

Sachsentourist Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Heinz Wittig e.K.

Informationen zu Sachsentourist Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Heinz Wittig e.K.
Öffnungszeiten
- Montag: 09:00–13:00 Uhr, 14:00–18:00 Uhr
- Dienstag: 09:00–13:00 Uhr, 14:00–18:00 Uhr
- Mittwoch: 09:00–13:00 Uhr, 14:00–18:00 Uhr
- Donnerstag: 09:00–13:00 Uhr, 14:00–18:00 Uhr
- Freitag: 09:00–13:00 Uhr, 14:00–18:00 Uhr
- Samstag: Geschlossen
- Sonntag: Geschlossen
gemeinsam haben wir in den vergangenen Jahren Höhen und Tiefen überwunden. Ich danke Ihnen für Ihre Treue, die das Überleben der „Sachsentourist Familie“ sichert. Für das Reisejahr 2024 wünsche ich Ihnen beste Gesundheit, viel Reiselust und Spaß mit den neuen Katalogen, auch im Namen aller Mitarbeiter.
Die Angebote zu den vertraglichen Reiseleistungen in diesem Prospekt entsprechen dem Stand bei Drucklegung. Bitte haben Sie jedoch Verständnis dafür, dass bis zur Übermittlung Ihres Buchungswunsches aus sachlichen Gründen Änderungen der Leistungen möglich sind, die wir uns deshalb ausdrücklich vorbehalten müssen. Über diese werden wir Sie selbstverständlich vor Vertragsschluss unterrichten.
Inflationsaufschläge sind auch für uns unvermeidbar. Auf Grund der aktuellen Preisentwicklung weisen wir darauf hin, dass auch wir Preiserhöhungen an Sie weiter geben müssen.
ab sofort erheben wir einen Treibstoffzuschlag für Mehrtagesfahrten in Höhe von 10,00€ und für Tagesfahrten in Höhe von 2,00€ pro Person. Wir bitten um Ihr Verständnis.
Gern beraten wir Sie in einem unserer Reisebüros ausführlich zu unseren Bus-, Gruppenflug - und Schiffsreisen. Kommen Sie einfach vorbei, wir freuen uns Sie kennenzulernen.
Sparen Sie zusätzlich 10€/Person bei Mehrtagesfahrten, wenn Sie hier genannte Zustiege nutzen! Für einen besonders günstigen Preis steigen Sie am Sparzustieg zu und nach Reiseende wieder aus.
Sachsentourist Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Heinz Wittig e.K.: Meinungen
Fantastische Erfahrung: Super organisierte Reisen.
Fantastische Erfahrung: Waren jetzt mit Sachsentourist Wittig in Bad Kudova. Alles super!
Fantastische Erfahrung: Tolle Beratung, immer wieder
Fantastische Erfahrung:
Hinterlassen Sie Ihre Meinung zu Sachsentourist Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Heinz Wittig e.K.:
Sachsentourist omnibus- und reiseverkehr heinz wittig e.k. wird in den folgenden auflistungen angezeigt:, andere reisebüros, die sie interessieren könnten.

Reisebüro am Käferberg

sonnenklar.TV Reisebüro Lutz Hoffmann Riesa

Reisebüro Belitz

DERTOUR Reisebüro

Weltmeister Reisen GmbH Riesa | Reisebüro

Reisebüro im real-Markt Riesa
Fügen sie ihr reisebüro kostenlos in unser verzeichnis ein.
Wenn Sie ein Reisebüro leiten und in unserem Verzeichnis erscheinen möchten, fügen Sie Ihre Unternehmensinformationen hinzu und Sie können völlig kostenlos erscheinen.
Fügen Sie Ihr Unternehmen kostenlos hinzu

Solicitar un cambio
Sind Sie der Eigentümer des Unternehmens?
Das größte Verzeichnis von Reisebüros in Germany
Finden Sie die besten Reisebüros in Ihrer Nähe
Wähle dein Land
Veröffentlichen Sie kostenlos Ihr Reisebüro
Further Information Literature
Related Reactions Corey-Chaykovsky Reaction Julia Olefination Peterson Olefination Schlosser Modification Seyferth-Gilbert Homologation Tebbe Olefination Wittig-Horner Reaction
Wittig Reaction
The Wittig Reaction allows the preparation of an alkene by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with the ylide generated from a phosphonium salt. The geometry of the resulting alkene depends on the reactivity of the ylide. If R is an electron withdrawing group, then the ylide is stabilized and is not as reactive as when R is alkyl. Stabilized ylides give predominantly ( E )-alkenes whereas non-stabilized ylides lead to ( Z )-alkenes (see also Wittig-Horner Reaction ).
Mechanism of the Wittig Reaction
(2+2) Cycloaddition of the ylide to the carbonyl forms a four-membered cyclic intermediate, an oxaphosphetane. Preliminary posultated mechanisms lead first to a betaine as a zwitterionic intermediate, which would then close to the oxaphosphetane. The intermediacy of such betaines plays an important role in the Schlosser Modification . Betaines may be stabilized by lithium salts leading to side products; therefore, suitable bases in the Wittig Reaction are for example: NaH, NaOMe, NEt 3 .
The driving force is the formation of a very stable phosphine oxide:
Reactive ylides give rapid reaction and subsequent rapid ring opening to give the ( Z )-alkene:
Recent Literature
Site Search any all words
Main Categories
- Organic Reactions
- Org. Chem. Highlights
- Presentations
- Chemistry Tools
- Ads & Imprint
Popular Subcategories
- Name Reactions
- Protecting Groups
- Organic Synthesis

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Wittig Reaction
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 66509
- Organic Reactions Wiki
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide (often called a Wittig reagent ) to give an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide.
The Wittig reaction was discovered in 1954 by Georg Wittig, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979. It is widely used in organic synthesis for the preparation of alkenes. It should not be confused with the Wittig rearrangement.
Wittig reactions are most commonly used to couple aldehydes and ketones to singly substituted phosphine ylides. With unstabilised ylides this results in almost exclusively the Z-alkene product. In order to obtain the E-alkene, stabilised ylides are used or unstabilised ylides using the Schlosser modification of the Wittig reaction can be performed.
Reaction mechanism
Classical mechanism.
The steric bulk of the ylide 1 influences the stereochemical outcome of nucleophilic addition to give a predominance of the betaine 3 (cf. Bürgi–Dunitz angle). Note that for betaine 3 both R 1 and R 2 as well as PPh3+ and O− are positioned anti to one another.
Carbon-carbon bond rotation gives the betaine 4 , which then forms the oxaphosphetane 5 . Elimination gives the desired Z-alkene 7 and triphenylphosphine oxide 6 . With simple Wittig reagents, the first step occurs easily with both aldehydes and ketones, and the decomposition of the betaine (to form 5 ) is the rate-determining step. However, with stabilised ylides (where R 1 stabilises the negative charge) the first step is the slowest step, so the overall rate of alkene formation decreases and a bigger proportion of the alkene product is the E-isomer. This also explains why stabilised reagents fail to react well with sterically hindered ketones.

Mechanistic studies have focused on unstabilized ylides, because the intermediates can be followed by NMR spectroscopy. The existence and interconversion of the betaine ( 3a and 3b ) is subject of ongoing research. Phosphonium ylides 1 react with carbonyl compounds 2 via a π²s/π²a [2+2] cycloaddition to directly form the oxaphosphetanes 4a and 4b . The stereochemistry of the product 5 is due to the addition of the ylide 1 to the carbonyl 2 and to the equilibration of the intermediates. Maryanoff and Reitz identified the issue about equilibration of Wittig intermediates and termed the process "stereochemical drift". For many years, the stereochemistry of the Wittig reaction, in terms of carbon-carbon bond formation, had been assumed to correspond directly with the Z/E stereochemistry of the alkene products. However, certain reactants do not follow this simple pattern. Lithium salts can also exert a profound effect on the stereochemical outcome.

Mechanisms differ for aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes and for aromatic and aliphatic phosphonium ylides. Evidence suggests that the Wittig reaction of unbranched aldehydes under lithium-salt-free conditions do not equilibrate and are therefore under kinetic reaction control. Vedejs has put forth a theory to explain the stereoselectivity of stabilized and unstabilized Wittig reactions.
Wittig reagents
Preparation of phosphorus ylides.
Wittig reagents are usually prepared from a phosphonium salt, which is in turn prepared by the quaternization of triphenylphosphine with an alkyl halide. The alkylphosphonium salt is deprotonated with a strong base such as n -butyllithium:
One of the simplest ylides is methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph 3 P=CH 2 ). It is also a precursor to more elaborate Wittig reagents. Alkylation of Ph 3 P=CH 2 with a primary alkyl halide R−CH 2 −X, produces substituted phosphonium salts:
These salts can be deprotonated in the usual way to give Ph 3 P=CH−CH 2 R.
Structure of the ylide

The Wittig reagent may be described in the phosphorane form (the more familiar representation) or the ylide form:
The ylide form is a significant contributor, and the carbon is nucleophilic.

Scope and limitations
The Wittig reaction is a popular method for the synthesis of alkene from ketones and aldehydes. The Wittig reagent can generally tolerate carbonyl compounds containing several kinds of functional groups such as OH, OR, aromatic nitro and even ester groups. There can be a problem with sterically hindered ketones, where the reaction may be slow and give poor yields, particularly with stabilized ylides, and in such cases the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons (HWE) reaction (using phosphonate esters) is preferred. Another reported limitation is the often labile nature of aldehydes which can oxidize, polymerize or decompose. In a so-called Tandem Oxidation-Wittig Process the aldehyde is formed i n situ by oxidation of the corresponding alcohol.
As mentioned above, the Wittig reagent itself is usually derived from a primary alkyl halide. Quaternization of triphenylphosphine with most secondary halides is inefficient. For this reason, Wittig reagents are rarely used to prepare tetrasubstituted alkenes. However the Wittig reagent can tolerate many other variants. It may contain alkenes and aromatic rings, and it is compatible with ethers and even ester groups. Even C=O and nitrile groups can be present if conjugated with the ylide- these are the stabilised ylides mentioned above. Bis-ylides (containing two P=C bonds) have also been made and used successfully.
One limitation relates to the stereochemistry of the product. With simple ylides, the product is usually mainly the Z-isomer, although a lesser amount of the E-isomer is often formed also – this is particularly true when ketones are used. If the reaction is performed in DMF in the presence of LiI or NaI, the product is almost exclusively the Z-isomer. If the E-isomer is the desired product, the Schlosser modification may be used. With stabilised ylides the product is mainly the E-isomer, and this same isomer is also usual with the HWE reaction.
Schlosser modification
The major limitation of the traditional Wittig reaction is that the reaction proceeds mainly via the erythro betaine intermediate, which leads to the Z-alkene. The erythro betaine can be converted to the threo betaine using phenyllithium at low temperature. This modification affords the E-alkene.
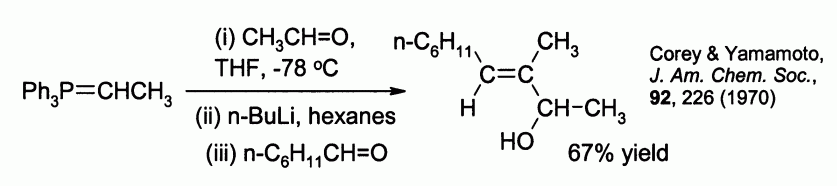
Allylic alcohols can be prepared by reaction of the betaine ylid with a second aldehyde. For example:
Because of its reliability and wide applicability, the Wittig reaction has become a standard tool for synthetic organic chemists.
The most popular use of the Wittig reaction is for the introduction of a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph 3 P=CH 2 ). Using this reagent even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative. In this case, the Wittig reagent is prepared in situ by deprotonation of methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide with potassium tert-butoxide. In another example, the phosphorane is produced using sodium amide as a base, and this reagent converts the aldehyde shown into alkene I in 62% yield. The reaction is performed in cold THF, and the sensitive nitro, azo and phenoxide groups are tolerated. The product can be used to incorporate a photostabiliser into a polymer, to protect the polymer from damage by UV radiation.
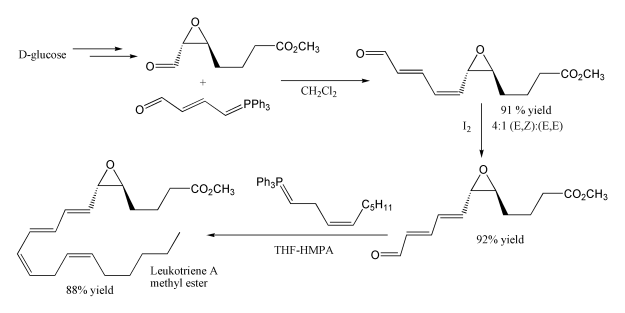
Another example of its use is in the synthesis of leukotriene A methyl ester. The first step uses a stabilised ylide, where the carbonyl group is conjugated with the ylide preventing self condensation, although unexpectedly this gives mainly the cis product. The second Wittig reaction uses a non-stabilised Wittig reagent, and as expected this gives mainly the cis product. Note that the epoxide and ester functional groups survive intact.
Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine is a Wittig reagent for the homologation of aldehydes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ihr Sachsentourist-Wittig-Team. Ihr Reisebüro ist für Sie da (bitte Änderungen im Aktuell-Bereich beachten!) Gern beraten wir Sie in einem unserer Reisebüros ausführlich zu unseren Bus-, Gruppenflug - und Schiffsreisen. Kommen Sie einfach vorbei, wir freuen uns Sie kennenzulernen.
April 2024 ; 20.04 : 1 Tag : Potsdam-Tulpenfest : 22.04 : 5 Tg : AIDAmar Kreuzfahrt : 25.04 : 1 Tag : Landesgartenschau Bad Dürrenberg : 25.04 : 1 Tag : Böhmische ...
www.sachsentourist-wittig.de
Hinterlassen Sie Ihre Meinung zu Sachsentourist Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Heinz Wittig e.K.: Ihren Namen Zinssatz von 1 bis 5 das Geschäft 5 4 3 2 1 1 = schlecht
Ostsee - Binz - Inselglück RügenGesundheitswoche in BinzSie wohnen im IFA Ferienpark hinter den Dünen direkt am Meer! Der IFA - Ferienpark bietet alle Annehmlichkeiten für einen erholsamen Ostseeurlaub. BINZ auf Rügen macht Sie fit: Die gesundheitsfördernde Wirkung der Ostseeluft weiß man seit jeher zu schätzen.
Firmenbeschreibung. 1955 gründete Heinz Wittig sein "Fuhrunternehmen" und arbeitete damals vor allem im Arbeiter-Berufs-Schülerverkehr. Die Fahrzeuge waren meistens "Marke Eigenbau". 1990 zu "Wende" nutzte Heinz Wittig die Chance seinen Betrieb zu einem modernen Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr zu erweitern. "Sachsentourist" wurde "geboren" und nahm dank der Reisefreiheit eine stürmische Entwicklung.
Für Sachsentourist Wittig Reisebüro in Riesa sind noch keine Bewertungen abgegeben worden. Wenn Sie Erfahrungen mit diesem Unternehmen gesammelt haben, teilen Sie diese hier mit anderen Seitenbesuchern. Geben Sie jetzt die erste Bewertung ab! Jetzt bewerten. Bewertung schreiben.
Sachsen-Tourist Wittig Sachsen-Tourist Wittig is a travel agency in Riesa, Meissen, Saxony located on Hauptstraße. Sachsen-Tourist Wittig is situated nearby to Zunftbaum and the police station Polizeirevier Riesa.
Verantwortlich für den Inhalt: Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Wittig e.K. Geschäftsführerin: Brigitte Wittig. Filderstädter Str. 1 04758 Oschatz. Tel: (03435) 930159
Find company research, competitor information, contact details & financial data for Omnibus- und Reiseverkehr Heinz Wittig e. K. of Oschatz, Sachsen. Get the latest business insights from Dun & Bradstreet.
Sachsentourist Wittig is a company that operates in the Wholesale industry. It employs 6-10 people and has $1M-$5M of revenue. The company is headq uartered in Oschatz, Saxony, Germany.
1,8 Mio. Firmen mit aggregierten Bewertungen von echten Menschen. Heinz Wittig Reisebüro in Oschatz wurde aktualisiert am 06.04.2024. Eintragsdaten vom 31.03.2024. Reisebüro | ⌚ Öffnungszeiten | Adresse | ☎ Telefonnummer | Bahnhofstr. 12 - 04758 Oschatz.
6 uy u eolfnw ]xu ;fn dxi hlqh odqjh xqg looxvwuh 7udglwlrq dov hlqhu ghu ehu ;kpwhvwhq .xuruwh ghu 5hjlrq 'dv khuyruudjhqgh +hlozdvvhu zlug vhlw -dku]hkqwhq ]xu /lqghuxqj
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent.Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph 3 P=CH 2).Using this reagent, even a sterically ...
The Wittig Reaction allows the preparation of an alkene by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with the ylide generated from a phosphonium salt. The geometry of the resulting alkene depends on the reactivity of the ylide. If R is an electron withdrawing group, then the ylide is stabilized and is not as reactive as when R is alkyl.
Page ID. The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide (often called a Wittig reagent) to give an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide. The Wittig reaction was discovered in 1954 by Georg Wittig, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979.