Pale Blue Dot at 30: Voyager 1's iconic photo of Earth from space reveals our place in the universe
The photo shows Earth as it truly is — a lonely outpost of life in an incomprehensibly vast cosmos.

Thirty years ago today, humanity got a chance to see itself in a whole new light.
On Feb. 14, 1990, NASA's Voyager 1 probe snapped a photo of Earth from 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) away. The image shows our home planet as it truly is — a tiny, lonely outpost of life in an incomprehensibly vast cosmos — and became iconic as a result.
The Voyager 1 team sensed at the time that the " Pale Blue Dot ," as the photo has come to be known, would be an important social document, said planetary scientist Candy Hansen, who served as the experiment representative for the Voyager imaging team and was the first person to set eyes on the Pale Blue Dot photo when it came down to Earth.
Related: Voyager at 40: 40 photos from NASA's epic 'Grand Tour' mission
The Cold War had not yet thawed completely in early 1990. The Pale Blue Dot had the potential to remind folks around the world that we're all in this together, no matter how many nuclear warheads one superpower may be aiming at another, Hansen explained. And the image remains vital today, because its message is timeless, she added.
"Now, we have climate change as an existential threat," Hansen, who now works for the Arizona-based Planetary Science Institute, told Space.com. "And we need to remind ourselves again that there's one planet that is hospitable to humans. Even if we colonize the moon or Mars one day, neither one of those bodies is really going to be able to support seven billion of us. So, we need to take care of this planet."

A family portrait
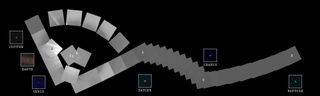
Voyager 1 launched a few weeks after its twin, Voyager 2 , back in 1977. Together, the two probes conducted an unprecedented "grand tour" of the solar system's giant planets, flying by Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The tour was over after the Neptune encounter, which Voyager 2 executed in August 1989. But the two spacecraft kept on flying, out toward the great unknown of interstellar space. Mission team members decided to turn off the two probes' cameras to save precious power during the long journey (and because they probably wouldn't have many chances to photograph interesting things out beyond Neptune anyway).
But Voyager 1 turned around to take one last look at home before closing its eyes. And not just its home planet — its home system. The probe took a "family portrait" series of 60 photos, capturing the sun, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune in addition to Earth. (Mercury was too close to the sun to be imaged, and sunlight bouncing around in the camera blocked Mars out.)
The Pale Blue Dot was the brainchild of famed astronomer, science communicator and Voyager imaging team member Carl Sagan , who first proposed snapping Earth with Voyager cameras in 1981 . And Sagan helped popularize the image and its message after the fact, writing a book called "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space" (Random House, 1994).
Earth was one of the last things Voyager 1 saw. The probe took the Pale Blue Dot photo at 0448 GMT on Feb. 14, 1990, just 34 minutes before its cameras were shut off forever. (The very last photos Voyager 1 took, however, were of the sun, Hansen said.)
All of the image data didn't come down to Earth until May 1, 1990, NASA officials wrote in a Pale Blue Dot explainer . Hansen couldn't wait to see our planet through Voyager 1's eyes — and, when she finally got the chance, doing so proved a bit more difficult than she had expected.
"It was actually kind of terrifying, because I didn't see it at first," she said. "Because of that beam of scattered light, it didn't pop out at me immediately. And then I was so afraid that we had missed it, or screwed up the exposure or something. So, it was such a relief when I spotted it."
That beam of scattered light may have briefly stopped Hansen's heart, but it adds a certain poetic flair to the Pale Blue Dot photo. It's almost as if the cosmos threw a spotlight onto our precious little world for a moment, to help us make it out in the abyss.
Related: Earth quiz: Do you really know your planet?
Still exploring
Both Voyagers kept flying long after February 1990. They cruised through the outer solar system and eventually popped free of the sun's sphere of influence into interstellar space.
Voyager 1 accomplished this unprecedented feat in 2012 , and its twin followed suit six years later. And both probes are still going strong. They should have enough power left to continue gathering data about their exotic surroundings through 2024 or so, mission team members have said.
The Voyager program has accomplished amazing things, shedding considerable light on the giant planets and the dark realms far beyond them. (Voyager 2, for example, is still the only spacecraft ever to get up-close looks at Uranus or Neptune.) And the Pale Blue Dot is a unique part of this diverse and layered legacy.
"The Earth picture reaches to our hearts, I would say, and all the rest goes in our heads," Hansen said.
- Photos from NASA's Voyager 1 and 2 probes
- Voyager 1's historic flyby of Jupiter in photos
- Voyager 1 spacecraft's road to interstellar space: A photo timeline
Mike Wall's book about the search for alien life, " Out There " (Grand Central Publishing, 2018; illustrated by Karl Tate ), is out now. Follow him on Twitter @michaeldwall . Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or Facebook .

OFFER: Save at least 56% with our latest magazine deal!
All About Space magazine takes you on an awe-inspiring journey through our solar system and beyond, from the amazing technology and spacecraft that enables humanity to venture into orbit, to the complexities of space science.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.
China to launch sample-return mission to the moon's far side on May 3
Satellites watch as 4th global coral bleaching event unfolds (image)
Yellowstone Lake's weird resistance to climate change could be about to crack
Most Popular
- 2 NASA's James Webb Space Telescope mission — Live updates
- 3 Best sci-fi movies with 90%+ on Rotten Tomatoes
- 4 Astronomers close in on the mystery of the erupting Orion star system (video)
- 5 Star Wars: Hunters launches in June for Nintendo Switch and mobile (video)

10 Things You Might Not Know About Voyager’s Famous ‘Pale Blue Dot’ Photo
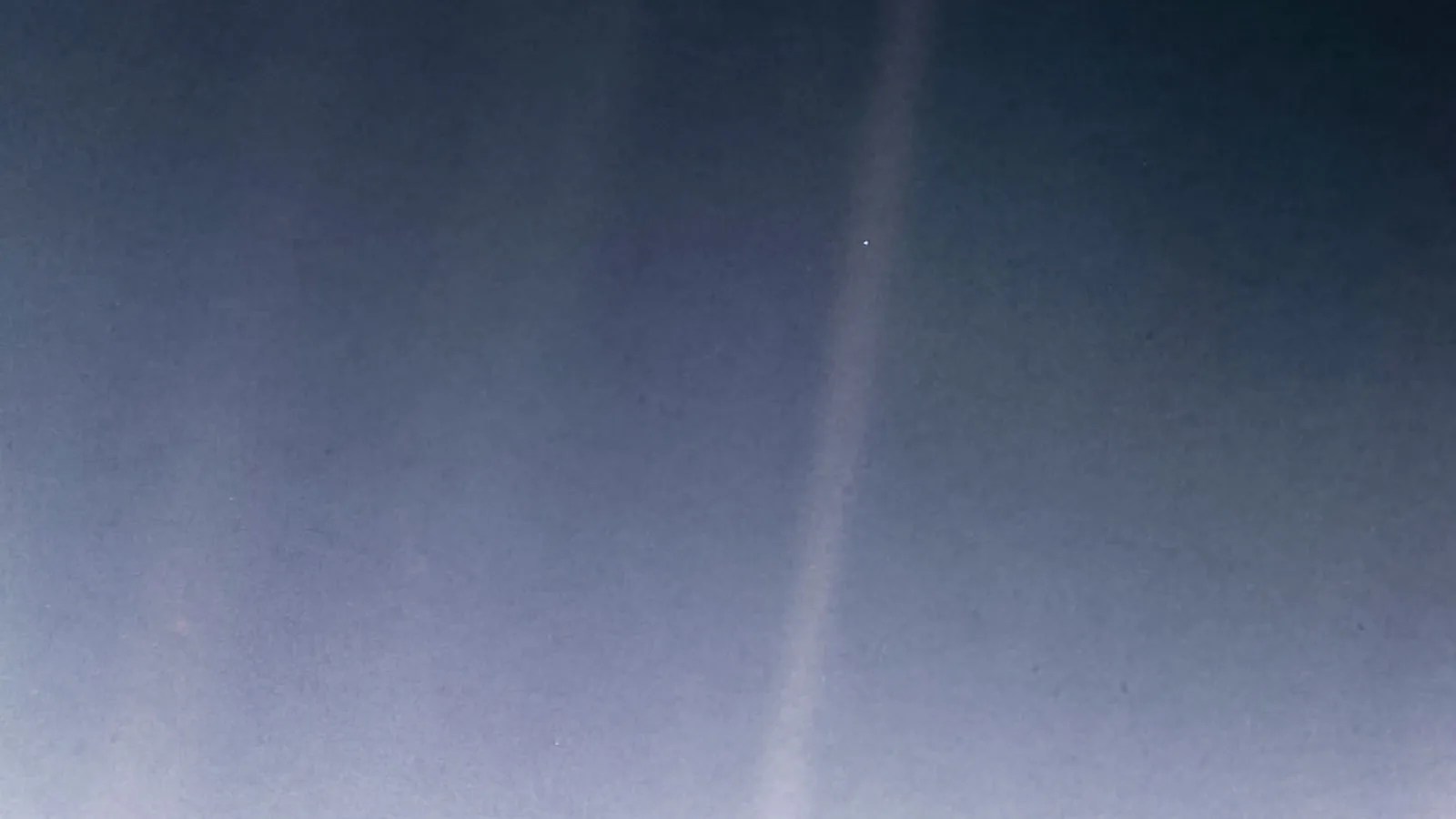

Thirty years ago on Feb. 14, 1990, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft sent home a very special Valentine: A mosaic of 60 images that was intended as what the Voyager team called the first “ Family Portrait ” of our solar system.
The spacecraft was out beyond Neptune when mission managers commanded it to look back for a final time and snap images of the worlds it was leaving behind on its journey into interstellar space.
It captured Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, Earth and Venus. A few key members didn’t make the shot: Mars was obscured by scattered sunlight bouncing around in the camera, Mercury was too close to the Sun and dwarf planet Pluto was too tiny, too far away and too dark to be detected. But the images gave humans an awe-inspiring and unprecedented view of their home world and its neighbors.
One of those images, the picture of Earth, would become known as the “ Pale Blue Dot .” The unique view of Earth as a tiny speck in the cosmos inspired the title of scientist Carl Sagan's book, "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space,"
But the image almost didn’t happen.
Here are 10 things you might not know about Voyager 1’s famous Pale Blue Dot photo.
1. Not in the Plan
Neither the “ Family Portrait ” nor the “ Pale Blue Dot ” photo was planned as part of the original Voyager mission. In fact, the Voyager team turned down several requests to take the images because of limited engineering resources and potential danger to the cameras from pointing them close to the Sun. It took eight years and six requests to get approval for the images.
2. A Unique Perspective
Voyager 1 remains the first and only spacecraft that has attempted to photograph our solar system. Only three spacecraft have been capable of making such an observation: Voyager 1 , Voyager 2 and New Horizons . ( Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 — the other two spacecraft headed into interstellar space — had similar vantage points, but technical challenges prevented them from getting such a shot.)
3. A Mote of Dust
The Voyager imaging team wanted show Earth’s vulnerability — to illustrate how fragile and irreplaceable it is — and demonstrate what a small place it occupies in the universe. Earth in the image is only about a single a pixel, a pale blue dot.
4. A Happy Coincidence
The image contains scattered light that resembles beams of sunlight, making the tiny Earth appear even more dramatic. In fact, these sunbeams are camera artifacts that resulted from the necessity of pointing the camera within a few degrees of the Sun.
Voyager 1 was 40 astronomical units from the Sun at the time so Earth appeared very near our brilliant star from Voyager's vantage point. One astronomical unit is 93 million miles, or 150 million kilometers That one of the rays of light happened to intersect with Earth was a happy coincidence.
Look again at that dot. That's here. That's home. That's us.

"Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space."
The prominent planetary scientist Carl Sagan ( 1934-1996) — a member of the Voyager imaging team — had the original idea to use Voyager’s cameras to image Earth in 1981, following the mission's encounters with Saturn. Sagan later wrote in poetic detail about the image and its meaning in his book, "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space."
6. Cold Cameras
Voyager 1 powered up its cameras for the images on Feb. 13 and it took three hours for them to warm up. The spacecraft’s onboard tape recorder saved all the images taken, for later playback to Earth.
7. Light Time
The images of Earth snapped by Voyager 1 captured light that had left our planet five hours and 36 minutes earlier. (This was, of course, reflected sunlight that had left the Sun eight minutes before that.)
8. Downloading...
Voyager 1 was so far from Earth it took several communications passes with NASA's Deep Space Network, over a couple of months, to transmit all the data. The last of the image data were finally downloaded on Earth on May 1, 1990.
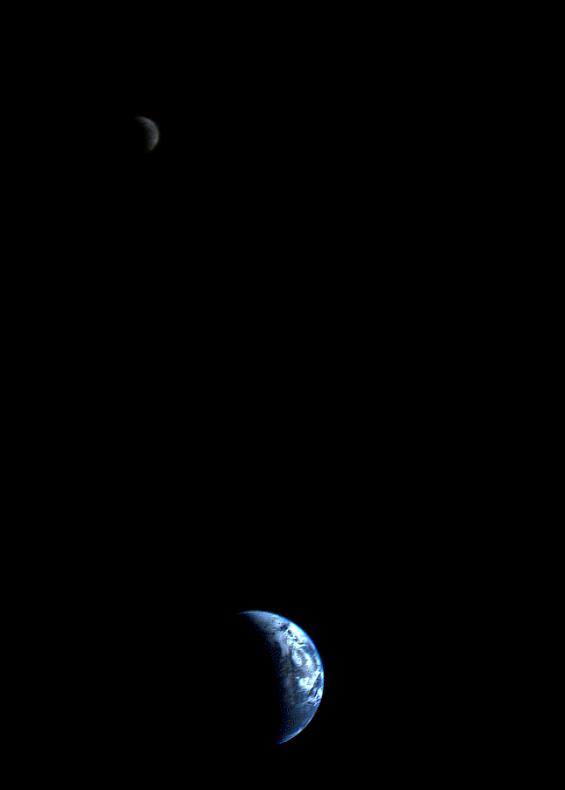

9. Another Unique Perspective
Voyager 1 also took the first image of the entire Earth and Moon together near the start of its mission on Sept. 18, 1977. The images were taken 13 days after launch at a distance of about 7.3 million miles (11.66 million kilometers) from Earth.
10. Parting Shot
After taking the images for “The Family Portrait” at 05:22 GMT on Feb. 14, 1990, Voyager 1 powered down its cameras forever. As of early 2020 the spacecraft is still operating, but no longer has the capability to take images.
- The Story Behind Voyager 1's Pale Blue Dot
- The Story Behind Voyager 1's Family Portrait
- Pale Blue Dot Poster
- Voyager 1 Mission Page
- Voyager 2 Mission Page
Acknowledgements: Amanda Barnett, Phil Davis and Preston Dyches contributed to this story. Some of the information in this article came from the account of the solar system family portrait detailed in Kosm ann , Hansen and Sagan, "The Family Portrait of the Solar System: The last set of images taken by Voyager 1 and the fascinating story of how they came to be," 70th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), IAC-19-F4.1.8, 2019.
Related Terms
- Voyager Program
Explore More

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers
The novel approach to estimating river water storage and discharge also identifies regions marked by ‘fingerprints’ of intense water use. A study led by NASA researchers provides new estimates of how much water courses through Earth’s rivers, the rates at which it’s flowing into the ocean, and how much both of those figures have fluctuated […]

NASA’s ORCA, AirHARP Projects Paved Way for PACE to Reach Space
It took the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission just 13 minutes to reach low-Earth orbit from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in February 2024. It took a network of scientists at NASA and research institutions around the world more than 20 years to carefully craft and test the novel instruments that allow PACE […]

NASA’s CloudSat Ends Mission Peering Into the Heart of Clouds
Over the course of nearly two decades, its powerful radar provided never-before-seen details of clouds and helped advance global weather and climate predictions. CloudSat, a NASA mission that peered into hurricanes, tallied global snowfall rates, and achieved other weather and climate firsts, has ended its operations. Originally proposed as a 22-month mission, the spacecraft was […]
Discover More Topics From NASA

Facts About Earth

Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
Kuiper Belt

BREAKING: Federal Reserve keeps interest rates at current levels as inflation holds its grip
Inside NASA's 5-month fight to save the Voyager 1 mission in interstellar space

After working for five months to re-establish communication with the farthest-flung human-made object in existence, NASA announced this week that the Voyager 1 probe had finally phoned home.
For the engineers and scientists who work on NASA’s longest-operating mission in space, it was a moment of joy and intense relief.
“That Saturday morning, we all came in, we’re sitting around boxes of doughnuts and waiting for the data to come back from Voyager,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for the Voyager 1 mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “We knew exactly what time it was going to happen, and it got really quiet and everybody just sat there and they’re looking at the screen.”
When at long last the spacecraft returned the agency’s call, Spilker said the room erupted in celebration.
“There were cheers, people raising their hands,” she said. “And a sense of relief, too — that OK, after all this hard work and going from barely being able to have a signal coming from Voyager to being in communication again, that was a tremendous relief and a great feeling.”
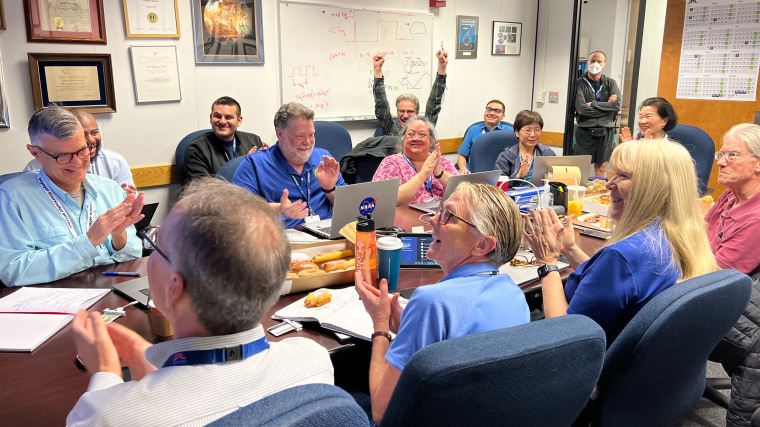

The problem with Voyager 1 was first detected in November . At the time, NASA said it was still in contact with the spacecraft and could see that it was receiving signals from Earth. But what was being relayed back to mission controllers — including science data and information about the health of the probe and its various systems — was garbled and unreadable.
That kicked off a monthslong push to identify what had gone wrong and try to save the Voyager 1 mission.
Spilker said she and her colleagues stayed hopeful and optimistic, but the team faced enormous challenges. For one, engineers were trying to troubleshoot a spacecraft traveling in interstellar space , more than 15 billion miles away — the ultimate long-distance call.
“With Voyager 1, it takes 22 1/2 hours to get the signal up and 22 1/2 hours to get the signal back, so we’d get the commands ready, send them up, and then like two days later, you’d get the answer if it had worked or not,” Spilker said.

The team eventually determined that the issue stemmed from one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers. Spilker said a hardware failure, perhaps as a result of age or because it was hit by radiation, likely messed up a small section of code in the memory of the computer. The glitch meant Voyager 1 was unable to send coherent updates about its health and science observations.
NASA engineers determined that they would not be able to repair the chip where the mangled software is stored. And the bad code was also too large for Voyager 1's computer to store both it and any newly uploaded instructions. Because the technology aboard Voyager 1 dates back to the 1960s and 1970s, the computer’s memory pales in comparison to any modern smartphone. Spilker said it’s roughly equivalent to the amount of memory in an electronic car key.
The team found a workaround, however: They could divide up the code into smaller parts and store them in different areas of the computer’s memory. Then, they could reprogram the section that needed fixing while ensuring that the entire system still worked cohesively.
That was a feat, because the longevity of the Voyager mission means there are no working test beds or simulators here on Earth to test the new bits of code before they are sent to the spacecraft.
“There were three different people looking through line by line of the patch of the code we were going to send up, looking for anything that they had missed,” Spilker said. “And so it was sort of an eyes-only check of the software that we sent up.”
The hard work paid off.
NASA reported the happy development Monday, writing in a post on X : “Sounding a little more like yourself, #Voyager1.” The spacecraft’s own social media account responded , saying, “Hi, it’s me.”
So far, the team has determined that Voyager 1 is healthy and operating normally. Spilker said the probe’s scientific instruments are on and appear to be working, but it will take some time for Voyager 1 to resume sending back science data.
Voyager 1 and its twin, the Voyager 2 probe, each launched in 1977 on missions to study the outer solar system. As it sped through the cosmos, Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn, studying the planets’ moons up close and snapping images along the way.
Voyager 2, which is 12.6 billion miles away, had close encounters with Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and continues to operate as normal.
In 2012, Voyager 1 ventured beyond the solar system , becoming the first human-made object to enter interstellar space, or the space between stars. Voyager 2 followed suit in 2018.
Spilker, who first began working on the Voyager missions when she graduated college in 1977, said the missions could last into the 2030s. Eventually, though, the probes will run out of power or their components will simply be too old to continue operating.
Spilker said it will be tough to finally close out the missions someday, but Voyager 1 and 2 will live on as “our silent ambassadors.”
Both probes carry time capsules with them — messages on gold-plated copper disks that are collectively known as The Golden Record . The disks contain images and sounds that represent life on Earth and humanity’s culture, including snippets of music, animal sounds, laughter and recorded greetings in different languages. The idea is for the probes to carry the messages until they are possibly found by spacefarers in the distant future.
“Maybe in 40,000 years or so, they will be getting relatively close to another star,” Spilker said, “and they could be found at that point.”
Denise Chow is a reporter for NBC News Science focused on general science and climate change.
Voyager 1 to Take Pictures of Solar System Planets

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft, having completed its mission along with Voyager 2 to explore the outer planets, will use its cameras February 13-14 to take an unprecedented family portrait of most of the planets in our solar system.
The collection of images will be from a unique point-of-view -- looking down on the solar system from a position 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane in which the planets orbit the Sun. No other spacecraft has ever been in a position to attempt a similar series of photos of most of the planets.
Voyager 1, launched in 1977, is now about 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles) from Earth. The Voyager spacecraft are controlled by and their data received at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
"This is not just the first time, but perhaps the only time for decades that we'll be able to take a picture of the planets from outside the solar system," said Voyager Project Scientist Dr. Edward C. Stone of Caltech. No future space missions are planned that would fly a spacecraft so high above the ecliptic plane of the solar system, he said.
Starting shortly after 5 p.m. (PST) on Feb. 13 and continuing over the course of four hours, Voyager 1 will point its wide- and narrow-angle cameras at Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, Earth and Venus. Mercury is too close to the Sun to be photographed by Voyager's cameras, and Pluto is too far away and too small to show up in images taken by the spacecraft. Beginning with the dimmest of the targets - Neptune -- and working toward the Sun, Voyager 1 will shutter about 64 images of the planets and the space between them.
The constellation Eridanus (The River), stretching behind the planets from Voyager 1's perspective, will provide the backdrop for the images.
Due to the schedules of several spacecraft being tracked by NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN), the images will be recorded on board Voyager 1 and played back to DSN receivers on Earth in late March. The Voyager imaging team estimates that processing the images to reveal as much detail as possible will take several weeks. Most of the planets will appear as relatively small dots (about one to four pixels, or picture elements, in the 800-by-800 pixel frame of one Voyager image).
The enormous scale of the subject matter makes it unlikely that the entire set of images can be mosaicked to produce for publication a single photograph showing all the planets. Even an image covering the planets out to Jupiter would easily fill a poster-sized photographic print. At the least, imaging team hopes to assemble a mosaicked image composed of the frames showing Earth, Venus and perhaps Mars together.
Voyager 1, rather than Voyager 2, received the solar system photo assignment largely because of Voyager 1's improved viewpoint of the planets.
Voyager 1 completed flybys of Jupiter and Saturn in 1979 and 1980, respectively. Voyager 2 flew past Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986 and Neptune last August. Both are now on missions that will take the spacecraft to the boundary of our solar system and into interstellar space.
According to Voyager engineers and scientists, the only potential damage from pointing the cameras toward the Sun is that the shutter blades of the wide-angle camera might warp. There are no plans, however, to use Voyager 1's cameras after the solar system photo series is completed.
The Voyager mission is conducted by Caltech's JPL for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe
Engineers spent months working to repair link with Earth’s most distant spacecraft, says space agency
Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday , JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X . “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries , including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.

Cosmic cleaners: the scientists scouring English cathedral roofs for space dust

Russia acknowledges continuing air leak from its segment of space station

Uncontrolled European satellite falls to Earth after 30 years in orbit

Cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko sets world record for most time spent in space

‘Old smokers’: astronomers discover giant ancient stars in Milky Way

Nasa postpones plans to send humans to moon

What happened to the Peregrine lander and what does it mean for moon missions?

Peregrine 1 has ‘no chance’ of landing on moon due to fuel leak
Most viewed.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission
Breaking News
After months of silence, Voyager 1 has returned NASA’s calls

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
For the last five months, it seemed very possible that a 46-year-old conversation had finally reached its end.
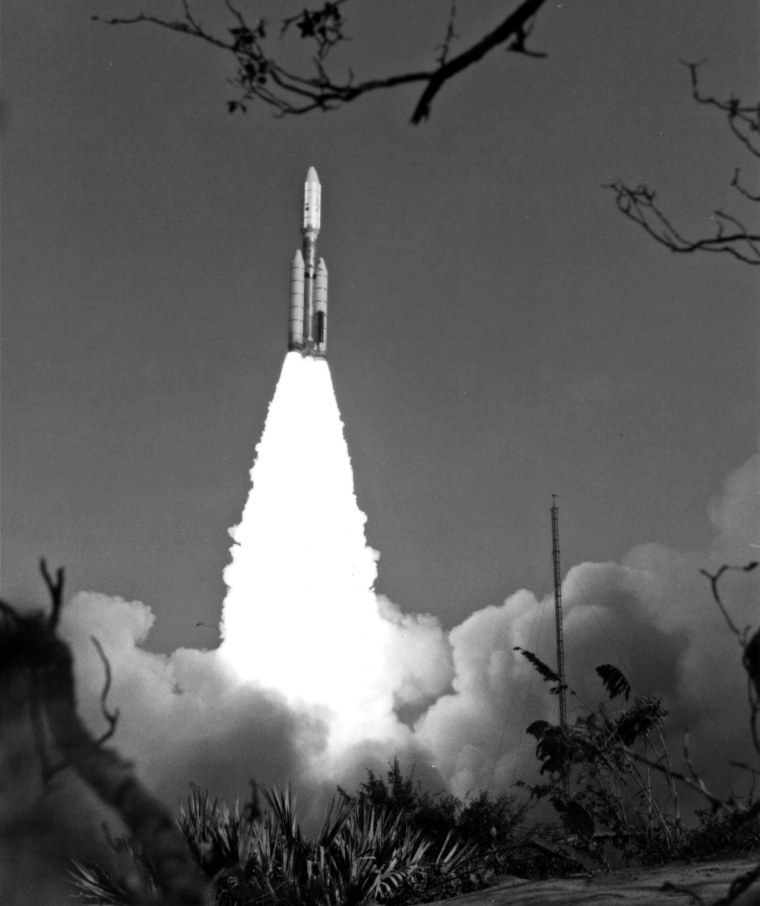
Since its launch from Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has diligently sent regular updates to Earth on the health of its systems and data collected from its onboard instruments.
But in November, the craft went quiet.
Voyager 1 is now some 15 billion miles away from Earth. Somewhere in the cold interstellar space between our sun and the closest stars, its flight data system stopped communicating with the part of the probe that allows it to send signals back to Earth. Engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge could tell that Voyager 1 was getting its messages, but nothing was coming back.
“We’re to the point where the hardware is starting to age,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for the Voyager mission. “It’s like working on an antique car, from 15 billion miles away.”
Week after week, engineers sent troubleshooting commands to the spacecraft, each time patiently waiting the 45 hours it takes to get a response here on Earth — 22.5 hours traveling at the speed of light to reach the probe, and 22.5 hours back.

Science & Medicine
This space artist created the Golden Record and changed the way we see the universe
Space artist Jon Lomberg has produced work that attempts to visualize what we can’t truly see, and to communicate with creatures we can’t yet imagine.
July 26, 2023
By March, the team had figured out that a memory chip that stored some of the flight data system’s software code had failed, turning the craft’s outgoing communications into gibberish.
A long-distance repair wasn’t possible. There wasn’t enough space anywhere in the system to shift the code in its entirety. So after manually reviewing the code line by line, engineers broke it up and tucked the pieces into the available slots of memory.
They sent a command to Voyager on Thursday. In the early morning hours Saturday, the team gathered around a conference table at JPL: laptops open, coffee and boxes of doughnuts in reach.
At 6:41 a.m., data from the craft showed up on their screens. The fix had worked .
“We went from very quiet and just waiting patiently to cheers and high-fives and big smiles and sighs of relief,” Spilker said. “I’m very happy to once again have a meaningful conversation with Voyager 1.”
Voyager 1 is one of two identical space probes. Voyager 2, launched two weeks before Voyager 1, is now about 13 billion miles from Earth, the two crafts’ trajectories having diverged somewhere around Saturn. (Voyager 2 continued its weekly communications uninterrupted during Voyager 1’s outage.)

Space shuttle Endeavour is lifted into the sky, takes final position as star of new museum wing
A shrink-wrapped Endeavour was hoisted and then carefully placed in its final location Tuesday at the still-under-construction Samuel Oschin Air and Space Center.
Jan. 30, 2024
They are the farthest-flung human-made objects in the universe, having traveled farther from their home planet than anything else this species has built. The task of keeping communications going grows harder with each passing day. Every 24 hours, Voyager 1 travels 912,000 miles farther away from us. As that distance grows, the signal becomes slower and weaker.
When the probe visited Jupiter in 1979, it was sending back data at a rate of 115.2 kilobits per second, Spilker said. Today, 45 years and more than 14 billion miles later, data come back at a rate of 40 bits per second.
The team is cautiously optimistic that the probes will stay in contact for three more years, long enough to celebrate the mission’s 50th anniversary in 2027, Spilker said. They could conceivably last until the 2030s.
The conversation can’t last forever. Microscopic bits of silica keep clogging up the thrusters that keep the probes’ antennas pointed toward Earth, which could end communications. The power is running low. Eventually, the day will come when both Voyagers stop transmitting data to Earth, and the first part of their mission ends.
But on the day each craft goes quiet, they begin a new era, one that could potentially last far longer. Each probe is equipped with a metallic album cover containing a Golden Record , a gold-plated copper disk inscribed with sounds and images meant to describe the species that built the Voyagers and the planet they came from.
Erosion in space is negligible; the images could be readable for another billion years or more. Should any other intelligent life form encounter one of the Voyager probes and have a means of retrieving the data from the record, they will at the very least have a chance to figure out who sent them — even if our species is by that time long gone.

JPL tries to keep Voyager space probes from disconnecting the world’s longest phone call
Keeping in touch with NASA’s two aging Voyager spacecraft is getting harder to do as they get farther away and their power sources dwindle.
Sept. 3, 2022
More to Read
Too expensive, too slow: NASA asks for help with JPL’s Mars Sample Return mission
April 15, 2024

NASA’s attempt to bring home part of Mars is unprecedented. The mission’s problems are not
March 25, 2024
Budget deal for NASA offers glimmer of hope for JPL’s Mars Sample Return mission
March 6, 2024

Corinne Purtill is a science and medicine reporter for the Los Angeles Times. Her writing on science and human behavior has appeared in the New Yorker, the New York Times, Time Magazine, the BBC, Quartz and elsewhere. Before joining The Times, she worked as the senior London correspondent for GlobalPost (now PRI) and as a reporter and assignment editor at the Cambodia Daily in Phnom Penh. She is a native of Southern California and a graduate of Stanford University.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Amid continued demonstrations, swastika drawn on USC’s campus

Climate & Environment
Lawsuit appears to be in peril for California children harmed by climate change

Timeline: UCLA’s night of violence before police moved in

California college campuses become lightning rods for pro-Palestinian protests
May 1, 2024

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.
NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels

NASA Scientists Gear Up for Solar Storms at Mars

NASA Uses Small Engine to Enhance Sustainable Jet Research
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

NASA Balloons Head North of Arctic Circle for Long-Duration Flights

NASA’s Hubble Pauses Science Due to Gyro Issue

NASA Selects Commercial Service Studies to Enable Mars Robotic Science
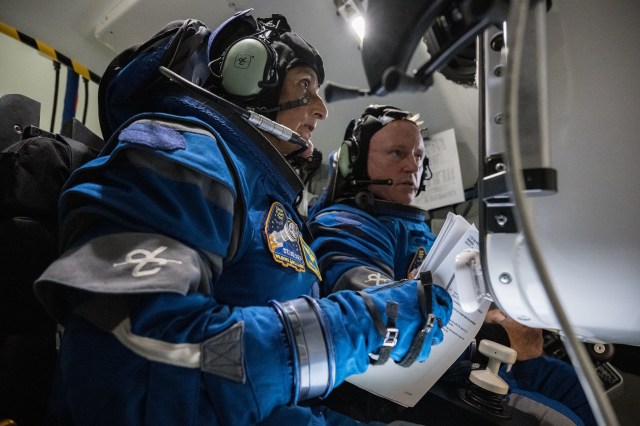

NASA’s Commercial Partners Deliver Cargo, Crew for Station Science


NASA Shares Lessons of Human Systems Integration with Industry

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers

NASA’s ORCA, AirHARP Projects Paved Way for PACE to Reach Space
Amendment 11: Physical Oceanography not solicited in ROSES-2024

What’s Up: May 2024 Skywatching Tips from NASA
May’s Night Sky Notes: Stargazing for Beginners
NASA’s Webb Maps Weather on Planet 280 Light-Years Away

Webb Captures Top of Iconic Horsehead Nebula in Unprecedented Detail

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Team Says Goodbye … for Now

Big Science Drives Wallops’ Upgrades for NASA Suborbital Missions

Tech Today: Stay Safe with Battery Testing for Space

NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars

Washington State High Schooler Wins 2024 NASA Student Art Contest

NASA STEM Artemis Moon Trees

NASA’s Commitment to Safety Starts with its Culture

NASA Challenge Gives Space Thruster Commercial Boost

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Voyager 1 image of saturn.

Voyager 1 looked back at Saturn on Nov. 16, 1980, four days after the spacecraft flew past the planet, to observe the appearance of Saturn and its rings from this unique perspective. A few of the spokelike ring features discovered by Voyager appear in the rings as bright patches in this image, taken at a distance of 5.3 million kilometers (3.3 million miles) from the planet. Saturn’s shadow falls upon the rings, and the bright Saturn crescent is seen through all but the densest portion of the rings. From Saturn, Voyager 1 is on a trajectory taking the spacecraft out of the ecliptic plane, away from the Sun and eventually out of the solar system (by about 1990). Although its mission to Jupiter and Saturn is nearly over (the Saturn encounter ends Dec. 18, 1980), Voyager 1 will be tracked by the Deep Space Network as far as possible in an effort to determine where the influence of the Sun ends and interstellar space begins. Voyager 1’s flight path through interstellar space is in the direction of the constellation Ophiuchus. Voyager 2 will reach Saturn on August 25, 1981, and is targeted to encounter Uranus in 1986 and possibly Neptune in 1989. The Voyager project is managed for NASA by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California.
Image Credt: NASA/JPL
Contact restored with NASA’s Voyager 1 space probe

Contact restored.
That was the message relieved NASA officials shared after the agency regained full contact with the Voyager 1 space probe, the most distant human-made object in the universe, scientists have announced.
For the first time since November, the spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems, NASA said in a news release Monday.
The 46-year-old pioneering probe, now 15.1 billion miles from Earth, has continually defied expectations for its life span as it ventures farther into the uncharted territory of the cosmos .
More: Voyager 1 is 15 billion miles from home and broken. Here's how NASA is trying to fix it.
Computer experts to the rescue
It wasn't as easy as hitting Control-Alt-Delete, but top experts at NASA and CalTech were able to fix the balky, ancient computer on board the probe that was causing the communication breakdown – at least for now.
A computer problem aboard Voyager 1 on Nov. 14, 2023, corrupted the stream of science and engineering data the craft sent to Earth, making it unreadable .
Although the radio signal from the spacecraft had never ceased its connection to ground control operators on Earth, that signal had not carried any usable data since November, NASA said. After some serious sleuthing to fix the onboard computer, that changed on April 20, when NASA finally received usable data.
In interstellar space
The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between the stars).
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally, NASA reports. Launched more than 46 years ago , the twin spacecraft are standouts on two fronts: they've operated the longest and traveled the farthest of any spacecraft ever.
Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
More: NASA gave Voyager 1 a 'poke' amid communication woes. Here's why the response was encouraging.
They were designed to last five years but have become the longest-operating spacecraft in history. Both carry gold-plated copper discs containing sounds and images from Earth, content that was chosen by a team headed by celebrity astronomer Carl Sagan .
For perspective, it was the summer of 1977 when the Voyager probes left Earth. "Star Wars" was No. 1 at the box office, Jimmy Carter was in the first year of his presidency, and Elvis Presley had just died.
Contributing: Eric Lagatta and George Petras
share this!
April 27, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
NASA hears from Voyager 1, the most distant spacecraft from Earth, after months of quiet
by Marcia Dunn

NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 again in a way that makes sense.
The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data last November. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft's coding to work around the trouble.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California declared success after receiving good engineering updates late last week. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data.
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space . The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Contact was never lost, rather it was like making a phone call where you can't hear the person on the other end, a JPL spokeswoman said Tuesday.
Launched in 1977 to study Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 has been exploring interstellar space — the space between star systems — since 2012. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 12.6 billion miles (20 billion kilometers) away and still working fine.
© 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Mystery behind huge opening in Antarctic sea ice solved
15 minutes ago

Do earthquake hazard maps predict higher shaking than actually occurred? Research finds discrepancy

New computer algorithm supercharges climate models and could lead to better predictions of future climate change

Improved AI process could better predict water supplies
57 minutes ago
Study: Airway hillocks challenge our understanding of lung biology

Religious intolerance predicts science denial, surveys suggest
2 hours ago

A 'cosmic glitch' in gravity: New model may explain strange behavior on a cosmic scale
3 hours ago

Why you can taste more ethanol in a cold pint of beer or warm glass of baijiu
Cell contraction drives the initial shaping of human embryos, study finds

Generating graph states of atomic ensembles via photon-mediated entanglement
Relevant physicsforums posts, solar wind particles, - reaching into earth's magnetic field.
24 minutes ago
The James Webb Space Telescope
9 hours ago
Documenting the setup of my new telescope
Apr 28, 2024
Quasi-Moons
Need help simplifying standard error formula for redshift.
Apr 27, 2024
Our Beautiful Universe - Photos and Videos
Apr 25, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth
Apr 22, 2024

NASA hears signal from Voyager 2 spacecraft after mistakenly cutting contact
Aug 1, 2023

NASA listens for Voyager 2 spacecraft after wrong command cuts contact
Jul 31, 2023

Engineers working to resolve issue with Voyager 1 computer
Dec 13, 2023
As Voyager 1's mission draws to a close, one planetary scientist reflects on its legacy
Mar 18, 2024

NASA back in touch with Voyager 2 after 'interstellar shout'
Aug 4, 2023
Recommended for you

New findings point to an Earth-like environment on ancient Mars

Citizen scientists help discover record-breaking exoplanet in binary star system
Apr 30, 2024

Novel calculations peg age of 'baby' asteroid

Clouds blanket the night side of the hot exoplanet WASP-43b

Enceladus spills its guts through strike–slip motion

Probing the effects of interplanetary space on asteroid Ryugu
Apr 29, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
NASA hears from Voyager 1, the most distant spacecraft from Earth, after months of quiet
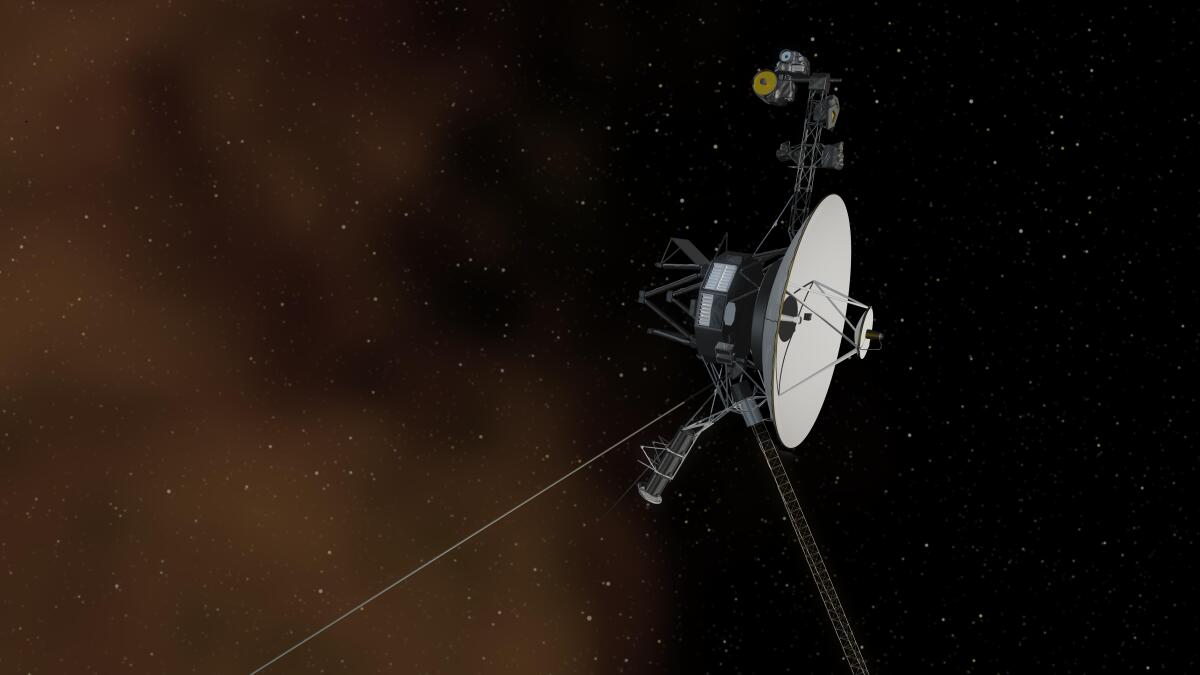
This illustration provided by NASA depicts Voyager 1. The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data in November 2023. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft’s coding to work around the trouble. In mid-April 2024, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory declared success after receiving good engineering updates. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data. (NASA via AP)
- Copy Link copied
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 again in a way that makes sense.
The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data last November. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft’s coding to work around the trouble.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California declared success after receiving good engineering updates late last week. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data.
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Contact was never lost, rather it was like making a phone call where you can’t hear the person on the other end, a JPL spokeswoman said Tuesday.
Launched in 1977 to study Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 has been exploring interstellar space — the space between star systems — since 2012. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 12.6 billion miles (20 billion kilometers) away and still working fine.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed 'Pale Blue Dot', is a part of the first ever 'portrait' of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic.
Earth was one of the last things Voyager 1 saw. The probe took the Pale Blue Dot photo at 0448 GMT on Feb. 14, 1990, just 34 minutes before its cameras were shut off forever.
The Pale Blue Dot - Revisited. The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA's Voyager 1 at a distance of 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) from the Sun. The image inspired the title of scientist Carl Sagan's book, "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space," in which he wrote: "Look again at that ...
Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken on February 14, 1990, by the Voyager 1 space probe from an unprecedented distance of approximately 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles, 40.5 AU), as part of that day's Family Portrait series of images of the Solar System.. In the photograph, Earth's apparent size is less than a pixel; the planet appears as a tiny dot against the vastness of ...
This picture of a crescent-shaped Earth and Moon - the first of its kind ever taken by a spacecraft - was recorded Sept. 18, 1977, by NASA's Voyager 1 when it was 7.25 million miles (11.66 million kilometers) from Earth. The Moon is at the top of the picture and beyond the Earth as viewed by Voyager.
This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed "Pale Blue Dot," is a part of the first ever "portrait" of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. › Full image and caption. These six narrow-angle color images were made from the first ever "portrait" of the solar system taken by Voyager 1, which was more than 4 billion miles from Earth and ...
This photo of Jupiter was taken by NASA's Voyager 1 on the evening of March 1, 1979, from a distance of 2.7 million miles (4.3 million kilometers). The photo shows Jupiter's Great Red Spot (top) and one of the white ovals. Credit: NASA/JPL . Full Image Details NASA's Voyager 1 acquired this image of a volcanic explosion on Io on March 4, 1979 ...
Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Feb 12, 2020. Article. This updated version of the iconic "Pale Blue Dot" image taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft uses modern image-processing software and techniques to revisit the well-known Voyager view while attempting to respect the original data and intent of those who planned the images. Credits: NASA/JPL ...
Images Voyager Took. The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft explored Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before starting their journey toward interstellar space. Here you'll find some of those iconic images, including "The Pale Blue Dot" - famously described by Carl Sagan - and what are still the only up-close images of Uranus and Neptune.
Solar System Portrait. This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed 'Pale Blue Dot', is a part of the first ever 'portrait' of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic.
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "Interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey through the Universe. In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
Today, Voyager 1 is the most distant spacecraft from Earth, more than 14 billion miles away and continuing on its journey out of our solar system. Forty years ago, it made its closest approach to Saturn. Although it was not the first to explore the giant ringed planet, as the Pioneer 11 spacecraft completed the first flyby in 1979, Voyager ...
First Close-up Image of Jupiter from Voyager 1 Full Resolution: TIFF (280.8 kB) JPEG (10.37 kB) 1996-09-26: Jupiter: Voyager: VG ISS - Narrow Angle: 500x500x3: PIA00455: Jupiter with Io Crossing Full Resolution: TIFF (412 kB) JPEG (15.15 kB) 1996-09-26
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the ...
A Titan/Centaur-6 launch vehicle carries NASA's Voyager 1 at the Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977. ... said the missions could last into the 2030s. Eventually, though, the probes will run out ...
Voyager 1, rather than Voyager 2, received the solar system photo assignment largely because of Voyager 1's improved viewpoint of the planets. Voyager 1 completed flybys of Jupiter and Saturn in 1979 and 1980, respectively. Voyager 2 flew past Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986 and Neptune last August.
Earth's most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.. Nasa's Jet Propulsion ...
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 again in a way that makes sense. The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data last November.
For the last five months, it seemed very possible that a 46-year-old conversation had finally reached its end. Since its launch from Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977, NASA's Voyager 1 ...
Voyager 1 looked back at Saturn on Nov. 16, 1980, four days after the spacecraft flew past the planet, to observe the appearance of Saturn and its rings from this unique perspective. A few of the spokelike ring features discovered by Voyager appear in the rings as bright patches in this image, taken at a distance of 5.3 million kilometers (3.3 ...
Contact restored. That was the message relieved NASA officials shared after the agency regained full contact with the Voyager 1 space probe, the most distant human-made object in the universe ...
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California declared success after receiving good engineering updates late last week. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data. It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space.