- Saudi International Travel Company


- Travel Tips
- +966 11 465 1887


Discover Riyadh in 5 days, for only 1,250$ Exquisite Experiences Await!
Welcome to samaya travel agency, our services, at sta, we offer a comprehensive range of travel services, including:.

Flight and Accommodation Booking

Tailored Tour Packages

Visa and Insurance Assistance

Corporate Travel Solutions

Concierge Services

Embark on Your Adventure with Samaya Travel Agency
Welcome to samaya travel agency – your ultimate partner in global connections., unlock the kingdom explore saudi arabia, travel tips and resources: your ultimate guide to seamless travelling, entertainment and events, important numbers, official holidays, transportation, capture moments, bring your camera, download the visit saudi app.

We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Search Menu
- Advance Articles
- Author Guidelines
- Open Access Options
- Self-Archiving Policy
- About International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
1. introduction, 2. overview of jeddah’s context, 3. governance frameworks in jeddah, 4. urbanization patterns and city structuring in jeddah, 5. comparative analysis of urban development: jeddah and similar cities, 6. strategic analysis of jeddah, 7. planning for the future city, 8. addressing the implementation challenges in jeddah’s urban planning, 9. recommendations and conclusions for jeddah’s urban development, author contributions.
- < Previous
Jeddah strategic approaches to sustainable urban development and vision 2030 alignment
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Haytham Alhubashi, Mohammed Alamoudi, Ayman Imam, Ahmad Abed, Ibrahim Hegazy, Jeddah strategic approaches to sustainable urban development and vision 2030 alignment, International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies , Volume 19, 2024, Pages 1098–1111, https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctae055
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This research article provides an in-depth look into the urban development trajectory of Jeddah, a historic port city in Saudi Arabia, which has developed into a vibrant urban center that reflects its rich past and ambitious future. The study systematically explores Jeddah’s journey through different lenses—its strategic geographical location as a maritime and pilgrimage gateway, its historical development dating back to the seventh century and its transformation influenced by diverse cultural and economic interactions. It comprehensively analyzes Jeddah’s social and economic fabric, demographic trends and the impact of these factors on the city’s urban landscape. This article examines the governance and regulatory frameworks that shape development policies in Jeddah and addresses how these frameworks are designed to meet the challenges of modern urbanization, including rapid population growth, infrastructure requirements and environmental sustainability. The research also examines the city’s response to these challenges, focusing on strategic planning, infrastructure development and sustainable urban initiatives that align with the goals of Saudi Vision 2030. This article provides an in-depth understanding of urban dynamics in Jeddah, presenting it as a case study for managing growth and modernization in rapid urban environments.
With its unique location along the Red Sea coast, Jeddah is an interesting case study in urban development, blending historical significance with rapid modernization. This research article embarks on a comprehensive exploration of Jeddah’s development, analyzing how its strategic geographical location made it a vital maritime and pilgrimage center and how this affected its social, economic and cultural landscape. The study traces the city’s transformation from a humble fishing village to a bustling, diverse metropolis, highlighting the role of historical events and cultural exchanges in shaping its urban identity.
Furthermore, the article delves into Jeddah’s demographic shifts and socioeconomic dynamics, examining how its population growth, characterized by diversity and rapid urbanization, poses challenges and opportunities for urban planning and development. The research examines Jeddah’s economic landscape, discussing the city’s transition from a trade-focused economy to a more diversified economic structure, with a particular focus on sectors such as tourism, finance and technology in line with Saudi Vision 2030.
The governance structures and planning frameworks guiding Jeddah’s urban development are analyzed in detail, revealing how these systems have adapted to the city’s growing needs and aspirations. The study provides a precise understanding of urbanization patterns, land use trends and key structuring elements that shape the current and future urban fabric of Jeddah. It identifies and assesses the city’s strategic issues, including housing needs, transportation systems, environmental sustainability and economic diversification and discusses comprehensive responses and planning strategies to address these challenges.
Finally, the article presents a multifaceted action plan for urban development in Jeddah, focusing on sustainable infrastructure projects, urban renewal initiatives, housing development strategies and integrating smart city and green urbanism principles. The recommendations emphasize the importance of comprehensive and sustainable urban planning that accommodates economic growth, social inclusion and environmental care, in line with the broader goals of Saudi Vision 2030. This expanded study enhances our understanding of Jeddah’s unique urban landscape and offers valuable insights and lessons for urban development strategies in fast-growing cities worldwide.
2.1. Geographic and historical background of Jeddah
Jeddah’s location on the Red Sea coast has been the cornerstone of its historical and economic importance ( Figure 1 ). Located halfway along the coast of Saudi Arabia, it enjoys a strategic advantage as a maritime gateway. The city’s coast extends over 60 km, providing a natural maritime trade and communications channel with the wider Red Sea region, East Africa and beyond. This geographical location made Jeddah a focal point in ancient and modern trade routes and a melting pot of different cultures and civilizations [ 1 ].
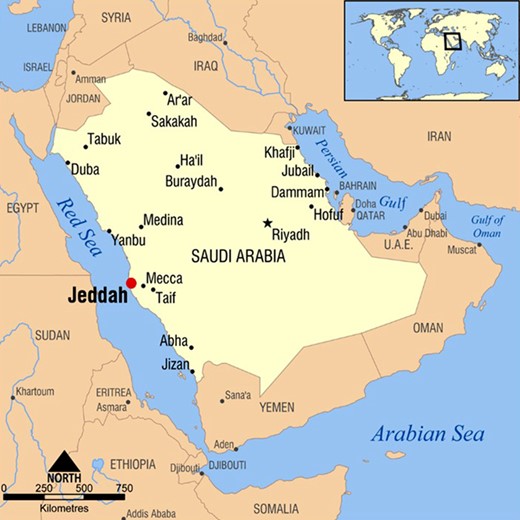
Jeddah geographic location.
Jeddah dates back to at least the seventh century, and its history is intertwined with the spread of Islam. Originally a small fishing village, its transformation into a bustling port city began when it became a gateway for Muslim pilgrims heading to the holy cities of Mecca and Medina. This status has greatly enhanced the importance of Jeddah, leading to its growth and prosperity.
Over the centuries, Jeddah has been influenced by various regional powers. Its architecture and urban fabric bear signs of Ottoman, Egyptian and other influences, making the city a tapestry of historical narratives. The Al Balad Historic District, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a testament to this rich history [ 2 ]. The area is known for its unique Red Sea-style architecture, characterized by multistory buildings made of coral stone and featuring intricately carved wooden windows (Roshan).
Today, Jeddah’s commercial center and Hajj gateway role have fostered a multicultural environment. Merchants and pilgrims from Africa, Asia and other parts of the Middle East brought their customs, languages and traditions, contributing to the city’s diverse cultural landscape. This cosmopolitan nature is evident in Jeddah’s cuisine, art and social customs, which blend Arab, African and Asian influences.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, Jeddah has continued to develop, embracing modernity while preserving its historical heritage. The discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia and the subsequent economic boom accelerated Jeddah’s growth. Modern infrastructure projects, such as King Abdulaziz International Airport and Jeddah Islamic Port—one of the largest and busiest ports in the Middle East—have been crucial in maintaining Jeddah’s role as a commercial and logistics hub [ 3 ].
Today, Jeddah is a historic and modern city known for its bustling commercial districts, sprawling residential neighborhoods and vibrant cultural scene. This combination of ancient heritage and modern development makes Jeddah a unique urban center, reflecting its historical heritage and contemporary importance in the region.
2.2. Demographic and socioeconomic aspects
The demographic profile of Jeddah is characterized by its rapid growth and diversity ( Figure 2 ). With over 3.4 million residents, it is the second-largest city in Saudi Arabia and one of the most diverse. This diversity is partly due to a large expatriate community comprising a large proportion of the population. These expatriates come from around the world, attracted by Jeddah’s economic opportunities and relatively open urban culture compared to other Saudi cities [ 4 ].
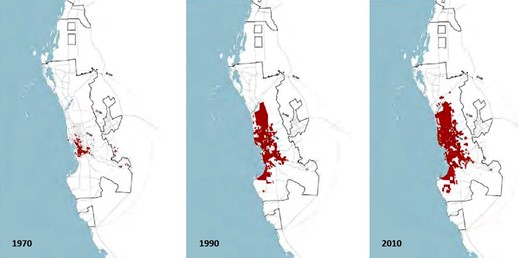
Jeddah urban area growth.
The city’s annual growth rate of about 2.5% is considered one of the highest rates in the region. This increase is due to natural population growth and migration [ 5 ]. Jeddah attracts individuals and families from other parts of Saudi Arabia and beyond with the promise of job opportunities, higher standards of living and the city’s unique cultural and social environment. This influx has resulted in a dynamic and constantly evolving demographic landscape, impacting the city’s social fabric, urban planning needs and infrastructure requirements.
Economically, Jeddah’s importance to Saudi Arabia is multifaceted. Jeddah Islamic Port is the cornerstone of the national economy [ 6 ]. The port handles more than 65% of the country’s imports by sea and is a trade asset and a vital link in Saudi Arabia’s supply chain. Port efficiency and capacity are crucial in facilitating international trade, impacting industries across the country.
Aside from its port, Jeddah’s economy is diverse and dynamic. The city is a major commercial center with busy markets, shopping malls and commercial areas. The retail sector thrives throughout the year and receives an additional boost during the Hajj season, as millions of pilgrims add to the consumer base.
Jeddah’s hospitality sector is also thriving, supported by religious tourism associated with Hajj and Umrah and a growing number of leisure and business travelers. The city’s hotels, restaurants and entertainment venues reflect this vitality, contributing significantly to its economy.
Transportation is another significant economic sector. The presence of King Abdulaziz International Airport, one of the busiest airports in the region, and the city’s position as a central transportation hub for the Hajj season increase its economic standing [ 7 ].
Furthermore, Jeddah’s social and economic landscape is being shaped by Saudi Vision 2030. This ambitious plan aims to diversify the economy away from dependence on oil, and Jeddah is expected to play a pivotal role in this transformation. Efforts are being made to develop nonoil sectors such as finance, technology and tourism, providing new job opportunities and stimulating economic growth.
3.1. Overview of the legal and institutional context
Jeddah operates within a comprehensive legal framework, which is part of the broader regulatory environment in Saudi Arabia. This framework, which includes national laws and regulations, governs various aspects of city life, including urban development and environmental management. These laws have been customized to suit the local context of the city of Jeddah by its administrative bodies [ 8 ].
The most important of these laws are the urban development and zoning laws that regulate land use and the building and zoning laws in Jeddah. These laws play an essential role in ensuring that urban development proceeds in an orderly and sustainable manner, in line with the city’s overall vision for growth and development. Environmental regulations are also crucial to this legal framework, especially for the city of Jeddah due to its coastal location. These regulations include pollution control, waste management, natural resource conservation and addressing the city’s unique environmental challenges [ 9 ]. Figure 3 provides a visual representation of the city’s layout, showcasing the areas governed by these laws and the jurisdiction of the Jeddah Municipality.
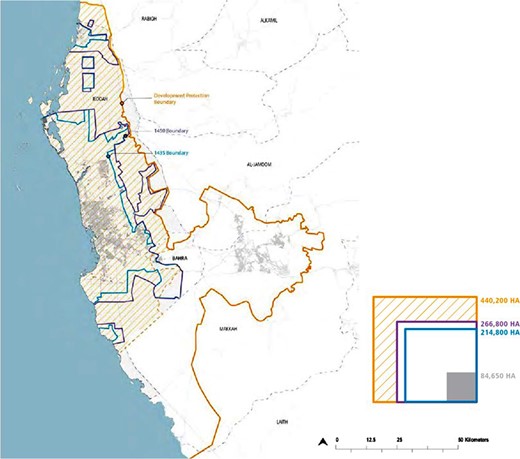
Jeddah administrative boundaries.
The institutional structure in Jeddah is led by the Jeddah Municipality, which is the main administrative body responsible for urban planning, municipal services and the implementation of development projects. The municipality operates under the supervision of the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs, working to align its policies and procedures with national goals. In addition, many other local and national authorities contribute to the administration of Jeddah. These bodies, which focus on sectors such as transportation, housing and economic development, often collaborate with the Jeddah Municipality to coordinate policies and projects.
Saudi Vision 2030, the strategic framework for the Kingdom’s future, greatly influences legal and institutional changes in Jeddah. This vision aims to diversify economically, reduce dependence on oil revenues and strengthen the tourism, finance and technology sectors. Due to its economic and geographical importance, the city of Jeddah plays a pivotal role in this transformation. The vision has stimulated numerous urban development projects in Jeddah, which aim to enhance infrastructure, public services and overall quality of life. These projects are guided by a legal and institutional framework that supports innovation, efficiency and sustainability. Modernizing infrastructure is a significant focus of this vision, which in Jeddah includes developing transportation systems such as the Jeddah Metro, enhancing port facilities and expanding the airport.
3.2. Description of planning instruments and procedures
3.2.1. characterization of urban planning mechanisms and protocols in jeddah.
Urban planning in Jeddah is a comprehensive endeavor that includes a set of tools and procedures that guide the sustainable and systematic development of the city. This framework addresses various aspects of urban life, including land use, infrastructure development, environmental protection and social services.
The Jeddah Strategic Plan is at the heart of this framework, which serves as a blueprint for the city’s future development. It sets long-term goals and strategies for critical sectors such as housing, transportation, public services and environmental management [ 10 ]. The plan takes into account Jeddah’s growing population and economic aspirations, with an emphasis on the need for sustainable development. It aims to create adequate housing, develop effective public transportation systems, improve public facilities and improve residents’ quality of life.
Another critical element is the Jeddah Urban Growth Boundary (JUGB). This tool plays a vital role in managing urban expansion, identifying areas where development is encouraged and areas where it is restricted [ 11 ]. By controlling urban sprawl, the Bank of Jordan helps focus development within specific areas, facilitating the efficient provision of public services and infrastructure. It encourages densification in designated areas, promoting sustainable land use patterns, reducing commuting times and preserving natural and agricultural lands.
The planning and implementation schema integrates four quintessential elements [ 12 ].
3.2.2. Zoning ordinances
Zoning regulations form the bedrock of Jeddah’s urban planning, orchestrating land use to align with the city’s developmental vision while preserving its natural and historical assets. These ordinances categorize territories into residential, commercial, industrial and recreational zones, each subject to specific guidelines and limitations to ensure compatibility with adjacent sectors and the overarching city goals.
Residential areas : Tailored to foster a salubrious living environment, these zones prioritize accessibility to essential services like education, healthcare and commerce alongside the physical milieu’s quality.
Commercial districts : Positioned to stimulate economic activities without encroaching on residential serenity, these zones serve as nuclei for business and trade, designed for optimal accessibility and growth potential.
Industrial sectors : Located to mitigate noise, pollution and traffic impacts on residential vicinities, these areas accommodate manufacturing and other industrial pursuits, contributing to Jeddah’s economic vibrancy while preserving residential living standards.
Green spaces : Essential for the city’s ecological health and residents’ well-being, these areas offer recreational spaces and act as urban green belts, bolstering urban biodiversity and climate resilience.
3.2.3. Development control mechanisms
Jeddah employs stringent development control tactics to ensure construction activities are congruent with the city’s planning ideals and benchmarks. This entails comprehensive construction plan assessments, ongoing oversight and rigorous enforcement of zoning, building and environmental norms.
Plan assessment and endorsement: Development proposals undergo meticulous scrutiny to ensure compliance with zoning statutes, building codes and environmental edicts, fostering seamless integration into the urban fabric.
Monitoring and adherence: Active construction undertakings are vigilantly monitored to affirm conformity with sanctioned plans, addressing infractions to uphold architectural and environmental integrity.
Urbanization challenge mitigation: In light of Jeddah’s expansion, development control is pivotal in managing urbanization effects, such as infrastructural demands, traffic bottlenecks and environmental wear, advocating for sustainable urban growth.
3.2.4. Stakeholder engagement
Acknowledging the criticality of resident and stakeholder involvement in the urban planning discourse, Jeddah adopts a participatory strategy to ensure developmental outcomes resonate with communal desires and expectations. Engagement channels encompass:
Workshops and public assemblies : Venues for community members to express opinions, provide feedback and actively partake in planning endeavors.
Surveys and digital interfaces : Using technology to engage a broader audience, leveraging online surveys and platforms for comprehensive community input, ensuring a more inclusive participation framework.
Developmental impact : This inclusive engagement methodology enriches the relevance and acceptance of urban projects, engendering a communal sense of ownership and accountability, thereby enhancing project success and sustainability.
3.2.5. Synchronization with national initiatives
Jeddah’s urban planning endeavors are cohesively aligned with Saudi Vision 2030, a strategic blueprint aimed at economic diversification and life quality enhancement for its citizenry. This congruence ensures that Jeddah’s developmental activities bolster national objectives:
Economic diversification : Jeddah’s support for nonoil industries catalyzes job creation and stimulates economic growth.
Social advancement : Urban planning in Jeddah tackles essential quality-of-life facets, such as housing, healthcare and education, fostering societal well-being.
Environmental sustainability : By embedding sustainability in urban development, Jeddah confronts climate change challenges and promotes efficient resource utilization in alignment with Saudi Vision 2030’s environmental goals.
Through these comprehensive strategies, Jeddah is transforming its urban landscape and making a substantial contribution to Saudi Arabia’s overarching developmental and transformative ambitions, epitomizing a holistic and visionary approach to urban planning.
4.1. Current urbanization trends in Jeddah: growth, expansion and emerging challenges
Jeddah is experiencing an essential phase of urbanization characterized by rapid demographic growth and spatial expansion. The city’s population has exceeded 3.4 million and is growing annually at about 2.5% ( Figure 4 ). This increase in population is considered the main driver of urban expansion in Jeddah, leading to various developments and changes in the cityscape [ 13 ].
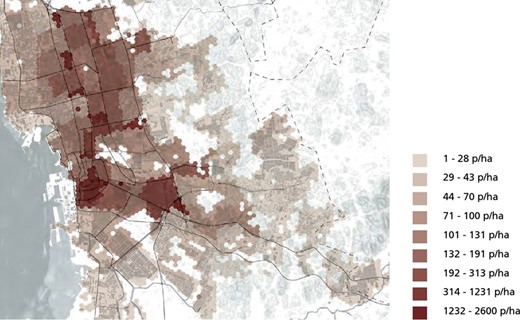
Jeddah current distribution of population density.
The physical growth of Jeddah is notable in its expanding urban footprint, which extends outward with new neighborhoods and developments, especially on the outskirts and along the coast. This expansion includes developing new residential areas, commercial areas and infrastructure projects. The demand for housing, fueled by a growing population, has increased residential construction projects. These projects range from high-density housing in the urban core to sprawling developments in the suburbs, diversifying the city’s housing market with options including luxury apartments and affordable family homes [ 14 ].
Alongside residential growth, Jeddah is also experiencing significant commercial development, reshaping its urban landscape. Demand for commercial and retail space has increased, leading to the construction of new shopping centers, business centers and mixed-use developments, particularly in new urban areas. Expanding the city’s commercial infrastructure caters to the growing consumer base and supports the local economy. Jeddah’s growth pattern shows a marked shift from a traditionally dense urban core to sprawling suburban areas. This trend is influenced by factors such as the desire for larger living spaces, land availability on the city’s outskirts and improved transportation networks that facilitate mobility.
However, with rapid urbanization come both challenges and opportunities. One of the main challenges is ensuring that infrastructure and public services keep pace with the city’s growth. This includes transportation networks, utilities, healthcare and educational facilities [ 15 ]. Urbanization in Jeddah also represents an opportunity to implement sustainable urban planning practices, including developing green spaces, enhancing public transportation and ensuring efficient use of resources.
The urbanization trend aligns with efforts to achieve economic diversification under Saudi Vision 2030. Jeddah’s growth could stimulate sectors other than oil, contributing to a more diversified and resilient economy. This includes the real estate, retail, tourism and services sectors.
4.2. Analysis of urban density and land use: trends, variations and strategic planning
In Jeddah, urban density varies throughout the city, reflecting the diversity of its history and stages of development. The central and older parts of Jeddah, such as Al Balad, are highly urbanized, characterized by a tight fabric of residential and commercial buildings with narrow streets and limited open spaces [ 16 ]. This high-density results from historical development patterns optimized to accommodate a growing population in a limited area.
In contrast, Jeddah’s suburban areas, developed more recently, show lower densities. These areas are characterized by larger residential plots and expansive commercial developments, reflecting the trend toward more spacious living spaces that meet the city’s residents’ diverse lifestyle preferences and economic capabilities [ 17 ].
Land-use patterns in Jeddah have evolved in response to rapid urban growth and changing social and economic dynamics ( Figure 5 ). Residential land use dominates, including a range of housing types from densely populated apartments downtown to single-family homes in the suburbs. There is a growing trend toward mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial and leisure spaces within a single area or building complex [ 18 ]. This approach supports an inclusive urban experience, reducing the need for long commutes and promoting integrated community living. In addition, there is an increasing focus on including recreational and green spaces in urban planning in response to the need for sustainable urban environments and the well-being of residents. Parks, waterfront development and public plazas are increasingly being considered in urban planning.
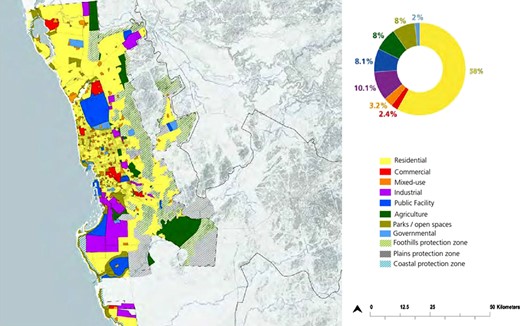
Jeddah land use plan.
The Jeddah City Master Plan reflects a strategic approach to urban development to achieve a balanced and sustainable urban environment. One of its goals is to reduce dependence on cars by creating more walkable neighborhoods, enhancing public transportation and ensuring residents have easy access to essential services and amenities. The plan also focuses on improving the overall quality of urban life by improving physical infrastructure and ensuring that urban spaces promote social interaction, cultural expression and recreational activities.
4.3. Key structuring elements shaping the City of Jeddah
4.3.1. transportation infrastructure.
A city’s transport infrastructure is vital to its development and connectivity. The extensive network of highways and major roads, such as the Jeddah-Makkah Expressway, plays a crucial role. This network facilitates efficient movement through the city and to other areas and influences urban expansion. New developments are often observed along these major transportation corridors, reflecting the impact of these routes on the city’s growth ( Figure 6 ).
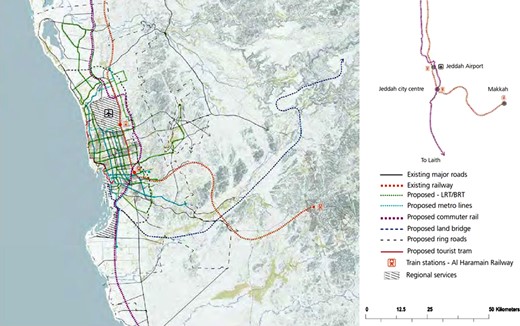
Jeddah transportation network plan.
In addition to the road network, the Haramain High-Speed Train greatly enhances the city’s connectivity. The modern railway system connects Jeddah to the important religious centers of Mecca and Medina. Railway stations act as public transport-oriented development centers and become focal points for new urban development. These developments include residential, commercial and mixed-use projects, further contributing to the city’s urban landscape.
King Abdulaziz International Airport is another significant element of the city’s transportation infrastructure. Known as one of the largest and busiest airports in the region, it plays a pivotal role in international and domestic travel. Its presence not only facilitates movement but also drives economic activity. The areas surrounding the airport have witnessed significant urban development, highlighting its impact on the region’s growth and urban expansion.
4.3.2. Economic drivers
The city’s economic engines are characterized by several key elements ( Figure 7 ), including the Jeddah Islamic Port. This port, which serves as a significant maritime center, drives economic activity and dramatically influences the development of adjacent industrial and commercial areas. Its continuous expansion and modernization have played a decisive role in strengthening Jeddah’s logistics and commercial center position. This has attracted businesses, enhancing the economic status of the city [ 3 ].
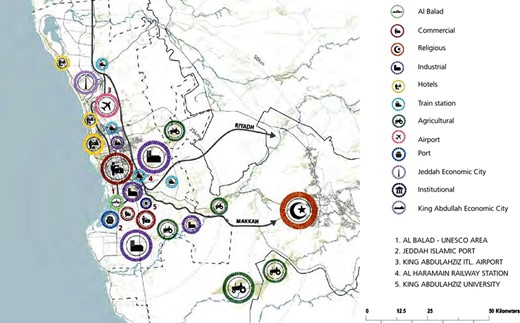
Jeddah major infrastructure and economic nodes.
The role of the port is complemented by industrial zones strategically spread throughout the city. These areas are considered pivotal in contributing to the economic diversification of Jeddah. As centers of manufacturing, logistics and trade, these regions profoundly impact land use patterns and job creation. Its strategic locations facilitate efficient operations and communication, strengthening the city’s economic framework and comprehensive development path [ 19 ].
4.3.3. Natural features
The city’s natural characteristics, especially the Red Sea coast, are essential in shaping its development. The coastline is a significant asset to the city of Jeddah, impacting various residential, commercial and tourism projects. Waterfront areas along the city’s coast are highly sought for real estate development. These areas are often the sites of high-end developments, luxury resorts and diverse entertainment facilities, making them significant attractions in the city’s landscape [ 10 ].
Environmental considerations are also an integral aspect of the city’s development, especially in the context of its natural features. There is increasing recognition of the need to preserve and protect these natural elements, including marine environments and beaches [ 20 ]. Efforts are being made to balance urban development and environmental sustainability. These efforts reflect the growing awareness of the importance of environmental stewardship in urban planning and ensuring that development occurs in harmony with the surrounding natural environment.
4.3.4. Cultural and historical sites
Cultural and historical sites are essential to the city’s identity and development. The historic Al-Balad region is a prominent example of this ( Figure 8 ). Al Balad is known for its traditional architecture and cultural significance and is considered an essential element of Jeddah’s identity. Preservation efforts in this historic area serve dual purposes. It protects and preserves the city’s cultural heritage and promotes cultural tourism. This promotion of cultural tourism has a tangible impact on land use in and around the area, reflecting the importance of the area in the city’s urban landscape [ 21 ].
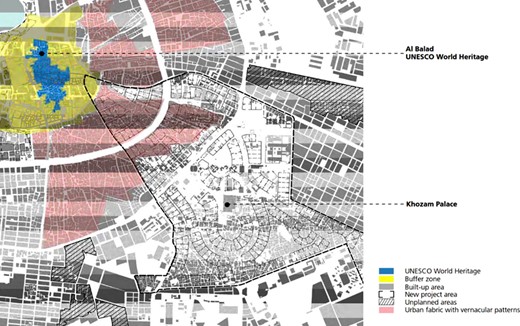
Historical Jeddah and UNESCO major sites.
Further emphasizing the role of culture in urban planning is the emphasis on cultural tourism throughout the city. Promoting cultural and historical sites for tourism has significant implications for urban planning and development. This involves developing and enhancing infrastructure to support tourism, such as improving accessibility and providing tourism facilities. Furthermore, integrating cultural heritage into broader urban development plans is a strategic approach, ensuring that these sites are preserved and showcased in the city’s growth and development context.
When comparing Jeddah’s urban development to similar cities, Istanbul, Cairo and Singapore are relevant benchmarks. These cities, like Jeddah, have experienced rapid urbanization, are significant cultural and economic hubs in their regions and face similar urban planning and development challenges.
Istanbul: Balancing historical preservation with modern development Istanbul exemplifies the challenge of preserving historical integrity amidst rapid urban growth. Jeddah can learn from Istanbul’s regulatory frameworks and community involvement strategies, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a city’s historical and cultural essence while accommodating modern infrastructure needs. This includes integrating innovative solutions to preserve historical sites and utilizing heritage as a lever for tourism and economic growth, without succumbing to over-commercialization.
Cairo: Addressing urban sprawl and traffic congestion Cairo’s experience with extensive urban sprawl and severe traffic congestion offers critical insights into managing these issues. Jeddah can apply Cairo’s comprehensive urban planning approaches, emphasizing the development of public transportation systems to alleviate traffic congestion. Additionally, upgrading informal settlements and ensuring inclusive development that provides equitable access to services and infrastructure are crucial lessons to ensure sustainable urban growth.
Singapore: Mastering high-density urban planning and sustainability Singapore’s highly efficient and sustainable urban planning model stands as an exemplary benchmark for Jeddah. The city-state’s strict zoning laws, commitment to green urbanism and robust public transportation infrastructure offer a blueprint for managing urban density while prioritizing environmental sustainability. Jeddah can adopt similar strategies, focusing on integrated urban development that harmonizes residential, commercial and recreational spaces with green initiatives and sustainable practices.
5.1. Strategic implementation for Jeddah
Regulatory and legal frameworks: Like Istanbul, Jeddah needs to establish strong legal and regulatory frameworks that protect its historical and cultural sites, ensuring that urban development does not erode its heritage.
Sustainable urban planning: Drawing from Singapore, Jeddah can prioritize sustainable urban planning, integrating green spaces and adopting energy-efficient building designs. This approach enhances the city’s livability and addresses environmental concerns.
Public transportation and infrastructure: Inspired by Cairo and Singapore, Jeddah should invest in developing a comprehensive public transportation system. This would reduce reliance on private vehicles, decrease traffic congestion and improve air quality.
Community engagement: Engaging local communities in the planning process, as seen in Istanbul and Cairo, ensures that development projects reflect the community’s needs and heritage. This participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership and satisfaction among residents.
Holistic development approach: Finally, adopting a holistic approach to urban development that balances economic growth with social and environmental sustainability, as Singapore exemplifies, can guide Jeddah toward a more sustainable and prosperous future.
By drawing on the experiences and strategies of Istanbul, Cairo and Singapore, Jeddah can navigate its urban development challenges more effectively, ensuring a balanced growth that respects its rich heritage while embracing modernity and sustainability.
6.1. Identification of main strategic issues in urban development
Rapid urbanization in Jeddah poses multiple challenges in housing and urban sprawl. A growing population has increased demand for housing, posing challenges to both supply and affordability. Different income levels require diverse housing options, but the rising cost of real estate makes affordability a critical issue. City sprawl often takes the form of suburban sprawl, raising concerns about sustainable land use, increased commute times, rising infrastructure costs and loss of green space. Accommodating the growing population requires adequate infrastructure and services, including utilities, healthcare, education and recreational facilities, ensuring that urban growth keeps pace.
Transportation and traffic congestion are major issues in Jeddah’s urban development. As the city grows, traffic congestion becomes a primary concern, affecting the quality of life and economic efficiency. The heavy reliance on private vehicles exacerbates this problem, highlighting the lack of a comprehensive and efficient public transportation system. Developing a robust public transport network, including buses, metro and trains, is essential to relieve traffic congestion and promote sustainable urban mobility.
Environmental sustainability and climate change are critical considerations in Jeddah’s urban planning. The city’s coastal location makes it vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels and extreme weather events. It is necessary to develop climate-resilient infrastructure and coastal protection measures. Urban heat islands and air pollution are major concerns, with solutions including promoting green building practices, increasing urban green spaces and improving waste and emissions management. Efficient water resource management is vital in Jeddah’s dry climate, necessitating strategies for water conservation, desalination and recycling.
Economic diversification and employment are consistent with broader national goals, requiring Jeddah to diversify its economy beyond the oil sector. Developing tourism, manufacturing, finance and technology sectors is crucial. Creating job opportunities, especially for young people and the growing population, is essential, including encouraging entrepreneurship, supporting small and medium enterprises and attracting foreign investment. These efforts are consistent with Saudi Vision 2030, which focuses on economic diversification, innovation and sustainable development.
6.2. The impact of strategic issues on Jeddah’s future urban development
The challenges facing Jeddah will significantly impact future urban planning and infrastructure development. Integrated urban planning is needed to address housing demand, transportation and urban sprawl comprehensively. This approach involves creating master plans incorporating land use, infrastructure development and environmental considerations. Infrastructure projects must be sustainable, focusing on building resilient structures, developing efficient public transport systems and ensuring new developments are connected and well-served. Managing urban sprawl is extremely important to prevent excessive expansion of services and infrastructure while adopting policies that promote densification, especially in central areas that enjoy good services, to manage growth sustainably.
The environmental challenges facing Jeddah require a strong focus on sustainability. Implementing green building standards and practices is essential to reduce the environmental footprint of new developments, which include energy-efficient buildings, water-saving technologies and sustainable materials. Increasing renewable energy sources, such as solar energy, is critical to reducing carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. Effective management of resources, including water and waste, is vital to achieving environmental sustainability, including investments in water recycling, desalination technologies and sustainable waste management practices.
Economic diversification is a crucial factor shaping urban development in Jeddah. Developing policies and infrastructure to support new and emerging industries is critical to achieving this diversification. This includes creating business-friendly environments, providing financial incentives and developing specialized economic zones. Fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship can drive economic growth, including supporting startups, incubators and initiatives.
Jeddah’s urban development also carries significant social and cultural implications. It should be comprehensive, meeting residents’ diverse needs, including affordable housing, accessible public services and community spaces. Preserving Jeddah’s cultural heritage, such as the historic Al Balad district, is essential for preserving the city’s unique identity, and urban development should integrate cultural heritage preservation with modernization. Involving local communities in planning ensures that development responds to their needs and aspirations.
7.1. Strategic responses to identified issues
The city’s development strategy includes various vital areas, addressing the challenges and opportunities its growth and modernization presents. These areas include the following:
Housing and urban expansion
With the rapid pace of urbanization and increasing demand for housing, the city is focusing on developing new housing projects and urban areas. These developments emphasize affordability and sustainability, meeting the needs of a growing population. Jeddah Municipality, for example, plans to develop new residential areas. These plans are about creating residential spaces and ensuring adequate infrastructure and services support these new communities.
Transportation and traffic management
Significant investments are being made in public transport infrastructure to address traffic congestion and enhance overall mobility. Significant projects include expanding the city’s road network, essential to facilitate traffic flow. In addition, a comprehensive public transportation system is being developed, including the metro and bus network. These projects aim to provide efficient and accessible transportation options for residents.
Environmental sustainability initiatives
Addressing environmental challenges is another critical focus area. Initiatives include implementing green building standards, encouraging renewable energy sources and enhancing water and waste management systems. Projects aimed at increasing green spaces and developing coastal areas are also part of these initiatives. These efforts are necessary to maintain environmental balance and ensure sustainable urban growth.
Economic diversification and job creation
Efforts are being made to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on the oil sector. This diversification includes strengthening industries such as tourism, finance and technology. This strategy includes developing specialized economic zones, supporting startups and promoting small businesses. These measures aim to create new job opportunities, stimulate economic growth and contribute to building a strong and dynamic economy.
7.2. Models for sustainable urban development
Jeddah’s approach to sustainable urban development can be analyzed from three main perspectives: Smart City Initiatives, the Compact City Model and Green Urbanism. Each model contributes uniquely to the city’s overall sustainability and livability goals.
7.2.1. Smart City initiatives
Jeddah’s transformation into a smart city, focusing on leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance urban life, is crucial to its urban development strategy. This reflects a commitment to innovation, efficiency and sustainability, aiming to improve its residents’ and visitors’ overall quality of life. This initiative includes the following:
The city uses advanced technologies in various sectors to streamline operations and improve service delivery. A notable example is the implementation of traffic lights and smart sensors designed to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion. These technologies are being integrated into the city’s traffic management systems to ensure smoother and more efficient transportation.
Digital governance platforms are being implemented to make municipal services more accessible to residents. These platforms allow efficient online access to various services, including bill payments, service requests and public feedback mechanisms. This shift toward electronic governance simplifies operations for residents and enhances the transparency and responsiveness of municipal services.
Deploying Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is crucial for real-time urban infrastructure monitoring. Sensors are used to monitor water and electricity use, assess the structural health of buildings and evaluate air quality. These monitoring systems enable proactive maintenance and management of city infrastructure, contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.
Jeddah embraces data analytics and artificial intelligence to improve city planning and operational efficiency. The city can make informed decisions regarding traffic patterns, urban development and resource management by analyzing data from various sources. This data-driven approach ensures that planning and development initiatives are based on accurate and up-to-date information, leading to more effective and sustainable urban solutions.
7.2.2. Compact city model
The Compact City Model adopted by Jeddah represents a strategic approach to urban planning that emphasizes the efficient use of space, enhanced urban connectivity and vibrant community interaction. This model is particularly relevant in addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization and sustainable development. It aims to create a city that is not only spatially efficient but also socially cohesive and environmentally friendly. This initiative includes the following:
The city is promoting high-density urban development to achieve more efficient use of land and resources. This approach involves developing mixed-use buildings and complexes with close residential, commercial and leisure facilities. In doing so, Jeddah aims to create more integrated and cohesive urban spaces that reduce the need for extensive travel and maximize the use of available land.
Great emphasis is placed on developing areas surrounding major public transportation hubs, such as metro stations. This transportation-oriented development is designed to encourage public transportation and reduce car reliance. By focusing development around transportation hubs, residents and workers have easier access to public transportation, thus facilitating more sustainable and efficient urban mobility.
Improving urban design to be more pedestrian- and cyclist-friendly is another crucial aspect of Jeddah’s approach. This includes creating wider sidewalks, pedestrian areas, bike paths and greenways. These features not only enhance urban esthetics but also encourage healthier and environmentally friendly modes of transportation. Improving walking and cycling infrastructure makes the city more accessible and enjoyable for residents and visitors.
Creating mixed-use neighborhoods is central to Jeddah’s vision of a compact urban form. These neighborhoods combine living, working and leisure activities, reducing the need to travel long distances. This approach fosters a stronger sense of community, encouraging interaction between residents in various aspects of their daily lives. Mixed-use neighborhoods provide a comprehensive living experience, contributing to the overall quality of life in the city.
7.2.3. Green urbanism
Green Urbanism in Jeddah emphasizes embedding sustainability and environmental responsibility in urban development. The focus is on creating a harmonious balance between urban growth and environmental preservation, ensuring the city’s and its residents’ sustainable future. This initiative includes the following:
A key aspect of this strategy is the development of urban green spaces. Jeddah focuses on creating parks, community gardens and green belts to provide recreational areas for residents. These green spaces provide areas for entertainment and relaxation and contribute to improving air quality and creating a healthier living environment. By integrating nature into the urban landscape, the city aims to enhance the overall well-being of its residents.
Sustainable building practices are encouraged to ensure new developments are environmentally friendly and resource-efficient. This involves using sustainable materials, incorporating energy-efficient designs and implementing water-saving technologies. By adopting these practices, Jeddah aims to reduce the environmental impact of its buildings and enhance sustainability in its urban fabric.
The city also focuses on climate-responsive design in its urban architecture. This approach includes designing buildings and spaces compatible with the specific climatic conditions of Jeddah. It includes improving natural lighting and ventilation and reducing energy use, thus creating comfortable, energy-efficient and environmentally friendly spaces.
The City of Jeddah is committed to preserving natural habitats and biodiversity in and around the city. This includes implementing measures to protect coastal and marine environments. Preserving these natural resources is vital to maintain the ecological balance and ensure the sustainability of the city’s development. By prioritizing environmental conservation, Jeddah is working to achieve a future in which urban growth and nature conservation go hand in hand.
Overall, sustainability initiatives collectively contribute to creating a more sustainable urban environment, reducing carbon footprint and improving resource efficiency. Enhanced livelihoods are achieved through improved transportation, green spaces and community-focused development, all of which improve the quality of life. Smart city initiatives can attract investment, foster innovation and improve economic efficiency, providing significant economic benefits. However, challenges may include the initial cost of implementing smart technologies, ensuring equitable access to these developments and striking a balance between rapid urbanization and environmental conservation.
Implementing urban development strategies in Jeddah involves intricate challenges beyond the initial planning stages. These can be broadly categorized into logistical, financial, political and social aspects, each with unique intricacies. Here is a detailed analysis of the challenges facing urban planning and development in Jeddah:
Logistical challenges: The complexity of executing large-scale urban projects cannot be overstated. This includes ensuring technological feasibility, coordinating various stakeholders and managing the disruption to daily city life. Integrating new infrastructure with existing systems requires careful planning to minimize disruptions and ensure long-term sustainability.
Financial constraints: Funding these ambitious projects is a significant hurdle. It involves securing the necessary capital and ensuring that the funds are allocated efficiently and transparently. To support these initiatives, the city may need to explore innovative financing models, such as public-private partnerships.
Political dynamics: The alignment of urban development with national policies is crucial. This requires navigating political landscapes, managing stakeholder interests and ensuring continuous support from various levels of government. The success of these projects often hinges on political will and stability.
Social and cultural factors: Gaining public support and addressing the concerns of local communities is paramount. This involves inclusive planning processes that consider the diverse socio-cultural fabric of Jeddah. Key considerations include preserving cultural heritage while promoting modernization and ensuring equitable development that benefits all segments of society.
Environmental considerations: Jeddah’s urban planning must also address environmental sustainability. This includes managing natural resources wisely, reducing carbon footprints and ensuring that urban expansion does not come at the cost of environmental degradation.
Adaptive planning: Finally, the ability to adapt to unforeseen challenges, whether they are economic fluctuations, technological advancements or social changes, is critical. An adaptive approach to urban planning, which allows for flexibility and responsiveness, is necessary in a rapidly evolving urban landscape like Jeddah.
In conclusion, addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that combines strategic planning with practical, on-ground solutions. It demands collaboration across different sectors, transparency in governance and a commitment to inclusive and sustainable development.
The recommendations to address urban development in Jeddah are multifaceted, covering spatial planning, institutional strengthening, legal frameworks and financial strategies. These recommendations aim to create a sustainable and balanced urban ecosystem.
Effective management of urban sprawl is essential. Urban growth limits can help control sprawl and encourage densification, leading to more efficient land use. Incorporating green spaces and ensuring a mix of residential, commercial and recreational land uses is vital to creating a balanced and livable urban environment. This approach not only promotes efficient land use but also enhances the quality of life for residents.
Strengthening local government institutions, especially the Jeddah Municipality, is crucial. Capacity building within these institutions will ensure they have the resources and skills to manage urban development effectively. This involves enhancing their ability to plan, implement and manage urban development projects and policies.
The legal framework, including zoning laws and building codes, needs to be updated to reflect the needs of a modern, sustainable city. Regulations should be geared toward sustainable practices, such as green buildings and efficient use of resources. This will support environmental sustainability and encourage developers and citizens to adopt more sustainable practices.
Leveraging public-private partnerships is a critical financial strategy. This approach could attract investment and expertise for infrastructure projects and urban services, reduce the financial burden on the public sector, and, at the same time, enhance innovation and efficiency. Diversifying revenue sources, such as property taxes or urban service fees, can provide sustainable infrastructure and financing for public services. In addition, investing in sustainable infrastructure projects such as renewable energy, public transportation and water conservation is crucial. These investments meet current needs while ensuring the long-term sustainability and resilience of the city.
The concluding remarks on the urban future of Jeddah and its alignment with Saudi Vision 2030 highlight the focus on urban resilience and sustainability. Future urban development in Jeddah should address environmental challenges and ensure a high quality of life for residents, in line with Saudi Vision 2030’s focus on sustainable living environments. Supporting economic diversification and innovation is vital to Jeddah’s future, as sectors such as technology, tourism and finance are strengthened to drive economic growth and job creation. Ensuring social inclusion and cultural preservation in urban development is vital, including community engagement and preservation of historical sites. Urban development in Jeddah must align with the broader goals of Saudi Vision 2030, which aims at economic diversification, sustainable development, improving quality of life, integrating advanced technologies, promoting environmental sustainability and ensuring economic stability. Top of Form.
Haytham Alhubashi (Investigation [equal], Writing—original draft [equal]), Mohammed Alamoudi (Data curation [equal], Formal analysis [equal], Funding acquisition [equal], Writing—original draft [equal]), Ayman Imam (Methodology [equal], Resources [equal]), Ahmad Abed (Resources [equal], Validation [equal], Visualization [equal]), Ibrahim Hegazy (Conceptualization [equal], Project administration [equal], Validation [equal], Writing—review and editing [equal]).
Massoud B . "Patterns" of Threshold Spaces in the Historical City of Jeddah: Investigating the Relationship Between the Public Spaces and Residential Units . Taylor & Francis , 2023 . https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003347675 .
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Alghamdi HS , Ibrahim A . 2023 . Reviving the identity of jeddah city through revitalizing the "Souq" in Al-Balad. In Mohamed M , Ibrahim A , Fekry M (eds). Cities of the Future: Challenges and Opportunities . Springer International Publishing . 85 – 103 .
Hegazy I , Helmi M , Qurnfulah E . et al. Assessment of urban growth of Jeddah: towards a liveable urban management . Int J Low Carbon Technol 2021 ; 16 : 1008 – 17 . https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctab030 .
Al Shomrany AS . Measuring land cover change due to Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia redevelopment project using GIS and remote sensing techniques . Egypt J Environ Change 2023 ; 15 : 39 – 54 . https://doi.org/10.21608/EJEC.2023.286641 .
Al-Kesmi F . The Potentials of Jeddah Neighborhoods to Adopt the Rapid Urban Development Approaches . Doctoral dissertation . Effat University , Jeddah, Saudi Arabia , 2023 .
Saeedi K , Visvizi A , Alahmadi D . et al. Smart cities and Households' recyclable waste management: the case of Jeddah . Sustain For 2023 ; 15 : 6776 . https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086776 .
Abouhassan M . 2023 . Sustainable Urban Street Design in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. In Hamdan A , Aldhaen ES (eds). Artificial Intelligence and Transforming Digital Marketing . Springer Nature Switzerland . 227 – 44 .
Aldegheishem A . Urban growth Management in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: an assessment of technical policy instruments and institutional practices . Sustain For 2023 ; 15 : 10616 . https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310616 .
Waheeb SA . Environmental and cultural sustainability of the architectural elements of two historical mosques in historic Jeddah . J Umm Al-Qura Univ Eng Arch 2023 ; 14 : 26 – 35 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s43995-022-00011-z .
Zaki SK , Hegazy IR . Investigating the challenges and opportunities for sustainable waterfront development in Jeddah City . Int J Low Carbon Technol 2023 ; 18 : 809 – 19 . https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctad062 .
Mubarak FA . Urban growth boundary policy and residential suburbanization: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia . Habitat Int 2004 ; 28 : 567 – 91 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2003.10.010 .
Helmi M . The Ability of the Local Planning Authority to Implement Zoning Regulations: A Case Study of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia . Doctoral dissertation . Newcastle University , 2015 . https://drepo.sdl.edu.sa/handle/20.500.14154/51691 .
Aljehani L . The impact of the Haramain high-speed train on land prices and urban growth in the neighborhoods of Tibah municipality, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia . Curr Urban Stud 2023 ; 11 : 415 – 46 . https://doi.org/10.4236/cus.2023.113023 .
Alqurashi AF , Kumar L . An assessment of the impact of urbanization and land use changes in the fast-growing cities of Saudi Arabia . Geocarto Int 2019 ; 34 : 78 – 97 . https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2017.1367423 .
Aljoufie M , Tiwari A . Exploring housing and transportation affordability in Jeddah . Hous Policy Debate 2023 ; 33 : 506 – 32 . https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2020.1815070 .
Shehata AM . Sustainable-oriented development for urban Interface of historic centers . Sustain For 2023 ; 15 : 2792 . https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032792 .
Almaimani A , Rahaman K . Planning for missing middle housing: an alternative option for combating housing crisis in Jeddah city . EQA Int J Environ Qual 2022 ; 51 : 20 – 31 . https://doi.org/10.6092/issn.2281-4485/16042 .
Aljoufie M . 2020 . Land use, transport, and sustainability: spatial analysis of commercial centers and public transport interaction in jeddah. In Amer M (ed). Urban and Transit Planning: A Culmination of Selected Research Papers from IEREK Conferences on Urban Planning, Architecture and Green Urbanism, Italy and Netherlands (2017) . Springer International Publishing , Netherlands , 289 – 95 .
AboSulaiman SS . Jeddah Islamic port: strategies for responding to the probable economic shocks of 2020-2030 . J King Abdulaziz Univ Mar Sci 2022 ; 32 : 51 – 73 . https://doi.org/10.4197/Mar.32-2.4 .
Al-Sheikh ABY . Management of environmental degradation of Jeddah coastal zone, Saudi Arabia, using remote sensing and geographic information systems . J Am Sci 2011 ; 7 : 665 – 73 .
Imam A , Helmi M , Alkadi A . et al. Exploring the quality of open public spaces in historic Jeddah . Arch City Environ 2023 ; 18 : 1 – 19 . http://hdl.handle.net/2117/390084 , https://doi.org/10.5821/ace.18.52.12123 .
Email alerts
Citing articles via, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 1748-1325
- Print ISSN 1748-1317
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Asia-Pacific
- Middle East & Africa

- Czech Republic

- France (English)
- France (Français)

- Switzerland

- Deutschland

- United Kingdom

- Indonesia (Bahasa)

- New Zealand

- Philippines

- South Africa

- United Arab Emirates
- الإمارات العربية المتحدة

- Cayman Islands

- Brazil (English)
- Brasil (Português)

- Mexico (English)
- México (Español)

- Canada(English)
- Canada(Français)

- United States

- SAB Online Log on
- SAB Invest Log on

Move to Borrowing navigation
- Compare Accounts
- Refer A friend
- Premier Account
- Advance Account
- General banking account
- Islamic Current Bank Account
- Commodity Investment Account
- Islamic Mudarabah Savings Account
- Wafer Account
- Green Deposit Account

Private Banking
- Private Banking Services
- Contact Us - Private Banking
- Credit Cards
- Apply for a Credit Card (Non-SAB customer)
- Apply Now for SAB Credit Card
- SAB Premier Credit Card
- SAB VISA Signature Credit Card
- SAB WORLD Mastercard Credit Card
- SAB Advance Visa Platinum
- SAB Platinum Mastercard Credit Card
- SAB VISA Platinum Credit Card
- SAB Titanium Mastercard
- SAB Visa "My Card" Credit Card
- Business Credit Card
- Privileges and Security
- Credit Card Payments
- SAB Debit Card
- Virtual Debit Card
Co-Brand Credit Cards
- SAB Emirates Signature Credit Card
- SAB ALFURSAN Mastercard Credit Card
- Cashback Credit Card
- SAB VISA Cashback Credit Card
Travel Card
- SAB Umlaty Multi Currency Card VISA
- Prepaid Card
- Household Salary Card
Card Benefits
- Alawwal Lounge By ALTANFEETHI
- Special Offers
- Cash on Call
- ICSAB+ Rewards Program
Prices of financing and savings products
- SAB Credit Card APR Calculator
- Product Disclosure Risk
- Bank Tariff
Wealth Management
- SAB Knowledge Centre
- Wealth Management Solutions
- BankingServices
- Investment Solutions
- Wide Range Asset Classes
- Safe Deposit Lockers
- Personal Finance
- Financing against Pledge of Cash Deposits Product
- Home Finance Products
- Non-salary Transfer PersonalFinance
Tools & Calculators
- Budget Planner
- Personal Finance Calculator
- Mortgage Calculator
International Transfers
- SAB Global View and Global Transfer
- Local Transfers
- Ways to Bank
e-Account opening
Sab 360°, open banking.
- SAB Branches & ATMs
Appointment Booking
E-statement, sms notification service, information security, interactive teller machine (itm), edesk+ machine, multi-currency atm, customer awareness, verify digital bank documents, update your information online, voice guidence atms, audio forms, handicap branches.
- Prices of Financing & Savings Products
- Premier Account Benefits
- Premier Account International
- You and Your Family
- Apply For Premier Account
- World Wide Assistance
- Growing your money with SAB Premier
- Preferred Banking
- International Banking Services
- Digital Banking Services
- Convenient Banking
- Credit Card Special Offers
- Travel Benefits
- Fees & Services
- CreditCard Special Offers
- SAB Visa "My Card" Credit Card - FAQs
- Credit Card Protection Feature
- SAB 3D Secure Service
- Cashback Calculator
- Dining & Groceries
- Automobiles
- Health & Fitness
- Cash on Call FAQs
- A beginner's guide to investing
- Myths about investing
- Saving vs investing
- What makes SAB different ?
- Off plan Product REDF Down Payment
- Ready Units Product REDF Down Payment
- Home and Liquidity
- Land Purchase
- Self-Construction
- Home Equity
- Ready units subsidized by REDF
- Self-construction product subsidized by REDF
- Under construction residential units (Off plan) by REDF
- Land and Financing Product Subsidized by REDF
- Home Equity Subsidized by REDF
- Under construction residential units (Off plan)
- Video Tutorials
- Demand Draft
- Local Transfer
- eForms - Account Opening
- TelexTransfer
Your browser is out of date
The browser you are using is outdated and may not display all the features of this website correctly. For the best online experience on sabb.com and improved safety features, we recommend that you update to the latest version of the browser.

- SAB Branches & ATMs
This link may allow you to access a non-SAB website. SAB has no control over the linked website and is not liable for your use of it. Proceed
This linkmay allow youto access a non-SAB website. SAB has no control over the linked website and is not liable for your use of it. Proceed
- Everyday Banking
SAB ATM offers you personalized Financial Services that allow you to conduct a range of transactions around the clock without having to visit the branch.
Discover the convenience of SAB’s ATM network
Banking and credit card services.
SAB ATMs offer the following Banking and Credit Card Services:
- Cash Withdrawal
- Balance Inquiry
- Statement Request
- Cash Deposit – most of our branches now have online cash deposit
- TM services
- PIN Change/Reset
- Mobile number change or reset
- Mini-statement for the last five transactions
- Initial Public Offering or Rights issue
Payment and Transfer Services
Payment and Transfer Services using a SAB ATM include:
- Transfers (to or from other SAB accounts or Credit Cards)
- Direct Pay (using a pre-defined beneficiary)
- SADAD bill payments
- Donations to Charity
- Ministry of Interior Services - MOI
SAB Branches & ATMs Locator
We think finding a SAB Branch & ATM should be easy. That's why our extensive ATM networks are designed to give you the accessibility you need to your money, no matter where life takes you.
What to do if you don't have an ATM Card
Please visit any of our branches to get an instant card issued or Call SAB Phone on 8001248888 (within Saudi) +9668001248888 (outside Saudi) to request a new/replacement card.
You can also request it through SAB Online .
Once you receive your new/replacement card, you can activate it through SAB Phone or by visiting the nearest SAB Branch.
Can a SAB client donate to charity through SAB ATMs?
Yes, SAB clients can donate to pre-identified charity accounts through SAB ATMs.
Can I change my ATM card PIN number through a SAB ATM?
Yes, you can change PIN as well as activate your card through any SAB ATM.
Can I get an account statement through SAB ATMs?
Yes, you can get a mini-statement or request a detailed account statement to be sent by mail.
Can I make credit card payments through SAB ATMs?
Yes, customers can make credit card payments at all SAB ATMs.
Can I pay my bills via ATM?
Yes, you can pay your bills through Utility payment at any SAB ATM.
Can I subscribe to an IPO at a SAB ATM?
Yes, you can subscribe to an IPO through any SAB ATM.
Can I transfer money locally and internationally via an ATM?
Yes, you can. If you're transferring money to a SAB client then all you need to complete the transaction through an ATM is the account number. For other local or international accounts you will need to add and activate the beneficiary before the transfer can be made.
Do SAB ATMs provide MOI payment services?
Yes, clients can make MOI payments through any SAB ATM.
How can I find the nearest SAB ATM?
Download the SAB Mobile App which will allow you to locate your nearest SAB ATM or Branch.
How can I report an ATM incident or ATM site issue?
In the case of an ATM/CDM error or site issue, please call us on ( 8001212221 ) or send an email to ( [email protected] ) making sure to include the device number in your statement.
How much is the daily cash withdrawal limit? And is it based on a 24hr time period?
The daily cash withdrawal limit from ATMs is 5000 SAR or its equivalent in foreign currency. The withdrawal limit gets updated daily.
I am a SAB customer and made a withdrawn from a non SAB ATM and my account was debited even though I did not get the money. What should I do?
You must submit a claim to the issuing bank to start the refund process. Please note that the claim will need to be authenticated before your account can be credited.
I am a SAB customer and made a withdrawn from a SAB ATM and my account was debited even though I did not get the money. What should I do?
In most cases, the amount will be credited to your account within 48 hour. If it has taken more time than that then you must submit a claim to the bank and the amount will be credited back after verifying its authenticity.
I am not a SAB customer and made a withdrawn from a SAB ATM and my account was debited even though I did not get the money. What should I do?
Is it possible to deposit foreign currency in a sab cash deposit machine.
No, CDMs can only accept SAR.
What is the daily limit of Self-Cash Deposit through CDM?
One hundred thousand Saudi Riyal
What should I do if I lose my ATM card?
Call SAB immediately to report lost or stolen cards so that the card can be deactivated.
What's the maximum amount of banknotes that cash deposit machines will accept?
One hundred banknotes is the maximum a CDM will accept.
Where do I find the ATM ID number?
ATM ID numbers are always printed on every transaction receipt. You can also find it on the identification panel above the ATM screen.
Why did the ATM capture my card?
There are a few reasons that include either:
- a problem with the card
- a problem with the account
- or an ATM technical error
- Compare SAB Credit Cards Cards
- Compare SAB Co-Brand Credit Cards
- SAB Travel Card
- Contact Centre
- Complaints & Feedback
- Terms &Conditions


- Hotel Booking
- International driving license
- Azerbaijan Visa
- Canada Tourist Visa
- Thailand Visa
- Vietnam Visa
- JAPAN eVisa
- Malaysia eVisa
- Russian Visa
- Turkish Visa
- Student Visa
- Become a vendor
Canada Tourist Visa
Visa Requirements for Temporary Resident Visa (Visit – Tourism):
1. Photo HD pdf (50 mm wide by 70 mm high) For complete guideline for photographs click at Canada photographs 2. Passport (The passport must be valid for a minimum of six months upon arrival at the Canadian Port of Entry.) 3. Residence Permit (Iqama) and its translation. 4. An employment letter stating position, salary, length of service & dates of contract. In case of (Self-employed: please provide a copy of your business CR.) 5. Immune status in Tawakkalna. (Health Passport) 6. National Address (Anwan Watani)
7. Bank statements covering six months prior to the date of your application
8. Previous Travel History with date
9. Last Educational Qualification Degree with Date
10. Valid national identity card (If you have)
10. Family Information
12. Additional Required Documents for Canada Visa for Pakistani Citizen
- FRC Family Registration Certificate (for Applicants & his Father)
- MRC Marriage Registration Certificate (In case you are traveling with your spouse)
- Invitation Letter / Sponsor Letter if any
- Only provide us all documentation scan copy of each document.
Price: SR 1190 (including visa & vfs 540SR fee & Iqama translation)
Need to go for Biometric at your nearest VFS center Application processing time from our side 3/4 Days, Visa approval time takes from Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada 1 Month to 6 Months.
SAB Travel process the Canadian Visit – Tourism VISA with easy documentation and procedures. Give us your documents and get relaxed. Visa is subjected to approval from embassy, fees is non-refundable in case of rejection. Office address:
SAB Travel & Tourism Al-Hayat Center – Behind RadissonBlu Hotel Madinah Road, Ash Sharafiyah 6945, Jeddah 23216 Saudi Arabia.
Google Map: Location
Apply Now
Get Updates & More
Thoughtful thoughts to your inbox
- Community Blog
- Work with Us
- Meet the Team
- Affiliate Program
- Privacy Policy
- SAB Education
Copyright © 2019 by Booking Core
Booking Core
or continue with
This website requires cookies to provide all of its features. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies. More info

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tourism, Visa Services, Education, Hotels, Tickets, Travel Insurance. [email protected]. USD EUR JPY ... Welcome to SAB Travel! Where would you like to go? Hotel Tour Car Flight Location . Check In - Out. 04/24/2024 - 04/25/2024. Guests . 1 Adult 1 Adults ...
Tourism, Visa Services, Education, Hotels, Tickets, Travel Insurance. [email protected]. SAR USD English ... Welcome to SAB Travel! Where would you like to go? Hotel Tour Car Flight Location . Check In - Out ...
SAB Travels, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. 14,674 likes · 7,608 talking about this · 7 were here. We take care of doing the cumbersome work of visa processing...
Post-COVID-19, the Saudi tourism industry appears to be gaining new ground. The 60-day Jeddah Season 2022 concluded in July with activities across 13 zones and event sites throughout the city. More than 6 million domestic and international tourists, representing 129 countries, attended and enjoyed entertainment, cultural, artistic, tourism, maritime sports, and other activities.
SAB Travel FOR INQUIRIES: Jeddah - +966 53 686 2740 Riyadh - +966 50 80 50240 ☎️Jeddah - 0122067877 Email Us: [email protected] SAB Travel & Tourism Al-Hayat Commercial Center -...
We take care of doing the cumbersome work of visa processing the application at your request. All you have to do is to contact us and provide us the necessar...
Special Fare Available..Book Now! SAB Travel & Tourism Al-Hayat Commercial Center - Behind RadissonBlu Hotel Madinah Road, Sharafeyah, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. • Website: alsabtravel.com • Tel:...
Riyadh. Established in 1980, Saudi International Travel Company is renowned for offering the best travel and tourism services. Over 42 years, we've earned a reputation for excellence in the diversity and quality of our offerings and the professionalism of our staff. We're proud of our ongoing, vital role in serving numerous government and ...
Payment Management Services ; SAB AMEX Corporate Payment Solutions ; ... Saudi Arabia has elevated its global tourism profile with the launch of e-tourist visas for nationals of 49 countries. ... At-Turaif District in ad-Dir'iyah (2010), Historic Jeddah, the Gate to Makkah (2014), and Rock Art in the Hail Region of Saudi Arabia (2015). ...
Saudi Awwal Bank, a listed joint stock company, incorporated in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with paid in capital of SAR 20,547,945,220, commercial registration certificate 1010025779, unified number 7000018668, P.O. Box 9084 Riyadh 11413, Kingdom ofSaudi Arabia, Tel. +966 11 4050677, www.sab.com, licensed pursuant to theCouncil of Ministers Resolution No. 198 dated 06/02/1398H and Royal ...
Almosafer is the Middle East's leading travel brand offering consumers seamless user experiences for domestic and international travel bookings through its omni-channel offerings across state-of-the-art online platforms, call centre, WhatsApp and retail locations. Providing hotel booking options for over 1.5 million properties around the ...
Domestic Packages. Explore the beauty of Saudi Arabia and discover hidden gems across the country. From Abha's mountain peaks and Al Baha's exotic forests to Jeddah's impressive museums and Taif's gorgeous scenery, you will never run out of fun experiences and thrilling adventures. We can help you book one of our domestic holiday packages ...
Welcome to Samaya Travel Agency - your ultimate partner in global connections. At Samaya Travel Agency, our mission is to connect people, places, and cultures through exceptional travel experiences, forging lifelong memories and inspiring a world of discovery. As we advance into the future, Samaya Travel Agency remains steadfast in our ...
At SAB Group, we are committed to providing sustainable and responsible tourism services. We prioritize eco-friendly practices and support local communities through our tourism activities. Our goal is to create a positive impact on the environment and society while providing our clients with an unforgettable travel experience.
Tourism, Visa Services, Education, Hotels, Tickets, Travel Insurance.
The Ministry of Tourism, before 2020 as the Saudi Commission for Tourism and National Heritage (SCTH), till 2015 as the Saudi Commission for Tourism and Antiquities (SCTA) and prior to 2008 as the Supreme Commission for Tourism (SCT), is a government ministry in Saudi Arabia that is concerned with the tourism sector of the country. Established in the year 2000 through a royal decree by King ...
SAB Travel process the Canadian Visit - Tourism VISA with easy documentation and procedures. ... Visa is subjected to approval from embassy, fees is non-refundable in case of rejection. Office address: SAB Travel & Tourism Al-Hayat Center - Behind RadissonBlu Hotel Madinah Road, Ash Sharafiyah 6945, Jeddah 23216 Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Awwal Bank, a listed joint stock company, incorporated in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with paid in capital of SAR 20,547,945,220, commercial registration certificate 1010025779, unified number 7000018668, P.O. Box 9084 Riyadh 11413, Kingdom ofSaudi Arabia, Tel. +966 11 4050677, www.sab.com, licensed pursuant to theCouncil of Ministers Resolution No. 198 dated 06/02/1398H and Royal ...
Saudi Tourist & Travel Bureau Ltd - Umrah STTB, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. 3,791 likes. The company's aim is to personally assist, attend and satisfactorily meet the requirements of the tour operators...
The government aims to attract 70 million international visitors by 2030, up from 27 million in 2023. AlUla is only one of the kingdom's massive projects, and the progress so far raises ...
Saudi Awwal Bank, a listed joint stock company, incorporated in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with paid in capital of SAR 20,547,945,220, commercial registration certificate 1010025779, unified number 7000018668, P.O. Box 9084 Riyadh 11413, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Tel. +966 11 4050677, www.sab.com, licensed pursuant to the Council of Ministers Resolution No. 198 dated 06/02/1398H and Royal ...
The urbanization trend aligns with efforts to achieve economic diversification under Saudi Vision 2030. Jeddah's growth could stimulate sectors other than oil, contributing to a more diversified and resilient economy. This includes the real estate, retail, tourism and services sectors. 4.2.
Saudi Awwal Bank, a listed joint stock company, incorporated in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with paid in capital of SAR 20,547,945,220, commercial registration certificate 1010025779, unified number 7000018668, P.O. Box 9084 Riyadh 11413, Kingdom ofSaudi Arabia, Tel. +966 11 4050677, www.sab.com, licensed pursuant to theCouncil of Ministers Resolution No. 198 dated 06/02/1398H and Royal ...
Tourism, Visa Services, Education, Hotels, Tickets, Travel Insurance. [email protected]. USD ... (Visit - Tourism): 1. Photo HD pdf (50 mm wide by 70 mm high) ... SAB Travel process the Canadian Visit - Tourism VISA with easy documentation and procedures. Give us your documents and get relaxed.