

Is Time Travel Possible?
We all travel in time! We travel one year in time between birthdays, for example. And we are all traveling in time at approximately the same speed: 1 second per second.
We typically experience time at one second per second. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA's space telescopes also give us a way to look back in time. Telescopes help us see stars and galaxies that are very far away . It takes a long time for the light from faraway galaxies to reach us. So, when we look into the sky with a telescope, we are seeing what those stars and galaxies looked like a very long time ago.
However, when we think of the phrase "time travel," we are usually thinking of traveling faster than 1 second per second. That kind of time travel sounds like something you'd only see in movies or science fiction books. Could it be real? Science says yes!
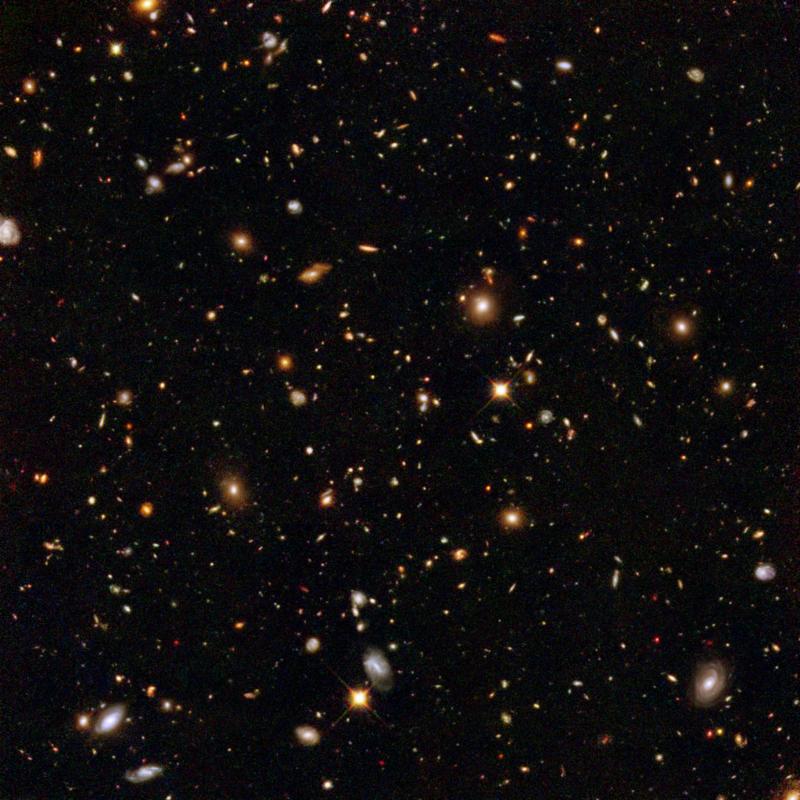

This image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies that are very far away as they existed a very long time ago. Credit: NASA, ESA and R. Thompson (Univ. Arizona)
How do we know that time travel is possible?
More than 100 years ago, a famous scientist named Albert Einstein came up with an idea about how time works. He called it relativity. This theory says that time and space are linked together. Einstein also said our universe has a speed limit: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
Einstein's theory of relativity says that space and time are linked together. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What does this mean for time travel? Well, according to this theory, the faster you travel, the slower you experience time. Scientists have done some experiments to show that this is true.
For example, there was an experiment that used two clocks set to the exact same time. One clock stayed on Earth, while the other flew in an airplane (going in the same direction Earth rotates).
After the airplane flew around the world, scientists compared the two clocks. The clock on the fast-moving airplane was slightly behind the clock on the ground. So, the clock on the airplane was traveling slightly slower in time than 1 second per second.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Can we use time travel in everyday life?
We can't use a time machine to travel hundreds of years into the past or future. That kind of time travel only happens in books and movies. But the math of time travel does affect the things we use every day.
For example, we use GPS satellites to help us figure out how to get to new places. (Check out our video about how GPS satellites work .) NASA scientists also use a high-accuracy version of GPS to keep track of where satellites are in space. But did you know that GPS relies on time-travel calculations to help you get around town?
GPS satellites orbit around Earth very quickly at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. This slows down GPS satellite clocks by a small fraction of a second (similar to the airplane example above).
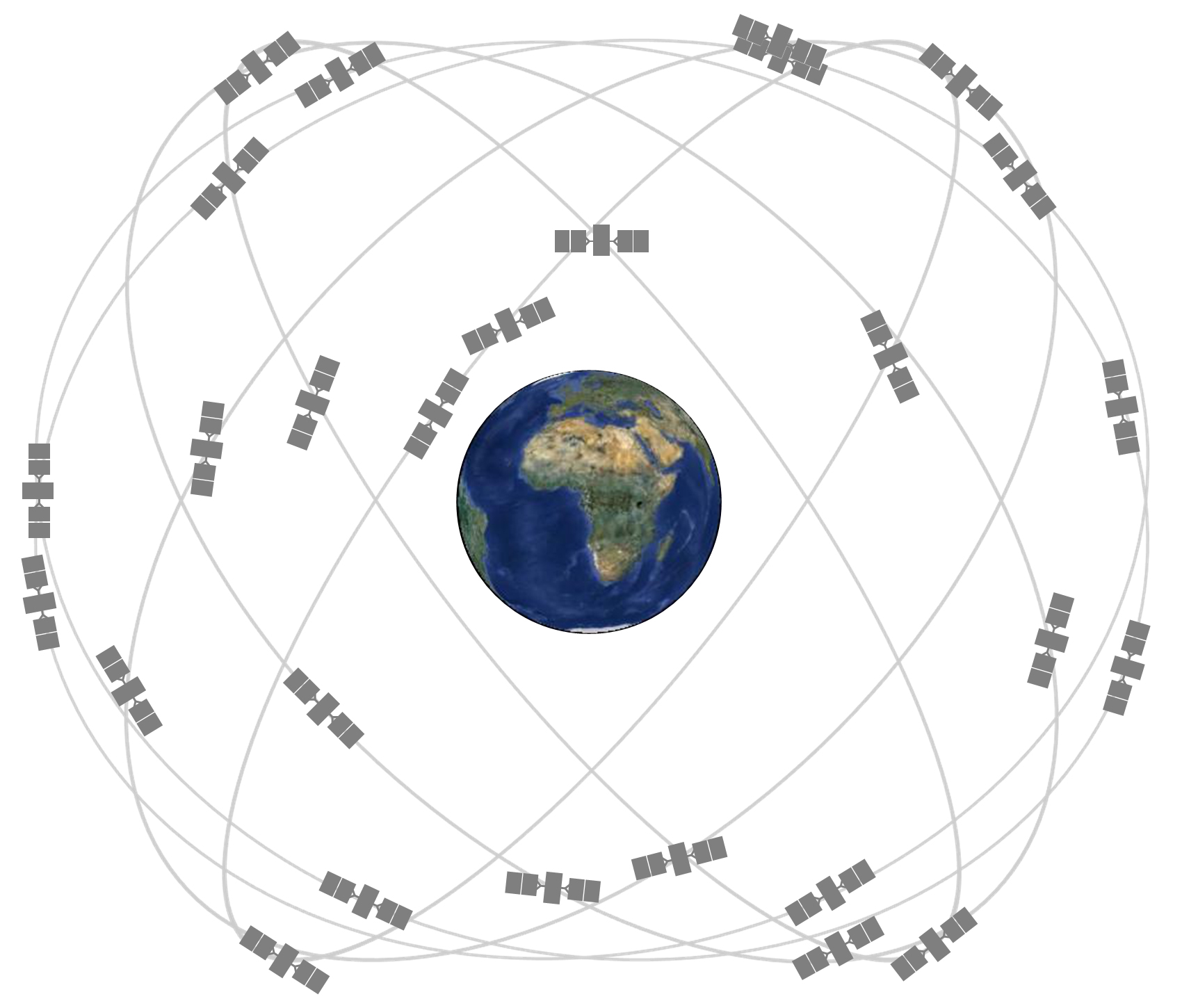
GPS satellites orbit around Earth at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. Credit: GPS.gov
However, the satellites are also orbiting Earth about 12,550 miles (20,200 km) above the surface. This actually speeds up GPS satellite clocks by a slighter larger fraction of a second.
Here's how: Einstein's theory also says that gravity curves space and time, causing the passage of time to slow down. High up where the satellites orbit, Earth's gravity is much weaker. This causes the clocks on GPS satellites to run faster than clocks on the ground.
The combined result is that the clocks on GPS satellites experience time at a rate slightly faster than 1 second per second. Luckily, scientists can use math to correct these differences in time.
If scientists didn't correct the GPS clocks, there would be big problems. GPS satellites wouldn't be able to correctly calculate their position or yours. The errors would add up to a few miles each day, which is a big deal. GPS maps might think your home is nowhere near where it actually is!
In Summary:
Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
If you liked this, you may like:
Can We Travel Through Time to the Past?
MARK GARLICK / Science Photo Library / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Astronomy
- Important Astronomers
- Solar System
- Stars, Planets, and Galaxies
- Space Exploration
- Weather & Climate
Traveling Into the Past
Black holes and wormholes, causality and alternate realities, wormhole warnings, so, is time travel to the past really possible.
- Ph.D., Physics and Astronomy, Purdue University
- B.S., Physics, Purdue University
Going back in time to visit an earlier era is a fantastic dream. It's a staple of SF and fantasy novels, movies, and TV shows. Who wouldn't like to go back and see the dinosaurs or watch the birth of the universe or meet their great-great grandparents? What could possibly go wrong Could someone travel to a previous era to right a wrong, make a different decision, or even completely alter the course of history? Has it happened? Is it even possible?
There are a lot of questions about travel into the past, but not very many solutions. The best answer science can give us right now is: it's theoretically possible. But, no one has done it.
It turns out that people time travel all the time, but only in one direction: from the past to the present and moving into the future . Unfortunately, no one has any control over how quickly that time passes and nobody can stop time and continue to live. It seems that time is a one-way street, always moving forward.
This is all right and proper. It also fits with Einstein's theory of relativity because time only flows in one direction—forward. If time flowed the other way, people would remember the future instead of the past. That sounds very counter-intuitive. So, on the face of it, traveling into the past seems to be a violation of the laws of physics.
But not so fast! It turns out that there are theoretical considerations to take into account if somebody wants to build a time machine that goes back to the past. They involve exotic gateways called wormholes, or some science fictional-sounding creation of gateways using a technology not yet available to science.
The idea of building a time machine, like those often depicted in science fiction films, is likely the stuff of dreams. Unlike the traveler in H.G. Wells's Time Machine, no one has figured out how to build a special carriage that goes from now to yesterday. However, astrophysics gives us one possible pathway: one could possibly harness the power of a black hole to venture through time and space. How would that work?
According to general relativity , a rotating black hole could create a wormhole —a theoretical link between two points of space-time, or perhaps even two points in different universes. However, there's a problem with black holes. They've long been thought to be unstable and therefore un-traversable. However, recent advances in physics theory have shown that these constructs could, in fact, provide a means of traveling through time. Unfortunately, we have almost no idea what to expect by doing so.
Theoretical physics is still trying to predict what would happen inside the wormhole, assuming one could even approach such a place. More to the point, there's no current engineering solution that would allow us to build a craft that would let make that trip safely. Right now, as it stands, once a ship enters the black hole, it's going to get crushed by incredible gravity. The ship, and everyone aboard are made one with the singularity at the heart of the black hole.
But, for the sake of argument, what if it were possible to pass through a wormhole? What would people experience? Some suggest it would probably be a lot like Alice falling through the rabbit hole. Who knows what we would find on the other side? Or in what time frame? Until someone can devise a safe way to make that trip, we aren't likely to find out.
The idea of traveling into the past raises all sorts of paradoxical issues. For instance, what happens if a person goes back in time and kills their parents before they can conceive their child? Lots of dramatic stories have been built around that one. Or, the idea that someone could go back and kill a dictator and change history, or save the life of a famous person. An entire episode of Star Trek was built around that idea.
It turns out that the time traveler effectively creates an alternate reality or parallel universe . So, if someone did travel back and prevent someone else's birth, or murdered someone, a younger version of the victim would never come to be in that reality. And, it might or might not carry on as if nothing had changed. By going back in time, the traveler creates a new reality and would, therefore, never be able to return to the reality they once knew. (If they then tried to travel into the future from there, they would see the future of the new reality, not the one they knew before.) Consider the outcome of the movie "Back to the Future". Marty McFly changes reality for his parents back when they were in high school, and that changes his own reality. He gets back home and finds his parents aren't quite the same as when he left. Did he create a new alternate universe? Theoretically, he did.
This brings us to another issue that is rarely discussed. The nature of wormholes is to take a traveler to a different point in time and space . So if someone left Earth and traveled through a wormhole, they could be transported to the other side of the universe (assuming they are even still in the same universe we currently occupy). If they wanted to travel back to Earth they would either have to travel back through the wormhole they just left (bringing them back, presumably, to the same time and place), or journey by more conventional means.
Assuming the travelers would even be close enough to make it back to Earth in their lifetimes from wherever the wormhole spat them out, would it still be the "past" when they returned? Since traveling at speeds approaching that of light makes time slow down for the voyager, time would proceed very, very quickly back on Earth. So, the past would fall behind, and the future would become the past... that's the way time works flowing forward !
So, while they exited the wormhole in the past (relative to time on Earth), by being so far away it's possible that they wouldn't make it back to Earth at any reasonable time relating to when they left. This would negate the whole purpose of time travel altogether.
Possible? Yes, theoretically. Probable? No, at least not with our current technology and understanding of physics. But perhaps someday, thousands of years into the future, people could harness enough energy to make time travel a reality. Until that time, the idea will just have to stay relegated to the pages of science-fiction or for viewers to make repeated showings of Back to the Future.
Edited by Carolyn Collins Petersen .
- Is Time Travel Possible?
- Time Travel: Dream or Possible Reality?
- Wormholes: What Are They and Can We Use Them?
- The Science of Star Trek
- Closed Timelike Curve
- What Is Time? A Simple Explanation
- Is Warp Drive From 'Star Trek' Possible?
- What Is the Twin Paradox? Real Time Travel
- Amazing Astronomy Facts
- Cosmos Episode 4 Viewing Worksheet
- An Introduction to Black Holes
- 9 Worst Science Mistakes in Movies
- Does Time Really Exist?
- The History of the Chinese Space Program
- Sub-light Speed in Star Trek: Can It Be Done?
- Movies That Realistically Present Physics
Will We Ever Be Able to Time Travel Into the Past?
Forward or back—which will it be?

Gear-obsessed editors choose every product we review. We may earn commission if you buy from a link. Why Trust Us?
You likely don’t realize it, but when you’re done reading this article, you will have traveled perhaps 90 seconds into the future. The truth is that it is easier, theoretically speaking, to travel forward in time than it is to travel backward, and that’s partly because we’re all moving forward in time naturally.
The possibility of time travel stems from Albert Einstein’s theory of special relativity, which, loosely speaking, describes the relationship between space and time. An outgrowth is something known as “time dilation,” which suggests that time can move at different rates for different observers—and therefore at different rates in different places. This theory is borne out by the (rather freaky) fact that clocks on the space shuttle—whether internal clocks or atomic clocks placed aboard for experimental purposes—run more slowly than reference clocks on Earth. In this sense, astronauts on extended missions may already be considered time travelers, as they arrive home very slightly later than the elapsed time measured on their own instruments would suggest. Moreover, “Time beats faster on the moon than on Earth, and time beats slower on Jupiter,” says celebrated physicist Michio Kaku of the City College of New York. “So if you were to simply camp out on the moon or Jupiter, you’d be going backward and forward in time. Now, of course, these are for fractions of a second.”
A more useful implication of time dilation is the fact that the closer to the speed of light you’re moving, the slower your internal clock will be ticking relative to time on Earth. “If you reach 99 percent of the speed of light and spend like a year moving at that speed—around the solar system, say—and then come back to Earth, you will find that the Earth has moved on, 100 to 200 years into the future,” says Dr. Ulvi Yurtsever, coauthor of a seminal paper on time travel. So, in theory, if we could improve propulsion systems enough, we could skip ahead centuries. But we still couldn’t move backward.
Indeed, backward time travel, while theoretically possible, is far trickier and would involve black holes and “tunable wormholes” and more energy than a kindergarten class on a sugar binge. “You can write down solutions of the equations,” says Clifford V. Johnson, a professor of theoretical physics at USC, “and those equations tell you two things: how you twist up space and time, and what matter you need to do that. And every time you get those weird twists in space and time that look like a time machine, the matter and energy you need to do that is in a form that may not exist in this universe. So that’s just a fancy way of saying that the jury is out.”
So from a technical standpoint, it seems far more likely that we’d move forward in time first. But how about from an ethical one? “Scientists and physicists may say ‘You know what, it’s much safer for us to go to the future, because if it’s possible to alter the past and therefore have that reverberate into the present—create a paradox—that’s pretty dangerous,’ ” says Bob Gale, who has spent some time thinking about this stuff, given that he cowrote the 1985 time-travel blockbuster Back to the Future. “So they would say ‘Well, to preserve the sanctity of the space-time continuum, we better go into the future, because that provides the least amount of risk.’ ”
So there you have it: 25th century, here we come.
Do you have unusual questions about how things work and why stuff happens? This is the place to ask them. Don’t be afraid. Nobody will laugh at you here. Email [email protected].
Want more Popular Mechanics? Get Instant Access!

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Science .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

The Maya Kingdom Collapsed Due to Burning Events

Pluto’s Heart—Now in 4D

Billiards With Memory Creates Intricate Patterns

‘Unprecedented’ Ancient Structure Found in France

The Overlooked, Powerful Role of Inorganic Carbon

The Moon Could Solve the Mystery of Stonehenge

Scientist Says AI Could Kill Us in About 200 Years

The CIA’s Secret Plan to Turn Psychics Into Spies

Pyrite Isn’t Looking So Foolish in the Lithium Age

Experts Confirm the Existence of Wigner Crystals

Is This the Real Iceberg That Sank the Titanic?

Time travel could be possible, but only with parallel timelines
Assistant Professor, Physics, Brock University
Disclosure statement
Barak Shoshany does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Brock University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
Brock University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA.
View all partners
Have you ever made a mistake that you wish you could undo? Correcting past mistakes is one of the reasons we find the concept of time travel so fascinating. As often portrayed in science fiction, with a time machine, nothing is permanent anymore — you can always go back and change it. But is time travel really possible in our universe , or is it just science fiction?
Read more: Curious Kids: is time travel possible for humans?
Our modern understanding of time and causality comes from general relativity . Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein’s theory combines space and time into a single entity — “spacetime” — and provides a remarkably intricate explanation of how they both work, at a level unmatched by any other established theory. This theory has existed for more than 100 years, and has been experimentally verified to extremely high precision, so physicists are fairly certain it provides an accurate description of the causal structure of our universe.
For decades, physicists have been trying to use general relativity to figure out if time travel is possible . It turns out that you can write down equations that describe time travel and are fully compatible and consistent with relativity. But physics is not mathematics, and equations are meaningless if they do not correspond to anything in reality.
Arguments against time travel
There are two main issues which make us think these equations may be unrealistic. The first issue is a practical one: building a time machine seems to require exotic matter , which is matter with negative energy. All the matter we see in our daily lives has positive energy — matter with negative energy is not something you can just find lying around. From quantum mechanics, we know that such matter can theoretically be created, but in too small quantities and for too short times .
However, there is no proof that it is impossible to create exotic matter in sufficient quantities. Furthermore, other equations may be discovered that allow time travel without requiring exotic matter. Therefore, this issue may just be a limitation of our current technology or understanding of quantum mechanics.

The other main issue is less practical, but more significant: it is the observation that time travel seems to contradict logic, in the form of time travel paradoxes . There are several types of such paradoxes, but the most problematic are consistency paradoxes .
A popular trope in science fiction, consistency paradoxes happen whenever there is a certain event that leads to changing the past, but the change itself prevents this event from happening in the first place.
For example, consider a scenario where I enter my time machine, use it to go back in time five minutes, and destroy the machine as soon as I get to the past. Now that I destroyed the time machine, it would be impossible for me to use it five minutes later.
But if I cannot use the time machine, then I cannot go back in time and destroy it. Therefore, it is not destroyed, so I can go back in time and destroy it. In other words, the time machine is destroyed if and only if it is not destroyed. Since it cannot be both destroyed and not destroyed simultaneously, this scenario is inconsistent and paradoxical.
Eliminating the paradoxes
There’s a common misconception in science fiction that paradoxes can be “created.” Time travellers are usually warned not to make significant changes to the past and to avoid meeting their past selves for this exact reason. Examples of this may be found in many time travel movies, such as the Back to the Future trilogy.
But in physics, a paradox is not an event that can actually happen — it is a purely theoretical concept that points towards an inconsistency in the theory itself. In other words, consistency paradoxes don’t merely imply time travel is a dangerous endeavour, they imply it simply cannot be possible.
This was one of the motivations for theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking to formulate his chronology protection conjecture , which states that time travel should be impossible. However, this conjecture so far remains unproven. Furthermore, the universe would be a much more interesting place if instead of eliminating time travel due to paradoxes, we could just eliminate the paradoxes themselves.
One attempt at resolving time travel paradoxes is theoretical physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov’s self-consistency conjecture , which essentially states that you can travel to the past, but you cannot change it.
According to Novikov, if I tried to destroy my time machine five minutes in the past, I would find that it is impossible to do so. The laws of physics would somehow conspire to preserve consistency.
Introducing multiple histories
But what’s the point of going back in time if you cannot change the past? My recent work, together with my students Jacob Hauser and Jared Wogan, shows that there are time travel paradoxes that Novikov’s conjecture cannot resolve. This takes us back to square one, since if even just one paradox cannot be eliminated, time travel remains logically impossible.
So, is this the final nail in the coffin of time travel? Not quite. We showed that allowing for multiple histories (or in more familiar terms, parallel timelines) can resolve the paradoxes that Novikov’s conjecture cannot. In fact, it can resolve any paradox you throw at it.
The idea is very simple. When I exit the time machine, I exit into a different timeline. In that timeline, I can do whatever I want, including destroying the time machine, without changing anything in the original timeline I came from. Since I cannot destroy the time machine in the original timeline, which is the one I actually used to travel back in time, there is no paradox.
After working on time travel paradoxes for the last three years , I have become increasingly convinced that time travel could be possible, but only if our universe can allow multiple histories to coexist. So, can it?
Quantum mechanics certainly seems to imply so, at least if you subscribe to Everett’s “many-worlds” interpretation , where one history can “split” into multiple histories, one for each possible measurement outcome – for example, whether Schrödinger’s cat is alive or dead, or whether or not I arrived in the past.
But these are just speculations. My students and I are currently working on finding a concrete theory of time travel with multiple histories that is fully compatible with general relativity. Of course, even if we manage to find such a theory, this would not be sufficient to prove that time travel is possible, but it would at least mean that time travel is not ruled out by consistency paradoxes.
Time travel and parallel timelines almost always go hand-in-hand in science fiction, but now we have proof that they must go hand-in-hand in real science as well. General relativity and quantum mechanics tell us that time travel might be possible, but if it is, then multiple histories must also be possible.
- Time travel
- Theoretical physics
- Time machine
- Albert Einstein
- Listen to this article
- Time travel paradox

Program Manager, Teaching & Learning Initiatives

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy
A beginner's guide to time travel
Learn exactly how Einstein's theory of relativity works, and discover how there's nothing in science that says time travel is impossible.

Everyone can travel in time . You do it whether you want to or not, at a steady rate of one second per second. You may think there's no similarity to traveling in one of the three spatial dimensions at, say, one foot per second. But according to Einstein 's theory of relativity , we live in a four-dimensional continuum — space-time — in which space and time are interchangeable.
Einstein found that the faster you move through space, the slower you move through time — you age more slowly, in other words. One of the key ideas in relativity is that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light — about 186,000 miles per second (300,000 kilometers per second), or one light-year per year). But you can get very close to it. If a spaceship were to fly at 99% of the speed of light, you'd see it travel a light-year of distance in just over a year of time.
That's obvious enough, but now comes the weird part. For astronauts onboard that spaceship, the journey would take a mere seven weeks. It's a consequence of relativity called time dilation , and in effect, it means the astronauts have jumped about 10 months into the future.
Traveling at high speed isn't the only way to produce time dilation. Einstein showed that gravitational fields produce a similar effect — even the relatively weak field here on the surface of Earth . We don't notice it, because we spend all our lives here, but more than 12,400 miles (20,000 kilometers) higher up gravity is measurably weaker— and time passes more quickly, by about 45 microseconds per day. That's more significant than you might think, because it's the altitude at which GPS satellites orbit Earth, and their clocks need to be precisely synchronized with ground-based ones for the system to work properly.
The satellites have to compensate for time dilation effects due both to their higher altitude and their faster speed. So whenever you use the GPS feature on your smartphone or your car's satnav, there's a tiny element of time travel involved. You and the satellites are traveling into the future at very slightly different rates.

But for more dramatic effects, we need to look at much stronger gravitational fields, such as those around black holes , which can distort space-time so much that it folds back on itself. The result is a so-called wormhole, a concept that's familiar from sci-fi movies, but actually originates in Einstein's theory of relativity. In effect, a wormhole is a shortcut from one point in space-time to another. You enter one black hole, and emerge from another one somewhere else. Unfortunately, it's not as practical a means of transport as Hollywood makes it look. That's because the black hole's gravity would tear you to pieces as you approached it, but it really is possible in theory. And because we're talking about space-time, not just space, the wormhole's exit could be at an earlier time than its entrance; that means you would end up in the past rather than the future.
Trajectories in space-time that loop back into the past are given the technical name "closed timelike curves." If you search through serious academic journals, you'll find plenty of references to them — far more than you'll find to "time travel." But in effect, that's exactly what closed timelike curves are all about — time travel

This article is brought to you by How It Works .
How It Works is the action-packed magazine that's bursting with exciting information about the latest advances in science and technology, featuring everything you need to know about how the world around you — and the universe — works.
There's another way to produce a closed timelike curve that doesn't involve anything quite so exotic as a black hole or wormhole: You just need a simple rotating cylinder made of super-dense material. This so-called Tipler cylinder is the closest that real-world physics can get to an actual, genuine time machine. But it will likely never be built in the real world, so like a wormhole, it's more of an academic curiosity than a viable engineering design.
Yet as far-fetched as these things are in practical terms, there's no fundamental scientific reason — that we currently know of — that says they are impossible. That's a thought-provoking situation, because as the physicist Michio Kaku is fond of saying, "Everything not forbidden is compulsory" (borrowed from T.H. White's novel, "The Once And Future King"). He doesn't mean time travel has to happen everywhere all the time, but Kaku is suggesting that the universe is so vast it ought to happen somewhere at least occasionally. Maybe some super-advanced civilization in another galaxy knows how to build a working time machine, or perhaps closed timelike curves can even occur naturally under certain rare conditions.

This raises problems of a different kind — not in science or engineering, but in basic logic. If time travel is allowed by the laws of physics, then it's possible to envision a whole range of paradoxical scenarios . Some of these appear so illogical that it's difficult to imagine that they could ever occur. But if they can't, what's stopping them?
Thoughts like these prompted Stephen Hawking , who was always skeptical about the idea of time travel into the past, to come up with his "chronology protection conjecture" — the notion that some as-yet-unknown law of physics prevents closed timelike curves from happening. But that conjecture is only an educated guess, and until it is supported by hard evidence, we can come to only one conclusion: Time travel is possible.
A party for time travelers
Hawking was skeptical about the feasibility of time travel into the past, not because he had disproved it, but because he was bothered by the logical paradoxes it created. In his chronology protection conjecture, he surmised that physicists would eventually discover a flaw in the theory of closed timelike curves that made them impossible.
In 2009, he came up with an amusing way to test this conjecture. Hawking held a champagne party (shown in his Discovery Channel program), but he only advertised it after it had happened. His reasoning was that, if time machines eventually become practical, someone in the future might read about the party and travel back to attend it. But no one did — Hawking sat through the whole evening on his own. This doesn't prove time travel is impossible, but it does suggest that it never becomes a commonplace occurrence here on Earth.
The arrow of time
One of the distinctive things about time is that it has a direction — from past to future. A cup of hot coffee left at room temperature always cools down; it never heats up. Your cellphone loses battery charge when you use it; it never gains charge. These are examples of entropy , essentially a measure of the amount of "useless" as opposed to "useful" energy. The entropy of a closed system always increases, and it's the key factor determining the arrow of time.
It turns out that entropy is the only thing that makes a distinction between past and future. In other branches of physics, like relativity or quantum theory, time doesn't have a preferred direction. No one knows where time's arrow comes from. It may be that it only applies to large, complex systems, in which case subatomic particles may not experience the arrow of time.
Time travel paradox
If it's possible to travel back into the past — even theoretically — it raises a number of brain-twisting paradoxes — such as the grandfather paradox — that even scientists and philosophers find extremely perplexing.
Killing Hitler
A time traveler might decide to go back and kill him in his infancy. If they succeeded, future history books wouldn't even mention Hitler — so what motivation would the time traveler have for going back in time and killing him?
Killing your grandfather
Instead of killing a young Hitler, you might, by accident, kill one of your own ancestors when they were very young. But then you would never be born, so you couldn't travel back in time to kill them, so you would be born after all, and so on …
A closed loop
Suppose the plans for a time machine suddenly appear from thin air on your desk. You spend a few days building it, then use it to send the plans back to your earlier self. But where did those plans originate? Nowhere — they are just looping round and round in time.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

How It Works has a special formula for making learning fun by answering questions on science, space, history, technology, transport and the environment with engaging articles, in-depth special features, global science news, and topical interviews. With impressive cutaway illustrations that show how things function, and mindblowing photography of the planet’s most inspiring spectacles, How It Works represents the pinnacle of engaging, factual fun for a mainstream audience keen to keep up with the latest tech and the most impressive phenomena on the planet and beyond. Written and presented in a style that makes even the most complex subjects interesting and easy to understand, How It Works is enjoyed by readers of all ages.
Get fantastic offers by subscribing to the digital and/or print edition now. Subscribers get 13 issues per year!
Hundreds of black 'spiders' spotted in mysterious 'Inca City' on Mars in new satellite photos
Scientists find one of the oldest stars in the universe in a galaxy right next to ours
World's thinnest gold leaf, dubbed 'goldene,' is just 1 atom thick
Most Popular
- 2 Giant, 82-foot lizard fish discovered on UK beach could be largest marine reptile ever found
- 3 Global 'time signals' subtly shifted as the total solar eclipse reshaped Earth's upper atmosphere, new data shows
- 4 Rare 'porcelain gallbladder' found in 100-year-old unmarked grave at Mississippi mental asylum cemetery
- 5 'I nearly fell out of my chair': 1,800-year-old mini portrait of Alexander the Great found in a field in Denmark
- 2 Hundreds of black 'spiders' spotted in mysterious 'Inca City' on Mars in new satellite photos
- 3 Plato's burial place finally revealed after AI deciphers ancient scroll carbonized in Mount Vesuvius eruption
- 4 China green-lights mass production of autonomous flying taxis — with commercial flights set for 2025
- 5 'We were in disbelief': Antarctica is behaving in a way we've never seen before. Can it recover?
Is time travel possible? Why one scientist says we 'cannot ignore the possibility.'

A common theme in science-fiction media , time travel is captivating. It’s defined by the late philosopher David Lewis in his essay “The Paradoxes of Time Travel” as “[involving] a discrepancy between time and space time. Any traveler departs and then arrives at his destination; the time elapsed from departure to arrival … is the duration of the journey.”
Time travel is usually understood by most as going back to a bygone era or jumping forward to a point far in the future . But how much of the idea is based in reality? Is it possible to travel through time?
Is time travel possible?
According to NASA, time travel is possible , just not in the way you might expect. Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity says time and motion are relative to each other, and nothing can go faster than the speed of light , which is 186,000 miles per second. Time travel happens through what’s called “time dilation.”
Time dilation , according to Live Science, is how one’s perception of time is different to another's, depending on their motion or where they are. Hence, time being relative.
Learn more: Best travel insurance
Dr. Ana Alonso-Serrano, a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Germany, explained the possibility of time travel and how researchers test theories.
Space and time are not absolute values, Alonso-Serrano said. And what makes this all more complex is that you are able to carve space-time .
“In the moment that you carve the space-time, you can play with that curvature to make the time come in a circle and make a time machine,” Alonso-Serrano told USA TODAY.
She explained how, theoretically, time travel is possible. The mathematics behind creating curvature of space-time are solid, but trying to re-create the strict physical conditions needed to prove these theories can be challenging.
“The tricky point of that is if you can find a physical, realistic, way to do it,” she said.
Alonso-Serrano said wormholes and warp drives are tools that are used to create this curvature. The matter needed to achieve curving space-time via a wormhole is exotic matter , which hasn’t been done successfully. Researchers don’t even know if this type of matter exists, she said.
“It's something that we work on because it's theoretically possible, and because it's a very nice way to test our theory, to look for possible paradoxes,” Alonso-Serrano added.
“I could not say that nothing is possible, but I cannot ignore the possibility,” she said.
She also mentioned the anecdote of Stephen Hawking’s Champagne party for time travelers . Hawking had a GPS-specific location for the party. He didn’t send out invites until the party had already happened, so only people who could travel to the past would be able to attend. No one showed up, and Hawking referred to this event as "experimental evidence" that time travel wasn't possible.
What did Albert Einstein invent?: Discoveries that changed the world
Just Curious for more? We've got you covered
USA TODAY is exploring the questions you and others ask every day. From "How to watch the Marvel movies in order" to "Why is Pluto not a planet?" to "What to do if your dog eats weed?" – we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer for you.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
13.7 Cosmos & Culture
Can we change the past.
Marcelo Gleiser

Who has no regrets about things done in the past? Wouldn't it be nice if, somehow, we could go back to tweak a couple of bad decisions?
This sounds (and as we will see, is, to a certain extent) like science fiction.
The laws of physics prohibit traveling backwards in time for many reasons. If we did travel backwards in time and changed the course of events, we would be altering the course of history. An example often cited is the grandfather's paradox: If you traveled back in time and killed your grandfather when he was still a high school student, he wouldn't have met your grandmother and your father and you wouldn't exist.
A popular example of traveling back in time is the fascinating Canadian TV series Travelers : In a distant future, the Earth is in shambles; humans are controlled by a benevolent artificial intelligence that finds a way to project the consciousness of people into unaware hosts in the 21st century. The idea is that travelers from the future take over the minds of people in the 21st century right before they are about to die. There is some obscure talk about quantum entanglement of consciousness between traveler and host, but this is secondary. The point of the show is that the travelers go back to try to change the course of history — so that the future looks better.
Putting humans or consciousness traveling back in time aside for the moment, is there anything in science even remotely similar? Surprisingly, yes. At the level of quantum particles (we are talking individual photons, elementary particles or individual atoms), there is something called Wheeler's delayed-choice experiments that show that actions in the present can influence the past.
The experiments use something called the wave-particle duality of light and of matter, the fact that the physical nature of quantum objects is undetermined until it is measured. In other words, this means that a particle of light, or of matter, can behave either as a wave (spreading out in space, showing interference) or as a particle (staying together as a small bundle) depending on the measuring apparatus. Long and ongoing discussions about the nature of quantum physics are still trying to work out what this actually means. Do our minds determine the nature of physical reality? The interested reader can see what I wrote about this in more detail in The Island of Knowledge: The Limits of Science and the Search for Meaning .
But experiments measure — they don't ask questions of meaning. John Wheeler , the physicist who proposed such experiments in the 1970s, would have been amazed if he had seen the current results. It does seem that the present can influence the past, at least at the level of quantum objects.
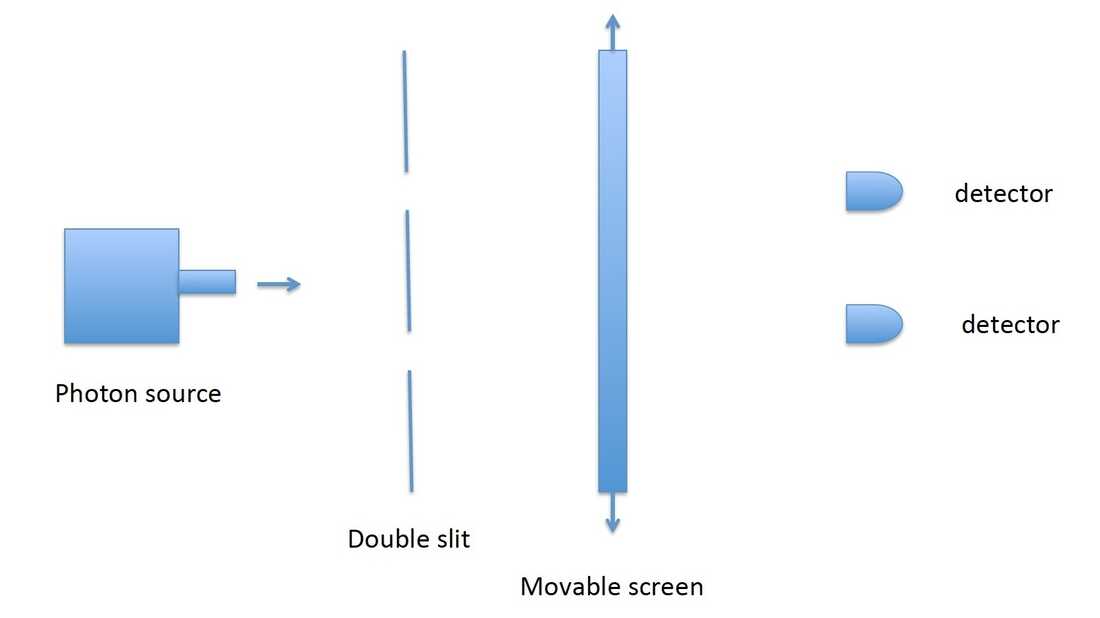
In the double-slit experiment, imagine that the setup — having or not having the screen — is decided after the photon goes through the slits. That is what the arrows in the diagram represent, the possibility that the screen is there — or is not. Courtesy of Marcelo Gleiser hide caption
In the double-slit experiment, imagine that the setup — having or not having the screen — is decided after the photon goes through the slits. That is what the arrows in the diagram represent, the possibility that the screen is there — or is not.
The picture to the right explains the story. Imagine that there is a source of photons (or other small quantum particle). The photons can pass through a double slit. Behind the double slit, there is a screen. If the photons hit the screen, those conducting the experiment observe an interference pattern of bright and dark fringes, typical of waves. If the screen is not there, and there are photon counters aligned with the slits, the photons will hit either one or the other, behaving like little bullets (or particles). So far, this is the typical setup for a double-slit experiment.
The "mystery which cannot go away" (as physicist Richard Feynman famously remarked) of the double-slit experiment, is that the person performing the experiment determines the physical nature of the particle — i.e., whether it is a wave or a particle. And, with Wheeler, the mystery deepens.
Imagine that the setup — having or not having the screen — is decided after the photon goes through the slits. That is what the arrows in the diagram represent, the possibility that the screen is there — or is not. In 2007, a group in France did exactly that , letting a single photon pass through a double slit and then, after it passed through, having a random number generator choose whether the screen would be there or not to detect it. As Wheeler wrote, "Thus one decides the photon shall have come by one route or by both routes after it has already done its travel." Since then, many other groups (for example, here ) have performed refined versions of the experiment, confirming Wheeler's intuition.
An important detail is that the switching over of detecting apparatus must be faster than the time the photon has to travel to the detectors. This way, there is no way the photon could "know" what to do. (If a photon knows anything, anyway.) Experiments presented in October extended the range of the photon's trip to about 2,200 miles, and still the photon seems to always choose the path consistent with the delayed choice. It is as if — Mike McRae wrote in this Science Alert piece — "that even after the horse has bolted 2,200 miles out of the gate, it can still wait until the finish line to decide which race it ran." That is, which path to the finish line it took.
Of course, photons are not people, and to sustain a quantum superposition is very difficult, especially as the size of the object increases. Still, there is something quite amazing and mysterious about this behavior, where the path in space taken by an object seems to be impervious to time; it is as if the two choices (particle or wave; one slit or two) are suspended in time and are only enacted once the spatial arrangement is decided upon. No wonder Wheeler liked to called such ideas as being indicative of a "participatory universe," that is, of a universe where our minds are somehow deeply connected with the very fabric of space and time. After all, the choices of the apparatus may be made by a random number generator, but the apparatus and the interpretation of the data require our intent and design.
Food for thought for the future. Or maybe the past?
Unfortunately, these experiments say very little about how we could interfere with the past in events relevant to the human scale. Better to think carefully about decisions than to try to fix them backwards.
Marcelo Gleiser is a theoretical physicist and writer — and a professor of natural philosophy, physics and astronomy at Dartmouth College. He is the director of the Institute for Cross-Disciplinary Engagement at Dartmouth, co-founder of 13.7 and an active promoter of science to the general public. His latest book is The Simple Beauty of the Unexpected: A Natural Philosopher's Quest for Trout and the Meaning of Everything . You can keep up with Marcelo on Facebook and Twitter: @mgleiser
- quantum particles
- delayed choice
- time travel
Advertisement
How Time Travel Works
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
Time Travel Into the Past

We've established that time travel into the future happens all the time. Scientists have proven it in experiments, and the idea is a fundamental aspect of Einstein's theory of relativity . You'll make it to the future; it's just a question of how fast the trip will be. But what about travel into the past? A glance into the night sky should supply an answer.
The Milky Way galaxy is roughly 100,000 light-years wide, so light from its more distant stars can take thousands upon thousands of years to reach Earth. Glimpse that light, and you're essentially looking back in time. When astronomers measure the cosmic microwave background radiation, they stare back more than 10 billion years into a primordial cosmic age. But can we do better than this?
There's nothing in Einstein's theory that precludes time travel into the past, but the very premise of pushing a button and going back to yesterday violates the law of causality , or cause and effect. One event happens in our universe, and it leads to yet another in an endless one-way string of events. In every instance, the cause occurs before the effect. Just try to imagine a different reality, say, in which a murder victim dies of his or her gunshot wound before being shot. It violates reality as we know it; thus, many scientists dismiss time travel into the past as an impossibility.
Some scientists like Einstein's theory of special relativity, have proposed the idea of using faster-than-light travel to journey back in time. After all, if time slows as an object approaches the speed of light , then might exceeding that speed cause time to flow backward? Of course, as an object nears the speed of light, its relativistic mass increases until, at the speed of light, it becomes infinite. Accelerating an infinite mass any faster than that is impossible. Warp speed technology could theoretically cheat the universal speed limit by propelling a bubble of space-time across the universe, but even this would come with colossal, far-future energy costs.
But what if time travel into the past and future depends less on speculative space propulsion technology and more on existing cosmic phenomena? Set a course for the black hole.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
September 2, 2014
Time Travel Simulation Resolves “Grandfather Paradox”
What would happen to you if you went back in time and killed your grandfather? A model using photons reveals that quantum mechanics can solve the quandary—and even foil quantum cryptography
By Lee Billings
On June 28, 2009, the world-famous physicist Stephen Hawking threw a party at the University of Cambridge, complete with balloons, hors d'oeuvres and iced champagne. Everyone was invited but no one showed up. Hawking had expected as much, because he only sent out invitations after his party had concluded. It was, he said, "a welcome reception for future time travelers," a tongue-in-cheek experiment to reinforce his 1992 conjecture that travel into the past is effectively impossible.
But Hawking may be on the wrong side of history. Recent experiments offer tentative support for time travel's feasibility—at least from a mathematical perspective. The study cuts to the core of our understanding of the universe, and the resolution of the possibility of time travel, far from being a topic worthy only of science fiction, would have profound implications for fundamental physics as well as for practical applications such as quantum cryptography and computing.
Closed timelike curves The source of time travel speculation lies in the fact that our best physical theories seem to contain no prohibitions on traveling backward through time. The feat should be possible based on Einstein's theory of general relativity, which describes gravity as the warping of spacetime by energy and matter. An extremely powerful gravitational field, such as that produced by a spinning black hole, could in principle profoundly warp the fabric of existence so that spacetime bends back on itself. This would create a "closed timelike curve," or CTC, a loop that could be traversed to travel back in time.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Hawking and many other physicists find CTCs abhorrent, because any macroscopic object traveling through one would inevitably create paradoxes where cause and effect break down. In a model proposed by the theorist David Deutsch in 1991, however, the paradoxes created by CTCs could be avoided at the quantum scale because of the behavior of fundamental particles, which follow only the fuzzy rules of probability rather than strict determinism. "It's intriguing that you've got general relativity predicting these paradoxes, but then you consider them in quantum mechanical terms and the paradoxes go away," says University of Queensland physicist Tim Ralph. "It makes you wonder whether this is important in terms of formulating a theory that unifies general relativity with quantum mechanics."
Experimenting with a curve Recently Ralph and his PhD student Martin Ringbauer led a team that experimentally simulated Deutsch's model of CTCs for the very first time, testing and confirming many aspects of the two-decades-old theory. Their findings are published in Nature Communications. Much of their simulation revolved around investigating how Deutsch's model deals with the “grandfather paradox,” a hypothetical scenario in which someone uses a CTC to travel back through time to murder her own grandfather, thus preventing her own later birth. ( Scientific American is part of Nature Publishing Group.)
Deutsch's quantum solution to the grandfather paradox works something like this:
Instead of a human being traversing a CTC to kill her ancestor, imagine that a fundamental particle goes back in time to flip a switch on the particle-generating machine that created it. If the particle flips the switch, the machine emits a particle— the particle—back into the CTC; if the switch isn't flipped, the machine emits nothing. In this scenario there is no a priori deterministic certainty to the particle's emission, only a distribution of probabilities. Deutsch's insight was to postulate self-consistency in the quantum realm, to insist that any particle entering one end of a CTC must emerge at the other end with identical properties. Therefore, a particle emitted by the machine with a probability of one half would enter the CTC and come out the other end to flip the switch with a probability of one half, imbuing itself at birth with a probability of one half of going back to flip the switch. If the particle were a person, she would be born with a one-half probability of killing her grandfather, giving her grandfather a one-half probability of escaping death at her hands—good enough in probabilistic terms to close the causative loop and escape the paradox. Strange though it may be, this solution is in keeping with the known laws of quantum mechanics.
In their new simulation Ralph, Ringbauer and their colleagues studied Deutsch's model using interactions between pairs of polarized photons within a quantum system that they argue is mathematically equivalent to a single photon traversing a CTC. "We encode their polarization so that the second one acts as kind of a past incarnation of the first,” Ringbauer says. So instead of sending a person through a time loop, they created a stunt double of the person and ran him through a time-loop simulator to see if the doppelganger emerging from a CTC exactly resembled the original person as he was in that moment in the past.
By measuring the polarization states of the second photon after its interaction with the first, across multiple trials the team successfully demonstrated Deutsch's self-consistency in action. "The state we got at our output, the second photon at the simulated exit of the CTC, was the same as that of our input, the first encoded photon at the CTC entrance," Ralph says. "Of course, we're not really sending anything back in time but [the simulation] allows us to study weird evolutions normally not allowed in quantum mechanics."
Those "weird evolutions" enabled by a CTC, Ringbauer notes, would have remarkable practical applications, such as breaking quantum-based cryptography through the cloning of the quantum states of fundamental particles. "If you can clone quantum states,” he says, “you can violate the Heisenberg uncertainty principle,” which comes in handy in quantum cryptography because the principle forbids simultaneously accurate measurements of certain kinds of paired variables, such as position and momentum. "But if you clone that system, you can measure one quantity in the first and the other quantity in the second, allowing you to decrypt an encoded message."
"In the presence of CTCs, quantum mechanics allows one to perform very powerful information-processing tasks, much more than we believe classical or even normal quantum computers could do," says Todd Brun, a physicist at the University of Southern California who was not involved with the team's experiment. "If the Deutsch model is correct, then this experiment faithfully simulates what could be done with an actual CTC. But this experiment cannot test the Deutsch model itself; that could only be done with access to an actual CTC."
Alternative reasoning Deutsch's model isn’t the only one around, however. In 2009 Seth Lloyd, a theorist at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, proposed an alternative , less radical model of CTCs that resolves the grandfather paradox using quantum teleportation and a technique called post-selection, rather than Deutsch's quantum self-consistency. With Canadian collaborators, Lloyd went on to perform successful laboratory simulations of his model in 2011. "Deutsch's theory has a weird effect of destroying correlations," Lloyd says. "That is, a time traveler who emerges from a Deutschian CTC enters a universe that has nothing to do with the one she exited in the future. By contrast, post-selected CTCs preserve correlations, so that the time traveler returns to the same universe that she remembers in the past."
This property of Lloyd's model would make CTCs much less powerful for information processing, although still far superior to what computers could achieve in typical regions of spacetime. "The classes of problems our CTCs could help solve are roughly equivalent to finding needles in haystacks," Lloyd says. "But a computer in a Deutschian CTC could solve why haystacks exist in the first place.”
Lloyd, though, readily admits the speculative nature of CTCs. “I have no idea which model is really right. Probably both of them are wrong,” he says. Of course, he adds, the other possibility is that Hawking is correct, “that CTCs simply don't and cannot exist." Time-travel party planners should save the champagne for themselves—their hoped-for future guests seem unlikely to arrive.
The Quantum Physics of Time Travel (All-Access Subscribers Only) By David Deutsch and Michael Lockwood
Can Quantum Bayesianism Fix the Paradoxes of Quantum Mechanics?
Astrophysicist J. Richard Gott on Time Travel

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Time Travel and Modern Physics
Time travel has been a staple of science fiction. With the advent of general relativity it has been entertained by serious physicists. But, especially in the philosophy literature, there have been arguments that time travel is inherently paradoxical. The most famous paradox is the grandfather paradox: you travel back in time and kill your grandfather, thereby preventing your own existence. To avoid inconsistency some circumstance will have to occur which makes you fail in this attempt to kill your grandfather. Doesn’t this require some implausible constraint on otherwise unrelated circumstances? We examine such worries in the context of modern physics.
1. Paradoxes Lost?
2. topology and constraints, 3. the general possibility of time travel in general relativity, 4. two toy models, 5. slightly more realistic models of time travel, 6. the possibility of time travel redux, 7. even if there are constraints, so what, 8. computational models, 9. quantum mechanics to the rescue, 10. conclusions, other internet resources, related entries.
- Supplement: Remarks and Limitations on the Toy Models
Modern physics strips away many aspects of the manifest image of time. Time as it appears in the equations of classical mechanics has no need for a distinguished present moment, for example. Relativity theory leads to even sharper contrasts. It replaces absolute simultaneity, according to which it is possible to unambiguously determine the time order of distant events, with relative simultaneity: extending an “instant of time” throughout space is not unique, but depends on the state of motion of an observer. More dramatically, in general relativity the mathematical properties of time (or better, of spacetime)—its topology and geometry—depend upon how matter is arranged rather than being fixed once and for all. So physics can be, and indeed has to be, formulated without treating time as a universal, fixed background structure. Since general relativity represents gravity through spacetime geometry, the allowed geometries must be as varied as the ways in which matter can be arranged. Alongside geometrical models used to describe the solar system, black holes, and much else, the scope of variation extends to include some exotic structures unlike anything astrophysicists have observed. In particular, there are spacetime geometries with curves that loop back on themselves: closed timelike curves (CTCs), which describe the possible trajectory of an observer who returns exactly back to their earlier state—without any funny business, such as going faster than the speed of light. These geometries satisfy the relevant physical laws, the equations of general relativity, and in that sense time travel is physically possible.
Yet circular time generates paradoxes, familiar from science fiction stories featuring time travel: [ 1 ]
- Consistency: Kurt plans to murder his own grandfather Adolph, by traveling along a CTC to an appropriate moment in the past. He is an able marksman, and waits until he has a clear shot at grandpa. Normally he would not miss. Yet if he succeeds, there is no way that he will then exist to plan and carry out the mission. Kurt pulls the trigger: what can happen?
- Underdetermination: Suppose that Kurt first travels back in order to give his earlier self a copy of How to Build a Time Machine. This is the same book that allows him to build a time machine, which he then carries with him on his journey to the past. Who wrote the book?
- Easy Knowledge: A fan of classical music enhances their computer with a circuit that exploits a CTC. This machine efficiently solves problems at a higher level of computational complexity than conventional computers, leading (among other things) to finding the smallest circuits that can generate Bach’s oeuvre—and to compose new pieces in the same style. Such easy knowledge is at odds with our understanding of our epistemic predicament. (This third paradox has not drawn as much attention.)
The first two paradoxes were once routinely taken to show that solutions with CTCs should be rejected—with charges varying from violating logic, to being “physically unreasonable”, to undermining the notion of free will. Closer analysis of the paradoxes has largely reversed this consensus. Physicists have discovered many solutions with CTCs and have explored their properties in pursuing foundational questions, such as whether physics is compatible with the idea of objective temporal passage (starting with Gödel 1949). Philosophers have also used time travel scenarios to probe questions about, among other things, causation, modality, free will, and identity (see, e.g., Earman 1972 and Lewis’s seminal 1976 paper).
We begin below with Consistency , turning to the other paradoxes in later sections. A standard, stone-walling response is to insist that the past cannot be changed, as a matter of logic, even by a time traveler (e.g., Gödel 1949, Clarke 1977, Horwich 1987). Adolph cannot both die and survive, as a matter of logic, so any scheme to alter the past must fail. In many of the best time travel fictions, the actions of a time traveler are constrained in novel and unexpected ways. Attempts to change the past fail, and they fail, often tragically, in just such a way that they set the stage for the time traveler’s self-defeating journey. The first question is whether there is an analog of the consistent story when it comes to physics in the presence of CTCs. As we will see, there is a remarkable general argument establishing the existence of consistent solutions. Yet a second question persists: why can’t time-traveling Kurt kill his own grandfather? Doesn’t the necessity of failures to change the past put unusual and unexpected constraints on time travelers, or objects that move along CTCs? The same argument shows that there are in fact no constraints imposed by the existence of CTCs, in some cases. After discussing this line of argument, we will turn to the palatability and further implications of such constraints if they are required, and then turn to the implications of quantum mechanics.
Wheeler and Feynman (1949) were the first to claim that the fact that nature is continuous could be used to argue that causal influences from later events to earlier events, as are made possible by time travel, will not lead to paradox without the need for any constraints. Maudlin (1990) showed how to make their argument precise and more general, and argued that nonetheless it was not completely general.
Imagine the following set-up. We start off having a camera with a black and white film ready to take a picture of whatever comes out of the time machine. An object, in fact a developed film, comes out of the time machine. We photograph it, and develop the film. The developed film is subsequently put in the time machine, and set to come out of the time machine at the time the picture is taken. This surely will create a paradox: the developed film will have the opposite distribution of black, white, and shades of gray, from the object that comes out of the time machine. For developed black and white films (i.e., negatives) have the opposite shades of gray from the objects they are pictures of. But since the object that comes out of the time machine is the developed film itself it we surely have a paradox.
However, it does not take much thought to realize that there is no paradox here. What will happen is that a uniformly gray picture will emerge, which produces a developed film that has exactly the same uniform shade of gray. No matter what the sensitivity of the film is, as long as the dependence of the brightness of the developed film depends in a continuous manner on the brightness of the object being photographed, there will be a shade of gray that, when photographed, will produce exactly the same shade of gray on the developed film. This is the essence of Wheeler and Feynman’s idea. Let us first be a bit more precise and then a bit more general.
For simplicity let us suppose that the film is always a uniform shade of gray (i.e., at any time the shade of gray does not vary by location on the film). The possible shades of gray of the film can then be represented by the (real) numbers from 0, representing pure black, to 1, representing pure white.
Let us now distinguish various stages in the chronological order of the life of the film. In stage \(S_1\) the film is young; it has just been placed in the camera and is ready to be exposed. It is then exposed to the object that comes out of the time machine. (That object in fact is a later stage of the film itself). By the time we come to stage \(S_2\) of the life of the film, it has been developed and is about to enter the time machine. Stage \(S_3\) occurs just after it exits the time machine and just before it is photographed. Stage \(S_4\) occurs after it has been photographed and before it starts fading away. Let us assume that the film starts out in stage \(S_1\) in some uniform shade of gray, and that the only significant change in the shade of gray of the film occurs between stages \(S_1\) and \(S_2\). During that period it acquires a shade of gray that depends on the shade of gray of the object that was photographed. In other words, the shade of gray that the film acquires at stage \(S_2\) depends on the shade of gray it has at stage \(S_3\). The influence of the shade of gray of the film at stage \(S_3\), on the shade of gray of the film at stage \(S_2\), can be represented as a mapping, or function, from the real numbers between 0 and 1 (inclusive), to the real numbers between 0 and 1 (inclusive). Let us suppose that the process of photography is such that if one imagines varying the shade of gray of an object in a smooth, continuous manner then the shade of gray of the developed picture of that object will also vary in a smooth, continuous manner. This implies that the function in question will be a continuous function. Now any continuous function from the real numbers between 0 and 1 (inclusive) to the real numbers between 0 and 1 (inclusive) must map at least one number to itself. One can quickly convince oneself of this by graphing such functions. For one will quickly see that any continuous function \(f\) from \([0,1]\) to \([0,1]\) must intersect the line \(x=y\) somewhere, and thus there must be at least one point \(x\) such that \(f(x)=x\). Such points are called fixed points of the function. Now let us think about what such a fixed point represents. It represents a shade of gray such that, when photographed, it will produce a developed film with exactly that same shade of gray. The existence of such a fixed point implies a solution to the apparent paradox.
Let us now be more general and allow color photography. One can represent each possible color of an object (of uniform color) by the proportions of blue, green and red that make up that color. (This is why television screens can produce all possible colors.) Thus one can represent all possible colors of an object by three points on three orthogonal lines \(x, y\) and \(z\), that is to say, by a point in a three-dimensional cube. This cube is also known as the “Cartesian product” of the three line segments. Now, one can also show that any continuous map from such a cube to itself must have at least one fixed point. So color photography can not be used to create time travel paradoxes either!
Even more generally, consider some system \(P\) which, as in the above example, has the following life. It starts in some state \(S_1\), it interacts with an object that comes out of a time machine (which happens to be its older self), it travels back in time, it interacts with some object (which happens to be its younger self), and finally it grows old and dies. Let us assume that the set of possible states of \(P\) can be represented by a Cartesian product of \(n\) closed intervals of the reals, i.e., let us assume that the topology of the state-space of \(P\) is isomorphic to a finite Cartesian product of closed intervals of the reals. Let us further assume that the development of \(P\) in time, and the dependence of that development on the state of objects that it interacts with, is continuous. Then, by a well-known fixed point theorem in topology (see, e.g., Hocking & Young 1961: 273), no matter what the nature of the interaction is, and no matter what the initial state of the object is, there will be at least one state \(S_3\) of the older system (as it emerges from the time travel machine) that will influence the initial state \(S_1\) of the younger system (when it encounters the older system) so that, as the younger system becomes older, it develops exactly into state \(S_3\). Thus without imposing any constraints on the initial state \(S_1\) of the system \(P\), we have shown that there will always be perfectly ordinary, non-paradoxical, solutions, in which everything that happens, happens according to the usual laws of development. Of course, there is looped causation, hence presumably also looped explanation, but what do you expect if there is looped time?
Unfortunately, for the fan of time travel, a little reflection suggests that there are systems for which the needed fixed point theorem does not hold. Imagine, for instance, that we have a dial that can only rotate in a plane. We are going to put the dial in the time machine. Indeed we have decided that if we see the later stage of the dial come out of the time machine set at angle \(x\), then we will set the dial to \(x+90\), and throw it into the time machine. Now it seems we have a paradox, since the mapping that consists of a rotation of all points in a circular state-space by 90 degrees does not have a fixed point. And why wouldn’t some state-spaces have the topology of a circle?
However, we have so far not used another continuity assumption which is also a reasonable assumption. So far we have only made the following demand: the state the dial is in at stage \(S_2\) must be a continuous function of the state of the dial at stage \(S_3\). But, the state of the dial at stage \(S_2\) is arrived at by taking the state of the dial at stage \(S_1\), and rotating it over some angle. It is not merely the case that the effect of the interaction, namely the state of the dial at stage \(S_2\), should be a continuous function of the cause, namely the state of the dial at stage \(S_3\). It is additionally the case that path taken to get there, the way the dial is rotated between stages \(S_1\) and \(S_2\) must be a continuous function of the state at stage \(S_3\). And, rather surprisingly, it turns out that this can not be done. Let us illustrate what the problem is before going to a more general demonstration that there must be a fixed point solution in the dial case.
Forget time travel for the moment. Suppose that you and I each have a watch with a single dial neither of which is running. My watch is set at 12. You are going to announce what your watch is set at. My task is going to be to adjust my watch to yours no matter what announcement you make. And my actions should have a continuous (single valued) dependence on the time that you announce. Surprisingly, this is not possible! For instance, suppose that if you announce “12”, then I achieve that setting on my watch by doing nothing. Now imagine slowly and continuously increasing the announced times, starting at 12. By continuity, I must achieve each of those settings by rotating my dial to the right. If at some point I switch and achieve the announced goal by a rotation of my dial to the left, I will have introduced a discontinuity in my actions, a discontinuity in the actions that I take as a function of the announced angle. So I will be forced, by continuity, to achieve every announcement by rotating the dial to the right. But, this rotation to the right will have to be abruptly discontinued as the announcements grow larger and I eventually approach 12 again, since I achieved 12 by not rotating the dial at all. So, there will be a discontinuity at 12 at the latest. In general, continuity of my actions as a function of announced times can not be maintained throughout if I am to be able to replicate all possible settings. Another way to see the problem is that one can similarly reason that, as one starts with 12, and imagines continuously making the announced times earlier, one will be forced, by continuity, to achieve the announced times by rotating the dial to the left. But the conclusions drawn from the assumption of continuous increases and the assumption of continuous decreases are inconsistent. So we have an inconsistency following from the assumption of continuity and the assumption that I always manage to set my watch to your watch. So, a dial developing according to a continuous dynamics from a given initial state, can not be set up so as to react to a second dial, with which it interacts, in such a way that it is guaranteed to always end up set at the same angle as the second dial. Similarly, it can not be set up so that it is guaranteed to always end up set at 90 degrees to the setting of the second dial. All of this has nothing to do with time travel. However, the impossibility of such set ups is what prevents us from enacting the rotation by 90 degrees that would create paradox in the time travel setting.
Let us now give the positive result that with such dials there will always be fixed point solutions, as long as the dynamics is continuous. Let us call the state of the dial before it interacts with its older self the initial state of the dial. And let us call the state of the dial after it emerges from the time machine the final state of the dial. There is also an intermediate state of the dial, after it interacts with its older self and before it is put into the time machine. We can represent the initial or intermediate states of the dial, before it goes into the time machine, as an angle \(x\) in the horizontal plane and the final state of the dial, after it comes out of the time machine, as an angle \(y\) in the vertical plane. All possible \(\langle x,y\rangle\) pairs can thus be visualized as a torus with each \(x\) value picking out a vertical circular cross-section and each \(y\) picking out a point on that cross-section. See figure 1 .
Figure 1 [An extended description of figure 1 is in the supplement.]
Suppose that the dial starts at angle \(i\) which picks out vertical circle \(I\) on the torus. The initial angle \(i\) that the dial is at before it encounters its older self, and the set of all possible final angles that the dial can have when it emerges from the time machine is represented by the circle \(I\) on the torus (see figure 1 ). Given any possible angle of the emerging dial, the dial initially at angle \(i\) will develop to some other angle. One can picture this development by rotating each point on \(I\) in the horizontal direction by the relevant amount. Since the rotation has to depend continuously on the angle of the emerging dial, circle \(I\) during this development will deform into some loop \(L\) on the torus. Loop \(L\) thus represents all possible intermediate angles \(x\) that the dial is at when it is thrown into the time machine, given that it started at angle \(i\) and then encountered a dial (its older self) which was at angle \(y\) when it emerged from the time machine. We therefore have consistency if \(x=y\) for some \(x\) and \(y\) on loop \(L\). Now, let loop \(C\) be the loop which consists of all the points on the torus for which \(x=y\). Ring \(I\) intersects \(C\) at point \(\langle i,i\rangle\). Obviously any continuous deformation of \(I\) must still intersect \(C\) somewhere. So \(L\) must intersect \(C\) somewhere, say at \(\langle j,j\rangle\). But that means that no matter how the development of the dial starting at \(I\) depends on the angle of the emerging dial, there will be some angle for the emerging dial such that the dial will develop exactly into that angle (by the time it enters the time machine) under the influence of that emerging dial. This is so no matter what angle one starts with, and no matter how the development depends on the angle of the emerging dial. Thus even for a circular state-space there are no constraints needed other than continuity.
Unfortunately there are state-spaces that escape even this argument. Consider for instance a pointer that can be set to all values between 0 and 1, where 0 and 1 are not possible values. That is, suppose that we have a state-space that is isomorphic to an open set of real numbers. Now suppose that we have a machine that sets the pointer to half the value that the pointer is set at when it emerges from the time machine.
Figure 2 [An extended description of figure 2 is in the supplement.]
Suppose the pointer starts at value \(I\). As before we can represent the combination of this initial position and all possible final positions by the line \(I\). Under the influence of the pointer coming out of the time machine the pointer value will develop to a value that equals half the value of the final value that it encountered. We can represent this development as the continuous deformation of line \(I\) into line \(L\), which is indicated by the arrows in figure 2 . This development is fully continuous. Points \(\langle x,y\rangle\) on line \(I\) represent the initial position \(x=I\) of the (young) pointer, and the position \(y\) of the older pointer as it emerges from the time machine. Points \(\langle x,y\rangle\) on line \(L\) represent the position \(x\) that the younger pointer should develop into, given that it encountered the older pointer emerging from the time machine set at position \(y\). Since the pointer is designed to develop to half the value of the pointer that it encounters, the line \(L\) corresponds to \(x=1/2 y\). We have consistency if there is some point such that it develops into that point, if it encounters that point. Thus, we have consistency if there is some point \(\langle x,y\rangle\) on line \(L\) such that \(x=y\). However, there is no such point: lines \(L\) and \(C\) do not intersect. Thus there is no consistent solution, despite the fact that the dynamics is fully continuous.
Of course if 0 were a possible value, \(L\) and \(C\) would intersect at 0. This is surprising and strange: adding one point to the set of possible values of a quantity here makes the difference between paradox and peace. One might be tempted to just add the extra point to the state-space in order to avoid problems. After all, one might say, surely no measurements could ever tell us whether the set of possible values includes that exact point or not. Unfortunately there can be good theoretical reasons for supposing that some quantity has a state-space that is open: the set of all possible speeds of massive objects in special relativity surely is an open set, since it includes all speeds up to, but not including, the speed of light. Quantities that have possible values that are not bounded also lead to counter examples to the presented fixed point argument. And it is not obvious to us why one should exclude such possibilities. So the argument that no constraints are needed is not fully general.
An interesting question of course is: exactly for which state-spaces must there be such fixed points? The arguments above depend on a well-known fixed point theorem (due to Schauder) that guarantees the existence of a fixed point for compact, convex state spaces. We do not know what subsequent extensions of this result imply regarding fixed points for a wider variety of systems, or whether there are other general results along these lines. (See Kutach 2003 for more on this issue.)
A further interesting question is whether this line of argument is sufficient to resolve Consistency (see also Dowe 2007). When they apply, these results establish the existence of a solution, such as the shade of uniform gray in the first example. But physicists routinely demand more than merely the existence of a solution, namely that solutions to the equations are stable—such that “small” changes of the initial state lead to “small” changes of the resulting trajectory. (Clarifying the two senses of “small” in this statement requires further work, specifying the relevant topology.) Stability in this sense underwrites the possibility of applying equations to real systems given our inability to fix initial states with indefinite precision. (See Fletcher 2020 for further discussion.) The fixed point theorems guarantee that for an initial state \(S_1\) there is a solution, but this solution may not be “close” to the solution for a nearby initial state, \(S'\). We are not aware of any proofs that the solutions guaranteed to exist by the fixed point theorems are also stable in this sense.
Time travel has recently been discussed quite extensively in the context of general relativity. General relativity places few constraints on the global structure of space and time. This flexibility leads to a possibility first described in print by Hermann Weyl:
Every world-point is the origin of the double-cone of the active future and the passive past [i.e., the two lobes of the light cone]. Whereas in the special theory of relativity these two portions are separated by an intervening region, it is certainly possible in the present case [i.e., general relativity] for the cone of the active future to overlap with that of the passive past; so that, in principle, it is possible to experience events now that will in part be an effect of my future resolves and actions. Moreover, it is not impossible for a world-line (in particular, that of my body), although it has a timelike direction at every point, to return to the neighborhood of a point which it has already once passed through. (Weyl 1918/1920 [1952: 274])
A time-like curve is simply a space-time trajectory such that the speed of light is never equaled or exceeded along this trajectory. Time-like curves represent possible trajectories of ordinary objects. In general relativity a curve that is everywhere timelike locally can nonetheless loop back on itself, forming a CTC. Weyl makes the point vividly in terms of the light cones: along such a curve, the future lobe of the light cone (the “active future”) intersects the past lobe of the light cone (the “passive past”). Traveling along such a curve one would never exceed the speed of light, and yet after a certain amount of (proper) time one would return to a point in space-time that one previously visited. Or, by staying close to such a CTC, one could come arbitrarily close to a point in space-time that one previously visited. General relativity, in a straightforward sense, allows time travel: there appear to be many space-times compatible with the fundamental equations of general relativity in which there are CTC’s. Space-time, for instance, could have a Minkowski metric everywhere, and yet have CTC’s everywhere by having the temporal dimension (topologically) rolled up as a circle. Or, one can have wormhole connections between different parts of space-time which allow one to enter “mouth \(A\)” of such a wormhole connection, travel through the wormhole, exit the wormhole at “mouth \(B\)” and re-enter “mouth \(A\)” again. CTCs can even arise when the spacetime is topologically \(\mathbb{R}^4\), due to the “tilting” of light cones produced by rotating matter (as in Gödel 1949’s spacetime).
General relativity thus appears to provide ample opportunity for time travel. Note that just because there are CTC’s in a space-time, this does not mean that one can get from any point in the space-time to any other point by following some future directed timelike curve—there may be insurmountable practical obstacles. In Gödel’s spacetime, it is the case that there are CTCs passing through every point in the spacetime. Yet these CTCs are not geodesics, so traversing them requires acceleration. Calculations of the minimal fuel required to travel along the appropriate curve should discourage any would-be time travelers (Malament 1984, 1985; Manchak 2011). But more generally CTCs may be confined to smaller regions; some parts of space-time can have CTC’s while other parts do not. Let us call the part of a space-time that has CTC’s the “time travel region” of that space-time, while calling the rest of that space-time the “normal region”. More precisely, the “time travel region” consists of all the space-time points \(p\) such that there exists a (non-zero length) timelike curve that starts at \(p\) and returns to \(p\). Now let us turn to examining space-times with CTC’s a bit more closely for potential problems.
In order to get a feeling for the sorts of implications that closed timelike curves can have, it may be useful to consider two simple models. In space-times with closed timelike curves the traditional initial value problem cannot be framed in the usual way. For it presupposes the existence of Cauchy surfaces, and if there are CTCs then no Cauchy surface exists. (A Cauchy surface is a spacelike surface such that every inextendable timelike curve crosses it exactly once. One normally specifies initial conditions by giving the conditions on such a surface.) Nonetheless, if the topological complexities of the manifold are appropriately localized, we can come quite close. Let us call an edgeless spacelike surface \(S\) a quasi-Cauchy surface if it divides the rest of the manifold into two parts such that
- every point in the manifold can be connected by a timelike curve to \(S\), and
- any timelike curve which connects a point in one region to a point in the other region intersects \(S\) exactly once.
It is obvious that a quasi-Cauchy surface must entirely inhabit the normal region of the space-time; if any point \(p\) of \(S\) is in the time travel region, then any timelike curve which intersects \(p\) can be extended to a timelike curve which intersects \(S\) near \(p\) again. In extreme cases of time travel, a model may have no normal region at all (e.g., Minkowski space-time rolled up like a cylinder in a time-like direction), in which case our usual notions of temporal precedence will not apply. But temporal anomalies like wormholes (and time machines) can be sufficiently localized to permit the existence of quasi-Cauchy surfaces.
Given a timelike orientation, a quasi-Cauchy surface unproblematically divides the manifold into its past (i.e., all points that can be reached by past-directed timelike curves from \(S)\) and its future (ditto mutatis mutandis ). If the whole past of \(S\) is in the normal region of the manifold, then \(S\) is a partial Cauchy surface : every inextendable timelike curve which exists to the past of \(S\) intersects \(S\) exactly once, but (if there is time travel in the future) not every inextendable timelike curve which exists to the future of \(S\) intersects \(S\). Now we can ask a particularly clear question: consider a manifold which contains a time travel region, but also has a partial Cauchy surface \(S\), such that all of the temporal funny business is to the future of \(S\). If all you could see were \(S\) and its past, you would not know that the space-time had any time travel at all. The question is: are there any constraints on the sort of data which can be put on \(S\) and continued to a global solution of the dynamics which are different from the constraints (if any) on the data which can be put on a Cauchy surface in a simply connected manifold and continued to a global solution? If there is time travel to our future, might we we able to tell this now, because of some implied oddity in the arrangement of present things?
It is not at all surprising that there might be constraints on the data which can be put on a locally space-like surface which passes through the time travel region: after all, we never think we can freely specify what happens on a space-like surface and on another such surface to its future, but in this case the surface at issue lies to its own future. But if there were particular constraints for data on a partial Cauchy surface then we would apparently need to have to rule out some sorts of otherwise acceptable states on \(S\) if there is to be time travel to the future of \(S\). We then might be able to establish that there will be no time travel in the future by simple inspection of the present state of the universe. As we will see, there is reason to suspect that such constraints on the partial Cauchy surface are non-generic. But we are getting ahead of ourselves: first let’s consider the effect of time travel on a very simple dynamics.
The simplest possible example is the Newtonian theory of perfectly elastic collisions among equally massive particles in one spatial dimension. The space-time is two-dimensional, so we can represent it initially as the Euclidean plane, and the dynamics is completely specified by two conditions. When particles are traveling freely, their world lines are straight lines in the space-time, and when two particles collide, they exchange momenta, so the collision looks like an “\(X\)” in space-time, with each particle changing its momentum at the impact. [ 2 ] The dynamics is purely local, in that one can check that a set of world-lines constitutes a model of the dynamics by checking that the dynamics is obeyed in every arbitrarily small region. It is also trivial to generate solutions from arbitrary initial data if there are no CTCs: given the initial positions and momenta of a set of particles, one simply draws a straight line from each particle in the appropriate direction and continues it indefinitely. Once all the lines are drawn, the worldline of each particle can be traced from collision to collision. The boundary value problem for this dynamics is obviously well-posed: any set of data at an instant yields a unique global solution, constructed by the method sketched above.
What happens if we change the topology of the space-time by hand to produce CTCs? The simplest way to do this is depicted in figure 3 : we cut and paste the space-time so it is no longer simply connected by identifying the line \(L-\) with the line \(L+\). Particles “going in” to \(L+\) from below “emerge” from \(L-\) , and particles “going in” to \(L-\) from below “emerge” from \(L+\).
Figure 3: Inserting CTCs by Cut and Paste. [An extended description of figure 3 is in the supplement.]
How is the boundary-value problem changed by this alteration in the space-time? Before the cut and paste, we can put arbitrary data on the simultaneity slice \(S\) and continue it to a unique solution. After the change in topology, \(S\) is no longer a Cauchy surface, since a CTC will never intersect it, but it is a partial Cauchy surface. So we can ask two questions. First, can arbitrary data on \(S\) always be continued to a global solution? Second, is that solution unique? If the answer to the first question is \(no\), then we have a backward-temporal constraint: the existence of the region with CTCs places constraints on what can happen on \(S\) even though that region lies completely to the future of \(S\). If the answer to the second question is \(no\), then we have an odd sort of indeterminism, analogous to the unwritten book: the complete physical state on \(S\) does not determine the physical state in the future, even though the local dynamics is perfectly deterministic and even though there is no other past edge to the space-time region in \(S\)’s future (i.e., there is nowhere else for boundary values to come from which could influence the state of the region).
In this case the answer to the first question is yes and to the second is no : there are no constraints on the data which can be put on \(S\), but those data are always consistent with an infinitude of different global solutions. The easy way to see that there always is a solution is to construct the minimal solution in the following way. Start drawing straight lines from \(S\) as required by the initial data. If a line hits \(L-\) from the bottom, just continue it coming out of the top of \(L+\) in the appropriate place, and if a line hits \(L+\) from the bottom, continue it emerging from \(L-\) at the appropriate place. Figure 4 represents the minimal solution for a single particle which enters the time-travel region from the left:
Figure 4: The Minimal Solution. [An extended description of figure 4 is in the supplement.]
The particle “travels back in time” three times. It is obvious that this minimal solution is a global solution, since the particle always travels inertially.
But the same initial state on \(S\) is also consistent with other global solutions. The new requirement imposed by the topology is just that the data going into \(L+\) from the bottom match the data coming out of \(L-\) from the top, and the data going into \(L-\) from the bottom match the data coming out of \(L+\) from the top. So we can add any number of vertical lines connecting \(L-\) and \(L+\) to a solution and still have a solution. For example, adding a few such lines to the minimal solution yields:
Figure 5: A Non-Minimal Solution. [An extended description of figure 5 is in the supplement.]
The particle now collides with itself twice: first before it reaches \(L+\) for the first time, and again shortly before it exits the CTC region. From the particle’s point of view, it is traveling to the right at a constant speed until it hits an older version of itself and comes to rest. It remains at rest until it is hit from the right by a younger version of itself, and then continues moving off, and the same process repeats later. It is clear that this is a global model of the dynamics, and that any number of distinct models could be generating by varying the number and placement of vertical lines.
Knowing the data on \(S\), then, gives us only incomplete information about how things will go for the particle. We know that the particle will enter the CTC region, and will reach \(L+\), we know that it will be the only particle in the universe, we know exactly where and with what speed it will exit the CTC region. But we cannot determine how many collisions the particle will undergo (if any), nor how long (in proper time) it will stay in the CTC region. If the particle were a clock, we could not predict what time it would indicate when exiting the region. Furthermore, the dynamics gives us no handle on what to think of the various possibilities: there are no probabilities assigned to the various distinct possible outcomes.
Changing the topology has changed the mathematics of the situation in two ways, which tend to pull in opposite directions. On the one hand, \(S\) is no longer a Cauchy surface, so it is perhaps not surprising that data on \(S\) do not suffice to fix a unique global solution. But on the other hand, there is an added constraint: data “coming out” of \(L-\) must exactly match data “going in” to \(L+\), even though what comes out of \(L-\) helps to determine what goes into \(L+\). This added consistency constraint tends to cut down on solutions, although in this case the additional constraint is more than outweighed by the freedom to consider various sorts of data on \({L+}/{L-}\).
The fact that the extra freedom outweighs the extra constraint also points up one unexpected way that the supposed paradoxes of time travel may be overcome. Let’s try to set up a paradoxical situation using the little closed time loop above. If we send a single particle into the loop from the left and do nothing else, we know exactly where it will exit the right side of the time travel region. Now suppose we station someone at the other side of the region with the following charge: if the particle should come out on the right side, the person is to do something to prevent the particle from going in on the left in the first place. In fact, this is quite easy to do: if we send a particle in from the right, it seems that it can exit on the left and deflect the incoming left-hand particle.
Carrying on our reflection in this way, we further realize that if the particle comes out on the right, we might as well send it back in order to deflect itself from entering in the first place. So all we really need to do is the following: set up a perfectly reflecting particle mirror on the right-hand side of the time travel region, and launch the particle from the left so that— if nothing interferes with it —it will just barely hit \(L+\). Our paradox is now apparently complete. If, on the one hand, nothing interferes with the particle it will enter the time-travel region on the left, exit on the right, be reflected from the mirror, re-enter from the right, and come out on the left to prevent itself from ever entering. So if it enters, it gets deflected and never enters. On the other hand, if it never enters then nothing goes in on the left, so nothing comes out on the right, so nothing is reflected back, and there is nothing to deflect it from entering. So if it doesn’t enter, then there is nothing to deflect it and it enters. If it enters, then it is deflected and doesn’t enter; if it doesn’t enter then there is nothing to deflect it and it enters: paradox complete.
But at least one solution to the supposed paradox is easy to construct: just follow the recipe for constructing the minimal solution, continuing the initial trajectory of the particle (reflecting it the mirror in the obvious way) and then read of the number and trajectories of the particles from the resulting diagram. We get the result of figure 6 :
Figure 6: Resolving the “Paradox”. [An extended description of figure 6 is in the supplement.]
As we can see, the particle approaching from the left never reaches \(L+\): it is deflected first by a particle which emerges from \(L-\). But it is not deflected by itself , as the paradox suggests, it is deflected by another particle. Indeed, there are now four particles in the diagram: the original particle and three particles which are confined to closed time-like curves. It is not the leftmost particle which is reflected by the mirror, nor even the particle which deflects the leftmost particle; it is another particle altogether.
The paradox gets it traction from an incorrect presupposition. If there is only one particle in the world at \(S\) then there is only one particle which could participate in an interaction in the time travel region: the single particle would have to interact with its earlier (or later) self. But there is no telling what might come out of \(L-\): the only requirement is that whatever comes out must match what goes in at \(L+\). So if you go to the trouble of constructing a working time machine, you should be prepared for a different kind of disappointment when you attempt to go back and kill yourself: you may be prevented from entering the machine in the first place by some completely unpredictable entity which emerges from it. And once again a peculiar sort of indeterminism appears: if there are many self-consistent things which could prevent you from entering, there is no telling which is even likely to materialize. This is just like the case of the unwritten book: the book is never written, so nothing determines what fills its pages.
So when the freedom to put data on \(L-\) outweighs the constraint that the same data go into \(L+\), instead of paradox we get an embarrassment of riches: many solution consistent with the data on \(S\), or many possible books. To see a case where the constraint “outweighs” the freedom, we need to construct a very particular, and frankly artificial, dynamics and topology. Consider the space of all linear dynamics for a scalar field on a lattice. (The lattice can be though of as a simple discrete space-time.) We will depict the space-time lattice as a directed graph. There is to be a scalar field defined at every node of the graph, whose value at a given node depends linearly on the values of the field at nodes which have arrows which lead to it. Each edge of the graph can be assigned a weighting factor which determines how much the field at the input node contributes to the field at the output node. If we name the nodes by the letters a , b , c , etc., and the edges by their endpoints in the obvious way, then we can label the weighting factors by the edges they are associated with in an equally obvious way.
Suppose that the graph of the space-time lattice is acyclic , as in figure 7 . (A graph is Acyclic if one can not travel in the direction of the arrows and go in a loop.)
Figure 7: An Acyclic Lattice. [An extended description of figure 7 is in the supplement.]
It is easy to regard a set of nodes as the analog of a Cauchy surface, e.g., the set \(\{a, b, c\}\), and it is obvious if arbitrary data are put on those nodes the data will generate a unique solution in the future. [ 3 ] If the value of the field at node \(a\) is 3 and at node \(b\) is 7, then its value at node \(d\) will be \(3W_{ad}\) and its value at node \(e\) will be \(3W_{ae} + 7W_{be}\). By varying the weighting factors we can adjust the dynamics, but in an acyclic graph the future evolution of the field will always be unique.
Let us now again artificially alter the topology of the lattice to admit CTCs, so that the graph now is cyclic. One of the simplest such graphs is depicted in figure 8 : there are now paths which lead from \(z\) back to itself, e.g., \(z\) to \(y\) to \(z\).
Figure 8: Time Travel on a Lattice. [An extended description of figure 8 is in the supplement.]
Can we now put arbitrary data on \(v\) and \(w\), and continue that data to a global solution? Will the solution be unique?
In the generic case, there will be a solution and the solution will be unique. The equations for the value of the field at \(x, y\), and \(z\) are:
Solving these equations for \(z\) yields
which gives a unique value for \(z\) in the generic case. But looking at the space of all possible dynamics for this lattice (i.e., the space of all possible weighting factors), we find a singularity in the case where \(1-W_{zx}W_{xz} - W_{zy}W_{yz} = 0\). If we choose weighting factors in just this way, then arbitrary data at \(v\) and \(w\) cannot be continued to a global solution. Indeed, if the scalar field is everywhere non-negative, then this particular choice of dynamics puts ironclad constraints on the value of the field at \(v\) and \(w\): the field there must be zero (assuming \(W_{vx}\) and \(W_{wy}\) to be non-zero), and similarly all nodes in their past must have field value zero. If the field can take negative values, then the values at \(v\) and \(w\) must be so chosen that \(vW_{vx}W_{xz} = -wW_{wy}W_{yz}\). In either case, the field values at \(v\) and \(w\) are severely constrained by the existence of the CTC region even though these nodes lie completely to the past of that region. It is this sort of constraint which we find to be unlike anything which appears in standard physics.
Our toy models suggest three things. The first is that it may be impossible to prove in complete generality that arbitrary data on a partial Cauchy surface can always be continued to a global solution: our artificial case provides an example where it cannot. The second is that such odd constraints are not likely to be generic: we had to delicately fine-tune the dynamics to get a problem. The third is that the opposite problem, namely data on a partial Cauchy surface being consistent with many different global solutions, is likely to be generic: we did not have to do any fine-tuning to get this result.
This third point leads to a peculiar sort of indeterminism, illustrated by the case of the unwritten book: the entire state on \(S\) does not determine what will happen in the future even though the local dynamics is deterministic and there are no other “edges” to space-time from which data could influence the result. What happens in the time travel region is constrained but not determined by what happens on \(S\), and the dynamics does not even supply any probabilities for the various possibilities. The example of the photographic negative discussed in section 2, then, seems likely to be unusual, for in that case there is a unique fixed point for the dynamics, and the set-up plus the dynamical laws determine the outcome. In the generic case one would rather expect multiple fixed points, with no room for anything to influence, even probabilistically, which would be realized. (See the supplement on
Remarks and Limitations on the Toy Models .
It is ironic that time travel should lead generically not to contradictions or to constraints (in the normal region) but to underdetermination of what happens in the time travel region by what happens everywhere else (an underdetermination tied neither to a probabilistic dynamics nor to a free edge to space-time). The traditional objection to time travel is that it leads to contradictions: there is no consistent way to complete an arbitrarily constructed story about how the time traveler intends to act. Instead, though, it appears that the more significant problem is underdetermination: the story can be consistently completed in many different ways.
Echeverria, Klinkhammer, and Thorne (1991) considered the case of 3-dimensional single hard spherical ball that can go through a single time travel wormhole so as to collide with its younger self.
Figure 9 [An extended description of figure 9 is in the supplement.]
The threat of paradox in this case arises in the following form. Consider the initial trajectory of a ball as it approaches the time travel region. For some initial trajectories, the ball does not undergo a collision before reaching mouth 1, but upon exiting mouth 2 it will collide with its earlier self. This leads to a contradiction if the collision is strong enough to knock the ball off its trajectory and deflect it from entering mouth 1. Of course, the Wheeler-Feynman strategy is to look for a “glancing blow” solution: a collision which will produce exactly the (small) deviation in trajectory of the earlier ball that produces exactly that collision. Are there always such solutions? [ 4 ]
Echeverria, Klinkhammer & Thorne found a large class of initial trajectories that have consistent “glancing blow” continuations, and found none that do not (but their search was not completely general). They did not produce a rigorous proof that every initial trajectory has a consistent continuation, but suggested that it is very plausible that every initial trajectory has a consistent continuation. That is to say, they have made it very plausible that, in the billiard ball wormhole case, the time travel structure of such a wormhole space-time does not result in constraints on states on spacelike surfaces in the non-time travel region.
In fact, as one might expect from our discussion in the previous section, they found the opposite problem from that of inconsistency: they found underdetermination. For a large class of initial trajectories there are multiple different consistent “glancing blow” continuations of that trajectory (many of which involve multiple wormhole traversals). For example, if one initially has a ball that is traveling on a trajectory aimed straight between the two mouths, then one obvious solution is that the ball passes between the two mouths and never time travels. But another solution is that the younger ball gets knocked into mouth 1 exactly so as to come out of mouth 2 and produce that collision. Echeverria et al. do not note the possibility (which we pointed out in the previous section) of the existence of additional balls in the time travel region. We conjecture (but have no proof) that for every initial trajectory of \(A\) there are some, and generically many, multiple-ball continuations.
Friedman, Morris, et al. (1990) examined the case of source-free non-self-interacting scalar fields traveling through such a time travel wormhole and found that no constraints on initial conditions in the non-time travel region are imposed by the existence of such time travel wormholes. In general there appear to be no known counter examples to the claim that in “somewhat realistic” time-travel space-times with a partial Cauchy surface there are no constraints imposed on the state on such a partial Cauchy surface by the existence of CTC’s. (See, e.g., Friedman & Morris 1991; Thorne 1994; Earman 1995; Earman, Smeenk, & Wüthrich 2009; and Dowe 2007.)
How about the issue of constraints in the time travel region \(T\)? Prima facie , constraints in such a region would not appear to be surprising. But one might still expect that there should be no constraints on states on a spacelike surface, provided one keeps the surface “small enough”. In the physics literature the following question has been asked: for any point \(p\) in \(T\), and any space-like surface \(S\) that includes \(p\) is there a neighborhood \(E\) of \(p\) in \(S\) such that any solution on \(E\) can be extended to a solution on the whole space-time? With respect to this question, there are some simple models in which one has this kind of extendability of local solutions to global ones, and some simple models in which one does not have such extendability, with no clear general pattern. The technical mathematical problems are amplified by the more conceptual problem of what it might mean to say that one could create a situation which forces the creation of closed timelike curves. (See, e.g., Yurtsever 1990; Friedman, Morris, et al. 1990; Novikov 1992; Earman 1995; and Earman, Smeenk, & Wüthrich 2009). What are we to think of all of this?
The toy models above all treat billiard balls, fields, and other objects propagating through a background spacetime with CTCs. Even if we can show that a consistent solution exists, there is a further question: what kind of matter and dynamics could generate CTCs to begin with? There are various solutions of Einstein’s equations with CTCs, but how do these exotic spacetimes relate to the models actually used in describing the world? In other words, what positive reasons might we have to take CTCs seriously as a feature of the actual universe, rather than an exotic possibility of primarily mathematical interest?
We should distinguish two different kinds of “possibility” that we might have in mind in posing such questions (following Stein 1970). First, we can consider a solution as a candidate cosmological model, describing the (large-scale gravitational degrees of freedom of the) entire universe. The case for ruling out spacetimes with CTCs as potential cosmological models strikes us as, surprisingly, fairly weak. Physicists used to simply rule out solutions with CTCs as unreasonable by fiat, due to the threat of paradoxes, which we have dismantled above. But it is also challenging to make an observational case. Observations tell us very little about global features, such as the existence of CTCs, because signals can only reach an observer from a limited region of spacetime, called the past light cone. Our past light cone—and indeed the collection of all the past light cones for possible observers in a given spacetime—can be embedded in spacetimes with quite different global features (Malament 1977, Manchak 2009). This undercuts the possibility of using observations to constrain global topology, including (among other things) ruling out the existence of CTCs.
Yet the case in favor of taking cosmological models with CTCs seriously is also not particularly strong. Some solutions used to describe black holes, which are clearly relevant in a variety of astrophysical contexts, include CTCs. But the question of whether the CTCs themselves play an essential representational role is subtle: the CTCs arise in the maximal extensions of these solutions, and can plausibly be regarded as extraneous to successful applications. Furthermore, many of the known solutions with CTCs have symmetries, raising the possibility that CTCs are not a stable or robust feature. Slight departures from symmetry may lead to a solution without CTCs, suggesting that the CTCs may be an artifact of an idealized model.
The second sense of possibility regards whether “reasonable” initial conditions can be shown to lead to, or not to lead to, the formation of CTCs. As with the toy models above, suppose that we have a partial Cauchy surface \(S\), such that all the temporal funny business lies to the future. Rather than simply assuming that there is a region with CTCs to the future, we can ask instead whether it is possible to create CTCs by manipulating matter in the initial, well-behaved region—that is, whether it is possible to build a time machine. Several physicists have pursued “chronology protection theorems” aiming to show that the dynamics of general relativity (or some other aspects of physics) rules this out, and to clarify why this is the case. The proof of such a theorem would justify neglecting solutions with CTCs as a source of insight into the nature of time in the actual world. But as of yet there are several partial results that do not fully settle the question. One further intriguing possibility is that even if general relativity by itself does protect chronology, it may not be possible to formulate a sensible theory describing matter and fields in solutions with CTCs. (See SEP entry on Time Machines; Smeenk and Wüthrich 2011 for more.)
There is a different question regarding the limitations of these toy models. The toy models and related examples show that there are consistent solutions for simple systems in the presence of CTCs. As usual we have made the analysis tractable by building toy models, selecting only a few dynamical degrees of freedom and tracking their evolution. But there is a large gap between the systems we have described and the time travel stories they evoke, with Kurt traveling along a CTC with murderous intentions. In particular, many features of the manifest image of time are tied to the thermodynamical properties of macroscopic systems. Rovelli (unpublished) considers a extremely simple system to illustrate the problem: can a clock move along a CTC? A clock consists of something in periodic motion, such as a pendulum bob, and something that counts the oscillations, such as an escapement mechanism. The escapement mechanism cannot work without friction; this requires dissipation and increasing entropy. For a clock that counts oscillations as it moves along a time-like trajectory, the entropy must be a monotonically increasing function. But that is obviously incompatible with the clock returning to precisely the same state at some future time as it completes a loop. The point generalizes, obviously, to imply that anything like a human, with memory and agency, cannot move along a CTC.
Since it is not obvious that one can rid oneself of all constraints in realistic models, let us examine the argument that time travel is implausible, and we should think it unlikely to exist in our world, in so far as it implies such constraints. The argument goes something like the following. In order to satisfy such constraints one needs some pre-established divine harmony between the global (time travel) structure of space-time and the distribution of particles and fields on space-like surfaces in it. But it is not plausible that the actual world, or any world even remotely like ours, is constructed with divine harmony as part of the plan. In fact, one might argue, we have empirical evidence that conditions in any spatial region can vary quite arbitrarily. So we have evidence that such constraints, whatever they are, do not in fact exist in our world. So we have evidence that there are no closed time-like lines in our world or one remotely like it. We will now examine this argument in more detail by presenting four possible responses, with counterresponses, to this argument.
Response 1. There is nothing implausible or new about such constraints. For instance, if the universe is spatially closed, there has to be enough matter to produce the needed curvature, and this puts constraints on the matter distribution on a space-like hypersurface. Thus global space-time structure can quite unproblematically constrain matter distributions on space-like hypersurfaces in it. Moreover we have no realistic idea what these constraints look like, so we hardly can be said to have evidence that they do not obtain.
Counterresponse 1. Of course there are constraining relations between the global structure of space-time and the matter in it. The Einstein equations relate curvature of the manifold to the matter distribution in it. But what is so strange and implausible about the constraints imposed by the existence of closed time-like curves is that these constraints in essence have nothing to do with the Einstein equations. When investigating such constraints one typically treats the particles and/or field in question as test particles and/or fields in a given space-time, i.e., they are assumed not to affect the metric of space-time in any way. In typical space-times without closed time-like curves this means that one has, in essence, complete freedom of matter distribution on a space-like hypersurface. (See response 2 for some more discussion of this issue). The constraints imposed by the possibility of time travel have a quite different origin and are implausible. In the ordinary case there is a causal interaction between matter and space-time that results in relations between global structure of space-time and the matter distribution in it. In the time travel case there is no such causal story to be told: there simply has to be some pre-established harmony between the global space-time structure and the matter distribution on some space-like surfaces. This is implausible.
Response 2. Constraints upon matter distributions are nothing new. For instance, Maxwell’s equations constrain electric fields \(\boldsymbol{E}\) on an initial surface to be related to the (simultaneous) charge density distribution \(\varrho\) by the equation \(\varrho = \text{div}(\boldsymbol{E})\). (If we assume that the \(E\) field is generated solely by the charge distribution, this conditions amounts to requiring that the \(E\) field at any point in space simply be the one generated by the charge distribution according to Coulomb’s inverse square law of electrostatics.) This is not implausible divine harmony. Such constraints can hold as a matter of physical law. Moreover, if we had inferred from the apparent free variation of conditions on spatial regions that there could be no such constraints we would have mistakenly inferred that \(\varrho = \text{div}(\boldsymbol{E})\) could not be a law of nature.
Counterresponse 2. The constraints imposed by the existence of closed time-like lines are of quite a different character from the constraint imposed by \(\varrho = \text{div}(\boldsymbol{E})\). The constraints imposed by \(\varrho = \text{div}(\boldsymbol{E})\) on the state on a space-like hypersurface are:
- local constraints (i.e., to check whether the constraint holds in a region you just need to see whether it holds at each point in the region),
- quite independent of the global space-time structure,
- quite independent of how the space-like surface in question is embedded in a given space-time, and
- very simply and generally stateable.
On the other hand, the consistency constraints imposed by the existence of closed time-like curves (i) are not local, (ii) are dependent on the global structure of space-time, (iii) depend on the location of the space-like surface in question in a given space-time, and (iv) appear not to be simply stateable other than as the demand that the state on that space-like surface embedded in such and such a way in a given space-time, do not lead to inconsistency. On some views of laws (e.g., David Lewis’ view) this plausibly implies that such constraints, even if they hold, could not possibly be laws. But even if one does not accept such a view of laws, one could claim that the bizarre features of such constraints imply that it is implausible that such constraints hold in our world or in any world remotely like ours.
Response 3. It would be strange if there are constraints in the non-time travel region. It is not strange if there are constraints in the time travel region. They should be explained in terms of the strange, self-interactive, character of time travel regions. In this region there are time-like trajectories from points to themselves. Thus the state at such a point, in such a region, will, in a sense, interact with itself. It is a well-known fact that systems that interact with themselves will develop into an equilibrium state, if there is such an equilibrium state, or else will develop towards some singularity. Normally, of course, self-interaction isn’t true instantaneous self-interaction, but consists of a feed-back mechanism that takes time. But in time travel regions something like true instantaneous self-interaction occurs. This explains why constraints on states occur in such time travel regions: the states “ ab initio ” have to be “equilibrium states”. Indeed in a way this also provides some picture of why indeterminism occurs in time travel regions: at the onset of self-interaction states can fork into different equi-possible equilibrium states.
Counterresponse 3. This is explanation by woolly analogy. It all goes to show that time travel leads to such bizarre consequences that it is unlikely that it occurs in a world remotely like ours.
Response 4. All of the previous discussion completely misses the point. So far we have been taking the space-time structure as given, and asked the question whether a given time travel space-time structure imposes constraints on states on (parts of) space-like surfaces. However, space-time and matter interact. Suppose that one is in a space-time with closed time-like lines, such that certain counterfactual distributions of matter on some neighborhood of a point \(p\) are ruled out if one holds that space-time structure fixed. One might then ask
Why does the actual state near \(p\) in fact satisfy these constraints? By what divine luck or plan is this local state compatible with the global space-time structure? What if conditions near \(p\) had been slightly different?
And one might take it that the lack of normal answers to these questions indicates that it is very implausible that our world, or any remotely like it, is such a time travel universe. However the proper response to these question is the following. There are no constraints in any significant sense. If they hold they hold as a matter of accidental fact, not of law. There is no more explanation of them possible than there is of any contingent fact. Had conditions in a neighborhood of \(p\) been otherwise, the global structure of space-time would have been different. So what? The only question relevant to the issue of constraints is whether an arbitrary state on an arbitrary spatial surface \(S\) can always be embedded into a space-time such that that state on \(S\) consistently extends to a solution on the entire space-time.
But we know the answer to that question. A well-known theorem in general relativity says the following: any initial data set on a three dimensional manifold \(S\) with positive definite metric has a unique embedding into a maximal space-time in which \(S\) is a Cauchy surface (see, e.g., Geroch & Horowitz 1979: 284 for more detail), i.e., there is a unique largest space-time which has \(S\) as a Cauchy surface and contains a consistent evolution of the initial value data on \(S\). Now since \(S\) is a Cauchy surface this space-time does not have closed time like curves. But it may have extensions (in which \(S\) is not a Cauchy surface) which include closed timelike curves, indeed it may be that any maximal extension of it would include closed timelike curves. (This appears to be the case for extensions of states on certain surfaces of Taub-NUT space-times. See Earman, Smeenk, & Wüthrich 2009). But these extensions, of course, will be consistent. So properly speaking, there are no constraints on states on space-like surfaces. Nonetheless the space-time in which these are embedded may or may not include closed time-like curves.
Counterresponse 4. This, in essence, is the stonewalling answer which we indicated in section 1. However, whether or not you call the constraints imposed by a given space-time on distributions of matter on certain space-like surfaces “genuine constraints”, whether or not they can be considered lawlike, and whether or not they need to be explained, the existence of such constraints can still be used to argue that time travel worlds are so bizarre that it is implausible that our world or any world remotely like ours is a time travel world.
Suppose that one is in a time travel world. Suppose that given the global space-time structure of this world, there are constraints imposed upon, say, the state of motion of a ball on some space-like surface when it is treated as a test particle, i.e., when it is assumed that the ball does not affect the metric properties of the space-time it is in. (There is lots of other matter that, via the Einstein equation, corresponds exactly to the curvature that there is everywhere in this time travel worlds.) Now a real ball of course does have some effect on the metric of the space-time it is in. But let us consider a ball that is so small that its effect on the metric is negligible. Presumably it will still be the case that certain states of this ball on that space-like surface are not compatible with the global time travel structure of this universe.
This means that the actual distribution of matter on such a space-like surface can be extended into a space-time with closed time-like lines, but that certain counterfactual distributions of matter on this space-like surface can not be extended into the same space-time. But note that the changes made in the matter distribution (when going from the actual to the counterfactual distribution) do not in any non-negligible way affect the metric properties of the space-time. (Recall that the changes only effect test particles.) Thus the reason why the global time travel properties of the counterfactual space-time have to be significantly different from the actual space-time is not that there are problems with metric singularities or alterations in the metric that force significant global changes when we go to the counterfactual matter distribution. The reason that the counterfactual space-time has to be different is that in the counterfactual world the ball’s initial state of motion starting on the space-like surface, could not “meet up” in a consistent way with its earlier self (could not be consistently extended) if we were to let the global structure of the counterfactual space-time be the same as that of the actual space-time. Now, it is not bizarre or implausible that there is a counterfactual dependence of manifold structure, even of its topology, on matter distributions on spacelike surfaces. For instance, certain matter distributions may lead to singularities, others may not. We may indeed in some sense have causal power over the topology of the space-time we live in. But this power normally comes via the Einstein equations. But it is bizarre to think that there could be a counterfactual dependence of global space-time structure on the arrangement of certain tiny bits of matter on some space-like surface, where changes in that arrangement by assumption do not affect the metric anywhere in space-time in any significant way . It is implausible that we live in such a world, or that a world even remotely like ours is like that.
Let us illustrate this argument in a different way by assuming that wormhole time travel imposes constraints upon the states of people prior to such time travel, where the people have so little mass/energy that they have negligible effect, via the Einstein equation, on the local metric properties of space-time. Do you think it more plausible that we live in a world where wormhole time travel occurs but it only occurs when people’s states are such that these local states happen to combine with time travel in such a way that nobody ever succeeds in killing their younger self, or do you think it more plausible that we are not in a wormhole time travel world? [ 5 ]
An alternative approach to time travel (initiated by Deutsch 1991) abstracts away from the idealized toy models described above. [ 6 ] This computational approach considers instead the evolution of bits (simple physical systems with two discrete states) through a network of interactions, which can be represented by a circuit diagram with gates corresponding to the interactions. Motivated by the possibility of CTCs, Deutsch proposed adding a new kind of channel that connects the output of a given gate back to its input —in essence, a backwards-time step. More concretely, given a gate that takes \(n\) bits as input, we can imagine taking some number \(i \lt n\) of these bits through a channel that loops back and then do double-duty as inputs. Consistency requires that the state of these \(i\) bits is the same for output and input. (We will consider an illustration of this kind of system in the next section.) Working through examples of circuit diagrams with a CTC channel leads to similar treatments of Consistency and Underdetermination as the discussion above (see, e.g., Wallace 2012: § 10.6). But the approach offers two new insights (both originally due to Deutsch): the Easy Knowledge paradox, and a particularly clear extension to time travel in quantum mechanics.
A computer equipped with a CTC channel can exploit the need to find consistent evolution to solve remarkably hard problems. (This is quite different than the first idea that comes to mind to enhance computational power: namely to just devote more time to a computation, and then send the result back on the CTC to an earlier state.) The gate in a circuit incorporating a CTC implements a function from the input bits to the output bits, under the constraint that the output and input match the i bits going through the CTC channel. This requires, in effect, finding the fixed point of the relevant function. Given the generality of the model, there are few limits on the functions that could be implemented on the CTC circuit. Nature has to solve a hard computational problem just to ensure consistent evolution. This can then be extended to other complex computational problems—leading, more precisely, to solutions of NP -complete problems in polynomial time (see Aaronson 2013: Chapter 20 for an overview and further references). The limits imposed by computational complexity are an essential part of our epistemic situation, and computers with CTCs would radically change this.
We now turn to the application of the computational approach to the quantum physics of time travel (see Deutsch 1991; Deutsch & Lockwood 1994). By contrast with the earlier discussions of constraints in classical systems, they claim to show that time travel never imposes any constraints on the pre-time travel state of quantum systems. The essence of this account is as follows. [ 7 ]
A quantum system starts in state \(S_1\), interacts with its older self, after the interaction is in state \(S_2\), time travels while developing into state \(S_3\), then interacts with its younger self, and ends in state \(S_4\) (see figure 10 ).
Figure 10 [An extended description of figure 10 is in the supplement.]
Deutsch assumes that the set of possible states of this system are the mixed states, i.e., are represented by the density matrices over the Hilbert space of that system. Deutsch then shows that for any initial state \(S_1\), any unitary interaction between the older and younger self, and any unitary development during time travel, there is a consistent solution, i.e., there is at least one pair of states \(S_2\) and \(S_3\) such that when \(S_1\) interacts with \(S_3\) it will change to state \(S_2\) and \(S_2\) will then develop into \(S_3\). The states \(S_2, S_3\) and \(S_4\) will typically be not be pure states, i.e., will be non-trivial mixed states, even if \(S_1\) is pure. In order to understand how this leads to interpretational problems let us give an example. Consider a system that has a two dimensional Hilbert space with as a basis the states \(\vc{+}\) and \(\vc{-}\). Let us suppose that when state \(\vc{+}\) of the young system encounters state \(\vc{+}\) of the older system, they interact and the young system develops into state \(\vc{-}\) and the old system remains in state \(\vc{+}\). In obvious notation:
Similarly, suppose that:
Let us furthermore assume that there is no development of the state of the system during time travel, i.e., that \(\vc{+}_2\) develops into \(\vc{+}_3\), and that \(\vc{-}_2\) develops into \(\vc{-}_3\).
Now, if the only possible states of the system were \(\vc{+}\) and \(\vc{-}\) (i.e., if there were no superpositions or mixtures of these states), then there is a constraint on initial states: initial state \(\vc{+}_1\) is impossible. For if \(\vc{+}_1\) interacts with \(\vc{+}_3\) then it will develop into \(\vc{-}_2\), which, during time travel, will develop into \(\vc{-}_3\), which inconsistent with the assumed state \(\vc{+}_3\). Similarly if \(\vc{+}_1\) interacts with \(\vc{-}_3\) it will develop into \(\vc{+}_2\), which will then develop into \(\vc{+}_3\) which is also inconsistent. Thus the system can not start in state \(\vc{+}_1\).
But, says Deutsch, in quantum mechanics such a system can also be in any mixture of the states \(\vc{+}\) and \(\vc{-}\). Suppose that the older system, prior to the interaction, is in a state \(S_3\) which is an equal mixture of 50% \(\vc{+}_3\) and 50% \(\vc{-}_3\). Then the younger system during the interaction will develop into a mixture of 50% \(\vc{+}_2\) and 50% \(\vc{-}_2\), which will then develop into a mixture of 50% \(\vc{+}_3\) and 50% \(\vc{-}_3\), which is consistent! More generally Deutsch uses a fixed point theorem to show that no matter what the unitary development during interaction is, and no matter what the unitary development during time travel is, for any state \(S_1\) there is always a state \(S_3\) (which typically is not a pure state) which causes \(S_1\) to develop into a state \(S_2\) which develops into that state \(S_3\). Thus quantum mechanics comes to the rescue: it shows in all generality that no constraints on initial states are needed!
One might wonder why Deutsch appeals to mixed states: will superpositions of states \(\vc{+}\) and \(\vc{-}\) not suffice? Unfortunately such an idea does not work. Suppose again that the initial state is \(\vc{+}_1\). One might suggest that that if state \(S_3\) is
one will obtain a consistent development. For one might think that when initial state \(\vc{+}_1\) encounters the superposition
it will develop into superposition
and that this in turn will develop into
as desired. However this is not correct. For initial state \(\vc{+}_1\) when it encounters
will develop into the entangled state
In so far as one can speak of the state of the young system after this interaction, it is in the mixture of 50% \(\vc{+}_2\) and 50% \(\vc{-}_2\), not in the superposition
So Deutsch does need his recourse to mixed states.
This clarification of why Deutsch needs his mixtures does however indicate a serious worry about the simplifications that are part of Deutsch’s account. After the interaction the old and young system will (typically) be in an entangled state. Although for purposes of a measurement on one of the two systems one can say that this system is in a mixed state, one can not represent the full state of the two systems by specifying the mixed state of each separate part, as there are correlations between observables of the two systems that are not represented by these two mixed states, but are represented in the joint entangled state. But if there really is an entangled state of the old and young systems directly after the interaction, how is one to represent the subsequent development of this entangled state? Will the state of the younger system remain entangled with the state of the older system as the younger system time travels and the older system moves on into the future? On what space-like surfaces are we to imagine this total entangled state to be? At this point it becomes clear that there is no obvious and simple way to extend elementary non-relativistic quantum mechanics to space-times with closed time-like curves: we apparently need to characterize not just the entanglement between two systems, but entanglement relative to specific spacetime descriptions.
How does Deutsch avoid these complications? Deutsch assumes a mixed state \(S_3\) of the older system prior to the interaction with the younger system. He lets it interact with an arbitrary pure state \(S_1\) younger system. After this interaction there is an entangled state \(S'\) of the two systems. Deutsch computes the mixed state \(S_2\) of the younger system which is implied by this entangled state \(S'\). His demand for consistency then is just that this mixed state \(S_2\) develops into the mixed state \(S_3\). Now it is not at all clear that this is a legitimate way to simplify the problem of time travel in quantum mechanics. But even if we grant him this simplification there is a problem: how are we to understand these mixtures?
If we take an ignorance interpretation of mixtures we run into trouble. For suppose that we assume that in each individual case each older system is either in state \(\vc{+}_3\) or in state \(\vc{-}_3\) prior to the interaction. Then we regain our paradox. Deutsch instead recommends the following, many worlds, picture of mixtures. Suppose we start with state \(\vc{+}_1\) in all worlds. In some of the many worlds the older system will be in the \(\vc{+}_3\) state, let us call them A -worlds, and in some worlds, B -worlds, it will be in the \(\vc{-}_3\) state. Thus in A -worlds after interaction we will have state \(\vc{-}_2\) , and in B -worlds we will have state \(\vc{+}_2\). During time travel the \(\vc{-}_2\) state will remain the same, i.e., turn into state \(\vc{-}_3\), but the systems in question will travel from A -worlds to B -worlds. Similarly the \(\vc{+}\) \(_2\) states will travel from the B -worlds to the A -worlds, thus preserving consistency.
Now whatever one thinks of the merits of many worlds interpretations, and of this understanding of it applied to mixtures, in the end one does not obtain genuine time travel in Deutsch’s account. The systems in question travel from one time in one world to another time in another world, but no system travels to an earlier time in the same world. (This is so at least in the normal sense of the word “world”, the sense that one means when, for instance, one says “there was, and will be, only one Elvis Presley in this world.”) Thus, even if it were a reasonable view, it is not quite as interesting as it may have initially seemed. (See Wallace 2012 for a more sympathetic treatment, that explores several further implications of accepting time travel in conjunction with the many worlds interpretation.)
We close by acknowledging that Deutsch’s starting point—the claim that this computational model captures the essential features of quantum systems in a spacetime with CTCs—has been the subject of some debate. Several physicists have pursued a quite different treatment of evolution of quantum systems through CTC’s, based on considering the “post-selected” state (see Lloyd et al. 2011). Their motivations for implementing the consistency condition in terms of the post-selected state reflects a different stance towards quantum foundations. A different line of argument aims to determine whether Deutsch’s treatment holds as an appropriate limiting case of a more rigorous treatment, such as quantum field theory in curved spacetimes. For example, Verch (2020) establishes several results challenging the assumption that Deutsch’s treatment is tied to the presence of CTC’s, or that it is compatible with the entanglement structure of quantum fields.
What remains of the grandfather paradox in general relativistic time travel worlds is the fact that in some cases the states on edgeless spacelike surfaces are “overconstrained”, so that one has less than the usual freedom in specifying conditions on such a surface, given the time-travel structure, and in some cases such states are “underconstrained”, so that states on edgeless space-like surfaces do not determine what happens elsewhere in the way that they usually do, given the time travel structure. There can also be mixtures of those two types of cases. The extent to which states are overconstrained and/or underconstrained in realistic models is as yet unclear, though it would be very surprising if neither obtained. The extant literature has primarily focused on the problem of overconstraint, since that, often, either is regarded as a metaphysical obstacle to the possibility time travel, or as an epistemological obstacle to the plausibility of time travel in our world. While it is true that our world would be quite different from the way we normally think it is if states were overconstrained, underconstraint seems at least as bizarre as overconstraint. Nonetheless, neither directly rules out the possibility of time travel.
If time travel entailed contradictions then the issue would be settled. And indeed, most of the stories employing time travel in popular culture are logically incoherent: one cannot “change” the past to be different from what it was, since the past (like the present and the future) only occurs once. But if the only requirement demanded is logical coherence, then it seems all too easy. A clever author can devise a coherent time-travel scenario in which everything happens just once and in a consistent way. This is just too cheap: logical coherence is a very weak condition, and many things we take to be metaphysically impossible are logically coherent. For example, it involves no logical contradiction to suppose that water is not molecular, but if both chemistry and Kripke are right it is a metaphysical impossibility. We have been interested not in logical possibility but in physical possibility. But even so, our conditions have been relatively weak: we have asked only whether time-travel is consistent with the universal validity of certain fundamental physical laws and with the notion that the physical state on a surface prior to the time travel region be unconstrained. It is perfectly possible that the physical laws obey this condition, but still that time travel is not metaphysically possible because of the nature of time itself. Consider an analogy. Aristotle believed that water is homoiomerous and infinitely divisible: any bit of water could be subdivided, in principle, into smaller bits of water. Aristotle’s view contains no logical contradiction. It was certainly consistent with Aristotle’s conception of water that it be homoiomerous, so this was, for him, a conceptual possibility. But if chemistry is right, Aristotle was wrong both about what water is like and what is possible for it. It can’t be infinitely divided, even though no logical or conceptual analysis would reveal that.
Similarly, even if all of our consistency conditions can be met, it does not follow that time travel is physically possible, only that some specific physical considerations cannot rule it out. The only serious proof of the possibility of time travel would be a demonstration of its actuality. For if we agree that there is no actual time travel in our universe, the supposition that there might have been involves postulating a substantial difference from actuality, a difference unlike in kind from anything we could know if firsthand. It is unclear to us exactly what the content of possible would be if one were to either maintain or deny the possibility of time travel in these circumstances, unless one merely meant that the possibility is not ruled out by some delineated set of constraints. As the example of Aristotle’s theory of water shows, conceptual and logical “possibility” do not entail possibility in a full-blooded sense. What exactly such a full-blooded sense would be in case of time travel, and whether one could have reason to believe it to obtain, remain to us obscure.
- Aaronson, Scott, 2013, Quantum Computing since Democritus , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511979309
- Arntzenius, Frank, 2006, “Time Travel: Double Your Fun”, Philosophy Compass , 1(6): 599–616. doi:10.1111/j.1747-9991.2006.00045.x
- Clarke, C.J.S., 1977, “Time in General Relativity” in Foundations of Space-Time Theory , Minnesota Studies in the Philosophy of Science , Vol VIII, Earman, J., Glymour, C., and Stachel, J. (eds), pp. 94–108. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
- Deutsch, David, 1991, “Quantum Mechanics near Closed Timelike Lines”, Physical Review D , 44(10): 3197–3217. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.44.3197
- Deutsch, David and Michael Lockwood, 1994, “The Quantum Physics of Time Travel”, Scientific American , 270(3): 68–74. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0394-68
- Dowe, Phil, 2007, “Constraints on Data in Worlds with Closed Timelike Curves”, Philosophy of Science , 74(5): 724–735. doi:10.1086/525617
- Earman, John, 1972, “Implications of Causal Propagation Outside the Null Cone”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 50(3): 222–237. doi:10.1080/00048407212341281
- Earman, John, 1995, Bangs, Crunches, Whimpers, and Shrieks: Singularities and Acausalities in Relativistic Spacetimes , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Earman, John, Christopher Smeenk, and Christian Wüthrich, 2009, “Do the Laws of Physics Forbid the Operation of Time Machines?”, Synthese , 169(1): 91–124. doi:10.1007/s11229-008-9338-2
- Echeverria, Fernando, Gunnar Klinkhammer, and Kip S. Thorne, 1991, “Billiard Balls in Wormhole Spacetimes with Closed Timelike Curves: Classical Theory”, Physical Review D , 44(4): 1077–1099. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.44.1077
- Effingham, Nikk, 2020, Time Travel: Probability and Impossibility , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198842507.001.0001
- Fletcher, Samuel C., 2020, “The Principle of Stability”, Philosopher’s Imprint , 20: article 3. [ Fletcher 2020 available online ]
- Friedman, John and Michael Morris, 1991, “The Cauchy Problem for the Scalar Wave Equation Is Well Defined on a Class of Spacetimes with Closed Timelike Curves”, Physical Review Letters , 66(4): 401–404. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.66.401
- Friedman, John, Michael S. Morris, Igor D. Novikov, Fernando Echeverria, Gunnar Klinkhammer, Kip S. Thorne, and Ulvi Yurtsever, 1990, “Cauchy Problem in Spacetimes with Closed Timelike Curves”, Physical Review D , 42(6): 1915–1930. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.42.1915
- Geroch, Robert and Gary Horowitz, 1979, “Global Structures of Spacetimes”, in General Relativity: An Einstein Centenary Survey , Stephen Hawking and W. Israel (eds.), Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press, Chapter 5, pp. 212–293.
- Gödel, Kurt, 1949, “A Remark About the Relationship Between Relativity Theory and Idealistic Philosophy”, in Albert Einstein, Philosopher-Scientist , Paul Arthur Schilpp (ed.), Evanston, IL: Library of Living Philosophers, 557–562.
- Hocking, John G. and Gail S. Young, 1961, Topology , (Addison-Wesley Series in Mathematics), Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Horwich, Paul, 1987, “Time Travel”, in his Asymmetries in Time: Problems in the Philosophy of Science , , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 111–128.
- Kutach, Douglas N., 2003, “Time Travel and Consistency Constraints”, Philosophy of Science , 70(5): 1098–1113. doi:10.1086/377392
- Lewis, David, 1976, “The Paradoxes of Time Travel”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 13(2): 145–152.
- Lloyd, Seth, Lorenzo Maccone, Raul Garcia-Patron, Vittorio Giovannetti, and Yutaka Shikano, 2011, “Quantum Mechanics of Time Travel through Post-Selected Teleportation”, Physical Review D , 84(2): 025007. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.84.025007
- Malament, David B., 1977, “Observationally Indistinguishable Spacetimes: Comments on Glymour’s Paper”, in Foundations of Space-Time Theories , John Earman, Clark N. Glymour, and John J. Stachel (eds.), (Minnesota Studies in the Philosophy of Science 8), Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press, 61–80.
- –––, 1984, “‘Time Travel’ in the Gödel Universe”, PSA: Proceedings of the Biennial Meeting of the Philosophy of Science Association , 1984(2): 91–100. doi:10.1086/psaprocbienmeetp.1984.2.192497
- –––, 1985, “Minimal Acceleration Requirements for ‘Time Travel’, in Gödel Space‐time”, Journal of Mathematical Physics , 26(4): 774–777. doi:10.1063/1.526566
- Manchak, John Byron, 2009, “Can We Know the Global Structure of Spacetime?”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part B: Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics , 40(1): 53–56. doi:10.1016/j.shpsb.2008.07.004
- –––, 2011, “On Efficient ‘Time Travel’ in Gödel Spacetime”, General Relativity and Gravitation , 43(1): 51–60. doi:10.1007/s10714-010-1068-3
- Maudlin, Tim, 1990, “Time-Travel and Topology”, PSA: Proceedings of the Biennial Meeting of the Philosophy of Science Association , 1990(1): 303–315. doi:10.1086/psaprocbienmeetp.1990.1.192712
- Novikov, I. D., 1992, “Time Machine and Self-Consistent Evolution in Problems with Self-Interaction”, Physical Review D , 45(6): 1989–1994. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.45.1989
- Smeenk, Chris and Christian Wüthrich, 2011, “Time Travel and Time Machines”, in the Oxford Handbook on Time , Craig Callender (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 577–630..
- Stein, Howard, 1970, “On the Paradoxical Time-Structures of Gödel”, Philosophy of Science , 37(4): 589–601. doi:10.1086/288328
- Thorne, Kip S., 1994, Black Holes and Time Warps: Einstein’s Outrageous Legacy , (Commonwealth Fund Book Program), New York: W.W. Norton.
- Verch, Rainer, 2020, “The D-CTC Condition in Quantum Field Theory”, in Progress and Visions in Quantum Theory in View of Gravity , Felix Finster, Domenico Giulini, Johannes Kleiner, and Jürgen Tolksdorf (eds.), Cham: Springer International Publishing, 221–232. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-38941-3_9
- Wallace, David, 2012, The Emergent Multiverse: Quantum Theory According to the Everett Interpretation , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199546961.001.0001
- Wasserman, Ryan, 2018, Paradoxes of Time Travel , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198793335.001.0001
- Weyl, Hermann, 1918/1920 [1922/1952], Raum, Zeit, Materie , Berlin: Springer; fourth edition 1920. Translated as Space—Time—Matter , Henry Leopold Brose (trans.), New York: Dutton, 1922. Reprinted 1952, New York: Dover Publications.
- Wheeler, John Archibald and Richard Phillips Feynman, 1949, “Classical Electrodynamics in Terms of Direct Interparticle Action”, Reviews of Modern Physics , 21(3): 425–433. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.21.425
- Yurtsever, Ulvi, 1990, “Test Fields on Compact Space‐times”, Journal of Mathematical Physics , 31(12): 3064–3078. doi:10.1063/1.528960
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Adlam, Emily, unpublished, “ Is There Causation in Fundamental Physics? New Insights from Process Matrices and Quantum Causal Modelling ”, 2022, arXiv: 2208.02721. doi:10.48550/ARXIV.2208.02721
- Rovelli, Carlo, unpublished, “ Can We Travel to the Past? Irreversible Physics along Closed Timelike Curves ”, arXiv: 1912.04702. doi:10.48550/ARXIV.1912.04702
causation: backward | determinism: causal | quantum mechanics | quantum mechanics: retrocausality | space and time: being and becoming in modern physics | time machines | time travel
Copyright © 2023 by Christopher Smeenk < csmeenk2 @ uwo . ca > Frank Arntzenius Tim Maudlin
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Time travel: Is it possible?
Science says time travel is possible, but probably not in the way you're thinking.

Albert Einstein's theory
- General relativity and GPS
- Wormhole travel
- Alternate theories
Science fiction
Is time travel possible? Short answer: Yes, and you're doing it right now — hurtling into the future at the impressive rate of one second per second.
You're pretty much always moving through time at the same speed, whether you're watching paint dry or wishing you had more hours to visit with a friend from out of town.
But this isn't the kind of time travel that's captivated countless science fiction writers, or spurred a genre so extensive that Wikipedia lists over 400 titles in the category "Movies about Time Travel." In franchises like " Doctor Who ," " Star Trek ," and "Back to the Future" characters climb into some wild vehicle to blast into the past or spin into the future. Once the characters have traveled through time, they grapple with what happens if you change the past or present based on information from the future (which is where time travel stories intersect with the idea of parallel universes or alternate timelines).
Related: The best sci-fi time machines ever
Although many people are fascinated by the idea of changing the past or seeing the future before it's due, no person has ever demonstrated the kind of back-and-forth time travel seen in science fiction or proposed a method of sending a person through significant periods of time that wouldn't destroy them on the way. And, as physicist Stephen Hawking pointed out in his book " Black Holes and Baby Universes" (Bantam, 1994), "The best evidence we have that time travel is not possible, and never will be, is that we have not been invaded by hordes of tourists from the future."
Science does support some amount of time-bending, though. For example, physicist Albert Einstein 's theory of special relativity proposes that time is an illusion that moves relative to an observer. An observer traveling near the speed of light will experience time, with all its aftereffects (boredom, aging, etc.) much more slowly than an observer at rest. That's why astronaut Scott Kelly aged ever so slightly less over the course of a year in orbit than his twin brother who stayed here on Earth.
Related: Controversially, physicist argues that time is real
There are other scientific theories about time travel, including some weird physics that arise around wormholes , black holes and string theory . For the most part, though, time travel remains the domain of an ever-growing array of science fiction books, movies, television shows, comics, video games and more.

Einstein developed his theory of special relativity in 1905. Along with his later expansion, the theory of general relativity , it has become one of the foundational tenets of modern physics. Special relativity describes the relationship between space and time for objects moving at constant speeds in a straight line.
The short version of the theory is deceptively simple. First, all things are measured in relation to something else — that is to say, there is no "absolute" frame of reference. Second, the speed of light is constant. It stays the same no matter what, and no matter where it's measured from. And third, nothing can go faster than the speed of light.
From those simple tenets unfolds actual, real-life time travel. An observer traveling at high velocity will experience time at a slower rate than an observer who isn't speeding through space.
While we don't accelerate humans to near-light-speed, we do send them swinging around the planet at 17,500 mph (28,160 km/h) aboard the International Space Station . Astronaut Scott Kelly was born after his twin brother, and fellow astronaut, Mark Kelly . Scott Kelly spent 520 days in orbit, while Mark logged 54 days in space. The difference in the speed at which they experienced time over the course of their lifetimes has actually widened the age gap between the two men.
"So, where[as] I used to be just 6 minutes older, now I am 6 minutes and 5 milliseconds older," Mark Kelly said in a panel discussion on July 12, 2020, Space.com previously reported . "Now I've got that over his head."
General relativity and GPS time travel

The difference that low earth orbit makes in an astronaut's life span may be negligible — better suited for jokes among siblings than actual life extension or visiting the distant future — but the dilation in time between people on Earth and GPS satellites flying through space does make a difference.
Read more: Can we stop time?
The Global Positioning System , or GPS, helps us know exactly where we are by communicating with a network of a few dozen satellites positioned in a high Earth orbit. The satellites circle the planet from 12,500 miles (20,100 kilometers) away, moving at 8,700 mph (14,000 km/h).
According to special relativity, the faster an object moves relative to another object, the slower that first object experiences time. For GPS satellites with atomic clocks, this effect cuts 7 microseconds, or 7 millionths of a second, off each day, according to the American Physical Society publication Physics Central .
Read more: Could Star Trek's faster-than-light warp drive actually work?
Then, according to general relativity, clocks closer to the center of a large gravitational mass like Earth tick more slowly than those farther away. So, because the GPS satellites are much farther from the center of Earth compared to clocks on the surface, Physics Central added, that adds another 45 microseconds onto the GPS satellite clocks each day. Combined with the negative 7 microseconds from the special relativity calculation, the net result is an added 38 microseconds.
This means that in order to maintain the accuracy needed to pinpoint your car or phone — or, since the system is run by the U.S. Department of Defense, a military drone — engineers must account for an extra 38 microseconds in each satellite's day. The atomic clocks onboard don’t tick over to the next day until they have run 38 microseconds longer than comparable clocks on Earth.
Given those numbers, it would take more than seven years for the atomic clock in a GPS satellite to un-sync itself from an Earth clock by more than a blink of an eye. (We did the math: If you estimate a blink to last at least 100,000 microseconds, as the Harvard Database of Useful Biological Numbers does, it would take thousands of days for those 38 microsecond shifts to add up.)
This kind of time travel may seem as negligible as the Kelly brothers' age gap, but given the hyper-accuracy of modern GPS technology, it actually does matter. If it can communicate with the satellites whizzing overhead, your phone can nail down your location in space and time with incredible accuracy.
Can wormholes take us back in time?
General relativity might also provide scenarios that could allow travelers to go back in time, according to NASA . But the physical reality of those time-travel methods is no piece of cake.
Wormholes are theoretical "tunnels" through the fabric of space-time that could connect different moments or locations in reality to others. Also known as Einstein-Rosen bridges or white holes, as opposed to black holes, speculation about wormholes abounds. But despite taking up a lot of space (or space-time) in science fiction, no wormholes of any kind have been identified in real life.
Related: Best time travel movies
"The whole thing is very hypothetical at this point," Stephen Hsu, a professor of theoretical physics at the University of Oregon, told Space.com sister site Live Science . "No one thinks we're going to find a wormhole anytime soon."
Primordial wormholes are predicted to be just 10^-34 inches (10^-33 centimeters) at the tunnel's "mouth". Previously, they were expected to be too unstable for anything to be able to travel through them. However, a study claims that this is not the case, Live Science reported .
The theory, which suggests that wormholes could work as viable space-time shortcuts, was described by physicist Pascal Koiran. As part of the study, Koiran used the Eddington-Finkelstein metric, as opposed to the Schwarzschild metric which has been used in the majority of previous analyses.
In the past, the path of a particle could not be traced through a hypothetical wormhole. However, using the Eddington-Finkelstein metric, the physicist was able to achieve just that.
Koiran's paper was described in October 2021, in the preprint database arXiv , before being published in the Journal of Modern Physics D.

Alternate time travel theories
While Einstein's theories appear to make time travel difficult, some researchers have proposed other solutions that could allow jumps back and forth in time. These alternate theories share one major flaw: As far as scientists can tell, there's no way a person could survive the kind of gravitational pulling and pushing that each solution requires.
Infinite cylinder theory
Astronomer Frank Tipler proposed a mechanism (sometimes known as a Tipler Cylinder ) where one could take matter that is 10 times the sun's mass, then roll it into a very long, but very dense cylinder. The Anderson Institute , a time travel research organization, described the cylinder as "a black hole that has passed through a spaghetti factory."
After spinning this black hole spaghetti a few billion revolutions per minute, a spaceship nearby — following a very precise spiral around the cylinder — could travel backward in time on a "closed, time-like curve," according to the Anderson Institute.
The major problem is that in order for the Tipler Cylinder to become reality, the cylinder would need to be infinitely long or be made of some unknown kind of matter. At least for the foreseeable future, endless interstellar pasta is beyond our reach.
Time donuts
Theoretical physicist Amos Ori at the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa, Israel, proposed a model for a time machine made out of curved space-time — a donut-shaped vacuum surrounded by a sphere of normal matter.
"The machine is space-time itself," Ori told Live Science . "If we were to create an area with a warp like this in space that would enable time lines to close on themselves, it might enable future generations to return to visit our time."
Amos Ori is a theoretical physicist at the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa, Israel. His research interests and publications span the fields of general relativity, black holes, gravitational waves and closed time lines.
There are a few caveats to Ori's time machine. First, visitors to the past wouldn't be able to travel to times earlier than the invention and construction of the time donut. Second, and more importantly, the invention and construction of this machine would depend on our ability to manipulate gravitational fields at will — a feat that may be theoretically possible but is certainly beyond our immediate reach.

Time travel has long occupied a significant place in fiction. Since as early as the "Mahabharata," an ancient Sanskrit epic poem compiled around 400 B.C., humans have dreamed of warping time, Lisa Yaszek, a professor of science fiction studies at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta, told Live Science .
Every work of time-travel fiction creates its own version of space-time, glossing over one or more scientific hurdles and paradoxes to achieve its plot requirements.
Some make a nod to research and physics, like " Interstellar ," a 2014 film directed by Christopher Nolan. In the movie, a character played by Matthew McConaughey spends a few hours on a planet orbiting a supermassive black hole, but because of time dilation, observers on Earth experience those hours as a matter of decades.
Others take a more whimsical approach, like the "Doctor Who" television series. The series features the Doctor, an extraterrestrial "Time Lord" who travels in a spaceship resembling a blue British police box. "People assume," the Doctor explained in the show, "that time is a strict progression from cause to effect, but actually from a non-linear, non-subjective viewpoint, it's more like a big ball of wibbly-wobbly, timey-wimey stuff."
Long-standing franchises like the "Star Trek" movies and television series, as well as comic universes like DC and Marvel Comics, revisit the idea of time travel over and over.
Related: Marvel movies in order: chronological & release order
Here is an incomplete (and deeply subjective) list of some influential or notable works of time travel fiction:
Books about time travel:

- Rip Van Winkle (Cornelius S. Van Winkle, 1819) by Washington Irving
- A Christmas Carol (Chapman & Hall, 1843) by Charles Dickens
- The Time Machine (William Heinemann, 1895) by H. G. Wells
- A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur's Court (Charles L. Webster and Co., 1889) by Mark Twain
- The Restaurant at the End of the Universe (Pan Books, 1980) by Douglas Adams
- A Tale of Time City (Methuen, 1987) by Diana Wynn Jones
- The Outlander series (Delacorte Press, 1991-present) by Diana Gabaldon
- Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban (Bloomsbury/Scholastic, 1999) by J. K. Rowling
- Thief of Time (Doubleday, 2001) by Terry Pratchett
- The Time Traveler's Wife (MacAdam/Cage, 2003) by Audrey Niffenegger
- All You Need is Kill (Shueisha, 2004) by Hiroshi Sakurazaka
Movies about time travel:
- Planet of the Apes (1968)
- Superman (1978)
- Time Bandits (1981)
- The Terminator (1984)
- Back to the Future series (1985, 1989, 1990)
- Star Trek IV: The Voyage Home (1986)
- Bill & Ted's Excellent Adventure (1989)
- Groundhog Day (1993)
- Galaxy Quest (1999)
- The Butterfly Effect (2004)
- 13 Going on 30 (2004)
- The Lake House (2006)
- Meet the Robinsons (2007)
- Hot Tub Time Machine (2010)
- Midnight in Paris (2011)
- Looper (2012)
- X-Men: Days of Future Past (2014)
- Edge of Tomorrow (2014)
- Interstellar (2014)
- Doctor Strange (2016)
- A Wrinkle in Time (2018)
- The Last Sharknado: It's About Time (2018)
- Avengers: Endgame (2019)
- Tenet (2020)
- Palm Springs (2020)
- Zach Snyder's Justice League (2021)
- The Tomorrow War (2021)
Television about time travel:

- Doctor Who (1963-present)
- The Twilight Zone (1959-1964) (multiple episodes)
- Star Trek (multiple series, multiple episodes)
- Samurai Jack (2001-2004)
- Lost (2004-2010)
- Phil of the Future (2004-2006)
- Steins;Gate (2011)
- Outlander (2014-2023)
- Loki (2021-present)
Games about time travel:
- Chrono Trigger (1995)
- TimeSplitters (2000-2005)
- Kingdom Hearts (2002-2019)
- Prince of Persia: Sands of Time (2003)
- God of War II (2007)
- Ratchet and Clank Future: A Crack In Time (2009)
- Sly Cooper: Thieves in Time (2013)
- Dishonored 2 (2016)
- Titanfall 2 (2016)
- Outer Wilds (2019)

Additional resources
Explore physicist Peter Millington's thoughts about Stephen Hawking's time travel theories at The Conversation . Check out a kid-friendly explanation of real-world time travel from NASA's Space Place . For an overview of time travel in fiction and the collective consciousness, read " Time Travel: A History " (Pantheon, 2016) by James Gleik.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Ailsa is a staff writer for How It Works magazine, where she writes science, technology, space, history and environment features. Based in the U.K., she graduated from the University of Stirling with a BA (Hons) journalism degree. Previously, Ailsa has written for Cardiff Times magazine, Psychology Now and numerous science bookazines.
Satellites watch as 4th global coral bleaching event unfolds (image)
Happy Earth Day 2024! NASA picks 6 new airborne missions to study our changing planet
Earth got hammered by cosmic rays 41,000 years ago due to a weak magnetic field
Most Popular
- 2 Mirrors in space could boost solar power production on Earth. Here's how.
- 3 NASA ends CloudSat Earth-observing mission after 18 years
- 4 Earth's weird 'quasi-moon' Kamo'oalewa is a fragment blasted out of big moon crater
- 5 Fortnite launches to the moon in new 'Lunar Horizons' simulation game
Time travel is theoretically possible, calculations show. But that doesn't mean you could change the past.
- Time travel is possible based on the laws of physics, according to researchers.
- But time-travelers wouldn't be able to alter the past in a measurable way, they say.
- And the future would essentially stay the same, according to the reseachers.

Imagine you could hop into a time machine, press a button, and journey back to 2019, before the novel coronavirus made the leap from animals to humans.
What if you could find and isolate patient zero? Theoretically, the COVID-19 pandemic wouldn't happen, right?
Not quite, because then future-you wouldn't have decided to time travel in the first place.
For decades, physicists have been studying and debating versions of this paradox: If we could travel back in time and change the past, what would happen to the future?
A 2020 study offered a potential answer: Nothing.
"Events readjust around anything that could cause a paradox, so the paradox does not happen," Germain Tobar, the study's author previously told IFLScience .
Tobar's work, published in the peer-reviewed journal Classical and Quantum Gravity in September 2020, suggests that according to the rules of theoretical physics, anything you tried to change in the past would be corrected by subsequent events.
Related stories
Put simply: It's theoretically possible to go back in time, but you couldn't change history.
The grandfather paradox
Physicists have considered time travel to be theoretically possible since Albert Einstein came up with his theory of relativity. Einstein's calculations suggest it's possible for an object in our universe to travel through space and time in a circular direction, eventually ending up at a point on its journey where it's been before – a path called a closed time-like curve.
Still, physicists continue to struggle with scenarios like the coronavirus example above, in which time-travelers alter events that already happened. The most famous example is known as the grandfather paradox: Say a time-traveler goes back to the past and kills a younger version of his or her grandfather. The grandfather then wouldn't have any children, erasing the time-traveler's parents and, of course, the time-traveler, too. But then who would kill Grandpa?
A take on this paradox appears in the movie "Back to the Future," when Marty McFly almost stops his parents from meeting in the past – potentially causing himself to disappear.
To address the paradox, Tobar and his supervisor, Dr. Fabio Costa, used the "billiard-ball model," which imagines cause and effect as a series of colliding billiard balls, and a circular pool table as a closed time-like curve.
Imagine a bunch of billiard balls laid out across that circular table. If you push one ball from position X, it bangs around the table, hitting others in a particular pattern.
The researchers calculated that even if you mess with the ball's pattern at some point in its journey, future interactions with other balls can correct its path, leading it to come back to the same position and speed that it would have had you not interfered.
"Regardless of the choice, the ball will fall into the same place," Dr Yasunori Nomura, a theoretical physicist at UC Berkeley, previously told Insider.
Tobar's model, in other words, says you could travel back in time, but you couldn't change how events unfolded significantly enough to alter the future, Nomura said. Applied to the grandfather paradox, then, this would mean that something would always get in the way of your attempt to kill your grandfather. Or at least by the time he did die, your grandmother would already be pregnant with your mother.
Back to the coronavirus example. Let's say you were to travel back to 2019 and intervene in patient zero's life. According to Tobar's line of thinking, the pandemic would still happen somehow.
"You might try and stop patient zero from becoming infected, but in doing so you would catch the virus and become patient zero, or someone else would," Tobar said, according to Australia's University of Queensland , where Tobar graduated from.
Nomura said that although the model is too simple to represent the full range of cause and effect in our universe, it's a good starting point for future physicists.
Watch: There are 2 types of time travel and physicists agree that one of them is possible
- Main content
- Newsletters
Time travel: five ways that we could do it
Cathal O’Connell
Cathal O'Connell is a science writer based in Melbourne.
In 2009 the British physicist Stephen Hawking held a party for time travellers – the twist was he sent out the invites a year later (No guests showed up). Time travel is probably impossible. Even if it were possible, Hawking and others have argued that you could never travel back before the moment your time machine was built.
But travel to the future? That’s a different story.
Of course, we are all time travellers as we are swept along in the current of time, from past to future, at a rate of one hour per hour.
But, as with a river, the current flows at different speeds in different places. Science as we know it allows for several methods to take the fast-track into the future. Here’s a rundown.
1. Time travel via speed
This is the easiest and most practical way to time travel into the far future – go really fast.
According to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, when you travel at speeds approaching the speed of light, time slows down for you relative to the outside world.
This is not a just a conjecture or thought experiment – it’s been measured. Using twin atomic clocks (one flown in a jet aircraft, the other stationary on Earth) physicists have shown that a flying clock ticks slower, because of its speed.
In the case of the aircraft, the effect is minuscule. But If you were in a spaceship travelling at 90% of the speed of light, you’d experience time passing about 2.6 times slower than it was back on Earth.
And the closer you get to the speed of light, the more extreme the time-travel.
Computer solves a major time travel problem
The highest speeds achieved through any human technology are probably the protons whizzing around the Large Hadron Collider at 99.9999991% of the speed of light. Using special relativity we can calculate one second for the proton is equivalent to 27,777,778 seconds, or about 11 months , for us.
Amazingly, particle physicists have to take this time dilation into account when they are dealing with particles that decay. In the lab, muon particles typically decay in 2.2 microseconds. But fast moving muons, such as those created when cosmic rays strike the upper atmosphere, take 10 times longer to disintegrate.
2. Time travel via gravity
The next method of time travel is also inspired by Einstein. According to his theory of general relativity, the stronger the gravity you feel, the slower time moves.
As you get closer to the centre of the Earth, for example, the strength of gravity increases. Time runs slower for your feet than your head.
Again, this effect has been measured. In 2010, physicists at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) placed two atomic clocks on shelves, one 33 centimetres above the other, and measured the difference in their rate of ticking. The lower one ticked slower because it feels a slightly stronger gravity.
To travel to the far future, all we need is a region of extremely strong gravity, such as a black hole. The closer you get to the event horizon, the slower time moves – but it’s risky business, cross the boundary and you can never escape.
And anyway, the effect is not that strong so it’s probably not worth the trip.
Assuming you had the technology to travel the vast distances to reach a black hole (the nearest is about 3,000 light years away), the time dilation through travelling would be far greater than any time dilation through orbiting the black hole itself.
(The situation described in the movie Interstellar , where one hour on a planet near a black hole is the equivalent of seven years back on Earth, is so extreme as to be impossible in our Universe, according to Kip Thorne, the movie’s scientific advisor.)
The most mindblowing thing, perhaps, is that GPS systems have to account for time dilation effects (due to both the speed of the satellites and gravity they feel) in order to work. Without these corrections, your phones GPS capability wouldn’t be able to pinpoint your location on Earth to within even a few kilometres.
3. Time travel via suspended animation
Another way to time travel to the future may be to slow your perception of time by slowing down, or stopping, your bodily processes and then restarting them later.
Bacterial spores can live for millions of years in a state of suspended animation, until the right conditions of temperature, moisture, food kick start their metabolisms again. Some mammals, such as bears and squirrels, can slow down their metabolism during hibernation, dramatically reducing their cells’ requirement for food and oxygen.
Could humans ever do the same?
Though completely stopping your metabolism is probably far beyond our current technology, some scientists are working towards achieving inducing a short-term hibernation state lasting at least a few hours. This might be just enough time to get a person through a medical emergency, such as a cardiac arrest, before they can reach the hospital.
In 2005, American scientists demonstrated a way to slow the metabolism of mice (which do not hibernate) by exposing them to minute doses of hydrogen sulphide, which binds to the same cell receptors as oxygen. The core body temperature of the mice dropped to 13 °C and metabolism decreased 10-fold. After six hours the mice could be reanimated without ill effects.
Unfortunately, similar experiments on sheep and pigs were not successful, suggesting the method might not work for larger animals.
Another method, which induces a hypothermic hibernation by replacing the blood with a cold saline solution, has worked on pigs and is currently undergoing human clinical trials in Pittsburgh.
4. Time travel via wormholes
General relativity also allows for the possibility for shortcuts through spacetime, known as wormholes, which might be able to bridge distances of a billion light years or more, or different points in time.
Many physicists, including Stephen Hawking, believe wormholes are constantly popping in and out of existence at the quantum scale, far smaller than atoms. The trick would be to capture one, and inflate it to human scales – a feat that would require a huge amount of energy, but which might just be possible, in theory.
Attempts to prove this either way have failed, ultimately because of the incompatibility between general relativity and quantum mechanics.
5. Time travel using light
Another time travel idea, put forward by the American physicist Ron Mallet, is to use a rotating cylinder of light to twist spacetime. Anything dropped inside the swirling cylinder could theoretically be dragged around in space and in time, in a similar way to how a bubble runs around on top your coffee after you swirl it with a spoon.
According to Mallet, the right geometry could lead to time travel into either the past and the future.
Since publishing his theory in 2000, Mallet has been trying to raise the funds to pay for a proof of concept experiment, which involves dropping neutrons through a circular arrangement of spinning lasers.
His ideas have not grabbed the rest of the physics community however, with others arguing that one of the assumptions of his basic model is plagued by a singularity, which is physics-speak for “it’s impossible”.
The Royal Institution of Australia has an Education resource based on this article. You can access it here .
Related Reading: Computer solves a major time travel problem
Originally published by Cosmos as Time travel: five ways that we could do it
Please login to favourite this article.

Time travel is possible, but it’s a one-way ticket
Chenoa van den Boogaard , Physics and Astronomy editor
The ability to travel through time, whether it is to fix a mistake in the past or gain insight into the future, has long been embraced by science fiction and debated by theoretical physicists. While the debate continues over whether travelling into the past is possible, physicists have determined that travelling to the future most certainly is. And you don’t need a wormhole or a DeLorean to do it.
Real-life time travel occurs through time dilation, a property of Einstein’s special relativity . Einstein was the first to realize that time is not constant, as previously believed, but instead slows down as you move faster through space.
As part of his theory, Einstein re-envisioned space itself. He coined the phrase “spacetime,” fusing the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single term. Instead of treating space as a flat and rigid place that holds all the objects in the universe, Einstein thought of it as curved and malleable, able to form gravitational dips around masses that pull other objects in, just as a bowling ball placed in the centre of a trampoline would cause any smaller object placed on the trampoline to slide towards the centre.
A computer-generated representation of Einstein’s curved spacetime. The Earth creates a gravitational dip in the fabric of spacetime which is deepest at its core. Courtesy and © of NASA
The closer an object gets to the centre of the dip, the faster it accelerates. The centre of the Earth’s gravitational dip is located at the Earth’s core, where gravitational acceleration is strongest. According to Einstein’s theory, because time moves more slowly as you move faster through space, the closer an object is to the centre of the Earth, the slower time moves for that object.
This effect can be seen in GPS satellites, which orbit 20,200 kilometres above the Earth’s surface. These satellites have highly precise clocks onboard that gain an average of 38 microseconds per day due to time dilation. While this time gain seems insignificant, GPS satellites rely on their onboard clocks to maintain precise global positioning. Running 38 microseconds fast would result in a positioning error of nearly 10 kilometres, an error that would increase daily if the time difference were not constantly corrected.
A more dramatic example of time dilation can be seen in the movie Interstellar when Matthew McConaughey and his crew land on a planet with an extreme gravitational field caused by a nearby black hole. Because of the black hole’s intense gravitational influence, time slows dramatically for the crew on the planet, making one hour on the surface equal to seven years on Earth. This is why, when the crew returns to Earth, Matthew McConaughey’s daughter is an old woman while he appears to be the same age as when he left.
So why hasn’t humanity succeeded in making such drastic leaps forward in time? The answer to this question comes down to velocity. In order for humanity to send a traveller years into the future, we would either have to take advantage of the intense gravitational acceleration caused by black holes or send the traveller rocketing into space at close to the speed of light (about 1 billion km/h). With our current technology , jumping a few microseconds into the future is all humans can manage.
But if technology one day allows us to send a human into the future by travelling close to the speed of light, would there be any way for the traveller to use time dilation to return to the past and report her findings? “Interstellar travel reaching close to the speed of light might be possible,” says Dr. Jaymie Matthews , professor of astrophysics at the University of British Columbia, “[but] this voyage is one way into the future, not back to the past.”
If we can’t use time dilation to return to the past, does this mean that the past is forever inaccessible? Perhaps not. Einstein proposed that time travel into the past could be achieved through an Einstein-Rosen bridge, a type of wormhole. Wormholes are theoretical areas of spacetime that are warped in a way that connects two distant points in space.
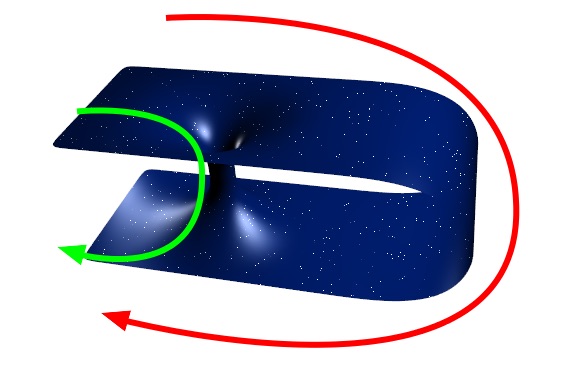
A visualization of a wormhole: The fabric of spacetime curves back upon itself, forming a bridge between two distant locations. Image by Panzi , CC-BY 3.0
Einstein’s equations suggested that this bridge in space could hypothetically connect two points in time instead if it were stable enough. “At the moment, even an Einstein-Rosen bridge cannot [be used to] go back in the past because it doesn’t live long enough – it is not stable,” Matthews explains.
“Even if it was stable, it [requires] other physics, which we don’t have. Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have “exotic” physical properties that would violate known laws of physics, such as a particle having a negative mass. That is why “wormholes” are only science fiction.”
While it would be fascinating to travel back in time to see the dinosaurs or to meet Albert Einstein and show him the reality of time travel, perhaps it is best if the past remains untouched. Travelling to the past invites the possibility of making an alteration that could destroy the future. For example, in Back to the Future , Marty McFly travels to the past and inadvertently prevents his parents from meeting each other, nearly preventing his own existence. But if he had undone his own existence, how could he have travelled back in time in the first place?
Marty’s adventures are a variation of the grandfather paradox: what happens if you go back in time and kill your grandfather before your father is conceived? If you are successful, how is it possible that you’re alive to kill your grandfather in the first place?
A recent study at the University of Queensland may have the answer to this baffling paradox. In this study, the researchers prove mathematically that paradox-free time travel is possible, showing that the universe will self-correct to avoid inconsistencies. If this is true, then even if we could travel back in time, we would never be able to alter events to create a different future.
While these new findings are enlightening, there appears to be more evidence that, although time dilation can allow us to glimpse the future, we will never be able to visit the past. As the late Stephen Hawking said in his book Black Holes and Baby Universes , “The best evidence we have that time travel [into the past] is not possible, and never will be, is that we have not been invaded by hordes of tourists from the future.”
Banner image by Alex Lehner, CC BY 2.0
240 thoughts on “ Time travel is possible, but it’s a one-way ticket ”
How do I go about time travel? what do I need how do I get those required things?
Very large ring magnets and some mathematics and will to see it in reality.
How about a sphere magnet ship…
hoe about 3d time and hemi synch or portals augmented reality,power of suggestion..drugs pcp binural tones frequency amplitude .virtual computing ie.
I’m a time traveling tourist, Stephen Hawking was wrong.
Time is simply a measurement of space under the amount given its mass and the amount of light and dark in which governs its mass in a 4dimensional reality step outside of the force in which permenates its flow one would reside there would be no past present or future there be a fixed permance of a constant here and now and so ok then what is to come.
Very well explained article !!
But I think if physics says time travel can be possible then it’s definitely possible. Considering not to go back to your childhood and fix things but rather can go to the past but as invisible person to them. So that,
No actions by you would impact your future.
Regards, Kirankumar DR
Tell me more
Yes.. I wish I can do this too 🙂
We will understand it better, by and by…
I have a theory for warp speed, but nasa would have to put it to the test…check my Facebook
I am reading for this drive , i am ready , without think my life safe or not
@Ravi chandila English translation please?
Please someone help me I just want to send a message to myself in my past.,to get the love of my life, he never revealed to me his feelings now my life is ruined by the decision of my elders Please help me, it’s question of my life and death. Nazneen
Is time travel machine is their, if the time travel machine is true can it move to the past . To bring back my lost life
That’s the problem you know.. it is not there that’s why we aren’t able to travel time..and yes it it will be built then you will be able to do so…..
damn my life is also lost and broken but still no one can give a time machine for free
DO NOT change the future. That’s why people like you couldn’t go. One wrong person to ruin it for the rest of us
On the point of time reversal, it is evidently impossible. The Uncertainty Principle prohibits spacetime reversal. The Universe is unable to remember its past (as a consequence of the Uncertainty Principle), therefore the Universe cannot reorganise itself.
Can I have to go on my past with another time travel it is a possible when just tell me about one thing that can I have to go in my past one year
we dont need magnets.we need a strong gravitational force to warp spacetime allowing us to travel through with speed of sound or speed of light or faster.we need to learn how to control such force carefully or it could be lethal.gravity slows down time.but it can theoratically work both ways.if we can reverse the gravity’s natural reaction we could speed up a spacecraft faster than light(its all relative(and theoratical))
I WAS ACTUALLY JUST THINKING THE SAME THINFG BEFORE READING YOUR PIECE. VERY WELL EXPLAINED, AND IT DOES MAKE ALOT OF SENSE. WELL DONE.
oh and I forgot to add it can be the key to look into the universe and also travelling time(theoratical).speed and gravity are the key to the universe(theory not proved)
All you really need is a crystal diode with 16 sides, a large pain of glass, and a frequency transmitter near a bathtub full of ice cold water….if you reach the right frequency you can travel through time forward and reverse…
Magnetized metal(VCR Reading Head), to read time out of the Magnetosphere all around earth. The Magnetosphere kills 2 birds with one stone- it protects earth and it records human time:
Mystery solved and I will explain, I was in a coma 3 months and I experienced things, I traveled time forward and backward, it is not a one way ticket. Movies and songs are recorded on magnetic tape in a VCR tape Cartridge or Cassette tape,  Magnetic tape recording works by converting electrical signals into magnetic energy, which imprints a record of the signal onto a moving tape covered in magnetic particles.  3D life on earth(a movie), and the Magnetosphere all around earth coming from the core of earth(MAGNETIC ACTIVITY) without Atom Made Tape, is like a movie on magnetic Atom made tape in a VCR tape cartridge. Revolution and Rotation is the motor(VCR).
This is why people have those freaky Deji’vu feelings like they have lived this before, BECAUSE YOU HAVE, and how people can be psychic, and how there is Prophecy in the Bible. When a person dies, their Spirit- MIND(Thoughts, Feelings, Urges(Physical and mental personality)) breaks out of human body- a stopped heart is what releases the spirit from the human body. Then the Soul(Life) with the memory of your existence in it breaks out of spirit and goes back to your birthday with a erased memory, meanwhile your spirit goes back in time to when you were a teenager starting the mental puberty, maturity from that adult spirit you died with in last life.In that old movie Star Wars or maybe it was the Empire Strikes Back, there is a scene where Princess Laya plays like a 3D movie, that is EXACTLY how its of life on earth.
Mr Snow, I believe you as I have seen it too. As humans we have deep knowledge of things we cannot rationally explain but you have done a great job here.
I thought that Analogy would be a better and easier way to explain, or in a picture of the earth from far out in space with the atmosphere around it looks like a DVD disk and the earth being the center sticker but is in 3D.
Actually you are on to several things here. I have also had the infusion of knowledge that also had to do with comparing life to recorded movies and music. I know you were using it to explain your theory, but I do think there is something there, I always have. When you watch a movie you are seeing the past. Why can’t you somehow use a recording as a base to go back into? I agree with everything you said here, and it’s worth looking into.
Jeffrey, very interesting idea!! Could be something to that. As far as your coma experiences, I think there are things we just do not understand and are nearly impossible to explain. Perhaps time IS like a video tape, or a DVD? Magnetism is one of the forces of nature. I too have had some odd experiences that suggest that we are able to perceive things beyond our five known senses.
I think if you have had a near death experience, such as being in a coma, then you have experienced the powerful hallucinations provided by the chemical substance DMT which your body creates naturally in times of extreme trauma, but also found in most plants and used recreationally by some who are brave enough and into that kind of thing. Your theory is interesting, but completely unproven and as far as I know untested. If things were so simple, I’m sure many scientists would have already thought of such an idea and tested it.
How do I travel through time
Be alive and live life to the fullest is the best way to travel through time ! OR Befriend grey aliens../ They may hold the key to the sum of all knowledge in the universe..
Sounds good will it work
Really log vaps mil sakte hau h kya
Can you plz explain I didn’t get it
You dont first all you are not experienced in the field of the space time continum and you could you upset the already fragile and multitude of alternate realitys that have looping due irresponsible ones who somehow gotten the technology causing another altered time frame there are a disarray multiple reality which are looping in earths 4dimensonal time frame time traveling is not for a vacation or just to get a joy ride its a serious and complex reality not be joked about it is a real thing and certain individual have are upset the balance of earths original time zone note now the gaurdians of this region of milky way the galatic order of the light keepers Angelic gaurdians of the (names with held)are working over time ooh nice pun (over TIME) ha wow to restore Earth back to a original time continum
Who said I want a joy ride, my life is devastated even my kids are suffering, I want to commit suicide but can’t leave my kids back, Being captive for most of my life, if my life is changed nothing will be disturbed, only thing happens is 3 life’s will be saved. And more so over I don’t want to travel I just want to send a message to myself in my past plz on the date of 30th May 1996. My life is ruined plz help me, it was my dad,brother, sister who pushed me into the dungeon and my husband and his family took over the charge of torturing me. Nazneen
I want to go back in time and tell my 5 year old self to burn the creepy dolls that my mom bought cause there is demons in it at the same time I will kidnap and torture my dad right now go back in time and show the younger version of my dad show him what will happen to his future self if he don’t get rid of those possessed objects and keeps letting my mom buy those antiques I’m 18 now I’m single no girlfriend no friend alone nothing very depressed too and I try to remember the positive things that happened in my life which there aren’t many tho but the demons keep squeezing my memory brain and my mom keeps on making so much loud noise including her damn mouth I have attempted to burn the demonic dolls but I only burned them for a minute or two with gas cause I was worried I might accidentally set my whole neighborhood on fire but then my mom threw it all in the recycle instead of the trash so the demons just keep bothering me its driving me nuts he he.
Access to a Quantum Computer Network on the web would be a good start. A series of ChatBots and webhook sites strategically placed in not only space, but in time. A series of algorithms and I think information can be transferred backwards to ones self…
How do we know that there are no horde of tourists among ourselves?
How do we know we’re all not tourists?
We’re all time travelers. We all travel into the future daily. 1 second at a time. Lol…
Agreed! I had the same thought!
Excellent question
If is possible, I would like to go back to: January the 1st 1975 & relive the 70’s as I prefer that decade to the awful one I am facing now, Back then We had more police our streets & left our front doors open, Those days were far much more better .
https://3netra.co.in/61-2/
Please do comment on my blog post regarding time travel
how about you ask the flash to help you
I need the time travel so I’m fails so many times i love time travel i have to go fast and future so i have no idea im travel is a my dream so my dream solution plz say me i have time travel so please help me someone please…..
I think you are over reacting
When we look at the stars now it is what they looked like years ago so what if we go to the stars and look down?
You cant go to the stars. It will just take billions and billions of years to go even to the next nearest star than our Sun- proxima centuri. Sorry to say, but do you think that you will be alive all those years??
You can do that without going to the stars… our planet reflects light as well thus making it visible from other parts of the universe…. has the word “reflection†crossed your mind ? 😉
Contact me on my hangout I will help you [email protected]
bro just time travel its not that hard
Please help me to time travel, can I see myself when I go back in time like Harmaini sees herself in Harry potter?? Or can I send messages to myself I know the particular date when to send. It’s not the mistake I had done in my past but it was done by my father and brother who are safe, happy enjoying their lives,my life is totally ruined Please help me. Nazneen
I want to go back in time to save my wife .it was a bad mastake she died .that could be changed i need to go back and save her. Please help me.yours gordon sutcliffe
Would love to hear more how it’s possible, as I am really so desperate to go back in time. I lost my wife 6mons back because of COVID and I will do the impossible things to make it happen.
DMT Experience
what is that?
Dmt experience. Time travel, out of body and sometimes superhuman capabilities.
Jump into a black hole
We have to lose something(the past) to gain something(the future) in time travel.Time cannot be played with.Am I correct.
you need to have d e t e r m i n a t i o n
Time machine is possible
speeder than light LOL
speeder than light cuz if the light break it limits it will move backward in time
Don’t Just don’t disturb the past
I want to go back in time and see my dad. I miss him.
mee too raina I lost my father the day before you posted the comment 18th may, crap it hurts me so much. I would rather die to bring those moments back….
Everything is connected . Time isn’t real .
It is universe we travel to and not a time line in one universe
Ask trump….Mandela effect…. dmt 5th dimension
u need an X-WING starfighter and a lightsaber to fight the knights at past and a R2-B2 to track
The fact that no one has time travelled to the past is the proof that time travelling will NEVER exist.
Others have. Portals open most of the time. Example: Miami Fl. Magnetic Material gets bombarded by the sun. Which fractures and formed portals within that area. Ley lines can lead to the portals of travel within miami for just to start. One can laugh or wonder if. In my experience jumping for the better the word of it (Movie Jumper) can be done. You can either Teleport or Time Travel. Our sun open these portals everyday. The best time when Sun spots start to emerge. All that electrons traveling at light speed is enough to rupture our magnetic fields on Earth. You will return of course. Like water on a lake or an ocean time will corrects itself. Your inner clock is your ticket back home. With a little math,fourth dimensional thinking,a magnetic meter, the right location,history research and luck. You may get to expirence it. First clue….cold spots…it may not be a ghost.
Plz can you help me please help me you can save my life
I wish I could help you, I can sense your sufferings.
You need a bag of hyperlink modules to start, then nuclear beepbeep gatangas, when you have that come back here and I will tell you what you need next.
You need high voltage beepbeep gatangas and a large broonasic magnet of about 450 Gauss, come back here when you have these and I will tell you the rest.
you need an old fashioned police box
If you rotate the center of the earth in the opposite direction, then the whole earth can be moved back in time, on the other hand, if you move the center of the earth and change its position by separating it from the part of the earth, then you will be able to time correctly. Let’s reach the other side.
How I could time travel any time travel machines inverted
give audition in the flash series..
I think that to go back in time you’d to travel faster than the speed of light since time stops at the speed of light but if you wanted to go back to say mlk’s assassination you would need to go at least 10 times the speed of light
You don’t want to, the moment you wrote that message is a historical point in time.
When time travel is possible, you should d̵͔̮͉̣̯̳͌iÍ’Ì̩̆͟ͅs͎̲̖͙̺ͬ̽̊͆͢r̖̹͆͂̚͘ê̛̫̪̱͇̘̩ͬgÍ̖͉̤͚ͣ̊̌͜a̯̗͚̬͑͂͒͡Í̱̦ṟͦ͗͘Ìd͋҉̪̖̥͔̟̟͚̻ ͧ̔Í͎̬i̧͚̫̻̇ͮͫ̆tÌ“Ì‚Ì•Ì©Ì»Í‰Ì©Ì˜Ì°Ì Ì« ̦̻̳̦̉͆̊̇̀i̴̗ͣ̈́Í̞͙͇mͦ̑ͦ̚Í͚̜̬̹̘̟ÌmÍ«ÌŒÍ†Í¡Ì±Í•Ì»Í‡Ì®Ì Ì°Ì¼e̢͈̜̱ͩd̵̦͙͔̃̿̈̚ͅÌ̹i̛̖̬͓͚̩ͯÌÌ—aÌ…ÌÍ̦͎ÌÌ£Ì̘͔͙ṯ̴̟ͥ̀͗e̵͎͗ͨ̂͒ÌÍ“ÌŸl̼͕͕ͦͦ͜y̸͙̯̺̘͉ͣ,͈̻͙̑ͫ͜Ì̺̘̞ ͔̗̣͒͜dÍ›Ì̶͇͚͉̦̞̗oÌ’Í©Í„Í€ÌžÌ®Ì»Ì²ÌœÍ…Ì Ì‰ÌÍ‚Ì̲̙̦̮̺̀nÌŒÍ Ì̞͖o͛ͩÌ̬͕̯̩͓̮̫͛͜Ìt̼̙̿͊͆̕ Ì̲͚̲̬̦̗̀m̢̹̜͗̆ͣÌÌ Ì¬ą̲̺̻͈̹͎̈́̇̉͛ǩ̜̪̱̀e̜̳͔͉̣͓̓͗͘ ̉҉̲̞̘͈ͅcÌ‹Í¥Ì̴̦̣Ì͇͈̙oÍ¯Í€Ì«Í‡Í‡Ì˜Ì»Ì Ì¹ÍŽn̺̹̣̦̔̇̾͢t͚̹͚̙̞̪̗̺̄͂͜a̞̗̖̻̩͉̋͛̆͘c͙̙̎͘tÌÍ§Í©Í„Ì•Ì»Ì Ì£Í‰Ì¹Ì Ì£Ì² ̶͕̗̬̿wͦÍÍ¡Í“ÌžÍ̹̰͖͉i͎̞̾ͦ̃̈́̕tÌ̜̺̖ͦ͞Ìh͙̰̬̖͎̰͛̇ͮͫ͡ ͣͯÍ͕̻͚̹̺ā̱̙͡Ì̦̤̼̥n̶͔̜ͥ͆̌̋y̷͓̻̺̺͉͇̻ͨọ̱͙̜̈́̉ͣ̔͟ņ̦̟͔̜̫̗̒ͬe̡͕̮̓͂̚ ̉Í̡͓̘͚͋̽Ì̹͔t̖͌͋͘ÍÍšÌ̬͈ͅÌẖ̗̖͚̼͔͕͆̓̾͜a̋ͦͩÍ͈̣͢ÍÍ•ÍtÌ̖̪̤̳͎̱͡ ÍƒÍ«Ì›Ì»Ì Ì¼Ì¬l̶̞̤̣͔̗͔̂ͅoÍ„Í¯Í Ì¹ÌžÌ¦Ì–ÍšÌ«ÌœÌ±o̧̯̱̪̓ͮ̋k͉͎̓ͧ̕ÌÌ»sÌ̤͈̪͟ ̤̞̳͔̔̂ͨ͜Ì̪̟̹hÍ—Ì…Ì̛̃Ì̲̰̻uÍ̇̈Í̜̙m̧̞̮̟̦̳̟̊aÍŠÍ›Ì̸͓̺̲̼̜n̶̳̮̒.͇̻͚͓̳̺̜̱͋ͬ͗ͩ͢
It’s Close I can feel it
Yes it becomes a history but my life also in the past changes and the present also with it. The way I’m suffering from the pain and want to end my life I’m 100% sure at least sure no one around me is or was as hopeless and horrible as my hubby I’m devastated I really want to send a message to my past it may not start but it will definitely change. I was forced, not given any option, my father and brother gave me wrong information and had no concerns for me. It was just survival for me. I repent for not killing myself when I had time, but now if I have a chance why not. Now when I’m out of my marriage I come to know a guy then had feelings for me, was madly in love and wanted to ask for my hand, now I want to inform my self and change everything plz help me.
I too would like to go back in time. I just wish he lived a happy eternal life. I would just like to repeat to come back in 2020.
I heard from a guy in Idaho that time travel is possible. You’ll need to go online and purchase a pogo stick looking device and make sure not to forget the crystals.
I think u need a black-hole-proof spaceship, go to the centre, escape the black hole and viola! You are now in the past. If you can’t escape, then you’d travel to a time where that black hole didn’t exist.
Believe me you time travel! If not physically then you do mentally,like you through dreams.
Though they sale it online, it would not take the chance. It is as simple as beating the speed of light and having some system to send you to the time you want. Time however is not real, and were just traving universes. It will all be in the open in 2028 according to other travelers.
All you need base on how to travel to time is very simple but had to find firstly find a way to get to space through a space rocket secondly find a very perfect consifigration for traveling to tiTme then find a very fast rocket that could create a form of force reaction in space in order yo enable fast speed in space for the break through of non gravity in space and make sure that while doing all you activities is not far away from planet and not also to close to planet earth and make sure that you are with wristwatchs whose time is set disame then you can to the future
Man you can get all you need for too build a time machine in your local store man, man I sure wished I’d kept mine but it frightened the heck off me man, sometimes when I fart I find a grape in my pants
time travel is a fake, baseless and delusional idea. If you believe in that crap then tell us if we are living in the future or in the past. To travel backward the entire system has to return all along with nature and events, it won’t be for you alone except time travel only happens in the mind.
you would need to get about 1,000,000 pounds of silicon and then somehow conduct enough energy to make 500 cars run without an engine and then go to a nuqular power plant and somehow make a portal. but the whole world could go out of orbit if you do that so I wouldent sugest it.
Time machine is good and bad because,with the time machine you will know about your future which is not good.
Is time travel actually a real thing because if it is then I need it because I am trying to go back in time to fix all of my mistakes
So what if time travel is the reason that we now believe there are other realities in our own world.this could be that a Time traveler we could only go back and couldn’t come back, and on doing so if you do something to change the past in stead make a new reality.making other things are deferent and ours realty stays the same . sometimes reality gets mixed up make the mandela effect that we see today
Time in the future it is faster then now. The past is slower so you can travel . It is up to you. One way is to meditate. You can travel and see any body you want right now. You can fly faster then light. That is one way. You go to the future. To go to the past you sleep for a long time. Some time you go to the future or the past. Your heart well stop and your body gets cold. Sometimes you can control it sometimes you can’t.
but how do we know that is really true ? i mean i want to figure this out, i want to time travel, but how is it that simple ? so many people have been trying to figure this out for many years and its that simple ?
Yeah what if you get stuck in there what do you do than
You cant go there in the first place. Dont worry. With current technology, we will only end up messing some few microseconds. Highly doubtful, if we can end up getting the news of travelling hundreds of years in our lifetime.
wait what would happen if someone saw you while you where in past/future i’m curious
Time is an illusion based on perceived reality and is only relative to our limitations. Time isn’t what it seems and all things can’t be figured out
Im on a school computer looking this up and i found this article and scrolling trough it and ive not heard one statement here as good as yours bro
This is blowing my mind people, then I see the school boy on the post. Great stuff, whoever reads this is already capable of travelling through time. Think about all people who have posted on this thread, now think about who will read mine. Now think of those €opposite trolls $ who never ever bother posting on you tube thread etc. But ONE comment from one of the time travellers who wrote on this thread. So that opposite troll is me,I don’t normally post.however because of previous comments I’m posting here. And I love the DMT shit I loved that and lived that one out in real life,,,,another day.
So my point is ifOne or two threads have made me write this….then what will my post make others write , think…..then I could travel back and not write this…. then what. Love the conception of time how can u travel something that doesn’t YOU perceive to be time, like a train can only run on its train tracks, a car can only drive on a road etc It’s posibble I know it is. Sometimes when u have fun times moves swift but locked in jail it goes snail pace. U c me. I write letters to myself from past from future. Remember everything that happens in present becomes part the past. But the future is what you hold in your hands. Question is, now you know….what the f are u gonna do about it?.. 01/04 ==== 21
Hahahah only realised school boy is named BIG dick pissing myself laughing I gotta go pee. Respect certified
so not halal mode
True so were not traveling in time. It is just different universe (on what we call) different time, day, tears, etc.
You would be scared for life
you will desepear
Maybe it has happened before and we just don’t know that they’re from the future. If people in the future time traveled, the would know that it’s dangerous to mess with the past and would pretend to be part of the past.
I believe time travel is already possible, however we cannot fix past mistakes without altering future predicaments. Say we stop JFK’s assasination, that would completely change the future from that point forward to one none of us can know/guess or conclude the effects? Other time travel purposes go to the future I think that from now our world will die off before 2096 basdd on overpopulation, global warming & polution as such creating islands of plastic waste in our oceans. The best thing my opinion go back to the garden of Eden, kill that Serpent Satan before he tricks Eve into the forbidden fruit. Then let God raise, enlighten & teach us how to be humanly sustainable on his planet & I guarantee technology & smart phones? Ain’t no part of it!!
Time travel possible but one n only theory of Stephen hawking
How it is possible to jump in time …??
Many ways. The most used is creating a black hole which can be done in a few ways. 1) traveling forwards or backwords faster than the speed of light 2) been known during heavy lightning strikes. Each way is a fast movement that opens the black hole. It has been done by the Government since the 1980s though they claimed they never beet the speed of light until 2002. However, Time is a illusion and their for we are actually traveling different universe that are differnt than ours even if the difference is by 1 thing. Each universe may have (what we call) different time, days and years. And each time we change that time line we created a new one. It is belief as CERN has said they destroy 5 universe, that they can travel to them. Since 2012 it has seem we been shifting and is now belief they have possibly came together. The event is known as The Mandela Effect.
No one has the right theory in my thinking. Only a few things are wrong. It is universes with (what we call) different time, days and years we are traveling to and not time itself as it is a illusion. Their is no stop to how much we can do, or where we can go. No limit as such say.
There is no God. No magical serpent or Garden of Eden ever existed. Basing a scientific theory on archaic stories does no one any good.
You choose a hopeless eternity. I choose hope through the promise of salvation through Christ for those who believe. You see, I have child in heaven. Thankfully, have a hopeful reality that I can embrace. There is a God. Our known universe is only 14 or so billion years old… is it mathematically possible that random molecules out of the Big Bang mixed in just the right way from to form a complex cellular organism… with DNA… and result in humans and such diversity of life forms? It’s naive to accept this as a result of chance. Think about it. How is that remotely possible without a creator?
Hahaha. You make it seem as tho the big bang happened, and we just popped into existence? Naw it’s called evolution baby, we started out as microscopic organisms, seriously, when did you drop out of school? But that’s like saying a some guy writes a book to explain away natural phenomenons that they were to stupid (un-evolved) to grasp and the concept good and bad and the eternal damnation, And thus, the Bible, and boom, everyone now was made by God, hahaha. When you can prove he/she exists, and that the Bible was a autobiography, and not just some twisted piece of Fiction, that has no real basis in reality, and cannot be proved to be more that a work of Fiction. Rather than being used as the16th Century control tact, ‘be good or you’ll go to hell’. But I guess that’s what they mean when they say ignorance is bliss, (maybe if I was as ignorant as y’all believers I’d believe to). But I can’t see how a ‘GOD’ would ever ask one of its creations to kill another.. Genocide, Crusades, all the ethnic cleansing.. All In the name of God Almighty! Hahahahahhaaa. Aliens are more believable than this shit, and theirs no proof they exist either. Hahahahaha. Fug’n Bible thumpers. ‘Step out side your faith and see the world for what it really is, a complex organism, mad of gravity and dust, quite a unique specimen! And we, yes Bible bangers, this includes you, are destroying it like the bubonic plague.’. ‘The end is coming and it’s our fault’
Have you taken the time to read The Old Testament and the prophecies therein that came to be ?.
How do you explain that ?.
My last post should read GS not G
You have not had an encounter yet with God. Don’t be so certain on yuour theory of evolution. He came and shook my reality to it’s core. Made thing possibly that no one could ever explain.
What are you talking about? Ur so wrong and funny in every way.
BlissfullyInformed just told me his comment was all an April fools prank. He believes in Jesus and was just fooling.
Time travel is very much possible just as you decided to come existence in this century meaning one can decide to be in another time zone . life is all about numbers, you just have to work on numbers
I’m pretty sure ppl don’t decide to come into existence. If that were true I wouldn’t be replying to your comment.
Un like your other reply, I understand what you mean. Each timeline (or universe as some see it) can easily be traveled to at will. No different than traveling threw your time you want to visit.
Science has proven a few things from the Bible is true. God does exist. Christians are confused with time and what it says. For a example. God created the world, as science even belives it was God who created the big bang, yet the bang has happen itself creating the moon, planets and stars. Christians also fail to understand chapter 1 and 2 of gen. spoke of two different creations which can be why we see dinosaurs before humans as chapter 1 spoke of animals first and humans 2nd. Their also was different time than, as without the moon a full day is 6 hours. It would take 4 days back than to equal are 1 day. Time is lost and Christians are just confuse on that time. That does not proof their is no God. As they have already found the robes of Jesus and remains of Noah’s ark, it proves much did happen. The bible only has less than 50% of what was written.
Changing the past is impossible, because if we went back into the past, that means we were already there during the time you experienced it.
We all know how to get into time travel but how do we get out……..
You don’t need time travel – all you need is life. And what is life? Life is the evolution of the impossible into the inevitable over an infinite amount of time.
if it is shown that if something, such as a solution to a particular class of equations, were possible, then two mutually contradictory things would be true, such as a number being both even and odd. The contradiction implies that the original premise is impossible.
This is called proof by impossibility. Thus if some traveled back in time far enough to kill his grandfather, we have the contradiction and therefore it is impossible.
You could argue that he would be able to time travel, but not kill his grandfather. However almost anything a person does going back in time would cause the same contradiction, thererfore it is the traveling back in time that is impossible.
Actually, it probably is possible to travel back in time, however to do so, you would also have to travel so far in space that you cannot see anything that happened before your current time due to the speed of light, because this to could affect the future.
The reason I am here is that, i really want to go back the day when our matriculation exam was just finished. Everything around me is peaceful and happy. Currently, I am living in dire situation. People are dying outside on the streets. Smokes everywhere. Everything is in doom. Ah, yeah. I really miss my past. If you are reading this, you can judge me in anyways. I just want to live peacefully and happily.
You must live in Portland
I entirely know what you say and how you feel, Robin. I am totally convinced that future is no promise to offer a better place to live. World is becoming unnecessarily more complex and more horrible and more insecure. Therefore, travelling back in time to a point where things were still far away from such ordeals is what I aspire. But I think if it is possible to travel back in time without the possibility of carrying our lived experiences with us, it will be useless as we will be repeating the same mistakes over and over again. Now, this begs the questions “in what type of physique could we imagine ourselves back there if such time travel becomes possible? That is, becoming younger again in a physical regression (as I said this would be a torture without having learned from all these later years)? Or appearing at our desired times in our present physique and age? I believe the most ideal one would be if we appeared at our desired point in time at the same age that we were at that point of time with a good feeling of our later lived experiences.
Mam all u need to do is just run faster as much as u can or visit the black hole because in both condition time just slow it down ….
Time travel is simple. If you do happen to travel to the past you create a new time line not affecting the time line you left. In essence you going to the past is now your future. Even if you were able to return you may never know if you remained in your time-line or created a new one. So even if you changed something in your travels it would happen in the future not the past.
Sorry time traveling is not possible, there is no way you can go into the past or the future â€â™‚ï¸. You can only be in the time you are already in.
Incorrect. General relativity allows time travel into the future. You need a space ship that can travel extremely fast though, approaching the speed of light, or you need to get close to a supermassive black hole.
It is travel into the past that there is no known practical way to do, and is probably impossible.
So what happens when we Die? Where do we go? I want to go back in time so I can meet my childhood friends…
Simple question from a simple mind:
At what point, when a person says they are from the future, do we stop throwing them in the funny farm and actually start listening??
When they show actual proof. Not just some random prediction of the future.
I don’t believe that “glimpses into the future” could be possible. If it were so, we could glimpse blueprints of the future that we could bring back to the present and build before they were invented. My personal.beleif is in any time frame there is only one active time which is the present. The past no longer exists and the future hasn’t occurred yet, so there is no such thing as ‘time travel’ except for the frame we are in now.
First off time is not real we make time if you travel anywhere all you are doing is beating the Earth speed try this for a mathematical equation the Earth travels a thousand miles per hour you’re not beating human time that is your own equation the Earth travels a thousand miles per hour a space shuttle travel 17,000 mph you can beat time that you made so time is not real you are only beating the Earth speed if you go in a space shuttle and go around the earth 17,000 miles per hour the Earth only travels a thousand miles per hour plus it has all types of gravitational pull from the Moon Earth’s access on the til t you figure out the mathematical equation I cannot time travel is real if you can beat the Earth speed and we can it has nothing to do with its 12:00 it’s 1:00 that’s not real time is made up as a mathematical equation you can beat the Earth speed you can go back into the Earth’s time in a space shuttle but you’re not beating anything except the Earth’s speed think about that one time is not real at all all it is is a mathematical equation think about that one real long
What I’m trying to say is this a space shuttle travel 17,000 mph the Earth travels a thousand you beat it 16 times faster that’s all you did you’re not beating any time you’re not beating 1:00 you’re not beating 3:00 all you’re doing is beating the Earth’s time you can go in reverse around the Earth 17,000 mph okay you can go forward with the Earth’s centrifugal force 17,000 miles per hour you’re not beating anything you’re beating a mathematically equation that we we created astronauts been traveling time for instance for years and haven’t told us because of the space shuttle that does travel 17,000 mph it beats the Earth speed 16 times a boggles my mind you have the Earth access the moon gravitational pull but you can get in a space shuttle and travel 17,000 miles per hour and beat the Earth’s speed 17 times think about it
If any scientist or anybody can actually answer this question how do you set up this equation with the Earth spinning a thousand miles per hour you have the moon pulling gravity the Earth’s access on until I want to know tell me then wondering for a while this equation popped into my head about 2 years ago I’m not a math whiz or anything I just thought about it weird how the mind works I’m not into space or any space stuff at all I’m Samanthas boy friend John antos wrote this
I liked your post and the knowledge you given. I also written a post on Time Travel.
how would any of that stuff be true because e’*34+Em would stop all the forss of vissecs and how would we do it if you now what i mean??? also thanks for the scuff for my project
I would love it if I had a real life time machine here with me now which could take me to anytime I want, the past, present or future. If I had a time machine here with me now, I would go to the past in September 2004 when I was born and give myself to another family that is actually rich and not this horrible family that I have now.
that not nice
Close but not quite right scientists of the idiotic variety, yes, you don’t want people to travel back in time to mess with their own pasts, of course, but you say it’s impossible, but it’s not, and I’m always ignored with my crazed crackpot theories, so what’s the harm in telling the truth as I see it, while it could be possible to travel to the past, here in lies the problem with rewriting the future, while some believe it’s possible to travel back in time, but it’s very expensive and definitely a one-way trip to the future or to the past. Basically Doc Brown got the mechanism for time travel almost right but the energy out put needs to be quadrupled instead, allowing for the ‘physical item, being or vehicle’ to transport through time without killing the time traveler in question. Wormholes are unpredictable, until warp speed for spaceships are a thing, it is not possible for the space ships to achieve time travel, unless they want to enter a black hole, which I would not recommend. as you need warp speed to survive the emptiness of the black hole, without being ripped to shreds. Say for example, Back to the future 1, the timeline doesn’t erase it continues on without the ‘said time traveler’ in existence basically the Marty from Wimpy George’s timeline did time travel to the past and messed with his parent’s meeting so to speak, but never return to the same timeline therefore Marty A went known as a Missing Child in timeline A, while it continues on without him, however Marty A became Marty B/C, in the Successful George Timeline. So that is what I’m talking about. the timeline changes only for the time traveler themselves the ones who are left behind don’t experience a thing of timeline rewritten-ism, as it would never happen in the first place. The other thing is if you want to mess with your own childhood, to make a better life for the past self, the key thing to remember it’s not really you. It’s an alternative version of you, that you interfered with. creating a parallel timeline to it’s original, yet slightly different. Yes it would be awkward to raise yourself. but as long as you are staying in the past, nothing should happen until the age you traveled back in time, unless of course you touched your past self and suddenly de-aged and merged with your past self, is an option 1, option 2 the future self explodes spreading guts all over the place and therefore the past self, of you became a murderer of your future self, I am more inclined to believe option 1 as option 2 seems a little too out there. Basically you would have two memories one of the former timeline and one of the current different timeline. Still traveling through time is truly a one way trip and if you want to travel through time, you would need some time travel mechanism, the way you scientist talk is basically a dream version, or an OBE version (OUT-OF-BODY-EXPERIENCE) which is basically a vivid/lucid dream which is not true time travel, the true time travel is based on the BTTF Trilogy not the idiotic versions you preach about. I believe I’ve said enough.
Mystery solved and I will explain, I was in a coma 3 months and I experienced things, I traveled time forward and backward, it is not a one way ticket. Movies and songs are recorded on magnetic tape in a VCR tape Cartridge or Cassette tape, Magnetic tape recording works by converting electrical signals into magnetic energy, which imprints a record of the signal onto a moving tape covered in magnetic particles. 3D life on earth(a movie), and the Magnetosphere all around earth coming from the core of earth(MAGNETIC ACTIVITY) without Atom Made Tape, is like a movie on magnetic Atom made tape in a VCR tape cartridge. Revolution and Rotation is the motor(VCR).
This is why people have those freaky Deji’vu feelings like they have lived this before, BECAUSE YOU HAVE, and how people can be psychic, and how there is Prophecy in the Bible. When a person dies, their Spirit- MIND(Thoughts, Feelings, Urges(Physical and mental personality)) breaks out of human body- a stopped heart is what releases the spirit from the human body. Then the Soul(Life) with the memory of your existence in it breaks out of spirit and goes back to your birthday with a erased memory, meanwhile your spirit goes back in time to when you were a teenager starting the mental puberty, maturity from that adult spirit you died with in last life.In that old movie Star Wars or maybe it was the Empire Strikes Back, there is a scene where Princess Laya plays like a 3D movie, that is EXACTLY how its of life on earth.
If only wish I could undo everything what I’ve done wrong in the past, I’d be more happier
And that my friend is absolutely what you do not or would not know. Everyone focuses on what they don’t or haven’t had rather than what positives they do have around them. To change the ingredients of a past life only changes the flavour you have in this life, it does not make you happier.
No, travel to the future is not possible. Like, future is unpredictable and always have been so give up on that field
Already has been, and has been proven.
Time travel is not so possible for every one , but there are already time travelers on earth #@*
Who are these time travelers?
Depends if it is the Governments (they done it since the 80s), or if it was a Accidental travel, or a simple us creating our own machine. Either way, one can easily find storys, and other evidence with a good research. I have a website that shows the effects of change cause by time travel.
They are out their (done by the government since the 80s) but the future is open with time travel (told its open since 2028) so they travel back much.
Time travel 101-
Create a closed loop circuit around a full metal structure, hermetically seal it and bring O2, Use two tesla coils to create north and south poles. (Artificial Magneto sphere.) Make sure to pain the outside in lead to prevent any cosmic rays from penetrating the materials on the inside. (Radiation = bad). Connect a ball made of w/e with wires that alternate the current from the coils to w/e panel on the outside of the structure to make it move via inductive magnetic / electric Lorentzo (Lorentzo = ExMfield = Velocity. = Antigravity) Create Antigravity by using forces from the inside reactor. (Pressurized Mercury, and Tesla Turbine.) Then Move 10-100x faster than light depending on the charged field, Friction will be added to the electric field instead of the craft allowing the G-forces not to crush you inside. The field will take the pressures of outer space, The temperature of space will allow for super conductivity of the structure.
Eventually you will arrive in the future, if you stay in one place. but account for the movement of earth in your travel log. To see outside you will need a monitor / camera system, as any leaks through a viewing area will cause death by radiation from the cosmic rays from the field you have created.
The O2 can be used as a backup generator, through air pressure and the tesla turbine.
There are many different ways to make wormholes, but the curvature of space is really hard to calculate to send a machine far out to the end and create a link with the machine that wants to travel there. And leaving one behind to get back.
If you can imagine it, it can be done. You just need the knowledge of not dying to complete it.
U.S.S. Tourist, You’re a time traveler or just insanely smart.
You don’t need to go the speed of light. Human Time is recorded in the magnetospere as a movie is record, ed on magnet VCR Tape or a song on a record. A VCR or record does not have to go light speed to retrieve the recorded info. All of life is recorded in 3D by our Magnetosphere. My Analogy is imagine a VCR tape cartridge being the earth, imagine life on earth being the movie but in 3D with out adom made tape, imagine Rotation and Revolution of Earth being the VCR putting all in to motion- playing. That is how its done, the magnetosphere kills two birds with one stone, it protects earth and records time, human time is in a magnetic bubble that is why the Bible refers our time is different from gods time and this is how God the maker(PLANET OF UNITED SUPREME BEINGS) can flip through our time to know everything. By the way long before life on earth, he built the original 7 wonders of world(Pyramids) to Pump the Seven gasses into the atmosphere of this planet found in the goldilocks zone, so Life can live on it, and that life of all types is his technological cyborgs that grow and multiply on earth also he seeded it with plant, trees, sea creature and things that fly,. Anyway that above is how time is recorded.
Until recently, I thought my neighbor was a crackpot until he actually invented a time machine. He utilized an ordinary closet, and showed me the sophisticated (to me) instrumentation he had installed. I was very skeptical at first, until he offered a small demonstration and entered the time coordinates and energized his invention. To my amazement, when I opened the door, the clock on the wall was 30 minutes later than when we stepped into the machine. OMG!!! Destroy this thing before it destroys us!!!.
So happy to have my husband back after 6 months of separation. get any kind of relationship/marriage help you want from….Robinsonbuckler11 @gmail com………………………
I find it odd that people say time travel isn’t possible yet… If time travel is possible, it has always existed. Meaning, there is not past present it future, only our perception of time. What we know as past present and future have always been occurring simultaneously, so travel was invited the moment the universe wss formed. Dinosaurs are roaming the earth right now, and forever. A version of me is typing this and has always been typing this, within this perceived moment of “time” and time travel has always happened, whether or not we exist in that reality at the right “time” to observe time travel is the only question.
I find it odd that people say time travel isn’t possible yet… If time travel is possible, it has always existed. Meaning, there is no past present or future, only our perception of time. What we know as past present and future have always been occurring simultaneously, so travel was invited the moment the universe was formed. Dinosaurs are roaming the earth right now, and forever. A version of me is typing this has always been typing this, within this perceived moment of “time” and time travel has always happened, whether or not we exist in that reality at the right “time” to observe time travel is the only question.
Their had to be one point however, when it was created and started, and for that, there was nothing but the current time. Once it was created, than we had a pass, present and future to which we can go back to millions of years to see Adam and Eve with the dinosaurs or go millions of years in the future. However, given the events that changes, each time a new time line has been created. We also have destroyed the planet and repopulated many times in the last million years. Each event changed, or something we do different (without traveling) enters a new universe where some things may be different or the same. Today are universe are shifting a lot.
To be fair, even if it is a one way trip into the past, that doesn’t stop machines going back. We could send a machine back and order it to do anything we want and then tell it to meet us at a certain time in the future. We send it back, then go straight to the meeting point we agreed and then we’ll be able to prove if it worked or not.
I’m a girl who has read a book about seeing future through a box. So is it actually possible?
Time travel has been done on purpose by the Government since the late 1980s. From research, the mostly use kids, or future Presidents. Their are some cases where people have been struck by lightning or came across some tragically event that cause them to leave their timeline either forward or behind in time. The Mandela Effect is the current cause of how things go wrong when time travel is not done right. Click on my name to see the website.
Even as traveling to a location as a future or pass date is possible as what people here mean. However, as you said, it is numbers. Time is a illusion and we do not travel threw time, just universe that are different than ours. What we call time dates and months is what changes each universe. We are all from different universes today as they came together. The mandela effect is a fine example.
thx to eleon wont we soon be able to digitize our conscious being, then accelerate that data pass the speed of light some how then download it into some android or something…..i dunno…..just a thought
I want to go to my elementary school again. Someone help me out, I know its Idiotic but stil.. I am not good at science. As far I understood, 1) we can trace through time if we travel fast than speed of light.. I think memory os the only thing that is faster than light, Yeah I can go to Paris within 1 sec in my memory but yeah its illustion, i want in real 2) Through Blackhole – I think its Bermuda triangle
if you travel back in time you will still be your age now. That is how it worked with others. No one gets younger otherwise traveling to far back would kill you. No school would let you return to school as a adult so not possible.
Plz help me I just want to send a message to myself in my past and save my self from a beast plz help Nazneen
Would love to experience many moments in life again for the first time again!
I think that time traveling should be left alone, for the sake of humanity. There are some things we’re not ready for yet.
Well stephen hawking may be wrong. I mean, the study proved that the universe self corrects itself to prevent inaccuracies. So maybe tourists from past do visit us but we don’t remember them as the universe alters our memory. If you guys have read about Butterfly Effect, a simple mistake today may grow through years to become a giant disaster in future so if you think of it, oncoming tourists from future may cause giant inaccuracies. Imagine this, You have travelled to past. You brought two cakes for yourself, so you pay the shopkeeper 20$. The shopkeeper invests the 20$ in stocks, strikes gold there and becomes a rich businessman.His daughter goes to Cambridge and marries someone else than the person she was supposed to marry according to time. Can you imagine the magnitude of inaccuracy after 100 years? Therefore, whatever the tourists from future do, is corrected by the universe and we don’t remember it. Creepy, but food for thought.It also adds a special meaning to the word ‘Fate’.
How much wacky terbacky (i.e. weed) you be smokin’ JOE JOE?
Hmmmm…. As brilliant of a mind as Stephen Hawkins was, how is he so sure that he would even recognize hordes of tourists from the future? Almost everyone is aware of the warning of the Butterfly Effect. So I’m sure any future visitors Intelligent enough for Past-Time travel would be amply attuned to this.
Most future people coming to the pass (our time) seems careless and not intelligent. Most are taking FBI lie detector test and telling us what is happening in the future. That is a bad idea, because if you tell us (example) who is the next President, and the Government does not like the person they than can change that event to let someone else in (as seen in 2020) One should never acknowledge who he or she is or why they are their. Most traveling is to get knowing of the pass or to pick up certain things. Since are pass is changing, events are changing and are timelines are messed up, someone made a mistake. The Mandela Effect is a fine example.
Wow that’s great plz help me go to my past plz,I can’t do it by my own at least help me send a msg to myself in my past Nazneen
I think it is possible, but time traveling is really just changing universe created by different time lines. Our whole solar system is in a whole different place now and Earth is much smaller in this universe from the one I grew up end. Someone has already changed the timeline.
Roads? Where we’re going, you don’t need roads!
Youre wrong about your measurement of speed for traveling, in order for time to slow down, with inside an object compared to outside. Scientists proved that time with inside an object at an excelorated speed actually appeared to have slown down during the duration of time for the test. The speed was far less then the terminal speed of a rocket for NASA at 256,000 kms p/h.
In to the volicity of space. Generating a vacuum of space, could be no different the the actual transport of matter over frequency where in fact matter can be carried by sound. It is believed that an alien civilization harnessed this energy in the form of bolisks that where believed to carry the same properities and in consideration of harmonic resinance, the simularities could be used in order to carry large weight. In accordance with a documentry on theoretical science.
However the properties, present the fact that a working property controdicts your counter intuative theory of gravitational deceloration of matter to colide within itself to absorb all things into non existance as to the transfer of matter into energy, rather then your idiolisms of transfer between dimentional space to another destination that is not linked or the transfer between time that isnt, either.
However to reproduce the fabric of time within space in a practical measurement as I have mentioned, would put an end to all the lunacy of an unmeasureable field, which people fail to identify. Like running into a glass window. Only to not know what forcefield is present.
Time travel into the past can be achieved simply going faster than the speed of light.
The closer you get to the speed of light the slower time goes
If you reach the speed of light time stops
If you go faster than the speed of light it starts to reverse
Why does no one seem to know this?
Christopher Reeves did this in Superman 3 brah.
Any time travel, pass and future, is by going faster than the speed of light. It is said by reversing that that you can go back in time. However, I assume since the Government has done this since the 80s they have better ways (maybe tying in a date) and not having to go to a unknown date.
I want to send a message to myself in the past on a particular date plz can you help me, this means a lot lot lot to me,plz help me Nazneen
Why don’t we drop the declaratory statements that it “is or isn’t possible!” Until someone actually does so. Just say “maybe”.
People have and their are records both to the pass and future. The Government has done it since the 80s as part of the “star wars project” and are much better at it today. This explains the black holes in the sky of 2019, and the CERN destroying 5 parallel universes in 2013. We also see changes because of time travel events changing time. The Mandela Effect is a find example.
I want to send a msg to myself and my family in the past ,is it possible plz help me my life will be saved one who helps me saves me and my kids from a pack of beasts,
The worst idea ever. We all want to do this and where does it stop. A lottery win does not sound bad if you knew the actual location, time and place. After a while though, would you not want to write that hit song, become the author of the Harry Potter books, stop 9/11? The idea of giving your pass self (a time time travel was not proven) information of the future could change things in a major way. This would cause one small thing to change creating many others to change. This has already happen in simple ways of the The Berenstein Bears changing to The Berenstain Bears. This is a small event but this event “The Mandela Effect” now has over 3,000 changes.
What if you decided to give your pass self information about a lottery ticket that would be a winner, bought late at night and he was hit by a car on the way to get it. Changes the whole future. However, If detailed right, done right, with no large changes, it may not effect much, but to know your being given info from yourself in a future time (when that was not known much or provrn back than) You would either assume it is a joke or you gone crazy.
I don’t want to win a lottery, my decision about my career and studying was right but my family and their cruelty has put me into this worst condition I just want to go back complete my studies and live a life like a human not like a animal or slave,help me plz Nazneen
Can someone take me to 2013? i can pay later to all of you in bitcoins so its a win win and you dont need to do anything, just wait
LOL but still complicating on my side
You travel in your dreams where time and space colloids ..That’s y sometimes the dream which you dreamt might be a 10 mins reel time but you felt dreaming whole time like 6 to 8hrs .. Probably even traveling to parallel universe
I agree. Dreams as we know it is not a simple sleep. The part of the brain we do not use while awake, we use at night. This is the phenomenon part of the brain that can do thing we feel a human can not do. We of course use less than 30% of our brain. By the use of 100% of the brain we would use both sides and be able to do common things such as read thoughts, move things without touching them etc. The idea of using this side of the brain, would be the theory we can leave our bodies and visit different universe, see what could of happen shall we done something different, and even see future events. This may be why we notice different memories to some things as we could of held some from another reality.
It would be very weird, however, if we were trapped in that universe, or another body and fail to return to ours. Is that how people die in their sleep?
i just fell like going to late 70’s, where i can see majority of family.. i am willing to trade life for it…..
Time travel to the pass is just as common as the future. However, as both has been done it is NOT travel threw time. Time is a illusion we created. We are actually traveling threw different universe with (what we call) different time, dates, years, etc. The Mandela Effect is a find example how traveling threw different reality’s change the time lines.
As a add on to the above, Time travel is not a theory, has been proven, and has been done by the Government since the 1980s. Their is many residue in our history to even show some time travel storys to be real.
Where can one get a reverse watch, is it really possible to go back in past with its help, is it sooo easy ,plz help me ??????? Nazneen
US20060073976A1- search this patent number,this describes the process for time travelling,I really don’t think magnetic energy will work,maybe heat focused on a specific point could expand the fabric of space and make a hole in it.even then I will the hole take you to another time.it would be one thing to time travel but selecting a point in time would be impossible.you could only travel to the time you device was built?
Is there a watch which back travels in time or reverse time watch? Is it true? How to get one? But with that how can I send a message to myself in my past, plz help Nazneen
I don’t believe such a watch exist and their are plenty of smart minds with huge funds trying to travel.right now there are only theories.
Thank you very much for your response. I just want to send a message to myself in my past. Nothing much will be changed but 3 literally dying devastating lives will be saved. We are suffering for the mistakes and egoistic arrogance of others so if possible plz help me
Traveling back in time isn’t just a when problem, it’s a *where* problem. Where was the place you’re standing right now a thousand years ago, or a thousandth of a second ago? There is no useful answer to those questions, so there’s nowhere to travel back in time to.
Traveling forward in time? You’re doing it now.
when you step through a door is time lost when you come back through? lets say you return days Later how much time did you loose. what exactly is Time,.? is dialation a safe way to return ,. a Blackhole will assist you in in travel, the question is will you arrive safe,.
Traveling back in time is impossible. 2 reasons why that are never taken into account.
A) The stuff you are made of ( subatomic material) is being used by something else. It I not like you are a facsimile of the already existing material. What you are made of is exactly the same existing material. The problem is exact stuff can not exist in 2 different places in the same point in time. You will either : Decompile or fall out of phase with the universe. Both bad outcomes for the time traveler.
B) Lets look at it from logical commonsense. You have a bar of gold . You intend to send the bar back 1 second in time. Now you have 2 bars of gold . You send those 2 bars back one second . You have 4 bars …… do that 50 times . You have over 900 trillion bars of gold. All made of the exact subatomic particles. The more the bars back the more the existing mass of the universe increase. What are the consequences of changing the mass of the universe . Hence the paradox . Information can not be destroyed., It also can not be created.
At least this is the way my brain perceives going back in time.
Time is a function of change. None of the 4 forces The strong force , The weak force , Electromagnetism and Gravity can not work without time.
I will figure out time travel one day but only for the past.
I wish I could travel back to 18th of June to save my mom.
Is time travel really a one way ticket? Theoretically, if you can go one way, you should be able to go back.
Time is not one way. It’s consequences are however irreparable given certain circumstances and is not something that should be taken lightly or thought of in a manner of disregard. I’ve only very recently decided to take to your social platforms regarding space and time.
You can try finding me on Instagram. I’m not familiar with these platforms to better direct you there. My Instagram name is johnrvh
On Twitter it seems to be @_JohnRvH
If I go forward I will have to pay extra bills and taxes. I don’t think I can afford it.
You’re the first person I’ve come across in this timeline that has a sense of humor. Thankfully, going forward is not possible if that future hasn’t been created yet.
timetraval is no joke if its created the whole universe could go out of orbit.
Cauchy problem converging to non minimal terraces as t → +∞
Stephen Hawking may he rest in peace a genius but not all knowing. As far as he knows we haven’t been flocked by tourists, in the same maybe these UFO sightings are actually time travelers from the future coming to the past to view how we really lived why things really happened the way they did, etc. To limit the imagination of possible and impossible is wrong then you create fantasy. And we have learned from history that there is truth in fantasy. I.e. the different mythos of the different ancient cultures from around the world including those of the Norse. Improbable and probable should be more appropriate. It’s possible because it can be imagined improbable die to the right math or this or that not existing or matching up. I also believe that if time travel to the past were possible that the changing of something in the past would create a new timeline running current with your timeline at which will inevitably collide and will cause the collapse of the universe at which point a new universe will be born.
so i think the speed of light is only relative to deciding a point of destination -initially- as specific gravity of destination needs to be ascertained to calculate the frequency needed to run an alcubierre-white engine to bend space correctly to cross space ‘quickly’, the point of reference may well be jupiter in our solar system for the fact of the moons that orbit it, i surmise that by using a ‘dead end ‘ equation that usually puts notable mathematicians into the outer regions by trying to solve it may actually be the key as calculations end in a loop of 4-2-1 ie 3N+1; this process of calculation creates a sine wave over time/distance relative to specific gravity of chosen destination – as time is determined by gravity therefore if the speed of light to a destination can be used to ascertain the specific gravity of a ‘body’ to visit ie a star or sun due to receivable resonant frequencies emitted by the body, then the constrictions of the speed of light do not exist other than to give a constant, by using the 3N+1 method of calculation ,once the speed of light and returning resonant frequencies of a destination are determined the calculation can be extrapolated to match the distance giving the end point -in doing this the sine wave required can be ascertained and be condensed to create a wormhole and allow the alcubierre-white engine to ‘bend or distort space enough so that the bubble you are in matches the required specific gravity of the destination – the frequency of the body nearest to the destination point should be used and resonated inside the bubble to create synchronicity of frequency and cause attraction i also believe that travelling through space require the ability to see things from different perspectives and it requires the ability to navigate through a series of what may be described as “Aims Windows” where your point of view needs to change inherently with a given position at a given point in the galaxy
Comments are closed.

Blogging from Canadian Perspectives
An inclusive digital science salon featuring Canadians blogging about a wide array of scientific disciplines.
Associate Sponsor


- [ November 30, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: December 2022 Night Sky
- [ November 22, 2022 ] James Webb Telescope Turns Its Attention To The Kuiper Belt News & Events
- [ November 1, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: November 2022 Night Sky
- [ October 4, 2022 ] Are Wormholes Fact or Fiction? General Astronomy
- [ October 1, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: October 2022 Night Sky
5 Bizarre Paradoxes Of Time Travel Explained
December 20, 2014 James Miller Astronomy Lists , Time Travel 58

There is nothing in Einstein’s theories of relativity to rule out time travel , although the very notion of traveling to the past violates one of the most fundamental premises of physics, that of causality. With the laws of cause and effect out the window, there naturally arises a number of inconsistencies associated with time travel, and listed here are some of those paradoxes which have given both scientists and time travel movie buffs alike more than a few sleepless nights over the years.
Types of Temporal Paradoxes
The time travel paradoxes that follow fall into two broad categories:
1) Closed Causal Loops , such as the Predestination Paradox and the Bootstrap Paradox, which involve a self-existing time loop in which cause and effect run in a repeating circle, but is also internally consistent with the timeline’s history.
2) Consistency Paradoxes , such as the Grandfather Paradox and other similar variants such as The Hitler paradox, and Polchinski’s Paradox, which generate a number of timeline inconsistencies related to the possibility of altering the past.
1: Predestination Paradox
A Predestination Paradox occurs when the actions of a person traveling back in time become part of past events, and may ultimately cause the event he is trying to prevent to take place. The result is a ‘temporal causality loop’ in which Event 1 in the past influences Event 2 in the future (time travel to the past) which then causes Event 1 to occur.
This circular loop of events ensures that history is not altered by the time traveler, and that any attempts to stop something from happening in the past will simply lead to the cause itself, instead of stopping it. Predestination paradoxes suggest that things are always destined to turn out the same way and that whatever has happened must happen.
Sound complicated? Imagine that your lover dies in a hit-and-run car accident, and you travel back in time to save her from her fate, only to find that on your way to the accident you are the one who accidentally runs her over. Your attempt to change the past has therefore resulted in a predestination paradox. One way of dealing with this type of paradox is to assume that the version of events you have experienced are already built into a self-consistent version of reality, and that by trying to alter the past you will only end up fulfilling your role in creating an event in history, not altering it.
– Cinema Treatment
In The Time Machine (2002) movie, for instance, Dr. Alexander Hartdegen witnesses his fiancee being killed by a mugger, leading him to build a time machine to travel back in time to save her from her fate. His subsequent attempts to save her fail, though, leading him to conclude that “I could come back a thousand times… and see her die a thousand ways.” After then traveling centuries into the future to see if a solution has been found to the temporal problem, Hartdegen is told by the Über-Morlock:
“You built your time machine because of Emma’s death. If she had lived, it would never have existed, so how could you use your machine to go back and save her? You are the inescapable result of your tragedy, just as I am the inescapable result of you .”
- Movies : Examples of predestination paradoxes in the movies include 12 Monkeys (1995), TimeCrimes (2007), The Time Traveler’s Wife (2009), and Predestination (2014).
- Books : An example of a predestination paradox in a book is Phoebe Fortune and the Pre-destination Paradox by M.S. Crook.
2: Bootstrap Paradox
A Bootstrap Paradox is a type of paradox in which an object, person, or piece of information sent back in time results in an infinite loop where the object has no discernible origin, and exists without ever being created. It is also known as an Ontological Paradox, as ontology is a branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of being or existence.
– Information : George Lucas traveling back in time and giving himself the scripts for the Star War movies which he then goes on to direct and gain great fame for would create a bootstrap paradox involving information, as the scripts have no true point of creation or origin.
– Person : A bootstrap paradox involving a person could be, say, a 20-year-old male time traveler who goes back 21 years, meets a woman, has an affair, and returns home three months later without knowing the woman was pregnant. Her child grows up to be the 20-year-old time traveler, who travels back 21 years through time, meets a woman, and so on. American science fiction writer Robert Heinlein wrote a strange short story involving a sexual paradox in his 1959 classic “All You Zombies.”
These ontological paradoxes imply that the future, present, and past are not defined, thus giving scientists an obvious problem on how to then pinpoint the “origin” of anything, a word customarily referring to the past, but now rendered meaningless. Further questions arise as to how the object/data was created, and by whom. Nevertheless, Einstein’s field equations allow for the possibility of closed time loops, with Kip Thorne the first theoretical physicist to recognize traversable wormholes and backward time travel as being theoretically possible under certain conditions.
- Movies : Examples of bootstrap paradoxes in the movies include Somewhere in Time (1980), Bill and Ted’s Excellent Adventure (1989), the Terminator movies, and Time Lapse (2014). The Netflix series Dark (2017-19) also features a book called ‘A Journey Through Time’ which presents another classic example of a bootstrap paradox.
- Books : Examples of bootstrap paradoxes in books include Michael Moorcock’s ‘Behold The Man’, Tim Powers’ The Anubis Gates, and Heinlein’s “By His Bootstraps”
3: Grandfather Paradox
The Grandfather Paradox concerns ‘self-inconsistent solutions’ to a timeline’s history caused by traveling back in time. For example, if you traveled to the past and killed your grandfather, you would never have been born and would not have been able to travel to the past – a paradox.
Let’s say you did decide to kill your grandfather because he created a dynasty that ruined the world. You figure if you knock him off before he meets your grandmother then the whole family line (including you) will vanish and the world will be a better place. According to theoretical physicists, the situation could play out as follows:
– Timeline protection hypothesis: You pop back in time, walk up to him, and point a revolver at his head. You pull the trigger but the gun fails to fire. Click! Click! Click! The bullets in the chamber have dents in the firing caps. You point the gun elsewhere and pull the trigger. Bang! Point it at your grandfather.. Click! Click! Click! So you try another method to kill him, but that only leads to scars that in later life he attributed to the world’s worst mugger. You can do many things as long as they’re not fatal until you are chased off by a policeman.
– Multiple universes hypothesis: You pop back in time, walk up to him, and point a revolver at his head. You pull the trigger and Boom! The deed is done. You return to the “present,” but you never existed here. Everything about you has been erased, including your family, friends, home, possessions, bank account, and history. You’ve entered a timeline where you never existed. Scientists entertain the possibility that you have now created an alternate timeline or entered a parallel universe.
- Movies : Example of the Grandfather Paradox in movies include Back to the Future (1985), Back to the Future Part II (1989), and Back to the Future Part III (1990).
- Books : Example of the Grandfather Paradox in books include Dr. Quantum in the Grandfather Paradox by Fred Alan Wolf , The Grandfather Paradox by Steven Burgauer, and Future Times Three (1944) by René Barjavel, the very first treatment of a grandfather paradox in a novel.
4: Let’s Kill Hitler Paradox
Similar to the Grandfather Paradox which paradoxically prevents your own birth, the Killing Hitler paradox erases your own reason for going back in time to kill him. Furthermore, while killing Grandpa might have a limited “butterfly effect,” killing Hitler would have far-reaching consequences for everyone in the world, even if only for the fact you studied him in school.
The paradox itself arises from the idea that if you were successful, then there would be no reason to time travel in the first place. If you killed Hitler then none of his actions would trickle down through history and cause you to want to make the attempt.
- Movies/Shows : By far the best treatment for this notion occurred in a Twilight Zone episode called Cradle of Darkness which sums up the difficulties involved in trying to change history, with another being an episode of Dr Who called ‘Let’s Kill Hitler’.
- Books : Examples of the Let’s Kill Hitler Paradox in books include How to Kill Hitler: A Guide For Time Travelers by Andrew Stanek, and the graphic novel I Killed Adolf Hitler by Jason.
5: Polchinski’s Paradox
American theoretical physicist Joseph Polchinski proposed a time paradox scenario in which a billiard ball enters a wormhole, and emerges out the other end in the past just in time to collide with its younger version and stop it from going into the wormhole in the first place.
Polchinski’s paradox is taken seriously by physicists, as there is nothing in Einstein’s General Relativity to rule out the possibility of time travel, closed time-like curves (CTCs), or tunnels through space-time. Furthermore, it has the advantage of being based upon the laws of motion, without having to refer to the indeterministic concept of free will, and so presents a better research method for scientists to think about the paradox. When Joseph Polchinski proposed the paradox, he had Novikov’s Self-Consistency Principle in mind, which basically states that while time travel is possible, time paradoxes are forbidden.
However, a number of solutions have been formulated to avoid the inconsistencies Polchinski suggested, which essentially involves the billiard ball delivering a blow that changes its younger version’s course, but not enough to stop it from entering the wormhole. This solution is related to the ‘timeline-protection hypothesis’ which states that a probability distortion would occur in order to prevent a paradox from happening. This also helps explain why if you tried to time travel and murder your grandfather, something will always happen to make that impossible, thus preserving a consistent version of history.
- Books: Paradoxes of Time Travel by Ryan Wasserman is a wide-ranging exploration of time and time travel, including Polchinski’s Paradox.
Are Self-Fulfilling Prophecies Paradoxes?
A self-fulfilling prophecy is only a causality loop when the prophecy is truly known to happen and events in the future cause effects in the past, otherwise the phenomenon is not so much a paradox as a case of cause and effect. Say, for instance, an authority figure states that something is inevitable, proper, and true, convincing everyone through persuasive style. People, completely convinced through rhetoric, begin to behave as if the prediction were already true, and consequently bring it about through their actions. This might be seen best by an example where someone convincingly states:
“High-speed Magnetic Levitation Trains will dominate as the best form of transportation from the 21st Century onward.”
Jet travel, relying on diminishing fuel supplies, will be reserved for ocean crossing, and local flights will be a thing of the past. People now start planning on building networks of high-speed trains that run on electricity. Infrastructure gears up to supply the needed parts and the prediction becomes true not because it was truly inevitable (though it is a smart idea), but because people behaved as if it were true.
It even works on a smaller scale – the scale of individuals. The basic methodology for all those “self-help” books out in the world is that if you modify your thinking that you are successful (money, career, dating, etc.), then with the strengthening of that belief you start to behave like a successful person. People begin to notice and start to treat you like a successful person; it is a reinforcement/feedback loop and you actually become successful by behaving as if you were.
Are Time Paradoxes Inevitable?
The Butterfly Effect is a reference to Chaos Theory where seemingly trivial changes can have huge cascade reactions over long periods of time. Consequently, the Timeline corruption hypothesis states that time paradoxes are an unavoidable consequence of time travel, and even insignificant changes may be enough to alter history completely.
In one story, a paleontologist, with the help of a time travel device, travels back to the Jurassic Period to get photographs of Stegosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Ceratosaurus, and Allosaurus amongst other dinosaurs. He knows he can’t take samples so he just takes magnificent pictures from the fixed platform that is positioned precisely to not change anything about the environment. His assistant is about to pick a long blade of grass, but he stops him and explains how nothing must change because of their presence. They finish what they are doing and return to the present, but everything is gone. They reappear in a wild world with no humans and no signs that they ever existed. They fall to the floor of their platform, the only man-made thing in the whole world, and lament “Why? We didn’t change anything!” And there on the heel of the scientist’s shoe is a crushed butterfly.
The Butterfly Effect is also a movie, starring Ashton Kutcher as Evan Treborn and Amy Smart as Kayleigh Miller, where a troubled man has had blackouts during his youth, later explained by him traveling back into his own past and taking charge of his younger body briefly. The movie explores the issue of changing the timeline and how unintended consequences can propagate.
Scientists eager to avoid the paradoxes presented by time travel have come up with a number of ingenious ways in which to present a more consistent version of reality, some of which have been touched upon here, including:
- The Solution: time travel is impossible because of the very paradox it creates.
- Self-healing hypothesis: successfully altering events in the past will set off another set of events which will cause the present to remain the same.
- The Multiverse or “many-worlds” hypothesis: an alternate parallel universe or timeline is created each time an event is altered in the past.
- Erased timeline hypothesis : a person traveling to the past would exist in the new timeline, but have their own timeline erased.
Related Posts
© Copyright 2023 Astronomy Trek

- Nostalgic Travel: Reliving Your Past Through Experiences
C oincidence and nostalgia intertwine as travelers seek a respite from the fast-paced world and technological overload. In a quest for freedom and a yearning to relive the past, a new trend of nostalgic travel has emerged. This article explores the allure of this phenomenon. Uncovering the reasons behind its appeal and showcasing destinations that allow travelers to embrace the magic of old films and the charm of a bygone era. Prepare to embark on a journey that takes you back in time, where memories are made and freedom is found.
This article all started when my husband and I were about to board our flight to Hawaii . We heard over the speakers the song “A Dream is a Wish Your Heart Makes.” It instantly made me think of Walt Disney World and put me in such a good mood. I told my husband what is it about Disney that is so nostalgic? Why does it have the power to make you feel all warm and fuzzy inside? Thats when my husband began to talk about Nostalgic travel. BINGO, I said. I know what my next article is going to be about.
I grew up traveling even though my family didn’t have a lot of money. My grandma used to play a game with us kids called “Destination Unknown.” When she would call us up on the phone and yell “Destination Unknown”, we knew we were going somewhere special. It wasn’t like grandma had a ton of money but as kids we never really knew that. She always seemed to make each trip special. Most of the time it wasn’t even out of the state of Oklahoma! She took us o many trips to Turner Falls State Park , Arbuckle Wilderness, Chickasaw National Recreation Area , and even to dig crystals at the Great Salt Plains .
Occasionally we got to go on long road trips. I remember this one trip, where we went to the Grand Canyon with all the grand kids piled into a van. On the way there we stopped to see the Petrified Forest, Meteor Crator and more. In the car we play roadside games as we didn’t have electronics back then. I remember grandma would always pack us a picnic lunch . These are memories that I will hold on to forever.
When I had kids, I decided to carry on this same tradition. In fact I guess you could say I got my travel bug from my grandma! Today we are going to talk about reliving your past with nostalgic travel. I would love for you to share some of your travel stories in the comments and relive your memories right along side you.
The rise of nostalgic travel
The rise of nostalgic travel reflects the growing desire for individuals to relive cherished memories and experiences from the past. In a world that is constantly changing and evolving, people are seeking solace and comfort in the familiarity of their childhood memories. Nostalgic travel allows them to revisit places that hold sentimental value and relive the moments that shaped their lives. It is a way of escaping the present and immersing oneself in the magic of the past.
For many, nostalgic travel is a way of reliving their past and reconnecting with their roots. It offers an opportunity to revisit the places that were once familiar and experience them with fresh eyes. Whether it’s a childhood home, a favorite vacation spot, or a beloved landmark, these destinations hold a special place in our hearts and evoke a sense of nostalgia that is hard to replicate.
Recreating experiences
Reliving your past through nostalgic travel is not just about revisiting physical locations; it is also about recreating the experiences and emotions associated with those memories. Whether it’s indulging in your favorite childhood treats , participating in activities that were once a part of your daily routine, or simply taking the time to reflect on the past, nostalgic travel allows you to reconnect with your true self and find solace in the simplicity of earlier times.
In a world that often feels chaotic and overwhelming, nostalgic travel offers a sense of freedom and escapism. It allows individuals to step away from their responsibilities and obligations and immerse themselves in the joy and innocence of their past. By reliving cherished memories and experiences, nostalgic travel provides a much-needed respite. It reminds us of the importance of slowing down and savoring the present.
Embracing retro vibes: Traveling back in time
Two popular ways of embracing retro vibes in travel are visiting vintage-inspired accommodations and exploring retro-themed attractions. This nostalgic travel trend has gained popularity among individuals who desire to relive the magic of the past while experiencing new adventures. Here are three key aspects of embracing retro vibes in travel:
- Vintage-Inspired Accommodations: Travelers are increasingly seeking out accommodations that transport them back in time. From boutique hotels decorated with retro furniture to cozy bed and breakfasts with a vintage flair, these accommodations provide a unique and nostalgic experience. The charm and character of these establishments allow guests to immerse themselves in a bygone era.
- Retro-Themed Attractions: Retro-themed attractions offer a trip down memory lane for those seeking a taste of the past. From retro arcades and amusement parks to vintage car shows and nostalgic music festivals. These attractions provide a sense of nostalgia and excitement. Visitors can relive their favorite childhood memories or experience the cultural trends of a specific era.
- Road Trips on Iconic Routes: Embarking on a road trip along iconic routes, such as Route 66 in the US. This allows travelers to explore the landscapes and towns that were once the lifeblood of the nation. These routes offer a glimpse into the past, with roadside diners, vintage motels, and breathtaking landscapes. It’s a way to disconnect from the modern world and embrace the freedom of the open road.
For those seeking a sense of freedom and a connection to the past, embracing retro vibes in travel provides a unique and enriching experience. Whether it’s staying in a vintage-inspired accommodation, exploring retro-themed attractions, or embarking on a road trip along iconic routes. Travelers can relive the magic of yesteryear and create lasting memories.
Wander through film history: Iconic movie locations
Visitors can immerse themselves in the cinematic world by exploring and reimagining iconic movie locations throughout history. This topic highlights the desire of travelers to experience the magic of their favorite films by visiting the actual shooting spots. Movie enthusiasts and avid fans seek to relive the enchantment of old films by stepping foot on locations associated with iconic movies. From India’s golden era of the 1950s and 1960s to the streets of New York City where countless blockbusters have been filmed, these destinations offer breathtaking scenery and a chance to relive cinematic moments.
In the current era of nostalgic travel, where travelers long for the comfort and charm of yesteryear, visiting vintage movie locations provides a unique and nostalgic experience. It allows for a journey that intertwines the present and the past, creating unforgettable memories for film enthusiasts. Moreover, this trend aligns with the desire for freedom in travel, as visitors can escape the screens and immerse themselves in the real-life settings of their favorite movies.
Seeking vintage magic: Unplanned experiences in nostalgic travel
An exploration of vintage locations offers travelers the opportunity to embark on unplanned experiences that evoke a sense of nostalgia and magic. In today’s fast-paced world, where technology dominates our lives, many people are seeking freedom and a break from the constant hustle and bustle. Nostalgic travel provides a way to escape the screens and immerse ourselves in the charm and comfort of yesteryear. Here are three reasons why seeking vintage magic through unplanned experiences in vintage locations is becoming increasingly popular:
- Escape from the ordinary: Vintage locations transport us back in time, allowing us to step away from the mundane and embrace a different era. These places offer a unique and nostalgic experience that cannot be replicated elsewhere.
- Connection with the past: By visiting vintage locations, we have the opportunity to relive the magic of old films and iconic moments. Whether it’s walking in the footsteps of our favorite actors or witnessing breathtaking scenery that was once captured on the silver screen, these destinations allow us to make a connection with the past.
- Authenticity and simplicity: Vintage travel offers an escape from modern amenities and a chance to experience raw and unplanned moments. Travelers seek to make connections with new faces, cultures, and languages, embracing the simplicity of a bygone era.
- We enjoy stopping by antique stores and thrift shops when we are on road trips. You never know what you are going to find.
In a world that constantly evolves, seeking vintage magic through unplanned experiences in vintage locations offers a sense of freedom and nostalgia that is increasingly appealing to travelers.
Making memories: Reliving the past in a changing world
The nostalgia for simpler times and the desire to relive cherished moments have prompted travelers to seek vintage-inspired accommodations and embrace the nostalgia travel trend. In a constantly evolving world, people long for the comfort and charm of yesteryear. They yearn for experiences that transport them back in time, where they can escape modern amenities and embrace a more raw and unplanned journey. Vintage travel offers a unique and nostalgic experience, allowing travelers to make connections and memories with new faces, cultures, and languages.
The current generation is increasingly drawn to retro vibes in travel. Vintage-inspired accommodations and retro-themed attractions have gained popularity, as travelers seek to relive the magic of the past. Road trips on iconic routes like Route 66 in the US offer a taste of the bygone era. Plus travelers are also embracing film and vintage cameras, seeking fewer photos and more unforgettable moments.
FREEDOM!!!!
For those who desire freedom, nostalgic travel offers an escape from the screens and virtual world that has consumed modern life. It provides an opportunity to disconnect and immerse oneself in the simplicity and charm of the past. As augmented and virtual reality devices continue to inspire participants to explore places physically, more and more travelers are seeking off-the-beaten-path locations to embrace nature and escape the crowds.
In a world where hotspots from years ago have lost their charm due to overcrowding, travelers are also considering off-peak season travel to save on expenses and avoid crowded destinations. The desire to explore places that have only been experienced virtually so far physically is strong, as travelers yearn for history to repeat itself through nostalgic travel.
You need more nostalgic travel!
In a world obsessed with progress and the latest trends, nostalgic travel offers a refreshing escape. By seeking solace in the past, travelers can relive the simplicity and charm of bygone eras. From vintage-inspired accommodations to iconic movie locations, these destinations offer a unique opportunity to immerse oneself in nostalgia. Ironically, in our quest to escape the overwhelming presence of screens. We find ourselves turning to the past for a much-needed break from the present.
Family Destinations & Articles You Should Check Out
- Branson Mo Roller Coasters: The Fast and The Furious
- Visit the Arbuckle Mountains and Turner Falls Oklahoma
- Free Printable License Plate Game : Road Trip Games in the Car
- Traveling Tips for Visiting LEGOLAND Florida
- Nickelodeon Resort Punta Cana
- Travel to Dog Friendly Orlando Florida
- Pretend Play for Kids : Free Printable Travel Set
- 5 Teen Friendly Attractions in OKC
- 10 Disney Vacation Tips You Need to Know
- Travel Gatlinburg – Theme Parks and Attractions
- Free Printable Road Trip Budget Planner
- Visit Old MacDonald’s Farm
- Great Wolf Lodge & Holiday Inn Review
- Things to Do in Branson with Kids
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA
- Facebook Group
- Explore Oklahoma Facebook Group
- Hot Deals Group
- Recipe Group
- Homesteading Facebook Group
- Don’t forget to invite your friend’s to our Facebook groups! We would also love to see your vacation pictures!
- Bryce Canyon Campgrounds: Where to Camp and RV
- Universal Studios Orlando Deals: Hotels, Park Tickets and More
- Free Events in Oklahoma City: Unlocking the Best of OKC
- Things to Do on Big Island Hawaii
The post Nostalgic Travel: Reliving Your Past Through Experiences appeared first on roamingmyplanetcom .

Advertisement
Supported by
Hot Oceans Worsened Dubai’s Dramatic Flooding, Scientists Say
An international team of researchers found that heavy rains had intensified in the region, though they couldn’t say for sure how much climate change was responsible.
- Share full article

By Raymond Zhong
Scenes of flood-ravaged neighborhoods in one of the planet’s driest regions stunned the world this month. Heavy rains in the United Arab Emirates and Oman submerged cars, clogged highways and killed at least 21 people. Flights out of Dubai’s airport, a major global hub, were severely disrupted.
The downpours weren’t a total surprise — forecasters had anticipated the storms several days earlier and issued warnings. But they were certainly unusual.
Here’s what to know.
Heavy rain there is rare, but not unheard-of.
On average, the Arabian Peninsula receives a scant few inches of rain a year, although scientists have found that a sizable chunk of that precipitation falls in infrequent but severe bursts, not as periodic showers. These rains often come during El Niño conditions like the ones the world is experiencing now.
U.A.E. officials said the 24-hour rain total on April 16 was the country’s largest since records there began in 1949 . And parts of the nation had already experienced an earlier round of thunderstorms in March.
Oman, with its coastline on the Arabian Sea, is also vulnerable to tropical cyclones. Past storms there have brought torrential rain, powerful winds and mudslides, causing extensive damage.
Global warming is projected to intensify downpours.
Stronger storms are a key consequence of human-caused global warming. As the atmosphere gets hotter, it can hold more moisture, which can eventually make its way down to the earth as rain or snow.
But that doesn’t mean rainfall patterns are changing in precisely the same way across every part of the globe.
In their latest assessment of climate research , scientists convened by the United Nations found there wasn’t enough data to have firm conclusions about rainfall trends in the Arabian Peninsula and how climate change was affecting them. The researchers said, however, that if global warming were to be allowed to continue worsening in the coming decades, extreme downpours in the region would quite likely become more intense and more frequent.
Hot oceans are a big factor.
An international team of scientists has made a first attempt at estimating the extent to which climate change may have contributed to April’s storms. The researchers didn’t manage to pin down the connection precisely, though in their analysis, they did highlight one known driver of heavy rain in the region: above-normal ocean temperatures.
Large parts of the Indian, Pacific and Atlantic Oceans have been hotter than usual recently, in part because of El Niño and other natural weather cycles, and in part because of human-induced warming .
When looking only at El Niño years, the scientists estimated that storm events as infrequent as this month’s delivered 10 percent to 40 percent more rain to the region than they would in a world that hadn’t been warmed by human activities. They cautioned, however, that these estimates were highly uncertain.
“Rainfall, in general, is getting more extreme,” said Mansour Almazroui, a climate scientist at King Abdulaziz University in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, and one of the researchers who contributed to the analysis.
The analysis was conducted by scientists affiliated with World Weather Attribution, a research collaboration that studies extreme weather events shortly after they occur. Their findings about this month’s rains haven’t yet been peer reviewed, but are based on standardized methods .
The role of cloud seeding isn’t clear.
The U.A.E. has for decades worked to increase rainfall and boost water supplies by seeding clouds. Essentially, this involves shooting particles into clouds to encourage the moisture to gather into larger, heavier droplets, ones that are more likely to fall as rain or snow.
Cloud seeding and other rain-enhancement methods have been tried around the world, including in Australia, China, India, Israel, South Africa and the United States. Studies have found that these operations can, at best, affect precipitation modestly — enough to turn a downpour into a bigger downpour, but probably not a drizzle into a deluge.
Still, experts said pinning down how much seeding might have contributed to this month’s storms would require detailed study.
“In general, it is quite a challenge to assess the impact of seeding,” said Luca Delle Monache, a climate scientist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in La Jolla, Calif. Dr. Delle Monache has been leading efforts to use artificial intelligence to improve the U.A.E.’s rain-enhancement program.
An official with the U.A.E.’s National Center of Meteorology, Omar Al Yazeedi, told news outlets that the agency didn’t conduct any seeding during the latest storms. His statements didn’t make clear, however, whether that was also true in the hours or days before.
Mr. Al Yazeedi didn’t respond to emailed questions from The New York Times, and Adel Kamal, a spokesman for the center, didn’t have further comment.
Cities in dry places just aren’t designed for floods.
Wherever it happens, flooding isn’t just a matter of how much rain comes down. It’s also about what happens to all that water once it’s on the ground — most critically, in the places people live.
Cities in arid regions often aren’t designed to drain very effectively. In these areas, paved surfaces block rain from seeping into the earth below, forcing it into drainage systems that can easily become overwhelmed.
One recent study of Sharjah , the capital of the third-largest emirate in the U.A.E., found that the city’s rapid growth over the past half-century had made it vulnerable to flooding at far lower levels of rain than before.
Omnia Al Desoukie contributed reporting.
Raymond Zhong reports on climate and environmental issues for The Times. More about Raymond Zhong
Japanese yen hits fresh 34-year low despite verbal intervention from authorities

The yen slipped past 155 against the U.S. dollar on Thursday, touching a new 34-year low against continued strength in the greenback.
The weakness comes as the Bank of Japan is due to release its monetary policy decision Friday and in spite of verbal warnings from Japanese authorities .
Some market watchers had speculated that the 155 level would prompt intervention after the currency languished at multi-decade lows for a month.
More from CNBC
- India markets face an ‘inevitable’ correction if Modi’s election win disappoints, Bernstein says
- ‘Chaotic era’ for Asian currencies: Bank of America is not bullish on any of them
- South Korea’s largest K-pop agency Hybe accuses sublabel executives of breach of trust
“For the BOJ to support the yen, it should acknowledge that policy has been too accommodative, that the next hike is as imminent as in June, and that the terminal rate would be higher than priced by the market,” Shusuke Yamada, head of Japan currency and rates strategy at BofA Securities Japan, said in a Tuesday note. Still, he said that’s unlikely at this week’s meeting.
The yen’s weakness has also been fueled by a stronger dollar. Stubborn U.S. inflation has spurred comments from Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell that suggest rate cuts may not come in the next several months.
“The Japanese authorities have stepped up verbal intervention, but it seems unlikely to be effective given that the move in the currency appears to reflect dollar strength against most currencies rather than being specific to the yen,” Idanna Appio, portfolio manager at First Eagle Investments, told CNBC.
Appio said this week’s BOJ meeting will be key for investors as they monitor inflation forecasts in light of the weaker yen, higher oil prices and strong wage growth.
Closing in on an intervention?
The yen has weakened 4.2% since the BOJ’s March meeting, worrying Japanese authorities and investors.
There has also been talk of a potential “coordinated intervention” with South Korea. If enacted, analysts believe such action could politically and economically benefit both nations, if it succeeded in supporting the yen and the Korean won.
As much as markets would like to see Japanese authorities take decisive action to stem the yen’s fall as soon as possible, analysts say it is unlikely that the central bank or the Ministry of Finance will act on it right away.
“The FX tail will not be allowed to wag the dog,” Vishnu Varathan, head of economics and strategy for Asia at Mizuho Bank, wrote in a note.
Varathan said yen weakness is a policy constraint, not a catalyst for the BOJ. He noted that the Japanese central bank will likely stick to its “dovish restraint” when it comes to tweaking rates. Instead, he said, authorities could opt for intervention through flexible bond purchase signals.
Shreyashi Sanyal is a correspondent for CNBC International in Singapore.
Train strikes in May 2024: Full list of dates and lines affected
Rail lines are set for disruption in the week following the first May bank holiday as train drivers at 16 rail companies strike on different days.
Thursday 25 April 2024 10:29, UK

Train drivers will stage a fresh wave of strikes and overtime bans in May, causing disruption to the rail network.
The strikes are part of a long-running dispute over pay.
Members of Aslef union at 16 rail companies will walk out on different days from 7 to 9 May.
Additionally, all members will refuse to work any overtime from 6 May to 11 May.
Here is a full list of the services affected by strikes and when.
Rail strike dates
Tuesday 7 May
Strikes will affect c2c, Greater Anglia, GTR Great Northern Thameslink, Southeastern, Southern, Gatwick Express and South Western Railway.
Wednesday 8 May
Strikes will affect Avanti West Coast, Chiltern Railways, CrossCountry, East Midlands Railway, Great Western Railway and West Midlands Trains.
Thursday 9 May
Strikes will affect LNER, Northern Trains and TransPennine Express.
Overtime ban dates
From Monday 6 May to Saturday 11 May union members will not work overtime.
Overtime bans, an action short of a strike, means some services may not be running or may be reduced as drivers refuse to work their rest days.
People are advised to check before they travel, as some areas may have no service.
Keep up with all the latest news from the UK and around the world by following Sky News
How do strikes and overtime bans affect services?
Strikes tend to mean services on lines where members are participating are extremely affected or cancelled entirely, whereas overtime bans often lead to reduced services.

Are there strikes on the Tube too?
There have been regular strikes on London Underground too recently, and while there aren't any planned walkouts for drivers, customer service managers are set to walk out on Friday 26 April in a dispute over terms and conditions.
There will also be an overtime ban for the customer service managers on the following days:
Monday 29 April
Tuesday 30 April
Wednesday 1 May
Tuesday 2 May
Wednesday 3 May
Thursday 4 May
Friday 5 May
The Transport Salaried Staffs' Association (TSSA) says the action by its members is likely to cause Tube stations to close at the last minute, including on the Saturday following the strike (27 April), while TfL has said on its website "some stations may need to close at short notice".
Despite the warning, a TfL spokesperson has said they aren't expecting significant disruption.
This action follows strike action taken by the same workers on 10 April, which the TSSA said had a "real impact" with "many stations shut at short notice".
They say they are "extremely concerned" about TfL's 'Stations Changes' proposals.
"We have made it clear that our union will not accept the continued threats to our members' roles, locations, terms, and conditions to stand unchallenged," a TSSA spokesperson said.
"We will continue to take sustained action until London Underground is prepared to negotiate with us in good faith."
Commenting on the impending strikes, a TfL spokesperson said: "We are disappointed that TSSA is continuing with this strike action following a consultation process.
"While we don't expect this action will cause significant disruption, we urge TSSA to continue to work with us to help find a resolution.
"There are no planned job losses as part of these vital changes which will improve the service we provide to customers at our stations."
How can I stay in the loop?
You can use the National Rail's journey planner to see when trains are running.
Be sure to check it close to when you plan to travel, as it will be updated regularly.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Why are the strikes still happening?
Aslef rejected a two-year offer of 4% in 2022 and another 4% this year, saying it is way below inflation, and is linked to changes in terms and conditions.
Aslef said train drivers have not had an increase in salary for five years, since their last pay deals expired in 2019.
The union said after its members voted overwhelmingly in February to continue taking industrial action, it asked the train operating companies to hold talks.
General secretary Mick Whelan said the year-old pay offer of 4% and another 4% was "dead in the water".
Related Topics
- London Underground
- Rail strikes

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Can we use time travel in everyday life? We can't use a time machine to travel hundreds of years into the past or future. That kind of time travel only happens in books and movies. But the math of time travel does affect the things we use every day. For example, we use GPS satellites to help us figure out how to get to new places.
Mallett posits that by twisting time into a loop, one could travel from the future back to the past - and then back to the future. And this is the idea of a wormhole, a sort of tunnel with two ...
The first page of The Time Machine published by Heinemann. Time travel is the hypothetical activity of traveling into the past or future.Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. In fiction, time travel is typically achieved through the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine.The idea of a time machine was popularized by H ...
Time travel makes regular appearances in popular culture, with innumerable time travel storylines in movies, television and literature. But it is a surprisingly old idea: one can argue that the ...
Traveling Into the Past . It turns out that people time travel all the time, but only in one direction: from the past to the present and moving into the future. Unfortunately, no one has any control over how quickly that time passes and nobody can stop time and continue to live. It seems that time is a one-way street, always moving forward.
Indeed, backward time travel, while theoretically possible, is far trickier and would involve black holes and "tunable wormholes" and more energy than a kindergarten class on a sugar binge.
In a peer-reviewed journal article, University of Queensland physicists say time is essentially self-healing. Changes in the past wouldn't necessarily cause a universe-ending paradox. Phew.
The understanding that this object could act as a time machine allowing one to travel to the past only happened in the 1970s, a few decades after scientists had discovered a phenomenon called ...
Time travel is the concept of moving between different points in time, just like you move between different places. ... As they peer into the vast expanse of the cosmos, they gaze into the past ...
The first time travel scene in the 1985 film 'Back to the Future.' Introducing multiple histories. But what's the point of going back in time if you cannot change the past?
Einstein found that the faster you move through space, the slower you move through time — you age more slowly, in other words. One of the key ideas in relativity is that nothing can travel ...
Is time travel possible? According to NASA, time travel is possible, just not in the way you might expect. Albert Einstein's theory of relativity says time and motion are relative to each other ...
A popular example of traveling back in time is the fascinating Canadian TV series Travelers: In a distant future, the Earth is in shambles; humans are controlled by a benevolent artificial ...
Accelerating an infinite mass any faster than that is impossible. Warp speed technology could theoretically cheat the universal speed limit by propelling a bubble of space-time across the universe, but even this would come with colossal, far-future energy costs. But what if time travel into the past and future depends less on speculative space ...
It was, he said, "a welcome reception for future time travelers," a tongue-in-cheek experiment to reinforce his 1992 conjecture that travel into the past is effectively impossible. But Hawking may ...
If time travel entailed contradictions then the issue would be settled. And indeed, most of the stories employing time travel in popular culture are logically incoherent: one cannot "change" the past to be different from what it was, since the past (like the present and the future) only occurs once.
Although many people are fascinated by the idea of changing the past or seeing the future before it's due, no person has ever demonstrated the kind of back-and-forth time travel seen in science ...
Time travel is theoretically possible, calculations show. But that doesn't mean you could change the past. Doc Brown and Marty McFly in "Back to the Future." Universal Pictures. Time travel is ...
Signup for your FREE trial to Wondrium here: http://ow.ly/f5Jw30rNLaD - Highly recommended!Chapters:0:00 - Einstein's predictions1:51 - How wormholes are pre...
According to Mallet, the right geometry could lead to time travel into either the past and the future. Since publishing his theory in 2000, Mallet has been trying to raise the funds to pay for a ...
Time travel is possible, but it's a one-way ticket. November 16, 2020 Science Borealis. Chenoa van den Boogaard, Physics and Astronomy editor. The ability to travel through time, whether it is to fix a mistake in the past or gain insight into the future, has long been embraced by science fiction and debated by theoretical physicists.
1: Predestination Paradox. A Predestination Paradox occurs when the actions of a person traveling back in time become part of past events, and may ultimately cause the event he is trying to prevent to take place. The result is a 'temporal causality loop' in which Event 1 in the past influences Event 2 in the future (time travel to the past ...
Nostalgic Travel: Reliving Your Past Through Experiences. Story by RoamingMyPlanet. • 1mo • 9 min read. Coincidence and nostalgia intertwine as travelers seek a respite from the fast-paced ...
All Time High Lyrics: A little cardio, we are on the clock / Travel lightly, fear of missing out / And people from our past have all turned in / Looks like we might be a dying breed / And I feel your
One recent study of Sharjah, the capital of the third-largest emirate in the U.A.E., found that the city's rapid growth over the past half-century had made it vulnerable to flooding at far lower ...
By Shreyashi Sanyal, CNBC. The yen slipped past 155 against the U.S. dollar on Thursday, touching a new 34-year low against continued strength in the greenback. The weakness comes as the Bank of ...
Rail strike dates. Tuesday 7 May. Strikes will affect c2c, Greater Anglia, GTR Great Northern Thameslink, Southeastern, Southern, Gatwick Express and South Western Railway. Wednesday 8 May ...