NASA's Voyager probes have been traveling through space for nearly 46 years. Here are 18 groundbreaking photos from their incredible mission.
- Nearly 46 years after their launch, Voyager 1 and 2 will likely soon reach the end of their scientific mission .
- NASA recently lost contact with Voyager 2 after sending it a bad command by mistake.
- Here are 18 pictures the probes took over the course of their forty-plus-year journey.

The Voyager probes are pioneers of science, making it farther into space than any other manufactured object. But now, they face a terminal problem: their power is running out.
The twin probes were originally sent on a four-year mission to tour the solar system, but they exceeded all expectations and are still going nearly 46 years later. That makes them NASA's longest-lived mission.
Scientists are now doing their best to keep the probes going for as long as possible. They recently found a clever hack to extend Voyager 2's life for another three years and plan to do the same with Voyager 1.
But these are old machines and NASA is constantly scrambling to fix mistakes. Last year, Voyager 1 started sending garbled data from the outside of the solar system. NASA ultimately figured out one of its computers had gone dead.
Voyager 2 is now in limbo , as the agency revealed Friday it had lost contact with the probe when someone sent a wrong command. It could be the end of Voyager 2's mission if NASA can't fix the mistake, which the agency probably won't be able to do before October.
As the probes are nearing the end of their scientific mission, here are 18 images from Voyager that changed science.

The Voyager probes were designed to visit Jupiter and Saturn.
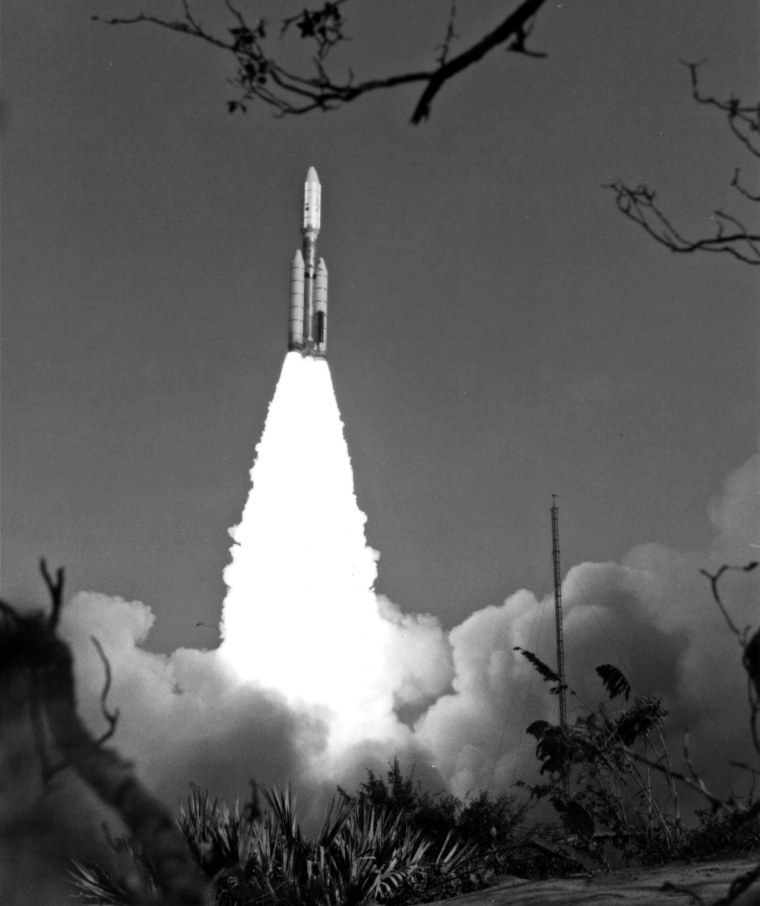
The Voyager mission included two probes — Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 — which NASA launched in 1977 within a few months of each other.
NASA took advantage of a rare planet alignment to turbocharge their journeys into space.
NASA originally built the probes to last five years, but they have exceeded that lifespan many times .
As of August 20 and September 5, 2023, Voyager 2 and Voyager 1 will have been traveling for 46 years, respectively.
This is what Voyager 1 saw on its approach to Jupiter.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 reached Jupiter in 1979.
As they flew by the planet, they took about 50,000 pictures of Jupiter. These blew away scientists, as the quality of the pictures was much better than those taken from Earth, according to NASA.
These snaps taught scientists important facts about the planet's atmosphere, magnetic forces, and geology that would have been difficult to decipher otherwise.
The probes discovered two new moons orbiting Jupiter: Thebe and Metis.
They also spotted a thin ring around Jupiter.
The probe captured this picture as it was looking back at the planet backlit by the Sun.
Voyager 1 discovered volcanoes at the surface of Io, one of Jupiter's moons.
Next stop: Saturn.
In 1980 and 1981, the probes reached Saturn . The flyby gave scientists unprecedented insight into the planet's ring structure, atmosphere, and moons.
Voyager snapped Saturn's rings in more detail than ever before.
And showed every secret that Enceladus, Saturn's moon, had to offer.
Saturn, snapped as the probe flew away, was shown in a new light.
By 1986, Voyager 2 had made it to Uranus.
By 1986, Voyager 1 has finished its grand tour of the solar system, and few out towards space. But Voyager 2 kept on its exploring our nearest planets, passing 50,600 miles away from Uranus in January 1986.
Voyager 2 discovered two extra rings around Uranus , revealing the planet had at least 11, not 9.
Voyager 2 also spotted 11 previously unseen moons around Uranus.
Here is a picture of Miranda, Uranus's sixth-biggest moon.
Voyager 2 was the first spacecraft to observe Neptune from a close distance.
In 1989, 12 years after its launch, Voyager 2 passed within 3,000 miles of Neptune.
Here's Nepture taken by Voyager 2, in all its blue glory.
Voyager 2 took this unflattering pic of Triton's rough face.
It captured Triton, Neptune's moon in unprecedented detail.
And snapped Triton's southern hemisphere.
As it flew by, Voyager 2 uncovered Neptune's rings.
As its parting gift, Voyager 2 took this beautiful picture of light grazing Neptune's south pole.
This is Voyager 2's last picture. Since it wouldn't come across another planet on its ongoing journey, NASA switched off its cameras after its flyby of Neptune to conserve energy for other instruments.
Voyager 1 had one last trick up its sleeve.
As its last photographic hurrah in 1990, Voyager 1 took 60 images of the solar system from 4 billion miles away.
It gave us the Earth's longest selfie, dubbed the "pale blue dot."
This remains the longest-range selfie: a portrait of the Earth taken by a human-made probe from 4 billion miles away.
After this picture, NASA switched off Voyager 1's cameras to save energy. NASA could switch the probes' cameras back on , but it is not a priority for the mission.
Beyond the solar system
Though the probes are no longer sending pictures, they haven't stopped sending crucial information about space.
In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first human-made instrument to cross into interstellar space by crossing the boundary between our solar system and the rest of the universe, called the heliopause.
Voyager 2 was second, crossing that threshold in 2018 . The probe revealed that there was yet another layer outside of our heliosphere.
The probes keep sending back measurements from interstellar space, like weird hums likely coming from vibrations made by neighboring stars.
Even after their instruments are switched off, the probes' mission continues.
NASA is planning to switch more of the probes' instruments in the hope of extending their life to the 2030s.
But even after all their instruments become quiet, their mission will carry on. As they drift off, they will still be carrying a golden record that carries crucial information about humanity. If intelligent extraterrestrial life exists, they could use that information to reach out to us.
This article was originally published on June 6, 2022, and is being updated with the latest developments about Voyager 1 and 2.
- Main content
- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration
Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
Rae Paoletta • Mar 03, 2022
The best space pictures from the Voyager 1 and 2 missions
Launched in 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 and 2 missions provided an unprecedented glimpse into the outer solar system — a liminal space once left largely to the imagination. The spacecraft provided views of worlds we’d never seen before, and in some cases, haven’t seen much of since.
The Voyager probes were launched about two weeks apart and had different trajectories, like two tour guides at the same museum. Only Voyager 2 visited the ice giants — Uranus and Neptune — for example.
The Voyagers hold a unique position in the pantheon of space history because they’re still making it; even right now, Voyagers 1 and 2 are the only functioning spacecraft in interstellar space. Both hold a Golden Record that contains sights and sounds of Earth in case alien life were to find one of the spacecraft.
As the Voyager missions voyage on, it’s good to look back at how they captured our solar system before leaving it.
This content is hosted by a third party (youtube.com), which uses marketing cookies. Please accept marketing cookies to watch this video.
Let’s Go Beyond The Horizon
Every success in space exploration is the result of the community of space enthusiasts, like you, who believe it is important. You can help usher in the next great era of space exploration with your gift today.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Voyager 1's Historic Flyby of Jupiter in Photos

On March 5, 1979, NASA's Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter , the largest planet in the solar system, in a historic encounter with the largest planet in our solar system. The photos of Jupiter beamed back by Voyager 1 were amazing, as was the science they returned. See Voyager 1's most amazing photos of Jupiter and its moons in our gallery here.
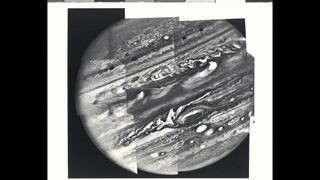
Parts of a Whole
Voyager 1 and 2 launched in 1977 to explore the cosmos. Voyager 1 took a series of images of Jupiter, which were compiled to create this mosaic of one entire hemisphere of the planet.
While the two spacecraft were originally designed for a five-year mission to explore Jupiter and Saturn, their successes and reliability allowed for additional exploration of Uranus, Neptune and more.
Credit: JPL

Standing Out in the Cosmos
Voyager 1 took three separate photos, using three different color filters, of Jupiter this day in 1979. Back on Earth in the Image Processing Lab at Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the images were combined, creating this colorful and breathtaking view of the Jovian planet.
Credit: JPL/NASA

A Planet and Two Moons
Io, Europa and Jupiter pose for a family photo. Io seems almost caught in Jupiter's Great Red Spot and glows with a very different color from Europa. Europa, on the other hand gives away very little detail about its composition with a glance from such a distance.
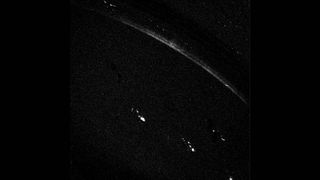
Jupiter's Night Light(s)
From within Jupiter's shadow Voyager 1 sent home this image detailing the planet's north pole, an aurora in action and possibly even some lightning. The image itself was taken over a long exposure of 3 minutes, 12 seconds with a wide angle camera.

A Window Inside?
Researchers believe this large brown oval, which was imaged Mar. 2, 1979, could allow a view into lower cloud levels of Jupiter if studied more closely.
Just above the brown spot lies the pale orange North Temperate Belt bordered to the south by the high speed North Temperate Current which moves with wind speeds up to 260 mi/hr (120 meters/sec).


A Big Ol' Spot
In early March 1979, Voyager 1 collected this image of the Great Red Spot and some other surrounding atmospheric activity. The smallest white ovals featured are 20 miles (30 km) across, some of which were observed four decades ago, at formation. The different disturbances in Jupiter's atmosphere move around the planet at different speeds.

Such Beautiful Contrast
Just below Jupiter's Great Red Spot, the planet's atmosphere has a great variation of textures and patterns. Using special computer processing, these details are enhanced to enable study in hopes of deepening understanding of the Jovian atmosphere.

Ring Around the Jupiter
On Mar. 4, 1979, this multiple exposure image provided the first evidence of a ring around the Jovian planet. Stars in the image appear as broken hairpins resulting from Voyager 1's motion during the more than 11 minute exposure. The image successfully completed it mission of searching for such rings at Jupiter.
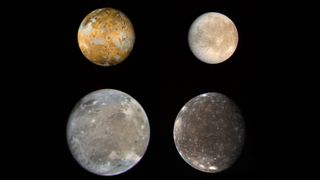
The Galilean Moons of Jupiter
In 1610, Galileo Galilei observed these four moons orbiting Jupiter. As a result, the group is referred to as the Galilean satellites of Jupiter. Shown here the relative sizes are compared — Io, on the top left; Europa, on the top right; Ganymede, on the bottom left; and Callisto, on the bottom right.
Ganymede and Callisto are larger than planet Mercury while Io and Europa are similar in size to Earth's moon. Io consists of active volcanoes and likely has a sulfurous composition. Ganymede and Callisto appear to consist mainly of water and water ice. Europa's make up is still largely a mystery waiting to be solved.

Active Volcanoes
To create this image of Jupiter's Io, several photos of the moon were snapped by Voyager 1 on Mar. 4, 1979. Centered on the moon a circular element has been connected to an known erupting volcano while across the image similar features can be identified. Io is the first-known body, other than Earth, where active volcanism has been seen.

Photobomber
While mapping Jupiter, Io snuck into the frame. Voyager 1 captured the side of the moon Jupiter never sees, revealing never-before-seen details of the Jovian satellite: several circles with dark centers and bright rims may be craters unknown on the moon until now. Without further study, researchers won't know if they are impact of volcanic craters.

Surprising Natural Colors
A color image of Jupiter's closest Galilean moon, Io, stuns viewers with its rich colors. Scientists believe the orange and red hues arise from sulfur compounds, salts and other volcanic sublimates. While volcanic craters and lava flows may explain the dark spots across the image.
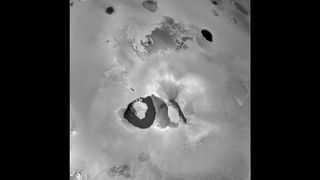
Loki, In Detail
The detailed structure of Loki, a volcano on Jupiter's Io, visualized clearly here in a Voyager 1 image. In this photo, the majority of the eruptive activity emanated from the possible rift in the dark linear feature. Also, a u-shaped "lava-lake" component reveals strange details, possibly solid sulfur "icebergs" in a liquid sulfur lake. This region claimed the hottest area on this moon at about 150 degrees Celsius.

Activity Afar
An active plume near the Loki volcano shines off the horizon of Io. The mosaic also presents views of fallout deposits from the active plume Pele at the heart-shaped feature to the southeast of Loki.
Credit: JPL/USGS/NASA
Small but Not Insignificant
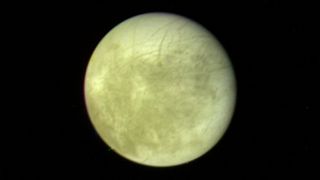
The smallest of the Galilean moons, Europa displays bright areas, surmised to be ice deposits, and darker spots expected to be rocky surfaces. Long linear structures across the northern hemisphere are features unique on the satellite. One theory suggests these lines could be fractures or faults in the moon's surface.

Similar but Not the Same
From about 2.6 million miles (4.2 million km) away, Voyager 1 snapped this image of Ganymede. Though larger than planet Mercury, the moon is much less dense. Ganymede, while reminiscent of Earth's moon, is four times as bright. Scientists speculate the Jovian moon could have areas, such as the north polar region, covered in water frost creating the brightness seen here.

Explaining the Sights
Several bright impact craters glow brightly in Voyager 1's image of Ganymede from Mar. 5, 1979. Many older impact craters, missing their rays, are visible as well. Some of the erosion may be caused by faulting of the surface materials.
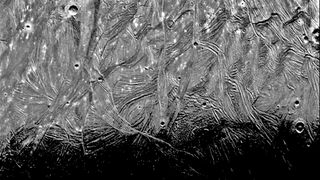
Strange Patterns
Jupiter's largest moon, Ganymede was imaged by Voyager 1 on Mar. 5, 1979. The image reveals intricate patterns of ridges and grooves. Scientists believe these features to be deformations in the satellite's thick icy crust.

A Trio of Info
Three images of Jupiter's Callisto combine to create this high resolution photo of the satellite. A large basin-like feature, discovered by Voyager 1, appears clearly on the upper left area of the moon. Across the center of this basin a brighter contrast is seen. Researchers believe these shining areas contain more clean ice as compared to the majority of Callisto's "dirty-ice" surface.
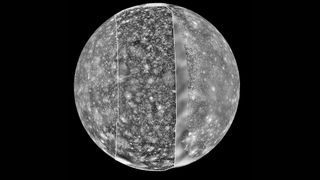
A Triad of Data
A mosaic of Callisto came from three different spacecraft. Voyager 1 contributed the left-side image and Voyager 2 provided the right-side image, both collected in 1979. The third, central portion originated from Galileo in September of 1996.
Credit: JPL/DLR/NASA
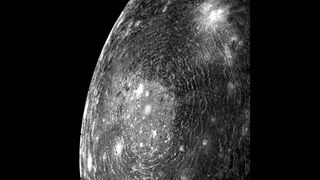
A Peak at What's Inside
March 6, 1979, Voyager 1 snapped this image of Callisto, one of Jupiter's largest moons, from almost 200,000 km away. The central focus of the image shows the complex circular structure that mirrors impact basins seen on Earth's moon and planet Mercury. Experts believe the patterns on Callisto demonstrate the planet's low density and lack of internal strength.

Christine Lunsford joined the Space.com team in 2010 as a freelance producer and later became a contributing writer, covering astrophotography images, astronomy photos and amazing space galleries and more. During her more than 10 years with Space.com, oversaw the site's monthly skywatching updates and produced overnight features and stories on the latest space discoveries. She enjoys learning about subjects of all kinds.
Satellites watch as 4th global coral bleaching event unfolds (image)
Happy Earth Day 2024! NASA picks 6 new airborne missions to study our changing planet
Russia vetoes UN resolution against nuclear weapons in space
Most Popular
- 2 Beavers are helping fight climate change, satellite data shows
- 3 Astronomers just discovered a comet that could be brighter than most stars when we see it next year. Or will it?
- 4 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 108 — Starliner: Better Late Than Never?
- 5 Boeing's Starliner spacecraft will not fly private missions yet, officials say
Voyager 1 to Take Pictures of Solar System Planets

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft, having completed its mission along with Voyager 2 to explore the outer planets, will use its cameras February 13-14 to take an unprecedented family portrait of most of the planets in our solar system.
The collection of images will be from a unique point-of-view -- looking down on the solar system from a position 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane in which the planets orbit the Sun. No other spacecraft has ever been in a position to attempt a similar series of photos of most of the planets.
Voyager 1, launched in 1977, is now about 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles) from Earth. The Voyager spacecraft are controlled by and their data received at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
"This is not just the first time, but perhaps the only time for decades that we'll be able to take a picture of the planets from outside the solar system," said Voyager Project Scientist Dr. Edward C. Stone of Caltech. No future space missions are planned that would fly a spacecraft so high above the ecliptic plane of the solar system, he said.
Starting shortly after 5 p.m. (PST) on Feb. 13 and continuing over the course of four hours, Voyager 1 will point its wide- and narrow-angle cameras at Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, Earth and Venus. Mercury is too close to the Sun to be photographed by Voyager's cameras, and Pluto is too far away and too small to show up in images taken by the spacecraft. Beginning with the dimmest of the targets - Neptune -- and working toward the Sun, Voyager 1 will shutter about 64 images of the planets and the space between them.
The constellation Eridanus (The River), stretching behind the planets from Voyager 1's perspective, will provide the backdrop for the images.
Due to the schedules of several spacecraft being tracked by NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN), the images will be recorded on board Voyager 1 and played back to DSN receivers on Earth in late March. The Voyager imaging team estimates that processing the images to reveal as much detail as possible will take several weeks. Most of the planets will appear as relatively small dots (about one to four pixels, or picture elements, in the 800-by-800 pixel frame of one Voyager image).
The enormous scale of the subject matter makes it unlikely that the entire set of images can be mosaicked to produce for publication a single photograph showing all the planets. Even an image covering the planets out to Jupiter would easily fill a poster-sized photographic print. At the least, imaging team hopes to assemble a mosaicked image composed of the frames showing Earth, Venus and perhaps Mars together.
Voyager 1, rather than Voyager 2, received the solar system photo assignment largely because of Voyager 1's improved viewpoint of the planets.
Voyager 1 completed flybys of Jupiter and Saturn in 1979 and 1980, respectively. Voyager 2 flew past Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986 and Neptune last August. Both are now on missions that will take the spacecraft to the boundary of our solar system and into interstellar space.
According to Voyager engineers and scientists, the only potential damage from pointing the cameras toward the Sun is that the shutter blades of the wide-angle camera might warp. There are no plans, however, to use Voyager 1's cameras after the solar system photo series is completed.
The Voyager mission is conducted by Caltech's JPL for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications.
Inside NASA's 5-month fight to save the Voyager 1 mission in interstellar space

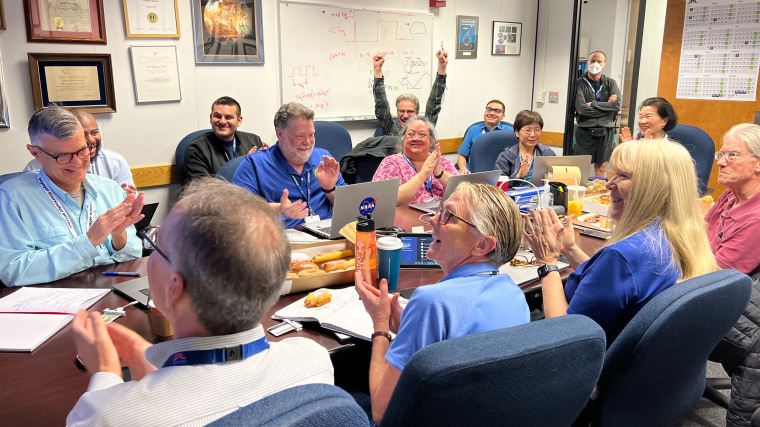
After working for five months to re-establish communication with the farthest-flung human-made object in existence, NASA announced this week that the Voyager 1 probe had finally phoned home.
For the engineers and scientists who work on NASA’s longest-operating mission in space, it was a moment of joy and intense relief.
“That Saturday morning, we all came in, we’re sitting around boxes of doughnuts and waiting for the data to come back from Voyager,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for the Voyager 1 mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “We knew exactly what time it was going to happen, and it got really quiet and everybody just sat there and they’re looking at the screen.”
When at long last the spacecraft returned the agency’s call, Spilker said the room erupted in celebration.
“There were cheers, people raising their hands,” she said. “And a sense of relief, too — that OK, after all this hard work and going from barely being able to have a signal coming from Voyager to being in communication again, that was a tremendous relief and a great feeling.”

The problem with Voyager 1 was first detected in November . At the time, NASA said it was still in contact with the spacecraft and could see that it was receiving signals from Earth. But what was being relayed back to mission controllers — including science data and information about the health of the probe and its various systems — was garbled and unreadable.
That kicked off a monthslong push to identify what had gone wrong and try to save the Voyager 1 mission.
Spilker said she and her colleagues stayed hopeful and optimistic, but the team faced enormous challenges. For one, engineers were trying to troubleshoot a spacecraft traveling in interstellar space , more than 15 billion miles away — the ultimate long-distance call.
“With Voyager 1, it takes 22 1/2 hours to get the signal up and 22 1/2 hours to get the signal back, so we’d get the commands ready, send them up, and then like two days later, you’d get the answer if it had worked or not,” Spilker said.

The team eventually determined that the issue stemmed from one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers. Spilker said a hardware failure, perhaps as a result of age or because it was hit by radiation, likely messed up a small section of code in the memory of the computer. The glitch meant Voyager 1 was unable to send coherent updates about its health and science observations.
NASA engineers determined that they would not be able to repair the chip where the mangled software is stored. And the bad code was also too large for Voyager 1's computer to store both it and any newly uploaded instructions. Because the technology aboard Voyager 1 dates back to the 1960s and 1970s, the computer’s memory pales in comparison to any modern smartphone. Spilker said it’s roughly equivalent to the amount of memory in an electronic car key.
The team found a workaround, however: They could divide up the code into smaller parts and store them in different areas of the computer’s memory. Then, they could reprogram the section that needed fixing while ensuring that the entire system still worked cohesively.
That was a feat, because the longevity of the Voyager mission means there are no working test beds or simulators here on Earth to test the new bits of code before they are sent to the spacecraft.
“There were three different people looking through line by line of the patch of the code we were going to send up, looking for anything that they had missed,” Spilker said. “And so it was sort of an eyes-only check of the software that we sent up.”
The hard work paid off.
NASA reported the happy development Monday, writing in a post on X : “Sounding a little more like yourself, #Voyager1.” The spacecraft’s own social media account responded , saying, “Hi, it’s me.”
So far, the team has determined that Voyager 1 is healthy and operating normally. Spilker said the probe’s scientific instruments are on and appear to be working, but it will take some time for Voyager 1 to resume sending back science data.
Voyager 1 and its twin, the Voyager 2 probe, each launched in 1977 on missions to study the outer solar system. As it sped through the cosmos, Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn, studying the planets’ moons up close and snapping images along the way.
Voyager 2, which is 12.6 billion miles away, had close encounters with Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and continues to operate as normal.
In 2012, Voyager 1 ventured beyond the solar system , becoming the first human-made object to enter interstellar space, or the space between stars. Voyager 2 followed suit in 2018.
Spilker, who first began working on the Voyager missions when she graduated college in 1977, said the missions could last into the 2030s. Eventually, though, the probes will run out of power or their components will simply be too old to continue operating.
Spilker said it will be tough to finally close out the missions someday, but Voyager 1 and 2 will live on as “our silent ambassadors.”
Both probes carry time capsules with them — messages on gold-plated copper disks that are collectively known as The Golden Record . The disks contain images and sounds that represent life on Earth and humanity’s culture, including snippets of music, animal sounds, laughter and recorded greetings in different languages. The idea is for the probes to carry the messages until they are possibly found by spacefarers in the distant future.
“Maybe in 40,000 years or so, they will be getting relatively close to another star,” Spilker said, “and they could be found at that point.”
Denise Chow is a reporter for NBC News Science focused on general science and climate change.

The Pale Blue Dot – Revisited
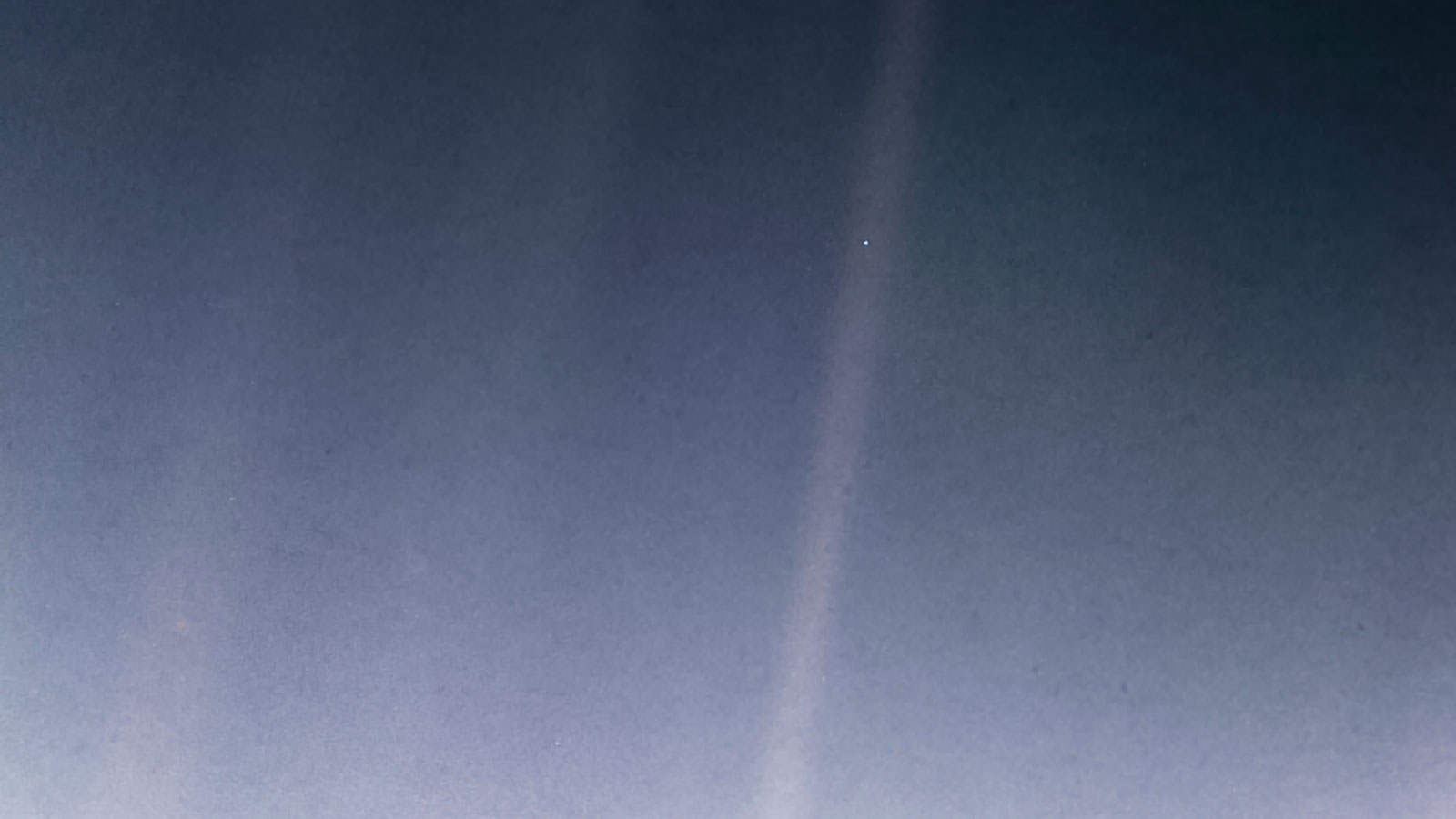

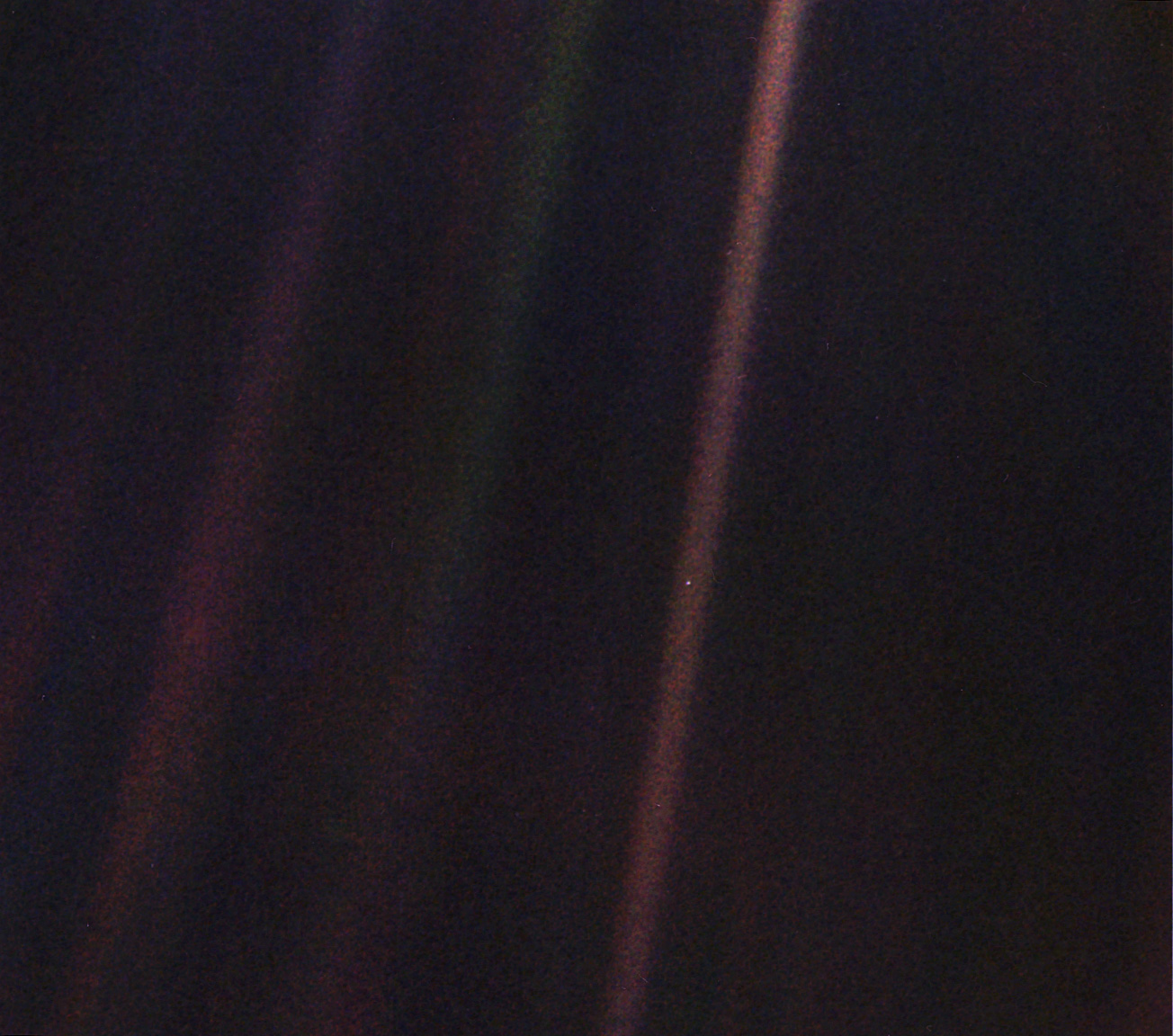
The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA’s Voyager 1 at a distance of 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) from the Sun. The image inspired the title of scientist Carl Sagan's book, "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space," in which he wrote: "Look again at that dot. That's here. That's home. That's us."
The revised image was processed by JPL engineer and image processing enthusiast Kevin M. Gill with input from two of the image's original planners, Candy Hansen and William Kosmann.
Original – Highest-Resolution (1990)
(tif) (4.32 MB)

Original (1990)
(jpg) (414.21 KB)
Pale Blue Dot Revisited (2020)
(tif) (29.85 MB)
More From Forbes
Nasa celebrates as 1977’s voyager 1 phones home at last.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar ... [+] space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
Voyager 1 has finally returned usable data to NASA from outside the solar system after five months offline.
Launched in 1977 and now in its 46th year, the probe has been suffering from communication issues since November 14. The same thing also happened in 2022 . However, this week, NASA said that engineers were finally able to get usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.
Fixing Voyager 1 has been slow work. It’s currently over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means a radio message takes about 22.5 hours to reach it—and the same again to receive an answer.
The problem appears to have been its flight data subsystem, one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers. Its job is to package the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth. Since the computer chip that stores its memory and some of its code is broken, engineers had to reinsert that code into a new location.
Next up for engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California is to adjust other parts of the FDS software so Voyager 1 can resume sending science data.
Google Issues ‘Critical’ Chrome Update For All Windows Users
New ios 18 ai security move changes the game for all iphone users, world war i tactics make a comeback as a ukrainian gunner in the back of a propeller plane shoots down a russian drone, beyond the ‘heliopause’.
The longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history, Voyager 1, was launched on September 5, 1977, while its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, was launched a little earlier, on August 20, 1977. Voyager 2—now 12 billion miles away and traveling more slowly—continues to operate normally.
Both are now beyond what astronomers call the heliopause—a protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the sun, which is thought to represent the sun’s farthest influence. Voyager 1 got to the heliopause in 2012 and Voyager 2 in 2018.
The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA’s Voyager 1 at a distance of ... [+] 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) from the sun. The image inspired the title of scientist Carl Sagan's book, "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space," in which he wrote: "Look again at that dot. That's here. That's home. That's us."
Pale Blue Dot
Since their launch from Cape Canaveral, Florida, aboard Titan-Centaur rockets, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have had glittering careers. Both photographed Jupiter and Saturn in 1979 and 1980 before going their separate ways. Voyager 1 could have visited Pluto, but that was sacrificed so scientists could get images of Saturn’s moon, Titan, a maneuver that made it impossible for it to reach any other body in the solar system. Meanwhile, Voyager 2 took slingshots around the planets to also image Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989—the only spacecraft ever to image the two outer planets.
On February 14, 1990, when 3.7 billion miles from Earth, Voyager 1 turned its cameras back toward the sun and took an image that included our planet as “a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam.” Known as the “Pale Blue Dot,” it’s one of the most famous photos ever taken. It was remastered in 2019 .
Wishing you clear skies and wide eyes.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Mission Status
Instrument status.
Where are the Voyagers now?
To learn more about Voyager, zoom in and give the spacecraft a spin. View the full interactive experience at Eyes on the Solar System . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
View Voyager
Space Flight Operations Schedule (SFOS)
SFOS files showing Voyager activity on Deep Space Network (DSN)
2024 Tracking Schedule
2023 tracking schedule, 2022 tracking schedule, 2021 tracking schedule, 2020 tracking schedule, 2019 tracking schedule, 2018 tracking schedule, 2017 tracking schedule, 2016 tracking schedule, 2015 tracking schedule, 2014 tracking schedule, 2013 tracking schedule, 2012 tracking schedule, 2011 tracking schedule, 2010 tracking schedule, 2009 tracking schedule, 2008 tracking schedule, 2007 tracking schedule, 2006 tracking schedule, 2005 tracking schedule, 2004 tracking schedule, 2003 tracking schedule, 2002 tracking schedule, 2001 tracking schedule, 2000 tracking schedule, 1999 tracking schedule, 1998 tracking schedule, 1997 tracking schedule, 1996 tracking schedule, 1995 tracking schedule, 1994 tracking schedule.
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access Only $1 for 4 weeks
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- Videos & Podcasts
- FT App on Android & iOS
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Premium newsletters
- Weekday Print Edition
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Premium Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Everything in Print
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
They took more than 33,000 pictures of Jupiter and its five major satellites. Saturn The Voyager 1 and 2 Saturn encounters occurred nine months apart, in November 1980 and August 1981. Voyager 1 is leaving the solar system. Voyager 2 completed its encounter with Uranus in January 1986 and with Neptune in August 1989, and is now also en route ...
Each Voyager space probe carries a gold-plated audio-visual disc in the event that the spacecraft is ever found by intelligent life forms from other planetary systems. Examine the images and sounds of planet earth. Images Voyager Took The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft explored Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before starting their journey ...
Here are 18 groundbreaking photos from their incredible mission. This montage shows examples of striking images of the solar system Voyager 1 and 2 took on their missions. NASA/JPL/Insider. Nearly ...
Early Voyager 1 Images of Jupiter Full Resolution: TIFF (491.5 kB) JPEG (21.78 kB) 1996-09-26: Jupiter: Voyager: Imaging Science Subsystem: 400x400x3: PIA00029: First Close-up Image of Jupiter from Voyager ...
This is an image of the planet Uranus taken by the spacecraft Voyager 2 in 1986. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech. Full Image Details. This image, taken by NASA's Voyager 2 early in the morning of Aug. 23, 1989, is a false color image of Triton, Neptune's largest satellite; mottling in the bright southern hemisphere is present.
Image: NASA / JPL / Ted Stryk. Saturn as seen by Voyager 1 The last picture from Voyager 1's approach to Saturn in which the entire planet and ring system can be seen in a single frame. Image: NASA/JPL/Björn Jónsson. Voyager 2's best view of Enceladus This was the Voyager mission's best view of Enceladus, captured by Voyager 2 on August 26 ...
PrevPage 1 of 15. This image of the Earth and moon are in a single frame. Voyager was the first spacecraft to achieve this and captured the iconic image on Sept. 18, 1977, by Voyager 1 when it was ...
On Feb. 14, 1990, NASA's Voyager 1 probe snapped a photo of Earth from 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) away. The image shows our home planet as it truly is — a tiny, lonely outpost of ...
On March 5, 1979, NASA's Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, in a historic encounter with the largest planet in our solar system. See the amazing photos here.
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. 45 years on, Voyager 1 and 2 continue to provide us with observations of the farthest reaches of space.. Our Voyager 1 spacecraft zoomed toward Jupiter in January and February 1979, capturing hundreds of images of Jupiter during its approach, including ...
Voyager 1's family portrait of six planets taken on Feb. 14, 1990, when the spacecraft was 3.7 billion miles from Earth. Remastered Voyager 1 photograph of Earth, Pale Blue Dot Revisited, taken from 3.7 billion miles away, released in February 2020. Earth is the tiny point of light near the image's center.
Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 1 spacecraft began an epic journey that continues to this day. The second of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 1 lifted off on Sept. 5, 1977, 16 days after its twin left on a similar voyage. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, managed the two spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets.
NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft, having completed its mission along with Voyager 2 to explore the outer planets, will use its cameras February 13-14 to take an unprecedented family portrait of most of the planets in our solar system. The collection of images will be from a unique point-of-view -- looking down on the solar system from a position 32 ...
Voyager 1 Perspective for Family Portrait Full Resolution: TIFF (2.496 MB) JPEG (336.9 kB) 2021-05-11: Voyager: 1241x427x3: PIA24572: Weak and Strong Plasma Oscillation Signals Full Resolution: TIFF (960.8 kB) JPEG (80.75 kB) 2021-11-30: Europa: Galileo Voyager: 1100x600x3: PIA24895: Three Views of Europa Full Resolution: ...
The Voyager 1 probe is the most distant human-made object in existence. After a major effort to restore communication with it, NASA announced success this week. IE 11 is not supported.
The Pale Blue Dot - Revisited. The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA's Voyager 1 at a distance of 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) from the Sun. The image inspired the title of scientist Carl Sagan's book, "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space," in which he wrote: "Look again at that ...
Voyager 1 got to the heliopause in 2012 and Voyager 2 in 2018. The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA's Voyager 1 at a distance of ... [+] 3.7 billion miles (6 ...
Voyager 1 looked back at Saturn on Nov. 16, 1980, four days after the spacecraft flew past the planet, to observe the appearance of Saturn and its rings from this unique perspective. A few of the spokelike ring features discovered by Voyager appear in the rings as bright patches in this image, taken at a distance of 5.3 million kilometers (3.3 ...
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first ...
Voyager 1's flight data system collects information from the spacecraft's science instruments and bundles it with engineering data that reflects its current health status. Mission control on ...
Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year. Distance from Sun: This is a real-time indicator of Voyagers' straight-line distance from the sun in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi ...
The craft embodies a golden age of space exploration. The writer is a science commentator. A ghost has come back to life. Voyager 1, a spacecraft dispatched in the 1970s that had been sending ...