Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week

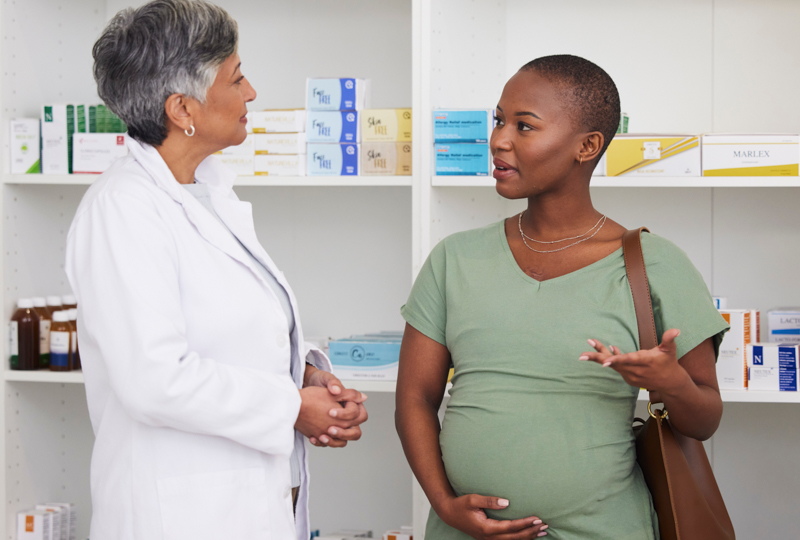
Prenatal care: 1st trimester visits
Pregnancy and prenatal care go hand in hand. During the first trimester, prenatal care includes blood tests, a physical exam, conversations about lifestyle and more.
Prenatal care is an important part of a healthy pregnancy. Whether you choose a family physician, obstetrician, midwife or group prenatal care, here's what to expect during the first few prenatal appointments.
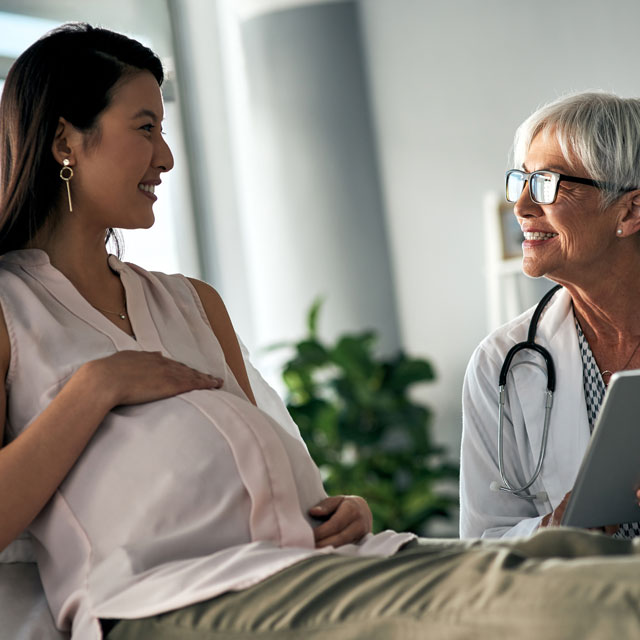
The 1st visit
When you find out you're pregnant, make your first prenatal appointment. Set aside time for the first visit to go over your medical history and talk about any risk factors for pregnancy problems that you may have.
Medical history
Your health care provider might ask about:
- Your menstrual cycle, gynecological history and any past pregnancies
- Your personal and family medical history
- Exposure to anything that could be toxic
- Medications you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins or supplements
- Your lifestyle, including your use of tobacco, alcohol, caffeine and recreational drugs
- Travel to areas where malaria, tuberculosis, Zika virus, mpox — also called monkeypox — or other infectious diseases are common
Share information about sensitive issues, such as domestic abuse or past drug use, too. This will help your health care provider take the best care of you — and your baby.
Your due date is not a prediction of when you will have your baby. It's simply the date that you will be 40 weeks pregnant. Few people give birth on their due dates. Still, establishing your due date — or estimated date of delivery — is important. It allows your health care provider to monitor your baby's growth and the progress of your pregnancy. Your due date also helps with scheduling tests and procedures, so they are done at the right time.
To estimate your due date, your health care provider will use the date your last period started, add seven days and count back three months. The due date will be about 40 weeks from the first day of your last period. Your health care provider can use a fetal ultrasound to help confirm the date. Typically, if the due date calculated with your last period and the due date calculated with an early ultrasound differ by more than seven days, the ultrasound is used to set the due date.
Physical exam
To find out how much weight you need to gain for a healthy pregnancy, your health care provider will measure your weight and height and calculate your body mass index.
Your health care provider might do a physical exam, including a breast exam and a pelvic exam. You might need a Pap test, depending on how long it's been since your last Pap test. Depending on your situation, you may need exams of your heart, lungs and thyroid.
At your first prenatal visit, blood tests might be done to:
- Check your blood type. This includes your Rh status. Rh factor is an inherited trait that refers to a protein found on the surface of red blood cells. Your pregnancy might need special care if you're Rh negative and your baby's father is Rh positive.
- Measure your hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein found in red blood cells that allows the cells to carry oxygen from your lungs to other parts of your body. Hemoglobin also carries carbon dioxide from other parts of your body to your lungs so that it can be exhaled. Low hemoglobin or a low level of red blood cells is a sign of anemia. Anemia can make you feel very tired, and it may affect your pregnancy.
- Check immunity to certain infections. This typically includes rubella and chickenpox (varicella) — unless proof of vaccination or natural immunity is documented in your medical history.
- Detect exposure to other infections. Your health care provider will suggest blood tests to detect infections such as hepatitis B, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and HIV , the virus that causes AIDS . A urine sample might also be tested for signs of a bladder or urinary tract infection.
Tests for fetal concerns
Prenatal tests can provide valuable information about your baby's health. Your health care provider will typically offer a variety of prenatal genetic screening tests. They may include ultrasound or blood tests to check for certain fetal genetic problems, such as Down syndrome.
Lifestyle issues
Your health care provider might discuss the importance of nutrition and prenatal vitamins. Ask about exercise, sex, dental care, vaccinations and travel during pregnancy, as well as other lifestyle issues. You might also talk about your work environment and the use of medications during pregnancy. If you smoke, ask your health care provider for suggestions to help you quit.
Discomforts of pregnancy
You might notice changes in your body early in your pregnancy. Your breasts might be tender and swollen. Nausea with or without vomiting (morning sickness) is also common. Talk to your health care provider if your morning sickness is severe.
Other 1st trimester visits
Your next prenatal visits — often scheduled about every four weeks during the first trimester — might be shorter than the first. Near the end of the first trimester — by about 12 to 14 weeks of pregnancy — you might be able to hear your baby's heartbeat with a small device, called a Doppler, that bounces sound waves off your baby's heart. Your health care provider may offer a first trimester ultrasound, too.
Your prenatal appointments are an ideal time to discuss questions you have. During your first visit, find out how to reach your health care team between appointments in case concerns come up. Knowing help is available can offer peace of mind.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
- Lockwood CJ, et al. Prenatal care: Initial assessment. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed July 9, 2018.
- Prenatal care and tests. Office on Women's Health. https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/prenatal-care-and-tests. Accessed July 9, 2018.
- Cunningham FG, et al., eds. Prenatal care. In: Williams Obstetrics. 25th ed. New York, N.Y.: McGraw-Hill Education; 2018. https://www.accessmedicine.mhmedical.com. Accessed July 9, 2018.
- Lockwood CJ, et al. Prenatal care: Second and third trimesters. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed July 9, 2018.
- WHO recommendations on antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal_perinatal_health/anc-positive-pregnancy-experience/en/. Accessed July 9, 2018.
- Bastian LA, et al. Clinical manifestations and early diagnosis of pregnancy. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed July 9, 2018.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 1st trimester pregnancy
- Can birth control pills cause birth defects?
- Fetal development: The 1st trimester
- Implantation bleeding
- Nausea during pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Prenatal care 1st trimester visits
Make twice the impact
Your gift can go twice as far to advance cancer research and care!

- Pregnancy Classes

Your First Prenatal Visit
If you did not meet with your health care provider before you were pregnant, your first prenatal visit will generally be around 8 weeks after your LMP (last menstrual period ). If this applies to you, you should schedule a prenatal visit as soon as you know you are pregnant!
Even if you are not a first-time mother, prenatal visits are still important since every pregnancy is different. This initial visit will probably be one of the longest. It will be helpful if you arrive prepared with vital dates and information. This is also a good opportunity to bring a list of questions that you and your partner have about your pregnancy, prenatal care, and birth options.
What to Expect at Your First Pregnancy Appointment
Your doctor will ask for your medical history, including:.
- Medical and/or psychosocial problems
- Blood pressure, height, and weight
- Breast and cervical exam
- Date of your last menstrual period (an accurate LMP is helpful when determining gestational age and due date)
- Birth control methods
- History of abortions and/or miscarriages
- Hospitalizations
- Medications you are taking
- Medication allergies
- Your family’s medical history
Your healthcare provider will also perform a physical exam which will include a pap smear , cervical cultures, and possibly an ultrasound if there is a question about how far along you are or if you are experiencing any bleeding or cramping .
Blood will be drawn and several laboratory tests will also be done, including:
- Hemoglobin/ hematocrit
- Rh Factor and blood type (if Rh negative, rescreen at 26-28 weeks)
- Rubella screen
- Varicella or history of chickenpox, rubella, and hepatitis vaccine
- Cystic Fibrosis screen
- Hepatitis B surface antigen
- Tay Sach’s screen
- Sickle Cell prep screen
- Hemoglobin levels
- Hematocrit levels
- Specific tests depending on the patient, such as testing for tuberculosis and Hepatitis C
Your healthcare provider will probably want to discuss:
- Recommendations concerning dental care , cats, raw meat, fish, and gardening
- Fevers and medications
- Environmental hazards
- Travel limitations
- Miscarriage precautions
- Prenatal vitamins , supplements, herbs
- Diet , exercise , nutrition , weight gain
- Physician/ midwife rotation in the office
Possible questions to ask your provider during your prenatal appointment:
- Is there a nurse line that I can call if I have questions?
- If I experience bleeding or cramping, do I call you or your nurse?
- What do you consider an emergency?
- Will I need to change my habits regarding sex, exercise, nutrition?
- When will my next prenatal visit be scheduled?
- What type of testing do you recommend and when are they to be done? (In case you want to do research the tests to decide if you want them or not.)
If you have not yet discussed labor and delivery issues with your doctor, this is a good time. This helps reduce the chance of surprises when labor arrives. Some questions to ask include:
- What are your thoughts about natural childbirth ?
- What situations would warrant a Cesarean ?
- What situations would warrant an episiotomy ?
- How long past my expected due date will I be allowed to go before intervening?
- What is your policy on labor induction?
Want to Learn More?
- Sign up for our weekly email newsletter
- Bonding With Your Baby: Making the Most of the First Six Weeks
- 7 Common Discomforts of Pregnancy
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Leg Cramps During Pregnancy

Prenatal Vitamin Limits

Skin Changes During Pregnancy
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
- First Trimester
- OB-GYN & Prenatal Care
What to Expect at the First Prenatal Visit
You got a positive pregnancy test —congratulations are in order! Now it’s time to plan your first prenatal visit. You might be feeling nervous (or is that morning sickness already?!), and you probably have lots of questions, but not to worry—your provider will be there every step of the way. In the meantime, you might want to brush up on what to expect at your first pregnancy appointment. Ready for answers? We’ve consulted with ob-gyns on all the important info.
When Should You Schedule Your First Prenatal Visit?
After you get that positive test, you can take a day or two to soak in the news and celebrate, but it’s a good idea to book that first prenatal visit with your chosen ob-gyn or midwife pretty soon after. (If you haven’t picked a provider yet , you’ll want to get on that ASAP!)
Andrea Braden , MD, IBCLC, an ob-gyn and founder of the lactation company Lybbie , advises to “be on the safe side and give the office a call as soon as you find out you’re pregnant.”
When Will Your First Prenatal Visit Happen?
It’s ideal to schedule your first prenatal visit for when you’re around 7 to 8 weeks pregnant, says Braden. Doctors recommend this timing because that’s when an ultrasound can likely detect baby’s heartbeat . (The earliest a fetal heartbeat can be detected is around week 6, according to Cleveland Clinic .)
If you’ve had complications in an earlier pregnancy, you may want to go in earlier than 7 to 8 weeks. “Sometimes we want to watch these early pregnancies closer because with a history of complications, you have an increased risk of having complications in a subsequent pregnancy,” notes Braden.
On the other hand, if you miss the 7-to-8-week mark, Braden says the goal would be to get you in before 12 weeks, when the first trimester ends. “After that point, just get in as soon as you can because there will be some catching up to do!” she adds.
How Can You Prepare for Your First Pregnancy Appointment?
Want a handy checklist for your first prenatal appointment? Here’s what you need to prepare, according to the experts.
- The date of your last menstrual period (LMP). During your first pregnancy appointment, your ob-gyn will compare the LMP to an ultrasound to determine your due date , says Braden. “If the last period was irregular or unpredictable, sometimes you need to know the first day of the period before that one,” she adds.
- Your medications and medical history. Gather a list of medications and dosages to bring to your provider to discuss their safety during pregnancy, advises Michael Platt-Faulkner , DO, an ob-gyn at St. Elizabeth Physicians in Northern Kentucky. “Writing down any significant personal medical or surgical history and family history of genetic diseases is also helpful information for your visit,” he adds.
- Your pharmacy information. Your doc might prescribe prenatal vitamins or other medications, depending on your medical history, so make sure you have a convenient pharmacy in mind.
- Any questions about symptoms or other concerns. Those first-trimester symptoms—nausea, fatigue, peeing all the time—can cause anxiety. Plus, figuring out what to eat (and not to eat) and questions like “ Can I have coffee while pregnant? ” can be confusing. Platt-Faulker suggests writing all your questions and concerns down for your provider, so you don’t forget them in the heat of the moment.
- Somewhere to track the rest of your pregnancy appointments. “There will be a lot of information coming at you,” says Braden. “You want to have a place to write down future appointments and take any notes.”
What Happens at Your First Prenatal Visit?
What happens at your first prenatal visit can vary widely depending on your state and the type of practice you’re visiting, says Braden. In some practices, you get both an ultrasound and a consultation during your first pregnancy appointment, while other providers’ offices split up these to-dos.
Here’s generally what to expect at your first prenatal appointment.
Your provider may perform an ultrasound to confirm the pregnancy, help determine your due date, check baby’s heart rate and check for any complications, according to Cleveland Clinic . “Oftentimes, an early-pregnancy ultrasound may use a vaginal probe and can be mildly uncomfortable—which can be helpful to know in order to be best prepared for your visit,” says Platt-Faulkner. By about 12 to 14 weeks of pregnancy, your provider will be able to hear baby’s heartbeat with a small device called a Doppler ultrasound, according to Mayo Clinic .
Medical history
“Your provider will review your pregnancy, medical and surgical histories in detail,” says Platt-Faulkner. “Your ob-gyn will [also] review how any medical diagnoses, pregnancy complications or surgical history may affect your pregnancy.” Your provider will also take a look at your medication list and discuss any pregnancy-related safety concerns with the medications you’re taking. Omoikhefe Akhigbe , MD, an ob-gyn at Pediatrix Medical Group in Maryland, adds that your provider may also discuss whether there are any specialty doctors you should start seeing or continue to see.
Lifestyle discussion
Your provider will discuss the lifestyle choices you plan to make during pregnancy. (Remember that, for starters, that means no smoking or alcohol .) “You’ll learn about foods that are safe to eat in pregnancy and the way to keep yourself healthy,” says Braden. “They will answer questions about exercise, diet, nutrition, rest, common symptoms and how to treat them and what to do if you do have discomfort in pregnancy.”
Genetic testing
At your first pregnancy appointment, your provider might perform or discuss future genetic testing. “There are genetic tests that are time-sensitive and can be done as early as 10 weeks,” says Braden. “There are some that are done with an ultrasound around 12 or 13 weeks pregnant, and some that are done in the second trimester. Depending on your history and what you desire, that’ll likely be brought up.” There are some specific tests your provider may offer based on your age or family history too, she adds.
Blood testing
You’ll likely get blood drawn during your first prenatal visit. You’ll be tested for a variety of conditions, including anemia, hepatitis B, syphilis and HIV, as well as for your blood type and Rh factor .
Urine testing
For starters, your provider might test a urine sample to confirm your pregnancy, as well as to test kidney function and screen for the presence of protein, as noted by the Cleveland Clinic .
Physical exam
You can expect a full physical exam at your first prenatal visit, which may include a pelvic examination and a breast exam. “If you’re due for a pap smear and you’re over 21 years of age, then you can expect that you’ll have a pap smear screening test done for cervical cancer along with an HPV test if indicated,” says Braden. “Typically, we also test for sexually transmitted infections at the time of the first prenatal visit.”
Questions to Ask at Your First Prenatal Visit
You’re likely full of questions—and that’s completely normal! Make sure to write them down—and bring this list to your first prenatal appointment in case you feel like you’re forgetting something.
- Questions about symptoms. Of course, you should bring any questions about symptoms to your appointment. Akhigbe says it’s also important to ask “when and where to call for an urgent question, what constitutes an emergency, what is an urgent question and what is a routine question that could probably wait for normal business hours.”
- Questions about testing. Which tests will you need during pregnancy? What will your insurance pay for? “Ask about common resources to use and where you can find the evidence-based information about your pregnancy and guidelines and information about tests,” advises Braden. A lot of people also want to know when they’ll find out baby’s sex , she adds. (Spoiler alert: With non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) , you can find out as early as 10 weeks.)
- Questions about your ultrasound plan. How many ultrasounds will you get? “Sometimes it depends on insurance, sometimes it depends on your medical history and sometimes it depends on your provider. Do they do them in-house or at a different center?” says Braden.
- Questions about lifestyle choices. Your doctor will review information about how to eat a healthy pregnancy diet with you, but if you have any specific concerns—such as about drinking alcohol or eating sushi—be sure to let them know.
- Questions about logistics. You’ve got a long journey ahead of you! Your provider will likely “review their practice structure, visit schedule and confirm the hospital where you’ll deliver,” says Platt-Faulkner. But if they’ve missed anything, Akhigbe recommends asking follow-up logistical questions, like how many providers you’ll see and which doctor is most likely to deliver baby. (Remember, there are no guarantees!)
There’s a lot of information to take in at your first prenatal visit. It might seem overwhelming, so make sure to bring questions, take notes and do whatever else you need to feel comfortable. Bringing your partner or a good friend along for the ride can help ease some nerves too. “If you have a support person that will be going along this journey with you, it’s always great to bring them to this visit if that’s allowed,” says Braden.
While it might feel like a lot to take in, know that your provider is there to make sure you and baby are healthy during your first prenatal visit and throughout your whole pregnancy—and that you’re making a wonderful first step in your pregnancy journey.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
15 Early Signs of Pregnancy
Pregnancy Checklist: Your First Trimester To-Dos
When Do You Start Showing in Pregnancy?
Omoikhefe Akhigbe , MD, is an ob-gyn and medical director at Pediatrix Medical Group in Maryland. She earned her medical degree from Meharry Medical College School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee.
Andrea Braden , MD, IBCLC, is an ob-gyn, board-certified lactation consultant and founder of the lactation company Lybbie . She earned her medical degree from the University of South Alabama School of Medicine.
Michael Platt-Faulkner , DO, is an ob-gyn at St. Elizabeth Physicians in Northern Kentucky. He earned his medical degree from the Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine at Ohio University.
Cleveland Clinic, Fetal Development , March 2023
Cleveland Clinic, Ultrasound in Pregnancy , September 2022
Mayo Clinic, Prenatal Care: 1st Trimester Visits , August 2022
Nemours KidsHealth, Prenatal Tests: First Trimester , July 2022
Cleveland Clinic, NIPT Test , October 2022
Cleveland Clinic, Your First Prenatal Appointment: What to Expect , December 2022
Learn how we ensure the accuracy of our content through our editorial and medical review process .
Navigate forward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.
Next on Your Reading List

- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Prenatal visits: What to expect and how to prepare
Regular prenatal visits are an important part of your pregnancy care. Find out how often you'll see a healthcare provider, what to expect at each appointment, and smart ways to prepare.

When to schedule a prenatal visit
Prenatal visitation schedule, how should i prepare for a prenatal visit, what happens during prenatal visits, how can i make the most of my pregnancy appointments.
Make an appointment for your first prenatal visit once you're aware you are pregnant – when you receive a positive home pregnancy test, for example. Booking it around week 8 of pregnancy is typical.
You'll come back regularly in the weeks and months following that initial appointment. Most people have between 8 and 14 prenatal visits throughout the course of their pregnancy.
During this time, you'll see a lot of your healthcare practitioner. That's why it's so important to choose someone you like and trust. If you're not comfortable or satisfied with your provider after your first visit or visits, don't be afraid to find someone with whom you have a better connection.
Typically, a pregnant woman will visit their doctor, midwife , or nurse practitioner every four weeks during the first and second trimesters. In the third trimester, you'll be seen more often – usually every other week until 36 weeks, and then every week until the baby is born.
For more information on what happens at these visits, see:
Your first prenatal visit
Second trimester prenatal visits (14 weeks to 27 weeks)
Third trimester prenatal visits (28 weeks through the end of pregnancy)
The specific number of scheduled appointments you'll have depends on if your pregnancy is considered to be high-risk. This is determined by your medical history and whether you have any complications or conditions that warrant more frequent checkups, such as gestational diabetes , high blood pressure , or a history of preterm labor . If you've had any medical problems in the past or develop any new problems during this pregnancy, you may need more prenatal visits than the average pregnant woman.
In the weeks before each visit, jot down any questions or concerns in a notebook or a notes app on your smartphone. This way, you'll remember to ask your practitioner about them at your next appointment. You may be surprised by how many questions you have, so don't miss the opportunity to get some answers in person.
For example, before you drink an herbal tea or take a supplement or an over-the-counter medication , ask your provider about it. You can even bring the item itself – or a picture of the label – with you to your next appointment. Then, your doctor, midwife, or nurse practitioner can read the label and let you know whether it's okay to ingest.
Of course, if you have any pressing questions or worries, or develop any new, unusual, or severe symptoms , don't wait for your appointment – call your practitioner right away.
In addition to your list, you may want to bring a partner, friend, family member, or labor coach with you to some or all of your prenatal visits. They can comfort you, take notes, ask questions, and help you remember important information.
The goal of prenatal visits is to see how your pregnancy is proceeding and to provide you with information to help keep you and your baby healthy. It's important that you go to all of your prenatal appointments, even if you're feeling just fine and believe that everything is progressing perfectly.
Your practitioner will start by asking how you're feeling physically and emotionally, whether you have any complaints or worries, and what questions you may have. They'll also ask you about your baby's movements once you begin to feel them, typically during the second trimester. Your practitioner will have other questions as well, which will vary depending on how far along you are and whether there are specific concerns.
Your midwife, doctor, or nurse practitioner will also:
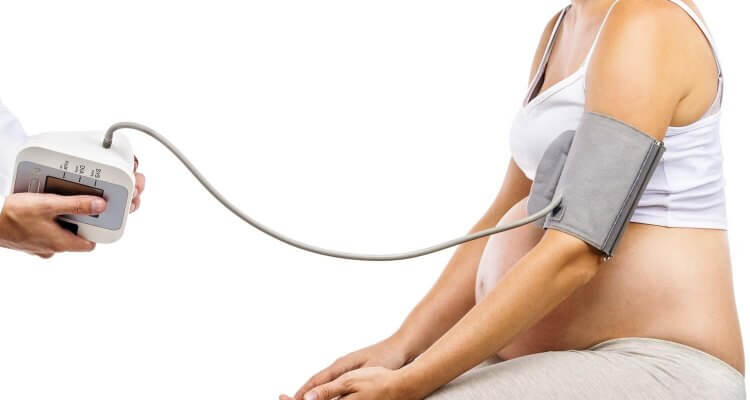
- Check your weight , blood pressure , and urine
- Check for swelling
- Measure your abdomen
- Check the position of your baby
- Listen to your baby's heartbeat
- Perform other exams and order tests, as appropriate
- Give you the appropriate vaccinations
- Closely monitor any complications you have or that you develop, and intervene if necessary
Near the end of your pregnancy, your provider may also do a pelvic exam to check for cervical changes. You will also discuss your delivery plan in more depth.
At the end of each visit, your practitioner will review their findings with you. They'll also explain the normal changes to expect before your next visit, warning signs to watch for, and the pros and cons of optional tests you may want to consider. Lifestyle issues will likely be a topic of discussion, as well. Expect to talk about the importance of good nutrition , sleep, oral health, stress management, wearing seatbelts, and avoiding tobacco , alcohol , and illicit drugs.
Many people look forward to their prenatal appointments but are disappointed to find that, with the exception of the first visit, they're in and out of the office in 10 minutes. A quick visit is typical and is usually a sign that everything is progressing normally. Still, you want to make sure your concerns are addressed – and that you and your baby are being well cared for.
Here are some things you can do to ensure that your prenatal visits are satisfying:
- Speak up. Your practitioner isn't a mind reader and won't be able to tell what you're thinking just by performing a physical exam. So, if anything is bothering you, say your piece. Are you having trouble controlling your heartburn ? Managing your constipation ? Suffering from headaches ? This is the time to ask for advice. Consult the notebook of questions you've been compiling. In addition to physical complaints, let your practitioner know if you have emotional concerns or fitness or nutrition questions.
- Ask the staff about the administrative stuff. Save your questions about things like insurance and directions to the hospital for the office staff so your practitioner has more time to answer your health-related questions. Go to the admin staff with any inquiries about payments, scheduling, office policies, and your contact information.
- Be open-minded. When talking with your doctor, midwife, or nurse practitioner, you should feel comfortable speaking freely. But remember to listen, too. Take notes if you find it helpful.
Keep in mind, too, that some days are busier than others. This is especially true during the COVID-19 pandemic. That doesn't mean your practitioner doesn't have to answer your questions, but sometimes a discussion can be continued at the next visit if it's a really busy day or if your practitioner needs to head to the hospital to deliver a baby.
At the same time, don't tolerate a healthcare practitioner who won't give you thorough answers, doesn't show reasonable compassion, or barely looks up from your chart. You and your baby deserve more than that.
Now that you know what to expect during all those prenatal visits, you might like a sneak peek at what else is in store. Here's an overview of the next nine months .
Learn more:
- The ultimate pregnancy to-do list: First trimester
- 12 steps to a healthy pregnancy
- When will my pregnancy start to show?
- Fetal development timeline
Was this article helpful?
What happens at second trimester prenatal appointments

What to expect at your first prenatal appointment

What to expect from third trimester prenatal appointments

Prenatal testing

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
MedlinePlus. (2021). Prenatal care in your first trimester. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000544.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
March of Dimes. (2017). Prenatal Care Checkups. https://www.marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/prenatal-care-checkups.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
Office on Women’s Health. (2019). Prenatal Care and Tests. https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/prenatal-care-and-tests Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
NIH: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2017). What happens during prenatal visits? https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/preconceptioncare/conditioninfo/prenatal-visits Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
NIH: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2017). What is a high-risk pregnancy? https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancy/conditioninfo/high-risk Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
NIH: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2018). What are some factors that make a pregnancy high-risk? https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/high-risk/conditioninfo/factors Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
March of Dimes. (2020). Over-the-Counter Medicine, Supplements, and Herbal Products During Pregnancy. https://www.marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/over-the-counter-medicine-supplements-and-herbal-products.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
Associates in Women’s Healthcare (2021). Preparing for Your First Prenatal Visit. https://www.associatesinwomenshealthcare.net/blog/preparing-for-your-first-prenatal-visit/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
National Health Service (UK). (2018). Your baby’s movements. https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/your-babys-movements/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
MedlinePlus. (2021). Prenatal care in your third trimester. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000558.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
UCLA Health. (2021). Schedule of prenatal care. https://www.uclahealth.org/obgyn/workfiles/Pregnancy/Schedule_of_Prenatal_Care.pdf Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
UCR Health. (2021). Healthy Pregnancy: The Importance of Prenatal Care. https://www.ucrhealth.org/2018/07/healthy-pregnancy-the-importance-of-prenatal-care/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]
Mayo Clinic. (2020). Prenatal care: 1 st trimesters visits. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/prenatal-care/art-20044882 Opens a new window [Accessed September 21, 2021.]

Where to go next


Set My Location
Providing your location allows us to show you nearby providers and locations.
The Ultimate Pregnancy Appointment Guide: What to Expect Week by Week at Your Prenatal Visits
Central to ensuring the health and well-being of you and your growing baby is seeing your care team regularly for touchpoints and milestones that are part of your pregnancy appointment schedule. Diana Kaufman, MD , UnityPoint Health, shares the recommended timeline for prenatal visits, and the importance of each test and discussion that’ll prepare you for a safe pregnancy and delivery.
Confirming Your Pregnancy
Every woman’s body is unique, but it’s a good idea to visit a doctor to confirm a pregnancy when you’re experiencing early symptoms, such as a missed period or you’ve received a positive home pregnancy test. Typically, this visit happens at 6-8 weeks of pregnancy.
Your doctor may confirm your pregnancy through urine tests, blood tests or ultrasounds.
Initial Prenatal Appointment: 5-12 Weeks
Your first prenatal visit consists of important screenings and discussions, so your healthcare team can create a care plan that ensures you and baby stay healthy throughout your pregnancy. Prepare a few things for this visit, including:
- Complete medical history: It’s important for your doctor to know your past and present health conditions or concerns, medications and any history of disease, substance abuse or known genetic conditions in your family.
- Insurance information: This includes consents for care, your insurance carrier and other paperwork
Here’s what to expect at your first pregnancy appointment
- A physical, which will likely include a breast and pelvic exam.
- A urine sample is collected to check for certain infections and conditions that can occur during pregnancy. Urine tests may be taken at your following prenatal visits as well. Urine drug screening tests are also recommended for women, or their partners, with a history of substance use — including smoking.
- Routine testing that includes blood draws to check your blood type and complete blood count (CBC) and look for specific diseases including hepatitis, HIV, syphilis and checking for immunity against rubella. Other testing that may occur includes genetic screening and testing for diabetes.
Your care team will review prenatal educational materials with you and remedies for any unpleasant pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea or vomiting . Your team also will provide an estimated due date for baby.
It’s also important to take good care of your teeth and gums during pregnancy. Changing hormone levels make your gums more sensitive to disease, which increases your risk for a low-birth weight or premature baby. Consider making an appointment to see your dentist during your first trimester.
Prenatal Appointment: Second Trimester (13 – 26 Weeks)
During weeks 13-26, you’ll see your doctor every four weeks. It’s a good idea to write down questions or concerns before your appointments to ensure they’re addressed.
At each appointment throughout the rest of your pregnancy, your care team will check the following:
- Blood pressure
- Position of baby
- Baby’s heartbeat
Here are some additional things to expect.
- Prenatal genetic testing: There are many different options for prenatal genetic testing. Your care team will review these with you.
- Pregnancy blood tests: These are tailored to your specific needs. Most patients are tested for anemia and diabetes of pregnancy between weeks 24-28. Other recommended tests will be reviewed with you.
- Ultrasound: It’s common to have an ultrasound in the first trimester to confirm the estimated due date. Ultrasound is also common at 20 weeks to check on baby's growth and development. Further ultrasounds could be needed if changes in your pregnancy make it necessary, such as concerns about baby’s growth or to see if baby is head down.
- Discuss preterm labor signs: Preterm labor refers to labor that begins before the 37th week of pregnancy and requires medical attention. Knowing what to look for — such as contractions, changes in vaginal discharge — is important for preventing potential complications.
- Childbirth classes: It’s a good idea to register for a class to help you prepare for baby’s arrival.
When to Call Your Doctor
Pregnancy creates new and unfamiliar symptoms in many women. However, some symptoms need attention. Here’s when to call your doctor in the second trimester:
- Vaginal bleeding, even a small amount
- Leg pain with numbness or leg weakness
- Pain or tenderness in one of both calves that doesn’t go away
- Thoughts of hurting yourself or others
- Severe headaches that don’t go away with Tylenol
- Persistent changes in vision such as blurriness or floaters
- More than five contractions in an hour
Now, your visits to your care team become more frequent — happening every two weeks until you’re 36 weeks pregnant. Your care team continues to monitor you and baby. Here’s what else to expect:
Prenatal Appointments: Third Trimester (27 Weeks – Baby’s Arrival)
- Check fetal movement: It’s important to be aware of your baby's movements. If you notice a sudden change or absence of fetal movement, let you care team know.
- Rhogam injections: If an Rh-negative blood type was found during your initial prenatal visit, you’ll receive an injection to prevent immune system complications for future pregnancies. This usually happens at 28 weeks.
- Additional prenatal testing: Around 35-37 weeks, you’re checked to see if you carry group B streptococcus bacteria . This is one of many bacteria that can live on our skin and typically does not cause problems. However, it can infect a newborn when you deliver. Antibiotics are given during delivery to prevent infection in a newborn if you test positive.
Prenatal Appointments: 36 Weeks – End of Pregnancy
Once you’ve reached 36 weeks, you’ll see your doctor every week until you deliver. These visits are essential for ensuring the well-being of both you and your little one, as well as preparing for a safe and smooth delivery. In addition to routine physical examinations and checking baby’s heartbeat and movement, here’s what else you can expect:
- Cervical exams: If you’re having frequent contractions or preparing to be induced, your doctor will likely need to perform this exam.
- Discuss labor signs: You’ll likely discuss signs of labor with your doctor and when to go to the hospital.
- Discuss birth preferences: It’s not necessary to have a birth plan. Your care team has that covered. Our goal is to keep you and your baby healthy throughout the entire pregnancy and delivery process. However, if you have strong desires or needs for delivery, please discuss those during a prenatal appointment. It’s also helpful to write these things down and bring them to the hospital, since you may not be able to fully express your wishes during labor.
Postpartum Visits
After delivering baby, but before you leave the hospital, call your doctor to make your postpartum appointment, if it hasn’t been scheduled yet. This visit typically occurs around 6 weeks after you deliver. Other visits are scheduled based on your individual needs.
These visits are a time for your doctor to check on your healing , discuss normal or abnormal postpartum bleeding, talk about your well-being and any signs of postpartum depression or anxiety , discuss when it’s safe to start exercising again and address other questions or concerns you may have .
Our UnityPoint Health care team is here to care for you and baby throughout the entirety of your pregnancy and beyond. Call us to schedule your first appointment or if you have questions about any future appointments.
More Maternity Content
Group B Strep in Pregnancy: Understanding Risks, Testing and Treatment
Second Time Mom Gets Wish of Vaginal Birth After C-Section
An OBGYN Answers 17 Questions to Help You Prepare for Postpartum
15 Crucial Questions Every Woman Needs to Ask Her OB/GYN During Pregnancy
Medical review policy, latest update:, what over-the-counter medications are safe, what about prescription meds that i might take, do i need to change my beauty routine, how much weight should i gain, what should i eat and avoid eating, what exercise is okay during pregnancy, what vaccinations should i get, how long can i work when i'm pregnant, what pregnancy symptoms are normal, and what's an emergency, first trimester, second trimester, third trimester, can we discuss my birth plan, what should i expect during my labor and delivery, who will deliver my baby, what's the likelihood i'll need a c-section, what should i know if i want a vbac, what support can i get if i want to breastfeed.
The bottom line: Don’t be afraid to call your practitioner if you’re unsure about anything. He or she knows this is likely a new experience for you, and can help you figure out what’s normal and what’s not.
What to Expect When You're Expecting , 5th edition, Heidi Murkoff. WhatToExpect.com, Your First Prenatal Appointment , January 2021. WhatToExpect.com, Medications During Pregnancy: What’s Safe and What’s Not? , March 2021. WhatToExpect.com, How Much Weight You Should Gain During Pregnancy , October 2020. WhatToExpect.com, 19 Best Foods to Eat During Pregnancy , May 2020. WhatToExpect.com, The Best Pregnancy Workouts and Exercises You Can Do While Expecting , July 2021. WhatToExpect.com, Signs of Labor , July 2021. WhatToExpect.com, How to Create a Birth Plan , June 2021. WhatToExpect.com, Having a C-Section (Cesarean Section) , July 2021. WhatToExpect.com, How a Lactation Consultant Can Help You Breastfeed , February 2019. WhatToExpect.com, The COVID-19 Vaccine During Pregnancy , July 2021. WhatToExpect.com, Vaccines to Get Before and During Pregnancy , July 2021. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Weight Gain During Pregnancy , 2020. American Family Physician, ACOG Updates Recommendations on Vaginal Birth After Previous Cesarean Delivery , January 2011. Food & Drug Administration, Advice about Eating Fish , December 2020. Kristina Mixer , M.D., OB/GYN, Spectrum Health United Hospital, Greenville, MI. Karen Deighan , M.D., OB/GYN, Loyola University Medical Center, North Riverside, IL.
Jump to Your Week of Pregnancy
Trending on what to expect, signs of labor, pregnancy calculator, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., top 1,000 baby girl names in the u.s., top 1,000 baby boy names in the u.s., braxton hicks contractions and false labor.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Health Topics
- Drugs & Supplements
- Medical Tests
- Medical Encyclopedia
- About MedlinePlus
- Customer Support
Prenatal care in your first trimester
Trimester means "3 months." A normal pregnancy lasts around 10 months and has 3 trimesters.
The word prenatal means before birth. The first trimester starts when your baby is conceived. It continues through week 14 of your pregnancy. Your health care provider may talk about your pregnancy in weeks, rather than in months or trimesters.
Your First Prenatal Visit
You should schedule your first prenatal visit soon after you learn that you are pregnant. Your doctor or midwife will:
- Draw your blood
- Perform a full pelvic exam
- Do a Pap smear and cultures to look for infections or problems
Your doctor or midwife will listen for your baby's heartbeat, but may not be able to hear it. Most often, the heartbeat cannot be heard or seen on ultrasound until at least 6 to 7 weeks.
During this first visit, your doctor or midwife will ask you questions about:
- Your overall health
- Any health problems you have
- Past pregnancies
- Medicines, herbs, or vitamins you take
- Whether or not you exercise
- Whether you smoke, use tobacco, drink alcohol or take drugs
- Whether you or your partner have genetic disorders or health problems that run in your family
You will have many visits to talk about a birthing plan. You can also discuss it with your doctor or midwife at your first visit.
The first visit will also be a good time to talk about:
- Eating healthy , exercising, getting adequate sleep, and making lifestyle changes while you are pregnant
- Common symptoms during pregnancy such as fatigue, heartburn, and varicose veins
- How to manage morning sickness
- What to do about vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy
- What to expect at each visit
You will also be given prenatal vitamins with iron if you are not already taking them.
Follow-up Prenatal Visits
In your first trimester, you will have a prenatal visit every month. The visits may be quick, but they are still important. It is OK to bring your partner or labor coach with you.
During your visits, your doctor or midwife will:
- Check your blood pressure.
- Check for fetal heart sounds.
- Take a urine sample to test for sugar or protein in your urine. If either of these is found, it could mean that you have gestational diabetes or high blood pressure caused by pregnancy.
At the end of each visit, your doctor or midwife will tell you what changes to expect before your next visit. Tell your doctor if you have any problems or concerns. It is OK to talk about them even if you do not feel that they are important or related to your pregnancy.
At your first visit, your doctor or midwife will draw blood for a group of tests known as the prenatal panel. These tests are done to find problems or infections early in the pregnancy.
This panel of tests includes, but is not limited to:
- A complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood typing (including Rh screen)
- Rubella viral antigen screen (this shows how immune you are to the disease Rubella)
- Hepatitis panel (this shows if you are positive for hepatitis A, B, or C)
- Syphilis test
- HIV test (this test shows if you are positive for the virus that causes AIDS)
- Cystic fibrosis screen (this test shows if you are a carrier for cystic fibrosis)
- A urine analysis and culture
Ultrasounds
An ultrasound is a simple, painless procedure. A wand that uses sound waves will be placed on your belly. The sound waves will let your doctor or midwife see the baby.
You should have an ultrasound done in the first trimester to get an idea of your due date. The first trimester ultrasound will usually be a vaginal ultrasound.
Genetic Testing
All women are offered genetic testing to screen for birth defects and genetic problems, such as Down syndrome or brain and spinal column defects.
- If your doctor thinks that you need any of these tests, talk about which ones will be best for you.
- Be sure to ask what the results could mean for you and your baby.
- A genetic counselor can help you understand your risks and test results.
- There are many options now for genetic testing. Some of these tests carry some risks to your baby, while others do not.
Women who may be at higher risk for these genetic problems include:
- Women who have had a fetus with genetic problems in earlier pregnancies
- Women, age 35 years or older
- Women with a strong family history of inherited birth defects
In one test, your provider can use an ultrasound to measure the back of the baby's neck. This is called nuchal translucency .
- A blood test is also done.
- Together, these 2 measures will tell if the baby is at risk for having Down syndrome.
- If a test called a quadruple screen is done in the second trimester, the results of both tests are more accurate than doing either test alone. This is called integrated screening. If the test is positive, an amniocentesis or cell-free DNA test may be recommended.
Another test, called chorionic villus sampling (CVS) , can detect Down syndrome and other genetic disorders as early as 10 weeks into a pregnancy.
A newer test, called cell free DNA testing, looks for small pieces of your baby's genes in a sample of blood from the mother. This test is newer, but offers a lot of promise for accuracy without risks of miscarriage. It may reduce the need for an amniocentesis, and so is safer for the baby.
There are other tests that may be done in the second trimester .
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your provider if:
- You have a significant amount of nausea and vomiting.
- You have bleeding or cramping.
- You have increased discharge or a discharge with odor.
- You have a fever, chills, or pain when passing urine.
- You have any questions or concerns about your health or your pregnancy.
Alternative Names
Pregnancy care - first trimester
Gregory KD, Ramos DE, Jauniaux ERM. Preconception and prenatal care. In:.Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 5.
Hobel CJ, Williams J. Antepartum care. In: Hacker N, Gambone JC, Hobel CJ, eds. Hacker & Moore's Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 7.
Magowan BA, Owen P, Thomson A. Antenatal and postnatal care. In: Magowan BA, Owen P, Thomson A, eds. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 22.
Symonds I. Early pregnancy care. In: Symonds I, Arulkumaran S, eds. Essential Obstetrics and Gynaecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 18.
Williams DE, Pridjian G. Obstetrics. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 20.
Review Date 4/19/2022
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Related MedlinePlus Health Topics
- Prenatal Care
- Infants & Toddlers
- Mental Health
- Weight Management
- Orthopedics & Spine
- Brain & Memory
- Breakthroughs
- Cold & Flu
- Ear, Nose & Throat
- Heart & Vascular
- Men’s Health
- Women’s Health

A trimester-by-trimester guide to pregnancy
By: My Vanderbilt Health
April 24, 2024
Learn how each stage of pregnancy can affect you physically — and how your medical team will be working to care for you and your growing baby.
While everyone’s experience will be different, there are some common changes you can expect throughout the stages of pregnancy.
Pregnancies last around 40 weeks, counting from the first day of your last menstrual period. Here’s what you can expect during each of your three trimesters.
First Trimester (Weeks 0-13)
The earliest symptoms of pregnancy include breast tenderness, mood changes and a missed period. By the second month, you may feel sick to your stomach and fatigued. During this stage of the pregnancy, your belly and breasts will grow and your clothes may start to feel tight. You may also experience headaches, dizziness, heartburn or constipation.
“The most common reasons people seek care during the first trimester are nausea, vomiting, spotting and bleeding,” said Dr. Jody L. Stonehocker, an obstetrician with Vanderbilt Women’s Health .
“I tell patients that if they’re experiencing bleeding, they should come in to get checked out,” said Stonehocker . “It doesn’t necessarily mean anything is wrong, but, especially if they haven’t had an ultrasound yet, we want to rule out ectopic pregnancy .”
First trimester tests include:
- A blood draw to scan for anemia, blood type, HIV and other conditions
- Urine samples
- Pelvic exam
- An ultrasound to confirm pregnancy, verify gestational age and determine if you’re carrying multiples
- The option to receive non-invasive prenatal testing , a blood test that screens for Down syndrome and other chromosomal conditions — and also allows you to find out the baby’s sex
Though you’ll see a provider regularly throughout pregnancy — appointments start out every 6 weeks and gradually become more frequent — don’t neglect the other aspects of your health.
Though you’ll see a provider regularly throughout pregnancy — appointments start out every 6 weeks and gradually become more frequent — don’t neglect the other aspects of your health. You can (and should!) go to your regular dental cleanings, and low-impact exercise like walking or yoga can improve your overall health.

Second Trimester (Weeks 14-27)
In the second trimester, you’ll start to feel your baby move. You’ll also feel more pressure on your bladder, stomach and other organs and may see a dark line emerge on your belly, called the linea nigra. You will also start gaining weight at a more regular pace — around 1 pound a week until you give birth. If you prefer not to track your weight, you can discuss modifications with your provider, like standing away from the scale’s display during appointments.
Second trimester tests include:
- Urine tests
- 20-week ultrasound to see the size, position and number of babies, check for physical issues and see the sex of the baby
- Blood sugar test to check for gestational diabetes
Third Trimester (Week 28-Birth)
As your baby grows, you may feel short of breath as your organs become more cramped. Your breasts will continue to grow, and milk may leak from your nipples. You will also start to feel minor contractions called Braxton-Hicks contractions . Also known as “false labor,” Braxton-Hicks contractions tend to be irregular and do not get stronger over time.
Third trimester tests include:
- Repeat testing for anemia, HIV and other conditions
- A swab for Group B streptococcus, a type of bacteria. If you’re positive, your obstetric care team will give you medicine during labor to lower the chance that your baby gets the bacteria.
In this stage of pregnancy, you should think through your birth plan so you can express your labor and postpartum preferences to your birthing partner and care team. This is also a great time to take any childbirth or breastfeeding classes, such as those offered by Vanderbilt Health .

Expert care for you and your baby
Each pregnancy and delivery is unique and yours should be too. Learn more about how Vanderbilt Health’s obstetrics and maternal fetal medicine teams bring together nationally ranked expertise and personalized care from your first prenatal visit to delivery and beyond.
To learn more, call 615-343-5700 or schedule an appointment online .
Related Articles
Making the most of your prenatal care
Early and continuous prenatal care can set you up for a supportive partnership with your health care provider throughout your pregnancy. Learn what to expect at your appointments.

What is an amniocentesis?
What to expect with this pregnancy screening procedure.

What to expect if you’re referred to a maternal-fetal medicine specialist
There are many reasons a pregnant woman may need to see this type of specialist. What to know.
Sign up for updates on My Vanderbilt Health
First Prenatal Visit: What Happens & How to Prepare
The first prenatal care visit is an exciting time but you may not know what to expect or how to prepare. Here’s an overview of what to expect.
- Written by Genevieve Howland
- Updated on May 24, 2019

From the time you pee on that pregnancy test to actually going to your first prenatal visit seems like an eternity. It. is. BRUTAL! I remember calling my midwife all giddy when I told her that I was pregnant and she said “I’ll see you in 10 weeks.” TEN WEEKS?!?! Are you crazy? What if something happens to the baby? What happens if I mess something up? What? Wha? Wha?
Then I remembered to breath… and I realized that there really isn’t anything a midwife could do to “save” my baby in these very precious early weeks. And so I surrendered. And waited. And wondered. What do I need to bring to my first prenatal visit? Can I prepare in any way? And what exactly goes on during the first prenatal visit?
Here’s what you can expect and how you can prepare.
When is my first prenatal visit?
Typically women see their healthcare provider for prenatal care between 8 and 12 weeks. If you are seeing a midwife they may suggest you wait until 10 – 12 weeks for your first appointment. This is because this is about the time when you can hear your baby’s heartbeat on a doppler. Don’t be sad or scared if they still can’t find the heartbeat, as it is really more like 12-14 weeks for a definite reading.
Many OBs and even family doctors expect you to schedule your first prenatal care appointment much earlier than this though.
An ultrasound can pick up a heartbeat as early as 6-7 weeks, and some women are led to believe that an early ultrasound is necessary for a healthy pregnancy. This analysis shows that routine ultrasound does not improve perinatal outcomes while this analysis shows no improvement in maternal outcomes.
Here’s a post dedicated to the risks vs. rewards of baby ultrasounds .
Another reason that some doctors want you to schedule an earlier appointment is for a full pelvic exam. The reasoning is that, for some women, prenatal care is their first or only chance to see a doctor and undiagnosed STDs can be dangerous for the baby.
Your provider may also take the opportunity to do a pap smear to check for cervical cancer. However, vaginal exams do carry a small risk of infection, so if you are relatively healthy and don’t have a history of ectopic pregnancy or other serious concerns, then you are probably fine to wait until around 12 weeks.
What should I expect at my first prenatal visit?
What happens during the first visit will vary from provider to provider, but for the most part you can expect to do four main things.
1. Build a relationship
One of the advantages to using midwives is that you have continuity of care, meaning that the midwife you see at each (or most) appointments will be the one who attends your birth. Even in a larger office with multiple midwives, at least each appointment was nice and long with plenty of time to talk and bond with these awesome ladies. By the end of my pregnancy, I knew I was in good hands no matter which midwife was on call and this is a very good feeling!
At the first prenatal visit you can get to know your midwife or doctor, learn about her background, and begin to build a relationship of trust. You can ask questions and get information on good books to read or specialists you may want to see during your pregnancy, such as a chiropractor or lactation consultant .
If you are using a family doctor, then you may have a similar continuity of care. With OBs in hospitals you aren’t likely to be able to choose the OB that attends your birth, so a prenatal visit won’t always focus on this kind of relationship building.
2. Assess your health
Your midwife will ask about your health history, family health history, and present health to get a baseline for what is normal for you. She will counsel you on nutrition, exercise and holistic healing and wellness. She will address common pregnancy complaints and offer holistic, natural remedies.
She will also ask if you are having unusual symptoms that may be a sign of something serious. Headaches are common in early pregnancy, but can also be a very early sign of preeclampsia. Your midwife will want to know if you are having headaches or other symptoms and will keep a record of them.
3. Routine tests
Your midwife will order a different blood tests that will tell her your blood type, red and white blood cell counts, hematocrit, hemoglobin, and platelet count. Your midwife needs to know your blood type for your safety, but the other tests should be optional.
These blood tests will also tell your midwife if you are Rh positive or negative. If you are positive (or you are negative and your partner is negative) you have nothing more to do. If you are negative and your partner is positive or you don’t know, your midwife may discuss your receiving an Rhlg shot to prevent any complications.
Your midwife will also tests for various Sexual Transmitted Diseases like syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, which could harmfully affect your pregnancy if not treated. She will also take your blood pressure, pulse, weight, and check the baby’s heartbeat if you are ok using a doppler, which contains ultrasound waves. I chose to use the doppler for the first appointment so I could really believe I was pregnant and then waited till 20 weeks to use the fetoscope for the baby’s heartbeat.
She may palpate your abdomen to check the fundal height (a measure of the size of your uterus). She will rule out any medical problems that may affect your pregnancy and assess whether a homebirth or birth center birth is safe for you (it usually is).
You will also be asked to test your urine for the presence of protein (a sign of toxemia), sugar (a sign of gestational diabetes), or bacteria (a sign of Group B Strep positive). You will pee into a cup and dip a test strip in. Depending on the brand of test strips you will read it after 60 second or immediately. You will do this test at every appointment until birth.
4. Paperwork
At your first prenatal visit you will probably have some paperwork to sign and your midwife or doctor’s office will probably need a copy of your health insurance card. Many midwives will give you an estimate costs for your pregnancy and birth care, so you are both on the same page in terms of cost.
Pregnant? Get my FREE week-by-week updates! – Week by Week Promo [In-article]
Track your baby’s growth, find safe and natural remedies, and have fun along the way!
How can I prepare for my first prenatal visit?
Prepare your questions.
Your first prenatal care appointment may be the first time you meet your midwife or doctor, so it’s a good idea to have questions prepared in order to get a feel for your provider’s background and philosophy. If you are seeing a doctor, ask what her thoughts are about: labor induction , ultrasounds, the glucola drink, treating GBS+ during birth, and natural childbirth in general. You can use these questions as a guide to see if your healthcare provider is a good fit for you.
If you’ve already interviewed your practitioner, you still may have some questions about what to expect during your pregnancy, what symptoms or concerns you may have, or how many weeks pregnant you may be.
I wrote down questions beforehand so that I wouldn’t forget anything during the actual appointment (between excitement, nervousness and pregnancy brain , I had a feeling I would forget a thing or two!)
Gather health info
Ask family members about pregnancy related health concerns that may run in the family. Write down any patterns of health you notice. Also take note of your partner’s family health history, especially genetic diseases. My mom had two c-sections so I wanted to get my midwife’s thoughts on if she thought I could have a vaginal birth.
Write down any past gynecological history, like an abnormal pap smear or a previous pregnancy or miscarriage. Write down any medications you are taking.
If you don’t know your due date, use our due date calculator before your appointment. If you do know your due date and want to know when you most likely conceived, use our reverse due date calculator . And here’s an article for you if you’re unsure how many weeks pregnant you are .
Do your research for prenatal care
Do your best to pick the practitioner who is right for you. But if you go to your first visit and don’t like him or her, remember that you can change at any time! My dear friend changed her care at 34 weeks! And she was so happy that she did.
Your midwife needs to know your blood type for your safety, but the other tests should be optional. A good practitioner will let you know at each appointment what tests or procedures will be coming up at the next appointment so you can have time to research and decide what’s best for you.
A good practitioner should also be able to guide you and answer any questions you have about tests and procedures.
Best wishes for your first prenatal visit!
The first prenatal care visit is an amazing and nerve-wracking time. You may get to hear the heartbeat for the first time! That’s why I would encourage your partner to come along for that first prenatal visit. Hearing your child’s heartbeat for the first time, together as parents, is truly a special and sacred moment. Plus, you now have more “proof” that you really are pregnant.
Knowing what to expect and how to prepare should ease your mind and let you enjoy the excitement of your pregnancy!
- https://www.emedicinehealth.com/complete_blood_count_cbc/article_em.htm
- Beech, BL. Ultrasound unsound? Association for Improvements in the Maternity Services. 1996

Read This Next…
- Constipation in Pregnancy: Natural Ways to Get Things Moving
- 9 Signs You’re Having a Girl (Plus How Accurate They Really Are!)
- Cramps During Pregnancy: What’s Normal? And What’s Not?
- How Accurate Are Pregnancy Tests?
- When Will My Baby Be Born? How Accurate Is Your Due Date?
- See 4 Comments
Add Comment
About the author.
Genevieve Howland is a childbirth educator and breastfeeding advocate. She is the bestselling author of The Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and Childbirth and creator of the Mama Natural Birth Course . A mother of three, graduate of the University of Colorado, and YouTuber with over 130,000,000 views, she helps mothers and moms-to-be lead healthier and more natural lives.
Meghan Quinn Jan 18 at 10:57 pm
Thank you for this info on what to expect! It eases my mind a bit.
Taylor Bishop Oct 26 at 11:22 am
I just wanted to thank you for going over what to expect for a prenatal visit. I didn’t know that it could be beneficial to maybe schedule this maybe 6-7 weeks in a pregnancy. My sister has been thinking of getting pregnant, so this could be good for her to know in the future.
Kendal Mar 12 at 8:52 pm
Thank you–I just had my first prenatal appointment, and this was really helpful! So glad I found your blog at the right time! I also was having trouble believing I was really pregnant, so it was relieving to see you wrote that same thought, and it helped me not feel so bad about also wanting the doppler to hear the heartbeat. Amazing!!
Sarah F. Feb 24 at 11:39 am
My first prenatal appointment led me to calling a local birth center for a meet and greet. My doctor, who I adore, suddenly became very pushy about flu shots. My (shy and quiet) husband had to argue with her about why I don’t get flu shots because after I told her I didn’t want it (they make me horribly sick, and I’d already been sick with bronchitis for 6 weeks), she ordered it anyway, until the husband put his foot down for me. I was on edge about hospital delivery before I even became pregnant, but it worries me that I couldn’t get my own doctor to listen to me over a flu shot. And there was no conceivable way for me to meet with more than 2 of the midwives and none of the OBs before I deliver in August! Hopefully everything clicks at the birth center and I can deliver there. Everyone I know who’s gone there has been thrilled with the care, and the hospitals around here seem quite notorious for C-sections. I wish my doctor had made me feel more confident, but I’m so much more comfortable with the idea that birth is normal and not a medical emergency.
Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required *
Your Comment *
See What’s Up With You & Baby Right Now - Week by Week Grid
Just tap your week of pregnancy:
- 1 st trimester
- 3 weeks -->
- 4 weeks -->
- 5 weeks -->
- 6 weeks -->
- 7 weeks -->
- 8 weeks -->
- 9 weeks -->
- 10 weeks -->
- 11 weeks -->
- 12 weeks -->
- 13 weeks -->
- 2 nd trimester
- 14 weeks -->
- 15 weeks -->
- 16 weeks -->
- 17 weeks -->
- 18 weeks -->
- 19 weeks -->
- 20 weeks -->
- 21 weeks -->
- 22 weeks -->
- 23 weeks -->
- 24 weeks -->
- 25 weeks -->
- 26 weeks -->
- 27 weeks -->
- 3 rd trimester
- 28 weeks -->
- 29 weeks -->
- 30 weeks -->
- 31 weeks -->
- 32 weeks -->
- 33 weeks -->
- 34 weeks -->
- 35 weeks -->
- 36 weeks -->
- 37 weeks -->
- 38 weeks -->
- 39 weeks -->
- 40 weeks -->
- 41 weeks -->
The world’s first natural pregnancy week-by-week. #1 bestseller. Over 125,000 copies sold!
Baby name finder.
Discover thousands of unique and popular baby names with Mama Natural’s NEW Baby Name Finder.
Trending Girl Names
Trending boy names.
25% OFF Suncare Collection* w/ code SUN25 | Free Shipping on all orders $50+

- > Prenatal Visit Schedule: What To Expect During Each Appointment
Prenatal Visit Schedule: What To Expect During Each Appointment
Prenatal care is an important part of a healthy pregnancy and allows your doctor to regularly monitor you and your baby . But what should you expect when it comes to your prenatal visit schedule?
Basically, you’ll visit your doctor once a month at the beginning of your pregnancy and then once a week at the end of your pregnancy. That said, it’s important to schedule your first prenatal visit as soon as you see a positive pregnancy test!
In this article, the experts at Mustela discuss how your prenatal visit schedule will most likely look and what to expect during each appointment.
Prenatal Visit Schedule: First Trimester

This is such an exciting time in your life! When you saw the positive pregnancy test , you were probably four to six weeks pregnant, so go ahead and call your doctor to schedule your first appointment.
During the first trimester , you will have your initial prenatal visit, and then your doctor will schedule your visits every four weeks or once a month.
Check with the doctor or staff for a printout of your prenatal visit schedule.
What To Expect At Your First Appointment
Your first prenatal visit will be around six to nine weeks and will most likely be the lengthiest of all your appointments, so block out a good bit of time on your calendar.
Your doctor will ask a good bit of detailed questions and perform a pretty thorough check. Let’s take a look at what they’ll do during this appointment.
Medical History
Your doctor will ask questions about your:
- Last menstrual cycle so they can give you a due date
- Gynecological history
- Obstetrical history (any past pregnancies)
- Personal and family medical history
- Supplements or medicines you’re taking (if any)
- Lifestyle (use of tobacco products, alcohol, and caffeine; eating and exercising habits)
- Recent travel adventures
- Feelings of depression or anxiety (if any)
Your doctor will order various lab work to check your blood for:
- Blood type and Rh status
- Hemoglobin levels
- Infections such as hepatitis B, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and HIV
- Thyroid levels
- Any other important screenings
Physical Exam
To give you and your baby the best care, your doctor will need to do a thorough physical exam, which most likely will also include a Pap smear to detect any abnormal cervical cells.
Your doctor’s observation also includes:
- Checking your blood pressure
- Measuring your height and weight to determine your recommended weight gain for a healthy pregnancy
- A breast exam
- A pelvic exam
- Screening your heart, lungs, and thyroid
Discuss any pregnancy discomforts , such as nausea and fatigue, with your doctor. Be honest with your doctor so they can take care of you and your baby to the best of their knowledge.

Some doctors also do an ultrasound during the first trimester to confirm or date your pregnancy. (Your first prenatal visit will vary based on the specific policies of your doctor’s office.)
What To Expect At Your 12-Week Appointment
You're nearing the end of your first trimester! During this appointment, you can expect your doctor to check the following:
- Weight and blood pressure
- Urine for sugar and protein levels
- Your baby’s heartbeat (This will be the first time you’ll hear it!)
- Size of your uterus
- Hands and feet for any swelling
Prenatal Visit Schedule: Second Trimester

Assuming you have a healthy pregnancy and no further examinations are necessary, this is what your prenatal visit schedule will look like during your second trimester :
- Four-month appointment (around 16 weeks)
- Five-month appointment (around 20 weeks)
- Six-month appointment (around 24 weeks)
What To Expect During Routine Appointments
Many of your appointments from here on out will look similar regarding what your doctor will check for. During these visits, you can expect your doctor to look at:
- Your baby’s heartbeat
- Your fundal height (The size of your uterus is used to assess fetal growth and development. Your doctor will get this measurement by measuring the length from the top of your uterus to the top of your pubic bone. This measurement should match how many weeks you are. Example: If you’re 20 weeks pregnant, your fundal height should equal 20 centimeters.)
- Hands and feet for swelling
- Any symptoms you’ve been experiencing
At this point in your pregnancy, you may notice your skin becoming dry and starting to stretch a bit. Don’t worry; it’s completely normal!
To tackle dry skin, try Mustela’s Stretch Marks Cream . This velvety, hard-working cream delivers immediate moisture and comfort to your skin!
And our Stretch Marks Oil treats recently formed stretch marks. It’s a fast-absorbing oil that hydrates your skin throughout your pregnancy!
What To Expect During Your 20-Week Sonogram:
Sometime around your 20-week appointment, your doctor will schedule an ultrasound to determine the gender of your baby! During this sonogram, your sonographer will take a look at:
- Baby’s size and all their major organs
- Amniotic fluid
- Location of placenta
Your sonographer passes this information to your doctor to give them a clear picture (literally!) of the overall health of your baby and your pregnancy.
Prenatal Visit Schedule: Third Trimester

During your third trimester , your prenatal visits will be every two weeks until the last month of your pregnancy, when you’ll have them every week. So that means your prenatal visit schedule will look like this:
What To Expect At Your Seventh- and Eighth-Month Visits
During your seventh and eighth months of pregnancy, expect your doctor to check the following:
- Urine for sugar and protein
- Your fundal height (top of your uterus)
- Size and position of your baby
- Feet and hands for swelling
- Varicose veins in your legs
- Glucose screen test (read below for more information)
- Group B strep test (read below for more information)
- Blood test for anemia
- Any symptoms you’ve been having

Glucose Screen Test
This test is used to determine if you have gestational diabetes. Once you arrive at your doctor’s office, be prepared to have your blood drawn first.
Next, you’ll drink a very sugary drink that tastes like flat orange soda. Some women enjoy the taste, while others feel a little queasy afterward!
After you consume the entire drink, you’ll wait one hour before having your blood drawn again. If your blood work comes back with elevated numbers, your doctor will order the next level of tests, which is used to officially diagnose gestational diabetes.
Should you need to take the second test (no studying required!), you’ll have to fast before the appointment. Just like with the initial round of tests, your doctor will draw your blood first and then have you consume the drink.
The only difference is this time, your blood will be drawn every hour for three hours. Be prepared to stay in your doctor’s office for three to four hours.
If the results from this test also come back elevated, your doctor will discuss management techniques for gestational diabetes.
But don’t let this information worry you. Most women who monitor their blood sugar levels and work closely with their doctor have perfectly normal pregnancies and healthy babies!

Group B Strep Test
Group B Strep (GBS) is bacteria that can be found in the vaginas of healthy women. (It’s not related to strep, the throat infection.)
If you are a carrier of GBS, your baby can catch the infection during delivery when they pass through the birth canal. While this bacteria isn’t harmful to you, it can be dangerous for your baby.
To check for GBS, your doctor will perform a test just like they would a Pap smear. If the test shows that you’re a carrier, you’ll receive antibiotics through an IV once you’re in labor. This way, you won’t pass the infection to your baby!
You’re routinely tested for GBS around the seventh or eighth month of pregnancy so your doctors can be prepared to give you the antibiotics at the onset of labor.
What To Expect During Your Ninth Month
Similar to months seven and eight, your doctor will closely monitor you and your baby during this time. Since you’re getting closer to your due date, expect a few additional observations from your doctor.
During your last month of pregnancy, they will take a look at:
- Your cervix by an internal examination to check for effacement (thinning) and dilation (opening)
- Baby’s heartbeat
- Baby’s size (At this point in your pregnancy, your doctor may give you an estimation of your baby’s weight. They can tell your baby’s presentation: head or bottom first, and their position: front- or rear-facing.)
- Any questions or concerns you may have about delivery
A Beautiful Pregnancy And Beautiful Skin

Throughout these nine months , your prenatal visits are special moments of checking on your sweet little baby. It’s exciting to see your belly grow with each visit! But that also means possible stretch marks.
The good news is that Mustela offers a line of prenatal products, including our Stretch Marks Cream and Bust Firming Serum , to soothe and hydrate your skin while you manage the busyness of your prenatal visit schedule.
Let Mustela help you start your beautiful pregnancy with beautiful skin!

Suggested Articles

6 Tips For Finding The Best Maternity Clothes

7 Breastfeeding Myths & Realities

The Best Postpartum Care Plan For New Mothers
Get tips, news and exclusive offers
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.

SARAH INÉS RAMÍREZ, MD, FAAFP
Am Fam Physician. 2023;108(2):139-150
Related AFP Community Blog: Practice Ancestry-Based Medicine, not Racial Essentialism
Related editorial: Perinatal Care of Transgender Patients, Adolescent Patients, and Patients With Opioid Use Disorder
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Well-coordinated prenatal care that follows an evidence-based, informed process results in fewer hospital admissions, improved education, greater satisfaction, and lower pregnancy-associated morbidity and mortality. Care initiated at 10 weeks or earlier improves outcomes. Identification and treatment of periodontal disease decreases preterm delivery risk. A prepregnancy body mass index greater than 25 kg per m 2 is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus, hypertension, miscarriage, and stillbirth. Advanced maternal and paternal age (35 years or older) is associated with gestational diabetes, hypertension, miscarriage, intrauterine growth restriction, aneuploidy, birth defects, and stillbirth. Rh o (D) immune globulin decreases alloimmunization risk in a patient who is RhD-negative carrying a fetus who is RhD-positive. Treatment of iron deficiency anemia decreases the risk of preterm delivery, intrauterine growth restriction, and perinatal depression. Ancestry-based genetic risk stratification using family history can inform genetic screening. Folic acid supplementation (400 to 800 mcg daily) decreases the risk of neural tube defects. All pregnant patients should be screened for asymptomatic bacteriuria, sexually transmitted infections, and immunity against rubella and varicella and should receive tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis (Tdap), influenza, and COVID-19 vaccines. Testing for group B Streptococcus should be performed between 36 and 37 weeks, and intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis should be initiated to decrease the risk of neonatal infection. Because of the impact of social determinants of health on outcomes, universal screening for depression, anxiety, intimate partner violence, substance use, and food insecurity is recommended early in pregnancy. Screening for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks is recommended for all patients. People at risk of preeclampsia, including those diagnosed with COVID-19 in pregnancy, should be offered 81 mg of aspirin daily starting at 12 weeks. Chronic hypertension should be treated to a blood pressure of less than 140/90 mm Hg.
Family physicians provide family-centered care for individuals and families before, during, and after the birth of a child. Well-coordinated prenatal care that follows an evidence-based, informed process results in fewer hospital admissions, improved education, greater care satisfaction, improved perinatal outcomes, and mitigates pregnancy-associated morbidity and mortality. 1 Family physicians are uniquely positioned to address social determinants of health while ensuring quality of care.
Prenatal Care Visits
Initiation of care between six and 10 weeks allows for identification of preexisting conditions that negatively affect maternal-fetal outcomes (e.g., diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity) 2 ; however, 22% of pregnant patients do not receive care during this time. 2 The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a reevaluation of the number of physician visits needed, with an emphasis on increased flexibility, allowing for a combination of virtual and in-person visits depending on risk. 3 Table 1 outlines the components of prenatal care. 1 , 4 – 22 Table 2 provides opportunities for educating pregnant patients during prenatal care visits. 6 , 8 , 14 – 19 , 23 – 29
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Weight, height, and blood pressure should be measured at the first prenatal visit. Early identification of periodontal disease and treatment decreases adverse pregnancy outcomes. 7 Treatment may be performed in the second trimester, and emergent treatment may be completed at any time during pregnancy. 7 A bimanual pelvic examination has poor predictive value for clinical pelvimetry and screening for disease (i.e., sexually transmitted infections and cancer) but may be used as a diagnostic aid in patients with a discrepancy between uterine size and gestational age, which warrants ultrasonography assessment. 30 A pelvic examination is also useful in a symptomatic patient for evaluating spontaneous labor (e.g., cervical dilation, rupture of amniotic membranes). The clinical breast examination is a diagnostic aid in the symptomatic patient and addresses breastfeeding concerns or barriers but does not demonstrate benefit in patients already receiving screening mammograms and does not decrease mortality. 31 – 33
MATERNAL WEIGHT GAIN AND NUTRITION
A prepregnancy body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg per m 2 is associated with preterm delivery, gestational diabetes, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia. A BMI greater than 30 kg per m 2 is also associated with an increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and obstructive sleep apnea. 6 Prepregnancy BMI informs the timing of fetal surveillance, nutritional counseling, and goals for gestational weight gain. Table 3 lists general dietary guidelines for pregnant people. 8 , 17 , 34 , 35 For Black and Hispanic people, a prepregnancy BMI greater than 25 kg per m 2 and the associated poor outcomes are worse compared with non-Hispanic White people. 36
PARENTAL AGE AT CONCEPTION
Advanced maternal and paternal age (35 years and older) is associated with poor outcomes (i.e., aneuploidy, birth defects, gestational diabetes, hypertension, intrauterine growth restriction [IUGR], miscarriage, and stillbirth). Activities focused on improving perinatal outcomes for this group, such as a detailed fetal anatomic screening on ultrasonography, may decrease morbidity and mortality. 37
PREGNANCY DATING AND ULTRASONOGRAPHY
Accurate gestational age estimation is critical to quality care because it enables more precise timing of interventions (e.g., aspirin for preeclampsia prevention, steroids for fetal lung maturity), screening tests, and delivery. Up to 40% of people estimate their last menstrual period incorrectly; therefore, ultrasonography is recommended if uncertainty exists and for patients with irregular menstrual cycles, irregular bleeding, and discrepancy between uterine size and gestational age. 1 , 38 Ultrasonography before 24 weeks decreases missed multiple gestations and post-term inductions. 39 Although routine third-trimester ultrasonography may increase detection of IUGR, it does not improve outcomes. 40 If malpresentation is suspected on physical examination, confirmation with ultrasonography is recommended. 4
ALLOIMMUNIZATION
For patients who are RhD-negative and carrying a fetus who is RhD-positive, the alloimmunization risk is 1.5% to 2% in the setting of spontaneous abortion and 4% to 5% with dilation and curettage. The risk is decreased by 80% to 90% with anti-D immune globulin. 41 Testing for the ABO blood group and RhD antibodies should be performed early in pregnancy. A 300-mcg dose of anti-D immune globulin is recommended for RhD-negative pregnant patients at 28 weeks and again within 72 hours of delivery if the infant is RhD-positive. 41
Iron deficiency anemia increases the risk of preterm delivery, IUGR, and perinatal depression. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found insufficient evidence to assess the benefits and harms of screening for anemia in pregnancy. 42 Screening is recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists early in pregnancy, with iron treatment if deficient. 43 Intravenous iron should be considered for patients who cannot tolerate oral iron or in whom oral iron has been ineffective at correcting the deficiency. 43 Patients with non–iron deficiency anemia, or if iron repletion is ineffective within six weeks, should be referred to a hematologist for further evaluation. Iron supplementation in the first trimester decreases the prevalence of iron deficiency. 43
INHERITED CONDITIONS
Pregnant patients should be counseled and offered aneuploidy (extra or missing chromosomes) screening in early pregnancy, regardless of age. 44 In the United States, 1 in 150 infants has a chromosomal condition, the most common being trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). 44 Table 4 compares screening tests for Down syndrome. 1 , 45 , 46 If a screening test is positive, amniocentesis at 15 weeks or more or chorionic villous sampling between 11 and 13 weeks is recommended. Both procedures have similar rates of fetal loss. 47 At 35 years of age, the risk of Down syndrome (1 in 294 births) is similar to that of fetal loss from amniocentesis. 47 Serum and nuchal translucency testing can screen for other trisomies, including 13 and 18, the protocols for which have lower sensitivities and higher specificities compared with screening protocols for trisomy 21 because they are rarer. 47
Additional genetic screening should be based on maternal and paternal personal and family histories. Race is a social construct, necessitating a shift in genetic risk stratification from race-based to ancestry-based. Sickle cell disease affects up to 100,000 people in the United States, but its inheritance pattern (1:10) is based on people with African ancestry, which includes much of the world. 48 Cystic fibrosis is inherited mainly by people of European ancestry (1:25), but ignoring the possibility of European ancestry in certain racial and ethnic groups results in an underestimation of its prevalence: African (1:61), Hispanic (1:40), and Mediterranean (1:29). 49
NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS
In the United States, neural tube defects affect approximately 2,600 infants per year, with the highest prevalence in Hispanic populations. 35 , 50 All pregnant patients should be counseled and offered screening with maternal serum alpha fetoprotein. 35 Folic acid, 400 to 800 mcg daily, started at least one month before conception and continued until the end of the first trimester, decreases the incidence of neural tube defects by nearly 78%. 35 Patients taking folic acid antagonists (e.g., carbamazepine, methotrexate, trimethoprim) or who have a history of carrying a fetus with a neural tube defect should take 4 mg of folic acid daily, starting at least three months before conception. 35
THYROID DISORDERS
There is no evidence that screening for thyroid disorders improves pregnancy outcomes. Thyroid-stimulating hormone levels should be measured if there is a history of thyroid disease or symptoms of disease. If the level is abnormal, a free thyroxine test helps determine the etiology. 51 Hypothyroidism complicates 1 to 3 per 1,000 pregnancies and increases the risk of fetal loss, preeclampsia, IUGR, and stillbirth. Hyperthyroidism occurs in 2 per 1,000 pregnancies and is associated with miscarriage, preeclampsia, IUGR, preterm delivery, thyroid storm, and congestive heart failure. 51 The effect of subclinical hypothyroidism on a child's neurocognitive development is not well understood, and the effectiveness of treatment with levothyroxine is unproven. 51
CERVICAL CANCER
Intervals for cervical cancer screening are based on patient age, cytology history, and history of the presence of high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV). Routine screening for people at average risk of cervical cancer should begin at 21 years of age. Screening can be performed with either cytology alone every three years, HPV screening alone every five years, or cytology plus HPV screening every five years starting at 25 years of age. Screening is not indicated for people 65 years and older with negative screening in the previous 10 years, and no history of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or higher in the past 25 years. 52 Colposcopy is indicated when the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 is greater than 4%. Surveillance of high-grade lesions should be performed every 12 to 24 weeks. 52 , 53 Although colposcopy and cervical biopsy can be safely performed during pregnancy, endocervical sampling should be deferred until postpartum. 53
Infectious Disease
Bacteriuria.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria complicates up to 15% of pregnancies in the United States, 30% of which progress to pyelonephritis if untreated. 54 All pregnant patients should be screened for bacteriuria at the first prenatal visit. 54 A culture from a midstream or clean-catch sample with greater than 100,000 colony-forming units per mL of a single pathogen is considered positive and treated to decrease the risk of pyelonephritis and subsequent preterm delivery. 54
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
Sexually transmitted infections can affect prenatal outcomes. 55 – 57 Table 5 lists routine screening and treatment for sexually transmitted infections in pregnancy. 55 , 56
Rubella immunity screening during the first prenatal visit is recommended. Postpartum vaccination should also be offered if the patient is not immune to prevent congenital rubella syndrome in subsequent pregnancies. 1 , 58 The presence of rubella immunoglobulin G should be interpreted with caution in patients recently migrating from areas where rubella is endemic because this may indicate a recent infection. 58 Rubella is a live vaccine and should not be administered during pregnancy but is safe during lactation after delivery. 59 , 60
Maternal varicella can result in congenital varicella syndrome (i.e., IUGR and limb, ophthalmologic, and neurologic abnormalities) and neonatal varicella; infection can occur from approximately five days before to two days after birth. A negative history of varicella infection or vaccination warrants serologic testing, and if immunoglobulin G is negative, varicella exposure should be avoided. Postpartum vaccination should be offered. 61
Although tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccination is recommended for anyone in close contact with the infant, only antenatal maternal vaccination ensures increased protection against neonatal pertussis. 62 Pregnant patients should receive a Tdap vaccine beginning at 27 weeks to maximize time for passive immunity to the fetus through the placental transfer of maternal antibodies; vaccination is recommended in each subsequent pregnancy. 62
INFLUENZA AND COVID-19
Influenza and COVID-19 infection in pregnancy increase the risk of intensive care unit admission, preterm delivery, stillbirth, and maternal death. 63 , 64 COVID-19 infection almost doubles the risk of developing preeclampsia 64 ; therefore, initiating low-dose aspirin (81 mg daily) starting at 12 weeks should be considered. 5 Pregnant patients and their household contacts should be vaccinated for influenza and COVID-19. 63 , 64
GROUP B STREPTOCOCCUS
In the United States, group B Streptococcus (GBS) is the leading cause of infection in the first three months of life; 25% of all pregnant patients are GBS carriers. 65 , 66 Screening with a vaginal-rectal swab for culture between 36 and 37 weeks is recommended. 67 Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis decreases neonatal mortality. Antibiotics are recommended when there is GBS bacteriuria with the current pregnancy, a history of a previous infant affected by GBS (e.g., septicemia, meningitis, pneumonia, death), or unknown GBS status and risk factors (e.g., preterm labor, rupture of membranes more than 18 hours before delivery, GBS in previous pregnancy). 67 Patients with GBS bacteriuria in the current pregnancy are assumed to be colonized and do not need subsequent screening. 67
Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health represent up to 80% of the factors that directly affect a person's health. 68 Physicians who provide prenatal care play a critical role in mitigating the burden that social determinants of health play on maternal-child health without compromising the quality of care delivered. 69 An increased burden from social determinants of health increases the risk of depression, anxiety, intimate partner violence, substance use, and food insecurity 70 , 71 ; therefore, universal screening is recommended early in pregnancy.
DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY-RELATED DISORDERS
After the COVID-19 pandemic, rates of perinatal depression and anxiety have increased. People who are non-White, 24 years or younger, or who have 12 years or less of education, lower socioeconomic status, or a history of intimate partner violence or sexual trauma are at higher risk. 11 , 72 , 73 If untreated, depression and anxiety-related disorders increase the risk of preeclampsia, preterm delivery, IUGR, substance use, maternal suicide, infanticide, psychosis, and homicide. 11
INTIMATE PARTNER VIOLENCE
Intimate partner–related homicide is the leading cause of death in the United States in pregnancy. Screening is recommended at the first prenatal visit and once per trimester. 13 Intimate partner violence increases the risk of miscarriage, placental abruption, premature rupture of membranes, IUGR, and preterm delivery. 13 Family physicians should be aware of the signs of intimate partner violence (e.g., frequent sexually transmitted infections, repeated requests for pregnancy tests when pregnancy is not desired, fear of asking a partner to use a condom), the effect of violence on health, and the increased risk of child abuse after delivery. 13
SUBSTANCE USE
Substance use during pregnancy increases the risk of IUGR, preterm delivery, stillbirth, fetal malformations, and maternal death. 74 The use of prescription opioids complicates 7% of pregnancies in the United States; of these, 20% of patients report misuse. 75 Opioid use in pregnancy increased by 131% from 2010 to 2017 in the United States, and the incidence of babies born with withdrawal symptoms in that time increased by 82%. 76 Fetal alcohol exposure is the leading cause of preventable neurodevelopmental disorders in the United States. 14 However, 14% of pregnant patients report current drinking, and 5% report binge drinking in the past 30 days. 77 Exposure to cigarette smoking in utero increases the risk of sudden intrauterine and infant death. 15
FOOD INSECURITY
Maternal food insecurity increases the risk of poor outcomes (e.g., IUGR, preterm delivery, gestational diabetes, hypertension, depression, anxiety). However, few patients disclose this due to concerns about social stigma; therefore, a universal approach to screening is encouraged. The Hunger Vital Sign tool may be used. 12
Complications of Pregnancy
Gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes complicates up to 14% of U.S. pregnancies, with up to 67% of patients developing type 2 diabetes later in life. 78 Racial and ethnic minorities are at the highest risk. 79 Gestational diabetes is associated with hypertension, macrosomia, shoulder dystocia, and cesarean deliveries. 80 Screening for undiagnosed type 2 diabetes at the initial prenatal visit is recommended for people at increased risk 80 ( Table 6 5 , 80 ) . Universal screening for gestational diabetes should occur between 24 and 28 weeks with a one-hour (50-g) glucose tolerance test and, if results are abnormal, should be followed by a confirmatory, fasting, three-hour (100-g) test. 80
HYPERTENSION
Blood pressure should be monitored at each prenatal visit, and education should be provided on preeclampsia warning signs. 5 Patients at increased risk of preeclampsia should be screened for thrombocytopenia, transaminitis, and renal insufficiency, including proteinuria, during the first or second trimester and started on prophylactic daily low-dose aspirin (81 mg) between 12 and 16 weeks 5 , 85 ( Table 6 5 , 80 ) . [Updated] Screening for proteinuria in isolation has little predictive value for detecting preeclampsia. 5 Chronic hypertension (hypertension before 20 weeks) is treated to less than 140/90 mm Hg. 81
PRETERM DELIVERY
Preterm delivery (between 20 and 37 weeks) is a significant cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality, complicating 10.5% of U.S. pregnancies. 2 Modifiable risk factors include prepregnancy BMI (less than 18.5 kg per m 2 and greater than 25 kg per m 2 ), substance use, and short interval between pregnancies (i.e., less than 18 months). 82 Several options are available for the prevention of preterm labor in a singleton pregnancy. 82 Patients with a previous preterm delivery before 34 weeks should have a cervical length assessment starting at 16 weeks through 24 weeks. 82 These patients should be treated with progesterone supplementation (vaginal or intramuscular). In the asymptomatic patient with a short cervix and without a history of spontaneous birth before 34 weeks, vaginal progesterone (200 mg) started between 16 and 20 weeks and continued through 36 weeks is recommended. 82
POST-TERM DELIVERY
Stillbirth complicates 3 per 1,000 post-term (42 weeks or greater) pregnancies. 20 Antenatal testing should be initiated at 41 weeks; if the results are not reassuring, induction of labor is recommended. 20 , 21
Cultural Considerations
Maternity care improves outcomes; however, vulnerable populations (i.e., racial, ethnic, and religious minorities) are less likely to engage in care if it is not culturally centered, which acknowledges the effect of culture on health conditions (e.g., depression) and enhances patient-physician trust. 83 Addressing cultural needs (e.g., doula, community health workers, interpreters) throughout pregnancy helps mitigate barriers and improves outcomes.
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Zolotor and Carlough 1 ; Kirkham, et al. 17 ; and Kirkham, et al. 84
Data Sources: A search was completed using the key terms prenatal care, COVID-19, oral health, pelvic examination, prepregnancy body mass index, pregnancy dating and ultrasound, maternal and paternal age and impact on pregnancy outcomes, aneuploidy screening, inheritance patterns of sickle cell disease and cystic fibrosis, anemia, cell-free DNA analysis, thyroid disease, cervical cancer screening, management of abnormal cervical cytology, screening guidelines for sexually transmitted infections in pregnancy, group B Streptococcus screening, social determinants of health and prenatal outcomes, intimate partner violence, polysubstance abuse, food insecurity, maternity care deserts, hypertension in pregnancy, progesterone for preterm birth prevention, post-term delivery, and preconception care. Also searched were PubMed, Essential Evidence Plus, the Cochrane database, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Cancer Society, American Family Physician , and reference lists of retrieved articles. Search dates: July 1, 2022; February 19, 2023; and June 16, 2023.
Zolotor AJ, Carlough MC. Update on prenatal care. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89(3):199-208.
Osterman MJK, Hamilton BE, Martin JA, et al. Births: final data for 2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023;72(1):1-53.
Peahl AF, Zahn CM, Turrentine M, et al. The Michigan Plan for appropriate tailored healthcare in pregnancy prenatal care recommendations. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138(4):593-602.
Superville SS, Siccardi MA. Leopold maneuvers. StatPearls . StatPearls Publishing. February 19, 2023. Accessed October 16, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560814
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia: practice bulletin, no. 222. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135(6):e237-e260.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Obesity in pregnancy: practice bulletin, no. 230. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137(6):e128-e144.
Nannan M, Xiaoping L, Ying J. Periodontal disease in pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes: progress in related mechanisms and management strategies. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:963956.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Antenatal care. August 19, 2021. Accessed October 11, 2022. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng201
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Ultrasound in pregnancy: practice bulletin, no. 175. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128(6):e241-e256.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Methods for estimating due date: committee opinion, no. 700. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129(5):e150-e154.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Screening and diagnosis on mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum: practice guideline, no. 4. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141(6):1232-1261.
Dolin CD, Compher CC, Oh JK, et al. Pregnant and hungry: addressing food insecurity in pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2021;3(4):100378.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Intimate partner violence: ACOG committee opinion, no. 518. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119(2 pt 1):412-417.
Ethen MK, Ramadhani TA, Scheuerle AE; National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Alcohol consumption by women before and during pregnancy. Matern Child Health J. 2009;13(2):274-285.
Bednarczuk N, Milner A, Greenough A. The role of maternal smoking in sudden fetal and infant death pathogenesis. Front Neurol. 2020;11:586068.
Krist AH, Davidson KW, Mangione CM; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for unhealthy drug use: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2020;323(22):2301-2309.
Kirkham C, Harris S, Grzybowski S. Prenatal care: part I. General prenatal care and counseling issues. Am Fam Physician. 2005;71(7):1307-1316.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Smoking cessation during pregnancy: committee opinion, no. 721. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(4):1.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy: committee opinion, no. 711. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(2):e81-e94.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Obstetric Practice; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Indications for outpatient antenatal fetal surveillance: committee opinion, no. 828. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137(6):e177-e197.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Obstetric Practice; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Medically indicated late-preterm and early-term deliveries: committee opinion, no. 831. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138(1):e35-e39.
Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy UM; Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal–Fetal Medicine Units Network. Labor induction vs. expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(6):513-523.
Meek JY, Noble L; Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2022;150(1):e2022057988.
Norman JE, Heazell AEP, Rodriguez A; AFFIRM investigators. Awareness of fetal movements and care package to reduce fetal mortality (AFFIRM) [published correction appears in Lancet . 2020; 396(10259): 1334]. Lancet. 2018;392(10158):1629-1638.
Haghighi MM, Wright CY, Ayer J; Climate Change and Heat-Health Study Group. Impacts of high environmental temperatures on congenital anomalies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(9):4910.
Shah-Kulkarni S, Lee S, Jeong KS, et al. Prenatal exposure to mixtures of heavy metals and neurodevelopment in infants at 6 months. Environ Res. 2020;182:109122.
Yoon I, Slesinger TL. Radiation exposure in pregnancy. StatPearls . May 8, 2022. Accessed October 18, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551690
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Solvents – reproductive health. May 1, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/repro/solvents.html
ACOG committee opinion, no. 733. Employment considerations during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(4):e115-e123.
ACOG committee opinion, no. 754. The utility of and indications for routine pelvic examination. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132(4):e174-e180.
Lee SJ, Thomas J. Antenatal breast examination for promoting breast-feeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008(3):CD006064.
Oeffinger KC, Fontham ET, Etzioni R; American Cancer Society. Breast cancer screening for women at average risk: 2015 guideline update from the American Cancer Society [published correction appears in JAMA . 2016; 315(13): 1406]. JAMA. 2015;314(15):1599-1614.
Ngan TT, Nguyen NTQ, Van Minh H, et al. Effectiveness of clinical breast examination as a ‘stand-alone’ screening modality: an overview of systematic reviews. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):1070.
MedlinePlus. Eating right during pregnancy. November 21, 2022. Accessed October 18, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000584.htm
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Neural tube defects: ACOG practice bulletin, no. 187. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(6):e279-e290.
Driscoll AK, Gregory ECW. Prepregnancy body mass index and infant outcomes by race and Hispanic origin: United States, 2020. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70(16):1-8.
Pregnancy at age 35 years or older: ACOG obstetric care consensus, no. 11 [published correction appears in Obstet Gynecol . 2023; 141(5): 1030]. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140(2):348-366.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion, no. 700: methods for estimating the due date. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129(5):e150-e154.
Kaelin Agten A, Xia J, Servante JA, et al. Routine ultrasound for fetal assessment before 24 weeks' gestation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021(8):CD014698.
Henrichs J, Verfaille V, Jellema P; IRIS study group. Effectiveness of routine third trimester ultrasonography to reduce adverse perinatal outcomes in low risk pregnancy (the IRIS study). BMJ. 2019;367:l5517.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Prevention of Rh D alloimmunization. ACOG practice bulletin, no. 181. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(2):e57-e70.
Siu AL. Screening for iron deficiency anemia and iron supplementation in pregnant women to improve maternal health and birth outcomes: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(7):529-536.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. Anemia in pregnancy: ACOG practice bulletin, no. 233. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138(2):e55-e64.
LeFevre NM, Sundermeyer RL. Fetal aneuploidy: screening and diagnostic testing. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(8):481-488.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics; Committee on Genetics; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities: practice bulletin, no. 226. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;136(4):e48-e69.
Dar P, Jacobsson B, MacPherson C, et al. Cell-free DNA screening for trisomies 21, 18, and 13 in pregnancies at low and high risk for aneuploidy with genetic confirmation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227(2):259.e1-259.e14.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics; Committee on Genetics; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities: ACOG practice bulletin, no. 226. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;136(4):e48-e69.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data and statistics on sickle cell disease. May 2, 2022. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/data.html#:~:text=In%20the%20United%20States&text=SCD%20affects%20approximately%20100%2C000%20Americans,sickle%20cell%20trait%20(SCT
Boston Medical Center. Genetic screening: ancestry based. Accessed September 30, 2022. https://www.bmc.org/genetic-services/ancestry-based
Mai CT, Isenburg JL, Canfield MA; National Birth Defects Prevention Network. National population-based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Res. 2019;111(18):1420-1435.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Thyroid disease in pregnancy: ACOG practice bulletin, no. 223. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135(6):e261-e274.
Fontham ETH, Wolf AMD, Church TR, et al. Cervical cancer screening for individuals at average risk: 2020 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(5):321-346.
Perkins RB, Guido RS, Castle PE; 2019 ASCCP Risk-Based Management Consensus Guidelines Committee. 2019 ASCCP risk-based management consensus guidelines for abnormal cervical cancer screening tests and cancer precursors [published correction appears in J Low Genit Tract Dis . 2020; 24(4): 427]. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24(2):102-131.
Smaill FM, Vazquez JC. Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019(11):CD000490.
Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70(4):1-187.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Bacterial vaginosis. July 22, 2021. Accessed October 11, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/bv.htm
Brocklehurst P, Gordon A, Heatley E, et al. Antibiotics for treating bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013(1):CD000262.
Mehta NM, Thomas RM. Antenatal screening for rubella—infection or immunity?. BMJ. 2002;325(7355):90-91.
ACOG committee opinion, no. 741: maternal immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
Rubella vaccine. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) . June 15, 2020. Accessed October 11, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501097
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chickenpox vaccination: what everyone should know. April 28, 2021. Accessed October 11, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/varicella/public/index.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tdap (pertussis) vaccine and pregnancy. August 10, 2017. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pregnancy/hcp-toolkit/tdap-vaccine-pregnancy.html
Grohskopf LA, Blanton LH, Ferdinands JM, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices – United States, 2022–23 influenza season. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2022;71(1):1-28.
Jamieson DJ, Rasmussen SA. An update on COVID-19 and pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;226(2):177-186.
Nanduri SA, Petit S, Smelser C, et al. Epidemiology of invasive early-onset and late-onset group b streptococcal disease in the United States, 2006 to 2015: multistate laboratory and population-based surveillance [published corrections appear in JAMA Pediatr . 2019; 173(3): 296, and JAMA Pediatr . 2019; 173(5): 502]. JAMA Pediatr. 2019;173(3):224-233.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Active bacterial core surveillance (ABCs) report. Emerging infections program network, group B Streptococcus , 2018. May 19, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/abcs/reports-findings/survreports/gbs18.pdf?CDC_AA_refVal= https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fabcs%2Freports-findings%2Fsurvreports%2Fgbs18.html
Prevention of group b streptococcal early-onset disease in newborns: ACOG committee opinion, no. 797 [published correction appears in Obstet Gynecol . 2020; 135(4): 978–979]. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135(2):e51-e72.
Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement. Going beyond clinical walls: solving complex problems. October 2014. Accessed October 11, 2022. https://www.icsi.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/1.SolvingComplexProblems_BeyondClinicalWalls.pdf
Partin M, Sanchez A, Poulson J, et al. Social inequities between prenatal patients in family medicine and obstetrics and gynecology with similar outcomes. J Am Board Fam Med. 2021;34(1):181-188.
Compton MT, Shim RS. The social determinants of mental health. Focus. 2015;13(4):419-425.
Kuhrau C, Kelly E, DeFranco EA. Social determinants of health associated with intimate partner violence in an urban obstetric population. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228(1):S110-S111.
Bauman BL, Ko JY, Cox S, et al. Vital signs: postpartum depressive symptoms and provider discussions about perinatal depression - United States, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(19):575-581.
Lombardi BN, Jensen TM, Parisi AB, et al. The relationship between a lifetime history of sexual victimization and perinatal depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2023;24(1):139-155.
Yazdy MM, Desai RJ, Brogly SB. Prescription opioids in pregnancy and birth outcomes. J Pediatr Genet. 2015;4(2):56-70.
Ko JY, D'Angelo DV, Haight SC, et al. Vital signs: prescription opioid pain reliever use during pregnancy–34 U.S. jurisdictions, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(28):897-903.
Hirai AH, Ko JY, Owens PL, et al. Neonatal abstinence syndrome and maternal opioid-related diagnoses in the US, 2010–2017 [published correction appears in JAMA . 2021; 325(22): 2316]. JAMA. 2021;325(2):146-155.
Gosdin LK, Deputy NP, Kim SY, et al. Alcohol consumption and binge drinking during pregnancy among adults aged 18–49 years–United States, 2018–2020 [published correction appears in MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2022; 71(4): 156]. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71(1):10-13.
Diaz-Santana MV, O'Brien KM, Park YM, et al. Persistence of risk for type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(4):864-870.
Bower JK, Butler BN, Bose-Brill S, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in diabetes screening and hyperglycemia among US women after gestational diabetes. Prev Chronic Dis. 2019;16:E145.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Gestational diabetes mellitus. ACOG practice bulletin, no. 190. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(2):e49-E64.
Tita AT, Szychowski JM, Boggess K, et al. Treatment for mild chronic hypertension during pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(19):1781-1792.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. Prediction and prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. ACOG practice bulletin, no. 234. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138(2):e65-e90.
Gopalkrishnan N. Cultural diversity and mental health: considerations for policy and practice. Front Public Health. 2018;6:179.
Kirkham C, Harris S, Grzybowski S. Evidence-based prenatal care: part II. Third-trimester care and prevention of infectious diseases. Am Fam Physician. 2005;71(8):1555-1560.
- Roberts JM, King TL, Barton JR, et al. Care plan for individuals at risk for preeclampsia: shared approach to education, strategies for prevention, surveillance, and follow-up. Am J Obstet Gynecol . 2023;229(3):193-213.
Continue Reading

More in AFP
More in pubmed.
Copyright © 2023 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your next prenatal visits — often scheduled about every four weeks during the first trimester — might be shorter than the first. Near the end of the first trimester — by about 12 to 14 weeks of pregnancy — you might be able to hear your baby's heartbeat with a small device, called a Doppler, that bounces sound waves off your baby's heart.
If you did not meet with your health care provider before you were pregnant, your first prenatal visit will generally be around 8 weeks after your LMP (last menstrual period ). If this applies to you, you should schedule a prenatal visit as soon as you know you are pregnant! Even if you are not a first-time mother, prenatal visits are still ...
The most common tests at your first prenatal visit will likely include: [3] Urine test. Your urine may be checked for protein, glucose (sugar), white blood cells, blood and bacteria. Bloodwork. A sample of your blood will be used to determine blood type and Rh status and check for anemia. Trusted Source Mayo Clinic Rh factor blood test See All ...
Many healthcare providers will schedule your first visit for when you're about 8 weeks pregnant. Some will see you sooner, particularly if you have an existing health condition, ... The first prenatal visit is a great opportunity to learn about how your body will change. It's also a good time to ask about nutrition, including which foods to ...
If your first prenatal appointment comes later in your pregnancy, around 10 or 12 weeks or later, your provider may use a traditional ultrasound or Doppler to check the fetal heartbeat. Earlier ...
Typical prenatal appointment schedule. The number of visits you'll have in a typical pregnancy usually total about 10 to 15, depending on when you find out you're expecting and the timing of your first checkup. In most complication-free pregnancies, you can expect to have a prenatal appointment with the following frequency: Weeks 4 to 28 ...
1st Trimester: 1st Prenatal Visit. It's the first doctor visit of your pregnancy. Congratulations! During this visit, your doctor will check your overall health and determine your due date. They ...
Genetic testing. At your first pregnancy appointment, your provider might perform or discuss future genetic testing. "There are genetic tests that are time-sensitive and can be done as early as 10 weeks," says Braden. "There are some that are done with an ultrasound around 12 or 13 weeks pregnant, and some that are done in the second ...
Weeks 1-4 Weeks 5-8 Weeks 9-12 Calculate due date Sharing news Twins or more Age 35+ Second trimester. Second trimester overview Weeks 13-16 ... Your first prenatal visit. This first visit will probably be the longest, because there's a lot to cover! To make sure you and your baby are off to a healthy start, we'll:
When to schedule a prenatal visit. Make an appointment for your first prenatal visit once you're aware you are pregnant - when you receive a positive home pregnancy test, for example. Booking it around week 8 of pregnancy is typical. You'll come back regularly in the weeks and months following that initial appointment.
Here's what to expect at your first pregnancy appointment. A physical, which will likely include a breast and pelvic exam. A urine sample is collected to check for certain infections and conditions that can occur during pregnancy. Urine tests may be taken at your following prenatal visits as well. Urine drug screening tests are also ...
While it's important to check with your own doctor first, these typically get the green light: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) for headache, pain or fever. Vitamin B6 and doxylamine (Unisom) or Diclegis for nausea and vomiting. Chlorpheniramine and tripelennamine for cold and allergy symptoms. Fiber supplement for constipation.
2. Write down your questions. It's hard to remember everything. So, it's a good idea to write down your questions and bring them with you to your first appointment. Check out our suggested list of questions here. 3. Take a prenatal vitamin. There are many good options for over-the-counter prenatal vitamins.
Visit #4: 20-22 weeks. Visit #5: 24-28 weeks. Visit #6: 32 weeks. Visit #7: 36 weeks. Visits #8-10: 38-40 weeks. Visit #1: 6-10 weeks. Your first prenatal appointment will be a bit longer than the rest, as it will involve a wide range of tests and exams to assess your overall health, establish baseline measurements and look for factors that ...
Weeks 4 to 28 — One prenatal visit every four weeks. Weeks 28 to 36 — One prenatal visit every two weeks. Weeks 36 to 40 — One prenatal visit every week. Each scheduled visit on the timeline ...
A doppler usually cannot detect a baby's heartbeat before 10 to 12 weeks of pregnancy. The provider may perform an ultrasound ... The first prenatal visit can be exciting yet stressful. With all ...
The first trimester starts when your baby is conceived. It continues through week 14 of your pregnancy. Your health care provider may talk about your pregnancy in weeks, rather than in months or trimesters. Your First Prenatal Visit . You should schedule your first prenatal visit soon after you learn that you are pregnant. Your doctor or ...
Each pregnancy and delivery is unique and yours should be too. Learn more about how Vanderbilt Health's obstetrics and maternal fetal medicine teams bring together nationally ranked expertise and personalized care from your first prenatal visit to delivery and beyond. To learn more, call 615-343-5700 or schedule an appointment online. Learn More
Download transcript. Your first prenatal care appointment will most likely be between weeks 7 and 12. After that, as long as your pregnancy is going normally, you'll have prenatal visits — either in person, online, or by phone — at about: 16 to 20 weeks. 21 to 27 weeks. 28 to 31 weeks.
The first prenatal visit is also an opportunity to ask any questions or discuss any concerns that you may have about your pregnancy. ... The most dramatic changes and development happen during the first trimester. During the first eight weeks, a fetus is called an embryo. The embryo develops rapidly and by the end of the first trimester, it ...
4. Paperwork. At your first prenatal visit you will probably have some paperwork to sign and your midwife or doctor's office will probably need a copy of your health insurance card. Many midwives will give you an estimate costs for your pregnancy and birth care, so you are both on the same page in terms of cost.
(Your first prenatal visit will vary based on the specific policies of your doctor's office.) What To Expect At Your 12-Week Appointment You're nearing the end of your first trimester! ... Third Trimester During your third trimester, your prenatal visits will be every two weeks until the last month of your pregnancy, when you'll have them ...
Should be determined at first prenatal visit; weight should be measured at all subsequent visits: Dental health 7: ... Recommended at each prenatal visit beginning at 20 weeks; should be plotted ...
New York will become the first state in the nation to expand access to prenatal care for pregnant women by granting up to 20 hours of leave for eligible employees to attend appointments, without impacting the existing twelve weeks of paid family leave. ... recognize the needs of military veterans, support First Nations, and invest in TGNCNB New ...