The Ordeal in the Hero's Journey
From Christopher Vogler's The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure
Moviepix / GettyImages
- Tips For Adult Students
- Getting Your Ged
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Deb-Nov2015-5895870e3df78caebc88766f.jpg)
- B.A., English, St. Olaf College
The Ordeal is the critical moment in every story, a major source of magic in heroic myth, according to Christopher Vogler, author of The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure. The hero stands in the deepest chamber of the inmost cave and faces a direct confrontation with his greatest fear. No matter what the hero came for, it’s Death that now stares back at her. She is brought to the brink of death in a battle with a hostile force.
The hero of every story is an initiate being introduced to the mysteries of life and death, Vogler writes. She must appear to die so she can be reborn, transformed.
The ordeal is a major crisis in the story, but it's not the climax, which happens closer to the end. The ordeal is usually the central event, the main event of the second act. A crisis, according to Webster’s, is when "hostile forces are in the tensest state of opposition."
The hero’s crisis, as frightening as it is, is the only way to victory, according to Vogler.
Witnesses are an important part of the crisis. Someone close to the hero witnesses the hero’s apparent death and the reader experiences it through their point of view. Witnesses feel the pain of death, and when they realize the hero still lives, their grief, as well as the reader’s, suddenly, explosively, turns to joy, Vogler states.

Readers Love to See Heroes Cheat Death
Vogler writes that in any story, the writer is trying to lift the reader, raise their awareness, heighten their emotions. Good structure works as a pump on the reader’s emotions as the hero’s fortunes are raised and lowered. Emotions depressed by the presence of death can rebound in an instant to a higher state than before.
Just as on a roller coaster, you’re hurled around until you think you might die, Vogler writes, and you get off elated that you’ve survived. Every story needs a hint of this experience or it’s missing its heart.
The crisis, a halfway point, is a divide in the hero’s journey : the top of the mountain, the heart of the forest, the depth of the ocean, the most secret place in his soul. Everything in the trip has to lead up to this point, and everything after is about going home.
There may be greater adventures to come, the most exciting even, but every journey has a center, a bottom or a peak somewhere near the middle. Nothing will ever be the same after the crisis.
The most common ordeal is some sort of battle or confrontation with the opposing force, which usually represents the hero’s own shadow, according to Vogler. No matter how alien the villain’s values, in some way they are the dark reflection of the hero’s own desires, magnified and distorted, her greatest fears come to life. The unrecognized or rejected parts are acknowledged and made conscious despite all their struggles to remain in darkness.
Death of the Ego
The ordeal in myth signifies the death of the ego. The hero has soared above death and now sees the connectedness of all things. The hero has risked his life for the sake of the larger collective.
The Wicked Witch is enraged that Dorothy and her friends have penetrated the inmost cave. She threatens each of them with death. She lights Scarecrow on fire. We feel the horror of his imminent death. Dorothy grabs a bucket of water to save him and ends up melting the witch. We watch her agonizing death instead. After a moment of being stunned, everyone is related, even the witch’s minions.
This article is part of our series on the hero's journey, starting with The Hero's Journey Introduction and The Archetypes of the Hero's Journey.
- The Approach to the Inmost Cave in the Hero's Journey
- The Resurrection and Return With the Elixir
- An Introduction to The Hero's Journey
- The Hero's Journey: Crossing the Threshold
- The Reward and the Road Back
- The Hero's Journey: Refusing The Call to Adventure
- The Ordinary World in the Hero's Journey
- The Role of Archetypes in Literature
- The Hero's Journey: Meeting with the Mentor
- Jean Paul Sartre's 'The Transcendence of the Ego'
- Ulysses (Odysseus)
- Freud: Id, Ego, and Superego Explained
- Amplification Definition and Examples in Rhetoric
- Falling Action in Literature
- The Heroes of Ancient Greece and Rome
- How to Write Great Ledes for Feature Stories
Exploring the 12 Stages of the Hero’s Journey Part 8: The Ordeal
We dive into this archetypal story concept, according to Joseph Campbell's The Hero's Journey and Christopher Vogler's interpreted twelve stages of that journey within his book, The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers ?
Welcome to Part 8 of our 12-part series ScreenCraft’s Exploring the 12 Stages of the Hero’s Journey , where we go into depth about each of the twelve stages and how your screenplays could benefit from them. Before we dive in, be sure to download our free e-book while it's still available:

The first stage — The Ordinary World — happens to be one of the most essential elements of any story, even ones that don't follow the twelve-stage structure to a tee.
Showing your protagonist within their Ordinary World at the beginning of your story offers you the ability to showcase how much the core conflict they face rocks their world. And it allows you to foreshadow and create the necessary elements of empathy and catharsis that your story needs.
The next stage is the Call to Adventure. Giving your story's protagonist a Call to Adventure introduces the core concept of your story, dictates the genre your story is being told in and helps to begin the process of character development that every great story needs.
When your character refuses the Call to Adventure, it allows you to create instant tension and conflict within the opening pages and first act of your story. It also gives you the chance to amp-up the risks and stakes involved, which, in turn, engages the reader or audience even more. And it also manages to help you develop a protagonist with more depth that can help to create empathy for them.
Along the way, your protagonist — and screenplay — may need a mentor. Meeting the Mentor offers the protagonist someone that can guide them through their journey with wisdom, support, and even physical items. Beyond that, they help you to offer empathetic relationships within your story, as well as ways to introduce themes, story elements, and exposition to the reader and audience.
At some point at the end of the first act, your story may showcase a moment where your protagonist needs to cross the threshold between their Ordinary World and the Special World they will be experiencing as their inner or outer journey begins. Such a moment shifts everything from the first act to the second, allowing the reader and audience to feel that shift so they can prepare for the journey to come.
It showcases the difference between the protagonist's Ordinary World and the Special World to come. And, even more important, we're introduced to the first shift in the character arc of the protagonist as they decide to venture out into the unknown.
And it's within this unknown that the protagonist faces many tests and meets their allies and enemies — all of which define the meat of your story by introducing the conflict, expanding the cast of characters, and offering a more engaging and compelling narrative.
Once you've put your protagonist through those tests and once they've met their allies and enemies, they're going to need to Approach the Inmost Cave of the story — preparing to face their greatest fears and conflicts. This is an essential element of your narrative, allowing the reader, audience, and characters to catch their breath, reflect, review, and plan ahead for the conflict just over the horizon. And it allows you, the writer, to build the necessary tension and anticipation that you need going into the midpoint of your story.
Everything within the first act — and beginning of the second — builds up to The Ordeal, which is the first real conflict that the protagonist must face.
What Is The Ordeal ?
It's the midpoint of your story where your protagonist faces their greatest conflict yet.
The protagonist has gone through the necessary trials and tribulations that prepare them for what they believe to be the ultimate test they've faced within their journey thus far — The Ordeal.
As they Approach the Inmost Cave of their story, we've learned everything we need to know about how they plan to handle the situation. But once they begin their approach, everything goes haywire. Unexpected setbacks occur. What they thought they knew was either wrong, misinterpreted, or has evolved into a far more difficult conflict than they could have ever imagined.
This is the point of the story where the protagonist and their allies (if any) face their greatest challenge thus far — usually amid great consequences. Sometimes it's life or death. Other times it's a metaphorical version of those stakes.
This is when the protagonist hits rock bottom, making them — as well as the reader and audience — feel as if they are at the dark end of their days.
Here are three ways that you can create the best Ordeal within your story.
1. Write The Ordeal as If It Was the Climax of the Story
Just because The Ordeal is the midpoint of your story doesn't mean that it can't pack a punch.
In essence, The Ordeal is a false climax.
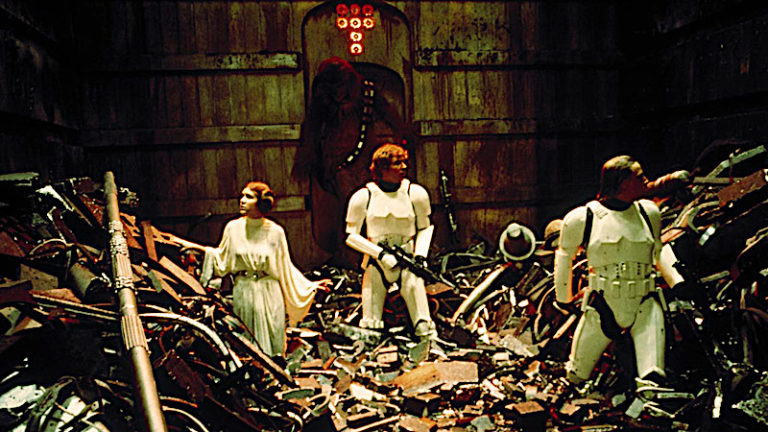
In Star Wars — as Kenobi goes off to deactivate the tractor beam so they can escape — Luke, Han, and Chewbacca discover that Princess Leia is being held on the Death Star with them. They rescue her, survive a hopeless situation within a trash compactor, and then escape to the Millennium Falcon, hoping that Kenobi has successfully deactivated the tractor beam.
Kenobi later sacrifices himself as Luke watches Darth Vader strike him down.
https://youtu.be/sq51w34Hg9I
This sequence feels like the end of the great space opera, but it's really launching us towards the true climax to come — the Battle of Yavin as the Rebellion takes on the Galactic Empire in an epic space battle.
The Ordeal represents what the protagonist believes is the final confrontation between themselves and the conflict that has rocked their Ordinary World.
In Mission: Impossible , the plan to perform a heist within the CIA Headquarters is worthy of being one of the most thrilling heist climaxes of all time.
https://youtu.be/2zRtOpW8gOs
https://youtu.be/5BcLRnMkI7Q
But it's really just the midpoint of the story that launches us forward with even more conflict to deal with.
In The Lord of the Rings: Fellowship of the Ring , Frodo and the rest of the Fellowship are forced to fend off hundreds, if not thousands, of orcs within Moria. They even have to deal with a towering cave troll. When they finally defeat the cave troll, orcs are about to overrun them until their numbers are scattered as the Balrog appears.
Gandalf fights the Balrog and casts him into a chasm. However, the Balrog drags Gandalf down with him to his apparent death.
It's hard to believe that this isn't the climax of the film.
When you develop The Ordeal within your story, write it as if it'd be the exciting climax of any other great novel or movie. When you do that, you're retaining the interest of the reader and audience through the most difficult part of your story — the second act.
And it works in any genre. The Ordeal can be a moment where the protagonist believes they are facing their greatest physical or emotional challenge. But then everything goes wrong, despite what they've learned through tests they've undergone in their journey.
2. Kill the Protagonist's Darlings
Allies and Mentors are the rock for most protagonists. They offer emotional and physical support. Mentors offer the hero the knowledge and perspective that they need to take on whatever conflict they're forced to face.
The Ordeal is all about taking your protagonist to their lowest of lows so that they can rise up and be resurrected in such a way that they can truly handle the major conflict once and for all.
And what greater way to take them as low as they can go than killing their allies and mentors.
In Jaws , Brody loses both his allies and mentors in Hooper and Quint.
During The Ordeal of that story, the shark attacks the shark cage and Hooper is thought to be lost.
Soon after, as their now sinking boat takes on water, the shark attacks and kills Quint, leaving Brody all by himself.
Note: The Ordeal in Jaws comes a little later than the Midpoint of the story. There are always variances within story structures.
Brody is now tasked with taking on the shark all by himself.
When you take away beloved characters, you create an empathetic reaction for the reader and audience. This leads to cathartic moments that make your story even more memorable and engaging.
We feel for the protagonist because we've fallen in love with these characters. We rely on them, just as the protagonist does.
Kill your darlings.
3. Give Opportunities Within The Ordeal for the Protagonist to be Resurrected
Two Hero's Journey stages away from The Ordeal is The Resurrection — The climax where the hero faces their final test, using everything they have learned to take on the conflict once and for all.
Within that Resurrection, your protagonist needs to have a moment of transformation. But before that transformation can occur, something has to push them to the brink — to their lowest point.
While losing an ally or mentor can help set the stage for the need for them to transform so that they can handle the final test, we need more. They need to lose hope, courage, or strength to carry on. The reader and audience need to feel as if there's no returning to the Ordinary World because that is how bad things are.
In Jaws , we know that Brody is afraid of the water. This character trait is showcased time and time again throughout the story. He's lost his allies and mentors, yes. But now he must face his greatest fear from his Ordinary World — the water. Not to mention the giant shark that is coming to eat him.
The Ordeal within that film sets up a necessary transformation that must occur before he can face his fear of the water and kill the shark once and for all.
Inject characterization throughout the first and second act of your script that can help you showcase a powerful transformation that will keep the reader and audience invested, engaged, and compelled.
The Ordeal is the midpoint of your story that works as a false climax, taking your protagonist to the depths of despair. It offers you the ability to create an engaging midpoint climax that takes you into the third act. It ups the stakes within your story by taking away beloved allies and mentors. And it sets up the necessary transformation that your protagonist must go through in order to prevail.
And remember...
"The Hero's Journey is a skeleton framework that should be fleshed out with the details of and surprises of the individual story. The structure should not call attention to itself, nor should it be followed too precisely. The order of the stages is only one of many possible variations. The stages can be deleted, added to, and drastically shuffled without losing any of their power." — Christopher Vogler, The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers
Joseph Campbell's 17-stage Monomyth was conceptualized over the course of Campbell's own text, The Hero with a Thousand Faces, and then later in the 1980s through two documentaries, one of which introduced the term The Hero's Journey .
The first documentary, 1987's The Hero's Journey: The World of Joseph Campbell , was released with an accompanying book entitled The Hero's Journey: Joseph Campbell on His Life and Work .
The second documentary was released in 1988 and consisted of Bill Moyers' series of interviews with Campbell, accompanied by the companion book The Power of Myth .
Christopher Vogler was a Hollywood development executive and screenwriter working for Disney when he took his passion for Joseph Campbell's story monolith and developed it into a seven-page company memo for the company's development department and incoming screenwriters.
The memo, entitled A Practical Guide to The Hero with a Thousand Faces , was later developed by Vogler into The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Storytellers and Screenwriters in 1992. He then elaborated on those concepts for the book The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure For Writers .
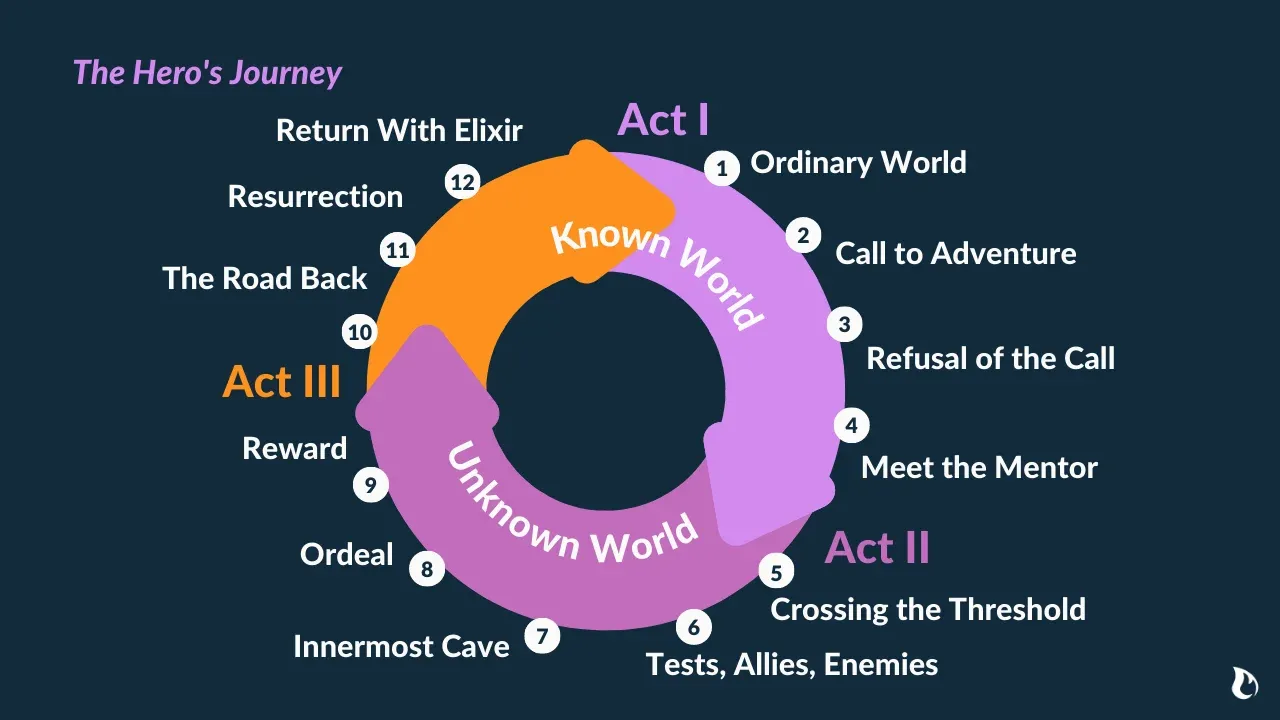
Christopher Vogler's approach to Campbell's structure broke the mythical story structure into twelve stages. We define the stages in our own simplified interpretations:
- The Ordinary World : We see the hero's normal life at the start of the story before the adventure begins.
- Call to Adventure : The hero is faced with an event, conflict, problem, or challenge that makes them begin their adventure.
- Refusal of the Call : The hero initially refuses the adventure because of hesitation, fears, insecurity, or any other number of issues.
- Meeting the Mentor : The hero encounters a mentor that can give them advice, wisdom, information, or items that ready them for the journey ahead.
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero leaves their ordinary world for the first time and crosses the threshold into adventure.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : The hero learns the rules of the new world and endures tests, meets friends, and comes face-to-face with enemies.
- The Approach : The initial plan to take on the central conflict begins, but setbacks occur that cause the hero to try a new approach or adopt new ideas.
- The Ordeal: Things go wrong and added conflict is introduced. The hero experiences more difficult hurdles and obstacles, some of which may lead to a life crisis.
- The Reward : After surviving The Ordeal, the hero seizes the sword — a reward that they've earned that allows them to take on the biggest conflict. It may be a physical item or piece of knowledge or wisdom that will help them persevere.
- The Road Back : The hero sees the light at the end of the tunnel, but they are about to face even more tests and challenges.
- The Resurrection : The climax. The hero faces a final test, using everything they have learned to take on the conflict once and for all.
- The Return : The hero brings their knowledge or the "elixir" back to the ordinary world.
Ken Miyamoto has worked in the film industry for nearly two decades, most notably as a studio liaison for Sony Studios and then as a script reader and story analyst for Sony Pictures.
He has many studio meetings under his belt as a produced screenwriter, meeting with the likes of Sony, Dreamworks, Universal, Disney, Warner Brothers, as well as many production and management companies. He has had a previous development deal with Lionsgate, as well as multiple writing assignments, including the produced miniseries Blackout , starring Anne Heche, Sean Patrick Flanery, Billy Zane, James Brolin, Haylie Duff, Brian Bloom, Eric La Salle, and Bruce Boxleitner. Follow Ken on Twitter @KenMovies
For all the latest ScreenCraft news and updates, follow us on Twitter, Facebook , and Instagram .
Get Our Screenwriting Newsletter!
Get weekly writing inspiration delivered to your inbox - including industry news, popular articles, and more!
Facebook Comments
Free download.

Screenwriting Resources:

$ 15.00 $ 12.00 Add to cart
Popular Posts

Recent Posts

Next Related Post

Get Our Newsletter!
Developing your own script.
We'll send you a list of our free eCourses when you subscribe to our newsletter. No strings attached.
You Might Also Like

- Hidden Name
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Connect With Us
Writing competitions, success stories.
© 2024 ScreenCraft | An Industry Arts Company
Wait! Subscribe to get our free Newsletter
Join our community of over 100,000 screenwriters and get weekly inspiration delivered to your inbox.
Screenwriting Newsletter
Join our community of over 100,000 screenwriters and get weekly inspiration delivered to your inbox:
✓ Popular blog posts and industry news ✓ New ScreenCraft online events ✓ Screenplay competition announcements!
" * " indicates required fields
Holiday Savings

cui:common.components.upgradeModal.offerHeader_undefined
The hero's journey: a story structure as old as time, the hero's journey offers a powerful framework for creating quest-based stories emphasizing self-transformation..

Table of Contents
Holding out for a hero to take your story to the next level?
The Hero’s Journey might be just what you’ve been looking for. Created by Joseph Campbell, this narrative framework packs mythic storytelling into a series of steps across three acts, each representing a crucial phase in a character's transformative journey.
Challenge . Growth . Triumph .
Whether you're penning a novel, screenplay, or video game, The Hero’s Journey is a tried-and-tested blueprint for crafting epic stories that transcend time and culture. Let’s explore the steps together and kickstart your next masterpiece.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey is a famous template for storytelling, mapping a hero's adventurous quest through trials and tribulations to ultimate transformation.
What are the Origins of the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey was invented by Campbell in his seminal 1949 work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces , where he introduces the concept of the "monomyth."
A comparative mythologist by trade, Campbell studied myths from cultures around the world and identified a common pattern in their narratives. He proposed that all mythic narratives are variations of a single, universal story, structured around a hero's adventure, trials, and eventual triumph.
His work unveiled the archetypal hero’s path as a mirror to humanity’s commonly shared experiences and aspirations. It was subsequently named one of the All-Time 100 Nonfiction Books by TIME in 2011.
How are the Hero’s and Heroine’s Journeys Different?
While both the Hero's and Heroine's Journeys share the theme of transformation, they diverge in their focus and execution.
The Hero’s Journey, as outlined by Campbell, emphasizes external challenges and a quest for physical or metaphorical treasures. In contrast, Murdock's Heroine’s Journey, explores internal landscapes, focusing on personal reconciliation, emotional growth, and the path to self-actualization.
In short, heroes seek to conquer the world, while heroines seek to transform their own lives; but…
Twelve Steps of the Hero’s Journey
So influential was Campbell’s monomyth theory that it's been used as the basis for some of the largest franchises of our generation: The Lord of the Rings , Harry Potter ...and George Lucas even cited it as a direct influence on Star Wars .
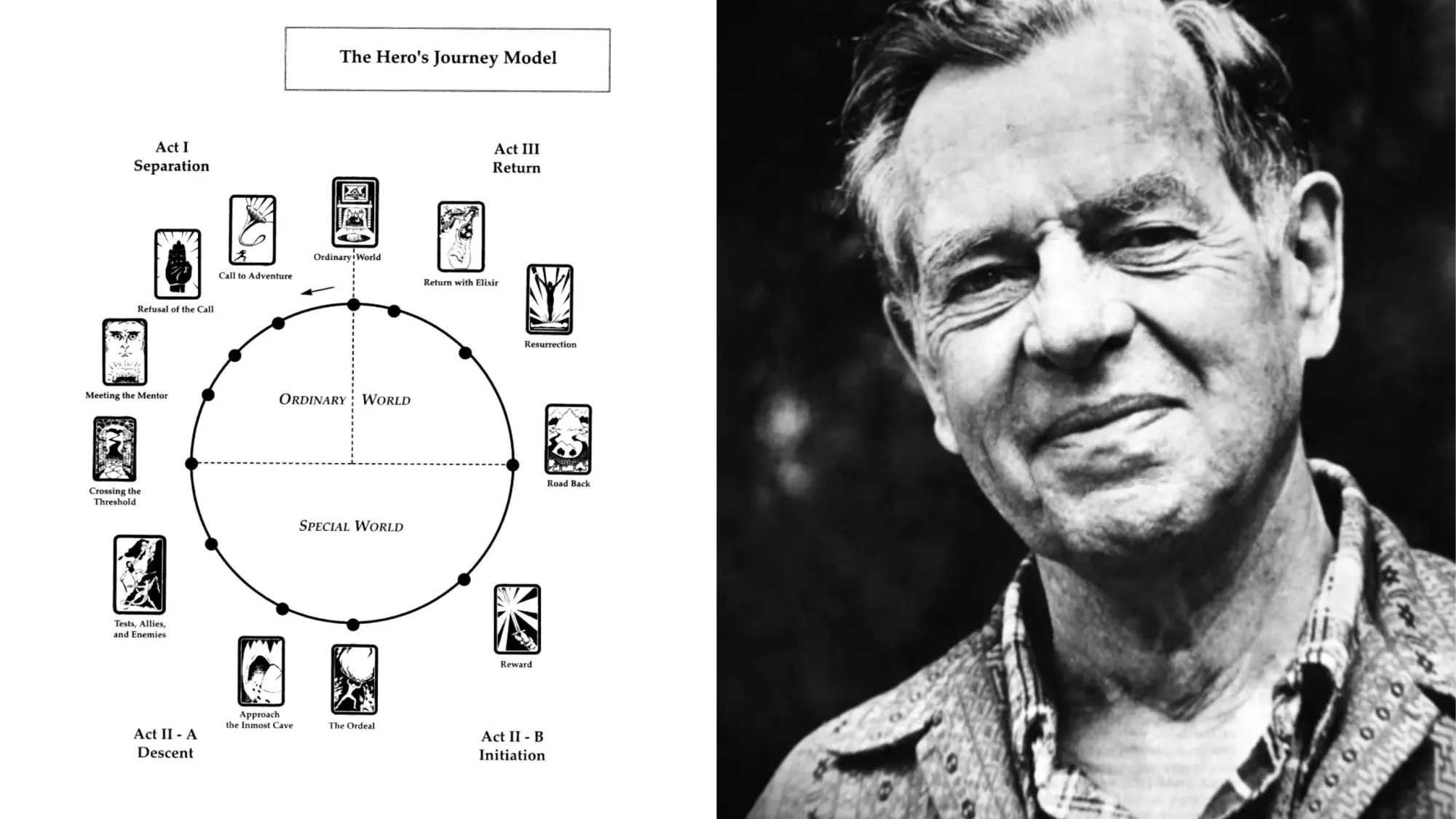
There are, in fact, several variations of the Hero's Journey, which we discuss further below. But for this breakdown, we'll use the twelve-step version outlined by Christopher Vogler in his book, The Writer's Journey (seemingly now out of print, unfortunately).

You probably already know the above stories pretty well so we’ll unpack the twelve steps of the Hero's Journey using Ben Gates’ journey in National Treasure as a case study—because what is more heroic than saving the Declaration of Independence from a bunch of goons?
Ye be warned: Spoilers ahead!
Act One: Departure
Step 1. the ordinary world.
The journey begins with the status quo—business as usual. We meet the hero and are introduced to the Known World they live in. In other words, this is your exposition, the starting stuff that establishes the story to come.
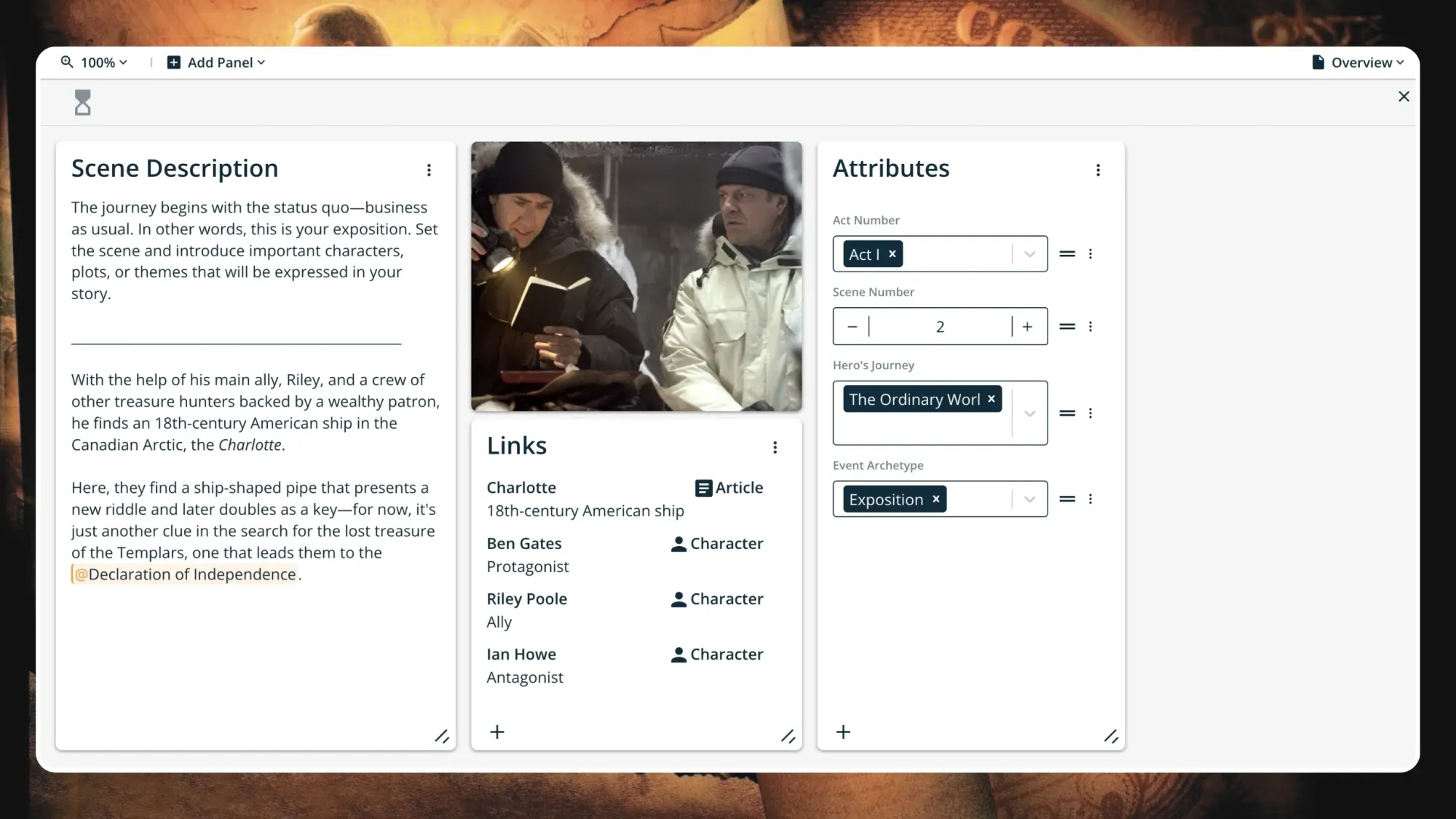
National Treasure begins in media res (preceded only by a short prologue), where we are given key information that introduces us to Ben Gates' world, who he is (a historian from a notorious family), what he does (treasure hunts), and why he's doing it (restoring his family's name).
With the help of his main ally, Riley, and a crew of other treasure hunters backed by a wealthy patron, he finds an 18th-century American ship in the Canadian Arctic, the Charlotte . Here, they find a ship-shaped pipe that presents a new riddle and later doubles as a key—for now, it's just another clue in the search for the lost treasure of the Templars, one that leads them to the Declaration of Independence.
Step 2. The Call to Adventure
The inciting incident takes place and the hero is called to act upon it. While they're still firmly in the Known World, the story kicks off and leaves the hero feeling out of balance. In other words, they are placed at a crossroads.
Ian (the wealthy patron of the Charlotte operation) steals the pipe from Ben and Riley and leaves them stranded. This is a key moment: Ian becomes the villain, Ben has now sufficiently lost his funding for this expedition, and if he decides to pursue the chase, he'll be up against extreme odds.
Step 3. Refusal of the Call
The hero hesitates and instead refuses their call to action. Following the call would mean making a conscious decision to break away from the status quo. Ahead lies danger, risk, and the unknown; but here and now, the hero is still in the safety and comfort of what they know.
Ben debates continuing the hunt for the Templar treasure. Before taking any action, he decides to try and warn the authorities: the FBI, Homeland Security, and the staff of the National Archives, where the Declaration of Independence is housed and monitored. Nobody will listen to him, and his family's notoriety doesn't help matters.
Step 4. Meeting the Mentor
The protagonist receives knowledge or motivation from a powerful or influential figure. This is a tactical move on the hero's part—remember that it was only the previous step in which they debated whether or not to jump headfirst into the unknown. By Meeting the Mentor, they can gain new information or insight, and better equip themselves for the journey they might to embark on.
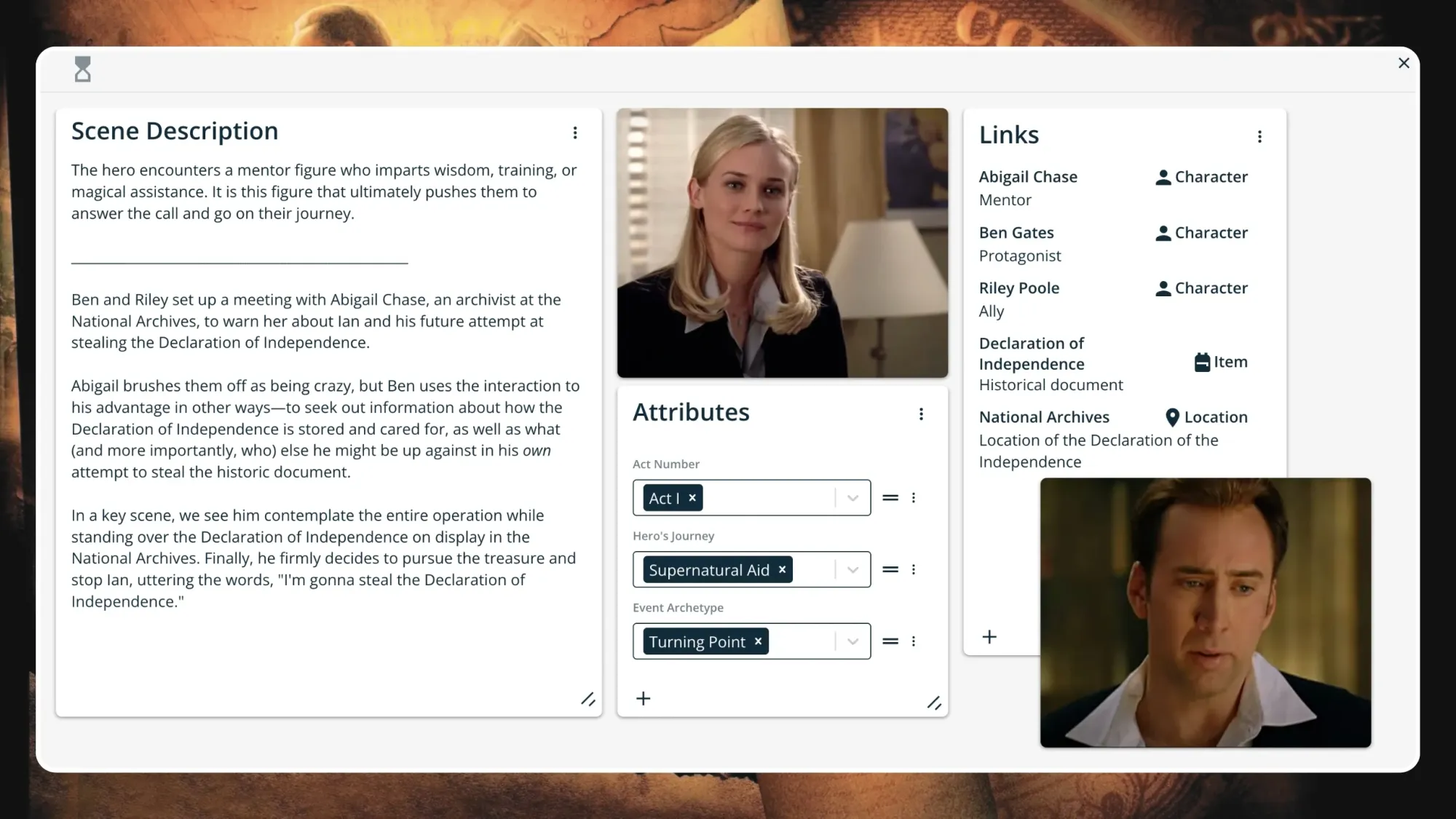
Abigail, an archivist at the National Archives, brushes Ben and Riley off as being crazy, but Ben uses the interaction to his advantage in other ways—to seek out information about how the Declaration of Independence is stored and cared for, as well as what (and more importantly, who) else he might be up against in his own attempt to steal it.
In a key scene, we see him contemplate the entire operation while standing over the glass-encased Declaration of Independence. Finally, he firmly decides to pursue the treasure and stop Ian, uttering the famous line, "I'm gonna steal the Declaration of Independence."
Act Two: Initiation
Step 5. crossing the threshold.
The hero leaves the Known World to face the Unknown World. They are fully committed to the journey, with no way to turn back now. There may be a confrontation of some sort, and the stakes will be raised.
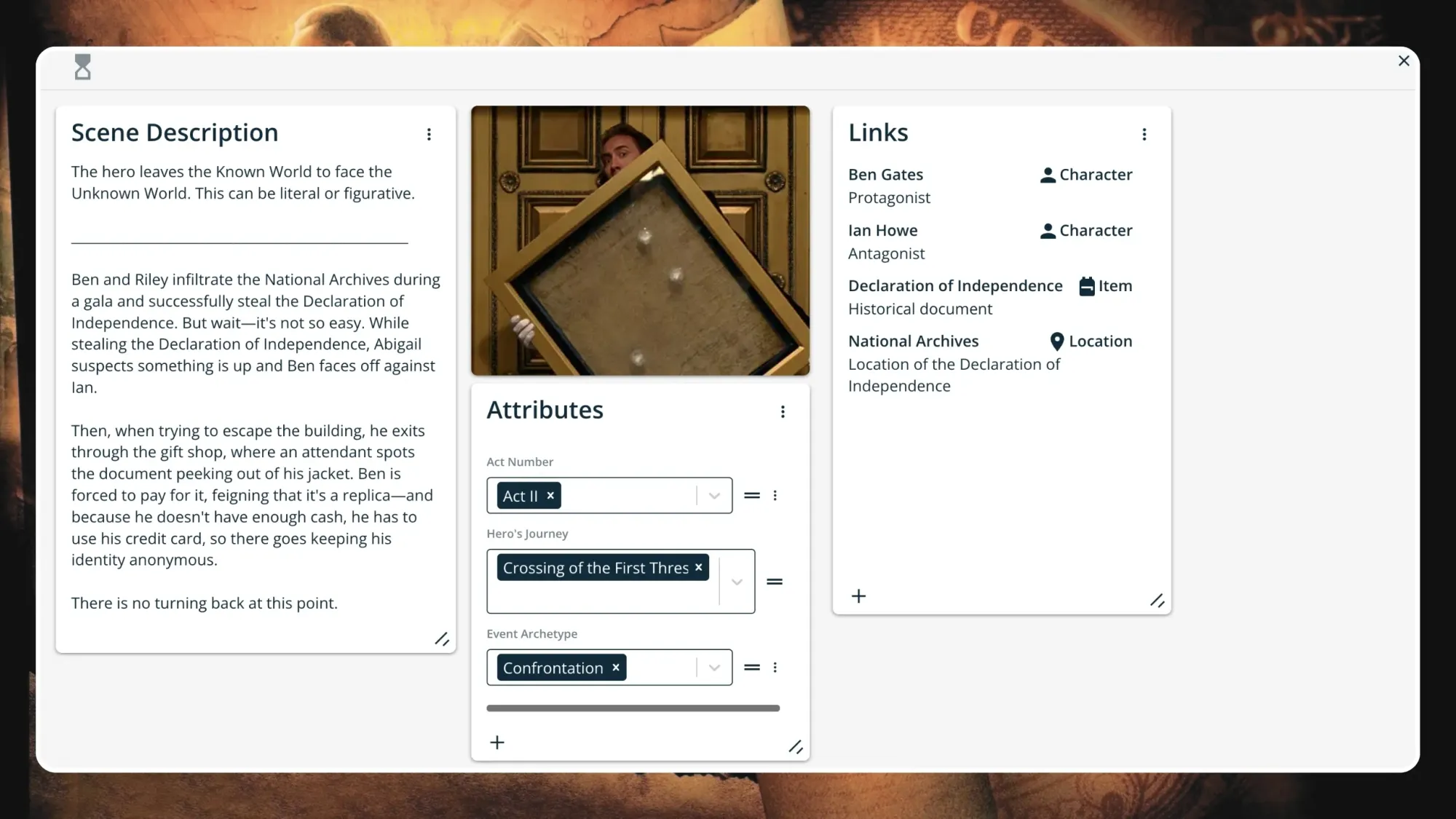
Ben and Riley infiltrate the National Archives during a gala and successfully steal the Declaration of Independence. But wait—it's not so easy. While stealing the Declaration of Independence, Abigail suspects something is up and Ben faces off against Ian.
Then, when trying to escape the building, Ben exits through the gift shop, where an attendant spots the document peeking out of his jacket. He is forced to pay for it, feigning that it's a replica—and because he doesn't have enough cash, he has to use his credit card, so there goes keeping his identity anonymous.
The game is afoot.
Step 6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
The hero explores the Unknown World. Now that they have firmly crossed the threshold from the Known World, the hero will face new challenges and possibly meet new enemies. They'll have to call upon their allies, new and old, in order to keep moving forward.
Abigail reluctantly joins the team under the agreement that she'll help handle the Declaration of Independence, given her background in document archiving and restoration. Ben and co. seek the aid of Ben's father, Patrick Gates, whom Ben has a strained relationship with thanks to years of failed treasure hunting that has created a rift between grandfather, father, and son. Finally, they travel around Philadelphia deciphering clues while avoiding both Ian and the FBI.
Step 7. Approach the Innermost Cave
The hero nears the goal of their quest, the reason they crossed the threshold in the first place. Here, they could be making plans, having new revelations, or gaining new skills. To put it in other familiar terms, this step would mark the moment just before the story's climax.
Ben uncovers a pivotal clue—or rather, he finds an essential item—a pair of bifocals with interchangeable lenses made by Benjamin Franklin. It is revealed that by switching through the various lenses, different messages will be revealed on the back of the Declaration of Independence. He's forced to split from Abigail and Riley, but Ben has never been closer to the treasure.
Step 8. The Ordeal
The hero faces a dire situation that changes how they view the world. All threads of the story come together at this pinnacle, the central crisis from which the hero will emerge unscathed or otherwise. The stakes will be at their absolute highest here.
Vogler details that in this stage, the hero will experience a "death," though it need not be literal. In your story, this could signify the end of something and the beginning of another, which could itself be figurative or literal. For example, a certain relationship could come to an end, or it could mean someone "stuck in their ways" opens up to a new perspective.
In National Treasure , The FBI captures Ben and Ian makes off with the Declaration of Independence—all hope feels lost. To add to it, Ian reveals that he's kidnapped Ben's father and threatens to take further action if Ben doesn't help solve the final clues and lead Ian to the treasure.
Ben escapes the FBI with Ian's help, reunites with Abigail and Riley, and leads everyone to an underground structure built below Trinity Church in New York City. Here, they manage to split from Ian once more, sending him on a goose chase to Boston with a false clue, and proceed further into the underground structure.
Though they haven't found the treasure just yet, being this far into the hunt proves to Ben's father, Patrick, that it's real enough. The two men share an emotional moment that validates what their family has been trying to do for generations.
Step 9. Reward
This is it, the moment the hero has been waiting for. They've survived "death," weathered the crisis of The Ordeal, and earned the Reward for which they went on this journey.
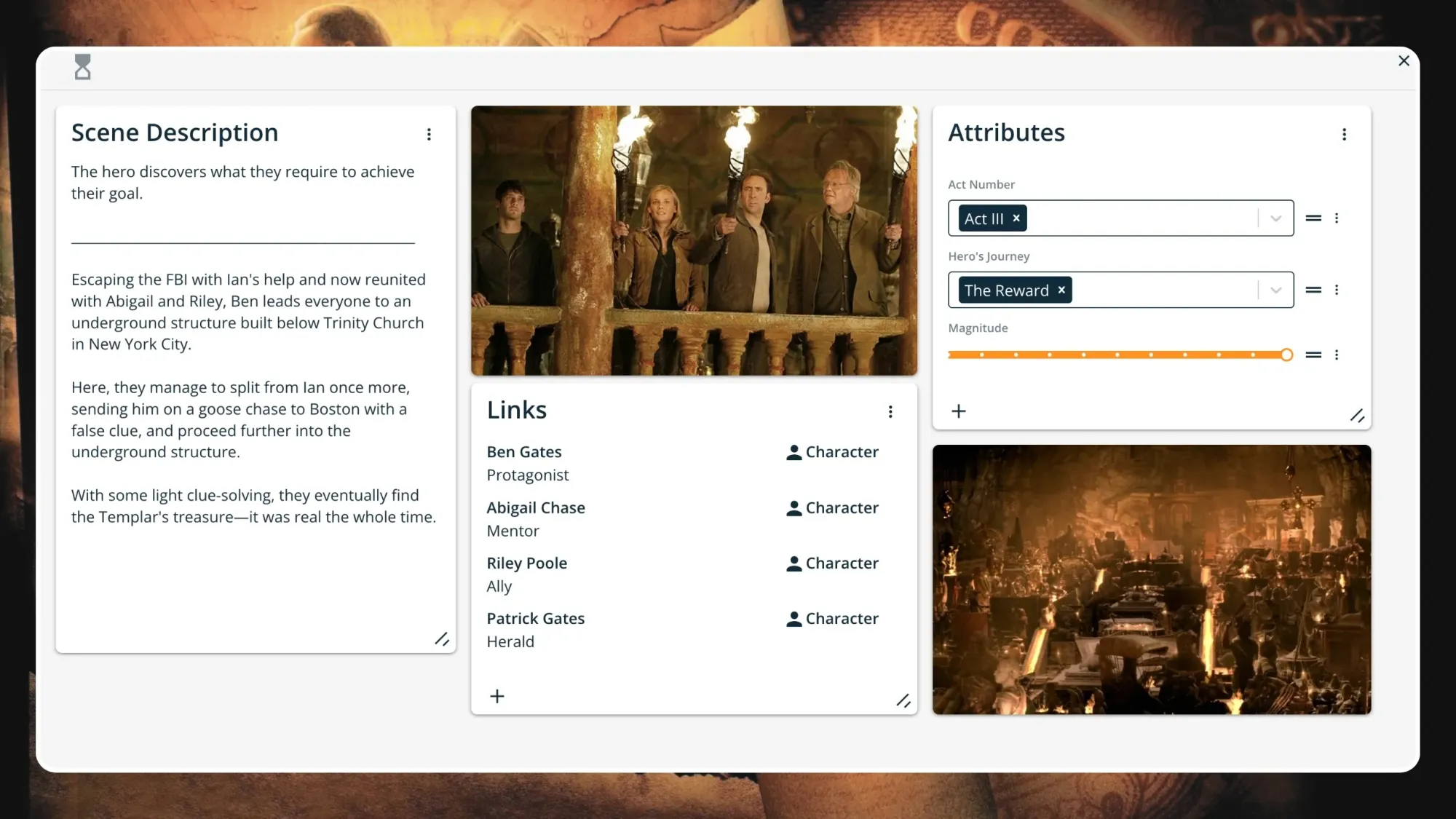
Now, free of Ian's clutches and with some light clue-solving, Ben, Abigail, Riley, and Patrick keep progressing through the underground structure and eventually find the Templar's treasure—it's real and more massive than they could have imagined. Everyone revels in their discovery while simultaneously looking for a way back out.
Act Three: Return
Step 10. the road back.
It's time for the journey to head towards its conclusion. The hero begins their return to the Known World and may face unexpected challenges. Whatever happens, the "why" remains paramount here (i.e. why the hero ultimately chose to embark on their journey).
This step marks a final turning point where they'll have to take action or make a decision to keep moving forward and be "reborn" back into the Known World.
Act Three of National Treasure is admittedly quite short. After finding the treasure, Ben and co. emerge from underground to face the FBI once more. Not much of a road to travel back here so much as a tunnel to scale in a crypt.
Step 11. Resurrection
The hero faces their ultimate challenge and emerges victorious, but forever changed. This step often requires a sacrifice of some sort, and having stepped into the role of The Hero™, they must answer to this.
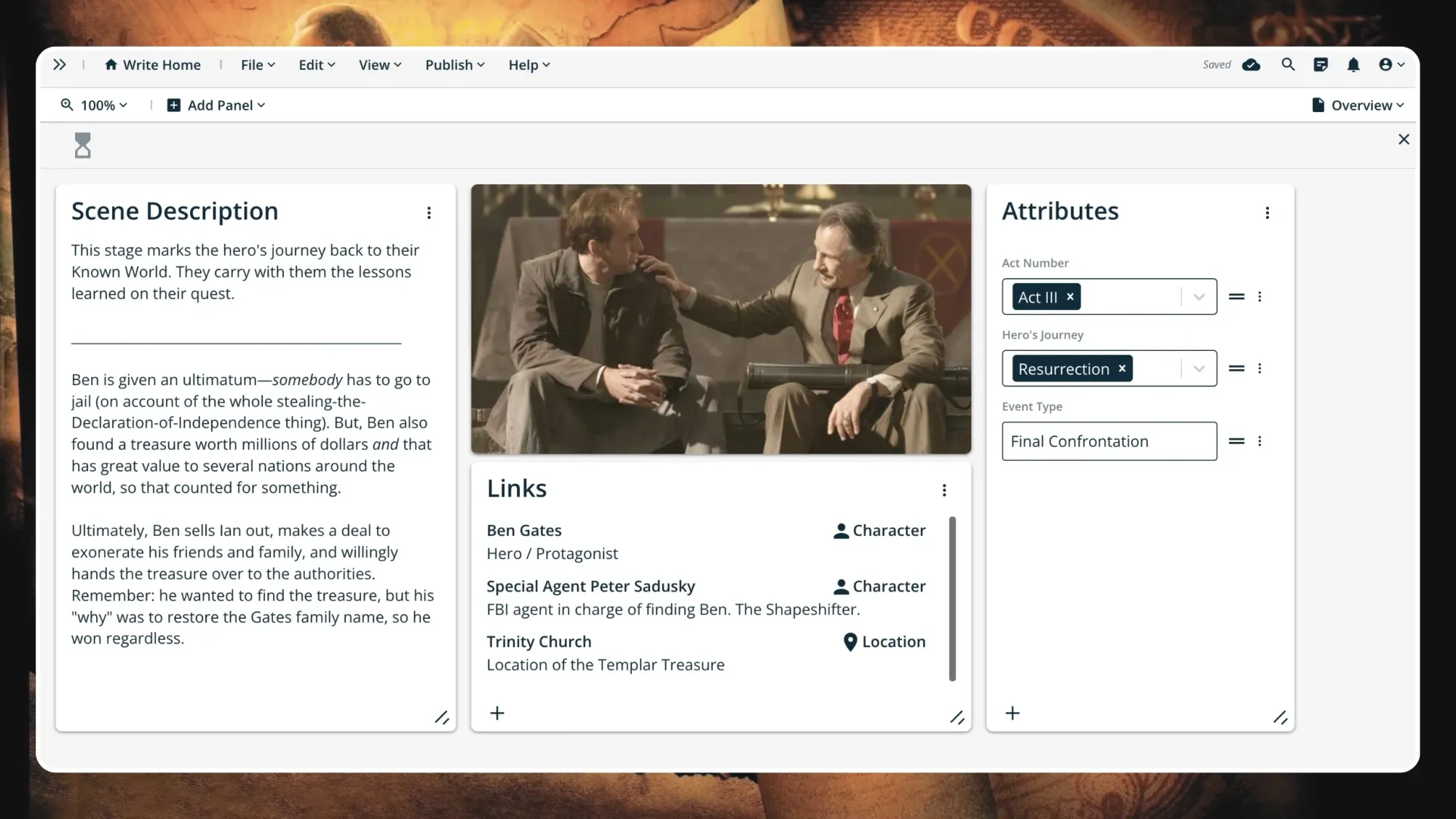
Ben is given an ultimatum— somebody has to go to jail (on account of the whole stealing-the-Declaration-of-Independence thing). But, Ben also found a treasure worth millions of dollars and that has great value to several nations around the world, so that counts for something.
Ultimately, Ben sells Ian out, makes a deal to exonerate his friends and family, and willingly hands the treasure over to the authorities. Remember: he wanted to find the treasure, but his "why" was to restore the Gates family name, so he won regardless.
Step 12. Return With the Elixir
Finally, the hero returns home as a new version of themself, the elixir is shared amongst the people, and the journey is completed full circle.
The elixir, like many other elements of the hero's journey, can be literal or figurative. It can be a tangible thing, such as an actual elixir meant for some specific purpose, or it could be represented by an abstract concept such as hope, wisdom, or love.
Vogler notes that if the Hero's Journey results in a tragedy, the elixir can instead have an effect external to the story—meaning that it could be something meant to affect the audience and/or increase their awareness of the world.
In the final scene of National Treasure , we see Ben and Abigail walking the grounds of a massive estate. Riley pulls up in a fancy sports car and comments on how they could have gotten more money. They all chat about attending a museum exhibit in Cairo (Egypt).
In one scene, we're given a lot of closure: Ben and co. received a hefty payout for finding the treasure, Ben and Abigail are a couple now, and the treasure was rightfully spread to those it benefitted most—in this case, countries who were able to reunite with significant pieces of their history. Everyone's happy, none of them went to jail despite the serious crimes committed, and they're all a whole lot wealthier. Oh, Hollywood.
Variations of the Hero's Journey
Plot structure is important, but you don't need to follow it exactly; and, in fact, your story probably won't. Your version of the Hero's Journey might require more or fewer steps, or you might simply go off the beaten path for a few steps—and that's okay!
What follows are three additional versions of the Hero's Journey, which you may be more familiar with than Vogler's version presented above.
Dan Harmon's Story Circle (or, The Eight-Step Hero's Journey)
Screenwriter Dan Harmon has riffed on the Hero's Journey by creating a more compact version, the Story Circle —and it works especially well for shorter-format stories such as television episodes, which happens to be what Harmon writes.
The Story Circle comprises eight simple steps with a heavy emphasis on the hero's character arc:
- The hero is in a zone of comfort...
- But they want something.
- They enter an unfamiliar situation...
- And adapt to it by facing trials.
- They get what they want...
- But they pay a heavy price for it.
- They return to their familiar situation...
- Having changed.
You may have noticed, but there is a sort of rhythm here. The eight steps work well in four pairs, simplifying the core of the Hero's Journey even further:
- The hero is in a zone of comfort, but they want something.
- They enter an unfamiliar situation and have to adapt via new trials.
- They get what they want, but they pay a price for it.
- They return to their zone of comfort, forever changed.
If you're writing shorter fiction, such as a short story or novella, definitely check out the Story Circle. It's the Hero's Journey minus all the extraneous bells & whistles.
Ten-Step Hero's Journey
The ten-step Hero's Journey is similar to the twelve-step version we presented above. It includes most of the same steps except for Refusal of the Call and Meeting the Mentor, arguing that these steps aren't as essential to include; and, it moves Crossing the Threshold to the end of Act One and Reward to the end of Act Two.
- The Ordinary World
- The Call to Adventure
- Crossing the Threshold
- Tests, Allies, Enemies
- Approach the Innermost Cave
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return with Elixir
We've previously written about the ten-step hero's journey in a series of essays separated by act: Act One (with a prologue), Act Two , and Act Three .
Twelve-Step Hero's Journey: Version Two
Again, the second version of the twelve-step hero's journey is very similar to the one above, save for a few changes, including in which story act certain steps appear.
This version skips The Ordinary World exposition and starts right at The Call to Adventure; then, the story ends with two new steps in place of Return With Elixir: The Return and The Freedom to Live.
- The Refusal of the Call
- Meeting the Mentor
- Test, Allies, Enemies
- Approaching the Innermost Cave
- The Resurrection
- The Return*
- The Freedom to Live*
In the final act of this version, there is more of a focus on an internal transformation for the hero. They experience a metamorphosis on their journey back to the Known World, return home changed, and go on to live a new life, uninhibited.
Seventeen-Step Hero's Journey
Finally, the granddaddy of heroic journeys: the seventeen-step Hero's Journey. This version includes a slew of extra steps your hero might face out in the expanse.
- Refusal of the Call
- Supernatural Aid (aka Meeting the Mentor)
- Belly of the Whale*: This added stage marks the hero's immediate descent into danger once they've crossed the threshold.
- Road of Trials (...with Allies, Tests, and Enemies)
- Meeting with the Goddess/God*: In this stage, the hero meets with a new advisor or powerful figure, who equips them with the knowledge or insight needed to keep progressing forward.
- Woman as Temptress (or simply, Temptation)*: Here, the hero is tempted, against their better judgment, to question themselves and their reason for being on the journey. They may feel insecure about something specific or have an exposed weakness that momentarily holds them back.
- Atonement with the Father (or, Catharthis)*: The hero faces their Temptation and moves beyond it, shedding free from all that holds them back.
- Apotheosis (aka The Ordeal)
- The Ultimate Boon (aka the Reward)
- Refusal of the Return*: The hero wonders if they even want to go back to their old life now that they've been forever changed.
- The Magic Flight*: Having decided to return to the Known World, the hero needs to actually find a way back.
- Rescue From Without*: Allies may come to the hero's rescue, helping them escape this bold, new world and return home.
- Crossing of the Return Threshold (aka The Return)
- Master of Two Worlds*: Very closely resembling The Resurrection stage in other variations, this stage signifies that the hero is quite literally a master of two worlds—The Known World and the Unknown World—having conquered each.
- Freedom to Live
Again, we skip the Ordinary World opening here. Additionally, Acts Two and Three look pretty different from what we've seen so far, although, the bones of the Hero's Journey structure remain.
The Eight Hero’s Journey Archetypes
The Hero is, understandably, the cornerstone of the Hero’s Journey, but they’re just one of eight key archetypes that make up this narrative framework.
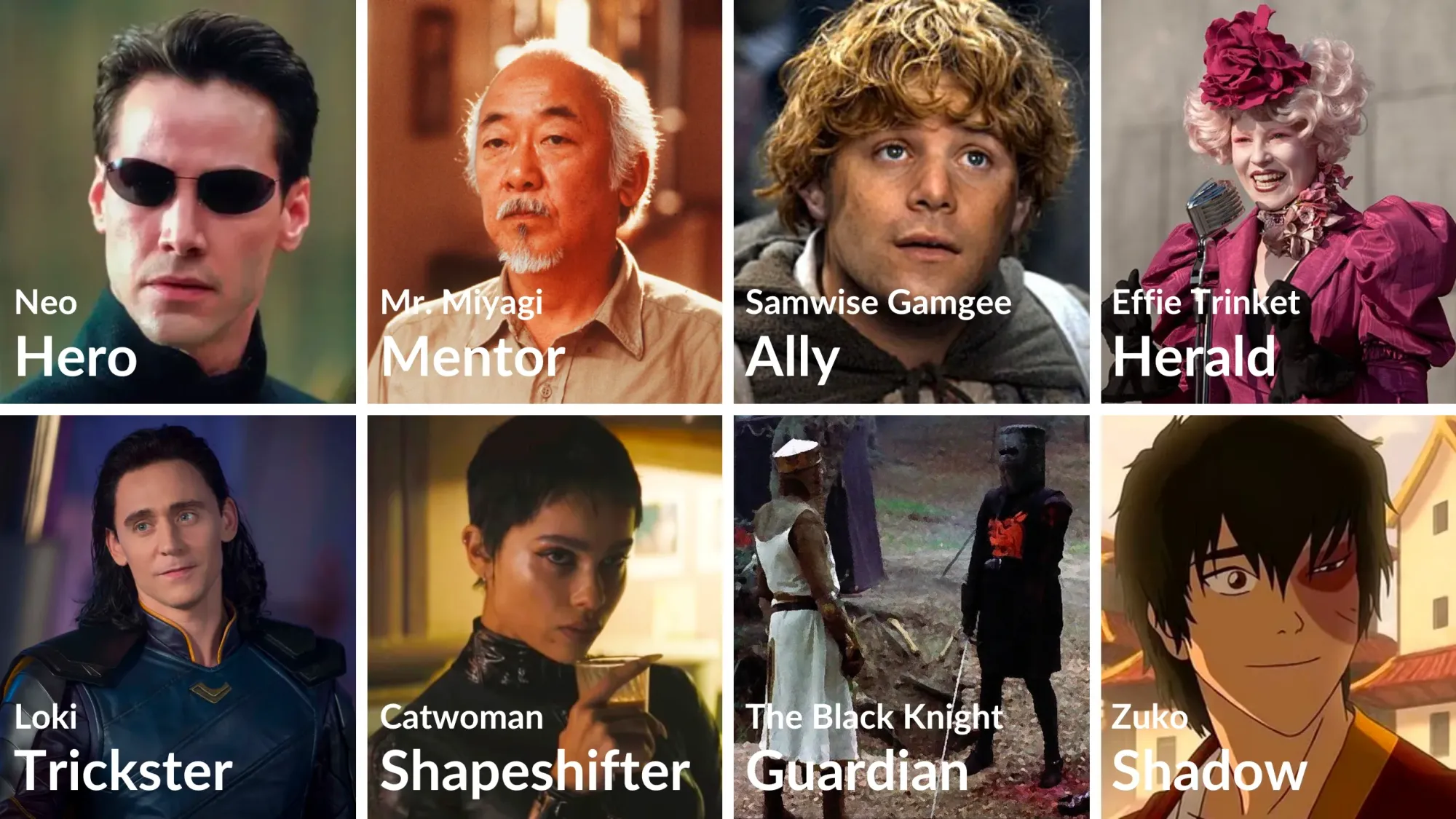

In The Writer's Journey , Vogler outlined seven of these archetypes, only excluding the Ally, which we've included below. Here’s a breakdown of all eight with examples:
1. The Hero
As outlined, the Hero is the protagonist who embarks on a transformative quest or journey. The challenges they overcome represent universal human struggles and triumphs.
Vogler assigned a "primary function" to each archetype—helpful for establishing their role in a story. The Hero's primary function is "to service and sacrifice."
Example: Neo from The Matrix , who evolves from a regular individual into the prophesied savior of humanity.
2. The Mentor
A wise guide offering knowledge, tools, and advice, Mentors help the Hero navigate the journey and discover their potential. Their primary function is "to guide."
Example: Mr. Miyagi from The Karate Kid imparts not only martial arts skills but invaluable life lessons to Daniel.
3. The Ally
Companions who support the Hero, Allies provide assistance, friendship, and moral support throughout the journey. They may also become a friends-to-lovers romantic partner.
Not included in Vogler's list is the Ally, though we'd argue they are essential nonetheless. Let's say their primary function is "to aid and support."
Example: Samwise Gamgee from Lord of the Rings , a loyal friend and steadfast supporter of Frodo.
4. The Herald
The Herald acts as a catalyst to initiate the Hero's Journey, often presenting a challenge or calling the hero to adventure. Their primary function is "to warn or challenge."
Example: Effie Trinket from The Hunger Games , whose selection at the Reaping sets Katniss’s journey into motion.
5. The Trickster
A character who brings humor and unpredictability, challenges conventions, and offers alternative perspectives or solutions. Their primary function is "to disrupt."
Example: Loki from Norse mythology exemplifies the trickster, with his cunning and chaotic influence.
6. The Shapeshifter
Ambiguous figures whose allegiance and intentions are uncertain. They may be a friend one moment and a foe the next. Their primary function is "to question and deceive."
Example: Catwoman from the Batman universe often blurs the line between ally and adversary, slinking between both roles with glee.
7. The Guardian
Protectors of important thresholds, Guardians challenge or test the Hero, serving as obstacles to overcome or lessons to be learned. Their primary function is "to test."
Example: The Black Knight in Monty Python and the Holy Grail literally bellows “None shall pass!”—a quintessential ( but not very effective ) Guardian.
8. The Shadow
Represents the Hero's inner conflict or an antagonist, often embodying the darker aspects of the hero or their opposition. Their primary function is "to destroy."
Example: Zuko from Avatar: The Last Airbender; initially an adversary, his journey parallels the Hero’s path of transformation.
While your story does not have to use all of the archetypes, they can help you develop your characters and visualize how they interact with one another—especially the Hero.
For example, take your hero and place them in the center of a blank worksheet, then write down your other major characters in a circle around them and determine who best fits into which archetype. Who challenges your hero? Who tricks them? Who guides them? And so on...
Stories that Use the Hero’s Journey
Not a fan of saving the Declaration of Independence? Check out these alternative examples of the Hero’s Journey to get inspired:
- Epic of Gilgamesh : An ancient Mesopotamian epic poem thought to be one of the earliest examples of the Hero’s Journey (and one of the oldest recorded stories).
- The Lion King (1994): Simba's exile and return depict a tale of growth, responsibility, and reclaiming his rightful place as king.
- The Alchemist by Paolo Coehlo: Santiago's quest for treasure transforms into a journey of self-discovery and personal enlightenment.
- Coraline by Neil Gaiman: A young girl's adventure in a parallel world teaches her about courage, family, and appreciating her own reality.
- Kung Fu Panda (2008): Po's transformation from a clumsy panda to a skilled warrior perfectly exemplifies the Hero's Journey. Skadoosh!
The Hero's Journey is so generalized that it's ubiquitous. You can plop the plot of just about any quest-style narrative into its framework and say that the story follows the Hero's Journey. Try it out for yourself as an exercise in getting familiar with the method.
Will the Hero's Journey Work For You?
As renowned as it is, the Hero's Journey works best for the kinds of tales that inspired it: mythic stories.
Writers of speculative fiction may gravitate towards this method over others, especially those writing epic fantasy and science fiction (big, bold fantasy quests and grand space operas come to mind).
The stories we tell today are vast and varied, and they stretch far beyond the dealings of deities, saving kingdoms, or acquiring some fabled "elixir." While that may have worked for Gilgamesh a few thousand years ago, it's not always representative of our lived experiences here and now.
If you decide to give the Hero's Journey a go, we encourage you to make it your own! The pieces of your plot don't have to neatly fit into the structure, but you can certainly make a strong start on mapping out your story.
Hero's Journey Campfire Template
The Timeline Module in Campfire offers a versatile canvas to plot out each basic component of your story while featuring nested "notebooks."
Simply double-click on each event card in your timeline to open up a canvas specific to that card. This allows you to look at your plot at the highest level, while also adding as much detail for each plot element as needed!
If you're just hearing about Campfire for the first time, it's free to sign up—forever! Let's plot the most epic of hero's journeys 👇
Lessons From the Hero’s Journey
The Hero's Journey offers a powerful framework for creating stories centered around growth, adventure, and transformation.
If you want to develop compelling characters, spin out engaging plots, and write books that express themes of valor and courage, consider The Hero’s Journey your blueprint. So stop holding out for a hero, and start writing!
Does your story mirror the Hero's Journey? Let us know in the comments below.

- My Storyboards
The Hero’s Journey
What is the Hero's Journey in Literature?
Crafting a heroic character is a crucial aspect of storytelling, and it involves much more than simply sketching out a brave and virtuous figure. The hero's journey definition is not the typical linear narrative but rather a cyclical pattern that encompasses the hero's transformation, trials, and ultimate return, reflecting the profound and timeless aspects of human experience. The writer's journey in this endeavor goes beyond the external actions of the hero and delves into the character's inner world. The hero arc is the heart of the narrative, depicting the character's evolution from an ordinary person to a true hero.
Narratology and Writing Instructions for Heroic Characters
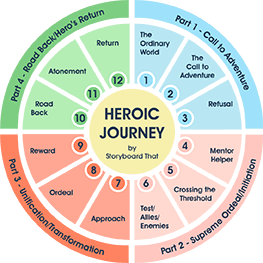
Related to both plot diagram and types of literary conflict , the ”Hero’s Journey” structure is a recurring pattern of stages many heroes undergo over the course of their stories. Joseph Campbell, an American mythologist, writer, and lecturer, articulated this cycle after researching and reviewing numerous myths and stories from a variety of time periods and regions of the world. He found that different writers take us on different journeys, however, they all share fundamental principles. Through the hero's trials, growth, and ultimate triumph, the narrative comes full circle, embodying the timeless pattern of the hero cycle. Literature abounds with examples of the hero cycle, illustrating how this narrative structure transcends cultural boundaries and remains a fundamental element of storytelling. This hero cycle in literature is also known as the Monomyth, archetype . The most basic version of Joseph Campbell's Monomyth has 12 steps, while more detailed versions can have up to 17 steps. His type of hero's journey diagram provides a visual roadmap for understanding the various stages and archetypal elements that protagonists typically encounter in their transformative quests. The wheel to the right is an excellent visual to share with students of how these steps occur. Hero's journey diagram examples provide a visual roadmap for understanding the various stages and archetypal elements that protagonists typically encounter in their transformative quests. Exploring the monomyth steps outlined by Joseph Campbell, we can see how these universal narrative elements have shaped countless stories across cultures and time periods.
Which Story Structure is Right for You?
The choice of story structure depends on various factors, including the type of story you want to tell, your intended audience, and your personal creative style. Here are some popular story structures and when they might be suitable:
- The Hero's Journey: Use this structure when you want to tell a story of personal growth, transformation, and adventure. It works well for epic tales, fantasy, and science fiction, but it can be adapted to other genres as well.
- Three-Act Structure: This is a versatile structure suitable for a wide range of genres, from drama to comedy to action. It's ideal for stories that have a clear beginning, middle, and end, with well-defined turning points.
- Episodic or Serial Structure: If you're creating a long-running series or a story with multiple interconnected arcs, this structure is a good choice. It allows for flexibility in storytelling and can keep audiences engaged over the long term.
- Nonlinear Structure: Experiment with this structure if you want to challenge traditional narrative conventions. It's suitable for stories where timelines are fragmented, revealing information gradually to build intrigue and suspense.
- Circular or Cyclical Structure: This structure is great for stories with recurring themes or for tales that come full circle. It can be particularly effective in literary fiction and philosophical narratives.
Ultimately, the right story structure for you depends on your creative vision, the genre you're working in, and the narrative you want to convey. You may also choose to blend or adapt different structures to suit your story's unique needs. The key is to select a structure that serves your storytelling goals and engages your target audience effectively.
What is a Common Theme in the Hero's Journey?
A common theme in the hero's journey is the concept of personal transformation and growth. Throughout the hero's journey, the protagonist typically undergoes significant change, evolving from an ordinary or flawed individual into a more heroic, self-realized, or enlightened character. This theme of transformation is often accompanied by challenges, trials, and self-discovery, making it a central and universal element of hero's journey narratives.
Structure of the Monomyth: The Hero's Journey Summary
This summary of the different elements of the archetypal hero's journey outlines the main four parts along with the different stages within each part. This can be shared with students and used as a reference along with the hero's journey wheel to analyze literature.
Part One - Call to Adventure
During the exposition, the hero is in the ordinary world , usually the hero’s home or natural habitat. Conflict arises in their everyday life, which calls the hero to adventure , where they are beckoned to leave their familiar world in search of something. They may refuse the call at first, but eventually leave, knowing that something important hangs in the balance and refusal of the call is simply not an option.

Part Two - Supreme Ordeal or Initiation
Once the hero makes the decision to leave the normal world, venture into the unfamiliar world, and has officially begun their mysterious adventure, they will meet a mentor figure (a sidekick in some genres) and together these two will cross the first threshold . This is the point where turning back is not an option, and where the hero must encounter tests, allies and enemies . Obstacles like tests and enemies must be overcome to continue. Helpers aid the hero in their journey.
Part Three - Unification or Transformation
Having overcome initial obstacles, in this part of the heroic cycle, the hero and their allies reach the approach . Here they will prepare for the major challenge in this new or special world. During the approach, the hero undergoes an ordeal , testing them to point near death. Their greatest fear is sometimes exposed, and from the ordeal comes a new life or revival for the hero. This transformation is the final separation from their old life to their new life. For their efforts in overcoming the ordeal, the hero reaches the reward . The hero receives the reward for facing death. There may be a celebration, but there is also danger of losing the reward.
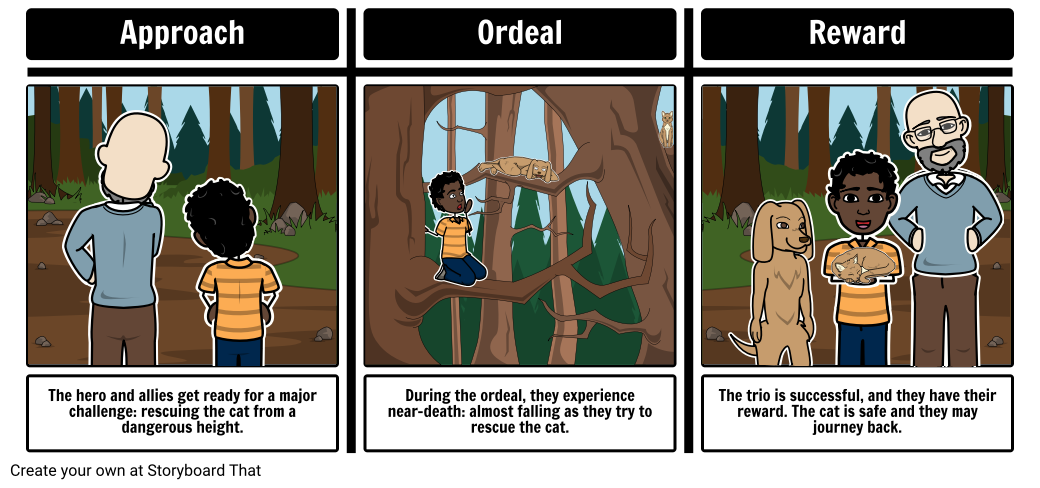
Part Four - Road Back or Hero's Return
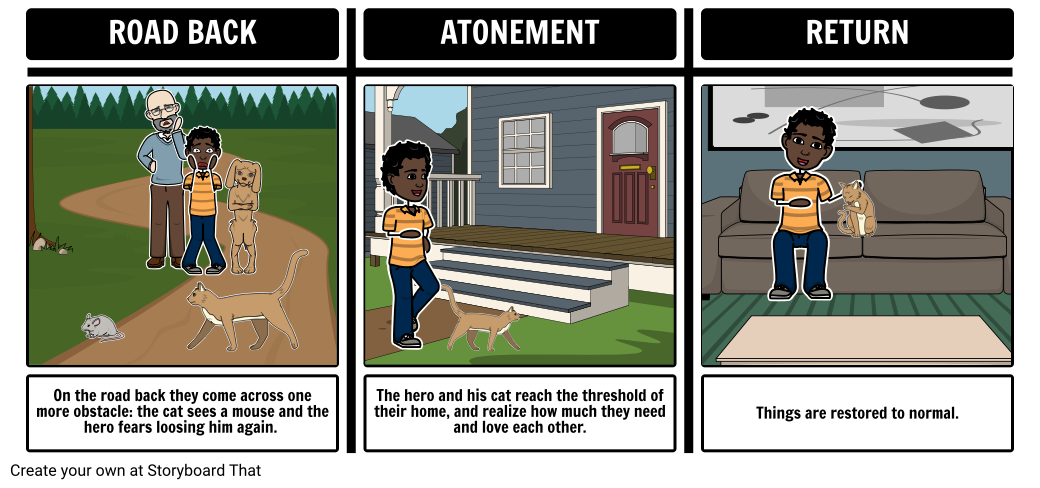
Once the hero achieves their goal and the reward is won, the hero and companions start on the road back . The hero wants to complete the adventure and return to their ordinary world with their treasure. This stage is often referred to as either the resurrections or atonement . Hero's journey examples that showcase the atonement stage often highlight the protagonist's inner turmoil and the difficult decisions they must make to reconcile with their past and fully embrace their heroic destiny. The hero becomes "at one" with themselves. As the hero crosses the threshold (returning from the unknown to their ordinary world), the reader arrives at the climax of the story. Here, the hero is severely tested one last time. This test is an attempt to undo their previous achievements. At this point, the hero has come full circle, and the major conflict at the beginning of the journey is finally resolved. In the return home, the hero has now resumed life in his/her original world, and things are restored to ordinary.
Popular Hero's Journey Examples
Monomyth example: homer's odyssey.
Monomyth examples typically involve a hero who embarks on an adventure, faces trials and challenges, undergoes personal transformation, and returns home or to society with newfound wisdom or a significant achievement, making this storytelling structure a powerful and timeless tool for crafting compelling narratives.
The hero's journey chart below for Homer’s Odyssey uses the abridged ninth grade version of the epic. The Heroic Journey in the original story of the Odyssey is not linear, beginning in media res , Latin for “in the middle of things”.)

To Kill a Mockingbird Heroic Journey

Did you know that many popular movies have heroes that follow this type of journey? It is true! In the "Star Wars" movies, Hollywood film producer George Lucas creates a journey for Luke Skywalker and Princess Leia. In "The Lion King", Simba goes on quite the adventure that ends in a final battle with his uncle Scar, a major turning point in the film before the hero returns to save his land. In "The Wizard of Oz", Dorothy takes on the role of the epic hero as she teeters between the two worlds of Kansas and Oz. These are just a few of the many examples of Campbell's theory in the cinematic realm.
Classroom Applications and Uses
Example exercises.
Create your own hero's journey examples using the Storyboard That Creator! Customize the level of detail and number of cells required for projects based on available class time and resources.
- Students identify the stages of the heroic journey in a piece of literature by creating one cell depicting each of the twelve steps.
- Students create storyboards that show and explain each stage found in the work of literature, using specific quotes from the text which highlight each part of the journey.
- Students create an outline of their own original story that follows the monomyth stages.
Common Core
- ELA-Literacy.RL.9-10.3 : Analyze how complex characters (e.g., those with multiple or conflicting motivations) develop over the course of a text, interact with other characters, and advance the plot or develop the theme
- ELA-Literacy.RL.9-10.7 : Analyze the representation of a subject or a key scene in two different artistic mediums, including what is emphasized or absent in each treatment (e.g., Auden’s “Musée des Beaux Arts” and Breughel’s Landscape with the Fall of Icarus)
- ELA-Literacy.W.9-10.6 : Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically
- ELA-Literacy.SL.9-10.2 : Integrate multiple sources of information presented in diverse media or formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) evaluating the credibility and accuracy of each source
- ELA-Literacy.RL.11-12.3 : Analyze the impact of the author’s choices regarding how to develop and relate elements of a story or drama (e.g., where a story is set, how the action is ordered, how the characters are introduced and developed)
- ELA-Literacy.RL.11-12.7 : Analyze multiple interpretations of a story, drama, or poem (e.g., recorded or live production of a play or recorded novel or poetry), evaluating how each version interprets the source text. (Include at least one play by Shakespeare and one play by an American dramatist.)
- ELA-Literacy.W.11-12.6 : Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information
- ELA-Literacy.SL.11-12.2 : Integrate multiple sources of information presented in diverse formats and media (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) in order to make informed decisions and solve problems, evaluating the credibility and accuracy of each source and noting any discrepancies among the data
Related Resources
- Plot Diagram and Narrative Arc
- Types of Conflict In Literature
- What is an Archetype?
- The Odyssey Teacher Guide
- Types of Heroes in Literature
How Teachers Can Use The Concept of The Heroic Journey To Help Students Better Understand Character Development In Literature
Introduce the concept of the heroic journey.
Teachers can introduce the concept of the heroic journey to students and explain the different stages involved in the journey. This will provide a framework for students to better understand how characters develop throughout the story.
Analyze Characters Using the Heroic Journey
Teachers can guide students through the stages of the heroic journey and ask them to identify where the character is in the journey. This will help students to understand the character's development and how their actions and decisions are influenced by the different stages of the journey.
Compare and Contrast Character Journeys
Teachers can ask students to compare and contrast the journeys of different characters within a story or across multiple stories. This will help students to gain a deeper understanding of how the heroic journey is used to develop characters in literature and how it can be applied across different genres and cultures.
Discuss the Role of Character Motivation
Teachers can encourage students to think critically about the motivations of characters at each stage of the journey. This will help students to understand why characters make certain decisions and how their motivations contribute to their development.
Apply the Concept to Real-Life Situations
Teachers can encourage students to apply the concept of the heroic journey to real-life situations. This will help students to see how the journey applies not only to literature, but also to their own lives and experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Hero's Journey
What is a "monomyth" or the "hero's journey" in literature.
In comparative mythology, the monomyth, or the hero's journey, is the series of stages that can be applied to a variety of stories from all genres. It involves a hero who is called to pursue an adventure, undergoes an ordeal, achieves their goal and returns home transformed.
What are the 12 Stages of the Hero's Journey in literature?
- Ordinary World
- Call to Adventure
- Meeting the Mentor / Helper
- Crossing the Threshold
- Test / Allies / Enemies
What is a common theme in the hero's journey?
The Hero's Journey usually follows the path of the main character from childhood or young adulthood through maturity. It is about the common human experiences of growth, challenges and change that are relatable to us all.
Why should students learn about the hero's journey?
The hero's journey is relevant for students in that it demonstrates the possibility of overcoming adversity and the potential for growth and change that is within us all. It is a common theme of literature and movies that once students understand, they will be able to identify over and over again. It is helpful for students to make the text-to-self connection and apply this thinking to their own life as a "growth mindset" . They can see that they are on their own hero's journey and that everyone has the ability to overcome obstacles to achieve their goals and affect positive change in their lives and the lives of others.
What are some of the best examples of the hero's journey?
The hero's journey stages appear in more books than students may realize! Here are just a few examples of popular books that contain the monomyth structure:
- The Graveyard Book
- The Hunger Games
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- The Odyssey
- The Lions of Little Rock
- Wednesday Wars
- One Crazy Summer
- Out of My Mind
- Brown Girl Dreaming
- The Lightning Thief
- The Miraculous Journey of Edward Tulane
- The Stars Beneath Our Feet
- Fish in a Tree
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Last updated on Aug 10, 2023
The Hero's Journey: 12 Steps to a Classic Story Structure
The Hero's Journey is a timeless story structure which follows a protagonist on an unforeseen quest, where they face challenges, gain insights, and return home transformed. From Theseus and the Minotaur to The Lion King , so many narratives follow this pattern that it’s become ingrained into our cultural DNA.
In this post, we'll show you how to make this classic plot structure work for you — and if you’re pressed for time, download our cheat sheet below for everything you need to know.

FREE RESOURCE
Hero's Journey Template
Plot your character's journey with our step-by-step template.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero's Journey, also known as the monomyth, is a story structure where a hero goes on a quest or adventure to achieve a goal, and has to overcome obstacles and fears, before ultimately returning home transformed.
This narrative arc has been present in various forms across cultures for centuries, if not longer, but gained popularity through Joseph Campbell's mythology book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces . While Campbell identified 17 story beats in his monomyth definition, this post will concentrate on a 12-step framework popularized in 2007 by screenwriter Christopher Vogler in his book The Writer’s Journey .
The 12 Steps of the Hero’s Journey
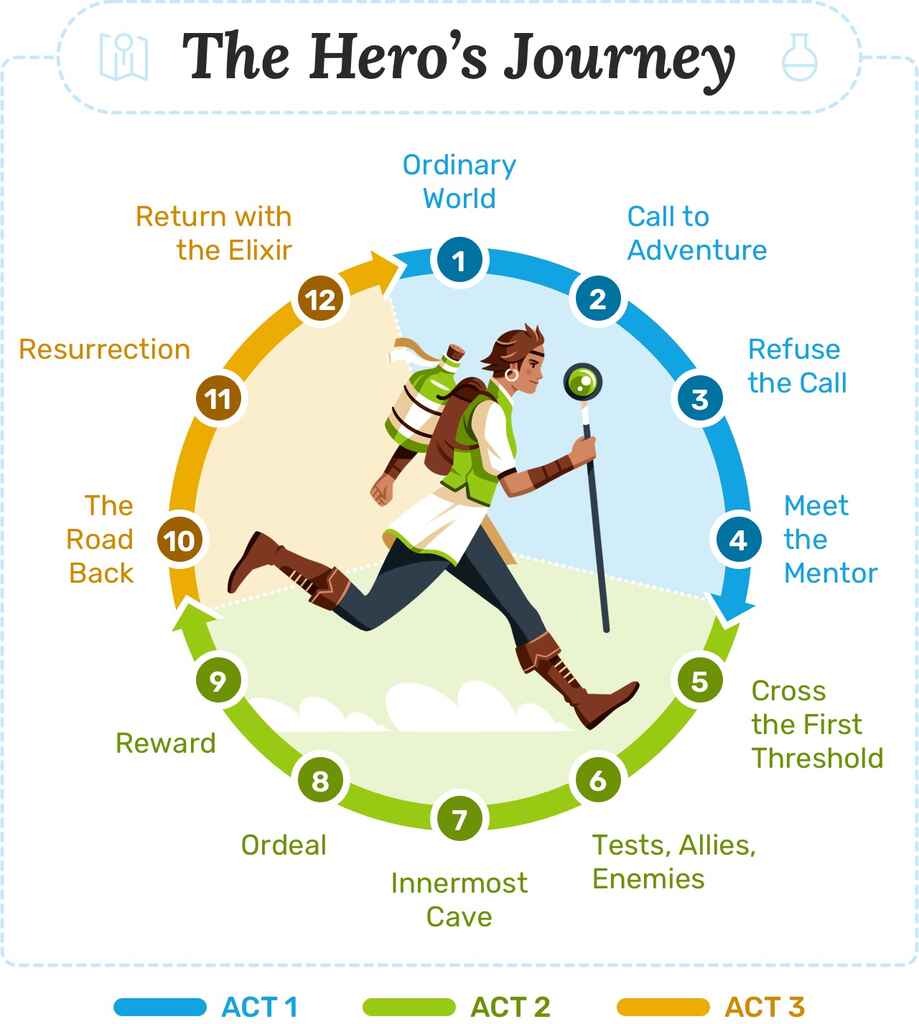
The Hero's Journey is a model for both plot points and character development : as the Hero traverses the world, they'll undergo inner and outer transformation at each stage of the journey. The 12 steps of the hero's journey are:
- The Ordinary World. We meet our hero.
- Call to Adventure. Will they meet the challenge?
- Refusal of the Call. They resist the adventure.
- Meeting the Mentor. A teacher arrives.
- Crossing the First Threshold. The hero leaves their comfort zone.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Making friends and facing roadblocks.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. Getting closer to our goal.
- Ordeal. The hero’s biggest test yet!
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Light at the end of the tunnel
- The Road Back. We aren’t safe yet.
- Resurrection. The final hurdle is reached.
- Return with the Elixir. The hero heads home, triumphant.
Believe it or not, this story structure also applies across mediums and genres (and also works when your protagonist is an anti-hero! ). Let's dive into it.
1. Ordinary World
In which we meet our Hero.
The journey has yet to start. Before our Hero discovers a strange new world, we must first understand the status quo: their ordinary, mundane reality.
It’s up to this opening leg to set the stage, introducing the Hero to readers. Importantly, it lets readers identify with the Hero as a “normal” person in a “normal” setting, before the journey begins.
2. Call to Adventure
In which an adventure starts.
The call to adventure is all about booting the Hero out of their comfort zone. In this stage, they are generally confronted with a problem or challenge they can't ignore. This catalyst can take many forms, as Campbell points out in Hero with a Thousand Faces . The Hero can, for instance:
- Decide to go forth of their own volition;
- Theseus upon arriving in Athens.
- Be sent abroad by a benign or malignant agent;
- Odysseus setting off on his ship in The Odyssey .
- Stumble upon the adventure as a result of a mere blunder;
- Dorothy when she’s swept up in a tornado in The Wizard of Oz .
- Be casually strolling when some passing phenomenon catches the wandering eye and lures one away from the frequented paths of man.
- Elliot in E.T. upon discovering a lost alien in the tool shed.
The stakes of the adventure and the Hero's goals become clear. The only question: will he rise to the challenge?

3. Refusal of the Call
In which the Hero digs in their feet.
Great, so the Hero’s received their summons. Now they’re all set to be whisked off to defeat evil, right?
Not so fast. The Hero might first refuse the call to action. It’s risky and there are perils — like spiders, trolls, or perhaps a creepy uncle waiting back at Pride Rock . It’s enough to give anyone pause.
In Star Wars , for instance, Luke Skywalker initially refuses to join Obi-Wan on his mission to rescue the princess. It’s only when he discovers that his aunt and uncle have been killed by stormtroopers that he changes his mind.
4. Meeting the Mentor
In which the Hero acquires a personal trainer.
The Hero's decided to go on the adventure — but they’re not ready to spread their wings yet. They're much too inexperienced at this point and we don't want them to do a fabulous belly-flop off the cliff.
Enter the mentor: someone who helps the Hero, so that they don't make a total fool of themselves (or get themselves killed). The mentor provides practical training, profound wisdom, a kick up the posterior, or something abstract like grit and self-confidence.

Wise old wizards seem to like being mentors. But mentors take many forms, from witches to hermits and suburban karate instructors. They might literally give weapons to prepare for the trials ahead, like Q in the James Bond series. Or perhaps the mentor is an object, such as a map. In all cases, they prepare the Hero for the next step.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
5. Crossing the First Threshold
In which the Hero enters the other world in earnest.
Now the Hero is ready — and committed — to the journey. This marks the end of the Departure stage and is when the adventure really kicks into the next gear. As Vogler writes: “This is the moment that the balloon goes up, the ship sails, the romance begins, the wagon gets rolling.”
From this point on, there’s no turning back.
Like our Hero, you should think of this stage as a checkpoint for your story. Pause and re-assess your bearings before you continue into unfamiliar territory. Have you:
- Launched the central conflict? If not, here’s a post on types of conflict to help you out.
- Established the theme of your book? If not, check out this post that’s all about creating theme and motifs .
- Made headway into your character development? If not, this character profile template may be useful:

Reedsy’s Character Profile Template
A story is only as strong as its characters. Fill this out to develop yours.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
In which the Hero faces new challenges and gets a squad.
When we step into the Special World, we notice a definite shift. The Hero might be discombobulated by this unfamiliar reality and its new rules. This is generally one of the longest stages in the story , as our protagonist gets to grips with this new world.
This makes a prime hunting ground for the series of tests to pass! Luckily, there are many ways for the Hero to get into trouble:
- In Jumanji: Welcome to the Jungle , Spencer, Bethany, “Fridge,” and Martha get off to a bad start when they bump into a herd of bloodthirsty hippos.
- In his first few months at Hogwarts, Harry Potter manages to fight a troll, almost fall from a broomstick and die, and get horribly lost in the Forbidden Forest.
- Marlin and Dory encounter three “reformed” sharks, get shocked by jellyfish, and are swallowed by a blue whale en route to finding Nemo.

This stage often expands the cast of characters. Once the protagonist is in the Special World, he will meet allies and enemies — or foes that turn out to be friends and vice versa. He will learn a new set of rules from them. Saloons and seedy bars are popular places for these transactions, as Vogler points out (so long as the Hero survives them).
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
In which the Hero gets closer to his goal.
This isn’t a physical cave. Instead, the “inmost cave” refers to the most dangerous spot in the other realm — whether that’s the villain’s chambers, the lair of the fearsome dragon, or the Death Star. Almost always, it is where the ultimate goal of the quest is located.
Note that the protagonist hasn’t entered the Inmost Cave just yet. This stage is all about the approach to it. It covers all the prep work that's needed in order to defeat the villain.
In which the Hero faces his biggest test of all thus far.
Of all the tests the Hero has faced, none have made them hit rock bottom — until now. Vogler describes this phase as a “black moment.” Campbell refers to it as the “belly of the whale.” Both indicate some grim news for the Hero.
The protagonist must now confront their greatest fear. If they survive it, they will emerge transformed. This is a critical moment in the story, as Vogler explains that it will “inform every decision that the Hero makes from this point forward.”
The Ordeal is sometimes not the climax of the story. There’s more to come. But you can think of it as the main event of the second act — the one in which the Hero actually earns the title of “Hero.”
9. Reward (Seizing the Sword)
In which the Hero sees light at the end of the tunnel.
Our Hero’s been through a lot. However, the fruits of their labor are now at hand — if they can just reach out and grab them! The “reward” is the object or knowledge the Hero has fought throughout the entire journey to hold.
Once the protagonist has it in their possession, it generally has greater ramifications for the story. Vogler offers a few examples of it in action:
- Luke rescues Princess Leia and captures the plans of the Death Star — keys to defeating Darth Vader.
- Dorothy escapes from the Wicked Witch’s castle with the broomstick and the ruby slippers — keys to getting back home.

10. The Road Back
In which the light at the end of the tunnel might be a little further than the Hero thought.
The story's not over just yet, as this phase marks the beginning of Act Three. Now that he's seized the reward, the Hero tries to return to the Ordinary World, but more dangers (inconveniently) arise on the road back from the Inmost Cave.
More precisely, the Hero must deal with the consequences and aftermath of the previous act: the dragon, enraged by the Hero who’s just stolen a treasure from under his nose, starts the hunt. Or perhaps the opposing army gathers to pursue the Hero across a crowded battlefield. All further obstacles for the Hero, who must face them down before they can return home.
11. Resurrection
In which the last test is met.
Here is the true climax of the story. Everything that happened prior to this stage culminates in a crowning test for the Hero, as the Dark Side gets one last chance to triumph over the Hero.
Vogler refers to this as a “final exam” for the Hero — they must be “tested once more to see if they have really learned the lessons of the Ordeal.” It’s in this Final Battle that the protagonist goes through one more “resurrection.” As a result, this is where you’ll get most of your miraculous near-death escapes, à la James Bond's dashing deliverances. If the Hero survives, they can start looking forward to a sweet ending.
12. Return with the Elixir
In which our Hero has a triumphant homecoming.
Finally, the Hero gets to return home. However, they go back a different person than when they started out: they’ve grown and matured as a result of the journey they’ve taken.
But we’ve got to see them bring home the bacon, right? That’s why the protagonist must return with the “Elixir,” or the prize won during the journey, whether that’s an object or knowledge and insight gained.
Of course, it’s possible for a story to end on an Elixir-less note — but then the Hero would be doomed to repeat the entire adventure.
Examples of The Hero’s Journey in Action
To better understand this story template beyond the typical sword-and-sorcery genre, let's analyze three examples, from both screenplay and literature, and examine how they implement each of the twelve steps.
The 1976 film Rocky is acclaimed as one of the most iconic sports films because of Stallone’s performance and the heroic journey his character embarks on.
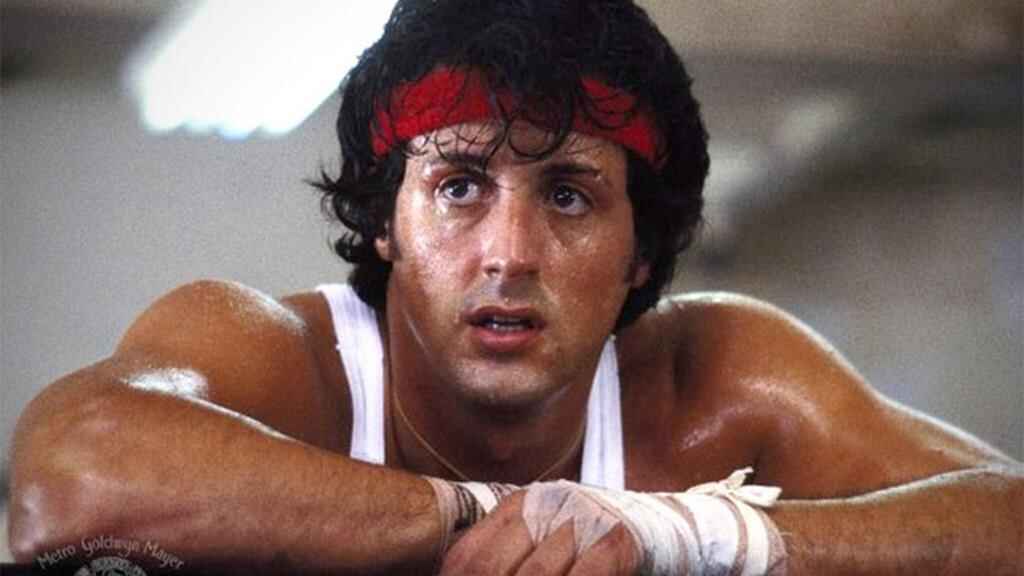

- Ordinary World. Rocky Balboa is a mediocre boxer and loan collector — just doing his best to live day-to-day in a poor part of Philadelphia.
- Call to Adventure. Heavyweight champ Apollo Creed decides to make a big fight interesting by giving a no-name loser a chance to challenge him. That loser: Rocky Balboa.
- Refusal of the Call. Rocky says, “Thanks, but no thanks,” given that he has no trainer and is incredibly out of shape.
- Meeting the Mentor. In steps former boxer Mickey “Mighty Mick” Goldmill, who sees potential in Rocky and starts training him physically and mentally for the fight.
- Crossing the First Threshold. Rocky crosses the threshold of no return when he accepts the fight on live TV, and 一 in parallel 一 when he crosses the threshold into his love interest Adrian’s house and asks her out on a date.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Rocky continues to try and win Adrian over and maintains a dubious friendship with her brother, Paulie, who provides him with raw meat to train with.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. The Inmost Cave in Rocky is Rocky’s own mind. He fears that he’ll never amount to anything — something that he reveals when he butts heads with his trainer, Mickey, in his apartment.
- Ordeal. The start of the training montage marks the beginning of Rocky’s Ordeal. He pushes through it until he glimpses hope ahead while running up the museum steps.
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Rocky's reward is the restoration of his self-belief, as he recognizes he can try to “go the distance” with Apollo Creed and prove he's more than "just another bum from the neighborhood."
- The Road Back. On New Year's Day, the fight takes place. Rocky capitalizes on Creed's overconfidence to start strong, yet Apollo makes a comeback, resulting in a balanced match.
- Resurrection. The fight inflicts multiple injuries and pushes both men to the brink of exhaustion, with Rocky being knocked down numerous times. But he consistently rises to his feet, enduring through 15 grueling rounds.
- Return with the Elixir. Rocky loses the fight — but it doesn’t matter. He’s won back his confidence and he’s got Adrian, who tells him that she loves him.
Moving outside of the ring, let’s see how this story structure holds on a completely different planet and with a character in complete isolation.
The Martian
In Andy Weir’s self-published bestseller (better known for its big screen adaptation) we follow astronaut Mark Watney as he endures the challenges of surviving on Mars and working out a way to get back home.
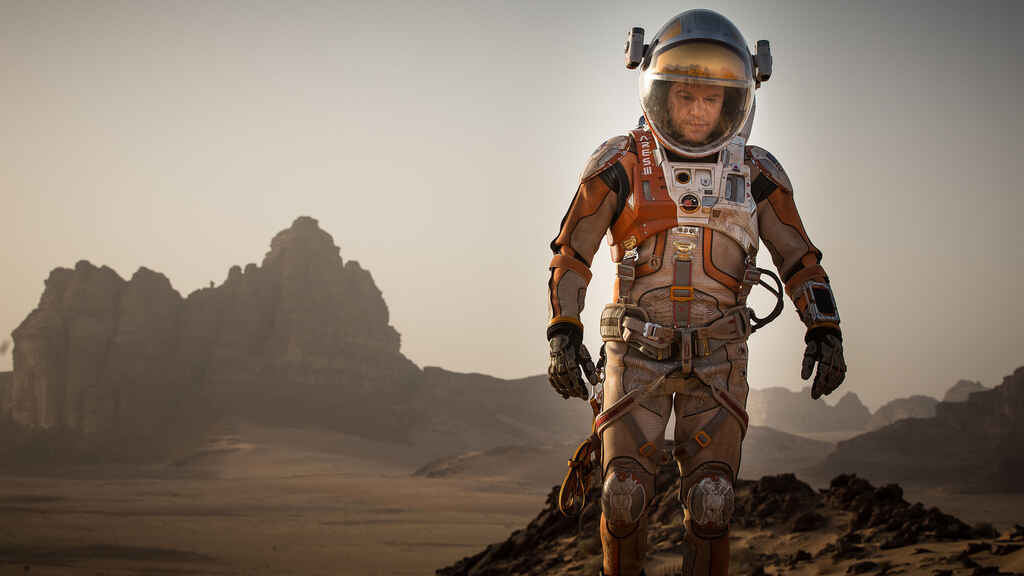

- The Ordinary World. Botanist Mark and other astronauts are on a mission on Mars to study the planet and gather samples. They live harmoniously in a structure known as "the Hab.”
- Call to Adventure. The mission is scrapped due to a violent dust storm. As they rush to launch, Mark is flung out of sight and the team believes him to be dead. He is, however, very much alive — stranded on Mars with no way of communicating with anyone back home.
- Refusal of the Call. With limited supplies and grim odds of survival, Mark concludes that he will likely perish on the desolate planet.
- Meeting the Mentor. Thanks to his resourcefulness and scientific knowledge he starts to figure out how to survive until the next Mars mission arrives.
- Crossing the First Threshold. Mark crosses the mental threshold of even trying to survive 一 he successfully creates a greenhouse to cultivate a potato crop, creating a food supply that will last long enough.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Loneliness and other difficulties test his spirit, pushing him to establish contact with Earth and the people at NASA, who devise a plan to help.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. Mark faces starvation once again after an explosion destroys his potato crop.
- Ordeal. A NASA rocket destined to deliver supplies to Mark disintegrates after liftoff and all hope seems lost.
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Mark’s efforts to survive are rewarded with a new possibility to leave the planet. His team 一 now aware that he’s alive 一 defies orders from NASA and heads back to Mars to rescue their comrade.
- The Road Back. Executing the new plan is immensely difficult 一 Mark has to travel far to locate the spaceship for his escape, and almost dies along the way.
- Resurrection. Mark is unable to get close enough to his teammates' ship but finds a way to propel himself in empty space towards them, and gets aboard safely.
- Return with the Elixir. Now a survival instructor for aspiring astronauts, Mark teaches students that space is indifferent and that survival hinges on solving one problem after another, as well as the importance of other people’s help.
Coming back to Earth, let’s now examine a heroine’s journey through the wilderness of the Pacific Crest Trail and her… humanity.
The memoir Wild narrates the three-month-long hiking adventure of Cheryl Strayed across the Pacific coast, as she grapples with her turbulent past and rediscovers her inner strength.

- The Ordinary World. Cheryl shares her strong bond with her mother who was her strength during a tough childhood with an abusive father.
- Call to Adventure. As her mother succumbs to lung cancer, Cheryl faces the heart-wrenching reality to confront life's challenges on her own.
- Refusal of the Call. Cheryl spirals down into a destructive path of substance abuse and infidelity, which leads to hit rock bottom with a divorce and unwanted pregnancy.
- Meeting the Mentor. Her best friend Lisa supports her during her darkest time. One day she notices the Pacific Trail guidebook, which gives her hope to find her way back to her inner strength.
- Crossing the First Threshold. She quits her job, sells her belongings, and visits her mother’s grave before traveling to Mojave, where the trek begins.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Cheryl is tested by her heavy bag, blisters, rattlesnakes, and exhaustion, but many strangers help her along the trail with a warm meal or hiking tips.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. As Cheryl goes through particularly tough and snowy parts of the trail her emotional baggage starts to catch up with her.
- Ordeal. She inadvertently drops one of her shoes off a cliff, and the incident unearths the helplessness she's been evading since her mother's passing.
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Cheryl soldiers on, trekking an impressive 50 miles in duct-taped sandals before finally securing a new pair of shoes. This small victory amplifies her self-confidence.
- The Road Back. On the last stretch, she battles thirst, sketchy hunters, and a storm, but more importantly, she revisits her most poignant and painful memories.
- Resurrection. Cheryl forgives herself for damaging her marriage and her sense of worth, owning up to her mistakes. A pivotal moment happens at Crater Lake, where she lets go of her frustration at her mother for passing away.
- Return with the Elixir. Cheryl reaches the Bridge of the Gods and completes the trail. She has found her inner strength and determination for life's next steps.
There are countless other stories that could align with this template, but it's not always the perfect fit. So, let's look into when authors should consider it or not.
When should writers use The Hero’s Journey?

The Hero’s Journey is just one way to outline a novel and dissect a plot. For more longstanding theories on the topic, you can go this way to read about the ever-popular Three-Act Structure or here to discover Dan Harmon's Story Circle and three more prevalent structures .
So when is it best to use the Hero’s Journey? There are a couple of circumstances which might make this a good choice.
When you need more specific story guidance than simple structures can offer
Simply put, the Hero’s Journey structure is far more detailed and closely defined than other story structure theories. If you want a fairly specific framework for your work than a thee-act structure, the Hero’s Journey can be a great place to start.
Of course, rules are made to be broken . There’s plenty of room to play within the confines of the Hero’s Journey, despite it appearing fairly prescriptive at first glance. Do you want to experiment with an abbreviated “Resurrection” stage, as J.K. Rowling did in Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone? Are you more interested in exploring the journey of an anti-hero? It’s all possible.
Once you understand the basics of this universal story structure, you can use and bend it in ways that disrupt reader expectations.
Need more help developing your book? Try this template on for size:

Get our Book Development Template
Use this template to go from a vague idea to a solid plan for a first draft.
When your focus is on a single protagonist
No matter how sprawling or epic the world you’re writing is, if your story is, at its core, focused on a single character’s journey, then this is a good story structure for you. It’s kind of in the name! If you’re dealing with an entire ensemble, the Hero’s Journey may not give you the scope to explore all of your characters’ plots and subplot — a broader three-act structure may give you more freedom to weave a greater number story threads.
Which story structure is right for you?
Take this quiz and we'll match your story to a structure in minutes!
Whether you're a reader or writer, we hope our guide has helped you understand this universal story arc. Want to know more about story structure? We explain 6 more in our guide — read on!
6 responses
PJ Reece says:
25/07/2018 – 19:41
Nice vid, good intro to story structure. Typically, though, the 'hero's journey' misses the all-important point of the Act II crisis. There, where the hero faces his/her/its existential crisis, they must DIE. The old character is largely destroyed -- which is the absolute pre-condition to 'waking up' to what must be done. It's not more clever thinking; it's not thinking at all. Its SEEING. So many writing texts miss this point. It's tantamount to a religions experience, and nobody grows up without it. STORY STRUCTURE TO DIE FOR examines this dramatic necessity.
↪️ C.T. Cheek replied:
13/11/2019 – 21:01
Okay, but wouldn't the Act II crisis find itself in the Ordeal? The Hero is tested and arguably looses his/her/its past-self for the new one. Typically, the Hero is not fully "reborn" until the Resurrection, in which they defeat the hypothetical dragon and overcome the conflict of the story. It's kind of this process of rebirth beginning in the earlier sections of the Hero's Journey and ending in the Resurrection and affirmed in the Return with the Elixir.
Lexi Mize says:
25/07/2018 – 22:33
Great article. Odd how one can take nearly every story and somewhat plug it into such a pattern.
Bailey Koch says:
11/06/2019 – 02:16
This was totally lit fam!!!!
↪️ Bailey Koch replied:
11/09/2019 – 03:46
where is my dad?
Frank says:
12/04/2020 – 12:40
Great article, thanks! :) But Vogler didn't expand Campbell's theory. Campbell had seventeen stages, not twelve.
Comments are currently closed.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
- Screenwriting \e607
- Cinematography & Cameras \e605
- Directing \e606
- Editing & Post-Production \e602
- Documentary \e603
- Movies & TV \e60a
- Producing \e608
- Distribution & Marketing \e604
- Fundraising & Crowdfunding \e60f
- Festivals & Events \e611
- Sound & Music \e601
- Games & Transmedia \e60e
- Grants, Contests, & Awards \e60d
- Film School \e610
- Marketplace & Deals \e60b
- Off Topic \e609
- This Site \e600
Unraveling The Concept of The Hero’s Journey in Filmmaking
This podcast featuring christopher vogler opens up a lot of storytelling ideas..
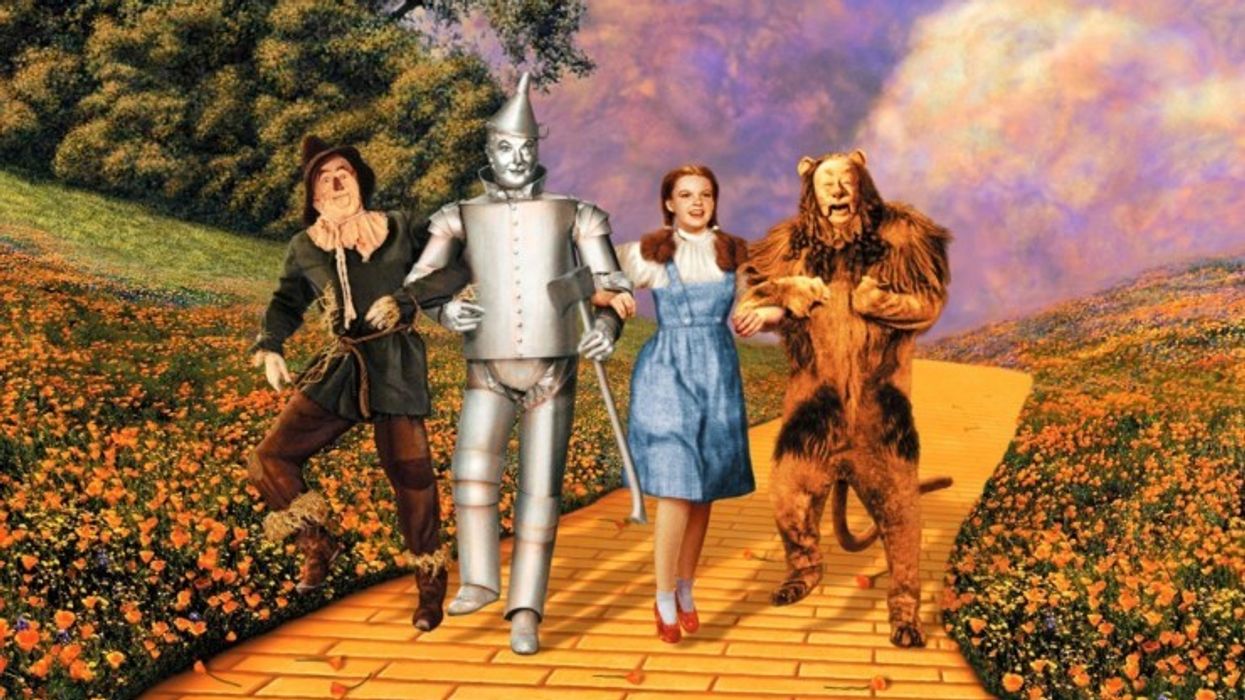

Many great stories, whether told through the written word or on the silver screen, share a common thread—a hero's journey. The Hero's Journey is a narrative structure that has been a fundamental part of storytelling for centuries, and it continues to be a powerful tool in filmmaking.
One of my favorite screenwriting books is ' The Writer’s Journey ', which details Joseph Campbell's journey through storytelling and takes the writer's POV.
This was the first book I read on screenwriting and one of the best.
Christopher Vogler wrote the book, and he was recently on the Film Crux podcast talking about these concepts. So check out the podcast and we'll talk after.
What is the Hero's Journey?
'Star Wars'
I figured that after the podcast you may need a refresher on Joseph Campbell and his concept of The Hero's Journey. This not a new concept; it dates back to ancient mythology and has been used by countless cultures throughout history.
Campbell was a scholar of comparative mythology and wrote a book called "The Hero with a Thousand Faces." He identified a common pattern in myths and stories from around the world, a pattern he called the monomyth or the Hero's Journey .
The Hero's Journey is a template that outlines the stages a hero typically goes through in a story. While there may be variations and adaptations, the core structure remains consistent.
It begins with the hero's ordinary world, followed by a call to adventure, a journey into the unknown, encounters with allies and enemies, a transformation or revelation, and finally, a return to the ordinary world with newfound wisdom or gifts.
A Diagram of The Hero's Journey
The Hero's Journey Diagram
Wikipedia Commons
The Hero's Journey is often depicted as a circular diagram, with each stage connected to the next in a cycle. there are many different names for the story beats in the circle.
The image above is from Wikipedia.
Here's a linear representation of Campbell's idea with beats I use when writing.
- Ordinary World : The hero's normal life before the adventure begins.
- Call to Adventure : The hero receives a call to leave their ordinary world and embark on a journey.
- Refusal of the Call : The hero hesitates or resists the call initially.
- Meeting the Mentor: The hero encounters a mentor or guide who provides advice or assistance.
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero commits to leaving the ordinary world and entering the unknown.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : The hero faces challenges, makes allies, and encounters adversaries.
- Approaching the Cave : The hero gets closer to the central challenge or conflict.
- Ordeal : The hero faces a major test, often their most significant challenge.
- Reward : The hero overcomes the ordeal and gains a reward or insight.
- The Road Back: The hero begins the journey back to the ordinary world.
- Resurrection : The hero faces one final, climactic challenge.
- Return with the Elixir: The hero returns to the ordinary world, transformed, and brings something valuable back.
Examples of The Hero's Journey in Film
'The Matrix'
Warner Bros.
Many iconic films have embraced the Hero's Journey structure to great effect. Here are a few examples:
- Star Wars : George Lucas drew heavily from Joseph Campbell's work when creating the Star Wars saga. Luke Skywalker's journey from a farm boy on Tatooine to a Jedi Knight follows the Hero's Journey pattern closely.
- The Lord of the Rings : J.R.R. Tolkien's epic fantasy trilogy, adapted into films by Peter Jackson, showcases the Hero's Journey through Frodo's quest to destroy the One Ring.
- The Matrix: The Wachowskis used the Hero's Journey to guide Neo's transformation from a computer hacker to "The One" who can save humanity.
- The Wizard of Oz: Dorothy's adventure in the Land of Oz is a classic Hero's Journey, complete with a call to adventure, allies, adversaries, and a return home with newfound wisdom.
How Filmmakers Utilize the Hero's Journey
- Creating Relatable Characters: One of the most significant advantages of the Hero's Journey in filmmaking is its ability to create relatable characters. Audiences connect with heroes who face challenges, make sacrifices, and experience personal growth. By following this narrative structure, filmmakers can craft characters that resonate with viewers on a deep emotional level.
- Building Tension and Conflict: The Hero's Journey provides a built-in framework for tension and conflict. As the hero progresses through the various stages, they encounter obstacles, adversaries, and setbacks, keeping the audience engaged and invested in the story's outcome.
- Engaging Audiences on an Emotional Level: The Hero's Journey is not just about physical challenges; it's also about the hero's internal journey. Filmmakers can use this structure to explore the hero's emotions, fears, and desires, allowing the audience to connect with the character on an emotional level.
- Crafting Memorable Endings: The return of the hero to the ordinary world at the end of their journey often leaves a lasting impact on the audience. Filmmakers can use this moment to deliver powerful messages, resolutions, or open-ended conclusions that leave viewers thinking long after the credits roll.
More Reading on The Hero's Journey
The Lion King (2019)
This is No Film School, of course we've written about this concept many times before. so here are some articles for you to peruse as well...
- What Are the Fundamentals of the Hero's Journey?
- What Is the 'Call to Adventure' in Storytelling?
- Joseph Campbell's Monomyth: A Brief History and Introduction
- Puppets Reenact Your Favorite Movie Moments to Explain Joseph Campbell’s ‘Hero’s Journey’
- The Other Hero's Journey: The Emotional Struggle of Screenwriting
- Over 48 Hours of Joseph Campbell Lectures Released for Free on Spotify
- This Supercut Takes You Through the Hero's Journey of over 50 Iconic Films
The Hero's Journey is a storytelling archetype deeply embedded in our collective consciousness. It provides filmmakers with a powerful tool to engage and captivate audiences.
By understanding and utilizing this narrative structure, filmmakers can create compelling stories with relatable characters, tension, and emotional depth.
Whether you're crafting a space opera or an intimate drama, the Hero's Journey remains a timeless blueprint for successful storytelling in filmmaking.
Let me know what you think in the comments.
- The Other Hero's Journey: The Emotional Struggle of Screenwriting ›
- This Supercut Takes You Through the Hero's Journey of over 50 Iconic Films ›
- What Are the Fundamentals of the Hero's Journey? ›
- Writing 101: What Is the Hero's Journey? 2 Hero's Journey ... ›
- The Hero's Journey: Joseph Campbell on His Life and Work (The ... ›
- Hero's journey - Wikipedia ›
What is the "Chosen One" Trope?
And how is it used in screenwriting for film and tv.
When it comes to telling stories about heroes, there are plenty of tropes surrounding the protagonist . The one I have the most trouble writing is called the Chosen One, but it's also one of my favorites to watch.
The Chosen One trope is one of the most common in literature, film and TV. It's at the center of two of the biggest franchises of all time, and every year people try to mimic the storytelling device to find their own fortune on the spec market .
So today, I'm going to crack into the trope, define it, show some examples, and try to catch you up to speed on it while learning about it myself.
Let's dive in.
The Chosen One Definition
The trope of the Chosen One is a literary device where an individual, often the protagonist, finds themselves singled out by destiny, a prophecy, or their unique lineage to fulfill a monumental task—usually to save the world.
Why We Love The Chosen One Trope
Wonder Woman 1984
This trope plays into people's needs and desires to feel special. We like reading or watching a character who has been annoyed out of the ordinary, or preordained to do something great.
Many people live boring lives. I am one of them. Sometimes it's nice to think there are parts of the cosmos that are pulling the strings and picking and choosing which one of us will find success or have an amazing life.
This trope is so popular that it's responsible for what I consider to be the two biggest franchises of all time, Harry Potter and Star Wars .
But the history is deeper than that.
The History of the Chosen One
The Chosen One trope has deep, ancient roots. Like from the beginning of storytelling time.
Mythologies often feature heroes or demigods who are divinely selected to perform extraordinary feats.
Think of figures like King Arthur, Perseus, or Moses—all guided by a higher purpose beyond their choosing. This theme weaves through religious narratives as well, with prophets and messiahs playing crucial roles dictated by their faith.
The Chosen One trope gained even more traction in the realm of fantasy literature and later transitioned seamlessly into film and television.
From Tolkien's Lord of the Rings to the modern phenomenon that is Game of Thrones , and its Prince That Was Promised, authors continue to tap into the trope's inherent appeal.
The Global Reach of the Chosen One Trope
Kung Fu Hustle
Columbia Pictures
The thing that's special about this trope is that it';s not just an American thing. It has its roots in Greek mythology, but also pops up across the world in different stories, meaning it has a universal appeal and imagination.
While the Chosen One trope flourishes in Western cinema, its presence extends far beyond.
Here are a few examples:
- Bollywood : Indian cinema embraces the idea of the Chosen One. Films like Baahubali and Krrish feature protagonists with exceptional abilities or divine origins tasked with defeating great evils.
- Chinese Cinema: Kung Fu Hustle and other martial arts movies often have unlikely heroes with hidden potential who emerge to face off against powerful villains. This theme stems from the Wuxia literary tradition in China.
- Japanese Anime : Chosen Ones are a mainstay of anime , from Naruto to Sailor Moon , where teenagers with extraordinary abilities become beacons of hope. The trope often connects with themes of legacy and inherited powers.
Examples of The Chosen One Trope in Film and TV
Star Wars: The Phantom Menace
We built it up enough, let's take a look at a few examples that I think properly highlight the trope.
Classic Examples:
- Neo from The Matrix : Quite literally "The One" prophesied to break the system and liberate humanity from the Matrix.
- Luke Skywalker from Star Wars : The son of a powerful Jedi, destined to use the Force to defeat the Galactic Empire and his own father, Darth Vader.
- Harry Potter from the Harry Potter series: "The Boy Who Lived," targeted by the dark wizard Voldemort, carries the prophecy to vanquish evil.
- Buffy Summers from Buffy the Vampire Slayer : The latest in a long line of vampire slayers, Buffy inherits extraordinary powers and the responsibility to protect the world from supernatural forces.
Slightly Tweaked Examples:
- Frodo Baggins from The Lord of the Rings : An unassuming hobbit becomes the unlikely ring-bearer, tasked with destroying the One Ring and ending the reign of Sauron.
- Katniss Everdeen from The Hunger Games : Initially a volunteer in the place of her sister, Katniss becomes a symbol of rebellion against the oppressive Capitol, defying expectations along the way.
- John Connor from the Terminator franchise: As the foretold leader of the human resistance against Skynet, John's very survival is crucial to humanity's future.
- Wonder Woman (Diana Prince) from DC Comics: Daughter of Zeus and Queen of the Amazons, she's destined to become a bridge between the world of the gods and humans, bringing peace and understanding.
Subversions of the Trope:
- Aang from Avatar: The Last Airbender : While technically the Chosen One (the Avatar), Aang is also a child who simply wants to have fun. The series explores the burden of responsibility even when one might not be 'ready'.
- Shrek from Shrek : An ogre living in a swamp, the opposite of a classic hero, finds himself thrust into a fairy tale quest, poking fun at the very concept of destiny along the way.
- Enola Holmes from Enola Holmes : While having a famous detective brother (Sherlock), Enola breaks from the mold. She carves her own path, using her wit and skills to solve her own mysteries, defying the expectation that the Chosen One must be male.
The Chosen One trope taps into a fundamental human desire for something greater than ourselves. We yearn for heroes in a complicated world.
These narratives offer hope and a sense of purpose, assuring us that even an ordinary person can rise to extraordinary challenges if fate calls upon them.
How Good is Sora Actually? An Interview with the Filmmakers Behind "Air Head"
Screenwriter michael arndt on how to write insanely great endings, what are the best thriller movies of all time, insta360’s free desktop editor studio takes major step forward with latest update, 50+ camera angles, shots, and movements, why is the fujifilm x100vi struggling to stay in stock, three gopro action cameras to take on the go, you can now sign a petition to add custom luts to the sony a7s iii, a filmmaker's guide to shooting the eclipse, what are the top 10 eclipses in movies and tv.

Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Hero's Journey 101: How to Use the Hero's Journey to Plot Your Story

Dan Schriever

How many times have you heard this story? A protagonist is suddenly whisked away from their ordinary life and embarks on a grand adventure. Along the way they make new friends, confront perils, and face tests of character. In the end, evil is defeated, and the hero returns home a changed person.
That’s the Hero’s Journey in a nutshell. It probably sounds very familiar—and rightly so: the Hero’s Journey aspires to be the universal story, or monomyth, a narrative pattern deeply ingrained in literature and culture. Whether in books, movies, television, or folklore, chances are you’ve encountered many examples of the Hero’s Journey in the wild.
In this post, we’ll walk through the elements of the Hero’s Journey step by step. We’ll also study an archetypal example from the movie The Matrix (1999). Once you have mastered the beats of this narrative template, you’ll be ready to put your very own spin on it.
Sound good? Then let’s cross the threshold and let the journey begin.
What Is the Hero’s Journey?
The 12 stages of the hero’s journey, writing your own hero’s journey.
The Hero’s Journey is a common story structure for modeling both plot points and character development. A protagonist embarks on an adventure into the unknown. They learn lessons, overcome adversity, defeat evil, and return home transformed.

Joseph Campbell , a scholar of literature, popularized the monomyth in his influential work The Hero With a Thousand Faces (1949). Looking for common patterns in mythological narratives, Campbell described a character arc with 17 total stages, overlaid on a more traditional three-act structure. Not all need be present in every myth or in the same order.
The three stages, or acts, of Campbell’s Hero’s Journey are as follows:
1. Departure. The hero leaves the ordinary world behind.
2. Initiation. The hero ventures into the unknown ("the Special World") and overcomes various obstacles and challenges.
3. Return. The hero returns in triumph to the familiar world.
Hollywood has embraced Campbell’s structure, most famously in George Lucas’s Star Wars movies. There are countless examples in books, music, and video games, from fantasy epics and Disney films to sports movies.
In The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers (1992), screenwriter Christopher Vogler adapted Campbell’s three phases into the "12 Stages of the Hero’s Journey." This is the version we’ll analyze in the next section.
For writers, the purpose of the Hero’s Journey is to act as a template and guide. It’s not a rigid formula that your plot must follow beat by beat. Indeed, there are good reasons to deviate—not least of which is that this structure has become so ubiquitous.
Still, it’s helpful to master the rules before deciding when and how to break them. The 12 steps of the Hero's Journey are as follows :
- The Ordinary World
- The Call of Adventure
- Refusal of the Call
- Meeting the Mentor
- Crossing the First Threshold
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies
- Approach to the Inmost Cave
- Reward (Seizing the Sword)
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return with the Elixir
Let’s take a look at each stage in more detail. To show you how the Hero’s Journey works in practice, we’ll also consider an example from the movie The Matrix (1999). After all, what blog has not been improved by a little Keanu Reeves?

#1: The Ordinary World
This is where we meet our hero, although the journey has not yet begun: first, we need to establish the status quo by showing the hero living their ordinary, mundane life.
It’s important to lay the groundwork in this opening stage, before the journey begins. It lets readers identify with the hero as just a regular person, “normal” like the rest of us. Yes, there may be a big problem somewhere out there, but the hero at this stage has very limited awareness of it.
The Ordinary World in The Matrix :
We are introduced to Thomas A. Anderson, aka Neo, programmer by day, hacker by night. While Neo runs a side operation selling illicit software, Thomas Anderson lives the most mundane life imaginable: he works at his cubicle, pays his taxes, and helps the landlady carry out her garbage.
#2: The Call to Adventure
The journey proper begins with a call to adventure—something that disrupts the hero’s ordinary life and confronts them with a problem or challenge they can’t ignore. This can take many different forms.
While readers may already understand the stakes, the hero is realizing them for the first time. They must make a choice: will they shrink from the call, or rise to the challenge?
The Call to Adventure in The Matrix :
A mysterious message arrives in Neo’s computer, warning him that things are not as they seem. He is urged to “follow the white rabbit.” At a nightclub, he meets Trinity, who tells him to seek Morpheus.
#3: Refusal of the Call
Oops! The hero chooses option A and attempts to refuse the call to adventure. This could be for any number of reasons: fear, disbelief, a sense of inadequacy, or plain unwillingness to make the sacrifices that are required.
A little reluctance here is understandable. If you were asked to trade the comforts of home for a life-and-death journey fraught with peril, wouldn’t you give pause?
Refusal of the Call in The Matrix :
Agents arrive at Neo’s office to arrest him. Morpheus urges Neo to escape by climbing out a skyscraper window. “I can’t do this… This is crazy!” Neo protests as he backs off the ledge.

#4: Meeting the Mentor
Okay, so the hero got cold feet. Nothing a little pep talk can’t fix! The mentor figure appears at this point to give the hero some much needed counsel, coaching, and perhaps a kick out the door.
After all, the hero is very inexperienced at this point. They’re going to need help to avoid disaster or, worse, death. The mentor’s role is to overcome the hero’s reluctance and prepare them for what lies ahead.
Meeting the Mentor in The Matrix :
Neo meets with Morpheus, who reveals a terrifying truth: that the ordinary world as we know it is a computer simulation designed to enslave humanity to machines.
#5: Crossing the First Threshold
At this juncture, the hero is ready to leave their ordinary world for the first time. With the mentor’s help, they are committed to the journey and ready to step across the threshold into the special world . This marks the end of the departure act and the beginning of the adventure in earnest.
This may seem inevitable, but for the hero it represents an important choice. Once the threshold is crossed, there’s no going back. Bilbo Baggins put it nicely: “It’s a dangerous business, Frodo, going out your door. You step onto the road, and if you don't keep your feet, there's no knowing where you might be swept off to.”
Crossing the First Threshold in The Matrix :
Neo is offered a stark choice: take the blue pill and return to his ordinary life none the wiser, or take the red pill and “see how deep the rabbit hole goes.” Neo takes the red pill and is extracted from the Matrix, entering the real world .
#6: Tests, Allies, and Enemies
Now we are getting into the meat of the adventure. The hero steps into the special world and must learn the new rules of an unfamiliar setting while navigating trials, tribulations, and tests of will. New characters are often introduced here, and the hero must navigate their relationships with them. Will they be friend, foe, or something in between?
Broadly speaking, this is a time of experimentation and growth. It is also one of the longest stages of the journey, as the hero learns the lay of the land and defines their relationship to other characters.
Wondering how to create captivating characters? Read our guide , which explains how to shape characters that readers will love—or hate.
Tests, Allies, and Enemies in The Matrix :
Neo is introduced to the vagabond crew of the Nebuchadnezzar . Morpheus informs Neo that he is The One , a savior destined to liberate humanity. He learns jiu jitsu and other useful skills.
#7: Approach to the Inmost Cave

Time to get a little metaphorical. The inmost cave isn’t a physical cave, but rather a place of great danger—indeed, the most dangerous place in the special world . It could be a villain’s lair, an impending battle, or even a mental barrier. No spelunking required.
Broadly speaking, the approach is marked by a setback in the quest. It becomes a lesson in persistence, where the hero must reckon with failure, change their mindset, or try new ideas.
Note that the hero hasn’t entered the cave just yet. This stage is about the approach itself, which the hero must navigate to get closer to their ultimate goal. The stakes are rising, and failure is no longer an option.
Approach to the Inmost Cave in The Matrix :
Neo pays a visit to The Oracle. She challenges Neo to “know thyself”—does he believe, deep down, that he is The One ? Or does he fear that he is “just another guy”? She warns him that the fate of humanity hangs in the balance.
#8: The Ordeal
The ordeal marks the hero’s greatest test thus far. This is a dark time for them: indeed, Campbell refers to it as the “belly of the whale.” The hero experiences a major hurdle or obstacle, which causes them to hit rock bottom.
This is a pivotal moment in the story, the main event of the second act. It is time for the hero to come face to face with their greatest fear. It will take all their skills to survive this life-or-death crisis. Should they succeed, they will emerge from the ordeal transformed.
Keep in mind: the story isn’t over yet! Rather, the ordeal is the moment when the protagonist overcomes their weaknesses and truly steps into the title of hero .
The Ordeal in The Matrix :
When Cipher betrays the crew to the agents, Morpheus sacrifices himself to protect Neo. In turn, Neo makes his own choice: to risk his life in a daring rescue attempt.
#9: Reward (Seizing the Sword)
The ordeal was a major level-up moment for the hero. Now that it's been overcome, the hero can reap the reward of success. This reward could be an object, a skill, or knowledge—whatever it is that the hero has been struggling toward. At last, the sword is within their grasp.
From this moment on, the hero is a changed person. They are now equipped for the final conflict, even if they don’t fully realize it yet.
Reward (Seizing the Sword) in The Matrix :
Neo’s reward is helpfully narrated by Morpheus during the rescue effort: “He is beginning to believe.” Neo has gained confidence that he can fight the machines, and he won’t back down from his destiny.

#10: The Road Back
We’re now at the beginning of act three, the return . With the reward in hand, it’s time to exit the inmost cave and head home. But the story isn’t over yet.
In this stage, the hero reckons with the consequences of act two. The ordeal was a success, but things have changed now. Perhaps the dragon, robbed of his treasure, sets off for revenge. Perhaps there are more enemies to fight. Whatever the obstacle, the hero must face them before their journey is complete.
The Road Back in The Matrix :
The rescue of Morpheus has enraged Agent Smith, who intercepts Neo before he can return to the Nebuchadnezzar . The two foes battle in a subway station, where Neo’s skills are pushed to their limit.
#11: Resurrection
Now comes the true climax of the story. This is the hero’s final test, when everything is at stake: the battle for the soul of Gotham, the final chance for evil to triumph. The hero is also at the peak of their powers. A happy ending is within sight, should they succeed.
Vogler calls the resurrection stage the hero’s “final exam.” They must draw on everything they have learned and prove again that they have really internalized the lessons of the ordeal . Near-death escapes are not uncommon here, or even literal deaths and resurrections.
Resurrection in The Matrix :
Despite fighting valiantly, Neo is defeated by Agent Smith and killed. But with Trinity’s help, he is resurrected, activating his full powers as The One . Isn’t it wonderful how literal The Matrix can be?
#12: Return with the Elixir
Hooray! Evil has been defeated and the hero is transformed. It’s time for the protagonist to return home in triumph, and share their hard-won prize with the ordinary world . This prize is the elixir —the object, skill, or insight that was the hero’s true reward for their journey and transformation.
Return with the Elixir in The Matrix :
Neo has defeated the agents and embraced his destiny. He returns to the simulated world of the Matrix, this time armed with god-like powers and a resolve to open humanity’s eyes to the truth.
If you’re writing your own adventure, you may be wondering: should I follow the Hero’s Journey structure?
The good news is, it’s totally up to you. Joseph Campbell conceived of the monomyth as a way to understand universal story structure, but there are many ways to outline a novel. Feel free to play around within its confines, adapt it across different media, and disrupt reader expectations. It’s like Morpheus says: “Some of these rules can be bent. Others can be broken.”
Think of the Hero’s Journey as a tool. If you’re not sure where your story should go next, it can help to refer back to the basics. From there, you’re free to choose your own adventure.
Are you prepared to write your novel? Download this free book now:

The Novel-Writing Training Plan
So you are ready to write your novel. excellent. but are you prepared the last thing you want when you sit down to write your first draft is to lose momentum., this guide helps you work out your narrative arc, plan out your key plot points, flesh out your characters, and begin to build your world..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Dan holds a PhD from Yale University and CEO of FaithlessMTG
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
The Hero’s Journey Climax: 3 Key Principles to Write the Ordeal Scene
by David Safford | 1 comment
Writing a Hero's Journey climax isn't easy. Even when you outline it properly, you might struggle to put the right words on the paper.
If you understand what makes a great Hero's Journey climax, however, you can defeat this daunting task easier.

In this article, you'll learn what the Hero's Journey climax, otherwise known as the Ordeal, is—and why it is so important.
You'll also learn writing tips that can help you write this well: how to raise the stakes and maintain the action without losing the heroic arc that your protagonist has learned along the way.
Understanding A Strong Hero's Journey Climax
As a judge of several writing contests, I've read many stories filled with action, violence, shouting, and assorted conflict. While a few of these stories pulled off their hero's journey climaxes, most of them bombarded me with noise, gore, curses, and even sexual activity—all while abandoning their protagonist's true journey.
When that happens, you can count your reader out.
Here's how to write your story's climax and keep your reader excitedly turning pages.
The Hero's Journey (Recap)
Joseph Campbell's Hero's Journey is a theory exploring a timeless, mythical story structure. Following a hero as they flee their everyday life, the hero's central conflict involves a quest for justice and rebirth that must come from defeating an evil force, usually called the Shadow.
This entire journey has been condensed into Christopher Vogler's 12 Steps of the Hero's Journey , an outline of story elements and the series of events leading from the beginning to the climactic event (the moment when the hero either achieves their goal or is defeated).
Prior to the climatic event, or the Hero's Journey Ordeal, there's an Approach to the Inmost Cave . Here, before the hero performs a big, decisive action, there is a brief pause. During this time the author establishes three key things:
- The villain guarding the goal is really, really nasty
- The cost of losing (known as stakes ) are extremely high
- The task that must be completed in order to achieve victory
Once this “calm before the storm” has occured, you are free to send your hero unto the breach so they can face the tests ahead.
Let's talk about how to do just that!
Hero's Journey Step 8: The Ordeal (the Climax)
In Hero's Journey-speak, the climax of the story is known as the Ordeal .
The Ordeal is a complicated and nearly-impossible task that your hero must accomplish in order to achieve their goal. Accomplishing it, however, cannot end the story, but merely reveal that the goal itself does not satisfy your hero's deepest need. But more on that later.
An easy way to think of the Ordeal is as an action sequence, but this may not always be the case. It could be a test of character, like in The Queen's Gambit. It could be a test of wit and wisdom, as in WandaVision. And it can be a test of loyalty, as in Pride and Prejudice.
But most often it is, in fact, a test of strength, strategy, and skill.
There is a “storming of the castle,” so to speak, where your hero must face a task that is greater than anything they have encountered so far. It's also likely your hero comes face to face with the villainous Shadow in this scene.
From 30,000 feet, though, remember that the goal of the Ordeal scene is to have your hero obtain the Goal of the quest.
This usually involves rescuing someone, acquiring a treasure or weapon, or fulfilling some other task (like destroying the One Ring of Sauron, à la The Lord of the Rings).
However, the act of doing so much reveal something about the Goal, the world it lives in, and/or the hero themselves that leads to dissatisfaction or fails to resolve the issues facing the story in a complete way.
3 Key Principles in a Hero's Journey Climax (Ordeal)
The Ordeal is a lengthy scene, filled with many beats, and each beat must be carefully designed to maximize its impact. This is the moment your reader has been waiting for, after all!
How do you write it so it is irresistibly good?
1. Focus on what got you here: Desire
It's easy to screw this up. When we plan and write a story, we spend a lot of time building up toward the exciting climactic event. So when we get there, it's easy to overdo it with physical details as we attempt to take the movie playing in our heads and put it down on paper.
Unfortunately, the same movie will never play in your reader's mind. There might not be a movie playing at all.
Instead, when readers confront pages of physical description and noise (whether they're depictions of fistfights, gun battles, sexual intimacy, or shouted opinions), they instinctively recoil.
This is especially true if the bombast isn't earned, but thrust too quickly or emphatically into the story.
This is natural. We avoid conflict , especially conflict that we can't comprehend or establish ourselves in, even as observers. It is imperative that your reader understands every piece of your story's action, and that they care about the outcome of each punch, jump, kiss, or insult.
That's why you need to focus on what got you here: Your protagonist's desire.
And along with that desire (for their want and need), is their fear. What do they have to lose? Why is success so important to them?
Each moment of action must be filtered through the protagonist's journey of hope and fear. Each step forward or retreat backward must come with hope, disappointment, terror, anticipation, belief, despair . . . all the emotions that accompany an active protagonist.
A great example can be found in George Lucas's epic space fantasy, Star Wars.
The final battle between the Rebellion and the Empire is ultimately a loud, bombastic explosion of lasers and engines screaming across the screen. But there are two elements infusing it with incredible emotion: Friendship and the Force.
First, Luke is fighting not just for the Rebellion, but for his friends. Leia, Chewbacca, and C-3PO are on Yavin-4, the planet about to be obliterated by the Death Star. And his best friend from home, Biggs, gets killed in the fight.
Then to add to it, Luke seems to know that computers and technology alone cannot win the battle for him. After all, they are fighting a massive machine (the Death Star) and a small machine (Darth Vader); clearly the Empire has the upper hand when it comes to dehumanizing control.
The scene , and his character, takes a massive turn when Luke listens to the voice of his master, speaking through the mystical energy field called the Force, instructing him to trust in it and use it.
Luke does, and this is what gives Star Wars' climactic moment its most powerful punch. Luke doesn't just desire to beat the Empire; he desires for his life to have meaning. The Force gives him that meaning that he deeply seeks.
2. Use beats of quiet contemplation or conversation
Another mistake authors make with their story climaxes is to load them with nonstop action.
Again, this may be a result of “writing the movie in your head,” as we hope to create a scene of pulse-pounding excitement, and write one blindingly exhausting scene after another.
But this isn't how the human mind processes things. It also doesn't allow much room for your hero to process how the stakes (and their dreams) are changing in the moment. Human beings are constantly evaluating and strategizing, and you need little moments of quiet thought or peaceful conversation to punctuate the sound and the fury of your story climax.
More movies do this than you might immediately realize. Rewatch your favorite action movie and you'll notice throughout the climactic action scenes just how often the story pauses for characters to think, reflect, and reorient themselves.
The Hunger Games excels at this.
Partially, author Suzanne Collins is at an advantage, since the Ordeal could include all of the “Games.” Yet the Games aren't packed with wall-to-wall violence. Take the relationship between Katniss and Rue.
Neither come from wealth or privilege. District 12 is hardly a paradise, and from what Katniss learns from Rue, neither is District 11. With an ordinary world in common, the two form a friendship which seems based on love and respect for life. It's these quiet, beautiful moments that make Rue's death so gut-wrenching. They are also why her death is such a critical moment in both the plot and Katniss's character development.
So add in a few moment for your characters to catch their breath and connect in the midst of the chaos. Your reader will probably need to do the same, too!
3. Don't give the hero what they want
One final trick that will make your climax unbelievably thrilling is to withhold the very thing the scene promises to deliver: The Goal.
This isn't just meant to mess with your reader. It's to reflect a painful reality of life: That what we want is often deeply unsatisfying, or at least not so easily won.
There are two ways to do this.
First, you can simply have the Goal be taken away. Destroy the MacGuffin. Kill off the character. Have the Shadow, or villain, hide the Goal or protect it in a more ultimate way.
Or secondly, and perhaps more meaningfully, let the hero obtain the Goal, only to feel a deep and hollow disappointment.
So often we orient our lives toward some physical goal, like money, fame, sex, or treasure, only to obtain that goal and find ourselves feeling emptier than ever before. We realize that no matter how much we believe we will be fulfilled by this “thing,” that no thing can ever fulfill as deeply as we'd hope.
That's why your hero must have something in addition to their object of desire: your hero must have an internal need .
Internal needs take the form of validation, acceptance, peace with oneself, spiritual harmony, reconciliation, forgiveness, acceptance of death, emotional/spiritual rebirth, and more. These needs are what will ultimately drive your Hero's Journey forward, because heroic journeys aren't just about getting prizes like weapons, money, or “peace.”
They're about peace within, and the peace all human beings long for in a world filled with so much injustice and suffering.
Such a story is the epic saga of Harry Potter .
This series is filled with several MacGuffin goals that J.K. Rowling sends her cast of characters out to find, but all of them point to the deeper problem lurking under the surface: Voldermort.
This is why Harry Potter will begin one of his adventures thinking he wants a magical object, like the Sorcerer's Stone, but soon learns that such a thing won't ultimately help him satisfy his deepest needs.
When Harry seeks to acquire the Sorcerer's Stone in order to prevent Voldemort from regenerating. Yet when he looks in the Mirror of Erised (that's Desire if you weren't reading this in a mirror), Harry realizes that he doesn't want a magic rock. He wants his family back. But because Voldemort destroyed it, he can never have what he truly wants.
What a powerful message to package into a children's book! Yet this is the reality of life, and great writers use their stories' climaxes to reflect it.
If you do this too, your story will also ripple with unfathomable power. Readers will gasp, but they won't give up. They'll have to keep reading, because what happens to the hero will say something about the readers' lives as well.
That's the kind of story we all want to write.
Ordeal/Climax: Action of the Heart
No matter what kind of climactic Ordeal your story requires, never forget that the most important action must occur in your protagonist's heart.
It can be so easy to compose physical imagery and believe it will thrill our readers. But without the necessary action of the heart—the action of wanting, hoping, fearing, disbelieving, and more—the physical action will fall painfully flat, leaving your reader disappointed.
Don't fall leave your reader wanting. Deliver an incredible reading experience by nailing your story's Ordeal.
What are your favorite climax scenes from stories you enjoy? What do you love about those scenes? Let us know in the comments .
To practice writing this crucial scene, freewrite for fifteen minutes about a high stakes choice. Here's all you need:
- Character (call them “A” or “B”)
- A goal (make it something simple, like a bottle of water)
- High stakes
Dream up ways for the pursuit to be challenging, heartbreaking, and filled with dilemmas in which the character must choose between two “best bad” options.
Then jump into the hero's psyche and react with thought or dialogue. Write how the hero processes this emotion physically: Do they sweat? Do their fingers become ice-cold? Does their vision blur?
Experiment with this physical-emotional back-and-forth to discover new ways of composing climactic action! Post your Practice in the box below, and be sure to leave a constructive critique on another writer's practice when you're done!
David Safford
You deserve a great book. That's why David Safford writes adventure stories that you won't be able to put down. Read his latest story at his website. David is a Language Arts teacher, novelist, blogger, hiker, Legend of Zelda fanatic, puzzle-doer, husband, and father of two awesome children.

A looked out the window. the clouds were blocking the sun, as usual. she put her chin in her hands and sighed woefully. She wanted to go outside, so so bad. To feel the rain, the wind, the grass, but mostly the sun. She would never be allowed outside. for her own good, of course. She flopped onto the bed as a nurse hurried in. the nurse closed the curtains and turned to A. “remember, honey, that the sun is dangerous. even a few rays through the clouds could be dangerous for your health!” She scolded. A whimpered, and looked at her pale hands. the hands of a ghost. “i’m dying anyways, why not let me look at the sun before I go?” The nurse softened, “we’re trying our best, and you’re a fighter. you’ll make it.” “What’s living, without the sun? There’s no purpose. always being inside, no nature. no LIGHT.” A waved her hand at the LED lights on the ceiling that were never on. It seemed the nurse couldn’t take the depressive state of A anymore, so she fled. tail between her legs. A sat up, conscious of the weakness in her limbs, and cautiously clambered out of the bed. she gribbed the edges to steady herself, and walked out the door. she made it out the door, only to trip, and stub her toe. She yelped in pain, drawing the attention of a doctor down a hallway. “Miss! miss! You’re not supposed to be out!” He started running toward A. A panicked, and fled the hallway, she stumbled and fell on her face, but, grunting in pain, she pushed herself up, her weak arms shaking from the strain of her bodyweight. she crawled, into an unused room, and sat with her back to the wall, breathing heavily and crying quietly. She couldn’t afford to be found, not yet. The doctor passed the room A is in, as she stifled her cries, his strong footsteps passed as he ran by. A wiped her tears, and held out her arms. the were weak, limp, and pale white. she flexed them, but couldn’t make out a muscle. A got up, and, gripping the walls, walked as quietly as possible into the hallway and the reception area of the hospital. the receptionist was busy with a phone call, her back turned toward the entrance. A could see the clouds pulling away, revealing the blue of the firmament, the green of the grass, the rolling hills, the purple, pink, white, yellow of flowers, the trees, the trunks, the bees the birds, A almost gasped, her heart was beating joy into her soul, her body coming alive again. A walked to the entrance door, the soles of her feet masking her footsteps. she carefully danced in the shadows around the light shining through the glass doors. she opened the door, the black metal warming her hand. she opened the door, and stepped out. She ran to the middle of the lawn, squealing and giggling. The wind mussing her hair, the grass irritating her feet, and the sun… the sun warming her body from head to toe. she squeezed her eyes shut as she felt the sun getting to her eyes, and the sensitivity keeping her from feeling the true joy of vitamin D. A laid on the prickly grass, her face towards the sky, and cried. Cried of joy, for being able to feel the sun, of sadness, that this is the last time, of content, for she’ll be joining her creator, and of happiness, that it was her, and not her sister, that was diagnosed with all the problems. The tears flowed freely, and it felt nice. nice to let her emotions out, nice to feel something other than cold shadows, and stiff beds. The door opened, and A heard footsteps. she let a few more tears escape, because it was over, then wiped her eyes. It hurt, to rub the sensitive, blistering skin around her eyes after being in the sun. The doctors and nurses rushed towards her, applying tonic and gels to the skin around her eyes, and her arms, which were quickly burning and showing signs of spider-web veins. They tried to pull her inside, but A refused, she wanted to spend her last moments outside, but they wouldn’t understand; what it’s liked to suffocate in a dark white room, with only shadows to comfort, and stiff beds to feel. “NO!” Finally, A pleaded, and slipped out of their grasps. “please..no. I only have a few more moments, why not spend it in nature?” She whispered, mostly to herself, but they heard, and answered. “But, A. We just got the news. You’re expected to live for months, maybe YEARS more!” A looked up, a sob building in her chest. years more of the agony of life. she cried out, in pain, to the heavens, and let the doctors and nurses take her to her stark white prison. Resigned to a state of choking on tonics and gels and liquids the demon nurses shove down her throat. “it’ll heal you…” they tell her. “It’ll HELP you…” they scream. but she knows its just another way of keeping her on the planet she doesn’t want to be on.. with the people she doesn’t know. when really, she just wants to be with her loved ones who have moved on. So she, moved on.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- The Hero’s Journey: How to Write the Climax of Your Story – Books, Literature & Writing - […] “Want to create a gripping climax? Give your hero a win-but-lose ending: there’s some success, but there’s also failure—or…
- The Hero's Journey: How to Build Suspense With a Fake-Out Ending - […] he or she confronts the big task, known as the Ordeal, and makes a decision that wins him or…
- The Hero's Journey: How to Write the Resurrection - […] they confront the big task, known as the Ordeal, and makes a decision that wins them the […]
- The Hero’s Journey: The Ultimate Guide to the Universal Structure of Great Stories - […] Learn more: Here’s how to craft Hero’s Journey Step #8: The Ordeal […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.

You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.

The 9 Stages of the Hero’s Journey and How to Use Them
by Lewis / July 14, 2018 / Story Structure
What is the true purpose of storytelling?
You might say it’s to uplift us, or to comfort us in times of trouble. Others will argue storytelling serves to teach us morality, the meaning of good versus evil, or the value of inner strength. Yet, Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey goes deeper than all of those things.
The Hero’s Journey is about exploring human nature and charting our common path from childhood to adulthood, regardless of who we are or what we struggle with. Not only that, but it embodies universal themes of growth and change, making it the perfect foundation to build your own unique story from!
What Is the Hero’s Journey?
- 1 What Is the Hero’s Journey?
- 2 Using the Hero’s Journey in Your Own Novel
- 3.1 The Ordinary World:
- 3.2 The Call to Adventure and Refusing the Call:
- 3.3 Overcoming Resistance and Meeting the Mentor:
- 3.4 Crossing the First Threshold:
- 3.5 Tests and Trials:
- 3.6 The Major Ordeal:
- 3.7 The Road Back:
- 3.8 Mastering the Journey:
- 3.9 Returning with the Elixir:
- 4 Understanding the Monomyth

Popularized by Joseph Campbell, the Hero’s Journey was part of his idea of the “Monomyth,” a term describing the universal progression of all human storytelling. He developed this while studying mythology from cultures across the world and throughout history, writing about them in The Hero With a Thousand Faces.
As a follow up, Christopher Vogler wrote The Writer’s Journey , further distilling the ideas of Campbell into a usable storytelling guide.
The result is one of the best storytelling tools around.
At its core, the Hero’s Journey is a form of story structure just like the Three Act Structure. However, in comparison the Hero’s Journey is much more broad, and is something you can see at play in almost every story—regardless of how anti-traditional it may be.
This is because the Monomyth builds on ever-present patterns of growth and change, something humans have been obsessed with forever.
- What is my purpose in life?
- What does it mean to grow up?
- Is there something greater out there?
- What will happen when I die?
These questions have always echoed in the human mind, and been reflected in our storytelling as a result. Thus, the Hero’s Journey is so powerful and omnipresent because it resonates with a core part of our human experience.
“A blunder—apparently the merest chance—reveals an unsuspected world, and the individual is drawn into a relationship with forces that are not rightly understood… They are the result of suppressed desires and conflicts. They are ripples on the surface of life, produced by unsuspected springs. And these may be very deep—as deep as the soul itself.” – Joseph Campbell, The Hero with a Thousand Faces
Using the Hero’s Journey in Your Own Novel
Of course, this is all well and good, but how can you use this Monomyth in your own writing?
Well, one of the best qualities of this structure is that it ties together both your characters and plot. Rather than just being a story structure, the Hero’s Journey can also act as something of a character arc. That’s the most helpful thing about these principles—they apply not only to your plot, but your protagonist’s arc as well, helping you build a more cohesive story.
When combined, you have a powerful recipe for engaging your readers!
Overall, the Hero’s Journey is split into two halves: The Ordinary World, and the Unknown World. The Ordinary World is exactly what it sounds like—your protagonist’s everyday life, complete with all of their flaws and insecurities.
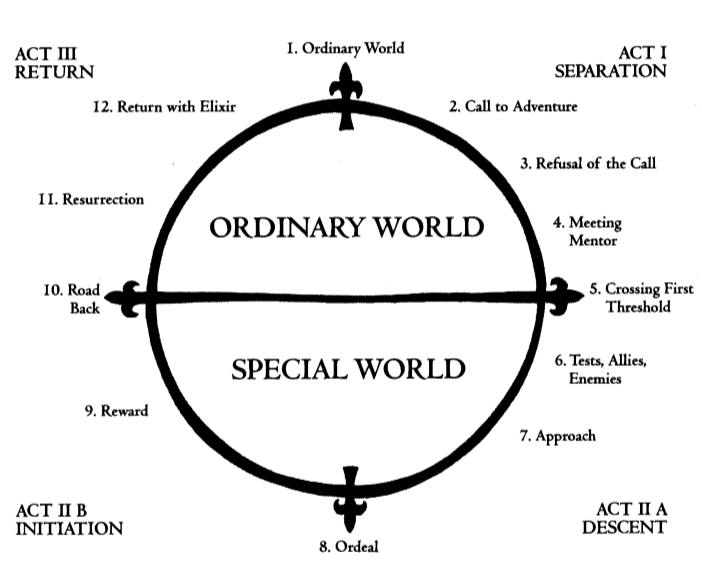
However, a problem is brewing beneath the surface, and this is what will force them to leave home and enter the Unknown World. This Unknown World is where they’ll be tested and forced to grow as a person. Along the way they’ll gain new allies and skills, until they finally return to their Ordinary World to heal it’s suffering and take their place among the heroes.
Throughout this structure, your protagonist’s inner development will mirror the conflict of the story, giving your novel a cohesive and resonant feel. With that said, let’s look at the nine stages of the Hero’s Journey and how to incorporate them in your own storytelling!
The 9 Stages of Campbell’s Monomyth
The ordinary world:.
The start of the Hero’s Journey finds us in the Ordinary World, where readers are introduced to your setting, meet the starting cast, and get to know your protagonist. Essentially, the Ordinary World provides a baseline that will make the Unknown World your protagonist later encounters stand out.
Because of this, you don’t want to neglect this important setup.
Without seeing where your hero is starting from, a world full of magical purple unicorn dragons could be entirely normal to them. Instead, you need to you start your story by showing their normal everyday life in suburban Wisconsin. It’s the contrast between these two worlds that makes them feel impactful.
Alongside this, the Ordinary World also sets up the inner struggle your protagonist will need to overcome during their character arc. It shows how they’ve been living before their journey begins and foreshadows the cracks under the surface. Without this critical knowledge of the Ordinary World, the reader has no metric by which to measure your character’s growth or the growth of their world.
The Call to Adventure and Refusing the Call:
If you’re already a fan of the Three Act Structure, then the Call to Adventure will likely feel at least somewhat familiar.
This is because the Call to the Adventure mimics the Inciting Event and Key Event from the Three Act Structure. Here, your protagonist will learn of the coming conflict and get their first taste of the journey to come—though sometimes they are whisked away with little choice. Most often they’ll also refuse this call, helping your reader better understand the stakes of your story.
If your protagonist has reason to be afraid, then your audience does as well.
This stage allows you to build suspense, foreshadow the power of your antagonist and the dangers ahead, and show off your protagonist’s flaws in action. Are they too timid, headstrong, selfish, or careless? Incorporate this into their Refusal of the Call and show how it will hinder them on the journey ahead.
Overcoming Resistance and Meeting the Mentor:
Now that a Call has been issued, your protagonist will be feeling afraid, hesitant, or even outright resistant to beginning their journey.
Overcoming this resistance requires a period of counsel, where they’ll get advice and encouragement from mentors and allies. Here you’ll prepare your protagonist and audience for what’s coming, while also fitting in some last minute worldbuilding and plot development before your story picks up steam.
Your protagonist will begin collecting the tools and wisdom needed for the road ahead, though they won’t be completely prepared for a while yet. Their inner struggles will continue pushing against them here, and they may neglect important information they’ll regret later on. Still, they’ll also show promise, usually in the form of some redeeming quality that lets your readers know there is hope for them to grow.
Crossing the First Threshold:
This is the true beginning of your story.
Here your protagonist will Cross the First Threshold into the new, Unknown World, officially committing themselves to the journey ahead. There is no turning back from this point, and no returning to the Ordinary World until they’ve completed their quest and grown past their flaws.
Your protagonist will have to prove themselves to make it this far of course, even though they haven’t overcome their inner struggle just yet.
Just as they showed a redeeming quality while Overcoming Resistance and Meeting the Mentor, they’ll need to prove this redeeming quality again to cross into the Unknown World. As an example, Bilbo Baggins temporarily overcomes his fearfulness and leaves the Shire, while Mulan overcomes her self-doubt and joins the Chinese army. However, some characters will be forced into this Unknown World, like when Simba is driven from the Pride Lands by Scar.
Tests and Trials:
Your story has officially entered the Unknown World, and this is when a period of Tests and Trials begin for your protagonist.
Here they’ll gain new allies, new enemies, and new skills. They’ll be beaten down repeatedly, only to get back up again that much stronger and wiser. Essentially, this period is all about preparing them for the bigger battles that lie ahead.
This means that the Tests and Trials period is important for a variety of reasons.
It provides a stark contrast from the more stable Ordinary World and thrusts your protagonist into their new life. However, it also gives them the opportunity—through their new experiences—to prove their strengths, befriend others in your cast, and begin to threaten your antagonist. Overall, these tests will form nearly a quarter of your story’s overall runtime as you approach the Major Ordeal.
The Major Ordeal:
Perhaps confusingly named, the Major Ordeal is not the Climax.
Instead it corresponds with the Midpoint of the Three Act Structure, and shifts your protagonist from a period of reaction to action. After this point, they’ll finally be able to actively drive your plot forward, rather than just being pushed along against their will. They’ll also be rewarded for their success, either through a new tool, new allies, or new knowledge.
The Major Ordeal itself will feature a moment of growth that cements your protagonist’s progress. They’ll have to face their biggest conflict yet, giving them a chance to show how far they’ve come from their Ordinary World. However, don’t let them get ahead of themselves.
They haven’t overcome their inner struggle yet, though they may think they have.
To pick on Mulan again, her Major Ordeal occurs when she retrieves the arrow from the top of the pole in the middle of camp, proving her cleverness and intelligence. She has gained the acceptance of her comrades, but she is still living in disguise. This will come back to punish her later, just as your protagonist’s flaw will come back to punish them.
The Road Back:
With the Major Ordeal behind them, the Road Back prepares your protagonist to face the finale of your story.
They’re now driving the plot, seeking out your antagonist or otherwise planning their defeat, and likely beginning the trek to wherever their final showdown will take place. Here your pacing will speed up as well. You’re preparing for a climactic showdown, and both your cast and your readers are ready to see this journey come to its conclusion.
This creates the perfect opportunity to remind your protagonist of the stakes.
In the afterglow of the Major Ordeal, you need to show them why their journey isn’t over yet. Reveal the cracks still left by their flaw, and remind them that no matter how much they try to cover them up, they must deal with them soon. The conflict is far from over, and there’s still danger ahead.
Mastering the Journey:
With your story coming to its close, its time for your protagonist to prove they’ve mastered their journey—and as you can probably guess, this overlaps with the Climax and the Climactic moment from the Three Act Structure. Here they’ll do battle against your antagonist and face their final test, hopefully overcoming their inner struggle in the process.
As a result, everything in your story needs to come together here.
All of your themes, subplots, characters, symbols, motifs—it’s called the Climax for a reason! Of course, this is also the culmination of your protagonist’s arc. Here they’ll face the most difficult test of their flaws, and will have to use all of the knowledge, skills, and alliances they’ve gained to survive.
Ultimately, without the journey they just went on, they would never be able to succeed.
Returning with the Elixir:
With your story’s conflict resolved, it’s now time for your protagonist to recover. To Return with the Elixir references the end of many myths where the hero brings the rewards of their journey back to their home village, healing the lives of everyone around them—not just their own. In terms of the traditional Three Act Structure, this mirrors your Resolution.
Essentially, your goal in these final scenes is to complete the circle of your story.
At the end of many adventures the protagonist returns home to their Ordinary World, experiencing echoes from the start of their journey. Yet everything feels different, and they quickly realize how their quest has changed them. Others don’t make a physical return, but instead see similar situations to those they struggled with or felt uncomfortable in at the start, this time unfazed by what seemed so intimidating before.
Either way, these final moments will be bittersweet, joyful, and maybe even a bit sad.
Most importantly, they’ll provide an important sense of catharsis for your readers, a release of the emotional tension your story created. So—to use this ending to its full effect—make sure you give your readers a moment to relax with your cast before they close the back cover.
Understanding the Monomyth
At the end of the day, the Hero’s Journey embodies patterns seen in almost all human storytelling, and it’s also a great tool for writers wanting to more deeply understand their own stories. While it’s not without it’s flaws, it can still serve as a great starting point for telling your own epic adventures!
Of course, the Hero’s Journey isn’t the only form of story structure out there. If you’re interested in exploring everything else story structure has to offer, I hope you’ll take a moment to check out The Complete Story Structure Series , a collection of articles on The Novel Smithy dedicated to everything structure.
How does the Hero’s Journey impact your stories? Let me know in the comments!
Thoughts on the 9 stages of the hero’s journey and how to use them.
Hi, I have four books out and a new one almost ready. This may be the best explanation of the Journey I’ve read. And, I’ve read a lot, including Hero with a Thousand Faces and the Writer’s Journey. I especially like your take on Crossing the Threshold and the Major Ordeal. Those two entries helped clear a lot of fog on the subject for me.
Thanks. Charles Hampton
Glad to hear it Charles! 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Hero’s Journey: A Guide to Becoming The Hero Of Your Story
What will your story be?
Be the hero of your story . It’s common advice from motivational speakers and life coaches, a call to arms to take centre stage and tackle life’s challenges head-on, to emerge victorious in the face of adversity, to transform through hardship.
As humans, hardwired to view the world and share experiences through the medium of stories, myths often act as powerful motivators of change. From ancient cave paintings to the Star Wars and its Death Star to Harry Potter and his battle against evil, the hero’s journey structure is a familiar one. It’s also one you need to know if you want to know how to write a book , but I digress.
This article will outline the stages, and psychological meaning, of the 12 steps of Joseph Campbell’s hero’s journey. So, are you ready to become the hero of your story? Then let the adventure begin…
Who is Joseph Campbell?
Joseph Campbell was an American professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College, and an expert of mythology that once spent five years in a rented shack, buried in books for nine hours each day. His greatest contribution is the hero’s journey, outlined in his book The Hero with A Thousand Faces . Campbell was able to synthesise huge volumes of heroic stories, distilling a common structure amongst them.
Near the end of his life, Campbell was interviewed by Bill Moyers in a documentary series exploring his work, The Power of Myth .
Throughout their discussion, Campbell highlighted the importance of myth not just in stories, but in our lives, as symbols to inspire us to flourish and grow to our full potential.
How is the hero’s journey connected to self development?
You might be wondering what storytelling has to do with self-development. Before we dive into the hero’s journey (whether that is a male or a female hero’s journey), context will be useful. Joseph Cambell was heavily inspired by the work of Carl Jung, the groundbreaking psychologist who throughout his life worked on theories such as the shadow, collective unconscious, archetypes, and synchronicity.

Jung’s greatest insight was that the unconscious is a vast, vibrant landscape, yet out sight from the ordinary conscious experience. Jung didn’t only theorize about the unconscious; he provided a huge body of work explaining the language of the unconscious, and the way in which it communicates with the conscious mind.
The nature of the unconscious
Due to its vast nature, the unconscious doesn’t operate like the conscious mind, which is based in language, logic, and rationality. The unconscious instead operates in the imaginal realm — using symbols and meaning that take time to be deciphered and understood consciously. Such symbols surface in dreams, visualizations, daydreams, or fantasies.
For Jung, the creative process is one in which contents of the unconscious mind are brought to light. Enter storytelling and character development — a process of myth-making that somehow captures the truth of deep psychological processes.
Campbell saw the power of myth in igniting the unconscious will to grow and live a meaningful life. With that in mind, his structure offers a tool of transformation and a way to inspire the unconscious to work towards your own hero’s journey.
The 12 steps of the hero’s journey
The hero’s journey ends where it begins, back at the beginning after a quest of epic proportions. The 12 steps are separated into three acts:
- departure (1-5)
- initiation (5-10)
- return (10-1)
The hero journeys through the 12 steps in a clockwise fashion. As Campbell explains:
“The usual hero adventure begins with someone from whom something has been taken, or who feels there is something lacking in the normal experience available or permitted to the members of society. The person then takes off on a series of adventures beyond the ordinary, either to recover what has been lost or to discover some life-giving elixir. It’s usually a cycle, a coming and a returning.”
Let’s take a closer look at each of the steps below. Plus, under each is a psychological symbol that describes how the hero’s journey unfolds, and how when the hero ventures forth, he undergoes an inner process of awakening and transformation.
1. The ordinary world
The calm before the storm. The hero is living a standard, mundane life, going about their business unaware of the impending call to adventure. At this point, the hero is portrayed as very, very human. There could be glimpses of their potential, but these circumstances restrict the hero from fulfilling them. Although well within the hero’s comfort zone, at this stage, it’s clear something significant is lacking from their life.
Psychological symbol
This is represented as a stage of ignorance, pre-awakening. Living life by the status quo, on other people’s terms, or simply without questioning if this is what you want. At this point life is lived, but not deeply satisfying.
2. Call to adventure
Next is a disruption, a significant event that threatens the ways things were. This is a challenge that the hero knows deep down will lead to transformation and change, and that the days of normality, “the way things are,” are numbered. The hero confronts the question of being asked to step into their deeper potential, to awaken the power within, and to enter a new, special world.
Many of us embark on inner-journeys following hardship in life — the death of a loved one, the loss of a job, physical or mental illness. This stage occurs when it becomes apparent that, to move through suffering, one has to look within, to adventure into the soul.
3. Refusal of the call
No compelling story would be complete without friction. The hero often resists this call to adventure, as fear and self-doubt surface at full force, and the purpose of this new life direction is questioned. Can the reluctant hero journey forth? Do they have the courage?
The only way to grow and live a deeply fulfilling life is to face the discomfort of suffering. Campbell himself once said: “ The cave you fear to enter holds the treasure you seek .” At this stage, fears, and anxieties about delving deep into the psyche arise. The temptation is to remain blissfully ignorant, to avoid discomfort, and to stay in your familiar world.
4. Meeting a mentor
As the hero faces a crisis of confidence , a wise mentor figure appears.
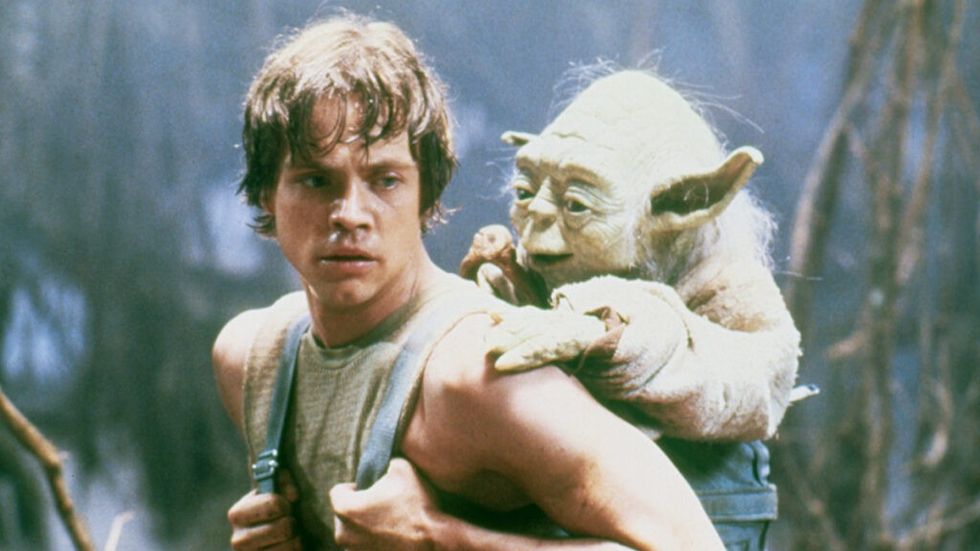

This character offers inspiration, guidance, or understanding that encourages the hero to have the self-belief to start this new adventure. In many stories, a mentor is someone else who has embarked on the hero’s journey, or someone who attempted, and failed. This person reflects the importance of this mission, reminding the hero their calling far exceeds their fear.
When the journey of exploration has to begin, people or situations enter your life at just the right time, guiding you in the right direction. This could be a close friend, a peer, a professional, such as a coach or therapist, or even a fictional character in a film or book. In most cases, these are chance encounters that contain a sense of knowing before the hero leaves on his or her adventure.
5. Crossing the threshold
This is a pivotal moment in the hero’s journey, as the initiation begins. This occurs when the hero fully commits to their quest, whether physical, emotional, or spiritual. This is the point of no return, where the reluctant hero embarks on their adventure, and has accepted that the way things were must change. The hero enters a new zone, one in which the call to adventure must be accepted. The hero’s resolve is hardened, and they understand they have a responsibility to confront what is ahead of them.
Whatever your life was before the call to action, this is a crossroads which is accepted, knowing your life may never be the same. This is a point of empowerment, where you realize that journeying within will lead you to greater self-understanding, even if those insights will dramatically change your life direction.
6. Test, allies, enemies
Now the hero has ventured outside of their comfort zone, the true test begins. This is a stage of acclimatizing to unknown lands. Unknown forces work against them, as they form bonds with allies who join them along the way, or face formidable enemies or encounters that have to be conquered. Throughout this testing time, the hero will be shaped and molded through adversity, finding deeper meaning in their life and mission.
Once the journey of self-discovery is underway, the initial burst of inspiration might be tested by the difficulty of the task. You might meet people who are able to offer advice or guide you, or those who reflect areas of yourself you have to work on.
Often, these are inner experiences, in the forms of memories, emotions, or outward tests, such as difficult circumstances that challenge your resolve and commitment to your new life direction.
7. Approach to the inmost cave
Having already crossed the threshold into the unknown and the uncertain, having faced obstacles and enemies, and having begun to utilize their qualities along the way, the next stage is another threshold.
This is the beating heart of the hero’s challenge, where again self-doubt and fear can arise, as another threshold has to be crossed. This is often a period of respite, giving the hero time to pause and reflect. Will the hero make the leap?
The hero’s journey has ups and downs. There may be quick wins in the beginning — your new life direction may go well, or inner-work may lead you to a new place of calm or confidence. But then, out of nowhere, comes an even bigger challenge, surfacing as a question mark to the person you’ve become. Life often has a way of presenting the right challenges at the right time…
This is the life-or-death moment. This can be a meeting with an ultimate enemy or facing the hero’s deepest fear. There is an awareness that if the hero fails, their new world, or their life, could be destroyed.
Everything the hero has fought for up to this point, all the lessons learned along the journey, all the hidden potentials actualized, will have to be utilized to survive this supreme ordeal, for the hero to be victorious. Either way, the hero will undergo a form of death, and leave the ordeal forever changed.
There are inner challenges that have to be confronted on the journey of self-discovery. This might be in the form of trauma that has to be confronted and healed, people with whom you have to have difficult conversations, or fears you have to face, actions that in the past you never thought you’d be capable of. But, with the skills you’ve learned along the way, this time you’ll be ready. But it won’t be easy.
9. Reward (seizing the sword)
Through great adversity comes triumph. Having confronted their greatest fear, and survived annihilation, the hero learns a valuable lesson, and is now fully transformed and reborn — with a prize as a reward.

This object is often symbolized as a treasure, a token, secret knowledge, or reconciliation, such as the return of an old friend or lover. This prize can assist in the return to the ordinary world — but there are still a few steps to come.
When confronting deep inner fears or challenges, you are rewarded with deep insights or breakthroughs. That might be in the form of achieving a significant goal or inwardly having a sense of peace or reconciliation with your past, or moments that have previously felt unresolved. As a spiritual process, this may also be the realization that behind suffering and pain lies freedom or inner peace.
10. The road back
Having traveled into distant, foreign lands and slain the dragon, now it’s time for the hero to make their return journey. This stage mirrors the original call to adventure and represents another threshold.
The hero may be understanding their new responsibility and the consequences of their actions, and require a catalyst to make the journey back to the ordinary world with their prize.
The hard work has been done, the ultimate fear confronted, new knowledge found. Now, what’s the next step? For many, the initial stages of growth come with a period of renunciation or are symbolized by an outward journey away from home, or away from familiarity.
Then comes the stage of returning to familiarity, or the things left behind — be it family, friends, locations, or even behaviors that were once loved and sacrificed during the journey.
11. Resurrection
When it appears the hero is out of the woods, there comes a final confrontation — an encounter with death itself. Transformed inwardly and with a personal victory complete, the hero faces a battle that transcends their individual quest, with its consequences far-reaching, for entire communities or even humanity itself.
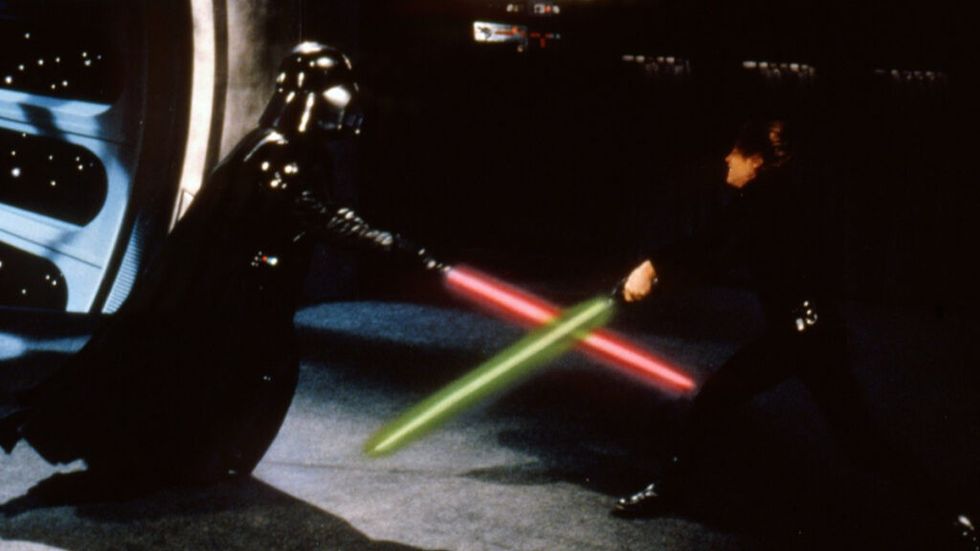

This purification solidifies the hero’s rebirth, as their new identity fully emerges just in time to return to the ordinary world.
In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, self-actualization is secondary to self-transcendence. In other words, once inner battles have been faced, and the alchemy of psychological transformation is underway, the next stage is to apply the newfound insights and knowledge to a bigger cause — supporting others, or standing up a mission that will benefit the wider world.
12. Return with the elixir
Following the final battle, the hero finally returns home. By now, personal transformation is complete, they’re returning home a different person. Having faced indescribable hardship, the hero returns with added wisdom and maturity. The elixir is the treasure they’ve returned with, ready to share with the ordinary world. This could be a sense of hope , freedom, or even a new perspective to assist those originally left behind.
The hero has a new level of self-awareness, seeing the ordinary world through fresh eyes. They’ve left internal conflict behind. There’s an understanding that things will never be the same, but that the hero’s journey was part of their destiny.
Then comes the ultimate prize: a final reconciliation, acceptance from the community, celebration, redemption. Whatever the prize, there are three elements: change , success , and proof of the journey .
Following a transformative psychic process, there’s an understanding of what is within your control. The “ordinary world” may have many elements that remain the same, but this is accompanied by a realization that when you change, so does your reality. Previously modes of thinking may be replaced, as bridges are built with your past, giving opportunity for a renewed approach to life.
What can we learn from the hero’s journey?
At the time of writing this article, I’m in the UK visiting my family for the first time in 18 months. As I walked down paths I’d walked throughout my childhood, I was struck by how much I’ve changed over the years. A passage from T.S Eliot’s poem Little Gidding came to mind:
“We shall not cease from exploration. And the end of all our exploring. Will be to arrive where we started. And know the place for the first time.”
I reflected on the notion of coming full circle — to begin a journey, outwardly or inwardly, before finding yourself back at the beginning, transformed. In spiritual traditions, the circle is a powerful symbol of timelessness, death and rebirth, totality, and wholeness. Aptly, the 12 steps of the hero’s journey are depicted as a circle. It’s not a coincidence.
What can we learn from the hero’s journey? In a way, it is similar to the writer’s journey. Above all else, it’s a reminder that we each within us have a purpose, a quest and a mission in this life that can and will invoke our truest potential. The path isn’t easy — there are many, many challenges along the way. But at the right time, people and situations will come to our aid.
If you’re able to confront the mission head-on and take bold steps along the way — just like all the heroes of fiction before you, from Shakespeare’s characters to Luke Skywalker and Rey from the universe brought to us by George Lucas — then you will be transformed, and then you can return to where you started, reborn, ready to share your gifts and your lessons with the world.
- hero's journey
- storytelling
Author exploring the soul of self-development, the mystery of existence, and the heartful path to maximising the human potential. Get your free copy of my book, Mindsets for Mindfulness , for practical guidance to overcome the ego on the journey of growth. More at MindThatEgo .com and on YouTube .

They’ve Been Divorced for 27 Years, but When His Ex-wife Got Sick, He Was the First to Step Up
Woman Stops Visiting Her Baby Daughter in the Hospital – So the Married Nurses Taking Care of Her Take Her In

Woman Wakes Up to Husband’s Dirty Dishes in the Sink – Instead of Cleaning Up, He Left Her a Note With 3 Words
- Script Studio
- Movie Outline 3
- Movie Outline Ebook
- Hollywood Script Express
- Movie Reference Plugins
- Online Store
- Competitive Upgrade
- Version Upgrade
- Educational Solutions
- Volume & Site Licenses
- Screenwriting Contest
- Screenwriting Articles
- Screenplay Format
- Step Outlining
- Script Writing Glossary
- Screenwriting Books
- Entertainment Law
- Screenwriting Tips
- ScriptTips Blog
- MFA in Screenwriting Degrees
- Knowledge Base
- Product Video Tour
- Download Free Trial
- Download Updates
- Register Software
- Press Releases
- Endorsements & Testimonials
- Reseller Application

The Hero's Journey - Mythic Structure of Joseph Campbell's Monomyth
By dan bronzite, to structure or not to structure that is the question....
Every story has a beginning, a middle and an end. In the beginning you setup your hero (or heroine) and his story, then you throw something at him that is a great source of conflict and takes him into a whole heap of trouble. After facing many foes and overcoming various obstacles the hero saves the day and wins the girl. If only writing a movie was that easy... The thing is, there are many forms of structure and some writers subscribe to one formula, while others subscribe to another. Some try not to subscribe to any and see the whole idea of structure as "evil", feeling that a story should evolve organically without rules confining ideas or obstructing the creative flow.

In the end, a story should dictate the kind of structure it follows or whether it shouldn't follow a structure at all. There's no point trying to write a comedy and forcing the structure of a thriller upon it - it won't work. Well, theoretically it won't but I'm sure someone will find a way! Let your characters define the story and your story define your structure and then use a formula if necessary to tighten your script. The trick is to initially let the ideas flow without paying too much attention to structure and then in your second pass begin to focus your story and separate the wheat from the chaff.
The 12 Stages of The Hero's Journey
A popular form of structure derived from Joseph Campbell's Monomyth from his book The Hero With A Thousand Faces and adapted by Christopher Vogler is the Twelve Stage Hero's Journey . This is essentially a more detailed Character Arc for your story's hero which is overlayed onto the more traditional three-act structure that many successful Hollywood movies such as Star Wars and The Wizard of Oz when analyzed appear to follow.
1. Ordinary World
This is where the Hero's exists before his present story begins, oblivious of the adventures to come. It's his safe place. His everyday life where we learn crucial details about our Hero, his true nature, capabilities and outlook on life. This anchors the Hero as a human, just like you and me, and makes it easier for us to identify with him and hence later, empathize with his plight.
2. Call To Adventure
The Hero's adventure begins when he receives a call to action, such as a direct threat to his safety, his family, his way of life or to the peace of the community in which he lives. It may not be as dramatic as a gunshot, but simply a phone call or conversation but whatever the call is, and however it manifests itself, it ultimately disrupts the comfort of the Hero's Ordinary World and presents a challenge or quest that must be undertaken.
3. Refusal Of The Call
Although the Hero may be eager to accept the quest, at this stage he will have fears that need overcoming. Second thoughts or even deep personal doubts as to whether or not he is up to the challenge. When this happens, the Hero will refuse the call and as a result may suffer somehow. The problem he faces may seem to much to handle and the comfort of home far more attractive than the perilous road ahead. This would also be our own response and once again helps us bond further with the reluctant Hero.
4. Meeting The Mentor
At this crucial turning point where the Hero desperately needs guidance he meets a mentor figure who gives him something he needs. He could be given an object of great importance, insight into the dilemma he faces, wise advice, practical training or even self-confidence. Whatever the mentor provides the Hero with it serves to dispel his doubts and fears and give him the strength and courage to begin his quest.
5. Crossing The Threshold
The Hero is now ready to act upon his call to adventure and truly begin his quest, whether it be physical, spiritual or emotional. He may go willingly or he may be pushed, but either way he finally crosses the threshold between the world he is familiar with and that which he is not. It may be leaving home for the first time in his life or just doing something he has always been scared to do. However the threshold presents itself, this action signifies the Hero's commitment to his journey an whatever it may have in store for him.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
Now finally out of his comfort zone the Hero is confronted with an ever more difficult series of challenges that test him in a variety of ways. Obstacles are thrown across his path; whether they be physical hurdles or people bent on thwarting his progress, the Hero must overcome each challenge he is presented with on the journey towards his ultimate goal. The Hero needs to find out who can be trusted and who can't. He may earn allies and meet enemies who will, each in their own way, help prepare him for the greater ordeals yet to come. This is the stage where his skills and/or powers are tested and every obstacle that he faces helps us gain a deeper insight into his character and ultimately identify with him even more.
7. Approach To The Inmost Cave
The inmost cave may represent many things in the Hero's story such as an actual location in which lies a terrible danger or an inner conflict which up until now the Hero has not had to face. As the Hero approaches the cave he must make final preparations before taking that final leap into the great unknown. At the threshold to the inmost cave the Hero may once again face some of the doubts and fears that first surfaced upon his call to adventure. He may need some time to reflect upon his journey and the treacherous road ahead in order to find the courage to continue. This brief respite helps the audience understand the magnitude of the ordeal that awaits the Hero and escalates the tension in anticipation of his ultimate test.
The Supreme Ordeal may be a dangerous physical test or a deep inner crisis that the Hero must face in order to survive or for the world in which the Hero lives to continue to exist. Whether it be facing his greatest fear or most deadly foe, the Hero must draw upon all of his skills and his experiences gathered upon the path to the inmost cave in order to overcome his most difficulty challenge. Only through some form of "death" can the Hero be reborn, experiencing a metaphorical resurrection that somehow grants him greater power or insight necessary in order to fulfill his destiny or reach his journey's end. This is the high-point of the Hero's story and where everything he holds dear is put on the line. If he fails, he will either die or life as he knows it will never be the same again.
9. Reward (Seizing The Sword)
After defeating the enemy, surviving death and finally overcoming his greatest personal challenge, the Hero is ultimately transformed into a new state, emerging from battle as a stronger person and often with a prize. The Reward may come in many forms: an object of great importance or power, a secret, greater knowledge or insight, or even reconciliation with a loved one or ally. Whatever the treasure, which may well facilitate his return to the Ordinary World, the Hero must quickly put celebrations aside and prepare for the last leg of his journey.
10. The Road Back
This stage in the Hero's journey represents a reverse echo of the Call to Adventure in which the Hero had to cross the first threshold. Now he must return home with his reward but this time the anticipation of danger is replaced with that of acclaim and perhaps vindication, absolution or even exoneration. But the Hero's journey is not yet over and he may still need one last push back into the Ordinary World. The moment before the Hero finally commits to the last stage of his journey may be a moment in which he must choose between his own personal objective and that of a Higher Cause.
11. Resurrection
This is the climax in which the Hero must have his final and most dangerous encounter with death. The final battle also represents something far greater than the Hero's own existence with its outcome having far-reaching consequences to his Ordinary World and the lives of those he left behind. If he fails, others will suffer and this not only places more weight upon his shoulders but in a movie, grips the audience so that they too feel part of the conflict and share the Hero's hopes, fears and trepidation. Ultimately the Hero will succeed, destroy his enemy and emerge from battle cleansed and reborn.
12. Return With The Elixir
This is the final stage of the Hero's journey in which he returns home to his Ordinary World a changed man. He will have grown as a person, learned many things, faced many terrible dangers and even death but now looks forward to the start of a new life. His return may bring fresh hope to those he left behind, a direct solution to their problems or perhaps a new perspective for everyone to consider. The final reward that he obtains may be literal or metaphoric. It could be a cause for celebration, self-realization or an end to strife, but whatever it is it represents three things: change, success and proof of his journey. The return home also signals the need for resolution for the story's other key players. The Hero's doubters will be ostracized, his enemies punished and his allies rewarded. Ultimately the Hero will return to where he started but things will clearly never be the same again.
Structuring With Color Using Script Studio's PowerView
Script Studio includes five default customizable templates:
- Hero's Journey
- 3 Act Screenplay
- 5 Act Stage Play
- One Hour TV Drama
- Half-Hour TV Sitcom
Each sample template is designed to help you structure your story and they include comprehensive information about each section, helping you understand how a particular type of story narrative works. They are, however, merely a guide and should not be rigidly adhered to. Creativity is far more important than sticking to a "formula" but they can help you pace your story and troubleshoot rewrites.
The default templates can be modified to suit your project's needs and you can even create your own templates from scratch or save templates from one project for use in another. Download a FREE Demo of Script Studio to see how its powerful screenplay formatting, character development and story structuring tools can help you make a better script!
About Dan Bronzite
Dan is a produced screenwriter and award-winning filmmaker , CEO of Buckle Up Entertainment , Nuvotech and creator of Script Studio screenwriting software . His writingcredits and written numerous specs and commissioned feature scripts including screenplay adaptations of Andrea Badenoch's Driven and Irvine Welsh's gritty and darkly comic novel Filth . Dan is a contributor to Script Magazine and has also directed three award-winning short films including his most recent All That Glitters which garnered over 50 international film festival selections and 32 awards. His supernatural horror feature Long Time Dead for Working Title Films was released internationally through Universal and his spec horror Do or Die sold to Qwerty Films. He is currently setting up his directorial feature debut and various US and UK feature and series projects.

New Release: Script Studio

Buy Script Studio Online

What the Pros Say...
I have tried every software application imaginable in quest of the perfect way to write a movie and when I put Movie Outline on my Mac I came to the end of the rainbow. Kieth Merrill Academy Award® Winner
I use Movie Outline all the time. It has many powerful features, is easy to use and makes writing and formatting a screenplay a breeze. No script writer should be without it. Kevin Williamson Screenwriter – Scream
If you're looking for a tool to help you nurture your idea for a movie into an actual shooting script I recommend this program without hesitation. Professor Richard Walter Chairman of the UCLA Graduate Screenwriting Program
This is the most complete package I've seen for the screenwriter in one application from outline to final draft. I recommend this program to all scribes – from novice to pro. Karl Iglesias UCLA Instructor & Author
I thoroughly enjoy working with Movie Outline and find it easy to use, well designed, helpful and entertaining. If you're a novice or a seasoned pro, this program can aid greatly in your creative process. Marc Scott Zicree Writer – The Next Generation
Movie Outline does a terrific job of helping writers organize their development process from beginning to end and has effectively raised the bar in the screenwriting software arena. Sean Kennelly Creative Screenwriting
Upgrade From Movie Outline

30 Day Money Back Guarantee

- wizard of oz
- character arc
- hero's journey
- ordinary world
Products & Services
- Hollywood Deconstructed Ebook
- Copyright Registration
- Script Copying & Shipping
Downloads & Demos
- Movie Outline Video Tour
- Compare Screenwriting Software
- Press Kit & Graphics
- Software Updates
- Upgrade Software
- Software Requirements
Screenwriting Resources
- Screenwriting Competition
- Screenplay Software
Company & Support
- Press & News
- Product Reviews
- Authorized Resellers
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
- Editing Services
- Academic Editing Services
- Admissions Editing Services
- Admissions Essay Editing Services
- AI Content Editing Services
- APA Style Editing Services
- Application Essay Editing Services
- Book Editing Services
- Business Editing Services
- Capstone Paper Editing Services
- Children's Book Editing Services
- College Application Editing Services
- College Essay Editing Services
- Copy Editing Services
- Developmental Editing Services
- Dissertation Editing Services
- eBook Editing Services
- English Editing Services
- Horror Story Editing Services
- Legal Editing Services
- Line Editing Services
- Manuscript Editing Services
- MLA Style Editing Services
- Novel Editing Services
- Paper Editing Services
- Personal Statement Editing Services
- Research Paper Editing Services
- Résumé Editing Services
- Scientific Editing Services
- Short Story Editing Services
- Statement of Purpose Editing Services
- Substantive Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Services
Proofreading
- Proofreading Services
- Admissions Essay Proofreading Services
- Children's Book Proofreading Services
- Legal Proofreading Services
- Novel Proofreading Services
- Personal Statement Proofreading Services
- Research Proposal Proofreading Services
- Statement of Purpose Proofreading Services
Translation
- Translation Services
Graphic Design
- Graphic Design Services
- Dungeons & Dragons Design Services
- Sticker Design Services
- Writing Services
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
The Hero's Journey: Stages, Steps, and Examples

Remember when you were younger, probably around middle school age, and your teacher introduced the Greek mythology lesson? It was such an exciting time of reading books like Rick Riordan's Percy Jackson & The Olympians: The Lightning Thief . Maybe you fell in love with Percy, a lovable and relatable young boy struggling with his identity. Or maybe you were a part of the dystopian crave and fell in love with Katniss Everdeen from Suzanne Collins' The Hunger Games . Either way, this may have been your first introduction to the hero's journey (we're sure you've seen the templates). After all, the hero's journey is all around us!
If you fell in love with reading a hero's journey archetype and want to try to create your own modern hero, then you've come to the perfect place. We're going to explore the crucial steps of a hero's journey and what they entail, so you can have a template through which to write your own story. Your questions act as our call to action (you'll understand what we mean by that shortly). But first, let's define a hero's journey. After all, how can we possibly evaluate the steps of a hero's journey if we don't even have a solid definition?
The hero's journey
A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: The hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man. The Hero With a Thousand Faces by Joseph Campbell
The hero's journey is the story of a hero who leaves the ordinary world to go on an adventure full of peril. On it, the hero will gain both adversaries and allies, and will face a great evil. The hero will also face his shadow self, which is perhaps the most frightening antagonist of all.
Campbell references 17 total steps in the hero's journey. Wait a minute, 17 steps? That seems like a lot. Don't worry! Depending on who you ask, the number of steps and what those steps look like will differ, though they all follow a similar template. The hero's journey is commonly accepted to have 12 main steps. To make it even simpler on you, these steps can actually be broken down into three stages: the departure, the initiation, and the return.
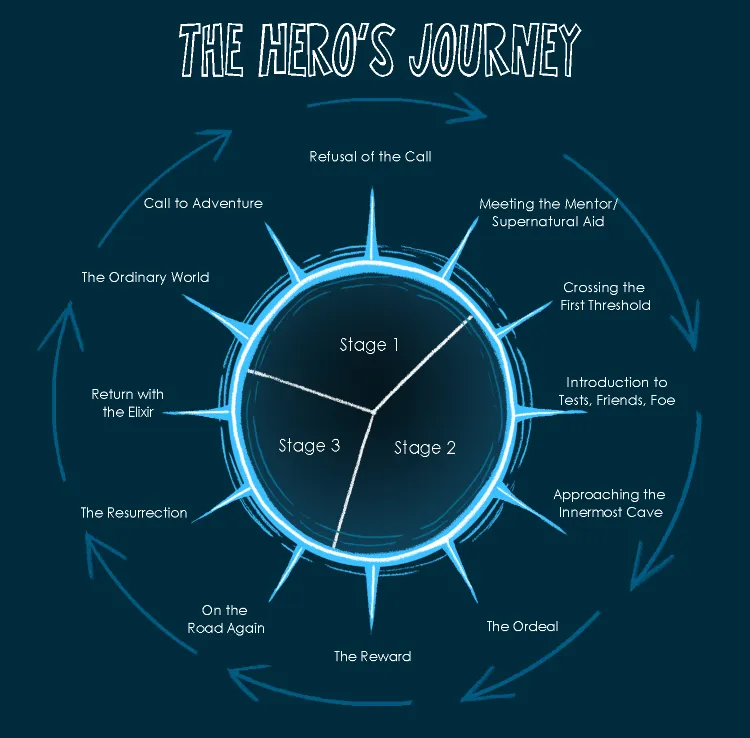
Stage 1: the departure

The departure is just as you might expect. This is the stage where the protagonist is introduced, typically in a modern, realistic setting, and we are introduced to some struggles the protagonist may be experiencing or questions they may have about their own identity. This stage can be broken into our first four steps.
- The ordinary world : As we said, we are first introduced to our protagonist and soon-to-be hero in the reality we know. It is just as the first step is listed: the ordinary world. There is no magic, mayhem, or supernatural creatures evident in this ordinary world. It is the world the protagonist has known all their life.
- Call to adventure : This is one of the steps you may be most familiar with, as it's one of the most commonly known phrases in literature. Regardless of what genre you are writing, your hero has a call to action. After all, there must be a reason why the protagonist leaves the mundane, comfortable lifestyle they've lived up until now. This is the moment where the journey or quest is initiated: a problem, challenge, or quest is presented to the protagonist, and they must decide to leave behind their ordinary lives to face new challenges. Whether the protagonist is immediately threatened, a family member is threatened, or they see something they shouldn't have, it is up to the protagonist to respond to the call.
- Refusal of the call : Wow, isn't it so cool that the hero was discovered by some other world (or they discovered it!) and now they get to embark on this awesome journey? Yes, well, sometimes. Despite how amazing it may seem to be called to accept a quest (hence the reason why this archetype is so popular in literature), the protagonist may not be feeling that excitement. In fact, it's likely that the protagonist is feeling nervous, anxious, scared, hesitant, and thus, resistant to the call at first (don't worry, they'll give in eventually).
- Meeting the mentor/supernatural aid : Okay, so the protagonist is done refusing the call. Maybe they've gotten over their fears, or maybe something happened that makes it impossible for them to continue to deny their inevitable quest. Yay! Now it's time for our protagonist to meet their mentor. The mentor can be supernatural or not, but they act as a teacher, trainer, and instructor for the protagonist. After all, the protagonist is going to need some serious guidance once they've been booted out of their ordinary world. This step involves a lot of trust, though, as the protagonist may barely know their mentor. This step also involves the passing on of certain tools and equipment the protagonist may need to succeed on their journey. These can be special powers or physical instruments.
Stage 2: the initiation

Now that you've spent a decent chunk of time introducing your protagonist (and hero!) and their conflict, it's time to head into the second stage of the hero's journey: the initiation. Before you do this, though, ensure you've checked off the first four items on the previous list. It is crucial that you meet these criteria for a successful hero's journey. After all, the hero can't be truly initiated into their new world if you have not established their old world, their main conflict, and the introduction of their next steps.
This next stage will take up the largest portion of your story. You should fill it with lots of new characters, settings, and trials and tests for your protagonist to endure. This is also a stage where you should focus a lot on character development for your protagonist. No person is going to go through a massive journey and end up the same person they once were when everything is said and done. Take this time to think about how you want your protagonist to change and what it's going to take to accomplish that change.
- Crossing the first threshold : This is the point at which the hero decides to embark on the adventure and cross over into the unknown, leaving his or her ordinary world behind. This is called the threshold because there is something or someone acting as a literal barrier between the protagonist's ordinary world and their new world. Beyond the threshold lies trials and tribulations and potential risks and dangers. Once the protagonist takes that first step beyond this threshold, there is no returning to the life they once knew. This is where the hero's actual journey truly begins.
- Introduction to tests, friends, and foe : This is the step of the story where the cast of characters expands and a new setting, the new world, is introduced. The protagonist may be lost in their new world, so they must evaluate the new people around them to identify potential allies, enemies, or morally ambiguous characters. Trust is established or denied. Just like anyone would struggle with encountering anew environment, the protagonist will endure some struggles of their own, but this is how they'll determine who is friend and who is foe, establishing other character roles in the process. The rules of the ordinary world do not apply to this new world, so hopefully the protagonist meets some good people who will teach him the new ways of life.
- Approaching the innermost cave : At this point on the hero's journey, they have left all semblance of the ordinary world behind. This step marks the preparation for the main event of the journey. The protagonist may gather materials and even other characters, if they're trustworthy enough, to take on the rest of the steps of the quest with them. The cave acts as a metaphor for what the protagonist is about to endure: risk, danger, darkness, and even potential loss. This step also includes some of the tests leading up to the large test yet, which happens to be the next step in the hero's journey.
- The ordeal : Buckle up, this is about to be a wild ride! That's right, your hero has finally made it to one of the biggest challenges of all. The protagonist is no longer approaching the innermost cave. Rather, the protagonist is now fully in the belly of the beast, and what a beast it is! The ordeal is usually not the climax of the story, but this is the moment where the protagonist truly transforms from an ordinary character into a true hero. It may involve their greatest fear or a physically or mentally demanding task.
- The reward : If your protagonist, now hero, succeeds in their greatest challenge, then they will be given a reward that makes the journey worth so much time, effort, and challenge. If they can succeed, then there is hope for them, that bright light that shines through the top of a dark cave and promises fulfillment and a future. This is what the hero has been fighting for this whole time. As for the reward itself, you should make sure it makes sense in the context of your story. It can be an object, a piece of knowledge, or even something entirely different, so long as its value matches the degree of the journey.
Stage 3: the return

Wahoo, your hero has endured so much and has finally gotten their reward! It's over, right? They can return to their ordinary life and reap the benefits of all their hard work? Wrong! Things are never as easy as they seem, especially in a hero's journey, so why would the road back to the ordinary world be any different for your hero?
- On the road again : This is the turning point, literally. The hero turns back around, hoping to return to their normal life after receiving their reward. But thing's are never that simple, so be sure to make sure that road is blocked. Traffic cones, stoplights, maybe a supernatural villain or catastrophic natural disaster! That should do the trick. If the road back home was easy, we'd be bored, so maintain the stakes with challenges for the hero to face as they make their way back home.
- The resurrection : Congratulations, you've finally reached the climax of your story. Remember how we said the ordeal was the moment where your protagonist transformed from an ordinary character into an actual hero, this is the moment where they can prove to us that they deserve the hero title, after all. The stakes become extremely high, as the hero does not want to fail after having endured so much already. This is the final test for the hero and the final opportunity for the villain or opposing forces to defeat the hero. If the hero comes out on top, then they will finally be able to reach that light at the end of the tunnel.
- Return with the elixir : The hero has finally completed all their challenges and is able to return home with their reward. Their transformation is complete, and they've most likely become a better person because of the journey. Or, if you want to add a twist to this step, you can always have the hero fail to return without they set out to receive, but you better be prepared to write a sequel and a whole other journey!
Following the template

Since we mentioned The Hunger Games at the very beginning, let's use Katniss Everdeen and her hero's journey as a model for this template.
- The ordinary world : Katniss Everdeen is introduced as a citizen on District 12, a poor mining district. She spends her days hunting in the woods to provide food for her family.
- The call to action : Every year, a reaping takes place where a male and female tribute from each district is randomly chosen to take place in the Hunger Games, a fight to the death. During the reaping, Katniss' sister Primrose is selected, so Katniss volunteers to take her place as the female tribute from District 12.
- Refusal of the call : As we mentioned, you may not include all 12 steps of the hero's journey in your own story. Katniss does not actually refuse the call, as she volunteered herself to save her sister. A refusal of the call is slightly seen in Peeta, Katniss' fellow tribute, as he is visibly nervous and shaken up. The nature of this story makes it so that a refusal is impossible.
- Meeting the mentor : Katniss meets Haymitch Abernathy, a previous Hunger Games victor from her District. He is her literal mentor and is meant to teach her how to make allies, get sponsors, and survive in the arena. She also finds a mentor in Cinna, the person in charge of her appearance for promotions.
- Crossing the threshold : Katniss is whisked out of District 12 and on the train to the gaudy, wealthy Capitol.
- Introduction to tests, friends, and foe : Katniss must attempt to learn who to trust while also earning sponsors and impressing the Game Makers. Katniss makes a reluctant alliance with Peeta and admires Rue from District 11. During training, it is evident that the Careers (tributes from the wealthier districts) are enemies.
- Approaching the innermost cave : Katniss enters the physical arena.
- The ordeal : The arena is full of challenges: tracker jackers, mutant wolves, poisonous berries, and other tributes trying to survive. The games themselves are the whole ordeal.
- The reward : Katniss and Peeta are the last tributes standing.
- On the road again : Although Katniss and Peeta have survived, there can only be one winner, and the Capitol wants to force them to select who lives and who dies.
- The resurrection : Katniss' bold attempt at a mutual suicide leads to both of them being allowed to live as victors, lest they become martyrs in front of the whole country.
- Return with the elixir : Katniss and Peeta return to District 12 as victors, allowing them to live lives of wealth and luxury. If you've read the books, you'll know this is nowhere near the end of Katniss' journey.
Reaping the rewards
If you've managed to check off all 12 steps on our hero's journey checklist, then you've got yourself an awesome hero's journey. If you're just starting out on your own journey of writing for a hero, then be sure to follow this template for maximum results. Be the hero in your own journey and remember to never give up as you face those roadblocks and challenges while buckling down and writing a story of your own!
Header photo by Zoltan Tasi .
Related Posts

How To Fix a Flat Character

Seven Indispensable Tricks for Writing Comic Books
- Book Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Academic Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Professional book editing services you can trust
- Story Writing Guides
12 Hero’s Journey Stages Explained (+ Free Templates)
From zero to hero, the hero’s journey is a popular character development arc used in many stories. In today’s post, we will explain the 12 hero’s journey stages, along with the simple example of Cinderella.
The Hero’s Journey was originally formulated by American writer Joseph Campbell to describe the typical character arc of many classic stories, particularly in the context of mythology and folklore. The original hero’s journey contained 17 steps. Although the hero’s journey has been adapted since then for use in modern fiction, the concept is not limited to literature. It can be applied to any story, video game, film or even music that features an archetypal hero who undergoes a transformation. Common examples of the hero’s journey in popular works include Star Wars, Lord of the Rings, The Hunger Games and Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone.
- What is the hero's journey?
Stage 1: The Ordinary World
Stage 2: call of adventure, stage 3: refusal of the call, stage 4: meeting the mentor, stage 5: crossing the threshold, stage 6: tests, allies, enemies, stage 7: the approach, stage 8: the ordeal, stage 9: reward, stage 10: the road back, stage 11: resurrection, stage 12: return with the elixir, cinderella example, campbell’s 17-step journey, leeming’s 8-step journey, cousineau’s 8-step journey.
- Free Hero's Journey Templates
What is the hero’s journey?
The hero’s journey, also known as the monomyth, is a character arc used in many stories. The idea behind it is that heroes undergo a journey that leads them to find their true selves. This is often represented in a series of stages. There are typically 12 stages to the hero’s journey. Each stage represents a change in the hero’s mindset or attitude, which is triggered by an external or internal event. These events cause the hero to overcome a challenge, reach a threshold, and then return to a normal life.
The hero’s journey is a powerful tool for understanding your characters. It can help you decide who they are, what they want, where they came from, and how they will change over time. It can be used to
- Understand the challenges your characters will face
- Understand how your characters react to those challenges
- Help develop your characters’ traits and relationships
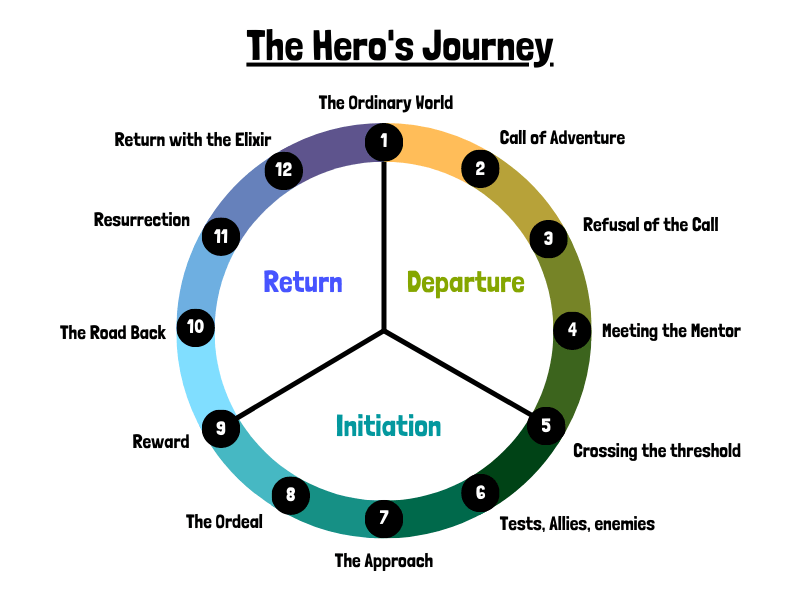
In this post, we will explain each stage of the hero’s journey, using the example of Cinderella.
You might also be interested in our post on the story mountain or this guide on how to outline a book .
12 Hero’s Journey Stages
The archetypal hero’s journey contains 12 stages and was created by Christopher Vogler. These steps take your main character through an epic struggle that leads to their ultimate triumph or demise. While these steps may seem formulaic at first glance, they actually form a very flexible structure. The hero’s journey is about transformation, not perfection.
Your hero starts out in the ordinary world. He or she is just like every other person in their environment, doing things that are normal for them and experiencing the same struggles and challenges as everyone else. In the ordinary world, the hero feels stuck and confused, so he or she goes on a quest to find a way out of this predicament.
Example: Cinderella’s father passes away and she is now stuck doing chores and taking abuse from her stepsisters and stepmother.
The hero gets his or her first taste of adventure when the call comes. This could be in the form of an encounter with a stranger or someone they know who encourages them to take a leap of faith. This encounter is typically an accident, a series of coincidences that put the hero in the right place at the right time.
Example: An invite arrives inviting the family to a royal ball where the Prince will choose a wife.
Some people will refuse to leave their safe surroundings and live by their own rules. The hero has to overcome the negative influences in order to hear the call again. They also have to deal with any personal doubts that arise from thinking too much about the potential dangers involved in the quest. It is common for the hero to deny their own abilities in this stage and to lack confidence in themselves.
Example: Cinderella accepts the call by making her own dress for the ball. However, her stepmother refuses the call for her by not letting her go to the ball. And her step-sisters ruin her dress, so she can not go.
After hearing the call, the hero begins a relationship with a mentor who helps them learn about themselves and the world. In some cases, the mentor may be someone the hero already knows. The mentor is usually someone who is well-versed in the knowledge that the hero needs to acquire, but who does not judge the hero for their lack of experience.
Example: Cinderella meets her fairy godmother who equips her with everything she needs for the ball, including a dress and a carriage.
The hero leaves their old life behind and enters the unfamiliar new world. The crossing of the threshold symbolises leaving their old self behind and becoming a new person. Sometimes this can include learning a new skill or changing their physical appearance. It can also include a time of wandering, which is an essential part of the hero’s journey.
Example: Cinderella hops into the carriage and heads off to the ball. She has transformed from a servant into an elegant young lady.
As the hero goes on this journey, they will meet both allies (people who help the hero) and enemies (people who try to stop the hero). There will also be tests, where the hero is tempted to quit, turn back, or become discouraged. The hero must be persistent and resilient to overcome challenges.
Example: At the ball, Cinderella meets the prince, and even see’s her stepmother and stepsister. She dances with Prince all night long making her step-sisters extremely jealous.
The hero now reaches the destination of their journey, in some cases, this is a literal location, such as a cave or castle. It could also be metaphorical, such as the hero having an internal conflict or having to make a difficult decision. In either case, the hero has to confront their deepest fears in this stage with bravery. In some ways, this stage can mark the end of the hero’s journey because the hero must now face their darkest fears and bring them under control. If they do not do this, the hero could be defeated in the final battle and will fail the story.
Example: Cinderella is having a great time at the ball and nearly forgets about the midnight rule. As she runs away in a hurry, her glass slipper falls off outside the palace.
The hero has made it to the final challenge of their journey and now must face all odds and defeat their greatest adversary. Consider this the climax of the story. This could be in the form of a physical battle, a moral dilemma or even an emotional challenge. The hero will look to their allies or mentor for further support and guidance in this ordeal. Whatever happens in this stage could change the rest of the story, either for good or bad.
Example: Prince Charming looks all over the kingdom for the mysterious girl he met at the ball. He finally visits Cinderella’s house and tries the slippers on the step-sisters. The prince is about to leave and then he sees Cinderella in the corner cleaning.
When the hero has defeated the most powerful and dangerous of adversaries, they will receive their reward. This reward could be an object, a new relationship or even a new piece of knowledge. The reward, which typically comes as a result of the hero’s perseverance and hard work, signifies the end of their journey. Given that the hero has accomplished their goal and served their purpose, it is a time of great success and accomplishment.
Example: The prince tries the glass slipper on Cinderella. The glass slipper fits Cinderella perfectly, and they fall in love.
The journey is now complete, and the hero is now heading back home. As the hero considers their journey and reflects on the lessons they learned along the way, the road back is sometimes marked by a sense of nostalgia or even regret. As they must find their way back to the normal world and reintegrate into their former life, the hero may encounter additional difficulties or tests along the way. It is common for the hero to run into previous adversaries or challenges they believed they had overcome.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming head back to the Prince’s castle to get married.
The hero has one final battle to face. At this stage, the hero might have to fight to the death against a much more powerful foe. The hero might even be confronted with their own mortality or their greatest fear. This is usually when the hero’s true personality emerges. This stage is normally symbolised by the hero rising from the dark place and fighting back. This dark place could again be a physical location, such as the underground or a dark cave. It might even be a dark, mental state, such as depression. As the hero rises again, they might change physically or even experience an emotional transformation.
Example: Cinderella is reborn as a princess. She once again feels the love and happiness that she felt when she was a little girl living with her father.
At the end of the story, the hero returns to the ordinary world and shares the knowledge gained in their journey with their fellow man. This can be done by imparting some form of wisdom, an object of great value or by bringing about a social revolution. In all cases, the hero returns changed and often wiser.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming live happily ever after. She uses her new role to punish her stepmother and stepsisters and to revitalise the kingdom.
We have used the example of Cinderella in Vogler’s hero’s journey model below:

Below we have briefly explained the other variations of the hero’s journey arc.
The very first hero’s journey arc was created by Joseph Campbell in 1949. It contained the following 17 steps:
- The Call to Adventure: The hero receives a call or a reason to go on a journey.
- Refusal of the Call: The hero does not accept the quest. They worry about their own abilities or fear the journey itself.
- Supernatural Aid: Someone (the mentor) comes to help the hero and they have supernatural powers, which are usually magical.
- The Crossing of the First Threshold: A symbolic boundary is crossed by the hero, often after a test.
- Belly of the Whale: The point where the hero has the most difficulty making it through.
- The Road of Trials: In this step, the hero will be tempted and tested by the outside world, with a number of negative experiences.
- The Meeting with the Goddess: The hero meets someone who can give them the knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- Woman as the Temptress: The hero is tempted to go back home or return to their old ways.
- Atonement with the Father: The hero has to make amends for any wrongdoings they may have done in the past. They need to confront whatever holds them back.
- Apotheosis: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level.
- The Ultimate Boon: The ultimate boon is the reward for completing all the trials of the quest. The hero achieves their ultimate goal and feels powerful.
- Refusal of the Return: After collecting their reward, the hero refuses to return to normal life. They want to continue living like gods.
- The Magic Flight: The hero escapes with the reward in hand.
- Rescue from Without: The hero has been hurt and needs help from their allies or guides.
- The Crossing of the Return Threshold: The hero must come back and learn to integrate with the ordinary world once again.
- Master of the Two Worlds: The hero shares their wisdom or gifts with the ordinary world. Learning to live in both worlds.
- Freedom to Live: The hero accepts the new version of themselves and lives happily without fear.
David Adams Leeming later adapted the hero’s journey based on his research of legendary heroes found in mythology. He noted the following steps as a pattern that all heroes in stories follow:
- Miraculous conception and birth: This is the first trauma that the hero has to deal with. The Hero is often an orphan or abandoned child and therefore faces many hardships early on in life.
- Initiation of the hero-child: The child faces their first major challenge. At this point, the challenge is normally won with assistance from someone else.
- Withdrawal from family or community: The hero runs away and is tempted by negative forces.
- Trial and quest: A quest finds the hero giving them an opportunity to prove themselves.
- Death: The hero fails and is left near death or actually does die.
- Descent into the underworld: The hero rises again from death or their near-death experience.
- Resurrection and rebirth: The hero learns from the errors of their way and is reborn into a better, wiser being.
- Ascension, apotheosis, and atonement: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level (sometimes a god-like level).
In 1990, Phil Cousineau further adapted the hero’s journey by simplifying the steps from Campbell’s model and rearranging them slightly to suit his own findings of heroes in literature. Again Cousineau’s hero’s journey included 8 steps:
- The call to adventure: The hero must have a reason to go on an adventure.
- The road of trials: The hero undergoes a number of tests that help them to transform.
- The vision quest: Through the quest, the hero learns the errors of their ways and has a realisation of something.
- The meeting with the goddess: To help the hero someone helps them by giving them some knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- The boon: This is the reward for completing the journey.
- The magic flight: The hero must escape, as the reward is attached to something terrible.
- The return threshold: The hero must learn to live back in the ordinary world.
- The master of two worlds: The hero shares their knowledge with the ordinary world and learns to live in both worlds.
As you can see, every version of the hero’s journey is about the main character showing great levels of transformation. Their journey may start and end at the same location, but they have personally evolved as a character in your story. Once a weakling, they now possess the knowledge and skill set to protect their world if needed.
Free Hero’s Journey Templates
Use the free Hero’s journey templates below to practice the skills you learned in this guide! You can either draw or write notes in each of the scene boxes. Once the template is complete, you will have a better idea of how your main character or the hero of your story develops over time:
The storyboard template below is a great way to develop your main character and organise your story:

Did you find this guide on the hero’s journey stages useful? Let us know in the comments below.

Marty the wizard is the master of Imagine Forest. When he's not reading a ton of books or writing some of his own tales, he loves to be surrounded by the magical creatures that live in Imagine Forest. While living in his tree house he has devoted his time to helping children around the world with their writing skills and creativity.
Related Posts

Comments loading...

Mastering The Hero's Journey: A Comprehensive Guide To Storytelling Success
Table of Contents
Origins of the Hero's Journey
The three-act structure, the 12 stages of the hero's journey, key archetypes in the hero's journey, the inner and outer journey, applying the hero's journey to your story, adaptations and variations of the hero's journey, case studies: the hero's journey in popular fiction, common mistakes and how to avoid them, writing tips for crafting a compelling hero's journey, frequently asked questions, further reading.
The concept of the Hero's Journey can be traced back to the work of renowned mythologist Joseph Campbell . In his seminal book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces (1949), Campbell examined myths and stories from various cultures around the world and identified a common narrative pattern that he dubbed the "monomyth."
According to Campbell, the monomyth is a universal story template that transcends time, culture, and geography. It consists of a series of stages that a hero must go through in order to fulfill their destiny or complete their quest. Campbell drew inspiration for this concept from the works of prominent scholars such as Carl Jung , whose theories on archetypes and the collective unconscious greatly influenced his thinking.
Another significant influence on Campbell's work was James Frazer , who studied comparative mythology and religion in his groundbreaking book, The Golden Bough (1890). Frazer's work helped Campbell recognize the similarities between myths from different cultures and formulate the idea of a shared, underlying narrative structure.
In The Hero with a Thousand Faces , Campbell outlined the basic structure of the monomyth, which he divided into three main stages: Departure, Initiation, and Return. These stages encompass various sub-stages that the hero encounters on their journey, creating a blueprint for the Hero's Journey that can be applied to countless stories.
While Campbell's work focused primarily on myths and legends, the Hero's Journey has been widely adopted by writers and filmmakers in crafting their narratives. Some of the most successful books and movies, such as Star Wars and The Lord of the Rings , have followed the basic structure of the monomyth, proving the enduring appeal of this timeless narrative framework.
Over the years, the Hero's Journey has been refined and expanded upon by other scholars and writers, most notably Christopher Vogler , who adapted Campbell's ideas for use in modern storytelling in his book The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers (1992). Vogler's work has made the Hero's Journey more accessible to contemporary writers, ensuring its continued relevance in the world of storytelling.
The Three-Act Structure is a widely-used storytelling model that divides a narrative into three distinct parts or "acts": Setup, Confrontation, and Resolution. This model has its roots in classical drama and has been adapted for use in modern storytelling, particularly in the realms of screenwriting and novel writing. The Three-Act Structure provides a framework for pacing and plot development, helping writers create a well-structured and engaging narrative.
Act One: Setup
The first act of a story serves to introduce the main characters, establish the setting, and provide important background information. During this act, the protagonist is typically confronted with an inciting incident that sets the story in motion and propels them into the main conflict. This act ends with a turning point or "plot point" that pushes the protagonist into the second act.
In the context of the Hero's Journey, Act One corresponds to the Departure stage, which includes elements such as the Call to Adventure, Refusal of the Call, and the Meeting with the Mentor. These events set the stage for the hero's transformation and the challenges they will face throughout their journey.
Act Two: Confrontation
The second act, often referred to as the "rising action," sees the protagonist facing a series of obstacles and challenges as they pursue their goal. This is the longest part of the story, as it delves into the hero's struggles, their growth, and their relationships with other characters. The second act also features a turning point or "midpoint" that raises the stakes and heightens the tension. This act concludes with another major plot point, often involving a crisis or setback for the protagonist, propelling them into the final act.
In the Hero's Journey, Act Two encompasses the Initiation stage, with events such as the Road of Trials, the Approach to the Inmost Cave, and the Ordeal. These challenges test the hero's mettle, forcing them to confront their fears, learn important lessons, and acquire the skills they need to succeed in their quest.
Act Three: Resolution
The third and final act of a story focuses on the resolution of the conflict and the protagonist's ultimate transformation. The climax of the story typically occurs near the beginning of this act, as the hero faces their final challenge or confrontation with the antagonist. After the climax, the story moves into the "falling action," where loose ends are tied up, and the consequences of the protagonist's actions are revealed. The story concludes with the "denouement," which provides closure and shows how the characters have been affected by the events of the story.
In the context of the Hero's Journey, Act Three corresponds to the Return stage, featuring events such as the Resurrection, the Atonement with the Father, and the Freedom to Live. These elements signify the hero's completion of their quest, their reconciliation with their past, and their newfound ability to live a more fulfilled and authentic life.
By following the Three-Act Structure, writers can effectively pace their stories and ensure that the narrative remains engaging and satisfying for their audience. When combined with the stages and elements of the Hero's Journey, this structure provides a powerful blueprint for crafting compelling and resonant tales.
While the Hero's Journey can be broken down into the Three-Act Structure, it is often further divided into 12 distinct stages that the hero must go through during their quest. These stages, as described by Joseph Campbell and adapted by Christopher Vogler, provide a more detailed roadmap for writers seeking to create a compelling Hero's Journey narrative. The 12 stages are as follows:
- The Ordinary World : This stage establishes the protagonist's normal life before their adventure begins. It provides important context and allows the audience to become familiar with the hero's circumstances, values, and motivations. ( source )
- The Call to Adventure : The hero is confronted with an event or challenge that disrupts their ordinary world and sets the stage for their adventure. This call can take many forms, such as a threat, a discovery, or a personal loss. ( source )
- Refusal of the Call : Initially, the hero may be hesitant or resistant to embark on their journey, often due to fear, doubt, or a sense of obligation to their ordinary world. This stage highlights the hero's internal conflict and the stakes involved in their decision. ( source )
- Meeting the Mentor : The hero encounters a wise figure or guide who provides advice, guidance, or magical assistance to help them on their journey. This mentor figure can take various forms, such as a teacher, a parent, or even a supernatural being. ( source )
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero makes the decision to leave their ordinary world and fully commit to their adventure. This stage signifies the hero's acceptance of the call to adventure and their willingness to face the unknown. ( source )
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : As the hero embarks on their journey, they encounter a series of obstacles, challenges, and antagonistic forces. They must also forge alliances with other characters who can help them along the way. This stage serves to develop the hero's character, test their resolve, and teach them valuable lessons. ( source )
- Approach to the Inmost Cave : The hero prepares for the central crisis or ordeal of their journey, often involving a confrontation with their greatest fear or the story's main antagonist. This stage often involves a period of introspection and reflection, as the hero gathers their strength and resources for the upcoming challenge. ( source )
- The Ordeal : The hero faces their most difficult challenge, which often involves a life-or-death situation or a confrontation with their greatest fear. This stage serves as the climax of the story and represents the hero's transformation, as they must overcome their inner and outer demons to succeed. ( source )
- Reward (Seizing the Sword) : After overcoming the ordeal, the hero receives a reward, which could be a physical object, a piece of knowledge, or personal growth. This stage signifies the hero's victory and the attainment of their goal. ( source )
- The Road Back : The hero begins their journey back to the ordinary world, often with a renewed sense of purpose and the knowledge or reward they gained during their adventure. This stage can involve additional challenges, as the hero's transformation may be met with resistance from their ordinary world. ( source )
- Resurrection : The hero faces a final test or confrontation that represents the culmination of their character growth and the ultimate resolution of the story's conflict. This stage often involves a symbolic "death" and "rebirth" for the hero, signifying their transformation and newfound wisdom. ( source )
- Return with the Elixir : The hero returns to their ordinary world, having been transformed by their experiences and armed with the knowledge or reward they gained during their journey. This stage signifies the completion of the Hero's Journey and the hero's newfound ability to make a positive impact on their world. ( source )
By incorporating these 12 stages into their narrative, writers can craft a rich and satisfying Hero's Journey that resonates with audiences and follows a time-tested pattern of storytelling.
In addition to the 12 stages, the Hero's Journey also features several key archetypes that frequently appear in these narratives. These archetypes, derived from the work of Carl Jung and popularized by Joseph Campbell, represent universal symbols and character types that resonate with audiences across cultures and time periods. By incorporating these archetypes into their story, writers can create a rich and engaging narrative that taps into the human psyche. Some of the most common archetypes in the Hero's Journey include:
- The Hero : The protagonist of the story, who embarks on a journey to achieve a goal or resolve a conflict. The hero undergoes a transformation, often involving personal growth, self-discovery, and the acquisition of new skills or knowledge. ( source )
- The Mentor : A wise and experienced figure who provides guidance, support, and knowledge to the hero. The mentor often possesses valuable information or abilities that the hero needs to complete their journey. ( source )
- The Threshold Guardian : A character or obstacle that tests the hero's resolve and commitment to their journey. Threshold guardians often appear at the beginning of the adventure, forcing the hero to prove their worth and overcome their initial fears or doubts. ( source )
- The Herald : A character or event that signals the beginning of the hero's journey and delivers the Call to Adventure. The herald may also appear later in the story to announce important events or changes. ( source )
- The Shapeshifter : A character whose allegiance, motives, or appearance are uncertain or subject to change. The shapeshifter often serves to create tension and intrigue within the story, as the hero and the audience are left unsure of their true intentions. ( source )
- The Shadow : The antagonist or opposing force in the story, often representing the hero's greatest fears, flaws, or challenges. The shadow serves as a foil to the hero, highlighting their weaknesses and forcing them to confront their inner demons. ( source )
- The Ally : A character who aids and supports the hero on their journey, often providing companionship, advice, or practical assistance. Allies can take many forms, from loyal friends to unlikely partners, and help the hero overcome the obstacles they face. ( source )
- The Trickster : A character who uses wit, cunning, or humor to challenge the status quo and disrupt the established order. The trickster often serves as comic relief, but can also play a more significant role in the hero's journey by introducing new perspectives or forcing the hero to question their assumptions. ( source )
Understanding these key archetypes can help writers create well-rounded characters and engaging narratives that resonate with their audience. By incorporating these archetypes into their Hero's Journey, writers can tap into universal themes and symbols that have captivated readers and viewers for generations.
The Hero's Journey is not just a physical quest but also a psychological one, often referred to as the Inner and Outer Journey. The Outer Journey represents the hero's external actions and experiences, while the Inner Journey delves into their emotional growth, personal development, and the transformation of their beliefs and values. Understanding these two aspects of the Hero's Journey can help writers create a more nuanced and emotionally resonant narrative. Here is an overview of the Inner and Outer Journey in relation to the Hero's Journey:
The Outer Journey
The Outer Journey focuses on the hero's physical actions, experiences, and obstacles they encounter throughout their adventure. This journey is primarily plot-driven and involves the hero's progression through the various stages of the Hero's Journey, such as the Call to Adventure, the Ordeal, and the Return with the Elixir. The Outer Journey often includes the following elements:
- Action and adventure
- Conflict and resolution
- Settings and world-building
- Interaction with other characters
Writers can use the Outer Journey to create engaging and dynamic narratives that keep the audience invested in the hero's plight and the outcome of their quest. ( source )
The Inner Journey
The Inner Journey delves into the hero's psychological and emotional transformation, which is often closely intertwined with the events of the Outer Journey. This journey is primarily character-driven and explores the hero's internal struggles, personal growth, and the evolution of their beliefs and values. The Inner Journey often includes the following elements:
- Character development and growth
- Emotional arcs and conflicts
- Inner demons and fears
- Moral dilemmas and choices
By incorporating the Inner Journey into their narrative, writers can create complex and relatable characters that resonate with their audience on a deeper, more personal level. ( source )
Both the Inner and Outer Journey are integral components of the Hero's Journey, and a successful narrative will weave these two aspects together to create a compelling and emotionally satisfying story. By understanding the interplay between the hero's external actions and their internal growth, writers can create a more nuanced and engaging Hero's Journey that resonates with their audience.
Now that you have a thorough understanding of the Hero's Journey and its various components, it's time to apply this framework to your own story. By incorporating the 12 stages, key archetypes, and the Inner and Outer Journey into your narrative, you can create a rich and engaging story that resonates with your audience. Here are some practical tips and guidelines for applying the Hero's Journey to your story:
1. Identify your hero
Start by identifying your protagonist or hero, the character who will embark on the journey and undergo a transformation. Consider their background, motivations, and personal flaws, as these elements will shape their journey and influence their character development. ( source )
2. Define the Call to Adventure
Determine the inciting incident or Call to Adventure that will propel your hero into their journey. This event should create a sense of urgency, challenge the hero's status quo, and set the stage for their transformation. ( source )
3. Outline the stages of the journey
Using the 12 stages of the Hero's Journey as a guide, outline the key events and turning points in your story. Consider how each stage contributes to the hero's growth and transformation, and ensure that your narrative follows a logical and satisfying arc. ( source )
4. Develop your archetypes
Introduce the key archetypes that will populate your story, such as the Mentor, the Threshold Guardian, and the Shadow. Consider how each archetype can contribute to the hero's journey and help to shape their character development. ( source )
5. Balance the Inner and Outer Journey
Ensure that your story effectively balances the hero's Inner and Outer Journey, weaving together their emotional growth and external experiences into a cohesive narrative. Consider how the events of the Outer Journey influence the hero's Inner Journey and vice versa, and use this interplay to create a compelling and emotionally resonant story. ( source )
6. Revise and refine your story
Once you have applied the Hero's Journey framework to your story, review and revise your narrative to ensure that it adheres to the principles of the Hero's Journey while remaining true to your unique vision and voice. Consider seeking feedback from others, such as critique partners, beta readers, or professional editors, to help you refine your story and bring it to its full potential. ( source )
By following these guidelines and incorporating the Hero's Journey into your narrative, you can create a rich and engaging story that resonates with your audience and follows a time-tested pattern of storytelling success.
While the Hero's Journey provides a useful framework for storytelling, it's important to recognize that not all stories will follow this structure exactly. Over time, various adaptations and variations of the Hero's Journey have emerged, offering different perspectives and approaches to storytelling. By exploring these adaptations, writers can gain a broader understanding of the narrative possibilities and apply these insights to their own work. Here are some notable adaptations and variations of the Hero's Journey:
1. The Heroine's Journey
The Heroine's Journey, first proposed by Maureen Murdock in her book "The Heroine's Journey: Woman's Quest for Wholeness," offers a gendered perspective on the Hero's Journey, focusing on the unique challenges and experiences faced by female protagonists. The Heroine's Journey emphasizes the importance of relationships, self-discovery, and the integration of masculine and feminine qualities within the individual. ( source )
2. The Writer's Journey
Christopher Vogler's "The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers" adapts the Hero's Journey for screenwriters and novelists, condensing Campbell's 17 stages into a more streamlined 12-stage structure. Vogler's adaptation has been widely embraced by the writing community and is particularly influential in the world of screenwriting. ( source )
3. The Virgin's Promise
Kim Hudson's "The Virgin's Promise" offers an alternative narrative structure that focuses on the protagonist's journey towards self-fulfillment and personal empowerment, rather than a quest to save others or restore balance to the world. The Virgin's Promise is particularly relevant to stories featuring female protagonists and themes of personal growth and transformation. ( source )
4. The Anti-Hero's Journey
The Anti-Hero's Journey explores the narrative arc of protagonists who do not possess traditional heroic qualities, such as moral integrity, courage, or selflessness. The Anti-Hero's Journey may involve a more morally ambiguous or complex character, who may not ultimately achieve redemption or success in the conventional sense.
5. The Collective Journey
The Collective Journey, as proposed by Jeff Gomez, focuses on the interconnected and collaborative nature of modern storytelling, particularly in transmedia narratives and shared storyworlds. In the Collective Journey, the focus shifts from the individual hero to a diverse ensemble of characters, each contributing to the narrative in unique and meaningful ways. ( source )
By exploring these adaptations and variations of the Hero's Journey, writers can gain a broader understanding of the possibilities for storytelling and create narratives that reflect their unique perspective and voice. Remember that the Hero's Journey is not a rigid formula, but rather a flexible framework that can be adapted and modified to suit the needs of your story and your characters.
To further illustrate the power and versatility of the Hero's Journey, let's examine some case studies of popular fiction that employ this narrative structure. By analyzing these examples, you can gain a deeper understanding of how the Hero's Journey can be applied to various genres, mediums, and story types.
1. The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien
Tolkien's epic fantasy trilogy is a prime example of the Hero's Journey, with its protagonist Frodo Baggins embarking on a quest to destroy the One Ring and save Middle-earth. The story follows the classic stages of the Hero's Journey, with Frodo facing numerous trials, allies, and enemies along the way, ultimately transforming from a humble Hobbit into a hero capable of great courage and sacrifice. ( source )
2. The Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling
Rowling's beloved fantasy series follows the young wizard Harry Potter as he embarks on a journey to defeat the dark wizard Voldemort. Over the course of the series, Harry undergoes the stages of the Hero's Journey, from the Call to Adventure (receiving his Hogwarts letter) to the Ordeal (battling Voldemort) and the Return with the Elixir (restoring peace to the wizarding world). The series also features a rich cast of archetypal characters, such as the Mentor (Dumbledore), the Shadow (Voldemort), and the Shapeshifter (Snape). ( source )
3. The Hunger Games trilogy by Suzanne Collins
Collins' dystopian series follows the journey of Katniss Everdeen, a young woman who becomes the symbol of rebellion against a tyrannical government. Katniss' journey reflects the Hero's Journey, as she faces trials in the Hunger Games arena, encounters allies and enemies, and ultimately leads a revolution to overthrow the Capitol. The series also incorporates elements of the Heroine's Journey, exploring themes of personal growth, relationships, and the integration of masculine and feminine qualities. ( source )
4. Star Wars by George Lucas
George Lucas' iconic space opera is heavily influenced by Joseph Campbell's work on the Hero's Journey, with its protagonist Luke Skywalker embarking on a quest to become a Jedi and defeat the evil Empire. The original Star Wars trilogy follows the stages of the Hero's Journey, with Luke undergoing a transformation from a simple farm boy to a powerful Jedi Knight. The series also features a cast of archetypal characters, such as the Mentor (Obi-Wan Kenobi), the Shadow (Darth Vader), and the Trickster (Han Solo). ( source )
These case studies demonstrate the enduring appeal and versatility of the Hero's Journey as a narrative structure. By applying the principles of the Hero's Journey to your own work, you can create compelling stories that resonate with audiences across genres, mediums, and cultures.
While the Hero's Journey can be a powerful tool for storytelling, it's essential to avoid some common mistakes when applying this framework to your work. By recognizing these pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, you can create a more engaging and original story that stands out in today's competitive market. Here are some common mistakes and tips for avoiding them:
1. Rigid adherence to the Hero's Journey
One of the most common mistakes writers make is treating the Hero's Journey as a rigid formula rather than a flexible framework. It's important to remember that not every story will follow the Hero's Journey exactly, and forcing your narrative to adhere to this structure can result in a predictable and uninspired story. Instead, use the Hero's Journey as a guide and adapt it to suit your unique vision and characters. ( source )
2. Stereotypical characters and archetypes
While the Hero's Journey relies on certain archetypal characters, it's essential to avoid creating one-dimensional, stereotypical characters that lack depth and complexity. Instead, strive to develop nuanced and multifaceted characters that challenge audience expectations and engage their emotions. This will result in a richer and more satisfying story. ( source )
3. Neglecting the Inner Journey
Another common mistake is focusing solely on the external events of the Hero's Journey and neglecting the protagonist's emotional growth and transformation. To create a truly compelling story, it's essential to balance the Inner and Outer Journey, ensuring that your hero's emotional development is intertwined with their external experiences. This will result in a more emotionally resonant and satisfying narrative. ( source )
4. Overemphasis on action and spectacle
While the Hero's Journey often involves high-stakes action and conflict, it's essential not to let these elements overshadow the emotional core of your story. Instead, focus on your characters' relationships, motivations, and personal growth, ensuring that the action and spectacle serve to enhance the emotional stakes and drive the narrative forward. ( source )
5. Ignoring cultural context and diversity
Finally, it's important to recognize that the Hero's Journey is rooted in a specific cultural context and may not apply universally to all stories and cultures. When crafting your narrative, be mindful of cultural diversity and strive to create stories that reflect and celebrate the rich tapestry of human experience. This will result in a more inclusive and engaging story that resonates with a broader audience. ( source )
By avoiding these common mistakes and applying the principles of the Hero's Journey thoughtfully and creatively, you can craft a powerful and engaging story that stands out in today's competitive market and resonates with your audience.
Creating a compelling Hero's Journey requires a thoughtful approach to storytelling, character development, and narrative structure. To help you craft a memorable and engaging story, consider these writing tips:
1. Understand the foundation of the Hero's Journey
Before attempting to write a Hero's Journey, familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts, stages, and archetypes outlined by Joseph Campbell and other scholars. This will provide a solid foundation for crafting your narrative and help you identify the essential elements of your story. ( source )
2. Develop compelling characters
Creating engaging, multidimensional characters is essential for a successful Hero's Journey. Focus on developing your protagonist, as well as the supporting cast of allies, enemies, and mentors, ensuring that each character is unique, relatable, and serves a purpose within the narrative.
3. Focus on emotional stakes
The emotional stakes of your story are crucial to maintaining reader engagement and investment in the Hero's Journey. Strive to create a narrative with high emotional stakes, where the protagonist's personal growth and relationships are intertwined with their external quest. ( source )
4. Use the Hero's Journey as a guide, not a template
While the Hero's Journey provides a useful framework for crafting your story, avoid treating it as a rigid formula. Instead, use the Hero's Journey as a starting point and adapt it to suit your unique vision, characters, and genre. This will result in a more original and engaging narrative. ( source )
To create a satisfying and well-rounded narrative, it's essential to balance the Inner Journey (the protagonist's emotional growth) with the Outer Journey (their external quest). Ensure that both aspects of the Hero's Journey are interconnected and contribute to the protagonist's overall transformation. ( source )
6. Embrace diversity and cultural context
When crafting your Hero's Journey, be mindful of cultural diversity and consider incorporating elements from various myths, legends, and cultural traditions. This will enrich your narrative and help it resonate with a broader audience. ( source )
7. Revise, revise, revise
Finally, remember that writing a compelling Hero's Journey is an iterative process that requires multiple drafts and revisions. Be prepared to revise your work, seeking feedback from beta readers, editors, and writing groups to refine your narrative and ensure that it effectively communicates your vision. ( source )
By applying these writing tips and maintaining a thoughtful, creative approach to storytelling, you can craft a compelling Hero's Journey that engages your audience and leaves a lasting impact.
Below are some frequently asked questions that will provide you with more information.
How can I adapt the Hero's Journey framework to my unique story?
Adapting the Hero's Journey to your unique story involves understanding its core principles and using them as a guide rather than a rigid template. Be creative and flexible, allowing your story's characters and themes to drive the narrative. Don't be afraid to deviate from the traditional Hero's Journey if it better serves your story's vision and purpose.
What are the key components of a compelling Hero's Journey narrative?
The key components of a compelling Hero's Journey narrative include a well-developed protagonist, a clear and meaningful quest, engaging character archetypes, high emotional stakes, and a balance between the Inner and Outer Journeys. Additionally, focusing on character growth and transformation can create a more emotionally resonant and satisfying story.
How can I avoid common mistakes when writing a Hero's Journey story?
Avoid common mistakes by not treating the Hero's Journey as a rigid formula, developing nuanced characters instead of stereotypes, focusing on emotional stakes, and considering cultural diversity. Also, be mindful of the balance between the Inner and Outer Journeys, ensuring that your protagonist's emotional growth is intertwined with their external quest.
What are some writing tips for crafting a compelling Hero's Journey?
Writing tips for crafting a compelling Hero's Journey include understanding the foundation of the Hero's Journey, developing compelling characters, focusing on emotional stakes, using the Hero's Journey as a guide rather than a template, balancing the Inner and Outer Journeys, embracing diversity and cultural context, and revising your work iteratively.
If you're interested in exploring the Hero's Journey further, here are three non-fiction books that delve into the topic and provide valuable insights:
In conclusion, mastering the Hero's Journey is a crucial skill for any writer seeking to create a compelling and resonant narrative. By understanding the origins of the Hero's Journey and its connections to myth, legend, and the human psyche, you can tap into a powerful framework for storytelling success.
The Hero's Journey provides a structure that can guide your narrative, helping you craft a story that engages readers and speaks to universal themes of personal growth, transformation, and triumph over adversity. By carefully studying the Three-Act Structure , the 12 Stages of the Hero's Journey , and the key archetypes that populate this narrative structure, you'll be better equipped to create a story that resonates with your audience.
Remember that while the Hero's Journey offers a valuable blueprint for storytelling, it's essential to adapt and personalize this framework to suit your unique vision and narrative goals. Be open to deviating from the traditional structure, incorporating diverse cultural elements, and exploring new ways to tell your story.
Finally, embrace the iterative nature of the writing process, seeking feedback from others and revising your work to ensure that your Hero's Journey effectively communicates your intended message and themes. By dedicating time and effort to mastering the Hero's Journey, you'll be well on your way to crafting a captivating and successful story.
Claim your free eBook today and join over 25,000 writers who have read and benefited from this ebook.
'It is probably one of the best books on writing I've read so far.' Miz Bent


Competitions
The hero’s journey breakdown: back to the future.
By Ken Miyamoto · June 21, 2020

How does Back to the Future follow Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey breakdown?
Welcome to another installment of our new series A Hero’s Journey Breakdown where we explore Joseph Campbell’s mythological storytelling structure and how iconic films fit into that mold.
Christopher Vogler’s approach to Campbell’s structure broke the mythical story structure into twelve stages. For this series, we define the stages in simplified interpretations:
- The Ordinary World : We see the hero’s normal life at the start of the story before the adventure begins.
- Call to Adventure : The hero is faced with an event, conflict, problem, or challenge that makes them begin their adventure.
- Refusal of the Call : The hero initially refuses the adventure because of hesitation, fears, insecurity, or any other number of issues.
- Meeting the Mentor : The hero encounters a mentor that can give them advice, wisdom, information, or items that ready them for the journey ahead.
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero leaves their ordinary world for the first time and crosses the threshold into adventure.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : The hero learns the rules of the new world and endures tests, meets friends, and comes face-to-face with enemies.
- The Approach : The initial plan to take on the central conflict begins, but setbacks occur that cause the hero to try a new approach or adopt new ideas.
- The Ordeal: Things go wrong and added conflict is introduced. The hero experiences more difficult hurdles and obstacles, some of which may lead to a life crisis.
- The Reward : After surviving The Ordeal, the hero seizes the sword — a reward that they’ve earned that allows them to take on the biggest conflict. It may be a physical item or piece of knowledge or wisdom that will help them persevere.
- The Road Back : The hero sees the light at the end of the tunnel, but they are about to face even more tests and challenges.
- The Resurrection : The climax. The hero faces a final test, using everything they have learned to take on the conflict once and for all.
- The Return : The hero brings their knowledge or the “elixir” back to the ordinary world.
Here we turn to the classic Back to the Future .
Note: As with any application of story structure or formula, this is just a hindsight interpretation and implementation of The Hero’s Journey to this cinematic tale. There can and will be variances.
The Ordinary World
Marty McFly is a teenager with dreams of becoming a rock star. The problem is that his family is caught in a web of failure spanning two generations.
Even Marty’s principal points out that no McFly ever amounted to anything — primarily because the McFly men are slackers, fearful of taking chances and inept at succeeding. This statement is proven when Marty and his band try out to play the school dance. They are quickly rejected.
Marty wants to become something. The trouble is, he doesn’t have the backbone to go the extra mile to make anything happen.
Call to Adventure
Marty’s call to adventure is subtle — and it’s a literal phone call that he receives from his eccentric friend Doc Brown, a crazy scientist. Doc wants Marty to meet him at the Twin Pines Mall at 1:15 am to witness a breakthrough in an experiment he’s been working on.
This call happens before we really see Marty within his ordinary world, but the true call to adventure occurs later that night when Marty has fallen asleep. Doc calls him, waking him up. He asks Marty to stop by his house to pick up his video camera.
Refusal of the Call
The initial Refusal of the Call is present when Doc initially asks Marty to meet him at such a late hour in the night. Marty scoffs at first. A more clear Refusal of the Call occurs that night when Marty has fallen asleep, subconsciously refusing the call by ignoring it.
It’s not until Doc calls that Marty is reminded. He quickly heads out.
Meeting the Mentor
Marty arrives at the Twin Pines Mall with the video camera. Doc Brown makes his entrance, and we quickly learn that he lives up to his eccentric reputation.
The interesting element to this story is that Marty actually has two mentors — 1985 Doc and 1955 Doc. Both are very different. It’s the 1955 Doc that is the true mentor of this story, and we don’t meet him until much later on in the second act.
Crossing the Threshold
While the time travel to 1955 seems like a proper threshold that is crossed, this stage actually happens a few moments before Marty makes the jump back in time.
When 1985 Doc sends his dog Einstein back in time — and then back to 1985 one minute later — Marty has indeed crossed the threshold. His Ordinary World of being an ordinary teenager dealing with ordinary problems is behind him. He’s witnessed something spectacular.
The time travel to come is the physical manifestation of him Crossing the Threshold while witnessing the discovery of time travel moments before is the emotional manifestation.
Test, Allies, and Enemies
Marty is put to the test when the Libyans come after Doc for stealing the Plutonium that he used to power the time machine. He’s crossed the threshold even more as he runs for his life. When Doc is seemingly gunned down, Marty must now take the initiative to survive.
He leaps into the DeLorean and tries to escape. They corner him as a rocket launcher is aimed at his vehicle. He shifts the car into a higher gear to outrun them and get out of range of the weapon. When he hits 88 mph, the flux capacitor is activated, thrusting Marty through time and into 1955.
Marty is then put through several initial tests within his journey as he acclimates to his new surroundings — Hill Valley circa 1955.
He meets his father…
… and manages to mess up the timeline by becoming the victim of his grandfather’s car — a fate that was supposed to happen to 1955 George McFly, Marty’s father.
To Marty’s dismay, 1955 Loraine (his mother) becomes infatuated with Marty. Marty quickly escapes and finds 1955 Doc Brown. He’s Marty’s only hope. But Marty must first convince the 1955 Doc that he truly is from the future.
The Approach
Once 1955 Doc is convinced, he’s dismayed when he realizes that DeLorean needs a substantial power source — and it’s no easy task finding Plutonium in 1955. Doc reveals that the only way to replicate the type of power they’d need to activate the flux capacitor is a bolt of lightning. Unfortunately, you never know when or where a bolt of lightning is going to strike.
Marty remembers that at a specific upcoming day — the coming Saturday night — the Hill Valley Clock Tower will be struck by lightning.
Doc figures out that if there’s some way to harness the energy from that bolt and into the flux capacitor, Marty can be sent back to the future.
Marty is excited. He figures he can hang out with Doc for a week until that Saturday, joking that Doc can show him around. Doc stops him and insists that he must not leave the house. He must not see anybody or talk to anybody. Any contact could cause severe repercussions to the timeline.
But Marty has already met his parents. And worse yet, he’s already changed the timeline.
Doc’s theory is proven when they look at the photo of Marty and his brother and sister. His brother’s head is disappearing. If Marty doesn’t get his mother and father together, they’ll never fall in love, marry, and have kids. That’s why his older siblings are falling out of existence — and if Marty doesn’t do anything, he’ll be the last to disappear.
Marty remembers his 1985 mother telling him the story of how she fell in love with his father back in 1955. It was at the Enchantment Under the Sea dance where they kissed for the first time.
The problem is that 1955 Loraine has a crush on Marty. So Marty must struggle to get them to go to the dance together. But it’s not working.
Biff doesn’t make things easier. When Marty continually stands up to Biff’s bullying ways, Loraine becomes more and more enamored with him.
Marty struggles to help George get the courage to ask Loraine out, but George is living up to what the principal declared — he’s a slacker. But Marty comes up with a plan. Since Loraine wants to go to the dance with him, he’s found a way that George can come to her rescue. They concoct a plan where Marty and Loraine will be in the parking lot outside the dance. Marty will make a move that forces a struggle between him and Loraine. George will come to the rescue, and he and Loraine will live happily ever after.
Meanwhile, Doc is setting everything up at the Hill Valley Clock Tower. Marty is tasked with connecting George and Loraine and then escaping the dance to go be sent back to the future.
Things don’t go as planned.
George loses track of time while in the dance.
Marty is doing his best to make things awkward between him and Loraine — and she’s doing just the same. Just when he thinks he’s being pulled out of the car by George, as planned, it’s revealed that a drunk Biff has found him. He seeks out revenge for the damage that Marty caused to his car.
He tosses Marty to his friends, and they stash Marty in the trunk of a car as Biff tries to take advantage of Loraine. Biff’s friends are chased away by the band members, but they can’t get into the trunk because the keys are in with Marty.
Meanwhile, George has arrived at the car, not knowing that Biff is the one assaulting Loraine. He opens the door, ready to play out the scripted scene, only to discover that it’s Biff.
But George manages to muster the courage to stand up to Biff. But that courage gets him into trouble as Biff blocks George’s punch and twists his arm, ready to break it.
The band members get Marty out of the trunk, slicing the hand of their guitarist as they do. Marty rushes towards the car just in time to see George take a stand and punch out Biff. Loraine is now enamored with George.
But it’s not over yet. The guitarist can’t play because of his cut hand, so Marty must take his place — without music at the dance, George and Loraine won’t have their first kiss moment that makes them fall in love.
As Marty plays and George and Loraine dance, there’s one final moment of conflict. Another student tries to cut in, forcing George to momentarily return to his old cowardly, slacker ways. Marty sees this and notices that his hand is about to disappear. He looks at the picture of him and his siblings — he’s the last one left, and he’s fading.
George musters his newfound courage once again, tosses the other student aside, and he and Loraine share a magical kiss. So magical that the disappearing Marty is brought back to life instantly, signaling that the timeline is safe once again.
The Road Back
Marty wishes his parents well and rushes to the Hill Valley Clock Tower as the storm hits.
Marty attempts to give Doc a letter that he wrote, warning him of his future death. But Doc refuses to read it, fearing the repercussions within the timeline. He rips it up.
The Resurrection
Setbacks occur, and Doc is forced to go to extreme measures to reconnect the cable that will send the bolt of lightning to the flux capacitor. Marty struggles to warn Doc about his future death, but it’s too late.
Marty rushes to ready the DeLorean, but it shuts down. As Doc reconnects the cable, Marty starts the car just in time and races towards it. He hits the proper 88 mph speed as the bolt of lightning connects with the cable, sending the necessary charge down to the DeLorean, sending it back to the future.
Marty is back in 1985. He’s set the time machine to arrive ten minutes early so that he can prevent the death of 1985 Doc. But the DeLorean breaks down. He’s forced to run to the mall and then realizes that he’s too late. He watches as Doc is gunned down — and then sees his past self successfully flee the Libyans as they crash to their apparent death after the DeLorean makes the jump into the past and disappears.
But Marty is shocked to see that Doc has survived. He put the letter back together. Everything is fine.
Doc goes back and gets the DeLorean running again. Marty bids him a farewell and Doc travels to the future.
Marty wakes up the next morning. He’s back in his house circa 1985. Was it all a dream? When he heads out of his room and into his house, he sees that everything is different. The McFly curse has been lifted.
1985 George is a successful author. His siblings are just as successful as well. 1985 Biff is now 1985 George’s underling. And Loraine looks wonderful.
Marty, as well as the whole McFly family, have been resurrected with much better fates, thanks to the actions of 1955 George McFly.
Marty is finally reunited with Jennifer when their kiss is interrupted by the arrival of the DeLorean. It’s Doc. He’s back from the future and needs to take both Marty and Jennifer back to the future to rescue their kids from a dismal fate.
For all the latest from The Script Lab, be sure to follow us on Twitter , Facebook , and Instagram .
And become a member of TSL 360 to enjoy the LARGEST screenwriting education content library, featuring masterclasses, deep-dive interviews, and lectures from Academy Award-winning screenwriters, TV show-runners, producers, literary managers, agents, studio executives, and leading educators – all in one place.
Download Free Trending Scripts

Raiders of the Lost Ark

Oppenheimer

Fargo (1996)

Poor Things

Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind

Mr. and Mrs. Smith

A Quiet Place

Next Related Article

The Great TV Writers: Gene Roddenberry
Martin Keady · June 16, 2020
Recent Articles
What is the wilhelm scream.
Ken Miyamoto from ScreenCraft · April 10, 2024

Sonic Stories: The Cinematic Magic of Movies About Music
Ken Miyamoto from ScreenCraft · April 8, 2024

2024 TSL Free Screenplay Contest Quarterfinalists
Admin · April 5, 2024

Deadline: April 15th, 2024

PAGE International Screenwriting Awards Competition

Slamdance Screenplay Competition
Deadline: April 24th, 2024
More Related Articles

The Great Screenwriters: Dalton Trumbo
Martin Keady · July 5, 2020

“The Einstein Technique” of Creative Thinking for Writers
Ken Miyamoto · June 26, 2020

How SOUTH PARK Creators Plot Better Scripts
Ken Miyamoto · June 12, 2020
© 2024 The Script Lab - An Industry Arts Company
Sign up for the TSL Newsletter
and get $50 off Final Draft 12
Stay up to date on the latest scripts & screenwriting articles.

'The Hijacking of Flight 601' Review: Monica Lopera's riveting performance holds the fort in Netflix series
CALI, COLOMBIA: 'The Hijacking of Flight 601' premiered on Netflix on Wednesday, April 10, depicting the true story of the 1973 takeover incident in Colombia.
If you were expecting ' The Hijacking of Flight 601 ' to be solely centered around violence and action, you might be surprised, as the series offers much more. Beyond the gripping hijacking storyline, the series also delivers poignant moments of friendship.
Starring Monica Lopera, Valentín Villafañe, Alián Devetac, Christian Tappan, Angela Cano, and Enrique Carriazo in pivotal roles, the series takes viewers on a riveting journey through the events surrounding the hijacking.
The series offers a compelling portrayal of the harrowing ordeal faced by the passengers and crew.
Monica Lopera's compelling portrayal elevates 'The Hijacking of Flight 601'
Monica Lopera delivers a remarkable performance as Edilma Perez in 'The Hijacking of Flight 601.'
Edilma, a flight attendant with three children, grapples with the challenge of balancing her professional duties with her personal life.
Monica's portrayal of Edilma is authentic and compelling, skillfully capturing the challenges and emotions involved in juggling both work and family responsibilities.
When the hijackers seized control of the plane, Monica's portrayal of Edilma's strength, resilience, and vulnerability makes her character relatable and compelling, drawing viewers into her emotional journey throughout the series.
Monica's acting feels so natural that she embodies the essence of a real flight attendant rather than merely portraying one as an actress.
From her initial struggles to secure a job to her courageous confrontation with the hijackers, Monica's portrayal of Edilma is incredibly compelling.
During moments of crisis, Edilma's character shines through as selfless and compassionate, prioritizing the safety and well-being of the passengers over her concerns.
Valentín Villafañe's performance in 'The Hijacking of Flight 601' leaves a lasting impression
Valentín Villafañe delivers a captivating performance as hijacker Ulises in 'The Hijacking of Flight 601.'
Valentín's performance masterfully captures the ruthlessness and determination of Ulises' character, creating a palpable sense of genuine threat that permeates throughout the series.
Valentín's presence on screen is magnetic, commanding attention in every scene he appears in. His performance is a masterclass in acting, showcasing his talent and versatility.
Valentín's portrayal of Ulises is nuanced and multifaceted, whether he's intimidating the passengers or manipulating the pilot.
He adeptly transitions between states of composed calculation and intense outbursts, ensuring viewers remain captivated and suspenseful throughout the series.
Valentín's acting is truly the standout element of 'The Hijacking of Flight 601,' making it a must-watch series that leaves a lasting impression on viewers long after the final credits roll.
During the initial episodes of 'The Hijacking of Flight 601,' Valentín's intentions are shrouded in mystery, adding to the suspense and tension of the series.
This element theoretically adds tension by placing viewers in the shoes of the confused passengers on the plane, who are uncertain of the hijackers' true intentions.
However, as the series progresses, Valentín eventually reveals his motives.
During intense scenes, the tension is palpable as the pilots and authorities negotiate with Ulises, heightening the stakes of a potential mid-air tragedy.
This gripping narrative keeps viewers engrossed, eagerly anticipating the resolution of the harrowing situation.
'The Hijacking of Flight 601' unfolds the emotional journey of passengers and crew
What sets 'The Hijacking of Flight 601' apart is its emphasis on the human aspects of the story.
In addition to the gripping hijacking plot, the series delves deep into the personal lives of its characters, showcasing their fears, aspirations, and the enduring bonds of friendship that form amid adversity.
The series does an excellent job of capturing the historical context of the hijacking, exploring the political and social climate of Colombia in 1973. This provides viewers with a broader understanding of the events that led to the hijacking.
Comprising six riveting episodes, the series skillfully portrays the camaraderie that develops among the passengers and crew amidst a high-stakes hijacking.
The captain and the flight attendants emerge as unsung heroes, their actions showcasing the best of humanity in the worst of circumstances.
Amid this chaos, the plane's captain and two flight attendants are tasked with the impossible: looking after the passengers and maintaining order in the face of imminent danger.
These instances of human connection add depth to the narrative, elevating it beyond a mere recounting of historical events.
Viewers witness how strangers from different walks of life come together, transcending their differences to unite against a common threat.
Despite some scenes that may momentarily reduce tension, the series ultimately builds to an impressive final chapter where some passengers are finally assured of their safety.
The attention to detail in recreating the 1973 hijacking incident in Colombia adds to the authenticity of the story, making it a riveting and immersive viewing experience.
It is a must-watch for anyone interested in historical dramas or captivating storytelling.
'The Hijacking of Flight 601' is now streaming on Netflix
Top 10 Ivanka Trump fashion moments

Briton who ran length of Africa says Congo kidnapping was only time he mulled quitting
- Medium Text

The Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter provides all the news you need to start your day. Sign up here.
Writing by Trevor Stynes in Krakow; Editing by Hugh Lawson
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Sports Chevron

Medvedev dumped out of Monte Carlo Masters by Khachanov
Former world number one Daniil Medvedev was once again drawn into a heated exchange with an umpire before crashing out of the Monte Carlo Masters following a 6-3 7-5 defeat by fellow Russian Karen Khachanov in the last 16 on Thursday.

Newcastle United's sponsor Sela are introducing haptic shirts which will allow deaf supporters and those with hearing loss to experience the raucous atmosphere at St. James' Park this weekend, the Premier League club said on Thursday.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Ordeal is the critical moment in every story, a major source of magic in heroic myth, according to Christopher Vogler, author of The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure. The hero stands in the deepest chamber of the inmost cave and faces a direct confrontation with his greatest fear.
In narratology and comparative mythology, the hero's journey, also known as the monomyth, is the common template of stories that involve a hero who goes on an adventure, ... It is in this ordeal that the hero may derive hope and assurance from the helpful female figure, by whose magic (pollen charms or power of intercession) they are protected ...
Two Hero's Journey stages away from The Ordeal is The Resurrection — The climax where the hero faces their final test, using everything they have learned to take on the conflict once and for all. Within that Resurrection, your protagonist needs to have a moment of transformation. But before that transformation can occur, something has to push ...
Learn more: Hero's Journey Step #8: The Ordeal. Step 9: The Reward. For their valiant efforts, the Hero must acquire the goal, yet the goal, as acquired, must be revealed to be inadequate. Usually this takes shape by the Hero reaching a crisis in their inner journey, where an inner need (for justice, peace, morality, etc) comes into conflict ...
The Hero's Journey offers a powerful framework for creating quest-based stories emphasizing self-transformation. Holiday Savings . cui:common.components.upgradeModal.description_undefined ... This is it, the moment the hero has been waiting for. They've survived "death," weathered the crisis of The Ordeal, and earned the Reward for which they ...
But, the hero's journey only increases its level of danger over time! So, the goddess tries to persuade the hero to stop the journey. Maybe the goddess tries to get the hero to run away together, ignore the troubles of the world and start a new life somewhere. Maybe the goddess tries to convince the hero that the hero has nothing to prove to ...
The Hero's Journey: Use this structure when you want to tell a story of personal growth, transformation, and adventure. It works well for epic tales, fantasy, and science fiction, but it can be adapted to other genres as well. Three-Act Structure: This is a versatile structure suitable for a wide range of genres, from drama to comedy to action.
The Hero's Journey, also known as the monomyth, is a story structure where a hero goes on a quest or adventure to achieve a goal, and has to overcome obstacles and fears, before ultimately returning home transformed. ... Ordeal. The hero's biggest test yet! Reward (Seizing the Sword). Light at the end of the tunnel; The Road Back. We aren't ...
The Hero's Journey is often depicted as a circular diagram, ... Ordeal: The hero faces a major test, often their most significant challenge. Reward: The hero overcomes the ordeal and gains a reward or insight. The Road Back: The hero begins the journey back to the ordinary world.
The Hero's Journey, or monomyth, is a common story structure first documented by Joseph Campbell that many writers use today to write engaging fiction stories. ... The Ordeal. The ordeal marks the hero's greatest test thus far. This is a dark time for them: indeed, Campbell refers to it as the "belly of the whale." ...
Prior to the climatic event, or the Hero's Journey Ordeal, there's an Approach to the Inmost Cave. Here, before the hero performs a big, decisive action, there is a brief pause. During this time the author establishes three key things: The villain guarding the goal is really, really nasty. The cost of losing (known as stakes) are extremely high.
The Hero's Journey is a narrative pattern identified by Joseph Campbell, most notably outlined in his book The Hero with a Thousand Faces. This pattern of adventure and transformation is a universal one that runs through all kinds of mythic traditions across the world. ... The Ordeal. The Hero faces his greatest challenge yet, in the form of ...
1 What Is the Hero's Journey? 2 Using the Hero's Journey in Your Own Novel; 3 The 9 Stages of Campbell's Monomyth. 3.1 The Ordinary World: 3.2 The Call to Adventure and Refusing the Call: 3.3 Overcoming Resistance and Meeting the Mentor: 3.4 Crossing the First Threshold: 3.5 Tests and Trials: 3.6 The Major Ordeal: 3.7 The Road Back: 3.8 ...
The Supreme Ordeal is the culmination of the entire Hero's Journey thus far. The goal that the hero established during the Call to Adventure is now within reach, but before they can meet it, they must confront the greatest obstacle in their path, often their greatest fear. They may still worry that they cannot succeed, but they will ...
But if the entire trilogy were to be seen as a Hero's Journey, Luke Skywalker's near-death encounter with Darth Vader in the dark depths of Cloud City is his supreme ordeal. The Lord of the Rings - Frodo's encounter with the spider Shelob, which paralyses him with venom and is on the verge of feeding on him before Sam comes to the rescue.
The hero's journey ends where it begins, back at the beginning after a quest of epic proportions. The 12 steps are separated into three acts: departure (1-5) ... Ordeal. This is the life-or-death moment. This can be a meeting with an ultimate enemy or facing the hero's deepest fear. There is an awareness that if the hero fails, their new ...
The 12 Stages of The Hero's Journey. A popular form of structure derived from Joseph Campbell's Monomyth from his book The Hero With A Thousand Faces and adapted by Christopher Vogler is the Twelve Stage Hero's Journey. This is essentially a more detailed Character Arc for your story's hero which is overlayed onto the more traditional three-act ...
The hero's journey is commonly accepted to have 12 main steps. To make it even simpler on you, these steps can actually be broken down into three stages: the departure, the initiation, and the return. The hero's journey is usually defined as having three stages subdivided into 12 steps total.
The 12 hero's journey stages represent a change or transformation in your story's main character or hero. Get a free hero's journey template. ... Stage 8: The Ordeal. The hero has made it to the final challenge of their journey and now must face all odds and defeat their greatest adversary. Consider this the climax of the story.
The Hero's Journey is probably the most well-known of all story structures. Its origins can be traced back to ancient mythology, where heroes embarked on transformative quests, facing trials and triumphs. However, it was Joseph Campbell, the renowned mythologist, who popularised its use and study. In his seminal work, "The Hero with a ...
Origins of the Hero's Journey. The concept of the Hero's Journey can be traced back to the work of renowned mythologist Joseph Campbell.In his seminal book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces (1949), Campbell examined myths and stories from various cultures around the world and identified a common narrative pattern that he dubbed the "monomyth." According to Campbell, the monomyth is a universal ...
The Ordeal: Things go wrong and added conflict is introduced. The hero experiences more difficult hurdles and obstacles, some of which may lead to a life crisis. The Reward: After surviving The Ordeal, the hero seizes the sword — a reward that they've earned that allows them to take on the biggest conflict. It may be a physical item or ...
The series offers a compelling portrayal of the harrowing ordeal faced by the passengers and crew. Monica Lopera's compelling portrayal elevates 'The Hijacking of Flight 601'
Cook arrived to a hero's welcome at Ras Angela in Tunisia on Sunday. His journey began last April in the South African village of L'Agulhas, Africa's most southerly point. Now he hopes his ...