- [email protected]

Home » Hot Topics » Germany per diem rates and how to manage employees travel expenses

Germany per diem rates and how to manage employees travel expenses
- 3 September 2022

One of the most frequently asked questions we get asked by our clients is how to manage employees travel expenses and Germany per diem rates. German regulations governing per diems, telecom expenses, hotel costs, meals reimbursements, mileage and so on, can often be confusing and different from an organization’s home-country rules.
Companies setting up shop in Germany are understandably concerned about how challenging it can be to stay compliant with German tax laws and want to avoid fines and reputational damage.
For this reason, we have decided to write this article with the aim of providing not only an overview on German travel expense reimbursements (as part of good expatriate management best practices ) but also to dissect and explain some of the finer details surrourding the complex circumstances companies face.
What are per diem rates?
According to Investopedia.com per diems (in German “ Tagespauschalen ”), from the Latin for “ by the day ”, refers to daily allowances paid to employees to cover costs incurred while on a business trip.
More specifically, the law in Germany talks about a lump sum for meals being paid to an individual as compensation for the expenses incurred in working outside their home and main workplace.
Moreover, an employment contract (or any other company issued policy) or collective bargaining agreement may also stipulate that per diems are to be used to reimburse employees.
Tax repercussions are likely (although as we will discuss in this article, not for all expenses categories) if employers choose to reimburse employees for actual expenses above the permitted per diem’s allowance instead.
On the other hand, there is less of an administrative burden for both companies and their employees when sticking with per diem rates as there is no need to:
– submit an itemized claim
– attach accompanying receipts
– update per diem rates each year in line the rising cost of living (the German Finance Ministry takes care of it)
What is not covered by Germany per diem rates
Now that we have a per diem definition and a law clarifying what per diem allowances are meant to cover in Germany, let us briefly look at what type of travel expenses, per diems are not meant to cover:
- Air fares
- Transport to and from the airport and/or meetings
- Hotel costs for staying overnight
- Breakfast, lunch and/or dinner whilst meeting clients
These types of expenses should be in fact be claimed as part of a separate expenses claim request (a template is provided towards the bottom of this article) for actual travel expenses incurred.
Per diem rates within Germany
When employees are traveling on business within Germany the costs of subsistence (drinks and meals) is typically reimbursed according to the applicable per diem rates which currently are:
– between 8-24 hours, 14 EUR
– for a full 24 hours day, 28 EUR
For the first and last day of travel, the applicable per diem rate is always 14 EUR.
Furthermore, there is also an overnight allowance of 20 EUR for accommodation.
In practice though, only self-employed individuals tend to claim this allowance via their German tax return as accommodation is usually fully paid by the employer for travelling employees.
Conditions for eligibility of per diem allowances
We have already discussed above what is not covered by per diem allowance.
Let us now look more specifically at what are some of the conditions to be fulfilled for employees to be eligible to claim the above mentioned per diem rates in full.
The main condition is that the full per diem meal allowances will only be paid if the employee actually covers the costs of their own food .
In the case of meals that the employee took and that are included for example in a hotel invoices (breakfast, lunch, dinner) or that the employer provided, there will be a compulsory reduction of the lump sum amount entitlement as follows:
– 20% reduction if breakfast is already included in hotel invoice
– 40% reduction if lunch / dinner are already provided by the employer.
It is also worth mentioning that meals provided by the employer for trips shorter than 8 hours are treated as fringe benefits and thus taxable on the employee are the following nominal values:
– breakfast, 1.77 EUR
– lunch or dinner, 3.30 EUR
Other conditions / rules attached to the eligibility for per diem rates in Germany include:
– hours can be added together for multiple trips within the same day
– The tax-free reimbursement can only be for 3 continuous months of business travel. These 3 months can then be reset after a 4 weeks break
– All expense invoices should be addressed to the company’s corporate address and if they exceed 150 EUR, they should state the VAT amount
Per diems outside of Germany
Considering that the cost of living between countries (and sometimes even between cities within the same country) can vary significantly, the German Ministry of Finance each year publishes a table with the up to date international per diem rates.
However, due to the Covid pandemic, the international per diem and overnight allowances issued by virtue of the German Federal Travel Expenses Act, have not been updated on January 1, 2022.
As a result, the tax-free per diem lump sums published by the BMF letter dated 3 December 2020 , on “Tax treatment of travel expenses and travel expense allowances for business and professional trips abroad from January 1, 2021” – Federal Tax Gazette Part I (BStBl I) page 1256, are also valid for the calendar year 2022.
Overview of other travel expense reimbursements in Germany
Entertainment.
Entertainment expenses for events in which only employees working for the same company took part are not accepted as an external party also needs to be involved.
Additionally, invoices for entertainment expenses reimbursements should clearly show the following information:
- Employee/s name/s
- Name/s of the people entertained
- The reason for the entertainment provided
- The place, date and signature
0.30 EUR/Km can be reimbursed tax-free. The lump sum rate covers all expenses related to the car such as insurance, depreciation, petrol / diesel, maintenance, car wash, etc.
Tax-free reimbursements for expenses incurred during business use for private cars can only be paid if the employees states on their expenses claims the driven KMs and other relevant details about the trip such as start / end KMs balance, details of the route taken and the reason for the trip.
Anything paid in addition to the 0.30 EUR/KM rate, will be deemed taxable.
This means that the amount will have to be split up in a tax-free part and a taxable part (taxed at individual income progressive tax rates).
Telecom expenses / home office
If the home telephone / mobile phone / internet contracts are between the telecommunication company and the employee and not between the telecommunication company and the employer, there are 4 possibilities to reimburse these expenses:
1) The employer can pay a monthly lump sum of 20% of the invoice amount up to a max. of 20 EUR tax free to the employee. Any additional reimbursements would be taxable.
2) If the employee highlights the costs incurred for the employer on the telecommunication company’s itemized bill every month, the employer can reimburse those costs tax-free.
3) If the employee highlights the costs incurred for the employer on the telecommunication company’s itemized bill for a period of 3 months, a typical percentage of total expenses concerning the employer can be calculated on the overall total bill, which can then be compensated tax free going forward every month. Any additional reimbursements above the calculated percentage apportionment would be taxable.
4) The employees could prove they have two different mobile phones / landline numbers so that they could clearly be differentiated between the one used for business purposes and the one used for private purposes. In such a scenario, all the expenses incurred for business purposes on the dedicated line / number can be reimbursed tax-free.
Hotel costs
Hotel stays during a business trip can be fully reimbursed tax free provided the invoice is addressed to the employer and not to the employee.
Other expenses
Other expenses such as flight, train or bus tickets can all be reimbursed in full tax-free.
Similarly, the following ancillary expenses can also be reimbursed tax-free for the full actual amount incurred:
– Storage of luggage (including luggage insurance)
– Letters to the employer or to business partners / clients
– Parking fees / tolls
– Rental car at the place of the destination
– Damages to the employee’s belongings if they are typical for business traveling
To help employees with their expenses claims, our travel expenses form may be downloaded here and used when submitting reimbursements requests (if the employer is not already providing one).
FAQ on Germany per diem rates and travel expenses reimbursements
Assuming the company chooses to reimburse the employee for the actual expenses amount incurred which happens to be above an allowable tax-free rate / per diem, does the employer have any compliance requirements in terms of reporting the difference .
(i.e. employer taxes and/or any requirements to report on the employee’s behalf with potential penalties if they don’t)?
Yes, the exceeding part is considered salary and as such subject to taxes and social security contributions.
As in the case of salary, the employer taxes the employee at source and has to fulfill his tax and social security obligations at all times.
The employee is the debtor of the income tax but the employer deducts it from him / her.
The employer is therefore responsible for withholding the applicable income taxes and social security contributions from the employee’s pay and thus liable, in case they do not.
Failure to do so could be deemed a criminal offence pursuant to Sec. 266a StGB (Criminal Law Act) .
Contact us should you require further clarifications on per diem rates and travel expenses reimbursements in Germany and/or have a look at some of the other insights we have published.
You might also be interested in:

Get our FREE International Expansion & Global Mobility guide now!

Telephone *
Company/Organisation *
Where are you located? * Choose a location Afghanistan Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua And Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bosnia And Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo Congo The Democratic Republic Of The Cook Islands Costa Rica Cote D ivoire Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic East Timor Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands (malvinas) Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island And Mcdonald Islands Holy See (vatican City State) Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Islamic Republic Of Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakstan Kenya Kiribati Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao People's Democratic Republic Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macau Macedonia The Former Yugoslav Republic Of Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia Federated States Of Moldova Republic Of Monaco Mongolia Montserrat Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestinian Territory Occupied Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Reunion Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Saint Helena Saint Kitts And Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Pierre And Miquelon Saint Vincent And The Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome And Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia And The South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard And Jan Mayen Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan Province Of China Tajikistan Tanzania United Republic Of Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad And Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks And Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States United States Minor Outlying Islands Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Viet Nam Virgin Islands British Virgin Islands U.s. Wallis And Futuna Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
Brief description of your enquiry * I accept * By entering your information, you permit us to reach out to you with future communications and you accept our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions – Privacy policy – Cookie policy
Privacy Overview
Travel Allowance (Fahrkostenzuschuss) and Taxation in Germany explained
Main points.
- The travel allowance is a salary supplement that you grant your team for the journey to work - regardless of which means of transport they choose. It is paid at a rate of 0.30 euros per kilometer (0.35 euros per kilometer from the 21st kilometer onwards) for the one-way journey between home and work, and only for the days on which your employees are at work.
- For whom. The travel allowance is available to all full-time employees, part-time employees, trainees, and mini-jobbers on a 520 euro basis.
- A complement to your employer branding strategy. The travel allowance is a mobility benefit and is suitable as a retention tool, especially for employees who live further away.
- Accounting & taxation. The allowance is a salary supplement and is paid out with the monthly salary. Travel allowances are taxed at a flat rate of 15% wage tax.
- What to look out for. The allowance can only be paid to employees who regularly commute to work and in many cases, there is an annual cap of 4,500 euros (the same cap as for income-related expenses). In addition: If you grant your employees a travel allowance, they can no longer claim these costs as income-related expenses in their tax return.
What is the travel allowance?
Here is our explanation and definition:
- The travel allowance is a monthly payment with your salary that you grant to your employees to compensate them for the costs of traveling to work. The travel allowance applies to all means of transport used for commuting to the office.
- Your team member is free to choose how they get to work, whether by bus, train, bicycle, or car. Important is that only the days on which your employees actually commute to work are taken into account. The allowance covers 0.30 Euro paid per kilometer, if your team member travels beyond 21 kilometers the compensation is 0.35 Euro per kilometer.
- All employees who regularly come to the office to work can receive a travel allowance, i.e. full-time and part-time employees as well as trainees and mini-jobbers. For full-time employees in your team who usually commute to work every day, the allowance can be applied for 15 days per month without further proof, according to the law.
- As a salary bonus, the travel allowance is paid out with the salary and taxed at a flat rate of only 15% wage tax. If your team works in the home office every day, you cannot pay your team a travel allowance.
- If your team comes to the office e.g. for two days a week, you can also grant the allowance to your team for these two days only.
Create the work place of tomorrow with NAVIT. We are happy to support you with designing the best mobility solution for your company. Get in touch with us!
For whom is the travel allowance worthwhile?
As with other mobility benefits, the travel allowance generally increases motivation and satisfaction at work and is thus an important employee retention tool.
For employees who live far from their workplace, the travel allowance is particularly valuable. As a general rule, travel allowances are worthwhile for distances greater than 17 kilometers.
Many employees benefit from flat-rate wage taxation of 15%. As a monthly supplement to their salary, the travel allowance offers your employees the convenience of not having to wait until the end of the year or until their tax return to receive reimbursements.
This is how travel allowances are taxed and accounted for: If your employees are entitled to a monthly travel allowance, they can receive 0.30 euros per distance kilometer (0.35 euros from the 21st kilometer), which is the otherwise deductible distance allowance. As an employer, you are responsible for paying the 15% flat-rate wage tax.
The travel allowance does not require social security contributions. To calculate the amount of the allowance, you use the shortest or most convenient route between your employee's place of residence and your company's office location.
If you decide to pay your employees a higher amount than € 0.30 per distance kilometer or to grant them an allowance for days on which they worked in their home office, this additional benefit is subject to the individual tax rate of your employees.
If you decide to offer your employees an additional mobility budget, this can be granted as a benefit in kind up to 50 euros per month tax-free (or taxed at a flat rate) on top of the salary.
What about if your employees only use public transport?
In this case, it makes more sense to offer a public transport-specific allowance, e.g. a job ticket. Since 2019, the job ticket can also be subsidized above the upper limit of the tax-free benefit in kind of 50 euros.
In this way, the tax-free benefit in the kind of 50 euros can be used for other mobility benefits, such as a flexible mobility budget.
With the job ticket, you as an employer provide your employees with free or discounted monthly tickets for public transport, which can be used not only for commuting to work but also for private journeys.
With regard to the tax return, it is important to note: If your employees receive a travel allowance, they cannot claim income-related expenses for travel to work in their tax return.
A travel allowance is therefore only attractive for your employees if the distance between home and work is at least 17 kilometers.
Our mobility experts at NAVIT would love to share their knowledge with you about the new mobility product. Feel free to get in touch with us!
What is the difference between the travel allowance and the commuter allowance?
The travel allowance is not the same as the commuter allowance.
While the travel allowance is a voluntary offer from you as an employer, the commuter allowance is a state offer to your employees and offers them the possibility to deduct their travel costs from their taxes.
What both offers have in common is the amount of 0.30 euros per kilometre (or 0.35 euros from the 21st kilometer).
Travel allowance and other mobility benefits
The travel allowance is a mobility benefit and thus an effective instrument for employee retention as an additional benefit to the salary.
You can offer the allowance to your employees either as a single mobility benefit or together with others, such as a flexible mobility budget.
If you grant your employees a higher amount than the already mentioned 0.30 euros per kilometer or offer them a credit in the form of a mobility budget for the use of public transport or sharing offers (e.g. car sharing, bike sharing, e-scooter sharing), your employees pay the individual additional wage tax.
In contrast to a mobility budget or a job ticket, the travel allowance is transferred directly to your employee's bank account as a monthly salary supplement. This means that your employees have this amount at their free disposal.
Information and content disclaimer
NAVIT hereby states that the information provided about benefits on our website is only for informational purposes only and does not represent any tax or legal advice. The content is not intended to replace any individual, binding tax and legal advice that addresses your specific tax or legal situation. We, therefore, declare that information provided is without guarantee of correctness and completeness.
We continue to provide updated information and research insights. We as a provider of this information cannot assume any liability for the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of the information provided. In particular, the information is of a general nature and does not constitute tax or legal advice in individual cases. For questions about taxes and legal topics, please consult a certified tax advisor or lawyer.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive the latest insights about our mobility solution products like the 49 eurojob ticket.

More mobility topics
What is micro-mobility and which vehicles are included? The contribution of micromobility to the mobility transition.
Why companies need to rethink corporate mobility and how the transition to a mobility policy can succeed.
How does a virtual credit card work and what advantages does it have as a mobility budget card?
Employers have various options for supporting their employees' mobility. What is the difference between a mobility budget, mobility allowance and mobility bonus?
How does non-cash remuneration affect salary and how are non-cash benefit done in payroll?

The implementation of a mobility budget works best with a mobility platform
The amount of a mobility budget depends on these factors.

What is meant with shared mobility? What sharing services are out there? How does it work?
How to choose the right benefit for your team. Five popular employee benefits and their providers compared.
The most important terms and definitions: Everything you need to know about employee benefits for your company.

The most important terms and trends from the world of New Work.
When and for whom are they best suited? An overview of the individual concepts.
Lease a bike or e-bike for employees: What is important to know? Key criteria for a provider comparison.
New Mobility: Trend terms and definitions. Everything you need to know about the latest mobility and transport topics.
E-Bike leasing for employers: Is it worth it? The benefits of E-Bike leasing for companies and employees.
How is the mobility budget implemented in other European countries? A comparison.
Why are employee benefits relevant for companies and why do mobility benefits become popular?
When it comes to business trips, a mobility budget can have advantages over a classic travel expense management.
Job ticket, company bike and company car at a glance - Which allowances can employees use at the same time?
Tax-free fuel voucher & fuel card: advantages, use & non-cash benefit in Germany for employers
The future of bicycle mobility. Bike leasing, bike subscription and bike sharing in Germany quickly explained.
Comparison: Car subscription, leasing or long-term rental as an alternative to a company car in German
how can you make the complex topic of taxation understandable to your finance department? In this article we show you how to make the right choice.
We provide tax optimisation tips that employers and employees should consider when applying mobility budget in Germany
Corporate benefits: 4 ideas for modern employee benefits 2024 in Germany

We explain how employers can provide their employees with a company bike tax-free through a bike lease program in Germany

What mobility budget providers are there on the market? A comparison of mobility budget platforms vs. expense and benefits platforms

Mobility budget: salary increase or salary conversion?
More companies are committed to effective climate protection. This also applies to mobility. We explain how this works in Germany
In depth comparison between Deutschlandticket, jobticket and mobilitybudget.
Find out who can benefit most from this ticket and for whom a job ticket is worthwhile in this article.
Read all pros and cons of the new ticket and how the 49 Euro Deutschland ticket affects the Job ticket in Germany
What are the pros and cons of a car subscription? Is it a viable alternative to traditional leasing and fleet management?
CO2 reporting, CSRD corporate social responsibility for companies from 2023 in Germany. Here are the new CSRD rules & requirements
How can the mobility budget for employees be implemented in your company? What are the current solutions? What do you have to pay attention to with the individual mobility budget providers? We will explain the various mobility solutions to you.
We show you the advantages of a mobility budget as an employee benefit that can help make a difference in your mobility management.
This article is to inform you about the fuel & charge card and what the advantages of a hybrid card are.
Here you find all the info about travel allowances (Fahrkostenzuschuss) and taxation in Germany.
In this article we will tell you about the job ticket. What is it? What do you have to consider in terms of tax law? How does it relate to the mobility budget?
This article is all about bike leasing as a supplement to the mobility budget. How does bike leasing work? What are the benefits of company bikes? What's the deal with salary conversion?
How can the mobility budget be integrated into corporate mobility management? Or can it even replace it? We'll clarify that in this article.
Read all information about mobility budget and ticket reimbursement usage. How do you reimburse your ticket? Which tax implications apply.
Mobility Budget Taxes, Taxation and Non-cash remuneration. We will give you a brief overview of how the individual means of transportation are taxed.
The mobility budget explained. What is a mobility budget? Which advantages does it have? How does it work? We give you all the answers.
How to calculate Germany’s per diem rates in 2023 / 2024

Published on November 28, 2023
)
Germany is known worldwide for its cultural commitment to efficiency and attention to detail. For the most part, these ideas have served the nation well - it boasts the fourth-largest economy in the world; first in Europe.
But in some cases, efficiency and precision butt heads against one another. And business trips are one of those cases.
Employees in German companies have fixed per diem rates to cover travel expenses . These are set by the government, which in theory makes things more efficient. Companies don’t need to create their own policies - they just follow the rules.
But there’s a problem: the rules are fairly complex, and lots of businesses struggle to follow them.
Efficiency, meet precision.
In this article, we’re going to give you a clear overview of the law for business travel within Germany and abroad.
Please note: This article contains per diem rates and rules for 2024 (in place since 2021). You can find applicable flat rates for the most common destinations further down in this article.

What are per diem rates?
This will probably be clear to most readers, but it’s important that we set out just what we’re talking about. While travelling for work, certain costs are incurred by the employee and should be reimbursed by the company .
Some costs are expected to be covered your per diem, and therefore don’t need to be claimed separately. You’ll simply want to keep these costs below the daily per diem rate you’ve been allocated.
Other costs aren’t covered by your per diem, which means you should include them in an expense claim .
Covered by per diem
These will fall under the fixed rates below, and should not be claimed separately .
Meals purchased while travelling for work
The law (see below) only talks about meals. Some employees will choose to include other small costs (metro tickets or stationery for example), rather than seeking reimbursement for these minor items.
Not covered by per diem
These expenses should still be reimbursed by the company as part of a separate expense claim .
Transport to and from the airport or meetings
Accommodation if staying overnight
Meals and other costs incurred while meeting clients
Keep this distinction in mind when travelling. Now, let’s look at the specific rules for per diems.
The law around German per diem rates
The applicable law in this case is the statute on income tax - more precisely section 9, paragraph 4(a) (link in German). This covers meals for travelling workers, and essentially states the following:
If the employee works outside their home and first place of work (external occupational activity), a lump sum for meals is paid in compensation for the additional expenses.
[The actual rates paid are in the next section of this post.]
Since it would be time-consuming, complicated, and potentially unfair to have individual businesses set their own rates, the government does it for them. So as long as the rates are easy to understand and make sense, this is a good thing.
It also prevents the need for itemized expense claims - something employees generally hate . You don’t need to submit every receipt and take hours filling in expense reports. If you travel for X number of days, you receive Y in reimbursement.
The rates depend on travel duration and destination (see table below).
Note : You can’t claim these rates twice.
Two fee rates for all business trips
At the end of each year, the Federal Ministry of Finance publishes the applicable meal allowances for the following year. For the first time in many years, the flat rate allowances for business travel were updated in 2020.
Although the lump sums have changed for some countries, the basic principle remains the same. Since January 1, 2014, only two meal per diems apply, both within Germany and abroad. These are based on the travel duration:
Small meal allowance : for business trips lasting more than eight hours and less than 24 hours. This rate also applies to arrival and departure days of multi-day business trips.
Large meal allowance : For business trips that last longer than 24 hours. This rate is applied to every single day.
Important note : The expense calculation is based on full calendar days . In fact, to claim a full day, the traveller actually has to be away from home (or the office) from 0:00 to 24:00.
Anyone who went on a business trip before 2014 will find that a few things have changed with the reform of travel expenses. The most important change: business trips with a duration of less than eight hours can no longer be billed .
Current per diem rates in Germany
The rates for business travel in Germany changed slightly in 2020, for the first time in years.
Even with the 2014 reform, only the categories were changed, but not the amount of the lump sums. So this 2020 update is worth noting.
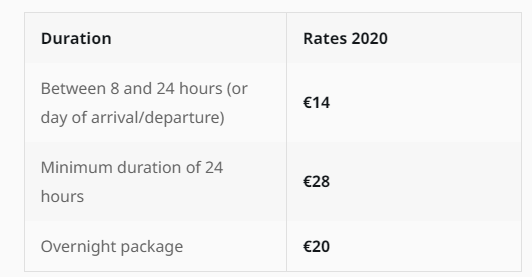
Today, these are the lump sum amounts for German per diems :
For business trips with a duration of less than 24 but more than eight hours, €14 can be noted in the travel expense report.
With a minimum duration of 24 hours, €28 euros can be claimed for each full day, and €14 euros for arrival and departure days (which will obviously be less than 24 hours).
The overnight flat rate is €20 - to be used for accommodation. In reality, accommodation will usually be covered fully by the employer , so travelling employees won’t claim this cost. But in cases where accommodation is not covered - for freelancers, for instance - this cost can usually be claimed through an individual’s income taxes.
Why is the overnight lump sum so low? One theory is that this should prevent fraudulent charges if business travellers choose to stay with friends or relatives.
You can find an example calculation in our free travel expense report template .
Exceptions to these rules
No good rules or regulations would be complete without exceptions. Thankfully, in this case they’re simple and quite brief.
First, the food allowance will only be paid in full if the business traveller actually pays for their own food . If the employer pays for meals on the trip, the rate will be reduced accordingly:
If breakfast is included (in the hotel fee, for example), 20 percent of the flat rate will be deducted for the day.
If lunch or dinner is provided by the employer, 40 percent of the fee will be removed.
For shorter business trips, it should be noted that meals provided by the employer are subject to income tax. Here are the so-called non-monetary benefits which must be taken into account in at tax time :
For breakfast, the value is currently €2.00.
For a lunch or dinner, €3.80 will be charged.
Foreign packages for business travel
As already mentioned, the categories for food allowances for business trips in Germany and abroad apply equally. But the rates of reimbursement may differ significantly depending on the country .
While an overnight stay in London, for example, costs €163, in Rome the value is only €150. For a day in Tokyo, the package is €50, but in Athens it's only €40.
The list also includes prices in different regions in the same country. For example, a stay in Miami is more expensive than in Los Angeles.
Unlike the lump sums for business travel within Germany, the rates for foreign destinations are frequently adjusted .
To help, we put together a list with the most frequented destinations and their respective meal allowances in this article. (at the bottom).
You can find the complete list here .
German per diems: clear as mud
Hopefully this article has helped to clear up some of the confusion around the German per diem system. In some ways it all seems unnecessarily complex, but once you have the basic concepts it should be fairly simple to repeat regularly.
The key parts to remember are the specific rates you can claim for each day, and that you can’t claim costs that have already been covered by your employer .
To help you manage your next business trip and keep on top of all spending (per diem or not), download our free Expense Report Template below.
More travel articles
VAT and expenses for UK businesses
10 excellent business travel management tools for 2023
The complete guide to corporate travel management
More reads on business travel spend.
)
The complete guide to company travel & expense management
)
UK per diem: how HMRC meal allowance rates work
Get started with spendesk.
Close the books 4x faster , collect over 95% of receipts on time , and get 100% visibility over company spending.
- Personal tools 🔒
- Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel
Central administration.

- Information
- Reimbursement amounts and scope
Daily allowance
Business travellers receive a daily allowance per calendar day as compensation for extra expenses for meals during the business trip. A daily allowance is not paid for trips at the place of work or residence. The amount of the daily allowance is based on the length of time away from home and on the focus of the business traveller's task.
The amount of daily allowance in Germany:
- Per full calendar day absent EUR 28
- For single-day trips and absent for over 8 hours EUR 14
- For trips lasting several days, for the days of departure and return , if the traveller has accommodation away from home, each EUR 14
If the business traveller receives the option of free board, 20% (5,60 EUR) for breakfast and 40% each for lunch and dinner (11,20 EUR) is deducted from the daily allowance. For full board, there will be no remaining daily allowance. This also applies if the boarding fees are included in the refundable travel expenses, overnight allowance or additional expenses (such as meals during a flight).
If the business trip lasts longer than 14 days in the same external business location, the daily allowance is reduced as from day 15 by 50%.
The amount of daily allowance abroad:
Please see the daily allowance 2024 for information on the amount of daily allowance abroad per calendar day in the event of 24 hr absence.
For single-day trips and absent for over 8 hours 80 % of the amounts stated in the list.
For trips lasting several days, for the days of departure and return , if the traveller has accommodation away from home, each 80% of the amounts stated in the list.
For regions or countries that are not included in the list mentioned above, the daily allowance abroad from Luxembourg is decisive. If lunches are had in a canteen (such as foreign university canteens), the daily allowance abroad amounts to 80% of the amounts stated in the list.
If the stay abroad lasts more than 14 days, not including the days travelling there and back, then 10% is deducted from the daily allowance abroad.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Search ITA Search

Germany Business Travel
Back to trade.gov/germany home
Business Travel
COVID-19 Travel Regulations Please review the latest updates published by the Federal Ministry of Interior and Community (BMI) before you travel.
U.S. citizens do not require a visa to enter Germany. Without a visa, however, they may not stay longer than three months every half-year or take up gainful employment requiring a work permit. If required, citizens may obtain a residence and/or work permit after entry.
For more information, visit the German Embassy website.
Welcome to Germany, the meeting, convention, and tourism destination for successful business representatives from around the world. What defines success in business also defines Germany: technology, innovation, flexibility, expertise, efficiency, organization, and mobility. Add the allure of Germany’s brilliant natural beauty, majestic castles and regal palaces, world-class culture and cities steeped in history, and you will come to see why no other destination for business travel even begins to compare. Visit the German National Tourist Board website and discover what attracts two-thirds of the world’s top international trade fairs to one place: Germany.
Getting around in Germany
Domestic flights are well developed. Frankfurt and Munich are hubs to Lufthansa, Germany’s national airline. Flying within Germany is quick, taking about 1 hour to get anywhere domestically.
International Airports in Germany (IATA-Code):
BER - Flughafen Berlin Brandenburg
DUS - Flughafen Düsseldorf (Rhein-Ruhr)
FRA - Flughafen Frankfurt am Main (Rhein-Main)
HAM - Flughafen Hamburg (Fuhlsbüttel)
HAJ - Flughafen Hannover (Langenhagen)
CGN - Flughafen Köln/Bonn (Konrad Adenauer)
MUC - Flughafen München (Franz-Josef-Strauß)
NUE - Flughafen Nürnberg
STR - Flughafen Stuttgart
National Airports in Germany (IATA-Code):
ZCC - Flugplatz Baden-Baden
BFE - Flugplatz Bielefeld
DTM - Flughafen Dortmund (Wickede)
DRS - Flughafen Dresden
FDH - Flughafen Friedrichshafen (Löwenthal)
HHN - Flughafen Hahn (Rheinland)
HOQ - Flughafen Hof
KEL - Flughafen Kiel
LHA - Flughafen Lahr (Schwarzwald)
LEJ - Flughafen Leipzig/Halle (Schkeuditz)
LBC - Flughafen Lübeck
MGL - Flughafen Mönchengladbach
FMO - Flughafen Münster/Osnabrück (Greven)
PAD - Flughafen Paderborn-Lippstadt
SCN - Flughafen Saarbrücken (Ensheim)
SGE - Flughafen Siegerland (Burbach)
The Deutsche Bahn AG offers a network that will get you almost anywhere in Germany. Rail travel is of no comparison to that in the United States. High-speed trains operate between major cities, making it an efficient alternative to flying, as rail stations are always located in the city center.
Germany’s highway - the Autobahn - is famous. They are in excellent condition and very well developed. However, to keep such quality, maintenance is necessary and construction sites are common.
From several seaports on the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, you may find your desired ferry connection .
There is a growing network of affordable long-distance bus routes in Germany. The following website identifies connections of various bus companies including booking (German only): http://www.busliniensuche.de
Additional Information
The German time zone is located within the Central European Time Zone.
To convert U.S. time to German time:
Eastern Standard (EST): +6 hours
Central Standard Time (CST): +7 hours
Mountain Standard Time (MST): +8 hours
Pacific Standard Time (PST): +9 hours
Alaska Standard Time (AST): +10 hours
Hawaii Standard Time (HST): +11 hours
Click here to receive more information about Germany’s currency and economy.
International Calls from the USA
To Germany: 011 + 49 + Area Code (disregard 0) + number
Example - German number 030 83051900: Dial 011 49 30 83051900 from the US.
To U.S.: 001 + Area Code + number
Mobile Phones
In Germany, cell phone coverage is almost 100% - you will always have service! However, frequencies throughout Europe differ from those used in North America. Your service provider can tell you if your phone is compatible with the German / European system and offer you alternatives if it is not. Network frequencies: EGSM 900 / GSM 1800 / GSM 1900
Computers & Internet
Bringing a laptop to Germany is simple: most run on both 110 volts, as in North America, or 230 volts, as found throughout Europe. Although the voltage is universal, you will still need an adapter to plug your computer into an electrical outlet.
While in Germany, the Internet is easily accessible. You can often log on at your hotel, either right from your room or in computer rooms, and at business centers, which offer internet access to guests. If neither is available, ask your hotel about an Internet café – chances are an excellent one is right around the corner!
Electric Current
Germany uses 230V. Therefore, a converter will be needed in order to use American 110V devices.
The climate is similar to that of the North Eastern U.S. More current weather information can be found here .
ATMs/ Banks: ATMs are as easily found in Germany as they are in North America. They are located at bank branches and in shopping, tourist and other busy areas. Major credit and debit cards, along with all other bank cards carrying the PLUS and NYCE symbols, are universally accepted. When located indoors, use your card to gain access if the door is locked.
Credit Cards: Credit cards are not commonly accepted in Germany, and they are not typically used for everyday expenses. Although, restaurants, hotels, stores, train stations, and other places regularly frequented by tourists will almost always accept them.
Tipping: The bill you receive at a hotel, restaurant, café, or bar often includes a service charge already. A tip is an indication of your satisfaction – 10% is average, whereas more than 10% indicates exceptional service. Tip taxi drivers about 10% and porters and others who assist you with baggage one euro per item.
Hours of Business
Stores in Germany generally open between 9 a.m. and 10 a.m, and most close between 6 p.m. and 10 p.m. Monday through Saturday. The regulations vary slightly between the federal states. On Sunday almost all stores are closed, the exceptions being gas stations and convenience stores, which carry some food items, snacks and beverages, newspapers, and journals as well as a basic supply of toiletry articles.
Banks and post offices are generally open from 8:30 a.m. to 1 p.m. and again from 2:30 p.m. to 4 p.m., Monday through Friday; some banks have extended hours on Thursday. Pharmacies open at 8 a.m.
Museums are generally closed on Mondays. Throughout the year, many cities have a “Long Night of the Museums,” where all the city’s museums are open throughout the night.
VAT Refunds & Tax-Free Shopping
Prices for goods and services in Germany always include a 19% value-added tax (VAT). Some or all of the VAT may be refundable for goods purchased at stores displaying the “Tax-Free for Tourists” sign. You will receive a tax-free form upon making a purchase. Before leaving the country and before checking any luggage, present the purchased goods, the tax-free form, and your receipt to German customs officials. They will certify the form as proof of legal export.
You may then obtain a cash refund at one of the Tax-Free Shopping Service counters located at all major border crossings, airports, ferry ports, and train stations.
Links to interesting pages:
- Webpage of the German Federal Government
- Information about Germany
- Get impressions of German travel destinations and German places

Travel allowances and non-monetary remuneration values 2023 for business trips
Additional subsistence expenses 2023.
As a general rule, employees traveling on business or official business are entitled to benefits to cover the cost of meals. Lump sums for additional meal expenses are commonly referred to as travel allowances. They are used to offset the cost of meals on business trips. Since the costs of meals incurred are generally higher than for meals at home, the flat rates are adjusted to the cost of living in the respective destination country.
As of 01.01.2023, the flat rates for travel expenses abroad will increase. The travel allowances for domestic travel do not increase. The same values apply here as in 2021 and 2022 .
The values for domestic travel :
- More than 8 hours: €14
- From 24 hours: €28
- Arrival and departure day: 14 € per day
The flat rates for all countries can be found in the letter from the Federal Ministry of Finance on the “ Tax treatment of travel expenses and travel expense reimbursements for business and work-related trips abroad from 1 January 2023 “.
Non-cash remuneration values 2023
The monthly value for meals will be increased to 288 euros as of Jan. 1, 2023. Thus, for meals provided at a reduced price or free of charge
- for a breakfast 2,00 Euro
- for lunch 3,80 Euro
- for dinner 3,80 Euro
per calendar day. The total value per day for catering is therefore 9.60 euros.
SPESENFUCHS
Legal notice
Privacy settings
Create travel expense report
Digitise receipts
All functions
Integrations


- Our Mission
- Opening a Bank Account
- Best Credit Card
- N26 Credit Card
- Health Insurance
- Liability Insurance
- Home Insurance
Per diem rates in Germany: All about business expenses
Especially consultants and sales people know the procedure all too well. As an employee in Germany working out of office, you are entitled to get a compensation for the extra costs. Usually, the costs of doing business include regular expenses as well so called per diems. In general, per diem rates in Germany are defined by the government and are a way to reimburse the employee for meals away from home. The German system of per diem rates with the Tagespauschale is rather unique compared to other countries. Therefore, this article will give you a quick overview of the daily allowances, covered costs and what to watch out for.
The difference between expenses and Per diem rates
Often, when working in client facing roles employees in Germany need to travel . An traveling incurs extra costs for the business. However, as these are business related expenses , a company will reimburse the employee for these costs. And since r eimbursements are based on days spent traveling for business, there is a certain daily (or latin per diem ) “allowance” for the employee. Interestingly here, the Ministry of Finance defines the amount of money included in the allowance every year . Also, the name Verpflegungsmehraufwand already implies the purpose of the allowance. To be precise, it covers living expenses (e.g. food and drinks) that are usually higher while traveling . Moreover, it is a fixed amount of money which employees receive regardless of what they have actually spent. Consequently, employees don’t need to collect receipts for meals and file an expense report for meals. Other expenses (such as public transit or taxi) are different and thus employees claim those expenses separately. In summary, a business trip of an employee causes two types of extra costs: general expenses and per diems . Per diem rates in Germany are regulated and the fixed sum covers meals. A dditional expenses are recorded based on the receipts collected during a business trip.
Which costs do Per diem rates cover?
Per diem rates are a simplification for calculating money an employee can spend on a business trip. On the one hand, per diems actually make things easier because the employee does not need to collect receipts . On the other hand, in rare cases unexpectedly high costs are not properly taken into account with these rigid rules . Generally, there are two types of costs an employer can cover:
- Meals : When traveling for business purposes, extra costs for food and drinks are meant to be covered by your per diem .
- Accommodation : A per diem rate for overnight stays is optional . There is a fixed rate of 20€ per night which can be reimbursed tax-free. This applies for example when you stay at a friend’s place on your business trip and there is no receipt. Ultimately, the employer can also choose to demand receipts and build their internal policy around this system.
Which costs are not covered by Per diem rates?
Naturally, there are other costs while traveling for business. This includes:
- transportation (by plane or train)
- transportation to and from airport/train station
- a ccommodation (see above)
- and meals with clients
Per diem rates explicitly do not cover these costs and employees claim them in a regular expense report.
Regulation around Per diem rates
Unsurprisingly, there is clear legislation around per diem rates in Germany. The regulation of income tax in Germany ( Sect. 9, § 4(a) ) defines the handling of meals and expenses for traveling employees. It says that employees on external occupational activities receive a lump sum to cover additional expenses.
In order to harmonize the system and increase fairness for employees, Germany decided that the government would set the per diem rates instead of individual firms and businesses. Effectively, employees of large and glamorous firms get the same daily allowance as employees of small and medium sized businesses . One could argue that this is excessive interference of the government, but as long as the system is logical and transparent , it might actually be a good thing.
For instance, it reduces the workload around itemized expense reports . Basically, you’ll spend less time about receipt and work that has nothing to do with your job. You’ll save valuable hours of painful filings for expenses. Instead, there’s a formula that tells you how much money you get from per diem rates in Germany based on the length of your trip.
How much are Per diem rates?
In general, the per diem rates in Germany only depend on destination and duration of your business trip. Let’s take Germany as an example:
Basically, there are only two types of per diem rates (it’s the same in other countries, just with different amounts of money). They are based on the length of your working days while traveling:
- Partial allowance : This per diem rate applies for business trips over 8h but under 24h . Moreover, the day of your arrival and the day of your departure will only allow a partial allowance.
- Full allowance : The full rate can only apply to full days of 24h . This means that every day between overnight stays on your multi-day trip, you receive the full allowance. Technically, this applies to days when you are away from the office from 0:00 to 24:00. Hence, an arrival at 1:00 am at night at the hotel will not qualify.
The internal policy of companies can actually set lower rates . However, your staff might feel treated poorly and it actually increases the amount of paperwork you need to do, so this is rather rare.
What do I need to consider as an employer or employee?
Per diems and their filing mean a little bit of administrative work . In return, they offer certain benefits though for employers and their employees . On the one hand, employees d o not need to keep every receipt for every coffee they bought on a two week trip. Your report at the end will be much simpler and you only need to keep track of departure date, arrival date and the respective times . And if you stay within the daily allowance or below, you can keep the difference . On the other hand, employers benefit a lot from per diem rates in Germany as well. Especially in travel-intensive industries like consulting or sales, it is much easier to predict travel expenses and cash-flow .
Per diem rates in Germany in 2020
Normally, per diem rates do not change very frequently in Germany. For 2020 they have been updated though, so here you can find the most recent rates:
This structure applies to business trips abroad as well . However, the per diem rates are different for each destination country .
Reimbursements and exceptions
No rule without exceptions. Similarly, per diem rates are not always as straightforward when it comes to reimbursement. For example, when talking about meals , it is important if you were offered a meal by e.g. a client or the hotel. The total allowance is split between breakfast , lunch , and dinner in a 20/40/40 ratio. Often, the hotel rate includes breakfast which is specified on the receipt due to the 19% VAT on food and 7% on lodging. If breakfast is included you need to deduct 20% off your daily allowance. If your client invites you to the on-site cafeteria for lunch or if it is included at a conference, you need to again deduct 40% . This leaves you with 40% of the per diem rate for dinner . If all your meals were provided at no extra cost for you, your per diem rates falls to zero. This makes sense as per diems should cover any extra expenses you have. In case this does not apply, you won’t need to be compensated.
Do you need assistance with Per diem rates in Germany?
This article is supposed to bring clarity to the field of per diem rates in Germany . Usually, your firm should have some kind of IT solution in place to assist you or follow the steps electronically. If you have further questions regarding expense management or best practices , feel free to reach out to our experts via the contact form . We are happy to help and get back to you within 24h.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Lisa Meier has more than ten years’ experience in providing strategic advice and legal guidance on international trade, administrative and legal matters to foreign companies, associations, and governments doing business in Germany. She advises companies in a broad range of industries on successfully navigating the German economic environment. Lisa brings a wealth of knowledge to Universal Hires’ marketing and client success team. In her free time, Lisa spends time exploring the unique city-life of Berlin and all the diversity that the East of Germany have to offer.
About Universal Hires
Universal Hires is Germany’s leading staffing provider. With expertise in recruitment and employer of record services, the company levarges its market entry support.
Related Links
- Employer of Record & PEO
- Talent Recruitment
- Executive Search & Headhunting
Write For Us
We are always looking for valuable contributions from industry experts. Interested?
Recommendations

Skilled Immigration Act in Germany: All you need to know

A Comparison of FinTech Markets in Germany and China

The Social Security Number in Germany – Explained

Active Sourcing in Germany – An Extensive Guide

The Impact of the Coronavirus on the Global Economy

The Importance of the Automobile to Germany
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Universal Hires Friedrichsstrasse 34 10117 Berlin, Germany
Staffing in Germany
© Universal Hires 2020
PRIVACY POLICY | TERMS OF USE | LEGAL NOTICE
Expenses per diem in Germany: this is how it works
Traveling on business as an employee in Germany? Then expenses per diem are the only way to tax-free reimburse you for your personal meals. What costs are covered as expenses per diem (or ‘Tagespauschale’ in German)? And what should you pay attention to? We give you a quick insight into these daily allowances within the German legislation.
The definition of expenses per diem.
While traveling for work as an employee in Germany , some costs you’ll make should be reimbursed by the company. However, these costs are expected to be covered per day, so the receipts don’t have to be claimed separately but are rather included in the “allowance”. This allowance, the so-called expense per diem is a specific amount of money, set by the German government, the employer gives an employee per day to cover living expenses when traveling for work. Per diems are the only way to reimburse you as an employee for personal meals tax-free while traveling on business.
What costs are covered by per diems?
The expenses per diems are a collection of a specific amount of money per day an employee is allowed to spend, without claiming all receipts separately.
- Personal meals: you may use per diems to cover for your additional meal costs when traveling on business.
- Overnight stays: Besides a daily rate that covers your meals, the option of a separate rate for overnight stays exists. Whilst using per diems for personal meals is the only tax-free reimbursement option, overnight stays on private locations can either be reimbursed on actual invoices or on per diems. Please check with your ultimate employer on their internal policy in this regard.
Other costs while traveling, like flights, transport to the airport, meals and other costs while meeting clients are not covered by per diem. These costs could be included in an expense claim.

The complexity of expenses per diems.
Per diems are quite complex, since the exact amount of the daily allowance can vary per country, city or region, all according to the individual estimated cost of living. These are updated annually and reflect the maximum amount to which you can be reimbursed tax-free. Please note that lower rates can be agreed upon, as per internal policy. Depending on the number of employees, this could result in a lot of administrative work for the employer.
Expenses per diem for employees and employers.
Apart from the administrative work, per diems have benefits for both employees and employers. Employees don’t have to keep documentation for every sandwich they buy while traveling. It eliminates a detailed expense report that needs receipts to document the amount spend on each day. They only have to stay within the limits of the amount per day. Expenses per diem are convenient for employers too since they have certainty and predictability in their travel expenses.
Current per diem rates 2020.
For the first time in five years, the rates for expenses per diem have changed. These are the lump sums for 2020 for traveling in Germany:
Working remote in Poland, thanks!

Thanks for helping me out in France!
You’re welcome, we’re Parakar

Per Diem - Additional Expenditures for Board During Domestic Travel
When traveling for business within Germany, you are entitled to a per diem to compensate for additional expenditures for meals (Section 6 German Travel Expenses Act - BRKG).
The reimbursed amount is based on Section 9 (4a) sentence 3 of the Income Tax Act (Einkommensteuergesetz). Pursuant to this act, effective 1 January 2014, you receive the following per diem for each day you are absent:
- 28 euros for each calendar day comprising 24 hours away from your home
- 14 euros for your days of departure and arrival, if you spend a night away from home prior to or following official travel
- 14 euros for each calendar day you are absent for more than 8 hours from your home or workplace at TU Berlin without an overnight stay
- 0 euros for travel lasting up to 8 hours
If your destination for official business is in the same city as your workplace or home, you are not entitled to a per diem.
Pursuant to Section 77 of the Berlin State Civil Service Act (Landesbeamtengesetz Berlin) and Section 23 (4) TV-L, you are also not entitled to a per diem if you travel to municipalities bordering Berlin or to Potsdam.
If you receive a free meal during official travel, your per diem for a full calendar day (28 euros) will be reduced by 20 percent for breakfast (5.60 euros) and 40 percent each for lunch and dinner (11.20 euros).
Reduction of per diem when receiving meals free of charge
The same applies if the costs for board are included in reimbursable travel, accommodation, or incidental expenses, such as longer flights or participation/conference fees.
In order to receive tax-free reimbursement from your employer, the cost of a standard meal may not exceed 60 euros as of 1 January 2014 . If the cost of a meal exceeds this amount, this can be reimbursed when submitting a travel expense report. However, you are required to pay tax on the full amount as part of your monthly income calculation. The Travel Expense Office arranges this for you together with Human Resources. If the costs for individual services are not clearly defined on a total invoice, the ratio of the individual partial services is to be assessed.
Your per diem is also reduced if you do not take meals provided free of charge without a valid reason.
Please refer to our page about international official travel for information about how your per diem is calculated when abroad. Similar rules apply with regards to meals provided free of charge.
Application
- Application for conducting travel by non-TU personnel (pdf, 115 KB)
- Application for official travel (pdf, 128 KB)
Reimbursement
- Attachement - Reimbursement for Travel Expenses (pdf, 159 KB)
- Attachment for Reimbursement Claim (pdf, 159 KB)
- Traveling expenses for interviews (docx, 39 KB)
- German Travel Expenses Act (BRKG)
- General BRKG Administrative Provisions
Contact & Location
Sandra Hoffmann
+49 30 314-22988
+49 30 314-24601
Torsten Radmann
Travel expenses in Germany
The Bezala travel expense app allows you to apply for local per diems and mileage allowances defined by the German Tax Office.
Bezala supports VAT rates, expenses claims, mileage allowances, and per diems in Germany.
The mileage allowances in Germany for the year 2024
When driving by own car or other motor vehicles (KFZ), the rate for tax-exempt Mileage allowance is 0.30 € / km. For motorcycles, scooters, and mopeds, the allowance is 0.20 € / km . Bezala makes claiming German mileage allowances easy.
Per diems in Germany for the year 2024
- Travel for less than 8 hours: No per diem
- Travel for 8-24 hours: Partial per diem (16 €)
- Travel for more than 24 hours, and it continues past midnight: Full per diem (32 €)
- Day of return: Partial per diem (16 €)
The accommodation allowance is 20 € per night if the employer does not provide the accommodation for the employee.
You can claim local and foreign Per Diems defined German Tax Administration with
Deductions from Per Diems
If the employer offers free meals to the employee during the travel, the meals should be deducted from the Per Diem paid to the employee.
Deductions:
- Breakfast: -20%
- Lunch: -40%
- Dinner: -40%
However, free meals are not to be deducted from the partial per diem.
Bezala – Europe's most automated expense software
Your team can easily file Receipts, Mileages and Per Diems and you can Approve them with one click. We'll remind your employees of missing credit card receipts and automatically take care of your accounting.
Integrations
Bezala has an integration to USA based ERP system NetSuite . In additional, you can create and modify csv files and we will send them directly to an SFTP server or e-mail. Check out our integrations . Sources: Akademie Herkert: Per diems and Mileages in Germany 2024
Foreign per diems 2024
Recent news
Bezala news 4/2024, bezala news 3/2024, bezala news 2/2024.
Germany Mileage
Compliance > Germany > Mileage
Get monthly compliance updates in your inbox
Please be aware that this resource is informational only, and many external factors, unique to your company might apply. Each company must make their own decisions about how they meet their tax obligations.
Approved mileage rates for business trips
Approved mileage rates for commute.
As an employer, you can pay an employee for using a personal vehicle for business trips. Business trips are trips to carry out business outside the place of work. You can pay your employee an approved amount of tax-exempt mileage allowance. The approved mileage allowance is 0,20 euro/km when using a motorbike, moped or scooter and 0,30 euro/km when using a car. The maximum amount per trip is 130 euros. You are allowed to pay an employee a higher amount but everything above the approved mileage allowance will be considered taxable income.
An employer can also pay an employee for their commute between the place of residence and the first place of work. You are allowed to pay an employee a higher amount but everything above the approved mileage allowance will be considered taxable income.
The approved amount of tax-exempt mileage allowance:
Additional notes on the approved mileage rates for commute:
- The increased amount of 0,38 euro per km as of the 21st kilometer is applicable from January 1st, 2022 until 2026;
- The commuter allowance is only applicable for days the employee commuted to the place of work;
- The maximum is 4500 euros per calendar year. A higher maximum of 4500 euros can be applied if the employee uses their car or a car that has been made available for him to use.
Last changed 2024-05-15
- NETHERLANDS
- SWITZERLAND
Expat Info Articles

How to claim travel expenses on your German tax return
The reason so many people choose to submit a tax return in Germany, even if they are not obliged to, is so that they can reduce their tax bill by taking advantage of deductions. One of the easiest deductions you can make is for your travel expenses to and from work. wundertax explains how it’s done.
Travel expenses for professional-related commutes can be claimed by taking advantage of the commuter allowance ( Entfernungspauschale ) on your German tax return and help increase your chances of a tax refund.
While some expenses are deducted as a set sum (e.g. per kilometre travelled), others can be deducted in full (e.g. the cost of tickets). Traditional employees can deduct these costs as income-related expenses ( Werbungskosten ) while freelancers / self-employed people can claim their travel expenses as business expenses ( Betriebsausgaben ). In this article we will be focusing on:
- Expenses for the commute from your residence to your primary workplace
- Travel costs for external activities and business trips
1. Deducting expenses for your work commute
You can claim a commuter allowance for commutes between your residence and primary workplace ( erste Tätigkeitsstätte ). This allowance amounts to 30 cents per kilometre for the first 20 kilometres of one-way travel to or from your workplace, regardless of means of transportation or actual incurred expenses.
That means this can be claimed whether you walk, ride a bike, drive a car, ride as a passenger, or take public transportation. The tax office will only accept deductions for the shortest possible route.
As of January 2021, the commuter allowance was increased to 35 cents from the 21st kilometre of one-way travel for long-distance commuters and from 2022 to 2026 it will be increased again to 38 cents from the 21st kilometre of one-way travel.
Is there a limit to the commuter allowance?
Generally, the tax office accepts 230 trips per year, but if you have a six-day work week you can claim up to 280 trips per year. Commuter expenses cannot be deducted for days spent home sick, on vacation, or working from home – days spent working from home can instead be claimed using the Home Office Lump Sum.
A maximum of 4.500 euros per year can be deducted with the commuter allowance. However, if you meet one of the following two exceptions, you should hang on to receipts as proof for the tax office:
- If you commute to work in your own personal or business vehicle you can claim more than 4.500 euros per year.
- If you commute to work by public transportation and the costs exceed 4.500 euros per year, you can enter and claim the actual expenses on your tax return.
Commuter costs for multiple workplaces
You can only have one primary workplace per employment role. If you work at several locations, this is considered external activity ( Auswärtstätigkeit ) and treated differently.
Rather than claiming a lump sum per kilometre, if you commute to external activities by public transport, you can have your actual expenses reimbursed (e.g. the cost of your tickets). If you travel by car, you can take advantage of the kilometre allowance ( Kilometerpauschale ). This applies to both the outward and return journey and amounts to 30 cents per kilometre.
If you have several different jobs in different locations, however, you can claim the commuter allowance for each primary workplace, so long as you travel home in between. When travelling from primary workplace to primary workplace, the distances can be added together, but then the commuter allowance can only be used for half of the total distance.
Mobility premium for long-distance commuters
As of 2021, long-distance commuters with a daily commute of 21 kilometres or more can apply for the new mobility premium ( Mobilitätsprämie ), which grants a bonus of 14 percent of the increased commuter allowance from the 21st kilometre of one-way travel.
To apply for this premium, your annual income cannot exceed the basic tax-free allowance ( Grundfreibetrag ), which amounts to 9.744 euros as of 2021. As of 2022, the basic tax-free allowance increased to 10.347 euros.
You can apply for the mobility premium in your tax return, and if you meet the requirements, it is transferred directly to your bank account. The assessment basis for the premium varies depending upon the difference between your annual taxable income and the basic tax-free allowance.
2. Costs for business trips
If you travel for work for any purpose including field services, further education, and trade fair visits, it’s recommended to claim the resulting expenses on your tax return (provided your employer didn’t already cover them). Your means of transport are irrelevant unless you’ve travelled in a company car, which is not tax-deductible.
Expenses for travel by public transport, ship, or aeroplane are all reimbursed in full so long as you travelled in the lowest class available. Train journeys in the next class up can be reimbursed if the travel time exceeds two hours.
If you travelled by car, you can either determine the actual incurred costs and claim them or use the kilometre allowance ( Kilometerpauschale ). Unlike the commuter allowance, the kilometre allowance can be applied to both the outward and return journeys.
Per kilometre travelled, the kilometre allowance amounts to:
- 30 cents for trips by car
- 20 cents for trips by motorcycle, scooter, moped, or e-bike
If your employer covered a portion of your business trip expenses, you have two options: You can either deduct the amount from the total expenses or you can write off the employer subsidies on your tax return.
If your business trip away from home and your primary workplace exceeds 8 hours, you can claim a flat rate of 14 euros for meals ( Verpflegungsmehraufwand ). If the trip exceeds 24 hours, you can claim a flat rate of 28 euros.
The rules surrounding commuter costs and other travel expenses can be complicated. wundertax helps you complete your tax return in as little as 17 minutes, while giving tips on deductible costs, so you can maximise your refund. Get started now .

Natascha Manthe
Natascha works as a Content Manager at wundertax. She loves to dive into tax topics and put them into easy-to-understand form. The other half of her heart belongs to acting:...
JOIN THE CONVERSATION (0)
Leave a comment
Service menu
- LOGIN Customs Portal
Subnavigation of Private individuals
- Private individuals
Staying in Germany
Postal consignments, internet order, customs portal, subnavigation of businesses.
- Businesses
Movement of goods
Movement of services and capital, aviation tax, subnavigation of service.
- Special online applications
- Forms and factsheets
- Regulations

Neither, under any circumstances, may the goods be imported for commercial purposes.
Restrictions on quantities and value
Tobacco products , if the importer is at least 17 years old :
- 200 cigarettes or
- 100 cigarillos or
- 50 cigars or
- 250 grammes tobacco (this also applies to heated tobacco products and water-pipe tobacco) or
- a proportionate combination of these goods.
Alcohol and beverages containing alcohol , if the importer is at least 17 years old:
- 1 litre of spirit drinks of an alcohol strength by volume exceeding 22 % or undenatured ethyl alcohol of an alcoholic strength by volume of 80 % or higher or
- 2 litres of alcohol and alcoholic beverages of an alcohol strength by volume up to 22 % or
- a proportionate combination of these goods and
- 4 litres of non-sparkling wine and
- 16 litres of beer
Medicinal products
- the quantity required for the traveller’s personal needs
Motor fuels
- for each motor vehicle the quantity in the vehicle’s main tank and up to 10 litres in a portable container
Other goods (including substitutes for tobacco products for persons aged 17 or older)
- up to a value of 300 euros
- up to a value of 430 euros for air/sea travellers
- up to a value of 175 euros for travellers under 15 years of age
Heated tobacco Heated tobacco as defined in section 1(2a) of the Tobacco Tax Act ( Tabaksteuergesetz-TabStG ) is smoking tobacco that is individually portioned (in "sticks") and designed to be consumed by inhalation of an aerosol or smoke produced in a "device".
Water-pipe tobacco Water-pipe tobacco pursuant to section 1(2b) ( Tabaksteuergesetz-TabStG ) is smoking tobacco intended to be smoked in a water-pipe and consisting of a mixture of tobacco and glycerine. It may also contain essential oils and extracts, molasses or sugar, and may also be flavoured with fruit. Products intended for use in a water pipe but not containing tobacco are also considered to be water-pipe tobacco.
Substitutes for tobacco products Substitutes for tobacco products are products which are suitable for the consumption of an aerosol or vapour produced by means of a device. This includes, for example, the liquids used in e-cigarettes. It does not include water-pipe tobacco or products assimilated to cigarettes or smoking tobacco. Products which are used exclusively for medical purposes and which are medicinal products within the meaning of the German Medicines Act are also excluded.
Tobacco Tax Act (in German)
There are other travellers’ allowances for alcohol, tobacco and products containing coffee and energy products when you enter Germany from an EU member state:
Alcohol, tobacco and products containing coffee Energy products
If the goods you are bringing with you exceed the travellers’ allowance, you must pay import duties.
If you enter Germany from another EU member state you must observe any specific national provisions of that member state.
Specific provisions for air and sea travel
Travellers are not considered to be air or maritime passengers if they enter this country as passengers on an inland waterway vessel or on board any private, non-commercial aircraft or vessel. An aircraft or vessel is deemed to be non-commercial if it is being used by its owner or lessee. Travellers entering Germany from Switzerland across Lake Constance are not considered to be maritime passengers. The exemption from duty in maritime travel depends on the waterway vessel having last called at a port outside the EU, or the port of a EU Member State’s region where Regulations 2006/112 EC and 2020/262 EU do not apply.
Specific provisions for value limits
- Please note that there are restrictions on quantities and value that apply to particular groups of persons such as the residents of municipalities near a border, or border commuters.
- The basis on which it is determined whether the value limits are being complied with or exceeded is the value of the goods including the foreign VAT .
- Several persons’ value limits may not be added together .
- If an item or product is non-divisible, such as a leather jacket or a piece of jewellery, and its value exceeds the travellers’ allowance , import duty must be paid on the total value of the product and not only on the portion of its value that exceeds the travellers’allowance.
A married couple enters Germany by car from Switzerland where they have bought four antique chairs and an old restored farmhouse cupboard. The duty-free limit per each traveller is 300 euros as they are entering by land, not by sea or air. Each chair costs 120 euros, and the cupboard 320 euros. Each of the travellers can import two chairs (240 euros) duty free within their allowance. The total value of the cupboard, at 320 euros, exceeds the value threshold, and import duty must be paid on its total value.
- Travellers can make use of the travellers’ allowance only once during any single journey. A journey comes to an end, when, for example, you have returned to your home in your own country or when you have arrived at your destination in Germany. You may not, therefore, repeatedly avail yourself of the travellers’ allowance by crossing the border several times in immediate succession.
A German holiday maker drives back to Germany from Switzerland. On returning to Germany he only brings in some souvenirs within the travellers’ allowance. He parks his car just over the border and walks back to Switzerland to the nearest hypermarket to buy more souvenirs. He then returns, entering Germany for a second time.
He must pay import duties for these purchases because he cannot avail himself of the travellers’ allowance for a second time on his return journey.
Contact and assistance
The Central Information Unit of the German customs administration ( Zentrale Auskunft Zoll ) is there to help you and will answer your questions by telephone, post, or e-mail.
Central Information Unit
Actions for this page:
Photo credits, hinweis zu de-mails.
Sie haben eine De-Mail-Adresse des Zolls angeklickt. Nachrichten per De-Mail können Sie nur an den Zoll versenden, wenn Sie selbst über ein De-Mail-Konto und eine De-Mail-Adresse verfügen.
Dafür müssen Sie sich bei einem Anbieter Ihrer Wahl registrieren (Infos unter: https://www.de-mail.info/).
De-mail:
Subnavigation of all website sections
Information.
- Customs offices
- Report accessibility issue
- User instructions

- Legal Notice
- Privacy statement
- Accessibility statement
© Central Customs Authority
Note on web analysis and the use of statistical cookies
In order to improve our website, we would like to analyse usage behaviour and compile access statistics. For this purpose, the web analysis software Matomo completely anonymously collects and evaluates statistical information. We will only store a statistical cookie on your device with your consent, and access device information required for this purpose. At no time will this data be linked to personal data or shared with third parties.
More information can be found in our data protection declaration. You can revoke your consent there at any time.
Data protection declaration
- How it works
- Try it out for free
- Expenses from Your Profession
Claim Travel Expenses on Your Tax Return
Travel expenses for professional-related commutes can be claimed as income-related expenses (Werbungskosten) on your tax return and help increase your chances of a tax refund. These expenses can include business trips, trips home in the case of double household management, or simply your daily commute to work – To learn more about deducting these on your tax return, keep reading this article!
Which travel expenses can be claimed?
Travel expenses incurred for professional reasons can be claimed on your tax return by entering the appropriate lump sums or flat rate and in some cases, these costs are fully deductible. These can be divided into 3 categories:
- Expenses for the commute from your residence to your primary workplace
- Travel costs from your secondary to primary residence in the case of double household management
- Travel costs for external activities & business trips
Traditional employees can deduct all of these costs as income-related expenses while freelancers/self-employed persons can claim their travel expenses as business expenses (Betriebsausgaben).
1. Your work commute
Primary profession: commuter allowance.
You can claim a commuter allowance (Entfernungs-/Pendlerpauschale) for the commutes between your residence and your primary profession . Primary profession refers to your main and permanent job. Freelancers can claim the commuter allowance for commutes to their first business location while students/trainees can claim it for commutes to their place of education.
The commuter allowance amounts to 30 cents per kilometer for the first 20 kilometers of one-way travel to or from your workplace, regardless of means of transportation or actual incurred expenses. That means this can be claimed whether you walk, ride a bike, drive a car, ride passenger, or take public transportation – just keep in mind that you can only claim one-way per working day. The tax office will only accept deductions for the shortest possible route (regardless of means of transport) and long detours would have to be justified, for example, if it’s more convenient and is a faster route (due to the shorter route having heavy traffic etc.).
Note: As of January 2021, the commuter allowance was increased to 35 cents from the 21st kilometer of one-way travel for long-distance commuters and from 2022 to 2026 it is increased again to 38 cents from the 21st kilometer of one-way travel.
Commuter allowance: Maximum limit
Generally, the tax office accepts a flat rate of 230 trips per year for a 5-day work week, and 280 trips for a 6-day work week. Commuter expenses can not be deducted for days spent home sick, on vacation, or working from home – days spent working from home can instead be claimed using the home office lump sum . A maximum of 4,500 euros per year can be deducted, unless you meet one of the following two exceptions :
- If you commute to work in your own personal or business vehicle and exceed 4,500 euros per year with the commuter allowance, the excess amount may be deducted.
- If you commute to work with public transportation and the costs exceed 4,500 euros per year, you can enter and claim the actual expenses on your tax return (not as a part of the commuter allowance).
If you meet either of these exceptions, hang on to your receipts as proof must be submitted upon the tax office’s request.
Commuter costs for multiple workplaces or professions
There can only be one primary workplace per profession, if you work at several locations they are considered external activity (Auswärtstätigkeit). Expenses for commuting to external activities can be reimbursed if you travel by public transport and the kilometer allowance (Kilometerpauschale) can be used if you travel by car. This applies to both the outward and return journey and amounts to 30 cents per kilometer.
If you have several professions , the commuter allowance can only be used for your primary profession if you travel between there and home on the same day. If you travel from workplace to workplace, the distances can be added, but then the commuter allowance can only be used for half of the total distance .
Mobility premium for long-distance commuters
As of 2021, long-distance commuters with a daily commute of 21 kilometers or more can apply for the new mobility premium (Mobilitätsprämie). In order to apply, your taxable income must not exceed the basic tax-free allowance (Grundfreibetrag) of 9,744 euros (as of 2021). The bonus is based on the 2021 commuter allowance increase and will remain valid until 2026. If eligible, you can apply for this premium directly on your tax return and receive it directly to your bank account. The premium grants a bonus of 14% to the already increased commuter allowance from the 21st kilometer of one-way travel to work and the assessment basis for the premium varies upon the difference between your annual taxable income and the basic tax-free allowance.
2. Commutes to your main residence with two households
Many employees manage two households for professional purposes and shorter commutes to the office, leading to common trips between their primary and secondary residences. One trip per week (or a total of 46 per calendar year) back to your primary residence can be deducted using the commuter allowance regardless of means of transportation. The same rules apply: either the outward or return journey can be deducted. The allowance can be deducted even if no costs were incurred from the trip, such as if you were given a ride.
In order to be eligible to deduct costs for double household management , your “life core” must take place at your primary residence, where you regularly stay and contribute at least 10% of the costs. It is not a prerequisite to have a spouse, partner, or child(ren) living at your primary residence.
The commuter allowance increase to 35 cents (2021) / 38 cents (2022) from the 21st kilometer also applies to trips home to your primary residence to see your family. Note: The maximum of 4,500 euros per year doesn’t apply to family trips home.
If you travel with public transportation and the costs exceed the benefits from the commuter allowance, you can instead deduct those costs individually on your tax return. If you fly home, you can only claim the price of the plane ticket.
Note: Weekly trips to your primary residence cannot be deducted if made with a company car. No tax must be paid on the first trip home with a company car as a non-cash benefit (geldwerter Vorteil), but it must be taxed from the second trip onwards.
3. Costs for business trips
Employers often pay for business trip expenses out of their own pocket – whether it be field service, further education, or visits to a trade fair. If the costs aren’t covered by your employer, it’s definitely worthwhile to claim them on your tax return. Means of transport are irrelevant unless you’ve traveled in a company car , which is not tax-deductible.
Expenses for travel by public transport, ship, or airplane are all reimbursed based on the lowest class available. Train journeys exceeding two hours in the next higher class can be reimbursed.
If you traveled by car, you can either determine the actual incurred costs and claim them or use the kilometer allowance (Kilometerpauschale). Unlike the commuter allowance, the kilometer allowance can be applied to both the outward and return journey .
Per kilometer traveled, the kilometer allowance amounts to:
- 30 cents for trips by car
- 20 cents for trips by motorcycle, scooter, moped, or e-bike
Tip: If your business trip away from home and your workplace exceeds 8 hours, you can claim a flat rate of 14 euros for room and board as well as meals (Verpflegungsmehraufwand). If the trip exceeds 24 hours, you can claim a flat rate of 28 euros.
Please note: The portion of travel expenses covered by your employer can no longer be included in your tax return. You can alternatively declare the costs in full if you also claim the employer subsidies for your travel costs.
Is it worth it for you to file a tax return?
Related articles.
- Tax Forms for your 2021 Tax Return
- What exactly is double household maintenance?
- How to Deduct Bahncard from Tax with Travel Expenses
Travel expenses as a self-employed person: How to use the mileage allowance in your tax return
As a self-employed person or freelancer, you don’t always work from home. Maybe you have your office in a coworking space, regularly drive to client meetings or even earn your money with a self-employed activity that requires you to drive back and forth, such as Amazon Flex delivery. As a self-employed person, you can claim these travel expenses on your tax return. This article explains the tax regulations and how you can claim the mileage allowance.
Basics in tax law: advertising costs and business expenses
In tax law, a distinction is made between income-related expenses and business expenses. Both employees and self-employed persons can deduct travel to the workplace as income-related expenses. This is often referred to as the commuter allowance. This refers to the regular journey to and from the workplace.
Self-employed persons can deduct all other travel expenses as business expenses. These can be trips to your customers, your business trips, or all travel costs of employed staff. As a self-employed person, you can deduct all travel expenses that are higher than the flat rates in the area of income-related expenses as business expenses.
💡Tip from Accountable: If you’re unsure whether you can deduct something, our free advertising expense calculator will be happy to help. Just enter your business expense and get an answer in seconds.
Private or company car?
However, you must take into account whether the vehicle used is your private one or whether it is part of the business assets. The decision on this depends on the respective use. If the business use is less than 10%, then the vehicle is allocated to your private assets. From 10% to 50% business use, you alone can decide whether you want to include the vehicle in your business assets or in your private assets. If the business use is over 50%, then the vehicle belongs to the business assets and can be used as a company car and accounted for accordingly for tax purposes. In this case, you can claim the travel costs, but also other things such as insurance.
If the vehicle remains part of your private assets, you can deduct the travel costs as income-related expenses (commuter allowance). If you decide to include the vehicle in your business assets, the travel costs will be charged as operating costs.
How do I deduct travel expenses? Mileage allowance vs. business expenses
Mileage allowance.
The simplest way to settle your travel expenses is with the commuting allowance. This can be claimed for expenses for the journey between home and the first place of business as well as family trips home, regardless of what means of transport you use. The mileage allowance, therefore, applies both if you travel by car and if you take a bicycle or use public transport. However, this flat rate cannot be claimed for air travel.
The flat rate is calculated as follows: each kilometer between your home and your first place of business is charged at €0.30. As of this year, you can also claim € 0.35 per kilometer for tax purposes from the 21st kilometer onwards. The actual working days in the respective calendar year are decisive for the calculation because you can only claim this flat rate once per working day. In total, you can claim up to € 4,500 for tax purposes in this way.
Business Expenses
If your travel costs exceed the maximum amount for the commuting allowance of €4,500, you can claim your travel costs as business expenses – even if the vehicle used is a private vehicle. In this case, however, you must provide evidence of the costs incurred. In addition to the expenses for fuel, this also includes the costs for vehicle tax, insurance, maintenance, and depreciation. The total costs are divided by the number of kilometers actually driven and an individual amount per kilometer is then calculated. This may well be higher than €0.30 per kilometer and you can claim an amount higher than €4,500 against tax.
If your vehicle is part of your business assets, then all your costs are counted as business expenses. In this case, you have to separate your private trips from business trips.
There are two ways to do this:
You can apply the so-called 1% rule . Under this rule, you are charged 1% of the official list price of the vehicle for its use each month as imputed income. For electric vehicles, only 0.5% of the list price is applied. With this regulation, all private journeys (e.g. also the vacation journey with the car) are covered and no further costs are incurred. However, this regulation can only be used if the share of business trips is over 50%.
As an alternative to the 1% rule, you can also account for the actual kilometers. For this, it is necessary that you keep a logbook . Every kilometer driven must be documented in detail with time and date.
💡Tip from Accountable: You can find more about the logbook here .
How do I deduct travel expenses with ELSTER?
Regardless of whether you decide in favour of the mileage allowance or claiming it as a business expense: You have to include it all in your tax return. If you submit your tax return via the ELSTER portal, there is space for the relevant details in the EÜR annex. You can enter motor vehicle costs and other traveling expenses in lines 81 to 86. The commuting allowance belongs in line 86. If your expenses exceed the commuting allowance, lines 85 and 86 are left blank.
How do I deduct travel expenses with Accountable?
Instead of ELSTER, you can also use software like Accountable . It is much easier for you since you only have to enter your expenses and Accountable will help you save it correctly and comply with the Finanzamt rules.
To do this, add a new expense. Under the category “Travel expenses” > “For the self-employed”, you can enter, for example, costs for bus and train, traveling to the office, but also flat-rate contributions, and mileage reimbursement. When using your vehicle, you can also record costs for insurance or leasing under “Vehicle”.
💡Tip from Accountable: If you want your complete bookkeeping and all tax returns in one solution, try the Accountable app . You keep full control over your taxes and finances and also get personal support from our tax coaches if you need help with German taxes.
Conclusion: Claiming travel expenses for tax purposes is worthwhile
It is definitely worth claiming travel expenses for tax purposes, as you can significantly reduce your tax burden. Whether you decide in favour of the flat rate or billing the actual costs depends on a number of individual conditions and the planned use. As a general rule, the use of lump sums significantly simplifies billing, but lump sums do not always cover all the costs incurred.
Flat rates can also lead to significantly more being paid than if the actual costs were recorded, for example, if private use is not desired because a second vehicle is available. With Accountable , however, you can manage your travel expenses easily and centrally in one place and always have access to your data from anywhere. Test it now for free!
All your taxes. Done.

Did you find what you were looking for?

Happy to hear!
Thank you for your feedback. 💜
Stay in the know! Leave your email to get notified about updates and our latest tips for freelancers like you.
We’re sorry to hear that.
Can you specify why this article wasn’t helpful for you?
Thank you for your response. 💜
We value your feedback and will use it to optimise our content.
What other freelancers are reading

Income tax for freelancers – how much tax do I have to pay in Germany?
Working as a self-employed professional has many advantages: You are your own boss and you...
Want to start a side hustle in addition to your full time job? Here’s what you need to know.
When it comes to freelancing in Germany, it doesn’t have to be all or nothing....
Registering as self-employed in Germany: Freelancer or tradesperson (Freiberufler vs Gewerbetreibender)?
In Germany, becoming self-employed isn’t only about having a great idea for your new venture....

A word about the author
This article is presented to you by the Accountable Team, a diverse group of accountants and seasoned freelancers active in Belgium. Thanks to the real-life experience and expertise in topics such as self-employment, taxes, bookkeeping, VAT, and many more, the Accountable Team is able to share insights and practical advice to empower others on their freelance journey. We are dedicated to helping the self-employed thrive in today’s dynamic work environment and fostering a community of independent professionals.

Try Accountable for free
Taxes can be this easy!
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access Only $1 for 4 weeks
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition
- Newsletters
Latest Live Coverage

Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico 'fighting for his life' in surgery

Live Broadcast
Watch Euronews live stream
Germany limits cash benefit payments for asylum-seekers as migration numbers increase

The new rule issues migrants a benefit card for local use, limiting cash withdrawals and banning international transfers.
A payment card exclusively for asylum-seekers has been introduced in Germany, following the recent parliamentary approval of a new rule.
Under the new regulation, migrants are issued a card to access their benefits, which can be used at local stores and for services, but it limits their cash withdrawals and bans international money transfers.
The aim is to prevent migrants from sending money to family and friends abroad, or to smugglers.
In Eichsfeld, Thuringia, 45-year-old Laca from Albania and her family were among the first in Germany to receive half of their government benefits as cashless payments on a plastic card.
“With half the money that is on the card, I can buy groceries, and with the other half (in cash) I can buy in every shop whatever I need for me and my children," Laca said.
Germany remains more reliant on cash payments than many other European countries, with some businesses still not accepting card payments.
Jihad Ammuri, a 20-year-old asylum-seeker from Syria, said that not all stores accept his payment card.
I tried to make a purchase in a shop, but they told me that they do not partner with this card. You can't buy with it from here. And it's also not working in all of Germany.
Migrant advocacy groups have criticised the new regulation as discriminatory and claim that it will possibly ostracise them further.
"It must be stated clearly that people are coming due to civil war and persecution; a payment card won't deter them," Wiebke Judith from Pro Asyl said.
Judith added, “The aim here is to create an instrument of discrimination and to bully refugees”.
Germany has been trying to clamp down on migration for months.
This latest measure comes just weeks before the European elections on 9 June.
Tougher migrant approach
Germany's far-right Alternative for Germany party (AfD) has effectively exploited the hardening attitudes of Germans towards migrants.
The AfD, known for its anti-migration stance, is expected to significantly increase its share of the vote from the 10.3% it secured in the 2021 federal election.
Attitudes toward migration have hardened in Germany as large numbers of asylum-seekers have arrived, in addition to refugees from Ukraine, and local authorities have struggled to find accommodation.
The number of people applying for asylum in Germany last year rose to more than 350,000 - an increase of just over 50% compared with the year before. The largest number of asylum-seekers came from Syria, followed by Turks and Afghans.
In January, lawmakers approved legislation intended to ease deportation of unsuccessful asylum-seekers.
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz has repeatedly said that authorities need to speed up deportations.
Germany, like several other European countries, has also started classifying some countries, such as Moldova and Georgia, as "safe countries of origin” - meaning asylum-seekers from there can be quickly rejected and deported faster than in the past.
You might also like
Majority of germany's 'open door' refugees have entered the labour force, new german legislation aims to make it easier to deport asylum seekers, germany tightens border controls as far-right afd party surges in the polls.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When employees are traveling on business within Germany the costs of subsistence (drinks and meals) is typically reimbursed according to the applicable per diem rates which currently are: - between 8-24 hours, 14 EUR. - for a full 24 hours day, 28 EUR. For the first and last day of travel, the applicable per diem rate is always 14 EUR.
The allowance is a salary supplement and is paid out with the monthly salary. Travel allowances are taxed at a flat rate of 15% wage tax. What to look out for. The allowance can only be paid to employees who regularly commute to work and in many cases, there is an annual cap of 4,500 euros (the same cap as for income-related expenses). In ...
The most important change: business trips with a duration of less than eight hours can no longer be billed. Current per diem rates in Germany. The rates for business travel in Germany changed slightly in 2020, for the first time in years. Even with the 2014 reform, only the categories were changed, but not the amount of the lump sums.
From 01.01.2024, various lump sums for travel expenses abroad will also increase. The flat rates for all countries can be found in the letter from the Federal Ministry of Finance on the "Tax treatment of travel expenses and travel expense allowances for business and work-related trips abroad from January 1, 2024″.
A daily allowance is not paid for trips at the place of work or residence. The amount of the daily allowance is based on the length of time away from home and on the focus of the business traveller's task. The amount of daily allowance in Germany: Per full calendar day absent EUR 28. For single-day trips and absent for over 8 hours EUR 14.
Example: Erika starts her business trip at 5 pm on Oct. 1st and ends at 1.30 am on Oct. 2nd. The duration of the business trip in total is 8,5 hours, which means a daily allowance of 14 euros applies. Employers can only offer tax-free reimbursement to employees for three months of continuous business travel.
Germany's Federal Ministry of Finance (BMF) has announced it will not change the per diem and overnight accommodation allowances for business trips abroad for 2022 as a result of the ongoing pandemic. The BMF issues an annual of allowable amounts that can be claimed back by employees to cover things such as meals while abroad. The rates that ...
Travel. Welcome to Germany, the meeting, convention, and tourism destination for successful business representatives from around the world. What defines success in business also defines Germany: technology, innovation, flexibility, expertise, efficiency, organization, and mobility. Add the allure of Germany's brilliant natural beauty ...
Tax treatment of travel expenses and travel expense reimbursements for business and work-related trips abroad as of 1 January 2022. The Federal Ministry of Finance has published information on the rates for additional subsistence expenses and accommodation costs for 2022. Due to the pandemic, foreign per diem and foreign overnight allowances ...
More than 8 hours: €14. From 24 hours: €28. Arrival and departure day: 14 € per day. The flat rates for all countries can be found in the letter from the Federal Ministry of Finance on the " Tax treatment of travel expenses and travel expense reimbursements for business and work-related trips abroad from 1 January 2023 ".
Often, when working in client facing roles employees in Germany need to travel.An traveling incurs extra costs for the business. However, as these are business related expenses, a company will reimburse the employee for these costs. And since reimbursements are based on days spent traveling for business, there is a certain daily (or latin per diem) "allowance" for the employee.
This allowance, the so-called expense per diem is a specific amount of money, set by the German government, the employer gives an employee per day to cover living expenses when traveling for work. Per diems are the only way to reimburse you as an employee for personal meals tax-free while traveling on business.
When traveling for business within Germany, you are entitled to a per diem to compensate for additional expenditures for meals (Section 6 German Travel Expenses Act - BRKG). ... Reduction of meal allowance for: Reimbursement in euros: Full board: € 0.00: Breakfast: € 22.40: Lunch: € 16.80: Dinner: € 16.80: Breakfast + Lunch: € 11.20 ...
For motorcycles, scooters, and mopeds, the allowance is 0.20 € / km. Bezala makes claiming German mileage allowances easy. Per diems in Germany for the year 2024. Travel for less than 8 hours: No per diem; Travel for 8-24 hours: Partial per diem (16 €) Travel for more than 24 hours, and it continues past midnight: Full per diem (32 €)
For domestic business trips, employees can receive the following Per Diems in Germany: Multi-day trips: €28 for every 24 hours that they're away from their home and primary workplace. €14 for the day of departure and arrival, if the employee doesn't spend the night at their own home. Single-day trips: €14 for the calendar day if the ...
You can pay your employee an approved amount of tax-exempt mileage allowance. The approved mileage allowance is 0,20 euro/km when using a motorbike, moped or scooter and 0,30 euro/km when using a car. The maximum amount per trip is 130 euros. You are allowed to pay an employee a higher amount but everything above the approved mileage allowance ...
Travel costs for external activities and business trips. 1. Deducting expenses for your work commute. You can claim a commuter allowance for commutes between your residence and primary workplace ( erste Tätigkeitsstätte ). This allowance amounts to 30 cents per kilometre for the first 20 kilometres of one-way travel to or from your workplace ...
The duty-free limit per each traveller is 300 euros as they are entering by land, not by sea or air. Each chair costs 120 euros, and the cupboard 320 euros. Each of the travellers can import two chairs (240 euros) duty free within their allowance. The total value of the cupboard, at 320 euros, exceeds the value threshold, and import duty must ...
Appendix 3 2023 2 Foreign Country Per Diem Allowance and Accommodation Costs (with proof), according to German Foreign Travel Expenses Ordinance / Auslandsreisekostenverordnung (ARV), valid as of 01.01.2023 Source: General administration regulation concerning the most recent determination of foreign country per diem allowance and accommodation costs dated 13.10.2022 (inofficial translation)
Commuter allowance: Maximum limit. Generally, the tax office accepts a flat rate of 230 trips per year for a 5-day work week, and 280 trips for a 6-day work week. Commuter expenses can not be deducted for days spent home sick, on vacation, or working from home - days spent working from home can instead be claimed using the home office lump sum.A maximum of 4,500 euros per year can be ...
Business Expenses. If your travel costs exceed the maximum amount for the commuting allowance of €4,500, you can claim your travel costs as business expenses - even if the vehicle used is a private vehicle. In this case, however, you must provide evidence of the costs incurred.
bundle is a set of rates. The simplest initial configuration of the travel allowance feature uses the statutory rate bundle provided by SAP Concur to create a configuration code. A Rate Bundle consists of rate types, calculation rules, trip types, meal types, lodging types, rates, deductions, and adjustments.
With a fixed daily type of travel allowance, the employee is reimbursed the fixed rate regardless of the actual amount of expenses. For example, assume that the fixed rate for meals (including incidentals) is 55.00 EUR per day. If the employee spends less than 55.00 EUR per day, the employee keeps the difference.
Germany is looking at tax breaks and welfare reforms to encourage people to work more, joining the UK and the Netherlands on a quest to tackle the region's economic malaise by reversing a big ...
Germany limits cash benefit payments for asylum-seekers as migration numbers increase Erdina Laca, a 45-year-old asylum seeker, shows her special payment card in front of a grocery store, in ...