
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets

Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Travel.State.Gov Newsroom
U.S. Passports News
International Travel News
U.S. Visas News
Intercountry Adoption News and Notices
Share this page:
Update on Change to U.S. Travel Policy Requiring COVID-19 Vaccination for nonimmigrant travel
Worldwide Visa Operations: Update
Employment-Based Fourth Preference (EB-4) Announcement
Suspension of Visa Services in Sudan
Diversity Visa 2024 Update
Nonimmigrant Visa Fee Increases to Take Effect June 17, 2023
India EB-3 Retrogression
Expiration of Covid-Era Visa Application Fee Receipts
Digital Visa Authorization (DVA) Proof of Concept
Final Rule Governing Public Charge Grounds of Visa Ineligibility
Visa Waiver Travel for Israeli Citizens
Important Update on Waivers of the Interview Requirement for Certain Nonimmigrant Visa Applicants
Department of State to Process Domestic Visa Renewals in Limited Pilot Program
Visa Information for Nationals of Haiti
Department of State/AILA Liaison Committee Meeting March 20, 2024
The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with an accepted COVID-19 vaccine to board a flight to the United States. CDC’s Amended Order Implementing Presidential Proclamation on Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic will no longer be in effect when the Presidential Proclamation Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic is revoked .
Please see: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/05/01/the-biden-administration-will-end-covid-19-vaccination-requirements-for-federal-employees-contractors-international-travelers-head-start-educators-and-cms-certified-facilities/
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Advertisement
Supported by
What to Know About the C.D.C. Guidelines on Vaccinated Travel
In updated recommendations, the federal health agency said both domestic and international travel was low risk for fully vaccinated Americans. But travel remains far from simple.
- Share full article

By Ceylan Yeginsu
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its guidance for fully vaccinated Americans in April, saying that traveling both domestically and internationally was low risk.
The long-awaited recommendations were issued by federal health officials after a series of studies found that vaccines administered in the United States were robustly effective in preventing infections in real-life conditions.
One is considered fully vaccinated two weeks after receiving the single dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, or two weeks after receiving the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna shots.
If you decide to travel, you might still have some questions. Here are the answers.
Will I still need to wear a mask and socially distance while traveling?
Yes. Under federal law, masks must be worn at airports in the United States, onboard domestic flights and in all transport hubs. The C.D.C. says that as long as coronavirus measures are taken in these scenarios, including mask wearing, fully vaccinated Americans can travel domestically without having to take a test or quarantine, although the agency warns that some states and territories may keep their local travel restrictions and recommendations in place.
For those wishing to travel internationally, a coronavirus test will not be required before departure from the United States unless mandated by the government of their destination. Vaccinated travelers are still required to get tested three days before travel by air into the United States, and are advised to take a test three to five days after their return, but will not need to self-quarantine.
Can I go abroad?
Yes, but only to countries that will have you.
More than half the world’s countries have reopened to tourists from the United States, including the countries of the European Union , which on June 18 added the United States to its “safe list” of countries, meaning that American travelers can now visit. While the European Union aims to take a coordinated approach to travel this summer, member states will be allowed to set their own requirements for travelers from individual countries based on their own epidemiological criteria, which means they may require testing or vaccination.
Some places like Turkey, Croatia and Montenegro had already been welcoming Americans with negative test results. Greece joined that growing list in May, ahead of most European countries, opening to fully vaccinated tourists and other foreigners with a negative test.
Many Caribbean nations have reopened to American tourists, but each has its own coronavirus protocols and entry requirements.
Here’s a full list of countries Americans can currently travel to.
What about domestic travel? Is it free and clear to cross state borders?
If you are fully vaccinated, the C.D.C. says you can travel freely within the United States and that you do not need to get tested, or self-quarantine, before or after traveling. But some states and local governments may choose to keep travel restrictions in place, including testing, quarantine and stay-at-home orders. Hawaii , for instance, still has travel restrictions in place.
Before you travel across state lines, check the current rules at your destination.
How are they going to check that I’m fully vaccinated?
Right now, the best way to prove that you have been vaccinated is to show your vaccine card .
Digital vaccine and health certificates showing that people have been vaccinated or tested are in various stages of development around the world and are expected, eventually, to be widely used to speed up travel.
The subject of “ vaccine passports ” is currently one of the most hotly debated topics within the travel industry, with questions over the equity of their use and concerns over health and data privacy.
In early April, Gov. Ron DeSantis of Florida issued an executive order that would ban local governments and state businesses from requiring proof of vaccination for services.
And in March, the European Union endorsed its own vaccine certificate , which some countries are already using, with more expected to adopt it by July 1.
But what about my kids? What’s the guidance on traveling with unvaccinated people?
The C.D.C. advises people against travel unless they have been vaccinated. If you must travel, the agency recommends testing one to three days before a trip and following all coronavirus guidance at your destination.
In May, the F.D.A. expanded its emergency use authorization of the Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus vaccine to include adolescents between 12 and 15 years of age.
All air passengers aged two and older coming into the United States, including fully vaccinated people, are required to have a negative Covid-19 test result taken no more than three days before they board their flight.
What is my moral obligation to the places I visit where most people are not vaccinated?
The United States inoculation rollout has been among the fastest in the world, but there is a stark gap between its rapid rollout and the vaccination programs in different countries. Some nations have yet to report a single dose being administered.
Many countries are currently seeing a surge in new cases and are implementing strict coronavirus protocols, including mask mandates in public spaces, capacity limits at restaurants and tourist sites and other lockdown restrictions.
It is important to check coronavirus case rates, measures and medical infrastructure before traveling to your destination and not to let your guard down when you get there. Even though you are fully vaccinated, you may still be able to transmit the disease to local communities who have not yet been inoculated.
You can track coronavirus vaccination rollouts around the world here.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation.
Ceylan Yeginsu is a London-based reporter. She joined The Times in 2013, and was previously a correspondent in Turkey covering politics, the migrant crisis, the Kurdish conflict, and the rise of Islamic State extremism in Syria and the region. More about Ceylan Yeginsu
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Vaccines for Travelers
Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places.
Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you’re traveling. It will also help make sure that you don’t bring any serious diseases home to your family, friends, and community.
On this page, you'll find answers to common questions about vaccines for travelers.
Which vaccines do I need before traveling?
The vaccines you need to get before traveling will depend on few things, including:
- Where you plan to travel . Some countries require proof of vaccination for certain diseases, like yellow fever or polio. And traveling in developing countries and rural areas may bring you into contact with more diseases, which means you might need more vaccines before you visit.
- Your health . If you’re pregnant or have an ongoing illness or weakened immune system, you may need additional vaccines.
- The vaccinations you’ve already had . It’s important to be up to date on your routine vaccinations. While diseases like measles are rare in the United States, they are more common in other countries. Learn more about routine vaccines for specific age groups .
How far in advance should I get vaccinated before traveling?
It’s important to get vaccinated at least 4 to 6 weeks before you travel. This will give the vaccines time to start working, so you’re protected while you’re traveling. It will also usually make sure there’s enough time for you to get vaccines that require more than 1 dose.
Where can I go to get travel vaccines?
Start by finding a:
- Travel clinic
- Health department
- Yellow fever vaccination clinic
Learn more about where you can get vaccines .
What resources can I use to prepare for my trip?
Here are some resources that may come in handy as you’re planning your trip:
- Visit CDC’s travel website to find out which vaccines you may need based on where you plan to travel, what you’ll be doing, and any health conditions you have.
- Download CDC's TravWell app to get recommended vaccines, a checklist to help prepare for travel, and a personalized packing list. You can also use it to store travel documents and keep a record of your medicines and vaccinations.
- Read the current travel notices to learn about any new disease outbreaks in or vaccine recommendations for the areas where you plan to travel.
- Visit the State Department’s website to learn about vaccinations, insurance, and medical emergencies while traveling.
Traveling with a child? Make sure they get the measles vaccine.
Measles is still common in some countries. Getting your child vaccinated will protect them from getting measles — and from bringing it back to the United States where it can spread to others. Learn more about the measles vaccine.
Find out which vaccines you need
CDC’s Adult Vaccine Quiz helps you create a list of vaccines you may need based on your age, health conditions, and more.
Take the quiz now !
Get Immunized
Getting immunized is easy. Vaccines and preventive antibodies are available at the doctor’s office or pharmacies — and are usually covered by insurance.
Find out how to get protected .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Coronavirus Updates
Cdc says travel is safe for fully vaccinated people, but opposes nonessential trips.
Rachel Treisman

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its domestic travel guidance for fully vaccinated people on Friday, lifting certain requirements while continuing to advise mitigation measures like mask-wearing and hand-washing. Angus Mordant/Bloomberg via Getty Images hide caption
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its domestic travel guidance for fully vaccinated people on Friday, lifting certain requirements while continuing to advise mitigation measures like mask-wearing and hand-washing.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has updated its domestic travel guidance for fully vaccinated people, lifting certain testing and self-quarantine requirements and recommending precautions like wearing a mask and avoiding crowds. But health officials continue to discourage nonessential travel, citing a sustained rise in cases and hospitalizations.
The CDC updated its website on Friday to reflect the latest scientific evidence, writing that "people who are fully vaccinated with an FDA-authorized vaccine can travel safely within the United States."
The announcement comes less than a month after the CDC first released updated guidance about gatherings for fully vaccinated people, which it described as a "first step" toward returning to everyday activities.
Air Travel Is Opening Up Again, But That Doesn't Mean The Pandemic Is Over
The CDC considers someone fully vaccinated two weeks after they receive the last dose of vaccine. Those individuals will no longer need to get tested before or after travel unless their destination requires it, and do not need to self-quarantine upon return.
The new guidance means, for example, that fully vaccinated grandparents can fly to visit their healthy grandkids without getting a COVID-19 test or self-quarantining as long as they follow other recommended measures while traveling, according to CDC Director Rochelle Walensky.
Those measures include wearing a mask over their nose and mouth, staying 6 feet from others and washing their hands frequently. Masks are required on all planes traveling into, within or out of the U.S., under an executive order issued by President Biden.
But Walensky, speaking at a White House COVID-19 Response Team briefing on Friday, nonetheless discouraged all nonessential travel, citing a continued increase in the seven-day average of cases and hospitalizations.
"While we believe that fully vaccinated people can travel at low risk to themselves, CDC is not recommending travel at this time due to the rising number of cases," Walensky said.

CDC Director Fears 'Impending Doom' If U.S. Opens Too Quickly
She said that while vaccinated people can do more things safely, most Americans are not yet fully vaccinated. Those who are not must have a negative test 1-3 days before they travel under CDC guidance. They must either get tested 3-5 days after they return and self-quarantine for 7 days, or self-quarantine for 10 days with no test.
Walensky said on Monday that there is more travel occurring now than throughout the pandemic, including the winter holidays. She acknowledged that people have been looking to get away over spring break or take advantage of what they perceive as a "relative paucity in cases," and she said the country was seeing an uptick in cases as a result.
"The thing that's different this time is that we actually have it in our power to be done with the scale of the vaccination," she said. "And that will be so much slower if we have another surge to deal with as well."
The U.S. is already seeing an uptick in domestic travel, and many Americans are looking to book trips in the coming months in what experts described to NPR as a sign of "clear pent up demand for travel."
As the country's supply of COVID-19 doses has grown, so has Biden's goal for the number of shots in arms during his first 100 days, doubling the target to 200 million by the end of this month. Many states have already expanded eligibility to all adults or are set to do so in the coming weeks, well ahead of the president's May 1 deadline.
According to NPR's vaccine tracker , 16.9% of the U.S. population is fully vaccinated, and 30% has had at least one dose. Researchers estimate that 70% to 85% of the country would need to have immunity for COVID-19 to stop spreading through communities.
International travel restrictions remain
The CDC is not lifting travel restrictions barring the entry of most non-U.S. citizens from places including China, Brazil, South Africa and parts of Europe. It will continue to require airline passengers entering the U.S. to get a test within three days of their departure and show proof of a negative result before boarding.
The travel industry has been pushing for some of these restrictions to end. A group of 26 organizations sent a letter to White House COVID-19 czar Jeffrey Zients urging the federal government "to partner with us to develop, by May 1, 2021, a risk-based, data-driven roadmap to rescind inbound international travel restrictions."

While Some Spring Breakers Swarm Beaches, Many Stay Home, Dreaming Of Summer Travel
"To be clear, at this time, we do not support removal or easing of core public health protections, such as the universal mask mandate, inbound international testing requirement, physical distancing or other measures that have made travel safer and reduced transmission of the virus," they wrote. "However, the data and science demonstrate that the right public health measures are now in place to effectively mitigate risk and allow for the safe removal of entry restrictions."
Travel and tourism have taken a considerable hit because of the pandemic with industry groups noting that overseas travel to the U.S. declined by 81% in 2020, causing billions of dollars in losses. Without lifting international travel bans, the U.S. Travel Association estimates that some 1.1 million American jobs will not be restored and billions in spending will be lost by the end of the year.
"Fortunately, enough progress has been made on the health front that a rebound for domestic leisure travel looks possible this year, but that alone won't get the job done," Roger Dow, the association's president and CEO, said in a statement . "A full travel recovery will depend on reopening international markets, and we must also contend with the challenge of reviving business travel."

Fauci Expects Surge In Vaccinations To Keep A 4th Coronavirus Wave At Bay
- COVID-19 vaccine
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
Measles — United States, January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024
Weekly / April 11, 2024 / 73(14);295–300
Adria D. Mathis, MSPH 1 ; Kelley Raines, MPH 1 ; Nina B. Masters, PhD 1 ; Thomas D. Filardo, MD 1 ; Gimin Kim, MS 1 ; Stephen N. Crooke, PhD 1 ; Bettina Bankamp, PhD 1 ; Paul A. Rota, PhD 1 ; David E. Sugerman, MD 1 ( View author affiliations )
What is already known about this topic?
Although endemic U.S. measles was declared eliminated in 2000, measles importations continue to occur. Prolonged outbreaks during 2019 threatened the U.S. measles elimination status.
What is added by this report?
During January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024, a total of 338 U.S. measles cases were reported; 29% of these cases occurred during the first quarter of 2024, almost all in persons who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status was unknown. As of the end of 2023, U.S. measles elimination status was maintained.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Risk for widespread U.S. measles transmission remains low because of high population immunity. Enhanced efforts are needed to increase routine U.S. vaccination coverage, encourage vaccination before international travel, identify communities at risk for measles transmission, and rapidly investigate suspected measles cases to reduce cases and complications of measles.
- Article PDF
- Full Issue PDF

Measles is a highly infectious febrile rash illness and was declared eliminated in the United States in 2000. However, measles importations continue to occur, and U.S. measles elimination status was threatened in 2019 as the result of two prolonged outbreaks among undervaccinated communities in New York and New York City. To assess U.S. measles elimination status after the 2019 outbreaks and to provide context to understand more recent increases in measles cases, CDC analyzed epidemiologic and laboratory surveillance data and the performance of the U.S. measles surveillance system after these outbreaks. During January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024, CDC was notified of 338 confirmed measles cases; 97 (29%) of these cases occurred during the first quarter of 2024, representing a more than seventeenfold increase over the mean number of cases reported during the first quarter of 2020–2023. Among the 338 reported cases, the median patient age was 3 years (range = 0–64 years); 309 (91%) patients were unvaccinated or had unknown vaccination status, and 336 case investigations included information on ≥80% of critical surveillance indicators. During 2020–2023, the longest transmission chain lasted 63 days. As of the end of 2023, because of the absence of sustained measles virus transmission for 12 consecutive months in the presence of a well-performing surveillance system, U.S. measles elimination status was maintained. Risk for widespread U.S. measles transmission remains low because of high population immunity. However, because of the increase in cases during the first quarter of 2024, additional activities are needed to increase U.S. routine measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination coverage, especially among close-knit and undervaccinated communities. These activities include encouraging vaccination before international travel and rapidly investigating suspected measles cases.
Introduction
Measles is a highly infectious acute, febrile rash illness with a >90% secondary attack rate among susceptible contacts ( 1 ). High national 2-dose coverage with the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine led to the declaration of U.S. measles elimination* in 2000 ( 2 ). However, this elimination status was threatened in 2019 because of two prolonged outbreaks among undervaccinated communities in New York and New York City; these outbreaks accounted for 29% of all reported cases during 2001–2019 ( 2 ). To assess U.S. measles elimination status after the 2019 outbreaks and to provide context for understanding more recent increases in measles cases in 2024, † CDC assessed the epidemiologic and laboratory-based surveillance of measles in the United States and the performance of the U.S. measles surveillance system during January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024.
Reporting and Classification of Measles Cases
Confirmed measles cases § ( 1 ) are reported to CDC by state health departments through the National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System and directly (by email or telephone) to the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. Measles cases are classified by the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists as import-associated if they were internationally imported, epidemiologically linked to an imported case, or had viral genetic evidence of an imported measles genotype ( 1 ); cases with no epidemiologic or virologic link to an imported case are classified as having an unknown source ( 1 ). For this analysis, unique sequences were defined as those differing by at least one nucleotide in the N-450 sequence (the 450 nucleotides encoding the carboxyl-terminal 150 nucleoprotein amino acids) based on the standard World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations for describing sequence variants ¶ ( 3 ). Unvaccinated patients were classified as eligible for vaccination if they were not vaccinated according to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendations ( 4 ). A well-performing surveillance system was defined as one with ≥80% of cases meeting each of the following three criteria: classified as import-associated, reported with complete information on at least eight of 10 critical surveillance indicators (i.e., place of residence, sex, age, occurrence of fever and rash, date of rash onset, vaccination status, travel history, hospitalization, transmission setting, and whether the case was outbreak-related) ( 5 ), and laboratory-confirmed.
Assessment of Chains of Transmission
Cases were classified into chains of transmission on the basis of known epidemiologic linkages: isolated (single) cases, two-case chains (two epidemiologically linked cases), and outbreaks (three or more epidemiologically linked cases). The potential for missed cases within two-case chains and outbreaks was assessed by measuring the interval between measles rash onset dates in each chain; chains with more than one maximum incubation period (21 days) between cases could indicate a missing case in the chain. This activity was reviewed by CDC, deemed not research, and was conducted consistent with applicable federal law and CDC policy.**
Reported Measles Cases and Outbreaks
CDC was notified of 338 confirmed measles cases with rash onset during January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024 ( Figure ); cases occurred in 30 jurisdictions. During 2020, 12 of 13 cases preceded the commencement of COVID-19 mitigation efforts in March 2020. Among the 170 cases reported during 2021 and 2022, 133 (78%) were associated with distinct outbreaks: 47 (96%) of 49 cases in 2021 occurred among Afghan evacuees temporarily housed at U.S. military bases during Operation Allies Welcome, and 86 (71%) of 121 cases in 2022 were associated with an outbreak in central Ohio. During 2023, 28 (48%) of 58 cases were associated with four outbreaks. As of March 28, 2024, a total of 97 cases have been reported in 2024, representing 29% of all 338 measles cases reported during January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024, and more than a seventeenfold increase over the mean number of cases reported during the first quarter of 2020–2023 (five cases).
Characteristics of Reported Measles Cases
The median patient age was 3 years (range = 0–64 years); more than one half of cases (191; 58%) occurred in persons aged 16 months–19 years ( Table ). Overall, 309 (91%) patients were unvaccinated (68%) or had unknown vaccination status (23%); 29 (9%) had previously received ≥1 MMR vaccine dose. Among the 309 cases among unvaccinated persons or persons with unknown vaccination status, 259 (84%) patients were eligible for vaccination, 40 (13%) were aged 6–11 months and therefore not recommended for routine MMR vaccination, and 10 (3%) were ineligible for MMR because they were aged <6 months. †† Among 155 (46%) hospitalized measles patients, 109 (70%) cases occurred in persons aged <5 years; 142 (92%) hospitalized patients were unvaccinated or had unknown vaccination status. No measles-associated deaths were reported to CDC.
Imported Measles Cases
Among all 338 cases, 326 (96%) were associated with an importation; 12 (4%) had an unknown source. Among the 326 import-associated cases, 200 (61%) occurred among U.S. residents who were eligible for vaccination but who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status was unknown. Among 93 (28%) measles cases that were directly imported from other countries, 34 (37%) occurred in foreign visitors, and 59 (63%) occurred in U.S. residents, 53 (90%) of whom were eligible for vaccination but were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status was unknown. One (2%) case in a U.S. resident occurred in a person too young for vaccination, two (3%) in persons who had previously received 1 MMR vaccine dose, and three (5%) in persons who had previously received 2 MMR vaccine doses. The most common source for internationally imported cases during the study period were the Eastern Mediterranean (48) and African (24) WHO regions. During the first quarter of 2024, a total of six internationally imported cases were reported from the European and South-East Asia WHO regions, representing a 50% increase over the mean number of importations from these regions during 2020–2023 (mean of two importations per year from each region).
Surveillance Quality Indicators
Overall, all but two of the 338 case investigations included information on ≥80% of the critical surveillance indicators; those two case investigations included information on 70% of critical surveillance indicators. Date of first case report to a health department was available for 219 (65%) case investigations; 127 (58%) cases were reported to health departments on or before the day of rash onset (IQR = 4 days before to 3 days after). Overall, 314 (93%) measles cases were laboratory confirmed, including 16 (5%) by immunoglobulin M (serologic) testing alone and 298 (95%) by real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR). Among 298 rRT-PCR–positive specimens, 221 (74%) were successfully genotyped: 177 (80%) were genotype B3, and 44 (20%) were genotype D8. Twenty-two distinct sequence identifiers (DSIds) ( 3 ) for genotype B3 and 13 DSIds for genotype D8 were detected (Supplementary Figure, https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/152776 ). The longest period of detection for any DSId was 15 weeks (DSId 8346).
Chains of Transmission
The 338 measles cases were categorized into 92 transmission chains (Table); 62 (67%) were isolated cases, 10 (11%) were two-case chains, and 20 (22%) were outbreaks of three or more cases. Seven (35%) of 20 outbreaks occurred during 2024. §§ The median outbreak size was six cases (range = three–86 cases) and median duration of transmission was 20 days (range = 6–63 days). Among the 30 two-case chains and outbreaks, more than one maximum incubation period (21 days) did not elapse between any two cases.
Because of the absence of endemic measles virus transmission for 12 consecutive months in the presence of a well-performing surveillance system, as of the end of 2023, measles elimination has been maintained in the United States. U.S. measles elimination reduces the number of cases, deaths, and costs that would occur if endemic measles transmission were reestablished. Investigation of almost all U.S. measles cases reported since January 2020 were import-associated, included complete information on critical surveillance variables, were laboratory-confirmed by rRT-PCR, and underwent genotyping; these findings indicate that the U.S. measles surveillance system is performing well. A variety of transmission chain sizes were detected, including isolated cases, suggesting that sustained measles transmission would be rapidly detected. However, the rapid increase in the number of reported measles cases during the first quarter of 2024 represents a renewed threat to elimination.
Most measles importations were cases among persons traveling to and from countries in the Eastern Mediterranean and African WHO regions; these regions experienced the highest reported measles incidence among all WHO regions during 2021–2022 ( 6 ). During November 2022–October 2023, the number of countries reporting large or disruptive outbreaks increased by 123%, from 22 to 49. Global estimates suggest that first-dose measles vaccination coverage had declined from 86% in 2019 to 83% in 2022, leaving almost 22 million children aged <1 year susceptible to measles ( 6 ).
As has been the case in previous postelimination years ( 7 ), most imported measles cases occurred among unvaccinated U.S. residents. Increasing global measles incidence and decreasing vaccination coverage will increase the risk for importations into U.S. communities, as has been observed during the first quarter of 2024, further supporting CDC’s recommendation for persons to receive MMR vaccine before international travel ( 4 ).
Maintaining high national and local MMR vaccination coverage remains central to sustaining measles elimination. Risk for widespread U.S. measles transmission remains low because of high population immunity; however, national 2-dose MMR vaccination coverage has remained below the Healthy People 2030 target of 95% (the estimated population-level immunity necessary to prevent sustained measles transmission) ( 8 ) for 3 consecutive years, leaving approximately 250,000 kindergarten children susceptible to measles each year ( 9 ). Furthermore, 2-dose MMR vaccination coverage estimates in 12 states and the District of Columbia were <90%, and during the 2022–23 school year, exemption rates among kindergarten children exceeded 5% in 10 states ( 9 ). Clusters of unvaccinated persons placed communities at risk for large outbreaks, as occurred during the central Ohio outbreak in 2022: 94% of measles patients were unvaccinated and 42% were hospitalized ( 10 ). Monitoring MMR vaccination coverage at county and zip code levels could help public health agencies identify undervaccinated communities for targeted interventions to improve vaccination coverage while preparing for possible measles outbreaks. As of March 28, 2024, a total of 97 confirmed measles cases have been reported in the United States in 2024, compared with a mean of five cases during the first quarter of each year during 2020–2023. Similar to cases reported during 2020–2023, most cases reported during 2024 occurred among patients aged <20 years who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status was unknown, and were associated with an importation. Rapid detection of cases, prompt implementation of control measures, and maintenance of high national measles vaccination coverage, including improving coverage in undervaccinated populations, is essential to preventing measles and its complications and to maintaining U.S. elimination status.
Limitations
The findings in this report are subject to at least three limitations. First, importations might have been underreported: 4% of reported cases during the study period had no known source. Second, case investigations resulting in discarded measles cases (i.e., a diagnosis of measles excluded) are not nationally reportable, which limits the ability to directly evaluate the sensitivity of measles case investigations. However, surveillance remains sufficiently sensitive to detect isolated cases and outbreaks, and robust molecular epidemiology provides further evidence supporting the absence of sustained measles transmission in the United States. Finally, the date of first case report to a health department was not available for 35% of case investigations.
Implications for Public Health Practice
The U.S. measles elimination status will continue to be threatened by global increases in measles incidence and decreases in global, national, and local measles vaccination coverage. Because of high population immunity, the risk of widespread measles transmission in the United States remains low; however, efforts are needed to increase routine MMR vaccination coverage, encourage vaccination before international travel, identify communities at risk for measles transmission, and rapidly investigate suspected measles cases to maintain elimination.
Corresponding author: Adria D. Mathis, [email protected] .
1 Division of Viral Diseases, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, CDC.
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. Stephen N. Crooke reports institutional support from PATH. No other potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
* Elimination is defined as the absence of endemic measles virus transmission in a defined geographic area for ≥12 months in the presence of a well-performing surveillance system.
† https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2024/han00504.asp
§ A confirmed measles case was defined as an acute febrile rash illness with laboratory confirmation or direct epidemiologic linkage to a laboratory-confirmed case. Laboratory confirmation was defined as detection of measles virus–specific nucleic acid from a clinical specimen using real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction or a positive serologic test for measles immunoglobulin M antibody.
¶ Genotyping was performed at CDC and at the Vaccine Preventable Disease Reference Centers of the Association of Public Health Laboratories.
** 45 C.F.R. part 46.102(l)(2), 21 C.F.R. part 56; 42 U.S.C. Sect. 241(d); 5 U.S.C. Sect. 552a; 44 U.S.C. Sect. 3501 et seq.
†† MMR vaccine is not licensed for use in persons aged <6 months.
§§ At the time of this report, six measles outbreaks have ended, and one outbreak is ongoing. A measles outbreak is considered to be over when no new cases have been identified during two incubation periods (42 days) since the rash onset in the last outbreak-related case.
- Gastañaduy PA, Redd SB, Clemmons NS, et al. Measles [Chapter 7]. In: Manual for the surveillance of vaccine-preventable diseases. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/surv-manual/chpt07-measles.html
- Mathis AD, Clemmons NS, Redd SB, et al. Maintenance of measles elimination status in the United States for 20 years despite increasing challenges. Clin Infect Dis 2022;75:416–24. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab979 PMID:34849648
- Williams D, Penedos A, Bankamp B, et al. Update: circulation of active genotypes of measles virus and recommendations for use of sequence analysis to monitor viral transmission. Weekly Epidemiologic Record 2022;97(39):481–92. https://reliefweb.int/report/world/weekly-epidemiological-record-wer-30-september-2022-vol-97-no-39-2022-pp-481-492-enfr
- McLean HQ, Fiebelkorn AP, Temte JL, Wallace GS; CDC. Prevention of measles, rubella, congenital rubella syndrome, and mumps, 2013: summary recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2013;62(No. RR-4):1–34. PMID:23760231
- World Health Organization. Measles: vaccine preventable diseases surveillance standards. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2018. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/vaccine-preventable-diseases-surveillance-standards-measles
- Minta AA, Ferrari M, Antoni S, et al. Progress toward measles elimination—worldwide, 2000–2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:1262–8. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7246a3 PMID:37971951
- Lee AD, Clemmons NS, Patel M, Gastañaduy PA. International importations of measles virus into the United States during the postelimination era, 2001–2016. J Infect Dis 2019;219:1616–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiy701 PMID:30535027
- Truelove SA, Graham M, Moss WJ, Metcalf CJE, Ferrari MJ, Lessler J. Characterizing the impact of spatial clustering of susceptibility for measles elimination. Vaccine 2019;37:732–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.12.012 PMID:30579756
- Seither R, Yusuf OB, Dramann D, Calhoun K, Mugerwa-Kasujja A, Knighton CL. Coverage with selected vaccines and exemption from school vaccine requirements among children in kindergarten—United States, 2022–23 school year. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:1217–24. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7245a2 PMID:37943705
- Tiller EC, Masters NB, Raines KL, et al. Notes from the field: measles outbreak—central Ohio, 2022–2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:847–9. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7231a3 PMID:37535476
FIGURE . Confirmed measles cases, by month of rash onset (N = 338) — United States, January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024
Abbreviations: IgM = immunoglobulin M; rRT-PCR = real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction; WHO = World Health Organization. * A case resulting from exposure to measles virus outside the United States as evidenced by at least some of the exposure period (7–21 days before rash onset) occurring outside the United States and rash onset occurring within 21 days of entering the United States without known exposure to measles during that time. † A case in a transmission chain epidemiologically linked to an internationally imported case. § A case for which an epidemiologic link to an internationally imported case was not identified, but for which viral sequence data indicate an imported measles genotype (i.e., a genotype that is not detected in the United States with a pattern indicative of endemic transmission). ¶ A case for which an epidemiologic or virologic link to importation or to endemic transmission within the United States cannot be established after a thorough investigation. ** Percentage is percentage of international importations. Four cases among persons who traveled to both the Eastern Mediterranean and African regions and one case in a person who traveled to both the Eastern Mediterranean and European regions were counted twice. †† Place of residence, sex, age or date of birth, fever and rash, date of rash onset, vaccination status, travel history, hospitalization, transmission setting, and whether the case was outbreak related. §§ Includes 65 cases among patients who received both positive rRT-PCR and positive IgM results. ¶¶ Percentage is percentage of total chains.
Suggested citation for this article: Mathis AD, Raines K, Masters NB, et al. Measles — United States, January 1, 2020–March 28, 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2024;73:295–300. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7314a1 .
MMWR and Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report are service marks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of the date of publication.
All HTML versions of MMWR articles are generated from final proofs through an automated process. This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users are referred to the electronic PDF version ( https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr ) and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Featured Clinical Reviews
- Screening for Atrial Fibrillation: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement JAMA Recommendation Statement January 25, 2022
- Evaluating the Patient With a Pulmonary Nodule: A Review JAMA Review January 18, 2022
Select Your Interests
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
- Download PDF
- Share X Facebook Email LinkedIn
- Permissions
Measles Outbreaks in US and Abroad Prompt CDC Vaccination Alert
- Medical News & Perspectives Measles Is Spreading Again in the US Melissa Suran, PhD, MSJ JAMA
Amid an uptick in measles cases and outbreaks both in the US and abroad, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued an alert on March 18 encouraging clinicians to work with schools and educators to ensure children are up-to-date on their measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccines. As of March 28, 97 measles cases had been reported in 18 US states this year. Most of the cases have been linked to international travel.
Full vaccination involves 2 doses of the MMR vaccine, with the first typically given when children are aged 12 to 15 months. However, children aged 6 to 11 months who will be traveling internationally should receive 1 dose before leaving.
Although the risk of broad transmission is low, measles is highly contagious, and “pockets of low coverage leave some communities at higher risk for outbreaks,” the CDC noted. Clinicians should consider measles as a potential cause when children present with a fever and generalized rash of raised red bumps alongside a cough, runny nose, or conjunctivitis.
Published Online: April 12, 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.5153
See More About
Harris E. Measles Outbreaks in US and Abroad Prompt CDC Vaccination Alert. JAMA. Published online April 12, 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.5153
Manage citations:
© 2024
Artificial Intelligence Resource Center
Cardiology in JAMA : Read the Latest
Browse and subscribe to JAMA Network podcasts!
Others Also Liked
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
CDC: Nearly a third of measles cases since 2020 happened in the past three months
Nearly a third of all U.S. measles cases in the past four years happened during a three-month stretch in 2024 , according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rise in measles, a highly infectious virus, is troubling, experts warned. Officials attribute it to the drop in the U.S. vaccination rate for the deadly and preventable virus amid a global surge in cases. For now, the risk of widespread transmission remains low due to existing immunity and robust public health responses to contain outbreaks, according to the report published Thursday .
The CDC documented nearly 340 measles cases since January 2020. Almost 100 of the infections happened in 2024, prior to March 28, with cases occurring in more than a dozen states. Since then, there have more than a dozen cases as of April 4 that aren’t included in the report.
“ Most of the outbreaks that we’ve seen during this period have been small and short due to high population immunity and rapid response by state and local health departments to control these outbreaks,” said Adria Mathis, a study author and the CDC’s lead epidemiologist for measles surveillance.
Measles 2024: Chicago moves to vaccinate people amid migrant shelter measles outbreak
At the start of the year, the CDC warned clinicians about signs of the virus amid the global uptick. The latest report shows measles spread mostly by unvaccinated U.S. residents who traveled abroad and then brought measles to schools or hospitals they visited.
Measles was once thought to be a disease of the past. Public health officials in 2000 declared measles eliminated in the U.S. after decades of people getting vaccinated which are highly effective at preventing the virus. While vaccines are still widely used, Mathis said, the report notes that more measures must be taken to curb the rise in cases and prevent further transmission within the U.S.
Many Americans have chosen not to vaccinate their children, which CDC officials said contributed to recent outbreaks of cases. The nationwide measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccination rate among American kindergartners is around 93%, below the 95% goal thought to provide adequate protection against measles.
The median age of a measles patient is 3, CDC's report said. About 90% of recent cases were in patients who weren't vaccinated or those for whom vaccination status was unknown.
New measles cases tend to primarily be caused by lack of vaccinations and an uptick in travel after the pandemic, experts said.
“This is akin to turning back the clock to the bad old days,” Dr. William Schaffner, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, told USA TODAY.
How deadly is measles?
Before vaccines, Schaffner said between 400 and 500 Americans died annually of the disease . Measles leaves about one-fifth of children hospitalized and about 1 in 1,000 with brain swelling. One to 3 children out of 1,000 die after contracting the disease.
Recent cases, Schaffner explained, are a result of parents delaying routine MMR vaccines, or withholding vaccines altogether from their children, which are typically required at U.S. public schools.
“The only way it can come back is if we stop vaccinating and permit the virus in other parts of the world to be imported into the United States and then spread,” he said.
The CDC report confirmed nearly all cases were introduced from abroad by people entering the U.S., primarily from other areas that the World Health Organization defines as the Eastern Mediterranean and African regions.
The nation's largest outbreak in 2024 has occurred at a Chicago migrant shelter , and city officials have identified over 60 cases so far . Local health officials have said it likely spread through local transmission. Cases haven't been linked to international travel, including among people who recently crossed the southern U.S. border, the city's top health official said in March .
U.S. residents traveling abroad accounted for two-thirds of imported cases. The report said imported cases were likely underreported.
“It doesn't bode well for what the future might bring,” Michael Osterholm, director of the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy , told USA TODAY. “Because we're just going to continue to see more and more international travel. Meanwhile, we're continuing to see even more widespread measles transmission around the world. And that combination is a very, unfortunately, deadly combination.”
The CDC report noted the U.S. needs to increase vaccination coverage, including for young children before international travel and among at-risk communities with low uptake.
U.S. Measles Cases Are Rising in 2024, CDC Warns
Health officials urge vaccination against the highly contagious virus, which has caused 121 infections in the country this year
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Will-Sullivan-photo.png)
Will Sullivan
Daily Correspondent
:focal(2126x1427:2127x1428)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f3/f3/f3f39245-16fd-406d-b296-25bcb309e825/gettyimages-930111236.jpg)
In the 1950s, an estimated three million to four million Americans were infected with the measles virus each year, resulting in 400 to 500 deaths and 48,000 hospitalizations annually. But since the first measles vaccine was developed in 1963, case numbers fell dramatically—and measles was declared eliminated in the United States in 2000. During the 21st century, the nation has clocked several years with fewer than 100 cases of measles.
But now, in the first quarter of 2024, the number of measles cases recorded in the U.S. was significantly higher than in recent years, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Americans have reported a total of 338 cases since January 1, 2020—and 97 cases, or 29 percent of the total, came between the start of 2024 and March 28, per the report. And as of April 11, the number of cases in 2024 had risen to 121 .
“What was surprising about 2024 is that we’ve seen a significant increase,” John Brownstein , an epidemiologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, tells ABC News ’ Mary Kekatos. “It’s an alarming number, because it indicates a trend going in the wrong direction for us, a virus that we have successfully controlled, a virus that we successfully have an effective vaccine for.”
Measles continues to be considered eliminated in the U.S., meaning there hasn’t been a sustained transmission chain lasting 12 consecutive months—the longest chain between 2020 and 2023 lasted 63 days. And the high level of immunity from vaccines means the risk for widespread transmission is low.
“However, the rapid increase in the number of reported measles cases during the first quarter of 2024 represents a renewed threat to elimination,” the authors write.
To prevent the spread of measles, the nation needs to maintain high levels of measles vaccine coverage, and undervaccinated communities should get immunized, the report says. More than 90 percent of people infected since the start of 2020 were either unvaccinated or had an unknown vaccination status.
“I think that people need to remember that this is a preventable disease,” Susan Hassig , an infectious disease researcher at Tulane University, says to Devi Shastri and Mike Stobbe of the Associated Press (AP). “It is a potentially dangerous disease for their children.”
Measles is a highly contagious virus, and its symptoms include high fever, cough, runny nose, red and watery eyes and a rash of small red spots. It can cause serious health complications, which young children are more likely to experience, such as pneumonia and inflammation of the brain . Around one in five unvaccinated people who get measles are hospitalized, and around one to three of every 1,000 infected children die from respiratory or neurological complications .
The virus spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and if nearby people are not protected, up to 90 percent tend to also become infected. The contagious virus can linger in a room for two hours .
Two outbreaks in 2019 in undervaccinated communities in New York and New York City caused a large spike in cases, threatening measles’ elimination status in the U.S. In 2020, 12 of the 13 total cases were reported before Covid-19 lockdowns started in March.
The 97 cases in the first quarter of 2024 represent a 17-fold increase over the average number of cases in the first quarters of 2020 to 2023, per the new report.
For all cases since 2020, the median patient age was 3 years old. Unvaccinated people accounted for 68 percent of all cases, and 23 percent of infected people had unknown vaccination statuses. Of 155 people hospitalized with measles, 70 percent were children younger than 5 years old, and 92 percent were either unvaccinated or their status was unknown. No deaths were reported.
Almost all cases were tied to an importation after travel outside the country, and the majority of these cases were among U.S. residents who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status was unknown. Increased rates of measles globally and decreased vaccination rates both increase the risk for importations, and the CDC recommends children get vaccinated before international travel.
“Public health jurisdictions are reaching out to communities and populations with low vaccination rates, and we feel this approach will be effective,” Marcus Plescia , chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, tells CNN ’s Deidre McPhillips. “However, the increase in misinformation about measles vaccination undermines these efforts and could ultimately endanger our elimination status.”
Officials want at least 95 percent of the population to be vaccinated, but coverage has remained below this threshold for three consecutive years. Vaccination coverage in kindergartners fell from 95.2 percent in the 2019-2020 school year to 93.1 percent in the 2022-2023 school year. Vaccine coverage estimates are below 90 percent in 12 states and Washington, D.C., per the new report.
The CDC recommends that all children get their first dose of the measles, mumps and rubella vaccine between the ages of 12 months and 15 months and their second and final dose between 4 and 6 years of age.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Will-Sullivan-photo.png)
Will Sullivan | | READ MORE
Will Sullivan is a science writer based in Washington, D.C. His work has appeared in Inside Science and NOVA Next .
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 5 - Melioidosis
- Section 5 - Pertussis / Whooping Cough
Meningococcal Disease
Cdc yellow book 2024.
Author(s): Lucy McNamara, Amy Blain
Infectious Agent
Transmission, epidemiology, clinical presentation.
INFECTIOUS AGENT: Neisseria meningitidis
Worldwide, but greatest incidence occurs in the meningitis belt of Africa (see Map 5-01 )
TRAVELER CATEGORIES AT GREATEST RISK FOR EXPOSURE & INFECTION
PREVENTION METHODS
Meningococcal disease is vaccine-preventable
DIAGNOSTIC SUPPORT
Neisseria meningitidis is a gram-negative diplococcus bacterium. Meningococci are classified into serogroups based on the composition of their capsular polysaccharide. The 6 major meningococcal serogroups associated with disease are A, B, C, W, X, and Y.
Meningococci spread through respiratory secretions and require close contact for transmission. Both asymptomatic carriers and people with overt meningococcal disease can be sources of infection. Asymptomatic carriage is transient and typically affects ≈5%–10% of the population at any given time.
N. meningitidis is found worldwide, but incidence is greatest in the “meningitis belt” of sub-Saharan Africa ( Map 5-01 ). Meningococcal disease is hyperendemic in this region, and periodic epidemics during the dry season (December–June) reach an incidence of up to 1,000 cases per 100,000 population. By contrast, rates of disease in Australia, Europe, South America, and the United States range from 0.10–2.4 cases per 100,000 population per year.
Although meningococcal disease outbreaks can occur anywhere in the world, they are most common in the African meningitis belt, where large-scale epidemics occur every 5–12 years. Historically, outbreaks in the meningitis belt were primarily due to serogroup A. With the introduction of a monovalent serogroup A meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MenAfriVac) in the region starting in 2010, however, recent meningococcal outbreaks in the meningitis belt have primarily been caused by serogroups C and W; serogroup X outbreaks also have been reported.
Outside the meningitis belt, infants, adolescents, and adults >80 years of age have the highest rates of disease. In meningitis belt countries, high rates of disease are seen in people ≤30 years old; the highest rates are in children and adolescents aged 5–14 years.
Unvaccinated travelers visiting meningitis belt countries and having prolonged contact with local populations during an epidemic are at greatest risk for meningococcal disease. The Hajj pilgrimage to Saudi Arabia also has been associated with outbreaks of meningococcal disease among returning pilgrims and their contacts, including 4 cases in travelers from the United States during a large Hajj-associated outbreak in 2000.
Map 5-01 The meningitis belt & other areas at risk for meningococcal meningitis epidemics
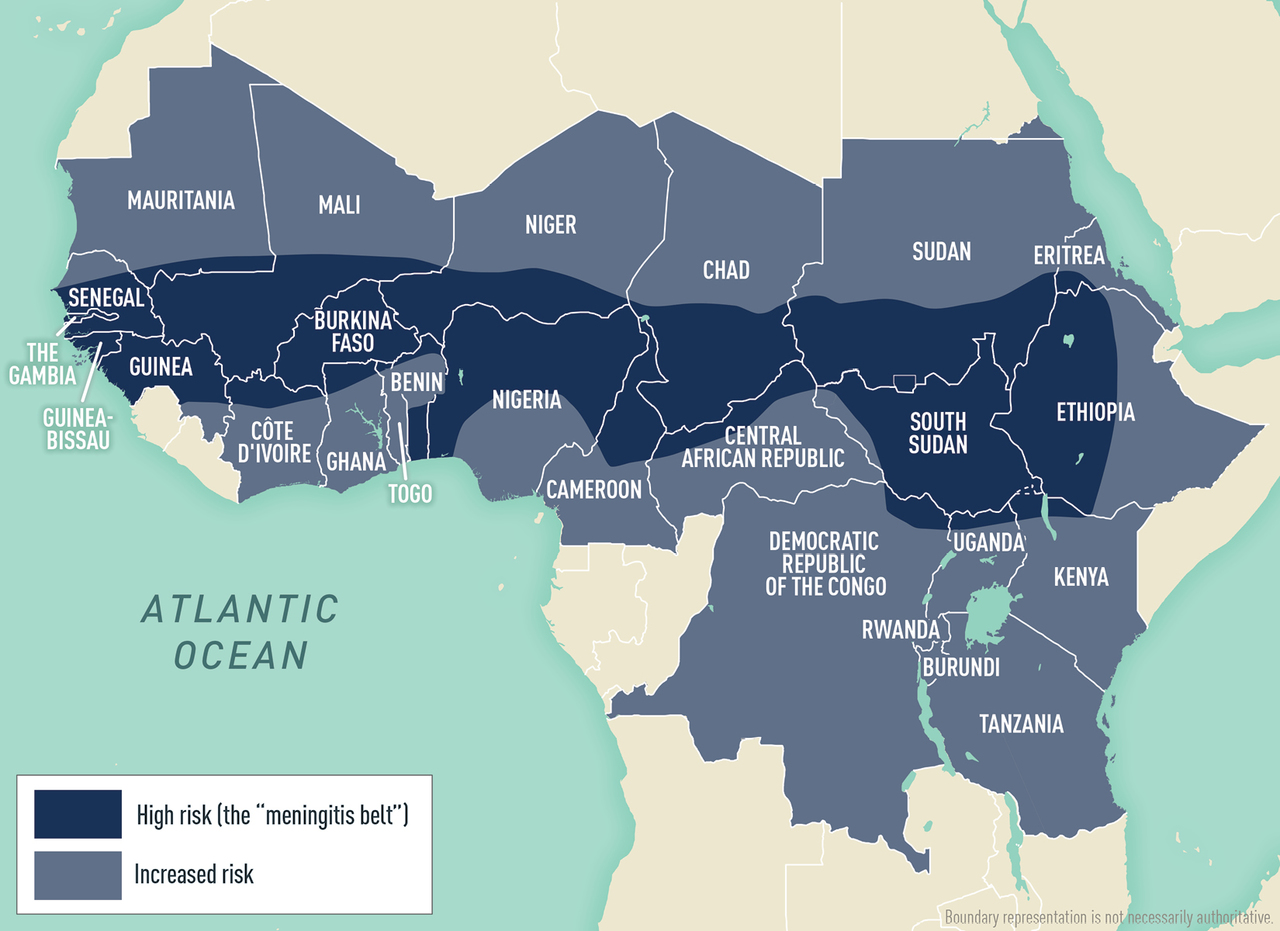
View Larger Figure
Disease data source: World Health Organization. International Travel and Health. Geneva, Switzerland: 2015.
Meningococcal disease generally occurs 1–10 days after exposure and presents as meningitis in ≈50% of cases in the United States. Meningococcal meningitis is characterized by sudden onset of headache, fever, and neck stiffness, sometimes accompanied by nausea, vomiting, photophobia, or altered mental status. Meningococcal disease progresses rapidly and has a case-fatality rate of 10%–15%, even with antimicrobial drug treatment. Without rapid treatment, fatality rates can be much higher.
Approximately 30% of people with meningococcal disease present with meningococcal sepsis, known as meningococcemia. Symptoms of meningococcemia can include abrupt onset of fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and a petechial or purpuric rash, which can progress to purpura fulminans. Meningococcemia often involves hypotension, acute adrenal hemorrhage, and multiorgan failure. An additional 15% of meningococcal disease cases in the United States, primarily among adults >65 years of age, present as bacteremic pneumonia.
Other presentations (e.g., septic arthritis) also occur. Among infants and children aged <2 years, meningococcal disease can have nonspecific symptoms. Neck stiffness, usually seen in people with meningitis, might be absent in this age group.
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical. If bacterial meningitis is suspected, collect blood for culture right away and perform a lumbar puncture (LP) to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for microscopic examination and Gram stain. In general, diagnosis is made by isolating N. meningitidis from a normally sterile body site (e.g., blood, CSF) either by culture or by PCR detection of N. meningitidis –specific nucleic acid. State health departments can provide diagnostic and testing support if needed.
Signs and symptoms of meningococcal meningitis are like those of other causes of bacterial meningitis (e.g., Haemophilus influenzae , Streptococcus pneumoniae ). Proper treatment and prophylaxis depend on correctly identifying the causative organism. Meningococcal disease is nationally notifiable in the United States; report cases to the state or local health department without delay.
Meningococcal disease can be rapidly fatal and should always be viewed as a medical emergency. As soon as disease is suspected and blood cultures and CSF have been collected, deliver appropriate treatment; if the LP is to be delayed for any reason (e.g., imaging studies of the head prior to LP), administer antimicrobial drugs immediately after collecting blood cultures. Begin empiric antimicrobial drug treatment early and prior to receiving diagnostic test results.
Third-generation cephalosporins are recommended for empiric treatment. Although ampicillin or penicillin also can be used for treatment, determine meningococcal isolate susceptibility before switching to one of these antibiotics; recent reports indicate emerging penicillin resistance among meningococcal isolates in the United States. If a patient presents with suspected bacterial meningitis of uncertain etiology, some treatment algorithms recommend empiric use of dexamethasone in addition to an antimicrobial drug until a bacterial etiology is established; if meningococcal meningitis is confirmed or suspected, steroids can be discontinued.
Five meningococcal vaccines (3 quadrivalent, 2 monovalent) are licensed and available in the United States. Travelers should receive vaccines 7–10 days before travel to enable time for protective antibody levels to develop. See Table 5-03 for more information about available meningococcal vaccines.
Table 5-03 Meningococcal vaccines licensed & available in the United States: recommendations for travelers to or residents of countries where meningococcal disease is hyperendemic or epidemic 1
Abbreviations: IM, intramuscular
1 Source: TABLE 9. Recommended vaccination schedule and intervals for people who travel to or are residents of countries where meningococcal disease is hyperendemic or epidemic—Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2020 ( www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/rr/rr6909a1.htm#T9_down ).
2 For people at continued risk, revaccination (booster) with meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-CRM, -D, or -TT) is recommended for the following age groups: <7 years old, a single dose 3 years after primary vaccination and every 5 years thereafter; ≥7 years old, a single dose 5 years after primary vaccination and every 5 years thereafter.
3 A 2-dose primary series (DOSE 2 given 8–12 weeks after DOSE 1) is recommended for the following groups: people with HIV; people with anatomic or functional asplenia; people with persistent complement component deficiency (C3, C5-9, properdin, factor D, factor H); and people taking a complement component inhibitor (e.g., eculizumab [Soliris] or ravulizumab [Ultomiris]).
4 Can be administered ≥8 weeks apart in travelers.
5 MenB-FHbp and MenB-4C are not interchangeable; the same vaccine should be used for all doses, including booster doses.
6 A 3-dose primary series (DOSE 2 given 1–2 months after DOSE 1; DOSE 3 given 6 months after DOSE 2) is recommended for the following groups: people with anatomic or functional asplenia; people with persistent complement component deficiency (C3, C5-9, properdin, factor D, factor H); people taking a complement component inhibitor (e.g., eculizumab [Soliris] or ravulizumab [Ultomiris]); microbiologists routinely exposed to Neisseria meningitidis isolates; and people at risk during a serogroup B meningococcal disease outbreak.
7 A single booster dose of MenB vaccine is recommended for people at increased risk due to a serogroup B meningococcus outbreak if they completed the MenB primary series ≥1 year prior (≥6 months might also be considered by public health professionals). See: www.cdc.gov/meningococcal/downloads/meningococcal-outbreak-guidance.pdf [PDF}].
8 A booster dose of MenB vaccine is recommended 1 year after completion of the primary vaccination series and every 2–3 years thereafter for people who remain at increased risk of serogroup B meningococcal disease for any other reason.
Routine Immunization
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends routine administration of a quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MenACWY) for all people aged 11–18 years. Administer a single dose of vaccine to patients at age 11 or 12 years and a booster dose at age 16 years. Routine immunization with MenACWY is not recommended for other age groups in the United States, except for people at increased risk for meningococcal disease, including those with a persistent complement component deficiency (C3, C5-9, properdin, factor D, factor H); people taking a complement component inhibitor (e.g., eculizumab [Soliris] or ravulizumab [Ultomiris]); people who have functional or anatomic asplenia; or people with HIV. ACIP describes vaccine, product, number of doses, and booster dose recommendations, based on age and risk factors for each risk group, in Meningococcal Vaccination: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2020 .
ACIP also recommends adolescents and young adults aged 16–23 years be vaccinated with a serogroup B meningococcal (MenB) vaccine series, based on shared clinical decision-making. A MenB vaccine series provides short-term protection against most strains of serogroup B meningococcus; 16–18 years is the optimal age for MenB vaccination. ACIP also recommends routine use of MenB vaccine for people aged ≥10 years who are at increased risk for meningococcal disease, including people who have persistent complement component deficiency and those with functional or anatomic asplenia. ACIP recommendations for use of MenB vaccines can be found in Meningococcal Vaccination: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices , United States, 2020.
Immunization For Travelers
Quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate (menacwy) vaccines.
ACIP recommends that travelers aged ≥2 months who visit or reside in parts of the meningitis belt of sub-Saharan Africa (see Map 5-01 ) during the dry season (December–June) receive vaccination with a MenACWY vaccine before travel. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issues advisories for travelers to other countries when outbreaks of meningococcal disease are recognized; travelers should check the CDC Travelers’ Health website before travel. There are 3 meningococcal vaccines licensed and available in the United States for children; the age at vaccine initiation and schedule differs for each. See Table 5-03 for more information about meningococcal vaccines for young children.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) requires travelers >2 years of age making the Umrah or Hajj pilgrimage to provide documentation of quadrivalent vaccine ≥10 days and ≤3 years before arrival for polysaccharide vaccine (MPSV4, no longer available in the United States) and ≤5 years before arrival for conjugate vaccine. Travelers should confirm visa requirements with the KSA embassy. Although the KSA Ministry of Health advises against travel to Hajj for pregnant people or children, these groups should receive meningococcal vaccination according to licensed indications for their age if they travel.
International travelers at risk for meningococcal disease who were previously vaccinated with a quadrivalent vaccine should receive a booster dose. For children who completed the primary dose or series at <7 years of age, administer a booster dose of MenACWY after 3 years and repeat every 5 years thereafter for those who live in or travel to hyperendemic areas. For people who received the primary dose or series at ≥7 years of age, administer a booster dose after 5 years and every 5 years thereafter for people who live in or travel to a hyperendemic area.
Monovalent Vaccines (Serogroups A, B & C)
In 2010, the Meningitis Vaccine Project introduced MenAfriVac, a monovalent serogroup A meningococcal conjugate vaccine, into meningitis belt countries through mass vaccination campaigns and the routine childhood immunization schedule. This vaccine is not licensed for use in the United States. US travelers going to live or work in the meningitis belt should receive a quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MenACWY) before leaving, to protect against 4 serogroups.
MenB vaccine is not recommended for people who live in or travel to meningitis belt countries, because serogroup B disease is extremely rare in this region. MenB vaccine is not routinely recommended for travelers to other regions of the world unless an outbreak of serogroup B disease has been reported.
In some countries outside the meningitis belt, meningococcal vaccination (e.g., monovalent conjugate C vaccine or MenB vaccine) might be recommended as part of the routine immunization program for infants. Clinicians can consider meningococcal vaccination for infants residing in these countries, according to the routine immunization recommendations of that country.
Safety & Adverse Reactions
Side effects after MenACWY vaccination include low-grade fevers and local reactions (e.g., injection-site pain, arm swelling, pain that limits movement of the injected arm). Symptoms are generally mild to moderate and resolve within 48–72 hours. Severe adverse events (e.g., high fever, chills, joint pain, rash, seizures) are rare (<5% of vaccinees).
Although no clinical trials of meningococcal vaccines have been conducted in people who are pregnant or lactating, post-licensure safety data have not identified any serious safety concerns to the mother or fetus. Pregnancy or lactation should not preclude vaccination with MenACWY if indicated.
Precautions & Contraindications
People with moderate or severe acute illness should defer vaccination until their condition improves. Vaccination is contraindicated for people who have had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccines or to a prior dose of the vaccine. A severe allergic reaction to any diphtheria toxoid- or CRM197-containing vaccine also is a contraindication for MenACWY-D and MenACWY-CRM; severe allergic reaction to any tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine is a contraindication for MenACWY-TT.
To avoid interference with the immune response to meningococcal vaccine, MenACWY-D should be given either before or at the same time as DTaP in children. MenACWY-D may be given at any time in relation to Tdap or Td.
All meningococcal vaccines are inactivated and can be given to people who are immunosuppressed.
Postexposure Prophylaxis
In the United States and most industrialized countries, antibiotic chemoprophylaxis is recommended for close contacts of a patient with invasive meningococcal disease to prevent secondary cases. Chemoprophylaxis ideally should be initiated within 24 hours after the index patient is identified; prophylaxis given >2 weeks after exposure has little value.
Antibiotics used for prophylaxis include ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, and rifampin. Ceftriaxone is recommended for pregnant people. CDC provides detailed information on meningococcal prophylaxis in the Manual for the Surveillance of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases .
CDC website: Meningococcal disease
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Sarah A. Mbaeyi, Lucy A. McNamara
Bibliography
American Academy of Pediatrics. Meningococcal infections. In: Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson M, Long SS, editors. Red Book: 2015 report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 30th edition. Elk Grove Village (IL): American Academy of Pediatrics; 2015. pp. 547–58.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Public health dispatch: Update: assessment of risk for meningococcal disease associated with the Hajj 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50(12):221–2.
Folaranmi T, Rubin L, Martin SW, Patel M, MacNeil JR. Use of serogroup B meningococcal vaccines in persons aged >/=10 years at increased risk for serogroup B meningococcal disease: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(22):608–12.
Halperin SA, Bettinger JA, Greenwood B, Harrison LH, Jelfs J, Ladhani SN, et al. The changing and dynamic epidemiology of meningococcal disease. Vaccine. 2012;30(Suppl 2):B26–36.
MacNeil JR, Rubin L, Folaranmi T, Ortega-Sanchez IR, Patel M, Martin SW. Use of serogroup B meningococcal vaccines in adolescents and young adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(41):1171–6.
Mbaeyi SA, Bozio CH, Duffy J, Rubin LG, Hariri S, Stephens DS, et al. Meningococcal vaccination: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2020. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2020;69(9):1–41.
McNamara LA, Potts C, Blain AE, Retchless AC, Reese N, Swint S, et al. Detection of ciprofloxacin-resistant, β-lactamase-producing Neisseria meningitidis serogroup Y isolates—United States, 2019–2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(24):735–9.
Patton ME, Stephens D, Moore K, MacNeil JR. Updated recommendations for use of MenB-FHbp serogroup B meningococcal vaccine—Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;66(19);509–13.
Trotter CL, Lingani C, Fernandez K, Cooper LV, Bita A, Tevi-Benissan C, et al. Impact of MenAfriVac in nine countries of the African meningitis belt, 2010–2015: an analysis of surveillance data. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17(8):867–72.
World Health Organization. Epidemic meningitis control in countries of the African meningitis belt, 2016. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2017;92(13):145–54.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Measles elimination in the U.S. is under 'renewed threat,' CDC warns
Measles has spread at a rapid clip this year. From January to March, the U.S. recorded around 30% of the total cases seen since the beginning of 2020.
From 2020 through 2023, the U.S. recorded an average of five measles cases in the first quarter of each year. Those low numbers were due, in part, to the Covid pandemic, when fewer people were interacting in person. By contrast, this year’s first-quarter tally was 97, according to a report the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released Thursday.
"The rapid increase in the number of reported measles cases during the first quarter of 2024 represents a renewed threat to elimination," the authors wrote.
Measles has been considered eliminated in the U.S. since 2000, meaning the disease is no longer constantly present, though there are still occasional outbreaks.
The country nearly lost that elimination status in 2019, when it recorded more than 1,200 cases — most of which were associated with outbreaks in Orthodox Jewish communities in New York. The high case load this year could put that elimination in jeopardy once again: As of April 4, the U.S. had already recorded seven outbreaks and 113 cases .
The CDC report called for more widespread vaccination coverage. Around 91% of measles cases recorded in the U.S. since January 2020 were among people who were unvaccinated or had an unknown vaccination status, it said.
One dose of the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine is 93% effective at preventing measles, and two doses are 97% effective.
This year so far, 83% of recorded cases have been in people who were unvaccinated or whose vaccination status is unknown. Half of the 2024 cases have been in children under age 5. So far, 65 people have been hospitalized.
No one has died of measles in the last four years, according to the CDC report.
Measles vaccination rates dipped in the last few years. Communities should have around 95% vaccination coverage to prevent sustained measles transmission, but 12 states and Washington, D.C., had rates below 90% as of the 2022-23 school year.
The share of U.S. kindergartners who had received two doses of the MMR vaccine fell from 95% in the 2019-20 school year to 93% in the 2022-23 school year. According to the CDC, that leaves around 250,000 kindergarteners susceptible to measles each year.
Vaccination coverage has also declined globally . Around 83% of people worldwide had received one dose of a measles vaccine in 2022, down from 86% in 2019, according to the CDC. Global coverage declined to 81% during the Covid pandemic — the lowest since 2008.
The CDC report encouraged vaccination before international travel, since the majority of measles cases are introduced to the U.S. from other countries. According to the CDC, the number of countries reporting “large or disruptive” measles outbreaks increased 123% from November 2022 to October 2023.
In the U.S., the largest outbreak this year began at a migrant shelter in Chicago. The city’s measles case total topped 60 this week. Since last month, the Chicago Department of Public Health has distributed more than 13,000 measles vaccines to help contain the spread.
Measles is highly contagious: An infected person can spread it to up to 90% of people close to them if those contacts aren’t immune.
However, the CDC report noted that the “risk for widespread U.S. measles transmission remains low because of high population immunity.”
Aria Bendix is the breaking health reporter for NBC News Digital.

COMMENTS
Highlights. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by: Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip. Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines. Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family's ...
Many diseases prevented by routine vaccination are not common in the United States but are still common in other countries. Check CDC's destination pages for travel health information. Check CDC's webpage for your destination to see what vaccines or medicines you may need and what diseases or health risks are a concern at your destination.
Vaccination (2-dose vaccine): Recommended for most travelers. --Administer 2 doses, at least 6 months apart. --At least 1 dose should be given before travel. Consultation: Advise patient to wash hands frequently and avoid unsafe food and water. Hepatitis B. Sexual contact, contaminated needles, & blood products, vertical transmission.
Q. What are the requirements for travelers entering the United States through land POEs? A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following: Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website. During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
The White House announced that vaccines will be required for international travelers coming into the United States, with an effective date of November 8, 2021. For purposes of entry into the United States, vaccines accepted will include FDA approved or authorized and WHO Emergency Use Listing vaccines. More information is available here.
Ned Price, Department Spokesperson. October 25, 2021. Today, the White House and CDC announced details of the new vaccination policy that will go into effect for international travelers on November 8. As of that date, foreign national air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination ...
CDC has determined that for purposes of travel to the United States, vaccines accepted will include FDA approved or authorized and World Health Organization (WHO) emergency use listed (EUL) vaccines.
The White House announced that vaccines will be required for international travelers coming into the United States, with an effective date of November 8, 2021. For purposes of entry into the United States, vaccines accepted will include FDA approved or authorized and WHO Emergency Use Listing vaccines. More information is available here.
CDC recommends: Everyone 5 years and older get 1 updated COVID-19 vaccine to protect against serious illness. Children aged 6 months - 4 years may need more than 1 updated COVID-19 vaccine to be up to date. People aged 65 years and older who received 1 dose of any updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna or Novavax) should ...
Last Updated: May 4, 2023. The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with ...
Get up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines before you travel and take steps to protect yourself and others.Consider wearing a mask in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor areas, including on public transportation and in transportation hubs. Take additional precautions if you were recently exposed to a person with COVID-19. Don't travel while sick. If you have a weakened immune system or are ...
Nov. 8, 2021. On Monday, the United States lifted travel restrictions for international visitors from 33 countries who are fully vaccinated against the coronavirus, ending an 18-month ban that has ...
What to Know About the C.D.C. Guidelines on Vaccinated Travel. In updated recommendations, the federal health agency said both domestic and international travel was low risk for fully vaccinated ...
Vaccines for Travelers. Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places. Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you're ...
Guidance released Friday allows fully vaccinated people to travel domestically without getting tested or self-quarantining, but advises them to keep practicing mitigation measures to protect others.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
0:00. 2:02. The U.S. is launching a new travel system on Nov. 8. Vaccinated foreign air travelers will need to show proof of full vaccination and test for COVID-19. The new travel system also adds ...
International travelers boarding flights to the United States will now be considered fully vaccinated two weeks after getting a single dose of either the Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccine any time ...
You should plan to be fully vaccinated at least 2 weeks before you depart. If your trip is less than 2 weeks away and you're not protected against measles, you should still get a dose of the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine. The MMR vaccine protects against all 3 diseases. Two doses of MMR vaccine provide 97% protection against measles.
Introduction. mRNA COVID-19 vaccines have been recommended for U.S. children and adolescents aged ≥5 years since November 2021 † (1).Two doses of Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine protected against COVID-19-related hospitalizations before and after emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (2,3).Throughout Omicron variant predominance (beginning in December 2021), estimated pediatric ...
Vaccination may be considered for children and adults who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission. Cholera - CDC Yellow Book. Hepatitis A. Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to India. Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A.
Methods Reporting and Classification of Measles Cases. Confirmed measles cases § (1) are reported to CDC by state health departments through the National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System and directly (by email or telephone) to the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.Measles cases are classified by the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists as import ...
Amid an uptick in measles cases and outbreaks both in the US and abroad, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued an alert on March 18 encouraging clinicians to work with schools and educators to ensure children are up-to-date on their measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccines. As of March 28, 97 measles cases had been reported in 18 US states this year.
The CDC report noted the U.S. needs to increase vaccination coverage, including for young children before international travel and among at-risk communities with low uptake. Featured Weekly Ad
April 15, 2024. The measles virus as seen through a transmission microscope. Rising numbers of measles cases in the U.S. threaten its eliminated status, according to a new CDC report. BSIP ...
Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked. Page last reviewed: December 15, 2023. Content source: National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) Division of Global Migration Health (DGMH) Official U.S. government health recommendations for traveling. Provided by the U.S ...
Five meningococcal vaccines (3 quadrivalent, 2 monovalent) are licensed and available in the United States. Travelers should receive vaccines 7-10 days before travel to enable time for protective antibody levels to develop. See Table 5-03 for more information about available meningococcal vaccines.
Measles vaccination rates dipped in the last few years. Communities should have around 95% vaccination coverage to prevent sustained measles transmission, but 12 states and Washington, D.C., had ...