
- Previous Chapter
- Next Chapter
This chapter addresses the importance of sound governmental tourism policies and strategies as foundations of sustainable tourism development. It explains differences in objectives, formats, ownership and timeframes of tourism policy, strategy, operational planning, master planning and other tourism planning instruments that are used in sustainable tourism management. A framework for tourism policy and strategy development and typical policy topics are provided and contentious issues in policy development are highlighted. Consultative processes for policy and strategy development are also briefly highlighted. In addition, techniques employed in destination competitive strategy development are explained addressing aspects such as competitive positioning, market and product segmentation and destination value chain assessment. Examples of policy and strategy development in South Africa are briefly discussed. The section concludes by highlighting two broad approaches in sustainable policy and strategy development namely sustainability as an underlying theme and good practice in tourism industry management and sustainability as a main thrust and key selling proposition for positioning destinations.
You are not authenticated to view the full text of this chapter or article.
Access options
Get access to the full article by using one of the access options below.
Other access options
Institutional Login
Log in with Open Athens, Shibboleth, or your institutional credentials

Table of Contents

- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.136]
- 81.177.182.136
Character limit 500 /500
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

Competitiveness
- Market Intelligence
Policy and Destination Management
- Product Development
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local.
The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance.
Governance has two specific dimensions:
- Directive capacity of government , determined by coordination and collaboration as well as by the participation of networks of stakeholders.
- Directive effectiveness, determined by institutional skills and resources that support the ways in which processes are conducted to define goals and search for solutions and opportunities for relevant stakeholders, and by the provision of tools and means for their joint execution.
In this sense, UN Tourism works to support its Members in their efforts to develop efficient governance models / structures and policies, focusing among others on:
- Tourism policy and strategic planning
- Governance and vertical cooperation, i.e. national-regional-local levels
- Public Private Partnership (PPP)
Destination Management
Destination management consists of the coordinated management of all the elements that make up a tourism destination. Destination management takes a strategic approach to link-up these sometimes very separate elements for the better management of the destination. Joined up management can help to avoid overlapping functions and duplication of effort with regards to promotion, visitor services, training, business support and identify any management gaps that are not being addressed.
Destination management calls for a coalition of many organizations and interests working towards a common goal, ultimately being the assurance of the competitiveness and sustainability of the tourism destination. The Destination Management Organization’s (DMO) role should be to lead and coordinate activities under a coherent strategy in pursuit of this common goal.
Though DMOs have typically undertaken marketing activities, their remit is becoming far broader, to become a strategic leader in destination development. This is a vital ingredient for success in every tourism destination and many destinations now have DMOs to lead the way.
From a traditionally marketing and promotion focus the trend is to become leading organizations with a broader mandate which includes strategic planning, coordination and management of activities within an adequate governance structure with the integration of different stakeholders operating in the destination under a common goal. Destinations wherein such an organization is not still in place are increasingly creating or plan to create a DMO as the organizational entity to lead the way.
UN Tourism has identified three areas of key performance in destination management at DMO level: Strategic Leadership, Effective Implementation and Efficient Governance.
UN Tourism supports its Members and Destination Management/Marketing Organizations through the UN Tourism.QUEST - a DMO Certification System. UN Tourism.QUEST promotes quality and excellence in DMOs planning, management and governance of tourism, by means of capacity building. UN Tourism.QUEST Certification evaluates the three areas of key performance in destination management at DMO level: Strategic Leadership, Effective Implementation and Efficient Governance. With a training and capacity building component, UN Tourism.QUEST is a strategic tool which allows the DMOs to implement an improvement plan to achieve the criteria and standards of the Certification with the aim of enhancing their management processes and thus contribute to the competitiveness and sustainability of the destinations they represent.
Events & Publications
- International Seminar on Destination Management
- 2nd Conference on Destination Management in the Mediterranean
- 6th International Conference on Destination Management
UN Tourism Guidelines for Institutional Strengthening of Destination Management Organizations (DMOs) – Preparing DMOs for new challenges
Many factors account for the increased focus on effective destination management, all of them urging destination management organizations (DMOs) to face and adapt to new challenges. From traditional marketing and promotion boards the trend is for these entities to increasingly enlarge their scope to become all embracing DMOs, aiming to enhance the competitiveness and sustainability of destinations within a harmonious relationship between the residents and visitors.
Competitiveness Committee (CTC)
The Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) is one of the technical committees of the UN Tourism and it is a subsidiary organ of the Executive Council . The Committee was established at the 95th session of the Executive Council in Belgrade, Serbia in May 2013 (CE/DEC/7(XCV). Its Rules of Procedure and the composition were approved by the Executive Council at its 96th session (Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe, August 2013) (CE/DEC/9(XCVI).
Since its establishment in 2013, CTC focused its work mainly on assessing the state of knowledge on the basic concept of “ tourism competitiveness ” and identifying its key factors . This process has also included identifying, developing and harmonizing concepts, models and operational definitions used in the tourism value chain .
Work priorities
(a) To support the Organization in fulfilling its normative role;
(b) To provide a dialogue mechanism between the public and private tourism stakeholders and academia to give guide in building and strengthening tourism competitiveness policies and strategies; and
(c) To build synergies and strategic alignments in the harmonization of the related activities of the Secretariat as well as other collaborating organizations/entities in order to ensure consistency and consensus in the delivery of the outputs and reinforce the official position of the Organization.
Provide UNWTO Members and other tourism stakeholders with a comprehensive and concise, operational, applicable and globally relevant conceptual framework to set the scene and contribute to establish a common ground for a clear harmonized understanding of:
i) concepts, models and operational definitions used in the tourism value chain;
ii) the quantitative and qualitative factors that explain competitiveness at the destination level which may be translated into technical guidelines facilitating a methodology for destinations to identify and evaluate their own factors of competitiveness.
As an outcome of the work of the CTC, the 22 nd Session of the General Assembly held in Chengdu, China (11-16 September 2017) adopted as Recommendations key definitions. Along with these definitions the Committee also focused on identifying the key quantitative and qualitative factors for “tourism competitiveness ” under two categories: i) governance, management and market dynamics, and ii) destination appeal, attractors, products and supply.
Full list of definitions adopted by the 22 nd Session of the General Assembly held in Chengdu, China (11-16 September 2017)
As part of the work of the UNWTO Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) in its mandate for the period 2015-2019 prepared a paper on " Tourism Policy and Strategic Planning " which delves into this factor for tourism competitiveness. This paper (available below in pdf) aims to:
- Provide UNWTO Members with a comprehensive understanding on national tourism policies and contribute to their successful formulation and implementation;
- Explore key areas which need to be addressed in tourism policy and strategic planning in order to ensure the competitiveness and sustainable development of tourism;
- Assess the key areas addressed by UNWTO Members in their tourism policies and provide case studies to illustrate key elements of a sound tourism policy; and
- Serve as a practical tool for UNWTO Members and tourism policymakers by including a set of recommendations.
Composition of the CTC (2019-2023)
Full Members
Bahamas Bahrain Brazil Fiji (Vice-chair) India Israel Kenya Republic of Moldova Senegal (Chair)
Representative of the Associate Members Macao, China (2019-2021) Puerto Rico (2021-2023)
Representative of the Affiliate Members FITUR, Spain (2019-2021) Asociación Empresarial hotelera de Madrid (AEHM), Spain (2021-2023)
Meetings of the CTC:
1st Meeting: 25 August, 2013, Victoria Falls, Zambia /Zimbabwe (during 20th UN Tourism General Assembly) 1st Virtual Meeting: 27 March, 2014 2nd Virtual Meeting: 3 July, 2014 3rd Virtual Meeting: 22 October, 2014 2nd Meeting: 28 January, 2015, Madrid, Spain 3rd Meeting: 13 September, 2015, Medellin, Colombia (during 21st UN Tourism General Assembly) 4th Meeting: 22 January, 2016, Madrid, Spain 4th Virtual Meeting: 21 April, 2016 5th Meeting: 20 January, 2017, Madrid, Spain 5th Virtual Meeting: 2 March, 2017 6th Meeting: 11 September, 2017, Chengdu, China (during 22nd UN Tourism General Assembly) 7th Meeting: 19 January, 2018, Madrid, Spain 8th Meeting: 10 September 2019, Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation (during 23rd UN Tourism General Assembly) 9th Meeting: 24 January, 2020, Madrid, Spain 10th Virtual Meeting: 30 July 2020 11th CTC Meeting: 30 November 2021, Madrid, Spain (during the 24th UN Tourism General Assembly) 12th Virtual Meeting: 12 September, 2022

11th CTC Meeting: 30 November 2021, Madrid, Spain
During the 24th un tourism general assembly.

Download PDF
- Position Paper on Tourism Policyand Strategic Planning
- UN Tourism Tourism Definitions
- Composition of the Committee on tourism and competitiveness

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Tourism Policy, Planning, and Development
General overview.
Tourism policy, planning, and development are all very connected and do not just occur when a geographic area decides to be a tourism destination. Policy, planning, and development are included in numerous aspects of communities.
continue but from different perspectives. An example would be the use of the destination/product lifecycle, discussed later. It is important to understand what tourism planning and development are individually as well as collectively. Planning is essential to effective development. Tourism is not always a beneficial industry for a geographical area, but without planning tourism can damage the area, including natural and cultural resources (Morrison et al., 2018). A destination might consider “Who, What, When, Where, Why” when working on a tourism plan. The same can be considered for tourism development, as well as other topics included in this alternative textbook (e.g., marketing and promotion).
Tourism Policy
A policy is essentially a course of action taken by some organization or institution (e.g., government, business, educational institution). A tourism policy as defined by Edgell et al. (2008) “is a progressive course of actions, guidelines, directives, principles, and procedures set in an ethical framework that is issues-focused and best represents the intent of a community (or nation) to effectively meet its planning, development, product, service, marketing, and sustainability goals and objectives for the future grown of tourism” (p. 7). Stated more simply, Hall and Jenkins (1995) suggest “tourism public policy is whatever governments choose to do nor not to do with respect to tourism” (p. 7-8). A tourism policy is essentially a framework including guidelines, goals, and initiatives to work toward achieving the goals. Where as an act by government, such as the Travel Promotion Act of 2009 establishing Brand USA, is a law or statute.
A policy for international travel is having a current passport and for many countries a Visa. The application for a Visa to visit a foreign country allows countries to approve who may visit the country and not allow individuals for a variety of reasons (e.g., security threat). The U.S also has the Visa Waiver Program, which is an agreement with 40 countries allowing citizens of those countries to visit the U.S. for business or leisure travel purposes for up to 90 days without a Visa, provided they meet other requirements (U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs, n.d.). The countries with the Visa Waiver Program also allows U.S. residents to travel to the respective countries with fairly similar criteria. The purpose of requiring a Visa is to regulate travel between countries. The Visa Waiver Program is an agreement to allow citizens of certain countries to visit without having to obtain a Visa if certain criteria are met. This essentially makes it easier to travel between the respective countries.
The International Trade Administration includes a Tourism Policy Council (TPC) to ensure national decision-making considers the national interests of travel and tourism (International Trade Administration, n.d.). The TPC provides resources to help with such issues or challenges as recovering from disaster, and links to Center for Disease Control (CDC), and many other potential issues or challenges for travel and tourism in the U.S.
At more local levels, Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism destinations can develop policies for development, marketing, tourist experiences, human resource issues, tourism organizations (e.g., structure), relationships throughout the community, quality assurance, and supporting services (e.g., safety and security).
Policy Setting Process
There are a series of recommended steps for the establishing policy (Morrison et al., 2018). First, identifying and assessing the circumstances related to the issue. This includes understanding contraints that you and/or will face. Constraints can be internal (e.g., locals’ awareness of tourism, training and education of employees in hospitality and tourism, budget) or external (e.g., economy, price of gas, natural disaster). The tourism organization/local industry has more control or ability to do something about internal constraints, while have little or no control over external constraints. For example, nothing can be done about bad weather or if a natural disaster occurs. However, if locals are not aware of tourism in the local community, education and information can be shared to make locals more aware. This step in the process can also make you aware of new opportunities (e.g., an attraction to develop, new target market).
The next step is typically to create a policy statement to provide guidelines, goals, and initiatives to help guide the organization, destination, etc. While not directly a policy statement, most CVB vision statements include something that provides a guideline with somewhat vague goals. For example, it might be to maintain and/or improve the quality of life for residents of the destination by promoting the destination for tourism and conventions, which would include an economic goal. A policy statement for this vision would be more specific with the goals and initiatives identified to fulfill the goals.
Consultation with government, local tourism businesses, and any other stakeholders is next. This step is to get feedback about the policy statement. Following the consultation and depending on the outcome, the policy statement might be rewritten or modified. Next would be another round of consultation and then rewriting until the the policy statement is approved.
Now is time to implement the policy statement. This will include identifying specific roles of individuals, committees, organizations, etc. This step also includes developing the budget and timeline for the initiative(s).
Finally, those involved evaluation the policy. Were the goals achieved? Why or why not? However, you do not wait until the end of the established timeline for the policy to evaluate. There should be constant assessment to identify if you are likely to achieve the goals. Remember there are numerous constraints that are external (e.g., weather, natural disaster) that might dictate the need to adjust the initiatives and other efforts related to the tourism policy.
Tourism Planning
Prior to tourism planning it is important to consider other types of planning for a community or geographic area. Planning is not new. Gunn and Var (2002) indicate physical planning goes back to early Greek and Roman times. Planning is done to manage visual appearance and land use. However, planning incorporates many disciplines and perspectives: “Planning is a multidimensional activity and seeks to be integrative. It embraces social, economic, political, psychological, anthropological, and technology factors. It is concerned with the past, present, and future” (Rose, 1984, p. 45).
Gunn and Var (2002) suggest when plans (not only tourism, but community, etc.) are created they often include very high or lofty goals and it is difficult to actually achieve such goals for numerous reasons. Planning is very vague and has no real theory behind it. For community plans the general goal is a better place to live. For tourism planning the goal might be to provide visitors with a good experience. As stated earlier, an effective tourism plan can also maintain or even improve the quality of life of residents, not just economically but the attractions provide activities for local residents as well as tourists.
Morrison et al. (2018) offer three primary reasons for tourism planning. The first two are related to impacts, to maximize the economic benefits and minimize damage to resources (i.e., natural, environmental, cultural). Another reason for a tourism plan is that tourism is constantly changing for many reasons (e.g., visitor expectations, needs, motives; politics; economy; technology). As a result, the plan needs to be adaptable.
Not all destinations have a tourism plan. Some reasons for not having a tourism plan include (Morrison et al., 2018):
- Objections – it should be taken care of by the private sector and there is no need for a formal plan.
- Cost – includes market research, consultations, and a lot of time.
- Complex – tourism is affected by numerous things, such as government policies, dynamic of the community and stakeholders.
- Diversity – various sectors involved directly or indirectly in tourism.
- Seasonality – in many destinations the jobs related to tourism can be seasonal (e.g., beach destinations, snow skiing destinations).
- Unpredictability – keep in mind the numerous things that affect and make tourism complex (e.g., natural disasters, crises, politics, economy).
Gunn and Var (2002) add the following tourism planning barriers:
- Lack of awareness of tourism impacts – which is ironic because it is a reason for a tourism plan.
- Do not understand tourism development – there needs to be a plan for developing tourism and then maintaining and even upgrading tourism (e.g., attractions, facilities, etc.).
- Inadequate infrastructure – might have deteriorated attractions, facilities, etc.
- Unorganized – no leadership to guide the process.
- Politics – usually various opinions among stakeholders (e.g., businesses, government, other stakeholders).
- Lack of hospitality training.
However, there can be serious consequences of unplanned tourism. In general, unplanned tourism is not likely to be sustainable tourism economically, environmentally, socially/culturally.
Tourism Planning Models or Approaches
Morrison et al. (2018) provide a seven step tourism destination planning model:
- Background analysis – including a SWOT analysis and assessments of government policies that affect tourism, inventory analysis (e.g., attractions, accommodations, restaurants, etc.), current demand for tourism at the destination.
- Research and analyses – identify/map locations of the inventory analysis, market survey of current visitors (e.g., motivations, what they like to do) and non-visitors (e.g., why have they not visited?, awareness of the destination, image/perception of the destination), competitive analysis (e.g., who are your competitors?, how can you differentiate your destination from competitors? what do and can you work to improve?).
- Where are we now? (position statement).
- Where would we like to be? (vision statement). Then, identify critical success factors or ways to measure and determine if you achieved your vision.
- Setting goals, establishing strategies, and setting objectives – develop a policy or (e.g., stimulate the economy). Set goals or achievable outcomes. Identify alternative strategies to achieve goals and select the most desired of the alternatives given environment or conditions (e.g., economy, resources, politics). Set objectives which are more short term goals to help monitor if you are going to achieve your longer term goals. If not, remember a tourism destination plan should be adaptable, which is the next step.
- Develop a plan – identify organizations and people to be involved and their roles, funding sources and budgets for different aspects of the plan, activities to implement your plan.
- Implement and monitor the plan – While the plan should be developed by input and participation by numerous stakeholders, it is generally implemented by a local tourism agency or organization (e.g., CVB). But, there should be committees derived of various stakeholders to which the agency is accountable. This helps monitor progress of implementing the tourism destination plan and adapt if needed.
- Evaluate the plan – measure performant of the various parts of the plan against the goals (e.g., did you achieve the goals? Why or why not?). Use the evaluation to see if and how you might adapt the plan moving forward.
Tourism Development
The tourism destination plan helps guide development of tourism. Destinations will be at various stages of development. So, it is not that the tourism plan is just for a destination just getting involved in tourism. As suggested by Mason (2003). development and change for destinations occurs as time progresses. The characteristics, motives, preferred activities and attractions, and many other things change over time and destinations redevelop to remain competitive. A fairly common way to view this is commonly referred to as “Butler’s Tourism Area Lifecycle”. There are five main stages to Butler’s Life Cycle (Butler, 1980):
- Exploration – at this stage there might be some tourism but not really an effort to provide traditional or common tourism attractions, facilities, etc. This stage mostly include tourists visiting facilities and local resources used by residents.
- Involvement – this is the beginning of the destination offering some facilities for tourists. The destination begins to more formally organize and provide or improve infrastructure, some attractions, and facilities for tourists at a local level.
- Development – the destination begins marketing and promoting the destination. This stage also begins development from outside organizations and/or businesses. The destination will begin to develop and look more like a noticeable tourist destination. More and more tourists will likely visit the destination as development progresses.
- Consolidation – at this stage the rate of increase in visitors will begin to decline. The rate of development will also begin to decline. Residents may become opposed to tourism with all of the non-locals who are in the community and there is more traffic and congestion. Some of the older attractions, facilities, etc. may also begin showing degradation.
- Decline – number of visitors will be begin to decrease as competitor destinations might have more appealing attractions, infrastructure, etc. The degradation of attractions, infrastructure, and other aspects of the destination will continue and possibly turn into what Butler (1980) refers to as a “veritable tourist slum” (p. 9).
- Rejuvenation – this outcome can occur by development of a new man-made attraction, which is likely to be followed by improvement of surrounding attractions, facilities, and other tourist needs. However, if competitor destinations also rejuvenate, the competition will remain and rejuvenation might be much less or possibly not rejuvenate and potentially decline. Another way Butler (1980) suggest rejuvenation can occur is to utilize natural resources that might not have been part tourism product throughout previous tourism development and marketing and promotion.
Butler (1980), as well as many other tourism scholars, suggest all of these efforts or stages of Tourism Area Life Cycle should be a collaborative effort within the community. For example, the government could offer incentives for private development of a new man-made attraction.
There are a number of potential ways to develop tourism. One way is to develop a “flagship” attraction, which are major attractions like a theme park (e.g., Disney Land, Disney World) and/or utilize natural attractions (e.g., ocean, lake, National Park). Gunn and Var (2002) offer recommendations for tourism destinations to develop destination zones. The zone would have clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) and a corridor connecting the clusters with some form of transportation. Clustering attractions provides tourists with more to do in a closer area so they spend more time at attractions and less traveling between attractions. The destination zone and clustering is a great example of planning and development and how integrated the two initiatives should be.
Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism involvement should be holistic. The holistic view would include consideration of the product (e.g., attractions, events, support facilities, transportation, infrastructure, etc.). Respective destinations could also ensure people (i.e., hosts, guests) are included to ensure there is community awareness and inclusion of local businesses, organizations, and residents. Morrison et al. (2018) also suggest visitor management (e.g., signage) and identifying the visitor mix of the destination. Packages (e.g., all inclusive, hotel and tickets to attraction) and programs (e.g., events, festivals, other activities) could also be developed to attract more tourists. However, destinations should approach tourism development and/or redevelopment from a sustainable approach to avoid overtourism (i.e., too many tourists).
Sustainable Tourism Development
Tourism development should also be sustainable and include the three impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural).
The United Nations (n.d.) proposes 17 goals to consider for economic development, which include economic (e.g., “No Poverty”, “Decent Work and Economic Growth”, environmental (e.g., “Clean Water and Sanitation”, “Affordable and Clean Energy”), and social/cultural (e.g., “Good Health and Well Being”, Quality Education”) goals. The 17th goal is “Partnerships For the Goals”, which are very important for tourism destinations, not only in tourism destination planning and development, but other aspects such as marketing and promotion.
Relating development back to the impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural). Sustainable development should include these impacts. Morrison et al. (2018) through applying the triple bottom line to tourism offers some examples of efforts for sustainable development in each of the three areas:
- Social – include residents, be sure development improves or at least maintains locals’ quality of life.
- Environmental – protect resources, educate visitors and residents of ways to protect resources.
- Economic – new employment opportunities, increase spending of visitors, find ways to have businesses purchase locally to minimize leakage.
Tourism Development Strategies
Various strategies exist to develop tourism. For example, flagship attractions (e.g., large amusement parks, National Parks) can provide something unique to market and promote. Development of clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) provide several attractions near each other so visitors do not have to drive long distances between attractions. Such districts could also include development of a circuit or trail for transportation via hiking or biking. Aside from man-made attractions, events can be developed by destinations to highlight such things as cultural or other unique aspects of a destination.
Considering all of the possible options of tourism development provides a holistic view. Not only the examples of attractions and events, but packages and programs can developed. Destinations need to also consider all of the elements of tourism in development (i.e., attractions, infrastructure, transportation, built/support facilities, service quality/hospitality). Again, not only businesses and organizations directly involved in tourism, but all stakeholders (e.g., residents, other local businesses) should be included and/or given the opportunity to provide feedback regarding the tourism development plan.
The general goals of tourism development should include improving visitors’ experiences, improving the local economy, not damaging natural resources, and integration throughout the destination so that tourism attractions and venues are not isolated from the rest of the community (Gunn & Var, 2002). Such goals of tourism development require all three sectors (i.e., private, non-profit, government) to be involved and collaborate.
Tourism Development Roles
The private sector, non-profit, government, and local community (e.g., residents) should be involved in tourism development. The private sector role is entrepreneurial and operations (Morrison et al., 2018). The entrepreneurial role is to identify investors to develop man-made attractions, accommodations, food and beverage, and other facilities for tourists. Once built their role becomes to hire workers, manage the operation and ensure it is successful. After all, they are taking a risk as entrepreneurs.
As discussed in the Tourism Organizations section, the non-profit organizations include CVBs to market and manage the destination, chambers of commerce, associations such as a local sports association to attract sporting events to the destination. The CVB typically works with all stakeholders and leads the marketing and sales (e.g., conventions, trade shows) for the destination. Chambers of commerce might be the tourism marketing and sales organization in smaller destinations. However, many of these non-profit types of organizations collaborate with each other, as well as with private or for-profit-sector (e.g., members of CVBs) and government (e.g., hotel tax dollars as a funding source). Non-profit organizations might also operate such things as museums and historical attractions, as well as festivals and events. Such organizations might be local cultural organizations.
The government really does not manage tourism attractions. However, there are exceptions, such as National Parks. Government roles are to stimulate development of tourism, as well as establish and enforce procedures, codes, such as zoning (e.g., business, residential). Government might also get involved for the following reasons: bankruptcy of an attraction where the government needs to help the business in some way, ensure cultural aspects of the community are conserved, encouraging private sector development, find ways to work with potential attractions and other elements of tourism provided through the private sector where businesses may have concerns about being profitable (Morrison et al., 2018).
Government might fulfill some of the above reasons for their role in tourism development by offering incentives (e.g., tax breaks) to entice development by the private sector. Government might also offer a piece of land for private sector development, which lowers the businesses cost to develop at attraction, supporting facilities, or other element of tourism.
While the sectors may have relatively unique roles in tourism development, it is also important the cooperate with each other for the good of the destination. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) offer a model whereby there are times each will work independently of the other two sectors, times when two sectors work together (e.g., private sector and government), and times when all three work together. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) call this “coopetition”. For example, while attractions compete within the destination for tourists to visit respective attractions, if all stakeholders cooperate the develop and manage tourism, the destination will do better overall.

Project Development Analyses
Prior to developing an attraction, hotel, or other element of tourism, there should be an assessment or analysis to determine the feasibility of being successful. Private sector developers who need be profitable will typically do feasibility studies. This may start with a pre-feasibility study, which is essentially to see if the project is even viable. For example, does the project make sense given what the destination already offers? Pre-feasibility studies might be conducted by whatever company or organization is interested in the project. If it does, the next step would be a more robust feasibility study to identify such things as potential sites for the product being considered, assess the market demand of the project, projected revenues and expenses, capital costs to develop the project, and will there be enough return on investment (ROI) if the project is developed. The full feasibility study is often conducted by an independent consulting company to minimize biases. The feasibility studies helps the company or organization identify if the project should move forward or not.
The market demand study within the full feasibility study would include secondary and primary research. Secondary research would include existing data, such as hotel metrics (e.g., supply, demand or rooms sold over a given period of time, occupancy, average daily rate (ADR), and revenue per available room (REVPAR) if the project is a hotel. Primary market analysis requires collection of data. This can include surveys (e.g., visitors of the destination to determine if the potential project is of interest), focus groups to get in-depth insight as to the interest of visitors. Surveys can also be conducted to potentially identify potential demand for the project.
If a project is not intended to be profitable, such as one being developed by the government or non-profit organization, a cost-benefit analysis can be conducted. Such a study essentially identifies the potential benefits to society are worth the cost of the investment.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area life cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer, XXIV (1), 5-12.
Draper, J., Woosnam, K. M., & Norman, W. C. (2011). Tourism use history: Exploring a new framework for understanding residents’ attitudes toward tourism. Journal of Travel Research, 50 (1), 64-77.
Edgell, D. L., Allen, M. D., Smith, G., & Swanson, L. E. (2008). Tourism policy and planning: Yesterday, today and tomorrow . Elsevier Inc.
Gunn, C. A., & Var, T. (2002). Tourism planning: Basics, concepts, cases (4th ed.). Routledge.
Hall, C. M., & Jenkins, J. M. (1995). Tourism and public policy . Routledge.
International Trade Administration. (n.d.). Tourism Policy Council (TPC). https://www.trade.gov/tourism-policy-council
Mason, P. (2003). Tourism impacts, planning and management . Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Morrison, A. M., Lehto, X. Y., & Day, J. G. (2018). The tourism system (8th ed.). Kendall Hunt.
Rose, E. A. (1984). Philosophy and purpose in planning. In M. J. Bruton (Ed.), The spirit and purpose of planning (2nd ed., pp. 31-65). Hutchinson.
United Nations. (n.d.). Department of Economic and Social Affairs: Sustainable Development. https://sdgs.un.org/goals
U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs. (n.d.) Visa Waiver Program. https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas/tourism-visit/visa-waiver-program.html
GHL 2365 - Tourism Copyright © 2024 by Jason Draper is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Why tourism planning is important
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Tourism planning should be an integral part of any destination’s tourism development plan in order to achieve the best results and satisfy all stakeholders. Tourism planning is key to maintaining sustainable tourism and whilst some destinations do this very well, others (often developing countries), fail the recognise the importance of effective tourism development planning.
In this post I will explain why tourism planning is so important and recommend some literature for further reading on this topic. This information on tourism planning should be helpful to a number of tourism stakeholders, including business entrepreneurs, Government bodies and tourism workers. It is also useful for those studying travel and tourism as well as those who have a general interest in the subject. For an introduction to the concept of tourism policy and planning visit this post- ‘ The different levels of tourism policy and planning ‘.
Wait! Before you read on, take a look at the short video that I created all about the importance of tourism planning!
What is tourism planning?
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, tourism planning is a very important part of this.
On a basic level, tourism development can be defined as creating strategies and plans to increase/develop/encourage tourism for a destination. The fundamental reason behind planning and implementing strategies for developing the tourism sector is primarily to make money and to subsequently increase the GDP of a country/area.
You might also be interested in my post- ‘ What is tourism? A definition of tourism ‘
Tourism development consists of many elements including, but not limited to: developing and managing private-public partnerships, assessing the competitors to gain competitive advantage, ensuring responsible and sustainable development, viewing tourism as an interconnected system and a demand-driven sector, assessing private sector investment and international cooperation, tourism clustering and involvement by the Government.
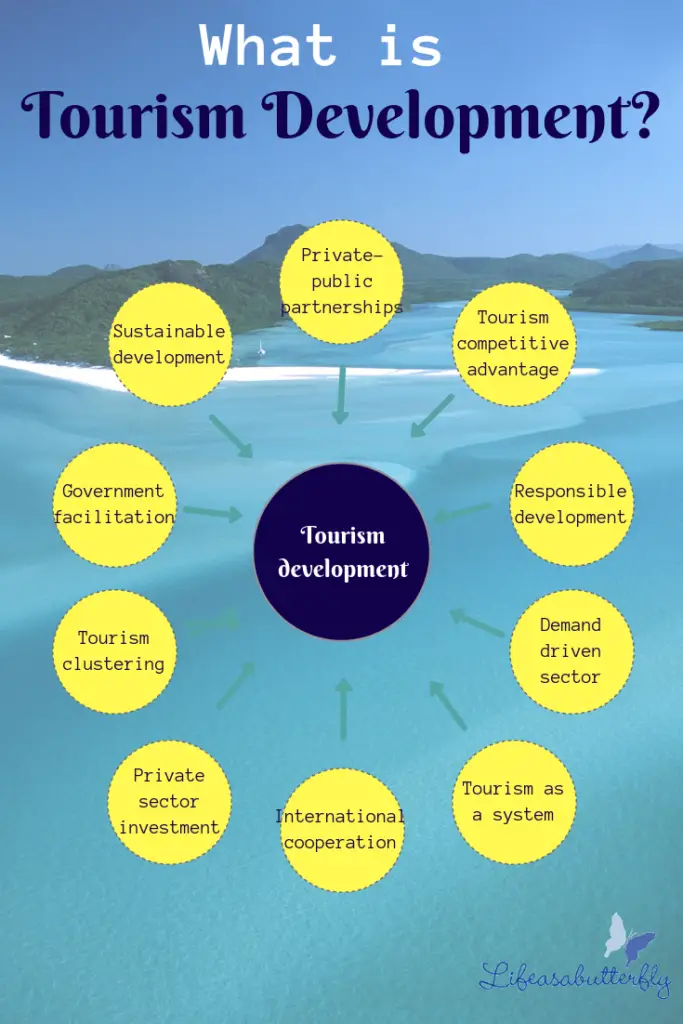
According to Williams cited in Mason (2003);
‘The aim of modern planning is to seek optimal solutions to perceived problems and that it is designed to increase and, hopefully maximise development benefits, which will produce predictable outcomes’.
And Getz (1987) cited in Pearce (1989) defines tourism planning as;
“A process, based on research and evaluation, which seeks to optimise the potential contribution of tourism to human welfare and environmental quality”
Tourism development planning should be an integral part of any destination’s tourism plan in order to achieve the best results and satisfy all stakeholders. Tourism development planning is key to maintaining sustainable tourism and whilst some destinations do this very well, others (often developing countries), fail the recognise the importance of effective tourism development planning.
What is tourism development planning?
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, planning is a very important part of this.
Basic stages in tourism development planning
Tourism development planning is no simple task and there are many variables to consider. There are also different levels of tourism planning and policy . Fortunately , destinations can learn lessons from other areas which have been successful or otherwise. Take for example, over dependence on tourism in Egypt as I explain in this post- Why Unpaid Business is Better than No Business: The Case of the Egyptian Boatman. It is also worthwhile to look at the tourism policies of similar destinations. Some strong examples include Jamaica and Cape Town .
On a basic level, the main stages in tourism development planning include: the analysis of previous tourist development; evaluation of the position of tourism in the area including competition; formulation of relevant tourism policy by Government; the defining of a development strategy and the formation of a programme of action.

The benefits of tourism development
Tourism development planning enables a range of benefits to all stakeholders involved, for example:
- It increases income and jobs from tourist spending
- It helps preserve cultural and natural heritage for tourists
- It increases understanding of other cultures
- It builds new facilities such as sewage for whole communities or new roads
The costs of tourism development
There are also some costs which must be considered and planned for, which include:
- Costs of implementing tourist facilities can be costly
- The environment can be destructed to make room for hotels etc. to be built
- Social standards may be undermined e.g. topless women in Dubai
- The natural environment may be polluted
Formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning
There are six ‘golden rules’ that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning, as outlined by Inskeep (1991).

- Goal oriented
Clear recognition of tourism’s role in achieving broad national and community goals
- Integrative
Incorporating tourism policy and planning into the mainstream of planning for the economy, land use and infrastructure, conservation and environment
- Market driven
Planning for tourism development that trades successfully in a competitive global marketplace
- Resource driven
Developing tourism which build on the destination’s inherent strengths whilst protecting and enhancing the attributes and experiences of current tourism assets
- Consultative
Incorporating the wider community attitudes, needs and wants to determine what is acceptable to the population
Drawing on primary or secondary research to provide conceptual or predictive support for planners including the experiences of other tourism destinations
Why tourism development planning is important
Tourism development planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community.
If done badly , tourism development can destroy the very environment or culture that it relies on. It can disrupt local economies, cause inflation and negative effects to local people and businesses. Unfortunately, developing countries tend to suffer the most from negative impacts such as these, largely as a result of limited education and experience in contrast with Western nations. For more on this topic, you can read this post.
If you wish to cite any of the content in the post please use reference ‘Stainton, Hayley. (2018) Lifeasabutterfly .’
§§cs§§
For more on what constitutes tourism planning I recommend that you refer to the texts Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow by Edgell and Swanson and Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing by Camilleri .
Tourism development planning is no simple task and there are many variables to consider. There are also different levels of tourism planning and policy. Fortunately, destinations can learn lessons from other areas which have been successful or otherwise. Take for example, over dependence on tourism in Egypt as I explain in this post- Why Unpaid Business is Better than No Business: The Case of the Egyptian Boatman. It is also worthwhile to look at the tourism policies of similar destinations. Some strong examples include Jamaica and Cape Town .

You might also be interested in my post- ‘ Best Universities In The UK To Study Travel and Tourism ‘
There are six ‘golden rules’ that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism planning and policy, as outlined by Inskeep (1991).

You might also be interested in my post- ‘ What is ‘begpacking’ and why is it so bad ?’
Tourism planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community.
If done badly, tourism development can destroy the very environment or culture that it relies on. It can disrupt local economies, cause inflation and negative effects to local people and businesses. Unfortunately, developing countries tend to suffer the most from negative impacts such as these, largely as a result of limited education and experience in contrast with Western nations.
For more on this topic, I recommend the following texts:
Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing
Leisure, Sport and Tourism, Politics, Policy and Planning
Tourism Planning: Policies, Processes and Relationships
Liked this article? Click to share!
Tourism Policy
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2018
- pp 5969–5975
- Cite this reference work entry

- María Velasco 2
27 Accesses
1 Citations
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Allen MD, Edgell DL, Smith G, Swanson J (2007) Tourism policy and planning, 1st edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Amsterdam
Google Scholar
Bramwell B, Lane B (2000) Tourism collaboration and partnerships : politics, practice and sustainability, 1st edn. Channel View Publications, Clevedon
Bramwell B, Lane B (2013) Tourism governance : critical perspectives on governance and sustainability. Routledge, Hoboken
Burns PM, Novelli M (eds) (2007) Tourism and politics. Taylor & Francis Ltd., GB
Deegan, J., & Dineen, D. A. (1997). Tourism policy and performance (1. publ. ed.).London [u.a.]: Internat, Thomson Business Press
Dredge D, Jamal T (2015) Progress in tourism planning and policy: a post-structural perspective on knowledge production. Tour Manag 51:285–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.06.002
Article Google Scholar
Dredge D, Jenkins J (eds) (2011) Stories of practice : tourism policy and planning. Ashgate, Burlington
Edgell DL (2015) International sustainable tourism policy. The Brown Journal of World Affairs 22(1):25
Edgell L, Swanson J, Allen D, Smith G (2013) Tourism policy and planning, Second edn. Routledge Ltd - M.U.A, GB. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203113332
Book Google Scholar
Gössling S (2002) Global environmental consequences of tourism. Glob Environ Chang 12(4):283–302
Hall CM (1994) Tourism and politics : policy, power and place. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Hall CM (2008) Tourism planning:policies, processes and relationships, 2nd edn. Pearson Education M.U.A, GB
Hall CM (2011) A typology of governance and its implications for tourism policy analysis. J Sustain Tour 19(4):437–457. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2011.570346
Hall CM (2014) Introduction to tourism policies, planning, and governance. In: Lew AA, Hall CM, Williams AM (eds) The Wiley Blackwell companion to tourism. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Oxford
Hall CM, Jenkins JM (1995) Tourism and public policy (1. publ. ed.). New York, Routledge
Hood C (1986) The tools of government. Chatam House, Chatam
Hood C, Margetts H (2007) The tools of government in the digital age. Palgrave Macmillan, London
Howlett M (1991) Policy instruments, policy styles, and policy implementation. Policy Studies Journal 19:1–21
Howlett M (2011) Designing public policies: principles and instruments. Routledge, Abingdon
ILO (2010) Developments and challenges in the hospitality and tourism sector. http://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---sector/documents/meetingdocument/wcms_162202.pdf
Jeffries D (2001) Governments and tourism (1. publ. ed.). Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann
Jenkins JM, Dredge D (eds) (2011) Stories of practice : tourism policy and planning. Ashgate, Farnham/Burlington
Johannesson GT, Ren C, Duim van der R (eds) (2015) Tourism encounters and controversies: Ontological politics of tourism development. Ashgate, Farnham/Burlington
Johnson P, Barry T (1992) Perspectives on tourism policy. Continuum International Publishing Group, London
MacCannell D (2013) The tourist. a new theory of the leisure class (With a new introduction). University of California Press, New York
McKercher B, Du Cros H (2002) Cultural tourism. Haworth Hospitality Press, New York
Moufakkir O (2012) Controversies in tourism. CABI, Wallingford
Scott, N (2011) Tourism policy: a strategic review. http://www.goodfellowpublishers.com/free_files/fileTourismPolicy.pdf
Velasco González M (2004) La política turística. Gobierno y Administración Turística en España. Tirant Lo Blanch, Valencia
Velasco González M (2011) La política turística una arena de acción autónoma. Cuadernos de Turismo 27:953–969
Wall G, Mathieson A (2006) Tourism: change, impacts, opportunities, 2nd edn. Pearson Education M.U.A, GB
WTO (1997) Towards new forms of public-private sector partnership : the changing role, structure and activities of national tourism administrations. World Tourism Organization, Madrid
WTO (1999) The future of national tourism administrations. Madrid, World Tourism Organization
WTO (2012a) Exploring the full economic impact of tourism for policy making. http://cf.cdn.unwto.org/sites/all/files/unwto_paper_t20_france.pdf
WTO (2012b) Positioning tourism in economic policy: evidence and some proposals. http://www2.unwto.org/es/node/30786
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
María Velasco
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to María Velasco .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Ali Farazmand
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Velasco, M. (2018). Tourism Policy. In: Farazmand, A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20928-9_2674
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20928-9_2674
Published : 16 June 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-20927-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-20928-9
eBook Packages : Economics and Finance Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This chapter addresses the importance of sound governmental tourism policies and strategies as foundations of sustainable tourism development. It explains differences in objectives, formats, ownership and timeframes of tourism policy, strategy, operational planning, master planning and other tourism planning instruments that are used in sustainable tourism management. A framework for tourism ...
Recent Trends. Tourism is an important part of OECD member and partner economies, and a key sector within a growing services economy. On average tourism directly contributes 4.4% of GDP, 6.9% of employment ( Figure 1.1) and 21.5% of service related exports to OECD countries. Global tourism has steadily expanded for over six decades.
Policy Statement - Tourism Policies for Sustainable and Inclusive Growth. natural and cultural resources; iv) improve competitiveness; and, v) promote inclusive growth and development within and across countries. We agree that for whole-of-government policy responses to be effective, they should, as appropriate:
The purpose of this paper is to explore the applicability of Importance-Perform ance Analysis (IPA) technique in the formulation and evaluation of tourism policy. The authors discuss the use of this survey research technique and the key elements in the development of an effective research design using IPA.
Public policy in tourism and hospitality are governance principles based on formal and informal institutions set out to guide the courses of action and constrain behavior of actors within the tourism and ... Consensus policy formulation in tourism. Tourism Management, 9 (3) (1988), pp. 199-212, 10.1016/0261-5177(88)90037-4. Google Scholar ...
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local. The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance. Governance has two specific dimensions:
Several institutions, organisations, and businesses have been established within a country to guide tourism policy formulation and implementation. An understanding of the tourism policy network structure facilitates the coordination between actors, and the reduced formal power of policy actors results in less influence on tourism policy directions.
Tourism policy has been the subject of extensive research over the past decades (Hall 1994, 2011; ... To formulate development strategies and programs. 2. To invest in better mobility systems in the tourism areas to help manage tourism flows and build of tourism-related infrastructure (like marinas or theme parks). ...
The need for formal tourism policy is being increasingly acknowledged. Nowhere is the need more pressing than in cases where economic and environmental forces clash to create social conflicts and industry inefficiencies. This article reviews one of the most complex and most costly policy studies undertaken in recent years.
A tourism policy is essentially a framework including guidelines, goals, and initiatives to work toward achieving the goals. Where as an act by government, such as the Travel Promotion Act of 2009 establishing Brand USA, is a law or statute. A policy for international travel is having a current passport and for many countries a Visa.
Tourism policy is an intentional course of action which goes beyond the level of theoretical. reflection and political intention materialized into real actions, invol ving the use o f public ...
1. Introduction. The sheer importance for the understanding of tourism policy-making and implementation has been emphasized by scholars due to the multi-faceted nature of tourism and the complexity in inter-organizational relations and collaborative policy-making (e.g. Bramwell & Sharman, 1999; Dredge & Jenkins, 2007; Lovelock, 2001; Pforr, 2006). ...
Policy makers, tourism developers, and tourism planners should pay attention to have the actual knowledge as well as an understanding of local communities, the dynamics of the influential factors ...
The national level of tourism planning is concerned with: tourism policy; infrastructure facilities and a physical structure plan which includes important tourist attractions, selected tourism development regions, international entry points, facilities, and services. It is also concerned with: the amount, kinds, and quality of accommodation and ...
E-mail: [email protected]. Babu George. Alaska Pacific University, 4101 Univer sity Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508, USA. E-mail: [email protected]. Abstract: This paper purports to narrow ...
The purpose of this paper is to explore the applicability of Importance-Perform ance Analysis (IPA) technique in the formulation and evaluation of tourism policy. The authors discuss the use of this … Expand
The formulation of tourism policy as an aid in the overall planning and management of tourism is explained in 4 sections: (1) gives a simple overview of the need for tourism policy formulation; (2) describes some of the important tourism policy concerns summarized under the headings of economic, sociocultural, and environmental issues; (3) presents some of the key influences on tourism policy...
Tourism policy formulation lacks the ability to macro-control the factors of production such as capital, land, technology and talent. (4) Increasing numbers of government departments are becoming involved in formulating tourism policy, but policy efforts have become more stable. Recent studies suggest that the effective operation of the tourism ...
Formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning. There are six 'golden rules' that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism planning and policy, as outlined by Inskeep (1991). Goal oriented; Clear recognition of tourism's role in achieving broad national and community goals.
Planning tends to assume current conditions and technologies, with some allowances for predictable change -policy formulation tends to emphasize a systematic destination of "what" should be done in long-term tourism development, while planning tends to emphasize the "how" for the achievement of specific destination goals
National Policy and Strategy List. A snapshot of gender equality and women's empowerment in national tourism strategies. The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), a United Nations specialized agency, is the leading international organization with the decisive and central role in promoting the development of responsible, sustainable and ...
Tourism policy has been the subject of extensive research over the past decades (Hall 1994, 2011; ... To formulate development strategies and programs. 2. To invest in better mobility systems in the tourism areas to help manage tourism flows and build of tourism-related infrastructure (like marinas or theme parks). ...
Article on Philippine Tourism Act of 2009: tourism policy formulation analysis from Multiple Streams, published in Journal of Policy Research in Tourism, Leisure and Events 8 on 2015-06-01 by Edieser Dela Santa+1. Read the article Philippine Tourism Act of 2009: tourism policy formulation analysis from Multiple Streams on R Discovery, your go-to avenue for effective literature search.