Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Cultural Tourism: A review of recent research and trends

2018, Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management
This review article traces the development of cultural tourism as a field of research over the past decade, identifying major trends and research areas. Cultural tourism has recently been reaffirmed by the UNWTO as a major element of international tourism consumption, accounting for over 39% of tourism arrivals. Cultural tourism research has also grown rapidly, particularly in fields such as cultural consumption, cultural motivations, heritage conservation, cultural tourism economics, anthropology and the relationship with the creative economy. Major research trends include the shift from tangible to intangible heritage, more attention for indigenous and other minority groups and a geographical expansion in the coverage of cultural tourism research. The field also reflects a number of 'turns' in social science, including the mobilities turn, the performance turn and the creative turn. The paper concludes with a number of suggestions for future research directions, such as the development of trans-modern cultures and the impacts of new technologies.
Related Papers
greg richards
This is the latest update to the ATLAS Cultural Tourism Bibliography, which is a work in progress rather than a comprehensive listing of cultural tourism research sources. All suggestions for additional references gratefully received. In line with the multilingual nature of ATLAS, we are happy to receive suggested references in languages other than English, preferably with an English language translation of the title. The latest revision includes references from the UNWTO report Tourism and Culture Synergies (2018).
ATLAS Cultural Tourism Bibliography 4.1
This is the updated version of the ATLAS Cultural Tourism Bibliography, produced with input from members of the group in September 2019.
KÜLTÜREL MİRAS Yönetim
Richards, G. (2019) Kültür Turizmi: Son Araştırmalar ve Eğilimlere Dair Bir İnceleme. In Özdemir, N. and Öger, A. KÜLTÜREL MİRAS Yönetimi. Ankara: Grafiker. pp. 583-614. ISBN: 978-605-2233-52-8
World Journal of Business and Management
Kostas Karamanis
This paper presents the development of tourism market through the alternative forms of tourism. Origins and main definitions are presented followed by an analysis of the complexity of classifying the alternative forms of tourism. It is about developing new forms of sustainable tourism that integrate local populations and both natural and human environments of host countries. Ecotourism, cultural tourism and creative tourism support a different philosophy of tourism. Ecotourism in recent years encloses many tourism forms focused on natural environment. In the concept of alternative tourism, the dynamic growth of cultural tourism can be explained by the fast growth of demand for trips to various cultural attractions and amenities. Τhe increase of the educated population around the world, the globalization and technology supported this growth. The cultural tourist, from consumer is transforming to producer of the cultural products and experiences. As culture tourists become more interactive and creative, cultural tourism needs to be repositioned and become more “creative” too. In this way, the present article offers useful information about the current trends in tourism market.
Tourism Management
greg richards , Brian E M King , Emmy Yeung
Highlights • Presents a large-scale survey of cultural experiences in attractions, events and tours • Identifies significant differences between visitor- and context-related influences on the experience • Underlines the importance of active involvement in producing satisfactory experiences • Illustrates the importance of affective experiences of cultural sites for local residents Abstract This paper develops a measurement scale for cultural experiences across different contexts, including attractions, events and tours, in Hong Kong. Four dimensions of experience (cognitive, conative, affective and novelty) are identified through structural equation modelling. The scale is applied to compare visitor- and context-related influences on the experience and on subsequent behavioural intentions. We find that the conative dimension of experience elicits the highest experience scores from visitors, but affective experiences are more significant in distinguishing between different experience contexts and visitor groups. The strongest experiences were attributed to event contexts, followed by tours, and finally permanent attractions. The experience is also enhanced when various sites are combined by visitors to provide a ‘destination journey’. Keywords Visitor experience; Attractions;Events;Tours; Cultural tourism;Hong Kong
Business & Entrepreneurship Journal
Between the 1970s and early 1980s new forms of tourism emerged in developing countries as an alternative solution to the " undesired " type of tourism " the mass tourism " or " the conventional/commercial tourism " or " the traditional tourism ". These forms of tourism appearing in different names and various models, served a more sensitive approach giving priority to natural and cultural resources at the front line of planning and development. The purpose of this paper is to describe the theoretical background of alternative tourism in which origins and main definitions are presented followed by an analysis of the complexity of classifying the alternative forms of tourism. Three of the many forms, seemed to be the core of alternative tourism, are distinguished and analyzed. The ecotourism, the cultural tourism and the creative tourism. Ecotourism in recent years, encloses many tourist forms focused on natural environment. Although these forms are closely related to ecotourism need to be distinguished from it as ecotourism presents many dimensions. In the concept of alternative tourism, the dynamic growth of cultural tourism can be explained by the fast growth of demand for trips to various cultural attractions and amenities. A rise in interest of tourists both to distant cultures and to the local heritage occurred through the increase of educated people around the world and the globalization. Moreover, technology supported this growth. The cultural tourist, from consumer is transforming to producer of the cultural products and experiences. As culture tourist become more interactive and creative, the cultural tourism need to be repositioned and to become more " creative ". In " creative tourism " there is a co-creation of creative experiences between visitors and hosts, usually expressed through the creation of networks, itineraries, courses and events. Finally, the paper ends with a brief mention on the current trends in alternative tourism and the concluding remarks.
GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites
Donatella Privitera
The aim of this study was to contribute to the literature on food tourism by proposing the concept of place and events linked to food, and to analyze the opportunity of gastronomic tourism for local development around Romania (Sibiu Region) and Italy (Sicily Region). The materials were 336 interviews with tourists. Specially designed questionnaire allowed fast data collection. The questions were of qualitative and quantitative type, useful to encode the expressed opinions of the tourists. The results highlight the need for destination marketing organizations to pay more attention to the link between destination image and food events. It concludes that tourism practices enable the continuity of local foods, reinterpreted in the light of urban consumption. Further research is needed to explain why, despite recommend a food tourism policy integrating upon the preservation and the development of the cultural and ethnic identity, in order to attract tourists. Key words: cultural heritage, food involvement, culinary events, Sicily, Sibiu.
Gurel Cetin
A B S T R A C T This study investigates whether and how Istanbul, Turkey is marketed and promoted as a culinary destination. Based on a critical literature review, a research framework was developed, and official brochures and websites for Istanbul, Turkey, were content-analyzed. The research findings suggest that although Istanbul has rich culinary resources and offers many domestic and international cuisines, the city is not well marketed and promoted as a culinary destination. This is one of the first studies discussing how far a leading urban destination in a developing country is not successfully marketed and promoted as a culinary destination. Based on the research findings, this study offers specific theoretical and practical implications on how Istanbul and similar destinations can better utilize their unique culinary resources.
Global heritage: A reader
Yujie Zhu , Noel B. Salazar
RELATED PAPERS
natalie ferranti
ENLIGHTENING TOURISM. A PATHMAKING JOURNAL (ET)
Alfonso Vargas-Sánchez
Devi Kausar
Dr. Ganga Bhavani M
Prince of Songkla University
Inderpal Virdee
TOURISM TODAY: A JOURNAL OF THE COLLEGE OF TOURISM AND HOTEL MANAGEMENT AND DEPARTMENT OF FAMILY AND CONSUMER SCIENCES, BALL STATE UNIVERSITY
Burçin Kırlar Can
Tourism Recreation Research
Brian E M King
Milena Ivanovic , Melville Saayman
A Research Agenda for Creative Tourism
greg richards , Nancy Duxbury
János Csapó
I Gde Agus Jaya Sadguna
International Journal of Tourism Research
Anna Carr , Anne Ford
anna pudianti
José G. Vargas-hernández
Polyxeni Moira
BOOK OF ABSTRACTS of the 3rd CREATOUR International Conference and Creative Tourism Showcase: Creative Tourism Dynamics: Connecting Travellers, Communities, Cultures, and Places
Alexandra Rodrigues Gonçalves , Mirian Nogueira Tavares
Book of Abstracts of the 3rd CREATOUR International Conference2019
Alexandra Rodrigues Gonçalves
Vahid Ghasemi
Second Global Report on Gastronomy Tourism
Ainara Rodriguez Zulaica
ToSEE – Tourism in Southern and Eastern Europe, Vol. 5
Nikola Vojnović
UNIVERSITI SAINS MALAYSIA
Nor Fatimah Abd Hamid
Journal of Tourism Consumption and Practice
greg richards , Daniela Jelinčić , Eliana Messineo
Hilary du Cros
Exploring Creative Tourism, Journal of Tourism Consumption and Practice
Lénia Marques , greg richards , Eliana Messineo
Asia-Pacific Journal of Innovation in Hospitality and Tourism (APJIHT)
James Bury , Emi Iwasaki
Herlan Wijaya
Bulletin of Geography. Socio-economic Series
Jarkko Saarinen
Journal of International Studies, Prince of Songkla University
Faizal Ayob
Mun Yee Lai , Ying Wang
Gülpınar AKBULUT ÖZPAY
Montse Crespi Vallbona , Melinda Jászberényi
Revista Espacios digital
Ignacio Sariego López , Maria de los Baños García-Moreno García
ENLIGHTENING TOURISM. A PATHMAKING JOURNAL (ET), Jun 27
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Open access
- Published: 23 March 2022
Research progress and knowledge system of world heritage tourism: a bibliometric analysis
- Juan Zhang 1 , 2 ,
- Kangning Xiong 1 ,
- Zhaojun Liu 1 &
- Lixiang He 2 , 3
Heritage Science volume 10 , Article number: 42 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
7836 Accesses
27 Citations
Metrics details
In the context of integrating culture and tourism, world heritage tourism research has become a focus in tourism research in recent years. There are increasing discussions in academic circles on the content and methods of this field. Clarifying the knowledge system of research is conducive to dialogue with international theoretical frontiers and integrating, analyzing, and predicting the progress and lineage from a more comprehensive perspective. Still, few studies on the knowledge system of world heritage tourism research have been conducted. To fill this gap, this study uses the SSCI and SCI sub-databases of Web of Science Core Collection as the data source with the help of CiteSpace and VOSviewer software to measure the knowledge system of world heritage tourism research. A bibliometric analysis of 567 publications between 1992 and 2020 was conducted to construct a framework of a knowledge system based on literature statistics and content analysis, revealing the geographic research regions, theories and methods, themes and contents, trend evolution, and future research inspiration. The results show that: (1) the number of publications tends to increase gradually, with the highest in 2019. The authors and research institutions are mainly concentrated in Europe, America, East Asia. China has the highest publications. More literature on cultural heritage as a geographical study area than natural heritage. (2) The research themes, objects, and methods of the sample literature have become more diversified with the advancement of the research stage. The literature on multi-stakeholder research is the largest, followed by tourism impacts and research on World Heritage Sites’ resource management techniques and methods. These studies provide a multifaceted interpretation of the sustainable development of World heritage tourism, mainly from the perspectives of both supply and demand. However, the theoretical system is still incomplete. (3) Future research should strengthen the theoretical system construction, research innovation, cooperation, and research exchange in world heritage tourism research. Pay more attention to the research on the pluralistic value system of world heritage. Focus on exploring research on world heritage tourism’s resilience and localization dilemmas under the impact of the New Crown epidemic. To reveal the synergistic mechanisms and paths of diversified livelihoods of World Heritage Sites’ residents in ecologically fragile and impoverished areas.
Introduction
Research on world heritage (WH) tourism began to emerge in the mid-twentieth century and has shown rapid growth in the early twenty-first century and continues today. A World Heritage Site (WHS) is a scarce area of outstanding universal value (OUV) that requires long-term protection, is non-renewable and irreplaceable, as identified by United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) and World Heritage Committee (WHC) [ 1 ]. World Heritage-listed areas typically receive an order of magnitude more tourist visits than their non-listed counterparts [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. These areas are also often used as a means of economic regeneration through tourism development [ 5 , 6 , 7 ], as they have a significant economic impact on local communities [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. In addition, WHSs contribute to national image building [ 12 , 13 , 14 ] and promote destination branding [ 13 , 15 , 16 ]. Thus various national and regional governments actively apply for WHSs [ 15 ]. As of December 2021, the total number of enlisted heritage sites is 1154, including cultural, natural, and mixed categories, registered in 167 countries. In recent decades, WHSs have attracted a great deal of attention in promoting tourism and economic development and heritage conservation, driven by the benefits of the “WH” brand. The series of impacts and challenges arising from the inscription and development frenzy has led to a lively debate and a re-examination of WH tourism in the light of the increasingly popular concept of sustainable tourism development.
Tourism utilization and WH conservation are inevitably intertwined, and there is a symbiotic or tension between the two [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]. The development of tourism can create new values and social relations for WHSs and is often seen as a tool to combat poverty and promote sustainable development [ 8 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. However, many WHSs also face challenges by the rapidly expanding tourism industry, population pressure, environmental pollution, conflicts between residents, tourists, government, and other stakeholders threaten WH conservation and sustainability. The interaction between conservation and use has become a vital issue in WH tourism research [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. Development pressure due to local socio-economic issues, poor legislation and management, and inappropriate tourism operations are the leading causes of conflicts between heritage conservation and tourism development [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ].
Controversies in academic circles regarding WH tourism research are becoming increasingly intense, and differences in positions and perspectives have divided the study into different categories. For example, environmentalists believe that WH and tourism are entirely contradictory. The development of tourism poses a threat to the environmental protection of WHSs [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. Scholars concerned with social development emphasize that tourism can promote the economic development of WHSs [ 5 , 8 , 22 ]. Socio-ecological conservation advocates focus on exploring the synergy between environmental conservation and tourism economic development in WHSs [ 34 , 35 ]. It is essential to clarify WH tourism research’s progress and academic dynamics to advance research in the field, thus explaining the unique research objects and focus.
Existing studies have been categorized and reviewed mainly in terms of fundamental issues of WH tourism destinations, tourism activities, tourists, and other stakeholders, mostly an analysis of the content of the literature. While review studies based on bibliometric analysis have emerged in recent years, integrated accounting and prognosis of the development lineage of WH tourism research are relatively rare. A knowledge system is structured knowledge that members of a discipline or field use to guide their practice or work [ 36 ], including a systematization of the structure, principles, and examples of professional knowledge generated by members through continuous discovery and validation. The organization of the knowledge system facilitates the self-reflective growth and reproduction of WH tourism research [ 37 ]. A single visual knowledge map can hardly reflect the intrinsic nature of the knowledge system, and a single content analysis method is slightly lacking in objectivity. To fill this gap, this study mainly uses two types of scientometric tools, CiteSpace and VOSviewer, which integrates quantitative analysis represented by scientometric analysis, knowledge mapping, and keyword clustering, and content analysis represented by topic reading to identify the research progress and knowledge system of WH tourism research. To provide a comprehensive and objective overview of the current state of research in the field and provide a scientific reference for subsequent research. To achieve this, we set the following objectives:
To reveal the basic characteristics of the literature (section 3: changes in the number of publications, authors, research institutions, geographical research areas).
To identify key areas of research progress (sections 4–5: key research areas and contents, research theories and methods, and evolution of research trends).
To build a framework of knowledge (sections 6–7).
Material and methods
Research methods.
Bibliometric analysis helps decipher and map the cumulative scientific knowledge and evolutionary nuances of well-established fields by making sense of large volumes of unstructured data in rigorous ways. It enables and empowers scholars to gain a one-stop overview, identify knowledge gaps, derive novel ideas for investigation, and position their intended contributions to the field [ 38 ]. In recent years, bibliometric analysis in heritage tourism has emerged sporadically [ 39 , 40 ]. However, there is a relative lack of bibliometrics on tourism research in WHSs.
Science mapping is a generic domain analysis and visualization [ 41 ]. It is a study of scientific knowledge and belongs to scientometrics [ 42 ]. Several valuable scientific knowledge mapping tools have been born in bibliometric analysis, such as CiteSpace, VOSviewer, Sci2, BibExcel, Carrot2, etc. CiteSpace software can more intuitively and quickly visualize the focus and evolutionary trends in a specific field than other visualization and analysis software. It can reveal the inner connection between knowledge bases, conducive to better grasping the key points and future research development direction. VOSviewer software has unique advantages in graph display and clustering technology and is often used to display large networks [ 43 ]. The combined use of CiteSpace and VOSviewer software visualizes the highlights and trend evolution of WH tourism research. Using bibliometric visualization software for statistical data analysis, combined with content analysis, we objectively interpret WH tourism research progress and construct a knowledge system framework to provide scientific reference for WH conservation and utilization.
Defining terms
WHS is a rare and irreplaceable treasure of humanity recognized by UNESCO and WHC as a heritage site and natural landscape of OUV. OUV is the criterion for being selected as a WHS. It means cultural and/or natural significance, which is exceptional to transcend national boundaries and be of common importance for present and future generations of all humanity. The World Heritage List (WHL) published by UNESCO divides WHS into three main categories: cultural site (including cultural landscapes), natural site, and mixed cultural and natural site. According to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (Convention) promulgated in 1972, world cultural heritage means cultural objects, architectural ensembles, and sites of OUV. World natural heritage refers to natural features of OUV, threatened animal and plant habitat areas, wild places of interest, or delineated natural areas. Only properties that partially or fully satisfy cultural and natural heritage definitions in Articles 1 and 2 of the Convention can be considered “mixed cultural and natural heritage.” Following the Convention’s definition of WH, we focus on the tourism development of world cultural, natural, and mixed heritage sites. Therefore, publications that meet the following conditions are excluded.
A study of heritage tourism unrelated to WHS.
Articles and comments on intangible heritage.
Document selection
In this study, we used the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection database as the data source, selected one of the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI) and Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) databases to search. The reason for using this database is that it is one of the most widely recognized international databases with data going back to 1900 and provides a rich, comprehensive collection of information from more than 18,000 authoritative, high-impact scholarly journals worldwide. Search the literature using 5 sets of keywords. (a) “world heritage” and “tourism,” (b) “world cultural heritage” and “tourism,” (c) “world natural heritage” and “tourism,” (d) “mixed heritage” and “tourism,” (e) “cultural landscape,” “world heritage” and “tourism.” Without limiting the starting time, the data were last updated on December 31, 2020.
Searches returned 672 documents (Fig. 1 ): (a) 604 documents for world heritage and tourism, (b) 29 documents for world cultural heritage and tourism, (c) 24 documents for world natural heritage and tourism, (d) 3 documents for mixed heritage and tourism, and (e) 12 documents for cultural landscape, world heritage and tourism. We excluded 10 documents not in English, and 28 documents that appeared in two searches or more (duplicates). Finally, a full-text assessment was carried out, resulting in 567 papers (Additional file 1 : Appendix S1).

Approach for the material selection
Document analysis
In the final data analysis phase, an analysis protocol has been applied to critically analyze the collected publications’ content and describe it in a structured way (Fig. 2 ). It sought to gather each document’s essential characteristics, focus, content, and existing gaps and needs in WH tourism research. Finally, a full-text assessment was conducted to summarize findings and problems with existing studies and present future research needs.
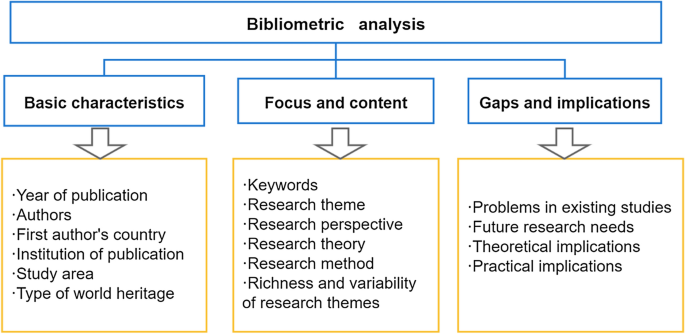
Analysis protocol for the material collection
Basic characteristics of the selected publications
Year of publication.
As shown in Fig. 3 , the number of publications generally showed an upward trend from 1992 to 2020. At the end of the twentieth century, related scholars began to pay attention to this emerging field, and the results appeared one after another. However, the number of articles published between 1992 and 2006 was small because of the initial research stage, with an average of only 2 articles per year. Since 2007, the number of articles has increased significantly, in 2019 was as high as 94, indicating that the academic community’s research on world heritage tourism is highly enthusiastic.
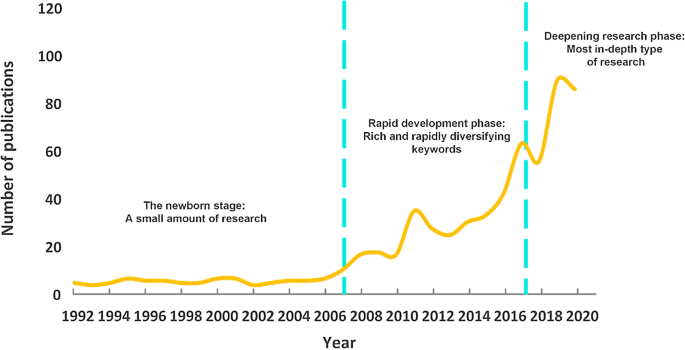
The number of publications per year
First author’s country
The sample literature came from more than 50 countries in total, and the top 10 countries in terms of the number of publications were mainly concentrated in East Asia, Europe, and America (Fig. 4 ). China has the most significant number of publications, accounting for 20%. The early research literature was mainly concentrated in developed countries like Australia and the United Kingdom. Research in China began to appear in 2003, with a significant increase in volume in 2009, and maintained the world’s top-ranking number of publications during 2014–2020. Since China joined the Convention in 1985, it has become one of the fastest-growing countries in the world in terms of the number of WHSs, attracting the attention of the academic community and increasing the number of research results year by year. By the 43rd World Heritage Conference, 55 WHSs have been successfully nominated, ranking first in the world with Italy. It can be seen that the geographical distribution of research literature is positively related to the level of regional economic development and the number of WHSs.
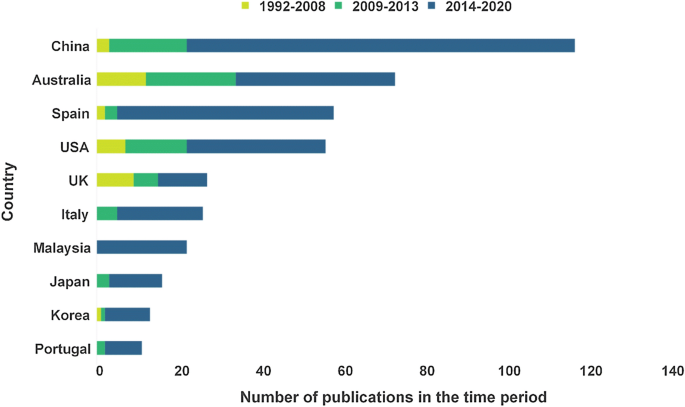
Number of publications from the top 10 countries at different periods
Authors and institutions
(1) authorship and cooperation networks.
There were 475 first authors on the 567 sample papers. In Fig. 5 , the larger font size of the authors’ names indicates more publications, and the larger nodes indicate more collaboration between authors. It shows that Su, Rasoolimanesh, Martinez-Perez A, Xu, and Buckley are the top five in terms of the total number of publications. And the collaborative network has a core–edge structure with fewer connections between the nodes, indicating that only a few researchers collaborate, and the majority of scholars are weakly connected. Most research teams were formed after 2011, indicating that research on WH tourism has gradually increased since then. For example, Su and Wall have collaborated on many publications on community engagement in heritage sustainable management research. Rasoolimanesh and Jaafar have produced many results around resident perception research in heritage sites, with 6 articles published in 2016.
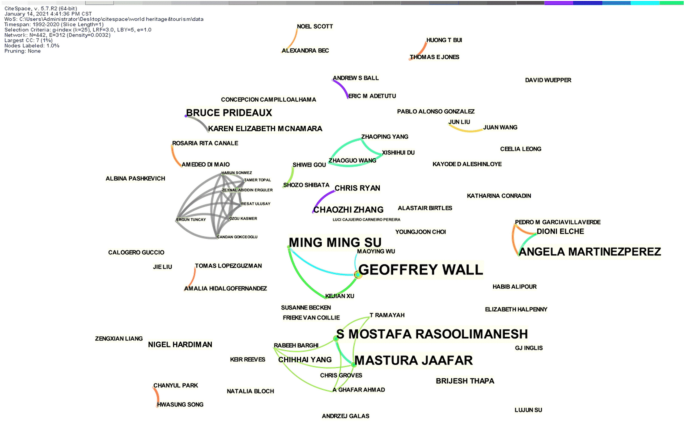
Author co-cited network
(2) Issuing institution
According to the frequency in Table 1 , the top ten research institutions in terms of the number of publications are mainly universities and colleges, and there are relatively few research institutes. Sun Yat-Sen University and the Renmin University of China are the primary research institutions in China. The rest of the research institutions are mainly located in Canada, Australia, Spain, and Malaysia. Research institutions have specialized WH tourism research groups, such as Sun Yat-sen University in China, whose primary literature is contributed by the team of Zhang, Xu, and Sun.
Geographical study area
There are 56 world natural heritage sites and 123 cultural heritage sites studied in 434 documents. 155 of these articles (36%) are about natural sites, 254 (59%) about cultural sites, and 25 about mixed heritage sites (5%). The WHSs that appeared more than 2 times in the sample literature were counted and sorted by their countries (Table 2 ). It shows that China, Australia, Spain, Malaysia, Korea, and Cambodia are the hot geographical areas of academic research, with the Great Barrier Reef (n = 18), Melaka and George Town (n = 15), and Angkor (n = 11) being the most prominent. In recent years, research results about Jiuzhaigou Valley Scenic and Historic Interest Area and Wulingyuan Scenic and Historic Interest Area in China and the archaeological heritage of the Lenggong Valley in Malaysia have increased.
Key research areas and content
Keywords are a condensation and distillation of the core content of the literature. A high frequency of keywords can reflect the focus in a particular area [ 44 ]. Using the CiteSpace keyword analysis function to identify the main topics of interest to the academic community. Table 3 shows the keywords with a word frequency greater than 10 times. It can be seen that management, conservation, impact, perception, satisfaction, sustainable tourism, and stakeholders are the concerns in WH tourism research. In addition, we found that keywords such as customized authenticity, adaptive management, social-ecological system, sustainable livelihood, and resilience had a word frequency of fewer than 5 times, giving us some clues to track the frontier. Although the high-frequency keywords can reflect the main focus of existing research, the article’s overall idea and the mainline cannot be seen through the keywords.
Research themes
After identifying the high-frequency keywords, the research themes in the field were further clarified. To avoid the limitation of keywords, combining keyword clustering with full-text reading, the key research areas of WH tourism research were summarized into the following 8 themes.
(1) Sustainable tourism
The sustainable tourism theme contains 86 articles (15% of total). Scientific research has always been very focused on assessing the sustainability of tourism [ 45 ]. The development of governmental sustainable management strategies (n = 25), community residents’ perceptions and attitudes towards participation in tourism development (n = 28), spatial evolution of destinations (n = 8), low-carbon environmental measures in ecotourism (n = 12), and community livelihood diversification (n = 13) have been studied as factors influencing sustainable tourism in WHSs. Among them, the most crucial academic attention has been paid to the relationship between community support and sustainable tourism. Several empirical studies have been conducted, showing that local and community participation in WH management is necessary for sustainable tourism [ 46 , 47 ]. Empowering local communities to participate effectively in tourism decision-making and to be able to share equitably in the benefits of tourism development is an essential principle of sustainable tourism [ 25 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 ]. Sustainable tourism has been widely accepted to mediate tensions and balance the relationship between heritage conservation, tourism management, social pressure, and economic development.
(2) Authenticity
The theme includes 14 articles (2% of total). The UNESCO have adopted authenticity as a critical principle for inscription on the WHL [ 1 ]. In the tourism context, three commonly used authenticity concepts are objective authenticity, constructive authenticity, and existential authenticity [ 53 ]. Studies of authenticity in WH tourism focus on existential authenticity (n = 10) and constructive authenticity (n = 4). Existential authenticity emphasizes tourists’ perceptions, experiences, and preferences of authenticity, including experiences, emotions, attachments, and identities [ 54 ]. Scholars generally agree that the authenticity of the tourist experience has a significant impact on satisfaction and loyalty and that the quality of WH tourism is enhanced by authenticity [ 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 ]. The perception of authenticity increases the heritage destination value [ 60 ]. Constructed authenticity discussions focus on customized authenticity that tourists can seek and embrace even in publicly staged or produced contexts [ 61 ]. The debate on the authenticity of WH tourism has shifted from the static perspective to how authenticity is interpreted [ 62 ]. The acceptance of authenticity itself depends on tourists’ perceptions.
Authenticity is a controversial concept in WH tourism studies [ 53 , 63 ]. Some scholars have even suggested that the concept should be abandoned because of its problematic nature [ 64 ]. Despite its clear importance, authenticity is a problematic and insufficiently explored concept, which hinders its practical application [ 53 ]. So fewer articles are examining the use of authenticity in WH tourism practice. However, with the rapid development of WH tourism and the microscopic shift in WH tourism research, Scholars have attempted to explore the impact of different authenticity on the visitor experience. They have confirmed that understanding how visitors interpret authenticity is vital for marketing and managing heritage sites [ 56 , 57 ]. After 2017, there has been a marked increase in research on the application of authenticity in WH tourism practice. The number of articles is relatively small because it is still exploratory.
(3) Management techniques and methods of tourism resources
The second-highest number of publications (22% of the total) studied management techniques and strategies for WH tourism resources, with 124 articles. Dynamic conservation and multidisciplinary research are fundamental approaches to planning and sustainable management of WH. The main focus is on techniques and methods for WH resource survey and assessment (n = 32), management and conservation enhancement (n = 57), presentation and education (n = 14), visitor flow forecasting (n = 3), visitor safety management (n = 6), and itinerary design (n = 12). Thanks to the continuous progress of technology, a series of new technologies and methods such as 3D technology [ 65 ], geoinformation technology, and remote sensing(RS) [ 66 , 67 ], augmented reality(AR) [ 68 ], and mixed reality (MR) [ 69 ] have facilitated the management and conservation of WH tourism resources. Western scholars focus on the physical conservation of heritage sites, and research and conservation also focus on achieving this goal through technology [ 65 , 70 , 71 ]. Recently, scholars have taken social-ecological system theory [ 34 ], adaptive management theory [ 72 ], and resilience theory [ 35 , 73 ] to analyze the resource conservation and tourism development contradictions and propose synergistic paths on this basis.
(4) Tourism impacts
There are 110 articles on the tourism impacts (20% of total). The impacts of tourism on WHSs is mainly environmental (n = 50), economic (n = 13), social (n = 15), and cultural (n = 5), with some studies discussing the combined impact (n = 27). There is a consensus in the academic community that demographic pressure from tourism remains a major threat to WHSs’ environmental and cultural integrity. Highly intensive tourist demand significantly challenges the sustainability of WHSs [ 74 , 75 ]. In addition, local socio-economic development pressures and mismanagement also pose challenges to its health. Most studies have examined the objective environmental impacts by assessing tourism environmental capacity, ecological tourism footprint, and eco-efficiency. The destruction of the natural environment and ecosystems of WHSs and the intensification of environmental pollution of air, water, vegetation, soil, etc. are the major negative environmental impacts [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 ], or assessing the environmental impacts from the perspective of residents’ perceptions [ 10 , 80 , 81 ]. Tourism development contributes to sustainable livelihoods, women’s empowerment and gender equality, and improved recreational facilities and public amenities in WHSs [ 9 , 22 , 23 , 82 , 83 , 84 ]. However, it can also result in negative impacts such as increased cost of living, rising real estate and prices, income imbalance, littering, and host-client conflict [ 85 ]. In addition, scholars represented by Jimura, Rasoolimanesh, and Kim have confirmed through their studies that the rapid development of WH tourism has improved the cultural identity of residents to some extent. Traditional arts and culture have been preserved and revived to some extent. Still, it has also weakened the local spirit of local communities and created a series of conflicts between village historical heritage conservation and tourism development [ 8 , 9 , 80 , 86 , 87 ].
(5) Stakeholders
This topic has the largest publications, including 143 articles (25% of total). WH tourism stakeholders were studied mainly by residents (n = 45), tourists (n = 54), government departments (n = 19), tourism enterprises (n = 10), and multiple stakeholder interactions (n = 15). Scholars often use perception studies as a breakthrough to study stakeholder synergy. Visitor perception studies are useful for understanding their motivations and expectations for undertaking WH tourism, strengthening visitor management, and promoting destination marketing and promotion. Studies have been conducted on visitor perceptions mainly from heritage presentation and interpretation, marketing, and management. The research mainly focuses on the relationship between tourists’ perceived value, quality of experience, satisfaction, and loyalty [ 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 ]. The perceived impact of tourism development by community residents is a key and necessary element of community engagement research [ 25 , 95 , 96 , 97 ]. Scholars have studied residents’ perceptions or attitudes through cross-sectional and longitudinal comparisons. They agree that socio-economic status, local attachment, environmental attitudes and values, and participation in the planning and decision-making process become the main factors determining residents’ perceptions of tourism impacts [ 98 , 99 ]. The local attachment is the most critical element [ 100 ].
As the leading force in the “inscription” process, the government is the guarantor of the rational development of heritage tourism resources and the involvement of stakeholders. Many issues hinder the sustainable development and management of heritage tourism in developing countries. Lack of political will, government priorities, and financial assistance are the main constraints to WH management [ 101 , 102 , 103 ]. Although governments do not hesitate to develop tourism, their mismanagement is inevitably criticized [ 104 , 105 , 106 ]. Travel agencies and tourism companies are an integral part of WH conservation. Research on tourism companies has focused on maximizing economic benefits and exploring breakthrough innovations at the firm level in the context of cultural tourism clusters [ 107 , 108 ]. The perceptions of corporate managers regarding their social responsibility in WH conservation have not received much attention from scholars [ 109 , 110 ].
(6) World heritage value
21 papers discuss the value of WH (4% of total). The study is mainly focused on OUV (n = 8), economic value (n = 6), and social value (n = 7). Research on OUV of WH focuses on different stakeholders’ perceptions of heritage values and the factors that influence them. Some studies focus on discussing OUV narration from a guide’s perspective [ 111 , 112 ]. However, the understanding and claiming of the pluralistic value of heritage has not been given much attention. Tourists’ tourism satisfaction and education level are the main factors influencing their perception of OUV [ 113 , 114 ]. Residents’ perception of OUV positively impacts local attachment and willingness to preserve heritage. The conditional value assessment method (CVM) is a commonly used method for estimating the economic value of WHSs, providing a scientific reference for admission management systems and better brand marketing [ 86 , 103 , 115 , 116 ]. In addition, recent studies have explored how to construct heritage social values based on OUV and have indicated that social values are beneficial to enhance the international and national image and tourism attractiveness of WH destinations [ 117 ]. Heritage values are artificially assigned by different heritage subjects rather than naturally generated and self-evidently existing. The identified OUV emphasizes the materiality of heritage with a Eurocentric perspective. However, there is also a need to focus on non-material content such as people and activities associated with WHSs to better convey heritage stories and a sense of place [ 112 , 118 ].
(7) Destination brand image building and marketing
The theme includes 40 articles (7% of total). Studies have focused on WH brand equity management (n = 11), marketing strategies, platforms and tools (n = 12), stakeholder perceptions of WHS brand image (n = 8), visitor market segmentation (n = 5), and heritage promotional discourse (n = 4). WH represents the international identity of the inducted country, and it can play an essential role in building a national image and the highly competitive global tourism market [ 12 ]. The success of the inscription is a great honor for the selected country, and the “WH” brand is widely used in marketing campaigns to promote national tourism and increase the destination’s visibility. Scholars generally agree that the WHL helps build destination images [ 13 , 119 ] and discusses using the WH brand for destination image building and marketing. It is also argued that establishing emotional attachment to build destinations and the interpretation of authenticity by tourists are vital issues in branding tourism destinations in today’s tourism market [ 56 , 120 ]. Although the WHL is a powerful brand that significantly impacts tourism, it still requires proper management to maintain brand equity. However, brand image building and marketing need to be integrated with the local culture [ 121 ], focus on local storytelling, and highlight the elements that characterize its heritage value to develop differentiated marketing.
(8) Impact of the World Heritage List on tourism demand
The literature examining the impact of the WHL on tourism demand includes 29 articles (5% of total). The majority of scholars see “inscriptions” and “accessions” as “magnets” that attract tourists and guarantee an increase in the number of visitors to heritage sites. They generally believe that “inscription” positively impacts local tourism demand (n = 22). It has been shown to have a positive impact on local tourism demand through the use of “inscription” in China [ 4 , 122 , 123 , 124 ], Italy [ 125 , 126 ], Spain [ 127 ], Israel [ 15 ], and other case studies confirm this finding. Contrary findings (n = 7) argue that the WHL does not necessarily promote tourism [ 128 , 129 , 130 ]. Some scholars in the recent literature have questioned the assumption of a linear relationship between the total number of WHSs and tourism demand in previous studies, emphasizing the need to distinguish between the different impacts of tangible and intangible heritage on tourism demand [ 131 ]. The effects of the WHL on heritage tourism vary from country to country and region to region, with findings running depending on the study area, research perspective, and methodology. The disagreement among scholars makes the research on the effect of WHL on tourism demand consistently popular [ 4 , 130 , 132 ].
Research theory and methodology
Given the small number of high-frequency keywords regarding research methods reflected in Table 3 , all keywords were analyzed in this paper to gain insight into the main theories and methods in the field. In addition, a glossary of terms representing specific research theories and methods was summarized by analyzing the content of the literature (Table 4 ). Various well-established theories such as sustainability development theory (n = 67), community participation theory (n = 62), stakeholder theory (n = 25), place attachment theory (n = 17), authenticity theory (n = 16), sustainable livelihood (n = 13), social-ecological system theory (n = 10), resilience theory (n = 7), social exchange theory (n = 6), and planned behavior theory (n = 5). Scholars have used these theories to argue for problem and pathway studies of WH tourism. Research methods are mainly qualitative (n = 151) and quantitative (n = 327), or a combination of both (n = 89), and quantitative analysis methods are becoming increasingly diverse.
Evolution of research trends
With the continuous advancement of WH conservation practices, WH tourism research themes are becoming increasingly diverse (Fig. 6 ). Based on the number of publications, keyword clustering analysis, and interpretation of the leading research content of the literature, the following stages are used to characterize the evolution of research trends in this field.
Evolution map of world heritage tourism research theme
The first stage (1992–2006): the newborn stage. The number of WHSs grew slowly during this period, and research in WH tourism is beginning to receive attention, but not much heat. The literature in this stage is small, and the clustering of keywords is not apparent because of the small amount of literature. The research package mainly includes the functional zoning planning of WHSs, the impact of tourism activities on the natural environment, and the impact of national tourism policies on the development of WHSs. More studies at the macro level mainly focus on proper conservation management of tourism resources and exploring sustainable development strategies. In addition, there are more studies on the management and conservation of WH based on tourists’ perspectives, emphasizing the management of tourists to promote the WH conservation. In terms of resource types, there are more case studies about the Great Barrier Reef, a world natural heritage site.
Phase 2 (2007–2017): rapid development phase. During this period, the proliferation of WHSs and the range of challenges and impacts of tourism overdevelopment have generated a lively debate in academic circles. The publications showed a rapid growth trend in 2007 and beyond, with increasingly rich keywords and rapidly diversifying research themes. Theoretical thinking and practical research have been expanded, and research perspectives have been broadened with distinctive interdisciplinary features. The research on WH conservation gradually changes from “balancing conservation and development” to the paradigm of “conservation for development.” Therefore, besides focusing on the conservation of heritage resources, the socio-economic benefits of WH are gradually being paid attention to, and the impact of WHL on tourism demand has become a more intense issue of debate among scholars. In addition, the conservation philosophy of world natural heritage sites is undergoing a shift from neglecting communities to valuing them, from absolute conservation to gradient conservation, and paying more attention to human needs and development. Therefore, studies on multiple stakeholders have become more prosperous. Residents’ perception, community involvement, local attachment, tourists’ experience, tourists’ loyalty, and satisfaction and the relationship between them have become the focus of scholars’ attention.
Phase 3 (2018-): deepening research phase. The WH has moved from rapid quantitative growth to enhanced conservation and management quality. Research in this period expands slowly and is the most in-depth type of research. New ideas such as digitalization, cultural creativity, and low-carbon tourism are also penetrated in WH resource conservation. Scholars began to focus on areas such as the evolution of cultural space in WHSs, the construction of WH brand assets, residents’ responsibility and attitude towards heritage conservation, well-being, and the resilience of socio-ecological systems. Meanwhile, further deepening research on the impact of the WHL on tourism continuity, the spatial and temporal evolution of residents’ perceptions, the promotion of destination images and brand effects, the construction of heritage authenticity, and sustainable livelihoods of communities. Continued attention is paid to exploring pathways for the management and sustainable tourism development of WHSs.
Knowledge system framework for world heritage tourism research
To better understand the progress and lineage of WH tourism research, a framework of knowledge system is constructed. This framework is based on the basic characteristics of the literature, the key research areas and content, research theories, the evolution of research trends, and future research gaps summarized in the previous section [ 133 ] (Fig. 7 ). The first box’s contents in the left column are derived from high-frequency keywords. The keywords in each box are sorted in word frequency from highest to lowest. For example, in the first box of the first column, the highest frequency is “management,” and the lowest is “conflict.” The sustainable tourism theme is summarized by extracting 11 keywords and interpreting the content of the literature and presented inside the first column of key research areas and content. The other 7 themes were extracted by the same method. The endpoint of the whole knowledge system framework points to two intersecting circles. It consists of three high-frequency keywords: “world heritage,” “tourism,” and “world heritage tourism,” indicating that world heritage and tourism are inseparable.
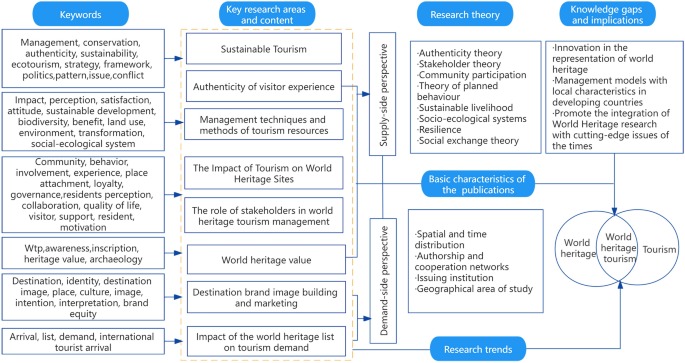
Knowledge system of world heritage tourism research
Around the binary debate of conservation and utilization, the conservation and management practices and the tourism and leisure practices of WHSs have become two main lines of research, respectively. Research perspectives are mainly cut from both supply and demand sides but are not discrete. For example, WH tourism authenticity focuses on both the interpretation of authenticity by tourists in the demand perspective and the management and development of heritage resources in the supply perspective. The supply-side perspective emphasizes the study of destination management, the tourism impacts on WHSs, and stakeholders such as communities and governments in management as the focus of WH tourism. In particular, the ecological, social, economic, and cultural impacts of tourism on WHSs, sustainable livelihoods, and community perceptions have received continued attention from scholars. The demand-side perspective focuses on WH tourism from a marketing perspective, with branding and marketing of destinations, the impact of the WHL on tourism demand, and the relationship between visitor experience, perception, and satisfaction as the primary research components.
In terms of research theories, academics mainly draw on relevant theories from sociology, anthropology, and ecology to explain and solve the contradiction between WH conservation and tourism development. The interdisciplinary trend is more prominent. However, there is a lack of theoretical research on geography. From the perspective of the human-land relationship system in WHS, future research should fully use geography’s comprehensive and systematic nature. And apply it more to the management techniques and methods of WH tourism resources to better understand the contradiction between WH conservation and tourism development and balance the relationship between them.
Knowledge gaps with implications for future research
WH tourism research focuses on the conservation and use of WHSs and examines the development of society through the interaction of the two. How to realize the synergy between WH conservation and tourism development will be a continuing focus of scholars in this field of research. Future research can focus on exploring the following areas.
Innovative ways of representing World Heritage
From a demand-side perspective, subsequent WH tourism demand research should focus on people’s subjective constructs, such as tourists’ cultural needs and preferences. To match consumer perceptions with the intrinsic values characterized by WH [ 14 ] and target brand building and marketing. Demand research on the supply side should explore how to cut through the origin and form of WH and bring heritage back to today’s social life through the industrialization of cultural tourism. The storytelling of WH and cultural communication in WH tourism should be the focus of scholars’ later research. Among them, local culture plays a vital role in the sustainable management of WHSs, and intangible elements such as memories, emotions, and feelings related to WHSs should also attract the attention of scholars. In addition, most of the current studies are on cultural heritage, while there is relatively little research literature on the cultural lineage of natural heritage. Future research should strengthen the value of natural heritage constructed based on OUV and pay attention to local spiritual maintenance and humanistic values. Mainly focus on exploring the mechanism of the construction of cultural confidence and cultural identity in WH conservation and exploring the synergistic path of heritage conservation and tourism development.
To explore world heritage management models with local characteristics in developing countries to synergize conservation and tourism development
Compared with leading foreign studies, WH tourism research in developing countries is more concerned with management systems, government policies, and community participation. Most of the existing studies have explored the issues themselves. There are more case studies and fewer studies that summarize the patterns. More attention needs to be paid to micro-area studies to draw on the results and paradigms of current research. Taking China as an example, localized management and development models should be explored in light of the unique characteristics of WHS, such as focusing on the sustainable development of WHS in karst ecologically fragile and poor areas. It is necessary to propose targeted WH tourism management policies based on adaptive and collaborative community management [ 77 ] and seek a win–win model for WH conservation and regional development. A multi-element, multi-scale and multi-system approach should be adopted to explore the evolutionary patterns of tourism development in WHSs. The aim is to strengthen the capacity to predict the evolution of WHSs’ spatial patterns and structures and improve the ability to regulate and support decision-making for sustainable development. In addition, it is necessary to build an inclusive, democratic, and dialogical space, deepen the research on the role mechanisms of different stakeholders in WH conservation and tourism development, pay attention to the research on the value perception and local attachment of tourism business managers, further clarify their social responsibilities, attitudes, and behaviors, and their influencing factors, and optimize their roles in heritage conservation and management. At the same time, it should strengthen the research on the localization dilemma of WH under the influence of the new corona epidemic and focus on the multiple livelihood synergy mechanism and path of residents in WHSs in ecologically fragile and poverty-stricken areas.
Promote the integration of World Heritage research with cutting-edge issues of the times
The help of modern science and technology such as big data, cloud computing, the internet of things, artificial intelligence, digital conservation technology, interactive display technology, information space management technology, and other vital technologies provide new paths for comprehensive, systematic, and complex research on WH. They provide scientific and technological support to expand further the depth and breadth of research on WH tourism. Subsequent research should focus on combining technology and local heritage characteristics, highlighting the “materialization” of technology while emphasizing humanistic care. In addition, the new crown epidemic has exposed and exacerbated tourism’s vulnerability, especially for communities that are highly dependent on tourism as a source of livelihood, and sustainability is threatened. At the same time, the epidemic has also had a tremendous impact on government management practices, tourist travel behavior, tourism business operation models, changes in management models, host-client relationships, market demand, and consumption habits. They are making it necessary to explore adaptive management models and future directions for the industry appropriate for local practices. Finally, resilience theory emphasizes studying the historical relationship between society and its environment. The study of the mechanism of community resilience on WH conservation may become a breakthrough point for adaptive management research. In the future, we need to pay attention to the study of the resilience path of WH tourism after the new crown epidemic to enhance the resilience of communities in WHSs.
Based on the “Web of Science” database, the knowledge mapping software CiteSpace and VOSviewer were applied, combined with bibliometric and content analysis methods, to reveal the knowledge system’s themes, trends, and frameworks of WH tourism research. From the essential characteristics of the literature, chronologically, the research began in the 1990s, achieved rapid development in the first decade of the twenty-first century, and is booming. It is mainly concentrated in countries and regions with rich WH resources, developed economies, and more mature tourism industries. Although a specific group of authors has been formed, a particular research circle has not yet been created. The cooperative relationship between most authors is weak. Research institutions are mainly concentrated in universities.
The increasing refinement of WH conservation concepts and tourism development practices has contributed to research trends. The evolution of the research phases shows that WH tourism research has gradually become more microscopic and specific, with further development of theoretical analysis and scientific practice and the expansion of the study to multiple stakeholders such as tourist objects and external societies. Research topics have shifted to the micro-level, such as residents’ perceptions of tourism impacts and the cultural and economic impacts on WHSs. As research deepened and diversified, several new concepts and techniques began to be applied to WH resource conservation and evaluation. Although the expansion of research has gradually slowed down, deepening research exploring the multidisciplinary intersection and multiple research methods and perspectives have further advanced.
The knowledge system has formed a multidisciplinary and multi-level comprehensive research situation. In terms of research methods, the combination of qualitative and quantitative is the main focus. The methods of quantitative analysis are becoming more and more diversified, mostly cutting from micro cases for empirical research, and the research content is mainly focused on both supply and demand of WH tourism. However, the theoretical system is not yet perfect. The knowledge mapping, constructed knowledge systems, and inherent knowledge linkages presented in WH tourism research have specific academic value. The evolution of the knowledge system further deepens the disciplinary innovativeness. Whether from supply or demand, future research should seek breakthrough points based on existing research, innovate WH representation, tell heritage stories, and strengthen research on the cultural lineage of natural heritage sites. To promote the integration of WH research with cutting-edge issues of the times, research the paths of resilience and localization dilemmas of WH tourism after the new crown epidemic, and focus on the inhabitants of WHSs in ecologically fragile and impoverished areas. We will also study the mechanism and paths of multi-livelihood synergy for residents in environmentally vulnerable and poor regions. We will strengthen theoretical system construction, research innovation, and exchange and cooperation to form a more prosperous and in-depth knowledge system of WH tourism research.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this manuscript as no datasets were generated or analyzed.
Abbreviations
World Heritage
World Heritage Site
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation
World Heritage Committee
World Heritage List
Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage
Conditional value assessment method
Geographic information system
Partial least square-structural equation modelling
Analytic hierarchy process
Principal component analysis
Analysis of variance
Remote sensing
Augmented reality
Mixed reality
UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Operational guidelines for the implementation of the world heritage convention. WHC.21/01. Paris: UNESCO, 2021. https://whc.unesco.org/en/guidelines/ . Accessed 17 Jan 2022.
Yang CH, Lin HL, Han CC. Analysis of international tourist arrivals in China: the role of world heritage sites. Tour Manag. 2010;31(6):827–37.
CAS Google Scholar
Gao YY, Su W. Is the world heritage just a title for tourism? Ann Tour Res. 2019;78: 102748.
Google Scholar
Han W, Cai JM, Wei YG, Zhang Y, Han Y. Impacts of the world heritage list inscription: a case study of Kaiping Diaolou and Villages in China. Int J Strateg Prop Manag. 2020;24(1):51–69.
Buckley R, Shekari F, Mohammadi Z, Azizi F, Ziaee M. World heritage tourism triggers urban–rural reverse migration and social change. J Travel Res. 2020;59(3):559–72.
Agapiou A. UNESCO World Heritage properties in changing and dynamic environments: change detection methods using optical and radar satellite data. Herit Sci. 2021;9(1):1–14.
Su MM, Wall G, Xu KJ. Heritage tourism and livelihood sustainability of a resettled rural community: mount Sanqingshan world heritage site, China. J Sustain Tour. 2016;24(5):735–57.
Jimura T. The impact of world heritage site designation on local communities—a case study of Ogimachi, Shirakawa-mura, Japan. Tour Manag. 2011;32(2):288–96.
Zhang X. Impact of rural tourism on residents’ well-being in traditional ancient villages: a case of North Guangxi. Herit Sci. 2021;9:138.
Slabbert E, Du Plessis E, Digun-Aweto O. Impacts of tourism in predicting residents’ opinions and interest in tourism activities. J Tour Cult Chang. 2021;19(6):819–37.
Christensen J, Jones R. World heritage and local change: conflict, transformation and scale at Shark Bay, Western Australia. J Rural Stud. 2020;74:235–43.
Silverman H. Border wars: the ongoing temple dispute between Thailand and Cambodia and UNESCO’s world heritage list. Int J Herit Stud. 2011;17(1):1–21.
Kim H, Stepchenkova S, Yilmaz S. Destination extension: a faster route to fame for the emerging destination brands? J Travel Res. 2019;58(3):440–58.
Wang ZG, Yuan BC. Harmonizing the branding strategy of world natural heritage in China: visitors’ awareness of the multiple brands of Wulingyuan, Zhangjiajie. Geoheritage. 2020;12:1–11.
Poria Y, Reichel A, Cohen R. World heritage site—is it an effective brand name? A case study of a religious heritage site. J Travel Res. 2011;50(5):482–95.
Xu HG, Ye T. Dynamic destination image formation and change under the effect of various agents: the case of Lijiang’, The Capital of Yanyu’. J Destin Mark Manag. 2018;7:131–9.
Li Y, Lau C, Su P. Heritage tourism stakeholder conflict: a case of a world heritage site in China. J Tour Cult Change. 2020;18(3):267–87.
Panzera E, De Graaff T, De Groot HL. European cultural heritage and tourism flows: the magnetic role of superstar world heritage sites. Pap Reg Sci. 2021;100(1):101–22.
Ryan C, Zhang CZ, Deng Z. The impacts of tourism at a UNESCO heritage site in China—a need for a meta-narrative? The case of the Kaiping Diaolou. J Sustain Tour. 2011;19(6):747–65.
Vargas A. The tourism and local development in world heritage context. The case of the Mayan site of Palenque, Mexico. Int J Herit Stud. 2018;24(9):984–97.
Lin YX, Chen MH, Lin BS, Su CH. Asymmetric effects of cultural and natural world heritage sites on tourism receipts. Curr Issue Tour. 2020;23(24):3134–47.
Su MM, Wall G, Xu KJ. Tourism-induced livelihood changes at Mount Sanqingshan world heritage site, China. Environ Manag. 2016;57(5):1024–40.
Maruyama NU, Woosnam KM. Representation of ‘mill girls’ at a UNESCO world heritage site in Gunma, Japan. J Sustain Tour. 2021;29(2–3):277–94.
Drost A. Developing sustainable tourism for world heritage sites. Ann Tour Res. 1996;23(2):479–84.
Rasoolimanesh SM, Jaafar M. Sustainable tourism development and residents’ perceptions in world heritage site destinations. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2017;22(1):34–48.
Zhen RC, Chao YF, Qian Z, Fu LC. Joint development of cultural heritage protection and tourism: the case of Mount Lushan cultural landscape heritage site. Herit Sci. 2021;9(1):1–16.
Rongna A, Sun J. Integration and sustainability of tourism and traditional livelihood: a rhythm analysis. J Sustain Tour. 2020;28(3):455–74.
Zhang CZ, Fyall A, Zheng YF. Heritage and tourism conflict within world heritage sites in China: a longitudinal study. Curr Issue Tour. 2015;18(2):110–36.
Bloch N. Evicting heritage: spatial cleansing and cultural legacy at the Hampi UNESCO site in India. Crit Asian Stud. 2016;48(4):556–78.
Allen A, Lennon M. The values and vulnerabilities of ‘Star Wars Island’: exploring tensions in the sustainable management of the Skellig Michael world heritage site. Int J Sust Dev World. 2018;25(6):483–90.
Thinh NA, Thanh NN, Tuyen LT, Hens L. Tourism and beach erosion: valuing the damage of beach erosion for tourism in the Hoi An world heritage site, Vietnam. Environ Dev Sustain. 2019;21(5):2113–24.
Simsek S, Günay G, Elhatip H, Ekmekci M. Environmental protection of geothermal waters and travertines at Pamukkale, Turkey. Geothermics. 2000;29(4–5):557–72.
Galas A. Problems of the environmental resources management around Colca Canyon, Peru. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi-Miner Resour Manag. 2008;24(2):135–52.
Van Dijk J, Broersma L, Mehnen N. Options for socioeconomic developments in ICZM for the tri-national Wadden area. Ocean Coast Manag. 2016;119:76–92.
Heslinga J, Groote P, Vanclay F. Understanding the historical institutional context by using content analysis of local policy and planning documents: assessing the interactions between tourism and landscape on the Island of Terschelling in the Wadden Sea Region. Tour Manag. 2018;66:180–90.
Varghese J, Crawford SS. A cultural framework for Indigenous, local, and science knowledge systems in ecology and natural resource management. Ecol Monogr. 2021;91(1): e01431.
Yang R, Duan ZW, Du MJ, Miao X. A comprehensive knowledge pedigree on environmental transparency. Pol J Environ Stud. 2020;30(1):535–54.
Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021;133:285–96.
Bhowmik P. Heritage tourism: a bibliometric review. Anatolia. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2021.1875250 .
Article Google Scholar
Kumar S, Sureka R, Vashishtha A. The journal of heritage tourism: a bibliometric overview since its inception. J Herit Tour. 2020;15(4):365–80.
Chen CM. Science mapping: a systematic review of the literature. J Data Inf Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1515/jdis-2017-0006 .
Powell TH, Kouropalatis Y, Morgan RE, Karhu P. Mapping knowledge and innovation research themes: using bibliometrics for classification, evolution, proliferation and determinism. Int J Entrep Innov Manag. 2016;20(3–4):174–99.
Feng Y, Cui SZ. A review of emergency response in disasters: present and future perspectives. Nat Hazards. 2021;105(1):1109–38.
Xie L, Wang JW, Lv JH. Knowledge mapping of international dark tourism research: a bibliometric analysis using CiteSpace. Resour Sci. 2019;41(3):454–66 ( In Chinese ).
Marinello S, Butturi MA, Gamberini R, Martini U. Indicators for sustainable touristic destinations: a critical review. J Environ Plan Manag. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2021.1978407 .
Orgaz-Agüera F, Castellanos-Verdugo M, AcostaGuzmán JA, Cobeña M, Oviedo-García MDLÁ. The mediating effects of community support for sustainable tourism, community attachment, involvement, and environmental attitudes. J Hosp Tour Res. 2020;12:1–24.
Rastegar R, Zarezadeh Z, Gretzel U. World heritage and social justice: insights from the inscription of Yazd, Iran. J Sustain Tour. 2021;29(2–3):521–40.
Zheng DN, Liang ZX, Ritchie BW. Residents’ social dilemma in sustainable heritage tourism: the role of social emotion, efficacy beliefs and temporal concerns. J Sustain Tour. 2020;28(11):1782–804.
Kaltenborn BP, Thomassen J, Wold LC, Linnell JD, Skar B. World heritage status as a foundation for building local futures? A case study from Vega in Central Norway. J Sustain Tour. 2013;21(1):99–116.
Lee TH. Influence analysis of community resident support for sustainable tourism development. Tour Manag. 2013;34:37–46.
Tavares AO, Henriques MH, Domingos A, Bala A. Community involvement in geoconservation: a conceptual approach based on the geoheritage of South Angola. Sustainability. 2015;7(5):4893–918.
Eslami S, Khalifah Z, Mardani A, Streimikiene D, Han H. Community attachment, tourism impacts, quality of life and residents’ support for sustainable tourism development. J Travel Tour Mark. 2019;36(9):1061–79.
Wang N. Rethinking authenticity in tourism experience. Ann Tour Res. 1999;26(2):349–70.
Su XY, Sigley GG, Song CQ. Relational authenticity and reconstructed heritage space: a balance of heritage preservation, tourism, and urban renewal in Luoyang Silk Road Dingding Gate. Sustainability. 2020;12(14):5830.
Park E, Choi BK, Lee TJ. The role and dimensions of authenticity in heritage tourism. Tour Manag. 2019;74:99–109.
Fu X. Existential authenticity and destination loyalty: evidence from heritage tourists. J Destin Mark Manag. 2019;12:84–94.
Katahenggam N. Tourist perceptions and preferences of authenticity in heritage tourism: visual comparative study of George Town and Singapore. J Tour Cult Chang. 2020;18(4):371–85.
Latiff K, Ng SI, Aziz YA, Basha NK. Food authenticity as one of the stimuli to world heritage sites. Br Food J. 2019;122(6):1755–76.
Shen SY, Guo JY, Wu YY. Investigating the structural relationships among authenticity, loyalty, involvement, and attitude toward world cultural heritage sites: an empirical study of Nanjing Xiaoling Tomb, China. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2014;19(1):103–21.
Kolar T, Zabkar V. A consumer-based model of authenticity: an oxymoron or the foundation of cultural heritage marketing? Tour Manag. 2010;31(5):652–64.
Wang Y. Customized authenticity begins at home. Ann Tour Res. 2007;34(3):789–804.
Lugosi P. Socio-technological authentication. Ann Tour Res. 2016;58:100–13.
Zhu YJ. Performing heritage: rethinking authenticity in tourism. Ann Tour Res. 2012;39(3):1495–513.
Reisinger Y, Steiner CJ. Reconceptualizing object authenticity. Ann Tour Res. 2006;33(1):65–86.
Aldighieri B, Testa B, Bertini A. 3D exploration of the San Lucano Valley: virtual geo-routes for everyone who would like to understand the landscape of the Dolomites. Geoheritage. 2016;8(1):77–90.
Orimoloye IR, Kalumba AM, Mazinyo SP, Nel W. Geospatial analysis of wetland dynamics: wetland depletion and biodiversity conservation of Isimangaliso Wetland, South Africa. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2020;32(1):90–6.
Liu J, Ren HG, Wang XY, Shirazi Z, Quan B. Measuring and predicting urban expansion in the Angkor region of Cambodia. Remote Sens. 2019;11(17):2064–85.
Koo S, Kim J, Kim C, Kim J, Cha HS. Development of an augmented reality tour guide for a cultural heritage site. J Comput Cult Herit. 2019;12(4):1–24.
Okura F, Kanbara M, Yokoya N. Mixed-reality world exploration using image-based rendering. J Comput Cult Herit. 2015;8(2):1–26.
Wright AM. Assessing the stability and sustainability of rock art sites: insight from southwestern Arizona. J Archaeol Method Theory. 2018;25(3):911–52.
Saintenoy T, Estefane FG, Jofré D, Masaguer M. Walking and stumbling on the paths of heritage-making for rural development in the Arica Highlands. Mt Res Dev. 2019;39(4):D1–10.
Wardell-Johnson G, Schoeman D, Schlacher T, Wardell-Johnson A, Weston M, Shimizu Y, et al. Re-framing values for a world heritage future: what type of icon will K’gari-Fraser Island become? Australas J Environ Manag. 2015;22(2):124–48.
Heslinga J, Groote P, Vanclay F. Towards resilient regions: policy recommendations for stimulating synergy between tourism and landscape. Land. 2020;9(2):44.
Li MM, Wu BH, Cai LP. Tourism development of world heritage sites in China: a geographic perspective. Tour Manag. 2008;29(2):308–19.
Berg F. Wear and tear of world heritage: preventive conservation and tourism in Norway’s stave churches. Stud Conserv. 2018;63(sup1):320–2.
Hardiman N, Burgin S. Effects of trampling on in-stream macroinvertebrate communities from canyoning activity in the Greater Blue Mountains world heritage area. Wetl Ecol Manag. 2011;19(1):61–71.
Lin MS, Xiao XN, Xu Y, Xie HB. The impact of water quality changes on tourism capacity at Golden Lake, China. J Food Agric Environ. 2013;11:1069–72.
Pan YD, Deng GP, Wang LZ, Cao Y, Pang WT, Wang QX, et al. Effects of in situ phosphorus enrichment on the benthos in a subalpine karst stream and implications for bioassessment in nature reserves. Ecol Ind. 2017;73:274–83.
Li QY, Wu JL, Zhou JC, Sakiev K, Hofmann D. Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) in soils around two typical lakes in the western Tian Shan Mountains (Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia): local burden or global distillation? Ecol Indic. 2020;108: 105749.
Rasoolimanesh SM, Jaafar M, Kock N, Ramayah T. A revised framework of social exchange theory to investigate the factors influencing residents’ perceptions. Tour Manag Perspect. 2015;16:335–45.
Türker N. Host community perceptions of tourism impacts: a case study on the world heritage city of Safranbolu, Turkey. Revista de Cercetare şi Intervenţie Socială. 2013;43:115–41.
Tucker H, Boonabaana B. A critical analysis of tourism, gender and poverty reduction. J Sustain Tour. 2012;20(3):437–55.
Qian C, Sasaki N, Jourdain D, Kim SM, Shivakoti PG. Local livelihood under different governances of tourism development in China—a case study of Huangshan Mountain area. Tour Manag. 2017;61:221–33.
Chen FF, Xu HG, Lew AA. Livelihood resilience in tourism communities: the role of human agency. J Sustain Tour. 2020;28(4):606–24.
Jha S. Can natural world heritage sites promote development and social harmony? Biodivers Conserv. 2005;14(4):981–91.
Kim SS, Wong KK, Cho M. Assessing the economic value of a world heritage site and willingness-to-pay determinants: a case of Changdeok Palace. Tour Manag. 2007;28(1):317–22.
Okech RN. Socio-cultural impacts of tourism on world heritage sites: communities’ perspective of Lamu (Kenya) and Zanzibar Islands. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2010;15(3):339–51.
Su DN, Nguyen NAN, Nguyen QNT, Tran TP. The link between travel motivation and satisfaction towards a heritage destination: the role of visitor engagement, visitor experience and heritage destination image. Tour Manag Perspect. 2020;34: 100634.
Hoang TDT, Brown G, Kim AKJ. Measuring resident place attachment in a world cultural heritage tourism context: the case of Hoi An (Vietnam). Curr Issue Tour. 2020;23(16):2059–75.
Shakoori A, Hosseini M. An examination of the effects of motivation on visitors’ loyalty: case study of the Golestan Palace, Tehran. Tour Manag Perspect. 2019;32: 100554.
Lee KY, Lee H. Traditional costume experience at a cultural heritage festival. Tour Manag Perspect. 2019;32: 100555.
Hew JJ, Leong LY, Tan GWH, Lee VH, Ooi KB. Mobile social tourism shopping: a dual-stage analysis of a multi-mediation model. Tour Manag. 2018;66:121–39.
Chen CF, Leask A, Phou S. Symbolic, experiential and functional consumptions of heritage tourism destinations: the case of Angkor world heritage site, Cambodia. Int J Tour Res. 2016;18(6):602–11.
Prayag G, Hosany S, Odeh K. The role of tourists’ emotional experiences and satisfaction in understanding behavioral intentions. J Destin Mark Manag. 2013;2(2):118–27.
Gannon M, Rasoolimanesh SM, Taheri B. Assessing the mediating role of residents’ perceptions toward tourism development. J Travel Res. 2021;60(1):149–71.
Escudero Gómez LA. Residents’ opinions and perceptions of tourism development in the historic City of Toledo, Spain. Sustainability. 2019;11(14):3854.
Md Noor S, Rasoolimanesh SM, Jaafar M, Barghi R. Inscription of a destination as a world heritage site and residents’ perceptions. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2019;24(1):14–30.
Benham CF. Editor understanding local community attitudes toward industrial development in the Great Barrier Reef region world heritage area: are environmental impacts perceived to overshadow economic benefits? Natural Resources Forum; 2017: Wiley Online Library.
Della Lucia M, Franch M. The effects of local context on world heritage site management: the Dolomites natural world heritage site, Italy. J Sustain Tour. 2017;25(12):1756–75.
Aleshinloye KD, Fu X, Ribeiro MA, Woosnam KM, Tasci AD. The influence of place attachment on social distance: examining mediating effects of emotional solidarity and the moderating role of interaction. J Travel Res. 2020;59(5):828–49.
Yan HL, Bramwell B. Cultural tourism, ceremony and the state in China. Ann Tour Res. 2008;35(4):969–89.
Sun JX, Zhou Y, Wang XJ. Place construction in the context of world heritage tourism: the case of ‘Kaiping Diaolou and Villages.’ J Tour Cult Chang. 2019;17(2):115–31.
Othman J, Rahajeng A. Economic valuation of Jogjakarta’s tourism attributes: a contingent ranking analysis. Tour Econ. 2013;19(1):187–201.
Nicholas LN, Thapa B, Ko YJ. Residents’ perspectives of a world heritage site: the pitons management area, St. Lucia. Ann Tour Res. 2009;36(3):390–412.
Gao X, Roder G, Jiao YM, Ding YP, Liu ZL, Tarolli P. Farmers’ landslide risk perceptions and willingness for restoration and conservation of world heritage site of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces, China. Landslides. 2020;17(8):1915–24.
Wardana A. Neoliberalizing cultural landscapes: Bali’s agrarian heritage. Crit Asian Stud. 2020;52(2):270–85.
Martínez-Pérez Á, Beauchesne M-M. Overcoming the dark side of closed networks in cultural tourism clusters: the importance of diverse networks. Cornell Hosp Q. 2018;59(3):239–56.
Martínez-Pérez Á, Elche D, García-Villaverde PM, Parra-Requena G. Cultural tourism clusters: social capital, relations with institutions, and radical innovation. J Travel Res. 2019;58(5):793–807.
Chi CG, Zhang CZ, Liu YY. Determinants of corporate social responsibility (CSR) attitudes: perspective of travel and tourism managers at world heritage sites. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-03-2018-0217 .
Su LJ, Hsu MK, Swanson S. The effect of tourist relationship perception on destination loyalty at a world heritage site in China: the mediating role of overall destination satisfaction and trust. J Hosp Tour Res. 2017;41(2):180–210.
Weng LS, Liang ZX, Bao JG. The effect of tour interpretation on perceived heritage values: a comparison of tourists with and without tour guiding interpretation at a heritage destination. J Destin Market Manag. 2020;16: 100431.
Gao J, Zhang CZ, Liu L. Communicating the outstanding universal value of world heritage in China? The tour guides’ perspective. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2020;25(9):1042–55.
Verma A, Rajendran G. The effect of historical nostalgia on tourists’ destination loyalty intention: an empirical study of the world cultural heritage site—Mahabalipuram, India. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2017;22(9):977–90.
Alazaizeh MM, Ababneh A, Jamaliah MM. Preservation vs. use: understanding tourism stakeholders’ value perceptions toward Petra Archaeological Park. J Tour Cult Change. 2020;18(3):252–66.
Baral N, Kaul S, Heinen JT, Ale SB. Estimating the value of the world heritage site designation: a case study from Sagarmatha (Mount Everest) National Park, Nepal. J Sustain Tour. 2017;25(12):1776–91.
Dong XW, Zhang J, Zhi RZ, Zhong SE, Li M. Measuring recreational value of world heritage sites based on contingent valuation method: a case study of Jiuzhaigou. Chin Geogr Sci. 2011;21(1):119–28.
Parga-Dans E, González PA, Enríquez RO. The social value of heritage: balancing the promotion-preservation relationship in the Altamira world heritage site, Spain. J Destin Mark Manag. 2020;18: 100499.
Santos PM. Crossed gazes over an old city: photography and the ‘experientiation’ of a heritage place. Int J Herit Stud. 2016;22(2):131–44.
Wuepper D, Patry M. The world heritage list: which sites promote the brand? A big data spatial econometrics approach. J Cult Econ. 2017;41(1):1–21.
Veasna S, Wu WY, Huang CH. The impact of destination source credibility on destination satisfaction: the mediating effects of destination attachment and destination image. Tour Manag. 2013;36:511–26.
Brown S, Baldwin C, Chandler L. Representation of Butchulla cultural heritage values in communication of K’gari (Fraser Island) as a tourism destination. Australas J Environ Manag. 2015;22(2):163–80.
Yang CH, Lin HY. Revisiting the relationship between world heritage sites and tourism. Tour Econ. 2014;20(1):73–86.
Su YW, Lin HL. Analysis of international tourist arrivals worldwide: the role of world heritage sites. Tour Manag. 2014;40:46–58.
Gao YY, Su W. The disclosure of quality on tourism performance: evidence from top tourist cities in China. J Travel Res. 2021;60(7):1492–509.
Patuelli R, Mussoni M, Candela G. The effects of world heritage sites on domestic tourism: a spatial interaction model for Italy. J Geogr Syst. 2013;15(3):369–402.
Cellini R. Is UNESCO recognition effective in fostering tourism? A comment on Yang, Lin and Han. Tour Manag. 2011;32(2):452–4.
Santa-Cruz FG, López-Guzmán T. Culture, tourism and world heritage sites. Tour Manag Perspect. 2017;24:111–6.
Huang CH, Tsaur JR, Yang CH. Does world heritage list really induce more tourists? Evid Macau Tour Manag. 2012;33(6):1450–7.
Cuccia T, Guccio C, Rizzo I. The effects of UNESCO world heritage list inscription on tourism destinations performance in Italian regions. Econ Model. 2016;53:494–508.
Ribaudo G, Figini P. The puzzle of tourism demand at destinations hosting UNESCO world heritage sites: an analysis of tourism flows for Italy. J Travel Res. 2017;56(4):521–42.
Bak S, Min CK, Roh TS. Impacts of UNESCO-listed tangible and intangible heritages on tourism. J Travel Tour Mark. 2019;36(8):917–27.
Yang Y, Xue L, Jones TE. Tourism-enhancing effect of world heritage sites: Panacea or placebo? A meta-analysis. Ann Tour Res. 2019;75:29–41.
Yu GX, Dai GQ. Construction of Chinese and English event study knowledge system based on tourism perspective. Tour Tribune. 2018;2(33):90–104 ( In Chinese ).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Guizhou normal university. We would also like to thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful and productive comments on the manuscript.
This work was supported by the Key Project of Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province (No. 5411 2017 Qiankehe Pingtai Rencai), the World Top Discipline Program of Guizhou Province (No.125 2019 Qianjiao Keyan Fa), the China Overseas Expertise Introduction Program for Discipline Innovation (No.D17016), the Strategic Action Plan of Guizhou Undergraduate Higher Education Institutions to Serve the Rural Industrial Revolution(No. Qianjiaohe KY[2018]086), the Postgraduate Education Innovation Program Project of Guizhou Province (No. Qianjiaohe YJSCXJH [2020] 112).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Karst Science, Guizhou Normal University/State Engineering Technology Institute for Karst Desertification Control, Guiyang, 550001, China
Juan Zhang, Kangning Xiong & Zhaojun Liu
School of Management Science, Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, Guiyang, 550025, China
Juan Zhang & Lixiang He
School of Urban and Environmental Sciences, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 430079, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JZ and KNX developed the concept of this work. JZ wrote the manuscript, KNX and ZJL reviewed the whole text and made comments and suggestions to improve it. LXH edited parts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kangning Xiong .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: appendix s1..
List of the 567 publications considered in bibliometric analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhang, J., Xiong, K., Liu, Z. et al. Research progress and knowledge system of world heritage tourism: a bibliometric analysis. Herit Sci 10 , 42 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-022-00654-0
Download citation
Received : 15 November 2021
Accepted : 21 January 2022
Published : 23 March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-022-00654-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- World natural heritage
- World cultural heritage
- Sustainable tourism
- Stakeholders
- Tourism impacts
- Conservation
- Development
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Ethics, culture and social responsibility.
- Global Code of Ethics for Tourism
- Accessible Tourism
Tourism and Culture
- Women’s Empowerment and Tourism
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
The convergence between tourism and culture, and the increasing interest of visitors in cultural experiences, bring unique opportunities but also complex challenges for the tourism sector.
“Tourism policies and activities should be conducted with respect for the artistic, archaeological and cultural heritage, which they should protect and pass on to future generations; particular care should be devoted to preserving monuments, worship sites, archaeological and historic sites as well as upgrading museums which must be widely open and accessible to tourism visits”
UN Tourism Framework Convention on Tourism Ethics
Article 7, paragraph 2
This webpage provides UN Tourism resources aimed at strengthening the dialogue between tourism and culture and an informed decision-making in the sphere of cultural tourism. It also promotes the exchange of good practices showcasing inclusive management systems and innovative cultural tourism experiences .
About Cultural Tourism
According to the definition adopted by the UN Tourism General Assembly, at its 22nd session (2017), Cultural Tourism implies “A type of tourism activity in which the visitor’s essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the tangible and intangible cultural attractions/products in a tourism destination. These attractions/products relate to a set of distinctive material, intellectual, spiritual and emotional features of a society that encompasses arts and architecture, historical and cultural heritage, culinary heritage, literature, music, creative industries and the living cultures with their lifestyles, value systems, beliefs and traditions”. UN Tourism provides support to its members in strengthening cultural tourism policy frameworks, strategies and product development . It also provides guidelines for the tourism sector in adopting policies and governance models that benefit all stakeholders, while promoting and preserving cultural elements.
Recommendations for Cultural Tourism Key Players on Accessibility
UN Tourism , Fundación ONCE and UNE issued in September 2023, a set of guidelines targeting key players of the cultural tourism ecosystem, who wish to make their offerings more accessible.
The key partners in the drafting and expert review process were the ICOMOS International Cultural Tourism Committee and the European Network for Accessible Tourism (ENAT) . The ICOMOS experts’ input was key in covering crucial action areas where accessibility needs to be put in the spotlight, in order to make cultural experiences more inclusive for all people.
This guidance tool is also framed within the promotion of the ISO Standard ISO 21902 , in whose development UN Tourism had one of the leading roles.
Download here the English and Spanish version of the Recommendations.
Compendium of Good Practices in Indigenous Tourism

The report is primarily meant to showcase good practices championed by indigenous leaders and associations from the Region. However, it also includes a conceptual introduction to different aspects of planning, management and promotion of a responsible and sustainable indigenous tourism development.
The compendium also sets forward a series of recommendations targeting public administrations, as well as a list of tips promoting a responsible conduct of tourists who decide to visit indigenous communities.
For downloads, please visit the UN Tourism E-library page: Download in English - Download in Spanish .
Weaving the Recovery - Indigenous Women in Tourism

This initiative, which gathers UN Tourism , t he World Indigenous Tourism Alliance (WINTA) , Centro de las Artes Indígenas (CAI) and the NGO IMPACTO , was selected as one of the ten most promising projects amoung 850+ initiatives to address the most pressing global challenges. The project will test different methodologies in pilot communities, starting with Mexico , to enable indigenous women access markets and demonstrate their leadership in the post-COVID recovery.
This empowerment model , based on promoting a responsible tourism development, cultural transmission and fair-trade principles, will represent a novel community approach with a high global replication potential.
Visit the Weaving the Recovery - Indigenous Women in Tourism project webpage.
Inclusive Recovery of Cultural Tourism

The release of the guidelines comes within the context of the International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development 2021 , a UN initiative designed to recognize how culture and creativity, including cultural tourism, can contribute to advancing the SDGs.
UN Tourism Inclusive Recovery Guide, Issue 4: Indigenous Communities

Sustainable Development of Indigenous Tourism
The Recommendations on Sustainable Development of Indigenous Tourism provide guidance to tourism stakeholders to develop their operations in a responsible and sustainable manner within those indigenous communities that wish to:
- Open up to tourism development, or
- Improve the management of the existing tourism experiences within their communities.
They were prepared by the UN Tourism Ethics, Culture and Social Responsibility Department in close consultation with indigenous tourism associations, indigenous entrepreneurs and advocates. The Recommendations were endorsed by the World Committee on Tourism Ethics and finally adopted by the UN Tourism General Assembly in 2019, as a landmark document of the Organization in this sphere.
Who are these Recommendations targeting?
- Tour operators and travel agencies
- Tour guides
- Indigenous communities
- Other stakeholders such as governments, policy makers and destinations
The Recommendations address some of the key questions regarding indigenous tourism:

Download PDF:
- Recommendations on Sustainable Development of Indigenous Tourism
- Recomendaciones sobre el desarrollo sostenible del turismo indígena, ESP
UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conferences on Tourism and Culture
The UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conferences on Tourism and Culture bring together Ministers of Tourism and Ministers of Culture with the objective to identify key opportunities and challenges for a stronger cooperation between these highly interlinked fields. Gathering tourism and culture stakeholders from all world regions the conferences which have been hosted by Cambodia, Oman, Türkiye and Japan have addressed a wide range of topics, including governance models, the promotion, protection and safeguarding of culture, innovation, the role of creative industries and urban regeneration as a vehicle for sustainable development in destinations worldwide.
Fourth UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference on Tourism and Culture: Investing in future generations. Kyoto, Japan. 12-13 December 2019 Kyoto Declaration on Tourism and Culture: Investing in future generations ( English, French, Spanish, Arabic, Russian and Japanese )
Third UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference on Tourism and Culture : For the Benefit of All. Istanbul, Türkiye. 3 -5 December 2018 Istanbul Declaration on Tourism and Culture: For the Benefit of All ( English , French , Spanish , Arabic , Russian )
Second UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference’s on Tourism and Culture: Fostering Sustainable Development. Muscat, Sultanate of Oman. 11-12 December 2017 Muscat Declaration on Tourism and Culture: Fostering Sustainable Development ( English , French , Spanish , Arabic , Russian )
First UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference’s on Tourism and Culture: Building a new partnership. Siem Reap, Cambodia. 4-6 February 2015 Siem Reap Declaration on Tourism and Culture – Building a New Partnership Model ( English )
UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage
The first UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage provides comprehensive baseline research on the interlinkages between tourism and the expressions and skills that make up humanity’s intangible cultural heritage (ICH).

Through a compendium of case studies drawn from across five continents, the report offers in-depth information on, and analysis of, government-led actions, public-private partnerships and community initiatives.
These practical examples feature tourism development projects related to six pivotal areas of ICH: handicrafts and the visual arts; gastronomy; social practices, rituals and festive events; music and the performing arts; oral traditions and expressions; and, knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe.
Highlighting innovative forms of policy-making, the UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage recommends specific actions for stakeholders to foster the sustainable and responsible development of tourism by incorporating and safeguarding intangible cultural assets.
UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage
- UN Tourism Study
- Summary of the Study
Studies and research on tourism and culture commissioned by UN Tourism
- Tourism and Culture Synergies, 2018
- UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage, 2012
- Big Data in Cultural Tourism – Building Sustainability and Enhancing Competitiveness (e-unwto.org)
Outcomes from the UN Tourism Affiliate Members World Expert Meeting on Cultural Tourism, Madrid, Spain, 1–2 December 2022
UN Tourism and the Region of Madrid – through the Regional Ministry of Culture, Tourism, and Sports – held the World Expert Meeting on Cultural Tourism in Madrid on 1 and 2 December 2022. The initiative reflects the alliance and common commitment of the two partners to further explore the bond between tourism and culture. This publication is the result of the collaboration and discussion between the experts at the meeting, and subsequent contributions.
Relevant Links
- 3RD UN Tourism/UNESCO WORLD CONFERENCE ON TOURISM AND CULTURE ‘FOR THE BENEFIT OF ALL’
Photo credit of the Summary's cover page: www.banglanatak.com
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Change of tourism organizations: implications from a review of cultural tourism research.

- 1 Alliance Manchester Business School, The University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
- 2 School of Event and Communication, Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, Shanghai, China
Change has been universally acknowledged as the perpetual theme for routine organizational life. As cultural tourism, a major element of global tourism consumption accounting for 40% of tourism employment, is becoming increasingly flourishing and promising, tourism organizations are also obliged to implement a series of organizational changes to adapt to the trending culturalization in the tourism domain. In light of this, this research, by outlining important sub-themes and trends of cultural tourism research, tracks the evolution of cultural tourism as a research field over the previous decades so as to analyze existing interconnections between the systematic review and tourism organizational change. Based on these interconnections, the research also manages to propose several potential implications for tourism organizations to optimize their future implement of daily organizational changes for the sake of adaptative survival and development.
Introduction
In a business environment that is increasingly volatile and dynamic, organizations strive consistently to adjust and adapt their operations to changing conditions ( Hope Hailey and Balogun, 2002 ). Existing literature on organizational management has widely admitted the centrality of change in organizational life ( North, 1996 ; Orlikowski, 1996 ; Weick, 1998 ; Al-Haddad and Kotnour, 2015 ; Errida and Lotfi, 2021 ). Thanks to the changing nature of all things in life ( James, 1996 ) as well as the fact that organizations are creations of human agents who are the main source of change seeds ( Feldman, 2000 ), organizational change has been universally accepted as a pervasive norm, an inevitable routine, and a consistent operation ( Tsoukas and Chia, 2002 ). As organizations have been increasingly regarded as an emergent property of change ( Errida and Lotfi, 2021 ), traditional misconception that change exists merely as an exception or an epiphenomenon ( Beer and Nohria, 2000 ) has gradually been weeded out. In other words, change is becoming the only certain stability in organizations, making change management a compulsory course for all kinds of organizations, including tourism organizations, to survive the elusory future ( Kickert, 2014 ; Soulard et al., 2019 ; Errida and Lotfi, 2020 ).
In addition to the common rationale for tourism organizations to adapt to changes (i.e., change management is compulsory for all kinds of organizations), the volatility of the tourism context proves to be a more urgent rationale for tourism organizations to change readily ( Smith et al., 2014 ). Specifically, recent decades have witnessed the inextricable link between culture and tourism turning into a specific form of consumption known as cultural tourism ( Richards, 2018 ), which is a significant revolution in the tourism context. Accounting for 40% of the global tourism revenues ( UNWTO, 2021 ), cultural tourism possesses unprecedentedly promising prospects by acquiring its place in the tourism policy of 89% UNWTO member countries around the world ( UNWTO, 2018 ; Petrei et al., 2020 ; UNESCO, 2022 ) as well as showing a market volume growth rate up to 130% during the recent 5 years ( OECD, 2018 ; UNWTO, 2021 ). Thus, it is inevitable for tourism organizations to make some changes to adapt to the rising of cultural tourism.
In light of this, the research first makes a systematic review that summarizes some of the most important sub-themes associated with cultural tourism research. It then analyzes the interconnections between each sub-theme of cultural tourism research and tourism organizational change management, based on which the research finally manages to figure out potential implications for tourism organizations to make and manage changes.

A review of cultural tourism research and interconnections with tourism organizational change
As cultural tourism is gaining plenty of popularity in both the tourism industry and the tourism literature, it is necessary to have a general understanding on extant cultural tourism research. Therefore, this multi-sectional part first reviews and summarizes cultural tourism literature in terms of such research topics as the current research status, definition, typology, important branches, and optimal development strategies. Then the review presented in each section functions as the primary evidence to figure out the interconnections between cultural tourism research and tourism organizational change (as is shown in Table 2 ), laying foundations for proposing potential implications in the next part.
Current status of cultural tourism research
To acquire a better understanding of the current research status of cultural tourism, we adopt a Google Scholar search for the term cultural tourism to generate the total number of cultural tourism research publications in each year of 1990–2021. Note that in order to improve the results accuracy, only publications specifically focusing on the term cultural tourism (i.e., excluding publications that only mention the full term or part of the term) are included in the samples. As is shown in Figure 1 , the recent three decades (1990–2021) have witnessed a significant uptrend on the total volume of cultural tourism research publications. Specifically, growth was particularly sharp between 2005 and 2020.
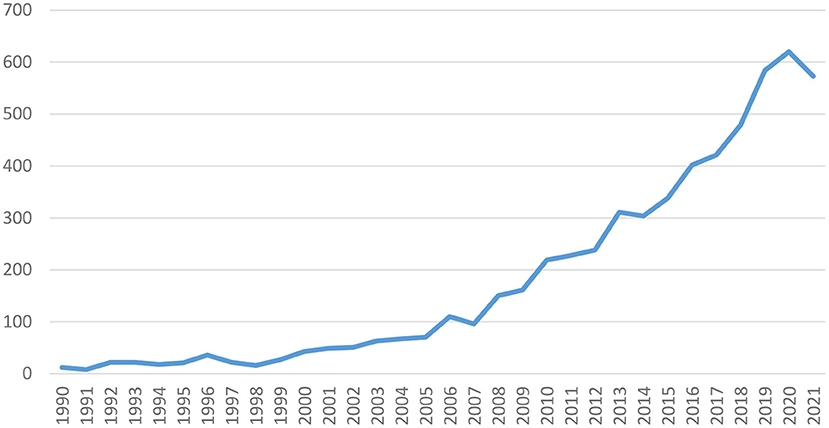
Figure 1 . 1990–2021 number of cultural tourism publications.
We then further figure out the proportion of high-quality publications in total publications for each year of 1990–2021 (data source: Google Scholar) so as to learn about the quality of cultural tourism publications. Note that we define high-quality publications as those published on journals with three-star or above based on the 2021 ABS academic journal guide. According to Figure 2 (i.e., the proportion of high-quality publications for each year of 1990–2021) and Figure 3 (i.e., the corresponding pie chart of Figure 2 ), we can learn that despite the obvious fluctuations, the general trend for each year's proportion of high-quality publications is still going up, demonstrating that the quality of cultural tourism research is also growing continuously.
Figure 2 . 1990–1992 proportion of high-quality publications.
Figure 3 . Pie chart for 1990–2022 proportion of high-quality publications.
Cultural tourism is also widely discussed in various research fields. According to Table 1 , cultural tourism is most frequently discussed in Economics (20.91%), followed by Management (20.29%; data source: Google Scholar). In terms of specific themes, such themes as connotations (i.e., a form of cultural consumption; e.g., Barbieri and Mahoney, 2009 ; Falk, 2011 ; Du Cros and McKercher, 2020 ), motivations and typology (e.g., Lee and Hsu, 2013 ; Chang et al., 2014 ; Packer and Ballantyne, 2016 ), cultural heritage tourism (e.g., Yankholmes and McKercher, 2015 ; Patuelli et al., 2016 ), gastronomy tourism (e.g., Everett and Aitchison, 2008 ; Montanari, 2009 ), shopping tourism (e.g., Rabbiosi, 2011 ; Saayman and Saayman, 2012 ; Choi et al., 2016b ), destination branding (e.g., Josiassen et al., 2013 ; Barnes et al., 2014 ; Mariani and Giorgio, 2017 ), and tourism experience (e.g., Chatterley et al., 2013 ) are frequently discussed in extant literature. Additionally, some research also shows some interest in themes such as economic effects (e.g., Cisneros-Martínez and Fernández-Morales, 2015 ; Ponferrada, 2015 ; Noonan and Rizzo, 2017 ; Artal-Tur et al., 2018 ; Guccio et al., 2018 ), creative economy (e.g., Ponzini et al., 2016 ; Fahmi et al., 2017 ; Mostafanezhad and Promburom, 2018 ), and anthropology (e.g., Ochoa Zuluaga, 2015 ; Pabel et al., 2017 ).
Table 1 . Proportion in various research fields.
Generally, cultural tourism is a flourishing topic in the tourism research, which is another evidence for cultural tourism to be a trending type of tourism. In light of this, tourism organizations have to adjust their strategy and positioning to better embrace culturedness , thus hedging the potential risks caused by the failure to comply with the promising trend in the tourism domain.
Thanks to the changing nature of cultural tourism, there exists no perfect definition that gives an absolutely thorough interpretation. Nevertheless, some definitions are of relatively widespread coverage and are illuminating for further identification of the notion. For example, Richards (2003 , 2007) believed that cultural tourism is the movement of people toward cultural attractions, somewhere other than their habitual place of residence, to obtain information and knowledge to fulfill their cultural demands. In 2017, the UNWTO updated the definition as “A type of tourism activity where the essential motivation of tourists is to learn, discover, experience and consume both tangible and intangible cultural resources in a tourism destination” ( UNWTO, 2017 , p. 30). Compared to Richards's definition, the new one expands the boundary of traditional physical-heritages-based cultural resources by including intangible ones, innovatively relating cultural tourism to ways of life, creativity, and everyday culture ( Richards, 2018 ; UNWTO, 2018 ). In 2018, Richards (2018) further defined cultural tourism as a collection of cultural practices engaged in by a wide range of actors, especially by tourists themselves. In light of this, it seems that cultural tourism is no longer regarded as a merely specific form of tourism or a coherent tourism market, but is attached with a new identification embracing expanding broadness and complexity ( Jovicic, 2016 ; Richards, 2018 ). With regard to this issue, tourism organizations are also expected to equip with transformative sense and dynamic thinking to adapt to the changing nature of cultural tourism.
Typology of cultural tourists
The typology of cultural tourists is also a popular topic in cultural tourism research. According to Barbieri and Mahoney (2009) , cultural tourists could be either general or specific based on their degree of mixing or omnivorousness in cultural tourism behavior. Apart from a general grouping like this, cultural tourists can also be classified into specific groups or segments based on cultural experience appetites (e.g., art museum lovers, movie fans, etc.; Baltaci and Cakici, 2022 ), age, physical contexts (e.g., holiday type and attraction setting; Richards and van der Ark, 2013 ), and motivations (i.e., the most common and effective criterion; Du Cros and McKercher, 2020 ). For example, younger visitors tend to consume contemporary art, creativity, and modern architecture, whereas older visitors tend to be frequenters of traditional monuments and museums ( Richards and van der Ark, 2013 ). Pearce (1982) divided the needs of tourists into five levels from low to high based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs. The higher the level of needs, the greater the sense of satisfaction felt by tourists. Correia et al. (2013) roughly divided the motivations of cultural tourists into two types: one is culture-seeking motivation, and the other is non-cultural motivation. Specifically, the former type usually includes culture learning, which is the stem of culture-seeking motivation and is frequently highlighted by scholars, while the latter, however, includes anything other than culture learning ( Packer and Ballantyne, 2016 ).
Based on the degree of culturedness ( Jovicic, 2016 ) presented by the two motivation types (i.e., cultural and non-cultural), cultural tourists can be further divided into two types: tourists who consider culture consumption as their main motivation, and those for whom culture consumption is only an alternative that is complementary, secondary, or even accidental ( Galí-Espelt, 2012 ). Note that the degree of culturedness could be measured in terms of the duration of visit and the frequency of cultural experiences ( Galí-Espelt, 2012 ; Jovicic, 2016 ), and that the majority of cultural tourists tend to seek a combination of learning and hedonic-entertainment consumption-related dimensions, or edutainment, a unique blend of education and entertainment, form the process of cultural tourism ( Geissler et al., 2006 ; Kay, 2006 ; Ballantyne and Packer, 2016 ; Jovicic, 2016 ).
Given that the diversity and complexity of cultural tourists are constantly increasing, tourism organizations are responsible to set up diverse functional departments to cover various demands of tourists up to the hilt.
Important sub-themes and branches
This section discusses several flourishing sub-themes or branches in cultural tourism research. In addition to cultural heritage tourism, which is the most lineal branch of cultural tourism research, this section also includes gastronomy tourism and shopping tourism, two promising cultural tourism sub-themes developed by the prosperous culturalization process in gastronomy and shopping domain ( Timothy, 2011 ; Báez-Montenegro and Devesa-Fernández, 2017 ; Redondo-Carretero et al., 2017 ; Richards, 2018 ).
Cultural heritage tourism
Originating from tourism managers' business instinct that cultural heritage can be a driver of tourism development, cultural heritage tourism is regarded as the most lineal branch of cultural tourism ( Smith, 2015 ; Gravari-Barbas, 2018 ). As Timothy (2011) put it, cultural tourism and heritage tourism have minimal distinction. According to Park (2013) , cultural heritage tourism is defined as visits or experiences of physical or immaterial relics of the past. It is also noted as a product of cultural patrimony that contains even smallest piece of existing cultures such as folkways and everyday scenes ( Timothy and Nyaupane, 2009 ; Richards, 2018 ).
Extant literature on cultural heritage tourism tend to show great interest in list of World Heritage Sites (WHS), especially in terms of the negative side. For example, Frey and Steiner (2011) are skeptical to the rationality of WHS list. They argued that the benefits of a WHS designation is limited to cultural destinations that fail to generate fair notability and related developmental resources, rather than to destinations that are already well-known and flourishing. Alberts and Hazen (2010) also questioned the credibility of the criteria for WHS designation by pointing out that these criteria could lead to ambiguous definitions and varying interpretations in different cultural settings. In addition, Patuelli et al. (2016) suggested that the existence of WHS list can be a primary fuse for an even fiercer inter-destination competition.
The conservation, preservation, and protection of cultural heritage is also a popular topic in cultural heritage tourism research. For example, Hall et al. (2016) identified that cultural landscapes, local rituals, built environments, buried archeology, and climate changes could be potential threats for the conservation of cultural heritages. They also proposed that strategies like planning time-scales, monitoring, management, maintenance, loss and obsolescence could be effective to deal with these challenges. By analyzing real-life cases of Hong Kong and Singapore, Li (2003) focused on the contradictions between the conservation and change of cultural heritage and concluded that the balance point between the two depends to the actual impacts (i.e., cultural or economic returns vs. residents' life quality) brought by the cultural heritages.
Other than the aforementioned two issues (i.e., WHS list and conservation), many researchers also pay attention to other issues in the development of cultural tourism. For example, Gravari-Barbas (2018, p. 3) concerned that tourism might become a “heritage-production machine,” as heritage tourism is tourist-centered and is subject to tourists demands ( Urry, 1992 ; Yang, 2011 ; Park, 2013 ; Dela Santa and Tiatco, 2019 ). Zhang (2022) argued that more and more local residents suffered from the over-tourism in their homelands and that the elimination of local perspectives and livelihoods may result in emigration and depopulation, which eventually affects the cultural site's viability. Generally, people are increasingly concentrating on the trade-off between further development and long-term sustainability.
According to this section, cultural heritage tourism, which is the stem of cultural tourism, is usually associated with various professional staff such as museum commentators, historic buildings maintenance engineers, and archaeologists etc. In light of this, tourism organizations are obliged to optimize personnel management through professional training, precise selection, and scientific evaluation.
Gastronomy tourism
Gastronomy tourism is known to be one of the most important sub-themes of cultural tourism research, for it is believed to be of much culturedness ( Jovicic, 2016 ). For most tourists, food is not only sustenance, but also a cultural artifact with a myriad of facets that can be enjoyed in various locations and through many different activities (e.g., food trails, events, and festivals; Everett and Aitchison, 2008 ). As Cohen (1992) put it, tourist cuisines are by nature new and sui generis cultural products whose tourists-adaptive transformation is not only mere fusion or hybridization of exotic and local elements but also a multidirectional and multidimensional innovation or creation. Meneguel et al. (2019) also suggested that gastronomy tourism is usually acknowledged as a cultural practice where typical cuisines are treated as sensory and experiential heritage and that the emergence of gastronomy tourism revitalizes and diversifies tourism, thus promoting gastronomy culture, multi-ethnicity, and global exposure. Another evidence for the cultural influence of gastronomy tourism is that it is by nature the swelling of cultural food consumption ( Montanari, 2009 ). As heritage unites with ritualistic elements, cultural food consumption, a symbolic portrayal of its root culture, helps to arouse the connection between individuals and their own cultural heritage ( Horng and Tsai, 2010 ; Wu et al., 2021 ). Additionally, such factors as dining atmospherics ( Ha and Jang, 2010 ; Jang et al., 2012 ; Jang and Ha, 2015 ), employees' appearance or ethnicity ( Baker and Kim, 2018 ), the presence of other customers ( Song et al., 2019 ), menu design ( Kim et al., 2017 ; Yu et al., 2020 ), and service innovation ( Su, 2011 ) will potentially influence consumers' cultural food consumption experiences, thus increasing the culturedness of gastronomy tourism ( Sims, 2010 ).
Throughout the 30-year research history of gastronomy in the tourism domain ( Okumus, 2021 ), gastronomy tourism has been acknowledged as a unifier in terms of multiple perspectives. In terms of major contents, gastronomy tourism, interchangeably named culinary tourism, food tourism, or taste tourism in some studies ( Okumus et al., 2018 ), is the combination of understanding, savoring, and consuming the local food and culture in tourist destinations and is usually associated with cuisine, gourmet, tasting, and wine tourism ( Smith and Xiao, 2008 ). Similarly, Henderson (2009) defined gastronomy tourism as the binding agent of a series of intentional and exploratory participating behaviors in gastronomy activities, such as food preparation, food display, cooking, and dining. In terms of involved parties, gastronomy tourism is also known as the bond between the primary and secondary food producers, food festivals, restaurants, and local food tasting sites ( Hall and Mitchell, 2000 ). In terms of its relevant domains, gastronomy tourism “represents a multifaceted research area rising in prominence” with the potential to function as an instrument that regenerates “academic research to the forefront of geographical theory, tourism policy, cultural studies, and sociological analysis” ( Everett and Aitchison, 2008 , p. 151).
In more recent research on gastronomy tourism, scholars tend to pay attention to such topics as gastronomy tourism experience, scale and measurement, and luxury gastronomy tourism. For example, many related studies tend to explore gastronomy experience in tourism through cognitive evaluations ( Berbel-Pineda et al., 2019 ; Sthapit et al., 2019 ; Lai et al., 2021 ), although Richards (2021) argued that the literature on gastronomy experience has shifted from a cognitive to an emotive approach. Specifically, a small group of scholars ( Williams et al., 2019 ; Mohamed et al., 2020 ; Promnil, 2021 ) got to realize that affective gastronomy experience turns out to be a stronger inspirer for tourists' satisfaction and behavioral intention than cognitive attributes do. In terms of scale and measurement, Bastiaansen et al. (2019) proposed a scale to measure local food preference, inspired by which Hsu et al. (2022) created a valid and reliable scale for measuring tourists' affective gastronomy experiences (TAGES) in tourism destinations. As for luxury gastronomy tourism, Balderas-Cejudo et al. (2022) found it a top type of gastronomy tourism and that its impacts on local development are usually shown through local Michelin-starred restaurants.
Thanks to the dominant role played by taste (i.e., one of the important involved senses) in tourists' ecological body-environment exchange, gastronomy, a burgeoning subfield of sociological and anthropological research ( Beardsworth et al., 2002 ), became a crucial precondition ( Hall and Sharples, 2008 ), a leading attraction ( Dann, 1996 ), and one of the most important components of tourism activities ( MacCannell, 1973 ; Urry, 1990 ; Cohen and Avieli, 2004 ). Meanwhile, as an indispensable branch of cultural tourism, gastronomy tourism proves to be economically ( Okumus et al., 2007 ), environmentally ( Hjalager and Richards, 2002 ), sociologically ( Richards, 2002 ), and psychologically ( Graburn, 1977 ; Cohen, 1986 ; Quan and Wang, 2004 ; Everett, 2008 ; Henderson, 2009 ; Björk and Kauppinen-Räisänen, 2017 ; Ellis and Mattison Thompson, 2018 ) influential. In light of this, gastronomy tourism is expected to keep on flourishing ( Hsu et al., 2022 ) and continue to be a priority of tourism and hospitality research in the next 75 years (2020–2095) ( Okumus, 2021 ) despite the worldwide health crisis. As [( Everett, 2019 ), p. 9] put it, “Food tourism research is still very much on a journey and has much still to offer, therefore I urge scholars to consider adding new empirical contributions which analyze new aspects of this form of tourism activity.”
Shopping tourism
Shopping tourism is another flourishing sub-theme of cultural tourism, for shopping is a common cultural activity among those forces driving the choice of tourism destinations, especially in cultural tourism destinations where cultural creative economy is prosperous and booming ( Saayman and Saayman, 2012 ). As a direct sociocultural experience, shopping is a mediator through which tourists manage to develop familiarity with the unique culture and distinct features of the target tourism destinations, thus improving tourists' satisfaction and pleasure ( Rabbiosi, 2011 ; Way and Robertson, 2013 ; Choi et al., 2016a ; Sun et al., 2017 ). When visitors are in shopping places, they can get in close touch with the cultural connotations of tourist destinations as well as create unique travel experiences of their own through interactive behaviors such as information search and counter-offer behavior ( Liu et al., 2019 ).
Initially proposed by Jansen-Verbeke (1991) , shopping tourism got its first definition as a tour with the main purpose of purchasing products from Timothy and Butler (1995) . It is then further defined as a specialized tour in which tourists tend to spend more than 50% of net tourism expenses (i.e., total tourism expenses excluding lodging and transportation costs) on pure shopping activities ( Michalkó and Varadi, 2004 ; Timothy, 2005 ; Saayman and Saayman, 2012 ; Jin et al., 2020 ). In more recent years, shopping tourism, combining both tangible (i.e., tangible consumer goods such as souvenirs and gifts) and intangible (i.e., intangible touristic experiences) stimulations, is defined as a contemporary form of tourism fostered by individuals for whom purchasing goods outside of their usual environment is a determining factor in their decision to travel ( UNWTO, 2015 ; Sharma et al., 2018 ; Jiang and Yu, 2020 ).
In addition to its culturedness and definition, extant literature on shopping tourism is also frequently focused on such topics as attributes of shopping tourism ( Baker et al., 1988 , 2002 ; Henderson et al., 2011 ; Albayrak et al., 2016 ; Lee and Choi, 2020 ), cross-border shopping ( Yeung et al., 2004 ; Wong and Wan, 2013 ), souvenir shopping ( Masset and Decrop, 2021 ), passengers' shopping motivations ( Lin and Chen, 2013 ), duty-free shopping ( Han and Hyun, 2018 ), the typology of shopping tourists ( Choi et al., 2016a ), and shopping risk management ( Hsieh and Tsao, 2014 ). In addition, Kattiyapornpong and Miller (2012) found that shopping tourism could function as one of the competitive advantages of tourism destinations, thus bringing tremendous economic benefits to local development. Lee and Choi (2020) examined the effects of asymmetric shopping tourism attributes on shopping destination satisfaction levels and designed two pyramid-shaped figures prioritizing both shopping-specific attributes and destination-specific attributes based on the categorization of their asymmetric impacts. Choi et al. (2018) examined the trust in the shopping destination as an antecedent of shopping tourists' perceptions of value based on an RFT framework. Correia et al. (2019) dug deep into Chinese tourist perceptions of luxury shopping visits to Hong Kong to explore the nature of luxury buying behavior.
According to Section Gastronomy tourism and Section Shopping tourism, gastronomy and shopping, the two representative components of general tourism, are both on their way to become part of cultural tourism through the process of culturalization. Therefore, it is necessary for tourism organizations to take on the culture-oriented strategy so as to conform to the inevitable trend of culturalization.
Optimization of the cultural tourism development
This section reviews literature on the optimization of cultural tourism development, including destination branding and consumer experience, two significant tools to optimize cultural tourism development.
Destination branding in tourism
Branding of tourism destinations is an essential tool for tourism destinations to attract more tourists and thus to flourish. By far, there is barely any research specifically focusing on destination branding in cultural tourism. However, destination branding in general tourism has generated a bunch of attention from scholars, from which we can capture some of the developmental patterns of destination branding in cultural tourism.
As the market competition intensifies, more and more companies and organizations get to realize that tourist destinations also need to make the most of such valuable assets as their developed brands to position and differentiate themselves properly ( Aaker, 2009 ). Therefore, tourism branding, usually known as destination branding, has become a key theme for tourism researchers since the late 1990's ( Liu et al., 2020 ). For example, Konecnik and Gartner (2007) explored the effectiveness of customer-based destination brand equity (CBDBE) and proposed a comprehensive evaluation system consisting of four dimensions: image, awareness, quality, and loyalty. Furthermore, the determinants of CBDBE have been identified from three main perspectives: tourists' travel-related factors (e.g., destination experience and consumption social visibility); DMOs' branding-related factors (e.g., DMOs' cooperation or power); and resident-related factors (e.g., tourist–resident interaction; Marzano and Scott, 2009 ; Josiassen et al., 2013 ; Barnes et al., 2014 ; Mariani and Giorgio, 2017 ). Applying traditional research methods of brand image and brand personality to tourism destinations, Hosany et al. (2006) found that destination image is closely related to destination personality and that the emotional component of destination image captures the majority of variance on destination personality dimensions. Taking the Gold Coast in Australia as a case study, Marzano and Scott (2009) concluded that a lack of unity and collaboration amongst stakeholders could barely affect the positive outcomes brought by a destination branding process. The authors also provided a detailed inventory of the interests advanced by stakeholders' power in the forms of persuasion and authority in a branding process.
In the past decade, the connotation of destination branding is becoming increasingly comprehensive. According to Campelo et al. (2014) , destination branding is meant to combine a tourism destination's environmental, social, and cultural capital, thus creating a unique and differential image of the destination. Pike and Page (2014) proposed that DMOs should also include local residents (other than visitors) into their target audience base during destination branding. Additionally, destination brand image is no longer an exclusive creation of DMOs alone, but a complex co-creation of thousands of social media users who tend to share their traveling experiences and feelings online ( Lo et al., 2011 ; Mak, 2017 ). In light of this, scholars began to explore the potential use of mainstream social media platforms (e.g., Instagram) for destination branding purposes ( Fournier and Avery, 2011 ; Fatanti and Suyadnya, 2015 ; Oliveira and Panyik, 2015 ). When it comes to the connection between consumers and destination branding, scholars tend to focus on destination brand love (DBL), which is usually defined as a multi-dimensional construct including passionate love, emotional attachment, self-brand integration, and self-brand identification in the context of tourism ( Tsai, 2014 ; Lee and Hyun, 2016 ; Aro et al., 2018 ; Zhang et al., 2020 ). Through manifesting their love toward certain destination brands, tourists manage to express their consumer identity and personality, getting closer to their ideal self ( Batra et al., 2012 ; Belk, 2014 ).
From the year 2020 on, research on destination branding has become more detail-oriented and innovative when a great many scholars tend to focus on topics that are either further extensions of existing ones or accumulative innovations. For example, further to the series of research on mainstream social media platforms for destination branding purposes, Filieri et al. (2021) explored how destination brand love (DBL) is expressed on Instagram using a mixed-methods approach. Pan et al. (2021) innovatively explore destination brand image from the perspective of gender, contributing greatly to the measurement scale development of destination gender, which is an important topic in destination branding literature. Considering New Zealand as a space tourism destination, Scott (2022) proposed that the destination branding of New Zealand should be updated with the development of the society to include cultural factors, geopolitical factors, and sustainability-related factors.
Consumer experience in cultural tourism
Consumer experience, a central concept in marketing ( Pine et al., 1999 ), is also a pivotal construct in the tourism industry and is usually known as tourism experience under touristic context ( Otto and Ritchie, 1996 ; Sørensen and Jensen, 2015 ). Extant literature on tourism experience has proved that the key to retain flow of tourists is to create a memorable tourism experience for them, which is also applicable for cultural tourism.
Many researchers have long been working on exploring the essence of tourism experiences. According to Chen et al. (2014) , a tourism experience is different from general consumer experiences in that it is strongly driven by service and hospitality. It usually occurs in distinct stages including at-home stage, at-the-destination stage, and after-returning stage ( Chatterley et al., 2013 ). In as early as 1979, Cohen found that the ultimate tourism experience could be compared as a religious experience or the result of pilgrimage, where tourists search for something less tangible than the trip and more rewarding than just being there ( Vallee, 1987 ). Mannell and Iso-Ahola suggested in 1987 that the core of leisure tourism experience is flow experience and that the search for the ultimate tourism experience is a quest for authenticity, center, meaning, or values. From the perspective of psychology, the main benefits of leisure tourism experiences emanate from the interplay of two forces: escaping (of routine and stressful environments) and seeking (for recreational opportunities of certain intrinsic rewards). However, it remains a problem to neatly distinct plain tourism experience from leisure experience ( Mannell and Iso-Ahola, 1987 ).
As the famous tourism anthropologist Cohen (1979) put it, different tourists need different tourism experiences, which is of special significance for tourists. For example, excitement-seeking tourists tend to show a special preference for adventure tourism, while food lovers turn out to be loyal customers of gastronomy tourism ( Gyimóthy and Mykletun, 2004 ; Konu, 2015 ; Sthapit, 2019 ). However, due to factors such as heterogeneity in customer preferences, uncertainties in destination choices, and contingencies related to group activities ( Hsiao et al., 2015 ), tourism experience proves to be a quite complex concept that is neither definition-friendly nor manipulation-friendly ( Mei, 2014 ). In light of this, many tourism firms begin to introduce co-creation, a tourism designing mode in which tourists function as independent co-creators rather than passive consumers to create value in interactive consumer-firm relationships ( Dalonso et al., 2014 ; Prebensen et al., 2017 ; Geng et al., 2022 ; Sun et al., 2022 ). In a high co-creation context, tourist wellbeing increases with increased active participation ( Björk, 2014 ). Moreover, thanks to all the individual resources devoted to the co-creation of tourism experience, psychological ownership also comes into play and enhances tourists' subjective value, thus stimulating tourists' loyalty (i.e., intentions to re-visit; Prebensen et al., 2013 ; Sugathan and Ranjan, 2019 ).
Tourism experience is usually recognized as a psychological phenomenon where expectations, individual sensing and perception, and memorizing are crucial components ( Larsen, 2007 ). Theoretically, the boundary of tourism experience can be extended to various psychological fields such as cognitive psychology and social psychology. For example, research on experiential consumption believes that from the perspective of tourist psychology, it is the experience of shopping at a tourism destination, rather than the physical goods purchased, that really matters in tourism consumption. Furthermore, as MacCannell (2002) put it, a tourism experience is by nature an experiential commodity whose value is legitimated by consumers' pursuit of ego fulfillment. Therefore, the essence of tourism consumption is also experiential consumption ( Moldes et al., 2019 ; Gilovich and Gallo, 2020 ; Puente-Díaz and Cavazos-Arroyo, 2021 ). Experiential consumption is a concept originally proposed by Van Boven and Gilovich (2003) . Using the experience sampling method, Kumar et al. (2020) found that experiential shopping would lead to more instant happiness, which is a sense of happiness perceived by consumers from a certain consumption behavior ( Dunn and Weidman, 2015 ). Experiential consumption will also lead to more positive emotions ( Carter and Gilovich, 2010 ; Barton et al., 2019 ), more jealousness ( Lin et al., 2018 ), more interactive behavior ( Chen et al., 2021 ), and fewer regrets ( Rosenzweig and Gilovich, 2012 ).
According to Section Destination branding in tourism and Section Consumer experience in cultural tourism, extant literature on cultural tourism development has been increasingly emphasizing the power of people. Specifically, optimizing destination branding and promoting tourist experience are both effective methods centered on destination-tourist bonding. In light of this, tourism organizational change in the future may as well center on people and thus pass on to the promising humanity-centered times.
Summary of interconnections
Combining all the sub-interconnections mentioned in the last paragraph of each section, the general interconnections between the review of cultural tourism research and the change of tourism organizations can be summarized as: tourism organizations are interconnected with cultural tourism research in terms of changes in strategy, structure, personnel management, and organizational culture, and thus are obliged to implement multi-facet changes to adapt to the volatile tourism industry. Table 2 summarizes and reviews all the aforementioned interconnections for quick check.
Table 2 . Summary of interconnections.
Implications for tourism organizational change
Based on the systematic literature review of cultural tourism research presented in Part 2 as well as its interconnections with tourism organizational change (as is shown in Table 2 ), several irradiative implications could be proposed for tourism organizations to implement feasible changes. In this part, all the potential implications will be presented section by section and will be further summarized into Table 3 .

Table 3 . Implications for tourism organizational changes.
Culture-based strategic change
Above all, it is inevitable for tourism organizations to change their traditional sightseeing-based strategies into culture-based ones. For one thing, cultural tourism, instead of traditional tourism, is gradually becoming a mainstream tourism type in the global tourism market ( UNWTO, 2018 , 2021 ). According to the aforementioned Figures 1 , 2 , cultural tourism research is becoming increasingly flourishing, which turns out to be another evidence for the growing status of cultural tourism. For another thing, traveling motivations of most tourists are more or less of some culturedness ( Jovicic, 2016 ) when traditional non-cultural motivations such as relaxation-seeking, sports-seeking, family-relationship-seeking, pressure-escaping, autonomy (freedom)-seeking ( Özel and Kozak, 2012 ), identity (achievement)-seeking ( Bond and Falk, 2013 ), and novelty-seeking ( Sugathan and Ranjan, 2019 ; Prayag et al., 2021 ; Pereira et al., 2022 ) are increasingly being reduced to appendants of cultural motivations. For example, gastronomy, which has long been acknowledged as a traditional mainstream touristic motivation way off cultural stuff, is now universally accepted as a cultural motivation by tourists ( Cohen, 1992 ; Everett and Aitchison, 2008 ; Jovicic, 2016 ). In addition, the swelling of cultural food consumption is gradually driving gastronomy tourism to become an important sub-sector of cultural tourism as well as an inevitable component of general tourism (i.e., gastronomy is a necessary component of all types of tourism activities; Montanari, 2009 ; Sims, 2010 ). Similar mechanism also applies in shopping, the closest companion of tourism ( Jansen-Verbeke, 1991 ). The boom of cultural souvenir shopping and tourists' evergreen shopping enthusiasm toward cultural intellectual properties (IP) are robust evidence for the prevailing sense of culturedness in touristic shopping activities ( Masset and Decrop, 2021 ). Therefore, tourism organizations, by launching a strategic change where culture-based strategy substitute for traditional sightseeing-based strategy, should quickly adapt to the cultural revolution in the tourism industry to survive the volatile future.
Personnel-based structural change
Thanks to the increasing complexity of cultural tourism connotation, tourism organizations are also subject to adaptive structural change that is focused on personnel management. According to Richards (2018) , the connotation of cultural tourism is increasingly focused on the pursuit of broadness by including concepts such as in-betweenness and non-tourism. The expanding broadness of cultural tourism connotation can also be reflected by diverse typologies of cultural tourists. Specifically, cultural tourists have been classified upon factors such as personal appetite ( Barbieri and Mahoney, 2009 ; Baltaci and Cakici, 2022 ), age ( Richards and van der Ark, 2013 ), physical contexts ( Richards and van der Ark, 2013 ; Richards, 2018 ), and motivations ( Pearce, 1982 ; Correia et al., 2013 ; Jovicic, 2016 ; Packer and Ballantyne, 2016 ; Du Cros and McKercher, 2020 ). As Russo and Richards (2016) put it, cultural tourists can no longer be regarded as static categories when most actors engaged in the process of cultural tourism begin to perform different roles relative to one another. Additionally, the increasing broadness and complexity of the connotation and typology enhance the connection between cultural tourism and some major academic disciplines such as management, sociology, economics, anthropology, and psychology, which is consistent with our finding that cultural tourism has been widely discussed in various research fields (see Table 1 ). In light of this, tourism organizations are obliged to launch a structural change by increasing the diversity and subdivision of their departments, thus adapting to the increasing complexity of the newly adopted culture-based strategy.
More importantly, structural changes are usually accompanied with personnel management such as new hiring, professional training, rotation of role and responsibilities, and scientific performance evaluation ( Graetz and Smith, 2010 ). By putting together a group of selected employees with enough expertise, position power, credibility, and leadership skills, proper personnel changes potentially solidify structural changes that took place in tourism organizations ( Kotter, 1995 ; Thomas et al., 2011 ). For example, hiring professional chefs to guarantee the authenticity of local ethnic restaurants ( Cohen and Avieli, 2004 ; Chatzopoulou et al., 2019 ; Meneguel et al., 2019 ; Yu et al., 2020 ), training restaurant employees to improve service awareness by removing the order barrier of tourists ( Lai et al., 2019 ; Yu et al., 2020 ), and properly arranging and balancing responsibilities of different departments to gather joint efforts ( Smith and Xiao, 2008 ), are all feasible ways for tourism organizations to make structural changes in preparation for the adoption of gastronomic culture-based strategies. In general, tourism organizations are suggested to make personnel-based structural changes to guarantee their readiness and capacity and thus to further consolidate their newly adopted culture-based strategy.
Humanity-centric organizational culture change
According to Section Destination branding in tourism and Section Consumer experience in cultural tourism, methods that are adopted to optimize the development of cultural tourism are increasingly centered on the importance of people. For example, more and more consumer psychological techniques are applied to destination branding when improving consumer experience becomes the key to attract a steady flow of tourists in most destinations. As Feldman (2000) put it, human agents are the initial source and trigger for all the potential development and changes. Therefore, tourism organizations are obliged to respect and take advantage of the value brought by people, including tourists and employees, thus prioritizing humanity within their organizational culture.
Tourist-oriented communication mechanism
Tourism organizations are first obligated to develop a tourist-oriented communication mechanism, for the final performances of organizational change are inclined to be examined and evaluated by consumers (i.e., tourists). A successful tourist-oriented communication mechanism is usually associated with fascinating destination branding ( Aaker, 2009 ), memorable tourism experience ( Sørensen and Jensen, 2015 ), and proper balance between authenticity and glocalization ( Soulard et al., 2019 ). Firstly, tourism organizations should adopt more tourist-oriented techniques such as arousing destination brand love ( Lee and Hyun, 2016 ), inspiring self-brand integration ( Tsai, 2014 ), as well as taking advantage of tourists' respect and trust toward authoritative titles (e.g., the list of World Heritage Sites; Jimura, 2011 ) to carry forward the brand of a target destination, thus strengthening the tourists-destination connection ( Aro et al., 2018 ; Zhang et al., 2020 ). Secondly, tourism organizations should also create a memorable tourism experience, which proves to be the key to attract a steady flow of tourists ( Mei, 2014 ), through bonding techniques such as encouraging co-creation of tourists ( Dalonso et al., 2014 ; Prebensen et al., 2017 ; Geng et al., 2022 ; Sun et al., 2022 ). Thirdly, endemic tourism destinations should maintain the balance between authenticity and glocalization to deal with the dilemma caused by tourists' curiosity toward a different culture and their limited tolerance toward a strange taste. For example, some endemic restaurants in tourism destinations try to slightly adapt their traditional cuisines to the taste of ecdemic tourists, thus bringing the authentic culture of the tourism destination and simultaneously improving tourists' dining satisfaction ( Cohen and Avieli, 2004 ; Soulard et al., 2019 ). Therefore, tourism organizations are recommended to launch a tourist-oriented communication change to better capture tourists' changeable demands and preferences.
Employee-centric emotion management
Tourism organizations are also obliged to properly manage employees' emotions toward upcoming organizational changes, which prove to be essential to the success of change implementation ( Errida and Lotfi, 2021 ). According to Al-Haddad and Kotnour (2015) , the general success rate of organizational change has long been under 30%, indicating a sustained need to improve the success rate by minimizing destructive barriers such as employees' negative emotions and attitudes toward change ( Rafferty et al., 2013 ). According to most literature on change management, employees' emotions toward change, usually known as the change motivation of employees, are inclined to represent organizational change readiness and capacity ( Project Management Institute, 2013 ; Combe, 2014 ; Alwheeb and Rea, 2017 ). As employees usually function as the active impellers of changes ( Mento et al., 2002 ), their change motivations and emotions, which are usually influenced by each interest-based personnel reshuffle during organizational change ( Shah et al., 2016 ), turn out to be determinants of the change success rate ( Fernandez and Rainey, 2006 ; Hodges, 2017 ). Therefore, it is vital for tourism organizations to optimize their employee-centric emotion management and thus to equip themselves with sustainable resilience, secure readiness, and excellent capabilities to successfully implement daily changes.
Additionally, these implications have been summarized into Table 3 for quick check.
This study, based on a brief review addressing the tremendous expansion of cultural tourism scholarship that has evolved into a well-defined research field incorporating multi-disciplinary perspectives, manages to figure out several feasible implications for tourism organizations to implement proper organizational changes for adaptative development. According to the evolutionary process from fragmentation to systematization in cultural tourism research ( Richards, 2018 ), cultural tourism is continuously growing from a niche market consisting of intellectuals and high-income tourists toward a mass-market open to a much wider range of people, becoming a promising trend that directs future change implementations of tourism organizations ( Noonan and Rizzo, 2017 ). In general, this study, based on a brief review of cultural tourism research that illustrates its interconnections with organizational changes, has figured out several implications in terms of changes in organizational strategy, organizational structure, personnel management, and organizational culture. Therefore, tourism organizations are recommended to pursue culturedness , accompanied by corresponding means to continuously implement proper changes to hedge the potential volatility in future development.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZZ: writing and final proofreading. MG: data collection, analysis, and producing figures and reference list. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aaker, D. A. (2009). Managing Brand Equity . New York, NY: Simon and Schuster.
Google Scholar
Albayrak, T., Caber, M., and Çömen, N. (2016). Tourist shopping: the relationships among shopping attributes, shopping value, and behavioral intention. Tour. Manag. Perspect . 18, 98–106. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2016.01.007
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Alberts, H. C., and Hazen, H. D. (2010). Maintaining authenticity and integrity at cultural world heritage sites. Geogr. Rev . 100, 56–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1931-0846.2010.00006.x
Al-Haddad, S., and Kotnour, T. (2015). Integrating the organizational change literature: a model for successful change. J. Organ. Chang. Manag . 28, 234–262. doi: 10.1108/JOCM-11-2013-0215
Alwheeb, M., and Rea, D. M. (2017). Assessing organizational readiness for the improvement and change initiatives in public hospitals. Manag. Issues. Healthcare. Syst . 3, 49–57. doi: 10.33844/mihs.2017.60346
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Aro, K., Suomi, K., and Saraniemi, S. (2018). Antecedents and consequences of destination brand love—a case study from Finnish Lapland. Tour. Manag . 67, 71–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.01.003
Artal-Tur, A., Briones-Peñalver, A. J., and Villena-Navarro, M. (2018). Tourism, cultural activities and sustainability in the Spanish Mediterranean regions: a probit approach. Tour. Manag. Stud . 14, 7–18. doi: 10.18089/tms.2018.14101
Báez-Montenegro, A., and Devesa-Fernández, M. (2017). Motivation, satisfaction and loyalty in the case of a film festival: differences between local and non-local participants. J. Cult. Econ . 41, 173–195. doi: 10.1007/s10824-017-9292-2
Baker, J., Berry, L. L., and Parasuraman, A. (1988). The marketing impact of branch facility design. J. Retail Bank . 10, 33–42.
Baker, J., Parasuraman, A., Grewal, D., and Voss, G. B. (2002). The influence of multiple store environment cues on perceived merchandise value and patronage intentions. J. Mark . 66, 120–141. doi: 10.1509/jmkg.66.2.120.18470
Baker, M. A., and Kim, K. (2018). The role of language, appearance, and smile on perceptions of authenticity versus rapport. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 74, 171–179. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.04.011
Balderas-Cejudo, A., Gavilan, D., and Fernandez-Lores, S. (2022). Michelin-starred Restaurants and Its Contribution to Luxury Gastronomy Tourism. The Emerald Handbook of Luxury Management for Hospitality and Tourism (Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited), 321–334. doi: 10.1108/978-1-83982-900-020211016
Ballantyne, R., and Packer, J. (2016). Visitors' perceptions of the conservation education role of zoos and aquariums: implications for the provision of learning experiences. Visit. Stud . 19, 193–210. doi: 10.1080/10645578.2016.1220185
Baltaci, M., and Cakici, A. C. (2022). Serendipitous Cultural Tourist: L. oliveira, Advances in Hospitality, Tourism, and the Services Industry (Pennsylvania, PA: IGI Global), 332–350. doi: 10.4018/978-1-7998-8528-3.ch018
Barbieri, C., and Mahoney, E. (2009). Cultural tourism behaviour and preferences among the live-performing arts audience: an application of the univorous–omnivorous framework. Int. J. Tour. Res . 2009, jtr.767. doi: 10.1002/jtr.767
Barnes, S. J., Mattsson, J., and Sørensen, F. (2014). Destination brand experience and visitor behavior: testing a scale in the tourism context. Ann. Tour. Res . 48, 121–139. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2014.06.002
Barton, G., Baguley, M., Kerby, M., and MacDonald, A. (2019). “Exploring how quality children's literature can enhance compassion and empathy in the classroom context,” in Compassion and Empathy in Educational Contexts , eds G. Barton and S. Garvis (Cham: Palgrave Macmillan). doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-18925-9_9
Bastiaansen, M., Lub, X. D., Mitas, O., Jung, T. H., Ascenção, M. P., Han, D.-I., et al. (2019). Emotions as core building blocks of an experience. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag . 31, 651–668. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-11-2017-0761
Batra, R., Ahuvia, A., and Bagozzi, R. P. (2012). Brand love. J. Mark . 76, 1–16. doi: 10.1509/jm.09.0339
Beardsworth, A., Bryman, A., Keil, T., Goode, J., Haslam, C., and Lancashire, E. (2002). Women, men and food: the significance of gender for nutritional attitudes and choices. Br. Food J . 104, 470–491. doi: 10.1108/00070700210418767
Beer, M., and Nohria, N. (2000). Cracking the code of change. Harv. Bus. Rev . 78, 133–141. Available online at: https://hbr.org/2000/05/cracking-the-code-of-change
Belk, R. (2014). Digital consumption and the extended self. J. Mark. Manag. 30, 1101–1118. doi: 10.1080/0267257X.2014.939217
Berbel-Pineda, J. M., Palacios-Florencio, B., Ramírez-Hurtado, J. M., and Santos-Roldán, L. (2019). Gastronomic experience as a factor of motivation in the tourist movements. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci . 18, 100171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2019.100171
Björk, P. (2014). Tourist experience value: tourist experience and life satisfaction. Creat. Exp. Value Tour . 2014, 22–32. doi: 10.1079/9781780643489.0022
Björk P. Kauppinen-Räisänen H. (2017). Interested in eating and drinking? How food affects travel satisfaction and the overall holiday experience. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour . 17, 9–26. doi: 10.1080/15022250.2016.1215871
Bond, N., and Falk, J. (2013). Tourism and identity-related motivations: why am I here (and not there)?: who am i and why am i here…and not there? Int. J. Tour. Res . 15, 430–442. doi: 10.1002/jtr.1886
Campelo, A., Aitken, R., Thyne, M., and Gnoth, J. (2014). Sense of place: the importance for destination branding. J. Travel Res . 53, 154–166. doi: 10.1177/0047287513496474
Carter, T. J., and Gilovich, T. (2010). The relative relativity of material and experiential purchases. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol . 98, 146–159. doi: 10.1037/a0017145
Chang, L. L., Backman, K., and Chih Huang, Y. (2014). Creative tourism: a preliminary examination of creative tourists' motivation, experience, perceived value and revisit intention. Int. J. Cult. Tour. Hosp. Res . 8, 401–419. doi: 10.1108/IJCTHR-04-2014-0032
Chatterley, C., Linden, K. G., and Javernick-Will, A. (2013). Identifying pathways to continued maintenance of school sanitation in Belize. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev . 3, 411–422. doi: 10.2166/washdev.2013.128
Chatzopoulou, E., Gorton, M., and Kuznesof, S. (2019). Understanding authentication processes and the role of conventions: a consideration of Greek ethnic restaurants. Ann. Tour. Res . 77, 128–140. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2019.06.004
Chen, J. S., Prebensen, N. K., and Uysal, M. (2014). Dynamic drivers of tourist experiences. Creat. Exp. Value Tour . 2014, 11–21. doi: 10.1079/9781780643489.0011
Chen, K., Wang, Q., Wang, X., and Xing, C. (2021). The difference between experiential and material consumption: research methods and effects. Adv. Psychol. Sci . 29, 1111–1121. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.01111
Choi, M., Law, R., and Heo, C. Y. (2016b). Shopping destinations and trust – tourist attitudes: Scale development and validation. Tour. Manag . 54, 490–501. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2016.01.005
Choi, M., Law, R., and Heo, C. Y. (2018). An investigation of the perceived value of shopping tourism. J. Travel Res . 57, 962–980. doi: 10.1177/0047287517726170
Choi, M. J., Heo, C. Y., and Law, R. (2016a). Developing a typology of Chinese shopping tourists: an application of the schwartz model of universal human values. J. Travel Tour. Mark . 33, 141–161. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2014.997961
Cisneros-Martínez, J. D., and Fernández-Morales, A. (2015). Cultural tourism as tourist segment for reducing seasonality in a coastal area: the case study of Andalusia. Curr. Issues Tour . 18, 765–784. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2013.861810
Cohen, E. (1979). A phenomenology of tourist experiences. Sociology 13, 179–201. doi: 10.1177/003803857901300203
Cohen, E., and Avieli, N. (2004). Food in tourism: attraction and impediment. Ann. Tour. Res . 31, 755–778. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2004.02.003
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychol. Bull . 112, 155. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155
Cohen, S. (1986). Contrasting the hassles scale and the perceived stress scale: who's really measuring appraised stress? Am. Psychol . 41, 716–718. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.41.6.716
Combe, M. (2014). Change Readiness: Focusing Change Management Where It Counts . Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
Correia, A., Kozak, M., and Ferradeira, J. (2013). From tourist motivations to tourist satisfaction. Int. J. Cult. Tour. Hosp. Res . 7, 411–424. doi: 10.1108/IJCTHR-05-2012-0022
Correia, A., Kozak, M., and Kim, S. (2019). Investigation of luxury values in shopping tourism using a fuzzy-set approach. J. Travel Res . 58, 77–91. doi: 10.1177/0047287517741005
Dalonso, Y. S., Lourenço, J. M., Remoaldo, P. C., and Panosso Netto, A. (2014). Tourism experience, events and public policies. Ann. Tour. Res . 46, 181–184. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2014.03.003
Dann, G. M. S. (1996). Tourists' images of a destination-an alternative analysis. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 5, 41–55. doi: 10.1300/J073v05n01_04
Dela Santa, E., and Tiatco, S. A. (2019). Tourism, heritage and cultural performance: developing a modality of heritage tourism. Tour. Manag. Perspect . 31, 301–309. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2019.06.001
Du Cros, H., and McKercher, B. (2020). Cultural Tourism . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9780429277498
Dunn, E. W., and Weidman, A. C. (2015). Building a science of spending: lessons from the past and directions for the future. J. Consum. Psychol . 25, 172–178. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2014.08.003
Ellis, D., and Mattison Thompson, F. (2018). The effect of wine knowledge type on variety seeking behavior in wine purchasing. J. Wine Res . 29, 71–86. doi: 10.1080/09571264.2018.1471393
Errida, A., and Lotfi, B. (2020). Measuring change readiness for implementing a project management methodology: an action research study. Acad. Strat. Manag. J . 19, 1–17. Available online at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Measuring-Change-Readiness-for-Implementing-a-an-Errida-Lotfi/8b4c99dafcbc04a5684b3dcca31b57a8f2736d98
Errida, A., and Lotfi, B. (2021). The determinants of organizational change management success: literature review and case study. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag ., 13, 184797902110162. doi: 10.1177/18479790211016273
Everett, S. (2008). Beyond the visual gaze? The pursuit of an embodied experience through food tourism. Tour. Stud . 8, 337–358. doi: 10.1177/1468797608100594
Everett, S. (2019). Theoretical turns through tourism taste-scapes: the evolution of food tourism research. Res. Hosp. Manag . 9, 3–12. doi: 10.1080/22243534.2019.1653589
Everett, S., and Aitchison, C. (2008). The role of food tourism in sustaining regional identity: a case study of Cornwall, South West England. J. Sustain. Tour . 16, 150–167. doi: 10.2167/jost696.0
Fahmi, F. Z., McCann, P., and Koster, S. (2017). Creative economy policy in developing countries: the case of Indonesia. Urban Stud . 54, 1367–1384. doi: 10.1177/0042098015620529
Falk, J. H. (2011). Contextualizing falk's identity-related visitor motivation model. Visit. Stud . 14, 141–157. doi: 10.1080/10645578.2011.608002
Fatanti, M. N., and Suyadnya, I. W. (2015). Beyond user gaze: how instagram creates tourism destination brand? Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci . 211, 1089–1095. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.11.145
Feldman, M. (2000). Organizational routines as a source of continuous change. Organ. Sci . 11, 611–629. doi: 10.1287/orsc.11.6.611.12529
Fernandez, S., and Rainey, H. G. (2006). Managing successful organizational change in the public sector. Public. Admin. Rev . 66, 168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-6210.2006.00570.x
Filieri, R., Yen, D. A., and Yu, Q. (2021). #ILoveLondon: an exploration of the declaration of love towards a destination on Instagram. Tour. Manag . 85, 104291. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104291
Fournier, S., and Avery, J. (2011). The uninvited brand. Bus. Horiz . 54, 193–207. doi: 10.1016/j.bushor.2011.01.001
Frey, B. S., and Steiner, L. (2011). World heritage list: does it make sense? Int. J. Cult. Policy . 17, 555–573. doi: 10.1080/10286632.2010.541906
Galí-Espelt, N. (2012). Identifying cultural tourism: a theoretical methodological proposal. J. Herit. Tour . 7, 45–58. doi: 10.1080/1743873X.2011.632480
Geissler, G. L., Rucks, C. T., and Edison, S. W. (2006). Understanding the role of service convenience in art museum marketing: an exploratory study. J. Hosp. Leis. Mark . 14, 69–87. doi: 10.1300/J150v14n04_05
Geng, R., Sun, R., Li, J., Guo, F., Wang, W., and Sun, G. (2022). The impact of firm innovativeness on consumer trust in the sharing economy: a moderated mediation model. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist . 34, 1078–1098. doi: 10.1108/APJML-10-2020-0748
Gilovich, T., and Gallo, I. (2020). Consumers' pursuit of material and experiential purchases: a review. Consum. Psychol. Rev . 3, 20–33. doi: 10.1002/arcp.1053
Graburn, N. (1977). The museum and the visitor experience. Roundtable Rep . 1977, 1–5.
Graetz, F., and Smith, A. C. T. (2010). Managing organizational change: a philosophies of change approach. J. Chang. Manag . 10, 135–154. doi: 10.1080/14697011003795602
Gravari-Barbas, M. (2018). Tourism as a heritage producing machine. Tour. Manag. Perspect . 25, 173–176. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2018.01.004
Guccio, C., Lisi, D., Mignosa, A., and Rizzo, I. (2018). Does cultural heritage monetary value have an impact on visits? An assessment using official Italian data. Tour. Econ . 24, 297–318. doi: 10.1177/1354816618758729
Gyimóthy, S., and Mykletun, R. J. (2004). Play in adventure tourism. Ann. Tour. Res . 31, 855–878. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2004.03.005
Ha, J., and Jang, S. (2010). Perceived values, satisfaction, and behavioral intentions: the role of familiarity in Korean restaurants. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 29, 2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2009.03.009
Hall, C. M., Baird, T., James, M., and Ram, Y. (2016). Climate change and cultural heritage: conservation and heritage tourism in the Anthropocene. J. Herit. Tour . 11, 10–24. doi: 10.1080/1743873X.2015.1082573
Hall, C. M., and Mitchell, R. (2000). Wine tourism in the Mediterranean: a tool for restructuring and development. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 42, 445–465. doi: 10.1002/1520-6874(200007/08)42:4<445::AID-TIE6>3.0.CO;2-H
Hall, C. M., and Sharples, L. (2008). Food events, festivals and farmers' markets: an introduction. Food and wine festivals and events around the world. Dev. Manag. Markets 2008, 3–22. doi: 10.4324/9780080887951
Han, H., and Hyun, S. S. (2018). Investigating customers' shopping behaviors at airport duty-free shops: impact of shopping flow and alternative shopping malls' attractiveness. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res . 23, 627–638. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2018.1485717
Henderson, J. C. (2009). Food tourism reviewed. Br. Food J . 111, 317–326. doi: 10.1108/00070700910951470
Henderson, J. C., Chee, L., Mun, C. N., and Lee, C. (2011). Shopping, tourism and retailing in Singapore. Manag. Leis . 16, 36–48. doi: 10.1080/13606719.2011.532599
Hjalager, A. M., and Richards, G. (2002). Tourism and Gastronomy (Vol. 11) . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9780203218617
Hodges, J. (2017). Building capabilities for change: the crucial role of resilience. Dev. Learn. Org ., 31, 5–8. doi: 10.1108/DLO-07-2016-0064
Hope Hailey, V., and Balogun, J. (2002). Devising context sensitive approaches to change: the example of glaxo wellcome. Long. Range. Plan . 35, 153–178. doi: 10.1016/S0024-6301(02)00035-3
Horng, J. S., and Tsai, C. T. (2010). Government websites for promoting East Asian culinary tourism: a cross-national analysis. Tour. Manag. 31, 74–85. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2009.01.009
Hosany, S., Ekinci, Y., and Uysal, M. (2006). Destination image and destination personality: an application of branding theories to tourism places. J. Bus. Res . 59, 638–642. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2006.01.001
Hsiao, C., Lee, Y. H., and Chen, W. J. (2015). The effect of servant leadership on customer value co-creation: a cross-level analysis of key mediating roles. Tour. Manag . 49, 45–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2015.02.012
Hsieh, M. T., and Tsao, W. C. (2014). Reducing perceived online shopping risk to enhance loyalty: a website quality perspective. J. Risk Res . 17, 241–261. doi: 10.1080/13669877.2013.794152
Hsu, F. C., Liu, J., and Lin, H. (2022). Affective components of gastronomy tourism: measurement scale development and validation. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag . 2021, 1112. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-09-2021-1112
James, W. (1996). A Pluralistic Universe . Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press.
Jang, S., and Ha, J. (2015). The influence of cultural experience: emotions in relation to authenticity at ethnic restaurants. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res . 18, 287–306. doi: 10.1080/15378020.2015.1051436
Jang, S., Ha, J., and Park, K. (2012). Effects of ethnic authenticity: investigating Korean restaurant customers in the U.S. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 31, 990–1003. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2011.12.003
Jansen-Verbeke, M. (1991). Leisure shopping: a magic concept for the tourism industry? Tour. Manag . 12, 9–14. doi: 10.1016/0261-5177(91)90024-N
Jiang, L., and Yu, L. (2020). Consumption of a literary tourism place: a perspective of embodiment. Tou. Geogr . 22, 127–150. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2019.1586985
Jimura, T. (2011). The impact of world heritage site designation on local communities – a case study of Ogimachi, Shirakawa-mura, Japan. Tour. Manag . 32, 288–296. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2010.02.005
Jin, H., Moscardo, G., and Murphy, L. (2020). Exploring Chinese outbound tourist shopping: a social practice framework. J. Travel Res . 59, 156–172. doi: 10.1177/0047287519826303
Josiassen, A., Lukas, B. A., Whitwell, G. J., and Assaf, A. G. (2013). The halo model of origin images: conceptualisation and initial empirical test: the country-image model. J. Consum. Behav . 12, 253–266. doi: 10.1002/cb.1405
Jovicic, D. (2016). Cultural tourism in the context of relations between mass and alternative tourism. Curr. Issues Tour . 19, 605–612. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2014.932759
Kattiyapornpong, U., and Miller, K. E. (2012). Propensity to shop: identifying who shops til they drop. J. Travel Tour. Mark . 29, 552–565. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2012.703027
Kay, P. (2006). “Tourist benefits research: old and new issues and uses in a cultural tourism context,” in CAUTHE 2006 City Proc. 16th Counc. Hosp. Tour. Educ. Conf (Melbourne, FL: Victoria University). 809–824.
Kickert, W. J. M. (2014). Specificity of change management in public organizations: conditions for successful organizational change in Dutch ministerial departments. Am. Rev. Public . 6, 693–717. doi: 10.1177/0275074013483871
Kim, J. H., Youn, H., and Rao, Y. (2017). Customer responses to food-related attributes in ethnic restaurants. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 61, 129–139. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2016.11.003
Konecnik, M., and Gartner, W. C. (2007). Customer-based brand equity for a destination. Ann. Tour. Res . 34, 400–421. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2006.10.005
Konu, H. (2015). Developing a forest-based wellbeing tourism product together with customers – an ethnographic approach. Tour. Manag . 49, 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2015.02.006
Kotter, J. P. (1995). Leading change: why transformation efforts fail. Harv. Bus. Rev . 1995, 59–67.
Kumar, A., Killingsworth, M. A., and Gilovich, T. (2020). Spending on doing promotes more moment-to-moment happiness than spending on having. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol . 88, 103971. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2020.103971
Lai, I. K. W., Liu, Y., and Lu, D. (2021). The effects of tourists' destination culinary experience on electronic word-of-mouth generation intention: the experience economy theory. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res . 26, 231–244. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2020.1851273
Lai, M. Y., Khoo-Lattimore, C., and Wang, Y. (2019). Food and cuisine image in destination branding: toward a conceptual model. Tour. Hosp. Res . 19, 238–251. doi: 10.1177/1467358417740763
Larsen, S. (2007). Aspects of a psychology of the tourist experience. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour . 7, 7–18. doi: 10.1080/15022250701226014
Lee, J. S., and Choi, M. (2020). Examining the asymmetric effect of multi-shopping tourism attributes on overall shopping destination satisfaction. J. Travel Res . 59, 295–314. doi: 10.1177/0047287519832373
Lee, K. H., and Hyun, S. S. (2016). The effects of perceived destination ability and destination brand love on tourists' loyalty to post-disaster tourism destinations: the case of Korean Tourists to Japan. J. Travel Tour. Mark . 33, 613–627. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2016.1167349
Lee, T. H., and Hsu, F. Y. (2013). Examining how attending motivation and satisfaction affects the loyalty for attendees at aboriginal festivals: how attending motivation and satisfaction affects loyalty. Int. J. Tour. Res . 15, 18–34. doi: 10.1002/jtr.867
Li, Y. (2003). Heritage tourism: the contradictions between conservation and change. Tour. Hosp. Res . 4, 247–261. doi: 10.1177/146735840300400305
Lin, R., van de Ven, N., and Utz, S. (2018). What triggers envy on Social Network Sites? A comparison between shared experiential and material purchases. Comput. Hum. Behav . 85, 271–281. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2018.03.049
Lin, Y. H., and Chen, C. F. (2013). Passengers' shopping motivations and commercial activities at airports – the moderating effects of time pressure and impulse buying tendency. Tour. Manag . 36, 426–434. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2012.09.017
Liu, H., Wu, L., and Li, X. (2019). Social media envy: how experience sharing on social networking sites drives millennials' aspirational tourism consumption. J. Travel Res. 58, 355–369. doi: 10.1177/0047287518761615
Liu, Y., Hultman, M., Eisingerich, A. B., and Wei, X. (2020). How does brand loyalty interact with tourism destination? Exploring the effect of brand loyalty on place attachment. Ann. Tour. Res . 81, 102879. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2020.102879
Lo, I. S., McKercher, B., Lo, A., Cheung, C., and Law, R. (2011). Tourism and online photography. Tour. Manag . 32, 725–731. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2010.06.001
MacCannell, D. (1973). Staged authenticity: arrangements of social space in tourist settings. Am. J. Sociol . 79, 589–603. doi: 10.1086/225585
MacCannell, D. (2002). Empty Meeting Grounds: The Tourist Papers . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9780203412145
Mak, A. H. N. (2017). Online destination image: comparing national tourism organisation's and tourists' perspectives. Tour. Manag . 60, 280–297. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2016.12.012
Mannell, R. C., and Iso-Ahola, S. E. (1987). Psychological nature of leisure and tourism experience. Ann. Tour. Res . 14, 314–331. doi: 10.1016/0160-7383(87)90105-8
Mariani, M. M., and Giorgio, L. (2017). The “Pink Night” festival revisited: meta-events and the role of destination partnerships in staging event tourism. Ann. Tour. Res . 62, 89–109. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2016.11.003
Marzano, G., and Scott, N. (2009). Power in destination branding. Ann. Tour. Res . 36, 247–267. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2009.01.004
Masset, J., and Decrop, A. (2021). Meanings of tourist souvenirs: from the holiday experience to everyday life. J. Travel Res . 60, 718–734. doi: 10.1177/0047287520915284
Mei, X. Y. (2014). Boring and expensive: the challenge of developing experience-based tourism in the Inland region, Norway. Tour. Manag. Perspect . 12, 71–80. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2014.09.003
Meneguel, C. R., de, A., Mundet, L., and Aulet, S. (2019). The role of a high-quality restaurant in stimulating the creation and development of gastronomy tourism. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 83, 220–228. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.10.018
Mento, A., Jones, R., and Dirndorfer, W. (2002). A change management process: Grounded in both theory and practice. J. Chang. Manag. 3, 45–59. doi: 10.1080/714042520
Michalkó, G., and Varadi, Z. (2004). Croatian shopping tourism in Hungary: the case study of Barcs. Tourism . 52, 13327461. Available online at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Croatian-shopping-tourism-in-Hungary%3A-the-case-of-Michalk%C3%B3-V%C3%A1radi/a1d5ea72964bfa71bb105ee75feb5f96497fea59
Mohamed, M. E. A., Hewedi, M. M., Lehto, X., and Maayouf, M. (2020). Egyptian food experience of international visitors: a multidimensional approach. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag . 32, 2593–2611. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-02-2020-0136
Moldes, O., Banerjee, R., Easterbrook, M. J., Harris, P. R., and Dittmar, H. (2019). Identity changes and well-being gains of spending money on material and experiential consumer products. J. Econ. Psychol . 72, 229–244. doi: 10.1016/j.joep.2019.04.003
Montanari, A. (2009). Geography of taste and local development in Abruzzo (Italy): project to establish a training and research centre for the promotion of enogastronomic culture and tourism. J. Herit. Tour . 4, 91–103. doi: 10.1080/17438730802366482
Mostafanezhad, M., and Promburom, T. (2018). ‘Lost in Thailand': the popular geopolitics of film-induced tourism in northern Thailand. Soc. Cult. Geogr . 19, 81–101. doi: 10.1080/14649365.2016.1257735
Noonan, D. S., and Rizzo, I. (2017). Economics of cultural tourism: issues and perspectives. J. Cult. Econ . 41, 95–107. doi: 10.1007/s10824-017-9300-6
North, D. (1996). “Epilogue: economic performance through time,” in Empirical Studies in Institutional Change , eds L. J. Alston, T. Eggertsson, and D. North (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 342–355. doi: 10.1017/CBO9781139174633.023
Ochoa Zuluaga, G. I. (2015). Global Tourism Chains and Local Development in the Amazon: Implications for Community Wellbeing . ‘s-Hertogenbosch: BOXPress BV.
OECD (2018). Cultural and Local Development . Venice.
Okumus, B. (2021). Food tourism research: a perspective article. Tour. Rev . 76, 38–42. doi: 10.1108/TR-11-2019-0450
Okumus, B., Koseoglu, M. A., and Ma, F. (2018). Food and gastronomy research in tourism and hospitality: a bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 73, 64–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.01.020
Okumus, B., Okumus, F., and McKercher, B. (2007). Incorporating local and international cuisines in the marketing of tourism destinations: the cases of Hong Kong and Turkey. Tour. Manag . 28, 253–261. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2005.12.020
Oliveira, E., and Panyik, E. (2015). Content, context and co-creation: digital challenges in destination branding with references to Portugal as a tourist destination. J. Vacat. Mark . 21, 53–74. doi: 10.1177/1356766714544235
Orlikowski, W. J. (1996). Improvising organizational transformation over time: a situated change perspective. Inform. Systems. Res . 7, 63–92. doi: 10.1287/isre.7.1.63
Otto, J. E., and Ritchie, J. R. B. (1996). The service experience in tourism. Tour. Manag . 17, 165–174. doi: 10.1016/0261-5177(96)00003-9
Özel, Ç. H., and Kozak, N. (2012). Motive based segmentation of the cultural tourism market: a study of Turkish domestic tourists. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour . 13, 165–186. doi: 10.1080/1528008X.2012.645199
Pabel, A., Prideaux, B., and Thompson, M. (2017). Tourists' preferences with Indigenous tourism experiences in the Wet Tropics of Queensland, Australia. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag . 31, 142–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2016.11.004
Packer, J., and Ballantyne, R. (2016). Conceptualizing the visitor experience: a review of literature and development of a multifaceted model. Visit. Stud . 19, 128–143. doi: 10.1080/10645578.2016.1144023
Pan, L., Lu, L., and Zhang, T. (2021). Destination gender: scale development and cross-cultural validation. Tour. Manag . 83, 104225. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104225
Park, H. Y. (2013). Heritage Tourism . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315882093
Patuelli, R., Mussoni, M., and Candela, G. (2016). The Effects of World Heritage Sites on Domestic Tourism: A Spatial Interaction Model for Italy. Spatial Econometric Interaction Modelling (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 281–315. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-30196-9_13
Pearce, P. L. (1982). Perceived changes in holiday destinations. Ann. Tour. Res . 9, 145–164. doi: 10.1016/0160-7383(82)90044-5
Pereira, V., Gupta, J. J., and Hussain, S. (2022). Impact of travel motivation on tourist's attitude toward destination: evidence of mediating effect of destination image. J. Hosp. Tour. Res . 46, 946–971. doi: 10.1177/1096348019887528
Petrei, F., Cavallo, L., and Santoro, M. T. (2020). Cultural tourism: an integrated analysis based on official data. Qual. Quant. 54, 1705–1724. doi: 10.1007/s11135-019-00929-y
Pike, S., and Page, S. J. (2014). Destination Marketing Organizations and destination marketing: a narrative analysis of the literature. Tour. Manag . 41, 202–227. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.09.009
Pine, B. J., Pine, J., and Gilmore, J. H. (1999). The Experience Economy: Work Is Theatre and Every Business a Stage . Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Ponferrada, M. L. V. (2015). Evolución del turismo en España: el turismo cultural. Int. J. Sci. Manag. Tour . 1, 75–95. Available online at: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=5665969
Ponzini, D., Fotev, S., and Mavaracchio, F. (2016). Place Making or Place Faking? The Paradoxical Effects of Transnational Circulation of Architectural and Urban Development Projects. Reinventing the Local in Tourism (Bristol: Multilingual Matters), 153–170. doi: 10.21832/9781845415709-012
Prayag, G., Alrawadieh, Z., and Alrawadieh, Z. (2021). Motivation, emotion and world heritage status in discerning the heritage tourists: a segmentation perspective. Tour. Manag. Perspect . 40, 100906. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100906
Prebensen, N. K., Chen, J. S., and Uysal, M. (2017). Co-creation in Tourist Experiences . New York, NY: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315645919
Prebensen, N. K., Vittersø, J., and Dahl, T. I. (2013). Value co-creation significance of tourist resources. Ann. Tour. Res . 42, 240–261. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2013.01.012
Project Management Institute (2013). Managing Change in Organizations: A Practice Guide . Newtown Square, PA: PMI.
Promnil, N. (2021). Community-based gastronomy tourism development-the case of Northern Thailand. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 12, 3228–3235. Available online at: https://turcomat.org/index.php/turkbilmat/article/view/9135/7065
Puente-Díaz, R., and Cavazos-Arroyo, J. (2021). Experiential gifts as meaningful moments and memories: their influence on nostalgia, and relive intention. Psychol. Mark . 38, 553–563. doi: 10.1002/mar.21455
Quan, S., and Wang, N. (2004). Towards a structural model of the tourist experience: an illustration from food experiences in tourism. Tour. Manag . 25, 297–305. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5177(03)00130-4
Rabbiosi, L. (2011). Subsidiary roles and reverse knowledge transfer: an investigation of the effects of coordination mechanisms. J. Int. Manag . 17, 97–113. doi: 10.1016/j.intman.2010.10.001
Rafferty, A. E., Jimmieson, N. L., and Armenakis, A. A. (2013). Change readiness: A multilevel review. J. Manag. 39, 110–135. doi: 10.1177/0149206312457417
Redondo-Carretero, M., Camarero-Izquierdo, C., Gutiérrez-Arranz, A., and Rodríguez-Pinto, J. (2017). Language tourism destinations: a case study of motivations, perceived value and tourists' expenditure. J. Cult. Econ . 41, 155–172. doi: 10.1007/s10824-017-9296-y
Richards, G. (2002). Tourism attraction systems. Ann. Tour. Res . 29, 1048–1064. doi: 10.1016/S0160-7383(02)00026-9
Richards, G. (2003). “Gastronomy: an essential ingredient in tourism production and consumption?” in Tourism and Gastronomy (Routledge), 17–34.
Richards, G. (2007). Cultural Tourism: Global and Local Perspectives . New York, NY: The Haworth Hospitality Press.
Richards, G. (2018). Cultural tourism: a review of recent research and trends. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag . 36, 12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2018.03.005
Richards, G. (2021). Evolving research perspectives on food and gastronomic experiences in tourism. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag . 33, 1037–1058. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-10-2020-1217
Richards, G., and van der Ark, L. A. (2013). Dimensions of cultural consumption among tourists: multiple correspondence analysis. Tour. Manag . 37, 71–76. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.01.007
Rosenzweig, E., and Gilovich, T. (2012). Buyer's remorse or missed opportunity? Differential regrets for material and experiential purchases. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol . 102, 215–223. doi: 10.1037/a0024999
Russo, A. P., and Richards, G. (2016). Reinventing the Local in Tourism: Producing, Consuming and Negotiating Place . Bristol: Channel View Publications. doi: 10.21832/9781845415709
Saayman, M., and Saayman, A. (2012). Determinants of spending: an evaluation of three major sporting events: determinants of spending of major sporting events. Int. J. Tour. Res . 14, 124–138. doi: 10.1002/jtr.841
Scott, M. (2022). A space tourism destination: environmental, geopolitical and tourism branding considerations for New Zealand as a ‘launch state'. J. Sustain. Tour . 30, 2240–2253. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1817049
Shah, N., Irani, Z., and Sharif, A. M. (2016). Big data in an HR context: exploring organizational change readiness, employee attitudes and behaviors. J. Bus. Res . 70, 366–378. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.010
Sharma, P., Chen, I. S. N., and Luk, S. T. K. (2018). Tourist shoppers' evaluation of retail service: a study of cross-border versus international outshoppers. J. Hosp. Tour. Res . 42, 392–419. doi: 10.1177/1096348015584439
Sims, R. (2010). Putting place on the menu: the negotiation of locality in UK food tourism, from production to consumption. J. Rural Stud . 26, 105–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2009.09.003
Smith, M. K. (2015). Issues in Cultural Tourism Studies . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315767697
Smith, R., King, D., and Sidhu, R. (2014). The Effective Change Manager's Handbook: Essential Guidance to the Change Management Body of Knowledge, 1st Edn. London: Kogan Page Ltd, APMG-International.
Smith, S. L. J., and Xiao, H. (2008). Culinary tourism supply chains: a preliminary examination. J. Travel Res . 46, 289–299. doi: 10.1177/0047287506303981
Song, H., Phan, B. V., and Kim, J. H. (2019). The congruity between social factors and theme of ethnic restaurant: Its impact on customer's perceived authenticity and behavioural intentions. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag . 40, 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2019.05.001
Sørensen, F., and Jensen, J. F. (2015). Value creation and knowledge development in tourism experience encounters. Tour. Manag . 46, 336–346. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.07.009
Soulard, J., McGehee, N. G., and Stern, M. (2019). Transformative tourism organizations and glocalization. Ann. Tour. Res . 76, 91–104. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2019.03.007
Sthapit, E. (2019). Memories of gastronomic experiences, savoured positive emotions and savouring processes. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour . 19, 115–139. doi: 10.1080/15022250.2017.1402702
Sthapit, E., Coudounaris, D. N., and Björk, P. (2019). Extending the memorable tourism experience construct: an investigation of memories of local food experiences. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 19, 333–353. doi: 10.1080/15022250.2019.1689530
Su, C. S. (2011). The role of service innovation and customer experience in ethnic restaurants. Serv. Ind. J . 31, 425–440. doi: 10.1080/02642060902829302
Sugathan, P., and Ranjan, K. R. (2019). Co-creating the tourism experience. J. Bus. Res . 100, 207–217. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.03.032
Sun, G., Sun, R., Li, J., Wang, W., and Johnson, L. (2022). Consumers' trust propensity and continuous use intention toward the sharing economy: a moderated mediation model. J. Consum. Behav . 21, 871–879. doi: 10.1002/cb.2045
Sun, G., Wang, W., Cheng, Z., Li, J., and Chen, J. (2017). The intermediate linkage between materialism and luxury consumption: evidence from the emerging market of China. Soc. Indic. Res . 132, 475–487. doi: 10.1007/s11205-016-1273-x
Thomas, R., Sargent, L. D., and Hardy, C. (2011). Managing organizational change: negotiating meaning and power-resistance relations. Organ. Sci . 22, 22–41. doi: 10.1287/orsc.1090.0520
Timothy, D. J. (2005). Shopping Tourism, Retailing and Leisure . Bristol: Multilingual Matters. doi: 10.21832/9781873150610
Timothy, D. J. (2011). Cultural Heritage and Tourism: An Introduction, Vol. 4 . Bristol: Channel View Publications. doi: 10.21832/9781845411787
Timothy, D. J., and Butler, R. W. (1995). Cross-boder shopping. Ann. Tour. Res . 22, 16–34. doi: 10.1016/0160-7383(94)00052-T
Timothy, D. J., and Nyaupane, G. P. (2009). Cultural Heritage and Tourism in the Developing World . New York, NY: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9780203877753
Tsai, S. P. (2014). Love and satisfaction drive persistent stickiness: investigating international tourist hotel brands: love and satisfaction drive persistent stickiness. Int. J. Tour. Res . 16, 565–577. doi: 10.1002/jtr.1950
Tsoukas, H., and Chia, R. (2002). On organizational becoming: rethinking organizational change. Organ. Sci . 13, 567–582. doi: 10.1287/orsc.13.5.567.7810
UNESCO (2022). Bringing Cultural Tourism Back in the Game . Paris.
UNWTO (2015). UNWTO Annual Report 2014 . Madrid: World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
UNWTO (2017). Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) . Madrid: World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
UNWTO (2018). Report on Tourism and Culture Synergies . Madrid: World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
UNWTO (2021). Big Data in Cultural Tourism: Building Sustainability and Enhancing Competitiveness . Madrid: World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
Urry, J. (1990). The consumption of tourism. Sociology 24, 23–35. doi: 10.1177/0038038590024001004
Urry, J. (1992). The tourist gaze “revisited”. Am. Behav. Sci . 36, 172–186. doi: 10.1177/0002764292036002005
Vallee, P. (1987). Authenticity as a Factor in Segmenting the Canadian Travel Market . Waterloo, ON: University of Waterloo.
Van Boven, L., and Gilovich, T. (2003). To do or to have? That is the question. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol . 85, 1193–1202. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.85.6.1193
Way, K. A., and Robertson, L. J. (2013). Shopping and tourism patterns of attendees of the bikes, blues and BBQ festival. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag . 22, 116–133. doi: 10.1080/19368623.2012.627261
Weick, K. (1998). Improvisation as a mindset for organizational analysis. Organ. Sci . 9, 543–555. doi: 10.1287/orsc.9.5.543
Williams, H. A., Yuan, J., and Williams, R. L. (2019). Attributes of memorable gastro-tourists' experiences. J. Hosp. Tour. Res . 43, 327–348. doi: 10.1177/1096348018804621
Wong, I. A., and Wan, Y. K. P. (2013). A systematic approach to scale development in tourist shopping satisfaction: linking destination attributes and shopping experience. J. Travel Res . 52, 29–41. doi: 10.1177/0047287512457263
Wu, L. L., Liu, S. Q., Huang, H., and Yu, X. (2021). Photo vs. art? The design of consumption guidance in cultural food consumption. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 97, 103008. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.103008
Yang, L. (2011). Ethnic tourism and cultural representation. Ann. Tour. Res . 38, 561–585. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2010.10.009
Yankholmes, A., and McKercher, B. (2015). Understanding visitors to slavery heritage sites in Ghana. Tour. Manag . 51, 22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2015.04.003
Yeung, S., Wong, J., and Ko, E. (2004). Preferred shopping destination: Hong Kong versus Singapore: Hong Kong versus Singapore. Int. J. Tour. Res . 6, 85–96. doi: 10.1002/jtr.474
Yu, X., Huang, H., Liu, S. Q., and Lu, Z. (2020). Signaling authenticity of ethnic cuisines via handwriting. Ann. Tour. Res . 85, 103054. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2020.103054
Zhang, M., Geng, R., Hong, Z., Song, W., and Wang, W. (2020). The double-edged sword effect of service recovery awareness of frontline employees: from a job demands-resources perspective. Int. J. Hosp. Manag . 88, 102536. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102536
Zhang, S. (2022). Agricultural heritage tourism development and heritage conservation: a case study of the Samaba Rice Terraces, Yunnan, China. J. Herit. Tour . 17, 357–370. doi: 10.1080/1743873X.2022.2028793
Keywords: tourism organizational change, change management, implications, brief review, cultural tourism research
Citation: Zhang Z and Guo M (2022) Change of tourism organizations: Implications from a review of cultural tourism research. Front. Psychol. 13:1000117. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1000117
Received: 21 July 2022; Accepted: 20 September 2022; Published: 05 October 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Zhang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ziling Zhang, zhangziling1412@gmail.com
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Can cultural tourism experience enhance cultural confidence? The evidence from Qingyuan Mountain
1 Tan Siu Lin Business School, Quanzhou Normal University, Quanzhou, China
Yanxin Kang
2 School of Tourism, Liming Vocational University, Quanzhou, China
Liping Hong
Yijun huang, associated data.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
A questionnaire survey was conducted among 600 visitors to the region using Qingyuan Mountain, a 5A picturesque location in Quanzhou City, Fujian Province, as the research site. A total of 489 valid questionnaires were received. The links between cultural involvement, cultural experience, cultural identity, cultural confidence, and cultural loyalty were experimentally examined using a structural equation modeling technique. The results showed that cultural experience was a mediating factor in the processes of the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity and the influence of cultural involvement on cultural confidence, but the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity and the influence of cultural involvement on cultural confidence were not supported. The study accordingly condenses theoretical contributions to academia and management insights for businesses.
Introduction
Culture is the sum of the material and spiritual productive capacity and the material and spiritual wealth created by human beings during social practice, and it provides the resource base for tourism, in which people are in fact learning about culture. Cultural tourism as a social phenomenon emerged after the Second World War; after all, it can improve cultural understanding and people’s understanding as well as help build the economy ( Richards, 2018 ). Cultural tourism as an academic study emerged in the 1980s. Cultural tourism reached a high point in the 1980s and 1990s as it became widely recognized as a good tourism product. There was a proliferation of research on cultural tourism, and different theories and research methods were applied to the field ( Smith and Richards, 2013 ). According to the World Tourism Organization’s Tourism and Culture Synergy Report (2018), 89% of the World Tourism Organization’s member states have included cultural tourism in their tourism development policies and are committed to further developing it. According to the report’s projections, cultural tourists will account for more than 40% of the overall tourism sector in the future ( UNWTO, 2018 ). Now is precisely the point in time when the report predicts the next 5 years of planning. Therefore, the current study on cultural tourism is very relevant and timely.
The study of cultural tourism was first defined by the World Tourism Organization as a form of culturally motivated tourism and is one of the oldest forms of ‘new’ tourism ( McKercher, 2020 ). These are tourism, cultural heritage, the experience and consumption of the product and the visitor. The element of tourism is undoubtedly the most fundamental attribute of cultural tourism, which not only facilitates the preservation and exchange of culture but also promotes economic development, revitalizing culture and sustaining its benefits ( Shi et al., 2021 ). Cultural heritage is one of the most dominant forms of cultural tourism and the hottest tourism product ( Seyfi et al., 2020 ). Heritage tourism has become an important ground for scholars to conduct research on cultural tourism. Experience and consumption are important elements of cultural tourism research; after all, cultural tourism involves subject areas such as economics and management, and the desire to maximize the benefits of cultural tourism while preserving it is shared by stakeholders such as tourism developers, local governments, community residents, and cultural custodians ( Ammirato et al., 2021 ). With the rise of the experience economy, the deep integration of cultural tourism and the experience economy has been consistently recognized by many scholars ( Su et al., 2020a ; Zhang et al., 2021 ). The study of tourists is a necessary part of any tourism product, and only if tourists accept, recognize and even recommend the tourism product will it have economic value and be sustainable ( Su et al., 2020b ). In this new era, the types of cultural tourism products are further enriched, and the boundaries between culture and tourism become increasingly blurred ( Yang et al., 2022 ).
Cultural confidence is a collective cultural identity, belonging and love based on an individual’s deep understanding, acceptance and practice of their own culture. It is a powerful spiritual motivator that leads to the formation of certain value dispositions and can lead to positive behavior ( Wan and Rucker, 2013 ; Ortiz-Ordoñez et al., 2015 ). And to form one’s cultural confidence, one must first have access to channels and opportunities to learn about excellent traditional culture ( Zhao, 2022 ). Traveling is a good learning opportunity, which not only enables the traveler to broaden his or her horizons and gain insight, but also generates a self-confidence from the inside out through this process ( Chen, 2022 ). And this self-confidence has positive implications for personal growth, external communication and patriotism ( Lin et al., 2022 ). Therefore, exploring the mechanisms by which cultural confidence is generated in tourists and its impact on tourism behavior can provide useful references for other scholars exploring similar topics, as well as providing more business management ideas for tourism business managers and valuable references for the education sector in patriotic education.
This study adopts a positivist paradigm to investigate the psychological feelings of tourists after experiencing cultural tourism, with the aim of understanding the experience of cultural tourism, cultural identity, cultural confidence and cultural loyalty and clarifying the interplay among them. This study is a good complement to the current hot research on cultural confidence, broadening the theoretical outreach of cultural tourism research, further enriching the content of cultural tourism and providing a theoretical basis for other scholars in similar research. In addition, the results of this study have certain management practice implications for tourism management departments and are of reference value for tourism developers to carry out targeted tourism marketing for tourists.
Literature review and hypotheses
Cultural involvement.
Involvement is the evaluation of the importance and relevance of objects by individuals according to their intrinsic needs, values and interests ( Zaichkowsky, 1985 ). According to this definition, cultural involvement can be thought of as tourists evaluating cultural tourism activities and consumption based on their own needs, values and interests ( Campos et al., 2017 ). Carlson and Güler (2018) argue that cultural involvement includes both the culture of origin and destination culture dimensions, while Gao et al. (2020) argue that cultural involvement includes three dimensions, namely, attraction, self-expression, and centrality, and Whang et al. (2016) argue that cultural involvement includes situational involvement and persistent involvement. The study by Jian et al. (2019) used a single dimension of persistent involvement. This study also adopts the concept of a single dimension of persistent involvement.
In a study conducted by Li et al. (2021) on residents’ attitudes toward tourism, cultural involvement was found to have a positive and significant effect on the cultural experience. Whang et al. (2016) argued that cultural transmission is a prerequisite for cultural involvement and that tourists’ experiences cannot be separated from cultural transmission. Lee and Chang (2017) found that cultural involvement was an antecedent variable for the cultural tourism experience in a survey of 901 tourists who visited Taiwan for diet tourism and found that cultural involvement was an antecedent variable of the cultural tourism experience. Lee and Chang’s (2017) study reconfirmed this result.
Jian et al.’s (2019) study found that cultural involvement has a positive impact on cultural identity, such as manifesting a love for a culture or becoming a fan of a culture. Similar results were confirmed in Koenig-Lewis et al.’s (2021) study, in which 1,335 tourists were interviewed, confirming not only the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity but also the relationship between cultural involvement and cultural experience. Carlson and Güler (2018) confirmed the same results in their study of immigrants as survey respondents.
Cultural confidence is a collective cultural identity, a sense of belonging and love based on an individual’s deep understanding, acceptance and practice of his or her own culture ( Pan et al., 2021 ). Guan et al. (2020) found that cultural involvement directly influenced students’ cultural confidence in a study on the extent of their red cultural identity in Hebei Province. Li et al. (2021) suggested that local governments and communities organize more cultural-themed activities to provide more opportunities for cultural exchange and enhance residents’ cultural involvement, thereby gaining more cultural confidence and cultural identity. At local cultural festivals, it was found that the cultural involvement of visitors was reinforced and helped them enhance their ethnic pride and cultural confidence.
Based on the above findings, this study makes the following hypotheses:
H1 : Cultural involvement positively influences cultural experience. H2 : Cultural involvement positively influences cultural identity. H3 : Cultural involvement positively influences cultural confidence.
Cultural experience
Cultural experiences are generally defined as trips to cultural tourism destinations for the purpose of acquiring knowledge and authentic experiences ( Crompton and McKay, 1997 ), a view that is related to that of Kim et al. (2009) , who found that learning knowledge and authentic experiences can be combined into one dimension through their rooted theory research. Kim and Eves (2012) reconfirmed this finding. The single dimension scale of Kim et al. (2009) was also used in this study.
Research on cultural experiences is well documented, with Koenig-Lewis et al. (2021) finding that travelers gained knowledge and enhanced their cultural identity through experiencing local cultural festivals. Similar results hold true for transient expatriates studying abroad, as El-Ouali and Mouhadjer (2019) and Li and Liu (2020) found that international students’ cultural experience of their host country helped them gain a sense of cultural identity and integrate into the local cultural life as soon as possible. In short, cultural identity is constructed on the basis of cultural experience ( Gao, 2021 ).
In terms of exploring the relationship between cultural experience and cultural confidence, Chen’s (2020) study found that university students’ creative design experiences enriched their knowledge of that culture and built up stronger cultural confidence. Mei (2022) found similar results through a study of university students’ experiences of their local culture, which had a significant effect on their cultural confidence.
Chen and Rahman (2018) interviewed tourists involved in cultural tourism and found correlations between engagement, cultural exposure, memorable travel experiences and loyalty to cultural tourism destinations, with memorable travel experiences being positively correlated with cultural tourism destinations. Ogunnaike et al. (2022) studied hotels and found that the cultural ambience of a hotel was crucial in attracting customers, as their cultural experience with the hotel directly influenced their loyalty to the hotel. Suhartanto et al. (2018) studied tourist loyalty using cultural tourism destinations and similarly found that the cultural experience of tourists had a significant direct impact on destination loyalty.
H4 : Cultural experience positively influences cultural identity. H5 : Cultural experience positively influences cultural confidence. H6 : Cultural experience positively influences cultural loyalty.
Cultural identity
Bhugra (2004) argues that cultural identity includes an individual’s adherence to and identification with elements of religion, language, customs, beliefs, rituals, and leisure activities. From the perspective of tourism, tourism contributes to the spread of culture, facilitates communication and brings in funds for the preservation of culture, and in this sense, tourism contributes to the cultural identity of tourists. Luo et al. (2019) conducted a study with tourists visiting the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road Museum and found that visitors who experienced the museum had a high cultural identity, and a strong study by Gao (2021) found that enhancing students’ national cultural identity helped build students’ national cultural self-confidence. Tian et al. (2020) conducted a study on tourists who participated in intangible cultural heritage experiences and found that tourists’ cultural identity would influence cultural destination loyalty through authenticity. Le and Le (2020) conducted a study of tourists visiting Thanh Hoa Province in Vietnam and obtained similar results. In addition to this finding for tourists, Lee et al. (2021) found similar results for Aboriginal people, whose identification with indigenous culture directly influenced their loyalty to that culture.
Based on these findings, this study makes the following hypotheses:
H7 : Cultural identity positively influences cultural confidence. H8 : Cultural identity positively influences cultural loyalty.
Cultural confidence
Pan et al. (2021) , based on previous definitions of self-confidence and through focus interviews with cultural and tourism experts, define cultural confidence as a collective cultural identity, belonging and love that is based on an individual’s deep understanding, acceptance and practice of his or her own culture. As the concept of cultural confidence has emerged only in recent years, research on cultural confidence is not yet very rich and currently focuses more on the integration of culture and identity. Zang and Liu (2021) found through their study of mobile learning among university students that cultural confidence among university students helped to enhance their sense of cultural loyalty. Li’s (2022) study found that Jia et al. (2022) argued that traditional culture should be included in the science and technology courses of university students because it has a direct impact on enhancing their cultural confidence and has a significant effect on their loyalty to their motherland and people, i.e., the enhancement effect. In light of this, this study argues the following:
H9 : Cultural confidence positively influences cultural loyalty.
Cultural loyalty
Cultural loyalty is an authority that derives from the voluntary allegiance of its members ( Parekh, 2001 ). Cultural loyalty is a very strong sense of people’s loyalty to their values, ideal beliefs and religious beliefs. It should include at least three voices, namely, the voice of ancestors, the voice of relationships and the voice of ethics ( Piquemal, 2005 ). Loyalty is an important concept that has received widespread scholarly attention, including national loyalty, ethnic loyalty and brand loyalty, among others. Cultural loyalty has received more widespread scholarly attention in recent years because it is more of an intangible soft power and a powerful emotional force, and some scholars have even proposed a cultural loyalty approach ( Karkabi, 2021 ). It is clear that an in-depth study of cultural loyalty is necessary and important.
Based on the above research findings and the comprehensive reasoning of this study, the following model is constructed in this study (see Figure 1 ):

The structure model.
Materials and methods
Located in southeastern Fujian Province, on the northeastern bank of the lower reaches of the Jinjiang River, Qingyuan Mountain is one of the eighteen scenic spots in Quanzhou and a national key scenic spot, consisting of three large areas: Qingyuan Mountain, Nine-Day Mountain and the Holy Tomb of Lingshan, with a total area of sixty-two square kilometers. It is a national 5A level tourist attraction in China. Qingyuan Mountain is a must-see attraction when visiting Quanzhou. The most famous statue of Laojun from the Song Dynasty is the Laojun Rock in the scenic area, which is the largest and most artistically valuable Taoist stone sculpture in China. The stone carving of praying for the wind at Jiuriyama is a precious source for studying the history of overseas transportation and the art of calligraphy in ancient China. The Holy Sepulchre is the place where the three sages and four sages, disciples of Muhammad, came to Quanzhou to preach and were buried, called the Islamic Holy Sepulchre. Qingyuan Mountain is not only beautiful but also an important cultural tourism destination. The number of visitors to Qingyuan Mountain is very high every year, peaking at 30,000 visitors per day. As the only 5A scenic spot in Quanzhou, it has become, to a certain extent, one of Quanzhou’s calling cards for external publicity and an important part of the composition of Quanzhou’s tourism image. Qingyuan Mountain has also become a commonly chosen case study site for local scholars engaged in cultural research, as well as attracting many scholars from around the world who are studying Quanzhou culture, Hokkien culture and the historical traces of Islamic culture. The study has therefore chosen this study site as a representative and viable one.
Scale design
This study used a self-statement scale for data collection, consisting of six parts, using a 7-point Likert scale design. The first section is cultural involvement, from a study by Jian et al. (2019) , the second section is cultural experience, from a study by Kim and Eves (2012) , the third section is cultural identity, from a study by He and Wang (2015) , the fourth section is cultural confidence, from a study by Pan et al. (2021) , the fifth section is cultural loyalty, from a study by Yang and Peterson (2004) , and the sixth part is demographic information.
Data collection
This study was conducted from September 10 to September 13, 2022, at the leisure hall at the exit of the main gate of the Qingyuan Mountain Scenic Area to interview visitors who had finished their visit. Two hundred copies were distributed each day, 100 in the morning and 100 in the afternoon. The research started from the first visitor returning in the morning until 100 copies were collected, and in the afternoon, due to the hot weather, there were many guests resting in the hall, so in order not to disturb the guests’ rest, the survey started from 3 o’clock until 100 copies were collected. A total of 600 questionnaires were distributed and 517 were returned, of which 489 were valid. The visitors were 259 men (52.97%) and 230 women (47.03%). In terms of age composition, 64 people (13.09%) were aged 18-25, 121 people (24.74%) were aged 26-35, 153 people (31.29%) were aged 36-45, 95 people (19.43%) were aged 46-55, 45 people (9.20%) were aged 56-65 and 11 (2.25%) were aged 66 or above. Regarding the composition of education levels, 132 (26.99%) were high school and below, 128 (26.18%) were college, 161 (32.92%) were bachelor’s degree and 68 (13.91%) were master’s degree and above.
SPSS 24.0 was used to test the quality of the dataset, and the analysis revealed that there were no missing values. The data had a skewness of 3 < and a kurtosis of <7, which basically met the requirements of a normal distribution. The reliability of the variables ranged from 0.845 to 0.918, all reaching the recommended value of >0.7 (see Table 1 ), and the corrected item total correlation (CITC) between the variables all reached the recommended value of >0.5. The data are of good quality and ready for the next step of analysis.
The results of confirmatory factor analysis ( n = 489).
std., standard estimate; CR, composite reliability.
Common method bias
To exclude the effect of common method bias, the one-way validation method of Harman (1976) was used in this study. That is, a factor analysis was performed on the dataset to check the cumulative explained variance of the first factor without rotation, and if it was below 50%, the common method bias of the dataset was not serious enough for further analysis. By testing, the cumulative explained variance of the first factor in this study was 25.322%, well below the recommended value of 50%.
Measurement model
Using Amos 24.0 for validated analysis of the dataset, the measurement model met the recommended values recommended by academics for the model fit indicators, except for AGFI, which was slightly below the recommendation of 0.9 (see Table 2 ; CFA). The factor loadings for each variable ranged from 0.671 to 0.874, with all questions reaching above 0.7 except for the Cid2 question item, which was slightly below 0.7; the reliability of each variable ranged from 0.846 to 0.919, meeting the scholarly recommendation of greater than 0.7; and the AVE ranged from 0.565 to 0.694, all meeting the recommendation of greater than 0.5. This study used Fornell and Larcker (1981) and Bagozzi and Yi (2012) recommended discriminant validity method to validate the dataset for discriminant validity, and the results showed that the discriminant validity met the criteria recommended by scholars (see Table 3 ).
The results of model fit measures.
The discriminant validity.
The square root of the AVE is presented in bold.
Structural equation modeling
Structural equation modeling was conducted using the maximum likelihood method of Amos 24.0. The model fit was showed in the table 2-structural. And the results of the path analysis were significant for all the paths except H2: cultural involvement has a positive impact on cultural identity and H3: cultural involvement has a positive impact on cultural confidence, which were not significant (see Figure 2 ; Table 4 ).

Structure model and path coefficient. * p < 0.05,** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Structure parameter estimates.
std., standard estimate. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Mediating effects
As the two paths of cultural involvement on cultural identity and cultural involvement on cultural confidence are not significant, and cultural experience is in the intermediary position between the two paths of cultural involvement and cultural identity and cultural involvement and cultural confidence, it is necessary to explore the mediating effect of cultural experience to further explore the relationships between cultural involvement and cultural identity and cultural involvement and cultural confidence. This paper uses the bootstrap (bootstrap = 2000) method to further verify the mediating effect of cultural experiences. The results are shown in Table 5 below, where cultural experiences play a mediating role in the pathways of the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity and cultural involvement on cultural confidence.
Mediation effect.
Cin, Cultural involve; CE, Cultural experience; Cid, Cultural identity.
Discussion and conclusion
This study takes the famous religious mountain located in Quanzhou City, Fujian Province, as an example and explores the relationships between cultural involvement, cultural experience, cultural identity, cultural confidence and cultural loyalty. The results showed that most of the hypotheses were tested, except for the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity and the influence of cultural involvement on cultural confidence, which were not tested. In addition, the mediating role of cultural experience in the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity and the influence of cultural involvement on cultural confidence was also tested.
From the results, the relationship between cultural involvement and the influence of cultural experience was verified, which is consistent with previous research ( Gao, 2021 ; Koenig-Lewis et al., 2021 ). After all, the higher the degree of cultural involvement, the more likely it is that the motivation to experience is generated, and once a person has generated motivation, it is easy to put it into action, that is, to produce the act of experiencing. When travellers have a cultural experience, they are bound to have certain feelings about the culture, which may be good or bad. If it is a good feeling, they are bound to appreciate, identify with or even love the culture, while if it is a bad feeling, they may reject the culture and fail to integrate into it ( Wei et al., 2020 ). This is common among new immigrants and explains why many immigrants are unable to adapt to the culture of the place they have moved to. In addition to giving identity, experience may also give rise to a sense of confidence and even pride, because culture is powerful and intangible, and culture is also a source of spiritual strength for people, as evidenced in the research at Karadağ et al. (2020) . Of course, when a culture has become a person’s spiritual strength, he is bound to cherish that strength and be loyal to that culture without reluctance, which explains the relationship between the influence of cultural involvement and cultural loyalty in this study.
Identity is the identification of people with something, a role or a culture. It is not just an acceptance but a high degree of emotional approval, so that identity is a positive psychological state that gives people positive energy and creates psychological confidence. When a person is highly identified with a culture or even becomes an integral part of his or her own culture, he or she is bound to be loyal to that culture because it is already an important part of his or her culture, psyche and spirit. Therefore, the influence of cultural identity on cultural confidence ( Luo et al., 2019 ; Gao, 2021 ) and the influence of cultural identity on cultural loyalty ( Tian et al., 2020 ; Lee et al., 2021 ) in this study are reasonable and in line with previous research.
Self-confidence is an absolutely positive psychological state in human beings; it is a spiritual motivation and source of strength that sustains one’s persistence, effort and perseverance, and this also applies in the field of culture. Therefore, the hypothesis that cultural confidence has a positive impact on cultural loyalty is valid and in line with the results of previous studies ( Zang and Liu, 2021 ; Jia et al., 2022 ; Li, 2022 ).
However, the hypothesis that cultural exposure has a positive impact on cultural identity has not been tested, contrary to the findings of previous studies. Cultural involvement is a superficial perception that may come from oral accounts, indirect knowledge from films, television, books, etc., or fragmented knowledge. This kind of knowledge makes it difficult to form a three-dimensional perception in the visitor’s mind, much less to make him or her feel good about it or accept, or even highly value, the culture ( Smolicz, 1981 ). This is therefore a good explanation for why cultural involvement does not hold true for the positive impact of cultural identity. Similarly, when visitors’ perceptions are only at this superficial level, it is not possible for them to develop a sense of confidence. Therefore, it is possible that the effect of cultural involvement on cultural confidence does not hold true. A study by McKercher and Du Cros (2002) found that approximately half of tourists are not influenced by cultural involvement when choosing a tourist destination.
It is of interest to note that cultural experience has an important place in this study, as it plays an extremely important role in the overall mechanism of cultural influence ( Armbrecht, 2014 ; Lembo and Martin, 2022 ). The influence of cultural involvement on cultural experience is present, as is the influence of cultural experience on cultural identity, cultural confidence and cultural loyalty. In addition to this, cultural experiences play a mediating role in the influence of cultural involvement on cultural identity, as well as in the influence of cultural involvement on cultural confidence. It is clear that it is difficult to develop cultural tourism without well-designed experiences to create identity and confidence in visitors, which explains exactly why the experience economy is so hot and the importance of experience quality in the tourism product.
Theoretical implications
This study enriches the theory of cultural tourism research. Cultural tourism has traditionally been a key area of research in the tourism sector, receiving much attention not only from tourism scholars but also from cultural scholars. However, it is rare to integrate cultural involvement, cultural experience, cultural identity, cultural confidence and cultural loyalty into one study, and it is also rare to conduct in-depth research and discussion on their interrelationships and mechanisms of influence. Therefore, the attempt of this study provides more references for subsequent research on cultural tourism.
The two hypotheses found to be unsupported in this study add to the previous research. Unlike in previous studies, the impact of cultural involvement on cultural identity and the impact of cultural involvement on cultural confidence are not supported in this study. This suggests that there are still some gaping points in the previous study and further clarifies the relationships among the three, which is also an important finding in this respect.
The two complete mediators found in this study further confirm the importance of cultural experience. Cultural experience has been extensively and thoroughly researched in previous studies, but its importance, especially in the field of cultural tourism, should be given more attention by scholars, as after all, tourists’ cultural identity and cultural confidence are based on good cultural experience. This result also provides a theoretical reference for other scholars to carry out similar studies in the future.
Implications for management practice
Cultural tourism development should pay attention to tourism promotion. The basis for a tourist’s motivation to travel is that he has some knowledge of this tourist destination. When information about a tourist destination is not disseminated to the minds of potential tourists, or when tourists are simply unaware of the existence of such a tourist destination or tourist product, they cannot be motivated to travel. Therefore, in the process of cultural tourism development, it is important to strengthen publicity efforts, broaden publicity channels, enrich publicity methods and focus on the effects of publicity. After all, in the current era of diverse information dissemination channels, the amount of information is exploding, and without timely and effective publicity, it is easily buried by new information.
Cultural tourism development should pay attention to experience design and improve the quality of the experience. The experience economy has been here for a long time, and the importance of experience marketing for products has become an irrefutable marketing approach to business management. However, previous experience marketing focused on tangible products, and after all, it can give people a real sense of presence; however, cultural products, including cultural tourism, are intangible products, and passive preaching has been unable to move the emotions of tourists or make them more likely to resonate. Therefore, intangible cultural tourism should pay more attention to the experience process and experience quality.
Cultural tourism development should strive to gain the recognition of tourists and work hard to create cultural confidence in them to form cultural loyalty. Whereas products bring limited benefits to an enterprise, brands bring unlimited, long-term benefits. Cultural tourism products can also be a good brand, but it is essential that visitors identify with the product and brand and develop national cultural self-confidence in it. Only in this way is it possible for visitors to develop loyalty to the cultural tourism brand, which is very useful and necessary to develop customer stickiness.
Research limitations and future study
Due to the openness of the study site and the human and material resource constraints of this study, this study adopts a convenience sampling method; the form of the data is cross-sectional, and the representativeness may be somewhat different from that of the random sampling method. Second, the case study site for this study is Qingyuan Mountain in Quanzhou City, Fujian Province. There are many other famous mountains and rivers with the same profound cultural heritage, and geographical differences may lead to cultural differences; therefore, the results of this study should be taken with caution when generalizing to other study sites.
Cultural tourism is a big topic that needs more scholars to be involved in it and more variables to be tapped to study the field of cultural tourism thoroughly and to provide a truly useful reference for the theoretical and industrial communities. Therefore, in future research, consideration could be given to adding contingent variables such as perceived value, cultural consistency, authenticity, etc., as well as moderating variables and multicluster analysis for different groups of people, to clarify the influence mechanisms of cultural tourism.
Data availability statement
Author contributions.
JL and YH conceived the study. JL, YK, LH, and YH wrote the manuscript. All authors designed the study, collected and analyzed the data, read and approved the manuscript, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
This paper was supported by Innovation Strategy Research Plan project of Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Department, “Research on Innovation ecosystem Construction of Digital Creative Industry” (2021R0120), and Education and Scientific Research Project of Young and Middle-aged Teachers in Fujian Province (Social Sciences) General project: Research on the development path of old-age tourism industry in Quanzhou City under the background of aging (JAS21638).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Ammirato S., Felicetti A. M., Linzalone R., Carlucci D. (2021). Digital business models in cultural tourism . Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 28 , 1940–1961. doi: 10.1108/IJEBR-01-2021-0070 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Armbrecht J. (2014). Use value of cultural experiences: a comparison of contingent valuation and travel cost . Tour. Manag. 42 , 141–148. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.11.010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bagozzi R. P., Yi Y. (2012). Specification, evaluation, and interpretation of structural equation models . J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 40 , 8–34. doi: 10.1007/s11747-011-0278-x, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhugra D. (2004). Migration, distress and cultural identity . Br. Med. Bull. 69 , 129–141. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldh007, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Campos A. C., Mendes J., do Valle P. O., Scott N. (2017). Co-creating animal-based tourist experiences: attention, involvement and memorability . Tour. Manag. 63 , 100–114. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2017.06.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carlson E., Güler A. (2018). Cultural involvement and preference in immigrant acculturation . J. Int. Migr. Integr. 19 , 625–647. doi: 10.1007/s12134-018-0554-4, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen J. (2020). Research on the cultivation of college students’ design originality from the perspective of cultural confidence . J. Contemp. Educat. Res. 4 , 47–49. doi: 10.26689/jcer.v4i10.1564 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen D. (2022). Study on the ways to integrate cultural confidence in the new era into the ideological and political class of college students . Int. J. Soc. Sci. Educat. Res. 5 , 238–243. doi: 10.47205/jdss.2021(2-iv)74 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen H., Rahman I. (2018). Cultural tourism: an analysis of engagement, cultural contact, memorable tourism experience and destination loyalty . Tour. Manag. Perspect. 26 , 153–163. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2017.10.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crompton J. L., McKay S. L. (1997). Motives of visitors attending festival events . Ann. Tour. Res. 24 , 425–439. doi: 10.1016/S0160-7383(97)80010-2, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- El-Ouali F. Z., Mouhadjer N. (2019). Cultural identity reconstruction in the study abroad context: the case of Algerian Sojourners . Glob. J. Foreign Lang. Teach. 9 , 214–225. doi: 10.18844/gjflt.v9i4.4366 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fornell C., Larcker D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error . J. Mark. Res. 18 , 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao F. (2021). Negotiation of native linguistic ideology and cultural identities in English learning: a cultural schema perspective . J. Multiling. Multicult. Dev. 42 , 551–564. doi: 10.1080/01434632.2020.1857389 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao J., Lin S. S., Zhang C. (2020). Authenticity, involvement, and nostalgia: understanding visitor satisfaction with an adaptive reuse heritage site in urban China . J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 15 :100404. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2019.100404 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guan C., Xiao L., Ma W. (2020). The status quo and problem analysis of Hebei red cultural value identification by English majors in Hebei Province . Open J. Modern Linguist. 10 , 125–131. doi: 10.4236/ojml.2020.102008 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harman H. H. (1976). Modern Factor Analysis. Chicago Horace: University of Chicago Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- He J., Wang C. L. (2015). Cultural identity and consumer ethnocentrism impacts on preference and purchase of domestic versus import brands: an empirical study in China . J. Bus. Res. 68 , 1225–1233. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2014.11.017 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jia X., Miao W., Yu D., Liu H., He C. (2022). Chinese culture integrated into the science and engineering courses . Sci. Soc. Res. 4 , 1–6. doi: 10.26689/ssr.v4i6.3977, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jian Y., Zhou Z., Zhou N. (2019). Brand cultural symbolism, brand authenticity, and consumer well-being: the moderating role of cultural involvement . J. Product Brand Manag. 28 , 529–539. doi: 10.1108/JPBM-08-2018-1981 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karadağ M., Altınay Aksal F., Altınay Gazi Z., Dağli G. (2020). Effect size of spiritual leadership: in the process of school culture and academic success . Sage Open 10 . doi: 10.1177/2158244020914638 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karkabi N. (2021). The impossible quest of Nasreen Qadri to claim colonial privilege in Israel . Ethn. Racial Stud. 44 , 966–986. doi: 10.1080/01419870.2021.1877314 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim Y. G., Eves A. (2012). Construction and validation of a scale to measure tourist motivation to consume local food . Tour. Manag. 33 , 1458–1467. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2012.01.015 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim Y. G., Eves A., Scarles C. (2009). Building a model of local food consumption on trips and holidays: a grounded theory approach . Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 28 , 423–431. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2008.11.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koenig-Lewis N., Palmer A., Asaad Y. (2021). Linking engagement at cultural festivals to legacy impacts . J. Sustain. Tour. 29 , 1810–1831. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1855434 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Le H. B. H., Le T. B. (2020). Impact of destination image and satisfaction on tourist loyalty: mountain destinations in Thanh Hoa province, Vietnam . J. Asian Finan. Econ. Bus. 7 , 185–195. doi: 10.13106/jafeb.2020.vol7.no4.185 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee T. H., Chang P.-S. (2017). Examining the relationships among festivalscape, experiences, and identity: evidence from two Taiwanese aboriginal festivals . Leis. Stud. 36 , 453–467. doi: 10.1080/02614367.2016.1190857 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee T. H., Lin Y. H., Wang C.-K. (2021). Can aboriginal images contribute to aboriginal cultural identity? Evidence from the perspective of tourists’ images . Curr. Issue Tour. 25 , 1–16. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2021.2005553 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lembo A., Martin J. L. (2022). The structure of cultural experience . Poetics 91 :101562. doi: 10.1016/j.poetic.2021.101562, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li J. (2022). The positive influence of traditional classical literature Reading promotion activities on mental heath . Forest Chem. Rev. 653–664. [ Google Scholar ]
- Li Y.-Q., Liu C.-H. (2020). Impact of cultural contact on satisfaction and attachment: mediating roles of creative experiences and cultural memories . J. Hosp. Market. Manag. 29 , 221–245. doi: 10.1080/19368623.2019.1611516 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li J., Pan L., Hu Y. (2021). Cultural involvement and attitudes toward tourism: examining serial mediation effects of residents’ spiritual wellbeing and place attachment . J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 20 :100601. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2021.100601 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin G., Hao L., Yong W. (2022). A study on the value of cultural self-confidence cultivated by the rise of . Acad. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 5 , 29–34. doi: 10.25236/ajhss.2022.050506 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luo Y., Chu D., Xing D., Pan J., Huang Y., Yu J. (2019). On museum tourism development from the perspective of cultural identity experience—taking the core area of the 21st century maritime silk road as an example. Paper presented at the 2nd International Seminar on Education Research and Social Science (ISERSS 2019).
- McKercher B. (2020). Cultural tourism market: a perspective paper . Tour. Rev. doi: 10.1108/TR-03-2019-0096 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McKercher B., Du Cros H. (2002). Cultural Tourism: The Partnership between Tourism and Cultural Heritage Management . New York: Haworth Hospitality Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mei T. (2022). New trends of culture response in contemporary China: a case study of cultural localization. Paper presented at the 2021 International Conference on Social Development and Media Communication (SDMC 2021).
- Ogunnaike O. O., Agada S. A., Ighomereho O. S., Borishade T. T. (2022). Social and cultural experiences with loyalty towards hotel services: the mediating role of customer satisfaction . Sustainability 14 :8789. doi: 10.3390/su14148789 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz-Ordoñez J. C., Stoller F., Remmele B. (2015). Promoting self-confidence, motivation and sustainable learning skills in basic education . Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 171 , 982–986. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.205, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pan L., Xu X. a., Lu L., Gursoy D. (2021). How cultural confidence affects local residents’ wellbeing . Serv. Ind. J. 41 , 581–605. doi: 10.1080/02642069.2018.1540595, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parekh B. (2001). Rethinking multiculturalism: cultural diversity and political theory . Ethnicities 1 , 109–115. doi: 10.1177/146879680100100112 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piquemal N. (2005). Cultural loyalty: aboriginal students take an ethical stance . Reflective Pract. 6 , 523–538. doi: 10.1080/14623940500300707 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Richards G. (2018). Cultural tourism: a review of recent research and trends . J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 36 , 12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2018.03.005, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seyfi S., Hall C. M., Rasoolimanesh S. M. (2020). Exploring memorable cultural tourism experiences . J. Herit. Tour. 15 , 341–357. doi: 10.1080/1743873X.2019.1639717 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shi Z., Cheng Q., Xu D. (2021). Spatial econometric analysis of cultural tourism development quality in the Yangtze River Delta . Asia Pacif. J. Tour. Res. 26 , 597–613. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2021.1886131 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith M. K., Richards G. (2013). The Routledge Handbook of Cultural Tourism . Oxon: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smolicz J. (1981). Core values and cultural identity . Ethn. Racial Stud. 4 , 75–90. [ Google Scholar ]
- Su X., Li X., Chen W., Zeng T. (2020a). Subjective vitality, authenticity experience, and intangible cultural heritage tourism: an empirical study of the puppet show . J. Travel Tour. Mark. 37 , 258–271. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2020.1740141 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Su X., Li X., Wang Y., Zheng Z., Huang Y. (2020b). Awe of intangible cultural heritage: the perspective of ICH tourists . SAGE Open 10:2158244020941467. doi: 10.1177/2158244020941467 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suhartanto D., Clemes M. D., Wibisono N. (2018). How experiences with cultural attractions affect destination image and destination loyalty . Tour. Cult. Communicat. 18 , 176–188. doi: 10.3727/109830418X15319363084463 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tian D., Wang Q., Law R., Zhang M. (2020). Influence of cultural identity on tourists’ authenticity perception, tourist satisfaction, and traveler loyalty . Sustainability 12 :6344. doi: 10.3390/su12166344 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNWTO (2018). Report on tourism and cultural synergies . Madrid: UNWTO. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wan E. W., Rucker D. D. (2013). Confidence and construal framing: when confidence increases versus decreases information processing . J. Consum. Res. 39 , 977–992. doi: 10.1086/666467 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wei C., Dai S., Xu H., Wang H. (2020). Cultural worldview and cultural experience in natural tourism sites . J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 43 , 241–249. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.04.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whang H., Yong S., Ko E. (2016). Pop culture, destination images, and visit intentions: theory and research on travel motivations of Chinese and Russian tourists . J. Bus. Res. 69 , 631–641. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.06.020 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang Z., Peterson R. T. (2004). Customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: the role of switching costs . Psychol. Mark. 21 , 799–822. doi: 10.1002/mar.20030 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang Y., Wang S., Cai Y., Zhou X. (2022). How and why does place identity affect residents’ spontaneous culture conservation in ethnic tourism community? A value co-creation perspective . J. Sustain. Tour. 30 , 1344–1363. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2021.1945070 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zaichkowsky J. L. (1985). Measuring the involvement construct . J. Consum. Res. 12 , 341–352. doi: 10.1086/208520, PMID: [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zang X., Liu X. (2021). Design of vocal music mobile learning platform based on digital information technology. Paper presented at the 2021 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Aided Education.
- Zhang Q., Liu X., Li Z., Tan Z. (2021). Multi-experiences in the art performance tourism: integrating experience economy model with flow theory . J. Travel Tour. Mark. 38 , 491–510. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2021.1952148 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao X. (2022). Evaluation of the modern value of imperial examination culture in the context of cultural confidence based on deep learning models . Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022 :9748146. doi: 10.1155/2022/9748146 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Research on Digital Transformation Driving the High-Quality Development of Cultural and Tourism Enterprises—Evidence Based on Listed Cultural and Tourism Companies
- Published: 29 April 2024
Cite this article

- Rui Tang 1 ,
- Pishi Xiu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7238-4272 2 &
- Haoxiang Dong 1
Digital transformation has become an important means for cultural and tourism enterprises to achieve high-quality development. The role of digital transformation in driving the development of cultural and tourism enterprises deserves to be fully explored. Based on the data of 98 listed cultural and tourism companies in China, this paper uses Python text mining, a two-way fixed effects model, and other methods to find that digital transformation could promote high-quality development of cultural and tourism enterprises. The positive effects of digital transformation are not limited by the nature of enterprise ownership, enterprise growth, or the competitive environment. The positive influence of digital transformation is significant when facing a high degree of marketization. Mechanism tests show that improvement in management efficiency, operational efficiency, quality of workforce, and industry spillovers are effective ways for digital transformation to promote high-quality development of cultural and tourism enterprises. The findings provide a decision-making basis for cultural and tourism enterprises to explore the potential of digital technology and cultivate digital transformation as an important driving force for high-quality development of enterprises.
Graphical Abstract
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Marketability index data is from China Provincial Marketization Index Database , the website is https://cmi.ssap.com.cn/ .
Abbas, J., Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Asif Amjid, M., Al-Sulaiti, K., Al-Sulaiti, I., & Aldereai, O. (2024). Financial innovation and digitalization promote business growth: The interplay of green technology innovation, product market competition and firm performance. Innovation and Green Development, 3 (1), 100111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.igd.2023.100111
Article Google Scholar
Abbasian Fereidouni, M., & Kawa, A. (2019). Dark side of digital transformation in tourism. In: N. Nguyen, F. Gaol, T. P. Hong, & B. Trawiński (Eds.), Intelligent Information and Database Systems . ACIIDS 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11432. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14802-7_44
Aboushouk, M. A. (2022). The impact of employees’ absorptive capacity on digital transformation of tourism and travel services: Evidence from the Egyptian travel agencies. In M. H. Bilgin, H Danis, E. Demir, & V. Bodolica (Eds.), Eurasian Business and Economics Perspectives. Eurasian Studies in Business and Economics , 23. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14395-3_9
Acemoglu, D., & Restrepo, P. (2019). Automation and new tasks: How technology displaces and reinstates labor. Journal of Economic Perspectives . American Economic Association, 33(2), 3-30, Spring. Handle: RePEc:aea:jecper:v:33:y:2019:i:2:p:3–30. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.33.2.3
Aqeel, M., Raza, S., & Aman, J. (2021). Portraying the multifaceted interplay between sexual harassment, job stress, social support and employees turnover intension amid COVID-19: A multilevel moderating model. Foundation University Journal of Business & Economics , 6 (2), 1–17. https://fui.edu.pk/fjs/index.php/fujbe/article/view/551
Ben Slimane, S., Coeurderoy, R., & Mhenni, H. (2022). Digital transformation of small and medium enterprises: a systematic literature review and an integrative framework. International Studies of Management & Organization, 52 (2), 96–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/00208825.2022.2072067
Busulwa, R., Pickering, M., & Mao, I. (2022). Digital transformation and hospitality management competencies: Toward an integrative framework. International Journal of Hospitality Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.103132
Camino-Mogro, S. (2022). TFP determinants in the manufacturing sector: The case of Ecuadorian firms. Applied Economic Analysis, 30 (89), 92–113. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEA-10-2020-0142
Chen, N., Sun, D., & Chen, J. (2022). Digital transformation, labour share, and industrial heterogeneity. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge , 7 (2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2022.100173
Cheng, X., Xue, T., Yang, B., & Ma, B. (2023). A digital transformation approach in hospitality and tourism research. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 35 (8), 2944–2967. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-06-2022-0679
Christou, P., Hadjielias, E., Simillidou, A., & Kvasova, O. (2023). The use of intelligent automation as a form of digital transformation in tourism: Towards a hybrid experiential offering. Journal of Business Research , 155 (Part B). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.113415
Ciarli, T., Kenney, M., Massini, S., & Piscitello, L. (2021). Digital technologies, innovation, and skills: Emerging trajectories and challenges. Research Policy , 50 (7). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2021.104289
Correani, A., De Massis, A., Frattini, F., Petruzzelli, A. M., & Natalicchio, A. (2020). Implementing a digital strategy: Learning from the experience of three digital transformation projects. California Management Review, 62 (4), 37–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/0008125620934864
Dahl, A. J., Peltier, J. W., & Milne, G. R. (2022). Reducing information asymmetry and increasing health value co-creation in a rural healthcare context. Journal of Consumer Affairs, 56 (2), 512–535. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12447
Elkhwesky, Z., El Manzani, Y., & Elbayoumi Salem, I. (2024). Driving hospitality and tourism to foster sustainable innovation: A systematic review of COVID-19-related studies and practical implications in the digital era. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 24 (1), 115–133. https://doi.org/10.1177/14673584221126792
Farmaki, A., & Pappas, N. (Eds.). (2021). Emerging transformations in tourism and hospitality (1st ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003105930
Fichman, R. G., Dos Santos, B. L., & Zheng, Z. (2014). Digital innovation as a fundamental and powerful concept in the information systems curriculum. MIS Quarterly, 38 (2), 329–353. https://doi.org/10.25300/MISQ/2014/38.2.01
Gu, R., Li, C., Yang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2023). The impact of industrial digital transformation on green development efficiency considering the threshold effect of regional collaborative innovation: Evidence from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration in China. Journal of Cleaner Production . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138345
Huang, Y. (2023). Can tax incentives promote digital transformation of enterprises. Contemporary Finance & Economics, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.13676/j.cnki.cn36-1030/f.20230728.003
Huang, B., Li, H., Liu, J., & Lei, J. (2023a). Digital technology innovation and the high-quality development of Chinese enterprises: Evidence from enterprise’s digital patents. Economic Research Journal, 58 (03), 97–115.
Google Scholar
Huang, Q., Xu, C., Xue, X., & Zhu, H. (2023b). Can digital innovation improve firm performance: Evidence from digital patents of Chinese listed firms. International Review of Financial Analysis . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2023.102810
Jawed, M. S., Tapar, A. V., & Dhaigude, A. S. (2023). Crisis, firm characteristics and stock performance: Evidence from hospitality and tourism sector. Tourism Recreation Research, 48 (2), 268–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2021.1899536
Kalia, P., Mladenović, D., & Acevedo-Duque, Á. (2022). Decoding the trends and the emerging research directions of digital tourism in the last three decades: A bibliometric analysis. SAGE Open , 12 (4). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221128179
Kumar, D. (2023). Economic and political uncertainties and sustainability disclosures in the tourism sector firms. Tourism Economics, 29 (6), 1694–1699. https://doi.org/10.1177/13548166221113434
Li, C., Zhou, D., & Dong, Z. (2023). Does capital market opening drive digital transformation of enterprises: Based on the quasi-natural experiment and text analysis method. Statistical Research, 40 (08), 96–109. https://doi.org/10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2023.08.008
Li, P., Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Wang, Q., Zhang, Q., & Shah, S. A. R. (2024). Impact of sectoral mix on environmental sustainability: How is heterogeneity addressed? Gondwana Research, 128 , 86–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2023.09.018
Li, Y., Al-Sulaiti, K., Dongling, W., & Al-Sulaiti, I. (2022). Tax avoidance culture and employees’ behavior affect sustainable business performance: The moderating role of corporate social responsibility. Frontiers in Environmental Science. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2022.964410
Liao, X., & Lyu, B. (2023). Sexual harassment in the workplace: Rituals as prevention and management strategies in COVID-19 crisis. Heliyon, 9 (9), e19530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19530
Lieberman, M. B., & Asaba, S. (2006). Why do firms imitate each other? Academy of Management Review, 31 (2), 366–385. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.2006.20208686
Liu, S., Jin, Y., & Kong, D. (2023a). Enterprise digital transformation and overcapacity. China Journal of Economics , 1–30. https://doi.org/10.16513/j.cnki.cje.20230215.004
Liu, F., Wang, C., & Kang, J. (2023b). Exploration and thinking on the training of new business applied talents under the background of digital economy: Take tourism management as an example. Journal of Human Resource Development, 5 , 41–49. https://doi.org/10.23977/jhrd.2023.050307
Madzík, P., Falát, L., Copuš, L., & Valeri, M. (2023). Digital transformation in tourism: bibliometric literature review based on machine learning approach. European Journal of Innovation Management, 26 (7), 177–205. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-09-2022-0531
Mamirkulova, G., Al-Sulaiti, I., Al-Sulaiti, K. I., & Dar, I. B. (2024). Mega-infrastructure development, tourism sustainability and quality of life assessment at world heritage sites: Catering to COVID-19 challenges. Kybernetes, 53 (2), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1108/K-07-2023-1345
Nguyen, D. K., Broekhuizen, T., Dong, J. Q., & Verhoef, P. C. (2023). Leveraging synergy to drive digital transformation: A systems-theoretic perspective. Information & Management , 60 (7). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2023.103836
Nie, J., Jian, X., Juanjuan, X., Nuo, X., Jiang, T., & Yang, Y. (2024). The effect of corporate social responsibility practices on digital transformation in China: A resource-based view. Economic Analysis and Policy, 82 , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2024.02.027
Nyagadza, B., Pashapa, R., Chare, A., Mazuruse, G., & Hove, P. K. (2022). Digital technologies, Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) & Global Value Chains (GVCs) nexus with emerging economies’ future industrial innovation dynamics. Cogent Economics & Finance, 10 , 1. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2021.2014654
Ozdemir, S., de Arroyabe, J. C. F., Sena, V., & Gupta, S. (2023). Stakeholder diversity and collaborative innovation: Integrating the resource-based view with stakeholder theory. Journal of Business Research . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.113955
Pennington-Gray, L., & Basurto, E. (2023). The role of crisis management in managing cultural heritage tourism in a Covid era. In P. L. Yu, T. Lertcharnrit, & G. S. Smith (Eds.), Heritage and Cultural Heritage Tourism . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44800-3_6
Qiang, M. (2022). Quantifying the loss of China’s tourism revenue induced by COVID-19. Current Issues in Tourism, 25 (24), 3919–3924. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2022.2067524
Roy, U., & Chakraborty, I. (2023). Market concentration, agency cost and firm performance: a case study on Indian corporate firms. Economic Change and Restructuring, 56 , 2645–2693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10644-023-09529-1
Rydzik, A., & Kissoon, C. S. (2022). Decent work and tourism workers in the age of intelligent automation and digital surveillance. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 30 (12), 2860–2877. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1928680
Schönherr, S., Eller, R., Kallmuenzer, A., & Peters, M. (2023). Organisational learning and sustainable tourism: the enabling role of digital transformation. Journal of Knowledge Management, 27 (11), 82–100. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-06-2022-0434
Shah, S. H., Fahlevi, M., Rahman, E. Z., Akram, M., Jamshed, K., & Aljuaid, M. (2023). Impact of green servant leadership in Pakistani small and medium enterprises: Bridging pro-environmental behaviour through environmental passion and climate for green creativity. Sustainability , 15 (20). https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014747
Styvén, M. E., & Wallström, Å. (2019). Benefits and barriers for the use of digital channels among small tourism companies. Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 19 (1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/15022250.2017.1379434
Svahn, F., Mathiassen, L., & Lindgren, R. (2017). Embracing digital innovation in incumbent firms: How Volvo Cars managed competing concerns. MIS Quarterly, 41 (1), 239–253. https://doi.org/10.25300/MISQ/2017/41.1.12
Tiantian, G., Hailin, C., Zhou, X., Ai, S., & Siyao, W. (2023). Does corporate digital transformation affect the level of corporate tax avoidance? Empirical evidence from Chinese listed tourism companies. Finance Research Letters, 57 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2023.104271
Tuncalı Yaman, T., & Başeğmez, H. (2023). Digital transformation in tourism: An intelligent information system proposition for hotel organizations. In C. Kahraman, & E. Haktanır (Eds.), Intelligent Systems in Digital Transformation. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems (p. 549). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16598-6_15
Vial, G. (2019). Understanding digital transformation: A review and a research agenda. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 28 (2), 118–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2019.01.003
Van Doorn, J., Smailhodzic, E., Puntoni, S., Li, J., Schumann, J. H., & Holthöwer, J. (2023). Organizational frontlines in the digital age: The consumer–autonomous technology–worker (CAW) framework. Journal of Business Research . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114000
Wang, K., Liu, W., & Fan, D. (2022). The impact of COVID-19 on tourism firm value in an emerging market during various pandemic prevention periods. Current Issues in Tourism, 25 (23), 3799–3814. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2022.2078689
Wen, J., & Deng, Y. (2023). How does intellectual property protection contribute to the digital transformation of enterprises? Finance Research Letters, 58 , Part A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2023.104340
Wooldridge, J. M. (1996). Estimating systems of equations with different instruments for different equations. Journal of Econometrics, 74 (2), 387–405.
Wu, F., Hu, H., Lin, H., & Ren, X. (2021). Enterprise digital transformation and capital market performance: Empirical evidence from stock liquidity. Journal of Management World, 37 (07), 130–144+10.
Yuan, S., & Pan, X. (2023). Inherent mechanism of digital technology application empowered corporate green innovation: Based on resource allocation perspective. Journal of Environmental Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118841
Yuan, C., Xiao, T., Geng, C., & Sheng, Y. (2021). Digital transformation and division of labor between enterprises: Vertical specialization or vertical lntegration. China Industrial Economics, 09 , 137–155.
Zeng, G., & Lei, L. (2021). Digital transformation and corporate total factor productivity: Empirical evidence based on listed enterprises. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society , vol. 2021, Article ID 9155861, 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9155861
Zhuo, C., & Chen, J. (2023). Can digital transformation overcome the enterprise innovation dilemma: Effect, mechanism and effective boundary. Technological Forecasting and Social Change . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122378
Download references
PRC National Social Science Foundation Youth Program, 23CJY047, Rui Tang.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Academy of Strategy for Innovation and Development, Anhui University, Hefei, Anhui, China
Rui Tang & Haoxiang Dong
School of Management, Wenzhou Business College, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pishi Xiu .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rui Tang is the first author, and Haoxiang Dong is the third author.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tang, R., Xiu, P. & Dong, H. Research on Digital Transformation Driving the High-Quality Development of Cultural and Tourism Enterprises—Evidence Based on Listed Cultural and Tourism Companies. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01972-3
Download citation
Received : 29 December 2023
Accepted : 04 April 2024
Published : 29 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01972-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Digital transformation
- High-quality development
- Cultural and tourism enterprises
- Total factor productivity
- Influence mechanism
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Digital Innovation and the Role of Cloud Transformation in Tourism and Culture, Digital instruments in the tourism and cultural ecosystem, and Cloud applications, 2024_ASSEGNI_DIG_45

Job Information
Offer description.
Research aims for the following goals: - analyze the degree of spread of digital tools within the Tourism supply chain, and in particular of accommodation facilities, travel agencies, and museums; - analyze the main areas of Cloud development in the digitalization of Tourism and Culture organizations; - analyze the benefits of Cloud transformation for Tourism and Culture; - investigate organizational aspects related to Cloud transformation; - support Digital Innovation Observatories in implementing the Cloud in the development, testing, management, maintenance, and enhancement of the Osservatori.net platform to disseminate research results.
Requirements
Additional information.
Relevance of qualifications with the research programme object of selection
Consistency of the candidate's overall profile with respect to the content of the research programme for selection
Close relevance of publications submitted with the research programme object of selection
Interview aimed at ascertaining the candidate's aptitude for the research object of the selection
Eligible destination country/ies for fellows:
Eligibility of fellows: country/ies of residence:
Eligibility of fellows: nationality/ies:
In order to participate in the selection, please read the call ("bando") available at the following website: https://www.polimi.it/en/faculty/working-at-the-politecnico/research-gr…
Work Location(s)
Where to apply.
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Photo by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, Official Photographer: Kuk Kyungwon
Harmony in Motion:
A night of korean arts & performance, friday, april 5, 2024, 5:00-7:30 pm location: 180 hagerty hall, the ohio state university, 1775 college road. columbus. oh. 43210.
5:00-6:00 PM: Flavors of Korea: A Prelude to the Performance (food and drinks)
6:00-6:05 PM: Opening remarks
6:05-6:10 PM: Welcome remarks by Prof. Mark Bender
6:10-6:25 PM: Korean Melodies: Musical Tribute
6:25-6:40 PM: Rhythm and Groove: A K-pop Dance Showcase
6:40-6:55 PM: Korean Poetry Reading
6:55-7:10 PM: Korean Speeches
7:10-7:20 PM: K-Martial Arts: Traditional Moves in Modern Times
7:20-7:30 PM: Pulse of Korea: Samulnori Percussion Ensemble
7:30 PM: Closing
7:35 PM: Refreshments and Networking
Dr. Christopher Lee Korean Studies Research Fund
Department of East Asian Languages and Literatures
East Asian Studies Center
Korean-American Community of Columbus
Acknowledgments:

We are honored to extend our sincerest gratitude to Dr. Christopher Lee, a retired faculty member from the Ohio State Department of Radiology, for his generous sponsorship of our Korean performance event. Dr. Lee’s philanthropic spirit and commitment to education have led to the establishment of the Dr. Lee Korean Studies Research Fund. This transformative gift is poised to elevate the Ohio State Korean program to the forefront of Korean studies programs nationwide, enabling advancements in research, performance funding, and the expansion of partnerships. Originally from South Korea, Dr. Lee pursued his medical education at Yonsei University in Korea before undertaking post-graduate training and a radiology fellowship at Ohio State. He had a distinguished career in private practice as well as imparted his knowledge and expertise as a clinical professor of radiology at Ohio State for a decade. Reflecting on his own journey, Dr. Lee emphasizes the profound impact of receiving a scholarship during his medical studies, which inspired his commitment to giving back. His unwavering dedication to supporting OSU students and faculty research exemplifies the spirit of generosity and community that defines our Korean program.
We would also like to acknowledge Prof. Chan Park, Professor Emeritus, who first initiated the Korean performance event at OSU, an initiative that is carried on by the current Korean faculty.
Event coordination team : Korean faculty at OSU (Danielle Pyun, Pil Ho Kim, Hayana Kim, Yonsoo Kang-Parker)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The growing body of cultural tourism scholarship is confirmed by a literature search on the term "cultural tourism" on Google Scholar. As Fig. 1 indicates, cultural tourism sources have risen from less than 100 in 1990 to over 6000 in 2016. Growth was particularly sharp between 2005 and 2015, and cultural tourism publications have risen as a proportion of all tourism publications, to reach ...
Abstract. This review article traces the development of cultural tourism as a field of research over the past decade, identifying major trends and research areas. Cultural tourism has recently been re-affirmed by the UNWTO as a major element of international tourism consumption, accounting for over 39% of tourism arrivals.
This review article traces the development of cultural tourism as a field of research over th e. past decade, identifying major trends and research a reas. Cultural tourism has recently been. re ...
At the same time, the expanding notion of cultural experience invites new economic research paths focusing on intangible cultural expressions, such as wine and gastronomy tourism (Hall et al., 2009; Hjalager and Richards, 2003), and developing new interpretative frameworks to account for the multidimensional forms of benefits in cultural tourism experiences.
Academic work on popular culture tourism is a novel, rapidly evolving area drawing upon perspectives from multiple disciplines, including tourism analysis, cultural studies, sociology, fandom research, geography, political economy, business, media studies, and information technology (cf. Beeton, 2010). In the literature, we can find focal ...
Abstract. In the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, the future of tourism is a much-debated topic both in academic and non-academic circles with commentators expounding contrasting perspectives. This conceptual paper contributes to such debates and aims at envisioning plausible futures of cultural tourism, in particular.
Heritage/cultural tourism is the fourth most relevant topic discovered in our analysis and has been a significant area of interest in hospitality and tourism research over the past three decades.
2018, Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management. This review article traces the development of cultural tourism as a field of research over the past decade, identifying major trends and research areas. Cultural tourism has recently been reaffirmed by the UNWTO as a major element of international tourism consumption, accounting for over 39% ...
Countries, through culture, forged new identities; regions and cities have adopted culture as an instrument for growth and development; cultural tourism is identified as good tourism, due to the ...
Culture has become a key product in the international tourism market, with tourists engaged in cultural activities accounting for 40% of international arrivals in 2016 (UNWTO, Citation 2016).Destinations build on cultural supplies to conform their tourism offer, given the interest of visitors for cultural attractions (OECD, Citation 2009).City tourism relies on culture as a major product (ETC ...
Cultural heritage includes tangible heritage—architectural, archaeological, movable, and immovable; and intangible heritage—oral expressions and traditions, festive events, social rituals, knowledge, and practices related to nature and skills linked to knowledge [17-19].The positioning of cultural heritage elements constitutes a legacy to contemporary tourism, in terms of production and ...
Culture and value. Wang and Leou (Citation 2015) conducted a component analysis of cultural and heritage tourism motivation and revealed that tourists' perceived value has three dimensions: scenic value, knowledge value and social value.These factors are important markers of perceived value that positively influence tourist destination loyalty. For example, halal destinations are expected to ...
Cultural Tourism Research Methods. The consumption of culture is one of the most important aspects of tourism activity. Cultural tourism includes experiencing local culture, traditions and lifestyle, participation in arts-related activities, and visits to museums, monuments and heritage sites. This book reviews a wide range of qualitative and ...
Qualitative research refers to research applying a methodology as well as one of a range of methods, which seeks to explore, interpret, understand, and potentially intervene into a given field or issue under study. Qualitative research in tourism takes its inspiration primarily from the humanities and the social sciences, such as cultural ...
Cultural heritage is the sum of material wealth and spiritual wealth left by a nation in the past. Because of its precious and fragile characteristics, cultural heritage protection and tourism development have received extensive global academic attention. However, application visualization software is still underused, and studies are needed that provide a comprehensive overview of cultural ...
This chapter reviews some of the key issues in doing survey research in cultural tourism through the lens of the Association for Tourism and Leisure Education (ATLAS) Cultural Tourism Research Project, probably the largest and longest-running global research project in cultural tourism. This analysis illustrates the advantages and disadvantages ...
In the context of integrating culture and tourism, world heritage tourism research has become a focus in tourism research in recent years. There are increasing discussions in academic circles on the content and methods of this field. Clarifying the knowledge system of research is conducive to dialogue with international theoretical frontiers and integrating, analyzing, and predicting the ...
This webpage provides UN Tourism resources aimed at strengthening the dialogue between tourism and culture and an informed decision-making in the sphere of cultural tourism. It also promotes the exchange of good practices showcasing inclusive management systems and innovative cultural tourism experiences.. About Cultural Tourism. According to the definition adopted by the UN Tourism General ...
A review of cultural tourism research and interconnections with tourism organizational change. As cultural tourism is gaining plenty of popularity in both the tourism industry and the tourism literature, it is necessary to have a general understanding on extant cultural tourism research. Therefore, this multi-sectional part first reviews and ...
Given the traditional hegemony of Western culture in behavioral research in tourism, marketing, and other business and management fields, part of the challenge for future research will be to validate these theories and models among some of the emerging geographical sources of outbound tourism, including the Asia-Pacific region, Africa, South ...
Cultural tourism as an academic study emerged in the 1980s. Cultural tourism reached a high point in the 1980s and 1990s as it became widely recognized as a good tourism product. There was a proliferation of research on cultural tourism, and different theories and research methods were applied to the field (Smith and Richards, 2013). According ...
[email protected]. Marjan Melkert, Researcher and Consultant, Centre of Expertise for Cultural Tourism, Zuyd University, New Eyckholt 300, PO Box 550, 6400 AN Heerlen, the Netherlands. E-mail: m ...
Digital transformation has become an important means for cultural and tourism enterprises to achieve high-quality development. The role of digital transformation in driving the development of cultural and tourism enterprises deserves to be fully explored. Based on the data of 98 listed cultural and tourism companies in China, this paper uses Python text mining, a two-way fixed effects model ...
She was the former Nodal Officer of the Indian Institute of Tourism and Travel Management (Ministry of Tourism, Govt. of India) South Campus, Nellore. A behavioral economist by research, she started her research at IIT Madras and earned a Ph.D. in Economics from Avinashilingam University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nādu, India.
It addresses various topics, including industrial heritage conservation, regeneration approaches, and cultural heritage tourism. The research focuses primarily on the value appraisal of industrial heritage, exploring revitalisation tactics and routes, as well as regional development models in urban-rural periphery areas.
The presence of a tourism village in Indonesia might be viewed as an opportunity to strengthen small, micro, and medium-sized businesses as a driving force in the local economy. The goal of Micro Small Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) development is to create a tourism village supported by MSMEs that combines natural and culture attractions, local gastronomic and artisan, and public service facilities.
Originally defining cultural. tourism as ' that form of tourism whose ob ject is, among other aims, the discovery of. monuments and sites' by 1999 the defini tion included 'any form of tourism to ...
Research aims for the following goals: - analyze the degree of spread of digital tools within the Tourism supply chain, and in particular of accommodation facilities, travel agencies, and museums; - analyze the main areas of Cloud development in the digitalization of Tourism and Culture organizations;
Photo by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, Official Photographer: Kuk Kyungwon. Harmony in Motion: A Night of Korean Arts & Performance. Friday, April 5, 2024, 5:00-7:30 pm ... enabling advancements in research, performance funding, and the expansion of partnerships. Originally from South Korea, Dr. Lee pursued his medical education ...