- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A Year Without Travel

For Planet Earth, No Tourism Is a Curse and a Blessing
From the rise in poaching to the waning of noise pollution, travel’s shutdown is having profound effects. Which will remain, and which will vanish?

By Lisa W. Foderaro
For the planet, the year without tourists was a curse and a blessing.
With flights canceled, cruise ships mothballed and vacations largely scrapped, carbon emissions plummeted. Wildlife that usually kept a low profile amid a crush of tourists in vacation hot spots suddenly emerged. And a lack of cruise ships in places like Alaska meant that humpback whales could hear each other’s calls without the din of engines.
That’s the good news. On the flip side, the disappearance of travelers wreaked its own strange havoc, not only on those who make their living in the tourism industry, but on wildlife itself, especially in developing countries. Many governments pay for conservation and enforcement through fees associated with tourism. As that revenue dried up, budgets were cut, resulting in increased poaching and illegal fishing in some areas. Illicit logging rose too, presenting a double-whammy for the environment. Because trees absorb and store carbon, cutting them down not only hurt wildlife habitats, but contributed to climate change.
“We have seen many financial hits to the protection of nature,” said Joe Walston, executive vice president of global conservation at the Wildlife Conservation Society. “But even where that hasn’t happened, in a lot of places people haven’t been able to get into the field to do their jobs because of Covid.”
From the rise in rhino poaching in Botswana to the waning of noise pollution in Alaska, the lack of tourism has had a profound effect around the world. The question moving forward is which impacts will remain, and which will vanish, in the recovery.
A change in the air
While the pandemic’s impact on wildlife has varied widely from continent to continent, and country to country, its effect on air quality was felt more broadly.
In the United States, greenhouse gas emissions last year fell more than 10 percent , as state and local governments imposed lockdowns and people stayed home, according to a report in January by the Rhodium Group, a research and consulting firm.
The most dramatic results came from the transportation sector, which posted a 14.7 percent decrease. It’s impossible to tease out how much of that drop is from lost tourism versus business travel. And there is every expectation that as the pandemic loosens its grip, tourism will resume — likely with a vengeance.
Still, the pandemic helped push American emissions below 1990 levels for the first time. Globally, carbon dioxide emissions fell 7 percent , or 2.6 billion metric tons, according to new data from international climate researchers. In terms of output, that is about double the annual emissions of Japan.
“It’s a lot and it’s a little,” said Jason Smerdon, a climate scientist at Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory . “Historically, it’s a lot. It’s the largest single reduction percent-wise over the last 100 years. But when you think about the 7 percent in the context of what we need to do to mitigate climate change, it’s a little.”
In late 2019, the United Nations Environment Program cautioned that global greenhouse gases would need to drop 7.6 percent every year between 2020 and 2030. That would keep the world on its trajectory of meeting the temperature goals set under the Paris Agreement, the 2016 accord signed by nearly 200 nations.
“The 7 percent drop last year is on par with what we would need to do year after year,” Dr. Smerdon said. “Of course we wouldn’t want to do it the same way. A global pandemic and locking ourselves in our apartments is not the way to go about this.”
Interestingly, the drop in other types of air pollution during the pandemic muddied the climate picture. Industrial aerosols, made up of soot, sulfates, nitrates and mineral dust, reflect sunlight back into space, thus cooling the planet. While their reduction was good for respiratory health, it had the effect of offsetting some of the climate benefits of cascading carbon emissions.
For the climate activist Bill McKibben , one of the first to sound the alarm about global warming in his 1989 book, “The End of Nature,” the pandemic underscored that the climate crisis won’t be averted one plane ride or gallon of gas at a time.
“We’ve come through this pandemic year when our lives changed more than any of us imagined they ever would,” Mr. McKibben said during a Zoom webinar hosted in February by the nonprofit Green Mountain Club of Vermont.
“Everybody stopped flying; everybody stopped commuting,” he added. “Everybody just stayed at home. And emissions did go down, but they didn’t go down that much, maybe 10 percent with that incredible shift in our lifestyles. It means that most of the damage is located in the guts of our systems and we need to reach in and rip out the coal and gas and oil and stick in the efficiency, conservation and sun and wind.”
Wildlife regroups
Just as the impact of the pandemic on air quality is peppered with caveats, so too is its influence on wildlife.
Animals slithered, crawled and stomped out of hiding across the globe, sometimes in farcical fashion. Last spring, a herd of Great Orme Kashmiri goats was spotted ambling through empty streets in Llandudno, a coastal town in northern Wales. And hundreds of monkeys — normally fed by tourists — were involved in a disturbing brawl outside of Bangkok, apparently fighting over food scraps.
In meaningful ways, however, the pandemic revealed that wildlife will regroup if given the chance. In Thailand, where tourism plummeted after authorities banned international flights, leatherback turtles laid their eggs on the usually mobbed Phuket Beach. It was the first time nests were seen there in years, as the endangered sea turtles, the largest in the world, prefer to nest in seclusion.
Similarly, in Koh Samui, Thailand’s second largest island, hawksbill turtles took over beaches that in 2018 hosted nearly three million tourists. The hatchlings were documented emerging from their nests and furiously moving their flippers toward the sea.
For Petch Manopawitr, a marine conservation manager of the Wildlife Conservation Society Thailand, the sightings were proof that natural landscapes can recover quickly. “Both Ko Samui and Phuket have been overrun with tourists for so many years,” he said in a phone interview. “Many people had written off the turtles and thought they would not return. After Covid, there is talk about sustainability and how it needs to be embedded in tourism, and not just a niche market but all kinds of tourism.”
In addition to the sea turtles, elephants, leaf monkeys and dugongs (related to manatees) all made cameos in unlikely places in Thailand. “Dugongs are more visible because there is less boat traffic,” Mr. Manopawitr said. “The area that we were surprised to see dugongs was the eastern province of Bangkok. We didn’t know dugongs still existed there.”
He and other conservationists believe that countries in the cross hairs of international tourism need to mitigate the myriad effects on the natural world, from plastic pollution to trampled parks.
That message apparently reached the top levels of the Thai government. In September, the nation’s natural resources and environment minister, Varawut Silpa-archa, said he planned to shutter national parks in stages each year, from two to four months. The idea, he told Bloomberg News , is to set the stage so that “nature can rehabilitate itself.”
An increase in poaching
In other parts of Asia and across Africa, the disappearance of tourists has had nearly the opposite result. With safari tours scuttled and enforcement budgets decimated, poachers have plied their nefarious trade with impunity. At the same time, hungry villagers have streamed into protected areas to hunt and fish.
There were reports of increased poaching of leopards and tigers in India, an uptick in the smuggling of falcons in Pakistan, and a surge in trafficking of rhino horns in South Africa and Botswana.
Jim Sano, the World Wildlife Fund’s vice president for travel, tourism and conservation, said that in sub-Saharan Africa, the presence of tourists was a powerful deterrent. “It’s not only the game guards,” he said. “It’s the travelers wandering around with the guides that are omnipresent in these game areas. If the guides see poachers with automatic weapons, they report it.”
In the Republic of Congo, the Wildlife Conservation Society has noticed an increase in trapping and hunting in and around protected areas. Emma J. Stokes, regional director of the Central Africa program for the organization, said that in Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park, monkeys and forest antelopes were being targeted for bushmeat.
“It’s more expensive and difficult to get food during the pandemic and there is a lot of wildlife up there,” she said by phone. “We obviously want to deter people from hunting in the park, but we also have to understand what’s driving that because it’s more complex.”
The Society and the Congolese government jointly manage the park, which spans 1,544 square miles of lowland rainforest — larger than Rhode Island. Because of the virus, the government imposed a national lockdown, halting public transportation. But the organization was able to arrange rides to markets since the park is considered an essential service. “We have also kept all 300 of our park staff employed,” she added.
Largely absent: the whir of propellers, the hum of engines
While animals around the world were subject to rifles and snares during the pandemic, one thing was missing: noise. The whir of helicopters diminished as some air tours were suspended. And cruise ships from the Adriatic Sea to the Gulf of Mexico were largely absent. That meant marine mammals and fish had a break from the rumble of engines and propellers.
So did research scientists. Michelle Fournet is a marine ecologist who uses hydrophones (essentially aquatic microphones) to listen in on whales. Although the total number of cruise ships (a few hundred) pales in comparison to the total number of cargo ships (tens of thousands), Dr. Fournet says they have an outsize role in creating underwater racket. That is especially true in Alaska, a magnet for tourists in search of natural splendor.
“Cargo ships are trying to make the most efficient run from point A to point B and they are going across open ocean where any animal they encounter, they encounter for a matter of hours,” she said. “But when you think about the concentration of cruise ships along coastal areas, especially in southeast Alaska, you basically have five months of near-constant vessel noise. We have a population of whales listening to them all the time.”
Man-made noise during the pandemic dissipated in the waters near the capital of Juneau, as well as in Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve . Dr. Fournet, a postdoctoral research associate at Cornell University, observed a threefold decrease in ambient noise in Glacier Bay between 2019 and 2020. “That’s a really big drop in noise,” she said, “and all of that is associated with the cessation of these cruise ships.”
Covid-19 opened a window onto whale sounds in Juneau as well. Last July, Dr. Fournet, who also directs the Sound Science Research Collective , a marine conservation nonprofit, had her team lower a hydrophone in the North Pass, a popular whale-watching destination. “In previous years,” she said, “you wouldn’t have been able to hear anything — just boats. This year we heard whales producing feeding calls, whales producing contact calls. We heard sound types that I have never heard before.”
Farther south in Puget Sound, near Seattle, whale-watching tours were down 75 percent last year. Tour operators like Jeff Friedman, owner of Maya’s Legacy Whale Watching , insist that their presence on the water benefits whales since the captains make recreational boaters aware of whale activity and radio them to slow down. Whale-watching companies also donate to conservation groups and report sightings to researchers.
“During the pandemic, there was a huge increase in the number of recreational boats out there,” said Mr. Friedman, who is also president of the Pacific Whale Watch Association . “It was similar to R.V.s. People decided to buy an R.V. or a boat. The majority of the time, boaters are not aware that the whales are present unless we let them know.”
Two years ago, in a move to protect Puget Sound’s tiny population of Southern Resident killer whales, which number just 75, Washington’s Gov. Jay Inslee signed a law reducing boat speeds to 7 knots within a half nautical mile of the whales and increasing a buffer zone around them, among other things.
Many cheered the protections. But environmental activists like Catherine W. Kilduff, a senior attorney in the oceans program at the Center for Biological Diversity, believe they did not go far enough. She wants the respite from noise that whales enjoyed during the pandemic to continue.
“The best tourism is whale-watching from shore,” she said.
Looking Ahead
Debates like this are likely to continue as the world emerges from the pandemic and leisure travel resumes. Already, conservationists and business leaders are sharing their visions for a more sustainable future.
Ed Bastian, Delta Air Lines’ chief executive, last year laid out a plan to become carbon neutral by spending $1 billion over 10 years on an assortment of strategies. Only 2.5 percent of global carbon emissions are traced to aviation, but a 2019 study suggested that could triple by midcentury.
In the meantime, climate change activists are calling on the flying public to use their carbon budgets judiciously.
Tom L. Green, a senior climate policy adviser with the David Suzuki Foundation , an environmental organization in Canada, said tourists might consider booking a flight only once every few years, saving their carbon footprint (and money) for a special journey. “Instead of taking many short trips, we could occasionally go away for a month or more and really get to know a place,” he said.
For Mr. Walston of the Wildlife Conservation Society, tourists would be wise to put more effort into booking their next resort or cruise, looking at the operator’s commitment to sustainability.
“My hope is not that we stop traveling to some of these wonderful places, because they will continue to inspire us to conserve nature globally,” he said. “But I would encourage anyone to do their homework. Spend as much time choosing a tour group or guide as a restaurant. The important thing is to build back the kind of tourism that supports nature.”
Lisa W. Foderaro is a former reporter for The New York Times whose work has also appeared in National Geographic and Audubon Magazine.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation.
Come Sail Away
Love them or hate them, cruises can provide a unique perspective on travel..
Cruise Ship Surprises: Here are five unexpected features on ships , some of which you hopefully won’t discover on your own.
Icon of the Seas: Our reporter joined thousands of passengers on the inaugural sailing of Royal Caribbean’s Icon of the Seas . The most surprising thing she found? Some actual peace and quiet .
Th ree-Year Cruise, Unraveled: The Life at Sea cruise was supposed to be the ultimate bucket-list experience : 382 port calls over 1,095 days. Here’s why those who signed up are seeking fraud charges instead.
TikTok’s Favorite New ‘Reality Show’: People on social media have turned the unwitting passengers of a nine-month world cruise into “cast members” overnight.
Dipping Their Toes: Younger generations of travelers are venturing onto ships for the first time . Many are saving money.
Cult Cruisers: These devoted cruise fanatics, most of them retirees, have one main goal: to almost never touch dry land .

14 important environmental impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
The environmental impacts of tourism have gained increasing attention in recent years.
With the rise in sustainable tourism and an increased number of initiatives for being environmentally friendly, tourists and stakeholders alike are now recognising the importance of environmental management in the tourism industry.
In this post, I will explain why the environmental impacts of tourism are an important consideration and what the commonly noted positive and negative environmental impacts of tourism are.
Why the environment is so important to tourism
Positive environmental impacts of tourism, water resources, land degradation , local resources , air pollution and noise , solid waste and littering , aesthetic pollution, construction activities and infrastructure development, deforestation and intensified or unsustainable use of land , marina development, coral reefs, anchoring and other marine activities , alteration of ecosystems by tourist activities , environmental impacts of tourism: conclusion, environmental impacts of tourism reading list.

The quality of the environment, both natural and man-made, is essential to tourism. However, tourism’s relationship with the environment is complex and many activities can have adverse environmental effects if careful tourism planning and management is not undertaken.
It is ironic really, that tourism often destroys the very things that it relies on!
Many of the negative environmental impacts that result from tourism are linked with the construction of general infrastructure such as roads and airports, and of tourism facilities, including resorts, hotels, restaurants, shops, golf courses and marinas. The negative impacts of tourism development can gradually destroy the environmental resources on which it depends.
It’s not ALL negative, however!
Tourism has the potential to create beneficial effects on the environment by contributing to environmental protection and conservation. It is a way to raise awareness of environmental values and it can serve as a tool to finance protection of natural areas and increase their economic importance.
In this article I have outlined exactly how we can both protect and destroy the environment through tourism. I have also created a new YouTube video on the environmental impacts of tourism, you can see this below. (by the way- you can help me to be able to keep content like this free for everyone to access by subscribing to my YouTube channel! And don’t forget to leave me a comment to say hi too!).
Although there are not as many (far from it!) positive environmental impacts of tourism as there are negative, it is important to note that tourism CAN help preserve the environment!
The most commonly noted positive environmental impact of tourism is raised awareness. Many destinations promote ecotourism and sustainable tourism and this can help to educate people about the environmental impacts of tourism. Destinations such as Costa Rica and The Gambia have fantastic ecotourism initiatives that promote environmentally-friendly activities and resources. There are also many national parks, game reserves and conservation areas around the world that help to promote positive environmental impacts of tourism.
Positive environmental impacts can also be induced through the NEED for the environment. Tourism can often not succeed without the environment due the fact that it relies on it (after all we can’t go on a beach holiday without a beach or go skiing without a mountain, can we?).
In many destinations they have organised operations for tasks such as cleaning the beach in order to keep the destination aesthetically pleasant and thus keep the tourists happy. Some destinations have taken this further and put restrictions in place for the number of tourists that can visit at one time.
Not too long ago the island of Borocay in the Philippines was closed to tourists to allow time for it to recover from the negative environmental impacts that had resulted from large-scale tourism in recent years. Whilst inconvenient for tourists who had planned to travel here, this is a positive example of tourism environmental management and we are beginning to see more examples such as this around the world.
Negative environmental impacts of tourism

Negative environmental impacts of tourism occur when the level of visitor use is greater than the environment’s ability to cope with this use.
Uncontrolled conventional tourism poses potential threats to many natural areas around the world. It can put enormous pressure on an area and lead to impacts such as: soil erosion , increased pollution, discharges into the sea, natural habitat loss, increased pressure on endangered species and heightened vulnerability to forest fires. It often puts a strain on water resources, and it can force local populations to compete for the use of critical resources.
I will explain each of these negative environmental impacts of tourism below.
Depletion of natural resources

Tourism development can put pressure on natural resources when it increases consumption in areas where resources are already scarce. Some of the most common noted examples include using up water resources, land degradation and the depletion of other local resources.
The tourism industry generally overuses water resources for hotels, swimming pools, golf courses and personal use of water by tourists. This can result in water shortages and degradation of water supplies, as well as generating a greater volume of waste water.
In drier regions, like the Mediterranean, the issue of water scarcity is of particular concern. Because of the hot climate and the tendency for tourists to consume more water when on holiday than they do at home, the amount used can run up to 440 litres a day. This is almost double what the inhabitants of an average Spanish city use.

Golf course maintenance can also deplete fresh water resources.
In recent years golf tourism has increased in popularity and the number of golf courses has grown rapidly.
Golf courses require an enormous amount of water every day and this can result in water scarcity. Furthermore, golf resorts are more and more often situated in or near protected areas or areas where resources are limited, exacerbating their impacts.
An average golf course in a tropical country such as Thailand needs 1500kg of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides per year and uses as much water as 60,000 rural villagers.

Important land resources include fertile soil, forests , wetlands and wildlife. Unfortunately, tourism often contributes to the degradation of said resources. Increased construction of tourism facilities has increased the pressure on these resources and on scenic landscapes.
Animals are often displaced when their homes are destroyed or when they are disturbed by noise. This may result in increased animals deaths, for example road-kill deaths. It may also contribute to changes in behaviour.
Animals may become a nuisance, by entering areas that they wouldn’t (and shouldn’t) usually go into, such as people’s homes. It may also contribute towards aggressive behaviour when animals try to protect their young or savage for food that has become scarce as a result of tourism development.
Picturesque landscapes are often destroyed by tourism. Whilst many destinations nowadays have limits and restrictions on what development can occur and in what style, many do not impose any such rules. High rise hotels and buildings which are not in character with the surrounding architecture or landscape contribute to a lack of atheistic appeal.
Forests often suffer negative impacts of tourism in the form of deforestation caused by fuel wood collection and land clearing. For example, one trekking tourist in Nepal can use four to five kilograms of wood a day!
There are also many cases of erosion, whereby tourists may trek the same path or ski the same slope so frequently that it erodes the natural landscape. Sites such as Machu Pichu have been forced to introduce restrictions on tourist numbers to limit the damage caused.

Tourism can create great pressure on local resources like energy, food, and other raw materials that may already be in short supply. Greater extraction and transport of these resources exacerbates the physical impacts associated with their exploitation.
Because of the seasonal character of the industry, many destinations have ten times more inhabitants in the high season as in the low season.
A high demand is placed upon these resources to meet the high expectations tourists often have (proper heating, hot water, etc.). This can put significant pressure on the local resources and infrastructure, often resulting in the local people going without in order to feed the tourism industry.
Tourism can cause the same forms of pollution as any other industry: Air emissions; noise pollution; solid waste and littering; sewage; oil and chemicals. The tourism industry also contributes to forms of architectural/visual pollution.

Transport by air, road, and rail is continuously increasing in response to the rising number of tourists and their greater mobility. In fact, tourism accounts for more than 60% of all air travel.
One study estimated that a single transatlantic return flight emits almost half the CO2 emissions produced by all other sources (lighting, heating, car use, etc.) consumed by an average person yearly- that’s a pretty shocking statistic!
I remember asking my class to calculate their carbon footprint one lesson only to be very embarrassed that my emissions were A LOT higher than theirs due to the amount of flights I took each year compared to them. Point proven I guess….
Anyway, air pollution from tourist transportation has impacts on a global level, especially from CO2 emissions related to transportation energy use. This can contribute to severe local air pollution . It also contributes towards climate change.
Fortunately, technological advancements in aviation are seeing more environmentally friendly aircraft and fuels being used worldwide, although the problem is far from being cured. If you really want to help save the environment, the answer is to seek alternative methods of transportation and avoid flying.
You can also look at ways to offset your carbon footprint .

Noise pollution can also be a concern.
Noise pollution from aircraft, cars, buses, (+ snowmobiles and jet skis etc etc) can cause annoyance, stress, and even hearing loss for humans. It also causes distress to wildlife and can cause animals to alter their natural activity patterns. Having taught at a university near London Heathrow for several years, this was always a topic of interest to my students and made a popular choice of dissertation topic .

In areas with high concentrations of tourist activities and appealing natural attractions, waste disposal is a serious problem, contributing significantly to the environmental impacts of tourism.
Improper waste disposal can be a major despoiler of the natural environment. Rivers, scenic areas, and roadsides are areas that are commonly found littered with waste, ranging from plastic bottles to sewage.
Cruise tourism in the Caribbean, for example, is a major contributor to this negative environmental impact of tourism. Cruise ships are estimated to produce more than 70,000 tons of waste each year.
The Wider Caribbean Region, stretching from Florida to French Guiana, receives 63,000 port calls from ships each year, and they generate 82,000 tons of rubbish. About 77% of all ship waste comes from cruise vessels. On average, passengers on a cruise ship each account for 3.5 kilograms of rubbish daily – compared with the 0.8 kilograms each generated by the less well-endowed folk on shore.
Whilst it is generally an unwritten rule that you do not throw rubbish into the sea, this is difficult to enforce in the open ocean . In the past cruise ships would simply dump their waste while out at sea. Nowadays, fortunately, this is less commonly the case, however I am sure that there are still exceptions.
Solid waste and littering can degrade the physical appearance of the water and shoreline and cause the death of marine animals. Just take a look at the image below. This is a picture taken of the insides of a dead bird. Bird often mistake floating plastic for fish and eat it. They can not digest plastic so once their stomachs become full they starve to death. This is all but one sad example of the environmental impacts of tourism.
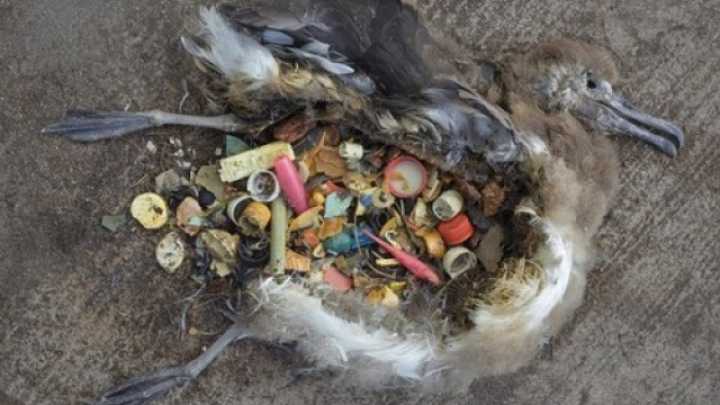

Mountain areas also commonly suffer at the hands of the tourism industry. In mountain regions, trekking tourists generate a great deal of waste. Tourists on expedition frequently leave behind their rubbish, oxygen cylinders and even camping equipment. I have heard many stories of this and I also witnessed it first hand when I climbed Mount Kilimanjaro .

The construction of hotels, recreation and other facilities often leads to increased sewage pollution.
Unfortunately, many destinations, particularly in the developing world, do not have strict law enrichments on sewage disposal. As a result, wastewater has polluted seas and lakes surrounding tourist attractions around the world. This damages the flora and fauna in the area and can cause serious damage to coral reefs.
Sewage pollution threatens the health of humans and animals.
I’ll never forget the time that I went on a school trip to climb Snowdonia in Wales. The water running down the streams was so clear and perfect that some of my friends had suggested we drink some. What’s purer than mountain fresh water right from the mountain, right?
A few minutes later we saw a huge pile of (human??) feaces in the water upstream!!
Often tourism fails to integrate its structures with the natural features and indigenous architecture of the destination. Large, dominating resorts of disparate design can look out of place in any natural environment and may clash with the indigenous structural design.
A lack of land-use planning and building regulations in many destinations has facilitated sprawling developments along coastlines, valleys and scenic routes. The sprawl includes tourism facilities themselves and supporting infrastructure such as roads, employee housing, parking, service areas, and waste disposal. This can make a tourist destination less appealing and can contribute to a loss of appeal.
Physical impacts of tourism development

Whilst the tourism industry itself has a number of negative environmental impacts. There are also a number of physical impacts that arise from the development of the tourism industry. This includes the construction of buildings, marinas, roads etc.

The development of tourism facilities can involve sand mining, beach and sand dune erosion and loss of wildlife habitats.
The tourist often will not see these side effects of tourism development, but they can have devastating consequences for the surrounding environment. Animals may displaced from their habitats and the noise from construction may upset them.
I remember reading a while ago (although I can’t seem to find where now) that in order to develop the resort of Kotu in The Gambia, a huge section of the coastline was demolished in order to be able to use the sand for building purposes. This would inevitably have had severe consequences for the wildlife living in the area.

Construction of ski resort accommodation and facilities frequently requires clearing forested land.
Land may also be cleared to obtain materials used to build tourism sites, such as wood.
I’ll never forget the site when I flew over the Amazon Rainforest only to see huge areas of forest cleared. That was a sad reality to see.
Likewise, coastal wetlands are often drained due to lack of more suitable sites. Areas that would be home to a wide array of flora and fauna are turned into hotels, car parks and swimming pools.

The building of marinas and ports can also contribute to the negative environmental impacts of tourism.
Development of marinas and breakwaters can cause changes in currents and coastlines.
These changes can have vast impacts ranging from changes in temperatures to erosion spots to the wider ecosystem.

Coral reefs are especially fragile marine ecosystems. They suffer worldwide from reef-based tourism developments and from tourist activity.
Evidence suggests a variety of impacts to coral result from shoreline development. Increased sediments in the water can affect growth. Trampling by tourists can damage or even kill coral. Ship groundings can scrape the bottom of the sea bed and kill the coral. Pollution from sewage can have adverse effects.
All of these factors contribute to a decline and reduction in the size of coral reefs worldwide. This then has a wider impact on the global marine life and ecosystem, as many animals rely on the coral for as their habitat and food source.
Physical impacts from tourist activities
The last point worth mentioning when discussing the environmental impacts of tourism is the way in which physical impacts can occur as a result of tourist activities.
This includes tramping, anchoring, cruising and diving. The more this occurs, the more damage that is caused. Natural, this is worse in areas with mass tourism and overtourism .

Tourists using the same trail over and over again trample the vegetation and soil, eventually causing damage that can lead to loss of biodiversity and other impacts.
Such damage can be even more extensive when visitors frequently stray off established trails. This is evidenced in Machu Pichu as well as other well known destinations and attractions, as I discussed earlier in this post.

In marine areas many tourist activities occur in or around fragile ecosystems.
Anchoring, scuba diving, yachting and cruising are some of the activities that can cause direct degradation of marine ecosystems such as coral reefs. As I said previously, this can have a significant knock on effect on the surrounding ecosystem.

Habitats can be degraded by tourism leisure activities.
For example, wildlife viewing can bring about stress for the animals and alter their natural behaviour when tourists come too close.
As I have articulated throughout this post, there are a range of environmental impacts that result from tourism. Whilst some are good, the majority unfortunately are bad. The answer to many of these problems boils down to careful tourism planning and management and the adoption of sustainable tourism principles.
Did you find this article helpful? Take a look at my posts on the social impacts of tourism and the economic impacts of tourism too! Oh, and follow me on social media !
If you are studying the environmental impacts of tourism or if you are interested in learning more about the environmental impacts of tourism, I have compiled a short reading list for you below.
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
Liked this article? Click to share!
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
- SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
- Competitiveness
- Innovation and Investments
- ETHICS, CULTURE AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
- TECHNICAL COOPERATION
- UN Tourism ACADEMY
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Sustainable development
"Tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities"
Sustainable tourism development guidelines and management practices are applicable to all forms of tourism in all types of destinations, including mass tourism and the various niche tourism segments. Sustainability principles refer to the environmental, economic, and socio-cultural aspects of tourism development, and a suitable balance must be established between these three dimensions to guarantee its long-term sustainability.
Thus, sustainable tourism should:
- Make optimal use of environmental resources that constitute a key element in tourism development, maintaining essential ecological processes and helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity.
- Respect the socio-cultural authenticity of host communities, conserve their built and living cultural heritage and traditional values, and contribute to inter-cultural understanding and tolerance.
- Ensure viable, long-term economic operations, providing socio-economic benefits to all stakeholders that are fairly distributed, including stable employment and income-earning opportunities and social services to host communities, and contributing to poverty alleviation.
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective measures whenever necessary.
Sustainable tourism should also maintain a high level of tourist satisfaction and ensure a meaningful experience to the tourists, raising their awareness about sustainability issues and promoting sustainable tourism practices amongst them.
COMMITTEE ON TOURISM AND SUSTAINABILITY (CTS)
Biodiversity
UN Tourism strives to promote tourism development that supports, in equal measure, the conservation of biodiversity, the social welfare and the economic security of the host countries and communities.
Climate Action
Tourism is both highly vulnerable to climate change while at the same time contributing to it. Threats for the sector are diverse, including direct and indirect impacts such as more extreme weather events, increasing insurance costs and safety concerns, water shortages, biodiversity loss and damage to assets and attractions at destinations, among others.
Global Tourism Plastics Initiative
The problem of plastic pollution in tourism is too big for any single organisation to fix on its own. To match the scale of the problem, changes need to take place across the whole tourism value chain.
Hotel Energy Solutions (HES)
Hotel Energy Solutions (HES) is a UN Tourism -initiated project in collaboration with a team of United Nations and EU leading agencies in Tourism and Energy .
Observatories (INSTO)
The UN Tourism International Network of Sustainable Tourism Observatories (INSTO) is a network of tourism observatories monitoring the economic, environmental and social impact of tourism at the destination level.
When responsibly planned and managed, tourism has demonstrated its capacity to support job creation, promote inclusive social integration, protect natural and cultural heritage, conserve biodiversity, generate sustainable livelihoods and improve human wellbeing. As the sector is experiencing tremendous growth, collective efforts to ensure its long-term sustainability are essential.
Resource Efficiency in Tourism
The report aims to inspire stakeholders and encourage them to advance the implementation of the SDGs through sustainable tourism.
Small Islands Developing States (SIDS)
Small Island Developing States face numerous challenges. For a significant number, their remoteness affects their ability to be part of the global supply chain, increases import costs - especially for energy - and limits their competitiveness in the tourist industry. Many are increasingly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change - from devastating storms to the threat of sea level rise.
Travel facilitation
Travel facilitation of tourist travel is closely interlinked with tourism development and can be a tool to foster increased demand and generate economic development, job creation and international understanding.
UNGA Sustainable Tourism Resolutions
The UN Tourism is regularly preparing reports for the General Assembly of the United Nations providing updates on sustainable tourism policies both from UN Tourism member States and States Members of the United Nations, as well as relevant agencies and programmes of the United Nations system.
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 May 2023
Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies
- Yunfeng Shang 1 ,
- Chunyu Bi 2 ,
- Xinyu Wei 2 ,
- Dayang Jiang 2 ,
- Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5446-7093 3 , 4 &
- Ehsan Rasoulinezhad ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7726-1757 5
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 275 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
8286 Accesses
7 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
Developing ecotourism services is a suitable solution to help developing countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. The primary purpose of this paper is to find out the effects of green governance variables and carbon dioxide emissions on ecotourism for 40 developing economies from 2010 to 2021. The results confirmed a uni-directional causal relationship between the green governance indicator and the inflation rate of the ecotourism indicator. In addition, with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. In comparison, with a 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries, ecotourism will increase by 0.32%. Moreover, ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to macroeconomic variables changes than in developed economies. Geopolitical risk is an influential factor in the developing process of ecotourism. The practical policies recommended by this research are developing the green financing market, establishing virtual tourism, granting green loans to small and medium enterprises, and government incentives to motivate active businesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Comprehensive green growth indicators across countries and territories

Role of foreign direct Investment and political openness in boosting the eco-tourism sector for achieving sustainability
Ways to bring private investment to the tourism industry for green growth
Introduction.
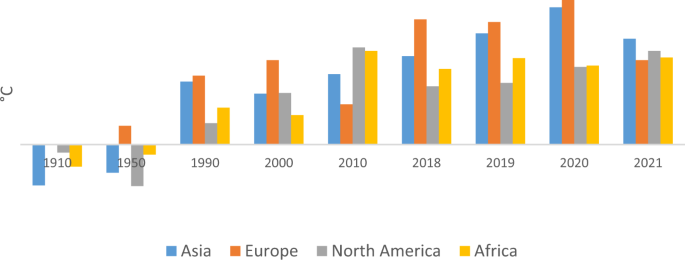
The challenge of climate change has become a primary threat to living on the Earth in the last centuries (Rasoulinzhad and Taghizadeh-Hesary, 2022 ). Many meetings of the countries at the regional and international level are held on the topics of environment and climate change. Regardless of environmental issues, population growth, and the lack of control of greenhouse gas emissions, industrialization has been the most crucial cause of the climate change crisis. Chao and Feng ( 2018 ) address human activity as the leading cause of climate change and express that this challenge is a potential threat to living on Earth. Woodward ( 2019 ) argued that climate change threats include the rise in global temperature, the melting of polar ice caps, and unprecedented disease outbreaks. Therefore, urgent policies and solutions are essential to control and lower the risk of global change. One of the signs of climate change is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s surface. Figure 1 shows the temperature data from 1910 to 2021 for the four continents of Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America.
Source: Authors from NOAA ( https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/climate-at-a-glance/global/time-series ).
The data in Fig. 1 shows that the air temperature has increased significantly over the past century, which has been more prominent in Asia and Europe. In 2021, we saw a decrease in temperature changes due to the spread of the Corona disease and a decrease in the rate of greenhouse gas emissions. However, the role of the Asian continent in increasing the global temperature has been more than other continents due to its large population and excessive consumption of fossil fuels.
During the past decades, the world’s countries have tried to formulate and implement various environmental policies collectively in the form of agreements or separately to fight environmental threats. Regarding international agreements, such things as the Paris Agreement of 2015, the Kyoto Protocol of 1997, the Montreal Protocol of 1987, and the Vienna Convention on the Protection of the Ozone Layer in 1985 can be addressed whose primary purpose is to integrate the goals and motivation of the international community to the world’s environmental threats. However, a group of earlier studies, such as Zheng et al. ( 2017 ), Takashima ( 2018 ), and Roelfsema et al. ( 2022 ), emphasized the inefficiency of these global agreements, especially after the left the USA from the Paris Agreement on 1 June 2017. The most important cause of this inefficiency has been the need for more motivation of countries to fulfill their international obligations towards environmental issues. However, many governments consider the threat of climate change only within their geographical boundaries and have tried to formulate and implement green policies to advance their environmental protection goals. These policies include green financial policies (green taxes, green subsidies), monetary policies (such as green loans and green financing), and cultural and social policies in line with sustainable development. The ultimate goal of these green policies is a green economy, an environmentally friendly economy, a zero carbon economy, or a sustainable economy. Lee et al. ( 2022 ) define the green economy as a broad concept comprising green industry, agriculture, and services. Centobelli et al. ( 2022 ) express that environmental sustainability should be more attention in the service sector owing to its penetration into social life and interactions.
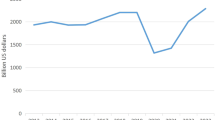
Tourism and travel-related services are among countries’ main parts of the service sector. By creating the flow of tourists, tourism services can lead to capital transfer, job creation, cultural exchange (globalization), and increasing welfare in the country hosting the tours. According to the Yearbook of Tourism Statistics published by the World Tourism Organization, international tourism has increased from 522.2 billion US dollars in 1995 to nearly 1.86 trillion US dollars in 2019. This increase shows the importance of tourism services in generating income for countries, especially in the era of Corona and post-corona. Casado-Aranda et al. ( 2021 ) express that tourism services can be a central driver of economic growth recovery in post COVID era. Jeyacheya and Hampton ( 2022 ) argue that tourism can make high incomes for host countries leading to job creation and economic flourishing in destination cities for tourists.
An important issue mentioned in the corona era and relies on the post-corona era is the revitalizing of green economic growth. An important issue mentioned in the corona era and relying on the post-corona era is the revitalizing green economic growth (Bai et al., 2022 ; Werikhe, 2022 ), an opportunity that countries should pay more attention to in order to rebuild their economic activities. In other words, countries should plan their return to economic prosperity with environmental issues in mind. To this end, the issue of tourism finds a branch called Ecotourism or sustainable tourism which has environmental concerns and tries to help countries to improve environmental protection policies. Ecotourism is an approach based on environmental criteria, which is opposed to over-tourism (a type of tourism that disrupts the protection of the environment and destroys natural resources). The International Ecotourism Society defines Ecotourism as an efficient way to conserve the environment and improve local people’s well-being. It can be said that Ecotourism, along with various economic advantages (income generation, job creation, globalization, poverty alleviation), will bring environmental protection to the world’s countries, achieving the goals of green economic growth recovery and sustainable development. Xu et al. ( 2022 ) consider Ecotourism as one of the essential components of achieving sustainable development in the post-corona era.
Ecotourism in developing countries has more priorities compared to developed economies. Firstly, developing countries are often countries with financial problems of the government, and the governments in these countries need more capital to advance sustainable development goals. Therefore, developing ecotourism services can be a suitable solution to help these countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. Second, due to the spread of the Corona disease, developing countries have experienced numerous bankruptcy in the tourism services sector. Therefore, promoting ecotourism in these countries is of great importance in the post-corona era. Third, developing countries have a high share in the emission of greenhouse gases in the world due to their high dependence on fossil fuels and the lack of advanced green technologies. Fourth, due to bureaucratic processes, high cost, and lack of market transparency, greenwashing may happen in developing economies’ ecotourism industry, meaning that a company serving ecotourism services makes its activities seem more sustainable and ethical than they are. The term “greenwashing” can harshly impact the future development path of the ecotourism industry in developing economies. According to the reasons mentioned above, developing ecotourism in developing countries can be an essential factor in controlling and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in these countries.
This paper tries to contribute to the existing literature from the following aspects:
Calculating the ecotourism index for selected countries based on the criteria for measuring sustainable tourism stated by the World Tourism Organization in the United Nations. Considering that there is no specific index for ecotourism, the calculation of ecotourism in this article will be innovative.
Measuring the green governance index as a proxy for environmental policies for selected countries based on the Environment Social and Governance (ESG) data.
Selecting a sample of 40 developing countries from different geographical regions to calculate the interconnections between ecotourism, green governance, and climate change
Making a further discussion to address the role of uncertainty and the developing level of countries in the relationship between ecotourism and explanatory variables.
The main results confirm the existence of a uni-directional causal relationship running from the green governance indicator and inflation rate to the ecotourism indicator. In addition, with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. A 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries accelerates ecotourism by 0.32%.
Moreover, ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to macroeconomic variables changes than in developed economies. Geopolitical risk is an influential factor in the developing process of ecotourism. The practical policies recommended by this research are developing the green financing market, establishing virtual tourism, granting green loans to small and medium enterprises, and government incentives to motivate active businesses.
The paper in continue is organized as follows: section “Literature review” provides a short literature review to determine the gaps this research seeks to fill. Section “Data and model specification” argues data and model specification. The following section represents empirical results. Section “Discussion” expresses discussion, whereas the last section provides conclusions, policy implications, research limitations, and recommendations to research further.
Literature review
This part of the article analyzes and classifies the previous literature on ecotourism and sustainable development in a rational and structured way. The importance of tourism in economic growth and development has been discussed in previous studies. However, the study of the effect of tourism on climate change has received little attention. Especially the relationship between sustainable tourism, climate change, and environmental policies is a problem that has yet to receive the attention of academic experts.
A group of previous studies has focused on the place of tourism in economic development and growth. Holzner ( 2011 ) focused on the consequences of tourism development on the economic performance of 134 countries from 1970 to 2007. They found out that excessive dependence on tourism income leads to Dutch disease in the economy, and other economic sectors need to develop to the extent of the tourism sector. In another study, Sokhanvar et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the causal link between tourism and economic growth in emerging economies from 1995 to 2014. The main results confirmed that the linkage is country-dependent. Brida et al. ( 2020 ) studied 80 economies from 1995 to 2016 to determine how tourism and economic development are related. The paper’s conclusions highlighted tourism’s-positive role in economic activities.
Another group of previous studies has linked tourism to sustainability targets. Sorensen and Grindsted ( 2021 ) expressed that nature tourism development has a positive and direct impact on achieving sustainable development goals of countries. In a new study, Li et al. ( 2022 ) studied the impacts of tourism development on life quality (as one of the sustainable development goals defined by the UN in 2015) in the case of Japan. They found that tourism development positively impacts the quality of life of age groups in the country. Ahmad et al. ( 2022 ) explored the role of tourism in the sustainability of G7 economies from 2000–2019. The primary findings revealed the positive impact of tourism arrivals on sustainable economic development. Zekan et al. ( 2022 ) investigated the impact of tourism on regional sustainability in Europe. They concluded that tourism development increases transport, leading to increased carbon dioxide emissions. Therefore, tourism development causes environmental pollution.
Tourism that can pay attention to environmental issues is called “ecotourism.” Many new studies have studied different dimensions of ecotourism. Lu et al. ( 2021 ) expanded the concept of the ecotourism industry. The significant results expressed that smart tourist cities are essential for efficient ecotourism in countries. Thompson ( 2022 ) expressed the characteristics of ecotourism development through survey methodology. The results confirmed the importance of transparent regulations, government support, and social intention to promote ecotourism. In another study, Heshmati et al. ( 2022 ) employed the SWOT analysis method to explore the critical success factors of ecotourism development in Iran. They found that legal documentation and private participation are major influential factors in promoting ecotourism in Iran. In line with the previous research, Hosseini et al. ( 2021 ) tried to explore the influential factors in promoting ecotourism in Iran by employing a SWOT analysis. They depicted that attracting investors is essential to enhance ecotourism projects in Iran. Hasana et al. ( 2022 ) reviewed research to analyze the earlier studies about ecotourism. The conclusions expressed that ecotourism is necessary for environmental protection. However, it is a challenging plan for the government, and they should carry out various policies toward ecotourism development. Kunjuraman et al. ( 2022 ) studied the role of ecotourism on rural community development in Malaysia. The significant results confirmed that ecotourism could transfer-positive impacts.
Several earlier studies have concentrated on the characteristics of ecotourism in different developed and developing economies. For example, Ruhanen ( 2019 ) investigated the ecotourism status in Australia. The paper concluded that the country could potentially make a larger share of ecotourism to the entire local tourism industry. Jin et al. ( 2022 ) studied the role of local community power on green tourism in Japan. They concluded that the concept of agricultural village activity and regional support positively influences the development of green tourism in Japan as a developed economy. Choi et al. ( 2022 ) sought to find aspects of ecotourism development in South Korea. The preliminary results confirmed the importance of green governance and efficient regulation to promote a sustainable tourism industry. Baloch et al. ( 2022 ) explored the ecotourism specifications in the developing economy of Pakistan. They found that Pakistan’s ecotourism needs government support and the social well-being of the visited cities. Sun et al. ( 2022 ) studied ecotourism in China. They concluded that there is imbalanced development of ecotourism among Chinese provinces due to the need for more capital to invest in all ecotourism projects throughout the Chinese cities. Tajer and Demir ( 2022 ) analyzed the ecotourism strategy in Iran. They concluded that despite various potentials in the country, insufficient capital, lack of social awareness, and political tension are the major obstacles to promoting a sustainable tourism industry in Iran.
Another group of earlier studies has drawn attention to promoting eco-tourism in the post COVID era. They believe that the corona disease has created an excellent opportunity to pay more attention to environmental issues and that countries should move towards sustainable development concepts such as sustainable (eco) tourism in the post-corona era. Soliku et al. ( 2021 ) studied eco-tourism in Ghana during the pandemic. The findings depicted the vague impacts of a pandemic on eco-tourism. Despite the short-term negative consequence of the pandemic on eco-tourism, it provides various opportunities for developing this sector in Ghana. Hosseini et al. ( 2021 ) employed the Fuzzy Dematel technique to find solutions for promoting eco-tourism during COVID-19. They found out that planning to increase the capacity of eco-tourism and incentive policies by governments can help promote the eco-tourism aspect under the pandemic’s consequences. Abedin et al. ( 2022 ) studied the consequence of COVID-19 on coastal eco-tourism development. The primary findings confirmed the negative impacts of a pandemic on the development of eco-tourism.
A review of previous studies shows that tourism can positively impact green growth and sustainable development. Sustainable tourism can be used as a policy to deal with the threat of climate change. This issue needs more attention in the corona and post-corona eras. Because in the post-corona era, many countries have sought to revive green economic growth, and ecotourism can be one of the tools to achieve it. As observed, a detailed study of the relationship between climate change, ecotourism, and environmental policies has yet to be done. Therefore, this research will address and fill this literature gap.
Data and model specification
Data description.
The paper seeks to find the relationship between climate change, ecotourism, and environmental policy for the panel of 40 developing economies from different regions from 2010 to 2021 (480 observations). The sample size could have been more extensive due to the lack of information on some variables. However, there are 480 observations in the data analysis of the data panel; therefore, the number of samples selected is acceptable.
To determine the proxies for main variables, CO2 emissions per capita are selected as the proxy for climate change. Many earlier studies (e.g., Espoir et al., 2022 ) have employed this variable as an appropriate variable representing the status of climate change. Regarding ecotourism, the World Tourism Organization proposed some measurements of sustainable tourism, and also following Yusef et al. ( 2014 ), the entropy weight method is employed to calculate a multi-dimensional ecotourism indicator comprising per capita green park area (square meters), gross domestic tourism revenue (US dollars), the ratio of good air quality (%), green transport, renewable water resources (km3) and deforestation rate (%). It is a novel ecotourism indicator that can show the ecotourism status in countries.
In addition, the green governance index is calculated as a proxy for environmental policy. Principally, the Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) data from World Bank are gathered to calculate this variable. With the improvement of the Green Governance Index, the quality of environmental policies will also increase, and vice versa. With the adverseness of the Green Governance Index, the efficiency of environmental policies will decrease.
Regarding control variables, the inflation rate as an influential factor in tourism flows is selected. The importance of this variable to promoting/declining tourism flows has been drawn to attention by some earlier studies, such as Liu et al. ( 2022 ). The inflation rate can raise the total cost of travel, causing a reduction in tourism flows, while any reduction in the inflation rate can increase the intention of tourists to travel. In addition, the KOF globalization index provided by the KOF Swiss Economic Institute is another control variable. A country with a higher degree of globalization means more readiness to accept tourists from countries with different cultures and religions.
Model specification
According to the variables mentioned above, 40 examined developing countries from 2010 to 2021, the panel co-integration model can be written as Eq. 1 :
ETOR indicates the ecotourism index, while CO2, GGI, INF, and GLOB denote Carbon dioxide emissions per capita, green governance index, inflation rate, and globalization index, respectively. i is 1,2,…,40 and shows examined developing economies, while t is time and contains 2010, 2011,..,2021.
Prior to the estimation of coefficients of Eq. 1 , the panel unit root tests are employed to find out whether the series is stationary. To this end, three tests of LLC (Levin et al., 2002 ), Breitung’s test ( 2000 ), and the PP-Fisher test (Philips and Perron, 1988 ). If all the variables are stationary at the first level of difference (I(1)), a panel co-integration test can be conducted to explore whether the model is spurious. To this end, Kao’s co-integration test ( 1999 ) and Pedroni’s residual co-integration test ( 2004 ) are conducted. If the co-integration relationship exists among variables, the panel causality test can be run to determine the causal linkages among variables. In this paper, the two steps of Engle and Granger (1987)‘s test, which is based on the error correction model (ECM) is used as Eqs. 2 – 6 :
In the above Equations, Δ is the first differences of variables, while θ and ECT represent the fixed country effect and error correction term.
The next step is the long-run panel co-integration estimations. To this end, Fully Modified OLS (FMOLS) and Dynamic OLS (DOLS) as robustness checks are conducted, which are two famous panel co-integration estimators (Rasoulinezhad, 2018 ). The FMOLS estimator has various advantages. It allows serial correlation, endogeneity, and cross-sectional heterogeneity (Erdal and Erdal, 2020 ).
Empirical results
In this section, we will implement the experimental research model. The purpose of implementing an econometric model based on panel data is to find the effects of green governance variables and carbon dioxide emissions on ecotourism. As the first step, the panel unit root tests are conducted. The results are reported in Table 1 as follows:
According to Table 1 , all three-panel unit root tests depict that all series are non-stationary at the level and become stationary after a first difference. Next, the panel co-integration tests are conducted, and their results are represented in Tables 2 and 3 :
The two-panel co-integration tests’ findings confirm the presence of co-integration linkages among variables.
The panel causality test studies the short-term and long-term causal relationship among variables. Table 4 reports the results of the panel causality check as follows:
According to Table 4 , there is a uni-directional causal relationship between the green governance indicator and the inflation rate of the ecotourism indicator. At the same time, there is a bi-directional causal relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and ecotourism indicators, confirming the existence of the feedback effect. In addition, there is only short-term causality from the green governance indicator to carbon dioxide emissions. In contrast, ecotourism and the globalization index have a uni-directional causal linkage. In the short term, improving ecotourism can cause globalization and reduce carbon emissions in developing economies. Regarding the long-term causality, it can be concluded that the ECT of ecotourism, green governance index, and globalization index are statistically significant. These three variables are major adjustment variables when the system departs from equilibrium.
In the last stage, the long-run estimations are done through FMOLS and DOLS estimators. Table 5 lists the results of the estimations by these two-panel co-integration estimators:
Based on FMOLS estimation, it can be concluded that the Green Governance index has a positive and significant coefficient in such a way that with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. By improving the state of green governance, the quality of formulated and implemented green policies in these countries will increase, improving the conditions of ecotourism development. This finding aligns with Agrawal et al. ( 2022 ) and Debbarma and Choi ( 2022 ), who believe that green governance is essential to sustainable development. In the case of carbon dioxide emissions, the coefficient of this variable is not statistically significant. In other words, the variable of carbon dioxide emissions per capita has no significant effect on ecotourism in developing countries. The inflation rate has a significant negative effect on ecotourism. With a 1% increase in the general prices of goods and services in developing countries, ecotourism will decrease by 0.34%. This finding aligns with Rahman ( 2022 ), who showed a negative relationship between inflation and sustainable development in their research. An increase in inflation means an increase in the total cost of a tourist’s trip to the destination country, inhibiting the growth of tourist services.
Regarding the globalization variable, this variable has a significant positive effect on the ecotourism of developing countries. With a 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries, ecotourism will increase by 0.32%. Globalization means more interaction with the world’s countries, acceptance of different cultures and customs, more language learning in society, more acceptance of tourism, and development of tourist services in the country. This finding is consistent with the results of Akadiri et al. ( 2019 ), who confirmed that globalization is one of the crucial components in tourism development.
The DOLS estimator was also used to ensure the obtained findings’ validity. The results of this method are shown in Table 5 . The signs of the coefficients are consistent with the results obtained by the FMOLS method. Therefore, the validity and reliability of the obtained coefficients are confirmed.
In this section, we will briefly discuss the relationship between ecotourism and climate change and the environmental policy considering the uncertainty and the relationship between variables in developed and developing countries.
Consideration of uncertainty
Uncertainty as a primary reason for risk has become a research issue in recent decades. Uncertainty can make the future unpredictable and uncontrollable, affecting economic decision-making. Regarding tourism, the impacts of uncertainty have been drawn to attention by several earlier studies (e.g., Dutta et al., 2020 ; Das et al., 2020 ; and Balli et al., 2019 ; Balli et al., 2018 ). In general, uncertainty in the tourism industry reflects tourists’ concerns and consumption habits in the way that by increasing uncertainty, it is expected that tourists make sense of risks and postpone their tourism activities, and vice versa; in the sphere of certainties, the various risks are clear, and tourists can make rational decisions for their tourism plans and activities. In order to explore the impacts of uncertainties on eco-tourism of the examined developing economies, the geopolitical risk index (GPR) as a proxy for economic policy uncertainty index is gathered and added as a control variable to Eq. 1 . The estimations results by FMOLS are reported in Table 6 as follows.
According to Table 6 , the uncertainty (geopolitical risk) has a negative coefficient meaning that with a 1% increase in geopolitical risk, the eco-tourism industry in the examined developing countries decreases by approximately 0.69%. The signs of coefficients of other variables align with the earlier findings, represented in Table 5 . In addition, the magnitude of the impact of geopolitical risk is larger than the impacts of other variables highlighting the importance of lower geopolitical risk in these economies to reach sustainable tourism targets.
Difference in developed and developing economies
Considering the different structures and financial power of these two groups of countries, the relationship between the variables mentioned in these two groups is expected to be different. In the previous section, the results for the group of developing countries showed that the Green Governance index has a positive and significant coefficient. In the case of carbon dioxide emissions, the coefficient of this variable is not statistically significant. The inflation rate has a significant negative effect on ecotourism. Regarding the globalization variable, it can be mentioned that this variable has a significant positive effect on the ecotourism of developing countries. In order to analyze the relationship between variables in the developed countries, the top 10 countries with the highest HDI in 2021 are selected (Switzerland (0.962), Norway (0.961), Iceland (0.959), Hong Kong (0.952), Australia (0.951), Denmark (0.948), Sweden (0.947) and Ireland (0.945)). The selected variables, explained in section “Data and model specification”, are collected from 2010 to 2021. The panel unit root tests confirmed that all series are non-stationary at the level and become stationary after a first difference. In addition, the presence of co-integration linkages among variables is revealed by the panel co-integration test. The panel co-integration estimator of FMOLS is employed to study the long-term relationship among variables. The findings are reported in Table 7 as follows:
According to the estimated coefficients, the green governance indicator positively and statistically significantly impacts ecotourism in the examined developed economies. However, the magnitude of the impact of this variable is more considerable for developing countries because these countries have more imbalances in markets and regulations. Therefore, the presence of good green tourism can have a more positive effect on advancing the goal of ecotourism. Contrary to the findings of developing countries, carbon dioxide emission in developed countries has a negative and significant effect, meaning that with an increase of 1% in carbon dioxide in developed countries, the level of ecotourism becomes more unfavorable by 0.034%. Moreover, inflation and globalization variables have significant negative and positive coefficients, respectively. However, the magnitudes of these two variables’ coefficients are also higher in developing countries. Ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to changes in macroeconomic variables such as green governance, globalization, and inflation.
Another difference between eco-tourism in developed and developing economies may be interpreted through the term “greenwashing,” introduced by Westerveld in 1986 (Maichum et al., 2016 ). In developing countries, due to the economic structure, limited knowledge, bureaucratic process, lack of legal eco-certification, and imperfect competition, a company involved in the eco-tourism industry makes an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into accepting the company’s services are in line with environmental protection policies. Hence, green governance in developing countries should have another role in regulating the eco-tourism market to lower the threat of greenwashing in eco-tourism services.
Conclusions and policy recommendations
Concluding remarks.
The findings of econometric modeling revealed the relationship between environmental policies, climate change, and ecotourism. Based on the findings of the econometric model, the following conclusions can be presented:
A uni-directional causal relationship runs from the green governance indicator and inflation rate to the ecotourism indicator, which means that any changes in green governance and inflation rate cause changes in ecotourism, which is vital for developing economies where governance and inflation rate are two crucial issues.
There is a bi-directional causal relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and ecotourism indicators, confirming the existence of the feedback hypothesis, expressing that in developing economies, any policies related to ecotourism cause changes in CO2 emissions and vice versa.
There is only short-term causality from the green governance indicator to carbon dioxide emissions, whereas there is a uni-directional causal linkage from ecotourism to the globalization index. In other words, in the short term, improving ecotourism can cause globalization and reduce carbon emissions in developing economies.
By improving green governance in developing economies, the quality of formulated and implemented green policies in these countries will increase, improving the conditions of ecotourism development.
An increase in the inflation rate raises the total cost of a tourist’s trip to developing economies, inhibiting the growth of eco-tourist services.
Globalization means more interaction with the world’s countries, acceptance of different cultures and customs, more language learning in society, more acceptance of tourism, and development of tourist services in developing countries.
Policy implications
In order to achieve the promotion of ecotourism in developing countries, the implementation of integrated and effective strategic and practical policies is of great importance. According to the concluding remarks mentioned, practical policies are presented as follows for enhancing ecotourism in developed countries. The development of ecotourism requires the improvement of various infrastructures and mechanisms, which depends on the implementation of projects related to ecotourism in developing countries. Because most countries do not have enough financial power to invest in such projects, developing the green financing market can be one of the critical practical solutions. The green financing tool can increase the investment risk and return on investment in such projects, and as a result, the participation of the private sector in these projects will increase. With information and communication technology development, virtual tourism can solve many environmental issues related to human physical presence. Virtual tourism is one of the branches of tourism services that provide people with destinations, places of interest, and tourist attractions with full quality but in virtual form. Another practical policy is granting green loans to small and medium enterprises active in ecotourism. Despite the organizational agility, these companies do not have the significant financial power to develop different sectors of ecotourism; therefore, the cooperation of the banking industry of developing countries by providing green loans (with low-interest rates) can motivate small and medium-sized companies in the field of activities related to ecotourism. Government incentives to motivate businesses active in ecotourism and government deterrent policies (green tax) from businesses active in the field of tourism to lead them to increase the share of ecotourism in their activities can be a proper operational strategy. In developing countries, the role of government and green governance is vital in advancing the goals of ecotourism. By improving the level of its green governance, the government can create efficient policies, regulations, and social tools to create motivation and desire to accept ecotourism, an essential and undeniable issue in developing societies. Creating a guarantee fund for ecotourism companies in developing countries is another practical policy to support these companies financially. Guarantee funds can be established with the participation of the people of ecotourism destinations in order to strengthen the financial strength of ecotourism companies in these destinations.
Limitations and recommendations to further research
This research had a practical and innovative contribution to the literature on ecotourism in developing countries. The findings obtained from the econometric model analysis provided appropriate practical and strategic policies to the policymakers of countries interested in the development of ecotourism. However, access to data related to the ecotourism index and sustainable development of developing countries due to the lack of community in a specific database is considered one of the critical limitations of this research. This limitation caused many developing countries to be excluded from the research sample, which may have created a deviation in the research. Adding more countries to the test sample in future research is suggested to obtain complete and accurate results. Also, due to the outbreak of the Corona pandemic at the end of 2019 and the Russia-Ukraine war since the beginning of 2022, it is suggested that these two variables be included in the econometric model as an illusion in order to analyze their effects on the ecotourism of the countries of the world. Using other econometric methods, such as artificial neural networks, is suggested to model ecotourism in different countries. Complex modeling by taking into account trends and trends to predict the relationship between variables in the future will be an essential step in formulating effective programs in ecotourism.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abedin Z, Handayani W, Zaky E, Faturrahman A (2022) Perceived risk and attitude’s mediating role between tourism knowledge and visit intention during the COVID-19 pandemic: implementation for coastal-ecotourism management. Heliyon 8(10):e10724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10724
Article Google Scholar
Agrawal A, Brandhorst S, Jain M, Liao C, Pradhan N, Solomon D (2022) From environmental governance to governance for sustainability. One Earth 5(6):615–621
Article ADS Google Scholar
Ahmad N, Youjin L, Hdia M (2022) The role of innovation and tourism in sustainability: why is environment-friendly tourism necessary for entrepreneurship? J Clean Prod 379(Part 2):134799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134799
Akadiri S, Alola A, Akadiri A (2019) The role of globalization, real income, tourism in environmental sustainability target. Evidence from Turkey. Sci Total Environ 687:423–432
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bai X, Wang K, Tran T, Sadiq M, Trung L, Khudoykulov K (2022) Measuring China’s green economic recovery and energy environment sustainability: econometric analysis of sustainable development goals. Econ Anal Policy 75:768–779
Balli F, Shahzad SJH, Uddin GS (2018) A tale of two shocks: what do we learn from the impacts of economic policy uncertainties on tourism? Tour Manag68:470–475
Balli F, Uddin GS, Shahzad SJH (2019) Geopolitical risk and tourism demand in emerging economies. Tour Econ 25(6):997–1005
Baloch Q, Shah S, Iqbal N, Sheeraz M, Asadullah M, Mahar S, Khan A (2022) Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism. Environ Sci Pollut Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22496-w
Breitung J (2000) The local power of some unit root tests for panel data. In: Baltagi B (ed.). Nonstationary panels, panel cointegration, and dynamic panels, advances in econometrics. vol. 15. JAI Press, Amsterdam. pp. 161–178
Brida J, Gomez D, Segarra V (2020) On the empirical relationship between tourism and economic growth. Tour Manag 81:104131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104131
Casado-Aranda L, Fernandez J, Bastidas-Manzano A (2021) Tourism research after the COVID-19 outbreak: insights for more sustainable, local and smart cities. Sustain Cities Soc 73:103126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103126
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Centobelli P, Cerchione R, Esposito E (2022) Environmental sustainability in the service industry of transportation and logistics service providers: systematic literature review and research directions. Transp Res Part D Trans Environ 53:454–470
Chao Q, Feng A (2018) Scientific basis of climate change and its response. Glob Energy Interconnect 1(4):420–427
Google Scholar
Choi Y, Oh C, Chon J (2022) Applying the resilience principles for sustainable ecotourism development: a case study of the Nakdong Estuary, South Korea. Tour Manag 83:104237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104237
Das D, Dutta A, Bhadra A, Uddin GS (2020) Role of presidential uncertainties on the hotel industry. Ann Tour Res 81:102762
Debbarma J, Choi Y (2022) A taxonomy of green governance: a qualitative and quantitative analysis towards sustainable development. Sustain Cities Soc 79:103693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103693
Dutta A, Mishra T, Uddin GS, Yang Y (2020) Brexit uncertainty and volatility persistence in tourism demand. Curr Issue Tour 24(16):2225–2232
Erdal H, Erdal G (2020) Panel FMOLS model analysis of the effects of livestock support policies on sustainable animal presence in Turkey. Sustainability 12:3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083444
Espoir D, Mudiangombe B, Bannor F, Sunge R, Tshitaka J (2022) CO2 emissions and economic growth: Assessing the heterogeneous effects across climate regimes in Africa. Sci Total Environ 804:150089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150089
Hasana U, Swain S, George B (2022) A bibliometric analysis of ecotourism: a safeguard strategy in protected areas. Region Sustain 3(1):27–40
Heshmati M, Gheitury M, Shadfar S (2022) Factors affecting possibility of ecotourism development and sustaining natural resources using SWOT approach in west Iran. Int J Geoheritage Parks 10(2):173–183
Holzner M (2011) Tourism and economic development: the beach disease. Tour Manag32(4):922–933
Hosseini S, Paydar M, Keshteli M (2021) Recovery solutions for ecotourism centers during the Covid-19 pandemic: utilizing Fuzzy DEMATEL and Fuzzy VIKOR methods. Exp Syst Appl 185:115594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115594
Hosseini S, Paydar M, Triki C (2021) Implementing sustainable ecotourism in Lafour region, Iran: applying a clustering method based on SWOT analysis. J Clean Prod 329:129716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129716
Jeyacheya J, Hampton M (2022) Pathway choice and post-Covid tourism: Inclusive growth or business as usual? World Dev Sustain 1:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wds.2022.100024
Jin C, Takao M, Yobuta M(2022) Impact of Japan’s local community power on green tourism. Asia Pacific J Region Sci 6:571–591
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Economet 90(1):1–44
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Kunjuraman V, Hussin R, Aziz R (2022) Community-based ecotourism as a social transformation tool for rural community: a victory or a quagmire. J Outdoor Recreat Tour 39:100524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jort.2022.100524
Lee C, Wang C, Ho S (2022) The dimension of green economy: Culture viewpoint. Econ Anal Policy 74:122–138
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CS (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Economet 108(1):1–24
Li J, Ridderstaat J, Yost E (2022) Tourism development and quality of life interdependence with evolving age-cohort-based population. Tour Manag 93:104621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104621
Liu A, Kim Y, Song H (2022) Toward an accurate assessment of tourism economic impact: a systematic literature review. Ann Tour Res Empirical Insight 3(2):100054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2022.100054
Lu C, Huang J, Chen C, Shu M, Hsu C, Bapu T (2021) An energy-efficient smart city for sustainable green tourism industry. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 47:101494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101494
Maichum K, Parichatnon S, Peng KC (2016) Application of the extended theory of planned behavior model to investigate purchase intention of green products among Thai consumers. Sustainability 8:1077
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theory 20(3):597–625
Phillips PCB, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regressions. Biometrika. 75(2):335–346
Rahman M (2022) The effect of taxation on sustainable development goals: evidence from emerging countries. Heliyon 8(9):e10512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10512
Rasoulinezhad E (2018) A new evidence from the effects of Russia’s WTO accession on its foreign trade. Eur Econ Rev 8(1):73–92
Rasoulinezhad E, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2022) Role of green finance in improving energy efficiency and renewable energy development. Energy Efficiency 15(2):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-022-10021-4
Roelfsema M, Soest H, Elzen M, Coninck HH, Kuramochi T, Harmsen M, Dagnomilis I, Hohne N, Vuuren D (2022) Developing scenarios in the context of the Paris Agreement and application in the integrated assessment model IMAGE: a framework for bridging the policy-modelling divide. Environ Sci Policy 135:104–116
Article CAS Google Scholar
Ruhanan L (2019) The prominence of eco in ecotourism experiences: an analysis of post-purchase online reviews. J Hosp Tour Manag 39:110–116
Sokhanvar A, Ciftcioglu S, Javid E (2018) Another look at tourism-economic development nexus. Tour Manag Perspect 26:97–106
Soliku O, Kyiire B, Mahama A, Kubio C (2021) Tourism amid COVID-19 pandemic: impacts and implications for building resilience in the eco-tourism sector in Ghana’s Savannah region. Heliyon 7(9):e07892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07892
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sorensen F, Grindsted T (2021) Sustainability approaches and nature tourism development. Ann Tour Res 91:103307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2021.103307
Sun Y, Ding W, Yang G (2022) Green innovation efficiency of China’s tourism industry from the perspective of shared inputs: Dynamic evolution and combination improvement paths. Ecol Indica 138:108824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108824
Tajer E, Demir S (2022) Ecotourism strategy of UNESCO city in Iran: applying a new quantitative method integrated with BWM. J Clean Prod 376:134284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134284
Takashima N (2018) International environmental agreements between asymmetric countries: a repeated game analysis. Jpn World Econ 48:38–44
Thompson B (2022) Ecotourism anywhere? The lure of ecotourism and the need to scrutinize the potential competitiveness of ecotourism developments. Tour Manag 92:104568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104568
Werikhe A (2022) Towards a green and sustainable recovery from COVID-19. Curr Res Environ Sustain 4:100124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crsust.2022.100124
Woodward A (2019) Climate change: disruption, risk and opportunity. Glob Trans 1:44–49
Xu L, Ao C, Liu B, Cai Z (2022) Cotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends. Environ Dev Sustain https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0
Yusef N, Rahman F, Jamil M, Iranmanesh M (2014) Measuring the quality of ecotourism services: case study–based model validation. Sage Open, https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244014538270
Zekan B, Weismayer C, Gunter U, Schuh B, Sedlacek S (2022) Regional sustainability and tourism carrying capacities. J Clean Prod 339:130624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130624
Zheng H, Dai H, Lai H, Wang W (2017) U.S. withdrawal from the Paris agreement: reasons, impacts, and China’s response. Adv Clim Change Rese 8(4):220–225
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Hospitality Administration, Zhejiang Yuexiu University, Zhejiang, China
- Yunfeng Shang
School of Economics, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China
Chunyu Bi, Xinyu Wei & Dayang Jiang
School of Global Studies, Tokai University, Tokyo, Japan
Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary
TOKAI Research Institute for Environment and Sustainability (TRIES), Tokai University, Tokyo, Japan
Faculty of World Studies, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Ehsan Rasoulinezhad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Yunfeng Shang , Dayang Jiang or Ehsan Rasoulinezhad .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shang, Y., Bi, C., Wei, X. et al. Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 275 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01777-w
Download citation
Received : 11 November 2022
Accepted : 18 May 2023
Published : 31 May 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01777-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Spatial effects of green finance development in chinese provinces under the context of high-quality energy development.
- Fangbin Qian
Economic Change and Restructuring (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Chapman University
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
Ecotourism Definition and Principles
Pros and cons.
- Examples of Ecotourism
- Frequently Asked Questions
Ecotourism is about more than simply visiting natural attractions or natural places; it’s about doing so in a responsible and sustainable manner. The term itself refers to traveling to natural areas with a focus on environmental conservation. The goal is to educate tourists about conservation efforts while offering them the chance to explore nature.
Ecotourism has benefited destinations like Madagascar, Ecuador, Kenya, and Costa Rica, and has helped provide economic growth in some of the world’s most impoverished communities. The global ecotourism market produced $92.2 billion in 2019 and is forecasted to generate $103.8 billion by 2027.
A conservationist by the name of Hector Ceballos-Lascurain is often credited with the first definition of ecotourism in 1987, that is, “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, as well as any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas.”
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES), a non-profit organization dedicated to the development of ecotourism since 1990, defines ecotourism as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education [both in its staff and its guests].”
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) looks at ecotourism as a significant tool for conservation, though it shouldn’t be seen as a fix-all when it comes to conservation challenges:
“There may be some areas that are just not appropriate for ecotourism development and some businesses that just won’t work in the larger tourism market. That is why it is so important to understand the basics of developing and running a successful business, to ensure that your business idea is viable and will be profitable, allowing it to most effectively benefit the surrounding environment and communities.”
Marketing an ecosystem, species, or landscape towards ecotourists helps create value, and that value can help raise funds to protect and conserve those natural resources.
Sustainable ecotourism should be guided by three core principles: conservation, communities, and education.
Conservation
Conservation is arguably the most important component of ecotourism because it should offer long-term, sustainable solutions to enhancing and protecting biodiversity and nature. This is typically achieved through economic incentives paid by tourists seeking a nature-based experience, but can also come from the tourism organizations themselves, research, or direct environmental conservation efforts.
Communities
Ecotourism should increase employment opportunities and empower local communities, helping in the fight against global social issues like poverty and achieving sustainable development.
Interpretation
One of the most overlooked aspects of ecotourism is the education component. Yes, we all want to see these beautiful, natural places, but it also pays to learn about them. Increasing awareness about environmental issues and promoting a greater understanding and appreciation for nature is arguably just as important as conservation.
As one of the fastest growing sectors of the tourism industry, there are bound to be some downsides to ecotourism. Whenever humans interact with animals or even with the environment, it risks the chance of human-wildlife conflict or other negative effects; if done so with respect and responsibility in mind, however, ecotourism can reap enormous benefits to protected areas.
As an industry that relies heavily on the presentation of eco-friendly components to attract customers, ecotourism has the inevitable potential as a vessel for greenwashing. Part of planning a trip rooted in ecotourism is doing research to ensure that an organization is truly providing substantial benefits to the environment rather than exploiting it.
Ecotourism Can Provide Sustainable Income for Local Communities
Sustainably managed ecotourism can support poverty alleviation by providing employment for local communities, which can offer them alternative means of livelihood outside of unsustainable ones (such as poaching).
Research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that communities in regions surrounding conservation areas in Costa Rica had poverty rates that were 16% lower than in areas that weren’t near protected parks. These protected areas didn’t just benefit from conservation funds due to ecotourism, but also helped to reduce poverty as well.
It Protects Natural Ecosystems
Ecotourism offers unique travel experiences focusing on nature and education, with an emphasis on sustainability and highlighting threatened or endangered species. It combines conservation with local communities and sustainable travel , highlighting principles (and operations) that minimize negative impacts and expose visitors to unique ecosystems and natural areas. When managed correctly, ecotourism can benefit both the traveler and the environment, since the money that goes into ecotourism often goes directly towards protecting the natural areas they visit.
Each year, researchers release findings on how tourist presence affects wildlife, sometimes with varying results. A study measuring levels of the stress hormone cortisol in wild habituated Malaysian orangutans found that the animals were not chronically stressed by the presence of ecotourists. The orangutans lived in the Lower Kinabatangan Wildlife Sanctuary, where a local community-managed organization operates while maintaining strict guidelines to protect them.
Ecotourism May Also Hurt Those Same Natural Ecosystems
Somewhat ironically, sometimes ecotourism can hurt ecosystems just as much as it can help. Another study in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution found that ecotourism can alter animal behaviors in ways that put them at risk. If the presence of humans changes the way animals behave, those changes may make them more vulnerable by influencing their reaction to predators or poachers.
It's not just the animals who are at risk. As ecotourism activities become too popular, it can lead to the construction of new infrastructure to accommodate more visitors. Similarly, more crowds mean more pressure on local resources, increased pollution, and a higher chance of damaging the soil and plant quality through erosion. On the social side, these activities may displace Indigenous groups or local communities from their native lands, preventing them from benefiting from the economic opportunities of tourism.
Ecotourism Offers the Opportunity to Experience Nature
Renown conservationist Jane Goodall has a famous quote: “Only if we understand, will we care. Only if we care, will we help. Only if we help, shall all be saved.” It can be difficult to understand something that we haven’t seen with our own eyes, and ecotourism gives travelers the opportunity to gain new experiences in natural areas while learning about the issues they face.
Ecotourism also educates children about nature, potentially creating new generations of nature lovers that could someday become conservationists themselves. Even adult visitors may learn new ways to improve their ecological footprints .
EXAMPLES OF ECOTOURISM
The East African country has some competitive advantages over its neighbors thanks to its rich natural resources, paired with the fact that it has allocated over 25% of its total area to wildlife national parks and protected areas. Because of this, an estimated 90% of tourists visit to Tanzania seeking out ecotourism activities. Ecotourism, in turn, supports 400,000 jobs and accounts for 17.2% of the national GDP, earning about $1 billion each year as its leading economic sector.
Some of Tanzania’s biggest highlights include the Serengeti, Mount Kilimanjaro , and Zanzibar, though the country still often goes overlooked by American tourists. Visitors can take a walking safari tour in the famous Ngorongoro Conservation area, for example, with fees going to support the local Maasai community.
The country is also known for its chimpanzees , and there are several ecotourism opportunities in Gombe National Park that go directly towards protecting chimpanzee habitats.
Galapagos Islands
It comes as no surprise that the place first made famous by legendary naturalist Charles Darwin would go on to become one of the most sought-after ecotourism destinations on Earth, the Galapagos Islands .
The Directorate of the Galapagos National Park and the Ecuadorian Ministry of Tourism require tour providers to conserve water and energy, recycle waste, source locally produced goods, hire local employees with a fair wage, and offer employees additional training. A total of 97% of the land area on the Galapagos is part of the official national park, and all of its 330 islands have been divided into zones that are either completely free of human impact, protected restoration areas, or reduced impact zones adjacent to tourist-friendly areas.
Local authorities still have to be on their toes, however, since UNESCO lists increased tourism as one of the main threats facing the Galapagos today. The bulk of funding for the conservation and management of the archipelago comes from a combination of governmental institutions and entry fees paid by tourists.
Costa Rica is well-known throughout the world for its emphasis on nature-based tourism, from its numerous animal sanctuaries to its plethora of national parks and reserves. Programs like its “Ecological Blue Flag” program help inform tourists of beaches that have maintained a strict set of eco-friendly criteria.
The country’s forest cover went from 26% in 1983 to over 52% in 2021 thanks to the government’s decision to create more protected areas and promote ecotourism in the country . Now, over a quarter of its total land area is zoned as protected territory.
Costa Rica welcomes 1.7 million travelers per year, and most of them come to experience the country’s vibrant wildlife and diverse ecosystems. Its numerous biological reserves and protected parks hold some of the most extraordinary biodiversity on Earth, so the country takes special care to keep environmental conservation high on its list of priorities.
New Zealand
In 2019, tourism generated $16.2 billion, or 5.8% of the GDP, in New Zealand. That same year, 8.4% of its citizens were employed in the tourism industry, and tourists generated $3.8 billion in tax revenue.
The country offers a vast number of ecotourism experiences, from animal sanctuaries to natural wildlife on land, sea, and even natural caves. New Zealand’s South Pacific environment, full of sights like glaciers and volcanic landscapes, is actually quite fragile, so the government puts a lot of effort into keeping it safe.
Tongariro National Park, for example, is the oldest national park in the country, and has been named by UNESCO as one of only 28 mixed cultural and natural World Heritage Sites. Its diverse volcanic landscapes and the cultural heritage of the indigenous Maori tribes within the create the perfect combination of community, education, and conservation.
How to Be a Responsible Ecotourist
- Ensure that the organizations you hire provide financial contributions to benefit conservation and find out where your money is going.
- Ask about specific steps the organization takes to protect the environment where they operate, such as recycling or promoting sustainable policies.
- Find out if they include the local community in their activities, such as hiring local guides, giving back, or through initiatives to empower the community.
- Make sure there are educational elements to the program. Does the organization take steps to respect the destination’s culture as well as its biodiversity?
- See if your organization is connected to a non-profit or charity like the International Ecotourism Society .
- Understand that wildlife interactions should be non-invasive and avoid negative impacts on the animals.
Ecotourism activities typically involve visiting and enjoying a natural place without disturbing the landscape or its inhabitants. This might involve going for a hike on a forest trail, mountain biking, surfing, bird watching, camping, or forest bathing .
Traveling in a way that minimizes carbon emissions, like taking a train or bike instead of flying, may also be part of an ecotourism trip. Because these modes of travel tend to be slower, they may be appreciated as enjoyable and relaxing ecotourism activities.
The Wolf Conservation Center ’s programing in New York State is an example of ecotourism. This non-profit organization is dedicated to the preservation of endangered wolf species. It hosts educational sessions that allow visitors to observe wolves from a safe distance. These programs help to fund the nonprofit organization’s conservation and wildlife rehabilitation efforts.
Stonehouse, Bernard. " Ecotourism ." Environmental Geology: Encyclopedia of Earth Science , 1999, doi:10.1007/1-4020-4494-1_101
" What is Ecotourism? " The International Ecotourism Society .
" Tourism ." International Union for Conservation of Nature .
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307712111
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033357
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010
https://doi.org/10.5897/JHMT2016.0207
" Galapagos Islands ." UNESCO .
" About Costa Rica ." Embassy of Costa Rica in Washington DC .
https://www.stats.govt.nz/information-releases/tourism-satellite-account-2019
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- Defeating Deforestation Through Rum, Chocolate, and Ecotourism
- Empowering Communities to Protect Their Ecosystems
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Sustainable Travel
- Why Bonobos Are Endangered and What We Can Do
- Why Are National Parks Important? Environmental, Social, and Economic Benefits
- IUCN President Tackles Biodiversity, Climate Change
- The World’s Smallest Tiger Is Inching Towards Extinction
- Ecuador Expands Protected Galapagos Marine Reserve by More Than 23,000 Square Miles
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- New Zealand Aims to Become World's Largest 'Dark Sky Nation'
- Utility Menu
International Sustainable Tourism Initiative
Tourism and environmental health in a changing climate.
The International Sustainable Tourism Initiative (ISTI) researched a new framework, the Holistic Environmental Accounting for Tourism Destinations (HEAT-D) to help local governments and national planning bodies to measure the Invisible Burden. The Invisible Burden is defined in the report, Destinations at Risk: The Invisible Burden of Tourism . This research helps to measure the Invisible Burden in Tunisia, via funding from GIZ.
Download Report: Tourism and Environmental Health in a Changing Climate

HEAT-D Framework was tested in Tunisia between July 2017-December 2018, primarily on the island of Djerba.
The report comes to the following conclusions :
- Without further monitoring at the destination level, tourism will play an increasingly energy and resource-intensive role that will not be accounted for in national planning and will leave local authorities without the resources to manage growth.
- Municipal leaders require data on the many unmonitored and unaccounted for impacts on local destinations to guide the development of more sustainable, efficient economies, in order to meet the Sustainable Development (SDG) Goals and lower GhG emissions in accord with the Paris Agreement.
As the impacts of climate change continue to escalate, governments and business have barely begun to deliberate on how the impacts of climate change will transform tourism-dependent countries and their communities. ISTI formulated a means to help industry and government measure, report, mitigate, and adapt in order to garner the substantial human and financial resources required to help local destinations decarbonize and deploy proven approaches to environmental protection and climate change mitigation and adaptation.

Tourism and Environmental Health in a Changing Climate: The ISTI Framework for Tourism Destinations
The International Sustainable Tourism Initiative (ISTI) Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health undertook research on the HEAT-D Framework in Tunisia on Djerba Island and Tozeur in 2017 with the support of GIZ (the German government development cooperation agency), to test a set of measures for destination authorities to manage their GhG emissions and the unaccounted-for costs of tourism growth, including energy, solid waste, waste water, water utility services and local land-use.
In its upcoming journal article based on this research, the project is summarized this way;
The framework measures per tourist requirements and direct/indirect impacts on energy, water, and wastewater treatment, solid waste, land-use and biodiversity to determine if consistent monitoring of this data could guide local policy makers on the management of both tourism resource uses and climate change related impacts.
The HEAT-D Framework designed by Research Manager, Sofia Fotiadou, uncovered the indirect costs of tourism development and revealed to local authorities how to avoid growth without adequate recompense for supporting sustainable infrastructure in host countries. It also took an in-depth look at land-use changes and measures required to protect coastal tourism destinations from the impacts of climate change.
Local authorities can apply this framework to investigate the precise costs for managing tourism development at the municipal level. The final report, linked here, demonstrated that tourism drove up energy usage, water demand, beachfront development, and waste generation at the expense of local needs. These findings ran contrary to national decision makers' opinion that tourism was providing strong economic benefits while not seriously increasing municipal costs for the island, undermining resilience to sea level rise, or causing significant increases in GhG emissions per tourist for the country at large.
The HEAT-D Framework is now being considered by agencies in a wide range of tourism destinations and the approach to this will be dictated by the following goals:
- Reveal the indirect costs of tourism growth, and the investment required to protect environmental health and local population well-being
- Measure municipal costs for servicing tourism and guide decision making on policies and infrastructure
- Help to develop strategic mitigation and adaptation plans to protect tourism economies and local populations when climate impacts worsen
- Trigger international funding, subsidies, and impact investment for sustainable infrastructure projects, such as solar energy and alternative waste treatment for tourism areas
- Create a new category of research based on empirical data to drive global research cooperation on destination planning
Contact Megan Epler Wood, Founding Director of our International Sustainable Tourism Initiative, for more information HERE .

Founding Director: Megan Epler Wood

Co-Principal Investigator: Dr. John Spengler

Co-Principal Investigator: Dr. Henry Lee

Team Member: Sofia Fotiadou , Research Manager
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism
Qadar bakhsh baloch.
1 Abasyn University, Peshawar, Pakistan
Syed Naseeb Shah
Nadeem iqbal.
2 Air University School of Management, Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan
Muhammad Sheeraz
3 Department of Commerce, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan
Muhammad Asadullah
4 IBA, Gomal University, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan
Sourath Mahar
5 University of Sialkot, Sialkot, Pakistan
Asia Umar Khan
6 Islamia College University Peshawar, Peshawar, Pakistan
Associated Data
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available on request.
The empirical research investigated the relationship between tourism development and environmental suitability to propose a framework for sustainable ecotourism. The framework suggested a balance between business and environmental interests in maintaining an ecological system with the moderating help of government support and policy interventions. The study population encompasses tourism stakeholders, including tourists, representatives from local communities, members of civil administration, hoteliers, and tour operators serving the areas. A total of 650 questionnaires were distributed to respondents, along with a brief description of key study variables to develop a better understanding. After verifying the instrument’s reliability and validity, data analysis was conducted via hierarchical regression. The study findings revealed that a substantial number of people perceive socio-economic benefits, including employment and business openings, infrastructure development from tourism development, and growth. However, the state of the natural and environmental capital was found to be gradually degrading. Alongside the social environment, social vulnerability is reported due to the overutilization of land, intrusion from external cultures, and pollution in air and water due to traffic congestion, accumulation of solid waste, sewage, and carbon emissions. The study suggested a model framework for the development of sustained ecotourism, including supportive government policy interventions to ensure effective conservation of environmental and natural resources without compromising the economic viability and social well-beings of the locals. Furthermore, the variables and the constructs researched can be replicated to other destinations to seek valuable inputs for sustainable destination management elsewhere.
Introduction
Tourism is a vibrant force that stimulates travel to explore nature, adventures, wonders, and societies, discover cultures, meet people, interact with values, and experience new traditions and events. Tourism development attracts tourists to a particular destination to develop and sustain a tourism industry. Moreover, environmental sustainability is the future-based conscious effort aimed at conserving socio-cultural heritage and preserving natural resources to protect environmental ecosystems through supporting people’s health and economic well-being. Environment sustainability can be reflected in clean and green natural landscaping, thriving biodiversity, virgin sea beaches, long stretches of desert steppes, socio-cultural values, and archeological heritage that epitomize tourists’ degree of motivation and willingness of the local community to welcome the visitors. In this context, tourism growth and environmental sustainability are considered interdependent constructs; therefore, the increase in tourism development and tourists’ arrivals directly affects the quality of sustained and green tourism (Azam et al. 2018 ; Hassan et al. 2020 ; Sun et al. 2021 ).
According to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism is one of the fastest-growing industries, contributing more than 10% to the global GDP (UNWTO 2017; Mikayilov et al. 2019 ). Twenty-five million international tourists in 1950 grew to 166 million in 1970, reaching 1.442 billion in 2018 and projected to be 1.8 billion by 2030. Mobilizing such a substantial human tourist’s mass is most likely to trickle environmental pollution along with its positive effects on employment, wealth creation, and the economy. The local pollution at tourist destinations may include air emissions, noise, solid waste, littering, sewage, oil and chemicals, architectural/visual pollution, heating, car use, and many more. In addition, an uncontrolled, overcrowded, and ill-planned tourist population has substantial adverse effects on the quality of the environment. It results in the over-consumption of natural resources, degradation of service quality, and an exponential increase in wastage and pollution. Furthermore, tourism arrivals beyond capacity bring problems rather than a blessing, such as leaving behind soil erosion, attrition of natural resources, accumulation of waste and air pollution, and endangering biodiversity, decomposition of socio-cultural habitats, and virginity of land and sea (Kostić et al. 2016 ; Shaheen et al. 2019 ; Andlib and Salcedo-Castro 2021 ).
Tourism growth and environmental pollution have been witnessed around the globe in different regions. The ASEAN countries referred to as heaven for air pollution, climate change, and global warming are experiencing economic tourism and pollution (Azam et al. 2018 ; Guzel and Okumus 2020 ). In China, more than fifty-eight major Chinese tourism destinations are inviting immediate policy measures to mitigate air pollution and improve environmental sustainability (Zhang et al. 2020 ). Similarly, Singapore, being a top-visited country, is facing negative ecological footprints and calling for a trade-off between tourism development and environmental sustainability (Khoi et al. 2021 ). The prior studies established that international tourism and the tourism-led growth surge tourists’ arrival, energy consumption, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions, and air pollution resultantly cause climate change (Aslan et al. 2021 ). South Asian countries, more specifically Sri Lanka and Pakistan, are on the verge of tourism growth and environmental pollution compared to other countries (Chishti et al. 2020 ; Tiwari et al. 2021 ).
Pakistan is acknowledged in the tourism world because of its magnificent mountains with the densest concentration of high peaks in the world, scenic beauty of Neelum Valley, Murree, Chitral, and swat Valleys’, Kaghan, Naran, Hunza, Gilgit Baltistan (Baloch 2007 ), sacred shrines of Sikhism, archeological sites of the Gandhara and Indus Valley civilizations such as Mohenjo-Daro, Taxila including pre-Islamic Kalasha community (Baloch and Rehman 2015 ). In addition, Pakistan’s hospitable and multicultural society offers rich traditions, customs, and festivals for the tourists to explore, commemorate, cherish, and enjoy. Pakistan’s geographical and socio-cultural environment represents its resource and an opportunity (Baloch and Rehman 2015 ); therefore, Pakistan is looking to capitalize on it as a promising source of the foreign reserve to compensate for its mounting trade deficit (Baloch et al. 2020 ).
Tourism expansion has been established as a very deleterious ecological cost vis-à-vis the socio-economic benefits it passes to the host communities (Pulido-Fernández et al. 2019 ; Simo-Kengne 2022 ). In this context, the research is motivated to investigate the relationships between Pakistan’s tourism development activities and environmental sustainability. Drawing from the arguments of Pulido-Fernández et al. ( 2019 ) and Simo-Kengne ( 2022 ), it is feared that Pakistan’s ongoing determination to tourism development is likely to cause environmental degradation in two ways. Firstly, the tourism infrastructure developmental process would consume natural resources in the form of air and water pollution, loss of nature, and biodiversity. Secondly, the proliferation of tourism-related energy-consuming activities harms the environment by adding CO 2 emissions (Andlib and Saceldo-Castro 2021 ; Chien et al. 2021a ). Therefore, to tape this tourism-rich potential without compromising the sustainability of the natural and socio-cultural environment in the area, there is a dire need to develop Pakistan’s tourism areas into environment-friendly destinations.
Against the backdrop of a widening level of trade deficit, Pakistan’s rich tourism potential is being perceived as an immediate alternative for earning revenue to compensate for the current account gap. However, the developing large-scale tourism industry is considered a threat to deforestation, and air and water pollution, endangering biodiversity trading on resilient ecological credentials. The research study attempts to find an all-inclusive and comprehensive answer to the socio-ecological environmental concerns of tourism development and growth. Therefore, the research investigates the relationship between tourism development and its environmental sustainability to suggest a model framework for the development and growth of Sustainable Ecotourism in Pakistan along with its most visited destinations.
Literature review
Tourism development and growth.
Tourism is considered a force of sound as it benefits travelers and communities in urban and suburban areas. Tourism development is the process of forming and sustaining a business for a particular or mix of segments of tourists’ as per their motivation in a particular area or at a specific destination. Primarily, tourism development refers to the all-encompassing process of planning, pursuing, and executing strategies to establish, develop, promote, and encourage tourism in a particular area or destination (Mandić et al. 2018 ; Ratnasari et al. 2020 ). A tourism destination may serve as a single motivation for a group of tourists or a mix of purposes, i.e., natural tourism, socio-cultural or religious tourism, adventure or business tourism, or a combination of two or more. Andlib and Salcedo-Castro ( 2021 ), drawing from an analysis approach, contended that tourism destinations in Pakistan offer a mix of promising and negative consequences concerning their socio-economic and environmental impressions on the host community. The promising socio-economic impacts for the local community are perceived in the form of employment and business opportunities, improved standard of living, and infrastructural development in the area. The adverse environmental outcomes include overcrowding, traffic congestion, air and noise pollution, environmental degradation, and encroachment of landscaping for the local community and the tourists. An extensive review of the literature exercise suggests the following benefits that the local community and the tourists accrue from the tour are as follows:
- Generate revenue and monetary support for people and the community through local arts and culture commercialization.
- Improve local resource infrastructure and quality of life, including employment generation and access to improved civic facilities.
- Help to create awareness and understanding of different ethnic cultures, social values, and traditions, connecting them and preserving cultures.
- Rehabilitate and conserve socio-cultural and historical heritage, including archeological and natural sites.
- Establishment of natural parks, protracted areas, and scenic beauty spots.
- Conservation of nature, biodiversity, and endangered species with control over animal poaching.
- Improved water and air quality through afforestation, littering control, land and soil conservation, and recycling of used water and waste.
Tourism and hospitality business incorporates various business activities such as travel and transportation through the air or other modes of travel, lodging, messing, restaurants, and tourism destinations (Szpilko 2017 ; Bakhriddinovna and Qizi 2020 ). A tourist’s tourism experience is aimed at leisure, experiencing adventure, learning the culture or history of a particular area or ethnic entity, traveling for business or health, education, or religious purposes. The chain of activities adds value to the Tourism experience. Every activity contributes toward economic stimulation, job creation, revenue generation, and tourism development encompassing infrastructure for all activities involved in the tourism process. Tourism growth expresses the number of arrivals and the time of their stay/trips over a period of time. Tourism growth is measured through the interplay between tourists’ arrivals, tourism receipts, and travel time duration (Song et al. 2010 ; Arifin et al. 2019 ). The following factors drive the degree and level of tourism development and growth:
- Environmental factors include scenic beauty, green spaces, snowy mountains, towering peaks, good climate and weather, the interconnectivity of destination, quality of infrastructure, etc.
- Socio-economic factors: the distinctiveness of community, uniqueness of culture and social values, hospitality and adaptability, accessibility, accommodation, facilities and amenities, cost-effectiveness, price index, and enabling business environment.
- Historical, cultural, and religious factors include historical and cultural heritage, religious sites, and cultural values and experiences.
The tourism development process and its different dynamics revolve around the nature of tourism planned for a particular destination or area, which can be specified as ecotourism, sustainable tourism, green tourism or regenerative tourism, etc. Ecotourism is “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education” (Cheia, 2013 ; TIES, 2015). According to the World Conservation Union (IUCN), ecotourism involves “ Environmentally responsible travel to natural areas, to enjoy and appreciate nature (and accompanying cultural features, both past, and present) that promote conservation, have a low visitor impact and provide for beneficially active socio-economic involvement of local peoples ”. Moreover, Blangy and Wood ( 1993 ) defined it as “ responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and sustains the well-being of local people ” (p. 32). The concept of ecotourism is grounded upon a well-defined set of principles including “environmental conservation and education, cultural preservation and experience, and economic benefits” (Cobbinah 2015 ; De Grosbois and Fennell 2021 ).
Ecotourism minimizes tourism’s impact on the tourism resources of a specific destination, including lessening physical, social, interactive, and psychosomatic impacts. Ecotourism is also about demonstrating a positive and responsible attitude from the tourists and hosts toward protecting and preserving all components of the environmental ecosystem. Ecotourism reflects a purpose-oriented mindset, responsible for creating and delivering value for the destination with a high degree of kindliness for local environmental, political, or social issues. Ecotourism generally differs from mass tourism because of its following features (Liang et al. 2018 ; Ding and Cao 2019 ; Confente and Scarpi 2021 ):
- Conscientious behavior focuses on the low impact on the environment.
- Sensitivity and warmth for local cultures, values, and biodiversity.
- Supporting the sustenance of efforts for the conservation of local resources.
- Sharing and delivering tourism benefits to the local communities.
- Local participation as a tourism stakeholder in the decision-making process.
- Educating the tourist and locals about the sensitivity and care of the environment because tourism without proper arrangement can endanger the ecosystems and indigenous cultures and lead to significant ecological degradation.
Sustainability aims to recognize all impacts of tourism, minimize the adverse impacts, and maximize the encouraging ones. Sustainable tourism involves sustainable practices to maintain viable support for the ecology of the tourism environment in and around the destination. Sustainable tourism is natural resource-based tourism that resembles ecotourism and focuses on creating travel openings with marginal impact and encouraging learning about nature having a low impact, conservation, and valuable consideration for the local community’s well-being (Fennell 2001 & 2020 ; Butowski 2021 ). On the other hand, ecotourism inspires tourists to learn and care about the environment and effectively participate in the conservation of nature and cultural activities. Therefore, ecotourism is inclusive of sustainable tourism, whereas the focus of sustainable tourism includes the following responsibilities:
- Caring, protecting, and conserving the environment, natural capital, biodiversity, and wildlife.
- Delivering socio-economic welfare for the people living in and around tourists' destinations.
- Identifying, rehabilitating, conserving, and promoting cultural and historical heritage for visitors learning experiences.
- Bringing tourists and local groups together for shared benefits.
- Creating wide-ranging and reachable opportunities for tourists.
Environment and sustainability of ecosystem
The term “environment” is all-inclusive of all the natural, organic living, inorganic, and non-natural things. The environment also denotes the interface among all breathing species with the natural resources and other constituents of the environment. Humans’ activities are mainly responsible for environmental damage as people and nations have contemplated modifying the environment to suit their expediencies. Deforestation, overpopulation, exhaustion of natural capital, and accumulation of solid waste and sewage are the major human activities that result in polluted air and water, acid rain, amplified carbon dioxide levels, depletion of the ozone, climate change, global warming, extermination of species, etc. A clean, green, and hygienic fit environment has clean air, clean water, clean energy, and moderate temperature for the healthy living of humans, animals, and biodiversity as nature is destined for them by their creatures. Maintaining and sustaining a clean environment is indispensable for human and biodiversity existence, fostering growth and development for conducting business and creating wealth. The environment can be sustained through conservation, preservation, and appropriate management to provide clean air, water, and food safe from toxic contamination, waste, and sewage disposal, saving endangered species and land conservation.
The globalization process, known for building socio-economic partnerships across countries, is also charged with encouraging environmental degradation through the over-consumption of natural resources and energy consumption, deforestation, land erosion, and weakening (Adebayo and Kirikkaleli 2021 ; Sun et al. 2021 ). Chien et al. ( 2021b ), while studying the causality of environmental degradation in Pakistan, empirically confirmed the existence of a significant connection between CO 2 emissions and GDP growth, renewable energy, technological innovation, and globalization. However, Chien et al. ( 2021a ) suggested using solar energy as a source of economic intervention to control CO 2 emissions and improve environmental quality in China. The danger of air pollution is hard to escape as microscopic air pollutants pierce through the human respiratory and cardiovascular system, injuring the lungs, heart, and brain. Ill-planned and uncontrolled human activities negatively affect ecosystems, causing climate change, ocean acidification, melting glaciers, habitation loss, eutrophication, air pollution, contaminants, and extinction of endangered species ( Albrich et al. 2020 ) .
Humans have a more significant effect on their physical environment in numerous ways, such as pollution, contamination, overpopulation, deforestation, burning fossil fuels and driving to soil erosion, polluting air and water quality, climate change, etc. UNO Agenda for 2030 “Sustainable Development and its Sustainable Development Goals” (SDGs) mirrors the common premise that a healthy environment and human health are interlaced as integral to the satisfaction of fundamental human rights, i.e., right to life, well-being, food, water and sanitation, quality of life and biodiversity to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages (SDG3)—which includes air quality that is dependent upon terrestrial ecosystems (SDG15), oceans (SDG14), cities (SDG11), water, cleanliness, and hygiene (SDG6) (Swain 2018 ; Opoku 2019 ; Scharlemann et al. 2020 ). The UNEP stated that 58% of diarrhea cases in developing economies is due to the non-provision of clean water and inadequate sanitation facilities resulting in 3.5 million deaths globally (Desai 2016 ; Ekins and Gupta 2019 ).
Climate change overwhelmingly alters ecosystems’ ability to moderate life-threatening happenings, such as maintaining water quality, regulating water flows, unbalancing the temporal weather and maintaining glaciers, displacing or extinction biodiversity, wildfire, and drought (Zhu et al. 2019 ; Marengo et al. 2021 ). Research studies advocate that exposure to natural environments is correlated with mental health, and proximity to green space is associated with lowering stress and minimizing depression and anxiety (Noordzij et al. 2020 ; Slater et al. 2020 ; Callaghan et al. 2021 ). Furthermore, the Ecosystem is affected by pollution, over-exploitation of natural resources, climate change, invasive and displacing species, etc. Hence, providing clean air and water, hygienic places, and green spaces enriches the quality of life: condensed mortality, healthier value-added productivity, and is vital to maintaining mental health. On the other hand, climate change aggravates environment-related health hazards through adverse deviations to terrestrial ecology, oceans, biodiversity, and access to fresh and clean water.
Tourism development denotes all activities linked with creating and processing facilities providing services for the tourists on and around a destination. Infrastructure development is vital for developing a tourism destination to advance tourists’ living conditions and preserve natural and cultural heritage by constructing new tourist facilities, the destinations administrative and supporting echelons, including community living, etc. Development for tourism infrastructure and land use often burdens natural capital through over-consumption, leading to soil erosion, augmented pollution, loss of natural habitats, and endangered species. Development of tourism infrastructure and construction work has profound implications on environmental degradation, reduction in green spaces, deforestation, solid waste and sewage, overutilization of air and water, emission of CO 2 and other gases contributing to air and water pollution, climate change, loss and displacement of biodiversity, and the degradation of ecosystems. These negative consequences of tourism development result in many problems for the tourists and the indigenous people in the foreseeable future (Azam et al. 2018 ; Hoang et al. 2020 ).
A report published by UNEP titled “Infrastructure for climate action” has suggested governments introduce sustainable infrastructure as the prevailing one is responsible for causing 79% of all greenhouse gas emissions in struggling climate change, alleviation, and adaptation efforts. Sustainable infrastructure signifies that structures’ planning, construction, and functioning do not weaken the social, economic, and ecological systems (UNEP 2021 ; Krampe 2021 ). Sustainable infrastructure is the only solution that ensures societies, nature, and the environment flourish together. Therefore, Sustainable Ecotourism supports adapting pro-environment and nature-based climate change strategies that help resilient biodiversity and ecosystem to impact climate change. The proposed strategy is to focus on the conservation and restoration of ecosystems to combat climate hazards, fluctuating rainfalls, soil erosion, temperature variations, floods, and extreme wind storms (Niedziółka 2014 ; Setini 2021 )
Pakistan’s tourism infrastructure suffered a colossal amount of damage during the earthquake of October 8, 2005, which left widespread demolition and destruction to its human, economic assets, and infrastructure networks, especially in Kashmir and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's tourism areas. The tourism-related infrastructure, including hotels, destination facilities of social service delivery and commerce, water channels, and communications networks, were either drained or virtually destroyed. The destruction in the aftermath of the earthquake was further added by the war against terror in tourism-hit areas, resulting in the redundancy of tourists and tourism facilities for a long time (Akbar et al. 2017 ; Zakaria and Ahmed 2019 ). The tourism revival activities during the post-earth quack, post-terrorism scenario, and COVID-19 period called for various entrepreneurial activities, including the construction of infrastructure, hotels, road networks, community living, etc. Development and reconstruction of the livelihood and hospitality infrastructure through entrepreneurship were undertaken intensively through a public-private partnership from national and international findings (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Sadiq 2021 ; Dogar et al. 2021 ).
The revival and reinvigoration of infrastructure in tourism areas were backed up by extensive deforestation, use of local green land, rebuilding of the road network, displacement of biodiversity, and overtaxing the consumption of water and other natural resources. The deforestation, extensive use of green land, and over-consumption of water and other natural resources have depleted the tourism value of the area on the one hand and degraded the environment on the other. However, it was the focused rehabilitation activities of earthquake and Pakistan’s Government’s socio-environment conservation strategy of the Billion Trees plantation program in the province, including dominating tourism areas. The afforestation and loss of green tops are being reclaimed through these efforts, and the tourism environment is soon expected to regenerate (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Rauf et al. 2019 ; Siddiqui and Siddiqui 2019 ).
Government support and policy interventions
Tourism generates wide-ranging benefits for the economy, community, and people. Tourism contributes to the economy through revenue generation and shares responsibility with the Government to alleviate poverty alleviation, create opportunities for job placements, protect environments, and conserve natural ecosystems and biodiversity. It is assumed that if the tourism industry is left to its own, it will most likely prefer its business interests over environments or biodiversity. Governments, custodians of the life and well-being of their subjects, are directly responsible for providing a clean environment, nature, and Ecosystem. Therefore, national and local governments are responsible for preparing and implementing tourism development plans and enforcing values and standards for tourism development in conformity with the prerequisites of environmental sustainability. Through institutional governance, governments help tourism development by providing financial and budgetary support, regulatory framework, land, physical resources, infrastructure, etc. Provision and facilitation for Sustainability of Ecotourism and conservation of environment and biodiversity are dependent upon Government-supported interventions as follows:
- The regulatory framework for setting up tourism-related entrepreneurship and quality standards can support ecotourism and prevent environmental degradation on any account.
- Provision of budgetary support for ecosystem conservation and regeneration of bio-diversity-related projects.
- Plan, rehabilitate if needed, promote conservation and protection of socio-cultural, historic, antique, and natural endowments in coordination with other public and private agencies, and deal with the defaulters, if any.
- Promoting and undertaking afforestation alongside land conservation and discouraging deforestation, soil erosion, accumulation of solid waste, littering, and any direct or indirect loss or threat to biodiversity.
- Setting restrictions for over-tourism beyond capacity and quality standards for transportation, restaurants, hotels, food and drinking water, etc.
- Placing enforcement mechanism necessary to ensure application of the regulatory framework and quality standards applicable along with all activities inclusive to the Ecotourism value chain.

Theoretical support and hypothesis development
According to the social disruption theory, rapidly expanding societies usually experience a period of widespread crisis and a loss of their conventional routines and attitudes. The crisis impacts people whose mental health, worldviews, behavioral patterns, and social networks may all be impacted (Çalişkan and Özer 2021 ). According to the social disruption theory, fast community change brought on by population growth will result in a variety of social issues that are signs of a generally disorganized community (Smith et al. 2001 ). Because some types of tourism communities experience rapid expansion accompanied by intensive development and rapid social change over a relatively short period of time, they seem to be great settings for studying various postulations of the social disruption theory.
Place change and social disruption theory are closely connected. According to this assumption, when a community undergoes fast expansion, it tends to experience a generalized crisis that might culminate in several social issues as changes spread throughout the community and among individuals (Rasoolimanesh et al. 2019 ). Place change can result from fundamental community restructuring due to economic development, new class divides, and migration of both long-term and temporary people (Nelson 2001 ). Social unrest, though, is not enduring. Instead, it is transitory; societies gradually adjust to these changes (Deery et al. 2012 ).
The standard of living may initially deteriorate, but due to the adaptability of people and communities, they will gradually reinvigorate and strengthen themselves accordingly. Furthermore, the social disruption proposition reinforces one of the challenges in analyzing the effects of tourism, particularly in emerging nations, since it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between the effects of tourism and the overall ongoing development (Park and Stokowski 2009 ) (Fig. (Fig.1 1 ).
- Tourism development and growth significantly affect natural environment resources.
- Tourism development and growth significantly affect environmental pollution.
- Tourism development and growth significantly affect the physical ecosystem of the environment.
- Tourism development and growth significantly affect the socio-cultural environment.
- Tourism development and growth significantly affect the economic environment of people and the community.
- Government policy and support significantly moderate the relationship between tourism development and growth and the environmental factors.

Conceptual framework
Methodology
The study aimed to investigate the association of tourism development and its impact on environmental factors. Therefore, a survey method was employed to collect data by including all the relevant people in the locality. The study is based on stakeholders’ opinions from Pakistan’s most visited tourist areas, including Murree, Swat, Chitral, Naran, Kaghan, Neelum Valley, Malam Jabba, Ayubia, and Nathia Gali. A total of 650 stakeholders were contacted from the above-mentioned tourist destinations through survey. The distribution of the sample is mentioned in Table Table1 1 .
Sample configuration
Field survey—2021
Using quantitative techniques, hierarchical linear regression analysis was employed to investigate the possible relationships between tourism growth and various dimensions of environmental sustainability. The results below reveal that tourism development translates into environmental deterioration, and the relationship between tourism and environmental sustainability is bidirectional.
Tourism growth and development were measured through a five-item scale. The environment was measured through 16 items combined scale with sub-dimensions; depletion of Natural Resources=3 items, Polluting Environment=3 items, Physical Effects on Ecosystem=4 items, Socio-Cultural Degradation=3 items, and Economic Environment=3-items. Similarly, our moderating variable, Government Interventions and Support, was measured using a 5-item scale. Table Table2 2 below presents the details of the instruments.
Instrument reliability
Analysis and results
Data were analyzed using SPSS Version 26. It includes correlation, linear regression, and stepwise hierarchal regression analysis.
Table Table3 3 above shows that our Tourism Growth and Development has significant and positive relationship with Polluting Environment ( r = 0.20**), Physical Effects on Ecosystem ( r = 0.19**), Depletion of Natural Resource ( r = 0.24**), Socio-Cultural Degradation ( r = 0.18**). However, Tourism Growth and Development has positive relationship with Economic Environment ( r = 0.29**) and Government Interventions and Support ( r = 0.13**).
Correlation matrix
* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01
Results of linear regression analysis at Table Table4 4 above depict that tourism growth and development predicts 4.1% variance in Depletion of Natural Resources ( β = 0.20, p <0.01), 3.9% variance in pollution ( β = 0.19, p <0.01), 6% variance in Physical Effects on Ecosystem ( β = 0.24, p <0.01), 3.6% variance in Socio-Cultural Degradation ( β = 0.18, p <0.01), and 8.8% variance in Economic Environment ( β = 0.29, p <0.01).
Regression analysis for H1–H5
** p < 0.01
The study analyzes the applied two-step hierarchal regression. In the first step, Tourism Growth and Government Interventions were treated as independent variables, and their significant impact was measured. In the second step, the interaction term Tourism and Growth× Government Interventions was added, and its impact was measured. The results suggest that Government Interventions and Support moderate the relationship between Tourism Growth and the Environmental variables (Table (Table5 5 ).
Moderation analysis
* p < 0.05;** p < 0.01
The study has reported unique findings regarding tourism and its environmental impacts. We found that tourism growth and development generate economic activity on the one hand. However, it has specific adverse environmental and socio-cultural outcomes on the other hand as well. Our study revealed that tourism growth and development predict a 4.1% variance in Depletion of Natural Resources ( β = 0.202*, p <0.01). This suggests that due to the expansion of tourism in the country, natural resources are continuously depleted to meet the needs of tourists. Studies also supported our findings and suggested that revival and reinvigoration of infrastructure in tourism areas were backed up by extensive deforestation, use of local green land, rebuilding of the road network, displacement of biodiversity, and overtaxing the consumption of water and other natural resources (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Sadiq 2021 ; Dogar et al. 2021 ). The prior studies are consistent with our hypothesis that “tourism development and growth significantly affect natural environment resources.”
We further found that tourism growth and development predict a 3.9% variance in pollution ( β = 0.198*, p <0.01), suggesting that tourism expansion may pollute the natural environment. Furthermore, recent national statistics depict that major human activities at local tourism destinations such as Kalam, Sawat, Muree, and Northern Areas have accumulated solid waste and sewage, resulting in polluted air and water. Further, research also suggests that the overflow of tourists to tourist destinations may adversely affect the environment due to human activities (Noordzij et al. 2020 ; Slater et al. 2020 ; Andlib and Salcedo-Castro 2021 ; Callaghan et al. 2021 ). Thus, it is safe to argue that the growth of tourism has a particularly detrimental effect on the environment. These findings also support our hypothesis, “Tourism development and growth significantly contribute to environmental pollution.”
The results reported that tourism growth and development predict a 6% variance in Physical Effects on the Ecosystem ( β = 0.245*, p <0.01). Studies have reported that deforestation and alteration in species’ natural environment for tourism facilities construction may adversely affect environmental health (Kuvan, 2010 ; Azam et al. 2018 ; Hoang et al. 2020 ; Andlib and Salcedo-Castro 2021 ). During post-terrorism and post-Covid-19 times in Pakistan, millions of local tourists moved to popular tourist destinations that required new infrastructure to accommodate these tourists. Consequently, colossal deforestation and other detrimental human activities have negatively affected ecosystem. These findings also support our hypothesis that tourism development and growth significantly affect the physical ecosystem of the environment.
The study reported a total of 3.6% variance in socio-cultural degradation ( β = 0.189*, p <0.01) due to tourism growth and development. These findings suggest that tourism’s growth and development may lead the inhabitants to imitate the foreign tourists regarding their living standards, which may endanger their traditional culture. Thus, our hypothesis that “tourism development and growth significantly affect the socio-cultural environment” is confirmed.
Further, it was found that tourism growth and development predict an 8.8% variance in the economic environment ( β = 0.297*, p <0.01). It is established from the literature that tourism growth and development generate economic activity in the country. Development projects such as the construction of infrastructure, hotels, and road networks generate economic activity to facilitate international and indigenous tourists, positively affecting the community’s living standard (Baloch et al. 2020 ). Thus, our hypothesis, “tourism development and growth significantly affect economic environment of people and community,” is confirmed.
Due to tourism growth and development, our study reported a 1.8% variance in Government Support and Interventions ( β = .133*, p <0.01). However, more recently, the Government of Pakistan has devised specific interventions that may help curb the adverse impacts of detrimental environmental factors. For example, developmental schemes such as the Billion Trees Plantation drive and Road-Infrastructure Network Development under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor initiative may prove moderators to curb the negative impacts of tourism growth on the environment (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Rauf et al. 2019 ; Siddiqui and Siddiqui 2019 ). Therefore, the hypothesis, Government policy and support, significantly moderates the relationship between tourism development and growth with the environment is confirmed based on these findings.
Suggested model for ecotourism framework
Through its detailed review of existing literature, prevailing tourism policies, and empirical inputs from the stakeholders’ perspectives, the study has identified a wide range of obstacles limiting the development and growth of ecotourism in Pakistan. The study suggests National Tourism Management authorities carefully invest in ecotourism destination’s planning and development in coordination with the environment development agency. The suggested model for ecotourism framework is initially meant for the tourism destinations specifically designated for ecotourism. However, selected points can also be extended to the quality management parameters set for the National Parks, Conservation and Protracted Areas, Museums, National or International event sites, etc. The national tourism authorities are to lay particular emphasis in their forthcoming National Tourism Policy on the development and promotion of Sustainable Ecotourism having, with focus on the following key areas:
- Identify and classify four to five ecotourism destinations, including ecotourism-centered activities of value chains for priority development, which are administratively possible within budgetary constraints. However, the development plan shall consider the integral benefits of other developmental schemes such as the Billion Trees Plantation drive, Road-Infrastructure Network Development under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor initiative, International Union for Conservation of Nature (ICUN) programs in the area.
- While staying within the alignment of UN Millennium Development Goals (MDG) calling for ‘environmental sustainability’ and the development vision of each designated destination, the Tourists Management System shall take into cognizance of issues like managing capacity of the place, quality parameters for the conservation of the environment, and allowable activities thereof.
- Identify degenerated destinations of religious, socio-cultural, or historical significance for their rehabilitation under the Regenerated tourism program.
- i. To deflect the tourist pressure upon these destinations, the potential tourists from nearby cities and metropolitan areas be provided with nearby alternative destinations for leisure tourism as stay-tourism sites.
- ii. To prevent the environment from air pollution, the traffic load on the destination be curtailed through an effective traffic management strategy, provision of off-destination parking for combustion engine vehicles, and encouraging electric driven or hybrid vehicles for nearby parking.
- iii. Provision of clean drinking water through public infiltration plants, public toilets, solid waste carriers, and recycling of sewage and used water is recommended in the most visited areas of the destination.
- iv. Signposting at appropriate places, giving social messages encouraging to maintain cleanliness, avoid littering, ensure nature conservation, and humility toward biodiversity.
- Develop all-inclusive, comprehensive execution plans to expedite the investments for the sustainable ecotourism, encouraging public–private cooperation, community involvement, and infrastructure mapping guaranteeing environmental conservation and safeguards.
- Develop and place on the ground an all-inclusive program of capacity building for sustainable ecotourism, regenerative and green tourism services.
- Develop and launch Pakistan tourism profile and Sustaining Ecotourism obligatory framework “to promote tourism on the one hand and nurture conscious ecological behavior among the potential tourists of the area”.
- In order to fetch local ownership for the ecotourism center developments, all efforts shall be made to share the socio-economic benefits integral to the development scheme with the local population for community development.
- As part of the destination management planning, identify complementary value chains and livelihood activities that could be developed as part of the overall ecotourism destination package.
- i. Setting new quality standards facilitating the promotion of ecotourism and environmental sustainability through acts of various bodies operating in the Ecotourism value chain, such as:
- Revision of Private hotels Management Act (1976) and Tourists Operators Act (1976) alongside introduction and promulgation of a new “Tourism Destination Management Act” incorporating new quality standards as of today.
- Promulgating laws to make all new construction/development projects responsible from any agency in the area, incorporating quality standards needed for environmental sustainability, and promoting ecotourism.
- Set measures for the preservation of the local biodiversity and preservation of endangered species, including seeking support from internationally active environment conservation agencies, declaring local hunting illegal, introducing licensing programs for hunting of certain selected animals/ birds on the payment of a handsome amount to be used for the welfare of the local community.
- Create awareness programs against deforestation, land conservation, and biodiversity, and maintain cleanliness, inculcating a culture of respecting and enjoying nature instead of spoiling it.
Conclusion, implications, and limitations of the study
The study premise was based on the contention that sustenance of ecotourism focuses on the economic viability of the business interests alongside the conservation and preservation of natural ecosystems, including ethical fairness to the socio-cultural environment of the host community. Ecotourism is a phenomenon that contributes to environmental sustainability through well-planned and careful destination management capable of balancing conflicting interests of business growth and environmental sustainability. Tourism-environment paradox suggests that the sustainability and survival of both are dependent upon the flourishing mode of each other. Quality of environment and sustainability of bio-ecosystem stimulates tourists’ arrivals and over-tourism beyond capacity with irresponsible behavior from tourists negatively influencing the environment and harming the ecosystem of nature. Ecotourism is not inevitably sustainable unless it is economically sustainable and environmentally maintainable besides being socio-culturally acceptable. Socio-culturally intolerable ecotourism means the activity which does not benefit locals and their socio-cultural values. Hence, the study concludes that ecotourism has to positively interplay between economy, environment, and culture without compromising one over others. The pursuit of sustainable ecotourism is not an end in meeting the little comforts of the business interests but rather a means to end the sustainability issues created due to ill-conceived tourism development and unmanageable growth.
Practical implications
Drawing from the findings and conclusions of the research, the study extends the following practical implications for effectively managing the process of tourism development and environmental sustainability in line with the dictates of the philosophy behind ecotourism:
- Paradoxically tourism necessitates ecological capitals as primary ingredients for the creation of tourism experiences on the one hand. However, it is also contingent upon the conservation and preservation of ecological integrity on the other. The study suggests that unbalancing this “resource paradox” results in the harshness and tenacity of adversarial climate change, natural calamities, environmental pollution, and endangered biodiversity.
- The research findings and the suggested framework for ecotourism imply that sustainable ecotourism principles-based planning is mandatory for destination management to assure effective trade-off between the business interests’ sustainability of the environmental ecosystem.
- Tourism development and growth shall be steered through ecotourism principles as its sustainable model offers enduring social, environmental and economic, ecological integrity, and social and cultural benefits for the local community. Therefore, ecotourism is a recipe for preventing environmental degradation and guarantees sustainability of ecosystems nature and its biodiversity. Hence, ecotourism shall stand central priority focus for strategic management to nurture quality experiences from sustainable tourism.
- To revive back the sustainability of the environment, in the areas where over-tourism has degraded the environment, schemes for regenerated tourism shall be immediately launched to mitigate the negative footprints on the sustainability of destinations, including reinforcing protracted conservation sites, biodiversity, and recouping endangered species, afforestation drives, recycling of water and solid waste, refurnishing of landscaping, preservation, and rehabilitation of cultural heritage and refurbishing of depleted infrastructure accordingly. Furthermore, to regenerate and sustain the tourism infrastructure of the destinations experiencing over-tourism, capacity building measures like capacity, recycling of water and solid waste, preventive measures to control air and water pollution, traffic control management, and spread of entertainment facilities shall be the focus of the regeneration plans.
- The study implies that government authorities and policymakers have a special role in placing their moderating intervention in terms of policy guidelines, regulatory framework, and budgetary support, provision of inter-organizational synergy in planning and implementation of ecotourism strategies, protection of environmental resource base and conservation of natural and biological ecosystem, sustenance of socio-cultural value of local community over and above their economic and social well-being/quality life for the long run.
- The study also implies that public and private policymakers lay down threshold criteria for responsible travel and tourism standards for destination management and its related supply chain. The laid criterion would facilitate management in nurturing “responsible behavior” to plan, protect, conserve, preserve, and sustain natural and cultural resources and responsible socio-economic development without compromising the sustainability of the environment and long-term well-being of the hoist community. The deep-seated adherence to social responsibility protocols by the tourism supply chain network can significantly increase the capacity of tourism destinations and improve the conscious awareness of green consumers along the tourism supply chain. Furthermore, the consciously responsible behavior among stakeholders and legislatures can strike a needed balance between the business interests and environments in favor of sustainability of socio-cultural, economic, and natural capital.
- The study elucidates that responsible behavior necessitates purpose-built eco-friendly infrastructure and policy parameters to support the sustainability of environments across destinations. The strategic planning aligned with the sustainability-focused objectives dictates the need for artistic, innovative, and talented people and quality intuitions in harnessing quality tourism services and responsible tourism behavior. Furthermore, the study encourages community involvement in the developmental process, enactment of structural policies, preservation of socio-cultural heritage, and conservation of natural biodiversity as it would foster emotional bondage between the people of the host community and the tourism undertakings. Therefore, community and value chain managers shall collaborate to maximize the perceived benefits of responsible tourism while developing cultural exchanges and planning opportunities for leisure and tourism.
- Regulatory measures help offset negative impacts; for instance, controls on the number of tourist activities and movement of visitors within protected areas can limit impacts on the ecosystem and help maintain the integrity and vitality of the site. Limits should be established after an in-depth analysis of the maximum sustainable visitor capacity. Furthermore, the variables and the constructs researched can be replicated to other destinations to seek valuable inputs for sustainable destination management elsewhere.
Study limitation
Besides the functional, practical applications, the study has some limitations. Besides having integral disadvantages of cross-sectional research, the respondents selected for the study were visitors on peak days with the highest tourist arrivals, thereby having experiences of a higher degree of environmental pollution and natural disorder. Furthermore, the research is limited to stakeholders’ perspectives instead of any scientifically generated data or mathematical or econometric model.
Author contribution
QBB: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. SNS: data curation and supervision. NI: visualization, editing, proofreading. MS: review and editing. MA: review and editing. SM: editing, data curation. AUK: review and editing.
Data availability
Declarations.
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. We also declare that we do not have human participants, data, or tissue.
We do not have any person’s data in any form.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Qadar Bakhsh Baloch, Email: moc.liamg@bqhcolabrd .
Syed Naseeb Shah, Email: moc.liamtoh@hahs_beesan .
Nadeem Iqbal, Email: moc.oohay@1labqimeedanrd .
Muhammad Sheeraz, Email: [email protected] .
Muhammad Asadullah, Email: moc.liamg@apmdasa .
Sourath Mahar, Email: moc.oohay@mhtaros .
Asia Umar Khan, Email: kp.ude.pci@ramu-aisa .
- Abir T, Khan MYH (2022) Importance of ICT advancement and culture of adaptation in the tourism and hospitality industry for developing countries. In: ICT as innovator between tourism and culture. IGI Global, pp 30–41
- Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D. Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalization, and technological innovation on environmental degradation in Japan: application of wavelet tools. Environ Dev Sustain. 2021; 23 (11):16057–16082. doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01322-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akbar J, Tanveer S, Khan MN, Naeem A. Role of facilities available and un-available in attracting of tourist in Swat Valley Pakistan. J Landsc Ecol. 2017; 10 (1):5–19. doi: 10.1515/jlecol-2017-0006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Albrich K, Rammer W, Seidl R. Climate change causes critical transitions and irreversible alterations of mountain forests. Glob Change Biol. 2020; 26 (7):4013–4027. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15118. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Andlib Z, Salcedo-Castro J. The impacts of tourism and governance on CO2 emissions in selected south Asian countries. ETIKONOMI. 2021; 20 (2):385–396. doi: 10.15408/etk.v20i2.17449. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Arifin M, Ibrahim A, Nur M. Integration of supply chain management and tourism: an empirical study from the hotel industry of Indonesia. Manage Sci Lett. 2019; 9 (2):261–270. doi: 10.5267/j.msl.2018.11.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aslam AM. Intertemporal relationship between tourism demand and environmental quality in Sri Lanka. Test Eng Manage. 2020; 82 (January-February):17841–17856. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aslan A, Altinoz B, Özsolak B. The nexus between economic growth, tourism development, energy consumption, and CO 2 emissions in Mediterranean countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2021; 28 (3):3243–3252. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10667-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Azam M, Alam MM, Hafeez MH. Effect of tourism on environmental pollution: further evidence from Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand. J Clean Prod. 2018; 190 :330–338. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.168. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bakhriddinovna AN, Qizi KDR (2020) Tourism logistics: relationship between tourism and logistics. Academy 7(58):22–23
- Baloch QB. Managing tourism in Pakistan: a case study of Chitral valley. J Manag Sci. 2007; 2 (2):169–190. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baloch QB, Rehman A. Regional integration of Pakistan tourism: exploring prospects. Abasyn Univ J Soc Sci. 2015; 8 (2):405–415. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baloch QB, Irshad M, Qamar FM, Naseebullahshah S (2020) Development of tourism’s sector in the face of scarce economy. The Discourse 6(1):75–96
- Blangy S, Wood ME (1993) Developing and implementing ecotourism guidelines for wildlands and neighboring communities. Ecotourism Society, pp 32–54
- Boers B, Cottrell S. Sustainable tourism infrastructure planning: a GIS-supported approach. Tour Geogr. 2007; 9 (1):1–21. doi: 10.1080/14616680601092824. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bramwell B, Lane B. Sustainable tourism: contributing to the debates. J Sustain Tour. 1999; 7 (1):1–5. doi: 10.1080/09669589908667323. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Briassoulis H, Van Der Straaten J (eds) (2013) Tourism and the environment: regional, economic, cultural and policy issues, vol 6. Springer Science & Business Media
- Butowski L. Sustainable tourism: a human-centered approach. Sustainability. 2021; 13 (4):1835. doi: 10.3390/su13041835. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Callaghan A, McCombe G, Harrold A, McMeel C, Mills G, Moore-Cherry N, Cullen W. The impact of green spaces on mental health in urban settings: a scoping review. J Ment Health. 2021; 30 (2):179–193. doi: 10.1080/09638237.2020.1755027. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Çalişkan U, Özer Ö. Relationship between local residents’ perceptions of tourism and support attitudes in post-communist countries: case of Turkestan (Kazakhstan) Tour Plan Dev. 2021; 18 (5):573–593. doi: 10.1080/21568316.2020.1837228. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheia G. Ecotourism: Definition and concepts. Revista De Turism-Studii Si Cercetari in Turism. 2013; 15 :56–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chien F, Ajaz T, Andlib Z, Chau KY, Ahmad P, Sharif A. The role of technology innovation, renewable energy and globalization in reducing environmental degradation in Pakistan: a step towards sustainable environment. Renew Energy. 2021; 177 :308–317. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.05.101. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chien F, Sadiq M, Nawaz MA, Hussain MS, Tran TD, Le Thanh T. A step toward reducing air pollution in top Asian economies: the role of green energy, eco-innovation, and environmental taxes. J Environ Manag. 2021; 297 :113420. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113420. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chingarande A, Saayman A. Critical success factors for tourism-led growth. Int J Tour Res. 2018; 20 (6):800–818. doi: 10.1002/jtr.2233. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chishti MZ, Ullah S, Ozturk I, Usman A (2020) Examining the asymmetric effects of globalization and tourism on pollution emissions in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(22):27721–27737 [ PubMed ]
- Cobbinah PB. Contextualizing the meaning of ecotourism. Tour Manag Perspect. 2015; 16 :179–189. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2015.07.015. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Confente I, Scarpi D. Achieving environmentally responsible behavior for tourists and residents: a norm activation theory perspective. J Travel Res. 2021; 60 (6):1196–1212. doi: 10.1177/0047287520938875. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de Grosbois D, Fennell DA. Sustainability and ecotourism principles adoption by leading ecolodges: learning from best practices. Tour Recreat Res. 2021 doi: 10.1080/02508281.2021.1875170. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deery M, Jago L, Fredline L. Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: a new research agenda. Tour Manag. 2012; 33 (1):64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2011.01.026. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dogar AA, Shah I, Elahi N. Sports tourism in post conflict peace building: evidence from Swat, Pakistan. J Contemp Issues Bus Government. 2021; 27 (1):480–489. [ Google Scholar ]
- Desai BH. 14. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Yearbook Int Environ Law. 2016; 27 :481–488. doi: 10.1093/yiel/yvx069. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ding ZF, Cao B. Exploring the factors in visitors’ behavioral intentions–mediation effects on perceived environmental involvement and ecotourism support. Appl Ecol Environ Res. 2019; 17 (1):1083–1092. doi: 10.15666/aeer/1701_10831092. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ekins P, Gupta J. Perspective: a healthy planet for healthy people. Global Sustainability. 2019; 2 (e20):1–9. doi: 10.1017/sus.2019.17. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fennell DA. A content analysis of ecotourism definitions. Curr Issue Tour. 2001; 4 (5):403–421. doi: 10.1080/13683500108667896. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fennell DA (2020) Ecotourism. Routledge
- Guzel AE, Okumus İ. Revisiting the pollution haven hypothesis in ASEAN-5 countries: new insights from panel data analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (15):18157–18167. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08317-y. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hassan A, Kennell J, Chaperon S. Rhetoric and reality in Bangladesh: elite stakeholder perceptions of the implementation of tourism policy. Tour Recreat Res. 2020; 45 (3):307–322. [ Google Scholar ]
- Harris R, Williams P, Griffin T (2012) Sustainable tourism. Routledge, Oxford
- Hill J, Gough G (2009) Can the conservation attitudes and behavioural intentions of tourists to tropical forest be improved through biodiversity interpretation? A case study from Australia. Principles and practice, ecotourism and environmental sustainability, pp 175–196
- Hoang TTH, Van Rompaey A, Meyfroidt P, Govers G, Vu KC, Nguyen AT et al (2020) Impact of tourism development on the local livelihoods and land cover change in the northern Vietnamese highlands. Environ Dev Sustain 22(2):1371–1395
- Holden A (2008) Tourism and the environment, 2nd edn. Routledge, New York
- Khoi NH, Le NH, Ngoc BH (2021) The effect of tourism development on the ecological footprint in Singapore: evidence from asymmetric ARDL method. Curr Issue Tour 25(15):2500–2517
- Kostić M, Milićević S, Nedeljković I. Research of tourists’ perception of the relationship between tourism and environment. Becтник aпк Cтaвpoпoлья 2016; S4 :32–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Krampe F (2021) Ownership and inequalities: exploring UNEP’s environmental cooperation for Peacebuilding program. Sustain Sci 16(4):1159–1172
- Kuvan Y. Mass tourism development and deforestation in Turkey. Anatolia. 2010; 21 (1):155–168. doi: 10.1080/13032917.2010.9687096. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liang Y, Wang L, Zhu Y. Using environmental sensitivity for discussing the correlation between ecotourism cognition and environmental attitude. Ekoloji. 2018; 27 (106):1653–1659. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mandić A, Mrnjavac Ž, Kordić L. Tourism infrastructure, recreational facilities and tourism development. Tour Hosp Manag. 2018; 24 (1):41–62. doi: 10.20867/thm.24.1.12. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marengo JA, Cunha AP, Cuartas LA, Deusdará Leal KR, Broedel E, Seluchi ME, Bender F (2021) Extreme drought in the Brazilian Pantanal in 2019–2020: characterization, causes, and impacts. Frontiers in Water 3:639204
- Mikayilov JI, Mukhtarov S, Mammadov J, Azizov M. Re-evaluating the environmental impacts of tourism: does EKC exist? Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019; 26 (19):19389–19402. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05269-w. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nelson CA. The development and neural bases of face recognition. Infant and Child Development: An International Journal of Research and Practice. 2001; 10 (1–2):3–18. doi: 10.1002/icd.239. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Niedziółka I. Sustainable tourism development. Reg Form Dev Stud. 2014; 8 (3):157–166. [ Google Scholar ]
- Noordzij JM, Beenackers MA, Groeniger JO, Van Lenthe FJ. Effect of changes in green spaces on mental health in older adults: a fixed effects analysis. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2020; 74 (1):48–56. doi: 10.1136/jech-2019-212704. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Park M, Stokowski PA. Social disruption theory and crime in rural communities: comparisons across three levels of tourism growth. Tour Manag. 2009; 30 (6):905–915. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2008.11.015. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Opoku A. Biodiversity and the built environment: implications for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Resour Conserv Recycl. 2019; 141 :1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pforr C (2001) Concepts of sustainable development, sustainable tourism, and ecotourism: definitions, principles, and linkages. Scand J Hosp Tour 1(1):68–71
- Pulido-Fernández JI, Cárdenas-García PJ, Espinosa-Pulido JA. Does environmental sustainability contribute to tourism growth? An analysis at the country level. J Clean Prod. 2019; 213 :309–319. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.151. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qamar F, Baloch QB (2017) Reviving tourism through entrepreneurial capabilities in swat, Dir & Chitral Triangle in post operation environment. Journal of Managerial Sciences 11(2):209–228
- Rasoolimanesh SM, Md Noor S, Schuberth F, Jaafar M. Investigating the effects of tourist engagement on satisfaction and loyalty. Serv Ind J. 2019; 39 (7–8):559–574. doi: 10.1080/02642069.2019.1570152. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ratnasari SL, Susanti EN, Ismanto W, Tanjung R, Darma DC, Sutjahjo G. An experience of tourism development: how is the strategy? J Environ Manag Tour. 2020; 11 (7):1877–1886. doi: 10.14505//jemt.v11.7(47).26. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rauf T, Khan N, Shah SJ, Zada M, Malik SY, Yukun C, Sadique A. Poverty and prosperity: impact on livelihood assets of billion trees afforestation program in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK), Pakistan. Forests. 2019; 10 (10):916. doi: 10.3390/f10100916. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Raza SA, Jawaid ST. Terrorism and tourism: a conjunction and ramification in Pakistan. Econ Model. 2013; 33 :65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2013.03.008. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sadiq N (2021) COVID-19, adaptive capacity and tourism governance: the case of Pakistan's tourism industry. In: Pandemics and travel. Emerald Publishing Limited, pp 49–66
- Scharlemann JP, Brock RC, Balfour N, Brown C, Burgess ND, Guth MK, Kapos V (2020) Towards understanding interactions between sustainable development goals: the role of environment–human linkages. Sustain Sci 15(6):1573–1584
- Setini M, Wardana I, Sukaatmadja I, Ekawati N, Yasa N, Astawa I. Policy models for improving ecotourism performance to build quality tourism experience and sustainable tourism. Manage Sci Lett. 2021; 11 (2):595–608. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaheen K, Zaman K, Batool R, Khurshid MA, Aamir A, Shoukry AM, Gani S. Dynamic linkages between tourism, energy, environment, and economic growth: evidence from top 10 tourism-induced countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019; 26 (30):31273–31283. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06252-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Siddiqui F, Siddiqui DA. Causality between tourism and foreign direct investment: an empirical evidence from Pakistan. Asian J Econ Mod. 2019; 7 (1):27–44. doi: 10.18488/journal.8.2019.71.27.44. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simo-Kengne BD. Tourism growth and environmental sustainability: trade-off or convergence? Environ Dev Sustain. 2022; 24 (6):8115–8144. doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01775-5. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slater SJ, Christiana RW, Gustat AJ (2020) Recommendations for keeping parks and green space accessible for mental and physical health during COVID-19 and other pandemics. Prev Chronic Dis 17:200204. 10.5888/pcd17.200204 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Smith MD, Krannich RS, Hunter LM. Growth, decline, stability, and disruption: a longitudinal analysis of social well-being in four western rural communities. Rural Sociol. 2001; 66 (3):425–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1549-0831.2001.tb00075.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Song H, Li G, Witt SF, Fei B. Tourism demand modelling and forecasting: how should demand be measured? Tour Econ. 2010; 16 (1):63–81. doi: 10.5367/000000010790872213. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stefănica M, Butnaru GI. Research on tourists’ perception of the relationship between tourism and environment. Procedia Econ Finance. 2015; 20 :595–600. doi: 10.1016/S2212-5671(15)00113-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sun Y, Yesilada F, Andlib Z, Ajaz T. The role of eco-innovation and globalization towards carbon neutrality in the USA. J Environ Manag. 2021; 299 :113568. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113568. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sunchindah A (2015) Transboundary haze pollution problem in Southeast Asia: reframing ASEAN’s response working papers DP-2015-82, economic research institute for ASEAN and East Asia (ERIA)
- Swain RB. Handbook of sustainability science and research. Cham: Springer; 2018. A critical analysis of the sustainable development goals; pp. 341–355. [ Google Scholar ]
- Szpilko D. Tourism supply chain—overview of selected literature. Procedia Eng. 2017; 182 :687–693. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.03.180. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tiwari AK, Nasreen S, Iqbal Z. Nexus between tourism and environmental pollution in South Asia: a comparative analysis using time-varying and non-parametric techniques. Curr Issue Tour. 2021; 24 (21):2996–3020. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1862070. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNEP (2021) New report reveals how infrastructure defines our climate. October, 12
- Zakaria M, Jun W, Ahmed H. Effect of terrorism on economic growth in Pakistan: an empirical analysis. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja. 2019; 32 (1):1794–1812. doi: 10.1080/1331677X.2019.1638290. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zakaria M, Jun W, Ahmed H. Effect of terrorism on economic growth in Pakistan: an empirical analysis. Economic Research-Ekonomska istraživanja. 2019; 32 (1):1794–1812. doi: 10.1080/1331677X.2019.1638290. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang L, Gao J. Exploring the effects of international tourism on China’s economic growth, energy consumption and environmental pollution: evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2016; 53 :225–234. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.08.040. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang N, Ren R, Zhang Q, Zhang T. Air pollution and tourism development: an interplay. Ann Tour Res. 2020; 85 :103032. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2020.103032. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhu L, Ives AR, Zhang C, Guo Y, Radeloff VC. Climate change causes functionally colder winters for snow cover-dependent organisms. Nat Clim Chang. 2019; 9 (11):886–893. doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0588-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Number of tourist arrivals
Somewhere on Earth this year
The World Counts • Impact through Awareness
The world counts impact through awareness, 45 arrivals every second.
There are over 1.4 billion tourists arriving at their destination every year. That’s 45 arrivals every single second.
Exponential growth of tourism
In 1950 there were 25 million international tourist arrivals, in 1970 the number was 166 million, and by 1990 it had grown to 435 million. From 1990 to 2018 numbers more than tripled reaching 1.442 billion. By 2030, 1.8 billion tourist arrivals are projected.
Negative environmental impacts of tourism
The negative environmental impacts of tourism are substantial. They include the depletion of local natural resources as well as pollution and waste problems. Tourism often puts pressure on natural resources through over-consumption, often in places where resources are already scarce.
Tourism puts enormous stress on local land use, and can lead to soil erosion, increased pollution, natural habitat loss, and more pressure on endangered species. These effects can gradually destroy the environmental resources on which tourism itself depends.
Tourism often leads to overuse of water
An average golf course in a tropical country, for example, uses as much water as 60,000 rural villagers. It also uses 1500 kilos of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides per year.
Tourism and climate change
Tourism contributes to more than 5 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions, with transportation accounting for 90 percent of this.
By 2030, a 25% increase in CO2-emissions from tourism compared to 2016 is expected. From 1,597 million tons to 1,998 million tons.
394,730,543
Tons of waste dumped
Globally, this year
Square kilometers of land area being degraded
793,184,608,700
Tons of freshwater used
Worldwide, this year
8,024,943,431
Tons of CO2 emitted into the atmosphere
The alternative: Eco-tourism
Eco-tourism offers a greener alternative. Eco-tourism is a rapidly growing industry, with potential benefits for both the environment and the economies of the tourist destinations.
Number of eco-tourist arrivals
- World Population
- The Consumer Economy
- Our Global Challenges
- The Project
- Keep the optimism
- Support green companies
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Sustainable tourism worldwide - statistics & facts
What are the effects of global tourism on the climate, traveler awareness of social and environmental responsibility, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Ecotourism market size worldwide 2022-2028
Tourism-related transport's share of carbon emissions worldwide 2016-2030
Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2023
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic.
Leisure Travel
Global carbon dioxide emissions from energy 1965-2022, by region
Related topics
Recommended.
- Tourism worldwide
- Hotel industry worldwide
- Sustainable tourism in the U.S.
- Sustainable fashion worldwide
Recommended statistics
Industry overview.
- Premium Statistic Ecotourism market size worldwide 2022-2028
- Premium Statistic Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2023
- Premium Statistic Sustainable initiatives travelers would adopt worldwide 2022, by region
- Premium Statistic Conscious travelers' challenges when traveling in a sustainable manner worldwide 2022
Market size of the ecotourism sector worldwide in 2022, with a forecast for 2028 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Share of travelers that believe sustainable travel is important worldwide in 2023
Sustainable initiatives travelers would adopt worldwide 2022, by region
Main sustainable initiatives travelers are willing to adopt worldwide in 2022, by region
Conscious travelers' challenges when traveling in a sustainable manner worldwide 2022
Challenges of travelers when trying to travel in a sustainable and socially conscious manner worldwide as of March 2022
Environmental impact
- Basic Statistic Global carbon dioxide emissions from energy 1965-2022, by region
- Premium Statistic Tourism-related transport's share of carbon emissions worldwide 2016-2030
- Premium Statistic Carbon footprint of tourism-related transport worldwide 2005-2030
- Premium Statistic Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
- Premium Statistic Carbon footprint of domestic tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Carbon dioxide emissions from energy worldwide from 1965 to 2022, by region (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide)
Tourism-related transport's share of carbon emissions worldwide 2016-2030
Share of carbon dioxide emissions coming from tourism-related transport worldwide in 2016, with a forecast for 2030
Carbon footprint of tourism-related transport worldwide 2005-2030
Carbon dioxide emissions from tourism-related transport worldwide in 2005 and 2016, with a forecast for 2030 (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide)
Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Transport-related emissions from international tourist arrivals worldwide in 2005 and 2016, with a forecast for 2030, by mode of transport (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide)
Carbon footprint of domestic tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Transport-related emissions from domestic tourist arrivals worldwide in 2005 and 2016, with a forecast for 2030 (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide), by mode of transport
International tourism figures
- Premium Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
- Basic Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
- Premium Statistic Countries with the highest number of inbound tourist arrivals worldwide 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Global air traffic - number of flights 2004-2024
- Premium Statistic Global air traffic - scheduled passengers 2004-2022
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 1950 to 2023 (in millions)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2005 to 2023, by region (in millions)
Countries with the highest number of inbound tourist arrivals worldwide 2019-2022
Countries with the highest number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in millions)
Global air traffic - number of flights 2004-2024
Number of flights performed by the global airline industry from 2004 to 2023, with a forecasts for 2024 (in millions)
Global air traffic - scheduled passengers 2004-2022
Number of scheduled passengers boarded by the global airline industry from 2004 to 2022 (in millions)
Opinions and behavior
- Premium Statistic Main drivers for visiting a country by people worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Share of outbound travelers planning to spend more worldwide 2022, by category
- Premium Statistic Share of global travelers that want to use green lodging in the next year 2016-2022
- Premium Statistic Interest in accommodation with high sustainability standard globally 2023, by country
- Premium Statistic Reasons global travelers stayed in sustainable lodging at least once last year 2022
- Premium Statistic Demand for sustainable hotels by global corporate travel managers 2022
Main drivers for visiting a country by people worldwide 2023
Reasons to visit a country according to respondents worldwide in 2023
Share of outbound travelers planning to spend more worldwide 2022, by category
Share of travelers planning to spend more on trips abroad in selected countries worldwide in 2022, by type of expenditure
Share of global travelers that want to use green lodging in the next year 2016-2022
Distribution of global travelers intending to stay at least once in an eco-friendly or green accommodation when looking at the year ahead from 2016 to 2022
Interest in accommodation with high sustainability standard globally 2023, by country
Share of travelers who look for accommodation with impressive sustainability innovation worldwide as of July 2023, by country
Reasons global travelers stayed in sustainable lodging at least once last year 2022
Main reasons travelers stayed in sustainable accommodation at least once over the past year worldwide in as of February 2022
Demand for sustainable hotels by global corporate travel managers 2022
Importance of hotel sustainability for business travel buyers worldwide as of October 2022
Further reports Get the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
- About Us 👨👩👧
Positive Impacts of Tourism on the Environment
If you asked random people from different countries whether tourism has negative or positive impacts on the environment, none of the answers would most likely prevail since their opinion will be based on their personal experience from travels. Tourism and environment have important, yet controversial relationship, that needs to be in a perfect balance to benefit each other.
Beautiful natural landscapes or unique flora and fauna are the main drivers of tourism into an area. But when too many tourists visit natural sites, environment and its inhabitants rather suffer from the negative impacts, which easily outweigh all the benefits due to exceeding the natural carrying capacity of a place .
On the other hand, when the number of visitors is balanced with respect for the natural environment, tourism has great potential in supporting or even starting out new conservation projects that protect unique areas and benefit local residents.
Sustainable tourism helps protect the environment
Many countries around the world depend on tourism as their main industry in providing jobs in rural areas and bringing in funds that would be otherwise out of their reach. Financial resources and employment are critical for local livelihoods and security. But as more and more countries focus on expanding their tourism sites, they often encounter problems with overconsumption of their finite natural resources, pollution, and degradation. This easily spirals into undesirable situations of negative impacts on the local environment and society.
Tourism as a fast-growing industry must follow the principles of sustainability in order to last long term while maintaining positive impacts for an area. In terms of environment, this means consumption of natural resources within acceptable limits, protecting biodiversity and making sure that essential ecological processes can take place, while providing a pleasant experience to visiting tourists [1] .
A part of striving towards sustainability is also raising awareness about the unique natural features of an area and educating visitors about their sustainable management. This helps them to understand the rules set in place and respect differences.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in relation to tourism
Tourism represents 10 percent of world GDP. The industry increasingly affects the environment, culture, and socio-economic development of a country. Due to such a great reach, it is a powerful tool in facilitating change.
According to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism contributes directly or indirectly to all the 17 goals of sustainable development (SDGs) that were defined together with additional 169 SDG targets to ensure safer future for life on Earth by 2030.
Since 2018, UNWTO operates even an online platform dedicated to achievement of SDGs through tourism. You can visit it here: https://tourism4sdgs.org/ . On the platform is detailed description of each sustainable development goal in relation to tourism. SDGs address areas ranging from the importance of biodiversity, protection of marine ecosystems to urgent call for sustainable production and consumption.
Following the guidelines, UNWTO has, for example, partnered with the United Nations Environment Programme and the Ellen MacArthur Foundation and launched a Global Tourism Plastics Initiative to mitigate the problem of plastic pollution in the industry.
What are the positive impacts of tourism on the environment?
Sustainable tourism is the only way to go forward if the industry wants to grow. But throughout the last couple decades, tourism has been already growing and has introduced many new places to foreign visitors. In some regions, having the option of welcoming paying guests, tourism has brought many positive impacts on the environment. Let’s see their examples.
#1 Awareness raising and first-hand experience
Beautiful landscapes, animals in their natural environment, exotic ecosystems attract visitors from around the world. They are the primary reason why people travel. To get rest from their daily blues and experience ultimate relaxation from the connection with natural world. Tourism is the best tool to raise awareness of environmental values.
You learn the best when you do get to experience something directly, when you see it, touch it, and when you witness what threatens to destroy it. Personal visit of natural areas introduces you to the values they have for life. It makes you care about them, since you get to enjoy their special feeling. And memories you will have will encourage you to be environmentally-conscious in travel and personal life.
In January 2021, alarming pictures of the most touristy beaches in Bali buried in plastic waste that washed up on the shore due to the monsoon weather, appeared on social media of travelers and in the news [2] . The images have drawn global attention and created a bad rep for single-use plastic items, making us (consumers) more aware of the true impact.
#2 Tourism for skills learning and education
This is a special side of tourism but plays also an important role in positive impacts of tourism on the environment. Visitors do not have to be drawn to places just for entertainment or relaxation, they may come with the primary mission of learning a new skill or gaining certain knowledge. Tourists come to see a special feature in an area and often pay for their stay, for food, or training, which is a nice way to support the work they came to admire. Additionally, they may also put the new knowledge to use for their own projects.
One nice example of this form of tourism could be visiting a permaculture farm with the purpose to learn about the practices applied on the farm and exchange ideas on what might work at home. Another example, that could inspire many, is spending time on edible forest farms, learning about planting diversity of low maintenance plants on your piece of land. Or visiting villages excelling in agroforestry farming practices which have allowed them to harvest variety of products from their lands, while protecting sensitive mountainous environments, where intensive farming would not be an option.
#3 Support of conservation and biodiversity protection activities
Africa is a prime example of a country where tourism has had a positive effect on wildlife protection. Wildlife tourism in Africa makes around 36 percent of the tourism industry, contributing over $29 billion to the continent’s economy and provides jobs to 3.6 million people [3] .
The opportunity of seeing wild animals in their natural environment is what Africa is the most known for. This form of tourism reduces poverty and helps to empower women directly by giving them jobs, but even indirectly by allocating funds to build infrastructure – schools, hospitals.
Africa, Asia, South America, and the South Pacific focus more and more on the value of their wild natural areas. With the growth of tourism appear even new national and wildlife parks that connect sustainable tourism with biodiversity preservation.
For example, iSimangaliso Wetland Park in South Africa offers amazing experience for tourists who can choose between diving, snorkeling, kayaking or horseback riding in a landscape of 25,000 years old coastal dunes and swamp forests, while protecting the area’s sensitive ecosystems and unique species. The coastline is Africa’s only remaining nesting place of Loggerhead and Leatherback turtles [4] .
#4 Protection of endangered species
Countries begin to realize that their rare and endemic species are their symbol in the eyes of foreign visitors who are often attracted to the place because of them. Wild animals, virgin forests and a colorful palette of exotic plants are becoming an unusual sight in an economically developed world. The remaining spots that are still a home to this disappearing world are often turn to nature reserves and protected areas. This ensures better safety for endangered species that inhabit them.
Virunga National Park in East Africa has a story of conservation success to tell, even despite years of civil unrest and war in the surrounding areas, it has been declared an ecological pillar for the entire East and Central African biodiversity, having the largest concentration of birds and reptiles over other protected areas [5] .
Thanks to the initiative of the World Wildlife Fund and United Nations, the park has endured hard years and granted protection to endangered mountain gorillas, who were almost driven to extinction by human encroachment into their already limited habitat. Thanks to these extraordinary efforts and persistence, gorillas from the Virunga recovered and their number rose from 480 to over 600 [6] . The park is one of the most attractive tourist destinations, where you can see gorillas, chimpanzees, and many other iconic animals.
#5 Prevention of illegal trade and exploitation
Tourism brings new opportunities even to most remote places. The growing interest of tourists in visiting places where people live in connection with nature and animals gives chance to locals to sustain their families far from urban areas. In many cases, local communities quickly realize the need to protect what they have in order to attract tourists, as the stream of income from tourism is long-term and more advantageous than one-time sales of finite resources or poached animals.
A glimmer of hope sparked by the vision of attracting tourists takes place in two villages in Nepal that are known for being a transit points for illegal trade in pangolin meat and scales to Tibet and India.
The villages have joined a community-based pangolin conservation and education project . The goal of the project is to discourage local poachers from selling scales of pangolins to illegal traders, and thus interrupt the illegal trade pathway while protecting endangered pangolins . Participants of the project are also trained to help with long-term monitoring of pangolin population (species ecology, identification of threats and distribution).
#6 Finance and job opportunities
One in ten jobs worldwide are directly or indirectly in the tourism industry. Tourism creates decent work opportunities and economic growth even in rural or remote areas. Tourism employs women and is often the first job experience of young people. Money from the tourism then often goes into improving local infrastructure, and sustainable management and protection of natural wonders that attract visitors.
Better infrastructure and services have a positive impact on the environment. They revolve around consumption of resources and their management. Modern infrastructure for wastewater cleaning saves water and promotes more efficient use of it. Waste management facilities focus on recycling materials rather than just dumping waste into sea or to landfills.
Tourism also directly helps to fund conservation activities of national parks, or other nature and wildlife preservation projects. Visitors are usually asked to pay entrance fees or a small tax that is meant to support the project.
Costa Rica has one of the most successful rainforest conservation strategies, which enables the country to protect and care for its incredibly biodiversity rich rainforests, while at the same time generating income from tourism. A part of this income goes back to the rainforest conservation maintenance, research, and professional training of park guards. The rest sustains regional economy and creates balanced life opportunities for locals.
#7 Adoption of sustainable practices and new legislation
We have partially tapped into this aspect already in the previous point. It is closely linked. More funds available to a region mean better possibilities to improve infrastructure and services. Modernization of infrastructure goes hand in hand with a transition to sustainable technologies and seeking of long-term solutions that will benefit people and the local environment.
Many travelers care about their impact on the environment. They are willing to pay for environmentally friendly services and accommodation when visiting a new place. Many destinations already follow the suit and are changing their approach to tourism by considering their environmental impact in their management.
Additionally, governments also respond to this pressure and often enforce regulations to further protect local natural resources by adopting sustainable practices in the industry.
You can see this trend in increasing numbers of eco-tourism lodges around the world; or recycling bins placed in public areas to collect different materials for more efficient waste management; in water saving measures and recommendations adopted by accommodation providers; or even large-scale renewable energy projects that power whole regions.
Several studies highlighted the benefits of renewable energy for maintaining healthy environment during the seasonal influx of tourists to island destinations. For example, a study of Mediterranean islands sees renewable energy projects as a tool to provide sufficient energy to residents and tourists during the periods of increased demand, while protecting already fragile and limited resources islands have.
Tourism and the environment could go well together
The success of tourism relies on good infrastructure and decent quality of services. The industry therefore helps the community development and brings new sources of inspiration and motivation for protection of biodiversity rich natural areas, wildlife, or whole ecosystems.
Many new conservation projects raise hope of local people in being able to sustain their families, while taking care of their home, of their legacy, of a place shaped by the nurturing hands of their ancestors. They hope that their effort will be appreciated and rewarded by respectful visitors.
Was this article helpful?
About greentumble.
Greentumble was founded in the summer of 2015 by us, Sara and Ovi . We are a couple of environmentalists who seek inspiration for life in simple values based on our love for nature. Our goal is to inspire people to change their attitudes and behaviors toward a more sustainable life. Read more about us .
- Agriculture
- Biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Endangered Species
- Green Living
- Solar Energy
Sliding Sidebar
TOURISM'S THREE MAIN IMPACT AREAS
Negative impacts from tourism occur when the level of visitor use is greater than the environment's ability to cope with this use within the acceptable limits of change. Uncontrolled conventional tourism poses potential threats to many natural areas around the world. It can put enormous pressure on an area and lead to impacts such as soil erosion, increased pollution, discharges into the sea, natural habitat loss, increased pressure on endangered species and heightened vulnerability to forest fires. It often puts a strain on water resources, and it can force local populations to compete for the use of critical resources.
DEPLETION OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Tourism development can put pressure on natural resources when it increases consumption in areas where resources are already scarce.
Water resources
Water, and especially fresh water, is one of the most critical natural resources. The tourism industry generally overuses water resources for hotels, swimming pools, golf courses and personal use of water by tourists. This can result in water shortages and degradation of water supplies, as well as generating a greater volume of waste water..

Golf course maintenance can also deplete fresh water resources. In recent years golf tourism has increased in popularity and the number of golf courses has grown rapidly. Golf courses require an enormous amount of water every day and, as with other causes of excessive extraction of water, this can result in water scarcity. If the water comes from wells, overpumping can cause saline intrusion into groundwater. Golf resorts are more and more often situated in or near protected areas or areas where resources are limited, exacerbating their impacts.
Local resources
Tourism can create great pressure on local resources like energy, food, and other raw materials that may already be in short supply. Greater extraction and transport of these resources exacerbates the physical impacts associated with their exploitation. Because of the seasonal character of the industry, many destinations have ten times more inhabitants in the high season as in the low season. A high demand is placed upon these resources to meet the high expectations tourists often have (proper heating, hot water, etc.).
Land degradation
Important land resources include minerals, fossil fuels, fertile soil, forests, wetland and wildlife. Increased construction of tourism and recreational facilities has increased the pressure on these resources and on scenic landscapes. Direct impact on natural resources, both renewable and nonrenewable, in the provision of tourist facilities can be caused by the use of land for accommodation and other infrastructure provision, and the use of building materials.
Forests often suffer negative impacts of tourism in the form of deforestation caused by fuel wood collection and land clearing. For example, one trekking tourist in Nepal - and area already suffering the effects of deforestation - can use four to five kilograms of wood a day.
Tourism can cause the same forms of pollution as any other industry: air emissions, noise, solid waste and littering, releases of sewage, oil and chemicals, even architectural/visual pollution.
Air pollution and noise
Transport by air, road, and rail is continuously increasing in response to the rising numbe reported that the number of international air passengers worldwide rose from 88 million in 1972 to 344 million in 1994. One consequence of this increase in air transport is that tourism now accounts for more than 60% of air travel and is therefore responsible for an important share of air emissions. One study estimated that a single transatlantic return flight emits almost half the CO2 emissions produced by all other sources (lighting, heating, car use, etc.) consumed by an average person yearly. (Mayer Hillman, Town & Country Planning magazine, September 1996. Source: MFOE ).
Transport emissions and emissions from energy production and use are linked to acid rain, global warming and photochemical pollution. Air pollution from tourist transportation has impacts on the global level, especially from carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions related to transportation energy use. And it can contribute to severe local air pollution. Some of these impacts are quite specific to tourist activities. For example, especially in very hot or cold countries, tour buses often leave their motors running for hours while the tourists go out for an excursion because they want to return to a comfortably air-conditioned bus.
Noise pollution from airplanes, cars, and buses, as well as recreational vehicles such as snowmobiles and jet skis, is an ever-growing problem of modern life. In addition to causing annoyance, stress, and even hearing loss for it humans, it causes distress to wildlife, especially in sensitive areas. For instance, noise generated by snowmobiles can cause animals to alter their natural activity patterns.
Solid waste and littering

In mountain areas, trekking tourists generate a great deal of waste. Tourists on expedition leave behind their garbage, oxygen cylinders and even camping equipment. Such practices degrade the environment with all the detritus typical of the developed world, in remote areas that have few garbage collection or disposal facilities. Some trails in the Peruvian Andes and in Nepal frequently visited by tourists have been nicknamed "Coca-Cola trail" and "Toilet paper trail".

Aesthetic Pollution
Often tourism fails to integrate its structures with the natural features and indigenous architectural of the destination. Large, dominating resorts of disparate design can look out of place in any natural environment and may clash with the indigenous structural design.
A lack of land-use planning and building regulations in many destinations has facilitated sprawling developments along coastlines, valleys and scenic routes. The sprawl includes tourism facilities themselves and supporting infrastructure such as roads, employee housing, parking, service areas, and waste disposal.
PHYSICAL IMPACTS
Attractive landscape sites, such as sandy beaches, lakes, riversides, and mountain tops and slopes, are often transitional zones, characterized by species-rich ecosystems. Typical physical impacts include the degradation of such ecosystems.
An ecosystem is a geographic area including all the living organisms (people, plants, animals, and microorganisms), their physical surroundings (such as soil, water, and air), and the natural cycles that sustain them. The ecosystems most threatened with degradation are ecologically fragile areas such as alpine regions, rain forests, wetlands, mangroves, coral reefs and sea grass beds. The threats to and pressures on these ecosystems are often severe because such places are very attractive to both tourists and developers.
Physical impacts are caused not only by tourism-related land clearing and construction, but by continuing tourist activities and long-term changes in local economies and ecologies.
Physical impacts of tourism development
- Construction activities and infrastructure development The development of tourism facilities such as accommodation, water supplies, restaurants and recreation facilities can involve sand mining, beach and sand dune erosion, soil erosion and extensive paving. In addition, road and airport construction can lead to land degradation and loss of wildlife habitats and deterioration of scenery.
In Yosemite National Park (US), for instance, the number of roads and facilities have been increased to keep pace with the growing visitor numbers and to supply amenities, infrastructure and parking lots for all these tourists. These actions have caused habitat loss in the park and are accompanied by various forms of pollution including air pollution from automobile emissions; the Sierra Club has reported "smog so thick that Yosemite Valley could not be seen from airplanes". This occasional smog is harmful to all species and vegetation inside the Park. (Source: Trade and Environment Database)
Deforestation and intensified or unsustainable use of land Construction of ski resort accommodation and facilities frequently requires clearing forested land. Coastal wetlands are often drained and filled due to lack of more suitable sites for construction of tourism facilities and infrastructure. These activities can cause severe disturbance and erosion of the local ecosystem, even destruction in the long term.
- Marina development Development of marinas and breakwaters can cause changes in currents and coastlines. Furthermore, extraction of building materials such as sand affects coral reefs, mangroves, and hinterland forests, leading to erosion and destruction of habitats. In the Philippines and the Maldives, dynamiting and mining of coral for resort building materials has damaged fragile coral reefs and depleted the fisheries that sustain local people and attract tourists. Overbuilding and extensive paving of shorelines can result in destruction of habitats and disruption of land-sea connections (such as sea-turtle nesting spots). Coral reefs are especially fragile marine ecosystems and are suffering worldwide from reef-based tourism developments. Evidence suggests a variety of impacts to coral result from shoreline development, increased sediments in the water, trampling by tourists and divers, ship groundings, pollution from sewage, overfishing, and fishing with poisons and explosives that destroy coral habitat.
Physical impacts from tourist activities
- Trampling Tourists using the same trail over and over again trample the vegetation and soil, eventually causing damage that can lead to loss of biodiversity and other impacts. Such damage can be even more extensive when visitors frequently stray off established trails.
- Anchoring and other marine activities In marine areas (around coastal waters, reefs, beach and shoreline, offshore waters, uplands and lagoons) many tourist activities occur in or around fragile ecosystems. Anchoring, snorkeling, sport fishing and scuba diving, yachting, and cruising are some of the activities that can cause direct degradation of marine ecosystems such as coral reefs, and subsequent impacts on coastal protection and fisheries.
- Alteration of ecosystems by tourist activities Habitat can be degraded by tourism leisure activities. For example, wildlife viewing can bring about stress for the animals and alter their natural behavior when tourists come too close. Safaris and wildlife watching activities have a degrading effect on habitat as they often are accompanied by the noise and commotion created by tourists as they chase wild animals in their trucks and aircraft. This puts high pressure on animal habits and behaviors and tends to bring about behavioral changes. In some cases, as in Kenya, it has led to animals becoming so disturbed that at times they neglect their young or fail to mate.
Advertisement
Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism
- Research Article
- Published: 19 August 2022
- Volume 30 , pages 5917–5930, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- Qadar Bakhsh Baloch 1 ,
- Syed Naseeb Shah 1 ,
- Nadeem Iqbal 2 ,
- Muhammad Sheeraz 3 ,
- Muhammad Asadullah 4 ,
- Sourath Mahar 5 &
- Asia Umar Khan 6
49k Accesses
79 Citations
3 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The empirical research investigated the relationship between tourism development and environmental suitability to propose a framework for sustainable ecotourism. The framework suggested a balance between business and environmental interests in maintaining an ecological system with the moderating help of government support and policy interventions. The study population encompasses tourism stakeholders, including tourists, representatives from local communities, members of civil administration, hoteliers, and tour operators serving the areas. A total of 650 questionnaires were distributed to respondents, along with a brief description of key study variables to develop a better understanding. After verifying the instrument’s reliability and validity, data analysis was conducted via hierarchical regression. The study findings revealed that a substantial number of people perceive socio-economic benefits, including employment and business openings, infrastructure development from tourism development, and growth. However, the state of the natural and environmental capital was found to be gradually degrading. Alongside the social environment, social vulnerability is reported due to the overutilization of land, intrusion from external cultures, and pollution in air and water due to traffic congestion, accumulation of solid waste, sewage, and carbon emissions. The study suggested a model framework for the development of sustained ecotourism, including supportive government policy interventions to ensure effective conservation of environmental and natural resources without compromising the economic viability and social well-beings of the locals. Furthermore, the variables and the constructs researched can be replicated to other destinations to seek valuable inputs for sustainable destination management elsewhere.
Similar content being viewed by others
Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins

Public transportation and sustainability: A review

Ecotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Tourism is a vibrant force that stimulates travel to explore nature, adventures, wonders, and societies, discover cultures, meet people, interact with values, and experience new traditions and events. Tourism development attracts tourists to a particular destination to develop and sustain a tourism industry. Moreover, environmental sustainability is the future-based conscious effort aimed at conserving socio-cultural heritage and preserving natural resources to protect environmental ecosystems through supporting people’s health and economic well-being. Environment sustainability can be reflected in clean and green natural landscaping, thriving biodiversity, virgin sea beaches, long stretches of desert steppes, socio-cultural values, and archeological heritage that epitomize tourists’ degree of motivation and willingness of the local community to welcome the visitors. In this context, tourism growth and environmental sustainability are considered interdependent constructs; therefore, the increase in tourism development and tourists’ arrivals directly affects the quality of sustained and green tourism (Azam et al. 2018 ; Hassan et al. 2020 ; Sun et al. 2021 ).
According to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism is one of the fastest-growing industries, contributing more than 10% to the global GDP (UNWTO 2017; Mikayilov et al. 2019 ). Twenty-five million international tourists in 1950 grew to 166 million in 1970, reaching 1.442 billion in 2018 and projected to be 1.8 billion by 2030. Mobilizing such a substantial human tourist’s mass is most likely to trickle environmental pollution along with its positive effects on employment, wealth creation, and the economy. The local pollution at tourist destinations may include air emissions, noise, solid waste, littering, sewage, oil and chemicals, architectural/visual pollution, heating, car use, and many more. In addition, an uncontrolled, overcrowded, and ill-planned tourist population has substantial adverse effects on the quality of the environment. It results in the over-consumption of natural resources, degradation of service quality, and an exponential increase in wastage and pollution. Furthermore, tourism arrivals beyond capacity bring problems rather than a blessing, such as leaving behind soil erosion, attrition of natural resources, accumulation of waste and air pollution, and endangering biodiversity, decomposition of socio-cultural habitats, and virginity of land and sea (Kostić et al. 2016 ; Shaheen et al. 2019 ; Andlib and Salcedo-Castro 2021 ).
Tourism growth and environmental pollution have been witnessed around the globe in different regions. The ASEAN countries referred to as heaven for air pollution, climate change, and global warming are experiencing economic tourism and pollution (Azam et al. 2018 ; Guzel and Okumus 2020 ). In China, more than fifty-eight major Chinese tourism destinations are inviting immediate policy measures to mitigate air pollution and improve environmental sustainability (Zhang et al. 2020 ). Similarly, Singapore, being a top-visited country, is facing negative ecological footprints and calling for a trade-off between tourism development and environmental sustainability (Khoi et al. 2021 ). The prior studies established that international tourism and the tourism-led growth surge tourists’ arrival, energy consumption, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions, and air pollution resultantly cause climate change (Aslan et al. 2021 ). South Asian countries, more specifically Sri Lanka and Pakistan, are on the verge of tourism growth and environmental pollution compared to other countries (Chishti et al. 2020 ; Tiwari et al. 2021 ).
Pakistan is acknowledged in the tourism world because of its magnificent mountains with the densest concentration of high peaks in the world, scenic beauty of Neelum Valley, Murree, Chitral, and swat Valleys’, Kaghan, Naran, Hunza, Gilgit Baltistan (Baloch 2007 ), sacred shrines of Sikhism, archeological sites of the Gandhara and Indus Valley civilizations such as Mohenjo-Daro, Taxila including pre-Islamic Kalasha community (Baloch and Rehman 2015 ). In addition, Pakistan’s hospitable and multicultural society offers rich traditions, customs, and festivals for the tourists to explore, commemorate, cherish, and enjoy. Pakistan’s geographical and socio-cultural environment represents its resource and an opportunity (Baloch and Rehman 2015 ); therefore, Pakistan is looking to capitalize on it as a promising source of the foreign reserve to compensate for its mounting trade deficit (Baloch et al. 2020 ).
Tourism expansion has been established as a very deleterious ecological cost vis-à-vis the socio-economic benefits it passes to the host communities (Pulido-Fernández et al. 2019 ; Simo-Kengne 2022 ). In this context, the research is motivated to investigate the relationships between Pakistan’s tourism development activities and environmental sustainability. Drawing from the arguments of Pulido-Fernández et al. ( 2019 ) and Simo-Kengne ( 2022 ), it is feared that Pakistan’s ongoing determination to tourism development is likely to cause environmental degradation in two ways. Firstly, the tourism infrastructure developmental process would consume natural resources in the form of air and water pollution, loss of nature, and biodiversity. Secondly, the proliferation of tourism-related energy-consuming activities harms the environment by adding CO 2 emissions (Andlib and Saceldo-Castro 2021 ; Chien et al. 2021a ). Therefore, to tape this tourism-rich potential without compromising the sustainability of the natural and socio-cultural environment in the area, there is a dire need to develop Pakistan’s tourism areas into environment-friendly destinations.
Against the backdrop of a widening level of trade deficit, Pakistan’s rich tourism potential is being perceived as an immediate alternative for earning revenue to compensate for the current account gap. However, the developing large-scale tourism industry is considered a threat to deforestation, and air and water pollution, endangering biodiversity trading on resilient ecological credentials. The research study attempts to find an all-inclusive and comprehensive answer to the socio-ecological environmental concerns of tourism development and growth. Therefore, the research investigates the relationship between tourism development and its environmental sustainability to suggest a model framework for the development and growth of Sustainable Ecotourism in Pakistan along with its most visited destinations.
Literature review
- Tourism development and growth
Tourism is considered a force of sound as it benefits travelers and communities in urban and suburban areas. Tourism development is the process of forming and sustaining a business for a particular or mix of segments of tourists’ as per their motivation in a particular area or at a specific destination. Primarily, tourism development refers to the all-encompassing process of planning, pursuing, and executing strategies to establish, develop, promote, and encourage tourism in a particular area or destination (Mandić et al. 2018 ; Ratnasari et al. 2020 ). A tourism destination may serve as a single motivation for a group of tourists or a mix of purposes, i.e., natural tourism, socio-cultural or religious tourism, adventure or business tourism, or a combination of two or more. Andlib and Salcedo-Castro ( 2021 ), drawing from an analysis approach, contended that tourism destinations in Pakistan offer a mix of promising and negative consequences concerning their socio-economic and environmental impressions on the host community. The promising socio-economic impacts for the local community are perceived in the form of employment and business opportunities, improved standard of living, and infrastructural development in the area. The adverse environmental outcomes include overcrowding, traffic congestion, air and noise pollution, environmental degradation, and encroachment of landscaping for the local community and the tourists. An extensive review of the literature exercise suggests the following benefits that the local community and the tourists accrue from the tour are as follows:
Generate revenue and monetary support for people and the community through local arts and culture commercialization.
Improve local resource infrastructure and quality of life, including employment generation and access to improved civic facilities.
Help to create awareness and understanding of different ethnic cultures, social values, and traditions, connecting them and preserving cultures.
Rehabilitate and conserve socio-cultural and historical heritage, including archeological and natural sites.
Establishment of natural parks, protracted areas, and scenic beauty spots.
Conservation of nature, biodiversity, and endangered species with control over animal poaching.
Improved water and air quality through afforestation, littering control, land and soil conservation, and recycling of used water and waste.
Tourism and hospitality business incorporates various business activities such as travel and transportation through the air or other modes of travel, lodging, messing, restaurants, and tourism destinations (Szpilko 2017 ; Bakhriddinovna and Qizi 2020 ). A tourist’s tourism experience is aimed at leisure, experiencing adventure, learning the culture or history of a particular area or ethnic entity, traveling for business or health, education, or religious purposes. The chain of activities adds value to the Tourism experience. Every activity contributes toward economic stimulation, job creation, revenue generation, and tourism development encompassing infrastructure for all activities involved in the tourism process. Tourism growth expresses the number of arrivals and the time of their stay/trips over a period of time. Tourism growth is measured through the interplay between tourists’ arrivals, tourism receipts, and travel time duration (Song et al. 2010 ; Arifin et al. 2019 ). The following factors drive the degree and level of tourism development and growth:
Environmental factors include scenic beauty, green spaces, snowy mountains, towering peaks, good climate and weather, the interconnectivity of destination, quality of infrastructure, etc.
Socio-economic factors: the distinctiveness of community, uniqueness of culture and social values, hospitality and adaptability, accessibility, accommodation, facilities and amenities, cost-effectiveness, price index, and enabling business environment.
Historical, cultural, and religious factors include historical and cultural heritage, religious sites, and cultural values and experiences.
The tourism development process and its different dynamics revolve around the nature of tourism planned for a particular destination or area, which can be specified as ecotourism, sustainable tourism, green tourism or regenerative tourism, etc. Ecotourism is “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education” (Cheia, 2013 ; TIES, 2015). According to the World Conservation Union (IUCN), ecotourism involves “ Environmentally responsible travel to natural areas, to enjoy and appreciate nature (and accompanying cultural features, both past, and present) that promote conservation, have a low visitor impact and provide for beneficially active socio-economic involvement of local peoples ”. Moreover, Blangy and Wood ( 1993 ) defined it as “ responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and sustains the well-being of local people ” (p. 32). The concept of ecotourism is grounded upon a well-defined set of principles including “environmental conservation and education, cultural preservation and experience, and economic benefits” (Cobbinah 2015 ; De Grosbois and Fennell 2021 ).
Ecotourism minimizes tourism’s impact on the tourism resources of a specific destination, including lessening physical, social, interactive, and psychosomatic impacts. Ecotourism is also about demonstrating a positive and responsible attitude from the tourists and hosts toward protecting and preserving all components of the environmental ecosystem. Ecotourism reflects a purpose-oriented mindset, responsible for creating and delivering value for the destination with a high degree of kindliness for local environmental, political, or social issues. Ecotourism generally differs from mass tourism because of its following features (Liang et al. 2018 ; Ding and Cao 2019 ; Confente and Scarpi 2021 ):
Conscientious behavior focuses on the low impact on the environment.
Sensitivity and warmth for local cultures, values, and biodiversity.
Supporting the sustenance of efforts for the conservation of local resources.
Sharing and delivering tourism benefits to the local communities.
Local participation as a tourism stakeholder in the decision-making process.
Educating the tourist and locals about the sensitivity and care of the environment because tourism without proper arrangement can endanger the ecosystems and indigenous cultures and lead to significant ecological degradation.
Sustainability aims to recognize all impacts of tourism, minimize the adverse impacts, and maximize the encouraging ones. Sustainable tourism involves sustainable practices to maintain viable support for the ecology of the tourism environment in and around the destination. Sustainable tourism is natural resource-based tourism that resembles ecotourism and focuses on creating travel openings with marginal impact and encouraging learning about nature having a low impact, conservation, and valuable consideration for the local community’s well-being (Fennell 2001 & 2020 ; Butowski 2021 ). On the other hand, ecotourism inspires tourists to learn and care about the environment and effectively participate in the conservation of nature and cultural activities. Therefore, ecotourism is inclusive of sustainable tourism, whereas the focus of sustainable tourism includes the following responsibilities:
Caring, protecting, and conserving the environment, natural capital, biodiversity, and wildlife.
Delivering socio-economic welfare for the people living in and around tourists' destinations.
Identifying, rehabilitating, conserving, and promoting cultural and historical heritage for visitors learning experiences.
Bringing tourists and local groups together for shared benefits.
Creating wide-ranging and reachable opportunities for tourists.
Environment and sustainability of ecosystem
The term “environment” is all-inclusive of all the natural, organic living, inorganic, and non-natural things. The environment also denotes the interface among all breathing species with the natural resources and other constituents of the environment. Humans’ activities are mainly responsible for environmental damage as people and nations have contemplated modifying the environment to suit their expediencies. Deforestation, overpopulation, exhaustion of natural capital, and accumulation of solid waste and sewage are the major human activities that result in polluted air and water, acid rain, amplified carbon dioxide levels, depletion of the ozone, climate change, global warming, extermination of species, etc. A clean, green, and hygienic fit environment has clean air, clean water, clean energy, and moderate temperature for the healthy living of humans, animals, and biodiversity as nature is destined for them by their creatures. Maintaining and sustaining a clean environment is indispensable for human and biodiversity existence, fostering growth and development for conducting business and creating wealth. The environment can be sustained through conservation, preservation, and appropriate management to provide clean air, water, and food safe from toxic contamination, waste, and sewage disposal, saving endangered species and land conservation.
The globalization process, known for building socio-economic partnerships across countries, is also charged with encouraging environmental degradation through the over-consumption of natural resources and energy consumption, deforestation, land erosion, and weakening (Adebayo and Kirikkaleli 2021 ; Sun et al. 2021 ). Chien et al. ( 2021b ), while studying the causality of environmental degradation in Pakistan, empirically confirmed the existence of a significant connection between CO 2 emissions and GDP growth, renewable energy, technological innovation, and globalization. However, Chien et al. ( 2021a ) suggested using solar energy as a source of economic intervention to control CO 2 emissions and improve environmental quality in China. The danger of air pollution is hard to escape as microscopic air pollutants pierce through the human respiratory and cardiovascular system, injuring the lungs, heart, and brain. Ill-planned and uncontrolled human activities negatively affect ecosystems, causing climate change, ocean acidification, melting glaciers, habitation loss, eutrophication, air pollution, contaminants, and extinction of endangered species ( Albrich et al. 2020 ) .
Humans have a more significant effect on their physical environment in numerous ways, such as pollution, contamination, overpopulation, deforestation, burning fossil fuels and driving to soil erosion, polluting air and water quality, climate change, etc. UNO Agenda for 2030 “Sustainable Development and its Sustainable Development Goals” (SDGs) mirrors the common premise that a healthy environment and human health are interlaced as integral to the satisfaction of fundamental human rights, i.e., right to life, well-being, food, water and sanitation, quality of life and biodiversity to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages (SDG3)—which includes air quality that is dependent upon terrestrial ecosystems (SDG15), oceans (SDG14), cities (SDG11), water, cleanliness, and hygiene (SDG6) (Swain 2018 ; Opoku 2019 ; Scharlemann et al. 2020 ). The UNEP stated that 58% of diarrhea cases in developing economies is due to the non-provision of clean water and inadequate sanitation facilities resulting in 3.5 million deaths globally (Desai 2016 ; Ekins and Gupta 2019 ).
Climate change overwhelmingly alters ecosystems’ ability to moderate life-threatening happenings, such as maintaining water quality, regulating water flows, unbalancing the temporal weather and maintaining glaciers, displacing or extinction biodiversity, wildfire, and drought (Zhu et al. 2019 ; Marengo et al. 2021 ). Research studies advocate that exposure to natural environments is correlated with mental health, and proximity to green space is associated with lowering stress and minimizing depression and anxiety (Noordzij et al. 2020 ; Slater et al. 2020 ; Callaghan et al. 2021 ). Furthermore, the Ecosystem is affected by pollution, over-exploitation of natural resources, climate change, invasive and displacing species, etc. Hence, providing clean air and water, hygienic places, and green spaces enriches the quality of life: condensed mortality, healthier value-added productivity, and is vital to maintaining mental health. On the other hand, climate change aggravates environment-related health hazards through adverse deviations to terrestrial ecology, oceans, biodiversity, and access to fresh and clean water.
Tourism development denotes all activities linked with creating and processing facilities providing services for the tourists on and around a destination. Infrastructure development is vital for developing a tourism destination to advance tourists’ living conditions and preserve natural and cultural heritage by constructing new tourist facilities, the destinations administrative and supporting echelons, including community living, etc. Development for tourism infrastructure and land use often burdens natural capital through over-consumption, leading to soil erosion, augmented pollution, loss of natural habitats, and endangered species. Development of tourism infrastructure and construction work has profound implications on environmental degradation, reduction in green spaces, deforestation, solid waste and sewage, overutilization of air and water, emission of CO 2 and other gases contributing to air and water pollution, climate change, loss and displacement of biodiversity, and the degradation of ecosystems. These negative consequences of tourism development result in many problems for the tourists and the indigenous people in the foreseeable future (Azam et al. 2018 ; Hoang et al. 2020 ).
A report published by UNEP titled “Infrastructure for climate action” has suggested governments introduce sustainable infrastructure as the prevailing one is responsible for causing 79% of all greenhouse gas emissions in struggling climate change, alleviation, and adaptation efforts. Sustainable infrastructure signifies that structures’ planning, construction, and functioning do not weaken the social, economic, and ecological systems (UNEP 2021 ; Krampe 2021 ). Sustainable infrastructure is the only solution that ensures societies, nature, and the environment flourish together. Therefore, Sustainable Ecotourism supports adapting pro-environment and nature-based climate change strategies that help resilient biodiversity and ecosystem to impact climate change. The proposed strategy is to focus on the conservation and restoration of ecosystems to combat climate hazards, fluctuating rainfalls, soil erosion, temperature variations, floods, and extreme wind storms (Niedziółka 2014 ; Setini 2021 )
Pakistan’s tourism infrastructure suffered a colossal amount of damage during the earthquake of October 8, 2005, which left widespread demolition and destruction to its human, economic assets, and infrastructure networks, especially in Kashmir and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's tourism areas. The tourism-related infrastructure, including hotels, destination facilities of social service delivery and commerce, water channels, and communications networks, were either drained or virtually destroyed. The destruction in the aftermath of the earthquake was further added by the war against terror in tourism-hit areas, resulting in the redundancy of tourists and tourism facilities for a long time (Akbar et al. 2017 ; Zakaria and Ahmed 2019 ). The tourism revival activities during the post-earth quack, post-terrorism scenario, and COVID-19 period called for various entrepreneurial activities, including the construction of infrastructure, hotels, road networks, community living, etc. Development and reconstruction of the livelihood and hospitality infrastructure through entrepreneurship were undertaken intensively through a public-private partnership from national and international findings (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Sadiq 2021 ; Dogar et al. 2021 ).
The revival and reinvigoration of infrastructure in tourism areas were backed up by extensive deforestation, use of local green land, rebuilding of the road network, displacement of biodiversity, and overtaxing the consumption of water and other natural resources. The deforestation, extensive use of green land, and over-consumption of water and other natural resources have depleted the tourism value of the area on the one hand and degraded the environment on the other. However, it was the focused rehabilitation activities of earthquake and Pakistan’s Government’s socio-environment conservation strategy of the Billion Trees plantation program in the province, including dominating tourism areas. The afforestation and loss of green tops are being reclaimed through these efforts, and the tourism environment is soon expected to regenerate (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Rauf et al. 2019 ; Siddiqui and Siddiqui 2019 ).
Government support and policy interventions
Tourism generates wide-ranging benefits for the economy, community, and people. Tourism contributes to the economy through revenue generation and shares responsibility with the Government to alleviate poverty alleviation, create opportunities for job placements, protect environments, and conserve natural ecosystems and biodiversity. It is assumed that if the tourism industry is left to its own, it will most likely prefer its business interests over environments or biodiversity. Governments, custodians of the life and well-being of their subjects, are directly responsible for providing a clean environment, nature, and Ecosystem. Therefore, national and local governments are responsible for preparing and implementing tourism development plans and enforcing values and standards for tourism development in conformity with the prerequisites of environmental sustainability. Through institutional governance, governments help tourism development by providing financial and budgetary support, regulatory framework, land, physical resources, infrastructure, etc. Provision and facilitation for Sustainability of Ecotourism and conservation of environment and biodiversity are dependent upon Government-supported interventions as follows:
The regulatory framework for setting up tourism-related entrepreneurship and quality standards can support ecotourism and prevent environmental degradation on any account.
Provision of budgetary support for ecosystem conservation and regeneration of bio-diversity-related projects.
Plan, rehabilitate if needed, promote conservation and protection of socio-cultural, historic, antique, and natural endowments in coordination with other public and private agencies, and deal with the defaulters, if any.
Promoting and undertaking afforestation alongside land conservation and discouraging deforestation, soil erosion, accumulation of solid waste, littering, and any direct or indirect loss or threat to biodiversity.
Setting restrictions for over-tourism beyond capacity and quality standards for transportation, restaurants, hotels, food and drinking water, etc.
Placing enforcement mechanism necessary to ensure application of the regulatory framework and quality standards applicable along with all activities inclusive to the Ecotourism value chain.
Theoretical support and hypothesis development
According to the social disruption theory, rapidly expanding societies usually experience a period of widespread crisis and a loss of their conventional routines and attitudes. The crisis impacts people whose mental health, worldviews, behavioral patterns, and social networks may all be impacted (Çalişkan and Özer 2021 ). According to the social disruption theory, fast community change brought on by population growth will result in a variety of social issues that are signs of a generally disorganized community (Smith et al. 2001 ). Because some types of tourism communities experience rapid expansion accompanied by intensive development and rapid social change over a relatively short period of time, they seem to be great settings for studying various postulations of the social disruption theory.
Place change and social disruption theory are closely connected. According to this assumption, when a community undergoes fast expansion, it tends to experience a generalized crisis that might culminate in several social issues as changes spread throughout the community and among individuals (Rasoolimanesh et al. 2019 ). Place change can result from fundamental community restructuring due to economic development, new class divides, and migration of both long-term and temporary people (Nelson 2001 ). Social unrest, though, is not enduring. Instead, it is transitory; societies gradually adjust to these changes (Deery et al. 2012 ).
The standard of living may initially deteriorate, but due to the adaptability of people and communities, they will gradually reinvigorate and strengthen themselves accordingly. Furthermore, the social disruption proposition reinforces one of the challenges in analyzing the effects of tourism, particularly in emerging nations, since it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between the effects of tourism and the overall ongoing development (Park and Stokowski 2009 ) (Fig. 1 ).
Tourism development and growth significantly affect natural environment resources.
Tourism development and growth significantly affect environmental pollution.
Tourism development and growth significantly affect the physical ecosystem of the environment.
Tourism development and growth significantly affect the socio-cultural environment.
Tourism development and growth significantly affect the economic environment of people and the community.
Government policy and support significantly moderate the relationship between tourism development and growth and the environmental factors.
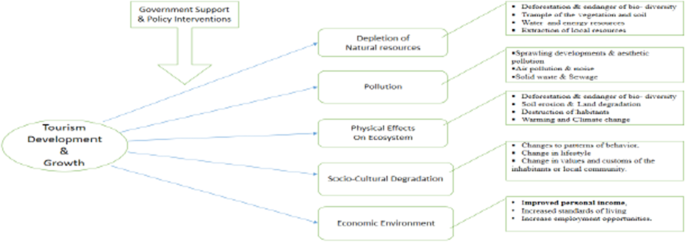
Conceptual framework
Methodology
The study aimed to investigate the association of tourism development and its impact on environmental factors. Therefore, a survey method was employed to collect data by including all the relevant people in the locality. The study is based on stakeholders’ opinions from Pakistan’s most visited tourist areas, including Murree, Swat, Chitral, Naran, Kaghan, Neelum Valley, Malam Jabba, Ayubia, and Nathia Gali. A total of 650 stakeholders were contacted from the above-mentioned tourist destinations through survey. The distribution of the sample is mentioned in Table 1 .
Using quantitative techniques, hierarchical linear regression analysis was employed to investigate the possible relationships between tourism growth and various dimensions of environmental sustainability. The results below reveal that tourism development translates into environmental deterioration, and the relationship between tourism and environmental sustainability is bidirectional.
Tourism growth and development were measured through a five-item scale. The environment was measured through 16 items combined scale with sub-dimensions; depletion of Natural Resources=3 items, Polluting Environment=3 items, Physical Effects on Ecosystem=4 items, Socio-Cultural Degradation=3 items, and Economic Environment=3-items. Similarly, our moderating variable, Government Interventions and Support, was measured using a 5-item scale. Table 2 below presents the details of the instruments.
Analysis and results
Data were analyzed using SPSS Version 26. It includes correlation, linear regression, and stepwise hierarchal regression analysis.
Table 3 above shows that our Tourism Growth and Development has significant and positive relationship with Polluting Environment ( r = 0.20**), Physical Effects on Ecosystem ( r = 0.19**), Depletion of Natural Resource ( r = 0.24**), Socio-Cultural Degradation ( r = 0.18**). However, Tourism Growth and Development has positive relationship with Economic Environment ( r = 0.29**) and Government Interventions and Support ( r = 0.13**).
Results of linear regression analysis at Table 4 above depict that tourism growth and development predicts 4.1% variance in Depletion of Natural Resources ( β = 0.20, p <0.01), 3.9% variance in pollution ( β = 0.19, p <0.01), 6% variance in Physical Effects on Ecosystem ( β = 0.24, p <0.01), 3.6% variance in Socio-Cultural Degradation ( β = 0.18, p <0.01), and 8.8% variance in Economic Environment ( β = 0.29, p <0.01).
The study analyzes the applied two-step hierarchal regression. In the first step, Tourism Growth and Government Interventions were treated as independent variables, and their significant impact was measured. In the second step, the interaction term Tourism and Growth× Government Interventions was added, and its impact was measured. The results suggest that Government Interventions and Support moderate the relationship between Tourism Growth and the Environmental variables (Table 5 ).
The study has reported unique findings regarding tourism and its environmental impacts. We found that tourism growth and development generate economic activity on the one hand. However, it has specific adverse environmental and socio-cultural outcomes on the other hand as well. Our study revealed that tourism growth and development predict a 4.1% variance in Depletion of Natural Resources ( β = 0.202*, p <0.01). This suggests that due to the expansion of tourism in the country, natural resources are continuously depleted to meet the needs of tourists. Studies also supported our findings and suggested that revival and reinvigoration of infrastructure in tourism areas were backed up by extensive deforestation, use of local green land, rebuilding of the road network, displacement of biodiversity, and overtaxing the consumption of water and other natural resources (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Sadiq 2021 ; Dogar et al. 2021 ). The prior studies are consistent with our hypothesis that “tourism development and growth significantly affect natural environment resources.”
We further found that tourism growth and development predict a 3.9% variance in pollution ( β = 0.198*, p <0.01), suggesting that tourism expansion may pollute the natural environment. Furthermore, recent national statistics depict that major human activities at local tourism destinations such as Kalam, Sawat, Muree, and Northern Areas have accumulated solid waste and sewage, resulting in polluted air and water. Further, research also suggests that the overflow of tourists to tourist destinations may adversely affect the environment due to human activities (Noordzij et al. 2020 ; Slater et al. 2020 ; Andlib and Salcedo-Castro 2021 ; Callaghan et al. 2021 ). Thus, it is safe to argue that the growth of tourism has a particularly detrimental effect on the environment. These findings also support our hypothesis, “Tourism development and growth significantly contribute to environmental pollution.”
The results reported that tourism growth and development predict a 6% variance in Physical Effects on the Ecosystem ( β = 0.245*, p <0.01). Studies have reported that deforestation and alteration in species’ natural environment for tourism facilities construction may adversely affect environmental health (Kuvan, 2010 ; Azam et al. 2018 ; Hoang et al. 2020 ; Andlib and Salcedo-Castro 2021 ). During post-terrorism and post-Covid-19 times in Pakistan, millions of local tourists moved to popular tourist destinations that required new infrastructure to accommodate these tourists. Consequently, colossal deforestation and other detrimental human activities have negatively affected ecosystem. These findings also support our hypothesis that tourism development and growth significantly affect the physical ecosystem of the environment.
The study reported a total of 3.6% variance in socio-cultural degradation ( β = 0.189*, p <0.01) due to tourism growth and development. These findings suggest that tourism’s growth and development may lead the inhabitants to imitate the foreign tourists regarding their living standards, which may endanger their traditional culture. Thus, our hypothesis that “tourism development and growth significantly affect the socio-cultural environment” is confirmed.
Further, it was found that tourism growth and development predict an 8.8% variance in the economic environment ( β = 0.297*, p <0.01). It is established from the literature that tourism growth and development generate economic activity in the country. Development projects such as the construction of infrastructure, hotels, and road networks generate economic activity to facilitate international and indigenous tourists, positively affecting the community’s living standard (Baloch et al. 2020 ). Thus, our hypothesis, “tourism development and growth significantly affect economic environment of people and community,” is confirmed.
Due to tourism growth and development, our study reported a 1.8% variance in Government Support and Interventions ( β = .133*, p <0.01). However, more recently, the Government of Pakistan has devised specific interventions that may help curb the adverse impacts of detrimental environmental factors. For example, developmental schemes such as the Billion Trees Plantation drive and Road-Infrastructure Network Development under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor initiative may prove moderators to curb the negative impacts of tourism growth on the environment (Qamar and Baloch 2017 ; Rauf et al. 2019 ; Siddiqui and Siddiqui 2019 ). Therefore, the hypothesis, Government policy and support, significantly moderates the relationship between tourism development and growth with the environment is confirmed based on these findings.
Suggested model for ecotourism framework
Through its detailed review of existing literature, prevailing tourism policies, and empirical inputs from the stakeholders’ perspectives, the study has identified a wide range of obstacles limiting the development and growth of ecotourism in Pakistan. The study suggests National Tourism Management authorities carefully invest in ecotourism destination’s planning and development in coordination with the environment development agency. The suggested model for ecotourism framework is initially meant for the tourism destinations specifically designated for ecotourism. However, selected points can also be extended to the quality management parameters set for the National Parks, Conservation and Protracted Areas, Museums, National or International event sites, etc. The national tourism authorities are to lay particular emphasis in their forthcoming National Tourism Policy on the development and promotion of Sustainable Ecotourism having, with focus on the following key areas:
Identify and classify four to five ecotourism destinations, including ecotourism-centered activities of value chains for priority development, which are administratively possible within budgetary constraints. However, the development plan shall consider the integral benefits of other developmental schemes such as the Billion Trees Plantation drive, Road-Infrastructure Network Development under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor initiative, International Union for Conservation of Nature (ICUN) programs in the area.
While staying within the alignment of UN Millennium Development Goals (MDG) calling for ‘environmental sustainability’ and the development vision of each designated destination, the Tourists Management System shall take into cognizance of issues like managing capacity of the place, quality parameters for the conservation of the environment, and allowable activities thereof.
Identify degenerated destinations of religious, socio-cultural, or historical significance for their rehabilitation under the Regenerated tourism program.
Tourism Destinations that have been over-consumed and exhausted (e.g., Murree, Galiaat, Naran, Malam Jabba) because of over-tourism shall be planned for their reclamation through regenerated tourism. However, to facilitate the success of the regeneration of their tourism potential following is to be catered for:
To deflect the tourist pressure upon these destinations, the potential tourists from nearby cities and metropolitan areas be provided with nearby alternative destinations for leisure tourism as stay-tourism sites.
To prevent the environment from air pollution, the traffic load on the destination be curtailed through an effective traffic management strategy, provision of off-destination parking for combustion engine vehicles, and encouraging electric driven or hybrid vehicles for nearby parking.
Provision of clean drinking water through public infiltration plants, public toilets, solid waste carriers, and recycling of sewage and used water is recommended in the most visited areas of the destination.
Signposting at appropriate places, giving social messages encouraging to maintain cleanliness, avoid littering, ensure nature conservation, and humility toward biodiversity.
Develop all-inclusive, comprehensive execution plans to expedite the investments for the sustainable ecotourism, encouraging public–private cooperation, community involvement, and infrastructure mapping guaranteeing environmental conservation and safeguards.
Develop and place on the ground an all-inclusive program of capacity building for sustainable ecotourism, regenerative and green tourism services.
Develop and launch Pakistan tourism profile and Sustaining Ecotourism obligatory framework “to promote tourism on the one hand and nurture conscious ecological behavior among the potential tourists of the area”.
In order to fetch local ownership for the ecotourism center developments, all efforts shall be made to share the socio-economic benefits integral to the development scheme with the local population for community development.
As part of the destination management planning, identify complementary value chains and livelihood activities that could be developed as part of the overall ecotourism destination package.
Governments at all levels and the tourism Development and Promotion Agencies Network in Pakistan shall join hands to chalk out and, with a strict enforcement mechanism, a “Regulatory Framework for Ecotourism Friendly Destination” to sustain the efforts and policies undertaken in this regard on the one hand and generate responsible behavior from the tourism stakeholders on the other. Some of the suggestive points could be:
Setting new quality standards facilitating the promotion of ecotourism and environmental sustainability through acts of various bodies operating in the Ecotourism value chain, such as:
Revision of Private hotels Management Act (1976) and Tourists Operators Act (1976) alongside introduction and promulgation of a new “Tourism Destination Management Act” incorporating new quality standards as of today.
Promulgating laws to make all new construction/development projects responsible from any agency in the area, incorporating quality standards needed for environmental sustainability, and promoting ecotourism.
Set measures for the preservation of the local biodiversity and preservation of endangered species, including seeking support from internationally active environment conservation agencies, declaring local hunting illegal, introducing licensing programs for hunting of certain selected animals/ birds on the payment of a handsome amount to be used for the welfare of the local community.
Create awareness programs against deforestation, land conservation, and biodiversity, and maintain cleanliness, inculcating a culture of respecting and enjoying nature instead of spoiling it.
Conclusion, implications, and limitations of the study
The study premise was based on the contention that sustenance of ecotourism focuses on the economic viability of the business interests alongside the conservation and preservation of natural ecosystems, including ethical fairness to the socio-cultural environment of the host community. Ecotourism is a phenomenon that contributes to environmental sustainability through well-planned and careful destination management capable of balancing conflicting interests of business growth and environmental sustainability. Tourism-environment paradox suggests that the sustainability and survival of both are dependent upon the flourishing mode of each other. Quality of environment and sustainability of bio-ecosystem stimulates tourists’ arrivals and over-tourism beyond capacity with irresponsible behavior from tourists negatively influencing the environment and harming the ecosystem of nature. Ecotourism is not inevitably sustainable unless it is economically sustainable and environmentally maintainable besides being socio-culturally acceptable. Socio-culturally intolerable ecotourism means the activity which does not benefit locals and their socio-cultural values. Hence, the study concludes that ecotourism has to positively interplay between economy, environment, and culture without compromising one over others. The pursuit of sustainable ecotourism is not an end in meeting the little comforts of the business interests but rather a means to end the sustainability issues created due to ill-conceived tourism development and unmanageable growth.
Practical implications
Drawing from the findings and conclusions of the research, the study extends the following practical implications for effectively managing the process of tourism development and environmental sustainability in line with the dictates of the philosophy behind ecotourism:
Paradoxically tourism necessitates ecological capitals as primary ingredients for the creation of tourism experiences on the one hand. However, it is also contingent upon the conservation and preservation of ecological integrity on the other. The study suggests that unbalancing this “resource paradox” results in the harshness and tenacity of adversarial climate change, natural calamities, environmental pollution, and endangered biodiversity.
The research findings and the suggested framework for ecotourism imply that sustainable ecotourism principles-based planning is mandatory for destination management to assure effective trade-off between the business interests’ sustainability of the environmental ecosystem.
Tourism development and growth shall be steered through ecotourism principles as its sustainable model offers enduring social, environmental and economic, ecological integrity, and social and cultural benefits for the local community. Therefore, ecotourism is a recipe for preventing environmental degradation and guarantees sustainability of ecosystems nature and its biodiversity. Hence, ecotourism shall stand central priority focus for strategic management to nurture quality experiences from sustainable tourism.
To revive back the sustainability of the environment, in the areas where over-tourism has degraded the environment, schemes for regenerated tourism shall be immediately launched to mitigate the negative footprints on the sustainability of destinations, including reinforcing protracted conservation sites, biodiversity, and recouping endangered species, afforestation drives, recycling of water and solid waste, refurnishing of landscaping, preservation, and rehabilitation of cultural heritage and refurbishing of depleted infrastructure accordingly. Furthermore, to regenerate and sustain the tourism infrastructure of the destinations experiencing over-tourism, capacity building measures like capacity, recycling of water and solid waste, preventive measures to control air and water pollution, traffic control management, and spread of entertainment facilities shall be the focus of the regeneration plans.
The study implies that government authorities and policymakers have a special role in placing their moderating intervention in terms of policy guidelines, regulatory framework, and budgetary support, provision of inter-organizational synergy in planning and implementation of ecotourism strategies, protection of environmental resource base and conservation of natural and biological ecosystem, sustenance of socio-cultural value of local community over and above their economic and social well-being/quality life for the long run.
The study also implies that public and private policymakers lay down threshold criteria for responsible travel and tourism standards for destination management and its related supply chain. The laid criterion would facilitate management in nurturing “responsible behavior” to plan, protect, conserve, preserve, and sustain natural and cultural resources and responsible socio-economic development without compromising the sustainability of the environment and long-term well-being of the hoist community. The deep-seated adherence to social responsibility protocols by the tourism supply chain network can significantly increase the capacity of tourism destinations and improve the conscious awareness of green consumers along the tourism supply chain. Furthermore, the consciously responsible behavior among stakeholders and legislatures can strike a needed balance between the business interests and environments in favor of sustainability of socio-cultural, economic, and natural capital.
The study elucidates that responsible behavior necessitates purpose-built eco-friendly infrastructure and policy parameters to support the sustainability of environments across destinations. The strategic planning aligned with the sustainability-focused objectives dictates the need for artistic, innovative, and talented people and quality intuitions in harnessing quality tourism services and responsible tourism behavior. Furthermore, the study encourages community involvement in the developmental process, enactment of structural policies, preservation of socio-cultural heritage, and conservation of natural biodiversity as it would foster emotional bondage between the people of the host community and the tourism undertakings. Therefore, community and value chain managers shall collaborate to maximize the perceived benefits of responsible tourism while developing cultural exchanges and planning opportunities for leisure and tourism.
Regulatory measures help offset negative impacts; for instance, controls on the number of tourist activities and movement of visitors within protected areas can limit impacts on the ecosystem and help maintain the integrity and vitality of the site. Limits should be established after an in-depth analysis of the maximum sustainable visitor capacity. Furthermore, the variables and the constructs researched can be replicated to other destinations to seek valuable inputs for sustainable destination management elsewhere.
Study limitation
Besides the functional, practical applications, the study has some limitations. Besides having integral disadvantages of cross-sectional research, the respondents selected for the study were visitors on peak days with the highest tourist arrivals, thereby having experiences of a higher degree of environmental pollution and natural disorder. Furthermore, the research is limited to stakeholders’ perspectives instead of any scientifically generated data or mathematical or econometric model.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Abasyn University, Peshawar, Pakistan
Qadar Bakhsh Baloch & Syed Naseeb Shah
Air University School of Management, Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan
Nadeem Iqbal
Department of Commerce, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan
Muhammad Sheeraz
IBA, Gomal University, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan
Muhammad Asadullah
University of Sialkot, Sialkot, Pakistan
Sourath Mahar
Islamia College University Peshawar, Peshawar, Pakistan
Asia Umar Khan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
QBB: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. SNS: data curation and supervision. NI: visualization, editing, proofreading. MS: review and editing. MA: review and editing. SM: editing, data curation. AUK: review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nadeem Iqbal .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. We also declare that we do not have human participants, data, or tissue.
Consent for publication
We do not have any person’s data in any form.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Baloch, Q.B., Shah, S.N., Iqbal, N. et al. Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30 , 5917–5930 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22496-w
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2021
Accepted : 08 August 2022
Published : 19 August 2022
Issue Date : January 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22496-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Environmental sustainability and degradation
- Natural environment
- Ecosystem and biodiversity
- Ecotourism framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition
Europe: Venice residents protest as city begins visitor charging scheme – as it happened
Locals say city is against plan and accuse authorities of turning Venice into a ‘theme park’ by charging day trippers for visits
- 6h ago Summary of the day
- 6h ago ‘Recipe for disaster’: Venice entry fee sparks confusion and protest on day one
- 6h ago Italian state broadcaster journalists to strike
- 7h ago Why is Spain’s prime minister considering resigning from office?
- 7h ago Spanish prosecutor seeks dismissal of case against prime minister's wife
- 10h ago Protests in Venice as city introduces fee
- 10h ago Amsterdam targets river cruises
- 10h ago 'What fee?' Tourists react to new Venice fee
- 12h ago NGO cautions about environmental impact of over-tourism
- 12h ago Venice access fee: what is it and how much does it cost?
- 12h ago Welcome to the blog
- 12h ago ‘Are we joking?’: Venice residents protest as city starts charging visitors to enter

Amsterdam targets river cruises
The latest target in Amsterdam’s decade-long battle against overtourism is an unlikely one: river cruises .
City finance chief Hester van Buren announced this month that the city wants to halve the number of river cruises by 2028, from the current total of 2125. Councillors have already voted to close an ocean cruise terminal in the city centre.
But local businesses have suggested visitors who take river boat tours from Amsterdam are not typically nuisance tourists. The 271,000 people are often older, enjoy a night at a hotel and spend an estimated €63 million.
However, it is all part of around 100 measures to try to stem tourism, which exploded after late mayor Eberhard van der Laan brokered a deal with Airbnb to officially allow holiday home rentals in 2014 – and take a cut of the tax.
Since 2023, smoking cannabis outside has been banned in the city centre, there are restrictions on alcohol sales, pubs have earlier closing times in the red light district, and the city plans to close 100 brothel windows and move them to an “erotic centre”. City tax is up and a “ stay away ” plan to dissuade nuisance young Brits hit the global headlines and will be expanded to other nations such as the French, Germans and Dutch themselves.
Despite all this, hotel overnights rose to over 20 million last year (not including holiday rentals) and although there’s an official ban on new hotels, 26 are being built. The Dutch came up with the word “overtourism” in 2017 and it’s still an everyday term.
'What fee?' Tourists react to new Venice fee
Tourists arriving in Venice on Thursday were welcomed by ticket controllers as the city became the first in the world to charge an entrance fee.
The hotly debated measure, targeted at day-trippers, kicked in at 8.30am. Most of the day-trippers arriving at Santa Lucia station came pre-prepared with a QR code proving they had payed the €5 toll, but the initiative sparked confusion among people staying in hotels who, even though they are exempt, were unaware they would still have to endure the rigmarole of going online to confirm their exemption.
A steward guided Yvonne McKenna and Ken Mehan, who had just arrived on an overnight train from Vienna, through the process, which took about 10 minutes.
“I knew about the new tax and I knew about the exemption but I didn’t know we would be doing this when we arrived,” said McKenna. “It does seem to take a long time...imagine if you weren’t so up on all the technology?”
Others were totally oblivious to the new measure. “What fee?” asked Elizabeth from America, before being taught how to pay online.
The initiative has caused much division in Venice, with opponents arguing that it is against the principle of freedom of movement and will do nothing to meaningfully address over-tourism.
Some who live in other tourist hotspots sympathise with their plight, but support the fee.
Jana Plevova, from Prague, is spending five nights in the city and so is exempt as she already pays a nightly tourist tax, but said she would have no problem paying €5 to enter for the day.
“I come from Prague which is also suffering from over-tourism so paying €5 is not that much for trying to preserve this beauty,” she said.

Only about one in ten people present in Venice have paid a €5 fee to access the city, Ansa reported today.

The daily Le Parisien ran a front page on the Venice scheme drawing comparisons with the challenges of over-tourism at some sites in France.
For example, the Calanques de Sugiton, in the Calanques national park near Marseille, has put in place a quota reservation system for hikers and swimmers at peak moments in the summer months to protect the ecosystem from erosion and overcrowding.
The paper cited an OpinionWay poll for Evaneos in which 60% of French people said they had suffered because of overtourism. Three quarters said they had given up on visiting a site because of overcrowding.
Éric Straumann , the mayor of the picturesque Alsace town of Colmar told the paper he was thinking about whether to introduce some kind of limited access to the Christmas market, which at weekends can reach 150,000 visitors in a town of 70,000 people.
There are islands in France which limit the number of daily visitors in the summer, for example the Île-de-Brehat in Brittany and at Porquerolles in the south. The Mont-Saint-Michel in Normandy does not have quotas, but shuttle buses to the site have been limited and car-park reservations introduced.

‘A family used to live here’: The Spanish sticker rebellion battling tourist lets
Incensed after finding out his rental home of 10 years was about to become a tourist apartment, Dani Romero took to social media.
What followed swiftly snowballed into a movement, as residents in Málaga began plastering stickers – reading “A family used to live here” or “Go home” – outside tourist lets across the southern Spanish city.
“I didn’t mean to arm a revolution,” said Romero. “I’m just looking for a house to live in.”
At the core of what one Spanish broadcaster called “the sticker rebellion” is not a rejection of tourism, said Romero. Instead, as city residents grapple with a record number of tourists, it’s a cri de coeur for a more balanced approach that could allow for a better coexistence between residents and tourists.
It’s a debate playing out across Europe, as cities from Athens to Amsterdam wrestle with how best to tackle overtourism.
Read the full story here .
NGO cautions about environmental impact of over-tourism
Transport & Environment, an NGO campaigning for cleaner transport, has warned about the impact of over-tourism.
”The current number of cruise ships globally is higher than it’s ever been, according to data from Clarksons Research,” the NGO said this morning.
“In 2022, Europe’s 218 cruise ships emitted as much sulphur oxides (SOx) as 1 billion cars, T&E’s Return of the Cruise report (2023) found,” it said, noting that “Europe’s cruise ships emit 8 million tonnes of CO2 every year.”
“In 2021 Venice banned large cruise ships from entering the city. This led to an 80% fall in SOX emissions from cruise ships. Barcelona is now Europe’s most polluted port,” Transport & Environment said.
Carlos Calvo Ambel , senior director for Non-Road Transport at T&E, added:
Europe’s luxury cruise ships emit as much toxic sulphur as a billion cars, and low-cost airlines are now polluting more CO2 than ever. The uncontrolled growth of these two sectors must come to an end. Cruise ships should plug into electricity if they want to dock, and the adoption of zero-emission fuels by cruises and airlines needs to happen fast. If cruise lines and airlines don’t radically change how they operate, they will increasingly be seen as unwanted guests.
Venice access fee: what is it and how much does it cost?
Why is this being introduced?
According to Simone Venturini, the city’s councillor for tourism, Venice “affixed itself” to mass tourism in the 1960s and since then visitor numbers have surged to the point that during the busiest periods of the year it attracts an average of 40,000 people a day.
That number has put pressure on the fragile lagoon, while pushing residents away from the main island. Brugnaro said he wanted to make Venice “livable” again.
However, the final push to enact the measure came after Unesco threatened last year to put Venice on its list of heritage sites in danger, citing mass tourism and rising water levels attributed to climate change.
How much is the charge and who has to pay?
The “Venice access fee” costs €5 (£4.30).
Read the full explainer .
Preparations were underway in Venice for the introduction of a new access fee.

‘Are we joking?’: Venice residents protest as city starts charging visitors to enter
Authorities in Venice have been accused of transforming the famous lagoon city into a “theme park” as a long-mooted entrance fee for day trippers comes into force.
Venice is the first major city in the world to enact such a scheme. The €5 (£4.30) charge, which comes into force today, is aimed at protecting the Unesco world heritage site from the effects of excessive tourism by deterring day trippers and, according to the mayor, Luigi Brugnaro, making the city “livable” again.
But several residents’ committees and associations have planned protests for Thursday, arguing that the fee will do nothing to resolve the issue.
“I can tell you that almost the entire city is against it,” claimed Matteo Secchi, who leads Venessia.com, a residents’ activist group. “You can’t impose an entrance fee to a city; all they’re doing is transforming it into a theme park. This is a bad image for Venice … I mean, are we joking?”
Once the heart of a powerful maritime republic, Venice’s main island has lost more than 120,000 residents since the early 1950s, driven away by a number of issues but predominantly a focus on mass tourism that has caused the population to be dwarfed by the thousands of visitors who crowd its squares, bridges and narrow walkways at the busiest times of the year.
Read the full story .
Welcome to the blog
Good morning and welcome to the blog. Today we will be delving into the issue of overtourism.
Send comments and tips to [email protected].
- Europe live

‘Recipe for disaster’: Venice entry fee sparks confusion and protest on day one

Venice mayor says he is brave like Marco Polo in charging day-trippers €5

Venice to limit tourist group size to 25 to protect historic city

Venice gondola capsizes after tourists refuse to sit down and stop taking selfies

Venice to trial €5 ticketing system for day visitors from 2024

I took my mum to Venice – it was instantly special
Most viewed.

Donate to Defend Our Planet
Drilling on public lands, mass wildlife extinctions, worsening climate change—our planet is in crisis. Help us fight back and your gift will be matched $1 for $1.
Fourteen Years After Deepwater Horizon, Drilling is Still a Threat
Despite the devastation of the BP Deepwater Horizon disaster, offshore drilling remains a threat to communities, our ocean, and the climate.

Oil supply boats use water cannons to fight fire and smoke rising from BP's mobile offshore drilling unit called Deepwater Horizon following an explosion on the rig in the Gulf of Mexico.
U.S. Coast Guard

- Share this page block
Fourteen years after the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, it could happen again. The devastating consequences of our dependence on fossil fuels are especially clear as we look back on one of the greatest environmental disasters in history. On April 20, 2010, barrels upon barrels of oil gushed into the Gulf of Mexico following an explosion on the BP Deepwater Horizon oil rig. The explosion took the lives of 11 workers stationed on the rig and unleashed roughly 3.19 million barrels (134 million gallons) of oil into the Gulf, which flowed for 87 days. To say that the spill was catastrophic for marine ecosystems, coastal communities, and Gulf South economies would be a grotesque understatement. The impacts of the disaster continue to reverberate throughout the Gulf South today.
Beyond the devastating impacts for marine ecosystems, the BP Deepwater Horizon disaster had a profound human impact. The spill oiled 1,300 miles of shoreline across Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas, and Florida. The surface oil slick cumulative extent totaled 43,300 square miles (approximately equal to the size of Virginia). Fishermen saw their livelihoods erased as state and federal fisheries were closed in the Gulf of Mexico . Coastal economies lost hundreds of millions of dollars in commercial fishing and tourism because of the fossil fuel industry’s reckless pursuit of profit. The fossil fuel industry is pushing for even more offshore drilling despite the clear evidence of what happens when they drill and who bears the consequences.
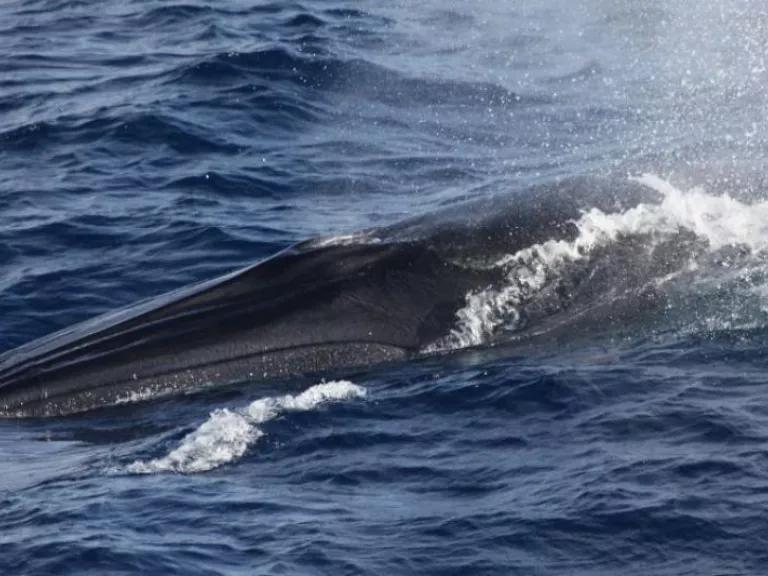

A Rice's Whale in the Gulf of Mexico. Credit: NOAA Fisheries/Laura Dias (Permit #14450)
Of the many species hit by the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill, one of the most impacted species was the Gulf of Mexico whale (also known as Rice’s whale). This whale is endemic to the Gulf of Mexico, and offshore drilling is hurtling the species toward extinction. Although the BP Deepwater Horizon drilling platform was outside the known habitat range of the Gulf whale, the spill killed roughly 17% of the whales outright . It caused reproductive failure and other misery in much of the rest of the population. There are fewer than 100 of these critically endangered whales alive today. A unique part of the region’s—and the country’s—natural history, the Gulf whale could be silenced forever if offshore drilling is allowed to continue.
At the same time, the same oil and gas companies polluting our waters are making billions in profits and still expecting taxpayers to foot the bill for cleaning up their messes. A recent report by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) states that over 2,700 wells and 500 platforms are actively deteriorating and endangering our oceans, wildlife, and Gulf Coast communities. At the same time, Big Oil recklessly continues to drill in public waters. Members of Congress agree , “The oil and gas companies, which are making record-breaking profits using our offshore waters, should be assuming the risks of their operations, not the American people.” Gulf South communities and ecosystems cannot afford another oil spill like Deepwater Horizon.
The Deepwater Horizon disaster was not an isolated incident but a symptom of an economy that functions off of exploitation of people and the environment to further the profits of a few over the prosperity of the many. Since the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill, millions more gallons of oil have spilled into the Gulf of Mexico. A fossil fuel economy does not have to be our reality or future. The anniversary of the BP Deepwater Horizon disaster is a reminder of the devastation that fossil fuels can have. Still, it is an opportunity to reflect on all we can save by ending our reliance on polluting industries for our energy system. It is time for accountability from the fossil fuel industry, and it is time for a fossil fuel phaseout. It is up to us to protect our coasts, our climate, and our futures because the fossil fuel industry certainly won’t.
Related Blogs

2023 Review: Offshore Drilling

The Biden Administration’s Risky Offshore Leasing Plan

Time for U.S. to Kick the Habit of Offshore Drilling
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Published March 7, 2021 Updated March 12, 2021. For the planet, the year without tourists was a curse and a blessing. With flights canceled, cruise ships mothballed and vacations largely scrapped ...
Solid waste and littering. Sewage. Aesthetic Pollution. Physical impacts of tourism development. Construction activities and infrastructure development. Deforestation and intensified or unsustainable use of land. Marina development. Coral reefs. Physical impacts from tourist activities.
The negative environmental impacts of tourism. Tourism sector has great influence over wellbeing of local residents. It is an industry that flourishes in large cities as well as remote rural areas rich in natural wonders. For many distant communities, tourism is the only opportunity of generating sufficient income to sustain their lifestyle and ...
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective ...
According to experts, tourism causes about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. "At first glance, that may not sound like much," says Wolfgang Strasdas, head of research at the Center for ...
Tourism is a significant contributor to the global economy, with potentially large environmental impacts. Origin and destination accounting perspectives are used to provide a comprehensive ...
In a 'business-as-usual' scenario, tourism would generate through 2050 an increase of 154% in energy consumption, 131% in greenhouse gas emissions, 152% in water consumption and 251% in solid waste disposal. This is why sustainability must now define tourism development in the 21 st century. UN Environment aims to mainstream sustainability ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
The influence of tourism development and economic policy uncertainties on environmental sustainability is substantial. Promoting responsible tourism and using sustainable tourism practises, like offering eco-friendly lodging, is a key part of protecting natural habitats and lowering carbon footprints. Hence, this study tries to examine the relationship between tourism development, economic ...
The reef has an economic, social and icon asset value of A$56bn. It supports 64,000 jobs and contributes $6.4bn to the Australian economy.". In order for the tourism industry to advocate for ...
Baloch Q, Shah S, Iqbal N, Sheeraz M, Asadullah M, Mahar S, Khan A (2022) Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism.
Sustainable tourism considers its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts by addressing the needs of its ecological surroundings and the local communities. This is achieved ...
Ecotourism can help a destination balance tourism revenue and environmental protection. ... and all of its 330 islands have been divided into zones that are either completely free of human impact ...
The International Sustainable Tourism Initiative (ISTI) researched a new framework, the Holistic Environmental Accounting for Tourism Destinations (HEAT-D) to help local governments and national planning bodies to measure the Invisible Burden. The Invisible Burden is defined in the report, Destinations at Risk: The Invisible Burden of Tourism. This research helps to measure the Invisible ...
The study has reported unique findings regarding tourism and its environmental impacts. We found that tourism growth and development generate economic activity on the one hand. However, it has specific adverse environmental and socio-cultural outcomes on the other hand as well.
Tourism is one of the most vital sectors and can contribute significantly to the environment and economy. Here are ways tourism can contribute to environmental conservation: 1. Better environmental planning and management. Management of tourism facilities can improve the natural environment within a tourist destination.
The negative environmental impacts of tourism are substantial. They include the depletion of local natural resources as well as pollution and waste problems. Tourism often puts pressure on natural resources through over-consumption, often in places where resources are already scarce. Tourism puts enormous stress on local land use, and can lead ...
Sustainable tourism, also known as ecotourism, or green tourism, is a form of tourism that attempts to take responsibility for its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts ...
Responsible tourism helps the environment by limiting ecological impact, supporting indigenous wildlife, respecting cultural heritage, and not taking away from a destination as a visitor, be it ...
Tourism is a large, diffuse global industry. Environmental aspects are little studied, with ∼1,500 publications in total. Impacts range from global contributions to climate change and ocean pollution to localized effects on endangered plant and animal species in protected areas. Environmental management is limited more by lack of adoption than by lack of technology. Government regulation is ...
The images have drawn global attention and created a bad rep for single-use plastic items, making us (consumers) more aware of the true impact. #2 Tourism for skills learning and education. This is a special side of tourism but plays also an important role in positive impacts of tourism on the environment.
The social, cultural, economic, and environmental impacts of tourist growth became subjects of serious study and research, and entered in the policy agendas of national and international organisations. Tourism is no longer considered a 'clean industry' as opposed, say, to heavy manufacturing. Tourism planning is advocated as a tool for ...
Changes in salinity and siltation can have wide-ranging impacts on coastal environments. And sewage pollution can threaten the health of humans and animals. Aesthetic Pollution. Often tourism fails to integrate its structures with the natural features and indigenous architectural of the destination.
The empirical research investigated the relationship between tourism development and environmental suitability to propose a framework for sustainable ecotourism. The framework suggested a balance between business and environmental interests in maintaining an ecological system with the moderating help of government support and policy interventions. The study population encompasses tourism ...
Tourism impacts tourist destinations in both positive and negative ways, encompassing economic, political, socio-cultural, environmental, and psychological dimensions. Economic effects: Increased tax revenue, personal income growth, enhanced The impacts of tourism , and the creation of additional employment opportunities.
DOI: 10.1007/s10668-024-04884-z Corpus ID: 269209205; Evaluation of economic, environmental, and social impacts of COVID on rural tourism @article{Muda2024EvaluationOE, title={Evaluation of economic, environmental, and social impacts of COVID on rural tourism}, author={Iskandar Muda and Sunil Kumar Vohra and Veer P. Gangwar and Bhadrappa Haralayya and Prabhdeep Singh and Ashish Kumar Pandey ...
The purpose of this research was to examine the impacts of the COVID pandemic on rural tourism by comparing the field both before and after the pandemic occurred along three key social, economic, and environmental dimensions. Survey methodology was employed for this quantitative research.
The demonstrators say they want a sustainable model that factors in environmental impacts such as water shortages in a warming climate, and which puts less pressure on costs and housing.
NGO cautions about environmental impact of over-tourism. Transport & Environment, an NGO campaigning for cleaner transport, has warned about the impact of over-tourism.
The impacts of the disaster continue to reverberate throughout the Gulf South today. Beyond the devastating impacts for marine ecosystems, the BP Deepwater Horizon disaster had a profound human ...