- Mission Statement
- Advisors to the Board
- Military Fellows
- Jobs at MDAA
- Arizona AETOS ’25
- Hawai’i Space Science Initiative
- USC SHIELD ’24
- USC SHIELD ’23
- USC SHIELD ’22
- USC SHIELD Alerts
- USC SHIELD in the News
- Ronald Reagan Missile Defense Site, Vandenberg SFB
- Kauai Veteran’s Eternal Memorial and Missile Defense Viewing Site
- Lessons Learned Series
- Write Your Representative
- April 12th, 2022 U.S. Missile Defense – An Overview of Past, Current, and Future Roles and Responsibilities
- Virtual CRT: U.S. Missile Defense – An Overview of Past, Current, and Future Roles and Responsibilities
- MDAA Alert: The Roles and Responsibilities of Missile Defense
- Threat News
- Missile Defense News
- Air Defense News
- MDAA in the News
- Threat Basics
- Ukrainian War Updates
- Taiwan Incursion Updates
- Global Missile Tracker
- Space Threats Updates
- Notable Missile Tests
- Combat Launches
- Future Missile Threats
- U.S. Missile Defense
- Missile Defense of U.S. Partners
- Missile Defense Intercept Test Record
- Operational Intercepts by System
- Future BMD Systems
- Discontinued Programs
- U.S. Air Defense
- Air Defense of U.S. Partners
- Future Air Defense Systems
- Alerts Archive
- MDAA U.S. Ballistic Missile Defense Overview
- MDAA System/Issue Briefs
- MDAA Country Briefs
- Foreign Military Sales by Country
- 3D Panoramas
- Additional Resources
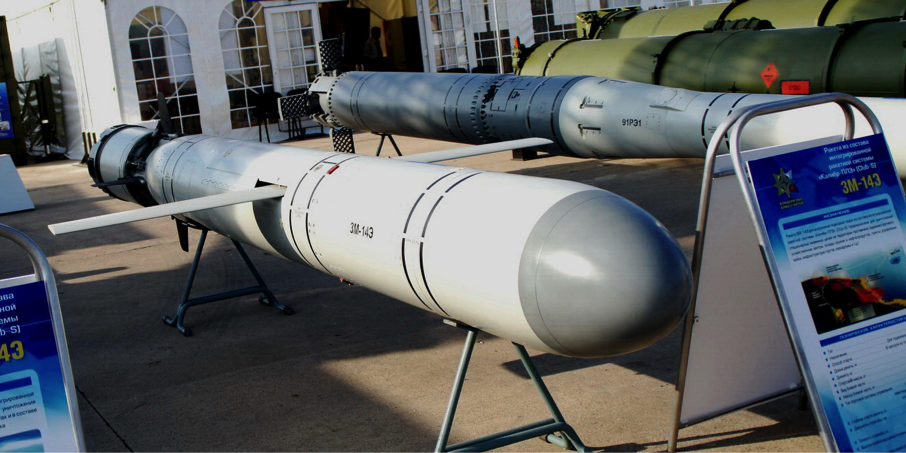

- Cruise Missile Basics

What is a cruise missile?
Cruise missiles, although similar to ballistic missiles in some regards, provide an alternate means to deliver a lethal payload rapidly and accurately to a target. Cruise missiles differ from ballistic missiles in that they fly towards their target at lower altitudes, remaining within the Earth’s atmosphere throughout their trajectory. Cruise missiles are defined as “an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target.” [1] Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned control-guided helicopters or aircraft can be included in this definition [2] , but will not be discussed on this page.
The cruise missile has its beginnings in World War I, when the U.S. Army developed the Kettering Bug, an unmanned aerial bomb designed to strike targets beyond the range of artillery and too dangerous for piloted aircraft. However, the Kettering Bug was never used in combat. [3] Instead, the modern cruise missile originates more from the V-1 Flying Bomb used by the Germany in the last months of World War II. [4]
Launch Platforms
Cruise missiles are capable of being launched from multiple ground, air, sea and submarine platforms. Both fighter and long-range bomber aircraft are capable of carrying and launching cruise missiles. [5] On the ground, cruise missiles are most commonly launched by road-mobile systems due to the inherent advantages of mobility, but they can also be launched from fixed platforms. [6]

Russian warships in the Caspian Sea launch Kalibr cruise missiles towards targets inside Syria.
At sea, various surface ships and submarines can launch cruise missiles. Submarines are capable of launching while surfaced or submerged using torpedo fixtures or vertical launch tubes. [7] In April 2010 Kontsern-Morinformsistema-Agat, a Russian company, began marketing a version of the Russian Kalibr cruise missile housed in and capable of being launched from a standard shipping container. [8] This would allow any vehicle capable of carrying a standard shipping container to become a discreet platform from which to launch cruise missiles. [9]
Propulsion and Flight
Cruise missiles utilize jet engines as their primary method of propulsion. Most cruise missiles are subsonic and use Turbofan and Turbojet engines. While less common, supersonic and hypersonic cruise missiles utilize Ramjet and Scramjet engines. [10] Some also use rocket motor propulsion as a booster in the first phase of flight [11] or to accelerate to supersonic speeds in the terminal phase. [12]
Cruise missiles can fly to their targets at varying altitudes as long as they remain within the atmosphere. The trajectory of most remains close to the Earth’s surface, sometimes skimming just meters above the ground. Their low flight path makes it much harder for most radar and sensor systems to detect the missile, unless the radar or sensor system is airborne and directed towards the ground. [13] Some cruise missiles will fly only at high altitudes and dive sharply down once they reach their target. Flying at high altitude can extend the range of the missile because it’s more fuel-efficient than flying at lower altitudes. However, this also makes the missile more susceptible to missile defense systems since today’s radars and sensors are typically positioned to detect and track high altitude threats. [14] Cruise missiles can also mix their flight trajectory between high and low altitude in order to get the benefits of both. In this instance, cruise missiles will typically fly at a high altitude early in their flight to help extend their range, but as they approach their target, or missile defenses, they will fly down to a lower sea skimming/terrain hugging altitude to help it evade detection and defenses. [15]
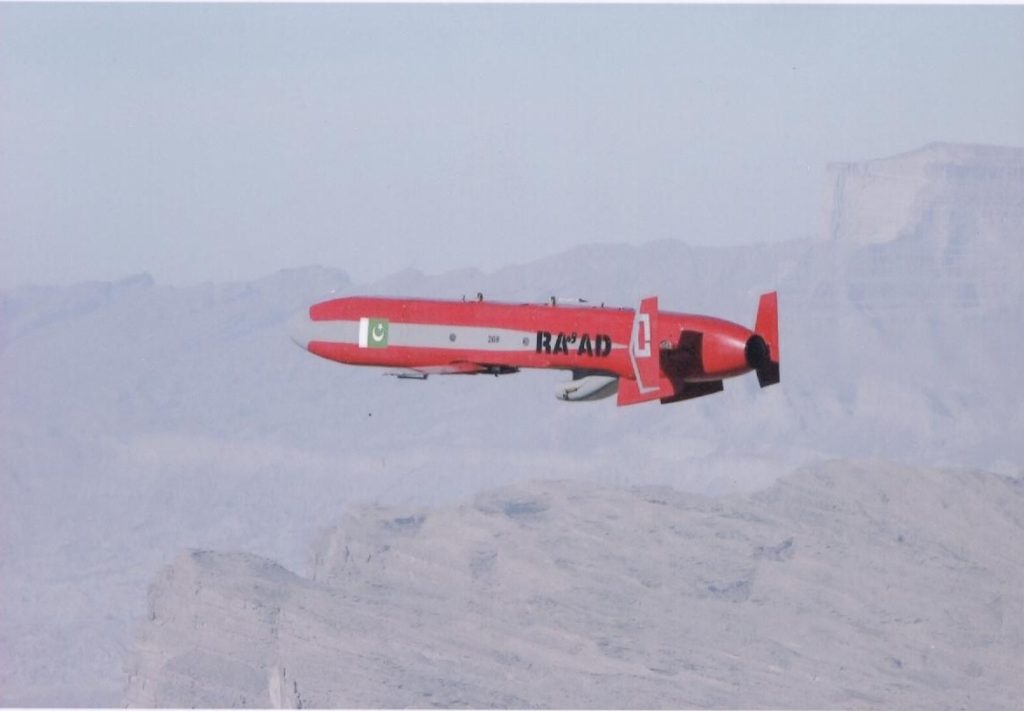

Flight test of Pakistan’s Ra’ad cruise missile.
Cruise missiles can use multiple guidance methods in order to accurately place their ordinance on the desired target and avoid missile defense systems. One of the first methods used by cruise missiles was inertial guidance, which is still used today and allows the missile to fly along a flight path programmed prior to launch. [16] Another guidance method is terrain contour matching (TERCOM), which compares a terrain map to the current terrain the missile is flying over to ensure the missile is flying on the correct path. [17] Some use GPS systems, which require connection to either GPS or GLONASS satellite system, but can help ensure the missile follows the correct flight path and strikes the final target using specific coordinates with a high degree of accuracy. [18]
Other guidance methods are primarily used in the terminal phase of flight to increase accuracy. One is a laser guided system which uses a sensor to detect its target painted by a laser, however this can be unreliable because dust and smoke can interfere with the laser or the missile may not always be able to see the laser or painted target. [19] Another terminal guidance method is TV guidance, in which an operator uses a camera in the nose of the missile to visually identify and manually guide the missile to the target in its final phase. This method also gives the operator the option to abort the strike in the final phase if an anomaly is detected. [20] A radar seeker is also used in the nose of some missiles to identify and/or keep the missile on target in the terminal phase. These radar seekers use either passive radar, which detect radar emissions of their target, or active radar, which emit their own radar to detect their target. [21] Infrared (IR) guidance – directing the missile towards heat emitting objects, such as engines [22] – may also be used by cruise missiles in the terminal phase. [23] However, because of its simplicity, IR guidance cannot differentiate between friendly, adversarial, or extraneous IR signals in a crowded battlefield, and is usually used in conjunction with other guidance systems. [24] The last guidance system used by cruise missiles is Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC), which uses a camera in the missile to find the desired target and match it to a stored image using an image correlator. [25]
Cruise missiles are typically armed with conventional or nuclear warheads, but can also be equipped with chemical or biological warheads. [26] The warhead weight and yield can vary widely, depending on the specific cruise missile and its mission.
[1] “Cruise Missiles.” Federation of American Scientists. http://fas.org/nuke/intro/cm/
[3] “Kettering Bug.” UAVGLOBAL. http://www.uavglobal.com/kettering-bug/ ; “War Machines: Cruise Missile.” National Geographic. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AD8Kr0f1tEY
[4] Hickman, Kennedy. “World War II: V-1 Flying Bomb.” About Education. http://militaryhistory.about.com/od/artillerysiegeweapons/p/v1.htm
[5] N.R.P. “Explained: How Cruise Missiles Work!” Defencyclopedia. https://defencyclopedia.com/2014/08/01/explained-how-cruise-missiles-work/
[8] Stott, Michael. “Deadly New Russian Weapon Hides in Shipping Container.” Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/us-russia-weapon-idUSTRE63P2XB20100426
[9] Lewis, Jeffrey, Nikolai Sokov. “Sokov on Russian Cruise Missiles.” Arms Control Wonk. http://www.armscontrolwonk.com/archive/207801/sokov-on-russian-cruise-missiles/
[11] Brain, Marshall. “How Cruise Missiles Work.” How Stuff Works. http://science.howstuffworks.com/cruise-missile.htm
[12] N.R.P. “Explained: How Cruise Missiles Work!” Defencyclopedia. https://defencyclopedia.com/2014/08/01/explained-how-cruise-missiles-work/
[22] Kopp, Carlo. “Heat-Seeking Missile Guidance.” Air Power Australia. http://ausairpower.net/TE-IR-Guidance.html
[23] N.R.P. “Explained: How Cruise Missiles Work!” Defencyclopedia. https://defencyclopedia.com/2014/08/01/explained-how-cruise-missiles-work/
[25] Brain, Marshall. “How Cruise Missiles Work.” How Stuff Works. http://science.howstuffworks.com/cruise-missile.htm
[26] “Ballistic and Cruise Missile Threat.” Federation of American Scientists. http://fas.org/irp/threat/missile/naic/part02.htm ; Norris, Robert S., Hans M. Kristensen. “Nuclear Cruise Missiles.” Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. http://bos.sagepub.com/content/63/6/60.full
Missile Threat and Proliferation
- Missile Payload Destruction Cost Comparisons
- Technological Threat Assessment
- War By 2025 Threat Analysis
- Ballistic Missile Basics
- Hypersonic Weapon Basics
- Rocket and Mortar Basics
- Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Basics
- Non-State Actors
- Israel-Hamas War Updates
- United States Incursion Tracker
- World Drone Comparison
- Dong Feng-16 (CSS-11)
- Dong Feng-15 (CSS-6)
- Dong Feng-11 (CSS-7)
- M-7 (8610)/CSS-8
- Dong Feng-12 (CSS-X-15)
- Dong Feng-3 (CSS-2)
- Dong Feng-21 (CSS-5)
- Dong Feng-21D (CSS-5)
- Dong Feng-26
- Dong Feng-4 (CSS-3)
- Dong Feng-5 (DF-5)
- Dong Feng-31 (CSS-10)
- Dong Feng-41(CSS-X-20)
- DH-10 / CJ-10
- Changjian-20 (CJ-20)
- DF-ZF Hypersonic Glide Vehicle
- Dong Feng-17
- Chinese Spy Balloons
- Hwasong-17/KN-27
- Pukguksong-3 (KN-26)
- KN-02 (Toksa)
- Hwasong-5 (Scud-B Variant)
- Hwasong-6 (Scud-C Variant)
- Hwasong-9 (Scud-ER/Scud-D Variant)
- Polaris-2 (Pukguksong-2/KN-15)
- Taepodong-1
- Hwasong-12/KN-17
- Taepodong-2
- KN-08 / Hwasong-13
- Hwasong-14/KN-20
- Hwasong-15/KN-22
- 3M22 Zircon
- Avangard (Hypersonic Glide Vehicle)
- RS-26 Rubezh
- OTR-21 Tochka (SS-21 Scarab)
- SS-1 Scud-A
- R-17 Elbrus (SS-1 Scud-B)
- S-300P Air and Missile Defense System
- S-300V Air and Missile Defense System
- S-400 Triumf Air Defense System
- SS-1d Scud-C
- R-17 VTO/SS-1e (Scud-D)
- Iskander-M (SS-26)
- Kh-47M2 Kinzhal (“Dagger”)
- SS-18 Satan/R-36M2 Voyevoda
- SS-19 Stiletto
- RS-12M Topol (SS-25 Sickle)
- SS-27 / Topol-M
- SS-27 Mod 2 / RS-24 Yars
- RS-28 Sarmat (Satan 2)
- AS-15 Kent (Kh-55 Granat)
- RK-55 Relief (SS-N-21 Sampson)
- 3M-54 Klub (SS-N-27 Sizzler)
- 3M-14 Kalibr (SS-N-30A)
- P-15 Termit (SS-N-2 Styx)
- P-6 Progress/SS-N-3C Shaddock
- P-120 Malakhit (SS-N-9 Siren)
- P-270 Moskit/SS-N-22 Sunburn
- P-500 Bazalt (SS-N-12 Sandbox)
- P-700 Granit/SS-N-19 “Shipwreck”
- KH-35 (SS-N-25 Switchblade)
- P-800 Oniks (SS-N-26 Strobile)
- P-1000 Vulkan
- R-29R / SS-N-18 Stingray
- R-29RM / SS-N-23 Skiff
- SS-N-30 Bulava
- Tondar-69 (M7, CSS-8)
- Natanz Enrichment Facility
- Fordow Uranium Enrichment Plant
- Arak Heavy Water Nuclear Reactor
International Cooperation
Missile Defense Advocacy Alliance
515 King Street Suite 330 Alexandria VA, 22314 Phone: 703.299.0060 [email protected]
Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
© Missile Defense Advocacy Alliance 2024
Advertisement
How Cruise Missiles Work
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

Tomahawk cruise missiles frequently appear in the news because they are the U.S. weapon of choice for a variety of quick-strike operations. With all of the missiles in the U.S. arsenal, have you ever wondered why cruise missiles seem to come up so often?
In this edition of HowStuffWorks , we will look at cruise missiles so that you can understand what they are, how they operate and why they are ideal for certain scenarios.

A cruise missile is basically a small, pilotless airplane . Cruise missiles have an 8.5-foot (2.61-meter) wingspan, are powered by turbofan engines and can fly 500 to 1,000 miles (805 to 1,610 km) depending on the configuration.
A cruise missile's job in life is to deliver a 1,000-pound (450-kg) high-explosive bomb to a precise location -- the target. The missile is destroyed when the bomb explodes. Since cruise missiles cost between $500,000 and $1,000,000 each, it's a fairly expensive way to deliver a 1,000-pound package.

Cruise missiles come in a number of variations (see the links at the end of the article for more information) and can be launched from submarines , destroyers or aircraft.

When you hear about hundreds of cruise missiles being fired at targets, they are almost always Tomahawk cruise missiles launched from destroyers.

Cruise missiles are 20 feet (6.25 meters) long and 21 inches (0.52 meters) in diameter. At launch, they include a 550-pound (250-kg) solid rocket booster and weigh 3,200 pounds (1450 kg).
The booster falls away once it has burned its fuel. The wings, tail fins and air inlet unfold, and the turbofan engine takes over.
This engine weighs just 145 pounds (65 kg) and produces 600 pounds of thrust burning RJ4 fuel. The fuel load is 800 to 1,000 pounds (about 450 kg) of fuel at launch, or approximately 150 gallons (600 liters). The missile has a cruising speed of 550 mph (880 kph).

The hallmark of a cruise missile is its incredible accuracy. A common statement made about the cruise missile is, "It can fly 1,000 miles and hit a target the size of a single-car garage." Cruise missiles are also very effective at evading detection by the enemy because they fly very low to the ground (out of the view of most radar systems ).
Four different systems help guide a cruise missile to its target:
- IGS - Inertial Guidance System
- Tercom - Terrain Contour Matching
- GPS - Global Positioning System
- DSMAC - Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation
The IGS is a standard acceleration-based system that can roughly keep track of where the missile is located based on the accelerations it detects in the missile's motion ( click here for a good introduction). Tercom uses an on-board 3-D database of the terrain the missile will be flying over. The Tercom system "sees" the terrain it is flying over using its radar system and matches this to the 3-D map stored in memory. The Tercom system is responsible for a cruise missile's ability to "hug the ground" during flight. The GPS system uses the military's network of GPS satellites and an onboard GPS receiver to detect its position with very high accuracy.
Once it is close to the target, the missile switches to a "terminal guidance system" to choose the point of impact. The point of impact could be pre-programmed by the GPS or Tercom system. The DSMAC system uses a camera and an image correlator to find the target, and is especially useful if the target is moving. A cruise missile can also be equipped with thermal imaging or illumination sensors (as used in smart bombs ).
Frequently Asked Questions
How do cruise missiles navigate to their target, what advancements have been made in cruise missile technology, lots more information, related articles.
- How Stinger Missiles Work
- How Sidewinder Missiles Work
- How Smart Bombs Work
- How MOAB Works
- How Patriot Missiles Work
- How Stealth Bombers Work
- How Apache Helicopters Work
- How F-15s Work
- How Airplanes Work
- How Gas Turbine Engines Work
- How Radar Works
- How GPS Receivers Work
- How Rocket Engines Work
More Great Links
- USAF Fact Sheet: AGM-86B/C Missiles
- U.S. navy Fact File: Tomahawk Cruise Missile
- BBC News: NATO's firepower: The cruise missile
- Time.com: Tomahawk Cruise Missile
- Analysis: Tomahawks, Submarines and the F-111
Launch systems
- Arleigh Burke Class (AEGIS) Guided Missile Destroyers, USA
- SSN Los Angles Class Attack Submarine, USA - U.S. subs that launch cruise missiles
- SSN Astute Class Attack Submarine, UK - Royal Navy subs that launch cruise missiles
- B-52H Stratofortress Long-Range Multi-Role Bomber, USA
- B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber, USA
Miscellaneous
- Williams F107-WR-101 Turbofan Engine
- Digital Imagery Workstation Suite (DIWS) - generates the Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC) reference scenes
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation
April 27, 2017
Fact Sheet: Ballistic vs. Cruise Missiles

Ballistic missiles are powered initially by a rocket or series of rockets in stages, but then follow an unpowered trajectory that arches upwards before descending to reach its intended target. Ballistic missiles can carry either nuclear or conventional warheads.
There are four general classifications of ballistic missiles based on their range, or the maximum distance the missile can travel:
- Short-range: less than 1,000 kilometers (approximately 620 miles), also known as “tactical” ballistic missiles.
- Medium-range: between 1,000 and 3,000 kilometers (approximately 620-1,860 miles), also known as “theater” ballistic missiles.
- Intermediate-range: between 3,000 and 5,500 kilometers (approximately 1,860-3,410 miles)
- Long-range: more than 5,500 kilometers (approximately 3,410 miles), also known as intercontinental or strategic ballistic missiles. Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) can fly much further than the minimum range; for example, Russia could hit Chicago with an ICBM launched from the Krasnoyarsk ICBM base, which is located 9,156 kilometers (5,689 miles) away.

Ballistic missiles have three stages of flight:
Boost Phase begins at launch and lasts until the rocket engine(s) stops firing and the missile begins unpowered flight. Depending on the missile, boost phase can last three to five minutes. Most of this phase takes place in the atmosphere.
Midcourse Phase begins after the rocket(s) stops firing. The missile continues to ascend toward the highest point in its trajectory, and then begins to descend toward Earth. This is the longest phase of a missile’s flight; for ICBMs, it can last around 20 minutes. During midcourse phase, ICBMs can travel around 24,000 kilometers per hour (15,000 miles per hour).
Terminal Phase begins when the detached warhead(s) reenter the Earth’s atmosphere and ends upon impact or detonation. During this phase, which can last for less than a minute, strategic warheads can be traveling at speeds greater than 3,200 kilometers per hour (1,988 miles per hour).

Cruise missiles remain within the atmosphere for the duration of their flight and can fly as low as a few meters off the ground. Flying low to the surface of the earth expends more fuel but makes a cruise missile very difficult to detect.
Cruise missiles are self-guided and use multiple methods to accurately deliver their payload, including terrain mapping, global positioning systems (GPS) and inertial guidance, which uses motion sensors and gyroscopes to keep the missile on a pre-programmed flight path. As advanced cruise missiles approach their target, remote operators can use a camera in the nose of the missile to see what the missile sees. This gives them the option to manually guide the missile to its target or to abort the strike.
To learn about missile defense, check out our fact sheet .
Sources: Department of Defense, Missile Defense Agency, Federation of American Scientists .

820 1st Street NE, Suite LL-180 Washington, D.C. 20002 Phone: 202.546.0795
The World’s First Hypersonic Cruise Missile Will Fly 20 Times Faster Than the Competition
Hypersonic Attack Cruise Missile (HACM) will be the first scramjet-powered weapon to enter production.
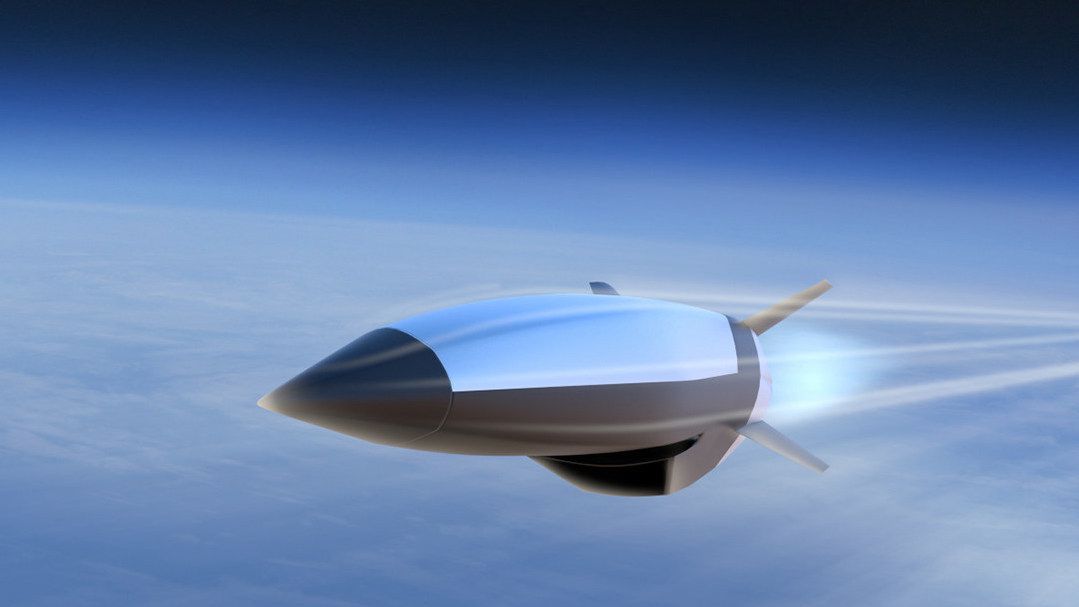

- Unlike most cruise missiles, however, this one travels way faster than the speed of sound , with the capability to fly at speeds in excess of Mach 5.
- Exactly how fast the new Hypersonic Attack Cruise Missile will be remains a mystery.
The Pentagon has plenty of cruise missiles in its arsenal, from the long-serving Tomahawk to the new JASSM-ER . But a new missile set to enter service in 2027 is radically different: the new Hypersonic Attack Cruise Missile (HACM) will fly up to 20 times faster, giving adversaries little time to escape its wrath. HACM will be the first mass-produced weapon to use air-breathing scramjet engines.
Raytheon and Northrop Grumman won a contract worth $985 million to develop the world’s first hypersonic cruise missile. HACM, developed for the United States and Australia, is an air-launched hypersonic cruise missile designed to quickly strike targets on the ground. Under the terms of the contract, the Pentagon should see the first operational missiles in 2027.

In 2020, the U.S. and Australia jointly began the Southern Cross Integrated Flight Research Experiment partnership, or SCIFiRE. Named after the constellation that appears on Australia’s national flag, SCIFiRE was meant to develop an air-breathing hypersonic weapon system designed to be carried on both U.S. and Australian aircraft, including the F/A-18 Super Hornet , F-35A Joint Strike Fighter , P-8A Poseidon aircraft, and others. The contract will mature the Raytheon SCIFiRE prototype into an actual weapon system.
HACM is a tactical weapon designed to be used on day one of a large-scale conventional conflict . “HACM will provide our commanders with tactical flexibility to employ fighters to hold high-value, time-sensitive targets at risk while maintaining bombers for other strategic targets,” Air Force Chief of Staff Gen. CQ Brown said in an Air Force statement last week.
Traditional cruise missiles are basically pilotless aircraft. Like many aircraft, turbofan engines power cruise missiles, propelling them at subsonic speeds. Cruise missiles fly low to avoid radar detection, and a slower speed helps them fly lower and hug the ground. Tomahawk cruise missiles , for example, fly at an altitude of between 98 and 164 feet at a speed of 550 miles per hour.
HACM is a hypersonic weapon, which means it flies at Mach 5 or faster—but we don’t know exactly how much faster it will fly. Most missiles that remain in the atmosphere, like air-to-air missiles , top out at around Mach 3+. SCIFiRE was descended from the earlier HIFiRE program , which tested a scramjet engine at speeds up to Mach 8.
HACM will be the world’s first operational weapon system to use a scramjet engine . Like turbofan engines, scramjets scoop up oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere to use as fuel. One key difference between the two is that a turbofan engine scoops up oxygen at subsonic speeds, while a scramjet scoops it up at supersonic speeds. More oxygen means more fuel for the scramjet engine, which enables it to propel the missile even faster. According to NASA , scramjet engines should work to at least Mach 15. That translates to 11,509 miles per hour, or fast enough to circle Earth in about two hours.

Hypersonic weapons are the new hotness in warfare. Most of the avowed nuclear powers have technically had hypersonic weapons for a half-century or more, as the ballistic missiles that carry nuclear warheads travel at hypersonic speeds, impacting their targets at up to 15,000 miles per hour. This new generation of hypersonic weapons is different in that it is non-nuclear in nature—at least so far—and would be used immediately in a conventional war.
There’s a lot we don’t know about HACM. We don’t know how fast it really flies, or how far it flies. All we know is it is small enough to be carried by a fighter jet and will be ready by 2027. One thing is for sure: HACM is awkward and we need a better name for it.

Kyle Mizokami is a writer on defense and security issues and has been at Popular Mechanics since 2015. If it involves explosions or projectiles, he's generally in favor of it. Kyle’s articles have appeared at The Daily Beast, U.S. Naval Institute News, The Diplomat, Foreign Policy, Combat Aircraft Monthly, VICE News , and others. He lives in San Francisco.
.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Pop Mech Pro: Military .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

China Could Rule the Seas With This New Tech

This Is the Most Lethal Submarine in the Sea

The Most Expensive Plane Crash in History

Can America’s Aging F-16 Overpower Russia’s Su-35?

Get to Know the Marines’ Favorite Ride

Meet the Navy’s New Radar-Killing Missile

Could the U.S. Army Fight and Win Without Tanks?

Why This Armored Vehicle Is the Army’s Unsung Hero

Why the U.S. Air Force Wants Flying Jeeps

Everything You Need to Know About Camouflage

Can We Turn Subs Into Undersea Aircraft Carriers?
- Air Warfare
- Cyber (Opens in new window)
- C4ISR (Opens in new window)
- Training & Sim
- Asia Pacific
- Mideast Africa
- The Americas
- Top 100 Companies
- Defense News Weekly
- Money Minute
- Whitepapers & eBooks (Opens in new window)
- DSDs & SMRs (Opens in new window)
- Webcasts (Opens in new window)
- Events (Opens in new window)
- Newsletters (Opens in new window)
- Events Calendar
- Early Bird Brief
- Digital Edition (Opens in new window)
Pentagon plan for homeland cruise missile defense taking shape
WASHINGTON — The Pentagon’s plan to defend the U.S. homeland from cruise missiles is starting to take shape after a prolonged period of development because until recently , the threat was perceived as a more distant regional one, a senior Air Force official said.
North American Aerospace Defense Command and U.S. Northern Command have been working for several years and across two presidential administrations to come up with a design that can effectively defend the continental U.S. from cruise missiles, according to Brig. Gen. Paul Murray, NORAD deputy director of operations.
NORAD and NORTHCOM, in consultation with the Missile Defense Agency and the Joint Integrated Air and Missile Defense Organization are closing in on a design framework for the mission, Murray said, just as the Pentagon enters a critical decision-making period as it formulates the fiscal 2024 budget request.
Once the design is created, “it’s time to go out and defend the design,” Murray said at a Center for Strategic and International Studies conference July 14. This translates to conducting modeling and simulation to prove out, in part, that the architecture will work.
It’s also not to say “my computer’s crunching numbers, buy me these capabilities,” he said, adding capabilities need to be demonstrated which includes partnering with the MDA and others to experiment.
Budgets for cruise missile defense of the homeland in fiscal 2022 and 2023 were modest, with combatant commands including NORTHCOM placing additional funding for development in so-called wish lists rather than in base budget requests and hoping that Congress ultimately supplies the dollars.
The cruise missile challenge
Land-attack cruise missiles can be launched from the air, ground or sea and because they fly at low altitudes under powered flight, it is difficult for radars to detect them.
Ballistic missiles can be detected much earlier, which allows more time to detect, track, decide and act. For cruise missiles, decision makers may have only a couple of minutes and salvos of cruise missiles can attack from different directions, complicating the approach to defeating the threat.
While the U.S. has been focused on ballistic missile defense of the homeland from adversaries including North Korea, Russia and China have made investments over several decades to develop cruise missiles capable of carrying out a non-nuclear attack.
The 2019 Missile Defense Review highlighted the need to focus on near-peer cruise missiles and directed the Pentagon to recommend an organization to have acquisition authority of cruise missile defense for the homeland. The designation requirement also appeared in the 2017 National Defense Authorization Act, but the Pentagon has yet to choose what organization will be in charge of the effort.
The lack of an acquisition authority can hamper the budget process. And budget requests during the Trump administration contained little to get moving on cruise missile defense. In President Joe Biden’s first two budgets, the mission also received very little funding save to conduct a cruise missile defense kill chain demonstration.
Previous attempts to figure out how to defend against cruise missiles hit roadblocks.
In 2015, for example, a large aerostat being evaluated for cruise missile defense at Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland broke free from its mooring and drifted across Pennsylvania. It’s long tether knocked out power lines and, once it landed in a grove of trees in Amish countryside, had to be shot at by State Troopers to get it to deflate.
The JLENS program was promptly canceled .
The debate over what part of the U.S. is most important to protect from cruise missiles also hindered progress because it was difficult to land on policy to help determine site locations, Peppi DeBiaso, a non-resident senior associate at CSIS, said during a panel discussion at the conference.
Impossible to protect everything
CSIS, in a report it debuted at the conference , said it will be impossible to protect everything. Lt. Gen. A.C. Roper, U.S. NORTHCOM deputy commander, said in a recording played at the event, that “placing a Patriot or a [Terminal High Altitude Area Defense] battery on every street corner is both infeasible and unaffordable.”
Missile Defense Agency fires Patriot missile from THAAD system
Mda has hit a milestone for integrating the terminal high altitude area defense system with the patriot air and missile defense system, firing an advanced patriot missile from thaad..
The CSIS report lays out a suggested architecture, implementation plan and cost estimate for a cruise missile defense capability to protect the homeland that uses systems already fielded today and leverages sensors and radars already working other jobs to provide early warning and information to aid detection and then decision making in the event of a cruise missile attack.
The design in the CSIS report consists of five layers implemented over three phases. The elements include over-the-horizon radars, towered sensors, an aerostat, three types of interceptors, command-and-control operations centers and a mobile airborne asset, all with a projected acquisition cost of $14.9 billion. Phased operations and sustainment costs are estimated to be $17.8 billion – or $32.7 billion over 20 years.
A study from the Congressional Budget Office in 2021 developed four architectures with 20-year acquisition and sustainment costs estimated between $77 billion and $466 billion. CSIS said the architecture designs from CBO were “hampered by methodological constraints and by element selection, resulting in brittle and expensive solutions.”
The authors of the report acknowledged that “no weapon system is perfect, and perfection is the enemy of the good,” but added, “even if limited and imperfect, a sufficient and affordable defense can complicate adversary planning and strengthen deterrence.”
Vista Rampart and beyond
NORAD and NORTHCOM held a wargame called Vista Rampart in March and April to further refine cruise missile defense concepts. Then NORAD took the design outside of the headquarters to the Globally Integrated War Game, which addressed the capabilities at a broader level with the services and combatant commands.
Other considerations will need to be made, Murray added, to include how to organize, train and equip the defensive systems.
How the architecture would tie into a broader defensive framework with allies and partners such as Canada will require further coordination and analysis. The U.S. and Canada are extensively partnered through a binational command, with capabilities including the North Warning System at the edge of the Arctic designed to detect airborne threats coming from the polar region.
The Pentagon is also keeping a close eye on how the establishment of a missile defense capability on Guam will inform a homeland cruise missile defense capability. The Missile Defense Agency revealed a relatively detailed plan for defending the island against ballistic, hypersonic and cruise missile attacks as well as other airborne threats and funded the initial development and fielding in the coming years to build it.
“I think as we develop a Guam architecture, working with the Army, working with the Navy, working with the joint staff and the services, I think we will learn a lot from that, how we want to operate that integrated kind of defense” Stan Stafira, Missile Defense Agency chief architect, said at the conference. “And then that area is kind of the size of what you’re looking at trying to defend, say, a limited area in CONUS,” he said.
Last fall the Joint Requirements Oversight Council approved an Integrated Air and Missile Defense priority requirements document through a portfolio management review process, Col. Tony Behrens, JIAMDO deputy director, said on the same panel.
“This process will enable a flexible and holistic approach to determining and prioritizing IAMD requirements. It established a priority framework that the combatant commands and Joint Force will help us review annually in developing what we’re calling the Integrated Air Missile Defense portfolio priority list, a holistic approach to the entire IAMD enterprise,” Behrens said.
The list is intended to aid senior decision makers balance budgetary needs and synchronize support across the services and DOD in support of missions like air and cruise missile defense of the homeland, he said.
As the Pentagon looks at cruise missile defense capability “there is a lot of capability out there,” Stafira said, “and all of the services have developed capabilities to defend against cruise missiles.”
Yet as the Defense Department looks at all of these capabilities it is going to need help from industry to answer, “how do you integrate different industry partners’ assets together to do that?”
Jen Judson is an award-winning journalist covering land warfare for Defense News. She has also worked for Politico and Inside Defense. She holds a Master of Science degree in journalism from Boston University and a Bachelor of Arts degree from Kenyon College.
More In Pentagon
Sea-Air-Space 2024: All the cutting-edge tech at Navy’s largest show
From an eclipse that yanked attendees to the waterfront to a surprise appearance by lance cpl. chesty xvi, here’s what you may have missed..
Space Force launches weather satellite to replace 1960s-era spacecraft
The launch is a first step toward modernizing the space force’s more than 60-year-old weather constellation, the defense meteorological satellite program..
Project Overmatch’s Small says EW is ‘killer app’ for unmanned tech
The navy is investing in unmanned systems — on the water, as well as above and below it — to augment existing and near-future firepower..
Space Force picks satellite providers for rapid delivery mission
The victus haze responsive space mission is slated to launch in 2025 with a focus on real-time threat response..
Secretive US cyber force deployed 22 times to aid foreign governments
“enhancing the security of government, private sector and critical infrastructure systems grows ever more imperative,” said air force gen. timothy haugh., featured video, despite being gravely wounded, this ranger refused to leave his men in the vietnamese jungle.
Troops get next-gen weapons and citizen heroes are honored | Defense News Weekly Full Episode, 4.6.2
What are the latest financial scams to watch out for? — Money Minute
101st Airborne unit receives the Next Generation Squad Weapon
Trending now, us air force issues $409 million award for long-sought pacific airfield, air force to get f-15e jet with fresh electronic warfare tech in summer, spy-7 radar tracks live space objects ahead of delivery to japan, how companies plan to ramp up production of patriot missiles, armenia deepens military ties with western allies.
Why it’s so hard to defend against cruise missiles
A recent conference raises the question: What kind of threat does this type of weapon pose to the United States?
By Kelsey D. Atherton | Published Jul 25, 2022 7:00 AM EDT

On July 14, the Center for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, DC held a one-day conference premised on a specific threat: What if, in the future, war comes to the United States via cruise missile? Pointing to new developments in cruise missile technology, and the limitations of existing early warning systems that are focused on the high arcing trajectories of ballistic missiles, the CSIS conference and accompanying report suggests that to defend the continental United States from such a threat, the military should adapt and deploy the kind of cruise missile defenses presently used as regional weapons.
Unlike ballistic missiles, which arc up into space before traveling back down towards earth, cruise missiles fly close to the ground, making it hard for radar on the ground that’s pointed up at space to see them.
The perceived threat from new cruise missiles is driven by tech developments occurring across the globe, as new materials, better aerodynamics, and sophisticated sensors and guidance systems make possible the fielding of weapons, like hypersonic missiles , that had mostly been just theoretical decades ago.
For the United States, the development of long-range bombers in the 1940s, followed by the development of intercontinental ballistic missiles, shattered the notion that the enormous distances of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans were enough to protect the continental US from direct attack. (During World War II, US territories in the Pacific came under direct attack, but the only long-range assault on the 48 states came in the form of incendiary-carrying balloons launched by Japan into the jet stream and carried over to the US.)
With atomic and then thermonuclear payloads, bombers and long-range missiles threatened devastation on an unprecedented scale, and the United States built an elaborate system of early warning sensors focused on detecting early signs of launch, and expanded its first-in-the-world nuclear arsenal to deter attack. North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) is run by both Canada and the United States, and maintains a series of radars and other sensors designed to detect early attacks across the Arctic or elsewhere. (Every December, NORAD highlights its existence by tracking Santa Claus, turning a system designed to detect oblivion into a kid-friendly Christmas tradition .)
At the conference held by CSIS, the threat from cruise missiles was discussed as a way that other countries could attack the United States that is hard to detect by employing existing, ICBM-focused measures. It is also considered hard to deter through threat of nuclear retaliation, operating on the assumption that if a cruise missile with a conventional warhead destroyed a building or killed people in the United States, the President would not immediately respond with a nuclear strike.
“You know, our adversaries are building diverse, expansive ranges of modern offensive missile systems, and we see them – we see them in the news every day,” Stan Stafira, Chief Architect of the Pentagon’s Missile Defense Agency, told the panel. “They’re capable of maneuvering in the midcourse and the terminal phases of their flight, like maneuvering reentry vehicles, multiple independent reentry vehicles, hypersonic glide vehicles, and cruise missiles.”
Part of the broader appeal of hypersonic weapons to nations like Russia, China, and the United States is that the speed and trajectories of the missiles make them harder to detect than ICBMs. The ballistic arc of ICBMs means the launch is visible to radar while it is still ascending, once it clears the horizon line. Meanwhile, both hypersonic glide vehicles and hypersonic cruise missiles, which travel at Mach 5 or above, are designed to fly below that radar horizon, with the cruise missile keeping a close trajectory to earth and the glide vehicle flying in the high atmosphere.
“I want to state that we absolutely believe that nuclear deterrence is the foundation of homeland defense,” said Lieutenant General AC Roper, deputy commander of Northern Command, the part of the US military responsible for North America. “However, we also must have credible deterrence options below the nuclear thresholds, options which allow for a balanced approach of deterrence by denial and deterrence by punishment or cost imposition.”
Deterrence, at its most straightforward, is a strategy of making a big threat on a condition: One country publicly declares it will launch nukes at another if it launches nukes at it, with the intended effect that neither country launches nukes. But because the payload of a cruise missile—it could be nuclear or conventional, unlike ICBMs, which are always nuclear—is unlikely to be known until impact, generals like Roper would prefer to have a range of weapons with which to respond.
Missile defense is one of those options, and the US already employs a few forms. Part of any missile defense system is the sensors, like specially focused radar, that can detect incoming attacks, and then track those weapons as they travel. These radars then send that tracking information to interceptors, which are missiles launched to fly and destroy the incoming attacking missile. Shooting missiles at other missiles is a hard problem because an incoming threat arrives at great speed, and because the cost calculus can favor an attacker. Interceptors, like shorter-ranged Patriot missiles or longer-ranged ballistic interceptors , are often more expensive than the missiles they are intercepting. And unlike interceptors, which have to hit precisely to work, missiles launched in attack can deploy decoys or countermeasures to redirect interceptors away, or can instead be fired in a greater volume, overwhelming interceptors through sheer numerical advantage.
“The resulting 20-year cost to provide even a light defense of a vast area ranged from $77 billion to $466 billion,” reads the CSIS report , citing an analysis from the Congressional Budget Office studying a range of cruise missile defense options. “The considerable cost variation is due to alternative combinations of sensors and interceptors and varying desired warning times of 5 or 15 minutes.”

Kelsey D. Atherton is a military technology journalist who has contributed to Popular Science since 2013. He covers uncrewed robotics and other drones, communications systems, the nuclear enterprise, and the technologies that go into planning, waging, and mitigating war.
Like science, tech, and DIY projects?
Sign up to receive Popular Science's emails and get the highlights.
Russia's firing new, long-range Kh-69 cruise missiles, war experts say, piling on the misery for Ukraine's dwindling air defense
- Russian forces have deployed a new cruise missile, the Institute for the Study of War said.
- The Kh-69 was used in an attack on a major power station near Kyiv this week.
- The Kh-69 is a leap forward in Russian tactical munitions.

Russian Forces are deploying a new, long-range cruise missile, known as the Kh-69, as it steps up attacks on Ukraine's energy infrastructure.
The Washington DC-based think tank, the Institute for the Study of War (ISW), noted in its Friday report that the new air-to-surface missiles were part of Russia's "continued efforts to improve strike packages and penetrate Ukraine's degraded air defense."
Russia has renewed its attacks against Ukraine's energy infrastructure in recent weeks, exploiting Kyiv's dwindling air defense systems.
"We need air defense systems and other defense assistance, not just turning a blind eye and having lengthy discussions," President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said in a post on X.
The post was in response to a Russian missile attack overnight on April 11 that destroyed the Trypillia Thermal Power Plant. The plant is one of the primary energy suppliers to Ukraine's capital, Kyiv. The plant was hit by the new Kh-69 missiles, according to the Ukrainian military.
"ISW has not previously observed the Russian use of Kh-69 missiles in Ukraine," it said.
"Russian forces have reportedly launched Kh-69 missiles from 400 kilometers away from their targets, exceeding a previous estimated range of 300 kilometers and the 200-kilometer range of the most recent Kh-59MK2 variant," wrote the ISW.
Related stories
Illia Yevlash, a spokesperson for Ukraine's Air Force, confirmed on Friday that Russia had launched the new missiles during its massive aerial assault on Thursday.
"This is an improved system of the Kh-59 version," Yevlash said.
"We are currently establishing what kind of missile it was, what type it was. These are fresh missiles with parts manufactured in 2023. That is, we can see that Russia is constantly trying to produce new missiles."
Yevlash said Russia was manufacturing the Kh-69 domestically, but that continued production relied on the ability to source key components from abroad. ISW analysts noted that while the Russian stockpiles and production capability of these Kh-69 missiles are unclear, "Russia is unlikely to be able to produce them at a significantly greater speed or quantity than its other domestically produced missiles."
The Kh-69 is Russia's latest cruise missile
Reports that Russia was employing the Kh-69 first appeared on Ukrainian Telegram channels in early February.
On February 7, a Ukrainian military blogger posted a photo on Telegram purporting to show the destroyed rear fins of a Kh-69. A Ukrainian war monitor account, which tracks Russian aviation activity, claimed that three Kh-69s were fired at Ukraine overnight on February 7-8.
In September last year, the UK-based International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) think tank reported that the Kh-69 was still undergoing testing. It described the missile as an "air-launched land-attack cruise missile likely akin to the European Storm Shadow or Taurus KEPD 350 missiles."
According to The War Zone, the Kh-69 was developed by Raduga, part of Russia's Tactical Missile Corporation. The missile weighs around 1,700 pounds, has an operating speed of up to 621 miles per hour, and has the option of either a penetration or a cluster warhead weighing up to 680 pounds. The missile's shape offers some degree of reduced radar signature.
Russian forces can launch the missiles from Su-34 and Su-35 tactical aircraft rather than solely from strategic bombers.
Watch: Ukraine says it shot down 6 hypersonic missiles over Kyiv during 'exceptional' night of attacks
- Main content
Ukraine’s New ‘Long Neptune’ Cruise Missile Could Strike Anywhere In Crimea—And Russian Territory Beyond
Kyiv knows it needs more domestic missiles
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
A Neptune test-shot.
Ukraine is developing a “long” version of its ground-launched Neptune cruise missile—one of its main weapons for striking Russian forces deep behind the front line of Russia’s 22-month wider war on Ukraine.
The coming of the Long Neptune is good news for advocates of a free Ukraine. Especially considering the possible throttling of U.S. support for the Ukrainian war effort. Throttling that’s being advanced by a minority of pro-Russian Republicans in the U.S. Congress.
The news broke on Monday in ArmyInform’s interview with Lt. Gen. Ivan Gavrylyuk, Ukraine’s deputy minister of defense. “Currently, work is underway to create the so-called ‘Long Neptune,’" Gavrylyuk said . “This is a new modification of the missile for the Neptune complex.”
It’s obvious what’s happening—and it’s obvious because it’s happened before, when other countries enhanced their cruise missiles by making them longer. In extending the 17-foot Neptune and filling the extra space with additional fuel for the missile’s turbofan engine, Ukraine could add a lot to its approximately 200-mile range.
Consider the Harpoon, the U.S. Navy’s classic anti-ship cruise missile, which also has land-attack modes. Ukraine operates a small number of donated Harpoons alongside its locally-produced Neptunes and other deep-strike munitions including air-launched Storm Shadow and SCALP-EG cruise missiles and ground-launched S-200 and Tochka ballistic missiles .
The basic surface-launched Harpoon ranges no farther than 75 miles. In 1991, arms-maker McDonnell Douglas—now Boeing—offered a new Block 1D model of the Harpoon that added two feet to the 13-foot missile. “A structural modification provides additional volume for fuel, thus doubling range,” McDonnell stated in a sales brochure .
The U.S. Navy never showed much interest in the Harpoon Block 1D at a time when a major war with Russia seemed like a distant prospect. But the new missile at least proved, again, how to extend the range of a cruise missile. Make it longer, add more fuel.
The trick is to rebalance the missile after the addition. In the case of the Harpoon 1D, that meant repositioning the wings, which the Americans “moved forward to maintain maneuverability and flying characteristics.”
The Neptune might undergo similar changes. Those tweaks, plus any related modifications to the missile’s truck-mounted launcher, should be straightforward. Luch, the Ukrainian design bureau responsible for the Neptune, for months has been teasing enhancements to the Neptune that would extend the missile’s range to 225 miles.
The longer body might not be the first modification to Neptune. The earliest models of the missile, which is a derivative of the Soviet-vintage Kh-35, had radar seekers that limited their role to anti-ship strikes. Indeed, the Neptune’s first victims were Russian warships, including the missile-cruiser Moskva , holed and sunk in the western Black Sea back in April 2022.
Many anti-ship cruise missiles also have ground-attack modes, but these same missiles often feature GPS-aided navigation.
The reason is simple. A radar seeker generally is enough for striking ships, as a ship reflects a clear radar signature relative to the flat water around it. Ground targets, by contrast, are surrounded by the clutter of buildings, trees and uneven terrain. But juice a radar-guided missile with GPS, and you might get enough discrimination to steer the munition through the clutter to its target.
Luch in its wisdom fitted the Neptune with GPS from the start. But the design bureau made additional tweaks to the missile’s seeker to optimize its land-attack mode, a Ukrainian official told The War Zone in April . “We are pretty close.”
The official wasn’t lying. Just four months after The War Zone interview, the Ukrainians began firing Neptunes at Russian air-defenses on land in occupied Crimea.
A Long Neptune that also has the improved seeker might be able to range more than 200 miles. Potentially a lot more. That could put all of occupied Crimea plus adjacent Russian territories within range of Ukrainian batteries firing missiles from well behind the front line.
The Long Neptune is just one of several domestic deep-strike munitions. They also include newly-produced copies of the classic Tochka ballistic missile. It’s not for no reason Kyiv is prioritizing the development of indigenous deep-strike missiles. Supplies of foreign deep-strike missiles are thin—and could get thinner.
The United States shocked observers this fall by supplying Ukraine with a batch of around 20 ground-launched M39 ballistic missiles—and then surprised them again by apparently not sending additional batches of the lethal munitions.
Money is one problem. U.S. president Joe Biden has warned that the Congressional funding his administration relies on for military support to Ukraine will run out this year.
Biden has proposed an additional $67 billion in funding, but a far-right fringe in the slim Republican majority in the Congress’s lower house—as well as that majority’s extremist leader, Rep. Mike Johnson—have made funding for Ukraine contingent on profound changes to the American system for offering asylum to refugees.
In essence, Republicans want to strip away the government’s power to offer asylum to populations fleeing natural disasters and other crises. Democrats in Congress have rejected this demand. Unless one side caves—or both reach a compromise—American money for Ukraine could run out soon.
That might mean no more U.S.-made long-range missiles for Ukraine’s deep-strike campaign. In that case, the Ukrainians would rely more on domestic missiles. Including the Long Neptune.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
North Korea says it tested a new cruise missile in the latest example of its expanding capabilities

SEOUL, South Korea — North Korea said Thursday it conducted its first flight test of a new cruise missile , as it expands its military capabilities in the face of deepening tensions with the United States and neighbors.
The report in state media came a day after South Korea’s military said it detected the North firing several cruise missiles into waters off its western coast. The South’s Joint Chiefs of Staff did not provide more specific assessments, including the number of missiles fired or their flight characteristics.
The North’s official Korean Central News Agency said the Pulhwasal-3-31 missile is still in its development phase and that the launch did not pose a threat to neighbors. It described the missile as “strategic,” implying an intent to arm them with nuclear weapons.
The cruise missile launches were North Korea’s second known launch event of the year, following a Jan. 14 test-firing of the country’s first solid-fuel intermediate-range ballistic missile , which reflected its efforts to advance its lineup of weapons targeting U.S. military bases in Japan and Guam.
North Korea’s cruise missiles are among its growing arsenal of weapons aimed at overwhelming missile defenses in South Korea and Japan. They supplement the country’s huge lineup of ballistic missiles, including intercontinental ballistic missiles designed to reach the U.S. mainland.
While North Korean cruise missile activities are not directly banned under U.N. sanctions, experts say those weapons potentially pose a serious threat to South Korea and Japan. They are designed to be harder to detect by radar, and North Korea claims they are nuclear-capable and their range is up to about 1,240 miles, a distance that would include U.S. military bases in Japan.
Since 2021, North Korea has conducted at least 10 rounds of tests of what it described as long-range cruise missiles fired from both land and sea.
Tensions in the region have increased in recent months as Kim continues to accelerate his weapons development and make provocative threats of nuclear conflict with the United States and its Asian allies. In response, the United States, South Korea and Japan have been expanding their combined military exercises, which Kim condemns as invasion rehearsals and uses as a pretext to further ramp up his military demonstrations.
There are concerns that Kim could dial up pressure in an election year in the United States and South Korea.
South Korean experts and officials say Kim’s weapons drive has put further strain on a broken economy, decimated by decades of mismanagement and U.S.-led sanctions over his nuclear ambitions.
In a separate report, KCNA said Kim during a two-day ruling party meeting held through Wednesday criticized officials for failures in sufficiently providing “basic living necessities including condiments, foodstuff and consumption goods” to people living in the countryside and less developed cities and towns.
Kim had called the meeting to discuss a 10-year project he announced last week to promote more balanced regional development, which includes a goal of building modern factories in every county nationwide.
Satellite images analyzed by The Associated Press this week suggest North Korea has torn down a huge arch in its capital that symbolized reconciliation with South Korea, a week after Kim dismissed decades of hopes for peaceful reunification with the war-divided peninsula’s south.
Kim last week described the Pyongyang monument as an “eyesore” and called for its removal while declaring that the North was abandoning long-standing goals of a peaceful unification with South Korea and ordering a rewriting of the North’s constitution to define the South as its most hostile foreign adversary. He accused South Korea of acting as “top-class stooges” of the Americans and repeated a threat that he would use his nuclear weapons to annihilate the South if provoked.
Analysts say North Korea could be aiming to diminish South Korea’s voice in the regional nuclear standoff and eventually force direct dealings with Washington as it looks to cement its nuclear status.
The Associated Press
Mapping the wide-scale Iranian drone and missile attacks
Iran launched waves of drones and missiles toward Israel on Saturday in retaliation for Israel’s attack on an Iranian site in Damascus, Syria, this month. A spokesperson for the Israel Defense Forces said Iran fired over 300 ballistic missiles, UAVs, suicide drones and cruise missiles. The vast majority were intercepted outside of Israeli territory, according to the IDF.
Iranian strikes have hit Irbil in northern Iraq and the Arad region in southern Israel. An Israeli air base was also hit, causing “minor damage to infrastructure,” according to the IDF. Targets were intercepted in Jerusalem and Dimona on Saturday night.
No UAVs managed to infiltrate Israel. Of 30 Iranian cruise missiles launched, zero entered Israeli airspace, 25 were downed by the Israeli Air Force outside of Israeli airspace, and 120 ballistic missiles were downed by Israeli aerial defense systems, the IDF said.
Iranian missile and drone attacks were launched at Israel from positions in Iran, Lebanon, Iraq and Yemen, according to the Iranian state-run Tasnim News Agency. In a statement, the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah said it targeted Israeli barracks in the Golan Heights, an Israeli-occupied strip along the border with Syria, with a barrage of rockets after midnight local time.
After the attack, the IDF highlighted the close coordination of a coalition led by U.S. Central Command, the U.K., France and other countries, highlighting the Aerial Defense Array and the defensive abilities of the Israeli Air Force’s aircraft.

Defense systems of Israel
1,000 miles
Each Iron Dome battery can defend an area of up to 58 square miles.
David’s Sling
Arrow System
25 to 186 miles
Up to 1,490 miles
Iron Dome is an Israeli mobile missile defense system designed to intercept short-range rockets and artillery. It is intended to counter unguided rocket and drone attacks.
Defense system intended to prevent attacks from aircraft, helicopters, bombers, cruise missiles, UAVs and stand-off weapons.
Firing Unit
Python-5 for short-range engagements and the Derby for medium-range.
20 Tamir missile
Missile range
3 to 43 miles
Up to 62 miles
Up to 6 miles
DAVID’S SLING
ARROW 2 AND 3
It is designed to intercept ballistic and cruise missiles. Capable of intercepting targets at altitudes of up to 15 km.
Upper layer of Israel’s missile defense system. The Arrow 3 is the longest-range interceptor currently fielded with the Arrow Weapon System, complementing the Arrow 2, which engages targets in the upper atmosphere.
6 to 12 Stunner
interceptor
Up to 6 missiles
Up to 1,491 miles
Up to 9 miles
Note: Not all of Israel’s defense systems are included.
Sources: CSIS, Rafael, Army Recognition

Defense systems
20 container launchers each
with one Tamir missile.
Two types of missiles, the Python-5 for short-range engagements and the Derby for medium-range.
6 to 12 Stunner interceptor

According to the IDF, out of over 120 ballistic missiles, only a few crossed into Israeli territory. They caused minor damage to infrastructure at the Nevatim Air Force Base. According to IDF spokesman Daniel Hagari, the IAF’s Adir jets were returning to the base from the aerial defense mission.

The Israeli Air Force’s F-35I Adir
Weapons capacity
F-35 Lightning II
It carries weapons internally in stealth configuration or externally in permissible environments.
The Israeli Air Force gave the F-35 the Hebrew name Adir, meaning “Mighty One”.
18,000 pounds
Above 50,000 feet
Manufacturer
Mach 1.6 (~1,200 mph)
Lockheed Martin
Source: Lockheed Martin

The escalation prompted airspace closures in neighboring countries during the attack. Egypt suspended flights to Jordan, Iraq and Lebanon, according to Egyptian state TV. Israeli authorities announced the reopening of the country’s airspace starting at 7:30 a.m. Sunday. The IDF described the wide-scale Iranian attack as a “major escalation.”
Israel-Gaza war
The Israel-Gaza war has gone on for six months, and tensions have spilled into the surrounding region .
The war: On Oct. 7, Hamas militants launched an unprecedented cross-border attack on Israel that included the taking of civilian hostages at a music festival . (See photos and videos of how the deadly assault unfolded ). Israel declared war on Hamas in response, launching a ground invasion that fueled the biggest displacement in the region since Israel’s creation in 1948 .
Gaza crisis: In the Gaza Strip, Israel has waged one of this century’s most destructive wars , killing tens of thousands and plunging at least half of the population into “ famine-like conditions. ” For months, Israel has resisted pressure from Western allies to allow more humanitarian aid into the enclave .
U.S. involvement: Despite tensions between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and some U.S. politicians , including President Biden, the United States supports Israel with weapons , funds aid packages , and has vetoed or abstained from the United Nations’ cease-fire resolutions.
History: The roots of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and mistrust are deep and complex, predating the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 . Read more on the history of the Gaza Strip .
- Most U.N. Security Council members condemn Iranian attack, urge ‘restraint’ 3 hours ago Most U.N. Security Council members condemn Iranian attack, urge ‘restraint’ 3 hours ago
- Why did Iran attack Israel? What to know about the strikes, U.S. response. April 14, 2024 Why did Iran attack Israel? What to know about the strikes, U.S. response. April 14, 2024
- Israel mulls response after U.S.-led alliance fends off Iranian barrage April 14, 2024 Israel mulls response after U.S.-led alliance fends off Iranian barrage April 14, 2024

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Israel says Iran launched more than 300 drones and missiles, 99% of which were intercepted
Loud booms were heard in Jerusalem after Iran launched missiles and drones at Israel.

Sirens and explosions could be heard in Jerusalem on Sunday after Iran fired drones and missiles towards Israel.

The Israeli military said it would do everything to defend Israel, as Iran launched a first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday, sending drones and ballistic missiles toward Israel. Iran’s state-run media reported that dozens of drones had been fired.

Iran launched a first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday, sending drones and cruise and ballistic missiles toward Israel.

Israeli military spokesman Rear Adm. Daniel Hagari said that Iran has launched drones from its territory at Israel. Israel has been preparing for the possibility of a direct attack from Iran and is ready “for any scenario,” Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said Saturday.

A group of hardliners gathered outside the British embassy in Tehran early Sunday to celebrate missile and drone attacks on Israel. Protesters chanted “Death to Israel” and thanked the revolutionary guard for the attacks.

Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said that Israel’s defenses are ready after Iran launched dozens of drones and ballistic missiles toward Israel on Saturday

Iran’s state TV confirmed early on Sunday that the country’s powerful Revolutionary Guard had launched drones and missiles at Israel. Iran launched drones toward Israel late Saturday, the Israeli military also announced, and Iran’s state-run media reported that dozens had been fired.

Iranian missiles or drones were intercepted in the sky above the Jordanian capital, Amman, on Sunday.

Objects flying over the sky were seen from the West Bank, while booms and air raid sirens have sounded in Jerusalem after Iran launched dozens of drones and ballistic missiles toward Israel in an unprecedented revenge mission that pushes the Middle East closer to a regionwide war.

A group of hardline supporters of the Iranian government gathered overnight in central Tehran to celebrate the country’s missile and drone attacks against Israel.

Missiles could be seen in the night sky over the West Bank early on Sunday as Iran launched a first direct military attack against Israel, sending drones and cruise and ballistic missiles toward Israel.
Israeli Iron Dome air defense system launches to intercept missiles fired from Iran, in central Israel, Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday. The Israeli military says Iran fired more than 100 bomb-carrying drones toward Israel. Hours later, Iran announced it had also launched much more destructive ballistic missiles. (AP Photo/Tomer Neuberg)
- Copy Link copied
Interceptors missiles are launched into the sky early Sunday, April 14, 2024, in Jerusalem. (AP Photo/Sam Mednick)
Iranian demonstrators chant slogans during an anti-Israeli gathering in front of the British Embassy in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
This is a locator map for Iran with its capital, Tehran. (AP Photo)
An Iranian cleric chants slogans while attending an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel Saturday. The Israeli military says Iran fired more than 100 bomb-carrying drones toward Israel. Hours later, Iran announced it had also launched much more destructive ballistic missiles. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
Iranian demonstrators wave a Palestinian flag during their anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
An Iranian demonstrator chants slogans while attending an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel Saturday. The Israeli military says Iran fired more than 100 bomb-carrying drones toward Israel. Hours later, Iran announced it had also launched much more destructive ballistic missiles. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
A demonstrator waves Iranian and Palestinian flags during an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel Saturday. The Israeli military says Iran fired more than 100 bomb-carrying drones toward Israel. Hours later, Iran announced it had also launched much more destructive ballistic missiles. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
This image made from a video provided to The Associated Press by a Mideast defense official shows a helicopter raid targeting a vessel near the Strait of Hormuz on Saturday, April 13, 2024. A video seen by The Associated Press shows commandos raiding a ship near the Strait of Hormuz by helicopter Saturday, an attack a Mideast defense official attributed to Iran amid wider tensions between Tehran and the West. The Mideast defense official spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss intelligence matters. (AP Photo)
An Iranian demonstrator holds a poster of the late Revolutionary Guard Gen. Mohammad Hadi Haj Rahimi, who was killed in an airstrike widely attributed to Israel that destroyed Iran’s Consulate in Syria on April 1, during an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel Saturday. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
Iranian demonstrators flash the victory sign as they hold an Iranian flag and a model of a bullet during an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
An Iranian demonstrator flashes a victory sign as he holds a model of a bullet during an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
An Iranian demonstrator ignites a flare as others carry a Palestinian flag during an anti-Israeli gathering at the Felestin (Palestine) Sq. in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel Saturday. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
In this image provided by the White House, President Joe Biden, along with members of his national security team, receive an update on an ongoing airborne attack on Israel from Iran, as they meet in the Situation Room of the White House in Washington, Saturday, April 13, 2024. From left to right, facing Biden are, Central Intelligence Agency Director William Burns; Avril Haines, Director of National Intelligence; Secretary of State Antony Blinken and National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan. Some papers on the desk have been blurred by the source for national security reasons. (Adam Schultz/The White House via AP)
Iranian demonstrators chant slogans during their anti-Israeli gathering in front of the British Embassy in Tehran, Iran, early Sunday, April 14, 2024. Iran launched its first direct military attack against Israel on Saturday. (AP Photo/Vahid Salemi)
Follow AP’s live updates on Iran’s attack against Israel .
JERUSALEM (AP) — Booms and air raid sirens sounded across Israel early Sunday after Iran launched hundreds of drones, ballistic missiles and cruise missiles in an unprecedented revenge mission that pushed the Middle East closer to a regionwide war. A military spokesman said the launches numbered more than 300 but 99% of them were intercepted.
Calling the outcome “a very significant strategic success,” Rear Adm. Daniel Hagari said Iran fired 170 drones, more than 30 cruise missiles and more than 120 ballistic missiles. Of those, several ballistic missiles reached Israeli territory, causing minor damage to an air base.
Rescuers said a 7-year-old girl in a Bedouin Arab town was seriously wounded in southern Israel, apparently in a missile strike, though they said police were still investigating the circumstances of her injuries.
In Washington, President Joe Biden said U.S. forces helped Israel down “nearly all” the drones and missiles and pledged to convene allies to develop a unified response.
The Iranian attack, less than two weeks after a suspected Israeli strike in Syria that killed two Iranian generals in an Iranian consular building, marked the first time Iran has launched a direct military assault on Israel, despite decades of enmity dating back to the country’s 1979 Islamic Revolution.
Condemnation from the United Nations chief and others was swift, with France saying Iran “is risking a potential military escalation,” Britain calling the attack “reckless” and Germany saying Iran and its proxies “must stop it immediately.”
Hagari said the vast majority of the intercepts came outside Israel’s borders, including 10 cruise missiles that were intercepted by warplanes.
Israel’s Iron Dome air defense system launches to intercept missiles fired from Iran, in central Israel, Sunday, April 14, 2024. (AP Photo/Tomer Neuberg)
“A wide-scale attack by Iran is a major escalation,” he said. Asked whether Israel would respond, Hagari said only that the army “does and will do whatever is required to protect the security of the state of Israel.” He said the incident was not over, and dozens of Israeli warplanes remained in the skies.
Israel’s military said its Arrow system, which shoots down ballistic missiles outside the atmosphere, handled most interceptions and noted that “strategic partners” were involved.
“At my direction, to support the defense of Israel, the U.S. military moved aircraft and ballistic missile defense destroyers to the region over the course of the past week,” Biden said in a statement. “Thanks to these deployments and the extraordinary skill of our service members, we helped Israel take down nearly all of the incoming drones and missiles.”
U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said in a separate statement that U.S. forces “intercepted dozens of missiles and UAVs en route to Israel, launched from Iran, Iraq, Syria and Yemen.”
Biden and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu spoke early Sunday, Israeli time, their governments said. Biden said in his statement that he reaffirmed “America’s ironclad commitment” to Israel’s security — a departure from his growing criticism of Israel’s conduct in its war on Hamas in Gaza.
Iran had vowed revenge since the April 1 airstrike in Syria , which Tehran accused Israel of being responsible for. Israel hasn’t commented on it.
Israel and Iran have been on a collision course throughout Israel’s six-month war against Hamas militants in Gaza. The war erupted after Hamas and Islamic Jihad, two militant groups backed by Iran, carried out a devastating cross-border attack on Oct. 7 that killed 1,200 people in Israel and kidnapped 250 others. An Israeli offensive in Gaza has caused widespread devastation and killed over 33,000 people, according to local health officials.
Almost immediately after the war erupted, Hezbollah, an Iranian-backed militant group in Lebanon, began attacking Israel’s northern border. The two sides have been involved in daily exchanges of fire, while Iranian-backed groups in Iraq, Syria and Yemen have launched rockets and missiles toward Israel.
In a statement carried late Saturday by Iran’s state-run IRNA news agency, the country’s paramilitary Revolutionary Guard acknowledged launching “dozens of drones and missiles towards the occupied territories and positions of the Zionist regime.”
In a later statement, the Revolutionary Guard issued a direct warning to the U.S.: “The terrorist U.S. government is warned any support or participation in harming Iran’s interests will be followed by decisive and regretting response by Iran’s armed forces.”
IRNA also quoted an anonymous official saying ballistic missiles were part of the attack. A ballistic missile moves on an arch trajectory, heading up into space before gravity brings the weapon down at a speed several times faster than the speed of sound.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said that Israel’s defenses are ready after Iran launched dozens of drones and ballistic missiles on Saturday.
Israel has a multilayered air-defense network that includes systems capable of intercepting a variety of threats including long-range missiles, cruise missiles, drones and short-range rockets. However, in a massive attack involving multiple drones and missiles, the likelihood of a strike making it through is higher.
Iran has a vast arsenal of drones and missiles. Online videos shared by Iranian state television purported to show delta-wing-style drones resembling the Iranian Shahed-136s long used by Russia in its war on Ukraine. The slow-flying drones carry bombs. Ukraine has successfully used both surface-to-air missiles and ground fire to target them.
Some Israelis watched the interceptions light up the night sky.
Air raid sirens were reported in numerous places including northern Israel, southern Israel, the northern West Bank and the Dead Sea near the Jordanian border.
Israel’s army ordered residents in the Golan Heights — near the Syrian and Lebanese borders — as well as the southern towns of Nevatim and Dimona and the Red Sea resort of Eilat into protective spaces. Dimona is home to Israel’s main nuclear facility, and Nevatim has a major air base. Loud booms were heard in Jerusalem and northern and southern Israel.
The army’s Home Front Command canceled school Sunday and limited public gatherings to no more than 1,000 people. Israel and some other countries in the region closed their airspace.
Earlier, Netanyahu warned: “Whoever harms us, we will harm them.”
In Washington, Biden convened a principals meeting of the National Security Council to discuss the attack.
Gen. Erik Kurilla, the head of the U.S. military’s Central Command, was in Israel over the weekend consulting with Israeli defense officials. The Central Command oversees U.S. forces in the Middle East.
Iran’s mission to the United Nations issued a warning to both Israel and the U.S. “Should the Israeli regime make another mistake, Iran’s response will be considerably more severe,” it wrote online. “It is a conflict between Iran and the rogue Israeli regime, from which the U.S. MUST STAY AWAY!”
For days, Iranian officials including Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei had threatened to “slap” Israel for the Syria strike.
In Iran’s capital, Tehran, witnesses saw long lines at gas stations early Sunday as people appeared worried about what may come next. Dozens of hard-liners demonstrated in support of the attack at Palestine Square.
Lebanon’s state-run National News Agency reported heavy Israeli airstrikes and shelling on multiple locations in south Lebanon following Iran’s launch of drones. The Lebanese militant group Hezbollah said it launched “dozens” of Katyusha rockets at an Israeli military site in the Golan Heights early Sunday. It was not immediately clear if there was any damage.
Iranian missiles or drones were intercepted in the sky above the Jordanian capital, Amman. In Lebanon’s capital, Beirut, and elsewhere in the country, residents reported seeing missiles in the sky and hearing explosions, likely from interceptions. In Syria, explosions were heard in the capital, Damascus, and elsewhere. Britain-based war monitor the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights reported that Syrian air defenses tried to shoot down Israeli attempts to intercept Iranian missiles.
Gambrell reported from Dubai, United Arab Emirates. AP correspondents Nasser Karimi in Tehran, Iran, Michael Balsamo in New York, Krutika Pathi in New Delhi, Stephen Graham in Berlin, Thomas Adamson in Paris, and Zeke Miller and Lolita C. Baldor in Washington contributed to this report.

- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition


Iran launches hundreds of drones and cruise missiles at Israel in unprecedented attack
Islamic Republic’s first ever direct attack on Jewish state involved more than 300 drones and missiles, and raises the risk of a broader regional conflagration
- Iran launches attack against Israel – live updates
- Iran missile and drone attack on Israel – what we know so far
Iran launched more than 300 drones and missiles at Israel on Saturday night, in the Islamic Republic’s first ever direct attack on the Jewish state, bringing a years-long shadow war into the open and threatening to draw the region into a broader conflagration.
Israel, with the help of key western allies including the US, UK and Jordan, claimed to have intercepted some 99% of the launches during the mass strike, but added that some ballistic missiles had reached Israel, damaging the key Nevatim air base in southern Israel which remained operational.
As the UN security council prepared to convene an emergency session, the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) said more than 350 missiles were launched during the attack from Iran , Lebanon, Syria and Yemen, and called the interception rate a “significant strategic success”.
Commenting on Israel’s response to the attack, Israel’s prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, posted on X: “We intercepted, we repelled, together we shall win.”
“The Iranian attack was foiled,” Israeli military spokesman Rear Admiral Daniel Hagari said in a televised statement adding that no drones or cruise missiles that had entered Israeli territory, and “only a few” ballistic missiles reached Israel.
Although Israel moved to reopen its air space, officials said the incident was not yet over.
As of Sunday morning, Israeli officials indicated no decision had been made about an Israeli response to the Iranian attack, as an official said any potential response would be discussed at the war cabinet meeting.
Israeli war planes, however, were reported to be bombing Hezbollah positions in southern Lebanon.
On the Gaza front of the fast expanding regional war, Netanyahu said Hamas had rejected a ceasefire proposal and that Israel would continue pursue its conflict there with “full force”.
While many of the missiles and drones were brought down outside Israel’s airspace others were intercepted over Israeli territory by the Iron Dome air defence interceptor system, which lit up the night sky with multiple detonations, while air raid sirens sounded in Tel Aviv, Jerusalem and other cities.
The roar of Israeli air force jets could be heard across the country in the early hours of Sunday.

Some projectiles penetrated the defensive shield. IDF spokesperson Daniel Hagari confirmed a direct hit on an airbase in southern Israel that caused “minor damage to infrastructure” though the base remains fully operational.
One young girl is in emergency care after the attack, he said.
When asked about possible retaliation by Israel, Hagari said: “We have plans, the situation is still ongoing, we are assessing the situation, we are showing the cabinet the plans, and we are ready to do what is necessary for the defence of Israel.”
The New York Times cited Israeli intelligence sources as saying the main targets appeared to be Israeli military installations in the occupied Golan Heights, in the far north, and the Negev desert, in the far south. Tehran’s ally in Lebanon, Hezbollah, fired volleys of rockets at the Golan at the same time as the Iranian bombardment, and the Iran-backed Houthi forces in Yemen, claimed they had also joined the attack.
Earlier on Saturday, Iran’s state-run IRNA news agency reported that the country’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) had boarded a ship in the Strait of Hormuz by helicopter assault and taken it into Iranian waters. The cargo ship, the MSC Aries, is Portugese-flagged but linked to an Israeli company.
Through its mission at the UN, Iran declared the mass aerial attack, which Tehran dubbed “Operation True Promise” was a retaliation for the bombing of an Iranian diplomatic building in Damascus on 1 April, and that it now considered the matter closed, unless there was further action by Israel.
“The matter can be deemed concluded, the statement said. However, should the Israeli regime make another mistake, Iran’s response will be considerably more severe,” the statement on the X social media platform said. “It is a conflict between Iran and the rogue Israeli regime, from which the US must stay away!”
Netanyahu spoke by phone for 25 minutes with US president Joe Biden at 4am Israeli time, as the aerial attack appeared to peter out.
After the call, Biden said he had reaffirmed to Netanyahu “America’s ironclad commitment to the security of Israel”.
“I told him that Israel demonstrated a remarkable capacity to defend against and defeat even unprecedented attacks – sending a clear message to its foes that they cannot effectively threaten the security of Israel,” Biden said, adding that on Sunday he would convene G7 leaders “to coordinate a united diplomatic response to Iran’s brazen attack”.
“My team will engage with their counterparts across the region. And we will stay in close touch with Israel’s leaders,” Biden said. “And while we have not seen attacks on our forces or facilities today, we will remain vigilant to all threats and will not hesitate to take all necessary action to protect our people.”
An IDF officer said the Israeli leadership would consider its response early on Sunday, and meanwhile Israel called for an emergency session of the UN security council to condemn the attack. The meeting is expected at 4pm on Sunday (9pm BST).
In the days leading up to the assault, US officials had predicted it would be an unprecedented operation launched from Iran on Israeli territory. They said that if it did not cause mass casualties, Washington would urge Israel to moderate its own response, to prevent tit-for-tat escalation spiralling out of control, drawing in other countries and the US itself.
Biden interrupted a weekend break at his house on Rehoboth Beach, Delaware, and arrived back at the White House just after the first drones had been launched, and met his top security officials in the underground situation room. US surveillance planes in the region tracked the incoming attack, and US fighter jets shot down incoming drones and missiles.
The Jordanian air force was also reported to have intercepted some of the projectiles over its territory, and the UK’s Royal Air Force said it was contributing fighters and refuelling planes, mostly to fill in for the US in conducting aerial patrols over Iraq and Syria as part of its campaign against the Islamic State, but the defence secretary, Grant Shapps, said British planes could also “intercept airborne attacks within range of our existing missions”.
There had been nearly two weeks of speculation about when, where and how Tehran or its proxy forces would respond to the 1 April strike on an Iranian diplomatic building in the Syrian capital of Damascus which killed Gen Mohammad Reza Zahedi, a senior figure in Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guards, and eight other officers.
Israeli officials almost never claim responsibility for attacks carried out on foreign soil. Tehran has blamed Israel for the strike.
Since the war in Gaza began six months ago, there have been near-daily exchanges of fire between Israeli forces and Hezbollah along the Israel-Lebanon border that have threatened to escalate into full-blown conflict.
A direct attack by Iran on Israel, however, was not believed to be on the cards: Tehran’s leaders have previously made clear that they are not seeking a war with Israel, which could also draw in the US.
Iran has never responded with such force to previous attacks, including many covert Israeli operations on its soil, or the US assassination of the powerful Quds Force leader Qassem Soleimani in Iraq in 2020.
- Middle East and north Africa
- US foreign policy
- US military

Live Middle East crisis live: UK foreign secretary condemns ‘reckless’ Iran attack on Israel as UN chief says region on ‘brink’

Israel on high alert as it weighs response to Iranian attack

‘I hope everything is behind us’: Israelis take stock after night of airstrikes

After Iran’s attack on Israel, the world must act: this is a crisis that threatens us all

How Iran’s attack on Israel was stopped

Bullish Iran hails attack on Israel as a success and says operation is over

Middle East crisis: visual guide to Iran’s attack on Israel

Why Israel’s attack on Iranian consulate in Syria was a gamechanger

Iran warns it will strike again with greater force if Israel or US retaliate

Iran launches drone and missile strike against Israel as Biden rushes back to White House
Most viewed.

Prelims 2024 CA | 2024 Test Series | March Monthly Compilations | Daily CA | Daily MCQs
Ballistic Missile vs. Cruise Missile, India’s Missile Systems, IGMDP
- August 2, 2019
- Indigenous Defence Technology , Science & Technology
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
We frequently notice news related to ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and various missile systems of India. Memorizing names and salient features of various Indian missiles is hard without having a broader understanding of the concept of ballistic missiles and cruise missiles, and major missile defence systems. It is better to give these concepts a holistic structure rather than learning them in bits and pieces.
Ballistic Missile vs. Cruise Missile
The Hindu | GS3 > indigenization of technology
The terms ‘ballistic missile’ and ‘cruise missile’ appear in news articles wherever there is a missile test. It is essential for us to understand these terms to understand various Indian missile defence systems.
Ballistic Missile
- A ballistic missile follows a ballistic trajectory to deliver one or more warheads on a predetermined target.
- A ballistic trajectory is the path of an object that is launched but has no active propulsion during its actual flight (these weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods of flight).
- Consequently, the trajectory is fully determined by a given initial velocity, effects of gravity, air resistance, and motion of the earth (Coriolis Force).
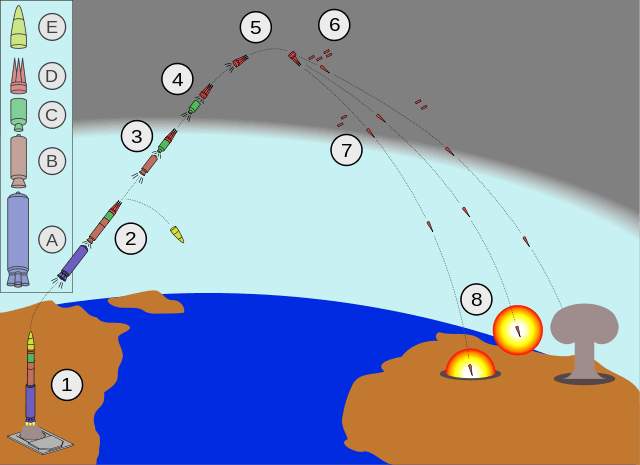
Image Credits: Wikipedia
- Shorter range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Longer-ranged intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), are launched on a sub-orbital flight trajectory and spend most of their flight out of the atmosphere.
Types of ballistic missiles based on the range
- Short-range (tactical) ballistic missile (SRBM): Range between 300 km and 1,000 km.
- Medium-range (theatre) ballistic missile (MRBM): 1,000 km to 3,500 km.
- Intermediate-range (Long-Range) ballistic missile (IRBM or LRBM): 3,500 km and 5,500 km.
- Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): 5,500 km +
Cruise missile
- A cruise missile is a guided missile (target has to be pre-set) used against terrestrial targets.
- It remains in the atmosphere throughout its flight.
- It flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed.
- Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
- Modern cruise missiles are capable of travelling at supersonic or high subsonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory.
Types of cruise missiles based on speed
- Hypersonic (Mach 5): these missiles would travel at least five times the speed of sound (Mach 5). E.g. BrahMos-II.
- Supersonic (Mach 2-3): these missiles travel faster than the speed of sound. E.g. BrahMos.
- Subsonic (Mach 0.8): these missiles travel slower than the speed of sound. E.g. Nirbhay.
Differences between Ballistic Missile and Cruise Missile
Integrated guided missile development programme (igmdp).
PIB | Source | The Hindu | 19-06-2019 | GS3 > indigenization of technology
- IGMDP was conceived by Dr. A P J Abdul Kalam to enable India attain self-sufficiency in missile technology.
- IGMDP was conceived in response to the Missile Technology Control Regime that decided to restrict access to any technology that would help India in its missile development program.
- To counter the MTCR, the IGMDP team formed a consortium of DRDO laboratories, industries and academic institutions to build these sub-systems, components and materials.
- IGMDP was started in 1983 and completed in March 2012.
- Keeping in mind the requirements of various types of missiles by the defence forces, the development of five missile systems was taken up.
- Prithvi: Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile (Prithivi means Earth Surface to Surface)
- Agni: Intermediate-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile
- Trishul: Short-range low-level surface-to-air missile
- Akash: Medium-range surface-to-air missile (Akash means Sky Surface to Air)
- Nag: Third generation anti-tank missile (Nag means Snake Nag slithers like a Snake to hit a tank!)
- After its success, the Agni missile program was separated from the IGMDP upon realizing its strategic importance.
India’s Missile Systems
PIB | Source | The Hindu | GS3 > indigenization of technology
SLBM: Sub-marine launched ballistic missile
Prithvi Missiles
All the Prithvi variants are surface-to-surface SRBMs.
Agni Missiles
MIRV: Multiple Independently targetable Re-entry Vehicle
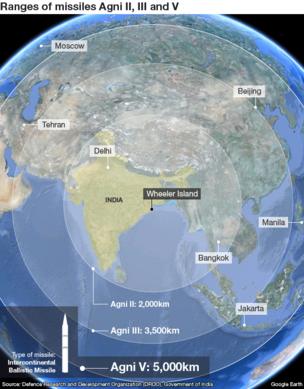
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT)
- In March 2019, India successfully tested its ASAT missile.
- The ASAT missile destroyed a live satellite in Low Earth orbit (283-kilometre).
- As per DRDO, the missile is capable of shooting down targets moving at a speed of 10 km per second at an altitude as high as 1200 km.
Newsletter Updates
Assured Discounts on our New Products!
Related Posts

Precision Farming, Geoinformatics for Precision Farming
- November 30, 2019

Genome, Whole Genome Sequencing, Genome India Project
- June 4, 2021
Lithium-ion battery, Internal Combustion Engine vs. Electric Vehicles
- November 9, 2019

India’s Three-Stage Nuclear Power Programme
- March 21, 2016
Nuclear Fission, Components of Nuclear Reactor, Types of Nuclear Reactors
- January 2, 2020
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance & Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- May 11, 2021

Kepler’s laws, Satellite Orbits, Launch Vehicles PSLV & GSLV
- December 3, 2020
Uranium & Thorium Distribution across India & World
- April 6, 2020
wonderful sir
Thanks a lot for this fantastic compilation sir!
I was unable to find such complied information on internet, but I found it here. Thanks a lot to PMFIAS
Thanks a lot
What a work sirji. Thank you so much
Thanks for very useful information and systematic content is systematic view of point very fantastic please keep it up latest update by geneon source like Hindu PIB arc etc
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
Trending now
Never miss an important update!
Advertisement
Israel Faced a Sophisticated Attack From Iran
The weapons Iran employed this weekend travel farther and are more precise than those Hamas and other allies have used against Israel in the past six months.
- Share full article

By Jin Yu Young
- April 14, 2024
Late Saturday, Iran began firing hundreds of drones and missiles at Israel, including weapons that experts say are more sophisticated than anything Israel had encountered until now in six months of fighting with Hamas and its allies in the region.
Previously, Israel had faced aerial attacks from Hamas and Islamic Jihad, whose rocket arsenal includes short-range (12 to 25 miles) and somewhat inaccurate 122-milimeter rockets of the Grad family, as well as Syrian-made M-302 rockets with a range of about 100 miles. Hamas also has Fajr-5 rockets from Iran and a similar, locally made version of the Fajr-5, both with a range of about 50 miles.
The weapons Iran used on Saturday can travel much farther, and some of them can travel much faster. Still, Israel said that nearly all of the missiles and drones that Iran fired were intercepted, many with help from U.S. forces.
In the attack, 185 drones, 36 cruise missiles and 110 surface-to-surface missiles were fired toward Israel, according to Israeli military officials. Most of the launches were from Iran, though a small portion came from Iraq and Yemen, the officials said.
Fabian Hinz, an expert on Iran’s military at the International Institute for Strategic Studies in Berlin, said in a post on X that Iran was probably using a cruise missile developed by the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps, the Paveh 351. It has a range of more than 1,200 miles — plenty to reach Israel from Iran.
According to his post, different versions of that missile have also been provided to the Houthis in Yemen and to the Iraqi Popular Mobilization Forces.
And Jeffrey Lewis, a member of the International Security Advisory Board at the U.S. State Department, said in a post on X that Iran was using land-attack cruise missiles that could carry around a ton of explosives.
He also noted that much of Iran’s ballistic missile arsenal has a long enough range to reach Israel. And though Iran’s drones carry much smaller explosive payloads than missiles, they have the advantage of being able to hover and shift targets.
In recent decades, Iran has largely been focused on deterrence, long-range missiles, drones and air defenses. It has one of the largest ballistic missile and drone arsenals across the Middle East, according to weapons experts, and is also becoming a major arms exporter globally.
Last year, after the attack by Hamas in October, Israel asked the United States for more precision-guided munitions for its combat aircraft and more interceptors for its Iron Dome missile defense system. Israel’s weapons arsenal includes Vietnam-era missiles, some of which have a failure rate as high as 15 percent.
Jin Yu Young reports on South Korea, the Asia Pacific region and global breaking news from Seoul. More about Jin Yu Young
Iran launches retaliatory attack on Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles
- Medium Text
- For a Reuters live page of coverage of the Iranian attack, click
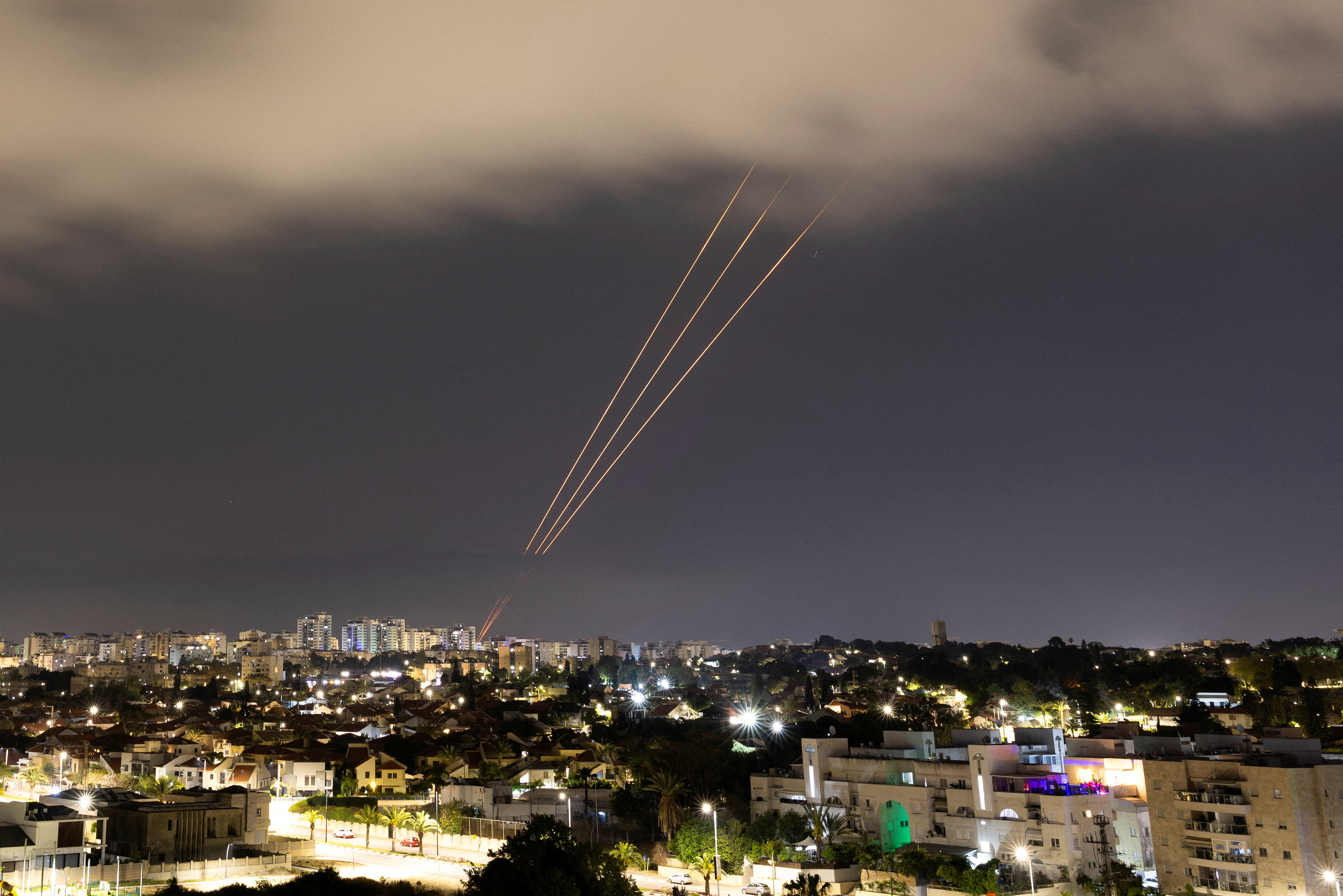

The Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter provides all the news you need to start your day. Sign up here.
Reporting by Dan Williams in Jerusalem, Parisa Hafezi in Dubai, Timur Azhari in Baghdad, Jeff Mason, Eric Beech and Doina Chiacu in Washington and Suleiman al-Khalidi in Amman and Lidia Kelly in Lisbon; Writing by Angus McDowall; Editing by Jonathan Oatis, Daniel Wallis, Chizu Nomiyama, Howard Goller and William Mallard
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

British security firm Ambrey said on Sunday that Israel Defence Forces (IDF) intercepted an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) near Eilat, stating that it assessed the UAV was launched from Yemen.

World Chevron

France, Germany and EU mark anniversary of Sudan war with funding push
Top diplomats from France, Germany and the European Union were set to push for more funding for Sudan on Monday at a meeting in Paris to mark the first anniversary of a war that commands far less global attention that those in the Middle East or Ukraine.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
Ballistic missiles are different than cruise missiles. Cruise missiles are self-propelled for the majority of their time in the air, flying in a relatively straight line and at lower altitudes thanks to a rocket propellant. Think of a ballistic missile's flight path as a large arc up and back down again, while that of a cruise missile — fired from a warship, for instance — is closer to a ...
cruise missile, type of low-flying strategic guided missile.The German V-1 missile used in World War II was a precursor of the cruise missile, which was developed by the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1960s and '70s. Capable of carrying either a nuclear or a conventional warhead, the cruise missile was designed to have a very low radar cross section and to hug the ground while ...
Cruise missiles are capable of being launched from multiple ground, air, sea and submarine platforms. Both fighter and long-range bomber aircraft are capable of carrying and launching cruise missiles. [5] On the ground, cruise missiles are most commonly launched by road-mobile systems due to the inherent advantages of mobility, but they can ...
The Basics. A cruise missile is basically a small, pilotless airplane. Cruise missiles have an 8.5-foot (2.61-meter) wingspan, are powered by turbofan engines and can fly 500 to 1,000 miles (805 to 1,610 km) depending on the configuration. A cruise missile's job in life is to deliver a 1,000-pound (450-kg) high-explosive bomb to a precise ...
Cruise missiles are self-guided and use multiple methods to accurately deliver their payload, including terrain mapping, global positioning systems (GPS) and inertial guidance, which uses motion sensors and gyroscopes to keep the missile on a pre-programmed flight path. As advanced cruise missiles approach their target, remote operators can use ...
The AGM-86 ALCM is an American subsonic air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) built by Boeing and operated by the United States Air Force.This missile was developed to increase the effectiveness and survivability of the Boeing B-52H Stratofortress strategic bomber.The missile dilutes an enemy's forces and complicates air defense of its territory.. The concept started as a long-range drone ...
A cruise missile is a subsonic guided missile that uses a turbojet, a smaller version of the jet engines that power today's airplanes, to reach its targets. Cruise missiles often have small ...
AGM-158 JASSM. The AGM-158 JASSM ( Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile) is a low detection standoff air-launched cruise missile developed by Lockheed Martin for the United States Armed Forces. [4] It is a large, stealthy long-range weapon with a 1,000-pound (450 kg) armor piercing warhead. It completed testing and entered service with the U.S ...
used land-attack cruise missiles for the first time during the conflict in Syria. The US Armed Forces are responsible for countering the ballistic and cruise missile threat through deterrence, and if necessary active suppression. Threat suppression may include attacks on missile systems, both before launch and during flight, and attacks on their
The Pentagon has plenty of cruise missiles in its arsenal, from the long-serving Tomahawk to the new JASSM-ER.But a new missile set to enter service in 2027 is radically different: the new ...
The Tomahawk is a long-range, unmanned weapon with an accuracy of about 5 metres (16 feet). The 5.6-metre- (18.4-foot-) long missile has a range of up to approximately 2,400 km (about 1,500 miles) and can travel as fast as 885 km (550 miles) per hour. Tomahawks are launched vertically from ships, but they can be launched horizontally from ...
Budgets for cruise missile defense of the homeland in fiscal 2022 and 2023 were modest, with combatant commands including NORTHCOM placing additional funding for development in so-called wish ...
Shooting missiles at other missiles is a hard problem because an incoming threat arrives at great speed, and because the cost calculus can favor an attacker. Interceptors, like shorter-ranged ...
Russian Forces are deploying a new, long-range cruise missile, known as the Kh-69, as it steps up attacks on Ukraine's energy infrastructure. The Washington DC-based think tank, the Institute for ...
A Neptune test-shot. Ukrainian government photo. Ukraine is developing a "long" version of its ground-launched Neptune cruise missile—one of its main weapons for striking Russian forces deep ...
The cruise missile launches were North Korea's second known launch event of the year, following a Jan. 14 test-firing of the country's first solid-fuel intermediate-range ballistic missile ...
In total, around 170 drones, more than 30 cruise missiles and more than 120 ballistic missiles were launched at Israel by Iran overnight Saturday, the military said.
Surface ships. Submarines. TELs. The Tomahawk ( / ˈtɒməhɔːk /) Land Attack Missile ( TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations. Developed at the Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins ...
Additionally, the MDAA says the Zircon is "a maneuvering anti-ship hypersonic cruise missile" with a range of somewhere between 500 and 1,000 kilometers (310 to 620 miles).
Of 30 Iranian cruise missiles launched, zero entered Israeli airspace, 25 were downed by the Israeli Air Force outside of Israeli airspace, and 120 ballistic missiles were downed by Israeli aerial ...
The Israeli army said Sunday that Iran launched dozens of suicide drones, cruise missiles and dozens of surface-to-surface missiles at Israel overnight. It is yet unclear which types of ballistic missiles Iran fired, but prior information and footage of boosters - missile parts that fell to the ground as part of the missile's flight path ...
JERUSALEM (AP) — Booms and air raid sirens sounded across Israel early Sunday after Iran launched hundreds of drones, ballistic missiles and cruise missiles in an unprecedented revenge mission that pushed the Middle East closer to a regionwide war. A military spokesman said the launches numbered more than 300 but 99% of them were intercepted.
Iran launched more than 300 drones and missiles at Israel on Saturday night, in the Islamic Republic's first ever direct attack on the Jewish state, bringing a years-long shadow war into the ...
Cruise missile. A cruise missile is a guided missile (target has to be pre-set) used against terrestrial targets. It remains in the atmosphere throughout its flight. It flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
The following is a list of cruise missiles. It doesn't include the specifically anti-ship missiles whose list is separate. Missile Type Country Max. range Max. Speed (Mach) Mass Warhead Warhead type Status Note AV-TM 300: Surface-to-surface missile
In the attack, 185 drones, 36 cruise missiles and 110 surface-to-surface missiles were fired toward Israel, according to Israeli military officials. Most of the launches were from Iran, though a ...
Iran launched explosive drones and fired missiles at Israel late on Saturday in its first direct attack on Israeli territory, a retaliatory strike that raised the threat of a wider regional ...
According to the army, Iran launched 30 cruise missiles, 120 ballistic missiles and 170 drones. The attacks were launched from Iran, Iraq, Yemen and Lebanon, marking the most serious multi-front ...