Conjugation verb visit
Model : obey
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: visit oneself / not visit
Contractions
- he/she/it visits
- you visited
- he/she/it visited
- they visited
Present continuous
- I am visiting
- you are visiting
- he/she/it is visiting
- we are visiting
- they are visiting
Present perfect
- I have visited
- you have visited
- he/she/it has visited
- we have visited
- they have visited
- I will visit
- you will visit
- he/she/it will visit
- we will visit
- they will visit
Future perfect
- I will have visited
- you will have visited
- he/she/it will have visited
- we will have visited
- they will have visited
Past continous
- I was visiting
- you were visiting
- he/she/it was visiting
- we were visiting
- they were visiting
Past perfect
- I had visited
- you had visited
- he/she/it had visited
- we had visited
- they had visited
Future continuous
- I will be visiting
- you will be visiting
- he/she/it will be visiting
- we will be visiting
- they will be visiting
Present perfect continuous
- I have been visiting
- you have been visiting
- he/she/it has been visiting
- we have been visiting
- they have been visiting
Past perfect continuous
- I had been visiting
- you had been visiting
- he/she/it had been visiting
- we had been visiting
- they had been visiting
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been visiting
- you will have been visiting
- he/she/it will have been visiting
- we will have been visiting
- they will have been visiting
- let's visit

Perfect participle
- having visited
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe.
You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site.
The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single goal: to provide you with rich, high-quality content. All this is possible thanks to the income generated by advertising and subscriptions.
By giving your consent or subscribing, you are supporting the work of our editorial team and ensuring the long-term future of our site.
If you already have purchased a subscription, please log in
How to conjugate "to visit" in English?
English "to visit" conjugation, full conjugation of "to visit", translations for "to visit", present continuous, simple past, past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, conditional present, conditional present progressive, conditional perfect, conditional perfect progressive, subjunctive, present subjunctive, past subjunctive, past perfect subjunctive, present participle, past participle.
Translations for "to visit" in our English dictionaries
Popular English verbs
Find out the most frequently used verbs in English.
CULTURE & TRAVEL
Why register, enjoy an enhanced experience.
- Access all dictionaries for free
- Browse the whole site in any of 24 languages
- Translation tool with additional allowance
Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.
'visit' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'V'
- Access the entire site, including the Easy Learning Grammar , and our language quizzes.
- Customize your language settings. (Unregistered users can only access the International English interface for some pages.)
- Submit new words and phrases to the dictionary.
- Benefit from an increased character limit in our Translator tool.
- Receive our weekly newsletter with the latest news, exclusive content, and offers.
- Be the first to enjoy new tools and features.
- It is easy and completely free !
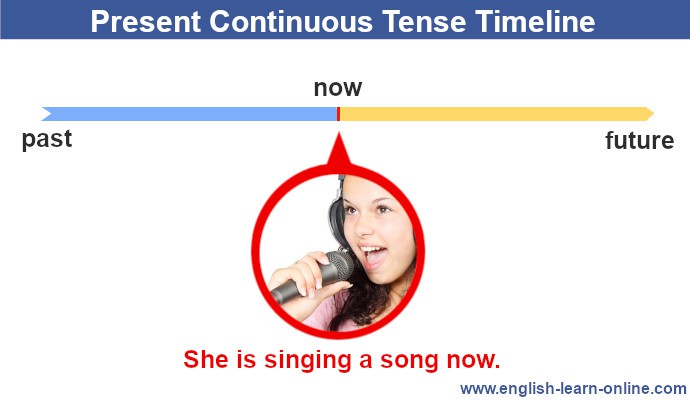
Understanding the Present Continuous Tense: Rules and Examples
Marcus Froland
March 28, 2024
Picture this: you’re sitting in your favorite coffee shop, sipping on the best latte ever. Around you, people are chatting, laughing, and working. This scene is happening right now, at this very moment. And that’s exactly what the present continuous tense is all about – capturing actions as they unfold in real-time.
In English, tenses can be tricky beasts to tame. But fear not! The present continuous isn’t as daunting as it may seem at first glance. It’s used far more often than we realize, sliding into our daily conversations with ease. From describing ongoing activities to talking about future plans made in stone, understanding its rules and examples can make a world of difference in how we express ourselves.
The question then becomes: How do we get from recognizing its use to flawlessly incorporating it into our own sentences? Well, that journey begins with the basics…
The Present Continuous tense is used to talk about actions happening right now or around this time. It’s formed with am/is/are plus the -ing form of the verb. For example, “I am eating,” “She is running,” and “They are watching.” This tense also describes plans or arrangements in the near future, like “We are meeting him tomorrow.” Remember, for actions that are currently in progress or set to occur in the near future, the Present Continuous tense is your go-to. It’s simple: use “am,” “is,” or “are” with a verb ending in -ing .
The Essentials of Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous tense is a fundamental grammatical construction used to denote ongoing actions or conditions that are currently unfolding or are expected to take place in the near future. The essence of this tense lies in its structure, which consists of the subject, the appropriate form of the auxiliary verb “be” (am/is/are), and the present participle (verb ending in “-ing”). This tense can be utilized to express actions in progress at the moment of speaking, new trends or developments, and habitual behaviors marked by keywords such as “always.” Examples include phrases like “I am swimming,” and “We are investigating a crime,” which demonstrate the present continuous in action.
It is important to remember that the Present Continuous tense is an essential part of Grammar Fundamentals , allowing you to express actions in their Present Progressive Form .
Utilizing the Present Continuous tense effectively entails a basic understanding of its key features. These features can be easily summarized and illustrate the various aspects of this versatile tense.
In order to harness the full potential of the Present Continuous tense, it is essential to have a firm grasp on these aspects. By understanding when and how to use the Present Continuous, you can aptly describe ongoing actions and effectively communicate your ideas in English.
Forming the Present Continuous Tense
In the Present Continuous tense, understanding the nuances of subject-verb agreement , the role of auxiliary verbs, and the process of adding “-ing” to main verbs is critical. By mastering these grammar rules , you’ll be able to confidently construct sentences that effectively convey ongoing actions and events. Let’s delve deeper into these essential components of Present Continuous tense formation.
Subject-Verb Agreement in Present Continuous
Providing accurate subject-verb agreement is a key aspect of forming the Present Continuous tense. The verb “be” must align with the subject in both person and number, ensuring proper grammar usage . Here are the precise combinations:
- First person singular: “am”
- Third person singular: “is”
- All other pronouns/plural subjects: “are”
For example, phrases like “I am running,” “She is singing,” and “They are studying” all adhere to these subject-verb agreement rules. It’s essential to remember that, in contracted form, “am” changes to “aren’t” rather than “amn’t” when used in questions, such as “Aren’t I reading a newspaper?”
The Role of Auxiliary Verbs
In the Present Continuous tense, auxiliary verbs play a fundamental role. They serve as helping verbs, connecting the subject with the main verb’s “-ing” form and creating the appropriate Present Progressive construction . Depending on the subject’s person and number, different forms of the auxiliary verb “be” are used:
- “am” for I
- “is” for third person singular subjects
- “are” for you/we/they and all plurals
Phrases such as “He is playing tennis” and “She is not practicing for the audition” demonstrate the crucial role auxiliary verbs play in constructing the Present Continuous tense.
Adding the -ing to Main Verbs
The “-ing” form of main verbs, or the Present Participle usage , is another critical element of the Present Continuous tense. To transform base verbs into their present participles, you’ll typically simply attach “-ing” to the end of the verb. However, in some cases, you’ll need to drop a silent ‘e’, as in “make” becoming “making,” or double the last consonant in a single-syllable verb ending in consonant-vowel-consonant, like “sit” becoming “sitting.”
The continuous form emphasizes that the action is currently in progress, as illustrated in phrases like “She is studying ,” or “The dog is running .” By following the progressive aspect guide outlined above, you’ll be adept at creating grammatically accurate Present Continuous sentences and accurately expressing ongoing actions and experiences.
Correct Usage of Present Continuous for Ongoing Actions
Using Present Continuous correctly plays a vital role in conveying the intended meaning while describing ongoing actions . The Present Continuous tense effectively portrays actions happening at the very moment of speaking or that are currently underway. In this section, we will discuss the Continuous Tense guidelines that can help you in effectively describing ongoing actions without any confusion.
Present Continuous tense can paint a vivid picture of activities, such as sitting, eating, waiting, and pondering, that are ongoing without a determined endpoint. This tense adds a layer of immediacy and dynamism, distinguishing itself from the past tense, which narrates completed actions. It is also used to express actions that may continue into the future and are frequently occurring, such as “Scott’s little sister is arriving at the diner.”
Here are a few guidelines to ensure you are using Present Continuous correctly :
- Identify the action you want to express. The action must be happening at the moment of speaking or currently ongoing to use the Present Continuous tense.
- Choose the appropriate auxiliary verb “be” (am/is/are) corresponding to the subject of the action.
- Form the main verb in its “-ing” form to create the present participle. This “-ing” form of the verb must be included to signal an ongoing action or condition.
- Construct the sentence with the subject, the auxiliary verb “be,” and the main verb in its “-ing” form.
For example, in the sentence “I am eating an apple,” the action of eating is happening now, the auxiliary verb “am” matches the subject “I,” and the main verb “eat” is transformed into its “-ing” form, “eating.”
Remember, using Present Continuous correctly not only helps you in describing ongoing actions but also aids in effective communication. Keep practicing and applying these guidelines to enhance your English language skills and avoid any confusion.
Distinguishing Between Present Simple and Present Continuous Tenses
Understanding when to use the Present Continuous tense over the Present Simple requires comprehension of the situational differences between them. The Present Continuous is the choice for activities currently in motion, while the Present Simple is used for habitual actions, general truths, or situations that are static or fixed. For instance, observe the two examples below:
“I’m working at the moment; can I call you back later?” (Present Continuous) “Regular exercise contributes to bodily and mental health, so I work out regularly.” (Present Simple)
Identifying Situational Differences
Present Continuous may denote actions about to be performed or future events, whereas Present Simple is reserved for clearly defined, scheduled future events or habits that repeat. Although both tenses are used in everyday English, it is essential to choose the correct tense based on the context and specific time-related information. Using the wrong tense leads to confusion and can distort the intended meaning.
Keyword Indicators for Tense Selection
Keywords serve as linguistic indicators that signal the appropriate selection of tense. Some words and phrases are more commonly associated with one tense, helping you make an informed decision about which tense to use. Check the table below to identify some relevant keywords for each tense:
It is important to recognize these keywords as they play a role in deciding whether an action is depicted as ongoing or as a habitual or permanent state. Be aware of these signal words as they can help you make a more accurate and grammatically correct choice when using Present Simple or Present Continuous tenses.
Applying Present Continuous to Discuss Future Plans
The Present Continuous tense boasts a distinctive application in the realm of expressing future intentions, plans, and arrangements. By using this tense, one can constructively convey the idea of an action or event that is scheduled or anticipated to occur in the future. In contrast to the Present Simple tense, which encapsulates more clearly defined or officially scheduled future events, the Present Continuous facilitates the description of less rigid, more tentative future plans. To better elucidate the differences between these two tense uses and understand their application in various contexts, consider the examples in the following table:
While utilizing the Present Continuous tense, phrases such as “ I am meeting with the client tomorrow ,” or “ They are leaving for vacation next week ,” display the versatility of the tense in articulating future intentions or arrangements with a certain level of certainty.
“I am attending a virtual conference in two weeks.”
Integrating the Present Continuous tense to discuss future events, as shown in the examples above, is just one of its many applications. By forming sentences using the subject, appropriate form of the auxiliary verb “be” (am/is/are), and the present participle (the “-ing” form), you can effectively express future intentions, plans, and scheduled appointments with ease and clarity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Present Continuous
As you continue to master the Present Continuous tense, there are some common mistakes to be aware of so you can use it effectively and accurately. Let’s explore two key areas where errors often occur: the misuse of stative verbs and the confusion of tense forms in negative and question structures.
Overusing the Tense with Stative Verbs
One of the most common mistakes in using Present Continuous is applying it to stative verbs that describe states of being, emotions, sensations, or beliefs, rather than dynamic actions. These verbs include “love,” “know,” “prefer,” “believe,” and “own,” among others. For instance, saying “I am loving this song” is incorrect; instead, one should say “I love this song.” Keep an eye out for such Stative Verb Errors and avoid overusing the Present Continuous Misuse inappropriately.
Mixing Up Tense Forms in Negative and Question Structures
Another area to pay close attention to when using the Present Continuous is the formation of negative constructs and questions. Mixing up these structures can lead to misunderstandings and impair the coherence of your sentences. Remember that in the negative form, “not” is placed between the auxiliary and main verb, resulting in contractions like “isn’t” and “aren’t.” However, the first-person form “am not” remains unchanged. When forming questions, the auxiliary verb “be” precedes the subject, as in “Are you studying?” or “Is the train leaving?” By avoiding these Common Grammar Mistakes and Negative Question Tense Mistakes , you’ll be well on your way to mastering the Present Continuous Structure Errors in English.

Subscribe now and transform your language skills with insider tips, tricks, and exclusive content!
You May Also Like:
What Is Alliteration? Discover the Rhythmic Literary Device
In the home or at the home which is correct, “on the platform” or “in the platform”: unraveling the correct usage, understanding “expectations of” vs. “expectations for” – your easy preposition guide, mastering the art of quoting: how to use ellipses for sentence clarity, contribute for, to, on, or in easy preposition guide, two minute english.
English Made Simple: Two-Minute Lessons for Busy Learners
Copyright © 2024 • TwoMinEnglish.com

Your way to the top of Grammar...
Present Continuous Tense: Full guide
- June 4, 2021
- Verb Tenses
The Present Continuous is a very popular tense in English.
We use the Present Continuous as often as the Present Simple! That is why you should know the Present Continuous well.
What is the Present Continuous?
Why is the Present Continuous so popular? Because we use this tense to talk about continuous actions that take place in the present, often at the very moment of speaking. And this is a huge number of actions that we do all the time!
These actions can be quick and short:
Look, I am jumping !
Or such actions can last for a long time and be global, slowly evolving:
I think the climate is changing …
Another reason for the popularity of the Present Continuous is that the Present Continuous carries several additional functions.
The Present Continuous is involved in the formation of several important grammatical constructions.
Sometimes English learners have difficulty with the fact that there is no analog of the Present Continuous in their native language. Even so, you will be able to understand what the Present Continuous is. It’s not difficult at all!

Present Progressive or Present Continuous?
This tense is often called either the Present Progressive or Present Continuous .
Both of these names are correct , and you can find any of them in various English grammar textbooks. We will call it the Present Continuous.
Meaning of Present Continuous
The main purpose of the Present Continuous is to show an action or process that takes place at the moment of speaking .
If you are walking down the street and someone asks:
What are you doing now?
Then you can safely use the Present Continuous, answering:
I am walking down the street.
Because you perform this action at the moment of speaking .
But this does not mean that if you suddenly stop in the middle of the street, you cannot say “I’m walking down the street”. You can say that! Even if you stop, you are still in the process of performing your action in the general sense, which is “walking down the street.”
We usually use the Present Continuous with words that indicate that the action is happening right at the moment of speaking:
- at the moment
- this minute
- right now etc.
How to form sentences
To form a sentence in the Present Continuous, we need two main components:
- Suitable form of the verb to be .
- The main verb with the -ing ending.
Now let’s take a closer look at these two components:
- We use the verb to be in the Present Continuous in the same forms as we use the verb to be in the Present Simple.
- The main verb is a verb that shows us what action happens in a sentence.
In the Present Continuous, the main verb changes as follows:
We use the verb in the base form and add the -ing ending to the verb.
- Jump – Jump ing
- Run – Runn ing
- Read – Read ing
- Talk – Talk ing
For some verbs, you can simply add the -ing ending. Some verbs take the -ing ending according to some rules.
How to form Affirmative (Positive) Sentences in Present Continuous
To form an affirmative (positive) sentence in the Present Continuous, we put the subject first in the sentence. After the subject, we put the right form of the verb to be. Then we put the main verb with the -ing ending. Then we put the rest of the sentence if necessary.
Subject (I, he, dog, people, John) + to be (am, is, are) + main verb with -ing (reading, jumping, playing) + the rest of the sentence
I am dancing in the dark. She is singing beautifully. These guys are running really fast.
How to form Interrogative (Question) Sentences in Present Continuous
We form questions in the Present Continuous in the following way:
We put first the right form of the verb to be ( am, is, are ), which serves as the auxiliary verb that shows that this is an interrogative (question) sentence. Then we put in the subject . After the subject, we put the main verb with the -ing ending. After which we put the rest of the sentence, if necessary.
to be (am, is, are) + subject (I, he, dog, people, John) + main verb with -ing (reading, jumping, playing) + the rest of the sentence
Am I dancing in the dark? Is she singing beautifully? Are these guys running really fast?
How to form Negative Sentences in Present Continuous
In negative sentences, we put the subject first. After the subject, we put the verb to be with the negative not . Then we put the main verb with the -ing ending. After which we put the rest of the sentence, if necessary.
Subject (I, he, dog, people, John) + to be (am, is, are) + not + main verb with -ing (reading, jumping, Playing) + rest of the sentence
I am not dancing in the dark. She is not singing beautifully. These guys are not running fast.
When we Use Present Continuous?
We use the Present Continuous in many cases. Let’s take a look at the most popular of them.
- We use the Present Continuous when we describe the action that occurs at the moment of speaking. In such sentences, we often use words that indicate that the action takes place exactly at the moment of speaking. These are words such as: “At the moment”, “Now”, “At this moment”.
I’m walking down the street now. She is reading a book at the moment.
- We use the Present Continuous to describe actions that are currently taking place, but not necessarily at the moment of speaking. Such actions could have begun a long time ago, even a very long time ago. The main thing is that these actions continue to last at the moment too. Often such actions are accompanied by words such as: currently, these days, etc.
I am watching a fascinating TV show. It has 50 episodes!
I am traveling around the world in my car.

- To describe two or more actions that occur simultaneously at the moment of speaking.
I’m walking down the street now, and my wife is running around the shops! At the moment I am working, and my children are running around me and screaming! They are just having fun.
- We use the Present Continuous to express dissatisfaction or resentment about someone or something. Because using the Present Continuous’ dynamics we add expression to the sentence. This is how we express our dissatisfaction or indignation. Such expressions can be accompanied by the words: Always, Constantly, Every time, Day after day, Without stopping, etc.
She is constantly complaining about her life. I am watching TV day after day! John is smoking too much.
- To talk about the unusual behavior of someone or something. Or when we want to tell about something that we have not seen before.
I can’t believe, Jessica is playing sports. He is eating too much these days!
Note: It is important to understand that we use the Present Continuous in such cases when we describe really unusual behavior that surprises us or attracts our attention.
- We use the Present Continuous to describe actions that are planned. It is important here to understand that we use the Present Continuous in this case when we are talking about the actions that we really planned and decided to do some time ago. In this case, we are confident that we will do what we have planned.
Often in such sentences, we use words that specify the time of our planned actions: “next day”, “next month”, “tomorrow”, “in two hours”, etc.
We are moving to a new home in two weeks. John and Jessica are going to the theatre tomorrow.
NOTE: When we use the Present Continuous to talk about our plans, we mean that we not only planned an action, but also did everything necessary to accomplish it. Therefore, the sentence “John and Jessica are going to the theatre tomorrow” means that John has made an agreement with Jessica and may have already bought tickets. It was indeed a planned action.
- Another interesting use of the Present Continuous when we talk about temporary situations. These are cases when we are talking about some actions, often from life, which are of a temporary nature.
Grandma stays with us for two weeks. John is using his father’s car while John’s car is being repaired.
Often in such sentences, we use additional words (until, during, while, etc.), which express that the action is temporary.
Note: It is important here to understand that the Present Continuous is used in the examples to show that Grandmother does not live there all the time, she just came to visit for two weeks. John will not drive his father’s car all the time, he took it for a while. If situations are not temporary, then we do not use the Present Continuous but the Present Simple.
For example:
I live in London. This sentence means that I live in London all the time . Probably whole my life.
I am living in London. This sentence means that I am living in London temporarily . Maybe I moved to London because of my job. I am not going to live in London for my whole life.

- We use the Present Continuous to describe a situation that is changing or evolving. In these cases, we use the Present Continuous to emphasize the dynamics of development or change. In such cases, we can use words like: become, start, change, etc.
Climate is changing. The children are growing up so fast! The situation is getting worse and worse.
- We use the Present Continuous with verbs of movement when talking about the near future. We can use verbs such as: Go, Come, Leave, Start, End, etc.
I’m going to visit Mark. John is starting a new business. I am leaving this party.
- We use the Present Continuous to say about something new, in the case when this something new is contrasted (put in comparison, compared) with the way it was before.
Unfortunately, I am watching TV all day, but I used to play sports. He quit his job, he is writing books now. People are working less these days than it was in the old days.
Time Clauses
Another use case for the Present Continuous is Time Clauses after Conjunctions:
Such sentences have two parts:
- Continuous action expressed in the Present Continuous.
- Short action expressed in the Present Simple.
Putting these two parts together, we describe some kind of ongoing action against the background of some kind of short action .
Conjunctions such as as long as, while, when , etc. help us connect the two. We often use this construction when we talk about ordinary life situations.
You call me at that moment when I am walking down the street. Call me back later! They make noise while John is trying to focus on his work!
How to use Stative verbs in Present Continuous
Action verbs in the Present Continuous can be used with the -ing ending. But in English, there is a group of verbs that we do not use with -ing. These are stative verbs , non-continuous verbs .
For example, verbs that describe feelings (love, want). We use these verbs with the Present Simple instead of the Present Continuous.
We can say in the Present Continuous:
I’m going home.
We cannot say in the Present Continuous:
I am understanding that it is time for me to go home.
To say this we use the Present Simple:
I understand that it is time for me to go home.
Stative verbs are not used with the -ing ending. They cannot be in the process of duration. Because it is impossible to see or feel their dynamics.
You can imagine how John runs , Jessica jumps , or a bird flies . These are all processes that can take place in dynamics. But how can the verb “ Understand ” occur in action?

Therefore, the group of Stative verbs includes verbs of feelings, emotions, thought processes, and perception, such as:
- satisfy etc.
What to do with these verbs? Nothing complicated! We just use these verbs in the Present Simple instead of the Present Continuous.
You can form a whole sentence using the Present Continuous with Action verbs. Then if we need to add a Stative verb to such a sentence, we just use the Present Simple.
Let’s write a sentence like this where all actions happen at the same time. We use some verbs in the Present Continuous because these verbs mean continuous actions. We use the Present Simple for others verbs from the group of Stative verbs:
I am playing with dolls, John is reading , but I think he don’t like the book.
You see, there is nothing complicated about it.
Cases when we can use Stative verbs
However, in English, there is an exception for every rule 🙂
Therefore, now I am going to tell you about a case when even a Stative verb can be used in the Present Continuous.
We can use Stative verbs in the Present Continuous to emphasize our emotions or feelings .
I am thinking ! Do not bother me! Yes, I am hating you right now!
See? In these examples, we want to emphasize that the Stative verb is very important at the moment of speaking. Therefore, we put the Stative verb in the progressive (continuous) form.
When we can use to have as a continuous verb (to have with -ing)
The verb to have is also a Stative verb. But we can use to have in the Present Continuous. We can add the -ing ending to the verb to have in the Present Continuous. We do this in some special cases.
For example, we use the verb to have with the -ing ending if the verb to have is a part of some Fixed Expressions:
- to have a breakfast
- to have a brake
- to have fun
We can use these constant expressions in the Present Continuous by adding -ing to the verb to have :
I am having breakfast. We are having fun!
When we can use to be as a continuous verb (to be with -ing)
The verb to be is also a Stative verb. But sometimes we can use the verb to be with the -ing ending in the Present Continuous.
IMPORTANT: In this case, I mean the verb to be in its base form without to – be . It is be that we can turn into being using the -ing ending.
be + -ing = being.
Remember: We cannot add the -ing ending to to be forms such as am, was, are, is, etc. We can only add -ing to one base form of the verb to be – be .
We use the verb to be in the form being when we want to emphasize that someone or something behaves in a certain way at a particular moment of speaking.
Stop being so rude. She is being so nice to our children. Look at her. She is being weird after I told her the secret.
In these examples, we emphasize the behavior of someone at the moment of speaking .
What is the difference between Present Continuous vs Present Simple. Examples.
The Present Simple and the Present Continuous are great friends. The Present Simple is often used in conjunction with the Present Continuous.
For example, when we tell a story. We tell some details of the story in the Present Simple and some in the Present Continuous. Thus, we can tell that some action takes place against the background of another action.
I go out into the garden where flowers are blooming, birds are singing and everything around is so beautiful!
But how do we know when we should USE the Present Continuous and when the Present Simple ? After all, both of these tenses refer to the present. Both of them are used very, very often.
Let’s take a look at the main differences between the Present Continuous and the Present Simple:
- We use the Present Simple with non-action verbs, non-progressive verbs that describe feelings, sensations, perceptions, thought processes. We use such verbs in the Present Continuous only in rare situations.
I want to eat. Right now , Jack is thinking about how much he loves Jessica.
- We use the Present Simple when talking about situations or actions that are permanent. We use the Present Continuous when we talk about temporary actions.
Grandma is living with us. Grandma lives with us.
In the first example, Grandma lives with us and this is temporary because she came to visit us. In the second example, Grandma lives with us all the time.

- We use the Present Simple to describe facts, truths that everyone knows. We use the Present Continuous to describe facts or truths that occur at the moment of speaking or are facts and truths at the moment of speaking.
The dog is running around the yard.
This means that the dog is rinning right at the moment of speaking.
The dog runs around the yard every day.
This means that the dog runs around the yard every day. The dog loves to run around the yard. The dog does it every day . This does not happen at the moment of speaking.
- We use the Present Simple to describe actions that do not occur at the moment of speaking and are not related to the present moment. The Present Continuous describes actions that are related to the present, even if they do not occur at the moment of speaking.
I jog three times a week. Lately, I am jogging a lot.
Markers of Present Continuous
The Present Continuous markers are words that indicate that actions occur at the moment of speaking:
- At the moment
- This minute
- In this situation
I’m busy right now , I am working! At this moment they are flying in an airplane over Paris.
Examples of Present Continuous
Take a look at some examples of the Present Continuous. These examples will help you understand this lesson better.
I cannot speak on the phone, I am driving. Mom is busy now, she is cleaning the kitchen. Watch your brother is dancing. I’m reading a book now. They are running very fast, look! He is walking in the park.
Related Posts

Past Continuous: Rules and Examples

Present Perfect and Past Simple: Difference

Future Continuous: Rules and Usage

To Be in Past Simple

Present Perfect: Formula and Rules

Past Perfect: How to Form and How to Use?
One comment.
Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!
Comments are closed.
Trending now

- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for visit
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "visit" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->

Present Continuous Sentences With Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
The present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are happening at the moment of speaking or actions that are ongoing. It is formed using “am/is/are” followed by the present participle (verb + ing), like in “They are watching a movie.” This tense emphasizes the current, ongoing nature of an action, unlike the simple present tense, which is used for habitual actions or general truths.
The present continuous tense in English is used to describe actions or states that are currently in progress or are ongoing. The structure of a present continuous sentence is:
Am/Is/Are + present participle
Let’s explore some examples to understand this better:
Example 1: I am reading a book. This sentence indicates that the speaker is in the middle of the action of reading a book right now. The action is happening at the moment of speaking.
Example 2: She is cooking dinner. This is an example of the present continuous used for an ongoing action. The action of cooking dinner is currently taking place.
Example 3: They are playing soccer in the park. This sentence shows an action that is happening right now. The action of playing soccer is occurring as we speak.
Example 4: We are not watching TV at the moment. This sentence expresses a negative ongoing action. The speaker and their companions are currently not engaged in the activity of watching TV.
Example 5: If you are looking for your keys, they are on the table. This is an example of the present continuous used in a conditional sentence. It suggests that the action of looking for the keys is currently happening.
The present continuous is formed by using “am/is/are” followed by the present participle of the verb. It’s crucial to use the correct form of the verb to maintain the tense.
Incorrect: She are reading a book.
We can see that the present continuous is often used to talk about actions happening right now, temporary situations, and future plans.
The words “ now ,” “ currently ,” “ at the moment ,” “ today ,” and “ this week ” are commonly used with the present continuous to add context about the timing of the action.
Present Continuous Sentence Examples
- I am studying for my exams. (The action of studying is happening right now.)
- She is running in the marathon today. (She is currently participating in the marathon.)
- They are building a new house. (The construction of the house is ongoing.)
- We are having lunch at the moment. (The action of having lunch is happening now.)
- He is not working today. (He is not engaged in work currently.)
- The children are playing in the garden. (The children are engaged in playing right now.)
- I am learning to play the guitar. (The action of learning is ongoing.)
- She is shopping for groceries. (The action of shopping is happening at this moment.)
- We are traveling to New York next week. (This is a future plan expressed in the present continuous.)
- He is reading the news online. (The action of reading is happening currently.)
- The teacher is explaining the lesson. (The explanation is taking place now.)
- They are discussing the new project. (The discussion is ongoing at the moment.)
- I am not feeling well today. (The state of not feeling well is current.)
- She is planning her vacation. (The planning is happening right now.)
- We are waiting for the bus. (The waiting is ongoing at this moment.)
- He is playing the piano. (The action of playing the piano is happening now.)
- The students are preparing for the exam. (The preparation is currently taking place.)
- You are always losing your keys. (This describes a repeated action in the present continuous to express annoyance.)
- I am visiting my grandparents this weekend. (A future plan expressed in the present continuous.)
- She is thinking about moving to a new city. (The thought process is happening now.)
The present continuous tense is versatile and is essential for describing ongoing actions, temporary situations, and near-future plans. Using this tense accurately helps convey the immediacy and ongoing nature of actions and states in English.
Related Articles:
- Questions in Present Continuous Tense with Examples
- Difference between Present Simple vs. Present Continuous with example
- Going to and Present Continuous for Future Plans and Arrangements
- Present Continuous Tense: How to Use It, With Examples
- Present Continuous Negative Sentences with Examples
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- 📝 VOCABULARY
- 🚀 GAMES/ACTIVITIES

Present Continuous Tense – With Usage Examples and Pictures

“Present continuous tense” or “present progressive tense” is a verb tense that describes the actions we are doing right now. It is used to express the actions that we are doing at the moment of speaking. The auxiliary verbs are “ am, is, are ” and we add “ -ing ” at the and of the verbs in present continuous tense.
⬤ Formation of present continuous tense
For affirmative sentences we use the formation of “am, is, are + Ving” . For negative sentences we use “not” after the auxiliaries “am, is, are”. To make questions just put “am, is, are” before the subject. See the animated sentences below to learn the structure of present continuous tense.
Examples with Pictures Dialogue exercise Sentence scramble game Translation exercise
⬤ Which auxiliary (helping verb) to use for present continuous tense?
The auxiliary verbs in present continuous tense are “ am, is, are “. We always add “ -ing ” at the end of the verbs in present continuous tense
- They are swimming.
- I am reading a book.
- He is playing football.
- Lucy is going home.
- Ali is helping his father.
⬤ Positive (Affirmative) sentences
For the formation of positive sentences in present continuous tense we add use “ am, is, are ” and a verb with “ -ing ” suffix at the end.
- I am not crying.
- He is not drinking tea.
- We aren’t waiting for the bus.
- I’m not going anywhere.
⬤ Negative sentences
For the formation of negative sentences in present continuous tense we use “ not ” together with “ am, is, are “. The short forms are “ ‘m not, isn’t, aren’t ”
- He did not want tea.
- We didn’t wait for the bus.
- I didn’t use your pen.
- Susan didn’t lie.
⬤ Interrogative sentences
For the formation of question sentences (interrogative) in present continuous we take “ am, is, are ” before the subject of the sentence.
- Is Mr. Gibbs having breakfast?
- Are you kidding?
- What are you looking at?
- Why are yo laughing?
⬤ Sentence forms in present continuous tense
SIMILAR PAGES: ❯❯ Learn verb to be here ❯❯ Learn simple present tense here ❯❯ Learn future simple tense (will) here ❯❯ Learn be going to future tense here ❯❯ Learn simple past tense here ❯❯ Learn past continuous tense here ❯❯ Learn present perfect tense here
⬤ Explanations and usages of present continuous tense
You can learn the explanations, usages and time adverbs of present continuous tense below.
⬤ 1- Activities that are happening at the time of speaking
Present continuous tense is used to describe activities that we do at the very moment of speaking.
- I am listening to music now.
- He is working in the office.
- Are you crying?
- What are you doing now? – I’m drinking tea.
⬤ 2- Longer and temporary actions
Temporary but continuous actions can also be expressed using present continuous tense.
- I writing a book on pets.
- I am studying maths at the university.
- We are staying in this hotel.
- She is selling flowers.
⬤ 3- Arrangements for near future
We can also use present continuous tense to talk about arrangements in near future
- We are going to the cinema tomorrow evening.
- He is meeting some friends this evening.
- Are you coming with us next week?
- We are celebrating the Eid two days later.
⬤ 4- Annoying situation
The word “always” can be used with the present continuous tense to give the idea of an annoying or bothering situation.
- He is always getting up late nowadays.
- You are always exaggerating the news.
- Sam is always talking loud.
⬤ 5- Non-progressive verbs
Some verbs have no progressive forms, so these verbs are used in simple present tense. Some of these verbs are:believe, know, remember, understand, need, hate, like, love, prefer, want, feel, mean etc.
- WRONG: I am knowing the answer. CORRECT: I know the answer.
- WRONG: I am loving you. CORRECT:I love you.
- WRONG: I am understanding it. CORRECT:I understand it.
- WRONG: He is liking ice-cream. CORRECT:He likes ice-cream.
- I know the answer.
- I like football.
- Do you remember my name?
- I don’t want tea.
- What do you mean?
⬤ Time expressions in present continuous tense
Time expressions are now, just now, at the moment, at present
⬤ Images and example sentences
In this section you can learn present continuous tense with images and example sentences.
⬤ A dialogue example
Below is a dialogue to learn present continuous tense. After reading the sentences, you can make similar dialogues.
I am coming home.
The dinner table is ready.
Are you coming with your office friends?
No, they are not coming.
Mike is going to london
and Sam is working at the office now.
They are busy.
Why is Sam working at this time of the day?
It is very late.
He has a lot to do.
OK. See you.
⬤ Translate the sentences below into your native language.
You will see random examples of present progressive tense below. You can translate them into your native language.
⬤ Sentence scramble game
You can see scrambled words of present continuous tense sentences. Click on the words in order to make meaningful sentences.
⬤ Example sentences
You can see many sentences below to learn present continuous tense in context.
➔ 10 examples of about present continuous tense
- Alex is running outside.
- He is playing with his toys now.
- Rose is going to school at the moment.
- Jack is driving fast.
- What are you drawing?
- I am thinking about my future.
- The doctor is examining the baby.
- I am not lying.
- She is wearing jeans at the moment.
- we are getting married next month.
- The phone is ringing.
⬤ Questions and answers
You can read the questions and the answers below to learn how to use about present continuous tense.
➔ 10 questions and answers about present continuous tense
- Why are they discussing? Because they are late.
- What are you drinking? I’m drinking lemonade.
- Where are you going? We are going to Italy.
- Are you sleeping? No, I am just resting my eyes.
- Is it snowing outside? Yes, it is.
- Are you crying? Yes. I am thinking about my family.
- Are the children playing in the garden? No. They are playing at home.
- Why is Nancy sitting alone? Because she wants to be alone.
- Are you coming with us tomorrow? Yes, I am.
- Is she studying English now? Yes, she is.
External resources: You can visit British Council page to learn present continuous tense , or watch a video from the popular movies to see example sentences . Here is a PDF document to learn present continuous tense.
related pages
Fill in the blanks quiz for present continuous tense, sentence scramble game for present continuous tense, accessories vocabulary 👓 exercises pictures audio, body parts in english 👨 with games and listed images, classroom objects vocabulary in english 📕 with games, clothes vocabulary in english 👕 learn with images and flashcards, colour names in english 🎈 with tests and images, computer parts (hardware) vocabulary: pictures audio, verb to be (am, is, are) – with examples and online exercises, modal “can” – with explanations exercises and activities, simple present tense (do-does) – with usage, pictures and example sentences, future simple tense (will) – with activities dialogue and exercises.
© www.english-learn-online.com All right reserved You can write us any mistakes or read our about page or see our privacy policy .
Conjugation English verb to visit
Simple present, present progressive/continuous, simple past, past progressive/continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive/continuous, past perfect, past perfect progressive/continuous, future progressive/continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, progressive, perfect progressive, translation to visit.
EnglishGrammarSoft

- 50 Sentences of Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense describes on-going actions at the time of speaking and happening right now, stressing that the doer is in the middle of the activity and hasn’t finished yet (the action is incomplete). For example, I am eating a burger.
See also : 12 Verb Tenses with Formula and Examples
Sentences of Present Continuous Tense
Here are 50 sentences of present continuous tense.
Affirmative Sentences
- Tom is learning grammar rules.
- You are the one who is giving information.
- I am taking breakfast now.
- Steve is reading a book now.
- Alice is talking with her friend.
- She is going to Spain Sunday.
- I am training to become a professional footballer.
- She is waiting for her friends.
- He is working hard to achieve the goal.
- The children are playing hide and seek.
- She is planting flowers around the tree.
- More and more people are using their headphones to listen to music.
- Our country is getting richer.
- The children are shivering from the cold.
- They are enjoying the party.
- The plumber is fixing the tap.
- He is eating chips while watching the television.
- The sun is rising in the east.
- I am running on the jogging track.
- The doctor is feeling the pulse of the patient.
- Jimmy is recording videos for his YouTube channel.
- He is looking for a job.
- Jon is playing the flute.
- The farmer is harvesting the crop.
- Alice is spending his valuable time reading books.
- Hundreds of families are living in this village.
- Robots are helping us in performing routine work.
- The birds are migrating from Siberia due to harsh weather.
- Jon is resigning from his job due to the low salary.
- I am attending a business meeting right now.
Negative Sentences
- The chef is not baking the cookies.
- He is not feeling ashamed of his act.
- Tom is not driving the car fast.
- They are not talking with each other after the last argument.
- The audience is not listening to the speaker.
- It is not raining outside.
- I am not going to Singapore.
- Peter is not paying attention to his handwriting.
- He is not preparing for the exam.
- The ship is not going to Manila.
Interrogative Sentences
- Who is making noise ?
- Who is ringing the bell ?
- Are you living in this town ?
- Is the postman delivering letters ?
- Is she betraying me ?
- Is the boy reading his lesson ?
- Where are the people gathering for the party ?
- How many workers are building the bridge ?
- Is he doing his duty diligently ?
- Is the mechanic fixing the car ?

Further Reading
- Simple Present Tense (Formula, Examples & Exercises)
- 50 Sentences of Simple Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense Worksheets
- Present Continuous Tense Formula, Examples & Usage
- Present Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Tense with Examples
- 50 Sentences of Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Examples, Exercise, & Structure
- 50 Sentences of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets
Similar Posts

Past Perfect Continuous Tense Sentences in English (Affirmative, Negative & Questions)
Past perfect progressive or continuous tense is very similar to the past perfect tense, only that the focus of this tense is the duration of…

Starting Sentences for Essays & Tips for Opening Sentences
Starting sentences for essays A good opening sentence can make or break your essay. It’s what catches the reader’s attention and makes them want to…

Sentences with Colon in them (40 Examples)
The colon is a punctuation mark consisting of two equally sized dots centered on the same horizontal line. The main use of a colon is…

Negative Interrogative Sentences of All Tenses
Negative interrogative sentences are used to ask questions that are negative in meaning. In this lesson, you will see 100+ negative interrogative sentences of all…

Sentences with 3 Adjectives (52 Examples)
You may be puzzled about how to make sentences with three (3) adjectives. Sometimes, you may find it tough to make sentences with more than…
Singular and Plural Nouns (15 Rules, 50 Examples & Worksheet)
What is singular noun? The singular nouns are words that only refer to one person or thing. They can be used as a subject, direct…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- English Grammar
- English Tenses
- Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense - Meaning, Definition, Formula, Uses, Structure with Examples
Are you wondering how the present continuous tense can be used? Well, fret no more. You just came across a sentence with the present continuous tense. In this article, you will learn all that you need to know about what the present continuous tense is, its definition, uses, structure and rules of usage. Along with these, with the examples and practice questions, you will surely be able to use the frame sentences using the present continuous tense accurately.

Table of Contents
Definition of the present continuous tense, structure of the present continuous tense, rules and points to remember when using the present continuous tense, uses of the present continuous tense, 10 sentences using the present continuous tense, test your understanding of the present continuous tense, frequently asked questions on present continuous tense, understanding the present continuous tense.
The present continuous tense, as the name suggests, is the form of tense that is used to denote an action that is ongoing or occurring in that current moment. It is also referred to as the present progressive tense as they represent the action that is progressing in the present. Let us now take a look at the definitions provided by various dictionaries about the present continuous tense.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines the ‘present continuous tense’ as “the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now.” According to the Collins Dictionary, the present continuous tense is defined as “a verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used especially to indicate that a present action or event is in progress, being repeated, or of a temporary nature or to express the future.” The present continuous tense is “the tense used to talk about actions or behaviour that are in progress now or planned for the future”, according to the Macmillan Dictionary.
There is definitely just one formula to mastering the present continuous tense and this is how it goes.
However, there is something more you should pay attention to. You should also learn how the sentences with the present continuous tense form of the verb are structured when they are positive, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative.
Have a look at the table given below to have a deeper understanding of the structure of the present continuous tense.
When using the present continuous tense, make sure you follow the sentence structure exactly.
- Always start with the subject when it is a positive or negative sentence and with the helping verb when it is in the interrogative format.
- A sentence with the present continuous tense consists of a helping verb (‘to be’ form of verbs) and a main verb . The helping verbs can be ‘am’ for the pronoun ‘I’, ‘is’ for singular subject and ‘are’ for a plural subject.
- Just note that like the other pronouns, the pronoun ‘am’ cannot be used in the negative form in an interrogative sentence. Instead of ‘amn’t’, ‘aren’t’ is used.
For example:
- Amn’t I reading a newspaper? Wrong
- Aren’t I reading a newspaper? Correct
- The present continuous tense can never be used with stative verbs .
Like the simple present tense , the present continuous tense is also generally used to talk about an action that is taking place in the present. The only difference is that it denotes an action that is continuing to happen or progressing at the current moment.
Take a look at the following points that elaborate on the more specific uses of the present continuous tense.
- It is used to represent an action that is happening or progressing in the moment that the speaker is speaking.
- My son is working on his science project.
- Santana is singing Don’t Rain on my Parade.
- It is used to depict a future event or arrangement.
- What are you planning to do tomorrow?
- I heard that Rachel is moving to Paris next month.
- It is used to denote an action that is going on or continuing at the time of speaking.
- Is she still working at the National Institute of Medical Sciences?
- I am currently taking guitar lessons so that I could play for your wedding.
Examples of Present Continuous Tense
Going through more and more examples can only make you an expert in the particular subject or topic. So , here you go. Check out the examples of sentences using the present continuous tense given below.
- My mom is cooking dinner.
- The band is playing all the classics.
- Monica and Rachel are going on a trip tomorrow.
- Sheethal is not practising for the final audition.
- I am trying out something new.
- They are not travelling to London next week.
- Are you watching a movie tonight?
- Is your phone working properly now?
- The children are loving the new park.
- Diana is playing the main role in the play.
Having gone through all the given examples, you should have understood really well. Check your understanding of the present continuous tense by filling in the blanks in the following sentence with the right form of tense using the verbs given in the brackets.
1. ______ the clock ________ (work)?
2. The teachers ___________ (plan) to dance to all the latest songs on Childrens Day.
3. ______ she ___________ (play – negative) the piano anymore?
4. The dog __________ (run) all around the garden.
5. We ____________ (go – negative) to the party tomorrow.
6. The Bellas ___________ (perform) the songs of the 80s.
7. Will, Smith and Sherlock ___________ (dance) well.
8. _______ I __________ (look) good today?
9. Trinita and Vinitha ____________ (ride) on their new cat.
10. _____ he still ________ (stand) there?
Ready to see if you got it all right. Check out the answers given below.
1. Is the clock working ?
2. The teachers are planning to dance to all the latest songs on Childrens Day.
3. Is she not playing the piano anymore?
4. The dog is running all around the garden.
5. We are not going to the party tomorrow.
6. The Bellas are performing the songs of the 80s.
7. Will, Smith and Sherlock are dancing well.
8. Am I looking good today?
9. Trinita and Vinitha are riding on their new cat.
10. Is he still standing there?
What is the present continuous tense?
The Present Continuous Tense, as the name suggests, is the form of tense that is used to denote the action that is ongoing or occuring in that current moment. It is also referred to as the present progressive tense as they represent the action that is progressing in the present.
What is the definition of the present continuous tense?
What is the formula to be followed when using the present continuous tense.
The formula to be kept in mind and used when writing or speaking a sentence in the present continuous tense is as follows: Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence
Give some examples of the present continuous tense.
Here are a few examples to show you how the present continuous tense is used.
What are the uses of the present continuous tense?
The present continuous tense can be used to talk about an action that
- is happening or progressing in the moment that the speaker is speaking.
- depicts a future event or arrangement.
- is going on or continuing at the time of speaking.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Entrar ¿Todavía no tienes una cuenta? Regístrate ¿Has olvidado tu contraseña?

Regístrate ¿Ya tienes cuenta? Entrar
Recuperar contraseña ¿Ya tienes cuenta? Entrar ¿Todavía no tienes una cuenta? Regístrate
Conjugador de verbos
Con nuestra herramienta podrás conjugar verbos en inglés: sólo tienes que introducir un verbo en inglés y automáticamente obtendrás las tablas de conjugación de todos sus tiempos verbales. Todos los tiempos Present simple Present continuous Past simple Past continuous Future simple Present perfect simple Present perfect continuous Past perfect simple Past perfect continuous Future perfect Conditional Conditional perfect Forma contracta Conjugar
Tabla de conjugación del verbo "To visit" Present Simple (Presente Simple) Affirmative I visit. You visit. We visit. He/She/It visits. You visit. They visit. Negative I do not visit. You do not visit. We do not visit. He/She/It does not visit. You do not visit. They do not visit. Interrogative Do I visit? Do you visit? Do we visit? Does he/she/it visit? Do you visit? Do they visit? Ir a la clase relacionada Present Simple Continuous (Presente Continuo) Affirmative I am visiting. You are visiting. We are visiting. He/She/It is visiting. You are visiting. They are visiting. Negative I am not visiting. You are not visiting. We are not visiting. He/She/It is not visiting. You are not visiting. They are not visiting. Interrogative Am I visiting? Are you visiting? Are we visiting? Is he/she/it visiting? Are you visiting? Are they visiting? Ir a la clase relacionada Past Simple (Pasado Simple) Affirmative I visited. You visited. We visited. He/She/It visited. You visited. They visited. Negative I did not visit. You did not visit. We did not visit. He/She/It did not visit. You did not visit. They did not visit. Interrogative Did I visit? Did you visit? Did we visit? Did he/she/it visit? Did you visit? Did they visit? Ir a la clase relacionada Past Continuous (Pasado Continuo) Affirmative I was visiting. You were visiting. We were visiting. He/She/It was visiting. You were visiting. They were visiting. Negative I was not visiting. You were not visiting. We were not visiting. He/She/It was not visiting. You were not visiting. They were not visiting. Interrogative Was I visiting? Were you visiting? Were we visiting? Was he/she/it visiting? Were you visiting? Were they visiting? Ir a la clase relacionada Future Simple (Futuro Simple) Affirmative I will visit. You will visit. We will visit. He/She/It will visit. You will visit. They will visit. Negative I will not visit. You will not visit. We will not visit. He/She/It will not visit. You will not visit. They will not visit. Interrogative Will I visit? Will you visit? Will we visit? Will he/she/it visit? Will you visit? Will they visit? Ir a la clase relacionada Present Perfect Simple (Presente Perfecto) Affirmative I have visited. You have visited. We have visited. He/She/It has visited. You have visited. They have visited. Negative I have not visited. You have not visited. We have not visited. He/She/It has not visited. You have not visited. They have not visited. Interrogative Have I visited? Have you visited? Have we visited? Has he/she/it visited? Have you visited? Have they visited? Ir a la clase relacionada Present Perfect Continuous (Presente Perfecto Continuo) Affirmative I have been visiting. You have been visiting. We have been visiting. He/She/It has been visiting. You have been visiting. They have been visiting. Negative I have not been visiting. You have not been visiting. We have not been visiting. He/She/It has not been visiting. You have not been visiting. They have not been visiting. Interrogative Have I been visiting? Have you been visiting? Have we been visiting? Has he/she/it been visiting? Have you been visiting? Have they been visiting? Ir a la clase relacionada Past Perfect Simple (Pasado Perfecto) Affirmative I had visited. You had visited. We had visited. He/She/It had visited. You had visited. They had visited. Negative I had not visited. You had not visited. We had not visited. He/She/It had not visited. You had not visited. They had not visited. Interrogative Had I visited? Had you visited? Had we visited? Had he/she/it visited? Had you visited? Had they visited? Ir a la clase relacionada Past Perfect Continuous (Pasado Perfecto Continuo) Affirmative I had been visiting. You had been visiting. We had been visiting. He/She/It had been visiting. You had been visiting. They had been visiting. Negative I had not been visiting. You had not been visiting. We had not been visiting. He/She/It had not been visiting. You had not been visiting. They had not been visiting. Interrogative Had I been visiting? Had you been visiting? Had we been visiting? Had he/she/it been visiting? Had you been visiting? Had they been visiting? Ir a la clase relacionada Future Perfect (Futuro Perfecto) Affirmative I will have visited. You will have visited. We will have visited. He/She/It will have visited. You will have visited. They will have visited. Negative I will not have visited. You will not have visited. We will not have visited. He/She/It will not have visited. You will not have visited. They will not have visited. Interrogative Will I have visited? Will you have visited? Will we have visited? Will he/she/it have visited? Will you have visited? Will they have visited? Ir a la clase relacionada Conditional (Condicional) Affirmative I would visit. You would visit. We would visit. He/She/It would visit. You would visit. They would visit. Negative I would not visit. You would not visit. We would not visit. He/She/It would not visit. You would not visit. They would not visit. Interrogative Would I visit? Would you visit? Would we visit? Would he/she/it visit? Would you visit? Would they visit? Ir a la clase relacionada Conditional Perfect (Condicional Perfecto) Affirmative I would have visited. You would have visited. We would have visited. He/She/It would have visited. You would have visited. They would have visited. Negative I would not have visited. You would not have visited. We would not have visited. He/She/It would not have visited. You would not have visited. They would not have visited. Interrogative Would I have visited? Would you have visited? Would we have visited? Would he/she/it have visited? Would you have visited? Would they have visited? Ir a la clase relacionada
Conjugación verbo visit - inglés
Modelo : obey
Auxiliar : have , be
Otras formas: visit oneself / not visit
Contracciones
- he/she/it visits
- you visited
- he/she/it visited
- they visited
Present continuous
- I am visiting
- you are visiting
- he/she/it is visiting
- we are visiting
- they are visiting
Present perfect
- I have visited
- you have visited
- he/she/it has visited
- we have visited
- they have visited
- I will visit
- you will visit
- he/she/it will visit
- we will visit
- they will visit
Future perfect
- I will have visited
- you will have visited
- he/she/it will have visited
- we will have visited
- they will have visited
Past continous
- I was visiting
- you were visiting
- he/she/it was visiting
- we were visiting
- they were visiting
Past perfect
- I had visited
- you had visited
- he/she/it had visited
- we had visited
- they had visited
Future continuous
- I will be visiting
- you will be visiting
- he/she/it will be visiting
- we will be visiting
- they will be visiting
Present perfect continuous
- I have been visiting
- you have been visiting
- he/she/it has been visiting
- we have been visiting
- they have been visiting
Past perfect continuous
- I had been visiting
- you had been visiting
- he/she/it had been visiting
- we had been visiting
- they had been visiting
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been visiting
- you will have been visiting
- he/she/it will have been visiting
- we will have been visiting
- they will have been visiting
- let's visit
Perfect participle
- having visited
Ayudando a millones de personas y grandes organizaciones a comunicar con más eficacia y precisión en todos los idiomas.

Visit Past Tense
visited past tense of visit is visited.
Visit verb forms
Conjugation of visit.
- What is the past tense of waterlog in English?
- What is the second form of verb watermark?
- What is the third form of verb waterproof in English?
- What is the conjugation of waterski in English?
- Conjugate wattle in English?
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.
Conjugación del verbo inglés to visit
Traducción to visit, simple present, present progressive/continuous, simple past, past progressive/continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive/continuous, past perfect, past perfect progressive/continuous, future progressive/continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, progressive, perfect progressive.

Conjugação verbo visit em inglês
Modelo : obey
Auxiliar : have , be
Outras formas: visit oneself / not visit
- he/she/it visits
- you visited
- he/she/it visited
- they visited
Present continuous
- I am visiting
- you are visiting
- he/she/it is visiting
- we are visiting
- they are visiting
Present perfect
- I have visited
- you have visited
- he/she/it has visited
- we have visited
- they have visited
- I will visit
- you will visit
- he/she/it will visit
- we will visit
- they will visit
Future perfect
- I will have visited
- you will have visited
- he/she/it will have visited
- we will have visited
- they will have visited
Past continous
- I was visiting
- you were visiting
- he/she/it was visiting
- we were visiting
- they were visiting
Past perfect
- I had visited
- you had visited
- he/she/it had visited
- we had visited
- they had visited
Future continuous
- I will be visiting
- you will be visiting
- he/she/it will be visiting
- we will be visiting
- they will be visiting
Present perfect continuous
- I have been visiting
- you have been visiting
- he/she/it has been visiting
- we have been visiting
- they have been visiting
Past perfect continuous
- I had been visiting
- you had been visiting
- he/she/it had been visiting
- we had been visiting
- they had been visiting
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been visiting
- you will have been visiting
- he/she/it will have been visiting
- we will have been visiting
- they will have been visiting
- let's visit
Perfect participle
- having visited
Ajudando milhões de pessoas e grandes organizações a comunicarem com mais eficiência e precisão em todas as línguas.
Coniugazione verbo visit inglese
Modello : obey
Ausiliare : have , be
Altre forme: visit oneself / not visit
Forme contratte
- he/she/it visits
- you visited
- he/she/it visited
- they visited
Present continuous
- I am visiting
- you are visiting
- he/she/it is visiting
- we are visiting
- they are visiting
Present perfect
- I have visited
- you have visited
- he/she/it has visited
- we have visited
- they have visited
- I will visit
- you will visit
- he/she/it will visit
- we will visit
- they will visit
Future perfect
- I will have visited
- you will have visited
- he/she/it will have visited
- we will have visited
- they will have visited
Past continous
- I was visiting
- you were visiting
- he/she/it was visiting
- we were visiting
- they were visiting
Past perfect
- I had visited
- you had visited
- he/she/it had visited
- we had visited
- they had visited
Future continuous
- I will be visiting
- you will be visiting
- he/she/it will be visiting
- we will be visiting
- they will be visiting
Present perfect continuous
- I have been visiting
- you have been visiting
- he/she/it has been visiting
- we have been visiting
- they have been visiting
Past perfect continuous
- I had been visiting
- you had been visiting
- he/she/it had been visiting
- we had been visiting
- they had been visiting
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been visiting
- you will have been visiting
- he/she/it will have been visiting
- we will have been visiting
- they will have been visiting
- let's visit
Perfect participle
- having visited
Aiutiamo milioni di persone e grandi organizzazioni a comunicare in modo più efficiente e preciso in tutte le lingue.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Conjugate the English verb visit: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate visit in context, with examples of use and definition.
'to visit' conjugation - English verbs conjugated in all tenses with the bab.la verb conjugator.
Firefox and Chrome users: install a shortcut ( Firefox or Chrome) then type "conj visit" in your address bar for the fastest conjugations.
The present continuous tense normally requires a dynamic verb. Verbs that instead describe a state of being such as emotion, belief, perception, or possession are called stative verbs. Some examples include "prefer," "appear," "exist," and "own.". Stative verbs should not be used in the present continuous tense.
Present Continuous I am visiting you are visiting he/she/it is visiting we are visiting you are visiting they are visiting
The present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are happening right now. Learn how to use it correctly with examples in this guide.
Conjugation of verb "To visit". Present Simple. Affirmative. I visit. You visit. We visit. He/She/It visits. You visit. They visit.
Master English grammar with "The Present Continuous tense (Rules and Examples)". Dive deep into usage, understand rules, and apply real-world examples effortlessly.
Learn how to use the Present Continuous tense with clear explanations and examples. Improve your English grammar and speaking skills with this full guide.
Conjugate the verb visit in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc.
Enhance your understanding of the present continuous through 50 carefully selected examples illustrating its use.
Present Continuous Tense - With Usage Examples and Pictures "Present continuous tense" or "present progressive tense" is a verb tense that describes the actions we are doing right now. It is used to express the actions that we are doing at the moment of speaking. The auxiliary verbs are " am, is, are " and we add " -ing " at the and of the verbs in present continuous tense.
Conjugation English verb to visit in several modes, tenses, voices, numbers, persons : indicative mode, subjunctive, imperative mood, conditional, participle form, gerund, present, past, future perfect, progressive.
50 Sentences of Present Continuous Tense. Present Continuous Tense describes on-going actions at the time of speaking and happening right now, stressing that the doer is in the middle of the activity and hasn't finished yet (the action is incomplete). For example, I am eating a burger. See also : 12 Verb Tenses with Formula and Examples.
Present Continuous Tense: Learn how to convey actions that are progressing or happening at the moment of speaking by going through this article on present continuous tense. Check out the formula, rules, uses and examples to develop a clear idea of the topic.
Conjugador de verbos Con nuestra herramienta podrás conjugar verbos en inglés: sólo tienes que introducir un verbo en inglés y automáticamente obtendrás las tablas de conjugación de todos sus tiempos verbales. visit: Tabla de conjugación del verbo.
Conjugación verbo visit en inglés, ver modelos de conjugación inglés, verbos irregulares. Definición y traducción en contexto de visit.
Learn the present continuous tense with our comprehensive A1 Elementary English grammar rules, examples and exercises.
This is a reference page for visit verb forms in present, past and participle tenses. Find conjugation of visit. Check past tense of visit here.
Simple present I visit you visit he visit s we visit you visit they visit
Conjugação verbo inglês visit: indicativo, passado, particípio, present perfect, gerúndio, modelos de conjugação e verbos irregulares. Traduzir visit em contexto, com exemplos de utilização.
Coniugazione del verbo inglese visit: past tense, present, past perfect, future. Verbi irregolari e modelli dei verbi inglesi. Traduzione in contesto di visit, con esempi d'uso reale.