Switch language:


Tomahawk Long-Range Cruise Missile
Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile in service with the surface ships and submarines of the US and the UK’s Royal Navy.
Long-range subsonic cruise missile
Manufacturer
US Navy and Royal Navy
Williams International F415 cruise turbo-fan
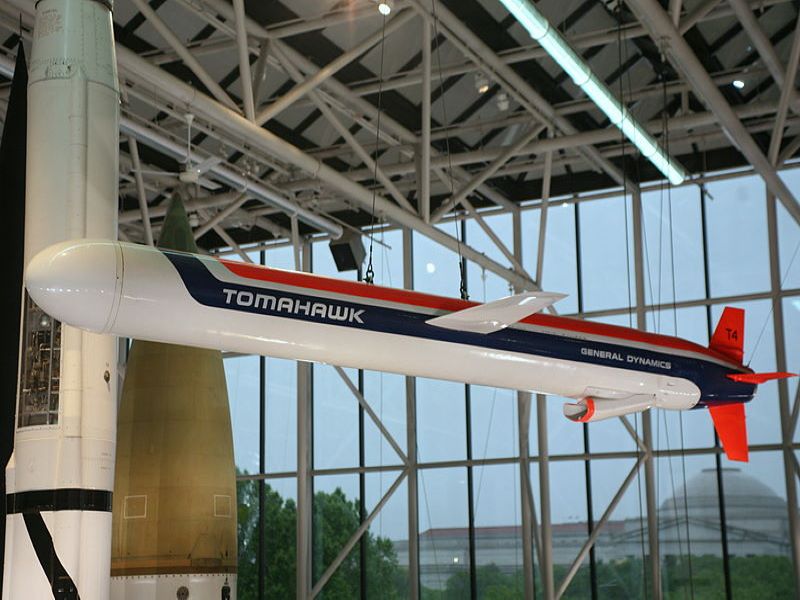

Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile in service with the surface ships and submarines of the US and the UK’s Royal Navy. Originally produced by General Dynamics, Tomahawk is currently manufactured by Raytheon.
The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) can strike high-value or heavily defended land targets. The Block II TLAM-A missile achieved initial operating capability in 1984. The missile was first deployed in combat during Operation Desert Storm in 1991.
Recommended White Papers
Angle of Arrival/Direction-Finding Techniques
Advanced geolocation capabilities, recommended buyers guides.
Military messaging and naval communications software providers for the naval defence industry
Maritime solutions: subsystems for the naval industry, tomahawk missile variants.
The Tomahawk family of missiles includes a number of variants, carrying different warheads. The UGM-109A Tomahawk (Block II TLAM-A) carries a W80 nuclear warhead.
RGM / UGM-109C (Block III TLAM-C) is a conventional unitary variant, carrying a 1,000lb-class warhead. RGM / UGM-109D (Block III TLAM-D) is a submunitions dispenser variant armed with 166 combined-effects bomblets.
RGM / UGM-109E Tomahawk (Block IV TLAM-E) is the latest member in the Tomahawk missile family. It carries a 1,000lb-class unitary warhead for a maximum range of 900nmi.
The Tomahawk Block IV missiles were converted and upgraded to Block V in 2017. The upgraded Tomahawk includes extended range, enhanced navigation and communication systems and modernised data-link radio.
The upgrades were performed at Raytheon’s Tucson, Arizona facility. The US Navy will use the upgraded Tomahawk cruise missiles beyond 2040. Raytheon was contracted to integrate the upgraded navigation and communication systems into the Block IV Tactical Tomahawk (TACTOM) missile in March 2020. The upgraded version is known as the Block V TACTOM.
The Block Va variants will be named Maritime Strike and have the capability of hitting a moving target. The Block Vb will feature the Joint Multi-Effects Warhead System.
Tomahawk design features
The Tomahawk is designed to operate at very low altitudes while maintaining high-subsonic speeds. Its modular design enables the integration of numerous types of warheads, guidance and control systems.
The missile carries a nuclear or conventional payload. It can be armed with a nuclear or unitary warhead or a conventional submunitions dispenser with combined-effect bomblets. The missile has a 5.56m length, 51.8cm diameter and a 2.67m wingspan. The weight of the missile is 1,315kg. It has a life span of 30 years.
The Tomahawk weapon system includes the Tomahawk missile, Theatre Mission Planning Centre (TMPC) / Afloat Planning System and the Tomahawk weapon control system (TWCS) for surface vessels or combat control system (CCS) for submarines.
Guidance and control
The Tomahawk Block IV uses GPS navigation and a satellite data-link to continue through a pre-set course. The missile can be reprogrammed in-flight to a new target.
The two-way satellite communications are used to perform post-launch mission changes throughout the flight. The on-board camera provides imagery of the target to the commanders before the strike.
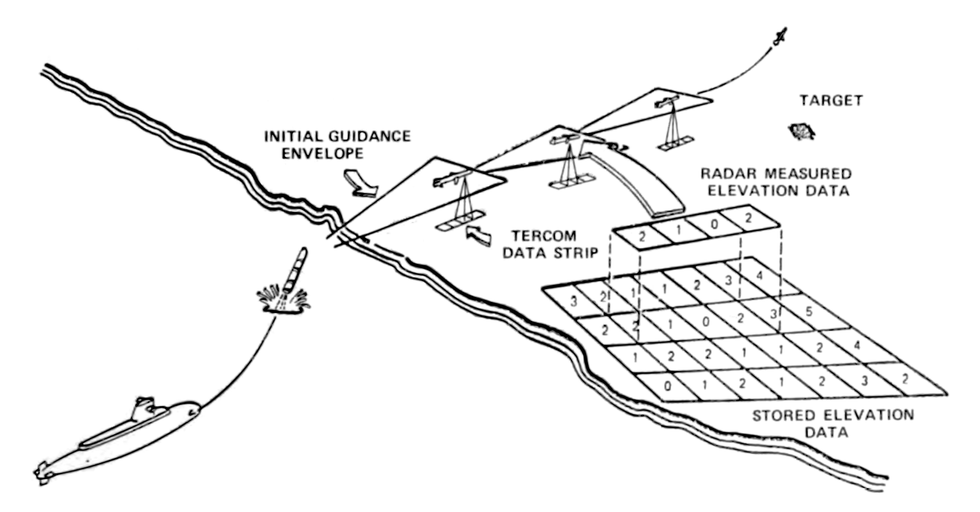
The guidance system is assisted by Terrain Contour Matching (TERCOM). The Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC) system or GPS provide terminal guidance.
The Tactical Tomahawk Weapons Control System (TTWCS) integrated within the ship’s systems computes the path to engage targets. The system enables the planning of new missions on board the launch vessel. TTWCS is also used to communicate with multiple missiles for reassigning the targets and redirecting the missiles in flight.
The Block IV Tomahawk missile is outfitted with advanced electronic support measure (ESM) seeker in Block IV Tomahawk missile. Its joint multi-effects warhead enables the commander to control the blast.
The Tomahawk Block IV missile is powered by a Williams International F415 cruise turbo-fan engine and ARC MK 135 rocket motor. The propulsion provides a subsonic speed of 880km/h.
Tomahawk launch platforms
The missile can be launched from over 140 US Navy ships and submarines and Astute and Trafalgar class submarines of the Royal Navy. All cruisers, destroyers, guided missile and attack submarines in the US Navy are equipped with a Tomahawk weapons system.
US Navy launch platforms were modified to accommodate upgraded Tomahawk missile variants. Four Ohio class nuclear ballistic missile submarines were converted into cruise missile submarines for firing Tomahawk missiles. The Virginia class submarines and the Royal Navy Astute class submarines were also fitted with new vertical launch modules for Tomahawk missile.
Tomahawk orders and deliveries
The US signed a foreign military sales (FMS) agreement with the UK in 1995 to supply 65 Tomahawks for use with the Royal Navy nuclear submarines. The first batch of missiles was delivered in 1998.
The US Government approved an agreement in 2003 to deliver 65 Tomahawk Block IV missiles for the UK. In August 2004, the US Navy placed a $1.6bn multi-year procurement contract with Raytheon for 2,200 Tomahawk Block IV missiles.
Raytheon was awarded a $346m production contract for 473 Tomahawk Block IV cruise missiles in March 2006. The contract includes 65 submarine torpedo tube-launched missiles for the Royal Navy. The Block IV entered service with the Royal Navy in March 2008.
Raytheon was awarded a $207m-worth firm-fixed-price contract in March 2009 for 207 Tomahawk Block IV All-Up-Round (AUR) missiles.
The 2,000th Tomahawk Block IV missile was delivered to the US Navy in February 2010.
The US Navy placed a $338m contract with Raytheon in June 2012 for the delivery of 361 Tomahawk Block IV tactical cruise missiles. Another contract worth $254.6m was awarded for Tomahawk Block IV in the same year.
Raytheon delivered the 3,000th Tomahawk Block IV to the US Navy in January 2014 as part of the ninth Block IV production contract.
The US Navy awarded a $251m contract to Raytheon for the production and delivery of Tomahawk Block IV missiles for both the US Navy and Royal Navy in September 2014.
A $25.9m contract for Tomahawk missile composite capsule launching systems (C/CLS) was awarded in December 2014. The C/CLS is integrated with the nuclear-powered fast-attack submarines and nuclear-powered guided-missile submarines, allowing the missile to be launched from submarines.
Tomahawk Block IV missile demonstrated its moving target capability in tests conducted in February 2015.
Raytheon received a $122m contract from the US Navy in March 2015 for the production of 114 Tomahawk Block IV all-up round missiles. Raytheon conducted an active seeker test flight for the Tomahawk Block IV cruise missile in January 2016.
The 4,000th Tomahawk Block IV missile was delivered to the US Navy in August 2017. The US Navy warships and submarines launched 66 GPS-enabled Tomahawk missiles at Syrian chemical weapon facilities in 2018.
Raytheon planned to undertake recertification and modernisation programmes for Tomahawk Block IV missile in 2019 to add maritime strike capability and multiple-effects warhead upgrades to the missiles.
Raytheon received a $349m contract for phase two of the Maritime Strike Tomahawk Rapid Deployment Capability to improve the Tomahawk cruise missile system in August 2019. Work will be executed in various locations across the US until February 2023.
Related Projects
More Projects
Transwing Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) UAS, US
Combat boat 90 (cb90), sweden, naval station mayport, jacksonville, florida, kings bay naval submarine base, sign up for our daily news round-up.
Give your business an edge with our leading industry insights.
Sign up to the newsletter
Your corporate email address.
Naval Technology In Brief
Global Defence Technology
Thematic Take
I consent to Verdict Media Limited collecting my details provided via this form in accordance with Privacy Policy
Thank you for subscribing
View all newsletters from across the GlobalData Media network.
Air Warfare
- Cyber (Opens in new window)
- C4ISR (Opens in new window)
- Training & Sim
- Asia Pacific
- Mideast Africa
- The Americas
- Top 100 Companies
- Defense News Weekly
- Money Minute
- Whitepapers & eBooks (Opens in new window)
- DSDs & SMRs (Opens in new window)
- Webcasts (Opens in new window)
- Events (Opens in new window)
- Newsletters (Opens in new window)
- Events Calendar
- Early Bird Brief
- Digital Edition (Opens in new window)
Watch this US Air Force cargo plane launch a cruise missile in Norway
WASHINGTON — The U.S. Air Force has for the first time in an overseas test used its Rapid Dragon system , in which cruise missiles on pallets are launched from the back of a mobility aircraft.
An MC-130J Commando II from the 352nd Special Operations Wing launched a Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile-Extended Range cruise missile using the system nicknamed “bomb bay in a box” in a range over the Norwegian Sea on Wednesday, the Air Force Research Laboratory said.
Dean Evans, the program manager for Rapid Dragon , said the successful test shows how quickly the program is progressing, noting that it moved from a concept on paper to a live-fire test in two years.
“Now, less than three years from the program’s inception, Rapid Dragon is being used by [U.S. Special Operations Command Europe] in the Arctic Circle,” Evans said in a release. “This is a testament to the team’s focus on rapid fielding to meet warfighter needs.”
The command posted a video online Wednesday that shows the test process at Norway’s Andøya Space Defense Range from multiple perspectives. A parachute attached to the Rapid Dragon deployment box is tossed from the open cargo bay of the MC-130, which then unfurls and swiftly pulls the pallet out of the aircraft.
The hurtling box sheds its deployment parachute and deploys a quartet of other parachutes that steady it. When the deployment box is vertical, it releases a JASSM-ER missile downward. Within seconds, the missile’s wings and tail snap open, and its engine engages, leaving a trail of exhaust in its wake.
This was the first live-fire Rapid Dragon test since the Air Force destroyed a target in the Gulf of Mexico in December 2021, and the first time the concept was used outside of the continental United States, the Air Force Research Lab said.
A longer video of the test posted by the Pentagon showed the cruise missile traveling over the sea for about 2 minutes before detonating. When asked if a target was destroyed, the lab did not respond directly, but said that all objectives were met.
An airman with the 352d Special Operations Wing conducts preflight operations on an MC-130J Commando II during the Atreus exercise at Andøya Space Defense Range in Norway on Nov. 8, 2022. Two U.S. Air Force Special Operations Command wings partnered in a total force initiative to conduct the first live-fire demonstration in the European theater of Rapid Dragon, a long-range palletized munitions system, in the U.S. European Command's area of responsibility. (Tech. Sgt. Brigette Waltermire/Air National Guard)
Additional photographs posted by the Air Force showed American and Polish airmen training to load palletized munitions onto a Polish C-130. That training took place Tuesday in Powidz, Poland.
The lab said the program has so far focused on kinetic munitions, but is now turning its attention to adding “palletized effects.” Those effects include intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance platforms, cargo resupply, and humanitarian aid delivery, the release said.
The Air Force hopes this concept will allow the U.S. and its allies to turn cargo aircraft into heavily armed bomb trucks that can engage enemies at a safe distance, giving combatant commanders more options to deliver firepower.
The lab said this test took place as part of U.S. European Command’s operational series Atreus, which aims to conduct training events on capabilities found in Europe. The 352nd Special Operations Wing is based at RAF Mildenhall in England, and the MC-130 was from the wing’s 67th Special Operations Squadron.
This test was the seventh Atreus event, and in addition to Norway also included allies from the United Kingdom, Poland, and Romania.
Previous Atreus training events focused on using the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System along with allies from Romania, the U.K., Sweden and Latvia.
Stephen Losey is the air warfare reporter for Defense News. He previously covered leadership and personnel issues at Air Force Times, and the Pentagon, special operations and air warfare at Military.com. He has traveled to the Middle East to cover U.S. Air Force operations.
More In Air Warfare
Defense Innovation Unit moves to ease commercial drone certifications
Diu wants to improve its process for vetting commercial drones, with the goal of making it easier for companies to sell their systems to the u.s. military..
Saab unveils technology incubator using Enforcer 3 as test bed
“we are trying to get capability to the fleet in months,” said erik smith, the chief executive of saab's u.s. branch..
Lockheed to supply Australia with air battle management system
Overhauling australia’s overhead defenses is expected to generate hundreds of local jobs as well as open the door to a multibillion-dollar export market..
Defense Innovation Unit prepares to execute $800 million funding boost
Diu director doug beck said he doesn’t foresee any issues with quickly putting to work the $983 million in fy-24 funding congress provided in march..
Army may swap AI bill of materials for simpler ‘baseball cards’
"we know innovation's happening in the open-source environment," said the army's bharat patel. "we also know who's contributing to the open source.", featured video, military times’ 2024 service members of the year.
From combat medic to Paralympian: What drives Ellie Marks?

The Navy petty officer ensuring the Carney stays focused on the fight
Ukraine-born airman’s translations aided allied efforts as war erupted
Trending now, here are the two companies creating drone wingmen for the us air force, french missile double punch adds new naval capability for europe, us army’s next-gen helicopter engine could fly in black hawk next year, us army to shift aviation force structure back to tailored brigades, us army to field long-range combat aircraft to first unit in fy31.
- Air Transport
- Defense and Space
- Business Aviation
- Aircraft & Propulsion
- Connected Aerospace
- Emerging Technologies
- Manufacturing & Supply Chain
- Advanced Air Mobility
- Commercial Space
- Sustainability
- Interiors & Connectivity
- Airports & Networks
- Airlines & Lessors
- Safety, Ops & Regulation
- Maintenance & Training
- Supply Chain
- Workforce & Training
- Sensors & Electronic Warfare
- Missile Defense & Weapons
- Budget, Policy & Operations
- Airports, FBOs & Suppliers
- Flight Deck
- Marketplace
- Advertising
- Marketing Services
- Fleet, Data & APIs
- Research & Consulting
- Network and Route Planning
Market Sector
- AWIN - Premium
- AWIN - Aerospace and Defense
- AWIN - Business Aviation
- AWIN - Commercial Aviation
- Advanced Air Mobility Report - NEW!
- Aerospace Daily & Defense Report
- Aviation Daily
- The Weekly of Business Aviation
- Air Charter Guide
- Aviation Week Marketplace
- Route Exchange
- The Engine Yearbook
- Aircraft Bluebook
- Airportdata.com
- Airport Strategy and Marketing (ASM)
- CAPA – Centre for Aviation
- Fleet Discovery Civil
- Fleet Discovery Military
- Fleet & MRO Forecast
- MRO Prospector
- Air Transport World
- Aviation Week & Space Technology
- Aviation Week & Space Technology - Inside MRO
- Business & Commercial Aviation
- CAPA - Airline Leader
- Routes magazine
- Downloadable Reports
- Recent webinars
- MRO Americas
- MRO Australasia
- MRO Baltics & Eastern Europe Region
- MRO Latin America
- MRO Middle East
- Military Aviation Logistics and Maintenance Symposium (MALMS)
- Asia Aerospace Leadership Forum & MRO Asia-Pacific Awards
- A&D Mergers and Acquisitions
- A&D Programs
- A&D Manufacturing
- A&D Raw Materials
- A&D SupplyChain
- A&D SupplyChain Europe
- Aero-Engines Americas
- Aero-Engines Europe
- Aero-Engines Asia-Pacific
- Digital Transformation Summit
- Engine Leasing Trading & Finance Europe
- Engine Leasing, Trading & Finance Americas
- Routes Americas
- Routes Europe
- Routes World
- CAPA Airline Leader Summit - Airlines in Transition
- CAPA Airline Leader Summit - Americas
- CAPA Airline Leader Summit - Latin America & Caribbean
- CAPA Airline Leader Summit - Australia Pacific
- CAPA Airline Leader Summit - Asia & Sustainability Awards
- CAPA Airline Leader Summit - World & Awards for Excellence
- GAD Americas
- A&D Mergers and Acquisitions Conference (ADMA)
- A&D Manufacturing Conference
- Aerospace Raw Materials & Manufacturers Supply Chain Conference (RMC)
- Aviation Week 20 Twenties
- Aviation Week Laureate Awards
- ATW Airline Awards
- Program Excellence Awards and Banquet
- CAPA Asia Aviation Summit & Awards for Excellence
- Content and Data Team
- Aviation Week & Space Technology 100-Year
- Subscriber Services
- Advertising, Marketing Services & List Rentals
- Content Sales
- PR & Communications
- Content Licensing and Reprints
- AWIN Access
Cruise Missiles Rise To Top Of U.S. Weapons Agenda

After successfully fielding only one new cruise missile during the past 30 years, the U.S. Defense Department hopes to multiply that result over the next decade.
Two new candidates for a future hypersonic cruise missile are currently in testing, while a third has entered the design phase. A subsonic replacement for a nuclear version of the Boeing AGM-86 air-launched cruise missile is in development. Another replacement for the Navy’s RGM/UGM-109 Tomahawk is on the drawing board and may be adapted for a nuclear role as well.
- Scramjet-powered cruise missiles gain traction
- INF Treaty demise restarts production of ground-launched cruise missiles
Meanwhile, new versions of the Lockheed Martin AGM-158 Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) and the Tomahawk missiles are set to enter production. Finally, a new class of air vehicle that blurs the line between a cruise missile and an unmanned aircraft system is gaining traction.
The Biden administration, however, might intervene. Two nuclear cruise missile projects—the Air Force’s Raytheon Long-Range Standoff (LRSO) and the Navy’s sea-launched cruise missile (SLCM-N)—could become targets of a pending review by President Joe Biden’s appointees of the $1.2 trillion nuclear modernization program. And the extent to which Biden’s national security team supports conventional hypersonic cruise missiles is not yet apparent.
But U.S. military support has never been higher for a powered alternative to ballistic missiles with the capability to maneuver during a flight without sacrificing speed.
In the category of hypersonic weapons, scramjet-powered cruise missiles are seen as a more affordable and versatile option than the larger and more expensive hypersonic glide vehicles, such as the air-launched Lockheed AGM-183A.
As recently as December 2018, senior defense officials viewed scramjet propulsion as less mature than rocket-boosted hypersonic gliders. But scramjet technology has evolved rapidly in wind tunnel testing.
In 2020, Aerojet Rocketdyne demonstrated that an 18-ft.-long scramjet engine could generate 13,000-lb. thrust in a wind tunnel. Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems achieved the same result with another scramjet design in 2019. Both engines are now set to enter flight testing in 2021 under DARPA’s Hypersonic Air-Breathing Weapon Concept program; Aerojet has partnered with Lockheed, and Northrop has teamed up with Raytheon. A follow-on operational prototyping program, known as the Hypersonic Attack Cruise Missile, is set to begin, and air-launched and sea-launched versions are possible.
A third option could enter the competition this year. In November, the Pentagon awarded Boeing a contract to complete a preliminary design and component-level testing of the Mach 5-plus HyFly 2, a concept for a dual-combustion, ramjet-powered cruise missile optimized for the Navy’s carrier decks.
All three conventional hypersonic cruise missiles are expected to enter service years before the Air Force fields the nuclear LRSO, but the program is making progress. The Air Force selected Raytheon over Lockheed to continue development of the LRSO, which will be armed with an upgraded W80-4 warhead.
The LRSO entered development under the Obama administration, but the SLCM-N joined the future arsenal following the Trump administration’s Nuclear Posture Review. A Navy analysis recommended developing the SLCM-N as a nuclear variant for the Next-Generation Land Attack Weapon (NGLAW), which is intended to replace the ship- and surface-launched Tomahawk.
As a bridge to the fielding of the NGLAW, the Tomahawk itself reentered production in 2020 to support the improved Block V variant. The Maritime Strike Tomahawk, which integrates a new seeker, is scheduled to enter service in 2023.
Ground-launched cruise missiles (GLCM) also are making a comeback since the demise of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty in August 2019. That 31-year-old pact compelled the Air Force to retire an arsenal of deployed BGM-109G Gryphon missiles. But conventional GLCMs will reenter the arsenal. Last November, the Army selected the BGM-109 Tomahawk to form half of a new Mid-Range Capability with a ground-launched version of the Raytheon SM-6 in 2023.
Lockheed’s AGM-158 JASSM provided the Air Force a stealthy option to strike targets at ranges of up to 500 nm. Although the AGM-158 fell far short of the AGM-86C conventional air-launched cruise missile, the Air Force allowed the latter to be retired from service with no direct replacement in November 2019. That gap will be addressed partially by the fielding in 2024 of the AGM-158D, a new version of the JASSM with a range of up to 1,000 nm and the same radar cross section.

Steve covers military aviation, missiles and space for the Aviation Week Network, based in Washington DC.
Related Content

Stay Connected. Stay Informed Grow Your Business.
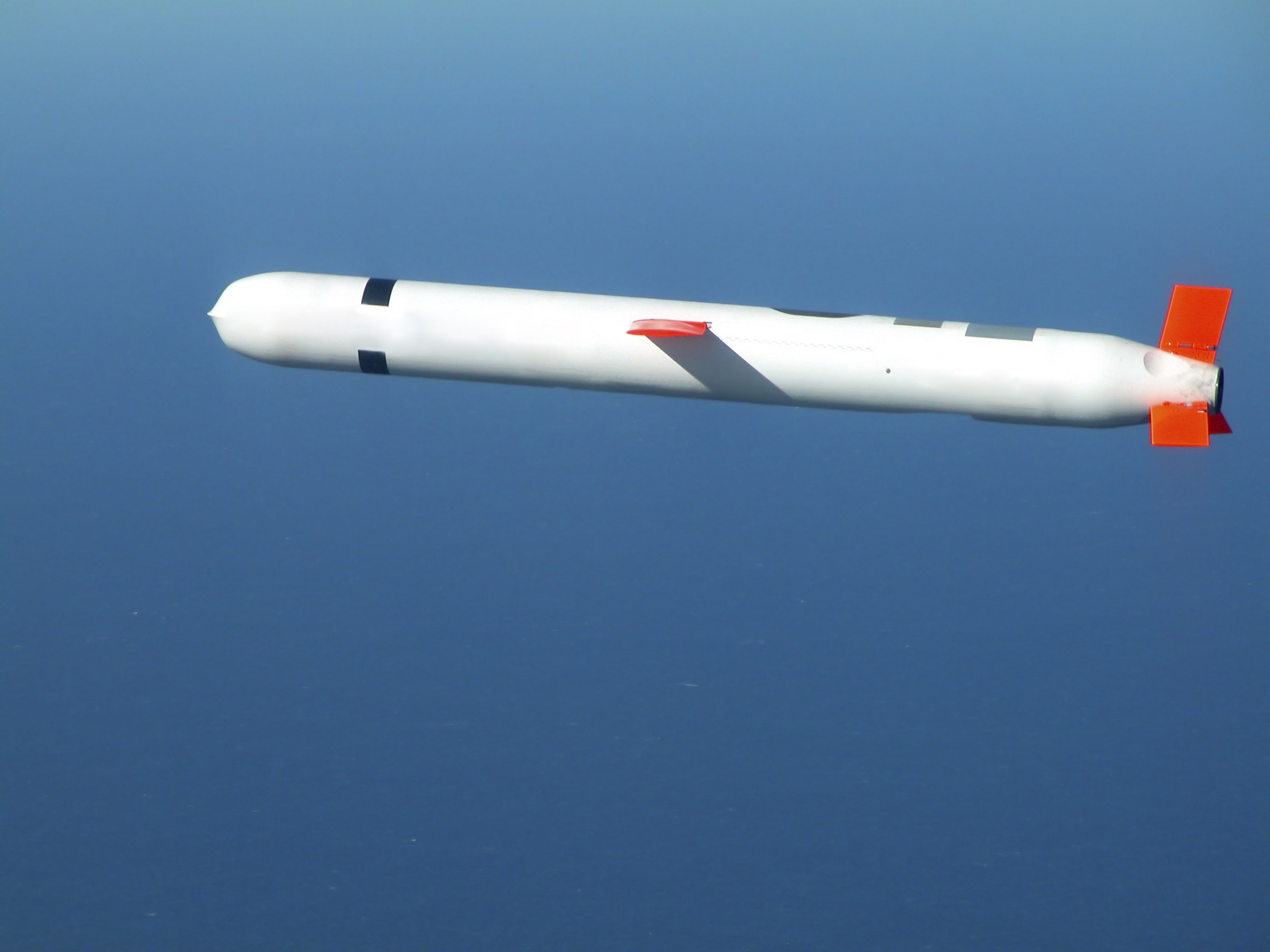

A Short History of Cruise Missiles: The Go-To Weapons for Conventional Precision Strikes
The slow, stubby-winged cruise missile has become a major part of modern warfare. This is its story.
- They’re not like other missiles; instead, cruise missiles work more like drones.
- Ironically, the inspiration for the first cruise missiles involved pilots—the infamous kamikazes of World War II .
One weapon that establishes a military power in a completely different category from the rest is the cruise missile. Originally designed to deliver nuclear weapons at long distances, it’s become the go-to weapon for conventional precision strikes, and is currently front and center in Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
But as the cruise missile is now in its fifth decade of use, there are signs it’ll need some adjustments to stay relevant on the modern battlefield .
Divine Wind
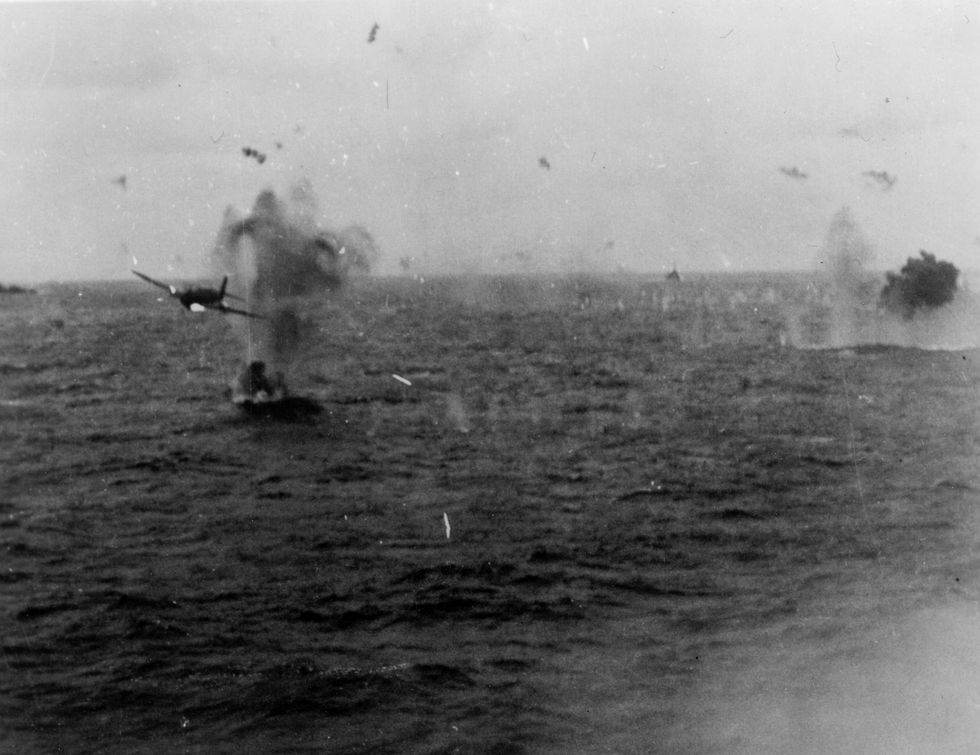

A cruise missile is a subsonic guided missile that uses a turbojet, a smaller version of the jet engines that power today’s airplanes , to reach its targets. Cruise missiles often have small, stubby wings to allow them to bank and turn, following an invisible flight path in the sky. Modern cruise missiles use satellite navigation to guide themselves to target, and some can even take pictures of the target area, allowing operators to retarget them in midair. The missile’s payload is typically a warhead in the 1,000-pound weight class, often with the ability to penetrate earth and concrete to target underground shelters.
The first cruise missiles were Japan’s kamikaze planes of World War II. The kamikaze, or “divine wind,” was part of the Japanese Special Attack Units. Created out of desperation and meant to curb the inexorable advance of U.S. forces across the Pacific, kamikaze pilots were sent on one-way missions to target ships of the U.S. Pacific Fleet. The planes were loaded with explosives, and the pilots flew low and fast to avoid detection until the last possible moment.
Kamikaze missions were incredibly successful. In the first four months of their use, an estimated 34 percent of all kamikazes reached their targets. Much of their success is likely attributable to American forces’ disbelief that pilots could commit suicide for their mission. But the low-flying mission profile and the pilot’s ability to recognize threats and avoid them were also undoubtedly factors. In the 1970s, when U.S. military planners originally conceived of the cruise missile, the kamikazes were likely not far from anyone’s mind.
How Cruise Missiles Work
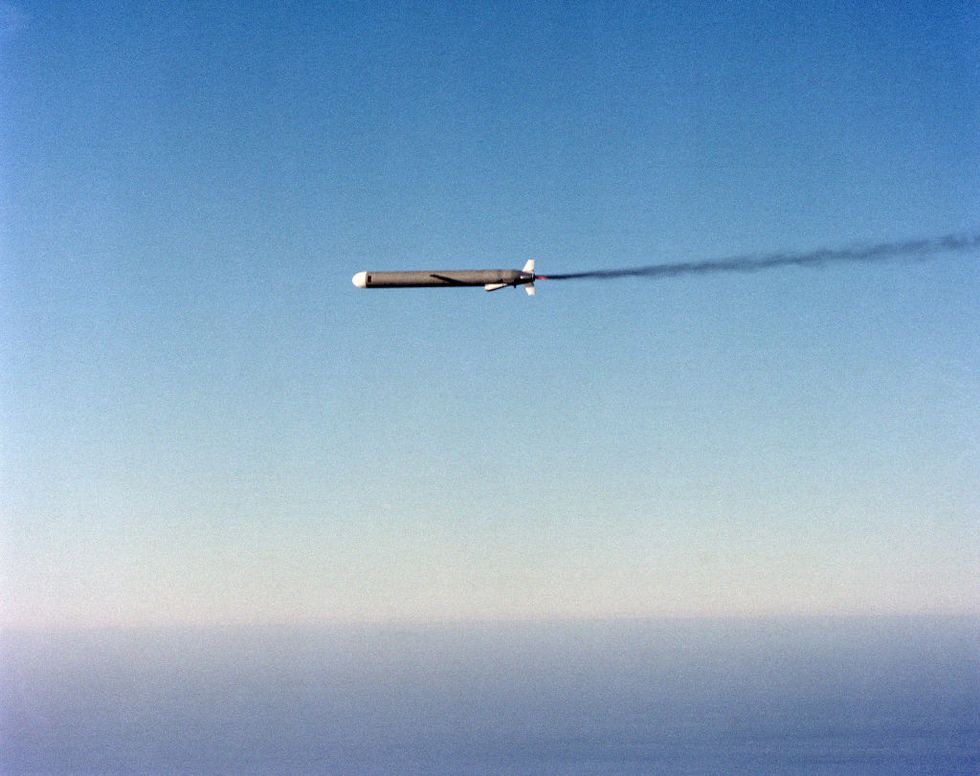

Cruise missiles were originally designed to carry nuclear weapons long distances, allowing bombers to strike their targets without entering the range of an adversary’s air-defense weapons. Conventional rocket-powered missiles didn’t fit the bill: rocket engines are designed to provide speed, and burn up fuel quickly. A cruise missile would need an enormous rocket engine to reach a distant target, with the result being a missile so big only a few would be able to fit inside a bomber.
Instead of rockets, engineers took a different tack: small turbofan engines that burn jet fuel. Turbofan engines are much more efficient, allowing a 21-foot-long missile to carry enough fuel to fly 1,000 miles, plus a 1,000-pound high-explosive warhead (or W-80 thermonuclear warhead ) and a guidance system. The downside was that a turbofan-powered cruise missile could not fly particularly fast, just about 500 miles per hour.
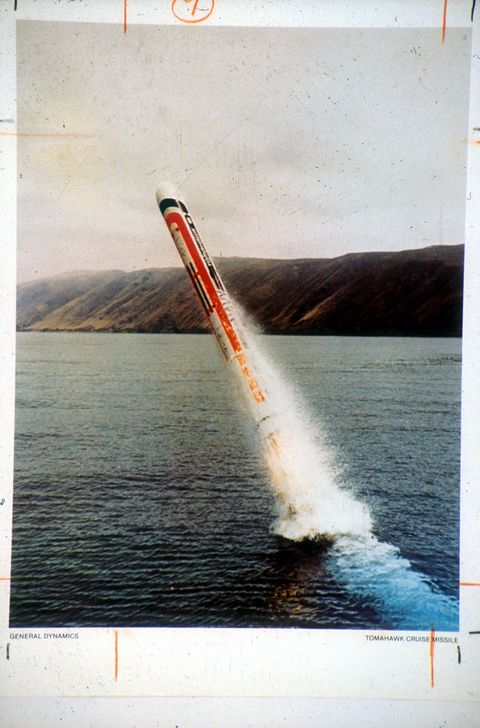

A subsonic cruise missile flying a straight flight path and unable to take evasive action would prove easy meat to any enemy interceptor that happened upon it. The first modern cruise missile, the American-made Tomahawk , was designed to fly low, less than 100 meters above the ground. This limited the range at which ground-based radars could detect a cruise missile, as radar waves conform to the curvature of Earth. This also frustrated enemy fighters, whose nose-mounted radars found it difficult to pick out a cruise missile against the clutter created by the ground below. While cruise missiles were too slow to become first-strike weapons, they were effective for retaliatory strikes against heavily defended airspace.
Early Tomahawk cruise missiles followed a pre-programmed flight path to target using a system called terrain contour matching (TERCOM). In TERCOM , a radar altimeter scans the terrain below the missile, then compares it to a terrain elevation map stored in its onboard computer brain. If the two match, the missile is on the right flight path; if they don’t match, the missile adjusts course. Programming TERCOM for a long-range mission was a notoriously time-consuming process, and had to be done at a computer terminal.
As the Tomahawk neared its target, it switched over to a completely different navigation system: digital scene matching and area correlation ( DSMAC ). DSMAC used an optical sensor that took pictures of the ground and compared them to actual sites on the final route to the target. Together, TERCOM and DSMAC delivered unheard of accuracy, allowing Tomahawks to fly hundreds of miles and strike specific parts of land targets, even specific parts of buildings.
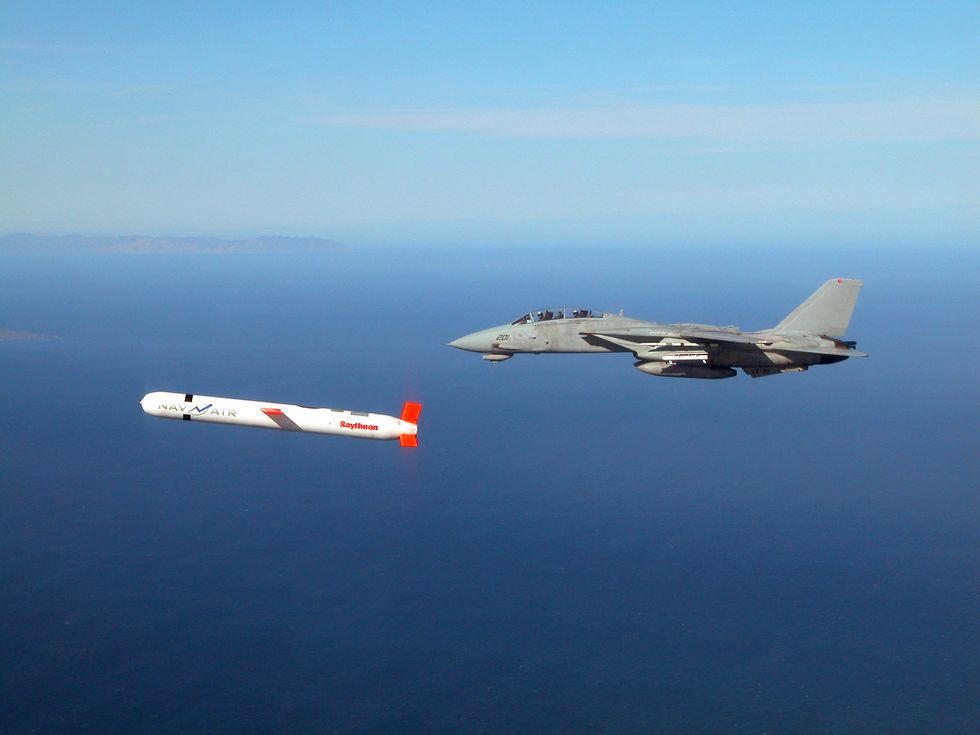

More recent cruise missiles, including newer versions of the Tomahawk, have done away with the old navigation systems in favor of using GPS to guide themselves to a fixed target. This has had the effect of making an already accurate missile even more accurate—reportedly to within 32 feet of a target. The Tomahawk Block IV version, introduced in the 2010s, included a camera that could send back imagery to the missile’s controllers, allowing a missile to be re-tasked in midair if its target was already destroyed. Block Va, the latest version, adds the ability to target and attack moving ships at sea.
The Tomahawk missile was the first cruise missile fired in anger. U.S. Navy warships fired a total of 288 Tomahawks during Operation Desert Storm in 1991. Tomahawk missiles have also been fired at Bosnia, Sudan, Syria , Yemen, Libya, Somalia, and Afghanistan. U.S. and U.K. forces have delivered just over 2,000 Tomahawk missiles against operational targets, with more than half against Iraq.
In recent years, other countries have also used cruise missiles in combat. In October 2017, Russia began cruise missile strikes against so-called terrorist targets in Syria. These Novator 3M14 Kalibr cruise missiles are very similar to Tomahawk missiles, but use Russia’s GLONASS satellite navigation system, an alternative to the American GPS. Russia has launched a steady stream of air- and sea-launched cruise missiles against Ukraine since the early hours of the invasion on February 24, 2022 , but a shrinking missile stockpile has led to the attacks becoming less frequent, supplemented by Iranian-made kamikaze drones.

The war in Ukraine has also seen the use of two European cruise missiles, the U.K.’s Storm Shadow and the French SCALP missile . The two are essentially the same, with a 340-mile range and 990-pound warhead. The missiles donated to Ukraine are launched from specially modified Su-24 Soviet-era strike jets . Storm Shadow/SCALP was also used against the Khaddafi regime in Libya in 2011, ISIS in 2015, and by Saudi Arabia against Yemeni rebels in 2016.
The Russo-Ukrainian War has also confirmed an important, long suspected fact: low-flying, subsonic cruise missiles are vulnerable to man-portable surface-to-air missiles. In 2022, a Ukrainian National Guardsman was filmed shooting down a Russian cruise missile with an Igla surface-to-air missile. It was the first known case of a shoulder-fired missile, typically carried by infantry, shooting down a multi-million dollar cruise missile. How this event will affect future cruise missiles remains to be seen.
The Takeaway
Cruise missiles have dramatically changed warfare, as one might expect from a weapon that can fly 1,000 miles and deliver a half-ton high-explosive warhead within 32 feet of a target. The missiles allow countries that can afford them the ability to execute precision strikes on heavily defended targets without endangering pilots or aircraft.
The war in Ukraine will likely impart lessons on the next generation of cruise missiles , but the platform isn’t going anywhere anytime soon.

Kyle Mizokami is a writer on defense and security issues and has been at Popular Mechanics since 2015. If it involves explosions or projectiles, he's generally in favor of it. Kyle’s articles have appeared at The Daily Beast, U.S. Naval Institute News, The Diplomat, Foreign Policy, Combat Aircraft Monthly, VICE News , and others. He lives in San Francisco.

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Pop Mech Pro .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

US Army Accepts Delivery of First M10 Assault Gun

Underwater UFO is a Threat, Says Ex-Navy Officer

DIY Car Key Programming: Why Pay the Dealer?
Use Induction Heat to Break Free Rusted Bolts

How to Replace Your Car’s Brakes

The Air Force is Resurrecting a B-1 Bomber

Who Killed Harry Houdini?

A New Hypersonic Missile Will Give the F-35 Fangs

The Navy’s New Drone Could Turn into a Ship-Killer

The CIA’s Secret Plan to Turn Psychics Into Spies

Is This the Real Iceberg That Sank the Titanic?
Why it’s so hard to defend against cruise missiles
A recent conference raises the question: What kind of threat does this type of weapon pose to the United States?
By Kelsey D. Atherton | Published Jul 25, 2022 7:00 AM EDT

On July 14, the Center for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, DC held a one-day conference premised on a specific threat: What if, in the future, war comes to the United States via cruise missile? Pointing to new developments in cruise missile technology, and the limitations of existing early warning systems that are focused on the high arcing trajectories of ballistic missiles, the CSIS conference and accompanying report suggests that to defend the continental United States from such a threat, the military should adapt and deploy the kind of cruise missile defenses presently used as regional weapons.
Unlike ballistic missiles, which arc up into space before traveling back down towards earth, cruise missiles fly close to the ground, making it hard for radar on the ground that’s pointed up at space to see them.
The perceived threat from new cruise missiles is driven by tech developments occurring across the globe, as new materials, better aerodynamics, and sophisticated sensors and guidance systems make possible the fielding of weapons, like hypersonic missiles , that had mostly been just theoretical decades ago.
For the United States, the development of long-range bombers in the 1940s, followed by the development of intercontinental ballistic missiles, shattered the notion that the enormous distances of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans were enough to protect the continental US from direct attack. (During World War II, US territories in the Pacific came under direct attack, but the only long-range assault on the 48 states came in the form of incendiary-carrying balloons launched by Japan into the jet stream and carried over to the US.)
With atomic and then thermonuclear payloads, bombers and long-range missiles threatened devastation on an unprecedented scale, and the United States built an elaborate system of early warning sensors focused on detecting early signs of launch, and expanded its first-in-the-world nuclear arsenal to deter attack. North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) is run by both Canada and the United States, and maintains a series of radars and other sensors designed to detect early attacks across the Arctic or elsewhere. (Every December, NORAD highlights its existence by tracking Santa Claus, turning a system designed to detect oblivion into a kid-friendly Christmas tradition .)
At the conference held by CSIS, the threat from cruise missiles was discussed as a way that other countries could attack the United States that is hard to detect by employing existing, ICBM-focused measures. It is also considered hard to deter through threat of nuclear retaliation, operating on the assumption that if a cruise missile with a conventional warhead destroyed a building or killed people in the United States, the President would not immediately respond with a nuclear strike.
“You know, our adversaries are building diverse, expansive ranges of modern offensive missile systems, and we see them – we see them in the news every day,” Stan Stafira, Chief Architect of the Pentagon’s Missile Defense Agency, told the panel. “They’re capable of maneuvering in the midcourse and the terminal phases of their flight, like maneuvering reentry vehicles, multiple independent reentry vehicles, hypersonic glide vehicles, and cruise missiles.”
Part of the broader appeal of hypersonic weapons to nations like Russia, China, and the United States is that the speed and trajectories of the missiles make them harder to detect than ICBMs. The ballistic arc of ICBMs means the launch is visible to radar while it is still ascending, once it clears the horizon line. Meanwhile, both hypersonic glide vehicles and hypersonic cruise missiles, which travel at Mach 5 or above, are designed to fly below that radar horizon, with the cruise missile keeping a close trajectory to earth and the glide vehicle flying in the high atmosphere.
“I want to state that we absolutely believe that nuclear deterrence is the foundation of homeland defense,” said Lieutenant General AC Roper, deputy commander of Northern Command, the part of the US military responsible for North America. “However, we also must have credible deterrence options below the nuclear thresholds, options which allow for a balanced approach of deterrence by denial and deterrence by punishment or cost imposition.”
Deterrence, at its most straightforward, is a strategy of making a big threat on a condition: One country publicly declares it will launch nukes at another if it launches nukes at it, with the intended effect that neither country launches nukes. But because the payload of a cruise missile—it could be nuclear or conventional, unlike ICBMs, which are always nuclear—is unlikely to be known until impact, generals like Roper would prefer to have a range of weapons with which to respond.
Missile defense is one of those options, and the US already employs a few forms. Part of any missile defense system is the sensors, like specially focused radar, that can detect incoming attacks, and then track those weapons as they travel. These radars then send that tracking information to interceptors, which are missiles launched to fly and destroy the incoming attacking missile. Shooting missiles at other missiles is a hard problem because an incoming threat arrives at great speed, and because the cost calculus can favor an attacker. Interceptors, like shorter-ranged Patriot missiles or longer-ranged ballistic interceptors , are often more expensive than the missiles they are intercepting. And unlike interceptors, which have to hit precisely to work, missiles launched in attack can deploy decoys or countermeasures to redirect interceptors away, or can instead be fired in a greater volume, overwhelming interceptors through sheer numerical advantage.
“The resulting 20-year cost to provide even a light defense of a vast area ranged from $77 billion to $466 billion,” reads the CSIS report , citing an analysis from the Congressional Budget Office studying a range of cruise missile defense options. “The considerable cost variation is due to alternative combinations of sensors and interceptors and varying desired warning times of 5 or 15 minutes.”

Kelsey D. Atherton is a military technology journalist who has contributed to Popular Science since 2013. He covers uncrewed robotics and other drones, communications systems, the nuclear enterprise, and the technologies that go into planning, waging, and mitigating war.
Like science, tech, and DIY projects?
Sign up to receive Popular Science's emails and get the highlights.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Japan signs agreement to purchase 400 Tomahawk missiles as US envoy lauds its defense buildup
Japanese and U.S. military officials and U.S. Ambassador to Japan Rahm Emanuel, fourth left, and Japanese Defense Minister Minoru Kihara, third right, stand behind a defense equipment procurement official as he signs a document for the Tomahawk purchase deal at the Japanese Defense Ministry, in Tokyo, Thursday, Jan. 18, 2023. Japan has signed a deal with the United States to purchase up to 400 Tomahawk cruise missiles as part of its ongoing military buildup in response to increased regional threats. U.S. Ambassador to Japan Rahm Emanuel attended a signing event at Japan’s Defense Ministry on Thursday. (AP Photo/Mari Yamaguchi)
- Copy Link copied
TOKYO (AP) — Japan signed a deal with the United States on Thursday to purchase up to 400 Tomahawk cruise missiles as part of its ongoing military buildup in response to increased regional threats.
Prime Minister Fumio Kishida’s government has pledged to double its annual defense spending to around 10 trillion yen ($68 billion) by 2027, which would make Japan the world’s third-biggest military spender after the United States and China.
Defense Minister Minoru Kihara announced in December a decision to accelerate deployment of some Tomahawks and Japanese-made Type 12 surface-to-ship missiles beginning in fiscal year 2025, a year before the original plan. The government says Japan is facing its “severest” security environment since World War II because of threats from China and North Korea, causing it to increase military cooperation with the U.S., Australia, Britain and other friendly nations.
In November, the U.S. approved a $2.35 billion sale of two types of Tomahawks — 200 Block IV missiles and 200 upgraded Block V versions. They can be launched from warships and hit targets 1,600 kilometers (1,000 miles) away, officials said.
The signing of the purchase agreement on Thursday was attended by Kihara and U.S. Ambassador to Japan Rahm Emanuel.
Japan and the United States agreed to expedite the deployment “in response to the increasingly severe security environment,” Kihara said.
Emanuel said training of Japanese servicemembers for the Tomahawks will start in March.
Late last year, Japan’s Cabinet eased a ban on exports of lethal weapons, allowing the sale of Japanese-made weapons and components made under license from other nations to those countries. The government quickly approved a shipment of Japanese-made Patriot missiles to the United States to complement the U.S. inventory.
Japan is accelerating its deployment of long-range cruise missiles capable of hitting targets in China or North Korea, while Japanese troops increasingly work side-by-side with the U.S. and other friendly nations and take on more offensive roles.
At a news conference earlier Thursday marking the end of his second year in Tokyo, Emanuel lauded Japan’s rapid move during that time to build up its military and strengthen its alliance with the U.S. to meet challenges in the region.
Under a new defense strategy adopted in December 2022, Japan has joined the United States, Australia, South Korea and many other regional partners “in an aligned vision of how to promote peace and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific and meet the challenges head on,” Emanuel said.
The U.S. approach to its partnership with Japan is “one of ensuring deterrence” and making sure there is no change in the region by military force, Emanuel said.
“There is a new Japan emerging, a more competent Japan,” he said.
North Korea says it tested ‘super-large’ cruise missile warhead and new anti-aircraft missile
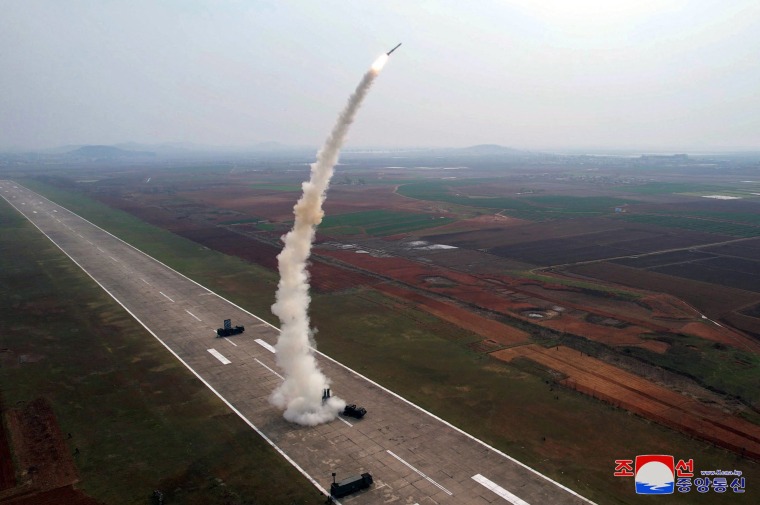

SEOUL, South Korea — North Korea said Saturday it tested a “super-large” cruise missile warhead and a new anti-aircraft missile in a western coastal area as it expands military capabilities in the face of deepening tensions with the United States and South Korea.
North Korean state media said the country’s missile administration on Friday conducted a “power test” for the warhead designed for the Hwasal-1 Ra-3 strategic cruise missile and a test-launch of the Pyoljji-1-2 anti-aircraft missile. It said the tests attained an unspecified “certain goal.”
Photos released by the North’s official Korean Central News Agency showed at least two missiles being fired off launcher trucks at a runway.
North Korea conducted a similar set of tests Feb. 2, but at the time did not specify the names of the cruise missile or the anti-aircraft missile, indicating it was possibly seeing technological progress after testing the same system over weeks.
KCNA insisted Friday’s tests were part of the North’s regular military development activities and had nothing to do with the “surrounding situation.”
Tensions on the Korean Peninsula are at their highest in years, with North Korean leader Kim Jong Un dialing up his weapons demonstrations, which have included more powerful missiles aimed at the U.S. mainland and U.S. targets in the Pacific. The United States, South Korea and Japan have responded by expanding their combined military training and sharpening their deterrence strategies built around strategic U.S. assets.
Cruise missiles are among a growing collection of North Korean weapons designed to overwhelm regional missile defenses. They supplement the North’s vast lineup of ballistic missiles, including intercontinental ballistic missiles aimed at the continental United States.
Analysts say anti-aircraft missile technology is an area where North Korea could benefit from its deepening military cooperation with Russia , as the two countries align in the face of their separate, intensifying confrontations with the U.S. The United States and South Korea have accused North Korea of providing artillery shells and other equipment to Russia to help extend its warfighting in Ukraine.
The Associated Press
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
North Korea fires ballistic missiles, South Korea, Japan say
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Hyunsu Yim in Seoul and Rocky Swift in Tokyo; Writing by Jack Kim Editing by Kim Coghill, Gerry Doyle and Toby Chopra
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Seoul-based reporter covering the Koreas with a focus on South Korean politics, North Korea's missile tests and the K-pop industry. Before joining Reuters, he worked at The Korea Herald.

World Chevron

Pictures of the Week
A selection of some of our top photography from around the world this week.

An Israeli strike in Lebanon's Beqaa region has killed two members of a Lebanese militant group that has fired rockets across the southern border at Israel, the group said on Friday.

Two earthquakes, the largest a 6.1 magnitude, struck Taiwan's eastern county of Hualien on Saturday, the island's weather administration said, with no immediate reports of damage.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Middle East crisis — explained
The conflict between Israel and Palestinians — and other groups in the Middle East — goes back decades. These stories provide context for current developments and the history that led up to them.
Israel launches missile strikes into Iran, U.S. military official says

Rob Schmitz

Peter Kenyon

Demonstrators wave a huge Iranian flag in an anti-Israeli gathering in front of an anti-Israeli banner on the wall of a building at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, on Monday. Vahid Salemi/AP hide caption
Demonstrators wave a huge Iranian flag in an anti-Israeli gathering in front of an anti-Israeli banner on the wall of a building at the Felestin (Palestine) Square in Tehran, Iran, on Monday.
The Israeli military has conducted missile strikes against Iran, a senior U.S. military official told NPR on Thursday. There are also reports of explosions in Iraq and Syria.
The strikes appear to be the response Israel vowed to carry out after an Iranian attack on Sunday, when Tehran fired hundreds of drones and missiles at Israel. Most of Iran's volleys were intercepted or caused little damage. The U.S. military official spoke on condition of anonymity Thursday.
The extent of Israel's strikes and the weapons used weren't clear.
Iran state news agency IRNA reported a military official in the central Iranian city of Isfahan, Brigadier General Mihan Dost, as saying loud sounds heard east of the city were the sound of air defenses intercepting what he called a "suspicious target" and that no damage was reported in the area.

What we know so far about Israel's strike on Iran — and what could happen next
Other Iranian news agencies had not reported any such strike and have concluded the sounds reported near Isfahan were the interception of one or more drones.
Israel's military and prime minister's office have not yet responded to NPR's request for comment.
The International Atomic Energy Agency has confirmed on social media that there is no damage to Iran's nuclear sites.
Meanwhile, Israel's hardline National Security Minister, Itamar Ben-Gvir, wrote on social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, that Israel's latest apparent strike against Iran was "weak" and too limited.
Commercial flights continue in and out of Israel, and the country's Home Front Command system, which is responsible for issuing threat alerts to civilians during tense military times, didn't change its threat level.
In Iran, flights were temporarily grounded in the morning, but resumed just a couple of hours later.
The U.S. and other western allies had been urging Israel to forego a military strike to avoid a regional conflict springing out of the Israel-Hamas war .
Those concerns rose when an air strike – which Iran blamed on Israel – killed two Iranian military commanders in the country's consulate in Damascus, Syria, on April 1.

How Iran and Israel became archenemies
Iran said Sunday's attack on Israel was in response to that.
The region has been on the edge of wider conflict since Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7, killing 1,200 people and taking more than 240 others hostage, according to Israel. Israel's military campaign in response in Gaza has killed more than 33,000 people, according to Gaza health officials.
Israel and Iran-backed Hezbollah have traded frequent fire over the northern Israel border. Houthi militants, also backed by Iran, have been going after international commercial vessels passing through the Red Sea in recent months. The group's leaders claim they're targeting ships with links to Israel in response to the country's ongoing invasion of Gaza.
What Iran’s attack on Israel revealed about its weapons arsenal
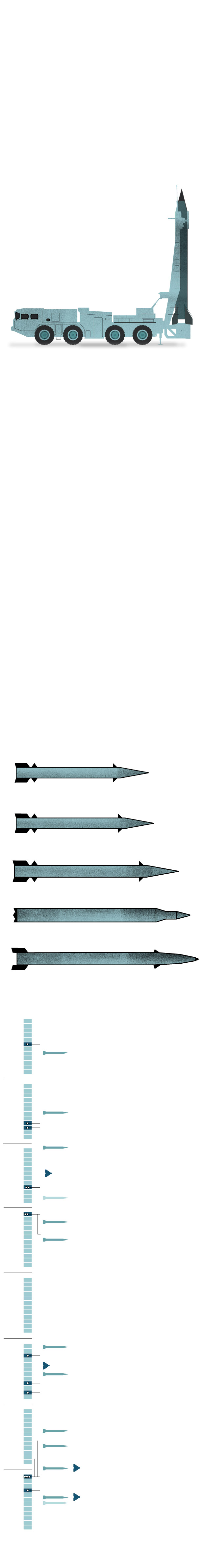
Iran’s first direct attack on Israel overnight Saturday demonstrated the country’s military might and the advances of its domestic weapons program, analysts said, while also revealing the limitations of its arsenal.
With more than 300 drones and missiles launched in a layered onslaught, it was Iran’s largest-ever conventional show of force . That it inflicted only minimal damage was due in part to the choreographed nature of the attack — giving Israel and the United States ample time to prepare air defense systems — but may also be attributed to shortcomings in its medium- and long-range capabilities.
“The operation showed that our armed forces are ready,” Iranian president Ebrahim Raisi told crowds gathered Wednesday in Tehran to mark Army Day. Parades in the Iranian capital featured many of the same munitions used in the attack on Israel.

What Iran used against Israel
110 ballistic
Iranian drones
These drones can deliver small payloads of explosives in self-detonating attacks.
Length: 11.5 ft.
Width: 8 ft.
Max. take off weight: 440 lb.
Max. speed: 115 mph
Range: About 1,100 - 1,500 miles
Its nose contains a warhead and can be equipped with a camera.
Length: 8 ft.
Width: 7 ft.
Max. take off weight: 300 lb.
The Shahed-131 is an earlier version of Shahed-136 with a similar principle of operation. The layout and aerodynamics are also identical.
Ballistic missiles
KHEIBAR SHEKAN
The Kheibar Shekan MRBM is a solid-propellant ballistic missile designed by the IRGC.
Length: 34 ft.
Diameter: 2.6 ft.
Max. range: 900 miles
Warhead weight: 1,100 lb.
Introduction: 2022
The Emad MRBM is an Iranian-designed, liquid-fuel ballistic missile based on Shahab-3.
Length: 54 ft.
Diameter: 4.1 ft.
Max. range: 1,056 miles
Warhead weight: 1,650 lb.
Introduction: 2015
The Ghadr-1 MRBM seems to be an improved variant of the Shahab-3A. It is also referred to as the Ghadr-101 and the Ghadr-110.
Max. range: 1,211 miles
Warhead weight: 1,760 lb.
Introduction: 2007
Cruise missile
Max. range: 1,025 miles
Introduction: 2023
What Iran did not use
The Sejjil-1 Iranian MRBM is a two-stage, solid-propellant, surface-to-surface missile.
Length: 60 ft
Max. range: 1,243 miles
Warhead weight: 1,540 lb.
Introduction: 2011
The Shahab-3 is a MRBM developed by Iran and based on the North Korean Nodong-1.
Diameter: 4.1 or 4.5 ft.
Max. range: 808 miles
Warhead: Single or multiple
with 5 warheads of 617 lb.
Introduction: 2003
Sources: OE Data Integration Network (ODIN),
CSIS Missile Defense Project

120 ballistic
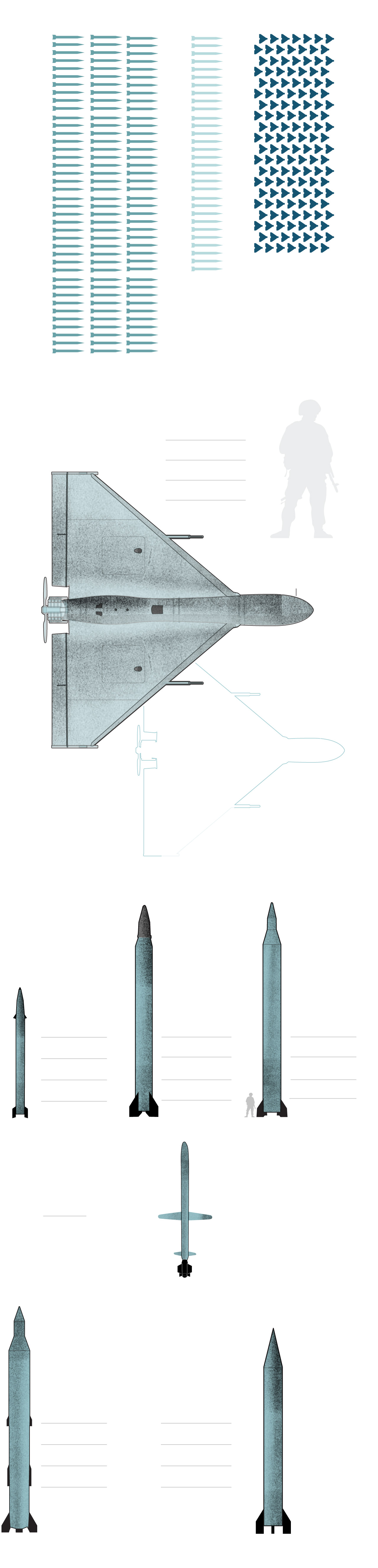
120 ballistic missiles
30 cruise missiles
Overhead view
1,211 miles
1,056 miles
Max. range:
Warhead weight:
Introduction:
Sources: OE Data Integration Network (ODIN), CSIS Missile Defense Project
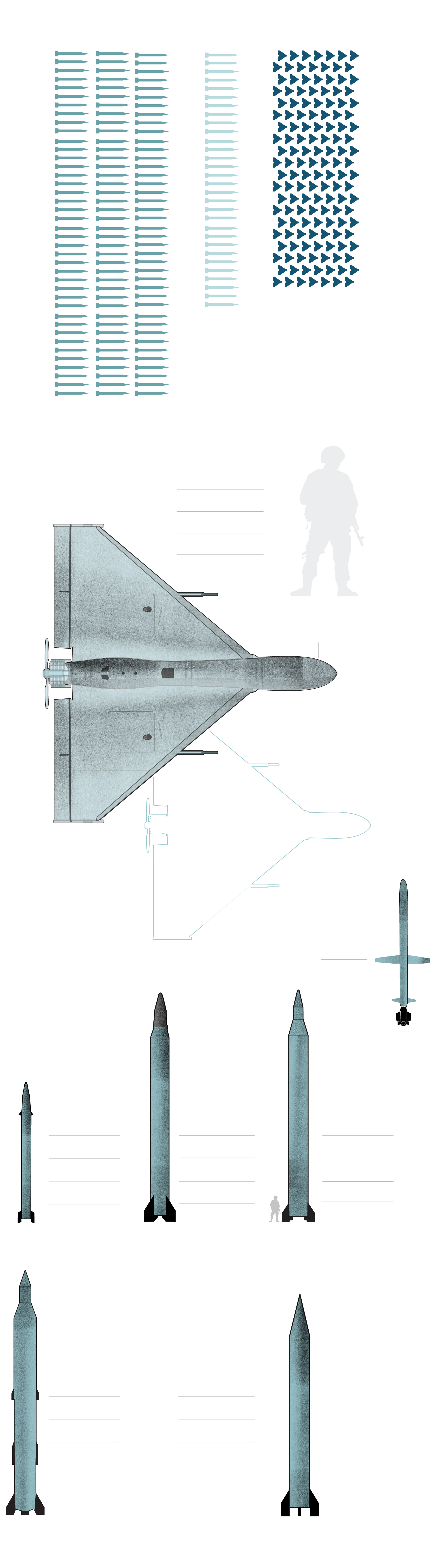
Raisi hailed the attack as a resounding “success,” but was also quick to qualify the strikes as “limited” and “not comprehensive.”
“If it was supposed to be a large-scale action, nothing would have been left of the Zionist regime,” he said. And if Israel retaliates, Raisi pledged, “they will be dealt with fiercely and severely.”
Yet after analyzing the munitions used in Saturday’s assault and the success of regional defense systems, researchers say it’s unclear how Iran could inflict greater damage on Israel through conventional military means.
“Iran basically threw everything it had that could reach Israel’s territory,” said John Krzyzaniak, a researcher who studies Iran’s missile programs at the Wisconsin Project on Nuclear Arms Control. Like other analysts interviewed for this story, he has spent the past several days studying launch videos, imagery of debris and interception information to identify the Iranian munitions.
His conclusion is that Tehran “used some of every system they have.” And experts said it made sense that the Sejjil-1 and Shahab-3 missiles were excluded from the attack.
Shahab-3 “wasn’t used because it’s so old,” said Fabian Hinz, an Iran analyst at the International Institute for Strategic Studies in Berlin. “The Sejjil is a bit of a mysterious missile,” he said, adding that Iran has “used it very, very little during maneuvers.”
Other analysts noted the Sejjil was expensive to produce and may no longer be in production.
The quantity of munitions used also provides new insights into Iran’s capabilities. The deployment of over 100 ballistic missiles in a single wave suggests that previous estimates that Iran has about 3,000 ballistic missiles stockpiled are probably accurate, and could even be on the low end.
“If this is just round one of an unknown number of rounds to come, you wouldn’t fire a significant fraction of what you have just in the first round,” Krzyzaniak said.
The firing of over 100 ballistic missiles in the space of a few minutes suggests Iran has at least 100 launchers, he added — a new data point for researchers.
“This shows that Iran has really faced no limitation in domestically producing missiles and launchers,” he said.
Iran’s ballistic missile arsenal, the largest of any country in the Middle East, is almost entirely homegrown. In recent years Iran has demonstrated the ability to upgrade some systems, improving their range and precision.
The spokesman for Iran’s armed forces, Abolfazl Shekarchi, said the munitions used in the strikes against Israel only represented “a fraction of” the country’s military’s might, according to a statement published on state-run media.
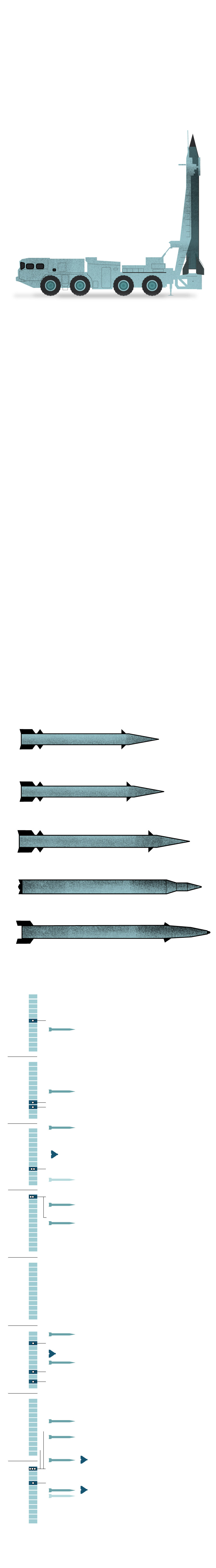
The evolution of Iran’s
missile program
In the mid-1980s, Tehran acquired Scud missiles from Libya, Syria and North Korea and also began adapting the technology for their own missile variants. During the eight-year war with Iraq, Tehran countered primarily with Scud B missiles, which have a range of 185 miles.
Shahab-1 , 186 miles
1994 to 2001
Iran developed its own version of the Scud B, the Shahab-1, and from 1994 to 2001 fired it at bases in Iraq used by the opposition group Mujahedin-e Khalq.
A new generation of missiles
After 16 years without firing new missiles, Iran showed its technological advances in 2017 striking on an ISIS command center with 6 Zolfaghars with a range of 430 miles. In early 2024, it launched strikes against Islamic State targets in northwest Syria using Kheibar Shekan missiles that travelled 745 miles from Iran to Syria.
Fahteh 110 , 181 miles
Fahteh 313 , 310 miles
Zolfaghar , 435 miles
Qiam 1 , 497 miles
Kheibar Shekan , 900 miles
IRAN ATTACKS
Against ISIS
6 ballistic missiles
Deir ez-Zor, Syria
Against Kurdish dissidents
7 ballistic missiles
Abu Kamal, Syria
Against Oil fields and facilities
18 drones + 7 cruise missiles
Abqaiq, S. Arabia
Khurais, S. Arabia
3 cruise missiles
Against U.S. forces
Erbil, Iraq
1 ballistic missile
Ain Al Asad, Iraq
15 to 22 ballistic missiles
Against “Israeli strategic centers”
At least 10 ballistic missiles
73 launches + at least 20 drones
and suicide drones
Sulaimaniyah,
Against IS targets
Harem, Syria
Israeli “spy headquarters”
Against Jaish ul Adl
Balochistan,
Missiles and drones
Against Israel
120 ballistic missiles,
170 drones,
Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF
The evolution of Iran’s missile program
IRAN TARGETS
KNOWN MISSILE
Zolfaghars,
Abqaiq, Saudi Arabia
Khurais, Saudi Arabia
Zolfaghars and
potentially
Ballistic missiles and suicide drones
Sulaimaniyah, Iraq
Kheibar Shekan
Balochistan, Pakistan
Missiles and drones against Jaish ul Adl
170 drones, 30 cruise missiles
Before the attack on Israel, Iran’s most significant use of ballistic missiles was in 2020, after a U.S. drone attack killed the powerful Iranian commander Qasem Soleimani.
Iran launched more than a dozen ballistic missiles at two U.S. military bases in Iraq, one in the country’s west and one in the north. While there were no fatalities, dozens of U.S. service members suffered traumatic brain injuries.
Iran also used ballistic missiles in strikes this year on Pakistan, Syria and Iraq.
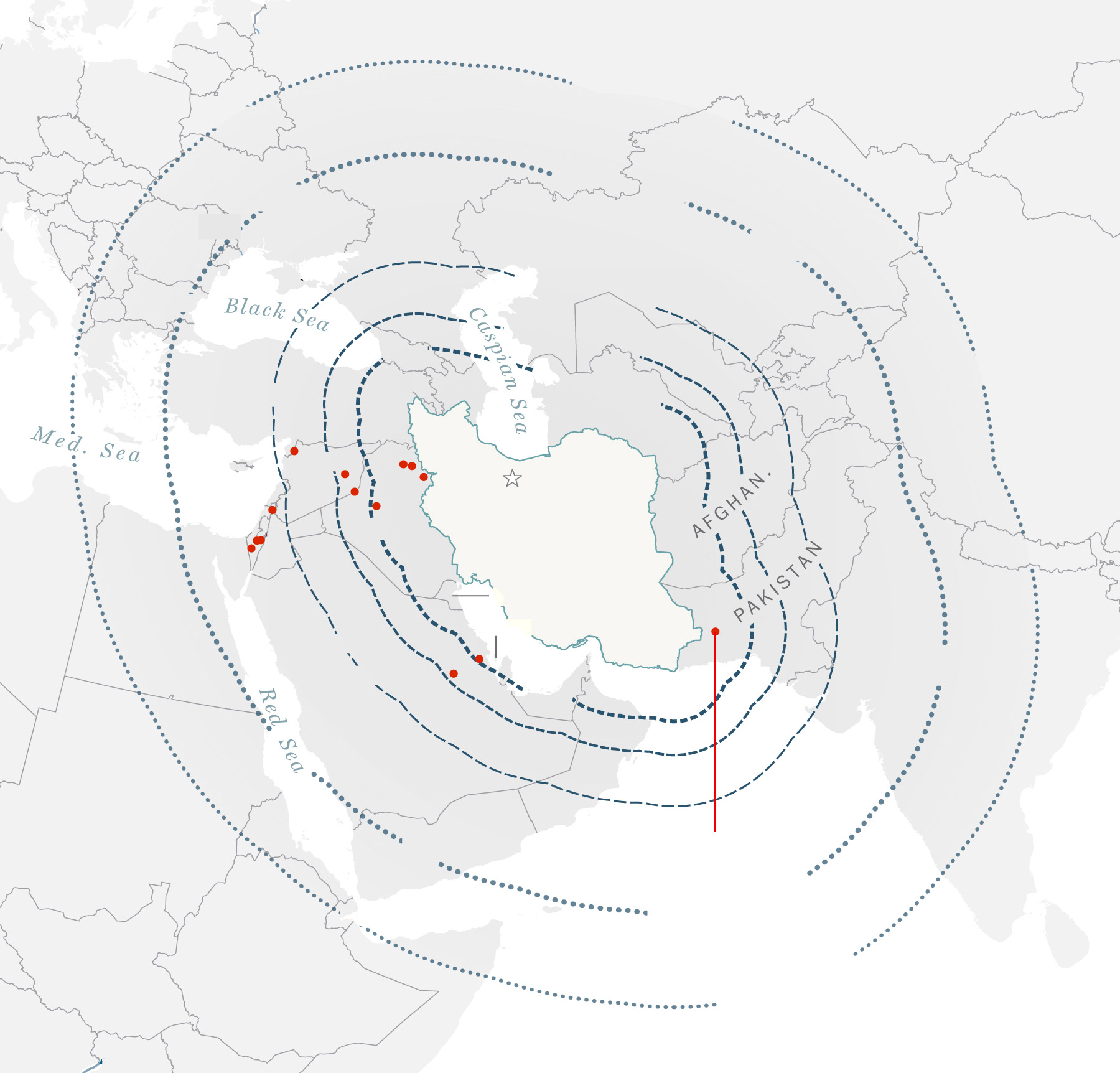
Iranian ballistic
missile ranges
1,240 miles
Locations of Iranian
missile strikes
INDIAN OCEAN
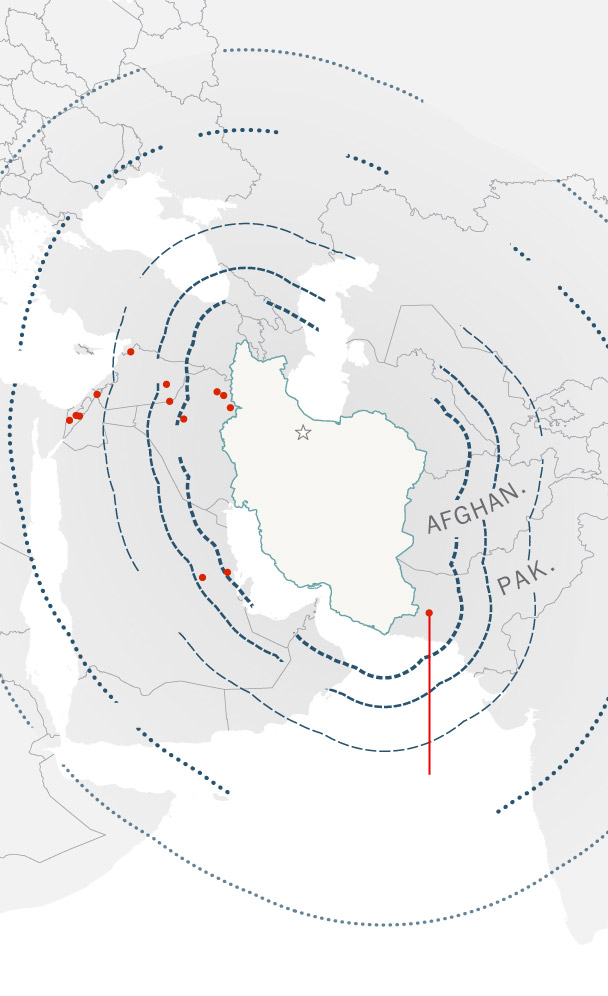
But the attack on Israel suggests that many of Iran’s munitions are of low quality. Israel’s military said 99 percent of the missiles and drones launched by Iran were intercepted or failed to launch.
“We saw that accuracy and precision are a work in progress,” said Behnam Ben Taleblu, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies who has written extensively about Iran’s missile program. “These weapons alone won’t win a war for Iran.”
Iranian drones made up the first wave of the attack. Cheap, effective and easy to produce, Iranian drones have been used in attacks across the Middle East for years. Iran has also supplied drones to Russia for its war in Ukraine , where they have been deadly.
During the attack on Israel, the slow-moving drones were probably deployed to occupy air defenses and allow more advanced munitions to get through. All the drones were shot down before entering Israeli airspace, the Israel Defense Forces said.
Ali Hamie, a Lebanese military analyst, said Iran had probably gleaned important lessons about Israel’s aerial defenses. Commentators on Iranian state television have made similar points.
“It could be a testing attack,” Hamie said, “and the Iranians got what they want. Making it past the air defenses is not only a symbolic victory, but real victory.”
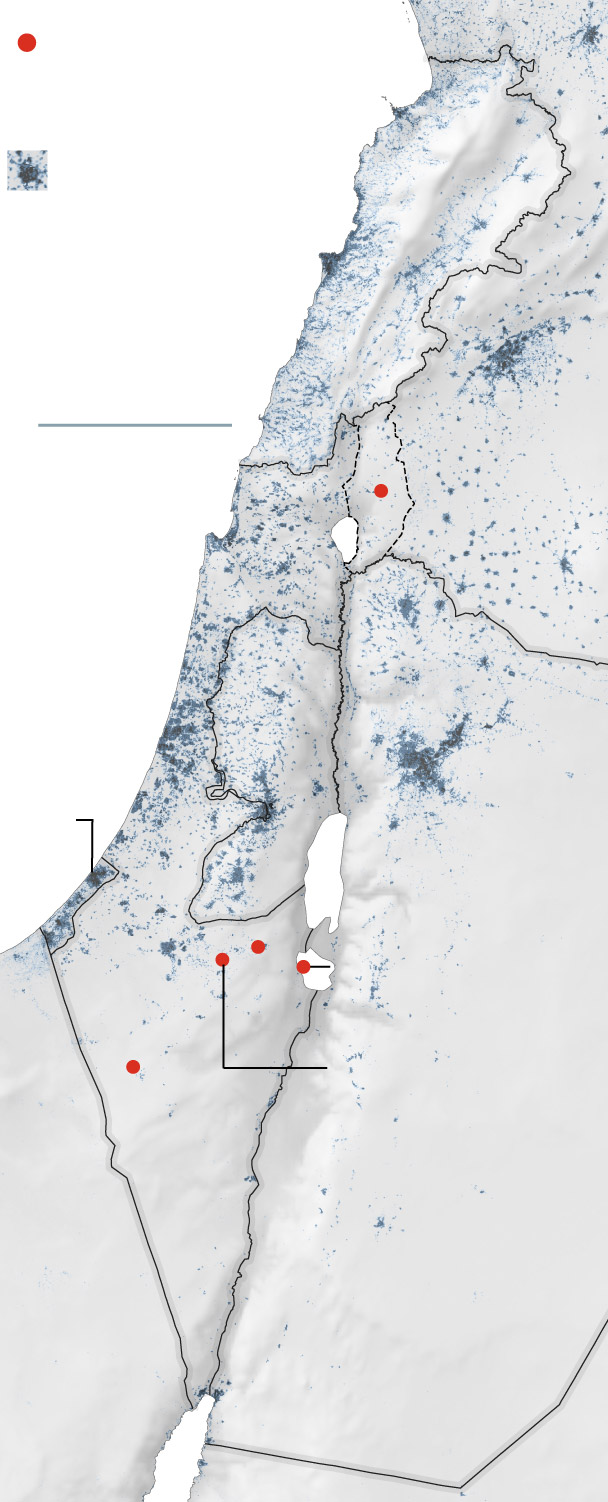
One of the few missiles to make it through the interceptors hit an Israeli air base in the Negev desert. Images of the strike were run on loop on many state-run Iranian broadcasters in the days after the attack. Israel characterized the damage as minor.
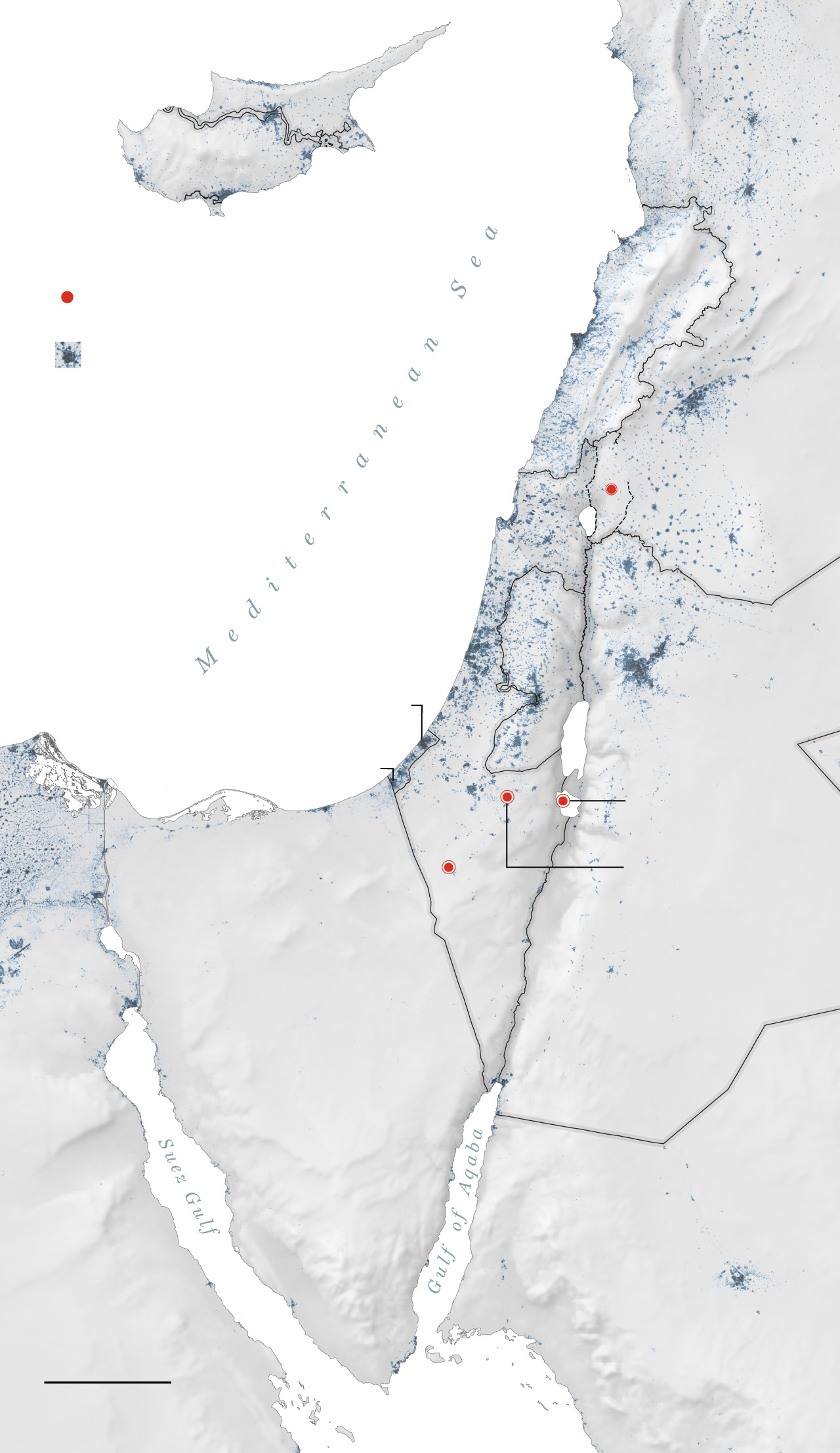
General location of missile strikes
that reached the ground.
Beirut—
Populated areas
Haifa—
Tel Aviv—
—Amman
—Jerusalem
An emad missile
was found here.
The barrage of
missiles from Iran
included targeting
the Nevatim
General location of
missile strikes that
reached the ground.
Mediterranean
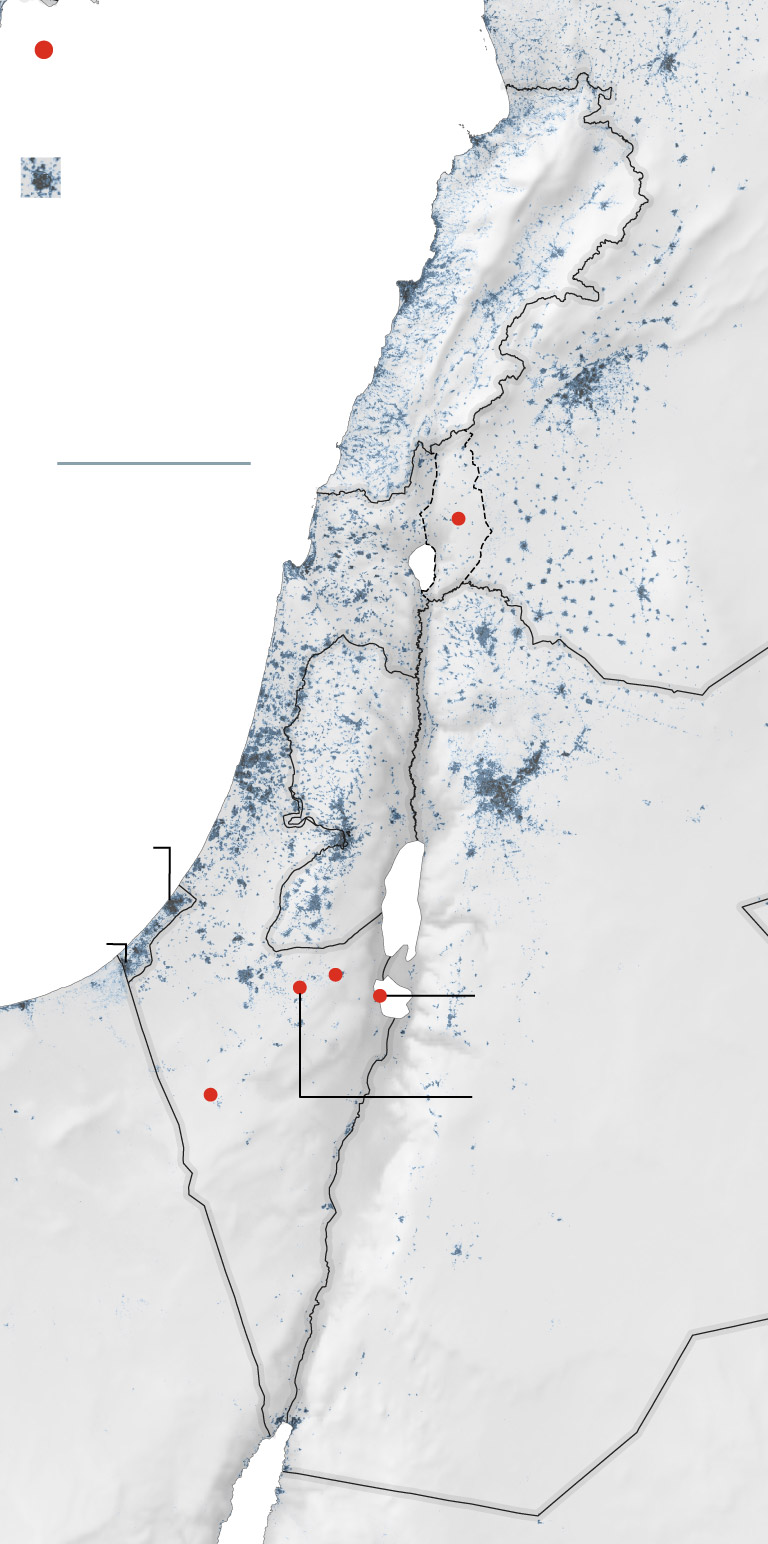
General location of missile
strikes that reached the
In addition to analyzing Israel’s air defenses, Tehran will probably also be studying the problems with its missile systems that reportedly led to failures at launch and in flight, according to Afshon Ostovar, a professor of national security affairs at the Naval Postgraduate School in California.
“Another attack could be more effective,” he said. But ultimately the kind of approach demonstrated in Saturday’s attack “is not really sustainable over a long-term conflict.”
Even if Iran changed the tempo of attacks and adjusted the munitions used, “they would still have to launch quite a lot of stuff for just a few [munitions] to get through,” he said.
Some Iranian officials have suggested they have held back their most dangerous weapons.
“We are prepared to use weapons we have never used before. We have plans for every scenario,” said Abolfazl Amoui, a parliamentary national security spokesman, in an interview with Lebanese broadcaster Mayadeen.
But analysts say it’s unlikely that any one type of munition could be a game changer. Rather, it’s more likely Iran would use the same kinds of munitions in a future attack, but in a different way: giving less warning, or launching the barrage in concert with allied militant groups in the region. The country’s proxy forces, from Lebanon to Iraq to Yemen, played little role in Saturday’s assault.
As Israel mulls its response , Tehran has warned that a counterattack would come in “a matter of seconds.”
“Iran will not wait for another 12 days to respond,” Deputy Foreign Minister Ali Bagheri Kani said Monday.
While the United States and Israel have celebrated the thwarting of Saturday’s attack, analysts are urging humility.
“The number of munitions it took to repel the attack was enormous, costly and could be difficult to replicate,” said Tom Karako, the director of the Missile Defense Project at the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
“Israel may have gotten lucky and Iran may have gotten very unlucky.”
William Neff and Suzan Haidamous contributed to this report.
Israel-Gaza war
The Israel-Gaza war has gone on for six months, and tensions have spilled into the surrounding region .
The war: On Oct. 7, Hamas militants launched an unprecedented cross-border attack on Israel that included the taking of civilian hostages at a music festival . (See photos and videos of how the deadly assault unfolded ). Israel declared war on Hamas in response, launching a ground invasion that fueled the biggest displacement in the region since Israel’s creation in 1948 .
Gaza crisis: In the Gaza Strip, Israel has waged one of this century’s most destructive wars , killing tens of thousands and plunging at least half of the population into “ famine-like conditions. ” For months, Israel has resisted pressure from Western allies to allow more humanitarian aid into the enclave .
U.S. involvement: Despite tensions between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and some U.S. politicians , including President Biden, the United States supports Israel with weapons , funds aid packages , and has vetoed or abstained from the United Nations’ cease-fire resolutions.
History: The roots of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and mistrust are deep and complex, predating the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 . Read more on the history of the Gaza Strip .
- After Israeli strike in Iran, both sides appear to downplay incident April 19, 2024 After Israeli strike in Iran, both sides appear to downplay incident April 19, 2024
- Homes burned, animals killed: Palestinians describe Israeli settler rampage April 16, 2024 Homes burned, animals killed: Palestinians describe Israeli settler rampage April 16, 2024
- Six months of the Israel-Gaza war: A timeline of key moments April 7, 2024 Six months of the Israel-Gaza war: A timeline of key moments April 7, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary ... and aircraft. The main outcome of the United States Navy submarine missile project was the SSM-N-8 Regulus missile, based upon the V-1. The United States Air Force's first operational ...
A USAF B-1 bomber drops a JASSM-ER missile during testing. U.S. Air Force photo. A Chinese attack on Taiwan could trigger a war involving two million Chinese troops, half a million Taiwanese ...
Surface ships. Submarines. TELs. The Tomahawk ( / ˈtɒməhɔːk /) Land Attack Missile ( TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations. Developed at the Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins ...
The U.S. Air Force secretly test-fired a long-range variant of a stealthy cruise missile from a B-2 stealth bomber late last year, defense contractor Northrop Grumman revealed Thursday. The ...
Naval Air Station Patuxent River Maryland 20670-1547. (240) 925-5305. Description The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is an all-weather, long range, subsonic cruise missile used for deep land ...
Budgets for cruise missile defense of the homeland in fiscal 2022 and 2023 were modest, with combatant commands including NORTHCOM placing additional funding for development in so-called wish ...
cruise missile, type of low-flying strategic guided missile.The German V-1 missile used in World War II was a precursor of the cruise missile, which was developed by the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1960s and '70s. Capable of carrying either a nuclear or a conventional warhead, the cruise missile was designed to have a very low radar cross section and to hug the ground while ...
Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile in service with the surface ships and submarines of the US and the UK's Royal Navy. Originally produced by General Dynamics, Tomahawk is currently manufactured by Raytheon. The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) can strike high-value or heavily defended land targets.
The Tomahawk cruise missile is a precision weapon that launches from ships, submarines, and ground launchers and can strike targets precisely from 1,000 miles away, even in heavily defended airspace. US strikes in Syria launched from USS Porter. Watch on.
A U.S. Air Force MC-130J Commando II executes the first-ever European-theater live-fire demonstration of a Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile during exercise Atreus in Norway on Nov. 9, 2022.
The Tomahawk is a long-range, unmanned weapon with an accuracy of about 5 metres (16 feet). The 5.6-metre- (18.4-foot-) long missile has a range of up to approximately 2,400 km (about 1,500 miles) and can travel as fast as 885 km (550 miles) per hour. Tomahawks are launched vertically from ships, but they can be launched horizontally from ...
The AGM-86 ALCM is an American subsonic air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) built by Boeing and operated by the United States Air Force. This missile was developed to increase the effectiveness and survivability of the Boeing B-52H Stratofortress strategic bomber. The missile dilutes an enemy's forces and complicates air defense of its territory ...
Ground-launched cruise missiles (GLCM) also are making a comeback since the demise of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty in August 2019. That 31-year-old pact compelled the Air Force to ...
The AGM-129A is a subsonic, turbofan-powered, air-launched cruise missile. It is harder to detect, and has greater range and accuracy than the AGM-86 air-launched cruise missile. The ACM achieves maximum range through its highly efficient engine, aerodynamics and fuel loading. B-52H bombers can carry up to six AGM-129A missiles on each of two ...
The AGM-86B air-launched cruise missile, or ALCM, and AGM-86C/D conventional air-launched cruise missile, or CALCM, were developed to increase the effectiveness of B-52H bombers. In combination, they dilute an enemy's forces and complicate defense of its territory. Features. The small, winged AGM-86B/C/D missile is powered by a turbofan jet ...
The U.S. Air Force has awarded Raytheon a contract to develop the service's next-generation stealth cruise missile. The Long Range Stand Off (LRSO) missile will arm B-21 Raider and B-52 ...
The US Air Force has tested a hypersonic cruise missile in the Pacific for the first time, in what analysts say is a signal to China that Washington still competes in a weapons arena where many ...
A cruise missile would need an enormous rocket engine to reach a distant target, with the result being a missile so big only a few would be able to fit inside a bomber. US Navy // Wikimedia Commons
The perceived threat from new cruise missiles is driven by tech developments occurring across the globe, as new materials, better aerodynamics, and sophisticated sensors and guidance systems make ...
Japan has signed a deal with the United States to purchase up to 400 Tomahawk cruise missiles as part of its ongoing military buildup in response to increased regional threats. U.S. Ambassador to Japan Rahm Emanuel attended a signing event at Japan's Defense Ministry on Thursday. (AP Photo/Mari Yamaguchi)
North Korea said Saturday it tested a "super-large" cruise missile warhead and a new anti-aircraft missile in a western coastal area as it expands military capabilities in the face of ...
Cruise missiles of the United States include cruise missiles designed, built, or operated by the United States. Subcategories. This category has only the following subcategory. N. Nuclear cruise missiles of the United States (1 C, 20 P) Pages in category "Cruise missiles of the United States"
Over 99% of the 350 incoming targets — drones, cruise missiles and ballistic missiles — was shot down, the majority outside Israeli airspace, according to the Israel Defense Forces.
The US has said it secretly delivered long-range ATACMS missiles to Ukraine. This has drawn focus to the debate over providing Taurus cruise missiles, a move the German chancellor continues to oppose.
North Korea fired "several" short-range ballistic missiles on Monday toward the sea off its east coast, South Korea's military said, drawing a swift condemnation from Seoul, which called it a ...
In this handout photo from the US Army, an early version of an Army Tactical Missile System is tested December 14, 2021, at White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico.
A cruise missile submarine is a submarine that carries and launches cruise missiles ( SLCMs consisting of land-attack cruise missiles and anti-ship missiles) as its primary armament. Missiles greatly enhance a warship 's ability to attack surface combatants and strike land targets; although torpedoes are a more discrete option for submerged ...
Israel launches missile strikes into Iran, U.S. military official says. Updated April 19, 2024 4:58 AM ET Originally published April 18, 2024 10:10 PM ET. By . Tom Bowman , Rob Schmitz ,
Hypersonic Cruise missile Air-launched cruise missile Anti-ship missile Land-attack missile Surface-to-surface missile India / Russia: 1,000 km (620 mi) 8.0?? ? Under Development: BrahMos-NG: Next Generation Air-launched cruise missile Land-attack missile Anti-ship missile India: 290 km (180 mi) 3.5?? ? Under Development: Nirbhay: Subsonic ...
30 cruise missiles. Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF. The evolution of Iran's . missile program. 1980s. Scud. ... the United States supports Israel with weapons, ...