Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Updated: April 17, 2024
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2022? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map at the last second?

The thing is — understanding your customer base can be very challenging. Even when you think you’ve got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

While it isn’t possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a convenient tool for keeping track of critical milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents

What is the customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, benefits of customer journey mapping, customer journey stages.
- What’s included in a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Customer Journey Design
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer’s journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I’ve worked with were confused about the differences between the customer’s journey and the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don’t wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process of considering, evaluating, and purchasing a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand’s place within the buyer’s journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer’s journey. When you create a customer journey map, you’re taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey instead of leaving it up to chance.
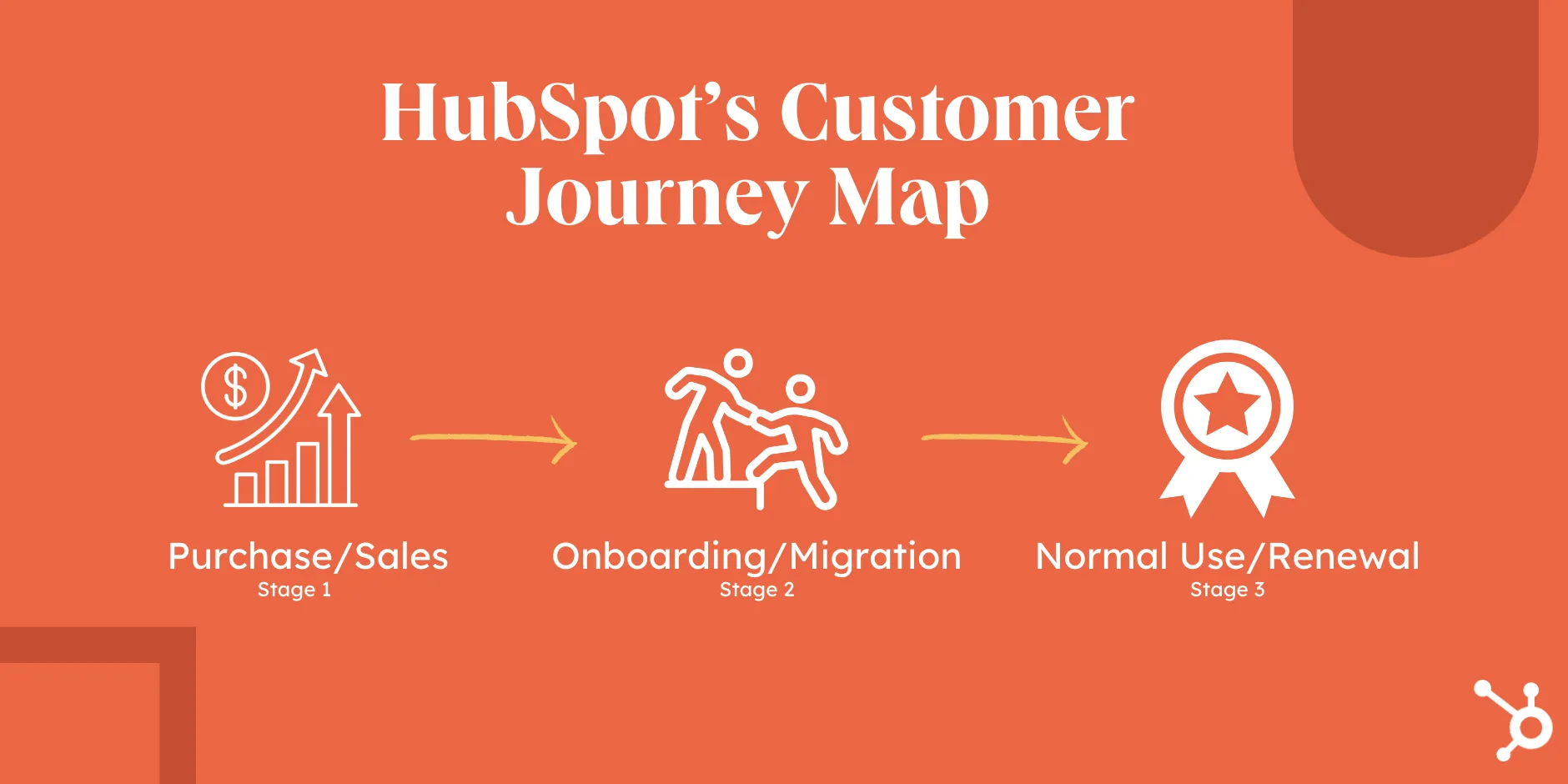
For example, at HubSpot, our customer’s journey is divided into three stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot’s free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer’s journey, a day in your customer’s life, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company’s buyer persona. This will improve your product and customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you’re creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don’t have one, I recommend creating a buyer persona . This persona is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics of your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics ready.
Don’t have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot’s Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Questionnaires and user testing are great ways to obtain valuable customer feedback. The important thing is to only contact actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you’ve learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a customer journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company. If you group too many personas into one journey, your map won’t accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it’s best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don’t worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
What is a touchpoint in a customer journey map?
A touchpoint in a customer journey map is an instance where your customer can form an opinion of your business. You can find touchpoints in places where your business comes in direct contact with a potential or existing customer.
For example, if I were to view a display ad, interact with an employee, reach a 404 error, or leave a Google review, all of those interactions would be considered a customer touchpoint.
Your brand exists beyond your website and marketing materials, so you must consider the different types of touchpoints in your customer journey map. These touchpoints can help uncover opportunities for improvement in the buying journey.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there’s no overlap.
This is essential in creating a customer journey map because it provides insight into your customers’ actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they’re quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you must also look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels.
- Email marketing.
- Third-party review sites or mentions.
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
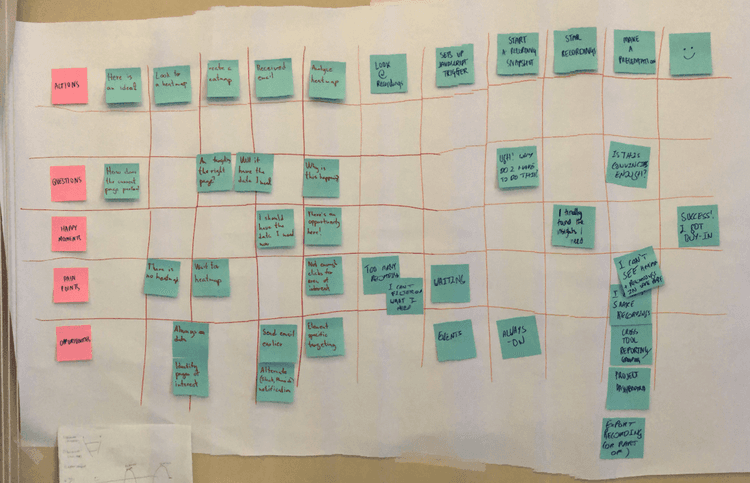
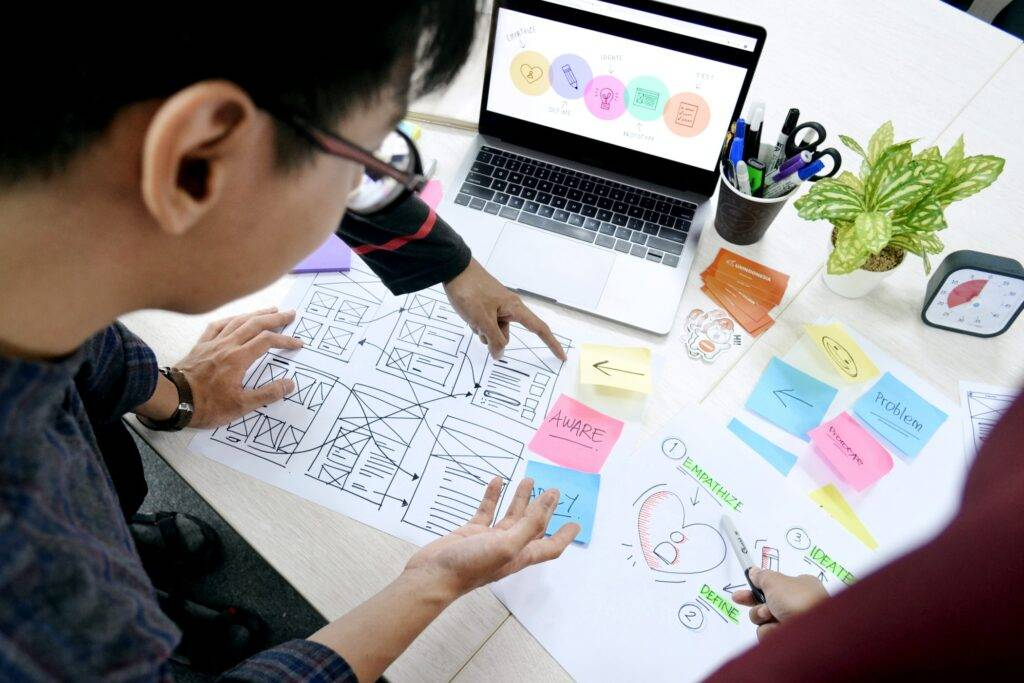
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding — you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![customer journey emotions How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey emotions How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey emotions Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![customer journey emotions How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
![customer journey emotions Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-experience-vs-user-experience_2.webp)
Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
Customer journey mapping in 2 and 1/2 days
How to create a customer journey map that improves customer success.
Last updated
Reading time.
There’s a common saying that you can’t understand someone until you’ve walked a mile in their shoes—and that’s exactly what customer journey maps do: they help you put yourself in different customers’ shoes and understand your business from their point of view.
Why should you do it? How should you do it? Find the answers in this guide, which we wrote after interviewing 10+ customer journey experts who shared methodologies, dos and don’ts, and pro tips with us.
On this page:
What is a customer journey map?
How to create a customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
4 benefits of customer journey mapping for your business
In later chapters, we dive deeper into customer journey analytics, workshops, and real-life examples.
Start mapping your customer journey
Hotjar lets you experience the customer journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of how customers interact with and experience your website, products, or business across multiple touchpoints.
By visualizing the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience, a customer journey map helps you better understand them and identify the pain points they encounter. This is essential if you want to implement informed, customer-focused optimizations on your site.
Mapping the customer journey: narrow vs. wide focus
A customer journey map can have a very narrow focus and only look at a few, specific steps of the customer experience or buyer’s journey (for example, a product-to-purchase flow on a website), or it can take into account all the touchpoints, online and offline, someone goes through before and after doing business with you.
Each type of customer journey map has its advantages:
A CJM with a narrow focus allows you to zero in on an issue and effectively problem-solve
A CJM with a wide focus gives you a broader, holistic understanding of how customers experience your business
Regardless of their focus, the best customer journey maps have one thing in common: they are created with real customer data that you collect and analyze . The insights are usually organized into a map (hence the name), diagram, or flowchart during a group workshop, which is later shared across the entire business so everyone gets a clear and comprehensive overview of a customer’s journey.
How to create your first customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
The process of creating a customer journey map can be as long or short as you need. Depending on how many people and stakeholders you involve, how much data you collect and analyze, and how many touchpoints there are across the business, you could be looking at days or even weeks and months of work.
If you’re new to customer journey mapping, start from a narrower scope before moving on to mapping every single customer touchpoint .
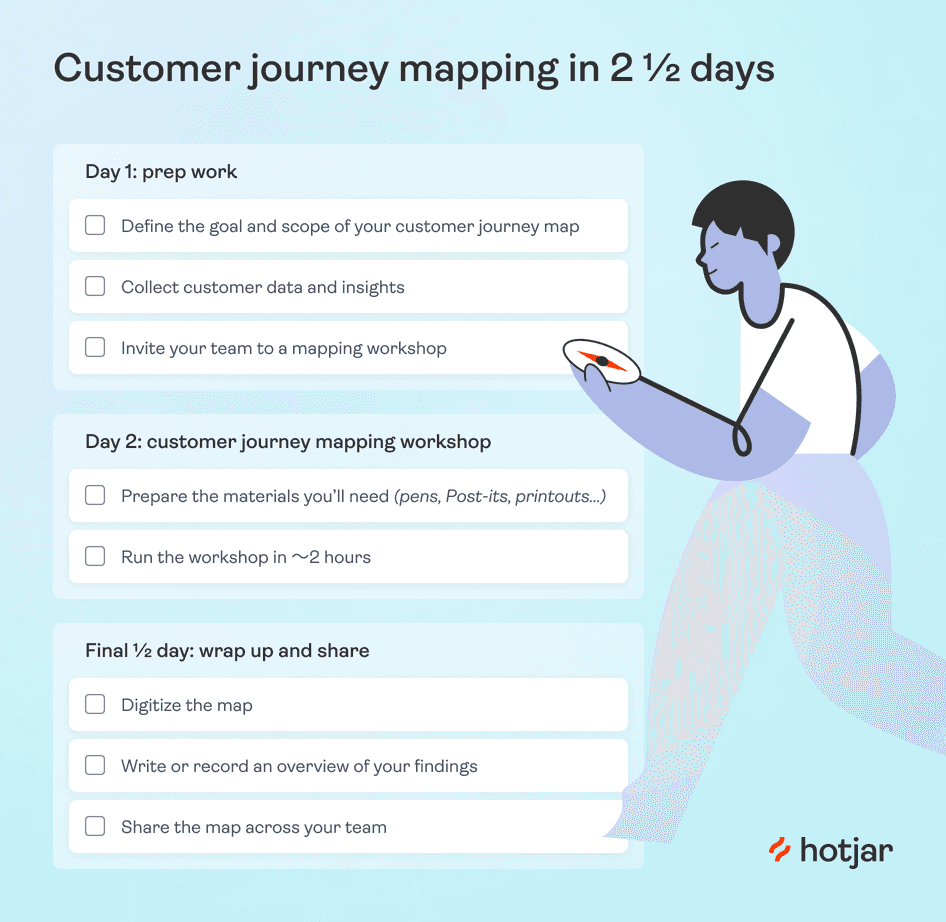
Here’s our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days:
Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work
Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop.
Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results
Download your free customer journey map checklist (as seen below), to mark off your tasks as you complete them.
On your first day, you have three essential tasks:
Define the goal and scope of your CJM
Collect customer data and insights
Invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
Step 1: define the goal and scope of your CJM
Clarifying what part(s) of the journey you're looking at, and why, helps you stay focused throughout the mapping process.
If this is your first map, start from a known issue or problematic area of your website. Keep the scope small, and focus on anything you can break down into four or five steps. For example:
If you have a high drop-off on a pricing page with five calls-to-action, each of which takes users to a different page, that’s enough for a mappable journey
If your purchase flow is made of five self-contained pages, each of which loses you potential customers, that’s a good candidate for mapping
✅ The output: a one- or two-sentence description of what your map will cover, and why, you can use whenever you need to explain what the process is about. For example: this map looks at the purchase flow on our website, and helps us understand how customers go through each step and the issues or obstacles they encounter. The map starts after users click ‘proceed to checkout’ and ends when they reach the 'Thank You' page .
Step 2: collect customer data and insights
Once you identify your goal and scope, the bulk of your first day should be spent collecting data and insights you’ll analyze as part of your mapping process. Because your map is narrow in focus, don’t get distracted by wide-scale demographics or data points that are interesting and nice to know, but ultimately irrelevant.
Get your hands on as much of the following information as you can:
Metrics from traditional analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) that give you insight into what’s happening, across the pages and stages your customer journey map covers
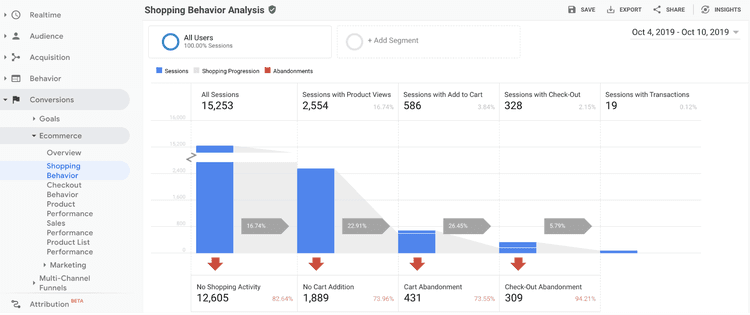
Data from analyzing your conversion ‘funnels’ , which record how many visitors end up at each stage of the user journey, so you can optimize those steps for potential customers and increase conversions
Behavior analytics data (from platforms like Hotjar) that show you how people interact with your site. For example, heatmaps give you an aggregate view of how users click, move and scroll on specific pages, and session recordings capture a user’s entire journey as they navigate your site
Quantitative and qualitative answers to on-site surveys relevant to the pages you’re going to investigate, as customer feedback will ultimately guide your roadmap of changes to make to improve the journey
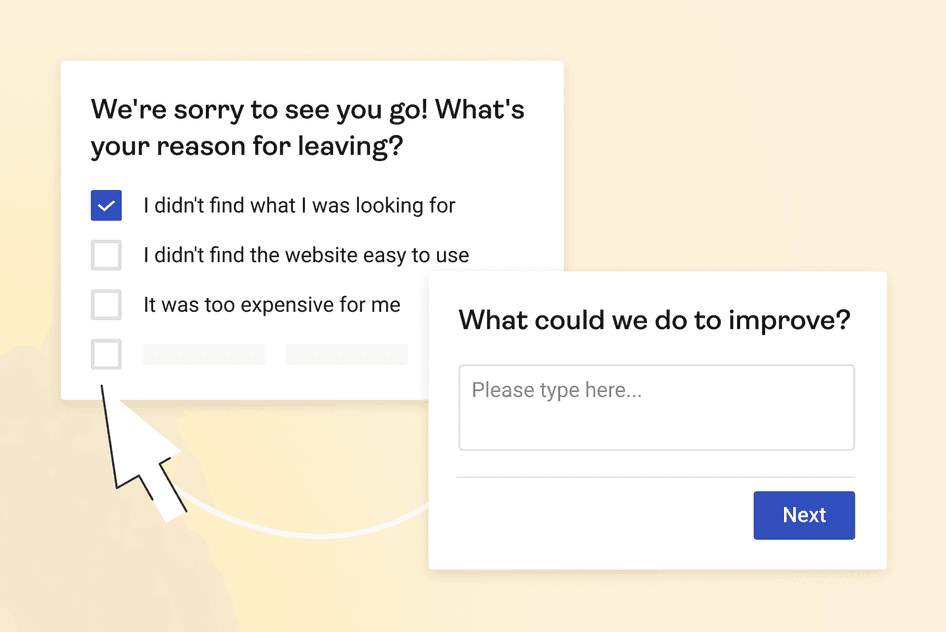
Any demographic information about existing user and customer personas that helps you map the journey from the perspective of a real type of customer, rather than that of any hypothetical visitor, ensuring the journey makes sense for your target audience
Any relevant data from customer service chat logs, emails, or even anecdotal information from support, success, and sales teams about the issues customers usually experience
✅ The output: quantitative and qualitative data about your customers' interactions and their experiences across various touchpoints. For example, you’ll know how many people drop off at each individual stage, which page elements they interact with or ignore, and what stops them from converting.
💡Pro tip: as you read this guide, you may not yet have most of this data, particularly when it comes to heatmaps, recordings, and survey results. That’s ok.
Unless you’re running your CJM workshop in the next 12 hours, you have enough time to set up Hotjar on your website and start collecting insights right now. The platform helps you:
Learn where and why users drop off with Funnels
Visualize interactions on key pages with Heatmaps
Capture visitor sessions across your website with Recordings
Run on-site polls with Surveys
When the time comes for you to start your customer journey mapping process, this data will be invaluable.
Step 3: invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
In our experience, the most effective way to get buy-in is not to try and convince people after things are done—include them in the process from the start. So while you can easily create a customer journey map on your own, it won’t be nearly as powerful as one you create with team members from different areas of expertise .
For example, if you’re looking at the purchase flow, you need to work with:
Someone from the UX team, who knows about the usability of the flow and can advocate for design changes
Someone from dev or engineering, who knows how things work in the back end, and will be able to push forward any changes that result from the map
Someone from success or support, who has first-hand experience talking to customers and resolving any issues they experience
✅ The output: you’ve set a date, booked a meeting space, and invited a group of four to six participants to your customer journey mapping workshop.
💡Pro tip: for your first map, stay small. Keep it limited to four to six people, and no main stakeholders . This may be unpopular advice, especially since many guides out there mention the importance of having stakeholders present from the start.
However, when you’re not yet very familiar with the process, including too many people early on can discourage them from re-investing their time into future CJM tasks. At this stage, it’s more helpful to brainstorm with a small team, get feedback on how to improve, and iterate a few times. Once you have a firm handle on the process, then start looping in your stakeholders.
On workshop day, you’ll spend half your time prepping and the other half running the actual session.
Step 1: prepare all your materials
To run a smooth workshop, ensure you do the following:
Bring stationery: for an interactive workshop, you’ll need basic materials such as pens, different colored Post-its, masking tape, and large sheets of paper to hang on the wall
Collect and print out the data: use the data you collected on Day 1. It’s good to have digital copies on a laptop or tablet for everybody to access, but print-outs could be the better alternative as people can take notes and scribble on them.
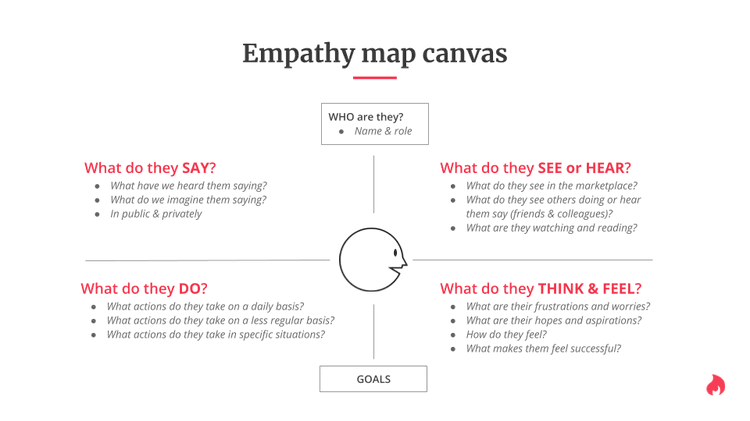
Print out an empathy map canvas for each participant: start the workshop with an empathy mapping exercise (more on this in Step 2). For this, hand each participant an empty empathy map canvas you can recreate from the template below.
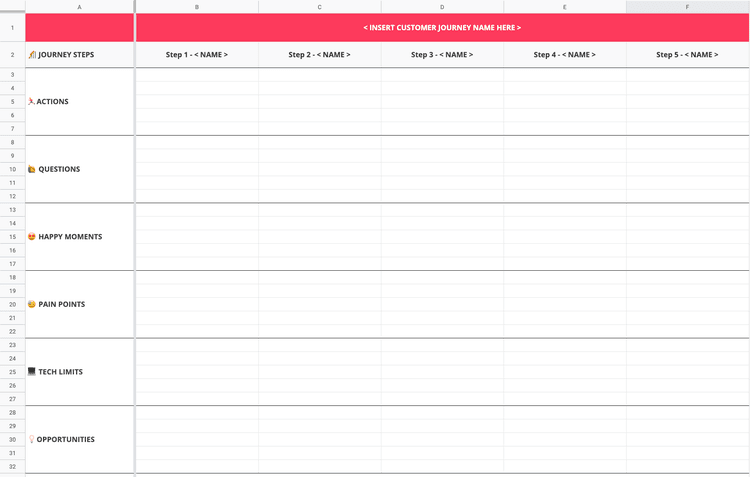
Set up a customer journey map template on the wall: use a large sheet of paper to create a grid you'll stick to the wall and fill in as part of the workshop. On the horizontal axis, write the customer journey steps you identified during your Day 1 prep work; on the vertical axis, list the themes you want to analyze for each step. For example:
Actions your customers take
Questions they might have
Happy moments they experience
Pain points they experience
Tech limits they might encounter
Opportunities that arise
Step 2: run the workshop
This is the most interactive (and fun) part of the process. Follow the framework below to go from zero to a completed draft of a map in just under 2 hours .
Introduction [🕒 5–10 min]
Introduce yourself and your participants to one another
Using the one-two sentence description you defined on Day 1, explain the goal and scope of the workshop and the activities it will involve
Offer a quick summary of the customer persona you’ll be referring to throughout the session
Empathy mapping exercise [🕒 30 min]
Using the personas and data available, have each team member map their observations onto sticky notes and paste them on the relevant section of the empathy mapping canvas
Have all participants take turns presenting their empathy map
Facilitate group discussions where interesting points of agreement or disagreement appear
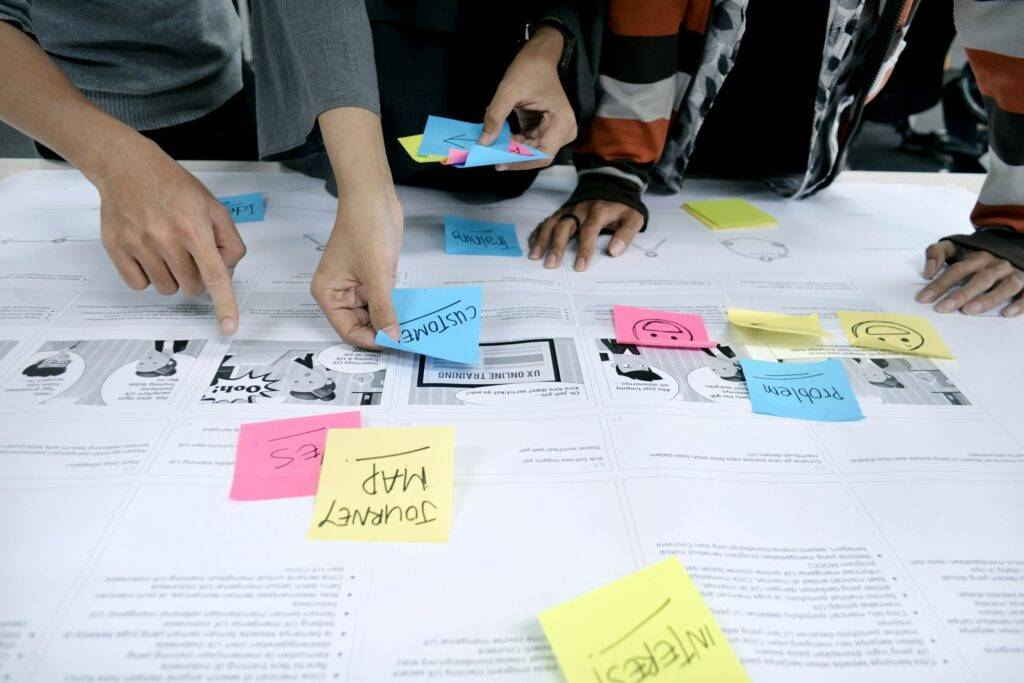
Customer journey mapping [🕒 60 min]
Using Post-its, ask each participant to fill in parts of the map grid with available information. Start by filling in the first row together, so everybody understands the process, then do each row individually (15–20 min). At the end of the process, you should have something like this:

Looking at the completed map, encourage your team to discuss and align on core observations (and take notes: they’ll come in handy on your final half day). At this point, customer pain points and opportunities should become evident for everybody involved. Having a cross-functional team means people will naturally start discussing what can, or cannot, immediately be done to address them (35–40 min).
Wrap up [🕒 5 min]
Congratulations! Your first customer journey map is complete. Finish the session by thanking your participants and letting them know the next steps.
Final half-day: wrap up and share
Once you’ve gone through the entire customer journey mapping workshop, the number one thing you want to avoid is for all this effort to go to waste. Instead of leaving the map hanging on the wall (or worse: taking it down, folding it, and forgetting about it), the final step is to wrap the process up and communicate the results to the larger team.
Digitize the map so you can easily update and share it with team members: it may be tempting to use dedicated software or invest time into a beautiful design, but for the first few iterations, it’s enough to add the map to your team’s existing workflows (for example, our team digitized our map and added it straight into Jira, where it’s easily accessible)
Offer a quick write-up or a 5-minute video introduction of the activity: re-use the description you came up with on Day 1, including who was involved and the top three outcomes
Clearly state the follow-up actions: if you’ve found obvious issues that need fixing, that’s a likely next step. If you’ve identified opportunities for change and improvement, you may want to validate these findings via customer interviews and usability testing.
4 benefits of customer journey mapping
In 2023, it’s almost a given that great customer experience (CX) provides any business or ecommerce site with a competitive advantage. But just how you’re supposed to deliver on the concept and create wow-worthy experiences is often left unsaid, implied, or glossed over.
Customer journey maps help you find answers to this ‘How?’ question, enabling you to:
Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
Create cross-team alignment around the business
Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
We’ve done a lot of customer journey work here at Hotjar, so we know that the above is true—but don’t just take our word for it: all the people we interviewed for this guide confirmed the benefits of journey mapping. Let’s take a look at what they shared.
1. Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
It’s one thing to present your entire team with charts, graphs, and trends about your customers, and quite another to put the same team in front of ONE map that highlights what customers think, want, and do at each step of their journey.
I did my first customer journey map at MADE.COM within the first three months of joining the company. I was trying to map the journey to understand where the pain points were.
For example, people who want to buy a sofa from us will be coming back to the site 8+ times over several weeks before making a purchase. In that time, they may also visit a showroom. So now I look at that journey, at a customer’s motivation for going to the website versus a physical store, and I need to make sure that the experience in the showroom complements what they're doing on-site, and vice-versa, and that it all kind of comes together.
The map helps in seeing that journey progress right up to the time someone becomes a customer. And it also continues after: we see the next touchpoints and how we're looking to retain them as a customer, so that they come back and purchase again.
A customer journey map is particularly powerful when you incorporate empathy into it, bringing to light specific emotions that customers experience throughout the journey.

2. Create cross-team alignment around the business
The best, most effective customer journey maps are not the solo project of the user experience (UX) or marketing team (though they may originate there).
Customer journey maps are a quick, easy, and powerful way to help everybody in your business get a clearer understanding of how things work from a customers’ perspective and what the customers’ needs are—which is the first step in your quest towards creating a better experience for them.
Our first goal for preparing a customer journey map was to improve understanding customers across the company, so that every employee could understand the entire process our clients go through.
For example, people from the shipping department didn't know how the process works online; people from marketing didn't know how customers behave after filing a complaint. Everything seems obvious, but when we shared these details, we saw that a lot of people didn't know how the company itself works—this map made us realize that there were still gaps we needed to fill.

If we discover that customers have a pain point in a specific section of the map, different teams can look at the same section from several angles; customer support can communicate why something is not possible, and engineering can explain why it’s going to take X amount of effort to get it done. Especially in cross-functional teams where we all come from really different disciplines, I find these maps to be an incredible way for us all to speak the same language.
3. Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
As a company grows in size and complexity, the lines of ownership occasionally become blurry. Without clarity, a customer might get bounced like a ping pong ball across Sales, Success, and Support departments—not great for the seamless and frictionless customer experience we all want to offer.
A central source of ‘truth’ in the form of a customer journey map that everybody can refer to helps clarify areas of ownership and handover points.
We were growing as a team, and we realized we needed to operationalize a lot of the processes that, before then, had just been manually communicated. We did it through a customer journey map. Our goal was to better understand where these hand-off points were and how to create a more seamless experience for our customers, because they were kind of being punted from team to team, from person to person—and often, it was really hard to keep tabs on exactly where the customer was in that entire journey.
4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
A customer journey map will take your team from 'It appears that 30% of people leave the website at this stage' to 'Wow, people are leaving because the info is incomplete and the links are broken.' Once everyone is aligned on the roadblocks that need to be addressed, changes that have a positive impact on the customer experience and customer satisfaction will happen faster.
The customer journey map brings it all together: it doesn't matter who you've got in the room. If you’re doing a proper journey map, they always get enlightened in terms of ‘Oh, my word. I did not know the customer's actually experiencing this.’ And when I walk out of the session, we have often solved issues in the business. Accountability and responsibilities have been assigned, and I find that it just works well.

Shaheema (right) working on a customer journey map
Collect the right data to create an effective customer journey map
The secret of getting value from customer journey mapping is not just building the map itself: it's taking action on your findings. Having a list of changes to prioritize means you can also measure their effect once implemented, and keep improving your customers' experience.
This all starts with collecting customer-centric data—the sooner you begin, the more information you’ll have when the time comes to make a decision.
Start mapping your customer journey today
Hotjar lets you experience your customer’s journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
FAQs about customer journey mapping
How do i create a customer journey map.
To create a useful customer journey map, you first need to define your objectives, buyer personas, and the goals of your customers (direct customer feedback and market research will help you here). Then, identify all the distinct touchpoints the customer has with your product or service in chronological order, and visualize the completion of these steps in a map format.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping provides different teams in your company with a simple, easily understandable visualization that captures your customers’ perspective and needs, and the steps they’ll take to successfully use your product or service.
Consider customer journey mapping if you want to accomplish a specific objective (like testing a new product’s purchase flow) or work towards a much broader goal (like increasing overall customer retention or customer loyalty).
What is the difference between a customer journey map and an experience map?
The main difference between an experience map and a customer journey map is that customer journey maps are geared specifically toward business goals and the successful use of a product or service, while experience maps visualize an individual’s journey and experience through the completion of any task or goal that may not be related to business.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Customer Journey Maps
What are customer journey maps.
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain points and opportunities to enhance customer experience and boost customer retention.
“ Data often fails to communicate the frustrations and experiences of customers. A story can do that, and one of the best storytelling tools in business is the customer journey map.” — Paul Boag, UX designer, service design consultant & digital transformation expert
In this video, Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, explains how you can include journey maps in your design process.
- Transcript loading…
Customer Journey Maps – Tell Customer Stories Over Time
Customer journey maps are research-based tools. They show common customer experiences over time To help brands learn more about their target audience.
Maps are incredibly effective communication tools. See how maps simplify complex spaces and create shared understanding.
Unlike navigation maps, customer journey maps have an extra dimension—time. Design teams examine tasks and questions (e.g., what-ifs) regarding how a design meets or fails to meet customers’ needs over time when encountering a product or service.
Customer journey maps should have comprehensive timelines that show the most essential sub-tasks and events. Over this timeline framework, you add insights into customers' thoughts and feelings when proceeding along the timeline. The map should include:
A timescale - A defined journey period (e.g., one week). This timeframe should include the entire journey, from awareness to conversion to retention.
Scenarios - The context and sequence of events where a user/customer must achieve a goal. An example could be a user who wants to buy a ticket on the phone. Scenarios are events from the first actions (recognizing a problem) to the last activities (e.g., subscription renewal).
Channels – Where do they perform actions (e.g., Facebook)?
Touchpoints – How does the customer interact with the product or service? What actions do they perform?
Thoughts and feelings – The customer's thoughts and feelings at each touchpoint.
A customer journey map helps you understand how customer experience evolves over time. It allows you to identify possible problems and improve the design. This enables you to design products that are more likely to exceed customers’ expectations in the future state.

How to Create a Customer Journey Map for Exceptional Experiences?
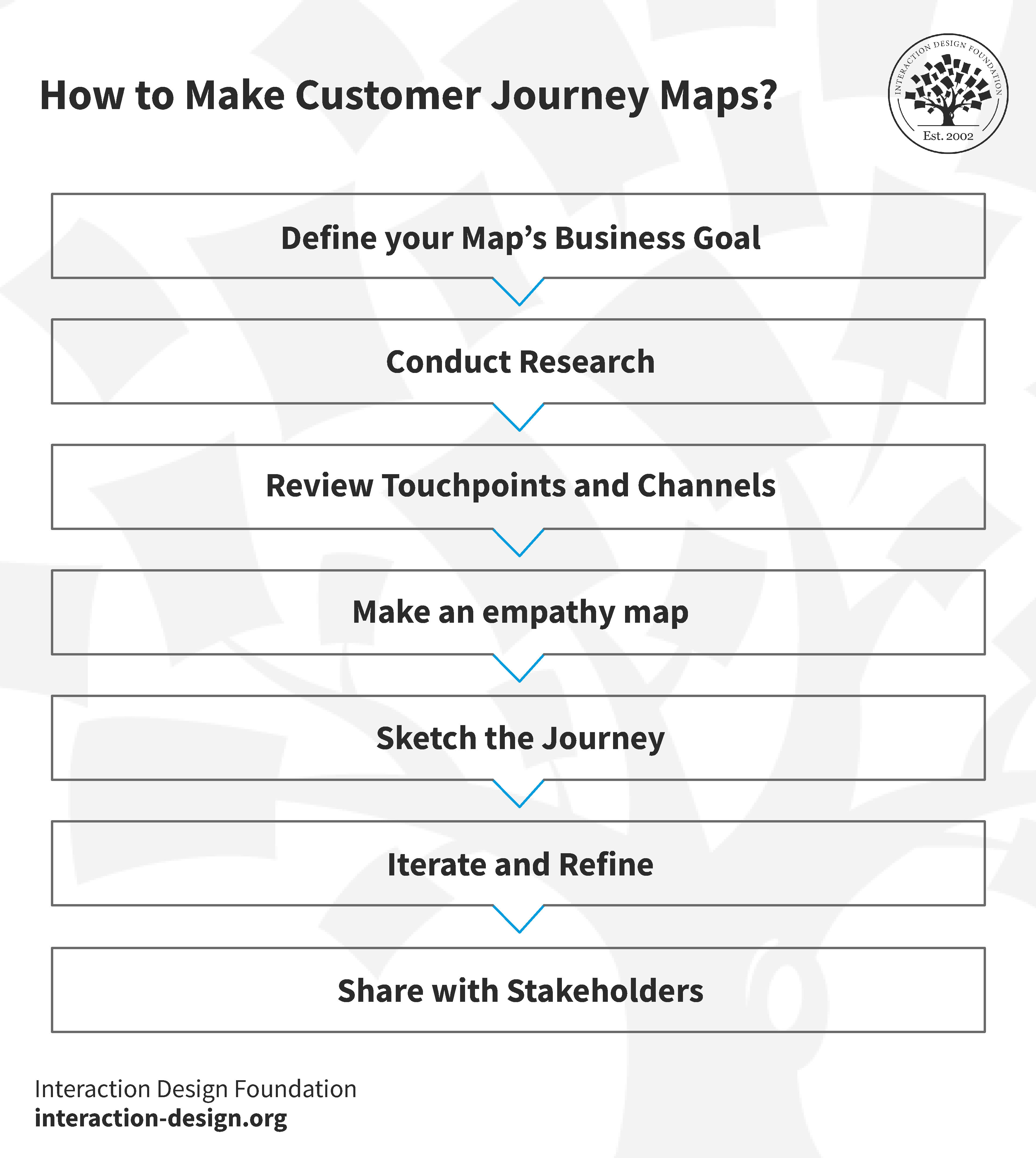
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Define Your Map’s Business Goal
Before creating a customer journey map, you must ask yourself why you're making one in the first place. Clarify who will use it and what user experience it will address.
Conduct Research
Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints. Get analytical/statistical data and anecdotal evidence. Leverage customer interviews, surveys, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
Watch user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen talk about how user research fits your design process and when you should do different studies.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Review Touchpoints and Channels
List customer touchpoints (e.g., paying a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for more touchpoints or channels to include.
Make an Empathy Map
Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc., in a given situation. Then, determine their needs and how they feel throughout the experience. Focus on barriers and sources of annoyance.
Sketch the Journey
Piece everything—touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.). Show a customer’s course of motion through touchpoints and channels across the timescale, including their feelings at every touchpoint.
Iterate and Refine
Revise and transform your sketch into the best-looking version of the ideal customer journey.
Share with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders understand your map and appreciate how its use will benefit customers and the organization.
Buyer Journey vs User Journey vs Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
You must know the differences between buyer, user, and customer journeys to optimize customer experiences. A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans.
Customer Journey
The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps:
1. Awareness : This is the first stage of the customer journey, where the customers realize they have a problem. The customer becomes aware of your brand or product at this stage, usually due to marketing efforts.
2. Consideration : Once customers know about your product or service, they start their research and compare brands.
3. Purchase : This is the stage where the customer has chosen a solution and is ready to buy your product or service.
4. Retention : After the purchase, it's about retaining that customer and nurturing a relationship. This is where good customer service comes in.
5. Advocacy : Also called the loyalty stage, this is when the customer not only continues to buy your product but also recommends it to others.
The journey doesn't end when the customer buys and recommends your solution to others. Customer journey strategies are cyclical and repetitive. After the advocacy stage, ideally, you continue to attract and retain the customers, keeping them in the cycle.
There is no standard format for a customer journey map. The key is to create one that works best for your team and product or service. Get started with customer journey mapping with our template:
This customer journey map template features three zones:
Top – persona and scenario.
Middle – thoughts, actions, and feelings.
Bottom – insights and progress barriers.
Buyer Journey
The buyer's journey involves the buyer's path towards purchasing. This includes some of the steps we saw in the customer journey but is specific to purchasing :
1. Awareness Stage : This is when a prospective buyer realizes they have a problem. However, they aren't yet fully aware of the solutions available to them.
2. Consideration Stage : After identifying their problem, the buyer researches and investigates different solutions with more intent. They compare different products, services, brands, or strategies here.
3. Decision Stage : The buyer then decides which solution will solve their problem at the right price. This is where the actual purchasing action takes place.
4. Post-Purchase Evaluation : Although not always included, this stage is critical. It's where the buyer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase. It includes customer service interactions, quality assessment, and attitudinal loyalty to the brand.
All these stages can involve many touchpoints, including online research, social media interactions, and even direct, in-person interactions. Different buyers may move through these stages at different speeds and through various channels, depending on a wide range of factors.
User Journey
The user journey focuses on people's experience with digital platforms like websites or software. Key stages include:
1. Discovery : In this stage, users become aware of your product, site, or service, often due to marketing efforts, word-of-mouth, or organic search. It also includes their initial reactions or first impressions.
2. Research/Consideration : Here, users dig deeper, exploring features, comparing with alternatives, and evaluating if your offering suits their needs and preferences.
3. Interaction/Use : Users actively engage with your product or service. They first-hand experience your solution's functionality, usability, and usefulness to achieve their goal.
4. Problem-solving : If they encounter any issues, how they seek help and resolve their issues fall into this stage. It covers user support, troubleshooting, and other assistance.
5. Retention/Loyalty : This stage involves how users stay engaged over time. Do they continue using your product, reduce usage, or stop altogether? It includes their repeated interactions, purchases, and long-term engagement over time.
6. Advocacy/Referral : This is when users are so satisfied they begin to advocate for your product, leaving positive reviews and referring others to your service.
Download this user journey map template featuring an example of a user’s routine.

Understanding these stages can help optimize the user experience, providing value at each stage and making the journey seamless and enjoyable.
Always remember the journey is as important as the destination. Customer relationships start from the first website visit or interaction with marketing materials. These initial touchpoints can influence the ongoing relationship with your customers.
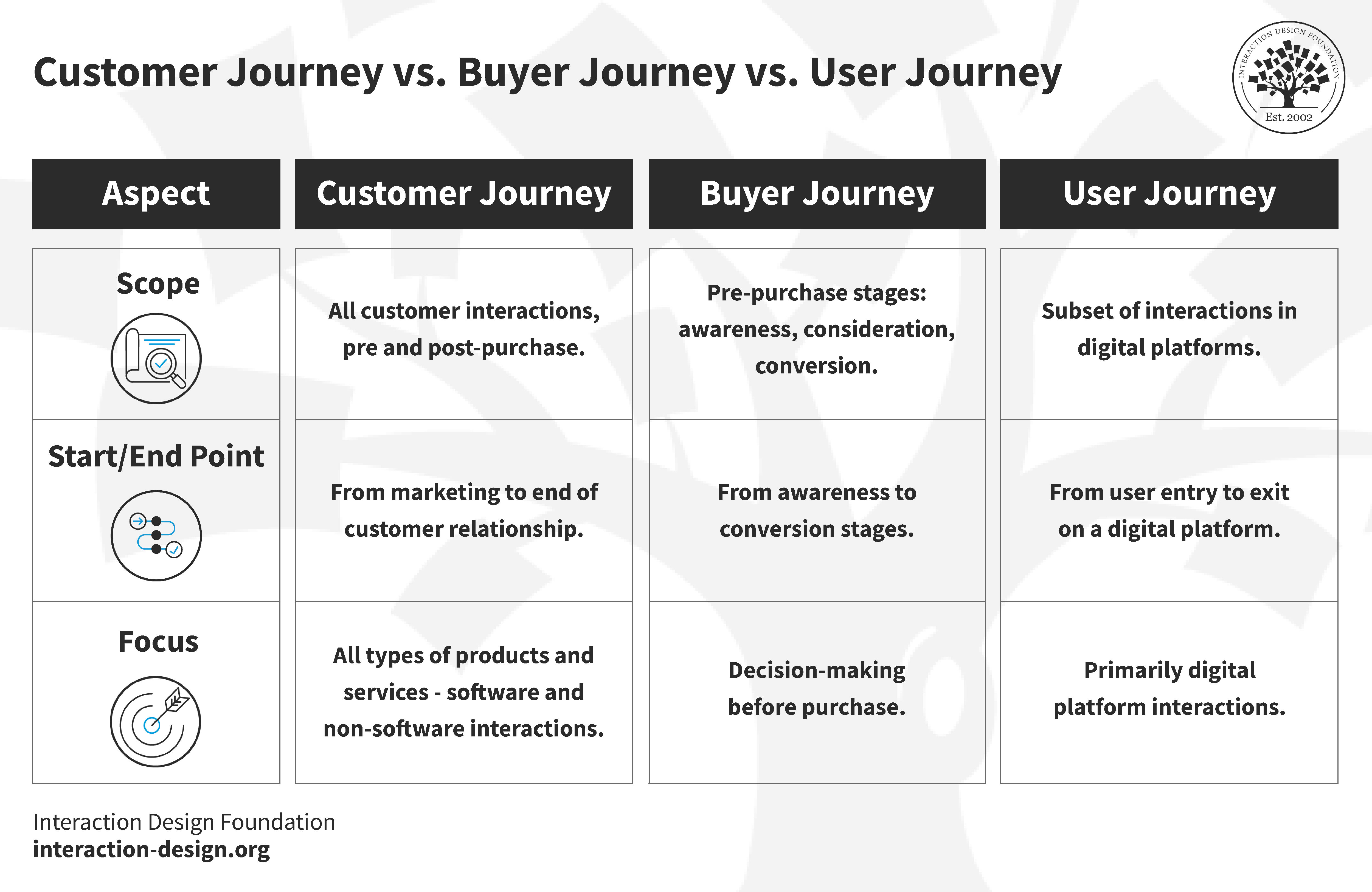
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
Drawbacks of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is valuable yet has limitations and potential drawbacks. Recognize these challenges and create more practical and realistic journey maps.
Over-simplification of Customer Experiences
Customer journey maps often risk simplifying complex customer experiences . They may depict varied and unpredictable customer behaviors as straightforward and linear. This simplification can lead to misunderstandings about your customers' needs and wants. As a result, you might overlook customers' diverse and unique paths.
Always remember that real customer experiences are more complex than any map. When you recognize this, you steer clear of decisions based on simple models.
Resource Intensity
Creating detailed customer journey maps requires a lot of resources and time. You must gather extensive data and update the maps to keep them relevant. This process can strain small businesses or those with limited resources.
You need to balance the need for comprehensive mapping with available resources. Efficient resource management and prioritization are crucial to maintaining effective journey maps.
Risk of Bias
Creating customer journey maps carries the inherent risk of biases . These biases can arise from various sources. They can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the maps.
Alan Dix, an expert in HCI, discusses bias in more detail in this video.
Common biases in customer journey mapping include:
Assumption Bias: When teams make decisions based on preconceived notions rather than customer data.
Selection Bias: When the data doesn’t represent the entire customer base..
Confirmation Bias : When you focus on information that supports existing beliefs and preferences. Simultaneously, you tend to ignore or dismiss data that contradicts those beliefs.
Anchoring Bias : Relying on the first information encountered (anchor) when making decisions.
Overconfidence Bias : Placing too much trust in the accuracy of the journey map. You may overlook its potential flaws.
These biases may misguide the team, and design decisions based on these maps might not be effective.
To address these biases, review and update journey maps with real user research data. Engage with different customer segments and gather a wide range of feedback to help create a more accurate and representative map. This approach ensures the journey map aligns with actual customer experiences and behaviors.
Evolving Customer Behaviors
Customer behaviors and preferences change with time. A journey map relevant today can become outdated. You need to update and adapt your maps to reflect these changes. This requires you to perform market research and stay updated with trends and customer feedback.
Getting fresh data ensures your journey map stays relevant and effective. You must adapt to evolving customer behaviors to maintain accurate and valuable customer journey maps.
Challenges in Capturing Emotions
Capturing emotions accurately in customer journey maps poses a significant challenge. Emotions influence customer decisions, yet you may find it difficult to quantify and represent them in maps. Most journey maps emphasize actions and touchpoints, often neglecting the emotional journey.
You must integrate emotional insights into these maps to understand customer experiences. This integration enhances the effectiveness of customer engagement strategies. You can include user quotes, symbols such as emojis, or even graphs to capture the ups and downs of the users’ emotions..
Misalignment with Customer Needs
Misalignments in customer journey maps can manifest in various ways. It can impact the effectiveness of your strategies. Common misalignments include:
Putting business aims first, not what customers need.
Not seeing or serving the varied needs of different customer types.
Not using customer feedback in the journey map.
Thinking every customer follows a simple, straight path.
Engage with your customers to understand their needs and preferences if you want to address these misalignments. Incorporate their direct feedback into the journey map. This approach leads to more effective customer engagement and satisfaction.
Over-Reliance on the Map
Relying too much on customer journey maps can lead to problems. These maps should serve as tools rather than definitive guides. Viewing them as perfect can restrict your responsiveness to customer feedback and market changes. Treat journey maps as evolving documents that complement direct customer interactions and feedback.
Make sure you get regular updates and maintain flexibility in your approach. Balance the insights from the map with ongoing customer engagement. This approach keeps your business agile and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Data Privacy Concerns
Collecting customer data for journey mapping poses significant privacy concerns. Thus, you need to create a balance. You must adhere to data protection laws and gather enough information for mapping.
You need a careful strategy to ensure customer data security. Stay vigilant to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and customer expectations. This vigilance helps maintain trust and compliance.
Learn More about Customer Journey Maps
Take our Journey Mapping course to gain insights into the how and why of journey mapping. Learn practical methods to create experience maps , customer journey maps, and service blueprints for immediate application.
Explore this eBook to discover customer journey mapping .
Find some additional insights in the Customer Journey Maps article.
Questions related to Customer Journey Maps
Creating a customer journey map requires visually representing the customer's experience with your product or company. Harness the strength of visual reasoning to understand and present this journey succinctly. Instead of detailing a lengthy narrative, like a book, a well-crafted map allows stakeholders, whether designers or not, to grasp the journey quickly. It's a democratized tool that disseminates information, unifies teams, and aids decision-making by illuminating previously unnoticed or misunderstood aspects of the customer's journey.
The customer journey encompasses five distinct stages that guide a customer's interaction with a brand or product:
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem.
Consideration: They research potential solutions or products.
Purchase: The customer decides on a solution and makes a purchase.
Retention: Post-purchase, the customer uses the product and forms an opinion.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences.
For a comprehensive understanding of these stages and how they intertwine with customer touchpoints, refer to Interaction-Design.org's in-depth article .
A perspective grid workshop is a activity that brings together stakeholders from various departments, such as product design, marketing, growth, and customer support, to align on a shared understanding of the customer's journey. These stakeholders contribute unique insights about customer needs and how they interact with a product or service. The workshop entails:
Creating a matrix to identify customers' jobs and requirements, not initially linked to specific features.
Identifying the gaps, barriers, pains, and risks associated with unmet needs, and constructing a narrative for the journey.
Highlighting the resulting value when these needs are met.
Discuss the implied technical and non-technical capabilities required to deliver this value.
Brainstorming possible solutions and eventually narrowing down to specific features.
The ultimate aim is to foster alignment within the organization and produce a user journey map based on shared knowledge.
Learn more from this insightful video:
Customer journey mapping is vital as it harnesses our visual reasoning capabilities to articulate a customer's broad, intricate journey with a brand. Such a depiction would otherwise require extensive documentation, like a book. This tool offers a cost-effective method to convey information succinctly, ensuring understanding of whether one is a designer or lacks the time for extensive reading. It also helps the team to develop a shared vision and to encourage collaboration. Businesses can better comprehend and address interaction points by using a journey map, facilitating informed decision-making and revealing insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Learn more about the power of visualizing the customer journey in this video.
Pain points in a customer journey map represent customers' challenges or frustrations while interacting with a product or service. They can arise from unmet needs, gaps in service, or barriers faced during the user experience. Identifying these pain points is crucial as they highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to enhance the customer experience and meet their needs more effectively. Pain points can relate to various aspects, including product usability, communication gaps, or post-purchase concerns. Explore the detailed article on customer journey maps at Interaction Design Foundation for a deeper understanding and real-world examples.
Customer journey mapping offers several key benefits:
It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting areas for improvement. This ensures that products or services meet users' needs effectively.
The process fosters team alignment, ensuring everyone understands and prioritizes the customer's perspective.
It helps identify pain points, revealing opportunities to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
This visualization allows businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring resources target the most impactful areas.
To delve deeper into the advantages and insights on journey mapping, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on key takeaways from the IXDF journey mapping course .
In design thinking, a customer journey map visually represents a user's interactions with a product or service over time. It provides a detailed look at a user's experience, from initial contact to long-term engagement. Focusing on the user's perspective highlights their needs, emotions, pain points, and moments of delight. This tool aids in understanding and empathizing with users, a core principle of design thinking. When used effectively, it bridges gaps between design thinking and marketing, ensuring user-centric solutions align with business goals. For a comprehensive understanding of how it fits within design thinking and its relation to marketing, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on resolving conflicts between design thinking and marketing .
A customer journey map and a user journey map are tools to understand the experience of users or customers with a product or service.
A customer journey map is a broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It considers physical and digital channels, multiple user personas, and emotional and qualitative aspects.
A user journey map is a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service. It only considers digital channels, one user persona, and functional and quantitative aspects.
Both are useful to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. However, they have different scopes, perspectives, and purposes. A customer journey map provides a holistic view of the entire customer experience across multiple channels and stages. A user journey map provides a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service.
While user journeys might emphasize specific tasks or pain points, customer journeys encapsulate the entire experience, from research and comparison to purchasing and retention.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience. It considers different user personas and emotional aspects.
A service blueprint shows how a service is delivered and operated by an organization. It focuses on the back stage of the service, which is what the customers do not see or experience. It considers one user persona and functional aspects. What are the steps that the customer takes to complete a specific task or goal within the service? What are the channels and devices that the customer interacts with at each step?
For an immersive dive into customer journey mapping, consider enrolling in the Interaction Design Foundation's specialized course . This course offers hands-on lessons, expert guidance, and actionable tools. Furthermore, to grasp the course's essence, the article “4 Takeaways from the IXDF Journey Mapping Course” sheds light on the core learnings, offering a snapshot of what to expect. These resources are tailored by industry leaders, ensuring you're equipped with the best knowledge to craft impactful customer journey maps.
Literature on Customer Journey Maps
Here’s the entire UX literature on Customer Journey Maps by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Customer Journey Maps
Take a deep dive into Customer Journey Maps with our course Journey Mapping .
This course will show you how to use journey mapping to turn your own complex design challenges into simple, delightful user experiences . If you want to design a great shopping experience, an efficient signup flow or an app that brings users delight over time, journey mapping is a critical addition to your toolbox.
We will begin with a short introduction to mapping — why it is so powerful, and why it is so useful in UX. Then we will get familiar with the three most common types of journey map — experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints — and how to recognize, read and use each one. Then you will learn how to collect and analyze data as a part of a journey mapping process. Next you will learn how to create each type of journey map , and in the final lesson you will learn how to run a journey mapping workshop that will help to turn your journey mapping insights into actual products and services.
This course will provide you with practical methods that you can start using immediately in your own design projects, as well as downloadable templates that can give you a head start in your own journey mapping projects.
The “Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project” includes three practical exercises where you can practice the methods you learn, solidify your knowledge and if you choose, create a journey mapping case study that you can add to your portfolio to demonstrate your journey mapping skills to future employers, freelance customers and your peers.
Throughout the course you will learn from four industry experts.
Indi Young will provide wisdom on how to gather the right data as part of your journey mapping process. She has written two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models . Currently she conducts live online advanced courses about the importance of pushing the boundaries of your perspective. She was a founder of Adaptive Path, the pioneering UX agency that was an early innovator in journey mapping.
Kai Wang will walk us through his very practical process for creating a service blueprint, and share how he makes journey mapping a critical part of an organization’s success. Kai is a talented UX pro who has designed complex experiences for companies such as CarMax and CapitalOne.
Matt Snyder will help us think about journey mapping as a powerful and cost-effective tool for building successful products. He will also teach you how to use a tool called a perspective grid that can help a data-rich journey mapping process go more smoothly. In 2020 Matt left his role as the Sr. Director of Product Design at Lucid Software to become Head of Product & Design at Hivewire.
Christian Briggs will be your tour guide for this course. He is a Senior Product Designer and Design Educator at the Interaction Design Foundation. He has been designing digital products for many years, and has been using methods like journey mapping for most of those years.
All open-source articles on Customer Journey Maps
14 ux deliverables: what will i be making as a ux designer.

- 1.2k shares
What are Customer Touchpoints & Why Do They Matter?
- 3 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

- 2 years ago
How to Resolve Conflicts Between Design Thinking and Marketing

How to Create a Perspective Grid
- 11 mths ago
4 Takeaways from the IxDF Journey Mapping Course
The Power of Mapping
User Story Mapping in Design
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Existing customer? Sign in

The Ultimate Guide to Customer Journey Mapping [Updated 2022]
![customer journey emotions The Ultimate Guide to Customer Journey Mapping [Updated 2022]](https://www.tracx.com/_astro/photo-1584652868574-0669f4292976.69af96b6_1RXYuN.jpg)
In a world full of choice, how are brands standing out?
By creating exceptional customer experiences.
Emotions play a large role in purchasing decisions. Brands that can create positive experiences are more likely to attract and retain customers, drive revenue, and experience growth.
For many businesses, customer journey mapping (CJM) is the first step towards creating these exceptional customer experiences.
We’ll talk about what customer journey mapping is, why customer journey mapping is especially important for offline-first businesses, and how to create your own customer journey map..

Customer journey mapping process, source: Unsplash
Customer journey definition
Your customer journey is the series of touchpoints your customer experiences as they interact with your brand on their way to making a purchase or after purchasing.
What is customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with your brand. It highlights the various touchpoints, actions, and goals a user has in the process of becoming your customer.
Since 56% of customer interactions happen across channels , there are many opportunities for cost savings, growth, and customer retention for your brand when you deepen your understanding of your customer’s journey. It’s best practice to map out your customer journey so you can identify pain points and opportunities for growth.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of your customer journey from the moment they first interact with your brand all the way through to when they become loyal advocates.
Customer journey mapping will help you step into your customers’ shoes and gain valuable insights into their real-world interactions with your brand – from clicking on your Google ad to stepping into your museum or store.
A strong customer journey map will provide insights into the aspects of the customer journey that are working well, not-so-well, and any aspects that may be missing altogether. These insights are an incredible resource as they help you to better understand your customers and pinpoint where you should be focusing your time and efforts.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
An exceptional customer experience is essential if you want to build brand equity, attract customers, and grow your business. Your customers interact with your organisation in a variety of ways. With the increasing complexity of interactions online and offline you’d think customer journey mapping features in most organisations’ customer experience (CX) plans.
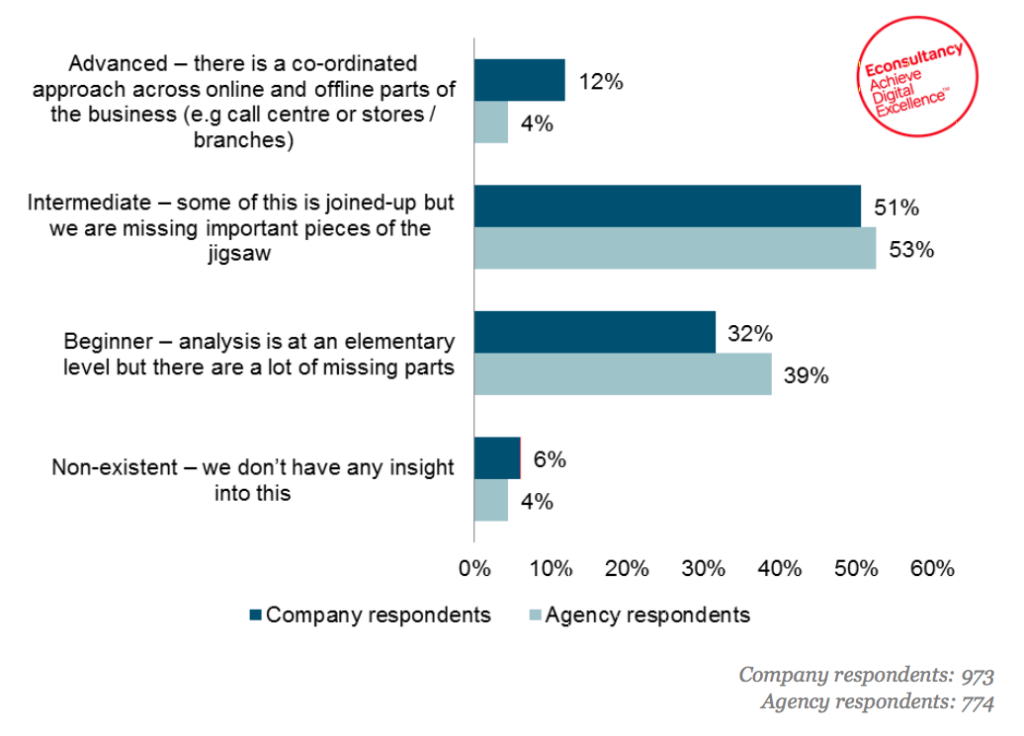
How would you best describe your understanding of the customer journey? Source: econsultancy.com
Yet, even though 81% of companies believe customer experience is a competitive advantage , only 8% report having a joined up omnichannel strategy. A full 33% admit they’re unable to track customer journeys at all.
It makes sense to spend some time creating your customer journey map – 71% of brands say that customer journey mapping has reduced their customer service costs by up to 20%. A further 77% of consumers say they view brands more favourably when they ask for feedback.
With 84% of consumers saying being treated like an individual is very important to winning their business, it’s critical that you understand your buyers’ desires and pain points at every interaction with your brand.
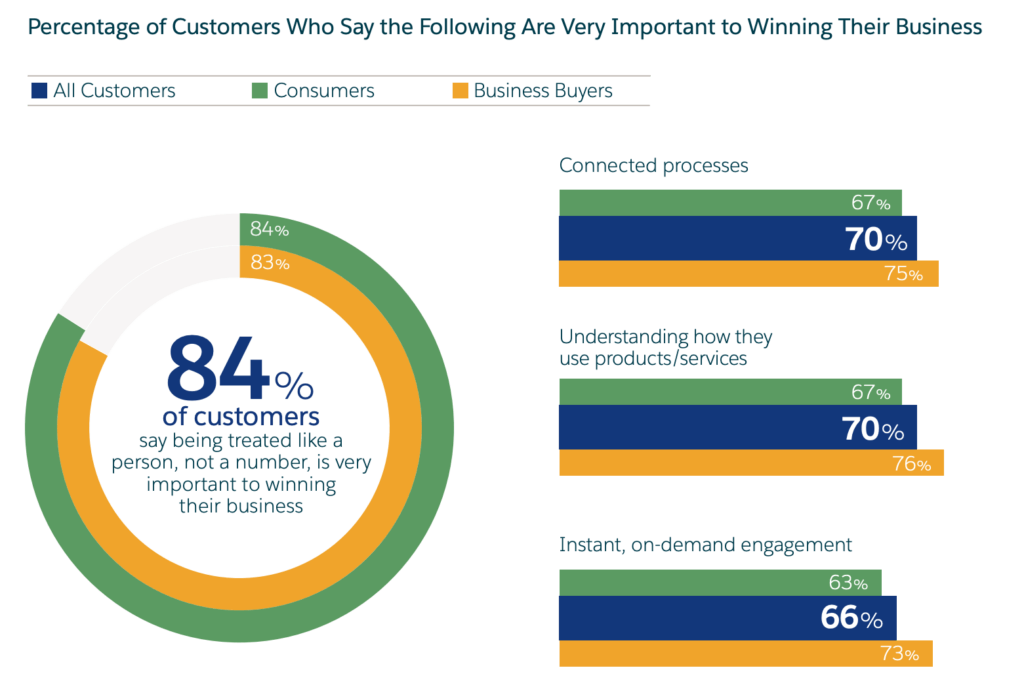
Source: salesforce.com
To create an exceptional customer experience , you need to have the proper data. Customer journey mapping is a strategic tool that helps you create personalised experiences along every step of the customer journey. It helps you meet short-term customer needs and expectations but also gives you a long-term view of their expectations so you can anticipate future needs. A customer journey map provides you with the insights you need to better understand your customers. This allows you to then create a customer experience that satisfies all their expectations.
The last mile of the customer journey is an important topic and customer journey mapping can help you identify opportunities for advanced forecasting, optimised delivery, intelligent insights, and real-time tracking.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
With information comes empowerment. By gaining a deeper understanding of your customer experiences through customer journey mapping, you will be empowered to make decisions that elevate your business.
By thoroughly mapping customer journeys, you can develop a customer-focused mentality, improve your customer retention rate, and gain a deeper understanding of your customers.
Customer journey mapping has several benefits , including:
- Uncovering the differences in behaviour between buyer personas
- Creating a logical buying process
- Optimising the onboarding process
- Benchmarking your customers’ experience against predictions
You can create a customer-focused mentality throughout the company
Although every department in your company is working towards the same goal, the objectives of each department may be slightly different. Everyone in the business wants to achieve growth. But while the marketing department focuses on building brand awareness, the accounting department focuses on profits and losses. Whatever the department’s objectives may be, the customer must always be at the heart of every action and goal.
By creating a customer journey map that illustrates the entire customer journey and the role each department plays in shaping the experience, you can unite departments over a shared customer-focused mentality. This shared mentality can help departments unite their objectives, improve the customer experience, and reach the same goals.
You can improve your customer retention rate
Customers are largely driven by emotion. If your business delivers a consistently positive experience, your customers are unlikely to take their business elsewhere.
By improving customer engagement and your customer retention rate through exceptional customer experiences, your business will likely also benefit from:
- Increased revenue. You are more likely to up-sell and cross-sell to existing customers. These revenue sources are often more profitable for your business.
- Improved external touchpoints. Your loyal customers will share positive referrals and reviews of your business to new potential customers.
- Cost efficiencies. It is generally more affordable to retain current customers than to attract new ones.
You can gain a deeper understanding of your customer
The best way to help your customer and create an exceptional customer experience is by understanding who they are and what they want. Diving into the actions and touchpoints your customers have along their journey will reveal the different goals they have and the outcomes they expect. This understanding will allow you to implement solutions and strategies that appeal directly to your customer’s wants and needs so you can continue creating those positive experiences and build brand loyalty.
A case against customer journey mapping
While there are many benefits to creating a customer journey map, it is not without its limitations. Some of these limitations include:
Little opportunity for flexibility. If you are a newer business without a pre-established customer journey in place, creating a customer journey map can limit your ability to test and experiment with different customer experience models or initiatives.
Excludes external factors. Inputs such as cost, implementation difficulty, and competition are not included in a customer journey map. However, these inputs have the potential to hold a notable influence on your overall customer experience and customer satisfaction.
Does not consider related journeys. Purchases don’t often happen in isolation, and your customer is likely engaging in a variety of related journeys with multiple businesses at the same time. CJM’s are not able to evaluate how these related journeys impact one another and influence the overall customer experience.
Despite its limitations, a customer journey map is still a great tool. Supplement CJM’s shortcomings by implementing additional tools that can work alongside your map.
The basic concepts of a customer journey map
A customer journey map combines a series of touchpoints, actions, emotions, and barriers that your customer experiences throughout their journey. Together, these inputs create one cohesive experience.
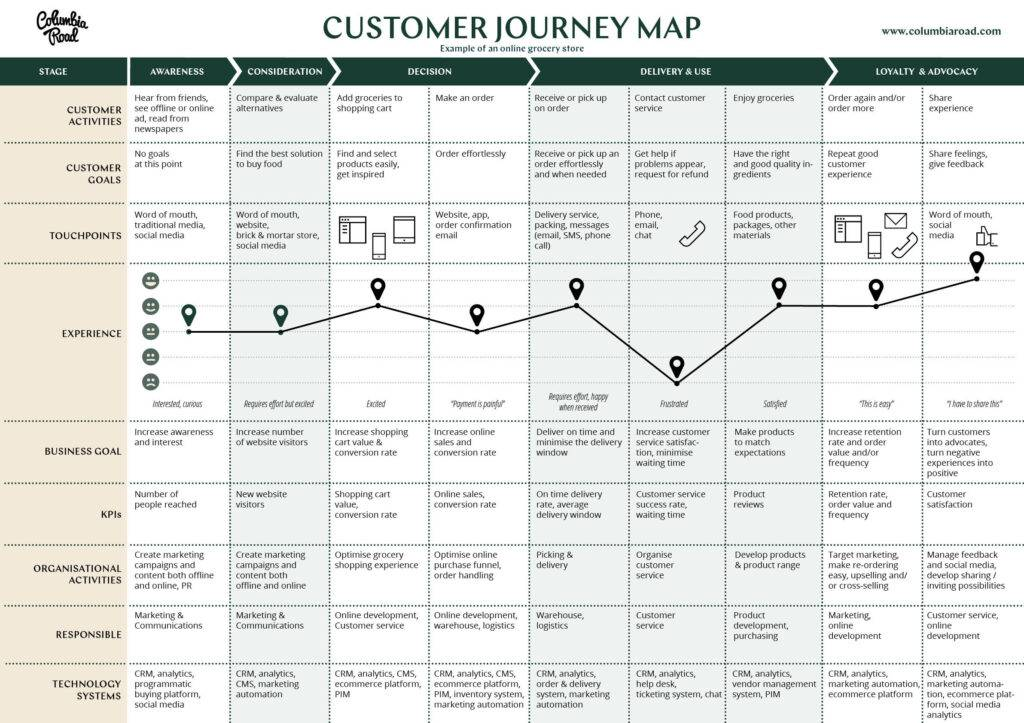
Example Customer Journey Map, source: Columbia Road
A strong journey map will include all these different inputs in detail so that you can make customer experience decisions based on complete and accurate information.
Touchpoints
A touchpoint is any interaction a customer has with your brand. This can include everything from in-store experiences and web searches to paid advertising and word-of-mouth referral. Essentially, a touchpoint is any interaction that allows your customer to form an opinion on your business.
Touchpoints are critical because their combined influence determines whether a user will become a customer. The challenge with touchpoints, however, is that many of them are outside of your control. Peer recommendations and user-generated content cannot be managed by your marketing department and depend upon the experiences of other customers with your brand.
Actions are any behaviour your customer engages in. This includes following your social media page, visiting your website, or coming to your store. While not all actions are equally important, they all play a role in determining whether a customer makes a purchase at the end of their journey.
Emotions & Motivations
Every customer has a different reason for purchasing from you. It may be because your product or service fulfils a functional need or because the customer aligns with your brand promise. Either way, the aspect uniting all purchasing motivations is emotion.
Customers’ decisions are largely based on how your business makes them feel. Ensuring you can fulfil customer’s functional needs while delivering a positive emotional experience is essential in creating a great customer journey.
Barriers & Pain Points
No customer journey is perfect, and at some point, your customer is likely to come across a barrier or pain point. Maybe your website load time is slow, or your return policy does not meet expectations. Whatever it is, most customer encounters a touchpoint or action that takes away from their overall experience.
Customers experience roadblocks, dead ends and frustration in their journey. The more friction we put in front of potential customers, the less likely they are to complete the journey Forbes
To create an outstanding customer experience, the first step is knowing where your barriers are. You need to identify these pain points and understand why they deter customers. With this information you can respond quickly and build effective solutions.
Current State
The most common type of customer journey map, is one that represents your customer journey as it currently exists. These customer journey maps outline the touchpoints, actions, emotions, and barriers that your users currently go through before and after becoming a customer. These types of CJM’s are great to help you acknowledge aspects of the customer journey that are working and identify growth opportunities.
Future State
A future state customer journey map, visualises your customer journey as you would like it to be. Future state CJM’s are aspirational by nature. They are great for creating a visual representation of your customer experience goals.
How do I create a customer journey map?

Source: https://unsplash.com/photos/w00FkE6e8zE
Your customer journey mapping should seek to address questions such as:
- Which customer segments am I targeting?
- What kinds of behaviours am I looking at – linear or cyclical?
- How can I start from the customer’s perspective?
- How can I recreate experiences across multiple channels and touch points?
- How can I represent important metrics and indicators such as NPS or CSAT scores?
There are many ways you can go about creating and designing your CJM, but for best results, we recommend following the following customer journey mapping methodology:
Conduct persona research
Many businesses believe they have an in-depth understanding of your customers and the customer experience. Yet, nothing beats speaking to your customers directly. For a strong customer journey map, conduct thorough research. Interview your customers via feedback surveys and questionnaires to get more complete and honest feedback on your current customer experience. Avoid making mistakes when surveying customers .
It is important to note when building your customer journey map, it is often best practice to focus on one customer persona at a time. Your customer base is diverse and so are their experiences with your brand. One CJM will not be enough to cover the variability in different customer journeys. Begin by focusing on one persona and slowly build out more maps from there to cover multiple personas.
Understand your customer’s goals
At every step along the customer journey, there is a goal your customer is trying to achieve. Whether that be trying to find your store hours when visiting your website, or wanting to learn more about your brand personality through social media. Every action is motivated by an end goal. By figuring out what these goals are at each stage of the customer journey, you will be able to determine if these goals are being satisfied effectively. You will also understand how these goals are evolving throughout the customer journey.
List all the touchpoints
The strongest CJM’s have lots of detail and are specific. Spend time identifying all the different touchpoints in your customer journey, to get a complete view of the experience.
Map the current state
To understand how you can improve your customer experience, you must first understand how the current journey is doing. Start by mapping the current state to create a baseline and identify opportunities for growth and improvement.
Take the customer journey yourself
Your real customers will be able to tell you a lot about your current customer experience. But most customers are not taking note of each and every touchpoint. They are likely to forget minor pain points or small moments of delight when questioned later on.
Going through your customer journey yourself is a great exercise. Approach with an unbiased perspective so you can experience first-hand the strengths and limitations of the journey. You’ll find deeper insight when you put yourself in your customer’s shoes.
Chart a sentiment line
Representing the emotional state of your customer throughout each stage of the journey is one of the most important aspects of your customer journey map. Each action taken by your customer is driven by emotion, so understanding how these emotions evolve throughout the journey and how they influence different actions is imperative. Include a sentiment line in your CJM that represents how emotions are evolving throughout the journey, and use this as a baseline when creating changes and improvements to your map.
Step-by-step: Customer journey mapping process
While it can be helpful to find other customer journey mapping examples, your customer journey map will be unique to your organisation’s goals and customers.
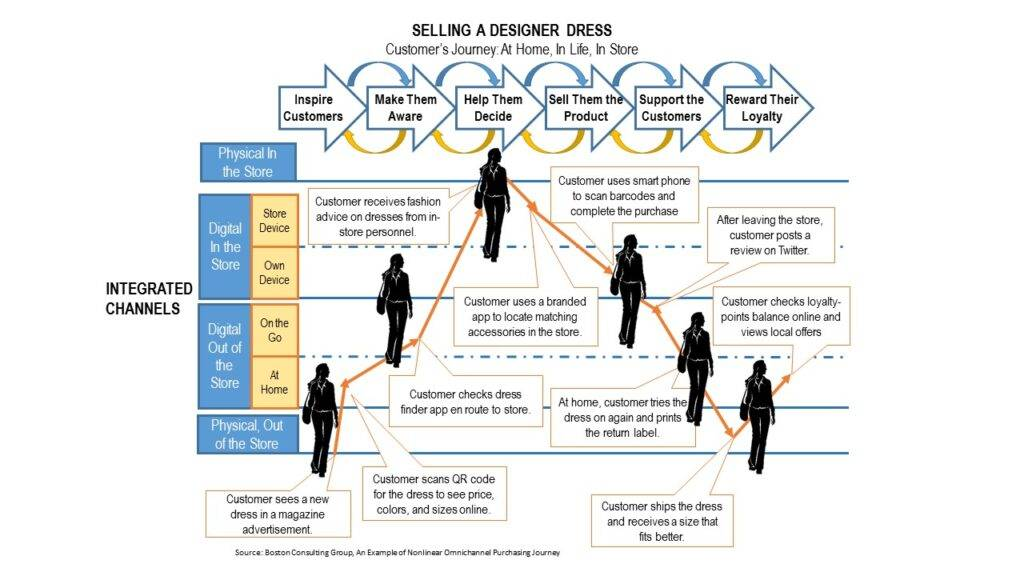
Source: davechaffey.com
We suggest the following 5 step process to build your customer journey map:
1. Gather the support of stakeholders
In the modern connected enterprise every department has a stake in the customer experience, not just customer support. Getting everyone involved early in the customer mapping process will help you define requirements and gather feedback further down the line.
2. Conduct customer research
Find out everything you can about your customers and their pain points through surveys , customer effort scores , and interviews. You can also use the data you have concerning your interactions with your customers, including your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tool , social media conversations, customer support calls, and complaint logs.
Build a complete picture of your customers using words and phrases you’ve heard them use, adding motivations, expectations, pain points and other emotional elements you’ve been able to gather.
When you’re building a customer journey map, don’t forget to include customers that didn’t purchase to uncover differences in their experiences. This can provide useful insights on their decision-making process, helping you to plug gaps in your product and service offerings you may be unaware of.
3. Create your customer personas
Armed with the results of your customer research, build a comprehensive profile of your customers. You may have one or several buyer personas. A buyer persona is an idealised profile of a customer but it will help you formulate an understanding of each customer type.
Your customer persona will also help you understand your customers’ motivations.
These can be:
- Price – At the research stage
- Information and guidance – At the purchasing stage
- Recognition from peers – Post purchase, such as when recommending your product or service to their friends and family
4. Draw your customer journey map
There are many ways (customer touchpoints) your customer comes into contact with your brand before, during and after purchasing.
Your map should capture these touch points adequately, highlighting those that have the highest impact. The point of sale is especially important for many businesses because this is the last interaction your would-be customer has with the brand before committing to a purchase.
For long customer journeys, break up your map into phases , taking care to document your customers’ mindset throughout each phase as they try to accomplish different goals.
Start with a customer journey map template if you’re unsure where to start. You may want to ask a graphic designer to give your map a professional finish to maximise its impact on stakeholders.
5. Refine your journey maps
Use qualitative and quantitative data to identify roadblocks and pain points in your customer journey. Also, mark areas where you’re excelling so you can build on them. Where there are roadblocks in your customer journey, drill further into the data and try to figure out where adjustments might have the biggest impact.
How can I improve my customer journey?
Once you understand your current customer journey, you will face the challenge of figuring out ways to make improvements. While each business will have different areas of focus, here are some guiding steps to follow when creating and implementing changes.
Your journey maps will be extensive, and there are likely many different areas you could focus your time on. To avoid getting overwhelmed or, feeling unsure of where to start, begin by setting specific goals of what you want to achieve. Maybe you want to focus on your social media presence or improve your customer service wait times, whatever it is, start small and set specific and tangible goals to guide your efforts.
Decide what to measure
When making improvements to your customer journey, it’s important to measure their impact. By defining metrics and measuring the success of different initiatives, you can track your progress and create a benchmark for future changes and opportunities.
Include KPIs
Changes to your customer journey won’t happen overnight. Set key performance indicators to help keep your team focused and on track as they work towards implementing outlined improvements. Align your KPI’s with your goals to help keep the improvement process organised and succinct.
Prioritise and fix issues
Once you’ve built your current state customer journey map, there will likely be quite a few customer pain points and improvement opportunities. To decide where to start, prioritise improvements based upon their significance in the customer journey, how frequently a customer interacts with that touchpoint, and the return on investment (ROI) they can deliver. Begin by fixing the highest priority items and work your way down the list.
Review and update each journey map after every major change
As your business evolves, so will your customer journey. Every time you launch a new product, service, or location be sure to update your CJM to reflect the changes. Customers expect a lot and being able to constantly improve your offerings while delivering consistently exceptional experiences will go a long way in building customer loyalty .
Set monthly, quarterly, or annual meetings to review the CJM as a team to help get you in the practice of making updates frequently.
Example customer journey maps
No two customer journey maps are alike. Depending on your industry and who your customers are, your customer journey map will hold different details and nuances to create a comprehensive and specific visual of your customer journey.
Although each CJM is unique, here are a few examples to help get you started.
Retail customer journey map example
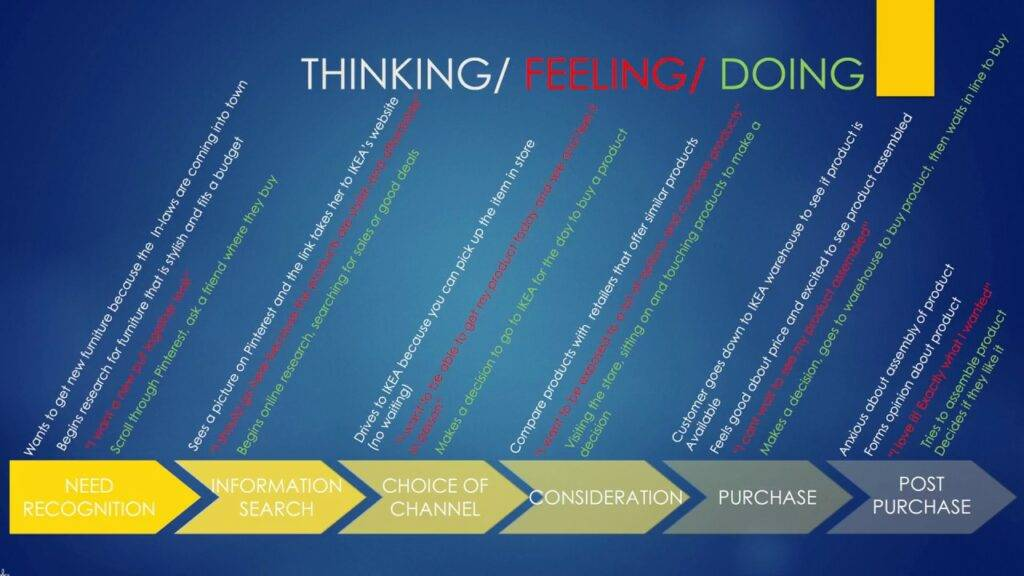
Source: IKEA
Customer journey mapping for big corporations can be tough. Ikea did a great job of developing a CJM that outlines the thoughts, behaviours, and emotions of a customer throughout their journey at the store. Visually appealing and easily digested, this map clearly describes the entire journey with all its complexities and nuances.
Bonus example: Omnichannel consumer journey map example
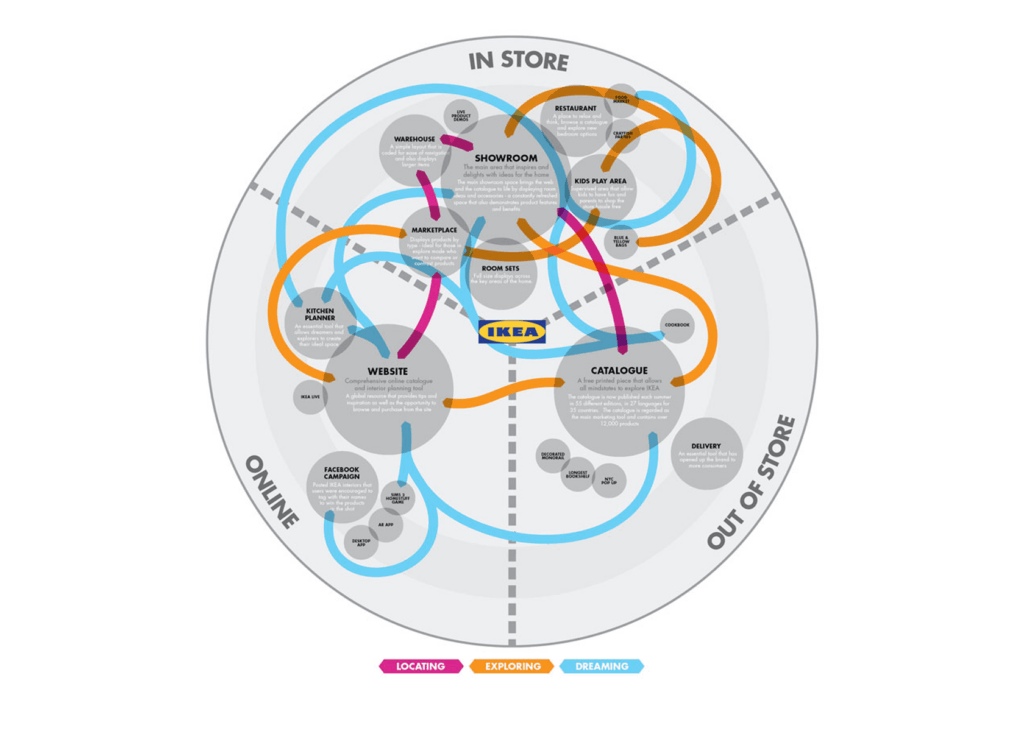
Source: Medium
It’s not a simple customer journey map, but this amazing graphic beautifully demonstrates how offline and online consumer journeys are connected as a buyer interacts with different touchpoints at IKEA.
B2B customer journey map example
Source: FedEx Business Insights
This customer journey map by FedEx is customer-focused and addresses the goal of the customer – global expansion. Through b2b international customer journey mapping, and by highlighting the customer journey from start to finish - and how FedEx plays a role in goal attainment - FedEx can position itself as an essential aspect of the B2B customer journey.
Circular customer journey map example
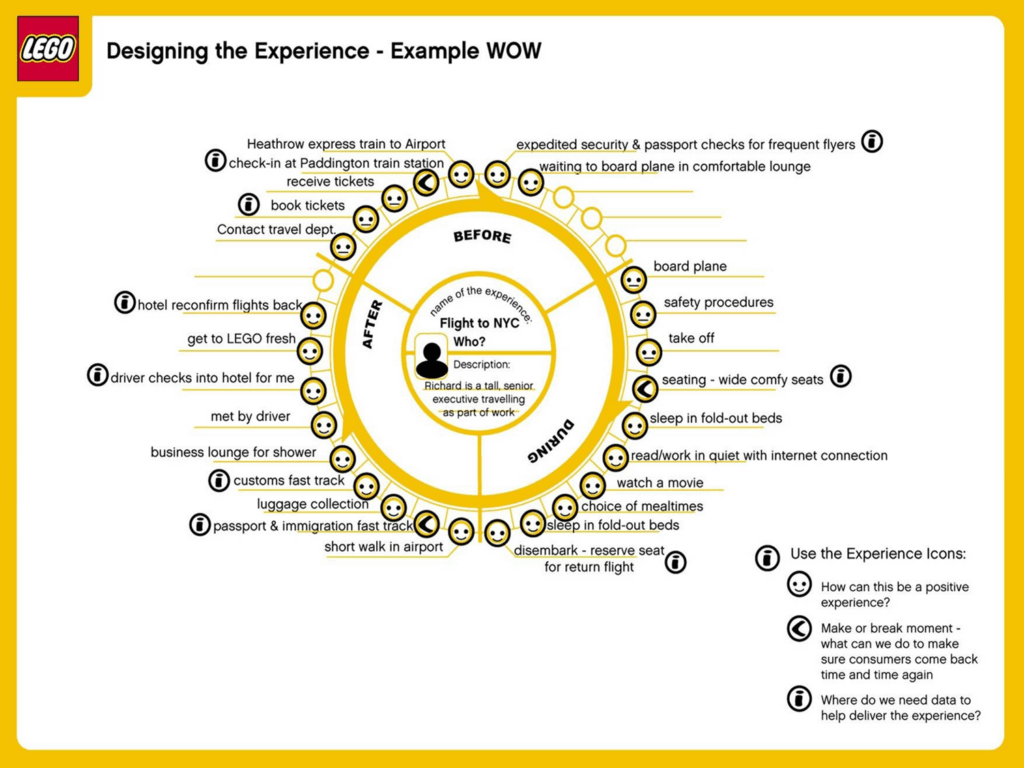
Customer Journey Map created by LEGO
A fun example of a circular customer journey map is the one from Lego, showing the customer experience of a Lego customer flying from Heathrow to New York City. In this example, Lego pays close attention to each step of the journey to create a detailed, unique, and exceptional LEGO customer journey.
Automotive customer journey map example
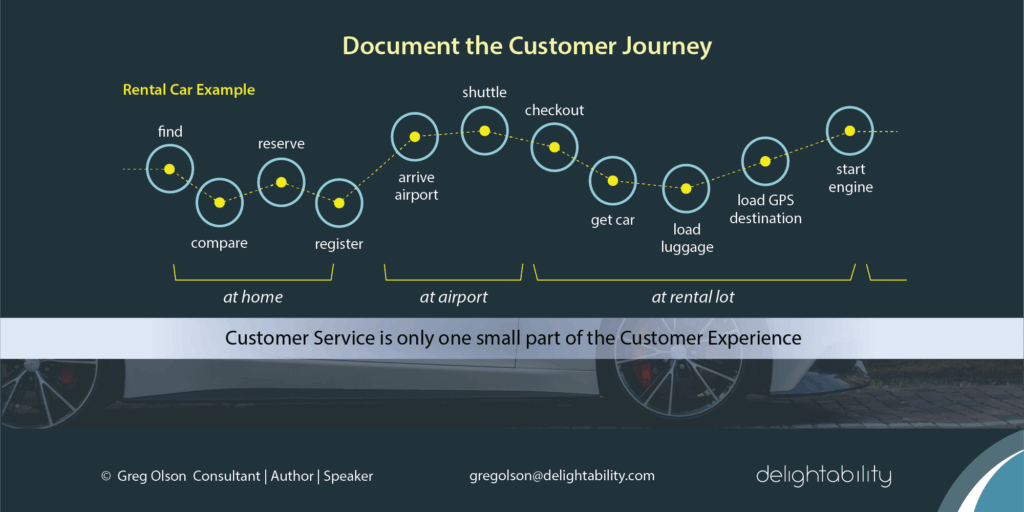
Car Rental Customer Journey Map created by Delightability
The image shows an automotive customer journey map using car rental. It’s taken from Gregory Olson’s book, The Experience Design Blueprint.
As you might notice, the relevance of each touchpoint on the journey depends largely on the audience. The company may have an interest in improving the overall experience when you’re trying to find a car to rent and using their app, but for someone renting a car for business travel, that might be less important than how easy it is to return the car at their destination.
So context matters. How you use the service as a business traveler will likely be very different from how you use it as a tourist.
The one thing we can all relate to is that most people have rented a car, so we can look at this map and think about all of our experiences in this context—and then consider how they could improve those parts that are more relevant to us based on what we do with them.
Use of customer journeys to improve customer satisfaction
Depending on what type of business you are in, the ideal customer experience will be different. By understanding who your customers are, what they need, and the experience they want to have, you can prioritise and implement the improvements that best align with your customer’s ideal experience.
In our world of change, competing on exceptional experiences is key to success. Make sure to use your journey map frequently and across departments to maintain your competitive advantage.
Tools to help you with your journey mapping
There are a variety of tools you can use to support the development of a strong customer journey map. Some of the tools that we recommend include:
Get everything done at once with Smaply.
A great tool to help you along the journey, Smaply helps you create customer personas, stakeholder maps, and customer journey maps. Includes various visualisation features and icons to help you add detail.
Create custom templates with Lucidchart
A great option for those looking to create a customised map. Lucidchart is a free online tool that allows you to develop a customer journey map using its suite of features.
Keep yourself on track with Asana.
After building your map, you will need a strong organisational system to keep you on track to implement journey improvements. Using a CRM journey map or work management platform like Asana helps you build out implementation projects, assign roles, and collaborate with your team to make customer journey changes quickly and efficiently.
15 free customer journey map templates
A customer journey map that looks great and is easily interpreted is more likely to be used by your team. Here are some great (free!) customer journey templates and customer journey canvas you can use to help develop your journey map:
- Practical Service Template
- Customer Journey Canvas
- Visual Paradigm Customer Journey Maps
- Invision App CJM Template
- Shopping & Purchases CJM Template
- Bundled Journey Map
- Graphic Customer Journey Maps
- Retail Customer Journey Template
- Miro Customer Journey Map
- Customize CJM
- Comprehensive CJM Template
- Simple Customer Journey Template
- Leisure & Entertainment CJM Template
- Restaurant Customer Journey Map
- Service Blueprint Template
Download your free customer journey map template using any of the links above.
Final Thoughts
To compete in our world of choice, you need to stand out from the crowd.
By delivering exceptional customer experiences you can stay competitive, build strong customer relationships, and drive profits.
Use the above steps, recommendations, and tools to build a strong customer journey map that will help you better understand your customers and grow your business.

Co-founder, TRACX
Tom is the co-founder of TRACX, a no-code marketing platform that allows local business owners to collect customer feedback and create engaging marketing campaigns. With over 17 years of experience in entrepreneurship, product development, and marketing for businesses large and small, Tom is currently responsible for developing product and marketing strategies for TRACX.
Give your business a boost with TRACX®
Sign up for free and get everything you need to turn visitors into customers, and customers into super-fans — all in one platform.
- TRACX is free forever
- Upgrade anytime, cancel anytime
- No coding necessary
- Get set up in seconds
- GDPR & CCPA-ready
- Hosted in EU datacentres
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The New Science of Customer Emotions
- Scott Magids,
- Alan Zorfas,
- Daniel Leemon

When a company connects with customers’ emotions, the payoff can be huge. Yet building such connections is often more guesswork than science. To remedy that problem, the authors have created a lexicon of nearly 300 “emotional motivators” and, using big data analytics, have linked them to specific profitable behaviors. They describe how firms can identify and leverage the particular motivators that will maximize their competitive advantage and growth. The process can be divided into three phases. First, companies should inventory their existing market research and customer insight data, looking for qualitative descriptions of what motivates their customers—desires for freedom, security, success, and so on. Further research can add to their understanding of those motivators. Second, companies should analyze their best customers to learn which of the motivators just identified are specific or more important to the high-value group. They should then find the two or three of these key motivators that have a strong association with their brand. This provides a guide to the emotions they need to connect with in order to grow their most valuable customer segment. Third, companies need to make the organization’s commitment to emotional connection a key lever for growth—not just in the marketing department but across every function in the firm.
A better way to drive growth and profitability
Idea in Brief
The Problem Companies know that emotions drive customer behavior, but most have little idea how to connect in ways that motivate the desired behaviors. The process is more guesswork than science.
The Solution The authors have created a lexicon of “emotional motivators” and, using big data analytics, have linked them to specific profitable behaviors.
The Opportunity By identifying the most powerful emotional motivators for a given customer segment, companies can design marketing and other strategies to leverage those motivators, giving them a new source of competitive advantage and growth.
When companies connect with customers’ emotions, the payoff can be huge. Consider these examples: After a major bank introduced a credit card for Millennials that was designed to inspire emotional connection, use among the segment increased by 70% and new account growth rose by 40%. Within a year of launching products and messaging to maximize emotional connection, a leading household cleaner turned market share losses into double-digit growth. And when a nationwide apparel retailer reoriented its merchandising and customer experience to its most emotionally connected customer segments, same-store sales growth accelerated more than threefold.
- SM Scott Magids is a cofounder and the CEO of Motista, a consumer intelligence firm.
- AZ Alan Zorfas is a co-founder and the chief intelligence officer of Motista, a consumer intelligence firm.
- DL Daniel Leemon is a director of CEB, a best-practice insight and technology company, and an advisor to Motista.
Partner Center

Trusted AI for Business
Enlighten Copilot
AI companion for contact center employees
Enlighten Autopilot
AI-driven customer self-service
Enlighten Actions
AI for CX leaders
All Enlighten AI Solutions
Complete CX Offerings
Digital and Self Service
Friction-free customer experiences driven by conversational AI
Workforce Engagement Management
Robust applications to optimize the employee experience (WEM)
Journey Orchestration and Routing
Seamless customer journeys across voice & digital channels
Agent Assist
AI-driven tools for real-time agent guidance and coaching
CX Analytics
Actionable insights to continuously enhance the customer experience
Open Cloud Platform
Innovative cloud-native foundation to rapidly scale extraordinary CX
All CX Offerings
By Industry
Healthy patient experiences
Delight customers where they shop
Financial Services
Customer experiences that count
Secure policyholder experiences
CX for Telecommunications
Travel and Hospitality
Strengthen traveler and guest loyalty
Business Process Outsourcers
Elevate citizen trust
By Business Initiative
Transform Experiences with AI
Identify behaviors that drive frictionless customer experiences.
Boost Customer Loyalty
Improve customer loyalty on every interaction across the journey
Drive Digital Transformation
Integrate digital technology at the center of the customer experience
Move to the Cloud
Elevate experiences and efficiencies by moving operations to the cloud
Increase Operational Efficiency
Leverage AI and automation to increase agent retention and reduce costs
Grow Revenues
Boost conversions and win rates to accelerate financial success
Improve Compliance
Protect your consumers with pre-built compliance solutions
Engage and Empower Employees
Create a workplace of truly engaged employees
Proactive Customer Engagement
Elevate customer satisfaction with proactive conversational AI
Call Center Software
Empower your agents to provide better experiences—on every channel.
Contact Center Services
Business Consulting
Partnership for successful transformations
Contact Center Training
Tailored education delivered by CX experts
Customer Support
Global support you can depend on
Professional Services
Relevant expertise, tools and know-how
Implementation Partners
NICE CXone certified implementation partners
Resource Library
Whitepapers, datasheets, demos and more
Self-Led Training
Professionally developed training courses
CX industry guidance by contact center experts
Analyst Perspective
Contact center reports from third party analysis
Upcoming events and webinars
Glossary of Terms
Detailed descriptions of industry-related terms
Frequently Asked Questions
Contact center focused FAQ
Customer Stories
Driving success in every customer story
Powering seamless experiences in the cloud
NICE Leadership
Meet our global leadership and executive team
View job openings and learn about our culture
Media Center
Media contacts and resources
Upcoming Events & Webinars
Market Leadership
Discover why NICE is the market leader
Press Releases
Find the latest updates from NICE
Investors relations, reports and filings
Corporate Responsibility
In a world where you can be anything, be NICE
Global Office Locations
Interactive map of office locations worldwide
- Get in Touch

6 Core Emotions in Customer Experience and Why They Matter

Sometimes “Customer Experience” feels like a book everyone talks about, but few people actually read. Luckily, the conversation is inspiring and a lot of fun. There's a rich and vibrant discourse on social media about customer experience and customer service, and so many thought leaders who are constantly pioneering the ways we think about the interactions between customers and companies. But at the end of the day, if the customer isn’t in on the conversation, we’re talking in abstraction.
Customer experience is emotion. Plain and simple. It is how a company makes a customer feel. That’s what experience really means, and that’s what really matters in any interaction with a customer. (Notice I didn’t write “customers.” I’m trying to avoid abstraction!)
Why do customer emotions matter? Because a customer is willing to spend more with; to talk positively about; and to stay loyal to companies that provide positive experiences. And of course, customer service is a big part of any customer’s experience with a brand. The customer really wants to feel good and he or she will reward you for delivering a good experience.
Oops, there I go again, talking in abstraction. “Good” isn’t exactly an emotion, and as an experience it's lackluster. That’s why merely satisfying the customer is no longer enough. Brands must inspire emotions that will evoke positive associations in the future.
There are six core emotions in customer experience: three positive and three negative. Consider each emotion a step, leading on the positive side to customer retention and on the negative side to the loss of the customer.

A customer feels Surprise immediately when he or she experiences customer service that is extraordinary or unexpected in a positive way. Even before he or she feels joy, there’s a feeling of surprise at an unexpected level of service.
Once surprise wears off, a customer is left with a feeling of Happiness. This is important not only in the moment, but in the future, because it is the beginning of the customer’s positive association with the brand.
Gratitude is the ultimate state of mind in customer experience. When a customer realizes he or she feels happy because of the actions of a brand, that happiness becomes a positive association with the whole brand experience, not just a single customer service exchange.

No one really wants to have a disgruntled customer, but the first negative emotion is an important opportunity. Anger means the customer is still emotionally connected to the brand. They haven’t given up yet and gone elsewhere. It is still possible to surprise and gratify them.
When a customer feels Frustration, it is typically after a period of anger. At this point he or she starts to slip away, contemplating a way out of this emotion and perhaps looking elsewhere, (to the competition) for relief. The customer is no longer sure you can help.
Disappointment is a dangerous emotion in customer experience because it is also the longest lasting emotion, meaning when a customer moves from feeling anger and frustration to disappointment it will be much harder to win them back. They have created a long-term negative association with the brand.
Disappointment leads to Apathy, and that's when the customer no longer feels anything toward the brand. In other words, they're gone.
We're talking about customer retention
A customer who has positive associations with a brand—who knows the brand will consistently surprise, delight, and resolve—is more likely to become a brand advocate, not only spending more over the long-term, but also bringing in new customers through word of mouth.
Happy customers stick around. On the other hand, once a customer makes a negative association with a brand, and once he or she is allowed to feel unresolved negative emotions because of problems that are not solved in a satisfactory way, he or she is moving down a path that leads to the competition.
A disappointed customer is not just unlikely to talk positively about a disappointing brand, he or she is very likely to tell others about the negative experience and to dissuade friends and colleagues from purchasing from the brand in the future.
If we agree that customer experience is important, and it’s clear we do, we need to start finding ways to surprise and delight customers, and we also need to pay attention to their language so we can cut through the noise and recognize how the customer is feeling at any given moment of a customer service exchange. Knowing the customer better is the key to understanding how he or she feels. If customer experience is a book, each customer is a chapter. You don’t have to know every page by heart, but you’ve got to know the most important parts of each customer’s story: Who they are, how they feel, which of your agents is most likely to connect, and how your brand can delight them. We’re here to help you do that.
To learn more about becoming a leader in customer service and the digital experience, we invite you to watch our webinar, " Digital-First Customer Service: The Future is Here Today ."
More from the blog
Earth month: top 5 ways renewable energy industry can power up customer experience, solving the staffing puzzle: workforce management wizardry for the digital age, how contact centers are using ai to meet their top business and cx priorities.
- Contact Center Glossary
- Customer experience management with AI
- NICE CX AI Platform
Interactions 2024 Event Details

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home QuestionPro QuestionPro Products
Emotional Journey Mapping: What it is + How to Create it?

A typical journey map is a visual representation of a person’s steps to achieve a goal, but an emotional journey mapping adds a new twist to this age-old technique.
Emotions are an excellent way to determine whether your customer is in a good, bad, or neutral mood while completing a purchase. This game-changer will teach you how to improve a journey map.
In this blog, we will learn what emotional journey mapping is and how to create one for your business. Let’s get started.
What is emotional journey mapping?
Emotional journey mapping is a way to understand and track how customers or users feel as they interact with a product, service, or brand.
The process involves finding the key touchpoints or interactions that the customer or user has with the product, service, or brand and figuring out the emotions that the customer or user may feel at each touchpoint.
The data is represented in a timeline or flowchart to discover customer experience regions that may create negative emotions and those that may be modified to increase positive feelings.
It can help businesses determine how to improve their customers’ experiences by understanding their emotional needs and want.
You may also check out this guide to learn how to build your own Customer Journey Map .
Importance of emotional journey mapping
Emotional journey mapping helps businesses to understand customers’ emotions and experiences throughout their interactions with the company. Some key importance is given below:
- Emotional journey mapping helps companies identify customer frustration and uncertainty. This data can then be used to improve the customer experience.
- Using emotional journey maps, companies can better understand the unique emotional needs of various customer segments. It can be used to customize experiences for different customer segments.
- Companies can develop stronger, more meaningful relationships by understanding customers’ emotions and experiences throughout their journey. Here, we will discuss some key importance of the emotional journey map below:
How to create emotional journey mapping?
Emotional journey maps show customer journeys. Here, the focus is on user satisfaction rather than product engagement. Understanding a user’s feelings helps create effective improvements. To create an emotional journey map, follow these steps:
- Create user persona
Create a user persona to begin creating the map. Consider your users and create a persona for each segment. Not all of your customers will have the same requirements (or ways of meeting those needs).
It is frequently preceded by user research. These personas can be developed using user interviews, focus group discussions, surveys, and prior user feedback.
- Create a scenario
We need a scenario that addresses users’ expectations and requirements to achieve their goal of creating emotional journey mapping. The scenario could be about interactions with people, events, or objects.
- Goals and tasks
The next step is to identify the goals and the tasks. A task is an action that the user needs to do in a certain amount of time or in a certain way. Each journey has a different set of goals and tasks. They provide structure for the rest of the customer journey map.
Example: A customer journey is a series of goals and tasks. Let’s say a family wants to go on vacation from place Y to place Z.
- Goal: The goal is to prepare for the trip from place Y to place Z.
Solution: supply a customer with a map of the place, hotels, restaurants, stopovers, etc.
- Task: The task is to rent transport to travel from place Y to place Z.
Solution : provide a quick and easy way to rent transport.
- Surveys or Interviews to gain understanding and real data
In this step, you need to ask questions to better understand your customers’ world, background, and experiences with your company. Surveys or interviews are the best options for knowing your customers’ thoughts.
You can ask customers about their feelings related to their experience to learn how and why they felt a specific way at each touchpoint, stage, and interaction during their journey with you.
Actively listen and analyze how they communicate and how they convey their experience.
- Interpreting data
You can organize all of your customer data, such as conversations, experiences, emotions, thoughts, and actions, based on how similar, important, and relevant they are.
Create a team to identify trends in the data.
Learn more about why understanding your Customer Journey transforms your CX program.
Sort conversations by where customers are in their journey and what they are thinking and experiencing. After that, customers’ emotions can be identified.
- Line up data-based evaluation points
In this step, draw a line graph to show how a customer’s feelings changed at each touchpoint and interaction. Do this for each different persona you create. The customer’s highs and lows are displayed using emoticons and an emotion graph throughout the entire journey, from start to finish.
- Analyze and improve the journey
Look at both the good and bad parts of the journey to learn more and understand it. Highlight points and possibilities to improve the emotional journey mapping.
- Implementation
After analyzing your emotional journey map, it’s time to implement it into your business. Make sure you implement your journey map properly to get the most advantage.
- Review and Monitor emotional journey mapping
It’s time to monitor your emotional journey map after the implementation step. You have to monitor how your customers respond to your journey map. Observe all the small or big things on your emotional journey map and take action according to them.
How can QuestionPro Cx enhance emotional journey mapping?
QuestionPro is survey software that allows users to create and distribute surveys to collect data about customer experiences and perceptions. QuestionPro CX can assist with emotional journey mapping by allowing you to create surveys that specifically target the various stages of a customer’s emotional journey.
Surveys are used to collect data on a customer’s feelings and perceptions at various stages of the journey, such as the awareness, consideration, and post-purchase stages. This data can then be used to map the customer’s emotional journey and identify areas for improvement.
QuestionPro CX also offers tools for analyzing and visualizing survey data, which can be used to gain insights and make decisions based on the customer’s emotional journey.
The goal of emotional journey mapping is to gain insight into how customers feel at various stages of their journey and identify areas for improvement to improve their overall experience.
It is a valuable method for understanding and improving the customer experience, and it can assist businesses in developing strong customer relationships.
Ow, it’s time to create your emotional journey mapping for your business. If you need any help regarding journey mapping, Contact QuestionPro!
QuestionPro is survey software that can be used to map emotional journeys. Users can use the platform to create and distribute surveys that target specific stages of the customer’s emotional journey.
QuestionPro can be a valuable tool for businesses looking to map their customers’ emotional journeys and improve their customer experience.
Try out QuestionPro today!
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro BI: From Research Data to Actionable Dashboards
Apr 22, 2024

21 Best Customer Advocacy Software for Customers in 2024
Apr 19, 2024

10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software for Every Data Scientist
Apr 18, 2024

11 Best Enterprise Feedback Management Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Customer Journey Map (CJM)

People expect some benefit when they use the products and services an organization provides. They want to get some job done, solve a problem, or experience a particular emotion.
It is only when they perceive this benefit as valuable they’ll give something in return – money, time, or attention.
To survive, organizations need to capture some value from their offerings. And value creation lies at the intersection of human interaction with the provider of a service.
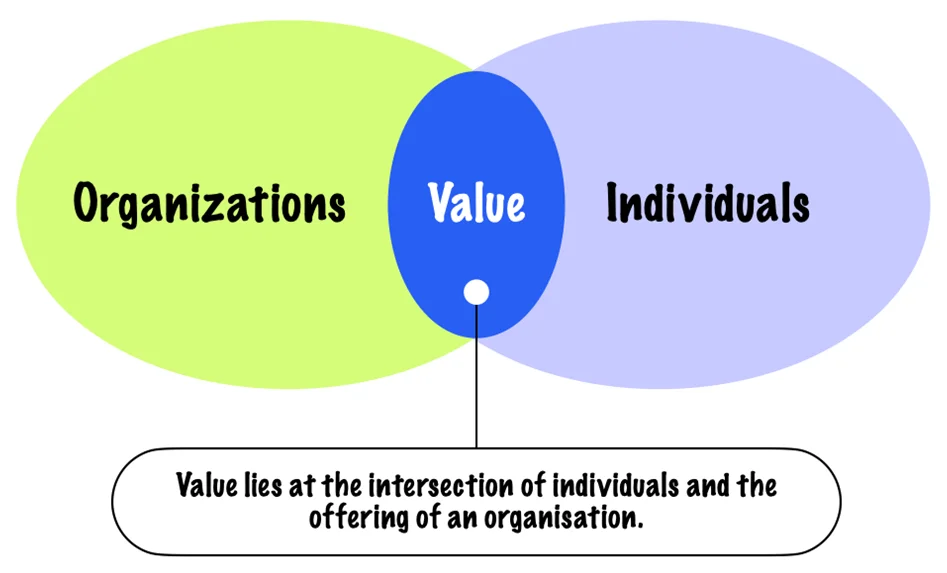
What is a Customer Journey Map
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) belongs to a class of diagrams called Alignment Diagrams [2] that help visualize the story of interaction between individuals and an organization.
They visually illustrate an individual customer’s needs, the series of interactions that are necessary to fulfill those needs, and the resulting emotional states a customer experiences throughout the process.
CJM shows the steps customers go through in engaging with a company, whether it be a product, an online experience, a retail experience, a service, or any combination.
CJMs are also called “cradle-to-grave maps” as they look at the entire arc of engagement. The more touchpoints a company has, the more complicated and necessary they become.
While the exact origin of the term customer journey map (CJM) is unclear, the basic idea of looking across touchpoints has its roots in Jan Carlzon’s concept of moments of truth. [3]
Importance of customer journey map
When most companies focus on customer experience, they think about individual touchpoints – the transactions through which customers interact with parts of the business.
While this is a logical approach and is relatively easy to build into operations, its siloed nature misses the bigger and more important picture – the customer’s end-to-end experience. [4]
A customer’s journey includes many things that happen before, during, and after the experience of a product or service. This journey can be long, stretching across multiple channels and touchpoints, and often lasts days or weeks.
Consider an example of a smartphone purchase, the CJM of which is as shown below.
Touchpoints that left negative emotions are depicted on the bottom of the vertical axis while positive ones are shown above. Each phase of the customer journey is indicated along the horizontal axis and moves from awareness to after-sale:
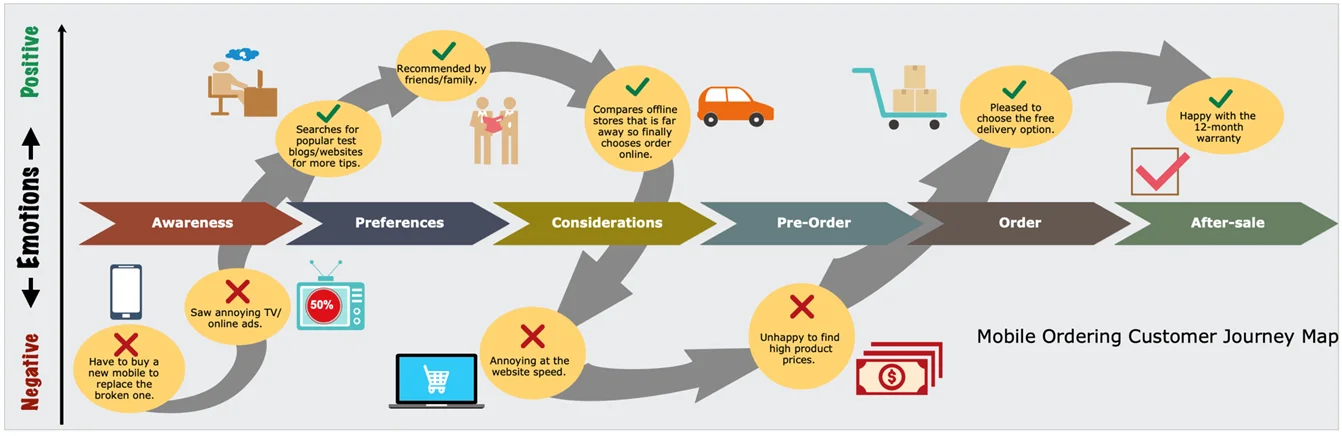
Notice how the customer’s journey involves interactions across multiple touchpoints such as adverts, physical stores, websites, emails, and (sometimes) sales/post-sales support.
A great sales process with a timely delivered smartphone could still lead to a bitter experience if the post-sales support (in case of a defect, for example) is not effective.
Likewise, a poorly designed advert may discourage a customer from considering the purchase in the first place.
Thus, only by looking at the customer’s experience through their own eyes along the entire journey taken can companies begin to understand how to meaningfully improve the overall performance.
Shown below is another, more complex CJM which details the process of installing a broadband and internet service:
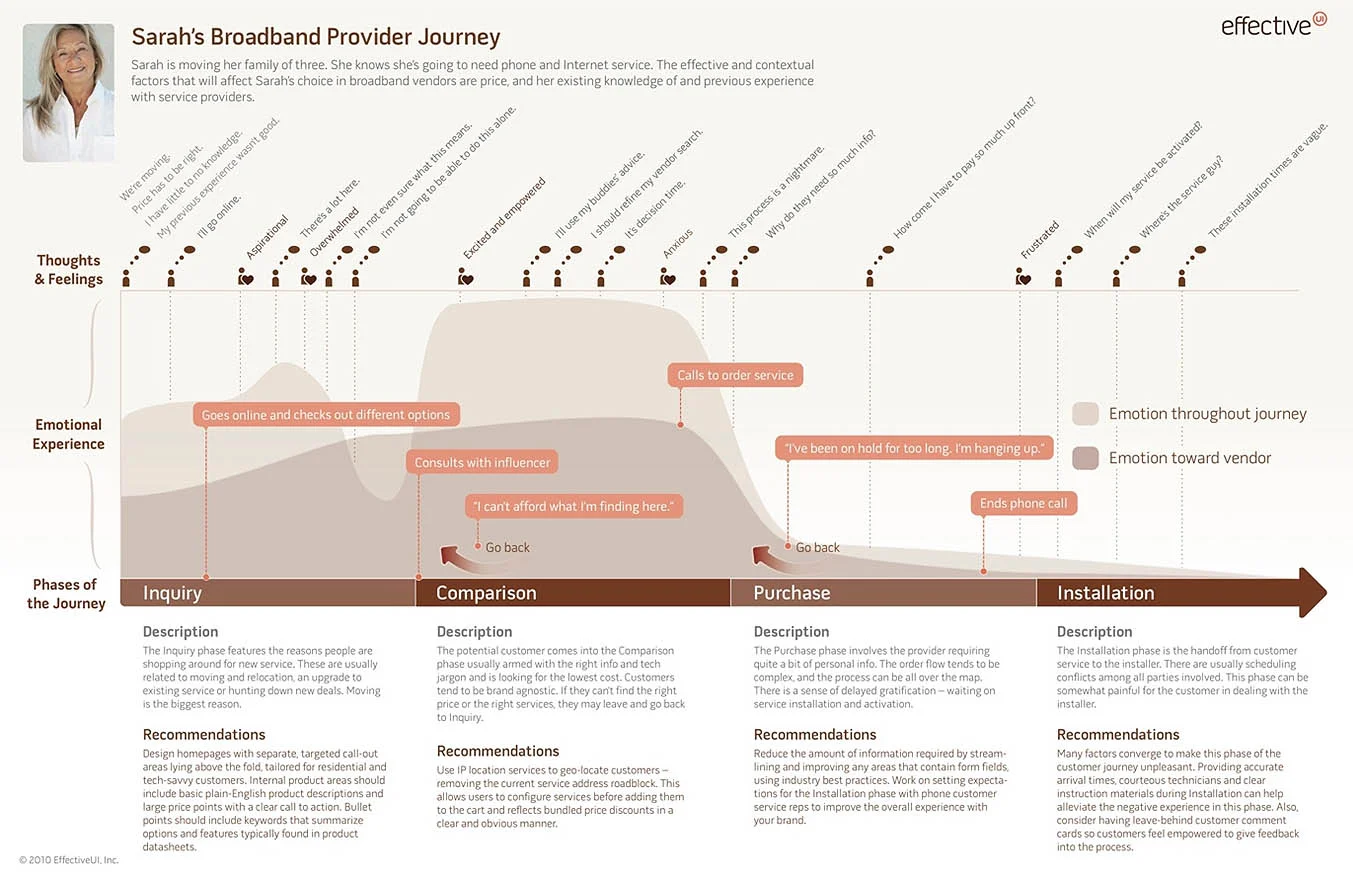
It focuses on the emotional aspects while highlighting the thoughts and feelings a customer typically goes through.
Since creating great experiences is not about individual touchpoint optimization but rather how touchpoints come together into a unified whole, CJMs play a crucial role as a strategic tool to visualize touchpoints and manage them more effectively.
What makes them much more powerful than simply delivering personas and scenarios is their ability to highlight the flow of the customer experience from the ups and downs along the way to those critical pain points where an organization’s attention and focus are most essential.
CJMs help better understand customer loyalty and improve customers’ experiences by answering questions such as:
- How can an organization better engage customers?
- How can it provide value so that customers keep coming back?
- How can it make services more relevant?
Components of a customer journey map
CJMs can range from very simple to complex illustrations that include personas, motivations, emotions, and key activities. To be effective, a CJM must be visually appealing, comprehensive, and understandable.
A CJM consists of the following key elements:
- Customer stages (or timeline) : identifies the stages in the customer journey. At a minimum, there are four stages: enquiry, comparison, purchase, and usage. Alternatively, this could also be a finite timeline (e.g., A week, month, year).
- Persona(s) : archetypal representations of existing subsets of the customer base who share similar goals, needs, expectations, behaviors, and motivation factors.
- Touchpoints : These are points of contact or interaction between a business and its customers. Information exchange at a touch point could be both unidirectional (e.g.: a banner advert) or bidirectional (physical store). To align the customer experience and identify pain points between channels and touchpoints, the map should also specify which channels are in focus.
- Emotions : CJMs must predict and specify customers’ emotions and feelings. This makes them useful for pinpointing potential pain points and successes.
- Channels : These are means by which interaction takes place. e.g. website, native app, call centre, in-store etc. This is where customers interact.
Optionally, they could also include:
- Barriers and pinpoints : These are areas where a customer is experiencing difficulties or issues with the product or service. This is more relevant when a CJM is developed for “as-is” conditions.
- Customer goals : a customer goal may not always remain constant throughout the journey. Identifying changing goals offers opportunities for improvements in the service.
- Positive experiences : Highlighting what is done well helps stakeholders understand which activities create a positive customer experience and add value.
Creating a customer journey map
While organizations use creative ways to develop customer journey maps, broadly the process includes the following steps:
1. Set objectives
Having a clear goal is a prerequisite to customer journey mapping. A company needs to first decide what it hopes to accomplish through the map, which customers to target (customer segmentation), and which types of experiences it expects the maps to highlight.
Objectives of the map are driven by the company’s strategic goal (e.g., increased revenue or improved customer retention).
For example, if the strategic goal is to improve customer experience, then the objective for the map could highlight key touchpoints, such as website interactions, customer support interactions, and post-purchase experiences, to identify areas for improvement and ultimately improve customer retention.
It is also important to decide on relevant metrics that can be tracked once the customer journey map is created and put to use. Without proper tracking, setting goals doesn’t mean much.
2. Collect customer data and insights
Firms should start the process by taking inventory of the customer knowledge they already have. Data must be gathered from every customer interaction. A marketing automation solution is a great way to collect this information.
For companies that do not have sufficient customer data, Voice of Customer (VoC) is an effective method to gain insights. [7]
Other methods could include mining databases and gathering reports, but the most significant insights will come from the stakeholders themselves. Valuable insights emerge when cross-functional groups are brought together to offer different perspectives on observations and ideas about customers and their experiences.
Data collected at this stage could be both qualitative and quantitative.
3. Distill customer segments into personas and define their goals
With internal and external research in hand, journey mapping leaders need to distill their findings about how customers interact with the company, their expectations from each interaction, and how they feel about each interaction.
Developing a customer persona helps capture the needs, goals, and value a customer brings to a company. Depending on the number of customer segments identified, more than one persona (and by extension, more than one customer map) might be developed.
This helps a company to successfully design experiences that support the specific needs of behaviorally distinct customers.
The benefits of a customer persona over typical customer models are as shown:
The more accurate a persona is, the more effective the CJM will be.
4. Identify touchpoints
Identifying touchpoints involves generating a list of customer touchpoints and the channels on which those touchpoints currently occur.
For example, the touchpoint could be “pay a bill”, and the channels associated with it could be “pay online”, “pay via mail” or “pay in person”.
Additionally, touchpoints could also be indirect, for example, reviews of a brand that customers read on third-party sites. As each touchpoint can drive customer conversion, it is critical to represent all possibilities.
5. Construct an empathy map
An empathy map is a collaborative visualization used to articulate what is known about a particular type of customer/user.
It externalizes knowledge about them to create a shared understanding of their needs, thereby aiding in decision-making.
Shown below is an example of an empathy map for a customer looking to purchase a television:
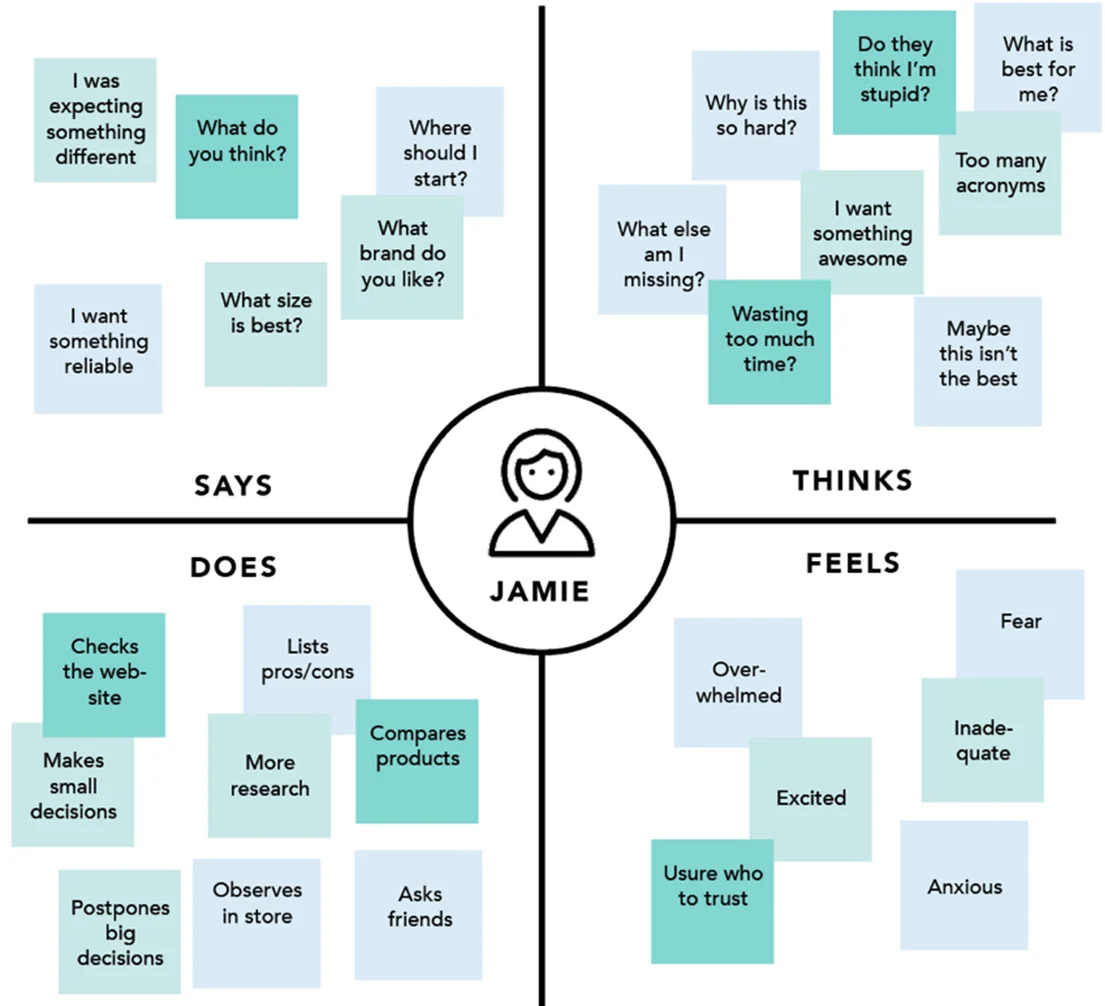
Empathy maps provide a foundation of material to fuel CJMs. They give a well-rounded sense of how it feels to be a particular persona in their experience, specifically focusing on what customers are thinking, feeling, seeing, hearing, saying, and doing.
6. Map the customer journey
This involves putting together all the pieces: timeline, touchpoints, channels, emotions, and even new ideas on how to improve the future customer journey.
The goal is to translate the analysis into a simple visual representation of customer processes, needs, and perceptions. With each interaction, the map should also define customer needs and identify how well the company currently meets those needs.
There are no standard rules or layouts to create a CJM. Even the timeline need not be a standard left-to-right. It could be circular or helical.
The below example shows the LEGO Group’s “experience wheel” which is a CJM built around the three basic stages of an executive’s visit to LEGO offices and the individual experiences that make up each stage.
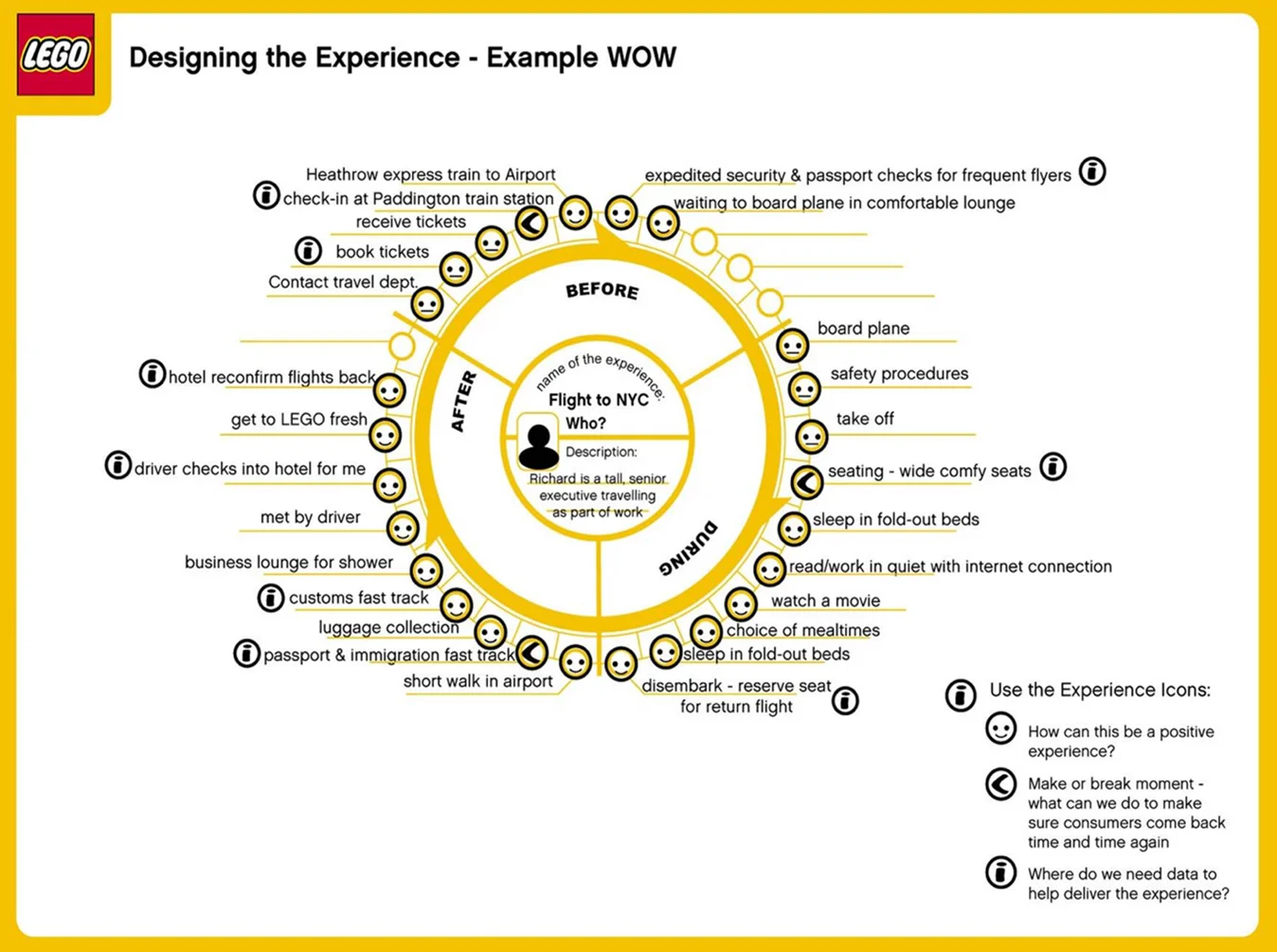
Notice how it starts with the description of a customer persona in the center (Richard, a senior executive in this case). It recognizes the timeline spread across three stages – before, during, and after the flight. It is easy to use and simple to understand.
Also at each interaction, the map defines customer needs and identifies how well the company currently meets those needs (in the form of smileys)
In terms of format, CJMs can be presented as either a comprehensive visual map in print/image form or an interactive digital form featuring clickable elements and embedded videos.
Steps to extract maximum value from CJMs
Developing CJMs won’t automatically realign an organization or improve customer experiences. Most lose momentum and are forgotten along with other research outputs.
To extract value, companies need to follow three practices: [8]
1. Share widely
To set the stage for broad customer experience improvements, the insights from CJMs must be shared with stakeholders across the company. This involves the following steps:
Involve internal stakeholders throughout the CJM process
Executives are more likely to buy into projects that they’re personally involved with. Hence, companies should actively engage decision-makers in the effort.
Those involved in the process early on are also more receptive to final conclusions (even if they are unpleasant) while those who stay out ultimately ignore recommendations.
Highlight key strengths
By design, CJMs are meant to identify problem areas where companies can make improvements. However, too many negatives can leave stakeholders choking.
Hence, to keep executives receptive, and not discourage efforts, a CJM should highlight both strengths as well as weaknesses.
Over time, as companies make improvements in their experiences, they can enjoy watching positive indicators overtake negative ones on their journey maps.
Use the organization’s native language
Companies aren’t accustomed to evaluating themselves from customers’ perspectives. To avoid resistance, it is necessary to tie CJMs to important elements of the existing corporate culture.
For example, explaining to stakeholders how new personas complement rather than replace existing segments.
Bring customer data to life
Engaging presentation techniques can bring CJMs to life.
This could include directly presenting the voice of the customer, showing videos of customers interacting with products or talking about their relationships with the company or audio recordings of customer service calls.
Some companies and consulting firms have used strategies like bringing persona cutouts into review meetings, building up physical rooms with customer research and even getting customers to participate in company meetings.
2. Act on insights
Since customer experience executives don’t manage all the organizational functions affected by the improvements identified in a CJM, this should be driven by leadership.
This calls for methodical identification and prioritization of opportunities while drawing on executive support and past successes. The following steps are important:
Exercise and expand executive support
Leadership should mandate that managers spend time interacting with customers and adopt
customer-focused metrics to measure performance. Without this level of support, customer experience leaders often face resistance from territorial channel and line-of-business leaders.
Another way of gaining executive buy-in is by competing pilot projects that demonstrate the process’s value.
Identify broken moments of truth
CJMs inevitably show companies the areas where they fail to meet their customers’ needs. But having a long list of poor experiences doesn’t tell what’s worth improving.
Companies need to focus on key moments of truth for customers – the interactions that they see as most important.
One way to prioritize is to plot interactions on a simple matrix, showing how important the quality of interactions is for customers:
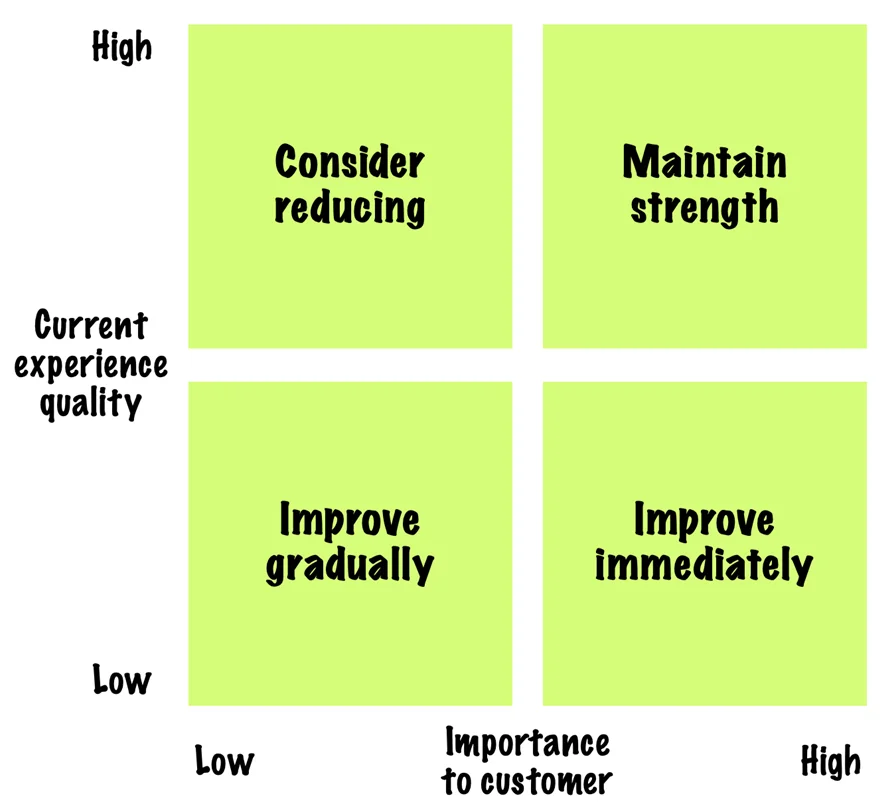
The importance of interaction can be decided through customer research or from simple surveys asking customers to rate experiences in terms of importance and quality.
Companies can also use the Kano Model [11] , which is an insightful way of understanding, categorizing, and prioritizing customer requirements.
The model shows the relationship between customer satisfaction and the attributes of products or services being (or to be) offered. It categorizes these attributes into five types:
- Threshold attributes (must-be qualities) : These attributes are taken for granted when fulfilled but result in dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. Customers expect these attributes and view them as basic; it is unlikely that they are going to tell the company about them when asked about quality attributes. For example, brakes in a car are a basic requirement which goes without saying.
- Performance attributes (one-dimensional qualities) : These attributes result in satisfaction when fulfilled and dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. These are attributes that are spoken about and the ones in which companies compete. A good suspension in a car that leads to a comfortable ride is such an attribute.
- Excitement attributes (attractive qualities) : These attributes provide satisfaction when achieved but do not cause dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. They are not normally expected and thus often unspoken. Offering a broader choice of colors for a car can potentially delight certain customers, but its absence may not necessarily dissuade them from making a purchase.
- Indifferent attributes : These aspects are neither good nor bad and have no effect, positive or negative, on customer satisfaction. For instance, a car equipped with heated seats in a region with a predominantly hot climate.
- Reverse qualities : If these aspects exist, they lead to dissatisfaction; if they do not exist, they do not lead to satisfaction.
- For example, in the case of customers primarily seeking a car for commuting on well-maintained roads, the presence of a four-wheel drive feature can lead to reduced fuel efficiency and discourage them from making a purchase.
With time, attributes that customers see as excitement (threshold attributes) move down and convert to performance or basic attributes.
For example, a decade ago, a smartphone battery that could last 12 hours was seen as a great feature, but as battery tech improved across generations, that attribute has shifted from delighter to less than a basic need.
This also highlights the fact that what may not be a broken moment of truth today could possibly be one in the future.
Prioritize opportunities based on value to the company
Even after filtering out low-value opportunities based on customer preference, most companies still face long lists of initiatives.
This can be narrowed down further by balancing their value to customers with elements of business value such as increased revenue, reduced service costs, and differentiation from competitors.
Potential improvements can then be plotted on a simple matrix to highlight improvements with high potential impact.
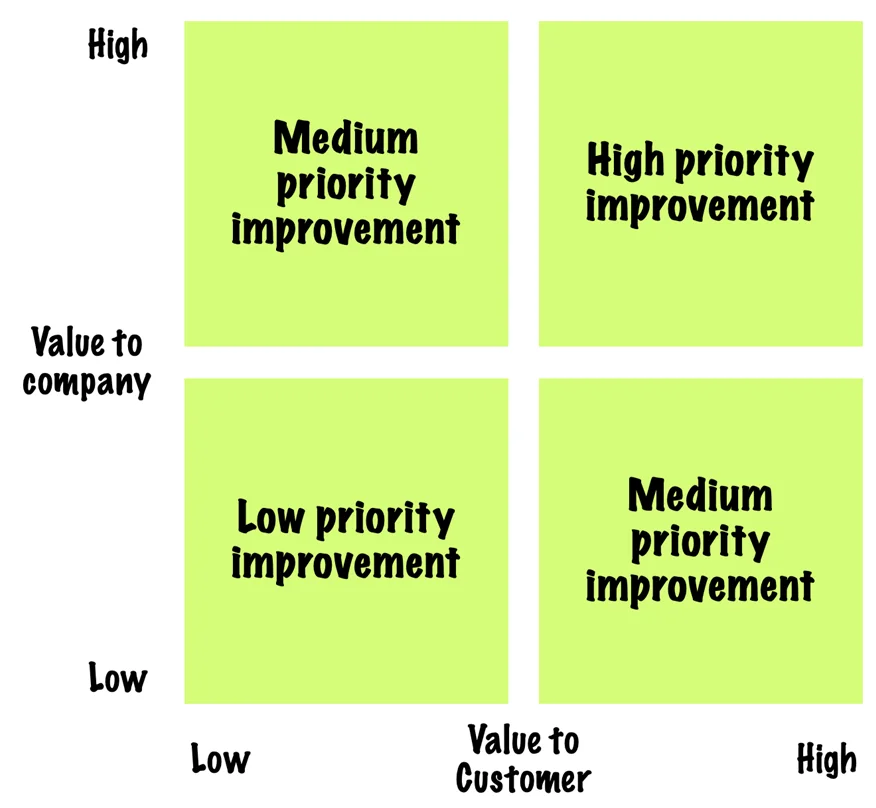
3. Sustain learnings over time
Companies derive maximum value when they treat the journey mapping process as an ongoing strategic initiative rather than a finite project. The following practices provide discipline to keep journey maps alive over time:
Assign long-term ownership
CJMs need to be linked to the overall strategic planning process of a company with well-defined ownership. Only then, will they remain live and relevant.
Monitor customer feedback and organizational progress over time
CJMs need to be refreshed periodically to remain valid. One way to implement this is by using the maps as the foundation of customer experience data.
Instead of updating findings periodically, fresh customer feedback and performance metrics can be directly fed into the journey maps.
As pointed out by the Kano Model, customer expectations change over time and an updated CJM helps companies sense these shifts early on and take action.
1. “Mapping Experiences: A Complete Guide to Creating Value through Journeys, Blueprints, and Diagrams”. James Kalbach, https://www.amazon.com/dp/1491923539 . Accessed 27 Sep 2023
2. “Alignment Diagrams”. Jim Kalbach, https://boxesandarrows.com/alignment-diagrams/ . Accessed 27 Sep 2023
3. “Moments of Truth”. Jan Carlzon, https://www.amazon.com/Moments-Truth-Jan-Carlzon/dp/0060915803 . Accessed 25 Sep 2023
4. “From touchpoints to journeys: Seeing the world as customers do”. McKinsey & Company, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/from-touchpoints-to-journeys-seeing-the-world-as-customers-do . Accessed 27 Sep 2023
5. “Mobile Ordering Customer Journey Map Template”. Edrawsoft, https://www.edrawsoft.com/template-mobile-ordering-customer-journey-map.html . Accessed 27 Sep 2023
6. “The Value of Customer Journey Maps: A UX Designer’s Personal Journey”. UX matters (Joel Flom), https://www.uxmatters.com/mt/archives/2011/09/the-value-of-customer-journey-maps-a-ux-designers-personal-journey.php . Accessed 27 Sep 2023
7. “Voice of the customer”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_of_the_customer . Accessed 26 Sep 2023
8. “Mapping The Customer Journey”. Forrester (Bruce Temkin), https://www.forrester.com/blogs/10-02-10-mapping_the_customer_journey/ . Accessed 26 Sep 2023
9. “Empathy Mapping: The First Step in Design Thinking”. Nielsen Norman Group, https://www.nngroup.com/articles/empathy-mapping/ . Accessed 26 Sep 2023
10. “LEGO’s Building Block For Good Experiences”. Bruce Temkin, https://experiencematters.wordpress.com/2009/03/03/legos-building-block-for-good-experiences/ . Accessed 26 Sep 2023
11. “What is the Kano Model?”. KanoModel, https://kanomodel.com/ . Accessed 27 Sep 2023
- Strategy Map: All You Need to Know
- Perceptual Map Explained
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

Customer Journey Mapping: How to Understand Your Buyers and Enhance Their Experience
- 14 min read
- 14 Dec, 2023
- No comments Share
The recent State of the Connected Customer Report by Salesforce revealed that for 80 percent of people, the experience a brand provides is as important as its product . With customer expectations at an all-time high, businesses must deliver the best service possible to satisfy consumers and stay competitive. For that, it’s crucial to understand what customers want and anticipate their actions.
A customer journey map is vital in this context. It helps businesses understand and manage interactions with their clientele at every touchpoint, from the first encounter to the final transaction. So this post is all about the tool that guides you in creating exceptional customer experiences and how you can get the most out of it.
What is customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping is creating a visual story of customers' interactions with the brand or product. It's like drawing a route people usually take from the moment they first become aware of your product or service all the way through to purchasing and even after-sales support.
A customer journey map includes all the touchpoints the customer can have with your brand, such as seeing a social media ad, visiting a store, calling customer support, and so on. Also, it should reflect the customers’ pain points , emotions, and reactions at every stage of the journey so that you understand them better and see how to improve their experience.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
Before we delve into the details of customer journey mapping, let’s say a few words about why do it at all. Here are some of its benefits.
Understand your customers better . Customer journey mapping helps you see your business through your customers' eyes. You get to understand what they like, what bothers them, and what makes them happy.
Find problems . Sometimes, there are bumps in the road that can make your customers unhappy, like a confusing website or long wait times. Journey mapping helps you spot these problems so you can address them.
Adjust your strategy . As you get to understand your customers better, you might realize that you have to tailor your offerings, pricing range, marketing campaigns, support team workflows, etc.
Improve customer experience and foster loyalty . When you know what your customers go through, you can make their journey smoother and more enjoyable. This means increased conversion and retention rates. Happy buyers are likelier to keep returning and recommend your brand to others. Research states that 88 percent of customers repeat the purchase if they like the customer service.
In essence, customer journey mapping is a tool that helps businesses empathize with their customers and improve their interaction journey, leading to better customer-brand relationships and business success.
Customer journey stages
As we start exploring a customer journey map, let’s first look at what a common customer journey looks like. Here are its main phases.

Awareness . This is the initial stage where potential customers realize they have a need or a problem that requires solving and become aware of a product or service.
Potential touchpoints at this stage: social media, industry events, online/offline ads, search results, etc.
Consideration . At this stage, customers look for solutions. They are considering different products or services and are researching to find the best option.
Potential touchpoints at this stage: your website, blog, knowledge base , reviews, testimonials, case studies, etc.
Decision . This is the point where the customer decides on a solution that best fits their needs.
Potential touchpoints at this stage: email newsletter, pricing information, your website, physical store, sales reps, etc.
Purchase . The customer buys the product or service and starts using it.
Potential touchpoints at this stage: customer support (phone, messages, chatbots), help desk/FAQ sections, etc.
Retention . A fter the purchase, the focus shifts to keeping the customer happy and engaged with the product or service. This stage is about building loyalty and encouraging repeat purchases.
Potential touchpoints at this stage: email, newsletters, sales reps, etc.
Please note that this is the typical scenario but not the only one. The stages can vary across industries and product types, so you might want to include other phases in your customer journey map. Or else, you might need to map out only one part of the journey, for example, pre-purchase, to better understand how your marketing campaigns work.
What’s included in a customer journey map?
When creating a customer journey map, you’ll evaluate your buyer’s interactions with your brand and look for opportunities to enhance their experience. So here are the main elements of a customer journey map.
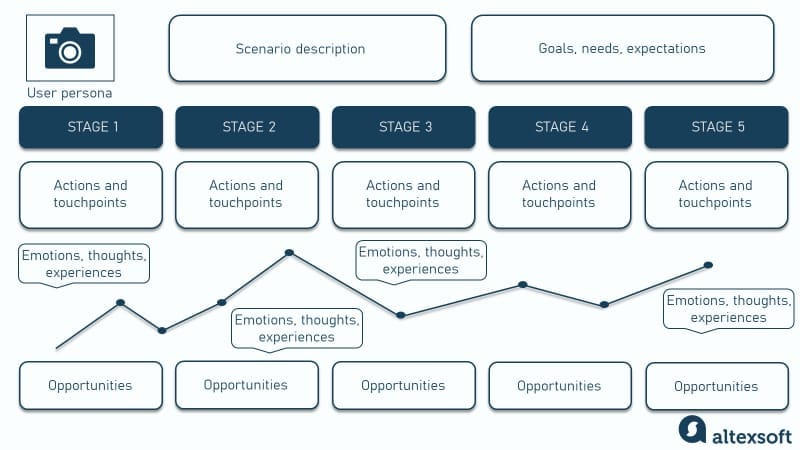
Elements of a customer journey map
Buyer/user/customer persona – a prototype of your target audience.
Scenario – a short description of the interaction story.
Customer’s goals/needs/expectations – why people turn to your brand.
Stages – the phases your customer goes through in the interaction scenario.
Actions and touchpoints – what customers do and where the interaction happens.
Emotions and experiences – what customers feel and think as they interact with your brand.
Emotional curve – the visual line of how the customer sentiment changes depending on their experience.
Opportunities – how you can improve the customer experience at each touchpoint or stage.
You can also include other elements like KPIs to track, designated people responsible for implementing improvements, and so on. T he complexity and elements of a customer journey map can vary based on the nature of your business, the type of customers, and your goals.
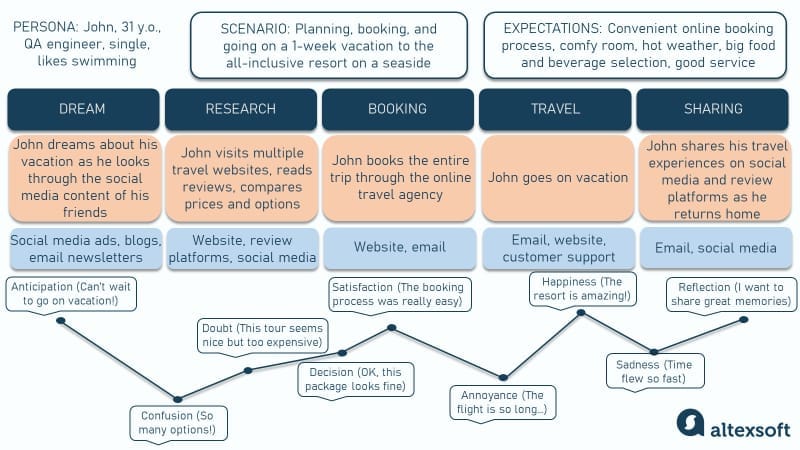
A simple example of a traveler journey map that an OTA or a hotel could create
The components of the customer journey map also depend on its type. There are many different modifications you can create for various business goals, so let’s talk about some of them.
Customer journey map types
Each customer journey map has its own focus and purpose. The choice of which one to use depends on your specific objectives, the complexity of your customer experience, and the information you want to capture. Here are some of the main types.
Current state journey maps provide a detailed view of the existing customer experience (just like in the illustration above). It’s the most basic map that documents touchpoints, interactions, and emotions “as is.”
Future state journey maps envision the ideal customer journey after implementing improvements or changes. They serve as a roadmap for designing and delivering a better customer experience and help teams set goals and prioritize initiatives to reach the desired state.
Day-in-the-life journey maps focus on a specific persona or customer segment's daily activities and how they interact with a product or service throughout their day. These maps help businesses understand a customer's routines and identify opportunities to provide value.
Channel-specific journey maps concentrate on a particular customer interaction channel, such as a website, mobile app, social media, or in-store experience. They help businesses optimize touchpoints within a specific channel.
Service blueprints go beyond the customer perspective and provide a comprehensive view of the entire service ecosystem. They include the customer journey, frontstage interactions (visible to the customer), and backstage processes (invisible to the customer). Service blueprints help improve alignment and coordination within an organization.
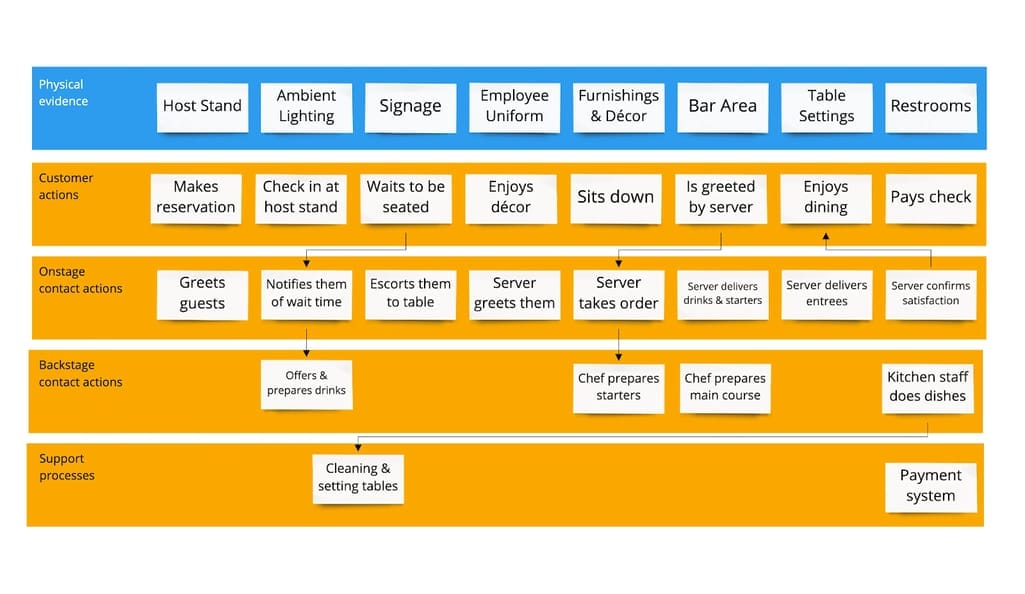
An example of a service blueprint for visiting a restaurant. Source: Miro
Some other types are emotional journey maps, lifecycle journey maps, cross-channel journey maps, etc. You can focus on a specific category or use a combination of these maps to better understand your customer journey and drive improvements in the customer experience.
How do you create and use a customer journey map ?
There’s no single best format for a customer journey map. It can be a linear timeline, flowchart, or any other visual representation that best suits your needs. You can draw it on paper, put sticky notes on a whiteboard , or design it in specialized software (we’ll talk about digital tools further on).
Since customer journey mapping is part of market research, usually, it’s the marketing or sales department that’s responsible for creating it. However, it’s worth engaging different teams in this process.
Define objectives
First of all, you have to decide on your goals – or why you want to analyze your customer journey. For example, it can be something as specific as checking how a particular marketing project works, i.e., how effective ad retargeting is. Or it can be a strategic business objective like attracting more customers, increasing sales volume per customer, or improving retentio n.
Pro tip: Make a customer journey map for a specific interaction scenario for a certain customer segment. This way, it won’t be too generic, so you’ll be able to explore your buyers’ sentiments more deeply at each stage of their way and get more concrete results to work with.
Create a buyer persona
As we said, you must create a fictional representative of your target audience. To understand their needs and pain points, design a persona with a specific traits -- professional background, motivations, lifestyle, goals, and so on.
Pro tip : Add as many details as possible to make the most accurate representation of your customer. Later on, it will help you better understand their perspective.
Identify touchpoints and map the customer journey
As we said, you have to define the ways customers interact with your brand at each stage. Make a list of all the potential touchpoints and then map them out on the customer journey stages.
Use various data sources such as website analytics, customer feedback, social media interactions, and sales data to gather information about where and how customers interact with your brand. Also, engage teams from various departments (sales, customer support, marketing) and encourage their input.
Pro tip : Look at your competitors to see where they engage with customers. This can provide insights into touchpoints you haven’t considered.
Understand the customer's perspective
As you record your customers' actions at each stage, remember to make the map from the customer's point of view. It must show what they think and feel at each touchpoint, what they're trying to achieve, and any challenges they might face.

Watch our expert explain customer research in product discovery
Get feedback directly from your customers through surveys, interviews , or email questionnaires to understand their experience at different touchpoints. Ask about their motivations and any difficulties they encountered.
Pro tip : Tools like website heat maps, open rates for emails, and engagement rates on social media can help you understand your customers’ behavior better.
Highlight emotions and experiences
A customer journey map goes beyond the actions customers take. It dives into their emotional experience, whether they're happy, frustrated, or confused at different stages.
It’s important to record both positive and negative emotions. The former exhibits opportunities to enhance the experience or exceed customer expectations, while the latter highlights pain points or bottlenecks where customers face challenges or frustrations.
Pro tip : Ask your customer support which questions they get most often. Also, pay attention to what customers say about your brand on social media, online review platforms, or other resources.
Identify opportunities for improvement
By mapping this journey, you can see where you're providing a great experience and where you fall short. This helps you find ways to enhance your strong sides and improve the weak ones. For example, some reasons for poor customer experience include long waiting times to get to customer service, unintuitive website interface, missing app functionality, high prices, and so on.
Pro tip : Conduct brainstorming sessions with different teams and encourage active cross-department collaboration. Also, try to go through the journey that you’ve depicted yourself to get first-hand experience.
Create a better customer experience
Ultimately, the goal is to use this map to make strategic decisions that enhance the customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty. Develop strategies and initiatives to address the pain points, optimize touchpoints, and leverage opportunities identified in the customer journey map.
Pro tip : Focus on your business goals when you analyze the impact of customer experience and prioritize your activities.
B2B customer journey map
If your company doesn’t work with individual customers but deals with other businesses, you can still take advantage of a customer journey map. A B2B customer journey map is a useful tool for managing client relationships. Just like the B2C analog, it visualizes the process they go through and experiences they have when interacting with your company. However, there are certain differences that impact the components of the customer journey map.
The complexity of the decision-making process . In the B2B context, there’s a more complex decision-making process, often with multiple stakeholders. The journey may include stages like RFP (Request for Proposal) submission, detailed product evaluations, approvals from different departments, and a longer negotiation phase. In B2C, the decision-making process is usually simpler and quicker, often involving only the individual consumer or their immediate family.
Length of sales cycle . B2B sales cycles are typically longer, sometimes lasting months or even years, as they involve higher-value transactions and more deliberation. B2C sales cycles are shorter, often concluding within a few days or even instantly.
Touchpoints . B2B touchpoints include industry events, professional networks, detailed product demos, and extensive follow-up communications. B2C touchpoints often focus more on mass marketing channels like social media, online ads, reviews, and retail environments.
Customer goals and expectations . Business customers often have specific, pragmatic goals like improving efficiency, increasing ROI, or integrating with existing systems. Meanwhile, individual consumer goals may be more diverse, including personal enjoyment, convenience, price, and brand alignment.
Relationship and engagement . B2B focuses more on building long-term relationships and ongoing engagement. In the B2C model, while repeat business is also important, engagement is often more transactional and less personalized unless it’s a high-value product or a niche market.
Just like in a B2C context, delivering a positive experience to your business clients is important. Customer journey mapping helps you understand how you can enhance your relationships.
Customer journey mapping softwa re
As we said, you can certainly map your customer journey on a sheet of paper, but we recommend you use a specialized digital tool instead. The software helps automate this process, allows for convenient collaboration, and enables easy editing, sharing, and so on. Besides, most platforms offer several editable templates for different purposes.
There are multiple tools available to help you with customer journey mapping. A simple online search will give you a list of relevant platforms. Some are designed specifically to manage customer experience, while others are more general-purpose and can be used for different scenarios.
When choosing a tool, we recommend you consider the following factors:
- available templates,
- integration options,
- interface intuitiveness,
- customization options,
- collaboration features, and
- customer support and training.
We’ll take a look at some of them to give you an idea of what’s out there. Please note that we don’t promote any of the tools; the choice was based on their popularity.
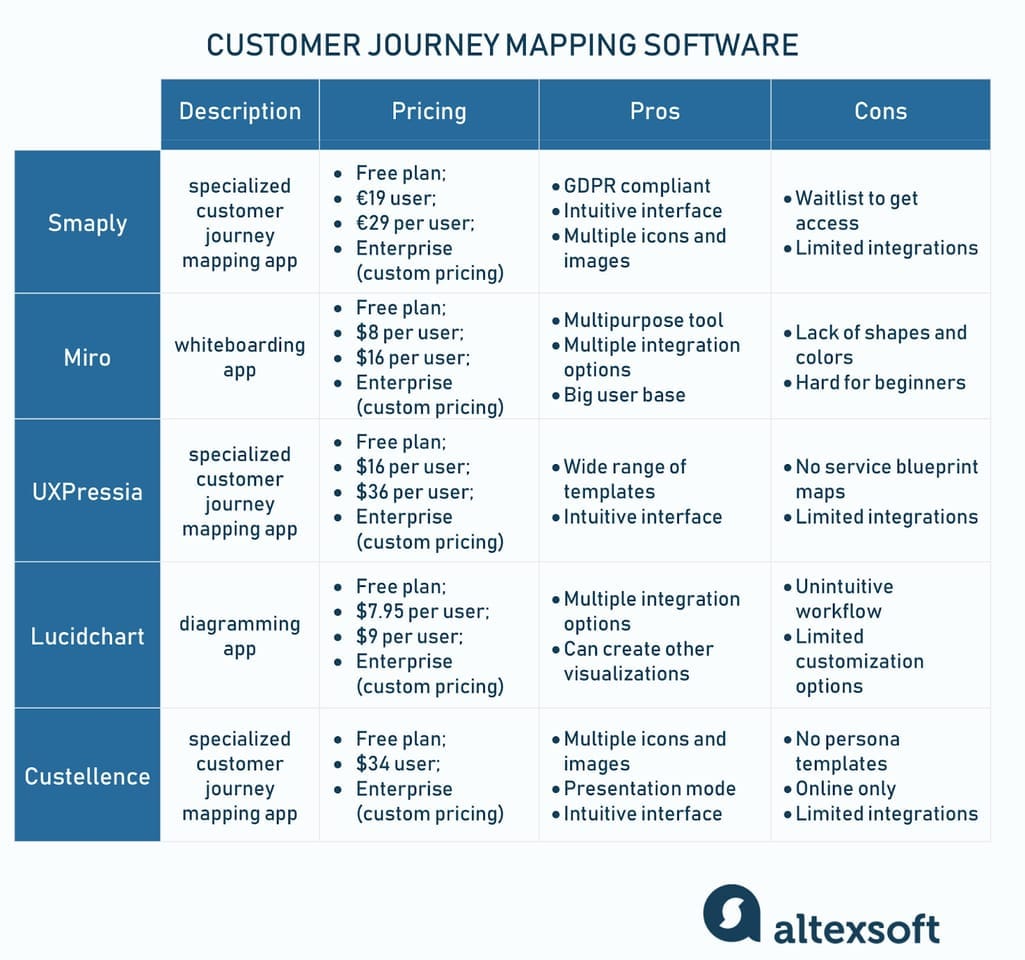
Customer journey mapping tools compared
Smaply is a specialized, user-friendly tool for journey mapping. It allows businesses to create detailed customer personas, journey maps, and other related visuals. It’s particularly good for visualizing complex customer interactions over multiple channels.
Miro is a multipurpose online collaborative whiteboarding platform. It offers numerous templates and tools for creating detailed customer journey maps, making it easier to visualize the customer experience.
UXPressia is specifically designed for creating customer journey maps with 100+ templates and customization options. It offers a persona creation feature, impact mapping, and the ability to integrate real data into your maps. You can also connect it to Jira, Google Analytics, and other external apps to add information to your maps.
Lucidchart is a diagramming app that helps create flowcharts, organizational charts, customer journey maps, etc. Besides creating visuals, it offers integration options with popular business tools like Google Workspace, Atlassian, and Slack.
Custellence is another focused customer journey mapping app. It has numerous templates for different industries and an intuitive, drag-and-drop user interface.
Customer journey map templates
As we’ve already mentioned, most software tools provide interactive templates for different scenarios. But if you don’t want to work on any focused platform, here are some downloadable templates for you:
- the most basic PDF template from Nielsen Norman Group,
- a collection of PowerPoint templates from HubSpot,
- an editable Google Docs template from WordStream, and
- a set of colored templates available in Google Slides or PowerPoint from Slidesgo.
We realize it might be confusing at the beginning when you don’t have a clear idea of how to approach customer journey mapping. For inspiration, check out some examples of how it might look.
Customer journey map examples
Companies create customer journey maps for a wide range of scenarios and with different purposes. While the objective isn’t always about getting more profit, it’s always about enhancing customer experience.
M ultiple use cases. UXPressia has a big section with customer journey map examples for many industries, including banking, travel, entertainment, and so on. Within each industry subsection, they cover multiple scenarios, plus they provide different user persona examples.
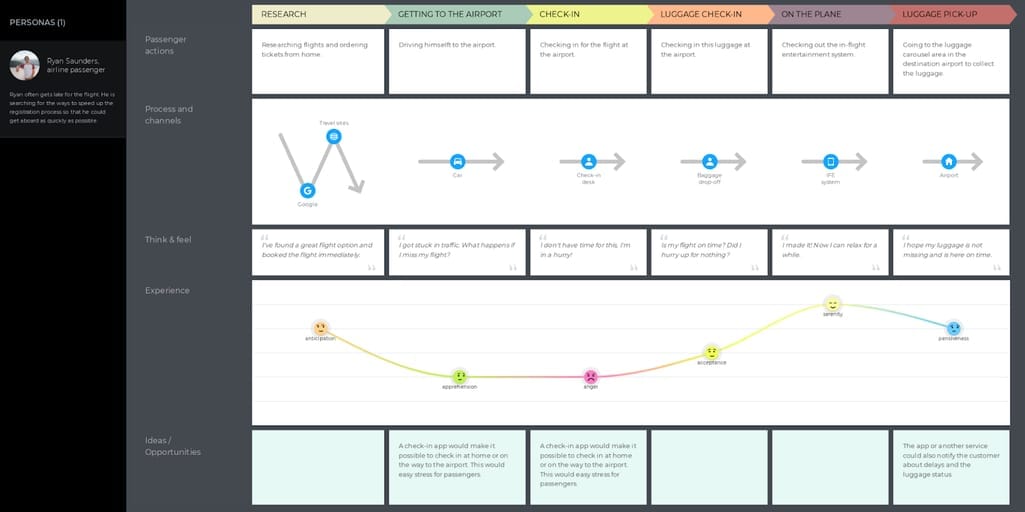
A customer journey map for an airplane passenger. Source: UXPressia
Attending city tours . Mural, a visual planning and collaboration tool, has created a customer journey map for travelers on guided city tours. The steps include browsing, booking, attending, and rating the tours.
Sharing music on Spotify . Meghana Bowen, a UX/UI designer, presented a customer journey map of using the Spotify app and sharing music with others. The author has also defined a user persona and depicted the following process of creating the sharing feature design.
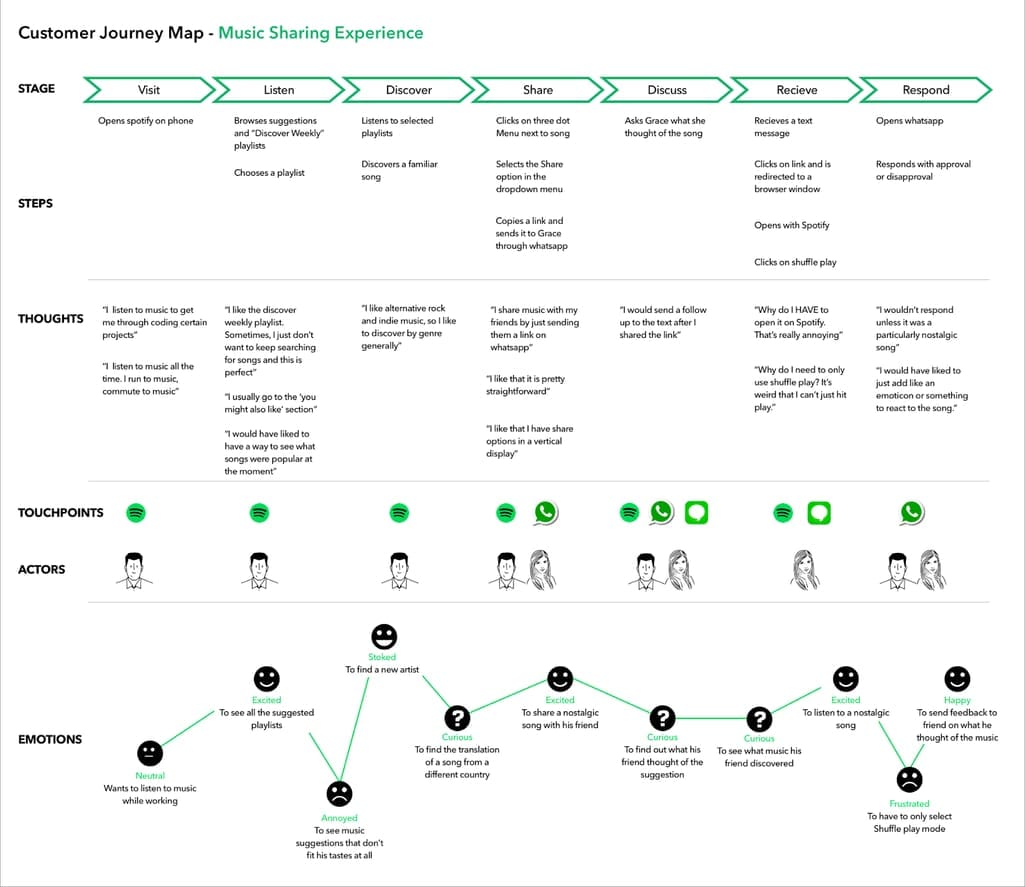
Spotify customer journey map. Source: Meghana Bowen
New students coming to the university campus . Iris Wu and Mei Xue created a service to facilitate traveling to Carnegie Mellon for incoming students. As part of their research, they’ve designed current and future customer journey maps to better understand the difficulties that international students encounter.
Best practices
We’ve already included some pieces of practical advice in the previous sections, but we still have a few more final tips.
Collaborate . We’ve mentioned it above but still want to emphasize the importance of cross-department collaboration when creating and working with the customer journey map. And, of course, involve your customers as well. Only in this case you’ll be able to have the most detailed information about your customer experience and improve it throughout all touchpoints.
Designate . As you implement changes, it’s crucial to assign responsibilities so that everyone knows their roles and tasks in these projects.
Track . It’s also important to develop KPIs so that you can track progress. The metrics you choose will depend on your objectives, but some examples are customer satisfaction score, net promoter score , conversion rate, or churn rate.
Update . Remember that the customer journey is dynamic and can change over time. Regularly revisit and update your customer journey map to reflect any changes in customer behavior or market conditions.
Published July 07, 2022
The art and science of measuring customer emotions: an essential guide for csms.
Do you know the best ways to measure customer emotions as a CSM? If not, check out this blog, wherein we have provided a comprehensive take on achieving this endeavor.

Whether we want them to be or not, emotions are substantial driving factors in any decision we make. And the same is true for your customers. They also make many emotional-based decisions. Whether they want to renew or leave for your competitors. So, one way CSMs can improve upon the customer’s experience is to focus on their emotions. In many cases, customer emotions are not measured, and this leads to an inability to manage it. So, in this guide, we’ll cover why measuring customer emotions are important and how to do it.
But First, The Basics, What are Customer Emotions?
Just so we’re on the same page about what we’re measuring, customer emotions are what customer feels about their experience with a product or company. Measuring customer sentiment is essential to keep customer happiness at the center and align overall goals. Emotions are a significant part of the customer journey and help drive the journey forward. Customer emotion data is how customers react to a product feature update or improvement.
Benefits of Measuring Customer Emotions
Here are the most significant benefits of measuring customer emotions.
Connecting With Your Customers
When you know how your customers feel about your company, you can forge a better bond with them based on their needs and what drives them. And when you understand their emotions, you’re able to help them get what they need more efficiently. So, by emotionally connecting with your customers, you can improved the overall customer experience .
Opportunity to Provide Value
When you measure customer emotions, you can accurately find ways to provide value to your customers. And this can allow you to help them achieve the value they signed up for, potentially increasing brand loyalty .

Like what you are reading? Sign up for our newsletter
Can improve targeting.
Customer emotion measurement can help understand target streaks and feelings behind customer behavior. You get an idea of what customer segments experience with the product and in what capacity. This way, you can build better bridges and improve segmentation and targeting.
Improved Product Scope
If you understand customer emotions, you can improve and give the product team a better understanding of feature updates or requests. You can enhance growth and measure product performance.
Top Ways to Measure Customer Emotions
Here are the top ways to measure customer emotions.
Ascertain Key Elements Like Who, How, and Where
Before you can measure your customer emotions, you have to segment them. Perhaps you want to measure the emotions of a specific customer segment . This targeting will help measure customer emotion so that you can personalize customer behavior.
You cannot assess the emotions of every customer. So, you’ll need to communicate with specific customers based on their engagement with the product. You must also choose the medium of interaction, for example, like sending a survey.
Use Net Promoter Score
You can also use the Net Promoter Score to determine how customers feel about the product. And it’ll help measure specific emotions in the customer journey. They’ll only need to answer one question—Will you recommend the product to your friends or family?
Calculate the Net Emotional Value
Another way to measure emotions is based on the Net Emotional Value metric. Net emotional value is when the company asks the customer to mention how their interaction is in one word. The NEV represents how the customer feels about the brand. You can eliminate neutral responses like fine, okay, decent, etc.
Net emotional value can help track the reasons for negative emotions.
Net Emotional Value = Total Positive Words – Total Negative Words
Perform a Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis measures the customer’s voice, messages, conversation context, word usage, etc. Sentiment analysis allows you to interpret all conversations objectively. Aspects you need to check include:
- How fast the customer speaks
- How frustrated the customer is
- How the customer responds to questions
- How the customer’s speech changes when offered solutions
How are Emotions Different From Sentiment?
Even though customer emotions and customer sentiment are similar feelings, there are some differences:
- Emotions are easy to change as compared to sentiment. A sentiment is a group of emotions on a specific topic.
- The sentiment builds over time while emotions are quick and intense.
- Emotions can vary, but the sentiment is either bad or good.
Bottom Line
Customer emotions are unique and can be managed if measured. Measuring customer emotion data and gauging sentiment is important to understand the customer experience better. And it’s important for CSMs to handle customer emotions and measure them in the right manner. And by using the methods mentioned above, you can measure customer emotion and take steps to improve customer experience .
You might also like:
- Emotional Intelligence Skills Every Customer Success Manager Should Have – Emotional Intelligence is a must-have skill for a Customer Success Manager. Read on the blog to know how to boost it and leverage profitability in no time.
- To see how SmartKarrot helps B2B companies streamline and scale customer success, Request a Demo .

Stanley Deepak is an accomplished sales and marketing professional with 15+ years of experience. He loves tech products and book reading. He writes on philosophy and culture on LinkedIn.
Published July 07, 2022, Updated March 02, 2023
- Customer Emotions ,
- Customer Sentiment ,
- Customer Success ,
- Customer Success Manager ,
- Measuring Customer Emotions
Featured Posts
- Intelligence, Automation, and the Future of Key Account Management Survey
- Advanced Systems for Customer Success – White Paper
- Income from Outcomes
If you're customer-obsessed, let's talk.
All blog posts.
Customer success is a journey of continuous learning. Embrace failure,...

26 Mar, 2024
Unlock collaborative success in Customer Success with the JOINT SUCCES...
11 Mar, 2024
Embark on a transformative journey with the SmartKarrot-Quint partners...

09 Feb, 2024
Get a live demo!
See how smartkarrot can transform your customer success outcomes..

Get Customer Success resources and insights straight to your inbox.
Sign up for SmartKarrot’s newsletter.
Take SmartKarrot for a spin
See how SmartKarrot can help you deliver winning customer outcomes at scale.


- THE STRATEGY JOURNEY Book
- Videos & Tutorials
- Strategy Journey Analyzer [QUIZ + WORKBOOK]
- COMMUNITY FORUMS
- Transforming Operating Models with Service Design (TOMS) Program
- ABOUT STRATABILITY ACADEMY
9 Steps to your Winning Customer Journey Strategy
By Julie Choo
Published: October 3, 2023
Last Update: January 9, 2024
TOPICS: Service Design
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, one thing remains constant: the customer is king. And to keep the king content, a well-defined customer journey strategy is paramount. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of customer journey strategy, exploring its intricacies, the importance of customer journey mapping, and how it all contributes to enhancing the customer experience. Buckle up; we’re about to embark on a journey of our own.
Customer Journey: What is it?
Step 1: define your objectives, step 2: identify customer personas, step 3: collect customer data, step 4: create a visual representation, step 5: define touchpoints, step 6: walk in your customers’ shoes, step 7: capture emotions and pain points, step 8: analyze and iterate, step 9: implement changes – bringing it all together, elevating customer experience: the north star of your strategy.
At its core, a customer journey represents the route a customer takes from their first interaction with your brand to the final purchase and beyond. Understanding this journey is the first step in crafting an effective customer journey strategy. It’s akin to setting up signposts along a road – guiding your customers on a seamless voyage.
A well-mapped customer journey not only benefits your customers but also your business. It enables you to anticipate customer needs, identify pain points, and optimize touchpoints to foster loyalty.
9 Steps of the Customer Journey Map
Customer journey mapping is the cartography of your customer’s experience. It’s where you take a deep dive into each step of their journey, from awareness to post-purchase engagement. Mapping allows you to see the journey from the customer’s perspective, highlighting pain points, moments of delight, and opportunities for improvement.
When crafting your map, consider customer personas, touchpoints, and channels. Visualizing the customer’s path helps in aligning your marketing, sales, and support teams to provide a cohesive and delightful experience.
Before setting sail, you need to chart your course. Start by defining your objectives. What specific aspects of the customer journey are you looking to understand or improve? Here’s a few common example of ideas to look at when considering your company’s objective
- Churn Reduction : One of the most common objectives is reducing churn or customer attrition. Your goal might be to pinpoint the exact stages in the customer journey where customers tend to drop off and identify strategies to retain them.
- Conversion Rate Optimization : If your primary aim is to increase conversions, your objectives could revolve around understanding the barriers that prevent prospects from moving smoothly through the sales funnel. What’s stopping them from becoming paying customers?
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty : For businesses seeking to boost customer loyalty, objectives may focus on identifying the touchpoints and interactions that contribute most to customer satisfaction. What can you do to turn satisfied customers into loyal advocates?
- Improved Customer Support : If customer support is a priority, you might aim to uncover pain points in the support journey. Are customers waiting too long for assistance? Are their issues resolved effectively? Your objectives could involve streamlining the support process for better customer experiences.
- Personalization and Engagement : In a world where personalization is key, objectives might be centered on tailoring the customer journey to individual preferences. What data points can you gather to offer more personalized recommendations and interactions?
- Cost Reduction : For cost-conscious businesses, objectives could revolve around optimizing the customer journey to reduce operational costs. Are there redundant touchpoints or inefficient processes that can be streamlined?
Practical implementation of this step involves convening a cross-functional team to brainstorm, discuss, and define your objectives. Each department, from marketing to customer support, should have input to ensure a comprehensive perspective.
Objectives should be documented, and their importance should be communicated throughout the organization. This clarity ensures that everyone is working toward a common goal, enhancing collaboration and alignment.
Every explorer needs a crew, and in this journey, your crew comprises customer personas. There are questions you should consider and ask. Create detailed profiles of your typical customers, considering;

- Demographics and Psychographics : Start by defining the basic demographics of your personas, such as age, gender, location, and income. Dive deeper into psychographics, understanding their values, interests, and lifestyle choices. For example, are your potential customers tech-savvy millennials seeking convenience, or are they older, price-conscious consumers looking for reliability?
- Goals and Pain Points: Delve into the goals and pain points of each persona. What are they trying to achieve when interacting with your brand? What obstacles or frustrations might they encounter along the way? Knowing these aspects allows you to provide solutions at critical touchpoints.
- Behavioral Patterns: Explore the behavioral patterns of your personas. How do they typically engage with your brand? Are they frequent visitors to your website, or do they prefer in-person interactions? Understanding these patterns helps in optimizing customer touchpoints.
- Communication Preferences: Identify how your personas prefer to communicate. Do they engage via email, social media, or phone calls? Tailor your communication channels to align with their preferences for more effective interactions.
- Decision-Making Process: Determine the decision-making process of your personas. Are they impulsive buyers, or do they conduct thorough research before making a purchase? This insight helps you align your marketing strategies and content with their decision journey.
In the realm of customer journey mapping, gathering customer data is akin to excavating precious gems of knowledge, crucial for achieving a deeper understanding of your audience and ensuring customer retention. It serves as the compass guiding your business through the intricate maze of customer preferences, behaviors, and expectations while minimizing customer churn. Effective data collection is not just a task but a strategic endeavor that requires precision and purpose, allowing you to engage with your target audience more effectively.
To embark on this data collection voyage, you must first identify the sources of valuable information within your reach. These sources span a spectrum, from website analytics and social media metrics to customer surveys designed to survey customers for insights. Categorize the data into distinct types, including demographic, behavioral, psychographic, and transactional data. For instance, understanding the preferences of tech-savvy millennials or the cautious spending habits of older customers can offer insights into customer churn and retention. Ensuring the quality and accuracy of this data is paramount, as it’s the cornerstone upon which insightful decisions are made. Implement data validation processes to minimize errors and uphold data integrity. Moreover, always respect customer privacy and adhere to data protection regulations, seeking clear consent for data collection to foster trust.
In practice, customer surveys can directly capture feedback and insights, uncovering a few examples of pain points or preferences that influence customer retention. Tools like Google Analytics help track website visitor behavior, providing essential data for tailoring your strategies. CRM systems centralize customer information, offering a unified view of interactions and preferences that can inform customer retention efforts. Social media listening uncovers sentiment and trends, guiding your engagement with the target audience. Additionally, data mining techniques reveal customer preferences that, when acted upon, boost customer retention. Regular data audits and cross-referencing data from various sources ensure data accuracy, while stringent data security measures and compliance with regulations protect sensitive information. By mastering the art of data collection, you not only unlock the secrets of the customer journey but also pave the way for crafting meaningful and personalized experiences that resonate with your target audience, thereby enhancing customer retention and reducing churn. With data as your guiding star, you’re equipped to navigate the seas of customer insights with confidence and purpose.
Now, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, pixels to screen) and create a visual representation of the customer journey. Use software or even a whiteboard to sketch out the different stages and touchpoints your customers go through. Each stage represents a milestone in their journey.
In the intricate tapestry of crafting an effective marketing strategy that caters to customer expectations and cultivates loyal customers. A touchpoint is any interaction between a customer and your brand, a moment when your customer journeys through your offerings, and their experience is shaped. Understanding and strategically defining these touchpoints empowers you to orchestrate a seamless, delightful journey that resonates with your audience.

To begin this journey of touchpoint definition, it’s essential to comprehensively map the customer’s journey. This involves identifying every instance where a customer comes into contact with your brand, whether it’s through a website visit, a social media interaction, a customer service call, or even an in-store experience. By recognizing these touchpoints, you can tailor your marketing strategy to meet customer expectations at each juncture.
The goal is to ensure that every interaction leaves a positive impression, fostering loyalty and trust among your customers. Whether it’s a user-friendly website interface or a personalized email campaign, every touchpoint is an opportunity to engage, delight, and convert customers into loyal advocates of your brand.
Creating a customer journey that truly engages and resonates with your audience is about stepping into your customers’ shoes, cultivating empathy, and fostering customer success. It’s not just about understanding their needs but also their emotions, challenges, and aspirations throughout their buying process.
To effectively walk in your customers’ shoes, start by revisiting your customer personas and immersing yourself in their characteristics, preferences, and pain points. Conduct interviews and surveys to gain deeper insights into their experiences and expectations. Organize workshops where cross-functional teams can collectively analyze the customer journey and identify areas for improvement. Employ mystery shopping and competitor benchmarking to uncover hidden gaps. Analyze customer feedback to spot recurring themes and issues.
Empathy should not be a one-time exercise but an integral part of your decision-making process. When empathy becomes ingrained in your organization’s culture, every team member considers its impact on customer success. By walking in your customers’ shoes, you gain a profound understanding of their journey, which becomes the foundation for designing meaningful interactions, fostering customer satisfaction, and driving brand advocacy. So, lace up those metaphorical shoes and embark on a journey to create a customer journey that ensures customer success throughout the buying process.
In the intricate world of customer journey mapping, Understanding your customer’s emotions and pain points plays a pivotal role in cultivating a deeper connection with your audience. This step revolves around the art of capturing emotions and pain points that shape customer interactions. Emotions are the driving force behind customer decisions and actions, while pain points represent the obstacles they encounter. Recognizing and understanding these aspects empowers businesses to create solutions that resonate with customers’ feelings and alleviate their concerns.
To capture emotions and pain points effectively, businesses can employ various strategies. Emotion-centric surveys can be designed to prompt customers to express their feelings and experiences at different touchpoints, be it during a purchase or while engaging with the customer service team. Empathy mapping workshops encourage collaborative creation of empathy maps, visually representing customer personas’ emotions and pain points throughout their journey. Customer interviews should go beyond the standard questions, urging customers to share emotional experiences and elaborate on their pain points.
Feedback analysis can be enriched by incorporating emotional tags to categorize responses and identify sentiments. Social media listening offers a real-time glimpse into customer emotions as they discuss brands online, providing opportunities for businesses to engage and gain a deeper understanding of their audience’s perspectives. Ultimately, applying these insights can transform ordinary interactions into memorable experiences, fostering customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy in the process.
In this step, we dive deeper into understanding and enhancing our customer journey maps. It’s like finding hidden treasures in a treasure hunt. First, we dig into all the information we’ve gathered about our customers, like feedback and surveys. Then, we use cool tools to turn this data into easy-to-understand pictures. These pictures show us how customers behave on their journey with our business.
But we don’t stop at just looking at pictures. We take action ! We listen to what customers say and what the numbers tell us. If something’s not right, like customers not staying with us for long, we figure out why and make changes. We also keep an eye on what other businesses are doing to see if we can do things better. It’s like always trying to make our customer journey maps more effective and exciting.
This isn’t a one-time job; it’s an ongoing adventure. As customers’ needs change, our journey maps should change with them. We work together across our teams to make sure our business strategy lines up with these maps. This way, we’re not just meeting but exceeding our customers’ expectations. And that’s how we keep them happy and coming back for more, making our business stand out from the crowd.
Once you’ve charted the course, it’s time to steer the ship. Implement changes and improvements based on your findings. Ensure that all departments and teams are aligned with the new strategy and understand their roles in enhancing the customer journey.
Through these nine steps, from defining objectives to implementing changes, we’ve embarked on a transformative journey ourselves. We’ve learned to see our business from the customer’s perspective, understand their emotions, and continuously adapt to meet their needs. By mastering these steps, we ensure that our customer journey maps are not just diagrams on a wall but effective tools that drive our business strategy. In doing so, we don’t just satisfy customers; we create loyal advocates who keep our business thriving. So, as we implement changes, we do it with a sense of purpose and a commitment to delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Customer experience (CX) is the heart and soul of your customer journey strategy. It’s not just about a single transaction; it’s about fostering long-term relationships. A positive CX ensures customers return, become brand advocates, and fuel business growth.
To enhance CX, focus on personalization, responsiveness, and consistency across all touchpoints. Leverage data and feedback to refine your strategy continuously. Remember, it’s the little things that make a big difference.
The Power of Customer Journey Mapping
Now that we’ve delved into the importance of customer journey mapping, let’s explore how it can transform your customer journey strategy.
Identifying Pain Points: Mapping helps pinpoint pain points in the customer journey, allowing you to address and eliminate them. This leads to a smoother and more enjoyable experience.
Optimizing Touchpoints: With a detailed map, you can optimize touchpoints, ensuring that each interaction aligns with your brand’s values and objectives.
Predicting Customer Behavior : A well-constructed customer journey map allows you to predict customer behavior, enabling you to proactively meet their needs.
Enhancing Personalization: Personalization is key to exceptional customer experiences. Mapping facilitates tailored interactions at each stage of the journey.
Measuring Success: By mapping the customer journey, you can establish clear metrics and KPIs to measure the success of your strategy.
In the realm of modern business, crafting a winning customer journey strategy is not just an option; it’s a necessity. A well-mapped customer journey, combined with a relentless focus on customer experience, can set your brand apart and drive sustainable growth.
About the author
Julie Choo is lead author of THE STRATEGY JOURNEY book and the founder of STRATABILITY ACADEMY. She speaks regularly at numerous tech, careers and entrepreneur events globally. Julie continues to consult at large Fortune 500 companies, Global Banks and tech start-ups. As a lover of all things strategic, she is a keen Formula One fan who named her dog, Kimi (after Raikkonnen), and follows football - favourite club changes based on where she calls home.
You might also like
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Strategy Journey Fundamentals , Transformation
The Impact of Co Creation in Modern Business
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Transformation
4 steps to create a Winning Game Plan
Service Design
Business Level Strategies: What are they, How to use it?
- EngageNow Suite Engage More Customers
- Convert More Customers
- Retain More Customers
- Our Product Suite Simplr EngageNow Suite
- Products Simplr Chatbot
- Simplr Human Cloud Network
- Simplr Platform
- Industries E-commerce
- Restaurants & Food Service
- SaaS & Technology
- Use Cases Pre-Sale Conversions
- Customer Retention
- CX Cost Cutting
- Case Studies
- The Economic Case for Simplr
- Simplr Blog
- Connect Events
Our fully managed service is designed for your brand and business. We provide the expertise needed to set up and maintain a high-quality, automation-first approach to CX.
Our Cognitive Paths™ reasoning engine ensures that our GenAI chatbot is trustworthy and emulates your best agents' behavior.
On-demand access to high-quality, AI-enabled customer service agents. “Gig 2.0" at its best.
Our Voice-to-Digital service enables brands to seamlessly shift incoming phone inquiries to digital channels.
Improve CSAT, and deliver industry-leading response times all while eliminating forecasting, coaching, and training.
Turn your CX from a cost center to a revenue-generating part of your business.
Simplr’s GenAI chatbot mirrors the best human agents engaging in complex interactions with multiple steps needed to resolve customer issues.
See what companies are saying about Simplr.
- Awards Our Mission Simplr is Asurion’s innovation center focused on applying generative AI to its entire suite of offerings. Launched in 2017, Simplr is a powerful extension of Asurion’s mission to leverage groundbreaking technologies to create consistently first-rate customer experiences that open up major new revenue streams for clients.
Customer Service Glossary
Table of contents, what is the customer emotional journey.
The customer emotional journey is an extension of the customer experience map, which details each touchpoint that a customer has with a brand. While similar to a customer experience map, the customer emotional journey focuses on consumer behaviour and the emotional status of the shopper at each stage of the purchasing experience.
Companies map the customer emotional journey using a curved line, emojis, cartoons, or pictograms to represent the specific, qualitative emotional steps of the shopping process. Then, brands can analyze the stages and identify areas of frustration, delight, or neutrality to improve the overall customer experience.
How the Customer Emotional Journey Impacts Customer Service
The customer emotional journey map uses data from marketing research, customer relationship management software, and other sources to visualize each shopper’s steps while they accomplish a goal, such as purchasing a product or obtaining a service.
Companies commonly use customer experience maps to describe what a customer does during the purchasing process. However, customer emotional journey maps analyze how the user feels as they complete each task. Understanding and applying customer emotional journey mapping can impact customer service departments in several ways, including:
1. Improved Customer Experience
Research conducted by Deloitte noted that a customer’s emotions directly impact the depth of their brand loyalty. In fact, more than 40% of customers interviewed in the study said that they would recommend a brand or product based solely on emotion.
With this in mind, your customer service agents can work to connect with their customers on a human level. By tracking user data and creating detailed customer profiles, agents can provide personalized care and empathize with the shopper at each stage of the journey.
2. Streamlined Customer Service Operations
Understanding each user’s emotional status during a customer service interaction enables agents to provide adequate care and assistance. For example, if a user reaches out at the peak anxiety stage, agents can address their concerns, soothe their worries, and guide them to the next stage.
3. Higher Customer Satisfaction Ratings
Finally, taking an emotionally-driven approach to customer service forges strong connections between users and agents. Users feel seen, heard, and valued. At the same time, customer emotional journey mapping empowers agents to learn more about each customer while implementing user feedback into the overall experience.
Elements of the Customer Emotional Journey
Customer emotional journey mapping consists of six interconnected elements, as follows.
1. The Users
Companies design user personas based on shared features and attributes, such as geographic location, occupation, or marital status.
2. The Circumstances
After developing user personas, brands consider certain circumstances and the needs or expectations that accompany them to create short biographies. Consider the following:
“John is a manager who oversees a team of 15 employees. He needs to find a lightweight project management platform to help organize projects, coordinate with staff members, and streamline the operations process in order to reach his goal of reducing inefficiencies within his department.”
3. The Goals
Next, your team should consider the tasks and goals involved in the customer journey. A goal represents the highest-level action that a user must complete, such as traveling to France. A task is a lower-level action which the user must complete during a certain time or under certain constraints, such as booking a flight.
4. The Likability
Likability indicates how likely shoppers are to continue and complete the customer journey. Support agents can increase the likelihood of task completion by engaging with customers at key points during the journey and building trust.
5. The Effort
Ease indicates how easily a shopper feels that they can complete a task. If tasks feel too tricky, you can work to remove roadblocks, reduce stress, or find another solution to streamline the process.
6. The Opportunity
Finally, you have a significant opportunity to learn more about your users through customer emotional journey mapping. The insights therein enable your team to improve interactions, boost satisfaction ratings, and increase customer loyalty.
Understanding the Customer Emotional Journey in Customer Support Departments
Customer emotional journey mapping impacts more than web content creation, site development and design, and advertising. Instead, customer support teams can leverage the stages of the customer emotional journey to provide personalized, real-time assistance and convert potential leads into loyal customers.
Related Resources and Information
- Online Customer Experience Done Right – 3 Awesome Examples
- Conversational AI for Customer Service – Pros and Cons in 2021
- 5 Live Chat Best Practices… For Converting Customers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Customer emotions on a journey map are expressed visually using an emotion graph. An emotion graph visualises customer sentiment, i.e. how customers feel at each interaction. Emotion icons or emoticons are a picture or image representation of facial expressions indicating a particular emotion—such as a 'smiley face' emoticon to indicate ...
A customer journey map generally includes a summary of your customer persona, purchase phases, touchpoints with your company, customer thoughts/actions/emotions and opportunities to improve the ...
Customer emotion is a measure of how customers feel about their experience with a company. The dynamics behind customer emotions are surprisingly complex. The increasing importance of customer emotion in customer experience can be summed up by appropriating an old quote: "Customers may not remember what the quality of your product was, but ...
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams. Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is convenient for cross-functional teams to provide feedback. Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team so they always keep the customer in mind.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of customers' processes, needs, and perceptions throughout their interactions and relationship with an organization. It helps ... Capturing emotion at the exact instant when it's felt is critical to understanding
Here's our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days: Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work. Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop. Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results.
By mapping the emotional journey of your customers, you can identify opportunities to create positive emotional experiences, leading to increased customer loyalty, retention, and advocacy. Additionally, by focusing on emotional engagement, you can differentiate your brand from the competition and create a more meaningful and memorable customer ...
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain ...
Retail customer journey map example. Source: IKEA. Customer journey mapping for big corporations can be tough. Ikea did a great job of developing a CJM that outlines the thoughts, behaviours, and emotions of a customer throughout their journey at the store.
Artwork: Hong Hao, My Things No. 5, 2002, scanned objects, digital c-print 120 x 210 cm. Summary. When a company connects with customers' emotions, the payoff can be huge. Yet building such ...
There are six core emotions in customer experience: three positive and three negative. Consider each emotion a step, leading on the positive side to customer retention and on the negative side to the loss of the customer. Positive emotions: Surprise, Happiness, and Gratitude. A customer feels Surprise immediately when he or she experiences ...
A typical journey map is a visual representation of a person's steps to achieve a goal, but an emotional journey mapping adds a new twist to this age-old technique.. Emotions are an excellent way to determine whether your customer is in a good, bad, or neutral mood while completing a purchase. This game-changer will teach you how to improve a journey map.
Among those listed in the 1970s by anthropologist Paul Eckman are anger, fear, surprise, disgust, joy and sadness. Others expanded the list to include aversion, courage, dejection, desire, despair ...
Choose the type of customer. Create a scenario. Define your main goals (1 to 4) and tasks (1-10) Prepare your Interviews and find your audience. Determine the user's emotions during each action. Prepare questions that will reveal the emotions of your user after completing a task. Lead the Moderated Interviews.
It's simple, professional and to-the-point, and covers all the basic elements that need to go into a journey map. 2. Gaming Customer Journey Map Template. This gaming customer journey map template is created with recreational mobile apps in mind, but you can use it for any tech, SaaS or other industry.
6. Map the customer journey. This involves putting together all the pieces: timeline, touchpoints, channels, emotions, and even new ideas on how to improve the future customer journey. The goal is to translate the analysis into a simple visual representation of customer processes, needs, and perceptions.
A customer journey map includes all the touchpoints the customer can have with your brand, such as seeing a social media ad, visiting a store, calling customer support, and so on. Also, it should reflect the customers' pain points , emotions, and reactions at every stage of the journey so that you understand them better and see how to improve ...
Emotional journey mapping is a valuable technique to understand and improve customer experience. To ensure success, you need to avoid relying on assumptions and biases, and instead use data and ...
Emotions are a significant part of the customer journey and help drive the journey forward. Customer emotion data is how customers react to a product feature update or improvement. Benefits of Measuring Customer Emotions. Here are the most significant benefits of measuring customer emotions. Connecting With Your Customers
Step 5: Define Touchpoints. Step 6: Walk in Your Customers' Shoes. Step 7: Capture Emotions and Pain Points. Step 8: Analyze and Iterate. Step 9: Implement Changes - Bringing It All Together. Elevating Customer Experience: The North Star of Your Strategy. The Power of Customer Journey Mapping. Conclusion.
The customer emotional journey is an extension of the customer experience map, which details each touchpoint that a customer has with a brand. While similar to a customer experience map, the customer emotional journey focuses on consumer behaviour and the emotional status of the shopper at each stage of the purchasing experience.
Despite the significance of evaluating emotions throughout the customer journey, there remains a dearth of empirical evidence regarding the assessment of ferry passenger emotions onboard, as most existing studies predominantly focus on conceptual frameworks. This literature gap underscores the necessity for further research that empirically ...
CX shift. Transitioning from customer journey to customer experience is crucial for brand loyalty and growth. Prioritize emotional connections in today's competitive landscape. Journey essentials ...
Here are four examples of how businesses can create an impactful customer journey while prioritizing trust and ethics. Empathetic customer support. Providing empathy in your customer support protocols goes beyond resolving issues; it involves understanding and empathizing with customers' emotions and concerns. Businesses that prioritize ...