
- Cars for Sale
- Research & Reviews
- News & Videos
- Sell Your Car
- Instant Offer
- Sign in with Google
- Sign in with Facebook
- Sign in with Apple

Does Cruise Control Save Gas?
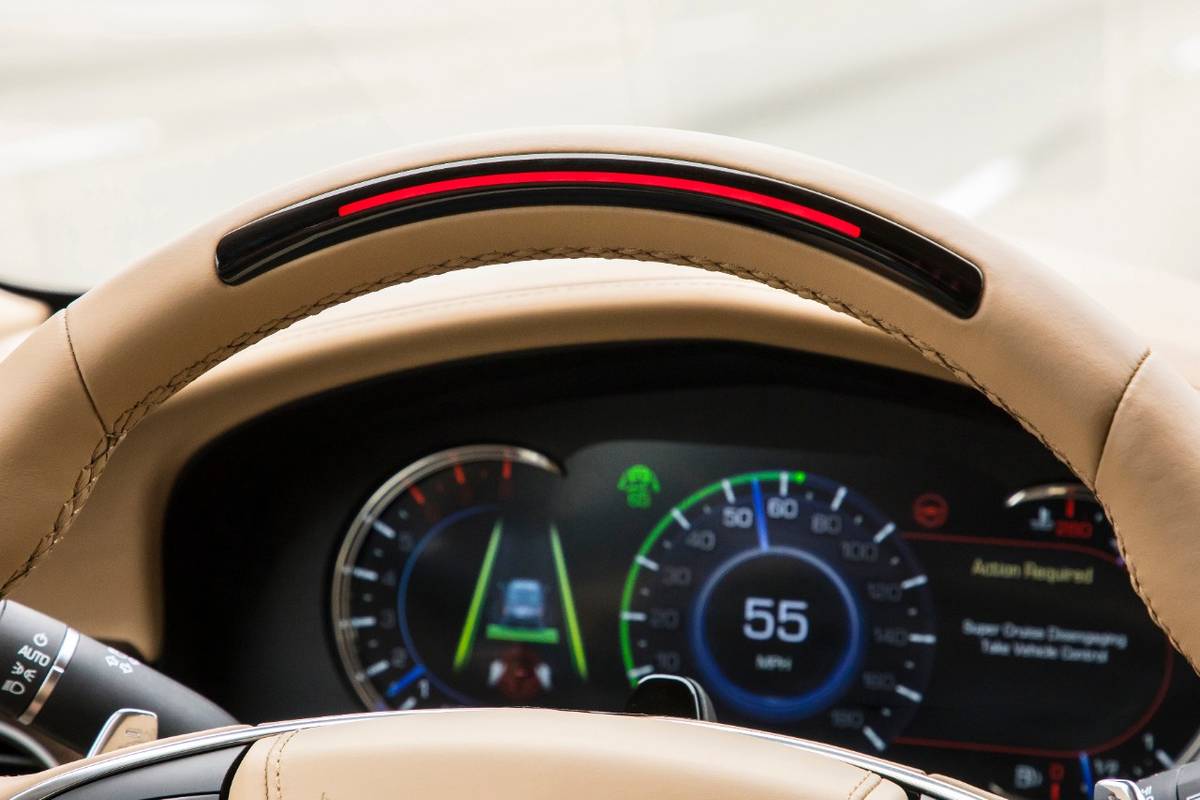

By Rick Popely
Is cruise control helpful for fuel efficiency? In a word, yes, though there isn’t much recent research that quantifies just how much it can save. Eliminating or reducing the number of times a vehicle slows down and then accelerates on the highway keeps the engine and transmission operating in their most efficient modes and, as a result, fuel economy will be higher when cruise control maintains a steady pace.
Related: Which Cars Have Self-Driving Features for 2020?
Notable highlights
- ${price_badge()}
- ${battery_badge()}${ev_report_link()}
- ${hot_car_badge()}
- ${award_badge()}
- ${cpo_badge()}
- ${href_to_vdp()}
${price_badge_description}
The EV Battery Rating is based on this vehicle's current expected range relative to the vehicles expected range when new. ${battery_badge_text}
Certified cars are manufacturer warrantied and typically go through a rigorous multi-point inspection.
This car is likely to sell soon based on the price, features, and condition.
${award_blurb}
${award_two_blurb}
Shop the 2020 Hyundai Palisade near you

Without cruise control, even the most attentive driver is bound to slow down and then speed up again from time to time. That uses more gas.
In addition, someone following 18-wheelers and other slower vehicles, especially when going uphill, might get antsy and floor the throttle to quickly get around those rolling roadblocks — a surefire way to use more fuel. Most cruise control systems allow increasing speeds in 1-mph increments, an approach that will use less fuel than flooring it.
The more often a vehicle changes speeds, the more that economy is likely to suffer. A study by Natural Resources Canada found that varying vehicle speed between roughly 47 and 53 mph every 18 seconds can increase fuel consumption by 20% compared to a steady speed. But because of wide variations among drivers, where a vehicle is being driven and the vehicles themselves, there is no set formula for how much cruise control can save and guidance about fuel economy often is vague.
For example, the federal website for fuel economy information says, “Aggressive driving (speeding, rapid acceleration and braking) wastes gas. It can lower your gas mileage by roughly 15% to 30% at highway speeds.”
The site is even less specific about cruise control: “Using cruise control on the highway helps you maintain a constant speed and, in most cases, will save gas.”
A study by Volvo and the National Renewable Fuel Laboratory released in 2019 concluded that adaptive cruise control can increase fuel economy by 5-7% compared to a vehicle being driven manually. Adaptive cruise control not only maintains a steady speed on the highway, it also gradually slows or speeds up a vehicle to maintain a preset distance from vehicles ahead.
More From Cars.com:
- How Much Car Insurance Do I Need? 5 Key Coverage Considerations
- What to Know Before Taking on a 72- or 84-Month Car Loan
- How Many Miles Is Too Many for a Used Car?
- What Does TPMS Mean?
- More Fuel Economy News
Whether a vehicle has adaptive or conventional cruise control, the system is supposed to recognize when it is going uphill or downhill and adjust the speed accordingly, and that’s an area where results can vary. Some cruise control systems are more aggressive than others when climbing hills and will increase engine speed sooner, induce the transmission to downshift faster and stay in full-speed-ahead mode longer.
In other cases, the cruise control may be less fuel-efficient than a patient driver with a light throttle foot. For example, in driving through the Rocky Mountains with the engine constantly changing speeds and the transmission hunting for the right gear, most drivers forget about fuel economy. They just want to cope with the inclines and traffic, and turning off cruise control might be the better choice.
On a relatively flat road, however, cruise control is likely to reduce fuel consumption.
Cars.com’s Editorial department is your source for automotive news and reviews. In line with Cars.com’s long-standing ethics policy, editors and reviewers don’t accept gifts or free trips from automakers. The Editorial department is independent of Cars.com’s advertising, sales and sponsored content departments.
Latest news
Here Are the 11 Cheapest Electric Vehicles You Can Buy

Electric Cars With the Longest Range

Toyota Teases Next-Generation 4Runner
Featured stories.

2025 Infiniti QX80 Up Close: Beautiful Behemoth
By Conner Golden

2024 Ford Ranger Raptor Review: Jumping for Joy

Car Loans: How to Get the Best Interest Rate
By Cars.com Editors
Latest expert reviews

Sustainability Success

Does Cruise Control SAVE Gas? (and what to AVOID)
Following the increasing prices of gas, most people are adopting simple measures to save on fuel. For this reason, I’ve been asked more and more often: does cruise control save gas?
Yes, using cruise control can save gas, especially when commuting at a constant speed on a highway. However, this is not always true and in some situations, cruise control may actually increase gas consumption. This depends on a number of factors like traffic, type of journey, and more.
How true is the notion that cruise control helps to save gas? Does this simple practice really work or is it just another old wives’ tale? Or does cruise control use more gas? Read on to find out!
Table Of Contents
Does Cruise Control Save Gas? And Why?
Yes, cruise control can actually help you save gas. But how can cruise control help to save gas?
The reason why cruise control can help to save gas is that when accelerating or decelerating by placing the foot over the pedals the engine uses more gas. However, using cruise control when driving eliminates the need to constantly use the accelerator, either when speeding up or slowing down.
Instead, the cruise control feature helps you maintain a continuous speed. And by avoiding pressing on the pedals, a practice that costs you more fuel, you get to save more on gasoline.
This is not just a myth, in fact, also an agency of the Canadian government is reporting that: cars that fluctuate their speeds between 75 to 85 kilometers per hour use up 20% more gas every 18 seconds. On the contrary, cars that maintained a constant speed of 80 kilometers per hour (thanks to cruise control) saved on fuel and did not deplete gas as easily.
Similarly, the US government agrees that speeding, accelerating rapidly and braking immediately wastes a lot of gas. In fact, such aggressive driving at highway speeds can reduce your gas mileage by approximately 15%-30%.
These research findings clearly demonstrate that, by maintaining cars at a constant speed, cruise control helps to save gas.
As a matter of fact, cruise control can help you save by as much as 5% to 15% on gas!
After all, the cruise control of the vehicle uses the powertrain control module ( PCM ) to maintain constant designated speeds. Hence, when you activate cruise control, you eliminate the “human” aspect of maintaining speeds. This ensures that there are no speed fluctuations that could lead to the car consuming more fuel than what’s needed.
When Should You Use Cruise Control?
It is good news to know that cruise control can help you save on fuel. However, this does not mean that you use this car system everywhere and every time; use of cruise control is only limited to certain conditions.
For example, the feature is only fuel-efficient if used on flat roads or mostly level highways that do not have any traffic congestion. Besides the level roads, cruise control can also be used on steady uphills or downhill drives.
When you should AVOID using cruise control
You are not recommended to use cruise control when driving up and down hills that incline sharply or change perpetually, such as highways that pass across rolling hills.
Instead of using the cruise control feature on such paths, target an average speed and then allow the vehicle to reduce speeds by 5-10 mph when going uphill. Also, when descending, rise by similar speeds, that is, 5-10 mph. Following this technique helps to save on gas when driving through mountainous terrains, as compared to using cruise control.
Furthermore, it is not advisable to use cruise control when driving on slippery roads, such as those caused by snow and rain.
Usually, such road conditions change instantly when driving, requiring you to be careful and drive in response to the current situation at hand. And since cruise control cannot master these changes immediately after they occur, it is advisable to turn it off when driving in such conditions.
Also, you should not use cruise control if you feel drowsy or are driving in stop-and-go traffic areas, such as roundabouts or at traffic lights.
Remember that cruise control reduces the actions you need to take by eliminating the need to constantly step on the pedal. This is a situation that may make you even more sleepy and less alert, increasing the risk of an accident.
Similarly, stop-and-go traffic zones require a high level of concentration, as well as the need to monitor your speeds. In such areas, you might need to accelerate immediately or slow down instantly. Since cruise control only maintains constant speeds with no acceleration or deceleration, it is advisable that you turn off the feature when driving in these areas.
Advantages of Cruise Control
Here are the advantages of using cruise control on your car!
1. Saves fuel
The main benefit of cruise control is that it saves on gas by keeping the car moving at a constant speed.
However, this fuel-efficient system offers more advantages than just cutting down on your overall fuel bills. Consider four other advantages that cruise control provides:
2. Reduces Fatigue
Stepping on the pedals to accelerate or decelerate may sound like a simple activity; even so, this action wears you down and may even cause you to feel fatigued, especially when driving long distances.
However, cruise control eliminates the need to constantly step on the pedal, allowing you some time to rest, hence reducing fatigue.
3. Helps You Avoid Speeding Tickets
Most of us accelerate fast, even exceeding the speed limit without realizing it. And if the police would pull you over due to speeding, you might end up paying high penalty fees at the very least.
When you use cruise control, you can set constant speeds that do not exceed the legal speed limit. This protects you from the risk of being charged with overspeeding.
4. Improves Sustainability
Burning gasoline and diesel releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Since cruise control saves gas, it not only reduces the number of trips to the gas station but also helps you to reduce the environmental footprint of your commute, and improve your personal economic sustainability .
The less gas is used, the less pollution is released into the environment. In turn, reducing the carbon footprint promotes better environmental sustainability of your movements.
So, if you would like to help the environment, reduce waste, and have a more sustainable lifestyle but can’t afford an electric car (learn the hybrid vs electric car differences as well as hybrid vs gas cars ) or can’t use public transport, try at least to reduce your fuel consumption. This will help both the environment and your pocket, going a small step closer to sustainable development .
Most of us spend thousands of dollars every year on gasoline. Actually, according to Yardeni Research, households in the U.S spent approximately $5,000 per year on gas. And the worst part is that, with inflation, gas prices are going higher and higher with no relief in sight.
That’s why an increasing number of people in the US and all over the world are looking for ways to save on gas. For this reason, many people are asking: does cruise control save gas?
Absolutely! Cruise Control minimizes the number of times the vehicle accelerates or decelerates immediately, keeping it at constant speeds that significantly save on gas.
This simple practice is helping people to save hundreds of dollars a year and is especially common among drivers who make lengthy commutes on the highway.
Di you know that among the pros and cons of Drive Safe and Save insurance, there is also saving gas as well as having discounts on your insurance premium? Yes, also this insurance can help you to drive more cautiously and save even more gas!
So if you are looking to save on that fuel money , and even reduce your environmental impact on the planet, while at it, simply start using the cruise control feature of your car today!
Suggested Articles

Car advice put simply.
Does cruise control save gas? – get more gas mileage
Find out how cruise control can unexpectedly save on fuel consumption..

In times where cruise control comes as a standard piece of equipment on new cars, one important question is raised – does cruise control save gas ? Yes, cruise control saves gas and could even result in up to 20% better fuel economy if properly used.
Still, there’s much more about cruise control and gas mileage than meets the eye, and our team set out to explore. We’ll give you all the details on how you can save fuel with this driving function, and provide insight into how it works. Keep reading to figure out whether it could work for your driving style.
What is cruise control and how does it work?
Cruise control was a big deal in the automotive industry back in the day, as it made the first step towards autonomous driving. Well, at least it does so with the latest forms of adaptive cruise control, but you can enjoy the benefits of standard cruise control in your everyday driving.
It’s not exactly handy for busy town roads but comes in quite beneficial during highway driving. Cruise control lets you maintain your ride at a certain speed level without having to deal with the gas pedal. So, there’s no commotion caused by constantly shifting gears and keeping your foot on the pedal. You can just lean back and enjoy a smooth ride.
It’s best to use cruise control on a straight road where you won’t have to slow down or make turns often. Once you build up your speed, turn the function on by pressing the cruise control setup button that’s mostly placed around the steering wheel.
It will keep your car going at the same rev per minute ( RPM ) range without you having to keep your foot on the gas pedal. So, it’s a convenient feature for keeping optimal speed, and for improving fuel economy on top of it.
Impact of the cruise feature on your gas mileage

Now that you know how handy a cruise control option can be, it’s time for us to dig deeper into its connection with fuel economy. It has to do with the power output from the engine and the RPM level that you tend to drive at.
For instance, revving your car and keeping the engine spinning at high RPMs will only burn more fuel. On the other hand, if you drive at a lower RPM level, the engine will burn less fuel, especially in a longer drive. That’s why the cruise control setup can kick in quite well in helping you waste less fuel while driving on the highway.
You can just set up the optimal speed and drive in a higher gear on a lower RPM level. Keeping the revs in a flat line is also crucial for your fuel economy, and cruise control lets you drive at a steady RPM rate. You’ll save much more fuel this way since any fluctuations in gear changes and revs consume more fuel.
In general, you can save from 7% to 20% more fuel by driving with cruise control activated. There’s no sudden pressure on the throttle caused by accelerations which could trigger more fuel injection. Your engine will keep operating in the set RPM range, and the torque range remains the same which results in less fuel spent.
When is it a bad idea to use cruise control?
It’s a bad idea to use the cruise control system while moving uphill or on busy roads. Especially if you are facing an elevating road that requires a higher power output, using cruise control is not advisable. Think of it this way – you might end up damaging the engine if the RPM level is too low due to the set cruise feature.
The car might struggle to maintain its speed and you’ll just do more harm than good trying to save up on fuel. Also, driving on busy city roads isn’t much better of an idea, since you need to control the throttle response in turns. On top of that, there are some cases where drivers report cruise control not working properly, so it’s also important for the system to be fully operational.
Overall, it’s only both safe and beneficial in terms of fuel economy to use the cruise control system on roads where you can maintain the same speed level.
Is cruise control bad for your car?
No, cruise control isn’t bad for your car and it can hardly do any damage to the drivetrain components. Moreover, it can even be beneficial to use this feature, since keeping the engine rolling at a steady speed can’t do any harm.
As you shift through the gears, the difference in power output and torque requires more fuel for combustion needed to accelerate. So, you can even reduce wear and tear on your engine components by making use of this convenient driving feature.
Do brakes cancel cruise control?
Yes, you can cancel the cruise control feature by stepping onto the brake pedal. From this point on, you can accelerate and slow down the same way you normally would without the system being active. The reason behind this is the signal that the brake pedal sends to the computer.
It acts the same as pressing the cancel button, but it comes in handier during driving since you won’t have to take your eyes off the road.
Can you speed up while using cruise control?
Yes, you can speed up while using cruise control on most modern cars. Recent models have a modern cruise control system with buttons on the steering wheel that let you increase the speed or slow down. This feature alone helps you save fuel while using the cruise control function.
It’s because most cars let you accelerate just by 1 mph each time that you press the button. This way, you won’t have to burn much fuel while accelerating, and then slowing down right after. It lets you set up your driving speed precisely, and the same goes for slowing down. Have in mind that stepping on the brake pedal will shut down the cruise control feature.
Don’t use it during bad weather

One thing to have in mind is that cruise control shouldn’t be used while it’s raining, or on snowy roads. Driving at certain speed levels could cause hydroplaning as the tires could lose their grip on the road. So, it’s best to put your foot back on the gas pedal and adjust the driving speed accordingly during bad weather.
On the other hand, it might seem like you have enough grip even during rain, but it all changes when you reach a part of the road soaked in water. To prevent any sliding or hydroplaning due to consistently fast driving speeds, turn off the cruise control during bad weather.
Eventually, we’ve dealt with the matter of whether cruise control saves gas. As much as it’s beneficial on highways and routes that require little to no turns, cruise control could be dangerous during bad weather. So, as much as you use it responsibly and still keep your eyes on the road, you should be able to save some fuel as well.
Adaptive cruise control systems in modern cars can even recognize another vehicle in case you get too close to it, but it’s still best if you use cruise control with a dose of precaution.

Filip is a lifelong car enthusiast with over 3 years of experience writing about cars and had worked as a mechanic apprentice for over 5 years, gaining hands-on expertise in automotive mechanics. At REREV, he combines his passion for cars with his comprehensive knowledge to provide readers with a unique blend of technical insight and engaging storytelling that sets the bar high for automotive content.
- Editorial Guidelines
Car Insights
- Years to avoid
- Collections

Does Using Cruise Control Really Save Gas? A Research-Based Analysis

A Quick Overview
Cruise control is a feature found in many modern vehicles that allows drivers to set a desired speed for their vehicle, which the car then maintains automatically. One common claim about cruise control is that it can help save gas, leading to increased fuel efficiency and potential cost savings for drivers. In this blog post, we will explore whether using cruise control actually leads to fuel savings, based on research and scientific analysis.
The Mechanics of Cruise Control
Before delving into the fuel-saving aspect of cruise control, it’s important to understand how the system works. When activated, cruise control uses electronic sensors to monitor the vehicle’s speed and adjust the throttle accordingly to maintain the set speed. This eliminates the need for drivers to manually modulate the throttle pedal, resulting in a consistent speed and potentially reducing speed fluctuations that can impact fuel consumption.
Fuel Efficiency and Cruise Control
To determine whether cruise control can genuinely save gas, several studies have been conducted to evaluate its impact on fuel efficiency. Here are some key findings:
Consistent Speed: Cruise control helps maintain a steady speed on highways or long stretches of road. This consistency can reduce the tendency for drivers to accelerate and decelerate frequently, which is a common behavior that negatively affects fuel efficiency.
Optimized Acceleration: Cruise control typically provides a smoother and more controlled acceleration compared to manual driving. This can prevent unnecessary aggressive acceleration, which can consume more fuel.
Reduction in Speed Variations: By minimizing speed fluctuations, cruise control helps eliminate the need for frequent adjustments to maintain a constant speed. This stability can positively impact fuel efficiency, as rapid acceleration and deceleration events tend to use more fuel.
Ideal for Long, Flat Roads: Cruise control is particularly effective on long, flat stretches of road where the vehicle can maintain a constant speed for extended periods. In these situations, cruise control can contribute to fuel savings by ensuring a consistent and optimized throttle input.
Factors Influencing Fuel Efficiency
Although cruise control can positively impact fuel efficiency, it is important to note that other factors also play a role. Here are a few considerations to keep in mind:
Terrain: Hilly or mountainous terrains may limit the effectiveness of cruise control in terms of fuel efficiency. The system may struggle to maintain a constant speed in such conditions, potentially leading to increased fuel consumption.
Traffic Conditions: In heavy traffic situations, cruise control may not be practical due to the need for frequent acceleration and braking. Stop-and-go traffic can negate the fuel-saving benefits of cruise control.
Weather Conditions: Adverse weather conditions, such as rain, snow, or strong winds, may affect the performance of cruise control. In such cases, it is important for drivers to exercise caution and rely on manual control to ensure safety.
Based on research and scientific analysis, it can be concluded that using cruise control has the potential to save gas and improve fuel efficiency under ideal conditions. Consistent speed, optimized acceleration, and reduced speed fluctuations contribute to these fuel-saving benefits. However, it is essential to consider external factors such as terrain, traffic conditions, and weather, which can impact the effectiveness of cruise control.
While cruise control can be a useful tool for maximizing fuel efficiency, it is important for drivers to be aware of their surroundings and adapt their driving style accordingly. By combining the benefits of cruise control with situational awareness, drivers can make informed decisions and strive for optimal fuel economy while enjoying the convenience offered by this technology.
👉 You may also like - What is Cruise Control and How Does it Function in a Car?
Does using cruise control really save gas?
Using cruise control can indeed save gas in certain situations. When engaged, cruise control helps maintain a consistent speed, preventing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration. This stability reduces fluctuations in fuel consumption, leading to potential fuel savings, especially during long highway drives where steady speed can be maintained. However, the extent of fuel savings may vary depending on factors such as terrain, traffic conditions, and individual driving habits.
Is using cruise control more fuel-efficient than manual speed control?
In general, using cruise control tends to be more fuel-efficient than manual speed control. Cruise control systems are designed to optimize fuel consumption by maintaining a steady speed, avoiding unnecessary acceleration, and minimizing speed variations. Compared to manual speed control, where drivers may unintentionally apply more throttle or vary their speed, cruise control can provide better fuel efficiency, especially on long, relatively flat stretches of road.
Are there any situations where using cruise control may not save gas?
While using cruise control can save gas in many scenarios, there are situations where its effectiveness may be limited. For example, in hilly or mountainous terrain, the cruise control system may continuously adjust the throttle to maintain the set speed, resulting in increased fuel consumption. Additionally, in heavy traffic or urban driving conditions with frequent stops and starts, the constant engagement and disengagement of cruise control may not yield significant fuel savings.
Does the type of vehicle impact the fuel savings achieved by using cruise control?
Yes, the type of vehicle can impact the fuel savings achieved through cruise control. Generally, vehicles with smaller engines or those optimized for fuel efficiency may experience more noticeable fuel savings when using cruise control. Larger, less aerodynamic vehicles or those with higher horsepower engines may have fewer fuel-saving benefits due to their inherent design and power requirements.
Are there any additional benefits to using cruise control besides fuel savings?
Yes, using cruise control offers additional benefits beyond potential fuel savings. It can help reduce driver fatigue during long trips by allowing the driver to maintain a constant speed without constantly pressing the accelerator pedal. Cruise control also promotes a smoother driving experience, which can enhance passenger comfort and reduce the likelihood of abrupt braking or acceleration.
Are there any downsides or considerations to using cruise control?
While cruise control can be beneficial, there are some downsides and considerations to keep in mind. It’s important to remain attentive and prepared to disengage the cruise control system if unexpected situations arise on the road. Additionally, using cruise control in certain weather conditions, such as heavy rain or icy surfaces, may not be recommended for safety reasons. It’s crucial to use cruise control responsibly and be aware of the potential limitations in specific driving scenarios.

How to Clean a MAP Sensor. A Step-by-Step Guide
How can you reset a map sensor your ultimate guide.

Mastering ASE Testing - The Ultimate Guide for Success

Keeping Current - Charging System Diagnosis and Repair

The complete ASE practice test with answers and explanations

Enhancing the Ride - Accessories Diagnosis and Repair

Does Cruise Control Save Gas? Is It Better For Gas Mileage?

Is cruise control more fuel efficient? As drivers seek ways to optimize their fuel consumption, we delve into the science behind cruise control’s impact on gas mileage. Let’s explore the facts to determine if this widely-used feature is indeed a fuel-saving hero.
Does Cruise Control Use More Fuel?
Cruise control can save 14% on fuel on highways and 7% on ga s on city streets. When you engage on relatively flat and open roads, it maintains a constant speed. This stability can lead to improved fuel economy by reducing rapid fuel consumption associated with frequent speed changes.

Additionally, the cruise control system is often designed to operate more efficiently than an average driver, making subtle adjustments to optimize fuel use. However, its effectiveness can diminish in hilly terrains or congested traffic, where the system may need to overcompensate, potentially negating the fuel-saving benefits.
Other Benefits Of Cruise Control Function
Here are some added advantages that cruise control brings.
Reduce Fatigue
While fatigue reduction is a widely acknowledged benefit, it’s crucial to emphasize its impact on overall safety. By maintaining a consistent speed, cruise control minimizes the physical strain on drivers during long journeys, allowing for a more relaxed and alert driving experience.
Enhance Sustainability
Cruise control contributes to sustainable driving habits by promoting fuel efficiency. By maintaining a steady speed, the system optimizes fuel consumption, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the vehicle. This will benefit the environment in the long run.
Help Avoid Getting Speeding Tickets
Cruise control acts as a built-in speed regulator, automatically maintaining the selected speed without exceeding the set limit. This feature can be a valuable ally in helping drivers avoid unintentional speeding, ultimately reducing the risk of getting speeding tickets and the associated fines.
When To Use Your Cruise Control
Effectively using cruise control can enhance your driving experience and fuel efficiency. Cruise control is most beneficial when you can maintain a consistent speed without the need for frequent braking or acceleration. Here are the times you should use this practical feature.
- Long, straight roads: Cruise control excels on extended, straight roads where consistent speed is feasible. This feature minimizes fatigue and contributes to fuel efficiency.
- Moderate traffic: On highways with mild traffic conditions and predictable flow, cruise control can help you maintain a consistent driving speed without the need for frequent acceleration and braking.
- Open highways: When the road is wide open with minimal interruptions, cruise control prevents unintentional speeding and offers a more relaxed driving experience.
When Not To Use Your Cruise Control
As beneficial as it is, this feature is not meant to be used all the time. You should not apply it in situations requiring more immediate control over speed and braking.
- Heavy traffic: In congested traffic situations, cruise control is not advisable. It’s essential to maintain awareness and have quick access to braking capabilities.
- Adverse weather: Rain, snow, and ice can make roads unpredictable. Disengage cruise control to ensure you have immediate control over your current vehicle in changing conditions.
- Hilly or winding roads: Cruise control struggles on hilly or winding terrains. These situations require constant speed adjustments and quick braking, making manual control crucial.
- City streets with many corners: In urban settings with frequent turns, stops, starts, and variable speeds, cruise control may not be practical. Manual control allows you to adapt to the dynamic traffic environment.
Tips To Save Fuel When Driving
Besides using cruise control, you can also apply the following tips to save fuel.
- Moderate speeds: Maintain average speeds, as fuel efficiency often drops significantly at highway speeds.
- Limit aggressive driving: Avoid aggressive driving habits like rapid acceleration and sharp braking, as they can dramatically impact fuel efficiency.
- Engine warm-up: Avoid prolonged idling for engine warm-up; modern engines are designed to warm up more efficiently while driving.
- Avoid excessive idling: Turn off the engine if you anticipate a long wait, as idling consumes fuel.
- Use overdrive gears: When applicable, use overdrive gears to reduce engine speed and improve fuel efficiency on the highway.
- Choose the right fuel: Use the recommended fuel for your vehicle; using premium gas in a car designed for regular unleaded fuel may not provide additional benefits.
- Aerodynamic considerations: Keep windows closed at higher speeds to reduce aerodynamic drag, and remove roof racks when not in use to improve fuel efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is cruise control bad for your car .
Cruise control is generally good for your engine when used appropriately. It maintains a steady speed, reducing strain and enhancing fuel efficiency. However, avoid using it in hilly terrains or heavy traffic, as constant speed adjustments may lead to increased engine stress and decreased overall efficiency.
Does Cruise Control Use More Battery?
No, the cruise control feature typically does not significantly impact the vehicle’s battery. It primarily relies on the engine’s power, and its electrical consumption is minimal. However, using other electrical features, like air conditioning, while cruise control is engaged may marginally contribute to battery usage.
The Bottom Line
While the effectiveness of cruise control varies, utilizing it judiciously in appropriate conditions can contribute to gas savings. Understanding the nuanced role of this feature empowers drivers in the quest for both efficiency and a smoother, controlled driving experience.

Petroleum Engineer At Rex Energy
I have worked in a variety of roles and professions, from quality engineering in the automotive industry to production engineer in the oil and gas sector. From a technical point of view, these roles have shown me how to design a process, ensure it is efficient and up to standard, and manage the execution of the said process from start to finish.
Leave a Comment
Related Articles

How to Dispose of Old Gas?

What Type of Gas Does My Car Take? (85, 87 or 89…)

What Temperature Does Gasoline Freeze? Gas Freezing Point

Tractor Fuel vs Reefer Fuel: Are They The Same?

What Is 85 Octane Gas? Can You use 85 octane instead of 87

What Happens When Your Car Runs Out of Gas?
- Hybrids & EVs
- Motorsports
- Tips, Tricks & Trends

Does Cruise Control Waste More Gas?
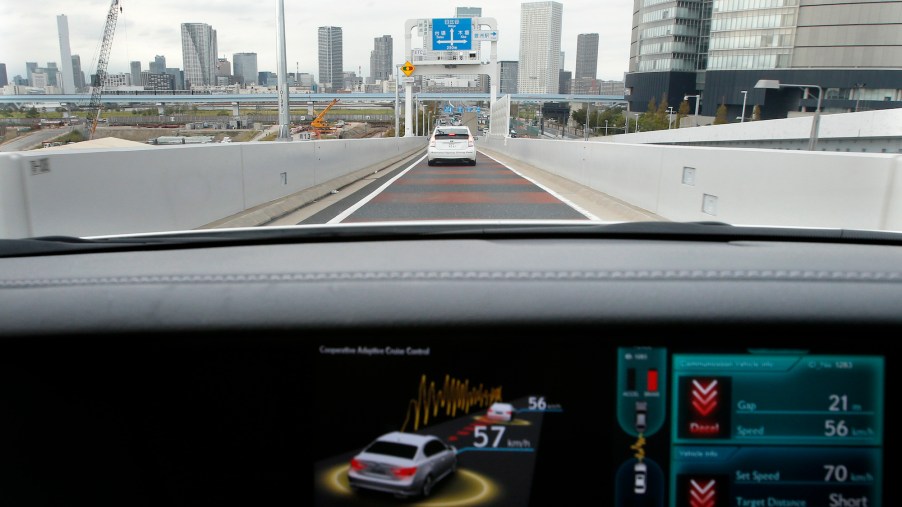
Many car shoppers seek models with advanced driver assists . Features such as automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assistance can safeguard occupants and keep the car’s resale value high. But there are tradeoffs with some advanced safety features. Some have a reputation for glitching; others are expensive to repair. And one notable feature — adaptive cruise control — might even negatively affect gas mileage and total ownership costs.
How does adaptive cruise control work?
Using inputs from thousands of data points, New #EPACE 's Driver Condition Monitor detects if you're beginning to feel drowsy, alerting you to take a break. Adaptive Cruise Control also maintains a set distance to the car in front for more relaxed, less tiring long distance trips. pic.twitter.com/unbYfEoej1 — Jaguar (@Jaguar) November 21, 2020
A modern variation on the traditional cruise control system, adaptive cruise control includes different systems that automatically adjust a vehicle’s position relative to its road position. One system known as automatic braking uses sensors to detect vehicles ahead and slow to avoid rear-ending them. When there is no longer an obstacle in front, adaptive cruise control will resume its previous speed automatically.
Dynamic set speed types can slow a car or speed it up without manual intervention to match current speed limits. These systems use GPS to gauge a vehicle’s position relative to speed limit signs and help drivers avoid unintentionally speeding on a highway or expressway.
As car manufacturers have worked to develop autonomous vehicles in recent years, the industry has developed a classification convention that includes features that allow a vehicle’s computer systems to share vehicle control with the driver or else take control entirely. Vehicles with adaptive cruise control are considered Level 1 autonomous vehicles. Level 1 vehicles usually also have features like parking assistance, lane-keep assistance, and automatic braking.
Are there drawbacks to adaptive cruise control systems?
Adaptive cruise control users are more likely to speed, IIHS study claims: https://t.co/WqwDjK9E5z pic.twitter.com/0CNGNbpRL8 — Autoblog (@therealautoblog) March 14, 2021
Adaptive cruise control doesn’t come standard on every vehicle. In fact, this system can be pricey depending upon the make and model. Though this feature can help mitigate accidents stemming from driver fatigue, it can also lull drivers into a false sense of security. A tired driver using adaptive cruise control might not resume control of the vehicle quickly enough in an accident or emergency.
According to a recent study cited by Kia , if a driver travels through hilly or mountainous terrain with many curves, adaptive cruise control systems might prove less fuel-efficient than presumed. The excessive increases and decreases in speed could cause vehicles to consume up to 20 percent more fuel than they might by using the gas and brake pedals.
However, in general, adaptive cruise control usually helps drivers conserve fuel, save money , and reduce total car ownership costs. Coupling this feature with driving in the right-hand lane and avoiding sudden acceleration and braking can result in serious fuel cost savings.
The origins of this car convenience feature
It’s helpful to understand what cruise control is and how it works . It’s a system that keeps a vehicle running at a constant speed the driver sets. Though it has precursors, the modern mechanism we know as cruise control was invented in 1948 and patented in 1950 by inventor Ralph Teeter. The device saw its first commercial use when installed on the 1958 Chrysler Imperial. Soon, the feature saw widespread adoption by auto manufacturers and surging popularity among consumers, especially during the oil crisis of the 1970s when consumers were eager to reduce the amount of gas they consumed.
In cars equipped with this feature, a driver brings the vehicle up to the speed they want and then enables cruise control with a switch or a button. The vehicle then pulls the throttle to maintain the speed. The driver can still accelerate, but once they take their foot off the gas pedal, the car decelerates to the previously set speed until cruise control is disabled. Traditional systems typically store the previously set speed in memory to restore that speed after braking.
Traditional cruise control systems also work best with vehicles with a continuously variable or automatic transmission. When using them with manual transmissions, shifting gears typically disengages the feature. It can also be hazardous to use during inclement weather and when making sharp turns. However, drivers can benefit from the increased fuel efficiency they provide, MotorTrend reports. Moreover, setting the speed at or below highway speed limits during long drives can help drivers avoid unintentionally speeding.
Is Adaptive Cruise Control Worth It? Absolutely

How to Escape a Car Submerged In Water

I Was Surprised By the Most Important Roadtrip Stretches

Escape Road Rage and Rush Hour in These 4 U.S. Towns Without Any Cars
Produced by Digital Editors
Our experienced team of Digital Editors works to produce all of our content from contributing authors, including everything from assigning headlines and crafting the angles that readers will be interested in, to editing and publishing the articles once they’re drafted. Our DEs are editors and writers in their own right, who each have several years of experience in digital media and publishing.
Each one caters their work to their specific interests.

Does Cruise Control Save Gas? (and Other FAQs)
With gas prices seemingly always on the rise, drivers are looking for ways to improve fuel efficiency. Many believe cruise control can help save gas by maintaining a steady speed.
But does this popular feature actually reduce fuel consumption? This article explores whether using cruise control can help you save money at the pump and when you should NOT be using cruise control.

Related: Does Running Your A/C Use More Gas?
Table of Contents
Does Using Cruise Control Save Gas?
Yes, in many cases, cruise control use can actually increase a vehicle’s fuel economy by as much as 5%-15%. While this might be surprising to some, there is good reasoning behind this decrease in fuel consumption.
Since fuel consumption is greatest during acceleration, it stands to reason that the best way of achieving peak fuel economy would be to maintain a set speed. This can be quite difficult to achieve by way of standard pedal application. However, maintaining a set speed is easily achieved through the use of cruise control.

Since designated speeds are maintained by way of PCM control when a vehicle’s cruise control is activated, the “human” aspect of speed maintenance is eliminated. In many cases, even speed fluctuations incurred while traveling uphill or downhill are quite minor, when using cruise control.
Read Also: What is ECO Mode? (and When Should You Use It?)
When Should You NOT Use Cruise Control?
The use of cruise control is not advised when driving in slippery conditions, such as those presented by rain or snow. This is due to the fact that road conditions can change in an instant when driving in these less than ideal conditions, thereby making it essential to drive in response to the situation at hand.
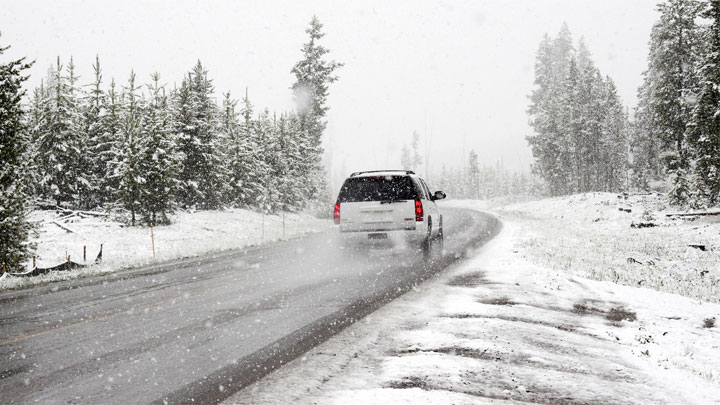

The use of cruise control is also not advised when one is drowsy or driving in congested conditions. Utilizing cruise control when tired only further eliminates one’s need to focus on the task of maintaining a set speed, often exacerbating this drowsiness.
Likewise, driving in stop-and-go traffic also requires a higher degree of concentration, as a significant amount of speed metering becomes necessary.
Does Cruise Control Use Brakes?
Cruise control, in its most basic form, does not use a vehicle’s brakes to meter speed. Quite the contrary, cruise control functions of this variety rely upon throttle plate actuation to maintain a constant speed, under an array of circumstances.
However, many late-model vehicles now feature adaptive cruise control, which does indeed utilize brake application as a means of slowing a vehicle’s speed. Systems of this type most often apply a vehicle’s brakes as a measure of accident avoidance, or to increase a vehicle’s trailing distance.
See Also: What Does the Overdrive Button Do?
Can Cruise Control Mess Up Your Transmission?
Contrary to popular belief, the use of cruise control does not accelerate transmission wear. In all actuality, regular cruise control use is actually capable of decreasing drivetrain wear, due to the significant reduction in manual throttle actuation.
A vehicle experiences the least amount of wear when operating at a constant, steady speed, for prolonged periods of time.
Many drivers are fooled into thinking that their vehicle’s transmission is being damaged when a vehicle’s cruise control causes an engine’s RPMs to spike during downshifting. In truth, this is not the case at all, as reasonably-timed downshifting is an accepted, and perfectly safe method of quickly decelerating any vehicle.
Where Should You Put Your Foot While Using Cruise Control?
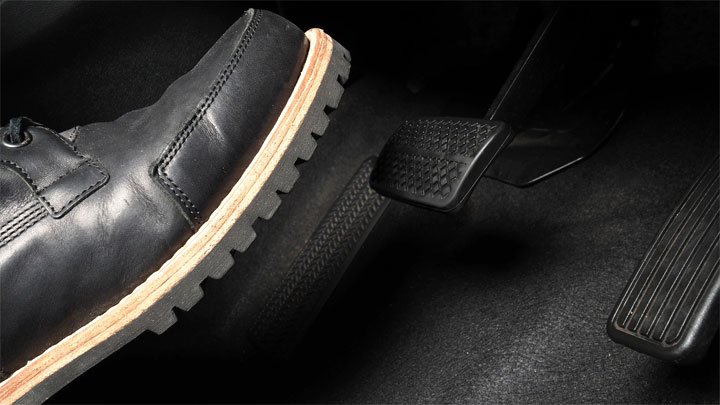

When using cruise control, it is always advised to keep your feet near a vehicle’s brake pedal at all times. Both road and traffic conditions can deteriorate in moments, necessitating additional input upon a driver’s behalf.
One is much more capable of mounting such a response in a timely manner, if their foot is near a vehicle’s brake pedal at all times.
This is even true when operating a vehicle that possesses adaptive cruise control. Though many drivers are lulled into a false sense of security when operating a vehicle under these conditions, one must be capable of maintaining full vehicle control at any given time.
That said, don’t drive with two feet (left foot over the brake, right foot over accelerator). Instead, keep your right foot near (not resting on top of) the brake pedal.
You may be tempted to cross your feet or legs (especially on a long drive) to stretch them out. But doing so severely impacts your reaction time when a situation calls for immediate braking.
Related: 5 Reasons Your Cruise Control Doesn’t Work
Are There Different Types of Cruise Control?
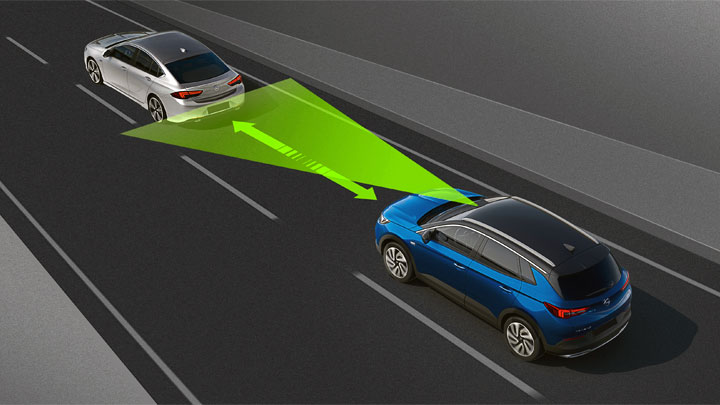
There are several different types of cruise control utilized by various vehicle manufacturers over the past several decades. The most basic of which is a standard, speed-limiting cruise control. As its name would suggest, a speed-limiting cruise control essentially governs a vehicle’s speed at a preset rate, thereby maintaining this speed under a variety of conditions.
Over the past decade, adaptive cruise control has also gained immense popularity. Systems of this type prove capable of maintaining a pre-set speed, while also metering a vehicle’s trailing distance, making any adjustments in speed as necessary. Systems of this nature rely upon a number of radar-based sensors, positioned along a vehicle’s exterior.
The latest form of cruise control to arrive on the scene has been that of a semi-autonomous design. Semi-autonomous cruise control systems meter a vehicle’s speed, braking, and steering, in response to traffic conditions. Systems of this type are capable of use in stop-and-go traffic, without driver intervention.
Related: 9 Benefits of Cruise Control
Can Cruise Control Be Added to a Vehicle?
In most cases, an aftermarket cruise control kit can be easily and affordably added to almost any vehicle. In fact, a number of aftermarket suppliers currently manufacture and market a variety of kits for this exact purpose.
Aftermarket cruise control kits typically include detailed installation instructions, and/or provide a direct phone number to the company’s technical support team. This eliminates much of the guesswork surrounding the installation of such systems.
It is also worth mentioning that aftermarket cruise control kits are available for vehicles with both cable and electronically actuated throttle linkages. While vehicles with the former of these two throttle configurations will require the installation of an additional throttle cable, the latter typically relies upon a module and basic wiring to facilitate operation.
- Recent Posts
- P1682 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Mar 28, 2024
- Toyota RCTA and BSM Malfunctions (Causes and Troubleshooting Advice) - Mar 25, 2024
- Getting a “Hill Start Assist Not Available” Message? (Here’s What to Do) - Mar 18, 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Local Giving
- Cenex ® TOP TIER™ Detergent Gasoline
- Cenex Roadmaster XL ® Premium Diesel
- Cenex ® Winterized Premium Diesel
- Cenex ® Ruby FieldMaster Premium Diesel ®
Renewable Fuels
- E-85/Other Blends And BioDiesel Blends
Fuel Services
- Automated Fuel Delivery
Featured Article
- Tracking Energy
Additional Information
- Cenex Total Protection Plan ®
- Safety Data Sheet Library
- Product Data Sheet Library
Engine Oils
- Diesel Engine Oils
- Gasoline Engine Oils
- Natural Gas Engine Oils
Hydraulic Oils
- Tractor Hydraulics Fluids
- Industrial Hydraulic Fluids
Transmission and Gear Oils
- Automatic Transmission Fluid
- Heavy Duty Transmission Fluid
Important Resources
- Equipment Lookup
Using Propane
- Residential
- Agriculture
- Transportation
- Propane Safety
Featured Articles
- Play it Safe With the Grill This Summer
- Flame Weeding. Powered by Propane
Corporate Information
- Energy Distribution
Cenex ®
- Join The Cenex ® Family
- Cenexperts ® Blog
Cenex ® Guarantee
- CenexExperts ® Blog

Fostering Community Connection Through Inclusive Sports
Read Blog Post
Does cruise control really save gas?
- By: Jenny Kraus
- Senior Marketing Specialist, CHS Refined Fuels
- in General Interest

For many of us, using cruise control comes second nature on a long drive. From speed-setting to automatic braking, it’s a handy feature to make lengthy trips a little bit easier. But have you ever wondered how cruise control affects your fuel efficiency?
It’s commonly assumed that cruise control saves on gas. As the thinking goes, by maintaining a steady speed, cruise control moderates fuel consumption more effectively than a driver manually pressing and releasing the gas pedal.
However, according to Autolist , that isn’t always the case. While it’s generally true that cruise control can improve fuel economy across long, flat stretches of road, there are no hard and fast rules.
How well your cruise control performs under different conditions depends on the make and model of your vehicle. No matter what you’re driving, though, keep these benefits in mind when determining whether to use cruise control on your next drive.
- It’s easy to use. Most systems have an on and off button in addition to buttons that allow you to change the speed in one-mph increments. In newer or more advanced systems, there may also be features like adaptive cruise control, which helps keep your car at a safe distance from others on the road.
- It can improve your focus. When the cruise control is set, you’re more available to focus on the road instead of worrying about maintaining a consistent speed. And since you don’t need to keep your foot on the gas, cruise control can also make driving more comfortable.
- It can help reduce speeding tickets. There are no guarantees, but if you’re notorious for racking up speeding tickets, cruise control may be your answer. Especially when used on the highway, cruise control can help tame your inner lead foot.
When is cruise control inefficient?
While cruise control can be helpful in many cases, there are occasions when you may not want to use it, including drives through hilly or rocky terrain. Many systems are unable to keep up with the changing inclines, which could decrease your fuel efficiency. In addition, although not related to fuel efficiently, remember that cruise control could be compromising when used in weather conditions like rain, ice and snow.
While cruise control systems vary, one thing that doesn’t is the need for quality fuels like CENEX TOP TIER™ DETERGENT GASOLINE . Find Cenex TOP TIER™ Detergent Gasoline at CENEX LOCATIONS NEAR YOU .
Spread The Word
Back to Cenexperts ® Blog


Providing Essential Food Resources to Children in Need
Find out how the Cenex Hometown Pride grant allowed the Hawley, Minn. based REACH® Inc. provides essential food resources to children in need.

Filling an Essential Community Gap to Support Small Town Families
Learn how a Hometown Pride Grant will help Kids Academy Daycare Center provide much-needed accessible childcare for its community.

What octane ratings really mean for your car
If you’ve ever contemplated which grade of gasoline to put in your tank, you’re not alone. Learn more about octane ratings and what they mean for your engine.

Battling Food Insecurity for Neighbors in Need
Learn how the Hometown Pride Grant will help the Backus Community Café provide solutions to hunger for its community.

Does Cruise Control Save Gas: Research-Based Guide

If you’re looking for a carefree way to travel, look no further than cruise control! This method of transportation is perfect for those who want to sit back and enjoy the ride. With cruise control, you can set your speed and relax while the car does the work. You can even take a nap if you’d like! Just be sure to keep an eye on the road in case you need to make any sudden stops.
With gas prices on the rise, many people are looking for ways to cut back on their fuel consumption. One method that is often touted as a way to save gas is using cruise control when driving on the highway. But does cruise control actually save gas, especially when driving on hills? In this research article, we will cover the answer to the question “Does Cruise Control Save Gas” in a detailed way.
Related Post: What Is Cruise Control In A Car Mystery Explained!
Does Cruise Control Save Gas

If you drive in a non-flat area such as in streets, heavy traffic, or hilly areas that increases fuel consumption due to repeatedly accelerating and braking. Non-flat areas increase fuel consumption because the cruise control cannot read the road the way the driver can.
The cruise control cannot read the gradient changes. It means that a surface on which one end or side is at a higher level than another, as a result, your cruise control will keep the power on for a little longer as it is unable to see slopes.
It depends upon where you drive, if you drive in a flat area such as a motorway, then it can save gas. Conversely, if you drive in a non-flat area such as in hills or heavy traffic, then it might not save you the gas. Now stick with me to break this down for you more comprehensively.
Cruise control can help you use less gas by driving on a long straight road; on the other hand, driving on streets or stop-and-go traffic does not save gas. According to greencarreports.com, the study showed a 5 to 7 percent drop in fuel consumption for cars driving with adaptive cruise control compared with human drivers.
In general, having a constant speed can increase fuel mileage even if you are not using cruise control. However, away from using constant speed even if you use the cruise control on non-flat roads or in stop-and-go traffic, you are still using high fuel.
Constant speed increases fuel efficiency, whereas varying the speed repeatedly from low to high and high to low can increase fuel consumption. According to natural resource Canada , you use 20% more fuel by varying speeds up and down between 55mph (90km/h) to 75mph (120km/h) compared to constant speed.
Related Post: The A-Z Of What Is Adaptive Cruise Control In A Car

Some people drive very aggressively, they accelerate heavily and suddenly brake, such kind of driving is not fuel-efficient, and this aggressive driving cause more fuel consumption. The harder you accelerate the more fuel you use, it is better to drive smoothly by using appropriate acceleration and brake.
This aggressive type of driving can increase fuel consumption. Because if you rapidly accelerate, you consume a high amount of fuel, which can travel you a few meters more. But if you brake in middle, you might not reach the point the consumed fuel can. As a result, your fuel is wasted.
According to fueleconomy.org , aggressive driving (rapid acceleration and braking) wastes gas. Aggressive driving can lower your gas mileage by roughly 15% to 30% at highway speeds and 10% to 40% in stop-and-go traffic.
So, using cruise control on flat areas such as motorways can help you save gas. It saves gas by driving at a constant speed since the driver does not accelerate and brakes frequently.
This is an Info Old cruise control systems might not save you much money as compared to modern cruise control systems. Because the old cruise controls aggressively return to the Resume speed by consuming a little more gas, but the modern cruise control accelerates gently and smoothly saving you a little more money.
Related Post: Cruise Control Symbol On Dashboard: Standard Symbol

By looking ahead at how the traffic is behaving; you can do good judgments in advance to slow down the car. So, you will consume less fuel by taking your foot off the accelerator pedal and saving more money. Try to maintain a steady speed and avoid unnecessary acceleration to save fuel.
Although, the latest version of adaptive cruise control will adapt the speed of the car by sensing the change in the car’s speed ahead of your car. According to research conducted in Europe, adaptive cruise control reduces fuel consumption by 2.8 percent on highways.
This is an Info In general, cruise control can be an extra drain on the battery of electric cars, which can reduce car traveling range. However, it will save the battery charge by keeping a steady speed compared to its uses.
About The Author
Related Posts

How To Turn OFF Cruise Control, When To Use It & When Not

How Does Cruise Control Work: We Have The Best Answer

Advantages & Disadvantages Of Adaptive Cruise Control
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- Advisories & Tips
- Apps & Software
- Buyer's Guide
- Maintenance

Cruise Control: How it Works, Types and Everything You Should Know
Learn how to effectively use cruise control in your vehicle. follow our simple instructions to optimize your driving experience.

Cruise control is a popular feature in modern vehicles that can make driving more comfortable and less stressful. There are several types of cruise control systems that drivers can choose from, depending on their driving conditions and preferences. Standard cruise control is the most basic system, which allows the driver to set a constant speed that the vehicle will maintain. Adaptive cruise control, on the other hand, uses sensors to detect the distance and speed of vehicles in front of the car, adjusting the vehicle’s speed accordingly to maintain a safe following distance.
Intelligent cruise control goes even further, using artificial intelligence to learn the driver’s behaviour and adjust the speed of the vehicle before the driver takes action. Stop-and-go cruise control is ideal for use in heavy traffic and can bring the vehicle to a complete stop if necessary, while speed limiters are designed to limit the maximum speed of the vehicle. Each type of cruise control system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and drivers should choose the one that best suits their needs.
What Is Cruise Control
Cruise control is a system within a vehicle that enables drivers to establish and sustain a specific speed without having to continuously press the accelerator pedal. The system uses electronic sensors to track the vehicle’s speed and automatically regulate the throttle and brakes to maintain the predetermined speed. Cruise controle is generally employed during extended trips on highways, where sustaining a constant speed can decrease driver tiredness and boost fuel economy. It is a common feature in modern automobiles, trucks, and other types of vehicles.
How it Works
Cruise control works by using a combination of electronic sensors, servos, and control algorithms to maintain a vehicle’s speed without requiring the driver to continuously press the accelerator pedal. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how cruise controle works:
- The driver activates cruise control by pressing a button or flipping a switch on the dashboard or steering wheel.
- The system uses electronic sensors to measure the vehicle’s speed and other factors such as throttle position, engine load, and road grade.
- The driver sets the desired speed by pressing a button or using a lever. The speed is usually displayed on the dashboard.
- Once the speed is set, the cruise controle system takes over and maintains the speed by sending signals to the throttle and brakes as necessary.
- If the vehicle encounters an incline or decline, the cruise control system adjusts the throttle to maintain a constant speed.
- If the driver needs to slow down or stop, they can deactivate the cruise control by pressing the brake or clutch pedal, or by turning off the system using the control button.
In some modern cars, the cruise control system is enhanced with additional sensors and algorithms that enable it to adapt to the surrounding traffic and road conditions. These advanced systems are known as adaptive cruise control, intelligent cruise control, or active cruise control.
How To Use Cruise Control
Cruise control is a feature commonly found in modern vehicles that allows the driver to maintain a constant speed without having to keep their foot on the accelerator pedal. Here’s how to use cruise control:
- Locate the cruise control button : The button is typically located on the steering wheel or dashboard. Check your owner’s manual if you’re having trouble finding it.
- Activate cruise control : Once you’ve found the cruise control button, press it to turn on the system. You should see a light on the dashboard indicating that cruise control is active.
- Accelerate to your desired speed : Using the accelerator pedal, accelerate to the speed you want to maintain.
- Set the speed : Press the “set” or “res” button on the steering wheel to set the speed. The vehicle will maintain this speed until you cancel cruise control or apply the brakes.
- Adjust the speed : To increase or decrease your speed, use the “+” or “-” buttons on the steering wheel.
- Cancel cruise control : To turn off cruise control, press the “off” or “cancel” button on the steering wheel, or press the brake pedal.
- Resume cruise control : If you cancel cruise control but want to resume it at the previous speed, press the “resume” button on the steering wheel.
Note: Always remember to pay attention to the road and adjust your speed as needed. Do not rely solely on cruise control while driving.
Advantages Of Cruise Control
- Reduces driver fatigue : With cruise control engaged, the driver does not have to maintain constant pressure on the accelerator pedal. This can help reduce driver fatigue, particularly during long trips.
- Conserves fuel : Cruise control helps maintain a consistent speed, which can result in better fuel efficiency. This is because the vehicle is not accelerating and decelerating as frequently, which can waste fuel.
- Helps avoid speeding tickets : Cruise control can help drivers avoid speeding tickets, as they can set the desired speed and avoid accidentally exceeding the speed limit.
- Improves safety : Maintaining a consistent speed with cruise control can help reduce the likelihood of sudden braking or acceleration, which can improve safety on the road.
- Enhances driving experience : Cruise control can make driving more comfortable and less stressful, particularly in heavy traffic or on long trips.
Disadvantages Of Cruise Control
- Limited use : Cruise controle is best suited for use on highways or other roads with minimal traffic and few curves. It may not be appropriate for use in heavy traffic or on winding roads, as it may not respond quickly enough to changing driving conditions.
- Increases risk in hazardous conditions : Using cruise controle in hazardous conditions such as rain, ice, or snow can be dangerous. The driver may not be able to react quickly enough to changing conditions, and the vehicle may lose traction or spin out of control.
- Can lead to complacency : Relying too heavily on cruise controle can lead to complacency and inattention while driving. The driver may become less aware of their surroundings or less attentive to the road.
- May cause speed variations : Cruise controle may cause speed variations due to changes in road elevation, wind, or traffic conditions. This can be a problem if the driver is not paying attention and fails to adjust the speed manually.
- May reduce driver engagement : Using cruise controle for extended periods of time may reduce driver engagement and enjoyment of the driving experience.
Types Of Cruise Control
Modern vehicles offer various types of cruise control systems to assist drivers in maintaining a steady speed. Here are some of the most common types of speed control.
1. Standard Cruise Control
Standard cruise control is the most basic form of speed control system that has been around for several decades. It allows the driver to set a desired speed and maintain it without having to keep their foot on the accelerator pedal. Once activated, the system uses electronic sensors to monitor the speed of the vehicle and automatically adjusts the throttle to maintain a constant speed.
With standard cruise controle, the vehicle will maintain the set speed regardless of changes in the road conditions, such as uphill or downhill slopes or curves. To deactivate the system, the driver can either apply the brakes or turn off the cruise control switch. Standard cruise controle can be found on many vehicles, from entry-level models to high-end luxury cars.
While it can help reduce driver fatigue and improve fuel economy on long drives, it requires the driver to remain attentive and adjust the speed manually if necessary. Therefore, it is important for drivers to use it responsibly and not rely solely on the system to maintain a safe driving experience.
Advantages of Standard Cruise Control
- Reduced driver fatigue : By allowing the driver to set a constant speed and not having to keep their foot on the accelerator pedal, standard cruise control can help reduce driver fatigue and make long drives more comfortable.
- Improved fuel efficiency : Maintaining a constant speed using cruise controle can improve fuel efficiency by reducing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, resulting in lower fuel consumption.
- Avoiding speeding tickets : Standard cruise control helps drivers avoid unintentionally exceeding the speed limit, which can result in costly speeding tickets.
- Easier driving in heavy traffic : When driving in heavy traffic, using cruise controle can help reduce stress and allow drivers to focus on other aspects of driving, such as changing lanes and looking out for other drivers.
- Consistent speed : By maintaining a consistent speed, standard cruise controle can provide a smoother driving experience, especially on long, open roads where it can be challenging to maintain a constant speed manually.
Disadvantages Of Standard Cruise Control
- Limited functionality : Standard cruise control can only maintain a constant speed and does not adjust the speed based on traffic or road conditions. As a result, drivers must be attentive and make manual adjustments if necessary, especially in situations such as steep hills, winding roads, or heavy traffic.
- Reduced control : By taking over the throttle, standard cruise controle can reduce the driver’s control over the vehicle, particularly in emergency situations that require quick acceleration or deceleration.
- Safety risks : Standard cruise controle may pose a safety risk in some situations, such as when driving on wet or icy roads, where sudden changes in road conditions could cause the vehicle to skid or lose control.
- Increased fuel consumption : In some cases, standard cruise controle can actually increase fuel consumption, particularly in stop-and-go traffic, where frequent acceleration and deceleration can lead to higher fuel consumption than maintaining a constant speed.
- Maintenance and repair costs : If the cruise controle system malfunctions, it can be costly to repair or replace.
2. Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is an advanced form of speed control that uses sensors and radar to detect the distance between the driver’s car and the vehicle ahead, unlike other types of cruise control systems. This type of cruise control automatically adjusts the speed of the vehicle to maintain a safe following distance and can even bring the vehicle to a complete stop if necessary.
The system uses sensors and radar to detect the distance between the driver’s car and the vehicle ahead. If the vehicle ahead slows down or stops, the ACC system automatically applies the brakes to slow down or stop the car, maintaining a safe distance. When the road clears or the vehicle ahead moves faster, the ACC system accelerates the car to the driver’s set speed or the maximum speed limit.
Some ACC systems also come with collision warning systems that alert the driver if the car gets too close to the vehicle ahead. Some systems can also detect pedestrians, animals, or other obstacles and apply the brakes if necessary.
Advantages Of Adaptive Cruise Control
- Enhanced safety : By automatically maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle ahead, adaptive cruise control can help reduce the risk of rear-end collisions, making it a valuable safety feature.
- Reduced driver fatigue : Adaptive speed control can reduce driver fatigue by taking over the task of maintaining a safe following distance, especially in heavy traffic.
- Increased convenience : ACC can make long drives more comfortable and less stressful, as the driver doesn’t have to constantly adjust the speed.
- Fuel efficiency : By maintaining a constant speed and reducing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, adaptive cruise control can help improve fuel efficiency.
Disadvantages Of Adaptive Cruise Control
- High cost : ACC systems are more expensive than traditional cruise control systems.
- Limited functionality : ACC may not work in all driving situations, such as on winding roads or in heavy rain or snow.
- Over-reliance : Drivers may become too reliant on the ACC system and neglect to pay attention to the road and other vehicles, which can lead to accidents.
- Complex operation : ACC systems can be complex and difficult to operate, requiring drivers to understand how the system works and how to use it correctly.
3. Intelligent Cruise Control
Intelligent Cruise Control (ICC), also known as Active Cruise Control (ACC), is an advanced form of cruise controle that uses sensors and cameras to detect the distance and speed of the vehicles ahead. ICC not only maintains a safe distance from the vehicle ahead but also adjusts the speed of the vehicle to match the flow of traffic.
The system uses a forward-facing camera and sensors to detect the speed and distance of the vehicle in front of the driver. If the vehicle ahead slows down or speeds up, ICC automatically adjusts the speed of the driver’s car to maintain a safe following distance. Unlike regular speed control, ICC can also bring the car to a complete stop and resume driving when the vehicle ahead starts moving again.
ICC systems can also recognize lane markings and keep the car centred within the lane, providing additional safety and convenience benefits. Some ICC systems can even detect and respond to pedestrians and other obstacles, providing an added layer of safety.
Advantages Of Intelligent Cruise Control
- Increased safety : By automatically adjusting the speed and maintaining a safe following distance, ICC can help prevent accidents and reduce the risk of collisions.
- Reduced driver fatigue : ICC can reduce driver fatigue and make long drives more comfortable, especially in heavy traffic.
- Improved fuel efficiency : By maintaining a constant speed and reducing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, ICC can help improve fuel efficiency.
- Enhanced convenience : ICC can make driving more convenient and less stressful, as the system takes care of maintaining a safe distance and speed.
Disadvantages Of Intelligent Cruise Control
- High cost : ICC systems can be expensive, especially in luxury cars.
- Complex operation : ICC systems can be complex and difficult to operate, requiring drivers to understand how the system works and how to use it correctly.
- Limited functionality : ICC may not work in all driving situations, such as on winding roads or in heavy rain or snow.
- Over-reliance : Drivers may become too reliant on the ICC system and neglect to pay attention to the road and other vehicles, which can lead to accidents.
4. Stop-and-Go Cruise Control
Stop-and-Go Cruise Control is an advanced form of speed control, Unlike other types of cruise controle systems. It can maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead, even in stop-and-go traffic. This type of cruise controle is designed to help drivers reduce stress and fatigue when driving in heavy traffic conditions. The system uses sensors and cameras to detect the distance and speed of the vehicle ahead.
When traffic slows down or comes to a stop, the Stop-and-Go Cruise Control system automatically applies the brakes to bring the car to a complete stop. When the traffic ahead starts moving again, the system automatically accelerates the car to follow the flow of traffic.
Stop-and-Go speed control systems can help reduce the stress and fatigue of driving in heavy traffic, as the system takes care of maintaining a safe distance and speed. Some systems also have the ability to recognize and respond to pedestrians and other obstacles, providing an added layer of safety.
Advantages Of Stop-and-Go Cruise Control
- Reduced driver fatigue : Stop-and-Go Cruise controle can reduce driver fatigue and make long drives in heavy traffic more comfortable.
- Increased safety : By automatically adjusting the speed and maintaining a safe following distance, Stop-and-Go Cruise controle can help prevent accidents and reduce the risk of collisions.
- Enhanced convenience : Stop-and-Go speed control can make driving in heavy traffic more convenient and less stressful, as the system takes care of maintaining a safe distance and speed.
- Improved fuel efficiency : By maintaining a constant speed and reducing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, Stop-and-Go Cruise controle can help improve fuel efficiency.
Disadvantages Of Stop-and-Go Cruise Control
- Limited functionality : Stop-and-Go speed control may not work in all driving situations, such as on winding roads or in heavy rain or snow.
- High cost : Stop-and-Go speed control systems can be expensive, especially in luxury cars.
- Complex operation : Stop-and-Go speed control systems can be complex and difficult to operate, requiring drivers to understand how the system works and how to use it correctly.
- Over-reliance : Drivers may become too reliant on the system and neglect to pay attention to the road and other vehicles, which can lead to accidents.
5. Speed Limiter
A speed limiter is a type of speed control system that is designed to limit the maximum speed of a vehicle. Unlike other types of cruise control systems, which maintain a set speed, a speed limiter prevents a vehicle from exceeding a certain speed limit.
Speed limiters can be installed in vehicles as a safety feature, particularly in commercial vehicles like trucks and buses. These vehicles are often required by law to have speed limiters installed, as they can help prevent accidents caused by excessive speed. In addition, speed limiters can help improve fuel efficiency and reduce wear and tear on the vehicle’s engine and brakes.
There are two main types of speed limiters :
Hard limiters : These limiters prevent a vehicle from exceeding a certain speed limit, typically set by the manufacturer. Once the limit is set, it cannot be exceeded, even in emergency situations. Soft limiters : These limiters allow the vehicle to exceed the set speed limit in certain situations, such as when overtaking or accelerating to merge onto a highway. However, the limiter will still prevent the vehicle from exceeding the maximum speed limit.
Advantages Of Speed Limiter
- Increased safety : Speed limiters can help prevent accidents caused by excessive speed, especially in commercial vehicles.
- Reduced fuel consumption : By limiting the maximum speed of a vehicle, speed limiters can help improve fuel efficiency.
- Reduced wear and tear : Speed limiters can help reduce wear and tear on a vehicle’s engine and brakes, extending the life of the vehicle.
- Compliance with regulations : In some countries, commercial vehicles are required by law to have speed limiters installed.
Disadvantages Of Speed Limiter
- Limited functionality : Speed limiters may not be effective in preventing all types of accidents or speeding violations.
- Reduced driver control : Some drivers may feel uncomfortable with a speed limiter installed, as it restricts their ability to control the vehicle’s speed.
- Maintenance costs : Speed limiters may require maintenance and calibration, which can be costly.
It’s important to remember that cruise control is not a substitute for attentive driving. Drivers should always remain aware of their surroundings and be ready to take control of the vehicle at any time. Additionally, drivers should not use speed control in certain situations, such as in heavy traffic, on wet or slippery roads, or when driving in mountainous terrain. Overall, it can be a helpful tool for long-distance driving on open roads, but drivers should always use it with caution and be aware of its limitations.
You Might Also Like
2023 toyota camry: features, specs and price in nigeria, 10 cheap cars with hidden fuel efficiency you should know, 2022 toyota camry: features, specs and price in nigeria, top 10 best cars for women to buy in nigeria (2024), 10 most affordable family cars in nigeria, sign up for daily newsletter, be keep up get the latest tech and auto news delivered straight to your inbox..
Email address:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Stay Connected
Latest news.

Xiaomi Redmi A3 Review: Specs and Price in Nigeria

How to Check Car Registration Status in Nigeria

Binance in Trouble: Nigeria Demands Massive $10B Fine

Infinix Hot 40 Pro Review: Specs and Price in Nigeria
Recent comments.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Why investigators are looking into ‘dirty fuel’ in Baltimore bridge collapse

“Dirty fuel” is one of several possible factors that may have caused the cargo ship Dali to lose power in the moments before it smashed into the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore on Tuesday, according to shipping industry experts.
The investigation by federal, state and local authorities into what went wrong on the Dali is just beginning. But the deadly events on the Patapsco River in the dark of night have shined a light on the travails of the global shipping industry, including a long-standing problem with dirty fuel.
According to a 2018 report for the Atlantic Council think tank, a “witches brew” of industrial products ends up in marine fuel, resulting in hundreds of engine failures in recent years that have left ships powerless and drifting across the high seas.
The Dali went dark as it lost electrical power just before the bridge disaster, and the pilot lost the ability to control the ship as it veered toward the support structure of the bridge. That power loss could have been caused by dirty fuel clogging filters that lead to the ship’s main generator, said Gerald Scoggins, a veteran chief engineer in the oil and gas industry and the CEO of the Houston company Deepwater Producers.
He noted that ships use different fuels for different portions of their cruise. While inside a port, as the Dali was before the collision, ships typically run on a relatively light diesel fuel. That also could have been contaminated. Common contaminants include water, dirt and algae, Scoggins said.
“He definitely could have had dirty fuel,” Scoggins said.
Fueling supply chain issues
Ian Ralby, the CEO of I.R. Consilium, a maritime and resource security consultancy, said heavy marine fuel loaded onto ships in port is mixed with what is called cutter stock, and is prone to being loaded with contaminants and is not closely regulated. Such dirty fuel could have “gummed up all of the fuel lines on the ship.”
Ralby, who co-authored the 2018 Atlantic Council report, said that waste products from refineries and other industrial operations have made their way illegally into shipping fuel, known as bunker fuel.
“The supply chain for bunker fuel is long, and relatively opaque,” the report states. “As a result, bunker fuel has become a final destination for the leftovers of the refining process.”
Merchant ships, the report states, then effectively function as incinerators for the refining industry. Inspectors have found bunker fuel contaminated with “used motor oil and by-products from the manufacture of plastics, rubber, cosmetics, fertilizers, and even paper goods.”
Baltimore bridge collapse

In the case of the Dali, Ralby said the possibility of a cyberattack should not be dismissed. It’s also possible that the ship had a purely mechanical failure in one of its critical systems.
The dirty fuel conjecture comes from observers with limited direct information about the ship, its fueling history and other potential mechanical problems that could have contributed to the loss of power and steering control.
Whatever the cause, the shipping industry has been roiled by the Baltimore disaster and other troubling developments, including attacks on Red Sea cargo ships by Houthi militants and low water in the Panama Canal . With those major shipping routes imperiled, the entire global supply chain has been rerouted, Ralby said — and that could exacerbate the dirty fuel problem.
“We may be in a situation where ships are going to be taking on fuel in places where they can’t guarantee the quality or caliber of fuel,” he said.
Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge collapsed after being hit by a cargo ship , sending at least eight people from a construction crew into the water. Follow live updates and see photos from the scene .
How it happened: The container ship lost power shortly before hitting the bridge, Maryland Gov. Wes Moore (D) said. Video shows the bridge collapse in under 40 seconds.
Victims: Divers recovered the bodies of two construction workers who died , while finding other vehicles trapped and probably containing the other victims, officials said. They were fathers, husbands and hard workers . The entire crew aboard the container ship Dali survived . First responders shut down most traffic on the four-lane bridge after the crew issued an urgent mayday call. It saved lives, Moore said.
Economic impact: The collapse of the bridge, which severed ocean links to the Port of Baltimore, adds a fresh headache to already struggling global supply chains . See how the collapse will disrupt the supply of cars, coal and other goods .
History: The Key Bridge was built in the 1970s and spanned the Patapsco River. Rebuilding the bridge will probably take years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars, experts said.

Toxicity bioassay of waste cooking oil-based biodiesel on marine microalgae
Affiliations.
- 1 Far Eastern Federal University, Sukhanova Street, 8, Vladivostok 690950, Russian Federation.
- 2 Laboratory of Toxicology, School of Medicine, University of Crete, Heraklion 71003, Greece.
- 3 University of Eastern Finland, School of Pharmacy, POB 1627, 70211 Kuopio, Finland.
- 4 The Federal Budgetary Establishment of Science "Federal Scientific Center of Hygiene named after F. F. Erisman" of the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing, 2 Semashko street, Mytishchi, Moscow Oblast', 141014, Russian Federation.
- 5 Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Department of Chemical Engineering, University Campus, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece.
- 6 University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, USA.
- 7 School of Life & Health Sciences, Pharmaceutics Dept., Aston University, B4 7ET, Birmingham, England, UK.
- 8 Pacific Geografical Institite FEB RAS, Vladivosotok, 690014, Russia.
- PMID: 30622905
- PMCID: PMC6317304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.12.007
The world biodiesel production is increasing at a rapid rate. Despite its perceived safety for the environment, more detailed toxicity studies are mandatory, especially in the field of aquatic toxicology. While considerable attention has been paid to biodiesel combustion emissions, the toxicity of biodiesel in the aquatic environment has been poorly understood. In our study, we used an algae culture growth-inhibition test (OECD 201) for the comparison of the toxicity of B100 (pure biodiesel), produced by methanol transesterification of waste cooking oil (yellow grease), B0 (petroleum diesel fuel) and B20 (diesel-biodiesel blended of 20% biodiesel and 80% petroleum diesel fuel by volume). Two marine diatoms Attheya ussuriensis and Chaetoceros muelleri , the red algae Porphyridium purpureum and Raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo were employed as the aquatic test organisms. A sample of biodiesel from waste cooking oil without dilution with petroleum diesel (B100) showed the highest level of toxicity for the microalgae A. ussuriensis , C. muelleri and H. akashiwo , compared to hexane, methanol, petroleum diesel (B0) and diluted sample (B20). The acute EC 50 in the growth-inhibition test (96 h exposure) of B100 for the four species was in the range of 3.75-23.95 g/L whereas the chronic toxicity EC 50 (7d exposure) was in the range of 0.42-16.09 g/L.
Keywords: Aquatic pollution; Biodiesel; Biodiesel blends; Ecotoxicology; Microalgae; Waste cooking oil biodiesel.
- Our mission and corporate values
- Key figures
- Public Reporting
All enterprises
- Procurement policy
- Protection of nuclear materials and facilities
- Anti-corruption policy
- Nuclear fuel cycle (sheme)
- Uranium mining
- Fuel and enrichment
- Machine building
- Engineering
- Power generation
- Nuclear Medicine
- Non-Nuclear Equipment Manufacturing
- Nuclear icebreaker fleet
- Other Non-Nuclear Applications
- International business development division
- International relations
- Nuclear and radiation safety
- Quality management
- Rosatom production system
- Environmental management
- Occupational safety
- Public council
- Disclosure policy
- Code of conduct
- Nuclear industry in the media
- Announcements
- Photoarchive
- Videogallery
- Corporate identity
- Rosatom newsletter
- Useful links
- Rosatom procurement system
- How to become a supplier
- Contacts for investors
- Credit Ratings and Public Borrowings
- Calendar of Events
© 2008–2024 The State Atomic Energy Corporation ROSATOM

- For journalists
- For suppliers
- For investors
2 enterprises

National Operator for Radioactive Waste Management

NIKIMT Atomstroy
Development and application of installation, maintenance, diagnostic and dismantling technologies for nuclear facilities with a focus on innovation; dismantlement of decommissioned nuclear facilities and construction of new infrastructure for nuclear...
Development and application of installation, maintenance, diagnostic and dismantling technologies for nuclear facilities with a focus on innovation; dismantlement of decommissioned nuclear facilities and construction of new infrastructure for nuclear decommissioning
14 enterprises

AKME Engineering

Alianstransatom
Integrated truck, minibuses and limousine transportation services for nuclear companies since 1945.

Angarsk Electrolysis Chemical Complex
Uranium enrichment since 1957; a host facility for the International Uranium Enrichment Centre (IUEC) operating under the auspices of the IAEA.
ASE Group provides engineering and construction of NPPs built to Russian technologies (all spectrum of front-end engineering and survey services associated with construction and retrofitting of nuclear power plants, including site selection, deve...
ASE Group provides engineering and construction of NPPs built to Russian technologies (all spectrum of front-end engineering and survey services associated with construction and retrofitting of nuclear power plants, including site selection, development of design and detailed engineering documentation, organisation of civil and installation works, supply of equipment and materials, commissioning, and startup operation).
Atom-Okhrana
Nuclear industry security agency established in 2002 to provide security services to nuclear companies, safeguard nuclear materials and equipment, and monitor access control policies at guarded facilities.

Atomenergomash Group
Atomenergoprom, atomenergoremont, atomenergosbyt.
Rosenergoatom's subsidiary AtomEnergoSbyt sells nuclear electricity and heat. It supplies electricity to organisations and peoples in the Central, North-West, Volga, Urals and Siberia federal districts of Russian Federation.
Federal nuclear icebreaker's fleet company

Atomic Reactor Research Institute
Atomkomplekt.
ROSATOM's organizer of tenders and procurement activities
Atomspetstrans
Transportation of nuclear materials and other radioactive substances and products inside and outside Russia since 2000.

Atomtechenergo
The specialized company, which was established in 1983 to provide repair and maintenance services for nuclear power plants.
5 enterprises
Production of high-precision instruments and machines, gas centrifuges for uranium enrichment, spent nuclear fuel containers, military products, gas meters and calibration tools.
Troitsk Institute for Innovation and Fusion Research
Turbine technology aaem limited liability company.

TVEL Fuel Company

Zababakhin Russian Research Institute for Technical Physics
One of the two national Federal Nuclear Centres engaged in both military and civilian research projects in a variety of fundamental and applied fields (material science, thermonuclear fusion, plasma physics, nuclear safety, nuclear materials mana...
One of the two national Federal Nuclear Centres engaged in both military and civilian research projects in a variety of fundamental and applied fields (material science, thermonuclear fusion, plasma physics, nuclear safety, nuclear materials management, computer modelling etc.)

Zarubezhatomenergostroy
Quality assurance and control functions (nuclear fuel acceptance, project design audit and quality audit) since 1973, 24 offices across Russia.
3 enterprises
Machine Building Plant

Mayak Production Association
Group of diversified manufacturing operations established in the late 1940s to produce plutonium for the Soviet nuclear industry; now focuses on spent nuclear fuel processing, isotope production and process automation; accounts for over a half of Rus...
Group of diversified manufacturing operations established in the late 1940s to produce plutonium for the Soviet nuclear industry; now focuses on spent nuclear fuel processing, isotope production and process automation; accounts for over a half of Russian isotope exports.
Mining and Chemical Plant
The enterprise of the Back End Management Division of ROSATOM, runs main radioactive waste (RAW) storage sites of Russian nuclear industry.

Science and Innovation
Management company established to coordinate activities of 13 research and development institutes within ROSATOM's Innovation Management Division engaged in development of new chemical, electrical and nuclear power technologies.

Siberian Chemical Plant
One of four enrichment facilities operating in Russia, subsidiary of the TVEL Fuel Company.
1 enterprise

Federal Center for Nuclear and Radiation Safety (JSC FCNRS)
FCNRS is the management company within ROSATOM Division for the Back-End of Nuclear Facilities Life Cycle, responsible for consolidation of assets and coordination of research and production activities of companies and organisations incorporated into...
FCNRS is the management company within ROSATOM Division for the Back-End of Nuclear Facilities Life Cycle, responsible for consolidation of assets and coordination of research and production activities of companies and organisations incorporated into the Division.
12 enterprises
RADON, FSUE
Rosatom emergency service.
ROSATOM's nuclear and radiation emergency response team is integrated into the national emergency response system; it includes a coordination centre in St. Petersburg, three operations centres across Russia, the Engineering and Training Centre fo...
ROSATOM's nuclear and radiation emergency response team is integrated into the national emergency response system; it includes a coordination centre in St. Petersburg, three operations centres across Russia, the Engineering and Training Centre for Robotics Research, and the EPRON Emergency and Underwater Rescue Service

Rosenergoatom
Management of radioactive waste and ionizing radiation sources, including transportation, collection, processing and storage, site rehabilitation, decommissioning of nuclear submarines, radioactive substance and radioactive waste control and accounti...
Management of radioactive waste and ionizing radiation sources, including transportation, collection, processing and storage, site rehabilitation, decommissioning of nuclear submarines, radioactive substance and radioactive waste control and accounting activities; operates through two subsidiaries – SevRAO in Ostrovnoy, Murmansk Region, and DalRAO in Vladivostok, Primorsky Krai
Rusatom International Network
Rusatom International Network has been established to develop and manage ROSATOM's regional representative offices all over the world. The main objectives of the company are to support the activity of ROSATOM's divisions on foreign markets, s...
Rusatom International Network has been established to develop and manage ROSATOM's regional representative offices all over the world. The main objectives of the company are to support the activity of ROSATOM's divisions on foreign markets, searching for new business opportunities, promoting the Russian nuclear industry's products and services on the global market.
Rusatom Overseas
Rusatom Overseas JSC is a company within the ROSATOM Group. It is responsible for promotion of the integrated offer for NPP construction projects in the international market.
Rusatom Service
Russian electrotechnical institute named after v.i. lenin, russian institute of precise chemistry technology (vniiht), russian research and development institute for nuclear power machinery.
Design and development of power machinery for conventional and nuclear power plants and special-purpose machinery for other industries since 1977.
Russian Research Institute for Chemical Technology
Design and development of uranium and pure metal production technologies since 1951 (ore processing, development of construction materials for the nuclear industry, production of ultra-pure gases for microelectronics and alternative power sources...
Design and development of uranium and pure metal production technologies since 1951 (ore processing, development of construction materials for the nuclear industry, production of ultra-pure gases for microelectronics and alternative power sources)
Russian Research Institute for Experimental Physics
One of the two national Federal Nuclear Centres engaged in both military and civilian projects in a variety of fundamental and applied fields (safety and reliability of Russian nuclear weapons, theoretical and mathematical physics, gas dynamics, ...
One of the two national Federal Nuclear Centres engaged in both military and civilian projects in a variety of fundamental and applied fields (safety and reliability of Russian nuclear weapons, theoretical and mathematical physics, gas dynamics, explosion physics, nuclear and radiation physics, lasers, high density energy, beam physics, etc.).
Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry
Research and development function established in 1918 to provide expertise in surface chemistry, adsorption, atomisation, electrode processes, corrosion protection, chemical kinetics and catalysis, radiation chemistry and high molecular weight compou...
Research and development function established in 1918 to provide expertise in surface chemistry, adsorption, atomisation, electrode processes, corrosion protection, chemical kinetics and catalysis, radiation chemistry and high molecular weight compounds.
NPK Khimprominzhiniring, JSC (a brand of UMATEX Group)
Dollezhal research and development institute of power engineering.
Major Russian research centre established in 1952 to develop reactor technologies and automation systems, concentrates research efforts on reactor physics, thermal physics, hydrodynamics, material engineering, nuclear safety, reactor core optimisatio...
Major Russian research centre established in 1952 to develop reactor technologies and automation systems, concentrates research efforts on reactor physics, thermal physics, hydrodynamics, material engineering, nuclear safety, reactor core optimisation, life cycle extension and nuclear decommissioning.

Venta, Mashine-building plant
Production of fans for NPP's.
VNIPIpromtechnologii National Research and Design Institute for Industrial Technology
Leading design and research institute specialising in end-to-end design engineering of uranium mining and processing facilities; to be reorganized into an engineering centre of ARMZ Uranium Holding
International Uranium Enrichment Centre

OKB Gidropress

OKBM Afrikantov
Specialized company, focused on the development and application of products from beryllium.

Bochvar National Research Institute for Inorganic Materials
Leading R&D institute, a subsidiary of TVEL Fuel Company, focused on the development and application of composite materials and alloys (including superconducting, high-melting, rare earth and ultra-pure materials).

The Branch Centre of the Capital Construction of ROSATOM
United corporation for innovations.
The United Innovation Corporation is the ROSATOM subsidiary engaged in the construction and fitting out of radionuclide diagnostic centres, both fixed and mobile, and of radionuclide diagnostic departments at medical institutions.
Toxicity bioassay of waste cooking oil-based biodiesel on marine microalgae
K.s. pikula.
a Far Eastern Federal University, Sukhanova Street, 8, Vladivostok 690950, Russian Federation
A.M. Zakharenko
V.v. chaika, a.k. stratidakis.
b Laboratory of Toxicology, School of Medicine, University of Crete, Heraklion 71003, Greece
M. Kokkinakis
c University of Eastern Finland, School of Pharmacy, POB 1627, 70211 Kuopio, Finland
V.N. Rakitskii
d The Federal Budgetary Establishment of Science “Federal Scientific Center of Hygiene named after F. F. Erisman” of the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing, 2 Semashko street, Mytishchi, Moscow Oblast’, 141014, Russian Federation
D.A. Sarigiannis
e Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Department of Chemical Engineering, University Campus, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece
f Environmental Health Engineering, School for Advanced Studies IUSS, Pavia, 27100, Italy
g University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, USA
M.D. Coleman
h School of Life & Health Sciences, Aston University, B4 7ET, Birmingham, England, UK
A. Tsatsakis
K.s. golokhvast.
i Pacific Geografical Institite FEB RAS, Vladivosotok, 690014, Russia
Associated Data
- • The individual components of the biodiesel had a lower toxicity threshold than in the complex mixture.
- • The B20 sample proved to be the most toxic for the red algae P. purpureum .
- • The B100 sample showed the highest level of toxicity for the microalgae A. ussuriensis , C. muelleri and H. akashiwo .
- • The sample of petroleum diesel B0 showed less toxicity compared to B20 and B100.
The world biodiesel production is increasing at a rapid rate. Despite its perceived safety for the environment, more detailed toxicity studies are mandatory, especially in the field of aquatic toxicology. While considerable attention has been paid to biodiesel combustion emissions, the toxicity of biodiesel in the aquatic environment has been poorly understood. In our study, we used an algae culture growth-inhibition test (OECD 201) for the comparison of the toxicity of B100 (pure biodiesel), produced by methanol transesterification of waste cooking oil (yellow grease), B0 (petroleum diesel fuel) and B20 (diesel-biodiesel blended of 20% biodiesel and 80% petroleum diesel fuel by volume). Two marine diatoms Attheya ussuriensis and Chaetoceros muelleri , the red algae Porphyridium purpureum and Raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo were employed as the aquatic test organisms. A sample of biodiesel from waste cooking oil without dilution with petroleum diesel (B100) showed the highest level of toxicity for the microalgae A. ussuriensis , C. muelleri and H. akashiwo , compared to hexane, methanol, petroleum diesel (B0) and diluted sample (B20). The acute EC 50 in the growth-inhibition test (96 h exposure) of B100 for the four species was in the range of 3.75–23.95 g/L whereas the chronic toxicity EC 50 (7d exposure) was in the range of 0.42–16.09 g/L.
1. Introduction
Biodiesel is a fuel composed of fatty acid alkyl esters made by transesterification of fatty acids (triglycerides) from plant oils or animal fats. Biodiesel was proposed as a “green” alternative for fossil fuel and with the intention of causing lower impact on human health and the environment by reduction of combustion derived hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and particulate matter (PM) [ 1 ]. However, concrete evidence which supports the reduced toxicity of biodiesel emissions is lacking. It is also apparent that biodiesel toxicity depends on the chemical composition and properties of the biodiesel made from diverse feedstocks which in turn can vary considerably. The impact of biodiesel on living systems is under intensive investigation using a variety of bioassays [ 2 ].
Residues of oils after cooking and from food waste, cleaning residues and animal fat wastes are a cheap source for biodiesel production and are widely used on an industrial scale. Used oils contain a high concentration of free fatty acids (FFA). According to the FFA content, used cooking oils are divided into two groups: yellow fat (FFA < 15%) and brown fat (FFA > 15% and water). Yellow fats are a common source of biodiesel and can be used after filtration and cleaning [ [3] , [4] , [5] ]. The world population growth has led to an increase in the volume of food industry wastes and by-products. The use of these wastes for biodiesel production has been encouraged as an effective utilization of an otherwise wasted resource. Thus, biofuels from waste edible oils, which can differ in the initial composition of fatty acids and, consequently, in properties and levels of toxicity often enter the market. The composition of the common fatty acids used in the production of biodiesel is described in a number of works [ [6] , [7] , [8] , [9] , [10] ].
Much of the work on the toxicity of biofuels has focused on comparison of hazardous properties of diesel engine emissions with biodiesel alternatives [ [11] , [12] , [13] ]. However, only limited information is available on the aquatic toxicity of biodiesel or other biofuels. Petroleum-related pollutants are a worldwide threat to aquatic organisms and humans [ [14] , [15] , [16] , [17] ], so the ecotoxicity of biodiesel biofuel needs to be examined in terms of its impact on such species.
Comparisons of published studies of biodiesel water toxicity can be problematic because procedures differ for preparation of oil-in-water dispersions (OWDs) or water-accommodated fractions (WAFs). The use of biodiesels from different feedstocks as well as the employment of different test organisms must be considered. Hence, there is a lack of uniformity in the conclusions reached; some studies suggest that the toxicity of petroleum diesel exceeds that of biodiesel with differences of up to 1000 fold [ [18] , [19] , [20] ]. Therefore, clarification of the risks of biodiesel to aquatic species must be made in view of the growing popularity and environmental exposure of these fuels.
In our study, we used an algae culture growth-inhibition test for evaluation of the toxicity of a petroleum diesel (B100) and a B20 blend (20% biodiesel and 80% petroleum diesel) of biodiesel from waste cooking oil. The use of a phytoplankton for the assessment of marine pollution is well documented [ 21 , 22 ]. These algae are one of the primary organisms in the food chain, playing a key role in toxin biomagnification to higher predators, such as zooplankton, fish and ultimately humans [ 23 ].
2. Material and methods
2.1. chemicals.
Fuel samples were obtained from the Primorsky Krai (Russian Federation) market as B100 (pure biodiesel), produced by methanol transesterification of waste cooking oil (yellow grease), B0 (diesel fuel) and B20 (diesel-biodiesel blend of 20% biodiesel and 80% diesel fuel by volume). Hexane and methanol were used for comparison control. Potassium bichromate (K 2 Cr 2 O 7 ) (source) was used as the positive control.
Propidium Iodide (PI), from Molecular Probes (Eugene, Oregon, USA), was used to measure cell death (or Growth-inhibition/vitality).
2.2. Microalgal cultures
Four species of seawater microalgae isolated from the Peter the Great Gulf (Sea of Japan, the Primorsky Krai, Far-Eastern Russia) were used as the test organisms. The test species included two marine diatoms Attheya ussuriensis and Chaetoceros muelleri , a red algae Porphyridium purpureum and Raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo and were cultured with Guillard’s f/2 medium [ 24 ]. Microalgal culture medium was provided by National Scientific Center of Marine Biology, Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (NSCMB FEB RAS).
Culturing and toxicity test conditions were according to OECD 201 standard and are presented in Table 1 .
Culturing and toxicity test conditions.
The suitability of the each microalgae species as a test organism for the assay was carried out with the toxicant potassium bichromate. The results of microalgae sensitivity testing are presented in Table 2 . Exposure of cells was carried out in 24-well plates. Each assay was run at concentrations of K 2 Cr 2 O 7 of 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 mg/L. For each concentration and control group (without toxicant), the experiment was conducted in 4 replications. The volume of microalgae aliquots in each replication was 1.5 mL. The number of living cells was determined using a CytoFLEX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, USA) after 96 h (acute toxicity) and after 7 days (chronic toxicity). The calculation of EC 50 (growth inhibition) was performed using GraphPad Prism 7.04.
Preliminary testing of microalgae cultures sensitivity, mg L −1 .
Thus, the species sensitivity trend from more sensitive to less sensitive was as follows:
P. purpureum > H. akashiwo > A. ussuriensis > C. muelleri
2.3. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC–MS) analysis
Diesel fuel (B0), blended sample (B20), and straight biodiesel (B100) were analyzed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS).
2.4. Flow cytometry analysis
The algae-bioassay (24 h, 96 h and 7 days) was carried out to test the toxicity of the fuel samples. Twenty-four-well plates were used for cultivation of the microalgal species with the biofuel at concentrations of 1, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 120 g/L. As comparison controls, the same bioassays with hexane and methanol at concentrations of 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 g/L were carried out. Wells with only f/2 medium were the control group. For each concentration and control group there were four replications. The volume of microalgae aliquots in each replication was 1,5 mL.
The accurate counting of algal cells was provided at 24 h, 96 h and 7 days by flow cytometer CytoFLEX (Beckman Coulter, USA) with the software package CytExpertv.2.0. Each sample was measured with a flow rate 40 μL/min during 75 s. Cells viability was determined by staining with Propidium Iodide (PI) according to standard protocol [ 25 ].
The parameters for determination of the target group of cells were made by the determination of cells having autofluorescence for chlorophyll a (light source - laser 488 nm, emission filter - PC5.5, 690 nm) in the FSC/PC5.5 dot diagram and elimination of dead cells from this range. The cells were considered dead if they had fluorescence in PI (light source - laser 488 nm, emission filter - ECD, 610 nm) in a FSC/ECD dot diagram.
2.5. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism 7.04 (GraphPad Software, USA).
3. Results and discussion
The results of the LC–MS analysis for the biodiesel (B100), blended sample (B20) and diesel fuel (B0) are presented in Table 3 .
LC–MS analysis of fuel samples.
The diesel fuel B0 consisted of alkanes (mainly n-heptane and n-hexane) plus methanol and ethanol (with latter two alcohols representing more than 10%) as additives. An insignificant content of unsaturated hydrocarbons was observed, including 0.1% of several aromatic compounds.
The blended sample B20 also consisted of alkanes (predominantly n-heptane), alcohols (about 23.5%) and a small amount of methyl esters of fatty acids.
The main components of the biodiesel sample B100 were methyl esters of fatty acids (77.6%). The predominant components were methyl esters of hexadecanoic acid (C16: 0) and methyl esters of saturated and unsaturated octadecanoic acids (C18: 0, C18: 1, C18: 2, C18: 3). In addition, BA100 contained ethanol (3.8%) and a significant amount of volatile organic compounds, such as 3-methylhexane (18.4%).
The toxicological properties of organic substances with different molecular structures often differ significantly. The assessment of individual hydrocarbons toxicity is based on the testing of model substances and the prediction of hazardous properties for substances having a similar structure; quantitative structure-activity relationship [ 26 ]. Hydrocarbons are divided into categories of substances with common properties by the number of carbon atoms, the content of common composite elements, the content of aromatic compounds, and the presence of components with unusual toxicity [ 4 ]. Consequently, the potential toxicity of individual hydrocarbons might be evaluating by using read-across hydrocarbons in general or to similar model substances for which the required data are available. To avoid underestimating the hazardous properties of a substance, the concept of a "reasonable worst case" is usually developed.
The toxic control and scientifically based regulation of petroleum or oil-based substances is a formidable challenge. Such chemicals of multi-constituent nature are defined as UVCB (Unknown or Variable Composition, Complex Reaction Products and Biological Materials) substances. Category read-across approaches for UVCBs may not always be sufficient. Thus, the concept of a potential hazardous chemical classification should be based on an integrative framework consisting of in vitro testing and high-throughput genomics data analyses for read-across assessment [ 27 , 28 ].
The only aliphatic hydrocarbon having an unusual toxicity is n-hexane. N-hexane is noted as an exception due to its toxicological properties that differ from the other aliphatic hydrocarbons with a similar structure or the same number of carbon atoms, including n-pentane, n-heptane, other hexane and heptane isomers, and cyclohexane. The unusual toxic properties of n-hexane are caused by the formation of a specific intermediate metabolite 2,5-hexanedione which, on the grounds of its structure, may interfere with the formation of microtubules and spindle fibers [ 29 , 30 ], leading to inhibition of meiosis [ 31 ].
Thus, in the existing literature, n-hexane and solvents containing n-hexane at levels > 5% are included in a separate category C6 (hexanes). C7-C9 (aliphatics) are classified separately. Among the tested samples n-heptane (B0- 70%, B20 - 68%) and 3-methylhexane (B100 - 18.4%) can be grouped into the category C7-C9.
According to McKee et al., [ 26 ] and the HPV documentation for this category of solvents [ 32 ], the C7–C9 aliphatic hydrocarbons are not genotoxic. The biodegradation of isoheptane in water was 51.3% after 28 days, and 60.2% after 60 days [ 33 ].
The toxicity of the fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) is still poorly understood. According to the OECD standard, FAMEs are not dangerous substances. All FAMEs are readily biodegrated in water, soil and sediment; within 10 days, 62% of FAMEs are biodegrated. However, the data on the water toxicity of biodiesel widely vary. The existing data on the water toxicity of the main components of the test samples on the most common small planktonic crustacean Daphnia magna and on the green algae Raphidocelis subcapitata (formerly known as Pseudokirchnerella subcapitata or Selenastrum capricornutum ) are presented in Table 4 .
EC 50 , aquatic toxicity of the main components of tested samples, mg L −1 .
In our work n-hexane and methanol were used as comparison controls. For all studied substances the concentrations were determined, at which the cell growth rate was reduced by 50% (EC 50 ) compared to the control. The EC 50 values (with 95% confidence intervals) based on flow cytometry analysis and determined by GraphPad Prism 7.04 are presented in Table 5 .
EC 50 values for microalgae species exposed to tested toxicants (g L −1 ).
According to the results of the experiments for microalgae A. ussuriensis , C. muelleri and H. akashiwo , the maximum level of toxicity was shown by a sample of pure biodiesel B100 and the diesel-biodiesel blend B20 sample for the red alga P. purpureum .
P. purpureum was the most sensitive of the tested species for potassium bichromate.
n-Hexane and methanol proved to be the most stable for B100 and B20. In addition, P. purpureum and H. akashiwo showed the ability to adapt to the presence of the tested pollutants. So, for P. purpureum , the EC 50 increased for hexane and methanol following 7 days of exposure (chronic toxicity) compared to 96 h (acute toxicity), while for B20 and B100, an increase in the EC 50 was observed from 24 h to 96 h. On the 7 th day of the experiment the EC 50 decreased. H. akashiwo during the experiment adapts only to B20, showing an increase in the EC 50 from 24 h to 96 h and a sharp decrease in the EC 50 by the 7 th day. For the diatoms of C. muelleri and A. ussuriensis , the level of toxicity increased in direct proportion to the increase of cells exposure time. C. muelleri and H. akashiwo demonstrated the highest acute toxic effect for B100. The highest chronic toxicity was shown by A. ussuriensis for B20 and B100.
Comparison of the mortality rates of the four microalgae species under 96 h exposure to toxicants is shown in Fig. 1 . The stimulating effect of low concentrations of n-hexane, B0 and B20 on the diatoms C. muelleri and A. ussuriensis is probably caused by a response to the presence of the petroleum hydrocarbons, using them as an additional source of carbon. The stimulation of microalgae growth due to low concentrations of the low molecular weight hydrocarbons is consistent with existing studies [ 42 ].

Mortality rates (mean) of four microalgae species in acute toxicity tests (96 h) of Hexane (blue), Methanol (red), Diesel fuel B0 (green), waste cooking oil biodiesel B100 (purple), diesel-biodiesel blend B20 (orange).
Many authors have reported biodiesel as a biodegradable and non-toxic fuel [ 5 , 43 , 44 ], but the sensitivity of these distinct species to different toxicants can widely vary, as indicated in the Fig. 2 . In particular, the sensitivity and stability of the algae to specific pollutants can be different for different species [ 45 ] and for more reliable bio-testing it is preferable to use several species. It has been reported that biodiesel from used cooking oils can pose a significant danger to aquatic organisms [ 18 ].

The sensitivity of the four microalgae species to B100 and B20.
The sensitivity trend for potassium bichromate, hexane, methanol and diesel fuel B0 for the four microalgae was the same. However, the B100 biodiesel was more toxic for H. akashiwo and C. muelleri and was the least toxic for P. purpureum . The species sensitivity trend for B100 (biodiesel) was: H. akashiwo > C. muelleri > A. ussuriensis > P. purpureum , which is quite different compared to preliminary testing of microalgae sensitivity by potassium bichromate.
The toxicity level of diesel-biodiesel blend B20 is mostly similar to B100. A notable difference, however, is observed for H. akashiwo , where the microalgae cells showed a significantly greater resistance to B20 compared to pure biodiesel B100.
It is noteworthy that for all the algae, the toxicity level of samples containing biodiesel from waste cooking oil (B20 and B100) was higher than it was for hexane, methanol or diesel fuel. The results of our studies showed that the sample B20 containing 68.1% n-heptane, 15% methanol and 8.5% ethanol was significantly more toxic for all species than pure hexane, pure methanol and the sample B0 containing about 70% n-heptane, but with a fraction of methanol and ethanol (˜5%).
Several groups have reported [ 46 , 47 ] that when biodiesel enters the aquatic environment, the biodegradation of fuel gradually increases the concentration of methanol that is formed as a result of hydrolysis that converted the transesterification reaction. Thus, it is most likely that the high toxicity of B20 is associated with an increased content of alcohol.
Quality biodiesel consists mainly of fatty acid methyl esters, the low toxicity and biodegradability of which determines their safety o for the environment. The low toxicity of FAMEs has been shown in several studies [ 48 , 49 ]. However, based on our results, sample B100 consisting of 77.6% of FAMEs exhibited the greatest aquatic toxicity among all the samples tested. This was probably caused by the presence of the aliphatic iso-paraffinic constituent 3-methylhexane (18.4%) included in C7-C9 category of petroleum pollutants. These paraffins have a high aquatic ecotoxicity potential, possibility due to the increasing concentration of methanol following FAME hydrolysis.
4. Conclusions
The properties of biodiesel as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative fuel may differ depending on the feedstock, the method of production and the chemical composition of the final product. Yassine, M. H., et al [ 50 ] remarked that the process of transesterification of biodiesel could be a critical factor in determining the aquatic toxicity of the fuel. At the same time, the combination of individual components with relatively low toxicity, can cause a synergistic effect and have unpredictable level of toxicity [ [51] , [52] , [53] , [54] ]. Judging from the literature and our results, the individual components of the biodiesel (n-hexane, n-pentane, methanol, FAMEs) had a lower toxicity threshold than in the complex mixture.
The B100 sample showed the highest level of toxicity for the microalgae A. ussuriensis , C. muelleri and H. akashiwo in comparison with hexane, methanol, B0 and B20. The acute EC 50 in the growth-inhibition test (96 h exposure) of B100 for the four species of microalgae was in the range 3.75–23.95 g/L, while the chronic toxicity EC 50 (7 d exposure) ranged from 0.42 to 16.09 g/L.
B20 proved to be the most toxic for the red algae P. purpureum . The acute C 50 of the diesel-biodiesel blend B20 for the four microalgae species was in the range 6.04–19.74 g/L; the chronic toxicity EC 50 was from 0.76 to 5.98 g/L.
A sample of petroleum diesel B0 showed less toxicity compared to B20 and B100. The diatom microalga C. muelleri proved to be much resistant to B0. The presence of B0 in concentrations up to 20 g/L caused an increase in the rate of cell growth. The acute EC 50 of B0 for the four microalgae species was in the range 9.01–54.31 g/L; the chronic toxicity EC 50 was in the range of 4.75–40 g/L.
The findings of this study provide an important foundation for further investigation into the effects of such products on coastal aquatic ecosystems.
Competing interests
AT is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article.
Transparency document
Acknowledgements.
The work was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (No. 15-14-20032-P).
The authors would like to thank the staff team of FEFU CCU (Center of Collective Use) ‘Interdepartmental center for analytical control of the environment’ and the Laboratory of Toxicology, University of Crete, Greece, for their dedicated involvement in this study.
- Interfax Group
- Due diligence & KYC
- Reputational Risk
- News Products
- Top Stories
- Exclusive Interviews
- Press Releases
- REQUEST A DEMO
Turkey's Yenigun to build waste-to-energy plant in Moscow Region for RT-Invest

KRASNOGORSK. Aug 6 (Interfax) - RT-Invest Group and Turkish construction company Yenigun have signed a contract to start construction of a waste-to-energy plant in the Naro-Fominsky district of Moscow Region, the Russian company told Interfax on Monday.
"As a result of a tender, Turkish corporation Yenigun was selected general contractor for construction. According to the design, the plant will process 700,000 tonnes of solid municipal waste per year and generate 75 MW of electricity," a company spokesman said.
Work has already begun at the construction site, he said.
Overall investment in the construction of the plant will exceed 30 billion rubles.
RT-Invest said the first stage of construction includes installation of temporary facilities, excavation of foundation pits, road construction and pouring of concrete for the main and auxiliary buildings.
The second stage includes construction of the main and auxiliary buildings and installations, laying of permanent utility lines and delivery of equipment.
It was reported earlier that a total of four waste-to-energy plants will be built in Moscow Region. They are scheduled to open on after another in 2021-2022. The first plant is being built in the Voskresensky district.
- Privacy Policy
News and other data on this site are provided for information purposes only, and are not intended for republication or redistribution. Republication or redistribution of Interfax content, including by framing or similar means, is expressly prohibited without the prior written consent of Interfax.
© 1991—2024 “Interfax Information Group” www.interfax.com. All rights reserved.

COMMENTS
A Natural Resources Canada study found that setting the cruise control at 80 kph (49.7 mph) versus cycling from 75 to 85 kph (46.6 to 52.8 mph) every 18 seconds consumes 20 percent less fuel (and ...
The study— published in IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine in June of 2019 —showed that consistent use of adaptive cruise control resulted in a 5 to 7 percent increase in gas mileage versus human throttle management. That said, one of the most effective ways of using less fuel is to drive at your car's optimal speed for fuel ...
It can lower your gas mileage by roughly 15% to 30% at highway speeds.". The site is even less specific about cruise control: "Using cruise control on the highway helps you maintain a constant ...
Cruise control is designed to help people traveling long distances drive comfortably, but it can also help save gas money. According to Progressive, cruise control works by letting the driver "set a speed for your car to maintain even if you take your foot off the gas.". Your car will remain at a constant speed for the duration of time you ...
These research findings clearly demonstrate that, by maintaining cars at a constant speed, cruise control helps to save gas. As a matter of fact, cruise control can help you save by as much as 5% to 15% on gas! After all, the cruise control of the vehicle uses the powertrain control module ( PCM) to maintain constant designated speeds.
That's why the cruise control setup can kick in quite well in helping you waste less fuel while driving on the highway. You can just set up the optimal speed and drive in a higher gear on a lower RPM level. Keeping the revs in a flat line is also crucial for your fuel economy, and cruise control lets you drive at a steady RPM rate.
Before delving into the fuel-saving aspect of cruise control, it's important to understand how the system works. When activated, cruise control uses electronic sensors to monitor the vehicle's speed and adjust the throttle accordingly to maintain the set speed. This eliminates the need for drivers to manually modulate the throttle pedal ...
When you engage cruise control, your vehicle maintains a constant speed, which helps optimize your fuel consumption. By eliminating unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, cruise control ensures that your engine operates at a consistent level of efficiency. This can lead to significant savings at the gas pump, especially during long highway ...
As drivers seek ways to optimize their fuel consumption, we delve into the science behind cruise control's impact on gas mileage. Let's explore the facts to determine if this widely-used feature is indeed a fuel-saving hero. Does Cruise Control Use More Fuel? Cruise control can save 14% on fuel on highways and 7% on gas on city streets ...
The fuel economy benefits of cruise control come from the system minimizing throttle openings, like when a driver lifts his or her foot off the accelerator a dozen times during a 10 minute drive. Therefore, a cruise control system that struggles on hills is not maximizing its ability to conserve fuel. However, with different systems in ...
The excessive increases and decreases in speed could cause vehicles to consume up to 20 percent more fuel than they might by using the gas and brake pedals. However, in general, adaptive cruise control usually helps drivers conserve fuel, save money, and reduce total car ownership costs. Coupling this feature with driving in the right-hand lane ...
The most basic of which is a standard, speed-limiting cruise control. As its name would suggest, a speed-limiting cruise control essentially governs a vehicle's speed at a preset rate, thereby maintaining this speed under a variety of conditions. Over the past decade, adaptive cruise control has also gained immense popularity.
RAY: We should add that in the old days, you could make the argument that cruise control could occasionally waste fuel. For instance, let's say you had it set to 65, and you cancelled it by stepping on the brake and then slowed down to 45. When you turned it back on, by hitting "Resume," older cruise-control systems would simply floor it until ...
Some drivers report seeing no difference in their gas mileage when using cruise control vs. not using it. Others wonder if perhaps the AC running makes a difference or windows up vs. windows down. On the other hand, some sources like CNN Money in 2007 said cruise control could save up to seven percent in fuel economy.
Moreover, aggressive driving (speeding, rapid acceleration, and braking) wastes a lot of gas. The federal website for fuel economy states that the decrease can be around 15% to 30% at highway speeds. In all the instances above, cruise control is detrimental to fuel economy. It negates the human factor and brings the speed under control, which ...
It's commonly assumed that cruise control saves on gas. As the thinking goes, by maintaining a steady speed, cruise control moderates fuel consumption more effectively than a driver manually pressing and releasing the gas pedal. However, according to Autolist, that isn't always the case. While it's generally true that cruise control can ...
Cruise control can help you use less gas by driving on a long straight road; on the other hand, driving on streets or stop-and-go traffic does not save gas. According to greencarreports.com, the study showed a 5 to 7 percent drop in fuel consumption for cars driving with adaptive cruise control compared with human drivers.
Different types of tires feature varying rolling resistances and create a unique degree of inertia which affect your fuel economy. Does Cruise Control Save Gas? We often hear - does cruise control waste gas? The answer depends on how you use it. When heading down the highway, cruise control can save gas by keeping your vehicle at a steady speed ...
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how cruise controle works: The driver activates cruise control by pressing a button or flipping a switch on the dashboard or steering wheel. The system uses electronic sensors to measure the vehicle's speed and other factors such as throttle position, engine load, and road grade.
Ralby, who co-authored the 2018 Atlantic Council report, said that waste products from refineries and other industrial operations have made their way illegally into shipping fuel, known as bunker ...
Aiming at the problems of slow response, poor comfort and high fuel consumption of the existing adaptive cruise control system under complex operating conditions, a multi-objective adaptive cruise control method of intelligent vehicles based on multi-mode switching is proposed.
In our study, we used an algae culture growth-inhibition test (OECD 201) for the comparison of the toxicity of B100 (pure biodiesel), produced by methanol transesterification of waste cooking oil (yellow grease), B0 (petroleum diesel fuel) and B20 (diesel-biodiesel blended of 20% biodiesel and 80% petroleum diesel fuel by volume).
The US Coast Guard says it is suspending its search and rescue efforts for the six individuals still missing after the collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore.
The specialized company, which was established in 1983 to provide repair and maintenance services for nuclear power plants. Production of high-precision instruments and machines, gas centrifuges for uranium enrichment, spent nuclear fuel containers, military products, gas meters and calibration tools.
Fuel samples were obtained from the Primorsky Krai (Russian Federation) market as B100 (pure biodiesel), produced by methanol transesterification of waste cooking oil (yellow grease), B0 (diesel fuel) and B20 (diesel-biodiesel blend of 20% biodiesel and 80% diesel fuel by volume). Hexane and methanol were used for comparison control.
According to the design, the plant will process 700,000 tonnes of solid municipal waste per year and generate 75 MW of electricity," a company spokesman said. Work has already begun at the construction site, he said. Overall investment in the construction of the plant will exceed 30 billion rubles.