

A Practical Guide to Joseph Campbell and the Hero’s Journey
OVERVIEW: What are the hero’s journey steps? That is, what’s the psychological process we go through that can lead to inner transformation? This guide answers these questions.
______________
Treasure, love, reward, approval, honor, status, freedom, and survival … these are some of the many things associated with the hero’s journey.
However, we don’t find the meaning of the hero’s journey in slaying the dragon or saving the princess.
These are but colorful metaphors and symbols for a more significant purpose.
Battling inner and outer demons, confronting bullies, and courting your ideal mate symbolize a passage through the often treacherous path of self-discovery toward adulthood.
If you complete one of these “adventures,” you’re different. Sometimes visually, but always internally.
Here, we’ll explore the meaning of the hero’s journey steps and see how it applies to psychological development and our ability to actualize our potential.
Let’s dive in …
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The hero’s journey refers to a common motif, or set of patterns, found in many ancient mythologies around the world.
The hero’s journey steps are said to be universal and found throughout recorded history.
The popularization of the hero’s journey is attributed to the late mythologist Joseph Campbell.
These stages lead an individual (the would-be hero) through a challenging process of change that often includes great hardships.
This well-known story structure is used in many modern films and storytelling. However, the true meaning of the hero’s journey motif is psychological in origin.
What is the Monomyth?
Joseph Campbell was a curious mythologist. In the field of comparative mythology, most scholars examine how one culture’s myths are different than another.
Instead of focusing on the many differences between cultural myths and religious stories, however, Campbell did the opposite: He looked for the similarities.
His studies resulted in what’s called the monomyth . The monomyth is a universal story structure.
Essentially, it’s a story template that takes a character through a sequence of stages. Campbell began identifying the patterns of this monomyth (the hero’s journey steps).
Over and over again, he was amazed to find this structure in the cultures he studied. He also observed the same sequence in many religions including the stories of Gautama Buddha, Moses, and Jesus Christ.
Campbell outlined the stages of the monomyth in his classic book The Hero with a Thousand Faces (1949).
What is the Hero?
The main character in the monomyth is the hero .
The hero isn’t a person, but an archetype —a set of universal images combined with specific patterns of behavior.
Think of a protagonist from your favorite film. He or she represents the hero.
The storyline of the film enacts the hero’s journey.
The Hero archetype resides in the psyche of every individual, which is one of the primary reasons we love hearing and watching stories.
What is a Myth?
We might ask, why explore the hero’s journey steps?
Sure, Hollywood uses it as their dominant story structure for its films (more on that later). But what relevance does it have for us as individuals?
Today, when we speak of “myth,” we refer to something that’s commonly believed, but untrue.
Myth, for minds like Campbell and Carl Jung however, had a much deeper meaning. Myths, for them, represent dreams of the collective psyche .
That is, in understanding the symbolic meaning of a myth, you come to know the psychological undercurrent—including hidden motivations , tensions, and desires—of the people and culture.
What is the Power of Myth?
Campbell explains to Bill Moyer in The Power of Myth : 1 Joseph Campbell, The Power of Myth , 1991, 193.
Mythology is not a lie, mythology is poetry, it is metaphorical. It has been well said that mythology is the penultimate truth–penultimate because the ultimate cannot be put into words. It is beyond words. Beyond images, beyond that bounding rim of the Buddhist Wheel of Becoming. Mythology pitches the mind beyond that rim, to what can be known but not told.
As Campbell eloquently puts it in The Hero with a Thousand Faces ,
Mythology is psychology misread as biography, history, and cosmology.
Because the hero’s journey steps represent a monomyth that we can observe in most, if not all, cultures, it represents a process that is relevant to the entire human family .

What is this Process Within the Hero’s Journey?
It’s the process of personal transformation from an innocent child into a mature adult.
The child is born into a set of rules and beliefs of a group of people.
Through the child’s heroic efforts, he must break free from these conventions (transcend them) to discover himself.
In the process, the individual returns to his soul.
If we think of the hero’s journey as a roadmap for self-development, it can hold a lot of value for us.
A Quick Note About Gender: Masculine vs Feminine
This psychological decoding is based on a “Jungian” understanding of the psyche.
The hero is ultimately a masculine archetype. The female counterpart would be the heroine. While the hero and the heroine certainly share many attributes, they are not the same.
Similarly, the hero’s journey is predominantly a process of development for the masculine psyche. The hero archetype is associated with autonomy, building structure, and learning about limitations, which are qualities associated with masculine energy.
However, note that “masculine” and “feminine” are not the same as “man” and “woman.” The psyche of a man has a feminine counterpart—what Jung called the anima . The psyche of a woman has a masculine archetype called the animus . For this reason, the hero’s journey does have universal relevance.
While Western culture seems riddled with gender confusion, there are distinct differences between the masculine and the feminine psyche.
Okay, now back to our story …
The 3 Main Stages of the Hero’s Journey
Okay, so now let’s begin to break down the structure and sequence of the hero’s journey.
As Campbell explains:
The usual hero adventure begins with someone from whom something has been taken, or who feels there is something lacking in the normal experience available or permitted to the members of society. The person then takes off on a series of adventures beyond the ordinary, either to recover what has been lost or to discover some life-giving elixir. It’s usually a cycle, a coming and a returning.
This cycle of coming and returning has 3 clear stages:
Stage 1: Departure
Campbell called the initial stage departure or the call to adventure . The hero departs from the world he knows.
Luke Skywalker leaves his home planet to join Obi-Wan to save the princess. Neo gets unplugged from The Matrix with the help of Morpheus and his crew.
In the Departure stage, you leave the safety of the world you know and enter the unknown.
Campbell writes of this stage in The Hero with a Thousand Faces :
This first step of the mythological journey—which we have designated the “call to adventure”—signifies that destiny has summoned the hero and transferred his spiritual center of gravity from within the pale of his society to a zone unknown.
That is, the hero must leave the known “conventional world” and enter a “special world” that is foreign.
Stage 2: Initiation
Now the hero must face a series of trials and tribulations. The hero’s journey isn’t safe.
The hero is tested in battle, skill, and conflict. He may not succeed in each action but must press on.
The protagonist will meet allies, enemies, and mentors with supernatural aid throughout the initiation stage.
Stage 3: Return
Having endured the trials and hardships of the adventure, the hero returns home.
But the hero is no longer the same. An internal transformation has taken place through the maturation process of the experience.
Luke is now a Jedi and has come to peace with his past. Neo embraces his destiny and liberates himself from the conventions of The Matrix.
The Hero’s Journey in Drama
In Three Uses of a Knife , famed playwright David Mamet suggests a similar three-act structure for plays and dramas: 2 David Mamet, Three Uses of the Knife: On the Nature and Purpose of Drama , 2000.
Act 1: Thesis . The drama presents life as it is for the protagonist. The ordinary world.
Act 2: Antithesis . The protagonist faces opposing forces that send him into an upheaval (disharmony).
Act 3: Synthesis . The protagonist attempts to integrate the old life with the new one.
We note that problems, challenges, and upheavals are the defining characteristic of this journey.
Without problems, the path toward growth is usually left behind. (More on this topic below.)
Assessing Your Place in the Hero’s Journey
Before we explore the stages of the monomyth more closely, let’s look at what these three phases reveal about self-mastery and psychological development.
Stage 1 represents our comfort zone. We feel safe here because it is known to us.
Stages 2 and 3, however, represent the unknown . Embracing the unknown means letting go of safety.
Abraham Maslow points out that we are confronted with an ongoing series of choices throughout life between safety and growth, dependence and independence, regression and progression, immaturity and maturity.
Maslow writes in Toward a Psychology of Being : 3 Abraham Maslow, Toward a Psychology of Being , 2014.
We grow forward when the delights of growth and anxieties of safety are greater than the anxieties of growth and the delights of safety.
Is it now clear why so many of us refuse the call to adventure?
We cling to the safety of the known instead of embracing the “delight of growth” that only comes from the unknown.
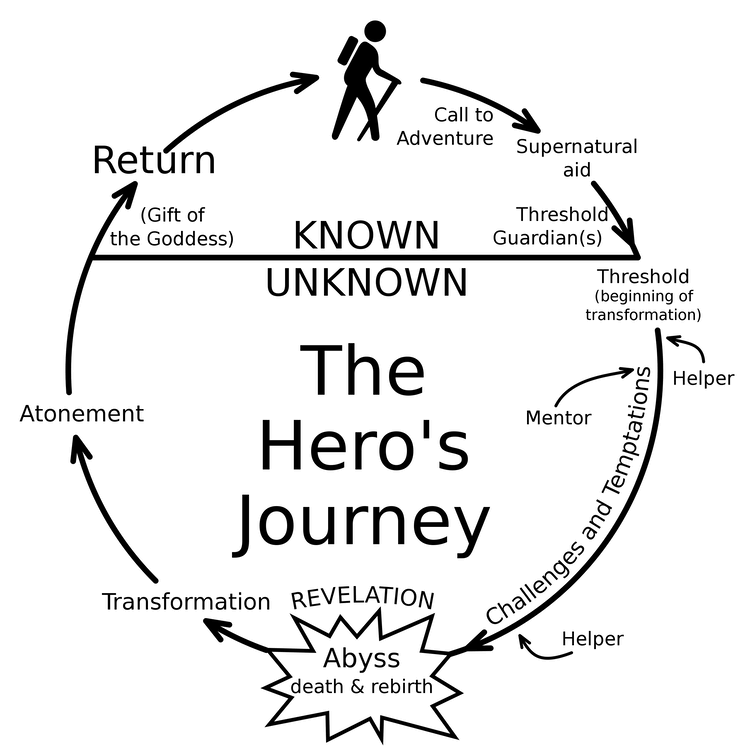
Campbell’s 17 Stages of the Hero’s Journey
Joseph Campbell didn’t just outline three stages of the monomyth. In The Hero with a Thousand Faces , he deconstructs every step along the journey.
The stages of the hero’s journey are the common sequence of events that occurred in the monomyth motif.
Technically speaking, Campbell outlined 17 stages in his The Hero with a Thousand Faces:
- 1: The Call to Adventure
- 2: Refusal of the Call
- 3: Supernatural Aid
- 4: The Crossing of the First Threshold
- 5: Belly of the Whale
- 6: The Road of Trials
- 7: The Meeting with the Goddess
- 8: Woman as the Temptress
- 9: Atonement with the Father
- 10: Apotheosis
- 11: The Ultimate Boon
- 12: Refusal of the Return
- 13: The Magic Flight
- 14: Rescue from Without
- 15: The Crossing of the Return Threshold
- 16: Master of the Two Worlds
- 17: Freedom to Live
These 17 stages or hero’s journey steps can be found globally in the myths and legends throughout recorded history.
The Modified 12 Hero’s Journey Steps
Now, let’s review these stages of the hero’s journey in more detail.
I’m going to outline these steps below using a slightly simplified version from Christopher Vogler’s The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers .
Vogler’s model, which is used throughout Hollywood, only has 12 steps (compared to 17), and I think it does a solid job of keeping the essence of Campbell’s monomyth structure intact.
As you read these hero’s journey steps, see if you can determine how they apply to your development.
Step 1: The Ordinary World
Before a would-be hero can enter the special world, he must first live in the ordinary world.
The ordinary world is different for each of us—it represents our norms, customs, conditioned beliefs, and behaviors. The ordinary world is sometimes referred to as the “conventional world.”
In The Hobbit , the ordinary world is the Shire where Bilbo Baggins lives with all the other Hobbits—gardening, eating and celebrating—living a simple life.
Novelist J.R.R. Tolkien contrasts this life in the Shire with the special world of wizards, warriors, men, elves, dwarfs, and evil forces on the brink of world war.
Step 2: The Call to Adventure
The first hero’s journey step is the call to adventure.
The call to adventure marks a transition from the ordinary world to the special world. The hero is introduced to his quest of great consequence.
Obi-Wan said to Luke, “You must come with me to Alderaan.” That is, Luke is invited to leave the ordinary world of his aunt and uncle’s farm life and go on an adventure with a Jedi knight.
Joseph Campbell explains: 4 Joseph Campbell, The Hero’s Journey: Joseph Campbell On His Life And Work , 1990.
The call to adventure signifies that destiny has summoned the hero and transferred his spiritual center of gravity from within the pale of this society to a zone unknown.
Step 3: Refusal of the Call
Fear of change as well as death, however, often leads the hero to refuse the call to adventure .
The ordinary world represents our comfort zone; the special world signifies the unknown.
Luke Skywalker immediately responds to Obi-Wan, “I can’t go with you,” citing his chores and responsibilities at home.

Step 4: Meeting the Mentor
Campbell called this archetype the “mentor with supernatural aid.”
Generally, at an early stage of the adventure, the hero is graced by the presence of a wise sage . Personified in stories as a magical counselor , a reclusive hermit, or a wise leader, the mentor’s role is to help guide the hero.
Think Obi-Wan, Yoda, Gandalf, Morpheus, or Dumbledore. Sometimes cloaked in mystery and secret language, a mentor manifests when the hero is ready.
Sadly, our modern world is depleted of wise elders or shamans who can effectively bless the younger generation. (A topic for a different day.) For most of us, it is best to seek wise counsel from your inner guide , the Self within.
Step 5: Cross the First Threshold
The hero resists change initially but is ultimately forced to make a critical decision: embark on the adventure or forever remain in the ordinary world with its illusion of security.
Although Luke refuses the call to adventure initially, when he returns home to see his aunt and uncle dead, he immediately agrees to go with Obi-Wan. He crossed the first threshold.
In one sense, the first threshold is the point of no return. Once the hero shoots across the unstable suspension bridge, it bursts into flames.
There’s no turning back, at least, not how he came.
The first threshold can mark a major decision in our personal lives:
- “I’m going to travel around the globe.”
- “I’m going to transform my physical health.”
- “I am going to write a book.”
- “I’m going to master the flute.”
- “I’m going to realize my true nature.”
This first breakthrough is a feat within itself; however, it is only the first of many turning points.
Step 6: Tests, Allies, Enemies
Along the hero’s journey, the main character encounters many obstacles and allies.
Luke meets Obiwan (mentor), Han Solo, Princess Leia, and the rebel alliance while fighting many foes. Neo meets Morpheus (mentor), Trinity, and the rest of the Nebuchadnezzar crew while having to fight Agents in a strange world.
Some people may try to stop you along your quest—possibly saying you’re unreasonable or unrealistic. These “dream-stoppers” are often cleverly masked as friends and family who appear to have positive intentions but hinder your development nonetheless.
Your ability to identify obstructions on your path and align with support along your adventure is critical to your adventure.
Unfortunately, because few complete their hero’s journey to mature adulthood, most people will unconsciously attempt to sabotage yours.
Step 7: Approach to the Inmost Cave
The next significant threshold is often more treacherous than the first.
Entering the villain’s castle or the evil billionaire’s mansion, this second major decision usually puts the hero at significant physical and psychological risks.
Neo decides to go save Morpheus who’s being held in a building filled with Agents.
Within the walls of the innermost cave lies the cornerstone of the special world where the hero closes in on his objective.
For a man, the innermost cave represents the Mother Complex, a regressive part of him that seeks to return to the safety of the mother. 5 Robert Johnson, He: Understanding Masculine Psychology, 1989. When a man seeks safety and comfort—when he demands pampering—it means he’s engulfed within the innermost cave.
For a woman, the innermost cave often represents learning how to surrender to the healing power of nurturance—to heal the handless maiden. 6 Robert Johnson, The Fisher King and the Handless Maiden: Understanding the Wounded Feeling Function in Masculine and Feminine Psychology , 1995.

Step 8: Ordeal
No worthwhile adventure is easy. There are many perils on the path to growth, self-discovery , and self-realization.
A major obstacle confronts the hero, and the future begins to look dim: a trap, a mental imprisonment, or imminent defeat on the battlefield.
It seems like the adventure will come to a sad conclusion, as all hope appears lost. But hope remains and it is in these moments of despair when the hero must access a hidden part of himself—one more micron of energy, strength, faith, or creativity to find his way out of the belly of the beast.
Neo confronts Agent Smith in the subway station—something that was never done before. The hero must call on an inner power he doesn’t know he possesses.
Step 9: Reward
Having defeated the enemy and slain the dragon, the hero receives the prize. Pulling the metaphorical sword from the stone, the hero achieves the objective he set out to complete.
Whether the reward is monetary, physical, romantic, or spiritual, the hero transforms. Usually, the initial prize sought by the hero is physical—the sword in the stone or a physical treasure of some kind.
Step 10: The Road Back
Alas, the adventure isn’t over yet. There usually needs to be one last push to return home. Now the hero must return to the world from which he came with the sacred elixir.
Challenges still lie ahead in the form of villains, roadblocks, and inner demons. The hero must deal with whatever issues were left unresolved at this stage of the journey.
Taking moral inventory, examining the Shadow , and performing constant self-inquiry help the hero identify weaknesses and blindspots that will later play against him.
Step 11: Resurrection
Before returning home—before the adventure is over—there’s often one more unsuspected, unforeseen ordeal.
This final threshold, which may be more difficult than the prior moment of despair, provides one last test to solidify the growth of the hero. This threshold represents the final climax.
Neo is shot and killed by Agent Smith. And, he literally resurrects to confront the enemy one last time following his transformation.
The uncertain Luke Skywalker takes that “one in a million” shot from his X-Wing to destroy the Death Star.
Step 12: Return with the Elixir
Often, the prize the hero initially sought (in Step 9) becomes secondary as a result of the personal transformation he undergoes.
Perhaps the original quest was financially driven , but now the hero takes greater satisfaction in serving others in need. The real change is always internal .
In this final stage, the hero can become the master of both worlds , with the freedom to live and grow, impacting all of humanity.
Returning with the prize, the hero’s experience of reality is different. The person is no longer an innocent child or adolescent seeking excitement or adventure.
Comfortable in his own skin, he has evolved and is now capable of handling the demands and challenges of everyday life.
The Hero’s Journey in Films
Are you now more aware of how these hero’s journey steps play out in popular films and television series?
George Lucas was friends with Joseph Campbell. Lucas used these hero’s journey steps from Campbell’s The Hero with a Thousand Faces to produce the original Star Wars film. 7 https://billmoyers.com/content/mythology-of-star-wars-george-lucas/
It’s difficult to appreciate the impact Star Wars still has on American culture and around the world. It’s even more difficult to articulate how much of that impact is attributed to Campbell’s insights.
However, one challenge our culture faces is that many popular film franchises produce movies that, most often, never complete the hero’s journey.
Many popular characters in action films like Marvel and DC Comics superheroes, James Bond, Ethan Hunt (Mission Impossible), Indiana Jones, etc. never actually transform.

These characters stay in the adolescent stage of development (and we tend to celebrate that reality).
These heroes don’t evolve into the warm, vulnerable, generative adults who no longer seek adventure and excitement.
That said, since I originally published this guide in early 2018, this has begun to change.
For example, in the final Bond film, No Time to Die (2021), James Bond did demonstrate some generative growth.
The same goes for Tony Stark’s character (Ironman) in Avengers: Endgame (2019).
Where Are You On Your Hero’s Journey?
More importantly, do you see how these hero’s journey steps are unfolding in your life?
Although each of our stories is unique, they have common threads—elements of this universal structure we all share.
Returning from the moment of despair—from inside the dragon’s lair—without the reward (or lesson), you are presented with a similar adventure repeated ad infinitum —until you either learn the lesson or give up.
In the beginning, the hero’s journey is about achievement.
Whether you’re trying to build a successful business, raise a family, write a screenplay, travel to a distant land, or become a skilled artist, these all represent external achievements that often launch us into our hero’s journey.
But through this external quest—if we become more conscious—the journey transitions to an emphasis on internal growth that leads to transformation.
The Hero isn’t an expression of mature adulthood. This archetype is a by-product of adolescence. The archetypes of adulthood are different, but to access them, we must complete the hero’s journey first .
The Primary Ingredient in Every Hero’s Journey
Compelling stories and real life comes down to one thing: problems .
The protagonist faces a problem and tries to overcome it. Problems represent the essence of drama and the key to good storytelling. Without problems, there’s no story. Problems engage us, tantalizing the human mind.
The hero must face his problems, surmount his fears, resolve his tensions, or fail.
The same is true for our development: without problems and tensions, there can be no growth.
Psychological development is the process of overcoming setbacks, limitations, and conditioned behavior to reach maturity.

Refusing the Call to Adventure
Few people ever fully embrace the Hero’s Journey, a psychological odyssey that leads the individual to wholeness .
Because of our fear of the unknown, many refuse the call to adventure. We delay our journey in many ways:
- Put important things aside.
- Procrastinate.
- Distract ourselves with TV, social media, and other people’s lives.
- Make excuses.
- Stay stuck in the lazy part .
- Focus on competing with others.
But something brews inside of us. An internal tension builds. The tension may be small at first, but it grows stronger in the darkness. Tensions are those opposing forces at play within us. This internal conflict creates disharmony.
Humans don’t like disharmony when it bubbles into consciousness, and so these internal tensions can catapult us out of the familiar. The feeling of discord can lead to action and ultimately, some resolution.
Maybe you’re currently embracing your hero’s journey. Or perhaps you’ve been refusing the call. It matters not. What matters is what you do today— right now .
How to Embrace Your Hero’s Journey, Step by Step
The main thing you need to do to embrace your hero’s journey is stay present.
Remember, as Campbell explained, “You are the hero of your own story.”
Psychological development is supposed to be a natural process. But we aren’t currently in a world that supports healthy development.
As such, it’s vital to listen within .
Here are a few guides that may serve you:
- Access Your Inner Guide
- How to Ground Yourself
- How to Stay in Your Center
- How to Overcome Internal Resistance
Ultimately, be mindful of your fears and aspirations.
Left unchecked, your fears can subconsciously lead you to endlessly refuse the call to adventure.
In contrast, your aspirations can help you embrace your adventure.
As Joseph Campbell often said,
Follow your bliss!
Videos Related to the Hero’s Journey Steps
Book related to the hero’s journey steps.
The hero’s journey steps are outlined in the books referenced throughout this guide:

The Hero with a Thousand Faces by Joseph Campbell

The Power of Myth by Joseph Campbell

Joseph Campbell’s Mythos Lecture Series (DVD)

The Writer’s Journey by Christopher Vogler

How to Be an Adult by David Richo
What Do You Think?
Are you going through the hero’s journey steps?
About the Author
Scott Jeffrey is the founder of CEOsage, a self-leadership resource publishing in-depth guides read by millions of self-actualizing individuals. He writes about self-development, practical psychology, Eastern philosophy, and integrated practices. For 25 years, Scott was a business coach to high-performing entrepreneurs, CEOs, and best-selling authors. He's the author of four books including Creativity Revealed .
Learn more >
I would like to understand the Hero’s journey. Joseph Campbell describes it as something that has been taken/lost or life giving. How do I know if my hero’s journey has been done?
If you’re examining the hero’s journey from the perspective of individuation — that is, the journey to mature adulthood — it takes many years to come to wholeness within oneself.
Psychologically speaking, the hero’s journey is inward. The characters you meet (like the Mentor) are within yourself. So it involves active imagination in bringing the archetype into some form of harmony within yourself.
You have mentioned a choice to stay in the comfort of safety or the unknow for growth. I am wondering if this is done in a Psychological manner where your life’s circumstances stay as they are or you physically live in a different environment, leaving your surroundings, people and material responsibilities etc.. Hope you can answer this for me.
If you’re a young adult, there’s often an external aspect to the hero’s journey — for example, leaving home and separating from one’s parents. But what Campbell was highlighting with the monomyth is ultimately a psychological process akin to Jungian individuation: https://scottjeffrey.com/individuation-process/
I want to share my thoughts on the heroes journey. After reading the twelve steps, and what you said- I quote “Step 12: Return with the Elixir Often, the prize the hero initially sought (in Step 9) becomes secondary as a result of the personal transformation he undergoes.
Perhaps the original quest was financially driven, but now the hero takes greater satisfaction in serving others in need.
The real change is always internal.
In this final stage, the hero can become the master of both worlds, with the freedom to live and grow, impacting all of humanity.”
My favorite movie for a while now has been The Peaceful Warrior, I have just watched Coach Carter. They seem to tell the same story and I think the story of The Heroes Journey. You have mentioned Star Wars, James Bond and the Matrix.
In the movies The Peaceful Warrior, and Coach Carter, the achievement earned is an inward spiritualism that is, I quote” impacting all of humanity.” Thank-you.
If The Peaceful Warrior is your favorite movie, read Dan Millman’s “The Way of the Peaceful Warrior” — the book the film is based on. Much deeper insights. It’s a magical book — especially when you’re just setting out on your self-discovery journey.
I have read about 25% so far, I am not a good reader. I give myself three pages each day, yet often I’m reading more. It is as if the movie is replaying and I’m able to go with it, imaging the main characters. There is more information from reading than watching the movie, though I am thinking there is a lot of fiction, as it has been described on the net. Though I just need to adhere to the believable parts. I don’t know if it is possible to remember the day’s events that happened during college. For example, what people said, what they were doing throughout the day. My college day’s I can only remember situations that happened all dispersed from one another, with only a few minutes recalled. Does someone like yourself able to recall conversations and put them as dialogs for a book? Or is it a writer’s privilege to invent these for the book?
“The Peaceful Warrior” is a work of fiction. The genre is technically called “visionary fiction.”
There is a passage in the book where Socrates say’s “Mind is an illusory reflection of cerebral fidgeting. It comprises all the random uncontrolled thoughts that bubble into awareness from the subconscious. Consciousness is not the mind; awareness is not mind; attention is not mind. Mind is an obstruction, an aggravation, a primal weakness in the human experiment. It is a kind of evolutionary mistake in the human being. I have no use for the mind.” I don’t think think this way because what we have as humans is natural and so it has a purpose. I am interested if you would give an opinion on this statement Socrates said.
For the most part, I agree with Millman’s statements. They are also consistent with much of the Eastern traditions. An essential aspect of the meditative traditions is to “pacify the mind”. They sometimes even use stronger longer of “killing the mind.” But at other times, they make the distinction between the “aware mind” versus the “monkey mind” or the “shining mind” versus the “stirring mind.” But in terms of the untrained mind (which is the mind of over 99% of people), I agree with Millman. I just wouldn’t call it “evolutionary.”
Millman would have already made ethical judgment towards any begger, so, he should not have thought twice about ignoring him. But because his story, is going through a transformation, he had these menacing mind talks. Do you think if you were in the same situation as him, would you give the begger money or use your self-consciousness to clear negative mind noise? I am wondering if a second time in the same situation would make one change their reaction…
This is quoted from the book; “A scrawny young teenager came up to me. “Spare some change, can’t you?” “No, sorry,” I said, not feeling sorry at all. As I walked away I thought, “Get a job.” Then vague guilts came into my mind; I’d said no to a penniless beggar. Angry thoughts arose. “He shouldn’t walk up to people like that!” I was halfway down the block before I realized all the mental noise i had tuned in to, and the tension it was causing – just because some guy had asked me for money and I’d said no. In that instant I let it go.”
I finished the peaceful warrior and found it enjoyable. The preview of Dan’s second book (Sacred Journey of the peaceful warrior) sums up what he was expressing through his life.
There was one part I have heard before where the dialog between Dan and Soc was flat, with no meaning. Thank-you.
I would like to balance the four functions Jung describes (thinking, feeling, sensation and intuition) in your Individuation Process page. How do I know when feeling and sensation are active in everyday events? Could you give me an example? Thank-you.
Brett, please use the related guide page to address your questions.
The Individuation process page has not got a comments section.
I was walking in the bush on a moonlit windy night. The moving branches displayed a moving shadow, I was startled at first thought someone was behind me. Then I put the moonlight and the moving branches together and summed up what had happened without turning around. Was my thinking a Feeling, thinking, intuition or sensation? Thank-you.
I didn’t realize the comment sections weren’t open on that other guide. The psychological types represent our dominant orientations for processing information. When you were startled, was your attention on your body or the fear itself? Was your mind focused on “what could that be”? No need to answer here.
But the main thing about psychological types, from a Jungian perspective, is to understand what your dominant and inferior types are so you can develop your weakest side. Taking an Enneagram assessment test can help you determine your dominant type. In that system, it’s either thinking, feeling, or sensing.
Thank-you for your reply. You gave me an example of what I believe would be my dominant (being the first impression of the event) type. The second instance you described, is that too my dominant type? I do already know what it was that brings me fear. Can you follow up with this scenario? I have done enneagram questions before, and I am hopeless in giving a true response as all multiple question apply to equally.
“I have done enneagram questions before, and I am hopeless in giving a true response as all multiple question apply to equally.”
In my experience, when people say things like this, it’s often because they are “out of center” and analyzing things in their heads. If, for example, you read detailed descriptions of each Type, there’s no way you’re going to relate equally to all of them. Only one (sometimes a few) will strike a deep cord within you. It may leave you feeling “raw” and exposed.
Using the example you provided isn’t really going to help in this context. Do you mostly live in your head (mind/thoughts/analysis), your body (gut/sensations/sensory perception), or feelings? We all use all of them, but one tends to be more dominant than the others.
Thank-you. I agree with you Quote “If, for example, you read detailed descriptions of each Type, there’s no way you’re going to relate equally to all of them”. You might think I’m procrastinating as I want to work this out. Quote” Superior Function versus Inferior Function We like to do things we’re good at and avoid doing things in which we feel inadequate. Thus, we develop specific skills while undeveloped capacities remain in the unconscious. Jung grouped these four functions into pairs: thinking and feeling, sensing and intuiting”. Follow me for a sec, I have determined my superior function is Thinking, that would leave my inferior function to feeling. I assume sensing and intuition would be in the middle. I’m going to give the answer that you will give to my question, how do I bring the four functions to the middle? Answer ; center yourself. Do you agree or tell me what I should be doing?
Brett, I can’t really speak to what you should be doing. From a Jungian perspective (as well as transpersonal psychology), you would develop your inferior function and grow in that line of intelligence. I borrow the concept of the Center from the Taoist tradition. Western psychology mainly seeks to build a healthy ego while Eastern traditions mainly focus on transcending the ego.
Is the answer to “center yourself”? Sure. But most likely you’ll only be able to do this temporarily (representing a “state” of consciousness), while if you develop via various practices, you establish different structural changes that become more stable.
How to Center Yourself.
I like this article and want to learn more. I’m sending you my questions in this article as there isn’t a comments section.
I have so many questions, do I really need these answered to be comfortable with learning? Or should I take a calming with acceptance approach, that will eventually find the answers I seek? Should I go ahead and ask… ok I will ask. In the four centers, take in information via the physical center, interpret experience via the emotional center, evaluate the world via the mental center. Could all be take in information? Thank-you.
Brett, I just opened the comment section on that centering guide. Please post your question there and then I’ll reply.
Is it always a Heroes journey to take on what seems an insurmountable task? I see this at the beginning of inspirational films. Thank-you.
Always be careful with the term “always.”
Remember that what Campbell was ultimately highlighting with his monomyth structure was a psychological process of development. So it’s best to keep that in context.
Insurmountable tasks can sometimes be a catalyst for one’s journey, but this is not always the case.
In films and storytelling, you need major a problem for the hero/protagonist to face. Otherwise, there’s no story.
With what you said in keeping the psychological process in context. I was thinking of the film where a football coach leaves a successful career in the city, to coach no-hoper orphans in the country. My first impression was that the coach is on a hero’s journey with much to lose but great inward comfort to gain. Now I think it is the orphan footballers who are on a hero’s journey, (by leading as an example of being an orphan and becoming successful to inspire them to do the same) to stand up with confidence to be equal to the rest of the world. The movie is twelve mighty orphans. Is this reasonable thinking and do you see different interpretation? Thank-you
I can’t really comment as I haven’t seen the film. In any decent film, multiple characters have “arcs.” In many cases, the coach in sports films plays the mentor/sage role but then has his own transformation as well. This is the case with Gandalf the Gray who has to “die” and be resurrected, transforming into Gandalf the White.
Merry Christmas Scott digital guide. Type to you soon:)
Does the hero’s journey have the same thoughts and feelings for a woman as a man?
From a Jungian perspective, the process would be different.
As Jungian Robert A. Johnson highlights in many of his books, the myths related to the feminine psyche are different than the myths related to the masculine. As such, they follow a different structure and aim.
That said, because there’s an anima in each male psyche and an animus in each female psyche, a part of us can relate to the hero’s journey in its totality. Hence, a heroine can go on a similar hero’s journey as a man.
What an excellent and thorough treatment. Thanks for these invaluable insights for my writing class.
Thank you for the feedback, Craig!
I love this observation about modern cinematic heroes: “Many popular characters in action films like Marvel and DC Comics superheroes, James Bond, Ethan Hunt (Mission Impossible), Indiana Jones, etc. never actually transform.”
Have you written elsewhere at greater length on this topic? I thought I read an article on this topic a few years back but don’t remember where! Certainly the weightiness of the observation was such a lightbulb moment.
Thanks and kind regards M.
You can find a more detailed archetypal decoding of the hero here:
https://scottjeffrey.com/hero-archetype/
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.

- Scriptwriting
Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey: A Better Screenplay in 17 Steps
- What is a Scene
- What is The Three Act Structure
- What is Story Structure
- What is a Story Beat
- What Is a Plot
- Plot vs Story
- What is a Non-Linear Plot
- What is a Plot Device
- What is Freytag’s Pyramid
- Screenplay Structure Examples
- What is a Story Mountain
- Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey
- What is Save the Cat
- Dan Harmon’s Story Circle
- What is Aristotle’s Poetics
- What is Exposition
- What is an Inciting Incident
- What is Rising Action
- What is the Climax of a Story
- What is the Falling Action
- What is Denouement
- How to Write the First Ten Pages of a Screenplay
- Plot Structure Tools
- The Ultimate Film Beat Sheet
- Secrets to Great Exposition in Screenwriting
- Writing Exposition in Film
- Best Inciting Incident Examples
- Examples of Midpoint In Movies
- Write Your Script For Free
dds are that if you’ve had any interest in writing a script within the past fifty years you’ve heard of the Hero’s Journey. A writer you got drinks with swore by it, a film professor suggested you read about it. Or you overheard the barista at your local coffee shop talking about how Die Hard is a picture-perfect template for it. But… what is it? I’ll explain all of the Hero’s Journey’s 17 steps and provide examples in the modern canon. Then you can kick writer’s block and get a strong script into the hands of agents and producers.
Watch: The Hero's Journey Explained
Subscribe for more filmmaking videos like this.
- Call to Action
- Refusal of Call
- Supernatural Aid
- Crossing The Threshold
- Belly of the Whale
- The Road of Trials
- Meeting the Goddess
- Atonement With the Father
- The Ultimate Boon
- Refusal of Return
- Magic Flight
- Rescue from Without
- Crossing the Return Threshold
- Master of Two Worlds
- Freedom to Live
Hero’s Journey Examples

The monomyth featuring three of your favorite franchises!
The hero's journey begins, 1. call to action.
Adventure is calling. Will your hero pick up?
The initial step in the first act of the Hero’s Journey - known as the departure - is the “call to action." The Hero is beckoned to go on a journey. Think Frodo Baggins meeting Gandalf. Or the Owl inviting Harry Potter to Hogwarts.
If having a tall wizard extend a hand may be a little too on the nose for you, don't worry. This comes in all forms. In Citizen Kane , the mystery surrounding Charles Foster Kane’s final words is the call to action for the reporter, Jerry Thompson, to get to work.
The Hero Hesitates
2. refusal of call.
Next is the Hero’s “refusal of call.” The Hero initially balks at the idea of leaving their lives. The Shire is beautiful, after all, who wants to embark on a dangerous journey across the world?
This refusal is typically because of a duty or obligation they have at home. Be it family, or work, it’s something our Hero cares deeply about. But, as pressure mounts, they eventually succumb and decide to leave with the help of “supernatural aid.”
The Hero Receives Assistance
3. supernatural aid.
Once the Hero has committed themselves to embarking on whatever that quest may be (keep in mind, a Hero’s Journey can apply to a modern, emotional story, as well), they receive “supernatural aid.”
Individuals give the Hero information or tools at the start of their journey to help their chances of completing the task. Rome wasn’t built in a day, and it definitely wasn’t built alone. Every hero has a set of allies helping them get the job done. From Luke, Han, and Chewie to Harry, Ron, and Hermoine, these teams are iconic and nearly inseparable.
The tools provided come in handy as the Hero begins…
The Hero Commits
4. crossing the threshold.
Now the hero ventures into a new, unfamiliar world where the rules and dangers are unknown. They’re not in Kansas anymore, Toto, and that becomes evidently clear when monkeys start flying.
This stage often requires a few examples to crystalize the change in environment from familiar to dangerous. The contrast is key to play up how ill-prepared they initially are.
The Hero is Challenged
5. belly of the whale.
Next thing you know, we're in “the belly of the whale.” The first point of real danger in the Hero’s Journey. Taken from the Biblical story of Jonah entering a literal whale’s belly, it’s here that the dangers we’ve been warned about are manifested into tangible characters. Like hungry Orcs with swords.
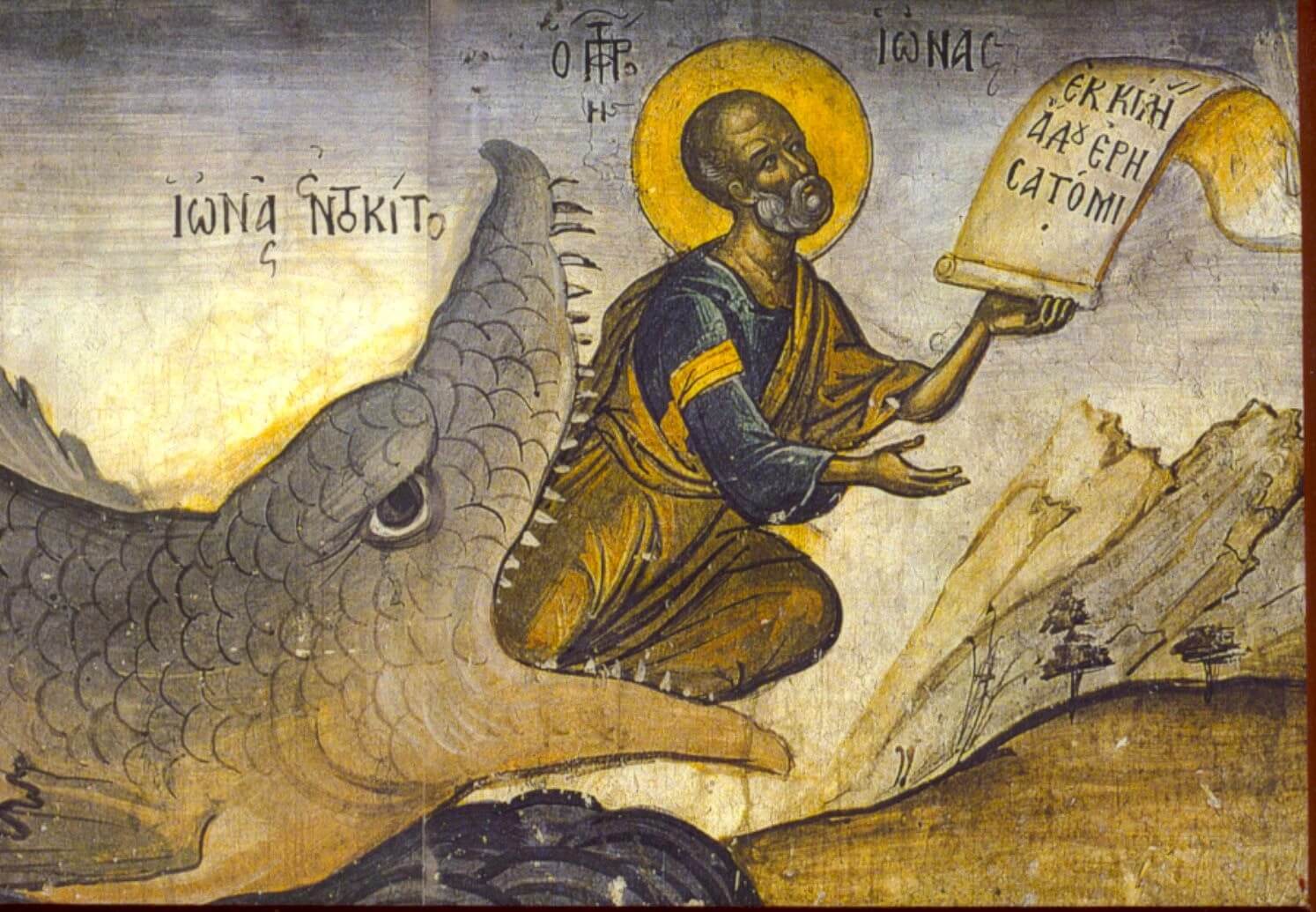

This is Jonah moments before actually being in the belly of the whale.
Now our Hero must make a decision to continue and, in turn, undergo a personal metamorphosis in the process.
They will not be the same individual at the end of this tale as they were in the beginning. This must be made clear while in the belly of the whale, as we enter Initiation, or act two. Which is the longest slice of the Hero’s Journey pie.
This part is filled with the most failure and risk, and ends with the climax. But first, it starts with...
The Hero is Tested
6. the road of trials.
“Road of trials” is a set of three tests that the Hero must take. Usually they will fail at least one of these tests. This could be a montage. It could also be a series of obstacles leading to a smaller goal in the journey.
Here is where the Hero learns to use his or her tools and allies while on their way to a...
The Great Advisor
7. meeting the goddess.
At this point in the monomyth, our Hero needs a break to adjust perspective and digest the ways they've changed. It’s here that they meet with an advisor, or a trusted individual, who will help them gain a better insight into the next steps of the journey. Frodo met with Galadriel, an elf who enlightened him with visions of potential futures.
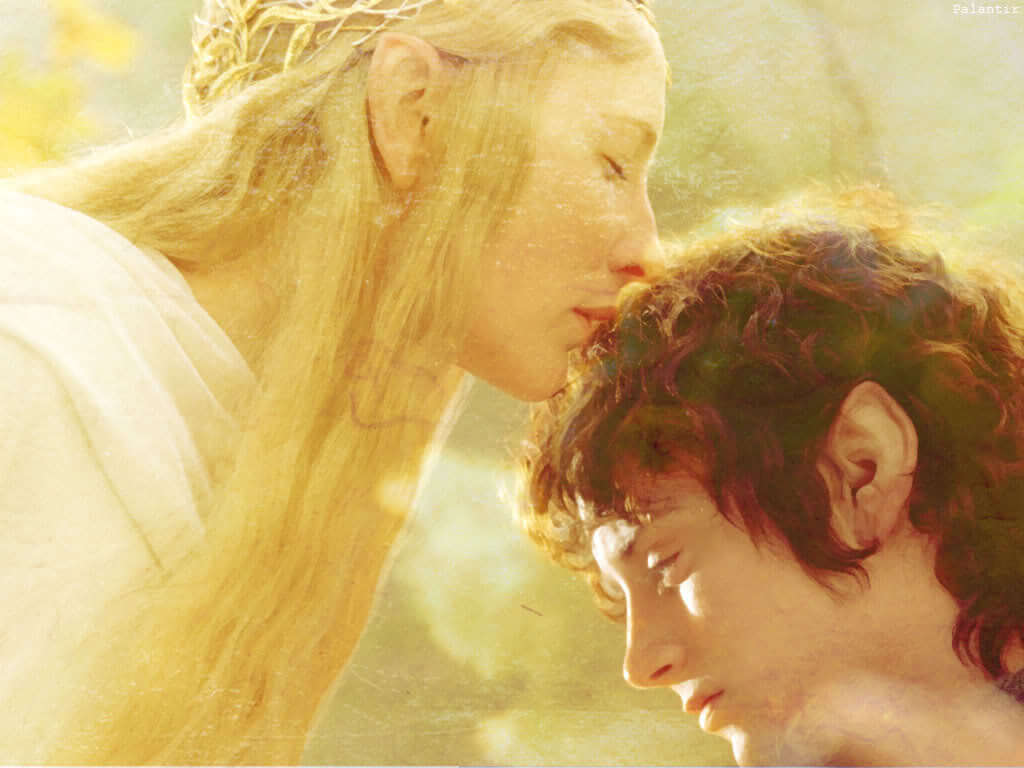

This is Frodo meeting with the goddess
Luke met Leia, and the two formed of a bond of kinship, motivating them to commit more to their cause. This individual doesn’t have to be a woman, but whoever it is our hero will gain something from the wisdom they impart.
But no good deed goes unpunished, and as we reward our Heroes in storytelling, we must also tempt them to failure.
The Hero is Torn
8. temptation.
Much like “road of trials,” “temptation” is a test in the Hero’s Journey. It presents a set of, well… temptations... that our Hero must either overcome or avoid. These temptations pick and pull at the insecurities of the Hero. A microcosm can be found in our own everyday lives with the simple act of getting out of bed.
The temptation to stay in the cozy confines of our comforters (and comfort zones) can be strong and sometimes overwhelming. This must be manifested in our story with some type of a cheap way out. Or an opportunity to throw in the towel. Our Hero must decline and press forward, nobly facing danger.
A Moment of Catharsis
9. atonement with the father.
Once they’ve thrown away their temptations, the Hero enters the “atonement with the father.” This is always an emotional part of the Hero’s Journey. It's a point in the monomyth where our protagonist must confront an aspect of their character from act one that has been slowing them down.
Something that could be fatal to their journey in the coming climactic stages. While this is actuated as a confrontation with a male entity, it doesn’t have to be.
The point here is that the Hero finds within themselves a change from who they were into someone more capable. Harry has to reconcile with the loss of his father figure, Dumbledore. Now take on Voldemort alone, using the lessons he’s learned on the way. Just like Luke...and every other hero ever. This is the emotional climax of the story.
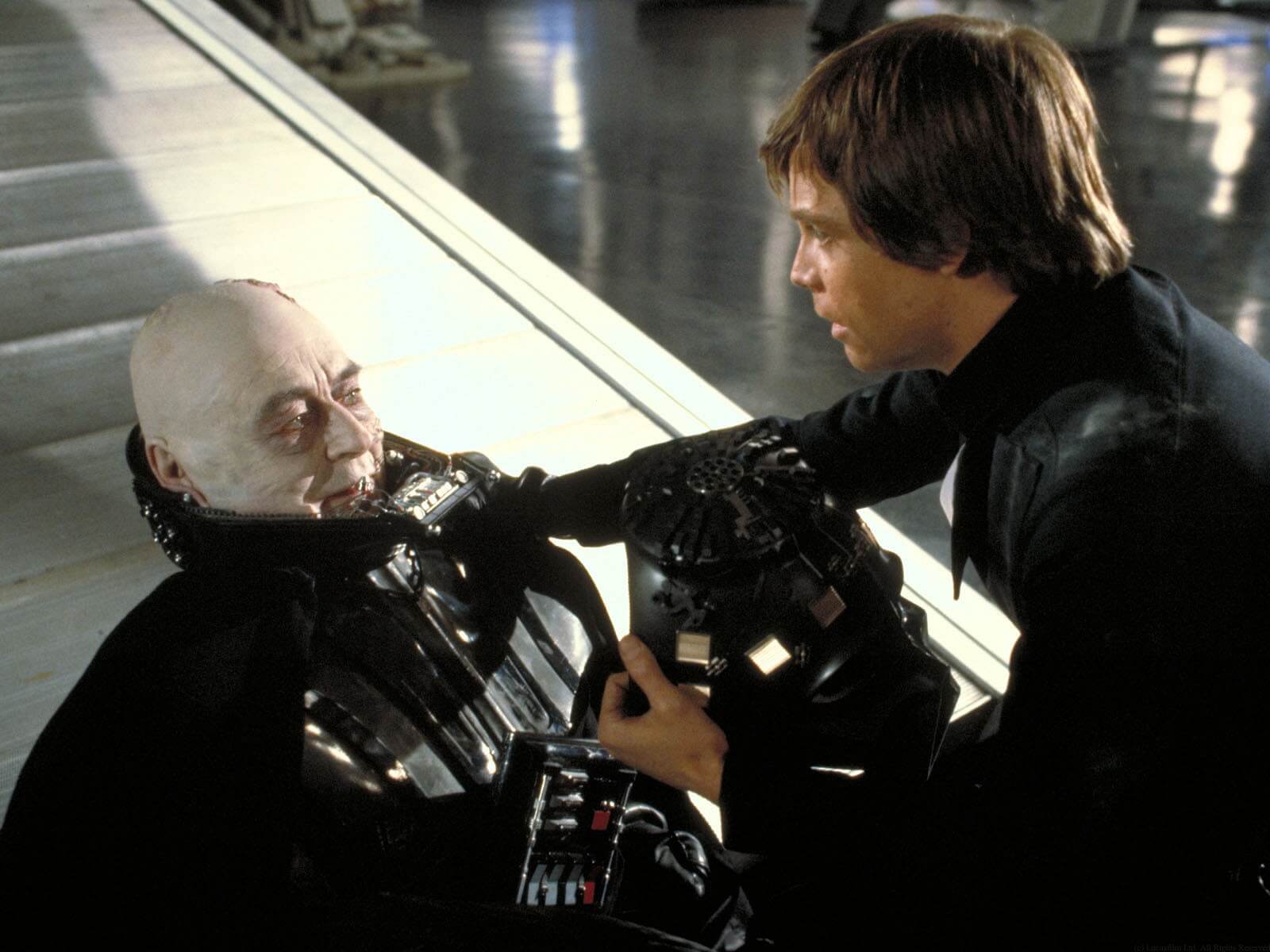
"Tell your sister... you were riiiiiiiiiight..."
Death of the hero, 10. apotheosis.
With a new sense of confidence and clarity we must then make our Hero deal with “apotheosis.” This is the stage of the Hero’s Journey where a greater perspective is achieved. Often embodied by a death of the Hero’s former self; where the old Frodo has died and the new one is born.
But this is sometimes interpreted as a more “a-ha!” moment — a breakthrough that leads to the narrative’s climax. This, too, can be tied to the death of Dumbledore and Harry’s reconciliation with the loss. This step is usually the final motivator for the Hero, driving the story into...
THe Hero Victorious
11. the ultimate boon.
This monomyth step is the physical climax of the story. This is often considered the MacGuffin of a film — the physical object that drives our Hero’s motivation. But it's a MacGuffin, to use Hitchcock's famous term, because ultimately... it doesn't matter.
In Pulp Fiction , we never find out what’s in the briefcase, but it’s the briefcase that led them on the wild journey. When we find out what “Rosebud” actually means, it simply forms a lynchpin to help us understand who Charles Foster Kane was. The mission is accomplished and the world can rest easy knowing that it is safe from evil.
The Hero's Journey Home
12. refusal of return.
Upon a successful completion of the Hero’s Journey, and a transformation into a different person, the Hero has a “refusal to return.” The Shire seems so boring now and the last thing Harry wants is to go back to that drawer under the stairs.
And, oftentimes, the return can be just as dangerous. This is the beginning of the third act of Campbell’s Hero’s Journey (known as the Return) and, while shorter, should still contain conflict. Our next step is an opportunity for that...
The Hero Transported
13. magic flight.
This is the point in the Hero’s Journey where they must get out alive, often requiring the help of individuals they met along the way. Dorothy still has to get back to Kansas, the solution to which may seem like a leap of faith.
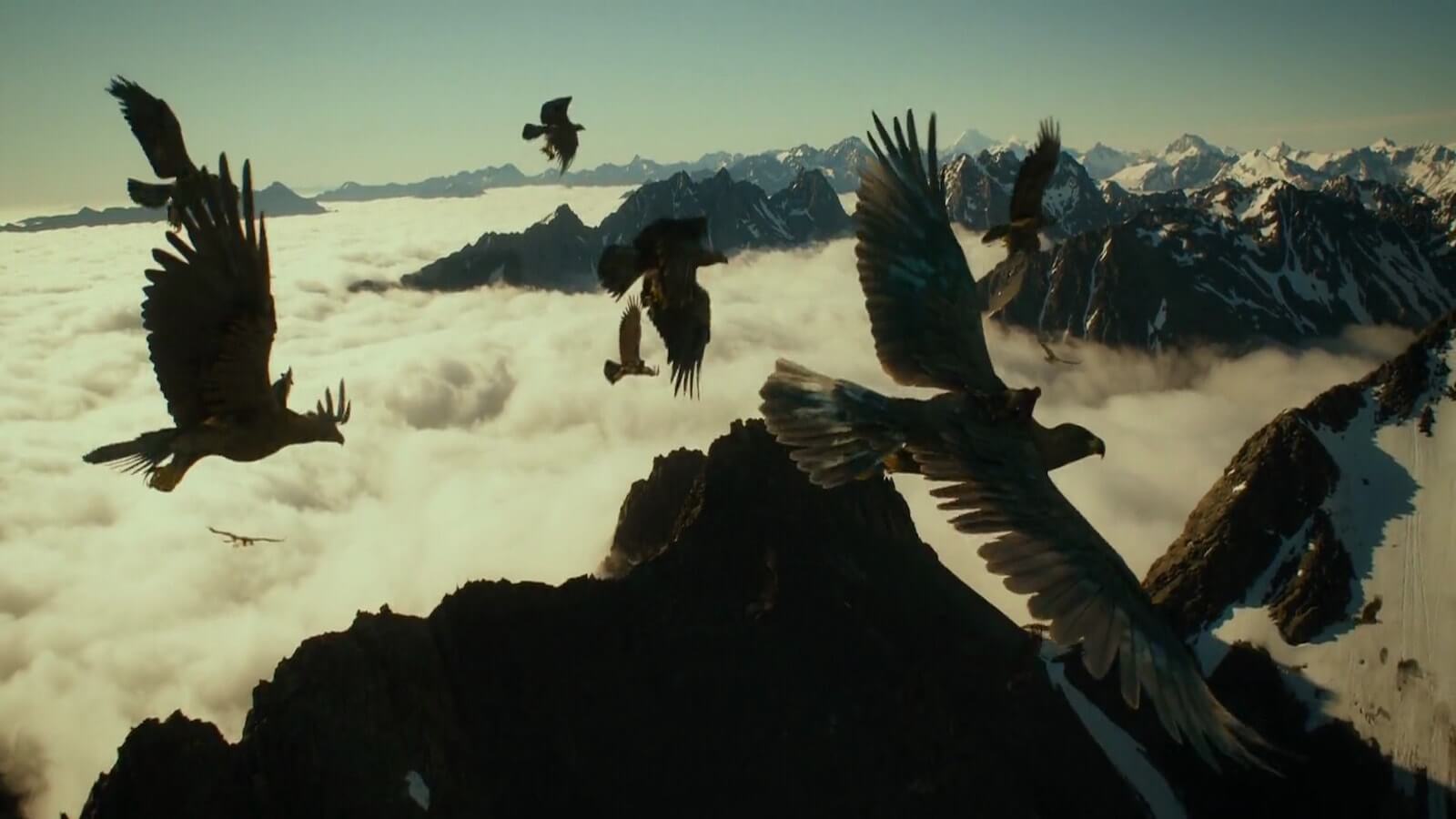

The eagles rescue from without with a magic flight to Frodo and friends
The hero's rescue, 14. rescue from without.
Bringing us to the “rescuers from without” point in the monomyth. Just because Frodo destroyed the one ring to rule them all doesn’t mean he gets a free ride back to the Shire. Remember those giant eagles we met a while back in act two? Well their back just in time!
Homeward Bound
15. crossing the return threshold.
Once the Hero is back home, it’s time to acknowledge their change in character. “Crossing the return threshold” is the stage in the monomyth where the hero has left the chaos of the outer world and return home.
But it's hard to adjust to the old world. Remember that scene where Frodo tried to enjoy a beer back at the shire? Hard to go back to normal when you essentially live with Dark Lord PTSD.
A Triumphant Return
16. master of two worlds.
The hero survived an adventure in the chaos realm, and now survives in the normal order realm. This makes him or her the master of two worlds. Not many people come back and live to tell the tale.
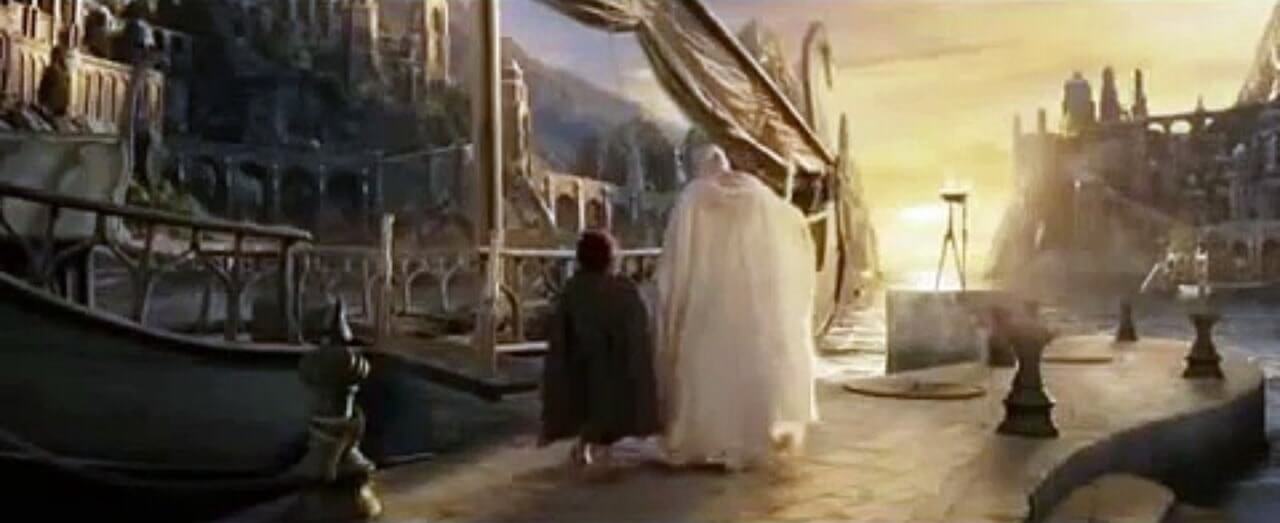

Frodo and Gandalf wandering off into the sunset post accomplishing their mission
Plus which, throughout the story, they’ve become someone much more capable and resilient than they were in act one. They've learned lessons, and brought what they learned home with them.
Whatever issues they may have had before embarking on this chaotic tale (often the ones preventing from taking the call to action) now pale in comparison with what they’ve been through.
It’s easier to deal with your annoying cousin, Dudley, after you’ve defeated Voldemort. This, in turn, leads to...
The New Status Quo
17. freedom to live.
In many ways the Hero's Journey is about death and rebirth. The story may manifest as the death of an aspect of character, and the birth of some new way of life. But the metaphor behind any story is one about mortality.
Change is constant. Hero's living through the Hero's Journey are models for us. Models that we can travers the constant change of existence, face our mortality, and continue. In a religious sense, and religions are all part of the monomyth, this is about the eternal spirit.
Look no farther than the prayer of St. Francis to understand this final step in the Hero's quest. "It is in dying that we are born to eternal life."

The Hero’s Journey Concludes
Cinematic heroes.
The monomyth is practically ubiquitous in Hollywood. As you’ve read earlier, Harry Potter , Star Wars , Lord of the Rings , and Citizen Kane all follow the Hero’s Journey. But, because this concept was built upon the foundations of major mythologies, it's truly a "tale as old as time."
Because Campbell discovered the Hero's Journey. He didn't make it up. Neither did those older myths. He realized as an anthropologist, that every culture all around the globe had the same story beats in all their myths.
Sure, some myths, and some movies, use 10 of the 17, or even just 5. But throughout human history, around the world, these story beats keep showing up. In cultures that had nothing to do with one another.
The Hero's Journey is a concept innate to being human.
And if remembering these 17 steps may seem a little daunting, fear not. Make sure to check out Dan Harmon's abridged 8-step variation of the Hero's Journey monomyth. Same structure, just made more digestible.
Dan Harmon’s Story Circle
Practically speaking, the Hero’s Journey is an excellent tool for structuring an outline in a clear and familiar way. It has the power to make your script much more powerful and emotionally resonant.
It’s circular, allowing for repeat adventures (which works well if you're learning how to write a TV pilot ) and each aspect drives the hero to the next. From the Goddess, the Hero finds temptation. From reconciling with the father, the Hero is now prepared for the final boon.
Story Circle • 8 Proven Steps to Better Stories
Using a Hero’s Journey worksheet can help you write a treatment or create a well-structured outline , which is a valuable tool for creating a strong first draft.
By putting in the 17 steps of the Hero’s Journey before building the outline, you can ensure that the writing process will flow smoothly and efficiently. Let us know in the comments how the monomyth has helped you craft a story that escalates with every beat to an exciting climax.
Up Next: Dan Harmon's Story Circle →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- TV Script Format 101 — Examples of How to Format a TV Script
- Best Free Musical Movie Scripts Online (with PDF Downloads)
- What is Tragedy — Definition, Examples & Types Explained
- What are the 12 Principles of Animation — Ultimate Guide
- What is Pacing in Writing — And Why It’s So Important
- 299 Facebook
- 238 Pinterest
- 12 LinkedIn
Kindlepreneur
Book Marketing for Self-Publishing Authors
Home / Book Writing / The Hero’s Journey: The 12 Steps of Mythic Structure
The Hero’s Journey: The 12 Steps of Mythic Structure
The Hero’s Journey plot structure is a common template for writing a compelling story. It also has a built-in character arc for the hero or heroine. Whether you write detailed outlines before getting into any prose, or you think writing is best done without an outline, the Hero’s Journey can help. Many writers fall somewhere in between, keeping in mind the broad strokes of a plot structure like the Hero’s Journey as they write.
Now, before you roll up your sleeves and get started with plotting your brand new idea, make sure it's viable to become a bestseller. Take just a few minutes to use book idea validation – without it, your book risks obscurity after it's published. If you have already written your book with a structure like the Hero's Journey and are looking to increase your sales, read how to make your book #1 on Amazon so you don't miss out on new readers.
One thing’s for sure: learning the twelve steps of the Hero’s Journey can only help your writing. This is why I recommend Plottr as an excellent tool to strengthen your writing. They have the Hero’s Journey and other well-known story archetypes to choose from so you can find one that best fits your particular story.
More on Plottr later. For now, let’s go on an adventure through the Hero’s Journey!
- The origins of the Hero’s Journey
- The 12 Steps of the Journey
- Examples of the Hero’s Journey
- How to incorporate this story structure into your writing
Table of contents
- What is the Hero’s Journey?
- The Hero’s Journey: An Overview
- 1. The Ordinary World
- 2. The Call to Adventure
- 3. Refusing the Call to Adventure
- 4. Meeting the Mentor
- 5. Crossing the Threshold
- 6. Test, Allies, and Enemies
- 7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
- 8. The Ordeal
- 9. The Reward
- 10. The Road Back
- 11. Resurrection
- 12. Return With the Elixir
- Star Wars: A New Hope
- The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring
- The Hunger Games
- Bonus Option: Use the Hero's Journey in a Series
- What Stories Work With the Hero’s Journey?
Get it for FREE here: Get the PDF Here
Popularized by mythologist Joseph Campbell in his book The Hero With a Thousand Faces , the Hero’s Journey is a story structure that has been used to tell exciting and captivating stories for centuries. Campbell, a literature professor, found that this was a common mythic structure. It’s widely known by the moniker the Hero’s Journey, but this name didn’t come around until well after Campbell’s 1949 book.
Campbell’s name for it was the monomyth.
Other scholars and storytellers have made tweaks to Campbell’s original monomyth structure, which has seventeen steps instead of the twelve I’ll be discussing today. The version of the Hero’s Journey widely used by screenwriters, authors, and playwrights today was popularized by screenwriter and producer Christopher Vogler .
You can apply this story structure to mythology, films, books, and even short stories.
There are three overall stages to the Hero’s Journey, each with individual story beats. These are 1) Departure, 2) Initiation, and 3) Return.
- The Ordinary World
- The Call to Adventure
- Refusing the Call to Adventure
- Meeting the Mentor
- Crossing the Threshold
- Test, Allies, and Enemies
- Approach to the Inmost Cave
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return With the Elixir
Format Beautiful Professional Books
Easy to use, and and full of amazing features, you can quickly turn your book into a professional book.
The Twelve Stages of the Hero’s Journey
Each of the twelve steps has its own story beats that happen. As we finish each stage, we’ll reflect on each story beat with an example from a famous movie.
The first step in the Hero’s Journey is your chance to familiarize the reader with the known world in which your story happens. This means giving the reader what they need to know to make sense of the world (otherwise known as exposition ). If your story takes place in a reality much like our own, you won’t have a lot to do. But if magic and mythical beasts are normal, or it’s far into the future and interstellar travel is possible, you’ll have a bit more work to do here. If you're having trouble picking which type of world is best for your book, research popular keywords in your genre to reveal settings that readers find interesting.
While you introduce the world, you’ll want to introduce the main character(s) as well. And in doing so, it’s important to give the reader a reason to like him, her, or them . While the protagonist is in their normal, ordinary world, they should want something more or different. And this want or need should dovetail nicely with the primary conflict of the story.
- Introduce the world and the character in an interesting way. Readers will give you some leeway at the beginning of the book, but if it reads like a textbook, you’ll lose them pretty quickly!
- Give the character personality and dimension . Needs, wants, flaws, and characteristics don’t all have to come out right away, but there should be enough for the reader to want to follow the hero through the story.
Tip: This first step should take the first 10-12% of the story.
Step two, the call to adventure, is also called the inciting incident. This is something disruptive that pulls the hero out of their ordinary world and toward a journey that will ultimately change their life . . . if they survive.
This call propels the rest of the story forward , so it should be exciting enough for the reader to want to continue with the story. This will change from genre to genre, so it’s important to know the tropes of whatever genre you’re writing in. On Amazon, there are thousands of genre categories to choose from, so research potential category options to better understand your market.
- Most heroes will resist this initial call to action. The stakes should be very real and clear to the reader at this point. In many stories, the stakes will be life or death.
- Remember that your story needs to grow in intensity until it peaks at the climax. So the call to action should be dramatic, but things will get worse for the protagonist from here.
Tip: The Call To Adventure should happen around the 12% mark.
Not every protagonist will refuse the call. Some may be ready to go. But if you pay attention to some of your favorite stories, you’ll likely see that most heroes resist initially until they have no choice.
Something should happen to make a refusing hero realize that they have no choice but to take on the challenge presented to them. For every refusal, some incident or information should come out that will raise the stakes and make the hero realize they must face the challenge . The hero ventures forth at the end of this section.
- It’s good to have the character refuse the call for a reason that ties in with the need or want established in the first step of the Hero’s Journey.
- Give them a good reason to refuse — and an even better reason to finally heed the call to adventure.
Tip: The refusal section starts around the 15% mark of the story.
At this point in the story, the protagonist has responded to the call to adventure. But their initial unease is still there. They don’t yet have the skills, items, or knowledge to succeed against such a challenge. This is where the mentor comes in.
The mentor helps the protagonist gain the confidence needed to continue on the journey. This is usually done in a multifaceted manner, with both physical and mental help. Much of the time, the mentor provides tough love, kicking the protagonist’s butt into action, so to speak. While mentors are often people, they can also take the form of information, like a map, a magic scepter, or any other number of things that help the hero along.
- Make it clear that, without the mentor, the protagonist would likely fall flat were they to continue on unaided.
- The hero’s time with the mentor should ultimately result in a revelation , giving the hero exactly what they need (or at least what they think they need) to face the antagonist or challenge.
Tip: Have this section start around the 20% mark of the story.
Step five of the Hero’s Journey is often called the point of no return. While the protagonist has learned from the mentor and gained confidence, this story beat forces them to engage fully with the challenge. Usually, this dramatic turning point is orchestrated by the antagonist, giving both the reader and the protagonist an idea of how powerful the villain really is.
One common tactic is to have the mentor killed in this section. Whatever you choose to do, make it pivotal and have it reinforce the central theme and conflict of the story . This is also the end of the Departure section, otherwise known as the first act.
- Until this point, the hero has had one foot in their ordinary world. Now, there’s no choice but to go forward into unknown territory, otherwise called the special world.
- The hero’s reaction to this pivotal story beat should be in line with what the reader knows about them. They need to work for any major changes that come about in this section.
Tip: Crossing the Threshold usually starts around the 25% mark.
This section marks the beginning of the second act. Building on everything that has come before, the protagonist should be challenged, putting their new abilities and knowledge to the test. It will become clear that the hero still needs help to resolve the main conflict of the story. This is where allies come into play. By teaming up with allies, the hero should continue to grow, playing off the other characters and working to overcome the tests or setbacks in the Special World.
Enemies are those that put the tests in their place, working actively against the hero and allies. The reader should learn to care about the allies, which means making them multifaceted characters. By the time this section is done, not all allies will have made it. Some may have even betrayed the hero. Likewise, enemies can also transform in this section, turning into allies.
- While the allies may want the same thing as the hero, they may have conflicting views on how to get it. Everyone in agreement all the time makes for a boring story.
- The hero’s abilities should be in doubt — both by the hero and the reader.
Tip: This section occurs around the 30% mark.
The approach to the inmost cave section gives the characters (and reader) a chance to reflect on the challenges of the previous section. Remember that the stakes and tension need to continue rising, so the previous section should have been the hardest challenge yet. The hero and allies are beaten and bruised — maybe one or more has died along the way — but the protagonist is still alive. The journey continues.
The group is closer to the goal — and to the place or time of ultimate danger. They’re regrouping and gathering their wits as they prepare to face the antagonist or some of the villain’s formidable forces.
- This is a good place for the characters to formulate a plan of attack, clarifying the price of failure and the prize for success.
- At this point, the hero has redoubled his effort and believes he is ready to face the challenge, despite his setbacks. The ordinary world is now far behind and impossible to get back to. The only way out is through.
Tip: This section happens around the 40% mark.
The ordeal is the biggest test yet and a transformative event that affects how the hero goes forward on their journey. This confrontation has the highest stakes so far, and it’s part of the central conflict. It brings the hero to their darkest point yet, and results in a metamorphosis of sorts that allows them to push through to the other side.
Campbell spoke of the ordeal in terms of death and rebirth for the protagonist. The hero uses all they have learned up to this point to push through the ordeal. A character close to the hero is often killed in this section, whether it be the mentor, a close ally, or a loved one. However, it’s not always a death. It could involve facing fears, going up against the biggest foe, or breaking through some seemingly insurmountable mental barrier. Whatever form the ordeal takes, the hero is broken down and comes out the other side stronger than before .
- This section is a long one, taking nearly a fifth of the story. It should be dramatic, compelling, and speak directly to the heart of both the external and internal conflicts of the story.
- Don’t be afraid to make things hard on your characters in this section. Even though the reader knows the hero will prevail, they should be left wondering in this section.
Tip: The Ordeal takes place from around the 50% mark.
Also called seizing the sword, this is the section in which the hero gets whatever they were searching for during the story. They’ve made it through the ordeal, and this is the reward. It can be an object, clarity, knowledge, or new skills/abilities. Whatever the reward is, it needs to be important in defeating the antagonist at the coming climax .
After the action and emotion of the ordeal, this section is a place for the reader and characters to regroup and catch their breath again. It can be a good place for a celebration of sorts, something to show for the sacrifices made so far. The hero may even reflect on all it took to get here.
- It should be clear to the reader how the reward will help the hero to finish the journey.
- This is a major milestone in the journey and should be treated as such. It also marks the end of act two.
Tip: The Reward section takes place around the 70% mark of the story.
Reward firmly in hand, the hero starts the journey back to the ordinary world. But every action has consequences, and those of claiming the reward block the hero’s road back. It becomes clear that things aren’t so simple, and the hero’s tribulations aren’t yet over.
The unforeseen consequences of claiming the reward make the hero realize they’re in more danger than ever before, and they must face the antagonist head-on before returning to the ordinary world. The hero prepares for the ultimate battle — the climax.
- It should be clear to the reader why the hero must face the antagonist once and for all. There should be no choice, given who the hero has become and the stakes they now face.
- This is a good place to re-establish the central conflict of the story and make clear the results of failure.
Tip: This section happens around the 75% mark.
This is the climax of the story — the ultimate showdown between hero and villain . The tension and the stakes are higher than they’ve been throughout the story. If the hero fails, the world as they know it will be forever changed for the worst. The hero uses all they have learned on the journey to defeat the antagonist.
The hero comes out of the confrontation changed, transformed into a true hero. This should be a dramatic transformation, completing the resurrection started earlier in the story.
- Like every other challenge, the hero needs to earn this victory by sacrificing something for it. In some stories, the hero may even sacrifice him or herself.
- By vanquishing the antagonist, the hero should find the strength or gain the knowledge to address their internal conflict in a satisfactory manner.
Tip: This section happens around the 85% mark .
The last section of the story details the hero’s return from the special world to the ordinary world. Sometimes called the magic flight, the hero now has changed for the better. Show what new skills, items, knowledge, or understanding of the world the hero brings with them (the elixir). This “elixir” can often be used to help those the hero left behind in the ordinary world.
In most stories, the hero will return to celebration. They’ve risked it all, saved lives, and learned important lessons. The people in the ordinary world are happy to have them back. The hero may decide to settle back into this world to use their newfound abilities. Or they may find they’ve outgrown it and have a taste for adventure.
- Re-establish the hero’s internal conflict and show how solving it has changed their view and life, completing the character arc .
- If you’re writing a series, provide a hook for the next story here by hinting at another conflict the hero will need to deal with.
Tip: This section happens around the 95% mark and finishes out the story!
Examples of the Hero’s Journey from Famous Works
In George Lucas's Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope , we can see the Hero's Journey in action. We also see it in The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring and The Hunger Games . Let’s take a look now.
- Luke Skywalker — an archetypal hero — in his Ordinary World, living with his aunt and uncle, hoping for adventure.
- Luke’s Call to Adventure comes when he activates a hidden message from Princess Leia that R2D2 is carrying for Obi-Wan Kenobi.
- Luke initially Refuses the Call — until he returns home to discover his aunt and uncle have been killed by Imperial forces.
- While Luke has already met his Mentor (Obi-Wan), the active mentoring really starts after Luke's home has been destroyed and the only family he's ever known killed.
- When Luke, Obi-Wan, and the droids step into the dangerous Mos Eisley Spaceport, it signifies the beginning of Luke's heroic journey and the Crossing of the Threshold.
- Luke and Obi-Wan hire a couple of Allies, Han Solo and Chewbacca, to transport them off the planet. Once on the Millennium Falcon, Luke's Tests begin.
- The Approach to the Inmost Cave happens when the Death Star captures the Falcon in a tractor beam and pulls them in.
- The Ordeal happens while Obi-Wan goes off to try and disengage the tractor beam. Luke, Han, and the others rescue Princess Leia. Obi-Wan confronts Darth Vader and sacrifices himself so the others can get away.
- With the Rewards (the Death Star plans and the princess), Luke thinks he should be able to defeat the Empire. And while Obi-Wan's death weighs on him, he can see success ahead.
- The Road Back is interrupted as the Falcon is attacked. They have no choice but to go to the Rebel base to deliver the Death Star plans, even though they’re being tracked.
- As the Rebels are attacking the Death Star, Obi-Wan's voice speaks to Luke, telling him to use the Force. Luke does, using all that he's learned and finally “sacrificing” his old self, embracing the Force and “Resurrecting” as a true hero. He fires and blows up the Death Star.
- Luke Returns to the Rebel base triumphant. Both he and Han Solo receive medals and accolades for delivering the (temporary) blow to the evil Empire.
- We get to see Frodo’s idyllic Ordinary World in the Shire. The idea of adventure is attractive to him, but not overly so.
- Frodo’s Call to Adventure begins after Bilbo disappears, leaving behind the Ring, which Gandalf entrusts to young Frodo.
- Frodo Refuses the Call not just once, but repeatedly throughout the story. He feels he is not the one to be entrusted with such a job of carrying and disposing of the Ring.
- Gandalf acts as Frodo’s Mentor, instructing him on what he must do to protect the Ring and, in so doing, protecting the Shire.
- Frodo and Sam quite literally Cross the Threshold as they leave the Shire after splitting from Gandalf.
- Frodo and Sam run into Allies Merry and Pippin on their way toward Bree. They are also Tested by Enemies as they’re pursued by the Nazgûl. These tests continue until the group gets to Rivendell.
- The Approach to the Inmost Cave is the group’s approach to the Mines of Moria — literal caves.
- The Ordeal happens inside the Mines of Moria as the group is attacked by orcs and then Balrog, which Gandalf fights off, falling down into the depths and presumed dead.
- The Reward is sparse in The Fellowship of the Rings. Gandalf is gone, and the group escapes with their lives.
- The Road Back isn’t signified in this story by a turn back to the Ordinary World. Instead, it’s Frodo’s stay in Lothlórien, where he sees the stakes of his failure in a vision.
- The Resurrection is the climax of the story, where the Uruk-hai catch up with the group and Boromir betrays Frodo, trying to take the ring from him. Frodo realizes he must travel alone to Mordor.
- The Return with the Elixir portion is Sam’s refusal to let Frodo journey alone. Frodo pulls him into the boat and they cross the river together. Meanwhile, the rest of the Fellowship are determined to save Merry and Pippin. To be continued . . .
- We see Katniss Everdeen living in her Ordinary World (District 12) with her mother and sister. It’s a bleak, depressing world, but it’s her Ordinary World nonetheless.
- After Prim, Katniss’s sister is called for Tribute, Katniss volunteers in her stead. This is the Call to Adventure.
- This is one example of a story with no real Refusal of the Call. She may not want to take part in the Hunger Games, but she makes the decision and sticks with it to save her sister.
- Katniss meets Haymitch, her Mentor. Though a drunk, he guides her on the politics and gives her tips on surviving the Games.
- Katniss Crosses the Threshold when she’s put on the train to the capital, leaving her Ordinary World behind.
- The Tests, Enemies, and Allies section starts when she has to navigate the preparation for the Games. She meets Rue and has Peeta as an ally, as well. The Careers are clearly enemies to contend with later.
- Katniss Approaches the Inmost Cave when the Hunger Games begin.
- The Ordeal is plain to see as the Games commence, and Katniss struggles to stay alive amid the chaos.
- The Reward comes when only Katniss and Peeta are left alive in the arena. They don’t have to fight, thanks to a rule change; they can both claim victory.
- It looks good for Katniss and Peeta until the Capital changes the rules again, putting an obstacle in the path of the Road Back. Suddenly, they’re forced to decide which of them gets to live.
- The Resurrection portion of the story plays out as Katniss and Peeta threaten to kill themselves, leaving no winner and possibly sowing the seeds of revolution. The Capital changes the rules again, allowing both of them to claim victory.
- Katniss gets to live, Returning from the Games as a hero. One who just may be able to make some real change to her Ordinary World.
Let's say you want to think big. Like a 12 book series big. One little fun way that I use the Hero's Journey is to use each of the 12 steps to represent an entire book as a whole. You could also condense this into 6 books, 3 books, etc.
For example, the original Star Wars trilogy does a fantastic job of fitting the hero's journey not only into the first movie (A New Hope) but also into the trilogy as a whole. The first movie could easily represent the first four steps of the hero's journey from a macro-perspective (as well as covering all 12 within its self-contained plot), with The Empire Strikes Back covering steps 5-8, and Return of the Jedi covering steps 9-12.
Seriously though, the OG Star Wars trilogy is a masterclass in plotting, you guys.
In other words, the Hero's Journey doesn't have to be used just for a single novel, it can be a great way to progress your character from a more zoomed out perspective through an entire series.
Now that you know what to look for, think about some of your favorite stories. See if you can see the beats of the Hero's Journey in them. From Harry Potter and Toy Story to the Lion King and The Hunger Games , you'll find evidence of this story structure.
Its uses aren't just for adventure stories, though. With a little tweaking, a sweet romance story could also follow this template pretty closely. The point of the Hero’s Journey plot template isn’t to lock you into a formula that you can’t deviate from. Instead, it’s a tool that can guide you along. When you know the tropes of your genre, you can marry them with the major beats of the Hero’s Journey to come up with a novel readers will love . Remember, however, that writing an incredible novel is only part of the battle to find loyal readers- it's also important to have a strong marketing strategy so people can actually discover your book, as outlined in my free e-book on how to become an Amazon bestseller.
To make story beats easier, I recommend giving Plottr a try. It’s a great storytelling tool for writers that can help keep you on track using structures like the Hero’s Journey, Dan Harmon’s Story Circle , the Three Act Structure , and more.
Dave Chesson
When I’m not sipping tea with princesses or lightsaber dueling with little Jedi, I’m a book marketing nut. Having consulted multiple publishing companies and NYT best-selling authors, I created Kindlepreneur to help authors sell more books. I’ve even been called “The Kindlepreneur” by Amazon publicly, and I’m here to help you with your author journey.
Related Posts
How to write an adventure story, parts of a book [from cover to cover], how to write a whodunit, sell more books on amazon, amazon kindle rankings e-book.
Learn how to rank your Kindle book #1 on Amazon with our collection of time-tested tips and tricks.
Join the community
Join 111,585 other authors who receive weekly emails from us to help them make more money selling books.

Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey: The Definitive Guide
Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey is a timeless blueprint that’s shaped storytelling across cultures and eras.
It’s a narrative pattern that guides our favorite heroes from humble beginnings to epic triumphs.
We’ll explore how this framework resonates in everything from ancient myths to modern blockbusters.
Get ready to uncover the stages that make characters’ adventures universally compelling.
Joseph campbells heros journey
Who was joseph campbell.
Joseph Campbell (March 26, 1904 – October 30, 1987) was an American mythologist, writer and lecturer, best known for his work in comparative mythology and comparative religion.
His work is vast, covering many aspects of the human experience.
He wrote and spoke about religion, mythology, paleontology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, anthropology, science, and psychology.
As a scholar he influenced a generation of modernist writers and thinkers.
Campbell’s work covers many different aspects of the human experience.
The Hero’s Journey: A Timeless Blueprint
The Hero’s Journey, conceptualized by Joseph Campbell, isn’t just a literary tool – it’s the backbone of countless storytelling traditions.
It has enabled writers and filmmakers to craft narratives that resonate deeply with audiences, regardless of cultural or temporal divides.
The familiarity of the journey’s pattern provides a comforting predictability that, paradoxically, allows for incredible creativity within its framework.
When we observe the Hero’s Journey in action, we can break down the narrative into several key stages.

Characters are first introduced in their ordinary world, then called to adventure and plunged into an entirely new and often hazardous domain.
The subsequent trials and revelations that they undergo help shape their character arcs and keep viewers and readers fully engaged.
Films like Star Wars and The Lord of the Rings have become timeless by employing this narrative structure.
In dissecting these iconic tales, one can clearly identify the crucial checkpoints of the Hero’s Journey such as the meeting with the mentor, the ordeal, and the eventual transformation.
Our connection to these films is no accident – the mastery of the journey’s blueprint in their storylines speaks directly to our collective unconscious.
This narrative device is also a critical tool for us in filmmaking.
Not only can it guide scriptwriting and character development, but it influences casting, cinematography, and editing too.
- Scriptwriting – aligning the plot to the stages of the journey ensures a solid narrative structure,
- Casting – selecting actors who can authentically embody the hero’s evolving persona,
- Cinematography and Editing – creating visuals and transitions that reflect the hero’s internal and external journeys.
By embracing the Hero’s Journey, we craft stories that are not only compelling but also strike the same mythic chords that have echoed throughout human history.
It’s our pathway to creating works that linger in hearts and memories long after the credits roll.
Understanding The Narrative Pattern
Understanding the narrative pattern of the Hero’s Journey helps us grasp why some stories stick with us long after the credits roll.
It’s not just about a sequence of events – it’s about a deep structure resonating with the human psyche.
The narrative unfolds typically across twelve stages, though some adaptations may vary.
These stages can be distilled into three distinct acts – the Departure, where the hero leaves the ordinary world; the Initiation, featuring trials and growth; and the Return, where the hero comes back transformed.
Each stage serves a unique purpose in forwarding the story and the character’s development.
Let’s look at a few:
- The Ordinary World – Here, the hero is introduced in their regular life.
- The Call to Adventure – Something disrupts the hero’s routine.
- Refusal of the Call – The hero hesitates to take on the challenge.
- Meeting the Mentor – Guidance is provided to the hero.
- Crossing the Threshold – The hero fully enters the new world of adventure.
Filmmakers apply these steps thoughtfully to produce unforgettable journeys.
For instance, films like The Matrix and Harry Potter thrive on this formula, ensuring audiences see parts of themselves in the heroes they admire.
By recognizing these patterns, we’re better positioned to construct our narratives or analyze those we find particularly compelling.
In doing so, we gain a clearer understanding of the magic woven into the fabric of classic and contemporary tales.
Uncovering The Stages Of The Hero’s Adventure
As we jump deeper into the heart of Joseph Campbell’s model, it’s essential to break down the Hero’s Journey into digestible segments.
These stages form a framework that artists have employed to craft some of the most compelling narratives in cinema.
Departure Act
The Departure Act marks the beginning of the Hero’s journey.

Here, call to adventure propels the protagonist into a world beyond their familiar boundaries.
- The Ordinary World – establishes the hero’s normal life,
- Call to Adventure – offers the initial spark for change,
- Refusal of the Call – highlights the hero’s reluctance,
- Meeting with the Mentor – provides guidance for the journey,
- Crossing the First Threshold – marks the hero’s commitment to the adventure.
Initiation Act
The Initiation Act, often the bulk of the journey, thrusts the hero into trials and tribulations.
Challenges faced here are pivotal for growth and transformation.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies – reveals the complexities of the new world,
- Approach to the Inmost Cave – signifies preparation for the central ordeal,
- Ordeal – tests the hero’s resolve in a fierce confrontation,
- Reward – confers an achievement or object of great value.
From Ancient Myths To Modern Blockbusters: How The Hero’s Journey Resonates
When we jump into the motifs of ancient myths, we uncover the timeless structure of the Hero’s Journey that continues to echo through modern cinema.
Films such as Star Wars and The Lord of the Rings have their foundations steeped in the classic stages of Joseph Campbell’s narrative framework.
Our fascination with heroic tales is not merely a cultural coincidence.
Instead, it’s deeply rooted in our collective psyche – propelling narratives from mere stories to profound journeys that mirror our own lives.
Blockbusters continue to draw on the Hero’s Journey for a very compelling reason – the universality of its theme.
Whether it’s the longing for adventure or the ultimate triumph over adversities, these stories tap into a shared human experience.
While the settings and characters change, the core stages of the Hero’s Journey remain as relevant in today’s stories as they were centuries ago.
As storytellers, we find a powerful ally in this narrative arc:
- Character development that fosters an emotional connection with the audience,
- Plot progressions that feel both exciting and familiar.
Our ability to reinvent and reimagine these stages keeps the Hero’s Journey fresh yet recognizable.
Heroes may falter and stray, but their stories will always find resonance with us, making their final return something we can all aspire to.
The Hero’s Journey isn’t just a template for crafting narratives; it’s a master key.
It unlocks the doors for us to create compelling, deep, and wide-reaching stories that span cultures and time periods.
The Compelling Nature Of Characters’ Adventures
The allure of the Hero’s Journey isn’t just in its structure; it’s deeply embedded in the characters we meet and the adventures they embark upon.
These are not just mere escapades; they are reflections of our own life’s quests.
Through their trials and triumphs, we see parts of ourselves, making their journey our journey.
Characters crafted on the bones of the Hero’s Journey reveal much about human nature and our eternal quest for meaning.
Whether it’s Luke Skywalker wrestling with his destiny in Star Wars or Dorothy seeking her way home in The Wizard of Oz , the narrative digs deep into the psyche, revealing universal truths through personal trials.
By taking note of these pivotal elements –
- Transformation,
- Inner conflicts,
- Mentorship,
- Ultimate boon.
We grasp the essence of why these stories resonate with us so profoundly.
It’s not merely the victory of the heroes that we celebrate; it’s their entire journey, marked by growth, resilience, and the human spirit’s indefatigable quest for a better self.
The immersion into fantastical worlds, whether it’s the expansive universe of The Lord of the Rings or the intricate politics and family drama of Game of Thrones , invites us to lose ourselves in stories that feel both incredibly distant yet intensely personal.
In witnessing the characters’ adventures unfold, we’re reminded of our potential for greatness in the face of adversity.
We’re not just passive observers; we’re participants in an emotional odyssey, rooting for characters as they make difficult choices that will forever change their worlds and ours.
Their journey becomes a mirror, and in that mirror, we catch glimpses of who we are and who we might become.
Joseph Campbells Heros Journey – Wrap Up
We’ve explored the depths of Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey and discovered its timeless impact on storytelling.
This narrative structure isn’t just a tool for writers; it’s a lens through which we view our own lives.
Our fascination with these tales stems from their universal appeal—they echo the very essence of the human experience.
By identifying with the hero’s trials and transformations, we’re inspired to embark on our personal quests.
As storytellers, we wield the power to craft narratives that not only entertain but also enlighten, offering a reflection of our collective journey.
The Hero’s Journey continues to guide us, proving that at the heart of every great story lies the potential for connection and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the hero’s journey.
The Hero’s Journey is a narrative structure that outlines a hero’s adventure and transformation through a series of stages.
It is divided into three acts: Departure, Initiation, and Return.
How Does The Hero’s Journey Influence Storytelling?
The Hero’s Journey serves as a blueprint for storytelling, resonating with human emotions and creating cinematic experiences that stick with audiences across different cultures and time periods.
What Are The Three Acts Of The Hero’s Journey?
The three acts are Departure, where the hero leaves the ordinary world; Initiation, where the hero faces trials and gains wisdom; and Return, where the hero comes back, often with something beneficial for their community.
Why Do Stories Following The Hero’s Journey Resonate With Audiences?
These stories tap into our collective psyche and reflect shared human experiences, such as growth, resilience, and the quest for self-improvement, making them universally compelling.
What Makes A Character’s Development In The Hero’s Journey Impactful?
Character development is impactful because it showcases a transformation that includes overcoming inner conflicts, learning from mentors, and enduring trials, which mirrors our own life’s quests.
How Does The Hero’s Journey Impact The Audience?
The audience participates emotionally, rooting for the characters as they encounter hardships and make choices that lead to personal growth and transformation, reflecting our own potential for greatness.
Best Jump Scare Movies: 20 Super Jumpy Movies
Shooting In The Rain: The Filmmaker's Definitive Guide
Matt Crawford
Related posts, what is past tense in writing for film narratives & literature: ultimate guide, teleplay vs screenplay vs script: what are the differences, good vs. evil in film & literature: a deep dive [with examples], what are framing devices in writing definition & examples, what is narrative paradigm in film & literature definitieve guide, what is an allusion definition, examples & tutorials, leave a reply cancel reply.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Registration is closed.
Pin It on Pinterest
Passion doesn’t always come easily. Discover your inner drive and find your true purpose in life.
From learning how to be your best self to navigating life’s everyday challenges.
Discover peace within today’s chaos. Take a moment to notice what’s happening now.
Gain inspiration from the lives of celebrities. Explore their stories for motivation and insight into achieving your dreams.
Where ordinary people become extraordinary, inspiring us all to make a difference.
Take a break with the most inspirational movies, TV shows, and books we have come across.
From being a better partner to interacting with a coworker, learn how to deepen your connections.
Take a look at the latest diet and exercise trends coming out. So while you're working hard, you're also working smart.
Sleep may be the most powerful tool in our well-being arsenal. So why is it so difficult?
Challenges can stem from distractions, lack of focus, or unclear goals. These strategies can help overcome daily obstacles.
Unlocking your creativity can help every aspect of your life, from innovation to problem-solving to personal growth.
How do you view wealth? Learn new insights, tools and strategies for a better relationship with your money.

Hero's Journey: A Guide to Becoming The Hero Of Your Story
What will your story be.
Be the hero of your story . It’s common advice from motivational speakers and life coaches, a call to arms to take centre stage and tackle life’s challenges head-on, to emerge victorious in the face of adversity, to transform through hardship.
As humans, hardwired to view the world and share experiences through the medium of stories, myths often act as powerful motivators of change. From ancient cave paintings to the Star Wars and its Death Star to Harry Potter and his battle against evil, the hero’s journey structure is a familiar one. It’s also one you need to know if you want to know how to write a book , but I digress.
This article will outline the stages, and psychological meaning, of the 12 steps of Joseph Campbell’s hero’s journey. So, are you ready to become the hero of your story? Then let the adventure begin...
Who is Joseph Campbell?
Joseph Campbell was an American professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College, and an expert of mythology that once spent five years in a rented shack, buried in books for nine hours each day. His greatest contribution is the hero’s journey, outlined in his book The Hero with A Thousand Faces . Campbell was able to synthesise huge volumes of heroic stories, distilling a common structure amongst them.
Near the end of his life, Campbell was interviewed by Bill Moyers in a documentary series exploring his work, The Power of Myth .
Throughout their discussion, Campbell highlighted the importance of myth not just in stories, but in our lives, as symbols to inspire us to flourish and grow to our full potential.
How is the hero’s journey connected to self development?
You might be wondering what storytelling has to do with self-development. Before we dive into the hero’s journey (whether that is a male or a female hero’s journey), context will be useful. Joseph Cambell was heavily inspired by the work of Carl Jung, the groundbreaking psychologist who throughout his life worked on theories such as the shadow, collective unconscious, archetypes, and synchronicity.
Jung’s greatest insight was that the unconscious is a vast, vibrant landscape, yet out sight from the ordinary conscious experience. Jung didn’t only theorize about the unconscious; he provided a huge body of work explaining the language of the unconscious, and the way in which it communicates with the conscious mind.
The nature of the unconscious
Due to its vast nature, the unconscious doesn’t operate like the conscious mind, which is based in language, logic, and rationality. The unconscious instead operates in the imaginal realm — using symbols and meaning that take time to be deciphered and understood consciously. Such symbols surface in dreams, visualizations, daydreams, or fantasies.
For Jung, the creative process is one in which contents of the unconscious mind are brought to light. Enter storytelling and character development — a process of myth-making that somehow captures the truth of deep psychological processes.
Campbell saw the power of myth in igniting the unconscious will to grow and live a meaningful life. With that in mind, his structure offers a tool of transformation and a way to inspire the unconscious to work towards your own hero’s journey.
The 12 steps of the hero’s journey
The hero’s journey ends where it begins, back at the beginning after a quest of epic proportions. The 12 steps are separated into three acts:
- departure (1-5)
- initiation (5-10)
- return (10-1)
The hero journeys through the 12 steps in a clockwise fashion. As Campbell explains:
“The usual hero adventure begins with someone from whom something has been taken, or who feels there is something lacking in the normal experience available or permitted to the members of society. The person then takes off on a series of adventures beyond the ordinary, either to recover what has been lost or to discover some life-giving elixir. It’s usually a cycle, a coming and a returning.”
Let’s take a closer look at each of the steps below. Plus, under each is a psychological symbol that describes how the hero’s journey unfolds, and how when the hero ventures forth, he undergoes an inner process of awakening and transformation.
1. The ordinary world
The calm before the storm. The hero is living a standard, mundane life, going about their business unaware of the impending call to adventure. At this point, the hero is portrayed as very, very human. There could be glimpses of their potential, but these circumstances restrict the hero from fulfilling them. Although well within the hero’s comfort zone, at this stage, it’s clear something significant is lacking from their life.
Psychological symbol
This is represented as a stage of ignorance, pre-awakening. Living life by the status quo, on other people’s terms, or simply without questioning if this is what you want. At this point life is lived, but not deeply satisfying.
2. Call to adventure
Next is a disruption, a significant event that threatens the ways things were. This is a challenge that the hero knows deep down will lead to transformation and change, and that the days of normality, “the way things are,” are numbered. The hero confronts the question of being asked to step into their deeper potential, to awaken the power within, and to enter a new, special world.
Many of us embark on inner-journeys following hardship in life — the death of a loved one, the loss of a job, physical or mental illness. This stage occurs when it becomes apparent that, to move through suffering, one has to look within, to adventure into the soul.
3. Refusal of the call
No compelling story would be complete without friction. The hero often resists this call to adventure, as fear and self-doubt surface at full force, and the purpose of this new life direction is questioned. Can the reluctant hero journey forth? Do they have the courage?
The only way to grow and live a deeply fulfilling life is to face the discomfort of suffering. Campbell himself once said: “ The cave you fear to enter holds the treasure you seek .” At this stage, fears, and anxieties about delving deep into the psyche arise. The temptation is to remain blissfully ignorant, to avoid discomfort, and to stay in your familiar world.
4. Meeting a mentor
As the hero faces a crisis of confidence, a wise mentor figure appears.
This character offers inspiration, guidance, or understanding that encourages the hero to have the self-belief to start this new adventure. In many stories, a mentor is someone else who has embarked on the hero’s journey, or someone who attempted, and failed. This person reflects the importance of this mission, reminding the hero their calling far exceeds their fear.
When the journey of exploration has to begin, people or situations enter your life at just the right time, guiding you in the right direction. This could be a close friend, a peer, a professional, such as a coach or therapist, or even a fictional character in a film or book. In most cases, these are chance encounters that contain a sense of knowing before the hero leaves on his or her adventure.
5. Crossing the threshold
This is a pivotal moment in the hero’s journey, as the initiation begins. This occurs when the hero fully commits to their quest, whether physical, emotional, or spiritual. This is the point of no return, where the reluctant hero embarks on their adventure, and has accepted that the way things were must change. The hero enters a new zone, one in which the call to adventure must be accepted. The hero’s resolve is hardened, and they understand they have a responsibility to confront what is ahead of them.
Whatever your life was before the call to action, this is a crossroads which is accepted, knowing your life may never be the same. This is a point of empowerment, where you realize that journeying within will lead you to greater self-understanding, even if those insights will dramatically change your life direction.
6. Test, allies, enemies
Now the hero has ventured outside of their comfort zone, the true test begins. This is a stage of acclimatizing to unknown lands. Unknown forces work against them, as they form bonds with allies who join them along the way, or face formidable enemies or encounters that have to be conquered. Throughout this testing time, the hero will be shaped and molded through adversity, finding deeper meaning in their life and mission.
Once the journey of self-discovery is underway, the initial burst of inspiration might be tested by the difficulty of the task. You might meet people who are able to offer advice or guide you, or those who reflect areas of yourself you have to work on.
Often, these are inner experiences, in the forms of memories, emotions, or outward tests, such as difficult circumstances that challenge your resolve and commitment to your new life direction.
7. Approach to the inmost cave
Having already crossed the threshold into the unknown and the uncertain, having faced obstacles and enemies, and having begun to utilize their qualities along the way, the next stage is another threshold.
This is the beating heart of the hero’s challenge, where again self-doubt and fear can arise, as another threshold has to be crossed. This is often a period of respite, giving the hero time to pause and reflect. Will the hero make the leap?
The hero’s journey has ups and downs. There may be quick wins in the beginning — your new life direction may go well, or inner-work may lead you to a new place of calm or confidence. But then, out of nowhere, comes an even bigger challenge, surfacing as a question mark to the person you’ve become. Life often has a way of presenting the right challenges at the right time…
This is the life-or-death moment. This can be a meeting with an ultimate enemy or facing the hero’s deepest fear. There is an awareness that if the hero fails, their new world, or their life, could be destroyed.
Everything the hero has fought for up to this point, all the lessons learned along the journey, all the hidden potentials actualized, will have to be utilized to survive this supreme ordeal, for the hero to be victorious. Either way, the hero will undergo a form of death, and leave the ordeal forever changed.
There are inner challenges that have to be confronted on the journey of self-discovery. This might be in the form of trauma that has to be confronted and healed, people with whom you have to have difficult conversations, or fears you have to face, actions that in the past you never thought you’d be capable of. But, with the skills you’ve learned along the way, this time you’ll be ready. But it won’t be easy.
9. Reward (seizing the sword)
Through great adversity comes triumph. Having confronted their greatest fear, and survived annihilation, the hero learns a valuable lesson, and is now fully transformed and reborn — with a prize as a reward.
This object is often symbolized as a treasure, a token, secret knowledge, or reconciliation, such as the return of an old friend or lover. This prize can assist in the return to the ordinary world — but there are still a few steps to come.
When confronting deep inner fears or challenges, you are rewarded with deep insights or breakthroughs. That might be in the form of achieving a significant goal or inwardly having a sense of peace or reconciliation with your past, or moments that have previously felt unresolved. As a spiritual process, this may also be the realization that behind suffering and pain lies freedom or inner peace.
10. The road back
Having traveled into distant, foreign lands and slain the dragon, now it’s time for the hero to make their return journey. This stage mirrors the original call to adventure and represents another threshold.
The hero may be understanding their new responsibility and the consequences of their actions, and require a catalyst to make the journey back to the ordinary world with their prize.
The hard work has been done, the ultimate fear confronted, new knowledge found. Now, what’s the next step? For many, the initial stages of growth come with a period of renunciation or are symbolized by an outward journey away from home, or away from familiarity.
Then comes the stage of returning to familiarity, or the things left behind — be it family, friends, locations, or even behaviors that were once loved and sacrificed during the journey.
11. Resurrection
When it appears the hero is out of the woods, there comes a final confrontation — an encounter with death itself. Transformed inwardly and with a personal victory complete, the hero faces a battle that transcends their individual quest, with its consequences far-reaching, for entire communities or even humanity itself.
This purification solidifies the hero’s rebirth, as their new identity fully emerges just in time to return to the ordinary world.
In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, self-actualization is secondary to self-transcendence. In other words, once inner battles have been faced, and the alchemy of psychological transformation is underway, the next stage is to apply the newfound insights and knowledge to a bigger cause — supporting others, or standing up a mission that will benefit the wider world.
12. Return with the elixir
Following the final battle, the hero finally returns home. By now, personal transformation is complete, they’re returning home a different person. Having faced indescribable hardship, the hero returns with added wisdom and maturity. The elixir is the treasure they’ve returned with, ready to share with the ordinary world. This could be a sense of hope, freedom, or even a new perspective to assist those originally left behind.
The hero has a new level of self-awareness, seeing the ordinary world through fresh eyes. They’ve left internal conflict behind. There’s an understanding that things will never be the same, but that the hero’s journey was part of their destiny.
Then comes the ultimate prize: a final reconciliation, acceptance from the community, celebration, redemption. Whatever the prize, there are three elements: change , success , and proof of the journey .
Following a transformative psychic process, there’s an understanding of what is within your control. The “ordinary world” may have many elements that remain the same, but this is accompanied by a realization that when you change, so does your reality. Previously modes of thinking may be replaced, as bridges are built with your past, giving opportunity for a renewed approach to life.
What can we learn from the hero's journey?
At the time of writing this article, I’m in the UK visiting my family for the first time in 18 months. As I walked down paths I’d walked throughout my childhood, I was struck by how much I’ve changed over the years. A passage from T.S Eliot’s poem Little Gidding came to mind:
“We shall not cease from exploration. And the end of all our exploring. Will be to arrive where we started. And know the place for the first time.”
I reflected on the notion of coming full circle — to begin a journey, outwardly or inwardly, before finding yourself back at the beginning, transformed. In spiritual traditions, the circle is a powerful symbol of timelessness, death and rebirth, totality, and wholeness. Aptly, the 12 steps of the hero’s journey are depicted as a circle. It’s not a coincidence.
What can we learn from the hero’s journey? In a way, it is similar to the writer’s journey. Above all else, it’s a reminder that we each within us have a purpose, a quest and a mission in this life that can and will invoke our truest potential. The path isn’t easy — there are many, many challenges along the way. But at the right time, people and situations will come to our aid.
If you’re able to confront the mission head-on and take bold steps along the way — just like all the heroes of fiction before you, from Shakespeare’s characters to Luke Skywalker and Rey from the universe brought to us by George Lucas — then you will be transformed, and then you can return to where you started, reborn, ready to share your gifts and your lessons with the world.
Hot Stories
Parents abandon baby at hospital after being horrified by his face - then one woman takes him in as her own, groom shaves bride's head on wedding day in front of guests, what happened to jenna marbles, one of youtube's first big stars, student banned from prom for wearing suit - so strangers stepped in to make it up to them in the best way, husband's controversial video on his wife wanting alone time goes viral, fortnite player calls mom and makes shocking announcement on livestream, single dad lets daughter say "whatever she wants" — her shocking words go viral.
Little Girl's Video on Self-Love Shocks Dad and Goes Viral
Jhovan "Jay" Galberth is a single dad whose parenting style is making jaws drop. The dadfluencer posted a shocking video that his young daughter, Tatum, recorded alone — and her surprising words say everything about how she is being raised.
His no-judgment approach brought a smile to millions of faces, but it also left some questioning the impact of his "let-it-all-out" parenting style.
Her Dad Gave Her 20 Seconds To Say Anything
A new challenge on ParentTok (short for TikTok parent content) is taking the internet by storm, and it's as simple as it is enlightening.
The trend involves parents giving their children 20 seconds in a room alone to say whatever they want, with the parent promising not to get mad. Jay Galberth ( @dadsdoittoo ), tried this challenge with his daughter, Tatum, expecting some silly antics or even a few bad words. Instead, what he got was a heartwarming lesson in self-love and positivity.
After telling Tatum she had 20 seconds, Jay closed the bathroom door and let the camera roll. The toddler's confidence and positivity caught everyone off guard. Rather than using the opportunity to make mischief, Tatum declared herself a "queen," a "superstar," and expressed her love for herself and her intelligence. "I'm beautiful, I'm smart, and I love myself," she proclaimed. Her infectious energy left viewers feeling inspired and energized.
Watch Jay Galberth's Video:
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Hey yall Its Tatum (@dadsdoittoo)
Barbie Gives a Shout-Out: Dad's Viral Video Gets a Glamorous Endorsement
Tatum's self-love-filled monologue was not only an inspiration to viewers but also caught the attention of some significant names. Among them was the official Barbie Instagram account, which left a comment under Jay's video, saying, "And don't you forget it 😉💖."
"I was proud. Seeing the things I instilled into her and hearing her speak the words of affirmation felt good to see." Jay Galberth
This unexpected recognition from the iconic doll brand added a touch of glamour and validation to the already viral video. It also highlighted the broader impact of the message Tatum was sending, which resonated with audiences of all ages. Jay and Tatum's story is a reminder that positivity and confidence, no matter how small the voice, can echo far and wide.
She Learned Self Love From Her Dad
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Jhovan Galberth (@movewitjay)
The powerful response to Tatum's words reflects the significant role parents play in shaping their children's self-esteem and sense of self-worth. Jay's dedication to instilling confidence and love in his daughter was evident in her positive words of self-affirmation.
In a world where self-doubt often takes center stage, Tatum's message of self-acceptance serves as a guiding light. Her father's positive influence is a testament to the impact that positive reinforcement and encouragement can have on a child's mindset. It’s not just about the words we say, but the actions we take to build our children's self-esteem and resilience.
"I try my best to motivate my daughter and build her up," he added. "This time she showcased her confidence and intelligence."
Jay Galberth's approach to parenting reminds us that nurturing a child's confidence can lead to a happier, more positive world. When parents shape their children's view of themselves with love and encouragement, they set the foundation for strong, self-assured adults. The viral video serves as a heartwarming reminder to always lift each other up and create a space for positivity and growth.
Bullies Play Homecoming Prank on Boy With Autism - So This Beauty Queen Steps In
Mom says her kid goes to school in stained clothing - strangers were taken by surprise, 16-year-old sentenced to 100 years in prison heads to law school, surprised mom finds random note at kmart - then, strangers find the mystery author, lamar odom regrets choosing khloe kardashian over taraji p henson, the kardashian redemption - an uncensored documentary, how did betrayal connect jennifer aniston and selena gomez, how tiffany haddish finally found the love she deserved, subscribe to our newsletter, the great takedown of nickelodeon’s dan schneider - how even small voices have the power for impact, chris gardner beyond the pursuit of happyness: the work begins, 100 powerful motivational quotes to help you rise above, wim hof: the iceman’s heroic journey to warming the hearts of millions, stranger insults middle school teacher online — but her clapback was a+.
School Teacher Gives Hater A Lesson They'll Never Forget
You've heard of fat shaming, you've heard of mommy-shaming, but have you ever heard of teacher-shaming?
Middle school teacher Ms. Amy Allen was on the receiving end of some serious hate when it came to how one stranger thought she conducted herself in the classroom. Thankfully, Ms. Allen was ready to teach this shamer a lesson — and in the most hilarious way possible.
This Middle School Teacher Just Wanted To Make Learning Fun Again
"I love teaching middle schoolers because they are awkward, and I’m awkward, so we get along." - Amy Allen
The comment read: "your a teacher act like it." For those who paid attention in English class, you'll notice the glaring grammatical errors. It was almost too easy. School was in session, and this was one teacher-shamer who was not going to be saved by the bell.
Ms. Allen's response was a classic teacher move. In a follow up video, she wrote the troll's comment on the whiteboard, then humorously corrected the errors, turning it into a mini-lesson for everyone watching. She added proper punctuation, fixed the grammar, and even included a tongue-in-cheek reminder to "Come see me if you have any further questions." Talk about schooling the critics!
The video quickly went viral, garnering millions of views and cheers from her followers. It wasn't just her clever correction that resonated; it was the way she handled criticism with grace and a touch of humor. After all, teachers are no strangers to spelling and grammar lessons, even when they come from unexpected places.
Watch Ms. Amy Allen's Video:
@_queenoftheclassroom Replying to @كل الكلبات تريد مني Come see me if you have any further questions. #qotc #iteachmiddleschool #weDEFINITELYdonthavefuninhere @Amy Allen ☀️ @Amy Allen ☀️ @Amy Allen ☀️ #Inverted
"My Students Are The Ultimate Hype People" – Her Class Was On Her Team
Despite the rude comment, Ms. Allen's students were firmly in her corner. They rallied behind her, tracking the video’s growing views like they were monitoring a pop quiz's success rate. As her comeback video gained traction, her class grew even more excited.
"What’s funny is I left my correction on the board accidentally, and the next day, students asked me what that was all about. When I explained it, they thought it was cool because 'why would anyone go after Ms. Allen'? At that point, the video had maybe 10,000 views. I never imagined the video would go viral." - Amy Allen
The views were racking up, so Ms. Allen made her fifth-period class a deal. If the video reached 1M views during their class time, they could sit wherever they wanted for an entire week. It was a deal too good to pass up. When the millionth view hit, the room erupted in cheers. Ms. Allen shared she was a classroom "rockstar." The support from her students was overwhelming, and it showed that a teacher's connection with their class goes beyond the four walls of the classroom.
It is moments like these that remind us why teachers do what they do. It's not just about teaching math, science, or grammar — it's about building a community where students feel supported and valued.
From Troll to Triumph — Ms. Allen Keeps It Cool and Classy
Despite the negativity from an online troll, Ms. Allen's response turned a mean-spirited comment into a viral success story. By demonstrating her teaching skills and her ability to laugh in the face of criticism, she showed everyone that the classroom is a place for learning, not just for the students, but sometimes for the critics too.
In the end, it's clear that Ms. Allen knows how to turn a classroom into a lively, welcoming space. She isn't afraid to play games, encourage laughter, and build a supportive environment. And when she faced an online troll, she handled it with the same playful energy that makes her classroom so special.
Her story is a reminder that even when faced with negativity, the best response is often a little humor, a lot of class, and a touch of teacher magic. So keep up the amazing work, Ms. Allen, because you're definitely teaching us all a thing or two about how to respond to haters with style and a smile.
Copyright © 2024 Goalcast
Get stories worth sharing delivered to your inbox
- Personal Development
The Hero's Journey, According to Joseph Campbell

The hero’s journey
The hero’s journey is a structure noted for its flexibility, as it’s capable of mutating without sacrificing its magic. The different phases attempt to explain the circular story in which a protagonist begins a journey that will change their life , facing different difficulties to achieve a goal and be able to return home.
The hero’s journey’s circularity mimics the world’s traditional compass : Life and death, order and chaos, consciousness and unconsciousness . The protagonist goes through several phases that take the action to the end, completing what’s called the hero’s journey arc: Their evolution.
“The cave you fear to enter holds the treasure you seek.” -Joseph Campbell-
The 17 phases of the One Myth structure
Campbell describes seventeen stages or steps along this journey, although very few myths fulfill all seventeen. Some add many of the stages and others only some. The seventeen stages can be organized in different ways.
To understand their development, they’re usually divided into three sections: Departure (sometimes called “separation”), initiation, and return .
The output deals with the adventure of the hero before fulfilling the mission. In this section, the following aspects are highlighted:
- The Ordinary World and the Call to Adventure: Amidst a context of normality, something happens that functions as a call to action.
- Refusal to the Call: Obligations, insecurity, weakness, and fear influence the hero to reject the call and prefer to remain as they are. But finally, by force, they must embark on the adventure.
- Supernatural Aid: The guide or instructor appears who will introduce the hero to this new world. They often prepare the hero for what’s to come and offer them tools and amulets of protection. In this way, the protagonist is prepared to cross the border from the ordinary world to the extraordinary world.
- The Crossing of the First Threshold: The hero enters the field of adventure, venturing into unknown and dangerous terrain where no rules or limitations are known. They have crossed the door. The hero is now ready to take action and truly begin their quest, be it physical, spiritual, or emotional.
- In the Belly of the Whale: This represents the hero’s final separation from the known self and world. By participating in this stage, they’re willing to undergo a metamorphosis.
The initiation deals with the hero’s various adventures along the way:
- The Road of Trials: This stage involves various tasks that are seemingly impossible, which the hero must overcome. They make mistakes and discover their weaknesses, strengths, and talents through them.
- The Meeting with the Goddess: The hero discovers how boundless and powerful love and unconditional surrender are. True love personified.
- Woman as the Temptress: Many activities, pleasures, and rewards tempt the hero to give up.
- Atonement with the Father/Abyss: The hero confronts whoever it is who holds the ultimate power in their life and is initiated.
- The Apotheosis: The ultimate metamorphosis or transformation elevates the hero to a higher plane.
- The Ultimate Boon: This symbolizes the achievement of the mission, the climax. All the previous steps served to prepare the hero for this moment in which he achieves that precious transcendental objective. This is the climax of the hero’s story where everything they love is put on the line.

Joseph Campbell & The Hero’s Journey
In 1949, scholar joseph campbell published his 1st book, the hero with a thousand faces. in this book, campbell introduced us to his theory that myths from around the globe share a fundamental structure, the monomyth ..
C ampbell formulated this theory over 5 years, spending 9 hours a day reading mythology from around the world. The Monomyth structure is divided into 3 events with additional stages in between. The stories of Osiris, Prometheus, Buddha, Moses, Jesus, and many other tales from history use this structure. It has inspired many artists and storytellers, such as, Jim Morrison of The Doors, Bob Dylan, creator of Star Wars George Lucas, Bob Weir, and Jerry Garcia of the band, The Grateful Dead. While countless stories follow this Monomyth structure, we will use the original Star Wars Trilogy as an example for exploring this process.
The Seventeen Stages of the Monomyth

The Cycle of Mythology
Stage 1: Separation
I n the first stage of the hero’s journey, we find our protangonist living life in a typically mundane situation. The Star Wars , Luke Skywalker lives as a talented yet lowly and pretty damn whiny moisture farmer on Tatooine.
Until…
1. Call to Adventure – By some chance the hero will become aware of information or actions that call for them to go on a quest. The lovable and recently acquired droid R2-D2 plays a holographic message of Princess Leia pleading for Luke’s soon to be mentor, Obi-Wan Kenobi’s assistance.
2. Refusal of the Call – Overwhelmed by the information, the hero refuses the call and makes excuses as to why they cannot answer it. Luke refuses Obi-Wan’s request to join him on his mission, stating that he has responsibilities at home.

Luke’s Supernatural Aid is in the form of a Lightsaber and newfound Knowledge of the Force
3. Supernatural Aid – Once a commitment to the quest is made by the hero, they are provided with a special weapon or power that will assist them along the way. Obi-Wan gifts Luke his fathers lightsaber and explains some Force 101.
4. Crossing the Threshold – The moment when the hero actually embarks upon the journey. After Luke discovers that his family has been murdered and that nothing is left for him at home, he decides to join Obi-Wan on the quest to save Princess Leia, cause that sounds way cooler than hanging at the farm where your entire family was just massacred.
5. Belly of the Whale – The final separation between the hero and their home. Luke and Kenobi bail out from Tatooine with their new bros Han Solo and Chewbacca.
Stage 2: Initiation

The Empire Strikes Back is nothing but a road of trials for our hero, Luke.
6. The Road of Trials – A series of usually 3 trials and tests, the hero often fails one or more of these test. In Luke’s journey the destruction of the Death Star is his first test and one that he passes. His second and third tests do not end so well. While training with Yoda on Dagobah, Luke fails in his truly mastering himself and the force. Thirdly, in the duel between himself and his newly revealed father, Darth Vader, he is defeated, injured, and almost killed.
7. The Meeting with the Goddess – Our hero experiences a love that has the power and significance to that of a mother. Luke begins to have strong feelings for Leia, his unbeknownst sister.
8. Woman as Temptress – The temptation to abandon the journey for material or other gain. Luke is close to being seduced to the dark side as the Emperor feeds his rage against his father and especially with the prospect that if he will not turn, perhaps his sister will.
9. Atonement with the Father – In this stage, the hero must confront and be initiated by whoever holds the ultimate power in their life. Luke battles Darth Vader and once again is on the losing side of the fight. Nearing death from the Emperor’s attacks, Luke begs his father to help save him from certain death.

Anakin & Luke Meet for the 1st Time
10. Apotheosis – The spiritual death and rebirth of the hero. Darth Vader hears his son’s cries for help and returns to the light, deciding to destroy the Emperor in a self sacrificial action. By bringing his father back to the light, Luke has finally become a true jedi.
11. The Ultimate Boon – The stage of achievement of the goal. Luke is a jedi, has defeated the Empire, the dark side, saved his father, and all his friends and family are safe.
12. Refusal of the Return – The hero basking in their newly found bliss, may not want to return to their previous life and share this bliss with his fellow man. Luke does the opposite of this, upon his reunification with his friends, he shares with Leia that they are siblings. He then goes on to train her and new jedi in the ways of the force.
Stage 3: Return
13. The Magic Flight – The daring escape made after obtaining the boon. Luke carries his fathers body onto a transport and flees the Death Star before its complete destruction.

The Millennium Falcon in Magical Flight
14. Rescue from Without – When powerful guides or mentors help bring the hero back to normal life. When Anniken, Obi-Wan, and Yoda appear from the ether to acknowledge Luke and his newfound jedi knighthood.
15. Crossing the Return Threshold – Retaining, integrating, and sharing wisdom learned on the quest. Luke shares his knowledge of the force with future jedi.
16. Master of Two Worlds – The hero has achieved a balance between the material and spiritual world. Luke has sorted all of his family issues, become a man and a jedi.
17. Freedom to Live – By becoming a master of the two worlds, the hero is free from regrets of the past and worries of the future, this leaves them to live in the moment. Luke has resolved all the conflicts in his life, he is free to live at one with the force.
Each of Us are the Heroes in Our own Journey
The Monomyth is a method of story telling that is innate to humans. Cultures from around the world share it’s structure in their stories. Every human, whether they are aware of it or not, is on their own hero’s journey. By studying Joseph Campbell’s work we can better our own understanding of the tests, trials, and progress along our journey.
About Author
Tamlorn Chase
Tamlorn Chase hails from the coastal town of Santa Barbara, where he works as a wilderness guide, wildlife filmmaker, and environmental activist. Protecting the natural world is his profession and passion.
Related Posts

Father Figures
Comments are closed.
Powered by themekiller.com
- Story Writing Guides
12 Hero’s Journey Stages Explained (+ Free Templates)
From zero to hero, the hero’s journey is a popular character development arc used in many stories. In today’s post, we will explain the 12 hero’s journey stages, along with the simple example of Cinderella.
The Hero’s Journey was originally formulated by American writer Joseph Campbell to describe the typical character arc of many classic stories, particularly in the context of mythology and folklore. The original hero’s journey contained 17 steps. Although the hero’s journey has been adapted since then for use in modern fiction, the concept is not limited to literature. It can be applied to any story, video game, film or even music that features an archetypal hero who undergoes a transformation. Common examples of the hero’s journey in popular works include Star Wars, Lord of the Rings, The Hunger Games and Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone.
- What is the hero's journey?
Stage 1: The Ordinary World
Stage 2: call of adventure, stage 3: refusal of the call, stage 4: meeting the mentor, stage 5: crossing the threshold, stage 6: tests, allies, enemies, stage 7: the approach, stage 8: the ordeal, stage 9: reward, stage 10: the road back, stage 11: resurrection, stage 12: return with the elixir, cinderella example, campbell’s 17-step journey, leeming’s 8-step journey, cousineau’s 8-step journey.
- Free Hero's Journey Templates
What is the hero’s journey?
The hero’s journey, also known as the monomyth, is a character arc used in many stories. The idea behind it is that heroes undergo a journey that leads them to find their true selves. This is often represented in a series of stages. There are typically 12 stages to the hero’s journey. Each stage represents a change in the hero’s mindset or attitude, which is triggered by an external or internal event. These events cause the hero to overcome a challenge, reach a threshold, and then return to a normal life.
The hero’s journey is a powerful tool for understanding your characters. It can help you decide who they are, what they want, where they came from, and how they will change over time. It can be used to
- Understand the challenges your characters will face
- Understand how your characters react to those challenges
- Help develop your characters’ traits and relationships
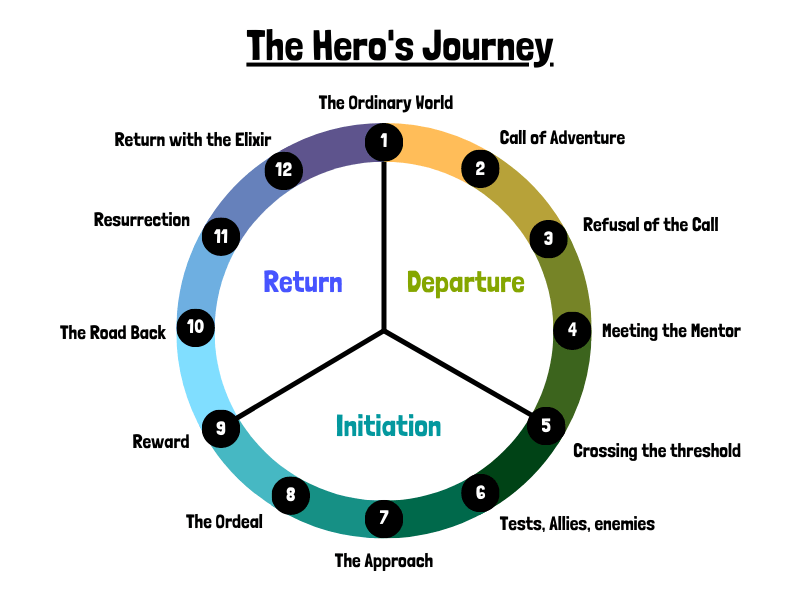
In this post, we will explain each stage of the hero’s journey, using the example of Cinderella.
You might also be interested in our post on the story mountain or this guide on how to outline a book .
12 Hero’s Journey Stages
The archetypal hero’s journey contains 12 stages and was created by Christopher Vogler. These steps take your main character through an epic struggle that leads to their ultimate triumph or demise. While these steps may seem formulaic at first glance, they actually form a very flexible structure. The hero’s journey is about transformation, not perfection.
Your hero starts out in the ordinary world. He or she is just like every other person in their environment, doing things that are normal for them and experiencing the same struggles and challenges as everyone else. In the ordinary world, the hero feels stuck and confused, so he or she goes on a quest to find a way out of this predicament.
Example: Cinderella’s father passes away and she is now stuck doing chores and taking abuse from her stepsisters and stepmother.
The hero gets his or her first taste of adventure when the call comes. This could be in the form of an encounter with a stranger or someone they know who encourages them to take a leap of faith. This encounter is typically an accident, a series of coincidences that put the hero in the right place at the right time.
Example: An invite arrives inviting the family to a royal ball where the Prince will choose a wife.
Some people will refuse to leave their safe surroundings and live by their own rules. The hero has to overcome the negative influences in order to hear the call again. They also have to deal with any personal doubts that arise from thinking too much about the potential dangers involved in the quest. It is common for the hero to deny their own abilities in this stage and to lack confidence in themselves.
Example: Cinderella accepts the call by making her own dress for the ball. However, her stepmother refuses the call for her by not letting her go to the ball. And her step-sisters ruin her dress, so she can not go.
After hearing the call, the hero begins a relationship with a mentor who helps them learn about themselves and the world. In some cases, the mentor may be someone the hero already knows. The mentor is usually someone who is well-versed in the knowledge that the hero needs to acquire, but who does not judge the hero for their lack of experience.
Example: Cinderella meets her fairy godmother who equips her with everything she needs for the ball, including a dress and a carriage.
The hero leaves their old life behind and enters the unfamiliar new world. The crossing of the threshold symbolises leaving their old self behind and becoming a new person. Sometimes this can include learning a new skill or changing their physical appearance. It can also include a time of wandering, which is an essential part of the hero’s journey.
Example: Cinderella hops into the carriage and heads off to the ball. She has transformed from a servant into an elegant young lady.
As the hero goes on this journey, they will meet both allies (people who help the hero) and enemies (people who try to stop the hero). There will also be tests, where the hero is tempted to quit, turn back, or become discouraged. The hero must be persistent and resilient to overcome challenges.
Example: At the ball, Cinderella meets the prince, and even see’s her stepmother and stepsister. She dances with Prince all night long making her step-sisters extremely jealous.
The hero now reaches the destination of their journey, in some cases, this is a literal location, such as a cave or castle. It could also be metaphorical, such as the hero having an internal conflict or having to make a difficult decision. In either case, the hero has to confront their deepest fears in this stage with bravery. In some ways, this stage can mark the end of the hero’s journey because the hero must now face their darkest fears and bring them under control. If they do not do this, the hero could be defeated in the final battle and will fail the story.
Example: Cinderella is having a great time at the ball and nearly forgets about the midnight rule. As she runs away in a hurry, her glass slipper falls off outside the palace.
The hero has made it to the final challenge of their journey and now must face all odds and defeat their greatest adversary. Consider this the climax of the story. This could be in the form of a physical battle, a moral dilemma or even an emotional challenge. The hero will look to their allies or mentor for further support and guidance in this ordeal. Whatever happens in this stage could change the rest of the story, either for good or bad.
Example: Prince Charming looks all over the kingdom for the mysterious girl he met at the ball. He finally visits Cinderella’s house and tries the slippers on the step-sisters. The prince is about to leave and then he sees Cinderella in the corner cleaning.
When the hero has defeated the most powerful and dangerous of adversaries, they will receive their reward. This reward could be an object, a new relationship or even a new piece of knowledge. The reward, which typically comes as a result of the hero’s perseverance and hard work, signifies the end of their journey. Given that the hero has accomplished their goal and served their purpose, it is a time of great success and accomplishment.
Example: The prince tries the glass slipper on Cinderella. The glass slipper fits Cinderella perfectly, and they fall in love.
The journey is now complete, and the hero is now heading back home. As the hero considers their journey and reflects on the lessons they learned along the way, the road back is sometimes marked by a sense of nostalgia or even regret. As they must find their way back to the normal world and reintegrate into their former life, the hero may encounter additional difficulties or tests along the way. It is common for the hero to run into previous adversaries or challenges they believed they had overcome.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming head back to the Prince’s castle to get married.
The hero has one final battle to face. At this stage, the hero might have to fight to the death against a much more powerful foe. The hero might even be confronted with their own mortality or their greatest fear. This is usually when the hero’s true personality emerges. This stage is normally symbolised by the hero rising from the dark place and fighting back. This dark place could again be a physical location, such as the underground or a dark cave. It might even be a dark, mental state, such as depression. As the hero rises again, they might change physically or even experience an emotional transformation.
Example: Cinderella is reborn as a princess. She once again feels the love and happiness that she felt when she was a little girl living with her father.
At the end of the story, the hero returns to the ordinary world and shares the knowledge gained in their journey with their fellow man. This can be done by imparting some form of wisdom, an object of great value or by bringing about a social revolution. In all cases, the hero returns changed and often wiser.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming live happily ever after. She uses her new role to punish her stepmother and stepsisters and to revitalise the kingdom.
We have used the example of Cinderella in Vogler’s hero’s journey model below:

Below we have briefly explained the other variations of the hero’s journey arc.
The very first hero’s journey arc was created by Joseph Campbell in 1949. It contained the following 17 steps:
- The Call to Adventure: The hero receives a call or a reason to go on a journey.
- Refusal of the Call: The hero does not accept the quest. They worry about their own abilities or fear the journey itself.
- Supernatural Aid: Someone (the mentor) comes to help the hero and they have supernatural powers, which are usually magical.
- The Crossing of the First Threshold: A symbolic boundary is crossed by the hero, often after a test.
- Belly of the Whale: The point where the hero has the most difficulty making it through.
- The Road of Trials: In this step, the hero will be tempted and tested by the outside world, with a number of negative experiences.
- The Meeting with the Goddess: The hero meets someone who can give them the knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- Woman as the Temptress: The hero is tempted to go back home or return to their old ways.
- Atonement with the Father: The hero has to make amends for any wrongdoings they may have done in the past. They need to confront whatever holds them back.
- Apotheosis: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level.
- The Ultimate Boon: The ultimate boon is the reward for completing all the trials of the quest. The hero achieves their ultimate goal and feels powerful.
- Refusal of the Return: After collecting their reward, the hero refuses to return to normal life. They want to continue living like gods.
- The Magic Flight: The hero escapes with the reward in hand.
- Rescue from Without: The hero has been hurt and needs help from their allies or guides.
- The Crossing of the Return Threshold: The hero must come back and learn to integrate with the ordinary world once again.
- Master of the Two Worlds: The hero shares their wisdom or gifts with the ordinary world. Learning to live in both worlds.
- Freedom to Live: The hero accepts the new version of themselves and lives happily without fear.
David Adams Leeming later adapted the hero’s journey based on his research of legendary heroes found in mythology. He noted the following steps as a pattern that all heroes in stories follow:
- Miraculous conception and birth: This is the first trauma that the hero has to deal with. The Hero is often an orphan or abandoned child and therefore faces many hardships early on in life.
- Initiation of the hero-child: The child faces their first major challenge. At this point, the challenge is normally won with assistance from someone else.
- Withdrawal from family or community: The hero runs away and is tempted by negative forces.
- Trial and quest: A quest finds the hero giving them an opportunity to prove themselves.
- Death: The hero fails and is left near death or actually does die.
- Descent into the underworld: The hero rises again from death or their near-death experience.
- Resurrection and rebirth: The hero learns from the errors of their way and is reborn into a better, wiser being.
- Ascension, apotheosis, and atonement: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level (sometimes a god-like level).
In 1990, Phil Cousineau further adapted the hero’s journey by simplifying the steps from Campbell’s model and rearranging them slightly to suit his own findings of heroes in literature. Again Cousineau’s hero’s journey included 8 steps:
- The call to adventure: The hero must have a reason to go on an adventure.
- The road of trials: The hero undergoes a number of tests that help them to transform.
- The vision quest: Through the quest, the hero learns the errors of their ways and has a realisation of something.
- The meeting with the goddess: To help the hero someone helps them by giving them some knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- The boon: This is the reward for completing the journey.
- The magic flight: The hero must escape, as the reward is attached to something terrible.
- The return threshold: The hero must learn to live back in the ordinary world.
- The master of two worlds: The hero shares their knowledge with the ordinary world and learns to live in both worlds.
As you can see, every version of the hero’s journey is about the main character showing great levels of transformation. Their journey may start and end at the same location, but they have personally evolved as a character in your story. Once a weakling, they now possess the knowledge and skill set to protect their world if needed.

Free Hero’s Journey Templates
Use the free Hero’s journey templates below to practice the skills you learned in this guide! You can either draw or write notes in each of the scene boxes. Once the template is complete, you will have a better idea of how your main character or the hero of your story develops over time:
The storyboard template below is a great way to develop your main character and organise your story:

Did you find this guide on the hero’s journey stages useful? Let us know in the comments below.

Marty the wizard is the master of Imagine Forest. When he's not reading a ton of books or writing some of his own tales, he loves to be surrounded by the magical creatures that live in Imagine Forest. While living in his tree house he has devoted his time to helping children around the world with their writing skills and creativity.
Related Posts

Comments loading...
ThinkWritten
The Hero’s Journey: A 17 Step Story Structure Beat Sheet
The Hero’s Journey is a classic plot structure made up of 17 steps. Learn how to craft an epic story using the Hero’s Journey story beats.

We may receive a commission when you make a purchase from one of our links for products and services we recommend. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Thank you for support!
Sharing is caring!
The Hero’s Journey is a story structure that tells how a hero starts in one place, goes on an adventure into an unknown world, and then returns to what they started with.
This blog post will explain the 17 steps of the Hero’s Journey and share how you can use this common plot structure to write your own story or novel.
What is the Hero’s Journey?

Joseph Campbell first introduced the Hero’s Journey in 1949. It is based on the idea that we can break down most stories into one basic story structure.
The plot structure of the Hero’s Journey is made up of 17 steps, all of which can be excellent guideposts for you when plotting your novel and planning your chapters.
To simplify the 17 steps of the Hero’s Journey, there are 3 main acts of the story: The Departure, The Initiation, and The Return.

Here’s an overview of all of the 17 steps of Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey:
Act One: The Departure
The Call to Adventure
Refusal of the call, supernatural aid.
- The Crossing of the First Threshold
Belly of the Whale
Act 2: The Initiation :
The Road of Trials
The meeting with the goddess, woman as the temptress, atonement with the father/abyss, the ultimate boon.
Act 3: The Return:
Refusal of the Return
The magic flight, rescue from without, the crossing of the return threshold, master of the two worlds, freedom to live.
In this post, we will cover each step of the Hero’s Journey and what it includes. If you are writing a novel , think of this as the ultimate beat sheet to help you plan and plot your novel !

To understand the 17 steps of the hero’s journey, we will share with you exactly what happens in each step and what it should include. We’ve divided the 17 steps into the three main acts: The Departure, The Initiation, and the Return.
Let’s dive on in, shall we?
The Departure

The Departure (Act 1) of the Hero’s Journey is all about your novel’s main characters and their ordinary lives. You want to show how they live before something happens that throws them into a world outside of what was normal for them.
In a nutshell, The Departure is when we see our heroes start in their current environment and set out on an adventure where they leave their comfort zone.
There are 5 steps of the Departure, each of which can help you base your chapters for your novel. Let’s look at these 5 steps in detail.

In the first 1 or 2 chapters of our book, our character is introduced and is given the call to adventure. Of course, the call to adventure is what sets our character on their journey. There is a moment when our hero realizes something isn’t right, and it’s time for them to become the hero of their own story.
The Call to Adventure should introduce your main characters and what part of life they are living before things start changing for them. You want this to be a scene that you can use to give your reader an idea of who they are and what their life is like.
The call to adventure is sometimes also called the inciting incident because it often comes from another character or situation in which our hero feels compelled to do something. This could come in the form of a problem or something that they’ve always wanted to accomplish.
Once we understand the character’s life and why they must go on their journey, we move onto the next crucial element: Refusal of the Call.

The Refusal of the Call sounds like it’s a bad thing, but in reality, it can help the hero grow and become more self-sufficient. In this step of the Departure, we see that our character isn’t sure if they are ready for such an adventure.
The refusal of the call is often used as a way for your reader to get more insight into some of your character’s weaknesses. It can also open up the character to seeing what they are missing in their life and get them a little more excited about going after it.
When writing your story, you will show your readers why your hero is reluctant to go on the journey. Why don’t they want to change? What are their fears? This step helps build your character arc, as well as builds some suspense in the story.
You also want to make sure in this step that the refusal of the call is resolved in some way. This can be through another character encouraging your hero or by realizing what they are missing out on if they don’t go on the journey.
Either way, you need to ensure this scene or chapter ends with the hero deciding to accept the challenge.
After your main character decides whether or not they want to go on this journey, we move onto Supernatural Aid.

Supernatural aid is the hero’s first experience with a mentor or teacher. While we use the term supernatural here, it does not necessarily have to be some mystical being.
It could be a random stranger giving our hero advice or someone who has been to this magical place before and knows the path. The important thing is this character is someone who will help your protagonist in their journey.
Supernatural aid helps your audience understand there will be obstacles along the way. The hero will need help. You will need a strong supporting character willing to give our main character advice on how they should proceed through their journey.
In this scene, you want to show us why you chose these characters for mentors. What qualities do they possess? Do they have experience with adventures like this? Why can they help the hero, and more importantly, why do they want to help the hero?
Once this person is introduced, we are ready for the next stage of the Hero’s Journey: Crossing the First Threshold.
Crossing the First Threshold

Crossing the first threshold is where your hero commits to going on the journey. They may have made some attempts at it before, but now they are fully committed and ready to go, even if that means leaving their comfort zone behind.
Your character will be doing something different than what they’ve done in the past, or perhaps this act will lead them into a dark and dangerous place.
For example, your hero may leave their home for the first time to go on this journey, or they are finally ready to go and confront someone who has been standing in their way of happiness.
In this 4th step of the Hero’s Journey, you want to show your reader why this is such a big change for the character.
You want to show your character scared and uncertain of what lies ahead for them while still being brave enough to continue on their journey! You don’t need to make this scene too long or spend time explaining every little detail; just put us in the headspace of your hero so we can understand what unknown dangers and fears are ahead.
Once our hero takes their first steps towards danger, we find ourselves in the Belly of the Whale.
The Belly of the Whale is the last step before the hero breaks away from their normal existence and sense of self. When someone enters this stage, they are showing that they want to change.
A typical element of the Belly of the Whale Scene is displaying a small problem or threat. These problems aren’t the major conflict of the story, but it is enough of an obstacle that we see the hero absolutely cannot go back to where they used to be and must change.
In this scene, it’s common to show a “dark night of the soul.” This is where they feel like everything in their life has been turned upside down, and things seem hopeless. Yet, they must commit to making a change and continuing on their journey in this final step of the Departure stage.
Now that we’ve covered all the steps of the Departure state let’s move onto Act 2: The Initiation.
The Initiation
The second act of our story, the Initiation, is the part where things get interesting. The character is now deeper into their journey and facing new challenges that they must overcome.
Not only are we focusing on our hero’s personal development, but our protagonist’s character traits start to change. They will be showing how they’ve become different from who they were in Act One and developing the traits needed for a successful journey.

The first scene or chapter of the Initiation stage of the Hero’s Journey is The Road of Trials. The Road of Trials is where the protagonist faces a series of tests that your hero must pass to move onto the next stage.
These trials will continue until our hero has shown they are ready for whatever is waiting ahead on their journey and have discovered what lessons they needed to learn along the way.
Usually, there is a series of 3 tests, and your hero will not ace all of them immediately. Sometimes, we will revisit the person introduced as a mentor or guiding force from Act One in these scenes, as the hero will certainly need some support in going through these trials.
In this scene, you want to make sure your reader sees how the hero experiences growth and changes. You want your reader to appreciate how far our hero has come along their journey, but there are still more experiences ahead for them!

The next step of the Initiation stage is The Meeting with the Goddess/Saviour. This is where we are introduced to someone who will give our protagonist a sense of love, peace, safety, and unity.
This character is essential because they offer our protagonist something he didn’t have before and will be the support that helps them through whatever journey lies ahead. Sometimes they appear as a love interest, but not always.
The Goddess figure is often human but could also be an animal or nature spirit. They are someone who will help your hero become whole again. They are an equal opposite of your hero.
In this scene, we want our hero to feel everything is going to be okay now. They will learn that they don’t need to face their problems alone; someone here with them understands what they are going through.
Of course, this doesn’t last forever as we move into the next chapter: Woman as the Temptress.

In this next step, the hero faces physical temptations that might cause them to be distracted from their quest. Again, it’s important to understand this does not mean you need to introduce a female character in this scene – the woman is only a metaphorical symbol.
Many things can tempt our heroes to stray from their path. It might be money, power, or fame. It could even be something as simple as food and drink. But, of course, these temptations are not meant actually to distract the protagonist from their path. Our hero must resist them to gain a greater reward at the end of this stage.
Throughout this scene, they may face several such temptations until our hero learns how to resist them and stay focused on what they really want.

The word Atonement means “reparations for a wrong or injury,” and the Father is a symbol for an authority figure in the hero’s life. Finally, the Abyss represents death or darkness.
In this scene, the hero must confront whatever it is that holds the most power over them. This could be another character or it could even be internal conflict where the hero must come face-to-face with the dark side of their personality and be willing to embrace it.
The goal of this step in the Hero’s Journey is to make your protagonist question their entire being. Only when they confront the most powerful obstacle in their path and reconcile with it can they move forward on their journey.
As with most characters, the father does not have to be an actual father or even a male figure. The important thing is this figure is a person of power and authority over the hero.
There are many ways the hero can reconcile with the father figure – they can defeat this person, win this person’s approval, or reconcile with a part of themselves that is related to the father.
This step is important because it forces your protagonist to face their biggest fears and insecurities. It gives them the opportunity and confidence boost to overcome these obstacles once and for all.

Apotheosis is another word for “the highest point of a person’s spiritual, moral or intellectual development.” It is when the protagonist transcends their humanity and becomes something more than they were before.
In this step of The Hero’s Journey, your protagonist will undergo an important change that brings them closer to being the ideal self they set out to be at the beginning.
In this stage of the Hero’s Journey, our hero learns something new about themselves that prepares them for the hardest part of their journey. This revelation gives them the necessary knowledge to complete their quest.
This step is often referred to as “the answer.” The protagonist will usually gain this new insight from a character who embodies wisdom or spiritual power, such as their mentor figure.
Now that our character has finally grown to where they need to be to accomplish their quest, they are ready for The Ultimate Boon’s next step.

The ultimate boon is the fulfillment of the purpose of the journey. This is when the hero finally achieves what they set out to accomplish.
All of the previous steps of the journey worked to this point to help the hero finally reach their goal.
In mythology, the “boon” is often something otherworldly. It could be the fountain of youth, an ancient scroll with sacred information, or a magical potion.
There are many ways to play out this step of The Hero’s Journey, so your character’s end goal will determine what the boon is.
This step of The Hero’s Journey often includes a battle with something that opposes your protagonist, such as an enemy or villain.
Our heroes might have to face their own dark side to achieve this final prize and complete their journey successfully. This could cause them to question whether or not they even want what the boon is.
When your protagonist achieves this final goal, it marks a major change in their life. Now we are ready to proceed to Act 3: The Return.
Act 3: The Return

Act Three of the Hero’s Journey often moves faster than the other acts of our story. In The Return, we see how the protagonist’s newfound knowledge and achievement of their goal affect their life and world.
This step of The Hero’s Journey is crucial because it gives us a glimpse as to what our character has learned from this journey, which is the ultimate test of whether they have truly successfully achieved their quest or not.
Let’s dive into the remaining scenes of our story.

The Refusal of the Return is when our protagonist does not want to return home after achieving their goal. They may be too frightened of what awaits them, or they may not want to give up the new life and world they have found themselves in.
Just as they were hesitant to go on the adventure in the beginning, they are also hesitant to go back.
They may be concerned with how their “boon” might affect the world – such as a magic potion or secret power that could get into the wrong hands. They may worry about what consequences they may face when they go back, or they may be afraid nothing is left for them to return to.
In some cases, our hero doesn’t want to leave because they have become comfortable with their new world and who they have become.
However, to truly finish the quest, our hero must return home. This refusal of return helps build up the tension to the final resolution of the story. This is when the reader questions whether the hero will return home – and wonders with great anticipation of what might happen when it happens.

The Magic Flight is the final conflict to the story where our protagonist must escape danger, sometimes using their newfound knowledge or boon. This is a way of symbolically proving that they have truly learned from this journey and are ready to bring it back home with them.
This part of The Hero’s Journey often involves a chase scene or battle against an opposing force. However, this is the final push necessary push they need to realize they must make the journey home because it becomes apparent they cannot stay where they are.

The Rescue From Without step of the Hero’s Journey is when the protagonist is rescued from danger by an outside source.
This outside source may be an ordinary person, or it might resemble deus ex machina, or god-like intervention, where something rescues our hero from an impossible situation, such as lightning striking that saves the day for our hero.
When you are writing the rescue scene, the circumstances of the rescue must be believable. Most people do not like the deus ex machina in writing simply because it’s too easy.
Those of us who have lived life long enough all know that a magic fairy godmother isn’t going to swoop us in, wave her wand and make all our problems disappear.
After being rescued, the hero truly has no other choice except to return home.

The Crossing of the Return Threshold is when our protagonist finally returns home after completing their adventure and achieving their goal.
This is the part of The Hero’s Journey where we see what they have learned from this journey and how it affects them.
In this story scene, you will want to answer the following questions: How has the hero changed from their journey? How is their old world different from when they left? How do they acclimate to being back home? Finally, how do others react to their return?

This is the part of The Hero’s Journey where our protagonist has reached their full potential. They have overcome their fears and grown in ways they could never have imagined.
They are a new person and have been forever changed by what they’ve experienced. Yet, it allows them to go back into society with heightened wisdom, power, skills, or resources that will help others in need when called upon again.
In this scene, we see the hero apply their knowledge and share it with the world.

After our hero has conquered all of their fears and has put their wisdom to good use, the hero finally has the freedom to do anything they want.
This is the resolution of our story – we see our heroes accomplish their “happily ever after.” Their fears or concerns no longer control them, and nothing exists between them and what they want.
More often than not, this closing chapter of the story gives the reader some closure. We want some type of affirmation that the story is truly complete. We get a glimpse of what our protagonist will do with their life now that they are free to live it.
If you’re looking for a story structure that is proven and effective, the Hero’s Journey might be perfect for you. With 17 stages of development, it will help you create an engaging plot with your readers and develop strong characters .
And of course, while the Hero’s Journey is the classic beat sheet for writers, remember you don’t always have to dedicate one chapter to each step. Sometimes you can combine 2-3 steps in one scene, while other steps might take several chapters to cover.
The important thing is you now know the Hero’s Journey! We hope this is helpful for you – whether you are writing your own novel or studying the Hero’s Journey arc in literature. Most of all, we hope that by breaking down each step of the Hero’s Journey, you can better understand all of it.
Do you have any thoughts or questions on the Hero’s Journey? We’d love to hear from you in the comments section below!
Chelle Stein wrote her first embarrassingly bad novel at the age of 14 and hasn't stopped writing since. As the founder of ThinkWritten, she enjoys encouraging writers and creatives of all types.
Similar Posts

How to Outline a Novel Plot in 5 Easy Steps

How to Avoid Over Planning Your Novel

160+ Character Development Questions & Free Printable Worksheet

Character Development: How to Write Strong Characters in Your Novel

Main Character vs. Supporting Characters in Story Development

5 Signs of a Strong Novel Plot
So if you’re writing an epic fantasy that will be a series, are these 17 steps strung out across the entire series, or redone in each book?
Thank you for such a helpful article. This has helped me fill in a glaring hole in my novel outline and shown me what was missing. I’m really grateful for this advice.
Glad it was helpful for you Laura!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Deep Dive: Joseph Campbell’s "Hero’s Journey"

Hannah Yang

What do Star Wars , the legend of Prometheus, and the epic tale Beowulf have in common? They all follow the stages of Joseph Campbell’s hero’s journey.
Whether you’re working on a novel or a short story, you can use the hero’s journey to plot and outline your work. If you’re new to the hero’s journey, start with our guide to using the hero’s journey as the backbone for your story.
The hero’s journey is so commonly used that it’s become an important narrative structure for any writer to understand. However, the idea that the hero’s journey is truly a "monomyth" is actually a myth of its own.
Understanding this narrative structure is important if you want to use it in your stories—but it’s also important if you want to subvert it and create something new.
Read on to see an analysis into how Joseph Campbell came up with the concept of the hero’s journey, as well as the common counterarguments to this well-known literary archetype.
What Is Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey?
How did joseph campbell develop the concept of the hero’s journey, what are the three stages of the hero’s journey, what were the original seventeen steps of the hero’s journey, what are the counterarguments to joseph campbell’s hero’s journey, how can you use the hero’s journey in your writing without making your story feel formulaic.
The hero’s journey is an archetypal narrative structure found in stories from cultures all over the world. Because it’s such a universal narrative structure, the hero’s journey is also known as the "monomyth"—the single great story with many variations.
The term was coined by Joseph Campbell, an American writer and editor who was fascinated by myths from various cultures and literary traditions. He noticed that many heroic stories follow the same narrative stages, no matter which culture or time period they come from.
Since 1949, countless stories have used the hero’s journey archetype, from George Lucas’s Star Wars to Disney’s The Lion King .
Joseph Campbell was born in New York City in 1904. As a child, he took frequent trips to Buffalo Bill’s Wild West exhibition and to the American Museum of Natural History, where he became fascinated by the Native American exhibits.
He began noticing parallels between stories from the Christian Bible and stories from Native American religions, which made him wonder whether other mythologies might also share those commonalities.
As an adult, Campbell studied English literature at Columbia University . He read and analyzed classic religious and mythological texts, such as those of the Buddha, Moses, Mohammed, Jesus, and countless others. Over time, he became convinced that mythologies worldwide have many similarities, and that they shared a universal narrative backbone—a "monomyth."

Besides studying classic stories, Campbell also studied the work of early 20th-century analytical psychologists. In particular, he became fascinated with the work of Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung. This was crucial to the development of the hero’s journey, as the transformative aspect of the structure closely resembles Jung’s theory of death and rebirth.
Campbell first coined the term "hero’s journey" in 1949, in his comparative mythology book The Hero with a Thousand Faces , which was later adapted into the TV show The Power of Myth . In this book, Campbell outlined the hero’s journey in three basic stages and seventeen detailed steps.
He wrote and edited many other texts on comparative mythology and storytelling. Aside from The Hero with a Thousand Faces (1949), his other major works include Myths and Symbols in Indian Art and Civilization (1946), The King and the Corpse (1948), Philosophies of India (1951), The Masks of God (1959–68), and The Power of Myth (1988).

In its simplest form, the hero’s journey can be described in three stages: departure, initiation, and return.
Departure: the hero leaves his home community to go on a quest.
Initiation: the hero faces trials and tribulations until he achieves victory on his quest.
Return: the hero goes home to his community with gifts and boons.
This is how Joseph Campbell summarized the hero’s journey in The Hero with a Thousand Faces (1949):
“A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man.”
Consider Star Wars , one of the most commonly cited examples of the hero’s journey.
In the departure stage, Luke Skywalker leaves his home planet of Tatooine with the goal of helping the rebellion defeat the Galactic Empire.
In the initiation stage, Luke undergoes various trials and tribulations on his heroic journey. He trains with Obi-Wan Kenobi to learn how to use the Force, rescues Princess Leia from the Death Star, and retrieves the Death Star plans and delivers them to the rebellion base. At last, he finally uses the Force to destroy the Death Star, fulfilling the purpose of his quest.
Finally, in the return stage, Luke returns to the rebellion base and wins a medal to commemorate his victory. He has helped his home world defeat the oppressive empire and gets to live as a hero.
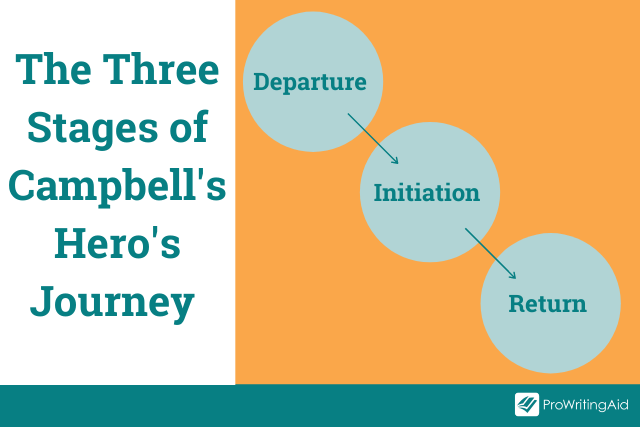
In The Hero with a Thousand Faces , Joseph Campbell outlined seventeen detailed steps of the hero’s journey.
These seventeen steps were later simplified to twelve steps by Christopher Vogler, a successful Hollywood consultant, in his book The Writer’s Journey (1992). These twelve steps are more commonly studied by writers today, since they’re easier to learn and remember than Campbell’s seventeen steps.
Here is Campbell’s original hero’s journey structure:
Stage 1: Departure
Call to Adventure: The hero receives an invitation to go on a quest.
Refusal of the Call: At first, the hero hesitates to accept the invitation, either because the journey is too dangerous, or because they have other obligations at home.
Supernatural Aid: Someone the hero looks up to inspires them to accept the call to adventure, or gives them tools that will help them on their quest.
Crossing the Threshold: The hero begins their quest and leaves the ordinary world and their everyday life.
Belly of the Whale: The hero encounters the first real danger in their quest, and wonders whether or not to turn back—but ultimately pushes forward.
Stage 2: Initiation
Road of Trials: The hero undergoes several trials and learns from their mistakes.
Meeting With the Goddess: The hero meets a mentor figure or ally, who offers help or advice.
Woman as Temptress: The hero encounters temptations that threaten to steer them away from their heroic journey, which they must nobly avoid.
Atonement with the Father: The hero undergoes a personal metamorphosis by confronting an aspect of their own character that has been preventing them from achieving success, such as their own fear, greed, or self-doubt.
Apotheosis: The hero transforms into a better person, and goes forward with new insight and clarity on what they must do to win.
Ultimate Boon: The hero achieves victory in their quest.
Stage 3: Return
Refusal of Return: At first, the hero is reluctant to go back to the familiar world after their exciting journey and transformation.
Magic Flight: Even though the hero has achieved victory on their quest, they still face dangers as they try to return home.
Rescue from Without: An outside ally or mentor helps guide the hero safely home.
Crossing the Return Threshold: The hero returns to the familiar world, and tries to adjust to their old life.
Master of Two Worlds: The hero finds a balance between their home life and the person they become on their quest.
Freedom to Live: The hero gets used to their normal life and lives peacefully.

In the past seventy years, many writers and editors have criticized Joseph Campbell’s monomyth. After all, Campbell lived in a society that strongly valued heroic individualism, and his theories were a product of his time. Our society has evolved since 1949, but the hero’s journey archetype has failed to evolve with it.
One of the most common criticisms of the hero’s journey is that it reduces the world to simple binaries: good and evil, victory and failure. If all stories followed the hero’s journey, writers wouldn’t be able to express a nuanced perspective of the world.
Another criticism is that the hero’s journey favors male protagonists, a tale about a hero leaving home to seek adventure in the outside world. In contrast, stories about women often involve looking inward, instead of looking outward, because of the domestic roles that women have traditionally been expected to fulfill.
The concept of the "heroine’s journey," also known as the female hero’s journey, was developed in 1990 by Maureen Murdock, a psychotherapist and a student of Joseph Campbell, in her book The Heroine’s Journey: Woman’s Quest for Wholeness .
Murdock wrote:
“The feminine journey is about going down deep into soul, healing and reclaiming, while the masculine journey is up and out, to spirit.”
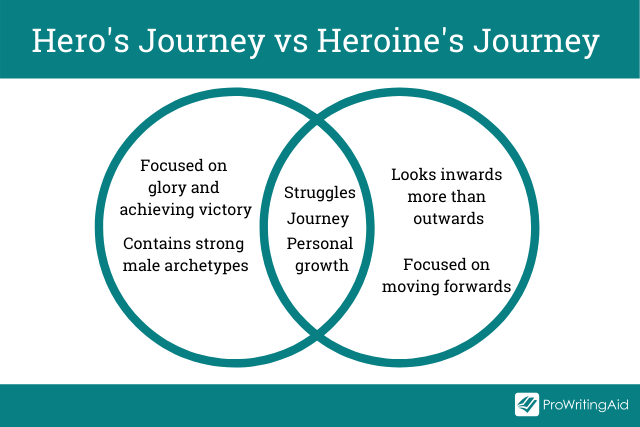
Similarly, stories about people of color or marginalized groups within our society sometimes follow different story archetypes. Joseph Campbell’s hero’s journey focuses on an individual hero, rather than a broader social context.
Stories about marginalized groups might center on communities reacting to oppression and navigating the rules set by the majority, instead of highlighting a single individual who proactively seeks adventure.
There’s nothing wrong with using the hero’s journey in your own work. After all, it’s been spectacularly successful for thousands of years—there’s a timeless appeal to this story of adventure and spiritual transformation.
However, the hero’s journey can be a useful tool even if you don’t use it the way Joseph Campbell originally intended. Readers who recognize these classic tropes can appreciate an unexpected twist. Innovative literary fiction often plays with traditional narrative structures in new ways.
Many writers have subverted the hero’s journey archetype to better reflect the stories they want to tell. For example, you can follow the hero’s journey throughout the first two stages, then withhold the hero’s victory in the third stage.

For more ideas, check out Steve Seager’s article on how to design a narrative more fitting to our contemporary context.
If it fits the needs of your story, consider changing up the hero’s journey in your own writing. You can build on Joseph Campbell’s time-honored literary tradition while also adding new twists of your own.
Do you want to know how to build a world your readers won’t forget? Download this free book now:

World-Building 101: How to Construct an Unforgettable World for Your Fantasy or Sci-Fi Story!
This guide is for all the writers out there who want to construct an unforgettable world that your readers can’t help but get lost in, learn how to invent species, gods, monsters, and more in our immersive guide..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey
Storytelling is one of the oldest forms of communication and the archetypal hero continues to be a key component. Whether…

Storytelling is one of the oldest forms of communication and the archetypal hero continues to be a key component. Whether it’s books or movies, fiction down the ages is replete with stories that focus on a hero’s journey. It was Joseph John Campbell, an American literature professor, who introduced the stages of a hero in his book, The Hero With A Thousand Faces (1949).
Joseph Campbell’s hero’s journey was part of his idea of the monomyth—a common story structure in which a character ventures into the unknown to retrieve something they need. Despite facing conflict and hardships, the hero returns home, triumphant and transformed.
Much like this classic plot structure, businesses value individuals who can rise to the occasion and persevere despite the challenges. The ability to go on an adventure, learn a lesson, be victorious and gain new knowledge are the defining principles of true leadership. Let’s look at the various ways in which Campbell’s hero’s journey makes sense in workplace settings.
The Evolution Of The Hero’s Journey
12 steps in hero’s journey , understanding hero’s journey in the context of women’s leadership, achieve transformative leadership.
While Campbell had originally proposed the hero’s journey structure, Christopher Vogler elaborated on the concept in his book, The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structures For Writers (1992). A Hollywood screenwriter, best known for working with Disney, Vogler expanded on Campbell’s three stages and defined 12 stages of a hero’s journey. Here are Campbell’s (i.e., the original) three stages in hero’s journey:
The Departure:
The hero leaves the familiar world when they receive a call for an adventure
The Initiation:
The hero ventures into the unknown i.e., the special world where they overcome a series of hurdles until they reach the journey’s climax—the main obstacle
The Return:
The hero returns to the familiar world, triumphant; the journey changes the hero as a person.
Vogler suggested a 12-stage hero’s journey that has a more detailed character arc. It goes beyond the three-act structure and highlights the inner and outer transformation of the journey.
12 Steps In Hero’s Journey:
The ordinary world.
The journey is yet to begin. The hero finds themselves in a familiar setting where they lead their everyday life. It gives a glimpse into their character before the journey begins. Hamartia (a fatal flaw or challenge) is likely to change the way a hero thinks or behaves.
Call To Adventure
This stage sets the story rolling as the hero receives a call to action. Something or someone interrupts the hero’s normal life and presents a threat, problem or opportunity. The hero must take a call whether they want to embark on the adventure and face the consequences.
Refusal Of The Call
The hero feels unprepared, not ready to take on the adventure. Their fears and insecurities surface and they hesitate to step outside their comfort zone. Second thoughts and self-doubt prevent them from embarking on the journey.
Meeting The Mentor
This is the crucial turning point of a hero’s journey as someone else comes along for guidance and support. As the hero is afraid to spread their wings and go out on an adventure, a mentor helps them. They provide the hero with necessary tools and resources; they give advice, motivate them and impart the wisdom that’s likely to change the hero’s mind.
Crossing The Threshold
The hero leaves the familiar world and their normal life behind. They’re finally ready to step out of their comfort zone and respond to the call to adventure. They’re spiritually, physically and emotionally ready to begin their quest. This signifies their commitment to take risks and overcome challenges.
Tests, Allies And Enemies
The hero finally confronts a series of challenges that obstruct their journey or progress. They learn the rules of the new and unfamiliar world. This stage helps them put their knowledge, experiences and skills to use. They gain a deeper insight into their character and identify others who can help them out.
Approach To The Inmost Cave
This is where the hero gets closer to their goal. This stage entails all the preparation that goes into facing the main challenge. However, there may be setbacks that prevent heroes from trying out new ideas or approaches. If they fail, they need to try again—it’s a lesson in persistence.
Supreme Ordeal
It refers to the main obstacle a hero faces in their journey. It may be a dangerous physical test or a deep inner crisis that they must face and overcome. Vogler refers to this stage as the ‘black moment’ as the hero must conquer their biggest fear. This further informs every decision that they make after this point.
After overcoming the biggest hurdle in the journey, a hero transforms into a new state. They emerge stronger and more resilient than ever. This is a moment of great success and the hero earns their reward for their accomplishment. This moment should be celebrated.
The Road Back
The journey isn’t over yet as the hero needs to return to the ordinary world—where they came from. They must commit to completing the journey and travel back. With new learnings and experiences, integrating them into old life in itself is a challenge.
The Resurrection
In this final test, the hero must use and apply everything they’ve learned or gathered over time. It reflects their personal growth and how well they can apply their knowledge to overcome obstacles. Vogler refers to this as the ‘final exam’ and the hero must give their best.
Return With The Elixir
The hero finally returns to the ordinary world i.e., their original setting. They’ve emerged victorious as they patiently addressed and overcame every challenge in their journey. They bring the elixir or the knowledge and that’s the true reward of their journey and transformation.
Although an increasing number of women are pushing their boundaries in leadership positions, the progress towards parity remains slow. The Women in the Workplace report (2020) published by McKinsey & Company suggests that women remain dramatically underrepresented in senior management roles.
Joseph Campbell hero’s journey can be used as a lens to identify the various challenges and opportunities that are instrumental to successful women’s leadership. This process of personal transformation is a roadmap for professional success. Women need appropriate tools and resources that can help them climb the corporate ladder. Organizations need to ensure that there’s sufficient support, guidance and mentorship so that women aren’t afraid to explore new challenges and opportunities. Create an environment where more and more women step outside their comfort zone.
Here are a few simple yet effective tips that’ll help you promote women’s leadership in the workplace. Help them explore their own version of the hero’s journey and enhance leadership qualities .
Address Basic Challenges
One of the biggest roadblocks to promoting women’s leadership is the accessibility of resources. It can include on-the-job training or guidance in general—individuals can sharpen necessary skills, capabilities and perspectives.
The Power Of Choice
Nudge women towards the right direction by helping them make choices and decisions independently. Encourage them to take ownership and provide them opportunities for professional and personal growth. C0-create a leadership development strategy.
Rethink And Challenge Assumptions
To make your work environment truly inclusive and supportive, address unconscious bias. Whether it’s your hiring process, salary increments or promotions, implement checks and balances and promote fair practices. Understand what women expect from their roles.
Create Appropriate Networks
A majority of women struggle to build strong professional networks. It’s crucial because the right relationships can help them access information, gain opportunities for career advancement and earn promotions. Effective leaders rely on good networks to influence and get results.
Invite Anonymous Feedback
Employees may not always be comfortable voicing their thoughts, ideas and opinions. In order to capture what they truly need and expect, ensure frequent and anonymous feedback surveys. Increase the overall comfort and transparency.
It’s an undeniable reality that women leaders face a unique set of obstacles at work. Studies show that women bring to the table better business outcomes, smarter problem-solving abilities and richer collaboration. They can be inspiring role models who lift others as they leap themselves.
Harappa’s Women’s Leadership Program pivots on five crucial outcomes that help learners raise the bar at the workplace. It brings a carefully curated selection of academically robust and application-oriented concepts that’ll help women leaders navigate demanding and challenging mandates. Help them achieve transformative leadership and let these heroes shine in their journeys!
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics such as Adult Learning Principles , Must-Have Skills For Leadership & The Importance Of Women’s Leadership that will help organizations tap into their employee’s potential.

Joseph Campbell’s 17 Stages of The Hero’s Journey

Mathematician

CALL TO ADVENTURE
Dananjaya Hetearachchi, Toastmaster’s 2014 winner got the call when he saw his mother cry tears of shame over what he had done.
“I want you to be a better man,” she said.
Presiyan Valselev, the 2013 winner gets his call when the voice in inside him says, “Reach out.”
Ryan Avery’s journey starts when Officer Snodgrass turned him over to his mother.
Lance Miller felt as if his life was going nowhere and, of his own volition, decided to take control.

On Tuesday, March 22nd, 2016, The World Champion Of Public Speaking Don Johnson inspired the audience with 1-hour presentation on 17 Stages of The Hero's Journey. If you master these 17 stages, you will become a proficient storyteller.
1. The Call to Adventure
The hero starts in the ordinary world and gets a call, sometimes from another person, sometimes of the person’s own volition. In Homer 's Odyssey , Odysseus is caught in the terrible winds of the angered god Poseidon and sent off to distant lands.
Throughout our own lives we see that necessity to answer the call and improve ourselves. Do you remember why and how you got involved in Toastmasters?
2. Refusal of the Call
The hero may refuse to pay attention to the call from fear, indifference, from insecurity, from a sense of inadequacy. Luke Skywalker refuses Obi Wan’s call. It’s difficult. It takes work.
Presiyan Vaselev refused the call three times. Presiyan’s refusal resulted in his situation getting worse.
3. Supernatural Aid
Cinderella had her fairy Godmother. Dorothy had Glenda, the good witch of the North. But it doesn’t necessarily have to be supernatural. It can be a parent or a grandparent or a friend giving a thought or aspiration. Dananjaya Hetearachchi’s Cool Dad’s friend says, “I see something in you.” Ryan Avery’s mother tells him, “Trust is a must.” Randy Harvey’s Fat Dad in Randy’s 2004 speech says, “Sometimes you’re the catcher; sometimes you’re the caught.”
It can be what we call miracles of coincidence where sometimes you’re saved from disaster seemingly miraculously.
Sometimes that supernatural aid is the resources within us.
4. The Crossing Of The First Threshold
This is the point where the person actually crosses into the field of adventure, leaving the known limits of his or her world and venturing into an unknown and dangerous realm where there aren’t any rules and limits. Beyond the guardian is darkness, the unknown and danger; just as beyond the parental watch is danger to the infant
You cross the threshold when you go off to college, join the services, or immigrate to another country.
5. The Belly of the Whale
It’s a common theme that appears not only in the Bible but in many other cultures as well. Remember Tom Thumb who was swallowed by a fish; the whale swallowed Pinocchio. The belly of the whale represents the final separation from the hero's known world and self. By entering this stage, the person shows willingness to undergo a metamorphosis.
6. The Road Of Trials
Once the hero accepts the call, the hero must face tasks and trial after trial and may have to face them alone, or may have assistance. The Yellow Brick Road is obvious. The road of trials is a series of tests, tasks, or ordeals that the person must undergo to begin the transformation. Dragons have now to be slain, bad witches overcome, and surprising barriers passed – again, again, and again.
A quitting smoker is plagued with withdrawal and cravings. A beginning speaker is plagued with stage fright.
7. The Meeting With The Goddess
This is the point when the person experiences an unconditional love that a fortunate infant may have experienced with his or her mother. This is a very important step in the process and is often represented by the person finding the other person that he or she loves most completely.
8. Woman As Temptress
This step is about those temptations that may lead the hero to abandon or stray from his or her quest, which does not necessarily have to be represented by a woman. Woman is a metaphor for the physical or material temptations of life, since the hero-knight was often tempted by lust from his spiritual journey. And he cannot acknowledge his own lust drives.
Throughout history men have refused to acknowledge their own faults and shortcomings and have conveniently attached them to someone else. And who is more convenient than the woman? The shining example is Eve in the creation myth.
The goddess that the man married has become a nag, a spendthrift. Women become the butt of men’s jokes. The marital problems are the fault of the spouse. But there is another side of the coin. The husband has transformed from Prince Charming into a big disappointment. He becomes lazy. He becomes a batterer. Men become the butt of women’s jokes.
9. Atonement with the Parent
In this step the person must confront and be initiated by whatever holds the ultimate power in his or her life. In many myths and stories this is the father, or a father figure who has life and death power. In Harry Potter he meets the images of his dead parents.
Dananjaya Hetearachchi’s mother and Ryan Avery’s mom were the parents with who they had to atone. With Presiyan Vaselev and Lance Miller it was their parent within.
10. Apotheosis
It’s the elevation or exultation to the rank of a god. The hero is treated as almost divine. The audience, having been led to identify with the hero, experiences the brink-of-death feeling with the hero and then is relieved by hero’s return from death. In all the winning International speeches we feel with the speaker at the moment of realization.
11. The Ultimate Boon
The ultimate boon is the achievement of the goal of the quest. It is what the person went on the journey to get. All the previous steps serve to prepare and purify the person for this step.
The scarecrow wanted intelligence, the lion wanted courage, and the tin woodman wanted compassion.
Maybe we’ve conquered our base desires and passions like lust or greed or indifference. We quit smoking. We got through our Icebreaker. We won the battle with stage fright. Now we feel we can confront any challenge.
12. Refusal of The Return
Having found bliss and enlightenment in the other world, the hero may not want to return to the ordinary world to bestow the boon onto his fellow man.
Even though we’ve discovered something we may have demons of doubts that have to be resolved. Our minds keep telling us there are other obstacles to be overcome. The person may one of those 40-year-olds that are still living at home.
13. The Magic Flight
Sometimes the hero must escape with the boon, if it is something that the gods have been jealously guarding. Jack climbed the beanstalk and stole the giant’s treasures. Glenda, the good witch of the North gave Dorothy magic slippers; Obi Wan Kenobi gave Luke Skywalker the light saber; Dumbo had a feather.
14. Rescue From Without
Heroes may need powerful guides and rescuers to bring them back to everyday life. More than likely, it’s an emotional wound. He she may succumb to recidivism or depression or negative attitudes. The mentor comes to the rescue.
15. The Crossing of The Return Threshold
The trick in returning is to retain the wisdom gained on the quest, to integrate that wisdom into our lives, and to share the wisdom with the rest of the world
16. Master Of Two Worlds
For a human hero, it may mean achieving a balance between the material and spiritual. If the hero has had to reach inside to discover his inner resources he must still realize that there is an outer world to be lived. But you can live both worlds more fully now.
17. Freedom To Live
Mastery leads to freedom from the fear of failure, which in turn is the freedom to live. This is sometimes referred to as living in the moment, neither anticipating the future nor regretting the past.
- Joseph Campbell, “The Hero with a Thousand Faces,” New World Library, Novato, California, Third Edition, 2008.
- Carl Jung, “Man and His Symbols,” Doubleday & Company, Inc., Garden City, New York,1964
- Grady Jim Robinson, “Did I Ever Tell You about the Time . . .? “ How to develop and deliver a speech using stories that get your message across, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2000.
- Kenneth C. Davis, “Don’t Know Much About Mythology, Everything You Need to Know About the Greatest Stories in Human History but never Learned,” Harper, New York, 2005.
- Robert L. Delevoy, “Symbolists and Symbolism,” Skira Rizzoli, New York, 1982
- https://donj31.wordpress.com/
MEET THE WORLD CHAMPION OF PUBLIC SPEAKING DON JOHNSON
Don Johnson, with over 38 years experience as a member of Toastmasters and the National Speakers Association is a veteran of countless talks to community and corporate groups. He has spoken to groups ranging from kindergartners to senior citizens, from recovering drug addicts to corporate managers, and community service organizations including Rotary clubs, Kiwanis and B'nai B'rith.
He served 4 years in the U.S. Navy, received his bachelor's degree at Clarkson University, his Masters at USC, and completed his Ph.D. coursework at UCLA. He has taught at Northrop University.
Don is District I's Tall-Tales champion, Region II's Humorous-Speech champion, and Toastmaster International’s World Champion of Public Speaking .
Don has spoken extensively for the American Heart Association, the March of Dimes and the American Cancer Society about health issues, has trained speakers for these organizations, and has chaired their speaker’s bureaus. He has facilitated stop-smoking programs and has trained others as facilitators.
He has taught comedy improv and has been a member of the Improv troupe: A Work in Progress , which performed regularly in the Los Angeles area. Don has taught How to Speak Like a Pro at the South Bay adult school in Manhattan Beach for 20 years, and is a Public Speaking consultant. He has been an announcer on the award-winning TV sensation, The Shelley Show .
His book, Would You Like to Swing on a Star; How You Can Create, Prepare, and Deliver a Winning Speech , gives insights into strengthening your talks and presentations and is a must for those who are considering competing. Two excerpts from the book have appeared in the Toastmaster Magazine .
His latest book Speaking from the Right Side of the Brain , is one that will boost your speaking to a new level by showing how to make more exciting, dynamic presentations by awakening unused, inner potential.
Don was a Cellist in the Beach Cities Symphony and is a painter whose works are on exhibit in the Parkhurst Gallery on 6th St. and in the Ports O’ Call Village Parkhurst Gallery, San Pedro.
Our 2024 Coverage Needs You
It's another trump-biden showdown — and we need your help, the future of democracy is at stake, your loyalty means the world to us.
As Americans head to the polls in 2024, the very future of our country is at stake. At HuffPost, we believe that a free press is critical to creating well-informed voters. That's why our journalism is free for everyone, even though other newsrooms retreat behind expensive paywalls.
Our journalists will continue to cover the twists and turns during this historic presidential election. With your help, we'll bring you hard-hitting investigations, well-researched analysis and timely takes you can't find elsewhere. Reporting in this current political climate is a responsibility we do not take lightly, and we thank you for your support.
Contribute as little as $2 to keep our news free for all.
Can't afford to donate? Support HuffPost by creating a free account and log in while you read.
The 2024 election is heating up, and women's rights, health care, voting rights, and the very future of democracy are all at stake. Donald Trump will face Joe Biden in the most consequential vote of our time. And HuffPost will be there, covering every twist and turn. America's future hangs in the balance. Would you consider contributing to support our journalism and keep it free for all during this critical season?
HuffPost believes news should be accessible to everyone, regardless of their ability to pay for it. We rely on readers like you to help fund our work. Any contribution you can make — even as little as $2 — goes directly toward supporting the impactful journalism that we will continue to produce this year. Thank you for being part of our story.
It's official: Donald Trump will face Joe Biden this fall in the presidential election. As we face the most consequential presidential election of our time, HuffPost is committed to bringing you up-to-date, accurate news about the 2024 race. While other outlets have retreated behind paywalls, you can trust our news will stay free.
But we can't do it without your help. Reader funding is one of the key ways we support our newsroom. Would you consider making a donation to help fund our news during this critical time? Your contributions are vital to supporting a free press.
Contribute as little as $2 to keep our journalism free and accessible to all.
Dear HuffPost Reader
Thank you for your past contribution to HuffPost. We are sincerely grateful for readers like you who help us ensure that we can keep our journalism free for everyone.
The stakes are high this year, and our 2024 coverage could use continued support. Would you consider becoming a regular HuffPost contributor?
The stakes are high this year, and our 2024 coverage could use continued support. If circumstances have changed since you last contributed, we hope you'll consider contributing to HuffPost once more.
Already contributed? Log in to hide these messages.
Popular in the Community
From our partner, more in contributor.
Holiday Savings

cui:common.components.upgradeModal.offerHeader_undefined
The hero's journey: a story structure as old as time, the hero's journey offers a powerful framework for creating quest-based stories emphasizing self-transformation..

Table of Contents
Holding out for a hero to take your story to the next level?
The Hero’s Journey might be just what you’ve been looking for. Created by Joseph Campbell, this narrative framework packs mythic storytelling into a series of steps across three acts, each representing a crucial phase in a character's transformative journey.
Challenge . Growth . Triumph .
Whether you're penning a novel, screenplay, or video game, The Hero’s Journey is a tried-and-tested blueprint for crafting epic stories that transcend time and culture. Let’s explore the steps together and kickstart your next masterpiece.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey is a famous template for storytelling, mapping a hero's adventurous quest through trials and tribulations to ultimate transformation.
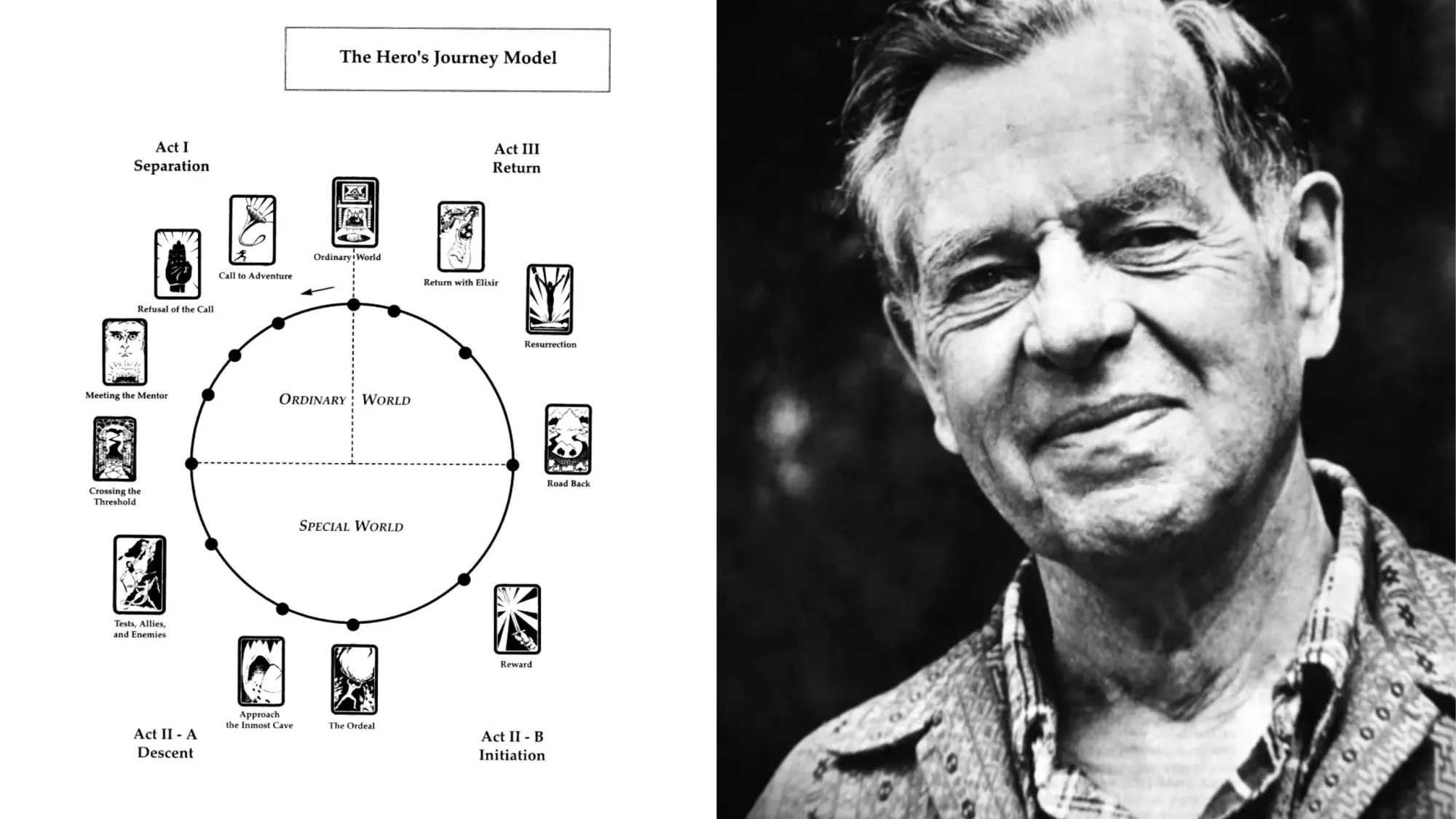
What are the Origins of the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey was invented by Campbell in his seminal 1949 work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces , where he introduces the concept of the "monomyth."
A comparative mythologist by trade, Campbell studied myths from cultures around the world and identified a common pattern in their narratives. He proposed that all mythic narratives are variations of a single, universal story, structured around a hero's adventure, trials, and eventual triumph.
His work unveiled the archetypal hero’s path as a mirror to humanity’s commonly shared experiences and aspirations. It was subsequently named one of the All-Time 100 Nonfiction Books by TIME in 2011.
How are the Hero’s and Heroine’s Journeys Different?
While both the Hero's and Heroine's Journeys share the theme of transformation, they diverge in their focus and execution.
The Hero’s Journey, as outlined by Campbell, emphasizes external challenges and a quest for physical or metaphorical treasures. In contrast, Murdock's Heroine’s Journey, explores internal landscapes, focusing on personal reconciliation, emotional growth, and the path to self-actualization.
In short, heroes seek to conquer the world, while heroines seek to transform their own lives; but…
Twelve Steps of the Hero’s Journey
So influential was Campbell’s monomyth theory that it's been used as the basis for some of the largest franchises of our generation: The Lord of the Rings , Harry Potter ...and George Lucas even cited it as a direct influence on Star Wars .
There are, in fact, several variations of the Hero's Journey, which we discuss further below. But for this breakdown, we'll use the twelve-step version outlined by Christopher Vogler in his book, The Writer's Journey (seemingly now out of print, unfortunately).

You probably already know the above stories pretty well so we’ll unpack the twelve steps of the Hero's Journey using Ben Gates’ journey in National Treasure as a case study—because what is more heroic than saving the Declaration of Independence from a bunch of goons?
Ye be warned: Spoilers ahead!
Act One: Departure
Step 1. the ordinary world.
The journey begins with the status quo—business as usual. We meet the hero and are introduced to the Known World they live in. In other words, this is your exposition, the starting stuff that establishes the story to come.
National Treasure begins in media res (preceded only by a short prologue), where we are given key information that introduces us to Ben Gates' world, who he is (a historian from a notorious family), what he does (treasure hunts), and why he's doing it (restoring his family's name).
With the help of his main ally, Riley, and a crew of other treasure hunters backed by a wealthy patron, he finds an 18th-century American ship in the Canadian Arctic, the Charlotte . Here, they find a ship-shaped pipe that presents a new riddle and later doubles as a key—for now, it's just another clue in the search for the lost treasure of the Templars, one that leads them to the Declaration of Independence.
Step 2. The Call to Adventure
The inciting incident takes place and the hero is called to act upon it. While they're still firmly in the Known World, the story kicks off and leaves the hero feeling out of balance. In other words, they are placed at a crossroads.
Ian (the wealthy patron of the Charlotte operation) steals the pipe from Ben and Riley and leaves them stranded. This is a key moment: Ian becomes the villain, Ben has now sufficiently lost his funding for this expedition, and if he decides to pursue the chase, he'll be up against extreme odds.
Step 3. Refusal of the Call
The hero hesitates and instead refuses their call to action. Following the call would mean making a conscious decision to break away from the status quo. Ahead lies danger, risk, and the unknown; but here and now, the hero is still in the safety and comfort of what they know.
Ben debates continuing the hunt for the Templar treasure. Before taking any action, he decides to try and warn the authorities: the FBI, Homeland Security, and the staff of the National Archives, where the Declaration of Independence is housed and monitored. Nobody will listen to him, and his family's notoriety doesn't help matters.
Step 4. Meeting the Mentor
The protagonist receives knowledge or motivation from a powerful or influential figure. This is a tactical move on the hero's part—remember that it was only the previous step in which they debated whether or not to jump headfirst into the unknown. By Meeting the Mentor, they can gain new information or insight, and better equip themselves for the journey they might to embark on.
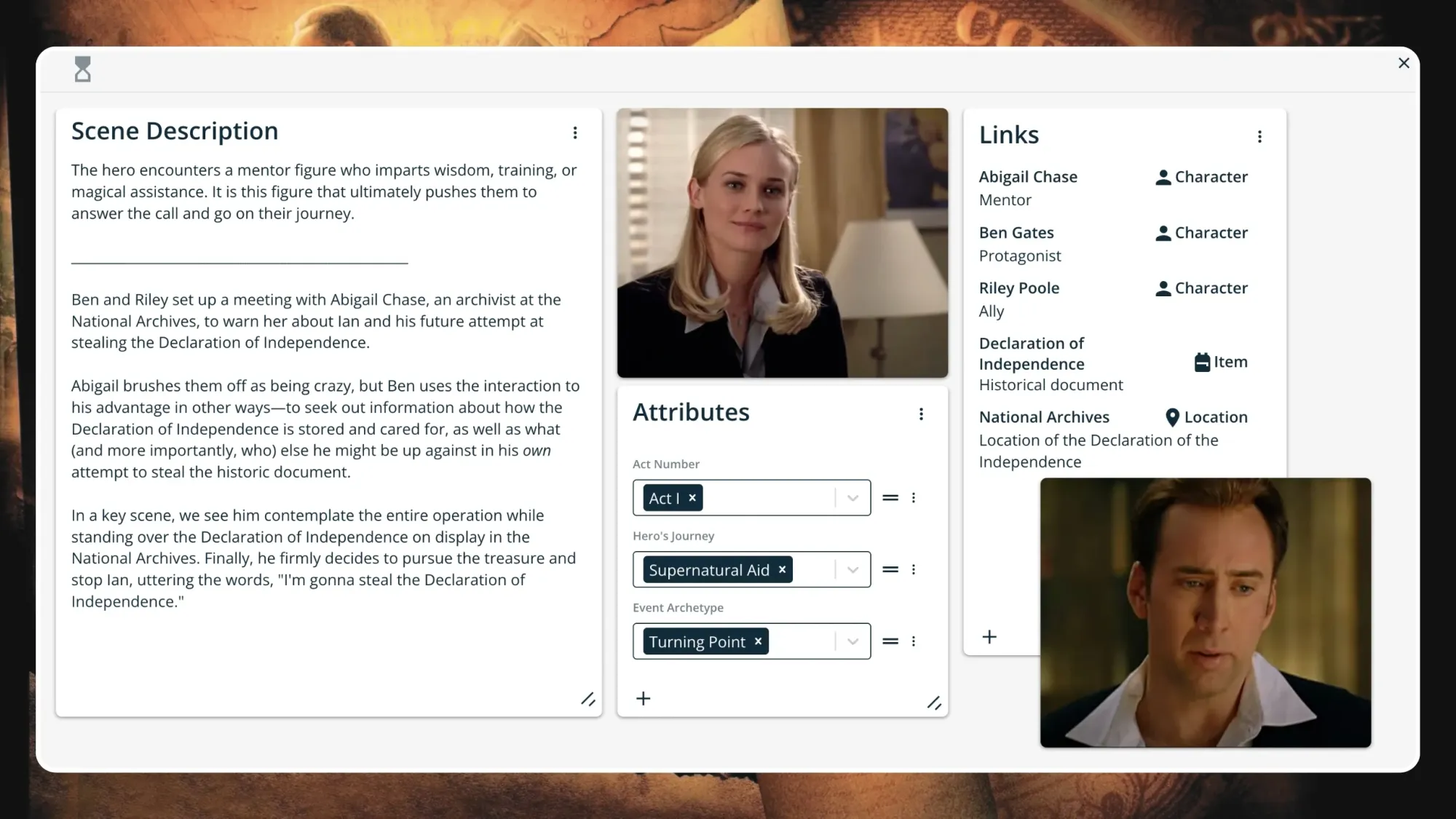
Abigail, an archivist at the National Archives, brushes Ben and Riley off as being crazy, but Ben uses the interaction to his advantage in other ways—to seek out information about how the Declaration of Independence is stored and cared for, as well as what (and more importantly, who) else he might be up against in his own attempt to steal it.
In a key scene, we see him contemplate the entire operation while standing over the glass-encased Declaration of Independence. Finally, he firmly decides to pursue the treasure and stop Ian, uttering the famous line, "I'm gonna steal the Declaration of Independence."
Act Two: Initiation
Step 5. crossing the threshold.
The hero leaves the Known World to face the Unknown World. They are fully committed to the journey, with no way to turn back now. There may be a confrontation of some sort, and the stakes will be raised.
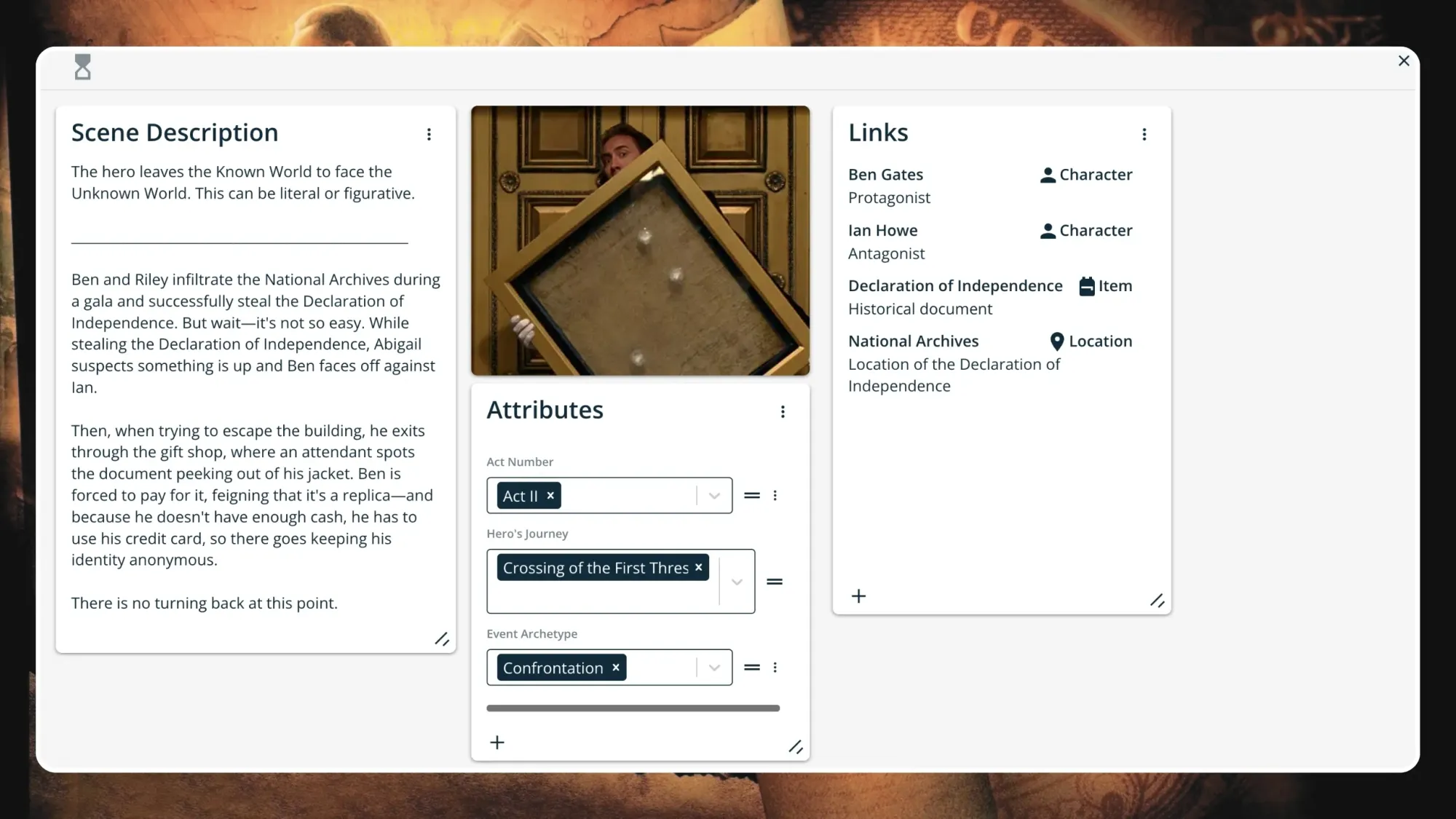
Ben and Riley infiltrate the National Archives during a gala and successfully steal the Declaration of Independence. But wait—it's not so easy. While stealing the Declaration of Independence, Abigail suspects something is up and Ben faces off against Ian.
Then, when trying to escape the building, Ben exits through the gift shop, where an attendant spots the document peeking out of his jacket. He is forced to pay for it, feigning that it's a replica—and because he doesn't have enough cash, he has to use his credit card, so there goes keeping his identity anonymous.
The game is afoot.
Step 6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
The hero explores the Unknown World. Now that they have firmly crossed the threshold from the Known World, the hero will face new challenges and possibly meet new enemies. They'll have to call upon their allies, new and old, in order to keep moving forward.
Abigail reluctantly joins the team under the agreement that she'll help handle the Declaration of Independence, given her background in document archiving and restoration. Ben and co. seek the aid of Ben's father, Patrick Gates, whom Ben has a strained relationship with thanks to years of failed treasure hunting that has created a rift between grandfather, father, and son. Finally, they travel around Philadelphia deciphering clues while avoiding both Ian and the FBI.
Step 7. Approach the Innermost Cave
The hero nears the goal of their quest, the reason they crossed the threshold in the first place. Here, they could be making plans, having new revelations, or gaining new skills. To put it in other familiar terms, this step would mark the moment just before the story's climax.
Ben uncovers a pivotal clue—or rather, he finds an essential item—a pair of bifocals with interchangeable lenses made by Benjamin Franklin. It is revealed that by switching through the various lenses, different messages will be revealed on the back of the Declaration of Independence. He's forced to split from Abigail and Riley, but Ben has never been closer to the treasure.
Step 8. The Ordeal
The hero faces a dire situation that changes how they view the world. All threads of the story come together at this pinnacle, the central crisis from which the hero will emerge unscathed or otherwise. The stakes will be at their absolute highest here.
Vogler details that in this stage, the hero will experience a "death," though it need not be literal. In your story, this could signify the end of something and the beginning of another, which could itself be figurative or literal. For example, a certain relationship could come to an end, or it could mean someone "stuck in their ways" opens up to a new perspective.
In National Treasure , The FBI captures Ben and Ian makes off with the Declaration of Independence—all hope feels lost. To add to it, Ian reveals that he's kidnapped Ben's father and threatens to take further action if Ben doesn't help solve the final clues and lead Ian to the treasure.
Ben escapes the FBI with Ian's help, reunites with Abigail and Riley, and leads everyone to an underground structure built below Trinity Church in New York City. Here, they manage to split from Ian once more, sending him on a goose chase to Boston with a false clue, and proceed further into the underground structure.
Though they haven't found the treasure just yet, being this far into the hunt proves to Ben's father, Patrick, that it's real enough. The two men share an emotional moment that validates what their family has been trying to do for generations.
Step 9. Reward
This is it, the moment the hero has been waiting for. They've survived "death," weathered the crisis of The Ordeal, and earned the Reward for which they went on this journey.
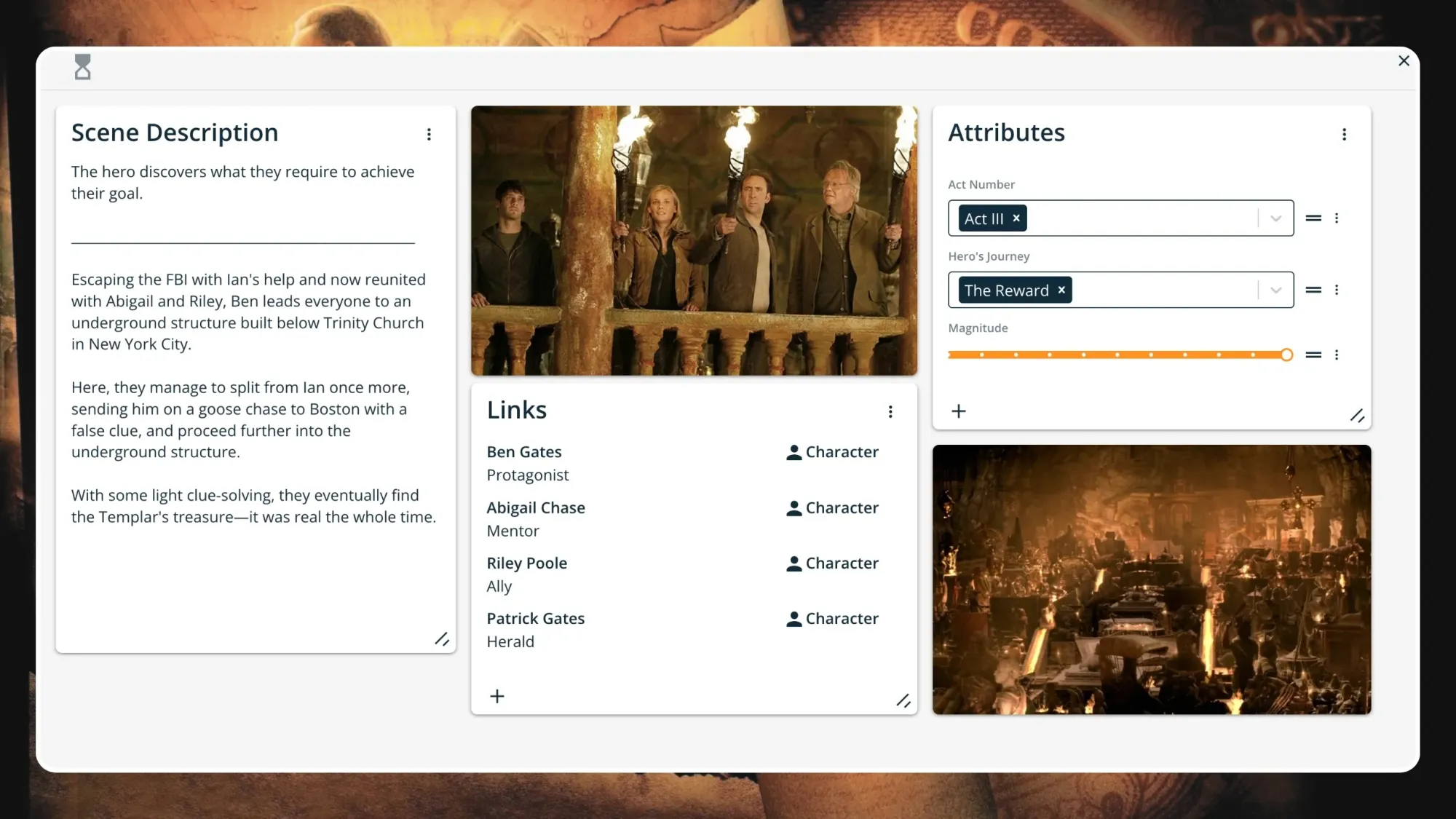
Now, free of Ian's clutches and with some light clue-solving, Ben, Abigail, Riley, and Patrick keep progressing through the underground structure and eventually find the Templar's treasure—it's real and more massive than they could have imagined. Everyone revels in their discovery while simultaneously looking for a way back out.
Act Three: Return
Step 10. the road back.
It's time for the journey to head towards its conclusion. The hero begins their return to the Known World and may face unexpected challenges. Whatever happens, the "why" remains paramount here (i.e. why the hero ultimately chose to embark on their journey).
This step marks a final turning point where they'll have to take action or make a decision to keep moving forward and be "reborn" back into the Known World.
Act Three of National Treasure is admittedly quite short. After finding the treasure, Ben and co. emerge from underground to face the FBI once more. Not much of a road to travel back here so much as a tunnel to scale in a crypt.
Step 11. Resurrection
The hero faces their ultimate challenge and emerges victorious, but forever changed. This step often requires a sacrifice of some sort, and having stepped into the role of The Hero™, they must answer to this.
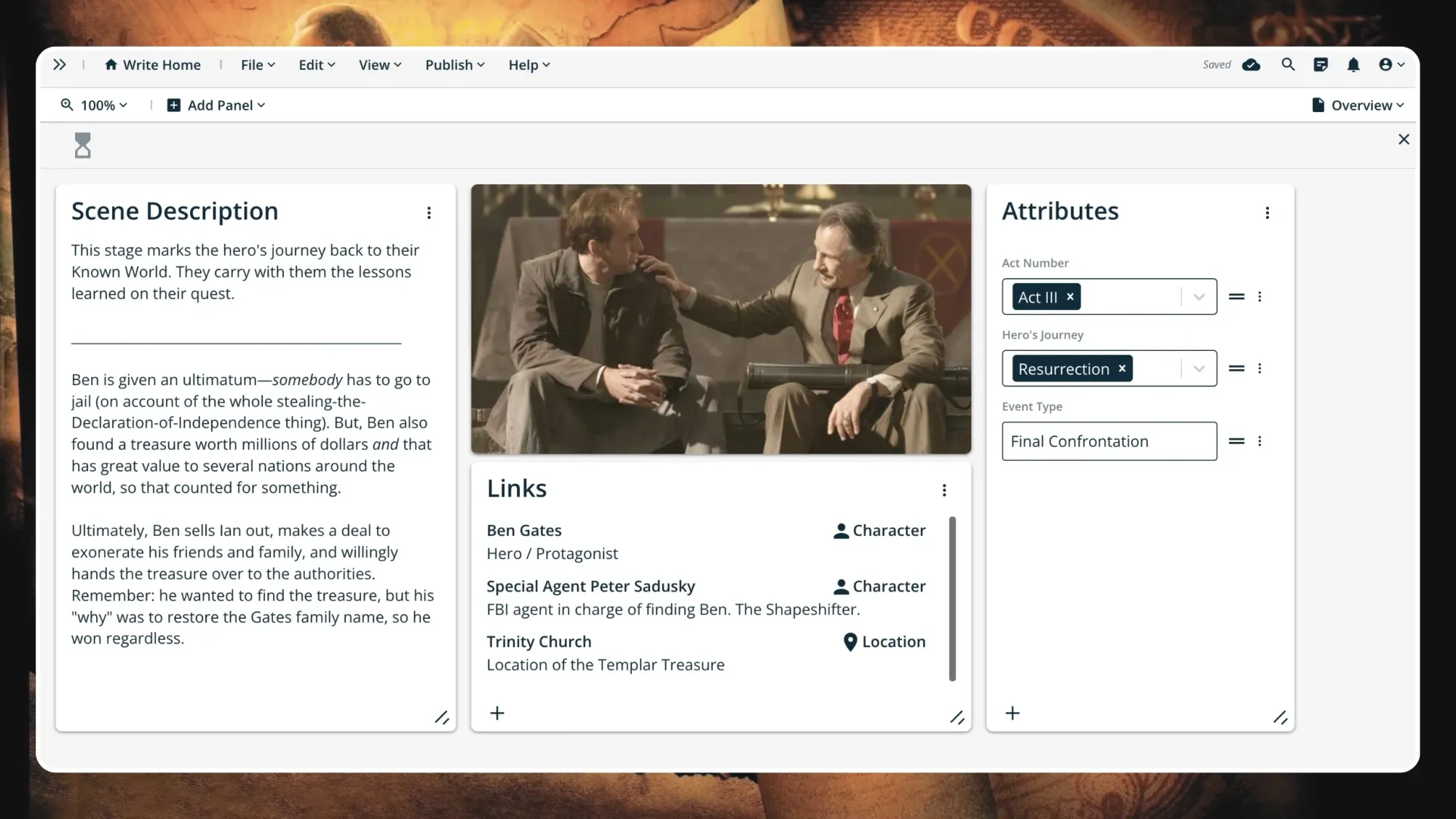
Ben is given an ultimatum— somebody has to go to jail (on account of the whole stealing-the-Declaration-of-Independence thing). But, Ben also found a treasure worth millions of dollars and that has great value to several nations around the world, so that counts for something.
Ultimately, Ben sells Ian out, makes a deal to exonerate his friends and family, and willingly hands the treasure over to the authorities. Remember: he wanted to find the treasure, but his "why" was to restore the Gates family name, so he won regardless.
Step 12. Return With the Elixir
Finally, the hero returns home as a new version of themself, the elixir is shared amongst the people, and the journey is completed full circle.
The elixir, like many other elements of the hero's journey, can be literal or figurative. It can be a tangible thing, such as an actual elixir meant for some specific purpose, or it could be represented by an abstract concept such as hope, wisdom, or love.
Vogler notes that if the Hero's Journey results in a tragedy, the elixir can instead have an effect external to the story—meaning that it could be something meant to affect the audience and/or increase their awareness of the world.
In the final scene of National Treasure , we see Ben and Abigail walking the grounds of a massive estate. Riley pulls up in a fancy sports car and comments on how they could have gotten more money. They all chat about attending a museum exhibit in Cairo (Egypt).
In one scene, we're given a lot of closure: Ben and co. received a hefty payout for finding the treasure, Ben and Abigail are a couple now, and the treasure was rightfully spread to those it benefitted most—in this case, countries who were able to reunite with significant pieces of their history. Everyone's happy, none of them went to jail despite the serious crimes committed, and they're all a whole lot wealthier. Oh, Hollywood.
Variations of the Hero's Journey
Plot structure is important, but you don't need to follow it exactly; and, in fact, your story probably won't. Your version of the Hero's Journey might require more or fewer steps, or you might simply go off the beaten path for a few steps—and that's okay!
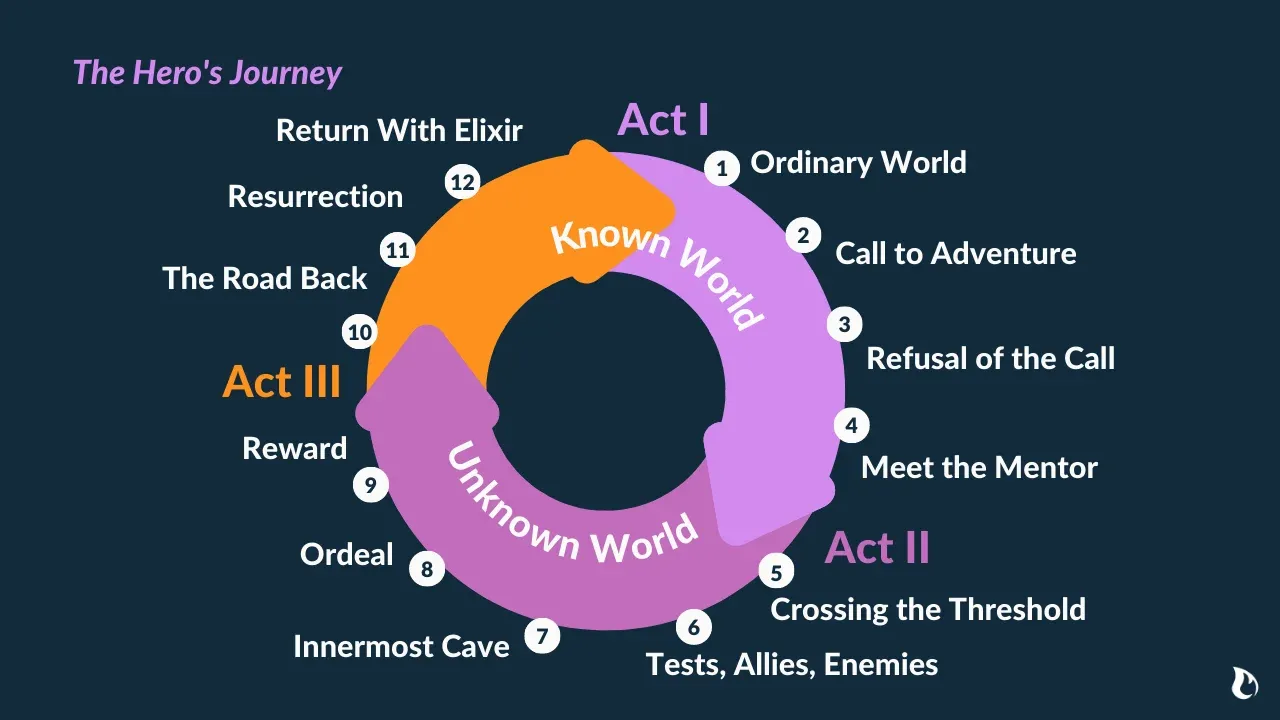
What follows are three additional versions of the Hero's Journey, which you may be more familiar with than Vogler's version presented above.
Dan Harmon's Story Circle (or, The Eight-Step Hero's Journey)
Screenwriter Dan Harmon has riffed on the Hero's Journey by creating a more compact version, the Story Circle —and it works especially well for shorter-format stories such as television episodes, which happens to be what Harmon writes.
The Story Circle comprises eight simple steps with a heavy emphasis on the hero's character arc:
- The hero is in a zone of comfort...
- But they want something.
- They enter an unfamiliar situation...
- And adapt to it by facing trials.
- They get what they want...
- But they pay a heavy price for it.
- They return to their familiar situation...
- Having changed.
You may have noticed, but there is a sort of rhythm here. The eight steps work well in four pairs, simplifying the core of the Hero's Journey even further:
- The hero is in a zone of comfort, but they want something.
- They enter an unfamiliar situation and have to adapt via new trials.
- They get what they want, but they pay a price for it.
- They return to their zone of comfort, forever changed.
If you're writing shorter fiction, such as a short story or novella, definitely check out the Story Circle. It's the Hero's Journey minus all the extraneous bells & whistles.
Ten-Step Hero's Journey
The ten-step Hero's Journey is similar to the twelve-step version we presented above. It includes most of the same steps except for Refusal of the Call and Meeting the Mentor, arguing that these steps aren't as essential to include; and, it moves Crossing the Threshold to the end of Act One and Reward to the end of Act Two.
- The Ordinary World
- The Call to Adventure
- Crossing the Threshold
- Tests, Allies, Enemies
- Approach the Innermost Cave
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return with Elixir
We've previously written about the ten-step hero's journey in a series of essays separated by act: Act One (with a prologue), Act Two , and Act Three .
Twelve-Step Hero's Journey: Version Two
Again, the second version of the twelve-step hero's journey is very similar to the one above, save for a few changes, including in which story act certain steps appear.
This version skips The Ordinary World exposition and starts right at The Call to Adventure; then, the story ends with two new steps in place of Return With Elixir: The Return and The Freedom to Live.
- The Refusal of the Call
- Meeting the Mentor
- Test, Allies, Enemies
- Approaching the Innermost Cave
- The Resurrection
- The Return*
- The Freedom to Live*
In the final act of this version, there is more of a focus on an internal transformation for the hero. They experience a metamorphosis on their journey back to the Known World, return home changed, and go on to live a new life, uninhibited.
Seventeen-Step Hero's Journey
Finally, the granddaddy of heroic journeys: the seventeen-step Hero's Journey. This version includes a slew of extra steps your hero might face out in the expanse.
- Refusal of the Call
- Supernatural Aid (aka Meeting the Mentor)
- Belly of the Whale*: This added stage marks the hero's immediate descent into danger once they've crossed the threshold.
- Road of Trials (...with Allies, Tests, and Enemies)
- Meeting with the Goddess/God*: In this stage, the hero meets with a new advisor or powerful figure, who equips them with the knowledge or insight needed to keep progressing forward.
- Woman as Temptress (or simply, Temptation)*: Here, the hero is tempted, against their better judgment, to question themselves and their reason for being on the journey. They may feel insecure about something specific or have an exposed weakness that momentarily holds them back.
- Atonement with the Father (or, Catharthis)*: The hero faces their Temptation and moves beyond it, shedding free from all that holds them back.
- Apotheosis (aka The Ordeal)
- The Ultimate Boon (aka the Reward)
- Refusal of the Return*: The hero wonders if they even want to go back to their old life now that they've been forever changed.
- The Magic Flight*: Having decided to return to the Known World, the hero needs to actually find a way back.
- Rescue From Without*: Allies may come to the hero's rescue, helping them escape this bold, new world and return home.
- Crossing of the Return Threshold (aka The Return)
- Master of Two Worlds*: Very closely resembling The Resurrection stage in other variations, this stage signifies that the hero is quite literally a master of two worlds—The Known World and the Unknown World—having conquered each.
- Freedom to Live
Again, we skip the Ordinary World opening here. Additionally, Acts Two and Three look pretty different from what we've seen so far, although, the bones of the Hero's Journey structure remain.
The Eight Hero’s Journey Archetypes
The Hero is, understandably, the cornerstone of the Hero’s Journey, but they’re just one of eight key archetypes that make up this narrative framework.
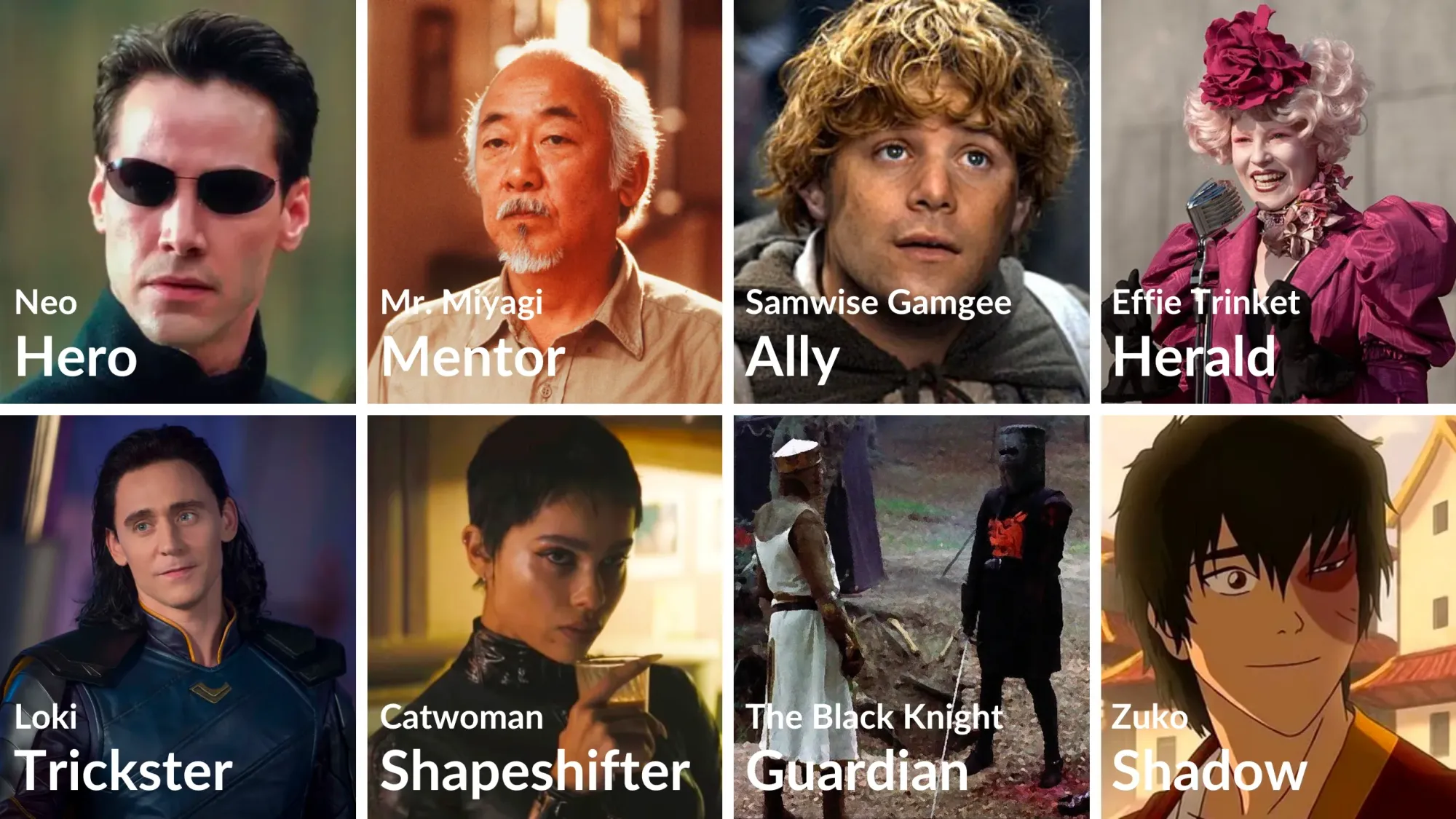

In The Writer's Journey , Vogler outlined seven of these archetypes, only excluding the Ally, which we've included below. Here’s a breakdown of all eight with examples:
1. The Hero
As outlined, the Hero is the protagonist who embarks on a transformative quest or journey. The challenges they overcome represent universal human struggles and triumphs.
Vogler assigned a "primary function" to each archetype—helpful for establishing their role in a story. The Hero's primary function is "to service and sacrifice."
Example: Neo from The Matrix , who evolves from a regular individual into the prophesied savior of humanity.
2. The Mentor
A wise guide offering knowledge, tools, and advice, Mentors help the Hero navigate the journey and discover their potential. Their primary function is "to guide."
Example: Mr. Miyagi from The Karate Kid imparts not only martial arts skills but invaluable life lessons to Daniel.
3. The Ally
Companions who support the Hero, Allies provide assistance, friendship, and moral support throughout the journey. They may also become a friends-to-lovers romantic partner.
Not included in Vogler's list is the Ally, though we'd argue they are essential nonetheless. Let's say their primary function is "to aid and support."
Example: Samwise Gamgee from Lord of the Rings , a loyal friend and steadfast supporter of Frodo.
4. The Herald
The Herald acts as a catalyst to initiate the Hero's Journey, often presenting a challenge or calling the hero to adventure. Their primary function is "to warn or challenge."
Example: Effie Trinket from The Hunger Games , whose selection at the Reaping sets Katniss’s journey into motion.
5. The Trickster
A character who brings humor and unpredictability, challenges conventions, and offers alternative perspectives or solutions. Their primary function is "to disrupt."
Example: Loki from Norse mythology exemplifies the trickster, with his cunning and chaotic influence.
6. The Shapeshifter
Ambiguous figures whose allegiance and intentions are uncertain. They may be a friend one moment and a foe the next. Their primary function is "to question and deceive."
Example: Catwoman from the Batman universe often blurs the line between ally and adversary, slinking between both roles with glee.
7. The Guardian
Protectors of important thresholds, Guardians challenge or test the Hero, serving as obstacles to overcome or lessons to be learned. Their primary function is "to test."
Example: The Black Knight in Monty Python and the Holy Grail literally bellows “None shall pass!”—a quintessential ( but not very effective ) Guardian.
8. The Shadow
Represents the Hero's inner conflict or an antagonist, often embodying the darker aspects of the hero or their opposition. Their primary function is "to destroy."
Example: Zuko from Avatar: The Last Airbender; initially an adversary, his journey parallels the Hero’s path of transformation.
While your story does not have to use all of the archetypes, they can help you develop your characters and visualize how they interact with one another—especially the Hero.
For example, take your hero and place them in the center of a blank worksheet, then write down your other major characters in a circle around them and determine who best fits into which archetype. Who challenges your hero? Who tricks them? Who guides them? And so on...
Stories that Use the Hero’s Journey
Not a fan of saving the Declaration of Independence? Check out these alternative examples of the Hero’s Journey to get inspired:
- Epic of Gilgamesh : An ancient Mesopotamian epic poem thought to be one of the earliest examples of the Hero’s Journey (and one of the oldest recorded stories).
- The Lion King (1994): Simba's exile and return depict a tale of growth, responsibility, and reclaiming his rightful place as king.
- The Alchemist by Paolo Coehlo: Santiago's quest for treasure transforms into a journey of self-discovery and personal enlightenment.
- Coraline by Neil Gaiman: A young girl's adventure in a parallel world teaches her about courage, family, and appreciating her own reality.
- Kung Fu Panda (2008): Po's transformation from a clumsy panda to a skilled warrior perfectly exemplifies the Hero's Journey. Skadoosh!
The Hero's Journey is so generalized that it's ubiquitous. You can plop the plot of just about any quest-style narrative into its framework and say that the story follows the Hero's Journey. Try it out for yourself as an exercise in getting familiar with the method.
Will the Hero's Journey Work For You?
As renowned as it is, the Hero's Journey works best for the kinds of tales that inspired it: mythic stories.
Writers of speculative fiction may gravitate towards this method over others, especially those writing epic fantasy and science fiction (big, bold fantasy quests and grand space operas come to mind).
The stories we tell today are vast and varied, and they stretch far beyond the dealings of deities, saving kingdoms, or acquiring some fabled "elixir." While that may have worked for Gilgamesh a few thousand years ago, it's not always representative of our lived experiences here and now.
If you decide to give the Hero's Journey a go, we encourage you to make it your own! The pieces of your plot don't have to neatly fit into the structure, but you can certainly make a strong start on mapping out your story.
Hero's Journey Campfire Template
The Timeline Module in Campfire offers a versatile canvas to plot out each basic component of your story while featuring nested "notebooks."
Simply double-click on each event card in your timeline to open up a canvas specific to that card. This allows you to look at your plot at the highest level, while also adding as much detail for each plot element as needed!
If you're just hearing about Campfire for the first time, it's free to sign up—forever! Let's plot the most epic of hero's journeys 👇
Lessons From the Hero’s Journey
The Hero's Journey offers a powerful framework for creating stories centered around growth, adventure, and transformation.
If you want to develop compelling characters, spin out engaging plots, and write books that express themes of valor and courage, consider The Hero’s Journey your blueprint. So stop holding out for a hero, and start writing!
Does your story mirror the Hero's Journey? Let us know in the comments below.

Breaking Down the Character Archetypes of the Hero’s Journey
You’ve read about George Lucas’s use of Joseph Campbell’s Monomyth found in his 1949 book, A Hero with a Thousand Faces , which is a common narrative pattern found in many stories from many different cultures worldwide. This narrative journey typically involves several character archetypes that affect the hero’s journey from beginning to end.
After the successful debut of Star Wars and Lucas’s discussions on using Campbell’s work as inspiration for his space opera, many producers, development executives, filmmakers, and screenwriters have explored the Monomyth with deeper and simplified approaches.

Christopher Vogler's Interpretation of the Hero's Journey
When Christopher Vogler, a development executive and screenwriter at Disney, was inspired by Joseph Campbell's concept of the story monomyth, he crafted a seven-page memo for Disney's development team and incoming screenwriters.
This memo, A Practical Guide to Joseph Cambell’s The Hero with a Thousand Faces , laid the groundwork for what would later become Vogler's 1992 book, The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Storytellers and Screenwriters . In this book, Vogler expanded upon Campbell’s ideas.
He adapted Campbell's mythical story structure into twelve distinct stages (from Campbell’s initial seventeen). Our concise interpretations of these stages include:
- The Ordinary World : We see the hero's normal life at the start of the story before the adventure begins.
- Call to Adventure : The hero faces an event, conflict, problem, or challenge that makes them begin their adventure.
- Refusal of the Call : The hero initially refuses the adventure because of hesitation, fear, insecurity, or any other issues.
- Meeting the Mentor : The hero encounters a mentor who can give them advice, wisdom, information, or items that ready them for the journey ahead.
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero leaves their ordinary world for the first time and crosses the threshold into adventure.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : The hero learns the rules of the new world and endures tests, meets friends, and comes face-to-face with enemies.
- The Approach : The initial plan to take on the central conflict begins, but setbacks cause the hero to try a new approach or adopt new ideas.
- The Ordeal : Things go wrong, and added conflict is introduced . The hero experiences more difficult hurdles and obstacles, some of which may lead to a life crisis.
- The Reward : After surviving The Ordeal, the hero seizes the sword — a reward that they've earned that allows them to take on the biggest conflict. It may be a physical item or piece of knowledge or wisdom that will help them persevere.
- The Road Back : The hero sees the light at the end of the tunnel, but they are about to face even more tests and challenges.
- The Resurrection : The climax. The hero faces a final test, using everything they have learned to take on the conflict once and for all.
- The Return : The hero brings their knowledge or the " elixir " back to the ordinary world.
Within these stages are character archetypes that help to shape the hero’s journey, and their eventual character arc throughout the story.
Read More: Exploring the Twelve Stages of the Hero’s Journey

'Tron: Legacy' (2010)
What Are Character Archetypes?
A character archetype is a common recurring representation of a character that embodies a set of universal and recognizable traits or characteristics. These archetypes are seen throughout literature, film, and other storytelling mediums—and they resonate with audiences because they are based on common human experiences or cultural norms.
Archetypes work well because they are instantly recognizable to readers and audiences. For writers, character archetypes can be adapted and molded with ease during character development.
Character archetypes are not specific characters in a story but rather broad categories or templates that individual characters can be based on or inspired by. They represent typical roles characters play in the narrative, and their actions and motivations are often predictable based on the archetype they represent.
However, writers can also choose to subvert those expectations to create a more dynamic character , as well as introduce much-needed twists and turns within the story.
Read More: 10 Character Archetypes in Comedies

'The Goonies' (1950)
The benefits of using character archetypes include:
- Universality : Archetypes are universally understood and have similar meanings across cultures and historical contexts. This can especially help in the cinematic realm as movies are released in multiple countries and languages.
- Symbolism : These character traits can symbolize a particular aspect of human experience or life. Once again, symbolism is identifiable across many cultures.
- Predictability : Because they are based on common patterns, their behaviors and roles in stories can often be anticipated . Because of that anticipation, writers can choose between subverting those expectations or using the predictability of the archetypes to service the story and protagonist with ease.
- Variability : While archetypes are typical patterns, they allow for variations and depth, meaning a single archetype can manifest in different ways across various stories, allowing writers can adapt these traits to any character.
Character archetypes can be used as tools to tell a compelling and universal story.

'Finding Nemo' (2003)
What Are the Character Archetypes in the Hero's Journey?
Many archetypes in the hero's journey—the threshold guardian, the herald, the shapeshifter, the trickster, the ally, and the tempter/temptress—are more defined in later interpretations and expansions of Campbell's work. People like Vogler applied his theories to modern storytelling so writers, readers, and audiences could more easily understand the dynamics of Campbell’s monomyth.
Here, we’ll break down the main character archetypes in the hero's journey utilized in Campbell’s Monomyth and Vogler’s expanded breakdowns and interpretations.
The hero is the central figure of the story (protagonist) who undergoes a journey, facing challenges and transformations. The hero often starts as an ordinary person who is then called to adventure. They are present throughout the entire journey , from the ordinary world to the return with newfound knowledge or power.
Luke Skywalker (Star Wars), Indiana Jones ( Raiders of the Lost Arc ), Katniss Everdeen ( The Hunger Games ), Barbie ( Barbie ), and Harry Potter (the Harry Potter series) are perfect examples of the hero character archetypes. You can include any protagonist within a story that goes on a physical or emotional journey.
As mentioned above, the hero in the hero’s journey usually begins their adventure within their ordinary world. This offers readers and audiences the chance to relate to the protagonist, empathize with their plight, and see the beginning of their character arc.
Read More: Why the 'Barbie' Movie is the Perfect Example of the Hero’s Journey
The shadow is the main antagonist of the story. The shadow reflects the darker aspects of the hero, sometimes represented as the mirror image (opposite) of the hero and their beliefs. Overall, they are the antagonist or villains present throughout the whole story in varied ways.
Read More: 15 Types of Villains Screenwriters Need to Know
The shadow can also be represented in metaphorical terms. If a story’s hero journey is the protagonist dealing with alcoholism or addiction, those vices can serve as the shadow/antagonist/villain.
The quintessential shadows in cinema include characters like Darth Vader ( Star Wars ), Voldemort (the Harry Potter series), and Sauron ( The Lord of the Rings series). But you can also find a less villainous shadow that takes on a lighter antagonistic role without purely evil intentions.
A perfect example of that would be Principal Rooney in Ferris Bueller’s Day Off . He doesn’t have evil intentions like a villain does. However, he is the shadow or mirror image of Ferris Bueller. Ferris believes in freedom an expression . Rooney believes in order and control of others.

'Ferris Bueller's Day Off' (1986)
This character serves as a guide or teacher to the hero, providing them with advice, training, or magical assistance. The mentor is often a wise or experienced figure, although there have been literary and cinematic variances.
Look no further than the likes of Obi-Wan Kenobi ( Star Wars ), Yoda ( The Empire Strikes Back ), Mr. Miyagi ( The Karate Kid ), and Gandalf ( The Lord of the Rings series ) as core examples of the mentor.

'The Karate Kid' (1984)
Allies are friends or companions who support and accompany the hero through their journey. They often complement the hero's skills and help them face challenges.
In Star Wars , the allies of Luke Skywalker include Han Solo, Chewbacca, and the droids. In The Lord of the Rings series , the fellowship companions of Frodo encompass this character archetype. You can also look to any sidekick-type character as the perfect example of an ally:
- Goose in Top Gun
- Patrick in Spongebob Squarepants
- Ron in Harry Potter
- Billy in Big
- Julie in Lady Bird
- Rod in Get Out
- Ned in the Spider-Man movies
- Sam in The Lord of the Rings
- Short Round in Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom
Allies can also be characters who aren’t as close to the hero but offer some type of help along the way.

'Lady Bird' (2017)
The Threshold Guardian
These characters serve as obstacles the hero must overcome or circumvent on their journey. They are not always enemies but are present within the story to test the hero and give them the belief and ability to continue on their adventure.
Little John in the Robin Hood stories is initially the threshold guardian of the Sherwood Forest.
He eventually becomes an ally to Robin. But he’s initially a threshold guardian.
You can turn to Monthy Python and the Holy Grail as well. The Black Knight isn’t necessarily King Arthur’s foe. However, he’s there to defend the bridge at all costs.
The Herald
The herald is the character that initiates the call to adventure, pushing the hero to action, or providing the news or event that triggers their journey.
In Star Wars , R2-D2 is the herald of Luke’s journey because he delivers the message from Princess Leia to him . If Luke doesn’t see that message, he doesn’t show it to Obi-Wan Kenobi. And if Obi-Wan doesn’t see that message, he doesn’t convince Luke to come with him to join the Rebellion.
In Barbie , Weird Barbie is the one who tells Barbie the truth about what she is going through and what she must do to seek out the answers she needs.
The herald can be a major character, a supporting character, or even a minor character. In The Lord of the Rings , Gandalf is both mentor and herald, as he is the one who appears to Frodo, telling him he must bring the ring to Mordor.
The Shapeshifter
This archetype's loyalty and role are often unclear, and they can serve as an ally or an enemy to the hero. Sometimes both. Their unpredictable nature adds complexity to the story, usually resulting in twists and turns within the plot.
Snape in the Harry Potter series is one of the greatest shapeshifters in literature and film. His motives are unknown, mistaken, and hidden. He acts as both a shadow to Harry and later an ally.
Jack Sparrow in the Pirates of the Caribbean series is another great example, embodying the role of an unpredictable ally whose loyalty is often questionable. Yes, he can be looked upon as an antihero protagonist of the movie. However, the clear hero of the story is Will.

'Pirates of the Caribbean: The Curse of the Black Pearl' (2003)
The Trickster
The trickster usually adds levity to the story through comic relief. They can be allies or enemies, but typically they cause trouble for both.
Jack Sparrow falls under this character archetype as well. But a better example may be Loki in the Marvel Cinematic Universe movies. He embodies the definition of a trickster. He brings more comic relief to the movies after his initial first appearance in Thor .
Perhaps the better example would be Genie in Disney's Aladdin . He uses his powers for humorous and unexpected effects, often bending the rules and adding a lighthearted element to the story.
Tempter/Temptress
This archetype can be of any gender and represents temptation or distraction that diverts the hero from their path.
Catwoman in the Batman movies often plays the role of a temptress to Batman, combining allure with a morally ambiguous character.
Many of the Bond Girls in the James Bond films serve as temptresses, combining allure and mystery and often leading Bond into dangerous situations.
The Indiana Jones variation would be Elsa from Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade .
One of the best examples of the Tempter playing a more pivotal role in the story is Avery Tolar in The Firm . He’s a senior partner at the law firm Bendini, Lambert & Locke. His role is crucial in seducing the protagonist, Mitch McDeere, into the luxurious and corrupt world of the law firm.
He has a charismatic and persuasive personality. He mentors Mitch and exposes him to the high-stakes, high-reward lifestyle that the firm offers, including wealth, prestige, and power. Tolar's character is complex. He is a nuanced character who embodies the charm and allure that the firm uses to entice and trap its young associates.
His influence on Mitch is significant, as he represents the allure of success and the moral compromises that often accompany it. Tolar's character effectively demonstrates how the tempter archetype can be used to explore themes of corruption, temptation, and ethical dilemmas in a narrative.
The character archetypes found within the h ero’s journey offer writers the ability to take universal character templates and mold them to fit into stories that embrace the monomyth structure or use it as a starting point to tell a compelling and engaging story.
Use them in whatever way you’d like. They can encompass the more traditional definition within your story, or you can use these archetypes to set up expectations and later subvert those expectations to create a more enthralling and surprising plot.
Read More: Is Joseph Campbell's "The Hero's Journey" Dead in Screenwriting Today?
CHECK OUT OUR PREPARATION NOTES SO YOU START YOUR STORY OFF ON THE RIGHT TRACK!
Ken Miyamoto has worked in the film industry for nearly two decades, most notably as a studio liaison for Sony Studios and then as a script reader and story analyst for Sony Pictures.
He has many studio meetings under his belt as a produced screenwriter, meeting with the likes of Sony, Dreamworks, Universal, Disney, Warner Brothers, as well as many production and management companies. He has had a previous development deal with Lionsgate, as well as multiple writing assignments, including the produced miniseries Blackout, starring Anne Heche, Sean Patrick Flanery, Billy Zane, James Brolin, Haylie Duff, Brian Bloom, Eric La Salle, and Bruce Boxleitner, the feature thriller Hunter’s Creed, and many Lifetime thrillers. Follow Ken on Twitter @KenMovies and Instagram @KenMovies76
Get Our Screenwriting Newsletter!
Get weekly writing inspiration delivered to your inbox - including industry news, popular articles, and more!
Facebook Comments
Free download.

Screenwriting Resources:

$ 15.00 Original price was: $15.00. $ 12.00 Current price is: $12.00. Add to cart
Popular Posts

Recent Posts

Next Related Post

Get Our Newsletter!
Developing your own script.
We'll send you a list of our free eCourses when you subscribe to our newsletter. No strings attached.
You Might Also Like

- Hidden Name
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Connect With Us
Writing competitions, success stories.
© 2024 ScreenCraft | An Industry Arts Company
Wait! Subscribe to get our free Newsletter
Join our community of over 100,000 screenwriters and get weekly inspiration delivered to your inbox.
Screenwriting Newsletter
Join our community of over 100,000 screenwriters and get weekly inspiration delivered to your inbox:
✓ Popular blog posts and industry news ✓ New ScreenCraft online events ✓ Screenplay competition announcements!
" * " indicates required fields
- Script Studio
- Movie Outline 3
- Movie Outline Ebook
- Hollywood Script Express
- Movie Reference Plugins
- Online Store
- Competitive Upgrade
- Version Upgrade
- Educational Solutions
- Volume & Site Licenses
- Screenwriting Contest
- Screenwriting Articles
- Screenplay Format
- Step Outlining
- Script Writing Glossary
- Screenwriting Books
- Entertainment Law
- Screenwriting Tips
- ScriptTips Blog
- MFA in Screenwriting Degrees
- Knowledge Base
- Product Video Tour
- Download Free Trial
- Download Updates
- Register Software
- Press Releases
- Endorsements & Testimonials
- Reseller Application

The Hero's Journey - Mythic Structure of Joseph Campbell's Monomyth
By dan bronzite, to structure or not to structure that is the question....
Every story has a beginning, a middle and an end. In the beginning you setup your hero (or heroine) and his story, then you throw something at him that is a great source of conflict and takes him into a whole heap of trouble. After facing many foes and overcoming various obstacles the hero saves the day and wins the girl. If only writing a movie was that easy... The thing is, there are many forms of structure and some writers subscribe to one formula, while others subscribe to another. Some try not to subscribe to any and see the whole idea of structure as "evil", feeling that a story should evolve organically without rules confining ideas or obstructing the creative flow.

In the end, a story should dictate the kind of structure it follows or whether it shouldn't follow a structure at all. There's no point trying to write a comedy and forcing the structure of a thriller upon it - it won't work. Well, theoretically it won't but I'm sure someone will find a way! Let your characters define the story and your story define your structure and then use a formula if necessary to tighten your script. The trick is to initially let the ideas flow without paying too much attention to structure and then in your second pass begin to focus your story and separate the wheat from the chaff.
The 12 Stages of The Hero's Journey
A popular form of structure derived from Joseph Campbell's Monomyth from his book The Hero With A Thousand Faces and adapted by Christopher Vogler is the Twelve Stage Hero's Journey . This is essentially a more detailed Character Arc for your story's hero which is overlayed onto the more traditional three-act structure that many successful Hollywood movies such as Star Wars and The Wizard of Oz when analyzed appear to follow.
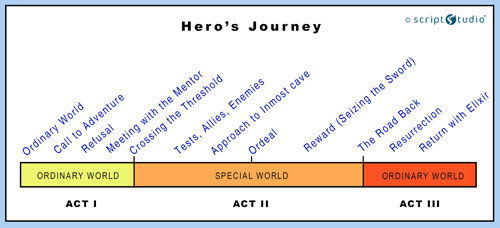
1. Ordinary World
This is where the Hero's exists before his present story begins, oblivious of the adventures to come. It's his safe place. His everyday life where we learn crucial details about our Hero, his true nature, capabilities and outlook on life. This anchors the Hero as a human, just like you and me, and makes it easier for us to identify with him and hence later, empathize with his plight.
2. Call To Adventure
The Hero's adventure begins when he receives a call to action, such as a direct threat to his safety, his family, his way of life or to the peace of the community in which he lives. It may not be as dramatic as a gunshot, but simply a phone call or conversation but whatever the call is, and however it manifests itself, it ultimately disrupts the comfort of the Hero's Ordinary World and presents a challenge or quest that must be undertaken.
3. Refusal Of The Call
Although the Hero may be eager to accept the quest, at this stage he will have fears that need overcoming. Second thoughts or even deep personal doubts as to whether or not he is up to the challenge. When this happens, the Hero will refuse the call and as a result may suffer somehow. The problem he faces may seem to much to handle and the comfort of home far more attractive than the perilous road ahead. This would also be our own response and once again helps us bond further with the reluctant Hero.
4. Meeting The Mentor
At this crucial turning point where the Hero desperately needs guidance he meets a mentor figure who gives him something he needs. He could be given an object of great importance, insight into the dilemma he faces, wise advice, practical training or even self-confidence. Whatever the mentor provides the Hero with it serves to dispel his doubts and fears and give him the strength and courage to begin his quest.
5. Crossing The Threshold
The Hero is now ready to act upon his call to adventure and truly begin his quest, whether it be physical, spiritual or emotional. He may go willingly or he may be pushed, but either way he finally crosses the threshold between the world he is familiar with and that which he is not. It may be leaving home for the first time in his life or just doing something he has always been scared to do. However the threshold presents itself, this action signifies the Hero's commitment to his journey an whatever it may have in store for him.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
Now finally out of his comfort zone the Hero is confronted with an ever more difficult series of challenges that test him in a variety of ways. Obstacles are thrown across his path; whether they be physical hurdles or people bent on thwarting his progress, the Hero must overcome each challenge he is presented with on the journey towards his ultimate goal. The Hero needs to find out who can be trusted and who can't. He may earn allies and meet enemies who will, each in their own way, help prepare him for the greater ordeals yet to come. This is the stage where his skills and/or powers are tested and every obstacle that he faces helps us gain a deeper insight into his character and ultimately identify with him even more.
7. Approach To The Inmost Cave
The inmost cave may represent many things in the Hero's story such as an actual location in which lies a terrible danger or an inner conflict which up until now the Hero has not had to face. As the Hero approaches the cave he must make final preparations before taking that final leap into the great unknown. At the threshold to the inmost cave the Hero may once again face some of the doubts and fears that first surfaced upon his call to adventure. He may need some time to reflect upon his journey and the treacherous road ahead in order to find the courage to continue. This brief respite helps the audience understand the magnitude of the ordeal that awaits the Hero and escalates the tension in anticipation of his ultimate test.
The Supreme Ordeal may be a dangerous physical test or a deep inner crisis that the Hero must face in order to survive or for the world in which the Hero lives to continue to exist. Whether it be facing his greatest fear or most deadly foe, the Hero must draw upon all of his skills and his experiences gathered upon the path to the inmost cave in order to overcome his most difficulty challenge. Only through some form of "death" can the Hero be reborn, experiencing a metaphorical resurrection that somehow grants him greater power or insight necessary in order to fulfill his destiny or reach his journey's end. This is the high-point of the Hero's story and where everything he holds dear is put on the line. If he fails, he will either die or life as he knows it will never be the same again.
9. Reward (Seizing The Sword)
After defeating the enemy, surviving death and finally overcoming his greatest personal challenge, the Hero is ultimately transformed into a new state, emerging from battle as a stronger person and often with a prize. The Reward may come in many forms: an object of great importance or power, a secret, greater knowledge or insight, or even reconciliation with a loved one or ally. Whatever the treasure, which may well facilitate his return to the Ordinary World, the Hero must quickly put celebrations aside and prepare for the last leg of his journey.
10. The Road Back
This stage in the Hero's journey represents a reverse echo of the Call to Adventure in which the Hero had to cross the first threshold. Now he must return home with his reward but this time the anticipation of danger is replaced with that of acclaim and perhaps vindication, absolution or even exoneration. But the Hero's journey is not yet over and he may still need one last push back into the Ordinary World. The moment before the Hero finally commits to the last stage of his journey may be a moment in which he must choose between his own personal objective and that of a Higher Cause.
11. Resurrection
This is the climax in which the Hero must have his final and most dangerous encounter with death. The final battle also represents something far greater than the Hero's own existence with its outcome having far-reaching consequences to his Ordinary World and the lives of those he left behind. If he fails, others will suffer and this not only places more weight upon his shoulders but in a movie, grips the audience so that they too feel part of the conflict and share the Hero's hopes, fears and trepidation. Ultimately the Hero will succeed, destroy his enemy and emerge from battle cleansed and reborn.
12. Return With The Elixir
This is the final stage of the Hero's journey in which he returns home to his Ordinary World a changed man. He will have grown as a person, learned many things, faced many terrible dangers and even death but now looks forward to the start of a new life. His return may bring fresh hope to those he left behind, a direct solution to their problems or perhaps a new perspective for everyone to consider. The final reward that he obtains may be literal or metaphoric. It could be a cause for celebration, self-realization or an end to strife, but whatever it is it represents three things: change, success and proof of his journey. The return home also signals the need for resolution for the story's other key players. The Hero's doubters will be ostracized, his enemies punished and his allies rewarded. Ultimately the Hero will return to where he started but things will clearly never be the same again.
Structuring With Color Using Script Studio's PowerView
Script Studio includes five default customizable templates:
- Hero's Journey
- 3 Act Screenplay
- 5 Act Stage Play
- One Hour TV Drama
- Half-Hour TV Sitcom
Each sample template is designed to help you structure your story and they include comprehensive information about each section, helping you understand how a particular type of story narrative works. They are, however, merely a guide and should not be rigidly adhered to. Creativity is far more important than sticking to a "formula" but they can help you pace your story and troubleshoot rewrites.
The default templates can be modified to suit your project's needs and you can even create your own templates from scratch or save templates from one project for use in another. Download a FREE Demo of Script Studio to see how its powerful screenplay formatting, character development and story structuring tools can help you make a better script!
About Dan Bronzite
Dan is a produced screenwriter and award-winning filmmaker , CEO of Buckle Up Entertainment , Nuvotech and creator of Script Studio screenwriting software . His writingcredits and written numerous specs and commissioned feature scripts including screenplay adaptations of Andrea Badenoch's Driven and Irvine Welsh's gritty and darkly comic novel Filth . Dan is a contributor to Script Magazine and has also directed three award-winning short films including his most recent All That Glitters which garnered over 50 international film festival selections and 32 awards. His supernatural horror feature Long Time Dead for Working Title Films was released internationally through Universal and his spec horror Do or Die sold to Qwerty Films. He is currently setting up his directorial feature debut and various US and UK feature and series projects.

New Release: Script Studio

Buy Script Studio Online

What the Pros Say...
I have tried every software application imaginable in quest of the perfect way to write a movie and when I put Movie Outline on my Mac I came to the end of the rainbow. Kieth Merrill Academy Award® Winner
I use Movie Outline all the time. It has many powerful features, is easy to use and makes writing and formatting a screenplay a breeze. No script writer should be without it. Kevin Williamson Screenwriter – Scream
If you're looking for a tool to help you nurture your idea for a movie into an actual shooting script I recommend this program without hesitation. Professor Richard Walter Chairman of the UCLA Graduate Screenwriting Program
This is the most complete package I've seen for the screenwriter in one application from outline to final draft. I recommend this program to all scribes – from novice to pro. Karl Iglesias UCLA Instructor & Author
I thoroughly enjoy working with Movie Outline and find it easy to use, well designed, helpful and entertaining. If you're a novice or a seasoned pro, this program can aid greatly in your creative process. Marc Scott Zicree Writer – The Next Generation
Movie Outline does a terrific job of helping writers organize their development process from beginning to end and has effectively raised the bar in the screenwriting software arena. Sean Kennelly Creative Screenwriting
Upgrade From Movie Outline

30 Day Money Back Guarantee

- wizard of oz
- character arc
- hero's journey
- ordinary world
Products & Services
- Hollywood Deconstructed Ebook
- Copyright Registration
- Script Copying & Shipping
Downloads & Demos
- Movie Outline Video Tour
- Compare Screenwriting Software
- Press Kit & Graphics
- Software Updates
- Upgrade Software
- Software Requirements
Screenwriting Resources
- Screenwriting Competition
- Screenplay Software
Company & Support
- Press & News
- Product Reviews
- Authorized Resellers
12 Stages of a Hero Journey
This essay about Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey outlines the twelve stages of this narrative framework, illustrating how a hero moves from an ordinary world to a realm of challenges and returns transformed. It starts with the hero in a familiar setting, facing a call to adventure which they initially refuse. With guidance from a mentor, they cross into an unknown world, facing tests and forming alliances. The central challenge occurs at the narrative’s midpoint, after which the hero receives a reward. The return to the ordinary world involves protecting this reward and a final resurrection where the hero must prove their transformation. The essay concludes with the hero’s return, bearing new wisdom or power. Campbell’s model not only serves as a blueprint for storytelling across cultures but also mirrors personal growth and life’s challenges, emphasizing the universal relevance of these narratives.
How it works
Joseph Campbell’s concept of the Hero’s Journey, as articulated in his influential work “The Hero with a Thousand Faces,” has embedded itself deeply within the fabric of narrative storytelling. This framework, comprising twelve stages, sketches the archetypal journey of a hero who ventures from an ordinary world into a realm of supernatural wonders, confronts formidable challenges, and returns transformed. The elucidation of these stages enriches our understanding of narrative structures and offers profound insights into human psychology and the universal process of transformation.
The journey begins in the Ordinary World, where the hero’s initial state of normalcy is depicted. It is in this familiar setting that they experience the Call to Adventure, which disrupts their regular life with an invitation to face the unknown. Often, heroes exhibit a Refusal of the Call, where fear, insecurity, or a strong sense of duty hinders their willingness to engage with this new quest. However, the arrival of a Mentor brings wisdom, encouragement, and sometimes magical gifts that equip the hero for the trials ahead, nudging them towards Crossing the First Threshold into the unknown.
As the hero advances into new territories, they navigate a series of Tests, form Allies, and confront Enemies. These experiences serve as preparation for the greater ordeals that lie ahead. Approaching the Inmost Cave, the hero must make significant preparations, facing setbacks and inner conflicts that test their resolve and readiness for the central challenge of their adventure.
The Ordeal, often positioned at the narrative’s midpoint, presents a formidable challenge that threatens the hero’s survival. This critical confrontation demands everything the hero has learned thus far. Upon surviving, the hero claims a Reward, which might be a crucial insight, a powerful artifact, or a significant personal transformation, marking their capability to face the final parts of their journey.
The hero then takes The Road Back to their Ordinary World, a journey that can be as fraught with danger and challenges as their initial departure. This stage often involves a pursuit that forces the hero to protect their reward. The Resurrection represents a final cleansing and rebirth, a test where the hero must prove that they have transformed by applying all their lessons and insights.
Finally, the hero Returns with the Elixir, bringing newfound wisdom, power, or perhaps a literal token from their journey back to the Ordinary World. This return signifies the completion of their cycle of growth and the potential to improve the lives of others with the knowledge or power they have gained.
The Hero’s Journey, with its deep roots in mythological studies, continues to be a dynamic tool for understanding storytelling across cultures and epochs. It resonates because it parallels the human experience of growth through adversity, reflecting our own life’s quests for meaning and transformation. As such, it transcends the boundaries of mere storytelling to offer a lens through which to view our own life’s journeys, portraying the indomitable human spirit and its unending quest for improvement. Through Campbell’s framework, we not only see a formula for crafting compelling narratives but also a map for personal development and understanding the transformative adventures of our lives.
Cite this page
12 Stages Of A Hero Journey. (2024, May 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/12-stages-of-a-hero-journey/
"12 Stages Of A Hero Journey." PapersOwl.com , 1 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/12-stages-of-a-hero-journey/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). 12 Stages Of A Hero Journey . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/12-stages-of-a-hero-journey/ [Accessed: 3 May. 2024]
"12 Stages Of A Hero Journey." PapersOwl.com, May 01, 2024. Accessed May 3, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/12-stages-of-a-hero-journey/
"12 Stages Of A Hero Journey," PapersOwl.com , 01-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/12-stages-of-a-hero-journey/. [Accessed: 3-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). 12 Stages Of A Hero Journey . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/12-stages-of-a-hero-journey/ [Accessed: 3-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Joseph Campbell explains: 4 Joseph Campbell, The Hero's Journey: Joseph Campbell On His Life And Work, 1990. The call to adventure signifies that destiny has summoned the hero and transferred his spiritual center of gravity from within the pale of this society to a zone unknown. Step 3: Refusal of the Call
Joseph Campbell. & the Hero's Journey. A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow men. The Hero With A Thousand Faces 23.
Joseph Campbell's Hero's Journey, while based on his study of mythology around the world, can be applied to more than just myth. In fact, it's applied to film frequently. One of the clearest examples of Campbell's Hero's Journey is none other than George Lucas's film Star Wars: A New Hope (1977). To this film we now turn.
The Great Advisor. 7. Meeting the Goddess. At this point in the monomyth, our Hero needs a break to adjust perspective and digest the ways they've changed. It's here that they meet with an advisor, or a trusted individual, who will help them gain a better insight into the next steps of the journey.
The Hero's Journey is a narrative pattern identified by Joseph Campbell, most notably outlined in his book The Hero with a Thousand Faces . This pattern of adventure and transformation is a universal one that runs through all kinds of mythic traditions across the world. Christopher Vogler has si
Popularized by mythologist Joseph Campbell in his book The Hero With a Thousand Faces, the Hero's Journey is a story structure that has been used to tell exciting and captivating stories for centuries.Campbell, a literature professor, found that this was a common mythic structure. It's widely known by the moniker the Hero's Journey, but this name didn't come around until well after ...
The Hero's Journey: A Timeless Blueprint. The Hero's Journey, conceptualized by Joseph Campbell, isn't just a literary tool - it's the backbone of countless storytelling traditions. It has enabled writers and filmmakers to craft narratives that resonate deeply with audiences, regardless of cultural or temporal divides.
The Hero's Journey is a common story structure for modeling both plot points and character development. A protagonist embarks on an adventure into the unknown. They learn lessons, overcome adversity, defeat evil, and return home transformed. Joseph Campbell, a scholar of literature, popularized the monomyth in his influential work The Hero ...
3 The Hero's Journey Breakdown Joseph Campbell's 17-stage Monomyth was conceptualized over the course of Campbell's own text, The Hero with a Thousand Faces, and then later in the 1980s through two documentaries, one of which introduced the term The Hero's Journey. The first documentary, 1987's The Hero's Journey: The World of Joseph Campbell,
The hero's journey ends where it begins, back at the beginning after a quest of epic proportions. The 12 steps are separated into three acts: departure (1-5) initiation (5-10) return (10-1) The hero journeys through the 12 steps in a clockwise fashion. As Campbell explains:
There are different theories, and one of them was proposed by Joseph Campbell. It describes a path of personal development, which he called The Hero's Journey, that each of us lives at different times in our lives. The choice of a path would depend a lot on the energetic resonance of the person, their courage, and their bravery in the face of ...
Joseph Campbell & The Hero's Journey. In 1949, scholar Joseph Campbell published his 1st book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces. In this book, Campbell introduced us to his theory that myths from around the globe share a fundamental structure, the Monomyth. C ampbell formulated this theory over 5 years, spending 9 hours a day reading mythology ...
View the full video and lesson at: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-makes-a-hero-matthew-winklerTo learn about how to leverage myth-making in marketing head ov...
The very first hero's journey arc was created by Joseph Campbell in 1949. It contained the following 17 steps: The Call to Adventure: The hero receives a call or a reason to go on a journey. Refusal of the Call: The hero does not accept the quest. They worry about their own abilities or fear the journey itself.
Here's an overview of all of the 17 steps of Joseph Campbell's Hero's Journey: Act One: The Departure. The Call to Adventure. Refusal of the Call. Supernatural Aid. The Crossing of the First Threshold. Belly of the Whale. Act 2: The Initiation: The Road of Trials.
This is a quick summary of The Hero's Journey stages by Joseph Campbell.Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCDlC2yGOv2RfN5W9moPZN1Q?ab_channel=RAWSpi...
The hero's journey is an archetypal narrative structure found in stories from cultures all over the world. Because it's such a universal narrative structure, the hero's journey is also known as the "monomyth"—the single great story with many variations. The term was coined by Joseph Campbell, an American writer and editor who was ...
12 Steps In Hero's Journey: The Ordinary World; ... Joseph Campbell hero's journey can be used as a lens to identify the various challenges and opportunities that are instrumental to successful women's leadership. This process of personal transformation is a roadmap for professional success. Women need appropriate tools and resources that ...
On Tuesday, March 22nd, 2016, The World Champion Of Public Speaking Don Johnson inspired the audience with 1-hour presentation on 17 Stages of The Hero's Journey. If you master these 17 stages, you will become a proficient storyteller. 1. The Call to Adventure. The hero starts in the ordinary world and gets a call, sometimes from another person ...
In this segment from the Netflix series Myths & Monsters, learn about Joseph Campbell's theories surrounding myths, storytelling and The Hero's Journey. In J...
The Hero's Journey is a famous template for storytelling, mapping a hero's adventurous quest through trials and tribulations to ultimate transformation. A portrait of Joseph Campbell (©Joseph Campbell Archives and Library); Christopher Vogler's model of the Hero's Journey from Myths and Movies (1999) by Stuart Voytilla.
Christopher Vogler's Interpretation of the Hero's Journey. When Christopher Vogler, a development executive and screenwriter at Disney, was inspired by Joseph Campbell's concept of the story monomyth, he crafted a seven-page memo for Disney's development team and incoming screenwriters. This memo, A Practical Guide to Joseph Cambell's The Hero with a Thousand Faces, laid the groundwork for ...
The phrase "the hero's journey", used in reference to Campbell's monomyth, first entered into popular discourse through two documentaries. The first, released in 1987, The Hero's Journey: The World of Joseph Campbell , was accompanied by a 1990 companion book, The Hero's Journey: Joseph Campbell on His Life and Work (with Phil Cousineau and ...
The 12 Stages of The Hero's Journey. A popular form of structure derived from Joseph Campbell's Monomyth from his book The Hero With A Thousand Faces and adapted by Christopher Vogler is the Twelve Stage Hero's Journey. This is essentially a more detailed Character Arc for your story's hero which is overlayed onto the more traditional three-act ...
Joseph Campbell's concept of the Hero's Journey, as articulated in his influential work "The Hero with a Thousand Faces," has embedded itself deeply within the fabric of narrative storytelling. This framework, comprising twelve stages, sketches the archetypal journey of a hero who ventures from an ordinary world into a realm of ...