Jira Software
Project and issue tracking
Content collaboration

Jira Service Management
High-velocity ITSM
Visual project management
- View all products
Marketplace
Connect thousands of apps and integrations for all your Atlassian products
Developer Experience Platform
Jira Product Discovery
Prioritization and roadmapping
You might find helpful
Cloud Product Roadmap
Atlassian Migration Program
Work Management
Manage projects and align goals across all teams to achieve deliverables
IT Service Management
Enable dev, IT ops, and business teams to deliver great service at high velocity
Agile & DevOps
Run a world-class agile software organization from discovery to delivery and operations
BY TEAM SIZE
Small Business
BY TEAM FUNCTION
Software Development
BY INDUSTRY
Telecommunications
Professional Services
What's new
Atlassian together.
Get Atlassian work management products in one convenient package for enterprise teams.
Atlassian Trust & Security
Customer Case Studies
Atlassian University
Atlassian Playbook
Product Documentation
Developer Resources
Atlassian Community
Atlassian Support
Enterprise Services
Partner Support
Purchasing & Licensing
Work Life Blog
Support for Server products ends February 15, 2024
With end of support for our Server products fast approaching, create a winning plan for your Cloud migration with the Atlassian Migration Program.
Assess my options

Atlassian Presents: Unleash
Product updates, hands-on training, and technical demos – catch all that and more at our biggest agile & DevOps event.
- Atlassian.com
Customer Journey Mapping
Journey mapping helps you visualize how customers experience your product or service, and how they feel along the way. Scroll to step 6 for a real-life example from one of our product teams!
USE THIS PLAY TO...
Understand the customer journey from a specific persona's perspective so that you can design a better experience.

Running the play
Depending on how many touchpoints along the customer journey you're mapping, you might break the journey into stages and tackle each stage in pairs.
Sticky notes
Whiteboards.io Template
Define the map's scope (15 min)
Ideally, customer journey mapping focuses on the experience of a single persona in a single scenario with a single goal. Else, the journey map will be too generic, and you'll miss out on opportunities for new insights and questions. You may need to pause creating a customer journey map until you have defined your customer personas . Your personas should be informed by customer interviews , as well as data wherever possible.
Saying that, don't let perfect be the enemy of good! Sometimes a team just needs to get started, and you can agree to revisit with more rigor in a few months' time. Once scope is agreed on, check your invite list to make sure you've got people who know the details of what customers experience when using your product or service.
Set the stage (5 min)
It's really important that your group understands the user persona and the goal driving their journey. Decide on or recap with your group the target persona and the scope of the journey being explored in your session. Make sure to pre-share required reading with the team at least a week ahead of your session to make sure everyone understands the persona, scope of the journey, and has a chance to delve deeper into research and data where needed. Even better- invite the team to run or attend the customer interviews to hear from customers first hand!
E.g. "We're going to focus on the Alana persona. Alana's role is project manager, and her goal is to find a scalable way for her team to share their knowledge so they spend less time explaining things over email. We're going to map out what it's like for Alana to evaluate Confluence for this purpose, from the point where she clicks that TRY button, to the point where she decides to buy it – or not."
Build a customer back-story (10 min)
Have the group use sticky notes to post up reasons why your target persona would be on this journey in the first place. Odds are, you'll get a range of responses: everything from high-level goals, to pain points, to requested features or services. Group similar ideas and groom the stickies so you can design a story from them.
These narratives should be inspired by actual customer interviews. But each team member will also bring a different perspective to the table that helps to broaden the lens.
Take a look at the example provided in the call out of this section. This back story starts with the pain points – the reasons why Alana would be wanting something like Confluence in the first place.
- E.g., "Her team's knowledge is in silos"
Then it basically has a list of requirements – what Alana is looking for in a product to solve the bottom pain points. This is essentially a mental shopping list for the group to refer to when mapping out the customer journey.
- E.g., "Provide structure"
Then it has the outcomes – goals that Alana wants to achieve by using the product
- E.g., "To keep my team focused on their work instead of distracted by unnecessary emails and shoulder-taps"
And finally the highest-level goal for her and her team.
- E.g., "Improve team efficiency"
Round off the back story by getting someone to say out loud what they think the overall story so far is, highlighting the main goals the customer has. This ensures a shared understanding that will inform the journey mapping, and improve the chances that your team will map it from the persona's point of view (not their own).
- E.g., "Alana and her team are frustrated by having to spend so much time explaining their work to each other, and to stakeholders. They want a way to share their knowledge, and organize it so it's easy for people outside their team to find, so they can focus more energy on the tasks at hand."

For example...
Here's a backstory the Confluence team created.
Map what the customer thinks and feels (30-60 min)
With the target persona, back story, and destination in place, it's time to walk a mile in their shoes. Show participants how to get going by writing the first thing that the persona does on a sticky note. The whole group can then grab stickies and markers and continue plotting the journey one action at a time.
This can also include questions and decisions! If the journey branches based on the answers or choices, have one participant map out each path. Keep in mind that the purpose of this Play is to build empathy for, and a shared understanding of the customer for the team. In order to do this, we focus on mapping the current state of one discrete end to end journey, and looking for opportunities for improvement.
To do a more comprehensive discovery and inform strategy, you will need to go deeper on researching and designing these journey maps, which will need to split up over multiple sessions. Take a look at the variation below for tipes on how to design a completely new customer journey.
Use different color sticky notes for actions, questions, decisions, etc. so it's easier to see each element when you look at the whole map.
For each action on the customer journey, capture which channels are used for the interactions. Depending on your context, channels might include a website, phone, email, postal mail, face-to-face, and/or social media.
It might also help to visually split the mapping area in zones, such as "frontstage" (what the customer experiences) versus "backstage" (what systems and processes are active in the background).
Journey mapping can open up rich discussion, but try to avoid delving into the wrong sort of detail. The idea is to explore the journey and mine it for opportunities to improve the experience instead of coming up with solutions on the spot. It's important not only to keep the conversation on track, but also to create an artefact that can be easily referenced in the future. Use expands or footnotes in the Confluence template to capture any additional context while keeping the overview stable.
Try to be the commentator, not the critic. And remember: you're there to call out what’s going on for the persona, not explain what’s going on with internal systems and processes.
To get more granular on the 'backstage' processes required to provide the 'frontstage' customer value, consider using Confluence Whiteboard's Service Blueprint template as a next step to follow up on this Play.

ANTI-PATTERN
Your map has heaps of branches and loops.
Your scope is probably too high-level. Map a specific journey that focuses on a specific task, rather than mapping how a customer might explore for the first time.
Map the pain points (10-30 min)
"Ok, show me where it hurts." Go back over the map and jot down pain points on sticky notes. Place them underneath the corresponding touchpoints on the journey. Where is there frustration? Errors? Bottlenecks? Things not working as expected?
For added value, talk about the impact of each pain point. Is it trivial, or is it likely to necessitate some kind of hack or work-around. Even worse: does it cause the persona to abandon their journey entirely?
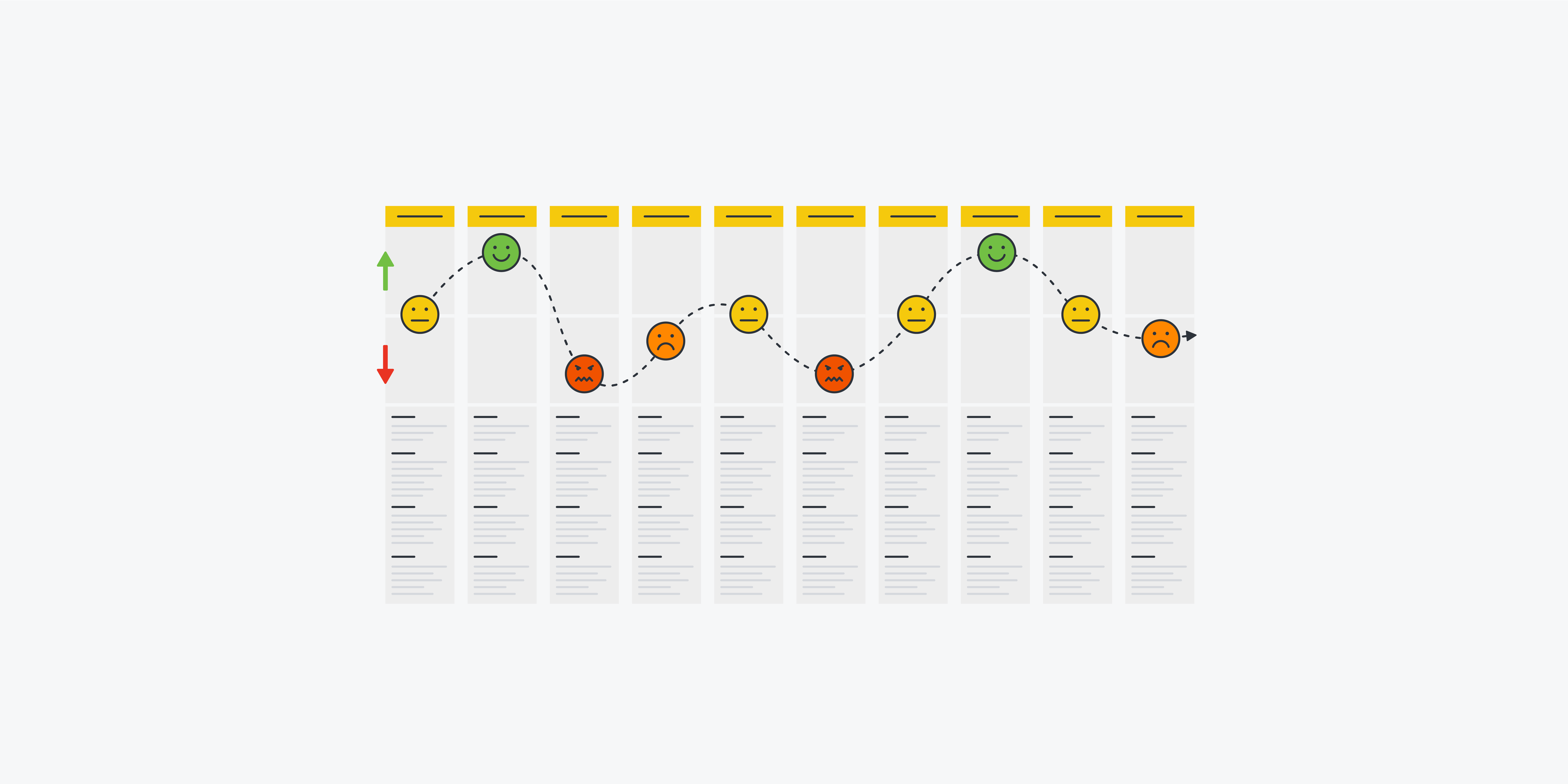
Chart a sentiment line (15 min)
(Optional, but totally worth it.) Plot the persona's sentiment in an area under your journey map, so that you can see how their emotional experience changes with each touchpoint. Look for things like:
- Areas of sawtooth sentiment – going up and down a lot is pretty common, but that doesn't mean it's not exhausting for the persona.
- Rapid drops – this indicates large gaps in expectations, and frustration.
- Troughs – these indicate opportunities for lifting overall sentiments.
- Positive peaks – can you design an experience that lifts them even higher? Can you delight the persona and inspire them to recommend you?
Remember that pain points don't always cause immediate drops in customer sentiment. Sometimes some friction may even buold trust (consider requiring verification for example). A pain point early in the journey might also result in negative feelings later on, as experiences accumulate.
Having customers in the session to help validate and challenge the journey map means you'll be more confident what comes out of this session.
Analyse the big picture (15 min)
As a group, stand back from the journey map and discuss trends and patterns in the experience.
- Where are the areas of greatest confusion/frustration?
- Where is the journey falling short of expectations?
- Are there any new un-met needs that have come up for the user type?
- Are there areas in the process being needlessly complicated or duplicated? Are there lots of emails being sent that aren’t actually useful?
Then, discuss areas of opportunity to improve the experience. E.g., are there areas in the process where seven steps could be reduced to three? Is that verification email actually needed?
You can use quantitative data to validate the impact of the various opportunity areas identified. A particular step may well be a customer experience that falls short, but how many of your customers are actually effected by that step? Might you be better off as a team focused on another higher impact opportunity?
Here's a user onboarding jouney map our Engaging First Impressions team created.
Be sure to run a full Health Monitor session or checkpoint with your team to see if you're improving.
MAP A FUTURE STATE
Instead of mapping the current experience, map out an experience you haven't delivered yet. You can map one that simply improves on existing pain points, or design an absolutely visionary amazeballs awesome experience!
Just make sure to always base your ideas on real customer interviews and data. When designing a totally new customer journey, it can also be interesting to map competitor or peer customer journeys to find inspiration. Working on a personalised service? How do they do it in grocery? What about fashion? Finance?
After the mapping session, create a stakeholder summary. What pain points have the highest impact to customers' evaluation, adoption and usage of our products? What opportunities are there, and which teams should know about them? What is your action plan to resolve these pain points? Keep it at a summary level for a fast share out of key takeaways.
For a broader audience, or to allow stakeholders to go deeper, you could also create a write-up of your analysis and recommendations you came up with, notes captured, photos of the group and the artefacts created on a Confluence page. A great way of sharing this information is in a video walk through of the journey map. Loom is a great tool for this as viewers can comment on specific stages of the journey. This can be a great way to inspire change in your organization and provide a model for customer-centric design practices.
KEEP IT REAL
Now that you have interviewed your customers and created your customer journey map, circle back to your customers and validate! And yes: you might learn that your entire map is invalid and have to start again from scratch. (Better to find that out now, versus after you've delivered the journey!) Major initiatives typically make multiple journey maps to capture the needs of multiple personas, and often iterate on each map. Remember not to set and forget. Journeys are rapidly disrupted, and keeping your finger on the pulse of your customer's reality will enable your team to pivot (and get results!) faster when needed.
Related Plays
Customer Interview
Project Poster
Want even more Playbook?
Drop your email below to be notified when we add new Health Monitors and plays.
Thanks! Now get back to work.
Got feedback?
Drop a question or comment on the Atlassian Community site.
Shared understanding
Different types of teams need to share an understanding of different things.
LEADERSHIP TEAMS
The team has a shared vision and collective purpose which they support, and confidence they have made the right strategic bets to achieve success.
Proof of concept
Project teams.
Some sort of demonstration has been created and tested, that demonstrates why this problem needs to be solved, and demonstrates its value.
Customer centricity
Service teams.
Team members are skilled at understanding , empathizing and resolving requests with an effective customer feedback loop in place that drives improvements and builds trust to improve service offerings.

Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2021? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map right at the last second?

The thing is -- understanding your customer base can be extremely challenging. And even when you think you've got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

Download Now
While it isn't possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a very handy tool for keeping track of important milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I'll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents
What is the customer journey?
Customer journey stages.
- What is a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
What's included in a customer journey map, steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
- Customer Journey Map Best Practices
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer's journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I've worked with were confused about the differences between the customer's journey and the buyer's journey. The buyer's journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don't wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process to consider, evaluate, and decide to purchase a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand's place within the buyer's journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer's journey. When you create a customer journey map, you're taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey, instead of leaving it up to chance.
Free Customer Journey Map Template
Fill out this form to access the free templates..
For example, at HubSpot, our customer's journey is divided into 3 stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
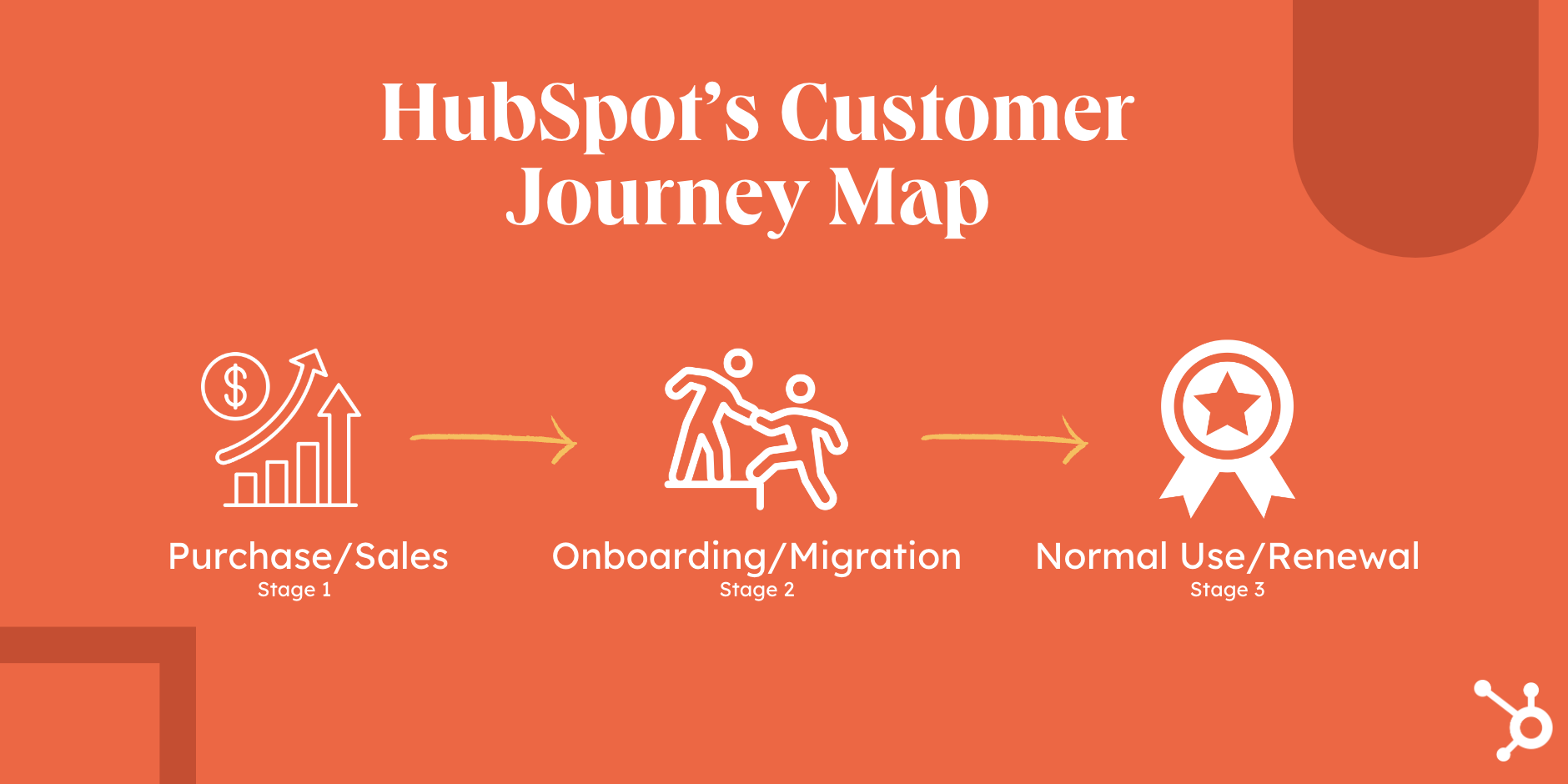
The stages may not be the same for you — in fact, your brand will likely come up with a set of unique stages of the customer journey. But where do you start? Let's take a look.
Generally, there are 5 phases that customers go through when interacting with a brand or a product: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Loyalty.
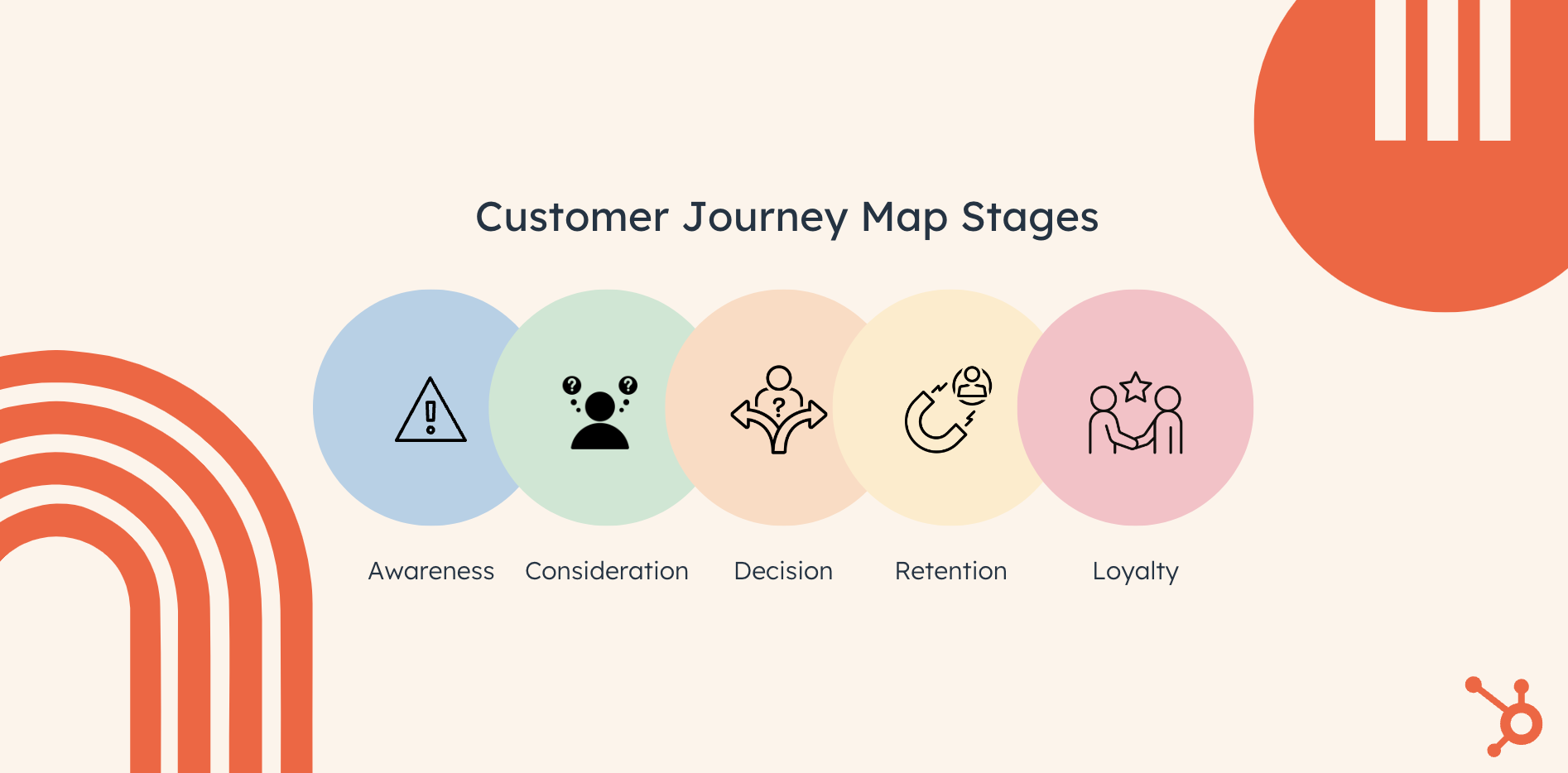
1. Awareness Stage
In the awareness stage, customers realize they have a problem. At this point, they may not know that they need a product or service, but they will begin doing research either way.
During this stage of the customer journey, brands should deliver educational content to help customers diagnose a problem and offer potential solutions. Your aim should be to help customers alleviate their pain point, not encourage a purchase.
Some educational content that I've created in the past are:
- How-to articles and guides
- General whitepapers
- General ebooks
- Free courses
Educational content may also be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Social media
- Search engines
2. Consideration
In the consideration stage, customers have done enough research to realize that they need a product or service. At this point, they begin to compare brands and offerings.
During this stage, brands should deliver product marketing content to help customers compare different offerings and, eventually, choose their product or service. The aim is to help customers navigate a crowded marketplace and move them toward a purchase decision.
Product marketing content may include:
- Product listicles
- Product comparison guides and charts
- Product-focused white papers
- Customer success stories or case studies
Product marketing content may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Your website
- Conferences
3. Decision Stage
In the decision stage, customers have chosen a solution and are ready to buy.
During this stage, your brand should deliver a seamless purchase process to make buying products as easy as possible. I wouldn't recommend any more educational or product content at this stage — it's all about getting customers to make a purchase. That means you can be more direct about wanting customers to buy from you.
Decision-stage content may include:
- Free consultations
- Product sign-up pages
- Pricing pages
- Product promotions (i.e "Sign up now and save 30%")
Decision-stage content may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
4. Retention Stage
In the retention stage, customers have now purchased a solution and stay with the company they purchased from, as opposed to leaving for another provider.
During this stage, brands provide an excellent onboarding experience and ongoing customer service to ensure that customers don't churn.
Retention-stage strategies may include:
- Providing a dedicated customer success manager
- Making your customer service team easily accessible
- Creating a knowledge base in case customers ever run into a roadblock
Retention-stage strategies may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
5. Loyalty Stage
In the loyalty stage, customers not only choose to stay with a company — they actively promote it to family, friends, and colleagues. The loyalty stage can also be called the advocacy stage.
During this phase, brands should focus on providing a fantastic end-to-end customer experience. This should span from your website content to your sales reps all the way to your social media team and your product's UX.
Most importantly, customers become loyal when they've achieved success with your product — if it works, they're more likely to recommend your brand to others.
Loyalty-stage strategies may include:
- Having an easy-to-navigate website
- Investing in your product team to ensure your product exceeds customer expectations
- Making it easy to share your brand with others via a loyalty or referral program
- Providing perks to continued customers, such as discounts
Loyalty-stage strategies may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Your products
To find out whether your customers have reached the loyalty stage, try a Net Promoter Score survey , which asks one simple question: "On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend us to a friend?" To deliver this survey, you can use customer feedback software like Service Hub .
Now, let's get to the good stuff. Let's talk about creating your customer journey map.
What is the customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer's experience with a company. It also provides insight into the needs of potential customers at every stage of this journey and the factors that directly or indirectly motivate or inhibit their progress.
The business can then use this information to improve the customer's experience, increase conversions, and boost customer retention.
Now, the customer journey map is not to be confused with a UX journey map. But, for clarity, let's distinguish these two below.
What is UX journey mapping?
A UX journey map represents how a customer experiences their journey toward achieving a specific goal or completing a particular action.
For example, the term "UX journey mapping" can be used interchangeably with the term "customer journey mapping" if the goal being tracked is the user's journey toward purchasing a product or service.
However, UX journey mapping can also be used to map the journey (i.e., actions taken) towards other goals, such as using a specific product feature.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
While the customer journey might seem straightforward — the company offers a product or service, and customers buy it — for most businesses, it typically isn't.
In reality, it's a complex journey that begins when the customer becomes problem-aware (which might be long before they become product-aware) and then moves through an intricate process of further awareness, consideration, and decision-making.
The customer is also exposed to multiple external factors (competitor ads, reviews, etc.) and touchpoints with the company (conversations with sales reps, interacting with content, viewing product demos, etc.).
Keep in mind that 80% of customers consider their experience with a company to be as important as its products.
By mapping this journey, your marketing, sales, and service teams can understand, visualize, and gain insight into each stage of the process.
You can then decrease any friction along the way and make the journey as helpful and delightful as possible for your leads and customers.
Customer journey mapping is the process of creating a customer journey map — the visual representation of a company's customer experience. It compiles a customer's experience as they interact with a business and combines the information into a visual map.
The goal of this process is to draw insights that help you understand how your customers experience their journeys and identify the potential bottlenecks along the way.
It's also important to note that most customer journeys aren't linear. Instead, buyers often experience a back-and-forth, cyclical, multi-channel journey.
Let's look at the stages that you should include in any customer journey.
- The Buying Process
- User Actions
- User Research
1. The Buying Process
To determine your customers' buying process, you'll want to pull data from all relevant sources (prospecting tools, CMS, behavior analytics tools, etc.) to accurately chart your customer's path from first to last contact.
However, you can keep it simple by creating broad categories using the typical buying journey process stages — awareness, consideration, and decision — and mapping them horizontally.
2. Emotions
Whether the goal is big or small, remember your customers are solving a problem. That means they're probably feeling some emotion — whether that's relief, happiness, excitement, or worry.
Adding these emotions to the journey map will help you identify and mitigate negative emotions and the pain points that cause them.
On HubSpot's journey map , we use emojis to represent potential emotions at different stages of the customer journey.
3. User Actions
This element details what a customer does in each stage of the buying process. For example, during the problem-awareness stage, customers might download ebooks or join educational webinars.
Essentially, you're exploring how your customers move through and behave at each stage of their journey.
4. User Research
Similar to the last section, this element describes what or where the buyer researches when they are taking action.
More than likely, the buyer will turn to search engines, like Google, to research solutions during the awareness stage. However, it's important to pay attention to what they're researching so you can best address their pain points.
5. Solutions
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot's free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer's journey, a day in the life of your customer, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company's buyer persona. Not only will this lead to improvements to your product, but also a better customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you're creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don't have one, I would recommend creating a buyer persona . This is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics representing your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics at the ready.
Don't have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot's Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Some great ways to get valuable customer feedback are questionnaires and user testing. The important thing is to only reach out to actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services and who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you've learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I would recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a UX journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company — so if you group too many personas into one journey, your map won't accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it's best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don't worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there's no overlap.
This is essential in creating a UX journey map because it provides insight into your customers' actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they're quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you also need to look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels
- Email marketing
- Third-party review sites or mentions
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand, impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding -- you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

HubSpot's free customer journey map template makes it easier than ever to visualize the buyer's journey. It saved me some time organizing and outlining my customer experience and it made it clear how a website could impact my user's lives.
The customer journey map template can also help you discover areas of improvement in your product, marketing, and support processes.
Download a free, editable customer journey map template.
Types of Customer Journey Maps and Examples
There are four types of customer journey maps , each with unique benefits. Pick the one that makes the most sense for your company.
Current State
These customer journey maps are the most widely used type. They visualize the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers currently experience while interacting with your company. They're best used for continually improving the customer journey.
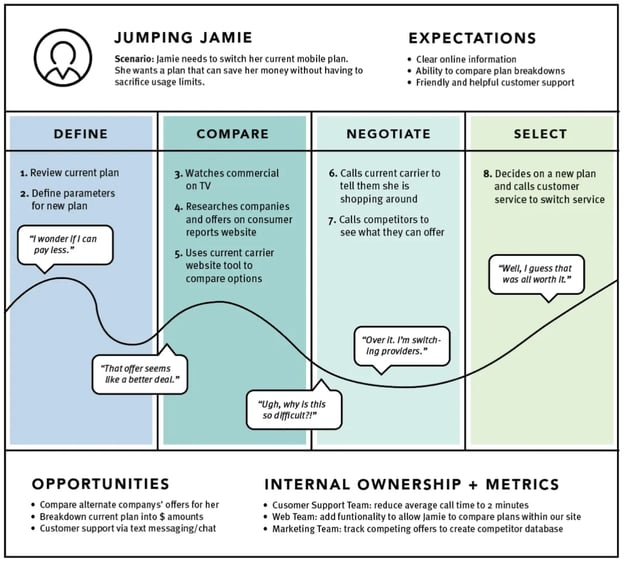
Image Source
Day in the Life
These customer journey maps visualize the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers currently experience in their daily activities, whether or not that includes your company.
This type gives a broader lens into your customers' lives and what their pain points are in real life.
Day-in-the-life maps are best used for addressing unmet customer needs before customers even know they exist. Your company may use this type of customer journey map when exploring new market development strategies .

Future State
These customer journey maps visualize what actions, thoughts, and emotions that your customers will experience in future interactions with your company. Based on their current interaction with your company, you'll have a clear picture of where your business fits in later down the road.
These maps are best for illustrating your vision and setting clear, strategic goals.
Service Blueprint
These customer journey maps begin with a simplified version of one of the above map styles. Then, they layer on the factors responsible for delivering that experience, including people, policies, technologies, and processes.
Service blueprints are best used to identify the root causes of current customer journeys or the steps needed to attain desired future customer journeys.
If you want a look at a real customer journey map that HubSpot has used recently, check out this interview we conducted with Sarah Flint, Director of System Operations at HubSpot. We asked her how her team put together their map (below) as well as what advice she would give to businesses starting from scratch.

Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Set a goal for the journey map.
- Survey customers to understand their buying journey.
- Ask customer service reps about the questions they receive most frequently.
- Consider UX journey mapping for each buyer persona.
- Review and update each journey map after every major product release.
- Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams.
1. Set a goal for the journey map.
Determine whether you aim to improve the buying experience or launch a new product. Knowing what the journey map needs to tell you can prevent scope creep on a large project like this.
2. Survey customers to understand their buying journey.
What you think you know about the customer experience and what they actually experience can be very different. Speak to your customers directly, so you have an accurate snapshot of the customer's journey.
3. Ask customer service reps about the questions they receive most frequently.
Sometimes, customers aren't aware of their specific pain points, and that's where your customer service reps come in.
They can help fill in the gaps and translate customer pain points into business terms you and your team can understand and act on.
4. Consider UX journey mapping for each buyer persona.
It's easy to assume each customer operates the same way, but that couldn't be further from the truth.
Demographics, psychographics, and even how long someone has been a customer can determine how a person interacts with your business and makes purchasing decisions.
Group overarching themes into buyer personas and create a UX journey map for each.
5. Review and update each journey map after every major product release.
Every time your product or service changes, the customer's buying process changes. Even slight tweaks, like adding an extra field to a form, can become a significant roadblock.
So, reviewing the customer journey map before and after implementing changes is essential.
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams.
Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is a convenient way for cross-functional teams to provide feedback.
Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team, so they always keep the customer top of mind.
Breaking down the customer journey, phase by phase, aligning each step with a goal, and restructuring your touchpoints accordingly are essential steps for maximizing customer success .
Here are a few more benefits to gain from customer journey mapping.
1. You can refocus your company with an inbound perspective.
Rather than discovering customers through outbound marketing, you can have your customers find you with the help of inbound marketing.
Outbound marketing involves tactics targeted at generalized or uninterested audiences and seeks to interrupt the customers' daily lives. Outbound marketing is costly and inefficient. It annoys and deters customers and prospects.
Inbound marketing involves creating helpful content that customers are already looking for. You grab their attention first and focus on the sales later.
By mapping out the customer journey, you can understand what's interesting and helpful to your customers and what's turning them away.
2. You can create a new target customer base.
You need to understand the customer journey properly to understand your customers' demographics and psychographics.
It's a waste of time and money to repeatedly target too broad of an audience rather than people who are actually interested in your offering.
Researching the needs and pain points of your typical customers will give you a good picture of the kinds of people who are trying to achieve a goal with your company. Thus, you can hone your marketing to that specific audience.
3. You can implement proactive customer service.
A customer journey map is like a roadmap to the customer's experience.
It highlights moments where people experience delight and situations where they might face friction. Knowing this ahead of time allows you to plan your customer service strategy and intervene at ideal times.
Proactive customer service also makes your brand appear more reliable. For example, when I worked in customer support, we would anticipate a surge in tickets around the holidays. To be proactive, we'd send out a message to customers letting them know about our team's adjusted holiday hours. We would aalso tell them about additional support options if we were unavailable and what to do if an urgent problem needed immediate attention.
With expectations set, customers won't feel surprised if they're waiting on hold a little longer than usual. They'll even have alternative options to choose from — like a chatbot or knowledge base — if they need to find a faster solution.
4. You can improve your customer retention rate.
When you have a complete view of the customer journey, it's easier to pick out areas where you can improve it. When you do, customers experience fewer pain points, leading to fewer people leaving your brand for competitors.
After all, 33% of customers will consider switching brands after just one poor experience.
UX journey mapping can point out individuals on the path to churn. If you log the common behaviors of these customers, you can start to spot them before they leave your business.
While you might not save them all, it's worth the try. Increasing customer retention rates by just 5% can increase profits by 25%-95%.
5. You can create a customer-focused mentality throughout the company.
As your company grows, it can be tricky to coordinate all your departments to be as customer-focused as your customer service, support, and success teams are. That's because each department has varying goals, meaning they might not be prioritizing customer needs -- they might focusing on website traffic, leads, product signups, etc.
One way to overcome this data silo is to share a clear customer journey map with your entire organization. The great thing about these maps is that they map out every single step of the customer journey, from initial attraction to post-purchase support. And, yes, this concerns marketing, sales, and service.
For more examples of customer journey maps, read on to the next section for a few templates you can use as a baseline for your company's map.
Customer Journey Mapping Examples
To help guide your business in its direction, here are examples to draw inspiration from for building out your customer journey map.
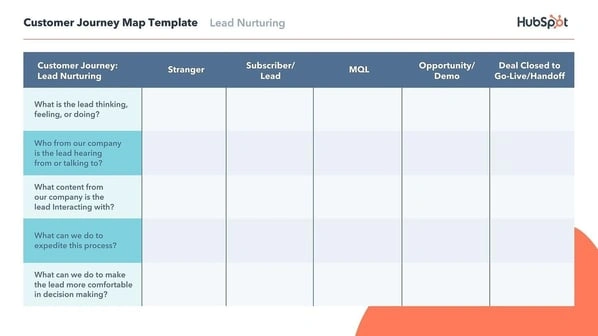
1. HubSpot's Customer Journey Map Templates
HubSpot's free Customer Journey Map Templates provide an outline for companies to understand their customers' experiences.
The offer includes the following:
- Current State Template
- Lead Nurturing Mapping Template
- A Day in the Customer's Life Template
- Customer Churn Mapping Template
- Customer Support Blueprint Template
Each of these templates helps organizations gain new insights into their customer base and help make improvements to product, marketing, and customer support processes.
Download them today to start working on your customer journey map.
2. B2B Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map clearly outlines the five steps Dapper Apps believes customers go through when interacting with them.
As you can see, it goes beyond the actual purchasing phase by incorporating initial research and post-purchase needs.
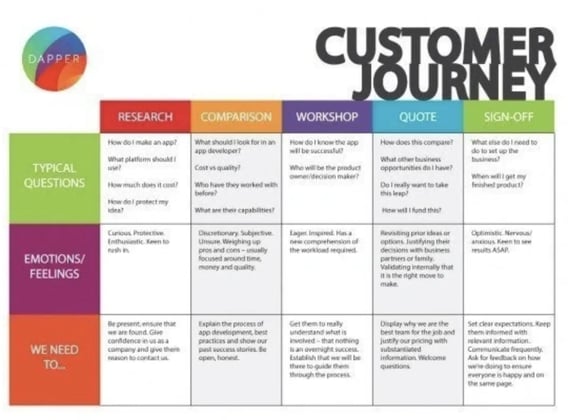
This map is effective because it helps employees get into the customers' minds by understanding the typical questions they have and the emotions they're feeling.
There are incremental action steps that Dapper Apps can take in response to these questions and feelings that will help it solve all the current problems customers are having.
3. Ecommerce Customer Journey Map Example
This fictitious customer journey map is a clear example of a day-in-the-life map.
Rather than just focusing on the actions and emotions involved in the customer's interaction with the company, this map outlines all the actions and emotions the customer experiences on a typical day.
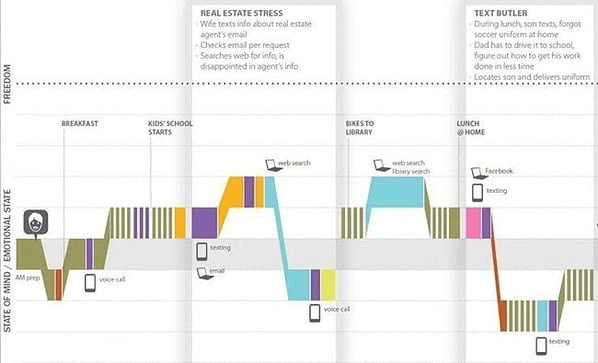
This map is helpful because it measures a customer's state of mind based on the level of freedom they get from certain stimuli.
This is helpful for a company that wants to understand what its target customers are stressed about and what problems may need solving.
4. Future B2C Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map, designed for Carnegie Mellon University, exemplifies the usefulness of a future state customer journey map. It outlines the thoughts, feelings, and actions the university wants its students to have.
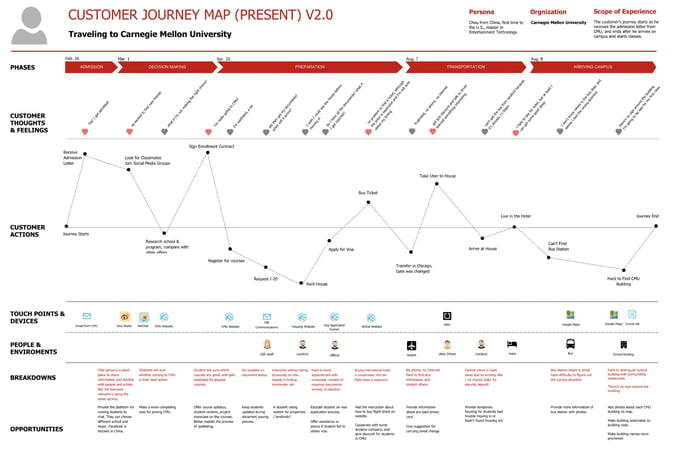
Based on these goals, CMU chose specific proposed changes for each phase and even wrote out example scenarios for each phase.
This clear diagram can visualize the company vision and help any department understand where they will fit into building a better user experience.
5. Retail Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map shows an in-depth customer journey map of a customer interacting with a fictitious restaurant.
It's clear that this style of map is more comprehensive than the others. It includes the front-of-stage (direct) and back-of-stage (non-direct or invisible) interactions a customer has with the company, as well as the support processes.
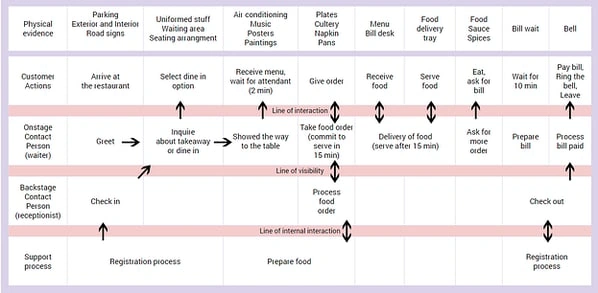
This map lays out every action involved in the customer experience, including those of the customer, employees directly serving diners, and employees working behind the scenes.
By analyzing how each of these factors influences the customer journey, a company can find the root cause of mishaps and problem-solve this for the future.
To get your business from point A — deciding to focus on customer journeys — to point B — having a journey map — a critical step to the process is selecting which customer mindset your business will focus on.
This mindset will determine which of the following templates you'll use.
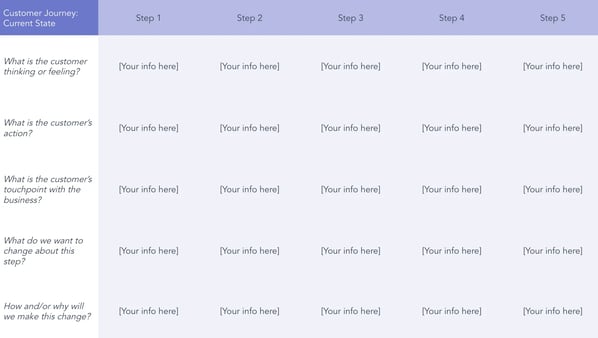
1. Current State Template
If you're using this template for a B2B product, the phases may reflect the search, awareness, consideration of options, purchasing decision, and post-purchase support processes.
For instance, in our Dapper Apps example, its phases were research, comparison, workshop, quote, and sign-off.
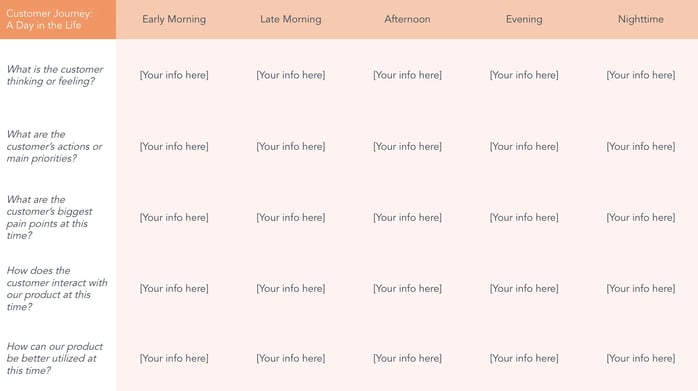
2. Day in the Life Template
Since this template reflects all the thoughts, feelings, actions, needs, and pain points a customer has in their entire daily routine — whether or not that includes your company — you'll want to map out this template in a chronological structure.
This way, you can highlight the times of day at which you can offer the best support.
Get an interactive day in the life template.
3. Future State Template
Similar to the current state template, these phases may also reflect the predicted or desired search, awareness, consideration of options, purchasing decision, and post-purchase support processes.
Since this takes place in the future, you can tailor these phases based on what you'd like the customer journey to look like rather than what it currently looks like.
Get an interactive future state template.

4. Service Blueprint Template
Since this template is more in-depth, it doesn't follow certain phases in the customer journey.
Instead, it's based on physical evidence — the tangible factors that can create impressions about the quality and prices of the service — that often come in sets of multiple people, places, or objects at a time.
For instance, with our fictitious restaurant example above, the physical evidence includes all the staff, tables, decorations, cutlery, menus, food, and anything else a customer comes into contact with.
You would then list the appropriate customer actions and employee interactions to correspond with each physical evidence.
For example, when the physical evidence is plates, cutlery, napkins, and pans, the customer gives their order, the front-of-stage employee (waiter) takes the order, the back-of-stage employee (receptionist) processes the order, and the support processes (chefs) prepare the food.
Get an interactive service blueprint template.

5. Buyer's Journey Template
You can also use the classic buyer's journey — awareness, consideration, and decision — to design your customer journey map.
Get an interactive buyer's journey template.
Charter the Path to Customer Success
Once you fully understand your customer's experience with your business, you can delight them at every stage of their buying journey. Remember, many factors can affect this journey, including customer pain points, emotions, and your company's touchpoints and processes.
A customer journey map is the most effective way to visualize this information, whether you're optimizing the customer experience or exploring a new business opportunity to serve a customer's unrecognized needs.
Use the free templates in this article to start mapping the future of customer success at your business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August, 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![customer journey step by step How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey step by step How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey step by step Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]
![customer journey step by step How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-journey-map_13.webp)
How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![customer journey step by step How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
What is customer journey mapping?
Customer journey map template, the customer journey mapping process, data inputs for your customer journey map, why should you use customer journey maps, the uses of customer journey mapping, how to improve a customer journey, tools to help you with your journey mapping, see how xm for customer frontlines works, customer journey mapping 101: definition, template & tips.
22 min read Find out about how to start customer journey mapping, and how to improve it for the benefit of your customers and the business.
If you want to improve your customer experience you need to be able to understand and adapt the customer journey you offer when someone interacts with your organization. Whether their journey is entirely online , offline, or a blend of both, there are multiple journeys a customer might undergo.
Understanding the customer journey in depth helps you identify and take action on customer pain points and repeat what’s working. By doing this, you will improve the overall experience that your customers have, which will have better outcomes for your business.
Outlining the potential customer journeys your audience might go through requires a process called customer journey mapping.
Free Course: Customer journey management & improvement
Creating a customer journey map is the process of forming a visual representation of customers’ processes, needs , and perceptions throughout their interactions and relationship with an organization. It helps you understand the steps customers take – the ones you see, and don’t – when they interact with your business.
It enables you to assess:
- Insights – from your existing customer journey, how to understand it better
- Impact – how to optimize budgets and effort for changes we want to make to the customer experiences
- Issues/opportunities – Diagnose the existing customer journey
- Innovation – where you might want to completely change the existing customer experience
A customer journey map gives you deeper insight into the customer, so you can go beyond what you already know. Many brands see the customer journey as something that is visible – where the customer interacts with the brand. But in reality, this is not true, and only accounts for a percentage of the entire customer journey. Creating a customer journey map gets you thinking about the aspects of the journey you don’t see, but have equal weight and importance to the entire experience.
When mapping out the customer journey, you are looking for the moments that matter – where there is the greatest emotional load.
If you’re buying a car, then the greatest moment of emotional load is when you go to pick the car up because it’s yours , after picking the color, choosing the model, and waiting for it to be ready.
Ensuring these moments match your customers’ expectations of your product, brand and service teams are key to helping you reach your business goals. But you can only do that by understanding the journey your customers go on in order to get there, what they’re thinking and needing from you at that time. Developing a customer journey map puts you in their shoes so you can understand them better than ever before.
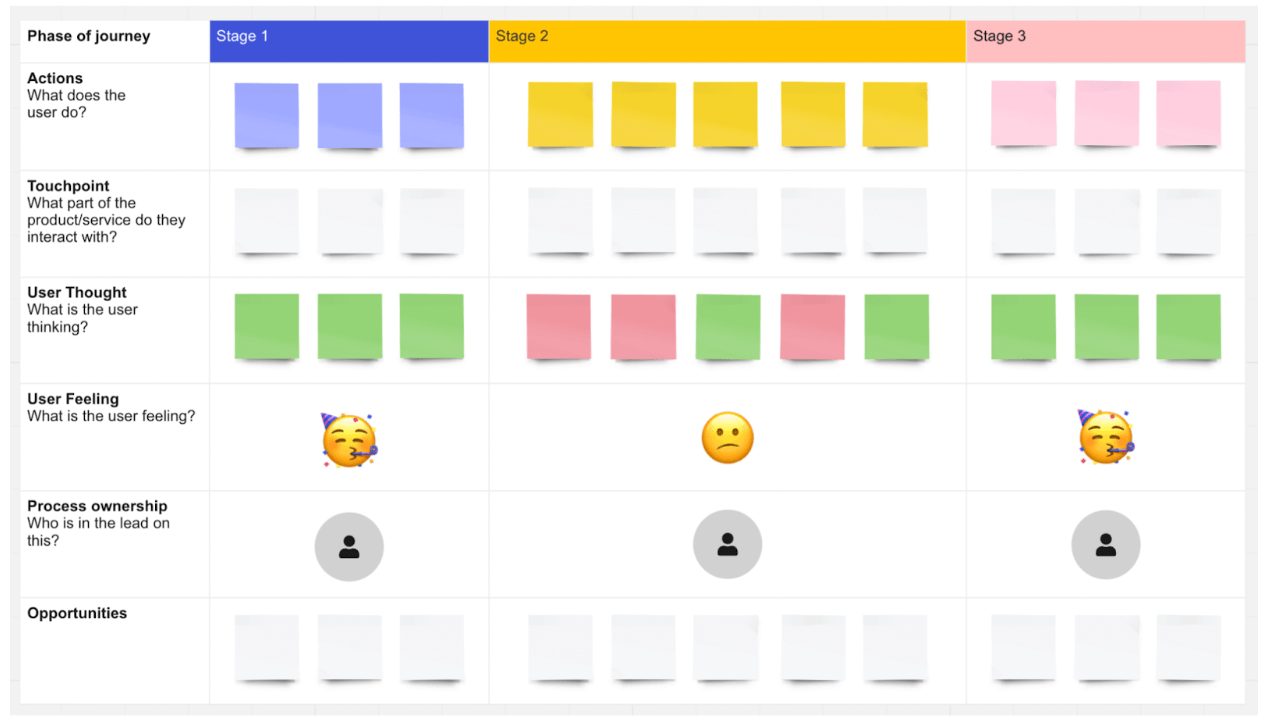
Getting started when creating a customer journey map template doesn’t have to be difficult. However, your customer journey map template will need to cover several elements in order to be effective.
There are several ingredients that make up the anatomy of a customer journey, all of which should be looked at carefully so that you can find out where the customer journey runs smoothly and meets customer needs at that moment in time – and where the experience does not, and needs some improvement.
Understanding their behaviors and attitudes also means you can fix bad experiences more effectively too because you know why you haven’t met your customers’ expectations and what you need to do to make amends. There may be times when things go wrong, but it’s how you adapt and what you do to fix these experiences that separates the best. Knowing how the customer will be feeling makes taking that decisive action much easier.
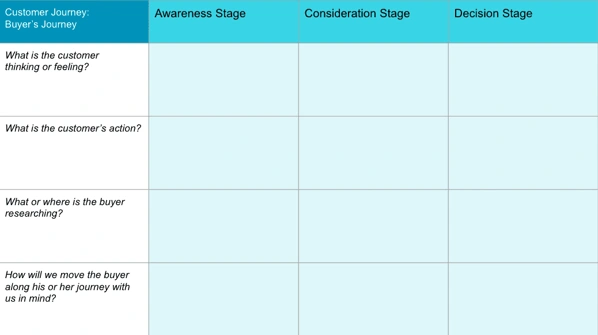
When exploring and visualizing the customer journey we are assessing:
- Customer behavior What is your customer trying to do?
- Customer attitudes What is your customer feeling/saying?
- The on-stage experience Who/what is your customer directly interacting with? (This includes various channels, such as TV ads or social media)
- The off-stage experience Who/what needs to be in place but which your customer is NOT directly aware of?
So what could the customer journey map examples look like when starting the process of buying a car?
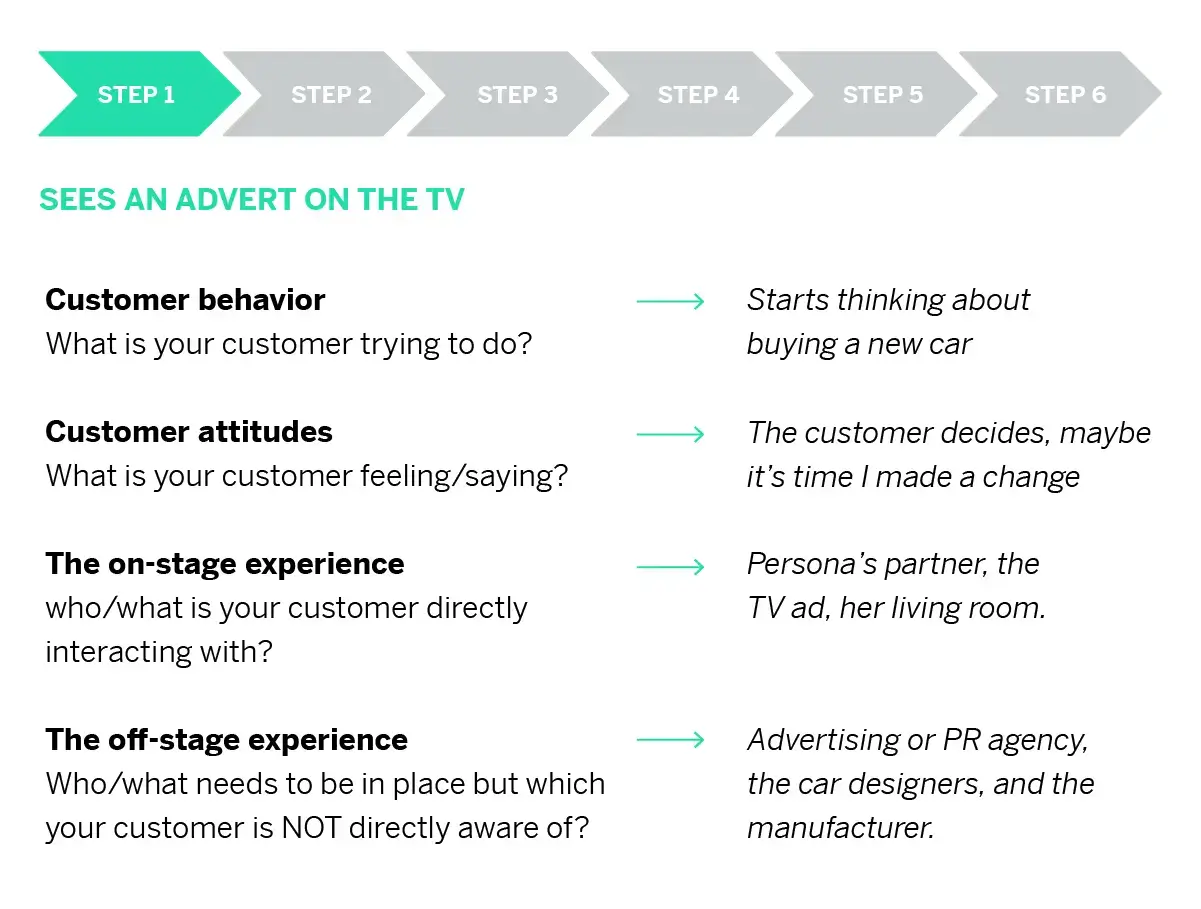
Customer journey vs process flow
Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map – otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you’re typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
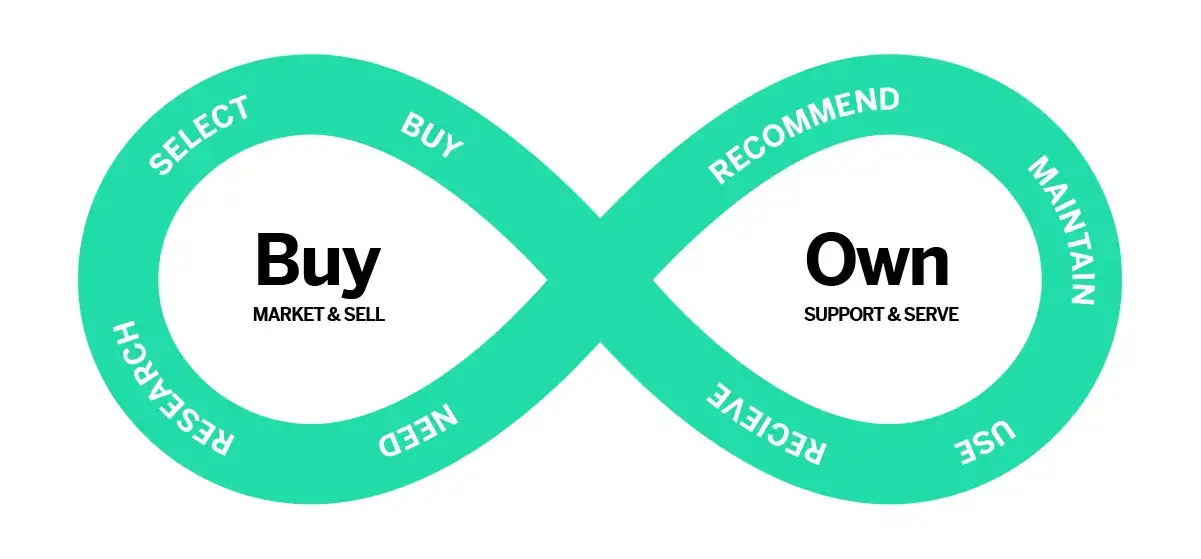
There is no single customer journey. In fact, there are multiple. The best experiences combine multiple journeys in a seamless way to create a continuous customer lifecycle as outlined below.
Getting started with customer journey map templates
To begin, start by choosing a journey that you would like to create a customer journey map for and outline the first step that customers will take.
You can use this customer journey map template below to work out the customer behaviors, attitudes, the on-stage and off-stage processes – and the KPIs attached to measuring the success of this experience.
Download our free journey mapping template here
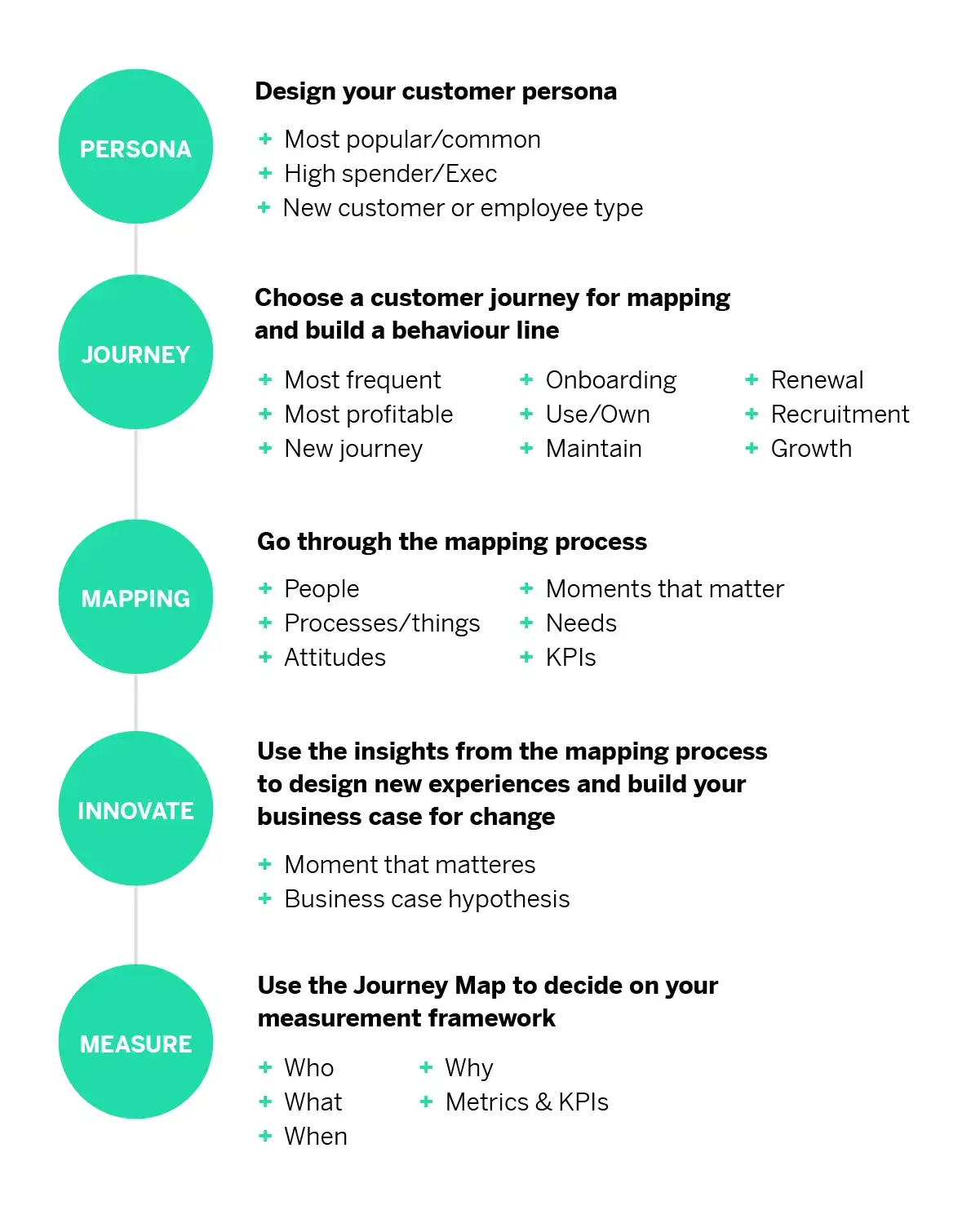
The step-by-step process of mapping the customer journey begins with the buyer persona .
Step 1 – Create a customer persona to test
In order to effectively understand the customer journey, you need to understand the customer – and this is where creating a persona really helps. You may base this around the most common or regular customers, big spend, or new customers you haven’t worked with before. This persona is beyond a marketing segment , but that can be a great place to begin if you’re just starting out on the mapping process for your organization.
What do you include? Start with these characteristics.
- Family status
- Professional goals
- Personal goals
These personas help you gain a deeper understanding of your customers and can be derived from insights and demographic data , or even customer interviews . This works for both B2B and B2C business models, but in B2B especially you’ll have multiple customers for each opportunity so it’s recommended you build out multiple personas.
To begin, start with no more than three personas to keep things simple.
Create a diverse team
When creating a customer journey map, you also need to build out a diverse mapping team to represent the whole business. Include frontline staff , day-to-day management, corporate teams, HR, and business support functions. They will give you vital feedback, advice, and perspectives you hadn’t thought of.
Step 2 – Choose a customer journey for mapping
Select a customer journey map to construct, then build a behavior line. This might be a new customer journey, renewal, or fixing a product issue. You might also choose this based on the most frequent customer journeys taken, or the most profitable.
Step 3 – Work through the mapping process
Ask yourself the following:
- Who are the people involved in this journey? E.g. if you’re in a car dealership, that might be the customer, the sales rep, and front-of-house staff.
- What are the processes or the things that happen during this journey?
- What are the customer attitudes ? What are they feeling at this time? Go beyond excitement or frustration. Bring these feelings to life. This car is my dream come true!
- What is the moment that matters? Identify the greatest moment of emotional load. The make or break where everything could be good up until that point, but if you get that moment of maximum impact wrong, then all that’s good is forgotten. The best experience brands get this moment right and identifying it is an important first step to achieving that. In that moment, ask yourself what are the things/people/processes involved? Think about this for the whole business – across your product , brand , and service teams.
- But beyond identifying this moment, you need to establish what your customers’ needs are. What are they getting out of this moment? How do their needs change if this experience goes badly? Knowing the answer to these questions can help you deliver experiences that will resonate , and respond quickly to unforeseen circumstances or issues.
- And finally, how do you measure how effectively you are meeting customer needs throughout the journey? Set KPIs to put benchmarks in place for your customer journey map and customer experience and track your progress.
Step 4 – Innovate
When you are mapping out your customer journey, brainstorm ideas for how to improve that moment that really matters . These ideas don’t need to be practical, but by putting together a diverse mapping team from around the business you can begin to filter through these ideas.
Then, test it.
Ask yourself: Is it feasible? Is it viable? Is it desirable? Don’t ask can we do it, ask should we do it? Then you can start to differentiate yourself from your competitors.
Step 5 – Measure
Use the customer journey map to decide on your measurement framework.
Who are you measuring? What are you measuring? When on the journey are you measuring it? And why? And finally, what metrics and KPI’s are in place to measure this?
Your customer journey map process will require you to use several different data inputs to get an accurate picture of how your customers behave and where you can improve their experience.
A customer journey map is often developed using data gleaned from customer feedback you’ve requested . While this type of market research is useful, your research process needs to be deeper to gain a richer, more accurate understanding of your customer’s behavior.
To create a customer journey map that accurately reflects the truth of customer actions and intentions, you need to take into account both solicited and unsolicited data.
Use solicited data to understand the voice of the customer
Solicited data includes the customer feedback you gain when you conduct research through surveys such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) or ask customers for feedback on social media. This approach can be very useful for understanding your customer’s point of view , rather than just making assumptions about how they think and behave.
However, your target audiences won’t tell you everything about what they plan to do when undergoing their customer journey. Though they might tell you that they’ve had a great experience in a particular part of their customer journey, this type of feedback presents a few issues:
- You have to know when to ask for feedback : You might already have a customer journey in mind when asking for feedback – but do you know all the routes a customer might take in your customer journey map?
- It’s a snapshot: When you survey customers, you’ll likely only get insights into their experience at that particular moment about a specific touchpoint
- It’s what customers say they think/will do, not what they actually think/will do: You’re relying on your customers to accurately reflect their sentiment and intentions in their responses, which isn’t always the case. For your customer journey map to be effective, you need to find the truth
- Your sample size might be too small : If you’re trying to understand how a relatively niche customer journey is doing, you might find that the number of customers who have not only taken the customer journey but are willing to respond with feedback is very limited. You can’t risk survey fatigue by polling the same audience several times, so your insights are limited
- You’re only getting part of the picture : You will likely have several types of useful customer data on file, but these are often not considered as part of the process when creating a customer journey design because solicited data takes precedence
You’ll need to infer how customers feel to be able to accurately predict the actions a customer takes. To do so, you’ll need to look at unsolicited data.
Unsolicited data
Unsolicited data covers everything your customers aren’t telling you directly when you ask them and contextual data that you likely already collect on them, such as purchase history. It can be taken from various sources, such as your website and social channels, third-party sites, customer calls, chat transcripts, frontline employee feedback , operational sources, and more.
This type of data is nuanced, but it allows you to establish the truth of your customers’ experience. The ability to gather unsolicited customer feedback from every channel enables you to see more than just what a customer tells you directly. Using real-time feedback gathering and natural language understanding (NLU) models that can detect emotion, intent, and effort, you’ll be able to understand your customers’ actions in a more profound way. Unsolicited data offers you a 100% response rate that better indicates what your customers actually think of each step in their customer journey.
Rather than be limited to a small sample size of customers who respond to surveys, you’ll be able to build an accurate picture of the average customer on each step of the customer journey map by using this richer insight data with your own operational data.
Why using solicited and unsolicited data is important data
With solicited data, you don’t always see why a customer behaves or thinks as they do. For example, a customer might tell you that they would recommend you to a friend or family – but they don’t renew their subscription with you. A customer might be an ideal candidate for a particular journey, but they abandon their basket when prompted to give their personal details. Understanding the why behind customer actions is key for designing a great customer journey, and that’s why both solicited and unsolicited data collection and evaluation are necessary for creating great customer journey maps.
Of course, knowing how customers will actually respond to your customer touchpoints is only part of the process. You may need to develop more than one customer journey map and create sub-audiences for your customer personas to accurately see where you can rectify pain points and improve outcomes. You will need to collect and analyze contextual data across all customer journey touchpoints and develop a highly detailed journey map that can unveil routes your customers might be taking without your knowledge.
Qualtrics’ Experience ID platform can overlay solicited and unsolicited data to provide an all-encompassing picture of your customer journey map, no matter how complex. Creating an effective customer journey map is easier with all your data collated and analyzed together, with actionable insights created automatically.
A customer journey map creates a common understanding for the organization of how a customer interacts during different stages of the customer lifecycle, and the roles and responsibilities of the different teams in charge of fulfilling that experience.
It will also bring an organization together, and foster empathy and collaboration between teams because people will know what is required from everyone in the business to deliver the experiences that customers expect. This will help you to develop a shared sense of ownership of the customer relationship, which ultimately drives a customer-centric culture . With everyone working towards a common goal, communication of what you learn about the customer and the journey they go through is vital in order to drive best practices throughout the organization.
Creating an accurate customer journey map will help your customer service team to focus on more specific issues, rather than handling problems generated by a less-tailored customer journey. Your customer experience will be improved with a customer journey that’s personalized to the specific personas you have generated. You’ll have put yourself in your customer’s shoes and adapted your strategy to reflect your customer’s perspective – which in turn will create more memorable experiences.
Creating a customer journey map will influence your journey analytics across the business. So for example, it will determine what you ask, who you ask, when you ask, why you ask it and how you ask questions in your Voice of the Customer Program .
So when should you use customer journey mapping?
There are four main uses:
- Assess the current state of your customer journey Understand and diagnose the specific issues in current experiences
- Understand what the future state of your customer journey should look like Design, redesign and create new experiences
- Blueprints For implementing change
- Communication Bringing teams together to train and scale up best practices.
Take stock and take action
To improve the customer journey you need a clear vision of what you want to achieve and you need to make a distinction between the present and the future.
- What is your customer journey right now?
- What does the future state of your customer journey look like?
This is why organizations blueprint their customer journey because they can see what works and act accordingly. By understanding your customers’ attitudes and needs at critical times in the journey, you can make amends to better meet them – and develop contingencies to cope when these needs aren’t or can’t be met. For example, during a sudden, unexpected surge in demand.
Orchestrate your customer journey
To offer your customers truly optimized experiences, you’ll need to go further than just creating a customer journey map. You’ll also need to orchestrate journeys using real-time customer behavior to adapt your strategy as your customers make choices. Orchestrating a journey means taking dynamic action towards optimizing your customer’s experience, using real-time customer behavior as informative data.
Improve your employee experience
Use your diverse mapping team to come up with ideas that incorporate experience from all aspects of the business to improve the customer journey – and remember that this has a significant payoff for your employees too. Improving the employee journey – by giving teams the tools to make a difference – can have a positive knock-on effect for the customer and improve their experience in those key moments. This is because employees have the autonomy and motivation in their roles to help their customers, and realize their own potential.
Your customer journey map isn’t just designed to improve the customer experience. Creating an accurate customer journey map can help you to improve your business outcomes.
Being able to link operational data to key touchpoints in a customer journey is transformative for organizations. This is because improving segments of the customer journey will see a direct impact on your business. The Qualtrics Journey Optimizer helps you do just that. By analyzing areas for improvement as outlined by your customer journey map, organizations can take actions that will have maximum benefit for their customers, and the business too.
With Qualtrics CustomerXM , you’ll:
- Create a common understanding throughout your workforce of how a customer interacts with your organization, and you’ll know the roles and responsibilities of your different teams
- Develop empathy and collaboration between teams, working together to achieve the same outcome
- Develop a shared sense of ownership of the customer relationship which ultimately drives a customer-centric culture
Free course: Customer journey management & improvement
Related resources
Customer Journey
B2B Customer Journey 13 min read
Customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, customer journey management 14 min read, customer journey stages 12 min read, buyer's journey 16 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Product Design Bundle and save
User Research New
Content Design
UX Design Fundamentals
Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
- UX training for teams
- Hire our alumni
- Journal of UX Leadership
- Our mission
- Advisory Council
Education for every phase of your UX career
Professional Diploma
Learn the full user experience (UX) process from research to interaction design to prototyping.
Combine the UX Diploma with the UI Certificate to pursue a career as a product designer.
Professional Certificates
Learn how to plan, execute, analyse and communicate user research effectively.
Learn the principles of content design, from mastering tone and style, to writing for interfaces.
Understand the fundamentals of UI elements and design systems, as well as the role of UI in UX.
Short Courses
Gain a solid foundation in the philosophy, principles and methods of user experience design.
Learn the essentials of software development so you can work more effectively with developers.
Give your team the skills, knowledge and mindset to create great digital products
Join our hiring programme and access our list of certified professionals.
Learn about our mission to set the global standard in UX education
Meet our leadership team with UX and education expertise
Members of the council connect us to the wider UX industry
Our team are available to answer any of your questions
Fresh insights from experts, alumni and the wider design community
Read stories from our students who have made successful careers in UX after completing our course
How to design a customer journey map (A step-by-step guide)
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how a user interacts with your product. Learn how to create a customer journey map in this practical step-by-step guide.
Free course: Introduction to UX Design
What is UX? Why has it become so important? Could it be a career for you? Learn the answers, and more, with a free 7-lesson video course.
Successful UX design is rooted in empathy. The best designers are able to step into their users’ shoes and imagine what they think, feel, and experience as they interact with a product or service.
One of the most effective ways to foster user empathy and consider different perspectives is to create customer journey maps—otherwise known as customer journey maps.
If you’re new to journey mapping, look no further than this guide. We’ll explain:
- What is a customer journey map?
Why create customer journey maps?
When to create customer journey maps, what are the elements of a customer journey map, how to create a customer journey map (step-by-step).
If you want to skip straight to the how-to guide, just use the clickable menu to jump ahead. Otherwise, let’s begin with a definition.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UX]
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map (otherwise known as a user journey map) is a visual representation of how a user or customer interacts with your product. It maps out the steps they go through to complete a specific task or to achieve a particular goal—for example, purchasing a product from an e-commerce website or creating a profile on a dating app.
Where does their journey begin? What’s their first point of interaction with the product? What actions and steps do they take to reach their end goal? How do they feel at each stage?
You can answer all of those questions with a user journey map.
A user journey map template from Miro .
Creating customer journey maps helps to:
- Centre the end user and foster empathy. Creating a user/customer journey map requires you to step into the end user’s shoes and experience the product from their perspective. This reminds you to consider the user at all times and fosters empathy.
- Expose pain-points in the user experience. By viewing the product from the user’s perspective, you quickly become aware of pain-points or stumbling blocks within the user experience. Based on this insight, you can improve the product accordingly.
- Uncover design opportunities. User journey maps don’t just highlight pain-points; they can also inspire new ideas and opportunities. As you walk in your end user’s shoes, you might think “Ah! An [X] feature would be great here!”
- Get all key stakeholders aligned. User journey maps are both visual and concise, making them an effective communication tool. Anybody can look at a user journey map and instantly understand how the user interacts with the product. This helps to create a shared understanding of the user experience, building alignment among multiple stakeholders.
Ultimately, user journey maps are a great way to focus on the end user and understand how they experience your product. This helps you to create better user experiences that meet your users’ needs.
User journey maps can be useful at different stages of the product design process.
Perhaps you’ve got a fully-fledged product that you want to review and optimise, or completely redesign. You can create journey maps to visualise how your users currently interact with the product, helping you to identify pain-points and inform the next iteration of the product.
You can also create user journey maps at the ideation stage. Before developing new ideas, you might want to visualise them in action, mapping out potential user journeys to test their validity.
And, once you’ve created user journey maps, you can use them to guide you in the creation of wireframes and prototypes . Based on the steps mapped out in the user journey, you can see what touchpoints need to be included in the product and where.
No two user journey maps are the same—you can adapt the structure and content of your maps to suit your needs. But, as a rule, user journey maps should include the following:
- A user persona. Each user journey map represents the perspective of just one user persona. Ideally, you’ll base your journey maps on UX personas that have been created using real user research data.
- A specific scenario. This describes the goal or task the journey map is conveying—in other words, the scenario in which the user finds themselves. For example, finding a language exchange partner on an app or returning a pair of shoes to an e-commerce company.
- User expectations. The goal of a user journey map is to see things from your end user’s perspective, so it’s useful to define what their expectations are as they complete the task you’re depicting.
- High-level stages or phases. You’ll divide the user journey into all the broad, high-level stages a user goes through. Imagine you’re creating a user journey map for the task of booking a hotel via your website. The stages in the user’s journey might be: Discover (the user discovers your website), Research (the user browses different hotel options), Compare (the user weighs up different options), Purchase (the user books a hotel).
- Touchpoints. Within each high-level phase, you’ll note down all the touchpoints the user comes across and interacts with. For example: the website homepage, a customer service agent, the checkout page.
- Actions. For each stage, you’ll also map out the individual actions the user takes. This includes things like applying filters, filling out user details, and submitting payment information.
- Thoughts. What is the user thinking at each stage? What questions do they have? For example: “I wonder if I can get a student discount” or “Why can’t I filter by location?”
- Emotions. How does the user feel at each stage? What emotions do they go through? This includes things like frustration, confusion, uncertainty, excitement, and joy.
- Pain-points. A brief note on any hurdles and points of friction the user encounters at each stage.
- Opportunities. Based on everything you’ve captured in your user journey map so far, what opportunities for improvement have you uncovered? How can you act upon your insights and who is responsible for leading those changes? The “opportunities” section turns your user journey map into something actionable.
Here’s how to create a user journey map in 6 steps:
- Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
- Define your persona and scenario
- Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions
- Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
- Identify opportunities
- Define action points and next steps
Let’s take a closer look.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UI DESIGN]
1. Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
The easiest way to create a user journey map is to fill in a ready-made template. Tools like Miro , Lucidchart , and Canva all offer user/customer journey map templates that you can fill in directly or customise to make your own.
Here’s an example of a user journey map template from Canva:
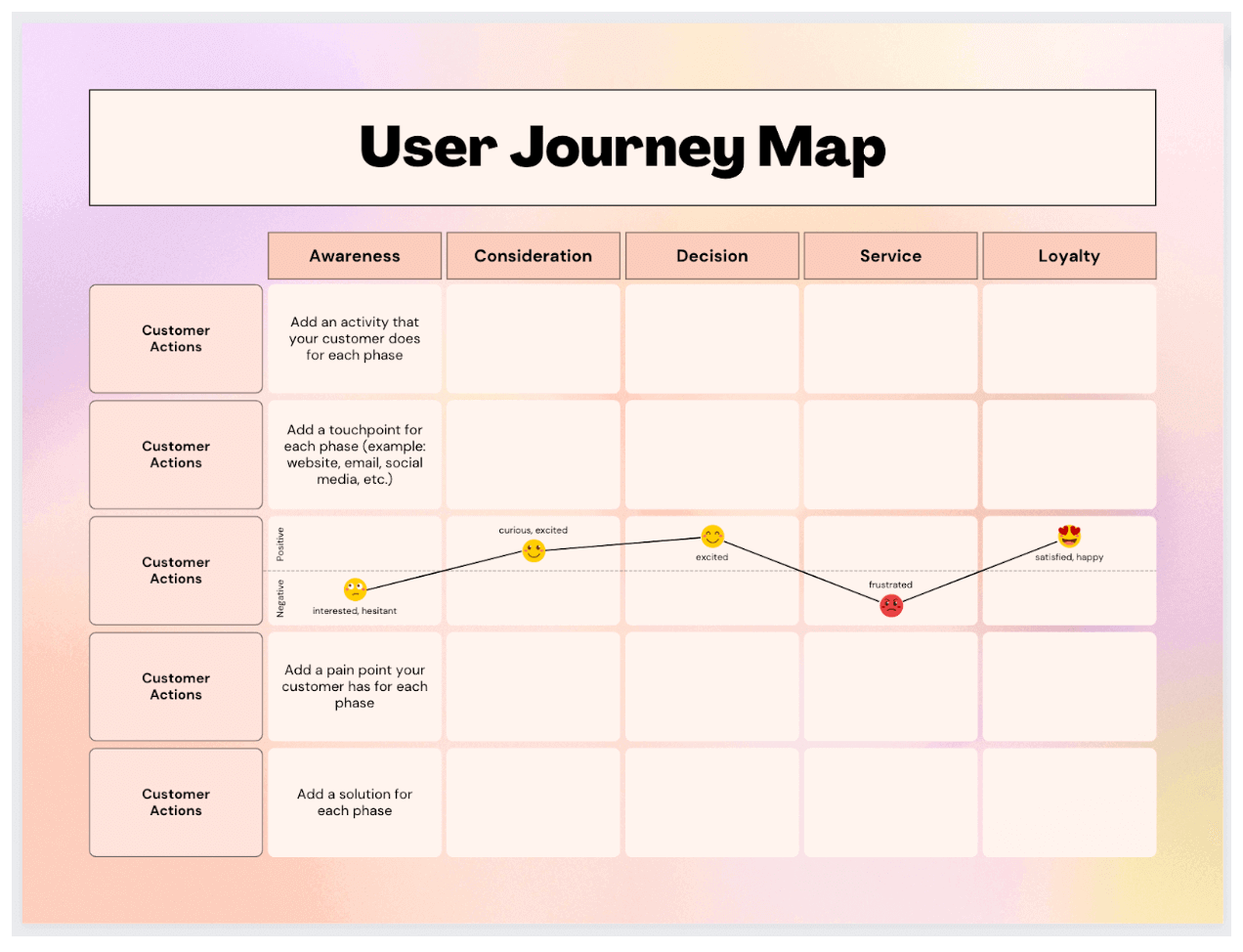
2. Define your persona and scenario
Each user journey map you create should represent a specific user journey from the perspective of a specific user persona. So: determine which UX persona will feature in your journey map, and what scenario they’re in. In other words, what goal or task are they trying to complete?
Add details of your persona and scenario at the top of your user journey map.
3. Outline key stages, actions, and touchpoints
Now it’s time to flesh out the user journey itself. First, consider the user scenario you’re conveying and think about how you can divide it into high-level phases.
Within each phase, identify the actions the user takes and the touchpoints they interact with.
Take, for example, the scenario of signing up for a dating app. You might divide the process into the following key phases: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Service, and Advocacy .
Within the Awareness phase, possible user actions might be: Hears about the dating app from friends, Sees an Instagram advert for the app, Looks for blog articles and reviews online.
4. Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
Next, step even further into your user’s shoes to imagine what they may be thinking and feeling at each stage, as well as what pain-points might get in their way.
To continue with our dating app example, the user’s thoughts during the Awareness phase might be: “ I’ve never used online dating before but maybe I should give this app a try…”
As they’re new to online dating, they may be feeling both interested and hesitant.
While looking for blog articles and reviews, the user struggles to find anything helpful or credible. This can be added to your user journey map under “pain-points”.
5. Identify opportunities
Now it’s time to turn your user pain-points into opportunities. In our dating app example, we identified that the user wanted to learn more about the app before signing up but couldn’t find any useful articles or reviews online.
How could you turn this into an opportunity? You might start to feature more dating app success stories on the company blog.
Frame your opportunities as action points and state who will be responsible for implementing them.
Here we’ve started to fill out the user journey map template for our dating app scenario:
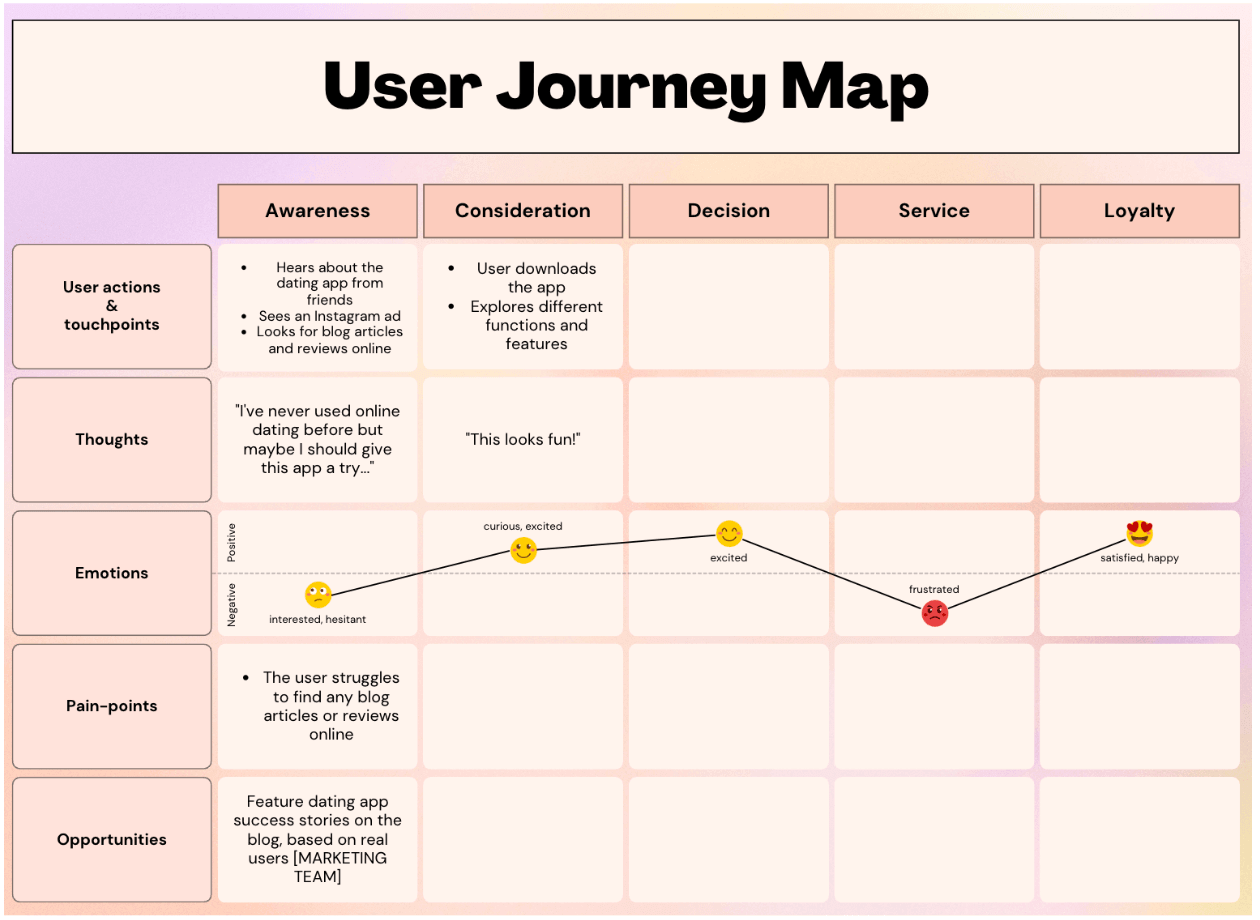
Repeat the process for each phase in the user journey until your map is complete.
6. Define action points and next steps
User journey maps are great for building empathy and getting you to see things from your user’s perspective. They’re also an excellent tool for communicating with stakeholders and creating a shared understanding around how different users experience your product.
Once your user journey map is complete, be sure to share it with all key stakeholders and talk them through the most relevant insights.
And, most importantly, turn those insights into clear action points. Which opportunities will you tap into and who will be involved? How will your user journey maps inform the evolution of your product? What are your next steps?
Customer journey maps in UX: the takeaway
That’s a wrap for user journey maps! With a user journey map template and our step-by-step guide, you can easily create your own maps and use them to inspire and inform your product design process.
For more how-to guides, check out:
- The Ultimate Guide to Storyboarding in UX
- How to Design Effective User Surveys for UX Research
- How to Conduct User Interviews
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the best UX insights and career advice direct to your inbox each month.
Thanks for subscribing to our newsletter
You'll now get the best career advice, industry insights and UX community content, direct to your inbox every month.
Upcoming courses
Professional diploma in ux design.
Learn the full UX process, from research to design to prototyping.
Professional Certificate in UI Design
Master key concepts and techniques of UI design.
Certificate in Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
Collaborate effectively with software developers.
Certificate in UX Design Fundamentals
Get a comprehensive introduction to UX design.
Professional Certificate in Content Design
Learn the skills you need to start a career in content design.
Professional Certificate in User Research
Master the research skills that make UX professionals so valuable.
Upcoming course
Build your UX career with a globally-recognised, industry-approved certification. Get the mindset, the skills and the confidence of UX designers.
You may also like

The ultimate guide to mobile app design: Follow these UI principles & best practices
The best online survey tools to use in 2024

What is colour theory? A complete introductory guide
Build your UX career with a globally recognised, industry-approved qualification. Get the mindset, the confidence and the skills that make UX designers so valuable.
The Complete Guide To Customer Journey Mapping (With Examples)


GorillaDesk Alternatives & Competitors
Explore the top GorillaDesk alternatives and competitors. Discover the best business management software solutions tailored to your industry.
FieldRoutes helps field service companies simplify, scale, and grow.
- Woopra Logo
- Platform Customers Pricing Resources Company
- Log in Start For Free
- Automations
- Integrations
- Documentation
How to Create a Customer Journey Map: A Step-By-Step Breakdown

There are often a lot of twists and turns in the customer journey, with each individual experience being unique.
That said, there is a predictable sequence of touchpoints throughout the sales funnel.
Mapping each customer touchpoint out effectively helps enhance the user experience and increases the chances of customer success.
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
Simply put, a customer journey map is a visualization of the process someone undertakes as they move through the various touchpoints of the customer journey.
It typically starts with the initial interaction they have, like visiting your website for the first time when gaining brand awareness, and then moves through the subsequent stages of consideration, purchase, retention, and advocacy.
Here’s an example of what a typical customer journey map may look like.
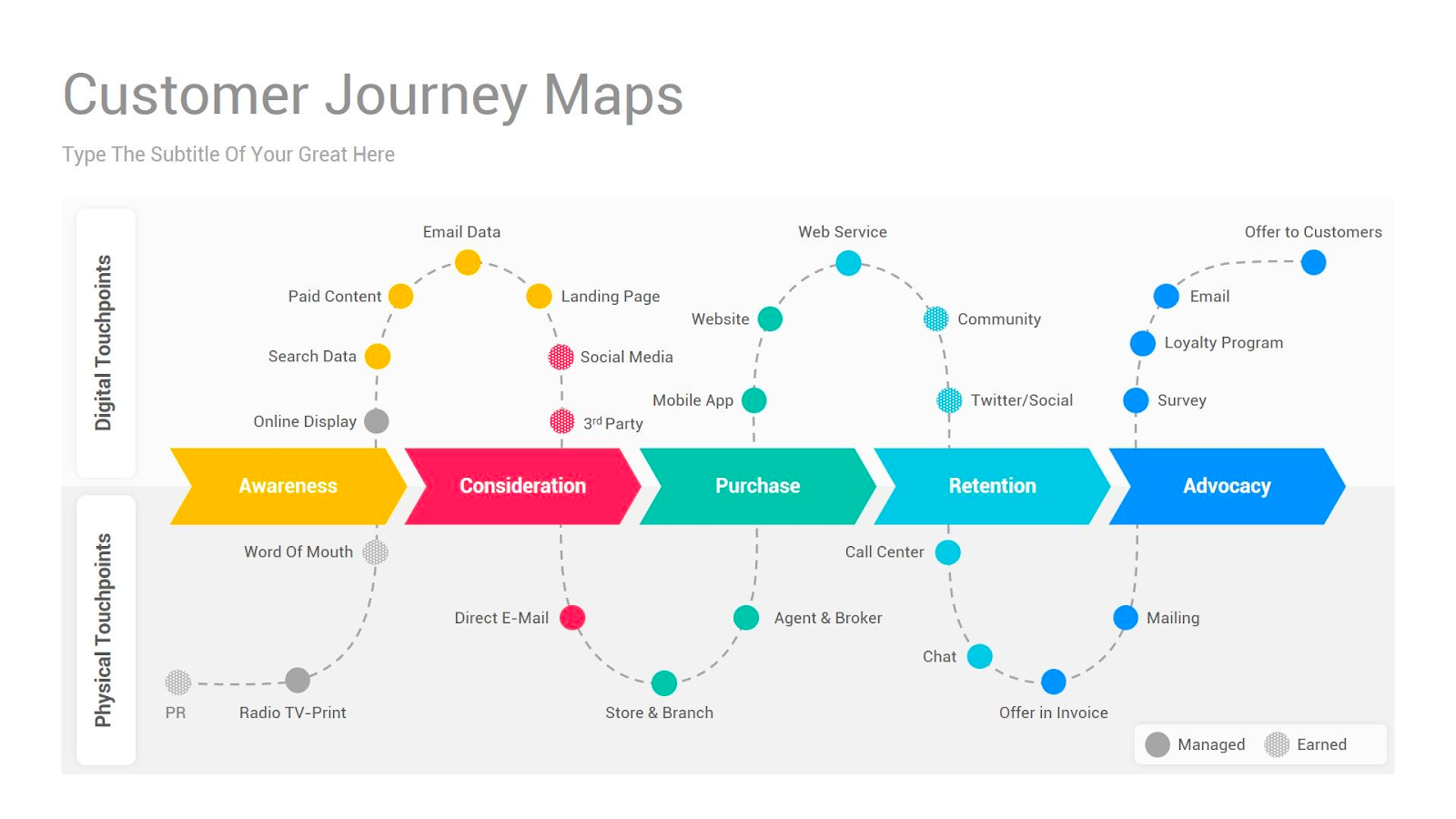
Notice how it concisely outlines the touchpoints customers take as they move throughout the customer journey.
It starts in the awareness stage with touchpoints like search results or paid content, moves on to the consideration stage with social media or email, then to the purchase stage, and so on.
There are four main purposes of customer journey mapping.
- Flesh out the step-by-step process someone takes from being a potential customer to a lead to an actual customer and ideally, a loyal advocate
- Understand the customer’s perspective
- Identify friction points that are causing issues with customer engagement
- Discover opportunities to reduce pain points and improve the overall customer experience
By doing so, you set the stage for better product design, more effective customer journey marketing, increased customer satisfaction, better customer retention, and ultimately, greater customer success.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
1. define business goals.
Before doing anything else, you’ll want to pinpoint exactly what you’re looking to accomplish with customer journey mapping.
Some common examples include:
- Optimizing each touchpoint in the customer experience
- Identifying areas with higher than average dropoff
- Resolving issues that are leading to excessive dropoff
- Improving the overall customer experience both during the buyer journey and post-purchase
Clearly articulating what you’re trying to achieve is essential because it will direct the path you take for subsequent steps of customer journey mapping.
Note that a big part of effectively defining business goals is getting input from multiple key stakeholders in your company who are responsible for different aspects of the customer experience.
For instance, you may want to get input from your marketing leaders when developing the awareness and consideration stages of your customer journey map, input from your sales leaders when ironing out the purchase stage, and input from your customer service leaders when constructing the retention and advocacy stages.
It’s also smart to perform extensive user research and incorporate customer feedback to ensure you address the right pain points and tackle the issues that are most pressing for creating a positive user experience and long-term customer loyalty.
This should make for cohesive CX journey mapping where touch points flow smoothly from one to the next.
2. Identify Key Stages in the Customer Journey
Next, you’ll want to pinpoint the exact sales funnel stages involved with the customer journey.
The sales funnel stages can vary slightly from company to company, but as we mentioned earlier, some common ones include:
- Consideration
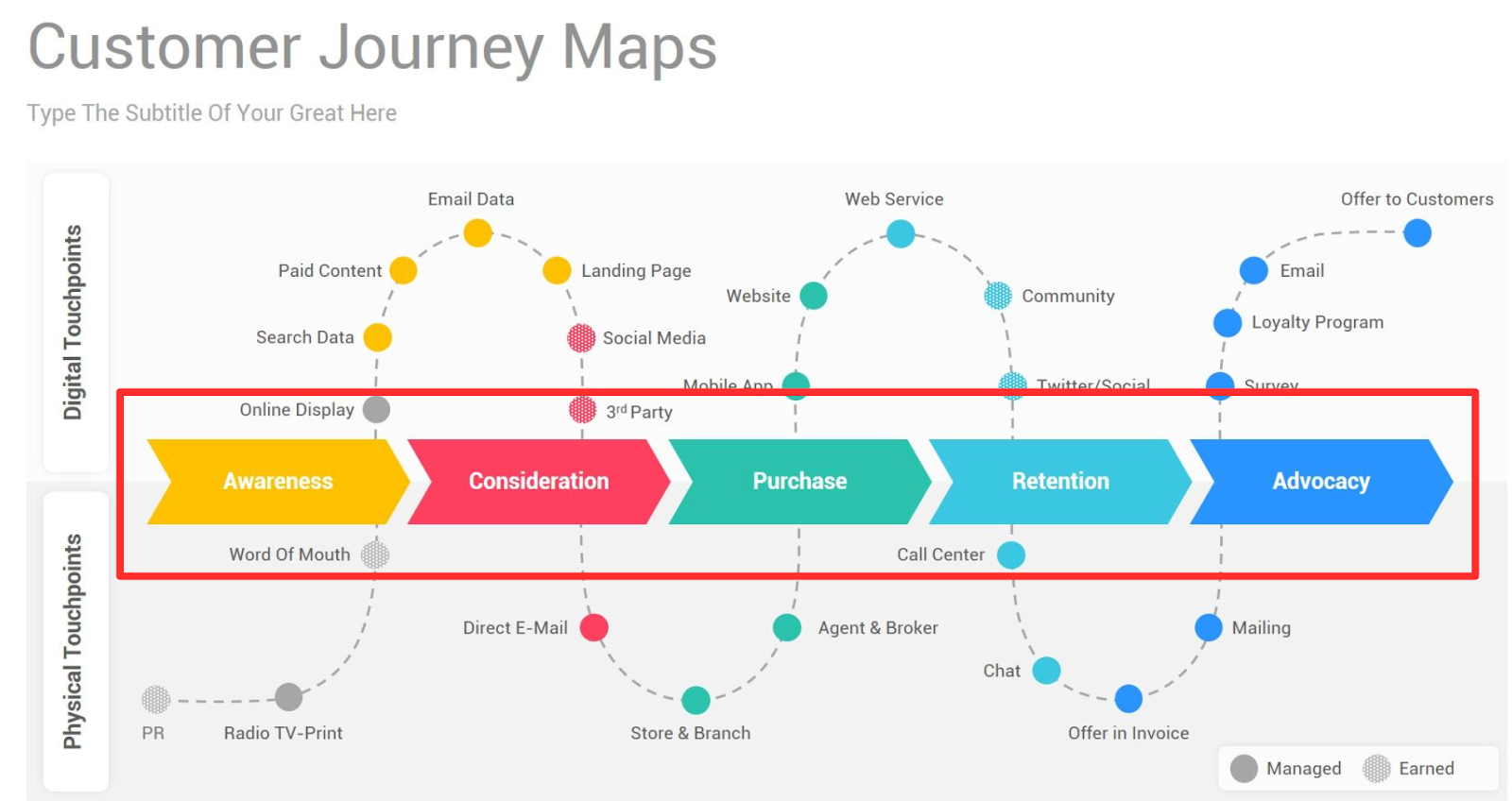
Fleshing the key stages out like this will show you the path users take as they go from being a prospect to a lead to a customer to an advocate.
By visualizing the key stages like this, you’ll see how each stage flows into the next — something that’s vital for making the customer journey as seamless as possible, meeting customer needs, and improving overall customer experience quality.
This is also what the next step in constructing customer journey maps is built on, which brings us to our next point.
3. Define Customer Touchpoints
You can think of the key stages in the customer journey on the macro level and the next step in the process — defining customer touchpoints — on the micro level.
These are the smaller interactions that customers take as they move from stage to stage in the user journey.
This can include digital touchpoints like becoming aware of your brand through an online ad, a search engine, paid content, and so on.
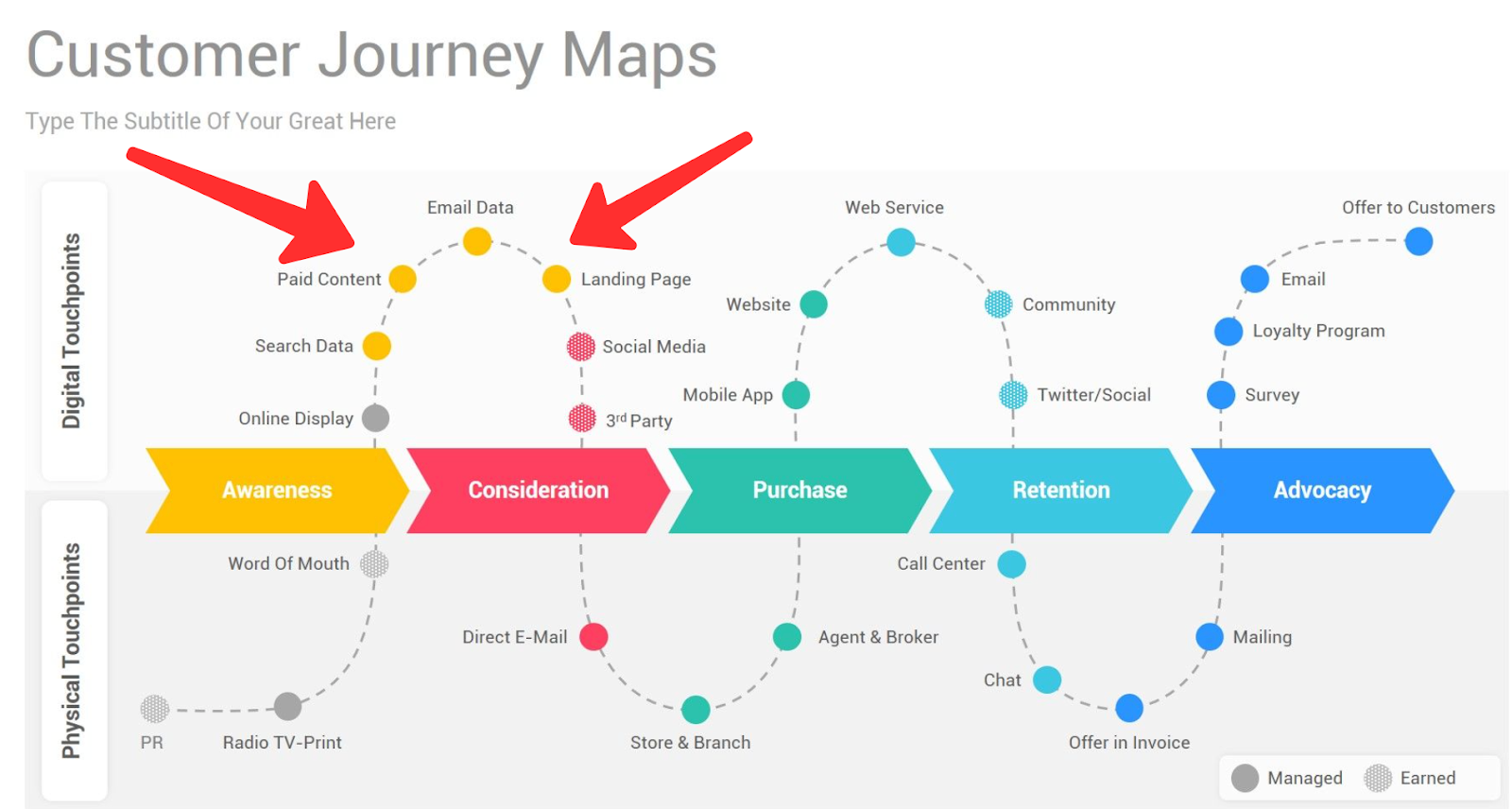
It can also include physical touchpoints like word-of-mouth.
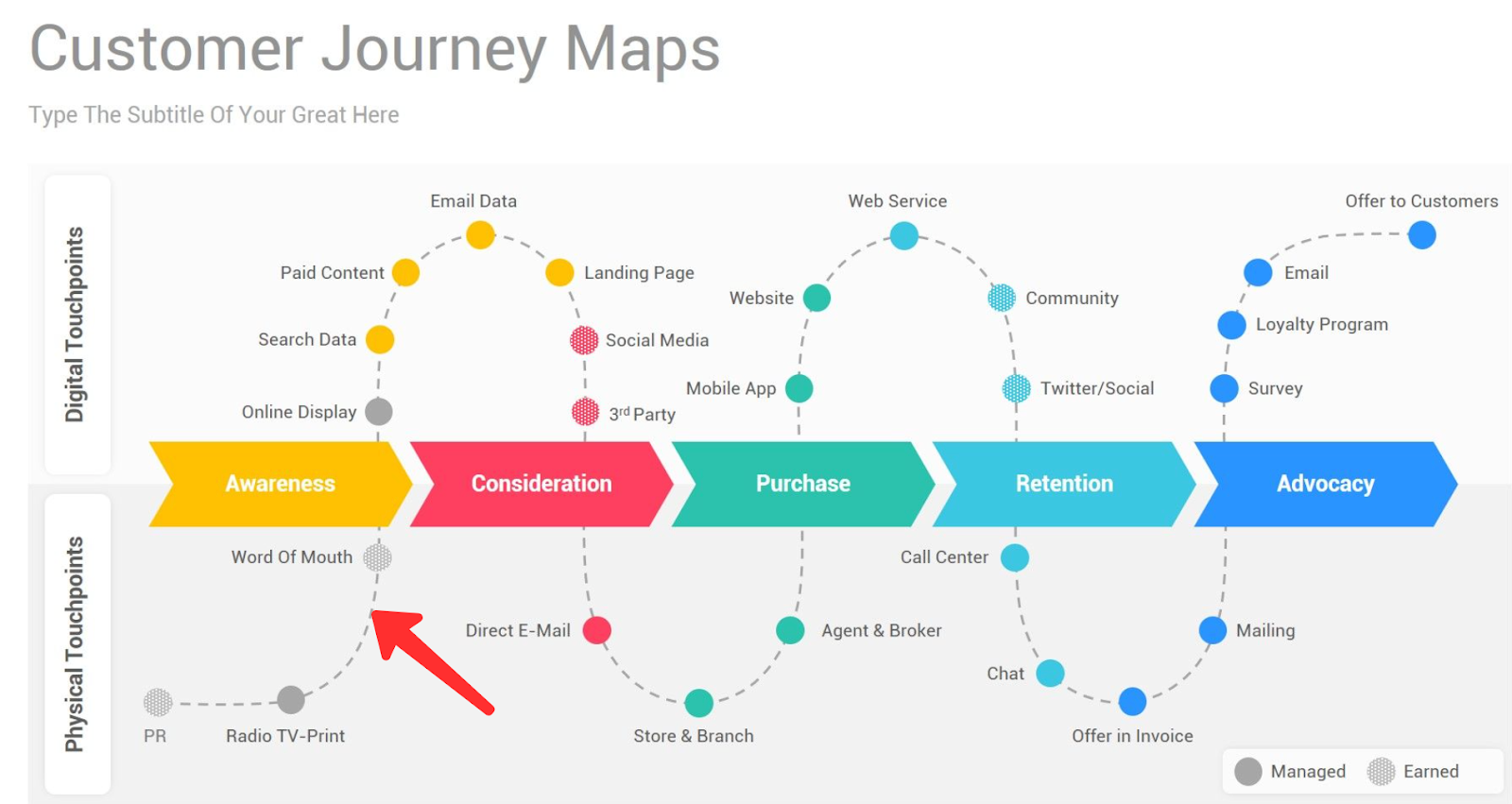
Customer touchpoints will account for the majority of your customer journey map and help you visualize how people interact with your brand.
The exact number of touchpoints can vary considerably, so defining them is highly individualistic.
When identifying them, you’ll want to carefully consider the typical customer journey and write down every step involved. Then, arrange each touchpoint sequentially so you can see the big picture.
4. Design a Visual Representation of the Customer Journey
After defining business goals, identifying key stages in the customer journey, and defining customer touchpoints, it’s time to actually create your customer journey map.
Here, you’ll create a visual representation of what your business’s specific customer journey looks like for a bird’s-eye view.
To do this effectively, it’s helpful to use strong visual elements like different colors, symbols, bullets, and emojis so you can easily see everything at a glance.
Here’s an example of what an online shopping customer journey map could look like.
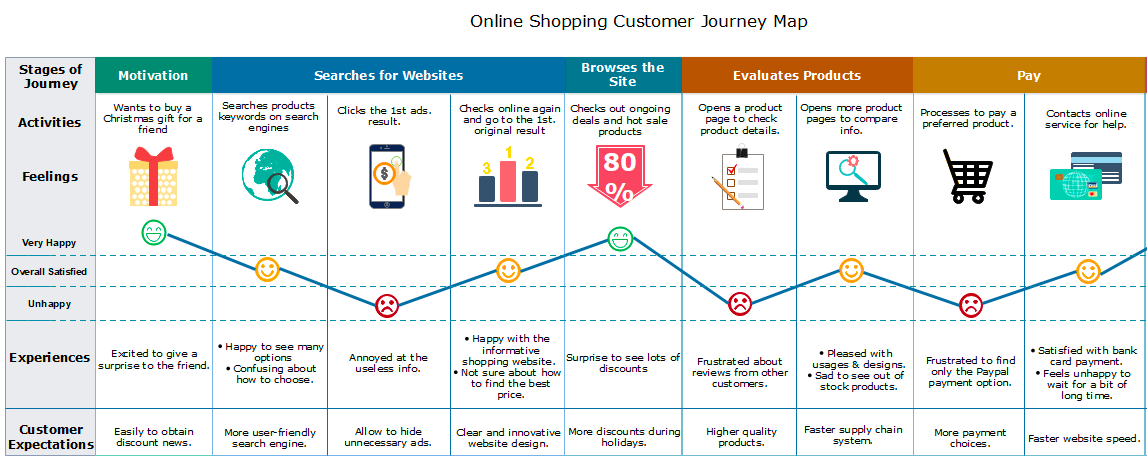
When it comes to customer journey mapping tools, there are several options available.
If you’re looking for something bare-bones and simple, you can use Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
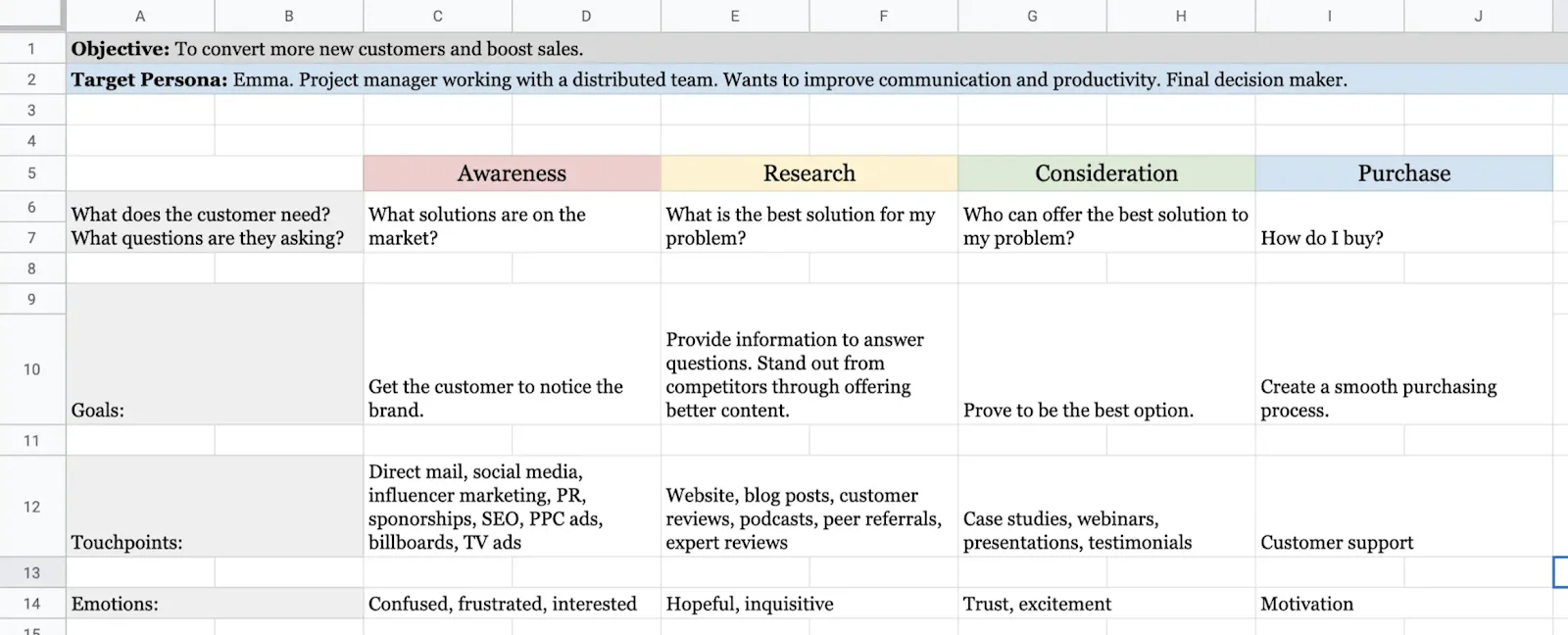
If you want something a bit more advanced, you can use HubSpot’s Customer Journey Map Template , which includes seven free templates (more on this later).

Or, if you want software with extensive features that are specifically designed for creating customer journey maps, you can find a list of the top 10 products here .
Note that most companies have more than one customer persona. Therefore, you may need to create multiple customer journey maps while targeting each individual buyer persona.
Customer Journey Map Templates
When most people think of customer journey mapping, they think of the classic buyer’s journey.
And they wouldn’t be wrong.
Generally, that’s the most commonly used customer journey map and the type of mapping we used in the customer journey map examples above.
But it’s certainly not the only type of mapping you can use.
As we’ll learn in a moment, there are also customer journey maps that target specific segments of the buyer’s journey and customer journey maps that focus on what you want your ideal journey to be like.
For the rest of this post, we’ll cover four of the most popular customer journey map templates you can use for different situations.
That way you can cover all the angles and increase the chances of customer success every step of the way.
Buyer’s Journey
As we just mentioned, this is widely considered the most classic type of customer journey mapping.
When mapping the buyer’s journey, you follow the key stages in the customer journey (awareness, consideration, purchase, etc.) like we outlined above, along with customer touchpoints.
Here’s a simple template journey map example for the buyer’s journey from HubSpot, which you can find for free here .
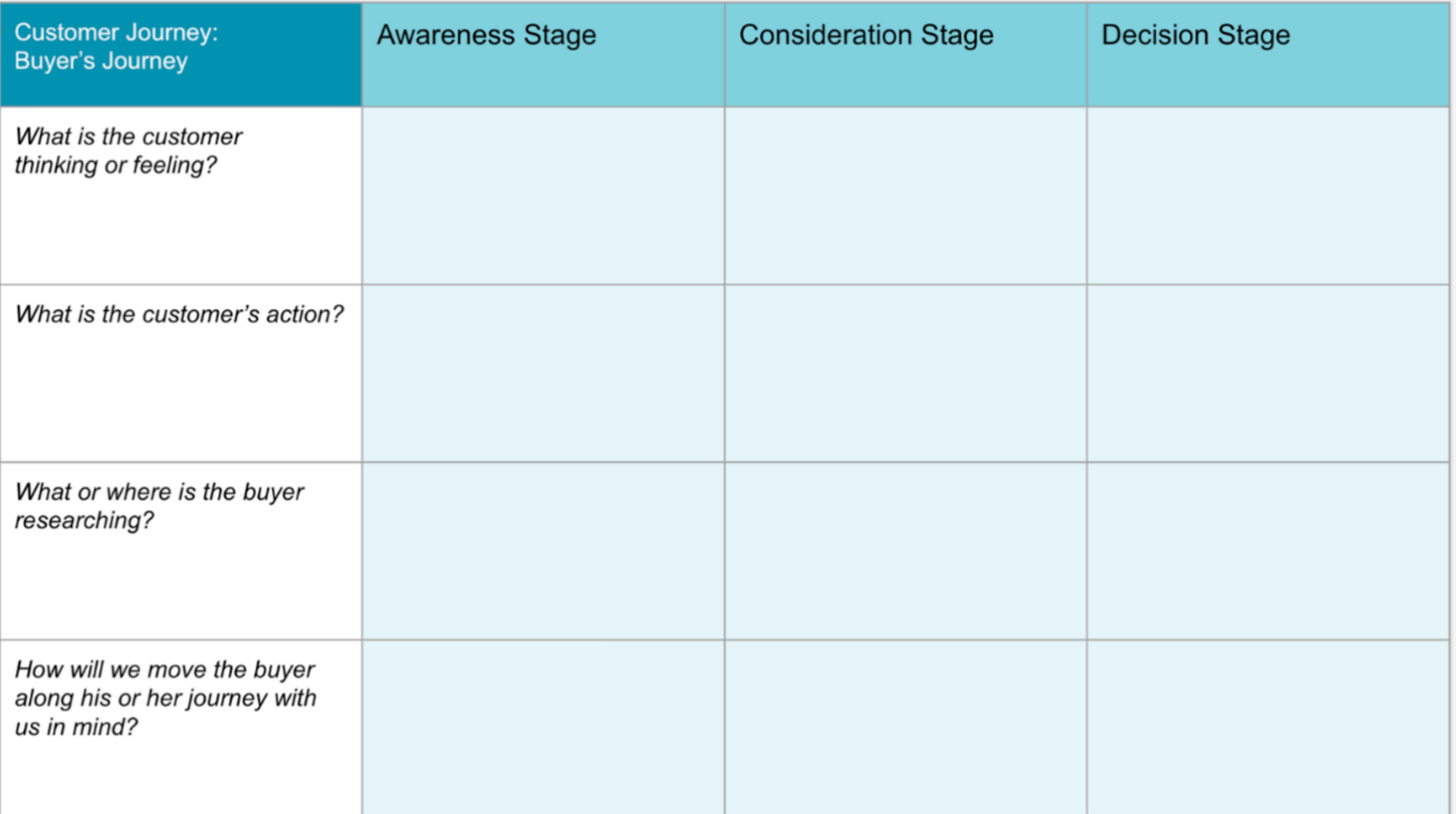
The default starting point is extremely simple. It includes just three stages and a handful of questions to understand customer interaction.
However, you can easily add more stages, questions, and additional information to fully customize the buyer’s journey so that it’s specific to your business.

This template, admittedly, won’t provide the same depth as some of the more advanced tools for creating customer journey maps, but it should be adequate for many business owners.
If you don’t need anything fancy and are testing out customer journey maps for the first time, HubSpot should be more than sufficient.
Whatever template you use, buyer’s journey mapping tends to be a good starting point as it helps you visualize the entire process from someone entering your sales funnel to converting to becoming a loyal customer.
This is integral for optimizing every aspect of the customer experience end-to-end, and from a product standpoint, is essential for achieving UX mastery.
It’s also worth mentioning that if you’re looking to improve your UX design skills, The Interaction Design Foundation is an excellent resource for doing so. They offer a wide variety of courses from the beginner to expert level and only charge a flat monthly fee for access to all courses.
Now that we’ve tackled buyer journey mapping, let’s look at three other popular types of customer journey map template options that are also available.
Future State
In most cases, the buyer’s journey is the current journey customers are taking.
While there will likely be several areas you’re satisfied with, your existing customer journey probably won’t be ideal and likely isn’t meeting customer expectations 100%.
For example, there may be friction points along the way where customers are attempting to accomplish a goal. Or, there may be higher than acceptable dropoff in a particular area like using core features or becoming a paid customer after using a free product version.
By the way, if you want to holistically understand the customer journey and generate objective customer data, you can use a customer journey analytics platform like Woopra . This enables you to analyze essential customer journey metrics so you can see what it looks like end-to-end.
With future state customer journey mapping, you design a new map with new touchpoints and engagements based on your ideal vision.
That way, you’ll know what needs to be done to create the optimal customer journey.
If you’ve already experimented with creating customer journey maps and are looking to take the next step to refine the customer experience, you’ll likely be interested in future state mapping.
HubSpot offers a free future state template as well, which allows you to outline the series of steps that need to be taken to make the customer journey as perfect as possible. And it’s completely customizable.
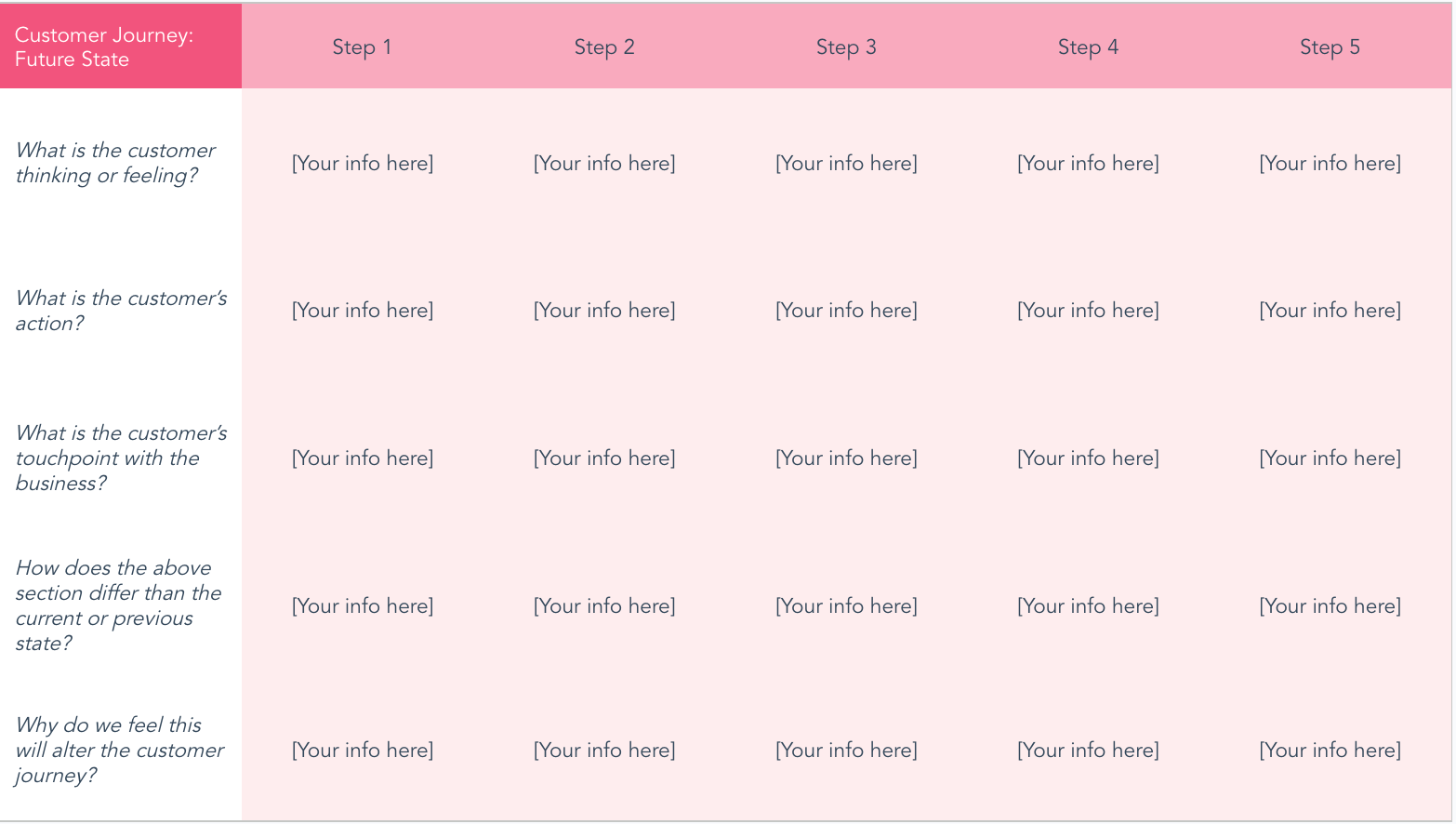
You simply list the steps you want to take to create an amazing customer experience and ask key questions regarding customer behavior.
It’s nothing over the top, but it should get the job done for many business owners.
Lead Nurturing
Although technically part of the buyer’s journey, some marketers choose to create a lead nurturing customer journey map because of the extreme importance of lead nurturing.
After all, any major holes in the lead nurturing process can disrupt sales as a whole. And no matter how good your marketing team is at generating leads, the impact will be negated if you can’t successfully nurture them.
To optimize this area of sales, you can create a lead nurturing map using a template like this one.
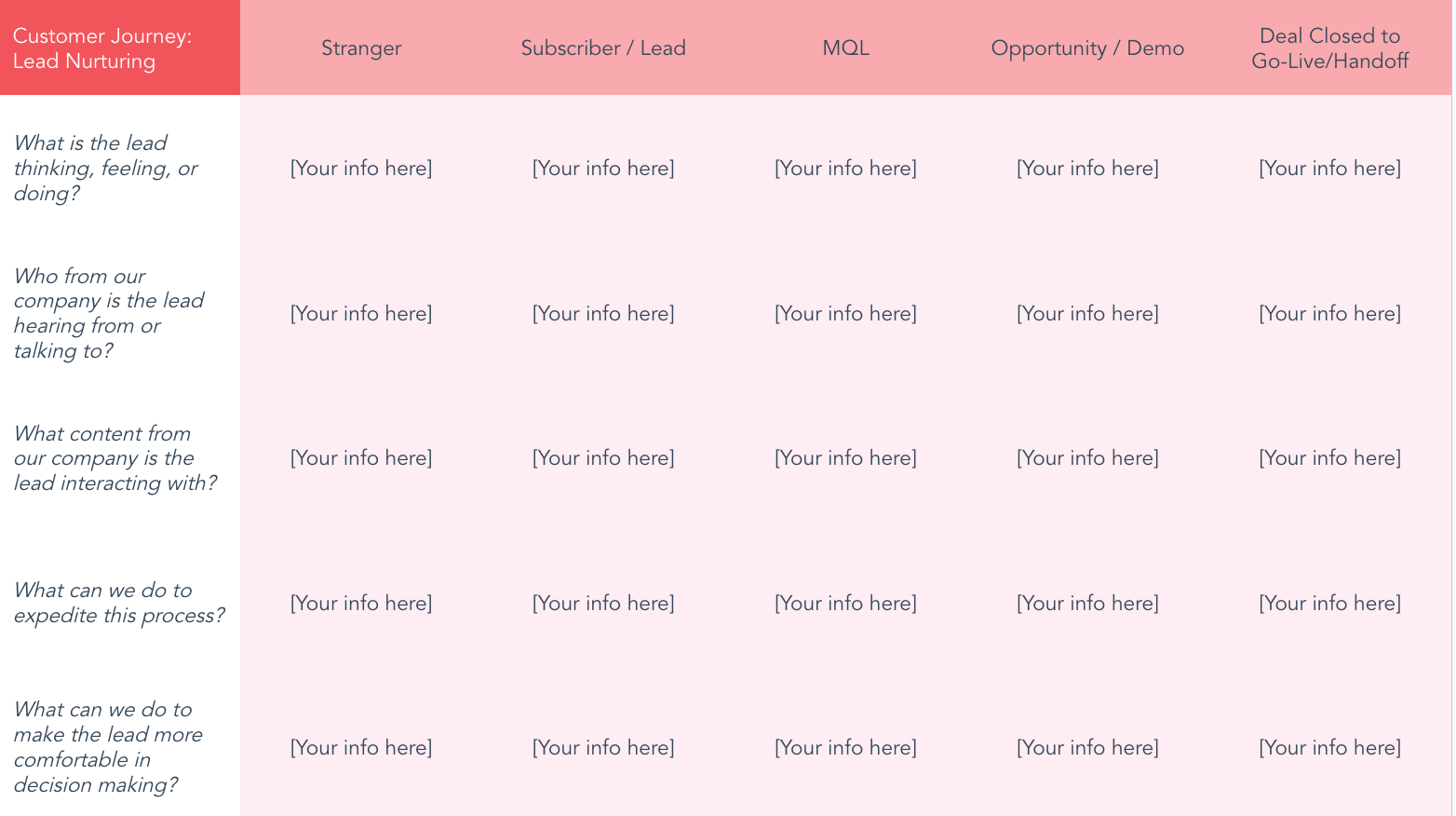
Here, the default starts with someone being a stranger, then moves on to them being a subscriber/lead, then a marketing qualified lead (MQL), a sales opportunity/demo, then a deal closed/handoff.
Again, everything is customizable, so you can adjust the lead nurturing customer journey to your exact specifications. And, it too, is available for free from HubSpot .
Customer Service and Support
Once again, a truly rewarding user experience goes beyond the purchase and ensures a customer is satisfied well after they’ve bought a product.
Like lead nurturing, customer service and support are also technically part of the buyer’s customer journey map.
However, it dives deeper into this area of the sales funnel with the intention of increasing customer retention and advocacy.
And I think we can all agree that this is incredibly important given that “Happy and satisfied customers are 87% more likely to purchase upgrades and new services.”
Here’s yet another free customer journey map template you can get from HubSpot that focuses specifically on customer service and support.

With it, you can follow how a customer goes from engaging in the normal use of a product to noticing an issue/having a complaint to asking for help/contacting customer support to speaking with support to conflict resolution.
Having a clear overview of the touchpoints involved with this process should help you fully understand the flow so you can 1) see things from a customer’s point of view and 2) identify issues that may be detrimental to customer support.
For inspiration from real-life major brands like Spotify, TurboTax, and Amazon, here’s a list of customer journey map examples you can learn from.
Crafting an Exceptional User Experience with Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is a simple yet effective way to visualize each touchpoint in the user journey holistically for each buyer persona.
From the initial moment someone becomes aware of your brand to the time of purchase and beyond, customer journey maps allow you to see how users move throughout the entire lifecycle.
And as we’ve learned, this serves several important purposes, including seeing the buying process from a customer’s point of view, identifying customer pain points, and unearthing opportunities to improve the customer experience end-to-end.
It’s just a matter of following the correct customer journey mapping guidelines and using the appropriate template to outline the buying process.
Then, tracking key customer journey metrics like engagement, churn rate, and customer satisfaction with an analytics platform like Woopra or Google Analytics should help you refine your customer journey mapping to fully optimize the customer experience.
Full insight into the customer journey. No SQL required.
Get started with Woopra for free to see who your customers are, what they do and what keeps them coming back.
Related Articles
The beginner’s guide to behavioral targeting to increase conversions.

How to get Started with Analytics

From Emails to Customers — Woopra Campaign Tracking
5 actionable methods to engage mobile customers, explore topics.
© Woopra, Inc. 600 California St 11th Floor San Francisco, CA 94108
- Request a demo
- Product Analytics
- Customer Analytics
- Customer Journey Analytics
- Google Analytics F.A.Q.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of service
What is a Customer Journey Map and How to Make One: A Step-by-Step Guide

A journey map, often referred to as a customer journey map or user journey map, is a visual representation that outlines the various steps and interactions a person or a customer goes through when engaging with a product, service, or organization. These maps are designed to provide a comprehensive view of the entire journey from the user’s or customer’s perspective, allowing businesses and organizations to better understand the experiences, emotions, and pain points of their users or customers.
How to Gain Valuable Insights from Your Customers with a Customer Journey Map
How to create a customer journey map, the customer journey mapping process, an example of a customer journey map, final thought.
Key components of a journey map typically include:
- Stages: The journey is divided into distinct stages or phases, which can vary depending on the context but often include stages like awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase.
- Touchpoints: These are the specific points of interaction between the user or customer and the product, service, or organization. Touchpoints can be both digital (e.g., website, app) and physical (e.g., in-store visit, phone call).
- Actions: The actions or activities that the user or customer takes at each touchpoint are documented. This may include researching products, making a purchase, seeking customer support, and more.
- Emotions: Emotions experienced by the user or customer are often included to provide insight into their feelings and reactions at different points along the journey. Understanding these emotions can help businesses tailor their interactions to create more positive experiences.
- Pain Points: Any difficulties, frustrations, or challenges that users or customers encounter during their journey are noted as pain points. Identifying these pain points is crucial for making improvements and enhancing the overall experience.
- Opportunities: Opportunities for improvement, innovation, or enhancement are also highlighted. These are areas where organizations can make changes to create better experiences or provide additional value.
- User or Customer Persona: In some journey maps, a user or customer persona is included to represent the typical characteristics and needs of the individuals going through the journey. This helps in personalizing the journey map.
- Data and Insights: Relevant data, research findings, and customer feedback may be incorporated to support the observations and conclusions made in the journey map.
Journey maps are valuable tools for businesses and organizations in several ways:
- Understanding the Customer: They help in gaining a deeper understanding of how customers engage with products and services, their needs, and their pain points.
- Improving Customer Experience: By identifying pain points and opportunities, organizations can make strategic improvements to enhance the overall customer experience.
- Alignment: Journey maps can be used to align various teams and departments within an organization to ensure a consistent and customer-centric approach.
- Innovation: They can inspire innovation by highlighting areas where new features, services, or strategies could be implemented to better meet customer needs.
- Decision Making: Journey maps provide valuable insights that can inform decision-making processes related to marketing, product development, and customer support.
Overall, journey maps are a powerful tool for businesses and organizations to empathize with their users or customers and make data-driven decisions to optimize the customer experience.
Customer journey maps are invaluable tools for businesses and organizations because they offer numerous benefits and insights that help improve the overall customer experience and drive business success. Here are some of the key reasons why customer journey maps are important:
- Understanding the Customer Perspective: Customer journey maps provide a detailed view of the customer’s perspective, helping organizations empathize with their customers. This understanding is crucial for tailoring products, services, and interactions to meet customer needs and expectations.
- Identifying Pain Points: Journey maps highlight pain points and challenges that customers face during their interactions with a brand. Recognizing these pain points allows organizations to address and resolve issues, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Optimizing Touchpoints: By analyzing the touchpoints where customers engage with a brand, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement. This may involve streamlining processes, enhancing digital interfaces, or providing better training to customer-facing teams.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: When organizations use journey maps to identify pain points and make improvements, it often results in a better overall customer experience. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal, repeat customers and advocates for the brand.
- Personalization and Segmentation: Journey maps help in creating personalized experiences for different customer segments or personas. By tailoring interactions to specific needs and preferences, organizations can increase engagement and conversion rates.
- Cross-Functional Alignment: Customer journey maps are collaborative tools that involve various departments within an organization, including marketing, sales, customer support, product development, and more. This alignment ensures a consistent and coordinated approach to customer interactions.
- Innovation and Product Development: Insights from journey maps can drive innovation by highlighting areas where new products or services can be developed to better meet customer needs. It guides product development efforts toward customer-centric solutions.
- Reducing Customer Churn: By identifying pain points and addressing them proactively, organizations can reduce customer churn. When customers have a positive and frictionless experience, they are less likely to switch to competitors.
- Measuring and Tracking Progress: Journey maps provide a baseline for measuring and tracking improvements over time. Organizations can use key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the impact of changes and make data-driven decisions.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that prioritize the customer experience and use journey maps to continually refine it gain a competitive advantage. Exceptional customer experiences can set a brand apart in a crowded market.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Engaged employees who understand the customer journey and their role in it are more motivated to deliver exceptional service. Journey maps help employees see the bigger picture and their contribution to it.
- Adaptation to Changing Market Conditions: As market dynamics evolve, customer journey maps can be updated to reflect changing customer behaviors and preferences. This adaptability ensures that organizations stay relevant and responsive to customer needs.
In summary, customer journey maps serve as powerful tools for enhancing the customer experience, increasing customer satisfaction, and driving business growth. By putting the customer at the center of their operations and decision-making processes, organizations can build lasting relationships and succeed in today’s competitive landscape.
Gaining valuable insights from your customers through a customer journey map involves a combination of research, analysis, and empathy. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to start the process by conducting user research:
1. Define Your Objectives: Begin by clearly defining your objectives for creating the customer journey map. What specific insights are you seeking? Are you looking to identify pain points, improve satisfaction, or optimize specific touchpoints?
2. Identify Your Target Audience: Determine which customer segments or personas you want to focus on. Your insights may vary depending on the characteristics and needs of different customer groups.
3. Gather Data: Collect relevant data from various sources to inform your journey map. This data can include:
- Surveys: Create surveys to collect quantitative data on customer preferences, satisfaction, and behaviors.
- Interviews: Conduct in-depth interviews with customers to gain qualitative insights into their experiences and emotions.
- Observation: Observe how customers interact with your product or service in real-life situations to understand their behaviors.
- Analytics: Analyze data from your website, app, or other digital platforms to uncover user behavior patterns.
- Customer Support Data: Review customer support tickets and inquiries to identify common issues and challenges.
- Feedback Forms: Analyze feedback forms, comments, and reviews from customers to identify recurring themes.
4. Create User Personas (If Applicable): Develop detailed user personas representing different customer segments. These personas should include demographic information, motivations, goals, and pain points.
5. Map the Customer Journey: Create a visual representation of the customer journey, including stages and touchpoints. Map out the customer’s interactions and experiences from initial awareness through post-purchase and beyond.
6. Document Insights: At each touchpoint, document key insights, observations, and data points. Include both quantitative data (e.g., satisfaction ratings) and qualitative data (e.g., customer comments and emotions).
7. Identify Pain Points: Pay special attention to pain points where customers encounter difficulties, frustrations, or obstacles. These are areas where immediate improvement can enhance the customer experience.
8. Highlight Opportunities: Identify opportunities where you can enhance the customer journey. These may involve introducing new features, communication channels, or support options to improve the overall experience.
9. Analyze Emotions: Consider the emotions customers experience at each touchpoint. Emotional data can provide insights into how customers feel during their interactions with your brand.
10. Prioritize Insights: Prioritize your insights based on their impact on the customer experience and alignment with your objectives. Focus on actionable insights that can drive meaningful improvements.
11. Share Insights and Collaborate: Share the customer journey map and insights with relevant teams and stakeholders within your organization. Collaborate with these teams to develop action plans for improvement.
12. Implement Changes: Execute the planned improvements and changes to address identified pain points and capitalize on opportunities. Monitor the impact of these changes on customer satisfaction and other relevant metrics.
13. Continuously Iterate: Customer journey mapping is an ongoing process. Regularly revisit the map and update it to reflect changing customer behaviors, preferences, and market conditions. Continuously gather new data and feedback to refine your insights.
Starting with user research is a critical first step in creating an effective customer journey map. By understanding your customers’ needs and experiences, you can develop a map that guides improvements and optimizations to enhance the overall customer experience.
The customer journey mapping process is a systematic approach to understanding and improving the customer experience. It involves several key steps to create a visual representation of the customer’s interactions with your product, service, or brand. Here’s a detailed overview of the customer journey mapping process:
- Define Objectives and Scope: Start by clearly defining the objectives you want to achieve with the customer journey map. Identify the specific aspects of the customer experience you want to explore and improve. Decide on the scope, which could be a specific user persona, product, service, or an end-to-end journey.
- Gather Data: Collect relevant data from various sources to inform your customer journey mapping process. This data may include customer feedback, surveys, interviews, analytics, support tickets, and any other sources of customer information. Ensure that your data reflects the chosen scope and objectives.
- Create User Personas (If Applicable): If you’re focusing on specific user personas, develop detailed personas that represent your target customers. Include demographic information, motivations, goals, pain points, and preferred communication channels.
- Identify Touchpoints: Determine the various touchpoints where customers interact with your brand, product, or service. These can include website visits, social media engagement, emails, phone calls, in-store visits, and more.
- Define Customer Journey Stages: Break down the customer journey into distinct stages or phases. Common stages include awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase. Customize these stages to match your specific context and objectives.
- Map the Journey: Start creating the visual representation of the customer journey map. For each stage, map out the touchpoints, actions, emotions, and pain points that customers experience. Consider using a visual format, such as a timeline, flowchart, or infographic.
- Document Insights: As you map the journey, document key insights, observations, and data points at each touchpoint. This should include both quantitative and qualitative information, such as customer behavior, feedback, and emotional responses.
- Analyze Pain Points and Opportunities: Identify pain points where customers face challenges or frustrations, as well as opportunities where you can enhance the customer experience. Use the insights you’ve gathered to pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Prioritize and Plan Improvements: Prioritize the pain points and opportunities based on their impact on the customer experience and alignment with your objectives. Develop an action plan to address these areas, which may involve changes to processes, products, or communication strategies.
- Share and Collaborate: Share the customer journey map with relevant teams and stakeholders within your organization. Collaborate with these teams to ensure alignment and a unified approach to improving the customer experience.
- Implement and Test Changes: Execute the planned improvements and changes to the customer journey. Monitor the impact of these changes and gather feedback from customers to ensure they are effective.
- Iterate and Update: The customer journey map is not a one-time effort. Continuously revisit and update it to reflect changes in customer behavior, market dynamics, and your business offerings. Regularly gather new data and feedback to refine the map and make ongoing improvements.
Throughout the customer journey mapping process, the goal is to gain a deep understanding of your customers, identify pain points, and create a more customer-centric approach to your business. By following this systematic process, you can enhance the overall customer experience and drive business growth.
Creating a full customer journey map typically involves various stages, from initial awareness to post-purchase experiences. Below, I’ll provide a simplified example of a customer journey map for a hypothetical e-commerce business. Please note that real customer journey maps can be much more detailed and complex, tailored to the specific needs and objectives of the organization. This example serves as a basic illustration:
Customer Persona: Sarah, a tech-savvy millennial looking to purchase a new smartphone online.
Stage 1: Awareness
- Action: Click on the ad to learn more.
- Emotion: Curious and interested.
- Action: Reads reviews and watches YouTube videos.
- Emotion: Informed and engaged.
Stage 2: Consideration
- Action: Browse product listings, read specifications, and compare prices.
- Emotion: Evaluative and selective.
- Action: Asks questions about camera quality and delivery options.
- Emotion: Inquisitive and eager for assistance.
Stage 3: Purchase
- Action: Fill in shipping and payment details.
- Emotion: Anxious but ready to buy.
- Action: Check her email for the confirmation and delivery date.
- Emotion: Relieved and anticipatory.
Stage 4: Post-Purchase
- Action: Tracks the package as it’s in transit.
- Emotion: Excited and informed.
- Action: Inspect the product, set it up, and explore features.
- Emotion: Satisfied and delighted.
- Action: Write a positive review on the e-commerce website.
- Emotion: Engaged and appreciative.
- Action: Clicks on links to explore recommended accessories.
- Emotion: Interested in enhancing the product.
This is a simplified example of a customer journey map. In reality, customer journey maps can be much more detailed, including additional stages, touchpoints, and layers of data such as user emotions, pain points, and metrics. The level of complexity and the specific touchpoints you include depends on the nature of your business and your research findings. The goal is to provide a comprehensive view of the customer’s interactions and emotions throughout their journey.
Explore the extensive collection of over 150 carefully crafted Customer Journey Map Templates and Examples and this Customer Journey Map Template .
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, understanding and optimizing the customer journey is paramount. As we conclude this step-by-step guide to crafting effective customer journey maps, remember that these maps are not just diagrams; they are invaluable tools that bridge the gap between your brand’s vision and your customers’ expectations.
By empathizing with your customers, conducting thorough research, and following a structured approach, you can create journey maps that drive meaningful change. These maps pave the way for enhanced customer experiences, improved satisfaction, and long-term loyalty.
In a world where customers hold the key to success, crafting exceptional journeys isn’t just an option—it’s a strategic imperative. So, embark on this journey of understanding, adaptability, and customer-centricity, and watch your business flourish in an age where the customer is truly king.
#CustomerJourneyMap #CXStrategy #CustomerExperience #JourneyMapping #UserResearch #CustomerEmpathy #CustomerInsights #StepByStepGuide #BusinessStrategy #CustomerCentric #UXDesign #DigitalMarketing #CustomerEngagement #MarketingStrategy #CustomerSuccess #UserExperience #CustomerFeedback #CustomerUnderstanding #CustomerSatisfaction #DataDrivenDecisions
Related Post
The top 5 ui ux design mistakes you must avoid, how to lead ux teams like a pro: top 7 strategies for building high-performance and collaboration, unleash the power of ui/ux to create captivating user experiences, leave a reply cancel reply, trending post, scrum 101: what is agile methodology and how to use it for business success, how to master time management for project leadership, unleashing the power of scrum: how agile methodology is revolutionizing business, how to achieve project management success with this proven formula.

Building a Customer Journey Map: A Step-by-Step Guide for Customer Success

A Customer Journey Map is the foundation of your Customer Success Strategy. Yet most CS leaders skip it.
Because it’s damn near impossible to find a simple explanation online of WHAT it is and HOW to accurately map it out. That ends here.
This article will outline what the customer journey map is, why you need it, how to create one with a few fun workshops, and how it can power every part of your customer success strategy.
Don’t be overwhelmed by the length of this article. TLDR – You’re going to put post-its on a wall. Four times.
If you can handle that, you can do a customer journey map.
Prefer to watch instead of read? Here’s an overview:
Customer Journey Mapping and Customer Success
What is Customer Success
Far too many people don’t understand what customer success is, or the benefits. While most of those people are OUTSIDE CS, here’s a simple definition you can use to explain CS to the rest of your company:
A Customer buys a product because they have a problem (A) and want to fix it using your product (B).
Customer success helps take the customer from A to B as quickly and easily as possible.
When you do that they will:
2) Tell their friends (free marketing and new sales!)
3) Buy more from you – because you’ve proven you are trustworthy and can get ^%#* done.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
If Customer Success is getting the customer from A to B, the customer journey map is HOW they get there.
It’s a visual representation of every step both the customer and your company need to take in order for the customer to get from A to B.
In many ways, it’s similar to a Success Map. The difference here is that a Success Map is customer-facing, whereas a customer journey map is internal and also contains some additional strategic guidance.
Pre-Sale vs. Post-Sale Customer Journey
One of the reasons Customer Success Leaders have trouble finding information on the Customer Journey is because Customer Success is relatively new, at least compared to Sales and Marketing, who have been using a Customer Journey for the buyer’s journey. So a Google search is a lot more likely to pull up information on that version. Here’s how they differ:
The Pre-sale Customer Journey Map includes:
User Actions
Pain Points
The Pre-sale customer journey map stages are:
Awareness – Customer becomes aware of their problem
Consideration – They discover there are solutions available and consider different providers
Decision – Customer lets the provider know they are interested in their product
Acquisition – Customer chooses provider and purchases the product
For a long time, most businesses thought that was the end of it. The customer wanted the product, they bought the product… why would there be an issue?
Well first of all, because these are humans and humans are not particularly logical. Second, products are almost never as intuitive as the provider thinks they are. Third, they give the customer too many choices.
The Post-Sale Customer Journey

The Post-Sale Customer Journey Map includes:
➡️ Every step the customer has to take on their end to achieve their desired outcome – and beyond
➡️ Every step the provider (aka your company) has to take on their end to ensure the customer achieves their desired outcome – and beyond
The Post-Sale customer journey map stages are:
Onboarding – Customer learns to use the product and is brought to first success milestone
Adoption – The product becomes part of their everyday life
*Achievement – Customer’s initial goal is achieved
Expansion – Customer’s goal expands to include additional products, services, or licenses
Renewal – What it sounds like…
Advocacy – Customer agrees to testimonials, referrals, social media posts, speaking engagements
While Achievement is not typically included in other articles I’ve read, I think it’s essential to know WHERE in the customer journey it occurs, since it’s, y’know, the whole point.
How they work together
These two journeys together define the customer experience. While it’s typical for Marketing and CS to develop them separately, it’s essential that they are combined to make sure the customer has a positive experience throughout – ESPECIALLY in the transitions between departments (marketing/sales/cs/support)
Customer Journey vs Customer Lifecycle
These can often be used interchangeably, but I like to think of it this way:
The customer journey is the customer’s perspective
The customer lifecycle is your company’s perspective . It’s a way to break up the journey to operationalize, analyze, and improve it.
Why is a Journey Map Important?
Far too many companies focus on themselves. What THEY have to do to drive business outcomes. That is, of course, important. Without that, nobody’s getting paid. (Don’t forget that!)
But by implementing a customer journey map focusing on what the customer is experiencing, and what they need to do internally, you are better able to guide them toward their goals.
It’s far too easy to miss the change management aspect of Customer Success. It’s not only the buyer who is going to use your product. You need to help them get buy-in from the end users. And without the guidance and enablement from CS, it’s 50-50 on whether that will ever happen. And if it doesn’t? An unused tool isn’t getting renewed.
You need more than one Customer Journey Map

I know, I know. Just doing ONE was overwhelming enough. But if you have different use cases, and/or different segments of customers, it will take a different set of steps to get them from A to B.
Even if you think you only have one use case, look at something like Calendly . They have segments for Customer Success, Recruiting, and Education… They don’t talk about booking meetings – they talk about increasing retention, decreasing time to hire, and planning office hours. Even though these customers are all using the same tool, they will use the features differently to achieve those outcomes.
Customer Journey Maps can help you better understand how customers interact with your product. They help you identify the steps and touchpoints customers take in order to achieve their goals. By creating multiple Customer Journey Maps, you can identify how different customer segments interact with different features of your product and how you can tailor your product to meet their needs and achieve better outcomes. With Customer Journey Maps, you can plan out how you can best guide customers from one step to the next, creating an optimal user experience.
How to create a Customer Journey Map
Creating a customer journey map is a great way to gain a better understanding of how customers interact with your business, website, or product. It is a visual representation of a customer’s experience of interacting with your business and is used to identify areas of improvement, create a more personalized experience, and increase customer satisfaction. To create a customer journey map, you will need to collect customer data and feedback, identify touchpoints along the customer journey, and map out the journey itself. You should also identify areas for improvement, and develop strategies to optimize the customer experience. With a customer journey map in hand, you will be able to better understand the customer experience and make improvements that will increase customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Alright enough talk. Let’s get down to action . Here’s how to create a customer-focused journey map.
Important – Customer Journey Mapping is a team sport
Here’s the great news. You cannot and should not do this alone! The best way to create a customer journey map is with your CSMs. Including them in this part of the strategy will give you much more insight into what actually goes on day to day with your customers, even if you are a player-coach. It also improves employee engagement and development because they can see how their thoughts drive results for the whole company. It’s respectful and it’s motivating. And as an added bonus, it’s less work for you.

1. Run Workshops
This will be an interactive brainstorming session between you and the CSMs. (Add CS Ops if you’ve got them!)
You will map the four views of the customer journey below in separate workshops. One for the customer journey, one for your company’s journey, and one or two to list pain points and opportunities for your target audiences.
Don’t overthink it. Get some post-it notes (or a miro board) and have everyone start listing every touchpoint, resource, action, and communication.
List Out All The Action Steps – Internal and External
Workshop 1. customer actions.
Starting with the customer perspective is essential. It’s the customer journey, not the company journey.
What is everything the customer needs to do internally to successfully:
- Onboard – including reaching their first success milestone
- Adopt – make it a part of their routine.
- Achieve their goal using your product
- Expand their use case – approvals etc.
- Renew the product – contracts, legal, finance
- Advocacy – have achieved impressive results using the product. May need to consult with legal
Have everyone create sticky notes for fifteen minutes, then put the stickies on a board and group them together. This will let you see where there is a repeated pattern of success and where customers act differently. Try to think about only SUCCESSFUL customers — those who have a good relationship with your company and either have renewed or have confirmed they will.
I prefer to split this session into two parts – 1) what they have to do to meet their original goal and 2) what has to happen for them to want to expand, renew, and tell their peers. If you don’t complete 1, you can’t get to 2…
*Bonus – Don’t only think of this in terms of the executive stakeholder. You have to consider the motivations of the end users as well.
Workshop 2. Your Company’s actions
Meet again with the same board you created the customer actions on. Then collaborate on the internal version – adding sticky notes in a DIFFERENT COLOR from the client actions.
What are all the internal steps and customer touchpoints your company has to take to ensure the customer meets their goals?
- What other departments get involved and where? (Sale-CS handoff, Implementation team to CS etc)
- Who are the key stakeholders?
- What standard interactions do you have with the customer? (Welcome email, kickoff call, etc.)
- What actions does the CSM take independently
- What are our success milestones?
Workshop 3. Customer Obstacles & Pain Points
No one wants to have points of friction in the customer journey, but it’s better to acknowledge them (internally) and plan around them. Ostriches make terrible CSMs.
- Where along this route have you found that customers complain or don’t complete the required actions?
- How do you get them back on track?
- Are there alternative routes to take if you know there’s going to be an issue?
4. Success Milestones & Opportunities
What are the milestones where the customer sees value? Where do they frequently comment that they liked something? These milestones can be great opportunities to ask for testimonials or prompt upsells (if their goal is within reach).

2. Let Data Be Your Guide
If you have data – USE IT. Data-driven customer journey maps are far more effective than relying on qualitative data. Here’s where you can learn how to use data to drive the customer journey )
The best bet is to use a three-pronged approach:
- CSM Feedback
- Customer Feedback
- Validate and Fill in the Gaps with Data
3. Talk to Customers to Understand Their Journey.
This is the step that seems to stop people in their tracks. This doesn’t have to be complicated. Talk to customers who are doing well with your product. Offer them a Starbucks or Amazon gift card to give some user insights. It’s less about the money ($10-$20 is plenty) and more about the fact that you are acknowledging their time is valuable. You don’t need to beat around the bush.
What to Ask
Give them an excuse to brag. Tell them they have a great use case and they are a great example of a well-done product rollout. Then ask:
- How did you start using the product?
- How does that differ from how you use it now?
- Change can be hard. What did you do internally to roll out the product?
- How do you motivate your employees to use the product?
- How does the product help you achieve your goals in your industry/niche
- What makes you want to keep using the product?
- Is there anything exciting enough about the product to make you recommend it to others?
Then track these on a Miro board (we have a template for this in CSLA ) over a quarter or two. Themes will start to emerge that you can then use to improve your first pass at the customer journey map.
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices

1. Set a Goal for the Journey Map.
No matter what the project is, or how complex the technologies, you have to begin with the end in mind. Otherwise, there’s no point. If I want to drive from New York to Austin, Texas, I could either enter a specific GPS, or I could drive SouthWest. One is going to get me where I want to go. The other will take twice as long and be pretty much pointless.
2. Done is better than perfect
Perfectionism is the enemy here. While you’re busy trying to make it perfect, you’re neglecting your clients. Do the post-its and get a baseline.
3. Measure and Iterate
Your customer journey is never done. But on the bright side it usually just requires some minor tweaks along the way. See what’s working and what’s not. Twice a year see if anyone has thoughts on how you might improve the customer journey. See if there are steps you can automate without the customer feeling the difference.
Try not to change more than two things at a time though. If you have a positive change you want to know what caused it. The same is true for a negative change.
4. Make the Customer Journey Map Accessible to Cross-functional Teams.
Silos are almost unavoidable in SaaS companies, but you can still do your part to be transparent. Share the customer journey with other departments. Communicate where it will be housed and be open to feedback. Yes, they may have different motivations, but you are all working together for the benefit of your company – not only the customer. Look for win-win situations.
Encourage collaboration and allow team members to offer input. This will help ensure the customer journey is up to date and that everyone is on the same page. Make sure to document the customer journey, so it is easy for cross-functional teams to access and reference. Additionally, consider creating a customer journey repository to store all customer journey maps, so that everyone is aware of how crucial the customer journey is to the success of the company.
I’d love to say you’re done, but a customer journey map is pretty useless just sitting in Google Drive. The whole point is to operationalize it.
Create Playbooks
A playbook is simply a set of step-by-step instructions to achieve a result. Create a separate playbook for each phase of the customer lifecycle:
Then create playbooks for
Expansion O pportunities
Advocacy Opportunities
Then add resources. This can be built as you go but will include things like email templates, slide presentations, calendar agendas, etc.
A final word
A Customer Journey Map is an incredibly powerful tool that allows organizations to understand and optimize the customer experience. It is a visual representation of every step a customer takes while interacting with an organization, from initial contact to post-purchase follow-up. By mapping out the journey and determining points of friction and areas for improvement, companies can create a more personal, and ultimately more successful, customer experience. Additionally, Customer Journey Maps can be used to identify opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, and they are the building blocks of what you will create in a CS tool . Utilizing a Customer Journey Map is an invaluable step in the customer success process and should be considered a priority for any business. PS – Want the templates that make this CS Strategy as easy as fill-in-the-blanks? Join CSLA!
Share this:
Related posts, why you should be a/b testing in customer success.
Jun 10, 2023
It honestly boggles my mind that A/B testing hasn't made it's way to Customer Success...As a Customer Success Leader, if you're not moving forward on strategy, you're not doing your job. Yet between being pressed for time and getting buy-in, it can feel almost...

Read This Before You Buy a Customer Success Tool (2023)
Jan 9, 2023
Looking to buy a customer success tool? WAIT!!! There is no easy button in Customer Success. No matter how amazing a CS tool is, YOU have to put in the work to get it there. Read below to learn what to do BEFORE you buy a Customer Success Tool so you do it right the...

Customer Advocacy: How to Turn Your Customers Into Brand Ambassadors
Dec 3, 2022
Customer advocacy is the act of publicly supporting a company or product. In the social media age, this takes the form of a positive online review, social media sharing, or even speaking at an industry event. There are many benefits to customer advocacy, such as...
Join the Discussion
Trackbacks/pingbacks.
- Customer Segmentation – The Next Level of Customer Success - Provan Success - […] Then start building a strategy for those. Start with your largest earning vertical and create a customer journey map…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Read More
Discover more from Provan Success
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Customer journey mapping: A six step expert guide

Hello SentiSum followers, readers and newcomers!
We teamed up with an industry expert to create a video guide for customer journey mapping.
That expert is Ed Deason, the current UK Head of Customer Service at British high street chain, Pret A Manger (find him on LinkedIn here ).
He's got a ton of experience behind him running customer experience and service teams.
And, customer journey mapping was actually one of the first things he did in his career.
Together, we wanted to make a truly actionable guide that would help both customer journey mapping newbies AND senior CX professionals navigate the process.
I suggest watching the full video lesson first, and then referring back to this shorter 'summary' blog post for a refresher.
If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us on LinkedIn.
(Follow us on LinkedIn for regular actionable content like this)
Watch the video here:
Customer journey mapping fundamentals
What is customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping is a way of creating a visual representation of the experience your customers go through when trying to achieve a goal with your brand, product or service.
It's a bit like graph, which you use to make data easier to understand and digest. Likewise, the customer journey map makes your customer's experience easy to understand and easy to digest for people across your company.
A 'customer journey map' is usually a step-by-step representation that outlines key events, motivations, customer satisfaction and experience scores at each touchpoint, which is ultimately presented as something that can be a resource for the wider organisation to use.
What is it used for? Who can use it and how do you use it?
They're probably three key reasons that your business might undertake customer journey mapping.
The first one is helping the wider organisation to understand the processes that your customers go through. This is helpful if you want to break down information silos and help teams see the bigger picture rather than just their own part of it.
Taking it down level, looking at it from your customer's point of view, the purpose of customer journey mapping is to identify points of friction for customers, perhaps unnecessary processes they go through or poor experiences they are having.
Taking it down another level, the purpose of customer journey mapping is to identify areas of waste and duplication within your internal processes. So where are there perhaps unnecessary handoffs between your teams that create delays that impact your customer.
Ultimately, reducing cost runs through a lot of customer journey mapping, because when go through customer journey mapping, what you're trying to do is identify problems and make things easier for your customers.
If you achieve that goal, you'll have fewer complaints, you'll have greater loyalty. You will have more sales.
It all comes down to improving the bottom line.
Who in a business would do this normally?
There isn't necessarily just one person who should do customer journey mapping.
Typically, it might sit with your customer experience team (if you have one).
So you might have a Customer Experience Manager or Chief Customer Officer and it may sit with them. But there's nothing really to stop any kind of customer facing team rom doing a customer journey map.
Whether you're working customer service, whether you work in sales, whether you work in operations, if you interact with customers, there's absolutely nothing to stop you from mapping out your customer journey.
In fact, it's useful to every team, customer facing or not, to stay closely in touch with how they impact the customer.
The six steps to customer journey mapping
Let's jump right in and answer the question, 'how do we do customer journey mapping?'.
There's six steps that you want to go through when you're starting out in customer journey mapping. The first one and probably the most important is to define the objective. To find what it is that you want to do when you start out.
The next steps are to pick a single customer journey to start with (simplify things for yourself), choose a customer persona (we'll cover what they are later), select the mapping approach that you want to take (high level or really detailed), make sure the right people are in the room, and finally, you want to overlay real qualitative and empirical data.
Here are those steps in greater detail.

1. Define your objective
This is the most important step in the process, it'll allow you to do your mapping exercise with a clear purpose.
There are typically three high level objectives:
- Helping the business understand the customer experience and breaking down silos between your teams.
This goal is about helping everyone in the organisation understand the overarching customer experience (a high level goal).
- Identifying areas of friction for your customers
This might be challenges with your returns process, for example it takes ages to contact you and reach a resolution.
- Identifying duplication and waste in your processes
This could be where you've got unnecessary handoffs between your teams that increase the time it takes to resolve what could be a simple resolution.
What objective you choose depends what role you're in. If you're a chief customer officer, perhaps what you want to do is actually help the business, understand the entire customer journey or the entire customer experience throughout the pre-purchase, purchase and after sales process.
Whereas if you're a department manager, you might want to be a lot more granular and look at where there are handoffs between your team and another team.
Could one customer journey map have multiple objectives?
In theory you could have a map that includes all three.
However, you would find that if you try to map out the very high level one, which is helping the business understand the customer experience, you will probably already have hundreds of potential touch points across 10 different departments.
So, if you tried to map that entire process at a customer friction level and to look at all the hand offs between teams, you would likely end up with a customer journey map that was so big as to be unusable.
With that in mind, I wouldn't suggest doing all three at once.
Potentially you can identify customer areas of friction and duplication and processes in one map. But I wouldn't then try and fold that into a high level, entire customer experience map.
Part of creating an actionable piece of work is picking something within reason. You've got to be pragmatic.
At the end of the day, the output has to be something that your teams can use, and if they have to scroll for 15 minutes just to find the bit of the map that's relevant to them, then they probably won't use it.
2. Pick a single journey to start with
Particularly if this is your first time having a go at customer journey mapping, pick a single journey and even pick one that is simple and straightforward.
So a returns process for your customer, for example. Something that has a kind of really clearly defined start and end and that probably doesn't have too many steps in there. So if you're starting out, pick something quite simple.
The reason is to reduce the complexity of the project, so that you can learn the ropes and grow the skill before taking on a bigger project.
What is a customer 'journey'?
When we talk about a journey, the best way to think about it is a clearly defined a set of steps that your customer will go through. Whether that is the steps to purchase your product (high level) or the process of making a complaint (detailed level).
What if this isn't your first rodeo?
If you've got a bit more experience in producing customer journey maps, what I would say is try and identify your largest volume areas.
Largest volume can be identified by sales or transactions or it could the area you know generates the most friction for customers or internal teams.
Either way, start where you know you'll have the biggest impact.
For example, if 80% of your sales comes through a particular channel, use that channel. That's your first customer journey map.
If the customer journey mapping process is new to the business, this is the best way to demonstrate value upfront.
Pick a high volume customer journey, identify some challenges in it and feed it back into the organisation.
And then once you're comfortable doing it (experienced or not) you can start doing more and more of then across the company.
Only then should you start to combine them and start to demonstrate to the organisation where they fit together and how a customer might travel through each of these different experiences.
"I think probably the first customer journey map I did was as a customer service manager. I wanted to map out multiple ways a customer could contact us and the time it took from receipt of that email through to resolution with the customer."
"By mapping out kind of the multiple touch points and the time in between each touch point and gave me a real good sense of how our customers were feeling about the experience."
3. Choose a customer persona
What is a customer persona.
A customer's persona is where you take a representation or maybe the key traits of your audience in order to generalise your view of them.
So for example, I work for Pret, so let's say one of our key customers is a busy professional. So she might be 35 to 45. She might live in the city and she might be prepared to pay more to save time and effort for herself. So that might be a customer persona and you'd give them a name.
It's best practice to choose a customer persona that's most valuable to the customer, one that spends the most with your brand or one that is experiencing a lot of friction at the moment.
Most companies have personas already. However, if you don't have existing customer personas, you still probably have a good sense of the kind of customers that purchase your products.
What you want to do is put yourself in that person's shoes. Get a sense of what the individual is looking for and how they will trabvel through your journey.
So you might want to ask yourself what: channels would they use? Are they more likely to call or are they might more likely to use online channels?
What times of day will they perhaps interact with you? And what is it that they need at each step?
Match the persona to your chosen journey
Once you chose your persona, what you would then do is think about how that customer persona would travel through the journey that you've just identified as the one that you want to focus on.
4. Select the right mapping approach for your goals
Which customer journey mapping template should i choose.
Each of the core objectives discussed in point (1) come into play here. You can use a slightly different map to fit your objective.
With this objective, you don't want to dive into masses of detail in your customer journey map. You want to stick to specific moments in the journey.
So that might be, awareness of your product, consideration, information gathering, purchase, and post-purchase behavior.
Split it into a few specific columns, but give a general sense of how a customer travels through that decision process of becoming aware of your organisation through to purchase and post-purchase experience (pictured below).
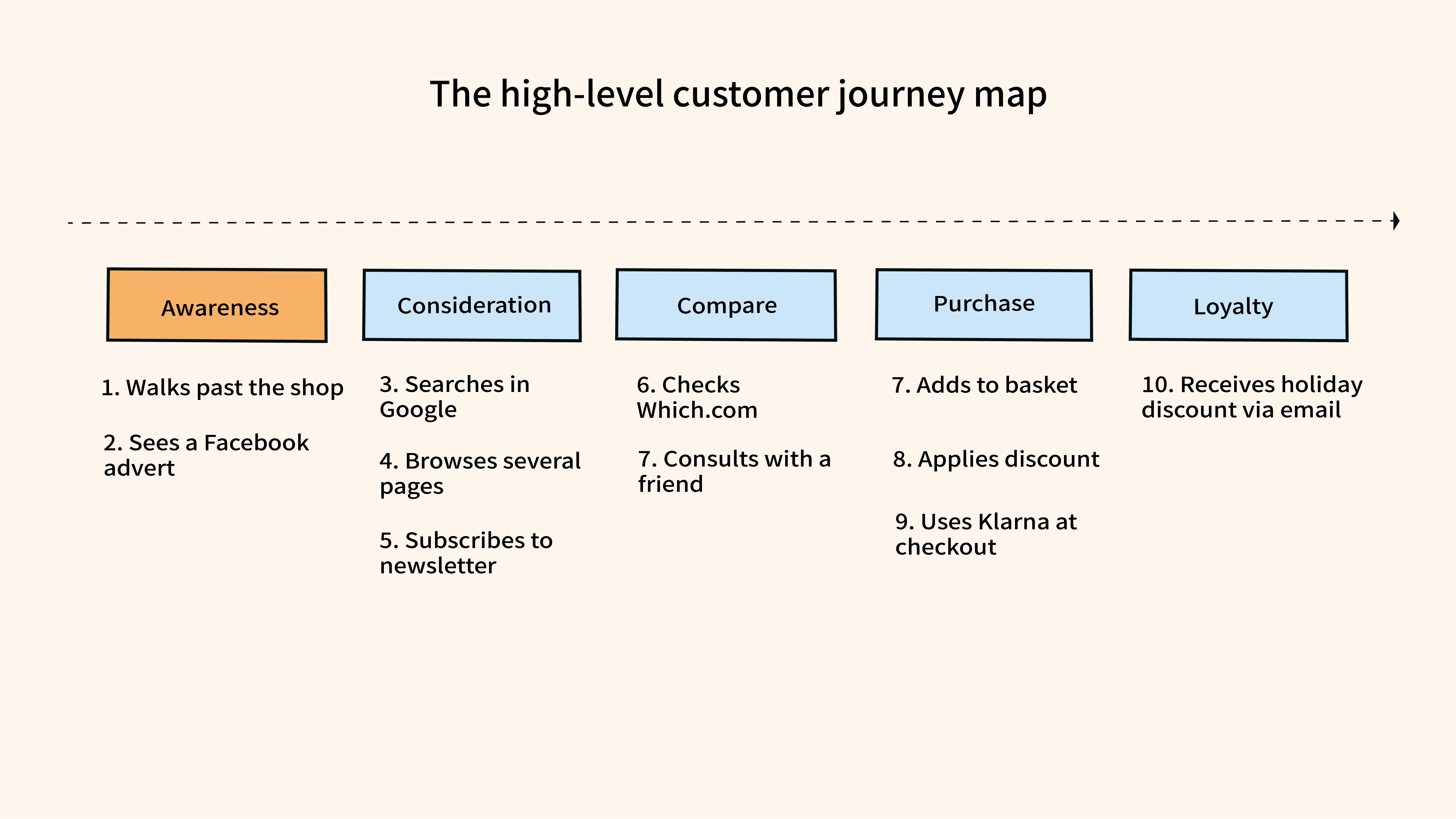
If you want to identify customer friction points, you should use a swim lane chart or a swim lane journey map. A basic swim lane splits the customer experience into two parts.
The top will be what the customer sees and underneath will be what the organisation sees.
You might have just a couple of points in the customer bit. For example, if we look at a customer service department, they swim lane points might just be 'send email' and then 'receive response' in the customer side of things. However, in the organisation side of things, you might have a number of steps in between for investigation, for writing a response, for actioning a check or a bank transfer for the customer.

The third map is like a more detailed version of the last point. It is another swim lane chart, but this one includes a lane for each department.
This is the map you want to use when you want to understand when there are handoffs and potentially duplication of work.
This one is where it's probably most useful to identify waste and duplication between your teams. You might turn out that you've got a handoff between your operations team and your customer service team three or four times when it could be once.
And that's something that if you take it out, it's going to make it quicker for your customer and easier for those two teams.

For example, if you look at the customer service team, a common issue is that you ask someone to confirm something for you and it's likely that they will come back with half the information you need. At which point you'll then have to write back to them for clarity and they'll comeback to you again.
That can happen three or four times.
So if you map this out then you identify that, if this happens frequently, there is an unnecessary point of friction.
"It's important to map what actually happens in the journey, not what should happen in theory. In reality, processes don't work like they should because of human error or something else."
5. Get the right people in the room
You must make sure the right stakeholders are in the room when you kick off this process. Why?
Because they will help you identify the 'real' customer journey—especially frontline staff
If you're asking yourself, 'how would I know that 50% of the time a particular process doesn't work?' then the answer is clear: you must get people who know the area of the business you're mapping to help.
"Don't map your customer journey on your own. You're never going to cover all of the touchpoints or all of the possible permutations. You're not going to have a full view of your customer's experience without a team there to help."
Frontline staff are particularly important. They often have the best insights.
Your customer service team will be able to instantly tell you three, four, five top issues that are frustrating your customer every single day.
That data is invaluable for your map.
Your executives may have a bit of a rose-tinted view of how your customers experience your journey, but your sales team and your customer service team can certainly talk them through issues and explain why that's perhaps not how it works. Include channel owners as well. Include your web team, your sales team, your guys that run the phone system or run your booking tool, make sure they're part of the process as well.
Executives are also important. Especially because they enable access and encourage action to take place.
It's tempting to miss people out, but you want all key stakeholders in the kick off meeting so you can identify core areas of focus.
Because people who are involved early on, are likely to be more cooperative when action is needed
Make sure those in charge of action at the end of the entire exercise are bought in early.
They should understand what you're trying to achieve, be clear on objectives and be able to influence those objectives, too.
"If you don't feel part of the origin story, it's easy to dismiss the output. You need to bring people along on the journey you're trying to achieve."
6. Overlay your data
Once you've chosen your persona, journey and map type, you need to start overlaying the data that you already have.
This data might be:
- Support ticket topics (Use support ticket analytics / tagging to identify high volume issues)
- Net promoter scores
- Customer satisfaction
- Churn rates
- Response times
- First call resolutions
- Trustpilot reviews
Overlay these data points onto the points within your map to breath life into the diagram you've created.
The more granular data you have the better. You should also be aware of bias so that you can trust the data to be actionable .
If you know a particular area is a challenge, but don't have much data on it, then you might want to start collecting data on that area about friction points—you'll find it within support tickets, survey results or other online feedback. You'
The Pareto principle dictates that 20% of your customer journey steps cause 80% of friction. So you'll soon start seeing where needs your attention most.
Trending articles
Voice of Customer Analytics: 5 Use Cases & Software Guide

Speech Analytics for Call Centers: 5 Use Cases & Tools
![customer journey step by step How Can Sentiment Analysis Improve the Customer Experience? [8 Use Cases]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/5ec6a20095cdf182f108f666/660d16a62c1cce18b30f45eb_Improve%20the%20Customer%20Experience.png)
How Can Sentiment Analysis Improve the Customer Experience? [8 Use Cases]
.png)
The accuracy of every NLP software depends on the context. Some industries and organisations have very complex issues, some are easier to understand. Our technology surfaces more granular insights and is very accurate compared to (1) customer service agents, (2) built-in keyword tagging tools, (3) other providers who use more generic AI models or ask you to build a taxonomy yourself. We build you a customised taxonomy and maintain it continuously with the help of our dedicated data scientists. That means the accuracy of your tags are not dependent on the work you put in. Either way, we recommend you start a free trial. Included in the trial is historical analysis of your data—more than enough for you to prove it works.
Frequently asked questions
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus, mi quis viverra ornare, eros dolor interdum nulla, ut commodo diam libero vitae erat. Aenean faucibus nibh et justo cursus id rutrum lorem imperdiet. Nunc ut sem vitae risus tristique posuere.
The customer journey — definition, stages, and benefits

Businesses need to understand their customers to increase engagement, sales, and retention. But building an understanding with your customers isn’t easy.
The customer journey is the road a person takes to convert, but this journey isn’t always obvious to business owners. Understanding every step of that journey is key to business success. After reading this article, you’ll understand the customer journey better and how to use it to improve the customer experience while achieving your business goals.
This post will discuss:
- What a customer journey is
Customer journey stages
Benefits of knowing the customer journey.
- What a customer journey map is
How to create a customer journey map
Use the customer journey map to optimize the customer experience, what is a customer journey.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. Businesses use the customer journey to better understand their customers’ experience, with the goal of optimizing that experience at every touchpoint.
Giving customers a positive customer experience is important for getting customers to trust a business, so optimizing the customer journey has never mattered more. By mastering the customer journey, you can design customer experiences that will lead to better customer relationships, loyalty, and long-term retention .
Customer journey vs. the buyer journey
The stages of the customer’s journey are different from the stages of the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey follows the customer experience from initial awareness of a brand to buying a product. The customer journey extends beyond the purchase and follows how customers interact with your product and how they share it with others.
Every lead goes through several stages to become a loyal customer. The better this experience is for customers at each stage, the more likely your leads are to stick around.
Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey:

1. Awareness
In the awareness phase, your target audience is just becoming aware of your brand and products. They need information or a solution to a problem, so they search for that information via social media and search engines.
For example, if someone searches on Google for pens for left-handed people, their customer journey begins when they’re first aware of your brand’s left-handed pen.
At this stage, potential customers learn about your business via web content, social media, influencers, and even their friends and family. However, this isn’t the time for hard sells. Customers are simply gathering information at this stage, so you should focus first on answering their questions and building trust.
2. Consideration
In the consideration phase, customers begin to consider your brand as a solution to their problem. They’re comparing your products to other businesses and alternative solutions, so you need to give these shoppers a reason to stick around.
Consideration-stage customers want to see product features that lean heavily toward solving problems and content that doesn’t necessarily push a sale. At this stage, businesses need to position their solution as a better alternative. For example, a nutrition coaching app might create content explaining the differences between using the app and working with an in-person nutritionist — while subtly promoting the benefits of choosing the app.
3. Purchase
The purchase stage is also called the decision stage because at this stage customers are ready to make a buying decision. Keep in mind that their decision might be to go with a competing solution, so purchase-stage buyers won’t always convert to your brand.
As a business, it’s your job to persuade shoppers at this stage to buy from you. Provide information on pricing, share comparison guides to showcase why you’re the superior option, and set up abandoned cart email sequences.
4. Retention
The customer journey doesn’t end once a shopper makes their first purchase. Once you’ve converted a customer, you need to focus on keeping them around and driving repeat business. Sourcing new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing clients, so this strategy can help you cut down on marketing costs and increase profits.
The key to the retention stage is to maintain positive, engaging relationships between your brand and its customers. Try strategies like regular email outreach, coupons and sales, or exclusive communities to encourage customer loyalty.
5. Advocacy
In the advocacy stage, customers are so delighted with your products and services that they spread the word to their friends and family. This goes a step beyond retention because the customer is actively encouraging other people to make purchases.
Customer journeys don’t have a distinct end because brands should always aim to please even their most loyal customers. In the advocacy stage of the customer journey, you can offer referral bonuses, loyalty programs, and special deals for your most active customers to encourage further advocacy.
Being aware of the customer journey helps shed more light on your target audience’s expectations and needs. In fact, 80% of companies compete primarily on customer experience. This means optimizing the customer journey will not only encourage your current customers to remain loyal but will also make you more competitive in acquiring new business.
More specifically, acknowledging the customer journey can help you:

- Understand customer behavior. Classifying every action your customers take will help you figure out why they do what they do. When you understand a shopper’s “why,” you’re better positioned to support their needs.
- Identify touchpoints to reach the customer. Many businesses invest in multichannel marketing, but not all of these touchpoints are valuable. By focusing on the customer journey, you’ll learn which of these channels are the most effective for generating sales. This helps businesses save time and money by focusing on only the most effective channels.
- Analyze the stumbling blocks in products or services. If leads frequently bail before buying, that could be a sign that something is wrong with your product or buying experience. Being conscious of the customer journey can help you fix issues with your products or services before they become a more expensive problem.
- Support your marketing efforts. Marketing requires a deep familiarity with your target audience. Documenting the customer journey makes it easier for your marketing team to meet shoppers’ expectations and solve their pain points.
- Increase customer engagement. Seeing the customer journey helps your business target the most relevant audience for your product or service. Plus, it improves the customer experience and increases engagement. In fact, 29.6% of customers will refuse to embrace branded digital channels if they have a poor experience, so increasing positive customer touchpoints has never been more important.
- Achieve more conversions. Mapping your customers’ journey can help you increase conversions by tailoring and personalizing your approach and messages to give your audience exactly what they want.
- Generate more ROI. You need to see a tangible return on your marketing efforts. Fortunately, investing in the customer journey improves ROI across the board. For example, brands with a good customer experience can increase revenue by 2–7% .
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Today, 94% of customers say a positive experience motivates them to make future purchases. Optimizing the customer journey helps you meet shopper expectations, which increases satisfaction and loyalty.

What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every step your customer takes from being a lead to eventually becoming an advocate for your brand. The goal of customer journey mapping is to simplify the complex process of how customers interact with your brand at every stage of their journey.
Businesses shouldn’t use a rigid, one-size-fits-all customer journey map. Instead, they should plan flexible, individual types of customer journeys — whether they’re based on a certain demographic or on individual customer personas. To design the most effective customer journey map, your brand needs to understand a customer’s:
- Actions. Learn which actions your customer takes at every stage. Look for common patterns. For example, you might see that consideration-stage shoppers commonly look for reviews.
- Motivations. Customer intent matters. A person’s motivations change at every stage of the customer journey, and your map needs to account for that. Include visual representation of the shopper’s motivations at each stage. At the awareness stage, their motivation might be to gather information to solve their problem. At the purchase stage, it might be to get the lowest price possible.
- Questions. Brands can take customers’ common questions at every stage of the customer journey and reverse-engineer them into useful content. For example, shoppers at the consideration stage might ask, “What’s the difference between a DIY car wash and hiring a professional detailer?” You can offer content that answers their question while subtly promoting your car detailing business.
- Pain points. Everybody has a problem that they’re trying to solve, whether by just gathering intel or by purchasing products. Recognizing your leads’ pain points will help you craft proactive, helpful marketing campaigns that solve their biggest problems.
Customer journey touchpoints
Every stage of the customer journey should also include touchpoints. Customer touchpoints are the series of interactions with your brand — such as an ad on Facebook, an email, or a website chatbot — that occur at the various stages of the customer journey across multiple channels. A customer’s actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will differ at each stage and at each touchpoint.
For example, a customer searching for a fishing rod and reading posts about how they’re made will have very different motivations and questions from when later comparing specs and trying to stay within budget. Likewise, that same customer will have different pain points when calling customer service after buying a particular rod.

It might sound like more work, but mapping the entire customer journey helps businesses create a better customer experience throughout the entire lifecycle of a customer’s interaction with your brand.
Before jumping into the steps of how to create the customer journey map, first be clear that your customer journey map needs to illustrate the following:
- Customer journey stages. Ensure that your customer journey map includes every stage of the customer journey. Don’t just focus on the stages approaching the purchase — focus on the retention and advocacy stages as well.
- Touchpoints. Log the most common touchpoints customers have at every stage. For example, awareness-stage touchpoints might include your blog, social media, or search engines. Consideration-stage touchpoints could include reviews or demo videos on YouTube. You don’t need to list all potential touchpoints. Only list the most common or relevant touchpoints at each stage.
- The full customer experience. Customers’ actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will change at every stage — and every touchpoint — during the customer journey. Ensure your customer journey map touches on the full experience for each touchpoint.
- Your brand’s solutions. Finally, the customer journey map needs to include a branded solution for each stage and touchpoint. This doesn’t necessarily mean paid products. For example, awareness-stage buyers aren’t ready to make a purchase, so your brand’s solution at this stage might be a piece of gated content. With these necessary elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map is a simple three-step process.
1. Create buyer personas
A buyer persona is a fictitious representation of your target audience. It’s a helpful internal tool that businesses use to better understand their audience’s background, assumptions, pain points, and needs. Each persona differs in terms of actions, motivations, questions, and pain points, which is why businesses need to create buyer personas before they map the customer journey.
To create a buyer persona, you will need to:
- Gather and analyze customer data. Collect information on your customers through analytics, surveys, and market research.
- Segment customers into specific buying groups. Categorize customers into buying groups based on shared characteristics — such as demographics or location. This will give you multiple customer segments to choose from.
- Build the personas. Select the segment you want to target and build a persona for that segment. At a minimum, the buyer persona needs to define the customers’ basic traits, such as their personal background, as well as their motivations and pain points.

For example, ClearVoice created a buyer persona called “John The Marketing Manager.” The in-depth persona details the target customer’s pain points, pet peeves, and potential reactions to help ClearVoice marketers create more customer-focused experiences.
2. List the touchpoints at each customer journey stage
Now that you’ve created your buyer personas, you need to sketch out each of the five stages of the customer journey and then list all of the potential touchpoints each buyer persona has with your brand at every one of these five stages. This includes listing the most common marketing channels where customers can interact with you. Remember, touchpoints differ by stage, so it’s critical to list which touchpoints happen at every stage so you can optimize your approach for every buyer persona.
Every customer’s experience is different, but these touchpoints most commonly line up with each stage of the customer journey:
- Awareness. Advertising, social media, company blog, referrals from friends and family, how-to videos, streaming ads, and brand activation events.
- Consideration. Email, sales calls, SMS, landing pages, and reviews.
- Purchase. Live chat, chatbots, cart abandonment emails, retargeting ads, and product print inserts.
- Retention. Thank you emails, product walkthroughs, sales follow-ups, and online communities.
- Advocacy. Surveys, loyalty programs, and in-person events.
Leave no stone unturned. Logging the most relevant touchpoints at each stage eliminates blind spots and ensures your brand is there for its customers, wherever they choose to connect with you.
3. Map the customer experience at each touchpoint
Now that you’ve defined each touchpoint at every stage of the customer journey, it’s time to detail the exact experience you need to create for each touchpoint. Every touchpoint needs to consider the customer’s:
- Actions. Describe how the customer got to this touchpoint and what they’re going to do now that they’re here.
- Motivations. Specify how the customer feels at this moment. Are they frustrated, confused, curious, or excited? Explain why they feel this way.
- Questions. Every customer has questions. Anticipate the questions someone at this stage and touchpoint would have — and how your brand can answer those questions.
- Pain points. Define the problem the customer has — and how you can solve that problem at this stage. For example, imagine you sell women’s dress shoes. You’re focusing on the buyer persona of a 36-year-old Canadian woman who works in human resources. Her touchpoints might include clicking on your Facebook ad, exploring your online shop, but then abandoning her cart. After receiving a coupon from you, she finally buys. Later, she decides to exchange the shoes for a different color. After the exchange, she leaves a review. Note how she acts at each of these touchpoints and detail her likely pain points, motivations, and questions, for each scenario. Note on the map where you intend to respond to the customer’s motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions. If you can create custom-tailored solutions for every stage of the funnel, that’s even better.
A positive customer experience is the direct result of offering customers personalized, relevant, or meaningful content and other brand interactions. By mapping your customers’ motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions, you’ll find opportunities to improve the customer experience. When you truly address their deepest needs, you’ll increase engagement and generate more positive reviews.
Follow these strategies to improve the customer experience with your customer journey map:
- Prioritize objectives. Identify the stages of the customer journey where your brand has the strongest presence and take advantage of those points. For example, if leads at the consideration stage frequently subscribe to your YouTube channel, that gives you more opportunities to connect with loyal followers.
- Use an omnichannel approach to engage customers. Omnichannel marketing allows businesses to gather information and create a more holistic view of the customer journey. This allows you to personalize the customer experience on another level entirely. Use an omnichannel analytics solution that allows you to capture and analyze the true cross-channel experience.
- Personalize interactions at every stage. The goal of mapping the customer journey is to create more personalized, helpful experiences for your audience at every stage and touchpoint. For example, with the right data you can personalize the retail shopping experience and customer’s website experience.
- Cultivate a mutually trusting relationship. When consumer trust is low, brands have to work even harder to earn their customers’ trust. Back up your marketing promises with good customer service, personalized incentives, and loyalty programs.
Getting started with customer journeys
Customer journeys are complicated in an omnichannel environment, but mapping these journeys can help businesses better understand their customers. Customer journey maps help you deliver the exact experience your customers expect from your business while increasing engagement and sales.
When you’re ready to get started, trace the interactions your customers have at each stage of their journey with your brand. Adobe Customer Journey Analytics — a service built on Adobe Experience Platform — can break down, filter, and query years’ worth of data and combine it from every channel into a single interface. Real-time, omnichannel analysis and visualization let companies make better decisions with a holistic view of their business and the context behind every customer action.
Learn more about Customer Journey Analytics by watching the overview video .
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/introducing-adobes-customer-journey-maturity-model
https://business.adobe.com/blog/how-to/create-customer-journey-maps
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-customer-journey-map

Customer Journey Visualization: How to Perform It + 3 Tools to Try
10 min read

Want to conduct customer journey visualization but not sure what’s the best way to do it?
This article shows you a step-by-step process for collecting customer data and creating easy-to-understand visual maps.
- A customer journey map represents the steps users take when interacting with your brand. Understanding these steps and the motivations behind them enables you to support customers in succeeding with your tool.
Customer journey visualization is the process of taking information from the customer journey map and representing it in a visually compelling way.
Benefits of customer journey mapping:
- Tailor marketing campaigns to the customer’s buying process.
- Build data-driven product roadmaps .
- Enhance customer experience.
- Improve free trial to paid conversion .
- Increase loyalty and revenue growth .
Key components to include when mapping the customer’s journey:
- Customer journey stages .
- User emotions .
- User actions .
- Proposed solution.
Stages included in the buyer journey
- Awareness stage
- Consideration stage
- Decision stage
- Activation stage
- Adoption stage
- Renewal stage
- Expansion stage
- Loyalty stage
Step-by-step guide for visualizing the customer journey:
- Identify your buyer persona .
- Segment your users with an in-app welcome survey .
- Identify key journey stages with path analysis .
- Spot customer touchpoints with heatmaps and session recordings .
- Find features that increase customer engagement and retention .
- Collect user feedback to tap into customer emotions .
- Visualize the journey with a customer journey map template .
Best practices to use when creating customer journey maps:
- Keep the visuals simple for all stakeholders .
- Use consistent symbols and colors .
- Iterate and continually update your journey maps .
Three journey mapping tools to improve the customer experience:
- Userpilot – Best data analysis tool to track user journeys.
- Miro – Best tool for customer journey map templates.
- UXPressia – Best for UX research into the customer’s journey.
Ready to create a customer journey visualization? Book a demo now to start collecting data with Userpilot .
Try Userpilot and Take Your Customer Experience to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation that illustrates the steps your customers go through when engaging with your brand. It also outlines their motivations, actions, and pain points at every stage.
The main purpose of a customer journey map is to provide a clear picture of all customer interactions with your business, from their initial contact to long-term retention.
What is customer journey visualization?
This helps understand complex customer interactions through diagrams, charts, or other graphical formats so all stakeholders can quickly glance through and grasp the emotions , needs , and goals at each customer touchpoint.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
A customer journey map that clearly outlines user activity at each journey stage has tons of benefits, including the following:
- Create targeted marketing campaigns : Journey maps reveal what motivates customers at different points—their needs, questions, and pain points. This lets you tailor messaging and offers to be most relevant where potential customers are in the buyer’s journey.
- Build data-driven product roadmaps : A customer journey map helps you understand which features move users to the next stage of the customer journey. This allows you to optimize your roadmaps and make product improvements based on real user needs.
- Enhance user experience : Positive customer experience is an easy way to stand out in a competitive landscape. The data from customer mapping enables you to deliver an improved user experience .
- Improve free trial to paid conversion : Understanding the journey from a free trial to a paid subscription helps identify the critical moments and factors influencing a customer’s decision to upgrade. This helps improve your trial conversion funnel and win more users.
- Increase loyalty and revenue growth : Customer journey mapping also enhances post-purchase experiences to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty . This allows you to take actions that foster stronger relationships, encourage repeat business , and generate more opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
What’s included in a customer journey map?
Customer journey maps can vary in complexity and detail but typically include the following key components:
- Customer journey stages : The major phases your customer goes through (e.g., awareness, consideration, activation, adoption, renewal).
- User emotions : How the customer feels at each stage—excited, frustrated, satisfied, etc. Understanding emotions adds depth to your customer journey visualization.
- User actions : What the customer does at each stage (e.g., visits the website, books a demo, engages with key activation features during onboarding, and so on).
- Proposed solution : Ideas for improving specific areas of the customer journey and addressing pain points .
Stages included in a customer journey
Each customer journey stage represents a unique mindset and set of objectives that, when understood, will help funnel users smoothly till they become paying and loyal users. Let’s go over the key journey stages :
- Awareness stage : The potential customer becomes aware of a problem or need and begins seeking general information, not necessarily focused on your product.
- Consideration stage : In this second stage of the buyer’s journey, potential customers begin actively researching for potential solutions. Using channels like friends, search engines, and social media, they compare different products, assessing features , benefits, and pricing to determine what best meets their needs.
- Decision stage : After their research, the customer makes a decision by booking a demo call , signing up for your free version , or going straight for the paid plan.
- Activation stage : The new user experiences your product’s core value for the first time and sees reasons to continue engaging.
- Adoption stage : After successful activation , the user incorporates your product into their workflow and continues using it regularly.
- Renewal stage : This is where the customer decides to renew their accounts to increase the ROI of using your product.
- Expansion stage : Here, the customer purchases add-ons, upgrades their accounts , or increases their usage. This signifies trust in your company and the value it provides.
- Loyalty stage : The loyalty stage is the holy grail of the SaaS customer journey. Customers in this stage not only expand and repeatedly renew their accounts but also advocate for you through word of mouth or social media.

Step-by-step guide for visualizing the customer journey
Customer journey visualization involves several steps, each contributing to a comprehensive view of the customer’s path from initial engagement to loyalty. Here’s how to approach it:
1. Identify your customer persona
The first step is to define the persona you wish to visualize—note that the customer journey will be slightly different for each of your customer personas because they have varying needs and goals.
Once you’ve decided on the persona to visualize, the next step is to list what you already know about them . This includes their pain points, goals, jobs to be done, and any relevant information you wish to add.
Here’s a template you can use:

2. Segment your users with an in-app welcome survey
Use a welcome survey to collect important data about new users. Keep the survey short and focus on asking questions about their company size, the end user’s role in the company, and their main use cases.
How is this important to the customer journey mapping process?
The data from your welcome survey helps segment users based on their needs, preferences, and initial impressions, allowing you to create more detailed and personalized customer journeys.

3. Identify key journey stages with path analysis
Define the goal(s) for each customer journey (e.g., activation of XYZ feature). Then, implement path analysis to find all the paths users take to achieve that goal. Filter through the noise to identify the shortest path and highlight all the stages involved.
For example, a path analysis can help you identify which features drive adoption by monitoring users’ journey from signing up to becoming paying customers.
You can track all the pages they visit or the events they conduct to understand key conversion drivers.

4. Spot customer touchpoints with heatmaps and session recordings
Heatmaps provide a visual representation of user actions on your website or app in terms of UI clicks and hovers so you can identify high-engagement areas.
Session recordings perform a similar function but are even more insightful as they provide video recordings of user clicks , scrolls, zoom-ins, and other mouse movements.
Combining these two customer analytics lets you identify the key touchpoints at each user journey stage.
5. Find features that drive engagement and retention
Use trend analysis to find popular features at every journey stage. This report highlights features that are visited most often in a given period so you can gain insights into key user problems and what solutions work best for them.

You can pair your trends report with cohorts analysis to find which features drive retention and loyalty.
These highly-used features likely fulfill a core need, address a significant pain point, or provide exceptional value. Identifying them helps you map out the moments of delight in the customer journey.

6. Collect user feedback to tap into customer emotions
Feedback surveys help you hear from the horse’s mouth. By asking the right questions, you can identify customer pain points and motivations at each journey stage.
For this survey, you want to prioritize open-ended questions over close-ended ones so users can freely express themselves.
For example, asking a question like “What are the top challenges your company is facing?” allows the respondents to think and provide detailed feedback .

7. Visualize the journey with a customer journey map template
With all the data and insights you collected from the previous steps, it’s time to visualize it. Use a customer journey map template to consolidate the customer data you’ve collected.
Examples of what to include:
- Customer journey stages
- Customer touchpoints
- User emotions
- User actions
- Opportunities
Here’s a customer journey map template from Miro you can use:

Best practices to use when creating customer journey maps
Follow these best practices to ensure your customer journey map is clear, actionable , and remains relevant over time.
Keep the visual representation simple
Your visualization should have just enough data for all stakeholders to understand user motivations . The map will lose its impact as a quick reference tool if it’s too cluttered or complex.
Here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Don’t use product jargon.
- Use illustrations to make it easy to visualize user feelings/emotions.
- Limit the detail level and attach summaries of each journey.
Use consistent symbols and colors
You’ll likely be working on multiple customer journeys across different user personas .
It’s easy to mix things up, so develop a visual key to represent different journey stages, touchpoints, emotions, and pain points .
Iterate and continually update your journey maps
Customer needs and preferences keep changing over time, so update the visualization based on new insights regularly.
Aim to conduct periodic data analytics to keep tabs on changes in the customer experience and track user behavior .
3 journey mapping tools to improve the customer experience
Below are three of the best customer journey mapping tools and what they help you accomplish.
1. Userpilot – Best data analysis tool to track user journeys
Userpilot is a product growth tool with powerful customer behavior analytics.
The platform lets you visualize customer journeys and create in-app experiences to improve your customer experience.
Relevant features:
- Funnel analysis : Visualize how users progress through each customer journey stage. The funnel analysis report shows friction points and areas where users move smoothly.

- Analytics reports : Dig into customer behavior data and uncover insights to facilitate better customer journey visualization with trend reports , cohort analysis , user paths , and heatmap analysis.
- Analytics dashboards : View all key data points from a single location with the analytics dashboard . There are different dashboards to choose from such as the product usage and core feature engagement dashboards. You can also build custom dashboards.

- Feature usage reports : Tag any feature of your choice and track all user interactions associated with it without having to involve your dev team.
- In-app surveys : From simple quantitative surveys to more in-depth, open-ended questions, Userpilot has several survey templates to make feedback collection easy.
2. Miro – Best tool for customer journey map templates
Miro is an online collaborative whiteboarding platform that enables teams to work more effectively, from brainstorming with digital sticky notes to planning and managing agile workflows.
Features that help with customer journey visualization include:
- Collaborative online whiteboards : Create and share customer journey maps in a visual and interactive environment. The workspace is flexible, allowing you to freely arrange text, shapes, and images to fit your visualization needs.
- Templates and frameworks : Access pre-built templates, including customer journey maps, to quickly start projects.
- Integration : Seamlessly integrate with tools such as Slack, Asana, and Google Drive to enhance team collaboration.

3. UXPressia – Best for UX research into the customer’s journey
UXPressia is a specialized platform dedicated to customer experience management, offering tools for customer journey mapping, persona creation, and impact mapping.
Here’s how it helps with customer journey visualization:
- Templates for customer journey mapping : Access a variety of industry-specific templates and customer journey mapping examples to streamline your mapping process with a user-friendly interface.
- Persona creation : Create personas by incorporating demographics, needs , and pain points to better understand the customer experience.
- Impact mapping : Identify and visualize the impact of different touchpoints on the customer’s experience and satisfaction.

By visualizing the steps users take to become loyal customers, you’ll spot ways to optimize your product and convert more customers.
Ready to begin? Book a Userpilot demo to access behavior analytics and user feedback for effective customer journey visualization.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Top 12 dashboard reporting tools for saas in 2024.
Aazar Ali Shad
8 Comprehensive Customer Journey Analytics Examples
14 best behavior analytics tools for tracking user activity.
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
A step-by-step guide to mapping the B2B customer journey (with real-life examples)
It’s tricky to effectively map out all the different user personas and purchasing processes in the B2B customer journey. But understanding your customer's experience is key to improving conversions and retaining users.
That’s why it’s essential for B2B companies to follow an effective customer journey mapping process.
Last updated
Reading time.

Use our step-by-step guide to create a map for your business-to-business (B2B) company that tracks your users’ unique journeys, giving you key insights into your customers and their needs.
Get valuable insights into your B2B customer journey
Hotjar helps you understand how buyers interact with key web and product touchpoints to improve their experience.
How to map out the B2B customer journey in 5 steps
Mapping the customer journey is essential in understanding your buyers and turning them into loyal customers.
Follow these steps to create an actionable B2B customer journey map that gives insights into who your customers are and helps you build an optimized user experience (UX) for them:
1. Set goals unique to your business
Before you start mapping out the customer journey, define your larger business and customer goals.
To begin, ask yourself what you want your customers to achieve—what are their jobs to be done (JTBD)? Does your business depend on repeat customers, or are your products one-off larger ticket items? Your customer journey will look different if you sell business clients a one-time-purchase product, like a hardware device, versus a subscription service.
For example, different B2B firms—like GE Renewable Energy and Hubspot—will have very different objectives. A company like GE Renewable Energy that sells large equipment to B2B customers may prioritize goals like generating more website conversions and creating brand advocates who recommend GE products to other businesses in the industry.
On the other hand, a software company like Hubspot will need to emphasize the customer journey's onboarding and renewal components to increase customer retention.
Know what your goals are before creating your B2B customer journey map to prioritize the most important steps for your customers and your business.
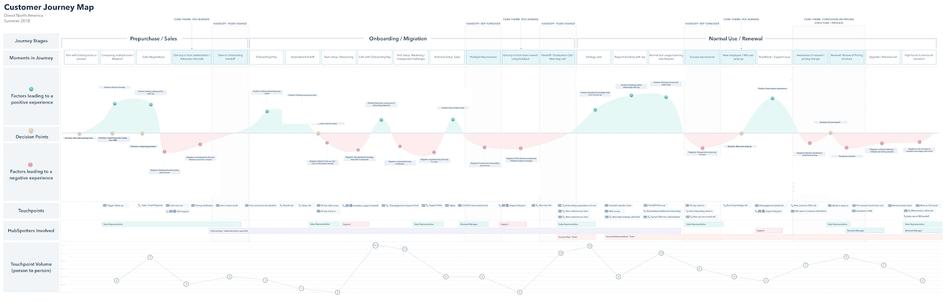
2. Identify your customer segments
The purchasing process is an especially nuanced cycle for B2B businesses, because the end users of your product or service are often not the same people making the purchasing decision .
John Forberger , founder of Forberger Communications , highlights this complexity:
Typically, multiple people have influence over a deal. Maybe one person researches how to replace a current tool, then a second person does a demo, and a third person actually cuts the check.
Don't just focus on the users who’ll try out your product or service, or on the C-level decision makers: understand every stakeholder involved in the purchasing process to map out an accurate B2B customer journey .
Consider the different needs of end users versus purchasers and think about how your user personas may differ depending on company size and type.
Take Canva, for example: the design tool is used by a variety of businesses, from freelancers to large corporations like PayPal and Danone. Understanding different user profiles and needs gave Canva the insight they needed to design their homepage for different B2B customer types who can choose their own adventure and head off on their most relevant user journey.
Pro tip: once you define your user profiles, learn more about different buyer types by asking the right survey questions . Use these questions to dig deeper into user goals and jobs to be done to better design the B2B customer journey.
3. Define the B2B customer journey stages
Once you have clear goals and user personas, it’s time to define the stages of the customer journey. Let’s take a look at a typical 7-stage B2B customer journey, using the popular SEO tool Ahrefs as an example.
Awareness: a buyer becomes aware of their problem and begins to search for solutions, which is when they discover your brand. In our example, a buyer knows they need to improve their website’s SEO performance, so they search for “best SEO tools” and come across Ahrefs. They visit the homepage, where the tool’s value proposition entices them to learn more.
Consideration: customers consider your product or service as a potential solution. Here, the buyer visits Ahref’s website and learns about the brand’s unique selling proposition , reads about features, watches a demo, explores resources like the Ahrefs blog and SEO guide, and weighs up whether Ahrefs is the product solution for them.
Decision: the buyer makes a decision and purchases the product or service that best fits their needs. In the case of Ahrefs, the buyer purchases the subscription (Lite, Standard, Advanced, or Enterprise) that’s right for them. The Ahrefs website guides users in the decision and purchasing process by displaying clear CTAs that encourage users to become paying customers.
Onboarding: the buyer starts to use the product, goes through the onboarding process, and gets familiar with the tool by reading guides and watching demos. They (ideally) start to adopt it into their everyday workflow.
Support: users contact customer teams as they need support. In our example, customers have easy access to customer support agents and the Ahrefs help center to smoothly resolve issues and questions.
Retention: customer retention is a key part of the B2B buyer journey, and at this stage, buyers decide whether or not they’ll remain loyal customers and continue using your product. Ahrefs offers a range of subscription models and gives users who sign up for an annual subscription a two-month free plan.
Advocacy: the final stage in an ideal customer journey is turning customers into brand advocates. Ahrefs has done a good job of this: the homepage shows reviews from real users who recommend the tool, including pro SEOs, content marketers, and agencies.
Pro tip: your product's user journey may look different depending on your company and customer types: a business customer purchasing a one-off product will have a very different journey from a company subscribing to a service.
Oleg Donets , founder and chief marketing officer at Real Estate Bees , points out how the stages of non-SaaS B2B customer journeys can differ from SaaS journeys :
"Since the vast majority of SaaS companies utilize subscription revenue models, this directly impacts the customer journey. B2B customer journeys often scale back a notch shortly after a sale has been made, but that’s when the customer journey of a SaaS company just starts kicking in."
4. List all possible B2B customer touchpoints
Once you map out the steps in your customer’s B2B journey, identify each ‘touchpoint’ where they interact with your company, from social media posts to your homepage CTAs and your product itself.
Let’s go back to the Ahrefs example.
A key touchpoint in the early awareness, consideration, and purchase stages of the B2B customer journey is their homepage and a clear call-to-action (CTA) button. These onsite touchpoints show customers what their next steps in the product experience (PX) should be and give them the information they need to make a decision.
In the next phases—onboarding and support—follow Ahrefs' example by making it easy for users to connect with your B2B business, resolve their issues, and upgrade. On the Ahrefs help center page, customers can reach out to representatives and receive support within minutes.
Make sure you continue mapping out how your users interact with your B2B after they become customers—in the retention and advocacy phases . How can you make it easier for them to renew their subscription? Do you offer any rewards for referrals?
As well as mapping out touchpoints by customer journey phase, consider the different touchpoints experienced by different user personas.
For example, the product experience of high-level executives who make the purchasing decision may not be the same as their employees who are your end-users.
By identifying key B2B customer journey touchpoints for different customers and purchasing stages, you can improve UX, making product advocates out of your buyers.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Observe tools—like Heatmaps and Recordings —to explore how your users interact with key B2B customer touchpoints on your website and product—and get the insights you need to improve their journey.
Hotjar Session Recordings show you how users experience your page to improve low-performing touchpoints
5. Measure and analyze the success of the customer journey
One of the most important customer journey mapping best practices is measuring the success of your customer journey.
Use the right customer journey mapping tools to help you evaluate the impact of your touchpoints. For best results, combine website analysis tools with software that offers more in-depth product experience insights and user feedback.
Use Hotjar's Observe tools to track how customers are engaging with your touchpoints. Then use Hotjar’s Ask tools—like Surveys and Feedback widgets—to learn what your users really think and feel about their B2B experience.
Tools like Google Analytics also help in mapping and analyzing the customer journey, giving you more general information on the types of users that visit your website and whether they convert or bounce.
Combine Hotjar with Google Analytics to dig deeper into B2B customer touchpoint insights to improve conversion rates and enhance the customer experience .
After you’ve mapped the customer journey, regularly check in on your key goals and what matters most to your customers. Keep measuring the outcomes of your customer journey to understand which aspects of the B2B customer journey are successful and what needs improvement.
Create a brilliant B2B user journey for happier customers
Successfully mapping out the B2B customer journey requires a deep understanding of all your buyers and how they interact with your brand and product.
Adapting these steps to your customers and company helps you create a customer journey map that identifies what your users need at each stage of the buying cycle to provide them with the best possible experience.
Use Hotjar to understand how buyers interact with key web and product touchpoints—and improve their experience with your B2B business.
FAQs about B2B customer journey mapping
Why do you need b2b customer journey mapping.
Visualizing the customer journey is the first step to understanding and improving it. B2B customer journey mapping helps you identify what type of experience customers have with your product at every stage .
Without B2B customer journey mapping, you won’t understand the process of converting potential buyers into loyal customers, meaning you have no way to make adjustments that enhance the customer journey.
How is the B2B customer journey different from other customer journeys?
With the B2B customer journey, there are often more stakeholders involved in the decision-making process than with a B2C customer journey. For that reason, the B2B customer journey is often much longer and depends on various decision-makers .
Plus, the B2B customer journey is often cyclical, as customer retention is such a key goal for many B2B companies.
What are some common mistakes of B2B customer journey mapping?
A big mistake in B2B customer journey mapping is failing to consider all user personas. B2B products often have a number of diverse customer profiles, whether that be different positions within one company (administrator vs. C-level executive) or different types of companies (like a small business vs. an enterprise).
Another common mistake is not taking into account the length and complexity of the B2B customer journey , which often has a lengthy approval process, and requires several different stakeholders to sign off on purchasing decisions.
CJM research
Previous chapter
Next chapter

- THE STRATEGY JOURNEY Book
- Videos & Tutorials
- Strategy Journey Analyzer [QUIZ + WORKBOOK]
- COMMUNITY FORUMS
- Transforming Operating Models with Service Design (TOMS) Program
- ABOUT STRATABILITY ACADEMY
9 Steps to your Winning Customer Journey Strategy
By Julie Choo
Published: October 3, 2023
Last Update: January 9, 2024
TOPICS: Service Design
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, one thing remains constant: the customer is king. And to keep the king content, a well-defined customer journey strategy is paramount. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of customer journey strategy, exploring its intricacies, the importance of customer journey mapping, and how it all contributes to enhancing the customer experience. Buckle up; we’re about to embark on a journey of our own.
Customer Journey: What is it?
Step 1: define your objectives, step 2: identify customer personas, step 3: collect customer data, step 4: create a visual representation, step 5: define touchpoints, step 6: walk in your customers’ shoes, step 7: capture emotions and pain points, step 8: analyze and iterate, step 9: implement changes – bringing it all together, elevating customer experience: the north star of your strategy.
At its core, a customer journey represents the route a customer takes from their first interaction with your brand to the final purchase and beyond. Understanding this journey is the first step in crafting an effective customer journey strategy. It’s akin to setting up signposts along a road – guiding your customers on a seamless voyage.
A well-mapped customer journey not only benefits your customers but also your business. It enables you to anticipate customer needs, identify pain points, and optimize touchpoints to foster loyalty.
9 Steps of the Customer Journey Map
Customer journey mapping is the cartography of your customer’s experience. It’s where you take a deep dive into each step of their journey, from awareness to post-purchase engagement. Mapping allows you to see the journey from the customer’s perspective, highlighting pain points, moments of delight, and opportunities for improvement.
When crafting your map, consider customer personas, touchpoints, and channels. Visualizing the customer’s path helps in aligning your marketing, sales, and support teams to provide a cohesive and delightful experience.
Before setting sail, you need to chart your course. Start by defining your objectives. What specific aspects of the customer journey are you looking to understand or improve? Here’s a few common example of ideas to look at when considering your company’s objective
- Churn Reduction : One of the most common objectives is reducing churn or customer attrition. Your goal might be to pinpoint the exact stages in the customer journey where customers tend to drop off and identify strategies to retain them.
- Conversion Rate Optimization : If your primary aim is to increase conversions, your objectives could revolve around understanding the barriers that prevent prospects from moving smoothly through the sales funnel. What’s stopping them from becoming paying customers?
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty : For businesses seeking to boost customer loyalty, objectives may focus on identifying the touchpoints and interactions that contribute most to customer satisfaction. What can you do to turn satisfied customers into loyal advocates?
- Improved Customer Support : If customer support is a priority, you might aim to uncover pain points in the support journey. Are customers waiting too long for assistance? Are their issues resolved effectively? Your objectives could involve streamlining the support process for better customer experiences.
- Personalization and Engagement : In a world where personalization is key, objectives might be centered on tailoring the customer journey to individual preferences. What data points can you gather to offer more personalized recommendations and interactions?
- Cost Reduction : For cost-conscious businesses, objectives could revolve around optimizing the customer journey to reduce operational costs. Are there redundant touchpoints or inefficient processes that can be streamlined?
Practical implementation of this step involves convening a cross-functional team to brainstorm, discuss, and define your objectives. Each department, from marketing to customer support, should have input to ensure a comprehensive perspective.
Objectives should be documented, and their importance should be communicated throughout the organization. This clarity ensures that everyone is working toward a common goal, enhancing collaboration and alignment.
Every explorer needs a crew, and in this journey, your crew comprises customer personas. There are questions you should consider and ask. Create detailed profiles of your typical customers, considering;

- Demographics and Psychographics : Start by defining the basic demographics of your personas, such as age, gender, location, and income. Dive deeper into psychographics, understanding their values, interests, and lifestyle choices. For example, are your potential customers tech-savvy millennials seeking convenience, or are they older, price-conscious consumers looking for reliability?
- Goals and Pain Points: Delve into the goals and pain points of each persona. What are they trying to achieve when interacting with your brand? What obstacles or frustrations might they encounter along the way? Knowing these aspects allows you to provide solutions at critical touchpoints.
- Behavioral Patterns: Explore the behavioral patterns of your personas. How do they typically engage with your brand? Are they frequent visitors to your website, or do they prefer in-person interactions? Understanding these patterns helps in optimizing customer touchpoints.
- Communication Preferences: Identify how your personas prefer to communicate. Do they engage via email, social media, or phone calls? Tailor your communication channels to align with their preferences for more effective interactions.
- Decision-Making Process: Determine the decision-making process of your personas. Are they impulsive buyers, or do they conduct thorough research before making a purchase? This insight helps you align your marketing strategies and content with their decision journey.
In the realm of customer journey mapping, gathering customer data is akin to excavating precious gems of knowledge, crucial for achieving a deeper understanding of your audience and ensuring customer retention. It serves as the compass guiding your business through the intricate maze of customer preferences, behaviors, and expectations while minimizing customer churn. Effective data collection is not just a task but a strategic endeavor that requires precision and purpose, allowing you to engage with your target audience more effectively.
To embark on this data collection voyage, you must first identify the sources of valuable information within your reach. These sources span a spectrum, from website analytics and social media metrics to customer surveys designed to survey customers for insights. Categorize the data into distinct types, including demographic, behavioral, psychographic, and transactional data. For instance, understanding the preferences of tech-savvy millennials or the cautious spending habits of older customers can offer insights into customer churn and retention. Ensuring the quality and accuracy of this data is paramount, as it’s the cornerstone upon which insightful decisions are made. Implement data validation processes to minimize errors and uphold data integrity. Moreover, always respect customer privacy and adhere to data protection regulations, seeking clear consent for data collection to foster trust.
In practice, customer surveys can directly capture feedback and insights, uncovering a few examples of pain points or preferences that influence customer retention. Tools like Google Analytics help track website visitor behavior, providing essential data for tailoring your strategies. CRM systems centralize customer information, offering a unified view of interactions and preferences that can inform customer retention efforts. Social media listening uncovers sentiment and trends, guiding your engagement with the target audience. Additionally, data mining techniques reveal customer preferences that, when acted upon, boost customer retention. Regular data audits and cross-referencing data from various sources ensure data accuracy, while stringent data security measures and compliance with regulations protect sensitive information. By mastering the art of data collection, you not only unlock the secrets of the customer journey but also pave the way for crafting meaningful and personalized experiences that resonate with your target audience, thereby enhancing customer retention and reducing churn. With data as your guiding star, you’re equipped to navigate the seas of customer insights with confidence and purpose.
Now, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, pixels to screen) and create a visual representation of the customer journey. Use software or even a whiteboard to sketch out the different stages and touchpoints your customers go through. Each stage represents a milestone in their journey.
In the intricate tapestry of crafting an effective marketing strategy that caters to customer expectations and cultivates loyal customers. A touchpoint is any interaction between a customer and your brand, a moment when your customer journeys through your offerings, and their experience is shaped. Understanding and strategically defining these touchpoints empowers you to orchestrate a seamless, delightful journey that resonates with your audience.

To begin this journey of touchpoint definition, it’s essential to comprehensively map the customer’s journey. This involves identifying every instance where a customer comes into contact with your brand, whether it’s through a website visit, a social media interaction, a customer service call, or even an in-store experience. By recognizing these touchpoints, you can tailor your marketing strategy to meet customer expectations at each juncture.
The goal is to ensure that every interaction leaves a positive impression, fostering loyalty and trust among your customers. Whether it’s a user-friendly website interface or a personalized email campaign, every touchpoint is an opportunity to engage, delight, and convert customers into loyal advocates of your brand.
Creating a customer journey that truly engages and resonates with your audience is about stepping into your customers’ shoes, cultivating empathy, and fostering customer success. It’s not just about understanding their needs but also their emotions, challenges, and aspirations throughout their buying process.
To effectively walk in your customers’ shoes, start by revisiting your customer personas and immersing yourself in their characteristics, preferences, and pain points. Conduct interviews and surveys to gain deeper insights into their experiences and expectations. Organize workshops where cross-functional teams can collectively analyze the customer journey and identify areas for improvement. Employ mystery shopping and competitor benchmarking to uncover hidden gaps. Analyze customer feedback to spot recurring themes and issues.
Empathy should not be a one-time exercise but an integral part of your decision-making process. When empathy becomes ingrained in your organization’s culture, every team member considers its impact on customer success. By walking in your customers’ shoes, you gain a profound understanding of their journey, which becomes the foundation for designing meaningful interactions, fostering customer satisfaction, and driving brand advocacy. So, lace up those metaphorical shoes and embark on a journey to create a customer journey that ensures customer success throughout the buying process.
In the intricate world of customer journey mapping, Understanding your customer’s emotions and pain points plays a pivotal role in cultivating a deeper connection with your audience. This step revolves around the art of capturing emotions and pain points that shape customer interactions. Emotions are the driving force behind customer decisions and actions, while pain points represent the obstacles they encounter. Recognizing and understanding these aspects empowers businesses to create solutions that resonate with customers’ feelings and alleviate their concerns.
To capture emotions and pain points effectively, businesses can employ various strategies. Emotion-centric surveys can be designed to prompt customers to express their feelings and experiences at different touchpoints, be it during a purchase or while engaging with the customer service team. Empathy mapping workshops encourage collaborative creation of empathy maps, visually representing customer personas’ emotions and pain points throughout their journey. Customer interviews should go beyond the standard questions, urging customers to share emotional experiences and elaborate on their pain points.
Feedback analysis can be enriched by incorporating emotional tags to categorize responses and identify sentiments. Social media listening offers a real-time glimpse into customer emotions as they discuss brands online, providing opportunities for businesses to engage and gain a deeper understanding of their audience’s perspectives. Ultimately, applying these insights can transform ordinary interactions into memorable experiences, fostering customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy in the process.
In this step, we dive deeper into understanding and enhancing our customer journey maps. It’s like finding hidden treasures in a treasure hunt. First, we dig into all the information we’ve gathered about our customers, like feedback and surveys. Then, we use cool tools to turn this data into easy-to-understand pictures. These pictures show us how customers behave on their journey with our business.
But we don’t stop at just looking at pictures. We take action ! We listen to what customers say and what the numbers tell us. If something’s not right, like customers not staying with us for long, we figure out why and make changes. We also keep an eye on what other businesses are doing to see if we can do things better. It’s like always trying to make our customer journey maps more effective and exciting.
This isn’t a one-time job; it’s an ongoing adventure. As customers’ needs change, our journey maps should change with them. We work together across our teams to make sure our business strategy lines up with these maps. This way, we’re not just meeting but exceeding our customers’ expectations. And that’s how we keep them happy and coming back for more, making our business stand out from the crowd.
Once you’ve charted the course, it’s time to steer the ship. Implement changes and improvements based on your findings. Ensure that all departments and teams are aligned with the new strategy and understand their roles in enhancing the customer journey.
Through these nine steps, from defining objectives to implementing changes, we’ve embarked on a transformative journey ourselves. We’ve learned to see our business from the customer’s perspective, understand their emotions, and continuously adapt to meet their needs. By mastering these steps, we ensure that our customer journey maps are not just diagrams on a wall but effective tools that drive our business strategy. In doing so, we don’t just satisfy customers; we create loyal advocates who keep our business thriving. So, as we implement changes, we do it with a sense of purpose and a commitment to delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Customer experience (CX) is the heart and soul of your customer journey strategy. It’s not just about a single transaction; it’s about fostering long-term relationships. A positive CX ensures customers return, become brand advocates, and fuel business growth.
To enhance CX, focus on personalization, responsiveness, and consistency across all touchpoints. Leverage data and feedback to refine your strategy continuously. Remember, it’s the little things that make a big difference.
The Power of Customer Journey Mapping
Now that we’ve delved into the importance of customer journey mapping, let’s explore how it can transform your customer journey strategy.
Identifying Pain Points: Mapping helps pinpoint pain points in the customer journey, allowing you to address and eliminate them. This leads to a smoother and more enjoyable experience.
Optimizing Touchpoints: With a detailed map, you can optimize touchpoints, ensuring that each interaction aligns with your brand’s values and objectives.
Predicting Customer Behavior : A well-constructed customer journey map allows you to predict customer behavior, enabling you to proactively meet their needs.
Enhancing Personalization: Personalization is key to exceptional customer experiences. Mapping facilitates tailored interactions at each stage of the journey.
Measuring Success: By mapping the customer journey, you can establish clear metrics and KPIs to measure the success of your strategy.
In the realm of modern business, crafting a winning customer journey strategy is not just an option; it’s a necessity. A well-mapped customer journey, combined with a relentless focus on customer experience, can set your brand apart and drive sustainable growth.
About the author
Julie Choo is lead author of THE STRATEGY JOURNEY book and the founder of STRATABILITY ACADEMY. She speaks regularly at numerous tech, careers and entrepreneur events globally. Julie continues to consult at large Fortune 500 companies, Global Banks and tech start-ups. As a lover of all things strategic, she is a keen Formula One fan who named her dog, Kimi (after Raikkonnen), and follows football - favourite club changes based on where she calls home.
You might also like
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Strategy Journey Fundamentals , Transformation
The Impact of Co Creation in Modern Business
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Transformation
4 steps to create a Winning Game Plan
Service Design
Business Level Strategies: What are they, How to use it?
- Case studies
- Expert advice
Activating your journey mapping: a four-step guide
Design and innovation are continuously evolving, making journey mapping an essential tool. However, a journey map has transcended beyond just being a diagram (and was it ever just that?). It now serves as a catalyst that unites teams and fosters new ideas. Jim Kalbach , known for his book "Mapping Experiences," talked about this change at our recent event. Jim sees journey maps as gathering points, like campfires, where teams can share ideas and insights.
This article looks into journey map activation, a way to use these maps as starting points for finding new opportunities and sparking creativity. Read it or watch the recording of the event with Jim at the end of the article.
Mapping experiences
Initially, nearly a decade ago, the conversation around customer journey and experience maps centered on their basic definitions and creation processes. Today, the prevailing questions have shifted towards the practical application of these maps: How can they drive innovation? How can they help teams uncover new opportunities?
How to understand customer experiences
Designing for complex human experiences filled with varied emotions and needs has led to innovative practices like service blueprinting and customer journey mapping . These tools enable a deep dive into customer experiences, guiding businesses to adapt their services and products more closely to user needs. Central to this approach is recognizing the importance of understanding the customer experience to appropriately apply technology, moving away from a technology-first mindset.
This customer-centric perspective has catalyzed the adoption of mapping techniques to visually articulate and discuss experiences, with the service blueprint standing out as a prime example.
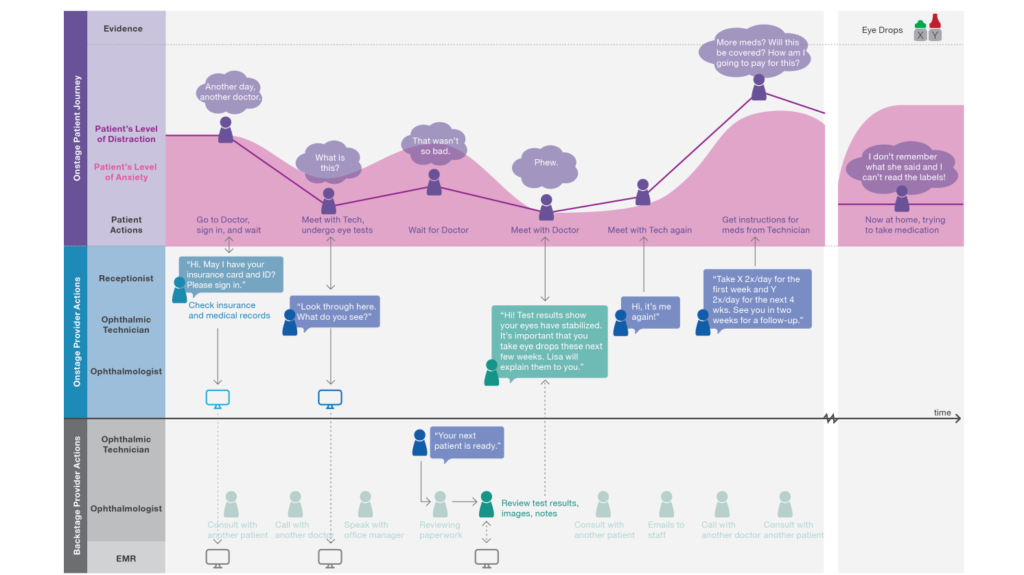
Such blueprints detail the customer's journey, including their actions, thoughts, and emotions, while mapping out the operational processes that underpin these experiences. They reveal the "backstage" activities, invisible to customers, like administrative tasks or preparation of medical equipment, emphasizing the seamless integration needed between customer experiences and organizational operations.
These tools align the delivery mechanisms — people, processes, or technology — with the customer's journey. This alignment ensures every element of the service is in sync with the customer's needs, enabling efficient and effective service delivery. The visualization offered by journey maps and service blueprints fosters a collective understanding among team members, bridging different perceptions and aligning them towards a unified goal.
Highlighting the importance of an "outside-in" approach, these mapping practices prioritize starting with the customer's perspective and then integrating technology to enhance that experience. This method contrasts with traditional approaches, encouraging a shift from focusing on internal processes to centering on the customer's needs. However, the ultimate value of journey maps extends beyond their creation. They are not meant to be static decorations but dynamic tools that facilitate continuous team improvement and alignment.
The act of mapping is a process of negotiation and shared understanding, serving as a catalyst for team alignment and insight generation. It's a dynamic exercise that, like a campfire, gathers team members for meaningful engagement, fostering the essential "inside-across" alignment for innovation and service improvement. Through this lens, journey mapping transcends being a mere deliverable to become a pivotal process in designing and delivering customer-centric services.
A step-by-step journey map activation
Journey mapping goes beyond workshops , serving as a key component of a holistic mapping strategy. Jim's book details a universal approach to creating maps like service blueprints or journey maps, involving stages of:
- initiation (scoping the project);
- investigation (basing the map on research);
- visualization (illustrating the findings);
- alignment (making the insights actionable through collaborative efforts).
This approach emphasizes transforming mapping insights into concrete strategies.
The journey mapping process is designed to deeply involve and engage the team at every step, integrating a social dimension to enhance collaboration and commitment. By focusing on making the journey map actionable and embedding team engagement from initiation through alignment, the process produces a valuable experience tool and cultivates a shared move towards practical outcomes.
Step 1. Initiate: make it relevant
In the journey mapping process, pinpointing specific customer segments and their paths is fundamental. This step, known as establishing the "point of view," involves choosing the focus — deciding which users or customers and their journeys to highlight.
It is essential to delineate the journey's scope, mark where it begins and ends, and determine the content the map will feature. These early focus, scope, and content decisions are crucial for every mapmaker.
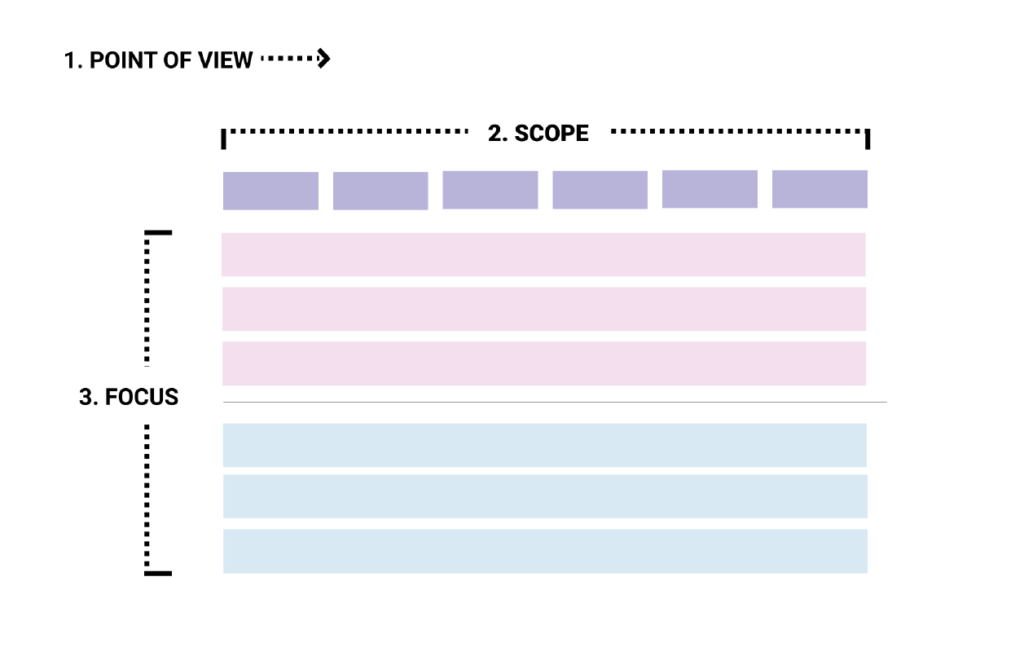
Engaging the team in these preliminary decisions ensures alignment and shared understanding. Activities like stakeholder mapping can clarify the map's domain and audience, underlining that the map's purpose is strategic insight, not mere decoration.
The journey map's primary audience is the internal team, making their involvement vital. Early discussions should identify key stakeholders and align the mapping effort with the organization’s strategic goals, enhancing the process with diverse insights.
It is a critical preparatory step to identify all relevant stakeholders — buyers, sellers, agents, etc. — and prioritize them according to business objectives when mapping the journey of home buyers in an online real estate service, for instance. Choosing to focus on home buyers and a specific aspect of their experience, like shopping for a new home, is made through collaborative team engagement. That ensures the journey map aligns with agreed priorities and organizational goals, fostering a collective sense of ownership and direction from the outset.
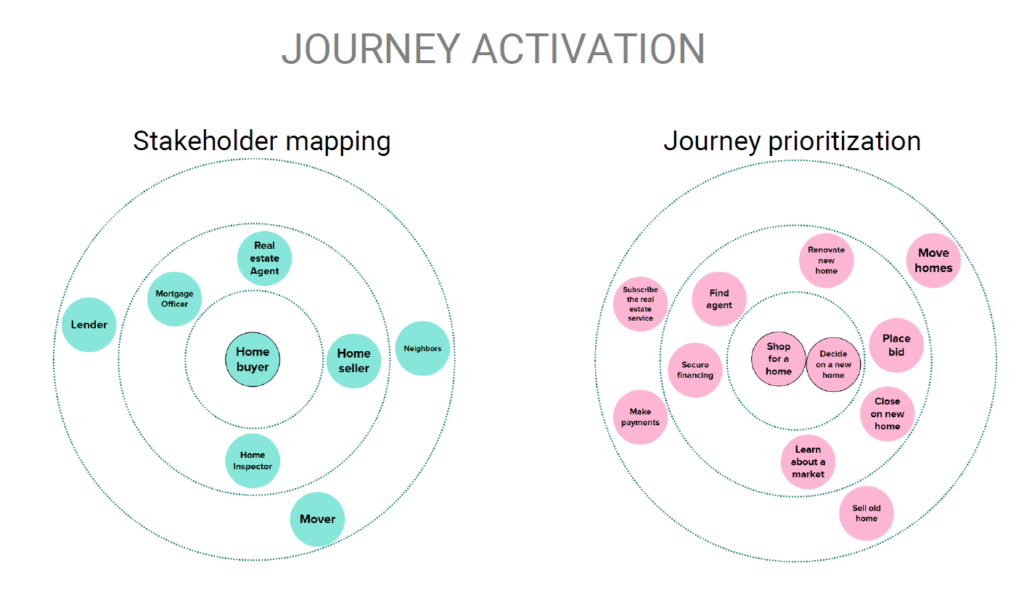
This collaborative approach to defining the mapping process's focus doesn't necessitate extensive research but can be achieved through straightforward, inclusive discussions. Continuous team engagement throughout the mapping ensures that the journey map remains relevant and aligned with the team's objectives and the broader organizational goals, preventing any later misalignment and ensuring the journey map effectively serves as a tool for strategic insight and team alignment.
Step 2. Investigate: make it real
During the investigation phase, tangible methods like ride-along interviews bring real user experiences to the forefront. Inviting team members to listen to conversations with home buyers, possibly through platforms like Zoom, offers a direct window into customer perspectives, grounding the process in reality. This approach not only enlightens team members unfamiliar with direct customer feedback but also aligns the team's understanding of customer needs.
Centering the journey mapping on home buyers' experiences is a collective decision that ensures alignment with organizational goals. Such decisions, facilitated through quick discussions or calls, aim to reflect the team's consensus on focus areas, avoiding any surprises in the journey map's later stages.
Involving stakeholders in the investigative phase, especially in activities like customer interviews , fosters a deep understanding and participation. This involvement cultivates a unified team perspective and engagement from note-taking to listening. Regular, inclusive engagement throughout the mapping process, as opposed to a single, extensive workshop, keeps the team aligned and informed.
For remote teams, sharing customer interviews within the organization thoughtfully is crucial. Maintaining interview participants' comfort while ensuring inclusivity suggests that non-active participants keep their cameras off and microphones muted, aware of the interview but not directly involved. This approach enhances the team's empathy and understanding of the customer experience, integrating real insights into the journey mapping process.
Step 3. Illustrate: make it visual
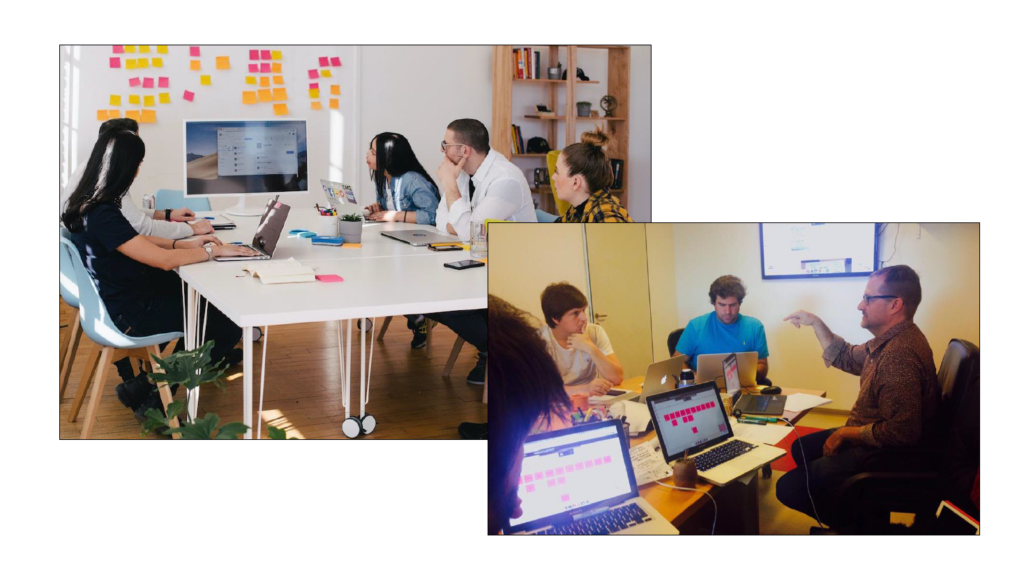

The visualization stage of journey mapping transforms insights into a tangible diagram, emphasizing collaboration in sketching and drawing. In this phase, while a mapmaker often compiles data and drafts the initial diagram, involving the entire team can deepen understanding and foster a sense of collective ownership. Active participation in creating the map, perhaps through digital platforms, encourages a shared insight and democratizes the process, making the team's collective knowledge and perspectives integral to the map's development.
This collaborative approach starts with engaging team members in the investigation phase, such as through silent observation during customer interviews on Zoom, ensuring a focused and intimate gathering of insights. Later, encouraging both team members and interviewees to contribute sketches or interpretations of the journey integrates diverse viewpoints directly into the visualization process.
Negotiating reality occurs as the team collaborates on the map's initial rough sketches, gathering stories and identifying patterns. This stage is characterized by its organic, somewhat disorganized nature, akin to a detective piecing together a case. Engaging the team in this chaotic phase demystifies the journey mapping process, illustrating that detailed, high-fidelity maps evolve from these simpler, collaborative beginnings.
Utilizing digital tools for map creation has proven effective in fostering dynamic, inclusive collaboration. It allows teams, whether remote or in-person, to co-create a map. This inclusive approach enhances the map with a rich tapestry of insights. It strengthens team alignment and ownership over the final journey map, underscoring the collective effort required to weave the gathered data into a coherent narrative.
Step 4. Align: make it actionable
The alignment phase of journey mapping shifts focus towards making the map actionable, emphasizing the importance of team collaboration to translate insights into strategic actions . That involves dedicating time for collective review and engagement with the created map through workshops that can span a few hours to a full day. These sessions integrate field insights, personas, and business needs, ensuring comprehensive understanding and alignment on the next steps.
Throughout the mapping process, embracing the initial chaos and collaboratively exploring insights is critical. Like detective work, the early stages involve identifying patterns and fostering a shared understanding. Digital tools like Mural facilitate this collaborative effort, whether conducted in person or remotely, enhancing team cohesion.
The alignment workshops serve as a platform for deep engagement with the journey map, encouraging interaction through activities like grading, voting, SWOT analysis, or role-playing. This hands-on approach ensures that the map evolves into a dynamic tool for continuous improvement rather than a static artifact.
Facilitation is crucial in this phase, bridging team perspectives with organizational goals and transforming the map into an actionable asset. Taking this step away from mere map creation towards facilitating meaningful discussions around customer experiences ensures that the journey map serves its intended strategic purpose and fosters deeper understanding and alignment within the team.
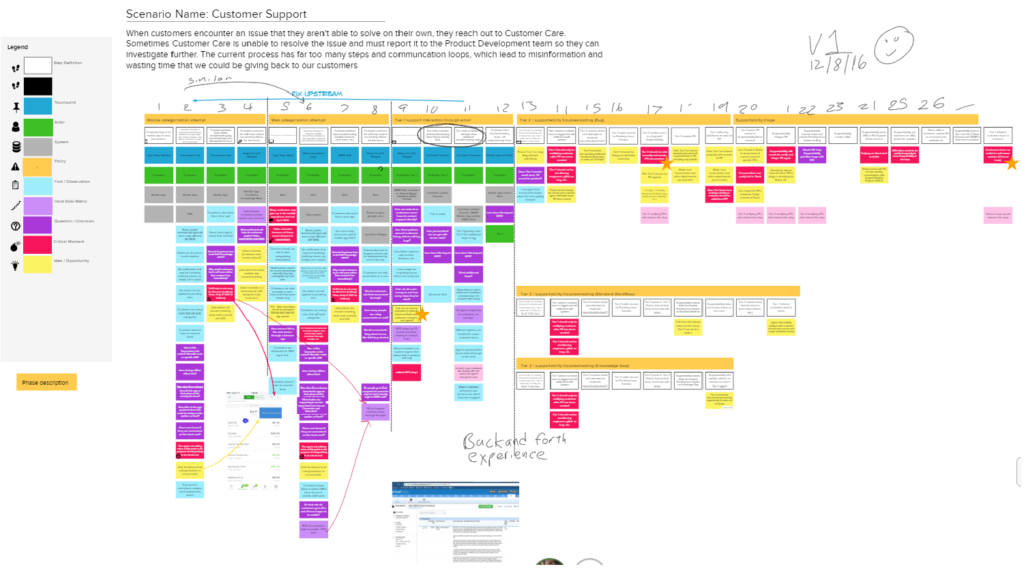
Mapping facilitation example from practice
In a collaborative digital mapping session with Intuit, Jim crafted a service blueprint enriched with visual cues and vibrant discussions. This blueprint identified key service moments, particularly a "moment of truth," derived from collective dialogue. This process demonstrated the profound value of mapping, not just in visual creation but in sparking meaningful conversations that lead to actionable insights and service improvements.
A notable session activity involved analyzing a specific customer interaction, marked by a screenshot on the map. This spurred discussions that pinpointed inefficiencies needing resolution, showcasing the dynamic interplay between visual elements and dialogue in driving toward solutions.
Further, an exercise had participants assess our company's customer support at various journey stages, revealing varied perceptions and highlighting discrepancies in service delivery understanding. This diversity in perspective prompted deeper investigations and aligned our strategic focus more closely with the customer experience.
The journey map acted as a pivotal storyboard, guiding discussions to remain customer-centric and evidence-based. Transitioning from map creation to facilitation, we employed resources like "Gamestorming" and "Innovation Games" to workshop pain points, emphasizing a design thinking approach to problem-solving that prioritizes customer needs.
The challenge extended beyond ideation to prioritizing and developing ideas into actionable solutions. Utilizing journey maps as strategic tools, the team focused on enhancing customer value, leading to rapid prototyping and usability testing to refine solutions based on real feedback. This process exemplified an efficient transition from concept to validation, ensuring solutions were grounded in genuine customer needs.
Ultimately, this mapping session underscored the importance of facilitation in driving discussions, integrating diverse insights for strategic alignment, and the need for a structured approach to transforming ideas into tangible outcomes, enhancing the overall customer journey.
Wrapping up
Journey mapping transcends the creation of a static map, becoming truly valuable through active facilitation and engagement that drives momentum. This shift from simply making a map to dynamic facilitation represents a move towards lean experimentation and continuous improvement. The map itself doesn't sustain progress; it's the proactive planning, workshops, and follow-ups that turn the mapping effort into a catalyst for innovation.
This approach challenges the traditional view of a map as a finished product, transforming it into a living tool that promotes understanding, collaboration, and actionable insights. It aims to ensure the journey map is fully integrated into strategic operations, preventing it from becoming mere "wallpaper" and instead serving as a springboard for ongoing development and team alignment.
Event recording
Want to hear it all with your ears? Watch (here's the paradox) the recording of the event that formed the basis of this article:
About the speaker
Jim Kalbach is a noted author, speaker, and instructor in innovation, design, and the future of work. He is currently the Chief Evangelist at Mural, the leading online whiteboard.
Jim is the author of several books: Designing Web Navigation (O’Reilly, 2007), Mapping Experiences, 2nd Ed. (O’Reilly, 2020), and The Jobs To Be Done Playbook (Rosenfeld, 2020). In 2023, he co-authored Collaborative Intelligence (Wiley, 2023) with Mariano Battan. Jim is also the Co-founder and Principal of the JTBD Toolkit, an online resource with learning, training, and content.
Related posts
Rate this post

Step-by-Step Guide for Customer Journey Templates
Home » Step-by-Step Guide for Customer Journey Templates
In the fast-paced digital marketplace, where every customer interaction can be a goldmine of insights, organizations are constantly seeking ways to harness this data effectively. The key to unlocking the potential of customer data lies in understanding the customer journey. A well-crafted Customer Journey Template can be the roadmap to enhanced customer experiences, increased loyalty, and ultimately, business growth. This write-up presents a step-by-step guide to creating a Customer Journey Template, leveraging the power of real-time data analysis and AI-assisted insights.
Understanding the customer journey is not just about mapping out touchpoints; it's about diving deep into the nuances of customer interactions, identifying pain points, and recognizing opportunities for improvement. The process begins with gathering comprehensive data from various customer interactions. This could include interview transcripts, customer feedback, support tickets, and more. The goal is to collate this data in a structured manner that allows for meaningful analysis.
Step 1: Data Collection
Begin by setting up a project folder to centralize all customer-related data. Import files from existing libraries or directly upload transcripts and other customer interaction records. This initial step ensures that all relevant information is accessible in one location, paving the way for efficient analysis.
Step 2: Data Analysis
Utilize AI tools, such as Insight Seven, to analyze the collected data with a single click. The AI's capabilities allow you to quickly identify themes, sentiments, and goals supported by the data. The analysis should result in a dashboard overview that highlights customer pain points, desires, and the opportunities that lie within.
Step 3: Insight Extraction
Delve into each identified theme to extract actionable insights. Look for patterns in customer interviews or conversations that reveal underlying issues or desires. Use AI research assistants to ask questions about the data and generate ideas for solutions to the problems mentioned.
Step 4: Customer Segmentation
Segment your customer base by relevant attributes such as revenue, employee size, industry, or any other meaningful criteria. This segmentation allows for a tailored analysis of different customer groups, helping to prioritize actions based on the top priorities for each segment.
Step 5: Template Creation
With the insights and segmentation in place, create a Customer Journey Template that maps out the customer experience from initial awareness to post-purchase behavior. Incorporate the insights to identify critical touchpoints where customers need more support or where opportunities for upselling may arise.
Step 6: Continuous Improvement
The Customer Journey Template is not a static document; it should evolve with ongoing customer feedback and data analysis. Revisit the template regularly to update it with new insights and ensure it remains relevant to the changing customer landscape.
In conclusion, a Customer Journey Template is an invaluable tool for any organization looking to deepen its understanding of customer needs and behaviors. By following this step-by-step guide and leveraging the power of AI-assisted data analysis, businesses can create a dynamic template that not only reflects the current state of customer interactions but also anticipates future needs and trends. This proactive approach to customer journey mapping is essential for staying ahead in a competitive market and fostering long-lasting customer relationships.
Customer Journey Mapping Software Comparison
Related posts, how to analyze focus group data and get actionable insights.
How to Generate Accurate Focus Group Summary with AI Tools
How to prepare focus group discussion reports in seconds, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Unlock Insights from Interviews 10x faster
- Request demo
- Get started for free
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads

Inspiration
Three things to look forward to at Insight Out
Tips and tricks
Make magic with your customer data in Dovetail

Four ways Dovetail helps Product Managers master continuous product discovery
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
Unlocking the B2B customer journey: step-by-step guide
Last updated
22 February 2024
Reviewed by
Regardless of your industry or the unique goals of your business, every customer interaction is important. From the time a customer discovers your product or service to when they make a purchase and beyond, you and every member of your team should pay attention to the impression you’re making. A positive customer experience can make the difference between a one-time sale and a customer for life.
The B2B customer journey helps businesses understand how customers perceive their products and services. It can assist sales representatives and customer service agents in uncovering opportunities to serve clients better and highlight ways to improve your products and services.
Whether you're new to the world of B2B or a seasoned marketer looking for new ways to serve your customer base, this guide will help you.
- What is a B2B customer journey?
A B2B customer journey contains all the touchpoints a customer has with a B2B business. This journey starts with the first interaction a customer has with your business and extends to the post-purchase timeframe.
The journey of a B2B customer generally takes longer than a B2C interaction (contact between a sales agent or customer service representative and the customer).
- The B2B customer journey stages
There are typically five stages of the B2B customer journey. The exact route can vary from organization to organization, but these five steps represent the basic outline of a customer journey:
1. Awareness stage
The awareness stage starts well before a customer discovers your business. It begins when a person becomes aware of a problem they have or a pain point that needs resolving and they begin to look for solutions.
Through your marketing and sales campaigns, you'll connect your product or solution with that customer's needs.
2. Consideration stage
During the consideration stage, a customer could be checking your website for reviews, reading case studies, or watching videos on your site to learn more about the product or service.
3. Customer conversion
When a customer decides to commit to your brand, they have entered the conversion stage of the B2B customer journey. The conversion stage doesn't necessarily have to be a purchase. It could be:
Signing up for a newsletter
Creating an account
Registering to receive a product demo
This stage can also include product delivery if a purchase is made, and onboarding work for your sales and customer service teams.
Conversion is only the midway point of the B2B customer journey. Once a customer has been converted, you'll need to continue to serve them via interactions with customer support. If a customer has questions or concerns, they must be handled promptly to keep satisfaction high.
5. Retention and advocacy
Ideally, you'll have a customer for life. Retaining customers and encouraging them to become brand advocates should be the goal of every business. After all, satisfied customers are more likely to not only purchase again but to encourage their friends and family to check out your business if they are in the market for a product like yours.
When creating your customer journey map, try to align the customer journey with your sales funnel. You'll create a symbiotic process that allows you to better control touchpoints and make it easier for your sales and service teams to track the customer's journey.
- The difference between B2C and B2B journeys
While B2B and B2C journeys share many similarities, including stages such as lead acquisition, there are also distinct differences.
B2B customer journeys tend to emphasize personalized engagement, while B2C journeys can feature a one-to-many mindset that prioritizes sales and marketing steps. Additionally, B2C marketing is often aimed at the general consumer. B2B is more industry-specific and focuses on target customers.
There can be multiple stakeholders involved in a B2B journey, while B2C journeys are usually individuals or families. Finally, B2B journeys involve greater discussion about return on investment (ROI), while B2C outcomes are often based on benefits to the individual or end user.
- How to create a B2B customer journey map in seven steps
Creating a B2B customer journey map can help your organization understand where to devote resources by identifying every point where a potential customer might come into contact with your business. When you can appropriately prepare your sales, marketing, and customer service teams, you'll be in a better position to retain more customers and grow market share.
Creating a customer journey map can take time and might involve contributions from multiple stakeholders. Here are the seven basic steps for journey mapping:
1. Analyze typical buying groups
While B2B journeys target specific customer groups rather than general consumers, multiple groups can often be involved.
You'll want to ensure you understand everyone involved in the journey and their requirements as you complete the journey mapping process.
Different groups might also have varying levels of influence on the buying process.
2. Understand your customers' goals
The first stage in a B2B customer journey is the awareness stage, when a customer becomes aware of a problem they need to solve or a goal they wish to complete. For the most successful customer interactions, familiarize yourself with your customers' motivations and concerns.
Take time to thoroughly understand their goals by reading your target customer personas and try to put yourself in their shoes. If you fully understand their needs, you'll be in a better position to address them.
3. Make use of data and analytics
Analytics are some of the most powerful tools in your arsenal. Data and analytics will give you factual insights into what's working and what isn't.
It's easy to make subjective decisions, especially when multiple stakeholders are involved. Use data from multiple sources, including your CRM, to figure out which touchpoints need more attention and which are functioning according to plan.
4. Build out the B2B customer journey stages
Every business has different goals and different definitions of success. You will have unique ideas of the customer journey, depending on your industry and the products and services you sell. Customize your customer journey accordingly.
It's a good idea to start with a standard outline of a customer journey, such as the stages highlighted above, and flesh it out as you go. Think from your target customer's point of view and sketch out components to account for the final journey mapping.
5. Outline the different touchpoints
It's important to identify all the areas where your customers interact with your business. These touchpoints can include direct contact such as:
Sales meetings
Phone calls
Onboarding sessions
They can also include indirect contact, such as:
Organic searches
Social media posts
Some of these touchpoints are more personalized and vital than others, but they should all be taken into account and mapped in your customer journey.
6. Define your goals
With any project, it's vital to have a goal in mind. Whether your end result is increased revenue, greater customer retention, or both, having a defined goal in place from the outset of your customer journey mapping can help you and your team stay focused and motivated.
Along the way, gather customer feedback to accurately capture the voice of the customer and refer to your analytics, to see how well you're doing at serving your customers and achieving your goals.
7. Monitor and improve as you go
Things rarely go perfectly from the outset. Even the best-laid plans (and the most carefully created customer journey maps) can have blind spots and weak areas. Rather than dwell on mistakes or slow starts, commit to improving your processes as you go.
The best way to do this is to closely monitor analytics as they come in to see at what points customers fall out of the funnel. For example, if you see a pattern of potential customers falling off after the initial conversion, look into those touchpoints and see how you can improve them.
- How to improve your customer journey for B2B
Shopping online, whether looking for a new product or a new service, can be time-consuming and stressful. For many consumers, especially those who don't consider themselves tech-savvy, the idea of spending time online making a purchase isn't a pleasant prospect.
As a marketer or someone who is in the business of pleasing customers, anything you can do to streamline this process is ideal. When you make your customer's life easier, there's a good chance they'll turn to you again and again.
Here are a few ways to improve your B2B customer journey:
Refer to buyer personas
Buyer personas are descriptions of your company's ideal customer. The buyer personas you define should guide your sales and marketing activities and help you better understand what your customers are looking for. This can help you create a stronger marketing funnel and enhance the touchpoints in your customer journey.
If you haven’t yet created any buyer personas, take time to make them. Include specifics such as:
Geographical location
Create quality content
The content you create and distribute has the power to attract, convert, and retain customers. It should be:
High quality and thoughtful
Crafted to address customers' needs
Aimed at improving the overall customer journey
Structure your content around issues that directly affect your customers. Never create and share content just for the sake of it.
Focus on the onboarding process
Arguably, the most important stage in the customer journey is the onboarding process. A smooth onboarding can make or break your future relationship with the customer.
This lays the groundwork for success and shows your customers you care about their experience.
Wherever possible, tailor the experience to their needs and hone in on potential weak points to streamline and eliminate problems before the customer comes across them.
Stay visible
Even as you work to gain new customers, make sure you stay front of mind for your current customers.
Stay in touch through email newsletters, boosted social posts, and other regular check-ins, so you can see how things are going and let them know you care about their experience. If the product they purchased is subscription-based, send a renewal notice promptly.
By simplifying and streamlining the customer journey in as many ways as possible, you'll be creating a customer for life. This can make the difference between a one-time purchase and multiple purchases and referrals.
The time you invest now in creating an efficient, effective customer journey can pay off hugely in the future.
- B2B customer journey map templates
Customer daily routine template
This template can help you consider how your target customer spends an average day. By highlighting what the customer thinks and feels throughout the day, you can figure out how your products or services fit in.
What is the customer thinking and feeling in the morning? By the afternoon? Late at night?
What are the customer's actions and priorities in the morning? By the afternoon? Late at night?
What are the customer's biggest pain points in a day?
How can the customer interact with our product in a way that resolves their pain points?
Service template
This template is focused on the factors that can create impressions about the quality and prices of the service, rather than on specific phases in a customer's journey. These questions can serve as a standalone template or be incorporated into a more hyper-focused template.
What is the customer feeling?
Why is the customer feeling like that?
How can we make the customer's experience better?
What actions can we take in the background?
What actions can we take when interacting with the customer?
Adjust the questions in the template to suit your industry. Every template should reflect the unique nature of your organization as well as your buyer personas.
Classic buyer's journey template
A classic buyer's journey, consisting of a series of defined stages, is an excellent starting point for any customer mapping journey. Here are some questions to consider:
What is the customer thinking and feeling during the awareness stage? The consideration stage? The conversion stage?
What is the customer's action during the awareness stage? The consideration stage? The conversion stage?
How is the customer researching products or services?
How can we move the buyer along in their journey during the awareness stage? The consideration stage?
Customer journey mapping is the most effective way to visualize how to serve your customers. Whether you're developing a new product or refining your customer service processes, creating a B2B customer journey map is an exciting opportunity to grow your business and build a more satisfied client base.
What are the 4 types of customers in B2B markets?
While B2B markets vary widely, many experts point to four types of business customers in B2B markets: producers, governments, resellers, and institutions. Producers are companies that purchase goods and services that they transform in to other products or services. Governments include local, state, and federal government agencies. Resellers are companies like Wal-Mart that sell goods and services produced by other companies. Institutions are primarily nonprofit organizations like churches, hospitals, and charitable organizations.
What is the B2B lifecycle?
The B2B lifecycle is generally thought to comprise four stages: discovery, evaluation, purchase, and loyalty. This is a more compressed form of a customer journey, which includes stages before and after a customer discovers a product or service. The B2B lifecycle only includes the stages that occur from the time a customer discovers a product to the moments after purchase when the customer chooses to either seek out other options to fulfill their needs or remain a loyal customer.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 22 April 2023
Last updated: 8 May 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2023
Last updated: 18 July 2023
Last updated: 9 July 2023
Last updated: 20 March 2024
Last updated: 21 March 2024
Last updated: 16 March 2024
Last updated: 5 April 2023
Last updated: 22 May 2023
Last updated: 29 May 2023
Last updated: 23 March 2024
Last updated: 25 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Define the map's scope (15 min) Ideally, customer journey mapping focuses on the experience of a single persona in a single scenario with a single goal. Else, the journey map will be too generic, and you'll miss out on opportunities for new insights and questions. You may need to pause creating a customer journey map until you have defined your ...
While many companies will put their own spin on the exact naming of the customer journey stages, the most widely-recognized naming convention is as follows: Awareness. Consideration. Decision. Retention. Advocacy. These steps are often then sub-categorized into three parts: Pre-sale. Sale/Purchase.
Breaking down the customer journey, phase by phase, aligning each step with a goal, and restructuring your touchpoints accordingly are essential steps for maximizing customer success. Here are a few more benefits to gain from customer journey mapping. 1. You can refocus your company with an inbound perspective.
The customer journey mapping process. The step-by-step process of mapping the customer journey begins with the buyer persona. Step 1 - Create a customer persona to test. In order to effectively understand the customer journey, you need to understand the customer - and this is where creating a persona really helps. You may base this around ...
How to create a customer journey map (step-by-step) Here's how to create a user journey map in 6 steps: Choose a user journey map template (or create your own) Define your persona and scenario. Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions. Fill in the user's thoughts, emotions, and pain-points. Identify opportunities.
Example 1: a mobile user journey. This user journey map template covers the digital experience of the persona who discovers a new mobile app, installs it, and uses the app for some time before deleting it. Open a full-size image in a new tab. Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank.
Step One - Create Your Customer Persona. A customer persona is an idealized image of the person you're marketing to. Simply trying to pull in anyone who'll open their wallets isn't beneficial to your business in the long term. You need people who suit your products and services.
This is also what the next step in constructing customer journey maps is built on, which brings us to our next point. 3. Define Customer Touchpoints. You can think of the key stages in the customer journey on the macro level and the next step in the process — defining customer touchpoints — on the micro level.
Step-by-step: Customer journey mapping process. While it can be helpful to find other customer journey mapping examples, your customer journey map will be unique to your organisation's goals and customers. Source: davechaffey.com. We suggest the following 5 step process to build your customer journey map: 1. Gather the support of stakeholders
The outcome will be your customer journey map. How to create a customer journey map. Here is a process to create an effective user journey map in 5 steps: Step 1: Define the behavioral stages. (Image source) Depending on your business, customers may go through different stages while navigating your site.
A journey map, often referred to as a customer journey map or user journey map, is a visual representation that outlines the various steps and interactions a person or a customer goes through when engaging with a product, service, or organization. These maps are designed to provide a comprehensive view of the entire journey from the user's or ...
Additionally, Customer Journey Maps can be used to identify opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, and they are the building blocks of what you will create in a CS tool. Utilizing a Customer Journey Map is an invaluable step in the customer success process and should be considered a priority for any business.
A 'customer journey map' is usually a step-by-step representation that outlines key events, motivations, customer satisfaction and experience scores at each touchpoint, which is ultimately presented as something that can be a resource for the wider organisation to use.
Customer Journey Mapping: Step-by-Step. There are seven basic steps to creating a good customer journey map. Let's dive into each of them. 1. Research Your Audience.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. ... With these necessary elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map is a simple three-step process. 1. Create buyer personas
6 minute read. Customer Journey Maps are a visual story about how people interact with your brand. They help brands gain a deep understanding of their customers and act as a bridge between business and buyers. In a single illustration, the journey map aims to capture the entire customer experience. No small task.
A step is like the title of an experience. In a journey map, each step (often also called touchpoint) is written in one horizontal row. Various steps can form one stage and group them into ...
We'll explore tips for optimizing the customer journey, ensuring that every step of the way, you're meeting — and exceeding — your customers' expectations. Tips for Optimizing the Customer Journey. Optimizing the customer journey is like being a gardener. Just as a gardener nurtures plants through different seasons, you need to tend ...
Customer journey stages. Step-by-step guide for visualizing the customer journey. Customer journey visualization involves several steps, each contributing to a comprehensive view of the customer's path from initial engagement to loyalty. Here's how to approach it: 1. Identify your customer persona
Mapping the customer journey is essential in understanding your buyers and turning them into loyal customers. Follow these steps to create an actionable B2B customer journey map that gives insights into who your customers are and helps you build an optimized user experience (UX) for them: 1. Set goals unique to your business.
Step 6: Walk in Your Customers' Shoes. Step 7: Capture Emotions and Pain Points. Step 8: Analyze and Iterate. Step 9: Implement Changes - Bringing It All Together. Elevating Customer Experience: The North Star of Your Strategy. The Power of Customer Journey Mapping. Conclusion.
Step 1. Initiate: make it relevant. In the journey mapping process, pinpointing specific customer segments and their paths is fundamental. This step, known as establishing the "point of view," involves choosing the focus — deciding which users or customers and their journeys to highlight.
The key to unlocking the potential of customer data lies in understanding the customer journey. A well-crafted Customer Journey Template can be the roadmap to enhanced customer experiences, increased loyalty, and ultimately, business growth. This write-up presents a step-by-step guide to creating a Customer Journey Template, leveraging the ...
2. Understand your customers' goals. The first stage in a B2B customer journey is the awareness stage, when a customer becomes aware of a problem they need to solve or a goal they wish to complete. For the most successful customer interactions, familiarize yourself with your customers' motivations and concerns.
Step 2: Listen actively to customers. Active listening plays a crucial role in resolving conflicts with customers. Give angry customers your undivided attention and demonstrate empathy. Let them vent their frustrations without interruption, and show that you genuinely care about their concerns.