Conjugation verb travel
Model : cancel
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: travel oneself / not travel
Contractions
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
The verb has several variants of conjugation, which may correspond to different meanings. Please use the menu to select one or all variants.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled

Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.

Select your English level
To personalize your experience.
- To Travel Conjugation
In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred.
Continuous Perfect
Conditional.
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely .

Travel Past Tense
Commonwealth travelled, US traveled past tense of travel is Commonwealth travelled, US traveled.
Travel verb forms
Conjugation of travel.
- What is the past tense of tup in English?
- What is the second form of verb TUPE?
- What is the third form of verb turbanize in English?
- What is the conjugation of turbinate in English?
- Conjugate turbocharge in English?
- turkey-trot
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.
To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe.
You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site.
The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single goal: to provide you with rich, high-quality content. All this is possible thanks to the income generated by advertising and subscriptions.
By giving your consent or subscribing, you are supporting the work of our editorial team and ensuring the long-term future of our site.
If you already have purchased a subscription, please log in
How to conjugate "to travel" in English?
English "to travel" conjugation.
- traveled; travelled
Full conjugation of "to travel"
Translations for "to travel", present continuous, simple past, past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, conditional present, conditional present progressive, conditional perfect, conditional perfect progressive, subjunctive, present subjunctive, past subjunctive, past perfect subjunctive, present participle, past participle.
Translations for "to travel" in our English dictionaries
Popular English verbs
Find out the most frequently used verbs in English.
Social Login
Conjugation English verb to travel
Simple present, present progressive/continuous, simple past, past progressive/continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive/continuous, past perfect, past perfect progressive/continuous, future progressive/continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, progressive, perfect progressive, translation to travel.

'travel' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'T'
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for travel
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "travel" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->
Verb "travel"
For the settings to take effect, you must restart the trainer Restart
Conjugation
Simple tense.
Present Simple
- he, she travels
- they travel
Past Simple
- I traveled ; travelled
- you traveled ; travelled
- he, she traveled ; travelled
- we traveled ; travelled
- they traveled ; travelled
Future Simple
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he, she will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Continuous Tense
Present Simple Continuous
- I am traveling ; travelling
- you are traveling ; travelling
- he, she is traveling ; travelling
- we are traveling ; travelling
- they are traveling ; travelling
Past Simple Continuous
- I was traveling ; travelling
- you were traveling ; travelling
- he, she was traveling ; travelling
- we were traveling ; travelling
- they were traveling ; travelling
Future Simple Continuous
- I will be traveling ; travelling
- you will be traveling ; travelling
- he, she will be traveling ; travelling
- we will be traveling ; travelling
- they will be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Tense
Present Perfect
- I have traveled ; travelled
- you have traveled ; travelled
- he, she has traveled ; travelled
- we have traveled ; travelled
- they have traveled ; travelled
Past Perfect
- I had traveled ; travelled
- you had traveled ; travelled
- he, she had traveled ; travelled
- we had traveled ; travelled
- they had traveled ; travelled
Future Perfect
- I will have traveled ; travelled
- you will have traveled ; travelled
- he, she will have traveled ; travelled
- we will have traveled ; travelled
- they will have traveled ; travelled
Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous
- I have been traveling ; travelling
- you have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she has been traveling ; travelling
- we have been traveling ; travelling
- they have been traveling ; travelling
Past Perfect Continuous
- I had been traveling ; travelling
- you had been traveling ; travelling
- he, she had been traveling ; travelling
- we had been traveling ; travelling
- they had been traveling ; travelling
Future Perfect Continuous
- I will have been traveling ; travelling
- you will have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she will have been traveling ; travelling
- we will have been traveling ; travelling
- they will have been traveling ; travelling
Conditional
- I would travel
- you would travel
- he, she would travel
- we would travel
- they would travel
- I would have traveled ; travelled
- you would have traveled ; travelled
- he, she would have traveled ; travelled
- we would have traveled ; travelled
- they would have traveled ; travelled
Present Continuous
- I would be traveling ; travelling
- you would be traveling ; travelling
- he, she would be traveling ; travelling
- we would be traveling ; travelling
- they would be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Continuous
- I would have been traveling ; travelling
- you would have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she would have been traveling ; travelling
- we would have been traveling ; travelling
- they would have been traveling ; travelling
- we Let's travel
Other verbs
Be the first to comment.
Add comment
English: travel
English verb 'travel' conjugated.
Here are the past tense forms of the verb travel
👉 Forms of verb travel in future and past simple and past participle. ❓ What is the past tense of travel.
Travel: Past, Present, and Participle Forms
What are the 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb travel.
🎓 What are the past simple, future simple, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect forms of the base form (infinitive) ' travel '? 👉 It's quite simple -->
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'
- the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses.
- the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense.
- the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
What are the past tense and past participle of travel?
What is the past tense of travel.
The past tense of the verb "travel" is "travelled (BrE)", or "traveled (AmE)", and the past participle is "travelled (BrE)" or "traveled (AmE)".
Verb Tenses
Past simple — travel in past simple travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (V2) . Future simple — travel in future simple is travel (will + V1) . Present Perfect — travel in present perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (have/has + V3) . Past Perfect — travel in past perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (had + V3) .
travel regular or irregular verb?
👉 Is 'travel' a regular or irregular verb? The verb 'travel' is regular verb .
Examples of Verb travel in Sentences
- These days we travelled 1400 km (Past Simple)
- We didn't travel that long (Past Simple)
- She has travelled extensively in the Philippines (Present Perfect)
- I can't travel without you (Present Simple)
- We usually travel to work by bus (Present Simple)
- A plane travels faster than a train (Present Simple)
- They are travelling together since 2018 (Present Continuous)
- You can travel by foot, why not? (Present Simple)
- Unfortunately you can't travel without a ticket, so please proceed to the ticket office (Present Simple)
- How many countries have you travelled to? (Present Perfect)
Along with travel, words are popular give and tell .
Verbs by letter: r , d , u , c , m , p , b , w , h , a , e , g , s , q , j , l , t , f , o , n , k , i , v , y , z .
English verbs
- 318 Irregular verbs
- 904 Regular verbs
- 5 Modal verbs
- 407 Phrasal verb
Online verb dictionary
We are currently working to add new verbs and examples to our website, along with detailed descriptions. Please send us a message if you have any requests or suggestions, and we will add them as quickly as we can. Thank you for your interest in our website!
our editor - Peter (Certified TEFL Tutor with over 8 years experience)
Have a question or find mistake?
Conjugation of verb (past tense) travel
Past simple, traveled; travelled, past participle.
- ⭐Conjugation
- Podmínkové věty
- Frázová slovesa
- ⭐Conditional
- ⭐Subjunktiv
- ⭐Participle
Conjugation of the regular verb [travel]
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking.
The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is known as declension). Also it is often restricted to denoting the formation of finite forms of a verb – these may be referred to as conjugated forms, as opposed to non-finite forms, such as the infinitive or gerund, which tend not to be marked for most of the grammatical categories.
Conjugation is also the traditional name for a group of verbs that share a similar conjugation pattern in a particular language (a verb class). A verb that does not follow all of the standard conjugation patterns of the language is said to be an irregular verb .
Present Continuous
Past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional of the regular verb [travel].
Causality (also referred to as causation or cause and effect ) is influence by which one event, process, state or object (a cause) contributes to the production of another event, process, state or object (an effect) where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be causal factors for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future.
The conditional mood (abbreviated cond) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual.
English does not have an inflective (morphological) conditional mood, except in as much as the modal verbs could, might, should and would may in some contexts be regarded as conditional forms of can, may, shall and will respectively. What is called the English conditional mood (or just the conditional) is formed periphrastically using the modal verb would in combination with the bare infinitive of the following verb. (Occasionally should is used in place of would with a first person subject – see shall and will. Also the aforementioned modal verbs could, might and should may replace would in order to express appropriate modality in addition to conditionality.)
Conditional present -->
Conditional present progressive -->, conditional perfect -->, conditional perfect progressive -->, subjunktiv of the regular verb [travel].
The subjunctive is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality such as: wish, emotion, possibility, judgement, opinion, obligation, or action that has not yet occurred; the precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is one of the irrealis moods, which refer to what is not necessarily real. It is often contrasted with the indicative, a realis mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact.
Subjunctives occur most often, although not exclusively, in subordinate clauses, particularly that-clauses. Examples of the subjunctive in English are found in the sentences "I suggest that you be careful" and "It is important that she stay by your side."
The subjunctive mood in English is a clause type used in some contexts which describe non-actual possibilities, e.g. "It's crucial that you be here" and "It's crucial that he arrive early." In English, the subjunctive is syntactic rather than inflectional, since there is no specifically subjunctive verb form. Rather, subjunctive clauses recruit the bare form of the verb which is also used in a variety of other constructions.
Present subjunctive -->
Past subjunctive -->, past perfect subjunctive -->, imperativ of the regular verb [travel].
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (you), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive).
Imperativ -->
Participle of the regular verb [travel].
The past participle is one of the most important parts of English grammar. It’s used to express perfect tenses and to form the passive voice. It’s also a useful tool for writing sentences that describe actions that started in the past and are still happening today. The past participles of irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern and can have numerous endings.
Present participle -->
Past participle -->, recent articles.
- Differences: past simple and past continuous
- Past simple sentences
- Past continuous structure
- Adverbs of past continuous tense
- Past continuous verbs
Start with any verb and browse through irregular verbs in alphabetical order
Use the button "Random choice"
Looking for a specific irregular verb?
regular verbs & Irregular verbs
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of travel verb from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
- 3 [ intransitive ] ( of food, wine, an object, etc. ) to be still in good condition after a long trip Some wines do not travel well.
- 4 [ intransitive ] to go fast Their car can really travel!
- 5 [ intransitive ] ( in basketball ) to move while you are holding the ball, in a way that is not allowed compare dribble
Other results
- travel light
Nearby words
Past Tense of Travel: Conjugations in Past and Present Participles

What is the past tense of “travel?” Most commonly, the past tense of the word “travel” is “traveled.” Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it’s used. For example, referencing “travel” in the present participle form will change it to “traveling,” but in the infinitive form, will be “travel.”
What is the past tense of the word "travel"
The past tense (past participle) form of “travel” is “traveled.” The infinitive of the word form is “travel.” The present participle form is “traveling.” The past tense form is “traveled” and past participle form is “traveled.”
Understanding verb tenses
The general grammar rules that govern past tenses are as follows. The simple past tense form is created by adding a -ed or -d affix to the root word of the verb. Some verbs use a -t variation where they end in a -t. For example, when "dream" turns into "dreamt."
The past perfect tense is formed for regular verbs (ending in -ed, -d, or -t) by adding "had" followed by the verb. For example, "I had finished ."
The past continuous tense is formed by the verb "be" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, " we were having dinner."
Lastly, the past perfect continuous tense is formed by adding "had been" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, "I had been building a castle with my sister."
For more information on forming all past tenses, visit our " understanding verb tenses " resource.
Sentence examples for the past tense of the word "travel"
- Infinitive: I travel.
- Present participle: She is traveling.
- Past tense: I traveled.
- Past particle: I have traveled.
Verb forms of the word "travel"
Example sentences in all verb forms:
Indefinite present tense
Present continuous tense.
She/he/it is traveling.
Present perfect continuous tense
She/he/it has/had traveled.
Present perfect tense
She/he/it has/had been traveling.
Simple past tense
She/he/it traveled.
Past continuous tense
She/he/it were traveling.
Past perfect tense
Perfect continuous tense.
She/he/it will/shall travel.
Simple future tense
She/he/it will/shall be traveling.
Future perfect tense
She/he/it will/shall have traveled.
Future perfect continuous tense
She/he/it will/shall have been traveling.
Sentence examples in all forms
Sentence examples in all participles and parts of speech :
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

Past Tense of Travel: Traveling Back in Time
By: Author Oliver
Posted on Last updated: August 12, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Welcome to our article on the past tense of travel! If you’re learning English grammar, you know that understanding verb tenses is an essential part of the language. The past tense is particularly important, as it allows us to talk about events and experiences that have already happened. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of English tenses, give an overview of the past tense, and focus specifically on how to use the past tense when talking about travel.
Travel is one of the most common topics of conversation, and being able to talk about past trips is a great way to connect with others and share experiences. However, using the past tense correctly can be tricky, especially when it comes to irregular verbs and complex sentence structures. In this article, we’ll provide plenty of examples and exercises to help you master the past tense of travel. We’ll also cover some common mistakes to avoid and provide additional resources for further learning.
So whether you’re planning your next trip or just want to improve your English skills, read on to learn everything you need to know about the past tense of travel!
Key Takeaways
- The past tense is essential for talking about past events and experiences, past tense of ‘travel’ is ‘traveled’
- By practicing with examples and exercises, you can improve your use of the past tense of travel and avoid common mistakes.

Past Tense of Travel
Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel.
To form the past tense of travel, we add “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- I traveled to Europe last summer.
- She traveled to Asia for business.
- We traveled to South America for vacation.
Simple Past
The simple past is used to describe a completed action in the past. Regular verbs like travel are formed by adding -ed to the base form. For example:
- I traveled to Paris last year.
Past Continuous
The past continuous is used to describe an action that was in progress at a specific point in the past. It is formed by using the past tense of “to be” (was/were) and the present participle (-ing) of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- I was traveling to Paris when I got a call from my boss.
Usage Examples
The past tense of travel is used to talk about a completed action in the past. Here are some examples:
- I traveled to Japan last year and had an amazing time.
- She traveled to Italy for her honeymoon and fell in love with the country.
- We traveled to Mexico for our anniversary and enjoyed the beautiful beaches.
We can also use the past tense of travel to talk about a past habit or routine. For example:
- When I was younger, I traveled to different countries every summer.
- She traveled for work every week and got used to living out of a suitcase.
- We traveled to visit our family every holiday season.
In conclusion, the past tense of travel is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb and is used to talk about completed actions or past habits. Practice using the past tense of travel in your own sentences to improve your English grammar skills.
Common Mistakes with Past Tense of Travel
If you are learning English, you might be struggling with the past tense of the verb “travel.” Here are some common mistakes people make and how to avoid them.
Mixing Past and Present Tenses
One of the most common mistakes is mixing past and present tenses. For example, saying “I travel to Paris last year” instead of “I traveled to Paris last year.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Present Participle
Another mistake is using the present participle instead of the past tense. For example, saying “I am traveling to London last week” instead of “I traveled to London last week.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb
Using the wrong auxiliary verb is also a common mistake. For example, saying “I was travel to Rome” instead of “I traveled to Rome.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the correct auxiliary verb (in this case, “did”) when forming the past tense.
Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences to help you practice using the past tense of “travel” correctly:
- I traveled to Japan last summer.
- She visited her grandparents in Florida last month.
- They took a road trip across the United States.
- We flew to Paris for our honeymoon.
- He backpacked through Europe after college.
Remember, practice makes perfect! Keep practicing using the past tense of “travel” correctly, and soon it will become second nature.
Exercises to Practice Past Tense of Travel
Learning English grammar can be challenging, especially when it comes to mastering the past tense of travel. To help you improve your skills, we have compiled a list of exercises that you can use to practice and perfect your past tense of travel.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are a great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to engage with the material and receive immediate feedback on your progress. Here are a few interactive exercises you can try:
- Fill in the Blank: In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense verb should go. Your task is to fill in the blank with the correct past tense verb. For example, “I ___ to Paris last year.” The correct answer would be “went.”
- Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, “flew” would match with “airplane.”
Written Exercises
Written exercises are another great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to focus on the material and practice at your own pace. Here are a few written exercises you can try:
- Sentence Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a travel-related word, and your task is to write a sentence using the correct past tense verb. For example, “train” could be used in the sentence, “I ___ to New York on a train.”
- Paragraph Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a prompt related to travel, and your task is to write a paragraph using the correct past tense verbs. For example, “Write a paragraph about your last vacation.” You could write, “Last summer, I ___ to Hawaii with my family. We ___ on the beach, ___ in the ocean, and ___ at some amazing restaurants.”
By practicing these exercises, you will improve your understanding and mastery of the past tense of travel. Keep practicing, and before you know it, you’ll be a pro at English grammar!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense of travel?
The past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second “l” in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?
As mentioned above, both spellings are correct. The difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English.
Which is correct travel or travelling?
Both “travel” and “travelling” are correct, but “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
What’s the difference between travel and Travelled?
“Travel” is the present tense of the verb, while “travelled” is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
What is the V2 form of travel?
The V2 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
What is the V3 form of travel?
The V3 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
The past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second \"l\" in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Which is correct travel or travelling?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Both \"travel\" and \"travelling\" are correct, but \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What's the difference between travel and Travelled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
\"Travel\" is the present tense of the verb, while \"traveled\" is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V2 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V2 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V3 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V3 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Safe: What It Is and How to Use It Correctly - October 3, 2023
- Purple Color Names: Different Hues of Purple - October 2, 2023
- Addition Transition Words for Clear and Cohesive Writing - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- Past Tense of Buy: How to Use them Correctly in English Grammar
- Mastering English Grammar: The Definitive Guide to Understanding the Past Tense of Cost
- Past Tense of Drag: Dragged Through Time
- Hoped or Hoped For? Mastering the Past Tense of Hope with Ease

English Grammar Here
Travel V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Travel

Verb; Travel
Meaning; trip, journey, voyage, peregrination, eyre
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Form of Travel
Synonym for Travel
- peregrination
- sightseeing
- cultivation
When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according to grammatical rules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in irregular verbs, this situation is slightly different. It may be a good start to make some memorization and learn how to use the verbs in the right places.
Here are Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 pdf
Related Posts

Omit V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Omit

Give Past Simple, Simple Past Tense of Give Past Participle, V1 V2 V3 Form Of Give

Freeze V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Freeze
About the author.
Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Travel Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Table of Contents
Travel past tense
Travel past participle, travel verb forms v1 v2 v3 v4, conjugation of travel, more verb past tense, you might also like.

Circulate Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Defeat Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Telecast Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Salvage Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Plug Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Become Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3
Travel Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
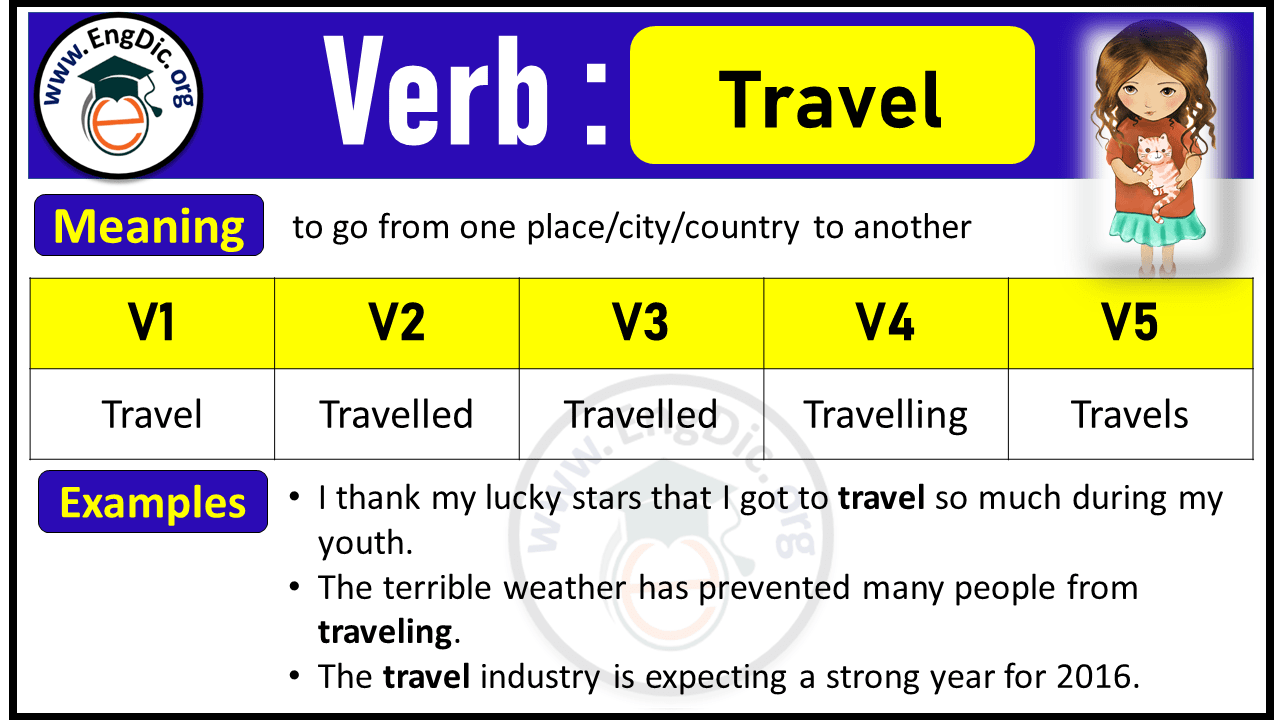
Meaning: to go from one place/city/country to another
Table of Contents
Travel Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
Travel past tense:.
Past Tense of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah Traveled by Train.
Travel Past Participle:
Past Participle Form of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah has Traveled by Train.
Travel Present Participle:
Present Participle Form of Travel is Travelling .
Example: Sarah is Travelling by Train.
Travel 3rd Person Singular:
3rd Person Singular of Travel is Travels .
Example: Sarah Travels by Train.
Travel Conjugation
Indefinite / simple present tense.
- I Travel by Train.
- We/You/They Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Travels by Train.
Present Continuous Tense
- I am Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They are Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam is Travelling by Train.
Present Perfect Tense
- I have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has Traveled by Train.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- I have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Past Tense
- I Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Traveled by Train.
Past Continuous Tense
- I was Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They were Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam was Travelling by Train.
Past Perfect Tense
- I had Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They had Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had Traveled by Train.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- I had been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They had been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Future Tense
- I will Travel by Train.
- We/You/They will Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will Travel by Train.
Future Continuous Tense
- I will be Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will be Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will be Travelling by Train.
Future Perfect Tense
- I will have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They will have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have Traveled by Train.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- I will have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have been Travelling by Train.
Past Tense of Travel Phrasal Verbs
Explore Other Verb Forms:
What is the Future Tense of Travel?
Future Tense of Travel is “ will Travel” .
What is the Present Tense of Travel?
Present Tense of Travel is “ Travel + s/es or ing” .
What is the Past Perfect Tense of Travel?
Past perfect tense of take is “ had Traveled ”.
Last updated on May 24th, 2023 at 02:22 am
Related Posts
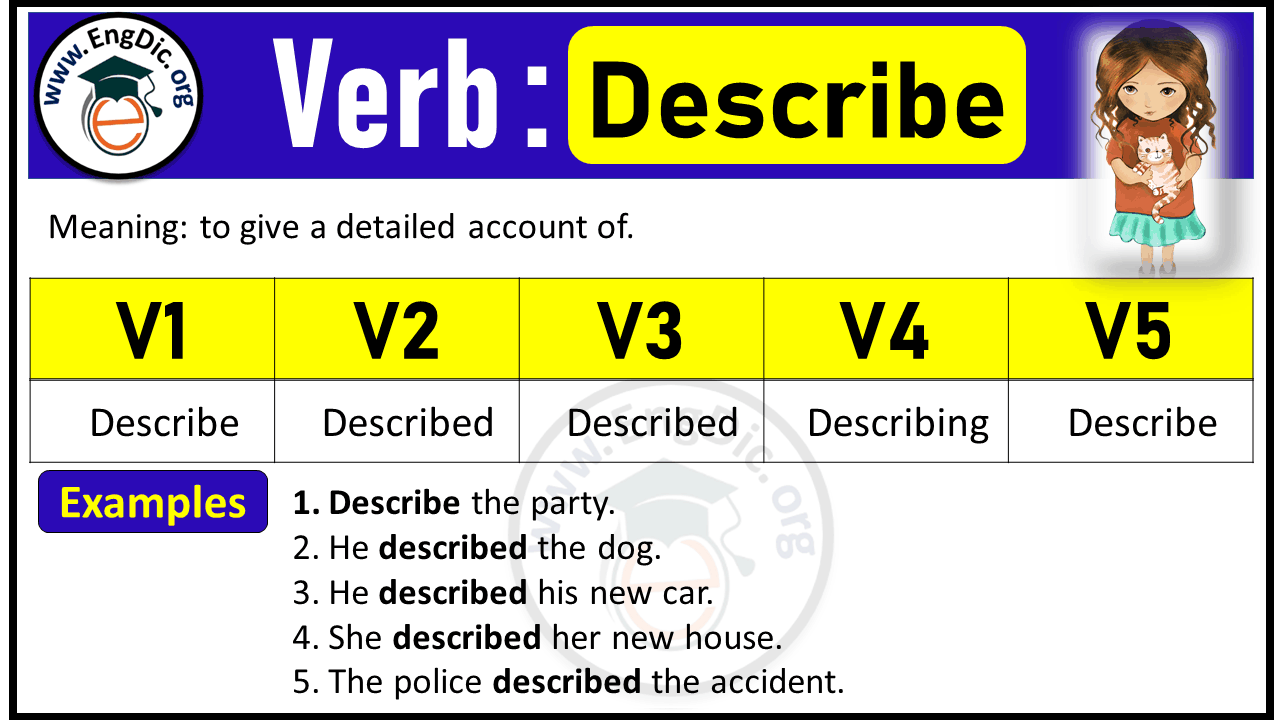
Describe Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

260 Verbs Starting with W (Complete List)
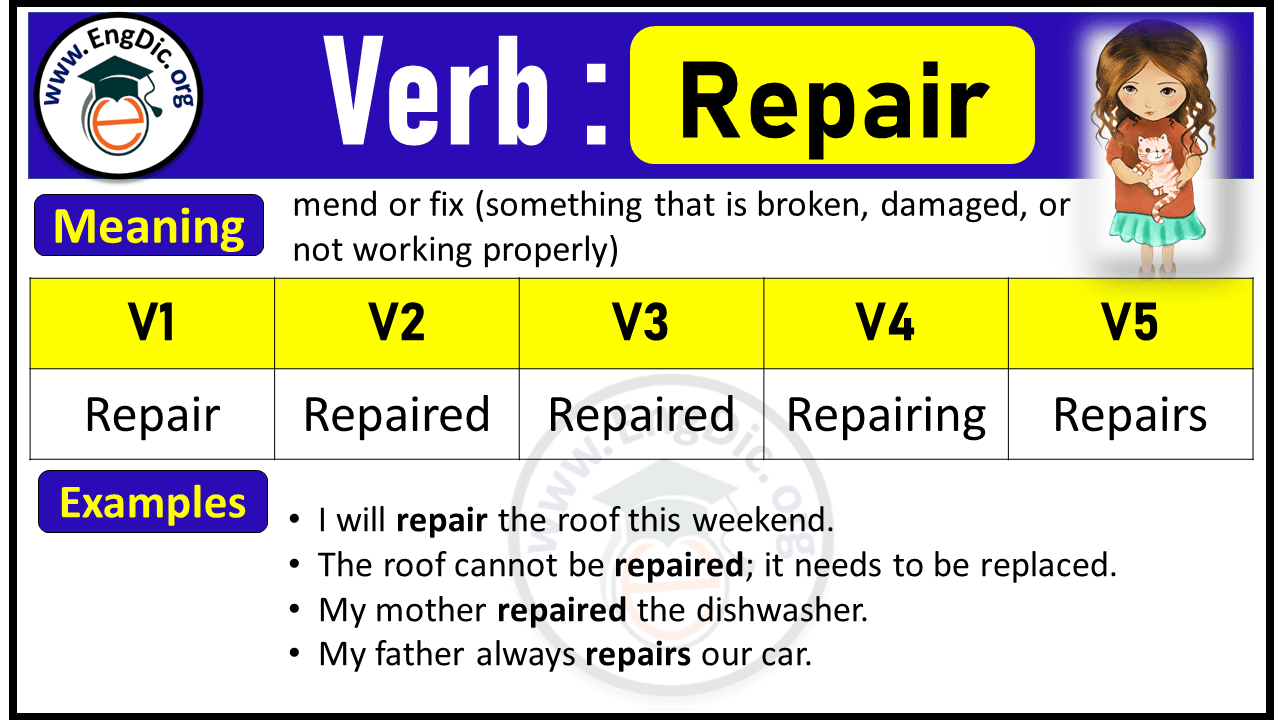
Repair Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Brush Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Let Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Reply Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.
Example: eat, ate, eaten
Past Perfect
Future perfect, present - conditional, perfect - conditional.
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of travel
(Entry 1 of 2)
intransitive verb
transitive verb
Definition of travel (Entry 2 of 2)
- peregrinate
- peregrination
Examples of travel in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'travel.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle English travailen, travelen to torment, labor, strive, journey, from Anglo-French travailler
14th century, in the meaning defined at intransitive sense 1a
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing travel
- pre - travel
- see / travel the world
- travel agency
- travel agent
- travel light
- travel sickness
- travel trailer
Articles Related to travel

Is it ‘traveling’ or...
Is it ‘traveling’ or ‘travelling’?
A tale of two variants

Noah Webster's Spelling Wins and Fails
Some of his biggest successes and defeats

8 Ways to Get Away From It All
Whether it's a jaunt or a junket, remember sunblock.
Dictionary Entries Near travel
Cite this entry.
“Travel.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/travel. Accessed 21 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of travel.
Kids Definition of travel (Entry 2 of 2)
Middle English travailen "torment, labor, strive, journey," from early French travailler "torment, labor," from an unrecorded Latin verb tripaliare "to torture," from Latin tripalium "an instrument of torture," literally "three stakes," derived from tri- "three" and palus "stake, pale" — related to pale entry 3 , travail
More from Merriam-Webster on travel
Nglish: Translation of travel for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of travel for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about travel
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day, noblesse oblige.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 19, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.

- English Tense Converter
- Basic English
- Parts of speech
- Daily tasks
- Verb of the day
- Quiz of the day
- Top 500 verbs list
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and conditions

Travel verb forms - Learn English Free Online | LTSenglish.com
Travel verb forms.

Travel present tense
Travel past tense, travel future tense, simple present tense of travel, present continuous tense of travel, present perfect tense of travel, present perfect continuous tense of travel, simple past tense of travel, past continuous tense of travel, past perfect tense of travel, past perfect continuous tense of travel, simple future tense of travel, future continuous tense of travel, future perfect tense of travel, future perfect continuous tense of travel.

© Copyright 2019 - 2024 ltsenglish.com
Meta working on travel mode for using Quest headsets during flights after Vision Pro launches with feature
Today I learned two things. First, apparently Meta Quest headsets don’t work on planes? I guess Apple knew to prioritize that feature for Vision Pro. And second, support is reportedly on the way. Add this to the list of ways competition from Vision Pro is making Meta Quest 3 a better product.
For April, Meta released software update v64 that makes Quest 3 passthrough more like Vision Pro, users say. Motion blur is more noticeable, but still clarity is increased. Meta has also added support for viewing spatial videos captured from iPhone 15 Pro.
Now Meta may be planning to introduce flight support as soon as v65 next month. Per @Lunayian on X ( via Nicholas Sutrich ), several code strings reference travel mode for use on a plane.
Early NUX render to introduce "Flight Mode" I found in Meta Quest OS v65 pic.twitter.com/oq2GzCiaZu — Luna (@Lunayian) April 18, 2024
Apple pushes watching movies and TV shows during flights as a key use case for Apple Vision Pro. It’s one of the first things you see at the top of Apple’s website currently.
Surely Meta has taken notice and prioritized travel mode as it positions Meta Quest 3 as a dramatically cheaper solution to Vision Pro with many of the same capabilities.
The most impactful change, however, would be around multitasking. Quest headsets are limited to three app windows at a time right now. Apple Vision Pro has plenty of other limitations, but there’s virtually no limit to how many windows can be placed around a room and used together.
- Zuckerberg says Meta Quest 3 is better than Apple Vision Pro
- Apple Vision Pro is already making the Meta Quest 3 better
- Vision Pro latency by far the best on passthrough; lags behind Meta on angular motion
- Meta confirms spatial video playback coming to Quest one day before Vision Pro launch
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.
Check out 9to5Mac on YouTube for more Apple news:

Zac covers Apple news, hosts the 9to5Mac Happy Hour podcast, and created SpaceExplored.com.
Cookie banner
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our site, show personalized content and targeted ads, analyze site traffic, and understand where our audiences come from. To learn more or opt-out, read our Cookie Policy . Please also read our Privacy Notice and Terms of Use , which became effective December 20, 2019.
By choosing I Accept , you consent to our use of cookies and other tracking technologies.
Follow The Ringer online:
- Follow The Ringer on Twitter
- Follow The Ringer on Instagram
- Follow The Ringer on Youtube
Site search
- What to Watch
- Bill Simmons Podcast
- 24 Question Party People
- 60 Songs That Explain the ’90s
- Against All Odds
- Bachelor Party
- The Bakari Sellers Podcast
- Beyond the Arc
- The Big Picture
- Black Girl Songbook
- Book of Basketball 2.0
- Boom/Bust: HQ Trivia
- Counter Pressed
- The Dave Chang Show
- East Coast Bias
- Every Single Album: Taylor Swift
- Extra Point Taken
- Fairway Rollin’
- Fantasy Football Show
- The Fozcast
- The Full Go
- Gambling Show
- Gene and Roger
- Higher Learning
- The Hottest Take
- Jam Session
- Just Like Us
- Larry Wilmore: Black on the Air
- Last Song Standing
- The Local Angle
- Masked Man Show
- The Mismatch
- Mint Edition
- Morally Corrupt Bravo Show
- New York, New York
- Off the Pike
- One Shining Podcast
- Philly Special
- Plain English
- The Pod Has Spoken
- The Press Box
- The Prestige TV Podcast
- Recipe Club
- The Rewatchables
- Ringer Dish
- The Ringer-Verse
- The Ripple Effect
- The Rugby Pod
- The Ryen Russillo Podcast
- Sports Cards Nonsense
- Slow News Day
- Speidi’s 16th Minute
- Somebody’s Gotta Win
- Sports Card Nonsense
- This Blew Up
- Trial by Content
- Wednesday Worldwide
- What If? The Len Bias Story
- Wrighty’s House
- Wrestling Show
- Latest Episodes
- All Podcasts
Filed under:
- Pop Culture
‘Conan O’Brien Must Go’ Is the Best Version of Conan
The comedian’s new travel show proves he’s at his best away from the rigid confines of late night
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: ‘Conan O’Brien Must Go’ Is the Best Version of Conan
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73287249/conanmustgo2_netflix_ringer.0.jpg)
After hundreds of episodes of Hot Ones , there’s little a guest can do to shake up the reliable formula of thoughtful questions combined with increasingly spicy chicken wings. But Conan O’Brien isn’t just any guest. Conan is someone who arrives with “Dr. Arroyo,” his personal physician, who, when asked where he went to medical school, answers “1998”; he deposits the remains of each wing into his jacket pocket; seemingly unfazed by the heat, he chugs hot sauces like they’re in tiny liquor bottles from a hotel minibar; he rubs the drumsticks on his hands, mouth, and, yes, nipples. Even as Conan’s pale complexion begins to resemble a ripe tomato, he remains committed to the bit, raising his body temperature by two degrees in a state of delirium. (According to Dr. Arroyo, of course.) Behold, the comedy GOAT:
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25405346/Screenshot_2024_04_12_at_9.53.49_AM.png)
Aside from being one of the funniest people on the planet, Conan seems to operate at the peak of his powers when surrounded by chaos. He was, for a time, our longest-tenured late-night host: He had a career on the airwaves that spanned nearly three decades, not unlike his icon, Johnny Carson. But while Conan could do the usual late-night beats in his sleep—the opening monologue, the celebrity interviews—he was never better than when things went completely off the rails. Consider: Conan used his last week as the short-lived host of The Tonight Show to waste NBC’s money on bringing a Kentucky Derby–winning horse to set; trolled his interns and staff in remote segments; introduced the world to his associate producer Jordan Schlansky, who gamely played a pretentious foil ; found an actual Tinder date with Dave Franco.
But some of Conan’s best work has been when he’s left the rigid confines of late night altogether. In 2015 Conan began a spinoff travel series, Conan Without Borders , in which he explored other countries armed with little more than his self-deprecating wit. “[Travel shows are] completely outside the realm of anything I do,” he explained to The New York Times in 2019. “They can be frightening because they take away a lot of control. I’m out there, I don’t often know what I’m going to encounter.” More often than not, it’s led to comedy gold. For instance, while he was taking a Japanese etiquette lesson, Conan’s instructor said that he wasn’t her type. The reason: “Face.”
Face . You could never script something so casually brutal; therein lies the magic. Most important, Conan never mocks other cultures to induce laughs—instead, he makes himself the butt of the joke, leaning into the bit of an ignorant tourist. But what truly elevated Conan Without Borders was how he could deftly weave in educational components and approach dark periods of a country’s history with genuine sensitivity. (Conan’s visit to the Armenian Genocide Memorial with his longtime assistant, Sona Movsesian, is among the most emotionally resonant moments of his career.) Thankfully, even though Conan has bowed out of the late-night scene, he’s doubling down on the travelogues.
On Thursday—Conan’s birthday, no less—Max released Conan O’Brien Must Go , a four-part series that takes him to Norway, Argentina, Thailand, and Ireland. These destinations were inspired by his podcast, Conan O’Brien Needs a Friend , which, in addition to celebrity interviews, features conversations with fans from around the globe. (The fans frequently invite Conan to come visit their neck of the woods; few would ever imagine he’d take them up on the offer.) While Conan O’Brien Must Go doesn’t rely on celebrity cameos, every episode opens with Werner Herzog voice-over narration about the grandeur of Mother Earth and how, to fully appreciate its natural wonders, we must sometimes “defile it.” Rest assured, Conan the Defiler is more than up to the task.
What separates Conan O’Brien Must Go from his first travel show is the incorporation of those fans, including a Norwegian fish farmer, an Irish medical student, and an Argentine painter. The fans understandably react to Conan showing up at their front door with a mixture of shock and glee, but before they even get a chance to compose themselves, he playfully roasts their respective living situations. Nobody gets it worse than Jarle, a young Norwegian rapper who still sleeps with soccer-themed bedsheets from childhood and has bread so stale it lands with an audible thud when Conan drops it. “I’ll wipe the floor with you,” Conan tells Jarle, “which actually might be a good idea, because I think you’d pick up a lot of lint.”
The Ringer ’s Streaming Guide

There’s a lot of TV out there. We want to help: Every week, we’ll tell you the best and most urgent shows to stream so you can stay on top of the ever-expanding heap of Peak TV.
But while it’s enjoyable in its own right to see Conan surprise fans, Conan O’Brien Must Go is never better than when he throws all caution to the wind mingling with the locals. One standout bit in Argentina involves a soccer team that invites Conan to its stadium, where he proceeds to take the sport’s reputation for theatrical diving to another level, with fake blood spurting out of his mouth. Argentina is also where Conan reunites with his archnemesis, Schlansky, who repeatedly corrects him on the proper pronunciation of tango over dinner. (Schlansky insists he’s right, even when the chefs disagree with him.) And while some comedians might have second thoughts if nobody seems entertained by their shenanigans, Conan always doubles down—if only for his own amusement. (The Argentine gauchos did not enjoy his singing talents.)
Despite all the silliness that’s part of the Conan experience, Conan O’Brien Must Go also manages to have moments of real profundity. For one, Conan uses the Ireland episode to explore his own heritage, culminating with a visit to the patch of rural farmland that belonged to his ancestors. It puts everything into perspective: His forebears fled the Irish famine for America, and their descendant returned with a camera crew and decades of fame and success under his belt. Truly, what are the odds? But what really tugs at the heartstrings is a brief video from the Norwegian fish farmer Kai, who explains how Conan’s visit to his small town completely changed his life. It’s genuinely heartwarming stuff, proving that comedy can achieve more than just laughs when it’s approached with curiosity and empathy.
It’s been three years since Conan last graced our screens, and his absence really underlined that he’s one of one. You can’t imagine anyone else showing up to a foreign country and reacting to situations on the fly without everything falling apart at the seams. But as Conan proved time and again during his late-night tenure, that’s where great comedy can be found: among the people, whether it’s in the streets of Harlem or a Civil War reenactment . Conan’s late-night career went through many phases , all of them worthy, but in retrospect, it feels like the format was holding him back. Conan O’Brien Must Go isn’t just a hilarious return to form: It’s one of the best things he’s ever done. Let’s hope the show’s Season 2 renewal will be a matter of when, not if. With Conan at the helm, there are so many more countries worth exploring—and defiling.
Next Up In TV
‘x-men ’97’ episodes 4-6 deep dive, a crazy week in bravoland plus, our most robust series of recaps ever..
- Coachella Thoughts, Alleged Taylor Swift Album Leak, and More!
- Self-Healing, WNBA Salaries, and What Jerrod Really Meant
- Apple Gets Into the Franchise Business, the Penultimate Episode of ‘Shogun,’ and ‘Ripley’ Episodes 4 and 5
- ‘Survivor’ Season 46, Episode 8
Sign up for the The Ringer Newsletter
Thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

Erik Spoelstra Is the NBA’s Best Coach and Power Ranking the League’s GOAT Dynasties
Austin and Pausha discuss Miami’s win over Chicago, the end of the Warriors dynasty, and a preview of the Magic vs. Cavaliers series

“The Real Stared You in the Face!”
A bonus episode discusses the Bulls-Heat play-in game, Chicago’s season ending on a sour note, and how Miami continues to succeed

The Hater’s Guide to the 2024 NBA Playoffs’ First Round
Which first-round series will produce the most jokes? From the dream Knicks-76ers clash to the Lakers-Nuggets "rivalry," we break down every matchup and the reputations at stake.

2024 NBA Playoff Predictions: Finals Picks, Upsets, and Summer Blockbusters
Which top seed could go down early? Who will ultimately make the Finals? And which star could be on the move after an early exit? We preview the postseason.

Mal and Jo discuss the stakes of the show, explain the role of shame in the series, and cover every romance while going over all that happened in the middle three episodes

Rachel and Callie guide you through the seemingly endless stream of news coming from the Bravosphere lately, while Jodi later hops on to recap recent episodes from ‘The Valley’ and ‘Vanderpump’

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conjugate the English verb travel: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate travel in context, with examples of use and definition. ... Other forms: travel oneself/not travel. Contractions. in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings.
travel. 'travel' is the model of its conjugation. In British English, the final consonant is doubled before -ing and -ed. infinitive: present participle: past participle: (to) travel. trave ll ing. trave ll ed.
English verb TO TRAVEL conjugated in all forms, with full audio, irregular highlighting, negative forms and contractions.
This is a reference page for travel verb forms in present, past and participle tenses. Find conjugation of travel. Check past tense of travel here. website for synonyms, antonyms, verb conjugations and translations ... PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present ...
'to travel' conjugation - English verbs conjugated in all tenses with the bab.la verb conjugator. To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe. You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site. The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single ...
Conjugation English verb to travel in several modes, tenses, voices, numbers, persons : indicative mode, subjunctive, imperative mood, conditional, participle form ...
Present Continuous. I am travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling he/she/it is travelling or traveling we are travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling they are travelling or traveling.
Conjugate the verb travel in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc.
Conjugation of the verb Travel in all tenses: future, present and past. 🎮 Conjugation trainer for memorizing forms. ... Verb forms. Base Form Past Simple Past Participle Gerund ; travel: traveled: traveled: travelled [ˈtrævl] [ˈtrævəld] [ˈtrævəld] [ˈtrævld] [ˈtræv(ə)l] [ˈtrævəld]
English: travel English verb 'travel' conjugated. Cite this page ...
Some wines do not travel well. [intransitive] travel (well) (of a book, an idea, etc.) to be equally successful in another place and not just where it began. These recipes travel well and don't require unusual ingredients or equipment. Some writing travels badly (= is not successful) in translation. [intransitive] to go fast. Their car can ...
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'. the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses. the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense. the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking. The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is ...
1 [intransitive, transitive] to go from one place to another, especially over a long distance to travel around the world I go to bed early if I'm traveling the next day. I love traveling by train. We always travel first class. We traveled to California for the wedding. When I finished college I went traveling for six months (= spent time visiting different places). travel something He traveled ...
The infinitive of the word form is "travel." The present participle form is "traveling." The past tense form is "traveled" and past participle form is "traveled." Understanding verb tenses. The general grammar rules that govern past tenses are as follows. The simple past tense form is created by adding a -ed or -d affix to the ...
Past Tense of Travel. Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel. Formation. To form the past tense of travel, we add "-ed" to the base form of the verb. For example: I traveled to Europe last summer. She traveled to Asia for business.
Verb; Travel. Meaning; trip, journey, voyage, peregrination, eyre. V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Form of Travel. Synonym for Travel. When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according to grammatical rules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in ...
Visit. Travelled is the past tense of the word travel. Travelled is the past participle of the word travel. travel past form, verb forms, v1v2v3, Inf.
Meaning: to go from one place/city/country to another Travel Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Base Form/Infinitive (V1): Travel Past Tense (V2): Traveled Past Participle Form (V3): Traveled Present Participle/Gerund (V4): Travelling 3rd Person Singular (V5): Travels Travel Past Tense: Past Tense of Travel is Traveled. Example: Sarah Traveled by Train. Travel Past Participle: Past Participle Form of ...
A tale of two variants. What to Know. When it comes to spelling the forms of the verb travel, traveled and traveling are more common in the U.S., and travelled and travelling are dominant everywhere else. Spelling is typically clear-cut in modern English: forty unfailingly betrays four; the sweet treat after dinner is spelled dessert, not desert.
Look up English verb forms - over 5000 verbs! Excellent resource for students and teachers. verb123.com Home Notes About. Example: eat, ate, eaten ...
travel: [verb] to go on or as if on a trip or tour : journey. to go as if by traveling : pass. associate. to go from place to place as a sales representative or business agent.
Travel Verb Forms. Base form (v1) Travel. Past form (v2) Travelled. Past Participle (v3) -ed form. Travelled. Present Participle (v4)
Surely Meta has taken notice and prioritized travel mode as it positions Meta Quest 3 as a dramatically cheaper solution to Vision Pro with many of the same capabilities. The most impactful change ...
Conan O'Brien Must Go isn't just a hilarious return to form: It's one of the best things he's ever done. Let's hope the show's Season 2 renewal will be a matter of when, not if.