- Patient Care & Health Information
- Diseases & Conditions
- Traveler's diarrhea
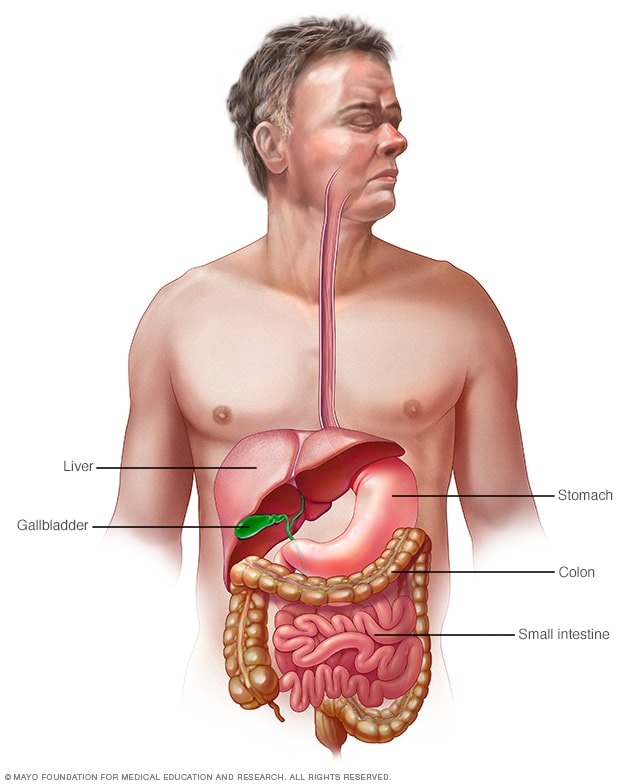

Gastrointestinal tract
Your digestive tract stretches from your mouth to your anus. It includes the organs necessary to digest food, absorb nutrients and process waste.
Traveler's diarrhea is a digestive tract disorder that commonly causes loose stools and stomach cramps. It's caused by eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water. Fortunately, traveler's diarrhea usually isn't serious in most people — it's just unpleasant.
When you visit a place where the climate or sanitary practices are different from yours at home, you have an increased risk of developing traveler's diarrhea.
To reduce your risk of traveler's diarrhea, be careful about what you eat and drink while traveling. If you do develop traveler's diarrhea, chances are it will go away without treatment. However, it's a good idea to have doctor-approved medicines with you when you travel to high-risk areas. This way, you'll be prepared in case diarrhea gets severe or won't go away.
Products & Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Book of Home Remedies
- A Book: Mayo Clinic on Digestive Health
Traveler's diarrhea may begin suddenly during your trip or shortly after you return home. Most people improve within 1 to 2 days without treatment and recover completely within a week. However, you can have multiple episodes of traveler's diarrhea during one trip.
The most common symptoms of traveler's diarrhea are:
- Suddenly passing three or more looser watery stools a day.
- An urgent need to pass stool.
- Stomach cramps.
Sometimes, people experience moderate to severe dehydration, ongoing vomiting, a high fever, bloody stools, or severe pain in the belly or rectum. If you or your child experiences any of these symptoms or if the diarrhea lasts longer than a few days, it's time to see a health care professional.
When to see a doctor
Traveler's diarrhea usually goes away on its own within several days. Symptoms may last longer and be more severe if it's caused by certain bacteria or parasites. In such cases, you may need prescription medicines to help you get better.
If you're an adult, see your doctor if:
- Your diarrhea lasts beyond two days.
- You become dehydrated.
- You have severe stomach or rectal pain.
- You have bloody or black stools.
- You have a fever above 102 F (39 C).
While traveling internationally, a local embassy or consulate may be able to help you find a well-regarded medical professional who speaks your language.
Be especially cautious with children because traveler's diarrhea can cause severe dehydration in a short time. Call a doctor if your child is sick and has any of the following symptoms:
- Ongoing vomiting.
- A fever of 102 F (39 C) or more.
- Bloody stools or severe diarrhea.
- Dry mouth or crying without tears.
- Signs of being unusually sleepy, drowsy or unresponsive.
- Decreased volume of urine, including fewer wet diapers in infants.
It's possible that traveler's diarrhea may stem from the stress of traveling or a change in diet. But usually infectious agents — such as bacteria, viruses or parasites — are to blame. You typically develop traveler's diarrhea after ingesting food or water contaminated with organisms from feces.
So why aren't natives of high-risk countries affected in the same way? Often their bodies have become used to the bacteria and have developed immunity to them.
Risk factors
Each year millions of international travelers experience traveler's diarrhea. High-risk destinations for traveler's diarrhea include areas of:
- Central America.
- South America.
- South Asia and Southeast Asia.
Traveling to Eastern Europe, South Africa, Central and East Asia, the Middle East, and a few Caribbean islands also poses some risk. However, your risk of traveler's diarrhea is generally low in Northern and Western Europe, Japan, Canada, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, and the United States.
Your chances of getting traveler's diarrhea are mostly determined by your destination. But certain groups of people have a greater risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Young adults. The condition is slightly more common in young adult tourists. Though the reasons why aren't clear, it's possible that young adults lack acquired immunity. They may also be more adventurous than older people in their travels and dietary choices, or they may be less careful about avoiding contaminated foods.
- People with weakened immune systems. A weakened immune system due to an underlying illness or immune-suppressing medicines such as corticosteroids increases risk of infections.
- People with diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, or severe kidney, liver or heart disease. These conditions can leave you more prone to infection or increase your risk of a more-severe infection.
- People who take acid blockers or antacids. Acid in the stomach tends to destroy organisms, so a reduction in stomach acid may leave more opportunity for bacterial survival.
- People who travel during certain seasons. The risk of traveler's diarrhea varies by season in certain parts of the world. For example, risk is highest in South Asia during the hot months just before the monsoons.
Complications
Because you lose vital fluids, salts and minerals during a bout with traveler's diarrhea, you may become dehydrated, especially during the summer months. Dehydration is especially dangerous for children, older adults and people with weakened immune systems.
Dehydration caused by diarrhea can cause serious complications, including organ damage, shock or coma. Symptoms of dehydration include a very dry mouth, intense thirst, little or no urination, dizziness, or extreme weakness.
Watch what you eat
The general rule of thumb when traveling to another country is this: Boil it, cook it, peel it or forget it. But it's still possible to get sick even if you follow these rules.
Other tips that may help decrease your risk of getting sick include:
- Don't consume food from street vendors.
- Don't consume unpasteurized milk and dairy products, including ice cream.
- Don't eat raw or undercooked meat, fish and shellfish.
- Don't eat moist food at room temperature, such as sauces and buffet offerings.
- Eat foods that are well cooked and served hot.
- Stick to fruits and vegetables that you can peel yourself, such as bananas, oranges and avocados. Stay away from salads and from fruits you can't peel, such as grapes and berries.
- Be aware that alcohol in a drink won't keep you safe from contaminated water or ice.
Don't drink the water
When visiting high-risk areas, keep the following tips in mind:
- Don't drink unsterilized water — from tap, well or stream. If you need to consume local water, boil it for three minutes. Let the water cool naturally and store it in a clean covered container.
- Don't use locally made ice cubes or drink mixed fruit juices made with tap water.
- Beware of sliced fruit that may have been washed in contaminated water.
- Use bottled or boiled water to mix baby formula.
- Order hot beverages, such as coffee or tea, and make sure they're steaming hot.
- Feel free to drink canned or bottled drinks in their original containers — including water, carbonated beverages, beer or wine — as long as you break the seals on the containers yourself. Wipe off any can or bottle before drinking or pouring.
- Use bottled water to brush your teeth.
- Don't swim in water that may be contaminated.
- Keep your mouth closed while showering.
If it's not possible to buy bottled water or boil your water, bring some means to purify water. Consider a water-filter pump with a microstrainer filter that can filter out small microorganisms.
You also can chemically disinfect water with iodine or chlorine. Iodine tends to be more effective, but is best reserved for short trips, as too much iodine can be harmful to your system. You can purchase water-disinfecting tablets containing chlorine, iodine tablets or crystals, or other disinfecting agents at camping stores and pharmacies. Be sure to follow the directions on the package.
Follow additional tips
Here are other ways to reduce your risk of traveler's diarrhea:
- Make sure dishes and utensils are clean and dry before using them.
- Wash your hands often and always before eating. If washing isn't possible, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol to clean your hands before eating.
- Seek out food items that require little handling in preparation.
- Keep children from putting things — including their dirty hands — in their mouths. If possible, keep infants from crawling on dirty floors.
- Tie a colored ribbon around the bathroom faucet to remind you not to drink — or brush your teeth with — tap water.
Other preventive measures
Public health experts generally don't recommend taking antibiotics to prevent traveler's diarrhea, because doing so can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Antibiotics provide no protection against viruses and parasites, but they can give travelers a false sense of security about the risks of consuming local foods and beverages. They also can cause unpleasant side effects, such as skin rashes, skin reactions to the sun and vaginal yeast infections.
As a preventive measure, some doctors suggest taking bismuth subsalicylate, which has been shown to decrease the likelihood of diarrhea. However, don't take this medicine for longer than three weeks, and don't take it at all if you're pregnant or allergic to aspirin. Talk to your doctor before taking bismuth subsalicylate if you're taking certain medicines, such as anticoagulants.
Common harmless side effects of bismuth subsalicylate include a black-colored tongue and dark stools. In some cases, it can cause constipation, nausea and, rarely, ringing in your ears, called tinnitus.
- Feldman M, et al., eds. Infectious enteritis and proctocolitis. In: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management. 11th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 25, 2021.
- LaRocque R, et al. Travelers' diarrhea: Microbiology, epidemiology, and prevention. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 26, 2021.
- Ferri FF. Traveler diarrhea. In: Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2023. Elsevier; 2023. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed April 28, 2023.
- Diarrhea. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diarrhea. Accessed April 27, 2023.
- Travelers' diarrhea. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2020/preparing-international-travelers/travelers-diarrhea. Accessed April 28, 2023.
- LaRocque R, et al. Travelers' diarrhea: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 26, 2021.
- Khanna S (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 29, 2021.
- Symptoms & causes
- Diagnosis & treatment
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
Make twice the impact
Your gift can go twice as far to advance cancer research and care!
Thanks for visiting! GoodRx is not available outside of the United States. If you are trying to access this site from the United States and believe you have received this message in error, please reach out to [email protected] and let us know.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Travelers diarrhea.
Noel Dunn ; Chika N. Okafor .
Affiliations
Last Update: July 4, 2023 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Traveler's diarrhea is a common ailment in individuals traveling to resource-limited destinations overseas. It is estimated to affect nearly 40 to 60 percent of travelers and is the most common travel-associated condition. Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections can cause symptoms, though bacterial sources represent the most frequent etiology. Although traveler's diarrhea is typically a benign, self-resolving condition, it can lead to dehydration and, in severe cases, significant complications. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of traveler's diarrhea and highlights the role of interprofessional team members in collaborating to provide well-coordinated care and enhance outcomes for affected patients.
- Identify the causes of traveler's diarrhea.
- Identify strategies to prevent traveler's diarrhea.
- Explain the management of traveler's diarrhea.
- Explain the importance of improving coordination amongst the interprofessional team to enhance care for patients affected by traveler's diarrhea.
- Introduction
Travelers’ diarrhea is a common ailment in persons traveling to resource-limited destinations overseas. Estimates indicate that it affects nearly 40% to 60% of travelers depending on the place they travel, and it is the most common travel-associated condition. Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections can cause symptoms, though bacterial sources represent the most frequent etiology. While travelers’ diarrhea is typically a benign self-resolving condition, it can lead to dehydration and, in severe cases, significant complications. [1] [2] [3]
The most common bacterial cause is enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), with estimates that the bacteria is responsible for nearly 30% of cases. Other common bacterial causes of travelers’ diarrhea include Campylobacter jejuni , Shigella , and Salmonella species. Norovirus is the most common viral cause while rotavirus is another source of infection. Giardia intestinalis is the most common parasitic source while Cryptosporidium and Entamoeba histolytica can also cause travelers’ diarrhea. The most common cause of travelers’ diarrhea varies by region, though the source is rarely identified in less severe cases. [4] [5] [6]
Traveler's diarrhea can occur in both short and long term travelers; in general, there is no immunity against future attacks. Traveler's diarrhea appears to be most common in warmer climates, in areas of poor sanitation and lack of refrigeration. In addition, the lack of safe water and taking short cuts to preparing foods are also major risk factors. In areas where food handling education is provided, rates of traveler's diarrhea are low.
- Epidemiology
Estimates place the incidence of travelers’ diarrhea at 30% to 60% of travelers to resource-limited destinations. Incidence and causal agent vary by destination, with the highest incidence reported in sub-Saharan Africa. Other locations with high incidence include Latin America, the Middle East, and South Asia. Risk factors are typically related to poor hygiene in resource-limited areas. These include poor hygienic practices in food handling and preparation; lack of refrigeration due to inadequate electrical supply; and poor food storage practices. Additional modifiable risk factors include proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use, recent antibiotic use, and unsafe sexual practices. Risk factors for severe complications are pregnancy, young or old age, travelers with underlying chronic gastrointestinal diseases, or people who are immunocompromised. [7] [8]
- Pathophysiology
Travelers’ diarrhea is most commonly spread by fecal-oral transmission of the causative organism, typically through consumption of contaminated food or water. The incubation period varies by causal agent, with viruses and bacteria ranging from 6 to 24 hours and intestinal parasites requiring 1 to 3 weeks before the onset of symptoms. The pathophysiology for travelers’ diarrhea differs by a causative agent but can be split into non-inflammatory or inflammatory pathways. Non-inflammatory agents cause a decrease in the absorptive abilities of the intestinal mucosa, thereby increasing the output of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Inflammatory agents on the other hand cause destruction of the intestinal mucosa either through cytotoxin release or direct invasion of the mucosa. The loss of mucosa surface again results in a decrease of absorption with a resultant increase in bowel movements. [9]
- History and Physical
The onset of symptoms will typically occur 1 to 2 weeks after arrival in a resource-limited destination, though travelers can develop symptoms throughout their stay or shortly after arrival. Travelers’ diarrhea is considered as three or more loose stools in 24 hours or a two-fold increase from baseline bowel habits. Diarrhea often occurs precipitously and is accompanied by abdominal cramping, fever, nausea, or vomiting. Patients should be asked about any blood in their stool, fevers, or any associated symptoms. A thorough travel history should be obtained including timeline and itinerary, diet and water consumption at their destination, illnesses in other travelers, and possible sexual exposures.
In most self-limited cases physical examination will show mild diffuse abdominal tender to palpation. Providers should assess for dehydration through skin turgor and capillary refill. In more severe cases patients may have severe abdominal pain, high fever, and evidence of hypovolemia (tachycardia, hypotension).
Laboratory investigation is typically not required in most cases. In patients with concerning features, such as with high fever, hematochezia, or tenesmus, stool studies can be obtained. Typical stool studies include stool culture, fecal leukocytes, and lactoferrin. The stool should be assessed for ova and parasites in patients with longer duration of symptoms. New multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) screens are becoming available and provide quick analysis of multiple stool pathogens. These screens, however, are expensive, are not widely available, and may not change the clinical management of patients. [4]
Radiological studies are not required in most cases. Kidneys, ureters, and bladder x-ray can be obtained to assess for acute intra-abdominal pathology or look for evidence of perforation in severe cases. An abdominal CT can also be used to assess for intraabdominal pathology in severe cases.
- Treatment / Management
Travelers should be counseled on risk reduction before travel, including avoiding tap water & ice, frequent hand washing, avoiding leafy vegetables or fruit that isn’t peeled, and avoiding street food. Bismuth subsalicylate (two tabs 4 times a day) can be used for prophylaxis and can reduce the incidence of travelers’ diarrhea by almost half, though it should be avoided in children and pregnant women due salicylate side effects. In short high-stakes travel, it may be reasonable to start antibiotics as prophylaxis but is generally avoided in longer-term travel. Rifaximin is a commonly used chemoprophylaxis due to its minimal absorption and minimal side effects. [10] [11] [12]
The foundation of diarrhea management is fluid repletion. In mild cases, travelers should focus on increasing water intake. Water is usually sufficient though sports drinks and other electrolyte fluids can be used. Pedialyte can be used for pediatric patients. Milk and juices should be avoided as this can worsen diarrhea. In more severe cases, oral rehydration salt can be used to ensure rehydration with adequate electrolyte repletion. In cases of severe dehydration, IV fluids may ultimately be required.
Treatment is supportive in mild-moderate cases. In patients without signs of inflammatory diarrhea, loperamide can be used for symptomatic relief. The typical dose for adults is 4 mg initially with 2 mg after each subsequent loose stool, not to exceed 16 mg total in a day.
Also, travelers can be given antibiotics to take as needed at the onset of symptoms. Ciprofloxacin is commonly used for treatment, though there are concerns with resistance with Campylobacter species. For this reason, fluoroquinolones are not often prescribed for travelers to Asia and azithromycin preferable. Also, azithromycin is often prescribed for pregnant travelers and children. A common regimen is 500 mg daily for three days, though evidence suggests that a single dose of 1000 mg may be slightly more effective. Parents can be given azithromycin powder with instructions to mix with water when needed. Rifaximin is a minimally absorbed antibiotic that is also available and is safe for older children and pregnant travelers.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Ischemic colitis
- Radiation-induced colitis
- Food poisoning
New Guidelines for Traveler's Diarrhea
- Travelers should be advised against the use of prophylactic antibiotics
- In high-risk groups, one may consider antibiotic prophylaxis
- Bismuth subsalicylate can be considered in any traveler.
- The antibiotic of choice is rifaximin
- Fluoroquinolones should not be used as prophylaxis
The outcomes in most patients with traveler's diarrhea are good. However, in severe cases, dehydration can occur requiring admission.
- Complications
- Dehydration
- Malabsorption
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome
- Reactive arthritides
- Postoperative and Rehabilitation Care
The majority of patients are managed as outpatients and need to do the following:
- Maintain hydration
- Hand washing
- Only take antimotility agents if prescribed by the healthcare provider
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- If diarrhea persists for more than 10 days, should follow up with the primary provider
- Deterrence and Patient Education
- Wash hands regularly
- Avoid shellfish from waters that are contaminated
- Wash all foods before consumption
- Drink bottled water when traveling
- Avoid consumption of raw poultry or eggs
- When traveling, consume dry foods and carbonated beverages
- Avoid water and ice from the street
- Avoid drinking water from lakes and rivers
- Pearls and Other Issues
There is a strong correlation with travelers’ diarrhea and the subsequent development of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), with some studies suggesting up to 50% incidence.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The key to traveler's diarrhea is preventing it. Today, nurses, the primary care provider and the pharmacists are in the prime position to educate the patient on the importance of hydration and good hygiene. The traveler should be educated on drinking bottled water and washing all fresh fruit and vegetables prior to consumption. Plus, travelers should be warned not to drink from lakes and streams. Carrying small packets of alcohol desansitizer to wash hands can be very helpful when hand washing is not possible.
The pharmacist should educate the traveler on managing the symptoms of diarrhea with over-the-counter medications or loperamide. Travelers should be discouraged from taking prophylactic antibiotics when traveling, as this leads to more harm than good. Finally, the traveler should be educated on the symptoms of dehydration and when to seek medical care. The primary care clinicians should monitor patients until there is a complete resolution of symptoms. Any patient that fails to improve within a few days should be referred to a specialist for further workup. With open communication between the team members, the morbidity of traveler's diarrhea can be reduced. [1] [8] (level V)
The prognosis for most patients with traveler's diarrhea is excellent. However, thousands of patients go to the emergency departments each year looking for a magical cure. Hydration is the key and admission is only required for severe dehydration and orthostatic hypotension. The elderly and children under the age of 4 are at the highest risk for developing complications, which often occur because of self-prescribing of over-the-counter medications. [13] [14] (Level V)
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Noel Dunn declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Chika Okafor declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Dunn N, Okafor CN. Travelers Diarrhea. [Updated 2023 Jul 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Travelers Diarrhea (Nursing). [StatPearls. 2024] Travelers Diarrhea (Nursing). Dunn N, Okafor CN, Knizel JE. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Review Travelers' Diarrhea: A Clinical Review. [Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Dru...] Review Travelers' Diarrhea: A Clinical Review. Leung AKC, Leung AAM, Wong AHC, Hon KL. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2019; 13(1):38-48.
- Review Travelers' diarrhea. [Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010] Review Travelers' diarrhea. Hill DR, Beeching NJ. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010 Oct; 23(5):481-7.
- Review [Travelers' diarrhea]. [Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013] Review [Travelers' diarrhea]. Burchard GD, Hentschke M, Weinke T, Nothdurft HD. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013 Aug; 138(33):1673-83; quiz 1684-6. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- Review Beyond immunization: travelers' infectious diseases. 1--Diarrhea. [J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2015] Review Beyond immunization: travelers' infectious diseases. 1--Diarrhea. El-Bahnasawy M, Morsy TA. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2015 Apr; 45(1):29-42.
Recent Activity
- Travelers Diarrhea - StatPearls Travelers Diarrhea - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- GP practice services
- Health advice
- Health research
- Medical professionals
- Health topics
Advice and clinical information on a wide variety of healthcare topics.
All health topics
Latest features
Allergies, blood & immune system
Bones, joints and muscles
Brain and nerves
Chest and lungs
Children's health
Cosmetic surgery
Digestive health
Ear, nose and throat
General health & lifestyle
Heart health and blood vessels
Kidney & urinary tract
Men's health
Mental health
Oral and dental care
Senior health
Sexual health
Signs and symptoms
Skin, nail and hair health
- Travel and vaccinations
Treatment and medication
Women's health
Healthy living
Expert insight and opinion on nutrition, physical and mental health.
Exercise and physical activity
Healthy eating
Healthy relationships
Managing harmful habits
Mental wellbeing
Relaxation and sleep
Managing conditions
From ACE inhibitors for high blood pressure, to steroids for eczema, find out what options are available, how they work and the possible side effects.
Featured conditions
ADHD in children
Crohn's disease
Endometriosis
Fibromyalgia
Gastroenteritis
Irritable bowel syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Scarlet fever
Tonsillitis
Vaginal thrush
Health conditions A-Z
Medicine information
Information and fact sheets for patients and professionals. Find out side effects, medicine names, dosages and uses.
All medicines A-Z
Allergy medicines
Analgesics and pain medication
Anti-inflammatory medicines
Breathing treatment and respiratory care
Cancer treatment and drugs
Contraceptive medicines
Diabetes medicines
ENT and mouth care
Eye care medicine
Gastrointestinal treatment
Genitourinary medicine
Heart disease treatment and prevention
Hormonal imbalance treatment
Hormone deficiency treatment
Immunosuppressive drugs
Infection treatment medicine
Kidney conditions treatments
Muscle, bone and joint pain treatment
Nausea medicine and vomiting treatment
Nervous system drugs
Reproductive health
Skin conditions treatments
Substance abuse treatment
Vaccines and immunisation
Vitamin and mineral supplements
Tests & investigations
Information and guidance about tests and an easy, fast and accurate symptom checker.
About tests & investigations
Symptom checker
Blood tests
BMI calculator
Pregnancy due date calculator
General signs and symptoms
Patient health questionnaire
Generalised anxiety disorder assessment
Medical professional hub
Information and tools written by clinicians for medical professionals, and training resources provided by FourteenFish.
Content for medical professionals
FourteenFish training
Professional articles
Evidence-based professional reference pages authored by our clinical team for the use of medical professionals.
View all professional articles A-Z
Actinic keratosis
Bronchiolitis
Molluscum contagiosum
Obesity in adults
Osmolality, osmolarity, and fluid homeostasis
Recurrent abdominal pain in children
Medical tools and resources
Clinical tools for medical professional use.
All medical tools and resources
Traveller's diarrhoea
Peer reviewed by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGP Last updated by Dr Toni Hazell Last updated 10 Feb 2023
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
In this series: Amoebiasis Giardia
Traveller's diarrhoea is diarrhoea that develops during, or shortly after, travel abroad. It is caused by consuming food and water, contaminated by germs (microbes) including bacteria, viruses and parasites. Other symptoms can include high temperature (fever), being sick (vomiting) and tummy (abdominal) pain. In most cases it causes a mild illness and symptoms clear within 3 to 4 days. Specific treatment is not usually needed but it is important to drink plenty of fluids to avoid lack of fluid in the body (dehydration). Always make sure that you get any advice that you need in plenty of time before your journey - some GPs offer travel advice but if yours doesn't then you may need to go to a private travel clinic.
In this article :
What is traveller's diarrhoea, what causes traveller's diarrhoea, are all travellers at risk, what are the symptoms of traveller's diarrhoea, how is traveller's diarrhoea diagnosed, when should i seek medical advice for traveller's diarrhoea, how is traveller's diarrhoea in adults treated, how is traveller's diarrhoea in children treated, side-effects of traveller's diarrhoea, how long does traveller's diarrhoea last, how can i avoid traveller's diarrhoea.
Continue reading below
Traveller's diarrhoea is diarrhoea that develops during, or shortly after, travel abroad. Diarrhoea is defined as: 'loose or watery stools (faeces), usually at least three times in 24 hours.'
Traveller's diarrhoea is caused by eating food, or drinking water, containing certain germs (microbes) or their poisons (toxins). The types of germs which may be the cause include:
Bacteria: these are the most common microbes that cause traveller's diarrhoea. Common types of bacteria involved are:
Escherichia coli
Campylobacter
Viruses: these are the next most common, particularly norovirus and rotavirus.
Parasites: these are less common causes. Giardia, cryptosporidium and Entamoeba histolytica are examples of parasites that may cause traveller's diarrhoea.
Often the exact cause of traveller's diarrhoea is not found and studies have shown that in many people no specific microbe is identified despite testing (for example, of a stool (faeces) specimen).
See the separate leaflets called E. Coli (VTEC O157) , Campylobacter, Salmonella, Cryptosporidium , Amoebiasis (dysentery information), Shigella and Giardia for more specific details on each of the microbes mentioned above.
Note : this leaflet is about traveller's diarrhoea in general and how to help prevent it.
Traveller's diarrhoea most commonly affects people who are travelling from a developed country, such as the UK, to a developing country where sanitation and hygiene measures may not meet the same standards. It can affect as many as 2 to 6 in 10 travellers.
There is a different risk depending on whether you travel to high-risk areas or not:
High-risk areas : South and Southeast Asia, Central America, West and North Africa, South America, East Africa.
Medium-risk areas : Russia, China, Caribbean, South Africa.
Low-risk areas : North America, Western Europe, Australia and New Zealand.
Sometimes outbreaks of diarrhoea can occur in travellers staying in one hotel or, for example, those staying on a cruise ship. People travelling in more remote areas (for example, trekkers and campers) may also have limited access to medical care if they do become unwell.
By definition, diarrhoea is the main symptom. This can be watery and can sometimes contain blood. Other symptoms may include:
Crampy tummy (abdominal) pains.
Feeling sick (nausea).
Being sick (vomiting).
A high temperature (fever).
Symptoms are usually mild in most people and last for 3 to 4 days but they may last longer. Symptoms may be more severe in the very young, the elderly, and those with other health problems. Those whose immune systems are not working as well as normal are particularly likely to be more unwell. For example, people with untreated HIV infection, those on chemotherapy, those on long-term steroid treatment or those who are taking drugs which suppress their immune system, for example after a transplant or to treat an autoimmune condition
Despite the fact that symptoms are usually fairly mild, they can often mean that your travel itinerary is interrupted or may need to be altered.
Traveller's diarrhoea is usually diagnosed by the typical symptoms. As mentioned above, most people have mild symptoms and do not need to seek medical advice. However, in some cases medical advice is needed (see below).
If you do see a doctor, they may suggest that a sample of your stool (faeces) be tested. This will be sent to the laboratory to look for any microbes that may be causing your symptoms. Sometimes blood tests or other tests may be needed if you have more severe symptoms or develop any complications.
As mentioned above, most people with traveller's diarrhoea have relatively mild symptoms and can manage these themselves by resting and making sure that they drink plenty of fluids. However, you should seek medical advice in any of the following cases, or if any other symptoms occur that you are concerned about:
If you have a high temperature (fever).
If you have blood in your stools (faeces).
If it is difficult to get enough fluid because of severe symptoms: frequent or very watery stools or repeatedly being sick (vomiting).
If the diarrhoea lasts for more than 5-7 days.
If you are elderly or have an underlying health problem such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, or kidney disease.
If you have a weakened immune system because of, for example, chemotherapy treatment, long-term steroid treatment, or HIV infection.
If you are pregnant.
If an affected child is under the age of 6 months.
If you develop any of the symptoms listed below that suggest you might have lack of fluid in your body (dehydration). If it is your child who is affected, there is a separate list for children.
Symptoms of dehydration in adults
Dizziness or light-headedness.
Muscle cramps.
Sunken eyes.
Passing less urine.
A dry mouth and tongue.
Becoming irritable.
Symptoms of severe dehydration in adults
Profound loss of energy or enthusiasm (apathy).
A fast heart rate
Producing very little urine.
Coma, which may occur.
Note : severe dehydration is a medical emergency and immediate medical attention is needed.
Symptoms of dehydration in children
Passing little urine.
A dry mouth.
A dry tongue and lips.
Fewer tears when crying.
Being irritable.
Having a lack of energy (being lethargic).
Symptoms of severe dehydration in children
Drowsiness.
Pale or mottled skin.
Cold hands or feet.
Very few wet nappies.
Fast (but often shallow) breathing.
Dehydration is more likely to occur in:
Babies under the age of 1 year (and particularly those under 6 months old). This is because babies don't need to lose much fluid to lose a significant proportion of their total body fluid.
Babies under the age of 1 year who were a low birth weight and who have not caught up with their weight.
A breastfed baby who has stopped being breastfed during their illness.
Any baby or child who does not drink much when they have a gut infection (gastroenteritis).
Any baby or child with severe diarrhoea and vomiting. (For example, if they have passed five or more diarrhoeal stools and/or vomited two or more times in the previous 24 hours.)
In most cases, specific treatment of traveller's diarrhoea is not needed. The most important thing is to make sure that you drink plenty of fluids to avoid lack of fluid in your body (dehydration).
Fluid replacement
As a rough guide, drink at least 200 mls after each watery stool (bout of diarrhoea).
This extra fluid is in addition to what you would normally drink. For example, an adult will normally drink about two litres a day but more in hot countries. The above '200 mls after each watery stool' is in addition to this usual amount that you would drink.
If you are sick (vomit), wait 5-10 minutes and then start drinking again but more slowly. For example, a sip every 2-3 minutes but making sure that your total intake is as described above.
You will need to drink even more if you are dehydrated. A doctor will advise on how much to drink if you are dehydrated.
Note : if you suspect that you are becoming dehydrated, you should seek medical advice.
For most adults, fluids drunk to keep hydrated should mainly be water. However, this needs to be safe drinking water - for example, bottled, or boiled and treated water. It is best not to have drinks that contain a lot of sugar, such as fizzy drinks, as they can sometimes make diarrhoea worse. Alcohol should also be avoided.
Rehydration drinks
Rehydration drinks may also be used. They are made from sachets that you can buy from pharmacies and may be a sensible thing to pack in your first aid kit when you travel. You add the contents of the sachet to water.
Home-made salt/sugar mixtures are used in developing countries if rehydration drinks are not available; however, they have to be made carefully, as too much salt can be dangerous. Rehydration drinks are cheap and readily available in the UK, and are the best treatment. Note that safe drinking water should be used to reconstitute oral rehydration salt sachets.
Antidiarrhoeal medication
Antidiarrhoeal medicines are not usually necessary or wise to take when you have traveller's diarrhoea. However you may want to use them if absolutely necessary - for example, if you will be unable to make regular trips to the toilet due to travelling.You can buy antidiarrhoeal medicines from pharmacies before you travel. The safest and most effective is loperamide.
The adult dose of this is two capsules at first. This is followed by one capsule after each time you pass some diarrhoea up to a maximum of eight capsules in 24 hours. It works by slowing down your gut's activity.
You should not take loperamide for longer than two days. You should also not use antidiarrhoeal medicines if you have a high temperature (fever) or bloody diarrhoea.
Eat as normally as possible
It used to be advised to 'starve' for a while if you had diarrhoea. However, now it is advised to eat small, light meals if you can. Be guided by your appetite. You may not feel like food and most adults can do without food for a few days. Eat as soon as you are able but don't stop drinking. If you do feel like eating, avoid fatty, spicy or heavy food. Plain foods such as bread and rice are good foods to try eating.
Antibiotic medicines
Most people with traveller's diarrhoea do not need treatment with antibiotic medicines. However, sometimes antibiotic treatment is advised. This may be because a specific germ (microbe) has been identified after testing of your stool (faeces) sample.
Fluids to prevent dehydration
You should encourage your child to drink plenty of fluids. The aim is to prevent lack of fluid in the body (dehydration). The fluid lost in their sick (vomit) and/or diarrhoea needs to be replaced. Your child should continue with their normal diet and usual drinks. In addition, they should also be encouraged to drink extra fluids. However, avoid fruit juices or fizzy drinks, as these can make diarrhoea worse.
Babies under 6 months old are at increased risk of dehydration. You should seek medical advice if they develop acute diarrhoea. Breast feeds or bottle feeds should be encouraged as normal. You may find that your baby's demand for feeds increases. You may also be advised to give extra fluids (either water or rehydration drinks) in between feeds.
If you are travelling to a destination at high risk for traveller's diarrhoea, you might want to consider buying oral rehydration sachets for children before you travel. These can provide a perfect balance of water, salts and sugar for them and can be used for fluid replacement. Remember that, as mentioned above, safe water is needed to reconstitute the sachets.
If your child vomits, wait 5-10 minutes and then start giving drinks again but more slowly (for example, a spoonful every 2-3 minutes). Use of a syringe can help in younger children who may not be able to take sips.
Note : if you suspect that your child is dehydrated, or is becoming dehydrated, you should seek medical advice urgently.
Fluids to treat dehydration
If your child is mildly dehydrated, this may be treated by giving them rehydration drinks. A doctor will advise about how much to give. This can depend on the age and the weight of your child. If you are breastfeeding, you should continue with this during this time. It is important that your child be rehydrated before they have any solid food.
Sometimes a child may need to be admitted to hospital for treatment if they are dehydrated. Treatment in hospital usually involves giving rehydration solution via a special tube called a 'nasogastric tube'. This tube passes through your child's nose, down their throat and directly into their stomach. An alternative treatment is with fluids given directly into a vein (intravenous fluids).
Eat as normally as possible once any dehydration has been treated
Correcting any dehydration is the first priority. However, if your child is not dehydrated (most cases), or once any dehydration has been corrected, then encourage your child to have their normal diet. Do not 'starve' a child with infectious diarrhoea. This used to be advised but is now known to be wrong. So:
Breastfed babies should continue to be breastfed if they will take it. This will usually be in addition to extra rehydration drinks (described above).
Bottle-fed babies should be fed with their normal full-strength feeds if they will take it. Again, this will usually be in addition to extra rehydration drinks (described above). Do not water down the formula, or make it up with less water than usual. This can make a baby very ill.
Older children - offer them some food every now and then. However, if he or she does not want to eat, that is fine. Drinks are the most important consideration and food can wait until the appetite returns.
Loperamide is not recommended for children with diarrhoea. There are concerns that it may cause a blockage of the gut (intestinal obstruction) in children with diarrhoea.
Most children with traveller's diarrhoea do not need treatment with antibiotics. However, for the same reasons as discussed for adults above, antibiotic treatment may sometimes be advised in certain cases.
Most people have mild illness and complications of traveller's diarrhoea are rare. However, if complications do occur, they can include the following:
Salt (electrolyte) imbalance and dehydration .
This is the most common complication. It occurs if the salts and water that are lost in your stools (faeces), or when you are sick (vomit), are not replaced by you drinking adequate fluids. If you can manage to drink plenty of fluids then dehydration is unlikely to occur, or is only likely to be mild and will soon recover as you drink.
Severe dehydration can lead to a drop in your blood pressure. This can cause reduced blood flow to your vital organs. If dehydration is not treated, your kidneys may be damaged . Some people who become severely dehydrated need a 'drip' of fluid directly into a vein. This requires admission to hospital. People who are elderly or pregnant are more at risk of dehydration.
Reactive complications
Rarely, other parts of your body can 'react' to an infection that occurs in your gut. This can cause symptoms such as joint inflammation (arthritis), skin inflammation and eye inflammation (either conjunctivitis or uveitis). Reactive complications are uncommon if you have a virus causing traveller's diarrhoea.
Spread of infection
The infection can spread to other parts of your body such as your bones, joints, or the meninges that surround your brain and spinal cord. This is rare. If it does occur, it is more likely if diarrhoea is caused by salmonella infection.
Irritable bowel syndrome is sometimes triggered by a bout of traveller's diarrhoea.
Lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance can sometimes occur for a period of time after traveller's diarrhoea. It is known as 'secondary' or 'acquired' lactose intolerance. Your gut (intestinal) lining can be damaged by the episode of diarrhoea. This leads to lack of a substance (enzyme) called lactase that is needed to help your body digest the milk sugar lactose.
Lactose intolerance leads to bloating, tummy (abdominal) pain, wind and watery stools after drinking milk. The condition gets better when the infection is over and the intestinal lining heals. It is more common in children.
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome
Usually associated with traveller's diarrhoea caused by a certain type of E. coli infection, haemolytic uraemic syndrome is a serious condition where there is anaemia, a low platelet count in the blood and kidney damage. It is more common in children. If recognised and treated, most people recover well.
Guillain-Barré syndrome
This condition may rarely be triggered by campylobacter infection, one of the causes of traveller's diarrhoea. It affects the nerves throughout your body and limbs, causing weakness and sensory problems. See the separate leaflet called Guillain-Barré syndrome for more details.
Reduced effectiveness of some medicines
During an episode of traveller's diarrhoea, certain medicines that you may be taking for other conditions or reasons may not be as effective. This is because the diarrhoea and/or being sick (vomiting) mean that reduced amounts of the medicines are taken up (absorbed) into your body.
Examples of such medicines are those for epilepsy, diabetes and contraception . Speak with your doctor or practice nurse before you travel if you are unsure of what to do if you are taking other medicines and develop diarrhoea.
As mentioned above, symptoms are usually short-lived and the illness is usually mild with most people making a full recovery within in few days. However, a few people with traveller's diarrhoea develop persistent (chronic) diarrhoea that can last for one month or more. It is also possible to have a second 'bout' of traveller's diarrhoea during the same trip. Having it once does not seem to protect you against future infection.
Avoid uncooked meat, shellfish or eggs. Avoid peeled fruit and vegetables (including salads).
Be careful about what you drink. Don't drink tap water, even as ice cubes.
Wash your hands regularly, especially before preparing food or eating.
Be careful where you swim. Contaminated water can cause traveller's diarrhoea.
Regular hand washing
You should ensure that you always wash your hands and dry them thoroughly; teach children to wash and dry theirs:
After going to the toilet (and after changing nappies or helping an older child to go to the toilet).
Before preparing or touching food or drinks.
Before eating.
Some antibacterial hand gel may be a good thing to take with you when you travel in case soap and hot water are not available.
Be careful about what you eat and drink
When travelling to areas with poor sanitation, you should avoid food or drinking water that may contain germs (microbes) or their poisons (toxins). Avoid:
Fruit juices sold by street vendors.
Ice cream (unless it has been made from safe water).
Shellfish (for example, mussels, oysters, clams) and uncooked seafood.
Raw or undercooked meat.
Fruit that has already been peeled or has a damaged skin.
Food that contains raw or uncooked eggs, such as mayonnaise or sauces.
Unpasteurised milk.
Drinking bottled water and fizzy drinks that are in sealed bottles or cans, tea, coffee and alcohol is thought to be safe. However, avoid ice cubes and non-bottled water in alcoholic drinks. Food should be cooked through thoroughly and be piping hot when served.
You should also be careful when eating food from markets, street vendors or buffets if you are uncertain about whether it has been kept hot or kept refrigerated. Fresh bread is usually safe, as is canned food or food in sealed packs.
Be careful where you swim
Swimming in contaminated water can also lead to traveller's diarrhoea. Try to avoid swallowing any water as you swim; teach children to do the same.
Obtain travel health advice before you travel
Always make sure that you visit your GP surgery or private travel clinic for health advice in plenty of time before your journey. Alternatively, the Fit for Travel website (see under Further Reading and References, below) provides travel health information for the public and gives specific information for different countries and high-risk destinations. This includes information about any vaccinations required, advice about food, water and personal hygiene precautions, etc.
There are no vaccines that prevent traveller's diarrhoea as a whole. However, there are some other vaccines that you may need for your travel, such as hepatitis A, typhoid, etc. You may also need to take malaria tablets depending on where you are travelling.
Antibiotics
Taking antibiotic medicines to prevent traveller's diarrhoea (antibiotic prophylaxis) is not generally recommended. This is because for most people, traveller's diarrhoea is mild and self-limiting. Also, antibiotics do not protect against nonbacterial causes of traveller's diarrhoea, such as viruses and parasites. Antibiotics may have side-effects and their unnecessary use may lead to problems with resistance to medicines.
Probiotics have some effect on traveller's diarrhoea and can shorten an attack by about one day. It is not known yet which type of probiotic or which dose, so there are no recommendations about using probiotics to prevent traveller's diarrhoea.
Further reading and references
- Bourgeois AL, Wierzba TF, Walker RI ; Status of vaccine research and development for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine. 2016 Mar 15. pii: S0264-410X(16)00287-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.02.076.
- Travellers' diarrhoea ; Fitfortravel
- Riddle MS, Connor BA, Beeching NJ, et al ; Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of travelers' diarrhea: a graded expert panel report. J Travel Med. 2017 Apr 1;24(suppl_1):S57-S74. doi: 10.1093/jtm/tax026.
- Giddings SL, Stevens AM, Leung DT ; Traveler's Diarrhea. Med Clin North Am. 2016 Mar;100(2):317-30. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2015.08.017.
- Diarrhoea - prevention and advice for travellers ; NICE CKS, February 2019 (UK access only)
Article History
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 9 Feb 2028
10 feb 2023 | latest version.
Last updated by
Peer reviewed by

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Our website uses cookies
This website uses cookies as well as similar tools and technologies to understand visitors’ experiences. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University’s usage of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice. (link opens in a new window)
Skip to content
Traveler's Diarrhea
Make an appointment.
Our team is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need.
Top of the page
Traveler's Diarrhea
- Conditions Basics
What is traveler's diarrhea?
Traveler's diarrhea is a common medical problem for people traveling from developed, industrialized countries to developing areas of the world.
High-risk areas for traveler's diarrhea include developing countries in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America. Low-risk areas include the developed countries of North America, Central Europe, Australia, and Japan.
What causes it?
Traveler's diarrhea is usually caused by a bacterial infection. Bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) , Campylobacter , Shigella , or Salmonella are the most common causes. These bacteria are in water contaminated by human or animal stools. Drinking water, water used to wash food, or irrigation water may be affected. When the traveler drinks this water or eats contaminated food, he or she is likely to get diarrhea.
Common sources of bacteria that cause diarrhea are undercooked or raw foods, contaminated food, or contaminated water (including ice cubes).
What are the symptoms?
Traveler's diarrhea can be mild to severe. Most people who develop traveler's diarrhea experience symptoms within the first 2 weeks, and often within 2 to 3 days, of arriving in a developing area. Symptoms include:
- Abdominal cramps.
- Mild to severe dehydration .
- General lack of energy, nausea, and vomiting.
- Fever, vomiting, and stools with blood or mucus. These symptoms mean you have serious diarrhea, which is more likely to lead to problems with dehydration. Dehydration may alter the effect of any medicines being taken, such as oral contraceptives or antimalarials.
How is traveler's diarrhea treated?
Treatment for traveler's diarrhea includes drinking fluids to avoid dehydration, taking nonprescription medicines, and in some cases, antibiotics and intravenous (I.V.) fluids.
- Take frequent, small sips of bottled or boiled water or a rehydration drink .
- If possible, drink a solution made with World Health Organization (WHO) oral rehydration salts. Packets of the salts are available at stores and pharmacies in most developing countries. Add one packet to boiled or treated water, making sure to read the instructions regarding the proper amounts of salts and water. Drink the solution within 12 hours if kept at room temperature, or within 24 hours if refrigerated.
- Let your stomach rest. Start to eat small amounts of mild foods if you feel like it. After your diarrhea is gone, you may eat a regular diet again.
Children 2 years old or younger are at high risk of dehydration from diarrhea. If your child has diarrhea:
- Give your child a solution of WHO rehydration salts in addition to your child's regular food as long as diarrhea continues. If your baby has trouble keeping the liquids down, try giving frequent sips by spoon.
- Continue breastfeeding normally. Bottle-fed babies should continue their usual formula.
- Feed your child starches, cereals, yogurt, fruits, and vegetables.
- Seek medical help immediately if you or your child has bloody diarrhea, fever, or persistent vomiting, and give rehydration fluids in the meantime.
- Your doctor may recommend an over-the-counter medicine. These may include bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) or loperamide (Imodium). Read and follow all instructions on the label. Do not use these medicines if your doctor does not recommend them.
- Be safe with medicines. If your doctor recommends prescription medicine, take it as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine. You will get more details on the specific medicines your doctor prescribes.
- If your doctor prescribes antibiotics, take them as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
How can you help prevent it?
The best way to prevent traveler's diarrhea is to avoid food or water that may be contaminated. Eating raw or uncooked seafood and meat puts you at higher risk for getting sick. Also avoid foods like salads, uncooked vegetables, and raw fruits that don't have a peel. Dry foods, such as breads, or fruits that you can peel are safe to eat.
Avoid drinking local water where you are traveling. Beverages that are usually safe to drink include:
- Tea and coffee if made with boiled water.
- Carbonated bottled water or soda pop.
- Bottled beer and wine.
Water also can be filtered or treated with iodine to make it safe to drink.
Also, be aware that contaminated water may be used to wash fruits and vegetables, clean utensils and plates, and make ice cubes. Brushing your teeth with untreated water also may increase your risk of infection.
Avoid eating food from street vendors where flies can transmit bacteria and poor hygiene practices are more likely to contaminate foods. If you purchase food at an outdoor market, make sure you boil it, cook it thoroughly, or peel it before you eat it.
Good hand-washing is important in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Washing with treated water or using alcohol wipes or antibacterial gels to disinfect your hands are good ways to reduce your risk of getting an infectious disease.
Talk with your doctor about antibiotics you can carry with you on your trip and instructions on when to use them just in case you should develop diarrhea.
Other information sources
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) maintains current information on infectious diseases around the world. Local health departments can access this information to help you determine what prevention measures-such as vaccines, antimalarial medicine, or supplies to treat water-are appropriate for the area of the world you are traveling to. The CDC website (www.cdc.gov/travel/default.aspx) also updates information for travelers.
Resources for medical care in a foreign country include embassies or consulates and major hotels. For English-speaking travelers, multinational corporations or credit card companies also may have referrals for local medical care in the foreign country.
- Related Information
- Diarrhea, Age 11 and Younger
- Diarrhea, Age 12 and Older
- Travel Health
Current as of: June 12, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Topic Contents
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use . Learn how we develop our content .

To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise.org .
© 1995-2024 Healthwise, Incorporated. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Best Traveler's Diarrhea Treatments for Symptom Relief
Sources of Bacteria, Prevention, and Medication Types
Complications
Frequently asked questions.
Traveler's diarrhea can turn a trip into a nightmare. Food and water contaminated by germs, also known as pathogens , is not uncommon in certain areas of the world that are popular travel destinations. Consuming even small amounts of these germs can cause loose, watery stool, the main sign of diarrhea , Luckily, treatment options are available.
This article explains the symptoms of traveler's diarrhea, how to treat it, and the best ways to prevent getting infected in the first place.
Luis Alvarez / Getty Images
Symptoms of traveler's diarrhea caused by bacteria or a virus usually appear six to 72 hours after eating or drinking something contaminated. With some types of pathogens, it may take a week or longer for stool to be affected.
Changes in your bowel habits it the main symptoms of diarrhea. At its mildest, diarrhea involves passing loose, watery stool three times a day. You may pass unformed stool 10 or more times a day in severe cases.
Other symptoms vary depending on the type of bacterial or virus you've been exposed to but may include:
- Stomach cramps
- Tenesmus , feeling you need to have a bowel movement even when your bowels are empty
- Mucous in stool
More severe cases of traveler's diarrhea may cause bloody stools .
Should You Go to a Doctor for Traveler's Diarrhea?
See a healthcare provider if your symptoms are accompanied by fever or bloody stools, or they last longer than 48 hours.
Traveler's Diarrhea Causes
The most common cause of traveler's diarrhea is probably poor hygiene (lack of cleanliness) in restaurants. You're most at risk when dining out in areas of Asia, the Middle East, Mexico, Africa, and South and Central America.
Pathogens are usually spread via the fecal-oral route . This means someone with the bacteria or virus excretes the germs in their feces. The feces may not be safely disposed of in a sanitary setting, or the infected person may not properly wash their hands before handling food and beverages. This allows germs to be transmitted to something you put into your mouth.
This cycle of contamination is most common in areas of the world that have specific conditions:
- Warmer climates that promote germ growth
- Poor sanitation (such as open sewage areas)
- Unreliable refrigeration
- Little education on safe food handling.
Common Bacterial Pathogens
The most common cause of traveler's diarrhea is bacteria, which are thought to lead to 80% to 90% of cases. These include:
- Escherichia coli or E-coli
- Campylobacter jejuni
Ingesting these bacterium causes gastroenteritis , which means the stomach and small intestines become inflamed. This leads to diarrhea.
Common Viral Pathogens
Viruses can also be transported via the fecal-oral route. The most common types of viruses that cause diarrhea include:
Viral infections of the digestive system are often referred to as stomach flu . The illness has no connection to respiratory influenza, but like the "flu," it usually lasts a short period.
Other Causes of Diarrhea
In addition to germs in your food and water, you could develop diarrhea from toxins, which cause the common symptoms of food poisoning .
Parasites , or protozoal pathogens, can also cause diarrhea. In these instances, you're more likely to develop symptoms one to two weeks after exposure to the pathogen.
Dehydration is one of the most common complications related to any form of diarrhea. Multiple bowel movements that release a lot of fluid can cause you to have too little water in your body.
Severe dehydration can lead to problems such as:
- Fatigue and muscle weakness or pain
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Increased heart rate and breathing
- Kidney Failure
Dysentery is a serious condition that can develop from exposure to Shigella or parasites. It usually causes bloody stool, fever, and extreme dehydration. It can be fatal if it's left untreated. In addition to being picked up from contaminated food or water, the bacteria or parasites that cause dysentery can be passed from person to person in close contact, or you can get it by swimming in unclean water.
Treatment for Traveler's Diarrhea
Getting sick while far from home is more than just inconvenient. The sudden onset and severity of symptoms can be frightening. Often, symptoms will last a few days and resolve on their own, but you may need to manage the condition and take medication.
Fluid Replacement
To manage dehydration, you want to concentrate on getting enough liquids even if you feel like you don't want to put anything in your stomach.
Drinking any safe fluids can manage mild cases of traveler's diarrhea. Since tap water may be a source of infection, you need to boil non-bottled water and let it cool before you drink it. You can also drink boiled broth or prepackaged (non-citrus) fruit juice. Sports drinks like Gatorade are good, too, but not essential.
For severe dehydration, an oral rehydration solution may be needed. These are mixes or packaged beverages that contain glucose and electrolytes such as potassium and sodium. Pedialyte is an example of an oral rehydration solution for kids.
Sweating can cause dehydration as well. Try to find a cool place out of the sun to rest while you rehydrate.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be used for traveler's diarrhea caused by bacterial infections. A stool test should be done to identify which antibiotic might work best.
Quinolone antibiotics such as Cipro (ciprofloxacin) are most often used when antibiotics are needed.
A single dose of 750 milligrams (mg) for adults is the typical treatment. Children may be given 20 to 30 mg per kilogram of weight per day.
In some areas, bacteria are resistant to quinolones, which means the medication won't help. This is especially a problem in Southeast Asia. Another antibiotic, azithromycin , may also be used in this case, although some strains are resistant to it.
Upset Stomach Medication
Pepto-Bismol can provide short-term relief of symptoms. However, it may not be effective in small doses, and high doses put you at risk for a health condition called salicylate toxicity. Additionally, Pepto-Bismol is not recommended for people younger than 18 years because there's a risk of a condition called Reye's syndrome .
Antidiarrheal Agents
It might seem logical to reach for an anti-diarrheal product such as Imodium (loperamide) or Lomotil (diphenoxylate). However, these products should not be used if your diarrhea is related to dysentery or if you see any signs of blood in your stools.
An antidiarrheal agent should only be taken with an antibiotic. When using an antidiarrheal for traveler's diarrhea, it is especially important to keep yourself well-hydrated. Discontinue the product if your symptoms worsen or you still have diarrhea after two days.
How Long Traveler's Diarrhea Lasts
Most cases of traveler's diarrhea last from one to five days. However, symptoms may linger for several weeks.
To help prevent traveler's diarrhea:
- Wash your hands with soap and water after going to the bathroom and before eating.
- At restaurants, only eat foods that are cooked and served hot.
- Drink beverages from factory-sealed bottles or containers.
- Don't get ice in your drink since it may be made with contaminated water.
There is evidence that Pepto-Bismol may protect against traveler's diarrhea. Studies have shown a protection rate of about 60%. However, not everyone should take Pepto-Bismol, including those who are pregnant or are 18 years of age and younger.
Don't take antibiotics or antidiarrheal medicine like Pepto-Bismol as prophylaxis—that is, to prevent traveler's diarrhea— unless it's been recommended to you by your healthcare provider.
Bacteria and viruses can live in water and food. These pathogens (germs) are most common in areas where the climate is warm, refrigeration is unreliable, and there isn't proper hand washing or bathroom sanitation. Infection with these pathogens (bacterial or viral) can cause traveler's diarrhea.
Traveler's diarrhea will often resolve on its own once the bacteria or virus is out of your system. However, you may need antibiotics. You may also need to manage symptoms by staying hydrated and using over-the-counter medications. You should contact your healthcare provider if symptoms last more than a few days.
When traveling to regions that have warm climates and relaxed hygiene practices, be sure to take steps to avoid eating or drinking anything that could have pathogens. Drink pre-packed or boiled water and ensure food is handled properly.
It's important to make sure that your child gets enough fluids. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration more quickly in kids than in adults. Check with your healthcare provider if your child has signs of dehydration such as dry mouth, few or no tears when crying, irritability, reduced urination, and drowsiness.
If you're pregnant, the most important thing to do is to drink enough fluids so you don't get dehydrated. Your doctor may suggest using azithromycin if you need an antibiotic. Don't use Pepto-Bismol (bismuth subsalicylate) when pregnant because of risks to the growing fetus.
Connor BA. Preparing international travelers: Travelers’ diarrhea . In: Brunette GW, ed. CDC Yellow Book 2020: Health information for international travel . Oxford University Press; 2017.
Leung AKC, Leung AAM, Wong AHC, Hon KL. Travelers’ diarrhea: a clinical review . Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov . 2019;13(1):38-48. doi:10.2174/1872213X13666190514105054
Shaheen NA, Alqahtani AA, Assiri H, Alkhodair R, Hussein MA. Public knowledge of dehydration and fluid intake practices: variation by participants' characteristics . BMC Public Health . 2018;18(1):1346. doi:10.1186/s12889-018-6252-5
Strachan SR, Morris LF. Management of severe dehydration . Pediatr Crit Care Med . 2017;18(3):251-255. doi:10.1177/1751143717693859
Riddle MS, Connor BA, Beeching NJ, et al. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of travelers’ diarrhea: a graded expert panel report . J Travel Med . 2017;24(suppl_1):S57-S74. doi:10.1093/jtm/tax026
Johns Hopkins Medicine. Traveler's Diarrhea.
Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth. Staying healthy while you travel.
Morof DF, Carroll ID. Family travel: Pregnant travelers . In: Brunette GW, ed. CDC Yellow Book 2020: Health information for international travel . Oxford University Press; 2017.
Wanke, Christine A. " Travelers' Diarrhea ." UpToDate .
By Barbara Bolen, PhD Barbara Bolen, PhD, is a licensed clinical psychologist and health coach. She has written multiple books focused on living with irritable bowel syndrome.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 11 - Respiratory Infections
- Section 11 - Dermatologic Conditions
Persistent Diarrhea in Returned Travelers
Cdc yellow book 2024.
Author(s): Bradley Connor
Although most cases of travelers’ diarrhea (TD) are acute and self-limited, a certain percentage of people afflicted will develop persistent (>14 days) gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Details on the management of acute TD are available in Sec. 2, Ch. 6, Travelers’ Diarrhea .
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of persistent diarrhea in returned travelers generally falls into one of the following broad categories: ongoing infection or co-infection with a second organism not targeted by initial therapy; previously undiagnosed GI disease unmasked by the enteric infection; or a postinfectious phenomenon.
Ongoing Infection
Most cases of TD are the result of bacterial infection and are short-lived and self-limited. In addition to immunosuppression and sequential infection with diarrheal pathogens, ongoing infection with protozoan parasites can cause prolonged diarrheal symptoms.
Individual bacterial infections rarely cause persistent symptoms, but travelers infected with Clostridioides difficile or enteroaggregative or enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 7, Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli ) can experience ongoing diarrhea. C. difficile –associated diarrhea can occur after treatment of a bacterial pathogen with a fluoroquinolone or other antibiotic, or after malaria chemoprophylaxis. The association between C. difficile and antimicrobial treatment is especially important to consider in patients with persistent TD that seems refractory to multiple courses of empiric antibiotic therapy. The initial work-up of persistent TD should always include a C. difficile stool toxin assay. Clinicians can prescribe oral vancomycin, fidaxomicin, or, less optimally, metronidazole to treat C. difficile .
As a group, parasites are the pathogens most likely to be isolated from patients with persistent diarrhea. The probability of a traveler having a protozoal infection, relative to a bacterial one, increases with increasing duration of symptoms. Parasites might also be the cause of persistent diarrhea in patients already treated for a bacterial pathogen.
Giardia (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 12, Giardiasis ) is the most likely parasitic pathogen to cause persistent diarrhea. Suspect giardiasis particularly in patients with upper GI–predominant symptoms. Untreated, symptoms can last for months, even in immunocompetent hosts.
PCR-based diagnostics, particularly the multiplex DNA extraction PCR, are becoming the diagnostic methods of choice to identify Giardia and other protozoal pathogens, including Cryptosporidium , Cyclospora , and Entamoeba histolytica . Diagnosis also can be made by stool microscopy, antigen detection, or immunofluorescence. In the absence of diagnostics (given the high prevalence of Giardia as a cause for persistent TD), empiric therapy is a reasonable option in the clinical setting. Rare causes of persistent symptoms include the intestinal parasites Cystoisospora , Dientamoeba fragilis , and Microsporidia .
Tropical Sprue & Brainerd Diarrhea
Persistent TD also has been associated with tropical sprue and Brainerd diarrhea. Tropical sprue is associated with deficiencies of vitamins absorbed in the proximal and distal small bowel and most commonly affects long-term travelers to tropical areas, as the name implies. The incidence of tropical sprue appears to have declined dramatically over the past 2 decades. Diagnosed only rarely in travelers, its cause is unknown.
Brainerd diarrhea is a syndrome of acute onset of watery diarrhea lasting ≥4 weeks. Symptoms include 10–20 episodes of explosive, watery diarrhea per day, fecal incontinence, abdominal cramping, gas, and fatigue. Nausea, vomiting, and fever are rare. Although the cause is believed to be infectious, a culprit pathogen has yet to be identified, and antimicrobial therapy is ineffective as treatment. Investigation of an outbreak of Brainerd diarrhea among passengers on a cruise ship to the Galápagos Islands in 1992 identified that individuals with persistent diarrhea (range: 7 to >42 months) were more likely to have consumed contaminated water or eaten raw fruits or vegetables washed with contaminated water.
Underlying Gastrointestinal Disease
Celiac disease.
In some cases, persistent symptoms relate to chronic underlying GI disease or to a susceptibility unmasked by the enteric infection. Most prominent among these is celiac disease, a systemic disease manifesting primarily with small bowel changes. In genetically susceptible people, exposure to antigens found in wheat causes villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, and malabsorption. Serologic tests, including tissue transglutaminase antibody testing, support the diagnosis; a small bowel biopsy showing villous atrophy confirms the diagnosis. Patients can be treated with a gluten-free diet.
Colorectal Cancer
Depending on the clinical setting and age group, clinicians might need to conduct a comprehensive search for other underlying causes of chronic diarrhea. Consider colorectal cancer in the differential diagnosis of patients passing occult or gross blood rectally or in patients with new-onset iron-deficiency anemia.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn’s disease, microscopic colitis, and ulcerative colitis, can occur after acute bouts of TD. One prevailing hypothesis is that in genetically susceptible people, an initiating exogenous pathogen changes the microbiota of the gut, thereby triggering inflammatory bowel disease.

Postinfectious Phenomena
In a certain percentage of patients who present with persistent GI symptoms, clinicians will not find a specific cause. After an acute diarrheal infection, patients might experience a temporary enteropathy characterized by villous atrophy, decreased absorptive surface area, and disaccharidase deficiencies, which can lead to osmotic diarrhea, particularly after consuming large amounts of fructose, lactose, sorbitol, or sucrose. Use of antimicrobial medications during the initial days of diarrhea might also lead to alterations in intestinal flora and diarrhea symptoms.
Occasionally, onset of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms occurs after a bout of acute gastroenteritis, known as postinfectious IBS (PI-IBS). PI-IBS symptoms can occur after an episode of gastroenteritis or TD. The clinical work-up for microbial pathogens and underlying GI disease in patients with PI-IBS will be negative. Whether using antibiotics to treat acute TD increases or decreases the likelihood of PI-IBS is unknown.
Traditional methods of microbial diagnosis rely on the use of microscopy. Examine stool specimens collected over 3 or more days for ova and parasites; include acid-fast staining for Cryptosporidium , Cyclospora , and Cystoisospora . Giardia antigen testing and a C. difficile toxin assay are appropriate elements of a work-up. In addition, a D-xylose absorption test can determine whether patients are properly absorbing nutrients. If underlying gastrointestinal disease is suspected, include serologic testing for celiac disease and consider inflammatory bowel disease during initial evaluation. Subsequently, studies to visualize both the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts, with biopsies, might be indicated.
Diagnostic tests to determine specific microbial etiologies in cases of persistent diarrhea have advanced in the past number of years. One of the most useful tools is high-throughput multiplex DNA extraction PCR. This technology uses a single stool specimen to detect multiple bacterial, parasitic, and viral enteropathogens simultaneously. Except for Cryptosporidium , these assays have high sensitivity and specificity; the clinical ramifications and the economic impact of using these diagnostic molecular panels have not been determined fully, however. In some cases, molecular testing detects colonization rather than infection, making it difficult for clinicians to interpret and apply the results properly.
Specific treatment of identified enteropathogens is usually indicated, and appropriate management of underlying gastrointestinal disease warranted (e.g., a gluten-free diet for celiac disease, medication for inflammatory bowel disease). Dietary modifications might help patients with malabsorption. Symptomatic treatment or the use of nonabsorbable antibiotics offer potential benefit if small intestinal bacterial overgrowth accompanies the symptom complex. Additionally, chronic diarrhea might cause fluid and electrolyte imbalances requiring medical management involving oral or intravenous replacement based on clinical presentation.
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Bradley A. Connor
Bibliography
Connor BA. Sequelae of traveler’s diarrhea: focus on postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41(Suppl 8):S577–86.
Connor BA. Chronic diarrhea in travelers. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2013;15(3):203–10.
Connor BA, Rogova M, Whyte O. Use of a multiplex DNA extraction PCR in the identification of pathogens in travelers’ diarrhea. J Trav Med. 2018;25(1):tax087.
Duplessis CA, Gutierrez RL, Porter CK. Review: chronic and persistent diarrhea with a focus in the returning traveler. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2017;3(9):1–17.
Hanevik K, Dizdar V, Langeland N, Hausken T. Development of functional gastrointestinal disorders after Giardia lamblia infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009;9:27.
Libman MD, Gyorkos TW, Kokoskin E, Maclean JD. Detection of pathogenic protozoa in the diagnostic laboratory: result reproducibility, specimen pooling, and competency assessment. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;76(7):2200–5.
Mintz ED, Weber JT, Guris D, Puhr N, Wells JG, Yashuk JC, et al. An outbreak of Brainerd diarrhea among travelers to the Galapagos Islands. J Infect Dis. 1998;177(4):1041–5.
Norman FF, Perez-Molina J, Perez de Ayala A, Jimenez BC, Navarro M, Lopez-Velez R. Clostridium difficile –associated diarrhea after antibiotic treatment for traveler’s diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(7):1060–3.
Porter CK, Tribble DR, Aliaga PA, Halvorson HA, Riddle MS. Infectious gastroenteritis and risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(3):781–6.
Spiller R, Garsed K. Postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1979–88.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
Travellers’ diarrhoea
Chinese translation.
- Related content
- Peer review
- Jessica Barrett , infectious diseases registrar 1 ,
- Mike Brown , consultant in infectious diseases and tropical medicine 1 2
- 1 Hospital for Tropical Diseases, University College London Hospitals NHS Trust, London WC1E 6AU, UK
- 2 Clinical Research Department, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, London, UK
- Correspondence to: J Barrett jessica.barrett{at}gstt.nhs.uk
What you need to know
Enterotoxic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is the most common cause of acute travellers’ diarrhoea globally
Chronic (>14 days) diarrhoea is less likely to be caused by bacterial pathogens
Prophylactic antibiotic use is only recommended for patients vulnerable to severe sequelae after a short period of diarrhoea, such as those with ileostomies or immune suppression
A short course (1-3 days) of antibiotics taken at the onset of travellers’ diarrhoea reduces the duration of the illness from 3 days to 1.5 days
Refer patients with chronic diarrhoea and associated symptoms such as weight loss for assessment by either an infectious diseases specialist or gastroenterologist
Diarrhoea is a common problem affecting between 20% and 60% of travellers, 1 particularly those visiting low and middle income countries. Travellers’ diarrhoea is defined as an increase in frequency of bowel movements to three or more loose stools per day during a trip abroad, usually to a less economically developed region. This is usually an acute, self limiting condition and is rarely life threatening. In mild cases it can affect the enjoyment of a holiday, and in severe cases it can cause dehydration and sepsis. We review the current epidemiology of travellers’ diarrhoea, evidence for different management strategies, and the investigation and treatment of persistent diarrhoea after travel.
We searched PubMed and Cochrane Library databases for “travellers’ diarrhoea,” and “travel-associated diarrhoea,” to identify relevant articles, which were added to personal reference collections and clinical experience. Where available, systematic reviews and randomised controlled trials were preferentially selected.
Who is at risk?
Variation in incidence 1 2 may reflect the degree of risk for different travel destinations and dietary habits while abroad. Destinations can be divided into low, medium, and high risk (see box 1). Rates of diarrhoea are likely to correlate closely with the quality of local sanitation.
Box 1: Risk of travellers’ diarrhoea according to destination 1 3
High risk destinations.
South and South East Asia*
Central America*
West and North Africa*
South America
East Africa
Medium risk
South Africa
North America
Western Europe
Australia and New Zealand
*Regions with particularly high risk of travellers’ diarrhoea
Backpackers have roughly double the incidence of diarrhoea compared with business travellers. 4 Travel in cruise ships is associated with large outbreaks of viral and bacterial gastroenteritis. 5 General advice is to avoid eating salads, shellfish, and uncooked meats. There is no strong evidence that specific dietary measures reduce incidence of diarrhoea, but studies examining this are likely to be biased by imperfect recall of what was eaten. 6 Risk factors for travellers’ diarrhoea are listed in box 2.
Box 2: Factors increasing risk of travellers’ diarrhoea 4 7 8 9
By increased dietary exposure.
Backpacking
Visiting friends and family
All-inclusive holidays (such as in cruise ships)
By increased susceptibility to an infectious load
Age <6 years
Use of H 2 receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors
Altered upper gastrointestinal anatomy
Genetic factors (blood group O predisposes to shigellosis and severe cholera infection)
What are the most important causes of travellers’ diarrhoea?
Most studies report a failure to identify the causative pathogen in between 40% and 70% of cases. 10 This includes multicentre studies based in high prevalence settings (that is, during travel). 3 10 11 12 This low diagnostic yield is partly due to delay in obtaining samples and partly due to the insensitivity of laboratory investigations. Older studies did not consistently attempt to identify enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC), and surveillance studies vary in reporting of other E coli species. 3 Where a pathogen is identified, bacteria are the commonest cause of acute travellers’ diarrhoea, with the remainder being caused by norovirus, rotavirus, or similar viruses (see table 1 ⇓ ). Protozoa such as Giardia lamblia can also cause acute diarrhoea, but they are more often associated with persistent diarrhoea, lasting more than two weeks. Cyclospora catayensis , another protozoan cause of diarrhoea, was identified in an increased number of symptomatic travellers returning from Mexico to the UK and Canada in 2015. 13
Frequency of pathogens causing travellers’ diarrhoea 2 3 10 11 12
- View inline
Table 1 ⇑ illustrates overall prevalence of causative agents in returning travellers with diarrhoea. However relative importance varies with country of exposure. Rates of enterotoxigenic E coli (ETEC) are lower in travellers returning from South East Asia than in those returning from South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, and Latin America, whereas rates of Campylobacter jejuni are higher. Norovirus is a more common cause in travellers to Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica are more common in travellers to South and South East Asia. 10
The importance of enterotoxigenic E coli as a cause for diarrhoea in travellers returning from Latin America has been decreasing over the past four decades. 10 A large scale analysis of EuroTravNet surveillance data shows increasing incidence of Campylobacter jejuni infection in travellers returning from India, Thailand, and Pakistan. 2
How does travellers’ diarrhoea present?
Most episodes of travellers’ diarrhoea start during the first week of travel, with the peak incidence on the second or third day after arrival. 8 14
Typically diarrhoea caused by enterotoxigenic E coli (“turista”) is watery and profuse, and preceded by abdominal cramps, nausea, and malaise. Symptoms are not a reliable guide to aetiology, but upper gastrointestinal manifestations such as bloating and belching tend to predominate with Giardia lamblia , while colitic symptoms such as urgency, bloody diarrhoea, and cramps are seen more often with Campylobacter jejuni and Shigella spp.
Most episodes will last between one and seven days, with approximately 10% lasting for longer than one week, 5% lasting more than two weeks, and 1% lasting more than 30 days. 8 During the illness, few patients will be severely incapacitated (in one large prospective cohort about 10% of 2800 participants were confined to bed or consulted a physician), but planned activities are often cancelled or postponed. 8
How can travellers’ diarrhoea be prevented?
Several controlled trials have failed to demonstrate an impact of food and drink hygiene advice on rates of diarrhoea. 15 However, the clear food-related source of most diarrhoeal pathogens means that general consensus among travel physicians is to continue to recommend boiling water, cooking food thoroughly, and peeling fruit and vegetables. 6 Other basic advice includes avoiding ice, shellfish, and condiments on restaurant tables, using a straw to drink from bottles, and avoiding salads and buffets where food may have been unrefrigerated for several hours. Travellers should be advised to drink bottled water where available, including in alcoholic drinks, as alcohol does not sterilise non-bottled water. If bottled water is not available, water can be purified by boiling, filtering, or use of chlorine based tablets. 16 There is some weak evidence that use of alcohol hand gel may reduce diarrhoea rates in travellers, 17 but, based on studies in non-travellers, it is reasonable to strongly encourage travellers to adhere to good hand hygiene measures. Two recent systematic reviews estimated hand washing with soap reduces the risk of diarrhoeal illness by 30-40%. 18 19
When is antibiotic prophylaxis recommended?
For most travellers antibiotic chemoprophylaxis (that is, daily antibiotics for the duration of the trip) is not recommended. While diarrhoea is annoying and distressing, severe or long term consequences from a short period of diarrhoea are rare, and routine use of chemoprophylaxis would create a large tablet burden and expose users to possible adverse effects of antibiotic therapy such as candidiasis and diarrhoea associated with Clostridium difficile .
Chemoprophylaxis should be offered to those with severe immune suppression (such as from chemotherapy for malignancy or after a tissue transplant, or advanced HIV infection), underlying intestinal pathology (inflammatory bowel disease, ileostomies, short bowel syndrome), and other conditions such as sickle cell disease or diabetes where reduced oral intake may be particularly dangerous (table 2 ⇓ ). 22 These patient groups may be unable to tolerate the clinical effects and dehydration associated with even mild diarrhoea, or the consequences of more invasive complications such as bacteraemia. For such patients, it is important to discuss the benefits of treatment aimed at preventing diarrhoea and its complications against the risks of antibiotic associated diarrhoea and other side effects. If antibiotics are prescribed then consideration should be given to any possible interactions with other medications that the patient is taking.
Antibiotic chemoprophylaxis options for immunosuppressed or other high risk travellers
A small comparative study in US soldiers showed that malaria prophylaxis with daily doxycycline has the added benefit of reducing rates of travellers’ diarrhoea caused by enterotoxigenic E coli and Campylobacter jejuni . 23
Do vaccines have a role in prevention of travellers’ diarrhoea?
Vaccines have been developed and licensed against Salmonella typhi , Vibrio cholerae , and rotavirus—all with reasonable efficacy. However, unlike enterotoxigenic E coli , none of these is a major cause of travellers’ diarrhoea, and only vaccines against S typhi are recommended for most travellers to endemic settings. Phase 3 trials of enterotoxigenic E coli toxin vaccines have been undertaken but have failed to demonstrate efficacy. 24 Studies suggest vaccines against enterotoxigenic E coli would have a major public health impact in high burden countries, and further candidate vaccines are in development. 25
What are the options for self administered treatment?
Table 3 ⇓ summarises the options for self treatment.
Summary of self treatment choices
Anti-motility agents and oral rehydration therapy
For most cases of travellers’ diarrhoea, oral rehydration is the mainstay of treatment. This can be achieved with clear fluids such as diluted fruit juice or soups. Young children, elderly people, and those at greater risk from dehydration (that is, those with medical comorbidities) are recommended to use oral rehydration salts (or a mixture of six level teaspoons of sugar and half a teaspoon of salt in a litre of clean water if rehydration salts are unavailable) (see http://rehydrate.org/rehydration/index.html ).
Anti-motility agents such as loperamide may be appropriate for mild symptoms, or where rapid cessation of diarrhoea is essential. Case reports of adverse outcomes such as intestinal perforation suggest anti-motility agents should be avoided in the presence of severe abdominal pain or bloody diarrhoea, which can signify invasive colitis. 26 Systematic review of several randomised controlled trials have demonstrated a small benefit from taking bismuth subsalicylate, but this has less efficacy in reducing diarrhoea frequency and severity than loperamide. 27
Antibiotics
Symptomatic treatment is usually adequate and reduces antibiotic use. However, some travellers will benefit from rapid cessation of diarrhoea, particularly if they are in a remote area with limited access to sanitation facilities or healthcare. Several systematic reviews of studies comparing antibiotics (including quinolones, azithromycin, and rifaximin) against placebo have shown consistent shortening of the duration of diarrhoea to about one and a half days from around three days. 28 29 30 Short courses (one to three days) of antibiotics are usually sufficient to effect a cure. 30
For some people travelling to high and moderate risk areas (see box 1) it will be appropriate to provide a short course of a suitable antibiotic, with advice to start treatment as soon as they develop diarrhoea and to keep well hydrated. Choice of antibiotic will depend on allergy history, comorbidities, concomitant medications, and destination. Avoid quinolones for both prophylaxis and treatment of travellers to South East and South Asia as levels of quinolone resistance are high. 31 Azithromycin remains effective in these areas, but resistance rates are likely to increase.
A meta-analysis of nine randomised trials showed that the addition of loperamide to antibiotic treatment (including azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, and rifamixin) resulted in statistically significantly higher rates of cure at 24 and 48 hours compared with antibiotic alone. 32 Travellers can be advised to add loperamide to their antibiotic treatment to reduce the time to symptomatic improvement as long as there are no features of invasive colitis such as severe pain, high fever, or blood visible in the diarrhoea. 30 If any of these symptoms develop, travellers are advised to seek medical advice immediately.
Returned travellers with persistent diarrhoea
Most bacterial causes mentioned do not cause persistent diarrhoea in immune competent adults. Travellers with diarrhoea persisting beyond 14 days may present in primary or secondary care on their return and require assessment for other underlying causes of persistent diarrhoea.
Table 4 ⇓ lists the important clinical history and symptoms that can point to the underlying cause.
Assessment of chronic diarrhoea
What investigations should be sent?
For diarrhoeal symptoms that persist beyond 14 days following travel (or sooner if there are other concerning features such as fever or dysentery), offer patients blood tests for full blood count, liver and renal function, and inflammatory markers; stool samples for microscopy and culture; and examination for ova, cysts, and parasites. Historically, advice has been to send three stool samples for bacterial culture, but this is unlikely to increase the diagnostic yield. Instead, stool microscopy can be used to distinguish inflammatory from non-inflammatory causes: a small observational study found presence of faecal leucocytes was predictive of a positive bacterial stool culture. 33 Yield from stool culture may be increased by dilution of the faecal sample, and the introduction of molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for common gastrointestinal pathogens such as Campylobacter spp may decrease turnaround times and increase yield. 34
Additional tests should be offered according to symptoms and risk (table 4 ⇑ ). If the patient has eosinophilia and an appropriate travel history, the possibility of schistosomiasis, strongyloides, and other helminthic infections should be considered. While schistosomiasis can rarely cause diarrhoea in the context of acute infection, serology may be negative in the first few months of the illness.
Imaging is required only if the patient has signs of severe colitis or local tenderness, in which instances toxic megacolon, inflammatory phlegmon, and hepatic collections should be excluded. Patients with severe colitis or proctitis may need joint assessment with gastroenterology and consideration of endoscopy, or laparotomy if perforation has occurred.
Where infectious and non-infectious causes have been appropriately excluded, the most likely diagnosis is post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome, although diarrhoea can also herald underlying bowel pathology and anyone with red flags for malignancy should be referred by the appropriate pathway for assessment. Post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome has an incidence of around 30% after an acute episode of travel associated gastroenteritis. 35 36 It is more commonly a sequela of prolonged episodes of diarrhoea or diarrhoea associated with fever and bloody stools. 36 There is weak evidence from small randomised trials suggesting that exclusion of foods high in fermentable carbohydrates (FODMAP) may be helpful. 37 Exclusion of dietary lactose and use of loperamide, bile acid sequestrants, and probiotics can also be tried, but there is limited evidence for long term benefit. 35 37 38
How should giardiasis be managed?
The most common pathogen identified in returning travellers with chronic diarrhoea is Giardia lamblia, particularly among people returning from South Asia. 39 Use of G lamblia PCR testing has increased detection, 40 which potentially will identify infection in some patients previously labelled as having post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome and in those whose diarrhoea may have been attributed to non-pathogenic protozoa. Most patients respond to 5-nitroimidazoles (a systematic review of a large number of trials has shown similar cure rates with tinidazole 2 g once only or metronidazole 400 mg three times daily for five days 41 ), but refractory cases are increasingly common and require investigation, identification of underlying risk factors, and repeated treatment (various antimicrobials have been shown to be effective but may have challenging risk profiles). .
Questions for future research
What is the justification for using antibiotics to treat a usually self limiting illness, in the wider context of rising levels of global antimicrobial resistance rates? What is the clinical impact of resistant enterobacteriaciae found in stool samples from returning travellers? 42 43
To what extent do host genetic factors increase susceptibility to gastrointestinal pathogens, and can this help to identify at risk populations and tailor treatments to individual patients?
What is the long term efficacy of new pharmacological treatments such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and rifaximin in post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome?
Tips for non-specialists
Include consideration of chemoprophylaxis for high risk individuals in pre-travel assessment
Advise all travellers on hygiene measures (such as hand washing and food consumption) and symptom management of diarrhoea
Avoid quinolones for prophylaxis or treatment in travellers to South East and South Asia
Where diarrhoea persists beyond 14 days, consider investigations to rule out parasitic and non-infectious causes. The presence of white blood cells on stool microscopy indicates an inflammatory cause
Additional educational resources
Resources for patients.
National Travel Health Network and Centre (NaTHNaC): http://travelhealthpro.org.uk/travellers-diarrhoea/
Provides pre-travel advice, as well as links to country-specific advice
Fit for Travel: www.fitfortravel.nhs.uk/advice/disease-prevention-advice/travellers-diarrhoea.aspx
Provides similar pre-travel advice on hygiene and disease prevention
Patient.co.uk: http://patient.info/doctor/travellers-diarrhoea-pro
Has patient leaflets and more detailed information about investigation and management of travellers’ diarrhoea
Resources for healthcare professionals
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention yellow book: http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2016/the-pre-travel-consultation/travelers-diarrhea
Provides a guide to pre-travel couselling
Rehydration Project website: http://rehydrate.org/rehydration/index.html
Has additional information about non-pharmacological management of diarrhoea
How patients were involved in the creation of the article
No patients were involved in the creation of this review.
Contributors: Both authors contributed equally to the preparation of this manuscript. MB is guarantor. We thank Dr Ron Behrens for sharing his extensive expertise on this subject.
Competing interests: We have read and understood BMJ policy on declaration of interests and have no relevant interests to declare.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
- ↵ Greenwood Z, Black J, Weld L, et al. GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Gastrointestinal infection among international travelers globally. J Travel Med 2008 ; 15 : 221 - 8 . doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2008.00203.x pmid:18666921 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Schlagenhauf P, Weld L, Goorhuis A, et al. EuroTravNet. Travel-associated infection presenting in Europe (2008-12): an analysis of EuroTravNet longitudinal, surveillance data, and evaluation of the effect of the pre-travel consultation. Lancet Infect Dis 2015 ; 15 : 55 - 64 . doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)71000-X pmid:25477022 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Health Protection Agency. Foreign travel-associated illness: a focus on travellers’ diarrhoea. HPA, 2010. http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http:/www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1287146380314 .
- ↵ Schindler VM, Jaeger VK, Held L, Hatz C, Bühler S. Travel style is a major risk factor for diarrhoea in India: a prospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015 ; 21 : 676.e1 - 4 . doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2015.03.005 pmid:25882361 . OpenUrl CrossRef
- ↵ Freeland AL, Vaughan GH Jr, , Banerjee SN. Acute gastroenteritis on cruise ships - United States, 2008-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016 ; 65 : 1 - 5 . doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6501a1 pmid:26766396 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ DuPont HL, Ericsson CD, Farthing MJ, et al. Expert review of the evidence base for prevention of travelers’ diarrhea. J Travel Med 2009 ; 16 : 149 - 60 . doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2008.00299.x pmid:19538575 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Bavishi C, Dupont HL. Systematic review: the use of proton pump inhibitors and increased susceptibility to enteric infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011 ; 34 : 1269 - 81 . doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04874.x pmid:21999643 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Pitzurra R, Steffen R, Tschopp A, Mutsch M. Diarrhoea in a large prospective cohort of European travellers to resource-limited destinations. BMC Infect Dis 2010 ; 10 : 231 . doi:10.1186/1471-2334-10-231 pmid:20684768 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Flores J, Okhuysen PC. Genetics of susceptibility to infection with enteric pathogens. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2009 ; 22 : 471 - 6 . doi:10.1097/QCO.0b013e3283304eb6 pmid:19633551 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Shah N, DuPont HL, Ramsey DJ. Global etiology of travelers’ diarrhea: systematic review from 1973 to the present. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2009 ; 80 : 609 - 14 . pmid:19346386 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ von Sonnenburg F, Tornieporth N, Waiyaki P, et al. Risk and aetiology of diarrhoea at various tourist destinations. Lancet 2000 ; 356 : 133 - 4 . doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02451-X pmid:10963251 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ Steffen R, Collard F, Tornieporth N, et al. Epidemiology, etiology, and impact of traveler’s diarrhea in Jamaica. JAMA 1999 ; 281 : 811 - 7 . doi:10.1001/jama.281.9.811 pmid:10071002 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ Nichols GL, Freedman J, Pollock KG, et al. Cyclospora infection linked to travel to Mexico, June to September 2015. Euro Surveill 2015 ; 20 . doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2015.20.43.30048 pmid:26536814 .
- ↵ Steffen R, Collard F, Tornieporth N, et al. Epidemiology, etiology, and impact of traveler’s diarrhea in Jamaica. JAMA. 1999 ; 281 : 811 - 7 . doi:10.1001/jama.281.9.811 pmid:10071002 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ DuPont HL. Systematic review: prevention of travellers’ diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2008 ; 27 : 741 - 51 . doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03647.x pmid:18284650 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ Clasen TF, Alexander KT, Sinclair D, et al. Interventions to improve water quality for preventing diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015 ; 10 : CD004794 . pmid:26488938 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Henriey D, Delmont J, Gautret P. Does the use of alcohol-based hand gel sanitizer reduce travellers’ diarrhea and gastrointestinal upset?: A preliminary survey. Travel Med Infect Dis 2014 ; 12 : 494 - 8 . doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2014.07.002 pmid:25065273 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Ejemot-Nwadiaro RI, Ehiri JE, Arikpo D, Meremikwu MM, Critchley JA. Hand washing promotion for preventing diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015 ; 9 : CD004265 . pmid:26346329 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Freeman MC, Stocks ME, Cumming O, et al. Hygiene and health: systematic review of handwashing practices worldwide and update of health effects. Trop Med Int Health 2014 ; 19 : 906 - 16 . doi:10.1111/tmi.12339 pmid:24889816 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- Hu Y, Ren J, Zhan M, Li W, Dai H. Efficacy of rifaximin in prevention of travelers’ diarrhea: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. J Travel Med 2012 ; 19 : 352 - 6 . doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2012.00650.x pmid:23379704 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- Alajbegovic S, Sanders JW, Atherly DE, Riddle MS. Effectiveness of rifaximin and fluoroquinolones in preventing travelers’ diarrhea (TD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev 2012 ; 1 : 39 . doi:10.1186/2046-4053-1-39 pmid:22929178 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Sommet J, Missud F, Holvoet L, et al. Morbidity among child travellers with sickle-cell disease visiting tropical areas: an observational study in a French tertiary care centre. Arch Dis Child 2013 ; 98 : 533 - 6 . doi:10.1136/archdischild-2012-302500 pmid:23661574 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Arthur JD, Echeverria P, Shanks GD, Karwacki J, Bodhidatta L, Brown JE. A comparative study of gastrointestinal infections in United States soldiers receiving doxycycline or mefloquine for malaria prophylaxis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1990 ; 43 : 608 - 13 . pmid:2267964 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Behrens RH, Cramer JP, Jelinek T, et al. Efficacy and safety of a patch vaccine containing heat-labile toxin from Escherichia coli against travellers’ diarrhoea: a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled field trial in travellers from Europe to Mexico and Guatemala. Lancet Infect Dis 2014 ; 14 : 197 - 204 . doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70297-4 pmid:24291168 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Bourgeois AL, Wierzba TF, Walker RI. Status of vaccine research and development for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine 2016 ; S0264-410X(16)00287-5 . pmid:26988259 .
- ↵ McGregor A, Brown M, Thway K, Wright SG. Fulminant amoebic colitis following loperamide use. J Travel Med 2007 ; 14 : 61 - 2 . doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2006.00096.x pmid:17241255 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Heather CS. Travellers’ diarrhoea. Systematic review 901. BMJ Clin Evid 2015 www.clinicalevidence.com/x/systematic-review/0901/overview.html .
- ↵ De Bruyn G, Hahn S, Borwick A. Antibiotic treatment for travellers’ diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000 ;( 3 ): CD002242 . pmid:10908534 .
- ↵ Ternhag A, Asikainen T, Giesecke J, Ekdahl K. A meta-analysis on the effects of antibiotic treatment on duration of symptoms caused by infection with Campylobacter species. Clin Infect Dis 2007 ; 44 : 696 - 700 . doi:10.1086/509924 pmid:17278062 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Steffen R, Hill DR, DuPont HL. Traveler’s diarrhea: a clinical review. JAMA 2015 ; 313 : 71 - 80 . doi:10.1001/jama.2014.17006 pmid:25562268 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Dalhoff A. Global fluoroquinolone resistance epidemiology and implictions for clinical use. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2012 ; 2012 : 976273 . pmid:23097666 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Riddle MS, Arnold S, Tribble DR. Effect of adjunctive loperamide in combination with antibiotics on treatment outcomes in traveler’s diarrhea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 2008 ; 47 : 1007 - 14 . doi:10.1086/591703 pmid:18781873 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ McGregor AC, Whitty CJ, Wright SG. Geographic, symptomatic and laboratory predictors of parasitic and bacterial causes of diarrhoea in travellers. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2012 ; 106 : 549 - 53 . doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2012.04.008 pmid:22818743 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Public Health England. Investigations of faecal specimens for enteric pathogens. UK Standards for Microbiology Investigations. B 30 Issue 8.1. 2014. www.hpa.org.uk/SMI/pdf .
- ↵ DuPont AW. Postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2008 ; 46 : 594 - 9 . doi:10.1086/526774 pmid:18205536 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Schwille-Kiuntke J, Mazurak N, Enck P. Systematic review with meta-analysis: post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome after travellers’ diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015 ; 41 : 1029 - 37 . doi:10.1111/apt.13199 pmid:25871571 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Halland M, Saito YA. Irritable bowel syndrome: new and emerging treatments. BMJ 2015 ; 350 : h1622 . doi:10.1136/bmj.h1622 pmid:26088265 . OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Orekoya O, McLaughlin J, Leitao E, Johns W, Lal S, Paine P. Quantifying bile acid malabsorption helps predict response and tailor sequestrant therapy. Clin Med (Lond) 2015 ; 15 : 252 - 7 . doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.15-3-252 pmid:26031975 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Swaminathan A, Torresi J, Schlagenhauf P, et al. GeoSentinel Network. A global study of pathogens and host risk factors associated with infectious gastrointestinal disease in returned international travellers. J Infect 2009 ; 59 : 19 - 27 . doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2009.05.008 pmid:19552961 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ Nabarro LE, Lever RA, Armstrong M, Chiodini PL. Increased incidence of nitroimidazole-refractory giardiasis at the Hospital for Tropical Diseases, London: 2008-2013. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015 ; 21 : 791 - 6 . doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2015.04.019 pmid:25975511 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Pasupuleti V, Escobedo AA, Deshpande A, Thota P, Roman Y, Hernandez AV. Efficacy of 5-nitroimidazoles for the treatment of giardiasis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014 ; 8 : e2733 . doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002733 pmid:24625554 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Tham J, Odenholt I, Walder M, Brolund A, Ahl J, Melander E. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in patients with travellers’ diarrhoea. Scand J Infect Dis 2010 ; 42 : 275 - 80 . doi:10.3109/00365540903493715 pmid:20121649 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Kantele A. A call to restrict prescribing antibiotics for travellers’ diarrhea--Travel medicine practitioners can play an active role in preventing the spread of antimicrobial resistance. Travel Med Infect Dis 2015 ; 13 : 213 - 4 . doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2015.05.005 pmid:26005160 . OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- Help & Feedback
- About epocrates
Traveler's diarrhea
Highlights & basics, diagnostic approach, risk factors, history & exam, differential diagnosis.
- Tx Approach
Emerging Tx
Complications.
PATIENT RESOURCES
Patient Instructions
Traveler's diarrhea is a common problem among travelers, typically caused by the consumption of contaminated food or water. Predominantly caused by bacteria.
Prevention strategies include careful selection of food and beverages, though these are not fail-safe. Prophylactic antibiotics are not recommended for most travelers.
Management is self-diagnosis while still traveling, followed by hydration, medications for symptom relief, and possibly, antibiotics. Antibiotic therapy is generally reserved for moderate to severe infections.
In healthy patients, resolution is typically within 3 to 5 days even without antibiotic treatment.
Quick Reference
Key Factors
diarrhea (with or without tenesmus), cramping, nausea, and vomiting
Dysentery (blood and fever), persistent diarrhea >14 days.
Other Factors
diarrhea without illness
Diagnostics Tests
1st Tests to Order
stool culture and sensitivity
Stool occult blood, multipathogen molecular diagnostic (polymerase chain reaction), stool ova and parasite exam.
Other Tests to consider
protozoal stool antigens
Clostridium difficile stool toxin, colonoscopy, endoscopy, and biopsy, hematology, blood chemistries, serology, treatment options.
presumptive
pre-travel prophylaxis
careful selection of food and beverages
rifaximin or bismuth subsalicylate
nonpregnant adults: mild diarrhea
loperamide or bismuth subsalicylate
rehydration
Classifications
Clinical entities
Mild (acute): diarrhea that is tolerable, is not distressing, and does not interfere with planned activities.
Moderate (acute): diarrhea that is distressing or interferes with planned activities.
Severe (acute): diarrhea that is incapacitating or completely prevents planned activities; all dysentery (passage of grossly bloody stools) is considered severe.
Persistent: diarrhea lasting ≥2 weeks.
Etiologic entities
Bacterial traveler's diarrhea: common infection usually due to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) and enteroaggregative E coli , Shigella , Salmonella (nontyphoid), Campylobacter jejuni , Yersinia , Aeromonas hydrophila , Plesiomonas shigelloides , and Vibrio (noncholera) species.
Viral traveler's diarrhea: diarrhea due to rotavirus (especially in infants and children), norovirus (e.g., on cruise ships), and other enteric viral infections.
Parasitic traveler's diarrhea: more persistent (>14 days) diarrhea due to parasitic infection with Giardia , Entamoeba , or Cryptosporidium .
Regional variation
Common Vignette
Other Presentations
Epidemiology
Pathophysiology.
- Mark Riddle, MD, MPH&TM, DrPH, C Trop Med, Certificate in Travel Health
- Acknowledgements
- Andrea Summer, MD
- Phil Fischer, MD

Traveler's diarrhea diagnosis during travel
Tolerable (mild): not distressing, does not interfere with planned activities
Distressing (moderate): interferes with planned activities
Incapacitating (severe): completely prevents planned activities.
Traveler's diarrhea diagnosis post-travel
Travel to a high-risk destination.
High risk destinations include: South and Southeast Asia; Central America; West and North Africa; South America; East Africa. [ 4 ]
age <30 years
Younger age is associated with increased risk-taking behavior and greater propensity for adventure travel in areas with high exposure to food and beverages from unhygienic sources.
prior TD susceptibility
Travelers unusually prone to TD may remain so on subsequent trips, even with proper food and water precautions. This may be because of an undiagnosed susceptibility to infection. Patients with diabetes mellitus or cancer, and travelers with known chronic illness, are also at greater risk for prolonged TD.
chronic disease, immunocompromise
Patients with diabetes mellitus or cancer, or those receiving immunomodulatory therapy, may be at greater risk for immunosuppression and increased susceptibility to TD. Furthermore, travelers with known chronic illness may also be at greater risk for prolonged, or more severe, TD-associated outcomes.
travelers with prior residence in developing country visiting friends and relatives
Travelers visiting friends and relatives are less likely to exercise food and water precautions, not recognizing that any previously acquired TD immunity is short-lived. These travelers are also much less likely to seek pretravel counseling. [ 14 ]
travel during hot and wet seasons
Risk may vary depending on the time of year. Hot and wet climate conditions are generally thought to support increased transmission risk for many of the common pathogens. [ 15 ]
decreased stomach acidity
Proton-pump inhibitors and H2 blockers decrease stomach acidity and thus may make it easier for bacteria contaminating food or water to survive transit through the stomach. However, few studies are available to directly evaluate this risk in the traveler. Consideration may be given to discontinuing use of these medications during travel, unless they are necessary for symptom control.
Typical symptoms of TD include cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diarrheal stools, with resolution in 3 to 5 days.
Bloody stools indicate an invasive organism and a serious, potentially systemic infection. Inflammatory bowel disease should also be considered if symptoms persist despite appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Parasitic infections do not respond to antibiotics and usually persist. Giardia is characterized by gassy diarrhea and belching with an odor of hydrogen sulfide. Amebic dysentery is associated with a mucoid bloody diarrhea.
Secondary lactose intolerance or bile acid malabsorption can occur, as well as tropical sprue. Symptoms lasting more than 30 days may indicate new onset functional gastrointestinal disorder, or unmasking of organic or structural disease.
Often termed "loose motions in travel".
Excess gas or an occasional loose stool without feeling ill could be related to new foods, changes in the normal timing of meals, stress, and changing bacterial flora.
identifies specific bacterial etiology with sensitivities
Use stool culture and sensitivity kit.
Not necessary for nonsevere TD or if traveler has not tried a course of appropriate antibiotic therapy.
blood suggests invasive organism or ulceration
May be obtained by digital rectal exam or specimen collection kit.
multiple pathogen etiologies common
Highly sensitive and relatively rapid identification of a broad range of pathogens known to cause acute diarrhea associated with travel.
Does not provide information on antibiotic sensitivities which may require reflex culturing of stool. [ 22 ]
identifies specific parasitic etiology (a negative acid-fast stain helps to exclude Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora )
Performed for persistent diarrhea (usually >14 days).
Use stool ova and parasite (O+P) collection kit.
Cryptosporidium is easily missed on stool O+P.
Cryptosporidium stool antigen test is specific for this organism.
Not as reliable as stool antigen test for detection of Giardia .
identifies Giardia , Cryptosporidium , Entameoba hystolitica
Reagents are commercially available for Cryptosporidium spp., Entamoeba histolytica , Giardia duodenalis .
identifies C difficile (pseudomembranous colitis)
Recommended in the scenario of inflammatory colitis in a returning traveler with recent antibiotic exposure.
identifies inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer, microscopic colitis, tropical sprue and malabsorptive conditions, and celiac disease
Recommended for chronic diarrhea to rule out structural or organic disease.
test based on individually derived differential diagnosis
C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and liver function tests identify organic disease.
White blood cells, and particularly eosinophilia, are indicative of extra-intestinal protozoa (e.g., strongyloides).
Celiac serologies considered depending on traveler family history and symptoms. [ 21 ]
Irritable bowel syndrome
Differentiating Signs/Symptoms
Diarrhea or constipation, both associated with abdominal pain. No weight loss, fever, or systemic symptoms. Symptom relief usually occurs after bowel movement. Post-TD irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is usually of the diarrhea subtype (IBS-D).
Differentiating Tests
Normal exam, and laboratory and bowel workup.
Secondary disaccharidase (or other dietary) deficiency
Exacerbation of symptoms with dairy products or other food class. Often difficult to solicit. Generally resolves in days to a week.
Normal exam and laboratory and bowel workup.
Malabsorptive conditions
Persistent diarrhea, may be unusually foul smelling or greasy. Can be attributed to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, or changes in microbiome or in structural absorptive capacity of microvilli.
Fecal fat, fecal bile acid, D-xylose, hydrogen/methane breath testing, colonoscopy/endoscopy may be revealing.
Pseudomembranous (Clostridium difficile) colitis
Persisting diarrhea with fever, abdominal pain/tenderness, and weight loss, often following use of antibiotics (with or without travel history).
C difficile stool toxin positive (enzyme immunoassay/polymerase chain reaction tests are available).
Celiac disease
Persisting diarrhea with malabsorption (with or without travel history).
May be associated with dermatitis herpetiformis.
AGA (IgA anti-gliadin antibodies), EMA (IgA anti-endomysium antibodies), AGG (IgG anti-gliadin antibodies), tTGA (IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase) may be positive.
Since IgA deficiency may interfere with celiac testing, an IgA level should also be obtained.
Crohn disease
Diarrhea (with or without travel history), abdominal pain, fever, perianal fistulae.
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, elevated fecal calprotectin, anemia, heme-positive stools. Colonoscopy differentiates most cases of Crohn disease from ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis always involves the rectum and is contiguous versus intermittent. Crohn disease often has perianal involvement, rectal sparing, and a tendency to form fistulae.
Ulcerative colitis
Bloody diarrhea (with or without travel history), abdominal pain, fever, no perianal disease.
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, elevated fecal calprotectin, anemia, heme-positive stools. Colonoscopy differentiates most cases of Crohn disease from ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis always involves the rectum and is contiguous versus intermittent. Terminal ileitis may be present in ulcerative colitis with pancolitis due to backwash.
Food poisoning
Predominant symptom is vomiting.
It is easy to confuse the symptoms of TD with those of food poisoning; the latter is of much earlier onset and is characterized more by vomiting than by diarrhea (excepting Clostridium ).
Food poisoning, while self-limited, does not respond to antibiotics.
Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus (both forming heat-stable toxins) or Clostridium perfringens (heat-labile toxins) cause most food poisoning cases.
Preformed toxins (from Staphylococcus or Bacillus ) produce symptoms (vomiting > diarrhea) within 1 to 6 hours, whereas Clostridium infections, with in vivo toxin formation, cause diarrheal symptoms within 8 to 16 hours. Most TD bacterial infections, on the other hand, become symptomatic 16 hours after ingestion. [ 13 ]
Typically diagnosed clinically, but bacterial cultures or virologic studies may elicit culprit organism.
Clinical criteria [ 1 ] [ 23 ]
Treatment Approach
Prophylaxis, rehydration, antibiotic therapy, adjunctive therapies, failure to respond to antibiotic therapy.
Selection of safe food and beverages is recommended.
Unsafe items include ice, tap water, salads, previously peeled fruits, and raw foods. Unpackaged condiments and sauces, such as guacamole, are frequently risky. Food from street vendors and buffets with poor food turnover also pose a significant risk of food poisoning.
Safe items include thoroughly cooked food served while still hot, boiled or bottled (properly sealed) water, commercially packaged foods, fresh breads, and fruits peeled by the traveler.
Primary Options
adults: 200-1100 mg/day orally given in 1-3 divided doses
Secondary Options
adults: 524-1048 mg orally four times daily
Prophylactic antibiotics are not recommended for most travelers. [ 1 ] [ 15 ] Occasional exceptions include short-term critical itineraries such as diplomatic missions, professional sports, and critical business/life event engagements; and chronically ill or immunocompromised patients on trips of <3 weeks' duration. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not usually recommended in children. Rifaximin is considered the treatment of choice for prophylaxis; it is effective at preventing TD with no increase in adverse effects (compared with placebo). [ 1 ] [ 16 ] [ 17 ]
Bismuth subsalicylate can reduce the incidence of TD by more than 60%; however, due to the number of tablets required and the inconvenient dosing, it is not commonly used as prophylaxis for TD. [ 19 ] [ 20 ] Studies have not established the safety of this drug when used for >4 weeks. [ 1 ] Adverse effects include salicylate toxicity (e.g., tinnitus) and blackening of the tongue or stools. [ 19 ]
Prophylaxis should be started before departure and discontinued after travel.
4 mg orally initially, followed by 2 mg after each unformed stool, maximum 16 mg/day
524 mg orally four times daily
Loperamide or bismuth subsalicylate are recommended for symptomatic relief in patients with mild diarrhea (i.e., diarrhea that is tolerable, is not distressing, and does not interfere with planned activities). [ 33 ]
Loperamide is an antimotility agent that controls cramping and diarrhea. [ 33 ] [ 34 ] Patients should be advised that it can take 1-2 hours for loperamide to take effect, and additional dosing should be spaced accordingly to avoid rebound constipation. Loperamide should not be used in patients with visible blood in the stool or high fever (characteristic of dysentery). Loperamide slows gastrointestinal transit time and, theoretically, may delay the expulsion of invasive bacteria.
The continued use of loperamide in patients with worsening symptoms, or the development of dysentery, is not recommended. [ 33 ]
Bismuth subsalicylate is an oral antidiarrheal agent. Adverse effects include salicylate toxicity (e.g., tinnitus) and blackening of the tongue or stools. [ 19 ] [ 20 ]
Fluid replacement is important in all patients. It is critical for older patients who are at risk of dehydration-related complications. Bowel rest should be avoided. Sports and energy drinks are not recommended as they are high in sugar and may worsen diarrhea.
nonpregnant adults: moderate diarrhea
loperamide and/or antibiotic therapy
1000 mg orally as a single dose, continue once daily dosing for up to 3 days if symptoms do not resolve within 24 hours; or 500 mg orally once daily for 3 days
200 mg orally three times daily for 3 days
750 mg orally as a single dose, continue once daily dosing for up to 3 days if symptoms do not resolve within 24 hours; or 500 mg orally once daily for 3 days
400 mg orally once daily for 1-3 days
500 mg orally once daily for 1-3 days
Treatment options for moderate diarrhea (i.e., diarrhea that is distressing or interferes with planned activities) include loperamide alone, antibiotic therapy alone, or loperamide plus antibiotic therapy. [ 1 ] However, guidelines are not consistent in regards to treatment of patients with moderate infection, and expert opinion on the choice of treatment varies.
Loperamide is an antimotility agent that controls cramping and diarrhea. [ 33 ] [ 34 ] Patients should be advised that it can take 1-2 hours for loperamide to take effect, and additional dosing should be spaced accordingly to avoid rebound constipation.
Loperamide should not be used in patients with visible blood in the stool or high fever (characteristic of dysentery). Loperamide slows gastrointestinal transit time and, theoretically, may delay the expulsion of invasive bacteria.
Antibiotic options for the treatment of TD include azithromycin, rifaximin, or a fluoroquinolone. [ 1 ]
Azithromycin is usually considered first-line because it is well tolerated with minimal adverse effects.
Rifaximin is a second-line agent; it may be the most suitable option for patients taking other medications as it is less likely to undergo drug-to-drug interactions. However, it may be less effective in Asia, where invasive pathogens (e.g., Campylobacter , Salmonella , Shigella ) are more likely. [ 1 ]
Fluoroquinolones are also considered a second-line option; however, they are only recommended for traveler's diarrhea when it is considered inappropriate to use other antibiotics that are commonly recommended for this infection due to the risk of serious, disabling, and potentially irreversible adverse effects (e.g., tendonitis, tendon rupture, arthralgia, neuropathies, and other musculoskeletal or nervous system effects). [ 31 ] [ 29 ] In 2016, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advised restricting fluoroquinolone antibiotic use for certain uncomplicated infections. [ 29 ] Subsequent FDA warnings reported on the potential increased risk of aortic dissection, significant hypoglycemia, and mental health adverse effects in patients taking fluoroquinolones. [ 36 ] [ 30 ]
Increased resistance against fluoroquinolones in South East Asia and other regions should be considered.
Antibiotic treatment, with adjunctive loperamide, consistently demonstrates the most rapid time to clinical cure (median 12-14 hours) compared with antibiotics alone (24-30 hours); however, antibiotic therapy (with or without adjunctive therapy) can be associated with a higher incidence of adverse effects, although these are often minor and self-limited. [ 26 ]
Many experts recommend taking antibiotics only until the patient feels better, usually 1-3 days (with the exception of rifaximin, which should be taken for the full 3-day course). If symptoms have not resolved after 24 hours, the regimen should be taken for up to 3 days. [ 1 ]
persistent diarrhea not responsive to first-line antibiotic
further workup
A medical evaluation is recommended for persistent diarrhea, but this is often unavailable or difficult for overseas travelers.
Failure to respond to antibiotic therapy suggests a parasitic or post-infectious etiology. Viral diarrhea usually resolves quickly.
Order a stool ova and parasite exam to test for parasites in patients with persistent diarrhea (>14 days), or consider using a culture-independent test which includes parasitic etiologies. [ 6 ] Treatment for the identified pathogen should be started once results are back.
If Clostridium difficile -associated disease is suspected, the patient should be managed according to current guidelines.
nonpregnant adults: severe diarrhea
antibiotic therapy
Antibiotics are always recommended in severe infection (i.e., diarrhea that is incapacitating or completely prevents planned activities; dysentery and febrile diarrhea are considered severe). [ 1 ]
Azithromycin is considered the first-line option in severe infection.
Rifaximin is a second-line option for nondysenteric TD. It may be the most suitable option for patients taking other medications as it is less likely to undergo drug-to-drug interactions. However, it may be less effective in Asia, where invasive pathogens (e.g., Campylobacter , Salmonella , Shigella ) are more likely. [ 1 ]
Many experts recommend taking antibiotics only until the patient feels better, usually 1 to 3 days (with the exception of rifaximin, which should be taken for the full 3-day course). If symptoms have not resolved after 24 hours, the regimen should be taken for up to 3 days. [ 1 ]
Loperamide controls cramping and diarrhea. [ 33 ] [ 34 ]
Patients should be advised that it can take 1-2 hours for loperamide to take effect, and additional dosing should be spaced accordingly to avoid rebound constipation. Loperamide should not be used in patients with visible blood in the stool or high fever (characteristic of dysentery). Loperamide slows gastrointestinal transit time and, theoretically, may delay the expulsion of invasive bacteria.
Antibiotic treatment, with adjunctive loperamide, consistently demonstrates the most rapid time to clinical cure (median 12-14 hours) compared with antibiotics alone (24-30 hours). [ 26 ]
Fluid replacement is an important part of treatment in all pregnant patients. Bowel rest should be avoided. Sports and energy drinks are not recommended as they are high in sugar and may worsen diarrhea.
Antibiotics are recommended in pregnant women with moderate to severe infection. Azithromycin is the treatment of choice. It is well tolerated with minimal adverse effects.
Many experts recommend taking antibiotics only until the patient feels better, usually 1-3 days. If symptoms have not resolved after 24 hours, the regimen should be taken for up to 3 days. [ 1 ]
Order a stool ova and parasite exam to test for parasites in patients with persistent diarrhea (>14 days), or consider using a culture-independent test which includes parasitic etiologies. [ 6 ] Treatment for the identified pathogen should be started once results are back. A specialist should be consulted for choice of drug and treatment course in pregnant women.
Rehydration is a key intervention for infants and younger children. Oral rehydration solutions (e.g., Pedialyte®) are very effective for the management of dehydration associated with diarrhea in infants. Oral rehydration salt solution or rice-based solutions are widely available overseas. Spoon-feeding oral rehydration salts is recommended if a child is vomiting. Sports and energy drinks are not recommended as they are high in sugar and may worsen diarrhea. Infants and children who are breast-fed should continue in spite of diarrhea. Bowel rest should be avoided.
children ≥6 years of age: consult specialist for guidance on dose
children ≥12 years of age: consult specialist for guidance on dose
Loperamide or bismuth subsalicylate are recommended for symptomatic relief in children, with some caveats. Loperamide is not generally recommended in children <6 years of age. Bismuth subsalicylate (an oral antidiarrheal agent) is not generally recommended in children aged <12 years, due to the risk of Reye syndrome; however, some physicians still use it with caution. It is not recommended in children aged <3 years. [ 15 ] Adverse effects include salicylate toxicity (e.g., tinnitus) and blackening of the tongue or stools. [ 19 ] [ 20 ]
10 mg/kg orally once daily for 1-3 days, maximum 500 mg/day
children ≥12 years of age: 200 mg orally three times daily for 3 days
20-30 mg/kg/day orally given in 1-2 divided doses for 1-3 days
Antibiotics are recommended in children with moderate to severe infection, especially when there is bloody or severe watery diarrhea, or evidence of systemic infection. Azithromycin is the treatment of choice in children. It is well tolerated with minimal adverse effects. Rifaximin or a fluoroquinolone may be used as an alternative in children; however, rifaximin is not approved for children aged <12 years, and fluoroquinolones should be used with caution in children as they may increase the risk of joint and tendon disorders. [ 15 ] [ 32 ]
Order a stool ova and parasite exam to test for parasites in patients with persistent diarrhea (>14 days), or consider using a culture-independent test which includes parasitic etiologies. [ 6 ] Treatment for the identified pathogen should be started once results are back. A specialist should be consulted for choice of drug and treatment course in children.
Prebiotics and probiotics
Cholera vaccine, diosmectite, primary prevention, secondary prevention, follow-up overview, post-td lactose intolerance.
Temporary lactose intolerance is quite common but usually self-limited.
post-TD irritable bowel syndrome
Although TD has been identified as a risk factor for the development of irritable bowel syndrome, postinfectious forms of irritable bowel syndrome are usually of the diarrhea predominant pathotype, and may have a better prognosis than idiopathic forms of the condition.
allergic reaction to antibiotic
Antibiotic should be discontinued if rash develops; patient is treated with antihistamines and prednisone if reaction is severe.
pseudomembranous (Clostridium difficile) colitis
Use of antibiotics occasionally provides favorable conditions for the overgrowth of C difficile in the gut. This organism may cause a range of symptoms from watery diarrhea to severe colitis.
ciprofloxacin-related tendonitis or tendon rupture
Rarely, tendon inflammation and rupture has occurred with prior ciprofloxacin use. Orthopedic referral is indicated.
In 2016, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advised restricting fluoroquinolone antibiotic use for certain uncomplicated infections. [ 29 ] The European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommends that fluoroquinolones should not be used for mild to moderate infections unless other appropriate antibiotics for the specific infection cannot be used, and should not be used in nonsevere, nonbacterial, or self-limiting infections.
Key Articles
Riddle MS, Connor BA, Beeching NJ, et al. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of travelers' diarrhea: a graded expert panel report. J Travel Med. 2017 Apr 1;24(suppl 1):S57-74. [Abstract] [Full Text]
De Bruyn G, Hahn S, Borwick A. Antibiotic treatment for travellers' diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD002242. [Abstract] [Full Text]
Johnson PC, Ericsson CD, DuPont HL, et al. Comparison of loperamide with bismuth subsalicylate for the treatment of acute travelers' diarrhea. JAMA. 1986 Feb 14;255(6):757-60. [Abstract]
Referenced Articles
1. Riddle MS, Connor BA, Beeching NJ, et al. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of travelers' diarrhea: a graded expert panel report. J Travel Med. 2017 Apr 1;24(suppl 1):S57-74. [Abstract] [Full Text]
2. Shah N, DuPont HL, Ramsey DJ. Global etiology of travelers' diarrhea: systematic review from 1973 to the present. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009 Apr;80(4):609-14. [Abstract]
3. Jiang ZD, DuPont HL. Etiology of travellers' diarrhea. J Travel Med. 2017 Apr 1;24(suppl_1):S13-S16. [Abstract] [Full Text]
4. Barrett J, Brown M. Travellers' diarrhoea. BMJ. 2016 Apr 19;353:i1937. [Abstract]
5. Ashbaugh HR, Early JM, Johnson ME, et al. A Multisite Network Assessment of the Epidemiology and Etiology of Acquired Diarrhea among U.S. Military and Western Travelers (Global Travelers' Diarrhea Study): A Principal Role of <i>Norovirus</i> among Travelers with Gastrointestinal Illness. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Nov;103(5):1855-1863. [Abstract] [Full Text]
6. Connor BA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Traveler's health: Persistent diarrhea in returned travelers. Jun 2019 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
7. Lalani T, Maguire JD, Grant EM, et al. Epidemiology and self-treatment of travelers' diarrhea in a large, prospective cohort of department of defense beneficiaries. J Travel Med. 2015 May-Jun;22(3):152-60. [Abstract] [Full Text]
8. Steffen R, Hill DR, DuPont HL. Traveler's diarrhea: a clinical review. JAMA. 2015 Jan 6;313(1):71-80. [Abstract]
9. Steffen R, Tornieporth N, Clemens SA, et al. Epidemiology of travelers' diarrhea: details of a global survey. J Travel Med. 2004 Jul-Aug;11(4):231-7. [Abstract] [Full Text]
10. DuPont H, Ericsson CD. Prevention and treatment of traveler's diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun 24;328(25):1821-7. [Abstract]
11. Lääveri T, Vilkman K, Pakkanen SH, et al. A prospective study of travellers' diarrhoea: analysis of pathogen findings by destination in various (sub)tropical regions. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017 Nov 10;24(8):908.e9-16. [Abstract]
12. Duplessis CA, Gutierrez RL, Porter CK. Review: chronic and persistent diarrhea with a focus in the returning traveler. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2017 May 4;3:9. [Abstract] [Full Text]
13. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Bad bug book: handbook of foodborne pathogenic microorganisms and natural toxins. Second edition. 2012 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
14. Bacaner N, Stauffer B, Boulware D, et al. Travel medicine considerations for North American immigrants visiting friends and relatives. JAMA. 2004 Jun 16;291(23):2856-64. [Abstract] [Full Text]
15. Connor BA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Travelers' diarrhea in CDC Yellow Book 2020: health information for international travel. June 2019 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
16. Hu Y, Ren J, Zhan M, et al. Efficacy of rifaximin in prevention of travelers' diarrhea: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. J Travel Med. 2012 Dec;19(6):352-6. [Abstract] [Full Text]
17. Alajbegovic S, Sanders JW, Atherly DE, et al. Effectiveness of rifaximin and fluoroquinolones in preventing travelers' diarrhea (TD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 28;1:39. [Abstract] [Full Text]
18. Martinez-Sandoval F, Ericsson CD, Jiang ZD, et al. Prevention of travelers' diarrhea with rifaximin in US travelers to Mexico. J Travel Med. 2010 Mar-Apr;17(2):111-7. [Abstract] [Full Text]
19. DuPont HL, Ericsson CD, Johnson PC, et al. Prevention of traveler's diarrhea by the tablet formulation of bismuth subsalicylate. JAMA. 1987 Mar 13;257(10):1347-50. [Abstract]
20. Brum JM, Gibb RD, Ramsey DL, et al. Systematic review and meta-analyses assessment of the clinical efficacy of bismuth subsalicylate for prevention and treatment of infectious diarrhea. Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Aug 8;:. [Abstract] [Full Text]
21. Connor BA, Riddle MS. Post-infectious sequelae of travelers' diarrhea. J Travel Med. 2013 Sep-Oct;20(5):303-12. [Abstract] [Full Text]
22. Vila J. New molecular diagnostic tools in traveller's diarrhea. J Travel Med. 2017 Apr 1;24(suppl 1):S23-28. [Abstract] [Full Text]
23. Riddle MS, DuPont HL, Connor BA. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of acute diarrheal infections in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016 May;111(5):602-22. [Abstract] [Full Text]
24. Shane AL, Mody RK, Crump JA, et al. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 29;65(12):1963-73. [Abstract] [Full Text]
25. Farthing M, Salam MA, Lindberg G, et al. Acute diarrhea in adults and children: a global perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;47(1):12-20. [Abstract] [Full Text]
26. De Bruyn G, Hahn S, Borwick A. Antibiotic treatment for travellers' diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD002242. [Abstract] [Full Text]
27. Kantele A, Lääveri T, Mero S, et al. Antimicrobials increase travelers' risk of colonization by extended-spectrum betalactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Mar 15;60(6):837-46. [Abstract] [Full Text]
28. Connor BA, Keystone JS. Antibiotic self-treatment of travelers' diarrhea: helpful or harmful? Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Mar 15;60(6):847-8. [Abstract] [Full Text]
29. US Food & Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA advises restricting fluoroquinolone antibiotic use for certain uncomplicated infections; warns about disabling side effects that can occur together. 12 May 2016 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
30. US Food & Drug Administration. FDA warns about increased risk of ruptures or tears in the aorta blood vessel with fluoroquinolone antibiotics in certain patients. 20 December 2018 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
31. European Medicines Agency. Quinolone- and fluoroquinolone-containing medicinal products. 19 March 2019 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
32. Bruzzese E, Giannattasio A, Guarino A. Antibiotic treatment of acute gastroenteritis in children. F1000Res. 2018 Feb 15;7:193. [Abstract] [Full Text]
33. Johnson PC, Ericsson CD, DuPont HL, et al. Comparison of loperamide with bismuth subsalicylate for the treatment of acute travelers' diarrhea. JAMA. 1986 Feb 14;255(6):757-60. [Abstract]
34. Riddle MS, Arnold S, Tribble DR. Effect of adjunctive loperamide in combination with antibiotics on treatment outcomes in traveler's diarrhea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2008 Oct 15;47(8):1007-14. [Abstract] [Full Text]
35. Riddle MS, Sanders JW, Putnam SD, et al. Incidence, etiology, and impact of diarrhea among long-term travelers (US military and similar populations): a systematic review. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006 May;74(5):891-900. [Abstract] [Full Text]
36. US Food & Drug Administration. FDA reinforces safety information about serious low blood sugar levels and mental health side effects with fluoroquinolone antibiotics; requires label changes. 10 July 2018 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
37. Nee J, Salley K, Ludwig AG, et al. Randomized clinical trial: Crofelemer treatment in women with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019 Dec;10(12):e00110. [Abstract] [Full Text]
38. Macarthur RD, Hawkins TN, Brown SJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of crofelemer for noninfectious diarrhea in HIV-seropositive individuals (ADVENT trial): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-stage study. HIV Clin Trials. 2013 Nov-Dec;14(6):261-73. [Abstract] [Full Text]
39. Guo Q, Goldenberg JZ, Humphrey C, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 30;(4):CD004827. [Abstract] [Full Text]
40. Pérez-Gaxiola G, Cuello-García CA, Florez ID, et al. Smectite for acute infectious diarrhoea in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 25;4:CD011526. [Abstract] [Full Text]
41. Public Health Agency of Canada. Statement on travellers' diarrhea. 2015 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
Published by
Infectious Diseases Society of America
American College of Gastroenterology
International Society of Travel Medicine
World Gastroenterology Organisation
US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Public Health Agency of Canada
Topic last updated: 2021-07-02
Mark Riddle , MD, MPH&TM, DrPH, C Trop Med, Certificate in Travel Health
Professor and Chair
Department of Preventive Medicine & Biostatistics
Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
Acknowledgements :
Dr Mark Riddle would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Gregory Juckett, the previous contributor to this topic.
Peer Reviewers
Andrea Summer , MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
Medical University of South Carolina
Phil Fischer , MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Department of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Disclaimer » Advertising
- HealthyChildren.org

- Previous Article
- Next Article
How much do you know about travelers’ diarrhea?
Dr. Meissner is professor of pediatrics at Floating Hospital for Children, Tufts Medical Center. He also is an ex officio member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases and associate editor of the AAP Visual Red Book.
- Split-Screen
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- CME Quiz Close Quiz
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Get Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
- Search Site
H. Cody Meissner; How much do you know about travelers’ diarrhea?. AAP News July 2015; 36 (7): 7. 10.1542/aapnews.2015367-7
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager

Diarrhea, a common travel-related problem for children and adults, generally is benign and self-limited. Treatment includes fluid replacement, antibiotics and anti-motility agents; the greatest concern is volume depletion.
The incidence of travelers’ diarrhea (TD) during a two-week trip is between 10% and 40% depending on the traveler’s destination and activities. The level of sanitation where the traveler purchases meals is the most important determinant of infection. TD occurs when food or water becomes contaminated with fecal material.
Which one of the following statements regarding TD is correct?
Travelers on cruise-based vacations have a higher incidence of TD compared to travelers on a land-based vacation.
The risk of TD varies from location to location and with the season of the year.
Children have a lower risk of acquiring TD compared to adults.
Men are more likely to experience TD than women.
Spices in food may cause TD.
Answer: b) is correct.
The risk of TD varies from location to location and with the season of the year. High-risk regions include the developing countries of Latin America, Asia, Africa and parts of the Middle East. Attack rates of TD are highest during summer months and rainy seasons.
Travelers on cruise-based trips have a lower incidence of TD than travelers on land-based vacations. This is despite the risk of norovirus outbreaks on cruise ships. Children have a greater risk than adults, perhaps because they consume more food and ingest a higher inoculum. The risk of TD is equal for men and women, although women are more likely to seek care once infected. Spices do not cause TD.
Diarrhea is one of the most common travel-related problems affecting children and adults. The classic definition of TD includes passage of three or more watery stools within 24 hours with varying degrees of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever and bloody stool, depending on the etiology.
Most TD is caused by bacteria, but viruses and parasites also may be transmitted in contaminated food or water. The development of bacterial TD is directly related to the number of viable bacteria that reach the intestine. Any factor that enables bacteria to survive in the intestine (such as proton pump inhibitors) will increase the risk of TD.
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli is the most common bacterial cause of TD followed by enteroaggregative E. coli , Salmonella spp., Campylobacter jejuni and Shigella spp. Rotavirus is the most common viral cause of TD followed by norovirus.
Parasites are less likely than bacteria or viruses to cause TD because parasitic contamination of food or water is uncommon in most locations. Sites where parasites are more likely to be acquired include Nepal and St. Petersburg, Russia, where Giardia or Cyclospora may be hyperendemic. Entamoeba histolytica is an uncommon cause of TD. Patients taking malaria prophylaxis may develop antibiotic-associated diarrhea due to Clostridium difficile , although overall this organism is an uncommon cause of TD.

Dr. Meissner
Preventive measures include avoidance of foods or beverages purchased from street vendors or other establishments where unhygienic conditions are present, avoidance of undercooked meat and seafood, and avoidance of raw fruits and vegetables unless peeled by the traveler.
Antibiotic chemoprophylaxis generally is not recommended for children or adults because of expense and side effects such as sun sensitivity, allergic reactions, yeast infections and risk of C. difficile colitis. Prophylaxis sometimes is considered for travelers at increased risk such as those with inflammatory bowel disease or ostomies.
For infants, breastfeeding is the best way to reduce the risk of foodborne and waterborne illness. Water served to young children, including water used to prepare infant formula, should be disinfected. In some parts of the world, even bottled water may be contaminated.
When proper hand-washing facilities are not available, alcohol-based hand sanitizers containing more than 60% alcohol can be used to clean hands, but they should not be relied on if organic material is visible. Alcohol-based hand washes are less effective against norovirus or the spores of C. difficile . Careful attention should be paid to cleaning bottles and pacifiers. Food available on aircraft generally is obtained at the site of departure.
TD generally is benign and self-limited, although dehydration may pose a health hazard to those with co-morbidities. Often, treatment is initiated without documentation of etiology. Routine stool culture is not warranted in most settings because various pathogenic strains of E. coli are not easily identified.
Treatment of TD includes fluid replacement, antibiotics and anti-motility agents. The greatest concern with TD is volume depletion. Patients with severe diarrhea should be treated with oral rehydration solution to replace electrolytes in the appropriate concentrations. For mild diarrhea, use of fluids generally is adequate. Self-medication may be appropriate.
For adults, ciprofloxacin will be active against most bacterial causes of TD. Azithromycin generally is the preferred agent for children. For children 12 years of age and older, rifaximin has similar efficacy as ciprofloxacin. Bismuth subsalicylate has the disadvantage of potential salicylate toxicity, the need to carry large quantities and the concern for Reye syndrome.
Anti-motility agents sometimes are used in combination with antibiotics to reduce the amount of stooling. Particularly with bloody diarrhea, anti-motility agents should be used with caution and only with an antibiotic.
Recipient(s) will receive an email with a link to 'How much do you know about travelers’ diarrhea?' and will not need an account to access the content.
Subject: How much do you know about travelers’ diarrhea?
(Optional message may have a maximum of 1000 characters.)
Advertising Disclaimer »
1. 4 million children lose Medicaid, CHIP insurance after public health emergency protections end
2. Autism diagnosis in primary care promotes equity, benefits families
3. Long hours, guilt, more compassion: Pediatrician moms share stresses, rewards
April issue digital edition

Subscribe to AAP News
Column collections, topic collections, affiliations, advertising.
- Submit a story
- American Academy of Pediatrics
- Online ISSN 1556-3332
- Print ISSN 1073-0397
- Pediatrics Open Science
- Hospital Pediatrics
- Pediatrics in Review
- AAP Grand Rounds
- Latest News
- Pediatric Care Online
- Red Book Online
- Pediatric Patient Education
- AAP Toolkits
- AAP Pediatric Coding Newsletter
First 1,000 Days Knowledge Center
Institutions/librarians, group practices, licensing/permissions, integrations.
- Privacy Statement | Accessibility Statement | Terms of Use | Support Center | Contact Us
- © Copyright American Academy of Pediatrics
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account

JOHNNIE YATES, M.D.
Am Fam Physician. 2005;71(11):2095-2100
Patient Information: Seen related handout on traveler’s diarrhea , written by the author of this article.
Acute diarrhea affects millions of persons who travel to developing countries each year. Food and water contaminated with fecal matter are the main sources of infection. Bacteria such as enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli , enteroaggregative E. coli , Campylobacter, Salmonella, and Shigella are common causes of traveler’s diarrhea. Parasites and viruses are less common etiologies. Travel destination is the most significant risk factor for traveler’s diarrhea. The efficacy of pretravel counseling and dietary precautions in reducing the incidence of diarrhea is unproven. Empiric treatment of traveler’s diarrhea with antibiotics and loperamide is effective and often limits symptoms to one day. Rifaximin, a recently approved antibiotic, can be used for the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea in regions where noninvasive E. coli is the predominant pathogen. In areas where invasive organisms such as Campylobacter and Shigella are common, fluoroquinolones remain the drug of choice. Azithromycin is recommended in areas with quinolone-resistant Campylobacter and for the treatment of children and pregnant women.
Acute diarrhea is the most common illness among travelers. Up to 55 percent of persons who travel from developed countries to developing countries are affected. 1 , 2 A study 3 of Americans visiting developing countries found that 46 percent acquired diarrhea. The classic definition of traveler’s diarrhea is three or more unformed stools in 24 hours with at least one of the following symptoms: fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, tenesmus, or bloody stools. Milder forms can present with fewer than three stools (e.g., an abrupt bout of watery diarrhea with abdominal cramps). Most cases occur within the first two weeks of travel and last about four days without treatment. 1 , 3 Although traveler’s diarrhea rarely is life threatening, it can result in significant morbidity; one in five travelers with diarrhea is bedridden for a day and more than one third have to alter their activities. 1 , 3
Destination is the most significant risk factor for developing traveler’s diarrhea. 1 – 4 Regions with the highest risk are Africa, South Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. Travelers who are immunocompromised and those with lowered gastric acidity (e.g., patients taking histamineH 2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors) are more susceptible to traveler’s diarrhea. Recently, a genetic susceptibility has been demonstrated. 5 Younger age and adventurous travel increase the risk of developing traveler’s diarrhea, 3 , 6 but persons staying at luxury resorts or on cruise ships also are at risk. 7 , 8
Food and water contaminated with fecal matter are the main reservoirs for the pathogens that cause traveler’s diarrhea. Unsafe foods and beverages include salads, unpeeled fruits, raw or poorly cooked meats and seafood, unpasteurized dairy products, and tap water. Eating in restaurants increases the probability of contracting traveler’s diarrhea 6 and food from street vendors is particularly risky. 9 , 10 Cold sauces, salsas, and foods that are cooked and then reheated also are risky. 6 , 11
In contrast to the largely viral etiology of gastroenteritis in the United States, diarrhea acquired in developing countries is caused mainly by bacteria 1 , 4 , 6 , 12 ( Table 1 ) . Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli is the pathogen most frequently isolated, but other types of E. coli such as enteroaggregative E. coli have been recognized as common causes of traveler’s diarrhea. 13 Invasive pathogens such as Campylobacter, Shigella, and non-typhoid Salmonella are relatively common depending on the region, while Aeromonas and non-cholera Vibrio species are encountered less frequently.
Protozoal parasites such as Giardia lamblia , Entamoeba histolytica , and Cyclospora cayetanensis are uncommon causes of traveler’s diarrhea, but increase in importance when diarrhea lasts for more than two weeks. 14 Parasites are diagnosed more frequently in returning travelers because of longer incubation periods (often one to two weeks) and because bacterial pathogens may have been treated with antibiotics. Rotavirus and noroviruses are infrequent causes of traveler’s diarrhea, although noroviruses have been responsible for outbreaks on cruise ships.
The prevalence of specific organisms varies with travel destination. 1 , 4 , 12 , 13 , 15 Available data suggest that E. coli is the predominant cause of traveler’s diarrhea in Latin America, the Caribbean, and Africa, while invasive pathogens are relatively uncommon. Enterotoxigenic E. coli and enteroaggregative E. coli may be responsible for up to 71 percent of cases of traveler’s diarrhea in Mexico. 13 In contrast, Campylobacter is a leading cause of traveler’s diarrhea in Thailand 15 – 17 and also is common in Nepal. 6 Regional variation also exists with parasitic causes of traveler’s diarrhea ( Table 2 ) . 12 , 13 For example, Cyclospora is endemic in Nepal, Peru, and Haiti.
Food poisoning is part of the differential diagnosis of traveler’s diarrhea. Gastroenteritis from preformed toxins (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus , Bacillus cereus ) is characterized by a short incubation period (one to six hours), and symptoms typically resolve within 24 hours. 18 Seafood ingestion syndromes such as diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, ciguatera poisoning, and scombroid poisoning also can cause diarrhea in travelers. These syndromes can be distinguished from traveler’s diarrhea by symptoms such as perioral numbness and reversal of temperature sensation (ciguatera poisoning) or flushing and warmth (scombroid poisoning). 19
Although travelers often are advised to “Boil it, cook it, peel it, or forget it,” data on the effectiveness of dietary precautions in preventing traveler’s diarrhea are inconclusive. 3 , 6 , 20 Many travelers find it difficult to adhere to dietary recommendations. 21 In a study 3 of American travelers, nearly one half developed diarrhea despite pretravel advice on avoidance measures; even persons who strictly followed dietary recommendations developed diarrhea. Avoiding high-risk foods and adventuresome eating behaviors may reduce the inoculum of ingested pathogens or prevent the development of other enteric diseases such as typhoid and hepatitis A and E.
Boiling is the best way to purify water. Iodination or chlorination is acceptable but does not kill Cryptosporidium or Cyclospora, and increased contact time is required to kill Giardia in cold or turbid water. 22 Filters with iodine resins generally are effective in purifying water, although it is uncertain whether the contact time with the resin is sufficient to kill viruses. Bottled water generally is safe if the cap and seal are intact.
DRUG PROPHYLAXIS
Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) even for high-risk travelers because it can lead to drug-resistant organisms and may give travelers a false sense of security. Although antibiotic prophylaxis does not prevent viral or parasitic infection, some health care professionals believe that it may be an option for travelers who are at high risk of developing traveler’s diarrhea and related complications (e.g., immunocompromised persons). Prophylaxis with fluoroquinolones is up to 90 percent effective. 23 Rifaximin (Xifaxan) may prove to be the preferred antibiotic because it is not absorbed and is well tolerated, although data on its effectiveness for prophylaxis have not yet been published.
Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) provides a rate of protection of about 60 percent against traveler’s diarrhea. 24 However, it is not recommended for persons taking anticoagulants or other salicylates. Because bismuth subsalicylate interferes with the absorption of doxycycline (Vibramycin), it should not be taken by travelers using doxycycline for malaria prophylaxis. Travelers should be warned about possible reversible side effects of bismuth subsalicylate, such as a black tongue, dark stools, and tinnitus.
Probiotics are a more natural approach to prophylaxis of traveler’s diarrhea. Probiotics colonize the gastrointestinal tract and theoretically prevent pathogenic organisms from infecting the gut. Studies 25 , 26 of Lactobacillus GG (Culturelle) have suggested protection rates of up to 47 percent. More studies are needed to confirm the efficacy of probiotic prophylaxis. Agents for the prophylaxis of traveler’s diarrhea are summarized in Table 3 .
Empiric Treatment
Counseling travelers about food precautions does not eliminate the risk of traveler’s diarrhea, and nonantibiotic prophylaxis requires frequent dosing to achieve only a modest reduction in risk. In addition, the traveler with diarrhea may have difficulty accessing medical care, the quality of care may be poor, and the quality of medications purchased abroad may be substandard. 27 However, because antibiotics reduce the duration and severity of traveler’s diarrhea and generally are well tolerated, 28 providing the traveler with the means for empiric self-treatment can effectively reduce morbidity from traveler’s diarrhea.
Waiting 24 hours to confirm the diagnosis of traveler’s diarrhea results in unnecessary discomfort and time away from activities. Therapy can be initiated after the first episode of “distressing” diarrhea (i.e., diarrhea that is uncomfortable or interferes with activities). 29 , 30 If symptoms resolve within 24 hours, no further treatment is necessary. 31 , 32 If diarrhea persists after one day, treatment should be continued for one or two more days. An algorithm for the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea is presented in Figure 1 . 33 , 34
Antibiotic selection is based on the likelihood that an invasive organism is present and on antibiotic resistance patterns. These factors are determined largely by travel destination. Although blood in the stool suggests invasive disease, fever is not a sensitive indicator of dysentery. Fluoroquinolones have been the drug of choice for traveler’s diarrhea in most parts of the world because of their efficacy against most enteropathogens. Rifaximin recently became available for the treatment of noninvasive diarrhea caused by E. coli . For persons traveling to destinations where noninvasive E. coli is the predominant pathogen (e.g., Mexico), rifaximin is a good choice. 35 , 36
In regions where invasive pathogens are responsible for a significant proportion of traveler’s diarrhea, quinolones should be used. Azithromycin (Zithromax) is recommended in places where quinoloneresistant Campylobacter is prevalent (e.g., Thailand). 15 , 16 Antibiotics used for the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea are listed in Table 4 . 16 , 32 , 37 Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra) and doxycycline are no longer recommended because of the development of widespread resistance. 12
Therapy that involves an antibiotic with loperamide (Imodium) often limits symptoms to one day. 38 , 39 Loperamide has antimotility and antisecretory effects and is taken as two 2–mg tablets after the first loose stool, followed by one tablet after each subsequent loose stool (maximum of 8 mg in 24 hours for two days). The use of loperamide in dysentery has been controversial because of concerns about prolonging illness, but it is now considered safe when combined with an antibiotic. 29 , 34 , 38 A conservative approach would be to use loperamide for dysentery only if combined with an antibiotic and if the traveler has a long trip or will have no toilet access.
Oral rehydration solutions generally are unnecessary in adults younger than 65 years. 40 However, all travelers with diarrhea should be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids and to replace lost electrolytes using foods such as salt crackers or broth.
Traveler’s Diarrhea in Infants, Children, and Pregnant Women
Traveler’s diarrhea is more common in young children than in adults, and they have a higher risk of dehydration and severe illness. 41 Parents should seek immediate medical attention if their child shows signs of moderate to severe dehydration, bloody diarrhea, a temperature higher than 39°C (102°F), or persistent vomiting. Few data exist on the treatment of diarrhea in children. The use of oral rehydration solutions is essential, and parents should include prepackaged packets (to be mixed with safe water) in their travel kits. These packets are available in camping stores in the United States or in pharmacies in other countries.
Because infants and toddlers normally can have three or more loose stools, an alternate definition of diarrhea in this age group is a twofold increase in the frequency of unformed stool. 37 Nursing infants should continue to breastfeed on demand, and infants and older children should be offered their usual food.
Fluoroquinolones are not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in children, and rifaximin is approved only for children 12 years and older. Therefore, azithromycin is the drug of choice for most children with traveler’s diarrhea. 37 Another option is nalidixic acid (Neggram) in a dosage of 55 mg per kg per day divided into four doses, not to exceed 1 g in 24 hours. 37 Loperamide is approved for children older than two years, but should not be used in children with dysentery. Bismuth subsalicylate should be avoided for prophylaxis in children because of the possible risk of Reye’s syndrome.
Pregnant women may be at higher risk of traveler’s diarrhea than nonpregnant women because of lowered gastric acidity and increased gastrointestinal transit time. 42 Quinolones (FDA pregnancy category C) generally are not advised during pregnancy, but azithromycin (FDA pregnancy category B) is safe. Oral rehydration should be emphasized. Although rifaximin is not absorbed, the safety of this medication in pregnant women has not been established. Loperamide (FDA pregnancy category B) may be used, but bismuth subsalicylate (FDA pregnancy category D) should be avoided. Being careful with food and water is particularly important during pregnancy because infections such as listeriosis can cause miscarriage, and hepatitis E can result in maternal mortality.
Complications
Dehydration is the main complication of traveler’s diarrhea, especially in children and older adults. Because E. coli O157:H7 is a rare cause of traveler’s diarrhea, there is little risk of hemolyticuremic syndrome. Other complications include Guillain-Barré syndrome after Campylobacter enteritis, Reiter’s syndrome (especially in persons who are HLA-B27 positive), Clostridium difficile colitis after antibiotic use, and postinfectious irritable bowel. These conditions may appear after the traveler has returned home.
If diarrhea persists despite antibiotic treatment, medical attention should be sought. Parasitic causes should be suspected in travelers who return with prolonged diarrhea or who do not respond to antibiotics. For those traveling to remote areas for extended periods, it is reasonable to discuss empiric treatment of protozoal infections (e.g., metronidazole [Flagyl] 250 mg three times a day for five days or tinidazole [Fasigyn] in a single 2–g dose for Giardia). 43
Resources such as the Travelers’ Health section of the CDC Web site ( http://www.cdc.gov/travel/diarrhea.htm ) or commercial sites such as Travel Health Online ( http://www.tripprep.com ) can keep physicians up to date on the epidemiology and resistance patterns of traveler’s diarrhea. Better preventive and prophylactic strategies will be needed until newer antibiotics become available and the sanitation and hygiene in developing countries improve.
von Sonnenburg F, Tornieporth N, Waiyaki P, Lowe B, Peruski LF , DuPont HL, et al. Risk and aetiology of diarrhoea at various tourist destinations.. Lancet. 2000;356:133-4.
Castelli F, Pezzoli C, Tomasoni L. Epidemiology of travelers’ diarrhea.. J Travel Med. 2001;8(suppl 2):S26-S30.
Hill DR. Occurrence and self-treatment of diarrhea in a large cohort of Americans traveling to developing countries.. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:585-9.
Steffen R, Sack RB. Epidemiology. In: Ericsson CD, DuPont HL, Steffen R, eds. Travelers’ diarrhea. Hamilton, Ont.: BC Decker, 2003:112–23.
Jiang ZD, Okhuysen PC, Guo DC, He R, King TM, DuPont HL, et al. Genetic susceptibility to enteroaggregative Escherichia coli diarrhea: polymorphism in the interleukin–8 promotor region.. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:506-11.
Hoge CW, Shlim DR, Echeverria P, Rajah R, Herrmann JE, Cross JH. Epidemiology of diarrhea among expatriate residents living in a highly endemic environment. JAMA. 1996;275:533-8.
Hardie RM, Wall PG, Gott P, Bardhan M, Bartlett LR. Infectious diarrhea in tourists staying in a resort hotel.. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:168-71.
Daniels NA, Neimann J, Karpati A, Parashar UD, Greene KD, Wells JG, et al. Traveler’s diarrhea at sea: three outbreaks of waterborne enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli on cruise ships.. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:1491-5.
Ansdell VE, Ericsson CD. Prevention and empiric treatment of traveler’s diarrhea.. Med Clin North Am. 1999;83:945-73
Mensah P, Yeboah-Manu D, Owusu-Darko K, Ablordey A. Street foods in Accra, Ghana: how safe are they?. Bull World Health Organ. 2002;80:546-54.
Adachi JA, Mathewson JJ, Jiang ZD, Ericsson CD, DuPont HL. Enteric pathogens in Mexican sauces of popular restaurants in Guadalajara, Mexico, and Houston, Texas.. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136:884-7.
Jiang ZD, Lowe B, Verenkar MP, Ashley D, Steffen R, Tornieporth N, et al. Prevalence of enteric pathogens among international travelers with diarrhea acquired in Kenya (Mombasa), India (Goa), or Jamaica (Montego Bay).. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:497-502.
Adachi JA, Jiang ZD, Mathewson JJ, Verenkar MP, Thompson S, Martinez-Sandoval F, et al. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli as a major etiologic agent in traveler’s diarrhea in 3 regions of the world.. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1706-9.
Taylor DN, Houston R, Shlim DR, Bhaibulaya M, Ungar BL, Echeverria P. Etiology of diarrhea among travelers and foreign residents in Nepal.. JAMA. 1988;260:1245-8.
Kuschner RA, Trofa AF, Thomas RJ, Hoge CW, Pitarangsi C, Amato S, et al. Use of azithromycin for the treatment of Campylobacter enteritis in travelers to Thailand, an area where ciprofloxacin resistance is prevalent.. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21:536-41.
Hoge CW, Gambel JM, Srijan A, Pitarangsi C, Echeverria P. Trends in antibiotic resistance among diarrheal pathogens isolated in Thailand over 15 years.. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:341-5.
Sanders JW, Isenbarger DW, Walz SE, Pang LW, Scott DA, Tamminga C, et al. An observational clinic-based study of diarrheal illness in deployed United States military personnel in Thailand: presentation and outcome of Campylobacter infection.. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:533-8.
Tauxe RV, Swerdlow DL, Hughes JM. Foodborne disease. In: Mandell GL, Douglas RG, Bennett JE, Dolin R, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone, 2000:1150–65.
Barbier HM, Diaz JH. Prevention and treatment of toxic seafoodborne diseases in travelers.. J Travel Med. 2003;10:29-37.
Kozicki M, Steffen R, Schar M. ‘Boil it, cook it, peel it or forget it’: does this rule prevent travellers’ diarrhoea?. Int J Epidemiol. 1985;14:169-72.
Mattila L, Siitonen A, Kyronseppa H, Simula II, Peltola H. Risk behavior for travelers’ diarrhea among Finnish travelers.. J Travel Med. 1995;2:77-84.
Backer H. Water disinfection for international and wilderness travelers.. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:355-64.
RendiWagner P, Kollaritsch H. Drug prophylaxis for travelers’ diarrhea.. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:628-33.
Steffen R, Heusser R, DuPont HL. Prevention of travelers’ diarrhea by nonantibiotic drugs.. Rev Infect Dis. 1986;8(suppl 2):S151-9.
Oksanen PJ, Salminen S, Saxelin M, Hamalainen P, Ihantola-Vormisto A, Muurasniemi-Isoviita L, et al. Prevention of travellers’ diarrhoea by Lactobacillus GG.. Ann Med. 1990;22:53-6.
Hilton E, Kolakowski P, Singer C, Smith M. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG as a diarrheal preventive in travelers.. J Travel Med. 1997;4:41-3.
World Health Organization. Substandard and counterfeit medicines. Fact sheet no. 275, November 2003. Accessed online April 6, 2005, at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/2003/fs275 .
De Bruyn G, Hahn S, Borwick A. Antibiotic treatment for travellers’ diarrhoea.. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;;1:CD002242.
Shlim DR. Self diagnosis and treatment of traveler’s diarrhea. In: Keystone JS, Kozarsky PE, Freedman DO, Nothdurft HD, Connor BA, eds. Travel medicine. St. Louis: Mosby, 2003:201–4.
Ericsson CD. Travelers’ diarrhea: epidemiology, prevention, and self-treatment.. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1998;12:285-303.
Salam I, Katelaris P, Leigh-Smith S, Farthing MJ. Randomised trial of singledose ciprofloxacin for travellers’ diarrhoea.. Lancet. 1994;344:1537-9.
Adachi JA, Ericsson CD, Jiang ZD, DuPont MW, Martinez-Sandoval F, Knirsch C, et al. Azithromycin found to be comparable to levofloxacin for the treatment of US travelers with acute diarrhea acquired in Mexico.. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37:1165-71.
DuPont HL, Mattila L. Antimicrobial treatment: an algorithmic approach. In: Ericsson CD, DuPont HL, Steffen R, eds. Travelers’ diarrhea. Hamilton, Ont.: BC Decker, 2003:227–37.
Adachi JA, OstroskyZeichner L, DuPont HL, Ericsson CD. Empirical antimicrobial therapy for traveler’s diarrhea.. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:1079-83.
DuPont HL, Jiang ZD, Ericsson CD, Adachi JA, Mathewson JJ, DuPont MW, et al. Rifaximin versus ciprofloxacin for the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial.. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:1807-15.
Steffen R, Sack DA, Riopel L, Jiang ZD, Sturchler M, Ericsson CD, et al. Therapy of travelers’ diarrhea with rifaximin on various continents.. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1073-8.
Stauffer WM, Konop RJ, Kamat D. Traveling with infants and young children. Part III: travelers’ diarrhea.. J Travel Med. 2002;9:141-50.
Murphy GS, Bodhidatta L, Echeverria P, Tansuphaswadikul S, Hoge CW, Imlarp S, et al. Ciprofloxacin and loperamide in the treatment of bacillary dysentery.. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118:582-6.
Taylor DN, Sanchez JL, Candler W, Thornton S, McQueen C, Echeverria P. Treatment of travelers’ diarrhea: ciprofloxacin plus loperamide compared with ciprofloxacin alone. A placebo-controlled randomized trial.. Ann Intern Med. 1991;114:731-4.
Caeiro JP, DuPont HL, Albrecht H, Ericsson CD. Oral rehydration therapy plus loperamide versus loperamide alone in the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea.. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28:1286-9.
Pitzinger B, Steffen R, Tschopp A. Incidence and clinical features of traveler’s diarrhea in infants and children.. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991;10:719-23.
Samuel BU, Barry M. The pregnant traveler.. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1998;12:325-54.
Drugs for parasitic infections. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2004;46:1-12.
Continue Reading
More in afp.
Copyright © 2005 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.
- Skip to content
- Accessibility help
Diarrhoea - adult's assessment: Scenario: Acute diarrhoea (less than 4 weeks)
Last revised in November 2023
Covers the primary care assessment, investigation, and referral of acute or persistent (less than 4 weeks' duration) diarrhoea in adults.
Scenario: Acute diarrhoea (less than 4 weeks)
From age 18 years onwards.
How should I assess a person with acute diarrhoea?
- The onset of symptoms within 6 hours of contaminated food suggests a pre-formed toxin of either Bacillus cereus or Staphylococcus aureus as the cause.
- More frequent stool passage suggests an infectious cause.
- Watery stools are associated with non-invasive and toxin-producing pathogens.
- Blood in the stool, which is usually seen with invasive pathogens or severe inflammation, e.g. ulcerative colitis.
- Recent hospital treatment or antibiotic treatment. For more information, see the CKS topic on Diarrhoea - antibiotic associated .
- Weight loss.
- Evidence of dehydration.
- Nocturnal symptoms — organic cause more likely.
- Also ask about sexual history (particularly in men who have sex with men) to exclude sexually transmitted enteric infection.
- Quantity and character of stools (watery, fatty, containing blood or mucus).
- Fever — often seen with invasive pathogens e.g. Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter , enteric viruses or a cytotoxic organism such as Clostridioides difficile .
- Recent contact with a person with diarrhoea.
- Exposure to possible sources of enteric infection (for example certain foodstuffs such as meat, shellfish, dairy, and eggs), having eaten meals out, or recent farm or petting zoo visits).
- Travel abroad — increases the likelihood of infection. Ask about potential exposures such as raw milk or untreated water.
- Being in a higher risk group such as food handlers, nursing home residents (greater risk of norovirus, Cryptosporidium, and Giardia ), and recently hospitalized people.
- Any new drugs, especially antibiotics or laxatives. For examples, see the Causes section on Acute diarrhoea .
- Stress or anxiety.
- Abdominal pain, which is often present in inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and ischaemic colitis.
- History of recent radiation treatment to the pelvis.
- Factors increasing the risk of immunosuppression (for example, human immunodeficiency virus infection, long-term steroid use, or chemotherapy).
- Any surgery or medical conditions (for example, endocrine disease) accounting for the diarrhoea.
- Diet and use of alcohol or substances such as sorbitol.
- Features indicating dehydration include increased pulse rate, reduced skin turgor, dryness of mucous membranes, delayed capillary refill time, decreased urine output, hypotension (check for postural changes), and altered mental status. For more detail, see Clinical features of dehydration .
- Also consider underlying conditions that may increase the risk of complications.
- Perform an abdominal examination to assess for pain or tenderness, distension, mass, increased or decreased bowel sounds, or liver enlargement.
- Consider a rectal examination to assess for rectal tenderness, stool consistency, blood, mucus, and possible malignancy.
- If acute causes have been excluded and the person has features suggestive of an early presentation of a chronic cause , see Scenario: Chronic diarrhoea (more than 4 weeks) .
Clinical features of dehydration
The following signs are observed in dehydration:
- Anorexia, nausea.
- Light-headedness.
- Postural hypotension.
- Usually no signs.
- Apathy/tiredness.
- Nausea/headache.
- Muscle cramps.
- Pinched face.
- Dry tongue or sunken eyes.
- Reduced skin elasticity.
- Tachycardia.
- Profound apathy.
- Confusion, leading to coma.
- Marked peripheral vasoconstriction.
- Systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg.
- Oliguria or anuria.
However, these signs and symptoms have been shown to have poor diagnostic accuracy (particularly in the elderly). Plasma or serum osmolality measurement is the gold standard for diagnosis, with a 90% sensitivity and 100% specificity for plasma osmolality.
[ Bunn, 2019 ; Lacey, 2019 ]
Basis for recommendation
These recommendations are based on the 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Infectious Diarrhea [ Shane, 2017 ], the Centers for Disease Control Yellow book Travelers' Diarrhea [ CDC, 2023 ], the BMJ Best Practice guide Assessment of acute diarrhoea [ BMJ Best Practice, 2023a ], and the review articles Diarrhea [ Nemeth, 2022 ] and Bacterial Diarrhea [ Akhondi, 2023 ].
How should I investigate acute diarrhoea in primary care?
- The person is systemically unwell; needs hospital admission and/or antibiotics.
- There is blood or pus in the stool.
- The person is immunocompromised.
- The person has recently received antibiotics, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or been in hospital — also request specific testing for Clostridioides difficile . For more information, see the CKS topic on Diarrhoea - antibiotic associated .
- Diarrhoea occurs after foreign travel — also request tests for ova, cysts, and parasites and state the countries visited on the form.
- Amoebae, Giardia , or cryptosporidium are suspected, particularly if diarrhoea is persistent (2 weeks or more) or the person has travelled to an at-risk area.
- There is a need to exclude infectious diarrhoea (for example, severe abdominal pain, exacerbation of inflammatory bowel disease, or irritable bowel syndrome).
- Diarrhoea in high-risk people (for example food handlers, healthcare workers, elderly residents in care homes).
- Suspected food poisoning (for example after a barbeque or restaurant meal or eating eggs, chicken, or shellfish).
- Outbreaks of diarrhoea in the family or community, when isolating the organism, may help pinpoint the source of the outbreak.
- Contacts of people infected with certain organisms, for example, Escherichia coli O157 or C. difficile , where there may be serious clinical sequelae to an infection.
- Close household contacts of a person with a Giardia infection.
- For more information on how to send a stool sample (such as what information to include), see Sending a stool sample .
- See the section on Investigations in the Scenario: Chronic diarrhoea (more than 4 weeks) for advice on which blood tests to request.
Sending a stool sample
- Send a single specimen (a quarter-full specimen pot is the minimum needed for routine microbiology investigation). Only send loose stools, as the laboratory will not examine formed stools.
- If diarrhoea occurs after exotic travel abroad, is recurrent, or prolonged, request ova, cysts, and parasites and give details of travel. Send three specimens a minimum of 2 days apart (ova, cysts, and parasites are shed intermittently).
- Clinical features (for example, fever; bloody stool; severe abdominal pain).
- History of immunosuppression.
- Food intake (for example, shellfish).
- Recent foreign travel (specify countries).
- Recent antibiotic therapy, proton pump inhibitor therapy, or hospitalization (suggestive of Clostridioides difficile infection).
- Exposure to untreated water (suggestive of infection with protozoa).
- Contact with other affected people or an outbreak.
- Repeat specimens are usually unnecessary unless advised by a specialist (microbiologist or consultant in public health), or ova, cysts and parasites are suspected.
- These recommendations are largely based on and extrapolated from UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) guidance M anaging specific infectious diseases (gastroenteritis chapter) [ UKHSA, 2023 ], the BMJ Best Practice guide Assessment of acute diarrhoea [ BMJ Best Practice, 2023a ], the review articles Diarrhea [ Nemeth, 2022 ] and Bacterial Diarrhea [ Akhondi, 2023 ].
Considering blood tests
- This recommendation is pragmatic and is based on what CKS considers to be good clinical practice.
When should I admit or refer a person with acute diarrhoea?
- The person is vomiting and unable to retain oral fluids, or
- They have features of severe dehydration or shock (for more information, see Clinical features of dehydration ).
- Older age (people 60 years of age or older are more at risk of complications).
- Home circumstances and level of support.
- Bloody diarrhoea.
- Abdominal pain and tenderness.
- Coexisting medical conditions — immunodeficiency, lack of stomach acid, inflammatory bowel disease, valvular heart disease, diabetes mellitus, renal impairment, rheumatoid disease, systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Drugs — immunosuppressants or systemic steroids, proton pump inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics.
- They are aged 40 and over with unexplained weight loss and abdominal pain, or
- They are aged 50 and over with unexplained rectal bleeding, or
- They are aged 60 and over with iron deficiency anaemia or changes in their bowel habit, or tests show occult blood in their faeces.
- Adults have a rectal or abdominal mass.
- Abdominal pain.
- Change in bowel habits.
- Iron-deficiency anaemia.
- Refer if the diagnosis remains uncertain after a primary care assessment — if infection and the other common causes of acute diarrhoea have been excluded and it is suspected that an episode of acute diarrhoea is due to a chronic cause .
These recommendations are extrapolated from an expert consensus guideline The management of infective gastroenteritis in adults. A consensus statement by an expert panel convened by the British Society for the Study of Infection [ Farthing, 1996 ], the BMJ Best Practice guide Assessment of acute diarrhoea [ BMJ Best Practice, 2023a ] and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline Suspected cancer: recognition and referral [ NICE, 2023 ].
Referral if the diagnosis remains uncertain
- CKS has based this recommendation on what it considers to be good clinical practice.
The content on the NICE Clinical Knowledge Summaries site (CKS) is the copyright of Clarity Informatics Limited (trading as Agilio Software Primary Care) . By using CKS, you agree to the licence set out in the CKS End User Licence Agreement .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Traveler's diarrhea is a digestive tract disorder that commonly causes loose stools and stomach cramps. It's caused by eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water. Fortunately, traveler's diarrhea usually isn't serious in most people — it's just unpleasant. When you visit a place where the climate or sanitary practices are ...
Treatment. Travelers' diarrhea (TD) is the most predictable travel-related illness. Attack rates range from 30%-70% of travelers during a 2-week period, depending on the destination and season of travel. Traditionally, TD was thought to be prevented by following simple dietary recommendations (e.g., "boil it, cook it, peel it, or forget ...
Traveler's diarrhea affects travelers and others who consume contaminated food or water. It's a brief but unpleasant gastrointestinal infection that typically causes loose stools and abdominal cramps. Most of the time, it's caused by bacteria, but sometimes viruses or parasites are to blame. International travelers are most at risk when ...
410-955-5000 Maryland. 855-695-4872 Outside of Maryland. +1-410-502-7683 International. Diarrhea is the term for bowel movements that are loose or watery. Traveler's diarrhea occurs within 10 days of travel to an area with poor public hygiene. It's the most common illness in travelers.
Travelers' diarrhea is the most common travel-related illness. It's an infection that usually occurs within the first 2 weeks of travel. There are steps you can take to minimize your risk of getting travelers' diarrhea. This includes paying special attention to what you eat and drink — or even taking some preventive medications.
Travelers' diarrhea is a common ailment in persons traveling to resource-limited destinations overseas. Estimates indicate that it affects nearly 40% to 60% of travelers depending on the place they travel, and it is the most common travel-associated condition. ... The onset of symptoms will typically occur 1 to 2 weeks after arrival in a ...
It can affect as many as 2 to 6 in 10 travellers. There is a different risk depending on whether you travel to high-risk areas or not: High-risk areas: South and ... Connor BA, Beeching NJ, et al; Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of travelers' diarrhea: a graded expert panel report. J Travel Med. 2017 Apr 1;24(suppl_1):S57-S74. doi ...
Travelers' Diarrhea. Travelers' diarrhea is the most common travel-related illness. It can occur anywhere, but the highest-risk destinations are in Asia (except for Japan and South Korea) as well as the Middle East, Africa, Mexico, and Central and South America. In otherwise healthy adults, diarrhea is rarely serious or life-threatening, but it ...
Traveler's diarrhea can be mild to severe. Most people who develop traveler's diarrhea experience symptoms within the first 2 weeks, and often within 2 to 3 days, of arriving in a developing area. Symptoms include: Diarrhea. Abdominal cramps. Mild to severe dehydration. General lack of energy, nausea, and vomiting.
For example, the parasite Giardia often causes symptoms that may take 2-4 weeks to resolve. ... Travelers' diarrhea: Update on the incidence, etiology and risk in military and similar ...
Antibiotics may be used for traveler's diarrhea caused by bacterial infections. A stool test should be done to identify which antibiotic might work best. Quinolone antibiotics such as Cipro (ciprofloxacin) are most often used when antibiotics are needed. A single dose of 750 milligrams (mg) for adults is the typical treatment.
Fever. Nausea and vomiting. Bloating. Urgent need to have a bowel movement. Malaise (weakness or discomfort) Explosive and painful gas. Stomach c ramps. Loss of appetite. Traveler's diarrhea ...
Traveler's diarrhea is a digestive tract disorder. It consists of abdominal cramps and diarrhea that's most often caused by consuming food or water that the body isn't familiar with.
The incidence of tropical sprue appears to have declined dramatically over the past 2 decades. Diagnosed only rarely in travelers, its cause is unknown. Brainerd diarrhea is a syndrome of acute onset of watery diarrhea lasting ≥4 weeks. Symptoms include 10-20 episodes of explosive, watery diarrhea per day, fecal incontinence, abdominal ...
Travellers' diarrhoea is defined as an increase in frequency of bowel movements to three or more loose stools per day during a trip abroad, usually to a less economically developed region. ... 5% lasting more than two weeks, and 1% lasting more than 30 days.8 During the illness, few patients will be severely incapacitated ...
Persistent: diarrhea lasting ≥2 weeks. ... Travelers' diarrhea in CDC Yellow Book 2020: health information for international travel. June 2019 [internet publication]. 16. Hu Y, Ren J, Zhan M, et al. Efficacy of rifaximin in prevention of travelers' diarrhea: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. J Travel Med ...
Diarrhea, a common travel-related problem for children and adults, generally is benign and self-limited. Treatment includes fluid replacement, antibiotics and anti-motility agents; the greatest concern is volume depletion.The incidence of travelers' diarrhea (TD) during a two-week trip is between 10% and 40% depending on the traveler's destination and activities.
Travellers' diarrhoea is defined as passing three or more unformed stools in a 24-hour period with at least one additional symptom, such as abdominal pain or cramps, nausea, vomiting, fever, or blood in the stools. Bacterial infection is the most common cause and is thought to account for 80-90% of cases of travellers' diarrhoea. The clinical ...
Travelers' diarrhea ( TD) is a stomach and intestinal infection. TD is defined as the passage of unformed stool (one or more by some definitions, three or more by others) while traveling. [2] [3] It may be accompanied by abdominal cramps, nausea, fever, headache and bloating. [3] Occasionally bloody diarrhea may occur. [5]
The Illness. Travellers' diarrhoea is when you have 3 or more bouts of loose, watery poo in 24 hours. Most cases are mild, but for some people it is severe. Travellers' diarrhoea tends to happen in the first week of travel. Symptoms last on average 3 to 5 days and usually get better without you needing specific treatment.
Most cases occur within the first two weeks of travel and last about four days without treatment. 1, 3 Although traveler's diarrhea rarely is life threatening, it can result in significant ...
Diarrhoea occurs after foreign travel — also request tests for ova, cysts, and parasites and state the countries visited on the form. Amoebae, Giardia, or cryptosporidium are suspected, particularly if diarrhoea is persistent (2 weeks or more) or the person has travelled to an at-risk area.