- +91 80 45621100
- +1-408-705-2240
- [email protected]

- RADAR Systems
- SONAR Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Airborne Telemetry Solutions
- Airborne Systems
- Naval Systems
- Automated Test Equipment (ATE)
- →Product Finder
- COTS Boards
- Signal Processing Engines
- RADAR Video and Display
- Rugged Graphics and Video
- Single Board Computers
- Switches/Routers
- COTS Systems
- Display Systems
- Small form-factor systems
- Storage & Data Recorders
- COTS Software
- Development Tools
- Safety Critical
- Operating Systems
- COTS Enclosures
Case Study on Digital System For Multi Object Traking RADAR
- MRD5165 SOM
- SnapDragon 820 Nano SOM
- Texas Instruments
- 60GHz Indl. AoP Module
- 60GHz Indl. AoPCB Module
- 77GHz AoPCB Automotive RoM
- AM65x Industrial SOM
- Jetson Neuron Board
- AI Sensor Fusion Kit Lite
- →Product Registration

APPLICATIONS
- Automotive & Electrification
- Drone Electronics
- Industrial Automation
- Internet of Things Services
- Medical & Assistive Electronics
- Scientific Applications
- SOCs and Platforms
- Wearable Electronics
- Embedded Android Development Services
- Embedded Linux Services
- High Density Interconnect PCB
- Image Sensors
- mmWave Technology
- Power Optimization and Management
- Qt Applications
- Sensor Integration
- VxWorks Development Services
- Mobile C4ISR Platforms
- Master Control Room
- Tactical Drones
- AI BASED VIDEO ANALYTICS
- Video Analytics & FR
- Video Synopsis Software
- Tethered Drone System
- Heavy Payload Drone
- Anti-Drone Solutions
- MISSION-CRITICAL COMMN.
- Integrated Command & Control
- 4G/5G Backhaul
- Digital Console System
- COFDM Body Worn Cameras

Case Study on Mobile Surveillance Vehicle for Pimpri-Chinchwad
Dos and Don’ts of Wi-fi connectivity: Maximizing Range and Reception
While installing Wi-fi solutions, a user may come up with a few impediments; specifically w.r.t the range and reception. It is very important to be aware of these impediments and see how they could affect the installation, before going in for a wireless solution.
The first thing to do is to check the construction of the walls. In theory, Wi-Fi signals are capable of passing through walls and other obstacles relatively easily. However, in reality, some walls are thicker or use reinforced concrete and may block some of the signals. Materials such as drywall, plywood, other kinds of wood and glass can be easily penetrated by wireless signals. However, materials such as brick, plaster, cement, metal, stone, and double-glazed glass may cause problems. The following facts should therefore be kept in mind:
- Metal bodies absorb Wi-Fi signals. Therefore, wireless surveillance solutions do not guarantee connectivity between floors of buildings and between thick reinforced concrete walls
- If the walls are made of non-porous materials, your wireless connection may have a shorter range or a slower speed
- Elevators block Wi-Fi signals to a great extent. When placing an IP camera; make sure the elevator does not come between the camera and the Wireless Access Point
- Tinted glass panes carry metal constituents. So if you have tinted glasses anywhere between WAP and the camera, you can expect a drop in signal strength.
Interference
The other thing to check for is potential interference with the Wi-Fi network’s frequency range. The 802.11 wireless standards communicate in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Interference can slow down a network significantly and reduce its range as well. The two most common sources of wireless network interference are wireless telephones and microwave ovens. Existing previously installed 802.11 networks can also cause interference.
Potential sources of interference in the 2.4GHz ISM band:
- Microwave ovens
- 2.4GHz cordless phones, DSSS and FHSS
- Fluorescent bulbs
- 2.4GHz video cameras
- Elevator motors
- Cauterizing devices
- Plasma cutters
- Bluetooth radios
- Nearby 802.11, 802.11b or 802.11g WLANs
- Wireless Internet Service Providers (WISPs)
Potential sources of interference in the 5GHz UNII bands include the following:
- 5GHz cordless phones
- Perimeter sensors
- Digital satellite
- Nearby 802.11a or 802.11n WLANs
- Outdoor wireless 5GHz bridges
A basic wireless surveillance set-up normally consists of the wireless IP cameras, the Wireless Access Point (WAP) and the Network Video Recorder (NVR) or the media server. In addition to the above, keep the following points in mind while installing a wireless surveillance solution:
- Keep the antennas straight pointing to the sky unless told to do otherwise
- A long hallway or corridor will most likely need an indoor semi-directional antenna for coverage as opposed to an omni-directional antenna. Do check the manufacturer’s recommendations. Anytime a type of antenna that is not recommended by the manufacturer is added, do keep in mind that the signal may be getting a boost beyond the legal limits of the country.
- Weather events such as rain, snow, and even wind can wreak havoc with wireless signals
- A high concentration of human bodies can attenuate the RF signal due to absorption
- Trees are notorious for absorbing signal energy
- Do not keep the Access Point device at a low level on the floor. If possible, try placing the WAP at a location equidistant from all the walls of the room. In other words, keep it in the middle of the room or desired area of coverage
- As far as possible, keep the WAP above all sources of obstruction. Even if it means overruling the earlier point. For example, in an office environment, keep the WAP above the height of all the cubicles. We would recommend it to be mounted close to the ceiling
- Try not to place the WAP near sources of heat or under the sun
- Do not operate multiple WAPs in close proximity (<100mts apart). Especially if the same SSID is used on both.
- Once again, do not place the wireless IP Cameras at a low level. It is best placed high on the wall or nearer to the roof (to avoid all kinds of obstacles like furniture, cubicles, etc.)
- Try not to place the cameras near sources of heat or under the sun
- Do not keep the cameras too close to the WAP (<2mts). The camera radio may automatically turn down its transmit output power which may result in connection loss
- Do not keep the cameras too close to each other (<2mts). This will cause signal interference between them.
A careful and thorough evaluation of your security requirements will help a great deal in identifying the prudence of using a wireless surveillance system.
Max Qty for this product is reached.
- Company Overview
- Executive Profiles
- System Engineering
- Software Develoment
- Audio & Video
- Cloud, Mobile and IoT Applications
- RADAR & Signal Processing Applications
- UI/UX HMI Applications (HMI Software Development)
- Board Design
- Industrial Design
- High Speed Digital Designs
- Mixed Signal Design
- Power Supply Design
- FPGA Design Services
- Verification and Validation Techniques (Testing and Validation Services)
- DO-178B/C, DO-254, DO-160 Testing
- FCC/CE Certification Testing
- Production Support
- Product Lifecycle Support
- Custom PCB Design Services (PCB Layout Design Services)
- 820 Nano SoM
- MRD5165 Eagle Kit
- AI Sensor Fusion Kit
- NVIDIA Neuron Board
- AM65x Development Kit
- 820 Development Kit
- COTS BOARDS
- COTS SOFTWARE
- COTS SYSTEMS
- COTS ENCLOSURES
- AI Analytics for Smart City
- Press Releases
- Media Coverage
- Work Culture
- Current Openings
- Upload Resume
- Collaterals
- Support Center
- Infographic Library
- Video Library
- Create Account

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

How to Boost Wi-Fi Signals Through Walls: A Comprehensive Guide
- Share on Facebook Facebook
- Share on Twitter Twitter
- Share on Reddit Reddit
- Share on WhatsApp WhatsApp
- Share via Email Email

The internet has become an essential part of our daily lives that we often take for granted. From our jobs to our hobbies, we rely heavily on the Internet for almost everything.
Weak Wi-Fi signals, on the other hand, can disrupt our experience while using the internet by causing buffering and slow connectivity, both of which are very frustrating. The problem at hand becomes even more complicated when there are obstacles in the way of the Wi-Fi signal, such as walls or other impediments.
In this article, we will discuss some effective techniques for how to boost Wi-Fi signals through walls so that you can maintain your connection without experiencing any disruptions.

What Weakens Wi-Fi Signal?
In their most basic form, Wi-Fi signals are radio waves that transmit data from one device to another via a set of predetermined frequencies. When these radio waves come into contact with obstacles such as walls, it weakens the Wi-Fi signals.
Wi-Fi signals can operate on either the 2.4GHz or 5GHz frequency bands , depending on which band is available. The 2.4GHz frequency band is more susceptible to interference and attenuation. The range for this kind of band can be limited, so they do not perform as well as 5GHz when trying to penetrate obstructions.
Data is transmitted over Wi-Fi networks using electromagnetic radiation, which moves in waves at the speed of light. These waves are capable of traveling through the air, but they are susceptible to being weakened or absorbed by obstacles in their path, such as walls, furniture, or other types of physical barriers. These obstructions either absorb or reflect the waves that we know as Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi signals can be disrupted not only by the height of the obstruction but also by its thickness and density. Thick walls made of materials such as brick, concrete, or metal are the hardest to penetrate. In a similar vein, obstacles such as water, mirrors, or glass can cause interference with Wi-Fi signals by reflecting them.
Additionally, other electronic devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices, have the potential to cause interference and disrupt Wi-Fi signals. This is due to the fact that they operate on similarly sized frequency bands, which can result in signals that overlap.
Check Out: Top 10 Things You Should Know About AI in 2023
How to Check Your Wi-Fi Signal Strength

Checking your Wi-Fi signal strength is an essential step to ensure that you have a stable and reliable internet connection. Here are three ways to check your Wi-Fi signal strength:
- Use a Wi-Fi Analyzer App : Wi-Fi analyzer apps are available for both Android and iOS devices. These apps scan the available Wi-Fi networks in your area and display their signal strength and other details like frequency, channel, and security type. They can also help you identify any interference or overlapping signals that may be affecting your Wi-Fi strength.
- Look for the Wi-Fi Signal Icon on Your Device: Most devices display a Wi-Fi signal icon on the status bar or in the network settings menu. The number of bars or the strength of the signal icon can indicate how strong or weak the Wi-Fi signal is. A full signal icon or all bars indicate a strong signal, while a weak signal icon shows fewer bars.
- Check the Router’s LEDs: Many routers have LED lights that indicate the strength and status of the Wi-Fi signal. These LEDs can help you identify any issues with your Wi-Fi connection, like a weak signal or interference. Check the user manual or manufacturer’s website for your router model to know which LED corresponds to the Wi-Fi signal strength.

How to Boost Wi-Fi Signals Through Walls

- Move your router to a more advantageous location, preferably one with less interference, and try using it again.
- Make the necessary adjustments to the antennas on the router to get the best possible signal coverage. Two distinct varieties of antennas can be used for routers: omnidirectional and directional. You can upgrade the antenna that is on your router to one that is of higher quality.
- Utilize a Wi-Fi range extender so that you can experience an improvement in the signal’s overall quality. There are many different types of Wi-Fi range extenders available, some of which include wall plugs, desktops, and even outdoor extenders. Make sure that you follow the instructions that are provided to successfully set up a Wi-Fi range extender.
- Installing a Wi-Fi mesh network will help improve coverage over large areas. A Wi-Fi mesh system is a network of nodes that work together to provide continuous coverage. These nodes communicate with one another to ensure seamless connectivity. Wi-Fi mesh networks work by relaying the signal from the router through several nodes.
- You should utilize a powerline adapter to extend the signal through the use of the electrical wiring in your home. This can be accomplished by using a powerline adapter. For a powerline adapter to function properly, it must be able to transmit a signal through the electrical wiring that is present in your home.
- Changing the channel of your Wi-Fi connection is an option if you want to have less interference from other Wi-Fi networks. Wi-Fi channels are the frequencies used by Wi-Fi networks to transmit data.
- Identify potential sources of Wi-Fi interference, such as microwave ovens, cordless phones, or other electronic devices, and then take steps to remove or disable them.

How to Maintain Strong Wi-Fi Signals

To maintain strong Wi-Fi signals, follow these tips:
- Download the most recent updates from the manufacturer to ensure that the firmware on your router is always current. Check for firmware updates regularly and install them as soon as they become available.
- Give some serious consideration to upgrading your existing router to a more recent model, one that not only improves the functionality of the device but also the quality of the signal that it transmits.
- When not in use, your router should be kept in an area that is dry, cool, and free from any potential sources of heat or moisture. Refrain from putting your router in a location where it will be too close to any walls or other obstacles that could potentially interfere with the signal.
- Maintain a distance of at least a few feet between your router and any other electronic devices to prevent electromagnetic interference.
- To protect your Wi-Fi network, enable WPA2 encryption and select a robust password.
- Disable guest networks to stop unauthorized users from accessing your Wi-Fi network.

What Is the Best Wi-Fi Range Extender for Thick Walls?
If you are looking at how to boost Wi-Fi signals through walls, the best Wi-Fi range extender for thick walls include options like NETGEAR Nighthawk X6S Tri-Band Wi-Fi Range Extender ($349+) , the TP-Link RE450 AC1750 Wi-Fi Range Extender ($59+) , and the Linksys AC1900 Gigabit Wi-Fi Range Extender ($19+) .
Can Aluminum Foil Boost Wi-Fi Signals?
Aluminum foil can reflect Wi-Fi signals, but it is not a reliable method to boost signal strength. It is recommended to use proper techniques such as repositioning the router or using a range extender for better signal coverage.
How Do I Check the Wi-Fi Signal Strength on My Router?
To check the Wi-Fi signal strength on your router, you can use a Wi-Fi analyzer app, look for the Wi-Fi signal icon on your device, or check the router’s LEDs.
How Often Should I Upgrade My Router?
The recommended timeframe for upgrading your router varies depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. However, it is generally recommended to upgrade your router every 3-5 years to ensure the best performance and security.
How Do I Secure My Wi-Fi Network?
To secure your Wi-Fi network, you can set a strong password, enable WPA2 encryption, disable guest networks, and update your router firmware regularly. Additionally, you can limit access to your network by using MAC address filtering or hiding your network’s SSID.
It is not impossible to boost Wi-Fi signals through walls, even though doing so can be difficult. If you are prepared with the right tools and strategies, you will be able to achieve uninterrupted connectivity while using the internet and have a pleasant experience overall. We have covered everything you need to know about boosting your Wi-Fi signals through walls, including moving your router, upgrading your antenna, and reducing interference. If you make sure to follow all of these recommendations, you will never have to worry about a Wi-Fi signal that is too weak again.
Subscribe For Weekly Updates
Sign up for our bi-weekly Nerdable recap, including technology, gadgets, collectibles, and more.

Does Wi-Fi Go Through Walls? – How to Boost the Signal

Wi-Fi, like all other radio waves, is interrupted by obstacles. The best way to get a clear, strong Wi-Fi connection is to stand right next to the router and modem, but that’s almost never likely going to happen. Walls, doors, fences, and garages are all thought to limit Wi-Fi signals, but do they actually have an impact?
So, does Wi-Fi go through walls? Yes, wi-fi can travel through walls, but dense materials such as solid metal and concrete can limit the frequency. It all depends on what’s inside the wall. In most cases, the hollowed nature of walls around houses doesn’t have too much of an effect on the strength of your Wi-Fi.
Throughout this article, you’ll also learn the following info:
- What affects Wi-Fi strength through walls?
- How can you boost the signal through walls?
» NAVIGATION «
Can Wi-Fi Signals Travel Through a Wall?
Wi-Fi is much more efficient than we give it credit for. It’s always annoying when you can’t get a solid signal to your devices, but as you learned above, walls aren’t always the culprit. Your Wi-Fi signal won’t be disrupted by hollow doors and walls, especially if you’re sitting close to its source.
Here are five factors that can impact the strength of your Wi-Fi signal when it’s traveling through a wall:
- What’s inside the wall ? Is it made out of metal, wood, drywall, etc.? Knowing the material will help you to figure out if it’s causing any problems. Wood is hard for a signal to pass through due to its density, while metal is known for reflecting Wi-Fi signals in the opposite direction. Drywall is pretty much never an issue.
- Do you have anything stored in or around the walls ? If you’re storing clothing or other belongings in a closet, you’ll definitely add to the barrier. Much like a hollow wall, clothes don’t add much of a blockade on their own. However, paired with a wall and other objects, the signal might fade a bit.
- Is your Wi-Fi’s router or modem blocked ? It might seem convenient to put them inside of an entertainment center or under your desk, but every little barrier builds up to make it harder and harder for the signal to go to you. Add a wall in between you and the source, and you could imagine the challenges.
- Remove bulbs, lamps, microwaves, and anything else that could distort the signal on its way to you . These obstacles can cause a quick disruption, so place them away from the wall that sits between you and the router and modem. By limiting the objects, big or small, that separate yourself from the source, you can greatly enhance the signal.
- Finally, if your walls are porous, then you shouldn’t have an issue . Non-porous materials prevent your signal from finding a way in, causing it to slow down instantly. There’s not much that you can do other than open a door or completely replace the wall in this situation, unfortunately.
How to Improve Your Wi-Fi’s Signal Through Walls
Even if there’s a slight disruption, it can be infuriating to deal with malfunctioning Wi-Fi signals. The good news is that you can try out a few suggestions to boost its strength and improve your chances of uninterrupted connection.
For example, you can point the antennas toward the room that’s having trouble. It might not change too much, but it definitely improves the direction and concentration of the signal in your favor.
Another thing that you could try is to remove any trees or other plants in between you and the Wi-Fi’s source. Trees can limit Wi-Fi signal since they’re made out of solid wood. Think about how hard it is to get a radio station to work in the middle of the forest!
Lastly, consider getting a Wi-Fi booster to enhance the signal in the direction of your room. This will give it the boost it needs to travel through walls and doors without a problem. The NetGear Wi-Fi Range Extender is one of the most popular and effective models on the market, and it’s not too expensive either.
Whichever solution you choose, there’s no denying that most walls have little to no impact on your Wi-Fi signal. Instead, you should try to remove other obstacles to limit the number of disruptions in service.
Final Words
Wi-Fi can travel through most walls as long as they’re hollow. However, distance, the wall’s material, and a few other factors can ruin the signal completely. Before you go and rip out your wall, try some of the tips provided throughout this article.
Wi-Fi boosters, new antennas, and removing trees can be enough to get rid of your frequency problem. You might even need a new router or modem. Unless your wall is non-porous, made of metal or wood, or it’s an elevator door (highly unlikely), then it won’t cause too many problems.

How to Sleep Sitting in a Chair (It’s Perfectly Doable!)

Flat vs. Fitted Sheets: Which Bedclothes Are Better?
Related posts.

What Color Walls Go With Brown Furniture: 10 Tips & Ideas

Neighbor Uses My Driveway to Turn Around: What Are My Options?

How to Keep Your Neighbors at a Distance: Different Strategies

How to Tackle Gaps Between Bathroom Vanity and Wall: Best 8 Ideas
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Does WiFi Go Through Walls? Understanding The Basics
By Author Jonah Matthes
Posted on Last updated: February 21, 2023
You’ve must’ve seen those memes asking, “What do you choose? Two days off work, or a thousand dollars and two days without WiFi?” Well, if you live your life online like us, you’d never take the money.
WiFi can go through walls because of how long its radio wavelengths are. They’ll lose a bit of strength, but they’ll still be strong enough to use. However, 2.4 GHz WiFi is much better than 5 GHz WiFi at going through walls because it has much longer wavelengths.
WiFi made its debut in the late ’90s, and today we talk through it, shop through it, and even date through it. So, you may have questions about the technology behind WiFi and how it works. We’ve put together this short guide for understanding the basics of wireless signals.
How Does WiFi Work Through Walls?

Yes, WiFi signals do pass through walls. But before we fully answer that question, we need to understand how WiFi works in general.
WiFi is based on electromagnetic radiation. And don’t worry, although the term sounds awfully dangerous, this form of electromagnetic radiation isn’t harmful. You won’t start to glow in the dark out of nowhere.
In fact, visible light, infrared light from cameras, and microwaves are all forms of electromagnetic radiation. WiFi utilizes a very low frequency of electromagnetic radiation that falls within the range of radio waves, a term used to describe frequencies between 3kHz and 300 GHz ( source ). WiFi works on two frequencies: 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
If you picture WiFi signals, billions of such waves are emitted from your router each second. These waves spread around the router. Then, your device’s antenna receives the waves, processes them, and sends data back to the router.
Now, what if there are solid objects like walls around? Will the WiFi signals still go through?
Yes. WiFi signals should pass through walls just fine, and that’s because radio waves have very long wavelengths. These signals penetrate objects such as walls and furniture, lose a bit of energy, and easily emerge on the other side. You could say that walls are as transparent to radio waves as glass is to visible light.
But this slight loss of energy makes WiFi susceptible to attenuation, which means that it weakens as it travels farther through the air or goes through solid objects. So each wall that the signal passes through reduces its power, and if you have too many thick walls around, your WiFi signal might be weak.
Which Building Materials Slow Down WiFi Signals?
Certain materials affect WiFi signals more than others. This is because these materials have a high density and absorb electromagnetic waves.
Here are a few examples:
- Concrete is the worst offender when it comes to slowing down WiFi signals. Reinforced concrete is embedded with iron rods which further block radio waves.
- Brick and masonry walls are not as dense as concrete but also absorb a significant amount of radio waves.
- A simple glass window might not block your WiFi, but double-paned insulating windows are almost as bad as brick walls.
- Metal in your windows, ceiling, or walls can also block WiFi signals.
- Wood and sheetrock walls are not so dense so they won’t affect WiFi much, but they can still cause minor signal loss.
Remember that thickness also affects the WiFi signals. A thick concrete wall will block a lot more than a single layer of brick and sheetrock.
Which WiFi-Band Goes Through Walls Better?
The radio wave is a broad term used to explain a range of electromagnetic waves. WiFi technology only uses a small portion of the radio wave spectrum, the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies.
The 2.4 GHz band means the router sends 2.4 billion signals each second. These signals have a larger wavelength, so even if they go through many walls, at least some will reach the connected device. As a result, 2.4 GHz provides extensive area coverage.
In a 5 GHz band, the router sends out 5 billion signals each second, giving it an advantage in speed and bandwidth. However, to accommodate the higher number, the wavelength of each signal is reduced, which means they lose more energy when passing through walls and can’t reach your devices if they’re at the other end of a building.
So, the 2.4 GHz band is always preferred when there are a lot of walls in the area. For example, offices and hospitals use the 2.4GHz band because the signals go through multiple walls. 5 GHz is better when it comes to pure speed and bandwidth.
However, the placement of the router also plays an important role. At the right spot, both bands will give the best performance.
Best Mesh WiFi Systems for Thick Walls

Just because you have many walls around doesn’t mean you can’t enjoy a stable WiFi connection. When it comes to covering dead zones and getting a strong signal all over the house, mesh WiFi systems are the way to go.
WiFi mesh uses your main router and several access devices strategically placed around your house. These smaller access points called ‘Nodes’ make a network that amplifies the signal from the parent router and then broadcasts it as a stronger signal to connected devices.
As a result, if you have thick walls, the nodes will compensate for the lost signal, and you’ll always enjoy stable WiFi.
Recommended Mesh WiFi Systems
Mesh WiFi systems are easy to set up and are perfect for large or multi-level homes. Below we have listed the best WiFi mesh systems for 2022.
Google WiFi AC1200 Mesh WiFi System (on Amazon)
With these sleekly designed packs, Google WiFi is one of the best mesh WiFi systems for the home. You’ll be able to cover 4500 sq feet with this pack and have that no buffering experience in every corner.
It also has parental control and device restriction features, so you can also schedule your kids’ internet time.
NETGEAR Orbi Whole Home Tri-band Mesh WiFi (on Amazon)
Equipped with the WiFi 6 technology and Netgear armor cybersecurity, Orbi WiFi will keep your devices safe and secure.
In addition, it has a 1.4 GHz powerful processor and promises 4.2 Gbps speed over WiFi. With the availability for 100 devices, you’ll get the best performance no matter how many devices you have in your home.
Amazon Eero Mesh WiFi System (on Amazon)
Another high-performance mesh WiFi system, Amazon eero, is one of the best WiFi mesh systems available in the market. With dual-band WiFi support and powerful processing, Amazon eero delivers powerful speed.
It also has tight security encryptions and works with Alexa to automate your WiFi around the house.
Meshforce M7 Tri-Band Mesh WiFi System (on Amazon)
Each pack covers up to 2000 square feet; Meshforce M7 is one of the most powerful mesh WiFi systems on the market. It’s compatible with both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz and uses high-power amplifiers for more robust output, essential if you have thick walls.
It also comes with the ‘My Mesh’ app guide to easily set up and manage the system from a mobile device.
If you have lots of thick walls around and your WiFi cannot reach your iPhone 10 on the other side of the home. Mesh WiFi is the solution to your issues.

- May 3, 2024 | HOW TO DO IT: Set up any DIRECTV remote to control the TV
- May 3, 2024 | Should you wait until “next year’s antennas” come out?
- May 2, 2024 | What’s the difference between a DIRECTV SWM and a DSWM?
- May 2, 2024 | Sustainability in the Workplace: How Electronics Can Reduce Environmental Footprints
- May 2, 2024 | THROWBACK THURSDAY: Five Years of weBoost Drive Reach
- May 2, 2024 | When should you use a Broadband DECA?
- May 1, 2024 | Fix marine satellite reception problems in one easy step
- May 1, 2024 | Ken Reid and Rolfe Kanefsky
- May 1, 2024 | Best of the Blog 2023, Volume 11
- May 1, 2024 | Does your TV work with MPEG-4? Here’s how to know for sure
- April 30, 2024 | Podcast #576: Nothing to stream already and it’s only April
- April 30, 2024 | NOW IN STOCK: The first ATSC 3.0 converter box at a fair price
- April 30, 2024 | Is it legal to get TV and radio broadcasts from another country?
- April 30, 2024 | REAL-WORLD TESTING: Solid copper vs. copper-clad steel
- April 29, 2024 | The BEST Charging Cable – 50% OFF
- April 29, 2024 | Do you need special cable in order to ground your equipment?
- April 29, 2024 | What’s the best preamp for an FM antenna?
- April 29, 2024 | Create Your First QR Code: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- April 28, 2024 | Lost DIRECTV local channels on your boat? Here’s what to do
- April 28, 2024 | Problems with 3rd party lenses and Blackmagic Design Cameras? Finally– a solution
How far can a wi-fi signal travel?

Posted By: Stuart Sweet May 30, 2013
Quick answer: further than you can imagine.
We’re often frustrated when our wi-fi doesn’t travel all the way from one end of the house to the other. We swear under our breath when it doesn’t go into the meeting room we’re about to enter. Yet, there is no reason that a wi-fi signal can’t travel miles, or hundreds of miles with the right equipment.
Wi-fi is just a radio transmission. Radio transmissions come thousands of light-years from space. There are two limitations to any form of transmission: broadcast power and obstruction. Wireless routers tend to use a very small amount of broadcast power, along the lines of a nightlight bulb. This is on purpose: wi-fi is designed to stay in smaller areas, so the same frequencies can be shared with millions of people and none of the signals interfere.
Up the power, or redesign the antenna, and you can get a huge difference in coverage. You have to be careful not to run afoul of the rules, though. An antenna like the one you see above can help you reach every area of your home or business while you’re operating your router at the maximum allowed power.
The other issue with any sort of radio signal is of course obstructions. Radio signals travel from faraway galaxies with nothing between them and us, through almost empty space. On the other hand, your wi-fi router has to go through walls full of wiring and possibly even metal studs. RF signals travel well through walls but nowhere near as well as they do through open space.
In the coming weeks, we’ll be showing you ways to build wi-fi networks that can serve even the largest spaces!
About the Author
Stuart Sweet
Related articles.

BREAKING: gotW3 brings back unlimited data plans!

Router, modem or switch — what is it?

Real customer service never goes out of style

Why do computers and phones get hot?
Up to 25% off most products - Start Shopping .

We're here to help. Call us! 1-855-846-2654

We’re here to help. Call us! 1-855-846-2654
How Much & Which Building Materials Block Cellular & WiFi Signals?
Dec 21, 2021

Have you ever wondered how much do various kinds of building materials block cell phone and Wi-Fi signals? Well, here's your chance to find out! If you have reception problem with your cell phone, you may find that you're a bit frustrated with trying to determine the cause of your weak signal. Your phone works in some spots outside of your home, but inside your abode, there is little to no signal at all. Obviously, there's something in the house which is stopping the reception, but what is it?
While Mother Nature does block cell signal from -5 to -25 dB where rain attenuates signal anywhere from -1dB to -5dB and foliage attenuates it anywhere from -1dB to -25dB, the odds are that it is your home building materials that blocks most of your signals. They are the number one cause of cell phone reception disruption. Knowing which materials can deflect your cell phone reception may help you to find solutions to increase or gain your signal using a cell phone signal booster or similar device. Or even help you reduce reception if you're concerned about radiation affecting your health. Either way, listed below are the top building materials that stop wifi and cell phone signals in its tracks.
Please note that while we mostly mention mobile signal strength attenuation figures below, wifi signal strength is similarly attenuated. The 802.11 standard provides several distinct radio frequency ranges for use in Wi-FI communications: 900 MHz 2.4 GHz, 3.6 GHz, 4.9 GHz, 5 GHz, 5.9 GHz and 60 GHz bands. Each range is divided into a multitude of channels. Therefore, we won't go into too many details to prevent getting sidetracked or distracted with all mobile and wifi frequencies and channels. Nevertheless, you will get a rough idea from the fully researched list below roughly how much of the signals will get attenuated by which products/ materials.
Clear Glass.
There's a misconception that clear glass fixtures, such as windows, are the best place to gain access to a signal. While the clear area is ideal for letting in light, they can bounce a signal around or reflect the signal away from the house. This is especially true for windows which are double insulated. There're triple pane windows in newer homes with reflect signals even more. The most deflecting ones are the latest low emission (Low-E) windows that keep the elements out to keep you warm or cool inside depending upon the weather outside. But if you're looking to improve cellular reception by standing next to a window, open that window for most impact. Blockage on windows can reach -4db.
Sheetrock and insulation.
Sheetrock is one of the lower blocking agents for a cell phone signal. However, it can cause your signal to be blocked completely if it is already weak. Keep in mind that 3G, 4G, 5G signals are generally the same as a radio signal and so you can see fluctuations in your signal of -2db. Closed rooms, meaning those which are not a part of an open floor plan, are more susceptible to cell phone signal disruption than sheet rocked rooms which are part of an open layout.
Although porous, fiberglass insulation in walls and attic can disrupt cell phone signals slightly, if it is thick enough. Foil-faced design of some insulation products helps keep out unwanted elements. However, foil facing used on insulation products like foam board or fiberglass batts can block radio frequency signals. Additionally, the interior walls made with denser materials can cut the reception down another -2db. In this manner, sheetrock and insulation has the potential to cut your cell phone reception before it even enters your home.
Plywood, Solid wood, Trees around the house.
Plywood which makes the majority of the structure and framework for many residential homes, reduces 3 and 4G networks up to -6db. Reduction is even higher at -9dB on 5G network. This number fluctuates a bit as there're different thicknesses of plywood, and different ways in which the plywood is compressed. Additionally, the cell phone reception loss can be increased should the plywood get damp/wet with numbers as low as -20db. But if the plywood on your house is wet, you have bigger issues to worry about(!)
Solid wood, such as that used in the flooring of the house builds upon the blocked signal of the plywood. While the finishing on the doors, floors, decking, etc. may be nice for that natural look, they are cell phone signal blockers. All wood slows down a signal. The thicker the wood, the more it will disrupt cell phone signal strength. Softer woods, such as pine, may not decrease the strength much, but you could still see a loss of -5 to -12db. Aside from indoor plants, trees outside including Pine trees that have branches with dense growth of leaves block signal to this or greater extent. The degree of blockage depends on the age or how old the trees are, and the size, or how large the trees are. Older and larger a tree surrounding a house, the more dead zones you can expect in the house.
Though incredibly sturdy against the elements, brick is one of the top materials for blocking a signal. First you have the thickness of the brick which slows the signal down. Secondly, you have mortar between the bricks which does not allow a signal. Additionally, brick generally has supplementary materials on the interior so that electronics, sheetrock, shelves, etc. can be added. The mere thickness of the wall combined with the density of this building material can block up to a whopping -28db scale.
When it comes to building materials, Metal is the top cell phone signal disrupter. Metal roofs as well as metal studs and interior metal will slow down the signal. While metal looks nice on a building, is durable against the elements, and can help with routing electricity and such away from the walls underneath, it can also route the signal away from the house. Most houses which have metal roofs will find that even if they live in an area where exterior signals are strong, interior signal strength will be weak if not non-existent. Ratings can drop as low as -32 to -50db, essentially making your home a dead zone. Along with 3G and 4G LTE, metal roofs deflect 5G signals the most because 5G uses higher frequencies that can penetrate metal the least.
Faraday Products.
If you're in a situation where you need to purposely block signals to prevent oscillation because your cell phone signal booster exterior and interior antennas are too close, then we carry high tech Faraday series maximum signal blocking materials to get the job done.
List of Materials and How Much They Block Cellular Signal:
Why should i care about the db and how can i increase my signal strength.
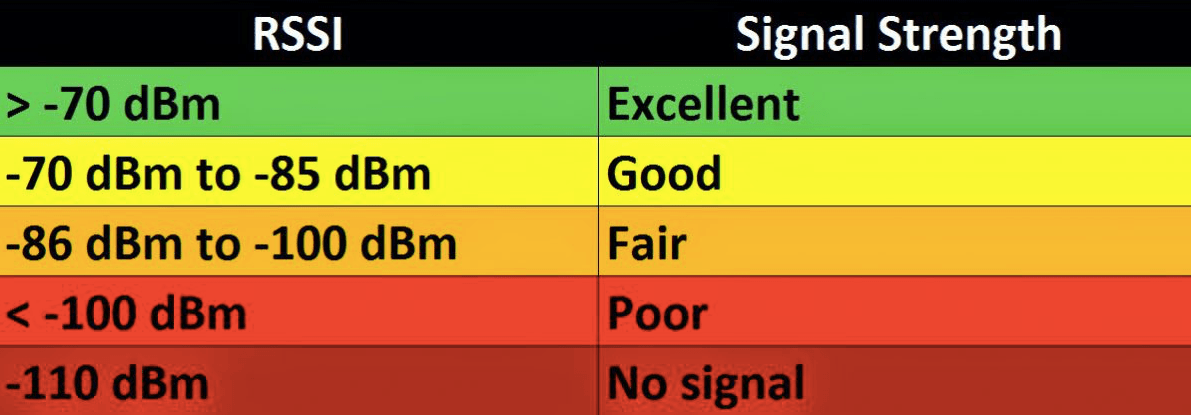
The decibels (dB) detected by your phone is how the signal strength is measured most accurately. This is true whether your phone is using 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, or 5G. A good signal strength metric is RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator. RSSI is a negative value, and the closer to 0, the stronger the signal. In other words, the closer to -50db you are, the better the signal because it typically ranges from -50 (strongest) to -120 (weakest). Keep in mind that a -120db is a deadzone while -50 is full bars. This is not to say that metal will put your phone at -120db though (dead zone). It may put it at -100db or more. The closer to -50 dB, the better the cell reception. Find out how to check signal strength in decibels on your phone or see the full scale chart showing the correlation of Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) in dBm or Decibel-Milliwatts versus corresponding Signal Strength in laymans terms below:
To increase your signal in your home, use a residential cell phone signal booster . Follow the steps in other articles on finding the best spot for your cell phone booster . Should you have questions about which booster is best for your home, business, or commercial space, try our phone booster selection tool or please call us - we would be happy to help you find the right phone booster.
Share this post
17 comments
- Tags: cell phone booster , cell phone signal booster
← Older Post Newer Post →
Metal roofs are generally not a problem in areas of otherwise good coverage. In fact, when I installed my new metal roof and then added thermal reflective barrier under the rafters I actually increased my reception for both wifi and cell coverage.
if things work out for the best, these reflective surfaces can create an excellent reflective surface to HELP with your reception. Do not think that just because a roof is metal that you lose reception and coverage. Just the opposite might be true!
Very good info. Was considering a metal roof on my manufactured home but thank the “cell gods” I didn’t do it. From my experience, you’re way better off with GSM for penetrating your house than CDMA. Nothing but grief with Verizon (on Straight Talk) in my house. Had to put my phone on a window sill facing the Hwy to stream anything. Switched to ATT sim (also Straight Talk) and poof! I can go anywhere in my house, in a closed closet or the bottom of the toilet and I can stream video without a glitch. The ATT and Verizon towers are in nearly all the same locations up and down the Hwy near my house (in the sticks in Northern Arizona – just South of the Grand Canyon) but the ATT GSM signals are tops in my house. Long live GSM!
Live in Mobile home with an aluminum roof with a tin roof over that with a 2 foot clearence. Will your product help with a straight talk phone. I get NO SERVICE inside my house. Leave out in the boonies. HELP!
Nothing is ever as easy as it looks. I appreciate the effort made to set these videos and instructions up but I am skeptical that things can be put into place so easily. Maybe I’m wrong. I just don’t want to buy a vehicle cell booster and get a migraine trying to put it in.
Interesting comments. I find it very interesting that since changing to T Mobile we have lots of dropped calls, garbled voices and texts that don’t send. I’m not sure why my iPhone 12 doesn’t work better, but it is a poor substitute for my old 7 iPhone. No problems there. Anyway, I called T Mobile and they said because it is the house, it isn’t their issue. I call BS… as the calls made on Verizon got through, very few dropped calls or text issues. Putting the problem on a building is making it a scapegoat. For what is paid to them for service every house should be able to capture a signal. Now answer me this… if people can use wifi for their phones, why do they need a phone company at all? Just use the wi-fi. Well, I hope you can tell that I’m frustrated with the technology, the companies and the expense for a service that isn’t… why should we pay if we can’t get the signal? Isn’t the contract with any cell phone for them to provide service to your phone and on to another phone and the other phone back to you? If that doesn’t work I think paying is usery… as we are paying for service we don’t get. Oh, BTW, T Mobile sent us a signal booster to help with our problem… it is a wi-fi booster… ironic since Nathan (our tech rep) said we need to turn off all wi-fi on our phones and just use their service. Why then did the company send us a wi-fi booster??? With all this bitchin’ I’m not unhappy with what I’ve read. this is a great discussion and thank you one and all for writing.
I never thought the glass would be what causes problems. My mind is blown. No way. jj
I had a steel roof installed on my home in late 2017. My cell phone reception was very sketchy after that.
Then I got a new cell phone, and most of my reception problems went away.
But Verizon is finishing up a 5G tower 200 feet from my back door, and that conceerns me greatly.
Also wondering if that tower may affect my property value in the future.
How far do Wi-Fi signals travel outside house your home typically an uninsulated home
Question. Carbon. Particularly paper. very thin caliper paper. Almost as “thick” as tracing paper. If something is being tracked by a powerfully strong signal locater, for instance a GPS sattelite in orbit. Would a thick sheet, or a number of thick carbon “wrapping” sheets be able to make the wrapped item undetectable?
My house has literally become a deadzone. I go outside and have decent to real good signal pretty much all the time but as soon as I come inside I lose any and all signal I have. I’ve tested my signal a lot lately mainly to see if the strength of the signal is by chance getting better but each time it’s the same. It’s consistently been between -115db and -130db with the last test I did being -126db. I have a metal roof but should it be causing complete loss of signal like that?
Is there a test method for testing the signal loss of 5G through materials? Is there a reference for the above data that we can access?
I must confess I was very interested and impressed with the thoroughness if your reporting; however, what I needed to convince me were links to the studies on which the reported facts were based. Are they available anywhere?
I’m glad there is research being done on what materials can block a wifi signal because this blog opened my eyes to what materials can block wifi signals. Unbeknownst to me, there are many materials that do so. That explains why there are so many iffy areas in my home where I get dropped calls or crummy reception. If someone wanted to figure out how to block a wifi signal from the router, they could come to my home. My back room has the worst wireless signal and I live in a smaller house. Thanks to this blog, I know how to get around these problems (besides buying a new home).
5G is a completely different animal. What on God’s Earth will block that nefarious signal ?
I look at this list of materials and I start to shudder. What can block a wifi signal? Pretty much everything that’s found in your home and office. Who would have imagined glass could block a wifi signal? Apparently, there’s a lot of research into what can block a wifi signal, as seen with the evidence here. A cell phone booster might be the way to go in my home, because I’m always having problems with signals. Glass? Oh man, it’s worse than I thought.
It looks like there aren’t many materials that help with signals. This pretty much measures up to what I’ve seen wherever I go. I’ve been in condos, townhouses, beachhouses, and homes, and there are always problems with cell coverage. I gotta say it is cool to know how to boost cell phone signal strength using these cell phone signal booster doo-dads.
I love this site. I learn so much about cell phone technology by browsing the various articles. I always thought a window was a surefire way to get a good signal while inside. Apparently not. It’s amazing how poor cell phone reception can be inside your home, even when you have a decent cell phone.
Leave a comment
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published.

Does 5Ghz WiFi Travel Through Walls? [Avoid These Obstacles]
If you use WiFi in different areas of your home or office, you may notice that devices connected to the 5GHz frequency occasionally experience weaker connections compared to those linked to a 2.4GHz band. Unfortunately this is because WiFi on 5GHz does not penetrate walls and solid objects as efficiently as 2.4GHz networks.
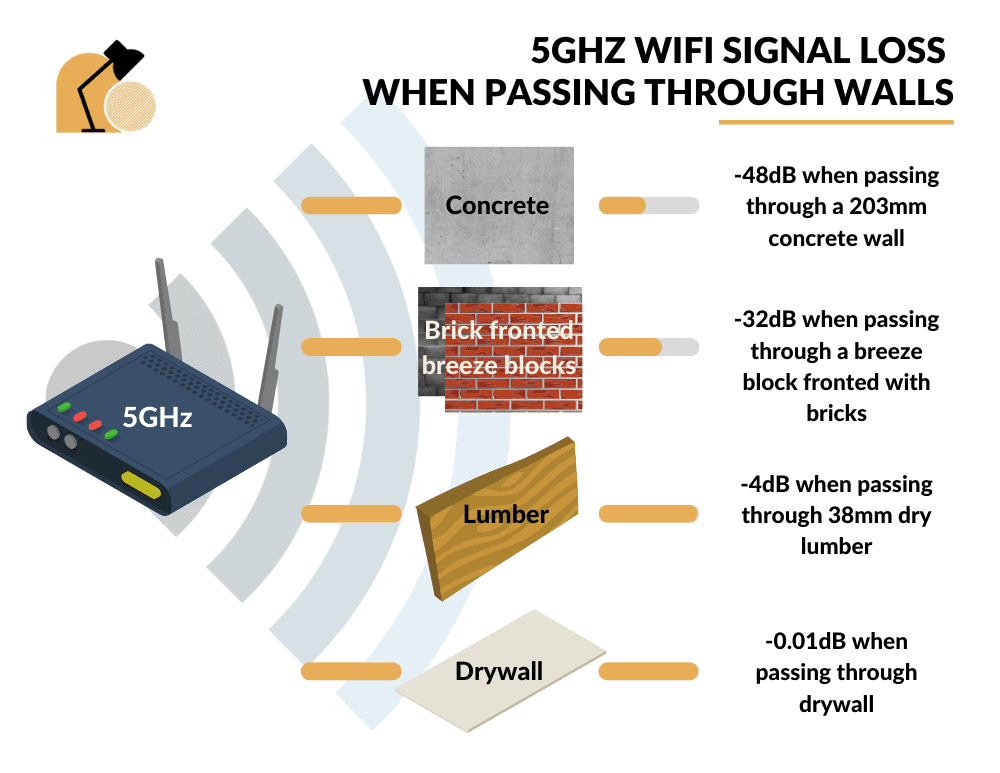
5GHz WiFi can travel through walls however its shorter wavelength is more susceptible to losing signal strength (vs 2.4GHz) when traveling through solid objects. Walls made from dense materials such as concrete and bricks can cause significant signal attenuation which may result in unreliable packet delivery.
Concrete at 203mm thickness was measured as causing -48dB, whilst brick faced masonry blocks caused -32dB. Lumber (-4dB) and drywall (-<1dB) barely impact the speed and reliability of a 5GHz WiFi connection.
This article looks at how walls and other materials slow WiFi and offer steps to make the best use of the 5GHz WiFi connection you have in your home or office. We’ll look at:
- Understand the difference between 2.4GHz and 5GHz WiFi
- Learn what types of materials block WiFi signals
- Choose the right spot for your WiFi router
- Use both 2.4 GHz and 5GHz WiFi networks
If despite implementing these steps you continue to have problems establishing a stable connection, you should consider investing in a WiFi extender for increased wireless coverage. Check out our article on WiFi boosters to learn more about choosing and setting up a WiFi extender.

2.4GHz is good at sending data at low speeds across greater distances whereas 5GHz offers faster speeds across shorter distances.
How does 5GHz WiFi compare to 2.4GHz?
The radio waves emitted on the 2.4GHz WiFi band are longer, allowing them to travel further through solid objects. This means 2.4GHz WiFi suffers less from signal degradation due to walls and other objects.
5GHz WiFi uses shorter radio waves, which is necessary for achieving faster speeds over a smaller range. However, these shorter radio waves are more easily affected by obstacles, such as walls.
However whilst 2.4GHz forms a better connection through walls and barriers, another factor to consider is that 5GHz is less prone to interference from other electronic devices.
Bluetooth devices and most WiFi-enabled electronics have been designed to use the 2.4GHz band, thus increasing the risk that interference may occur to a 2.4GHz network.
What type of walls block a WiFi signal?
Walls, floors, and ceilings impact WiFi signals. However, some building materials and objects are more likely than others to negatively impact your network.
The attenuation of 5GHz through different different building materials was explored in a controlled experiment by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Here are some of the materials that may block a WiFi signal, listed in order of severity:
- Metal
- Concrete
- Plaster with metal lath
- Ceramic tile
- Glass and mirrors
- Drywall
What is WiFi signal attenuation?
WiFi signal attenuation is measured in decibel loss, which has a non-linear relationship with signal strength. For example a 3dB of loss (-3 dB) halves the signal strength whilst 10dB loss (-10dB) provides ten times less signal strength.
If you’re interested in a little more information on signal strength, I’ll leave a link to a more in-depth guide here .
The main thing you need to be aware of for our purpose is that the greater the decibel loss the weaker the WiFi connection you can expect to receive.
Wi-Fi connections become unstable at -80dB, which is approximately the minimum value required to create a connection. At -90dB it’s unlikely a signal will be established.
Where should I put my router to boost a 5GHz signal?
Try to place the router in a position that offers the most direct path to the area where you plan on using your wireless devices. You should also pay attention to the proximity of WiFi-blocking materials. Fish tanks, large appliances, and electronics may limit the strength of your signal.
Placing a router in a central area can help provide better coverage to all corners of your property. Yet, you may only need increased connectivity in a specific room or area of your home.
You should also try to minimize exposure to the objects and materials listed above. Imagine a line between the router and your wireless device. Move the router to limit the number of objects that block a direct path.
How can I improve my 5GHz WiFi?
Along with finding the right spot for your router, you can improve the 5GHz WiFi connection by continuing to use the 2.4GHz network. Using devices on both networks helps keep one network from dealing with too many devices.
Use the 2.4GHz network for low bandwidth activities, such as browsing the Internet or checking your email. 5GHz networks offer the bandwidth needed for online gaming and HD video streaming.
You can also enhance your 5GHz WiFi coverage by adding a WiFi extender. Place the extender on another floor or the room where you are most likely to use WiFi.
Does 5GHz WiFi go through walls? Yes, any WiFi signal can travel through a wall. However, walls can interfere with WiFi connections, especially when using 5GHz WiFi.
5GHz WiFi is more prone to interference from obstructions, resulting in a weaker signal. You can improve your 5GHz WiFi connection by placing your router in a central location. Choosing an area that offers a more direct path to your devices may improve the signal.
Similar posts
Jbl speaker hidden features: jbl charge 4 & jbl pulse 4.

Why Does My Mouse Lag On A Second Monitor? [SOLVED]

WiFi Can Read Through Walls!
In this research, we have taken a completely different approach to tackle this challenging problem by focusing on tracing the edges of the objects instead. The interaction of an edge with the incident RF signal is dictated by the Keller's Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (GTD). More specifically, when a given wave is incident on an edge point, a cone of outgoing rays emerges according to the GTD, referred to as a Keller cone. We then introduce Wiffract: a new method to image the edges of still objects by exploiting the GTD and utilizing the corresponding Keller cones. More specifically, our approach develops a mathematical model that uses the footprints that the resulting Keller cones leave on a receiver grid, in order to infer the corresponding edge angles via hypothesis testing. Once it identifies high-confidence edge points, it then propagates their inferred angles to the rest of the imaging space using Bayesian information propagation. We can finally further improve the resulting edge map using advances in the area of computer vision. We extensively test the proposed methodology with several experiments. In particular, we show how our proposed approach can enable the first demonstration of WiFi reading the English alphabet (even through walls). This application is in particular informative as the English alphabet presents complex details that can be used to test the performance of our proposed imaging system.
- It only uses the radio waves of off-the-shelf WiFi transceivers for imaging.
- It does not require any prior RF data for training a machine learning system for RF sensing.
- It exploits edge diffraction and uses the corresponding signatures that the Keller Cones leave on the 2D receiver grid to develop a mathematical framework for edge tracing.
- In one example application, it can image and read (i.e., classify) uppercase letters of the English alphabet, even through walls, thus enabling the first demonstration of WiFi reading through walls.
Here, we briefly summarize our proposed approach and show sample experimental results. See the Publications for more details.
Team Members
Back to top
Publication Information
Summary of our approach.
In this work, we present a new foundation for imaging still objects with only WiFi power measurements of a 2D grid of COTS receivers. Consider the scenario shown in Fig. 1, where a fixed wireless transmitter (located at \(\mathbf{p}_t \in \mathbb{R}^3\)) emits radio signals which interact with a set of objects located at \(\mathbf{p}_o \in \Theta \subset \Psi\), where \(\Theta\) is the set of all object locations and \(\Psi\) is our imaging space of interest. The signals scattered from these objects are then captured by a uniform two-dimensional RX grid.
Sample Experimental Results
Experiments in Areas 1 and 2:
Experiments in Area 3:
Acknowledgments
National Science Foundation
Office of Naval Research
Copyright © 2007-2023
How Far Does Wifi Reach

- Internet & Connectivity
- WiFi & Ethernet

Introduction
Wifi, short for wireless fidelity, has become an integral part of our daily lives. It allows us to connect our devices to the internet without the need for cables, giving us the freedom to work, browse, and stream from anywhere within its range. But have you ever wondered how far wifi signals can actually reach?
Understanding the range of wifi signals is essential for optimizing our internet connectivity and ensuring reliable performance. In this article, we will explore the factors that influence wifi range and discuss how different devices may have varying signal capacities. We will also delve into ways to extend the reach of your wifi signal , so you can enjoy a seamless internet experience throughout your home or office.
Before we dive deeper into this topic, it’s important to understand how wifi signals work. Wifi operates on radio frequencies, typically either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, and uses electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive data. These waves can travel through walls, floors, and other obstacles, but their strength diminishes as the distance increases.
Now, let’s explore the various factors that can affect the range of wifi signals.
Understanding Wifi Signals
Wifi signals are a form of wireless communication that allow devices to connect to the internet wirelessly. These signals operate on radio frequencies, which are designated for wifi use. Understanding how wifi signals function can help in optimizing the performance and range of your wifi network .
Wifi signals are transmitted using electromagnetic waves, similar to radio or television signals. These waves propagate through the air and can travel through walls, floors, and other obstacles, although their strength diminishes as the distance increases.
The range of a wifi signal is determined by a combination of factors, including the frequency band being used, the transmitting power of the router, and the presence of any obstructions. Most wifi routers operate on either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.
The 2.4 GHz frequency band has a longer range but is more susceptible to interference from other devices, such as microwaves and cordless phones, as well as congested wifi networks in densely populated areas. On the other hand, the 5 GHz frequency band provides faster data transfer speeds but has a shorter range and is less prone to interference.
The transmitting power of the router also plays a crucial role in determining the range of a wifi signal. Routers with higher transmitting power can cover larger areas, ensuring a wider range for wifi connectivity.
Additionally, the presence of physical obstructions, such as walls, floors, and furniture, can affect the strength and range of wifi signals. Thick walls and metallic objects can block or weaken the signal, leading to reduced coverage in certain areas.
Understanding these factors can help you position your router strategically and make adjustments to optimize the range and performance of your wifi network.
Next, let’s explore the different factors that can impact the range of wifi signals for different devices.
Factors Affecting Wifi Range
Several factors can affect the range and coverage of wifi signals. Understanding these factors can help you optimize your wifi network and improve the connectivity throughout your space.
1. Wifi Router Placement: The placement of your wifi router plays a vital role in determining the range and coverage of the signal. Placing the router in a central location, away from obstructions, ensures that the signal can reach all areas of your home or office. Avoid placing the router near walls, metal objects, or other electronic devices that can interfere with the signal.
2. Antenna Type and Position: The type and position of the antenna on your wifi router can also affect the range of the signal. Some routers have external antennas, which can be adjusted to direct the signal in specific directions. Experimenting with different antenna positions can help you find the optimal setup for maximizing wifi coverage.
3. Interference from Other Devices: Wifi signals can be affected by interference from other electronic devices, such as cordless phones, microwave ovens, and Bluetooth devices. These devices operate on similar frequencies and can disrupt or weaken the wifi signal, leading to a reduced range. To minimize interference, keep your wifi router away from such devices or switch to a less crowded wifi channel.
4. Wifi Channel Congestion: In areas with multiple wifi networks, overlapping channels can result in interference and decreased wifi range. Using a wifi analyzer tool, you can determine the least congested wifi channel and manually set your router to operate on that channel to minimize interference and maximize wifi range.
5. Building Materials and Obstacles: The construction materials used in your home or office can impact the range of your wifi signal. Thick walls made of concrete or brick can significantly reduce signal strength, especially at long distances. Additionally, large furniture and metal objects can obstruct the signal, causing dead spots or weak coverage. Positioning your router in an open space and minimizing obstructions can help improve wifi range.
6. Quality of Wifi Equipment: The quality and capabilities of your wifi router and connected devices can also affect the range of your wifi signal. Investing in a high-quality router with advanced features, such as beamforming technology or multiple antennas, can extend the coverage of your wifi network. Similarly, using devices that support the latest wifi standards, such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax, can ensure optimal performance and range.
By considering and addressing these factors, you can optimize the range and coverage of your wifi network, ensuring a seamless and reliable internet connection throughout your space.
Next, let’s explore the typical wifi range for different devices and how you can extend it when needed.
Wifi Range for Different Devices
The wifi range for different devices can vary depending on various factors, including the device’s hardware capabilities and antenna design. While wifi range is primarily influenced by the transmitting power of the router, it’s essential to understand the typical range expectations for different devices.
Laptops and Desktop Computers: Laptops and desktop computers usually have built-in wifi adapters that can connect to wifi networks. The range for these devices is similar to other devices using wifi, typically ranging between 100 to 150 feet indoors. However, this range can be influenced by the quality of the wifi adapter and the strength of the router’s signal.
Smartphones and Tablets: Smartphones and tablets also have built-in wifi capabilities and can connect to wifi networks. The range for these devices is generally around 50 to 100 feet indoors, depending on the signal strength and any potential obstructions.
Smart TVs: Smart TVs have built-in wifi adapters and allow users to stream content from various online platforms. The range for smart TVs is similar to smartphones and tablets, typically around 50 to 100 feet indoors. However, it’s important to ensure a stable wifi connection for seamless streaming experiences.
Smart Home Devices: Smart home devices, such as smart speakers, thermostats, and security cameras, may have varying wifi range capabilities. Some devices may have weaker wifi adapters, resulting in shorter wifi range. It is crucial to position these devices within a reasonable distance from the wifi router or consider using wifi extenders or mesh systems to improve connectivity in larger spaces.
Gaming Consoles and Streaming Devices: Gaming consoles and streaming devices, such as Xbox, PlayStation, or Roku, require a stable wifi connection for online gaming or streaming content. These devices usually have reliable wifi adapters and can achieve similar ranges to smartphones and tablets, around 50 to 100 feet indoors.
Wifi Extenders and Mesh Systems: If you have areas in your home or office with weak wifi signals or dead spots, wifi extenders or mesh systems can help extend the range and improve coverage. Wifi extenders boost the existing wifi signal, while mesh systems create a network of interconnected devices to provide seamless coverage throughout your space.
Keep in mind that these ranges are approximate and can vary depending on the specific environment and the quality of the wifi equipment being used. Additionally, factors such as interference, obstacles, and network congestion can affect the effective range of wifi signals.
Now that we have explored the typical wifi ranges for different devices, let’s discuss methods to extend the range of your wifi network when needed.
Extending WiFi Range
When faced with weak wifi signals or dead spots in certain areas of your home or office, there are several ways to extend the range of your wifi network and improve connectivity:
1. Position Your Router Strategically: Ensure that your wifi router is placed in a central location, away from obstructions and interference. Consider elevating the router to a higher position, such as on a shelf or mounted on a wall, to provide better coverage throughout your space.
2. Use a WiFi Extender : WiFi extenders, also known as repeaters or boosters, are devices that amplify and retransmit the existing wifi signal. They pick up the signal from the main router and extend its coverage to areas with weak signals or dead spots. Place the extender within the range of the existing wifi signal for optimal performance.
3. Invest in a Mesh WiFi System: Mesh wifi systems utilize multiple devices, called nodes or access points, to create a seamless wifi network with extended coverage. These systems provide a unified wifi network, allowing devices to switch between nodes as you move around your home or office. Mesh systems are ideal for larger spaces or multi-story buildings where a single router may not provide adequate coverage.
4. Optimize Your WiFi Channel: Congested wifi channels can lead to decreased range and slower speeds. Use a wifi analyzer tool to determine which wifi channels are least congested in your area and manually set your router to operate on that channel. This will minimize interference from other wifi networks and improve overall wifi performance.
5. Upgrade Your WiFi Equipment: If you have an older router or wifi devices that do not support the latest wifi standards, upgrading to newer, more advanced equipment can improve the range and performance of your wifi network. Look for routers with higher transmitting power and features like beamforming, which focuses the wifi signal towards the connected devices.
6. Minimize Interference: Reduce potential sources of interference by keeping your wifi router away from devices that operate on similar wireless frequencies, such as cordless phones, microwaves, or Bluetooth devices. Additionally, ensure that the router is not placed near dense walls or large metallic objects that can obstruct the wifi signal.
7. Use Ethernet or Powerline Adapters: For devices that require a stable and high-speed internet connection, consider using ethernet or powerline adapters. These devices allow you to connect your devices directly to the router using wired connections, eliminating the need for wifi and providing a reliable connection in areas with poor wifi coverage.
By implementing these methods, you can effectively extend the range of your wifi network and ensure a reliable and seamless connection across your home or office.
Now that we have explored various ways to extend wifi range , let’s summarize the key points discussed in this article.
Wifi signals have become an essential part of our daily lives, allowing us to connect our devices to the internet wirelessly. Understanding the range of wifi signals and the factors that affect it is crucial for optimizing our wifi networks and ensuring reliable connectivity.
In this article, we discussed how wifi signals operate on radio frequencies and can travel through walls and obstacles, although their strength diminishes with distance. Factors such as wifi router placement, antenna type, interference from other devices, channel congestion, building materials, and the quality of wifi equipment can impact the range of wifi signals.
We also explored the typical wifi range for different devices, such as laptops, smartphones, smart TVs, and gaming consoles. Additionally, we discussed methods to extend the range of wifi networks, including strategic router placement, wifi extenders, mesh wifi systems, optimization of wifi channels, equipment upgrades, interference minimization, and the use of ethernet or powerline adapters.
By applying these strategies and techniques, you can improve wifi coverage and ensure a seamless internet experience throughout your home or office. Keep in mind that wifi range can vary depending on the specific environment and equipment being used. It is important to experiment and find the optimal setup for your unique situation.
Now that you have a better understanding of how far wifi signals can reach and how to extend their range, you can make informed decisions to enhance your wifi network. Enjoy the freedom of reliable wifi connectivity and make the most out of your internet experience!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Crowdfunding
- Cryptocurrency
- Digital Banking
- Digital Payments
- Investments
- Console Gaming
- Mobile Gaming
- VR/AR Gaming
- Gadget Usage
- Gaming Tips
- Online Safety
- Software Tutorials
- Tech Setup & Troubleshooting
- Buyer’s Guides
- Comparative Analysis
- Gadget Reviews
- Service Reviews
- Software Reviews
- Mobile Devices
- PCs & Laptops
- Smart Home Gadgets
- Content Creation Tools
- Digital Photography
- Video & Music Streaming
- Online Security
- Online Services
- Web Hosting
- WiFi & Ethernet
- Browsers & Extensions
- Communication Platforms
- Operating Systems
- Productivity Tools
- AI & Machine Learning
- Cybersecurity
- Emerging Tech
- IoT & Smart Devices
- Virtual & Augmented Reality
- Latest News
- AI Developments
- Fintech Updates
- Gaming News
- New Product Launches
Learn To Convert Scanned Documents Into Editable Text With OCR
Top mini split air conditioner for summer, related post, comfortable and luxurious family life | zero gravity massage chair, when are the halo awards 2024, what is the best halo hair extension, 5 best elegoo mars 3d printer for 2024, 11 amazing flashforge 3d printer creator pro for 2024, 5 amazing formlabs form 2 3d printer for 2024, related posts.

Why Is My Ps4 Not Connecting To Wifi

How Many Wifi Extenders Can You Use

13 Amazing WiFi Booster And Signal Amplifier for 2024

12 Best Tp-Link N300 WiFi Range Extender for 2024

13 Amazing WiFi Boosters For The House for 2024

How Far Does A Wifi Extender Reach

How To Connect Traeger To New Wifi

15 Amazing WiFi Extenders Signal Booster For Home for 2024
Recent stories.

Fintechs and Traditional Banks: Navigating the Future of Financial Services

AI Writing: How It’s Changing the Way We Create Content

How to Find the Best Midjourney Alternative in 2024: A Guide to AI Anime Generators

How to Know When it’s the Right Time to Buy Bitcoin

Unleashing Young Geniuses: How Lingokids Makes Learning a Blast!

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
Using Wi-Fi to “see” behind closed doors is easier than anyone thought
- Emerging Technology from the arXiv archive page
Wi-Fi fills our world with radio waves. In your home, in the office, and increasingly on city streets, humans are bathed in a constant background field of 2.4- and 5-gigahertz radio signals. And when people move, they distort this field, reflecting and refracting the waves as they go.
That’s given more than one group of researchers an interesting idea. In theory, they say, it ought to be possible to use this changing electromagnetic field to work out the position, actions, and movement of individuals. Indeed, several groups have created imaging systems that use Wi-Fi to “see” through walls .
But all these systems have drawbacks. For example, they rely on knowing the exact position of the Wi-Fi transmitters involved and need to be logged in to the network so that they can send known signals back and forth.
That isn’t possible for the ordinary snooper or peeping tom, who might typically have access only to off-the-shelf Wi-Fi sniffers such as those built into smartphones. This kind of set-up is just too basic to reveal any useful detail about what goes on behind closed doors, other than the presence of the Wi-Fi network itself.
At least, that’s what everybody thought. Today that changes thanks to the work of Yanzi Zhu at the University of California, Santa Barbara, and colleagues. These guys have found a way to see through walls using ambient Wi-Fi signals and an ordinary smartphone.
They say the new technique allows an unprecedented invasion of privacy. “Bad actors using smartphones can localize and track individuals in their home or office from outside walls, by leveraging reflections of ambient Wi-Fi transmissions,” they say.
First some background. If humans were able to see the world as Wi-Fi does, it would seem a bizarre landscape. Doors and walls would be almost transparent, and almost every house and office would be illuminated from within by a bright light bulb—a Wi-Fi transmitter.
But despite the widespread transparency, this world would be hard to make sense of. That’s because walls, doors, furniture, and so on all reflect and bend this light as well as transmitting it. So any image would be impossibly smeared with confusing reflections.
But this needn’t be an issue if all you are interested in is the movement of people. Humans also reflect and distort this Wi-Fi light. The distortion, and the way it moves, would be clearly visible through Wi-Fi eyes, even though the other details would be smeared. This crazy Wi-Fi vision would clearly reveal whether anybody was behind a wall and, if so, whether the person was moving.
That’s the basis of Zhu and co’s Wi-Fi-based peeping tom. It looks for changes in an ordinary Wi-Fi signal that reveal the presence of humans.
The challenge is actually even harder than described, because Wi-Fi sniffers don’t produce an image at all. The data that Zhu and co use is just a measurement of the signal strength at a specific location. That doesn’t tell you anything about the location of the transmitter. And without knowing that, it’s impossible to say where any human that distorts the field would be.
So the first step in the researchers’ approach is to locate the Wi-Fi transmitter. They do this by measuring the change in the signal strength as they walk around outside the target building or room. Indeed, they have created an app that uses the smartphone’s built-in accelerometers to record this movement and then analyzes the change in signal strength as they move. In that way, it is possible to number-crunch the position of the transmitter, even in the presence of numerous reflections and distortions.
It is even possible to work out exactly where the transmitter sits inside a house, because floor plans of most homes and offices in the US are downloadable from places such as real estate websites.
The researchers say that by walking back and forth a few times outside a room or building, they can reliably locate the transmitter. “We found that consistency check across 4 rounds of measurements is sufficient to achieve room level localization of 92.6% accuracy on average,” they say.
Having done that, it’s just a question of waiting. Provided nothing moves inside the target building, the Wi-Fi signal will be constant. But any small movement changes the signal in a way that is straightforward to measure.
Zhu and co show how various movements change the signal in different ways. For example, opening a door changes the field in two adjacent rooms and thus is straightforward to spot. Walking around creates large distortions, and even an action like typing creates small changes that a smartphone Wi-Fi receiver can pick up.
The team go on to say that they have tested this approach using Nexus 5 and Nexus 6 Android smartphones to peer into 11 different offices and apartments that the team had permission to observe, many of which contained several Wi-Fi transmitters.
Additional transmitters improve the accuracy of the approach. “We see that with more than 2 Wi-Fi devices in a regular room, our attack can detect more than 99% of the user presence and movement in each room we have tested,” say the researchers.
It’s not hard to imagine how a malicious actor might use this to work out if a building was occupied or empty.
The team say there are various defenses against this type of attack, such as geofencing Wi-Fi signals, but these are difficult to implement and have limited effectiveness. The most promising form of defense seems to be adding noise to the signals; the researchers are hoping to develop this in more detail in future.
In the meantime, this work suggests that the mere presence of Wi-Fi signals is a significant risk to privacy. “While greatly improving our everyday life, [wireless transmissions] also unknowingly reveal information about ourselves and our actions,” say Zhu and co. For the moment, this risk has been largely overlooked. That will need to change quickly.
It’s time to retire the term “user”
The proliferation of AI means we need a new word.
- Taylor Majewski archive page
How ASML took over the chipmaking chessboard
MIT Technology Review sat down with outgoing CTO Martin van den Brink to talk about the company’s rise to dominance and the life and death of Moore’s Law.
- Mat Honan archive page
- James O'Donnell archive page
Why it’s so hard for China’s chip industry to become self-sufficient
Chip companies from the US and China are developing new materials to reduce reliance on a Japanese monopoly. It won’t be easy.
- Zeyi Yang archive page
Modernizing data with strategic purpose
Data strategies and modernization initiatives misaligned with the overall business strategy—or too narrowly focused on AI—leave substantial business value on the table.
- MIT Technology Review Insights archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.

Does Wi-Fi Go Through Walls? The simple guide
Have you ever wondered what today’s world of connectivity would be like without the comforts of Wi-Fi-ready gadgets? If Wi-Fi keeps most of us connected even while we are on the go, it’s reasonable to wonder if there are barriers that block or hinder Wi-Fi connection. You may even keep on wondering: does Wi-Fi go through walls? If so, how do the walls affect the signal?
Wi-Fi signals can generally penetrate through walls, and some walls are easier to penetrate than others. In terms of how deep it can penetrate barriers, the strength of Wi-Fi connectivity largely depends on the thickness and, in most instances, the type of material was used to make the walls.
There is a reason why your fancy hotel, Air BNB, or a nearby Starbucks have Wi-Fi connectivity even if you are not situated close to their modem. Oftentimes, an efficient router will provide effective distribution of the wider Internet system. Read on to find out more about modems, routers, and why some buildings have smoother Wi-Fi connectivity than others.

What Are Modems And Routers?
Do you wonder how your portable electronic gadgets are picking up Internet signals even if you are in areas that do not have an internet connection? Part of this has to do with the fact that phone networks provide ready internet connectivity through cell towers, even without Wi-Fi. But how about other electronic gadgets that are not subscribed to a phone network? How do modems and routers play into this?
The modem is the box that connects a subscribed home or small business network to the internet, and modems are the main source of a building or a home’s internet connectivity.
A router is a box that allows wired and wireless electronic devices of a home or a building to use an internet connection from the modem. Routers also enable various devices to connect with each other.
It is interesting to know what the mostly unseen boxes of modems and routers do to help make your life easier when you want to connect to the world wide web. These unsung heroes of connectivity seem to perform miracles to make your life better. Continue below to find out if modems and routers can help you avoid obstructions and interferences to your Internet connections.
What Causes Wi-Fi Obstruction?
While sipping your favorite cold brew at a nearby Starbucks, you may have wondered: why do I have an excellent Wi-Fi connection here? You were also curious about the fact that Wi-Fi connectivity is not always the best when you are traveling for work. You thought it was all about the price you pay for your network provider subscription, but is it?
Internet obstruction and interference have little to do with the efficiency of your network provider. The main causes of internet blockage and intrusion in a Wi-Fi network are a direct result of the thickness and the materials used in constructing the walls of a building.
Wi-Fi signals can penetrate physical dividers but are affected by depth and certain materials used during construction.
Modems and routers are the unseen heroes of your portable connectivity. But both are helpless if the walls are too thick or if the materials used in making the walls are just too tough for Wi-Fi signals to penetrate. Keep reading to figure out how thick a wall or what materials used to create the wall can affect your Wi-Fi connectivity.
How Is Wi-Fi Strength Measured?
After establishing awareness that Wi-Fi signals are affected by the make and thickness of materials that serve as room dividers and barriers, are you curious about how Wi-Fi strength measured?
How will the strength of your network Wi-Fi hold up against barriers made of materials that deter Wi-Fi connection?
Wi-Fi power is measured in decibel milliwatts (dBm) and expressed in negative values .
(Newth, 2018)
Now that you know how Wi-Fi strength is measured, you can strategically place devices to maximize your connectivity strength. If you experience interference, you will understand what causes it and can remedy the situation. Keep reading to find out what type of materials affect Wi-Fi connections.

What Materials Affect Wi-Fi Signals?
You may be one of those who travel for work and depend largely on a Wi-Fi internet connection to get the job done. Since you know the type of construction materials that affect Wi-Fi signals, you now need to know how to prepare yourself if you are on the road and need to get an internet connection, especially for business or work.
Construction materials made of concrete create the toughest barriers for Wi-Fi signals to penetrate. Materials that can also adversely affect Wi-Fi connectivity include:
- Double-glazed glass
Thickness of material will vary. A more accurate indicator in determining Wi-Fi resistance is material impermeability. The least porous materials are the most resistant to Wi-Fi. Below are examples:
It is interesting to know that some materials can block or suppress the strength of Wi-Fi. We all thought that technology knows no barriers! Well, we thought wrong. Certain construction materials in our homes and buildings serve as barriers to our Wi-Fi connectivity. But is it just building materials that interfere with Wi-Fi? Keep reading to see what other factors hinder connectivity.
How Does Wi-Fi Travel?
You may have noticed that every time your microwave oven is on, your Wi-Fi connection is slower. This has kept you guessing as to what other potential factors can adversely affect your wireless connectivity. You are interested to know how Wi-Fi signal strength and speed are affected by various factors.
Wi-Fi signals travel in different bandwidths. Wireless connectivity frequency bands travel in:
A lower frequency bandwidth has a longer connectivity range but is slower at data transmission. The higher frequency bandwidth transmits data faster but has a limited range.
Every time you use Wi-Fi and experience interference, it does help to know how to remedy the situation. Is your frustration because you want faster downloads, or are you hoping for a stronger connection? Going back to the microwave, you cannot help but ask: How is Wi-Fi connection affected by other factors besides the materials used for walls?
Does Bandwidth Affect Connectivity?
Now that you know that wireless signals travel at different frequencies, do you know how connections are affected per bandwidth? There are different ways your Wi-Fi connections can be hindered. Chances are, speed, strength, or even a combination of the two can have interference depending on what bandwidth your network provider uses.
The bandwidth frequency at which Wi-Fi travels determines the type of connectivity interference.
Possible sources of signal obstruction in 2.4GHz frequency band:
- Microwave appliances
- 2.4GHz wireless telephones
- Incandescent light bulbs
- 2.4GHz camcorders
- Cauterizing machines
- Plasma cutting devices
- Bluetooth aided devices
- Adjacent 802.11, 802.11b, or 802.11g Wireless Local Area Networks
- Wireless Internet Service Providers
Potential sources of interference in the 5GHz frequency bands include the following:
- 5GHz wireless telephones
- Radio Detection And Ranging
- Perimeter sensing devices
- Satellites using digital technology
- Adjacent 802.11a or 802.11n Wireless Local Area Networks
- 5GHz Wireless bridges
Depending on the frequency your Wi-Fi connection travels, the list above provides factors that may interfere with and block your signal. It is important for you to be aware of what to avoid and minimize if you want to maximize the strength of connectivity and the speed of your network connection.
Does the Raspberry Pi computer use Wi-Fi?
I’ve written pretty extensively on the Raspberry Pi line of computers on this website. If you’re wondering about the Wi-Fi capabilities of these single board computers, you should check out my guide about their capabilities here .
Conclusion:
We have established the fact that Wi-Fi signals go through walls and barriers. However, it will eventually depend on the thickness and, more accurately, the type of materials used for building such barriers to determine if wireless signals can penetrate them. It seems the less porous and more solid the barriers and walls, the more interference and even blocking of your wireless signals you will experience.
Wireless signals also travel in different frequencies. How Wi-Fi signals are affected can and will be influenced by other factors outside of the type of materials used for barriers that separate rooms in houses and buildings. For you to maximize signal strength and speed of connectivity for your Wi-Fi devices, your routers must be placed near the modem or in areas where barriers are more porous with minimum electrical and electronic appliances that may also suppress maximum connectivity.
References:
Dos and Don’ts of Wi-Fi connectivity: Maximizing Range and Reception. (n.d.). Retrieved from Mistral Solutions: https://www.mistralsolutions.com/articles/dos-donts-wi-fi-connectivity-maximizing-range-reception/
Modem vs. Router: What’s the Difference? (2021, February 11). Retrieved from Wirecutter: https://www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/blog/modem-vs-router/
Newth, J. D. (2018, February 28). Wi-Fi Signal Strength: What Is a Good Signal And How Do You Measure It? Retrieved from Eyesaas.com: https://eyesaas.com/wi-fi-signal-strength/
Which Building Materials Can Block Wi-Fi Signals? (2019, December). Retrieved from Eye Networks: https://eyenetworks.no/en/wifi-signal-loss-by-material/
Recent Posts
How To Change Modems. A helpful, illustrated guide.
Changing an old modem for a new one is a do-it-yourself project anyone can accomplish in short order with the right know-how. If you've never swapped modems before, the process might intimidate you....
Do Routers Make A Difference? Here's the truth!
At first glance, routers are all the same. Multiple antennas stick out of a rectangular black box that grants several people and dozens of devices the ability to connect to the internet through the...
How to Boost the WiFi Signal Through Walls
Having a strong and reliable WiFi signal is essential for most of us nowadays. Whether you need to work from home, stream movies, or simply browse the internet, a weak or unstable WiFi signal can be frustrating and hinder your productivity.
One of the most common reasons for a weak WiFi signal is the presence of walls or other obstacles that interfere with the signal.
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to boost your WiFi signal through walls, and in this article, we will explore some of the best tips and tricks to improve your WiFi signal strength and quality.
We will discuss the basics of WiFi signals, how walls and obstacles affect the signal strength, and then dive into different methods to optimize your WiFi signal, such as adjusting network settings, using signal boosters/repeaters, upgrading your router, and more. So, let’s get started on improving your WiFi signal!
- Understanding WiFi Signal
Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) is a technology that allows devices to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables.
WiFi uses radio waves to transmit data between devices, and the quality of the signal is influenced by a range of factors such as distance, interference, and the presence of obstacles like walls.
Understanding how WiFi signals work and how they are affected by obstacles like walls is essential for optimizing your home or office WiFi network.
In this section, we will explore the basics of WiFi signals, how walls and obstacles affect signal strength, and the types of WiFi signals available.
Basics of WiFi Signals
WiFi signals are transmitted using radio waves, which are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can travel through the air. These waves are transmitted at a specific frequency and can be picked up by a device that has a compatible receiver.
The most common frequencies used for WiFi signals are 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
When a device connects to a WiFi network, it sends and receives data packets over the network. The signal strength and quality determine the speed at which these packets can be transmitted and received.
How Walls and Obstacles Affect Signal Strength
The presence of walls and other obstacles can significantly affect the strength and quality of WiFi signals. The signal can be blocked or weakened by the presence of obstacles, leading to poor connectivity or dropped connections.
Walls made of materials such as concrete, brick, or metal can significantly weaken WiFi signals. The signal can also be affected by other wireless devices like cordless phones or baby monitors, which can cause interference.
The distance between the WiFi router and the device also affects signal strength. The further the distance, the weaker the signal will be.
Types of WiFi Signals
There are two types of WiFi signals available: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. The 2.4GHz signal is the most common and has a longer range but can be affected by interference from other devices. The 5GHz signal, on the other hand, has a shorter range but is less affected by interference.
Some newer routers support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz signals, allowing devices to switch between the two depending on which signal is stronger at the time.
- Tips to Boost WiFi Signal Through Walls
Optimize Router Placement
One of the most effective ways to boost your WiFi signal through walls is by optimizing the placement of your router. The placement of the router can significantly affect the strength and quality of the WiFi signal.
Central Location
The first step in optimizing router placement is to find a central location in your home or office. This location should be as close to the center of the building as possible. This will help ensure that the signal can reach all parts of the building with minimal interference.
Elevated Position
Another factor that affects WiFi signal strength is the height of the router. Placing the router in an elevated position can help to improve the signal strength by minimizing the obstacles that can block the signal. The ideal location for the router would be on a high shelf or a wall mount.
Avoid Interference
Avoid placing the router near other wireless devices that can interfere with the signal, such as smart home appliances, wireless headphones, or microwaves.
These devices operate on the same frequency as WiFi signals and can interfere with the signal, resulting in a weaker or unstable connection.
Update Firmware
Updating firmware is an essential step in optimizing your router’s performance and improving your WiFi signal strength.
Firmware is software that controls the functions of your router, and updating it can fix bugs, improve security, and add new features.
Importance of Updates
Firmware updates can improve the performance and reliability of your router. These updates may address security issues, improve network stability, or add new features.
Without regular firmware updates, your router may become more susceptible to security threats or connectivity issues.
Steps to Update Firmware
Updating the firmware on your router is a straightforward process, and it can usually be done through the router’s web interface. The following are general steps for updating the firmware on your router:
- Check for firmware updates: Go to your router manufacturer’s website and look for the latest firmware update available for your specific router model.
- Download the firmware update: Download the firmware update and save it to your computer.
- Log in to your router’s web interface: Open your web browser and enter your router’s IP address. You will then need to enter your login credentials to access the router’s settings.
- Find the firmware update section: Look for the firmware update section in the router’s settings. This section may be under the “Advanced” or “Administration” tab.
- Upload the firmware update: Select the firmware update file you downloaded and upload it to the router.
- Wait for the firmware update to complete: The router will usually restart after the firmware update is complete. This process can take a few minutes, and you should not interrupt the router during this time.
It’s important to follow the instructions provided by the router manufacturer carefully when updating firmware. Failure to do so may result in a bricked router, which can be difficult or impossible to fix.
Use Signal Boosters/Repeaters
Signal boosters and repeaters work by amplifying or extending the WiFi signal, allowing it to reach areas that were previously out of range.
What are Signal Boosters/Repeaters?
A signal booster, also known as a range extender, is a device that amplifies the existing WiFi signal, allowing it to reach areas that were previously out of range.
A repeater, on the other hand, is a device that receives the existing WiFi signal and then broadcasts it to extend the range of the signal.
Signal boosters and repeaters are typically easy to install and do not require any technical expertise. They are available in different shapes and sizes, and some can be plugged directly into a power outlet.
How to Choose the Right Booster/Repeater
- Compatibility: Ensure that the booster or repeater is compatible with your router and the frequency of your WiFi signal.
- Coverage Area: Determine the coverage area you need. Some boosters or repeaters are designed for small areas, while others can cover large homes or office buildings.
- Speed: Consider the speed of the booster or repeater. Some boosters may slow down your WiFi speed, while others may be faster.
- Features: Look for additional features such as parental controls or guest networks.
Upgrade Antennas
Antennas play a critical role in transmitting and receiving WiFi signals, and upgrading to a higher quality or better-designed antenna can significantly boost signal strength.
Types of Antennas
There are three main types of antennas used in WiFi networks:
- Omni-Directional Antennas: These antennas send and receive signals in all directions. They are commonly used in homes or small offices and provide good coverage in all directions.
- Directional Antennas: These antennas focus the signal in one direction and are useful for reaching longer distances or specific locations. They are commonly used in outdoor or long-distance applications.
- Panel Antennas: These antennas are a type of directional antenna and are used to cover larger areas. They are commonly used in indoor or outdoor applications, such as in large homes or warehouses.
Benefits of Upgrading Antennas
Upgrading your antenna can have several benefits, including:
- Increased Signal Strength: Upgrading to a higher quality or better-designed antenna can significantly improve signal strength, allowing you to access WiFi signals from greater distances or through walls.
- Extended Range: A better antenna can extend the range of your WiFi signal, allowing you to access the internet from areas that were previously out of range.
- Improved Stability: Upgrading to a better antenna can help improve the stability of your WiFi signal, reducing the likelihood of dropped connections or slow speeds.
- Better Quality: A better antenna can provide a higher quality WiFi signal, resulting in faster internet speeds and better overall performance.
It’s important to note that not all routers allow you to upgrade the antenna. If your router does not allow antenna upgrades, you may need to consider other methods of improving your WiFi signal strength.
Adjust Network Settings
Network settings control how your WiFi signal is transmitted and received, and changing these settings can improve signal strength and reduce interference.
Change WiFi Channel
Changing the WiFi channel can help reduce interference from other WiFi networks and devices. When multiple WiFi networks are using the same channel, they can interfere with each other, resulting in a weaker or unstable signal.
Changing the channel can help reduce this interference and improve signal strength.
Increase Transmit Power
Increasing the transmit power of your router can help improve the signal strength and range of your WiFi signal.
However, it’s important to note that increasing transmit power can also increase interference with other WiFi networks and devices.
It’s best to experiment with different transmit power levels to find the optimal setting for your specific situation.
Use Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) is a network setting that prioritizes certain types of traffic, such as video streaming or online gaming, over other types of traffic, such as email or web browsing.
Using QoS can help ensure that high-bandwidth applications receive the necessary bandwidth, resulting in a more stable and faster connection.
Change WiFi Frequency
Changing the frequency of your WiFi signal can also help improve signal strength and reduce interference.
Most routers operate on either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency, and changing the frequency can help reduce interference from other devices that operate on the same frequency.
Use Mesh Networks

Mesh networks use multiple access points or nodes to create a seamless and reliable WiFi network that covers a large area.
What Are Mesh Networks?
Each node in the mesh network communicates with the other nodes, allowing the network to adapt to changes in the environment and provide optimal coverage. Mesh networks are easy to set up and can be expanded as needed by adding more nodes.
Advantages of Using Mesh Networks
Using a mesh network can provide several advantages, including:
- Improved Coverage: Mesh networks can cover large areas and provide reliable WiFi signal strength throughout the entire area. This is particularly useful for large homes or office buildings where traditional routers may not provide sufficient coverage.
- Seamless Connectivity: Mesh networks provide seamless connectivity as you move from room to room or from one access point to another. The network automatically switches to the strongest and most reliable signal, providing a smooth and uninterrupted experience.
- Scalability: Mesh networks are easy to expand by adding more nodes. This allows you to customize the network to your specific needs and expand the coverage area as needed.
- Self-Healing: Mesh networks are self-healing, meaning that if one node fails or goes offline, the other nodes will automatically adapt to maintain the network’s integrity and reliability.
- Easy to Manage: Mesh networks are easy to manage, with most systems offering a mobile app or web-based interface for configuring and managing the network.
Use Powerline Adapters
Powerline adapters can be a useful solution. Powerline adapters use the existing electrical wiring in your home or office to transmit data, providing a stable and reliable internet connection.
What Are Powerline Adapters?
Powerline adapters, also known as HomePlug adapters, use the existing electrical wiring in your home or office to transmit data between devices.
The adapters come in pairs, with one adapter connected to your router and the other adapter connected to the device that requires an internet connection.
The adapters communicate with each other through the electrical wiring, providing a stable and reliable internet connection.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Powerline Adapters
Using powerline adapters can provide several advantages, including:
- Stable and Reliable Connection: Powerline adapters provide a stable and reliable internet connection, even in areas where the WiFi signal is weak or blocked by walls or obstacles.
- Easy to Install: Powerline adapters are easy to install and require no technical expertise. Simply plug the adapters into a power outlet and connect them to your router and device.
- Cost-Effective: Powerline adapters are often less expensive than other solutions, such as mesh networks or wireless access points.
However, powerline adapters also have some disadvantages, including:
- Limited Range: Powerline adapters have a limited range and may not be effective in larger homes or office buildings.
- Susceptible to Interference: Powerline adapters can be susceptible to interference from other electrical devices, such as appliances or motors.
- Dependent on Electrical Wiring: Powerline adapters require a stable electrical wiring infrastructure to provide a reliable connection. Older homes or buildings with outdated wiring may not provide a stable connection.
Upgrade Router
If you’re experiencing weak WiFi signal strength despite trying all other solutions, it may be time to upgrade your router. Upgrading your router can provide significant improvements in signal strength and overall network performance.
When to Upgrade

It may be time to upgrade your router if you’re experiencing any of the following:
- Slow Internet Speeds: If your internet speeds are slower than what your service provider promised, it may be time to upgrade your router.
- Weak Signal Strength: If you’re experiencing weak WiFi signal strength, despite trying other solutions, it may be time to upgrade your router.
- Outdated Hardware: If your router is more than five years old, it may not be capable of supporting newer technologies, such as faster internet speeds or new WiFi standards.
Best Routers for Boosting WiFi Signal
When choosing a new router, there are several factors to consider, including:
- WiFi Standards: Look for a router that supports the latest WiFi standards, such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax.
- Antennas: Look for a router with external antennas that can be adjusted or replaced. This will allow you to optimize the signal strength and range.
- Dual-Band: Look for a router that supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. This will allow you to switch between frequencies to reduce interference and improve signal strength.
- Features: Look for additional features such as parental controls, guest networks, or built-in security.
Some of the best routers for boosting WiFi signal include:
- TP-Link AXE5400 (Archer AXE75)
- ASUS AX6000 (RT-AX88U)
- Netgear Nighthawk AX8 (RAX70)
Add Antenna if Possible
If your new router has external antennas, adding a high-quality antenna can further improve signal strength and range.
External antennas can be adjusted or replaced, allowing you to optimize the signal direction and strength.
It’s important to experiment with different solutions to find the best solution for your specific situation. What works for one person may not work for another, so it’s essential to try different solutions until you find the optimal solution.
Additionally, it’s important to note that WiFi technology is continually evolving, and new solutions may become available in the future.
Keeping up-to-date with the latest technologies and advancements can help ensure that your WiFi network is always performing at its best.
In summary, improving your WiFi signal strength may take some time and experimentation, but with the right solutions and tools, you can achieve a strong and reliable internet connection.
Don’t let weak WiFi signal strength hold you back – try some of the solutions outlined in this guide and enjoy a faster, smoother, and more reliable internet experience.
Table of Contents
Editor’s pick, what is a 2-in-1 laptop blending portability with power, why twitter is so toxic: uncovering the root causes, the disadvantages of incognito mode: the security illusion, you might also like, how to identify a fast charger: key specs to look for, easy steps to use a second monitor with your laptop, boosting online presence for franchise businesses: tips & tricks.
© 2018 - 2024 Tech Review Advisor


Can Bluetooth Signals Go Through Walls? (Solved!)
There’s no doubt that Bluetooth technology has made our lives easier in many ways. But one question that continues to come up is whether or not Bluetooth signals can go through walls. So can Bluetooth signals go through walls?
Yes. Bluetooth signals can travel through walls. However, there are some things you need to know to make sure your signal travels effectively. The strength of your Bluetooth signal will be determined by two main factors: the power of your transmitter and the construction of your walls.
In this article, I will take a closer look at what determines if the Bluetooth signal can travel through a wall and different ways to strengthen the signal.

Can Bluetooth Signals Travel through Walls?
Bluetooth signals are transmitted via radio waves, a type of electromagnetic radiation. This means that they can travel through objects, including walls.
However, the strength of the signal will be weakened when it passes through these obstacles.
The following factors will determine how well your signal travels through walls:
READ MORE! Can Neighbors Connect to your Bluetooth Devices? (Solved)
The Power of Your Bluetooth Transmitter
The transmitter is the device that emits the Bluetooth signal. The power of your transmitter will determine how far your signal can travel.
If you have a powerful transmitter, your signal will be able to reach a longer distance.
The Construction of Your Walls
The type of material your walls are made out of will also affect the strength of your Bluetooth signal. Solid concrete walls will weaken your signal more than drywall.
If you’re trying to transmit a signal through a wall, it’s best to use an unobstructed path.
The Bluetooth Version
There are different versions of Bluetooth, and each one has a different range. The latest version of Bluetooth, Bluetooth LE, has a range of up to 400 feet.
This means that your signal can travel through multiple walls before it weakens.
Objects between the Bluetooth Connection
The number of objects between your Bluetooth connection will also affect the strength of your signal.
If there are a lot of objects, such as furniture, between the connection, it will weaken the signal.
The Range of the Device
This is the maximum distance your Bluetooth device can be from the transmitter and still receive a signal. The range will be determined by the power of your transmitter and the construction of your walls.
The wider the range, the more likely it is that your signal will be able to travel through walls.
The range of your device is determined by:
- The Bluetooth Spectrum Brand – Bluetooth uses different frequencies to transmit data. The most common is Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), which has a range of up to 400 feet, and Classic Bluetooth, which has a range of up to 30 feet.
- The Output Power- This is the amount of power that your device uses to emit the signal. The higher the output power, the further your signal can travel.
- The Sensitivity of Your Device – This is the ability of your device to receive a signal. The higher the sensitivity, the further your signal can travel. The Bluetooth devices normally have a sensitivity of -90 dBm. This means that your signal can travel through multiple walls before it weakens.
- Transmit Power – This is the power that your device uses to emit the signal. The higher the transmit power, the further your signal can travel.
- The Design of the Antenna – The efficiency of your Bluetooth device’s antenna will also play a role in whether your signal can travel through a wall or not. A more efficient antenna will be able to transmit a signal further than a less efficient one.
How to Improve the Signal of Your Bluetooth so It Easily Goes Through Walls?
If you want to make sure your Bluetooth signal is able to travel through walls, there are a few things you can do:
Use a Powerful Transmitter
Use an unobstructed path.
If you’re trying to transmit a signal through a wall, it’s best to use an unobstructed path. This means that there should be no objects, such as furniture, between the connection.
Use the Latest Version of Bluetooth
The latest version of Bluetooth, Bluetooth LE, has a range of up to 400 feet. This version has a much longer range than previous versions and is more likely to be able to travel through walls.
Upgrade the Devices to Have a Similar Bluetooth Version
If you’re using multiple devices, make sure they all have the same Bluetooth version. This will ensure that the signal is compatible and transmitted between devices without any issues.
Use a Bluetooth signal Repeater
The signal repeater will receive the Bluetooth signal and then transmit it, which will help to improve the range. You should place the repeater in an area where there is a clear path to the devices.
For example, if you’re trying to connect to a device in another room, the repeater should be placed between the two rooms.
READ MORE! 7 Genius Tips To Improve Your Bluetooth Connection
Advantages of Having a Strong Bluetooth Signal That Can Pass through Walls
A strong Bluetooth signal that can travel through walls has a few advantages.
You Won’t Have to Worry about Losing Your Connection If you’re in a Different Room
You’ll also be able to connect to far away devices, such as speakers in another room. This will give you the ability to control the audio in your home from any room.
If you have a strong Bluetooth signal, you’ll be able to use your devices in more places.
For example, you’ll be able to use your headphones while you’re in the backyard or take your speaker outside without losing the connection.
Your Connection Will Be More Stable
A stronger Bluetooth signal will also give you a more stable connection. This means that you won’t have to worry about your signal cutting out or becoming patchy.
If you’re looking for a Bluetooth device with a strong signal, make sure to check the specifications. The range and power of the transmitter are important factors to look for.
Potential Risks of Using Strong Bluetooth Signals in Closed Places Like Homes and Offices
Interference with other electronic devices.
A strong Bluetooth signal has the potential to interfere with other electronic devices. This can cause problems with your Wi-Fi connection or cause static on your phone line.
If you’re using a strong Bluetooth signal in an office, it’s important to make sure that it doesn’t interfere with any sensitive equipment. This includes things like computers, printers, and copiers.
READ MORE! Do Microwaves Affect Bluetooth Signals?
Health Risks
It’s also important to be aware of the potential health risks of using strong Bluetooth signals. These signals are electromagnetic waves, and exposure to them has been linked to cancer and other health problems.
If you’re concerned about the potential risks, it’s important to take precautions. For example, you can limit your exposure by turning off your Bluetooth device when you’re not using it.
You can also reduce your exposure by keeping your device away from your body. For example, you can use a hands-free headset or keep your phone in your purse or backpack instead of in your pocket.
Can Bluetooth Signals Go Through Walls?
The strength of your Bluetooth signal will determine if it can travel through walls. If you have a powerful transmitter and an unobstructed path, your signal should be able to travel through multiple walls.
Does The Type of Wall Affect the Strength of the Signal?
The type of material your walls are made out of will affect the strength of your signal. If you’re trying to transmit a signal through a wall, it’s best to use an unobstructed path.
Do All Bluetooth Devices Have the Same Range?
No, all Bluetooth devices do not have the same range. The range of your device will depend on the specifications of the device.
How Can You Troubleshoot Common Bluetooth Problems?
If you’re having trouble with your Bluetooth connection, you can try a few things. First, make sure that your devices are within range of each other. If they are, try restarting both devices.
If you’re still having trouble, try moving your devices to another location. Sometimes, walls or other objects can block the signal. In order for the signal to pass through walls, it has to have a powerful transmitter that will make the signal stronger.
It is also possible that your devices are not compatible with each other. In this case, you’ll need to consult the user manuals for both devices.
Finally, if you’re still having problems, you can contact customer support for both devices. They may be able to help you troubleshoot the problem.
Final Thoughts
Bluetooth signals can travel through walls. However, the strength of the signal will be determined by the power of the transmitter, the construction of your walls, and the number of objects between the connection.
I hope this article has helped you know how you can improve the strength of your Bluetooth signal to get the best out of your Bluetooth devices.

Espen is the Director of ProPairing and has written extensively about Bluetooth devices for years. He is a consumer product expert and has personally tested Bluetooth devices for the last decade.
Related Posts:
- Can Construction Workers Use Bluetooth Headphones? (Solved)
- 7 Genius Tips To Improve Your Bluetooth Connection
- What is the Best Bluetooth TV Transmitter In 2022?
- Can Neighbors Connect to your Bluetooth Devices? (Solved)
- Can Bluetooth Be Used To Measure Distance? (Explained!)
- Are Bluetooth Devices allowed on planes? (Solved)
Similar Posts

What Is The PIN For Bluetooth Keyboard? (Solved!)

What Are The Benefits Of A Backlit Keyboard? (Explained!)

My Apple Watch Face Came Off: What to Do?

Does a Bluetooth FM Transmitter Drain Your Car Battery?

AirPods Not Working On Phone Calls (Easy Fix Here!)

Can You Use Apple Watch or Fitbit Without Bluetooth?

This article was last updated by Deepika Adhikari on April 2, 2023
Does 5GHz WI-FI Penetrate Through Walls?
- by Salman Gurung
- April 2, 2023
Do you get a fast Wi-Fi signal when sitting near your 5GHz router but instantly lose connection when moving to another room?
Do not blame your internet speed because the problem may be in your router signal all this time but Wi-Fi bandwidth.
Although faster and more robust than previous connections, 5 GHz Wi-Fi will fail to penetrate through walls.
Although Wi-Fi signals are known to pass through surfaces, 5GHz may not do the job, requiring significant upgrades.
Read on to find out how wall material, thickness, Wi-Fi band, and radio connection may affect the level of your Wi-Fi signal.
Table of Contents Show
Does wi-fi signal go through walls, how far can 5 ghz wi-fi travel, 1. size of your home, 2. obstacles or materials, 3. signal interferences, 4. interference with 2.4 ghz router, 5. location of the router, 5ghz vs. 2.4ghz wi-fi signals, tips to improve 5 ghz wi-fi, the bottom line.
Wi-Fi or Wireless Fidelity is a long radio wave that quickly passes through any surface, including walls and doors.
Therefore, users install a router in one room and effectively connect to it from different parts of the home.
That being said, the level of signal attenuation will depend on the surface material it passes through.
Some surfaces are thicker and more compact, affecting Wi-Fi’s signal attenuation (penetration), such as internet speed, penetration, and connectivity.

Therefore, you can connect and effectively use Wi-Fi when separated by a glass wall compared to a concrete or steel wall.
For instance, a concrete wall with reinforced concrete contains 8″ thick slabs, usually applied in commercial or residential buildings.
Hence, the internet connection could be weaker through concrete than the drywall that is hardly 2″ thick.
Similarly, the Wi-Fi signal could be more robust in the upper stories separated by standard ceilings than in an adjoining room separated by a thick load-bearing wall.
Therefore, the signal has to penetrate the load-bearing wall, leading to weaker signal attenuation.
Here is the list of surface materials and their signal attenuation to give your a better idea.
Does 5GHz Wi-Fi Penetrate Through The Wall?
Although 5 GHz guarantees faster internet speed, it may fail to penetrate the thick walls of your home or office.
GHz stands for gigahertz, where the higher the GHz number, the faster the speed.
5 GHz, also known as 5G, has become popular for many internet users who demand higher and faster internet speed, especially for gaming, streaming, and work.
However, it lacks the latency that helps the signal travel farther distances, primarily through hurdles like walls and ceilings.
With a much shorter range, it may be easily blocked by concrete and dry walls.
Therefore, if installing a new router with 5 GHZ speed, you should be wary about where you will be seated when using the internet.
The lower the GHz, the farther it will travel. For example, 2 GHz or 2G can travel 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors.
Similarly, 3G and 4G can travel about 100 feet indoors when obstructed.
However, the 5GHz or 5G wavelength is the shortest and can only travel about 50 feet (15 meters) when unobstructed.
Due to this, the 5G signals can easily be blocked by physical barriers at home, like walls and electronic devices.
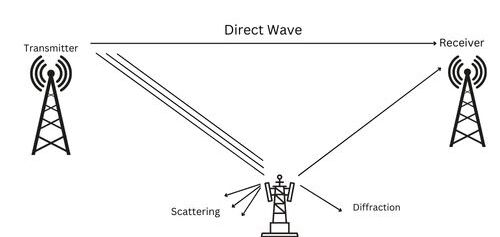
What May Restrict The 5 GHz Signal? (With Solutions)
5 GHz signal boasts a short wavelength compared to older generations of signal; therefore, it is often interrupted by different factors.
Here are a few factors that may restrict the 5 GHz signal.
The larger the home, the weaker the Wi-Fi signal. As previously mentioned, 5 GHz boasts a shorter wavelength, limiting the signal to a specific distance.
The obstacles that may come in between in the form of walls, ceilings, and furnishings may limit its range.
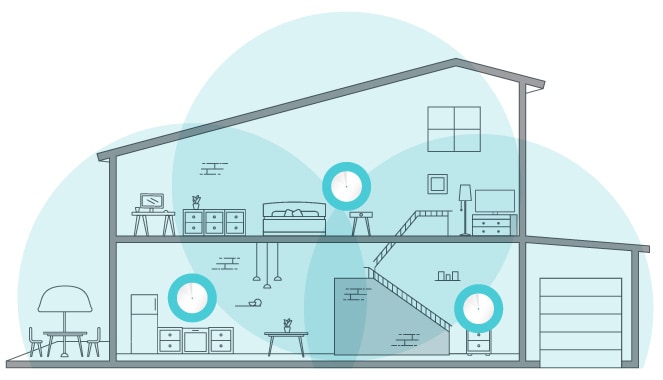
One effective way to solve this issue is to add an extender replicating the 5 GHz signal to other home parts.
It is recommended to plug the extender halfway between the router and the area you wish to reach.
Placing the extender farther from the router may risk losing significant signal speed.
Obstacles such as metal blinds, doors, walls, reinforced surfaces, and furniture will significantly restrict the 5 GHz Wi-Fi signal.
Remember, metal is good at absorbing electromagnetic signals such as Wi-Fi, limiting the signal attenuation.
Similarly, the signal will be affected by reinforced concrete walls, plaster, and metal lath used in plaster, ceramic tiles, tinted glass, and low-emissivity surfaces.
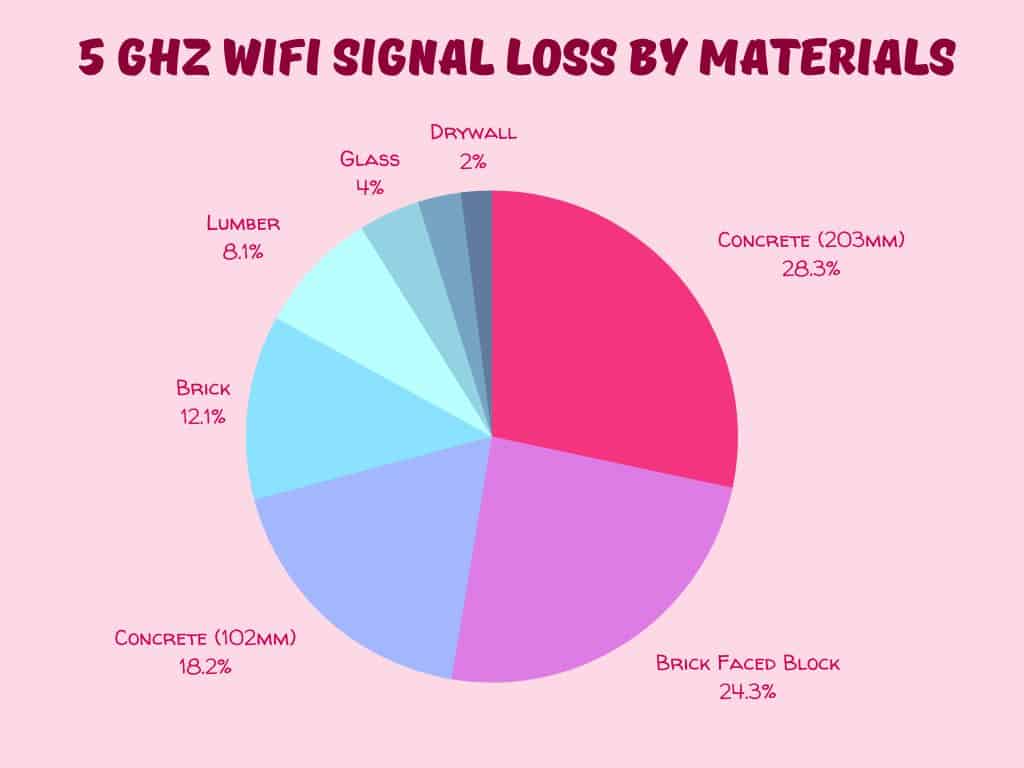
Some other materials such as mirrors, drywall, and neighbor’s Wi-Fi network will also affect 5 GHz signal attenuation.
Try placing the router and using it in home parts with fewer obstacles; otherwise, invest in an excellent extender to replicate the Wi-Fi signal.
The 5 GHz band may work very well at a short distance but often encounters interferences with other signals.
Some standard household devices like Bluetooth, baby monitors, garage door openers, Walkie, and Microwave may interfere with the 5 GHz signal.
5 GHz operates at a more significant number of unique channels, which would work well when less overlapped with other signals.
Therefore, keeping the device and router closer will solve this problem.
Otherwise, installing the router at a higher elevation near the ceiling, sideboard, or shelf may also help combat this problem.
Mixing the 5 GHz bands with the 2.4 GHz bands can be a grave mistake.
The 5 GHz router does not readily mix with the 2.4 GHz router, creating interferences that may disqualify both 5 GHz networks.
As a solution, you should upgrade to a single router with a dual-band, so neither signal interferes.
On the other hand, the 2.4 GHz band upgraded to 802.11g speed will run faster than the 5 GHz bands, eliminating the need to get the latter band altogether.
If you have two different routers at home, consider placing them far from each other to eliminate interference.
You may also find the Wi-Fi signal is better in a different part of the House, such as a room without reinforced and load-bearing walls.
Similarly, they are better kept in the adjoining room or a straight line as the line of sight is essential for radio wave travel.
Alternatively, consider adding the Wi-Fi repeater to another part of the home using a cable to improve the signal.
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi signals vary regarding wavelength range, speed, and usage.

Here are brief differences between the two frequencies.
Here are a few tips to improve the 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection.
- Place your router in an elevated region and as close to the device as possible.
- Avoid placing it inside a room with steel beams and reinforced concrete walls.
- Upgrade your 5 GHz router with antennas to boost internet speed, even up to 1 Gbps.
- Choose the right Wi-Fi channel, as 5 GHz has up to 24 channels. For the laptop channel, close to 5.83, and for the phone channel, 5 will be better.
- Keep your router updated by upgrading firmware or router updates.
- Prevent bandwidth hoggers from stealing bandwidth from other devices.
- Use performance-enhancing features like Multi-user MIMO , beam forming, etc., to boost internet speed.
- Protect your Wi-Fi router with a password, so hackers may not get easy access.
- Buy a Wi-Fi repeater or extender as needed to extend the signal throughout the area.
- Regularly reboot your router to refresh the connection and the router’s memory cache.

The 5 GHz Wi-Fi signals are best for modern-day activities and devices but may fail to penetrate through walls.
Therefore, boosting the Wi-Fi connection using different methods may help eliminate frequent interferences.
Otherwise, upgrading the router with a better connection and placing the device closer to the router will help solve the problem.
Follow this guide to find effective ways to improve your 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection.
- Slow Internet
- Work From Home
Salman Gurung
Your Go-to guy to know about everything related to technology, home office, and more. I love everything about technology, home improvement, interior decoration, and DIY for creating stuff out of nothing. Follow me to learn more about setting up a home office, home office hacks, computer hacks, and other stuff.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Also Like

- 7 minute read
Why is my Wireless Charging Pad not Working?
- November 8, 2022
- No comments

- 10 minute read
Top 10 Compact All-in-One Printer For Home Office Use
- by Manavi Shrestha
- March 27, 2023

How to Get Wifi Signal Through Brick Walls
Do you ever feel like your wifi signal needs to reach farther? Or there are certain areas in your home or office where access has never been easy due to brick walls and other physical barriers.

Although it’s common knowledge that brick walls can be a massive obstacle for wifi signals, there is no need to resign yourself to slow speeds or, even worse: no connection at all. There are actually several viable methods you can deploy right away in order to maximize the range of your network and get an even better signal through those pesky brick walls!
In this blog post, we will discuss precisely what these solutions look like so that you can say goodbye to irritating dead zones. So let’s dive in and find out how to get wifi signal through brick walls!
What Will You Need?
Before we get started, let’s look at the equipment you’ll need for this project.
- A Wi-Fi router
- Wi-Fi range extender
- A directional antenna
- Powerline adapter
- Mesh network system
Let’s now look at each piece of equipment in turn and what they can do to help with your brick wall problem!
10 Easy Steps on How to Get Wifi Signal Through Brick Walls
Step 1. choose the right wi-fi router.
When trying to solve any wifi signal issue, choosing a router that is up to the task is important. Make sure to research what models are best for your budget and needs, as well as consider the size of your home or office and the number of devices you plan to connect. If you’re having trouble deciding, consult our handy guide to choosing the right router.

Step 2. Install a Wi-Fi Range Extender
To increase the range of your wifi signal, it is recommended that you install a range extender in between your router and brick wall barrier . This device will amplify any incoming signals from the router so that they can easily pass through brick walls without losing strength. Remember to make sure that the extender is secured with a strong password for maximum security.
Step 3. Set Up a Directional Antenna
Another way to make sure that wifi signals don’t lose strength when passing through brick walls is to set up a directional antenna on one side of the wall. This will help direct the signal toward its ultimate destination, which can be especially useful if you connect multiple devices in different rooms. As always, make sure to secure your network with a strong password.
Step 4. Use a Powerline Adapter
If you don’t want to use any additional hardware, then a powerline adapter is your best option. This device uses the existing wiring in your home or office to boost and extend wifi signals to pass through brick walls easily. This adapter also eliminates any interference from other networks in the vicinity.
Step 5. Invest in a Mesh Network System
Investing in a mesh network system is one of the most effective ways to get wifi signals through thick walls. This type of system will work as one single unit, so even if there are multiple walls to penetrate, your wifi signal will easily reach its destination. If you’re looking for the best, check out our guide to the top mesh network systems.

Step 6. Place Your Router High Up
When it comes to the placement of your router, make sure that you put it as high up as possible in order for the signal to extend further without losing strength. This should also help avoid any interference from other electronic devices like microwaves or cordless phones, which can negatively impact performance. Moreover, try to keep your router away from windows and other areas where there may be a lot of outside interference.
Step 7. Move Your Router Away From Brick Walls
This is particularly important if you have a router situated close to a brick wall, as this can cause signal degradation due to interference with the material itself. Ensure enough space between your router and any nearby brick walls to ensure optimal performance. You can also use a range extender to make sure that there is no interference.
Step 8. Use a Metal Reflector
If you’re trying to send your wifi signal through an outdoor brick wall, then a metal reflector can be very helpful. This device works by reflecting the signal so that it is directed toward its destination while avoiding any interference caused by the bricks themselves. Another great benefit is that it’s extremely portable and easy to install.
Step 9. Upgrade Your Antenna
Finally, if none of these solutions seem to work for you, then it might be worth considering upgrading your router’s antenna. A stronger antenna can help amplify signals so that they don’t degrade or get blocked when passing through thick walls like those made from brick or concrete. It will also help to reduce the number of dead zones in your home or office.

Step 10. Use a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a great way to ensure that any wifi signals passing through brick walls are completely secure. By encrypting your connection, you can be sure that no one else can access or intercept your data as it passes through. Remember to choose a reputable VPN provider with strong encryption protocols for maximum security.
By following these ten simple tips, you’ll be well on your way to getting the best wifi signal through those pesky brick walls. Whether you choose to use a range extender, directional antenna, powerline adapter, mesh network system, or VPN – you can rest assured that your wifi connection will be strong, secure, and reliable.
5 Additional Tips and Tricks
- Make sure that your router is placed in a central location. This way, it will be more likely to reach all areas of the house, including behind thick brick walls.
- If you have an external antenna, position it in the direction of a wall that is blocking your signal. This can help draw the wifi signal to the other side of the wall and strengthen its reach.
- Use repeaters or extenders to amplify your wifi signal behind brick walls. These devices can boost weak signals and provide better coverage for large homes with thick walls.
- Check if your router supports higher frequencies, like 5GHz instead of 2.4GHz, which will often penetrate through brick walls more easily than lower frequencies.
- Ensure all doors and windows are closed when attempting to get wifi signal through brick walls – this will reduce interference from outside sources such as neighbors’ wifi signals.
These tips and tricks can help you to get the most out of your wifi signal, even through thick brick walls. With a little effort and the right equipment, you should enjoy reliable connectivity no matter where you are in your home.
5 Things You Should Avoid
- Position your router as close to brick walls as possible. This will only cause the signal to be blocked and not penetrate through.
- Don’t use old or outdated routers – they may not support frequencies that are more likely to penetrate brick walls, like 5GHz instead of 2.4GHz.
- Don’t place metal objects in front of the router or nearby, as they can interfere with the wifi signal’s reach.
- Avoid placing any other electronics that produce EMFs (electromagnetic fields) near your router, as these can also weaken signals and make it difficult for them to pass through thick walls.
- And finally, don’t forget to keep your router updated with the latest firmware – this will ensure that you’re getting the best performance from your device.

These are just a few tips and tricks to remember when attempting to get wifi signal through brick walls. With the right tools and know-how, you should enjoy seamless connectivity no matter where you are in your home or office.
Now that you know how to get wifi signal through brick walls, you can always stay connected regardless of where you are in your house or office. You have the knowledge and tools to enhance your internet connectivity and ensure that no matter what type of walls are separating you from your router, they won’t stop you from having a strong wireless connection.
With this newfound ability comes freedom and confidence—the assurance that the wifi will reach you no matter where in your home or office you may be! And if something goes wrong with your connection, you know how to troubleshoot it quickly so that no time is wasted.
Knowing how to get Wifi through brick walls is certainly a practical skill, thus, knowing how never hurts. So take advantage of this new knowledge and keep up with any changes or updates related to network technology.
Hopefully, this article has helped teach you how to get a wifi signal through brick walls. Now go forth and enjoy the freedom of always staying connected no matter what type of wall separates you from your router!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How WiFi Signals Travel Through Walls. When an electromagnetic wave (in this case, WiFi signals) strikes a surface, it can do one of these three things: 1 - pass through (refraction) 2 - get reflected (reflection) 3 - get absorbed (absorption) When an object reflects a particular wavelength of visible light, the color associated with that ...
Walls. The first thing to do is to check the construction of the walls. In theory, Wi-Fi signals are capable of passing through walls and other obstacles relatively easily. However, in reality, some walls are thicker or use reinforced concrete and may block some of the signals. Materials such as drywall, plywood, other kinds of wood and glass ...
Use 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. Due to wavelength physics, 2.4 GHz waves penetrate and refract around most objects better than 5 GHz waves. In most cases, this makes 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi a better option when you want to prioritize coverage. You do have to be careful about interference when using 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, though.
For a variety of technical reasons, comparing lower (mid range 433MHz) and higher frequency 2.4GHz) compares like this: The lower frequency signals travel further than because the energy is higher and more concentrated in a single steady fashion that isn't absorbed as easily by air, which consists of a good deal of moisture.
Here are three ways to check your Wi-Fi signal strength: Use a Wi-Fi Analyzer App: Wi-Fi analyzer apps are available for both Android and iOS devices. These apps scan the available Wi-Fi networks in your area and display their signal strength and other details like frequency, channel, and security type.
2. Walls (Concrete & Brick) Walls are made of materials that can block Wi-Fi signals, but the extent to which that happens depends on various factors, including the type of wall material and thickness. Concrete and brick walls, in particular, can be challenging for Wi-Fi signals to penetrate. Concrete walls are more effective at blocking Wi-Fi ...
Remove bulbs, lamps, microwaves, and anything else that could distort the signal on its way to you. These obstacles can cause a quick disruption, so place them away from the wall that sits between you and the router and modem. By limiting the objects, big or small, that separate yourself from the source, you can greatly enhance the signal.
Yes. WiFi signals should pass through walls just fine, and that's because radio waves have very long wavelengths. These signals penetrate objects such as walls and furniture, lose a bit of energy, and easily emerge on the other side. You could say that walls are as transparent to radio waves as glass is to visible light.
WiFi signals travel through airwaves and can sometimes struggle to penetrate thick walls, especially concrete ones. ... How To Boost WiFi Signals Through Walls: 5 Ways That Are Simple Yet Effective. While too many walls aren't ideal for WiFi connectivity, any location can't go without them. And not just walls but other objects and ...
Radio signals travel from faraway galaxies with nothing between them and us, through almost empty space. On the other hand, your wi-fi router has to go through walls full of wiring and possibly even metal studs. RF signals travel well through walls but nowhere near as well as they do through open space.
Sheetrock and insulation. Sheetrock is one of the lower blocking agents for a cell phone signal. However, it can cause your signal to be blocked completely if it is already weak. Keep in mind that 3G, 4G, 5G signals are generally the same as a radio signal and so you can see fluctuations in your signal of -2db.
5GHz WiFi can travel through walls however its shorter wavelength is more susceptible to losing signal strength (vs 2.4GHz) when traveling through solid objects. Walls made from dense materials such as concrete and bricks can cause significant signal attenuation which may result in unreliable packet delivery.
WiFi signals don't travel well through walls, especially concrete ones. But don't worry, we have the ultimate guide to boosting your wifi signal through concrete walls. In this blog post, we ...
Keller Cones: The Interaction of Wireless Signals with Edges As discussed earlier, when a wave is incident on an edge point, i.e., a point of discontinuity on the object's surface normal direction, a cone of outgoing rays emerge according to Keller's Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (GTD). The angle of the cone is equal to the angle between the incident ray and the edge (which is also the ...
Wifi operates on radio frequencies, typically either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, and uses electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive data. These waves can travel through walls, floors, and other obstacles, but their strength diminishes as the distance increases. Now, let's explore the various factors that can affect the range of wifi signals.
These guys have found a way to see through walls using ambient Wi-Fi signals and an ordinary smartphone. They say the new technique allows an unprecedented invasion of privacy. "Bad actors using ...
Wi-Fi signals travel in different bandwidths. Wireless connectivity frequency bands travel in: 2.4 GHz; 3.6 GHz; ... We have established the fact that Wi-Fi signals go through walls and barriers. However, it will eventually depend on the thickness and, more accurately, the type of materials used for building such barriers to determine if ...
WiFi signals are transmitted using radio waves, which are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can travel through the air. These waves are transmitted at a specific frequency and can be picked up by a device that has a compatible receiver. ... One of the most effective ways to boost your WiFi signal through walls is by optimizing the ...
Bluetooth signals are transmitted via radio waves, a type of electromagnetic radiation. This means that they can travel through objects, including walls. However, the strength of the signal will be weakened when it passes through these obstacles. The following factors will determine how well your signal travels through walls: READ MORE!
However, it lacks the latency that helps the signal travel farther distances, primarily through hurdles like walls and ceilings. How Wi-Fi signal passes through different surfaces in the home (Source: Zen.co.uk) With a much shorter range, it may be easily blocked by concrete and dry walls.
Researchers in the US have developed a system called RF Capture that uses wireless signals to detect and track human motion throughout a building, even when people are behind walls or furniture, or are in rooms at the opposite end of the building. In a paper that will be presented at the SIGGRAPH Asia 2015 conference next month, researchers ...
Step 2. Install a Wi-Fi Range Extender. To increase the range of your wifi signal, it is recommended that you install a range extender in between your router and brick wall barrier. This device will amplify any incoming signals from the router so that they can easily pass through brick walls without losing strength.
Wi-Fi signals track and distinguish people through walls. Two years ago, researchers at MIT used Wi-Fi signals to see through walls and track a person's movements. The same team has now come up ...