- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media

Follow the timeline of the Titan submersible’s journey from departure to tragic discovery
A submersible carrying five people to the Titanic imploded near the site of the shipwreck and killed everyone on board, authorities said Thursday, bringing a tragic end to a saga that included an urgent around-the-clock search and a worldwide vigil for the missing vessel. (June 22)

The Titan submersible was touted for its unconventional design. After its catastrophic underwater implosion that killed five people, the question remains, was the design destined for disaster? (June 23) (AP Video/Production: Rodrique Ngowi)

The U.S. Coast Guard says a debris field has been found near the Titanic as rescuers search for a missing submersible en route to the ship’s wreckage. The Coast Guard put the statement on Twitter on Thursday. (June 22)
FILE - This photo provided by OceanGate Expeditions shows a submersible vessel named Titan used to visit the wreckage site of the Titanic. The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions. (OceanGate Expeditions via AP, File)
- Copy Link copied
FILE - The Titanic leaves Southampton, England, on her maiden voyage on April 10, 1912. The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions. (AP Photo/File)
FILE - This 2004 photo provided by the Institute for Exploration, Center for Archaeological Oceanography/University of Rhode Island/NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration, shows the remains of a coat and boots in the mud on the sea bed near the Titanic’s stern. The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions. (Institute for Exploration, Center for Archaeological Oceanography/University of Rhode Island/NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration, File)
FILE - In this satellite image provided by Maxar Technologies, from top to bottom, the vessels Horizon Arctic, Deep Energy and Skandi Vinland search for the missing submersible Titan, Thursday, June 22, 2023, in the Atlantic Ocean. The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions. (Satellite image ©2023 Maxar Technologies via AP, File)
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions.
THE BUILDUP
The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner’s watery gravesite. Three missions involving other teams had been scrapped due to bad weather in the previous four weeks, but the latest OceanGate Expeditions group was hopeful.
“A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,” renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram. “More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
THE DIVE DOWN
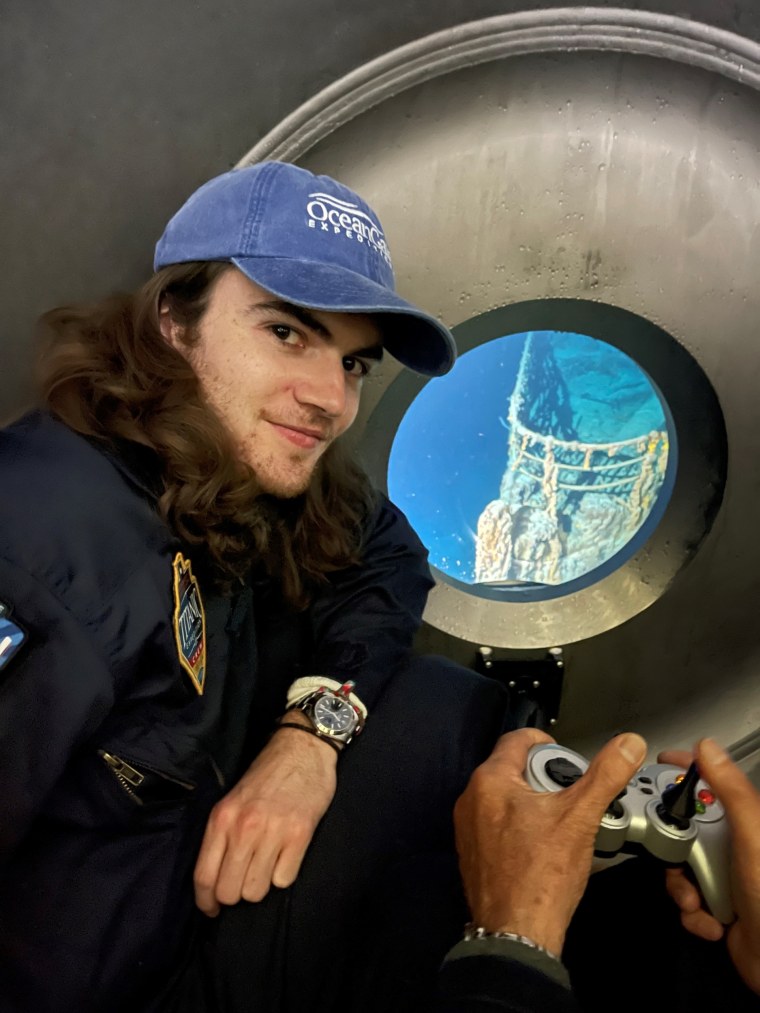
Moving about the Polar Prince, mission participants were required to wear water-activated life vests, bright orange jackets, helmets and steel-toed boots, said Arnie Weissmann, a journalist who spent eight days aboard the support ship in May before his mission was aborted. Just before a dive, they’d change into fleece vests, black flight suits bearing the OceanGate logo and warm socks — no shoes allowed on the submersible.
The team was carried to the Titan’s launch and recovery platform by one of two inflatable dinghies named Stewie and Max. Once inside, they would sit on a platform, with their legs crossed or out straight.
“You could not be in that thing if you’re claustrophobic,” Weissmann said. “It’s literally like being in a tin can because it’s got rounded sides.”
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
“Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean,” the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. “The descent takes approximately two hours but it feels like the blink of an eye.”
On Sunday, the vessel lost contact with the Polar Prince around 10:45 a.m.
At 5:40 p.m., nearly three hours after the Titan was expected to resurface and nearly eight hours after the last communication, the Polar Prince notified the U.S. Coast Guard that the vessel was overdue, setting off an intense international search and rescue.
After the craft was reported missing, the U.S. Navy analyzed its acoustic data and found an anomaly that was “consistent with an implosion or explosion in the general vicinity of where the Titan submersible was operating when communications were lost,” a senior Navy official later told The Associated Press. Though it wasn’t made public at the time, the Navy passed on that information on Sunday to the Coast Guard, which continued its search because the Navy did not consider the data to be definitive, according to the official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive technology.
By Monday afternoon, a C-130 Hercules aircraft from North Carolina and a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar equipment joined the search. Tuesday brought better weather and increased visibility, and by that morning, 10,000 square miles (25,900 square kilometers) had been searched.
A U.S. Air National Guard crew arrived that day, as did a Bahamian research vessel, Deep Energy, which deployed camera-equipped, remote-operated robots.
Meanwhile, sonar equipment detected banging noises Tuesday night and Wednesday morning, sparking hope that those aboard the Titan were still alive.
“We are smack dab in the middle of search and rescue, and we’ll continue to put every available asset that we have in an effort to find the Titan and the crew members,” Captain Jamie Frederick of the First Coast Guard District said at a news conference Wednesday afternoon.
By then, crews had scoured an area twice the size of Connecticut in waters 2½ miles (4 kilometers) deep. More resources were on the way, including multiple remote-operated vehicles, a salvage system capable of recovering heavy undersea objects and a mobile hyperbaric recompression chamber. Time was running out. The submersible was only equipped with enough air to last until sometime the next morning.
THE DISCOVERY:
On Thursday morning, a robotic vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan on the ocean floor, followed by the front and back ends of the Titan’s hull.
“The debris is consistent with the catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber,” said Rear Adm. John Mauger of the First Coast Guard District.
On its website before the expedition, OceanGate told future participants what to expect upon resurfacing.
“Once on deck, you will be welcomed back by the expedition crew and be able to share the story of your incredible accomplishment,” said the company, which already had scheduled dates for a 2024 expedition.
On Thursday, the company issued a statement mourning those killed, including company CEO and pilot Stockton Rush. In addition to Rush and Harding, the others on board were Titanic expert Paul-Henri Nargeolet and two members of a prominent Pakistani family, Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood.
“These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans,” OceanGate said. “We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
Patents, lawsuits, safety concerns — then tragedy. A timeline of OceanGate's Titan sub.

A mission to explore the remains of the Titanic went horribly awry on June 18, riveting the world as search crews raced against time to find a submersible that vanished during an attempted dive to the ocean floor, where paying passengers and Stockton Rush III, founder of the submersible company OceanGate, could view the Titanic wreckage.
On Thursday the U.S. Coast Guard announced pieces of the submersible were found scattered across a debris field a third of a mile from the Titanic . OceanGate issued a statement saying, "We grieve the loss of life" of those aboard.
Also aboard the vessel were French explorer Paul-Henry Nargeolet, British explorer and jet dealer Hamish Harding and Shahzada Dawood of a prominent Pakistani family and his son Suleman.
Records show the tragedy was preceded by a long path toward developing a craft that would reach the ocean depths where the Titanic rests. They also show a history of safety concerns .
Retrace the development of OceanGate, a Bahamian-registered corporation, and its submersibles, and the search for the missing Titan, with this timeline.
2009: OceanGate is founded
A provider of manned deep-sea submersibles, OceanGate starts operations on the West Coast, the company has stated in news releases. Its founder is Stockton Rush III, who graduated from Princeton University with a BSE in aerospace, aeronautical and astronautical engineering in 1984 and obtained an MBA at the University of California Berkeley's Haas School of Business in 1989, according to his biography on OceanGate’s website.
February 2012: OceanGate expands to Florida and the Caribbean
It's registered as a corporation in Miami, with Guillermo Sohnlein as president and Rush as secretary. Documents state the company incorporated in Washington State in Dec. 2011.
May 2013: Collaboration announced with University of Washington
OceanGate says it will collaborate with the school's Applied Physics Lab on Project Cyclops I, a new 3000-meter 5-person submersible. (The University clarified on June 23 that they only completed about $650,000 worth of work on a $5 million research collaborative agreement before parting ways. The collaboration resulted in a steel-hulled vessel that can only travel to a depth of 500 meters, the University stated.)
June 2013: Studies invasive fish
OceanGate teams up with Nova Southeastern University to study invasive lionfish in Florida.
August 2013: Submersible feasibility study concludes
OceanGate announces University of Washington completes design feasibility study for hull design for Cyclops I submersible.
June 2015: Report published on submersible
Rush and science and technology director Erika Montague, publish a report on Cyclops I with Peter Brodsky, an engineer at the University of Washington.
November 2015: Some of the earliest paying customers sign up for trip
Marc and Sharon Hagle sign a contract and pay $10,000 deposits to OceanGate to participate in an expedition to the Titanic.
June 2016: OceanGate submersible dives to wreck
One of the company's submersibles dives over the wreck of the Andrea Doria off Nantucket.
March 2017: OceanGate announces Titanic dive
Company announces it will conduct the first manned submersible dives to Titanic since 2005, and that private citizens may join the expedition as mission specialists for $105,129 each.
Mid-2017: Refund or not?
The Hagles begin pondering whether to ask OceanGate for a refund of their deposit. Rush visits their home to reassure them.
August 2017: One step completed
OceanGate completes assembly of core pressure vessel, bonding two titanium rings to the ends of a 56-inch wide, 100-inch-long carbon-fiber cylinder.
January 2018: Launch and recovery testing
OceanGate tweets it successfully tested the launch and recovery platform of Cyclops 2.
February 2018: Cyclops 2 becomes Titan
Engineering team hands over Cyclops 2 to operations team, renames submersible vessel.
The Hagles wire OceanGate an additional $190,258 to pay for their planned Titan expedition.
March 2018: Safety concerns raised
A trade group, the Marine Technology Society, sends a letter to OceanGate — Reported by the New York Times in June 2023 — to express unanimous concern regarding development of the Titan submersible and its planned Titanic Expedition.
April 2018: Expedition canceled
Hagles say OceanGate cancels June 2-9, 2018 expedition and reschedules it to July 2019.
July 2018: Lawsuit emerges
OceanGate sues former director of marine operations David Lochridge and his wife, Carole Reid Lochridge in Washington state .
August 2018: Safety concerns
Lochridges file a counterclaim in the lawsuit, alleging a series of safety concerns about the Titan submersible .
November 2018: Case dismissed
Parties settle in the OceanGate v. Lochridge case.
December 2018: Another milestone
CBS This Morning publishes a story saying Rush reached a depth of 13,000 feet during a dive in the Titan in the Bahamas, a key milestone in his plan to dive to the Titanic in 2019.
April 2019: A new patent
U.S. Patent Office assigns OceanGate a patent for systems to recover objects in aquatic environments.
June 2019: Expedition delay
OceanGate delays 2019 Titanic expedition, says it will take place in June 2020.
October 2019: Expedition canceled
Hagles receive email saying OceanGate cancels 2020 expedition.
January 2020: Raising money
OceanGate announces it has raised $18 million in equity financing, which it will use to expand its fleet of deep-sea submersibles to set the stage for 2021 dives to the Titanic.
February 2020: NASA to partner
NASA announces it will partner with OceanGate to develop and manufacture new carbon fiber pressure vessels. (NASA told USA TODAY on June 23 that it "consulted on materials and manufacturing processes for the submersible." Lance Davis, acting news chief for the Marshall Space Flight Center, said the agency "did not conduct testing and manufacturing via its workforce or facilities, which were done elsewhere by OceanGate.")
November 2020: Tourist dives to start
Dozens of international news stories say OceanGate will start its first tourist dives to the Titanic in 2021.
March 2021: Astronaut joins expedition
OceanGate and NASA astronaut and physician Dr. Scott Parazynski announce he will join the Titanic expedition.
May 2021: OceanGate provides plans to federal overseer
The U.S. District Court oversees legal issues involving the Titanic under an open 1993 court case. In May 2021, David Concannon, a legal and operations consultant to OceanGate, sent a letter to the court outlining its expedition plans, saying it will be "the first of many" and will be conducted under NOAA guidelines.
"The exploration team will conduct annual surveys of the wreck in collaboration with scientific and imaging experts from multiple organizations as part of an on-going long-term study to document the current conditionof the Titanic maritime heritage site."
The letter assured the court the vessel would not move or retrieve any artifacts and would deposit any ballast "well clear of the wreck and debris field." It ended with an invitation to the judge to join the expedition as a guest of OceanGate.
June 2021: Another patent
U.S. patent issued to OceanGate for systems and methods for launching and recovering objects in aquatic environments.
July 2021: Titanic success
OceanGate completes its first submersible dive to the Titanic, with a team that includes Rush, Scott Griffith and PH Nargeolet, a former French Naval commander and submersible pilot. The company says a series of yearly expeditions will help record the Titanic’s rate of decay and map the artifacts found on the site.
September 2021: A patent for monitoring integrity
OceanGate receives patent for systems for curing, testing, validating, rating and monitoring the integrity of composite structures.
November 2021: Tickets for sale for next expedition
OceanGate announces 2022 expedition to Titanic , price to ride rises to $250,000.
May 2022: OceanGate updates court on expedition plans
OceanGate sends a letter notifying the District Court that it plans five photographic and scientific survey "missions" to the wreck site of the Titanic during the summer of 2022 and includes a copy of its draft science plan.
"Every effort will be made to avoid contact with the wreck itself, and no artifacts or scientific samples will be collected from the wreck itself. However, this year the expedition does plan to take free floating water samples throughout the water column and on the bottom, as part of OceanGate’s scientific efforts to collect environmental DNA in conjunction with its partners at the University of North Carolina and University of Edinburgh."
July 2022: Expedition encounters difficulties
CBS correspondent David Pogue goes on a Titanic expedition with OceanGate . On one dive, the submersible never finds the Titanic .
August 2022: Video shows submersible dive
OceanGate releases high definition video from its 2022 trip to the Titanic.
January 2023: A tally of dives so far
A Guardian story reports OceanGate Expeditions has taken about 60 customers and 15-20 researchers down to the Titanic in its submersible.
February 2023: Couple alleges fraudulent inducement
The Hagles sue Rush in Orange County, Florida circuit court, alleging fraudulent inducement and violation of Florida’s Deceptive and Unfair Trade Practices Act.
April 2023: OceanGate sends 2023 plan to court
Concannon sends a letter to the District Court saying the 2023 expedition will begin in early May and continue in 8-day segments through the end of June.
"Each dive will consist of the deployment of the 5-person submersible Titan, which has a 4,000m/13,120 ft. depth capability (with a comfortable safety margin). Constructed of titanium and filament wound carbon fiber, the innovative vessel has proven to be a safe and comfortable vessel proven to withstand the enormous pressures of the deep ocean," the letter states.
The participating scientists and archaeologists on previous dives "are compiling and analyzing theirfindings. The company and science team collaborated with eDNAtec, headquartered in St. John’s Newfoundland, to analyze environmental DNA found in water samples collected near the wreck and at a natural reef site nearby. This collaboration will continue in 2023. eDNAtec intends to make all gene sequences available through GenBank at the conclusion of their analysis."
May 26, 2023: Titanic expedition underway
Ocean Gate Expeditions tweets a photo of 24 people on deck, saying: "It's been an exciting week with our Mission 2 crew!"
June 1, 2023: In the 'middle of the North Atlantic'
OceanGate Expeditions tweets "Despite being in the middle of the North Atlantic, we have the internet connection we need to make our #Titanic dive operations a success - thank you @Starlink!"
June 15, 2023: Missions underway
OceanGate tweets: "Despite being in the middle of the North Atlantic, we have the internet connection we need to make our #Titanic dive operations a success - thank you @Starlink !"
June 17, 2023: Harding posts dive planned next day
Hamish Harding, chairman of Action Aviation, posts on Facebook that he has joined OceanGate Expeditions for the Titan mission and will be on an attempted dive on June 18.
June 18, 2023: Day ends in disaster
8:00 a.m. – Titan begins a descent from the Canadian research vessel the Polar Prince to the Titanic wreck, a trip expected to take two hours to reach the ocean floor, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
9:45 a.m. – Communications cease between the Titan and its mothership , about 90 minutes into the trip.
Unknown time – Navy acoustic equipment detects an "anomaly" in the vicinity of the site.
3:00 p.m. – Titan fails to appear at the expected time for resurfacing
5:40 p.m. – Coast Guard receives a report on an overdue 21-foot submersible, with five people on board, diving to view the wreckage of the Titanic , approximately 900 nautical miles East of Cape Cod.
June 19, 2023: Search underway
Coast Guard says one of its C-130 Hercules aircraft and crew, as well as a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar capability, are searching for the submersible.
June 20, 2023: Hope flares
The Canadian aircraft reports hearing "underwater noises in the search area."
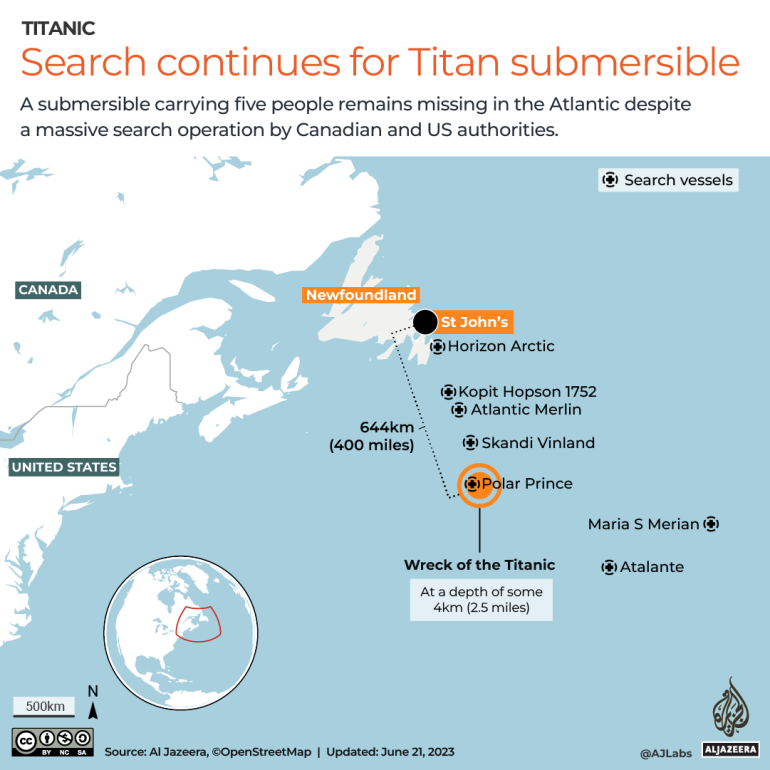
Coast Guard establishes a command to help coordinate multiple vessels conducting search operations, says 10,000 square miles have been searched, including a Bahamian research vessel using a remotely operated vehicle and another C-130 crew. Coast Guard reports eight vessels enroute, including five Canadian ships, a French research vessel, the motor vessel Horizon Arctic and the commercial vessel Skandi Vinland.
June 21, 2023: Search continues
Coast Guard reports a third C-130 enroute, as well as a Magellan ROV. The Navy is sending experts and a Deep Ocean Salvage System designed to lift underwater objects.
June 22, 2023: Debris field located
11:48 a.m. Coast Guard announces a debris field has been discovered by an ROV from the Horizon Arctic near the Titanic, likely the result of a catastrophic implosion.
OceanGate announces the crew of the Titan has been lost.
June 23, 2023: Lawsuit dropped
The Hagles, adventurers who became the first married couple on a commercial spaceflight last year , drop their lawsuit. They state: “Money is a driving force in our economy, but honor, respect and dignity are more important to the human soul."
June 24, 2023: Canada to investigate
Canada's Transportation Safety Board says it will investigate the Polar Prince , Titan's mothership, owned by Horizon Maritime. The company also owns the Horizon Arctic, the ship whose crew found the Titan wreckage.
June 25, 2023: Coast Guard to investigate
The Coast Guard says its Marine Board of Investigation will lead an investigation into the loss of the Titan. The MBI'S chairman, Capt. Jason Neubauer, says his primary goal is to "prevent a similar occurrence by making the necessary recommendations to advance the safety of the maritime domain worldwide."
June 28, 2023: Titan debris recovered
The Horizon Arctic vessel brings pieces of the Titan back to shore in St. John's, Newfoundland. After consulting with international partners, the Coast Guard intends to take the evidence to a U.S. port for further analysis and testing. A news release says medical professionals will conduct " a formal analysis of presumed human remains that have been carefully recovered within the wreckage ."
July 2, 2023: OceanGate shutting down
OceanGate Expeditions updates its website to say it is ceasing operations .
Contributing: Grace Hauck
Missing sub: Mapping and visualizing debris found near titanic
Follow the timeline of the Titan submersible's journey from departure to tragic discovery
How the wrecks of the titanic and the titan came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions., by holly ramer • published june 24, 2023 • updated on june 24, 2023 at 9:14 am.
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions.
The buildup
The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner's watery gravesite. Three missions involving other teams had been scrapped due to bad weather in the previous four weeks, but the latest OceanGate Expeditions group was hopeful.
“A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,” renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram. “More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
We're making it easier for you to find stories that matter with our new newsletter — The 4Front. Sign up here and get news that is important for you to your inbox.
The dive down
Moving about the Polar Prince, mission participants were required to wear water-activated life vests, bright orange jackets, helmets and steel-toed boots, said Arnie Weissmann, a journalist who spent eight days aboard the support ship in May before his mission was aborted. Just before a dive, they’d change into fleece vests, black flight suits bearing the OceanGate logo and warm socks — no shoes allowed on the submersible.
The team was carried to the Titan’s launch and recovery platform by one of two inflatable dinghies named Stewie and Max. Once inside, they would sit on a platform, with their legs crossed or out straight.
U.S. & World
The day's top national and international news.

Tupac's estate threatens to sue Drake over diss track using what appears to be late rapper's AI-generated voice

New York appeals court overturns Harvey Weinstein's 2020 rape conviction from landmark #MeToo trial
“You could not be in that thing if you’re claustrophobic,” Weissmann said. “It’s literally like being in a tin can because it’s got rounded sides.”
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
“Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean,” the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. “The descent takes approximately two hours but it feels like the blink of an eye.”
On Sunday, the vessel lost contact with the Polar Prince around 10:45 a.m.
At 5:40 p.m., nearly three hours after the Titan was expected to resurface and nearly eight hours after the last communication, the Polar Prince notified the U.S. Coast Guard that the vessel was overdue, setting off an intense international search and rescue.
After the craft was reported missing, the U.S. Navy analyzed its acoustic data and found an anomaly that was “consistent with an implosion or explosion in the general vicinity of where the Titan submersible was operating when communications were lost,” a senior Navy official later told The Associated Press. Though it wasn’t made public at the time, the Navy passed on that information on Sunday to the Coast Guard, which continued its search because the Navy did not consider the data to be definitive, according to the official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive technology.
By Monday afternoon, a C-130 Hercules aircraft from North Carolina and a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar equipment joined the search. Tuesday brought better weather and increased visibility, and by that morning, 10,000 square miles (25,900 square kilometers) had been searched.
A U.S. Air National Guard crew arrived that day, as did a Bahamian research vessel, Deep Energy, which deployed camera-equipped, remote-operated robots.
Meanwhile, sonar equipment detected banging noises Tuesday night and Wednesday morning, sparking hope that those aboard the Titan were still alive.
“We are smack dab in the middle of search and rescue, and we’ll continue to put every available asset that we have in an effort to find the Titan and the crew members,” Captain Jamie Frederick of the First Coast Guard District said at a news conference Wednesday afternoon.
By then, crews had scoured an area twice the size of Connecticut in waters 2½ miles (4 kilometers) deep. More resources were on the way, including multiple remote-operated vehicles, a salvage system capable of recovering heavy undersea objects and a mobile hyperbaric recompression chamber. Time was running out. The submersible was only equipped with enough air to last until sometime the next morning.
The discovery
On Thursday morning, a robotic vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan on the ocean floor, followed by the front and back ends of the Titan’s hull.
“The debris is consistent with the catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber,” said Rear Adm. John Mauger of the First Coast Guard District.
On its website before the expedition, OceanGate told future participants what to expect upon resurfacing.
“Once on deck, you will be welcomed back by the expedition crew and be able to share the story of your incredible accomplishment,” said the company, which already had scheduled dates for a 2024 expedition.
On Thursday, the company issued a statement mourning those killed, including company CEO and pilot Stockton Rush. In addition to Rush and Harding, the others on board were Titanic expert Paul-Henri Nargeolet and two members of a prominent Pakistani family, Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood.
“These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans,” OceanGate said. “We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
This article tagged under:
Titan sub timeline: When did it go missing and other key events
A timeline of events surrounding the trip to the Titanic wreck for the submersible that suffered a ‘catastrophic implosion’.

The five people on board a submersible visiting the wreck of the Titanic died after a “catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber.”
A “debris field” matching the submersible was discovered by a robotic deep-sea vessel on Thursday.
Keep reading
Titanic sub: crews exploring undersea noises in ‘complex’ search, titanic sub suffered ‘catastrophic implosion’: all we know, ‘catastrophic’: missing titanic sub likely imploded, killing crew.
Here is a timeline of the events leading up to the discovery:
Friday, June 16
The expedition sets off from St John’s, Newfoundland, Canada.
We've been working hard to get ready for our 2023 Titanic Expedition that begins next month. We moved @OceanGate 's sub, Titan, to The Launch at the @marineinstitute for final preparations. The Launch has brand-new facilities with everything we need to prepare for expedition! pic.twitter.com/iLgs6CJXUI — OceanGate Expeditions (@OceanGateExped) April 21, 2023
Saturday, June 17
British billionaire and adventurer Hamish Harding , one of those on board the submersible, posts on Facebook: “Due to the worst winter in Newfoundland in 40 years, this mission is likely to be the first and only manned mission to the Titanic in 2023. A weather window has just opened up, and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow.”
“More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
This was his last post on Facebook.
Sunday, June 18
04am ET (08:00 GMT) – This is when the submersible was originally planned to start its descent, according to a post by Harding on Instagram . But the descent starts four hours later, according to the US Coast Guard.
8am ET (12:00 GMT) – Titan submersible starts what should be a two-hour descent to the Titanic wreck, which lies at a depth of 13,000 feet (4,000 meters) in the North Atlantic, US Coast Guard says.
9:45am ET (13:45 GMT) – Communications between the submersible and the surface vessel are lost an hour and 45 minutes after starting its descent, the US Coast Guard says.
3pm ET (19:00 GMT) – The submersible is scheduled to return to the surface, the US Coast Guard says. It fails to appear.
5:40pm ET (21:40 GMT) – Coast Guard receives a report about an overdue submersible from the Canadian research vessel Polar Prince with five people on board diving to view the Titanic wreck about 900 nautical miles (1667km) east of Cape Cod on the US coast.

Monday, June 19
US and Canadian ships and planes are swarming the area, some dropping sonobuoys that can monitor to a depth of 13,000 feet (4,000 metres), US Coast Guard Rear Admiral John Mauger says. He adds it is a remote area and a challenge to conduct a search. Officials have also asked commercial vessels for help.
Officials say if the submersible is still intact, it is estimated to have between 70 and 96 hours of oxygen.
Tuesday, June 20
Morning – The family of Pakistani-born businessman Shahzada Dawood confirms he is on board with his 19-year-old son Suleman.
10:50am ET (14:50 GMT) – France says it will help with the search by deploying Atalante, a ship equipped with a deep-sea diving vessel.
During the day – Sounds detected over several hours by Canadian Lockheed P-3 Orion aircraft, equipped with gear to trace submarines. The US Coast Guard – which announces this on Wednesday – does not give a precise timing.
Media reports say Canadian aircraft detected banging sounds at 30-minute intervals.
Harding’s friend, Jannicke Mikkelsen, says: “And as it stands right now, it would be a miracle if they are recovered alive.”
The search becomes a big international operation . More ships, underwater vessels and aircraft join the mission.

Wednesday, June 21
During the day – US Coast Guard, US Navy, Canadian Coast Guard and OceanGate Expeditions establish a unified command to handle the search .
2am ET (06:00 GMT) – US Coast Guard announces Canadian P-3 aircraft detected underwater noises . It says remotely operated vehicle (ROV) searches are directed to the area of the sounds and the data are also sent to US Navy experts for analysis.
Thursday, June 22
6am (10:00 GMT) – Rough deadline for when the oxygen in the submersible will run out, based on the US Coast Guard’s estimate. The vessel has 96 hours of supply from the time it is sealed, according to its specifications. This depends on the vessel being intact and other factors, such as whether the sub still has power in the icy depths.
2pm (18:00 GMT) – A debris field that was found near the wreckage of the Titanic in the North Atlantic contains the pieces of the Titan submersible, officials said.
3pm (19:00 GMT) – The debris was consistent with loss of the pressure chamber and an implosion, the US Coast Guard said. There were no survivors, it added.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Titan submersible: timeline of vessel’s voyage
As the US Coast Guard announces the vessel suffered a ‘catastrophic implosion’, we chart its journey over the last week
- Titanic sub: latest updates
The expedition sets off from St John’s, Newfoundland, Canada.
The British billionaire and adventurer Hamish Harding , one of those onboard the submersible, posts on Facebook: “Due to the worst winter in Newfoundland in 40 years, this mission is likely to be the first and only manned mission to the Titanic in 2023. A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow.”

8am GMT/ 4am ET: Time the submersible originally aimed to start its descent, according to a post by Harding on Instagram. It actually started its descent later, according to the US Coast Guard.
12pm GMT/ 8am ET: The submersible starts what should be a two-hour descent to the Titanic wreck, nearly 4,000 metres down, according to the US Coast Guard.
1 .45pm GMT/ 9.45am ET: Communications between the submersible and the surface vessel are lost 1 hour and 45 minutes after starting its descent.

7pm GMT/ 3pm ET: Titan is scheduled to return to the surface, the US Coast Guard says, but fails to appear.
9.40pm GMT/ 5.40pm ET: US Coast Guard receives report about an overdue submersible from the research vessel Polar Prince about 900 nautical miles east of Cape Cod on the US coast.
US and Canadian ships and planes are swarming the area , some dropping sonar buoys that can monitor to a depth of almost 4,000 metres, US Coast Guard R Adm John Mauger says. Officials have also asked commercial vessels for help.
2.50pm GMT/ 10am ET: France says it will help with search by deploying Atalante, a ship equipped with a deep-sea diving vessel. It is expected to arrive late on Wednesday.

During the day: Sounds detected over several hours by Canadian Lockheed P-3 Orion aircraft, equipped with gear to trace submarines. CNN and Rolling Stone magazine report banging sounds at 30-minute intervals had been detected.
US Coast Guard, US Navy, Canadian Coast Guard and OceanGate Expeditions establish a unified command to handle the search.
6 am GMT/ 2am ET: US Coast Guard confirms Canadian P-3 aircraft detected underwater noises . It says remotely operated vehicle (ROV) searches are directed to the area of the sounds and the data is also sent to US Navy experts for analysis.
5pm GMT/1pm ET: US Coast Guard says more underwater noises were detected and that the search area had increased to “two times the size of Connecticut”.
Late on Wednesday: More vessels, including a French research ship, equipped with a deep-sea diving vessel, were due to arrive to assist the “complex response effort”, which covers an area twice the size of Connecticut.

10 am GMT/ 6am ET: Approximate deadline for when the air in the submersible was expected to run out, based on the US Coast Guard’s estimate that the Titan could have up to 96 hours of air supply from the time it was sealed.
Around 12pm GMT/8am ET: Two remotely operated vehicles have been deployed as part of the search effort. Experts say it is still unclear whether the submersible is on the surface or on the seabed, and warn “weeks of intense survey” may be required to locate it.
Around 3pm GMT/11am ET: Canadian navy ship carrying a medical team specialising in dive medicine arrives on the scene.
3.48pm GMT/ 11.48am ET: The US Coast Guard say a debris field was discovered within the search area by a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) near the Titanic wreck.
7pm GMT/ 3pm ET: US Coast Guard to hold press conference after announcing discovery of debris.
8pm GMT/4pm ET: Five crew members aboard the submersible Titan were probably killed instantly in a “catastrophic implosion”, the US Coast Guard said. Rear Adm John Mauger, the First Coast Guard District commander, said a remotely operated vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan sub and the debris is “consistent with a catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber”. A large debris field containing five major pieces of the vessel wasspotted by a remotely operated vehicle scouring the seabed near the Titanic wreck site 400 miles south of St John’s, Newfoundland, officials said.

This article was amended on 22 June 2023 to correct the time conversion from GMT to ET.
- Titanic sub incident
- The Titanic

Mother of teenager who died on Titan sub says she gave her place to son

Ross Kemp turned down trip on Titanic submersible over safety fears

Titan submersible: why was its implosion not announced sooner?

Investigations under way into loss of Titan sub as questions grow over its design

US navy says it picked up ‘anomaly’ hours after sub began mission – as it happened

Titanic sub crew believed to have died instantly in ‘catastrophic implosion’
Titanic sub: what we know about the victims of deep-sea tragedy.

Titan submersible: 19-year-old was a student at university in Glasgow

Titan sub implosion: what we know at a glance
Most viewed.
Titan: Timeline of the sub from departure to tragic discovery
'A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,' renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram
Author of the article:
You can save this article by registering for free here . Or sign-in if you have an account.
Article content
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions.
Titan: Timeline of the sub from departure to tragic discovery Back to video
The buildup.
The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner’s watery gravesite. Three missions involving other teams had been scrapped due to bad weather in the previous four weeks, but the latest OceanGate Expeditions group was hopeful.
Enjoy the latest local, national and international news.
- Exclusive articles by Conrad Black, Barbara Kay, Rex Murphy and others. Plus, special edition NP Platformed and First Reading newsletters and virtual events.
- Unlimited online access to National Post and 15 news sites with one account.
- National Post ePaper, an electronic replica of the print edition to view on any device, share and comment on.
- Daily puzzles including the New York Times Crossword.
- Support local journalism.
Create an account or sign in to continue with your reading experience.
- Access articles from across Canada with one account.
- Share your thoughts and join the conversation in the comments.
- Enjoy additional articles per month.
- Get email updates from your favourite authors.
Don't have an account? Create Account
“A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,” renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram. “More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
THE DIVE DOWN
Moving about the Polar Prince, mission participants were required to wear water-activated life vests, bright orange jackets, helmets and steel-toed boots, said Arnie Weissmann, a journalist who spent eight days aboard the support ship in May before his mission was aborted. Just before a dive, they’d change into fleece vests, black flight suits bearing the OceanGate logo and warm socks — no shoes allowed on the submersible.
The team was carried to the Titan’s launch and recovery platform by one of two inflatable dinghies named Stewie and Max. Once inside, they would sit on a platform, with their legs crossed or out straight.
“You could not be in that thing if you’re claustrophobic,” Weissmann said. “It’s literally like being in a tin can because it’s got rounded sides.”
Get a dash of perspective along with the trending news of the day in a very readable format.
- There was an error, please provide a valid email address.
By signing up you consent to receive the above newsletter from Postmedia Network Inc.
A welcome email is on its way. If you don't see it, please check your junk folder.
The next issue of NP Posted will soon be in your inbox.
We encountered an issue signing you up. Please try again
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
“Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean,” the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. “The descent takes approximately two hours but it feels like the blink of an eye.”
On Sunday, the vessel lost contact with the Polar Prince around 10:45 a.m.
At 5:40 p.m., nearly three hours after the Titan was expected to resurface and nearly eight hours after the last communication, the Polar Prince notified the U.S. Coast Guard that the vessel was overdue, setting off an intense international search and rescue.
After the craft was reported missing, the U.S. Navy analyzed its acoustic data and found an anomaly that was “consistent with an implosion or explosion in the general vicinity of where the Titan submersible was operating when communications were lost,” a senior Navy official later told The Associated Press. Though it wasn’t made public at the time, the Navy passed on that information on Sunday to the Coast Guard, which continued its search because the Navy did not consider the data to be definitive, according to the official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive technology.
By Monday afternoon, a C-130 Hercules aircraft from North Carolina and a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar equipment joined the search. Tuesday brought better weather and increased visibility, and by that morning, 10,000 square miles (25,900 square kilometers) had been searched.
A U.S. Air National Guard crew arrived that day, as did a Bahamian research vessel, Deep Energy, which deployed camera-equipped, remote-operated robots.
Meanwhile, sonar equipment detected banging noises Tuesday night and Wednesday morning, sparking hope that those aboard the Titan were still alive.
“We are smack dab in the middle of search and rescue, and we’ll continue to put every available asset that we have in an effort to find the Titan and the crew members,” Captain Jamie Frederick of the First Coast Guard District said at a news conference Wednesday afternoon.
By then, crews had scoured an area twice the size of Connecticut in waters 2 1/2 miles (4 kilometers) deep. More resources were on the way, including multiple remote-operated vehicles, a salvage system capable of recovering heavy undersea objects and a mobile hyperbaric recompression chamber. Time was running out. The submersible was only equipped with enough air to last until sometime the next morning.
THE DISCOVERY
On Thursday morning, a robotic vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan on the ocean floor, followed by the front and back ends of the Titan’s hull.
“The debris is consistent with the catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber,” said Rear Adm. John Mauger of the First Coast Guard District.
On its website before the expedition, OceanGate told future participants what to expect upon resurfacing.
“Once on deck, you will be welcomed back by the expedition crew and be able to share the story of your incredible accomplishment,” said the company, which already had scheduled dates for a 2024 expedition.
On Thursday, the company issued a statement mourning those killed, including company CEO and pilot Stockton Rush. In addition to Rush and Harding, the others on board were Titanic expert Paul-Henri Nargeolet and two members of a prominent Pakistani family, Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood.
“These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans,” OceanGate said. “We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
Our website is the place for the latest breaking news, exclusive scoops, longreads and provocative commentary. Please bookmark nationalpost.com and sign up for our newsletters here .
Postmedia is committed to maintaining a lively but civil forum for discussion. Please keep comments relevant and respectful. Comments may take up to an hour to appear on the site. You will receive an email if there is a reply to your comment, an update to a thread you follow or if a user you follow comments. Visit our Community Guidelines for more information.
FIRST READING: The unintended consequences of the capital gains hike are starting to pile up
Cupe president silences members who call her out for wearing keffiyeh at union meeting, carson jerema: toronto star, cbc debase themselves with poilievre hit job.

'Nessie' photo at Scotland's Loch Ness puts Canadians in media spotlight
Jamie sarkonak: want to save canada save marriage, new star wars lego sets released for 2024.
Celebrating 25 years of Star Wars LEGO
Sun’s out, legs out! Here are 5 stylish shorts and skirts to try this season
From pleated skirts to 24-7 shorts, Rebecca Tay showcases five options to set up for the season ahead.
Advertisement 2 Story continues below This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Fashion brands that prioritize sustainable manufacturing
How these fashion brands are prioritizing sustainability
Top spring cleaning tips from Melissa Maker of YouTube’s Clean My Space
Maker celebrates International Creator Day

Best Buy’s electronic recycling trade-in program a simple way to contribute to circular economy
Celebrate Earth Day and upgrade your tech
This website uses cookies to personalize your content (including ads), and allows us to analyze our traffic. Read more about cookies here . By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy .
You've reached the 20 article limit.
You can manage saved articles in your account.
and save up to 100 articles!
Looks like you've reached your saved article limit!
You can manage your saved articles in your account and clicking the X located at the bottom right of the article.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Credit card rates
- Balance transfer credit cards
- Business credit cards
- Cash back credit cards
- Rewards credit cards
- Travel credit cards
- Checking accounts
- Online checking accounts
- High-yield savings accounts
- Money market accounts
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Car insurance
- Home buying
- Options pit
- Investment ideas
- Research reports
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Follow the timeline of the Titan submersible's journey from departure to tragic discovery
Titanic tourist sub tick tock.
- Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later. More content below
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions.
THE BUILDUP
The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner's watery gravesite. Three missions involving other teams had been scrapped due to bad weather in the previous four weeks, but the latest OceanGate Expeditions group was hopeful.
“A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,” renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram. “More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
THE DIVE DOWN
Moving about the Polar Prince, mission participants were required to wear water-activated life vests, bright orange jackets, helmets and steel-toed boots, said Arnie Weissmann, a journalist who spent eight days aboard the support ship in May before his mission was aborted. Just before a dive, they’d change into fleece vests, black flight suits bearing the OceanGate logo and warm socks — no shoes allowed on the submersible.
The team was carried to the Titan’s launch and recovery platform by one of two inflatable dinghies named Stewie and Max. Once inside, they would sit on a platform, with their legs crossed or out straight.
“You could not be in that thing if you’re claustrophobic,” Weissmann said. “It’s literally like being in a tin can because it’s got rounded sides.”
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
“Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean,” the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. “The descent takes approximately two hours but it feels like the blink of an eye.”
On Sunday, the vessel lost contact with the Polar Prince around 10:45 a.m.
At 5:40 p.m., nearly three hours after the Titan was expected to resurface and nearly eight hours after the last communication, the Polar Prince notified the U.S. Coast Guard that the vessel was overdue, setting off an intense international search and rescue.
After the craft was reported missing, the U.S. Navy analyzed its acoustic data and found an anomaly that was “consistent with an implosion or explosion in the general vicinity of where the Titan submersible was operating when communications were lost,” a senior Navy official later told The Associated Press. Though it wasn’t made public at the time, the Navy passed on that information on Sunday to the Coast Guard, which continued its search because the Navy did not consider the data to be definitive, according to the official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive technology.
By Monday afternoon, a C-130 Hercules aircraft from North Carolina and a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar equipment joined the search. Tuesday brought better weather and increased visibility, and by that morning, 10,000 square miles (25,900 square kilometers) had been searched.
A U.S. Air National Guard crew arrived that day, as did a Bahamian research vessel, Deep Energy, which deployed camera-equipped, remote-operated robots.
Meanwhile, sonar equipment detected banging noises Tuesday night and Wednesday morning, sparking hope that those aboard the Titan were still alive.
“We are smack dab in the middle of search and rescue, and we’ll continue to put every available asset that we have in an effort to find the Titan and the crew members,” Captain Jamie Frederick of the First Coast Guard District said at a news conference Wednesday afternoon.
By then, crews had scoured an area twice the size of Connecticut in waters 2½ miles (4 kilometers) deep. More resources were on the way, including multiple remote-operated vehicles, a salvage system capable of recovering heavy undersea objects and a mobile hyperbaric recompression chamber. Time was running out. The submersible was only equipped with enough air to last until sometime the next morning.
THE DISCOVERY:
On Thursday morning, a robotic vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan on the ocean floor, followed by the front and back ends of the Titan’s hull.
“The debris is consistent with the catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber,” said Rear Adm. John Mauger of the First Coast Guard District.
On its website before the expedition, OceanGate told future participants what to expect upon resurfacing.
“Once on deck, you will be welcomed back by the expedition crew and be able to share the story of your incredible accomplishment,” said the company, which already had scheduled dates for a 2024 expedition.
On Thursday, the company issued a statement mourning those killed, including company CEO and pilot Stockton Rush. In addition to Rush and Harding, the others on board were Titanic expert Paul-Henri Nargeolet and two members of a prominent Pakistani family, Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood.
“These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans,” OceanGate said. “We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
Recommended Stories
Based on the odds, here's what the top 10 picks of the nfl draft will be.
What would a mock draft look like using just betting odds?
Broncos, Jets, Lions and Texans have new uniforms. Let's rank them
Which new uniforms are winners this season?
Jamie Dimon is worried the US economy is headed back to the 1970s
JPMorgan's CEO is concerned the US economy could be in for a repeat of the stagflation that hampered the country during the 1970s.
Luka makes Clippers look old, Suns are in big trouble & a funeral for Lakers | Good Word with Goodwill
Vincent Goodwill and Tom Haberstroh break down last night’s NBA Playoffs action and preview several games for tonight and tomorrow.
These are the cars being discontinued for 2024 and beyond
As automakers shift to EVs, trim the fat on their lineups and cull slow-selling models, these are the vehicles we expect to die off soon.
Everyone's still talking about the 'SNL' Beavis and Butt-Head sketch. Cast members and experts explain why it's an instant classic.
Ryan Gosling, who starred in the skit, couldn't keep a straight face — and neither could some of the "Saturday Night Live" cast.
Dave McCarty, player on 2004 Red Sox championship team, dies 1 week after team's reunion
The Red Sox were already mourning the loss of Tim Wakefield from that 2004 team.
Ryan Garcia drops Devin Haney 3 times en route to stunning upset
The 25-year-old labeled "mentally fragile" by many delivered the upset for the ages.
WNBA Draft winners and losers: As you may have guessed, the Fever did pretty well. The Liberty? Perhaps not
Here are five franchises who stood out, for better or for worse.
Arch Manning dominates in the Texas spring game, and Jaden Rashada enters the transfer portal
Dan Wetzel, Ross Dellenger & SI’s Pat Forde react to the huge performance this weekend by Texas QB Arch Manning, Michigan and Notre Dame's spring games, Jaden Rashada entering the transfer portal, and more
Chiefs make Andy Reid NFL's highest-paid coach, sign president Mark Donovan, GM Brett Veach to extensions
Reid's deal reportedly runs through 2029 and makes him the highest-paid coach in the NFL.
Yankees' Nestor Cortés told by MLB his pump-fake pitch is illegal
Cortés' attempt didn't fool Andrés Giménez, who fouled off the pitch.
Here’s when people think old age begins — and why experts think it’s starting later
People's definition of "old age" is older than it used to be, new research suggests.
Donald Trump nabs additional $1.2 billion 'earnout' bonus from DJT stock
Trump is entitled to an additional 36 million shares if the company's share price trades above $17.50 "for twenty out of any thirty trading days" over the next three years.
Retirement confidence in the US ticks up; new rule for financial advisors is set to start
Two-thirds of Americans reported that they feel confident they have enough money for a comfortable retirement, up a notch from last year.
2024 NFL mock draft: With one major trade-up, it's a QB party in the top 5
Our final 2024 mock draft projects four quarterbacks in the first five picks, but the Cardinals at No. 4 might represent the key pivot point of the entire board.
GDP: US economy grows at 1.6% annual pace in first quarter, falling short of estimates
The reading of first quarter economic growth comes at a crucial time as investors digest the potential impacts of the Fed holding interest rates higher for longer.
Oakland University outfielders combine to make spectacular catch vs. Northern Kentucky
Oakland University outfielders John Lauinger and Reggie Bussey combined on what could be college baseball's best catch of the 2024 season against Northern Kentucky.
Dylan Edwards set to be latest Colorado running back to enter transfer portal
All four rushers who had more than 10 carries in 2023 for the Buffaloes are transferring.
NBA Playoffs: Lillard sinks the Pacers, Celtics-Heat controversy, plus injury concerns for Kawhi & Embiid
Vincent Goodwill and Amin Elhassan react to (just about) every Round 1 game of the NBA Playoffs after the first games have been played over the weekend.
Follow live: The Supreme Court tackles claims that Trump has total immunity from criminal charges. Listen to live arguments.
Titan passengers share eerie accounts of safety issues on the submersible's past expeditions
The Titan was touted as a groundbreaking submersible that could give tourists the extraordinary chance to visit the deep-sea grave of the Titanic — but past passengers have shared chilling accounts of safety issues, communication failures and design concerns.
The desperate search for the missing submersible ended Thursday with the Coast Guard announcing that debris from the vessel was found. The five passengers are presumed dead.
It brings a close to the four-day race to find the Titan after it lost contact with its mother ship during a Sunday dive to the Titanic, 12,500 feet below the surface.
The 21-foot, carbon fiber and titanium submersible fit five people, with no seats and a curtained-off area for a makeshift bathroom.
Malfunctions left passengers like 'sitting ducks'
Brian Weed, 42, a camera operator for Discovery Channel’s “Expedition Unknown,” did a test dive on the Titan in May 2021 and said, “The moment we started the test dive, things started going wrong.”
The submersible descended, but not all the way to the shipwreck.
The launch was “clumsy,” and less than a quarter of the dive in, “there were malfunctions with the propulsion system,” leaving the passengers like “sitting ducks in the water,” Weed said.
“This was supposedly two months before they were supposed to take their first dive down to the Titanic, and that was very worrying for me. We were supposed to be on one of those first dives,” he said.
He was also concerned that the door was bolted from the outside, saying, “There’s still a potential that there’s no way out even if you’re on the surface.”
But it was the allure of the Titanic — the ocean liner that sank on its maiden voyage from England to New York in 1912 — that drew him to the project.
“The thought of going down and seeing the Titanic really clouds your mind. You want this to be possible. You want this to be true. Your brain is willing to overlook some really glaring problems,” he said.
“The thought of going down and seeing the Titanic really clouds your mind. You want this to be possible. You want this to be true. Your brain is willing to overlook some really glaring problems.”
Weed declined an invitation to dive again a week later.
Weed, no stranger to risky situations, said that “something about this felt like there wasn’t a plan” and that “the reward is not worth the risk.”
Josh Gates, the host of “Expedition Unknown,” told NBC News’ Tom Costello on that dive: “We had issues with thruster control. We had issues with the computers aboard. We had issues with comms."
“I just felt as though the sub needed more time and it needed more testing, frankly,” he said.
OceanGate completed successful expeditions to the wreckage in 2021 and 2022 before the Titian disappeared on the third trip.
Lost communications; wandering for hours underwater
Colin Taylor, who went on the submersible when it explored the Titanic site last July with his 22-year-old son, described the communication system as “very difficult.”

“There’s a text-based communication system that’s two-way, very slow,” he said. “I mean, when you’re sending signals through that amount of water, it’s very, very difficult.”
Mike Reiss, a writer and producer who has worked on “The Simpsons,” told ABC News he went on four 10-hour dives with OceanGate, including to the Titanic. The crews lost communication with the host ship each time.
When his vessel touched the bottom of the ocean on one of his OceanGate journeys to the Hudson Canyon, “a loud squawk came on the radio,” he recalled in an e pisode of the podcast “What Am I Doing Here?” that aired a year ago.
“The sonar, the computers, the lights all stopped working. We went back to the surface immediately,” he said.
Two years later, he took another expedition to the Titanic site in the submersible, describing it as “a car that you drunkenly drove into the ocean” steered by a video game controller.
When the team touched down, they faced a myriad of issues.
"We were nowhere near the Titanic. There were underwater currents pushing us farther and farther in the wrong direction. The sonar wasn’t working, and the compass kept flopping from east to west, north to south," he said. "There was also a time crunch. We started late, and there was a hurricane rolling in on the surface.”
David Pogue, a CBS News correspondent, tweeted that last year the submersible got “lost on the seafloor" for about five hours when he was on an OceanGate expedition to the Titanic’s resting place. A segment on the trip aired in November .
Pogue wasn’t in the Titan — he was in a control room on a ship at the surface.
“They could still send short texts to the sub, but did not know where it was. It was quiet and very tense,” he tweeted Monday.
Former employee warned Titan's shell wasn't tested to descend deep safely
A former OceanGate pilot, David Lochridge, who was hired to run manned tests of submersibles, claimed five years ago in court papers that he was fired after he warned that the Titan’s carbon shell was not properly tested to ensure it could descend safely to 4,000 meters, the estimated depth of the Titanic.
He also claimed OceanGate refused to pay extra for a viewport that could be used safely at a depth of 4,000 meters.
When he complained that OceanGate would be endangering customers, Lochridge said in the court papers, he was given “10 minutes to immediately clear out his desk.”
Lochridge’s claims, which were first reported by The New Republic , were in his counterclaim to a 2018 breach of contract lawsuit OceanGate filed saying he was not an engineer. The two sides settled a few months later. The details of the settlement were unclear.
Expeditions are always a 'risk'
Aaron Newman, a former passenger on the missing Titan and an investor in OceanGate, said he felt “safe” during his journey but acknowledged that risks are involved in such expeditions.
“They were a professional crew. They did a lot of training around safety and the backup systems around dropping weights,” Newman said. “We’re going places that a very few people have been. This is inventing things. There are risks, right? And we know that.”
Newman said the explorers on the missing submersible — OceanGate CEO Stockton Rush, British billionaire Hamish Harding, French dive expert Paul Henry Nargeolet, and prominent Pakistani businessman Shahzada Dawood and his son, Suleman — are a “good set of people” who were likely doing what they could “to stay alive.”
Arthur Loibl, 61, a retired businessman and adventurer from Germany, went on a voyage to the Titanic site in 2021 with Rush and Nargeolet, he told The Associated Press .
He said that while he was able to get a view of the iconic ocean liner, in hindsight he felt “a bit dubious” about how the dive was carried out.
“I was a bit naive, looking back now,” he said. “It was a kamikaze operation.”
Breaking News Reporter
Melissa Chan is a reporter for NBC News Digital with a focus on veterans’ issues, mental health in the military and gun violence.
Follow the Timeline of the Titan Submersible's Journey From Departure to Tragic Discovery
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet and 111 years of history
Follow the Timeline of the Titan Submersible's Journey From Departure to Tragic Discovery

FILE - This photo provided by OceanGate Expeditions shows a submersible vessel named Titan used to visit the wreckage site of the Titanic. The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions. (OceanGate Expeditions via AP, File)
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions.
THE BUILDUP
The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner's watery gravesite. Three missions involving other teams had been scrapped due to bad weather in the previous four weeks, but the latest OceanGate Expeditions group was hopeful.
“A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,” renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram. “More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
THE DIVE DOWN
Moving about the Polar Prince, mission participants were required to wear water-activated life vests, bright orange jackets, helmets and steel-toed boots, said Arnie Weissmann, a journalist who spent eight days aboard the support ship in May before his mission was aborted. Just before a dive, they’d change into fleece vests, black flight suits bearing the OceanGate logo and warm socks — no shoes allowed on the submersible.
Photos You Should See - April 2024

The team was carried to the Titan’s launch and recovery platform by one of two inflatable dinghies named Stewie and Max. Once inside, they would sit on a platform, with their legs crossed or out straight.
“You could not be in that thing if you’re claustrophobic,” Weissmann said. “It’s literally like being in a tin can because it’s got rounded sides.”
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
“Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean,” the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. “The descent takes approximately two hours but it feels like the blink of an eye.”
On Sunday, the vessel lost contact with the Polar Prince around 10:45 a.m.
At 5:40 p.m., nearly three hours after the Titan was expected to resurface and nearly eight hours after the last communication, the Polar Prince notified the U.S. Coast Guard that the vessel was overdue, setting off an intense international search and rescue.
After the craft was reported missing, the U.S. Navy analyzed its acoustic data and found an anomaly that was “consistent with an implosion or explosion in the general vicinity of where the Titan submersible was operating when communications were lost,” a senior Navy official later told The Associated Press. Though it wasn’t made public at the time, the Navy passed on that information on Sunday to the Coast Guard, which continued its search because the Navy did not consider the data to be definitive, according to the official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive technology.
By Monday afternoon, a C-130 Hercules aircraft from North Carolina and a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar equipment joined the search. Tuesday brought better weather and increased visibility, and by that morning, 10,000 square miles (25,900 square kilometers) had been searched.
A U.S. Air National Guard crew arrived that day, as did a Bahamian research vessel, Deep Energy, which deployed camera-equipped, remote-operated robots.
Meanwhile, sonar equipment detected banging noises Tuesday night and Wednesday morning, sparking hope that those aboard the Titan were still alive.
“We are smack dab in the middle of search and rescue, and we’ll continue to put every available asset that we have in an effort to find the Titan and the crew members,” Captain Jamie Frederick of the First Coast Guard District said at a news conference Wednesday afternoon.
By then, crews had scoured an area twice the size of Connecticut in waters 2½ miles (4 kilometers) deep. More resources were on the way, including multiple remote-operated vehicles, a salvage system capable of recovering heavy undersea objects and a mobile hyperbaric recompression chamber. Time was running out. The submersible was only equipped with enough air to last until sometime the next morning.
THE DISCOVERY:
On Thursday morning, a robotic vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan on the ocean floor, followed by the front and back ends of the Titan’s hull.
“The debris is consistent with the catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber,” said Rear Adm. John Mauger of the First Coast Guard District.
On its website before the expedition, OceanGate told future participants what to expect upon resurfacing.
“Once on deck, you will be welcomed back by the expedition crew and be able to share the story of your incredible accomplishment,” said the company, which already had scheduled dates for a 2024 expedition.
On Thursday, the company issued a statement mourning those killed, including company CEO and pilot Stockton Rush. In addition to Rush and Harding, the others on board were Titanic expert Paul-Henri Nargeolet and two members of a prominent Pakistani family, Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood.
“These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans,” OceanGate said. “We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
Copyright 2023 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , Massachusetts , world news
Related Articles
Best states.

America 2024

Best States Rankings
- # 2 Washington
- # 4 Nebraska
- # 5 Minnesota
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
Why utah is the best state.
Elliott Davis Jr. May 2, 2023

The 10 Best States in America

New York Appeals Court Overturns Harvey Weinstein’s 2020 Rape Conviction From Landmark #MeToo Trial
Associated Press April 25, 2024

Union Pacific's First-Quarter Profit Creeps up 1% as Railroad Limits Expenses

More Arrested in Pro-Palestinian Campus Protests Ahead of College Graduation Ceremonies

Columbia's President, No Stranger to Complex Challenges, Walks Tightrope on Student Protests

US Abortion Battle Rages on With Moves to Repeal Arizona Ban and a Supreme Court Case

Army Reservist Who Warned About Maine Killer Before Shootings to Testify Before Investigators

South Carolina Senate Approves $15.4B Budget After Debate on Bathrooms and Conference Switching
Associated Press April 24, 2024

Senators Demand Accounting of Rapid Closure Plan for California Prison Where Women Were Abused

What is the OceanGate Titan submersible and how does it work?
- Medium Text
Sign up here.
Compiled by Jonathan Allen; editing by Jonathan Oatis, Nick Zieminski and Grant McCool
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron
Harvey weinstein's conviction overturned by top new york court.
New York's highest court on Thursday overturned the 2020 sex crimes conviction of former Hollywood producer Harvey Weinstein, in the case that helped trigger the #MeToo movement.

Latest Headlines | What was the timeline of the Titan…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Entertainment
- Multimedia/Video
Breaking News
Latest headlines | new york appeals court overturns harvey weinstein’s 2020 rape conviction from landmark #metoo trial, latest headlines, latest headlines | what was the timeline of the titan submersible’s journey.

The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised temporary hopes and left lingering questions.
THE BUILDUP
The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner’s watery gravesite. Three missions involving other teams had been scrapped due to bad weather in the previous four weeks, but the latest OceanGate Expeditions group was hopeful.
“A weather window has just opened up and we are going to attempt a dive tomorrow,” renowned adventurer Hamish Harding said Saturday on Instagram. “More expedition updates to follow IF the weather holds!”
THE DIVE DOWN
Moving about the Polar Prince, mission participants were required to wear water-activated life vests, bright orange jackets, helmets and steel-toed boots, said Arnie Weissmann, a journalist who spent eight days aboard the support ship in May before his mission was aborted. Just before a dive, they’d change into fleece vests, black flight suits bearing the OceanGate logo and warm socks — no shoes allowed on the submersible.
The team was carried to the Titan’s launch and recovery platform by one of two inflatable dinghies named Stewie and Max. Once inside, they would sit on a platform, with their legs crossed or out straight.
“You could not be in that thing if you’re claustrophobic,” Weissmann said. “It’s literally like being in a tin can because it’s got rounded sides.”
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard.
“Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean,” the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. “The descent takes approximately two hours but it feels like the blink of an eye.”
On Sunday, the vessel lost contact with the Polar Prince around 10:45 a.m.
At 5:40 p.m., nearly three hours after the Titan was expected to resurface and nearly eight hours after the last communication, the Polar Prince notified the U.S. Coast Guard that the vessel was overdue, setting off an intense international search and rescue.
After the craft was reported missing, the U.S. Navy analyzed its acoustic data and found an anomaly that was “consistent with an implosion or explosion in the general vicinity of where the Titan submersible was operating when communications were lost,” a senior Navy official later told The Associated Press. Though it wasn’t made public at the time, the Navy passed on that information on Sunday to the Coast Guard, which continued its search because the Navy did not consider the data to be definitive, according to the official, who spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive technology.
By Monday afternoon, a C-130 Hercules aircraft from North Carolina and a Canadian P8 aircraft with underwater sonar equipment joined the search. Tuesday brought better weather and increased visibility, and by that morning, 10,000 square miles (25,900 square kilometers) had been searched.
A U.S. Air National Guard crew arrived that day, as did a Bahamian research vessel, Deep Energy, which deployed camera-equipped, remote-operated robots.
Meanwhile, sonar equipment detected banging noises Tuesday night and Wednesday morning, sparking hope that those aboard the Titan were still alive.
“We are smack dab in the middle of search and rescue, and we’ll continue to put every available asset that we have in an effort to find the Titan and the crew members,” Captain Jamie Frederick of the First Coast Guard District said at a news conference Wednesday afternoon.
By then, crews had scoured an area twice the size of Connecticut in waters 2½ miles (4 kilometers) deep. More resources were on the way, including multiple remote-operated vehicles, a salvage system capable of recovering heavy undersea objects and a mobile hyperbaric recompression chamber. Time was running out. The submersible was only equipped with enough air to last until sometime the next morning.
THE DISCOVERY:
On Thursday morning, a robotic vehicle discovered the tail cone of the Titan on the ocean floor, followed by the front and back ends of the Titan’s hull.
“The debris is consistent with the catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber,” said Rear Adm. John Mauger of the First Coast Guard District.
On its website before the expedition, OceanGate told future participants what to expect upon resurfacing.
“Once on deck, you will be welcomed back by the expedition crew and be able to share the story of your incredible accomplishment,” said the company, which already had scheduled dates for a 2024 expedition.
On Thursday, the company issued a statement mourning those killed, including company CEO and pilot Stockton Rush. In addition to Rush and Harding, the others on board were Titanic expert Paul-Henri Nargeolet and two members of a prominent Pakistani family, Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood.
“These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans,” OceanGate said. “We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
More in Latest Headlines

Crime & Public Safety | Boston police arrest 108 at Emerson College pro-Palestinian tent encampment

Migrants staying at Yarmouth motel move off Cape Cod, blindsiding Massachusetts town

SUBSCRIBER ONLY
New england patriots | patriots 2024 nfl mock draft: three biggest needs filled early.

Politics | Beacon Hill Democrats want to spend $426M on state-run shelters amid cash crunch
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
What to Know About the Titan Submersible
Officials believe the vessel that set out to reach the Titanic shipwreck with five passengers suffered a “catastrophic implosion,” a U.S. Coast Guard spokesman said.

By Yonette Joseph and Eric Schmitt
A submersible watercraft with five people on board that went missing after setting out early Sunday to explore the Titanic shipwreck in the North Atlantic most likely suffered a “catastrophic implosion” with no survivors, a U.S. Coast Guard spokesman said on Thursday.
The U.S. Navy had detected “an anomaly consistent with an implosion or explosion” in the area of the vessel around the time communications were lost on Sunday, two senior Navy officials said on Thursday.
The identification was “not definitive,” one official said, and it was shared with the search effort. But officials made the decision to continue searching to “make every effort to save the lives on board.”
Here’s what else to know.
When and where did the submersible disappear?
The 22-foot carbon-fiber and titanium craft , called the Titan, was deployed by a Canadian expedition ship, the Polar Prince, to travel nearly 13,000 feet down to the shipwreck site, on the ocean floor off Newfoundland.
The Titan lost contact with the surface ship an hour and 45 minutes after it started to dive, the U.S. Coast Guard said.
Who was on board?
Five people were in the submersible: Stockton Rush , the founder and chief executive of OceanGate Expeditions, which operated the vessel; Hamish Harding, a British businessman and explorer; another British businessman, Shahzada Dawood and his son, Suleman , from one of Pakistan’s wealthiest families; and Paul-Henri Nargeolet , a French maritime expert who had been on more than 35 dives to the Titanic wreck.
OceanGate said in a statement that everyone on the submersible had “sadly been lost.”
It added: “These men were true explorers who shared a distinct spirit of adventure, and a deep passion for exploring and protecting the world’s oceans. Our hearts are with these five souls and every member of their families during this tragic time. We grieve the loss of life and joy they brought to everyone they knew.”
Why was the Titan diving?
OceanGate, a private company based in Everett, Wash., organizes expeditions that can last up to nine days to travel to shipwrecks and underwater canyons.
According to the company’s website , OceanGate also provides crewed submersibles for commercial projects and scientific research.
Mr. Rush, an aerospace engineer and pilot, co-founded the company in 2009.
OceanGate called the Titan the only crewed submersible in the world that can take five people as deep as 4,000 meters — more than 13,100 feet — below the surface of the ocean.
The company has taken people on tours of the Titanic site since 2021, and guests have paid $250,000 to travel to the wreckage.
In 2018, leaders in the submersible craft industry were so worried about what they called the “experimental” approach of OceanGate that more than three dozen of them signed a letter to the company, obtained by The New York Times. They warned of possible “catastrophic” problems with the submersible’s development and the planned voyage to the Titanic wreckage.
Where is the Titanic wreck, exactly?
The R.M.S. Titanic , the biggest steamship in the world at the time, hit an iceberg four days into its first trans-Atlantic voyage in April 1912.
It sank to the bottom of the ocean, and more than 1,500 people died. The wreck was discovered in pieces in 1985, about 400 miles off Newfoundland.
Searchers scoured the sea.
The U.S. Coast Guard coordinated with the Canadian authorities and commercial vessels to search for the Titan.
A remotely operated vehicle, or R.O.V., from the Canadian vessel Horizon Arctic searched the sea floor, and a French vessel deployed its R.O.V. at the site, the U.S. Coast Guard said on Thursday on Twitter .
The U.S. Navy also sent a machine that can help recover heavy objects from the sea. Sonar buoys were deployed, and sonar was used to try to locate the submersible underwater. Aircraft from the United States and Canada, along with vessels, also scanned the ocean surface.

‘Unforgiving environment’
Search teams picked up underwater banging noises, but they did not appear to have any relation to the submersible’s wreckage, Rear Adm. John Mauger of the U.S. Coast Guard said at a news conference on Thursday.
He said a debris field found on the surface led to the discovery of the Titan’s tail cone and other pieces on the ocean floor Thursday morning, about 1,600 feet from the bow of the Titanic wreck.
The discovery was consistent with a “catastrophic loss of the pressure chamber” in the submersible, he said, adding that it was too early to tell when the vessel imploded and that investigators were working on a time line of events.
Asked about the prospect of recovering the remains of the victims, Admiral Mauger said he did not have an answer: “This is an incredibly unforgiving environment down there on the sea floor.”
He also said, “On behalf of the United States Coast Guard and the entire unified command, I offer my deepest condolences to the families.”
Reporting was contributed by Nicholas Bogel-Burroughs , Daniel Victor , Derrick Bryson Taylor , Mike Ives , William J. Broad , Anna Betts , Emma Bubola , Amanda Holpuch , John Ismay , Jesus Jiménez , Victoria Kim , Salman Masood , Matt Richtel and Alan Yuhas .
Yonette Joseph is a senior news editor on The New York Times’s International Desk. More about Yonette Joseph
Eric Schmitt is a senior writer who has traveled the world covering terrorism and national security. He was also the Pentagon correspondent. A member of the Times staff since 1983, he has shared four Pulitzer Prizes. More about Eric Schmitt
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Here's the latest on the missing Titan submersible and the race to rescue passengers
Emily Olson
Ayana Archie

U.S. Coast Guard Capt. Jamie Frederick speaks during a press conference about the search efforts for the submersible that went missing near the wreck of the Titanic in Boston on Tuesday. Joseph Prezioso/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
U.S. Coast Guard Capt. Jamie Frederick speaks during a press conference about the search efforts for the submersible that went missing near the wreck of the Titanic in Boston on Tuesday.
For the latest updates on the search for the missing submersible, head here.
As of Tuesday night, five passengers aboard a submersible in the North Atlantic are the subject of an international search. The vessel is owned by OceanGate, and designed to explore the site of the Titanic.
Authorities estimate there's only enough oxygen in the submersible to last for less than two days.
Here's what we know:
When and where did the vessel go missing?

Missing submersible: Rescuers race to find Titan after detecting underwater noises
The 21-foot vessel, which is named Titan , lost communication with its control center on Sunday morning, roughly 1 hour and 45 minutes into its scheduled dive, the U.S. Coast Guard wrote on Twitter.
Titan had been deployed by a Canadian expedition ship, the Polar Prince, about 435 miles (380 nautical miles) south of St. John's in Newfoundland, not far from the site of the iconic shipwreck.
Why was the submersible diving?
The missing vessel is owned by OceanGate, a company based in Washington state that offers underwater voyages to explore the remains of the Titanic from the seafloor.

'Tiny sub, big ocean': Why the Titanic submersible search is so challenging
OceanGate is a major chronicler of the ship's decay and shared the first-ever full-size digital scan of the wreck site in May.
OceanGate is also a pioneer in the deep sea tourism economy. For $250,000 a person, the company takes adventurers on a deep sea tour lasting eight days and stretching hundreds of miles.
From St. John's in Newfoundland, Canada, explorers travel 380 miles offshore and 2.4 miles below the surface.

A remarkable new view of the Titanic shipwreck is here, thanks to deep-sea mappers
If successful, they can catch a glimpse of what's left of the 1912 iceberg-crash disaster, which took the lives of all but 700 of the Titanic's 2,200 passengers and crew. Today, the ship is slowly succumbing to a metal-eating bacteria , which may cause it to fully disintegrate in a matter of decades.
Mike Reiss , who joined OceanGate to glimpse the deteriorating wreck in 2022, said the trip is less tourism than it is true exploration — and the people who dare to try it are made well aware of the risks.
"You sign a massive waiver that lists one way after another that you could die on the trip," he told the BBC in an interview Tuesday. "They mention death three times on page one. So it's never far from your mind. As I was getting on to the sub, that was my thought: That this could be the end."
'You sign a massive waiver that you could die on the trip' As search teams race against time to find the small sub that went missing during a dive to the wreck of the Titanic, writer Mike Reiss told #BBCBreakfast about taking the same trip last year https://t.co/FNeiSyZfLl pic.twitter.com/2STvm7YDbz — BBC Breakfast (@BBCBreakfast) June 20, 2023
Who was on board?
The Titanic-touring vessel contained one pilot and four paid passengers called "mission specialists," according to the U.S. Coast Guard. "Mission specialists" take turns operating sonar equipment and performing the tasks necessary to complete a dive.
Among those paid passengers was British businessman Hamish Harding, according to a statement from Action Aviation , a company where Harding works as chairman.
Harding holds three Guinness World Records, including the longest duration (4 hours, 15 minutes) at a full ocean depth (2.88 miles) by a crewed vessel. He has also trekked to the South Pole, circumnavigated the Earth in less than 48 hours and visited space in Blue Origin's New Shepard rocket .

Newly released footage of a 1986 Titanic dive reveals the ship's haunting interior
Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman, two members of a prominent Pakistani family known for investing, were also on board the vessel, according to a statement shared with outlets such as The Associated Press .
A fourth person on board is Paul-Henri Nargeolet, a French expert on the Titanic, his agent has confirmed to several outlets, including The New York Times . Nargeolet serves as director for RMS Titanic Inc. , the U.S. company that owns the salvage rights to the Titanic site. The Times reports that Nargeolet has completed over 35 dives to the wreckage, including a previous Titan expedition.
Titan's pilot and the fifth person has been identified as OceanGate CEO Stockton Rush.
Why did the vessel go missing?

This 2004 photo shows the remains of a coat and boots in the mud on the sea bed near the Titanic's stern. Institute for Exploration, Center for Archaeological Oceanography/AP hide caption
This 2004 photo shows the remains of a coat and boots in the mud on the sea bed near the Titanic's stern.
It's still unclear why the submersible lost communication with its control crew on the expedition ship.
Ahead of its launch, OceanGate said it would rely on the satellite-based internet company Starlink for the communications necessary for carrying out the expedition. A text-message-based system relying on underwater acoustic positioning normally allows the Titan to communicate with the control ship, according to an Australian researcher writing for The Conversation.
OceanGate says its vessels are "equipped with some basic emergency medical supplies and 96 hours of life support," according to the company's website .

Pop Culture Happy Hour
'titanic' was king of the world 25 years ago for a good reason.
And for good reason: This is not the first time an OceanGate submersible has gotten lost, according to David Pogue, a correspondent for CBS Sunday Morning .
Pogue, who traveled on an OceanGate expedition to see the Titanic last summer, recalled that the control room was unable to help the submersible locate the wrecked liner for roughly three hours due to technical difficulties.

James Cameron aims to finally put that 'Titanic' door debate to rest, 25 years later
"The difference this year is that it seems like they lost contact with the ship," Pogue told NPR. "They can't even reach the sub and that's really scary."
He added that factors like bad weather and mechanical issues mean the submersible vessels rarely make it to the Titanic, despite the expensive price tag. This season has seen zero successful dives, Pogue said.
What's it like inside the Titan?
Videos from Pogue's initial CBS Sunday Morning report on OceanGate show him reading from the "mission specialist" waiver, which points out that Titan has not been approved or certified "by any regulatory body."
"I couldn't help noticing how many pieces of this sub seem improvised," Pogue adds.
“Hope is quickly fading” to find the missing submersible that left for a mission to the wreckage of the Titanic, says @Pogue , who went on board the same sub last year. He says it could be impossible to rescue the passengers if the sub is still underwater. pic.twitter.com/n0NTsLYkIJ — CBS Mornings (@CBSMornings) June 20, 2023
A single plastic bottle and some Ziploc bags stand in for a toilet. An Xbox game controller and an elevator-esque up/down button serve as the vessel's primary controls. The interior lighting is from Camping World, notes OceanGate founder Stockton Rush.
In whole, the space inside is about the size of a minivan, not tall enough for someone to fully stand.
In an interview with NPR's All Things Considered , Pogue said there are seven different ballast mechanisms that can help the Titan rise from great depths.
"Some of these work even if the power is out or even if everyone on board is passed out," Pogue said.
The fact that rescue crews haven't spotted the vessel on the ocean's surface might mean that the Titan is snagged or its 5-inch-thick carbon fiber hull was penetrated, Pogue said.
Either situation could be catastrophic for the people on board.
What's the latest on the search efforts?
As of Tuesday at 1 p.m. ET, the Titan had about 40 hours of oxygen left, said Capt. Jamie Frederick, a response coordinator for the U.S. Coast Guard overseeing the search.
A unified command including the U.S. Coast Guard, the U.S. Navy, the Canadian Coast Guard and OceanGate are working together to steer the search efforts, but so far, has come up unsuccessful, Frederick said during a press conference.

TED Radio Hour
Robert ballard: what hidden underwater worlds are left to discover.
"We wouldn't be searching and putting all effort out there" if the submersible wasn't recoverable, Frederick said, adding that the crews contain the "nation's best experts."
Several Canadian Coast Guard vessels were en route to the scene, as were several additional private vessels.
The teams in place are continuing to use aircraft to scan the ocean, an effort that may get easier on Tuesday as Monday's heavy fog was lifting, said a Coast Guard spokesperson.
Sonar devices are also being employed to detect possible underwater sounds coming from the submersible. Crews have covered 7,600 square miles — an area bigger than the state of Connecticut.

How (and why) this man plans to live underwater for 100 days
The teams also expanded their underwater search capability on Tuesday by adding a remotely operated vehicle in order to reach lower depths. That search is ongoing.
But even if the crews can locate the vessel at a low depth, hauling it up to the surface is another task. The Titan could be at a depth of over 13,000 feet and a distance of over 900 miles offshore. Frederick said the search and rescue crews did not yet have salvage equipment in place.
David Marquet, a retired U.S. Navy submarine captain, told NPR's Morning Edition that the odds of survival are "about 1%."
A former OceanGate executive voiced safety concerns years ago
A fired OceanGate employee urged for additional testing on the hull of the Titan years earlier, according to a 2018 lawsuit. Former director of marine operations David Lochridge sent a report he authored in January 2018, which voiced concerns that the hull used carbon fiber and not a metallic composition. The Titan was being designed to travel 4,000 meters below the surface, which had never been done by an OceanGate vessel with a hull made of carbon fiber, Lochridge stated in court documents.
Furthermore, Lochridge said vessel's viewport, which allows passengers to look outside, was only certified by the manufacturer to withstand pressures at 1,300 meters below the surface. That was due to OceanGate's design of the vessel, which did not meet federal standards, according to the complaint.
Lochridge said he encouraged a nondestructive scan of the hull to check for any defects, rather than solely relying on acoustic monitoring. According to Lochridge, acoustic monitoring only detects a problem in the hull right before it fails.
Lochridge said his concerns were ignored and he was told equipment did not exist for the type of test he was asking for. "The paying passengers would not be aware, and would not be informed, of this experimental design, the lack of non-destructive testing of the hull, or that hazardous flammable materials were being used within the submersible," court documents state. Lochridge was fired in January 2018. In its lawsuit against Lochridge, OceanGate said they did not hire him to do engineering work. However, Lochridge says he made the report at the request of CEO Stockton Rush because the plans for the Titan were being passed from the engineering team to his operations department. Lochridge, who has experience as a submersible pilot and diver, was hired by OceanGate in May 2015 as an independent contractor and later became an employee, according to documents. OceanGate sued Lochridge for fraud, breach of contract, misappropriation of trade secrets and nearly $24,000, claiming that he repeatedly violated the nondisclosure agreement he signed by talking to at least two people about plans for the Titan.
The agreement stated he would not disparage the company and would "hold [OceanGate's] confidential information in strict confidence, and not disclose or use it except as authorized by [OceanGate] and for [OceanGate's] benefit." Lochridge denied violating the NDA, saying it was not properly executed and that his report was not critical of the company. He countersued for wrongful termination, though the parties ultimately reached a settlement.
NPR's Juliana Kim and Tovia Smith contributed reporting.
Correction June 20, 2023
A previous version of this story stated that the submersible has a 5-foot-thick carbon fiber hull. In fact, the hull is 5 inches thick.
- deep sea exploration
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 12, 2024 | Original: November 9, 2009

The RMS Titanic, a luxury steamship, sank in the early hours of April 15, 1912, off the coast of Newfoundland in the North Atlantic after sideswiping an iceberg during its maiden voyage. Of the 2,240 passengers and crew on board, more than 1,500 lost their lives in the disaster. Titanic has inspired countless books, articles and films (including the 1997 Titanic movie starring Kate Winslet and Leonardo DiCaprio), and the ship's story has entered the public consciousness as a cautionary tale about the perils of human hubris.
The Building of the RMS Titanic
The Titanic was the product of intense competition among rival shipping lines in the first half of the 20th century. In particular, the White Star Line found itself in a battle for steamship primacy with Cunard, a venerable British firm with two standout ships that ranked among the most sophisticated and luxurious of their time.
Cunard’s Mauretania began service in 1907 and quickly set a speed record for the fastest average speed during a transatlantic crossing (23.69 knots or 27.26 mph), a title that it held for 22 years.
Cunard’s other masterpiece, Lusitania , launched the same year and was lauded for its spectacular interiors. Lusitania met its tragic end on May 7, 1915, when a torpedo fired by a German U-boat sunk the ship, killing nearly 1,200 of the 1,959 people on board and precipitating the United States’ entry into World War I .
Did you know? Passengers traveling first class on Titanic were roughly 44 percent more likely to survive than other passengers.
The same year that Cunard unveiled its two magnificent liners, J. Bruce Ismay, chief executive of White Star, discussed the construction of three large ships with William J. Pirrie, chairman of the shipbuilding company Harland and Wolff. Part of a new “Olympic” class of liners, each ship would measure 882 feet in length and 92.5 feet at their broadest point, making them the largest of their time.
In March 1909, work began in the massive Harland and Wolff shipyard in Belfast, Ireland, on the second of these three ocean liners, Titanic, and continued nonstop for two years.
On May 31, 1911, Titanic’s immense hull–the largest movable manmade object in the world at the time–made its way down the slipways and into the River Lagan in Belfast. More than 100,000 people attended the launching, which took just over a minute and went off without a hitch.
The hull was immediately towed to a mammoth fitting-out dock where thousands of workers would spend most of the next year building the ship’s decks, constructing her lavish interiors and installing the 29 giant boilers that would power her two main steam engines.
‘Unsinkable’ Titanic’s Fatal Flaws
According to some hypotheses, Titanic was doomed from the start by a design that many lauded as state-of-the-art. The Olympic-class ships featured a double bottom and 15 watertight bulkhead compartments equipped with electric watertight doors that could be operated individually or simultaneously by a switch on the bridge.
It was these watertight bulkheads that inspired Shipbuilder magazine, in a special issue devoted to the Olympic liners, to deem them “practically unsinkable.”
But the watertight compartment design contained a flaw that was a critical factor in Titanic’s sinking: While the individual bulkheads were indeed watertight, the walls separating the bulkheads extended only a few feet above the water line, so water could pour from one compartment into another, especially if the ship began to list or pitch forward.
The second critical safety lapse that contributed to the loss of so many lives was the inadequate number of lifeboats carried on Titanic. A mere 16 boats, plus four Engelhardt “collapsibles,” could accommodate just 1,178 people. Titanic could carry up to 2,435 passengers, and a crew of approximately 900 brought her capacity to more than 3,300 people.
As a result, even if the lifeboats were loaded to full capacity during an emergency evacuation, there were available seats for only one-third of those on board. While unthinkably inadequate by today’s standards, Titanic’s supply of lifeboats actually exceeded the British Board of Trade’s requirements.
Passengers on the Titanic
Titanic created quite a stir when it departed for its maiden voyage from Southampton, England, on April 10, 1912. After stops in Cherbourg, France, and Queenstown (now known as Cobh), Ireland, the ship set sail for New York with 2,240 passengers and crew—or “souls,” the expression then used in the shipping industry, usually in connection with a sinking—on board.
As befitting the first transatlantic crossing of the world’s most celebrated ship, many of these souls were high-ranking officials, wealthy industrialists, dignitaries and celebrities. First and foremost was the White Star Line’s managing director, J. Bruce Ismay, accompanied by Thomas Andrews, the ship’s builder from Harland and Wolff.
Absent was financier J.P. Morgan , whose International Mercantile Marine shipping trust controlled the White Star Line and who had selected Ismay as a company officer. Morgan had planned to join his associates on Titanic but canceled at the last minute when some business matters delayed him.
The wealthiest passenger was John Jacob Astor IV, heir to the Astor family fortune, who had made waves a year earlier by marrying 18-year-old Madeleine Talmadge Force, a young woman 29 years his junior, shortly after divorcing his first wife.
Other notable passengers included the elderly owner of Macy’s, Isidor Straus, and his wife Ida; industrialist Benjamin Guggenheim, accompanied by his mistress, valet and chauffeur; and widow and heiress Margaret “Molly” Brown, who would earn her nickname “ The Unsinkable Molly Brown ” by helping to maintain calm and order while the lifeboats were being loaded and boosting the spirits of her fellow survivors.
The employees attending to this collection of First Class luminaries were mostly traveling Second Class, along with academics, tourists, journalists and others who would enjoy a level of service and accommodations equivalent to First Class on most other ships.
But by far the largest group of passengers was in Third Class: more than 700, exceeding the other two levels combined. Some had paid less than $20 to make the crossing. It was Third Class that was the major source of profit for shipping lines like White Star, and Titanic was designed to offer these passengers accommodations and amenities superior to those found in Third Class on any other ship of that era.
Titanic Sets Sail
Titanic’s departure from Southampton on April 10 was not without some oddities. A small coal fire was discovered in one of her bunkers–an alarming but not uncommon occurrence on steamships of the day. Stokers hosed down the smoldering coal and shoveled it aside to reach the base of the blaze.
After assessing the situation, the captain and chief engineer concluded that it was unlikely it had caused any damage that could affect the hull structure, and the stokers were ordered to continue controlling the fire at sea.
According to a theory put forth by a small number of Titanic experts, the fire became uncontrollable after the ship left Southampton, forcing the crew to attempt a full-speed crossing; moving at such a fast pace, they were unable to avoid the fatal collision with the iceberg.
Another unsettling event took place when Titanic left the Southampton dock. As she got underway, she narrowly escaped a collision with the America Line’s S.S. New York. Superstitious Titanic buffs sometimes point to this as the worst kind of omen for a ship departing on her maiden voyage.
The Titanic Strikes an Iceberg
On April 14, after four days of uneventful sailing, Titanic received sporadic reports of ice from other ships, but she was sailing on calm seas under a moonless, clear sky.
At about 11:30 p.m., a lookout saw an iceberg coming out of a slight haze dead ahead, then rang the warning bell and telephoned the bridge. The engines were quickly reversed and the ship was turned sharply—instead of making direct impact, Titanic seemed to graze along the side of the berg, sprinkling ice fragments on the forward deck.
Sensing no collision, the lookouts were relieved. They had no idea that the iceberg had a jagged underwater spur, which slashed a 300-foot gash in the hull below the ship’s waterline.
By the time the captain toured the damaged area with Harland and Wolff’s Thomas Andrews, five compartments were already filling with seawater, and the bow of the doomed ship was alarmingly pitched downward, allowing seawater to pour from one bulkhead into the neighboring compartment.
Andrews did a quick calculation and estimated that Titanic might remain afloat for an hour and a half, perhaps slightly more. At that point the captain, who had already instructed his wireless operator to call for help, ordered the lifeboats to be loaded.
Titanic’s Lifeboats
A little more than an hour after contact with the iceberg, a largely disorganized and haphazard evacuation began with the lowering of the first lifeboat. The craft was designed to hold 65 people; it left with only 28 aboard.
Tragically, this was to be the norm: During the confusion and chaos during the precious hours before Titanic plunged into the sea, nearly every lifeboat would be launched woefully under-filled, some with only a handful of passengers.
In compliance with the law of the sea, women and children boarded the boats first; only when there were no women or children nearby were men permitted to board. Yet many of the victims were in fact women and children, the result of disorderly procedures that failed to get them to the boats in the first place.
Exceeding Andrews’ prediction, Titanic stubbornly stayed afloat for close to three hours. Those hours witnessed acts of craven cowardice and extraordinary bravery.
Hundreds of human dramas unfolded between the order to load the lifeboats and the ship’s final plunge: Men saw off wives and children, families were separated in the confusion and selfless individuals gave up their spots to remain with loved ones or allow a more vulnerable passenger to escape. In the end, 706 people survived the sinking of the Titanic.
Titanic Sinks
The ship’s most illustrious passengers each responded to the circumstances with conduct that has become an integral part of the Titanic legend. Ismay, the White Star managing director, helped load some of the boats and later stepped onto a collapsible as it was being lowered. Although no women or children were in the vicinity when he abandoned ship, he would never live down the ignominy of surviving the disaster while so many others perished.
Thomas Andrews, Titanic’s chief designer, was last seen in the First Class smoking room, staring blankly at a painting of a ship on the wall. Astor deposited his wife Madeleine into a lifeboat and, remarking that she was pregnant, asked if he could accompany her; refused entry, he managed to kiss her goodbye just before the boat was lowered away.
Although offered a seat on account of his age, Isidor Straus refused any special consideration, and his wife Ida would not leave her husband behind. The couple retired to their cabin and perished together.
Benjamin Guggenheim and his valet returned to their rooms and changed into formal evening dress; emerging onto the deck, he famously declared, “We are dressed in our best and are prepared to go down like gentlemen.”
Molly Brown helped load the boats and finally was forced into one of the last to leave. She implored its crewmen to turn back for survivors, but they refused, fearing they would be swamped by desperate people trying to escape the icy seas.
Titanic, nearly perpendicular and with many of her lights still aglow, finally dove beneath the ocean’s surface at about 2:20 a.m. on April 15, 1912. Throughout the morning, Cunard’s Carpathia , after receiving Titanic’s distress call at midnight and steaming at full speed while dodging ice floes all night, rounded up all of the lifeboats. They contained only 706 survivors.
Aftermath of the Titanic Catastrophe
At least five separate boards of inquiry on both sides of the Atlantic conducted comprehensive hearings on Titanic’s sinking, interviewing dozens of witnesses and consulting with many maritime experts. Every conceivable subject was investigated, from the conduct of the officers and crew to the construction of the ship. Titanic conspiracy theories abounded.
While it has always been assumed that the ship sank as a result of the gash that caused the bulkhead compartments to flood, various other theories have emerged over the decades, including that the ship’s steel plates were too brittle for the near-freezing Atlantic waters, that the impact caused rivets to pop and that the expansion joints failed, among others.
Technological aspects of the catastrophe aside, Titanic’s demise has taken on a deeper, almost mythic, meaning in popular culture. Many view the tragedy as a morality play about the dangers of human hubris: Titanic’s creators believed they had built an unsinkable ship that could not be defeated by the laws of nature.
This same overconfidence explains the electrifying impact Titanic’s sinking had on the public when she was lost. There was widespread disbelief that the ship could not possibly have sunk, and, due to the era’s slow and unreliable means of communication, misinformation abounded. Newspapers initially reported that the ship had collided with an iceberg but remained afloat and was being towed to port with everyone on board.
It took many hours for accurate accounts to become widely available, and even then people had trouble accepting that this paragon of modern technology could sink on her maiden voyage, taking more than 1,500 souls with her.
The ship historian John Maxtone-Graham has compared Titanic’s story to the Challenger space shuttle disaster of 1986. In that case, the world reeled at the notion that one of the most sophisticated inventions ever created could explode into oblivion along with its crew. Both tragedies triggered a sudden collapse in confidence, revealing that we remain subject to human frailties and error, despite our hubris and a belief in technological infallibility.
Titanic Wreck
Efforts to locate the wreck of Titanic began soon after it sank. But technical limitations—as well as the vastness of the North Atlantic search area—made finding it extremely difficult.
Finally, in 1985, a joint U.S.-French expedition located the wreck of the RMS Titanic . The doomed ship was discovered about 400 miles east of Newfoundland in the North Atlantic, some 13,000 feet below the surface.
Subsequent explorations have found that the wreck is in relatively good condition, with many objects on the ship—jewelry, furniture, shoes, machinery and other items—are still intact.
Since its discovery, the wreck has been explored numerous times by manned and unmanned submersibles—including the submersible Titan, which imploded during what would have been its third dive to the wreck in June 2023.

HISTORY Vault: Titanic's Achilles Heel
Did Titanic have a fatal design flaw? John Chatterton and Richie Kohler of "Deep Sea Detectives" dive the wreckage of Titanic's sister ship, Britannic, to investigate the possibility.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard. "Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper and deeper into the ocean," the company wrote on its website when it advertised the expedition. "The descent takes approximately two hours but it ...
8:00 a.m. - Titan begins a descent from the Canadian research vessel the Polar Prince to the Titanic wreck, a trip expected to take two hours to reach the ocean floor, according to the U.S ...
The Titan submerged at 8 a.m. EDT Sunday, according to the U.S. Coast Guard. "Once the submersible is launched you will begin to see alienlike lifeforms whizz by the viewport as you sink deeper ...
OceanGate CEO Stockton Rush, who died aboard Titan, pictured in March 2015. OceanGate was a private company, founded in 2009 by Stockton Rush and Guillermo Söhnlein.From 2010 until the loss of the Titan submersible, OceanGate transported paying customers in leased commercial submersibles off the coast of California, in the Gulf of Mexico, and in the Atlantic Ocean.
Titan sub timeline: When did it go missing and other key events. A timeline of events surrounding the trip to the Titanic wreck for the submersible that suffered a 'catastrophic implosion'.
The Titan submersible, as seen in an undated handout photo issued by OceanGate Expeditions. ... Ross Kemp turned down trip on Titanic submersible over safety fears. 24 Jun 2023.
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised ...
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. The Polar Prince, a Canadian icebreaker ship, steamed out of Newfoundland on Friday, June 16, towing the experimental Titan submersible and carrying the five-man team headed to explore the iconic ocean liner's watery gravesite. "A weather window has just opened up ...
Titan began each trip with 96 hours of life support, which had set a Thursday morning target for the multinational team of rescuers racing to find the vessel and its passengers over the past few days.
OceanGate completed successful expeditions to the wreckage in 2021 and 2022 before the Titian disappeared on the third trip. Lost communications; wandering for hours underwater
AP. Experts from within and outside OceanGate raised concerns about the safety of its Titan submersible as far back as 2018, years before it went missing during a deep-sea dive to the Titanic ...
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised ...
CNN —. Time is running out to find five people aboard a submersible missing since Sunday on what was supposed to be a roughly 10-hour round trip to see the wreck of the Titanic. Oxygen levels ...
A former passenger details what it's like inside the missing Titan submersible. This undated photo provided by OceanGate Expeditions in June 2021 shows the company's Titan submersible. The missing ...
RMS Titanic was a British ocean liner that sank on 15 April 1912 after striking an iceberg on the ship's maiden voyage from Southampton, England to New York City, United States. Titanic, operated by the White Star Line, was carrying passengers and mail.Of the estimated 2,224 passengers and crew aboard, approximately 1,500 died, making the incident the deadliest sinking of a single ship at the ...
* Titan weighs 9,525 kg (21,000 lbs), and can travel at a speed of 3 knots (3-1/2 miles per hour) using electric thrusters. OceanGate says it is equipped with powerful LED lights, a sonar ...
Titanic, British luxury passenger liner that sank on April 14-15, 1912, during its maiden voyage, en route to New York City from Southampton, England, killing about 1,500 people. One of the most famous tragedies in modern history, it inspired numerous works of art and has been the subject of much scholarship.
By Jenny Gross. June 23, 2023. During a trip on board the Titan off the coast of the Bahamas in April 2019, Karl Stanley, an expert in submersibles, knew immediately that something was off: He ...
The wrecks of the Titanic and the Titan sit on the ocean floor, separated by 1,600 feet (490 meters) and 111 years of history. How they came together unfolded over an intense week that raised tempo…
The Titan lost contact with the surface ship an hour and 45 minutes after it started to dive, the U.S. Coast Guard said. Image The Titan preparing for its trip to the wreck of the Titanic on Sunday.
The Titan, a minivan-size submersible, was carrying five people to the Titanic's watery grave when it lost contact. The vessel has enough oxygen to keep its passengers alive for about 40 more hours.
Titanic. Updated: March 12, 2024 | Original: November 9, 2009. The RMS Titanic, a luxury steamship, sank in the early hours of April 15, 1912, off the coast of Newfoundland in the North Atlantic ...