
Written by Vasilena Markova • September 27, 2023 • 12:58 pm • Internet

Round-Trip Time (RTT): What It Is and Why It Matters
Round-Trip Time (RTT) is a fundamental metric in the context of network performance, measuring the time it takes for data packets to complete a round trip from source to destination and back. Often expressed in milliseconds (ms), RTT serves as a critical indicator for evaluating the efficiency and reliability of network connections. In today’s article, we dive into the concept of RTT, exploring how it works, why it matters in our digital lives, the factors that influence it, and strategies to enhance it. Whether you’re a casual internet user seeking a smoother online experience or a network administrator aiming to optimize your digital infrastructure, understanding this metric is critical in today’s interconnected world.
Table of Contents
What is Round-Trip Time (RTT)?
Round-Trip Time is a network performance metric representing the time it takes for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination and back to the source. It is often measured in milliseconds (ms) and is a crucial parameter for determining the quality and efficiency of network connections.
To understand the concept of RTT, imagine sending a letter to a friend through the postal service. The time it takes for the letter to reach your friend and for your friend to send a reply back to you forms the Round-Trip Time for your communication. Similarly, in computer networks, data packets are like those letters, and RTT represents the time it takes for them to complete a round trip.
How Does it Work?
The concept of RTT can be best understood by considering the journey of data packets across a network. When you request information from a web server, for example, your device sends out a data packet holding your request. This packet travels through various network devices in between, such as routers and switches, before reaching the destination server. Once the server processes your request and prepares a response, it sends a data packet back to your device.
Round-Trip Time is determined by the time it takes for this data packet to travel from your device to the server (the outbound trip) and then back from the server to your device (the inbound trip). The total RTT is the sum of these two one-way trips.
Let’s break down the journey of a data packet into several steps so you can better understand the RTT:
- Sending the Packet: You initiate an action on your device that requires data transmission. For example, this could be sending an email, loading a webpage, or making a video call.
- Packet Travel: The data packet travels from your device to a server, typically passing through multiple network nodes and routers along the way. These middle points play a significant role in determining the RTT.
- Processing Time: The server receives the packet, processes the request, and sends a response back to your device. This processing time at both ends also contributes to the Round-Trip Time.
- Return Journey: The response packet makes its way back to your device through the same network infrastructure, facing potential delays on the route.
- Calculation: It is calculated by adding up the time taken for the packet to travel from your device to the server (the outbound trip) and the time it takes for the response to return (the inbound trip).
Why does it matter?
At first look, Round-Trip Time (RTT) might seem like technical terminology, but its importance extends to various aspects of our digital lives. It matters for many reasons, which include the following:
- User Experience
For everyday internet users, RTT influences the sensed speed and responsiveness of online activities. Low Round-Trip Time values lead to a seamless experience, while high RTT can result in frustrating delays and lag during tasks like video streaming, online gaming, or live chats.
- Network Efficiency
Network administrators and service providers closely monitor RTT to assess network performance and troubleshoot issues. By identifying bottlenecks and areas with high RTT, they can optimize their infrastructure for better efficiency.
- Real-Time Applications
Applications that rely on real-time data transmission, such as VoIP calls, video conferencing, and online gaming, are highly sensitive to RTT. Low RTT is crucial for smooth, interruption-free interactions.
In cybersecurity, Round-Trip Time plays a role in detecting network anomalies and potential threats. Unusually high RTT values can be a sign of malicious activity or network congestion.
Factors Affecting Round-Trip Time (RTT)
Several factors can influence the metric, both positively and negatively. Therefore, understanding these factors is crucial, and it could be very beneficial for optimizing network performance:
- Distance: The physical distance between the source and destination plays a significant role. Longer distances result in higher RTT due to the time it takes for data to travel the network.
- Network Congestion: When a network experiences high volumes of traffic or congestion, data packets may be delayed as they wait for their turn to be processed. As a result, it can lead to packet delays and increased RTT.
- Routing: The path a packet takes through the network can significantly affect RTT. Efficient routing algorithms can reduce the time, while not-so-optimal routing choices can increase it.
- Packet Loss: Packet loss during transmission can occur due to various reasons, such as network errors or congestion. When lost, packets need to be retransmitted, which can seriously affect the Round-Trip Time.
- Transmission Medium: It is a critical factor influencing RTT, and its characteristics can vary widely based on the specific medium being used. Fiber optic cables generally offer low RTT due to the speed of light in the medium and low signal loss. In contrast, wireless mediums can introduce variable delays depending on environmental factors and network conditions.
How to improve it?
Improving Round-Trip Time (RTT) is a critical goal for network administrators and service providers looking to enhance user experiences and optimize their digital operations. While some factors affecting it are beyond our control, there are strategies and practices to optimize Round-Trip Time for a smoother online experience:
- Optimize Routing: Network administrators can optimize routing to reduce the number of hops data packets take to reach their destination. This can be achieved through efficient routing protocols and load balancing .
- Optimize Network Infrastructure: For businesses, investing in efficient network infrastructure, including high-performance routers and switches, can reduce internal network delays and improve RTT.
- Upgrade Hardware and Software: Keeping networking equipment and software up-to-date ensures that you benefit from the latest technologies and optimizations that can decrease RTT.
- Implement Caching: Caching frequently requested data closer to end-users can dramatically reduce the need for data to travel long distances. The result really helps with lowering RTT.
- Monitor and Troubleshoot: Regularly monitor your network for signs of congestion or packet loss. If issues arise, take steps to troubleshoot and resolve them promptly.
Discover ClouDNS Monitoring service!
Round-Trip Time (RTT) is the silent force that shapes our online experiences. From the seamless loading of web pages to the quality of our video calls, RTT plays a pivotal role in ensuring that digital interactions happen at the speed of thought. As we continue to rely on the Internet for work, entertainment, and communication, understanding and optimizing this metric will be crucial for both end-users and network administrators. By reducing it through strategies, we can have a faster, more responsive digital world where our online activities are limited only by our imagination, not by lag.
Hello! My name is Vasilena Markova. I am a Marketing Specialist at ClouDNS. I have a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Economics and am studying for my Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity Management. As a digital marketing enthusiast, I enjoy writing and expressing my interests. I am passionate about sharing knowledge, tips, and tricks to help others build a secure online presence. My absolute favorite thing to do is to travel and explore different cultures!

Related Posts

Ping Traffic Monitoring: Ensuring Network Health and Efficiency
March 28, 2024 • Monitoring
In an era where digital connectivity is the lifeline of businesses and individuals alike, maintaining optimal network performance is more ...
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recent Posts
- Network Monitoring: Ensuring the Pulse of Digital Communications
- rDNS explained in detail
- What is Authoritative DNS server?
- IPv4 vs IPv6 and where did IPv5 go?
- What is a Secondary DNS server?
- Cloud Computing
- DNS Records
- Domain names
- Load balancing
- SSL Certificates
- Web forwarding
- DNS Services
- Managed DNS
- Dynamic DNS
- Secondary DNS
- Reverse DNS
- DNS Failover
- Anycast DNS
- Email Forwarding
- Enterprise DNS
- Domain Names
Home > Learning Center > Round Trip Time (RTT)
Article's content
Round trip time (rtt), what is round trip time.
Round-trip time (RTT) is the duration, measured in milliseconds, from when a browser sends a request to when it receives a response from a server. It’s a key performance metric for web applications and one of the main factors, along with Time to First Byte (TTFB), when measuring page load time and network latency .
Using a Ping to Measure Round Trip Time
RTT is typically measured using a ping — a command-line tool that bounces a request off a server and calculates the time taken to reach a user device. Actual RTT may be higher than that measured by the ping due to server throttling and network congestion.
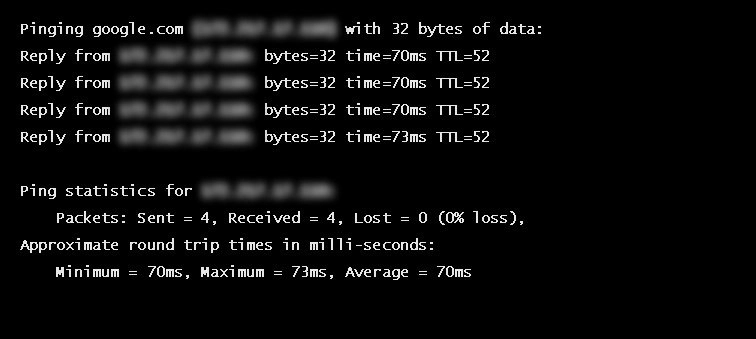
Example of a ping to google.com
Factors Influencing RTT
Actual round trip time can be influenced by:
- Distance – The length a signal has to travel correlates with the time taken for a request to reach a server and a response to reach a browser.
- Transmission medium – The medium used to route a signal (e.g., copper wire, fiber optic cables) can impact how quickly a request is received by a server and routed back to a user.
- Number of network hops – Intermediate routers or servers take time to process a signal, increasing RTT. The more hops a signal has to travel through, the higher the RTT.
- Traffic levels – RTT typically increases when a network is congested with high levels of traffic. Conversely, low traffic times can result in decreased RTT.
- Server response time – The time taken for a target server to respond to a request depends on its processing capacity, the number of requests being handled and the nature of the request (i.e., how much server-side work is required). A longer server response time increases RTT.
See how Imperva CDN can help you with website performance.
Reducing RTT Using a CDN
A CDN is a network of strategically placed servers, each holding a copy of a website’s content. It’s able to address the factors influencing RTT in the following ways:
- Points of Presence (PoPs) – A CDN maintains a network of geographically dispersed PoPs—data centers, each containing cached copies of site content, which are responsible for communicating with site visitors in their vicinity. They reduce the distance a signal has to travel and the number of network hops needed to reach a server.
- Web caching – A CDN caches HTML, media, and even dynamically generated content on a PoP in a user’s geographical vicinity. In many cases, a user’s request can be addressed by a local PoP and does not need to travel to an origin server, thereby reducing RTT.
- Load distribution – During high traffic times, CDNs route requests through backup servers with lower network congestion, speeding up server response time and reducing RTT.
- Scalability – A CDN service operates in the cloud, enabling high scalability and the ability to process a near limitless number of user requests. This eliminates the possibility of server side bottlenecks.
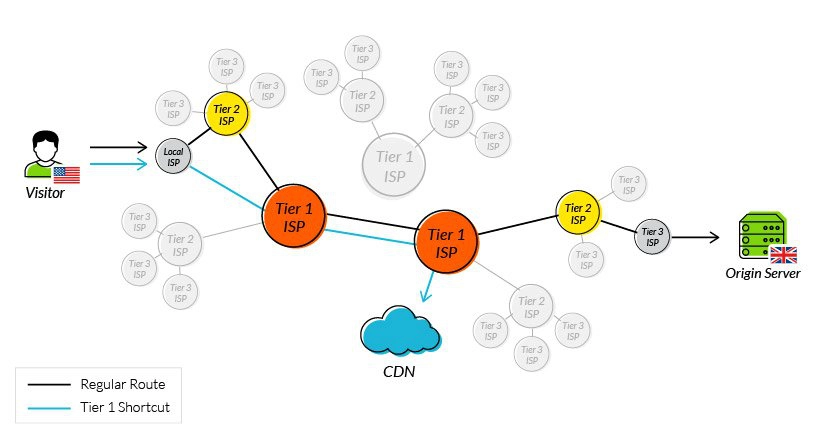
Using tier 1 access to reduce network hops
One of the original issues CDNs were designed to solve was how to reduce round trip time. By addressing the points outlined above, they have been largely successful, and it’s now reasonable to expect a decrease in your RTT of 50% or more after onboarding a CDN service.
Latest Blogs

Grainne McKeever
Feb 26, 2024 3 min read

Erez Hasson
Jan 18, 2024 3 min read

Luke Richardson
Dec 27, 2023 6 min read

Dec 21, 2023 2 min read

Dec 13, 2023 5 min read

Dec 7, 2023 6 min read

- Imperva Threat Research

, Gabi Stapel
Nov 8, 2023 13 min read

Nov 7, 2023 1 min read
Latest Articles
- Network Management
163.8k Views
152.4k Views
99.9k Views
97.8k Views
58.4k Views
54.4k Views
Protect Against Business Logic Abuse
Identify key capabilities to prevent attacks targeting your business logic
The 10th Annual Bad Bot Report
The evolution of malicious automation over the last decade
The State of Security Within eCommerce in 2022
Learn how automated threats and API attacks on retailers are increasing
Prevoty is now part of the Imperva Runtime Protection
Protection against zero-day attacks
No tuning, highly-accurate out-of-the-box
Effective against OWASP top 10 vulnerabilities
An Imperva security specialist will contact you shortly.
Top 3 US Retailer
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- English (US)
Round Trip Time (RTT)
Round Trip Time (RTT) is the length time it takes for a data packet to be sent to a destination plus the time it takes for an acknowledgment of that packet to be received back at the origin. The RTT between a network and server can be determined by using the ping command.
This will output something like:
In the above example, the average round trip time is shown on the final line as 26.8ms.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
- What is Latency?
- What are Different Types of Passwords used in Securing Cisco Router?
- Why is YouTube using TCP but not UDP?
- What is RTS(Real Time Streaming)?
- DNS vs VPN - What's the Difference?
- Types of switches in Computer Network
- TCP Fast Open and TCP/IP Acceleration
- Satellite and Fibre Internet
- What is P2P (Peer-to-Peer Process)?
- TCP vs UDP for Video Streaming
- Spanning Tree Port States
- TCP/IP in Computer Networking
- VIRUS Full Form
- What is WRAN (Wireless Regional Area Network)?
- What is E2EE(End to End Encryption)?
- What is a Next generation Firewall?
- How does Frame Relay Work?
- How Data Encapsulation & De-encapsulation Works?
- How to Mitigate a DDoS Attack?
What is RTT(Round Trip Time)?
RTT (Round Trip Time) also called round-trip delay is a crucial tool in determining the health of a network. It is the time between a request for data and the display of that data. It is the duration measured in milliseconds.
RTT can be analyzed and determined by pinging a certain address. It refers to the time taken by a network request to reach a destination and to revert back to the original source. In this scenario, the source is the computer and the destination is a system that captures the arriving signal and reverts it back.

RTT(Round Trip Time) Measurement
What Are Common Factors that Affect RTT?
There are certain factors that can bring huge changes in the value of RTT. These are enlisted below:
- Distance: It is the length in which a signal travels for a request to reach the server and for a response to reach the browser,
- Transmission medium: The medium which is used to route a signal, which helps in faster transfer of request is transmitted.
- Network hops: It is the time that servers take to process a signal, on increasing the number of hops, RTT will also increase.
- Traffic levels: Round Trip Time generally increases when a network is having huge traffic which results in that, for low traffic RTT will also be less.
- Server response time: It is the time taken by a server to respond to a request which basically depends on the capacity of handling requests and also sometimes on the nature of the request.
Applications of RTT
Round Trip Time refers to a wide variety of transmissions such as wireless Internet transmissions and satellite transmissions. In Internet transmissions, RTT may be identified by using the ping command. In satellite transmissions, RTT can be calculated by making use of the Jacobson/Karels algorithm.
Advantages of RTT
Calculation of RTT is advantageous because:
- It allows users and operators to identify how long a signal will take to complete the transmission.
- It also determines how fast a network can work and the reliability of the network.
Example: Let us assume there are two users, one of which wants to contact the other one. One of them is located in California while the other one is situated in Germany. When the one in California makes the request, the network traffic is transferred across many routers before reaching the server located in Germany. Once the request reverts back to California, a rough estimation of the time taken for this transmission could be made. This time taken by the transmitted request is referred to as RTT. The Round Trip Time is a mere estimate. The path between the two locations can change as the passage and network congestion can come into play, affecting the total period of transmission.
How Does Round-Trip Time Work?
Consider a topology where an appliance named “Exinda” is located between the client and the server. The diagram shown below depicts how the concept of RTT works:

RTT Calculation
For the calculation of Average RTT, RTTS for server and client needs to be calculated separately. The performed calculations are shown below:
Server RTT: RTT1 = T2 – T1 RTT2 = T5 – T4
Client RTT: RTT3 = T3 – T2 RTT4 = T7 – T6
Average RTT: Avg Server RTT = (RTTs1 + RTTs2) / 2 Avg Client RTT = (RTTc1 + RTTc2) / 2 Avg Total RTT = Avg Server RTT + Avg Client RTT
You can refer to the Program to calculate RTT for more details.
Measures To Reduce RTT
A significant reduction in RTT can be made using Content Delivery Network (CDN) . A CDN refers to a network of various servers, each acquiring a copy of the content on a particular website. It addresses the factors affecting RTT in the enlisted ways:
- Points of Presence (PoP)
- Web caching
- Load distribution
- Scalability
- Tier 1 access
CDN has been largely successful in reducing the value of RTT and due to this, a decrease in RTT by 50% is achievable.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- 10 Best Slack Integrations to Enhance Your Team's Productivity
- 10 Best Zendesk Alternatives and Competitors
- 10 Best Trello Power-Ups for Maximizing Project Management
- Google Rolls Out Gemini In Android Studio For Coding Assistance
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Round-Trip Time (RTT)
Last Edited
In the intricate domain of computer networking, Round-Trip Time, popularly known as RTT, plays an instrumental role. RTT signifies the time it takes for a data packet to travel from a source to a destination and back again. It serves as a key performance metric in networking, helping diagnose network speed and efficiency.
What is RTT?
To understand what RTT is, envision playing catch with a ball. You throw the ball (this represents the data packet), and your friend catches it (this is the packet reaching its destination). Then, your friend throws the ball back to you (the packet’s return journey). The total time from the initial throw to catching the ball again is akin to RTT in networking.
RTT is not about how quickly the ball is thrown or caught; rather, it’s about the total duration of the journey. Similarly, in the digital world, RTT measures the full journey of a data packet, irrespective of the data size or transmission speed.
The Importance of Round-Trip Time
RTT is pivotal for network administrators because it helps to measure network latency or delay. It’s a vital metric used to determine the performance of network connections, allowing administrators to identify potential issues and gauge the quality of the network.
A lower Round-Trip Time indicates a faster connection, resulting in improved data transfer and a superior user experience. Conversely, a high RTT may suggest network congestion, poor routing, or other issues leading to increased latency.
How to Measure RTT?
A common method to measure RTT is by using the ‘ping’ command . This command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) request to a specified server, which then sends an ICMP reply back. The time it takes for this round-trip journey is the RTT, typically measured in milliseconds (ms).
Another method involves using Traceroute, a command-line tool that displays the path that a packet takes to reach its destination, recording the latency at each hop.
RTT and Its Impact on Applications
RTT is particularly critical for real-time applications such as video conferencing, VoIP calls, online gaming, and live streaming. High Round-Trip Time values in these applications can lead to noticeable delays, buffering, and synchronization issues, disrupting the user experience.
In non-real-time applications, like email or file transfer, high RTT might not be immediately noticeable to the user but could slow down overall data transfer rates.
Understanding RTT is a fundamental aspect of grasping how networks operate. It allows us to measure and diagnose network performance, directly impacting how we experience the internet and online services. By paying attention to RTT, network administrators can ensure optimal network performance, paving the way for efficient, seamless digital communication.
- RFC 7982 – Measurement of Round-Trip Time and Fractional Loss Using Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN)
Capterra Glossary
RTT (Round-trip Time)
Round-trip time (RTT) or round-trip delay (RTD) is the number of milliseconds it takes for a network request to reach a destination, such as a server, and return to its starting point. Network administrators use this calculation to determine network latency and connection speeds. Various factors can influence RTT, such as:
The distance the signal has to travel to reach its destination and return to its starting point
The amount of traffic on the network
The time it takes for the server to respond to the network request
What Small and Midsize Businesses Need to Know About RTT (Round-trip Time)
SMBs should pay close attention to RTT because it can reveal the efficiency of a network. Networks with high latency might impact website performance, resulting in a poor user experience that jeopardizes sales and engagement.
Related Terms
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Business Intelligence (BI) Services
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Analytics and Business Intelligence (ABI)
- Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR)
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Managed Service Provider (MSP)
- Advanced Clinical Research Information Systems (ACRIS)
- Business Analytics
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Remote Work
- AMO (Application Management Outsourcing)
- Procurement
- Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy
- MSO (Management Services Organization)
- Fri. Apr 12th, 2024
ZP Enterprises
Cyber Security with a flare
What is round-trip time? | RTT definition
By zpenterprises

Round-trip time (RTT) is the millisecond duration (ms) for a network request to go from a starting point to a destination and back to the starting point.
What is round-trip time.
Round-trip time (RTT) is the millisecond duration (ms) for a network request to go from a starting point to a destination and back to the starting point. RTT is an important metric in determining the health of a connection on a local network or the larger Internet and is commonly utilized by network administrators to diagnose the speed and reliability of network connections.
Reducing RTT is a primary goal of a CDN . Improvements in latency can be measured by reducing round-trip time and eliminating instances where roundtrips are required, such as by modifying the standard TLS/SSL handshake .
The ping utility, available on virtually all computers, is a method of estimating round-trip time. Here’s an example of several pings to Google with the round-trip time calculated at the bottom. Notice that one of the ping times – 17.604ms – is higher than the rest.

How does round-trip time work?
Round-trip time represents when it takes data to go roundtrip to another location. Borrowing from the lesson on CDN latency benefits , let’s say that a user in New York wants to contact a server in Singapore.
When the user in New York requests, the network traffic is transferred across many routers in different physical locations before terminating at the server in Singapore. The server in Singapore then sends a response back across the Internet to the location in New York. Once the request terminates in New York, a rough estimate can be made of the time it takes to go round trip between the two locations.

It’s important to remember that round-trip time is an estimate and not a guarantee; the pathway between the two locations can change over time, and other factors, such as network congestion, can affect the overall transit time. Regardless, RTT is an important metric in understanding if a connection can be made and roughly how long it will take to make the trip.
What are the common factors that affect RTT?
Infrastructure components, network traffic, and physical distance along the path between a source and a destination are all potential factors that can affect RTT.
List of factors affecting RTT:
- The nature of the transmission medium – how connections are made affects how fast the connection moves; connections made over optical fiber will behave differently than connections made over copper. Likewise, a connection made over a wireless frequency will behave differently than that of a satellite communication.
- Local area network (LAN) traffic – the amount of traffic on the local area network can bottleneck a connection before it ever reaches the larger Internet. For example, if many users use streaming video services simultaneously, round-trip time may be inhibited even though the external network has excess capacity and functions normally.
- Server response time – the amount of time it takes a server to process and respond to a request is a potential bottleneck in network latency. When a server is overwhelmed with requests, such as during a DDoS attack , its ability to respond efficiently can be inhibited, resulting in increased RTT.
- Node count and congestion – depending on the path a connection takes across the Internet, it may be routed or “hop” through a different number of intermediate nodes. Generally speaking, the greater the number of nodes a connection touches, the slower it will be. A node may also experience network congestion from other traffic, slowing the connection and increasing RTT.
- Physical distance – although a connection optimized by a CDN can often reduce the number of hops required to reach a destination, there is no way of getting around the limitation imposed by the speed of light; the distance between a start and end point is a limiting factor in network connectivity that can only be reduced by moving content closer to the requesting users. A CDN will cache content closer to the requesting users to overcome this obstacle, reducing RTT.
How can a CDN improve RTT?
By maintaining servers inside internet exchange points and having preferred relationships with Internet service providers and other network carriers, a CDN can optimize network pathways between locations, reducing RTT and improving latency for visitors accessing content cached inside the CDN.
Explore the CDN performance lesson to learn how caching, data center placement, file size reductions, and other optimizations reduce latency and improve RTT.

Related Post
Millions of customers’ data found on dark web in latest at&t data breach, cyberattack hits pennsylvania court system, how to minify css for better website performance.
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of round trip
Examples of round trip in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'round trip.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1837, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near round trip
round-trip ticket
Cite this Entry
“Round trip.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/round%20trip. Accessed 13 Apr. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on round trip
Nglish: Translation of round trip for Spanish Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 12, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
- +Plus ayuda
- Cerrar sesión
Significado de round trip en inglés
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- break-journey
- circumnavigation
round trip | Diccionario de Inglés Americano
Round trip | inglés de negocios, ejemplos de round trip, traducciones de round trip.
¡Obtén una traducción rápida y gratuita!

Palabra del día
acting or speaking together, or at the same time

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Palabras nuevas
Aprende más con +Plus
- Recientes y Recomendados {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definiciones Explicaciones claras del uso natural del inglés escrito y oral inglés Learner’s Dictionary inglés británico esencial inglés americano esencial
- Gramática y sinónimos Explicaciones del uso natural del inglés escrito y oral gramática sinónimos y antónimos
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- inglés-chino (simplificado) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- inglés-chino (tradicional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- inglés–holandés holandés-inglés
- inglés-francés francés-inglés
- inglés-alemán alemán-inglés
- inglés-indonesio indonesio-inglés
- inglés-italiano italiano-inglés
- inglés-japonés japonés-inglés
- inglés-noruego noruego–inglés
- inglés-polaco polaco-inglés
- inglés-portugués portugués-inglés
- inglés-español español-inglés
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Listas de palabras
- Inglés Noun
- Negocios Noun
- Translations
- Todas las traducciones
Añadir round trip a una de tus listas, o crear una lista nueva.
{{message}}
Ha ocurrido un error
El informe no pudo enviarse.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is round-trip time? Round-trip time (RTT) is the duration in milliseconds (ms) it takes for a network request to go from a starting point to a destination and back again to the starting point. RTT is an important metric in determining the health of a connection on a local network or the larger Internet, and is commonly utilized by network ...
3. Round Trip Time. The RTT is the time between sending a message from a source to a destination (start) and receiving the acknowledgment from the destination at the source point (end). We can also see RTT referred to as Round Trip Delay (RTD). Sometimes, the acknowledgment is sent from the destination to the source almost immediately after the ...
Round-trip time definition. Round-trip time (RTT) is the millisecond duration for a packet of data to travel from the source to the destination and back. It is a crucial metric in networking to measure the efficiency and performance of data transmission across a network or the internet. RTT is closely related to latency, but it includes the ...
The round-trip time (RTT) from the client's network to the AWS Region that the WorkSpaces are in should be less than 100ms. If the RTT is between 100ms and 200ms, the user can access the WorkSpace, but performance is affected. If the RTT is between 200ms and 375ms, the performance is degraded. If the RTT exceeds 375ms, the WorkSpaces client ...
Round-Trip Time is a network performance metric representing the time it takes for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination and back to the source. It is often measured in milliseconds (ms) and is a crucial parameter for determining the quality and efficiency of network connections. To understand the concept of RTT, imagine ...
Factors Influencing RTT. Actual round trip time can be influenced by: Distance - The length a signal has to travel correlates with the time taken for a request to reach a server and a response to reach a browser.; Transmission medium - The medium used to route a signal (e.g., copper wire, fiber optic cables) can impact how quickly a request is received by a server and routed back to a user.
Round Trip Time (RTT) is the length time it takes for a data packet to be sent to a destination plus the time it takes for an acknowledgment of that packet to be received back at the origin. The RTT between a network and server can be determined by using the ping command. This will output something like: In the above example, the average round ...
Round-trip time (RTT) in networking is the interval it takes a network request to go from a source to a destination and back. It is expressed in milliseconds (ms). RTT is influenced by propagation, transmission, processing, and queueing delays. Low RTT is preferred for responsive network applications, while high RTT can cause sluggishness. RTT ...
Overview, Formula & Usage. Okta. Updated: 02/14/2023 - 11:30. Time to read: 3 minutes. Round trip time, or RTT, is a measurement of the milliseconds required for a data packet to head to a destination and for that destination server to send back an acknowledgment of the packet.
Last Updated : 13 Apr, 2023. RTT (Round Trip Time) also called round-trip delay is a crucial tool in determining the health of a network. It is the time between a request for data and the display of that data. It is the duration measured in milliseconds. RTT can be analyzed and determined by pinging a certain address.
Round-trip time (RTT) is the time it takes for a packet to go from the sending endpoint to the receiving endpoint and back. There are many factors that affect RTT, including propagation delay, processing delay, queuing delay, and encoding delay. These factors are generally constant for a given pair of communicating endpoints.
Round-Trip Time (RTT) In the intricate domain of computer networking, Round-Trip Time, popularly known as RTT, plays an instrumental role. RTT signifies the time it takes for a data packet to travel from a source to a destination and back again. It serves as a key performance metric in networking, helping diagnose network speed and efficiency.
Round-trip time (RTT) or round-trip delay (RTD) is the number of milliseconds it takes for a network request to reach a destination, such as a server, and return to its starting point. Network administrators use this calculation to determine network latency and connection speeds. Various factors can influence RTT, such as: The distance the ...
En este vídeo hablamos del concepto de RTT -ROUND TRIP TIME- y cómo medirlo. ¡Ojo! A pesar de que en el vídeo damos a entender que la latencia y el RTT son s...
Round-trip time (RTT) is the millisecond duration (ms) for a network request to go from a starting point to a destination and back to the starting point. RTT is an important metric in determining the health of a connection on a local network or the larger Internet and is commonly utilized by network administrators to diagnose the speed and ...
round trip ⓘ One or more forum threads is an exact match of your searched term. Spanish definition ... round-trip translation Total round trip time not null - information technology. Visit the Spanish-English Forum. Help WordReference: Ask in the forums yourself.
ROUND TRIP Significado, definición, qué es ROUND TRIP: 1. If you make a round trip, you go on a journey and return to where you started from. 2. If you…. Aprender más.
Round trip time, or RTT, is a measurement of the milliseconds required for a data packet to head to a destination and for that destination server to send back an acknowledgement of the packet. What is RTT in networking? Think of RTT as a type of timed confirmation receipt. As soon as you send something, the timer starts.
round trip n. (journey to a destination and back) viaje de ida y vuelta nm + loc adj. The round trip only takes four hours by car. El viaje de ida y vuelta en auto sólo te lleva cuatro horas. round-trip n as adj. (to a place and back again) de ida y vuelta loc adj. A round-trip ticket is usually cheaper than two one-way tickets.
Round-trip time (RTT) or round-trip delay (RTD) is the number of milliseconds it takes for a network request to reach a destination, such as a server, and return to its starting point. Network administrators use this calculation to determine network latency and connection speeds. Various factors can influence RTT, such as: -The distance the ...
round trip n. noun: Refers to person, place, thing, quality, etc. (journey to a destination and back) viaje de ida y vuelta nm + loc adj. The round trip only takes four hours by car. El viaje de ida y vuelta en auto sólo te lleva cuatro horas. round-trip n as adj. noun as adjective: Describes another noun--for example, " boat race," " dog food."
round-trip: [noun] a trip to a place and back usually over the same route.
round trip significado, definición, qué es round trip: 1. If you make a round trip, you go on a journey and return to where you started from. 2. If you…. Saber más.
At the same time, the amount the UK spends on defence as a percentage of its total economy is in the ditch by historical standards - down from 7% in the 1960s, to just over 2% now.