Available travel vaccines
The following vaccinations are available for people travelling abroad.

Cholera vaccination
Vaccination against cholera isn't routinely needed for most travellers.
But in some cases it may be recommended for aid workers and people likely to have limited access to medical services – for example, people working in refugee camps or after natural disasters.
Most cases of cholera are confined to regions of the world with poor sanitation and water hygiene, such as parts of:
- South America
The vaccine is usually given as a drink in 2 separate doses, taken 1 to 6 weeks apart.
Children aged 2 to 6 years old should have a third dose taken 1 to 6 weeks after the second dose.
You should make sure you have the final dose of this vaccine at least a week before you travel.
A single booster dose or full revaccination is usually recommended if you have previously been vaccinated against cholera and you're planning to travel to an area where the infection is common.
Diphtheria vaccination
A combined vaccination that protects against diphtheria , polio and tetanus is routinely given to all children in the UK.
You should make sure you and your children are up-to-date with your routine vaccinations before travelling.
Further booster doses are usually only recommended if you're going to visit parts of the world where diphtheria is widespread and your last vaccination dose was more than 10 years ago.
Diphtheria is more common in parts of the world where fewer people are vaccinated, such as:
- Central and Southeast Asia
- Eastern Europe
Additional doses of the vaccination are given in a single 3-in-1 Td/IPV (tetanus, diphtheria and polio) injection.
Hepatitis A vaccination
Vaccination against hepatitis A is recommended if you're travelling to countries where there are poor levels of sanitation and hygiene, and hepatitis A is common.
Ask your GP, pharmacy or travel clinic if you should have the hepatitis A vaccine if you're travelling to:
- Sub-Saharan and North Africa
- the Middle East
- South and Central America
The vaccination against hepatitis A is usually given as a single initial injection, with a second dose 6 to 12 months later. Two doses should protect you for at least 25 years.
You should preferably have the initial dose at least 2 weeks before you leave, although it can be given up to the day of your departure if needed.
Jabs that offer combined protection against hepatitis A and hepatitis B or typhoid are also available if you're likely to also be at risk of these conditions.
Hepatitis B vaccination
Vaccination against hepatitis B is recommended if you're travelling in parts of the world where hepatitis B is common, especially if you'll be doing activities that increase your risk of developing the infection.
Hepatitis B is spread through blood and body fluids. Things like having sex, injecting drugs or playing contact sports on your travels can increase your risk.
Anyone travelling for long periods or who's likely to need medical care while abroad is also at increased risk.
Hepatitis B is found worldwide, but it's more common in parts of:
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Southern and Eastern Europe
The hepatitis B vaccination generally involves a course of 3 injections. Depending on how quickly you need protection, these may be spread over a period as long as 6 months or as short as 3 weeks.
A combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B jab is also available if you're likely to be at risk of both these conditions while travelling.
Japanese encephalitis vaccination
Vaccination against Japanese encephalitis is usually recommended if you're planning a long stay (usually at least a month) in a country where you could get the condition.
It's particularly important if:
- you're visiting during the rainy season or there's a year-round risk because of a tropical climate
- you're going to visit rural areas, such as rice fields or marshlands
- you'll be taking part in any activities that may increase your risk of becoming infected, such as cycling or camping
Japanese encephalitis is found throughout Asia and beyond. The area it's found in stretches from the western Pacific islands in the east, across to the borders of Pakistan in the west.
It's found as far north as Northeastern China and as far south as the islands of the Torres Strait and Cape York in Northeastern Australia.
Despite its name, Japanese encephalitis is now relatively rare in Japan because of mass immunisation programmes.
Find out more about risk areas on the Travel Health Pro website
Vaccination against Japanese encephalitis usually consists of 2 injections, with the second dose given 28 days after the first.
Ideally, you need to have the second dose a week before you leave.
Meningococcal meningitis vaccination
Vaccination against some types of meningococcal meningitis is usually recommended if you're travelling to areas at risk and your planned activities put you at higher risk – for example, if you're a long-term traveller who has close contact with the local population.
High-risk areas for meningococcal meningitis include:
- parts of Africa
- Saudi Arabia during the mass gatherings of Hajj or Umrah
All travellers to Saudi Arabia for the Hajj or Umrah pilgrimages are required to show proof of vaccination.
If travelling to a high-risk area, you should be vaccinated against meningococcal meningitis with a MenACWY vaccine , also known as the quadrivalent meningococcal meningitis vaccine.
This is a single injection that should be given 2 to 3 weeks before you travel. Babies under a year old need 2 injections.
You should have the MenACWY vaccine before travelling to high-risk areas, even if you had the meningitis C vaccine as a child.
Read more about the meningococcal meningitis vaccines .
Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccination
The MMR vaccine that protects against measles , mumps and rubella is routinely given to all children in the UK.
You should make sure you and your children are up-to-date with routine vaccinations, including MMR, before travelling.
If you haven't been fully vaccinated against these conditions or you're not already immune, you should ask about MMR vaccination before you travel.
The MMR vaccine is given as 2 injections. These are usually given when a child is 3 years and 4 months old.
But if vaccination has been missed previously, adults can have the doses 1 month apart, and children can have them 3 months apart if necessary.
Read more about the MMR vaccine .
Polio vaccination
A combined vaccination that protects against diphtheria, polio and tetanus is routinely given to all children in the UK.
Further booster doses are usually only recommended if you're going to visit parts of the world where polio is, or has recently been, present and your last vaccination dose was more than 10 years ago.
Currently the condition is most common in Pakistan and Afghanistan, but it's also a risk in other regions of the world.
Read more about the Td/IPV (3-in-1) vaccine .
Rabies vaccination
Vaccination against rabies is advised if you're travelling to an area where you could get rabies, particularly if:
- you're staying for a month or more
- there's unlikely to be quick access to appropriate medical care
- you plan to do activities that could put you at increased risk of exposure to rabies, such as cycling or running
Rabies can be found in many parts of the world. GOV.UK provides a detailed list of countries that have rabies in domestic animals or wildlife .
Vaccination involves a course of 3 injections before you travel, usually given over a period of 28 days.
If you're bitten, licked or scratched by an animal in a country where rabies is a problem, further doses of rabies vaccine (with or without a special anti-rabies injection given around the wound) may be required as emergency treatment.
Find out more about the rabies vaccine
GOV.UK: Rabies risks for travellers
Tetanus vaccination
A combined vaccination that protects against diphtheria, polio and tetanus is routinely given to all children in the UK.
Further booster doses are usually only recommended if:
- you're travelling to areas where access to medical services is likely to be limited and your last vaccination dose was more than 10 years ago
- you've not had two booster doses
Read more about the Td/IPV (3-in-1) vaccine .
Tick-borne encephalitis vaccination
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is usually recommended for anyone who plans to live or work in a high-risk area, or hike and camp in these areas during late spring or summer.
The ticks that cause TBE are mainly found in forested areas of central, eastern and northern Europe, although at-risk areas also include eastern Russia and some countries in east Asia, including some regions of China and Japan.
The vaccination requires a course of 3 injections for full protection. The second dose is given 1 to 3 months after the first and provides immunity for about a year.
A third dose, given 5 to 12 months after the second, provides immunity for up to 3 years.
The course can sometimes be accelerated if necessary. This involves 2 doses being given 2 weeks apart.
Booster doses of the vaccine are recommended every 3 years, if necessary.
Tuberculosis (TB) vaccination
The BCG vaccine (which stands for Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine) protects against tuberculosis , which is also known as TB.
The BCG vaccine isn't given as part of the routine NHS vaccination schedule. It's given on the NHS only when a child or adult is thought to have an increased risk of coming into contact with TB.
When preparing for travel abroad, the BCG vaccine is recommended for any unvaccinated people under 16 who'll be living or working with friends, family or local people for more than 3 months in a country where TB is common or the risk of multi-drug resistant TB is high.
The BCG vaccine is given as a single injection.
Areas of the world where the risk of TB is high enough to recommend BCG vaccination for previously unvaccinated travellers include:
- parts of South and Southeast Asia
Read more about the BCG vaccine .
Typhoid vaccination
Vaccination against typhoid fever is recommended if you're travelling to parts of the world where the condition is common, particularly if you'll:
- have frequent or prolonged exposure to conditions where sanitation and food hygiene are likely to be poor
- be staying or working with local people
High-risk areas include:
- parts of South and Central America
Two main vaccines are available for typhoid fever in the UK. One is given as a single injection, and the other is given as 3 capsules to take on alternate days.
It's also possible to have a combined hepatitis A and typhoid jab.
Ideally, the typhoid vaccine should be given at least 1 month before you travel, but it can be given closer to your travel date if necessary.
Booster vaccinations are recommended every 3 years if you continue to be at risk of infection.
Read more about the typhoid vaccine .
Yellow fever vaccination
Vaccination against yellow fever is advised if you're travelling to areas where there's a risk of getting yellow fever.
Some countries require a proof of vaccination certificate before they let you enter the country.
Yellow fever occurs in some areas of tropical Africa and Central and South America. More information about yellow fever and areas where it's found is available on Travel Health Pro .
A single dose of the yellow fever vaccine is thought to provide lifelong protection. For most people, a booster dose is no longer recommended.
You must have a yellow fever vaccination at least 10 days before you travel. You will also need to complete a yellow fever vaccination checklist to make sure you can have the vaccine.
Find out more about the yellow fever vaccination checklist on the Travel Health Pro website
You should be issued with an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis when you have the vaccine. This certificate is valid for life.
Some people cannot have the yellow fever vaccine.
Read more about the yellow fever vaccine and who can have it .
When to get further advice
Speak to your GP before having any vaccinations if:
- you're planning to get pregnant
- you're pregnant
- you're breastfeeding
- you have an immune deficiency
- you have any allergies
Page last reviewed: 16 March 2023 Next review due: 16 March 2026
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
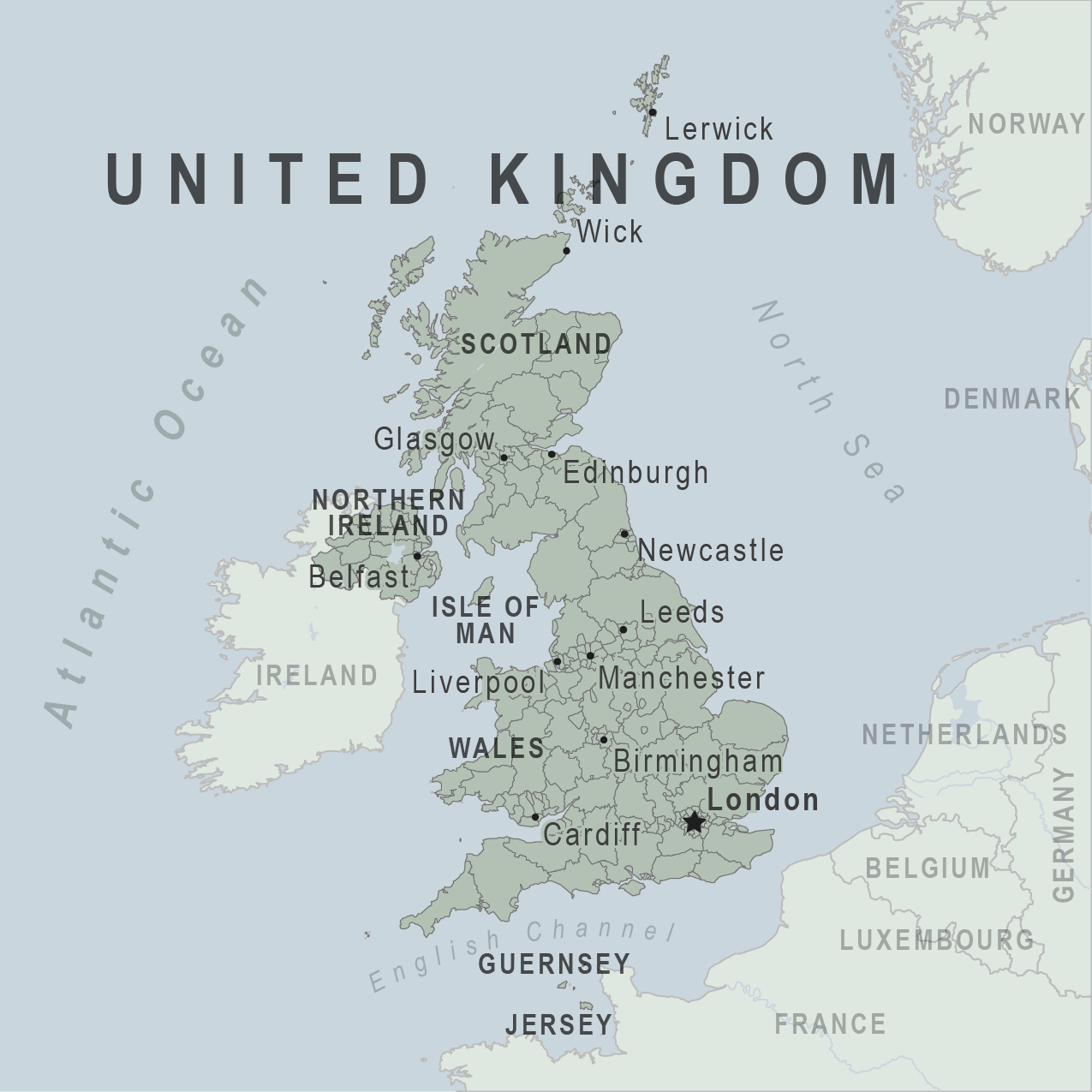
United Kingdom, including England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
There are no notices currently in effect for United Kingdom, including England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis A
Consider hepatitis A vaccination for most travelers. It is recommended for travelers who will be doing higher risk activities, such as visiting smaller cities, villages, or rural areas where a traveler might get infected through food or water. It is recommended for travelers who plan on eating street food.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to the United Kingdom. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to the United Kingdom.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
the United Kingdom is free of dog rabies. However, rabies may still be present in wildlife species, particularly bats. CDC recommends rabies vaccination before travel only for people working directly with wildlife. These people may include veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers working with specimens from mammalian species.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Tick-borne Encephalitis
Avoid bug bites
Learn more about tick-borne encephalitis at your destination .
Tick-borne Encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Airborne & droplet.
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in the United Kingdom, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Although the United Kingdom is an industrialized country, bug bites here can still spread diseases. Just as you would in the United States, try to avoid bug bites while spending time outside or in wooded areas.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Consider using permethrin-treated clothing and gear if spending a lot of time outside. Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in the United Kingdom include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip:
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in the heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if you are driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance for things your regular insurance will not cover.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medicines you take.
- Bring copies of your prescriptions for medicine and for eye glasses and contact lenses.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call the United Kingdom’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Make sure there are seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in the United Kingdom, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in the United Kingdom.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for United Kingdom for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Travel health advice and travel vaccinations
You should make an appointment for a travel health risk assessment if you’re travelling abroad and think you need:
- a malaria risk assessment
- further advice
A travel health professional will take you through your travel health risk assessment.
Your GP is no longer your point of contact for a travel health risk assessment, including travel vaccines.
NHS travel health service
NHS Scotland provides a travel health service that includes some free vaccines.
To find information on how to make an appointment for a travel health risk assessment in Scotland, contact the NHS health board where you live.
Private travel clinics
You can also visit an independent (private) travel clinic for:
- a travel health risk assessment
- travel advice
- other travel vaccines
You should arrange a travel health risk assessment 6 to 8 weeks before you travel. This gives time for any vaccines you need to become fully effective.
If your trip is sooner, remember it’s never too late to get advice.
Travel health risk assessment
If you’re planning to travel outside the UK, your travel health needs will depend on your individual situation. This includes:
- your destination
- how long you’ll stay
- what you’ll be doing
- your general health
The fitfortravel website provides country-specific advice on:
- recommended vaccines
- other risk prevention advice
If you think you need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional.
A travel health risk assessment is also recommended for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets aren’t required. This includes:
- older people
- those with a weakened immune system
- those with long-term conditions that need medications
- pregnant women
Travel vaccines
The following travel vaccines are free on the NHS in Scotland:
- diphtheria, polio and tetanus (combined booster)
- hepatitis A
It’s likely that you’ll have to pay for vaccines against:
- yellow fever
- Japanese encephalitis
- tick-borne encephalitis
You may also have to pay for the following vaccines if they’re only needed for travel purposes:
- hepatitis B
- tuberculosis (TB)
Proof of vaccination
To enter some countries you may need proof that you have had particular vaccines. This includes the yellow fever vaccine.
Yellow fever vaccines are only available from designated centres. To find out if you need a yellow fever vaccine or proof of the vaccine, you should contact a yellow fever clinic.
To request a list of any other vaccines held on your GP record, contact your GP practice. GP practices cannot provide proof of COVID vaccine.
Preventing risk while travelling
Vaccines or anti-malarial tablets will not protect against all travel health risks. This means you’ll need to take extra steps to protect your health whilst travelling abroad.
The fitfortravel website has further advice on preventing health risks whilst travelling. This includes information on:
- general travel advice
- disease prevention
Travelling abroad to visit friends and relatives
If you’re travelling abroad to visit friends or relatives, you may be at higher risk of developing travel-related illnesses. For example, malaria or typhoid. This could be because:
- you may be living with the local community
- your trip might be longer than the average holiday
- you might be visiting more rural areas where it’s difficult to take precautions that reduce your risk
The fitfortravel website provides information and advice on visiting friends and family abroad .
Travel safety advice
You can find country-specific safety and security advice through the UK government website .

Travel insurance advice
Many countries don’t have the same access to medical treatments as the UK and can be expensive.
It’s recommended that all travellers get comprehensive travel insurance before travelling.
When you return home
If you become unwell and/or develop a fever when you return home, it’s important to get medical advice as soon as possible. You should seek medical help even if it’s up to 1 month after you’ve been travelling.
Always make sure you tell the health professional that you’ve recently travelled abroad. This is especially important if you have been to a country where malaria is a risk.
Donating blood after travelling abroad
Travel outside the UK can affect whether you can give blood donations. This is because some infections may be caught abroad. This is usually through mosquito or other insect bites.
There are conditions for donating blood if you’ve been to certain countries. This can depend on your length of stay and some other factors.
Further information on donating blood after travelling abroad

Source: Public Health Scotland - Opens in new browser window
Last updated: 01 March 2024
Help us improve NHS inform
Your feedback has been received
Don’t include personal information e.g. name, location or any personal health conditions.

- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition
As foreign travel rules ease, what is required to enter the UK?
With a range of proofs needed, the market for fake Covid test and vaccination certificates is booming
- Coronavirus – latest updates
- See all our coronavirus coverage
When the UK reopens for foreign travel on Monday, a number of requirements for entry to the UK will be in force, involving a number of different types of tests and certificates.
The black market for pandemic-related products, including fake negative Covid tests and fake vaccination certificates, is booming.
Border officials have warned that an estimated 100 fake negative Covid tests were being caught each day even before the borders are opened further for foreign travel.
What is required to enter the UK?
The details are to be confirmed, but it’s expected that up to three polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests will be required: one before entry showing a negative result, and up to two afterwards, depending on the country from which a traveller has arrived.
PCR tests cost an average of £120 a test for each person.
What about other countries?
Countries have differing requirements, but some, including EU states, have said a requirement involving vaccination will be required to enter them.
What do you need certificates for in the UK?
To enter the UK, certificates are needed to provide evidence of a negative Covid-19 test. The test result must be in either English, French or Spanish.
Depending on the country of origin, up to two more tests could be required, both of which would need a certificate to prove a negative result.
What about vaccination?
The government has suggested it will incorporate a vaccination status into the existing NHS Covid app.
However, there are currently no requirements to prove vaccination status when entering the UK. The level of vaccination progress will be taken into account when determining how countries should be classified.
What checks are there?
Border Force officers at airports and ports are responsible for checking the certificates, although no specific training is provided.
Some Border Force officers said the certificates can be easy to spot as they often have spelling mistakes or punctuation errors. But as there is no single template for a negative test, it can be challenging.
What is the scale of the use of fakes?
Border Force staff have said that by their nature it is challenging to estimate the true scale of the use of fake certificates. However, union officials have said that at least 100 fake certificates are caught each day – equal to thousands a month.
Cybersecurity researchers said there were more than 1,200 vendors on the dark web offering fake certificates, vaccines, treatment drugs and protective equipment. Individual channels on encrypted messaging apps have more than 1,000 subscribers.
- Coronavirus
- Vaccines and immunisation
- Immigration and asylum
Most viewed
Working to make government more effective
- Accessiblility
- Media centre
- Partner with us
Covid international travel rules
Testing and quarantine requirements have been progressively removed since the start of 2022.

Are there any rules for international travel to the UK?
Testing and quarantine requirements have been progressively removed since the start of 2022. Testing and quarantine requirements were removed for fully vaccinated individuals and under 18s on 11 February, and then for unvaccinated individuals on 18 March, along with passenger locator forms for all arrivals. [1] Remaining restrictions were also removed in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. [2]
International travel for leisure in England had first resumed in May 2021. Initially countries were given a red, amber, or green rating with different rules for testing and quarantining on return.
The government simplified this system in October 2021, with only the red list remaining, and the red list was cleared of all countries on 1 November. In late November and early December 2021, some countries were added again, amid concerns about the Omicron variant. These countries were removed again as it became clear that Omicron was circulating widely within the UK. [3]
Arrivals from red list countries were required to take a pre-departure test and book a 10-day stay in a managed quarantine hotel with day 2 and day 8 tests, regardless of vaccination status. For countries not on the red list, arrival requirements depended on vaccination status, with vaccinated travellers subject to fewer requirements than unvaccinated arrivals by the end of 2021.
The government has stated that it has contingency plans in place for a new variant but these have not been set out in detail. [4]
Is this in line with what other countries are doing?
A small number of countries have also removed all travel restrictions – including Ireland, Iceland, Norway. But many still have some entry requirements, particularly when it comes to testing. Others are also still restricting access for unvaccinated individuals or, in a few cases, for most non-residents. [5]
How do Covid passports for travel work?
Although travel to the UK is no longer dependent on vaccination status, many countries still require proof of vaccination.
A Covid passport for travel is incorporated into the existing NHS app (which is different from the NHS Covid-19 contact tracing app). [6] The app is also available for Welsh residents, while Northern Ireland and Scotland have their own apps. Fully vaccinated children aged 12 to 15 can now request an NHS Covid pass letter for travel. From 3 February 2022 children aged 13 and over will be able to access a Covid pass for travel through the app, and those 12 and over will be able to request a PDF online. [7]
What are the potential challenges ahead?
Since the spread of the Delta variant in spring 2021, with questions about whether India should have been added to the red list sooner, the government has faced a tricky balance between the pressure to open up travel and the need for continued caution about Covid transmission and the spread of new variants.
All travel restrictions when entering the UK have now been removed. However, most other countries still retain some restrictions, meaning that travel from the UK is still affected.
The major question remaining is what the government will do if a new variant emerges. It has said that contingency plans are in place to respond to any future variants but has not set out in detail what those plans would mean for travel. [8]
- Department for Transport and Department of Health and Social Care, Travel to England from another country during coronavirus (COVID-19), 22 June 2021, www.gov.uk/guidance/travel-to-england-from-another-country-during-coronavirus-covid-19 ; Department for Transport, Department of Health and Social Care, The Rt Hon Sajid Javid MP, and The Rt Hon Grant Shapps MP, All COVID-19 travel restrictions removed in the UK, 14 March 2022, www.gov.uk/government/news/all-covid-19-travel-restrictions-removed-in-the-uk
- Department for Transport and Department of Health and Social Care, Travel to England from another country during coronavirus (COVID-19), 22 June 2021, www.gov.uk/guidance/travel-to-england-from-another-country-during-coronavirus-covid-19 ; Scottish Government, Coronavirus (COVID-19): international travel, www.gov.scot/publications/coronavirus-covid-19-international-travel-quarantine ; Welsh Government, International travel to and from Wales: coronavirus, 4 October 2021, https://gov.wales/rules-international-travel-and-wales-coronavirus ; NI Direct Government Services, Coronavirus (COVID-19): travel advice, www.nidirect.gov.uk/articles/coronavirus-covid-19-travel-advice
- Department for Transport, Department of Health and Social Care, The Rt Hon Sajid Javid MP, and The Rt Hon Grant Shapps MP, Travel Update: 47 countries and territories removed from red list, 7 October 2021, www.gov.uk/government/news/travel-update-47-countries-and-territories-removed-from-red-list ; Department for Transport and Department of Health and Social Care, Travel to England from another country during coronavirus (COVID-19), 22 June 2021, www.gov.uk/guidance/red-list-of-countries-and-territories
- BBC News, Covid travel restrictions have ended in the UK, 18 March 2022, www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-60789979
- GOV.UK, Foreign travel advice, www.gov.uk/foreign-travel-advice
- The app is available to individuals over 16 who are registered with a GP surgery in England. Individuals who cannot access the app can get a paper certificate by calling the NHS 119 helpline after 17 May. Certificates will be available from five days after a second vaccine dose: see Department of Health and Social Care, Using your NHS COVID Pass for travel abroad and at venues and settings in England, 7 May 2021, www.gov.uk/guidance/demonstrating-your-covid-19-vaccination-status-when-travelling-abroad
- Welsh Government, Get your NHS COVID Pass, https://gov.wales/nhs-covid-pass-prove-your-vaccination-status#section-70614 ; NI Direct Government Services, Apply for a Travel COVID vaccination certificate, www.nidirect.gov.uk/services/coronavirus-covid-19-covid-certificate-ni-residents ; www.nhsinform.scot/covid-19-vaccine/after-your-vaccine/get-a-record-of-your-coronavirus-covid-19-vaccination-status ; www.gov.uk/guidance/nhs-covid-pass#children
- BBC News, Covid travel restrictions have ended in the UK, 18 March 2022, www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-60789979
Related content
Coronavirus hotel quarantine: key questions for the government.
The gaps and challenges the government must answer if it wants its quarantine system to be a success.
Covid passports
The government must address concerns over how, where and when Covid passports would be used.
In conversation with Rt Hon Thérèse Coffey MP
Former deputy prime minister, health secretary and environment secretary Thérèse Coffey joined us to reflect on her nine years as government minister.
The Rwanda Act: what next in the courts?
What are the possible legal challenges to the government's Rwanda asylum plan?
Blog UK Health Security Agency

https://ukhsa.blog.gov.uk/2023/05/22/staying-well-when-travelling-abroad-this-summer/
Staying well when travelling abroad this summer

Dr Shreya Singhal is currently practising as a junior doctor and Academic Foundation Trainee working in West London, as well as being a keen backpacker. She has worked in Infectious Diseases and General Practice and has shared her top tips for people looking to travel this summer.
Lots of people will be travelling abroad this year. I’ve written this blog post as a handy guide for how to travel safely and minimise risks to your health, these tips can be applied by those setting off for an adventure of a lifetime or those just seeking a week of summer sunshine.
The risks to your health vary depending on the type of trip you’re going on – so whether you’re off for a week of sunbathing or taking a lengthier backpacking trip, it’s worth being prepared. It’s important to check your destination before you travel and be prepared by staying up to date with the latest outbreaks and events.
Before you travel
Vaccinations/pre-medications
Before you travel, it is vital to ensure you are up to date with your UK vaccination schedule, both for your protection and for the benefit of the health of the those around you.
Many countries have different diseases circulating and some of these could potentially be dangerous. It’s possible to pick up an illness that we don’t routinely see in the UK, and important to remember that some can have serious consequences for vulnerable people.
Viruses such as measles is more common in some parts of Africa, Asia and the mainland Europe, so please check that you are up to date with your childhood vaccine schedule .
You may need additional vaccinations and preventative medications for the countries you are visiting. For example, if you’re visiting parts of rural Asia and the Far East Japanese encephalitis may be a risk, and the vaccination could be recommended.
There are also places where the rabies vaccination may be needed and; for malaria risk areas, you may need to take malaria prevention tablets; it’s important to bear in mind that some countries require proof of yellow fever vaccination even if there is no risk of infection.
Always check your country of travel for recommended vaccinations , review the NHS Advice on Travel Vaccinations and keep a close eye on outbreaks in your country of travel .
For advice on vaccinations and preventative medicines, you can contact your local travel health clinic or GP surgery. With most vaccines it is advised you arrange your vaccination 4 to 6 weeks before you arrive at your destination.
Other factors to consider
- Your own underlying health should be stable before travelling. Carry your own medication supplies sufficient for the length of your trip (e.g. if you have asthma, make sure you carry your inhalers and rescue packs).
- Carry common medicines or a small first aid kit you might need, as you do not know what medicines/provisions the country you are travelling to will have.
- It’s also important to check the rules around using and importing medication in your target country, what might be a common medication in the UK could be outlawed in another.
During your travel
General health measures
While abroad, especially in more remote/rural places, be conscious of hand hygiene, your water supply, food safety, sun exposure , and your sexual health.
Be sure to pack condoms, suncream and hand sanitiser before you leave and where possible drink bottled water and wash your hands with soap and warm water after using the toilet and before eating. For general advice, this helpful blog covers top tips for each of these.
It’s more common in some countries but traveller’s diarrhoea, which results from consuming unsafe food/water, is something to be aware of. You can have quite significant fluid loss from this, so if you experience these symptoms while travelling, it is a good idea to take lots of rest, drink plenty of bottled fluids - if possible topped up with rehydration salts (If you feel particularly unwell, seek medical attention whilst abroad as you may require medical treatment for dehydration).
Particular diseases to be aware of
Mosquito bites are a particular risk, and can cause malaria, dengue, chikungunya, among many other diseases. Mosquito bite avoidance advice includes wearing long-sleeved clothing to cover exposed skin, using repellents (at least 50% DEET), and mosquito nets.
Suspected malaria is a medical emergency and must be quickly diagnosed and treated. If you visit a malaria risk country, which include countries in large areas of Africa, Asia, and Central and South America, and have a fever, flu-like symptoms or any unusual symptoms during or after travelling you must get urgent medical attention. Don’t wait until you return to the UK if you are unwell.
Rabies is transmitted by a bite or scratch from an infected animal, usually a dog, and can be fatal if not recognised, or because post-exposure treatment is not available.
Avoid animal bites, and check if you would benefit from a pre-exposure vaccine. All travellers who have a possible exposure to the rabies virus, whether by bites, scratches, or other means, should seek medical advice without delay. You can find full rabies advice here .
Sexual health
Practising safer sex while abroad will reduce the risk of STIs and HIV, as well as infections that spread through close personal contact, such as mpox.
You can reduce your risk by using condoms and having an open conversation about HIV, STIs and mpox before any sexual contact, and avoid sharing items such as towels, clothing or bedding with someone who has mpox or mpox symptoms.
Mpox is a virus which can be spread from an infected animal to a person, or by close personal contact with a person with mpox or materials where a person has shed the virus.
Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle ache, joint pain, and a rash with scabs which often begins on the face then spreads to other parts of the body which can include the mouth, genitals and anus (considered contagious until all scabs fall off and skin is intact).
In 2022, there was an international outbreak of mpox across more than 100 countries, where mpox was spread during sexual contact, particularly among men who are gay, bisexual or have sex with other men, and some countries are still reporting new infections.
Those at risk, including those who have been in contact with someone who has mpox, may be able to get the mpox vaccination. More information can be found here .
If you have had condomless sex while abroad, get yourself tested for STIs before having sex with anyone else – depending on where you live you could get a self-sampling kit or simply attend your local sexual health clinic .
Returning to the UK
When you return to the UK, if you feel unwell, seek medical attention and ensure you inform your healthcare provider that you have been travelling recently.
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about this blog.
The official blog of the UK Health Security Agency, providing expert insight on the organisation's work and all aspects of health security.
Sign up and manage updates
Recent posts.
- Who’s eligible for the 2024 COVID-19 vaccine, or ‘Spring Booster’? 16 April 2024
- What is whooping cough and how can I prevent my children catching it? 12 April 2024
- What is Lyme disease and why do we need to be tick-aware? 21 March 2024
- Skip to content
- Accessibility help
Immunizations - travel: Travel vaccinations
Last revised in July 2023
Travel vaccinations
- Travel to subtropical or tropical destinations is now common, and potentially dangerous diseases are more likely to be endemic in these areas.
- Extended travel abroad may increase the likelihood of exposure to tropical diseases.
- Travel to rural areas and adventure travel can increase the likelihood of contracting an illness. Medical treatment in remote areas may be hard to obtain.
- Many countries will not accept travellers who have recently visited areas in which yellow fever is endemic unless they can prove that they have been vaccinated or are medically exempt from yellow fever vaccination.
- Saudi Arabia requires proof of vaccination against meningococcal meningitis ACWY for Hajj and Umrah pilgrims.
- Travellers contracting tropical diseases abroad and importing them back to the UK pose a significant problem. General practitioners are encouraged to report and refer to specialist centres people returning from travel who may have symptoms of tropical disease.
[ PHE, 2016 ; PHE, 2020a ; NaTHNaC, 2021a ]
The content on the NICE Clinical Knowledge Summaries site (CKS) is the copyright of Clarity Informatics Limited (trading as Agilio Software Primary Care) . By using CKS, you agree to the licence set out in the CKS End User Licence Agreement .

- Public health
- Immunisation
Travel vaccinations
If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world. If possible, see a GP or a private travel clinic at least eight weeks before you are due to travel.
Some vaccines need to be given well in advance to allow your body to develop immunity. Some will involve a number of doses spread over several weeks or months.
Check which vaccinations you need
You can find out which vaccinations are necessary or recommended for the areas you will be visiting on these websites:
- Travel Health Pro
- GOV.UK - Foreign travel advice
- NHS - Travel vaccinations
- NHS - Fit for travel
Up to: Immunisation
Updated: 13 December 2022

Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
United Kingdom
Travel Advisory July 26, 2023
United kingdom - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in the United Kingdom due to terrorism.
Country Summary: Terrorist groups continue plotting possible attacks in the United Kingdom. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting tourist locations, transportation hubs, markets/shopping malls, local government facilities, hotels, clubs, restaurants, places of worship, parks, major sporting and cultural events, educational institutions, airports, and other public areas.
There is also a risk of isolated violence by dissident groups in Northern Ireland, focused primarily on police and military targets.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to the United Kingdom.
If you decide to travel to the United Kingdom:
- Be aware of your surroundings when traveling to tourist locations and crowded public venues.
- Follow the instructions of local authorities.
- Monitor local media for breaking events and adjust your plans based on new information.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter.com/Travelgov
- Review the Country Security Report for the United Kingdom.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel and return to the United States.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Must be valid for the duration of your stay in the United Kingdom (If you have onward travel to countries outside the United Kingdom, you should check the passport validity requirements for each additional country on their respective information pages.)
Must have at least one page
Not required for stays less than six months.
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy london.
33 Nine Elms Lane London, SW11 7US United Kingdom Telephone: +(44)(20) 7499-9000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(44)(20) 7499-9000 Fax: +(44) (20) 7891-3845 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Edinburgh, Scotland 3 Regent Terrace, Edinburgh EH7 5BW Scotland Telephone: 013-1556-8315 / from the United States: 011 (44)(13) 1556-8315 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 020-7499-9000 / from the United States: 011 (44)(20) 7499-9000 Fax: 0131-557-6023 /from the United States: 011 (44) 131-557-6023 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Belfast, Northern Ireland Danesfort House, 223 Stranmillis Road, Belfast BT9 5GR Northern Ireland, United Kingdom Telephone: 028-9038-6100 / from the United States: 011 (44)(28) 9038-6100 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 01253-501106 / from the United States: 011 (44) 1253-501106 Fax: 028-9068-1301 / from the United States: 011 (44)(28) 9068-1301 Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
- To enter the United Kingdom, your passport must be valid for the entire duration of your planned stay.
- Starting June 2019, U.S. passport holders will be able to use the ePassport Gates upon arrival in the United Kingdom. U.S. citizens who had previously registered for the UK’s Registered Traveller Service (RTS) should now also use the ePassport Gates on arrival in the UK.
- If you are planning onward travel after departing the UK, note that many other countries require at least six months’ remaining validity on your passport to enter. If you are bound for Continental Europe, please see our U.S. travelers in Europe page for additional details.
- Visas for specific categories of visitors must be obtained prior to travel. Visit the UK Visas and Immigration (UKVI) website to determine if you need a visa to enter the United Kingdom. We cannot intervene on your behalf when you apply for a UK visa, nor can we advocate for your admission into the UK if you are denied entry.
- Students and prospective students should visit the UKVI website to determine if they need a visa.
- For some U.S. travelers, especially students, an entry stamp is required. Please consult this website for more information.
- Unpaid and paid workers, interns, volunteers, charity workers, and temporary workers can find information about obtaining a visa on the UKVI website .
- Visitors traveling to the United Kingdom to get married, even if they do not plan to reside there, must obtain a visa in advance. See the UKVI website for visa information.
- Surcharges apply to certain categories of visas, generally those involving work, study, or residency for more than six months. More information is available on the UKVI website and in our Health section below.
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of the United Kingdom.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Terrorist groups continue plotting possible near-term attacks in Europe. The UK Security Service publishes specific reasons for any changes in the threat level and recommended actions for the public via its UK threat levels website .
There is the potential for isolated violence related to the political situation in Northern Ireland. The Police Service of Northern Ireland assesses there is a continued threat of violence from dissident groups in Northern Ireland, focused primarily on police and military targets, and may involve the use of firearms and explosives . Tensions may be heightened during the summer marching season (April to August), particularly on and around the July 12 public holiday.
Avoid areas of demonstrations if possible, and be careful within the vicinity of demonstrations. Demonstrations occur frequently in and around city centers and areas where tourists frequent. Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and possibly escalate to violence.
The phone number for police/fire/ambulance emergency services is 999 in the United Kingdom and 112 in Gibraltar. You should also use these numbers to report security threats or suspicious packages. Also see information for contacting police from abroad .
- Be cautious and aware of your surroundings.
- Be vigilant, as pickpocketing , mugging, and “snatch and grab” theft of mobile phones, watches and jewelry can occur.
- Do not leave bags unattended in restaurants, pubs, hotel lobbies, and parked cars.
- Be alert to other criminal schemes, such as impostors posing as undercover police officers and “fining” tourists for bogus minor offenses. A legitimate Metropolitan Police Services officer will never demand an immediate cash payment.
- Use only licensed Black Cabs or pre-ordered car services (minicabs) . Unlicensed taxis or private cars posing as taxis may offer low fares, but in some instances, travelers have been robbed or sexually assaulted while using these cars. See Transport for London for additional information on cabs and car services .
- Avoid using ATMs that look temporary in structure or location or are located in isolated areas – they may not be legitimate. Use ATMs located inside a bank branch.
Scams : Before sending any money to individuals you have never met in person, visit the Embassy London website for more information about internet financial scams and how to protect yourself.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information on scams.
Victims of Crime : Report crimes to the local police at 999 (United Kingdom) or 112 (Gibraltar) and contact the U.S. Embassy at +(44) (20) 7499-9000.
- Local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- help you find appropriate medical care
- assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- provide a list of local attorneys
- provide our information on victim compensation programs in the United States
- The Victim Support website is maintained by an independent UK charity to help people cope with the effects of crime
- A Northern Ireland-based independent charity maintains a similar victim support website
- In Scotland, victims of crime should contact Victim Support Scotland
- provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support if you are destitute
- help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- replace a stolen or lost passport
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence may contact the Embassy for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is generally regulated and rules are regularly enforced. Hazardous areas/activities are identified with appropriate signage and professional staff is typically on hand in support of organized activities. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is widely available throughout the country. Outside of a major metropolitan center, it may take more time for first responders and medical professionals to stabilize a patient and provide life-saving assistance. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
- You will be arrested if you bring pocket knives, blades, mace or pepper spray canisters, or any part of a gun into the United Kingdom . Please refer to the UK government publication Travelling to the UK , which details the items visitors are prohibited from bringing into the United Kingdom.
- Penalties against alcohol-related and other in-flight crimes committed aboard aircraft to and from the United Kingdom are stiff and are enforced with prison sentences . Please also see our information on U.S. customs regulations covering your return to the United States.
- Controlled Substances: UK law prohibits possession and trafficking of controlled substances and narcotics, including some substances that may be legal to possess under the law of certain U.S. states. More information on controlled substances is available here . Individuals who violate UK drug laws may face penalties including fines or prison sentences.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained in the United Kingdom, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Special Circumstances:
- The legal drinking age in the United Kingdom is 18. Parents and organizers of school trips should read our Students Abroad website to help plan a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Scotland’s “drink drive limit” law was amended to a lower level (roughly .05 BAC) and is stricter than the rest of the United Kingdom (roughly .08 BAC). This means that driving after even one drink can result in a charge of driving under the influence.
- The United Kingdom has very strict gun control laws, and importing firearms is extremely complicated. Information on applying for a firearm and/or shotgun certificate can be found on the London Metropolitan Police Firearms licensing webpage . Licenses from England or Wales may not be valid in Scotland; please check with the appropriate authorities. For firearms certificates for Scotland, please check with Police Scotland .
Faith-Based Travelers: See our following webpages for details:
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in the United Kingdom.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance:
- UK law requires that all public service providers (except in the transportation sector) make “reasonable adjustments” to ensure their services are available to persons with disabilities. Nevertheless, code exemptions permit many older buildings to have steps up from the street.
- Getting around in cities may be difficult at times because sidewalks can be narrow and uneven.
- Most London Underground and UK National Rail System stations are not readily accessible for people with disabilities. Many stations do not have elevators, and have stairways and long corridors for changing trains or exiting to the street. Many UK buses are equipped with lowering platforms for limited-mobility or sight- or hearing-disabled travelers.
- Many taxis have swivel-entry seats or retractable ramps to ease entry.
- Disabled parking permits (known as “blue badges”) are issued by local government councils throughout the country. Visit the UK government website for contact information. Some councils may not offer permits to temporary visitors.
The Transport for London and National Rail websites provide information for passengers with disabilities.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for women travelers .
While medical services are widely available, free medical care under the National Health System (NHS) is allowed only for UK residents, certain EU nationals, and some visa holders.
An NHS surcharge is assessed on certain visa applicants at the time of application. Tourists and short-term visitors will not be assessed the surcharge, but will be charged 150 percent of the cost of any medical treatment they receive from the NHS. Unpaid balances of £1,000 or more can result in being barred from return to the United Kingdom.
- The U.S. government does not pay medical bills, and U.S. Medicare is not valid overseas.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas . Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments . See our webpage for more information on insurance coverage overseas.
- We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Carry prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Traveling with sufficient supplies to last the duration of your trip is recommended. Mailing prescriptions is prohibitive and may be delayed or rejected by British customs.
Certain prescriptions available in the United States are classified as a "controlled drug" in the United Kingdom and cannot be brought into the country without applying for and obtaining a prior license. This includes prescriptions for medical marijuana or products containing CBD and THC. Please visit the https://www.gov.uk/travelling-controlled-drugs for additional information.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended for international travel by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Road conditions in the United Kingdom can differ significantly from those in the United States.
- In contrast to the United States, UK traffic drives on the left. Read the Highway Code before driving.
- Emergency call boxes (orange telephone booths with “SOS” printed on them) are found at half-mile intervals along motorways. White and blue poles point in the direction of the nearest call box. Call boxes dial directly to a motorway center. Use these phones rather than a personal cell phone, because motorway center personnel will immediately know your exact location.
- Generally, pedestrians do not have the right of way and should not expect vehicles to stop for them.
Many U.S. citizen pedestrians are injured, some fatally, every year in the United Kingdom, because they forget that oncoming traffic approaches from the opposite direction than in the United States. Exercise extra care when crossing streets; remain alert and look both ways before stepping into the street.
Traffic Laws:
- UK penalties for driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs are strict and often result in prison sentences .
- Using a hand-held cell phone or similar device while driving is illegal in the United Kingdom. Only hands-free phones may be used. You will be fined , or in the case of an accident, arrested and serve time in prison .
- The speed limit on highways/motorways in the United Kingdom is 70 mph, or lower when posted.
- You will be detained and arrested if you cannot provide a UK address to receive a subpoena or are about to depart the United Kingdom and have to be brought to court quickly for a motoring offense.
- In Central London, a congestion charge is levied on all drivers who pass through the congestion zone. You will be fined or arrested if you do not pay the charge. See Transport for London for more information about driving in London.
Public Transportation: Public transport in the United Kingdom is extensive.
- Information on disruptions to London transportation services can be found on the Transport for London website.
- Information about the status of National Rail Services can be found on the National Rail Enquiries website.
- Bus and train service information in Northern Ireland can be found on the Translink website.
- Bus and train service information in Scotland can be found on the Traveline Scotland website.
See our Road Safety page for more information. For specific information concerning UK driving permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, and mandatory insurance, refer to the UK Department for Transport website or the Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency website.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of the United Kingdom’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of United Kingdom’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to the United Kingdom should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts at www.marad.dot.gov/msci . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website and the NGA broadcast warnings website (select “broadcast warnings”).
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in the United Kingdom . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, united kingdom map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Check passport expiration dates carefully for all travelers! Children’s passports are issued for 5 years, adult passports for 10 years.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- International travel, immigration and repatriation during COVID-19
- Entering England during COVID-19
Quarantine-free travel to resume on 19 July for fully vaccinated passengers returning from amber list countries
The guidance on travel to and from amber list countries to England will change 19 July 2021.
This news article was withdrawn on 7 September 2021
Read the latest information on international travel .

- from 19 July, arrivals who have been fully vaccinated with an NHS administered vaccine in the UK (plus 14 days), or are on a formally approved UK vaccine clinical trial, returning to England from amber list countries will no longer need to quarantine – passengers will need to provide proof of their vaccination status to carriers in advance of travel
- pre-departure testing and day 2 testing measures to remain
- children under the age of 18 to be exempt from quarantine on returning to England from amber countries
- the recommendation for people to not travel to amber countries will also be removed from 19 July – people should continue to check FCDO travel advice before booking travel
- news marks the next step in the cautious reopening of international travel, following the Prime Minister setting out plans earlier this week to ease COVID-19 restrictions in England from step 4 of the roadmap
The government has today (8 July 2021) set out the details to enable people who have been fully vaccinated with an NHS administered vaccine, plus 14 days, to travel to amber list countries without having to quarantine on their return to England, from Monday 19 July. The recommendation for people not to travel to amber list countries will also be removed from 19 July.
The changes will come into force from Monday 19 July at 4am. Those who have been fully vaccinated with an NHS administered vaccine in the UK and are returning from amber countries will still be required to complete a pre-departure test before arrival into England, alongside a PCR test on or before day 2 after arrival. They will not have to take a day 8 test or self-isolate. Any positive results will be genomically sequenced to continue to manage the risk from importing variants.
France – important information
The changes to the amber list rules for fully UK vaccinated people will not apply to France .
Children under the age of 18 will not have to isolate when returning to England. While the recommendation that people should not travel to amber countries is being removed, children aged 4 and under will continue to be exempt from any travel testing. Children aged 5 to 10 will only need to do a day 2 PCR and 11 to 18 year olds will need to take both a pre-departure test and a day 2 PCR – as is the case for arrivals from green list countries.
The success of our vaccine programme has been aided by those selflessly taking part in clinical trials and those who are part of approved COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials in the UK will therefore be treated as vaccinated.
At this stage, there will be no changes to requirements for those returning from green or red list countries – even when they are fully vaccinated, nor for unvaccinated passengers travelling from amber countries who do not have a valid exemption.
Transport Secretary, Grant Shapps said:
Thanks to our successful vaccine rollout, we’re now able to widen quarantine-free travel to NHS administered fully vaccinated adults and children under the age of 18, and take another step towards fully reopening international travel. As we continue with the domestic unlocking, it’s only right we get people travelling again – whether that’s for business to help create jobs, overdue holidays or reconnecting family and friends. However, protecting public health still remains our priority and we will act swiftly if action is needed.
Health Secretary, Sajid Javid said:
Vaccinations have severely weakened the link between COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations and deaths, building a wall of protection across the country. As we learn to live with this virus, due to the tremendous progress of the vaccine programme – with more than 3 in 5 people now double jabbed – we can safely take steps to ease restrictions on travel, as we are doing at home. Allowing quarantine-free travel for fully vaccinated people means they can be reunited with loved ones overseas and we can return to normality as quickly as possible.
The government is taking a phased approach to amending requirements and is already exploring plans to remove quarantine for vaccinated non- UK residents arriving from amber countries later this summer where it is safe to do so. The Test to Release scheme scheme remains an option for non-fully vaccinated travellers returning from amber countries to shorten their quarantine period, by paying for a private test and being released early if they receive a negative COVID-19 test result.
Travel continues to be different from usual, and while some restrictions remain in place passengers should expect their experience to be different and may face longer wait times than they are used to – although the government is making every effort to speed up queues safely. We will continue to rollout e-gates over the summer, with many already in operation across airports and more to be added over the coming months.
Carriers will have a critical role in carrying out primary checks on all passengers before boarding, checking people have the right COVID-19 certification documents to ensure we can continue to safeguard against new variants. Anyone not complying with health measures could face a fine, and carriers will be required to ensure proper checks are carried out.
Airlines UK CEO Tim Alderslade said:
This is a positive move towards the genuine reopening the sector has been looking for. Opening up the market for the rest of the summer, this announcement will provide far greater opportunities to travel, do business and see family and friends, and enable many more of our customers to book with certainty. The summer season essentially starts here. Airlines look forward to working with government to continue this momentum and further open up the market.
All passengers will still need to complete their passenger locator form , which will include the requirement to declare vaccination status and provide proof of their pre-departure test. Amber arrivals will be required to prove their full vaccination status to carriers before departing, either via the NHS app or via an NHS COVID Pass letter which can be obtained by calling 119 for travelling overseas (which could take 5 days to arrive by post).
Airport Operators Association Chief Executive Karen Dee said:
This is a significant step forward that will be a boost to airports and the local economies that rely on them. Many airports staff will be able to get back to what they do best: supporting businesses to reach customers abroad, enabling people to visit friends and relatives and help people take a well-deserved holiday abroad after a difficult period.
If travelling abroad, you need to take steps to keep safe and prepare in case things change before you go or while you are there. Check the booking terms and conditions on flexibility and refunds because the situation remains fluid. Many travel firms have changed their terms to be fully flexible. Check and subscribe to FCDO travel advice updates to understand the latest entry requirements and COVID-19 rules at their destination – and passengers are advised to check all entry requirements and FCDO travel advice before they book any foreign travel.
Quarantine and testing requirements for children
Share this page.
The following links open in a new tab
- Share on Facebook (opens in new tab)
- Share on Twitter (opens in new tab)
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Foreign travel advice. Get advice about travelling abroad, including the latest information on coronavirus, safety and security, entry requirements and travel warnings. Search for a country or ...
Travel vaccination advice. If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world. Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever, typhoid and hepatitis A. In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule ...
The Transport Secretary, Grant Shapps, has today (17 September 2021) announced a simplified system for international travel in light of the success of the UK 's domestic vaccine rollout ...
From 4am 2 August 2021, passengers who are fully vaccinated in the EU with vaccines authorised by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) or in the USA with vaccines authorised by the Food and Drug ...
Advice about getting vaccinated before travelling abroad and information about common travel vaccines. Travel vaccination advice Available travel vaccines Country-by-country advice ... GOV.UK: foreign travel advice www.gov.uk. Support links. Home; Health A to Z; Live Well; Mental health; Care and support; Pregnancy; NHS services; Coronavirus ...
Only fully-vaccinated adults can travel to Malta, and don't need a negative test. Children aged 5-11 can travel with fully-vaccinated adults, but need a negative test. Under-5s don't need a test ...
Available travel vaccines The following vaccinations are available for people travelling abroad. Cholera vaccination ... GOV.UK provides a detailed list of countries that have rabies in domestic animals or wildlife. Vaccination involves a course of 3 injections before you travel, usually given over a period of 28 days. ...
BBC News. People coming to the UK must show proof of a negative Covid test before they travel, as new rules to limit spread of the Omicron variant come into effect. Contacts of a suspected Omicron ...
It is thought more than 80 holiday destinations around the world still require all UK travellers to take a pre-departure PCR test before arrival. UK-issued Covid passes can be used throughout the ...
UKHSA urges overseas travellers, including Hajj pilgrims, to check well in advance to ensure they are up to date and have all necessary vaccinations. From: UK Health Security Agency. Published. 11 ...
Yes, if you live in England and have had two Covid-19 vaccine doses administered in the UK. The vaccines must have been given 14 days prior to travel. The policy begins on 19 July. Authorities in ...
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include. Chickenpox (Varicella) Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis; Flu (influenza) Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR) Polio; Shingles; Immunization schedules. COVID-19: All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines.
Travel health advice and travel vaccinations. You should make an appointment for a travel health risk assessment if you're travelling abroad and think you need: vaccines. a malaria risk assessment. further advice. A travel health professional will take you through your travel health risk assessment. Your GP is no longer your point of contact ...
The government has suggested it will incorporate a vaccination status into the existing NHS Covid app. However, there are currently no requirements to prove vaccination status when entering the UK.
International travel for leisure in England had first resumed in May 2021. Initially countries were given a red, amber, or green rating with different rules for testing and quarantining on return. The government simplified this system in October 2021, with only the red list remaining, and the red list was cleared of all countries on 1 November.
It should be valid for the whole of your stay. You may also need a visa to come into or travel through the UK, depending on your nationality. Check which documents you'll need to come to the UK ...
Always check your country of travel for recommended vaccinations, review the NHS Advice on Travel Vaccinations and keep a close eye on outbreaks in your country of travel. For advice on vaccinations and preventative medicines, you can contact your local travel health clinic or GP surgery. With most vaccines it is advised you arrange your ...
Travellers can greatly reduce the risk of contracting certain infections by being vaccinated before potential exposure. Travel to subtropical or tropical destinations is now common, and potentially dangerous diseases are more likely to be endemic in these areas. Extended travel abroad may increase the likelihood of exposure to tropical diseases.
GOV.UK - Foreign travel advice; NHS - Travel vaccinations; NHS - Fit for travel; Up to: Immunisation. Updated: 13 December 2022 ... If possible, see a GP or a private travel clinic at least eight weeks before you are due to travel. Timescales. Some vaccines need to be given well in advance to allow your body to develop immunity. Some will ...
All testing measures for eligible fully vaccinated travellers arriving in the UK will be removed from 4am on 11 February, as the government goes one step further to reopen the travel sector.. The ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
The government has today (8 July 2021) set out the details to enable people who have been fully vaccinated with an NHS administered vaccine, plus 14 days, to travel to amber list countries without ...