

Bali Travel Regulations
Bali entry requirments and regulations.
Stay updated with the official government regulations regarding Bali Entry Requirements .
General Travel
General travel requirements to Bali include Customs, Covid Vaccination status, plus more.
Below we will answer all the questions you may have about your eligibility to enter Bali.
Visa Regulations
Bali Visa regulations relate to how long you plan to stay in Bali, Visa on Arrival, B211a, Valid and expired passports etc.
You may find on our Bali Visa Page .
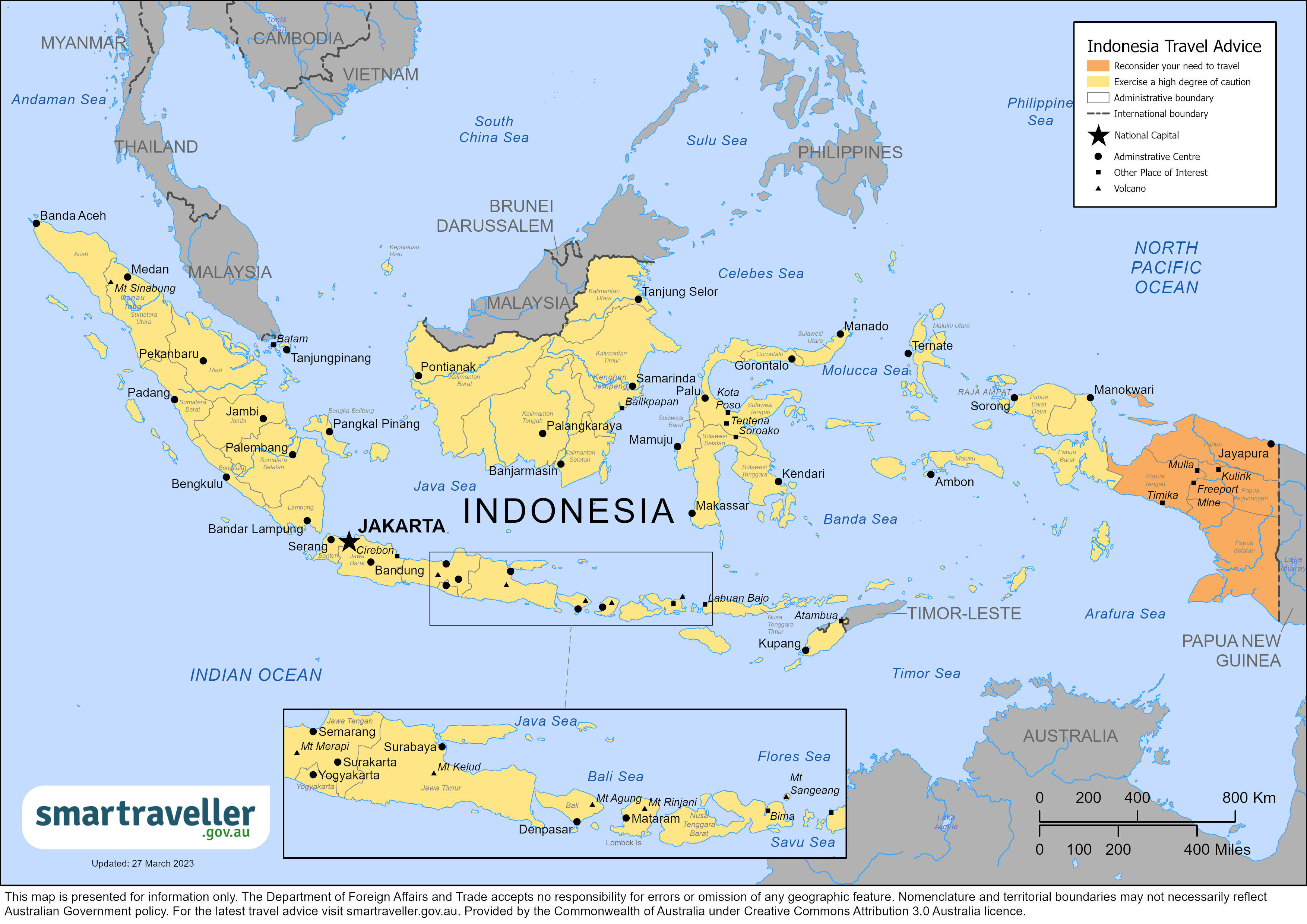
Bali Quarantine and Travel Requirements
Are there international flights to bali.
ABSOLUTELY. The number of flights to Bali may be lesser than before. Still, airlines are gradually including it again in their schedules, with airfares increasing significantly due to the pandemic – Singapore Air, KLM, Qatar, and Jetstar are among them. However, they aren’t as frequent anymore.
Do I Need a Visa to Enter Bali?
Depending on your nationality, the purpose of travel and the duration of stay, you can find out what documents are required for your visit. Please click the button below to check which visa requirements apply to you.
Bali Visa Regulations.
Do I Need a B211A Visit Visa?
If your country is not included in the list of visa-free and Visa on Arrival to Bali countries, or if you are planning to stay for more than 60 days, then a B211A Visit Visa is necessary. It’s worth noting that the original Visa on Arrival has been improved, so it now covers business meetings, sourcing and purchasing goods, transit activities, and government duties.
Can I Visit Bali Now?
Exciting news for international travellers! Indonesia has relaxed most of its travel restrictions and visa requirements, enabling visitors to explore the country’s gorgeous landscapes. However, specific steps still need to be taken to enter Indonesia safely and hassle-free; let this page guide you through these crucial details so your trip is smooth sailing!
Covid Requirements for Travelling to Bali?
Travellers who are fully vaccinated DO NOT need to quarantine and can now travel into Indonesia without a PCR test.
After receiving two (or more) doses of Pfizer, Moderna, Johnson & Johnson, or other approved COVID-19 vaccinations , travellers can confidently enter Bali, Indonesia with peace of mind that they are safe from any potential risk of catching it more in Bali than anywhere else in the world.
Unvaccinated
For the unvaccinated, entry into Bali/Indonesia is possible; however, only with a Medical Exemption Letter. Your doctor should provide this letter and explain any comorbid diseases or other conditions that would prevent you from receiving vaccinations.
However, this will not apply if you remain unvaccinated due to personal choices rather than medical reasons – in which case entry will unfortunately not be permitted.
If you have already recovered from Covid-19 and only received one dose of the vaccine, a recovery certificate will be required to travel to Bali. This document proves that you are no longer an active transmitter of Covid-19. Without this certificate, entry into Bali is strictly prohibited.
Proof of Vaccination
To travel to Bali, Indonesia, you must present a valid digital or printed proof of Covid Vaccination with the final dose taken 14 days prior. Although officials may not check your status upon arrival in Indonesia, airlines typically verify this requirement when checking in. Therefore, you must meet this criterion for entry.
Date of Vaccination (Expiry)
Currently, Indonesia does not have an expiration date for vaccinations; instead, it simply monitors the number of vaccinated people.
At this moment, no other quarantine conditions are necessary. You will be qualified to enter Indonesia following the abovementioned regulations, or you won’t be able to make your way into the country.
Regulations can often fluctuate, and different airlines may enforce the rules more strictly than others. Unfortunately, some carriers might even struggle to stay up-to-date with changing regulations and could ask for documentation that is no longer necessary. Consequently, verifying your airline’s requirements before you travel to Indonesia is essential to avoid any unnecessary complications during your trip.
What Other Documents Do I Need for Bali?
Accelerate your arrival in Bali by completing the ONLINE Customs Declaration Form: E-CD (Electronic Custom Declaration).
Airlines and immigration authorities may require you to have a return ticket within the time frame of your visa validity.
Also, ensure that your passport is valid for at least six months from arrival, or they will deny entry! Finally, fill out all paperwork BEFORE you arrive to save time in airport customs when visiting Bali.
It is essential to ensure your passport has an empty page before embarking on any international journey.
Additionally, please be aware that Emergency Passports and Temporary Travel Documents are no longer acceptable forms of travel documentation.
To assist with a smooth transition amid this pandemic, we strongly recommend downloading a “Travel Health App” before travelling abroad for all necessary health advisories and updates.
Bali Travel Regulations FAQs
Those under 18 years of age typically don’t require vaccinations; however, if they apply for a B211A Visa (not the one issued upon arrival), they must provide a medical statement indicating why vaccination is impossible.
Following January 2023, the President officially abolished all COVID-related travel limitations (PPKM measures), such as testing and mask-wearing. As a result, the situation is entirely under control, with so many millions of people now vaccinated.
Forget about the dreaded PCR Test when entering Bali / Indonesia; all travellers must be fully vaccinated unless they have a medical exemption stating otherwise.
With multiple medical insurance providers available with a simple Google search, finding coverage for your trip to Bali is easier than ever. However, it’s important to note that travel medical insurance isn’t required. Here’s our top-rated Bali insurance provider .
It depends on where you are flying from; however, if you don’t have the funds to fly direct to Bali, no worries! You can still get a ticket from Jakarta at an affordable 50-150 USD rate. In addition, airlines such as Citilink, Batik Air, Air Asia, Lion Air and Garuda offer regular flights that make this journey possible easily. So if the direct flight is too expensive for your budget, it might be well worth considering a domestic flight.
To ensure compliance with local regulations, please refrain from bringing more than the equivalent of IDR 100,000,000 (ca. AUD 10,000) cash into the country.
Travelers to Bali need at least one COVID-19 vaccination. For air travel, a PCR test no older than 48 hours is mandatory. For other transports, an antigen test within 24 hours is sufficient.
Visitors need a valid visa and an undamaged passport. Additionally, certain forms and apps are required upon arrival, and transit rules apply.
Tourists must stay in registered hotels and villas. Unlicensed accommodations like certain Airbnb rentals are not permitted.
International travelers must complete an Indonesia e-CD form, applicable to all parts of Indonesia, including Bali.
Travelers should be up-to-date with routine vaccinations like measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, and influenza before visiting Bali.
Australians need a valid passport with six months’ validity and at least one blank page. Temporary passports are not accepted.
Australians require a passport with at least 6 months validity, a return or onward flight booking, and proof of COVID-19 vaccinations.
Foreign travelers must undergo a health check upon arrival in Indonesia, including body temperature checks.
A new law prohibiting cohabitation and sex outside marriage is set to come into effect in three years, potentially impacting tourism.
Australian passport holders need a visa to enter Bali, available upon arrival at Indonesian airports for certain stay durations.
Bringing more than IDR 100 million (around $6,500 USD) requires declaration at customs.
Travelers are allowed to bring 1 liter of alcoholic products per person. Excess amounts are subject to fines or confiscation.
It’s a mandatory form for declaring personal or excess goods for tax purposes, to be completed before arrival.
Mosquitoes can be prevalent in Bali, so it’s advisable to use repellents and take precautions, especially during the rainy season.
Bali is generally safe for tourists, with only a few experiencing problems. Common sense and awareness are key to a safe visit.
The Visa on Arrival for Bali costs around AUD$50 (IDR 500,000).
Consult with a healthcare provider for specific advice. Commonly recommended items include pain relievers, antihistamines, and medications for stomach ailments.
Yes, it’s important to consider travel insurance for Bali to cover unforeseen medical and travel-related incidents.
Bali’s governor has stated that tourists’ marital status will not be checked under the new law, which is not yet in effect.
The Visa on Arrival costs approximately USD $35, valid for 30 days and extendable for another 30 days at a local immigration office.
While new laws criminalizing sex outside marriage are pending, tourists are currently not charged under these laws.
Australian drivers need both their national license and an international permit for proper insurance coverage and legality in Bali.
Cash is generally preferred in smaller towns and rural areas, while cards are widely accepted in larger cities.
You can use your phone in Bali by getting an Indonesian SIM card, provided your phone is unlocked.
Most Australian debit cards, especially those affiliated with Mastercard or Visa, are widely accepted in Bali. Before traveling, inform your bank of your trip to avoid unexpected card cancellations.
Travelers to Indonesia are allowed to carry a reasonable amount of perfume, along with specific allowances for tobacco and alcohol, adhering to the customs regulations.
Declare all purchased items, gifts, and business-related goods at customs. This includes duty-free purchases and items received as gifts or for business use.
Australians require a tourist visa for visits up to 30 days in Bali, effective from May 2022.
The Bali visa-on-arrival fee can be paid in several currencies, including AUD, at designated airport counters.
Bali’s departure tax is now included in the airline ticket price, eliminating the need for separate payment at the airport.
Ibuprofen and similar over-the-counter medications are generally allowed in Bali, but prescription drugs should be accompanied by a doctor’s note, especially if they contain controlled substances like codeine.
Australians traveling to Bali need a valid passport, visa, EVOA application, and compliance with COVID-19 health measures, including the PeduliLindungi app.
While holding hands is common, more intimate gestures like kissing are generally not practiced in public in Bali, in line with local customs.
Despite laws against cohabitation and extramarital relations, unmarried tourists commonly share rooms in Bali without legal issues.
Pre-arranging a visa online is recommended to avoid long queues at the airport, allowing more time for vacation activities.
Tourists can bring up to IDR 100 million (around US $6,500) without declaring it. Amounts exceeding this limit must be declared.
Two men can share a room in Bali without issues, though public displays of affection are generally discouraged.
Moderate public displays of affection like hugging are acceptable in Bali, especially among friends, but overtly sexual behavior is frowned upon.
Australians can stay in Bali for 30 days with a Visa on Arrival, with the possibility of a 30-day extension through specific agencies.
Our NEW Bali Travel Guide is out. Shop now! | Book Our Bali Vacation Planning Service
- Island Stays
- Welike Travels: The World
- Welike travels: Europe
- Island Talks
- BOAT TICKETS NUSA LEMBONGAN (15% OFF!)
- GET STARTED: BALI TRAVEL GUIDE
- FAMILY TRIP: BALI KIDS GUIDE
- DESIGN YOUR BALI HOLIDAY WITH US
- 1-ON-1 BALI CALL
- RENT A MOTORBIKE IN BALI
- BALI GUIDES
- TRAVEL PLANNING SERVICE
- GUIDES & SERVICES
- ONLINE SHOP
- BALI STORES
- Work with us
- Bali Stores
- AED AFN ALL AMD ANG AUD AWG AZN BAM BBD BDT BGN BIF BND BOB BSD BWP BZD CAD CDF CHF CNY CRC CVE CZK DJF DKK DOP DZD EGP ETB EUR € FJD FKP GBP GMD GNF GTQ GYD HKD HNL HUF IDR ILS INR ISK JMD JPY KES KGS KHR KMF KRW KYD KZT LAK LBP LKR MAD MDL MKD MMK MNT MOP MUR MVR MWK MYR NGN NIO NPR NZD PEN PGK PHP PKR PLN PYG QAR RON RSD RWF SAR SBD SEK SGD SHP SLL STD THB TJS TOP TTD TWD TZS UAH UGX USD UYU UZS VND VUV WST XAF XCD XOF XPF YER
Your Cart is Empty
- €0.00 Subtotal
UPDATE: BALI TRAVEL CHECK-LIST Rules to enter Indonesia + Everything to prepare for a smooth arrival
February 24, 2023

So, you are planning your trip to Bali or booked your tickets? Stoke levels are high! But now comes the rest... it isn’t a no brainer anymore as it was to just buy your ticket and suitcase and go. Although entry is finally possible again for foreign travelers - which is the most amazing news after 2,5 years of no international tourism for the island! - there are certain travel conditions and regulations. To make your life a little easier we made a checklist for all things you need to know, bring and do when traveling to Bali now.
Make sure to prepare well for a smooth arrival.
Important note: with the quickly changing rules and regulations for traveling to and within Indonesia - please inform with your local authorities as well. We are not responsible for any unforseen changes.
We update this Bali Travel Checklist each time we receive new updates.
Have a safe flight and have the most amazing time on the island. Make sure to share your tropical adventures with us by tagging @welikebali in your stories and posts!
1. Flight Tickets
If you arrive on Visa on Arrival make sure your return date or date that you’re flying to another country is within 60 days.
2. Your Passport
At least valid for another 6 months.
To enter Bali you need a visa. For your vacation you need a Visa on Arrival (VOA). The VOA will cost IDR 500.000 (around 32 euros) per person (children as well). You can buy the visa when you arrive on the airport in Denpasar with cash (IDR, USD or Euro), Mastercard or Visa.
You can also apply for an eVOA before arrival with a dedicated immigration lane, eliminating much of the waiting-in-line delays. Details (including the full list of eligible countries) can be find here.
The VOA is a single entry visa and valid for 2 x 30 days. So you can stay max 60 days in total. This visa is not extendable. If you plan to stay longer than 30 days you will need an extension halfway at 30 days. You can arrange this with a local visa agent and will need to go on a specific time to the immigration office in Jimbaran for fingerprints. Note: because it's very busy at the moment at most visa agents, make sure to arrange this already a week after you arrive in Bali.
If you plan to stay longer than 60 days, a B211A visa might be better for you. This visa you will need to apply for 10-15 days before your departure and costs around IDR 4.500.000 per person. Contact Bali Solve to arrange: WhatsApp on +62 812 37726811 (mention 'Welikebali'!).
4. Download the Peduli Lindungi App
Before it was required to fill in the e-HAC but at the moment it's not necessary anymore. Just download the app on your phone, and they might be asking for it to show at the check-in and when arriving in Bali.
Fill in this form before departure and follow instructions at the customs desk.
6. Double vaccination certificate (or 1 J&J vaccination)
Bring paper based proof. Unfortunately without vaccination you currently can not enter Indonesia yet, but there are talks that this might change.
Children under 18 can enter without proof of vaccination but must travel with a parent or guardian who meets all requirements.
Some websites state it's possible to do quarantine when not vaccinated but this is strictly only if you have a proof of medical exemption.
Just to confirm which rules do not apply and what is not mandatory anymore;
No PCR test is needed when you arrive in Denpasar on an international flight and no quarantine booking needed.
Officially also the insurance paper proof that COVID is covered is also not mandatory anymore when you arrive in Indonesia.
NEW: IMPORTANT NOTE
Domestic travel doesn't require a PCR test nor proof of vaccination.

Go faster through all the checks?
You can also book a special VIP fast track service for 35 USD per person. Someone will meet you when you get out of the plane and walk with you through all the checks. They will now at this time with all the regulations collect your documents via Whatsapp before you fly out to Bali, so they have everything on hand when you arrive in Bali to get you through fast and stress free. They also collect your luggage while you can chill in the lounge area.
We always book Mrs. Malini from Bali VIP Fast Track, you can send her a Whatsapp to book your VIP arrival on +62 82147208677.
Airport Pickup
We always advice to arrange your pick-up transfer before arriving to Bali. Book a driver for pikc-up at your first stay or contact our personal driver Pak Made via whatsapp on: +62 812-8532-1860. Make sure to always share your flight details with the driver so they can track your flight in case of delays.
Another option is to walk outside the arrival hall and take an official Airport Bluebird taxi.

BALI TRAVEL GUIDE ISSUE 005
Feeling overwhelmed about where to start, where to stay, what travel route to create and how not to miss the most incredible places to explore? Our Island eGuide for the creative traveler is all you need to plan your dream vacation to Bali and surrounding islands. Consider us your hosts showing you through the best of the island, with our 13 years in Bali we know our way around!
Our Islandlife eGuide is filled with 150 pages of everything you need to know to prepare for your trip to Bali, inspirational photography with an overview of our all-time favorite restaurants, cafes, beaches, surf spots, island stays, tropical escapes, shops, spas and tips for traveling Bali and the Gili Islands, Nusa Islands and Flores. Every place is personally visited and photographed by us.
Instant download Our Bali Travel eGuide comes as a downloadable PDF guide. Easy to bring with you on your smartphone or notebook while traveling. After completing your order, you’ll receive the download link instantly!
What's inside our Bali Guide?
- 150 pages filled with all the Bali information, our curated spots and stays and more.
- Everything you need to know before you go (from arrival to visa to money, the Gojek app, getting around and online, tips on traveling safe, addresses of hospitals and local doctors and more!)
- Explaining the areas in Bali and where to go
- Our recommended island stays per area, from pool villas to boutique hotels, ocean view bungalows to tropical glamping, there's something for every budget. All tried, tested & loved! Includes easy links to book directly!
- 100+ favorite restaurants and cafes
- The most beautiful beaches you can't miss out on, best surf spots (and where to learn how to surf!) and beach clubs
- Where to shop, have the best massages, getting your nails done
- Best gyms and workout spots per area and where to do yoga
- Our favorite addresses and tips for The Gili Islands, Nusa Lembongan, Ceningan and Penida, Flores & The Komodo Islands (including our contacts to book your boat tickets and local tour guides!)

7 Responses
March 02, 2023
Any rumors or news on releasing the 2 dose vaccinations requirement soon?
March 25, 2022
Wat als je voor je trip naar Bali, Corona hebt gehad en een herstel bewijs hebt. Is het dan nog wel mogelijk om naar Bali te komen? Kans is groot dat je met je PCR positief test.
Groet! Youri
Hi, do we still need to do PCR on day 3 of arrival? What do we do after we have done the test, do we need to submit?
March 24, 2022
Hoi Willemijn,
Misschien zie je dit nog. De pcr test betreft voor je vertrek. Anders wordt het natuurlijk een lastig verhaal. Daarna heb ik via mijn zorgverzekering een engelse verklaring gekregen dat ik gedekt ben voor kosten, dit was een standaard optie om aan te vragen ( ze hebben het vaker gehoord). Dit ga ik zelf meenemen! Hopelijk lees je het nog. Gr Sanne
March 19, 2022
Is that 2 tests 24 hours before we go? Or one test 48 hours before we go?
Thank you so much. G
March 18, 2022
Hi Ladies, ik vlieg volgende week weer lekker naar Bali, alles bijna geregeld. Ik heb 2 vragen waar ik niet helemaal uit kom, dus hopelijk kunnen jullie helpen.
7. PCR Test negative result 2×24 hour before departure → Wordt dan gekeken naar de Departure vanaf Nederland of vanaf de overstap op Singapore? 10. Travel insurance → Als Nederlanders zijn we natuurlijk goed verzekerd alleen ik zie nergens de medische kosten overzicht terug komen. Hoe moet ik dat bewijzen?
Hi. Can someone please advise if the Puri Saron Seminyak hotel is CHSE certified
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.
Also in Stories

Atlas Super Club Canggu

Renting a motorbike in Bali — Tips + Everything you need to know

NIEUWE editie We Like Bali reisgids lanceert 1 maart!
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Indonesia set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact Indonesia’s embassy in the UK .
Death from COVID-19 in Indonesia
If COVID-19 is given as cause of death and you would like to arrange a local cremation and repatriation of ashes, you will need to make contact with a local undertaker within 4 hours of the death registration to give your instructions. If you do not do this, it is likely that a local burial will take place.
You will also require a letter of no objection from the Embassy. This will be issued on the next working day.
Passport validity requirements
Make sure your passport is valid for at least 6 months from your date of entry into Indonesia.
Check with your travel provider or the nearest Indonesian Embassy or Consulate to make sure your passport and other travel documents meet the requirements.
Dual nationality
Indonesian law does not allow dual nationality for those aged 18 and older. If you are a British national who has retained Indonesian nationality, you could have difficulties with immigration in Indonesia. You might have to renounce your nationality or hand in your Indonesian passport.
Visa requirements
You can apply for an e-visa before arrival on the Indonesian immigration website .
Visas on arrival
British nationals who visit Indonesia for the following reasons can also apply for a visa on arrival at a cost of 500,000 Indonesian rupiah:
- official visit or government duties
- business or official meeting
- procurement of goods
The visa is valid for 30 days. It can be extended once (for a maximum of 30 days) by making an application to an immigration office within Indonesia. Make sure you extend your visa within the initial 30 days to avoid an overstay fine of 1 million rupiah a day.
KITAS extension (stay or work permit)
KITAS holders with expiring stay permit but currently outside Indonesia can apply for an extension through a sponsor. The sponsor must submit the application to the immigration office attaching a copy of the passport and proof of leaving Indonesia. The application is submitted without biometric sampling. The sponsor must report the foreigner’s arrival within 30 days.
Beware of visa scams by fake visa agents who, having taken your money, may fail to provide a visa or supply the wrong visa. This could result in your overstaying and a fine of 1 million Indonesia rupiah per day, detention, deportation and possible re-entry ban. Use the Indonesian Immigration self-service portal.
Visa scams are increasing in Indonesia. Some travellers have lost significant amounts of money. Others have been deported despite paying large fees to an agent to get the correct visa or extension.
If you choose to use to use an agent check they are reputable.
Overstaying your visa
Visitors who overstay without the proper permissions can be held in detention or refused permission to leave the country until a fine of 1 million Indonesian rupiah per day is paid.
If you have overstayed your visa for less than 60 days, you must pay your fine at the airport. After 60 days, you will be detained until the fine is paid.
If your visa will expire during a period of hospitalization or detention, contact Indonesian Immigration before your visa expires to avoid any overstay fines. The British Embassy Jakarta can assist with this.
Proof of onward travel
Immigration officials in Indonesia may ask you for proof of onward travel (such as a return or onward air ticket). Make all reservations before leaving for Indonesia. Some airlines have refused to board passengers without evidence of onward travel.
Airport tax
Airport tax is included in the cost of all domestic flights within Indonesia. For some international flights departing Indonesia, airport tax might not be included in the price of the ticket. Check with your airline or travel agent before you travel.
Tourist levy
On 14 February 2024, the Bali Provincial Government will introduce a tourist levy of 150,000 Indonesian rupiah per person (approximately £8) to all foreign tourists arriving in Bali. Payment can be made online or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali’s airport and seaport. Further information can be found on the Bali Provincial Government’s official website .
Vaccination requirements (other than COVID-19)
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and vaccination certificates you may need on TravelHealthPro .
Depending on your circumstances, these may include:
- yellow fever
Accommodation
Registering.
If you stay in private accommodation in Indonesia (not a hotel) you must register your presence with the local police at the nearest police station. You could be fined 5 million Indonesia rupiah if you do not register. If you stay in a hotel you will be registered automatically.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

- All Posts 39
- Latest Updates 7
- Entry & Exit Requirements 4
- Travellers Info 9
- Health & Safety 4
- Official Sites & Useful Links 6
- Campaigns 9

- Entry & Exit Requirements
Visa & Entry Requirements
Latest update on visa requirements and how to apply to enter Bali, as of 14 February 2024
Bali introduces IDR150,000 tourism levy from February 14, 2024
In an effort to safeguard Bali's rich customs, traditions, arts, and local wisdom, the Bali Provincial government has introduced the International Tourism Levy.
Apply and Pay for your Visa On Arrival Online e-VOA
e-VOA is a single-entry visa which is valid for 30 days stay in Indonesia with the purpose of Tourism, Government Visit, Business Meeting, Goods Purchasing, or Transit only.
Customs Declaration Online
e-CD Customs Declaration Form must be completed online. You will receive a QR code once you have completed all the information.
Trending Now
E-cd customs declaration form.
Bali International Airport Customs Electronic Customs Declaration
CHSE Certified Hotels In Bali
Looking to book your stay in Bali with your favourite hotel?
About the information on this site
All information presented on Welcome Back To Bali is reviewed regularly by our editorial team to ensure content is up-to-date, accurate and from official sources. Updated February 14, 2024
- Latest Updates
- Travellers Info
- Health & Safety
- Official Sites & Useful Links
Share This Content
Please ensure that you carefully read and understand our disclaimer.
This website is presented by the Bali Hotels Association[BHA]. It's purpose is to share travel advice and information with the public about Bali. BHA endeavours to provide up-to-date and accurate advice on this website, However, BHA does not guarantee the accuracy, reliability, currency or completeness of any material on this or any linked site. BHA accepts no legal liability arising from or connected to any material on this website or on any linked site. Welcome Back To Bali content The information on Welcome Back To Bali, is to help travellers to Bali to make informed decisions about traveling to Bali and staying in Bali. This includes information in official destination-specific travel advisories and general advice. All travelers need to take responsibility for their travel decisions. The information on Welcome Back To Bali isn't intended to be, nor should it be relied on, as a substitute for legal or other professional advice. Users should obtain any appropriate professional advice relevant to their particular circumstances. Articles are reviewed regularly by our editorial team to ensure that the content is up to date and accurate. Please return to the site as required and subscribe to updates to ensure you have the latest advice. Links and third-party content The material on this website may include the views or advice of third parties. It also includes links to external websites. These do not necessarily reflect the views of BHA
Due to the ever-changing nature of the regulations, we strongly advise that you check with your airline before you travel.
Situation in Haiti April 5, 2024
U.s. citizens in haiti, update april 12, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 24, 2023
Indonesia - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in Indonesia due to terrorism and natural disasters. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do Not travel to:
- The provinces of Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and Highland Papua (Papua Pegunungan) due to civil unrest.
Terrorists continue plotting possible attacks in Indonesia. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting police stations, places of worship, hotels, bars, nightclubs, markets/shopping malls, and restaurants.
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis or volcanic eruptions may result in disruptions to transportation, infrastructure, sanitation, and the availability of health services.
Demonstrations occur frequently and have the potential to become violent. Avoid demonstrations and crowds.
Indonesia’s revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. It is unclear how Indonesian authorities will implement the revised criminal code.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Indonesia.
If you decide to travel to Indonesia:
- Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to adjust your plans.
- Visit the websites for Badan Geologi (Indonesian Geological Agency, Indonesian language only) for the latest information from the Government of Indonesia on current natural disasters.
- Review the CDC’s suggestions on how to prepare for natural disasters.
- Be aware of your personal safety and security at all times.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Ensure your passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay.
- Follow the Department of State Facebook and Twitter . Follow the U.S. Embassy Jakarta on Facebook , Instagram , and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Indonesia.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Central Papua and Highland Papua– Level 4: Do Not Travel
In Central Papua and Highland Papua, violent demonstrations and conflict could result in injury or death to U.S. citizens. Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Armed separatists may kidnap foreign nationals.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Central Papua and Highland Papua as U.S. government employees must obtain special authorization before traveling to those areas.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Six months beyond arrival date. Indonesia does not accept the 12-page U.S. emergency passport for entry into Indonesia.
Two blank visa pages required for entry stamp
Yes, Visa or Visa on Arrival
100,000,000 Indonesian rupia (approx. $7,000 USD)
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy jakarta.
Jl. Medan Merdeka Selatan No. 3 - 5 Jakarta 10110, Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(21) 5083-1000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(21) 5083-1000 ext. 0 (operator) Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Surabaya Jl. Citra Raya Niaga No. 2 Surabaya 60217 Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(31) 297-5300 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(811) 334-183 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consular Agency Bali Jalan Hayam Wuruk 310, Denpasar, Bali Telephone: +(62)(361) 233-605 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: Please contact the U.S. Consulate in Surabaya:+(62)(811) 334-183 Email: [email protected]
American Consulate Medan, Sumatra Uni Plaza Building 4th Floor (West Tower) Jl. Let. Jend. MT Haryono A-1 Medan 20231, Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(61) 451-9000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(61) 451-9000 Email: [email protected]
The U.S. Consulate in Medan provides only emergency assistance to U.S. citizens and does not offer routine consular services.
Destination Description
See the Department of State’s Fact Sheet on Indonesia for information on U.S.- Indonesia relations.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Entry Requirements: To enter Indonesia, your passport must have at least two blank pages and be valid for at least six months beyond the date of your arrival in Indonesia. If your passport does not meet these requirements, you will be denied entry into Indonesia. The Government of Indonesia will not admit travelers holding the 12-page U.S. emergency passport, issued by U.S. embassies and consulates overseas.
Visa-on-Arrival: If you meet the requirements, you can apply for a visa on arrival at some international airports, seaports, or land crossings. To apply for the visa on arrival, you must have an ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter and the date you plan to leave Indonesia and a return or onward flight booking to another country. There is a 500,000 Indonesian Rupiah fee (about $35). The visa on arrival is valid for up to 30 days. You may extend a Visa-on-Arrival once at the immigration office one week before it expires for an additional 30 days for a maximum of 30 additional days, for another 500,000 Rupiah.
- Official visit or government duties;
- Business meeting;
- Procurement of goods;
- Official meeting; or
Electronic Visa-On-Arrival: You may also apply for an electronic Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) in advance if you are entering Indonesia at Soekarno-Hatta International Airport in Jakarta or Ngurah Rai International Airport in Bali. Check the e-VOA requirements from Indonesian Immigration before applying. To apply for an e-VOA see https://molina.imigrasi.go.id/ .
Visa: Travel for more than 30 days and travel for non-VOA purposes, including employment and journalism, requires that the appropriate visa be obtained from an Indonesian embassy or consulate before arrival. If you are traveling on an emergency passport, you must obtain a visa before arrival in Indonesia.
If you overstay your visa, you are subject to a fine of 1 million Indonesian rupiah (about $70 USD at current exchange rates; fees may change at any time) per day and may be detained and deported. U.S. citizens have been jailed for visa overstays or entering the country on the wrong visa class for their purpose of travel . Travelers coming to Indonesia for non-tourism purposes are strongly encouraged to consult Indonesian Immigration’s website. Travelers should generally carry a copy of their passport with them whenever possible to establish their identity and proof of Indonesian visa.
You must exit Indonesia using the same passport that you used to enter. If this passport is replaced for any reason before you depart Indonesia, you must apply with Immigration to obtain a “special pass” (exit permit) in your new passport prior to departing.
Dual-Nationality: Indonesia has laws that prohibit Indonesian citizens from holding additional nationalities. If you are an Indonesian with dual nationality, you could be compelled to renounce your Indonesian nationality through a formal act of renunciation. Please research Indonesian nationality laws and consult with a local attorney regarding any specific circumstance.
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Indonesia. The Government of Indonesia screens incoming passengers in response to reported outbreaks of pandemic illnesses.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorist groups and those inspired by such organizations are intent on attacking U.S. citizens abroad. Terrorists are increasingly using less sophisticated methods of attack – including knives, firearms, and vehicles – to target crowds. Frequently, their aim is unprotected or vulnerable targets, such as:
- High-profile public events (sporting contests, political rallies, demonstrations, holiday events, celebratory gatherings, etc.)
- Hotels, clubs, and restaurants frequented by tourists
- Places of worship
- Shopping malls and markets
- Public transportation systems (including subways, buses, trains, and scheduled commercial flights)
Extremists in Indonesia aspire to carry out violent attacks against Indonesian and foreign targets, and police have arrested more than 1,200 individuals on terrorism-related charges since 2018. Extremists may target both official and private establishments, including government offices, hotels, bars, nightclubs, shopping areas, restaurants, and places of worship. Be aware of your personal safety and security at all times.
Recent incidents of extremist violence include a December 2022 suicide bombing at a police station in Bandung, West Java that killed one police officer, a March 2021 bomb attack against a church in Makassar, South Sulawesi which injured 20 civilians, and May 2018 bomb attacks against three churches in Surabaya, East Java which killed 15 civilians and injured 50.
Demonstrations are very common in Jakarta, Surabaya, and other large cities, but less common in Bali. You should avoid demonstrations and other mass gatherings, since even those intended to be peaceful can become violent. U.S. citizens have been detained for participating in protests. Demonstrations may become more frequent ahead of the Indonesian general elections scheduled for February 2024.
Currently, travel by U.S. government personnel to the provinces of Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and Highland Papua (Papua Pegunungan) is restricted to mission-essential travel that is approved in advance by the Embassy. Papuan separatists have kidnapped foreigners in the past and a New Zealand national was kidnapped by a separatist group in Nduga Regency in February 2023.
For more information, see our Terrorism page.
Crime: In the last year several American citizens were victims of violent and serious crimes in Indonesia, particularly in Bali. As with any major tourist destination, U.S. citizens traveling in Indonesia are especially encouraged to always remain vigilant of their surroundings and read the following advisories carefully. Take sensible measures to protect yourself and your belongings. Closely monitor bags and luggage and carry only essential items. Take particular care of your passport and bank cards and avoid traveling alone.
Police presence and responsiveness is less than it is in the United States, making it more difficult to report crimes quickly and receive police attention. U.S. citizens often cite language barriers as a major hindrance when reporting crimes.
Pickpocketing, sexual assault, vehicle theft, armed car-jacking, snatch and grab robberies of cell phones and purses, and residential break-ins are common. Avoid traveling to isolated areas late at night. Be aware of your surroundings, particularly vehicles or individuals that might be following you.
Use a reputable taxi company or hire a taxi either at a major hotel or shopping center and ensure the driver’s identity card is visible. If you are booking a car via a mobile app, always ensure that the driver is the same as the person on the app, share your journey with a friend via the in-app option, and know the contact information for the app’s security center. Be aware of drivers falsely claiming to be registered with online ride hailing apps.
Credit card fraud is a common problem in Indonesia. Criminals have “skimmed” credit/debit cards to access and drain bank accounts. Use an ATM in a secure location, such as a major bank branch, and check the machine for evidence of tampering. Monitor your account statements regularly.
Tourists and Indonesians have suffered from serious illness and have even died from "drink-spiking” and drink poisoning incidents, particularly in clubs and nightspots in urban and tourist areas. There have been reports of sexual assaults and drink spiking in Bali, Lombok, and the Gili Islands. Make sure drinks are prepared in your sight and be careful about accepting drinks from strangers at clubs and parties or leaving drinks unattended. Tourists have also been robbed after taking visitors to their hotel rooms, and in some cases have found that their drinks were spiked. There have also been deaths and serious illnesses caused by drinking alcoholic drinks contaminated with methanol. These cases have occurred in bars, shops, and hotels in popular tourist areas like Bali, Lombok, the Gili Islands, and Sumatra.
Sexual Assault: Women travelling alone may be subject to harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault, harassment, and rape occur. To minimize the risk, avoid travelling alone, especially at night; remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas; and be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances. Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum, or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery. Local authorities may not respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the U.S. Embassy or U.S. Consulate General.
Demonstrations occur frequently. They may take place in response to political or economic issues, on politically significant holidays, and during international events.
- Demonstrations can be unpredictable. Avoid areas around protests and demonstrations.
- Past demonstrations have turned violent.
- Check local media for updates and traffic advisories.
- Participating in demonstrations on a tourist visa can lead to deportation.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Internet romance and financial scams occur in Indonesia. Scams are often initiated through Internet postings/profiles or by unsolicited emails and letters. Scammers almost always pose as U.S. citizens who have no one else to turn to for help. Common scams include:
- Romance/Online dating
- Money transfers
- Lucrative sales
- Gold purchase
- Contracts with promises of large commissions
- Grandparent/Relative targeting
- Free Trip/Luggage
- Inheritance notices
- Work permits/job offers
- Bank overpayments
Victims of Crime:
Sexual assault: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault should seek prompt medical assistance, contact the Embassy or nearest Consulate, and call the local police at 112. For a criminal investigation to be initiated by the police, the victim must make a full statement to the local police, in person. Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime. U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault may choose to be accompanied by a translator.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- Provide a list of local attorneys
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution. Follow this link for more information
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the Embassy for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism and recreational activity industries are unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. Water sports, especially diving, can be hazardous in Indonesia with operators lightly regulated and hyperbaric chambers available only in Bali and Ambon. Traffic is hazardous in Indonesia and U.S. citizens are frequently injured while riding rented motorbikes. Wearing a helmet is required by law. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities, and only basic stabilization may be available. Serious injuries require medical evacuation to another country. First responders are generally unable to provide urgent medical treatment or to access areas outside of major cities. Boat and ferry incidents are frequent; vessels rarely carry appropriate sizes and numbers of safety vests; passengers are encouraged to bring their own. U.S. citizens are strongly encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage ( http://travel.state.gov/content/passports/en/go/health/insurance-providers.html ).
Please note: The U.S. Embassy and Consulates do not pay the medical expenses of private U.S. citizens in Indonesia. It is the traveler’s responsibility to ensure adequate medical insurance coverage or funds for medical expenses.
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to Indonesian laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Criminal cases can take months or even years to resolve, and suspects can be held without charges for up to 60 days, and in many cases longer. Indonesia‘s revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to stay up-to-date.
If you are convicted of possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Indonesia, you may be subject to heavy fines, long jail sentences, and even the death penalty. Some prescription medications that are available in the United States are illegal in Indonesia. Some drugs used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are illegal in Indonesia. Marijuana, Cannabis, hash, “edibles,” and products containing CBD or THC remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation, or the death penalty. Illegal drug convictions often result in lengthy prison sentences, even at the simple possession level. Indonesian prison conditions are harsh and do not meet U.S. standards. Many prisons are overcrowded and provide minimal services. The costs of basic services, including healthcare, often must be borne by the prisoner.
Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- nternational Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTQI+ Travelers: LGBTQI+ status or conduct is not illegal, but local authorities sometimes take legal action against, or tolerate harassment of people engaging in LGBTQI+ relationships or openly expressing LGBTQI+ identity. Some local governments have passed laws criminalizing LGBTQI+ relationships. Same-sex marriages or civil unions recognized as valid in other countries are not legally recognized in Indonesia. The Indonesian Parliament revised the criminal code to include penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions, however, will not come into force until January 2026, and how they will be implemented is unclear.
See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details .
Sharia Law: Sharia law is enforced in Aceh province and may exist unofficially or through local legislation in other areas. The law is intended for Muslims and should not apply to non-Muslims or foreign visitors. You should be respectful of local traditions, mindful of social norms, and seek guidance from local police if confronted by Sharia authorities.
Earthquakes and Tsunamis: There are approximately 4,000 earthquakes per year in Indonesia, or more than 10 per day on average. While most earthquakes are mild, some cause significant destruction and can trigger tsunamis. Tsunami warning systems may not be operable, or reports of tremors and tsunamis may be delayed. Local construction standards are lower than in the United States, and many structures including hotels and malls are prone to damage or collapse in an earthquake. Access to disaster-affected areas is often difficult and assistance from the U.S. Embassy may be limited.
If a major earthquake or landslide occurs close to shore, you should follow the instructions of local authorities, bearing in mind that a tsunami could arrive within minutes. The Indonesia Tsunami Early Warning Centre issues tsunami warnings when a potential tsunami with significant impact is imminent or expected.
Volcanoes: There are 127 active volcanoes in Indonesia. Eruptions frequently cause travel delays, displace local populations, and disrupt economic activities.
Environmental Quality: Air quality in Indonesia’s major cities can range from "unhealthy for sensitive groups" to "unhealthy." Current air quality data for Jakarta can be found on the Embassy’s Air Quality page. Tap water is not potable throughout Indonesia and should not be consumed.
Mountain Hiking: When hiking in mountainous areas, obtain current information on local conditions, travel with a reputable guide, have overseas medical insurance, and carry a local mobile phone. Never go hiking or climbing alone. Particularly dangerous trails may not be clearly labeled as such. Hikers on Puncak Jaya in Papua should have realistic primary and backup plans for climbing down the mountain. Tour operators have abandoned climbers. Taking shortcuts through private property is considered trespassing and is not a safe or legal alternative to a proper plan. If possible, ensure your hiking plans are registered and known to local authorities and/or tourism operators, as this helps identify your presence in these areas in the event of an emergency.
Dual Nationality: Indonesian law does not recognize dual nationality for adults over 18 years of age. U.S. citizens who are also Indonesian nationals may be required to renounce their Indonesian citizenship and may also be deported. Please visit our Dual Nationality page .
Travelers with Disabilities: Persons with disabilities will face severe difficulties in Indonesia as most public places and transportation facilities do not accommodate disabled people. The law in Indonesia prohibits discrimination against persons with mental and physical disabilities, but the law is seldom enforced. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States. Expect accessibility to be extremely limited in public transportation, lodging, communication/information, and general infrastructure.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Women traveling alone may be subject to harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault, harassment, and rape occur. To minimize the risk, avoid travelling alone, especially at night; remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas; and be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances. Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum, or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery. While domestic violence is illegal in Indonesia, these laws are rarely enforced. Local authorities may not respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the U.S. Embassy or U.S. Consulate General and seek medical attention. See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
The Government of Indonesia requires all non-Indonesian citizens entering the country to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
Medical Care: For emergency services in Indonesia dial 112.
Sanitation and health care conditions in Indonesia are far below U.S. standards. Routine medical care is available in all major cities, although most expatriates leave the country for all but the most basic medical procedures. Physicians and hospitals often expect payment or sizable deposits before providing medical care, even in emergency and/or life-threatening situations. See our Embassy's website for a list of English-speaking doctors and hospitals, but keep in mind that even in large cities the quality of English-speaking medical personnel will vary and there are often communication difficulties. In remote areas there may be no English-speaking medical personnel. Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities, with hospital-based care only available through government institutions.
Ambulance services are not widely available, and training and availability of emergency responders may be below U.S. standards. Ambulances are not staffed with trained paramedics and often have little or no medical equipment. Injured or seriously ill travelers may prefer to take a taxi or private vehicle to the nearest major hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation, which can exceed over $100,000 per person.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Be aware that Indonesian authorities may consider some prescription drugs as illegal narcotics. The Indonesian government does not publish a list of which pharmaceuticals are considered contraband, and these decisions may be arbitrary.
U.S. citizens are advised against mailing or shipping by courier any medications to Indonesia. Indonesian authorities pay close attention to packages containing pharmaceuticals and may detain or arrest recipients of both prescription and over the counter medications. Even if a medication is legal or has been prescribed in the United States, it may be considered an illegal narcotic in Indonesia. U.S. citizens are advised to only hand carry prescription medications into the country, in the original packaging with a copy of any prescription. The U.S. Embassy and Consulates cannot assist you with the importation and/or release of medications.
Marijuana, Cannabis, hash, “edibles,” and products containing CBD or THC remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal.
Local pharmacies carry a range of products of variable quality, availability, and cost. Counterfeit pharmaceuticals are a significant risk; patronize only reputable pharmacies. Malaria, dengue, Japanese encephalitis, and Zika virus are mosquito borne diseases in Indonesia. Prevention of mosquito bites is strongly encouraged; malaria preventive medication is needed in some areas. Pregnant women should be aware that Indonesia is a CDC Zika risk area and that Zika can be spread by mosquitos as well as sexual contact . Diarrheal diseases are very common throughout Indonesia and food and water precautions are recommended. Rabies is prevalent in animals and animal contact should be avoided.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates. See the OPTIONAL stock language below for additional suggestions.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals. We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for information on Medical Tourism, the risks of medical tourism, and what you can do to prepare before traveling to Indonesia.
- We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation in the event of unforeseen medical complications.
- Your legal options in case of malpractice are very limited in Indonesia.
Pharmaceuticals
- Exercise caution when purchasing medication overseas. Pharmaceuticals, both over the counter and requiring prescription in the United States, are often readily available for purchase with little controls. Counterfeit medication is common and may prove to be ineffective, the wrong strength, or contain dangerous ingredients. Medication should be purchased in consultation with a medical professional and from reputable establishments.
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Water Quality
- Tap water is not potable. Bottled water and beverages are generally safe, although you should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Be aware that ice for drinks may be made using tap water.
Adventure Travel
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
General Health Language
The following diseases are prevalent:
- Tuberculosis
- Chikungunya
- Use the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended mosquito repellents and sleep under insecticide-impregnated mosquito nets. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended for all travelers even for short stays.
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Resources for Travelers regarding specific issues in Indonesia.
Air Quality
- Air pollution is a significant problem in several major cities in Indonesia. Consider the impact smog and heavy particulate pollution may have on you and consult your doctor before traveling if necessary. People at the greatest risk from particle pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema
- People with heart disease or diabetes
- People who work or are active outdoors
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Traffic in Indonesia is hazardous, congested, and undisciplined. Traffic signals are frequently ignored and often in disrepair. Motor vehicles share the roads with other forms of transportation such as pedicabs and pushcarts. Buses and trucks are often dangerously overloaded and travel at high speeds. Accidents between a car and a motorcycle are viewed as the fault of the driver of the car. Consider these risks before driving your own vehicle, especially if you are unaccustomed to Indonesian road conditions. When an accident results in personal injury, Indonesian law requires both drivers to await the arrival of a police officer to report the accident.
Public Transportation: Air, ferry, and road accidents that result in fatalities, injuries, and significant damage are common. While all forms of transportation are regulated in Indonesia, oversight is spotty, maintenance may not be properly performed, and rescue and emergency capacity are limited. Indonesia has experienced several fatal plane crashes and non-fatal runway overruns in recent years. Also in recent years, several ferry accidents and a train collision resulted in dozens of fatalities and even more injuries because of over-crowding and unsafe conditions.
See our Road Safety page for more information. Also, visit Indonesia's national tourist office online for road safety information.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Indonesia’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Indonesia’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Since 2014, several private pilots have inadvertently crossed into Indonesian airspace and have been detained and paid heavy fines. If you intend to fly on private aircraft through Indonesian airspace, get clearances from Indonesian aviation authorities before you depart.
Maritime Safety and Security: Inter-island travel by boat or ferry can be dangerous: storms can appear quickly, vessels may be over-crowded and lack basic safety equipment, and safety standards vary. Ferries have sunk, resulting in loss of life. The Indonesian Search and Rescue Agency records boat and ferry accidents resulting in injuries and deaths yearly. Boats and ferries used in tourism or general transportation frequently break down, stranding passengers or capsizing; not all boats are equipped with adequate life vests. Make sure you are satisfied with safety equipment and life jackets before travelling.
Piracy: Maritime piracy and other related crimes in and around Indonesian waters continue. Recent reports include thefts of valuables or cargo from boats that are in port and out at sea. Before traveling by sea, especially in the Strait of Malacca between Riau Province and Singapore, and in the waters north of Sulawesi and Kalimantan, review the current security situation with local authorities. Be vigilant, reduce opportunities for theft, establish secure areas on board, and report all incidents to the coastal and flag state authorities.
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Indonesia should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts on the Maritime Administration website . Information may also be posted to the websites of the U.S. Coast Guard and the National Geospace Intelligence Agency (select “broadcast warnings”).
In recent years, private vessels have inadvertently anchored in Indonesian waters, especially near Singapore, and have been detained and paid heavy fines.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Indonesia . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, indonesia map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall due to security risks.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
Indonesia (PDF 699.19 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire services, ambulance and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 110 or 112.
Tourist Police, Bali
Call (+0361) 759 687.
Tourist Police, Jakarta
Call (+201) 526 4073.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall.
Reconsider your need to travel to the provinces of Papua (Papua), Papua Highlands (Papua Pegunungan), Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and South Papua (Papua Selatan).
Reconsider your need to travel to the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan due to the risk of serious security incidents or demonstrations that may turn violent.
- There's an ongoing risk of terrorist attack in Indonesia. Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities. Popular tourist areas may be the target of terrorist attacks.
- Public protests and events that draw large groups of people occur regularly and can turn violent with little notice. Expect traffic delays and restricted access to locations if there are protests. Avoid protests and demonstrations and monitor local media for the latest updates.
- Many of Indonesia's volcanoes are active and can erupt without warning. Adhere to exclusion zones around volcanoes, which can change at short notice, and follow the advice of local authorities. Domestic and international flights can be disrupted. Monitor Indonesia's Volcano Observatory Notice for the latest volcanic activity (Bahasa Indonesia and English), Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System and the Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre for updates.
- There's been tension, including demonstrations and violence, in certain towns in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan in recent years. Armed groups have stated that they're targeting foreigners, including Australians. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited. Armed groups have shot at aircraft, including commercial planes, in remote airports in Papua Pegunungan and Papua Tengah provinces.
- Petty and violent crime occurs in Indonesia. Opportunistic crime, such as pickpocketing occurs. Drinks may be spiked or mixed with toxic substances. Crimes involving taxis and taxi drivers occur. Solo women are at higher risk. Be alert in taxis, public transport, crowds, bars and nightclubs.
- Legal disputes over real estate are common, including in Bali. Before entering into an agreement or providing financial details, do your research and get legal advice.
- Natural disasters such as severe weather, floods, landslides, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and tsunamis occur regularly. Weather conditions can change quickly during the wet season (October – April). Regularly check weather reports, monitor media and speak to your travel provider before continuing with planned activities. Follow the advice of local authorities.
- When undertaking adventure activities, ensure that functioning safety equipment is available, that you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for these activities.
Full travel advice: Safety
- The standard of medical facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than in Australia. Many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities.
- Some medications, including prescription medications, drugs for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), all cannabis-based products including medicinal cannabis, cannabis-based oils and creams, hemp-based products, CBD, THC, hash and edibles, are illegal in Indonesia. Harsh penalties, such as arrest and jail time, can apply even if you have a prescription. Make sure your medication is legal in Indonesia .
- Purchasing prescription medication online or over the counter in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller before your purchase.
Full travel advice: Health
- Indonesia has revised its criminal code, which includes penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions will not come into force until January 2026.
- Penalties for drug offences include heavy fines, long prison sentences and the death penalty. Police target tourist destinations.
- Some medications are illegal in Indonesia. Harsh penalties can apply even if you have a prescription. It is also illegal to purchase prescription medications online or over the counter without an Indonesian prescription. Ensure you have a valid Indonesian prescription. See ' Health '.
The death penalty exists for some crimes in Indonesia.
- Standards of dress and behaviour are conservative in many parts of Indonesia. Learn about local customs. Take care not to offend.
- Aceh province upholds aspects of sharia law. Sharia law applies to everyone, including travellers. Inform yourself about the laws, and be careful not to offend or break local laws. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- The Idul Fitri holiday period will take place from 10 April. Many people will travel across Indonesia until 22 April, with many expected to move in and out of the greater Jakarta area. This may impact traffic and public transport, including airports, seaports, highways, toll roads, train and bus stations across Indonesia. Airports are expected to be busy. Plan your travel carefully and prepare for significant delays. Contact your travel provider for up-to-date details.
- The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the e-Visa on Arrival or the Visa on Arrival. Cashless payments can be made online prior to travel or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali's airport and seaport. See the Bali Provincial Government's official website and FAQs for further information.
- If you're travelling to Indonesia for tourism, official government duties or business meetings, you can apply for an e-Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) online at least 48 hours before your travel to Indonesia. This also applies if you're transiting through Indonesia at international airports, seaports and land crossings. You can get a Visa on Arrival (VOA) at some international airports, seaports or land crossings.
- To apply for the e-VOA or VOA, you must have an ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter (we also recommend having at least 6 months of passport validity from the date you plan to leave Indonesia, to avoid any issues for your departure or onward travel) and a return or onward flight booking to another country.
- You may need to apply for a visa in advance to enter Indonesia for purposes not covered by the e-VOA or VOA. Check the latest entry requirements with your travel provider or an Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before travel. Entry, exit and transit conditions can change at short notice. Monitor media for the latest updates.
- You'll be required to complete an e-customs declaration for arrival. You can complete this within 3 days of departure to Indonesia.
- Travel requirements may change at short notice, including travel to Bali and Jakarta by air, land or sea. Contact your travel provider and monitor media for up-to-date details.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter tells you what the Australian Government can and can't do to help when you're overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy, Jakarta , the Australian Consulate-General, Bali , the Australian Consulate-General, Makassar or the Australian Consulate-General, Surabaya .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
The terrorist threat in Indonesia is ongoing. Attacks could happen anywhere and anytime. This includes places that foreigners visit.
Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities. Remain respectful of religious and local customs.
Indonesian authorities continue to investigate and disrupt terrorist groups in Indonesia, including Bali.
Terrorist attacks are motivated by extreme beliefs. Both local grievances as well as events in other parts of the world could motivate extremists in Indonesia towards violence.
Recent terrorist attacks
In December 2022, an explosion occurred at a police station in Bandung, Jawa Barat, killing 2 and injuring 11.
In March 2021, 2 suicide bombers attacked a church in Makassar, injuring dozens.
In the past, police have said that terrorist suspects remain at large and may seek Western targets.
Indonesian security agencies continue to conduct operations against terrorist groups.
Terrorists in Indonesia may carry out small-scale violent attacks with little or no warning.
Be alert in places of worship, especially during periods of religious significance.
Terrorists have targeted places of worship in:
As well as places of worship, other possible targets by terrorists include:
- Indonesian government facilities, premises and symbols associated with the Indonesian Government
- police stations and checkpoints
- bars, nightclubs, cafes and restaurants
- cinemas and theatres
- shopping centres, public transport and transport hubs
- airports and airlines
- clubs, including sporting clubs
- tourist areas and attractions, tour buses and tour groups
- outdoor recreation events
Supporters have committed additional acts of violence in response to high-profile extremists being detained or killed.
To protect yourself during a terrorist attack:
- leave the area as soon as it's safe
- follow the advice of local authorities
- don't gather in a group after an attack
- don't gather in a group if you're evacuated from a building
Security remains at a high level at:
- the Australian Embassy in Jakarta
- the Consulates-General in Bali, Makassar and Surabaya
More information:
Civil unrest and political tension
Most events are announced before they happen; however, protests may occur with little or no notice.
Protests and events are often held near major government buildings and embassies in Jakarta, including the Australian Embassy.
Protests may also occur at any of Australia's Consulates-General in Surabaya, Bali and Makassar, at government buildings, or the offices of international organisations in Indonesia.
You can expect traffic delays and restricted access to locations if there are protests.
Phone or email ahead for an appointment before going to the Embassy or the Consulates-General (see Local contacts ).
Demonstrations and acts of violence can happen when courts try and sentence extremists.
Conflict between different communities can sometimes occur, including in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited.
Local violence can also be directed at minority groups in other parts of Indonesia, including in Java.
If you're found to endanger security or public order, you may be prosecuted under Indonesia's Immigration laws, which may result in imprisonment or deportation.
To protect yourself from possible violence:
- avoid protests and demonstrations
- monitor local media for the latest security updates
- plan your activities to avoid potential unrest on significant dates
- be prepared to change your travel plans
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Armed conflict
The provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan experience regular violent clashes involving armed groups, civilians, Indonesian police, and the military. Armed groups have stated that they are targeting foreigners, including Australians. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited.
Many people have been killed and injured in clashes. This includes members of security forces, armed groups and civilians. Violent attacks have occurred in several areas of these provinces, including in and around Jayapura. There's a risk of more attacks.
On 23 February 2023, a riot broke out in Wamena, Papua Pegunungan, when a crowd attacked Indonesian security personnel following the arrest of two people accused of child kidnapping. 12 civilians and rioters were killed.
Violent attacks have occurred around the Freeport Mine in Papua Tengah.
Armed groups have:
- taken a New Zealand pilot hostage in Paro, Papua Pegunungan
- shot at aircraft, including commercial planes, at Beoga airport in Pupua Tengah province and Nop Goliat Dekai airport in Papua Pegunungan province.
- killed people in attacks, including one Australian
- attacked vehicles using the road between Grasberg and Timika
- killed people in violent attacks in Puncak Jaya District, Papua Tengah
- more attacks are possible and could target infrastructure and national institutions.
A range of crimes, including violent crime, occur in Indonesia. Crimes can happen in popular tourist locations in Bali.
To protect yourself from crime:
- be aware of your surroundings
- be alert in crowds
- understand the potential crime risks
Theft, robbery and bag and phone snatching have occurred. These crimes can sometimes involve violence. Opportunistic crime such as pickpocketing occurs.
Be careful of thieves:
- on motorcycles targeting pedestrians
- in upmarket shopping malls
- in crowded public transport
- at traffic lights targeting people in stopped cars
- at bars and nightclubs
- when entering accommodation, including villas in Bali
Keep bags and valuables out of sight in vehicles.
If you're travelling on foot, walk:
- on footpaths
- away from the curb
- with your bag held away from traffic
Sexual assault
If you're a victim of sexual assault :
- get immediate medical assistance. If you have any doubts about seeking medical assistance after a sexual assault, contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate in Indonesia (see Local contacts ) as quickly as possible.
- make a full statement to local police, in person, so they can conduct a criminal investigation. You may wish to seek consular help before you visit the police station. Contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate (see Local contacts ).
Local police can only investigate a crime after you've left Indonesia if you've reported it.
Your sworn statement, or statements by witnesses, can be used as evidence in criminal court proceedings.
You don't always need to be in Indonesia for trial. Neither do witnesses who live outside of Indonesia.
Counselling support
Should you wish to speak to a counsellor, you can call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate (see Local contacts ). They can connect you to counselling hotlines and services.
- Reducing the risk of sexual assault

Bars and nightclubs
Be alert in bars and nightclubs. Drink-spiking and snatching of valuables may occur if you're not alert.
Drinks may be contaminated with drugs or toxic substances. See Health .
Don't leave your food or drinks unattended.
Never accept drinks, food, gum, cigarettes, vapes or e-cigarettes from people you've just met.
- Partying safely
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card, online banking and ATM fraud occurs in Indonesia.
Check your bank statements.
Make sure your bank doesn't block your cards. Tell your bank you'll be visiting Indonesia.
Never let your card out of your sight. This includes when you pay in restaurants.
Shield your PIN from sight.
Some vendors install hidden cameras and use card skimmers.
Don’t click on unknown links in WhatsApp or mobile phone text messages, particularly if your phone is linked to mobile banking.
Use ATMs at controlled and secure places, such as:
- shopping centres
Scams and confidence tricks
Beware of scams and confidence tricks.
Only exchange money at authorised money changers. Authorised money changers can also be found on the Bali Foreign Exchange website . Unauthorised money changers have been known to scam foreign tourists in Bali and elsewhere.
All types of gambling are illegal in Indonesia.
Australians have lost large sums of money in card game scams run by organised gambling gangs, particularly in Bali. See Local laws
Some tourists have been robbed or planted with drugs after taking new acquaintances back to their hotel rooms. In some cases, their drinks were spiked.
Legal disputes over the purchase of real estate are common, including in Bali, involving:
- holiday clubs and resorts
- timeshare schemes
Before entering into an agreement or providing financial details:
- thoroughly research the proposal
- get legal advice and know your rights, especially before you sign any documents
Using taxis
Only use licensed official metered taxis. Crimes involving unregistered taxis include:
- taxis departing before the passenger can take their baggage from the vehicle
- taxi drivers robbing or temporarily holding passengers, including in urban areas
- taxi drivers forcing passengers to withdraw money at ATMs before releasing them
Lone female travellers are at higher risk of crime.
If you're in an incident involving a taxi, leave the taxi and the immediate area if it's safe to do so.
To protect yourself from overcharging and scams:
- only travel in licensed taxis with signage, a "taxi" roof sign and meters working
- ensure the driver's identification card is visible
- book via your phone, on an official taxi company mobile app, from inside an airport, or at stands at major hotels
See Travel .
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas while travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including destinations that are typically at lower risk.
On 7 February 2023, a New Zealand pilot was taken hostage by an armed group in Paro, Papua Pegunungan.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Adventure activities
Many businesses don't follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes transport and tour operators, water sports providers, hotels, restaurants and shops.
It may affect adventure activities, such as:
- bungee jumping
- scuba diving and snorkelling
- chairlift or gondola rides
In the past, Australians have been seriously injured or died while participating in adventure activities. If you require intensive care medical treatment, emergency surgery or medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about safety, search and rescue procedures
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
- check with your travel provider on vessel capacity limits before embarking on sea, land or air travel
- check weather and ocean conditions, and whether the vessel has had any mechanical issues, on the day and before continuing with water activities or sea travel
- check where the nearest medical facilities are
If proper safety equipment isn't available or you're unsure of the provider's safety or maintenance procedures, use another provider.
Trekking and climbing
Some mountain treks suit only experienced climbers. Travel with a guide and check the level of difficulty beforehand.
Many trekking options may be on or around an active volcano. Many of Indonesia's volcanoes are active and can erupt without warning. Volcanic and seismic activity may continue for some time. Adhere to exclusion zones around volcanoes, which can change at short notice, and follow the advice of local authorities. If you're planning to travel to an area near an active volcano, check with local authorities before climbing and check:
- Bureau of Meteorology Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre
- MAGMA Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia) for daily updates on status and alert levels
- National Disaster Management Authority (BNPB) (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Swimming safety
People have drowned in coastal areas, including in Bali, due to rough seas, strong currents, or from swimming, snorkelling or scuba diving in areas where there is frequent passage of boats, resulting in collisions.
Local beach rescue services may not be of the same standard as in Australia.
Saltwater crocodiles are in rivers throughout Indonesia. Avoid swimming around river estuaries and seek local advice in other locations.
If you plan to spend time in or on the water:
- regularly check weather reports as sea conditions can change rapidly
- take warnings seriously
- check media and local sources for information about potential dangers
- speak to your travel provider about safety equipment and weather conditions before continuing with planned activities
- take a friend or family member with you when you undertake swimming or water activities
- be careful when swimming, snorkelling or scuba diving near motor-powered boats or where there is frequent passage of boats
- ensure you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for planned activities
Ensure you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for planned activities.
Climate and natural disasters
Indonesia experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- landslides and mudslides
- volcanic eruptions
- earthquakes
- storms resulting in turbulent sea conditions
- tsunamis and high wave events
If there's a natural disaster or severe weather:
- always carry your passport in a waterproof bag
- keep in contact with family and friends
- check the media and local sources for information
- don't undertake sea, land or air travel if it's not safe to do so
- Indonesian Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency (BMKG) (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
Floods and mudslides
Floods , landslides and mudslides occur regularly during the wet season from October to April, with some severe events resulting in injury, displacement, death or damaged infrastructure.
Heavy rains can cause significant flooding in urban areas, including the greater Jakarta region, causing disruption to transportation. Monitor the local media for updates.
Walking and driving in flooded areas can be dangerous. Flood waters may hide uncovered drainage ditches.
Volcanic activity may escalate with little or no notice, leading to flight disruptions and airport closures, including in surrounding provinces. Contact your airline for the latest flight information.
There are 147 volcanoes in Indonesia. 76 of them are active volcanoes and could erupt at any time.
Volcanic alert levels and exclusion zones may rise quickly. You may be ordered to evacuate at short notice. Volcanic activity can disrupt domestic and international flights. There are 4 volcano alert levels in Indonesia; 1 - normal, 2 - advisory, 3 - watch, 4 - warning.
Before you travel to areas that are prone to volcanic activity, monitor media and ensure you read the Indonesian Government's latest advice on current volcanic activity, including:
- Volcanic Activity Report by Indonesia's Multiplatform Application for Geohazard Mitigation and Assessment (MAGMA) (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Volcano Activity and Observatory Notices (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- MAGMA Indonesia Map of Latest Volcano Levels and Climate Information (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Bureau of Meteorology's Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre
If there's volcanic activity:
- avoid the area
- take official warnings seriously and adhere to exclusion zones
- follow the instructions and advice of local authorities
- follow evacuation orders
- read our advice on Volcanic eruptions while travelling
Volcanic ash can cause breathing difficulties. The risk is higher for people with chronic respiratory illnesses, including:
Recent and frequent volcanic activity has included:
- Mount Ile Lewetolok in East Nusa Tenggara (Nusa Tenggara Timur)
- Mount Lewotobi Laki Laki in East Flores Regency, Nusa Tenggara Timur
- Mount Marapi in West Sumatra
- Mount Anak Krakatau, to the south of Sumatra
- Mount Merapi, near Yogyakarta
- Mt Dukono in North Sulawesi
- Mount Semeru, near Malang, East Java
- Mount Agung in Bali
- Mount Sinabung in North Sumatra
Some trekking routes are on or near active volcanoes, including Mount Agung and Mount Batur in Bali, Mount Marapi in West Sumatra, Mount Merapi near Yogyakarta, Mount Rinjani in Lombok, Mount Bromo and Mount Ijen in East Java. See 'Trekking and climbing'.
If you're planning to travel to an area near an active volcano, make sure you have comprehensive travel insurance and check if any restrictions apply.
If a volcanic eruption occurs:
- make a backup plan in case you're affected
- contact your airline or travel insurer to confirm flight schedules and get help
- keep in touch with family and friends
- Learn more about volcanic eruptions (Geoscience Australia)
- See practical advice and information about volcanic eruptions (US CDC)
- See worldwide volcanic activity reports in real-time (GDACS)
Earthquakes
Indonesia is in an active earthquake region. It has a high level of earthquake activity, that sometimes triggers tsunamis.
There are approximately 4,000 earthquakes across Indonesia every year. Around 70 to 100 of these are over 5.5 magnitude.
Earthquakes can cause death, injury and significant damage to infrastructure.
Strong earthquakes can occur anywhere in Indonesia. They are less common in Kalimantan and south-west Sulawesi.
To stay safe during an earthquake:
- know the emergency plans at your accommodation
- take precautions to avoid exposure to debris and hazardous materials, including asbestos
- MAGMA Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Indonesia's Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency (Bahasa Indonesia) or BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Indonesia)
- Indonesia's Centre for Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation (Bahasa Indonesia)
- US Federal Emergency Management Agency advice on what to do before, during and after an earthquake (English)
Forest fires and smoke haze
During the dry season in April to November, widespread forest fires can cause smoke haze resulting in poor air quality across parts of Indonesia, particularly the Riau Islands, central Sumatra and Kalimantan.
Smoke haze could affect your health and travel plans.
Keep up to date with local information and seek medical advice on appropriate precautions.
- ASEAN Regional Haze Situation
- Smartraveller advice on Bushfires
Tsunamis and high wave events
The Indian and Pacific Oceans experience more frequent, large and destructive tsunamis than other parts of the world.
There are many large earthquakes along major tectonic plate boundaries and ocean trenches.
High wave events can happen throughout coastal regions and between islands. They're caused by strong weather conditions and storms.
If you plan to surf, undertake water activities or travel by sea, check local conditions regularly.
If there’s a tsunami or high wave event:
- don't travel by sea if it's not safe to do so
- Indonesia Tsunami Early Warning Centre issues warnings when a potential tsunami with significant impact is expected
- Indonesia's Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency with the latest list of earthquakes with a magnitude greater than 5.0 on the Richter scale (Bahasa Indonesia) or BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- US Federal Emergency Management Agency page on what to do before, during and after an earthquake
Piracy occurs in the coastal areas of Indonesia.
The International Maritime Bureau (IMB) issues weekly piracy reports.
If you decide to travel by boat in these regions:
- check IMB piracy reports
- get local advice
- arrange security measures
- Travelling by boat
- Going on a cruise
- International Maritime Bureau
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including emergency treatment and medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
Before you travel, confirm:
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away, including on all forms of transport you plan to take
- whether it covers medical evacuation in the event of hospitalisation or injury
- any exclusions to your policy
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some drugs used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are illegal in Indonesia.
If you plan to bring over-the-counter or prescription medication, check if it's legal in Indonesia by contacting the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra well in advance of your planned travel. Take enough legal medicine for your trip and carry it in its original packaging. Purchasing prescription medication online in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller prior to your purchase.
Carry a copy of your prescription and a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medicine is
- your required dosage
- that it's for medical treatment or use
If you're caught with illegal medicine, you could face detention, fines or harsher penalties. You could face charges even if an Australian doctor prescribed the medication.
Ask the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra for advice before you travel.
Medicinal cannabis and cannabis-based products
Cannabis-based products such as cannabis oil and creams, hemp, CBD, THC, hash and edibles remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation or the death penalty.
- Medications
Health Risks
Critical care for Australians who become seriously ill, including in Bali, is significantly below the standard available in Australia. Medical evacuation may not be possible.
The Australian Government cannot guarantee your access to hospitals and other health services in Indonesia.
Medical evacuation to Australia for medical conditions, is possible but is very expensive and may not be covered by travel insurance. Check your policy before you travel.
Ban on sale of liquid/syrup medication
The Indonesian Ministry of Health (MoH) has advised local health workers and pharmacists to stop selling liquid/syrup medication, including commonly used medications containing paracetamol and cough syrups. MoH and the Indonesian Paediatrician Association (IDAI) received reports of a sharp increase in cases of Atypical Progressive Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in children , especially under the age of 5 years.
Insect-borne illnesses
Insect-borne illnesses are common throughout the year.
To protect yourself from disease:
- research your destination
- ask locals for advice
- make sure your accommodation is mosquito-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Dengue occurs throughout Indonesia, including Bali, Jakarta and other major cities.
Dengue is common during the rainy season.
Australian health authorities have reported an increase in dengue infections in people returning from Bali in recent years.
There are now two dengue vaccines, but they are not currently available in Australia. For further information, contact your doctor.
Zika virus can occur in Indonesia.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites.
The Australian Department of Health and Aged Care advises pregnant women to:
- discuss any travel plans with their doctor
- consider deferring non-essential travel to affected areas
Malaria , including chloroquine-resistant strains, is widespread in rural areas, particularly in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah, Papua Selatan, Papua Barat Daya, Papua Barat, Maluku and Nusa Tenggara Timur. There is no malaria transmission in Jakarta.
- Consider taking medicine to prevent malaria.
Japanese encephalitis and filariasis
Japanese encephalitis and filariasis occur in Indonesia, especially in rural agricultural areas.
Japanese encephalitis has been present in Australian travellers returning from Indonesia, including Bali.
Vaccination is recommended for certain groups of travellers.
- Infectious diseases
Drink poisoning
People have been poisoned by alcoholic drinks contaminated with harmful substances, including methanol and arak (a traditional rice-based spirit). Locals and foreigners, including Australians, have died or become seriously ill from poisoned drinks.
Cases of drink poisoning have been reported in Bali and Lombok.
Contaminated drinks have included:
- local spirits
- spirit-based drinks, such as cocktails
- brand name alcohol
To protect yourself from drink poisoning:
- consider the risks when drinking alcoholic beverages
- be careful drinking cocktails and drinks made with spirits
- drink only at reputable licensed premises
- avoid home-made alcoholic drinks
Labels on bottles aren't always accurate.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning can be similar to drinking too much. However, they are usually stronger.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning include:
- vision problems
Vision problems may include:
- blindness, blurred or snowfield vision
- changes in colour perception
- difficulty looking at bright lights
- dilated pupils
- flashes of light
- tunnel vision
If you suspect that you or someone you're travelling with may have been poisoned, act quickly. Urgent medical attention could save your life or save you from permanent disability.
Report suspected cases of methanol poisoning to the Indonesian police.
Magic mushrooms
Don't consume magic mushrooms. They're illegal.
Australians have become sick or injured after taking magic mushrooms.
Australians have been in trouble with local police after taking magic mushrooms, particularly in Bali.
Magic mushrooms can cause major health problems, including:
- erratic behaviour
- severe hallucinations
Rabies is a risk throughout Indonesia, especially in:
- Nusa Tenggara Timur, including Labuan Bajo
- South Sulawesi
- West Kalimantan
- Nias, off the west coast of Sumatra
To protect yourself from rabies:
- avoid direct contact with dogs
- don't feed or pat animals
- avoid contact with other animals, including bats and monkeys.
Talk to your doctor about getting a pre-exposure rabies vaccination.
If bitten or scratched by an animal:
- immediately use soap and water to wash the wound thoroughly for 15 minutes
- seek urgent medical attention.
Rabies treatment in Indonesia may be limited, including the rabies vaccine and immunoglobulin availability. If you're bitten, you may need to return to Australia or travel to another country for immediate treatment.
You're at risk of contracting rabies if you visit a market where live animals and fresh food are sold because:
- live rabies-positive dogs may be present
- rabies-positive dog meat may be sold as food
Selling dog meat for human consumption is a breach of government disease control regulations.
Avoid contact with monkeys, even in places where you're encouraged to interact with them. This includes:
- popular markets
- tourist destinations
- sanctuaries
Legionnaires' disease
Cases of Legionnaires' disease have been reported in people who have travelled to Bali. Travellers who are unwell with flu-like symptoms within 10 days of returning from Bali are advised to consult their GPs.
- Legionnaires' disease warning for Bali travellers (Western Australian Government Department of Health)
- Legionnaires’ disease (Better Health Channel, Victorian Government Department of Health)
- Legionnaires' disease (World Health Organization)
Cases of poliovirus (type 1) have been reported in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan. Poliovirus (type 2) cases have been reported in the provinces of Aceh, East, West and Central Java. There may be unreported cases in other provinces in Indonesia.
Ensure that you're vaccinated against polio.
- Factsheet on poliovirus types (World Health Organization)
- Health emergencies information for Indonesia (World Health Organization)
Periodic outbreaks of measles continue to be reported in Indonesia, including Bali.
You need 2 doses of vaccine 4 weeks apart to be fully vaccinated against measles.
If you have symptoms of measles, seek medical attention.
Measles is highly infectious. Call before attending a healthcare facility.
Nipah Virus and Yellow Fever
There are no cases of Nipah virus or Yellow Fever in Indonesia. You may be temperature checked on arrival at international and domestic airports. If you have fever symptoms, you may be referred to the airport clinic for further tests and asked to seek medical treatment. See your doctor or travel clinic before you travel to plan any vaccinations you need.
HIV/AIDS is a risk for travellers. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are widespread. These include:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- boil drinking water or drink bottled water
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw food, such as salads
To minimise the risk of food poisoning, only eat meat from reputable suppliers.
Seek urgent medical attention if you suspect food poisoning or have a fever or diarrhoea.
Seafood toxins
You can become sick from naturally occurring seafood toxins, including:
- ciguatera fish poisoning
- scombroid (histamine fish poisoning)
- toxins in shellfish
Avoid temporary black henna tattoos. The dye often causes serious skin reactions.
Before you get any tattoo, check the hygiene and safety of your tattoo provider.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than Australia. Many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities.
Hospitals expect families to provide support to patients, including all financial support.
Psychiatric and psychological services are limited in Indonesia. Hospital staff may use physical restraints on patients.
When diving in Indonesia, there is a risk that you may experience decompression illness. An illness may occur when a diver ascends to the water surface too quickly and may have severe consequences. Understand the risks before you dive.
Decompression chambers are available in various areas, including the following locations:
- Bali's Sanglah General Hospital
- Siloam Hospital in Labuan Bajo
- Hospitals in Jakarta, Balikpapan, Bintan, Medan, Makassar, Raja Ampat (Waisai), Maluku, Tual and Manado near popular dive sites
Before admitting patients, hospitals usually need:
- guarantee of payment from the patient or their next of kin (family or friend)
- confirmation of medical insurance
- deposit payment
There's no reciprocal healthcare agreement between Australia and Indonesia.
The Australian Government cannot provide guarantee of payment, confirmation of medical insurance or a deposit payment for services.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you may need to be evacuated to a place with better care. Medical evacuation can be very expensive. Check your insurance policy before you travel. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs. It's best to check with your travel provider on the location and functionality of decompression chambers and other medical facilities available in the area before undertaking remote travel.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
Indonesian Parliament has passed revisions to its criminal code, which includes penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions will not come into force until January 2026.
Indonesia has signed into law revisions to the Electronic and Information Transactions Law (ITE Law). Tough penalties apply for defamation, hate speech, spreading hoaxes and uploading immoral content to the Internet. The law applies both within and outside Indonesia.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
- Arrested or jailed
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
You may face heavy fines or jail for consuming or possessing even small amounts of drugs, including marijuana. Cannabis-based products such as cannabis oil and cream, hemp, CBD, THC, hash and edibles remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation or the death penalty.
Some prescription medications that are available in Australia are illegal in Indonesia. Purchasing prescription medication online or over the counter in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller before your purchase.
Magic mushrooms are illegal. Indonesian police work to prevent their distribution.
Police target illegal drug use and possession across Indonesia. Police often target popular places and venues in Bali, Lombok and Jakarta.
- Carrying or using drugs
Local labour laws can change at short notice. This can affect expatriate workers.
Under Indonesian law, you must always carry identification. For example, your:
- Australian passport; and
- Resident's Stay Permit (if applicable)
Gambling is illegal.
Property laws are strict, seek legal advice before acquiring property in Indonesia.
It's sometimes illegal to take photographs in Indonesia. Obey signs banning photography. If in doubt, get advice from local officials. See Safety .
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Local customs
Standards of dress and behaviour are conservative in many parts of Indonesia. Take care not to offend.
Find out what customs apply at your destination.
If in doubt, seek local advice.
LGBTI information
Same-sex relationships are legal in Indonesia, except in the province of Aceh. Same-sex relationships in Aceh may attract corporal punishment. Visible displays of same sex relationships could draw unwanted attention.
Some laws and regulations can be applied in a way that discriminates against the LGBTI community, including for pornography and prostitution.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
The Islamic holiday month of Ramadan is observed in Indonesia. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws at this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking and smoking may be illegal in public during this time. If you're not fasting, avoid these activities around people who are. Seek local advice to avoid offence and follow the advice of local authorities.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Aceh is governed as a special territory, not a province, and has a degree of special autonomy.
Some aspects of sharia law are upheld. This includes regulations and punishments that don't apply in other parts of Indonesia.
Local sharia police enforce sharia law.
Sharia law applies to anyone in Aceh, including:
- foreigners (expats and travellers)
- non-Muslims
Sharia law doesn't allow:
- drinking alcohol
- prostitution
- same-sex relationships
- extra-marital sex
- co-habitation before marriage
It also requires a conservative standard of dress.
Learn about the laws in Aceh. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Dual citizenship
Indonesia doesn't allow dual nationality for adults, and you may be prosecuted by Immigration authorities should you be found to hold valid passports of two nationalities. If you entered Indonesia on your non-Australian citizenship passport, Indonesian Immigration will require you to exit Indonesia on that nationality's passport.
A child of Indonesian and Australian parents can maintain citizenship of both countries until the age of 18 years. Before a dual Australian-Indonesian citizen minor travels from Indonesia, additional identity documentation may be required from Indonesian Immigration. Check with Indonesian Immigration or the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra well in advance of your planned travel.
- Embassy and Consulate of Indonesia
- Information on limited dual citizenship
- Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Bali Tourism Levy
The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the e-Visa on Arrival or the Visa on Arrival. Cashless payments can be made online prior to travel or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali's airport and seaport. Exemption from payment of the levy applies to transit passengers and certain visa holders. See the Bali Provincial Government's official website and FAQs for further information.
e-Visa on Arrival and Visa on Arrival
You can apply for an e-Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) no later than 48 hours prior to travelling to Indonesia if you are travelling for tourism, business meetings, purchasing goods or transiting only. Check the e-VOA requirements from Indonesian Immigration before applying.
You can still apply for a regular Visa on Arrival (VOA) at certain international airports, seaports and land crossings, including Jakarta, Bali, Surabaya, Makassar, Lombok, Batam, Medan, Manado, Aceh, Padang, Tanjung Pinang and Yogyakarta, if you do not apply for an e-VOA at least 48 hours in advance of your travel to Indonesia.
The e-VOA or VOA can be used for tourism, official government duties, business meetings, or to transit through Indonesia. You cannot transit in Indonesia without an e-VOA or VOA.
Additional requirements apply if you are travelling on government duties.
For the latest list of entry points for the e-VOA or VOA, refer to the Directorate General of Immigration's list of land border crossings, international airports, and international seaports .
The e-VOA and VOA cost IDR 500,000 (approximately $A 50), with the e-VOA charging a small online processing fee.
For the VOA, some airports, including Jakarta's international airport, are only accepting cash payment. Card payment facilities are available at Bali's international airport. ATM facilities may be in high demand. Be prepared to pay in cash if required.
The visa is valid for a 30 day stay and can be extended once (for a maximum of 30 days) by applying at an immigration office within Indonesia. Ensure you extend your visa within the initial 30 days to avoid an overstay fine and deportation.
To apply for a regular VOA, you must show:
- your ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter (we also recommend having at least 6 months passport validity from the date you plan to leave Indonesia, to avoid any issues for your departure or onward travel)
- a return flight booking to Australia or onward flight booking to another country
Contact your travel agent, airline, or your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia for details.
Other visas
If you're entering Indonesia from a port or airport that does not issue a visa on arrival, or you're visiting Indonesia for a purpose not allowed under the e-VOA or VOA conditions, you must apply for a visa in advance of travel. Check the Indonesian Immigration website for further information, or contact your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia .
Overstaying your permit may result in fines, detention and/or deportation.
- check your visa and permit, and contact the Directorate General of Immigration (DGI) for advice specific to your needs
- if you use an agent to extend your visa or stay permit, use only reputable companies
- if you have specific enquiries on visas or stay permits, contact DGI's Customer Service team via WhatsApp on +62 821 1295 3298
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest Embassy or Consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and entry rules.
You can't work or conduct research in Indonesia unless you have the appropriate visa. Fines of IDR1,000,000 (approx. $A 100) per day apply for the maximum 60 day overstay period.
If you breach Indonesian immigration regulations, you may face:
- deportation
- re-entry bans
You may not be allowed to enter Indonesia if you have a criminal record. This is regardless of how long ago the offence took place. If you're concerned, contact an Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before you travel.
Indonesian Immigration and visa decisions are final. The Australian Government can't help you.
- Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia
Border measures
You'll be required to complete an e-customs declaration for arrival . You can complete this within 3 days of departure to Indonesia.
Check entry requirements with your travel provider or the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before you travel.
You may be temperature checked on arrival at international and domestic airports. If you have fever symptoms, you may be referred to the airport clinic for further tests and asked to seek medical treatment. See your doctor or travel clinic before you travel to plan any vaccinations you need.
Departure from Indonesia
Indonesia, including Bali, currently has an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease affecting animals. In preparing to travel to Australia, read Smartraveller's advice on biosecurity and border controls . Measures include cleaning dirty shoes, clothing or equipment before boarding your flight to Australia and not packing meat or dairy products. On your Incoming Passenger Declaration, you must declare any meat, dairy or animal products and any of your travel in rural areas or near animals (e.g., farms, zoos, markets).
Other formalities
If you're staying in a private residence, not a hotel, register when you arrive with both:
- the local Rukun Tetangga Office
- local police
If you plan to be in Indonesia for more than 30 days:
- register with the local immigration office
- make sure you have the right visa
- Embassy of Indonesia in Canberra
Indonesia won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave Indonesia. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over. You can end up stranded or returned back to your previous port overseas at your own cost, if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months from the date you enter and the date you plan to leave Indonesia.
Indonesia does not accept entry with an emergency passport, even if it is valid for more than 6 months. Ensure you enter Indonesia on a valid ordinary, official, or diplomatic passport.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply these rules inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian Embassy, Consulate or High Commission.
Damaged Passports
Indonesian authorities have strict standards for damaged passports, and travellers have been refused entry into Indonesia with a damaged passport. Normal wear and tear, including water damage, minor tears or rips to the pages, can be considered damaged.
It's important that:
- there are no tears or cuts in the passport pages, especially the photo page
- everything on the photo page is legible and clear
- there are no marks across your photo or in the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) on the photo page
- no pages have been removed
- there is no alteration or tampering
If you're not sure about the condition of your passport, call the Australian Passport Office on 131 232 or contact your nearest Australian embassy or consulate overseas . We may need to see your passport to assess it.
- Passport Services
- Damaged and faulty passports
- Using and protecting your passport
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
The local currency is the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR).
Declare cash in excess of IDR100,000,000 or equivalent when you arrive and leave. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
IDR100,000,000 is worth about $A10,000.
Local travel
Idul fitri 2024.
The Idul Fitri holiday period will take place from 10 April. Many people will travel across Indonesia until 22 April, with many expected to move in and out of the greater Jakarta area. This may impact traffic and public transport, including airports, seaports, highways, toll roads, train and bus stations across Indonesia. Airports are expected to be busy. Plan your travel carefully and prepare for significant delays. Contact your travel provider for up-to-date details.
Travel Permits
You may need a travel permit or Surat Keterangan Jalan to travel to some areas of the Papua provinces.
Check if you need a permit with the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia or with your travel provider.
Mobile Phone Reception and Wi-Fi
Mobile phone reception and Wi-Fi are not always available, including in remote areas and some resort islands.
If you plan to stay in Indonesia for more than 90 days and would like to use your mobile phone purchased overseas, you'll need to register your mobile phone IMEI number with Indonesian Customs within the first 60 days of your stay.
If you plan to stay in Indonesia for less than 90 days, you can visit the local cellular operator/provider booth at the airport to get an access period to use the Indonesian cellular network, which is only valid for 90 days and includes data roaming.
A customs payment may be required, or a tourist SIM card can be purchased for short-term stays. You can use Wi-Fi networks without registration.
To stay in communication and avoid mobile service interruptions:
- check mobile coverage with your service provider
- register your mobile device with Indonesian Customs on arrival if you plan to connect to the mobile network
Driving permit
To drive in Indonesia, you need either:
- an Indonesian licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Check that your licence or permit is appropriate for the type of vehicle you're driving.
Your Australian licence isn't enough.
Your travel insurer will deny any claims you make if:
- you're unlicensed
- you don't hold the correct class of licence
Road travel
Traffic can be extremely congested.
Road users are often unpredictable or undisciplined.
You're more likely to be killed in a motor vehicle accident in Indonesia than in Australia. Drive defensively. Some traffic incidents can escalate into violent disputes quickly.
Consider hiring a taxi or a driver who is familiar with local roads and traffic conditions.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Motorcycle accidents have killed and injured foreigners, including Australians. This includes in tourist areas, particularly Bali, Lombok and the Gili Islands.
If you're riding a motorbike and there's an accident, you'll often be assumed to be at fault. You may be expected to compensate all parties.
If you hire a motorbike:
- make sure your insurance policy covers you
- check if any policy restrictions apply, for example if you're not licensed to ride a motorcycle in Australia
Always wear a helmet.
Public transport
Buses, trains and the metro rail can be crowded, particularly:
- around public holidays
- during peak commute times
Safety standards may not be observed.
- Transport and getting around safely
Only use licensed official metered taxis.
- only travel in licensed taxis with signage, a "taxi" roof sign and meters
- book via phone or an official taxi company mobile app
You can book licensed official metered taxis
- on the taxi company's official mobile app
- from inside airports
- at stands at major hotels
Unofficial operators can have taxis that look similar to those run by reputable companies. Make sure the taxi meter is working before you get into the taxi.
See Safety .
Rail travel
Inter-city rail networks operate on the islands of Java, Sumatra and Sulawesi.
Commuter trains operate in Java, including Jakarta.
Trains can be crowded, particularly:
- during peak commuter times
Travel between islands
Travel by ferry or boat can be dangerous.
Passenger and luggage limits aren't always observed.
Equipment may not be properly maintained, and they may not have GPS or emergency communications equipment.
There may not be enough life jackets. It's unlikely that the crew will have life jackets for children.
In March 2024, a ferry sank in the Thousand Islands off the coast of Jakarta, resulting in one death, and a liveaboard boat caught fire and sank in Raja Ampat, Papua Barat Daya, requiring several passengers to be rescued.
In August 2023, two crew died after a boat carrying passengers sank in the Banyak Islands, Aceh, and three people went missing after a ship sank in the Thousand Islands off the coast of Jakarta.
In July 2023, 15 people died after a ferry sank off Sulawesi Island.
In January 2023, 23 passengers and 6 crew were rescued after an inter-island ferry sank while returning from Nusa Penida to Sanur Beach, Bali.
In May 2022, 19 people died after a ferry sank in the Makassar Strait.
In June 2018, a ferry sank on Lake Toba in Sumatra and 100s of people died.
If you plan to travel by sea between islands:
- make sure any ferry or boat you board has appropriate safety equipment, GPS and communication equipment, and life jackets
- wear a life jacket at all times
- take enough life jackets for all children travelling with you
- ask your tour operator or crew about safety standards before you travel
- check sea, weather conditions and forecasts before embarking on boat or ferry travel, and delay travel if conditions are not safe
If appropriate safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Avoid travelling by water after dark unless the vessel is properly equipped. Avoid travel during wet weather or storms.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Indonesia's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
The European Union (EU) has published a list of airlines that have operating bans or restrictions within the EU. See the EU list of banned airlines .
Australian travellers should make their own decisions on which airlines to travel with.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Search and rescue services
Medical emergencies and ambulance.
SMS 1717 for Jakarta Police
Police Stations in Bali
Refer to the Bali Tourism Board’s list of police stations in Bali
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australian Embassy, Jakarta
Jalan Patra Kuningan Raya Kav. 1-4 Jakarta Selatan 12950
Phone: (+62 21) 2550 5555 Email: [email protected] Website: indonesia.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australian Embassy Jakarta, Indonesia X: @DubesAustralia Instagram: @KeDubesAustralia
Make an appointment online or call (+62 21) 2550 5500 or (+62 21) 2550 5555.
Australian Consulate-General, Bali
Jalan Tantular 32 Renon Denpasar Bali 80234
Phone: (+62 361) 2000 100 Email: [email protected] Website: bali.indonesia.embassy.gov.au X: @KonJenBali Instagram: @konjenbali
Australian Consulate-General, Makassar
Wisma Kalla Lt. 7 Jalan Dr Sam Ratulangi No. 8 Makassar South Sulawesi 90125
Phone: (+62 411) 366 4100 Email: [email protected] Website: makassar.consulate.gov.au Facebook: Australian Consulate-General, Makassar, Sulawesi X: @KonJenMakassar Instagram: @konjenmakassar
Australian Consulate-General, Surabaya
Level 3 ESA Sampoerna Center Jl. Dokter.Ir. H. Soekarno No. 198 Klampis Ngasem, Sukolilo, Surabaya
Phone: (+62 31) 9920 3200 Email: [email protected] Website: surabaya.consulate.gov.au Instagram: @KonJenSurabaya
Check the websites for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Indonesia?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Accessibility Links

Can I travel to Bali? The entry requirements explained
Here’s what you need to know about travelling to bali, from pre-departure testing and visas to mask-wearing requirements.

B ali, the ever-popular Indonesian holiday island in the Java Sea, has long attracted visitors who come to marvel at its crumbly temples, hippy villages and black-sand beaches (emblazoned with cracking sunsets). The island’s reliance on international tourism has made for a challenging two years — it’s been largely closed to outside visitors since the pandemic began in March 2020. Just 45 international tourists arrived between January to October 2021 — a far cry from the nine million who landed on its shores in 2019.
In March 2022, it reopened to international tourism as part of a pilot scheme to welcome visitors back.
Here’s everything you need to know about entry requirements, pre-departure testing and regulations on the ground in Indonesia.
Main photo: Mount Agung on Bali and fishing boats, Gili Isles, Indonesia (Alamy)
What are Bali’s entry requirements?
British visitors can enter Bali without quarantine or applying for a visa in advance if they’re fully vaccinated, with the last dose being administered more than 14 days prior.
Advertisement
A visa will be issued on arrival at a cost of IDR 500,000 (around £30) which is valid for 30 days (although there is the option of extending the visa for an extra fee) — visitors applying for this via a mobile app will have to show proof of vaccination.
Arriving passengers aged 18 and over must be fully vaccinated to enter (two doses); or in the case of only one jab, have a Covid recovery certificate. It’s advisable to have a booster jab if you intend to travel domestically, or you may be asked for a negative Covid test result.
They will also have a temperature check on arrival, and if showing symptoms of Covid, undertake a PCR test.

Can I travel to Bali unvaccinated?
Yes, if you have proof of a medical exemption. Otherwise, unvaccinated visitors will have to take a PCR test on arrival and quarantine for five days, with a second negative PCR result needed to exit isolation.
What are the restrictions when there?
Masks should be worn inside. Travellers can expect strict Covid protocols such as temperature checks and sanitising stations at hotels.
Get inspired
• Bali travel guide • Best hotels in Bali • Best villas in Bali
Take me there
Inspired to book a Bali trip? Find the best options with Tui and Virgin Holidays .
Sign up for the Times Travel Newsletter here .
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
- Accommodations

Bali Entry Requirements During the New Normal Period
Wayan Koster, the Governor of the Province of Bali and the Head of the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19, issued Circular Letter Number 305/GUGASCOVID19/VI/2020 on the Traffic Control of Travellers Entering Bali During the Adaptation of New Normal Towards a Productive and Free from COVID-19 Community, which will be in effect starting from 5 July 2020.
This regulation will be imposed for travelers entering Bali, apart from tourism purposes, in which tourism is guided by separate requirements. Apart from wearing masks, implementing social distancing, routine hand-washing as a mandatory protocol for travelers, this Circular Letter also regulates the requirements for domestic and international travelers intending to visit Bali.
Requirements for Domestic Travellers
Travelers conducting their journey by personal vehicles, public transportation by land, sea, and air are mandated to:
1 | Provide identification, KTP, or other forms of identification.
2 | Provide a non-reactive rapid test result, which is valid for 14 days from the issuance. It is also mandatory for persons conducting logistical travel purposes, officials from government institutions, and employees of private enterprises performing their duties to stay in Bali for more than seven (7) days. This regulation is also imposed on travelers that do not own Bali KTP, but for exceptional circumstances residing in Bali by completing a statement and guarantee letter, which can be downloaded at https://cekdiri.baliprov.go.id/
3 | For transit travelers who do not intend to visit Bali, it is mandatory to provide a valid non-reactive rapid test health result.
4 | Visitors must register online to https://cekdiri.baliprov.go.id/
5 | Visitors must download app EHac from Google Play Store (Android) or App Store (Apple), fill their complete data, and claim a barcode which will be checked at the departure gate in the airport in Bali. The app is mandatory for the purpose of tracking down travelers during the New Normal period. Additional Requirements for the Entry of Domestic Travelers (Optional)
Any visitors who enter Bali can download PeduliLindungi app from Google Play Store (Android) or App Store (Apple) to check the red/yellow/green zone status of the area that will be visited on Bali.
Requirements for International Travellers
Requirements for Non-Migrant Workers:
1 | Mandatory to provide a valid negative swab test PCR result health certificate
2 | For travelers that do not possess valid negative swab test PCR result health certificate, it is mandatory to conduct an independent swab test at the Government Hospital or at a dedicated laboratory designated by the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19
Requirements for Indonesian Migrant Workers:
1 | It is mandatory for migrant workers that do not have an official agency to conduct a swab test at a designated area assigned by the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19 and to conduct self-quarantine until the result is issued.
2 | Migrant workers with a health certificate from the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19 may conduct self-quarantine with the supervision of its local Gotong Royong Task Force.
3 | The Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19 is responsible to coordinate with migrant worker agencies in relation to the repatriation of migrant workers and shipmates to provide accommodation until the issuance of the swab test result.
Additional Requirements for all International Travellers:
1 | All International Travellers with a positive swab test result will be handled directly by the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19.
2 | International Travellers that have been deemed recovered would be escorted by the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19, which would then be placed under self-quarantine.
3 | International Travellers that do not own a Bali KTP but for special circumstances residing in Bali are permitted to stay in Bali by providing a negative swab test PCR result and completing a statement and guarantee letter, which can be downloaded at https://cekdiri.baliprov.go.id/
The implementation of this Bali Entry Requirements during the New Normal involves all regents/mayors in Bali as well as traditional villages through the Paikaten Pacalang by facilitating and informing the control of persons entering Bali by coordinating with the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19.
Suggested for you

We are Ensuring You Have a Safe Trip

Mandatory Requirements for Airplane Passengers During the COVID-19 Emergency Period

8 FAQs You Need To Know About Indonesia Today

Minister of Tourism and Creative Economy Encourages Tourism Stakeholders to Implement Strict Health Protocol to Welcome the “New Normal”

Visit our other website
This is the official website of the Ministry of Tourism, Republic of Indonesia. The contents listed on this website are intended for informational purposes rather than commercial. Any displayed sale is meant as a token of partnership and will always redirect you to our partners' sites.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Indonesia Travel Regulations, Entry Requirements and Tourist Tax for Bali Planning your trip to Bali? On this page you will find all you need to know about General Travel Requirements in relation to Customs, Tourist Tax, Passport, and some essential tips.. The following FAQ below will guide you through the general regulations that apply to all international travelers, so you can plan your trip ...
On 10 November 2022, the government also launched an Electronic Visa on Arrive (eVOA) program to provide foreign travelers with an easier entry process. According to the Circular Letter of the Directorate General of Immigration No. IMI-0794.GR.01.01 of 2022 concerning the Immigration Policy regarding Electronic Visit Visa Services, Visit Visa ...
Besides the entry requirements for Bali, another important thing about Bali travel requirements 2024 is preparing related documents. Below is a list of the documents required for traveling to Bali: Valid Passport; B211A E-Visa (or cash or credit cards if obtaining Indonesia Visa on Arrival, available at select international airports).
To travel to Bali, Indonesia, you must present a valid digital or printed proof of Covid Vaccination with the final dose taken 14 days prior. Although officials may not check your status upon arrival in Indonesia, airlines typically verify this requirement when checking in. Therefore, you must meet this criterion for entry.
The upcoming visitors going to the island by air must present a COVID-19 negative certificate that has been subjected to the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) from a government hospital laboratory or a COVID-19 Task Force designated laboratory. The COVID-19 negative certificate has a validity period of seven days from the time of arrival at one ...
Below are the frequently asked questions regarding the arrival requirements to Bali. ... There are several entrances for international travelers to visit Indonesia. As for Bali in particular, ... Upon arrival at the entry points, foreign travelers must undergo a COVID-19 symptom check, including a body temperature check, with the following ...
2. Your Passport. At least valid for another 6 months. 3. Visa. To enter Bali you need a visa. For your vacation you need a Visa on Arrival (VOA). The VOA will cost IDR 500.000 (around 32 euros) per person (children as well). You can buy the visa when you arrive on the airport in Denpasar with cash (IDR, USD or Euro), Mastercard or Visa.
Passport validity requirements. Make sure your passport is valid for at least 6 months from your date of entry into Indonesia. Check with your travel provider or the nearest Indonesian Embassy or ...
Customs Declaration Online. e-CD Customs Declaration Form must be completed online. You will receive a QR code once you have completed all the information. Read More... Applies to International Travellers. Published 01 07 2021 Updated 28 03 2024 976574 Entry & Exit Requirements.
x VoA-Visa on Arrival entitles for a single Entry into Bali/Indonesia, stay up to 30 days and can be maximum 1 times extended at Immigration Office (charge may be applied). x Payment can be done by: Visa Card ... x Travel insurance that covers Covid-19 and its related expenses at USD 25.000 insurance coverage per person (booking on line through
Entry Requirements: To enter Indonesia, your passport must have at least two blank pages and be valid for at least six months beyond the date of your arrival in Indonesia.If your passport does not meet these requirements, you will be denied entry into Indonesia. The Government of Indonesia will not admit travelers holding the 12-page U.S. emergency passport, issued by U.S. embassies and ...
Tourist Police, Bali. Call (+0361) 759 687. Tourist Police, Jakarta. Call (+201) 526 4073. Latest update. We've reviewed our advice for Indonesia and continue to advise exercise a high degree of caution. The Idul Fitri holiday period will take place between 10 - 22 April. ... Check the latest entry requirements with your travel provider or an ...
Advertisement. A visa will be issued on arrival at a cost of IDR 500,000 (around £30) which is valid for 30 days (although there is the option of extending the visa for an extra fee) — visitors ...
Bali entry requirements. Vaccinated tourists from 43 nationalities can fly directly to Bali and obtain EITHER a Visa on Arrival (VoA) or Visa Exemption Arrangement Facility.The VOA allows them to stay on the island for 30 days, and can be extended for another 30 days. Meanwhile, those who qualify for the latter can only stay for a maximum of 30 days.
VOA and eVOA can be granted for below travel: Tourism. Official government visits. Business meetings. Transit. Requirements to apply for VOA or eVOA: A legal and valid passport that must be valid at least 6 months before the expiration date. An international ticket for return or onward travel. The fee for VOA is IDR 500,000, payable in cash.
If you have had to put off traveling to Bali, Indonesia due to the pandemic, the wait is now over. Travel restrictions have been slowly easing up for Bali for the past few months and fully vaccinated international travelers can now visit Bali without additional testing. In this article, you will find details Covid-19 restrictions and requirements, as well as ...
Wayan Koster, the Governor of the Province of Bali and the Head of the Bali Provincial Task Force for the Acceleration of Handling of COVID-19, issued Circular Letter Number 305/GUGASCOVID19/VI/2020 on the Traffic Control of Travellers Entering Bali During the Adaptation of New Normal Towards a Productive and Free from COVID-19 Community, which will be in effect starting from 5 July 2020.
Ensure your flight tickets are booked and your passport is valid for at least another 6 months before you travel to Bali. For entry into Bali, you will need a Visa on Arrival (VOA) which costs IDR 500,000 per person and is valid for a stay of 2 x 30 days.
Tourism fee. From 14 February 2024, the Balinese government is introducing a new tourism fee to help preserve the nature and culture of Bali. The fee will cost IDR150,000 (approx. AUD$14.40) and is payable by all international tourists travelling to Bali. To save time at the airport, please ensure that you pay the fee ahead of your flight to ...