

भारतीय ध्वज की जानकारी | Indian Flag History in Hindi
Indian Flag History in Hindi
हर एक आज़ाद देश का अपना एक ध्वज है। एक आज़ाद देश की यही सबसे बड़ी पहचान होती है। ब्रिटिश राज से 15 अगस्त 1947 को आज़ाद होने के कुछ दिनों पहले ही भारत के राष्ट्रिय ध्वज को निर्वाचक असेंबली ने 22 जुलाई 1947 को स्वीकारा था। 15 अगस्त 1947 से 26 जनवरी 1950 तक यही हमारा स्वतंत्र ध्वज था। भारतीय ध्वज को ‘तिरंगा’ Tiranga भी कहा जाता है।
जिसके तले पूरा राष्ट्र एक सूत्र में बंधा होता है। उसी तरह हमारे भारत देश का एक राष्ट्रीय ध्वज तिरंगा – Indian Flag है,जो कि भारत देश की आन, बान और शान है।
भारत में अलग-अलग धर्मों और जातियों के लोग रहते हैं, जिनमें भाषा, पहनावा, रीति-रिवाज समेत कई तरह की असमानताएं हैं, जिसकी वजह से कई बार आपसी मतभेद भी देखने को मिलता है लेकिन इतनी सारी विविधता होने के बाबजूद भी भारत देश में एकता है।
जब भी देश की बात आती है, आपसी झगड़े को भूलकर देशवासी राष्ट्रीय ध्वज तिरंगे के नीचे एक सूत्र में बंध जाते हैं। यह तिरंगे की सबसे बड़ी खासियत है और देश की एकता का प्रतीक भी है।
“सभी देशो के लिये उनका राष्ट्रिय ध्वज काफी मायने रखता है। लाखो लोगो ने इसकी सुरक्षा के लिये अपने प्राण गवाए है। हमारा राष्ट्रिय ध्वज ही हमारी राष्ट्रिय एकता को दर्शाता है।”

Flag of India – भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज की रचना में कई बार बदलाव हुए। पहले ध्वज का इस्तेमाल आजादी के प्रति अपनी निष्ठा को दर्शाने के लिए होता था। इसके बाद में राष्ट्रीय ध्वज राजनीतिक विकास का भी प्रतीक बना। जिसें तिरंगा कहा जाता है।
लेकिन क्या आप जानते हैं कि भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को तिरंगा क्यों कहा जाता है, इसके लिए हम आपको बता दें कि – भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज तीन रंगों से मिलकर बना है इसलिए इसे “तिरंगा” – Tiranga कहा जाता है।
जानें तिरंगे में हुए बदलाव और इसके तीन रंगों के दार्शनिक महत्व के बारे में –
भारतीय राष्ट्रिय ध्वज की जानकारी – Indian Flag History in Hindi
15 अगस्त 1947 में जब हमारा भारत देश अंग्रेजों के चंगुल से आजाद हुआ था। आजादी के वक्त अलग-अलग तरह के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इस्तेमाल किया गया था। भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को इसके वर्तमान स्वरुप में 22 जुलाई 1947 को आयोजित भारतीय संविधान सभा की बैठक के दौरान लाया था।
आपको बता दें कि ये बैठक 15 अगस्त 1947 को अंग्रेजों से भारत की स्वतंत्रता के कुछ ही दिन पहले ही की गई थी। इसे 15 अगस्त 1947 और 26 जनवरी 1950 के बीच भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के रूप में अपनाया गया और इसके बाद भारतीय गणतंत्र ने इसे अपनाया और भारत में “तिरंगे” का अर्थ भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज है।
हम आपको बता दें कि भारत में सबसे पहले 7 अगस्त 1906 को कोलकाता के ग्रीन पार्क में ध्वज फहराया गया था। जो कि एकदम अलग था, इसकी बनावट और रंगों में काफी अंतर था।
इसके अंदर तीन रंग थे। सबसे ऊपर हरा बीच में पीला और नीचे लाल रंग था हरे रंग के ऊपर कमल के फूल के निशान थे और बीच में पीले रंग के ऊपर “वंदे मातरम” लिखा हुआ था वहीं सबसे नीचे लाल रंग के ऊपर एक चांद और सूरज का चित्र बना हुआ था।
उसके बाद साल 1907 में तिरंगा दूसरी बार जर्मनी के Stuttgart दूसरी इंटरनेशनल सोशलिस्ट कांग्रेस सभा में फहराया गया था। उस तिरंगे को मैडम भिकाजी कामा ने फहराया था। वहीं इस बार भी तिरंगे में कुछ बदलाव किए गए थे।
इसके बाद साल 1917 में एक और ध्वज बनाया गया था, ये ध्वज भी फाइनल ध्वज नहीं था और न ही पहले और दूसरे ध्वज की तरह था। ये ध्वज पहले बनाए गए दोनों ध्वजों से एकदम अलग थे।
आपको बता दें कि इसके अंदर पांच लाल रंग की और चार हरे रंग की पट्टी लगाई गई थी और इसके अलावा इसके अंदर 7 स्टार को लगाया गया था। और एक चांद को लगाया गया था। यूनियन चैक के साथ इसको बनाया गया था।
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में लगातार हो रहे बदलाव के दौरान साल 1921 में एक बार फिर से भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में कई बदलाव किए गए थे जो कि पहले वाले तीनों ध्वज से एकदम अलग थे।
आपको बता दें कि गांधी जी को ये ध्वज विजयवाड़ा के रहने वाले नौजवानों ने डिजाईन करके दिया था, लेकिन इस ध्वज के बाद भी कई बदलाव की जरूरत महसूस हुई इस जो की पहले वाले तीनों ध्वज से बिल्कुल अलग था।
इसके अंदर सिर्फ लाल और हरा 2 ही रंग लगाए गए थे। लाल रंग हिंदू और हरा कलर मुस्लिम को दर्शाता था। लेकिन इसके बाद भारत के राष्ट्रपिता महात्मा गांधी जी ने इस ध्वज में कुछ बदलाव किए।
उन्होनें इस तिरंगे में सफेद रंग को और जोड़ दिया जाए ताकि बाकी सभी धर्मों के लोगों को सफेद रंग दर्शाए और इस झंडे को पहले वाले तीनो ध्वज से अलग डिजाईन किया गया था। इस ध्वज में इसके अंदर चरखे के निशान को लगाया गया था।
वही ध्वज के अंदर चरखा लगाने का तरीका हंसराज जी का था, इस झंडे को डिजाइन करने के बाद इसको बनाने का काम महात्मा गांधी जी ने पिंगली वेंकय्या जी को सौंप दिया था। इस तरह पिंगली वैंकय्या ने हमारे राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को डिजाइन किया।
भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज पहले इंडियन नेशनल कांग्रेस पार्टी का प्रतीक था, जो कि पूरे भारत के अंदर इस्तेमाल किया गया था। आपको बता दें कि 1947 में कांग्रेस पार्टी के ध्वज को राष्ट्रीय ध्वज बनाने की कोशिश की गई थी।
लेकिन प्राइम मिनिस्टर ऑफिस के ऑफिसर बदरुद्दीन तैयब जी की पत्नी इस ध्वज में चरखा लगाने की बजाय अशोक चक्र को लगाना चाहती थी क्योंकि चरखा महज एक पार्टी का निशान था और ये ध्वज राष्ट्र की पहचान के लिए था।
वहीं ऐसे कुछ बदलाव के बाद तिरंगे के वर्तमान स्वरूप में लाया गाय गया, जिसमें केसरिया सफेद और हरा रंग में है और उसके बीच में नीले रंग का अशोका चक्र बना हुआ है।
इस तिरंगे को राष्ट्रीय ध्वज घोषित किया गया, तब से लेकर अभी तक यही हमारा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज है। आपको बता दें कि झंडे को राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के रूप में अपनाने के लिए डॉ. राजेंद्र प्रसाद के नेतृत्व में एक कमेटी का गठन किया गया। भारतीय संविधान सभी में इसे 22 जुलाई 1947 को राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के तौर पर स्वीकृति मिली थी।
संविधान सभा में स्वीकृति मिलने के बाद सबसे पहला राष्ट्रीय ध्वज 16 अगस्त 1947 को लाल किले पर फहराया गया। झंडे को पंडित जवाहर लाल नेहरू ने फहराया था।
पहले राजकीय जगहों के अतिरिक्त किसी और स्थान पर राष्ट्रीय ध्वज फहराने की अनुमति नहीं थी। बाद में 26 जनवरी 2002 में ध्वज संहिता में संशोधन किया गया। इसके तहत भारतीय नागरिक घरों, कार्यालयों और फैक्टरियों में कभी भी राष्ट्रीय ध्वज फहरा सकते हैं।
भारतीय ध्वज के रंगों का अर्थ – Indian National Flag Meaning
जैसे कि हम सभी भारतीय जानते हैं कि हमारे देश के तिरंगे झंडे में तीन रंग हैं – जिसमें सबसे ऊपर केसरिया बीच में सफेद और नीचे हरा रंग है। सफेद पट्टी के बीच में गहरे नीले रंग का एक चक्र है। यह चक्र अशोक की राजधानी के सारनाथ के शेर के स्तंभ पर बना हुआ है।
इसका व्यास लगभग सफेद पट्टी की चौड़ाई के बराबर होता है और इसमें 24 तीलियां है, जो कि दिन के 24 घंटों को दर्शाता है और यह समय की बहुमूल्यता का भी प्रतीक है।
देश के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में इस चक्र को प्रदर्शित करने का आशय यह है कि जीवन गतिशील है और इसके रुकने का अर्थ मृत्यु है। तिरंगे की चौड़ाई और लंबाई का अनुपात 3 और 2 है।
देश के झंडे में शामिल तीनों रंगों का अपना अलग महत्व है। केसरिया रंग जहां शक्ति का प्रतीक है। वहीं सफेद रंग शांति को दर्शाता है। जबकि हरा रंग हरियाली और संपन्नता को दिखाता है। ये रंग मिलकर देश के गौरव का प्रतीक बनाते हैं और भाईचारे के संदेश के साथ ही जीवन को लेकर ज्ञान भी देते हैं।
अब हम आपको अपने इस लेख में भारत के तिरंगे झंडे में रंगों के अर्थ के बारे में बताएंगे कि तिरंगे के तीन रंग केसरिया, सफेद और हरे रंग का क्या महत्व है और यह रंग किसका प्रतीक माने जाते हैं –
Indian Flag Colors
बलिदान, साहस, और ताकत का प्रतीक है केसरिया रंग
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में सबसे ऊपर केसरिया रंग की पट्टी है, इस केसरिया रंग को त्याग,बलिदान, शक्ति, साहस औऱ ताकत का प्रतीक माना जाता है। यह रंग राष्ट्र के प्रति हिम्मत और निस्वार्थ भावनाओं को दिखाता है।
शांति, स्वच्छता, सत्य और सद्भाव की निशानी है सफेद रंग
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में बीच की पट्टी का रंग सफेद रहता है। तिरंगे में सफेद रंग देश में सुख, शांति, शुद्धता, सच्चाई और ईमानदारी का संदेश देता है। इसके साथ ही स्वच्छता और सद्धाव की निशानी भी माना गया है।
भारतीय दर्शन शास्त्र के मुताबिक, सफेद रंग को ज्ञान का भी प्रतीक माना गया है। राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का सफेद रंग हमेशा ईमानदारी से और सच्चाई की राह पर चलने के लिए प्रेरित करता है।
उर्वरता, खुशहाली, प्रगति और समृद्धि का प्रतीक हरा रंग
भारत राष्ट्र का सम्मान का प्रतीक तिरंगा झंडा के सबसे नीचे हरा रंग रहता है। ये हरा रंग विश्वास, उर्वरता, खुशहाली, समृद्धि, प्रगति, बुद्धि और भाईचारा का प्रतीक माना जाता है।
इसके अलावा हरा रंग भारत में हरियाली को दर्शाता है और आंखों को सुकून भी देता है। जिस प्रकार प्रकृति जीवन का संदेश देती है, उसी तरह इस रंग से भी जीवन का गहरा संबंध है।
अशोक चक्र – Ashoka Chakra
ध्वज में लगने वाला धर्म चक्र 3 री शताब्दी के मौर्य शासक सम्राट अशोक के सारनाथ स्तम्भ से लिया गया है। यह चक्र जीवन साइकिल (चक्र) और मृत्यु की गतिहीनता को दर्शाता है।
26 जनवरी 2002 को भारतीय ध्वज कोड में आज़ादी के बहुत सालो बाद बदलाव किया गया था, जिसमे भारत के नागरिको को अपने घर, ऑफिस और फैक्ट्री में स्वतंत्रता दिवस पर ध्वज फहराने की आज़ादी दी गयी। आज हम भारतीय शान से हमारे घर या ऑफिस पर कभी-कभी भारतीय ध्वज लहरा सकते है।
लेकिन यदि कोई नागरिक राष्ट्रध्वज का अपमान करते हुए पाया गया तो उसे दंड अवश्य दिया जाता है।
“हम भारतीयों, मुस्लिम, क्रिस्चियन, पारसी और सभी धर्मो के लोगो के जीने और मरने के लिये एक ध्वज का होना बहुत जरुरी है। जिससे उनके देश का पता चल सके।” – महात्मा गांधी
ध्वज को फहराने से संबंधित कुछ नियम भी है, जो 26 जनवरी 2002 के कानून में बताये गए है। इसमें निचे दी गयी बाते शामिल है।
क्या करना चाहिये:
राष्ट्रिय ध्वज को किसी भी शैक्षणिक संस्था (स्कूल, कॉलेज, स्पोर्ट कैंप, स्काउट कैंप इत्यादि) जगहों पर पुरे सम्मान के साथ फहरा सकते है। फहराते समय राष्ट्र वचन लेना भी बहुत जरुरी है।
सामाजिक, प्राइवेट संस्था या फिर किसी शैक्षणिक संस्था के सदस्य भी छुट्टी के दिन या फिर स्वतंत्रता दिवस पर पुरे सम्मान के साथ ध्वज फहरा सकते है।
सेक्शन 2 के तहत कोई भी प्राइवेट नागरिक सम्मान के साथ अपनी ईमारत में राष्ट्रिय ध्वज को लहरा सकता है।
क्या नही करना चाहिये:
ध्वज का उपयोग सांप्रदायिक लाभ, कपडे की दुकान या फिर कपड़ो के रूप में नही कर सकते। हो सके तो सूरज निकालने के बाद और डूबने से पहले तक ही इसे रहने देना चाहिये।
राष्ट्रिय ध्वज जमीन पर गिरा हुआ या जमीन को छुआ नही होना चाहिये और ना ही पानी में भीगा हुआ होना चाहिये। ध्वज कपड़ो की खुटी पर भी टंगा हुआ नही होना चाहिये। और ना ही रेल, बस के आगे या पीछे लगा हुआ होना चाहिये।
इस ध्वज से ऊँचा दूसरा कोई भी ध्वज नही होना चाहिये। बल्कि ध्वज के उपर फुल या फिर कोई वस्तु भी नही चाहिये। हम तिरंगे का उपयोग रिबन या फिर ध्वजपट के लिये भी नही कर सकते।
भारत का राष्ट्रिय ध्वज भारत के लोगो की आशा और प्रेरणा का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। राष्ट्रिय ध्वज हमारे देश का गर्व है। पिछले पाँच दशको से बहुत से लोगो ने, बल्कि इंडियन आर्मी के नौजवानों ने भी तिरंगे की शान और सुरक्षा के लिये अपने प्राणों की आहुति दी है। आज इन्ही लोगो की वजह से हमारा तिरंगा हवा में शान से फहराता है
भारतीय राष्ट्रिय ध्वज हमारा राष्ट्रिय गर्व है और किसी भी देश का राष्ट्रिय ध्वज उसका सबसे सम्माननीय प्रतिक होता है। बाद में भारत के प्रधानमंत्री जवाहरलाल नेहरू ने राष्ट्रिय ध्वज को केवल देश की आज़ादी नही बल्कि देश के लोगो की आज़ादी का प्रतिक बताया।
भारतीय ध्वज पर सुविचार – Quotes On Indian Flag
“शांति और सामंजस्य, एकता और मजबूती से जीने के लिये एक सब को एक साथ, एक देश और एक ही ध्वज में रहना होंगा।”
“मै तब हाईस्कूल में ही था जब पंडित जवाहरलाल नेहरु ने नयी दिल्ली में ध्वज फहराया था।” – A.P.J Abdul Kalam
“मेरा मानना है की हमारा ध्वज कपडे और स्याही से कई बढ़कर है। यही हमारी अंतर्राष्ट्रीय पहचान है जो हमें आज़ाद रखती है। यही हमारे देश का इतिहास है और देश के लिये बलिदान देने वाले लोगो का परिणाम है।”
“हमारा ध्वज केवल वह नही जिसे हम राजनैतिक अंदाज़ से देखते है। बल्कि हमारा ध्वज ही हमारी राष्ट्रिय एकता का प्रतिक है।”
“हमारा ध्वज उनका सम्मान करता है जिन्होंने इसकी रक्षा के लिये अपने प्राणों की आहुति दी है और यही हमें हमारे देश के संस्थापको और हीरो के बलिदान को याद दिलाता है।”
“गणराज्य से आपकी क्या आशा है? एक देश, एक भाषा और एक ध्वज!”
“देशभक्त और नागरिक बनने से कयी ज्यादा ख़ुशी देश के ध्वज को फहराने में है।”
- भारत के प्रमुख राष्ट्रीय प्रतीक
- जन गन मन भारत का राष्ट्रगान
- “राष्ट्रिय गीत” वन्दे मातरम्
- Pingali Venkayya
- Essay on India
I hope you find this post about ”Indian Flag History In Hindi” useful. if you like this article please share it on Facebook & Whatsapp.
Note: We try hard for correctness and accuracy. please tell us If you see something that doesn’t look correct in this article About Indian Flag in Hindi… And if you have more information History of Indian Flag then helps with the improvements in this article.
7 thoughts on “भारतीय ध्वज की जानकारी | Indian Flag History in Hindi”
Kya aap sab jaan te hai ki hamare bharat ke jhande ko tiranga kyu kaha jata hai?? Chalo me hi bata deti hu hamare bharat ka jhanda 3 rang milakar Banta hai ti=three , ranga=colours
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Gyan ki anmol dhara
Grow with confidence...
- Computer Courses
- Programming
- Competitive
- AI proficiency
- Blog English
- Calculators
- Work With Us
- Hire From GyaniPandit
Other Links
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policy
- संस्कृत श्लोक एवम अर्थ
- वेडिंग स्पेशल
- टिप्स और ट्रिक्स
- उपयोगी लाभकारी घरेलु नुस्खे और उपाय
- महाभारत रामायण कहानी | Mahabharat Ramayan in Hindi
- हमसे संपर्क करे
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज इतिहास महत्त्व निबंध Indian National Flag history Essay Significance in Hindi
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज इतिहास व महत्त्व, निबंध ( Indian National Flag Essay history and Significance in hindi )
भारतीय राष्ट्रिय ध्वज हमारी स्वाधीनता का प्रतीक है. देश में अपना ध्वज लहराने का मतलब है कि वो देश आजाद है. आजादी के बाद पहले प्रधानमंत्री जवाहरलाल नेहरु ने कहा था ‘राष्ट्रीय ध्वज सिर्फ हमारी स्वतंत्रता नहीं है, बल्कि ये देश की समस्त जनता की स्वतंत्रता का प्रतीक है.’ भारतीय लॉ के अनुसार राष्ट्रीय ध्वज खादी के कपड़े का होना चाहिए. शुरुआत में राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इस्तेमाल आम नागरिकों द्वारा सिर्फ राष्ट्रीय दिवस जैसे स्वतंत्रता दिवस व गणतन्त्र दिवस को ही होता था, बाकि के दिनों में वे उसको नहीं फेहरा सकते थे. लेकिन कुछ समय के बाद यूनियन कैबिनेट ने इसमें बदलाव किया और आम नागरिकों द्वारा इसके उपयोग को शुरू कर दिया गया.

Table of Contents
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को सभी लोग ‘तिरंगा’ नाम से जानते है, इसका मतलब है तीन रंग. तीनों कलर समतलीय एक बराबर हिस्सों में बटे हुए होते है. सबसे उपर केसरिया, उसके नीचे सफ़ेद व सबसे नीचे हरा रंग होता है. तिरंगा की चोडाई व् लम्बाई 2:3 अनुपात में होती है. तिरंगा के बीच में सफ़ेद रंग के उपर नीले रंग का अशोक चक्र होता है, जिसमें 24 धारियां होती है.
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का महत्व
हमारा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज हमारे देश की संस्कृति, सभ्यता और इतिहास को दर्शाता है। हवा में लहराता हुआ हमारा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज हमारे देश की स्वतंत्रता को प्रदर्शित करता है। यह हमारा ध्वज हमारे देश के नागरिकों की स्वतंत्रता के साथ-साथ अंग्रेजों के अत्याचार से मुक्त हो होने पर अपना एवं अपने देशवासियों का गौरवयुक्त अभिमान है। हमारे राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में तीन महत्वपूर्ण है, इसलिए है, जो हमारे देश की अखंडता, एकता और वीरता को दर्शाता है। हमें गर्व है, कि हम एक ऐसे देश के वजह से जहां पर वीरों और महापुरुषों ने जन्म लिया।
तिरंगा के तीनों रंगों का विस्तार से विवरण –
केसरिया – केसरिया रंग तिरंगे में सबसे उपर होता है, यह साहस, निस्वार्थता व शक्ति का प्रतीक है.
सफ़ेद – तिरंगा में सफ़ेद रंग सच्चाई, शांति व पवित्रता का प्रतीक है. यह रंग देश में सुख शांति की उपयोगिता को दर्शाता है.
हरा – हरा रंग विश्वास, शिष्टता, वृद्धि व हरी भरी भूमि की उर्वरता का प्रतीक है. यह सम्रधि व जीवन को दर्शाता है.
अशोक चक्र – इसे धर्म चक्र भी कहते है. नीले रंग का अशोक चक्र तीसरी शताब्दी में सम्राट अशोक द्वारा बनाया गया था. जिसे तिरंगा में बीच में लगाया गया है, इसमें 24 धारियां होती है. अशोक चक्र जीवन के गतिशील होने को दर्शाता है, इसका न होना मतलब म्रत्यु है.
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इतिहास (Indian National Flag history)–
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज स्वतंत्रता के लिए, भारत की लम्बी लड़ाई व राष्ट्रीय खजाना का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है. यह स्वतंत्र भारत के गणतंत्र का प्रतीक है. देश आजाद होने के कुछ दिन पूर्व 22 जुलाई 1947 को स्वतंत्र भारत के संविधान को लेकर एक सभा आयोजित की गई थी, जहाँ पर पहली बार राष्ट्रीय ध्वज तिरंगा को सबके सामने प्रस्तुत किया गया. इसके बाद 15 अगस्त 1947 से 26 जनवरी 1950 तक राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को भारत के अधिराज्य के रूप में प्रस्तुत किया गया. 1950 में संविधान लागु होने पर इसे स्वतंत्र गणतंत्र का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज घोषित किया गया. राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को पिंगली वेंक्क्या द्वारा बनाया गया था.
भारत के सभी राष्ट्रीय ध्वजों का इतिहास (All National Flag History)–
- 1904-06 – भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इतिहास आजादी के पहले से जुड़ा हुआ है. 1904 -06 के आसपास पहली बार राष्ट्रीय ध्वज लोगो के सामने आया था. उस समय इसे स्वामी विवेकानंद की आयरिश शिष्या सिस्टर निवेदिता ने बनाया था. कुछ समय बाद इस ध्वज को सिस्टर निवेदिता ध्वज कहा जाने लगा. इस ध्वज का रंग पीला व लाल था. जिसमें लाल रंग आजादी की लड़ाई व पीला रंग जीत का प्रतीक था. इस पर बंगाली भाषा में ‘वोंदे मतोरम’ जिसका अर्थ वंदेमातरम् है लिखा गया था. इस पर भगवान इंद्र का शस्त्र वज्र व सेफ कमल का चित्र भी बनाया गया था. वज्र ताकत व कमल पवित्रता का प्रतीक था.
- 1906 – सिस्टर निवेदिता की रचना के बाद 1906 में एक बार फिर नए ध्वज का निर्माण हुआ. इसमें तीन रंग समाहित थे, सबसे उपर नीला फिर पीला व सबसे नीचे लाल रंग था. इसमें सबसे उपर नीली पट्टी में 8 अलग अलग तरह के सितारे बने हुए थे. सबसे नीचे की लाल पट्टी में एक ओर सूर्य व दूसरी ओर आधा चन्द्रमा व एक तारा बना हुआ था. पिली पट्टी में देवनागरी लिपि से वंदेमातरम् लिखा गया था.
इसी साल इस ध्वज में थोडा बदलाव किया गया, इसमें तीन रंग ही थे, लेकिन उन रंगों को बदल दिया गया. इसमें केसरिया, पीला व हरा रंग था, जिसे कलकत्ता ध्वज कहा गया. इसमें सबसे उपर 8 आधे खिले हुए कमल बनाये गए थे, इसलिए इसे कमल ध्वज भी नाम दिया गया. इसे सचिन्द्र प्रसाद बोस व सुकुमार मित्रा ने बनाया था. इस ध्वज को 7 अगस्त 1906 में कलकत्ता के पारसी बागन चौराहे पर सुरेन्द्रनाथ बैनर्जी द्वारा फ़हराया गया था. उस समय बंगाल का विभाजन हुआ था, उसी के विरोध में ये प्रदर्शन किया गया था.
- 1907 – 1907 में इसमें मैडम भिकाजी कामा, विनायक दामोदर सावरकर व् श्यामजी कृष्णा वर्मा द्वारा फिर बदलाव किये गए. इसे मैडम भिकाजी कामा ध्वज भी कहा गया. 22 अगस्त 1907 में मैडम भिकाजी कामा द्वारा इस ध्वज को जर्मनी में फ़हराया गया था. ऐसा पहली बार था, जब भारतीय ध्वज को देश के बाहर विदेशी जमीन पर फ़हराया गया था. इस समारोह के बाद इसे ‘बर्लिन कमिटी ध्वज’ भी कहा गया. इस ध्वज में सबसे उपर हरा बीच में केसरिया व् सबसे नीचे लाल रंग था.
- 1916 – 1916 में पिंगली वेंकय्या नाम की लेखिका ने एक ध्वज बनाया, जिसमें पुरे देश को साथ लेकर चलने की उनकी सोच साफ झलक रही थी. वे महात्मा गाँधी से भी मिली और उनकी राय ली. गांधीजी ने उनको उसमें चरखा भी जोड़ने की बात कही. पिंगली ने पहली बार ध्वज को खादी के कपड़े से बनाया था. इसमें 2 रंग लाल व् हरे रंग से बनाया गया व् बीच में चरखा भी बनाया गया. इस ध्वज को महात्मा गाँधी ने देख कर नकार दिया, उनका कहना था लाल रंग हिन्दू व् हरा रंग मुस्लिम जाति का प्रतीक है. इस ध्वज से देश एकजुट नहीं प्रतीत होता है.
- 1917 – 1917 में बाल गंगाधर तिलक ने नए ध्वज को राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के रूप में अपनाया. इस ध्वज पर सबसे उपर यूरोपियन देश का झंडा भी जुड़ा हुआ था, बाकि जगह में 5 लाल व् 5 नीली लाइनें थी. इसमें 7 स्टार जिसे सप्तऋषि कहते है, हिन्दुओं की धार्मिकता को दर्शाने के लिए बनाये गए. इसमें अर्द्धचन्द्रमा व् एक तारा भी बनाया गया था.
- 1921 – महात्मा गाँधी चाहते थे कि भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में देश की एक जुटता साफ साफ झलके, इस वजह से एक ध्वज का निर्माण किया गया. इस ध्वज में भी 3 रंग थे, सबसे उपर सफ़ेद फिर हरा आखिरी में लाल. इस ध्वज में सफ़ेद रंग देश के अल्पसंख्यक, हरा रंग मुस्लिम जाति व् लाल रंग हिन्दू और सिख जाति को दर्शाता था. बीच में चरखा भी जोड़ा गया, जो सारी जाति की एकजुटता को दर्शाता था. इस ध्वज को कांग्रेस पार्टी ने नहीं अपनाया, लेकिन फिर भी ये आजादी की लड़ाई में राष्ट्रीयता का प्रतीक बना हुआ था.
- 1931 – ध्वज में साम्प्रदायिक व्याख्या से कुछ लोग बहुत नाराज थे. इन्ही सब बातों को ध्यान में रखते हुए ध्वज में लाल रंग को गेरू कर दिया गया. ये रंग हिन्दू मुस्लिम दोनों जाति को प्रकट करता है. लेकिन इसके बाद सिख जाति के लोगो ने राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में अपनी जाति को प्रकट करने के लिए एक अलग मांग की. इसके फलस्वरूप पिंगली ने एक नया ध्वज बनाया, जिसमें सबसे उपर केसरिया फिर सफ़ेद अंत में हरा रंग था. इसमें बीच में सफ़ेद के उपर नीले रंग का चरखा था. 1931 में कांग्रेस पार्टी की मीटिंग में इसे पास कर दिया गया, जिसके बाद ये कांग्रेस का आधिकारिक ध्वज बन गया.
- 1947 – 1947 में जब देश आजाद हुआ, तब देश के प्रथम राष्ट्रपति व कमिटी प्रमुख राजेन्द्र प्रसाद जी ने राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के बारे में बात करने के लिए एक सभा बुलाई. वहां सबने एक मत होकर कांग्रेस से उनका ध्वज लेने की बात मानी. 1931 में बनाये गए उस ध्वज में बदलाव के साथ उसे अपनाया गया. बीच में चरखे की जगह अशोक चक्र ने ली. इस प्रकार अपने देश का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज तैयार हो गया.
ध्वज का निर्माण कार्य –
ब्यूरो ऑफ़ इंडियन स्टैण्डर्ड (BIS) ने ध्वज के निर्माण के लिए मानक सेट किया. उन्होंने उसके निर्माण से जुड़ी हर छोटी बड़ी बात जैसे उसका कपड़ा, धागा, रंग उसका अनुपात सब कुछ रुल के अनुसार सेट किया, यहाँ तक कि उसके फेहराने से जुड़ी बातें भी रुल में लिखी गई.
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज से जुड़ी कुछ जरुरी बातें –
यह एक राष्ट्रीय प्रतीक है, जिसका सम्मान हर भारतीय करता है. राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के सम्मान से जुड़ी कुछ बातें आम आदमी को हमेशा याद रखनी चाइये –
- जब राष्ट्रीय ध्वज उठाया जाये, तब हमेशा ध्यान रखें केसरिया रंग सबसे उपर हो.
- कोई भी ध्वज या प्रतीक राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के उपर नहीं होना चाहिए.
- अगर कोई और ध्वज फेहराये जा रहे है, तो वे हमेशा इसके बायीं ओर पंक्ति में फेहराये जाये.
- अगर कोई जुलुस या परेड निकल रही हो, तो राष्ट्रीय ध्वज दाहिने ओर होना चाइये या फिर बाकि ध्वजों की पंक्ति में बीच में होना चाइये.
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज हमेशा मुख्य सरकारी ईमारत व् संस्थान जैसे राष्ट्रपति भवन, संसद भवन, सुप्रीम कोर्ट, हाई कोर्ट आदि में फेहरा हुआ होना चाइये.
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज किसी भी पर्सनल व्यवसाय या काम के लिए उपयोग नहीं किया जा सकता.
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज शाम को सूर्यास्त के समय उतार देना चाइये.
रोचक तथ्य –
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को 29 मई 1953 में दुनिया के सबसे उचें पर्वत माउंट एवेरेस्ट पर फ़हराया गया था.
- मैडम भीखाजी खामा पहली इन्सान है, जिन्होंने राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को विदेशी जमीन पर फ़हराया था.
- 1984 में राकेश शर्मा द्वारा इसे अंतरीक्ष पर फ़हराया गया.
- दिसम्बर 2014 में चेन्नई में 50 हजार लोगो ने राष्ट्रीय ध्वज बनाकर एक रिकॉर्ड कायम किया था.
- दिल्ली के सेंट्रल पार्क में सबसे ऊँचा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज फ़हराया गया, जिसकी लम्बाई 90 फीट व् चोड़ाई 60 फीट थी.
- भारत के राष्ट्रीय चिन्ह और उनका अर्थ
- भारतीय के राष्ट्रीय पर्व
- सरोजनी नायडू जीवन परिचय
- भारत का इतिहास
More on Deepawali
शनि देव जयंती 2024 में कब है, क्या है..., गणेश चतुर्थी और विनायक चतुर्थी 2024 व्रत महत्व कहानी..., आतंकवाद विरोधी दिवस 2024 निबंध भाषण शायरी anti..., महाराणा प्रताप व चेतक का इतिहास व 2024 जयंती..., similar articles, आतंकवाद विरोधी दिवस 2024 निबंध भाषण शायरी anti terrorism day in hindi, काले पानी की सजा- सेल्यूलर जेल के बारे में पूरा इतिहास, नोबेल शांति पुरस्कार क्या है, नोबेल पुरस्कार विजेताओं की सूची 2023 (what is nobel prize in hindi), leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- How To Get Pregnant
- Infertility
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Second Pregnancy
- Giving Birth
- Post Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Development
- Browse Names
- Play & Activities
- Coloring Pages
- Food & Nutrition
- Health & Fitness
- Style & Beauty Care
- Collaborations
- New Parents
- Single Parenting
- Relationships
- Baby Eye Color Calculator
- Online Pregnancy Test
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- Implantation Calculator
- hCG Calculator
- Period Calculator
- ovulation calculator
- pregnancy due date calculator
- Child Height Predictor
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Breast Milk Calculator
- Child Growth Percentile Calculator
- Baby Cost Calculator
- BMI Calculator For Kids & Teens
- Contraction Calculator
- Immunization Scheduler and Chart
- C-Section Checklist
- Online Twin Pregnancy Quiz
- Numerology calculator
- Child Blood Type Calculator
- Nakshatra Calculator
- Diaper Bag Checklist
- Baby Name Combiner
Home • हिंदी • किशोरावस्था
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us .
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज (तिरंगा) का इतिहास और महत्वपूर्ण तथ्य | About Indian National Flag In Hindi

नृपेंद्र बाल्मीकि एक युवा लेखक और पत्रकार हैं, जिन्होंने उत्तराखंड से पत्रकारिता एवं जनसंचार में स्नातकोत्तर (एमए) की डिग्री प्राप्त की है। नृपेंद्र विभिन्न विषयों पर लिखना पसंद करते हैं, खासकर स्वास्... read full bio
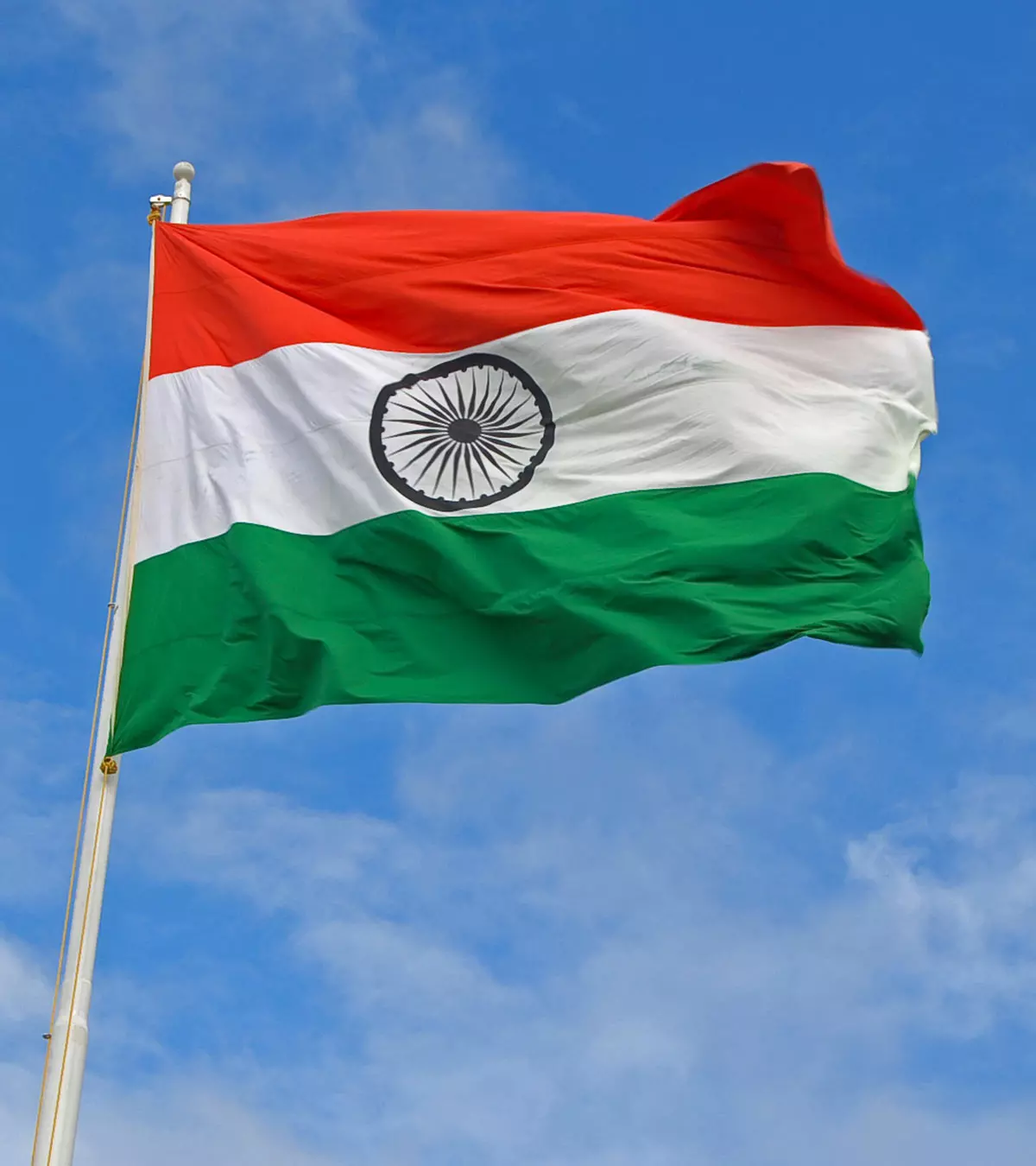

हर देश का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज उसकी स्वतंत्रता का प्रमाण और उसकी पहचान होता है। यही कारण है कि बचपन से हमें तिरंगे का सम्मान करने की सीख दी जाती है। हर 26 जनवरी और 15 अगस्त को लोग अपने-अपने घरों, दफ्तरों, स्कूल व कॉलेज आदि में तिरंगा फेहराते तो हैं, लेकिन राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के इतिहास की जानकारी कम लोग को ही होती है। इस बात को ध्यान में रखते हुए माॅमजंक्शन के इस लेख में भारत के झंडे से जुड़ी कुछ ऐसी जानकारी दी गई है, जिसके बारे में जानना हर किसी के लिए जरूरी है। इस लेख में आप तिरंगे के इतिहास के साथ जानेंगे ध्वज का विकास, उसे फहराने का सही तरीका और उससे जुड़े कुछ अन्य रोचक तथ्य।
आइए, कुछ वक्त पीछे चलते हैं और आपको बताते हैं हमारे राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इतिहास।
तिरंगे का इतिहास
भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज आज जिस स्वरूप में उसे 22 जुलाई 1947 को कॉन्स्टिटुएंट असेंबली में हुई मीटिंग के दौरान मान्यता मिली थी। इसे तिरंगा इसलिए कहा जाता है, क्योंकि यह तीन रंगों से मिलकर बना है – केसरिया, सफेद और हरा। साथ ही बीच में मौजूद सफेद रंग के ऊपर गहरे नीले (नेवी ब्लू) रंग का अशोक चक्र भी मौजूद होता है (1) ।
इस निराले तिरंगे की विकास यात्रा को जानने के लिए पढ़ते रहें यह लेख।
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का विकास
1947 से पहले राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का स्वरूप पांच बार बदला गया था, जो इस प्रकार है (1) :
- 1906 : राष्ट्रीय ध्वज पहली बार 7 अगस्त, 1906 को उस समय के कलकत्ता यानी आज के कोलकता में फहराया गया था। इस झंडे में तीन रंग थे – हरा, पीला और लाल। सबसे ऊपर हरा रंग, जिस पर कमल बने थे, बीच में पीले रंग पर “वंदे मातरम्” लिखा था और सबसे नीचे लाल रंग पर एक तरफ चांद व एक तरफ सूरज बना था।
- 1907 : यह जानकर शायद आपको हैरानी होगी कि भारत का दूसरा झंडा 1907 में मेडम कामा और उनके साथी क्रांतिकारियों द्वारा पेरिस में फहराया गया था। यह झंडा लगभग पहले वाले झंडे की तरह ही था। फर्क सिर्फ इतना था कि सबसे ऊपर वाली पट्टी पर कमल की जगह सात सितारे थे, जो सप्त ऋषियों को सर्मित थे।
- 1917 : भारत का तीसरा झंडा 1917 में होम रूल मूवमेंट के दौरान डॉ. एनी बैसैंट और बाल गंगाधर तिलक द्वारा फहराया गया था। इस झंडे में पांच लाल और चार हरीआड़ी पट्टियां (horizontal strips) थीं। ऊपर बाएं तरफ यूनियन जैक (ब्रिटेन का झंडा) और दूसरी ओर एक चांद और सितारा था। इसके अलावा, इस झंडे के दाहिने तरफ निचले छोर से ऊपरी बाएं छोर तक (diagonally) सितारे थे।
- 1921 : इस साल बेसवाड़ा (अब विजयवाड़ा) में ऑल इंडिया कांग्रेस कमीटी ने एक झंडा बनाया और उसे गांधी जी के पास ले गए। इस झंडे में दो रंग थे – लाल और हरा, जो भारत के दो मुख्य समुदायों – हिंदू और मुस्लिम को दर्शाते थे। इस झंडे को देखकर, गांधी जी ने इसके बीच में भारत के अन्य समुदायों को दर्शाने के लिए सफेद रंग जोड़ने की सलाह दी। साथ ही, इस सफेद रंग पर चरखा भी बनाया गया, जो भारत की प्रगति को दर्शाता था।
- 1931 : यह ऐतिहासिक साल था। इस साल तिरंगे झंडे को भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के रूप में अपनाने का प्रस्ताव पारित किया गया। इस झंडे में तीन रंग थे – केसरी, सफेद और हरा। इस प्रस्ताव को पारित करते समय यह साफ कर दिया गया था कि ये रंग किसी समुदाय के प्रतीक नहीं है और इसे इसी तरह अपनाया जाएगा। इन रंगों के साथ झंडे के बीच में एक चरखा भी बनाया गया।
- 1947 : 22 जुलाई 1947 को तिरंगे को आजाद भारत के राष्ट्रीय झंडे के रूप में अपनाया गया। देश की आजादी के बाद, इस तिरंगे के रंगों को नहीं बदला गया, सिर्फ चरखे को बदलकर उसकी जगह अशोक चक्र को जगह दी गई। इसके बाद, 15 अगस्त 1947 से 26 जनवरी 1950 तक भारत का प्रभुत्व झंडा (national flag of the Dominion of India) माना गया और उसके बाद इसे भारत गणराज्य (Republic of India) का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज माना गया।
क्या आप जानते हैं कि तिरंगे को फहराने के कुछ नियम भी हैं?
भारतीय ध्वज फहराने के लिए आचार संहिता
भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज फहराते समय कुछ नियमों का पालन करना जरूरी है। इन नियमों के बारे में नीचे विस्तार से बताया गया है (2) :
- तिरंगे को शिक्षण संस्थान जैसे स्कूल, कॉलेज, स्पोर्ट्स कैंप आदि पर फहराया जा सकता है। इसे फहराते समय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के पूर्ण सम्मान के बारे में ध्यान रखना जरूरी है।
- तिरंगे को सीधा लहराते समय केसरी रंग सबसे ऊपर आना चाहिए और आड़ा (horizontaly) लहराते समय केसरी रंग दाहिनी ओर से सबसे ऊपर की ओर होना चाहिए।
- खुले में फहराते समय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को किसी भी मौसम में सूरज उगने से लेकर शाम को ढलने तक ही फहराया जा सकता है।
- अगर तिरंगा फटा हुआ हो या किसी अन्य तरह से क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाए, तो उसे नहीं फहराया जा सकता।
- किसी भी अन्य झंडे को तिरंगे से ऊंचा नहीं फहराया जा सकता।
- हर हाल में इस बात का ध्यान रखना जरूरी है कि राष्ट्रीय ध्वज जमीन पर न गिरे या पानी को न छुए।
आगे जानिए राष्ट्रीय ध्वज से जुड़े कुछ रोचक तथ्यों के बारे में।
भारतीय ध्वज के बारे में 25 रोचक तथ्य
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का डिजाइन : भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को पिंगली वेंकय्या नामक एक स्वतंत्र सेनानी ने डिजाइन किया गया था। वह मछलीपट्टनम, आंध्र प्रदेश के निवासी थी। वह भूविज्ञान और कृषि के विशेषज्ञ थे। उन्होंने अपने नगर में एक शैक्षिक संस्थान भी स्थापित किया था।
- तिरंगे का अनुपात : भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज की चौड़ाई-लंबाई का अनुपात (width-to-length ratio) 2:3 है। इसके तीनों रंगों की पट्टियां बराबर होती हैं और बीच में अशोक चक्र होता है।
- तिरंगे के रंगों का अर्थ : तिरंगे में मौजूद केसरी रंग शक्ति और साहस का प्रतीक है। वहीं, सफेद का अर्थ है शांति और सत्य। राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में मौजूद हरा रंग देश की प्रगति और भारतीय जमीन की उर्वरता का प्रतीक है।
- अशोक चक्र : तिरंगे के बिल्कुल बीच में सफेद रंग की पट्टी पर अशोक चक्र बना होता है। इसे धर्म चक्र भी कहा जाता है। इसमें 24 धारियां होती हैं और इसका व्यास (diameter) सफेद पट्टी की लंबाई के बराबर होता है। यह चक्र दर्शाता है कि चलते रहना जीवन और रुक जाना मृत्यु है। अशोक चक्र इस तरह से प्रिंट होना चाहिए कि वह तिरंगे के दोनों ओर से साफ नजर आए।
- फहराने का तरीका : जब तिरंगा फहराया जाता है, तब उसकी डोर को तेजी से खींचा जाता है, वहीं जब तिरंगे को उतारा जाता है, तो धीरे-धीरे उतारा जाता है (2) ।
- तिरंगे का कपड़ा : तिरंगा बनाने के लिए सिर्फ बुनने वाला ऊन/कॉटन/सिल्क/खादी का उपयोग किया जा सकता है (2) ।
- स्वराज झंडा : 1921 में ब्रिटिश सरकार ने भारत का झंडा फहराने पर पाबंदी लगा दी थी। इसके बाद स्वतंत्रता सैलानियों ने स्वराज झंडे को विरोध के प्रतीक के रूप में उपयोग किया था। यह एक तिरंगा था, जिस पर अशोक चक्र की जगह चरखा बना था।
- भारतीय ध्वज संहिता : भारतीय ध्वज संहिता 26 जनवरी, 2002 को पेश की गई थी। यह वे नियम और कानून हैं, जिनके अनुसार भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को फरहाया जाता है। ध्वज संहिता को तीन भागों में विभाजित किया गया है: पहले भाग में ध्वज का वर्णन है, दूसरे भाग में सार्वजनिक, निजी और शैक्षिक संगठनों के लिए प्रदर्शन कोड का उल्लेख है। कोड के तीसरे भाग केंद्रीय में राज्य और उनकी एजेंसियों द्वारा तिरंगा फहराने के नियमों के बारे में बताया गया है।
- तिरंगा बनाने की प्रक्रिया : भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को बनाने की प्रक्रिया के कुल 6 स्टेप्स हैं :
- कताई (Hand spinning)
- बुनाई (Hand weaving)
- ब्लीच करना और रंगना (Bleaching and dyeing)
- अशोक चक्र बनाना (Making of the Ashoka Chakra)
- बांधना (Toggling)
- तिरंगे का साइज : कानूनन तिरंगे के 9 प्रकार के साइज हैं, जिसके बारे में हम नीचे टेबल के जरिए बता रहे हैं (2) :
- भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज प्रदर्शित करने के प्रोटोकॉल : राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के प्रदर्शन के समय हर बार नीचे बताई गई बातों को ध्यान में रखना जरूरी है :
- किसी भी परिस्थिति में तिरंगा जमीन को न छुए।
- इसका उपयोग किसी भी वस्तु को ढकने के लिए न किया जाए।
- तिरंगे को कभी भी उल्टा न फहराया जाए।
- तिरंगे को किसी भी व्यक्ति, वस्तु या संस्था के सामने झुकाया न जाए।
- तिरंगे के कपड़े में फलों के अलावा किसी चीज को न लपेटा जाए।
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का विनिर्माण (manufacturing) : भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के डिजाइन और निर्माण को ब्यूरो ऑफ इंडियन स्टैंडर्ड्स (बीआईएस) द्वारा विनियमित किया जाता है। सामग्री, डाई का रंग, आकार और विनिर्देश, सभी का परीक्षण बीआईएस प्रयोगशालाओं में किया जाता है। बीआईएस द्वारा हां बोलने के बाद ही झंडे को बेचा जा सकता है।
- नागरिकों को झंडा फहराने का अधिकार : 2002 में फ्लैग कोड में संशोधन से पहले भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को प्रदर्शित करने के अधिकार केवल सरकारी अधिकारियों और एजेंसियों तक ही सीमित थे। 2002 में, निजी संगठनों और व्यक्तियों को सम्मान के साथ राष्ट्रीय ध्वज फहराने करने का अधिकार मिला। यह भारतीय संविधान के अनुच्छेद 19 (i) (ए) के तहत प्रत्येक नागरिक का एक मौलिक अधिकार है।
- अंतरिक्ष में तिरंगा : विंग कमांडर राकेश शर्मा ने 1984 में अंतरिक्ष मिशन के दौरान अपने अंतरिक्ष सूट पर पदक के रूप में भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को पहना था।
- चांद पर तिरंगा : 15 सितंबर, 2008 को 08:34 बजे IST, चंद्रयान-I की मदद से मून प्रोब (एक तरह का स्पेसक्राफ्ट) को अंतरिक्ष में भेजा गया था। उस प्रोब के सभी तरफ भारतीय ध्वज बना हुआ था और इसी के साथ चंद्रमा पर अपना झंडा उतारने वाला भारत चौथा देश बन गया।
- माउंट एवेरेस्ट पर तिरंगा : माउंट एवेरेस्ट पर भारतीय ध्वज पहली बार 29 मई, 1953 को तेनजिंग नोर्गे द्वारा फहराया गया। फिलहाल, वह ध्वज राष्ट्रपति भवन संग्रहालय, नई दिल्ली में संरक्षित है।
- आधा उतरा झंडा : आधा उतरा तिरंगा शोक का प्रतीक होता है, जिसकी अवधि भारत के राष्ट्रपति द्वारा तय की जाती है। जब ध्वज को आधा उतारने का निर्णय लिया जाता है, तो यह अनिवार्य है कि ध्वज को पहले ऊपर तक उठाया जाए और फिर धीरे-धीरे नीचे उतारा जाए। गणतंत्र दिवस और स्वतंत्रता दिवस पर झंडे को कभी आधा झुकाया नहीं जाता है।
- राज्य और सैन्य अंतिम संस्कार : शहीदों और राज्य के गणमान्य व्यक्तियों के कॉफिन को ढकने के लिए तिरंगे का उपयोग जाता है, लेकिन उस समय भी कॉफिन को जमीन पर नहीं रखा जाता और न ही तिरंगे को शरीर के साथ जलाया जाता है।
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र का ध्वज : आमतौर पर राष्ट्रीय ध्वज दाहिनी ओर फहराया जाता है, लेकिन संयुक्त राष्ट्र के ध्वज के किसी भी ओर इसे फहराया जा सकता है। संयुक्त राष्ट्र की मीटिंग के दौरान, भारत का झंडा अन्य देशों के झंडों की बराबर की लंबाई का होना चाहिए।
- सबसे ऊंचा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज : भारत का सबसे ऊंचा तिरंगा 12 मार्च, 2018 को बेलागवी, कर्नाटक में फहराया गया। इस झंडे की ऊंचाई 110 मीटर (365 फीट) है और लंबाई व चौड़ाई 120×80 फीट है। इसे बेलागवी के जिला मंत्री रमेश जारकीहोली ने फहराया था।
- मानव राष्ट्रीय ध्वज : 2014 में चेन्नई में 50,000 से अधिक स्वयंसेवकों द्वारा सबसे बड़े ‘मानव’ भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज बनाया गया था। यह अब तक का सबसे बड़ा मानव ध्वज था।
- कपड़ों पर तिरंगा : संहिता में एक संशोधन के बाद 2005 में भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को विभिन्न प्रकार के कपड़ों के लिए उपयोग करने की अनुमति दी गई थी, लेकिन इसे केवल कमर के ऊपर पहना जाना चाहिए जैसे शर्ट के ऊपर।
- राष्ट्रीय ध्वज समिति : डॉ. राजेंद्र प्रसाद भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के लिए गठित पहली समिति के प्रमुख थे।
- भारत जैसा ध्वज : भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज कई देशों के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज की तरह दिखता है। यह सबसे ज्यादा नाइजर के झंडे की तरह दिखता है। ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि नाइजर का झंडा भी केसरी, सफेद और हरे रंग से बना है। फर्क सिर्फ इतना है कि उनके झंडे पर सफेद पट्टी पर अशोक चक्र की जगह केसरी रंग का गोल बिंदु है।
- पोडियम पर ध्वज : किसी वक्ता के पोडियम पर राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को हमेशा वक्ता के दाहिनी ओर रखा जाता है।
1. History Of Indian Tricolor by Know India 2. Flag Code of India by Know India
- मुख्य सामग्री पर जाएं
- मुख्य पृष्ठ
- भारत की राष्ट्रीय पहचान के प्रतीक
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज
- यह पेज प्रिंट करें

राष्ट्रीय ध्वज तिरंगे में समान अनुपात में तीन क्षैतिज पट्टियां हैं: केसरिया रंग सबसे ऊपर, सफेद बीच में और हरा रंग सबसे नीचे है। ध्वज की लंबाई-चौड़ाई का अनुपात 3:2 है। सफेद पट्टी के बीच में नीले रंग का चक्र है।
भारत की संविधान सभा ने राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का प्रारूप 22 जुलाई 1947 को अपनाया।
भारतीय झंडा संहिता, 2002
राष्ट्रीय गौरव अपमान निवारण अधिनियम, 1971
स्रोत: इंडिया बुक 2020 - एक संदर्भ वार्षिक
भारत के बारे में
भारत विश्व की सबसे पुरानी सभ्यताओं में से एक है जिसमें बहुरंगी विविधता और समृद्ध सांस्कृतिक विरासत है। इसके साथ ही यह अपने-आप को बदलते समय के साथ ढ़ालती भी आई है। आज़ादी पाने के बाद भारत ने बहुआयामी सामाजिक और आर्थिक प्रगति की है। भारत कृषि में आत्मनिर्भर बन चुका है और अब दुनिया के सबसे औद्योगीकृत देशों की श्रेणी में भी इसकी गिनती की जाती है। विश्व का सातवां बड़ा देश होने के नाते भारत शेष एशिया से अलग दिखता है जिसकी विशेषता पर्वत और समुद्र ने तय की है और ये इसे विशिष्ट भौगोलिक पहचान देते हैं। उत्तर में बृहत् पर्वत श्रृंखला हिमालय से घिरा यह कर्क रेखा से आगे संकरा होता जाता है। पूर्व में बंगाल की खाड़ी, पश्चिम में अरब सागर तथा दक्षिण में हिन्द महासागर इसकी सीमा निर्धारित करते हैं।
हमें फ़ॉलो करें

भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज

भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज एक राष्ट्रीय प्रतीक है जिसे क्षैतिज आयताकार में बनाया गया है। इसे तीन रंगों की मदद से सजाया गया है जिसमें गहरा केसरिया (सबसे ऊपर), सफेद( बीच में) और हरा (सबसे नीचे)। सफेद रंग के बीचों-बीच एक नीले रंग का अशोक चक्र (अर्थात कानून का चक्र) बना हुआ है जिसमें 24 तिलियाँ है। 22 जुलाई 1947 में भारत के संविधान सभा ने एक मीटिंग में राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के वर्तमान स्वरुप को स्वीकार किया था। भारत के सत्ताधारियों द्वारा वर्तमान राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को अधिकारिक रुप से स्वीकार किया गया था। तीन रंगों का होने के कारण इसे तिरंगा भी कहा जाता है। ये स्वराज ध्वज पर आधारित है (अर्थात भारतीय राष्ट्रीय काँग्रेस का ध्वज, पिंगाली वेंकैया द्वारा रुपांकित)।
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज (Indian Flag in Hindi)
Find below information about Indian Flag in Hindi language:
भारत के लोगों के लिये राष्ट्रीय ध्वज बहुत मायने रखता है। भारत के लोगों के लिये ये बेहद महत्वपूर्ण और गौरव का विषय है। भारतीय ध्वज को एक खास किस्म के कपड़े से बनाया गया है जिसे ख़ादी कहते है (हाथ से काता हुआ जिसे महात्मा गाँधी द्वारा प्रसिद्ध किया गया)। इसके निर्माण और डिज़ाइन के लिये भारतीय स्टैन्डर्ड ब्यूरो जिम्मेदार होता है जबकि, ख़ादी विकास एवं ग्रामीण उद्योग कमीशन को इसके निर्माण का अधिकार है। 2009 में राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का अकेला निर्माण कर्ता कर्नाटक ख़ादी ग्रामोंद्योग संयुक्त्त संघ रहा है। राष्ट्रीय प्रतीक से संबंधित कानून के साथ ही भारतीय ध्वज की प्रथा (किसी दूसरे राष्ट्र या ग़ैर राष्ट्रीय ध्वज) को भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज नियमावली संचालित करता है। किसी भी निजी नागरिक (किसी भी राष्ट्रीय दिवस को छोड़कर) के द्वारा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इस्तेमाल पूरी तरह प्रतिबंधित है। जबकि, नवीव जिंदल (निजी नागरिक) के अनुरोध पर 2002 में, सुप्रिम कोर्ट के आदेशानुसार भारत की सरकार (भारत की केन्द्रीय कैबिनेट) द्वारा ध्वज के सीमित उपयोग के कानून में बदलाव किया गया। ध्वज के अतिरिक्त इस्तेमाल के लिये 2005 में इसमें दुबारा बदलाव किया गया।
भारतीय ध्वज का अर्थ और महत्व
तीन रंगों में होने की वजह से भारतीय ध्वज को तिरंगा भी कहते है। ख़ादी के कपड़ों, बीच में चक्र और तीन रंगों का इस्तेमाल कर भारतीय ध्वज को क्षितिज के समांतर दिशा में डिज़ाइन किया गया है। ब्रिटीश शासन से भारतीय स्वतंत्रता के परिणाम स्वरुप 22 जुलाई 1947 को राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को स्वीकार किया गया था। इसकी लम्बाई और चौड़ाई का अनुपात क्रमशः २:३ होता है। आजादी और राष्ट्रीयता के प्रतीक के रुप में भारतीय ध्वज को बनाया और स्वीकार किया गया।
हमारे लिये भारतीय ध्वज का बहुत महत्व है। अलग-अलग विचारधारा और धर्म जैसै हिन्दू, मुस्लिम, सिक्ख, ईसाई आदि का होने के बावजूद भी ये सभी धर्मो को एक राह पर ले जाता है और हमारे लिये एकता के प्रतीक के रुप में है। इसमें मौजूद तीन रंग और अशोक चक्र का अपना अर्थ है जो इस प्रकार है:
केसरिया रंग राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का सबसे ऊपरी भाग केसरिया रंग है; जो बलिदान का प्रतीक है राष्ट्र के प्रति हिम्मत और नि:स्वार्थ भावना को दिखाता है। ये बेहद आम और हिन्दू, बौद्ध और जैन जैसे धर्मों के लिये धार्मिक महत्व का रंग है। केसरिया रंग विभिन्न धर्मों से संबंधित लोगों के अहंकार से मुक्ति और त्याग को इंगित करता है और लोगों को एकजुट बनाता है। केसरिया का अपना अलग महत्व है जो हमारे राजनीतिक नेतृत्व को याद दिलाता है कि उनकी ही तरह हमें भी किसी व्यक्तिगत लाभ की इच्छा के पूरे समर्पण के साथ राष्ट्र की भलाई के लिये काम करना चाहिये।
सफेद रंग राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के बीच का भाग सफेद रंग से डिज़ाइन किया गया है जो राष्ट्र की शांति, शुद्धता और ईमानदारी को प्रदर्शित करता है। भारतीय दर्शन शास्त्र के मुताबिक, सफेद रंग स्वच्छता और ज्ञान को भी दर्शाता है। राष्ट्र के मार्गदर्शन के लिये सच्चाई की राह पर ये रोशनी बिखेरता है। शांति की स्थिति को कायम रखने के दौरान मुख्य राष्ट्रीय उद्देश्य की प्राप्ति के लिये देश के नेतृत्व के लिये भारतीय राजनीतिक नेताओं का ये स्मरण कराता है।
हरा रंग तिरंगे के सबसे निचले भाग में हरा रंग है जो विश्वास, उर्वरता ; खुशहाली ,समृद्धि और प्रगति को इंगित करता है। भारतीय दर्शनशास्त्र के अनुसार, हरा रंग उत्सवी और दृढ़ता का रंग है जो जीवन और खुशी को दिखाता है। ये पूरे भारत की धरती पर हरियाली को दिखाता है। ये भारत के राजनीतिक नेताओं को याद दिलाता है कि उन्हें भारत की मिट्टी की बाहरी और आंतरिक दुश्मनों से सुरक्षा करनी है।
अशोक चक्र और 24 तिलीयाँ हिन्दू धर्म के अनुसार, पुराणों में 24 संख्या बहुत महत्व रखता है। अशोक चक्र को धर्म चक्र माना जाता है जो कि समय चक्र भी कहलाता है। अशोक चक्र के बीच में 24 तिलीयाँ है जो पूरे दिन के 24 बहुमूल्य घंटों को दिखाता है। ये हिन्दू धर्म के 24 धर्म ऋषियों को भी प्रदर्शित करता है जो “गायत्री मंत्र” की पूरी शक्ति को रखता है (हिन्दू धर्म का सबसे शक्तिशाली मंत्र)। हिमालय के सभी 24 धर्म ऋषियों को 24 अक्षरों के अविनाशी गायत्री मंत्र के साथ प्रदर्शित किया जाता है (पहला अक्षर विश्वामित्र जी के बारे वर्णन करता है वहीं अंतिम अक्षर यज्ञवल्क्या को जिन्होंने धर्म पर शासन किया)।
भारतीय झंडे के मध्य में अशोक चक्र होने के पीछे भी एक बड़ा इतिहास है। बहुत साल पहले, भगवान बुद्ध को मोक्ष की प्राप्ति हुई अर्थात गया में शिक्षा मिली। मोक्ष की प्राप्ति के बाद वो वाराणसी के सारनाथ आ गये जहाँ वो अपने पाँच अनुयायी (अर्थात् पाँच वर्जीय भिक्क्षु) कौनदिन्या, अश्वजीत, भद्रक, महानाम और कश्यप से मिले। धर्मचक्र की व्याख्या और वितरण कर बुद्ध ने उन सबको अपना पहला उपदेश दिया। इसे राजा अशोक द्वारा अपने स्तंभ के शिखर को प्रदर्शित करने के लिये लिया गया जो बाद में भारतीय ध्वज के केन्द्र में अशोक चक्र के रुप में इस चक्र के उत्पत्ति का आधार बना। राष्ट्रीय झंडे के बीच में अशोक चक्र की मौजूदगी राष्ट्र में मजबूत संबंध और बुद्ध में विश्वास को दिखाता है।
12 तिलीयाँ भगवान बुद्ध के अध्यापन को बताता है जबकि दूसरी 12 तिलीयाँ अपने बराबर की प्रतीकों के साथ जोड़ें में है जैसे-अविध्या (अर्थात् ज्ञान की कमी), सम्सकारा (अर्थात् आकार देने वाला), विजनाना (अर्थात् चेतना), नमरुपा (अर्थात् नाम और रुप), सदायातना ( अर्थात् छ: इन्द्रिय जैसे- कान, आँख, जीभ, नाक, शरीर और दिमाग), स्पर्श (अर्थात् संपर्क), वेदना ( अर्थात् दर्द), तृष्णा (अर्थात् प्यास), उपदना (अर्थात् समझना), भाव (अर्थात् आने वाला), जाति (अर्थात् पैदा होना), जरामरना (अर्थात् वृद्धावस्था), और मृत्यु।
अशोक चक्र क्यों नौसेना की तरह नीले रंग में है ? राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के सफेद पट्टी के केन्द्र में अशोक चक्र का नीला रंग, ब्रह्माण्ड की सच्चाई को दिखाता है। ये आकाश और समुद्र के रंग को भी प्रदर्शित करता है।
24 तिलियाँ क्या प्रदर्शित करती है ? हिन्दू धर्म के अनुसार, राष्ट्रीय ध्वज की सभी 24 तिलीयाँ जीवन को दर्शाती है अर्थात् धर्म जो इस प्रकार है: प्रेम, बहादुरी, धैर्य, शांति, उदारता, अच्छाई, भरोसा, सौम्यता, नि:स्वार्थ भाव, आत्म-नियंत्रण, आत्म बलिदान, सच्चाई, नेकी, न्याय, दया, आकर्षणशीलता, नम्रता, हमदर्दी, संवेदना, धार्मिक ज्ञान, नैतिक मूल्य, धार्मिक समझ, भगवान का डर और भरोसा (भरोसा या उम्मीद)।
भारतीय तिरंगे (ध्वज) का इतिहास
एक ध्वज किसी देश का प्रतीक बनता है इसलिये किसी भी आजाद देश को एक राष्ट्र के रुप में एक अलग पहचान के लिये एक ध्वज की जरुरत पड़ती है। संविधान सभा की मीटिंग में 22 जुलाई 1947 को भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को इसके वर्तमान स्वरुप में स्वीकार किया गया था, 15 अगस्त 1947 को ब्रिटिश शासन से देश की आजादी से कुछ दिनों पहले। इसे तीन रंगों, अशोक चक्र और खादी की मदद से पिंगाली वेंकैया के द्वारा डिज़ाइन किया गया था।
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को क्षैतिज आकार में डिज़ाइन किया गया है जिसमें सभी तीन रंग अपने बराबर अनुपात में है। झंडे की चौड़ाई से इसके लंबाई का अनुपात 2:3 का है। बीच की सफेद पट्टी में नीले रंग का एक पहिया बना हुआ है जो 24 तिलीयों से युक्त अशोक चक्र का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है।
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के अंतिम स्वीकारोक्त्ति के पहले, अपनी पहली शुरुआत से ये विभिन्न अद्भुत् बदलावों से गुजरा। ब्रिटिश शासन से आजादी के लिये राष्ट्रीय संघर्ष के दौरान देश को अलग पहचान के लिये राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के आविष्कार और खोज अभियान की शुरुआत हुई।
भारतीय ध्वज का क्रमिक विकास

ऐसा कहा जाता है, कलकत्ता (वर्तमान कोलकाता) के ग्रीन पार्क (पारसी बागान स्क्वैयर) में 7 अगस्त 1906 में राष्ट्रीय झंडे को फहराया गया। ये साधारण रुप से डिज़ाइन किया गया ध्वज था जिसमें तीन रंगों (लाल, पीला, और हरा) से तीन क्षैतिज पट्टीयों का इस्तेमाल किया गया था। सबसे उपरी हरे रंग की पट्टी में 8 सफेद कमल के फूल बने हुए थे। बीच की पीली पट्टी में हिन्दी में “वन्दे मातरम्” लिखा हुआ था और सबसे नीचे की लाल पट्टी में अर्धचन्द्राकार बना हुआ था (किनारे के बाएँ तरफ) और सूरज (दाँयी तरफ)।

इतिहास के मुताबिक, ऐसा कहा गया कि 1907 में अपने निर्वासित क्रांतिकारी मण्डली के साथ मैडामें कामा द्वारा पेरिस में दूसरी बार भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को फहराया गया था। बाद में बर्लिन के सामाजिक सम्मेलन में उसी झंडे को प्रदर्शित किया गया था। पहले से दूसरा ध्वज थोड़ा अलग था। इसमें सबसे ऊपरी पट्टी में नारंगी रंग था जिसमें एक कमल और सात सितारे (भेदक सप्तऋषि) बने थे। मध्य के पीले रंग की पट्टी में हिन्दी में “ वन्दे मातरम् ” लिखा था और सबसे नीचे की हरे रंग की पट्टी में बाँयी तरफ सूरज और दाँयी तरफ अर्धचन्द्र और सितारे बने हुए थे।

इसे तीसरी बार 1917 में डॉ ऐंनी बेसेंट और लोकमान्य तिलक द्वारा होमरुल आंदोलन के दौरान फहराया गया। इसे एकान्तर तरीके में पाँच लाल और चार हरी क्षैतिज पट्टीयों में डिज़ाइन किया गया था। इसमें सात भेदक सप्तऋषि सितारों के साथ बाँये शिखर में एक यूनियन जैक और दाँयी ओर शिखर पर अर्धचन्द्र और सितारा था।

1921 में, भारतीय काँग्रेस कमेटी ने बेजवाड़ा (विजयवाड़ा) में लाल और हरी रंग की दो पट्टीयों वाली ध्वज (जिसमें लाल और हरा रंग हिन्दू और मुस्लिम समुदायों को प्रदर्शित करता है) तैयार की और उसे महात्मा गाँधी के पास ले गये। जहाँ पर उन्होंने बीच में एक सफेद पट्टी (दूसरे समुदायों के लिये) और एक नीले पहिये (चक्र) को लगाने का सुझाव दिया जो राष्ट्र के प्रगति को प्रदर्शित करे।

अंतत:, भारत में तिरंगे झंडे (गाँधी जी के सुझाव पर) को अंगीकृत करने के लिये 1931 में एक प्रस्ताव पास हुआ था। इसमें सबसे ऊपर नारंगी, बीच में सफेद और सबसे नीचे हरा रंग है। बीच की सफेद पट्टी के मध्य में एक घूमता हुआ पहिया बना हुआ है।

हालाँकि, संविधान सभा के सम्मेलन में 22 जुलाई 1947 में इसे पूरी तरह से अपना लिया गया था फिर भी उन लोगों ने ये फैसला किया कि थोड़े बदलाव के साथ राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को स्वीकार किया जाएगा, राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में प्रतीक के रुप में राजा अशोक के धर्म चक्र को घूमने वाले पहिये से बदला गया। यही ध्वज अंतत: आजाद भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज बना।
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज की नियमावली क्या है ?
भारतीय ध्वज राष्ट्रीय गौरव का प्रतीक है जो लोगों की अभिलाषा और उम्मीद को दिखाता है। भारत की आजादी से अभी तक हमारे भारतीय सेनाओं ने दुश्मनों से तिरंगे को बचाया है और इसके सम्मान को बनाये रखा है।
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज की नियमावली पहले से निर्धारित कानूनों का समुच्चय है जो दूसरे देश के लोगों और भारतीयों द्वारा तिरंगे के उपयोग को संचालित करता है। निर्धारित मानकों (1968 में बना और 2008 में सुधार हुआ) के आधार पर भारतीय स्टैंडर्ड ब्यूरो को इसके निर्माण, डिज़ाइन, और सही इस्तेमाल के लिये नियमन करने का अधिकार दिया गया है।
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज नियमावली को 2002 में लिखा गया और उन्हें कुछ धाराओं के साथ मिलाया गया जैसे: “प्रतीकों के प्रावधान और नाम (गलत इस्तेमाल से रोकथाम के लिये) धारा 1950 (1950 का संख्या 12), धारा 1971 के तहत राष्ट्रीय सम्मान को ठेस पहुँचाने से निवारण के लिये (1971 के संख्या 69)। अंततोगत्वा, “भारत, के ध्वज नियमावली 2002” के रुप में 26 जनवरी 2002 में ध्वज नियमावली प्रभावी हुआ। इसके तीन भाग है जैसे कि:
- पहले भाग में राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के सामान्य विवरण दिये हुए है।
- दूसरे भाग में सरकारी, निजी संस्था और शिक्षण संस्थानों द्वारा इसके उपयोग को लेकर दिशा-निर्देश दिये गये है।
- और तीसरे भाग में केन्द्रीय और राज्य सरकार तथा इनकी एजेँसीयों के द्वारा इसके इस्तेमाल को लेकर हिदायत दी गयी है।
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के उपयोग को लेकर सभी नियम, कानून और अधिकार अधिकारिक रुप से भारत के ध्वज कानून के अंतर्गत वर्णित किये गये है जो इस प्रकार है: “ सबसे ऊपरी पट्टी का रंग भारतीय केसरिया और सबसे नीचे की पट्टी का रंग भारतीय हरा होना चाहिये। बीच की पट्टी सफेद होनी चाहिये, तथा इसी पट्टी के मध्य में नीले रंग के चक्र में समान दूरी पर 24 तिलियाँ होनी चाहिये।”
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को यदि किसी के द्वारा खादी या हाथ से बुने हुए कपड़ों के अलावा किसी और कपड़ो का इस्तेमाल करता है तो जुर्माने के साथ तीन साल की सजा का प्रावधान है। ख़ादी के लिये कॉटन, सिल्क और वुल के अलावा किसी और कपड़ों का इस्तेमाल की सख्त मनाही है। दो प्रकार के ख़ादी से झंडा तैयार होता है (ध्वज के ढ़ाँचे को बनाने के लिये ख़ादी ध्वजपट और पोल को थामे रखने के लिये ध्वज के अंतिम छोर को तैयार करने के लिये मटमैले रंग का कपड़ा आर्थात् ख़ादी-ड्क)। साथ ही कपड़े के हर एक स्क्वैयर सेंटीमीटर पर केवल 150 धागे ही रहेंगे, एक सिलाई पर चार धागे और एक स्क्वैयर फीट कपड़े का वजन 205 ग्राम होना चाहिए।
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के नियमावली के नियम और विनियमन क्या है ?
26 जनवरी 2002 के कानून पर आधारित भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज कानून के अनुसार, झंडा फहराने के कुछ कायदे-कानूनों को जरुर ध्यान में रखना चाहिये:
- अपने राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के सम्मान के लिये विद्यार्थीयों के प्रेरणा स्वरुप इसे शिक्षण संस्थानों (जैसे कि स्कूल, कॉलेज, विश्वविद्यालय, खेल कैम्प, स्कॉउट आदि) में फहराने की इज़ाजत दी गयी। झंडा फहराने के साथ ही शिक्षण संस्थानों में संकल्प की प्रतिबद्धता का पालन अवश्य होना चाहिए।
- ध्वज के सम्मान और गरिमा का ध्यान रखते हुए किसी भी राष्ट्रीय अवसर पर सरकारी या निजी संस्थान द्वारा राष्ट्रीय ध्वज को फहराया जा सकता है। नये नियम के सेक्शन 2 के अनुसार, आम आदमी भी अपने परिसर के अंदर झंडा फहरा सकता है।
- ध्वज का किसी सांप्रदायिक या व्यक्तिगत लाभ के लिये कपड़े के रुप में इस्तेमाल नहीं करना है। इसे कहीं भी केवल सूर्योदय से सूर्यास्त के समय तक फहराना है।
- इसको जानबूझकर ज़मीन, फर्श या पानी में घसीटना नहीं है।
- किसी भी स्थिति में इसका इस्तेमाल कार, हवाई जहाज़, ट्रेन, बोट आदि के ऊपर, नीचे या किनारों को ढ़कने के लिये नहीं होना चाहिये।
- यदि कोई राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के साथ किसी दूसरे ध्वज का उपयोग कर रहा/रही है तो उसे इस बात का एहसास जरुर होना चाहिए कि किसी दूसरे ध्वज की ऊँचाई हमारे राष्ट्रीय ध्वज से अधिक नहीं होनी चाहिए। कोई भी इसके ऊपर नहीं रखा जा सकता या इसे सज़ावट के लिये इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता।
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज के बारे में महात्मा गाँधी के विचार
“सभी राष्ट्रों के लिये ध्वज जरुरी है। लाखों इसके लिये कुर्बान हुए। इसमें कोई शक नहीं कि एक प्रकार की मूर्तिपूजा है जो पाप का नाश करने के लिये होगी। ध्वज आदर्श को प्रस्तुत करता है। यूनियन जैक का फहराना अंग्रेजी अन्त:करण भावनाओं को उत्पन्न करता है जिसकी मजबूती को मापना कठिन है। अमेरिकन के लिये सितारे और पट्टी एक दुनिया है। इस्लाम में सर्वोच्च बहादुरी सितारों और अर्धचन्द्र को आगे ले जाना है”
“ये हमारे लिये जरुरी है कि भारतीय मुस्लिम, ईसाई, यहूदी, पारसी और उन सभी के लिये जो भारत को अपना घर मानते है एक ध्वज के लिये जीयें और मरें। ”-महात्मा गाँधी
भारतीय ध्वज से संबंधित भाव
- मै तब हाई स्कूल में था जब पंडित नेहरु ने नई दिल्ली में झंडा फहराया था- ए.पी.जे.अब्दुल कलाम
- “शांति और समरसता में जीने के लिये, एकता और मजबूती, के साथ हमें एक लोग, एक राष्ट्र और एक ध्वज को मानना चाहिये।“- पॉलिन हैंसन
- “मेरा मानना है कि हमारा ध्वज कपड़े और स्याही से कुछ ज्यादा है। ये विश्वभर में पहचाने जाने वाला प्रतीक है जो उदारता और आजादी के लिये खड़ा होता है। ये हमारे राष्ट्र का इतिहास है, और ये उनके खून से लिखा हुआ है जो इसे बचाने मे शहीद हुए।“- जॉन थुने
- “हमारा ध्वज बहुत राजनीतिक विचारों में केवल एक नहीं है, बल्कि, ये हमारी राष्ट्रीय एकता की पहचान है।”- एंड़्रियन क्रोनाउर
- “हमारा ध्वज उनका सम्मान करता है जो इसकी सुरक्षा के लिये लड़ते है, और हमारे राष्ट्र के निर्माणकर्ताओं के बलिदान को याद दिलाता है। अमेरिका के ऐतिहासिक कहानियों के सर्वश्रेष्ठ प्रतिरुप के रुप में इस राष्ट्र के सबसे उत्कृष्ठ सितारों और पट्टीयों को प्रदर्शित करते है। ”- जो बार्टोन
- “क्या बची हुई उम्मीद है लोगों की ? एक देश, एक भाषा, एक ध्वज! ”- एलेक्जेंडर हेनरिक
- “एक देशभक्त और नागरिक होने से ज्यादा ध्वज को उठाना और संकल्प लेने में है।”- जेसे वेनचुरा
- “र्निदोष लोगों की हत्या के शर्म को ढ़कने के लिये कोई भी बड़ा ध्वज कम पड़ जाएगा। ”-हॉवर्ड जिन्न
- “ध्वज को लहराने में देशभक्ति नहीं होती, लेकिन इस प्रयास में कि हमारा देश अवश्य ईमानदार और मजबूत होना चाहिये।”- जेम्स ब्रिस
- “हम अपना सिर! और हमारा दिल! देते है अपने देश को! एक देश! एक भाषा! एक ध्वज! ”-कर्नल जॉर्ज.टी.बाल्क “दिलों का संयोजन, हाथों का मिलन और एकता का ध्वज हमेशा के लिये। ”- जार्ज पोप मॉरिस
- “चलिये एक ही ध्वज के तहत जन्म ले जिसमें हम हर आवश्यकता में रैली करें, हमारा एक देश है, एक संविधान है, एक किस्मत है। ”- डेनियल वेबस्टर
- “हमारे पास केवल एक ध्वज है, एक देश है; चलिये एक साथ होते है। हमलोग रंगों में अलग हो सकते है लेकिन भावनाओं में नहीं। बहुत कुछ मेरे बारे कहा गया है जो गलत है और जो श्वेत और काले लोग यहाँ है, जो कि शुरु से अंत तक युद्ध में मेरे साथ रहे, मेरा खंडन कर सकते है। ”- नॉथन बेडफोर्ड फौरेस्ट
गणतंत्र दिवस
गणतंत्र दिवस पर निबंध
गणतंत्र दिवस पर भाषण
गणतंत्र दिवस पर कविता
गणतंत्र दिवस परेड
संबंधित पोस्ट

भारत के राष्ट्रीय प्रतीक
भारत के राष्ट्रपति (presidents of india).

भारत के प्रधानमंत्री

भारत का राष्ट्रगीत – वन्दे मातरम्

भारत का राष्ट्रगान (जन गण मन)

- वर्ल्ड लाफ्टर डे “World Laughter Day” पर प्रश्न और उत्तर
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय खदान जागरूकता दिवस के बारे में प्रश्न और उत्तर
- “23 अप्रैल” हनुमान जयंती 2024:- पवनपुत्र हनुमान जी पर प्रश्न और उत्तर
- पृथ्वी दिवस क्विज 2024: महत्वपूर्ण जीके प्रश्न और उत्तर पृथ्वी पर हिंदी में
- “21अप्रैल” जानिये राष्ट्रीय सिविल सेवा दिवस (National Civil Service Day) क्या है ख़ास और क्विज
Best for GK , Current Affairs , Samanaya Gyan in Hindi
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज और इसका इतिहास सम्पूर्ण जानकारी हिंदी में
Complete information about of indian flag in hindi, history of indian flag, essay on indian flag.
हम सब जानते है की हर स्वतंत्र देश का अपना झंडा (ध्वज) होता है जो उस देश की पहचान होती है हर आजाद देश के राष्ट्रिय ध्वज का अपने आप में अलग अलग अभिप्राय होता है।
भारत का ध्वज (तिरंगा झंडा) एवं इसके चिन्ह की जानकारी – Information about India’s flag and its symbols in Hindi
वहीँ तीन रंगों केसरिया, सफेद और हरे से मिलकर बने भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज जिसे तिरंगा भी कहते है। जोकि हर भारतीय नागरिक के आन वान और शान है, जिसके लिए वीरों ने अपनी जान तक कुर्वान की है । जिसकी अभिकल्पना पिंगली वैंकैया ने की थी। तो आइये जानें भारत के तिरंगे के इतिहास व् उसके सभी रंगों के बारे में विस्तार से जानकारी।
भारतीय तिरंगे की जानकारी – Information about the Indian Tricolor
स्वतंत्र भारत देश के राष्ट्रिय ध्वज की कुल लम्बाई एवं चौड़ाई का अनुपात 2/3 है। भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज में सबसे प्रथम केसरिया, बीच में सफ़ेद व सबसे नीचे हरा रंग होता है। भारत के राष्ट्रिय ध्वज के सभी रंगों का अपने में अलग अलग मतलब है ।
भारतीय ध्वज के रंगों की जानकारी – Information about the colors of the Indian flag
- भारत के ध्वज में सबसे उपरी भाग में केसरिया रंग होता है जो देश की ताकत एवं साहस का परिचायक है।
- बीच में सफ़ेद रंग की पट्टी शांति एवं सत्यता को दर्शाती है।
- और भारत के ध्वज में सबसे निचले भाग में हरे रंग की पट्टी धरती की उर्वरता, विकास एवं पवित्रता की परिचायक है।
भारतीय ध्वज में अशोक चक्र का मतलब – The meaning of Ashok Chakra in the Indian flag
भारतीय तिरंगे में सफ़ेद रंग के बीच में एक चक्र बना हुआ होता है जिसमे 24 तीलियाँ होती है ये चक्र इस बात को दर्शित करता है कि जीवन गतिमान है जबकि मृत्यु निश्चलता का नाम है।
भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का इतिहास – History of the National Flag of India
भारत का प्रथम राष्ट्रिय ध्वज 1904 से 1906 के बीच बनाया गया जिसे स्वामी विवेकानंद की आयरिश भक्त भगिनी निवेदिता ने बनवाया था। जिसे आगे भगिनी निवेदिता ध्वज के नाम से भी जाना गया था। भगिनी निवेदिता ध्वज में लाल और पीले रंग की पट्टियाँ थी। जिसमे लाल रंग आज़ादी के संघर्ष और पिला रंग जीत को दर्शाता था। भगिनी निवेदिता ध्वज में लाल और पीले रंग की पट्टियाँ थी। और वज्र, हथियारों के देवता ‘इंद्र’ और ध्वज के मध्य कमल को दर्शाया गया था। बता दे कि भारत में यह पहले ध्वज नहीं है इससे पहले भी कई ध्वज रह चुके हैं भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का विकास आज के इस रूप में पहुंचने के लिए अनेक दौरों में से गुजरा। आइयें जाने
1907 में पेरिस में मैडम कामा द्वारा दूसरा राष्ट्रिय ध्वज लहराया गया था। जिसमे उपरी रेखा की जगह एक कमल और स्टार था।
1917 तीसरा ध्वज में लहराया गया जिसमे पाँच लाल और चार हरी रेखाए थे वही इसके दाहिने हाथ के उपरी किनारे पर एक यूनियन जैक (एकता चिन्ह) भी था।
1921 में महात्मा गांधीजी जी को बेजवाडा में होने वाली ऑल इंडिया कांग्रेस कमिटी में आंध्र के कुछ युवको एक ध्वज बनाकर सौपा। इस ध्वज में लाल और हरे दो रंग थे जो हिन्दू और मुस्लिम पर आधारित था ।
1931 में स्वर्णिम युग का ध्वज आज के ध्वज की तरह जहा उपर केसरिया, बीच में सफ़ेद और फिर हरा रंग और ध्वज के मध्य महात्मा गांधी जी का चरखे का चिन्ह था।
22 जुलाई 1947 में भारत के ध्वज को निर्वाचक असेंबली स्वीकार और भारत की आजादी होने पर महात्मा गांधी जी के चरखे की जगह अशोक चक्र को भारत के ध्वज के बीच में चिन्निहित किया गया।
भारत देश में अक्सर किसी राष्ट्रिय या निजी परेड, कार्यक्रम, जलूस आदि में ध्वज को सम्मान के साथ फेहराया जाता है जैसे गणतन्त्र दिवस, स्वंत्रता दिवस, स्कूल फंक्शन आदि में।
हमे उम्मीद है की अपने यहाँ से “भारत के राष्ट्रीय ध्वज ” से संबधित सही और सटीक सामान्य ज्ञान जानकारी अर्जित की होगी यदि फिर भी कुछ ऐसा जो हमने यहाँ गणतंत्र दिवस के बारे में कुछ प्रकाशित नहीं किया या कुछ सुधार करना हो तो कृपया आप हमे ईमेल करे।
भारत का राष्ट्रीय प्रतीक
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Hp 10th result 2024.
- CBSE 10th Result 2024
- CBSE 12th Result 2024
- HP Board Result 2024
- CG Board Result 2024
- CISCE Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- general knowledge
Flag Of India: Complete Journey of Indian National Tricolour
Republic day 2024: every year on the occasion of republic day, the president of india unfurls the tricolour on the red fort. this article will help you know the rich history behind the evolution of the national flag. let us have a look at the history and journey of the evolution of the indian national flag and when it was adopted in its present form..

Republic Day 2024: Republic Day marks and celebrates the date on which the Constitution of India came into effect on 26 January 1950. It replaced the Government of India Act 1935 as the governing document of India, thus turning the nation from a dominion into a republic separate from British Raj. Republic Day was established on January 26, 1930, the day the Indian National Congress proclaimed the Declaration of Indian Independence. This year, marks the 75th anniversary of Republic Day and it will be celebrated with themes, "Viksit Bharat" (Developed India) and "Bharat - Loktantra ki Matruka" (India - Mother of Democracy).
This article will help you know about the history of India's tricolour.
About National Flag
The National Flag of India has a horizontal strip of three colours including deep saffron (Kesaria) at the top, white in the middle, and dark green at the bottom. The ratio of the flag width to its length is 2:3. In the white band, at the centre, a Navi-blue wheel is there which represents the chakra.
- The top saffron colour indicates the strength and courage of the country.
- The white middle band indicates peace and truth with Dharma Chakra.
- The green shows the fertility, growth, and auspiciousness of the land.
- The design of the wheel appears like the wheel on the abacus of the Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka. Its diameter is approximately the width of the white band and it has 24 spokes.
Let us tell you that on 22 July 1947, the design of the National Flag was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India.
Now, we shall study the evolution or Journey of the tricolour National Flag of India
Several changes took place in our National Flag since its first inception. Through several vicissitudes, our National Flag evolution sailed to arrive at what it today is. We can say that it reflects the political developments in the nation. The historical milestones in the evolution of the National Flag are as follows:
1. The evolution of the Indian flag dates back to the pre-independence era. In 1904-1906 , the first Indian flag came into existence and it was made by an Irish disciple of Swami Vivekananda, Sister Nivedita. After some time the flag came to be known as Sister Nivedita's flag . The flag is comprised of red and yellow colours. Red signified the freedom struggle and yellow, is a symbol of victory. In Bengali words "Bonde Matoram" was written. It also contained a figure of 'Vajra', the weapon of the god 'Indra', and a white lotus in the middle. The symbol 'Vajra' depicts strength and lotus purity.
2. Another flag was also designed in 1906 . It was a tricolour flag with three equal strips of blue at the top, yellow in the middle, and red at the lower. The blue strip consists of eight stars of slightly different shapes. The red strip had two symbols, one of the sun and the other of a star and a crescent moon. In the yellow strip, 'Vande Mataram' was written in the Devanagari script.
3. On 7 August 1906 , the first unofficial national flag in India have bee
n hoisted in the Parsee Bagan Square (Green Park) in Calcutta now Kolkata. The flag consists of three horizontal stripes of red, yellow, and green colour. It came to be known as 'Calcutta Flag or 'Lotus Flag' . In the middle of it is written Vande Matram. The red strip had two symbols, one of the sun and the other a crescent moon. The green strip had eight half-open lotuses on it. It is believed that the flag was designed by Sachindra Prasad Bose and Sukumar Mitra. Let us tell you that the unfurling of the flag was being observed as "boycott day" against the partition of Bengal and the flag was hoisted by Surendranath Banerjee to mark the unity of India.

4. On 22 August 1907 , the flag was unfurled by Madam Cama at Stuttgart, Germany. It is believed that the flag was collectively designed by Madam Cama, Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, and Shyamji Krishna Varma. The flag attained the status of the first Indian flag that was hoisted in a foreign land. It was also referred to as the "Berlin Committee flag". The flag was similar to the first flag except that the top strip. It also consists of three colours namely green at the top, golden saffron in the middle, and red colour at the bottom.

5. In 1916 Pingali Venkaya also designed a flag after approval from Mahatma Gandhi. Pingali Venkaya was a writer and a geophysicist. Mahatma Gandhi told him to incorporate a charkha in the flag as a symbol of the economic regeneration of India. He created a flag from handspun yarn 'Khadi' and had two colours namely red and green and the 'Charkha' was drawn across them. But Mahatma Gandhi did not approve it. According to him, the red represented the Hindu community and the green Muslims, but the other communities of India were not represented in the flag.
6. In 1917 , the Home Rule League adopted a new flag. Let us tell you that the Home Rule League was formed by Bal Gangadhar Tilak. It was the time when Dominion status was being demanded in India. The flag consists of the Union Jack at the top, near the hoist. The rest of the flag had five red and four blue strips. In the shape of the 'Saptarishi' constellation, it had seven stars. It consists of a crescent moon and a star at the top fly end. But this flag did not gain popularity among the masses.

7. In the All India Congress Committee session which took place at Bezwada in 1921 (now Vijayawada) an Andhra youth prepared a flag and took it to Gandhiji. The flag was made up of two colours red and green that represent the two major communities Hindus and Muslims. At that time Gandhiji suggested adding a white strip in the flag that will represent the other communities of India and the spinning wheel to symbolise the progress of the nation. We can say that the flag was unofficially adopted in 1921.

8. In the history of the flag, 1931 year is important. This year, a resolution was passed of adopting a tricolour flag as our national flag. It consists of three colours including saffron, white, and green with Mahatma Gandhi's spinning wheel at the centre. It also stated that it bore no communal significance and was to be interpreted thus. Therefore, we can say that this flag was adopted in 1931.

9. The Constituent Assembly on 22 July 1947 adopted it as Free India National Flag. After Independence, the colours and significance remained the same. Only the change that took place was instead of the spinning wheel, the Dharma Chakra of Emperor Ashoka was adopted as the emblem of the national flag. Eventually, the tricolour flag of the Congress Party became the tricolour flag of Independent India.

What is Flag Code?
The Flag Code of India was modified on 26 January 2002 and after several years of independence; Indian citizens were finally allowed to hoist the flag of India over their homes, offices, and factories on any day and not just the National days as was the case earlier. According to the flag code, any Indian can proudly display the national flag anywhere and anytime, but should not disrespect the tricolour. Therefore, the Flag Code of India, 2002, has been divided into three parts. In Part, I, a general description of the National Flag is given. In Part II, it is mentioned that the display of the National Flag members of the public, private organisations, educational institutions, etc. In Part III, the display of the National Flag by Central and State Governments and their organisations and agencies. Let us tell you that there are some rules and regulations on how to fly the flag according to the 26 January 2002 legislation.
Get here current GK and GK quiz questions in English and Hindi for India , World, Sports and Competitive exam preparation. Download the Jagran Josh Current Affairs App .
- IPL Schedule 2024
- Fastest 50 in IPL 2024
- India T20 World Cup Squad 2024
- World Press Freedom Day 2024 Theme
- IPL 2024 Points Table
- Hanuman Jayanti 2024
- Ram Navami 2024
- Purple Cap in IPL 2024
- HP Board 10th Result 2024
- tnresults.nic.in 2024
- India Events
- History Facts
Latest Education News
HPBOSE Class 10th Result 2024 OUT:हिमाचल बोर्ड के नतीजे जारी, 74 फीसदी हुए पास , लिंक एक्टिव होने में लगेगा समय
HP Board Class 10 Result 2024 OUT with Jagran Josh: Check Your HPBOSE 10th Result Quickly Here!
HPBOSE HP Board 10th Topper List 2024: एचपी बोर्ड 10वीं में रिद्धिमा शर्मा ने किया टॉप , यहां देखें पूरी लिस्ट
[CHECK LINK] HP Board 10th Result 2024 Released: Check HPBOSE 10th Results at hpbose.org with Roll No, 74% Student Pass and Toppers List
[रिजल्ट लिंक] HPBOSE 10th Result 2024 OUT LIVE: एचपी बोर्ड धर्मशाला दसवीं का रिजल्ट hpbose.org पर Roll Number से करें चेक
HP Board 10th Topper List 2024 OUT: Ridhima Sharma Tops HPBOSE Class 10 Exam, Check Toppers Name, School-wise and District Details
HPBOSE 10th Result 2024 OUT: Where and How to Check HP Board Class 10 Results Online
[Result LINK] hpbose.org 10th Result 2024 Declared: Official Site to Check HP Board 10th Result and Download Marksheet
HP Board 10th Result 2024 Link जारी: रोल नंबर के साथ हिमाचल बोर्ड कक्षा 10 के परिणाम ऑनलाइन चेक करें, देखें Steps
[डायरेक्ट लिंक] hpbose.org 10th Result 2024 OUT: परिणाम जारी, टॉप 10 में 72 लड़कियां, तुरंत डाउनलोड करें मार्कशीट
NEET 2024 Answer Key: Download Question Paper Solution in PDF (All Sets)
DU Result 2024 OUT on exam.du.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
RPSC Sr Teacher Counselling Schedule 2024 Released at rpsc.rajasthan.gov.in: Here's Latest Update
Find 3 Differences Within This Fruit Harvesting In 24 Seconds
HPBOSE Result 2024 Roll Number: Easy Steps to Check Your HP Board 10th Results Online with Name and Other Details Here
[यहां देखें] HPBOSE Result 2024: Check हिमाचल प्रदेश बोर्ड Result Online at Jagran Josh and hpbose.org
[CHECK] HPBOSE 10th Result 2024: हिमाचल प्रदेश बोर्ड Class 10 Result Online at Jagran Josh and hpbose.org
HP Board 10th Result 2024 Today at 10:30 AM, Check HPBOSE Result Latest Updates at hpbose.org
(Updated) RR vs DC Head to Head in IPL: Check Stats, Records and Results
SSC GD Result 2024 Live: Constable Results on ssc.gov.in; Check Expected Cut Off, Merit List Date, Marking Scheme
Journey of the Indian National Flag – Its History & Significance

We are always interested to know about the journey of celebrities, film stars, sports personalities, etc but how many of us are aware of the Journey of the Indian National Flag?
When someone says the National Flag of India, the first thing that comes to our mind is ‘the horizontal tricolors with saffron at the top, white in the middle, and dark green at the bottom. And a navy-blue wheel in the center of the white band in the middle.’
But there is more to it.
Before going into the evolution of the Indian Nation Flag. Let’s explore all the details and descriptions of the National Flag of India in today’s time.
National Flag of India
#1 unofficial flag of india in 1906 – calcutta flag, #2 the berlin committee flag, #3 the flag used during home rule movement in the year 1917, #4 the flag unofficially adopted in the year 1921, #5 the flag adopted in 1931, #6 the present tricolour flag of india – the national flag of india, colors and meaning of the indian national flag, the indian flag code: do’s and don’ts, who designed the indian national flag, what is the ratio of the length and width of the indian national flag, who suggested ashoka chakra in the indian flag, what is a half-mast flag.
As per the official website ,
The National Flag is a horizontal tricolor of India saffron (kesaria) at the top, white in the middle and India green at the bottom in equal proportion. The ratio of width of the flag to its length is two to three. In the center of the white band is a navy-blue wheel with 24 equally spaced spokes which represents the Ashoka Chakra. The design of the National Flag was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India on 22 July 1947. knowindia.india.gov.in

A detailed explanation of the Indian National Flag…
The National Flag is a horizontal tricolor of deep saffron (kesaria) at the top, white in the middle, and dark green at the bottom in equal proportion. The ratio of the width of the flag to its length is two to three. In the center of the white band is a navy-blue wheel that represents the chakra.
The top saffron color indicates the strength and courage of the country. The white middle band indicates peace and truth with Dharma Chakra. The green shows the fertility, growth, and auspiciousness of the land.
Its design is that of the wheel which appears on the abacus of the Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka. Its diameter approximates the width of the white band and it has 24 spokes. The design of the National Flag was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India on 22 July 1947.
It is really amazing to see the various changes that our National Flag went through since its first inception. It was discovered or recognized during our national struggle for freedom. The evolution of the Indian National Flag sailed through many vicissitudes to arrive at what it is today.
History, Evolution and Journey of Indian National Flag

Indian National Flag is not just a flag made of cloth; it is a symbol of our nation’s struggle for Independence. In this post, we attempt to throw light on the journey of our nation’s most precious treasure.
It will be necessary for us Indians – Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Jews, Parsis and all others to whom India is their home – to recognize a common flag to live and die for. Mahatma Gandhi
The journey began in the year 1906 when the first unofficial Indian National Flag was hoisted in the Parsee Bagan Square of Kolkata.
This flag which was composed of three horizontal stripes of red, yellow, and green was also known as the Calcutta flag.

The second flag was unfurled in the year 1907 in Paris by one of the most prominent Indian freedom fighters, Madame Cama along with her band of exiled revolutionaries.
This was also the first time an Indian Flag was being hoisted on foreign soil. Co-designed by Cama, Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, and Shyamji Krishna Varma, it was famously known as the Saptarishi flag.

The third flag was hoisted by a British socialist, Dr. Annie Besant, and the “Father of the Indian unrest”, Lokmanya Tilak in the year 1917 .
This flag was different from the previous two flags; it had five red and four green horizontal strips arranged alternately, with seven stars in the Saptarishi configuration super-imposed on them.
In the left-hand top corner was the Union Jack. There was also a white crescent and star in one corner. This flag, however, was not able to gain popularity among the masses.

The fourth flag was designed in the year 1921 by Pingali Venkayya who was an Indian freedom fighter from the city of Vijayawada of Andhra Pradesh.
It was initially made of two colors- red and green which represented Hindus and Muslims.
However, on the suggestion of Mahatma Gandhi, a white stripe was added to represent the remaining communities of India along with a spinning wheel to signify the progress of the nation.

The fifth flag was adopted in the year 1931 as some people disagreed with the communal interpretation of the flag of 1921; therefore the red color was replaced with saffron which is a symbol of both Hindu yogis as well as Muslim darvesh.

And finally, the Tiranga was adopted on July 22, 1947 , after India got independence.
Tiranga is a modification of the flag of 1931 where Charkha was replaced with Chakra and this is how our Indian National Flag completed its journey.

Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru proposed the flag at the Constituent Assembly on 22 July 1947.
It is a horizontal tricolor of deep saffron, white and dark green, with the Ashoka wheel in blue in the center of the white band.
Nehru presented two flags to the assembly. One was in khadi silk and the other in khadi cotton. The resolution was approved unanimously. Nehru’s choice of the flag as the national flag of India continues today.
It’s been the national flag of the Dominion of India from 15 August 1947 to 26 January 1950 and has served as the flag of the Republic of India since then.
The national flag of India is a tri-colored flag, with the national colors of saffron (yellow) in the top band, white (middle band), and green (lower band) at the bottom.
The Saffron in the top band represents the strength and courage of the country.
The White band symbolizes peace and truth with Dharma Chakra.
The green band at the bottom represents the fertility, growth, and auspiciousness of the land.
Dharmachakra in the middle represents the “wheel of the law”. The wheel of dharma, or the wheel of the law, represents life in movement and death in stagnation.
Here are HEX and RGB codes of the Indian National Flag color scheme,
- Colour scheme – Orange (Saffron) | White | Green | Navy Blue
- HEX – #FF9933 | #FFFFFF | #138808 | #000080
- RGB – 255-153-51 | 255-255-255 | 19-136-8 | 0-0-128
Indian National Flag represents the hopes of countless Indians. It is the symbol of national pride. Insulting and disrespecting the national flag is an offense that is punishable under the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971 .
Originally the Indian National Flag code restriction didn’t permit civilians to fly the national flag except on national holidays such as Independence Day and Republic Day .
In 2002, the original Indian Flag Code was amended to allow individuals to hoist the flag on any day, subject to their liberty in protecting the dignity, honor, and respect of the flag.
Based on 26 January 2002 legislation ( The Flag Code of India, 2002 ) there are some rules to fly the Indian National Flag:

- The National Flag of India should be rectangular in shape and should be made of hand-spun and hand-woven wool/cotton/silk. The ratio of the length and width of the flag should be 3:2.
- The saffron band should always be placed at the top.
- The Flag should be flown in public only between sunrise and sunset.
- Displaying a damaged flag is an act of disrespect.
- The National Flag may be flown in educational institutions on special occasions to inspire respect for the Flag. An oath of allegiance to the Flag has been included in the flag-hoisting ceremony.
- You can’t put any objects on top of the tricolor, including flowers, garlands, or symbols.
- The Flag should never be used for commercial purposes without the government’s permission.
- The Indian flag is forbidden to touch the ground, floor, or water. It cannot be draped over the hood, top, and sides or back of any vehicle, train, boat, or aircraft.
- Plastic flags should not be used because they are not biodegradable. Further, the disposal of plastic flags is a problem, with dignity.
- The national flag is only to be used as a flag for the country.
- It’s never to be used for decorations or as a festoon, rosette, or bunting. No other colors are allowed to be combined with it.
- The flag should never be flown at half-mast. In the event of the death of a dignitary such as the Prime Minister, this rule does not apply entirely.
A flag not only of freedom for ourselves, but a symbol of freedom to all people. Jawaharlal Nehru
Times have come where people have started to define Independence Day as merely a day when people change their WhatsApp display picture to Indian Flag.
Flags can be found lying around street corners on the next day. That needs to change.
Our flag is a symbol of our freedom, unity, and abilities. Respect and only utmost respect is what it deserves.
FAQs – Indian Nationa Flag
Let’s take a look at some Frequently Asked Questions about the Indian flag and its history –
Pingali Venkayya designed the National Flag of India. While the flag has undergone changes in the past decades, it was Pingali Venkayya who presented it to the All India Congress Committee in 1921. During that session, he suggested that the flag be made of two colors: Red and Green, representing the two main communities i.e. Hindus and Muslims.
The National Flag shall be rectangular in shape. The ratio of the length and width of the Indian National Flag should be 3:2.
Mahatma Gandhi first spoke about the need for an Indian flag in 1921 in his journal, Young India. He proposed a flag with the spinning wheel (Charkha) at the center.
When the flag is to be flown at half-mast, the position of the flag is about halfway up a mast or pole and then slowly lowered. The flag is flying from the middle of the pole, not the top. At the half-mast position, the flag signifies state mourning.
Share this article
10+ New Year Resolution Ideas You Should Consider in 2023 & Learn on How to Stick to Your Resolutions

How to look Intelligent / Intellectual – Step by Step Guide

Kakori Conspiracy (Kakori Kand day) – Kakori Ke Veeron Se Parichay


Here’s Why 8th March The Women’s Day Does Not Define Me

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Notify me when new comments are added.
Sign me up for the newsletter.
- International
- Today’s Paper
- Premium Stories
- Express Shorts
- Health & Wellness
- Board Exam Results
- Brand Solutions
Explained: How did India get its national flag?
The final design of the indian national flag, hoisted by pm nehru on august 16, 1947 at red fort, had a history of several decades preceding independence..
On July 22, 1947, when members of the Constituent Assembly of India met in the Constitution Hall in Delhi, the first item on the agenda was reportedly a motion by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, about adopting a national flag for free India.
It was proposed that “the National Flag of India shall be horizontal tricolour of deep saffron (kesari), white and dark green in equal proportion.” The white band was to have a wheel in navy blue (the charkha being replaced by the chakra), which appears on the abacus of the Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka.

While the finer nuances were subsequently discussed in the meeting, the final design of the Indian National Flag, hoisted by Prime Minister Nehru on August 16, 1947 at Red Fort, had a history of several decades preceding independence.
The first national flag of India
While an Indian flag was reportedly designed by Sister Nivedita, an Irish disciple of Swami Vivekananda, between 1904-1906, arguably the first national flag of India is said to have been hoisted on August 7, 1906, in Kolkata at the Parsee Bagan Square (Green Park).
It comprised three horizontal strips of red, yellow and green, with Vande Mataram written in the middle. Believed to have been designed by freedom activists Sachindra Prasad Bose and Hemchandra Kanungo, the red strip on the flag had symbols of the sun and a crescent moon, and the green strip had eight half-open lotuses.

Next year, in 1907, Madame Cama and her group of exiled revolutionaries hoisted an Indian flag in Germany in 1907 — this was the first Indian flag to be hoisted in a foreign land.
In 1917, Dr Annie Besant and Lokmanya Tilak adopted a new flag as part of the Home Rule Movement. It had five alternate red and four green horizontal stripes, and seven stars in the saptarishi configuration. A white crescent and star occupied one top corner, and the other had Union Jack.
Also in Explained | How the Quit India movement gave a new direction to India’s freedom struggle
The origins of the present-day flag
The design of the Indian tricolour is largely attributed to Pingali Venkayya, an Indian freedom fighter who reportedly first met Mahatma Gandhi in South Africa during the second Anglo-Boer War (1899-1902), when he was posted there as part of the British Indian Army.
Years of research went into designing the national flag. In 1916, he even published a book with possible designs of Indian flags. At the All India Congress Committee in Bezwada in 1921, Venkayya again met Gandhi and proposed a basic design of the flag, consisting of two red and green bands to symbolise the two major communities, Hindus and Muslims. Gandhi arguably suggested adding a white band to represent peace and the rest of the communities living in India, and a spinning wheel to symbolise the progress of the country.

Several changes continued to be made till a decade later, when in 1931 the Congress Committee met in Karachi and adopted the tricolour as our national flag. Red was replaced with saffron and the order of the colours was changed. The flag was to have no religious interpretation.
📣 Express Explained is now on Telegram . Click here to join our channel (@ieexplained) and stay updated with the latest
A Flag for Independent India
The Tricolour was altered to become the flag of Independent India. Saffron on top symbolises “strength and courage”, white in the middle represents “peace and truth” and green at the bottom stands for “fertility, growth and auspiciousness of the land”. The Ashok Chakra with 24 spokes replaced the spinning wheel as the emblem on the flag. It is intended “to show that there is life in movement and death in stagnation”.
Controversies regarding its creator
In 2013, a controversy arose when historian Panduranga Reddy stated that the national flag was designed by Hyderabad -born Surayya Tyabji. With the resolution in the Constituent Assembly mentioning no names, the attributions are open to argument. While there is no consensus on who recommended the change from charkha to the Ashok Chakra in 1947, in 2018, in an article titled “How the Tricolour and Lion Emblem Really Came to Be”, Laila Tyabji, founding member of crafts NGO Dastkar, wrote that her parents, Badruddin and Surayya Tyabji, had suggested the change.
The website of the Flag Foundation of India, a non-profit organisation formed by industrialist and Congress politician Naveen Jindal, states, “The design of the National-flag for Independent India submitted by Mrs. Suriaya Badr-ud-Din Tyabi was finally approved and accepted by the Flag Committee on 17th July 1947. She was an artist of repute and her husband B.H.F.Tyabji (ICS) was then a Deputy Secretary in the Secretariat of the Constituent Assembly.”
- Why Congo's latest Mpox outbreak is concerning
- The flight of Prajwal Revanna: How diplomatic passports, visa regimes work
- Why is a Reliance Capital Ltd investor challenging its resolution plan?
Venkayya, who passed away in 1963, was posthumously honoured with a postage stamp in 2009 for his contribution towards Indian freedom struggle. In 2014, his name was also proposed for the Bharat Ratna.

Laapataa Ladies: A fantasy by those who have never lived Subscriber Only

What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and why are people Subscriber Only

Modi appears to be throwing away his own lead in Subscriber Only

The clean energy transition has become messy Subscriber Only

Message from Rae Bareli, Amethi: Rahul Gandhi de-risks, Priyanka still Subscriber Only

Though not a native to India, gulmohar trees have become Subscriber Only

How Real Madrid went from the dizzying days of Galacticos Subscriber Only

UPSC Key | Artificial General Intelligence, Tiger translocation, India-Myanmar Relations Subscriber Only

Heeramandi: Sanjay Leela Bhansali directs the most offensive scene of
- Express Explained
- Independence Day
- Vande Mataram

MI rises from bottom to 9th in IPL 2024 points table after 4th win, while Gujarat Titans remain at 10th. KKR takes top spot after demolishing Lucknow Super Giants, followed by RR, CSK, and SRH. Top four teams will qualify for playoffs, with top two playing in first Qualifier and winner advancing to final. Next match: Delhi Capitals vs Rajasthan Royals on Tuesday.

More Explained

Best of Express

EXPRESS OPINION

May 07: Latest News
- 01 Nearly half of MPs who represented Mumbai since 1951 were non-Marathis
- 02 Unused EU recovery funds should go towards defence, Polish ministers say
- 03 IPL 2024 Purple cap update: Jasprit Bumrah extends lead at the top after MI vs SRH
- 04 Holocaust researchers use AI to search for unnamed victims
- 05 Russian drone attack disrupts power supply to parts of Ukraine’s Sumy region
- Elections 2024
- Political Pulse
- Entertainment
- Movie Review
- Newsletters
- Gold Rate Today
- Silver Rate Today
- Petrol Rate Today
- Diesel Rate Today
- Web Stories
Read-Write-Smile-Listen-Love
Find me on Plurk

Find me on Facebook

- October 2018
- August 2018
- November 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- August 2015
- December 2014
- October 2014
- February 2014
- December 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- September 2012
- August 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- November 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
Journey of Indian Flag
Before moving on to the history of Indian flag, let me answer,
Why Do Countries Need a Flag? Each country needs a flag as a visual representation of its people—and to distinguish it from other nations. A flag is also a code of honor. When anyone sees an Indian flag, he gets reminded of a country called the India and its people.
Where on earth did the word flag come from? From Vexillum, a latin word meaning flag or banner. Over 4,000 years ago, the first flags were called vexilloid and they were made of metal or wooden poles with carvings.
They helped ancient armies coordinate on the battlefield—identify the allies from the enemies. They were also used to honor those who lost their lives in the fight.
Today, every country has a national flag made of fabric. It is hoisted on a flagpole and flown so that everyone can be reminded of the values and history of the country.
Flying a flag is also a way to show pride and ownership. If you find a building anywhere in the world with the Indian flag, you can be sure it is Indian territory—a consulate, embassy, or headquarters.
A country’s flag also helps to unite people. By having the same flag, we Indians have a common symbol to bring us closer together—at home or abroad.
Flags show ideas which would otherwise take many words. On sad occasions, country flags are flown at half-mast to honor the dead, and draped over the coffins of national heroes.
Countries usually design their flag with certain colors or shapes to stand for specific meanings. Sometimes, a flag is altered to represent new messages or events. And so is the Indian flag, altered at various times in history.
Below is the journey of Indian Flag.
1880 – British india flag
1880 – Flag of British India.
This is the first single indian flag raised by British. The flag included the Union Flag in the upper-left quadrant and a star of India capped by the royal crown in the middle of the right half.
Unofficial flag of India in 1906
1906 – Unofficial flag of India in 1906
It is said that, the national flag was first time hoisted on 7th of August in 1906 in the Green Park (also called as Parsee Bagan Square) in the Calcutta (current Kolkata). It was a simply designed flag using three horizontal strips of tri colours (red, yellow and green). The uppermost green colour strip contains eight (8) white lotus flowers. The middle yellow colour strip is written in the center with “Vande Matram” in Hindi. And the lowermost red colour strip contains a crescent (left side corner) and a Sun (right side corner).
1907 – Indian flag
1907 – The Berlin committee flag, first raised by Bhikaiji Cama in 1907
According to the history, it is said that Indian national flag was hoisted second time in the Paris by the Madame Cama with her banished revolutionary band in 1907. Later that flag was exhibited in the social conference of Berlin. The second flag was little different from the first one. The uppermost orange colour strip contains one lotus flower and seven stars (identifying the Saptarishis). The middle yellow colour strip is written with “Vande Matram” in Hindi in the center. And the lowermost green colour strip contains a Sun in the left corner and a white crescent and star in the right corner.
flag used during the Home Rule movement in 1917
1917 – The flag used during the Home Rule movement in 1917
The third flag went up in 1917 when our political struggle had taken a definite turn. Dr. Annie Besant and Lokmanya Tilak hoisted it during the Home rule movement. This flag had five red and four green horizontal strips arranged alternately, with seven stars in the saptarishi configuration super-imposed on them. In the left-hand top corner (the pole end) was the Union Jack. There was also a white crescent and star in one corner.
The flag unofficially adopted in 1921
1921 – The flag unofficially adopted in 1921
During the session of the All India Congress Committee which met at Bezwada in 1921 (now Vijayawada) an Andhra youth prepared a flag and took it to Gandhiji. It was made up of two colours-red and green-representing the two major communities i.e. Hindus and Muslims. Gandhiji suggested the addition of a white strip to represent the remaining communities of India and the spinning wheel to symbolise progress of the Nation.
The flag adopted in 1931. This flag was also the battle ensign of the Indian National Army
1931 – The flag adopted in 1931. This flag was also the battle ensign of the Indian National Army
The year 1931 was a landmark in the history of the flag. A resolution was passed adopting a tricolor flag as our national flag. This flag, the forbear of the present one, was saffron, white and green with Mahatma Gandhi’s spinning wheel at the center. It was, however, clearly stated that it bore no communal significance and was to be interpreted thus.
The present Tricolour flag of India
1947 – The present Tricolour flag of India
On July 22, 1947, the Constituent Assembly adopted it as Free India National Flag. After the advent of Independence, the colours and their significance remained the same. Only the Dharma Charkha of Emperor Asoka was adopted in place of the spinning wheel as the emblem on the flag. Thus, the tricolour flag of the Congress Party eventually became the tricolour flag of Independent India.
Tags: 15th august 70 years of independence countries flags history of Indian flag independence day indian independence day patriotism struggle for freedom why countries need a flag
RimpleSanchla
a girl believing in "simple living, high thinking". love challenges, music, gadgets, admire nature, honest, soft-hearted, friendly, love to enjoy each and every moment of life. smile n me are synonymous! its alwys der wid me like my best friend
You may also like...
Day 2 bhagavad gita – side stories, why do boys need a friend who is a girl, there are plenty of opportunities for mo….
- Next Paralysed life of locals in Kashmir
- Previous Thousand Splendid Suns

Cultural India
Rediscovering India
Unveiling the Significance and History of Indian National Flag

The Indian national flag is a symbol of unity and pride for the country and its people. The flag is designed with three equal horizontal bands of saffron (top), white, and green with a blue wheel (Ashoka Chakra) in the center. The significance of the colors and the Ashoka Chakra on the flag holds a deep meaning and history. The flag is not just a symbol of the country but also a representation of its rich culture and heritage. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the history of the Indian flag, the meaning of its colors, and its importance in the nation’s identity.
Table of Contents
Significance of the Indian flag and its colors
The Indian national flag is a symbol of unity and pride for the country and its people. The flag is designed with three equal horizontal bands of saffron (top), white, and green with a blue wheel (Ashoka Chakra) in the center. Each color and the Ashoka Chakra on the flag holds a deep meaning and significance.
The saffron color represents sacrifice, courage and selflessness. The white color symbolizes peace and truth, and the green color represents faith and chivalry. Together, the three colors represent the ideals of sacrifice, peace, and faith that form the foundation of the Indian nation.
The Ashoka Chakra in the center of the flag, which is a 24-spoke wheel, is derived from the Ashoka Chakra of the Sarnath Lion Capital, which was erected by the Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC. The Ashoka Chakra symbolizes the eternal wheel of law and justice and represents the continuity of the Indian civilization.
Furthermore, the flag is not just a symbol of the country but also a representation of its rich culture and heritage. The flag is a reminder of the sacrifices made by the freedom fighters and the struggles for independence. It also symbolizes the unity and diversity of the country, representing the various religious, linguistic, and cultural identities that make India unique. The flag is a source of national pride and inspiration for all citizens, and it is a symbol of India’s sovereignty, integrity and national identity.

The History of the Indian Flag
The evolution of the indian flag and its different versions.
The evolution of the Indian national flag has been a long and interesting journey, reflecting the country’s political and social changes over the years.
The first version of the Indian national flag was hoisted on August 7, 1906, at the Parsee Bagan Square in Calcutta (now Kolkata) by Madam Bhikaji Cama, Dr. Pherozeshah Mehta, and Veer Savarkar. The flag featured three horizontal bands of green, yellow and red, with eight lotuses arranged in a row on the middle yellow band, and a crescent and a star on the top green band.
In 1921, the Indian National Congress adopted a new flag, which featured a red background with the Union Jack in the top left corner and the star of India in the center. The flag was used during the Non-Cooperation Movement and was also hoisted on the Congress’s session in 1923.
In 1931, the Indian National Congress adopted a new flag, which featured a tricolor of saffron, white and green with a spinning wheel in the center. This flag was hoisted by the Congress party on December 31, 1929, in Lahore by Jawaharlal Nehru. The spinning wheel represented the progress of the nation and the flag was used during the Civil Disobedience Movement.
In 1947, the Constituent Assembly of India adopted the current national flag, which is a tricolor of saffron, white, and green with a blue wheel in the center. The saffron color represents sacrifice, courage and selflessness. The white color symbolizes peace and truth, and the green color represents faith and chivalry.
The Indian flag has undergone several changes over the years, reflecting the country’s political and social changes. The current national flag, which was adopted in 1947, is a symbol of unity and pride for the country and its people, and represents the ideals of sacrifice, peace, and faith that form the foundation of the Indian nation.
The Designers and the Significance of the flag
The current Indian national flag was designed by Pingali Venkayya, a freedom fighter and agricultural scientist from Andhra Pradesh, India. The flag was designed in 1921 and was adopted by the Indian National Congress in 1931.
The flag’s design was inspired by the colors of the Indian National Congress and the idea of a spinning wheel, which represented the progress of the nation. The colors of the flag, saffron, white, and green, were chosen to represent the ideals of sacrifice, peace, and faith that form the foundation of the Indian nation.
The Ashoka Chakra in the center of the flag was taken from the Ashoka Chakra of the Sarnath Lion Capital, which was erected by the Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC. The Ashoka Chakra symbolizes the eternal wheel of law and justice and represents the continuity of the Indian civilization.
The significance of the flag lies in its ability to unite the diverse population of India and to represent the country’s sovereignty and integrity. The flag is a reminder of the sacrifices made by the freedom fighters and the struggles for independence. It also symbolizes the unity and diversity of the country, representing the various religious, linguistic, and cultural identities that make India unique. The flag is a source of national pride and inspiration for all citizens.

The Meaning of the Colors
The Indian national flag is designed with three equal horizontal bands of saffron (top), white, and green with a blue wheel (Ashoka Chakra) in the center. Each color on the flag holds a deep meaning and significance.
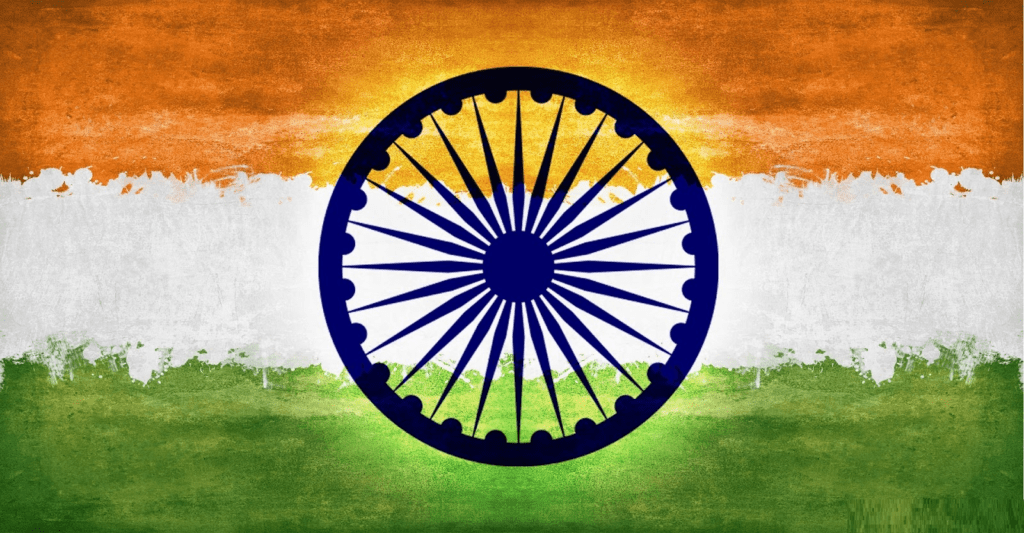
The saffron color represents sacrifice, courage and selflessness. It is believed that the color saffron represents the sacrifices of the people who fought for India’s freedom. It also symbolizes the spiritual power and strength of the nation.
The white color symbolizes peace and truth. The white color on the flag represents the country’s commitment to peace and non-violence. It also symbolizes the country’s unity and purity of purpose.
The green color represents faith and chivalry. The green color on the flag represents the country’s agricultural and natural wealth. It also symbolizes the country’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage and the welfare of its people.
Together, the three colors represent the ideals of sacrifice, peace, and faith that form the foundation of the Indian nation. The flag is a symbol of unity and pride for the country and its people, and represents the various religious, linguistic, and cultural identities that make India unique.
The Ashoka Chakra in the center of the flag, which is a 24-spoke wheel, is derived from the Ashoka Chakra of the Sarnath Lion Capital, which was erected by the Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC. The Ashoka Chakra symbolizes the eternal wheel of law and justice and represents the continuity of the Indian civilization. The chakra is navy blue in color and contains 24 spokes which represent the 24-hour cycle of the day and the 24-spoke wheel represents the continuous movement of the nation towards progress.
Significance of the Ashoka Chakra in the center
The Ashoka Chakra in the center of the Indian national flag is a significant symbol that holds both historical and symbolic significance.
The Ashoka Chakra is derived from the Ashoka Chakra of the Sarnath Lion Capital, which was erected by the Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC. The Ashoka Chakra symbolizes the eternal wheel of law and justice and represents the continuity of the Indian civilization. The chakra is navy blue in color and contains 24 spokes which represent the 24-hour cycle of the day and the 24-spoke wheel represents the continuous movement of the nation towards progress.
The Ashoka Chakra also represents the country’s commitment to the values of justice, righteousness, and moral order. It symbolizes the country’s adherence to the principles of dharma, which is the moral law that governs individual conduct and social order in Indian philosophy. The Ashoka Chakra also represents the country’s commitment to the rule of law, equality, and non-violence.
The Ashoka Chakra is also significant because it represents the country’s continuity with its ancient heritage and its commitment to progress and modernization. The Ashoka Chakra also represents the country’s commitment to the welfare of its people, as well as its commitment to promoting peace and harmony among all its citizens.

The Importance of the Indian Flag
The role of the flag in national unity and pride.
The Indian national flag plays a significant role in promoting national unity and pride among the citizens of India.
The flag serves as a symbol of the country’s sovereignty and integrity. It represents the ideals of sacrifice, peace, and faith that form the foundation of the Indian nation. The flag is a reminder of the sacrifices made by the freedom fighters and the struggles for independence. It also symbolizes the unity and diversity of the country, representing the various religious, linguistic, and cultural identities that make India unique.
The flag serves as a source of inspiration and motivation for all citizens, promoting a sense of national pride and unity. It is a symbol of the country’s heritage and culture, and it represents the aspirations and hopes of the people of India.
The flag is also an important symbol of national identity. It is a unifying symbol that brings together the diverse population of India, promoting a sense of belonging and shared identity among all citizens.
The flag plays an important role in fostering national unity and pride, particularly during national holidays and celebrations such as Independence Day and Republic Day. The flag is hoisted, paraded and honored as a symbol of the nation’s unity, sovereignty and integrity. The flag also serves as a reminder of the country’s rich cultural heritage and the sacrifices made by the freedom fighters.
In conclusion, the Indian national flag plays a significant role in promoting national unity and pride among the citizens of India. It serves as a symbol of the country’s sovereignty and integrity, a source of inspiration, motivation, and a unifying symbol that promotes a sense of shared identity, belonging and pride among all citizens.
The laws and regulations regarding the use and handling of the flag
The use and handling of the Indian national flag are regulated by the Flag Code of India, 2002, which outlines the guidelines and regulations for the proper display and respect of the flag.

According to the Flag Code of India, the national flag should be flown on all days, including national holidays, and should be flown at half-mast as a mark of respect on days of national mourning.
The flag should be treated with respect at all times and should not be used for commercial or personal gain. The flag should not be used as clothing, drapery, or as a covering for objects. It should also not be defaced by writing or printing on it.
The flag should be flown in a dignified manner and should not be allowed to touch the ground or the floor or be flown in a manner that is likely to allow it to be damaged or disrespected.
It is mandatory to hoist the National flag on certain days like Independence Day, Republic Day, Mahatma Gandhi’s Birthday, and National Days like National Flag Day, etc.
The Flag Code of India also states that the national flag should be flown on buildings and vehicles of the central and state governments, as well as on all government-aided educational institutions.

In conclusion, the Indian national flag is a symbol of unity and pride for the country and its people. It represents the ideals of sacrifice, peace, and faith that form the foundation of the Indian nation. The flag’s design, with three equal horizontal bands of saffron, white, and green with a blue wheel (Ashoka Chakra) in the center, holds a deep meaning and significance. The Ashoka Chakra symbolizes the eternal wheel of law and justice, the continuity of the Indian civilization, the commitment to justice, righteousness, moral order, non-violence, the rule of law and equality. The flag serves as a reminder of the sacrifices made by the freedom fighters and the struggles for independence, it also symbolizes the unity and diversity of the country, representing the various religious, linguistic, and cultural identities that make India unique. The flag plays an important role in promoting national unity and pride, particularly during national holidays and celebrations such as Independence Day and Republic Day. The laws and regulations regarding the use and handling of the flag are outlined in the Flag Code of India, which ensures that the flag is treated with respect and displayed in a dignified manner at all times.
Is it legal to use the national flag on clothing or other personal items?
According to the Flag Code of India, it is not legal to use the national flag on clothing or other personal items. The Flag Code of India, 2002 states that the national flag should not be used as clothing, drapery, or as a covering for objects. It also states that the flag should not be defaced by writing or printing on it. The Flag Code of India also states that the flag should be treated with respect at all times and should not be used for commercial or personal gain. It should be flown in a dignified manner and should not be allowed to touch the ground or the floor or be flown in a manner that is likely to allow it to be damaged or disrespected. It’s worth noting that there are also penalties for disrespectful treatment of the national flag as per the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971.
Are there any laws or penalties for disrespectful treatment of the national flag?
Yes, there are laws and penalties for disrespectful treatment of the national flag in India. The Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971, provides for the punishment of persons who prevent the use of the Indian National Flag or show disrespect to it. The Act states that whoever in any public place or in any other place within public view burns, mutilates, defaces, defiles, disfigures, destroys, tramples upon or otherwise shows disrespect to or brings into contempt (whether by words, either spoken or written, or by acts) the Indian National Flag or any part thereof, shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to three years, or with fine, or with both.
What should be done if the national flag becomes damaged or is no longer in a presentable condition?
If the Indian national flag becomes damaged or is no longer in a presentable condition, it should be disposed of in a respectful manner. The Flag Code of India has specific guidelines for the disposal of worn or damaged national flags. The flag should not be thrown away or treated disrespectfully. One option is to burn the flag in a private ceremony. The flag should be folded into a triangle, and then set on fire in a dignified manner, with those present standing at attention and saluting the flag as it burns. The ashes should then be buried or scattered in a respectful location. Another option is to bury the flag in a dignified manner. The flag should be folded into a triangle and then placed in a flag case or a plain box, and then buried in a dignified location. It is also possible to donate the flag to an organization that will properly dispose of it, such as a veterans’ group or a historical society. In any case, it is important to ensure that the flag is disposed of in a dignified and respectful manner, as a symbol of the nation’s unity, sovereignty and integrity.
Related Posts:

One thought on “ Unveiling the Significance and History of Indian National Flag ”
- Pingback: The Evolution Of India's Republic Day Celebrations | Cultural India
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Follow us here
Submit you article here.
Recent Posts
- How does Rajasthan SSO ID support digital initiatives?
- Online MBA Courses – Benefits, Eligibility and Career Scope
- Locate Psychotherapist in Delhi City Who Can Help You.
- The World of App Development Perspectives from Perth, Australia, and India
- Tawaifs in India’s Fight for Independence

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Indian History /
Evolution of the Indian Flag: All Phases

- Updated on
- May 7, 2024

The National Flag of India, a symbol of its years’s years-long struggle for independence and autonomous identity, was adopted on July 22, 1947. Throughout its history, the Indian national flag has undergone different significant transformations that represent the country’s political and social developments. In this blog, we will explore the glorious evolution of the Indian flag.
The Phases Of The Indian National Flag
Below we have mentioned the different phases of the evolution of the Indian flag.
1906 : The journey of India’s national flag began with the hoisting of the first national flag in the Parsee Bagan Square in Calcutta (now Kolkata). It all happened during the Swadeshi and Boycott struggle of the Indian subcontinent. The flag featured three horizontal stripes of red, yellow, and green, with the words Vande Mataram inscribed in Hindi language.
1907 : The second national flag of India was hoisted in Paris by Madam Bhikaji Cama and other exiled revolutionaries. Although it was quite similar to the previous flag, it bore minimal differences. For instance, the Berlin Committee flag of 1907 replaced the seven lotus flowers at the top with seven stars representing the Saptarishi. Moreover, the arrangement of colour horizontal stripes was also shifted from green at the top to orange. Interestingly, this flag was exhibited at a socialist conference in Berlin.
Also Read: Maratha Empire (1674-1818): History, Wars, Important Leaders
1917 : The third flag was hoisted by Annie Besant and Bal Gangadhar Tilak in 1917 during the Home Rule movement. It signified the political struggle of the nation and the need for establishing the Indian subcontinent as autonomous. This flag featured alternating red and green stripes with seven white stars arranged in the saptarishi formation. Along with this, the flag included a Union Jack in the top left corner and a white crescent and star in the top right corner.
1921 : A young freedom fighter known by the name Pingali Venkaiah presented the design of India’s national flag to Mahatma Gandhi . It all happened during the Bezwada (Vijayawada) session of Congress. This flag had three stripes of white, green, and reddish-orange colour. As evident, the co-existence of multiple colours signified the existence of multiple communities living peacefully in India. Apart from this, it featured a spinning wheel i.e. Ashoka Chakra in the centre, signifying the country’s progress and development post-independence.
Also Read: Lodi Dynasty- Exploring India’s Medieval History
1931 : In 1931, a resolution was passed to adopt a tricolour flag as the national flag of India. This flag came with three horizontal stripes of saffron at the top, white in the middle, and green at the bottom. Along with this, it featured a blue spinning wheel at the centre.
1947 : The year 1947 was a truly revolutionary year for India. The Constituent Assembly adopted the flag of free India in July 1947. The colours and their placement remained the same. However, Mahatma Gandhi’s spinning wheel was replaced by Ashoka’s Dharma Chakra, symbolizing truth and life. This is what we call the Tiranga of India.
Relevant Blogs
In this way, the transformation of the Indian flag reflects the nation’s journey from colonial rule to an independent democracy. This was all about the evolution of the Indian flag. If you wish to read more such informative blogs, check out our general knowledge page.
Parul Sharma
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Hinduism, Indian culture, Vedic Science, Yoga, Spirituality, India

Evolution of India’s National Flag
It is really amazing to see the various changes that our National Flag went through since its first inception. It was discovered or recognized during our national struggle for freedom. The evolution of the Indian National Flag sailed through many vicissitudes to arrive at what it is today. Some of the historical milestones in the evolution of our National Flag involve the following:
1906 – First Flag
- Also called Calcutta Flag or Lotus Flag
- The flag was first hoisted on 7 August 1906 at Parsee Bagan Square in Calcutta.
- This flag was composed of three colors – Green, Yellow and Red with the word – Vande Matram ( वन्देमातरम् ) inscribed in centre.
- The red strip at the top had eight white lotuses embossed on it in a row. On the yellow strip the words Vande Mataram were inscribed in deep blue in Devanagari characters. The green strip had a white sun on the left and a white crescent and star on the right.
1907 – Second Flag
- In 1907, the second form of Indian flag was hoisted in Paris by Madam Cama and her group of revolutionaries.
- Except for a few changes, the flag was similar to the first one.
- This flag was also exhibited at a socialist conference in Berlin.
1917 – Third Flag
- The third flag went up in 1917 when our political struggle had taken a definite turn. Dr. Annie Besant and Lokmanya Tilak hoisted it during the Home rule movement.
- This was the most colorful version of the Indian flag.
- This flag had five red and four green horizontal strips arranged alternately, with seven stars in the saptarishi configuration super-imposed on them. In the left-hand top corner (the pole end) was the Union Jack. There was also a white crescent and star in one corner.
- The presence of the Union Jack, however made the flag generally unacceptable.
1921 – Fourth Flag
- During the session of the All India Congress Committee which met at Bezwada in 1921 (now Vijayawada) an Andhra youth prepared a flag and took it to Gandhiji.
- The red and green color in the flag represents two communities – -Hindus and Muslims. As per Gandhiji’s suggestion, a white strip was included which indicated other religions and communities and a spinning wheel which portrays the progress of India.
- This was the flag approved by Gandhi in 1921.
- This flag was not formally adopted by the Indian National Congress, but nevertheless widely used.
1931 – Fifth Flag
- The year 1931 was a landmark in the history of the flag. A resolution was passed adopting a tricolor flag as our national flag.
- The three colors include saffron, white and green with Mahatma Gandhi’s spinning wheel or charkha in the center.
Flag of August 15 1947 – The present flag of India
- Our National Flag, which was born on July 22, 1947 with Nehruji’s words, “Now I present to you not only the Resolution, but the Flag itself”.
- This flag was first hoisted at the Council House on August 15, 1947
- In the national flag of India the top band is of Saffron color, indicating the strength and courage of the country. The white middle band indicates peace and truth with Dharma Chakra. The last band is green in color shows the fertility, growth and auspiciousness of the land.
- This Dharma Chakra depicted the “wheel of the law” in the Sarnath Lion Capital made by the 3rd-century BC Mauryan Emperor Ashoka. The chakra intends to show that there is life in movement and death in stagnation.
~Nikuni Jain
You may also like

10 Compelling Reasons to Visit the Ram Temple in Ayodhya

The Ram Temple in Ayodhya: A Confluence of Historical Faith and Modern Progress

The hanging pillar and wonders of Lepakshi
Sanskriti calendar 2024.

Search the website
Like us on facebook.
Get daily updates via Email
Enter your email address:, recent posts.

Navratri Series – Day 9: Goddess Siddhidatri – The Bestower of Supernatural Powers
Celebrate the conclusion of Navratri with Goddess Siddhidatri on Day 9. Learn about her powers to bestow siddhis and her role in achieving spiritual enlightenment. #Navratri2024 #GoddessSiddhidatri #SpiritualJourney

Navratri Series – Day 8: Goddess Mahagauri – The Beacon of Purity and Serenity
Day 8 of Navratri is dedicated to Goddess Mahagauri, known for her purity and tranquility. Discover how she symbolizes cleanliness and moral integrity, offering peace and renewal to all.

Navratri Series – Day 7: Goddess Kalaratri – The Fierce Protector
Explore the might and mystique of Goddess Kalaratri on Day 7 of Navratri. Learn about her role as the destroyer of darkness and her powerful protection against evil.

Navratri Series – Day 6: Goddess Katyayani – The Warrior of Righteousness
“Discover the powerful essence of Goddess Katyayani on Day 6 of Navratri. Learn how she embodies courage and fights for righteousness, symbolizing victory over evil.

Navratri Series – Day 5: Goddess Skandamata – The Mother of Wisdom and Courage
Day 5 of Navratri is dedicated to Goddess Skandamata, embodying maternal love and warrior strength. Discover how she imparts wisdom and courage in our lives.

Sanskriti comes from the Sanskrit root “kr” which means to do or to make prefix “sam” is applied before it to convey a sense of embellishment. It means actions done for the holistic refinement and perfection all the potentialities within a human being.
Important Links
“The term “Rishi” in Sanskrit originates from a root that means “To See.” Rishis, quite literally, “see” truths that are unveiled to them in elevated states of consciousness. .These are recorded in Sacred texts called Upanishads , Vedas etc. The wisdom imparted by ancient Rishis has not only enriched the realm of inner science but has also played a pivotal role in shaping and advancing modern scientific understanding. Let us Explore……
Sanskriti Social
Copyright © 2024. Sanskriti Magazine
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
History of Indian Flag Archived 2019-12-20 at the वेबैक मशीन भारतीय तिरंगे का इतिहास Archived 2014-08-24 at the वेबैक मशीन भारतीय ध्वज संहिता Archived 2009-10-07 at the वेबैक मशीन , गृह मंत्रालय ...
भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज लेफ्टिनेंट श्री पिंगली वेंकय्या द्वारा डिजाइन किया गया था।. भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज का सफर. सन 1904 में, अस्तित्व ...
Journey of National Flag : भारतीय तिरंगे का इतिहास, विकास और महत्व Tiranga yatra स्वतंत्र भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज कैसे बना?
Indian Flag History in Hindi. हर एक आज़ाद देश का अपना एक ध्वज है। एक आज़ाद देश की यही सबसे बड़ी पहचान होती है। ब्रिटिश राज से 15 अगस्त 1947 को आज़ाद होने के कुछ दिनों पहले ही भारत के ...
History of Indian National Flag (Timeline): Every independent nation of the world has its own flag which is the symbol of the independent country. The national flag of India in its present form was adopted during the meeting of the Constituent Assembly held on 22 July 1947, a few days before India's independence from the British on 15 August 1947.
History of Indian National Flag- Tiranga in HindiThe first flag was made in the beginning of the British rule in 1857,Then the first flag of India by any Ind...
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय ध्वज इतिहास व महत्त्व, निबंध ( Indian National Flag Essay history and Significance in hindi ) भारतीय राष्ट्रिय ध्वज हमारी स्वाधीनता का प्रतीक है. देश में अपना ध्वज लहराने का ...
हर देश का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज उसकी स्वतंत्रता का प्रमाण और उसकी पहचान होता है। यही कारण है कि बचपन से हमें तिरंगे का सम्मान करने की सीख दी जाती है। हर 26 जनवरी ...
भारत के बारे में. भारत विश्व की सबसे पुरानी सभ्यताओं में से एक है जिसमें बहुरंगी विविधता और समृद्ध सांस्कृतिक विरासत है। इसके साथ ही यह अपने-आप को ...
राष्ट्रीय ध्वज (Indian Flag in Hindi) Find below information about Indian Flag in Hindi language: भारत के लोगों के लिये राष्ट्रीय ध्वज बहुत मायने रखता है। भारत के लोगों के लिये ये बेहद महत्वपूर्ण और ...
Complete Information about of Indian Flag in Hindi, History of Indian Flag, Essay on Indian Flag. हम सब जानते है की हर स्वतंत्र देश का अपना झंडा (ध्वज) होता है जो उस देश की पहचान होती है हर आजाद देश के राष्ट्रिय ध्वज ...
Jan 25, 2024, 15:48 IST. Journey of the Indian National Flag. Republic Day 2024: Republic Day marks and celebrates the date on which the Constitution of India came into effect on 26 January 1950 ...
The national flag of India is a tri-colored flag, with the national colors of saffron (yellow) in the top band, white (middle band), and green (lower band) at the bottom. The Saffron in the top band represents the strength and courage of the country. The White band symbolizes peace and truth with Dharma Chakra.
While an Indian flag was reportedly designed by Sister Nivedita, an Irish disciple of Swami Vivekananda, between 1904-1906, arguably the first national flag of India is said to have been hoisted on August 7, 1906, in Kolkata at the Parsee Bagan Square (Green Park). It comprised three horizontal strips of red, yellow and green, with Vande Mataram written in the middle.
Below is the journey of Indian Flag. 1880 - British india flag. 1880 - Flag of British India. This is the first single indian flag raised by British. The flag included the Union Flag in the upper-left quadrant and a star of India capped by the royal crown in the middle of the right half. Unofficial flag of India in 1906.
Gaurav January 24, 2023 1. Spread the love. The Indian national flag is a symbol of unity and pride for the country and its people. The flag is designed with three equal horizontal bands of saffron (top), white, and green with a blue wheel (Ashoka Chakra) in the center. The significance of the colors and the Ashoka Chakra on the flag holds a ...
The national flag of India, colloquially called Tiraṅgā (the tricolour), is a horizontal rectangular tricolour flag, the colours being of India saffron, white and India green; with the Ashoka Chakra, a 24-spoke wheel, in navy blue at its centre. It was adopted in its present form during a meeting of the Constituent Assembly held on 22 July 1947, and it became the official flag of the Union ...
10 Facts About Indian Flag in Hindi (1-10) स्टूडेंट्स के लिए Facts About Indian Flag in Hindi यहाँ दिए गए है : भारत का राष्ट्रीय ध्वज केसरिया, सफेद और हरे रंग से मिलकर बना है जिसके ...
The National Flag of India was designed by Lt. Shri Pingali Venkayya. Journey of the Indian National Flag. In 1904, the first ever Indian flag that came into existence was designed by Sister ...
India's freedom. • In 1906, during the Swadeshi and Boycott struggle, a flag of India was hoisted for the first time in the Parsee Bagan Square in Calcutta (present-day Kolkata). • In 1907, a similar flag with slight modifications was raised by Madam Bhikaji Cama in Paris. This flag was also exhibited in
The phases of the Indian National Flag. Below we have mentioned the different phases of the evolution of the Indian flag. 1906: The journey of India's national flag began with the hoisting of the first national flag in the Parsee Bagan Square in Calcutta (now Kolkata).It all happened during the Swadeshi and Boycott struggle of the Indian subcontinent.
This flag was first hoisted at the Council House on August 15, 1947. In the national flag of India the top band is of Saffron color, indicating the strength and courage of the country. The white middle band indicates peace and truth with Dharma Chakra. The last band is green in color shows the fertility, growth and auspiciousness of the land.
A flag flying at half-mast is the universal symbol of mourning. A ship's signal of distress is made by hoisting the national ensign reversed—i.e., upside down. Flag of India, horizontally striped flag of saffron, white, and green with a 24-spoked blue chakra (wheel) in the center.