An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.


COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Coronavirus Updates
The u.s. lifts the pandemic travel ban and opens the doors to international visitors.
The Associated Press

Passengers walk through Salt Lake City International Airport, Oct. 27, 2020. More than a year and a half after COVID-19 concerns prompted the U.S. to close its borders to international travelers from countries including Brazil, China, India, South Africa, the U.K. and much of Europe, restrictions are shifting to focus on vaccine status. Rick Bowmer/AP hide caption
Passengers walk through Salt Lake City International Airport, Oct. 27, 2020. More than a year and a half after COVID-19 concerns prompted the U.S. to close its borders to international travelers from countries including Brazil, China, India, South Africa, the U.K. and much of Europe, restrictions are shifting to focus on vaccine status.
The U.S. lifted restrictions Monday on travel from a long list of countries including Mexico, Canada and most of Europe, allowing tourists to make long-delayed trips and family members to reconnect with loved ones after more than a year and a half apart because of the pandemic.
Starting Monday, the U.S. is accepting fully vaccinated travelers at airports and land borders, doing away with a COVID-19 restriction that dates back to the Trump administration. The new rules allow air travel from previously restricted countries as long as the traveler has proof of vaccination and a negative COVID-19 test. Land travel from Mexico and Canada will require proof of vaccination but no test.
Airlines are expecting more travelers from Europe and elsewhere. Data from travel and analytics firm Cirium showed airlines are increasing flights between the United Kingdom and the U.S. by 21% this month over last month.
The change will have a profound effect on the borders with Mexico and Canada, where traveling back and forth was a way of life until the pandemic hit and the U.S. shut down nonessential travel.
Malls, restaurants and Main Street shops in U.S. border towns have been devastated by the lack of visitors from Mexico. On the boundary with Canada, cross-border hockey rivalries were community traditions until being upended by the pandemic. Churches that had members on both sides of the border are hoping to welcome parishioners they haven't seen during COVID-19 shutdown.
Loved ones have missed holidays, birthdays and funerals while nonessential air travel was barred, and they are now eager to reconnect.
River Robinson's American partner wasn't able to be in Canada for the birth of their baby boy 17 months ago because of pandemic-related border closures. She was thrilled to hear the U.S. is reopening its land crossings to vaccinated travelers.
"I'm planning to take my baby down for the American Thanksgiving," said Robinson, who lives in St. Thomas, Ontario. "If all goes smoothly at the border I'll plan on taking him down as much as I can. Is crazy to think he has a whole other side of the family he hasn't even met yet."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the U.S. will accept travelers who have been fully vaccinated with any of the vaccines approved for emergency use by the World Health Organization, not just those in use in the U.S. That means that the AstraZeneca vaccine, widely used in Canada, will be accepted.
For air travelers, the airlines are required to verify vaccine records and match them against ID, and if they don't, they could face fines of up to nearly $35,000 per violation. Airlines will also collect information about passengers for contact tracing efforts. There will be CDC workers spot-checking travelers for compliance in the U.S. At land borders, Customs and Border Protection agents will check vaccine proof.
The moves come as the U.S. has seen its COVID-19 outlook improve dramatically in recent weeks since the summer delta surge that pushed hospitals to the brink in many locations.
Travel Restrictions to Prevent the Spread of Disease

Credit: David Snyder
Disease is just a flight away. To protect America’s health, CDC partners with the Department of Homeland Security to prevent the spread of serious contagious diseases during travel. CDC uses a Do Not Board list to prevent travelers from boarding commercial airplanes if they are known or suspected to have a contagious disease that poses a threat to the public’s health. Sick travelers are also placed on a Lookout list so they will be detected if they attempt to enter the United States by land or sea. These tools can be used for anyone who poses a threat to the public’s health.
Local and state public health officials can request CDC’s assistance if a person who poses a public health threat intends to travel. CDC helps ensure these people do not travel while contagious.
Placing people on the lists
The criteria for adding people to the Do Not Board and Lookout lists are
- not aware of diagnosis or not following public health recommendations, or
- Likely to travel on a commercial flight involving the United States or travel internationally by any means; or
- Need to issue travel restriction to respond to a public health outbreak or to help enforce a public health order.
Criteria number one plus one of the three subsets must be met for a person to be placed on the Do Not Board and Lookout lists.

Credit: David Heaberlin
Once a person is placed on these lists, airlines will not issue a boarding pass to the person for any commercial flight within, arriving to, or departing from the United States.
The Do Not Board and Lookout lists have been used for people with suspected or confirmed infectious tuberculosis (TB), including multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and measles. During 2020-2022, CDC used these authorities to restrict travel of people with COVID-19 and close contacts who were recommended to quarantine. These authorities were also used for mpox during 2022. Travel restrictions can also be used for other suspected or confirmed contagious diseases that could pose a public health threat during travel, including viral hemorrhagic fevers such as Ebola.
Preventing people with contagious diseases from traveling also helps to make sure they get or continue medical treatment, such as for infectious tuberculosis.
Taking people off the lists
Once public health authorities confirm a person is no longer contagious, the person is removed from the lists (typically within 24 hours). Also, CDC reviews the records of all persons on the lists every two weeks to determine whether they are eligible for removal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Travel Restrictions to Prevent the Spread of Disease
- Importation
- Southern Border Health and Migration
- Travelers' Health
- Vessel Sanitation Program
- Funding and Guidance for State and Local Health Departments
- Emergency Preparedness and Response
- Division of Global Migration Health
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets
Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
What is COVID-19?
Who can get covid-19, can i travel if i recently had covid-19, what can travelers do to prevent covid-19, more information.
CDC Respiratory Virus Guidance has been updated. The content of this page will be updated soon.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. The virus spreads mainly from person to person through respiratory droplets and small particles produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. The virus spreads easily in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor settings.
People with COVID-19 have reported a wide range of symptoms – ranging from no or mild symptoms to severe illness. Symptoms may appear 2–14 days after exposure to the virus. Possible symptoms include fever, chills, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle aches, headache, new loss of taste and smell, sore throat, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Anyone can get COVID-19. However, some people are more likely than others to get very sick if they get COVID-19. These include people who are older, are immunocompromised , or have certain disabilities , or have underlying health conditions . Vaccination, past infection, and timely access to testing and treatment can help protect you from getting very sick from COVID-19.
Yes, you can travel once you have ended isolation . Check CDC guidance for additional precautions, including testing and wearing a mask around others. If you recently had COVID-19 and are recommended to wear a mask, do not travel on public transportation such as airplanes, buses, and trains if you are unable to wear a mask whenever around others.
Get up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines before you travel and take steps to protect yourself and others . Consider wearing a mask in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor areas, including on public transportation and in transportation hubs. Take additional precautions if you were recently exposed to a person with COVID-19. Don’t travel while sick.
If you have a weakened immune system or are at increased risk for severe disease talk to a healthcare professional before you decide to travel. If you travel, take multiple prevention steps to provide additional layers of protection from COVID-19, even if you are up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines. These include improving ventilation and spending more time outdoors, avoiding sick people, getting tested for COVID-19 if you develop symptoms, staying home if you have or think you have COVID-19, and seeking treatment if you have COVID-19.
Consider getting travel insurance in case you need medical care abroad .
Consider getting a COVID-19 test if you:
- Develop COVID-19 symptoms before, during, or after travel.
- Will be traveling to visit someone who is at higher risk of getting very sick from COVID-19.
- Were in a situation with a greater risk of exposure during travel (e.g., in an indoor, crowded space like an airport terminal while not wearing a mask).
If you traveled and feel sick, particularly if you have a fever, talk to a healthcare professional, and tell them about your recent travel.
- Masking During Travel
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
U.S. to lift restrictions Nov 8 for vaccinated foreign travelers
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by David Shepardson; additional reporting by Tyler Clifford; Editing by Jonathan Oatis;
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron
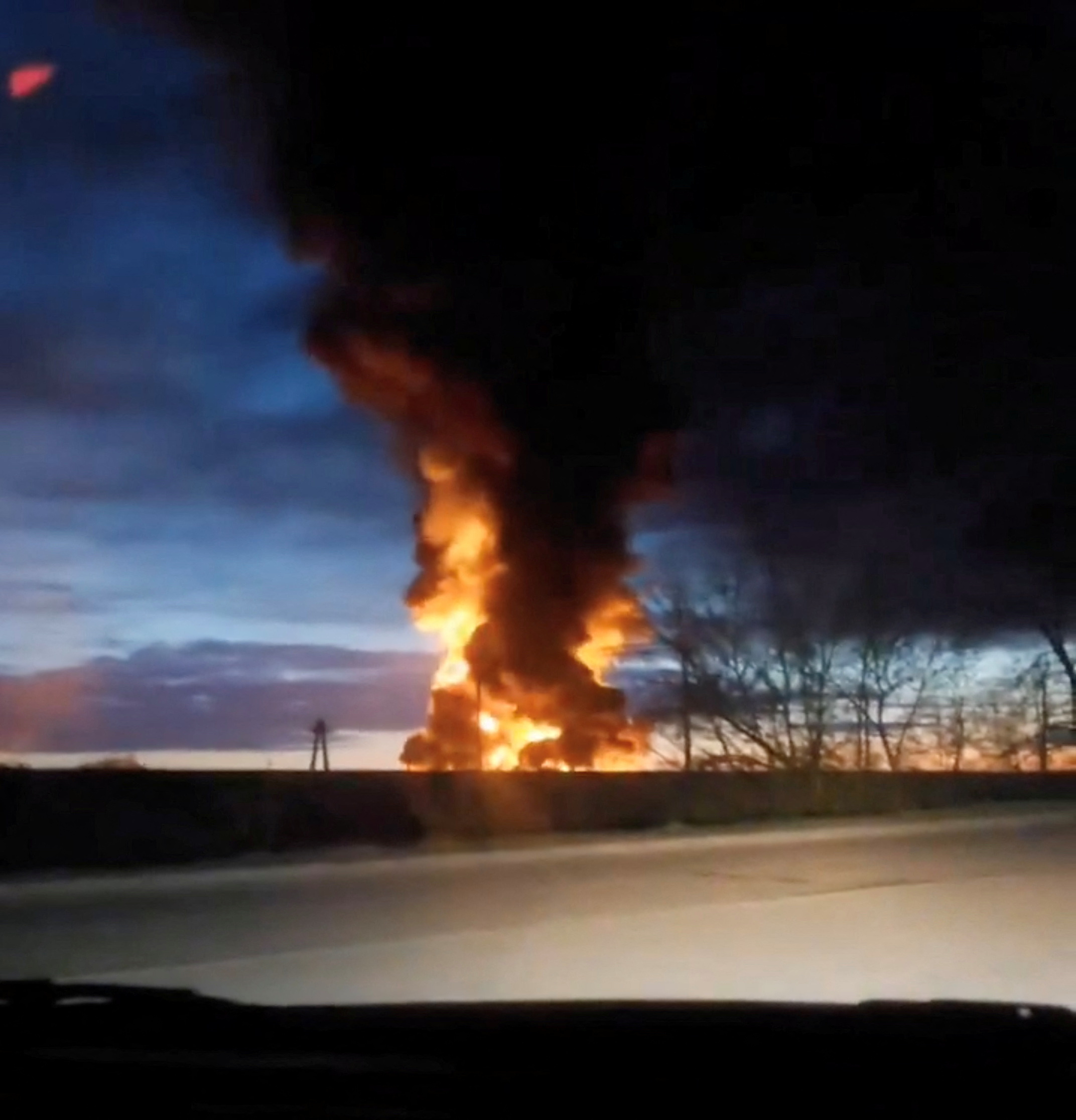

Ukrainian drones struck two Rosneft oil depots in attack, Kyiv source says
Drones sent by Ukraine's SBU security service struck two Rosneft-owned oil depots in Russia's Smolensk region in an overnight attack on Wednesday, a Ukrainian intelligence source said.

Morning Rundown: Tucker Carlson and Trump blamed for Ukraine aid delay, National Enquirer admits making up Ted Cruz father story, loose horses run amok in London
Map: Coronavirus travel restrictions by state
Guidance on traveling and travel restrictions varies across the United States as the country faces new surges in Covid-19 cases .
The patchwork of restrictions between regions highlights the ability of states to take different approaches while dealing with the coronavirus pandemic.
While all of the Northeast and most of the mid-Atlantic states have implemented statewide travel restrictions, more than half the states, including two of the biggest, Texas and Florida, have no such restrictions.
States hit the hardest when the epidemic began in the United States last spring, such as New York, New Jersey and Connecticut, have some of the most stringent travel restrictions.
Instead of opting for statewide restrictions, some local officials have imposed restrictions on travel to the most populous cities.
Check the interactive map below to see the latest guidance on travel and possible travel restrictions. This map will be updated weekly.
See NBC News’ coverage of the coronavirus , and see a map of coronavirus cases around the world or charts showing the day-by-day number of infections in the U.S. and worldwide .
CORRECTION (Dec. 18, 2020, 5:30 p.m.): A previous version of this map used the wrong colors for states with recommended travel restrictions and those with city-level travel restrictions. The colors were flipped: Recommendations should be orange (not yellow), and city-level restrictions should be yellow (not orange). The map has been fixed.
Matt Marshall is an associate producer for NBC News Now's "Top Story with Tom Llamas."
Kanwal Syed is a researcher for the Plan Your Vaccine interactive tool on NBCNews.com.
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

COVID-19 Restrictions on U.S. Visas and Entry
This page tracks U.S. visa and entry restrictions related to COVID-19. See NAFSA's Coronavirus Critical Resources Page for related information and resources.
Page Contents
- COVID Vaccine Requirement for Nonimmigrant Air Travelers End May 11 (updated 05/10/2023)
- Geographic Proclamations No Longer in Effect (updated 12/31/2021)
- General Resumption of Visa Services (updated 10/21/2022)
- COVID-19 Surge Impacts Nonimmigrant Visa Appointments in China (updated 1/12/2023)
- Expansion of Renewal Visa Interview Waivers (updated 12/27/2022)
- Vaccination requirements for individuals traveling through land ports of entry at the Canadian and Mexican borders scheduled to end at 12:01 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on May 12, 2023. (updated 05/10/2023)
- Mask Mandate Vacated (updated 4/18/2022)
- CDC Terminates COVID Test Requirement for Passengers Flights Originating in PRC ( updated 03/10/23) )
- COVID Viral Tests No Longer Required for Boarding All U.S.-Bound Flights Effective June 12, 2022 (updated 06/11/2022)
COVID Vaccine Requirement for Nonimmigrant Air Travelers
From November 8, 2021 through May 11, 2023, Presidential Proclamation 10294 of October 25, 2021, Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic , required all "noncitizens who are nonimmigrants" entering the United States through an air POE to show proof that they were fully vaccinated with an acceptable COVID vaccine. Presidential Proclamation of May 9, 2023, Revoking the Air Travel COVID-19 Vaccination Requirement , revokes Proclamation 10294's vaccination requirement effective 12:01 a.m. eastern daylight time on May 12, 2023.
For details, see NAFSA's page: COVID Vaccine and Test Requirements for U.S. Entry .
Geographic COVID-19 Proclamations No Longer in Effect
There are currently no geographic COVID-19 entry ban proclamations in effect.
- See NAFSA's page COVID Vaccine and Test Requirements for U.S. Entry for other current COVID-19 entry requirements and restrictions.
- See NAFSA's page Archive: Geographic COVID-19 Proclamations Affecting Entry from Certain Countries for historical information on revoked geographic COVID-19 proclamations.
U.S. Consular and Visa Services
The Department of State Visa Office does not maintain a COVID-19 portal page with information dedicated to U.S. visas, although the DOS travel.state.gov website does list COVID-19-related news alerts on its U.S. Visa News page . This NAFSA page has highlights from that and other sources.
Advocacy on Visa Delays
Senators ask dos to address visa backlog for international students.
On August 10, 2021, U.S. Senator Alex Padilla (D-Calif.) led a group of 23 Senators in calling on Secretary of State Antony Blinken and the State Department to address the backlog of visas for international students, which grew significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic. Read NAFSA's press release .
NAFSA Meets With Department of State Regarding Consular Operations
On July 12, 2021, Esther Brimmer, DPhil, NAFSA's executive director and CEO, met with U.S. State Department Acting Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary for Consular Affairs, Edward Ramotowski, to discuss growing concerns regarding limited visa appointment availability and processing delays affecting international students and scholars planning to arrive on U.S. campuses this fall. NAFSA members can read a meeting summary .
General Resumption of Visa Services
The Department of State suspended routine visa services worldwide in March 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. On July 13, 2020, DOS tweeted the following update from @TravelGov: " US embassies and consulates are beginning the phased resumption of routine visa services. The dates for each embassy or consulate will depend on local conditions. We are unable to provide details for each location. Please monitor the embassy or consulate website for updates. "
Read DOS' October 21, 2022 Update on Worldwide Visa Operations , transcribed below, for a DOS progress report.
" Update on Worldwide Visa Operations Last Updated: October 21, 2022 Worldwide Visa Operations Are Recovering Faster than Expected from the COVID-19 Pandemic The Department of State is successfully lowering visa interview wait times worldwide, following closures during the pandemic. We’ve doubled our hiring of U.S. Foreign Service personnel to do this important work, we are recovering faster than projected, and this year we will reach pre-pandemic processing levels. Backlogs and Wait Times – How We Got Here As for many service providers, the COVID-19 pandemic forced profound reductions in the Department’s visa processing capacity in two main ways. First, restrictions on travel to the United States, and local restrictions on public places like our overseas consular waiting rooms, curbed our ability to see visa applicants. As most applicants are required by U.S. law to appear in person, these restrictions forced a reduction in the number of visa applications the Department could process. Second, as revenue from the application fees that fund visa processing operations was cut nearly in half, the Department was forced to leave more than 300 overseas consular officer positions unfilled in 2020 and 2021. This further reduced the number of visa applications we could process. Where We Are Now Since COVID-19 restrictions have been lifted, we are back in business worldwide. Ninety-six percent of our embassies and consulates are again interviewing visa applicants, and we are processing nonimmigrant visa applications at 94 percent of pre-pandemic monthly averages and immigrant visa applications at 130 percent. In the past 12 months (through September 30, 2022), we processed 8 million non-immigrant visas, well above our best-case projections. We are well on the way to meeting and exceeding pre-pandemic visa processing capacity. Improved efficiency through Interview Waivers During the pandemic, the Department of State coordinated with the Department of Homeland Security to waive in-person interviews for several key visa categories, including for many students and temporary workers integral to supply chains. In addition, applicants renewing nonimmigrant visas in the same classification within 48 months of their prior visa’s expiration are now eligible to apply without an in-person interview in their country of nationality or residence. This has already reduced the wait time for an interview appointment at many embassies and consulates. We estimate 30 percent of worldwide nonimmigrant visa applicants may be eligible for an interview waiver, freeing up in-person interview appointments for those applicants who still require an in-person interview. Building on Success Our focused efforts during the pandemic recovery period have yielded substantial results in facilitating travel to the United States. Here are just some of our successes in the last year: We reduced the immigrant visa (IV) backlog and reunited families: As of October 2022, our consular sections worldwide have reduced the overall IV interview scheduling backlog by 25 percent (nearly 135,000 applicants), from its peak in July 2021. Our embassies in El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras eliminated an IV backlog of 22,000 applicants, and our consulate in Ciudad Juarez reduced the IV backlog for Mexican applicants by nearly 44 percent. We set records for student and academic exchange visitor visas. Consular sections worldwide adjudicated more student visas in July 2022 than in any other month since 2016, with nearly 180,000 F, M, and academic J visas processed. We exceeded pre-pandemic levels of visa processing for seasonal agricultural and nonagricultural workers who are vital links in the nation’s food supply chain and help ease labor shortages and inflation, with more than 395,000 H-2 visas issued in fiscal year 2022. We issued thousands of crewmember visas essential for maintaining the global supply chains that support both the U.S. and global economy. By Summer 2022, the issuance rates of crewmember visas were comparable to pre-pandemic levels. We issued all available E-3 visas in FY 2022, the immigrant visa category most sought by healthcare workers, who are crucial to the health and wellbeing of our communities. We issued 54,334 Diversity Visas during the DV-2022 program year. That is the highest number of DVs issued in 25 years, and all available DV numbers were exhausted when that total was combined with the domestic adjustments of status approved by USCIS under the DV program. For Those Navigating Long Interview Wait Times Our goal is to provide a visa interview for every applicant who requires one, worldwide, in a reasonable timeframe. Although our processing capacity is rebounding faster than projected, we know that visa applicants still face lengthy wait times at some embassies and consulates. We urge any visa applicant who can travel to another embassy or consulate with shorter wait times to consider doing so. There is no penalty for applying anywhere appointments are available, even outside your home country. For the latest information about wait times, see https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas.html ."
To find embassy or consulate websites, go to https://www.usembassy.gov/ . The embassy links get you to the right embassy website, but you will have to do some clicking to find relevant COVID-19 information, as each embassy website is structured a bit differently.
COVID-19 Surge Impacts U.S. Mission China Visa Appointments
Update from U.S. Mission China Consular Services for December 15, 2022
"Due to the operational impacts caused by the surge of COVID-19 infections across China, U.S. Embassy Beijing and U.S. Consulate General Shanghai are providing passport and emergency citizen services only. U.S. Consulates General Wuhan, Shenyang, and Guangzhou will only be providing emergency consular services until further notice. Please go to https://china.usembassy-china.org.cn/services/ for more information on emergency consular services. All routine Visa Services, with the exception of some previously scheduled for Consulate General Shanghai — are temporarily suspended; all regularly scheduled appointments at Embassy Beijing and the other Consulates General have been canceled."
Update from U.S. Mission China for December 27, 2022
"Consular Sections at the U.S. Embassy in Beijing, and Consulates Guangzhou and Shenyang will resume routine consular services on January 3. Consulate General Wuhan has resumed providing limited U.S. citizen services. Shanghai will continue operating in emergency operations status until further notice. Please note that the number of appointments available for routine services will be based on staffing."
Expansion of Visa Interview Waivers
In a December 23, 2022 announcement , DOS extended until December 31, 2023 the discretionary authority given to consular officers to waive the in-person interview requirement for certain "F, M, and Academic J Visa Holders" and "Petition-Based H, L, O, P, and Q Visa Holders."
See NAFSA's page for additional details .
Controls at Land Ports of Entry on Canadian and Mexican Borders
From January 22, 2022 through May 11, 2023, all noncitizens who are nonimmigrants had to show proof that they were fully vaccinated with an acceptable COVID-19 vaccine under the same vaccine standards as air travelers. Unlike air travel, however, travelers entering through land or ferry ports of entry were never subject to a pre-entry COVID-19 testing requirement. The U.S.-Canada-Mexico COVID restrictions ceased to have effect as of 12:01 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on May 12, 2023, under a pair of Federal Register Notice published on May 10, 2023. Canada notice | Mexico notice .
Airports and Flights
Mask mandate vacated.
Executive Order 13988 of January 21, 2021 , titled Executive Order on Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel, directed relevant agencies to incorporate, to the extent feasible, CDC recommendations on public modes of transportation and at ports of entry to the United States, including recommendations such as mask-wearing, physical distancing, appropriate ventilation, timely testing, and possibly self-quarantine after U.S. entry. See NAFSA's page on Executive Order 13988 for details.
CBP announced that on February 2, 2021 it began "enforcing the requirement that travelers wear face masks at all air, land and sea ports of entry in the United States in accordance with President Biden's Executive Order on Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order Regarding the Requirement for Persons to Wear Masks While on Public Conveyances and at Transportation Hubs...With limited exceptions, travelers must wear a face mask while physically present at a U.S. air, land, or sea port of entry. CBP Officers will require travelers to temporarily lower their mask during the inspection process to verify their identity."
However, On April 18, 2022, a Federal District Court judge in Tampa, Florida issued a ruling that the "Mask Mandate exceeds the CDC's statutory authority and violates the procedures required for agency rulemaking under the APA. Accordingly, the Court vacates the Mandate and remands it to the CDC." The case was Health Freedom Defense Fund, Inc. et al. v. Biden. Case 8:21-cv-01693-KKM-AEP.
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) followed up with an April 18, 2022 statement saying: "Due to today’s court ruling, effective immediately, TSA will no longer enforce its Security Directives and Emergency Amendment requiring mask use on public transportation and transportation hubs. TSA will also rescind the new Security Directives that were scheduled to take effect tomorrow. CDC continues to recommend that people wear masks in indoor public transportation settings at this time."
CDC Terminates COVID Test Requirement For PRC Travelers
The Centers for Disease Control announced on March 10, 2023, that:
"On March 10, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) rescinded the Order titled “ Requirements for Negative Pre-Departure COVID-19 Test Result or Documentation of Recovery from COVID-19 for Aircraft Passengers Traveling to the United States from the People’s Republic of China .”
This rescission takes effect for flights departing to the United States from the People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Designated Airports* at or after 3:00pm ET (8:00pm GMT) on March 10, 2023 , and will be published in the Federal Register.
This means that starting March 10, 2023 at 3pm ET, air passengers will no longer need to get tested and show the negative COVID-19 test result, or show documentation of recovery from COVID-19, prior to boarding a flight to the U.S. from the People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong, and Macau, or through a Designated Airport.
* Designated Airports included Incheon International Airport (ICN) in Seoul, Republic of Korea; Toronto Pearson International Airport (YYZ) in Canada; and Vancouver International Airport (YVR) in Canada.
View the Rescission [PDF – 5 pages] ."
The requirement had applied to air passengers regardless of nationality and vaccination status, if they wanted to enter the United States on a flight:
- originating from the PRC, Hong Kong, or Macau; or
- transiting Incheon International Airport, Toronto Pearson International Airport, or Vancouver International Airport on their way to the United States, if they have been in the PRC in the last 10 days.
Covered travelers had to take an acceptable COVID test ("such as a PCR test or an antigen self-test administered and monitored by a telehealth service or a licensed provider and authorized by the Food and Drug Administration or the relevant national authority") no more than 2 days before their departure to the United States, and the traveler must show a negative test result to the airline upon departure.
CDC Rescinds Order Requiring all Passengers on U.S.-Bound Flights to Have COVID-19 Viral Test, Effective June 12, 2022
Proclamation 10294 of October 25, 2021 did not institute new negative COVID-19 test requirements. Rather, in addition to being subject to the proof of vaccination requirements instituted by Proclamation 10294, nonimmigrants who were entering the United States through an air port of entry prior to June 12, 2022 were also subject to CDC rules that required all travelers ( regardless of citizenship ) to present proof of receiving a negative pre-departure viral test result for COVID-19. Nonimmigrants subject to Proclamation 10294 of October 25, 2021 must, however, still show both proof of being fully vaccinated (or qualify under one of the narrow exceptions) in order to enter the United States.
Update from the CDC website :
"As of 12:01AM ET on June 12, 2022 , CDC will no longer require air passengers traveling from a foreign country to the United States to show a negative COVID-19 viral test or documentation of recovery from COVID-19 before they board their flight. For more information, see Rescission: Requirement for Negative Pre-Departure COVID-19 Test Result or Documentation of Recovery from COVID-19 for all Airline or Other Aircraft Passengers Arriving into the United States from Any Foreign Country ."
See NAFSA's page COVID Vaccine and Test Requirements for U.S. Entry for additional details.
Related Content
Regulatory resources.
Advertisement
Supported by
U.S. Ends Last Covid Travel Barrier, Vaccine Mandate for Foreign Arrivals

By Ceylan Yeginsu
- Share full article
International passengers traveling to the United States no longer have to show proof of vaccination against Covid as of midnight Thursday, when the coronavirus health emergency officially ended .
The Biden administration dropped its requirement for coronavirus testing last June but kept in place its vaccination policy for foreign travelers. In February, the House of Representatives voted to end the last remaining pandemic restrictions on May 11.
“As we continue to monitor the evolving state of Covid-19 and the emergence of virus variants, we have the tools to detect and respond to the potential emergence of a variant of high consequence,” President Biden said in a proclamation published on May 1.
“Considering the progress that we have made, and based on the latest guidance from our public health experts, I have determined that we no longer need the international air travel restrictions that I imposed in October 2021,” he added.

Why It Matters: Most other countries have dropped restrictions.
For 18 months during the height of the pandemic, the U.S. closed its borders to international travelers, separating families and costing the global travel industry billions of dollars.
In November 2021, those restrictions were eased, and international travelers were welcomed back to the United States with great fanfare. But foreign travelers were still required to be vaccinated and take a coronavirus test within three days of travel to all U.S. ports of entry. When the administration dropped its testing rule in June last year but kept vaccinations in place, it argued that they were still necessary to slow the spread of new variants of the virus entering the country.
As of last summer, the U.S. was one of the few remaining countries to maintain coronavirus travel restrictions, causing many travelers to choose alternative destinations that welcome them unconditionally.
The rules barred the world’s No. 1-ranked tennis player, Novak Djokovic, from competing in the U.S. Open in 2022 because he is not vaccinated.
Background: Spending by foreign travelers in the U.S. still lags.
The initial U.S. travel ban on international travel decimated the U.S. economy’s tourism sector and resulted in losses of nearly $300 billion in visitor spending and more than one million American jobs, according to the U.S. Travel Association, an industry group.
Until April last year, all passengers traveling to or within the U.S. were required to wear masks on airplanes — a contentious mandate that led to fistfights and altercations on planes and put off some international travelers from taking long-haul flights.
Even after the restrictions were eased, spending by international travelers in the U.S. was still down by 78 percent in March 2022 compared to 2019 levels and by 56 percent for business travel, the group said.
“Today’s action to lift the vaccine requirement eases a significant entry barrier for many global travelers, moving our industry and country forward,” Geoff Freeman, the chief executive of the association, said in a statement after the May 11 end date was announced.
Ceylan Yeginsu is a travel reporter. She was previously a correspondent for the International desk in Britain and Turkey, covering politics; social justice; the migrant crisis; the Kurdish conflict, and the rise of Islamic State extremism in Syria and the region. More about Ceylan Yeginsu
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
This travel advice also covers American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and United States Virgin Islands.
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and any specific travel advice that applies to you:
- women travellers
- disabled travellers
- LGBT+ travellers
- solo and independent travel
- volunteering and adventure travel
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
About FCDO travel advice
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Here are the travel restrictions across Central and South America due to COVID-19

Editor's note: An updated version of this story is available here .
Thinking about making a trip to Central or South America soon? You may want to get familiar with each country's travel restrictions.
Entry requirements for U.S. travelers vary country by country, with some enforcing strict testing or quarantine mandates while others list very few COVID-19-related rules. Either way, most travelers will have to take at least one coronavirus test during their trip to reenter the United States.
Travelers can also take a look at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's travel recommendations to see the agency's COVID-19 risk assessment for each country. Many of the countries listed below have a "high" or "very high" risk of COVID-19, which means travelers should make sure they are fully vaccinated before visiting or avoid the destination altogether, according to the CDC.
►Which EU countries are open to US tourists? A breakdown of EU travel restrictions by country
Learn more: Best travel insurance
►Hilton, Hyatt and Marriott get flexible with rewards programs: Here are the updates in loyalty memberships
Can U.S. tourists enter? As of Nov. 1 , non-resident foreign tourists can enter Argentina.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? All travelers, regardless of vaccination status, will need to take a negative PCR test no more than 72 hours before arrival. If they are not fully vaccinated, they will be subject to a seven-day quarantine period .
What else do I need to know? All travelers entering or leaving the country must submit an electronic sworn statement within two days before their arrival or departure. Travelers must also have travel insurance that would cover any COVID-related hospitalization or quarantine.
Last updated: Nov. 2
Can U.S. tourists enter? Yes.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Unvaccinated travelers must show proof of a negative PCR test taken within 72 hours of arrival or a negative rapid antigen test taken within 48 hours of arrival. As of March 1, travelers who can show proof of full vaccination do not need to test prior to entry.
What else do I need to know? Travelers must purchase travel health insurance to enter Belize. International tourists must book their stay at a property approved by the Belize Tourism Board.
Last updated: March 8
► Hold off on that flight to the Caribbean: CDC raises travel alert level for Belize, Saint Kitts and Nevis
Can U.S. tourists enter? Yes.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Travelers 5 and older must show proof of a negative PCR test taken 72 hours prior to departure.
What else do I need to know? All travelers must quarantine at least 10 days after arrival and must take another coronavirus test seven days after arrival. Visitors must also submit a sworn statement of where they'll be staying. Nonresidents will need health insurance with COVID-19 coverage to enter.
Last updated: Sept. 17
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Travelers must show a negative coronavirus test administered by an accredited laboratory and taken 72 hours prior to check-in for international flights. Children under 2 and children under 12 who are accompanied by parents or guardians are exempt. Travelers will also need to submit a health affidavit form.
What else do I need to know? Travelers cannot stay more than 90 days.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Chile allows fully vaccinated foreigners who test negative for COVID-19 within 72 hours prior to travel. Travelers vaccinated outside of Chile must verify full vaccination through a "mobility pass," which can take two to three weeks to obtain. Travelers with a mobility pass will need to quarantine five days at a private residence or hotel and comply with a 14-day follow-up process that includes self-reporting of their health status and location. The country says it "may" require travelers to test for COVID-19 again on "several occasions," including at the point of entry or during the 14-day follow-up period.
Starting Dec. 1, travelers with a booster shot will not have to quarantine or take additional PCR tests upon arrival.
What else do I need to know? Visitors must complete an online "travelers' affidavit" form prior to travel. Visitors must also have travel insurance that will cover any medical expenses related to COVID-19 with a minimum coverage of $30,000.
Last updated: Nov. 24
Do I need a vaccine or testing? No, the country does not require any coronavirus testing or vaccinations to enter.
Can U.S. tourists enter? Yes, U.S. citizens can enter via air, land and sea.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Unless they are fully vaccinated, adult travelers will need to provide proof of a medical insurance policy that covers COVID-19 related medical treatments or quarantine lodging. All visitors must also complete a health pass online 7hours prior to arrival. These entry requirements are set to be lifted April 1.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Visitors must provide a negative coronavirus test 72 hours prior to travel or proof of full vaccination.
El Salvador
Do I need a vaccine or testing? As of Nov. 17, travelers do not need to show proof of vaccination or a negative coronavirus test to enter.
Last updated: Nov. 19
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Travelers 10 and older who are not fully vaccinated must show a negative coronavirus test or proof of recovery to enter.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Vaccinated travelers who have a negative PCR test taken within 72 hours of their scheduled flight may enter.
What else do I need to know? All travelers must also submit a passenger locator form 24 hours prior to travel.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Travelers must show proof of full vaccination or carry proof of a negative PCR or rapid test result taken less than 72 hours before entry.
What else do I need to know? All travelers must complete an immigration precheck form to enter and should carry a printout of the confirmation email during their trip.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Yes. Travelers must show a negative test at the airport taken less than 72 hours prior to entry. Test results should also be sent to the airline electronically before the travel date. Land borders also require a negative coronavirus test.
What else do I need to know? Travelers must fill out an online form and submit it at least seven days prior to arrival.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Visitors must show proof of vaccination or a negative COVID-19 test to enter. Unvaccinated tourists will be subject to at least 72 hours of quarantine.
What else do I need to know? All travelers must show a completed health affidavit to their airline or carrier before boarding.
► Traveling to Panama?: Be prepared to quarantine if unvaccinated
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Visitors older than 12 must show a negative coronavirus test result prior to entering, regardless of vaccination status. Visitors who have recently recovered from COVID-19 are exempt from the testing requirement.
Visitors older than 12 who cannot show proof of full vaccination must also quarantine five days after the date of their pre-departure test and take another test on the fifth day. If the test is positive, they must quarantine another seven days.
What else do I need to know? All air travelers should complete a health declaration form within 24 hours of entering the country.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Visitors must complete a health form and offer a negative coronavirus test to enter, if they cannot present proof of v.
What else do I need to know? Children under 12 can show a medical certificate of good health in lieu of a negative test.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Fully vaccinated people may enter without a quarantine period as long as they show proof of vaccination, a negative PCR test less than 72 hours old and valid travel documents. Unvaccinated visitors can only enter for essential purposes and must show a negative coronavirus test and undergo a seven-day quarantine.
Can U.S. tourists enter? As of Nov. 1, foreign travelers who are fully vaccinated and present a negative PCR test can enter the country, according to the Embassy of Uruguay in the U.S.
Do I need a vaccine or testing? Travelers must show a negative PCR test taken less than 48 hours before arrival to enter.
What else do I need to know? U.S. citizens must apply for a visa to enter.
Follow USA TODAY reporter Bailey Schulz on Twitter: @bailey_schulz .
International Travel Restrictions by Country
Find out where you can travel and covid-19 policies.
Select origin country, search destination or select a country on the map to see travel restrictions.
The travel status of individual countries can change suddenly, and we know it can be hard to stay on top of it all. That's why we're getting you the information you need to consider when planning travel. Learn about country-specific entry requirements such as the border status, COVID-19 testing requirements, and quarantine requirements. Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers.
Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official government site.
Destinations you can travel to now
Dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Filter by region, status and more
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Albania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Algeria.
American Samoa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter American Samoa.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Angola.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Anguilla.
Antigua And Barbuda
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Antigua And Barbuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Argentina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Armenia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Aruba.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Australia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Austria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Azerbaijan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bahrain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bangladesh.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Barbados.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belgium.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belize.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Benin.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bermuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bhutan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Botswana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brazil.
British Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the British Virgin Islands.

Brunei Darussalam
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brunei Darussalam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bulgaria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Burundi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cambodia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cameroon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Canada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cape Verde.
Caribbean Netherlands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Caribbean Netherlands.
Cayman Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cayman Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chad.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chile.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter China.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Colombia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Comoros.
Cook Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cook Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Costa Rica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Croatia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Curaçao.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cyprus.
Czech Republic
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Czech Republic.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Denmark.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Djibouti without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Dominica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Dominican Republic.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, need to quarantine to enter East Timor.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ecuador.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Egypt.
El Salvador
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter El Salvador.
Equatorial Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Equatorial Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eritrea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Estonia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eswatini.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ethiopia.
Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas).
Faroe Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Faroe Islands.
Federated States of Micronesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Federated States of Micronesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Fiji.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Finland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter France.
French Guiana
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Guiana.
French Polynesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Polynesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gabon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Gambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Georgia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Germany.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ghana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gibraltar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greece.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greenland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Grenada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guadeloupe.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guatemala.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea.
Guinea-Bissau
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea-Bissau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guyana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Honduras.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hong Kong.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hungary.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Iceland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter India.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Indonesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ireland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Italy.
Ivory Coast
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ivory Coast.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jamaica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Japan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jersey.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jordan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kazakhstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kenya.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kiribati.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kosovo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kuwait.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kyrgyzstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Laos.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Latvia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lesotho.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liberia.
Liechtenstein
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liechtenstein.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lithuania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Luxembourg.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Macau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Madagascar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malawi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malaysia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Maldives.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malta.
Marshall Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Marshall Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Martinique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritius.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mayotte.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mexico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Moldova.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mongolia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montenegro.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montserrat.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mozambique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Namibia.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Nauru without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nepal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Netherlands.
New Caledonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Caledonia.
New Zealand
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Zealand.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nicaragua.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Niger without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nigeria.
North Macedonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter North Macedonia.
Northern Mariana Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Northern Mariana Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Norway.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Oman.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Pakistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Palau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Panama.
Papua New Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Papua New Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Paraguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Peru.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Philippines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Poland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Portugal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Puerto Rico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Qatar.
Republic of the Congo
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Republic of the Congo without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Réunion.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Romania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Rwanda.
Saint Barthélemy
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Barthélemy.
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Saint Lucia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Lucia.
Saint Martin
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Martin.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Samoa.
São Tomé and Príncipe
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter São Tomé and Príncipe.
Saudi Arabia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saudi Arabia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Senegal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Serbia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Seychelles.
Sierra Leone
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sierra Leone.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Singapore.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovakia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovenia.
Solomon Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Solomon Islands.
South Africa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Africa.
South Korea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Korea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Spain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sri Lanka.
St. Maarten
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter St. Maarten.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sudan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Suriname.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sweden.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Switzerland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Taiwan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tajikistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tanzania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Thailand.
The Bahamas
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter The Bahamas.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Togo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tonga.
Trinidad and Tobago
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Trinidad and Tobago.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tunisia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Türkiye.
Turkmenistan
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Turkmenistan.
Turks and Caicos Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tuvalu.
U.S. Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uganda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Arab Emirates.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Kingdom.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uruguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uzbekistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vanuatu.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vietnam.
Wallis and Futuna
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Wallis and Futuna.
Western Sahara
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Western Sahara.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zimbabwe.

Get trip-ready with at-home COVID-19 tests
How often is the data on this page updated.
We check for travel restriction information from government authorities daily, and update the page any time we get new information. The following information regarding travel restrictions for each country is correct to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication.
How many countries are closed to visitors?
As of Sep 11, 2 countries have completely restricted entry to non-citizens and 5 are open but require quarantine and/or a negative COVID test.
Where can I travel without COVID restrictions?
Currently you can travel from the United States to 197 countries without restrictions. Please check our map to learn more.
Are there any other types of travel restrictions besides COVID-19 tests and quarantines?
These are the two main types of restrictions or requirements needed to travel into another country. However, the COVID-19 testing options are continually widening as new methods are developed. Different countries may accept results from different or multiple test types, so be sure to check the individual country's specific requirements.
What should I do if I get COVID-19 while in another country?
If you get COVID-19 while in another country, follow the local authority's recommendations. These may include hospitalization, self-isolating and testing in that country. Be sure to contact your travel insurance company and travel provider as well and inform them of your situation.
What should I do if the borders of the country I am visiting close?
Depending on your home country, you may need to change your departure date and return home as soon as possible. If that's the case, contact your travel provider to find the earliest departure.
Additional resources
- What you need to know
- Airline policies
- Hotel policies
- Car policies
- Tips for flying
- Tips for hotel
- Tips for vacation rental
If you're looking for personalized travel advice for your own travel plans like whether or not a restriction applies to your trip, we won't be able to answer any questions or offer advice. Please consult your local government's resources.
- Latest Latest
- The West The West
- Sports Sports
- Opinion Opinion
- Magazine Magazine
Pandemic policies under scrutiny: American voters question COVID-19 measures
A new poll shows a majority of voters say covid-19 measures infringed on personal freedom.
By Brigham Tomco
A majority of American voters believe COVID-19 public health measures infringed on personal freedoms, according to a new Deseret News poll.
The poll also found that a significant plurality of registered voters judge pandemic-related restrictions to have had an overall negative impact on their life.
This gloomy view reflects missteps by institutions like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and state governments as well as the general pain associated with natural disasters, according to public health insiders and outside analysts.
A fair accounting of the nation’s COVID-19 reaction is unlikely in today’s polarized environment, they said. But four years after being hit by a wave of impromptu pandemic policies, many Americans still look back on lockdowns, mandates and the organizations that recommended them with distrust — a fact that could impede future public health responses.
“We tend to be rejecting a lot of our traditional institutions and that will have a price because we’ll have to see all those lessons learned again,” said former Utah Gov. Mike Leavitt, who served as Health and Human Services Secretary in the George W. Bush administration. “But,” he added, “that’s the way history teaches.”
How voters feel about COVID restrictions
A Deseret News/HarrisX poll, which was conducted among 1,010 U.S. registered voters between March 25-26, found that voters do not have a net positive perception of any COVID-19 closures or restrictions.

Half of respondents (49%) said closures of non-essential retail businesses, like restaurants and department stores, had some or a strong negative impact on them personally. One-fifth (20%) said it had some or a strong positive effect on their lives and 30% said it had no impact. Respondents felt similarly about stay-at-home orders, work office closures and having to wear masks.
A plurality of voters said school closures did not impact them personally, likely because only 30% of respondents had at least one child living at home. But among those who said they were personally impacted, 64% said it was negative.
Dissatisfaction with pandemic polices was mostly uniform across race, education and income but diverged sharply between voters with different political affiliations. Self-identified Republicans were consistently more likely to have negative views of COVID-19 restrictions than Democrats by 20 to 30 percentage points, with independents hovering between the two.
The divide was clear on COVID-19 church closures. Over half (55%) of Republican voters said restricting access to places of worship had some or a negative impact on their life, compared to 26% of Democrats and 31% of independents.
Around half of Democrats and independents said church closures did not impact them personally. Less than one-third of Republicans felt the same way.
A majority (55%) of voters said government measures to slow the spread of COVID-19 infringed on personal freedoms. The percentage jumped to 73% among Republicans and fell to 39% among Democrats, with independents sitting at 53%.
The poll has a margin of error of +/- 3.1 percentage points.

Why many voters look back on pandemic policy with distrust
It is no surprise voters have a generally negative recollection of the COVID-19 years, said Dr. Andrew Pavia, who leads the division of pediatric Infectious diseases at University of Utah Health and directs hospital epidemiology at Primary Children’s Medical Center.
“What I read from those poll numbers is really a recounting of the trauma that we all went through,” Pavia told the Deseret News.
During the pandemic, Pavia served as an adviser to the CDC and the Utah Department of Health on COVID-19. He is also a member of the National Institutes of Health COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel where he was the pediatric team lead.
“Were all of the decisions perfect? Of course not. Were most of them made in good faith with the best available data? I think so,” he said.
However, major mistakes that hurt peoples’ perception of public health agencies were made, Pavia said.
One example was an early effort by the CDC to preserve medical masks for health care workers. Instead of explaining that masks were likely helpful but that they were in short supply, CDC guidance came across as “We don’t think masks will protect people that much,” Pavia said. The CDC’s position on masks was later completely reversed to the bewilderment of many. As Pavia put it, “The message was botched.”
But the problems with COVID-19 policy ran much deeper than bad public relations or political malfeasance, according to Bethany McLean and Joe Nocera, co-authors of “The Big Fail: What The Pandemic Revealed About Who America Protects and Who It Leaves Behind.”
“For any public health figure to say it was just the fault of politicians exploiting it is not to look in the mirror about their own mixed messaging. And for any politician to say, ‘I was just confused because public health was unclear’ is to avoid responsibility for their own flawed leadership,” said McLean, who works as a contributing editor for Vanity Fair magazine.
For McLean, and for many Americans, it is easy to rattle off a list of “incoherent” pandemic guidelines coming from political or public health officials.
Whether it was California Gov. Gavin Newsom imposing harsh lockdowns on public schools while continuing to send his own children to private academies; states shutting off access to certain outdoor spaces despite evidence there was nowhere safer to be; or — what McLean sees as the most egregious — the continued insistence that healthy children were at risk from COVID-19 despite the opposite being true.
“It served to widen our divides and to cause people to lose trust in institutions instead of bringing us together and strengthening our trust in institutions. And I think that’s potentially quite, quite dangerous,” McLean said.
Nocera, a business journalist who has written for the Free Press, Fortune, New York Times and Bloomberg, gave political and public health leaders a pass for policies enacted during the spring panic of 2020. But by that fall many course corrections were obviously needed that never came.
“What’s particularly painful about this is that if you compare lockdown states with non-lockdown states, there’s virtually no difference,” Nocera said. “So, after all this — shutting things down, making people angry, forcing people to stay out of church — in the end, it didn’t even make any difference.”
The United States had one of the highest pandemic death tolls of any wealthy country — an outcome likely associated with high levels of obesity and low levels of full vaccination, according to a New York Times analysis. But California, which had some of the strictest and longest pandemic restrictions, had a significantly higher death rate than Florida, which had relatively fewer and shorter restrictions.
Lessons from America’s COVID-19 response
Nocera, a “left-leaning independent,” praised Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis for making evidence-based decisions that took into account factors other than just the COVID-19 case count.
“As a general precept, Republican governors did a better job of saying, ‘COVID isn’t the only thing going on in our world,’” Nocera said. “The Democrats were much more attuned to the idea, ‘If public health tells us this, we have to do it, we can’t question it.’”
The most glaring inconsistency between what was said by public health officials and the facts on the ground, according to Nocera, had to do with vaccines. Figures like Anthony Fauci, former chief medical adviser to the president, and Rochelle Walensky, former director of the CDC, “wildly oversold the vaccines” by saying they would stop transmission of COVID-19 which turned out to be false and actually could not have been known from the vaccine testing process, Nocera said.
But it may have been the way that false or questionable claims were used to restrict people’s freedom or quiet dissident voices that had the most lasting damage on the country, Nocera said.
“The next time there’s a health emergency, many fewer people are going to listen to, or believe, anything public health says, or the government says, because a lot of people, even people in blue states, who did everything they were supposed to do, feel like they were not told the truth, the whole truth, and nothing but the truth,” he said.
According to a 2023 Harvard study , only one-third of U.S. adults had high levels of trust in the CDC. Trust in government sources for COVID-19 vaccine information fell throughout the pandemic, especially among Republicans, KFF polling found.
Pavia: Grace for public health officials
Pavia said striking the balance between “save the most lives and cause the least disruption,” all while trying to communicate uncertainty surrounding a novel virus, “is the hardest thing that anyone in public health ever does.”
Public health officials should be given grace for making human errors in their judgement or communication because without their knowledge, public health crises would be much worse, Pavia said.
“What we’ve seen among many people is sort of a wholesale discounting of expertise, and that’s really harmful because nobody knows the answers to everything but there are experts who come closer ... and while they may make mistakes, they still are probably the best positioned to give us the best advice,” he said.
While the usefulness of old models for new pandemics is limited, Pavia said increased preparation could have helped improve the country’s pandemic response. A pandemic preparedness playbook spearheaded by Leavitt during the Bush administration was dismantled “in the year leading up to the pandemic,” Pavia said.
According to Leavitt, it is always difficult for public health experts to convey the importance of learning from past pandemics to be more prepared for the next one.
“I came to understand that no matter what you say in advance of a pandemic, it sounds alarmist. After a pandemic starts, no matter what you do, it’s inadequate,” Leavitt said. “And that proved out during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
One of the big takeaways from COVID-19, according to Pavia, is “we all have to be better at communicating the uncertainty and accepting that as we learn more things will change quickly.”
McLean agreed.
“One of the lessons I wish we would learn is that ‘Follow the science’ must be one of the dumbest things that has ever been said because science at its best is a way of asking a question,” she said. “I hope we can learn some open mindedness coming out of this, learn some flexibility, instead of becoming so dogmatic. And I hope that our leaders, maybe all of us, can learn to say, ‘I don’t know.’”
Danielle Smith picked ’contrarian’ doctor to lead COVID review to get 'a broad range of perspectives'
In 2021, Dr. Gary Davidson claimed hospital admission numbers were overblown and being manipulated to justify public health restrictions
Author of the article:
You can save this article by registering for free here . Or sign-in if you have an account.
Article content
EDMONTON — Alberta Premier Danielle Smith says it’s a good idea to have a physician who accused the province of exaggerating COVID-19’s impact on hospitals now lead a review of pandemic-era health data.
Smith says Dr. Gary Davidson was selected to lead the data review because she wants to hear a range of viewpoints, including from those “shouted down in the public sphere.”
Enjoy the latest local, national and international news.
- Exclusive articles by Conrad Black, Barbara Kay, Rex Murphy and others. Plus, special edition NP Platformed and First Reading newsletters and virtual events.
- Unlimited online access to National Post and 15 news sites with one account.
- National Post ePaper, an electronic replica of the print edition to view on any device, share and comment on.
- Daily puzzles including the New York Times Crossword.
- Support local journalism.
Create an account or sign in to continue with your reading experience.
- Access articles from across Canada with one account.
- Share your thoughts and join the conversation in the comments.
- Enjoy additional articles per month.
- Get email updates from your favourite authors.
Don't have an account? Create Account
“I needed somebody who was going to look at everything that happened with some fresh eyes and maybe with a little bit of a contrarian perspective because we’ve only ever been given one perspective,” Smith told reporters at the legislature Tuesday.
“I left it to (Davidson) to assemble the panel with the guidance that I would like to have a broad range of perspectives.”
The work of the task force is nearly complete but few details have been publicized since it was struck in 2022.
The Globe and Mail reported Tuesday that Davidson, the former chief of emergency medicine at the Red Deer Regional Hospital Centre, was appointed chair of the task force a year ago.
During the height of the fourth wave of the pandemic in 2021, Davidson claimed hospital admission numbers were overblown and being manipulated to justify public health restrictions.
The provincial health authority, Alberta Health Services, rejected those accusations as false.
Your guide to the world of Canadian politics. (Subscriber exclusive on Saturdays)
- There was an error, please provide a valid email address.
By signing up you consent to receive the above newsletter from Postmedia Network Inc.
A welcome email is on its way. If you don't see it, please check your junk folder.
The next issue of First Reading will soon be in your inbox.
We encountered an issue signing you up. Please try again
Davidson did not immediately respond Tuesday to a request for comment.
In 2022, Smith swept to power in a vote by United Conservative Party members. Her campaign capitalized on and promised to redress COVID-19 grievances.
Smith promised to seek amnesty for those who violated COVID public health restrictions. She did not follow through, saying later she did not realize she didn’t have the authority to do so.
In late 2022, Smith directed the creation of what would become Davidson’s task force with a mandate to review data and to offer recommendations on how to better manage a future pandemic.
Smith said Tuesday she wanted it to look at how to better analyze public health data and to fact-check concerns about vaccine side-effects.
The government earmarked $2 million for the project, but Smith said she expects it to come in under budget. The final report is expected to go to the government next month and Smith has said the findings will be made public.
It is the second third-party COVID analysis ordered up by Smith’s government.
Former Reform Party leader Preston Manning filed a report last year reviewing Alberta’s COVID experience through the lens of improving laws and regulations governing future pandemics.
Manning’s report recommended the province consider “alternative scientific narratives” as part of a “balanced response” in future crises.
When asked why the details of the Davidson task force weren’t publicized by the government as much as the work of the Manning panel, Smith replied, “We wanted them to do their work.”
Opposition New Democrat Leader Rachel Notley lambasted the panel and Smith, calling it a waste of public money to launch a secret consultation led by someone with “fringe views.”
Notley said, “I believe the Earth is round, and I don’t think that the people of Alberta should be paying for people who believe it’s flat to be engaging in the conversation.”
During COVID, Smith publicly questioned the efficacy of pandemic rules and gathering restrictions, particularly when compared with the potential for long-term harms to mental and physical well-being.
Smith questioned the mainstream science approach to the pandemic and endorsed debunked COVID-19 treatments, such as horse dewormer ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
She embraced the Great Barrington Declaration, a theory that called for protecting the elderly and frail but otherwise letting COVID-19 run free to build up herd immunity.
Our website is the place for the latest breaking news, exclusive scoops, longreads and provocative commentary. Please bookmark nationalpost.com and sign up for our newsletters here .
Postmedia is committed to maintaining a lively but civil forum for discussion. Please keep comments relevant and respectful. Comments may take up to an hour to appear on the site. You will receive an email if there is a reply to your comment, an update to a thread you follow or if a user you follow comments. Visit our Community Guidelines for more information.
Michael Taube: Why Canada’s banks should avoid halal mortgages at all costs
Capital gains tax changes about 'intergenerational fairness,' trudeau says as opposition grows, subscriber only. john ivison: trudeau’s budget comeback tour isn’t proving popular enough to save his career, first reading: islamophobia czar's wild claim that anti-israel extremism is a "few individual protesters", vivian bercovici: trudeau's response to ottawa hate rally too little, too late, fashion brands that prioritize sustainable manufacturing.
How these fashion brands are prioritizing sustainability
Top spring cleaning tips from Melissa Maker of YouTube’s Clean My Space
Maker celebrates International Creator Day
Advertisement 2 Story continues below This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Best Buy’s electronic recycling trade-in program a simple way to contribute to circular economy
Celebrate Earth Day and upgrade your tech
Can this pocket tripod enhance your travel experience?
This unassuming phone stand folds up to credit card size
Beauty Buzz: La Prairie Skin Caviar Eye Lift Serum, Marc Anthony Strictly Curls Curl Envy Leave-In Conditioner, and Ghlee Lip Balm
We tried these three beauty products this week. Here are our thoughts.
This website uses cookies to personalize your content (including ads), and allows us to analyze our traffic. Read more about cookies here . By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy .
You've reached the 20 article limit.
You can manage saved articles in your account.
and save up to 100 articles!
Looks like you've reached your saved article limit!
You can manage your saved articles in your account and clicking the X located at the bottom right of the article.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What we know about unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S.
The unauthorized immigrant population in the United States reached 10.5 million in 2021, according to new Pew Research Center estimates. That was a modest increase over 2019 but nearly identical to 2017.
The number of unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S. in 2021 remained below its peak of 12.2 million in 2007. It was about the same size as in 2004 and lower than every year from 2005 to 2015.
The new estimates do not reflect changes that have occurred since apprehensions and expulsions of migrants along the U.S.-Mexico border started increasing in March 2021 . Migrant encounters at the border have since reached historic highs .
Pew Research Center undertook this research to understand ongoing changes in the size and characteristics of the unauthorized immigrant population in the United States. The Center has published estimates of the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population for more than two decades. The estimates presented in this research are the Center’s latest, adding new and updated annual estimates for 2017 through 2021.
Center estimates of the unauthorized immigrant population use a “residual method.” It is similar to methods used by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Office of Immigration Statistics and nongovernmental organizations, including the Center for Migration Studies and the Migration Policy Institute . Those organizations’ estimates are generally consistent with ours. Our estimates also align with official U.S. data sources, including birth records, school enrollment figures and tax data, as well as Mexican censuses and surveys.
Our “residual” method for estimating the nation’s unauthorized immigrant population includes these steps:
- Estimate the total number of immigrants living in the country in a particular year using data from U.S. censuses and government surveys such as the American Community Survey and the Current Population Survey.
- Estimate the number of immigrants living in the U.S. legally using official counts of immigrant and refugee admissions together with other demographic data (for example, death and out-migration rates).
- Subtract our estimate of lawful immigrants from our estimate of the total immigrant population . This provides an initial estimate of the unauthorized immigrant population .
Our final estimate of the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population, as well as estimates for lawful immigrants, includes an upward adjustment. We do this because censuses and surveys tend to miss some people . Undercounts for immigrants, especially unauthorized immigrants, tend to be higher than for other groups. (Our 1990 estimate comes from work by Robert Warren and John Robert Warren; details can be found here .)
The term “unauthorized immigrant” reflects standard and customary usage by many academic researchers and policy analysts. The U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Office of Immigration Statistics also generally uses it. The term means the same thing as undocumented immigrants, illegal immigrants and illegal aliens.
For more details on how we produced our estimates, read the Methodology section of our November 2018 report on unauthorized immigrants.
The unauthorized immigrant population includes any immigrants not in the following groups:
- Immigrants admitted for lawful residence (i.e., green card admissions)
- People admitted formally as refugees
- People granted asylum
- Former unauthorized immigrants granted legal residence under the 1985 Immigration Reform and Control Act
- Immigrants admitted under any of categories 1-4 who have become naturalized U.S. citizens
- Individuals admitted as lawful temporary residents under specific visa categories
Read the Methodology section of our November 2018 report on unauthorized immigrants for more details.
Pew Research Center’s estimate of unauthorized immigrants includes more than 2 million immigrants who have temporary permission to be in the United States. (Some also have permission to work in the country.) These immigrants account for about 20% of our national estimate of 10.5 million unauthorized immigrants for 2021.
Although these immigrants have permission to be in the country, they could be subject to deportation if government policy changes. Other organizations and the federal government also include these immigrants in their estimates of the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population.
Immigrants can receive temporary permission to be in the U.S. through the following ways:
Temporary Protected Status (TPS)
In 2021, there were about 500,000 unauthorized immigrants with Temporary Protected Status . This status provides protection from removal or deportation to individuals who cannot safely return to their country because of civil unrest, violence or natural disaster.
Deferred Enforced Departure (DED) is a similar program that grants protection from removal. The number of immigrants with DED is much smaller than the number with TPS.
Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA)
Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals is a program that offers protection from deportation to individuals who were brought to the U.S. as children before June 15, 2007. As of the end of 2021, there were slightly more than 600,000 DACA beneficiaries , largely immigrants from Mexico.
Asylum applicants
Individuals who have applied for asylum but are awaiting a ruling are not legal residents yet but cannot be deported. There are two types of asylum claims, defensive and affirmative .
Defensive asylum applications are generally filed by individuals facing deportation or removal from the U.S. These are processed by the Department of Justice’s Executive Office for Immigration Review. At the end of 2021, there were almost 600,000 applications pending.
Affirmative asylum claims are made by individuals already in the U.S. who are not in the process of being deported or removed. These claims are handled by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). At the end of 2021, more than 400,000 applications for affirmative asylum were pending, some covering more than one applicant.
Here are key findings about how the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population changed from 2017 to 2021:
- The most common country of birth for unauthorized immigrants is Mexico. However, the population of unauthorized immigrants from Mexico dropped by 900,000 from 2017 to 2021 , to 4.1 million.
- There were increases in unauthorized immigrants from nearly every other region of the world – Central America, the Caribbean, South America, Asia, Europe and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Among U.S. states, only Florida and Washington saw increases to their unauthorized immigrant populations , while California and Nevada saw decreases. In all other states, unauthorized immigrant populations were unchanged.
- 4.6% of U.S. workers in 2021 were unauthorized immigrants , virtually identical to the share in 2017.
Trends in the U.S. immigrant population
The U.S. foreign-born population was 14.1% of the nation’s population in 2021. That was very slightly higher than in the last five years but below the record high of 14.8% in 1890.
As of 2021, the nation’s 10.5 million unauthorized immigrants represented about 3% of the total U.S. population and 22% of the foreign-born population. These shares were among the lowest since the 1990s.
Between 2007 and 2021, the unauthorized immigrant population decreased by 1.75 million, or 14%.
Meanwhile, the lawful immigrant population grew by more than 8 million, a 29% increase, and the number of naturalized U.S. citizens grew by 49%. In 2021, naturalized citizens accounted for about half (49%) of all immigrants in the country.
Where unauthorized immigrants come from
Unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S. come from many parts of the world, with Mexico being the most common origin country.
The origin countries for unauthorized immigrants have changed since the population peaked in 2007, before the Great Recession slowed immigration. Here are some highlights of those changes:
The number of unauthorized immigrants from Mexico living in the U.S. (4.1 million in 2021) was the lowest since the 1990s. Mexico accounted for 39% of the nation’s unauthorized immigrants in 2021, by far the smallest share on record .
The decrease in unauthorized immigrants from Mexico reflects several factors:
- A broader decline in migration from Mexico to the U.S.
- Mexican immigrants to the U.S. continuing to return to Mexico
- Expanded opportunities for lawful immigration from Mexico and other countries, especially for temporary agricultural workers.
The rest of the world
The total number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. from countries other than Mexico has grown rapidly. In 2021, this population was 6.4 million, up by 900,000 from 2017.
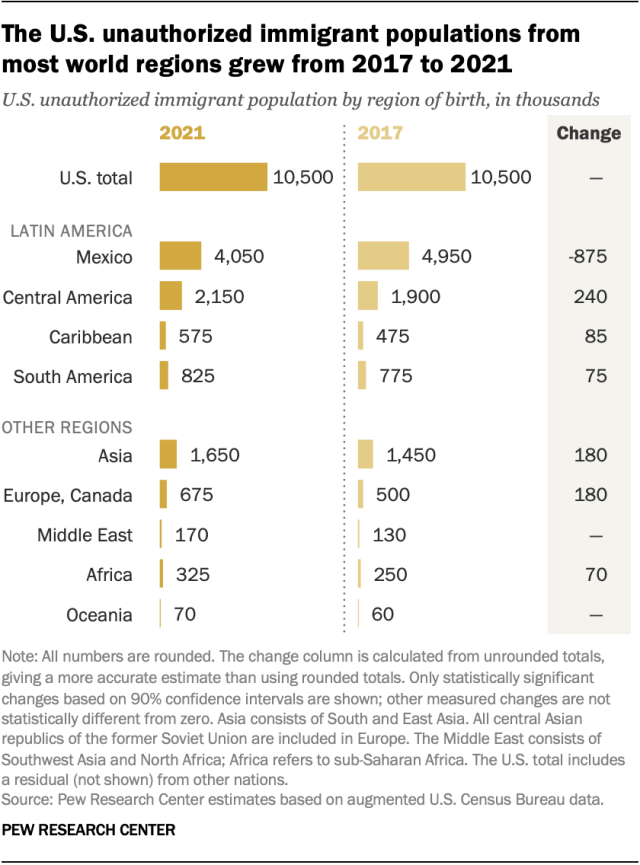
Almost every region in the world had a notable increase in the number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. from 2007 to 2021. The largest increases were from Central America (240,000) and South and East Asia (180,000).
After Mexico, the countries of origin with the largest unauthorized immigrant populations in the U.S. in 2021 were:
- El Salvador (800,000)
- India (725,000)
- Guatemala (700,000)
- Honduras (525,000)
India, Guatemala and Honduras all saw increases from 2017.
The Northern Triangle
Three Central American countries – El Salvador, Honduras and Guatemala – together represented 2.0 million unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. in 2021, or almost 20% of the total. The unauthorized immigrant population from the Northern Triangle grew by about 250,000 from 2017 and about 700,000 from 2007.
Other origin countries
Venezuela was the country of birth for 190,000 U.S. unauthorized immigrants in 2021. This population saw particularly fast growth, from 130,000 in 2017 and 55,000 in 2007.
Among countries with the largest numbers of U.S. unauthorized immigrants, India, Brazil, Canada and former Soviet Union countries all experienced growth from 2017 to 2021.
Some origin countries with significant unauthorized immigrant populations showed no change, notably China (375,000) and the Dominican Republic (230,000).
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrant population by region and selected country of birth (and margins of error), 1990-2021 (Excel)
U.S. states of residence of unauthorized immigrants
The unauthorized immigrant population in most U.S. states stayed steady from 2017 to 2021. However, four states saw significant changes:
- Florida (+80,000)
- Washington (+60,000)
- California (-150,000)
- Nevada (-25,000)
States with the most unauthorized immigrants
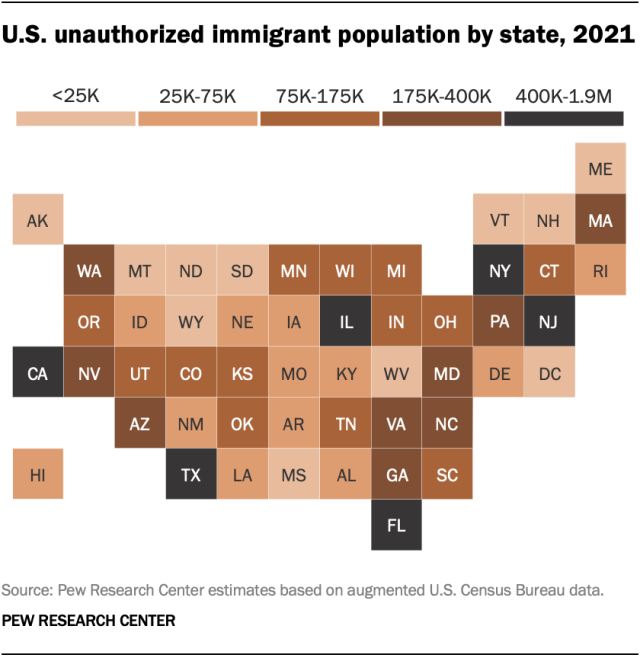
The six states with the largest unauthorized immigrant populations in 2021 were:
- California (1.9 million)
- Texas (1.6 million)
- Florida (900,000)
- New York (600,000)
- New Jersey (450,000)
- Illinois (400,000)
These states have consistently had the most unauthorized immigrants since 1990 and earlier .
At the same time, the unauthorized immigrant population has become less geographically concentrated. In 2021, these six states were home to 56% of the nation’s unauthorized immigrants, down from 80% in 1990.
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrant population for states (and margins of error), 1990-2021 (Excel)
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrants and characteristics for states, 2021 (Excel)
Unauthorized immigrants in the labor force
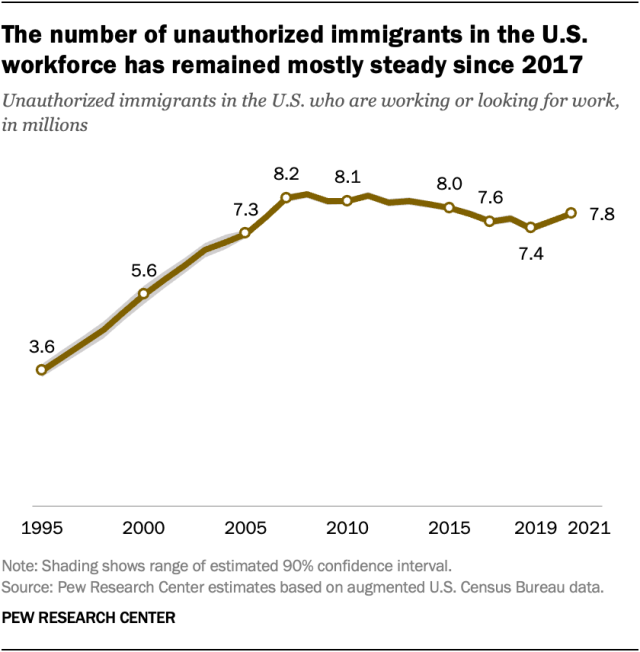
The share of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. workforce was slightly less than 5% in 2021, compared with 3% of the total U.S. population.
Demographics help explain the difference: The unauthorized immigrant population includes relatively few children or elderly adults, groups that tend not to be in the labor force.
Overall, about 7.8 million unauthorized immigrants were in the U.S. labor force in 2021. That was up slightly from 2019 but smaller than every year from 2007 through 2015.
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrants in the labor force for states, 2021 (Excel)
Here are some additional findings about unauthorized immigrants as a share of the workforce nationwide and in certain states:
- Since 2003, unauthorized immigrants have made up 4.4% to 5.4% of all U.S. workers, a relatively narrow range.
- Fewer than 1% of workers in Maine, Montana, Vermont and West Virginia in 2021 were unauthorized immigrants.
- Nevada (9%) and Texas (8%) had the highest shares of unauthorized immigrants in the workforce.
- Immigrant Populations
- Immigration Issues
- Unauthorized Immigration

Jeffrey S. Passel is a senior demographer at Pew Research Center

Jens Manuel Krogstad is a senior writer and editor at Pew Research Center
Key facts about Asian Americans living in poverty
Latinos’ views on the migrant situation at the u.s.-mexico border, key facts about the nation’s 47.9 million black americans, key facts about the wealth of immigrant households during the covid-19 pandemic, 8 facts about recent latino immigrants to the u.s., most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
COMMENTS
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
Last Updated: May 4, 2023. The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with ...
Starting Monday, the U.S. begins accepting fully vaccinated travelers at airports and land borders, doing away with a COVID-19 restriction that dates back to the Trump administration.
To protect America's health, CDC partners with the Department of Homeland Security to prevent the spread of serious contagious diseases during travel. ... CDC used these authorities to restrict travel of people with COVID-19 and close contacts who were recommended to quarantine. These authorities were also used for mpox during 2022 ...
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply.
0:00. 2:02. The U.S. is launching a new travel system on Nov. 8. Vaccinated foreign air travelers will need to show proof of full vaccination and test for COVID-19. The new travel system also adds ...
Get up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines before you travel and take steps to protect yourself and others.Consider wearing a mask in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor areas, including on public transportation and in transportation hubs. Take additional precautions if you were recently exposed to a person with COVID-19. Don't travel while sick. If you have a weakened immune system or are ...
However, if the CDC raises a country's COVID-19 THN to a Level 4, the State Department's Travel Advisory for that country will also be raised to a Level 4: Do Not Travel due to COVID-19. This update will leave approximately 10% of all Travel Advisories at Level 4: Do Not Travel. This 10% includes Level 4 Travel Advisories for all risk ...
What to Know: U.S. Travel Restrictions. Lauren Hard 📍 Reporting from New Jersey. Reuters. The new policy ends an 18-month ban on nonessential travel from 33 countries, including China, Brazil ...
The White House on Friday will lift COVID-19 travel restrictions for fully vaccinated international visitors starting Nov. 8, ending historic restrictions that had barred much of the world from ...
Section 1. Policy. Science-based public health measures are critical to preventing the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by travelers within the United States and those who enter the ...
The basics. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has lifted its requirement for travelers to test negative for Covid-19 before entering the United States. Ad Feedback. After nation ...
Key Points. The U.S. on Monday will lift a pandemic travel ban on international visitors from more than 30 countries after 19 months. New rules will replace the ban, requiring international ...
Find which ones across the United States have implemented travel restrictions to curb the spread of COVID-19. Print Aug. 7, 2020, 4:27 PM UTC / Updated Dec. 17, 2020, 10:28 PM UTC
CNN —. US travel restrictions instituted in the early months of the Covid-19 pandemic by states have been eliminated. However, the US Centers of Disease Control and Prevention suggests delaying ...
× External Link. You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State. Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein.
Before travel, all visitors must submit a health authorization form, the completion of which includes the purchase of mandatory Covid-19 insurance. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level ...
As for many service providers, the COVID-19 pandemic forced profound reductions in the Department's visa processing capacity in two main ways. First, restrictions on travel to the United States, and local restrictions on public places like our overseas consular waiting rooms, curbed our ability to see visa applicants.
Even after the restrictions were eased, spending by international travelers in the U.S. was still down by 78 percent in March 2022 compared to 2019 levels and by 56 percent for business travel ...
FCDO travel advice for USA. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
You may want to get familiar with the countries' COVID-19 travel restrictions. ... Here are the travel restrictions across Central and South America due to COVID-19. Bailey Schulz.
Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers. Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official ...
A majority of American voters believe COVID-19 public health measures infringed on personal freedoms, according to a new Deseret News poll. The poll also found that a significant plurality of registered voters judge pandemic-related restrictions to have had an overall negative impact on their life. This gloomy view reflects missteps by ...
Executive Order 13910 of March 23, 2020 (Preventing Hoarding of Health and Medical Resources to Respond to the Spread of COVID-19), Executive Order 13991 of January 20, 2021 (Protecting the ...
And in India, two Christians died after being beaten in police custody; they had been accused of violating COVID-19 curfews in the state of Tamil Nadu. Authorities and social groups in several countries blamed religious groups for spreading the virus. In 18 countries, authorities linked religious groups or gatherings to the spread of COVID-19.
Photo by JASON FRANSON / THE CANADIAN PRESS. EDMONTON — Alberta Premier Danielle Smith says it's a good idea to have a physician who accused the province of exaggerating COVID-19's impact on ...
The unauthorized immigrant population in the United States reached 10.5 million in 2021, according to new Pew Research Center estimates. That was a modest increase over 2019 but nearly identical to 2017. The number of unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S. in 2021 remained below its peak of 12.2 million in 2007.