

Countries most dependent on tourism
Travel to many top destinations around the world was severely curtailed or even stalled for much of 2020 as the world grappled with the coronavirus pandemic. A year later, these locations are beginning to welcome the return of visitors.
Stacker consulted the World Bank’s TCdata360 database released in 2020 in order to rank the 50 countries most dependent on tourism. To make the list, countries had to be a member of the United Nations. Rankings were determined by the percentage that tourism contributes to the GDP, with all monetary values given in U.S. dollars. We've additionally layered in context around what draws tourists to these locations.
As you could expect, many of the spots are islands in places such as the Caribbean, the South Pacific, and the Indian Ocean. Tourists are drawn by the warm weather, the fine beaches, and outdoor activities such as swimming and hiking. Others are in Europe and Africa, where travelers seek out cultural experiences and adventures.
Keep reading to discover which countries are most dependent on tourism.

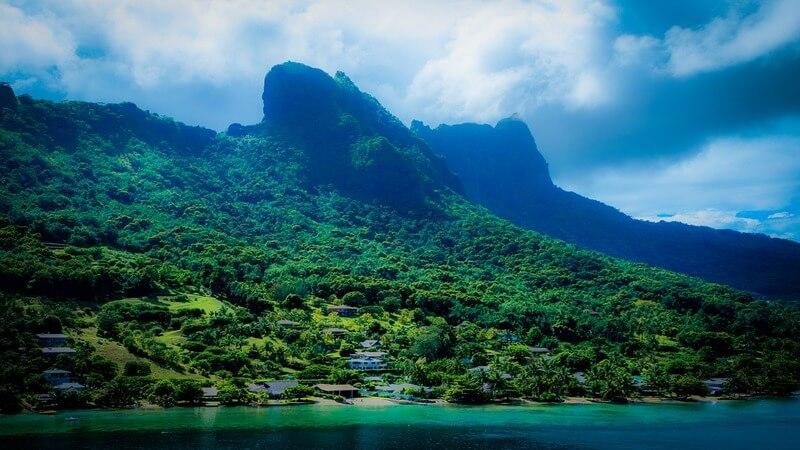
#50. Lesotho
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $320.6 million (13.7% of total GDP; 821.9% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 92,300 (13% of total jobs)
Lesotho is beautiful, culturally rich, and features affordable accessibility from South Africa. The country’s highlands offer top-rate hiking, mountain lodges, and trading posts. The footprint of one of the largest dinosaurs believed to have lived on the continent was found in the country’s Roma Valley in 2016. Lesotho features nature preserves and Qacha’s Nek Snake Park.

#49. Syrian Arab Republic
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $2.4 billion (14% of total GDP; 6.2% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 177,100 (8.3% of total jobs)
Before Syria’s decade-long civil war , which drew in the Islamic State and al-Qaeda, tourists flocked to Damascus’ old streets and the country’s historic sites. They visited Syria’s largest market, the al-Hamidiyah Souq , which is inside the old walled city of Damascus. Elsewhere, tourists traveled to the ancient city Palmyra; the Bosra theater, a large ancient Roman theater; and the citadels of Homs and Aleppo.

#48. Namibia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $1.9 billion (14.1% of total GDP; 1.4% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 103,000 (14.2% of total jobs)
Namibia takes its name from the world's oldest desert, the Namib , and its landscape is varied, from the mountains inland, to rivers, canyons, and the plains of the Kalahari. A big draw is the chance to watch wildlife at Etosha National Park, including big cats, elephants, and black rhinos. It gained independence in 1990 from South Africa after a war of almost 25 years.

#47. Tunisia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $5.9 billion (14.4% of total GDP; 19.2% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 478,300 (13.2% of total jobs)
Fodor’s Travel calls Tunisia a “fascinating melange” of a northern African country, an Islamic one since the first century A.D., and a former French colony. Its capital, Tunis, incorporates the ancient remains of Carthage, founded by the Phoenicians in the 8th century B.C., and its old walled medina includes souqs, palaces, and mosques. Another trip to take: Jeep safaris to small Berber villages.

#46. Panama
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $9 billion (14.6% of total GDP; 97.5% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 273,900 (14.6% of total jobs)
From beaches to parks to cultural sites, Panama offers tourists a wealth of experiences . Visitors can see the oldest Spanish fort and the first European settlement in the Pacific, meet two of the country’s indigenous people, the Guna and the Emberá, and learn more about their well-preserved traditions or try the food of Panama’s Afro-Caribbean community. And of course, there is the Panama Canal, starting at the visitor center at Miraflores.

#45. Austria
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $62.3 billion (14.6% of total GDP; 2.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 717,000 (15.9% of total jobs)
Austria is rich with attractions, from Renaissance palaces such as the Schloss Ambras in Innsbruck, to hikes in the Alps. Tourists can visit the Staatsoper , Vienna’s opera and ballet hall, watch the Lipizzaner stallions at the Spanish Riding School perform, or check out the largest accessible ice caves in Eisriesenwelt. See where Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was inspired by the old town in Salzburg or painter Gustav Klimt by the light in Attersee.

- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $60 million (14.8% of total GDP; 90% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 5,300 (15.9% of total jobs)
Tonga is made up of 176 islands, 40 of them inhabited, so there are many places to explore. The archipelago offers beaches, rainforests, coral atolls, active volcanoes, and ocean activities like kayaking, snorkeling, sailing, and fishing. The islands’ monarchy is the only surviving one in the South Pacific and is more than 1,000 years old. The kingdom observes Sunday as a day of rest and businesses and shops are closed by law.

- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $201.9 billion (14.9% of total GDP; 10.6% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 2.9 million (15% of total jobs)
Spain has a myriad of attractions : the beaches of the Canary Islands, the Gaudi architecture of Barcelona, flamenco shows, and Spanish guitar music in Seville, Granada’s Alhambra , the palace built by the Moors, and the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao in Basque country. In the north, pilgrims each year follow the St. James’ Way to Santiago de Compostela, the capital of Galicia, and its cathedral.

#42. Honduras
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $3.5 billion (15.1% of total GDP; 62.8% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 538,800 (13.3% of total jobs)
Honduras has white beaches, the world’s second-largest barrier reef, pine-covered mountains, and white-water rivers. Visitors can see Mayan ruins or colonial cities, fortresses and bird reserves, take a coffee tour or one of a cigar factory, or go diving or bird watching.

#41. Azerbaijan
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $5.9 billion (15.1% of total GDP; 144.3% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 636,800 (13.8% of total jobs)
Azerbaijan’s capital, Baku , is on the edge of the Caspian Sea. Its walled Old City or Icherisheher includes its oldest structure, the Maiden Tower, and the 15th-century Palace of the Shirvanshahs. Outside of the capital, tourists can visit traditional villages, hike in the Caucasus Mountains, or explore Sheki, once a stop on the Silk Road. Armenia and Azerbaijan reached a peace agreement in late 2020 over the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region.

#40. Estonia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $4.1 billion (15.5% of total GDP; 2.4% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 100,500 (15.5% of total jobs)
Estonia promotes its capital, Tallinn, as the best-preserved medieval city in Northern Europe. The country is about 50% forest, with more than 2,000 islands. You'll find traces of Viking culture, and the Estonian Song Celebration, which dates to 1869, attracts thousands of singers every five years.

#39. Mexico
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $191 billion (16.1% of total GDP; 18.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 8.8 million (16.6% of total jobs)
Mexico is famous for its beaches , including Cancun or Playa del Carmen along the Caribbean Sea, and those of Oaxaca on the Pacific Ocean. There are archaeological sites to explore, Chichén Itzá and Tulum on the Yucatan Peninsula, or the ancient city of Teotihuacán, where you'll find the pyramids of the sun and the moon. In Mexico City , most tourist attractions are in the historic city center.

#38. Madagascar
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $1.8 billion (16.2% of total GDP; 141.1% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 797,500 (13.6% of total jobs)
Five percent of all known plant and animal species can be found on the island and only here, the Lonely Planet guide notes. It is best known for the lemur but there also are mongoose, baobabs, sharks, orchids, and turtles. The landscape is varied, from desert to rainforest, and there are national parks to explore and remote resorts to visit.

#37. Armenia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $1.9 billion (16.2% of total GDP; 274.4% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 169,300 (14.4% of total jobs)
Armenia promotes its long winemaking tradition , which has seen renewed interest in the last 10 years with wine bars, wine festivals, and winery tours. A 6,100-year-old winery was found in 2007. Other attractions: hiking, caving, rope jumping, and other outdoor activities or explore the country’s history through its fortresses, petroglyphs, and other historic sites. Armenia and Azerbaijan reached a peace agreement in late 2020 over the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region.

#36. Dominican Republic
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $13.6 billion (17.2% of total GDP; 6.3% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 696,500 (15.9% of total jobs)
This Caribbean island has nearly 1,000 miles of coastline, and 250 miles of pristine beaches. A white marlin tournament is held in May. In the capital, Santo Domingo, tourists can visit Colonial City , the first European settlement of the Americas. Founded by Bartholomew Columbus, Christopher Columbus’ brother, in 1498, it was originally called La Isabela.

#35. Portugal
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $40 billion (17.8% of total GDP; 64.9% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 1 million (21.1% of total jobs)
Portugal was founded in the 12th century in the north in Porto and the surrounding area. Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia , across the Douro River, are known for port, which is shipped around the world, and there are many places to sample the fortified wine. Visitors can take a wine-tasting trip through the Douro Valley. Lisbon , the country’s capital, is characterized by its seven hills and cobblestone alleys.

#34. New Zealand
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $33.9 billion (17.9% of total GDP; 5.8% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 526,900 (21.8% of total jobs)
New Zealand consists of the North Island and the South Island and both have top things for travelers to do. Explore the capital, Wellington, and its food scene; visit the Waitomo Caves; and hike the Pouakai Crossing in Egmont National Park. On the South Island, take in Aoraki/Mount Cook, New Zealand’s highest peak, and the Victorian Larnach Castle in Dunedin.

#33. Morocco
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $20.8 billion (18.6% of total GDP; 69.8% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 1.9 million (16.4% of total jobs)
Visitors come to see the cities of Marrakesh, Fez, and Tangier , and shop in the souqs or markets. There are archaeological sites to see such as the Roman city of Volubilis or Lixus and its ruins of an amphitheatre and a mosaic depicting Neptune. Hike in the desert and spend the night in luxury tents. After the desert, there are the mountains, the High Atlas and the Rif , to explore.

#32. Lebanon
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $9.8 billion (19.1% of total GDP; 285.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 386,800 (18.4% of total jobs)
Lebanon offers swimming in the Mediterranean Sea and skiing in the mountains. It was home to the Phoenicians in its coastal cities of Byblos, Sidon, and Tyre, and the inland city of Baalbek, where today visitors can see the remains of Roman temples. But Lebanon’s economy is in freefall , and Beirut is still rebuilding from the explosion in its port in 2020 that damaged much of the city, including its historic homes.

#31. Jordan
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $8.2 billion (19.7% of total GDP; 12.7% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 229,500 (20.1% of total jobs)
Amman, Jordan’s capital, is built on a series of hills, with the Citadel on the highest. Among the country's attractions: Petra , the Nabataean city carved into sandstone; the desert landscape of Wadi Rum ; Aqaba, a city on the Red Sea; the Roman ruins at Jerash; and the Dana Biosphere Reserve.

#30. The Gambia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $225.6 million (20.2% of total GDP; 55.3% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 109,700 (17% of total jobs)
Visitors to The Gambia come for the beaches on the Atlantic Ocean, tours of its villages and the River Gambia, and craft and wood carving markets. The Gambia has six protected areas for its more than 500 species of birds, and other national parks for wildlife, including monkeys and the threatened hippopotamus.

#29. Greece
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $41.8 billion (20.2% of total GDP; 55.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 987,200 (25.4% of total jobs)
Tourists are drawn to the sites of ancient Greece , the Acropolis in Athens, the Parthenon and the Erechtheion temple, and other historic places throughout the country. There are also the islands to visit , Santorini, Mykonos, and the Cyclades, among them.

#28. Kiribati
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $40 million (20.9% of total GDP; 85.6% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 5,300 (17.3% of total jobs)
Kiribati is made up of 33 islands in the central Pacific Ocean, 21 of which are inhabited. Part of Micronesia, the republic offers fishing, surfing, diving and snorkeling, bird watching, and picturesque tours. The islands were invaded by the Japanese in 1941 and there are a number of World War II historical sites.

#27. Philippines
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $70.3 billion (21.1% of total GDP; 77.6% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 8.3 million (19.1% of total jobs)
The Philippines offer everything from beach resorts, surfing, and scuba diving to hiking in national parks. There are waterfalls, a marine reserve on Palaui Island, and a national park on Hundred Islands. The Yap-Sandiego House is a preserved historical Filipino house or there are festivals such as the Coconut Festival , a weeklong celebration honoring the patron saint, Paul the Hermit.

#26. Thailand
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $102.1 billion (22.1% of total GDP; 41.4% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 6.2 million (16.1% of total jobs)
Tourists come to Thailand for outstanding beaches, temples, and food. Eating tours showcase noodles in Bangkok or seafood in Phuket. Join a meditation retreat, visit a temple such as Wat Pho or Wat Phra Kaew, or observe the country’s religious festivals. Besides the coasts, there are 1,400 islands to explore.

#25. Cyprus
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $5 billion (23.1% of total GDP; 14.8% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 88,600 (23.3% of total jobs)
Cyprus has been divided since 1974 between the two-thirds controlled by Greek Cypriots and the one-third controlled by Turkish Cypriots. Most visitors head to the Greek section where they find beaches throughout, diving, sailing, and other water sports. Birdwatchers can look out for flocks of flamingos on the island’s salt lakes. Tourism in the northern, Turkish section is less developed but prices are lower.

#24. Grenada
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $262.7 million (23.3% of total GDP; 0.3% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 10,500 (21.5% of total jobs)
Grenada is actually a state in the southern Caribbean made up of three islands —Grenada, Carriacou, and Petite Martinique—that calls itself the Spice Island. It has what it says is the world’s first underwater sculpture park, as well as waterfalls and white-sand beaches. Both the French and the British controlled the island and today it retains those influences as well as Amerindian and African customs.

#23. Mauritius
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $3.2 billion (23.4% of total GDP; 4% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 130,500 (22.4% of total jobs)
An island in the Indian Ocean, Mauritius is known for beaches, reefs, and lagoons. In the capital, Port Louis, tourists can visit Eureka House, a Creole-style house, or the Pamplemousses Botanical Garden , also known as the Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam Botanical Gardens, created in the 18th century. Take in the views from the Trou aux Cerfs volcano crater. In the interior of the island, which is mountainous, there is the Black River Gorges National Park, with hiking trails through rainforests and waterfalls.

#22. St. Vincent and the Grenadines
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $193.7 million (23.9% of total GDP; 18.2% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 9,700 (22% of total jobs)
St. Vincent and the Grenadines is made up of 36 volcanic islands north of Grenada, featuring white-sand beaches and visited by beach-goers and boaters. There are coral reefs around the islands, some of which are private, and opportunities for diving and snorkeling. The capital, Kingstown, has preserved its colonial buildings and cobblestoned streets.

#21. São Tomé and Príncipe
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $106.1 million (24.1% of total GDP; 226.1% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 14,800 (23.5% of total jobs)
São Tomé and Príncipe is an island country off the west coast of Africa, in the Gulf of Guinea, with beaches and rainforests. The islands, just north of the Equator, are part of a volcano chain. The Obo National Park makes up nearly 30% of the two islands and features more than 230 types of birds.

#20. Montenegro
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $1.2 billion (25.1% of total GDP; 54.9% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 39,200 (20% of total jobs)
The Budva Riviera along the Adriatic coast is one of the most popular spots in Montenegro. An old town in Budva, Stari Grad, features Venetian walls and marble streets. The summer Sea Dance Festival attracts international musicians and fans from around the world. The Bay of Kotor was an important cultural and artistic center in the Middle Ages.

#19. Croatia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $14.2 billion (25.1% of total GDP; 45% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 319,800 (23.4% of total jobs)
Old-town Dubrovnik is distinctive with its red-tiled roofs by the Adriatic Sea. Many of the tiles had to be replaced after the Balkan wars of the 1990s, and new ones were made in Toulouse, France. More recently, Croatia has become the backdrop of Game of Thrones , drawing a new category of tourists.

#18. Albania
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $3.6 billion (26.3% of total GDP; 176.1% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 302,500 (24.3% of total jobs)
Albania’s borders were closed during a large part of the 20th century, but that changed with the end of its communist government in 1992. Since then tourists have been discovering its beaches, castles, and Greek and Roman sites. Rough Guides recommends visiting Tirana, the capital, and booking a food tour to try the traditional Albanian dishes.

#17. St. Kitts and Nevis
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $263.7 million (26.8% of total GDP; 9.6% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 6,500 (25.6% of total jobs)
Lying between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, St. Kitts and Nevis is known for its beaches and mountains, a volcano that rises above rainforests, and offshore coral beds. Its capital is Basseterre , founded in 1627 as a French colony.

- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $3.3 billion (26.9% of total GDP; 14.1% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 55,100 (28.1% of total jobs)
The Maltese archipelago is south of Sicily and north of Africa at the center of the Mediterranean Sea. It is made up of three islands (Malta, Gozo, and Comino), and its capital is Valletta. Some top things to do : Explore the streets of its medieval capital, Mdina, known as the Silent City; take a cruise around Valletta’s Grand Harbor; or visit St. John’s Co-Cathedral and see the “Beheading of St John” by Caravaggio.

#15. Georgia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $4.9 billion (31.3% of total GDP; 107.5% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 489,100 (27.3% of total jobs)
Lonely Planet calls Georgia the most visited country in the South Caucasus and notes its varied landscapes and rich culture. Old churches, vineyards, restaurants, and wine bars in the capital, Tbilisi, are popular with tourists. One famous attraction: Vardzia , a cave monastery dating from the 12th century.

#14. Cambodia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $7.5 billion (31.6% of total GDP; 356.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 2.7 million (30.5% of total jobs)
The most famous religious landmark is the Temple at Angkor Wat . Another notable location is a museum filled with human skulls and bones , a remembrance of the 1.7 million people killed in the 1970s during the reign of the Khmer Rouge’s Pol Pot. Other places to visit: beaches, colonial towns, and forests.

#13. Jamaica
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $4.9 billion (33.7% of total GDP; 26.2% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 368,100 (30.5% of total jobs)
The Caribbean country of Jamaica is known for white-sand beaches and its reggae music, but also rivers, waterfalls, mountains, and plains. There are three main resort areas: Montego Bay, Negril, and Ocho Rios. The capital, Kingston, offers theater, music, and shopping.

#12. Iceland
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $8.9 billion (35% of total GDP; 75.5% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 70,400 (36.6% of total jobs)
The usual attractions of Iceland gained a new one in 2021, when a volcano erupted in the Geldingadalur region of Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula. It is about 25 miles from the capital city, Reykjavik. More typically visitors are enjoying the Northern Lights , geothermal spas, waterfall, and rides on the island’s distinctive Icelandic horses .

#11. Dominica
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $199.9 million (37.6% of total GDP; 59.2% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 12,900 (34.5% of total jobs)
This Caribbean island is branding itself “the nature island,” featuring its diving and snorkeling, hiking for all levels, rainforest spas, birding, fishing, and farm-to-table dining. There are three national parks , including Morne Trois Pitons, where Boiling Lake is believed to be the world’s second-largest fumarole, or opening in the Earth’s crust.

- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $2 billion (39.3% of total GDP; 28.1% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 117,200 (35.7% of total jobs)
Fiji is a South Pacific archipelago with more than 300 islands . On the water , visitors dive, surf, snorkel, kayak in the ocean, and raft on the river. There is hiking in the rainforests and visits to remote villages with overnight stays to get an understanding of Fiji culture. Fiji also has a large Indian community that celebrates Hindu festivals during the year.

#9. Barbados
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $2 billion (41.2% of total GDP; 9.5% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 54,000 (41.3% of total jobs)
Barbados has fine sandy beaches and surfing, gardens away from the coast, and lively nightlife. Its capital, Bridgetown , is a UNESCO World Heritage-listed site with more than 100 historic buildings, forts, and museums to visit.

- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $794 million (41.8% of total GDP; 81.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 61,400 (37.1% of total jobs)
In Belize , on the east coast of Central America, visitors can see the Mountain Pine Ridge Forest Reserve; the Lamanai, once a major Mayan city; the Belize Zoo; and Blue Hole, an underwater sinkhole off the coast. Belize has the second-largest barrier reef in the world, the largest being Australia’s.

#7. St. Lucia
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $654.2 million (43.3% of total GDP; 18.1% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 40,300 (52.4% of total jobs)
An island in the Caribbean, St. Lucia is known for the Pitons mountains on its coast. There are white-sand beaches, diving, and festivals such as Jounen Kwéyòl or Creole Day, distinguished by feasts and music throughout the night. Saint Lucia Jazz and Arts Festival attracts top musicians.

#6. Cabo Verde
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $807.1 million (44.4% of total GDP; 235.5% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 95,400 (38.9% of total jobs)
Cabo Verde is a chain of islands west of Senegal in the Atlantic Ocean, a mix of beaches, high mountains, and volcanic landscapes . The highest peak is Pico do Fogo , which is still an active volcano. There are music clubs and bars and colonial architecture to see in Mindelo on São Vicente.

#5. Vanuatu
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $380.4 million (45.9% of total GDP; 21.6% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 30,800 (39.2% of total jobs)
Vanuatu is a country in the South Pacific with about 80 islands. Visitors can go scuba diving in the coral reefs and explore the SS President Coolidge, a World War II troopship that sank as it tried to pass through the Segond Channel, forcing its evacuation. Community tours demonstrate ancient ways of living, dances, and other cultural heritage.

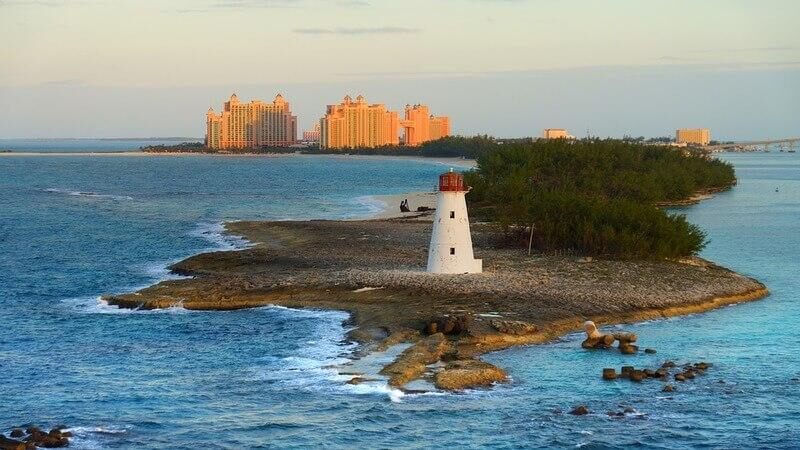
#4. The Bahamas
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $4.5 billion (48.3% of total GDP; 4.4% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 114,900 (56.2% of total jobs)
The Bahamas comprises 16 major islands in the Atlantic Ocean. Tourists can choose between exploring the capital, Nassau, enjoying Paradise Island, swimming with the wild pigs on Big Major Cay , or visiting Eleuthera’s pink-sand beaches.

#3. Antigua and Barbuda
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $806.1 million (52.4% of total GDP; 29.5% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 17,000 (46.2% of total jobs)
The islands , former British colonies in the Caribbean, both have beautiful beaches. Antigua is the busier of the two and the capital, St. John’s, is a port for cruise ships. It offers museums and colonial buildings to tour. Barbuda has the well-known Frigate Bird Sanctuary .

#2. Seychelles
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $999.9 million (64.2% of total GDP; 13.5% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 29,700 (63.7% of total jobs)
An archipelago of 115 granite and coral islands off East Africa in the Indian Ocean, the Seychelles boasts beaches, nature preserves, and coral reefs, and nature reserves. Among the wildlife are the giant Aldabra tortoises. The capital, Victoria, is on Mahé, which also has the Morne Seychellois National Park.

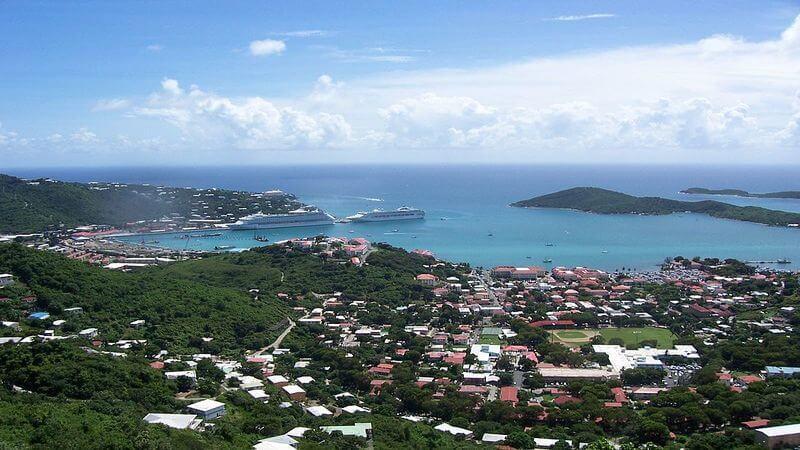
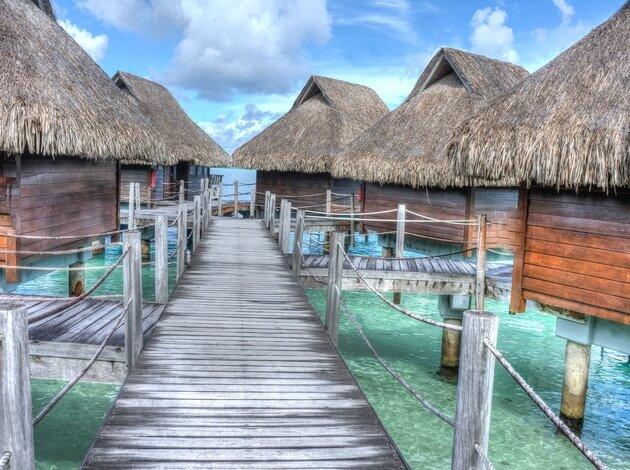
#1. Maldives
- Tourism total contribution to GDP: $3 billion (75.1% of total GDP; 44.2% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 80,400 (36.7% of total jobs) The Maldives is made up of 1,200 islands in the Indian Ocean, among them atolls, coral reefs, and coral islands. Only about 200 of them are inhabited. Tourists visit beaches and the reef formations for which the Maldives is known, and can go kayaking, snorkeling, and picnicking on one of the uninhabited islands. But the Maldives also is disappearing under the rising water caused by climate change.
Trending Now
Best drama movies from the last decade.

Best Law & Order SVU episodes

45 of the best college movies

Top 100 country songs of all time

The COVID-19 travel shock hit tourism-dependent economies hard
- Download the paper here

Subscribe to the Hutchins Roundup and Newsletter
Gian maria milesi-ferretti gian maria milesi-ferretti senior fellow - economic studies , the hutchins center on fiscal and monetary policy.
August 12, 2021
The COVID crisis has led to a collapse in international travel. According to the World Tourism Organization , international tourist arrivals declined globally by 73 percent in 2020, with 1 billion fewer travelers compared to 2019, putting in jeopardy between 100 and 120 million direct tourism jobs. This has led to massive losses in international revenues for tourism-dependent economies: specifically, a collapse in exports of travel services (money spent by nonresident visitors in a country) and a decline in exports of transport services (such as airline revenues from tickets sold to nonresidents).

This “travel shock” is continuing in 2021, as restrictions to international travel persist—tourist arrivals for January-May 2021 are down a further 65 percent from the same period in 2020, and there is substantial uncertainty on the nature and timing of a tourism recovery.
We study the economic impact of the international travel shock during 2020, particularly the severity of the hit to countries very dependent on tourism. Our main result is that on a cross-country basis, the share of tourism activities in GDP is the single most important predictor of the growth shortfall in 2020 triggered by the COVID-19 crisis (relative to pre-pandemic IMF forecasts), even when compared to measures of the severity of the pandemic. For instance, Grenada and Macao had very few recorded COVID cases in relation to their population size and no COVID-related deaths in 2020—yet their GDP contracted by 13 percent and 56 percent, respectively.
International tourism destinations and tourism sources
Countries that rely heavily on tourism, and in particular international travelers, tend to be small, have GDP per capita in the middle-income and high-income range, and are preponderately net debtors. Many are small island economies—Jamaica and St. Lucia in the Caribbean, Cyprus and Malta in the Mediterranean, the Maldives and Seychelles in the Indian Ocean, or Fiji and Samoa in the Pacific. Prior to the COVID pandemic, median annual net revenues from international tourism (spending by foreign tourists in the country minus tourism spending by domestic residents overseas) in these island economies were about one quarter of GDP, with peaks around 50 percent of GDP, such as Aruba and the Maldives.
But there are larger economies heavily reliant on international tourism. For instance, in Croatia average net international tourism revenues from 2015-2019 exceeded 15 percent of GDP, 8 percent in the Dominican Republic and Thailand, 7 percent in Greece, and 5 percent in Portugal. The most extreme example is Macao, where net revenues from international travel and tourism were around 68 percent of GDP during 2015-19. Even in dollar terms, Macao’s net revenues from tourism were the fourth highest in the world, after the U.S., Spain, and Thailand.
In contrast, for countries that are net importers of travel and tourism services—that is, countries whose residents travel widely abroad relative to foreign travelers visiting the country—the importance of such spending is generally much smaller as a share of GDP. In absolute terms, the largest importer of travel services is China (over $200 billion, or 1.7 percent of GDP on average during 2015-19), followed by Germany and Russia. The GDP impact for these economies of a sharp reduction in tourism outlays overseas is hence relatively contained, but it can have very large implications on the smaller economies their tourists travel to—a prime example being Macao for Chinese travelers.
How did tourism-dependent economies cope with the disappearance of a large share of their international revenues in 2020? They were forced to borrow more from abroad (technically, their current account deficit widened, or their surplus shrank), but also reduced net international spending in other categories. Imports of goods declined (reflecting both a contraction in domestic demand and a decline in tourism inputs such as imported food and energy) and payments to foreign creditors were lower, reflecting the decline in returns for foreign-owned hotel infrastructure.
The growth shock
We then examine whether countries more dependent on tourism suffered a bigger shock to economic activity in 2020 than other countries, measuring this shock as the difference between growth outcomes in 2020 and IMF growth forecasts as of January 2020, just prior to the pandemic. Our measure of the overall importance of tourism is the share of GDP accounted for by tourism-related activity over the 5 years preceding the pandemic, assembled by the World Travel and Tourism Council and disseminated by the World Bank . This measure takes into account the importance of domestic tourism as well as international tourism.
Among the 40 countries with the largest share of tourism in GDP, the median size of growth shortfall compared to pre-COVID projections was around 11 percent, as against 6 percent for countries less dependent on tourism. For instance, in the tourism-dependent group, Greece, which was expected to grow by 2.3 percent in 2020, shrunk by over 8 percent, while in the other group, Germany, which was expected to grow by around 1 percent, shrunk by 4.8 percent. The scatter plot of Figure 2 provides more striking visual evidence of a negative correlation (-0.72) between tourism dependence and the growth shock in 2020.

Of course, many other factors may have affected differences in performance across economies—for instance, the intensity of the pandemic as well as the stringency of the associated lockdowns. We therefore build a simple statistical model that relates the “growth shock” in 2020 to these factors alongside our tourism variable, and also takes into account other potentially relevant country characteristics, such as the level of development, the composition of output, and country size. The message: the dependence on tourism is a key explanatory variable of the growth shock in 2020. For instance, the analysis suggests that going from the share of tourism in GDP of Canada (around 6 percent) to the one of Mexico (around 16 percent) would reduce growth in 2020 by around 2.5 percentage points. If we instead go from the tourism share of Canada to the one of Jamaica (where the share of tourism in GDP approaches one third), growth would be lower by over 6 percentage points.
Measures of the severity of the pandemic, the intensity of lockdowns, the level of development, and the sectoral composition of GDP (value added accounted for by manufacturing and agriculture) also matter, but quantitatively less so than tourism. And results are not driven by very small economies; tourism is still a key explanatory variable of the 2020 growth shock even if we restrict our sample to large economies. Among tourism-dependent economies, we also find evidence that those relying more heavily on international tourism experienced a more severe hit to economic activity when compared to those relying more on domestic tourism.
Given data availability at the time of writing, the evidence we provided is limited to 2020. The outlook for international tourism in 2021, if anything, is worse, though with increasing vaccine coverage the tide could turn next year. The crisis poses particularly daunting challenges to smaller tourist destinations, given limited possibilities for diversification. In many cases, particularly among emerging and developing economies, these challenges are compounded by high starting levels of domestic and external indebtedness, which can limit the space for an aggressive fiscal response. Helping these countries cope with the challenges posed by the pandemic and restoring viable public and external finances will require support from the international community.
Read the full paper here.
Related Content
February 18, 2021
Eldah Onsomu, Boaz Munga, Violet Nyabaro
July 28, 2021
Célia Belin
May 21, 2021
The author thanks Manuel Alcala Kovalski and Jimena Ruiz Castro for their excellent research assistance.
Economic Studies
The Hutchins Center on Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Gian Maria Milesi-Ferretti, Alexander Conner
April 19, 2024
Belinda Archibong, Peter Blair Henry
April 18, 2024
Witney Schneidman
April 17, 2024
These are the 10 places that rely most on tourism for jobs

90% of Antigua's employment is related to the travel and tourism industry. Image: Unsplash
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Rosamond Hutt

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Travel and Tourism is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, fairer economies.
- Globally 10% of jobs and GDP were in travel and tourism in 2019.
- 197.5 million jobs in the industry could be at risk if coronavirus-related travel restrictions and quarantines remain in place, according to the World Travel & Tourism Council.
- Caribbean islands rely heavily on tourism for employment. More than 90% of jobs in Antigua and Barbuda in 2019 were in the sector.
Last year one in 10 people worked in travel and tourism-related jobs , contributing $8.9 trillion, or around 10.3%, to the global economy.
In the five years to 2019, the sector was responsible for one in four of all net new jobs created globally.
That was before COVID-19 struck. While many popular destinations are cautiously welcoming visitors again, the industry is continuing to haemorrhage jobs and revenues. And the worst may be yet to come.
Have you read?
Covid-19: these countries are most at risk from falling tourism, here are some of the innovative ways people are going on holiday during coronavirus, chart of the day: these countries normally have the highest international tourist numbers.
The United Nations World Tourism Organization estimated in May that international tourist numbers could fall 60-80% in 2020.
And some 197.5 million jobs in the sector could be lost , the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC) said in June. That figure was based on a “worst-case scenario” where barriers, such as blanket travel restrictions and quarantines, remain in place.
The first global pandemic in more than 100 years, COVID-19 has spread throughout the world at an unprecedented speed. At the time of writing, 4.5 million cases have been confirmed and more than 300,000 people have died due to the virus.
As countries seek to recover, some of the more long-term economic, business, environmental, societal and technological challenges and opportunities are just beginning to become visible.
To help all stakeholders – communities, governments, businesses and individuals understand the emerging risks and follow-on effects generated by the impact of the coronavirus pandemic, the World Economic Forum, in collaboration with Marsh and McLennan and Zurich Insurance Group, has launched its COVID-19 Risks Outlook: A Preliminary Mapping and its Implications - a companion for decision-makers, building on the Forum’s annual Global Risks Report.
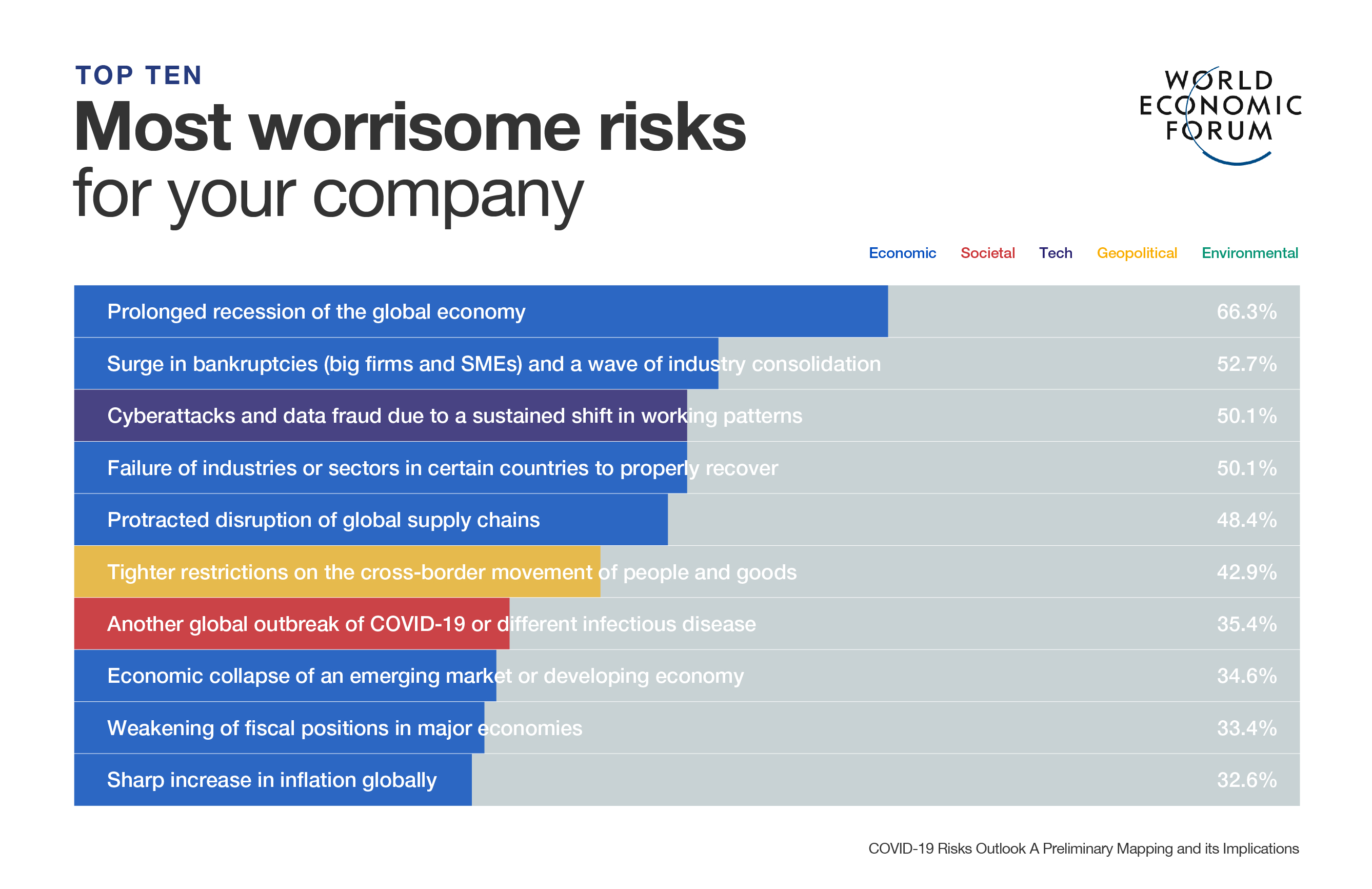
Companies are invited to join the Forum’s work to help manage the identified emerging risks of COVID-19 across industries to shape a better future. Read the full COVID-19 Risks Outlook: A Preliminary Mapping and its Implications report here , and our impact story with further information.
Lifeblood of economies
Travel and tourism is a big employer worldwide, but for some places it’s the main – even only – source of jobs and income

Caribbean islands rely heavily on travel and tourism for employment – the industry accounted for 90.7% of jobs in Antigua and Barbuda in 2019.
This is according to the latest WTTC report on the economic and employment impact of travel and tourism in 185 countries and 25 geographic or economic regions.
Next was Aruba, where tourism jobs made up 84.3% of total employment last year. St Lucia followed with 78.1%, then the US Virgin Islands (68.8%) and the British Virgin Islands (66.4%).
The glitzy Asian city of Macau (65.5%) and Indian Ocean paradise the Maldives (59.6%) were also on the list.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Industries in Depth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Nearly 15% of the seafood we produce each year is wasted. Here’s what needs to happen
Charlotte Edmond
April 11, 2024

How Paris 2024 aims to become the first-ever gender-equal Olympics
Victoria Masterson
April 5, 2024

5 ways CRISPR gene editing is shaping the future of food and health
Douglas Broom
April 3, 2024

How Japan is attracting digital nomads to shape local economies and innovation
Naoko Tochibayashi and Naoko Kutty
March 28, 2024

The Paris Olympics aims to be the greenest Games in history. Here's how

These vibrant new food dyes are 100% natural
- The Inventory
Support Quartz
Fund next-gen business journalism with $10 a month
Free Newsletters
These are the countries most reliant on your tourism dollars
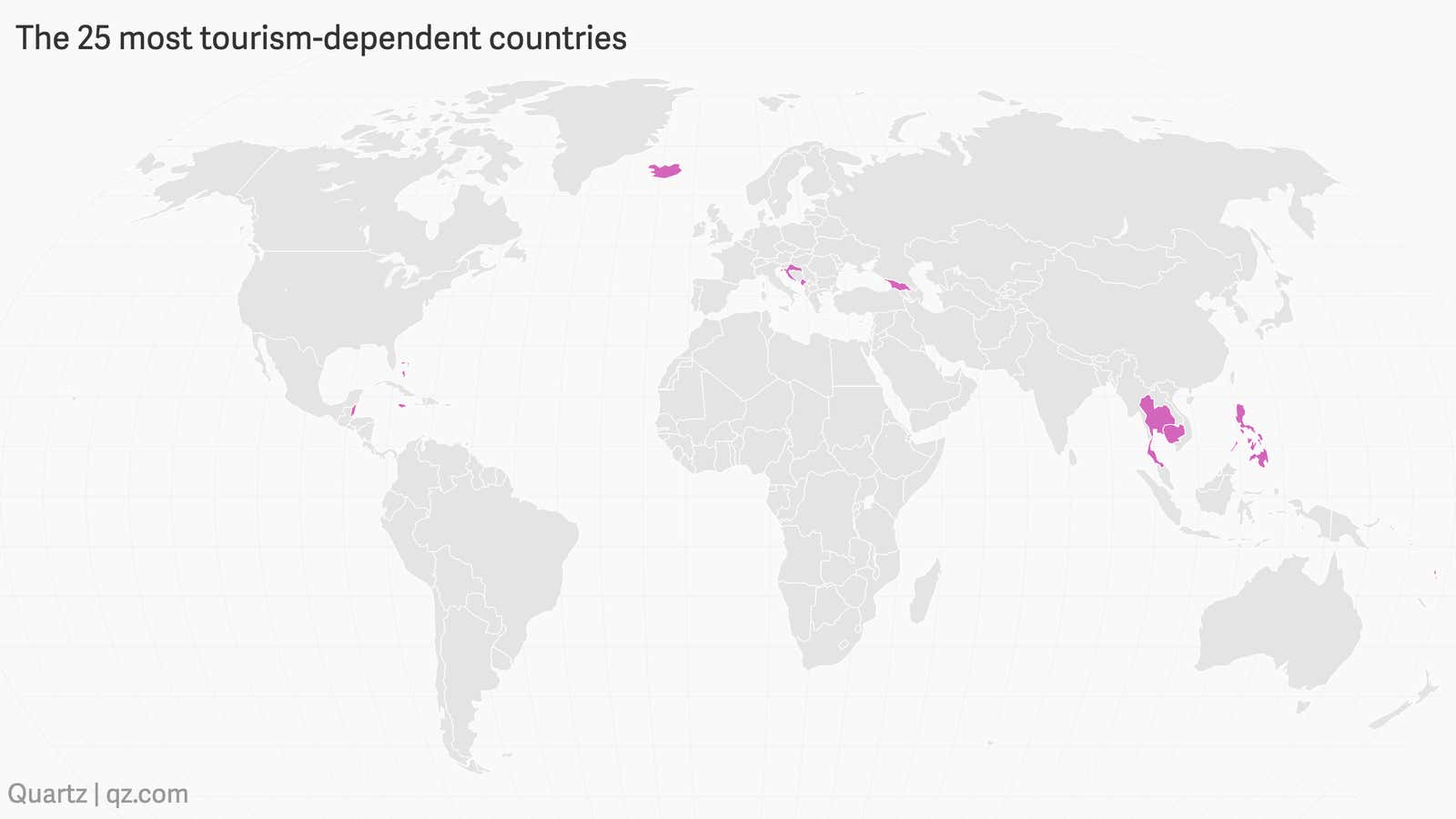
Almost 1.5 million people went to the Maldives in 2018. For these vacationers, their visits were restful opportunities to lie on beaches and suck down fruity drinks. For the island nation’s 430,000 people, they had a far more critical function: contributing more than a third of the country’s GDP.
The Maldives, located in the Indian Ocean, is the country most reliant on tourism. Around 20 others across the world derive more than 10% of their gross domestic product from tourism. Most are small, with a population well below a million people. The vast majority are in the developing world, where luxury resorts stand in stark relief to the reality of most locals.
Troublingly, more than half are islands and archipelagos. With few natural resources beyond pristine beaches and breathtaking views, tourism is an obvious economic focus. Unfortunately, these countries are extremely vulnerable to climate change, and have a huge amount to lose, including their tourist industry. They’re at high risk from rising sea levels obliterating resorts and coastal properties, the death of coral reef, and soil salinization threatening crops, as well as extreme weather events.
Source: The World Bank
📬 Sign up for the Daily Brief
Our free, fast, and fun briefing on the global economy, delivered every weekday morning.
The world’s most tourism-dependent countries
Rafat Ali, Skift
March 9th, 2013 at 4:02 AM EST
Fascinating list, if only to understand how vital the links -- literally -- to the outside world are for these countries, for their own economic growth.
When you’re a remote island, about the only means of building up an economy is tourism. World Travel & Tourism Council has come out with some data — along with its overall 2012-2013 numbers — that shows the extent to which these top tourism-dependent countries rely on that flow of tourists and the money they bring.
Beyond the GDP contribution that the tourists bring, this is also the largest sector for employment on these islands, as well as the largest investment sector in these countries.
In these top 10 countries, Caribbean, South Pacific and Indian Ocean island nations dominate, because of their remoteness from mainlands and also because they happen to be in temperate climate that encourages tourism. They have also developed good air and shipping links with mainland hubs, mainly as a result of their history under Western imperialism.
Among the few exceptions to the island rule is Macau, which might as well be a safe haven “island” for Chinese gambling-bound tourists, and has the highest proportion of GDP dependence on these travelers, along with being the biggest source of employment.
In the Western nations, only Ireland shows up on this list, as one of the top nations heavily investing in travel and tourism infrastructure.
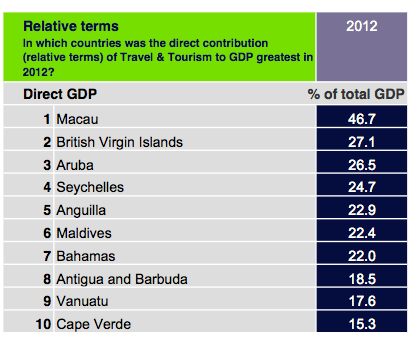
Without further ado, the world’s most tourism dependent countries, calibrated against four different measure of direct GDP contribution, employment, visitor exports (tourism dollars inflow compared to overall external inflow) and capital investment into the tourism economy:
The Daily Newsletter
Our daily coverage of the global travel industry. Written by editors and analysts from across Skift’s brands.
Have a confidential tip for Skift? Get in touch
Tags: economy , macau , tourism , wttc
Photo credit: Rendezvous Bay on the island of Anguilla. Andrea Zanivan / Flickr.com
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Global Health
Countries balance needed tourism with coronavirus concerns.

Joanna Kakissis

Eyder Peralta
Michael Sullivan
Nations that are heavily dependent on tourism are trying to walk a fine line between the need to reopen their beaches and resorts and the risk of importing more cases of the coronavirus.
DAVID GREENE, HOST:
There is a debate about how fast things can or should return to normal here in the United States, but little discussion of when the country should reopen to international visitors. This is a crucial question, though, for leaders of countries that are far more dependent on the tourist industry. They have to balance desperately needed income and employment against the potential risk to their citizens of infection from the outside.
We're getting different views of this dilemma from some of our regular reporters on three different continents. Joanna Kakissis is in Athens. NPR's Eyder Peralta is in Nairobi. Michael Sullivan is in Thailand. They're all with us. Hi, everybody.
JOANNA KAKISSIS, BYLINE: Hello.
EYDER PERALTA, BYLINE: Hey, David.
MICHAEL SULLIVAN, BYLINE: Hi.
GREENE: Well, Joanna, let me start with you. I mean, you're in Greece. This is a country that has gotten some pretty good marks for how they've handled this pandemic. The death toll has been, you know, thankfully, very low. But tourism is, like, 20% of GDP in Greece. So what are the Greeks going to do here?
KAKISSIS: Well, you know, Greece absolutely needs tourism revenue right now. Something like 700,000 jobs are indirectly or directly dependent on tourism. And Greece just recovered from this long economic depression. Now the fallout from the pandemic is expected to shrink the economy by up to 13% this year. So Greece wants to bring in as many tourists as possible to counter that. On June 15, it led in tourists from the European Union. Unfortunately, not many of them have shown up.
So on July 1, Greece hopes to open itself up to tourists from the rest of the world. But it's not clear which countries will be approved by the European Union. Greece is working with other EU member states on the list of which tourists can enter. Making the cut depends entirely on how well these countries are managing the pandemic. And at the moment, the list includes Australia, China, Uganda, but not the United States. The U.S. is considered too risky right now because the infection rate is so high.
GREENE: Well, Eyder, some African countries I know are almost as dependent on the tourism industry as Greece is. But it sounds like they're doing things differently.
PERALTA: Yeah, because everything is still at a standstill here in Africa. The borders of around 40 countries are still totally shut down. So very few tourists are flying in for safaris. I mean, even us - right? - like, we would love to be at the beach right now. But that is impossible because we're not allowed to leave Nairobi. And we are getting to what is usually peak tourism season here. It's the great wildebeest migration is around the corner. But, right now, it doesn't look like very many people will be here to see it.
GREENE: Michael is any of this sounding familiar to you as you've been watching things play out in Thailand?
SULLIVAN: Oh, yeah. I mean, Thailand, like Greece, depends on tourism for as much as 20% of its GDP. That's gone with international travel closed since March. And the lockdown hit Thailand's manufacturing sector, too. So altogether, it's put millions out of work - at least temporarily. Manufacturing is starting up again now that the lockdown has been lifted. But tourism isn't coming back for a while. And, of course, it won't look the same when it does.
The first people that are going to be allowed back here will be foreign businesspeople and foreigners with family here and people coming for medical tourism. They're going to be allowed next week after July 1. But most will still have to be quarantined for 14 days. As for tourists, Asian countries with low infection rates, they're going to be the first allowed back as the region pursues these travel bubbles you've been hearing about, safe country-to-country travel. But even that probably won't happen for another month or so, not until August or September.
GREENE: Well, let's talk about, I mean, more about the pressure that these countries are under to keep citizens safe. Eyder, African countries, I mean, you know, need the money. They need the employment from tourism. But is that just outweighed by the fear of more infection coming from overseas?
PERALTA: I mean, that's what the governments are discussing right now, right? I mean, at the moment, most African countries have actually been very successful at keeping infection rates down. But the thing is that the health care systems here are so weak in many countries that even a tiny spike in infections could overwhelm them. I mean, here in Kenya, for example, hospitals are already reaching capacity. And we just crossed the 5,000-case mark - not very many, relatively.
So opening up the borders would absolutely help economically. But, you know, it could also tip the country into a huge health crisis. And the president here says that opening up would just be irresponsible.
GREENE: Joanna, I mean, you said that the Greek government is hoping to bring as many tourists in as they can to help the economy. What are the fears, though, of more coronavirus?
KAKISSIS: You know, Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis says, you know, he wants to - he wants people to consider Greece the safest destination in the world. So he's trying to point out that he's taking the steps to keep tourists safe. But, you know, he's taking those same - the government is taking those same precautions to also keep the Greeks safe, too, because, like other countries that don't have a whole lot of money, the health care system here can't stand - can't withstand a huge outbreak.
As far as the tourists go, what - the way the prime minister is trying to lure people here is saying, look; you know, the people in the hospitality industry have to wear masks. The government, you know, we're going to have health workers on standby in case of outbreaks. And he tried to emphasize that these measures won't ruin anybody's vacation. He was on the island of Santorini earlier this month. And he pointed to this gorgeous sunset on the sea and said this.
(SOUNDBITE OF ARCHIVED RECORDING)
PRIME MINISTER KYRIAKOS MITSOTAKIS: You can sit on a veranda with this wonderful view, you know, have your nice Assyrtiko wine, enjoy the beach. But we don't want you crowded in a beach bar.
KAKISSIS: And that's because social distancing will be enforced.
GREENE: I mean, that is such a thing that we're going to be hearing so much of. Go on vacation. Do your thing. But, like, don't crowd into a bar. And it's going to be so dependent of whether people actually listen to that.
KAKISSIS: That's right.
GREENE: Michael, what - any timeframe at all in Thailand for when the country could open up to visitors from Europe, from here in the United States?
SULLIVAN: Don't hold your breath, David. A senior tourism authority official that I spoke to last week said maybe October or November at the earliest, probably not until next year. As I mentioned earlier, it'll be Asian tourists welcomed back first until the Thais are satisfied that the U.S. and European countries have the problem sorted. And who knows when that will be. Their attitude now is, better safe than sorry.
They've had no domestic infections for more than a month now, only 30 - well, fewer than 3,200 total with only 58 deaths. And they want to keep it that way. And Vietnam, which has done even better than Thailand in containing the spread of the virus, it's wary of foreigners, too. And it's allowing some businesspeople to come back this week. But the prime minister said yesterday that Vietnam is in no hurry to allow foreign tourists back.
GREENE: Eyder, can I just come back to you? You mentioned safaris. I mean, so much of a part of the experience visiting different parts of Africa. I mean, not having that, that's going to keep people unemployed. But doesn't that also damage conservation efforts that depend on those dollars?
PERALTA: Yeah. I was talking to Kaddu Sebunya, who's the CEO of the African Wildlife Foundation. And he says this pandemic has shown that conservation depends too much on tourism. He says we're starting to see encroachment into protection areas because people have lost their jobs. And now they're looking to the land to make a living. So he thinks, he worries, that this - that conservation efforts could be erased by this economic crisis.
GREENE: Eyder Peralta in Nairobi. Joanna Kakissis in Athens. Michael Sullivan in Thailand. Thank you all so, so much for this.
PERALTA: Thanks, David.
KAKISSIS: You're welcome, David.
SULLIVAN: You're welcome, David.
(SOUNDBITE OF GABRIEL GARZON-MONTANO'S "THE GAME")
Copyright © 2020 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
Post-pandemic travel: Consider a visit to these tourism-dependent countries

Global tourism has been one of the hardest-hit industries as the coronavirus pandemic drags on. The U.N.'s World Tourism Organization believes that tourist numbers in 2020 will drop a whopping 80%, while the World Travel & Tourism Council reported in June 2020 that nearly 200 million industry jobs could be lost as travel restrictions continue.
As devastating as the pandemic has been on those who love to travel, it's been far worse for countries that depend on a steady stream of visitors to bolster their economies and support local jobs. The Statista chart below shows which countries have been the most vulnerable when it comes to travel and tourism's contribution to GDP.
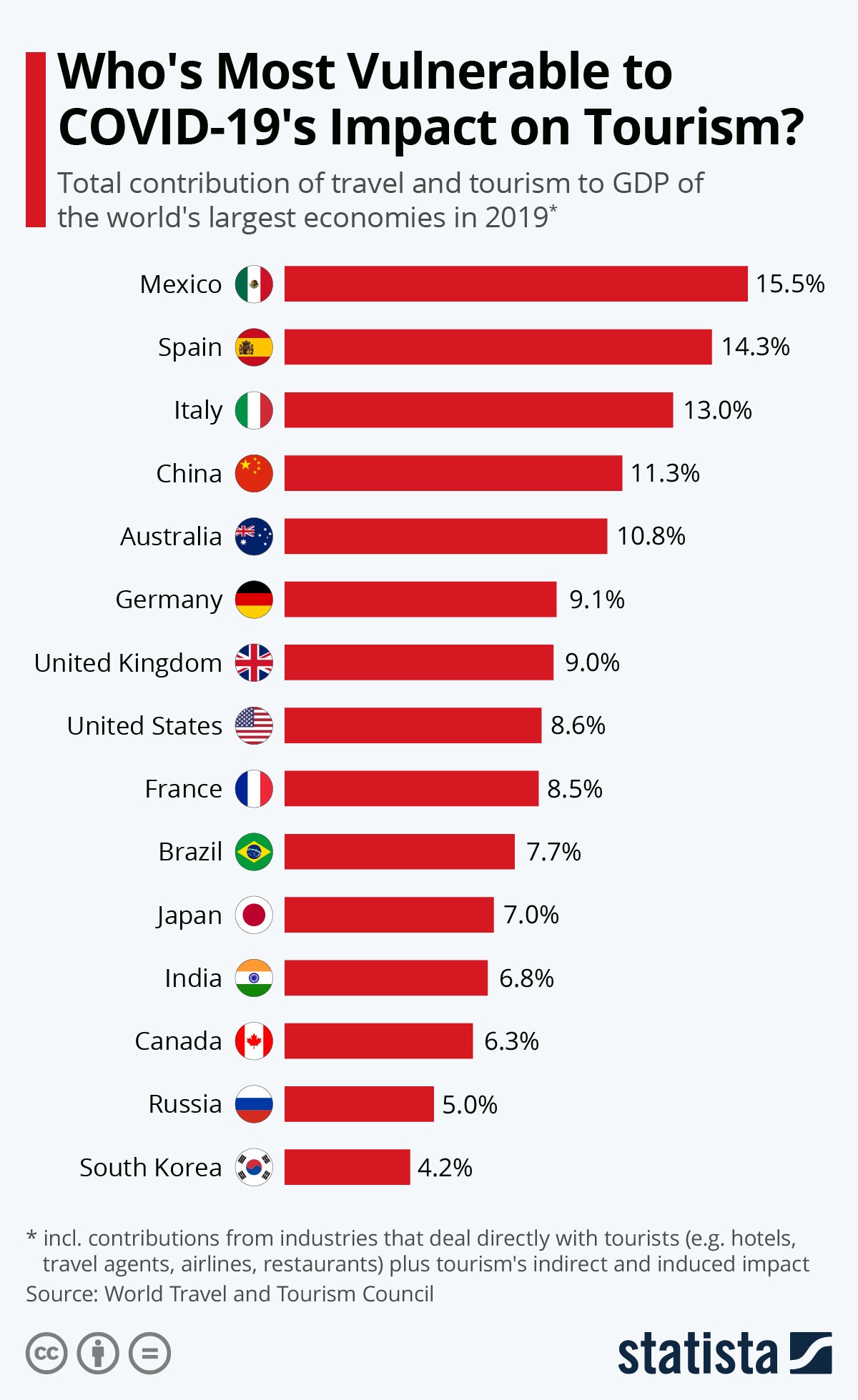
So with COVD-19 vaccines on the horizon and as we look to (hopefully) resume travel in 2021 and beyond, you should consider visits to the countries below to help them rebuild their tourism infrastructure and bring in badly needed dollars.

While the CDC has currently assigned Mexico a Level 4 "very high" COVID-19 designation and said that "all travel" to the country should be avoided, in normal times, it's a huge tourist destination, especially for Americans. In 2018 alone, Mexico made $22.51 billion in tourism revenue, according to Statista .
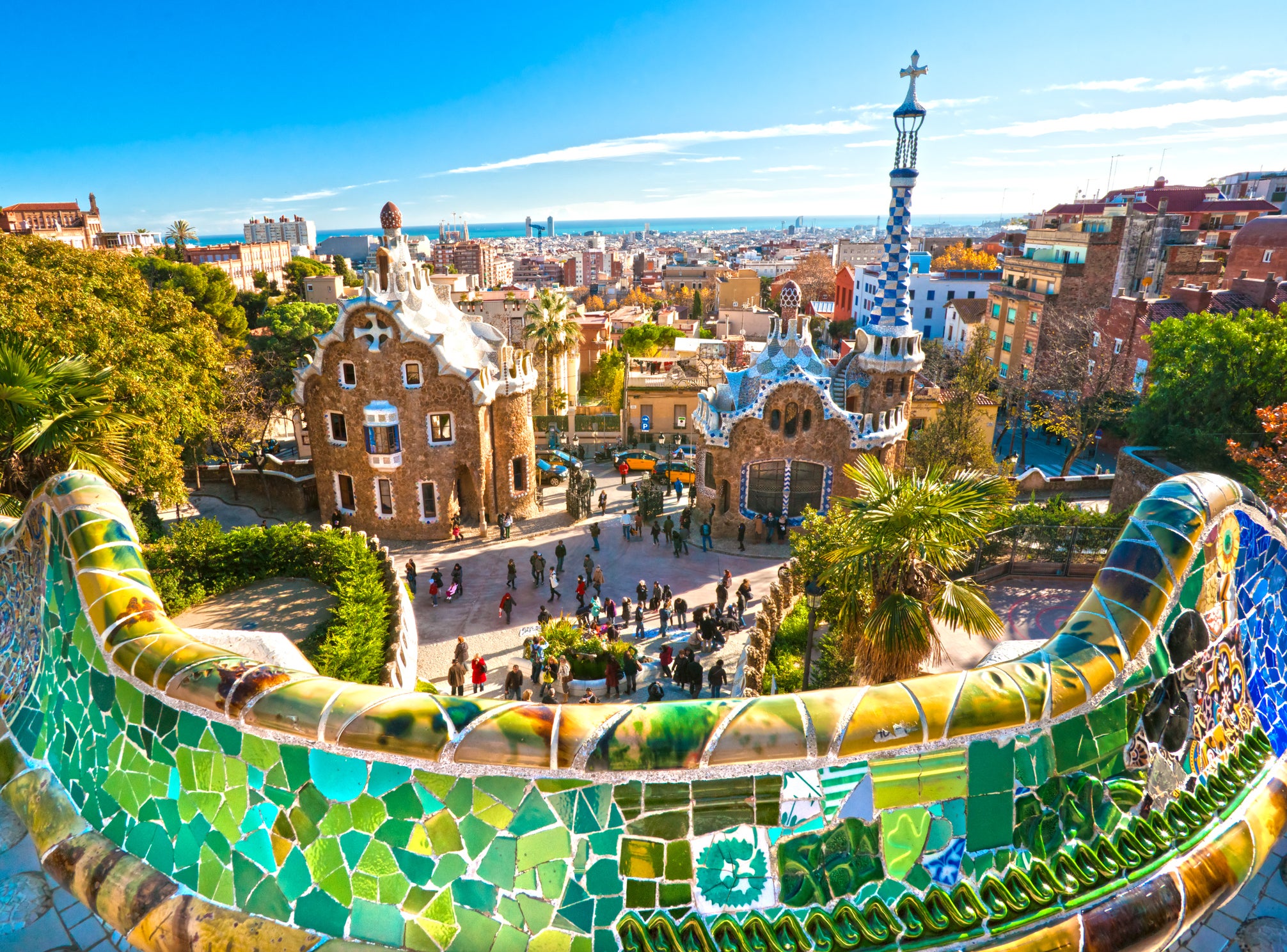

Spain saw a whopping 75% year-over-year drop in tourism in July 2020 because of the pandemic. The country is spending $2.4 million on a new campaign designed to lure tourists back, by showing it's a safe destination with information on safe travel, what to expect on arrival and how to prepare for the trip home. Information on the Travel Safe program is updated daily on the spain.info website.
The website highlights cities including Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Malaga and the Canary Islands. It also puts the spotlight on your choice of travel plans: contemporary architecture, Spain by bike, flamenco dancing and sleeping in unique accommodations.
Related: 5 lesser-known spots for a vacation in Spain
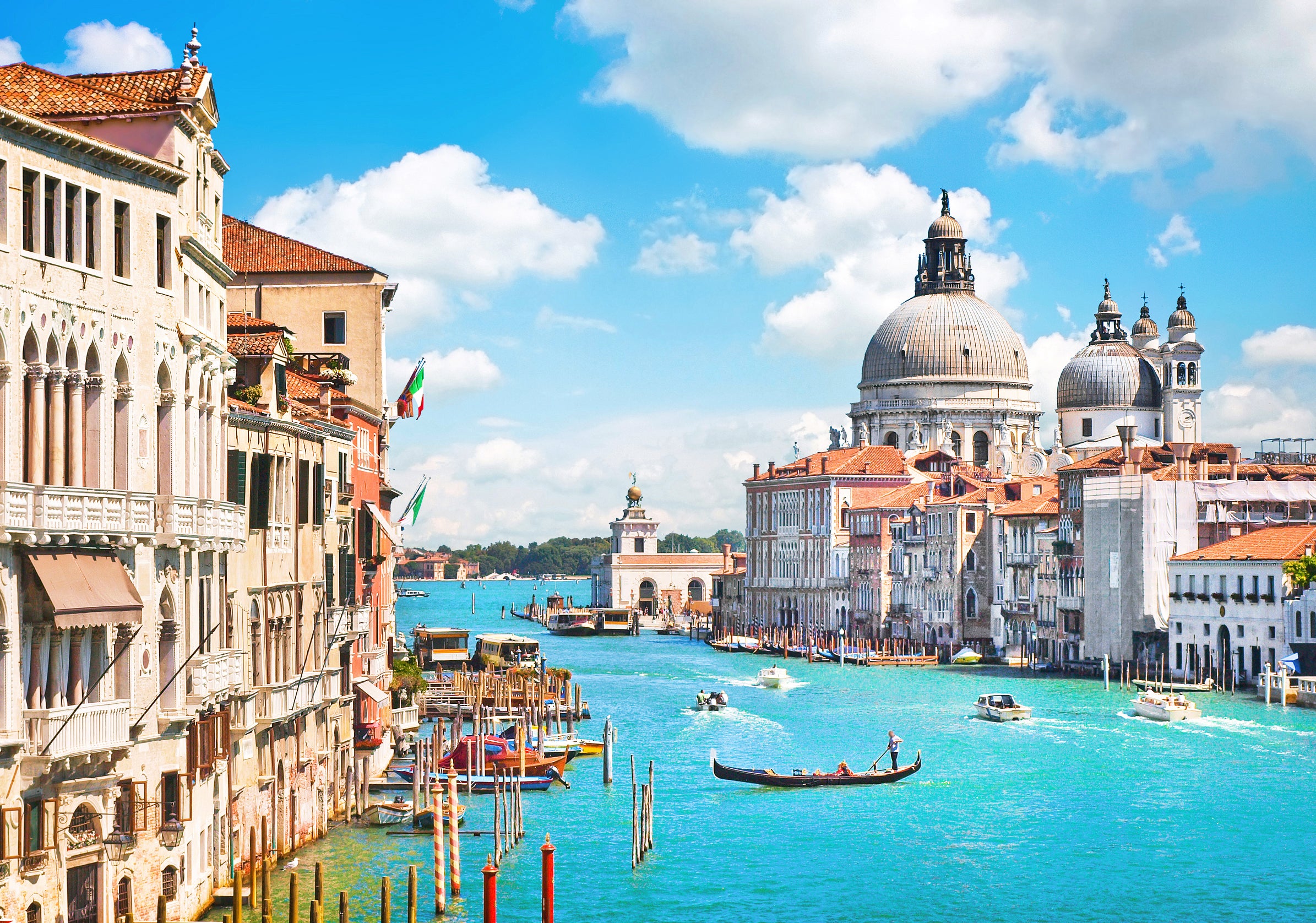

Italy was among the countries hardest hit by the coronavirus pandemic. It had one of Europe's strictest lockdowns and was the first country in Europe to do it after experiencing a surge of coronavirus cases and deaths in the spring.
However, the Italian Tourist Board is looking ahead to 2021. It has launched the Travel to Italy, #TravelResponsibly campaign, to protect the right to travel and ensure that people travel responsibly to support tourist businesses and the economy.
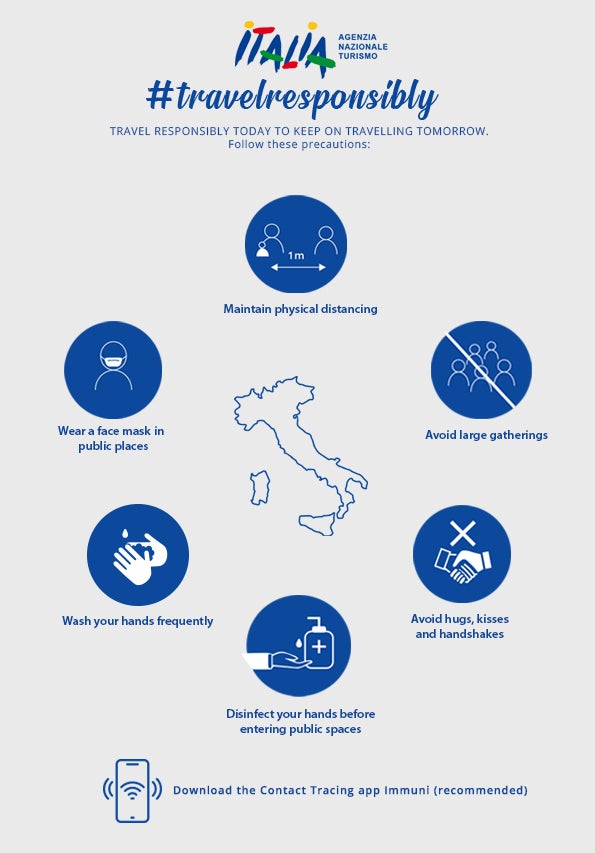
In the meantime, Delta Air Lines plans to launch quarantine-free, COVID-19-free travel between Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport (ATL) and Aeroporti di Roma Fiumicino (FCO) beginning Dec. 19, even though a spike in the country has emptied tourist destinations.
Related: An overview of Italy's best destinations for tourists
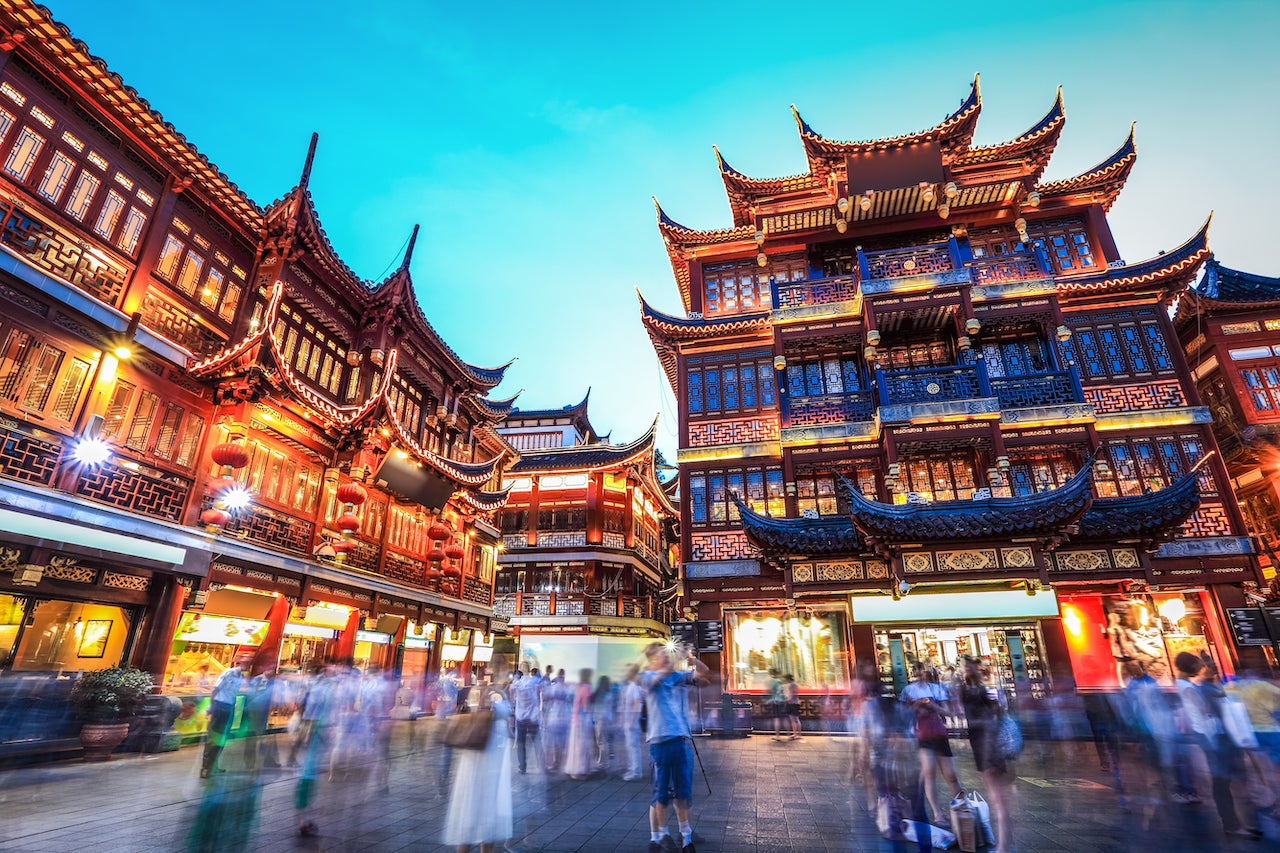

It's well known that Wuhan, China, was ground zero for the coronavirus pandemic. As a result, the government barred most foreign visitors from entering the country in March 2020 over fears the virus could reignite the outbreak there.
Now that COVID-19 outbreaks are largely under control in China, the country has seen air travel increase, driven by a surge in domestic flights, since international trips are still mostly off-limits. China will reclaim its top position as the primary source market for international tourism during 2021, according to a report released by COTRI China Outbound Tourism Research Institute.
Related: American Airlines returns to Shanghai after 10-month coronavirus hiatus
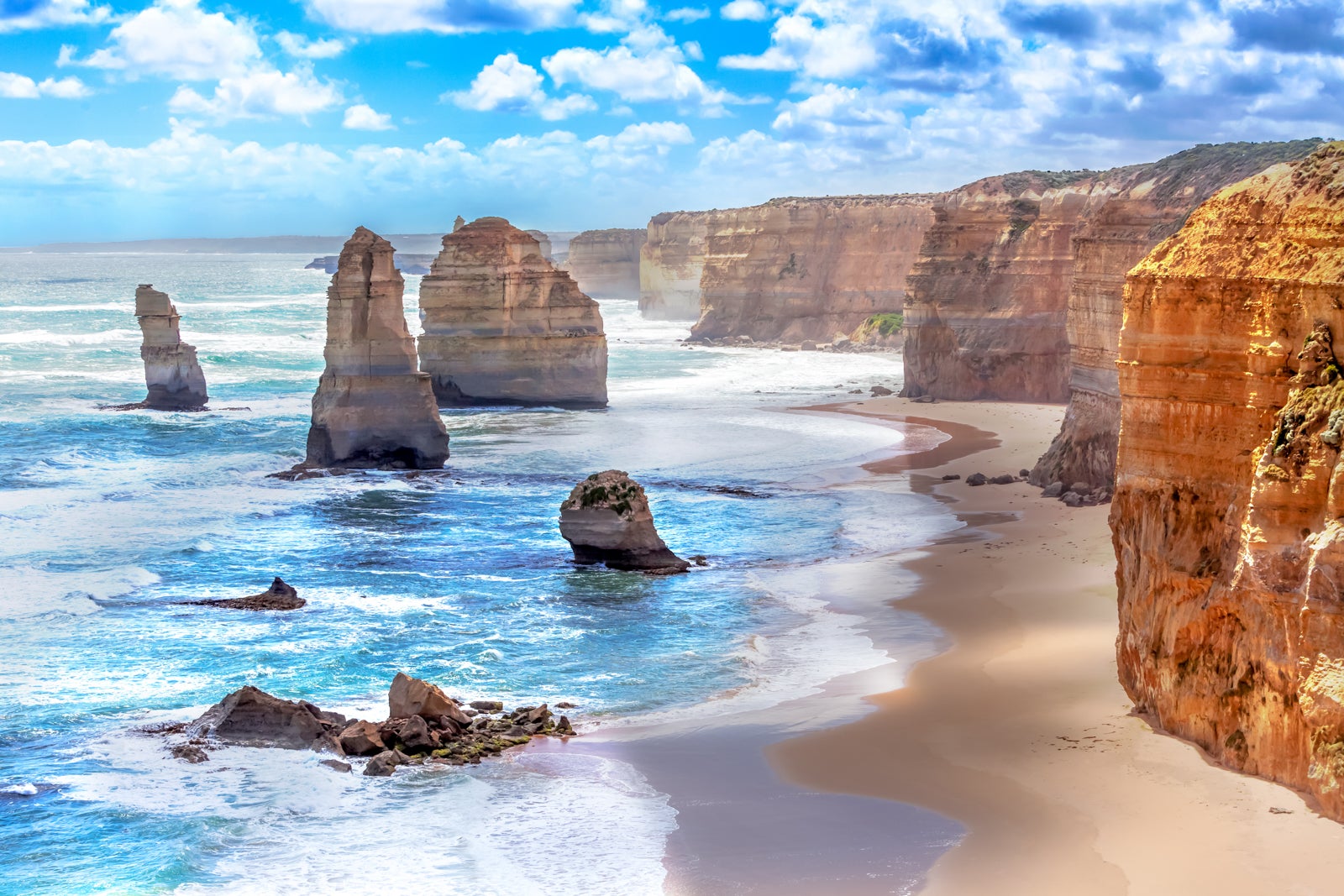

Australia took a draconian approach to combating the COVID-19 pandemic by banning foreign tourists from entering the country. While the government is opening travel bubbles to allow residents to leave the country beginning in the first quarter in 2021, foreign travelers won't be able to enter Australia again until late 2021.
Related: Qantas has stopped selling most international flights until March 2021
Bottom line
The world's tourism sector could lose at least $1.2 trillion, or 1.5% of the global gross domestic product (GDP) due to the coronavirus pandemic, according to a report by the U.N. Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). In its most pessimistic scenario with a 12-month break in international tourism, that number could grow to $3.3 trillion or 4.2% of global GDP.
As these and other countries are looking to rebuild their decimated tourism industries in 2021, now may be the time to look ahead and consider spending your dollars in the countries that need them most.
15 Countries That Rely On Tourism
Nature has blessed many countries in the world. Unparelleled natural landscapes and unadulterated beauty have been bestowed on these countries. With time, these places have become popular with tourists and their economies have become more and more dependent on tourism as a source of income. The following list are the countries that rely on tourism in the world:

The small country of Macau has a per capita tourism income of $16,797. Travel and tourism contributes to 51% of the total employment of the country. So remember on your vacation to this sin city, you're gambling for a good cause!
2. Seychelles
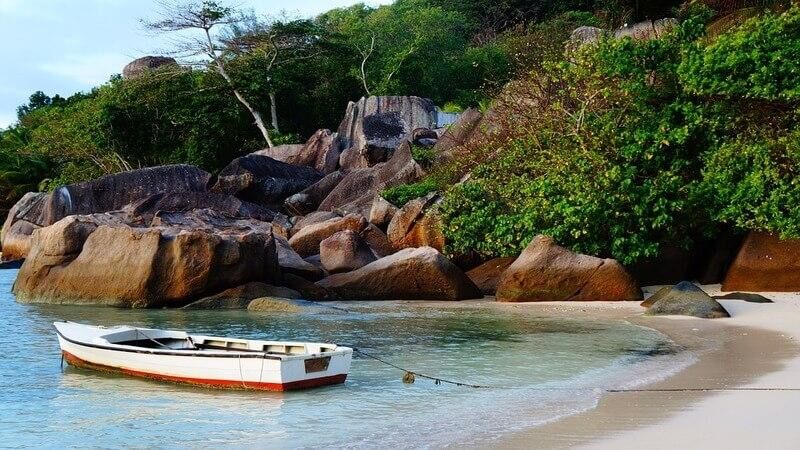

Travel and Tourism contributes to 24.7% of the total GDP of this country. About 26.3% of the total employed people are engaged in tourism activities. This island paradise was quite affected due to the slump in major economies. Hence, you can consider Seychelles as one of the popular countries with tourist based economy.
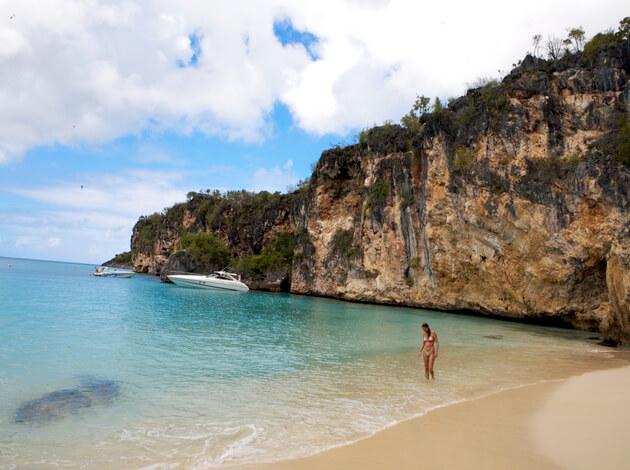
3. Anguilla

Anguilla has a per capita tourism income of $5319. Tourism also heavily contributes to the employment of this country- to the tune of 24.1 %. Anguilla also has the highest visitor exports compared to any other country in this list,at 86.1%.

Get year around hotel deal with TripHobo Hotels. Book Now, Pay Later!

About 30% of the labour force is employed by the tourism industry in Bahamas. The favorite island getaway of Americans, this island town is entirely dependent on tourism for its well being. 22% of its GDP comes from tourism and its allied activities. The per capita tourism income is $6288.

5. Antigua and Barbuda

Antigua and Barbudo has a per capita tourism income of $4947. About 18.5% of the total GDP comes from tourism. These Caribbean islands are a true marvel and see a huge number of tourists on their shores every year.Visitor exports stood at 80.4% as of 2012

6. St Lucia
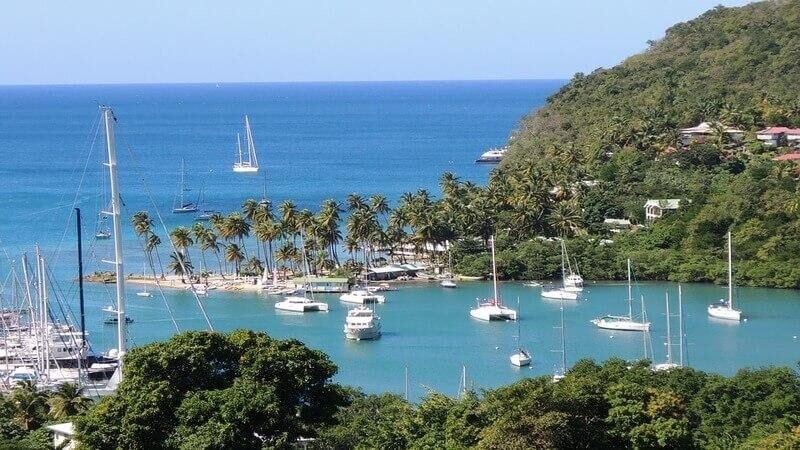

St Lucia welcomes over 300,000 visitors per year. Altough the economc slowdown and natural calamities have heavily impacted the economy, this country's gorgeous beauty can't keep visitors away forever. Torusim contributes to 13.8% of the total GDP of this country. The highest contributor after tourism is bananas.
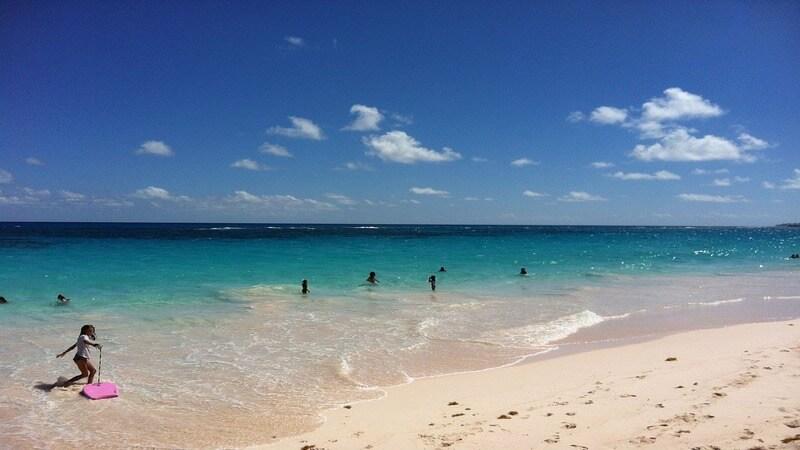

Bermuda has a per capita tourism income of $5451. An average tourist spends about $1305 in this country. With the huge amount of hotels here, it is no wonder that that most of the labour force is employed by this industry.
8. Cayman Islands

PC: Pixabay.com

The per capita tourism income of the Cayman islands is $12,042. Average tourist spend over here is about $1995. The Cayman Islands are one of the most popular toursit attractions in the world.
9. Turks and Caicos

The per capita tourism income here is $12,420. The total number of tourist arrivals were 1,069,497 as of 2013.
10. US Virgin Islands

PC: Wikimedia Commons

The US Virgin islands have a capital investment of 42.9% in the tourism sector. The per capita tourism income is $12,446

About 29.9% of the total employed force works in the tourism industry. Tourism and allied activities contribute to 26.5% of the total GDP here. The per capita tourism income is $14,771
12. British Virgin Islands

Tourism employs about 32% of the total worforce on these islands. The per capita tourism income here is $17,621. The contribution of tourism is 27.1% of total GDP.

13. French Polynesia

Who doesn't dream of a honeymoon at Bora Bora ? This tourist based country welcomed 164,000 visitors in the year 2013. The per capita tourism income is $2076. The average tourist spends about $2610 here.

14. Tanzania

Tanzania saw 1,063,000 tourists in 2013. Its teeming wildlife and natural beauty is the reason why so many tourists visit every year. Travel and Tourism contributes 12.7% to the total GDP.

Fiji saw 660,590 arrivals in 2012. The islands are popular tourist pullers and are heavily reliant on tourism for a living.
Countries that rely on tourism have historically had highly sensitive economies that have been gravely affected with financial cycles. Each of these small countires have invested heavily in the tourist's comfort and entertainment. This makes them a sheer joy to visit- not just because of their rich natural diversity but also because they've gone that extra mile for you and me. Every buck you spend at these places contributes majorly to their employment and national income. Planning a vacation now feels like a noble cause, doesn't it?
You May also Like to Read
- 20 Best Countries to Live in the World
Happiest Countries in the World
8 Smallest Countries in The World
Countries with exotic and Rare Fruits in the World
- 8 Smallest Countries Across The World That Are Worth A Visit
- 12 Countries With an Ideal Work Life Balance Status
- 19 Countries With The Cleanest Tap Water To Drink
- 8 Countries For Millionaires To Migrate
PREVIOUS ARTICLE
NEXT ARTICLE
Hundred countries that rely on tourism?
Where is India on the world tourism index? At what rank?

India is on rank 34th on the World Tourism Index
- Topics ›
- Travel and tourism in Europe ›
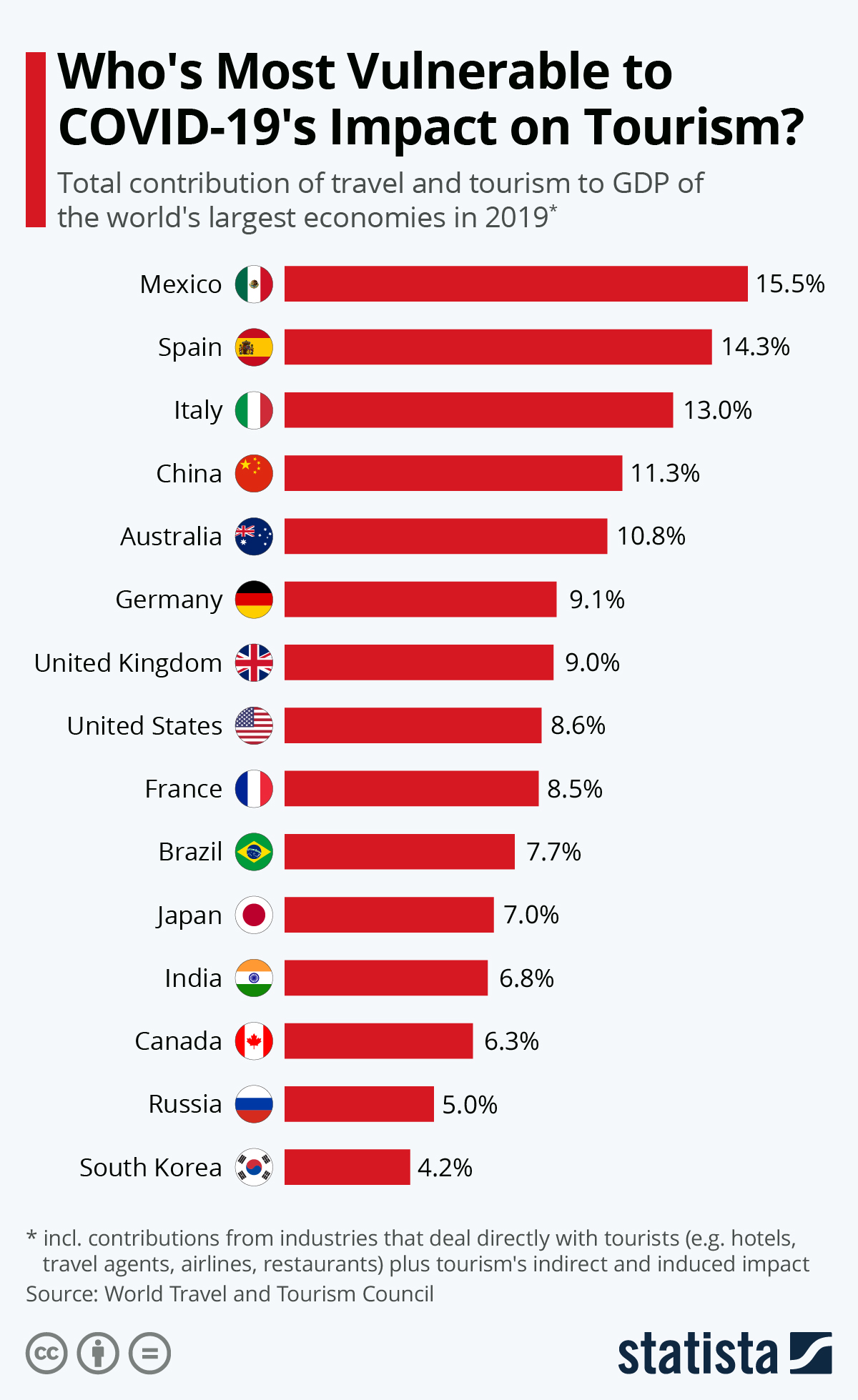
Who's Most Vulnerable to COVID-19's Impact on Tourism?
Economic impact of covid-19.
Italy and Spain have been among the countries hit earliest and hardest by the coronavirus pandemic. With more than 34,000 and 28,000 confirmed deaths at the time of this writing, both Italy and Spain have experienced the deadly force of the novel coronavirus, which killed more than 600,000 people globally and brought public life to a standstill across the globe.
As if the deadly impact of COVID-19 weren't enough, Italy and Spain are also among the countries most vulnerable to the economic fallout of the pandemic. Both countries rely heavily on travel and tourism, which has come to a screeching halt in the past months and remains very limited to this day despite gradual reopenings. Moreover, both countries have struggled economically even before the outbreak, with high levels of public debt and unemployment rates among the highest of all OECD countries.
As the following chart, based on data from the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), shows, travel and tourism contributed 14.3 and 13.0 percent, respectively, to Spain’s and Italy’s GDP last year, including direct contributions from hotels, travel agents, airlines, restaurants and others as well as ripple effects from the billions of dollars, or euros for that matter, that tourists bring to their shores. In the United States for example, the total impact of travel and tourism was considerably smaller at 8.6 percent of GDP. Even at that lower rate, travel and tourism directly support more than 6 million jobs in the United States, with the total contribution to employment amounting to 16.8 million jobs in the U.S. according to WTTC.
Description
This chart shows the total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP of countries worst affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Can I integrate infographics into my blog or website?
Yes, Statista allows the easy integration of many infographics on other websites. Simply copy the HTML code that is shown for the relevant statistic in order to integrate it. Our standard is 660 pixels, but you can customize how the statistic is displayed to suit your site by setting the width and the display size. Please note that the code must be integrated into the HTML code (not only the text) for WordPress pages and other CMS sites.
Infographic Newsletter
Statista offers daily infographics about trending topics, covering: Economy & Finance , Politics & Society , Tech & Media , Health & Environment , Consumer , Sports and many more.
Related Infographics
Climate financing, the yawning climate financing gap, covid 4 years on, mixed thoughts on chances of a new pandemic, 2022 credit card late fees cost consumers record $15 billion, sponsored post by booking.com, top 10 nature destinations in southeast asia, the how of improving social cohesion with local tourism, international women's day, black women four times as likely to die in pregnancy, european hospitality sector experiences unprecedented levels of bankruptcies, top 10 history and culture destinations in southeast asia, effective policies for reducing tourism-related emissions, hotels faring significantly better than strs on the japanese travel accommodation market, tourist accommodation, are short-term rentals more popular than hotels.
- Who may use the "Chart of the Day"? The Statista "Chart of the Day", made available under the Creative Commons License CC BY-ND 3.0, may be used and displayed without charge by all commercial and non-commercial websites. Use is, however, only permitted with proper attribution to Statista. When publishing one of these graphics, please include a backlink to the respective infographic URL. More Information
- Which topics are covered by the "Chart of the Day"? The Statista "Chart of the Day" currently focuses on two sectors: "Media and Technology", updated daily and featuring the latest statistics from the media, internet, telecommunications and consumer electronics industries; and "Economy and Society", which current data from the United States and around the world relating to economic and political issues as well as sports and entertainment.
- Does Statista also create infographics in a customized design? For individual content and infographics in your Corporate Design, please visit our agency website www.statista.design
Any more questions?
Get in touch with us quickly and easily. we are happy to help.
Feel free to contact us anytime using our contact form or visit our FAQ page .
Statista Content & Design
Need infographics, animated videos, presentations, data research or social media charts?
More Information
The Statista Infographic Newsletter
Receive a new up-to-date issue every day for free.
- Our infographics team prepares current information in a clear and understandable format
- Relevant facts covering media, economy, e-commerce, and FMCG topics
- Use our newsletter overview to manage the topics that you have subscribed to
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Pandemic will weigh heaviest on tourism-dependent economies, warns IMF
But impact over rest of decade will not be as bad as that following financial crisis of 2008
- Coronavirus – latest updates
- See all our coronavirus coverage
Scars from the pandemic will prevent the global economy from making a full recovery, though the impact over the rest of the decade will not be as severe as that of the 2008 financial crisis , the International Monetary Fund has said.
Tourism-dependent countries in the Pacific Islands and in the Caribbean – such as Barbados – would be among those to suffer the most, the Washington-based organisation said. It expected global output to be about 3% lower in 2024 than projected before the Covid-19 pandemic.
A speedy rollout of Covid-19 vaccines in the US, China and the UK among others is expected to raise the forecast for growth when the IMF provides a fresh outlook for this year and next, despite a third wave of the virus spreading across Europe and parts of south America that will dampen the rebound.
In its most recent economic update in January , the IMF said the global economy was on course to recover from a 3.5% fall in GDP in 2020 with growth of 5.5% in 2021, up slightly compared with October’s forecast.
However, in a summary of its twice-yearly world economic outlook, to be published next week, the IMF said a freeze on business investment in the early months of the pandemic and the hit to consumer spending that still affects most countries for business failures and job losses would have longer term repercussions for the recovery.
In a separate report, the World Trade Organization revised up its forecast for growth this year of global goods trade after a decline in 2020 that was far less severe than its expectation when the coronavirus first struck.
The WTO said it expected merchandise trade would grow this year by 8.0% after a fall of 5.3% in 2020. That compared with figures in October of respectively 7.2% growth and a 9.2% decline.
The Geneva-based trade body said that trade growth should slow to 4.0% in 2022, below its pre-pandemic trend.
IMF managing director Kristalina Georgieva warned that the effects of the disruption would be uneven and most damaging in emerging markets, which could become caught in debt crisis.
She warned that a flight of funds out of local currencies into dollar assets “would pose major challenges, especially to middle-income countries with large external financing needs and elevated debt levels.”
The IMF said in a blogpost to accompany its forecast that the path to recovery would also remain challenging for poorer countries that relied heavily on some of the hardest hit industries such as tourism.
“Unlike what happened during the global financial crisis, emerging market and developing economies are expected to have deeper scars than advanced economies, with losses expected to be the largest among low-income countries,” it said.
This was true for the Caribbean or the Pacific Islands, with gross domestic product in the latter estimated to be 10% lower in 2024 than pre-pandemic projections, the IMF said.
The pandemic could also have a bigger impact on the labour market over the medium- and longer term as workers are forced to leave sectors that shrink because contact industries fall out of favour or digital processes become more prevalent, the IMF said.
- Coronavirus
- Economic recovery
- Pacific islands
- World Trade Organization
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Economic policy
Most viewed
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Strikes, Inflation, Now War: Uncertainty Escalates for Europe’s Travel Season
As pandemic restrictions lifted, the travel industry was looking forward to a strong summer season. But they may be disappointed.

By Ceylan Yeginsu
Diego Sanz, a tour guide on Spain’s southeastern Mediterranean coast, received his first international group booking in more than a year in mid February. It was, he thought, an augury of better things to come.
“Here we live in paradise, and we were sure that when Covid restrictions were lifted, we would not have any more problems and tourists would come back to us like the honeybees come to the nectar,” said Mr. Sanz, sitting in a quiet cafe in late March in the port city of Alicante.
Then Russia invaded Ukraine and brought new international bookings to a grinding halt. In the first week of the war alone, airline bookings within Europe fell by 23 percent and trans-Atlantic bookings to European countries fell by 13 percent, according to the travel data company ForwardKeys.
“We are in the middle of a big storm,” said Mr. Sanz, speaking both literally and figuratively. Outside the window of the cafe, the Costa Blanca region was enduring one of the heaviest rainstorms in its history, with 18 consecutive days of heavy downpour that caused flash flooding and washed-out roads.
“The sun will come back, but what will happen with the war and the economic problems?” he continued. “I don’t know if we will be able to make any profit this summer.”
Many of the European countries including Spain, Greece, Italy and Croatia that are heavily dependent on tourism had hoped to start the travel season early to make up for lost revenue from the pandemic. That’s now looking unlikely. So far, the worst-hit destinations are those in proximity to Ukraine, including Poland, Bulgaria, Croatia, Estonia and Hungary, which saw a decrease in bookings between 30 to 50 percent, according to ForwardKeys. Many travel operators in those countries are swept up in efforts to help refugees fleeing Russian forces, unable to contemplate what impact the war might have on their livelihoods.
Across the continent, damage is already being felt with rising fuel costs, supply chain issues, inflation and labor strikes. Energy prices in Italy have surged in recent months, worrying hotel operators. Truck drivers in Spain have been on strike for more than 10 days, causing sporadic food and goods shortages. Hotels and restaurants are scrambling to find affordable replacements for key supplies like wheat and sunflower seed oil, of which 75 to 80 percent of the world’s supply comes from Russian and Ukraine, according to the United Nations World Food Program.
“We are trying to be flexible and find replacements for products in short supply, like we use olive oil instead of sunflower oil, so it does not impact the customer experience,” said Javier Garcia Cuenca, the vice president of Magic Costa Blanca Hotels and Resorts. “But the problem is managing cost, it becomes more expensive.”
Croatia often ranks among Europe’s most tourism-dependent economies, with tourism accounting for about one-fifth of the small nation’s gross domestic product, according to the Croatian Bureau of Statistics . The country’s main attraction, its slice of the Adriatic coast, drew most of the 13.8 million visitors and 84.1 million overnight stays to Croatia in 2021. It drove a 10.4 percent growth in G.D.P. year-over-year according to the Bureau of Statistics .
Although cancellations have been minimal in Croatia so far this year, the country is also experiencing a slowdown in bookings.
Dubrovnik Boats, a private excursion and charter company with a vast majority of clients from the United States, was expecting a record year before the war. But then the rate of bookings suddenly fell by 70 percent.
“To a foreigner, we’re one centimeter away from Ukraine on a map,” said Niksa Smojver, the owner.
A significant concern this year for marine charter companies is rising gas prices and the potential for fuel shortages. For Dubrovnik Boats, operating a round trip between the hot spots of Dubrovnik and Hvar now costs around $750 more than it did last year. So far, the company has not passed the increase to passenger fares, but may have to.
Still, Mr. Smojver remains hopeful. “After corona, people are fed up and everyone wants to travel. This season could be one of the better ones we’ve had. Not a record, but strong,” he said.
In other parts of Europe, particularly in countries dependent on tourism, the outlook was bleaker. Cancellations in Italy dampened an increasingly optimistic attitude among tour guides and operators, even as some expressed hope that the war would end and salvage the season.
“The mood in general is depressive, because everything seemed to be over and instead there’s been a new downturn,” said Margherita Capponi, a tour guide based in Rome.
Bernabò Bocca, the president of the Italian hotel association Federalberghi , said he was most concerned over energy costs, which have surged in Italy in recent months. “Hotels are energy-intensive companies, they’re open seven days a week, 24 hours a day,” he said. “The cost of energy has become a very important component, a price the entire world is paying.”
Before the pandemic, tourism accounted for about 14 percent of Italy’s G.D.P., according to the country’s tourism ministry, and Italy’s national tourism agency, ENIT , said that in 2019 more than 63 million foreigners traveled to Italy.
At a recent trade show, Italy’s tourism minister, Massimo Garavaglia, cited a February poll of American travel sentiment by the market research firm MMGY Global , which reported that 47 percent of the 4,500 surveyed were waiting to see how the situation in Ukraine evolves before they make plans to visit Europe. “It’s clear that if half of Americans don’t come to Europe, it’s going to be a drama,” he said.
However, other travel operators both large and small still express optimism for the upcoming season, despite concerns over the war and the coronavirus. Last week, the online travel agency Expedia announced a forecast for a strong summer in Europe, saying search interest among U.S. travelers looking to travel to Britain, Germany and France this summer increased fivefold compared to the same period in 2020.
On Costa Blanca, members of the local hotel industry have signed fixed-price contracts with tour operators, which are likely to result in fewer cancellations. The main challenge for hotels will be managing rising costs and adapting to supply chain problems.
Mr. Cuenca, of Magic Costa Blanca, said he had not yet increased rates and fees at his hotels and expressed cautious optimism about the summer, after already booking about half of his hotel rooms for the season. “We will have to watch inflation and may have to adjust our rates to keep our profit margins,” he said.
Last year the hotel chain had a successful summer season by attracting the domestic Spanish market, but Mr. Cuenca was unable to open one of his hotels because of little demand from the international market, particularly from British tourists who faced stringent, unpredictable travel rules at home.
“We will not have as strong a year as we expected,” he said. “But there is still strong demand as people realized during Covid that they could die and they will not live forever so they prioritize holidays and leisure.”
Sitting in the lobby of the Port Benidorm Hotel last week, Toni Mayor, president of the HOSBEC , the Costa Blanca hotel association, said the 89 percent hotel occupancy, mainly of British tourists, was very encouraging. “They are coming back,” he said.
Wendy Hartfield, a history tutor from Yorkshire, England, arrived in Benidorm last week hoping to get some sunshine and play golf, but instead spent most of her vacation reading indoors because of the rainstorms.
“I want to come back in the summer, but with the way everything is going it might be too expensive,” Ms. Hartfield said. “First we have to pay the bills at home.”
Elisabetta Povoledo contributed reporting from Rome, and Joe Orovic from Zadar, Croatia.

52 Places for a Changed World
The 2022 list highlights places around the globe where travelers can be part of the solution.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places list for 2022 .
Ceylan Yeginsu is a travel reporter. She was previously a correspondent for the International desk in Britain and Turkey, covering politics; social justice; the migrant crisis; the Kurdish conflict, and the rise of Islamic State extremism in Syria and the region. More about Ceylan Yeginsu
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
Mumbai: Spend 36 hours in this fast-changing Indian city by exploring ancient caves, catching a concert in a former textile mill and feasting on mangoes.
Kyoto: The Japanese city’s dry gardens offer spots for quiet contemplation in an increasingly overtouristed destination.
Iceland: The country markets itself as a destination to see the northern lights. But they can be elusive, as one writer recently found .
Texas: Canoeing the Rio Grande near Big Bend National Park can be magical. But as the river dries, it’s getting harder to find where a boat will actually float .
Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Tips
Which Country Is Heavily Dependent On Tourism For Its Livelihood?
Published: December 12, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Neely Bonner
- Plan Your Trip
Introduction
Tourism plays a vital role in the global economy, providing employment opportunities, driving economic growth, and contributing to the cultural exchange between nations. While many countries heavily rely on tourism as an industry, there are some nations that are particularly dependent on this sector for their livelihood. These countries, often characterized by their stunning natural landscapes, diverse cultures, and historical attractions, have built their economies around tourism, making it a primary source of income for both individuals and the government.
Heavy dependency on tourism refers to the situation where a country’s economy is significantly reliant on income generated from the tourism industry. This reliance can be due to various factors such as limited alternative economic opportunities, geographical advantages, or the country’s unique attractions that draw in a large number of visitors.
The importance of tourism for these countries cannot be understated. It not only brings in foreign exchange but also creates job opportunities for the local population, helps in infrastructure development, and promotes cultural preservation. However, it also poses certain challenges and risks, such as economic vulnerability, environmental degradation, and over-dependence on external factors.
In this article, we will explore the concept of heavy dependency on tourism, understand the factors contributing to it, and examine the economic impact and challenges associated with this dependence. We will also discuss sustainable tourism strategies that can help these countries address the risks and ensure long-term economic stability. To illustrate these points, we will focus on the profile of a specific country heavily dependent on tourism, highlighting its unique characteristics, successes, and potential pitfalls.
Definition of Heavy Dependency
Heavy dependency on tourism refers to a situation where a country’s economy is heavily reliant on the income generated from the tourism industry. In these countries, tourism plays a critical role in driving economic growth, providing employment opportunities, and contributing to the overall livelihood of the population.
When a country is considered to have a heavy dependency on tourism, it means that a significant portion of its revenue, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), and employment comes directly from the tourism sector. These countries often prioritize tourism as a strategic industry and invest heavily in promoting their destinations to attract visitors from around the world.
The metrics used to measure heavy dependency on tourism include the percentage of GDP contributed by tourism, the number of jobs created in the tourism industry, and the level of foreign exchange earnings from tourism-related activities. Countries with a high percentage of tourism contribution to their GDP, a large workforce engaged in tourism-related jobs, and substantial foreign exchange earnings are often considered to have a heavy dependency on tourism.
It is important to note that heavy dependency on tourism is not necessarily a negative thing. In fact, many countries have successfully leveraged their natural, cultural, and historical assets to build robust tourism industries that provide significant economic benefits. However, it does come with certain risks and challenges, which we will explore further in this article.
Importance of Tourism for Livelihood
Tourism plays a crucial role in providing livelihood opportunities for individuals and communities in countries heavily dependent on this industry. Here are some key reasons why tourism is vital for the livelihood of these nations:
- Employment Opportunities: Tourism creates a wide range of jobs, from hotel staff and tour guides to artisans and transportation providers. In countries heavily dependent on tourism, these employment opportunities are often significant, absorbing a significant portion of the local workforce. The tourism industry provides direct employment as well as indirect employment through related sectors such as hospitality, transportation, and retail. It helps reduce unemployment rates and alleviates poverty by offering income-generating activities to local communities.
- Economic Growth: Tourism is a significant contributor to the economic growth of countries heavily dependent on this industry. The revenue generated from tourism activities, such as accommodation, food and beverage services, and entertainment, directly contributes to the country’s GDP. This economic growth leads to increased government revenue, which can be reinvested in infrastructure development, healthcare, education, and other public services, further improving the livelihood of the population.
- Promotion of Cultural Exchange: Tourism promotes cultural exchange between visitors and the local community. Visitors have the opportunity to learn about the local customs, traditions, and way of life, providing a platform for cultural understanding and appreciation. This cultural exchange can lead to the preservation and promotion of traditional arts, crafts, and heritage, contributing to the livelihood of artisans and cultural practitioners.
- Infrastructure Development: With the growth of tourism, countries heavily dependent on this industry often invest in improving their infrastructure. This includes the construction of airports, roads, hotels, and other tourism-related facilities. As a result, the local population benefits from improved transportation networks, better access to basic services, and enhanced connectivity, which ultimately improves their overall quality of life.
- Promotion of Small-Scale Enterprises: Tourism provides opportunities for small-scale enterprises to thrive. Local entrepreneurs can set up businesses that cater to the needs of tourists, such as souvenir shops, restaurants, and tour operations. This promotes economic diversification, reduces income inequalities, and fosters entrepreneurship within the local community.
Overall, the importance of tourism for livelihood in countries heavily dependent on this industry cannot be overstated. It provides employment opportunities, drives economic growth, promotes cultural exchange, facilitates infrastructure development, and supports the growth of small-scale enterprises. However, it is essential to address the risks and challenges associated with heavy dependency on tourism to ensure long-term sustainability and balanced economic development.
Factors Contributing to Heavy Dependency on Tourism
Several factors contribute to the heavy dependency on tourism in certain countries. These factors vary based on the country’s unique characteristics, resources, and development strategies. Here are some common factors that contribute to the heavy dependency on tourism:
- Natural Attractions: Many countries heavily dependent on tourism possess remarkable natural attractions such as pristine beaches, lush forests, majestic mountains, or unique wildlife. These captivating landscapes draw in a large number of tourists seeking unforgettable experiences and breathtaking scenery. Countries like Costa Rica, Maldives, and New Zealand have strategically developed their tourism industry around their natural wonders.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Countries rich in cultural and historical heritage often attract tourists interested in exploring these aspects. Ancient temples, archaeological sites, traditional festivals, and vibrant cultural traditions can draw significant tourism demand. Countries such as Italy, Egypt, and India have harnessed their cultural and historical treasures to become major tourist destinations.
- Geographical Advantages: Some countries enjoy geographical advantages that make them natural hubs for tourism. These advantages can include favorable climate conditions, strategic location in relation to major tourist destinations, or proximity to popular attractions. For example, countries in the Caribbean region benefit from their naturally beautiful islands and warm tropical climate, attracting tourists from around the world.
- Government Support and Investment: Government policies and support can significantly contribute to the heavy dependency on tourism. When governments prioritize tourism as a strategic industry and invest in infrastructure development, marketing campaigns, and promoting the country as a tourist destination, it can fuel the growth of the tourism sector. This support creates an enabling environment for the industry to thrive, leading to heavy dependency on tourism for economic prosperity.
- Limited Alternative Economic Opportunities: In some cases, countries heavily rely on tourism due to limited alternative economic opportunities. Factors such as lack of natural resources, limited industrial capacity, or remote locations can make tourism the most viable and sustainable option for economic development. These countries often invest in developing tourism infrastructure and services to capitalize on their unique selling points and attract visitors.
These factors are not exhaustive and can differ from country to country. However, they illustrate the main drivers behind the heavy dependency on tourism. It is crucial for countries to recognize these factors and develop sustainable strategies to maintain a balanced economy, mitigate risks, and ensure long-term prosperity.
Country Profile: [Country Name]
[Country Name] is a nation that exemplifies heavy dependency on tourism. With its unique attractions, cultural heritage, and stunning landscapes, it has established itself as a prominent destination for travelers from around the globe. Let’s delve into the profile of this country to understand its key characteristics and the factors contributing to its heavy reliance on tourism.
Geographical Location: [Country Name] is situated in [geographical location], offering a diverse range of natural landscapes and ecosystems. From beautiful coastlines and tropical rainforests to rugged mountains and deserts, it has an abundance of natural wonders that attract nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers.
Cultural Richness: [Country Name] is home to a vibrant and diverse culture, with a rich tapestry of traditions, festivals, and historical landmarks. Its cultural heritage, including ancient temples, archaeological sites, and UNESCO World Heritage sites, offers visitors an opportunity to immerse themselves in the country’s history and traditions.
Unique Attractions: [Country Name] boasts unique attractions that set it apart from other destinations. It could be its iconic landmarks, like [famous landmark], or its exceptional wildlife, such as [unique wildlife species]. These attractions contribute to the country’s allure and make it an enticing choice for tourists seeking extraordinary experiences.
Tourism Infrastructure: To accommodate the influx of visitors, [Country Name] has invested in a well-established tourism infrastructure. It offers a wide range of accommodation options, from luxury resorts to budget-friendly guesthouses, ensuring that travelers of all budgets can find suitable accommodations. Moreover, efficient transportation systems, such as airports, roads, and public transportation, facilitate easy access to different regions of the country.
Government Initiatives: The government of [Country Name] has recognized the potential of tourism as a significant source of revenue and employment. Through proactive policies, they have actively promoted the country as a tourist destination and implemented measures that support the growth of the tourism industry. This includes marketing campaigns, sustainability efforts, and partnerships with industry stakeholders to enhance visitor experiences.
Community Involvement: The local communities in [Country Name] play a crucial role in the tourism sector. They contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage, act as custodians of natural areas, and provide unique experiences through community-based tourism initiatives. These endeavors not only benefit the local economy but also foster a deeper connection between visitors and the local culture.
It is important to note that while [Country Name] has reaped numerous benefits from its heavy reliance on tourism, there are also challenges and risks associated with this dependence. It is essential for the country to strike a balance between economic development and sustainability to ensure the long-term well-being of both the tourism industry and the local communities.
Economic Impact of Heavy Dependency on Tourism
The heavy dependency on tourism has a profound economic impact on countries that rely heavily on this industry. While tourism can bring significant benefits to the economy, it also poses certain challenges and risks. Here, we explore the economic impact of heavy dependency on tourism:
- Revenue Generation: One of the primary benefits of heavy dependency on tourism is the generation of revenue. Income from tourists, including expenditures on accommodations, meals, transportation, attractions, and souvenirs, contributes directly to the country’s GDP. This revenue can help fund infrastructure development, public services, and other critical sectors of the economy.
- Employment Opportunities: Heavy reliance on tourism creates a substantial number of jobs, covering a wide range of sectors. This includes positions in hospitality, travel agencies, transportation, tour guides, handicrafts, and more. The employment opportunities generated by tourism help reduce unemployment rates, provide income for local communities, and improve standards of living.
- Foreign Exchange Earnings: Tourism is often a significant source of foreign exchange earnings for countries heavily dependent on this industry. The influx of international visitors brings in foreign currency, strengthening the country’s foreign reserves. This currency can be used for imports, debt repayments, or investment in other sectors of the economy.
- Infrastructure Development: The growth of tourism requires significant investment in infrastructure development, which benefits not only the tourism industry but also the overall economy. To cater to the needs of travelers, countries heavily reliant on tourism invest in transportation networks, airports, hotels, restaurants, and other tourism-related facilities. This infrastructure development also enhances the country’s attractiveness as a destination for other industries and investors.
- Multiplier Effect: The economic impact of tourism extends beyond direct revenue generation. It has a multiplier effect, meaning that money spent in the tourism sector circulates throughout the economy, benefiting various industries. For example, income earned by hotel employees can be spent on local businesses, such as shops, restaurants, and services. This multiplier effect stimulates economic activity and supports a diverse range of sectors.
However, heavy dependency on tourism also presents certain risks and challenges that need to be addressed. Economic vulnerability, fluctuations in visitor numbers, and over-reliance on external factors can leave countries susceptible to economic shocks. It is essential for these nations to diversify their economies, promote sustainable tourism practices, and invest in other industries to reduce their vulnerability and ensure long-term economic stability.
Understanding the economic impact of heavy dependency on tourism is crucial for countries to develop strategies that maximize the benefits while mitigating the risks. By nurturing a sustainable tourism industry and diversifying their economies, countries can strive for a balanced and resilient economic future.
Challenges and Risks of Heavy Dependency on Tourism
While heavy dependency on tourism can bring economic benefits, it also poses various challenges and risks for countries heavily reliant on this industry. It is essential to recognize and address these challenges to ensure long-term sustainability. Here are some key challenges and risks associated with heavy dependency on tourism:
- Economic Vulnerability: Depending heavily on tourism makes a country economically vulnerable. Fluctuations in visitor numbers, global economic downturns, natural disasters, or political unrest can severely impact the tourism industry and result in significant revenue loss. Without diversification, the economy becomes highly susceptible to these external shocks, potentially leading to economic instability and unemployment.
- Seasonality and Overcrowding: Many tourist destinations experience seasonality, with peak periods attracting a large influx of visitors and off-peak periods facing a decline in tourist numbers. This seasonality can lead to challenges in managing resources efficiently, such as balancing hotel occupancy rates, maintaining consistent employment levels, and providing quality services during peak times. Overcrowding due to high tourist numbers can also strain infrastructure and negatively impact the local environment, culture, and quality of life for residents.
- Dependency on External Factors: Heavy reliance on tourism means being dependent on external factors beyond the control of the country. Changes in travel trends, economic policies of tourist-generating countries, currency exchange rates, and global events can significantly affect the number of visitors, their spending patterns, and the overall tourism industry. This dependency exposes the country to risks that it may have limited control over, making long-term planning and stability challenging.
- Environmental Degradation: Tourism, if not managed sustainably, can lead to environmental degradation. Increased infrastructure development, overuse of natural resources, pollution, and habitat destruction can harm ecosystems and biodiversity. This not only affects the natural attractions that draw tourists but also disrupts the delicate balance of the local environment, potentially leading to negative consequences for the long-term sustainability of the tourism industry itself.
- Social and Cultural Impact: Heavy tourism can have social and cultural impacts on local communities. The influx of tourists may lead to increased pressure on local resources and amenities, potentially causing conflicts with residents. In some cases, the authenticity of local culture and traditions may be commodified or compromised for commercial interests. Maintaining the integrity of local communities, preserving cultural heritage, and ensuring equitable distribution of tourism benefits are crucial challenges for countries dependent on tourism.
Recognizing these challenges and risks is vital for countries heavily dependent on tourism to develop strategies that mitigate the negative impacts. Diversification of the economy, promotion of sustainable tourism practices, investing in other industries, and actively engaging local communities in decision-making can help countries strike a balance between reaping the benefits of tourism and preserving their natural, social, and cultural integrity.
Sustainable Tourism Strategies
For countries heavily dependent on tourism, adopting sustainable tourism strategies is crucial to ensure the long-term viability of the industry and minimize negative impacts on the environment, communities, and cultural heritage. Here are some key sustainable tourism strategies that these countries can implement:
- Environmental Conservation: Implementing environmental conservation measures is essential to preserve natural resources, biodiversity, and the integrity of ecosystems. This includes promoting responsible tourism practices such as waste management, energy efficiency, water conservation, and protection of sensitive areas. Encouraging eco-friendly transportation options and promoting sustainable activities that respect the environment, such as wildlife viewing and nature trails, can also contribute to environmental preservation.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in the development and management of tourism is vital for sustainable outcomes. Empowering local residents through job opportunities, entrepreneurship, and capacity building enhances their sense of ownership and pride in tourism activities. Engaging communities in decision-making processes, preserving cultural heritage, and promoting community-based tourism can help ensure that local people benefit from tourism and actively participate in its sustainable development.
- Diversification of Tourism Products: Relying on a single type of tourism product can increase vulnerability to external factors. Countries should diversify their tourism offerings to cater to a broader range of tourists and attract visitors during off-peak seasons. This can include promoting cultural tourism, adventure tourism, ecotourism, and sustainable agriculture tourism. By diversifying the tourism product, countries can distribute the benefits of tourism more evenly and reduce seasonality-related challenges.
- Strengthening Destination Management: Effective destination management is critical for sustainable tourism. This involves establishing clear regulations, codes of conduct, and guidelines for tourism activities, ensuring that they align with sustainability principles. Collaborating with stakeholders, including local communities, tour operators, accommodation providers, and government agencies, can help create a coordinated approach towards sustainable tourism development. Monitoring visitor flows, managing carrying capacities, and minimizing negative social and environmental impacts are integral to effective destination management.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education and awareness among tourists, local communities, and industry stakeholders is vital for sustainable tourism. Encouraging responsible traveler behavior, such as respecting local customs, cultures, and natural environments, can minimize negative impacts. Providing training and education programs for tourism professionals on sustainable practices can also enhance the quality of tourism experiences and ensure that sustainable principles are embedded throughout the industry.
By implementing these sustainable tourism strategies, countries heavily dependent on tourism can strive towards a balanced approach that optimizes social, economic, and environmental benefits. Embracing sustainability not only safeguards the natural and cultural treasures but also ensures the long-term livelihoods of local communities and the resilience of the tourism industry as a whole.
Heavy dependency on tourism can provide significant economic benefits to countries, including revenue generation, employment opportunities, and infrastructure development. However, it also presents various challenges and risks that must be addressed to ensure long-term sustainability. Countries heavily dependent on tourism need to implement sustainable tourism strategies that strike a balance between economic growth and environmental and cultural preservation.
Understanding the factors contributing to heavy dependency on tourism, such as unique attractions, geographical advantages, and government support, is crucial for these countries. While natural wonders and cultural heritage attract tourists, governments play a pivotal role in promoting tourism, developing infrastructures, and supporting the industry’s growth.
Evaluating the economic impacts of heavy dependency on tourism reveals the importance of revenue generation, job creation, and foreign exchange earnings. However, vulnerabilities such as economic downturns, seasonality, and external factors necessitate diversification of the economy and investment in other industries to reduce risks and ensure stability.
The challenges and risks associated with heavy dependency on tourism, including economic vulnerability, seasonality, environmental degradation, and cultural impacts, call for sustainable tourism strategies. Conserving the environment, engaging local communities, diversifying tourism products, strengthening destination management, and promoting education and awareness are key components of sustainable tourism development.
In conclusion, countries heavily dependent on tourism must prioritize sustainable practices and long-term planning to ensure the balance between economic growth and the preservation of their natural and cultural assets. By adopting a holistic approach, these countries can continue reaping the benefits of tourism while safeguarding their unique heritage for future generations and fostering the well-being of both visitors and local communities.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Top Ten. Bangladesh - 9 jobs per tourist (944 per 100) India - 2 jobs per tourist (172 per 100) Pakistan - 2 jobs per tourist (154 per 100) Venezuela - 1 job per tourist (101 per 100 ...
Mexico. - Tourism total contribution to GDP: $191 billion (16.1% of total GDP; 18.7% increase since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 8.8 million (16.6% of total jobs) Mexico is famous for its beaches, including Cancun or Playa del Carmen along the Caribbean Sea, and those of Oaxaca on the Pacific Ocean.
10. Anguilla. 51%. 3,800. 15,000. Showing 1 to 10 of 44 entries. Previous Next. Croatia, another tourist hotspot, is hoping to reopen in time for peak season—the country generated tourism revenues of $13B in 2019. With a population of over 4 million, travel and tourism contributes to 25% of its workforce.
Waj / Shutterstock. #49. Syrian Arab Republic. - Tourism total contribution to GDP: $2.4 billion (14% of total GDP; 6.2% decrease since 1998) - Jobs reliant on tourism: 177,100 (8.3% of total jobs ...
Countries that rely heavily on tourism, and in particular international travelers, tend to be small, have GDP per capita in the middle-income and high-income range, and are preponderately net debtors.
This is according to the latest WTTC report on theeconomic and employment impact of travel and tourismin 185 countries and 25 geographic or economic regions. Next was Aruba, where tourism jobs made up 84.3% of total employment last year. St Lucia followed with 78.1%, then the US Virgin Islands (68.8%) and the British Virgin Islands (66.4%).
The Maldives, located in the Indian Ocean, is the country most reliant on tourism. Around 20 others across the world derive more than 10% of their gross domestic product from tourism. Most are ...
The world's most tourism-dependent countries. Rafat Ali, Skift. March 9th, 2013 at 4:02 AM EST. ... as one of the top nations heavily investing in travel and tourism infrastructure.
The October World Economic Outlook projected the global economy would contract by 4.4 percent in 2020. The shock in tourism-dependent economies will be far worse. Real GDP among African countries dependent on tourism will shrink by 12 percent. Among tourism-dependent Caribbean nations, the decline will also reach 12 percent.
Nations that are heavily dependent on tourism are trying to walk a fine line between the need to reopen their beaches and resorts and the risk of importing more cases of the coronavirus.
In its most pessimistic scenario with a 12-month break in international tourism, that number could grow to $3.3 trillion or 4.2% of global GDP. As these and other countries are looking to rebuild their decimated tourism industries in 2021, now may be the time to look ahead and consider spending your dollars in the countries that need them most.
The following list are the countries that rely on tourism in the world: 1. Macau. Private Tour: Macau Day Trip From Hong Kong 6 Reviews. USD 586.67. Book. The small country of Macau has a per capita tourism income of $16,797. Travel and tourism contributes to 51% of the total employment of the country.
It is likely that when countries are heavily dependent on tourism or tourism delivers benefits to a large group of low-income households, tourism expansion can reduce income inequality. ... In developing countries, tourism development is closely related to government intervention, whereas in developed countries, tourism development is largely ...
As if the deadly impact of COVID-19 weren't enough, Italy and Spain are also among the countries most vulnerable to the economic fallout of the pandemic. Both countries rely heavily on travel and ...
In this article, we will explore the top countries that heavily depend on tourism and delve into the reasons behind their popularity among travelers. These countries have managed to capture the attention of tourists with their diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, historical landmarks, and vibrant cities.
Tourism-dependent countries in the Pacific Islands and in the Caribbean - such as Barbados - would be among those to suffer the most, the Washington-based organisation said. It expected global ...
For places that rely heavily on travellers spending big, this task couldn't be more urgent. In 2019, Montenegro's reliance on tourism was closely followed by Croatia 's. The coastal Balkan ...
4. Seychelles. 25.74%. 5. Bahamas. 19.23%. Unsurprisingly, many of the countries where tourism is most important to the economy are located in popular island destinations. The country with the ...
Each year, a growing number of destinations and communities heavily dependent on tourism — countries like Thailand, India and Madagascar — are hit hard by the impacts of climate change, in the ...
Emilio Parra Doiztua for The New York Times. Many of the European countries including Spain, Greece, Italy and Croatia that are heavily dependent on tourism had hoped to start the travel season ...
Economic Growth: Tourism is a significant contributor to the economic growth of countries heavily dependent on this industry. The revenue generated from tourism activities, such as accommodation, food and beverage services, and entertainment, directly contributes to the country's GDP. This economic growth leads to increased government revenue ...
However, WTTC indicates the total contribution from travel and tourism accounts for around 16.8 million jobs. The US has the world's highest Covid-19 death rate, according to data from Johns ...
3. Data. To study the relationship between tourist activities and house prices, we collect annual data from 2000 to 2018 for eight countries heavily dependent on tourism in terms of exports - Australia, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Iceland, New Zealand, Portugal and Spain.
The Dominican Republic, known for good weather, will have 124 fewer "outdoor days" in 75 years — implying a huge hit to its quality of life and its tourism-dependent economy. Here's how ...
France is more likely to protect people from financial hardship caused by out-of-pocket payments for health care than most other countries in the European Union (EU), but gaps in coverage remain a challenge for households with low incomes, a new WHO/Europe report reveals.According to the report, "Can people afford to pay for health care? New evidence on financial protection in France", the ...