

Sizing A Circuit Breaker: Breaker Size Calculator + Amp Chart
Sizing a circuit breaker is never easy. But it’s also not all that difficult . Everybody knows that we need an adequately sized circuit breaker that allows for sufficient electric current. If we undersize a breaker, the breaker will likely catch on flame. No pressure here.

How do you go about picking the correct circuit breaker size? Do you need a 10A, 15A, 20A, 30A, 40A, 50A breaker, etc?
Standard breaker sizes are 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 35A, 40A, 45A, 50A, 60A, 70A, 80A, 90A, 100A, 110A, 125A, 150A, 175A, 200A, 225A, 250A, 300A, 350A, 450A, 500A, 600A, 700A, 800A, 1000A, 1200A, 1600A, 2000A, 2500A, 3000A, 4000A, 5000A, and 6000A.
Sizing a circuit breaker is actually quite easy. You just need to know a couple of rules. These are:
- 80% NEC breaker rule. This is the most basic NEC (National Electric Code) rule that states that you can’t push the current over 80% of its specified ampacity. Example: If you have a 20 amp breaker, you can only allow for a 16A current. 16A is 80% of the max. the specified ampacity of the circuit breaker. This is a safety measure; you better have a bit of overhead to prevent the circuit from frying. You can read the full Article 240.4(B) in NEC 2014 on this here .

If you know how to calculate the amps and account for the 80% breaker rule, you can calculate the size of the breaker yourself.
To help everybody sizing these breakers out, we will explain how to determine the right size of a breaker. On top of that, we include a Circuit Breaker Size Calculator further on (just insert watts and volts, and you get the correct breaker size).
At the end, we also included the ‘just tell me the breaker size I need’ Breaker Size Chart that tells you what breaker size you need for devices with different wattages (from 50W units to big 20,000W devices).
Let’s look at how breaker size can be calculated manually (you can also use the calculator or/and chart below):
Table of Contents
How To Calculate Size Of A Circuit Breaker?
This is the easiest to explain with an example.
Let’s say that we have a simple 1,500-watt space heater running on a standard 120V circuit. What size amp breaker do you need for a 1,500-watt space heater?
First, you need to calculate how many amps does this heater draw like this:
Current (Amps) = Power (Watts) / Voltage (Volt)
In our situation this is:
Current = 1,500W / 120V = 12.5 Amps
Now we know that the 1,500W space heater draws 12.5 amps. We have to account for the 80% breaker rule. This means that these 12.5 amps should represent 80% of the breaker amps. To calculate the size of the circuit breaker needed, we have to multiply the amp draw by 1.25 factor like this:
Minimum Circuit Breaker Size = 12.5A × 1.25 = 15.63 Amps
We can’t use a 15A breaker because the breaker ampacity should be at least 15.63A. The next breaker size is 20 amps; that means we need to use a 20A breaker for a 1,500W space heater running on 120V standard circuit.

Here is the basic step-by-step procedure we did to determine the size of a circuit breaker:
- Calculate the amp draw. We use the basic electric power equation for this. If we know the wattage and voltage, we can quite easily calculate the amp draw.
- Multiply amp draw by 1.25 to account for the 80% breaker rule. The resulting amps are the minimum ampacity a correctly sized circuit breaker should have.
- Choose a circuit breaker size. We usually pick between 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 35A, 40A, 50A, 60A circuit breakers, and so on.
This is how breaker sizing is done manually. The easiest way is to use a dynamic calculator. You simply input that wattage and the voltage, and the calculator will tell you what is the minimum size of a circuit breaker you need. You can use this calculator here:
Circuit Breaker Size Calculator
Here is how this breaker sizing calculator works:
Let’s say you have a big 5,000W air conditioner (this is usually a 5-ton unit). It runs on a 220V circuit. What size circuit breaker do you need?
Just slide the wattage slider to ‘5000’ and voltage slides to ‘220’ and you get ‘28.41 Amps’. Therefore you need a circuit breaker with at least 28.41A ampacity. 25A breaker is too small; you need a 30A breaker .
You can do this for literally any device running on any voltage. You can also play around with numbers to see how the amps change.
If you want the ‘just tell me the circuit breaker I need’ you can consult this chart:
Breaker Size Chart (For 120V And 220V Circuits)
You just need to know the wattage of the device you need a circuit breaker for and you can check what size breaker you need if you run it on a standard 120V circuit or an upgraded 220V circuit:
As you can see, calculating what size breaker you need is not all that hard. Of course, with bigger amp draws, you can connect several 30A or 50A in parallel to increase the total breaker ampacity.
We hope this illustrates how everybody can figure out the size of circuit breaker they need. If you have any questions regarding this breaker sizing, you can use the comments below and we’ll try to help you out.
Related posts:
- 50 Amp Wire Size Details: Gauge, Breaker, 220/240V Example
- Thermostat Not Reaching Set Temperature: 7 Causes + Fixes
- Wire Gauge Wattage Charts For AWG Wires (4/0 AWG To 14 AWG)
- How Many Outlets On A 15 Amp, 20 Amp, 30 Amp Circuit? (NEC 210.21)
- Thermostat Wire Color Codes For 3-8 Wire Thermostats (Color-By-Color)
12 thoughts on “Sizing A Circuit Breaker: Breaker Size Calculator + Amp Chart”
Thank you, this is very help full.
very much help full
Excelente information. Thank you.
The most amazing easy method. very Helpfull.
Thank you, Imran, we try to simplify it as much as possible. It’s nice to see a bit of recognition.
Helpful. 1,500-watt space heater running on a standard 120V circuit. What size amp breaker do you need for a 1,500-watt space heater? how can I use 120 v circuit.
Hi Masum, alright, 1500W heater on 120V draws 1500W/120V = 12.5 amps. To apply the 80% rule, you have to multiply this current by 125% like this: 12.5A × 1.25 = 15.63 amps. So, a 15A breaker won’t cut it, but a 20A breaker will be great for a 1500-watt space heater on a 120V circuit. Hope this helps.
Hi I have a 1200 watt generator , the breaker has gone bad and there is no size printed on the breaker. Im not sure if you can calculate the size the same way you would for a AC unit. What size would you suggest ? Thanks
Hi Renald, the size of the breaker you need for a 1,200 watt generator really depends on the amps it will give out. You can calculate the amps if you know the voltage. Generators can have 12V DC, 24V DC, 110-120V AC, 240V AC voltages. Example: Let’s say your 1200W generator has a 24V DC voltage. You can calculate the amps like this: 1200W/24V = 50 Amps. This is the current in the wire. You can calculate the minimum required breaker size for this generator like this: 50 Amp × 1.25 = 62.5 Amps. In this case you can go for 70A breaker, or 3x30A breakers, since their capacity if north of 62.5 amps. Hope this helps.
This article is flawless thank you!
Great info! Much appreciated but I’m trying to determine what breaker or breakers I need for my bass boat. 3x 12V in series for my 36V trolling motor and 1x 12 V for my electronics and starting battery which also powers the various pumps and aerators. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Hi Tom, the wattage you need is the key here. Electronics will have lower wattage but pumps and aerators… that should like high wattage stuff. Example: If you would put in 60A amp breaker on 36V voltage, and apply the 80% breaker rule, you will get 1,728W of power. It’s really hard to advise here without wattages but from the looks of it – 36V and energy-demanding pumps – the first presumption would be that you need big breakers, at least 60A. Hope this helps.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Basic Electrical
- Electrical Laws
- Electrical Tools
- Electrical Formulas & Equations
- Electrical Calculators
- Preventive Maintenance
- Electrical Procedures
- Electrical Projects
- Electrical Notes & Articles
- Electrical How to
- Troubleshooting
- Electrical Symbols
- Excel Tools
- Transformers
- Electric Motors
- Generations
- Transmission
- Distribution
- Measurement
- Control Systems
- Electrical Safety
- Electrical Interview
- Electrical MCQ
- Instrumentation & Control
- Renewable Energy
- Electrical Vehicles
- Submit Articles
- Freelance Job
- Privacy Policy
- Electrical Essentials
Breaker Size Calculator
Breaker size calculator is a online calculator tool (electrical calculator) that may be used to determine the proper size of a circuit breaker for a certain electrical circuit.
It takes into consideration a wide range of requirements such as voltage, power consumed by appliances/devices connected to the circuit, wire type, and safety regulations.
Several standards, including BS 7671 and the National Electrical Code (NEC) , specify “Ampacity” for different types of materials.
When a circuit overload or fault occurs, a circuit breaker used to protects the electrical appliances.
When the breaker trips, devices linked to the same circuit are cut off from the more current, causing them to lose power.
How do I calculate breaker size?
In general, a breaker should be sized to withstand 125% of the load (or 25% more capacity) and no less.
Oversized breakers might cause wires to overheat without interrupting the current flow. Undersized breakers, on the other end, may trip continuously under normal operation.
A circuit breaker has a rating in amperes (A), which tells us how much electricity may safely pass through the breaker before it trips. A 10 A breaker, for example, enables for up to 10 A of total load to be interconnected at the same time.
The desired breaker for electrical system equipment is chosen by a calculation known as breaker sizing.
Formula to determine Breaker Size
If we understand the wattage of every appliance in the circuit, we may use different formulae based on the kind of current to calculate their relative loads.
Load in DC Supply
I – Current in Amps (A)
W – Load Connected in Watts (W)
V – Voltage in Volts (V)
Load in AC Single Phase Supply
I = W/(V x P.F)
P.F – Power Factor
Load in AC Three Phase Supply
I = W/(V x P.F x √3)
What is Safety Factor (S.F)?
A specific overload condition can be operated for a specific period of time on some equipment. When sizing breakers, overload conditions are taken into consideration for increased protection. A safety factor is the 25% increase in current over the rated current, such as in the case of a motor that has a 100 A rating but can operate at 125 A for an hour.
The safety factor of common loads are listed below (Choose based on the connected load) :
Click here for more Electrical Calculators
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Short circuit current calculator, vt ratio calculator, ct ratio calculator.
- Related Post: Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCB, RCD or RCCB Circuit Breakers
Table of Contents
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A Circuit breaker (CB) is a control and protection device which:
- Control (make or break) a circuit manually or by remote control under normal and fault conditions.
- Break a circuit automatically under fault conditions (like over current, short circuit , etc).
A circuit breaker is used for switching mechanism and protection of the system
A circuit breaker is a switching as well as protection device used for ON/OFF operation of the circuit as well as prevent the electric shock. For accurate operation an d protection, even complex designs are used with circuit breaker like fuses , relays, switches , earthing & grounding etc.
- Related Post: Main Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
How Does a Circuit Breaker Work?
In normal conditions when the circuit current rating is lower than the circuit breaker rating, the circuit operation is normal and it can be changed by manual operation. In case of fault or short circuit when the value of current exceeds the circuit breaker current, It will automatically trip i.e. break the circuit from the main supply.
For example, a 30 amp circuit breaker will trip at 30 amp no matter if is it continuous or non continuous load. That’s why we must select 20-25% higher size of current for circuit breaker than the flowing current in the cables and wires to the connected device.
If we use a 100A circuit breaker for 30A circuit, it wont protect the circuit from fault currents and may burn and damage the device as more than 30 amperes current won’t trip the circuit breaker. In short, we must use the proper size of circuit breaker according to the device i.e. CB current should not be lower nor highest but 125% of circuit’s current.
Related Posts:
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) – Types, Construction, Working & Applications
- Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) – Types, Construction , Operation & Applications
Circuit Breaker Size Calculator
The following circuit breaker sizing calculator will show the difference in % to the load, voltage level in different countries and exact size of breaker in amperes.
Related Calculators:
- Wire & Cable Size Calculator in AWG
- Electrical Wire & Cable Size Calculator (Copper & Aluminum)
Circuit Breaker Size Calculation for Single Phase Supply
To determine the appropriate size of circuit breaker for single phase supply, it depends on multiple factors like type of load, cable material and environment temperature etc.
The general rule of thumb is that circuit breaker size should be 125% of the ampacity of cable and wire or the circuit which has to be protected by the CB. Let see the following solved examples:
Suppose a 12-gauge wire is to be used for a 16-ampere lighting circuit with a 120V single-phase supply. What is the best size of a circuit breaker for that 16 Amp circuit?
Circuit Current: 16 A
Circuit Breaker Size: ?
CB size should be 125% of the circuit current.
= 125% x 16 A
= 1.25 x 16 A
Circuit Breaker Size = 20A
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Determine the Right Size Capacity of a Subpanel?
What is the appropriate size of circuit breaker for 1920W, single phase 240V AC Supply?
- Load: 1920W
- Voltage: 120V (Single Phase)
Circuit Current:
According to the ohm’s law,
- I = 1920 W / 240V
Circuit Breaker Size:
Simply, Multiply 1.25 (safety factor) to the load current.
Circuit Breaker Size = 10 A
What is the suitable size of circuit breaker for 230V, 2.760 kW load single phase circuit?
- Current = Power / Voltage
- I = 2760 W / 230V
The minimum and recommended size of circuit breaker :
= 12A x 1.25
- Related Post: Smart WiFi Circuit Breaker – Construction, Installation and Working
Circuit Breaker Size Calculation for Three Phase Supply
To find the breaker size for three phase supply voltage, we must know the exact kind of load as there are many factors affecting the load current. In other words, same rule won’t apply to the different types of loads i.e. light, motor, inductive or capacitive load as motor takes initially very high current during the starting process as well as power factor involvement. For residential use, we may follow the same formula as above for single phase with taking the √3 (1.732) due to three phase power formula.
Good to know: For the same load, the breaker size in three phase is less than the breaker size used in single phase AC circuits.
Lets find the correct size of circuit breaker for three phase circuits as follow.
Example 1: Which size circuit breaker is needed for 6.5kW, three phase 480V load?
Power in Three Phase: P = V x I x √3
Current: P / V x √3
- I = 6.5kW / (480V x 1.732) … (√3 = 1.732)
- I = 6.5kW / 831.36
The recommended size of circuit breaker is
1.25 x 7.82A = 9.77A
The next closest standard of circuit breaker is 10A .
Example 2: Find the appropriate size of CB for 3-Phase 415V, 17kW load?
- Current = Power / (Voltage x √3)
- I = 17000W / (415V x 1.732)
Recommended Size of Circuit Breaker: 1.25 x 23.65A = 29.5A . The next closest value is 30A .
- Related Post: Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
Circuit Breaker Size Calculation for Continuous & Non-contentious Load
As circuit breakers (CBs) and Overcurrent Protection Devices (OCPD) are designed for 100% rated current i.e. a 30A circuit breaker can safely carry the exact 30A current but NEC suggests 80% as a safe current limit as compared to the rated current of CBs. This is because all loads are not same i.e. some loads are simultaneous (continuous) while other are non-simultaneous (non-continuous).
In case of contentious loads for three or more hours, the load current should not exceed 80% of the rated current of circuit breaker and OCPD.
The 80% of a 30A circuit breaker is 24A. This way, a 30A circuit can be safely used for 24A circuit.
In other words, a load circuit having 24A, the appropriate size of breaker would be:
24A / 0.8 = 30A.
Example 1: CB Size for 30A Non-contentious Load
- An exact 100% rated for 30A circuit breaker can be used for 30A non-continuous load.
Example 2: CB Size for 28A Contentious Load
- In case of continuous load, rate of %125 is applicable.
- 1.25 x 28 A = 35A
Example 3: CB Size for 30A Non-contentious Load & 28A contentious Load
- = 125% Continuous Load + 100% Non-continuous load
- = (1.25 x 28A ) + (30A)
Related Post: Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
Good to Know:
- An over sized breaker used for protection can damage the water heater or other connected appliances even leads to the fire due to overheat.
- An undersized breaker or same rating with load current breaker can trip and reset the circuit again and again. Use the correct size breaker.
- A single phase circuit breaker can’t be used for three phase supply voltage levels.
- A 3-Poles circuit breaker can be used on 3-Phase system using either 2 or 3 poles.
- A 3-Poles circuit breaker can be used on 1-Phase system only and only if indicated by the markings or instructed by user manual.
- 30A Breaker and 10 gauge wire can be used on 240V AC Supply.
- Breaker cannot be larger than ampacity of wire except for some loads like more loads.
In addition, A Circuit breaker rated for:
- 120V can only be used for 120V.
- 240V can be used for 120V, 240V but not for 277V (Commercial applications)
- 120-277 can be used for 120V, 240V and 277V.
- 120V can’t be used on 240V circuit and vice versa.
- 15A, 120V can’t be used on 20A, 120V circuit.
Related Post: How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
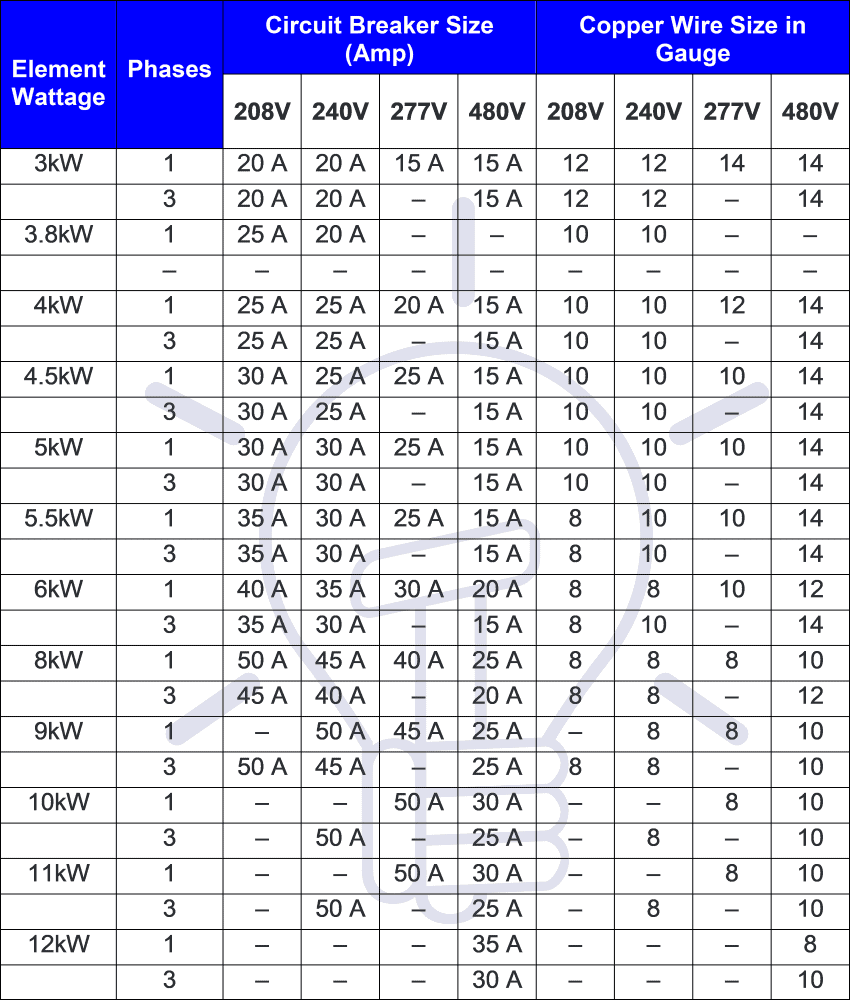
Circuit Breaker Size % and Amps Charts
The maximum safe current limit is 80% of the rated size of breaker except some motors. Keep in mind that the breaker size should not increase the max amperage rating of cable and wire. Below is the given chart showing the % of max current rating of breaker size for different types of load currents.
* Motors except Hermetically Sealed 00-250% NEC
The following two charts shows the suitable circuit breaker sizes with wire gauge and different level of voltages.
- How to Find the Right Wire Size for 100 Amp in AWG?
- What is the Right Wire Size for a 4.8kW, 240V Range: #10 or #12?
- American Wire Gauge “AWG” Chart – Wire Size & Ampacity Table
- How to Read MCB Nameplate Data Rating Printed on it?
- How to Wire a Single Element Water Heater and Thermostat?
- How to Find the Size of Earth Conductor, Earthing Lead & Earth Electrodes?
- How to Find the Value of Burnt Resistor ( By Four Handy Methods )
- Resistor Color Code Calculator – 3, 4, 5 & 6 Band Resistors Calculation
- Circuit Breaker, Fuse and Protection Symbols
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- How to Wire Single-Phase, 230V Consumer Unit with RCD? IEC, UK & EU
- How to Wire a Garage Consumer Unit?
- Single Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in Home – NEC & IEC
- Three Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in Home – NEC & IEC
Electrical Technology
Related articles.

A Complete Guide About Solar Panel Installation. Step by Step Procedure with Calculation & Diagrams

How to Size a Single Phase and Three Phase Transformer in kVA? Calculator

How to Calculate the Battery Charging Time & Battery Charging Current – Example

Automatic UPS / Inverter Connection Diagram to the Home Panel Board

How To Calculate Your Electricity Bill. Electric Bill Calculator with Examples

How to Find the Proper Size of Wire & Cable: Metric & Imperial Systems
17 comments.
I went Drive calculating process
NEC 240 first sections have requirements for max OCPD based on wire gauge up to #12. 20A max unless special cases in NEC (motor loads, HVAC etc.)
Please forward me all this information if it is free. Thanks
Love to always get updates. Thank you.
may i have a link to download this books
i have really enjoyed the lesson concerning the correct size of circuit breaker to be used for controlling electrical equipments for both domestic and industrial purposes… i will be happy if you could send me copy of the lessons through my email address provided below. Thank You.
The solved examples clear the confusing concept of sizing a circuit breaker. Thanks for explanation.
Very nice engineering field for polytechnic student read about electrical engineering& technology
CB used for protection of electrical equipment& machines.
There in no mention of operating time. Why?
Please post on ckt breaker maintenance Thank you
Certain aspects on this needs review
It is not correct that a 30A circuit breaker will trip at 30A.
The specifications clearly state that it shall carry 100%of the rated current
Further, hydraulic magnetic circuit breakers carry 100% of rated current continously and comply with UL specifications
Good update
Keep me updated please,really good!
Thanks very much for the Lesson…can you send to me through my emails, please?
Dear Owner, My name is Darrel Wolf with Pro Interior Designers LLC. I’m interested in your company ordering some circuit breakers for a electrical project am working on for my client. I want you to get back to me how much it will cost to order the 3-Pole Circuit Breaker, 200A, T3 Type for Symmetra PX250/500kW PD3P200AT3B. I will appreciate if you can send me an estimate to my company email address [email protected] and the the lead time on these order and i will gladly call you back to pay everything in advance for you to order them in to be collected from your store.Thank you and i will look forward to your reply soon.Please feel free to text me on 817-900-2949 if you have any question.
Sincerely, Mr. Darrel Wolf
HELLO, CAN ANYONE HELP ME OUT. I HAVE A CRABTREE (36 YEARS OLD) MCBs BOX WITH 11 WAYS ALL USED. FITTED WITH VARIOUSE SIZED TYPE 1 MCBs. THIS PROBLEM HAS ONLY JUST ARROS, WHEN PLUGGING IN MY 240 VOLT STICK WELDER THE 32 AMP MCB CLICKED OUT, I THEN PUSHED IT BACK IN, BUT HAVE NO POWER AT MY SOCKET, THE FUSE IS OK. IF THE MCB IS DAMAGED WHAT TYPE SIZE MCB SHOULD I INSTALL IE B C 32 OR 40 AMP PLEASE HELP IF YOU CAN, MANY THANKS
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Breaker Size Calculator
Importance of circuit breaker sizing calculations, how to calculate breaker size, how to use this circuit breaker calculator.
If you want to learn how to calculate breaker sizes, this circuit breaker size calculator is for you. Properly sizing your circuit breakers will not only help you avoid constantly resetting your tripped circuit breakers but can also help you protect yourselves from fire hazards.
Keep on reading to learn:
- The importance of circuit breaker sizing calculations;
- How to calculate breaker size; and
- How to use this circuit breaker calculator.
Sizing a breaker depends on how much load we anticipate it to handle. Basically, a breaker cuts off the flow of electricity when it detects an unsafe amperage flowing through it . With that said, we rate circuit breakers in amperes.
In a structure, we group our outlets and other electrical loads (e.g., lighting fixtures, ceiling fans, etc.) so that a circuit breaker only handles a section of the structure. A bedroom can have one circuit breaker assigned to its outlets, and the entire floor can share one circuit breaker for all its lighting fixtures.
For parts of the structure that demand high current flow, we can assign more than one circuit breaker for their outlets or use a larger size breaker.
As a rule of thumb, we size a breaker at 125% of the load we anticipate it to handle. Typically, we see appliance power ratings in watts. With the help of Watt's Law , we can find the amperage requirement of each appliance that we anticipate to belong to a circuit. Let's discuss more of the calculation process in the next section of this text.
Say, we need to find the advisable breaker size for a kitchen where we anticipate using a 120-W refrigerator and 900-W (max) microwave oven simultaneously at some point. Assuming these appliances function at 0.9 power factor and the house has a load distribution of 220-volt single-phase AC , let's find each appliance's amperage using the Watt's Law shown below:
- I I I is the amperage requirement of an appliance;
- W W W is the power consumption or wattage rating of an appliance;
- V V V is the voltage of the power source; and
- p f pf p f is the power factor of the appliance.
To find the amperage of our refrigerator, we plug in our known values to our formula, as shown here:
On the other hand, we calculate the amperage for our microwave oven as follows:
After finding our appliances' current requirements, we add them up to obtain the total load ( I total I_\text{total} I total ) and multiply the sum by 125% (or 1.25) to get our minimum breaker size ( I min I_\text{min} I min ), as we can see below:
Our last step is to choose the closest larger breaker size from the list of standard sizes of circuit breakers. Here are the standard circuit breaker sizes:
✅ Since the closest larger breaker size to our calculated minimum amperage requirement is 15A, we will use a 15A circuit breaker for this circuit.
Other amperage formulas
Our sample calculation above works for any single-phase AC systems only. If you need to find an appliance's amperage for three-phase AC and DC systems, here are the formulas you need to use:
For three-phase AC:
After finding each appliance's amperage, find the total amperage for your considered circuit, multiply the sum by 125% , and select the closest larger circuit breaker size from the list shown earlier.
If you need to calculate more than one circuit breaker size, you can use our breaker size calculator for convenience. Read on to learn how to use this breaker size calculator.
Using our circuit breaker size calculator is very easy. Here are the steps to follow when using it:
- Pick the current type or your power source. It could be DC , AC single-phase , or AC three-phase .
- Enter how much voltage your power source supplies.
- Select the appliance type of the appliance you anticipate using in a particular circuit. Choose Other if your appliance type is not on the list. We call your first appliance as Appliance A.
- Enter the quantity of Appliance A.
- Input Appliance A's wattage rating.
- If you anticipate other appliances simultaneously using this circuit, then repeat steps 3 to 5 for them. You can enter up to five devices in this tool.
- If you selected either AC single-phase or AC three-phase for the current type , you can use our tool in Advanced mode to enter or edit the power factor values for each of your appliances. Click on the Advanced mode button below our tool to toggle to that mode.
At this point, our tool will already have a recommendation for your breaker size for this circuit.
This tool is for informational purposes only. Please consult a certified electrician before buying your circuit breakers.
Capacitors in series
Schwarzschild radius.
- Astrophysics ( 17 )
- Atmospheric thermodynamics ( 11 )
- Continuum mechanics ( 21 )
- Conversion ( 15 )
- Dynamics ( 20 )
- Electrical energy ( 12 )
- Electromagnetism ( 18 )
- Electronics ( 34 )
- Fluid mechanics ( 29 )
- Kinematics ( 21 )
- Machines and mechanisms ( 20 )
- Math and statistics ( 34 )
- Optics ( 15 )
- Physical chemistry ( 15 )
- Quantum mechanics ( 14 )
- Relativity ( 9 )
- Rotational and periodic motion ( 17 )
- Thermodynamics ( 31 )
- Waves ( 14 )
- Other ( 33 )

Circuit Breaker Size Calculator
About circuit breaker size calculator (formula).
The Circuit Breaker Size Calculator is a tool used in electrical engineering to determine the appropriate size or amperage rating of a circuit breaker for a specific electrical circuit. It helps ensure the safety and proper functioning of electrical systems by preventing overloads and short circuits.
The formula for calculating the circuit breaker size depends on the electrical load or current draw of the connected devices and the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines.
The general formula for calculating the circuit breaker size is:
Circuit Breaker Size (Amperes) = 1.25 * (Total Load Current)
- Circuit Breaker Size is the amperage rating of the circuit breaker needed for the electrical circuit.
- Total Load Current is the sum of the currents drawn by all the devices connected to the circuit.
It’s important to note that the 1.25 multiplier is typically used to provide a safety margin and avoid continuous tripping of the circuit breaker. However, local electrical codes and specific applications may have different safety factors.
The Circuit Breaker Size Calculator is essential for electricians, electrical engineers, and anyone involved in electrical installations. By accurately calculating the circuit breaker size, it prevents electrical circuits from being overloaded, which could lead to overheating, damage to equipment, and even electrical fires.
The calculator considers various factors such as the types of devices connected, their individual currents, and the total current drawn by all devices to ensure that the circuit breaker is appropriately sized to handle the load.
In some cases, special considerations, such as motor starting currents or specific applications, may require different calculations or adjustments to the circuit breaker size.
Overall, the Circuit Breaker Size Calculator is a valuable tool for electrical safety and compliance with electrical codes and standards. It helps ensure that electrical circuits are protected adequately and function reliably under different operating conditions. For precise results, it is essential to adhere to local electrical regulations and seek professional assistance for complex electrical installations.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
allin1calculator
Circuit Breaker Trip Calculator
How to Calculate Circuit Breaker Trip Settings
Each circuit breaker in your breaker panel is labeled with the maximum amperage (current) capacity for that circuit. This may differ among circuits, so always check each breaker's capacity individually when calculating the electrical load that will cause that breaker to trip. Standard household circuits in the U.S. are 120 volts, but some circuits have double that capacity for appliances such as stoves and air conditioners. These breakers have 240-volt capacities and will be approximately twice the size of 120-volt breakers. Wattage is the easiest measure of power load to calculate and monitor so you don't accidentally trip your breakers.
Advertisement
Look for the amperage notation on the breaker switch. This will generally be 15 or 20. Also look for the voltage notation, which may be on the breaker switch as well, and will be 120 or 240. If you cannot locate the voltage, assume that breakers that take up one panel slot are 120 volts and breakers that take up two slots are 240 volts.
Video of the Day
Multiply the amps by the volts. In most circuits, this will be 20 x 120 = 2400 or 15 x 120 = 1800. The number resulting from this equation is the maximum wattage load you can place on the circuit before tripping the breaker.
Apply the same calculation to 240-volt circuits. For example, a 240-volt circuit with a 30-amp capacity would allow 7200 watts (30 x 240 = 7200).
Check the wattage for all electrical fixtures and appliances on the circuit. If the total wattage is over your maximum calculation, the breaker will trip.
Report an Issue
Screenshot loading...
Current Calculator – Calculate Amps
Use the current calculator below to calculate amps given the voltage, power, or resistance.
Have a Question or Feedback?
Calculation formulas:.
scroll down

On this page:
- Current Calculator

How to Calculate Electric Current
Current formula, how to calculate current from power, how to calculate current for ac circuits, three-phase ac current formula.

Joe is the creator of Inch Calculator and has over 20 years of experience in engineering and construction. He holds several degrees and certifications.

Aditya holds a PhD in electrical engineering from Stanford University and specializes in signal processing, algorithms, and machine learning.
In an electrical circuit, current is a measure of the flow of charged particles moving through a conductor. Current is measured in units of amperes (usually referred to as amps).
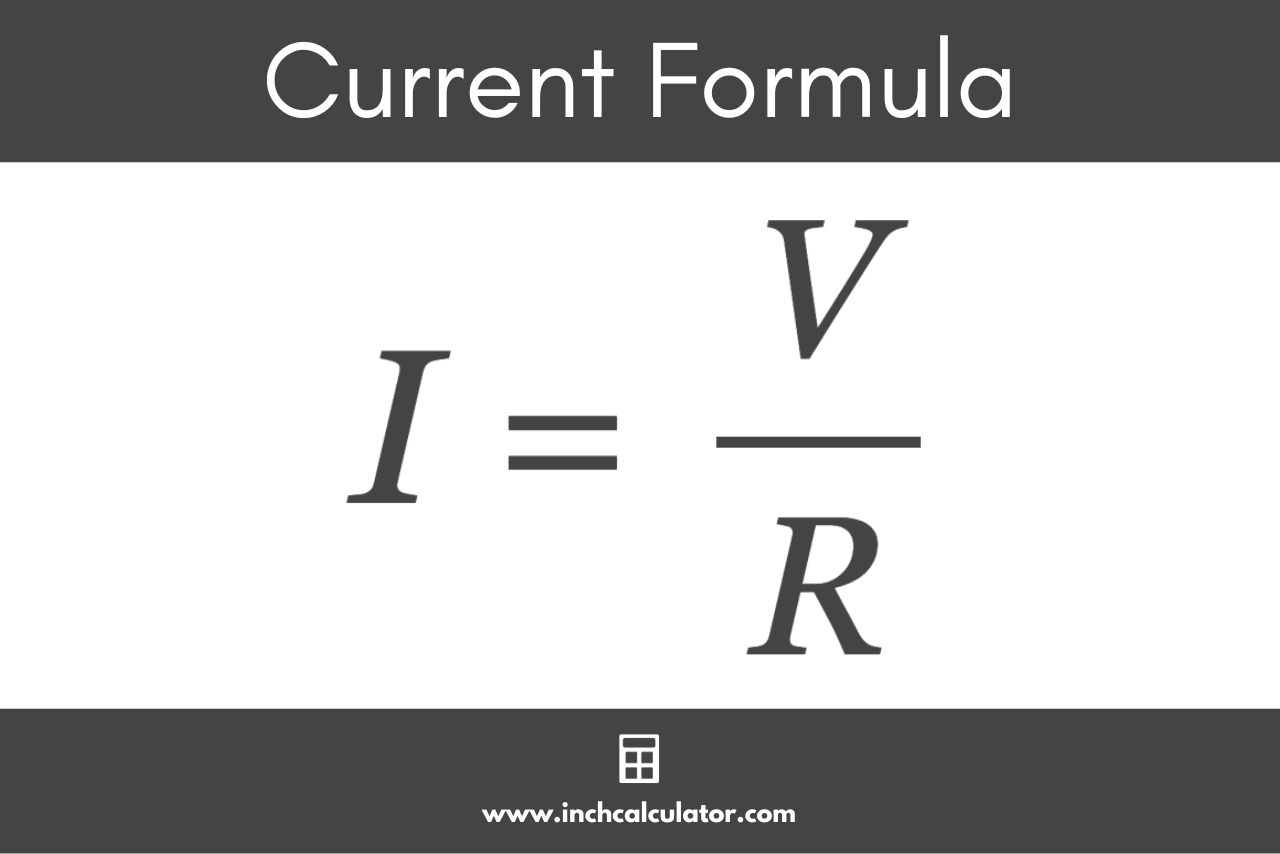
You can calculate the current flowing through a conductor using Ohm’s Law , which states that the current through a circuit element is directly proportional to the potential difference (also known as voltage) applied to it and inversely proportional to its electrical resistance . [1]
The Ohm’s Law formula to calculate current is I = V/R , where I is the current through the conductor in amps, V is the potential difference across or voltage across the conductor in volts, and R is the resistance of the conductor in ohms. [2]
Thus, the current I flowing through a conductor is equal to the voltage V across the conductor divided by the resistance R of the conductor.
You can also calculate electric current in amps if you know the power drawn from the circuit using the Watt’s Law power formula . The power formula states that the current in amps is equal to the power in watts divided by the voltage. [3]
I (A) = P (W) / V (V)
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the voltage V .
You can use our watts to amps calculator or volts to amps calculator to calculate current in amps, given voltage in volts and power in watts.
For a single-phase AC circuit given a power factor, you can calculate the current using the following formula.
I (A) = P (W) / V (V) × PF
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the voltage V and the power factor PF .
You can calculate the power factor using a power factor calculator if needed.
To calculate the current for three-phase AC circuits, you need to use a different formula to account for the three phases.
Line-to-Line Voltage Formula
If you know the line-to-line voltage in a three-phase AC circuit, you can use the following formula to calculate the current: [3] [4]
I (A) = P (W) / V L-L(V) × PF × √3
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the line-to-line voltage V in volts, the power factor PF , and the square root of 3.
This formula calculates the current draw for a single pair of wires in three-phase systems. You will need to multiply the result by 3 to calculate the total current for all three pairs.
Line-to-Neutral Voltage Formula
If you know the line-to-neutral voltage in a three-phase AC circuit, you can use the following formula to calculate the current:
I (A) = P (W) / V L-N(V) × PF × 3
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the line-to-neutral voltage V in volts, the power factor PF , and 3.
This formula calculates the total current for all three wires in a three-phase system. You will need to divide the result by 3 to find the current for a single wire in the circuit.
Once you identify how much current you’re working with, you can use our wire ampacity calculator to determine which conductor size is appropriate for the project.
Recommended Electrical Resources
- Power Factor Calculator
- Voltage Drop Calculator
- Ohm’s Law Calculator
- 2024 Electricity Cost Calculator
- Series and Parallel Capacitor Calculator
- Brandon Mitchell, Robert Ekey, Roy McCullough, and William Reitz, A Fan-tastic Quantitative Exploration of Ohm’s Law, https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1119/1.5021431
- National Institute of Standards and Technology, Ampere: The Present, https://www.nist.gov/si-redefinition/ampere-present
- Miller, C., NFPA's Electrical References, National Fire Protection Association , 2004, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 67-75. https://www.google.com/books/edition/NFPA_s_Electrical_References/raUyIi7i-asC
- Miller, C., Ugly’s Electrical References, 2020 Edition, 2020, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 16-23. https://books.google.com/books?id=1kS8DwAAQBAJ
Voltage Drop Calculator
This is a calculator for the estimation of the voltage drop of an electrical circuit. The "NEC data" tab calculates based on the resistance and reactance data from the National Electrical Code (NEC). The "Estimated resistance" tab calculates based on the resistance data estimated from the wire size. Click the "Other" tab to use customized resistance or impedance data, such as data from other standards or wire manufacturers.
When electrical current moves through a wire, it is pushed by electrical potential (voltage) and it needs to surpass a certain level of contrary pressure caused by the wire. The voltage drop is the amount of electrical potential (voltage) loss caused by the contrary pressure of the wire. If the current is alternating, such contrary pressure is called impedance. Impedance is a vector, or two-dimensional quantity, consisting of resistance and reactance (reaction of a built-up electric field to a change of current). If the current is direct, the contrary pressure is called resistance.
Excessive voltage drop in a circuit can cause lights to flicker or burn dimly, heaters to heat poorly, and motors to run hotter than normal and burn out. It is recommended that the voltage drop should be less than 5% under a fully loaded condition. This can be achieved by selecting the right wire, and by taking care in the use of extension cords and similar devices.
There are four major causes of voltage drop:
The first is the choice of material used for the wire. Silver, copper, gold, and aluminum are among the metals with the best electrical conductivity. Copper and aluminum are the most common materials used for wires due to their relatively low price compared with silver and gold. Copper is a better conductor than aluminum and will have less voltage drop than aluminum for a given length and wire size.
Wire size is another important factor in determining voltage drop. Larger wire sizes (those with a greater diameter) will have less voltage drop than smaller wire sizes of the same length. In American wire gauge, every 6-gauge decrease doubles the wire diameter, and every 3-gauge decrease doubles the wire cross sectional area. In the Metric Gauge scale, the gauge is 10 times the diameter in millimeters, so a 50 gauge metric wire would be 5 mm in diameter.
Still another critical factor in voltage drop is wire length. Shorter wires will have less voltage drop than longer wires for the same wire size. Voltage drop becomes important when the length of a run of wire or cable becomes very long. Usually this is not a problem in circuits within a house, but may become an issue when running wire to an outbuilding, well pump, etc.
Finally, the amount of current being carried can affect voltage drop levels; an increase in current through a wire results in an increased voltage drop. Current carrying capacity is often referred to as ampacity, which is the maximum number of electrons that can be pushed at one time – the word ampacity is short for ampere capacity.
The ampacity of a wire depends on a number of factors. The basic material from which the wire is made is, of course, an important limiting factor. If alternating current is being sent through the wire, the speed of alternation can affect ampacity. The temperature in which the wire is used can also affect ampacity.
Cables are often used in bundles, and when they are brought together, the total heat which they generate has an effect on ampacity and voltage drop. There are strict rules about bundling cables which must be followed for this reason.
Cable selection is guided by two main principles. First, the cable should be able to carry the current load imposed on it without overheating. It should be able to do this in the most extreme conditions of temperature it will encounter during its working life. Second, it should offer sufficiently sound earthing to (i) limit the voltage to which people are exposed to a safe level and (ii) allow the fault current to trip the fuse in a short time.
Voltage drop calculation
Ohm's Law is a very basic law for calculating voltage drop:
V drop = I·R
where: I: the current through the wire, measured in amperes R: the resistance of the wires, measured in ohms
The resistance of the wires is often measured and given as length-specific resistance, normally in the unit of ohms per kilometer or ohms per 1000 feet. Also, the wire is round-tripped. Therefore, the formula for a single-phase or direct current circuit becomes:
V drop = 2·I·R·L
The formula for a three-phase circuit becomes:
V drop = √ 3 ·I·R·L
where: I: the current through the wire R: the length-specific resistance of the wires L: the one-way length
Typical AWG wire sizes
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a wire gauge system used predominantly in North America for the diameters of round, solid, non-ferrous, electrically conducting wire. The following is a list of typical AWG wires and their sizes:

Calculate amperes with the Ampere Calculator

The Ampere Calculator allows you to calculate the amperage in amperes based on the electrical voltage in volts and the power in watts of an electrical appliance or system. Simply enter the existing voltage in volts and the power in watts, and the Ampere Calculator will then automatically determine the corresponding amperage in amperes.
Instead of calculating the amperage, you want to calculate the voltage in volts or the power in watts? Then use our guide pages with the Volt Calculator or the Watt Calculator .
Contents on the topic "Calculating Amperes"
Why do you need to calculate amperes.
Calculating amperes is important to ensure that electrical circuits and equipment operate safely and efficiently. In many electrical applications, such as installing electrical wiring, choosing the right fuses or sizing electric motors, it is necessary to calculate the required amperage in amperes. If the amperage is too high, this can lead to overheating, fires or even explosions. If the amperage is too low, the performance of the appliance or circuit may be affected. Therefore, it is important to calculate the correct amperage to ensure safe and effective operation.
An example is choosing the correct battery size for an electronic device. If the battery does not supply enough current, the device will not function properly. However, if the battery supplies too much current, it can cause overheating and damage to the device.
In electronics, it is also important to know the current requirements of components such as LEDs, transistors or microcontrollers to ensure that they are operating at the correct amperage. Calculating amperes is therefore an essential part of planning and implementing electrical projects.
What is Ampere actually?
Ampere is the unit of electrical current strength and is represented by the unit symbol "A". It is named after the French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère, who made important contributions to the study of the magnetic field and electrodynamics. An ampere defines the current that flows through a conductor when an electric charge of one coulomb flows through it in one second. In mathematical terms, one ampere corresponds to one coulomb per second (1A = 1C/s). Electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. When a voltage is applied to a conductor, electrons are moved through the conductor in a certain direction, resulting in the generation of an electric current.
What is the formula for amperes?
The current in amperes is obtained by dividing the electrical power in watts by the voltage in volts. The formula is therefore:
This formula indicates the amount of current required by an electrical appliance or device when the voltage and power are known. Voltage (V) is measured in volts and indicates how much electrical potential difference there is between two points, while power (W) is measured in watts and indicates how much electrical current flows through a component in a given time. By dividing the power by the voltage, you get the amperage (in amperes) that the appliance or system requires.
How does the Ampere Calculator work?
In the ampere calculator, the current in amperes is already preset under "What should be calculated?” According to the formula Ampere (A) = Power (W) / Voltage (V) , the ampere calculator still needs the two remaining entries for the power in watts and the voltage in volts to calculate the amperage in amperes. These two required inputs are described below:
Voltage in volts
Power in watts, how many amps does an e-bike have.
The battery of an e-bike requires a certain amperage, which is calculated from its values for voltage in volts and power in watts. If the battery of the e-bike has an output voltage of 36 volts and a power of 480 watts, the Ampere Calculator will calculate as follows:
Video on "How to calculate amps from watts"
Finally, a video on the subject of calculating amperes:
What other readers have also read
More online calculators, source information.
As source for the information in the 'Convert Volts, Watts & Amps' category, we have used in particular:
Last update
This page of the 'Convert Volts, Watts & Amps' category was last edited or reviewed by Stefan Banse on March 22, 2023. It corresponds to the current status.
Changes in this category "Convert Volts, Watts & Amps"
Rate our article with just one click.
Cloud Services

Desktop Software

Mobile Apps

- Login / Register
Power Load Calculator
Difference:.
TheNewsIndependent
How do you calculate ampere trip and ampere frame?
Table of Contents
Multiply the amps by the volts. In most circuits, this will be 20 x 120 = 2400 or 15 x 120 = 1800. The number resulting from this equation is the maximum wattage load you can place on the circuit before tripping the breaker.
How do you calculate ampere trip?
Divide the wattage by the voltage. The answer will be the amperage the device draws on your circuit. For example, a 150-watt device on a 120-volt circuit will draw 150 ÷ 120 = 1.25 amps.
What is ampere frame?
Ampere Frame [AF] it is the rating breaker current [maximum. current which the breaker will withstand for a long. time]. Ampere trip [AT] it is the current set to trip the. circuit [usually from 60% up to 100% of the AF].
What does trip mean on Breakerbox?
A circuit breaker “trips” (shuts off the electrical flow) in order to protect the circuit from overheating. It’s a safeguard that helps prevent damage and electrical fires.
What is frame size in Mccb?
Industrial-grade MCCBs are available in frame sizes from 100 amperes to 3000 amperes. ICCBs are available in frame sizes from 400 to 5000 amperes. The 400-ampere-frame ICCB is typically the same size and cost as the 800-ampere frame but is equipped with smaller-ratio current sensors.
What is the frame size of a 30a circuit breaker?
2-Space Square D Homeline Circuit Breaker 30A
How do you read a tripping curve?
The Trip Curve
- The X axis represents a multiple of the operating current of the circuit breaker.
- The Y axis represents the tripping time. A logarithmic scale is used in order to show times from . 001 seconds up to 10,000 seconds (2.77 hours) at multiples of the operating current.
What is breaker frame?
Frame – This is considered the body of the circuit breaker. It is the molded, insulated housing, fabricated from a glass-polyester, thermoset composite resin, or thermo-plastic glass fiber material. Trip unit – this is considered the brain of a circuit breaker.
What is the Kaic rating?
It stands for Kilo Ampere Interrupting Capacity and is sometimes referred to as Thousand Ampere Interrupting Capacity. KAIC in electricity refers to refers to measurements of the ability of a circuit breaker to withstand a short circuit or overload.
What does trip mean in electricity?
A trip unit is the part of a circuit breaker that opens the circuit in the event of a thermal overload, short circuit or ground fault. An open circuit will not conduct electricity because either air, or some other insulator has stopped or broken the flow of current in the loop.
What causes power to trip?
Common reasons for your circuit breaker tripping are because of either a circuit overload, short circuit or a ground fault. Here’s some information about the differences between a circuit overload, a short circuit and a ground fault to help you solve your circuit breaker and electrical systems issues.
What is frame of breaker?
Frame – This is considered the body of the circuit breaker. It is the molded, insulated housing, fabricated from a glass-polyester, thermoset composite resin, or thermo-plastic glass fiber material.
Online Calculators and Tables to Help You Determine Proper Wire Size
The Advanced Wire Size Calculator will calculate the proper wire size for a circuit based on circuit amps, preferred (or available) wire insulation, conductor type and installation specifications. This calculator also provides wire size correction factors for temperature, number of conductors in a raceway, and voltage drop for long wire runs.
Search Amazon for your Electrical products such as wire, tools, extension cords, and accessories.
- Advanced Wire Size Calculator
Enter the information below to calculate the appropriate wire size.
Voltage - Enter the voltage at the source of the circuit. Single-phase voltages are usually 115V or 120V, while three-phase voltages are typically 208V, 230V or 480V.
Amperes - Enter the maximum current in amps that will flow through the circuit. For motors, it is recommended to multiply the nameplate FLA by 1.25 for wire sizing.
Phases - Select the number of phases in the circuit. This is typically single-phase or three-phase. For single-phase circuits, three wires are required. For three-phase circuits, four wires are required. One of these wires is a ground wire which can be sized down. To calculate ground wire size, use the Ground Wire Size Calculator .
Insulation - Select the thermal rating of the insulation on the wire.
Conductor - Choose the material used as a conductor in the wire. Common conductors are copper and aluminum.
Installation - Choose the installation method for the circuit. This is typically in a raceway (cable-tray or conduit), in a cable, burried in the Earth, or in open air.
Voltage Drop - Choose the maximum percentage of the source voltage drop. It is recommended not to exceed a voltage drop of 5%.
Distance - Enter the one-way length of the wires in the circuit in feet.
Note : It's recommended to check the ampacity of a wire after doing a voltage drop calculation. Always use the total length of the circuit for calculations. Consult with an engineer if your application requires more complex calculations.
Source: NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, Table 310.15(B)(16-17)
For simpler circuits that do not need temperature or number of conductors correction factors, use the Wire Size Calculator .
For long conductor runs where voltage drop may be an issue, use the Voltage Drop Calculator to determine voltage drop and the Circuit Distance Calculator to determine maximum circuit length. Visit the Tables page to view reference tables such as Maximum Ampacity for Current-Carrying Conductors .
Visit the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy for this site. Your feedback is greatly appreciated. Let us know how we can improve.
Link Navigation
- Wire Size Chart
- Calculator List and Descriptions
- Wire Size Calculator
- Wire Ampacity Calculator
- Advanced Wire Ampacity Calculator
- Arc Flash Calculator
- Voltage Drop Calculator
- Circuit Distance Calculator
- Ohm's Law Calculator
- Motor Wire Size Calculator
- Ground Wire Size Calculator
- Distance Between Conduit Supports Calculator
- Resistor Color Code Calculator
- Table List and Descriptions
- Maximum Wire Ampacity for Current-Carrying Conductors in Raceway 30°C Table
- Maximum Wire Ampacity for Current-Carrying Conductors in Free Air 30°C Table
- Maximum Wire Ampacity for Current-Carrying Conductors in Raceway 40°C Table
- Maximum Wire Ampacity for Current-Carrying Conductors in Free Air 40°C Table
- Full-Load Current for Three-Phase AC Motors Table
- Three-Phase AC Motor Wire Sizes and Circuit Protection Table
- Arc Flash Tables
- Ground Conductor Size Table
- Distance Between Rigid Conduit Supports Table
- Wire Ampacity Correction Factors Table
Watt Calculator
Table of contents
With our watt calculator, you'll have a better understanding of what is Watt's law and the electrical power unit. Would you like to learn how to find watts? What about what connects volts, amps, watts, and ohms? Well, to do that, we need to dive in and discover what the power equation is!
If you want to know how the type of current affects how to calculate watts in a circuit, check out our watts to amps calculator .
How do you calculate watts? - Watt's equation
Our calculator is based on the two laws that describe simple electrical circuits. One of them - Watt's law - states that:
Power = Voltage * Current - in symbols: P = V * I .
This power equation, as well as the power unit, were named after James Watt - a Scottish engineer. One watt is the power at which the work performed in one second is equal to one joule:
1W = 1J / 1s
In electrical circuits, one Watt is defined as the rate of work when a current of one ampere flows through a conductor which has an electrical potential difference (voltage) of one volt :
1W = 1V * 1A
So what is power? Power, in an electric circuit, is the rate of transferring electrical energy per unit of time. Learn more in the electrical power calculator .
Ohm's law: volts, amps, and ohms
Our watt calculator uses a second formula - Ohm's law. It states that:
Voltage = Current * Resistance , or V = I * R
What do those names mean?
Electric Current is a measure of the quantity of charge (electrons) passing through any point of a wire per unit of time. Its SI unit is an ampere [A].
Resistance describes the strength of a given wire to oppose the flow of electrons. The resistance unit is an ohm [Ω].
Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points of a wire. The SI unit of voltage is a volt [V].
Power, Voltage, Resistance, Current
With Ohm's and Watt's equations you can calculate four variables - power, voltage, resistance and current. If you know the values of two of these variables, you can transform the above equations according to your needs. Underneath we list all of these transformations:
- Resistance:
- I = √(P / R)
- V = √(P * R)
Keep reading to see a couple of examples where we learn how to find watts and calculate amps from watts and volts!
Examples of conversion between volts, amps, watts, and ohms
To use our watt calculator, all you need to do is input two numbers, and all the other fields will be filled on their own. But, if you want to learn how to calculate these things by yourself, here are some examples that you might find helpful:
Let's consider a 60 Watt light bulb with 120 Volts of electric potential. How to calculate amps from watts and volts? Find the correct formula, and input the numbers in the correct places:
I = P / V = 60 W / 120 V = 0.5 A
Your light bulb needs 0.5 amps of current.
Let's look at another example. A resistor has a voltage of 4 volts and a resistance of 8 ohms. How to find watts? You need to combine both Ohm's and Watt's law. Then, you will get:
P = V² / R = (4V)² / 8Ω = 2 watts
Would you like to challenge yourself a bit? Check out the power factor calculator to find out more about the power equation and the components of power: real power, reactive power, and apparent power !
What does a Watt measure?
A Watt (W) is a unit of electric power (P) that measures the rate at which electric work is done when the potential difference (V) drives current (A) through a circuit.
How many volts are in a Watt?
One Watt is the electric work done when a current of one amp passes through a circuit with a voltage of one volt.
How many volts are in one Watt depends on how much amps of current is flowing in the circuit. The higher the current in one Watt, the lower the voltage.
How many kilowatts are in a Watt?
One Watt is equal to 10 -3 kilowatts.
1 W = 10 -3 kW = 0.001 kW
1 kW = 1000 W
How many BTUs are in a Watt?
British thermal unit per hour (BTU/h) is a unit of power for heating and cooling systems sometimes used in North America and the United Kingdom instead of watts. It is commonly shortened from BTU/h to just BTU.
How many BTUs are in a 1500 Watt heater?
One watt is approximately equal to 3.412142 BTU/h. So a 1500 W heater is equivalent to a 5118 BTU/h rated heater.
How do I calculate the Watt hours of a battery?
To calculate the Watt-hours (Wh) of a battery, follow these steps:
Find the battery's voltage (V) and amp-hours (Ah) from its specifications. For example, a 12V50 battery has 12 V voltage and 50 amp-hours capacity.
Multiply the battery's voltage by its amp-hours to get the battery's capacity in Watt-hours:
capacity (in Wh) = voltage × amp-hours
Voltage (V)
Current (I)
Resistance (R)

- Popular Routes

Easy EV Trip Planner
Leave range anxiety in the dust.

All estimates listed are estimated and may not be 100% precise. Service brands are trademarks of their respective owners, and we are not affiliated with them. All rights reserved. Read our privacy policy. 2023 © AmpTrip - EV Trip Planner
Relay Tripping Time Calculator
This free Inverse Definate Mean Time Calculator (IDMT) calculates the tripping time of a protection relay based on IEC 60255 and IEEE C37.112.
Calculation Notes
The IDMT (Inverse Definite Minimum Time) curve is an important element in power system protection. It enables the selective detection and clearance of faults by coordinating the operation of multiple relays. The curve ensures quick fault isolation, system stability, and equipment protection. It also enhances overall system safety by promptly interrupting fault currents, reducing the risk of hazards.
This calculator uses formuals found in the IEC Standard 60255 and the IEEE C37.112 standard to calculate the tripping times.
The formula used in the IEC 60255 calculation is;
Where; I is the fault current in Amps, TMS is the Time Multiplier setting on the protection relay, I s is the relay pickup current in Amps and K and p are contants defined in the table below.
The formula used in the IEEE C37.112 calculation is;
Where; I is the fault current in Amps, TMS is the Time Multiplier setting on the protection relay, I s is the relay pickup current in Amps and A, B and p are contants defined in the table below.
Related Calculators
Subscribe to our newsletter, get updates and learn from the best, recent posts, understanding voltage drop, as/nzs3008, understanding power cable insulation, understanding induction motors nameplate, understanding the power triangle, understanding why switching the neutral conductor is a bad idea, as/nzs3000.
Copyright © 2024 Powered by SparkyCalc . All rights reserved.
Lets share the love
Ohio man, 81, fatally shoots Uber driver, 61, after scammers target both of them, officials say
An 81-year-old Ohio man has been charged in the fatal shooting of an Uber driver he believed was working with a scammer, according to officials who said the victim was sent to the home by the same scammer.
William Brock told investigators he shot Loletha Hall, 61, outside his home March 25 because he thought she was working with a man who called him pretending to be an officer at the local court, Lt. Kristopher Shultz of the Clark County Sheriff's Office said.
"Mr. Brock received some scam call by a person purporting to be someone from our courts who informed him a family member was incarcerated and that he had a bond of a significant amount of money," Shultz said. "The calls turned from 'I'm an officer in the court' to 'We have this subject hostage, this is a ransom demand.'"
The person who called Brock, or an accomplice, requested an Uber ride to his South Charleston home to pick up the money, Shultz said.
"Ms. Hall did not have any idea," he added.
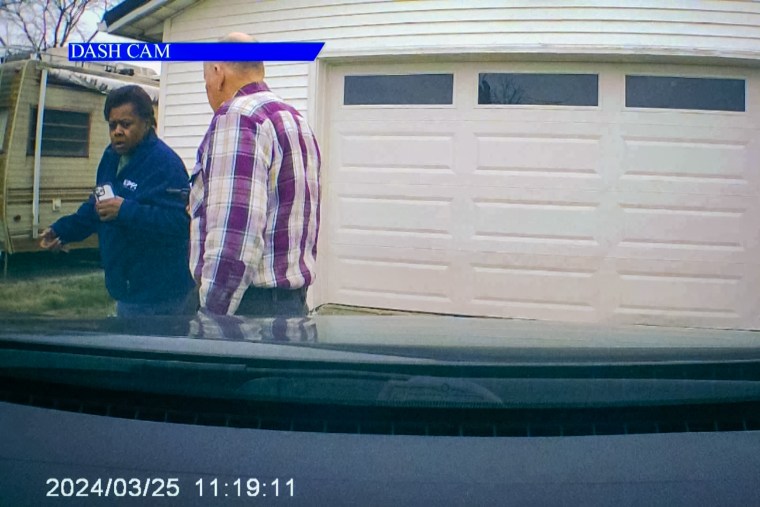

When Hall arrived at the home and approached the front door, Brock confronted her with a gun and asked her who she was working for, Shultz said. He took her cellphone and prevented her from getting in her vehicle and driving away.
“When she tried to get away, he shot her once, then there was more exchange between them," Shultz said. "Mr. Brock was at some point injured to his head, and he shot Ms. Hall a second time. There was more conversation, and then he shot her a third time. Only after he shot her a third time did he then make contact with authorities to report the incident."
Hall did not threaten Brock, have a weapon or assault him, according to the sheriff's office and a complaint filed in Clark County Municipal Court. She was taken to a hospital where she died from her injuries, according to the complaint.
In a statement, Uber said the company had spoken with Hall's family.
"This is a horrific tragedy and our hearts continue to be with Loletha’s loved ones as they grieve," an Uber spokesperson said. "We have been in contact with law enforcement and remain committed to supporting their investigation."

The Uber spokesperson said the account of the person who ordered a car to Brock's house has been banned. Officials have not identified the person who requested the Uber and have not said whether they have made any additional arrests in connection with the case.
In a grand jury presentation Monday, Brock was indicted on three counts of murder, one count of felonious assault and one count of kidnapping, Shultz said. He will be arraigned on those charges later this week.
It was not immediately clear whether he has an attorney.
Brock was originally arraigned on a murder charge in the Municipal Court of Clark County on Wednesday and posted a $200,000 bond. If convicted of that charge, he could be sentenced to 15 years to life in prison or a $15,000 fine.
Breaking news reporter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To calculate circuit breaker and wire size: Write down an approximation of the total load you will connect to the circuit breaker.; Get a circuit breaker rated for 125% of this load.; Make sure the wire it will be paired with has a higher ampacity than the circuit breaker's rating. Otherwise, the current may heat the wire above safety levels under normal operation.
Breaker sizing calculator parameter: Choose the method: provide load (in kilowatts or watts) and current (in amps) If current selected: rated current of equipment and required safety factor (S.F) to be entered If load selected: For option: For DC, 1∅ AC and 3∅ AC. For DC circuits: voltage (in volts), power (in watts or kilowatts) and safety factor (S.F) (in percentage) are required
To calculate the size of the circuit breaker needed, we have to multiply the amp draw by 1.25 factor like this: Minimum Circuit Breaker Size = 12.5A × 1.25 = 15.63 Amps. We can't use a 15A breaker because the breaker ampacity should be at least 15.63A.
650. Breaker size calculator is a online calculator tool (electrical calculator) that may be used to determine the proper size of a circuit breaker for a certain electrical circuit. It takes into consideration a wide range of requirements such as voltage, power consumed by appliances/devices connected to the circuit, wire type, and safety ...
An exact 100% rated for 30A circuit breaker can be used for 30A non-continuous load. Example 2: CB Size for 28A Contentious Load. In case of continuous load, rate of %125 is applicable. 1.25 x 28 A = 35A. Example 3: CB Size for 30A Non-contentious Load & 28A contentious Load. = 125% Continuous Load + 100% Non-continuous load.
Using our circuit breaker size calculator is very easy. Here are the steps to follow when using it: Pick the current type or your power source. It could be DC, AC single-phase, or AC three-phase.; Enter how much voltage your power source supplies.; Select the appliance type of the appliance you anticipate using in a particular circuit. Choose Other if your appliance type is not on the list.
Short-time pickup is adjustable from 1.5 to 10 times the trip unit ampere setting (Ir). For example, a 1000 ampere frame can be adjusted to trip anywhere from 1500 to 10,000 amps. The switch also has an "OFF" position to eliminate short-time pickup and short-time delay. Short-time pickup used for selective tripping.
The general formula for calculating the circuit breaker size is: Circuit Breaker Size (Amperes) = 1.25 * (Total Load Current) Where: Circuit Breaker Size is the amperage rating of the circuit breaker needed for the electrical circuit. Total Load Current is the sum of the currents drawn by all the devices connected to the circuit.
Circuit Breaker Trip Calculator. Rated Current (Amps): Trip Current (Amps): Calculate Trip Time.
Step 1. Look for the amperage notation on the breaker switch. This will generally be 15 or 20. Also look for the voltage notation, which may be on the breaker switch as well, and will be 120 or 240. If you cannot locate the voltage, assume that breakers that take up one panel slot are 120 volts and breakers that take up two slots are 240 volts.
I (A) = P (W) V L-N (V) × PF × 3. The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the line-to-neutral voltage V in volts, the power factor PF, and 3. This formula calculates the total current for all three wires in a three-phase system. You will need to divide the result by 3 to find the current for a single ...
Consider a scenario where a 40 amp circuit breaker was specified for an electric motor circuit. It means that the circuit breaker will trip at 40 amp regardless of the type of load the motor is subjected to. From this example, it would make sense to use a 100 A circuit breaker for a 40 A motor circuit, right? Wrong!
Ideally, a circuit breaker should never trip while carrying its rated current. Looking further down the graph to where it should trip, we find that a 30 Amp breaker will trip in about 10 seconds if carrying 60 Amps (200% of rating). A short pulse of 200% overload (say, 5 seconds) will not cause a trip, but a continuous 200% overload will, after ...
This free voltage drop calculator estimates the voltage drop of an electrical circuit based on the wire size, distance, and anticipated load current. ... the word ampacity is short for ampere capacity. ... (ii) allow the fault current to trip the fuse in a short time. Voltage drop calculation. Ohm's Law is a very basic law for calculating ...
The Ampere Calculator allows you to calculate the amperage in amperes based on the electrical voltage in volts and the power in watts of an electrical appliance or system. Simply enter the existing voltage in volts and the power in watts, and the Ampere Calculator will then automatically determine the corresponding amperage in amperes.
Power Load Calculator. This tool will help you calculate the load on a circuit to see if it is excessive. You can also calculate the minimum circuit breaker size for the given load. This is very useful when you are in pre-production as you will easily be able to calculate in advance whether or not you will need an external generator, and how many.
The calculator is designed to accept the total line voltage and current of the combined three cables. The equation for the area of a single wire is modified to: A = \frac {\sqrt 3 I \varrho L} {V} A = V 3I ϱL. The factor of \sqrt 3 3 is needed to convert between the system's phase current and line current.
In most circuits, this will be 20 x 120 = 2400 or 15 x 120 = 1800. The number resulting from this equation is the maximum wattage load you can place on the circuit before tripping the breaker. How do you calculate ampere trip? Divide the wattage by the voltage. The answer will be the amperage the device draws on your circuit.
Calculation with line to line voltage. The phase current I in amps (A) is equal to the power P in watts (W), divided by square root of 3 times the power factor PF times the line to line RMS voltage VL-L in volts (V): I(A) =. P(W) √3 × PF × VL-L(V) The power factor of resistive impedance load is equal to 1.
Advanced Wire Size Calculator. Enter the information below to calculate the appropriate wire size. Voltage - Enter the voltage at the source of the circuit. Single-phase voltages are usually 115V or 120V, while three-phase voltages are typically 208V, 230V or 480V. Amperes - Enter the maximum current in amps that will flow through the circuit.
For example, a 12V50 battery has 12 V voltage and 50 amp-hours capacity. Multiply the battery's voltage by its amp-hours to get the battery's capacity in Watt-hours: capacity (in Wh) = voltage × amp-hours. Our watt calculator helps you understand the relationship between power, voltage, current and resistance.
AmpTrip is completely free to use. Get started with AmpTrip today and transform your EV travel experience. AmpTrip is a simple EV trip planner designed to eliminate range anxiety, showcasing charging stations en route. Save money, reduce emissions, and enjoy stress-free travel with every electric adventure.
This calculator uses formuals found in the IEC Standard 60255 and the IEEE C37.112 standard to calculate the tripping times. The formula used in the IEC 60255 calculation is; t (i)=\left ( \frac {K} { { (\frac {I} {I_s}})^ {p}-1} \right) *TMS. Where; I is the fault current in Amps, TMS is the Time Multiplier setting on the protection relay, Is ...
By Mirna Alsharif. An 81-year-old Ohio man has been charged in the fatal shooting of an Uber driver he believed was working with a scammer, according to officials who said the victim was sent to ...
CEO Elon Musk is due to arrive in India next week for a visit that is expected to include a meeting with Prime Minister Narendra Modi and confirmation that Tesla plans to build a factory in the ...