The magazine of Glion Institute of Higher Education
- What is tourism and hospitality?
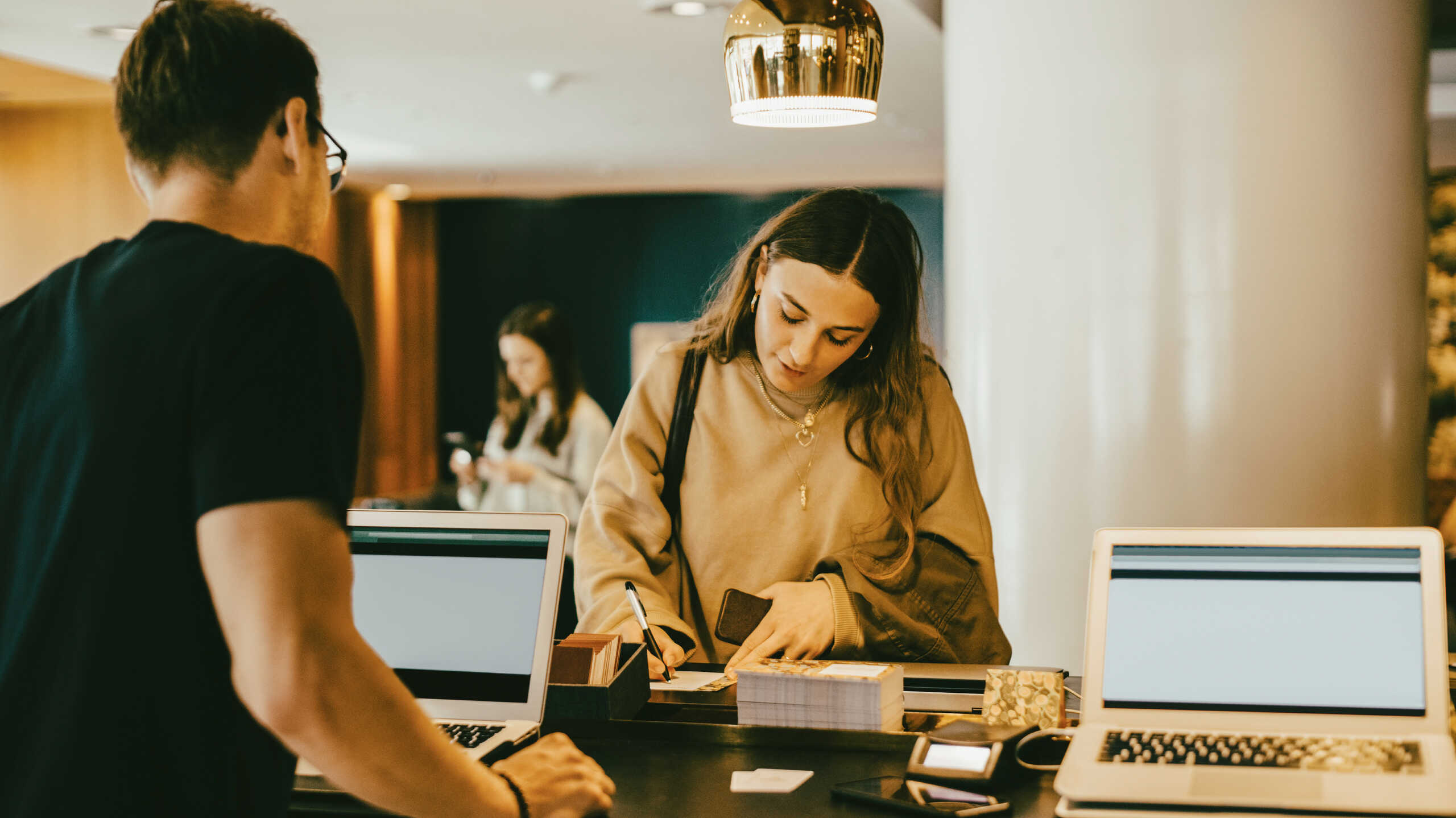

Tourism and hospitality are thriving industries encompassing many sectors, including hotels, restaurants, travel, events, and entertainment.
It’s an exciting and dynamic area, constantly evolving and adapting to changing customer demands and trends.
The tourism and hospitality industry offers a diverse range of career opportunities that cater to various interests, skills, and qualifications, with positions available from entry-level to executive management.
The booming tourism and hospitality industry also offers job security and career growth potential in many hospitality-related occupations.

What is tourism?
Tourism is traveling for leisure, pleasure, or business purposes and visiting various destinations, such as cities, countries, natural attractions, historical sites, and cultural events, to experience new cultures, activities, and environments.
Tourism can take many forms, including domestic, or traveling within your country, and international tourism, or visiting foreign countries.
It can also involve sightseeing, adventure tourism , eco-tourism, cultural tourism, and business tourism, and it’s a huge contributor to the global economy, generating jobs and income in many countries.
It involves many businesses, including airlines, hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, tour operators, and transportation companies.
What is hospitality?
Hospitality includes a range of businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, bars, resorts, cruise ships, theme parks, and other service-oriented businesses that provide accommodations, food, and beverages.
Hospitality is all about creating a welcoming and comfortable environment for guests and meeting their needs.
Quality hospitality means providing excellent customer service, anticipating guests’ needs, and ensuring comfort and satisfaction. The hospitality industry is essential to tourism as both industries often work closely together.
What is the difference between tourism and hospitality?
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries.
Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including transportation, accommodation, and attractions.
Transform your outlook for a successful career as a leader in hospitality management
This inspiring Bachelor’s in hospitality management gives you the knowledge, skills, and practical experience to take charge and run a business

Is tourism and hospitality a good career choice?
So, why work in hospitality and tourism? The tourism and hospitality industry is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world, providing a colossal number of job opportunities.
Between 2021 and 2031, employment in the hospitality and tourism industry is projected to expand faster than any other job sector, creating about 1.3 million new positions .
A tourism and hospitality career can be a highly rewarding choice for anyone who enjoys working with people, has a strong service-oriented mindset, and is looking for a dynamic and exciting career with growth potential.
Growth and job opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Tourism and hospitality offers significant growth and job opportunities worldwide. The industry’s increasing demand for personnel contributes to economic and employment growth, particularly in developing countries.
The industry employs millions globally, from entry-level to high-level management positions, including hotel managers, chefs, tour operators, travel agents, and executives.
It provides diverse opportunities with great career progression and skill development potential.
Career paths in tourism and hospitality

There are many career opportunities in tourism management and hospitality. With a degree in hospitality management, as well as relevant experience, you can pursue satisfying and fulfilling hospitality and tourism careers in these fields.
Hotel manager
Hotel managers oversee hotel operations. They manage staff, supervise customer service, and ensure the facility runs smoothly.
Tour manager
Tour managers organize and lead group tours. They work for tour companies, travel agencies, or independently. Tour managers coordinate a group’s transportation, accommodations, and activities, ensuring the trip runs to schedule.
Restaurant manager
Restaurant managers supervise the daily operations of a restaurant. They manage staff, ensure the kitchen runs smoothly, and monitor customer service.
Resort manager
Resort managers supervise and manage the operations of a resort. From managing staff to overseeing customer service, they ensure the entire operation delivers excellence.
Entertainment manager
Entertainment managers organize and oversee entertainment at venues like hotels or resorts. They book performers, oversee sound and lighting, and ensure guests have a great experience.
Event planner
Event planners organize and coordinate events, such as weddings, conferences, and trade shows. They work for event planning companies, hotels, or independently.
vent planners coordinate all aspects of the event, from the venue to catering and decor.
Travel consultant
Travel consultants help customers plan and book travel arrangements, such as flights, hotels, and rental cars. They work for travel agencies or independently. Travel consultants must know travel destinations and provide superb customer service.
What skills and qualifications are needed for a career in tourism and hospitality?

Tourism and hospitality are rewarding industries with growing job opportunities. Necessary qualifications include excellent skills in communication, customer service, leadership, problem-solving, and organization along with relevant education and training.
Essential skills for success in tourism and hospitality
A career in the tourism and hospitality industry requires a combination of soft and technical skills and relevant qualifications. Here are some of the essential key skills needed for a successful career.
- Communication skills : Effective communication is necessary for the tourism and hospitality industry in dealing with all kinds of people.
- Customer service : Providing excellent customer service is critical to the success of any tourism or hospitality business . This requires patience, empathy, and the ability to meet customers’ needs.
- Flexibility and adaptability : The industry is constantly changing, and employees must be able to adapt to new situations, be flexible with their work schedules, and handle unexpected events.
- Time management : Time management is crucial to ensure guest satisfaction and smooth operations.
- Cultural awareness : Understanding and respecting cultural differences is essential in the tourism and hospitality industry, as you’ll interact with people from different cultures.
- Teamwork : Working collaboratively with colleagues is essential, as employees must work together to ensure guests have a positive experience.
- Problem-solving : Inevitably, problems will arise, and employees must be able to identify, analyze, and resolve them efficiently.
- Technical skills : With the increasing use of technology, employees must possess the necessary technical skills to operate systems, such as booking software, point-of-sale systems, and social media platforms.
Revenue management : Revenue management skills are crucial in effectively managing pricing, inventory, and data analysis to maximize revenue and profitability
Master fundamental hospitality and tourism secrets for a high-flying career at a world-leading hospitality brand
With this Master’s degree, you’ll discover the skills to manage a world-class hospitality and tourism business.

Education and training opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Education and training are vital for a hospitality and tourism career. You can ensure you are prepared for a career in the industry with a Bachelor’s in hospitality management and Master’s in hospitality programs from Glion.
These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of the guest experience, including service delivery and business operations, while developing essential skills such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving. You’ll gain the knowledge and qualifications you need for a successful, dynamic, and rewarding hospitality and tourism career.
Preparing for a career in tourism and hospitality
To prepare for a career in tourism and hospitality management, you should focus on researching the industry and gaining relevant education and training, such as a hospitality degree . For instance, Glion’s programs emphasize guest experience and hospitality management, providing students with an outstanding education that launches them into leading industry roles.
It would help if you also worked on building your communication, customer service, and problem-solving skills while gaining practical experience through internships or part-time jobs in the industry. Meanwhile, attending industry events, job fairs, and conferences, staying up-to-date on industry trends, and networking to establish professional connections will also be extremely valuable.
Finding jobs in tourism and hospitality
To find jobs in tourism and hospitality, candidates can search online job boards, and company career pages, attend career fairs, network with industry professionals, and utilize the services of recruitment agencies. Hospitality and tourism graduates can also leverage valuable alumni networks and industry connections made during internships or industry projects.
Networking and building connections in the industry
Networking and building connections in the hospitality and tourism industry provide opportunities to learn about job openings, meet potential employers, and gain industry insights. It can also help you expand your knowledge and skills, build your personal brand, and establish yourself as a valuable industry professional.
You can start networking by attending industry events, joining professional organizations, connecting with professionals on social media, and through career services at Glion.
Tips for success in tourism and hospitality

Here are tips for career success in the tourism and hospitality industry.
- Gain relevant education and training : Pursue a hospitality or tourism management degree from Glion to gain fundamental knowledge and practical skills.
- Build your network : Attend industry events, connect with colleagues and professionals on LinkedIn, and join relevant associations to build your network and increase your exposure to potential job opportunities.
- Gain practical experience : Look for internships, part-time jobs, or volunteering opportunities to gain practical experience and develop relevant skills.
- Develop your soft skills : Work on essential interpersonal skills like communication, empathy, and problem-solving.
- Stay up-to-date with industry trends : Follow industry news and trends and proactively learn new skills and technologies relevant to tourism and hospitality.
- Be flexible and adaptable : The tourism and hospitality industry constantly evolves, so be open to change and to adapting to new situations and challenges.
- Strive for excellent guest service : Focus on delivering exceptional guest experiences as guest satisfaction is critical for success.
Tourism and hospitality offer many fantastic opportunities to create memorable guest experiences , work in diverse and multicultural environments, and develop transferable skills.
If you’re ready to embark on your career in tourism and hospitality, Glion has world-leading bachelor’s and master’s programs to set you up for success.
Photo credits Main image: Maskot/Maskot via Getty Images

BUSINESS OF LUXURY

HOSPITALITY UNCOVERED

LISTENING TO LEADERS

GLION SPIRIT

WELCOME TO GLION.
This site uses cookies. Some are used for statistical purposes and others are set up by third party services. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you accept the use of cookies
Privacy Overview

- Why Study hospitality?
- Your Future Career
- Why Choose EHL?
- Awards & Rankings
- Our History
- Academic Governance
- Accreditations & Memberships
- Professional Path to the Bachelor Degree
- Preparatory Year
- Student Business Projects
- Bachelor Internships
- Direct Entries & Transfers
- EHL Junior Academy Campus Lausanne
- EHL Junior Academy Campus Singapore
- EHL Junior Academy Campus Passugg
- Master's Degrees
- MBA Programs
- Culinary & Restaurant Management Certificate (CREM)
- Bachelor in Lausanne
- University Transfers & Direct Entries
- Bachelor in Singapore
- Fees for Bachelor students eligible for A-HES
- Learning Philosophy
- Our Faculty
- Swiss Education Excellence
- Research Projects & Publications
- Inauguration
- Student Life in Lausanne
- Campus Lausanne Guided Tour
- Explore Lausanne & Switzerland
- Campus Lausanne Contacts
- Student Life at EHL Campus (Singapore)
- Explore Singapore
- Explore the Region
- Campus (Singapore) Contacts
- Contact our Program Advisors
- Chat with our Students
What is hospitality?
Hospitality means extending a welcome to guests or offering a home away from home, and the word is derived from the Latin word “hospes” meaning host, visitor or stranger. The hospitality and tourism industry is a vast sector that includes all the economic activities that directly or indirectly contribute to, or depend upon, travel, tourism and hospitality.
This industry sector includes:
- Hotels & Resorts
- Restaurants & Catering
- Night Clubs & Bars
- Travel & Transportation
- Spas & Wellness
- Cruise Liners & Bus tours
- Cultural & Sports
- Business Administration (events, communication, customer experience, and many more )

Bachelor of Science in International Hospitality Management
Discover the EHL Bachelor's program meticulously crafted by our Hospitality Management School to meet the evolving needs of the hospitality and tourism industry.
Our curriculum strikes a balance between hands-on experience, academic excellence, and business acumen. It also provides a unique opportunity for students to study in two premier locations: Switzerland and Singapore.
Immerse yourself in practical courses, workshops and two six-month internships, providing real-world insights aligned with industry demands.

The History of Hospitality & Tourism
Hospitality is one of the oldest businesses, going way back to the innkeepers and taverns of biblical times. Tourism, on the other hand, is a more recent invention which began in Europe, with Switzerland being one of the first countries to develop special accommodation and services for travelers.
In the late 1800’s, the concept of leisure tourism and hospitality spread across Europe, bringing flocks of wealthy travelers to Switzerland. It began with visitors seeking cultural and natural exposure on guided tours in the Swiss Alps, train rides and wellness tourism. Palace-style hotels, thermal baths and ski resorts became icons of luxury tourism in Switzerland.
This new generation of wealthy guests had higher expectations for comfortable accommodations, convenient services and fine dining. The leisure travel phenomenon gave birth to hospitality management schools: EHL was founded as the first hotel management school in 1893 in Lausanne, and it has pioneered in hospitality management education since then.
Hospitality is one of the most resilient, adaptable and dynamic industries on the planet. It is an industry of constant change, where technology and innovation are being integrated to improve the guest experience.

What is Tourism and Hospitality Management?
Careers in hospitality management.
Hospitality management is a broad career field that provides many opportunities for international career progression. In the core of the hospitality industry alone (hotels, events, restaurants, etc.) graduates with a hospitality degree can become managers in a variety of departments and sectors, or choose to specialize in one area.
The career paths are as diverse as the industry, and with so many new hospitality concepts and innovation changing the industry, the career paths will continue to grow and evolve with technology and trends of the 21st.
Hospitality education at EHL teaches students to love learning because it takes a scientific approach that sparks curiosity and involves the five senses.
_Faculty%20&%20Students%20Discussion%201.jpg)
What are Hospitality Management Skills?
Studying at ehl, the world's 1st hospitality management school.
In the field of hospitality management, customer satisfaction is key, and the primary goal is to ensure the best customer experience possible. Therefore, hospitality management courses teach both professionally-focused hard skills (room pricing, cost-control, accounting, scheduling, etc. ) and soft skills which are related to how one acts, and interacts in a professional environment.
Training for soft-skills is critical to succeed in the 21st century: critical thinking, agility and adaptability, effective communication, imagination and curiosity: these are all skills students develop at EHL in our hospitality management courses and degrees.
#hospitality-industry
See More Articles

The potential of green financing for hotel real estate in Asia
April 4, 2024

The future of hotel distribution channels: Seizing opportunity in channel disruption
April 3, 2024

Customer experience management: Business vs. Customer expectations
March 28, 2024
- Bachelor Degree in Hospitality
- Pre-University Courses
- Master’s Degrees & MBA Programs
- Executive Education
- Online Courses
- Swiss Professional Diplomas
- Culinary Certificates & Courses
- Fees & Scholarships
- Bachelor in Hospitality Admissions
- EHL Campus Lausanne
- EHL Campus (Singapore)
- EHL Campus Passugg
- Host an Event at EHL
- Contact our program advisors
- Join our Open Days
- Meet EHL Representatives Worldwide
- Chat with our students
- Why Study Hospitality?
- Careers in Hospitality
- EHL Network of Excellence
- Career Development Resources
- Route de Berne 301 1000 Lausanne 25 Switzerland
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Terms
© 2024 EHL Holding SA, Switzerland. All rights reserved.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” [1] . The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
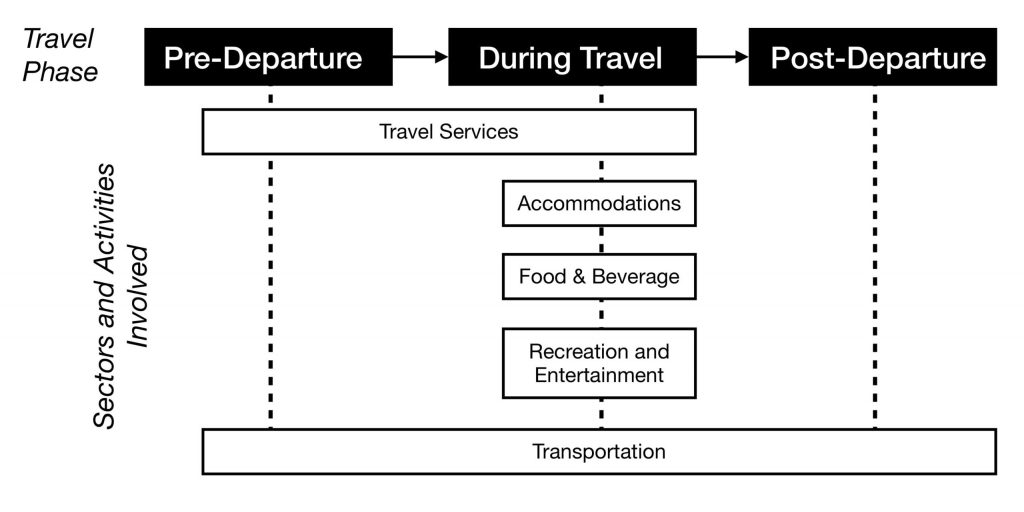
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Media Attributions
Front Desk © Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial) license
- (LinkBC, 2008, p.8) ↵
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism Copyright © 2020 by NSCC is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: What is Tourism?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 9308

- Morgan Westcott & Wendy Anderson et al.
Before engaging in a study of tourism, let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism, travel, and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4, respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
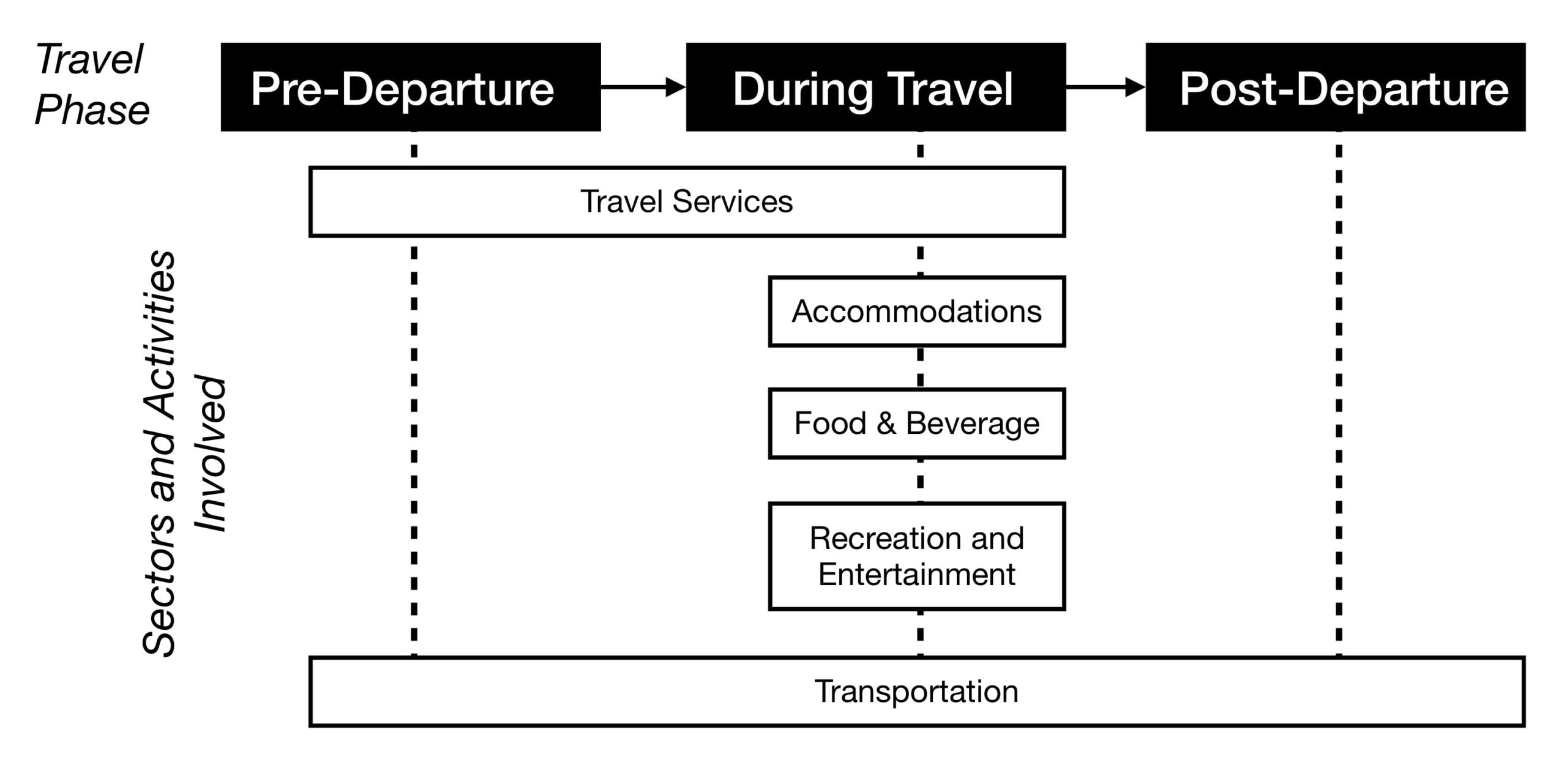
The original version of this chapter contained H5P content. You may want to remove or replace this element.
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
Learning Objectives
- Specify the commonly understood definitions of tourism and tourist
- Classify tourism into distinct industry groups using North American Industry Classification Standards (NAICS)
- Define hospitality
- Gain knowledge about the origins of the tourism industry
- Provide an overview of the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism worldwide
- Understand the history of tourism development in Canada and British Columbia
- Analyze the value of tourism in Canada and British Columbia
- Identify key industry associations and understand their mandates
What Is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure ( United Nations World Tourism Organization , 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure).
Definition of Tourist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 156 countries and over 400 affiliates such as private companies and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website : http://www2.unwto.org/.
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business — whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground — are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

The Hospitality Industry
When looking at tourism it’s important to consider the term hospitality . Some define hospitality as “t he business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, ¶ 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry. You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4, respectively.
Before we seek to understand the five industry groupings in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Global Overview
Origins of tourism.
Travel for leisure purposes has evolved from an experience reserved for very few people into something enjoyed by many. Historically, the ability to travel was reserved for royalty and the upper classes. From ancient Roman times through to the 17th century, young men of high standing were encouraged to travel through Europe on a “grand tour” (Chaney, 2000). Through the Middle Ages, many societies encouraged the practice of religious pilgrimage, as reflected in Chaucer’s Canterbury Tales and other literature.
The word hospitality predates the use of the word tourism , and first appeared in the 14th century. It is derived from the Latin hospes , which encompasses the words guest, host , and foreigner (Latdict, 2014). The word tourist appeared in print much later, in 1772 (Griffiths and Griffiths, 1772). William Theobald suggests that the word tour comes from Greek and Latin words for circle and turn, and that tourism and tourist represent the activities of circling away from home, and then returning (Theobald, 1998).
Tourism Becomes Business
Cox & Kings, the first known travel agency, was founded in 1758 when Richard Cox became official travel agent of the British Royal Armed Forces (Cox & Kings, 2014). Almost 100 years later, in June 1841, Thomas Cook opened the first leisure travel agency, designed to help Britons improve their lives by seeing the world and participating in the temperance movement. In 1845, he ran his first commercial packaged tour, complete with cost-effective railway tickets and a printed guide (Thomas Cook, 2014).
The continued popularity of rail travel and the emergence of the automobile presented additional milestones in the development of tourism. In fact, a long journey taken by Karl Benz’s wife in 1886 served to kick off interest in auto travel and helped to publicize his budding car company, which would one day become Mercedes Benz (Auer, 2006). We take a closer look at the importance of car travel later this chapter, and of transportation to the tourism industry in Chapter 2.
Fast forward to 1952 with the first commercial air flights from London, England, to Johannesburg, South Africa, and Colombo, Sri Lanka (Flightglobal, 2002) and the dawn of the jet age, which many herald as the start of the modern tourism industry. The 1950s also saw the creation of Club Méditérannée (Gyr, 2010) and similar club holiday destinations, the precursor of today’s all-inclusive resorts.
The decade that followed is considered to have been a significant period in tourism development, as more travel companies came onto the scene, increasing competition for customers and moving toward “mass tourism, introducing new destinations and modes of holidaying” (Gyr, 2010, p. 32).
Industry growth has been interrupted at several key points in history, including World War I, the Great Depression, and World War II. At the start of this century, global events thrust international travel into decline including the September 11, 2001, attack on the World Trade Center in New York City (known as 9/11), the war in Iraq, perceived threat of future terrorist attacks, and health scares including SARS, BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), and West Nile virus (Government of Canada, 2006).
At the same time, the industry began a massive technological shift as increased internet use revolutionized travel services. Through the 2000s, online travel bookings grew exponentially, and by 2014 global leader Expedia had expanded to include brands such as Hotels.com, the Hotwire Group, trivago, and Expedia CruiseShip Centers, earning revenues of over $4.7 million (Expedia Inc., 2013).
A more in-depth exploration of the impact of the online marketplace, and other trends in global tourism, is provided in Chapter 14. But as you can already see, the impacts of the global tourism industry today are impressive and far reaching. Let’s have a closer look at some of these outcomes.
Tourism Impacts
Tourism impacts can be grouped into three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations.
Economic Impacts
According to a UNWTO report, in 2011, “international tourism receipts exceeded US$1 trillion for the first time” (UNWTO, 2012). UNWTO Secretary-General Taleb Rifai stated this excess of $1 trillion was especially important news given the global economic crisis of 2008, as tourism could help rebuild still-struggling economies, because it is a key export and labour intensive (UNWTO, 2012).

Tourism around the world is now worth over $1 trillion annually, and it’s a growing industry almost everywhere. Regions with the highest growth in terms of tourism dollars earned are the Americas, Europe, Asia and the Pacific, and Africa. Only the Middle East posted negative growth at the time of the report (UNWTO, 2012).
While North and South America are growing the fastest, Europe continues to lead the way in terms of overall percentage of dollars earned (UNWTO, 2012):
- Europe (45%)
- Asia and the Pacific (28%)
- North and South America (19%)
- Middle East (4%)
Global industry growth and high receipts are expected to continue. In its August 2014 expenditure barometer, the UNWTO found worldwide visitation had increased by 22 million people in the first half of the year over the previous year, to reach 517 million visits (UNWTO, 2014a). As well, the UNWTO’s Tourism 2020 Vision predicts that international arrivals will reach nearly 1.6 billion by 2020 . Read more about the Tourism 2020 Vision : http://www.e-unwto.org/doi/abs/10.18111/9789284403394
Social Impacts

In addition to the economic benefits of tourism development, positive social impacts include an increase in amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts and culture, celebration of First Nations people, and community pride. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents.
However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP, 2003a), negative social impacts of tourism can include:
- Change or loss of indigenous identity and values
- Culture clashes
- Physical causes of social stress (increased demand for resources)
- Ethical issues (such as an increase in sex tourism or the exploitation of child workers)
Some of these issues are explored in further detail in Chapter 12, which examines the development of Aboriginal tourism in British Columbia.
Environmental Impacts
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can have severe negative impacts. According to UNEP (2003b), these can include:
- Depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.)
- Pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering)
- Physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity)
The environmental impacts of tourism can reach outside local areas and have an effect on the global ecosystem. One example is increased air travel, which is a major contributor to climate change. Chapter 10 looks at the environmental impacts of tourism in more detail.
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world, and the industry is transforming at a staggering rate. But before we delve deeper into our understanding of tourism, let’s take a look at the development of the sector in our own backyard.
Canada Overview
Origins of tourism in canada.
Tourism has long been a source of economic development for our country. Some argue that as early as 1534 the explorers of the day, such as Jacques Cartier, were Canada’s first tourists (Dawson, 2004), but most agree the major developments in Canada’s tourism industry followed milestones in the transportation sector: by rail, by car, and eventually, in the skies.
Railway Travel: The Ties That Bind

The dawn of the railway age in Canada came midway through the 19th century. The first railway was launched in 1836 (Library and Archives Canada, n.d.), and by the onset of World War I in 1914, four railways dominated the Canadian landscape: Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), Canadian Northern Railway (CNOR), the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR), and the Grand Trunk Pacific (GTP). Unfortunately, their rapid expansion soon brought the last three into near bankruptcy (Library and Archives Canada, n.d.).
In 1923, these three rail companies were amalgamated into the Canadian National Railway (CNR), and together with the CPR, these trans-continentals dominated the Canadian travel landscape until other forms of transportation became more popular. In 1978, with declining interest in rail travel, the CPR and CNR were forced to combine their passenger services to form VIA Rail (Library and Archives Canada, n.d.).
The Rise of the Automobile
The rising popularity of car travel was partially to blame for the decline in rail travel, although it took time to develop. When the first cross-country road trip took place in 1912, there were only 16 kilometres of paved road across Canada (MacEachern, 2012). Cars were initially considered a nuisance, and the National Parks Branch banned entry to automobiles, but later slowly began to embrace them. By the 1930s, some parks, such as Cape Breton Highlands National Park, were actually created to provide visitors with scenic drives (MacEachern, 2012).
It would take decades before a coast-to-coast highway was created, with the Trans-Canada Highway officially opening in Revelstoke in 1962. When it was fully completed in 1970, it was the longest national highway in the world, spanning one-fifth of the globe (MacEachern, 2012).
Early Tourism Promotion
As early as 1892, enterprising Canadians like the Brewsters became the country’s first tour operators, leading guests through areas such as Banff National Park (Brewster Travel Canada, 2014). Communities across Canada developed their own marketing strategies as transportation development took hold. For instance, the town of Maisonneuve in Quebec launched a campaign from 1907 to 1915 calling itself “Le Pittsburg du Canada.” And by 1935 Quebec was spending $250,000 promoting tourism, with Ontario, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia also enjoying established provincial tourism bureaus (Dawson, 2004).
National Airlines
Our national airline, Air Canada, was formed in 1937 as Trans-Canada Air Lines. In many ways, Air Canada was a world leader in passenger aviation, introducing the world’s first computerized reservations system in 1963 ( Globe and Mail , 2014). Through the 1950s and 1960s, reduced airfares saw increased mass travel. Competitors including Canadian Pacific (which became Canadian Airlines in 1987) began to launch international flights during this time to Australia, Japan, and South America ( Canadian Geographic, 2000). By 2000, Air Canada was facing financial peril and forced to restructure. A numbered company, owned in part by Air Canada, purchased 82% of Canadian Airline’s shares, with the result of Air Canada becoming the country’s only national airline ( Canadian Geographic, 2000).
Parks and Protected Areas
A look at the evolution of tourism in Canada would be incomplete without a quick study of our national parks and protected areas. The official conserving of our natural spaces began around the same time as the railway boom, and in 1885 Banff was established as Canada’s first national park. By 1911, the Dominion Forest Reserves and Parks Act created the Dominion Parks Branch, the first of its kind in the world (Shoalts, 2011).
The systemic conservation and celebration of Canada’s parks over the next century would help shape Canada’s identity, both at home and abroad. Through the 1930s, conservation officers and interpreters were hired to enhance visitor experiences. By 1970, the National Park System Plan divided Canada into 39 regions, with the goal of preserving each distinct ecosystem for future generations. In 1987, the country’s first national marine park was established in Ontario, and in the 20 years that followed, 10 new national parks and marine conservation areas were created (Shoalts, 2011).
The role of parks and protected areas in tourism is explored in greater detail in Chapter 5 (recreation) and Chapter 10 (environmental stewardship).
Global Shock and Industry Decline
As with the global industry, Canada’s tourism industry was impacted by world events such as the Great Depression and the World Wars.
More recently, global events such as 9/11, the SARS outbreak, and the war in Iraq took their toll on tourism receipts. Worldwide arrivals to Canada dropped 1% to 694 million in 2003, after three years of stagnant growth. In 2005, spending reached $61.4 billion with domestic travel accounting for 71% (Government of Canada, 2006).
Tourism in Canada Today
In 2011, tourism created $78.8 billion in total economic activity and 603,400 jobs. Tourism accounted for more of Canada’s gross domestic product (GDP) than agriculture, forestry, and fisheries combined (Tourism Industry Association of Canada, 2014).
Spotlight On: The Tourism Industry Association of Canada (TIAC)
Founded in 1930 and based in Ottawa, the Tourism Industry Association of Canada (TIAC) is the national private-sector advocate for the industry. Its goal is to support policies and programs that help the industry grow, while representing over 400 members including airports, concert halls, festivals and events, travel services providers, and businesses of all sizes. For more information, visit the Tourism Industry Association of Canada’s website : http://tiac.travel/About.html
Unfortunately, while overall receipts from tourism appear healthy, and globally the industry is growing, according to a recent report, Canada’s historic reliance on the US market (which traditionally accounts for 75% of our market) is troubling. Because three out of every four international visitors to Canada originates in the United States, the 55% decline in that market since 2000 is being very strongly felt here. Many feel the decline in American visitors to Canada can be attributed to tighter passport and border regulations, the economic downturn (including the 2008 global economic crisis), and a stronger Canadian dollar (TIAC, 2014).
Despite disappointing numbers from the United States, Canada continues to see strong visitation from the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Australia, and China. In 2011, we welcomed 3,180,262 tourists from our top 15 inbound countries (excluding the United States). Canadians travelling domestically accounted for 80% of tourism revenues in the country, and TIAC suggested that a focus on rebounding US visitation would help grow the industry (TIAC, 2014).
Spotlight On: The Canadian Tourism Commission
Housed in Vancouver, Destination Canada , previously the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC), is responsible for promoting Canada in several foreign markets: Australia, Brazil, China, France, Germany, India, Japan, Mexico, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and the United States. It works with private companies, travel services providers, meeting professionals, and government organizations to help leverage Canada’s tourism brand, Canada. Keep Exploring . It also conducts research and has a significant image library (Canadian Tourism Commission, 2014). For more information, visit Destination Canada website : http://en.destinationcanada.com/about-ctc.
As organizations like TIAC work to confront barriers to travel, the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC) is active abroad, encouraging more visitors to explore our country. In Chapter 8, we’ll delve more into the challenges and triumphs of selling tourism at home and abroad.
The great news for British Columbia is that once in Canada, most international visitors tend to remain in the province they landed in, and BC is one of three provinces that receives the bulk of this traffic (TIAC, 2012). In fact, BC’s tourism industry is one of the healthiest in Canada today. Let’s have a look at how our provincial industry was established and where it stands now.
British Columbia Overview
Origins of tourism in bc.
As with the history of tourism in Canada, it’s often stated that the first tourists to BC were explorers. In 1778, Captain James Cook touched down on Vancouver Island, followed by James Douglas in 1842, a British agent who had been sent to find new headquarters for the Hudson’s Bay Company, ultimately choosing Victoria. Through the 1860s, BC’s gold rush attracted prospectors from around the world, with towns and economies springing up along the trail (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
Railway Travel: Full Steam Ahead!
The development of BC’s tourism industry began in earnest in the late 1800s when the CPR built accommodation properties along itsnewly completed trans-Canada route, capturing revenues from overnight stays to help alleviate their increasing corporate debt. Following the 1886 construction of small lodges at stops in Field, Rogers Pass, and Fraser Canyon, the CPR opened the Hotel Vancouver in May 1887 (Dawson, 2004).
As opposed to Atlantic Canada, where tourism promotion centred around attracting hunters and fishermen for a temporary infusion of cash, in British Columbia tourism was seen as a way to lure farmers and settlers to stay in the new province. Industry associations began to form quickly: the Tourist Association of Victoria (TAV) in February 1902, and the Vancouver Tourist Association in June of the same year (Dawson, 2004).
Many of the campaigns struck by these and other organizations between 1890 and 1930 centred on the province’s natural assets, as people sought to escape modern convenience and enjoy the environment. A collaborative group called the Pacific Northwest Travel Association (BC, Washington, and Oregon) promoted “The Pacific Northwest: The World’s Greatest Out of Doors,” calling BC “The Switzerland of North America.” Promotions like these seemed to have had an effect: in 1928, over 370,000 tourists visited Victoria, spending over $3.5 million (Dawson, 2004).
The Great Depression and World War II
As the world’s economy was sent into peril during the Great Depression in the 1930s, tourism was seen as an economic solution. A newly renamed Greater Victoria Publicity Bureau touted a “100 for 1” multiplier effect of tourism spending, with visitor revenues accounting for around 13.5% of BC’s income in 1930. By 1935, an organization known as the TTDA (Tourist Trade Development Association of Victoria and Vancouver Island) looked to create a more stable industry through strategies to increase visitors’ length of stay (Dawson, 2004).
In 1937, the provincial Bureau of Industrial and Tourist Development (BITD) was formed through special legislation with a goal of increasing tourist traffic. By 1938, the organization changed its name to the British Columbia Government Travel Bureau (BCGTB) and was granted a budget increase to $105,000. This was soon followed by an expansion of the BC Tourist Council designed to solicit input from across the province. And in 1939, Vancouver welcomed the King and Queen of England and celebrated the opening of the Lions Gate Bridge, activities that reportedly bolstered tourism numbers (Dawson, 2004).
The December 1941 Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in Hawaii had negative repercussions for tourism on the Pacific Rim and was responsible for an era of decreased visitation to British Columbia, despite attempts by some to market the region as exciting. From 1939 to 1943, US visits to Vancouver (measured at the border) dropped from over 307,000 to approximately 183,600. Just two years later, however, that number jumped to 369,250, the result of campaigns like the 1943 initiative aimed at Americans that marketed BC as “comrades in war” (Dawson, 2004).
Post-War Rebound
We, with all due modesty, cannot help but claim that we are entering British Columbia’s half-century, and cannot help but observe that B.C. also stands for BOOM COUNTRY. – Phil Gagliardi, BC Minister of Highways, 1955 (Dawson, 2004, p.190)
A burst of post-war spending began in 1946, and although short-lived, was supported by steady government investment in marketing throughout the 1950s. As tourism grew in BC, however, so did competition for US dollars from Mexico, the Caribbean, and Europe. The decade that followed saw an emphasis on promoting BC’s history, its “Britishness,” and a commodification of Aboriginal culture. The BCGTB began marketing efforts to extend the travel season, encouraging travel in September, prime fishing season. It also tried to push visitors to specific areas, including the Lower Fraser Valley, the Okanagan-Fraser Canyon Loop, and the Kamloops-Cariboo region (Dawson, 2004).

In 1954, Vancouver hosted the British Empire Games, investing in the construction of Empire Stadium. A few years later, an increased emphasis on events and convention business saw the Greater Vancouver Tourist Association change its name in 1962 to the Greater Vancouver Visitors and Convention Bureau (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
The ski industry was also on the rise: in 1961, the lodge and chairlift on Tod Mountain (now Sun Peaks) opened, and Whistler followed suit five years later (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009). Ski partners became pioneers of collaborative marketing in the province with the foundation of the Ski Marketing Advisory Committee (SMAC) supported by Tod Mountain and Big White, evolving into today’s Canada’s West Ski Area Association (Magnes, 2010). This pioneer spirit was evident across the ski sector: the entire sport of heliskiing was invented by Hans Gosmer of BC’s Canadian Mountain Holidays, and today the province holds 90% of the world’s heliskiing market share (McLeish, 2014).
The concept of collaboration extended throughout the province as innovative funding structures saw the cost of marketing programs shared between government and industry in BC. These programs were distributed through regional channels (originally eight regions in the province), and considered “the most constructive and forward looking plan of its kind in Canada” (Dawson 2004, p.194).
Tourism in BC continued to grow through the 1970s. In 1971, the Hotel Room Tax Act was introduced, allowing for a 5% tax to be collected on room nights with the funds collected to be put toward marketing and development. By 1978, construction had begun on Whistler Village, with Blackcomb Mountain opening two years later (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009). Funding programs in the late 1970s and early 1980s such as the Canada BC Tourism Agreement (CBCTA) and Travel Industry Development Subsidiary Agreement (TIDSA) allowed communities to invest in projects that would make them more attractive tourism destinations. In the mountain community of Kimberley, for instance, the following improvements were implemented through a $3.1 million forgivable loan: a new road to the ski resort, a covered tennis court, a mountain lodge, an alpine slide, and nine more holes for the golf course (e-Know, 2011).
Around the same time, the “Super, Natural British Columbia” brand was introduced, and a formal bid was approved for Vancouver to host a fair then known as Transpo 86 (later Expo 86). Tourism in the province was about to truly take off.
Expo 86 and Beyond
By the time the world fair Expo 86 came to a close in October 1986, it had played host to 20,111,578 guests. Infrastructure developments, including rapid rail, airport improvements, a new trade and convention centre at Canada Place (with a cruise ship terminal), and hotel construction, had positioned the city and the province for further growth (PricewaterhouseCooopers, 2009). The construction and opening of the Coquihalla Highway through to 1990 enhanced the travel experience and reduced travel times to vast sections of the province (Magnes, 2010).
Take a Closer Look: The Value of Tourism
Tourism Vancouver Island, with the support of many partners, has created a website that directly addresses the value of tourism in the region. The site looks at the economics of tourism, social benefits of tourism, and a “what’s your role?” feature that helps users understand where they fit in. Explore the Tourism Vancouver Island website : http://valueoftourism.ca/.
By 2000, Vancouver International Airport (YVR) was named number one in the world by the International Air Transport Association’s survey of international passengers. Five years later, the airport welcomed a record 16.4 million passengers (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
Going for Gold
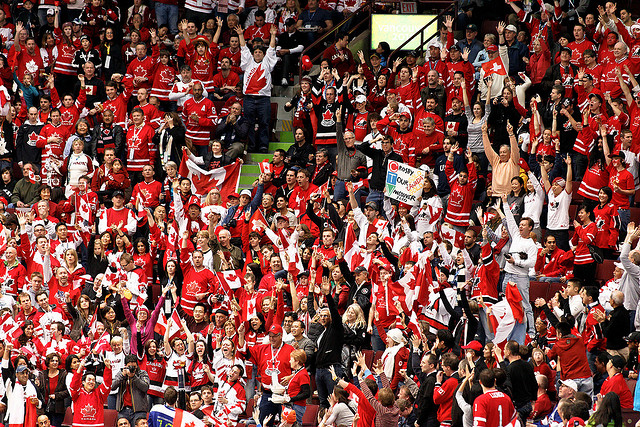

In 2003, the International Olympic Committee named Vancouver/Whistler as the host city for the 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games. Infrastructure development followed, including the expansion of the Sea-to-Sky Highway, the creation of Vancouver Convention Centre West, and the construction of the Canada Line, a rapid transport line connecting the airport with the city’s downtown.
As BC prepared to host the Games, its international reputation continued to grow. Vancouver was voted “Best City in the Americas” by Condé Nast Traveller magazine three years in a row. Kelowna was named “Best Canadian Golf City” by Canada’s largest golf magazine, and BC was named the “Best Golf Destination in North America” by the International Association of Golf Tour Operators. Kamloops, known as Canada’s Tournament City, hosted over 100 sports tournaments that same year, and nearby Sun Peaks Resort was named the “Best Family Resort in North America” by the Great Skiing and Snowboarding Guide in 2008 (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
By the time the Vancouver 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Games took place, over 80 participating countries, 6,000 athletes, and 3 billion viewers put British Columbia on centre stage.
Spotlight On: Destination British Columbia
Destination BC is a Crown corporation founded in November 2012 by the Government of British Columbia. Its mandate includes marketing the province as a tourist destination (at home and around the world), promoting the development and growth of the industry, providing advice and recommendations to the tourism minister on related matters, and enhancing public awareness of tourism and its economic value to British Columbia (Province of British Columbia, 2013b).
Tourism in BC Today
Building on the momentum generated by hosting the 2010 Winter Olympic Games, tourism in BC remains big business. In 2012, the industry generated $13.5 billion in revenue.
The provincial industry is made up of over 18,000 businesses, the majority of which are SMEs (small to medium enterprises), and together they employ approximately 127,300 people (Tourism Industry Association of BC, 2014). It may surprise you to learn that in British Columbia, tourism provides more jobs than high tech, oil and gas, mining, and forestry (Porges, 2014).
Spotlight On: The Tourism Industry Association of BC
Founded in 1993 as the Council of Tourism Associations, today the Tourism Industry Association of BC (TIABC) is a not-for-profit trade association comprising members from private sector tourism businesses, industry associations, and destination marketing organizations (DMOs). Its goal is to ensure the best working environment for a competitive tourism industry. It hosts industry networking events and engages in advocacy efforts as “the voice of the BC tourism industry.” Students are encouraged to join TIABC to take advantage of their connections and receive a discount at numerous industry events. For more information, visit the Tourism Industry Association of BC’s website : http://www.tiabc.ca/student-membership
One of the challenges for BC’s tourism industry, it has long been argued, is fragmentation. Back in September 1933, an article in the Victoria Daily Times argued for more coordination across organizations in order to capitalize on what they saw as Canada’s “largest dividend payer” (Dawson, 2004). Today, more than 80 years later, you will often hear BC tourism professionals say the same thing.
On the other hand, some experts believe that the industry is simply a model of diversity, acknowledging that tourism is a compilation of a multitude of businesses, services, organizations, and communities. They see the ways in which these components are working together toward success, rather than focusing on friction between the groups.
Many communities are placing a renewed focus on educating the general public and other businesses about the value of tourism and the ways in which stakeholders work together. The following case study highlights this in more detail:
Take a Closer Look: Tourism Pays in Richmond, BC
The community of Richmond, BC, brings to life the far-reaching positive economic effects of tourism in action. Watch the short video called “Tourism Pays” to see what we mean!: http://vimeo.com/31624689

Throughout the rest of this textbook, you’ll have a chance to learn more about the history and current outlook for tourism in BC, with in-depth coverage of some of the triumphs and challenges we’ve faced as an industry. You will also learn about the Canadian and global contexts of the tourism industry’s development.
As we’ve seen in this chapter, tourism is a complex set of industries including accommodation, recreation and entertainment, food and beverage services, transportation, and travel services. It encompasses domestic, inbound, and outbound travel for business, leisure, or other purposes. And because of this large scope, tourism development requires participation from all walks of life, including private business, governmental agencies, educational institutions, communities, and citizens.
Recognizing the diverse nature of the industry and the significant contributions tourism makes toward economic and social value for British Columbians is important. There remains a great deal of work to better educate members of the tourism industry, other sectors, and the public about the ways tourism contributes to our province.
Given this opportunity for greater awareness, it is hoped that students like you will help share this information as you learn more about the sector. So let’s begin our exploration in Chapter 2 with a closer look at a critical sector: transportation.
- British Columbia Government Travel Bureau ( BCGTB) : the first recognized provincial government organization responsible for the tourism marketing of British Columbia
- Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) : a national railway company widely regarded as establishing tourism in Canada and BC in the late 1800s and early 1900s
- Destination BC: the provincial destination marketing organization (DMO) responsible for tourism marketing and development in BC, formerly known as Tourism BC
- Destination Canada: the national government Crown corporation responsible for marketing Canada abroad, formerly known as the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC)
- Destination marketing organization (DMO): also known as a destination management organization; includes national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus
- Diversity: a term used by some in the industry to describe the makeup of the industry in a positive way; acknowledging that tourism is a diverse compilation of a multitude of businesses, services, organizations, and communities
- Fragmentation: a phenomenon observed by some industry insiders whereby the tourism industry is unable to work together toward common marketing and lobbying (policy-setting) objectives
- Hospitality: the accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings
- North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) : a way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis
- Tourism: the business of attracting and serving the needs of people travelling and staying outside their home communities for business and pleasure
- Tourism Industry Association of BC ( TIABC) : a membership-based advocacy group formerly known as the Council of Tourism Associations of BC (COTA)
- Tourism Industry Association of Canada (TIAC): the national industry advocacy group
- Tourist: someone who travels at least 80 kilometres from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or pleasure or other reasons; can be further classified as domestic, inbound, or outbound
- United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) : UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide
- List the three types of tourist and provide an example of each.
- What is the UNWTO? Visit its website, and name one recent project or study the organization has undertaken.
- List the five industry groups according to the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Using your understanding of tourism as an industry, create your own definition and classification of tourism. What did you add? What did you take out? Why?
- In 2011, how much money was generated by tourism worldwide? What percentage of this money was collected in Europe? Where was the least amount of money collected?
- According to UNEP, what are the four types of negative environmental tourism impact? For each of these, list an example in your own community.
- What major transportation developments gave rise to the tourism industry in Canada?
- Historically, what percentage of international visitors to Canada are from the United States? Why is this an important issue today?
- Name three key events in the history of BC tourism that resonate with you. Why do you find these events of interest?
- Watch the video in the “Take a Closer Look” feature on Richmond. Now think about the value of tourism in your community. How might this be communicated to local residents? List two ways you will contribute to communicating the value of tourism this semester.
- Choose one article or document from the reference list below and read it in detail. Report back to the class about what you’ve learned.
Case Study: Tourism – Canada’s Surprise Blind Spot
In a 2014 episode of the Voice of Canadian Business , the Canadian Chamber of Commerce’s podcast, host Mary Anne Carter sat down with Greg Klassen, the CTC’s president and CEO, and Michele Saran, executive director of Business Events Canada. Their discussion highlighted the reasons Canada is struggling to remain competitive within the sector, and underscores the role and impact Canada’s tourism industry has on the economy.Listen to the 14-minute podcast on tourism in Canada and answer the following questions: www.chamber.ca/media/pictures-videos/140407-podcast-tourism/
- Why are governments around the world starting to invest in tourism infrastructure? What does this mean for the competitive environment for Canada’s tourism product?
- How do we compare to the United States as a destination for business travel?
- According to Greg, why is the $200 million investment in Brand USA a “double-edged sword” for tourism in Canada? What is beneficial about this? Why does it make things more difficult?
- What is the relationship between tourism and people’s understanding of a country’s image?
- What ranking is Canada’s brand? What other industries are affected by this brand?
- Describe one activity the CTC participates in to sell Canadian tourism product abroad.
- Name two “sectors of excellence” for Canada. Why is the CTC focussing their business events sales strategies on these industries?
- What does the CTC consider to be the benefits of Vancouver hosting the 2014 and 2015 TED conferences?
Brewster Travel Canada. (2014). About Us – Brewster History . Retrieved from http://www.brewster.ca/corporate/about-brewster/brewster-history/
British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training . (2013a). BC Stats: Industry Classification . Retrieved from http://www.bcstats.gov.bc.ca/StatisticsBySubject/BusinessIndustry/IndustryClassification.aspx
British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training. (2013b). Bill 3 – 2013: Destination BC Corp Act . Retrieved from https://www.leg.bc.ca/39th5th/1st_read/gov03-1.htm
Canadian Geographic . (2000, September). Flying through time: Canadian aviation history . Retrieved from http://www.canadiangeographic.ca/magazine/so00/aviation_history.asp
Canadian Tourism Commission. (2014). About the CTC. Retrieved from http://en-corporate.canada.travel/about-ctc
Chaney, Edward. (2000). The evolution of the grand tour: Anglo-Italian cultural relations since the Renaissance . Portland OR: Routledge.
Cox & Kings. (2014). About us – History. Retrieved from http://www.coxandkings.co.uk/aboutus-history
Dawson, Michael. (2004). Selling British Columbia: Tourism and consumer culture, 1890-1970 . Vancouver, BC: UBC Press.
Discover Hospitality. (2015). What is hospitality? Retrieved from http://discoverhospitality.com.au/what-is-hospitality/
e-Know. (2011, November). Ogilvie’s past in lock step with last 50 years of Kimberley’s history. Retrieved from www.e-know.ca/news/ogilvie’s-past-in-lock-step-with-last-50-years-of-kimberley’s-history/
Expedia, Inc. (2013). Expedia: Annual report 2013. [PDF] Retrieved from http://files.shareholder.com/downloads/EXPE/3546131959x0x750253/48AF365A-F894-4E9C-8F4A-8AB11FEE8D2A/EXPE_2013_Annual_Report.PDF
Flightglobal. (2002). Sixty years of the jet age. Retrieved from http://www.flightglobal.com/features/jet-age/
Globe and Mail, The. (2014, March 28). Ten things you don’t know about Air Canada. Retrieved from http://www.theglobeandmail.com/life/travel/travel-news/10-things-you-likely-dont-know-about-air-canada/article17725796/?page=all
Government of Canada. (2006). Building a national tourism strategy. [PDF] Retrieved from https://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/034.nsf/vwapj/tourism_e.pdf/$FILE/tourism_e.pdf
Government of Canada. (2013, July 5). Appendix E: Tourism industries in the human resource module . Retrieved from http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/13-604-m/2013072/appe-anne-eng.htm
Griffiths, Ralph, Griffiths, G. E. (1772). Pennant’s tour in Scotland in 1769. The Monthly Review; or, Literary Journal XLVI : 150 . Retrieved from Google Books .
Gyr, Ueli. (2010, December 3). The history of tourism: Structures on the path to modernity. European History Online (EHO). Retrieved from http://ieg-ego.eu/en/threads/europe-on-the-road/the-history-of-tourism
Latin definition for hospes, hospitis. (2014).In Latdict – Latin Dictionary and Grammar Resources . Retrieved from http://www.latin-dictionary.net/definition/22344/hospes-hospitis
Library and Archives Canada. (n.d.). Ties that bind: Essay. A brief history of railways in Canada. Retrieved from http://www.collectionscanada.gc.ca/trains/021006-1000-e.html
LinkBC. (2008). Transforming communities through tourism: A handbook for community tourism champions. [PDF] Retrieved from http://linkbc.ca/siteFiles/85/files/TCTT.pdf
MacEachern, A. (2012, August 17). Goin’ down the road: The story of the first cross-Canada car trip. The Globe and Mail . Retrieved from http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/national/goin-down-the-road-the-story-of-the-first-cross-canada-car-trip/article4487425/
McLeish. (2014, July 23). History of heliskiing in Canada. Retrieved from www.lastfrontierheli.com/news/1607/history-of-heliskiing-in-canada/
Magnes, W. (2010, May 26). The evolution of British Columbia’s tourism regions: 1970-2010 [PDF] . Retrieved from http://linkbc.ca/siteFiles/85/files/LinkBCMagnesPaper2011.pdf
Porges, R. (2014, September). Tell me something I don’t know: Promoting the value of tourism. Tourism Drives the Provincial Economy . Presentation hosted by the Tourism Industry Association of BC, Vancouver, BC.
PricewaterhouseCooopers, LLC. (2009). Opportunity BC 2020: Tourism sector. [PDF] Prepared for the BC Business Council. Retrieved from http://www.bcbc.com/content/558/2020_200910_Mansfield_Tourism.pdf
Shoalts, A. (2011, April). How our national parks evolved: From Grey Owl to Chrétien and beyond, 100 years of Parks Canada. Canadian Geographic . Retrieved from http://www.canadiangeographic.ca/magazine/apr11/national_parks_evolution.asp
Theobald, William F. (1998). Global Tourism (2nd ed.). Oxford, England: Butterworth–Heinemann, pp. 6-7.
Thomas Cook Group of Companies. (2014). Thomas Cook history. Retrieved from http://www.thomascook.com/thomas-cook-history/
Tourism Industry Association of BC. (2014). Value of tourism toolkit: Why focus on the value of tourism? Retrieved from http://www.tiabc.ca/value-of-tourism-toolkit
Tourism Industry Association of Canada. (2014, October 14). Travel industry poised to boost Canadian exports: US market and border efficiencies central to growth potential . Retrieved from http://tiac.travel/cgi/page.cgi/_zine.html/TopStories/Travel_Industry_Poised_to_Boost_Canadian_Exports_US_Market_and_Border_Efficiencies_Central_to_Growth_Potential
Tourism Industry Association of Canada, HLT Advisory. (2012). The Canadian tourism industry: A special report [PDF] . Retrieved from http://www.hlta.ca/reports/The_Canadian_Tourism_Industry_-_A_Special_Report_Web_Optimized_.pdf
United Nations and World Tourism Organization. (1995). Recommendations on tourism statistics. [PDF] Retrieved from http://unstats.un.org/unsd/newsletter/unsd_workshops/tourism/st_esa_stat_ser_M_83.pdf
United Nations Environment Programme. (2003a). Negatives Socio-cultural impacts from tourism . Retrieved from http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/Socio-CulturalImpacts/NegativeSocio-CulturalImpactsFromTourism/tabid/78781/Default.aspx
United Nations Environment Programme. (2003b). Tourism’s three main impact areas. Retrieved from http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/TheTourismandEnvironmentProgramme/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/EnvironmentalImpacts/TourismsThreeMainImpactAreas/tabid/78776/Default.aspx
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2008). Understanding tourism: Basic glossary . Retrieved from http://media.unwto.org/en/content/understanding-tourism-basic-glossary
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2012, May 7). International tourism receipts surpass US$ 1 trillion in 2011. Retrieved from http://media.unwto.org/en/press-release/2012-05-07/international-tourism-receipts-surpass-us-1-trillion-2011
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2014a). UNWTO world tourism barometer, 12 [PDF] (1). Retrieved from http://dtxtq4w60xqpw.cloudfront.net/sites/all/files/pdf/unwto_barom14_04_august_excerpt_0.pdf
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2014b). Who we are. Retrieved from http://www2.unwto.org/content/who-we-are-0
Attributions
Figure 1.1 Selkirk College and Nelson by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.2 Capilano University’s Team by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.3 Vancouver Island University by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.4 Canadian Pacific 4-4-0 A-2-m No 136 by Peter Broster is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.5 Vancouver Island University by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.6 Switzerland vs. Canada by s.yume is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.7 CTC’s Boardroom by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC Copyright © 2015 by Capilano University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

When figuring out what hospitality even means in the events industry, we looked to define it first.
- Merriam Webster’s Dictionary defines hospitality as, “generous and friendly treatment of visitors and guests or hospitable treatment.”
- Dictionary.com goes further to define it as, “the friendly and generous reception and entertainment of guests, visitors, or strangers.”
For those working in hospitality, this transcends only working in hotels or food and beverage. This extends to anyone providing pieces of an event that provides a friendly, welcoming environment that defines hospitality.
Provide exceptional hospitality with an easy CRM
Get A Free Demo
What Does Hospitality Mean for Hotels in the Digital Age?
As a hotel owner or staff member, your first and foremost job is ensuring that your customers are satisfied. But so what does hospitality mean in a world where customers can get what they need at their fingertips? In the digital age, what does hospitality actually mean?
There are a few things that we think are more important than ever and can set your property apart from your competitors.

1. Be prompt, responsive, and specific with feedback
The digital age means that consumers are always looking for reviews and information about hotels and properties. Good hospitality – and frankly good business – means you need to be as prompt as possible when responding to both positive and negative feedback from guests.
When you are prompt with guest feedback, be responsive and specific as well. This means answering that feedback directly. If a consumer complain comes in, a simple, apologies for the inconvenience won’t cut it. Finding ways to earn trust back can mean the world to a customer. Even if feedback is negative, many consumers will respond that management was sympathetic to their plight and attempted to solve the problem.
The same goes for your online presence. If a customer leavse a negative online review, take the time to respond promptly.
What does it mean to be hospitable when customers can get what they need at their fingertips? Click To Tweet
2. Positive feedback provides a sales opportunity
What does hospitality mean if the customer has a positive experience? That means you’ve done your job!
The internet is full of deals, coupons, and opportunities for consumers. What sets a property apart from others is that positive feedback and nothing is worth more to your business. However, don’t miss the opportunity to get it.
In the digital age, you must take every opportunity to differentiate yourself and your hospitality from others. When you receive positive feedback, thank the customer and then insert a statement about another area where you are looking to improve or are trying to emphasize. Someone taking the time out of their day to give you a positive review is more likely to come back to your property. They’ll view your response as an example of showing digital hospitality.
3. Tell customers what you’re going to do, what you are doing, and what you did
Providing solid customer service encapsulates a big portion of hospitality. And the best way to manage customer expectations is to be clear in the message. Tell them what you’re going to do, what you’re doing while you’re doing it, and then tell them you’ve done it.
Oftentimes, customer frustrations arise when they feel they aren’t being heard. What does hospitality mean in this situation? It means keeping customers informed every step of the way, digitally especially, to show they’re heard.
On the flip side, the digital age has increased the number of distractions and the things competing for customer’s attention. In order to keep your hospitality in the top tier of your visitor’s minds, you have to stay top of mind. Are you getting a brand new lobby bar? Start a marketing campaign keeping customers informed about the process. Then, when it’s complete, tell them about the grand opening celebration. Showing customers that they’re part of the process is a unique way to show hospitality.
4. Add a touch of personalization
More and more, customers are expecting their visits to be customized to them. Keeping up with hospitality means doing as much as you can to meet this desire.
Amazon Echo or other digital assistants inside guest rooms is a great way to add personalization without putting personal information at risk. If the guest visits your property often, keep a file on the different activities they’ve participated in or restaurants they’ve dined in. The next time they arrive, offer coupons or discounts for the same or similar experiences. Additionally, in between visits, send your guests emails about experiences they’ve participated in when they’ve stayed with you.
How about showing personalization in smaller steps? Instead of your generic email, ensure you use the customer’s first name in the subject line and salutation. Ensure that your employees greet and interact with the guest by name as much as possible. And, customize check-in folders, and guest key card envelopes.
Respond to group business faster with an easy CRM
Get Started Now
The digital age places a larger emphasis on hospitality. Ensuring that your visitors feel that their stay is special, the better you’ll be able to differentiate yourself from your competitors.
20 Ways Event-Focused Hotel Employees Can Elevate Hospitality

There’s a lot you can do to collaborate with event planners. Here are some creative ideas to get you started!
1. Giving event planners insider information on important people.
Briefing the event check-in staff on repeat guests and VIPs will help them provide better service. Share details like seating preferences, membership status, and accessibility needs to help them better manage your best clients. You can even offer to personally meet them at the entrance and walk them through the check-in process.
2. Provide access to collaborative event plans.
Knowing the details of the event (what it’s all about, how guests can benefit from attending) can help sell more tickets . And, at the very least, hotel staffers will be able to answer questions. Guests often assume that front desk representatives and greeters know the inner workings of everything at the hotel anyways.
3. Have backup options for event music ready to go.
Last minute DJ cancellations, busted speakers, and equipment rental delays are more common than you might think. Fortunately a solid hotel sponsored phone or laptop hooked up to popular playlist apps like Spotify will do in a pinch. You can also prepare user friendly manuals (with photos and quick start instructions) for sound technology just in case an inexperienced event staff member has to take on the role.
4. Brainstorm supplemental add-ons or upgrades you can offer event attendees.
For example, if they’re attending a business conference, sell them on a relaxing spa day after they’ve finished work. Or suggest a local happy hour where they can continue mixing and mingling with attendees and locals. Viewing the experience from their perspective can be helpful. But keep in mind that you really don’t have to go too far out of your way either. Chances are you already have something fabulous on your hotel menu that might not have thought of for themselves.
5. Incentivize repeat business by partnering with event hosts to give away special discount codes.
Get repeat attendance by starting ticket sales for next year’s event right now. Share unique links or use the hotel employees’ first names as the referral code. That way they’ll get credited for the upsell. You can even turn it into a contest with a cash prize or a giveaway. The best hotel employee incentive programs offer things like a 30 minute massage at the spa, a free dinner at the hotel’s restaurant, or a gift card for popular ecommerce sites like Amazon.
6. Seek out complimentary local events to recommend to guests.
For example, if guests are visiting for a music festival, let them know about the annual chili cookoff locals like to attend nearby. The key is to pick something you or a colleague has been to and can verify its quality. It’s also great to search within the Facebook Local app to find something slightly off the beaten path on any given day.
7. Add event ticket upselling to your front desk and greeter scripts.
If the event promoters have an add-on experience or side event they’d like their guests to attend, have your staff tell them. Limit the offer to a line or two. And make sure to powwow with the event team to get more information on ways they can personalize the exchange with this particular audience.
8. Create a unique, special offer that only event attendees can use.
For example, free spa amenities pass or a complimentary fitness evaluation in the workout room are an extra special treat anyone can appreciate. And, if it’s popular enough, you may even want to add it to your services menu in the future. Again, you can choose something that makes sense with your hotel’s theme and amenities as well as the event’s overall purpose.
9. Offer the event planner a presentation and technology assistant.
Sometimes, in the heat of the moment, dealing with gadgets and software programs and WiFi can be overwhelming for event planners. They have a lot of people and activities to monitor so help them out by providing a hotel representative who has worked with the equipment before. If you’re low on staff, at the very least designate someone to charge all relevant tools the night before. And purchase backup batteries and auxiliary cords for multiple phone types while you’re at it.
10. Have an event emergency kit on hand.
Yes, you already have the required onsite medical supplies and first aid kits. But event emergencies are a different beast entirely. Stock them with extra phone chargers, tealight candles, extension cords, permanent markers, zip ties, a variety of tapes, and a basic tool box.
Provide the best hospitality with an easy group manager
11. keep a list of trusted local vendors that you can call in case the event host experiences last minute cancellations. .
It happens from time to time. And hotel employees can help by keeping a list of partners on hand for emergencies. Just make sure you communicate with these vendors to let them know they’re on the list. You can go a step further by keeping a printed copy of their last minute booking policies printed and put into a binder at the front desk.
12. Accumulate information on frequently asked questions and last minute hiccups that event planners experience at your venue over time.
Even if these issues have nothing to do with your space or your employees, you can learn from their experiences. When you do, make sure you have the right tool or plan in place so that if it ever happens again you can help troubleshoot. For example, do event planners tend to forget about their limited access to power outlets? If so, set an email reminder a day or two before each event. Then provide some extra power strips the day of.
13. Have a couple hotel staffers on call the day of the event in case the planners need extra hands.
Event staffing can be tricky. People call out sick the day of or get lost and stuck in traffic. If you can afford to keep some emergency backup assistants onsite, this could be a lifesaver for your event planner. If not, consider partnering with a trusted local event staffing company and strike a deal with them for situations like this one.
14. Invest in some dry erase signage boards to help assist with lobby traffic.
About 3-5 signs max should do the trick for large lobby areas. Keep erasers, markers, and board cleaner on hand too.
15. Prime the waiting area outside the event space to accommodate attendees.
You never quite know where the crowd will want to hang out so have your common areas well stocked. Add extra water pitchers, cups, trash cans and chairs to formal seating areas. And use some folding chairs in areas outside of bathrooms or near the coat check and valet areas just in case.
16. Give event-goers a special discount for onsite laundry, dry-cleaning or tailoring services for formal affairs.
Keeping clothes neat while traveling is no easy task. So if your hotel already offers these services, help attendees look great for the event with coupons or freebies. Or, at the very least, offer them one of these great DIY dry cleaning product samples.

17. Dedicate a convenient section of the valet area to event guests.
Use signage to help them find their loading space. And send out a map of which space event planners can expect to send guests to.
18. Set out extra branded pens and notepads for attendees who may have forgotten theirs.
If a lecturer or workshop is taking place, you’ll have the opportunity to help guests learn as much as possible. It’s also great for branding. For example, you can try doing a limited print of your hotel’s regular notepads but in the colors of the event itself.
19. Give away detailed welcome packets for event-goers with information like the event agenda, parking, etc.
Or, if you’d like to be more eco-friendly, ask to send out a digital copy of the materials to everyone who confirmed their attendance to the event. You can also use this same list to send out your own personal thank you notes after it’s all over.
20. Keep extra name tags on hand for event presenters.
Whether they’re pinned, sticky, or hanging from lanyards, your event planners will really appreciate you having this item around.
Now You Know What Hospitality Means for Event Professionals!

Up next, discover secrets to delivering a personalized experience for groups .
What does hospitality mean to you? Tell us your hospitality stories on Twitter!
Bring hospitable events to life, no stress
Have more questions about what hospitality means.
Merriam Webster’s Dictionary defines hospitality as, “generous and friendly treatment of visitors and guests or hospitable treatment.” It also refers to the industry in which hotels, caterers, and event planners largely operate.
In a job, hospitality means pretty much the same thing as it does in everyday life – generous and friendly treatment of guests and customers.
- Free Planner Tools
- Event Seating Software
- Event Check-In Software
Venue Tools
- Event Diagramming Software
- Interactive Floor Plans
- Photo-Realistic 3D
- Lead Capture Tools
- Event Planning
- Guides & Webinars
- Customer Stories
- Contact Sales: +1 (877) 973-2863
- About Cvent
- Cvent Community
- Help & Support
- Training & Certification
- Status & Uptime
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- +1 (877) 973-2863 - Option 1
- [email protected]

Copyright 2024 Cvent Inc. All rights reserved.

- German Soccer Sensation Finds a Home with the Bobcats
- From Air Force Veteran to the Middle of the Atlantic
- Career Assistance 44 Years After Graduation
- Admissions by Day. Filmmaking by Night.
- Admissions Process
- Alumni Updates
- Bryant & Stratton College News
- Business Degrees
- Career Services
- College Life
- Continuing Education
- Criminal Justice Studies
- Degree Insights
- Education Programs
- Financial Aid
- Healthcare Degrees
- Human Resources
- Military Relations
- Online Education
- Social Media
- Student Services
- Technology & Design
- Video Posts

Tourism vs. Hospitality - Decoding the Differences
Bryant & Stratton College Blog Staff

The hospitality and tourism industries are closely connected, but they are not the same thing. Though both connect to travel and leisure, these two industries have distinct differences that need to be understood if you are considering a degree or career in the field. By knowing how they are different, you can choose the right degree that will help you achieve your desired career path.
What is the Difference Between Tourism and Hospitality?
Hospitality is a field that focuses on providing accommodations to visitors at hospitality-related industries, such as hotels, motels, restaurants, cruise ships, country clubs, casinos, and convention centers, while tourism is focused on providing quality attractions and events in order to entice tourists to come.
For each of these fields to be successful, they focus on specific ways to keep people satisfied so they will return. Hospitality businesses must build strong relationships with their guests to not only prevent them from going to a competitor, but to keep them coming back. Many tourism businesses are classified as hospitality businesses as they must also have meaningful relationships, but they are more focused on traveling activities that may include heavy planning and marketing.
What are the Similarities Between Tourism and Hospitality?
Both the hospitality and tourism industries focus on serving people when they travel. These are highly competitive and always-changing fields that require people to be able to adapt to a changing market and work environment. Both tourism and hospitality professionals need to be good marketers to draw potential clients and customers to their industries.
What Jobs are there in the Travel and Tourism Industry?
The travel and tourism industry focuses on helping people plan and execute their travel arrangements. Some jobs in tourism management include:
Travel Agent
A travel agent is a great career path for people who majored in tourism. Travel agents work with their clients to plan their trips, so they must be highly organized and have a knowledge of the travel industry so they can book resorts, cruise ships, airline travel, and more for their clients.
Travel agents also assist clients with their travel budgets by calculating travel costs and helping clients choose trips and adventures that fit within their budget. They also can assist clients with getting their passports or other paperwork in order so they can legally travel.
The pay for a travel agent varies because they often earn commissions based on the trips and services they book, as well as the setting they work in. Travel agents can work independently or work with a travel agency, depending on the demand in their area.
Flight Attendant
A flight attendant works in an airline to help travelers get to their destination safely and comfortably. While travelers often see the simple work of the flight attendant, such as passing out snacks and collecting garbage, flight attendants are also trained on how to help protect passenger safety if something goes wrong.
Flight attendants need to be good at working with people, even those who are not in a good mood or who face frustration when they travel. One of the main benefits of this profession is getting to travel to and explore many destinations around the world.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that the demand for flight attendants will increase by 17% from 2019 to 2029, so it is a great time to pursue this career path.
What Jobs Are There in the Hospitality Industry?
Jobs within hotels, restaurants, and event centers tend to fall in the hospitality industry category. Hotel managers, event managers, hotel clerks, bar managers, and chefs are just a few examples in this industry, with details as follows:
Hotel Manager
A hotel manager makes sure that guests are comfortable during their stay in a hotel or resort. They may have to arrange for blankets or other amenities to be taken to hotel rooms, oversee the employees of the hotel, and ensure that supplies, like soap and shampoo, are ordered in a timely manner. On a resort property, the hotel manager may also be in charge of entertainment. The exact setting or location will dictate exact duties and responsibilities for this role. Overall, it is the manager's job to handle customer service needs that pop up during a guest's stay.
Event Manager
An event manager or event planner helps plan large events to ensure all attendees enjoy the experience. These individuals, like others in the hospitality industry, need to be highly organized. Event managers will plan all of the details, gather bids from venues and vendors, coordinate transportation for attendees, arrange for food, and even connect with local hotels to ensure people have a place to stay. They help their clients manage and maximize their budgets and ensure that everything is ready when the special event starts.
The BLS estimates that this career will grow 8% from 2019-2029, which is much faster than average. Approximately 10,800 new jobs will be created in this field, so it is a great time to consider pursuing a position in event management.
A concierge is employed by a resort or event center to help guests book entertainment and enjoy their stay more fully. These professionals need to know their local area well so they can connect guests to the entertainment options that best fit their tastes and desires for their trip.
Concierge professionals tend to be employed by high-end resorts and luxury hotels. Distinguished guests expect to have someone to help them book their services and are willing to tip well for this service.
Restaurant and Catering Professionals
The hospitality industry is also the industry that covers restaurants and catering services. While those interested in opening a restaurant or catering business will also need to explore foodservice training, training in hospitality will help them understand the customer service side of this industry. These professionals can work anywhere where food and beverage are prepared and served, including hotels, resorts, and restaurants.
Start Your Hospitality or Tourism Journey Today!
If the tourism and hospitality industries are appealing to you, then finding a career in these fields or industry may require further education. Bryant & Stratton College has a number of hospitality degree programs , including associate degrees and diplomas, that can help you get started in this field. Reach out to the admissions team at Bryant & Stratton College to learn more about these programs and to determine if they are the right fit for your career path.
Related Articles

Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Tips
What Is The Hospitality And Tourism Industry
Published: December 12, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Ingunna Whipple
- Hotel Reviews
- Sustainability
Introduction
Welcome to the exciting world of the hospitality and tourism industry! This dynamic and ever-growing sector offers an array of opportunities for those with a passion for travel, leisure, and providing exceptional customer experiences. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of the hospitality and tourism industry, its definition, scope, key players, employment opportunities, challenges, and trends.
The hospitality and tourism industry encompasses a wide range of businesses and services that cater to the needs of travelers, tourists, and individuals seeking leisure activities. It includes establishments such as hotels, resorts, restaurants, airlines, cruise lines, travel agencies, theme parks, and more. These diverse entities all work together to create memorable experiences for guests and visitors.
As global travel continues to increase year after year, the hospitality and tourism industry plays a crucial role in the global economy. Not only does it provide employment opportunities to millions of people worldwide, but it also contributes to the growth of local economies and promotes cultural exchanges between different regions and countries.
Nowadays, people’s expectations for travel and hospitality experiences have evolved. It’s no longer just about offering a comfortable stay or a delicious meal; guests seek unique and personalized experiences that resonate with them. This shift has led to the rise of experiential travel, where travelers immerse themselves in the local culture, try authentic cuisines, and engage in activities that give them a deeper understanding of a destination.
The hospitality and tourism industry is driven by the concept of hospitality, which entails providing an exceptional level of service and attention to guests. Whether it’s warmly welcoming guests at a hotel, anticipating their needs at a restaurant, or ensuring smooth travel arrangements, hospitality professionals strive to create a positive and memorable experience for every visitor.
Furthermore, the industry’s success relies heavily on effective customer service and customer relationship management. Building strong relationships with guests and fostering loyalty are essential for businesses to thrive in this competitive landscape. Word-of-mouth recommendations and positive online reviews have a significant impact on a company’s reputation and customer acquisition.
As we delve deeper into the hospitality and tourism industry, we will uncover the various sub-sectors, discuss the employment opportunities they offer, explore the challenges faced by professionals in the field, and highlight the latest trends shaping the industry’s future. So, let’s embark on this journey together and discover the countless possibilities that await in the vast world of hospitality and tourism.
Definition of Hospitality and Tourism Industry
The hospitality and tourism industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving sector that encompasses a wide range of businesses and services. It revolves around providing exceptional customer experiences to individuals who are seeking leisure activities, travel, and accommodation. This industry plays a crucial role in the global economy, offering employment opportunities to millions of people worldwide and contributing to the growth of local economies.
At its core, the hospitality and tourism industry is defined by its focus on hospitality, which involves delivering outstanding service and creating memorable experiences for guests. Whether it’s a luxury hotel, a quaint bed and breakfast, a fine dining restaurant, or an adventurous travel agency, the industry is united by its commitment to catering to the needs and desires of travelers and tourists.
Tourism, a significant component of the industry, refers to the activities individuals engage in when visiting different destinations. These activities can include sightseeing, exploring cultural landmarks, participating in outdoor adventures, and immersing oneself in the local culture. The tourism sector relies on various services within the hospitality industry to provide comfortable accommodation, dining options, transportation, and entertainment.
The hospitality and tourism industry includes a wide array of businesses and services:
- Hotels and resorts: These establishments provide accommodation for travelers, ranging from budget-friendly options to luxury experiences.
- Restaurants and food services: From casual dining to Michelin-starred restaurants, these establishments offer a variety of culinary experiences.
- Travel agencies and tour operators: These organizations assist individuals in planning and booking their travel arrangements, including flights, accommodations, and itinerary.
- Airlines, cruise lines, and transportation services: These companies facilitate the movement of travelers, providing air, sea, and land transportation options.
- Entertainment and attractions: Theme parks, museums, historical sites, and other attractions offer leisure activities and entertainment for tourists.
- Event planning and management: This sector handles the organization and execution of various events, such as conferences, weddings, and corporate functions.
The hospitality and tourism industry is highly customer-oriented and focuses on creating positive experiences that meet and exceed the expectations of guests. It requires individuals with excellent communication skills, attentiveness, problem-solving abilities, and a genuine passion for providing top-notch service.
As the industry continues to evolve, the definition of hospitality and tourism has expanded beyond traditional boundaries. It now encompasses new trends such as eco-tourism, wellness tourism, experiential travel, and the integration of technology in enhancing guest experiences. This adaptability ensures that the industry remains relevant and responsive to the changing preferences and demands of travelers worldwide.
Scope and Importance of the Hospitality and Tourism Industry
The scope of the hospitality and tourism industry is vast and encompasses a wide range of activities, businesses, and services. From providing accommodation and dining options to organizing travel arrangements and offering entertainment, this industry plays a crucial role in shaping the experiences of travelers and tourists worldwide.
One of the primary purposes of the hospitality and tourism industry is to cater to the needs and desires of individuals seeking leisure activities and travel experiences. It offers a diverse range of services that provide comfort, convenience, and entertainment to guests, ensuring their satisfaction and enjoyment.
One of the key aspects of the industry’s scope is the provision of accommodation options. Hotels, resorts, bed and breakfasts, and other lodging establishments offer visitors a place to stay while exploring a destination. These accommodations can range from budget-friendly options to luxury suites, catering to the preferences and budgets of various travelers.
In addition to accommodation, the industry also encompasses an array of dining options. Restaurants, cafes, food trucks, and other establishments provide visitors with the opportunity to sample local cuisine, indulge in gourmet experiences, or simply grab a quick bite to eat. These dining experiences often add a cultural element to travelers’ journeys, allowing them to savor the flavors of a particular region or country.
The transportation sector is another critical component of the industry’s scope. Airlines, cruise lines, car rental services, and other transportation providers ensure that individuals can reach their desired destinations conveniently and safely. This seamless connectivity helps facilitate travel and allows visitors to explore multiple locations during their trips.
Entertainment and attractions are also significant contributors to the industry’s scope. Theme parks, museums, historical sites, natural landmarks, and other attractions offer leisure activities and unique experiences for tourists. These destinations play a vital role in attracting visitors, increasing local tourism, and promoting cultural exchanges.
The importance of the hospitality and tourism industry cannot be overstated. Economically, it generates substantial revenue for destinations, stimulates local businesses, and creates employment opportunities for millions of people worldwide. It supports a wide range of industries, including hospitality, transportation, food and beverage, and retail.
Socially, the industry encourages cultural exchange, promoting understanding and appreciation of different cultures and traditions. It fosters connections between people from diverse backgrounds, enabling the exchange of ideas, customs, and perspectives.
Furthermore, the hospitality and tourism industry contributes to the preservation and promotion of natural and cultural heritage. By highlighting and showcasing these assets, it raises awareness about the importance of conservation and sustains the value of unique landmarks and ecosystems.
Key Players in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry
The hospitality and tourism industry consists of numerous key players, each playing a crucial role in delivering exceptional experiences to travelers and tourists. These players include a diverse range of businesses and organizations that contribute to the overall success and growth of the industry.
Hotels and resorts are major players in the industry, offering accommodation options to guests. This includes luxury chains, boutique hotels, budget-friendly establishments, and everything in between. These properties provide a variety of amenities and services to ensure a comfortable and enjoyable stay for visitors.
Restaurants and food services are also significant players in the hospitality and tourism industry. From high-end fine dining establishments to casual cafes and street food vendors, these businesses cater to the culinary needs of travelers and locals alike. They offer a wide range of cuisines, flavors, and dining experiences to satisfy diverse palates.
Travel agencies and tour operators play a vital role in planning and organizing travel arrangements. These players assist individuals and groups in booking flights, accommodations, transportation, and activities. They curate itineraries, provide expert guidance, and offer personalized recommendations to create unforgettable travel experiences.
Airlines and cruise lines are essential players in the transportation sector of the industry. They facilitate travel by air and sea, connecting travelers to various destinations around the world. These players focus on providing safe, efficient, and comfortable travel options for guests, ensuring a seamless journey from start to finish.
Attractions and entertainment providers contribute to the industry’s vibrancy and appeal. Theme parks, museums, zoos, national parks, and cultural heritage sites offer unique and engaging experiences for visitors. They showcase local history, art, nature, and provide opportunities for entertainment and adventure.
Event planning and management companies are important players in the industry, organizing conferences, conventions, weddings, and other events. They ensure that every aspect of an event, from venue selection to logistics and execution, meets the highest standards and exceeds the expectations of attendees.
Tourist boards and destination marketing organizations (DMOs) play a critical role in promoting tourism and attracting visitors to specific destinations. They collaborate with businesses, governments, and local communities to develop marketing campaigns, initiatives, and strategies aimed at showcasing the unique offerings and attractions of a place.
In addition to these key players, technology companies have also become increasingly important in the hospitality and tourism industry. Online travel agencies (OTAs), hotel booking platforms, and travel review websites have transformed the way travelers search, book, and review accommodations and experiences. The integration of technology has revolutionized the industry, providing greater convenience and options for travelers.
Collaboration and synergy between these key players are essential for the industry’s success. By working together, they can create seamless, memorable experiences for travelers, enhance destination offerings, and drive the growth and sustainability of the hospitality and tourism industry as a whole.

Sub-Sectors of the Hospitality and Tourism Industry
The hospitality and tourism industry is vast and comprises several sub-sectors that cater to the diverse needs and preferences of travelers and tourists. These sub-sectors offer specialized services and experiences, contributing to the overall richness and appeal of the industry. Let’s explore some of the key sub-sectors:
Hotels and Accommodation: This sub-sector includes various types of lodging options, ranging from luxury hotels and resorts to budget-friendly motels and hostels. It encompasses full-service hotels, boutique properties, bed and breakfasts, serviced apartments, and vacation rentals. Each lodging category provides different amenities, styles, and experiences to cater to the needs of travelers.
Food and Beverage: Restaurants, cafes, bars, and food services form an integral part of the hospitality industry. This sub-sector caters to both locals and tourists, offering a wide array of culinary delights that showcase local and international cuisines. From fine dining establishments to street food vendors, the food and beverage sub-sector delivers diverse and memorable dining experiences.
Travel and Tourism Agencies: This sub-sector encompasses travel agencies, tour operators, and online travel agencies (OTAs). These entities specialize in organizing and facilitating travel arrangements for individuals and groups. Whether it’s booking flights, accommodations, transportation, or activities, travel agencies play a pivotal role in creating seamless and hassle-free travel experiences for customers.
Transportation: Airlines, cruise lines, car rental services, and transportation companies fall under this sub-sector. They ensure the smooth movement of travelers from one destination to another. Airlines connect cities and countries through air travel, while cruise lines offer leisurely journeys by sea. Car rental services and transportation companies provide options for convenient and efficient travel within destinations.
Entertainment and Attractions: This sub-sector comprises a variety of attractions and entertainment venues that enhance the overall travel experience. Theme parks, museums, art galleries, amusement parks, zoos, botanical gardens, and cultural heritage sites all fall under this category. These attractions offer visitors the opportunity to explore local history, culture, and natural beauty, providing unique and engaging experiences.
Event Planning and Management: This sub-sector specializes in organizing and managing various events, such as conferences, conventions, weddings, and exhibitions. Event planning companies coordinate every aspect of an event, including venue selection, logistics, catering, and audiovisual arrangements. They ensure that events run smoothly and leave a lasting impression on attendees.
Destination Marketing: Tourist boards and destination marketing organizations (DMOs) play a crucial role in this sub-sector. They promote specific destinations, highlighting their unique attractions, cultural heritage, and activities to attract visitors. DMOs collaborate with local businesses, governments, and communities to develop marketing campaigns and initiatives that boost tourism and drive economic growth.
Technology and Online Platforms: This emerging sub-sector encompasses technology companies that provide online booking platforms, travel review websites, and other travel-related services. These platforms have revolutionized the way travelers plan, book, and review accommodations and experiences. Through the integration of technology, travelers have access to a vast array of choices and can personalize their travel experiences.
Each sub-sector of the hospitality and tourism industry plays a vital role in creating a comprehensive and enjoyable travel experience. By working together, these sub-sectors contribute to the overall success and growth of the industry, ensuring that travelers have a plethora of options and experiences to choose from.
Employment Opportunities in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry
The hospitality and tourism industry offers a vast array of employment opportunities for individuals with a passion for customer service, travel, and creating memorable experiences. From entry-level positions to managerial roles, this diverse industry provides a wide range of careers that cater to different skills, interests, and qualifications.
Overall, the hospitality and tourism industry is a dynamic and promising field for employment. It offers a wide range of opportunities for individuals seeking a career that combines their passion for travel, customer service, and creating unforgettable experiences. Whether it’s in hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, attractions, or event planning, there is a career path for individuals with diverse backgrounds and interests in this ever-evolving industry.
Challenges and Trends in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry
The hospitality and tourism industry operates in a dynamic and highly competitive environment, continuously evolving to meet the changing needs and expectations of travelers. While the industry offers numerous opportunities, it also faces various challenges. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and trends shaping the industry today.
Challenges:
1. Economic Factors: Economic instability, fluctuating currency rates, and geopolitical issues can significantly impact the industry. Economic downturns can lead to reduced travel budgets and lower consumer spending, affecting businesses’ profitability and sustainability.
2. Seasonality and Demand Variability: Many tourist destinations experience peaks and troughs in visitor numbers due to seasonality. Managing staffing levels, inventory, and operations to meet fluctuating demand can be a complex challenge for businesses.
3. Competition: The industry is highly competitive, with businesses constantly vying for customers. From large hotel chains to online travel agencies and local establishments, businesses must differentiate themselves and offer unique experiences to attract and retain guests.
4. Changing Consumer Behavior: Consumers’ preferences and expectations are continually evolving. Travelers now seek experiential travel, personalized recommendations, sustainable practices, and seamless digital experiences. Adapting to these changing demands requires continual innovation and investment in technology.
5. Technological Advancements: While technology presents opportunities for growth, it also poses challenges. Online booking platforms, review websites, and social media influence consumer decisions and can impact a business’s reputation. Staying up-to-date with technological advancements and leveraging them strategically is key to staying competitive.
1. Sustainable and Responsible Tourism: In response to growing environmental concerns, travelers are embracing sustainable and responsible tourism practices. Businesses are implementing eco-friendly policies, reducing waste, and supporting local communities to meet the rising demand for environmentally conscious travel experiences.
2. Experiential Travel: Travelers are seeking immersive and authentic experiences. They want to connect with local cultures, participate in unique activities, and explore off-the-beaten-path destinations. Businesses are catering to these desires by offering curated experiences, cultural immersion programs, and adventure tourism options.
3. Personalization and Customization: Personalization is a key trend in the industry. Travelers appreciate tailored recommendations and experiences that cater to their specific preferences and interests. Businesses are utilizing technology and data analytics to understand customer preferences and provide personalized offers and services.
4. Technology Integration: Technology continues to transform the industry, with advancements such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and mobile apps enhancing customer experiences. Key trends include mobile check-ins, contactless payments, chatbots for customer service, and personalized digital concierge services.
5. Rise of Sharing Economy: The sharing economy, represented by platforms such as Airbnb and Uber, has disrupted traditional hospitality and transportation sectors. It has provided travelers with alternative accommodation options and transportation choices, forcing businesses to adapt and find innovative ways to compete.
By staying informed about these challenges and trends, businesses in the hospitality and tourism industry can adapt their strategies, invest in technology, and provide exceptional experiences that meet the evolving needs and expectations of travelers. The industry’s ability to navigate these challenges and embrace trends will determine its success and resilience in the ever-evolving global marketplace.
The hospitality and tourism industry holds immense potential as a thriving and vibrant sector that caters to the needs of travelers and tourists worldwide. Throughout this article, we have explored the definition, scope, key players, employment opportunities, challenges, and trends of this dynamic industry.
The industry’s definition is centered around providing exceptional service and creating memorable experiences for guests. It encompasses a wide range of businesses and services, including hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, airlines, attractions, and event planning organizations.
The scope and importance of the hospitality and tourism industry cannot be understated. It drives economic growth, generates employment opportunities, fosters cultural exchange, and promotes the preservation of natural and cultural heritage.
The key players in the industry each play a significant role in delivering outstanding experiences to travelers, ensuring their comfort, satisfaction, and enjoyment during their journeys.
The numerous sub-sectors within the industry, such as hotels, food and beverage, travel agencies, attractions, event planning, and technology, offer diverse employment opportunities for individuals with a range of skills and interests.
While the industry presents exciting opportunities, it also faces challenges, including economic factors, competition, changing consumer behavior, and technological advancements. Businesses must embrace these challenges and stay attuned to the latest trends in order to provide exceptional experiences and stay competitive.
The trends shaping the industry, including sustainable and responsible tourism, experiential travel, personalization, technology integration, and the rise of the sharing economy, offer new avenues for growth and innovation for businesses in the industry.
In conclusion, the hospitality and tourism industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving sector that offers a wide range of opportunities for individuals seeking a career that combines their passion for travel, customer service, and creating unforgettable experiences. By adapting to changing consumer preferences, embracing technology, and providing exceptional service, businesses in the industry can continue to thrive and contribute to the growth and success of this exciting and vital industry.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
16 Chapter 16 Hospitality & Tourism
Richard Parsons; Stephen Skripak; Anastasia Cortes; Anita Walz; and Gary Walton
Learning Objectives
- Understand what tourism is: definition, components, and importance.
- Understand the economic, social and environmental benefits and costs of tourism.
- Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition.
- Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined.
- Examine the different categories of food service operations.
- Understand the different types of events, meetings and conventions.

The tourism industry is often cited as the largest industry in the world, contributing 10% of the world’s GDP. In 2016 there were over 1.2 billion international tourists: that’s a substantial economic impact and movement of goods and services! 1 Tourism is also considered an export and is unique in that the consumers come to the product where it is consumed on-site. Before we dig any deeper, let’s explore what the term “tourism” means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
A social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure. 2
In other words, tourism is the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure). It is important to understand the various groups and constituencies involved in this movement. Of course it includes the tourist, but also the vast array of businesses providing goods and services for the tourist, the government and political structure of a destination, and the local residents of the destination community itself. Each of these components are necessary parts of a successful tourism destination and operate within private and public sectors, the built environment, and the natural environment. All these come together to create the processes, activities, and outcomes of tourism.
If it all seems a little overwhelming, it might be helpful to break tourism down into broad industry groups, each of which will be covered in this chapter:
Accommodation and Lodging
- Food and Beverage Services (F & B)
Recreation and Entertainment
- Convention & Event Management
Travel Services
- Private Clubs
Benefits and Costs of Tourism
Tourism impacts can be grouped into three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations. Some impacts gain more attention than others. It is also important to recognize that different groups and constituencies are impacted differently.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The tourism industry has a huge economic impact that continues to expand to new markets and destinations. According to the UNWTO, in 2016 “The total export value from international tourism amounted to US$ 1.5 trillion.” 3 Regions with the highest growth in terms of tourism dollars earned (2016 vs 2015) are Africa, Asia and the Pacific, the Americas Europe. Only the Middle East posted negative growth at the time of the report. As well, the UNWTO’s Tourism 20 3 0 Vision report predicts that international arrivals will reach nearly 1.8 billion by 2030. 4 Figure 16.2 provides additional information about the impact of tourism worldwide.

Positive impacts from this economic boom include robust foreign exchange, increases in income, and GDP growth. Tourism can also offer diverse employment opportunities, can be developed with local products, and is often compatible with other economic activities within a destination. Tourism often injects money into the community that leads to secondary economic development as well. For example, successful resorts may create the need for a commercial laundry facility or a pet boarding business.
However, there are also negative impacts. Property values may increase to the point of unaffordability for local residents, and the seasonality of the tourism industry may create a feast-or-famine economy. As with any economy, if too many resources are focused on just one industry, communities may be vulnerable to any unexpected economic, social, or environmental changes. One example is the New Jersey shore after the devastation of Hurricane Sandy in 2012. The tourism industry was severely impacted, leaving no economic fallback for local residents.
Social Impacts of Tourism
In addition to the economic benefits of tourism development, positive social impacts include an increase in amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts, culture, heritage and tradition, celebration of indigenous communities, and community pride. Tourism also has the potential to break down language, socio-cultural, religious, and political barriers. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents and promotes a positive image of the destination.
However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme, negative social impacts of tourism can include: change or loss of indigenous identity and values; culture clashes; changes in family structure; conflict within the community for the tourism dollar; and ethical issues, including an increase in sex tourism, crime, gambling, and/or the exploitation of child workers. 5
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. In some destinations, there is a great appreciation of the environmental resources as the source of the tourism industry, and as such there are environmental protection policies and plans in place. Tourism has helped to save many delicate ecosystems and their flora and fauna. Preservation of these important resources benefits not only the tourist but also the local residents as well.
Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can still have severe negative economic impacts. According to The United Nations Environment Programme, these can include the depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.), pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering), and physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity, and spread of disease). 6
The environmental impacts of tourism can reach beyond local areas and have an effect on the global ecosystem. One example is increased air travel, which is often identified as a major contributor to climate change.
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world, and the industry is transforming at a staggering rate.
The original version of this chapter contained H5P content. This content is not supported in cloned books. You may want to remove or replace this section.
The Hospitality Industry
When looking at tourism it is important to consider the term hospitality. Some define hospitality as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves.” 7 Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry.

The pineapple has long been the symbol of hospitality. The Caribs, indigenous people of the Lower Antilles in the Caribbean, first used it as such a symbol. The Spaniards knew they were welcome if a pineapple was placed at the entrance to the village. This symbolism spread across Europe and North America where it became the custom to carve the shape of a pineapple into the columns at the entrance of the plantation. 8 Charles Carter added a three and a half foot wooden pineapple to the peak of the roof at Shirley Plantation, the first plantation in Virginia. 9 It is now common to see the image of the pineapple as a sign of welcome, warmth and hospitality.
The types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business — whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground — are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation and lodging . Figure 16.4 summarizes the various groupings within the industry.
Hotel Types
Hotels are typically referred to by hotel type or other classifications. Hotel type is determined primarily by how it will function and what amenities will be included within the property. Size, location, service levels and type of business or targeted market segments are additional classifications. Industry also classifies hotels by chain scale…separating hotels into categories determined by their average daily rates. Various ownership structures and brand affiliations also differentiate hotels.
Classifications
Hotels may be classified on a number of different variables. Type of Hotel : There are numerous classifications by hotel type including all-inclusive hotels, all-suite properties, B&B/Inns, boutique, convention/conference centers, condo hotels, resort, extended stay, full service, casino, limited service and timeshare properties. Size and Complexity: A hotel can be classified by the number of guest rooms it has; hotel sizes can range from a small boutique hotel with fewer than 50 rooms to a large resort hotel with more than 1,000 rooms. The complexity of the hotel is determined by the volume and number of additional revenue generating functions such as the square feet of available conference space, number of F&B operations and additional services and amenities like pools, fitness centers, spas, golf, etc. Location: The location of a hotel can also determine the type of guest served. An airport hotel may be very different from a city-center property in an urban environment, or a remote island resort or a small quaint bed and breakfast located on top of a mountain. Hotels that specialize in conferences, may locate near entertainment destinations like Las Vegas or Disney theme parks to provide pre-post conference activities for attendees. Service Level: The level of service provided is also a key variable, ranging from an inexpensive budget or economy hotel, (Limited or Focused Service Hotels) which may have limited services and amenities, to upscale and luxury hotels (Full Service Hotels) with many services and a wide range of amenities. Market Segmentation: Figure 16.5 on the next page outlines the characteristics of specific hotel types that have evolved to match the needs of a particular traveler segment. As illustrated, hotels adapt and diversify depending on the markets they desire and need to drive occupancy levels and generate revenues. Some hotels will specialize in a specific market segment, but in today’s competitive environment, most hotels will target a combination of these segments.
There are several other industry related organizations, such as Forbes and AAA which provide Consumer Ratings for individual hotels….another form of classifying a property. Forbes has traditionally awarded 1 to 5 “Stars” and AAA, 1 to 5 “Diamond” ratings. Additionally, many social media applications like Trip Advisor offer hotel property ratings to consumers.
Chain Scale: Smith Travel Research (STR) is an organization that provides the lodging industry with global data benchmarking, analytics and marketplace insights. STR classifies the lodging industry into six chain scale segments according to their respective brand Average Daily Rate (ADR). The six segments are defined as Luxury ; Upper Upscale ; Upscale ; Mid-Scale with F&B ( Upper Mid-Scale ); Mid-Scale without F&B ( Mid-Scale ) and Economy . Through STR’s 30 –plus years of service to the hospitality industry, they have developed vital benchmarking performance solutions, established market trend transparency and provided data used by the investment community to support hotel development projects. Their core product, the STAR report, provides hotel owners and operators with comparative performance data between their property and a defined set of market competitors and allows you to follow trends in hotel occupancy, average daily rate (ADR) and revenue per available room (RevPar). Developers, investors, industry analysts, hotel brands and management companies all utilize STR data when determine what type of hotel to build and what location would provide maximum opportunity for success.

The type of ownership, brand affiliation and management are also very important variables in the classification of hotels. Owners may manage their own hotels independently but in today’s competitive environment, they would likely sign a Franchise Agreement with a nationally recognized brand as well as a Management Contract with a hotel management company to manage the property. A hotel chain such as Marriott, Hilton, Hyatt or IHG (Intercontinental Hotel Group) is comprised of multiple brands: Marriott, following their recent merger with Starwood currently has 30 different hotel brands, with each name representing a different level of price, service or targeted market segments.
Branding Decision
Selecting a brand affiliation is one of the most significant decisions hotel owners must make. 10 The brand affiliation selected will largely determine the cost of hotel development or conversion of an existing property to meet the standards of the new brand. The affiliation will also determine a number of things about the ongoing operation including the level of services and amenities offered, cost of operation, marketing opportunities or restrictions, and the competitive position in the marketplace. For these reasons, owners typically consider several branding options before choosing to operate independently or to adopt a brand affiliation.
Franchise Agreements
Another managerial and ownership structure is franchising. A hotel franchise enables individuals or investment companies (the franchisee) to build or purchase a hotel and then buy or lease a brand name to become part of a chain of hotels using the franchisor’s hotel brand, image, loyalty program, goodwill, procedures, cost controls, marketing, and reservations systems. 11
A franchisee becomes part of a network of properties that use a central reservations system with access to electronic distribution channels, regional and national marketing programs, central purchasing, revenue management support, and brand operating standards. A franchisee also receives training, support, and advice from the franchisor and must adhere to regular inspections, audits, and reporting requirements.
Selecting a franchise structure may reduce investment risk by enabling the franchisee to associate with an established hotel company. Franchise fees can be substantial, and a franchisee must be willing to adhere to the contractual obligations with the franchisor. 12 Franchise fees typically include an initial fee paid with the franchise application and continuing fees paid during the term of the agreement. These fees are usually a percentage of revenue but can be set at a fixed fee. The total percentage of sales ranges significantly for hotels from 3.3% – 14.7% with a median of 11.8%. 13

Management Contracts
It is common for ownership to utilize a management contract , which is a service offered by a management company to manage a hotel or resort for its owners. Owners have two main options for the structure of a management contract. One is to enter into a management agreement with an independent third-party hotel management company to manage the hotel. There are hundreds of these companies, but some of the large organizations include Aimbridge, Benchmark Hospitality, Crescent Hotels, Interstate Hotels, and White Lodging. A slightly different option is for owners to select a single company to provide both the brand and the expertise to manage the property. Marriott, Hilton, and Hyatt, are companies that provide this second option to owners.

Food and Beverage Services

The food and beverage sector is commonly known to industry professionals by its initials F&B. The F&B sector grew from simple origins to meet the basic needs for food and beverage services to increasing demand for unique experiences and broader options. As the interests of the public became more diverse, so too did the offerings of the F&B sector. The increasing awareness and demand for organic, sustainable, local or craft options as well as special dietary needs in food and beverage continue to challenge this industry. In addition, in order to better attract and serve a diverse array of diners, the F&B industry now consists of a variety of segments. The following is a discussion of each.
Quick Service Restaurants
Formerly known as fast-food restaurants, examples of quick-service restaurants , or QSRs, include Chick-fil-A, Subway, and Pizza Hut. This prominent portion of the food sector generally caters to both residents and visitors, and it is represented in areas that are conveniently accessed by both. Brands, chains, and franchises dominate the QSR landscape. While the sector has made steps to move away from the traditional “fast-food” image and style of service, it is still dominated by both fast food and food fast; in other words, food that is purchased and prepared quickly, and generally consumed quickly as well.

Fast Casual Restaurants
Fast Casual restaurants focus on higher quality ingredients than QSR’s and provide made-to-order food in an environment that does not include table service. Customers usually queue and order at a counter. The seating area is more upscale and comfortable. Examples would include Chipotle Mexican Grill, Panera and Jason’s Deli.

Full-Service Restaurants
Full-service restaurants are perhaps the most fluid of the F&B operation types, adjusting and changing to the demands of the marketplace. Consumer expectations are higher here than with QSRs. 14 The menus offered are varied, but in general reflect the image of the restaurant or consumer’s desired experience. Major segments include fine dining, family/casual, ethnic, and upscale casual. Fine dining restaurants are characterized by highly trained chefs preparing complex food items, exquisitely presented. Meals are brought to the table by experienced servers with sound food and beverage knowledge in an upscale atmosphere with table linens, fine china, crystal stemware, and silver-plate cutlery. The table is often embellished with fresh flowers and candles. In these businesses, the average check, which is the total sales divided by number of guests served, is quite high (often reviewed with the cost symbols of three or four dollar signs: $$ \$\$\$ or \$\$\$\$ $$.) Examples include the Inn at Little Washington, Ruth’s Chris Steakhouse and Capitol Grille.

Casual restaurants serve moderately-priced to upscale food in a more casual atmosphere. Casual dining comprises a market segment between fast casual establishments and fine dining restaurants. Casual dining restaurants often have a full bar with separate bar staff, a larger beer menu and a limited wine menu. This segment is full of chains such as Chili’s, Outback, Red Robin and Cracker Barrel as well as many independent restaurants in regional or local markets.
Family restaurants offer affordable menu items that span a variety of customer tastes. They also have the operational flexibility in menu and restaurant layout to welcome large groups of diners. An analysis of menus in family/casual restaurants reveals a high degree of operational techniques such as menu item cross-utilization, where a few key ingredients are repurposed in several ways. Both chain and independent restaurant operators flourish in this sector. Examples of chains in this category would be Golden Corral, Cici’s Pizza and Ponderosa Steakhouse.
Ethnic restaurants typically reflect the owner’s cultural identity, Vietnamese, Cuban, Thai, etc. The growth and changing nature of this sector reflects the acceptance of various ethnic foods within our communities. Ethnic restaurants generally evolve along two routes: toward remaining authentic to the cuisine of the country of origin or toward larger market acceptance through modifying menu items. 15 Examples would be P.F. Chang’s, Tara Thai or Pei Wei.
Bars, Wineries, and Craft Distilling
The beverage industry continues to evolve as well with a strong focus on local craft beers, wines, cider and distilling. Wineries exist in almost every state, with over 250 in Virginia as of 2015. 16 Wine, bourbon, cider trails and brew pub crawls, etc. are used to generate awareness and create experiences for customers. Wineries often use event space or festivals to take advantage of the beauty of the winery and supplement their revenues.
Institutional Food Service
Institutional f ood s ervice is large scale and often connected to governmental (National Parks) or corporate level organizations. Often run under a predetermined contract, the institutional F&B sector includes:
- Educational institutions
- Prisons and other detention facilities
- Corporate staff cafeterias
- National Park restaurants and concessions
- Cruise ships
- Airports and other transportation terminals and operations
Examples of companies who focus on Institutional Food Service are Compass, Sodexho, Aramark.

Accommodation Food Service
This sector includes hotel restaurants and bars, room service, and self-serve dining operations (such as a breakfast room). Hotel restaurants are usually open to the public and reliant on this public patronage in addition to business from hotel guests. Collaborations between hotel and restaurant chains have seen reliable pairings such as the combination of Shula’s Steakhouse and Marriott Hotels.
Restaurant Industry Profitability and Cost Control
According to the National Restaurant Association, QSRs have the highest pre-tax profit margin at 6.3%, while full-service restaurants have a margin of 4.7%. There will be significant variances from these percentages at individual locations, even within the same brand. 17
A number of costs influence the profitability of an F&B operation. Some of the key operating expenses (as a percentage of revenue) are detailed in Figure 16.16, above, where food cost and salaries & wages are the two major expenses, each accounting for approximately a third of the total. Other expenses include rental and leasing of venue, utilities, advertising, and depreciation of assets. These percentages represent averages, and will vary greatly by sector and location.
Cost control and containment is essential for all F&B businesses. Demanding particular attention are the labor, food, and beverage costs, also known as the operator’s primary costs. In addition to these big ticket items, there is the cost of reusable operating supplies such as cutlery, glassware, china, and linen in full-service restaurants.
Recreation can be defined as the pursuit of leisure activities during one’s spare time 19 and can include vastly different activities such as golfing, sport fishing, and rock climbing. Defining recreation as it pertains to tourism, however, is more challenging.
Let’s start by exploring some recreation-based terms that are common in the tourism industry. Outdoor recreation can be defined as “outdoor activities that take place in a natural setting, as opposed to a highly cultivated or managed landscape such as a playing field or golf course.” 20 This term is typically applied to outdoor activities in which individuals engage close to their community. When these activities are further away, and people must travel some distance to participate in them, they are often described as “adventure tourism”. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), adventure tourism is “a trip that includes at least two of the following three elements: physical activity, natural environment, and cultural immersion.” 21

Ultimately, categorization is based on a combination of several factors, including manner of engagement in the activity (risk exposure, experience requirement, group or solo activity), the distance travelled to access the activity, and the type of environment (proximity to nature, level of challenge involved) in which the activity occurs.
A 2013 adventure tourism market study discovered that people who travel for adventure experiences tend to be well-educated, with 48% holding a four-year degree or higher credential. They value natural beauty and rank this factor highest when choosing a destination. The most cited reasons for their travel are “relaxation, exploring new places, time with family, and learning about different cultures.” 22
Globally, it is estimated that the continents of Europe, North America, and South America account for 70% of adventure tourism, or US$263 billion in adventure travel spending. 23
Entertainment
Entertainment is a very broad category which overlaps with many of the areas discussed elsewhere in this chapter, like hotels and accommodation. Two major types of entertainment that we’ll discuss here are gaming and theme parks.
Gaming has grown significantly in the U.S. and globally. The number of casinos in the U.S. has been growing since 2010, and in 2013, there were over 500 commercial casinos, as shown in Figure 16.16. Casinos are found all over the U.S. in major cities, riverboats, and on Native American lands. However, U.S. casino revenue has been relatively flat, while global gaming revenues have been on the increase, largely due to Asian market growth. Most casinos involve other facets of the Hospitality industry such as lodging, F&B, golf, entertainment, spas, etc., but they also have the added challenges of casino operations.

Theme Parks
Theme parks have a long history dating back to the 1500’s in Europe, and have evolved ever since. Today, it is hard not to compare any amusement park destination to Disneyland and Disney World. Opened in 1955 in sunny California, Disneyland set the standard for theme parks. Theme parks outside of California and Florida are often highly seasonable operations challenged with significant staffing and training requirements each year.

Convention and Event Management
A convention is a large meeting of people with similar interests who meet for a period of at least a few days to discuss their field. An event is a gathering at a given place and time, usually of some importance, often celebrating or commemorating a special occasion.
Both conventions and events can be extremely complex projects, which is why, over time, the role of meeting planners has taken on greater importance. The development of education, training programs, and professional designations such as CMPs (Certified Meeting Planners), CSEP (Certified Special Events Professional), and CMM (Certificate in Meeting Management) has led to increased credibility in this business and demonstrates the importance of the sector to the economy.
Meeting planners may be independent contractors hired to facilitate the planning process, work directly for the company full time to coordinate their meeting, or work for hotels, conference centers and event venues directly.
- The various tasks involved in meeting and event planning include:
- Conceptualizing/theming
- Site inspection & selection
- Logistics and planning
- Human resource management
- Marketing and public relations
- Budgeting and financial management
- Sponsorship procurement
- Management and evaluation
Event Categories
Mega events.
A m ega-event is a large scale, highly prestigious event such as the Olympic Games, the FIFA World Cup, or a global economic summit. These events typically gain tremendous media coverage and have major economic impacts on the host location, both positive and negative. High levels of tourism (1 million+ visitors) associated with a mega-event brings revenue, but the revenue may be outweighed by substantial capital and social costs incurred by the host. The events are often awarded to host destinations through a bidding process and gain tremendous media coverage.

Special Events
A special event is a one-time or infrequent specific ritual, presentation, performance, or celebration. Special events are planned and created to mark a special occasion, such as a presidential inauguration or the Queen of England’s 90 th birthday. Like mega-events, there may be significant media coverage and economic impact for the host city or destination.
Hallmark Event
A hallmark event is a unique event that is often identified with the location where it is held, like Carnival in Rio de Janeiro or Oktoberfest in Munich. Hallmark events contribute significant economic benefits and even can create a competitive advantage for the host city or destination that attracts tourists.

A festival is a themed public celebration that conveys, through a kaleidoscope of activities, certain meaning to participants and spectators. Festivals are often celebrations of community or culture and feature music, dance, or dramatic performances. Examples include Lollapalooza, the Cannes Film Festival, and Junkanoo in the Bahamas.
Local Community Events
A local community event is generated by and for locals; although it may attract tourists, its main audience is the local community. The community may experience measurable economic impacts, as might happen at The Steppin’ Out Street Fair in Blacksburg (think hotel stays and eating out). Fundraisers and community picnics are also examples in this category.
Meetings and Conventions
The tourism industry also has a long history of creating, hosting, and promoting meetings and conventions that draw business travelers. In fact, Convention and Visitor Bureau’s (CVB’s) work hard to attract these meetings and conventions to their city to drive economic benefit for hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, etc.
There are several types of such events.
Conventions generally have very large attendance, and are held on a regular schedule but in different locations. They also often require a bidding process. Political conventions are one such example.
Association M eetings or C onferences are held regionally and nationally for hundreds of associations or events focused on specific themes. Examples would be the National Restaurant Association Annual Convention, ComicCon, or the National Auto Show.
Corporate M eetings will vary significantly in size and purpose and include regional or national sales meetings, shareholder meetings, training sessions, or celebrations. The location will vary depending on the nature of the meeting. They may be held at an airport property, a traditional corporate meeting facility or even an upscale resort.
Trade S hows and T rade F airs can be stand-alone events, or adjoin a convention or conference.
S eminars , W orkshops , and R etreats are examples of smaller-scale events.
As meeting planners have become more creative, meeting and convention delegates have been more demanding about meeting sites. No longer are hotel meeting rooms and convention centers the only type of location used; non-traditional venues have adapted and become competitive in offering services for meeting planners. These include architectural spaces such as airplane hangars, warehouses, or rooftops and experiential venues such as aquariums, museums, and galleries. 24
Transportation and travel services are another large element of the tourism industry. This area includes cruise ships, airlines, rail, car rentals, and even ride sharing such as Uber and Lyft. Each of these segments is impacted significantly by fuel costs, safety issues, load factors and government regulation.
If you’ve ever been on a cruise, you are in good company. According to CLIA (Cruise Lines International Association), 23 million passengers were expected to go on a cruise worldwide on 62 member lines in 2015. 25 The industry employs over 900,000 people. 26
Over 55% of the world’s cruise passengers are from North America, and the leading destinations (based on ship deployments), according to CLIA are: 27
- The Caribbean (36%)
- The Mediterranean (20%)
- Northern Europe (11%)
- Australia/New Zealand (6%)
- Alaska (6%)
- South America (3%)

The t ravel services sector is made up of a complex web of relationships between a variety of suppliers, tourism products, destination marketing organizations, tour operators, and travel agents, among many others. Under the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), the travel services industry group includes “establishments primarily engaged in travel arrangement and reservation services. Examples … are tourist and travel agencies; travel tour operators and wholesale operators; convention and visitors’ bureaus; airline, bus, railroad and steamship ticket offices; sports and theatrical ticket offices; and airline, hotel and restaurant reservation offices.” 28 Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveler (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travelers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveler and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies. 29 Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
Online travel agencies (OTAs)
Online travel agents (OTAs) are companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include Booking.com, Expedia.com, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs are gaining popularity with the travelling public; in 2012, they reported online sales of almost $100 billion 30 and almost triple that figure, upward of $278 billion, in 2013. 31 Over 40% of U.S. travelers booked flights online in 2014. 32
Tour operators
A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveler. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies. 33 Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveler could by purchasing individually.
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs)
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” 34 .
Country Clubs
Country c lubs are another part of the Hospitality industry with a very different service strategy focusing on serving members who will develop relationships with the staff compared to a more transactional service interaction in lodging, restaurants or airlines.
Country clubs do not focus as strongly on profit as they do on maximizing member satisfaction, retention and growth while maintaining an attractive fee structure. Country (or city) clubs, will typically have restaurant and bar operations, catered events and other amenities such as golf, tennis, pool, fitness facilities, etc. Depending on the type of club, family and youth events are important to maintain and grow membership.
Strong customer service, culinary, event management and general management skills are necessary to be successful in clubs.

Chapter Video
As in any other fast-moving industry, the landscape in Hospitality and Tourism is always changing. This video explores 10 of the more important current trends impacting the industry.
(Copyrighted material)
Key Takeaways
- The Tourism industry is the largest industry in the world with significant benefit and costs to a region. The global competition for the tourism dollar is significant within the US and between countries.
- Hotels vary significantly in size, quality, purpose, chain affiliation, and ownership. The complexity of the operation and leadership vary as well.
- Food and Beverage is made up of a wide variety of restaurant types from QSR, Fast Casual, Fine Dining and Ethnic. Institutional food service in business , hospitals, education, parks and concessions are a significant part of the Food and Beverage industry.
- The evolution of tastes and consumer expectations in food and beverage continue to provide opportunity and challenges in the industry for ethnic sustainable, organic, local, craft, and other unique experiences.
Chapter 16 References and Image Credits
Portions of this chapter were adapted from Westcott, Morgan (Ed) Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC. CC BY 4.0 https://opentextbc.ca/introtourism Available for free at: http://open.bccampus.ca
Image Credits: Chapter 16
Figure 16.1: JackMac34 (2015). “Untitled.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/italy-burano-postcards-971575/
Figure 16.2: “The Impact of Global Tourism.” (2016) Data retrieved from: http://www2.unwto.org/content/why-tourism
Figure 16.3: Yellowute (2007). “Shirley Plantation.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shirley_Plantation_2006.jpg
Figure 16.6 “Example of a Hotel Market segmentation by STR’s chain scale” Author’s own work. Licensed CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 16.7: Christina Hsu (2009). “San Diego City and Bay at Night.” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://flic.kr/p/6KZ5Cv
Figure 16.8: Anastasia Cortes (2016). “The Inn at Virginia Tech.” Public domain. Provided by author.
Figure 16.9: Dale Cruse (2014). “New Zealand langoustines at Troquet.” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dalecruse/8551895022/
Figure 16.10: Imzadi1979 (2012). “An example of a typical American logo sign.” Public domain photograph. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logo_sign#/media/File:Logo_Sign.svg
Figure 16.11: J. Winters (2008) “A Red Robin Restaurant in Tukwila, Washington.” Public domain photograph. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Red_Robin_in_Tukwila,_Washington.jpg
Figure 16.12: “Le Procope.” © Michael Rys. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restaurant#/media/File%3AInside_Le_Procope.jpg
Figure 16.13 “The restaurant industry career path” Author’s own work. Licensed CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 16 .15 : JohnSM (2013). “Rafting in Turkey.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/rafting-turkey-travel-1125213/
Figure 16 .16 : Graph data sources: Statista (2016). “ Number of commercial casinos in the United States from 2005 to 2013.” Retrieved from: http://www.statista.com/statistics/187972/number-of-us-commercial-casinos-since-2005/ and “ Global casino gaming revenue from 2006 to 2015 (in billion U.S. dollars).” Retrieved from: http://www.statista.com/statistics/271577/global-casino-gaming-market-revenue/ and “ U.S. casino gaming market revenue from 2004 to 2015 (in billion U.S. dollars) .” Retrieved from: http://www.statista.com/statistics/271583/casino-gaming-market-in-the-us/
Figure 16 .17 : Josh Hallett (2009). “ The ‘Big Bang’ at Wishes – Magic Kingdom – Walt Disney World .” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/hyku/3830182777
Figure 16.18: Peter23 (2011). “Beijing National Stadium.” CC BY- SA 3.0 . Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beijing_National_Stadium#/media/File:Beijing_national_stadium.jpg
Figure 16.19 : Skeeze (2014). “Mardi Gras in New Orleans.” Public domain. Retrieved from: https://pixabay.com/en/mardi-gras-new-orleans-festival-1176483/
Figure 16 . 20 : Roger W. (2012). “ Charlotte Amalie – Panorama (Postcard) ” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/24736216@N07/7170231567
Figure 16 . 21 : Dan Perry (2006). “Riviera Country Club in Pacific Palisades, California.” CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Country_club#/media/File:Riviera_Country_Club,_Golf_Course_in_Pacific_Palisades,_California_(168828797).jpg
Video Credits: Chapter 16
Sisyanti, Ling Ling, Wasim Amsal,Ella Qiu, and Rebecca Catherine Stephany. “10 trends in Hospitality and Tourism Industry.” February 6, 2015. Retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SJ8Momwv7Qk
References: Chapter 16
Chapter 16 Hospitality & Tourism Copyright © 2018 by Richard Parsons; Stephen Skripak; Anastasia Cortes; Anita Walz; and Gary Walton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Before engaging in a study of tourism, let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism, travel, and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
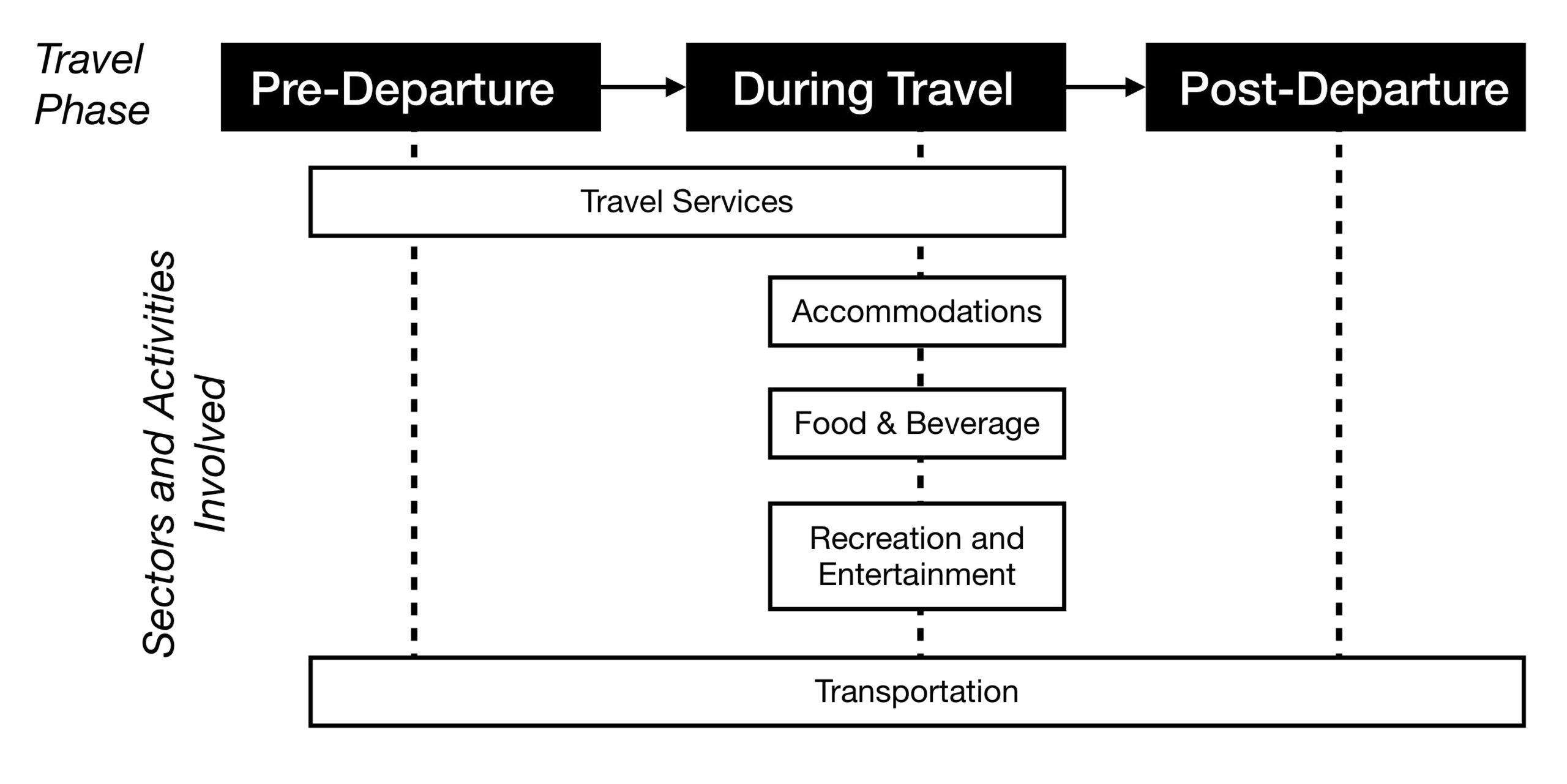
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Conceptualising, defining and theorising hospitality

2019, Tourism Today
This paper critically explores the extant literature associated with the rather convoluted journey that the hospitality academy has taken over the past few decades in its attempt both to realise a universally acceptable definition of hospitality and establish the 'boundaries' of the hospitality phenomenon. To both these issues credible solutions are proposed in an attempt to end this seemingly endless endeavour. From the proposed definition of hospitality its fundamental dimensions are established and articulated to form a basis for further conceptual development and empirical enquiry. In addition, the revolutionary and evolutionary forces, or 'tectonics', lying behind the manifestation of similar and divergent 'Hospitality Morphologies' are identified and discussed in relation to the development and use of theoretical concepts and approaches to establish a more robust 'comparative' theoretical approach to explain temporal and spatial similarities and differences between the incidence of alternative empirical hospitality morphologies.
Related Papers
International Journal of Hospitality Management
Kate Purcell
Bob Brotherton
This is a conceptual paper that explores the issues of the uniqueness, or otherwise, of the hospitality concept, the lack of any systematic theoretical framework to explain and predict the incidence and nature of hospitality in both temporal and spatial contexts and the identification of the key dimensions of the hospitality concept. In doing so it presents a theoretical and logical justification for the separation of hospitality from tourism and/or leisure using the General Systems Theory concepts of necessary and sufficient incidence, postulates a general theoretical model of hospitality that identifies the key variables comprising the model and proposes that the concept of hospitality per se can be operationalised through the use of four main dimensions to facilitate comparative analysis of hospitality occurences both spatially and temporally.
Trâm Nguyễn
Anil Bilgihan
Purpose-The purpose of this conceptual paper is to provide a critical reflection on the role of hospitality in society. Specifically, this research criticizes contemporary conceptualizations of hospitality in academic research and practice and suggests a reconceptualized approach for capturing the full potential of hospitality to elicit transformative social change. Design/methodology/approach-This paper is based on a critical analysis of hospitality research and practice as reflected in the extant literature. A typological approach to conceptualization is used to develop a framework that views hospitality from three distinct epistemological pathways. Findings-Hospitality has largely been conceptualized as an industry-or a business-level context in which economic activity takes place, a pathway referred to as application. This paper offers the hospitality-oriented society of tomorrow (HOST) framework, which urges researchers and practitioners to explore two additional pathwaysinfusion and transformationthrough which hospitality can contribute to society. The nonrecursive relationships between these three pathways and the five pillars of sustainable development espoused by the United Nations 2030 Agenda are proposed to form the basis of future inquiry into the role of hospitality in society. Practical implications-The HOST model provides a framework whereby stakeholders within and outside of the traditional contours of the hospitality industry can benefit from a broader conceptualization and implementation of the hospitality phenomenon. Originality/value-The paper offers a thought-provoking assessment of the fundamental tenets of hospitality as an academic discipline and social phenomenon. It offers a unique framework that should inform the evolution of hospitality research and practice if the discipline is to bolster its social significance.
Richard Kearney
in 'Ethos europäischer Gastlichkeit/Contours of an Ethos of European Hospitality' edited by Michael Staudigl and Andris Breitling, Velbrück Wissenschaft, 2015
Journal of Hospitalityand Tourism Management
Kevin D O'Gorman
This article presents a summary of findings from a continuing investigation into the historical origins of hospitality in the ancient and classical worlds, focusing mainly on the Greek and Roman civilisations. After considering the etymology of hospitality, the article goes on to explore hospitality and mythology, hospitality and the household, public hospitality, commercial hospitality and hospitality in contemporaneous religious writings. The evaluation of the outcomes leads to the identification of five dimensions of hospitality (honourable tradition, fundamental to human existence, stratified, diversified and central to human endeavour) that have been evolving from the beginning of human history.
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management
International Journal of Tourism Research
Alison Morrison
Tourism and Hospitality Planning & Development
This paper presents a critical review of the results from a pilot study designed to explore the validity of a data collection instrument and procedure, based upon the use of associative and metaphorical projection techniques, as a vehicle for generating hotel guest perceptions of the physical and service aspects of hospitality within given hospitality environments. The pilot study was undertaken in two case-study UK hotels where 89 face-to-face interviews were conducted using a pre-designed questionnaire. The results from this include the words guests most associate with ‘hospitality’ in genera, the colour, animal and season of the year they used to describe both the physical and service aspects of the hospitality they encountered in the case-study hotels, and the reasons why they chose these. In addition, the results also explore whether any relationship between these choices and a range of respondent variables, e.g. gender, age, educational level, ethnicity, occupational type, nature of stay, etc., should be hypothesized and tested in future studies. The results are also examined in relation to the operational definition of hospitality posited by Brotherton (2002) that suggests the hospitality concept is comprised of four basic dimensions – physical, temporal, behavioural and spatial.
Discussing the nature of Hospitality: why alcohol is present in these types of rites?. Volume 2, Issue 2. July 2013. (pp. 51-74) International Journal of Human Potential Development. Society for Human and Social Potential Development, Kanpur, India. ISSN 2277-1980
Maximiliano E. Korstanje
Abstract The encounter between hosts and guests may be troublesome from many perspectives. Sometimes tourists are targets of criminal activity, but others they are involved in illegality consumption of drugs or alcohol. Alcohol seems to be present in almost all tourist destinations, and some policy makers suggested to officials to restrict its consumption in public events, and hotels. We early said “troublesome” simply because guests are not familiar with the visited city, which merits protection. At the same time, hosts do trace the history or antecedents of tourists by means of diverse mechanism which ranges from Visa to steps for identity validation at airports. Going beyond the boundaries of home, people experience an increase of uncertainty and fear, which is reduced by means of hospitality. Not only tourists but also natives feel a wide-range sentiment of distrust each other. This means that hospitality is something more than a hotel industry or a sign of good manner. Hospitality represents an ancient institution that facilitates the encounter of travellers, eliminating not only the risks but also their differences. Alcohol, Music, Sex, Banquets and Foods are part of the instrument to make this encounter more suitable. Hospitality traverses all cultures and times. As a result of this, one might question, is alcohol a problem for leisure and tourism?. Alcohol is of paramount importance in order for ensuring the success of tourist encounters. This paper explores the connection of tourism, hospitality and alcohol from an anthropological view. Unlike the existent specialized literature that emphasizes on the negative or effects resulted from the abuse of alcohol, this research proposes a new theory, where alcohol is the stepping stone of hospitality and also an important piece of tourism as well. Key Words. Encounter, Liminiality, Anxiety, Alcohol-Consumption, State, and Hospitality.
RELATED PAPERS
Curso Básico
David Landivar
Influencia de la danza en el proyecto de vida: una experiencia en la fundación artística Cochaviva danza
Praxis Pedagógica
Laura Prado
marcella vacca
Lise Nielsen
Tiago Balem
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems
Rahib Abiyev
Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi JIE
Setyo Wahyu Sulistyono
Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
Thomas Platz
Dana Blahútová
Ecological Psychology
Journal of Clinical Psycology
hamid yaghubi
Mediterr J Pharm Pharm Sci
Patient Education and Counseling
Nguyen Cong Khai SK20V1Q524
2018 3rd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Engineering (ICITE)
Deepeka Garg
International journal of health sciences
Anshika Jaiswal
Carolina Flinz
Comprehensive psychiatry
Journal of Clinical Oncology
Advances in Space Research
Victor Sergeev
Proyección: Teología y mundo actual
Francisco A . Castro Pérez
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Fahri Ramadhan
Khotibul Umam
See More Documents Like This
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Understanding the Hospitality Industry and Its Services
Here is what you should know about hospitality if you’re getting into the service sector. We’ve covered some information and tips that you can utilize while embarking on this route.
What is hospitality?
Before you delve further into the article, it’s vital to know the definition of hospitality. The hospitality definitions have multiple meanings on various websites. So, how to define hospitality in a sentence? In simple terms, it’s a kind gesture and service towards guests, clients, strangers or visitors. And this kind of treatment is mainly involved in the service sector, such as:
- Travel and tourism
- Hotel industry
- Food and beverages
- Entertainment and recreation
These sectors thrive on effective customer care services. Besides,the core theme of this sector revolves around providing effective customer care to guests, tourists, clients, etc.
Regardless, it’s important to show hospitality even in our regular course of life. It cost no harm to be kind and warm towards a stranger or any individual. The hospitality synonym, according to the thesaurus, is warmth. In addition, it is also similar to cordial, friendly and accommodating.
The core sectors in the hospitality industry
The hospitality sector is growing at a fast phase. It is one of the biggest job generators in the world. So, what is hospitality services? It is broadly classified into four sectors:
The travel and tourism sector relies on the service it gives to its clients, guest or visitors. And it includes services such as travel agents, car rental companies, bus tours and sightseeing.
Globally, the tourism market is growing. It had a slump phase during COVID-19. However, now that normalcy is getting back gradually, the industry is sure to thrive. This sector requires effective communication and reliance to provide excellent service to their guest or visitors. And communication is vital because one can expect visitors or clients from different countries.
The hotel industry also thrives on the services it offers to their guest and visitors. And if you’re planning to get into this sector, hospitality is the primary factor you should delve into. The hotel hospitality market is growing at a fast rate. And globally, the market annual revenue generation falls over at around $500 billion.
Hospitality plays a crucial role in the hotel industry. One bad customer review might ward off the possible ten guests that you might get. So, it’s vital to offer the best service if you’re planning to get into this sector.
For example, you plan for a trip and look for hotels to book. And what would you do first? Naturally, you would check for reviews online. And you’d see negative reviews made by customers towards a specific hotel. Eventually, you would book the one with good feedback.
Among the hospitality sector, Food and beverages (F&B) rely heavily on customer care and services. It is also the largest sector within the hospitality industry. It goes beyond providing drinks or food. Along with the meal, an individual should present to customers with a warm smile and kindness.
F&B includes restaurants, pubs, coffee shops and night clubs etc. A good service is crucial in this sector. In addition, it’s also vital to have good communication. It will help to develop a good relationship between you and the customer or guests.
Communication is one of the crucial factors in the hospitality sector. Hence, it’s essential to get yourself acquainted with hospitality work before embarking on this route.
Entertainment and recreation are other sectors that work closely with the service sector. It includes museums, cultural events, music concerts, sporting events, art and performance.
Hospitality service plays an essential role in this sector. From amateur to professional, many take part in entertainment and recreational activities. And service is vital to provide guidance, especially in amusement parks, sports and music concerts.
Why is hospitality important?
Now that you know the definition of hospitality and its services, it’s crucial to understand its importance. The core aspect of hospitality is providing service in the best possible way. Since these sectors thrive on customer care and service, hospitality plays a primary role.
Whether you’re running a restaurant or trying to get into F&B, hospitality is essential. It will help if you have customers’ good reviews or feedbacks to run your business efficiently. And it’s vital to have good customer retention as well. If your service is good, the guest or customer will come back to your café or hotel.
Furthermore, the age of digital media is both good and bad for the hospitality sector. One bad review on a well-known site can tarnish the whole image of the restaurant or a bar. But if your service is excellent and gets a good review, it will be like hitting the jackpot. In addition, through positive word of mouth, you will get new customers too.
Building a good brand reputation is vital in any sector. Likewise, your service should be synonym with good reviews. It will be of great help to get some knowledge about hospitality management. Here are some of the schools for this course:
- Cornell university school of hotel administration, USA.
- Les Roches International School of hotel management (Switzerland, China and Spain).
- Ecole Hoteliere de Lausanne, Switzerland.
- University of Central Florida Rosen College of Hospitality Management, USA.
- Hotelschool The Hague, Netherland.
You can get a bachelor’s degree in hospitality management online from the University of Florida or Alabama. Furthermore, you can also get a hospitality management course online. Some institutes offer this course online, such as the eCornell suite. Along with another course, you can pursue this as a side course online.
Hospitality management definition in a simple term is the study of various service industries such as:
- Event management
- Food & Beverages,
- Travel and accommodation.
Getting knowledge about this course helps you to get an idea about how to deal within the industry. And it also helps to work on business ethics and discipline yourself. In this sector, these factors are vital to maintaining a good relationship with the guest or visitors.
Basic principles of hospitality that you should know
When it comes to hospitality, there are some basic principles that you should adhere to. It will help to carry the service effectively without any hiccups. Undeniably, mistakes are bound to happen. However, with preventive measures, it is avoidable.
Here are some of the principles that you can apply:
- The first impression is the last
It’s the natural tendency of humans to judge. And in the service industry, judgments are bound to happen. Bad feedback or a review can tarnish the image of a hotel or a café. Hence, it’s crucial to offer quality service to the customers or guests. It will allow a good impression on the visitors’ end and will revisit your business establishment. The first impression lasts longer, and if it’s not good, your guest or customer will have a prejudice against your café or hotel.
- Be cordial, warm and friendly.
If you’re in the hospitality industry, being warm, courteous and friendly is a necessity. These are the USP (Unique Selling Point) in the service sector. Greeting the visitors and saying goodbye will make them happy and set a good tone for your hotel.
- Be knowledgeable
Before you go for a job interview, you do proper research about the specific company you’re applying for. It is to help you get an idea about the company and be answerable to the recruiter. Likewise, in the hospitality sector, it’s essential to know what you’re providing. If you’re running a hotel or a park, you should instill your team with proper knowledge about it.
There are times when a guest or a customer might want to know about a specific product or food. And if you didn’t know about it, then it would create a negative impression. Hence, it’s always necessary to be prepared than to be sorry.
- Efficient service
Along with a good personality, it’s crucial to have efficient service. At the peak time, it would not be easy to attend to every guest. You wouldn’t want your guest to express their bad hospitality experience online. However, if you organize and execute it well, then it will run smoothly. Hence, efficiency is a vital factor in the service sector.
- Flexibility
Flexibility is also another vital aspect of the hospitality industry. There would be times when a customer would opt for a different course instead of following the regular course meal. So, you need to be able to bend the rule and provide what the customer prefers. It’s not easy at times; however, you need to deal with calm and patience. And if your café or restaurant has good flexibility, it would be a bonus.
- Consistency
Consistency is crucial in every aspect of life or work. Being consistent helps you work with ease and offer excellent service. And in the hospitality industry, it’s vital to stay consistent with your work.
One of the vital factors to have a good business cycle is consistency. A customer or guest comes back to your establishment because they like the food or the service you’ve offered. And you wouldn’t want to miss the chance of losing your valuable customer. Hence, be consistent with your work and offer the best service.
- Effective communication skill
One of the crucial factors in the service sector is to have excellent communication skills. When it comes to the service sector, you’re bound to interact with guests or visitors from different countries or backgrounds. Hence, it’s necessary to have a team that has excellent communication skills. It will allow you to understand customers’ needs and preferences and solve the issue without any hassle. Good communication also avoids misunderstandings between the host and guest.
What is hospitality experience?
As we’ve talked about hospitality experience in the article, it’s crucial to understand its aspect.
So, how to one define hospitality experience? In a narrow term, it’s an amalgamation of multiple aspects put into one. Broadly, it revolves around various factors such as food, ambiance, timing and customer care etc. All these factors are taken into consideration that leads to either a good or bad experience.
Therefore, in the service sector, you need to meet the customers’ expectations and needs. If you’re taking this route, you should be meticulous in your work. Furthermore, it would help if you have an effective team that has a good personality.
To have a good hospitality experience for your guest, you need to look into the tiniest detail. From being punctual to cleanliness, you shouldn’t miss out on any aspect. Some of the factors that you need to consider for your guest to have a good experience are:
- You should set a proper tone for your place or venue. Many people do proper online research before visiting an establishment.
- Another critical factor is to provide excellent service without any hiccups in the process.
- Effective management of customers.
Furthermore, you will communicate with people from different backgrounds, colors, or races in the service sector. In addition, some customers might be rude or not understanding.
As with the recent incident , an angry customer threw a warm soup at the manager’s face. Here the manager tried to deal with the customer calmly, but the customer was not paying heed. And cases like this are bound to happen. But you need to understand the situation and deal with calm, just like the manager.
The hospitality industry is an adventurous sector. If you’re willing to go beyond your comfort zone, then this would be a good call for you. Before you embark on this route, ask yourself what does hospitality means to you. Because along with the perks, you will face multiple challenges. However, once you understand all the pros and cons, then you’re good to go. What you do should come within, especially in this sector.
Furthermore, it would be better to take a course in hospitality management to understand this field better. It will help you have a clear perspective and apply your knowledge to it.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 16 Hospitality and Tourism
Learning Objectives
- Understand what tourism is: definition, components, and importance.
- Understand the economic, social, and environmental benefits and costs of tourism.
- Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition.
- Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined.
- Examine the different categories of food service operations.
- Understand the different types of events, meetings, and conventions.

The tourism industry is often cited as the largest industry in the world, contributing 10 percent of the world’s GDP. In 2016 there were over 1.2 billion international tourists: that’s a substantial economic impact and movement of goods and services! [1] Tourism is also considered an export and is unique in that the consumers come to the product where it is consumed on-site. Before we dig any deeper, let’s explore what the term “tourism” means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
A social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure. [2]
In other words, tourism is the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure). It is important to understand the various groups and constituencies involved in this movement. Of course it includes the tourist, but also the vast array of businesses providing goods and services for the tourist, the government and political structure of a destination, and the local residents of the destination community itself. Each of these components are necessary parts of a successful tourism destination and operate within private and public sectors, the built environment, and the natural environment. All these come together to create the processes, activities, and outcomes of tourism.
If it all seems a little overwhelming, it might be helpful to break tourism down into broad industry groups, each of which will be covered in this chapter:
Accommodation and Lodging
- Food and Beverage Services (F & B)
Recreation and Entertainment
- Convention & Event Management
Travel Services
- Private Clubs
Benefits and Costs of Tourism
Tourism impacts can be grouped into three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations. Some impacts gain more attention than others. It is also important to recognize that different groups and constituencies are impacted differently.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
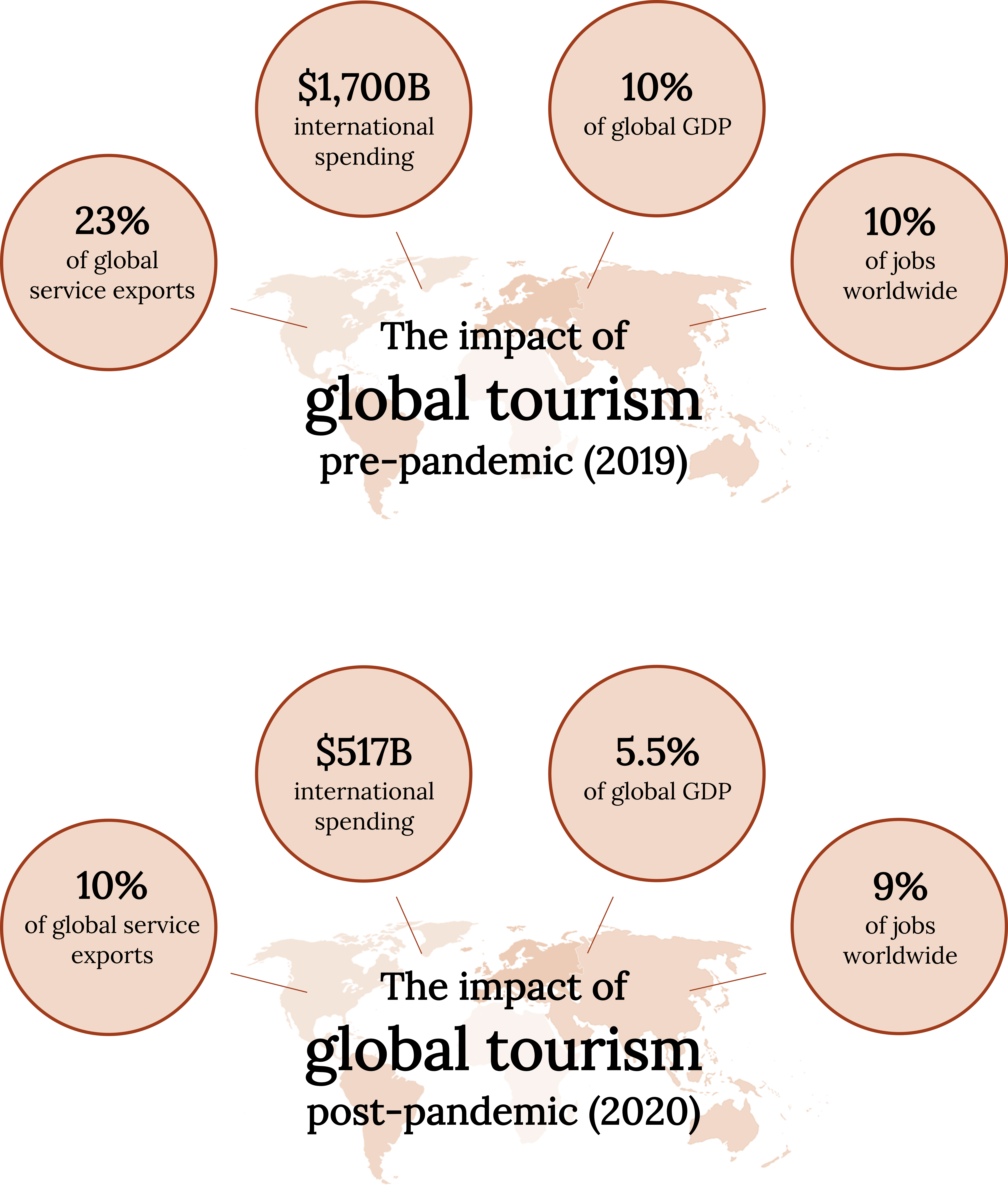
The tourism industry has a huge economic impact that continues to expand to new markets and destinations. According to the UNWTO, in 2016 “The total export value from international tourism amounted to US$ 1.5 trillion.” [3] Regions with the highest growth in terms of tourism dollars earned (2016 vs 2015) are Africa, Asia and the Pacific, the Americas Europe. Only the Middle East posted negative growth at the time of the report. As well, the UNWTO’s Tourism 20 3 0 Vision report predicts that international arrivals will reach nearly 1.8 billion by 2030. [4] Figure 16.2 provides additional information about the impact of tourism worldwide. The global pandemic of 2020 which limited or in some cases ceased any citizen travel has had a direct and significant impact on global tourism, as outlined in Figure 16.2.
Positive impacts from the prior economic boom include robust foreign exchange, increases in income, and GDP growth. Tourism can also offer diverse employment opportunities, can be developed with local products, and is often compatible with other economic activities within a destination. Tourism often injects money into the community that leads to secondary economic development as well. For example, successful resorts may create the need for a commercial laundry facility or a pet boarding business.
However, there are also negative impacts. Property values may increase to the point of unaffordability for local residents, and the seasonality of the tourism industry may create a feast-or-famine economy. As with any economy, if too many resources are focused on just one industry, communities may be vulnerable to any unexpected economic, social, or environmental changes. One example is the New Jersey shore after the devastation of Hurricane Sandy in 2012. The tourism industry was severely impacted, leaving no economic fallback for local residents.
Social Impacts of Tourism
In addition to the economic benefits of tourism development, positive social impacts include an increase in amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts, culture, heritage and tradition, celebration of indigenous communities, and community pride. Tourism also has the potential to break down language, socio-cultural, religious, and political barriers. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents and promotes a positive image of the destination.
However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme, negative social impacts of tourism can include: change or loss of indigenous identity and values; culture clashes; changes in family structure; conflict within the community for the tourism dollar; and ethical issues, including an increase in sex tourism, crime, gambling, and/or the exploitation of child workers. [5]
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. In some destinations, there is a great appreciation of the environmental resources as the source of the tourism industry, and as such there are environmental protection policies and plans in place. Tourism has helped to save many delicate ecosystems and their flora and fauna. Preservation of these important resources benefits not only the tourist but also the local residents as well.
Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can still have severe negative economic impacts. According to The United Nations Environment Programme, these can include the depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.), pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering), and physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity, and spread of disease). [6]
The environmental impacts of tourism can reach beyond local areas and have an effect on the global ecosystem. One example is increased air travel, which is often identified as a major contributor to climate change.
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world, and the industry is transforming at a staggering rate.
The Hospitality Industry
When looking at tourism it is important to consider the term hospitality. Some define hospitality as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves.” [7] Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry.

The pineapple has long been the symbol of hospitality. The Caribs, indigenous people of the Lower Antilles in the Caribbean, first used it as such a symbol. The Spaniards knew they were welcome if a pineapple was placed at the entrance to the village. This symbolism spread across Europe and North America where it became the custom to carve the shape of a pineapple into the columns of residences. [8] It is now common to see the image of the pineapple as a sign of welcome, warmth and hospitality.
The types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business—whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground—are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation and lodging . Figure 16.4 summarizes the various groupings within the industry.
Figure 16.4: The scope of the hospitality industry.
Hotel Types
Hotels are typically referred to by hotel type or other classifications. Hotel type is determined primarily by how it will function and what amenities will be included within the property. Size, location, service levels and type of business or targeted market segments are additional classifications. Industry also classifies hotels by chain scale … separating hotels into categories determined by their average daily rates. Various ownership structures and brand affiliations also differentiate hotels.
Classifications
Hotels may be classified on a number of different variables. Type of Hotel : There are numerous classifications by hotel type including all-inclusive hotels, all-suite properties, B&B/Inns, boutique, convention/conference centers, condo hotels, resort, extended stay, full service, casino, limited service and timeshare properties. Size and Complexity: A hotel can be classified by the number of guest rooms it has; hotel sizes can range from a small boutique hotel with fewer than 50 rooms to a large resort hotel with more than 1,000 rooms. The complexity of the hotel is determined by the volume and number of additional revenue generating functions such as the square feet of available conference space, number of F&B operations and additional services and amenities like pools, fitness centers, spas, golf, etc. Location: The location of a hotel can also determine the type of guest served. An airport hotel may be very different from a city-center property in an urban environment, or a remote island resort or a small quaint bed and breakfast located on top of a mountain. Hotels that specialize in conferences, may locate near entertainment destinations like Las Vegas or Disney theme parks to provide pre-post conference activities for attendees. Service Level: The level of service provided is also a key variable, ranging from an inexpensive budget or economy hotel, (Limited or Focused Service Hotels) which may have limited services and amenities, to upscale and luxury hotels (Full Service Hotels) with many services and a wide range of amenities. Market Segmentation: Figure 16.5 outlines the characteristics of specific hotel types that have evolved to match the needs of a particular traveler segment. As illustrated, hotels adapt and diversify depending on the markets they desire and need to drive occupancy levels and generate revenues. Some hotels will specialize in a specific market segment, but in today’s competitive environment, most hotels will target a combination of these segments.
Figure 16.5: Types of hotel market segments and their key characteristics.
There are several other industry related organizations, such as Forbes and AAA which provide Consumer Ratings for individual hotels … another form of classifying a property. Forbes has traditionally awarded one to five “Stars” and AAA, one to five “Diamond” ratings. Additionally, many social media applications like Trip Advisor offer hotel property ratings to consumers.
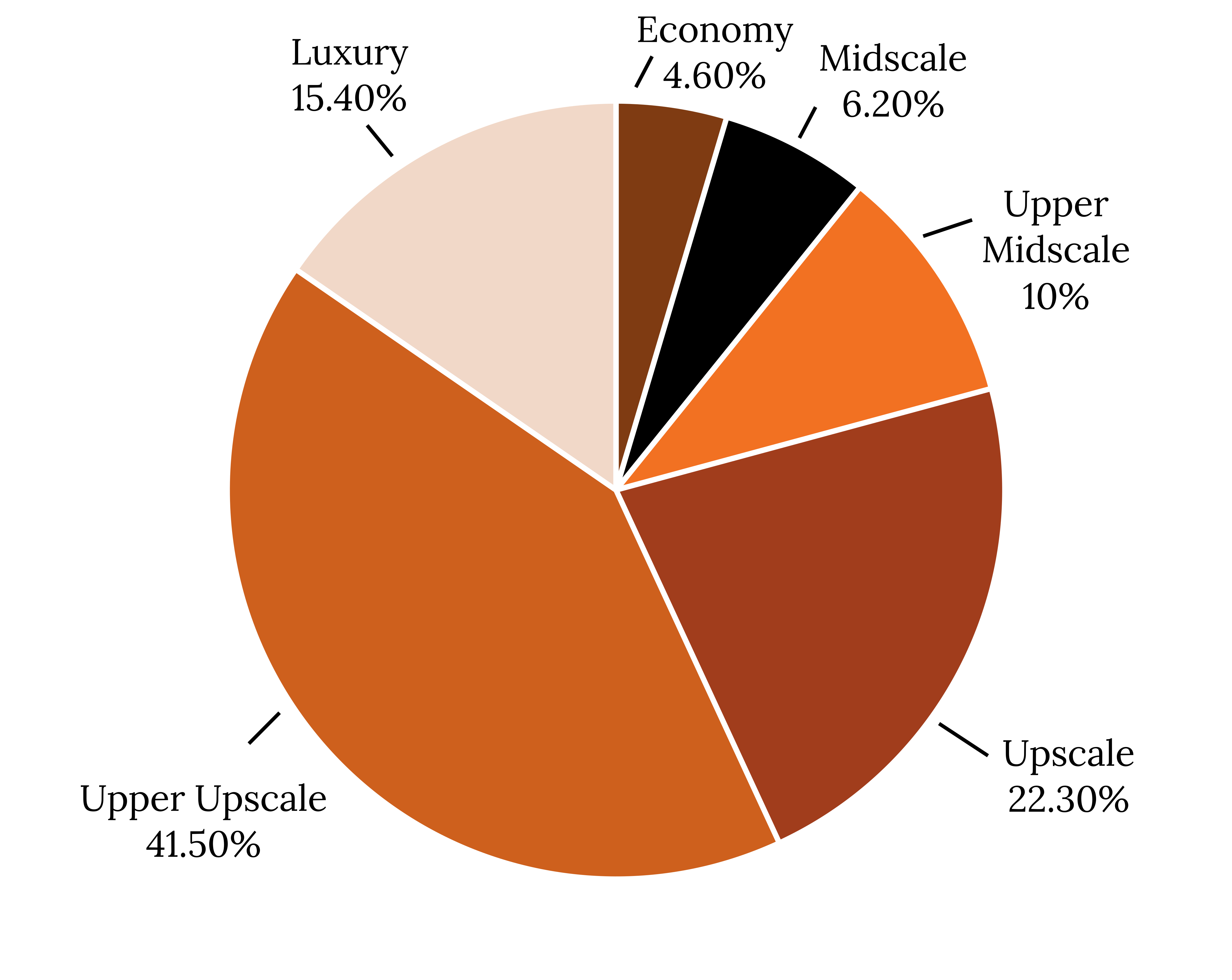
Chain Scale: Smith Travel Research (STR) is an organization that provides the lodging industry with global data benchmarking, analytics and marketplace insights. STR classifies the lodging industry into six chain scale segments according to their respective brand Average Daily Rate (ADR). The six segments are defined as Luxury ; Upper Upscale ; Upscale ; Mid-Scale with F&B ( Upper Mid-Scale ); Mid-Scale without F&B ( Mid-Scale ) and Economy . Through STR’s 30—plus years of service to the hospitality industry—they have developed vital benchmarking performance solutions, established market trend transparency and provided data used by the investment community to support hotel development projects. Their core product, the STAR report, provides hotel owners and operators with comparative performance data between their property and a defined set of market competitors and allows you to follow trends in hotel occupancy, average daily rate (ADR) and revenue per available room (RevPar). Developers, investors, industry analysts, hotel brands and management companies all utilize STR data when determine what type of hotel to build and what location would provide maximum opportunity for success.
The type of ownership, brand affiliation and management are also very important variables in the classification of hotels. Owners may manage their own hotels independently but in today’s competitive environment, they would likely sign a Franchise Agreement with a nationally recognized brand as well as a Management Contract with a hotel management company to manage the property. A hotel chain such as Marriott, Hilton, Hyatt or IHG (Intercontinental Hotel Group) is comprised of multiple brands: Marriott, following their recent merger with Starwood currently has 30 different hotel brands, with each name representing a different level of price, service or targeted market segments.
Branding Decision
Selecting a brand affiliation is one of the most significant decisions hotel owners must make. [9] The brand affiliation selected will largely determine the cost of hotel development or conversion of an existing property to meet the standards of the new brand. The affiliation will also determine a number of things about the ongoing operation including the level of services and amenities offered, cost of operation, marketing opportunities or restrictions, and the competitive position in the marketplace. For these reasons, owners typically consider several branding options before choosing to operate independently or to adopt a brand affiliation.
Franchise Agreements
Another managerial and ownership structure is franchising. A hotel franchise enables individuals or investment companies (the franchisee) to build or purchase a hotel and then buy or lease a brand name to become part of a chain of hotels using the franchisor’s hotel brand, image, loyalty program, goodwill, procedures, cost controls, marketing, and reservations systems. [10]

A franchisee becomes part of a network of properties that use a central reservations system with access to electronic distribution channels, regional and national marketing programs, central purchasing, revenue management support, and brand operating standards. A franchisee also receives training, support, and advice from the franchisor and must adhere to regular inspections, audits, and reporting requirements.
Selecting a franchise structure may reduce investment risk by enabling the franchisee to associate with an established hotel company. Franchise fees can be substantial, and a franchisee must be willing to adhere to the contractual obligations with the franchisor. [11] Franchise fees typically include an initial fee paid with the franchise application and continuing fees paid during the term of the agreement. These fees are usually a percentage of revenue but can be set at a fixed fee. The total percentage of sales ranges significantly for hotels from 3.3–14.7 percent with a median of 11.8 percent. [12]
Management Contracts

It is common for ownership to utilize a management contract , which is a service offered by a management company to manage a hotel or resort for its owners. Owners have two main options for the structure of a management contract. One is to enter into a management agreement with an independent third-party hotel management company to manage the hotel. There are hundreds of these companies, but some of the large organizations include Aimbridge, Benchmark Hospitality, Crescent Hotels, Interstate Hotels, and White Lodging. A slightly different option is for owners to select a single company to provide both the brand and the expertise to manage the property. Marriott, Hilton, and Hyatt, are companies that provide this second option to owners.
Food and Beverage Services

The food and beverage sector is commonly known to industry professionals by its initials F&B. The F&B sector grew from simple origins to meet the basic needs for food and beverage services to increasing demand for unique experiences and broader options. As the interests of the public became more diverse, so too did the offerings of the F&B sector. The increasing awareness and demand for organic, sustainable, local or craft options as well as special dietary needs in food and beverage continue to challenge this industry. In addition, in order to better attract and serve a diverse array of diners, the F&B industry now consists of a variety of segments. The following is a discussion of each.
Quick-Service Restaurants

Formerly known as fast-food restaurants, examples of quick-service restaurants , or QSRs, include Chick-fil-A, Subway, and Pizza Hut. This prominent portion of the food sector generally caters to both residents and visitors, and it is represented in areas that are conveniently accessed by both. Brands, chains, and franchises dominate the QSR landscape. While the sector has made steps to move away from the traditional “fast-food” image and style of service, it is still dominated by both fast food and food fast; in other words, food that is purchased and prepared quickly, and generally consumed quickly as well.
Fast-Casual Restaurants

Fast-Casual restaurants focus on higher quality ingredients than QSR’s and provide made-to-order food in an environment that does not include table service. Customers usually queue and order at a counter. The seating area is more upscale and comfortable. Examples would include Chipotle Mexican Grill, Panera and Jason’s Deli.
Full-Service Restaurants
Full-service restaurants are perhaps the most fluid of the F&B operation types, adjusting and changing to the demands of the marketplace. Consumer expectations are higher here than with QSRs. [13] The menus offered are varied, but in general reflect the image of the restaurant or consumer’s desired experience. Major segments include fine dining, family/casual, ethnic, and upscale casual.

Fine dining restaurants are characterized by highly trained chefs preparing complex food items, exquisitely presented. Meals are brought to the table by experienced servers with sound food and beverage knowledge in an upscale atmosphere with table linens, fine china, crystal stemware, and silver-plate cutlery. The table is often embellished with fresh flowers and candles. In these businesses, the average check, which is the total sales divided by number of guests served, is quite high (often reviewed with the cost symbols of three or four dollar signs: $$$ or $$$$.) Examples include the Inn at Little Washington, Ruth’s Chris Steakhouse and Capitol Grille.
Casual restaurants serve moderately-priced to upscale food in a more casual atmosphere. Casual dining comprises a market segment between fast casual establishments and fine dining restaurants. Casual dining restaurants often have a full bar with separate bar staff, a larger beer menu and a limited wine menu. This segment is full of chains such as Chili’s, Outback, Red Robin and Cracker Barrel as well as many independent restaurants in regional or local markets.
Family restaurants offer affordable menu items that span a variety of customer tastes. They also have the operational flexibility in menu and restaurant layout to welcome large groups of diners. An analysis of menus in family/casual restaurants reveals a high degree of operational techniques such as menu item cross-utilization, where a few key ingredients are repurposed in several ways. Both chain and independent restaurant operators flourish in this sector. Examples of chains in this category would be Golden Corral, Cici’s Pizza and Ponderosa Steakhouse.
Ethnic restaurants typically reflect the owner’s cultural identity, Vietnamese, Cuban, Thai, etc. The growth and changing nature of this sector reflects the acceptance of various ethnic foods within our communities. Ethnic restaurants generally evolve along two routes: toward remaining authentic to the cuisine of the country of origin or toward larger market acceptance through modifying menu items. [14] Examples would be P.F. Chang’s, Tara Thai or Pei Wei.
Wineries, Cideries, Local Craft Beer, and Distilleries
The beverage industry continues to evolve as well with a strong focus on local craft beers, wines, cider and distilling. Wineries exist in almost every state, with over 300 in Virginia as of 2022. [15] Wine, bourbon, cider trails and brew pub crawls, etc. are used to generate awareness and create experiences for customers. Wineries often use event space or festivals to take advantage of the beauty of the winery and supplement their revenues.
Alcohol sales, in many ways, have continued to evolve as a unique source of tourism revenue across the United States and around the world. From wine tours in Napa, California to scotch whisky tastings in Edinburgh, Scotland consumers are seeking different tastes as a part of their travels. Alcohol producers range from small first-generation entrepreneurs to wineries that have carried a family name for decades. The size of operation can also vary considerably from small wineries that produce very small batches to huge corporations, like Constellation Brands, that control and sell multiple brands of wine, beer and liquor from producers around the world. Constellation Brands – www.cbrands.com

Wine and wineries have attracted consumer dollars and consumer interest for hundreds of years. Consumers not only purchase wine to taste, but many also purchase wine to collect and even use as an investment. With respect to tourism, wineries are uniquely positioned to provide a special consumer experience. Wineries are often on beautiful, well-manicured farms with elaborate tasting rooms and event venues. Growers, as a part of their story or sales pitch, will review the local terroir. The “terroir” is the blend of culture, climate, soil and terrain factors that allow for the unique growing conditions of one or more grape varieties, from which the wine is made. [16]
Because of the dependency on climate, the industry is constantly evolving due to climate change. New varietals are introduced in areas where they could not grow even 50 years ago. An interesting example is the recent popularity of the “British Sparkler”. Across the English Channel, French wine and champagne brands are well-known. However, in recent years, British wine growers have been able to create exceptional sparkling wines from similar chalky soil and the same Chardonnay varietal. [17]
Cideries and Industry Legislation
The Craft Beverage Modernization and Reform Act of 2015 (CBMA) was a huge shot in the arm for entrepreneurs in the beverage industry. Overall, this act loosened the alcohol control laws permitting growers, brewers and distillers to distribute product easier. [18] , [19] A portion of this act was referred to as the “Cider Act” as it enabled farmers to open Cider tasting rooms and more easily distribute canned and bottled product. [20] Multiple states like Connecticut followed suit in easing state alcohol tax and control laws. [21] Cider was the fastest growing segment of the beverage industry between 2013-2014, with a growth rate of over 75%, stealing market share from wine and beer. [22] Another version of the CBMA was passed in 2019 further extending consumer access to cider.
Local Craft Beer

In most parts of the world the offering of a cold beer goes hand in hand with hospitality. While a few global corporations do control large portions of world-wide distribution, in the United States there has been a steady growth in American Craft beer, in recent decades. The combination of the growing popularity of home brewing clubs in the 1970’s and 1980’s, combined with the use of the internet to share and promote brews in the 1990’s and then the easing of alcohol distribution laws has created the craft brewing category. Total breweries in the United States including Regional Craft, Microbreweries, Taprooms, Brewpubs and large commercial breweries have grown from 4847 in 2015 to 8884 in 2020, according to the Brewers Association www.brewersassocaition.org. These brewery categories vary mainly based on size of production and the percent of beverage sales vs. onsite food sales. [23]
Craft beer makers typically pick from three very different growth strategies. The first strategy is more personal and closer to the rebel mentality of many craft beer makers. These brewers strive to leverage local resources and develop new local traditions to promote their products. Many of these brewers self-distribute their product, if it is sold outside of the brewery tasting rooms. Nearly every mid-size city in the country has an example this localized strategy. Big Lick Brewing in Roanoke, VA is an ideal example of this approach.
The second strategy is the “grow and sell” plan. A successful local brewer may fall into this plan, with a little luck, or it may be a strategy from the start to help support large scale growth. In this strategy the success of the brewer grows from a local market to a regional market. Their beer is distributed by one or more distributors who is aligned with a large national brewer. The national brewer takes note of the regional brewer growth and rather than compete directly, they purchase the regional brewer; they buy their competitor. For the smaller brewer this deal is often significant and it represents an ideal retirement strategy. The acquisition of Devils Back Bone by Anheuser Busch/Inbev is a good example. [24]
The third strategy is rarer. In this case the local brewer has more access to resources and is able to grow the brand on a large scale, moving from local to regional to a national brand, on their own. To help propel the growth of this brand it must be exceptional. To distribute the beer outside of the local market this brewer will develop multiple relationships with distributors to help support strategic growth, as market share and production grow. Sierra Nevada out of Chico, CA is one of the few such beer brands that has been able to thread this needle.
Distilleries and Mixology
Like wine and beer, distilled spirits often are a reflection of the local culture and geography. In the United States as of August 2021 there were 2290 craft sprit producers with about a third of those focused on whisky production. [25] Consumer brand preferences run strong in many categories and liquor is no exception. Craft distillers strive to create powerful branding, to not just sell the next drink, but to create customers for life. These branding programs share the brands history, geography, chemistry and culture with customers as part of an educational tasting experience. The Makers Mark Ambassador program and its sprawling distillery operation, with multiple tasting rooms, is a perfect example.
In the last few years, tequila has been the spirits category with the best growth. In 2020 it was North America’s fastest growing alcoholic beverage category with 5.7 billion dollars in annual sales. [26] Celebrity endorsements along with changing consumer demographics has helped fuel the growth in this category. According to US Census Reports, Hispanic and Latino demographic growth was 23% between the 2010 and 2020 census. [27] This change in consumer demographics certainly modified the overall market composition and created new opportunities for some distillers.
The evolving industry
The COVID pandemic has let the “genie out of the bottle” in more ways than one. Restaurant owners appealed to lawmakers for some flexibility in providing alcohol to customers, in the name of saving industry jobs, and in 2019 another revision of a Craft Beverage Modernization Act 2019 was passed. [28] Many states took alcohol control laws a step further, in favor of retailer and bar owners, and permitted cocktails to go as a new legal revenue stream for business owners. Multiple states have since made the changes permanent, while some continue to have the laws on the books, as a temporary relief strategy, during the pandemic. [29]
Institutional Food Service
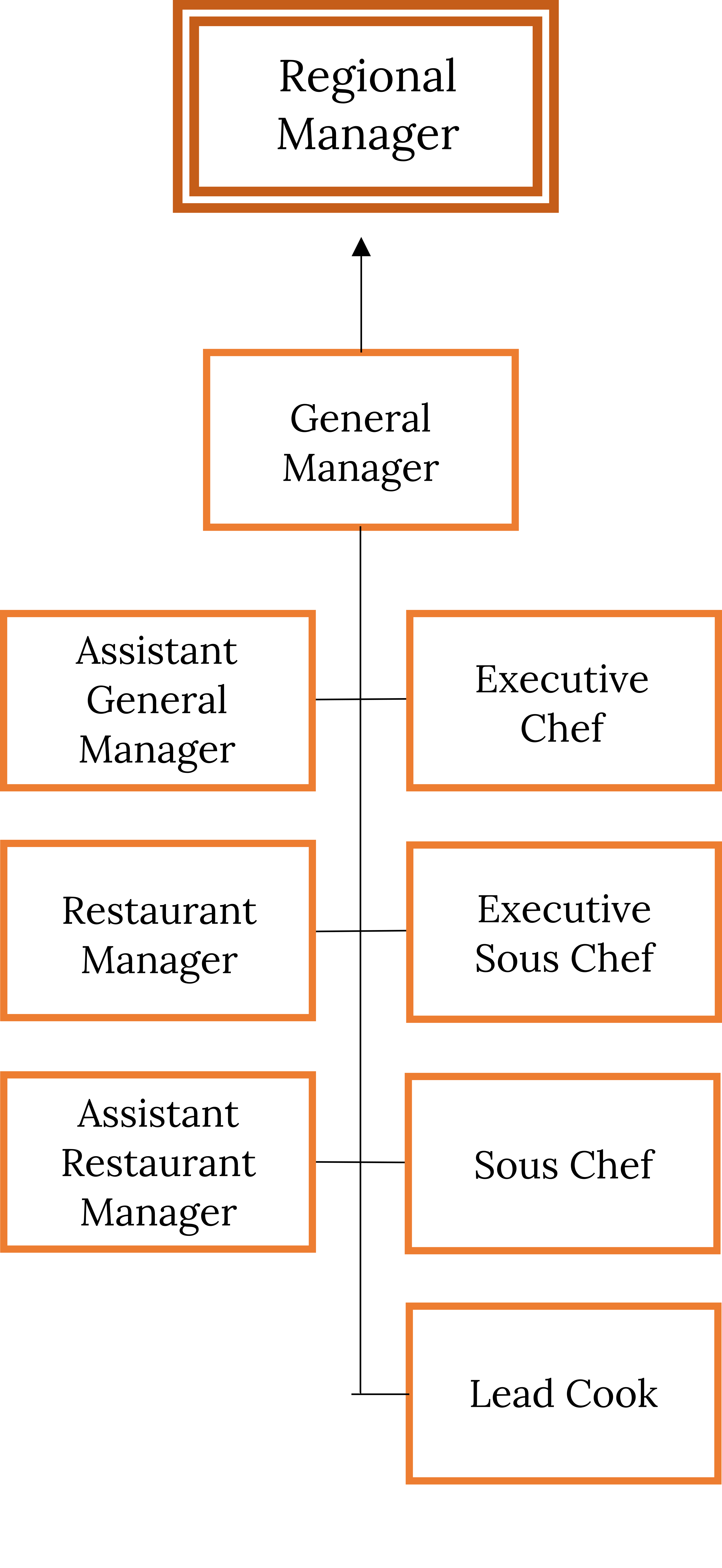
Institutional f ood s ervice is large scale and often connected to governmental (National Parks) or corporate level organizations. Often run under a predetermined contract, the institutional F&B sector includes:
- Educational institutions
- Prisons and other detention facilities
- Corporate staff cafeterias
- National Park restaurants and concessions
- Cruise ships
- Airports and other transportation terminals and operations
Examples of companies who focus on Institutional Food Service are Compass, Sodexho, Aramark.
Accommodation Food Service
This sector includes hotel restaurants and bars, room service, and self-serve dining operations (such as a breakfast room). Hotel restaurants are usually open to the public and reliant on this public patronage in addition to business from hotel guests. Collaborations between hotel and restaurant chains have seen reliable pairings such as the combination of Shula’s Steakhouse and Marriott Hotels.
Restaurant Industry Profitability and Cost Control
According to the National Restaurant Association, QSRs have the highest pre-tax profit margin at 6.6 percent, while full-service restaurants have a margin of 6.1 percent. There will be significant variances from these percentages at individual locations, even within the same brand. [30]
Figure 16.16: Restaurant operating expenses as a percent of revenue.
A number of costs influence the profitability of an F&B operation. Some of the key operating expenses (as a percentage of revenue) are detailed in figure 16.16 [31] , above, where food cost and salaries & wages are the two major expenses, each accounting for approximately a third of the total. Other expenses include rental and leasing of venue, utilities, advertising, and depreciation of assets. These percentages represent averages, and will vary greatly by sector and location.
Cost control and containment is essential for all F&B businesses. Demanding particular attention are the labor, food, and beverage costs, also known as the operator’s primary costs. In addition to these big ticket items, there is the cost of reusable operating supplies such as cutlery, glassware, china, and linen in full-service restaurants.
Recreation can be defined as the pursuit of leisure activities during one’s spare time [32] and can include vastly different activities such as golfing, sport fishing, and rock climbing. Defining recreation as it pertains to tourism, however, is more challenging.

Let’s start by exploring some recreation-based terms that are common in the tourism industry. Outdoor recreation can be defined as “outdoor activities that take place in a natural setting, as opposed to a highly cultivated or managed landscape such as a playing field or golf course.” [33] This term is typically applied to outdoor activities in which individuals engage close to their community. When these activities are further away, and people must travel some distance to participate in them, they are often described as “adventure tourism”. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), adventure tourism is “a trip that includes at least two of the following three elements: physical activity, natural environment, and cultural immersion.” [34]
Ultimately, categorization is based on a combination of several factors, including manner of engagement in the activity (risk exposure, experience requirement, group or solo activity), the distance travelled to access the activity, and the type of environment (proximity to nature, level of challenge involved) in which the activity occurs.
According to the 2021 Global Adventure Tourism Market Report, the global adventure travel market is expecting an elevation of $2.02 billion (in U.S. dollars) by 2030 and is witnessing a compound annual growth rate of 10.7 percent from 2020-30. [35]
Entertainment
Entertainment is a very broad category which overlaps with many of the areas discussed elsewhere in this chapter, like hotels and accommodation. Two major types of entertainment that we’ll discuss here are gaming and theme parks.
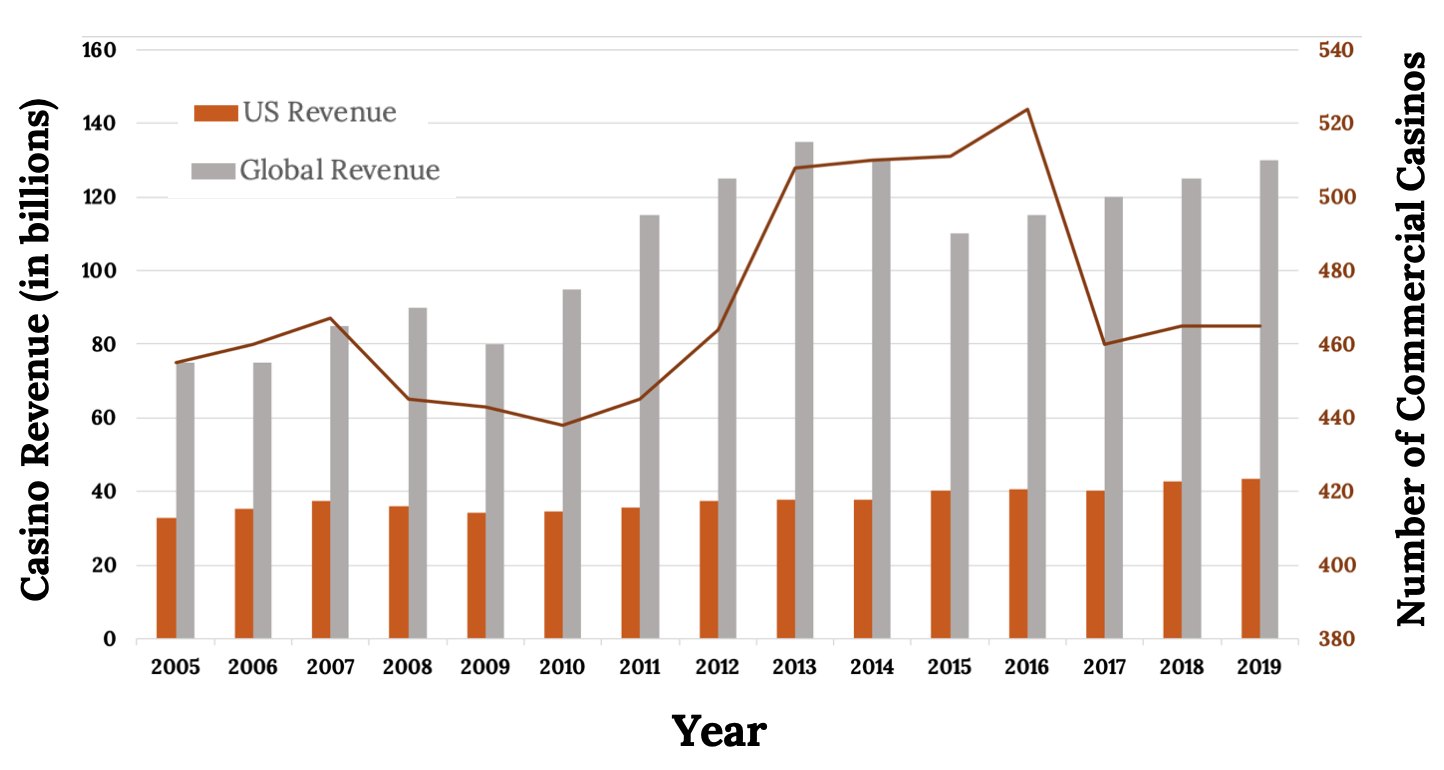
Gaming has grown significantly in the United States and globally. The number of casinos in the United States has been growing since 2010, as shown in figure 16.18. Casinos are found all over the United States in major cities, riverboats, and on Native American lands. However, US casino revenue has been relatively flat, while global gaming revenues have been on the increase, largely due to Asian market growth. Most casinos involve other facets of the Hospitality industry such as lodging, F&B, golf, entertainment, spas, etc., but they also have the added challenges of casino operations.
Theme Parks

Theme parks have a long history dating back to the 1500’s in Europe, and have evolved ever since. Today, it is hard not to compare any amusement park destination to Disneyland and Disney World. Opened in 1955 in sunny California, Disneyland set the standard for theme parks. Theme parks outside of California and Florida are often highly seasonable operations challenged with significant staffing and training requirements each year.
Convention and Event Management
A convention is a large meeting of people with similar interests who meet for a period of at least a few days to discuss their field. An event is a gathering at a given place and time, usually of some importance, often celebrating or commemorating a special occasion.
Both conventions and events can be extremely complex projects, which is why, over time, the role of meeting planners has taken on greater importance. The development of education, training programs, and professional designations such as CMPs (Certified Meeting Planners), CSEP (Certified Special Events Professional), and CMM (Certificate in Meeting Management) has led to increased credibility in this business and demonstrates the importance of the sector to the economy.
Meeting planners may be independent contractors hired to facilitate the planning process, work directly for the company full time to coordinate their meeting, or work for hotels, conference centers and event venues directly.
- The various tasks involved in meeting and event planning include:
- Conceptualizing/theming
- Site inspection & selection
- Logistics and planning
- Human resource management
- Marketing and public relations
- Budgeting and financial management
- Sponsorship procurement
- Management and evaluation

Event Categories
Mega-events.
A m ega-event is a large scale, highly prestigious event such as the Olympic Games, the FIFA World Cup, or a global economic summit. These events typically gain tremendous media coverage and have major economic impacts on the host location, both positive and negative. High levels of tourism (1 million visitors) associated with a mega-event brings revenue, but the revenue may be outweighed by substantial capital and social costs incurred by the host. The events are often awarded to host destinations through a bidding process and gain tremendous media coverage.
Special Events
A special event is a one-time or infrequent specific ritual, presentation, performance, or celebration. Special events are planned and created to mark a special occasion, such as a presidential inauguration or the Queen of England’s 90 th birthday. Like mega-events, there may be significant media coverage and economic impact for the host city or destination.
Hallmark Events

A hallmark event is a unique event that is often identified with the location where it is held, like Carnival in Rio de Janeiro or Oktoberfest in Munich. Hallmark events contribute significant economic benefits and even can create a competitive advantage for the host city or destination that attracts tourists.
A festival is a themed public celebration that conveys, through a kaleidoscope of activities, certain meaning to participants and spectators. Festivals are often celebrations of community or culture and feature music, dance, or dramatic performances. Examples include Lollapalooza, the Cannes Film Festival, and Junkanoo in the Bahamas.
Local Community Events
A local community event is generated by and for locals; although it may attract tourists, its main audience is the local community. The community may experience measurable economic impacts, as might happen at The Steppin’ Out Street Fair in Blacksburg (think hotel stays and eating out). Fundraisers and community picnics are also examples in this category.
Meetings and Conventions
The tourism industry also has a long history of creating, hosting, and promoting meetings and conventions that draw business travelers. In fact, Convention and Visitor Bureau’s (CVB’s) work hard to attract these meetings and conventions to their city to drive economic benefit for hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, etc.
There are several types of such events
Conventions generally have very large attendance, and are held on a regular schedule but in different locations. They also often require a bidding process. Political conventions are one such example.
Association M eetings or C onferences are held regionally and nationally for hundreds of associations or events focused on specific themes. Examples would be the National Restaurant Association Annual Convention, ComicCon, or the National Auto Show.
Corporate M eetings will vary significantly in size and purpose and include regional or national sales meetings, shareholder meetings, training sessions, or celebrations. The location will vary depending on the nature of the meeting. They may be held at an airport property, a traditional corporate meeting facility or even an upscale resort.
Trade S hows and T rade F airs can be stand-alone events, or adjoin a convention or conference.
S eminars , W orkshops , and R etreats are examples of smaller-scale events.
As meeting planners have become more creative, meeting and convention delegates have been more demanding about meeting sites. No longer are hotel meeting rooms and convention centers the only type of location used; non-traditional venues have adapted and become competitive in offering services for meeting planners. These include architectural spaces such as airplane hangars, warehouses, or rooftops and experiential venues such as aquariums, museums, and galleries. [36]
Transportation and travel services are another large element of the tourism industry. This area includes cruise ships, airlines, rail, car rentals, and even ride sharing such as Uber and Lyft. Each of these segments is impacted significantly by fuel costs, safety issues, load factors and government regulation.

If you’ve ever been on a cruise, you are in good company. According to CLIA (Cruise Lines International Association), 23 million passengers were expected to go on a cruise worldwide on 62 member lines in 2015. [37] The industry employs over 900,000 people. [38]
Over 55 percent of the world’s cruise passengers are from North America, and the leading destinations (based on ship deployments), according to CLIA are: [39]
- The Caribbean (36 percent)
- The Mediterranean (20 percent)
- Northern Europe (11 percent)
- Australia/New Zealand (6 percent)
- Alaska (6 percent)
- Asia (5 percent)
- South America (3 percent)
The t ravel services sector is made up of a complex web of relationships between a variety of suppliers, tourism products, destination marketing organizations, tour operators, and travel agents, among many others. Under the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), the travel services industry group includes “establishments primarily engaged in travel arrangement and reservation services. Examples … are tourist and travel agencies; travel tour operators and wholesale operators; convention and visitors’ bureaus; airline, bus, railroad and steamship ticket offices; sports and theatrical ticket offices; and airline, hotel and restaurant reservation offices.” [40] Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveler (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travelers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveler and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies. [41] Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
Online Travel Agencies (OTAs)
Online travel agents (OTAs) are companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include Booking.com, Expedia.com, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs are gaining popularity with the travelling public. Revenue of leading online travel agencies (OTAs) worldwide rose in 2021 over the previous year, after dropping sharply in 2020 due to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. Despite the substantial increase, however, the figures did not catch up yet with pre-pandemic levels. Overall, Booking was the OTA recording the highest revenue in 2021, generating nearly 11 billion U.S. dollars. Expedia placed second on the ranking, with roughly 8.6 billion U.S. dollars that year. [42]
Tour Operators
A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveler. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies. [43] Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveler could by purchasing individually.
Destination Marketing Organizations (DMOs)
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” [44] .
Country Clubs

Country c lubs are another part of the Hospitality industry with a very different service strategy focusing on serving members who will develop relationships with the staff compared to a more transactional service interaction in lodging, restaurants or airlines.
Country clubs do not focus as strongly on profit as they do on maximizing member satisfaction, retention and growth while maintaining an attractive fee structure. Country (or city) clubs, will typically have restaurant and bar operations, catered events and other amenities such as golf, tennis, pool, fitness facilities, etc. Depending on the type of club, family and youth events are important to maintain and grow membership.
Strong customer service, culinary, event management and general management skills are necessary to be successful in clubs.
Chapter Video
As in any other fast-moving industry, the landscape in Hospitality and Tourism is always changing. This video explores 10 of the more important current trends impacting the industry.
Key Takeaways
- The Tourism industry is the largest industry in the world with significant benefit and costs to a region. The global competition for the tourism dollar is significant within the US and between countries.
- Hotels vary significantly in size, quality, purpose, chain affiliation, and ownership. The complexity of the operation and leadership vary as well.
- Food and Beverage is made up of a wide variety of restaurant types from QSR, Fast Casual, Fine Dining and Ethnic. Institutional food service in business , hospitals, education, parks and concessions are a significant part of the Food and Beverage industry.
- The evolution of tastes and consumer expectations in food and beverage continue to provide opportunity and challenges in the industry for ethnic sustainable, organic, local, craft, and other unique experiences.
Portions of this chapter were adapted from Westcott, Morgan (Ed) Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC. CC BY 4.0. https://opentextbc.ca/introtourism . Available for free at: http://open.bccampus.ca.
Figure 16.1: Tourists gather at the Eiffel Tower. Siebe Warmoeskerken. 2018. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/mxNrtFzOd-I .
Figure 16.2: The impact of global tourism before and after the pandemic. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 . Data from https://wttc.org/Portals/0/Documents/Reports/2021/Global%20Economic%20Impact%20and%20Trends%202021.pdf [international spending, GDP, and jobs]; https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/BX.GSR.TRVL.ZS [global service exports]. https://archive.org/details/16.2_20220627 .
Figure 16.3: The Pineapple Hotel in Liverpool. Rodhullandemu. 2012. CC BY-SA 3.0 . https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pineapple,_Park_Road,_Liverpool.jpg .
Figure 16.6: Example of a hotel market segmentation by STR’s Chain Scale. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 . https://archive.org/details/16.6_20220627 .
Figure 16.7: The San Diego Marriott. Christina Hsu. 2009. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 . https://flic.kr/p/6KZ5Cv .
Figure 16.8: The Inn at Virginia Tech, managed by Benchmark Hospitality. Anastasia Cortes. 2016. Public domain. Provided by Steve Skripak.
Figure 16.9: Fine dining. Delightin Dee. 2021. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/_WI3DGseB3g .
Figure 16.10: Subway is a quick-service restaurant. Szymon12455. 2018. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/-jv94-xYy-E .
Figure 16.11: Panera is a fast-casual restaurant. Mike Mozart. 2014. CC BY 2.0 . https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Panera_Bread_(13883443466).jpg .
Figure 16.12: A fine-dining restaurant in the Netherlands. Ronan Kruithof. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/PCE0T5i4pDI .
Figure 16.13: Afton Mountain Vineyards, VA. Kevin Oliver. 2017. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 . https://flic.kr/p/V9h6v5 .
Figure 16.14: Beer being brewed in steam-fired kettles in a Brazillian brewery. Roberta keiko Kitahara Santana. 2019. Unsplash license. https://unsplash.com/photos/RfL3l-I1zhc .
Figure 16.15: Restaurant industry career path. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 . https://archive.org/details/16.15_202206 .
Figure 16.16: Restaurant operating expenses as a percent of revenue. Adapted from National Restaurant Association (2016). Restaurant Operations Report 2016 Edition. Washington, D.C.
Figure 16.17: Adventure tourism: whitewater rafting in Argentina. Jonatan Lewczuk. 2018. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/hN7jhC_YWk0 .
Figure 16.18: U.S. and global casino revenues (2005-2019). (2005-2015) Data Retrieved from: https://gaming.unlv.edu/reports/national_annual_revenues.pdf ; 2016 data retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20170301070205/http://gaming.unlv.edu/reports/national_monthly.pdf ; 2017 data retrieved from: https://www.americangaming.org/resources/state-of-the-states-2018-the-aga-survey-of-the-commercial-casino-industry/ ; 2018 data retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20190201140714/https://gaming.unlv.edu/reports/national_monthly.pdf ; 2019 data retrieved from: https://abcnews.go.com/Entertainment/wireStory/us-commercial-casinos-won-436-billion-2019-37-71069042; Global revenue data retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/271577/global-casino-gaming-market-revenue/ ; Number of commercial casinos data retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/187972/number-of-us-commercial-casinos-since-2005/ .
Figure 16.19: Disney is one of the most well-known theme parks. Bastien Nvs. 2020. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/g3CR0UJ1CyM .
Figure 16.20: The Bejing olympics is an example of a mega-event. zhang kaiyv. 2021. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/VAnriQouDIw .
Figure 16.21: Mardi Gras in New Orleans, 2018. Cayetano Gil. 2018. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/T0tb5Olqkis .
Figure 16.22: Cruise ship near St. Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands. Peter Hansen. 2017. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/MeGmdPNe36w .
Figure 16.23: The Old Course at Half Moon Bay, CA. Cristina Glebova. 2022. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/ihZwGiVMUCY .
- World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2015). “Why Tourism?” Retrieved from: http://www2.unwto.org/content/why-tourism ↵
- United Nations Statistics Division (2010, December). “Tourism as an Internationally Traded Service and Beyond.” Newsletter of the Interagency Task Force on Statistics of International Trade in Services. No. 6. p. 1. Retrieved from: http://unstats.un.org/unsd/tradeserv/tfsits/newsletter/TFSITS_newsletter_6.pdf ↵
- World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2015). “Exports from International Tourism Rise 4% in 2015.” Retrieved from: http://media.unwto.org/press-release/2016-05-03/exports-international-tourism-rise-4-2015 ↵
- Association of Bhutanese Tour Operators (2010). “UNWTO Tourism Vision 2020 Forecast Released.” Retrieved from: http://www.abto.org.bt/2010/06/unwto-tourism-2020-vision-forecast-released/ ↵
- United Nations Environment Programme (2016). “Negative Socio-Cultural Impacts from Tourism.” Retrieved from: http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/Socio-CulturalImpacts/NegativeSocio-CulturalImpactsFromTourism/tabid/78781/Default.aspx ↵
- United Nations Environment Programme (2016). “Tourism’s Three Main Impact Areas.” Retrieved from: http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/TheTourismandEnvironmentProgramme/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/EnvironmentalImpacts/TourismsThreeMainImpactAreas/tabid/78776/Default.aspx ↵
- Discover Hospitality (2015). “What is Hospitality?” Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20150814071021/http://discoverhospitality.com.au/what-is-hospitality ↵
- L. P. Coyle (1982). “Pineapple” in World Encyclopedia of Food . New York: Facts on File. p. 517. ↵
- C. Crandell, K. Dickinson, and G. I. Kanter (2004). "Negotiating the hotel management contract" In Hotel Asset Management: Principles & Practices . East Lansing, MI: University of Denver and American Hotel & Lodging Educational Institute. ↵
- S. Rushmore (2005). “What Does a Hotel Franchise Cost?” Canadian Lodging Outlook. Retrieved from: www.hotel-online.com/News/PR2005_4th/Oct05_FranchiseCost.html ↵
- Ibid.; N. Migdal (n.d.). “Franchise Agreements vs. Management Agreements: Which One Do I Choose?” Hotel Business Review. Retrieved from: hotelexecutive.com/business_review/2101/test-franchise-agreements-vs-management-agreements-which-one-do-i-choose ↵
- Stephen Rushmore Jr., Erin S. Bagley (2014). “2014 United States Hotel Franchise Fee Guide.” HVS. Retrieved from: http://www.hvs.com/article/7097/2014-united-states-hotel-franchise-fee-guide/ ↵
- H. G. Parsa, K. R. Lord, S. Putrevu, and J. Kreeger (2015). “Corporate Social and Environmental Responsibility in Services; Will Consumers Pay for It?” Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. Vol. 22. pp. 250-260. ↵
- A. H. Mak, M. Lumbers, A. Eves, and R. C. Change (2012). “Factors Influencing Tourist Food Consumption.” International Journal of Hospitality Management. Vol. 31. No. 3. pp. 928-936. ↵
- Virginia is for Wine Lovers. (n.d.) Virginia is for Lovers. Retrieved from: https://www.virginia.org/things-to-do/food-and-drink/wineries ↵
- Kathleen Willcox, July 6, 2017, “Climate change is putting English Sparkling Wine on the Map” Retrieved from https://www.vinepair.com/articles ↵
- Craft Beverage Modernization and Tax Reform Act of 2015, S. 1562, 114th Cong. (2015). Retrieved from: https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/senate-bill/1562/text ↵
- Wyden, Ron (2015). One Pager Craft Beverage Modernization and Tax Reform Act of 2015. Retrieved from: https://www.wyden.senate.gov/imo/media/doc/One%20Pager.pdf ↵
- CIDER Act, H. R. 600, 114th Cong. (2015). Retrieved from: https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/house-bill/600/text ↵
- Pazniokas, Mark and Moore, Maya. (2019) CT Legislature Passes Law to Help Beer, Cider Makers, Hartford Business Journal. Retrieved from: https://www.hartfordbusiness.com/article/ct-legislature-passes-law-to-help-beer-cider-makers ↵
- Jaken Emen, “What the Country’s New Cider Act Means for You” Retrieved from: https://www.eater.com/2016/1/28/10854324/new-us-cider-act ↵
- Brewers Association (n.d.), For Small & Independent Craft Brewers, Brewers Association. Retrieved from: https://www.brewersassociation.org ↵
- Hudson Lindenberger, June 16, 2021 , “Alcohol Consumption In the US Saw Its Most Significant Volume Gain in Almost Two Decades” Retrieved from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/hudsonlindenberger/2021/06/16/alcohol-consumption-in-the-united-states-saw-its-most-significant-volume-gain-in-almost-two-decades-in-2020/?sh=5b55ed8b724d ↵
- Maisey, Jeff (2016, May 19). Devil of a Deal, Virginia Craft Beer. Retrieved from: https://virginiacraftbeer.com/devil-of-a-deal ↵
- Maker’s Mark Ambassador Program (n.d.) Maker’s Mark Ambassador Experience. Retrieved from: https://www.makersmark.com/ambassadors ↵
- Fortune Business Insights (n.d.). Tequila Market Share, Size & COVID-19 Impact Analysis. Report ID: FBI104172. Retrieved from: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/tequila-market-104172 ↵
- U.S. Census Bureau, (2021, August 12). 2020 Census Illuminates Racial and Ethnic Composition of the Country. Retrieved from: https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2021/08/improved-race-ethnicity-measures-reveal-united-states-population-much-more-multiracial.html ↵
- Pete Johnson, P. (2020, November 17). Craft Beverage Modernization and tax reform act. Brewers Association. Retrieved from: https://www.brewersassociation.org/current-issues/craft-beverage-modernization-and-tax-reform-act-24 ↵
- Lucas, A. (2021, June 1). To-Go Cocktails Will Stick Around in at Least 20 States After the Pandemic. CNBC. Retrieved from: https://www.cnbc.com/2021/05/28/to-go-cocktails-will-stick-around-in-at-least-20-states-after-covid.html ↵
- American Restaurant Association and Deloitte Development LLC (2016). 2016 Restaurant Operations Report . Washington, D.C.: National Restaurant Association. p. 5. ↵
- Ibid. ↵
- J. Tribe (2011). The Economics of Recreation, Leisure, and Tourism , 4th ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier. ↵
- Tourism BC (2013). “2009/2010 Outdoor Recreation Study.” Destination British Columbia. Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Research-by-Activity/Outdoor-Recreation-Study-2009-2010,-January-2013/Outdoor-Recreation-for-Distribution-14Jan13-FINAL-DRAFT-(2).pdf.aspx ↵
- United Nations World Tourism Organization (2014). Global Report on Adventure Tourism . UNWTO and the Adventure Tourism Trade Association. p. 12. Retrieved from: http://cf.cdn.unwto.org/sites/all/files/pdf/final_1global_report_on_adventure_tourism.pdf ↵
- Publisher. (2021, August 16). Adventure Travel is Trending Upward. Leisure Group Travel. Retrieved from: https://leisuregrouptravel.com/adventure-travel-is-trending-upward/ ↵
- K. Colston (2014, April 24). "Non-Traditional Event Venues – Endless Entertainment." Retrieved from: http://helloendless.com/non-traditional-event-venues/ ↵
- CLIA (2016). CLIA 2015 Annual Report: One Voice: Advancing Our Industry Together . Cruise Lines International Association. p. 10. Retrieved from: http://www.cruising.org/docs/default-source/market-research/clia_2015_annualreport_web.pdf?sfvrsn=0 ↵
- CLIA (2015). CLIA 2015 Cruise Industry Outlook: Cruising to New Horizons and Offering Travelers More . Cruise Lines International Association. p. 28. Retrieved from: http://www.cruising.org/docs/default-source/research/2015-cruise-industry-outlook.pdf ↵
- Government of Canada (2014). “NAICS 2007: 5615 Travel Arrangement and Reservation Services.” Statistics Canada. Retrieved from: http://stds.statcan.gc.ca/naics-scian/2007/cs-rc-eng.asp?criteria=5615 ↵
- C. Goeldner and B. Ritchie (2003). Tourism: Principles, Practices, Philosophies , 9th ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ↵
- Published by Statista Research Department, & 24, M. (2022, May 24). Revenue of Leading OTAs Worldwide 2021. Statista. Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/934995/revenue-of-leading-otas-worldwide/ ↵
- The Destination Marketing Association International (2014). “The value of DMOs.” Retrieved from: http://www.destinationmarketing.org/value-dmos ↵
Chapter 16 Hospitality and Tourism Copyright © by Adapted by Ron Poff is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Sustainability Dimensions of Hospitality and Tourism: Care for Our Common Home
- First Online: 18 May 2022
Cite this chapter

- Omowumi Ogunyemi 11 &
- Andrew Onwudinjo 11
Part of the book series: Humanism in Business Series ((HUBUS))
230 Accesses
Hospitality and tourism are important industries for human flourishing. They are sources of revenue and contribute to economic development and they serve as avenues for attaining aspects of flourishing, since they cater to individuals who wish to take leisure breaks or business trips. Sustainability is key to caring for the earth in order to ensure that resources are sufficient today and for future generations. The contributions of hospitality and tourism centres to sustainability depend on the appropriate use of the resources available such that they can satisfy their clients’ needs and make profits. Sustainability involves care of others and thus requires a humanistic approach. In addition, hospitality and tourism have effects on environmental sustainability and, as our common home, ought to be managed in such a way that, although we depend on it for our sustenance, we care for it so that it can sustain us. This chapter seeks a nexus between tourism and hospitality and subthemes of sustainability. It explores connections between pillars of sustainability (specifically with regard to climate change and environmental sustainability) and hospitality and tourism. It then proposes ways in which clients of the industry and their hosts contribute to attaining some of the targets of sustainability.
- Hospitality
- Environmental Sustainability
- Social sustainability
- Human flourishing
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Becken, S., & Hay, J. E. (2007). Tourism and climate change: Risks and opportunities . Channel View Publications.
Google Scholar
Camilleri, M. A. (2018). Travel marketing, tourism economics and the airline product . Springer Nature.
Francis, P. (2015). Laudato Si: On care for our common home . Our Sunday Visitor.
Hall, C. M. (2001). Trends in ocean and coastal tourism: The end of the last frontier? Ocean and Coastal Management .
Hall, C. M., & Higham, J. (2005). Introduction: Tourism, recreation and climate change. In C. M. Hall & J. Higham (Eds.), Tourism, recreation and climate change (pp. 3–28). Channel View Publications.
Jones, A., & Phillips, M. (2011). Introduction: Disappearing destinations: Climate change and future challenges for coastal tourism. In A. Jones & M. Phillips (Eds.), Disappearing destinations: Climate change and future challenges for coastal tourism (pp. 1–9).
Kunwar, R. R. (2017). What is hospitality? The Gaze: Journal of Tourism and Hospitality, 8, 55–115.
Lashley, C. (2015). Hospitality and hospitableness. Research in Hospitality Management, 5 (1), 1–7.
Article Google Scholar
Lickorish, L. J., & Jenkins, C. L. (1997). An introduction to tourism . Butterworth-Heinemann.
Mijatov, M., Pantelic, M., Dragin, A., Peric, M., & Markovic, S. (2018). Application of sustainable development principles in hotel business. Journal of the Geographical Institute Jovan Cvijic SASA, 68 (1), 101–117.
Mashika, H., Davydenko, I., Olshanska, O., Sydorov, Y., Komarnitskyi, I., & Lypnytska, Y. (2020). Modelling of development of ecological tourism. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 9 (4), 683–688.
Morelli, J. (2011). Environmental sustainability: A definition for environmental professionals. Journal of Environmental Sustainability, 1 (1), 1–9.
Muhanna, E. (2006). Sustainable tourism development and environmental management for developing countries. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 4 (2), 14–30.
Oladokun, O. J., Adedara, T. M., & Adedadamola, J. O. (2015). Tourism and climate change: Combating climate change effects on tourism participation in Nigeria. Journal of Tourism, Hospitality and Sports, 5 , 1–5.
Orams, M. B. (2003). Sandy beaches as a tourism attraction: A management challenge for the 21st century. Journal of Coastal Research (Special Issue No. 35).
Organisation for Economic Cooperation & Development/ United Nations Environmental Programme. (2011). Climate change and tourism policy in OECD countries . OECD.
Păvăluc, C., Anichiti, A., Niţă, V., & Butnaru, G. I. (2020). Analysing the relationship between tourism development and sustainability by looking at the impact on the environment: A study on the European Union countries. CES Working Papers, 12 (1).
Scott, D. (2021). Sustainable tourism and the grand challenge of climate change. Sustainability, 13 , 1–16.
Skripak, S. J., & Ron, P. (2020). Fundamentals of business (3rd ed.). VT Publishing.
Sunlu, U. (2003). Environmental impacts of tourism. In D. Camarda & L. Grassini (Eds.), Local resources and global trades: Environments and agriculture in the Mediterranean region (pp. 263–270). CIHEAM
Tsagbey, S. A., Mensah, A. M., & Nunoo, F. K. E. (2009). Influence of tourist pressure on beach litter and microbial quality—Case study of two beach resorts in Ghana. West African Journal of Applied Ecology, 5 (1).
United Nations Environmental Programme & World Tourism Organisation. (2005). Making tourism more sustainable: A guide for policy makers . United Nations Environmental Programme and World Tourism Organisation.
Walker, J. R., & Walker, J. T. (2014). Introduction to hospitality management. Pearson Education Limited.
Yazdi, S. (2012). Sustainable tourism. American International Journal of Social Science, 1 (1), 50–56.
Zaei, M. E., & Zaei, M. E. (2013). The impacts of tourism industry on host community. European Journal of Tourism Hospitality and Research, 1 (2), 12–21.
Zahedi, S. (2008). Tourism impact on coastal environment. WIT Transactions on the Built Environment, 99 , 45–57.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Humanities, Pan-Atlantic University, Lagos, Nigeria
Omowumi Ogunyemi & Andrew Onwudinjo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Omowumi Ogunyemi .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Lagos Business School, Pan-Atlantic University, Lagos, Nigeria
Kemi Ogunyemi
Afara Leadership Centre, Lagos, Nigeria
Ebele Okoye
Omowumi Ogunyemi
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Ogunyemi, O., Onwudinjo, A. (2022). Sustainability Dimensions of Hospitality and Tourism: Care for Our Common Home. In: Ogunyemi, K., Okoye, E., Ogunyemi, O. (eds) Humanistic Perspectives in Hospitality and Tourism, Volume II. Humanism in Business Series. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95585-4_12
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95585-4_12
Published : 18 May 2022
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-95584-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-95585-4
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- The Tourism Academy Learning Management System (LMS)
- Platform Functionality - Instructors
- Marketing Your Course
- Course Creator Tools
- Selling Courses
- Tourism Essentials
- Tools for Academy Administrators
- Business Class Podcast
- Knowledge Base
Do you have a glossary of travel, tourism & hospitality terms?
Every industry has its own jargon and lingo. tourism is no different. here's a great list of tourism terms that you should know..
The list has been compiled by the world-class team of strategists, consultants, educators and established tourism experts at the nonprofit Tourism Academy . Our team offers relationship powered professional development, trade marketing, tourism development and consulting solutions.
Glossary of Tourism Terms

adventure travel: a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion
affinity group : a group of people linked by a common interest or purpose. See also pre- formed group.
agent : one who acts or has the power to act as the representative of another. A person whose job it is to arrange travel for end clients (individuals, groups, corporations), confirming travel components and simplifying the planning process for customers, providing consultation services and travel packages.
American Bus Association (ABA) : A trade organization consisting of member bus lines throughout the country. www.buses.org
American National Standards Institute (ANSI): A private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. www.ansi.org
American Society of Travel Agents (ASTA): The oldest and largest travel agent organization in the world with travel agents being the primary members. Other companies providing travel industry products and services can be associate members. www.astanet.com
Application Programming Interface ( API) : a code that allows two software programs to communicate with each other.
attrition : Shortfall of sleeping room block pick-up or food-and-beverage projections from numbers agreed to in a contract. Penalties for attrition may be outlined in a contract’s attrition clause.
Average Daily Rate (ADR) : a statistical unit that represents the average rental income per paid occupied room in a given time period.
back of house : a business term that refers to parts of a business operation that customers do not see. This may refer to mechanical rooms, accounting offices, kitchens, and those persons who are engaged in those areas.
block : a group of rooms, tickets, seats or space reserved for a specific customer - usually for a set period of time. Room blocks are commonly reserved for conventions, meetings or groups in general. Room blocks may also be allocated to high volume buyers (wholesale, receptive, tour) who intend to sell them as tour components on an ongoing basis. A room block is usually under a firm agreement and is for a set period of time.
Brand USA : A public/private partnership to promote inbound tourism to the United States and communicate US entry/exit policies. Also known as the Corporation for Travel Promotion. www.thebrandusa.com
bulk pricing : the practice of offering exceptionally low, typically non-commissionable rates to high volume buyers who purchase a specified number of units to resell at a mark up.
campaign : A specific, defined series of activities used in marketing a new or changed product or service, or in using new marketing channels and methods.
Certified Tour Professional (CTP) : A designation administered by the National Tour Foundation and conferred upon tour professionals who complete prescribed evaluation requirements.
certificate: an official document attesting to a fact such as a level of achievement in a course of study or training.
certification: the action or process of providing someone or something with an official document attesting to a status or level of achievement. See also: American National Standards Institute
certified: officially recognized as possessing certain qualifications or meeting certain standards.
Certified Travel Counselor (CTC) : A designation conferred upon travel professionals who have completed a travel management program offered by the Institute of Certified Travel Agents.
Certified Meeting Planner (CMP) : A designation conferred upon convention and meeting management professionals who have completed an application and written exam offered by the Events Industry Council.
channel manager : a system or platform that coordinates the distribution of product details, inventory and pricing in real time across multiple sales “channels”
charter : to hire for exclusive use any aircraft, motorcoach, cruise ship or other vehicle
class of service : a parameter used to differentiate the types of accommodation offered by travel suppliers, often denoted by fare code on air tickets. Classes may reflect differences in space, comfort, amenities and cabin service. Ex: First Class, Business Class, Coach Class or please hold this chicken until we land.
commercial rate : A special rate given by a hotel or rental car, motor coach, bus or passenger transport company to an organization based on either the volume of business done or the type of accommodation or rental car. Also referred to as a corporate rate.
commission : The varying amount paid by suppliers to travel agents for the sale of travel products and services.
commissioned tours : A tour available for sale through retail and wholesale travel agencies, which provides for a payment of an agreed upon sales commission either to the retail or wholesale seller.
complementary : goods or services that add to the value of another good or service. Ex: peanut butter complements jelly
complimentary (comp) : Service, space or item given at no charge.
complimentary (comp) ratio : The number of rooms, tickets, meals or service items provided at no cost based on the number of occupied rooms.
- The industry standard is one complimentary room per 20-50 rooms occupied per day.
- The industry standard for ticketed attractions and restaurants is one complimentary admission/meal per 10-20 paid.
complimentary registration : Waiver of registration fees.
concierge : a hotel employee whose job is to assist guests by arranging tours, local transportation, making reservations for theater or restaurants, etc.
Convention & Visitors Bureau (CVB) : A nonprofit organization supported by bed taxes, government budget allocations, private memberships or a combination of these. A CVB promotes tourism, encourages groups to hold meetings and trade shows in its city, and assists groups before and during meetings.
consolidator : a person or company which forms groups to travel using group rates on to increase sales, earn override commissions or reduce the possibility of tour cancellations.
consortium : a loosely knit group of independently owned and managed companies such as travel agencies, tour operators, hotels, or other suppliers, with a joint marketing distribution process
convention and visitors bureau (CVB) : a nonprofit local organizations charged with representing (and promoting) a specific destination. CVBs are funded by transient room taxes, government budget allocations, private membership dues, sponsorship sales and program participation fees, or a combination of these mechanisms. See also: destination marketing organization
co-op marketing: outreach activities that help multiple suppliers reach the target audience by sharing costs, resources and tactics.
course: a series of lessons or modules to teach the skills and knowledge for a particular job or activity.
destination : a place where travelers might visit. This may be any neighborhood, city, region or country that can be marketing as a single entity for tourists.
destination management company (DMC) : Company or professional individual engaged in organizing tours, meetings of all types and their related activities. Also referred to as a ground operator.
destination marketing organization (DMO) : A nonprofit marketing organization for a city, state, province, region or area whose primary purpose is the promotion of the destination. See also: convention & visitors bureau
direct spend : the value of goods and services purchased by tourists (e.g., attraction ticket, hotel room rate and meals)
double double : refers to a room containing two separate double beds, capable of sleeping up to four guests comfortably, sometimes referred to as a “quad”
double occupancy rate : the price per person for a room that will be shared between two people
dynamic pricing : the practice of varying the price for a product or service to reflect changing market conditions, in particular the charging of a higher price during times of greater demand. This is the opposite of static pricing.
educational travel : a type of niche tourism, built around learning objectives, often to the benefit of students and/or those who share a common interest, hobby or profession
emerging market : A group of customers who do not provide as much business as the target markets, but show interest in the destination.
escort : a person employed or contracted by a seller of packaged travel product who accompanies tour participants from point to point often acting as a the tour operator liaison and onsite problem solver.
escorted tour : a packaged, pre-planned itinerary that includes the services of a tour manager or tour escort who accompanies participants for the full duration of the tour
escrow : a legal concept and financial instrument whereby assets are held by a third party on behalf of two other parties that are in the process of completing a transaction. In many places, agents and tour operators are required by law to maintain customer deposits and pre-payments in escrow until the time of service.
excursion : a trip made for leisure, education or physical purposes. It is often an adjunct to a longer journey, cruise or visit to a place.
familiarization tour (FAM) : A program designed to acquaint participants with specific destinations or services. Offered in groups and on an individual basis.
folio : an itemized record of guest charges and credits, often referred to as a guest bill or statement.
frequent independent travel (FIT) : A custom-designed, pre-paid travel package with many individualized arrangements. An FIT operator specializes in preparing FITs documents at the request of retail travel agents. FITs usually receive travel vouchers to present to onsite services as verification or pre-payment. Also known as foreign individual/independent travel or frequent individual travel.
front office : a business term that refers to a company’s departments that come in direct contact with customers.
gateway : a city, airport, port or area where visitors arrive. International gateway refers to places where foreign visitors may first enter a country.
ground operator : a company or individual providing local accommodations, transfers, ticketing and related services. See also: receptive operator
group booking : Reservation for a block of rooms for a single group.
group tour : A prearranged, prepaid travel program for a group usually including transportation, accommodations, attraction admissions and meals. Also referred to as a package tour.
guaranteed departure : a tour that will definitely operate on the day it is scheduled and will not be cancelled.
Horizontal Market : audiences for products or services that are not easily distinguished by consumer characteristics. Examples of horizontal markets include those for computer security, legal or accounting services.
Hospitality Sales and Marketing Association International (HSMAI): A trade association for hotel sales, marketing and revenue management professionals.
hotel classifications : Classification of a hotel by its amenities, facilities, service and cost. Qualifications and terms may vary by country.
- limited service or economy is generally a reasonably priced, generally providing a bed, telephone, TV, shower and free parking. They often do not have room service or a restaurant.
- full service may refer to a property of any price category that offers some meeting space and features a restaurant onsite
- moderate medium-priced property with services and amenities such as a restaurant and possibly conference rooms.
- upper moderate is a property that offers special services such as a first-rate restaurant, banquet and conference rooms, valet service, room service, cable TV, and a host of other amenities.
- luxury or deluxe is a top-grade hotel or resort offering the highest service and the maximum variety of amenities. All rooms have a private bath, and all the usual public rooms and services are provided.
- boutique is loosely used to describe properties that have typically between 10 and 100 rooms and often contain luxury facilities in unique or intimate settings with full service accommodations.
hub and spoke : a style of tour that has guests staying in a single location with excursions to nearby destinations
incentive tour : travel experience offered to stimulate employee productivity or as a reward for sales agents
incidentals : items not included in the package price
inclusive : referring to a package or product price that includes all of the varying components, taxes and gratuities for a flat rate. An inclusive tour may include transportation, lodging, transfers, etc. for a set price. An inclusive meal might include food, drink, tax and gratuity.
independent tour : a style of travel packaging that allows visitors to move about without the accompaniment of a tour manager or escort
indirect spend : the value of all goods and services used to produce tourism output. (e.g., toiletries for hotel guests, ingredients for meals and plastic used in souvenirs)
International Inbound Travel Association (IITA) : A trade association of inbound receptive tour operators and suppliers from the US. Formerly RSAA Receptive Services Association of America.
incentive travel : A travel reward given by companies to employees to stimulate productivity. Also known as an incentive trip.
inclusive tour : A specific package in which all components of the package are part of the price. Generally, an inclusive package includes transportation, lodging, meals, gratuities and taxes, and some form of sightseeing or rental car. The terms and conditions of a tour contract should specify exactly what is covered. Also referred to as an all-expense tour and an all-inclusive tour.
inclusive rate : The rate charged to an operator that includes all service, tax, gratuities and additional fees.
IPW : A computerized scheduled appointment show for international tour operators always held in the United States and sponsored by U.S. Travel Association. Formerly known as Pow Wow.
itinerary : a schedule of travel components put together by an agent or operator.
leg : a portion of a journey between two scheduled stops.
lesson: an amount of teaching given at one time; a period of learning or teaching.
market segment : a group of consumers or buyer types that share one or more common characteristics, lumped together for sales or marketing purposes.
markup : the difference between the cost of a good or service and its selling price.
meet and greet : Pre-purchased service for meeting and greeting a client upon arrival in a city, usually at the airport, and assisting the client with entrance formalities, baggage and transportation.
microlearning : a tool for training, teaching and development that delivers content in small, very specific bursts.
module: each of a set of standardized parts or independent units that can be used to construct a more complex structure such as an item of furniture or a building. multiple lessons may be combined to create a module.
motor coach : A large, comfortable, well-powered bus that can transport groups and their luggage over long distances. Motor coaches are normally able to accommodate 46 to 54 passengers.
motor coach tour operator : A company that creates tours in which group members are transported via motor coach to their destination, itinerary activities and back.
mystery tour : a short journey, usually in a bus, that people make for pleasure without knowing where they are going.
NAJ : Producers of the RTO (receptive tour operator) summit and similar small trade show formats with a regional focus. Also referred to as North American Journeys
net rate : A wholesale rate for groups (usually 10-15 people) which an operator may add a mark up.
NTA (formerly National Tour Association) : A trade association of North American motor coach tour operators. www.ntaonline.com
occupancy : the percentage of available rooms in use during a given period.
online travel agent (OTA) : a travel website that specialized in the sale of travel products to consumers
outbound operator (or outbound tour) : A company or tour that takes groups from a given city or country to another city or country.
Ontario Motor Coach Association (OMCA) : A trade association of motorcoach operators based in and around Ontario province.
package : Travel arrangements with two or more components offered for one price, inclusive of all taxes. Also refers to a single-fee booth package offered by show management.
packager : An individual or organization that coordinates and promotes the development of a package tour and establishes operating procedures and guidelines for that tour.
performance tour operator : A tour operator company that focuses on planning trips for groups that must perform while traveling like school bands, choral groups, etc.
plus plus : a term used to describe a product price that does not include taxes, gratuities and/or service charges. Ex: The meal is $15 plus tax and gratuity OR $15++.
pre- and post-trip tours : Optional extension or side trip package offered before or after a meeting, gathering or convention.
pre-formed group : a group that contacts the tour operator to plan travel exclusively for the group members.
rack rate : the normal rate of a product or service, before any discounts, commissions or net price arrangements
receptive operator : A tour operator who provides local services, transfers, sightseeing, guides, etc. Many large receptive operators develop packages and sell them through wholesale tour operators in foreign countries. Also referred to as a ground operator, an inbound tour operator, a land operator, an RTO and a receiving agent.
retail tour : A tour put together by a tour operator and sold to individuals.
request for proposal (RFP) : A document that stipulates what services the organization wants from an outside contractor and requests a bid to perform such services.
retailer : one who sells directly to the consumer. See also: travel agent
return on investment (ROI) : Net profit divided by net worth. A financial ratio indicating the degree of profitability.
revenue per available room (RevPAR) : A measure used by hotels that divides revenue for a given time period by the number of available rooms for the same time period.
sales mission : Intense selling effort in a particular locality; calling upon qualify leads. Usually performed by a group of people who may or may not all be in a sales capacity but have an interest in meeting with the same buyers.
Seasons (from a buyer/operator perspective):
- looking The time of year when tour operators are looking at for new activities & vendors to include in future trips. Also known as product or catalog development season.
- selling The time of year when tour operators are focused on reaching out to their customers, promoting future trips and selling packaged travel programs.
- booking The time of year when tour operators are booking and confirming tour components they plan to utilize.
- travel The time of year when the majority of the tour operators’ customers are traveling.
Seasons (from a supplier perspective):
- off-season The time of year when tourist traffic, and often rates, are at their lowest because of decreased demand. Also referred to as low season, off-peak or value season.
- peak season The time of year when demand and price is at a premium. Also known as high season.
- shoulder season The season between peak season and off-season when demand is average and the travel product will not produce the highest price but does not need a deep discount to generate traffic.
series : describing a piece of business or scheduled itinerary that takes place on a regular frequency
site inspection : Personal, careful survey of property, facility or area.
Skål is a professional, fraternal organization of tourism leaders around the world, promoting global tourism and friendship.
SMERF : Meetings acronym for a category of meeting market segments including social, military, educational, religious and fraternal type groups. These organizations often are looking for value when selecting a meeting destination.
supplier : The actual provider of a travel product such as the hotel, attraction, restaurant, airline or car rental agency; not the travel agent or tour operator selling the product.
STAR (STR) Report : a tool used to measure hotel performance against competitive aggregates and within local markets. Data is collected and distributed by strglobal
static pricing : the practice of maintaining the same price for a product or service at all times regardless of changing market conditions, trends and demand. This is the opposite of dynamic pricing.
Student Youth Travel Association (SYTA) : a trade association representing tour operator companies that specialize in student travel. www.syta.com
tariff : a schedule of rates for a good or services provided by a supplier
tiered pricing : A pricing structure that offers a variety of price points for different customer types. For more or suggested rates by buyer type.
tour operator : A person or company that negotiates discount rates, packages travel products, prints brochures, and markets these travel products through travel agents or to the general public.
tour vouchers : Documents issued by tour operators to be exchanged for accommodations, meals, sightseeing, admission tickets and other services. Also referred to as coupons and tour orders.
tourism : travel for business or pleasure; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. Tourism may be international, or within the traveler’s country.
tourism ambassador: an individual possessing the knowledge, skill and training to represent a destination, assist tourists and create better visitor experiences.
Tourism Cares : A charitable organization that focuses on helping preserve the travel experience for future travelers. www.tourismcares.org
trade association : Group of persons employed in a particular trade.
trade publication : A magazine or newsletter that targets a specific industry.
trade show : Exhibit of products and services that is targeted to a specific clientele and not open to the public.
travel agent (or travel agency) : Person or firm qualified to advise and arrange for travel needs such as hotel rooms, meals, transportation, tours and other travel elements. Represents all travel suppliers worldwide. Also referred to as a retailer.
Travel Alliance Partners (TAP) : A member-owned organization of tour operators that work together to develop unique itineraries within their respective regions, cross-promote products offered by other members and leverage their collective buying power. www.tapintotravel.com
travel receipt : purchase of travel and tourism related goods and services by visitors. These goods and services include food, lodging, recreation, gifts, entertainment, local transportation and other items incidental to travel.
United Motor Coach Association (UMA) : North America's largest association for operators of motorcoach companies providing charter, tour and regular route services. www.uma.org
United States Tour Operators Association (USTOA) : A nationwide organization of tour operators offering protection for travelers purchasing member travel products by way of a multi-million-dollar bond. www.ustoa.com
Upsell : sales technique where a seller induces the customer to purchase more expensive items, upgrades or other add-ons in an attempt to make a more profitable sale
U.S. Travel Association : The national, nonprofit association representing all components of the U.S. travel industry. (formerly known as TIA - Travel Industry Association of America) www.ustravel.org
Vertical Market : used to identify areas where vendors offer goods & services specific to a group of customers with specialized needs. Examples may include customers identified by their areas of origin, age range(s) or interest types.
Visa : a conditional authorization granted by a country to a foreigner, allowing them to enter, remain within, or to leave that country.
voluntourism : the act or practice of doing volunteer or charitable work as needed in the communities where one is vacationing
voucher : documents or digital codes issued to consumers by tour operators that may be exchanged for tour components
walk-through : Review of meeting details, or inspection of function room or trade show floor prior to event.
webinar : Short for web-based seminar, a presentation, lecture, workshop or seminar that is transmitted over the web. A key feature of the webinar is its interactive elements – the ability to give, receive and discuss information. Contrast with webcast in which the data transmission is one way and does not allow interaction between the presenter and the audience.
wholesaler : A company that creates and markets inclusive tours and FITs for sale through travel agents. Often used interchangeably with “tour operator,” but several distinctions should be drawn: a wholesaler presumably sells nothing at retail, a tour operator does both; a wholesaler does not always create his or her own products, a tour operator virtually always does; and a wholesaler is less inclined than a tour operator to perform local services.
World Tourism Organization (WTO) : An organization created to promote and develop tourism in the interest of the economic, social and cultural progress of all nations. www.world-tourism.org
About the Author
Stephen Ekstrom is the Chief Strategist at The Tourism Academy | tourismacademy.org, featured speaker at numerous tourism industry conferences, travel writer and host of the Business Class podcast.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Accommodation and Lodging The Hospitality Industry. When looking at tourism it is important to consider the term hospitality. Some define hospitality as "the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves." [7] Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest ...
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries. Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including ...
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
The hospitality and tourism industry is a vast sector that includes all the economic activities that directly or indirectly contribute to, or depend upon, travel, tourism and hospitality. This industry sector includes: Hotels & Resorts. Restaurants & Catering. Night Clubs & Bars. Travel & Transportation.
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as "the ...
Main Body. Chapter 1. History and Overview. Learning Objectives. Specify the commonly understood definitions of tourism and tourist. Classify tourism into distinct industry groups using North American Industry Classification Standards (NAICS) Define hospitality. Gain knowledge about the origins of the tourism industry.
Dictionary.com goes further to define it as, "the friendly and generous reception and entertainment of guests, visitors, or strangers.". For those working in hospitality, this transcends only working in hotels or food and beverage.
The hospitality and tourism industries are closely connected, but they are not the same thing. Though both connect to travel and leisure, these two industries have distinct differences that need to be understood if you are considering a degree or career in the field. ... While travelers often see the simple work of the flight attendant, such as ...
Definition of Hospitality and Tourism Industry. The hospitality and tourism industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving sector that encompasses a wide range of businesses and services. It revolves around providing exceptional customer experiences to individuals who are seeking leisure activities, travel, and accommodation.
Understand the economic, social and environmental benefits and costs of tourism. Define hospitality and the pineapple tradition. Identify the types of hotel categories and how they are determined. Examine the different categories of food service operations. Understand the different types of events, meetings and conventions.
proliferation of sites of hospitality and of means of giving and receiving it make any simple definition laughable. Exceptions and complications abound. Brotherton's own delineation of the "dimensions of hospitality" shows that, even having worked through all the problems of previous definitions, cloudi-ness remains.
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
Hospitality industry definition for hotels. Hotels are at the very heart of the hospitality industry, and have been for hundreds of years. The definition of a hotel - an establishment providing lodging and often meals, entertainment and other personal services for the public - aligns closely with the hospitality industry definition that we've explored above.
Hospitality industry. The hospitality industry is a broad category of fields within the service industry that includes lodging, food and beverage services, event planning, theme parks, travel agency, tourism, hotels, restaurants, nightclubs, and bars .
The chapter discusses how marketing applies to the field of tourism and hospitality. It also described the core principles of marketing. These include information gathering, the marketing mix, marketing planning, and customer relationship management. Further, this chapter presents some of the reasons for studying tourism and hospitality marketing.
Download PDF. Conceptualising, defining and theorising Hospitality Conceptualising, defining and theorising hospitality¹ Bob Brotherton [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper critically explores the extant literature associated with the rather convoluted journey that the hospitality academy has taken over the past few decades in its ...
Travel and tourism; The travel and tourism sector relies on the service it gives to its clients, guest or visitors. And it includes services such as travel agents, car rental companies, bus tours and sightseeing. ... Hospitality management definition in a simple term is the study of various service industries such as: Event management; Food ...
Accommodation and Lodging The Hospitality Industry. When looking at tourism it is important to consider the term hospitality. Some define hospitality as "the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves." [7] Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest ...
Sustainability involves care of others and thus requires a humanistic approach. In addition, hospitality and tourism have effects on environmental sustainability and, as our common home, ought to be managed in such a way that, although we depend on it for our sustenance, we care for it so that it can sustain us.
Glossary of Tourism Terms. Add-on: a product or service not included in the list or package price. See also: Upsell. adventure travel: a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion. affinity group: a group of people linked by ...
The hospitality and tourism cluster includes many entry-level opportunities that can build toward higher-level positions. For example, an entry-level worker may start restaurant work as a dishwasher or table busser and eventually move into cooking, waiting tables, or even management. Many opportunities under this cluster do not require training ...