WhatsApp Our Local Electrician To Get a Fast Response & Quote For Your Electrical Needs.


What Causes Circuit Breakers To Trip?
- April 2, 2024
If your circuit breakers keep tripping, there’s no need to stress. This is a typical situation. Below, you’ll find details on the reasons behind this and tips for avoiding it going forward. Get a handle on your circuit breaker issues!
Table of Contents
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers are protection devices for electrical circuits. When too much current passes, the breaker trips, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage. This can be caused by faulty wiring, too many appliances on one circuit, or a ground fault.
Overloading can cause tripping. This happens when too many devices are connected to a single circuit. Heat builds up in the wires, which can start fires or cause damage. To prevent this, distribute loads across multiple circuits and don’t connect too many appliances to one outlet.
Short circuits also lead to tripping. This happens when two wires with opposite charges come in contact or when a wire touches something grounded. This causes an immediate surge in current that triggers the breaker. Check for exposed wires or insulation damage, and call an electrician if you spot any signs of trouble.
Ground faults can also cause tripping. This happens when there’s an unintentional connection between a live wire and a conductive surface. Install GFCIs to avoid this.
In short, know what causes circuit breakers to trip. Identify potential hazards like overloading, short circuits, and ground faults. Take steps to prevent accidents and ensure your electrical equipment is safe. If you’re unsure how to handle electrical problems, call a licensed electrician.
Overloading Causes
Circuit breakers trip to stop overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical parts. Plugging in too many devices can cause the circuit to become overloaded, so the breaker trips to cut off the power.
Short circuits are like a blind date gone wrong. They can be explosive, and often end in disaster. This happens when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or insulation/water. This throws off the electric balance, causing danger and tripping.
Short Circuit Causes
A short circuit happens when a low-resistance path appears between two points in the circuit that aren’t usually connected. This can cause too much current to flow, making a circuit breaker trip. Insulation or wiring damage, faulty appliances, and circuit overload are the most common reasons for a short circuit. It’s critical to identify and fix the root cause quickly to avoid electrical fires and other dangers .
When too much power passes through a circuit, the circuit breaker will automatically turn off. It’s designed to protect wiring and guard against electrical accidents . But if the breaker trips regularly, there may be underlying issues that need investigation and repair. Often times, this means upgrading or replacing components.
Sometimes short circuits are caused by human error or wear and tear. But they may also come from design or installation problems. Planning and upkeep from local electricians can keep electrical systems running safely and appropriately for a long time. If your circuit breaker is tripping a lot, get an experienced technician to review your system and suggest solutions that match your needs and budget .
Overheating Causes
Circuit breakers are essential safety features. They stop electrical fires and protect your appliances. When overloaded, too much current flows, producing heat. This causes the breaker to trip!
Other factors can cause overheating. Damaged insulation on wires increases resistance. Loose connections add resistance and heat. High temperatures and poor ventilation worsen the situation.
It’s important to maintain and service the electrical system. Checks of all components will make sure they work efficiently. To avoid tripping, prevent overheating. This will reduce energy consumption and safeguard equipment. So, let’s learn about circuit breakers and how they deal with overloads!
Circuit Breaker Types
Circuit breakers are essential for any electrical system. They prevent overloaded and faulted circuits . There are different types of circuit breakers suitable for specific electrical loads.
See the table below for the different types of circuit breakers and their functions:
It is crucial to select the right type of breaker. Each one has its own advantages in specific situations. For instance, thermal circuit breakers are perfect for small appliances like hair dryers or irons . Meanwhile, magnetic circuit breakers are great for bigger loads such as air conditioners or refrigerators .
Remember, circuit breakers are like Beyoncé – they can handle a lot, but have their limits.
Circuit Breaker Ratings and Specifications
Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. To ensure that circuits and appliances are safe, the ratings and specifications of circuit breakers need to be understood.
If a circuit breaker trips often, it may mean there’s an issue. It’s best to get professional help in these cases. Time to go on a hunt for your electrical wiring!
Troubleshooting Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers can flip out for multiple reasons, like overloads , short circuits , and ground faults .
Overloads happen when too much electricity passes through the circuit, creating too much heat and tripping the breaker. Short circuits are when two or more wires touch, resulting in extra current. Ground faults occur when the power takes an unexpected route, like through a person’s body.
To figure out why your circuit breaker is tripping, it’s important to figure out what is going on and act accordingly. Inspections and maintenance can also help avoid future tripping.
Stop your circuit breaker from misbehaving with these prevention tips!
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping
A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping:
- Know the electrical load – work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one circuit. Don’t overload them by spreading high-energy equipment across multiple circuits .
- Look after your appliances – ensure all your appliances & devices are in good condition, with no damaged cords or frayed wires.
- Upgrade your system – if you’re tripping breakers often you may need to upgrade the electrical system with higher capacity breakers or more circuits.
Plus, investing in surge protectors can also assist in preventing circuit overload and subsequent tripping of breakers. By following these steps you can make sure your home’s electricity runs safely and without interruption due to circuit breakers tripping.
Remember: these precautions will keep you from tripping more than just your circuit breakers!
Safety Precautions
Safety must be taken seriously when dealing with circuit breakers . Always switch off the main power supply before beginning work. Wear protective gear such as insulated gloves and boots to stay safe from electrocution. Never touch wires or components inside the box without proper training. Keep the area around the breaker box free from any flammable substances. Inspect breakers for damage or wear regularly .
Label each circuit breaker correctly . Test them frequently for functionality. This will help identify circuits quickly in case of an emergency. These precautions and practices ensure safety while dealing with circuit breakers. When in doubt, blame it on the circuit breaker – it’s always a good scapegoat for electrical woes!
Circuit breakers are essential components of any electrical system. They stop too much current flowing and thus, protect against potential fires . The most common cause for tripping is overload. But, other causes like short circuits and ground faults can also cause the breaker to trip. When it trips, there is something wrong that needs to be fixed right away.
Short circuits occur when two wires touch each other. This creates a low resistance path which allows a lot of current to flow with no load. Ground faults occur when the hot wire touches something incorrectly wired or with a damaged cord.
To prevent tripping, regular maintenance of the electrical system is needed. Keeping appliances in good condition, replacing worn-out cords and fixtures, and periodically checking for loose wires all help reduce the chances of tripping. In summary, understanding why the breaker trips and taking precautionary measures will keep you safe and save you repair costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what causes a circuit breaker to trip.
There are several possible causes, including overheating due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, and age-related wear and tear.
2. How can I prevent my circuit breaker from tripping?
You can avoid overloading your circuit by keeping the number of electrical appliances used on one circuit to a minimum, regularly checking wires for signs of wear and tear, and not using too many extension cords.
3. What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If your circuit breaker is constantly tripping, it is important to identify and fix the underlying issue. Contact an electrician to inspect and repair any faulty wiring or electrical devices.
4. Can a circuit breaker trip without an overload?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip due to a short circuit or a ground fault, which may occur without an overload.
5. How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker?
To reset a tripped circuit breaker, turn it off and then back on again. Make sure to identify and correct the underlying issue that caused the trip before restoring power.
6. What is the lifespan of a circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on usage and other factors. However, most circuit breakers last between 10 and 30 years.
Related posts:
- Moving Offices? Here’s How a Commercial Electrician Can Help
- Possible Causes of a Blown Fuse and What to Do
- How to Make an Electrical Plan for a New Home in Puchong
- How to Prepare Your Business in Kuala Lumpur for Power Outage Impacts
How to Fix a Circuit Breaker That Keeps Tripping

Dec 18, 2023
Electrical issues in a home or office can be frustrating and potentially dangerous. One common problem is a circuit breaker that continually trips. This article provides a detailed guide on how to troubleshoot and fix a circuit breaker that keeps tripping, ensuring your electrical system is safe and functional.
Understanding Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is an essential component of your home’s electrical system . It acts as a safety device that cuts off electrical power when there is an overload or a short circuit. Regular tripping can indicate a serious electrical issue.
Common Causes for a Tripping Circuit Breaker
Overloaded Circuit
The most common cause is an overloaded circuit. When too many appliances are running simultaneously, it exceeds the circuit’s capacity.
Short Circuit
Another cause could be a short circuit, a more dangerous issue where a hot wire touches a neutral wire.
Ground Fault
Similar to a short circuit, a ground fault occurs when a hot wire touches the ground wire or the metal wall box.
Steps to Fix a Tripping Circuit Breaker
1. identify the cause.
Start by identifying which circuit is tripping. Unplug all the appliances connected to that circuit.
2. Reset the Breaker
Once you have identified and addressed the potential cause, reset the breaker by turning it off and then on.
3. Check for Overloads
Reconnect the devices one at a time to identify if an overload is the cause. If the breaker trips again, you’ve likely found the culprit.
4. Inspect for Short Circuits
If the breaker trips immediately after reset, without anything plugged in, you might have a short circuit. Look for any obvious signs of damage to wires or outlets.
5. Test for Ground Faults
Ground faults in areas with high moisture, like bathrooms or kitchens, can cause tripping. Specialized testers can help detect these faults.
Understanding Your Home’s Electrical Load
Balancing the Load
Balancing the electrical load across different circuits is key in preventing tripping. Ensure that high-energy appliances are evenly distributed and not all connected to a single circuit.
Monitoring Power Usage
Invest in a power monitor to keep track of the electrical load on each circuit. This helps in identifying potential overload situations before they cause a breaker to trip.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Using energy-efficient appliances not only saves on your electricity bills but also reduces the likelihood of overloading circuits. Look for appliances with a high energy star rating.
Periodic Professional Inspections
Even with regular self-checks, having a professional electrician inspect your electrical system periodically is advisable. They can identify potential issues that might not be obvious to a layperson.
Maintenance Tips for Your Circuit Breaker
1. Regular Check-Ups
Conducting regular check-ups of your electrical panel and circuit breakers is vital. Look for any signs of wear, overheating, or rust. Regular maintenance can prevent many issues that cause circuit breakers to trip.
2. Upgrade When Necessary
As your power needs increase, your old electrical panel might not keep up. Upgrading your panel can prevent circuit overload and reduce the risk of tripping breakers.
3. Label Your Circuit Breakers
Properly labeling each circuit breaker with the area of the house it controls simplifies troubleshooting. This step is especially helpful during emergencies or routine checks.
4. Educate Your Household
Educating everyone in your household about the importance of electrical safety and how to respond to a tripped breaker is crucial. This awareness can prevent misuse and overloading of circuits.
When to Call a Professional
If you are unable to identify the cause or if the problem involves a short circuit or ground fault, it’s time to call a licensed electrician. Electrical work can be hazardous, and professional help ensures safety and compliance with local electrical codes .
Preventing Future Trips
To prevent future issues:
1. Avoid overloading circuits by spreading out high-energy appliances.
2. Regularly inspect your electrical system for any signs of damage or wear.
3. Consider upgrading your electrical panel if it’s old or inadequate for your current power needs.
Q: What should I do first when my circuit breaker trips?
A: Firstly, unplug all devices from the affected circuit and reset the breaker.
Q: Can I fix a short circuit by myself?
A: It’s not recommended to fix a short circuit yourself due to the risk involved. Consult a professional electrician.
Q: How can I tell if my circuit is overloaded?
A: If the breaker trips when multiple devices are used simultaneously, it’s likely an overload.
Q: Is it normal for a circuit breaker to trip occasionally?
A: Occasional tripping can happen, but frequent tripping indicates a problem.
Q: Can an old circuit breaker cause tripping issues?
A: Yes, as circuit breakers age, they can become less efficient and may trip more often.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the reasons behind a circuit breaker tripping is crucial in maintaining a safe and efficient electrical circuit in your home. Whether it’s due to a circuit overload, a tripped circuit breaker, or other electrical issues, addressing these problems promptly can prevent more significant concerns. Regular monitoring of your breaker panel and installing ground fault circuit interrupters in key areas can greatly reduce the risk of electrical fires. Remember, when a circuit breaker trips, it’s a warning sign that shouldn’t be ignored. Proactive measures and quick responses ensure that your electrical system remains in top condition, safeguarding your home and family.
If your circuit breaker keeps tripping, it’s a clear indication that your home’s electrical system requires attention. It could signal an overload, a ground fault, or an issue with the breaker panel itself. Regular checks, understanding the capacity of your electrical circuit, and professional inspections are vital steps in preventing and resolving these issues. Taking these precautions not only enhances the safety and functionality of your electrical system but also extends its lifespan. By staying vigilant and responsive to the signs of electrical issues, you can ensure a safe and uninterrupted power supply in your home.
Similar Blogs
Tips for reducing your home’s electrical consumption.
Mar 31, 2024
Steps to make a home energy efficient are the actions that not only save money on utility bills, but on a larger scale, ensure a healthy environment.
The Role of Grounding in Electrical Safety
Mar 21, 2024
Grounding in electrical safety serves as an essential shield against potential hazards, ranging from electric shocks to lightning strikes.
How to Remove a Ceiling Fan Like a Pro
Feb 18, 2024
We’ll walk you through removing a ceiling fan without damaging it or hurting yourself, with straightforward instructions and a few basic tools.
Powering Up Your Home: Will Adding a Generator Increase Its Value?
Jan 26, 2024
Does having a power generator also increase the value of our homes? This is a question that many homeowners may have when considering purchasing a power generator.

Why Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping and How to Fix It
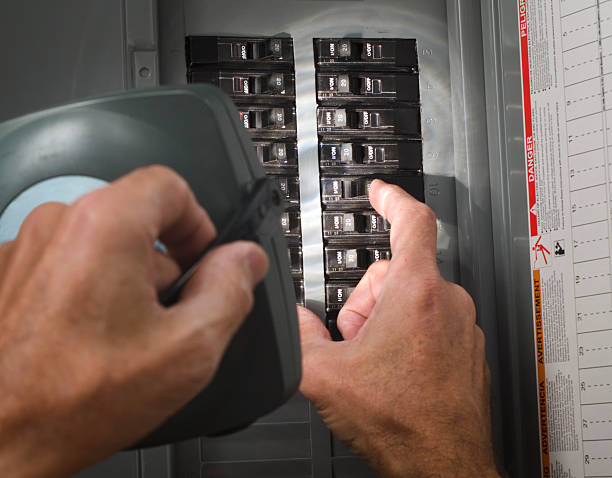

A breaker that keeps tripping can be a frustrating and concerning issue for homeowners. Not only does it disrupt your daily routine, but it could also signal a more significant problem with your electrical system.
This comprehensive guide aims to help you understand why your breaker is tripping and how to address the issue. We’ll cover common causes, prevention tips, and when to call a professional electrician.
Why Does a Breaker Keep Tripping?
Circuit breaker trips.
Circuit breakers are designed to protect your home from electrical overloads or short circuits. When a breaker trips, it’s doing its job to prevent damage to your electrical system and minimize the risk of fire. Here are some common reasons why a breaker may trip frequently:
1. Overloaded Circuit
An overloaded circuit is the most common reason for a breaker to trip. This occurs when the electrical demand on the circuit exceeds its capacity. When too many devices or appliances are running at the same time, the breaker trips to protect the circuit from overheating.
2. Short Circuit
A short circuit happens when an unintended path is created for electricity to flow, leading to an excess of current. This can occur when a live wire comes into contact with a neutral or grounded wire . Short circuits can generate a significant amount of heat, increasing the risk of fire. Breakers trip to prevent this dangerous situation.
3. Ground Fault
A ground fault is similar to a short circuit, but it occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a grounded object, such as a metal outlet box or water pipe. Ground faults can be hazardous and cause electrocution, so the breaker trips to protect you and your home.
4. Faulty Breaker
Although rare, sometimes the breaker itself is the issue. Breakers can wear out over time or become damaged, leading to tripping even when there’s no overload, short circuit, or ground fault.
How to Prevent Your Breaker from Tripping
Tripped circuit breaker.
To prevent your breaker from tripping, follow these simple tips:
1. Distribute Electrical Load
Avoid overloading a single circuit by distributing electrical devices and appliances evenly throughout your home. Be mindful of high-wattage appliances, such as microwaves and air conditioners, which can quickly cause an overload if used simultaneously on the same circuit.
2. Unplug Unused Devices
Unplugging devices that are not in use can reduce the overall load on your circuits, lowering the risk of an overload.
3. Upgrade Your Electrical System
If your home’s electrical system is outdated or lacks the capacity to handle your needs, consider upgrading to a higher-capacity system. This may involve adding additional circuits, upgrading your electrical panel, or increasing the amperage of your service.
4. Regular Maintenance
Inspect your electrical system regularly for signs of wear or damage. If you notice any frayed wires , loose connections, or damaged outlets, take action to fix the issue and prevent potential problems.
When to Call a Professional Electrician
Electrical circuit overload.
If you’ve tried troubleshooting your breaker issue and it continues to trip, it’s time to call a professional electrician. Don’t attempt to fix electrical problems yourself, as it can be dangerous and potentially worsen the issue. An electrician will be able to diagnose and repair the problem safely and efficiently.
Here are some signs that it’s time to call an electrician:
1. Frequent Tripping
If your breaker trips repeatedly, even after you’ve redistributed the electrical load or unplugged devices, it could indicate a more significant issue that requires professional attention.
2. Persistent Short Circuits or Ground Faults
If you suspect a short circuit or ground fault, call an electrician immediately. These issues can be dangerous and require an expert to identify and repair the problem safely.
3. Burning Smell or Signs of Heat
If you notice a burning smell, visible smoke, or signs of heat near your electrical panel or outlets, contact an electrician immediately. These symptoms could indicate a severe issue, such as a damaged wire or faulty breaker, that needs prompt attention.
4. Outdated Electrical System
Older homes may have outdated electrical systems that struggle to handle modern electrical demands. If you suspect your system is inadequate or outdated, consult with an electrician to discuss potential upgrades.
5. Inadequate Circuit Breaker
If you believe your circuit breaker is not sufficient for your home’s electrical needs, an electrician can assess your situation and recommend appropriate upgrades.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips: Loose or Corroded Wires and Faulty Electrical Switches
Circuit breaker tripping.
Loose or corroded wires can cause circuit overloads and lead to breaker tripping. It is essential to inspect your electrical system periodically to identify any loose connections or signs of corrosion. Additionally, a faulty electrical switch can also cause the breaker to trip. If you suspect a switch is malfunctioning, it is crucial to have it checked and replaced by a professional electrician to avoid further issues.
The Importance of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters and Understanding Hot and Ground Wires
Ground fault circuit interrupter.
Circuit breakers protect your home by monitoring electrical power flow and shutting off the supply when an overload or short circuit occurs. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are essential safety devices that can detect an imbalance between the active electrical wire (hot wire) and the ground wire. In case of an imbalance, the GFCI cuts off the power supply to prevent electrocution or electrical fires.
It is crucial to have GFCIs installed in areas with a high risk of water exposure, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets. By understanding the function of hot and ground wires and the importance of GFCIs, you can take proactive steps to ensure a safer electrical system in your home. Regular maintenance of circuit breakers, GFCIs, and the entire electrical system is necessary to minimize the risk of electrical fires and other hazards.
Repair Electrical Cords
A breaker that keeps tripping can be an annoyance, but it’s essential to remember that it’s doing its job to protect your home and keep you safe. Understanding the causes of tripping and taking steps to prevent it can help ensure a stable electrical system. However, when in doubt or faced with persistent issues, always consult with a professional electrician. Not only will they diagnose and fix the problem, but they will also ensure your home’s electrical system is functioning safely and efficiently.
Similar Posts

How Do I Redirect My Air Vent Under My Bed?
There are a few ways to redirect a vent in your bedroom. Most of them involve moving the vents cover or removing the cover and installing a new one.

Why Is Pex Plumbing Bad?
There are several downsides of PEX plumbing. These accumulate to make it an unsuitable choice for your house.

The Importance of Underlayment for Tile Installation
The process of tile installation, while intricate, is not complete without the critical component of underlayment. Serving as a protective intermediary layer between the subfloor and the tile, the underlayment has a pivotal role in ensuring the durability and the aesthetic appeal of the installed tile. This article aims to demystify the concept of underlayment…

Unmasking the Magic of Plumbers Putty
Plumbing can be a challenging and messy task without the right materials, and that’s where plumber’s putty steps in. Serving as a wonder product in the plumbing industry, this simple yet effective solution is a must-have in every homeowner’s toolkit. Here’s an extensive dive into the world of plumber’s putty, exploring its significance, applications, and…

Roof Washing: Enhance Your Home’s Curb Appeal
When it comes to maintaining your home’s exterior, it’s easy to overlook one crucial component – your roof. Covered in lichen, moss, and algae, a neglected roof doesn’t just look unattractive; it can potentially damage your home. The solution? Roof washing. One effective way to ensure a thorough and professional roof washing is by enlisting…

Teak Oil: Revitalizing Your Woodwork Naturally
Renowned for its deep penetration and protective qualities, teak oil is the secret behind the enduring allure of garden furniture, decks, and indoor woodwork.
Top home improvement website with expert advice on all things home, garden, decor and more.
Quick links
- [email protected]
- 44 Milton Ave Alpharetta, GA 30004
- 770-848-5939
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Home and Garden
- Home Maintenance
- Electrical Maintenance
- Electrical and Electronic Circuits
Does Your Circuit Breaker Keep Tripping? Here’s How to Find the Cause
Last Updated: May 6, 2023 Fact Checked
Common Causes of Tripped Circuits
Finding overloaded circuits, finding short circuits, finding ground faults.
This article was co-authored by Jesse Kuhlman and by wikiHow staff writer, Johnathan Fuentes . Jesse Kuhlman is a Master Electrician and the Owner of Kuhlman Electric based in Massachusetts. Jesse specializes in all aspects of home and residential wiring, troubleshooting, generator installation, and WiFi thermostats. Jesse is also the author of four eBooks on home wiring including "Residential Electrical Troubleshooting" which covers basic electrical troubleshooting in residential homes. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 20,245 times.
Picture this: you’re watching TV or browsing on your phone when, suddenly, half the lights in your home turn off. You check your circuit breaker and flip one of the switches back to “ON,” but an hour later it trips again…and again. Sound familiar? Having your circuit breaker trip over and over can be frustrating, but don’t sweat. In this article, we’ll explain the most common causes of a tripped circuit breaker. Keep reading to learn which causes might apply to your situation, when to try do-it-yourself fixes, and when it’s best to call an electrician.
Things You Should Know
- The most common causes of tripped circuit breakers are overloaded circuits, short circuits, and ground faults.
- Test for overloaded circuits by resetting your breaker and plugging in devices until it trips again. The device that caused the trip is overloading the circuit.
- Test for short circuits by resetting your breaker and plugging in items into different sockets. The device or socket that always trips the breaker likely has a short circuit.
- Have an electrician test for ground faults if you’ve already ruled out overloaded and short circuits. Ground faults are too dangerous to test for on your own.

- For example, if your bathroom and kitchen are part of the same circuit—that is, the plugs in your kitchen and bathroom are all connected to the same switch on your circuit breaker—then the breaker might trip if you run your microwave and hair dryer at the same time.

- Short circuits often happen when wires come loose or get damaged by corrosion or wear and tear, or even from an animal chewing through them. [3] X Research source
- Short circuits can occur in the wiring in your home or in individual devices. For instance, a refrigerator can have a short circuit due to a loose wire.

- Ground faults often happen due to water leaking into outlets or devices. They also occur when loose or corroded wires come into contact with ground wires, or when defective devices cause electricity to flow to a ground wire.

- If you have multiple devices sharing a single outlet in the area affected by the tripped breaker, it’s likely that that group of devices is causing the overload. [6] X Research source

- Wear safety goggles or stand to the side of a breaker when flipping a switch to “ON” in case of sparks.
- If the switches aren’t labeled, narrow down the affected area by flipping the switch to “ON” and checking which devices and lights turn on again.
- If multiple switches tripped at the same time, there might be an overloaded circuit in more than one area of your home, or you may have another issue such as a short circuit or ground fault.

- If none of the devices immediately trip the circuit breaker, it’s possible that your circuit isn’t getting overloaded right away. Leave the devices plugged in and turned on for a few minutes to see if the breaker trips again.
- If the breaker trips after several minutes, try the process again, but leave 1-2 less important devices unplugged. Eventually, you’ll find a combination of devices that doesn’t trip the circuit breaker.

- Leave your devices plugged in and on for a few hours. If the circuits are not overloaded, the circuit breaker shouldn’t trip.
- If the circuit breaker trips for the same part of your home again, plug additional devices into other outlets. You may need to try different combinations of plugs and outlets to see which combination doesn’t overload your circuits.
- If you try several combinations and the breaker continues to trip, it’s possible that you have a short circuit or ground fault somewhere in your home.

- If devices are plugged into surge protectors, unplug each device from the surge protector before unplugging the surge protector itself.

- If the circuit breaker trips whenever you plug something into a particular outlet, you probably have a short circuit in that outlet.
- If one particular device always trips the breaker, but other devices don’t, you probably have a short circuit in that particular device.

- If the device you want to test is too large to move—such as a kitchen refrigerator or washing machine—use a long extension cord to reach other outlets.

- If you find a short circuit in an individual device, check if your product is covered by a warranty. If it is covered, you might be able to get it fixed or replaced for free. [14] X Trustworthy Source Federal Trade Commission Website with up-to-date information for consumers from the Federal Trade Commisson Go to source

- Tell your electrician which outlet or area of your home is affected by the tripped circuit breaker. This will help them narrow down the exact problem.
- Avoid using sockets that appear water-logged or that show signs of water damage.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://nps.edu/documents/111291366/111353794/SafetyGram_Circuit_Breaker_Panels.pdf/eab72177-f7b7-4f6f-b7bc-f7efde96df4f?t=1423776819000
- ↑ https://engineering.mit.edu/engage/ask-an-engineer/what-is-a-short-circuit/
- ↑ https://www.coynecollege.edu/how-to-deal-unsafe-electrical-wiring/
- ↑ https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/2018-12/fy07_sh-16586-07_4_electrical_safety_participant_guide.pdf
- ↑ https://ask-the-electrician.com/how-to-fix-a-overloaded-circuit-breaker-problem/electrical-wiring-2/
- ↑ http://thecircuitdetective.com/treeshort.php
- ↑ https://consumer.ftc.gov/articles/warranties
- ↑ https://tools.niehs.nih.gov/wetp/public/Course_download2.cfm?tranid=2495
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Fix a Circuit Breaker That Keeps Tripping: A Comprehensive Guide

Understanding Circuit Breakers
- What is a Circuit Breaker?
- How Do Circuit Breakers Work?
- Causes of Tripped Circuit Breakers
Safety First: Precautions Before You Begin
- Importance of Safety Measures
- Necessary Tools and Equipment
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a Tripped Circuit Breaker
When to call a professional electrician.
- Signs of Complex Electrical Issues
- Professional Expertise and Assessment
Preventive Measures to Avoid Tripped Circuit Breakers
- Distributing Electrical Load
- Regular Circuit Maintenance
- How do I know if a circuit breaker has tripped?
- Can I simply keep resetting the circuit breaker?
- Why does my circuit breaker trip when I use certain appliances?
- Is it safe to replace a circuit breaker myself?
- What should I do if I smell burning near an outlet?

Are you tired of living in a dimly lit home? Installing a new ceiling light can significantly impact the appearance and atmosphere of a room. But if you're unsu...

Are you still using incandescent light bulbs in your home or business? If so, it's time to upgrade to LED lighting. LED lights are not just more energy-efficien...

Electrical issues are among many of the country's most common causes of home fires. Because electricity is so convenient in our daily lives, it's easy to overlo...
- Join Insider
Follow This Old House online:
Site search, why do circuit breakers trip.
Master electrician Heath Eastman shows host Kevin O’Connor everything he needs to know about why and how breakers trip.
Heath Eastman talks about circuit breakers. Heath shows Kevin O’Connor that while resetting these breakers is simple, these are complex devices that monitor and protect circuits. First, the two talk about the different sizes of breakers before moving on to the different types. Finally, Heath shows Kevin how to test certain breakers to ensure they’re working properly.
Circuit breakers exist to protect people, appliances, and homes from dangerous electrical current. However, few people understand why the trip and how they operate. Master electrician Heath Eastman shows host Kevin O’Connor why this happens, and even explains a few different types of breakers.
All About Electrical Systems
Breakers protect circuits.
When electricity comes into the house, it flows through the electrical service panel. From there, the electricity flows out through different branches in the house, each controlled by a circuit breaker. Should a branch begin to overload and overheat, the breaker will trip to prevent damage.
Breaker Sizes
There are two main sizes of breakers in a house: 15 amp and 20 amp. The amp rating explains how much current the breaker can handle before it will trip, and each requires a certain size of wire. Fifteen-amp breakers require a 14-gauge wire, while 20-amp breakers require a 12-gauge wire.
How They Work
A 15-amp breaker won’t necessarily trip the moment it experiences a spike above 15 amps. Many devices draw more amps upon start-up, and these breakers allow those temporary spikes. However, should the breaker sense elevated amperage for longer than is typical, it will trip to prevent the circuit from overheating.
GFCIs and AFCIs
Beyond circuit overload protection, there are other types of breakers that offer additional coverage. These include GFCI breakers and relatively-new AFCI breakers .
GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) breakers need to experience the same amount of current going out as coming back through the circuit. If the breaker experiences a drop in returning current, it assumes that the circuit is leaking, whether it be through a water source or a person. When this imbalance occurs, the GFCI trips immediately.
AFCI (arc fault circuit interrupter) breakers sense when the circuit, a device, or an appliance is arcing (the current is jumping from the circuit and onto something else or someone). When the breaker recognizes the arc signature, it trips immediately. These breakers are relatively new and look similar to GFCI breakers, but they’re becoming a code requirement in most locations.
How to Test Breakers
Homeowners, electricians, and inspectors can test their breakers. There are devices that users can plug into an outlet and replicate an error. These devices, known as AFCI/GFCI testers, can trip the breaker altogether or replicate a ground or arc fault, triggering the breaker. This is one of the best ways to ensure that a breaker is working properly.
When to Call a Professional
If a circuit is continuously tripping, or you know that it should be tripping and isn’t, be sure to call in a professional. An electrician will be able to determine the cause of the issue and make sure your circuit breakers and electrical system are safe.
Heath explains what a circuit breaker is, why they trip and how it protects a home. A circuit breaker is a device, installed in the electrical panel, that controls whether power can be sent from the panel through a circuit. Heath explains this ability is controlled by a switch that can be operated either manually—like when a person wants to interrupt power for service—or automatically, like a breaker trip.
He says power overloads, current “leaks”, and arcs are the three reasons that would cause a breaker to trip. A Power overload happens when a device is calling for more power than a receptacle , or a circuit is designed to provide. Current “leaks” are caused when current strays from the circuit for whatever reason, though it happens most commonly when moisture is present. Arcs can happen when the wire breaks down over time (due to overloads but also due to other factors, like animals chewing the wire and other decay) but what Heath sees the most is human error.
If a specific receptacle is consistently tripping the breaker, Heath advises to have a licensed electrician identify the problem to ensure the work is done safely.
Next Up In Electrical
- How to Label a Circuit Breaker
- Simple Guide for Selecting a Home Generator
- All About Portable Power Stations
- Simple Guide to Installing a Generator Hook-Up
- How to Build a Utility Cover
- Understanding Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Sign up for the Newsletter
Get the latest This Old House news, trusted tips, tricks, and DIY Smarts projects from our experts–straight to your inbox.

Understanding Trip Circuit: Breakers, Overloads, and Solutions for Short Circuits
Understanding circuit breakers and how to deal with constant tripping.
When the circuit breaker in your home trips, it’s important to reset it in the fusebox to restore power. This may require a trip under the stairs or down to the garage, depending on where your circuit breaker is located. Circuit breakers are designed to interrupt the electrical current when the switch is tripped, ensuring the safety of your electrical system.
While circuit breakers are essential safety devices, constant tripping and repeated resetting can be frustrating. However, if you can identify the cause of the frequent trips, you can take steps to address the issue.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
Every home and business premises have electrical circuits controlled and protected by a switching device located in a consumer unit or fuse panel. Modern systems typically use circuit breakers for control and protection, while older systems might still rely on fuses that blow when overloaded. The main purpose of a circuit breaker is to cut off the flow of electricity to prevent circuits from overheating, which can cause damage and even lead to electrical fires.
How Does a Circuit Breaker Work?
A circuit breaker is a switching device that can be operated manually or automatically. It trips and disconnects the circuit to cut off the electricity supply if there’s an excessive current flow or an overload that the switch can’t handle. The circuit breaker is designed to protect your electrical power system and any devices connected to it.
Why Does a Circuit Breaker Trip?
A circuit breaker will trip when there is an electrical fault that could damage the circuit. This fault typically falls into three categories:
- Overloads: The most common reason for circuit breakers to trip is overloading. This occurs when you draw more electrical power from a circuit than it can handle. For example, running multiple appliances simultaneously or exceeding the circuit’s capacity. When a circuit overheats due to an overload, it puts all connected appliances at risk. The circuit breaker ensures the wires don’t excessively heat up and protects against fire hazards.
- Power Surges: Power surges can also cause circuit breakers to trip. These surges happen when there is a sudden increase in electrical voltage, often caused by lightning strikes or faulty wiring in the electrical system. Circuit breakers act as a defense mechanism against power surges by cutting off the excessive flow of electricity.
- Faulty Components: Another reason for circuit breakers to trip is faulty components within the electrical system. This can include damaged wires, short circuits, or defective appliances. When these faults occur, the circuit breaker detects the problem and interrupts the current flow to prevent damage.
Dealing with Constant Tripping
If your circuit breaker is frequently tripping, it indicates that you are demanding too much power from the circuit. To resolve this issue:
- Redistribute Appliances: Distribute your appliances and devices onto different circuits. Avoid overloading a single circuit by spreading the load across multiple ones. This ensures that each circuit operates within its designed capacity.
- Upgrade Your Electrical System: If your system doesn’t have enough circuits to meet modern demands, consider upgrading your electrical system. This may involve installing additional circuits or replacing outdated wiring and panels. A professional electrician can assess your needs and recommend the best solution.
By understanding how circuit breakers work and taking appropriate measures, you can prevent constant tripping, protect your electrical system, and ensure the safety of your home or business.
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping: Short Circuits and Ground Fault Surges
Have you ever experienced a sudden power outage in your home or office? Chances are, it was due to a circuit breaker tripping. Understanding the causes of circuit breaker tripping, such as short circuits and ground fault surges, is crucial for ensuring the safety of your electrical system. Let’s explore these common issues in more detail:
1. Short Circuits
Short circuits are a common reason for circuit breaker tripping and should be taken seriously due to their potential danger. A short circuit occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a neutral wire, resulting in an abnormal electrical connection. This can happen in electrical outlets or due to faulty wiring in appliances or plugs.
When a short circuit occurs, the normal electrical resistance is overridden, causing an excessive flow of current through the circuit. This generates excessive heat, which can lead to fires. If you notice a burning smell or dark discoloration around the circuit breaker, it is an indication of a short circuit.
2. Ground Fault Surges
Similar to short circuits, ground fault surges involve a live wire touching a bare copper ground wire or a part of a metal outlet box connected to the ground wire. When this happens, an excess flow of electricity occurs, triggering the circuit breaker to trip. Discoloration around the outlet is also a visible sign of a ground fault surge.
Both short circuits and ground fault surges are not only inconvenient but also pose serious risks to your safety. If your circuit breakers frequently trip, it is crucial to seek professional assistance to identify and resolve the underlying electrical issues. Attempting to solve electrical problems on your own can lead to further complications and put your premises at risk.
Remember, the safety of your electrical system should be entrusted to trained professionals. Don’t hesitate to call for professional help to ensure the proper functioning and safety of your electrical circuits.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Circuit Breaker Tripping: Troubleshooting Guide
Hubert Miles | Licensed Home Inspector, CMI, CPI
Updated on January 5, 2024

A circuit breaker tripping results from short circuits, overloaded circuits, and ground faults. In each case, an unintended excessive flow of current triggers the trip. You must reset the circuit breaker by flipping it back on to restore power.
Circuit breakers trip because they cannot handle the amount of current running through them. Tripping the circuit breaker interrupts the flow of electricity and protects your devices or appliances from damage.

Get FREE estimates from licensed electricians in your area today. Whether you need to replace an outlet, hang a ceiling fan, a new electrical panel, or repair wiring, We Can Help!
Without electrical circuit breakers , the possibility of electrical fires would be much higher.
This guide looks at what causes circuit breakers to trip, what you can do, and how to identify a bad breaker.
What Would Cause a Circuit Breaker to Trip
There are three leading causes of circuit breaker trips:
- circuit overload
- electrical faults (i.e., ground faults and arc faults)
- short circuits
Below are factors that can cause circuit breaker trips.
Circuit Overload
A circuit overload happens when the flow of electric current running through the circuit exceeds the amperage of the devices it serves.
For example, if your microwave is a 12.5 amp appliance, you can run it on a 15 amp circuit. That means your microwave is safe as long as the amperage running through the circuit is 15 amps .
However, if the circuit receives an excessive electrical load over 15 amps , it will automatically trip to protect your device from damage. If the circuit doesn’t trip, the excess current will fry the circuit in your microwave.
Also, if you operate too many appliances and devices on one circuit, its internal mechanism heats up, causing the breaker to trip.
Circuit overload is the most common reason for breakers tripping.
Ground Faults
A ground fault occurs when the active wire comes into contact with a ground wire made of bare copper. Sometimes, this fault may happen when the hot wire touches the metal box connected to the ground wire.
Excessive current flows once the active wire touches the ground wire, flowing into the earth. If you step on the affected area, ground faults can cause shock and even electrocution. The uncontrolled flow of electricity will cause the circuit breaker to trip.
Arc Faults
An arc fault happens when exposed faulty wiring touches, causing the electric current to arc at the meeting point. As a result, sparks occur, which can ignite an electric fire.
A corroded or loose connection is the main culprit for arc faults. Circuit overloads, ground faults, or short circuits trip an AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) circuit breaker.
Arc faults result from damaged, loose, or corroded terminals and wires. The arc fault builds up over time as the heat due to the cable damage and terminals build up to the point of ignition.
Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when an active wire touches a neutral wire, and the electrical current takes an unintended path of least resistance.
The common cause of short circuits is frayed wires coming into contact when the wires touch. The electrical current flow increases significantly, causing the circuit breaker to trip to stop the electricity from damaging appliances.
It is a short circuit because the current bypasses the proper circuit wiring channels and flows through a shorter, unplanned pathway.
Short circuits occur
- When insulation melts and wires are exposed
- Within appliances with damaged internal wiring
- Due to damaged and frayed extension or appliance cords
How do You Fix a Breaker that Keeps Tripping?
A dedicated circuit breaker tripping indicates too much current flowing through the wiring or connection to the outlet.
Here is a step-by-step guide to follow when you notice the first trip:
- Begin by turning off all the appliances and unplug electrical devices from the outlet. Also, switch off light fixtures and unplug those that you can. This prevents any appliances from damaged when the breaker is reset and a sudden surge of power comes through.
- Open the circuit panel or box and locate the on and off buttons of the circuit breaker. You may notice an orange or red color on the breaker when it is off.
- Flip the switch from off to on to reset the circuit breaker. Once the breaker is reset, you can switch and test the appliances to see if the electrical power is flowing.
- Keep safe as you reset the breaker by working from the side of the electrical box instead of the front. That way, you will avoid any sparks (should there be any) when you switch the breaker back on.
- Some people prefer to switch the main electrical switch when working on the circuit breaker for added safety.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Standard circuit breaker.
Standard circuit breakers monitor the modulation of the electric current coming into your devices and appliances.
This circuit breaker stops the current from flowing when it detects the excessive flow of electricity.
Standard circuit breakers come in two forms:
- Single-pole circuit breakers
- Double pole circuit breakers
Single-Pole Circuit Breakers
Single-pole circuit breakers are the most common breakers in homes and buildings. They monitor the electric current’s flow in one wire and trip if that wire experiences a very high influx of electricity.
These breakers deliver only 120 volts and work well for 15 to 30 amp circuits. Single-pole circuit breakers come with one switch in the back.

Double-Pole Circuit Breakers
The double-pole circuit breakers monitor the current in two wires simultaneously. You will notice two switches on the back of these breakers.
The double-pole circuit breakers will trip even if only one of the wires receives too much current. They can accommodate between 15 to 200 amps while delivering 240 volts.
Single-pole breakers are a good fit for lighting fixtures and other standard home outlets. On the other hand, double-pole breakers work for larger appliances like dryers and washing machines.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
The GFCI circuit breaker interrupts the line due to ground faults. They trip when the current starts to follow an uncharted path into the ground. These ground fault surges occur when a foreign conductor, like water, comes in contact with a receptacle .
At the same time, they offer protection against circuit overloads and short circuits.
GFCI circuit breakers come built into specialized outlets required for wet areas in the home, including :
- Outdoor areas like the balcony, patio, porches, and decks
- Laundry rooms
- Swimming pools
- Six feet from a sink
- Six feet from the bathroom
These breakers help prevent shock or electrocution should the electrical outlet contact water.
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI)
The AFCI circuit breaker detects normal and abnormal arc faults, so it will trip when it detects a dangerous arc fault that can cause a fire.
The AFCI circuit breaker doesn’t work to protect devices and appliances plugged into an outlet. It works to prevent electrical fires due to faulty connections and wiring. The internal sensing mechanism in the circuit breaker senses the conditions of an electric arc, and the circuit trips to avoid an electric fire.
AFCI protection can also be built into an outlet. The National Electrical Code (NEC) requires these types of breakers to feature in :
- Common rooms
- Laundry areas
AFCI and GFCI circuit breakers can co-exist and complement each other for the best protection.
Combination All Fault Circuit Interrupter (CAFCI)
The CAFCI breaker senses and reacts to any electrical fault, including ground and arc faults.
CAFCI is a relatively new technology that meets new NEC requirements for circuits requiring arc and ground fault protection.
Do Circuit Breakers Get Weak?
A circuit breaker can wear out and become weak. If a breaker trips frequently, the thermal or magnetic element can lose calibration, causing it to trip at lower amp loads than intended. A breaker constantly under thermal stress caused by overloading the circuit will eventually trip more frequently.
Let’s not forget breakers are not impervious to damage. As the internal mechanical parts wear out, they become very sensitive and may not hold under normal load amperage and temperatures.
Electricians refer to this as a bad breaker .
Will a Bad Breaker Keep Tripping
By definition, bad breaker malfunctions, so it will keep tripping until it is either replaced or rectified .
A licensed electrician performs this simple test to see if a breaker will keep tripping and determine if it can be repaired or replaced in the following steps.
- The electrician will switch off all the fixtures and appliances in the house. Also, unplug everything.
- Find the malfunctioning circuit breaker . The electrician will go to the electrical box and locate the breaker lighting orange or red or the one with the switch off.
- They will ascertain that it is the correct circuit breaker. After that, the electrician puts the breaker off.
- With the switch on, the breaker is back on as well. The electrician will plug the appliances into the outlet with the problem circuit breaker. Now, they will turn the devices and appliances on.
If the breaker trips, the electrician will investigate the circuit’s current amount. The breaker is bad if the current is according to the appliance’s rating.
How You know if a Circuit Breaker is Bad
Breakers do wear out after a while. It has a problem if the breaker doesn’t stay on after resetting it.
Since the circuit breaker controls the electric flow in the house, it is essential to monitor it and catch signs that it has gone bad early.
Here are key signs that denote a bad circuit breaker :
It Frequently Trips
Frequent tripping could be because of a bad breaker. After tripping and resetting, your circuit breaker should stay on unless it detects high current flow.
To ensure that the issue is not the electricity but the circuit breaker, call an electrician to examine your electricity’s flow and determine whether it is the cause of the constant tripping.
If it is not, then the circuit breaker is the problem.
The Breaker Overheats
Electrical systems will heat up when active. Typically a breaker can heat to about 60°C (140°F) before problems arise.
Terminations for standard rated breakers: UL 489 Paragraph 7.1.4.2.2 says the temperature rise on a wiring terminal at a point to which the insulation of a wire is brought up as in actual service shall not exceed 50°C (122°F). Terminations for 100% rated breakers: UL489 Paragraph 7.1.4.3.3 says the temperature rise on the termination shall not exceed 60°C (140°F). Handles, knobs, and other user surfaces: UL489 Paragraph 7.1.4.1.6 says the maximum temperature on handles, knobs, and other surfaces subject to user contact during normal operation shall not exceed 60°C (140°F) on metallic and 85°C (185°F) on nonmetallic surfaces. Source: https://www.clipsal.com/faq/fa173839
Call an electrician immediately if the breaker becomes too hot.
There are Scorch Marks
Scorch marks around receptacles, appliances, and the electrical box should tell you your circuit breaker has gone bad.
The burn marks indicate that wiring insulation has melted off and the circuit wires are now sparking and emanating heat or fire. That means that the circuit breaker did not interrupt the excess current and reached the wires and burned them.
You may see melted wire sheathing on the wire where it connects to the breaker.
Professional electricians can use a thermal imaging infrared camera to locate the heat source. The infrared camera allows them to pinpoint the problem area through the walls and other construction material.
A Burning Smell
Sometimes you may smell the insulation burning, but no scorch marks are present to denote which outlet is the problem.
With the help of the infrared camera, an electrician can help locate electrical issues.
If you encounter a burning odor, shut off the main power and call for emergency service from an electrician.
The electrical wires burn because power surges through the circuit, melting the wire insulation.
What is Nuisance Tripping
Nuisance tripping is when a breaker trips without a fault to warrant the interruption to the electric current flow.
Nuisance tripping occurs due to several reasons:
Stringent Protection on Circuits
Sometimes the circuit is protected by stringent conditions that detect any variance as a fault and cause a trip.
Such stringent conditions can be tuned to accommodate the home’s or building’s electric needs.
A Highly Sensitive Circuit Breaker
In some cases, the circuit breaker has been set to susceptible settings so that they can detect even the slightest fault, even a minor average variance.
For example, the manufacturer can set an AFCI circuit breaker to sensitive standards to detect another circuit’s arc. This common issue may occur in a daisy chain where the circuit breakers connect in a linear series. There may be a faulty electrical outlet you are unaware of on the circuit. It is common for multiple rooms to share a breaker in older houses.
The Breaker Encounters Power Under Different Conditions
The variation in the current is normal, but the breaker responds to it by tripping because the flow is outside the breaker’s regular operation.
Your circuit breaker is tripping because the voltage it is encountering is not within the standard operation. You will need to adjust the circuit breaker or the voltage to eliminate nuisance tripping.
The Breaker Trips with Nothing Plugged in
A breaker tripping with nothing plugged in occurs when a hot, neutral wire is touching somewhere in the circuit. The common causes include frayed or damaged electrical wires, loose connections, faulty electrical receptacles, light switches , or dimmers.
Electrical wire damage happens when:
- wiring is chewed by animals such as rats, squirrels , raccoons, etc
- wire sheathing and insulation ages and become frayed
- wires rub against sharp edges such as punch-outs with missing grommets or wire clamps
Loose connections often occur when electrical wire nuts come loose or electrical tape wears out causing wires to touch.
Defective wiring can be anywhere along the circuit, so it’s best to contact a licensed electrician to troubleshoot why the breaker is tripping.
Replacing a Bad Circuit Breaker
- Check the electrical panel to see the compatible approved circuit breaker brands. Also, make a note of the brand of the electric panel . This is to help you determine if there are upgrades they could recommend for the hardware.
- Order online or go to the hardware store and purchase the breaker of the same voltage as the one you are replacing.
- Go and open the electrical box and switch off the bad breaker. Loosen the terminals and remove the wires using a pair of needle-nosed pliers. Ensure the pliers have rubber insulated handles to avoid shock or electrocution since you will use the pliers to grab the live wires from the terminal. That is a safety measure.
- Remove the bad breaker. Replace it with the new breaker and slip its clips into place. Remember to switch off the replacement breaker.
- Next, using the pliers, hold the wiring and tighten the screws on the terminal. It is crucial to ensure that the wires and screws in the terminals are in the right place.
- Turn the breaker on and replace the electrical panel cover.
Can a Breaker Fail Without Tipping
If you have a newer electrical panel , it’s not likely for a breaker to fail and not trip. However, in older breaker boxes like Federal Pacific , the breaker failing to trip is common.
The main reason Federal Pacific was investigated by the Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC) was widespread structure fires involving breakers failing to trip when an electrical overload was present. They found that the circuit breaker contacts would fuse to the bus bar.
Modern breakers will trip when a failure occurs as an added layer of safety. Most older breakers did not have these safeguards.
With AFCI breakers, if the Internal sensing mechanism fails, the breaker reverts to a standard breaker. The AFCI sensor mechanism will no longer work, but the breaker would still trip from overcurrent protection. Therefore, you should test the AFCI breaker regularly.
Conclusion
Listen to your circuit breaker . It’s alerting you of a problem when it trips. That communication could be a problem with the breaker itself, the circuit, or the amount of electric current coming into your home.
Hubert Miles is a licensed home inspector (RBI# 2556) with more than two decades of experience in inspection and construction. Since 2008, he has been serving South Carolina through his company, Patriot Home Inspections LLC. As a Certified Master Inspector, Hubert is dedicated to providing his expertise in home inspections, repairs, maintenance, and DIY projects.
Continue Reading

Watts to Amps Calculator: DC/AC Wattage to Amps Conversion

70 Amp Wire Size: Breaker & Wiring Gauge Guide

80 Amp Wire Size: Breaker & Wiring Gauge Guide

200 Amp Wire Size: Service Length & Wiring Gauge Guide

10/2 or 10/3 Wire for Mini Split: A Professional Guide

GFI vs GFCI: Understanding the Key Differences

Founded by Hubert Miles, Certified Master Inspector
Home Inspectors
Calculators
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
©2024 Home Inspection Insider 898 Whispering Pines Rd, Johnsonville, SC 29555 843-250-1882
(912) 602-3068 | Need Power? Call Clocktower!

(912) 602-3068
How to Fix a Tripped Circuit Breaker That Won’t Reset

- March 26, 2024
- Electrical Tips
Have you ever had a circuit breaker trip and found that it won’t reset? It’s a common problem, and one that can be frustrating when you’re not sure what to do.
The most common reasons for a circuit breakers that won’t reset are:
- Damaged breakers
- Electrical shorts
- Loose wiring
- Damaged insulation
In this post, we’ll walk you through how to check for each of these common reasons, and discuss how to fix them.
Why circuit breakers trip
A circuit breaker is a safety device in your home designed to stop the flow of electricity if there’s an overload, which can help prevent fires. When the current flowing through the circuit breaker becomes too much for it to handle, it “trips” and shuts off the power to prevent a fire from starting.
Most of the time, resetting a tripped circuit breaker is a simple matter of flipping the switch back to the “on” position. However, sometimes the breaker won’t reset no matter how many times you flip it.
First, try to reset the tripped circuit breaker
First, we should perform a basic test to make sure the breaker is actually malfunctioning. If you haven’t already tried manually resetting the circuit breaker, this is the place to start.
Locate your circuit breaker box and open the cover. Once you’ve located the tripped breaker, flip it to the “Off” position. Then, flip it back to the “On” position. You should hear a click as the breaker resets. If the breaker trips again, or simply won’t reset, there may be a problem with your wiring.
How to fix a tripping circuit breaker
Check to see if the circuit breaker is damaged.
If the circuit breaker trips and won’t reset, the first thing you should do is check to see if the switch is damaged. Circuit breakers are designed to trip when they become overloaded, which means they’re also designed to be flipped back on when the overload is resolved. However, if the switch itself is damaged or the electrical panel is outdated , it may not reset properly.
To check for damage, first make sure that there’s no power going to the breaker box by flipping all the switches to the “off” position. Then open up the panel and visually inspect the faulty breaker for any signs of burned or blackened areas. If you see any charring or burning around the switch, it’s likely time to replace it.
In some cases, you may be able to reset a damaged breaker by gently bending the switch back into place. However, this is only a temporary fix and the breaker will eventually need to be replaced.
We recommend that if you see any damage, it’s best to replace the entire circuit breaker rather than just the switch.
Check to see if there’s an electrical short
Another reason why your circuit breaker won’t reset after tripping is because there’s an electrical short somewhere in your home. An electrical short occurs when there’s too much current flowing through a wire, causing it to overheat and potentially start a fire.
To figure out if there’s an electrical short, the first thing you should do is turn off all of the switches in your breaker box. Once everything is off, go around your home and look for any signs of an electrical fire, such as burning smells or smoke. If you see or smell anything suspicious, call a licensed electrician right away.
If you don’t see any signs of a fire, the next step is to identify which circuit is causing the problem. Start by flipping on one switch at a time and seeing if the breaker trips. If it does, leave that switch off and move on to the next one. Repeat this process until you’ve found the problem circuit.
Once you’ve identified the problem circuit, the next step is to figure out where the electrical short is located. The easiest way to do this is to start at the breaker box and work your way down the circuit until you find the problem.
If you’ve followed these steps and you believe there may be an electrical short, it’s important to call an electrician right away. They’ll be able to locate the source of the problem and fix it before it causes any further damage.
Check for loose wiring
Another common reason for a circuit breaker to trip is because of loose wiring. Over time, wires can loosen and become frayed, which can cause them to short circuit.
The best way to check for loose wiring is to listen to your devices and appliances for the sound of buzzing or crackling. One common culprit is buzzing light switches or outlets. If you don’t find a faulty appliance, note that this can also be true around the breaker.
If you hear these noises and suspect that your circuit breaker is tripping because of loose wiring, the best thing to do is call an electrician as soon as possible. Trying to fix the problem yourself could result in injury or even death.
An electrician will be able to quickly diagnose the problem and make the necessary repairs. In most cases, they’ll also be able to prevent the problem from happening again in the future.
Look for signs of corrosion
Another common reason for a circuit breaker to trip is corrosion. This is especially true if you notice any moisture or wetness in the electrical panel . Corrosion can cause the metal parts of the breaker to break down, which in turn can cause a short circuit.
Corrosion usually appears in the form of a white, chalky substance building up around screw terminals. Look for signs of corrosion, rust, or moisture around the circuit breaker.
If you suspect that corrosion is the culprit, call an electrician to have a look at the problem. Trying to clean or repair the corrosion yourself could result in serious injury.
Check for damaged insulation
Sometimes circuit breakers will have insulation around them to stop cold air from entering through the box itself. Damaged insulation is another common cause of tripped circuit breakers. If you have insulation around the box, inspect it to see if it looks damaged.
If the insulation around your electrical wiring is damaged, it could cause a short circuit. Once again, if you suspect that this is the problem, call an electrician rather than trying to repair the problem yourself.
Is it dangerous if a circuit breaker keeps tripping?
We are often asked if tripping circuit breakers are dangerous. If your circuit breaker keeps tripping, it could be a sign of an electrical problem in your home, up to and including serious fire risks. While it’s not necessarily dangerous if your circuit breaker trips occasionally, if it happens frequently, it should be fixed right away.
If your circuit breaker trips and won’t reset, don’t panic! Many times the problem is something minor that you can easily fix yourself. However, if you’re unsure of what to do or think the problem may be something more serious, always err on the side of caution and call an electrician . Trying to fix the problem yourself could result in serious injury or even death.
Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is a relatively simple process that most people can do on their own. However, if the breaker trips repeatedly or if you have any questions about your electrical system, it’s always best to contact a professional electrician for assistance.
If you have any questions about resetting your circuit breaker or if you need assistance from a professional, don’t hesitate to contact us . We’re here to help!
Latest Articles

Average Electrician Cost to Install an EV Charger

Light Switch Buzzing: Causes, Dangers, and Fixes

How Many Things Can I Plug Into One Outlet Safely?
Commercial Outlet Vs Residential Outlets: Which is Right for You?

Are Ungrounded Outlets Dangerous? Understanding the risks

Why is My Outlet Smoking? Potential causes and how to fix them

Copyright © 2023 Clocktower Electric, LLC. All rights reserved. St. Simon’s Island, GA 31522
Contact Us | Privacy Policy | Site Map

How to Fix a Breaker That Keeps Tripping
"Ok, where's the flashlight?"
We've all had to deal with tripped circuit breakers . They're annoying and happen at the worst times. As a licensed electrician, I've seen my fair share of breakers, tripped or otherwise.
Circuit breakers monitor the flow of electricity through a circuit. If it exceeds a preset amount, it opens the circuit to stop the current flow. They're a vital piece of your home's electrical system. And when they trip, they're trying to tell you something.
Occasional trips are not something to be alarmed about. But if a circuit breaker in your home keeps tripping, it could be a sign something's wrong.
How To Know if Your Circuit Breaker Is Tripping
If your breaker trips, go to your electrical panel and open the front cover. There should be two columns of circuit breakers and, hopefully, nice labels indicating what circuits each one controls. Most breakers will be on, so look for the one with the handle in a different position than the others.
On every breaker, there will be an "On" and "Off" position. On a tripped breaker, the handle will be in the middle, neither On nor Off. To reset, flip the handle to Off first, then to On. Stand to the side of the panel and turn your face away when flipping breakers. If an arc flash occurs, it may save your life.
Why Does My Circuit Breaker Keep Tripping?
Circuit breakers trip when too much electricity flows through the breaker. Circuit breakers are rated based on how much electricity can safely flow through the electrical circuit they're protecting. When that's exceeded, the breakers trip. A 20-amp breaker trips when more than 20 amps of current is on the circuit.
Circuit breakers trip for three main reasons:
- Short circuits;
- Ground faults.
What Is a Circuit Overload?
An overloaded circuit has too many things running on it at once.
Imagine a kitchen with a microwave and an air fryer next to each other. Kitchen small appliance circuits are 20 amps. A 1,200-watt microwave draws 10 amps. A 1,700-watt air fryer draws about 14 amps. Running both appliances at the same time puts 24 amps on a circuit designed for 20 amps.
Over time, those extra amps will damage the wires by generating excessive heat. A circuit breaker stops this overload condition by opening the circuit.
What Is a Short Circuit?
A short circuit happens when a hot wire comes in contact with another hot wire, or the neutral or ground. When a circuit operates normally, current flows on the hot wire from your electrical panel to a light, appliance or other load. Then it goes back to the panel via the neutral.
If the hot and neutral accidentally touch each other, the current takes a "shortcut" back to the panel instead of going to the load. The electricity generated by this contact is many times higher than if it was being used by a light or appliance. It's an extremely dangerous situation that can cause shocks and fires.
What Is a Ground Fault?
A ground fault is a type of short circuit. Ground faults happen when a hot wire touches a non-current carrying part of the electrical circuit, like a metal box or pipe. It's important for that unintentional, really high current to have a place to go, so non-current-carrying parts of your home's electrical system are bonded together and connected to a ground.
If there's no purposeful path to channel that ground fault current safely, it will go through anything available, including you. Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) are specifically designed to monitor for ground faults, but regular circuit breakers also provide protection.
How To Fix a Circuit Breaker That Keeps Tripping
If your breaker keeps tripping, investigate and fix the problem. Here are a few ways to narrow down the possibilities. Always call a licensed electrician if the issue becomes too involved.
Check for overload
Figure out which area of the house the tripped breaker controls, then turn off and unplug everything in that area. Lights, microwaves, computers, everything. Then go turn on the breaker. If the breaker trips immediately, even with nothing plugged in, it's likely you have a short, not an overload.
If the breaker holds, go back to the room and start plugging things in and turning them on one by one. After each item, pause, then do the next one. When the breaker trips again, you know you've reached your limit for that circuit. Redistribute the loads more evenly between circuits if possible.
Check for a short in a specific appliance
Shorts and ground faults can occur within an appliance or other electrical device when a hot wire touches the housing.
Note the last thing you plugged in when the breaker tripped while checking for an overload. If you plug that appliance or device into another circuit, does that circuit trip as well? If so, unplug the device immediately and don't use it until it's replaced or serviced.
Call an electrician for shorts and ground faults in the wiring
If the breaker trips immediately upon resetting, even with nothing plugged in or turned on, it's likely something in your home's wiring causing the problem. This could be a loose connection at a receptacle or other device, or something more complicated, like worn insulation within your walls.
If you have electrical experience and can determine which device is causing the short, replace the device or correct the loose wire. If you're not experienced, or you smell something burning or see scorch marks on your walls, call a professional licensed electrician. Do the same if you have repeated problems with flickering lights or tripping breakers.
Electrical fires and shocks are dangerous, and shorts and ground faults are difficult to find. A pro can diagnose and fix the issue, providing peace of mind.
- About Team Austin
- Club Austin
- Service Area
- Explore Partnership Opportunities
- Plumbing Services
- Drain Cleaning
- Sump, Sewage & Grinder Pump Services
- Air Conditioning
- Water Heaters
- Air Duct Cleaning
- Wells & Pumps
- Water Conditioning
- Emergency Services
Mon – Fri: 7 AM – 5 PM
Why Do Circuit Breakers Trip? Common Reasons + Next Steps

No power at certain outlets? You may find your circuit breaker tripped. But why? And is it safe to turn back on? Our Master Tradesman responds.
Is it safe to reset a circuit breaker?
It is safe to reset a circuit breaker only if the breaker was tripped by an overloaded circuit, which we will get to later in this article. Resetting a breaker repeatedly can become a safety hazard due to arcing. If your circuit breaker is tripped and won’t reset, you will need a qualified electrician to investigate and troubleshoot the cause of the problem.
How to reset a tripped circuit breaker
A tripped breaker doesn’t always look tripped. Most breakers have a red or orange indicator showing that it has been tripped. Here are a few things to know before resetting the tripped circuit.
SAFETY TIP: Touch the electric panel using only one hand
- A breaker handle that is pointed to the outer edge of an electrical panel is off
- A breaker handle that is pointed towards the centerline of the electrical panel is on
- A breaker handle that is in the center is tripped
Follow these steps to reset a tripped breaker:
- First, slide the breaker handle all the way towards the outside edge of the panel
- Next, slide the breaker panel towards the center of the electrical panel
- The handle should stay on
- If you hear it the breaker trip again or if it returns to the center, call for service
How does a circuit breaker work?
A home’s circuit breaker serves a very important purpose by installing shut offs or cutting the power to circuits in the home. Without a working circuit breaker, routine and normal electrical failures could turn into a fire or cause electrocution. The inner workings of the circuit breaker are quite complicated, but this electrical safety device works by instantly shutting off the power to prevent electrical hazards and fires that can result from overloaded circuits or shorts in electric wires.
- An average home has 15-25 circuits
- Some circuits in a home are dedicated, which means only one electrical consuming appliance is on that circuit. Common examples with dedicated circuits would be electric ovens, well pumps, water heaters and air conditioners.
- Each circuit in the home is protected by a circuit breaker
- The circuit breaker in the electric panel also serves as a handy on/off switch for the area of the house it serves
- Circuit breakers should be labeled so you know the general area served by the breaker
The main circuit breaker: What can cause it to trip?
Sitting above all of the individual circuit breakers in a panel is the main circuit breaker. This breaker is one that controls the power to the entire home and any subpanels in the home after the main breaker. The main breaker also acts as a throttle, limiting the amount of total electricity usage of your home. Lightning strikes and other power surges coming from the electric grid are typically causes of a main breaker tripping, but on rare occasions an issue inside the breaker panel can cause issues with the main breaker.
Next steps if the main breaker is tripped
Whole home surge protectors are a great investment if you commonly find the main breaker of your home tripped. They can also prevent electrical emergencies and emergency repairs. These surge protectors work to absorb the power surge so further damage to the electrical system and your home’s electrons is prevented.
Failed Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers have a useful life of around 30 years and are under use and strain anytime there is a load on the electrical current that they serve. Circuit breakers also get warm and over time the mechanism inside the breaker wears and will eventually fail or trip for no reason. Common causes of a faulty breaker are overuse of the breaker (turning on and off a circuit often) and an overloaded circuit that doesn’t quite trip the breaker. If you have simultaneous use of high draw electrical motors and frequent overload happening on a circuit, this will cause failure as well.
- Water damage causes breaker failure
- Frequent usage of the breaker will cause wear
- Constant overload on the circuit will eventually cause the breaker to fail
- Loose wire connections at the breaker or inside the panel can cause overheating and fire
- Failed breakers can make it seem like you have a circuit overload or shorts even if you don’t
What to do if your circuit breaker is faulty
Replacement of a circuit breaker should only be done by a qualified electrician and is very dangerous. Because of this, if you suspect a failed circuit breaker, you should call Austin Plumbing, Heating, Air & Electric for evaluation and repair.
Overloaded Circuits
By far the most common cause of tripped circuit breakers is an overload in that circuit. Each electrical load that is on a circuit (outlet, light, appliance) has a total potential power draw while the circuit is being used. Wire also has load ratings. The circuit breaker’s job is to sense the load on the circuit and to interrupt or trip if the load gets too high. The reason for this is to protect the wire from starting on fire or getting hot and causing safety issues. When too much power travels through the circuit, danger increases.
Overloads are very common and usually easy to identify. If the circuit tripped when you started using an electrical appliance, then it’s likely that a combination of all of the electrical devices being used caused a simple overload.
Next steps if you have an overloaded circuit
Unplug or turn off the electric component that you think caused the system to overload and reset the breaker. If the breaker resets and everything seems fine, then you chalk up this breaker trip to an overloaded circuit breaker. If on the other hand the breaker trips again, something else may be going on.
The key to resolving an overloaded breaker is to lessen the load on it and the circuit it serves. Ways to do this include finding alternative places to plug in appliances, such as vacuums, and if you have several plugs running to the same outlet, consider using outlets in different areas of the home.
Short Circuits
A short circuit, or a dead short as many electricians call it, is a condition where two hot wires are touching together or touching something else metal. These short circuits can happen in jacketed wire, in electrical junction boxes, inside the panel or in the electrical appliance or equipment. Almost all residential home wiring utilizes three wires in order to make electricity work properly. One wire is live or also called hot (and covered with a black jacket), the second wire (covered with a white jacket) is called the neutral wire, and a bare copper ground wire.
What happens when the hot wire touches something it shouldn’t? This eliminates the electrical resistance and allows too much current to flow through the wire, which overloads the circuit breaker.
Many parts of the electrical system can be to blame for a short circuit, but loose wire connections, failed appliance cords, and damage to internal home wiring are among common causes we find.
Short circuits are dangerous because of the sparks that occur. It is quite common to see smoke, and the potential for a house fire due to a short circuit is high. If you happen to be touching the metal that the hot wire is shorting to, you run the risk of being burnt and electrocuted. If you see char marks on any electrical component, use caution!!!
Next steps for a short circuit
Because of the danger associated with a short circuit, a professional electrician should be called in to troubleshoot the root cause of the short.
Grounded Fault Surge
A ground fault surge is a specific type of short circuit that occurs when the black hot wire touches the ground wire or something metal in the electrical or plumbing system that ground wire is connected to.
Grounded faults are caused by the same thing that causes many shorts. Either the insulation on the wire is damaged or a connection gets loose allowing the hot wire to touch the ground.
From a safety point of view, ground faults can be more dangerous than short circuits, especially when the fault is caused by water. Modern homes and modern electrical code requires electrical outlets near water be protected with a special type of ground fault interrupter called a GFCI. GFCI stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. The code says that any outlet within six feet from a source of water must use a GFCI outlet. GFCI’s are commonly found in bathrooms, outdoor receptacles, kitchens, near sump pumps and in garages and basements.
GFCI’s provide an extra level of protection against grounded fault surges and are a critical safety component of modern electrical systems.
How to handle a tripped GFCI
GFCI receptacles are equipped with a reset. If you find the GFCI tripped, try simply resetting the outlet to see if that works. If pressing the reset button or test button several times does not restore the problem, call Team Austin for help.
Aged or Damaged Wire
The wire that carries the current from your electrical panel to the electrical appliance (aka load) has to be properly sized, properly insulated and installed correctly to prevent circuit breaker tripping and other electrical issues in the home. In very old homes, the wire insulation becomes degraded and brittle, which can cause various types of electrical shorts. As we learned earlier, this will cause the breakers to trip. Over the years as the electrical industry has improved, the flow of electricity with the quality of wire, wire nuts and other fasteners has also gotten better. If you have an old electrical system that has worn significantly and you continually have tripped breakers, you may consider a whole home rewire.
Next steps for aged or damaged wire
If you simply have damaged wire in a small area, the electrical pros at Austin Plumbing, Heating, Air & Electric can repair it in a cost effective manner. However, an aged or obsolete electrical system that involves rewiring a whole home or a section of the home will require design and a comprehensive plan for the best outcome. Both wire repairs and wire replacement is best suited for licensed electricians.
SE Wisconsin’s Electrical Experts & Full Trades Service
Austin Plumbing, Heating, Air & Electric has been solving the comfort, power and water problems of SE Wisconsin for over 80 years. If you’re having troubles with your electrical system or any other system in your home, you can trust the professional electricians at Team Austin for upfront pricing, honest recommendations and electrical repairs and replacements that will stand the test of time. Learn more about our electrical services on our electrical services main page or call 262-367-3808.
Table of Contents
— Air Conditioning
— Wells & Pumps
— Water Conditioning

10 Signs Your AC Needs a Repair (Or Replacement)
How Long Do Circuit Breakers Last?

The Ultimate Guide to Water Softener Troubleshooting: 20 Tips & Tricks

What Size Generator Does My Home Need?

The Actual Cost to Install an Automatic Whole-House Generator

Well Inspector? Or Septic Pumper in Disguise? Why Wisconsin Home Buyers Should NEVER Let Sellers’ Agents Pay for Well Inspections
Schneider Electric Blog
Home > Energy Management > Decarbonizing electrical networks means more switching, how can we remain sustainable?
Energy Management
Decarbonizing electrical networks means more switching, how can we remain sustainable?
April 18, 2024
3 min read | Guest Blogger
This audio was created using Microsoft Azure Speech Services
The circuit breaker challenge in a decarbonized energy future
As we transition to a decarbonized energy future, the demand for renewable energy sources is surging. The share of renewable energy in the European Union has risen dramatically over the years. In 2004, renewables accounted for only 9.6% of the EU’s energy mix, but this figure has more than doubled, reaching 22.1% by 2020. This substantial increase in the share of renewable sources highlights concerted efforts to transition towards a more sustainable energy landscape.
However, the intermittent nature of these sources necessitates more frequent switching of energy, the process of transferring electrical power from one source to another through the use of switches. This can involve changing the direction of power flow, turning power on or off, or redirecting power to different circuits. This poses a challenge for industries like grid (utility), automotive & process plants, and data centers. As the demand for energy resulting from electrification increases, a shift in perspective will mainly be influenced by the growing frequency at which power is being switched. If End Users continue using outdated circuit breakers, it can lead to higher maintenance and replacement costs for crucial equipment like circuit breakers.

Understanding the operational constraints of circuit breakers
Circuit breakers have a finite lifespan , measured in the number of operations they can perform before needing replacement. The average lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on several factors. Circuit breakers are designed to last a long time, typically 30 to 40 years. The lifespan of a circuit breaker is closely tied to the health of your electrical system.
High-quality circuit breakers tend to last longer. This can eliminate the need for frequent replacements, saving valuable time and reducing operational expenses. Therefore, end users are under pressure to maintain their equipment to the highest standards while prioritizing proper maintenance and investing in high-quality equipment to strive to reduce operational costs in the face of rising energy demands and electrification.
Electricity 4.0, through digital innovation, connected equipment is the backbone of improvements.
Decarbonizing our energy sources brings about a greater dependence on sustainable technologies. Unplanned downtime and the lifespan of a circuit breaker can have a significant impact on business operations and revenue.
This is where the convergence of Electricity 4.0 with real-life applications becomes crucial. Electricity 4.0 through digital innovation is revolutionizing the energy sector by making it smarter, more efficient, and ultimately more sustainable. By embracing sustainable technologies, businesses can decarbonize their operations while maximizing uptime and longevity.
To learn more about the transformative potential of Electricity 4.0, check out this article: Electricity 4.0: Revolution Is The Only Solution (forbes.com) .
EvoPacT HVX: The next-generation circuit breaker redefining resilience and longevity
One of the main advantages of new-generation circuit breakers is to push the boundaries of specifications, especially resilience and longevity, with new equipment capable of performing over 30,000 operations. This can potentially last the entire lifespan of a switchboard which is a fundamental component of an electrical distribution system that acts as a centralized hub, enabling the safe and controlled distribution of power throughout the system. This longevity of the switchboard means less demanding applications, saving time and reducing operational expenses for maintenance teams. By also integrating wireless sensors, digitally native breakers allow for real-time monitoring of equipment health status, reducing the need for manual checks and enabling more predictive and condition-based maintenance. This can help to avoid downtime and ensure optimal performance of switchboards.
The good news is that these advancements are available today, with a new generation MV Circuit Breaker called EvoPacT™ HVX . Furthermore, by combining EvoPacT™ HVX with condition monitoring services, end users can experience up to a 40% reduction in downtime and maintenance costs. EcoCare is a comprehensive membership program provided by Schneider Electric, offering condition monitoring, predictive maintenance recommendations, 24/7 expert support, and access to innovative tools for managing and monitoring electrical assets. This not only enhances the reliability and performance of equipment but also helps to reduce the environmental impact of operations.
Transforming ambition into action: The power of IMPACT Makers in the new energy landscape
The EvoPacT™ HVX is designed with sustainability in mind which enables us to meet the demands of a decarbonized energy landscape while also navigating the challenges of frequent switching and remaining committed to a greener and more sustainable world.
Together we can make a sustainable and long-lasting IMPACT with powerful EvoPacT™ HVX to build a future where decarbonization and sustainability go hand in hand, ensuring a resilient and environmentally conscious electrical infrastructure for generations to come.
If you’d like to learn more, we encourage you to watch the video below:
Discover how digital transformation of power systems can help you achieve digital transformation goals with active connectivity and IoT technology: How to Transform Electrical Distribution with Data (schneider-electric.com)
About the author

Soham Ghosh, General Manager – Global Medium Voltage Component Product category Leader
Soham Ghosh has left an indelible mark in the field of Medium Voltage (MV) components. His journey began as a Tendering and Project Manager at Areva T&D in 2006, where he spearheaded critical projects related to MV equipment such as AIS, GIS, RMU, and PSS. 2020 to 2023 marked a pivotal phase in Soham’s career. As the Lead Channel Manager and Operational Marketing Head for the East and South regions, he oversaw a network of approximately 30 channels, comprising MV panel builders, MV Lic Partners, and Distributors. Under his leadership, a successful business model emerged, resulting in a remarkable 3x growth within just three years. Notably, his efforts played a crucial role in elevating RMU Lic business to record heights for Schneider. In July 2023, Soham embarked on a new global role as the Medium Voltage Component Category Manager and Launch Leader. His responsibilities now encompass managing the MV component portfolio, overseeing the P&L, devising strategic initiatives, and orchestrating new offer launches across countries worldwide. Soham Ghosh’s journey exemplifies resilience, innovation, and unwavering commitment to excellence. As he continues to shape the MV landscape globally, he remains at the forefront of understanding, defining, and delivering solutions that power the infrastructures of the future.
Tags: circuit breaker , Condition Monitoring , energy future , Impact maker , medium voltage circuit breaker , power distribution , predictive maintenance , resilience , switchboards
Understand [ edit ]
Overlooking the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, Khabarovsk is the second largest city in the Russian Far East , approaching 600,000 residents and growing. It is also the capital of both Khabarovsk Krai and the Far Eastern Federal District . Unlike Vladivostok, the city has never been closed to foreigners, and retains a distinct international feel, rare for the Russian provincial centers – a feeling propped up by an increasing Asian presence with arrivals from Asian countries now numbering over a million each year. In turn, Asians come here to experience a piece of Europe close to home, with the fortunate effect that the city is spending huge swaths of money renovating the city, in which old classical buildings were spared much of the destructive effects of the 1917-23 civil war, to provide its visitors with just that feeling. From a European's perspective, Soviet city planning has unmistakably taken its toll, but it is still far more attractive than your average Siberian city.
Climate [ edit ]
The climate is temperate and monsoonal, with a cold, dry winter and a hot and humid summer. The average temperature for a full year is just 2°C, but covers over wide span of monthly averages ranging from a bone chilling −20°C in January to a quite warm +21°C average in July. The city sees an average of 686 mm precipitation in a year, but unfortunately the lions' share falls in the warm summer months. The number of sunny days per year is 70, which is higher than Moscow's 54. Climate-wise, end of May - early June or end of August - early September are the best time for a visit.
Get in [ edit ]
By plane [ edit ], by train [ edit ].
- 48.49659 135.07283 2 Khabarovsk railway station ( Habarovsk 1 ), Leningradskaya, 58 , ☏ +7 4212 38-39-40 . Khabarovsk station, listed as Habarovsk 1 in most train schedules, is a major stop on the Trans-Siberian Railway . There are several trains each day bound for Vladivostok (800 km) and Moscow (about 8500 km) along the main Trans-Siberian line. Other options include trains #386 or #035 to Blagoveshchensk , #325 for Tynda, #667э for Komsomolsk , #943э Vanino , all on the Baikal-Amur Mainline . Vanino is an interesting option as it allows ferry connections to Sakhalin and further on to Wakkanai in Japan – more details in the Russia to Japan via Sakhalin itinerary. The international trains are Khabarovsk- Harbin , ongoing twice a week and Khabarovsk- Pyongyang on special days.
By boat [ edit ]
- 48.46904 135.0581 3 River Port , Shevchenko 1 .
If you want to go to places upstream on the Amur river, the Meteor speedboats will often be your transport of choice, but only during the summer when the river is navigable. However, in 2008, the water level in the river was at a historic low, so that the Meteor traffic had to be stopped. If Meteor traffic functions normally, you can go some 1,000 km downstream to the Ul'chi municipal district (rayon), a region mostly inhabited by indigenous Ul'chi people.
- Fuyuan – In spring and summer there are daily hydrofoil services to Fuyuan in northeastern China , departing from the ferry terminal facing the Amur river.
- Komsomolsk – If you are heading for the BAM line up north, an interesting option is to take a hydrofoil cruising up the Amur river to Komsomolsk (6 hours), and catch a train from there.
Get around [ edit ]

The best thing to start with is to walk around the center of the city. Have a nice walk from Lenin Square to the Amur River via the main street, Muravieva-Amurski. You will find all sorts of shops and places to eat.
By tram [ edit ]
The city has a network of four tram lines (there is no line 3 or 4). The most useful section for visitors is the stretch of the network running from the main railway station along Amursky Boulevard, before making a left turn down Volochaevskaya St. (near the market), and crossing Muravyov-Amursky Street one block west of Lenina Square, it then continues south intersecting Lenina Street roughly at its halfway point, before a stop at the botanical gardens (Lines 1, 2 & 6). The remainder of the network mainly extends into the sleepy suburbs. Line 5 serves the North, Line 1 and 2 the South along Krasnorechenskaya St.
By bus [ edit ]
The electric trolleybuses also has a few useful sections for visitors, Line 1 runs between the Airport and Komsomolskaya Square (River promenade, Museum cluster) along Karla Marksa and Mureava Amursky streets.
The regular bus number 1, is a useful circle line. It starts at the Railway station, turns down Seryshev street (a block north of Amursky Boulevard) until it reaches the river park at Lenin Stadium. Turns down Komsomolskaya Street (and square) and runs south until Lenina Street. It then runs the entire length of Lenina street before north at the City History Museum and returns to the train station.
Major destinations [ edit ]
- Airport 18, T1, T2, T4
- Botanical Gardens' 9, 25, 29, 33, 54
- City History Museum 1, 54, 56, 57, T5
- Komsomolskaya Square 1, 9, 14, 19, 29, 34, 38, 55, 56, T1, T3
- Lenina Square 14, 19, 21, 29, 34, 38, 55, 56, T1, T3
- Railway Station 1, 6, 7, 11, 13, 20, 22, 24, 26, 34, 54, 57, T2, T5
- Slavy (Glory) Square 1, 9, 29, 33, 34, 56
See [ edit ]

The Far Eastern Museums [ edit ]
There is a fantastic cluster of top notch museums along Shevchenko Street, just behind the tall blue-domed Church of Theotokos on Komsomolskaya Square towards the river and stadium. Not only are the museums some of the best in the far east, they also make their home in some impressive century-old buildings dating back to before the revolution. After a visit, the nice river promenade is just a short walk away, so you can wash all that new found knowledge away with some pivos in good company.

Tugged away just across the next street behind the military museum, you also find the Archeology Museum on Turgeneva street.
Learn [ edit ]
The Pacific National University [dead link] , formally a Polytechnic Institute, is now a full fledged university, with over 21.000 students enrolled. Has a single Masters programme in Computer Sciences in cooperation with a German university, which is taught in English.
The Far Eastern State University of Humanities [dead link] offers a summer course in Russian language in July as well as courses during the academic year.
The Far-Eastern State Medical University [dead link] is a major medical institution in Eastern Siberia.
The Far-Eastern State University of Railways being one of the largest universities includes the course of Russian-Americam Programme.
The Far-Eastern State Scientific Library is an old and beautiful Art-Nouveau building in the city's center and has American, German and Japanese centers.
Japanese Center in Khabarovsk offers course of Japanese language as well as participation in business seminars
Connect [ edit ]
Phones [ edit ].
Khabarovsk has the usual set of Russian mobile operators:
GSM 900/1800:
- Beeline ( by Vympelcom ), ☏ +7 4212 64-90-64 .
- Megafon , toll-free: +7 800 333 0500 .
- MTS ( Mobile TeleSystems ), toll-free: +7 800 333 0890 .
- Skylink , Dzerzhiskogo, 4 ( Near Amur hotel. ), ☏ +7 4212 74-44-44 . The all-Russian CDMA operator, having less subscribers, than GSM operators, but popular for faster and cheaper mobile Internet service.
- Megafon , ☏ +7 800 333 0500 . new standart of mobile internet.
Check roaming prices, especially for mobile Internet, before using any non-Russian SIM card. Some mobile connection standards are not supported in Russia , e.g. those for Japan and the United States .
If you're staying in Russia for a week or more, it's definitely worth it to buy a local SIM card, but be aware, that a passport is needed for that. The easiest way to refill a local mobile account is to use an ATM. Most ATMs have bilingual interfaces, allowing numerous kinds of payments, including those for mobile services by local operators. You can also do it through terminals spread all over the city - like Qiwi or mobile shops.
Post [ edit ]
The General post office at 28 Muravyov-Amurskiy St. If you plan on calling anyone, Khabarovsk is UTC +10 (or 7 hours ahead of Moscow).
The post-office at the railway station is located on 13 Leningradsky per. about 200 m from the station building.
Navigation menu
Recreation Center Sosnovka

View prices for your travel dates
- Excellent 0
- Very Good 0
- English ( 0 )
Own or manage this property? Claim your listing for free to respond to reviews, update your profile and much more.
RECREATION CENTER SOSNOVKA (Khabarovsk) - Specialty Hotel Reviews & Photos - Tripadvisor
Boutique-Hotel Khabarovsk City

View prices for your travel dates
- Excellent 239
- Very Good 132
- All languages ( 399 )
- Russian ( 335 )
- English ( 40 )
- Japanese ( 8 )

" Avoid if you dont want to share your passport details with someone who you dont know "
" Cleanliness and kindness of staffs "
" Check out the room before you settle in. "

" My room was a studio. It was comfortable and cozy. "
" building work on a site on the East side, so choose room on opposite side. "
Own or manage this property? Claim your listing for free to respond to reviews, update your profile and much more.
BOUTIQUE-HOTEL KHABAROVSK CITY - Reviews (Russia)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Devices charging slowly. Electrical outlets not working. Flickering lights. Scorch marks on outlets and light switches. If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for ...
If you suspect a short circuit, unplug your appliances and check the wires for melted coverings. You might also notice a burning smell coming from the outlet. Call in a professional electrician to find the source of the problem. 3. Circuit Overload. Circuit overloads are the most common reason that a breaker trips.
Flip Back to ON Position. When you find the circuit breaker That's switched off, flip it back into the ON position. You should feel a slight resistance when flipping the lever and hear a clicking sound signaling that it's been flipped back on. This should restore power but if it doesn't, you may need to flip your breaker one more time.
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping. A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping: Know the electrical load - work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one ...
A tripping circuit breaker can be an annoying problem. There are, however, three possible causes of your tripping circuit breaker that are easy to DIY.Possib...
1. Identify the Cause. Start by identifying which circuit is tripping. Unplug all the appliances connected to that circuit. 2. Reset the Breaker. Once you have identified and addressed the potential cause, reset the breaker by turning it off and then on. 3. Check for Overloads.
1. Overloaded Circuit. An overloaded circuit is the most common reason for a breaker to trip. This occurs when the electrical demand on the circuit exceeds its capacity. When too many devices or appliances are running at the same time, the breaker trips to protect the circuit from overheating.
Leave the devices plugged in and turned on for a few minutes to see if the breaker trips again. If the breaker trips after several minutes, try the process again, but leave 1-2 less important devices unplugged. Eventually, you'll find a combination of devices that doesn't trip the circuit breaker. 4.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a Tripped Circuit Breaker. 1. Identifying the Affected Circuit. Commence your circuit repair journey by pinpointing the specific circuit at fault. Locate the corresponding switch that has shifted to the "off" position within the breaker panel. 2. Unplugging or Turning Off Devices.
A circuit breaker is a device, installed in the electrical panel, that controls whether power can be sent from the panel through a circuit. Heath explains this ability is controlled by a switch that can be operated either manually—like when a person wants to interrupt power for service—or automatically, like a breaker trip.
Short circuits are a common reason for circuit breaker tripping and should be taken seriously due to their potential danger. A short circuit occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a neutral wire, resulting in an abnormal electrical connection. This can happen in electrical outlets or due to faulty wiring in appliances or plugs.
The electrical current flow increases significantly, causing the circuit breaker to trip to stop the electricity from damaging appliances. It is a short circuit because the current bypasses the proper circuit wiring channels and flows through a shorter, unplanned pathway.
A professional electrician may recommend that you replace your electrical panel if the circuit breaker continues to trip, especially if your current panel is over 40 years old. The cost the replace your electrical panel ranges from $500 to $4,000 , depending on the type of panel and how much amperage is required to run your everyday appliances ...
Locate your circuit breaker box and open the cover. Once you've located the tripped breaker, flip it to the "Off" position. Then, flip it back to the "On" position. You should hear a click as the breaker resets. If the breaker trips again, or simply won't reset, there may be a problem with your wiring.
When it is said that a circuit breaker "trips," it means that circuit has detected what's known as a fault condition and has shut itself off to prevent the wiring from overheating and potentially igniting itself. Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is generally pretty easy - you just need to go back to the electrical panel, find the ...
If your breaker trips, go to your electrical panel and open the front cover. There should be two columns of circuit breakers and, hopefully, nice labels indicating what circuits each one controls ...
A circuit breaker is a switch inside your breaker box that monitors the flow of electricity on a circuit and turns off or trips if the circuit becomes damaged or overloaded. If the circuit is not damaged, running too many high-amp electrical appliances at a time is often the cause of a tripped breaker.
Follow these steps to reset a tripped breaker: First, slide the breaker handle all the way towards the outside edge of the panel. Next, slide the breaker panel towards the center of the electrical panel. The handle should stay on. If you hear it the breaker trip again or if it returns to the center, call for service.
Switch the breaker fully to the off position. Return the breaker to the on position. If multiple circuits have tripped, this may indicate a more serious electrical issue in your home's wiring and should contact an electrician. GFCI and AFCI breakers follow the same procedures as regular breakers.
The average lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on several factors. Circuit breakers are designed to last a long time, typically 30 to 40 years. The lifespan of a circuit breaker is closely tied to the health of your electrical system. High-quality circuit breakers tend to last longer. This can eliminate the need for frequent ...
Khabarovsk ice festival. Khabarovsk or Chabarovsk (Russian: Хаба́ровск, khah-BAH-ruhvsk) is a city on the Amur river in the Russian Far East, near the Chinese border. Often overlooked due to its proximity to Vladivostok, Khabarovsk could easily be a highlight in the long line of predominately dull cities along the Trans-Siberian Railway.But while most cities look their best when the ...
Service. 4.5. Value. 4.1. Parus Hotel is located in the business, cultural and administrative center of Khabarovsk on the right bank of the Amur River in a park area. The Amur River Embankment, the Rock, the Dormition Cathedral are situated nearby. The Central building is an old two-storied mansion built in the late 19th century.
Recreation Center Sosnovka, Khabarovsk: See traveller reviews, user photos and best deals for Recreation Center Sosnovka at Tripadvisor.
4.7. Service. 4.6. Value. 4.3. Boutique-hotel Khabarovsk City is located a few steps away from the main street - Muravyov-Amurskij Street, being in close proximity to most famous sights and attractions of the city. Its 50 guest rooms and suites are very spacious and carefully designed for a refreshing and comfortably relax.