- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

After a 12.3-billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
Emily Olson
Ayana Archie

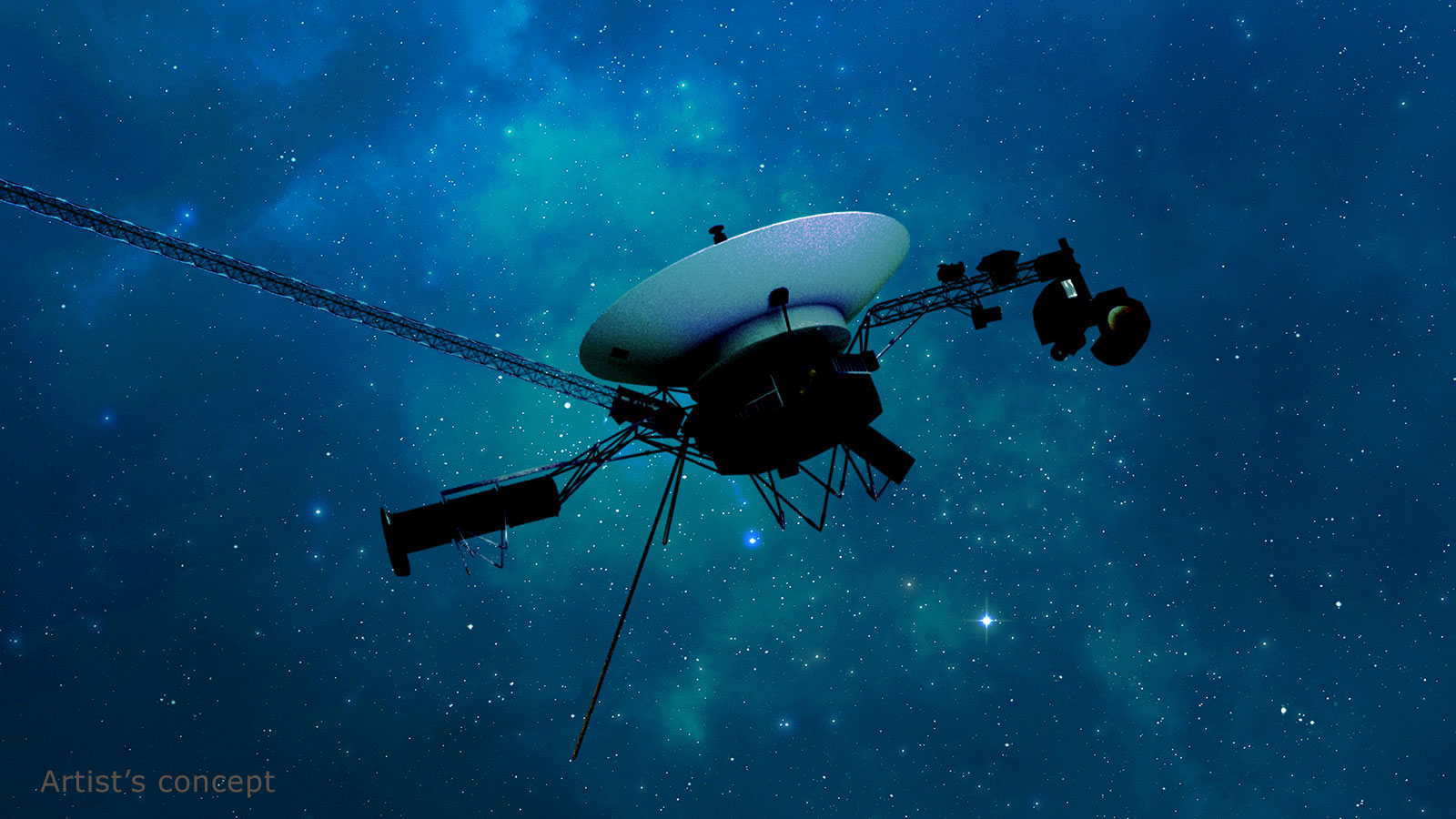
A NASA image of one of the twin Voyager space probes. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after mistakenly pointing its antenna 2 degrees away from Earth. On Friday, contact was fully restored. NASA/Getty Images hide caption
A NASA image of one of the twin Voyager space probes. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after mistakenly pointing its antenna 2 degrees away from Earth. On Friday, contact was fully restored.
Talk about a long-distance call.
NASA said it resumed full communications with the Voyager 2 on Friday after almost two weeks of silence from the interstellar spacecraft.
The agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory said a series of ground antennas, part of the Deep Space Network, registered a carrier signal from Voyager 2 on Tuesday. However, the signal was too faint.
A Deep Space Network facility in Australia then sent "the equivalent of an interstellar 'shout' " to the Voyager 2 telling it to turn its antenna back toward Earth. The signal was sent more than 12.3 billion miles away and it took 37 hours to get a response from the spacecraft, NASA said.
Scientists received a response at about 12:30 a.m. ET Friday. Voyager 2 is now operating normally, returning science and telemetry data, and "remains on its expected trajectory," NASA said.
NASA said Friday that it lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after "a series of planned commands" inadvertently caused the craft to turn its antenna 2 degrees away from the direction of its home planet.

NASA is keeping Voyager 2 going until at least 2026 by tapping into backup power
What might seem like a slight error had big consequences: NASA previously said it wouldn't be able to communicate with the craft until October, when the satellite would go through one of its routine repositioning steps.
"That is a long time to wait, so we'll try sending up commands several times" before October, program manager Suzanne Dodd told The Associated Press.

These are the 4 astronauts who'll take a trip around the moon next year
Even if Voyager 2 had failed to reestablish communications until fall, the engineers expected it to stay moving on its planned trajectory on the edge of the solar system.
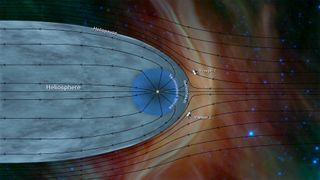
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space in November 2018 — more than 40 years since it launched from Cape Canaveral, Fla. To this day, Voyager 2 remains one of only two human-made objects to ever operate outside the heliosphere, which NASA defines as "the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun."
Its primary mission was to study the outer solar system, and already, Voyager 2 has proved its status as a planetary pioneer . Equipped with several imaging instruments, the spacecraft is credited with documenting the discovery of 16 new moons, six new rings and Neptune's "Great Dark Spot."

Voyager 2 Bids Adieu To The Heliosphere, Entering Interstellar Space
Voyager 2 is also carrying some precious cargo, like a message in a bottle, should it find itself as the subject of another world's discovery: a golden record containing a variety of natural sounds, greetings in 55 languages and a 90-minute selection of music.
Last month's command mix-up foreshadows the craft's inevitable end an estimated three years from now.
"Eventually, there will not be enough electricity to power even one instrument," reads a NASA page documenting the spacecraft's travels . "Then, Voyager 2 will silently continue its eternal journey among the stars."
Meanwhile, Voyager 2's sister spacecraft, Voyager 1, is still broadcasting and transmitting data just fine from a slightly farther vantage point of 15 billion miles away.
Correction Aug. 3, 2023
A previous version of this article implied that Voyager 2 flew past Uranus in 2018 when, in fact, the spacecraft concluded its encounter with the planet and started heading toward Neptune in 1986. Voyager 2 entered interstellar space in November 2018.
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory
NASA's interstellar Voyager 2 probe resumes communication with Earth
The spacecraft is healthy and has reestablished full communications with Earth.

Voyager 2 has reestablished communication with Earth and is operating normally.
NASA's long-running Voyager 2 mission , which launched from Earth in 1977 and is currently about 12.4 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) from Earth , lost contact with our planet after a set of commands accidentally moved Voyager 2's antenna two degrees away from Earth on July 28.
A "heartbeat" signal was picked up on Tuesday (Aug. 1) according to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), letting mission controllers know the probe was still healthy despite being unable to communicate fully with it. Voyager 2 is programmed to automatically reset its orientation a few times a year in case of troubles like this, but the next window would have been in October.
On Friday (Aug. 4), JPL announced in a mission update that NASA's Deep Space Network facility in Canberra, Australia was able to send a command into interstellar space that reoriented the spacecraft and pointed its antenna back towards Earth. Mission controllers had to wait 37 hours to learn if the command was successful. And it was.
"The spacecraft began returning science and telemetry data, indicating it is operating normally and that it remains on its expected trajectory," JPL said in the statement.
Related: NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
"Can you hear me now? Last night, I reestablished full communications with Earth thanks to some quick thinking and a lot of collaboration. I'm operating normally and remain on my expected trajectory," the Voyager Twitter account wrote in a statement posted to the social media platform on Friday (Aug. 4). "So glad I can finally phone home."
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Voyager 2 flew to space from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on August 20, 1977. After swinging by the four gas giant planets of the solar system between the 1970s and 1990s, it entered interstellar space on Dec. 10, 2018.
Its twin craft Voyager 1 is also operational, flying far away at about 15 billion miles (24 billion km) from Earth. It was the first object to move beyond the gravitational influence of our star, the sun , in 2012.
— After 45 years, the 5-billion-year legacy of the Voyager 2 interstellar probe is just beginning
— Voyager 2 bounces back from glitch in interstellar space
— Voyager turns 45: What the iconic mission taught us and what's next
The missions are slowly losing power from their nuclear radioisotope generators , but engineers have made several alterations to preserve their systems where possible. The heaters have been shut off, for example, and in April 2023 engineers disabled Voyager 2's surge protector (or voltage regulator).
These steps remove a bit of backup for the spacecraft while allowing their power supplies to last longer. The 2023 step alone has postponed one of the instrument shutdowns for Voyager 2 by three years, extending space data collection until at least 2026, officials said at the time.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
Car-size asteroid gives Earth a super-close shave with flyby closer than some satellites
SpaceX launches advanced weather satellite for US Space Force (video)
This Week In Space podcast: Episode 106 — Space Potpourri!
Most Popular
- 2 Tiny black holes left over from the Big Bang may be prime dark matter suspects
- 3 'You could feel the energy and wonder': Despite clouds, totality wows crowds during solar eclipse in Syracuse
- 4 In a virtual reality universe, upcoming 'JUICE' mission flies by Jupiter's moon Callisto
- 5 Artemis 2 Orion spacecraft starts testing ahead of moon mission with astronauts in 2025 (video)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Earth to Voyager 2: After a Year in the Darkness, We Can Talk to You Again
NASA’s sole means of sending commands to the distant space probe, launched 44 years ago, is being restored on Friday.

By Shannon Stirone
In the nearly 44 years since NASA launched Voyager 2 , the spacecraft has gone beyond the frontiers of human exploration by visiting Uranus, Neptune and, eventually, interstellar space .
Last March, the agency was compelled to shut down its only means of reaching 12 billion miles across the heavens to this robotic trailblazer . On Friday, Earth’s haunting silence will come to an end as NASA switches that communications channel back on, restoring humanity’s ability to say hello to its distant explorer.
Because of the direction in which it is flying out of the solar system, Voyager 2 can only receive commands from Earth via one antenna in the entire world. It’s called DSS 43 and it is in Canberra, Australia. It is part of the Deep Space Network, or DSN , which along with stations in California and Spain, is how NASA and allied space agencies stay in touch with the armada of robotic spacecraft exploring everything from the sun’s corona to the regions of the Kuiper belt beyond the orbit of Pluto . (Voyager 2’s twin, Voyager 1, is able to communicate with the other two stations.)
A round-trip communication with Voyager 2 takes about 35 hours — 17 hours and 35 minutes each way .
DSS 43 is a 70-meter dish that has been operating since 1973. It was long overdue for upgrades, especially with new robotic missions headed to Mars this year and even more preparing to launch to study other worlds in the months and years to come. So last year, the dish was switched off and dismantled, even though the shutdown posed considerable risk to the geriatric Voyager 2 probe.
Like everything in 2020, what would have been a normal antenna upgrade was anything but. Usually, the mission’s managers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California would send about 30 experts to oversee the dish’s makeover. But restrictions imposed during the Covid-19 pandemic reduced the team to four.
At the Canberra station, the crew working on the upgrade had to be separated into three smaller teams, said Glen Nagle, outreach manager at the Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex. “So there was always a backup team in case anybody got sick, and you could put that team in isolation, and the other team could come in and cover for them.” They also split the teams into morning and evening shifts to ensure social distancing.
While Voyager 2 was able to call home on the Canberra site’s smaller dishes during the shutdown, none of them could send commands to the probe. If anything had gone wrong aboard the probe during the last year, NASA would have been powerless to fix it.
Although NASA has been unable to send full commands to Voyager 2, it did send one test message to the spacecraft at the end of October when the antenna was mostly reassembled. A device on board called the command loss timer, something like a dead man’s switch, is used to help the spacecraft determine whether it’s lost contact with Earth and should protect itself by going into a form of electronic slumber. The October test reset the timer, and successfully told the spacecraft to continue operating.
“I think there was probably a big sigh of relief there,” Mr. Nagle said. “And we were very pleased to be able to confirm that the spacecraft was still talking to us.”
The work got high marks from NASA officials in the United States.
“The DSN folks in Canberra did a remarkable job under the pandemic conditions just to upgrade DSS 43,” said Suzanne Dodd, the Voyager mission project manager and director of the Interplanetary Network Directorate at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. “I’ve got 100 percent confidence in that antenna, that it will operate just fine for a few more decades. Long past when the Voyagers are done.”
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 hold the records for the farthest a spacecraft has ever traveled and for the longest operating mission. Voyager 2 has had a few hiccups over the years, but it is still feeling its way around in the dark, making discoveries about the boundaries that separate our solar system from the rest of the Milky Way galaxy .
“I’ve seen scientists whose backgrounds are in astrophysics now looking at Voyager data and trying to match that up with data they have from ground-based telescopes or other space-based telescopes,” Ms. Dodd said. “That’s kind of exciting to go from a planetary mission to the heliophysics mission and now, practically into an astrophysics mission.”
While Voyager 2 keeps chugging along, Ms. Dodd and her colleagues are preparing to switch off the heater for one of its scientific sensors, the Low Energy Charged Particle instrument. Doing so will ensure that the spacecraft’s limited power supply can keep its other systems, particularly its communications antenna, warm enough to function.
While Ms. Dodd thinks taking such steps could reduce the spacecraft’s scientific output, the main goal now is longevity.
“The challenge is not in the new technology, or the great discoveries,” Ms. Dodd said. “The challenge is in keeping it operating as long as possible, and returning the science data as long as possible.”
The team estimates that both spacecraft can operate for another four to eight years, and NASA last year granted the team three more years of flying time.
“The spacecraft continues to plug along,” Ms. Dodd said. “It always surprises me.”

Sync your calendar with the solar system
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other astronomical and space event that's out of this world.

Exploring the Solar System
A guide to the spacecraft beyond Earth’s orbit.
Using information from a NASA official, an earlier version of this article misstated a change that was made to the Voyager 2 spacecraft. The heater for the spacecraft's Low Energy Charged Particle instrument was switched off, not the instrument itself.
How we handle corrections
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
A new set of computer simulations, which take into account the effects of stars moving past our solar system, has effectively made it harder to predict Earth’s future and reconstruct its past.
Dante Lauretta, the planetary scientist who led the OSIRIS-REx mission to retrieve a handful of space dust , discusses his next final frontier.
A nova named T Coronae Borealis lit up the night about 80 years ago. Astronomers say it’s expected to put on another show in the coming months.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA’s Fermi Mission Sees No Gamma Rays from Nearby Supernova

The Ocean Touches Everything: Celebrate Earth Day with NASA

The April 8 Total Solar Eclipse: Through the Eyes of NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

NASA Open Science Initiative Expands OpenET Across Amazon Basin
A Solar Neighborhood Census, Thanks to NASA Citizen Science

NASA Motion Sickness Study Volunteers Needed!

NASA Selects New Crew for Next Simulated Mars Journey
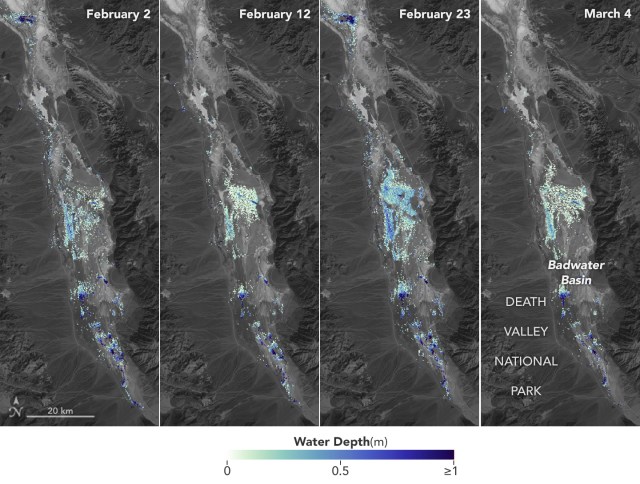
SWOT Satellite Helps Gauge the Depth of Death Valley’s Temporary Lake
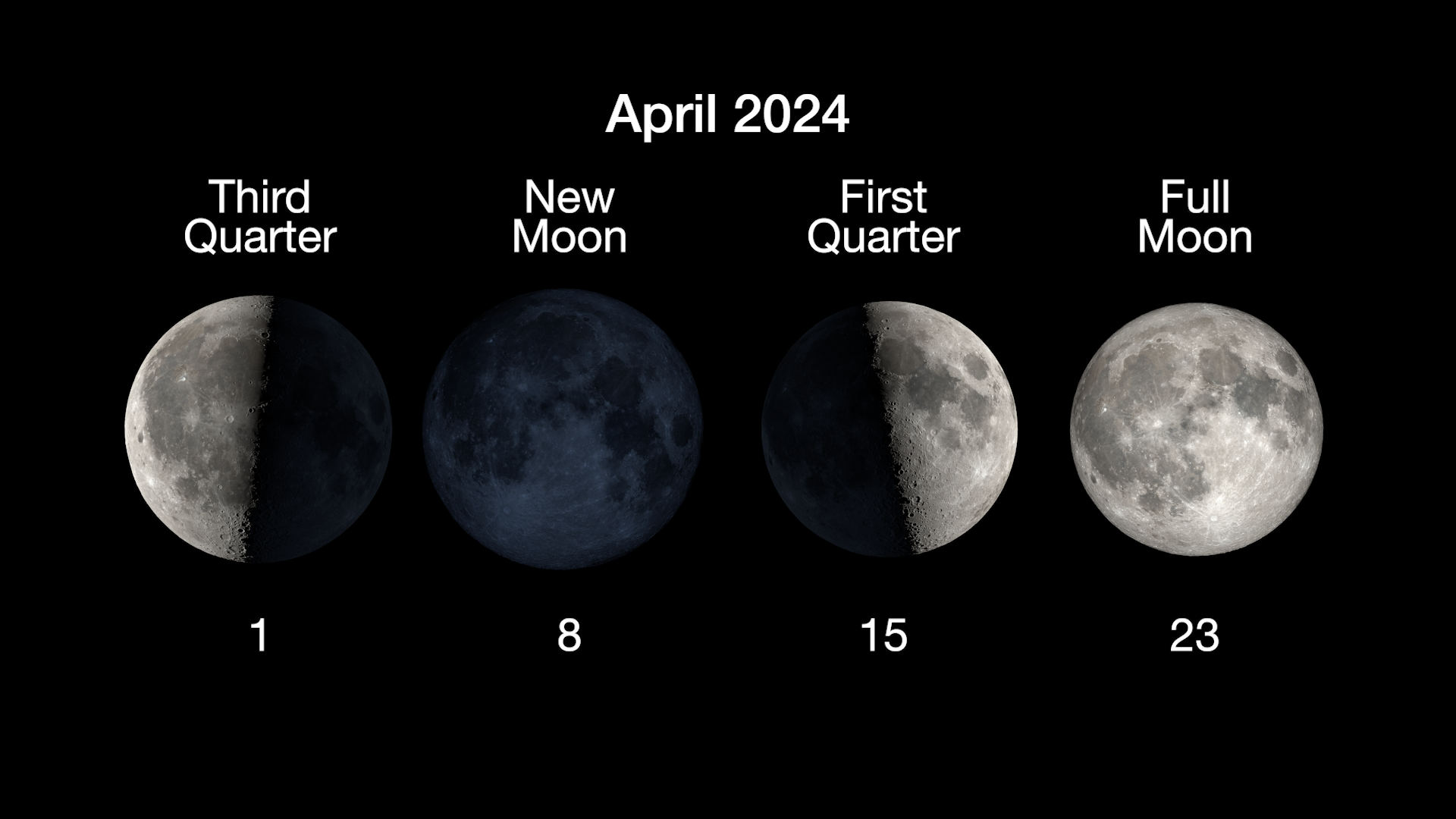

The next full Moon is the Pink Moon, Sprouting Grass Moon, Egg Moon, Fish Moon, the Pesach or Passover Moon
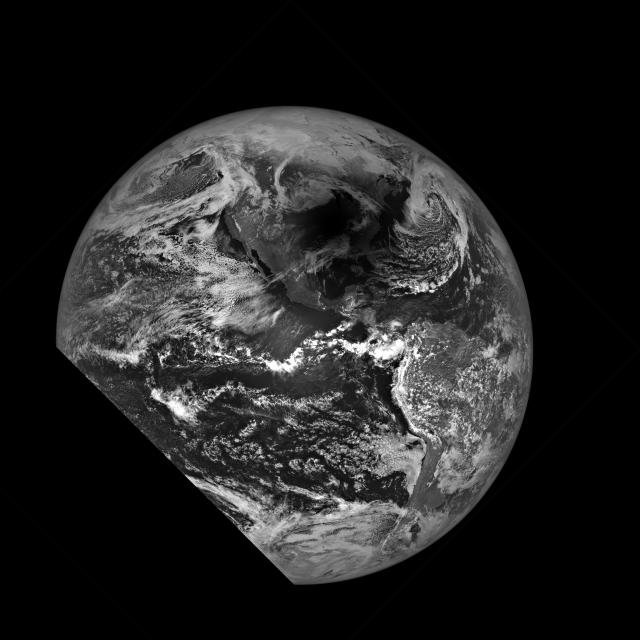

NASA’s LRO Observes 2024 Solar Eclipse Shadow

Hubble Spots a Galaxy Hidden in a Dark Cloud

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

ARMD Solicitations
NASA Noise Prediction Tool Supports Users in Air Taxi Industry


Tech Today: Folding NASA Experience into an Origami Toolkit
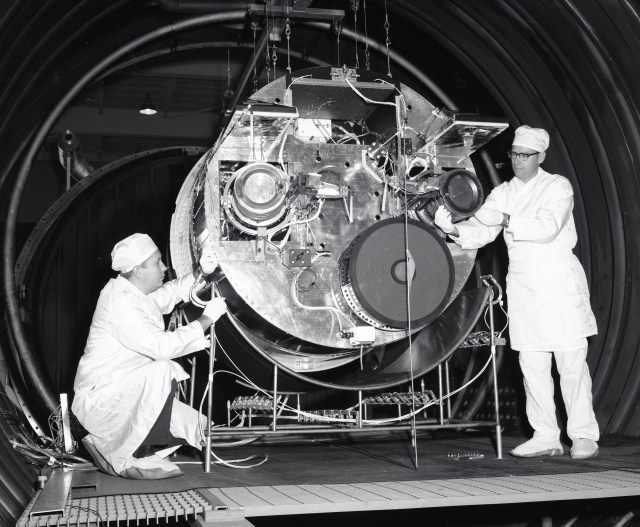
NASA’s SERT II: ‘A Genuine Space Success Story’

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge
Earth Day 2024: Posters and Virtual Backgrounds

NASA Partnerships Bring 2024 Total Solar Eclipse to Everyone

NASA Receives 13 Nominations for the 28th Annual Webby Awards

La presentación del X-59 de la NASA personifica la tradición aeronáutica
45 years ago: voyager 2 begins its epic journey to the outer planets and beyond, johnson space center.
Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 2 spacecraft left Earth to begin an epic journey that continues to this day. The first of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 2 lifted off on Aug. 20, 1977. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, manages the spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets and beyond. Taking advantage of a rare planetary alignment to use the gravity of one planet to redirect the spacecraft to the next, the Voyagers initially targeted only Jupiter and Saturn, but Voyager 2 went on to explore Uranus and Neptune as well. The Voyagers carried sophisticated instruments to conduct their in-depth explorations of the outer planets. Both spacecraft continue to return data as they make their way out of our solar system and enter interstellar space.
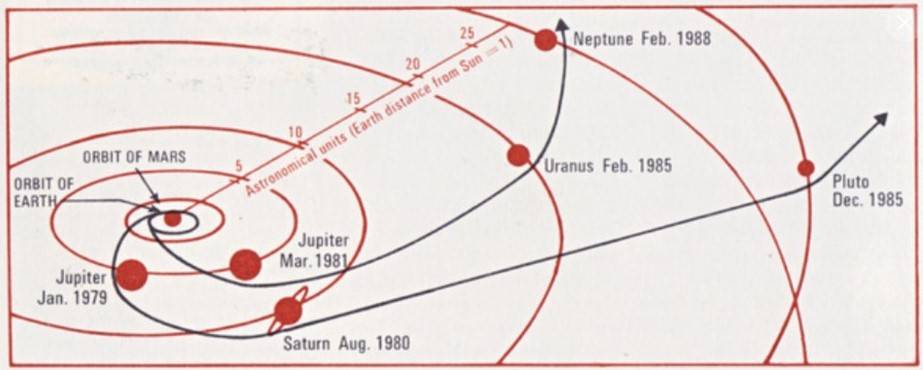
In the 1960s, mission designers at JPL noted that the next alignment of the outer planets that occurs only every 175 years would happen in the late 1970s. Technology had advanced sufficiently that spacecraft could take advantage of this rare alignment to flyby Jupiter and use its gravity to bend their trajectories to visit Saturn, and repeat the process to also visit Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Launching several missions to visit each planet individually would take much longer and cost much more. The original plan to send two pairs of Thermoelectric Outer Planet Spacecraft on these Grand Tours proved too costly leading to its cancellation in 1971. The next year, NASA approved a scaled-down version of the project to launch a pair of Mariner-class spacecraft in 1977 to explore just Jupiter and Saturn. On March 7, 1977, NASA Administrator James C. Fletcher announced the renaming of these Mariner Jupiter/Saturn 1977 spacecraft as Voyager 1 and 2. Scientists held out hope that one of them could ultimately visit Uranus and Neptune, thereby fulfilling most of the original Grand Tour’s objectives – Pluto would have to wait many more years for its first visit.
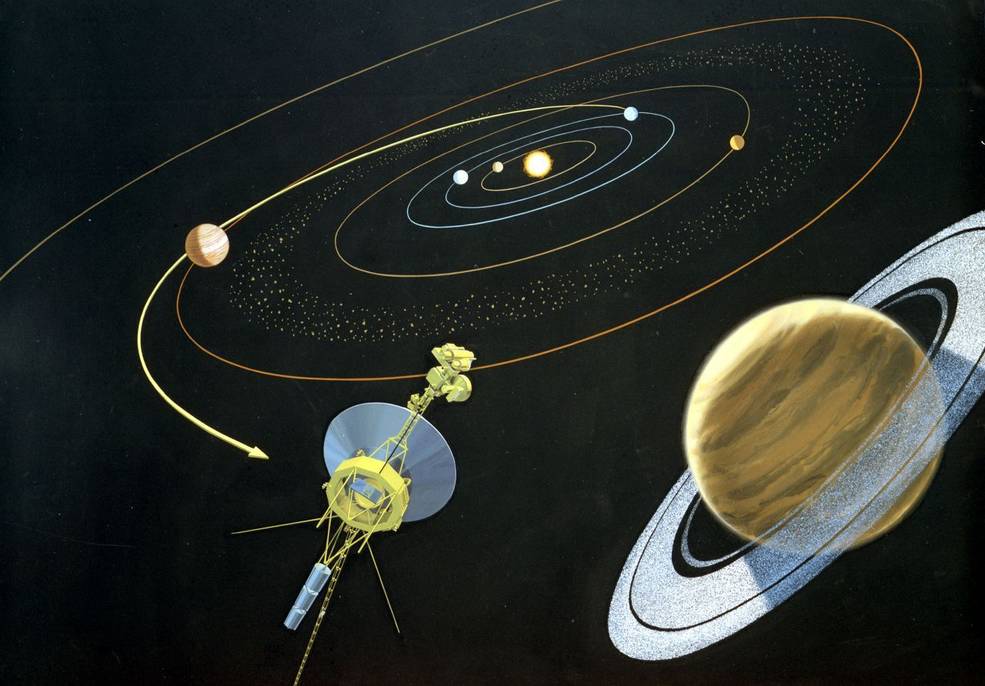
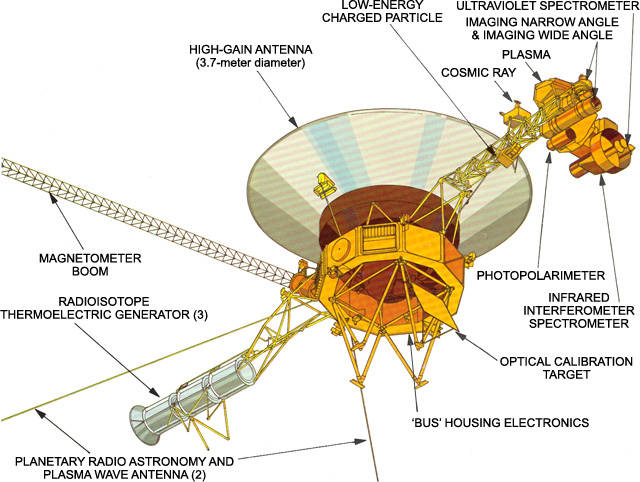
Each Voyager carried a suite of 11 instruments to study the planets during each encounter and to learn more about interplanetary space in the outer reaches of the solar system, including:
- An imaging science system consisting of narrow-angle and wide-angle cameras to photograph the planet and its satellites.
- A radio science system to determine the planet’s physical properties.
- An infrared interferometer spectrometer to investigate local and global energy balance and atmospheric composition.
- An ultraviolet spectrometer to measure atmospheric properties.
- A magnetometer to analyze the planet’s magnetic field and interaction with the solar wind.
- A plasma spectrometer to investigate microscopic properties of plasma ions.
- A low energy charged particle device to measure fluxes and distributions of ions.
- A cosmic ray detection system to determine the origin and behavior of cosmic radiation.
- A planetary radio astronomy investigation to study radio emissions from Jupiter.
- A photopolarimeter to measure the planet’s surface composition.
- A plasma wave system to study the planet’s magnetosphere.
Voyager 2 left Earth first, lifting off on Aug. 20, 1977, atop a Titan IIIE-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, now Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, in Florida. Although its twin launched two weeks later, it traveled on a faster trajectory and arrived at Jupiter four months earlier. Voyager 2 successfully crossed the asteroid belt between Dec. 10, 1977, and Oct. 21, 1978. In April 1978, its primary radio receiver failed, and it has been operating on its backup receiver ever since.
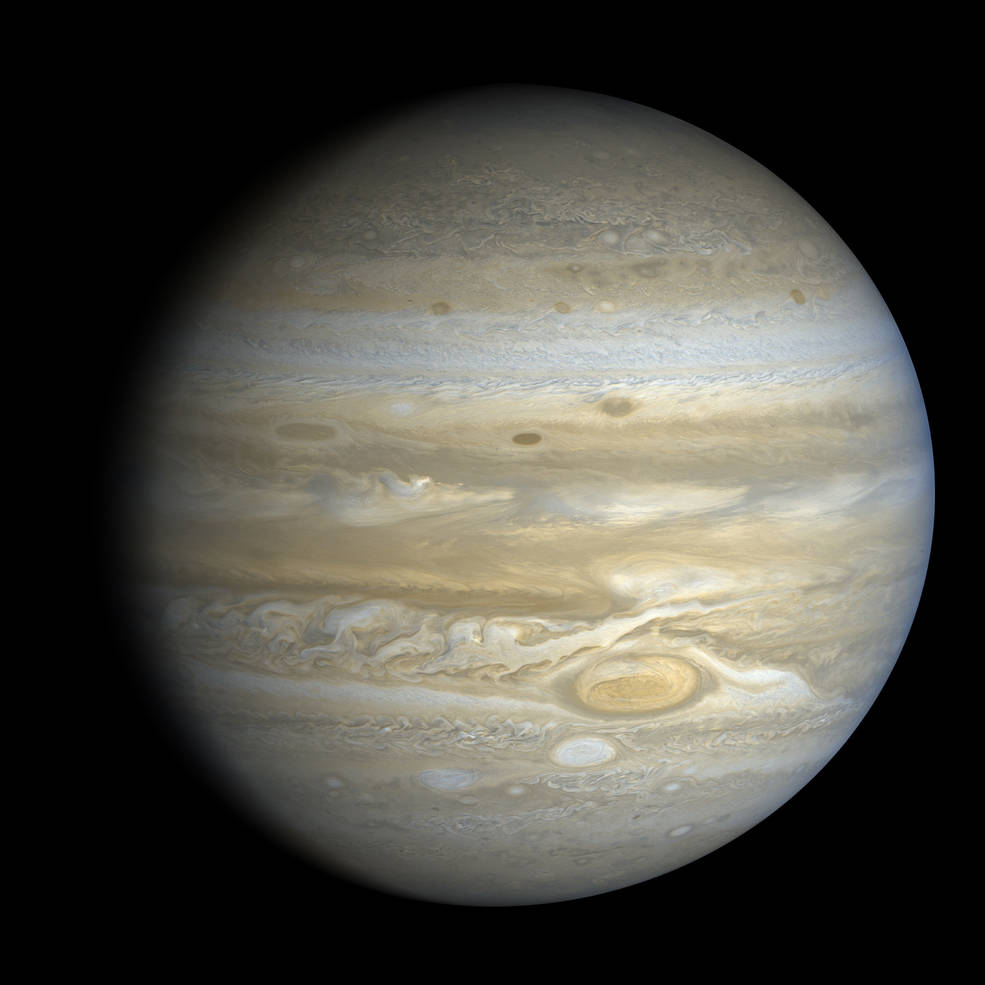

Voyager 2 conducted its observations of Jupiter between April 24 and Aug. 5, 1979, making its closest approach of 350,000 miles above the planet’s cloud tops on July 9. The spacecraft returned 17,000 images of Jupiter, many of its satellites, and confirmed Voyager 1’s discovery of a thin ring encircling the planet. Its other instruments returned information about Jupiter’s atmosphere and magnetic field. Jupiter’s massive gravity field bent the spacecraft’s trajectory, accelerating it toward Saturn. Voyager 2 began its long-range observations of the ringed planet on June 5, 1981, passed within 26,000 miles of the planet’s cloud tops on Aug. 26, and concluded its studies on Sept. 4. The spacecraft captured 16,000 photographs of the planet, its rings, and many of its known satellites. It discovered several new ones, while its instruments returned data about Saturn’s atmosphere. Saturn’s gravity sent Voyager 2 on to Uranus.
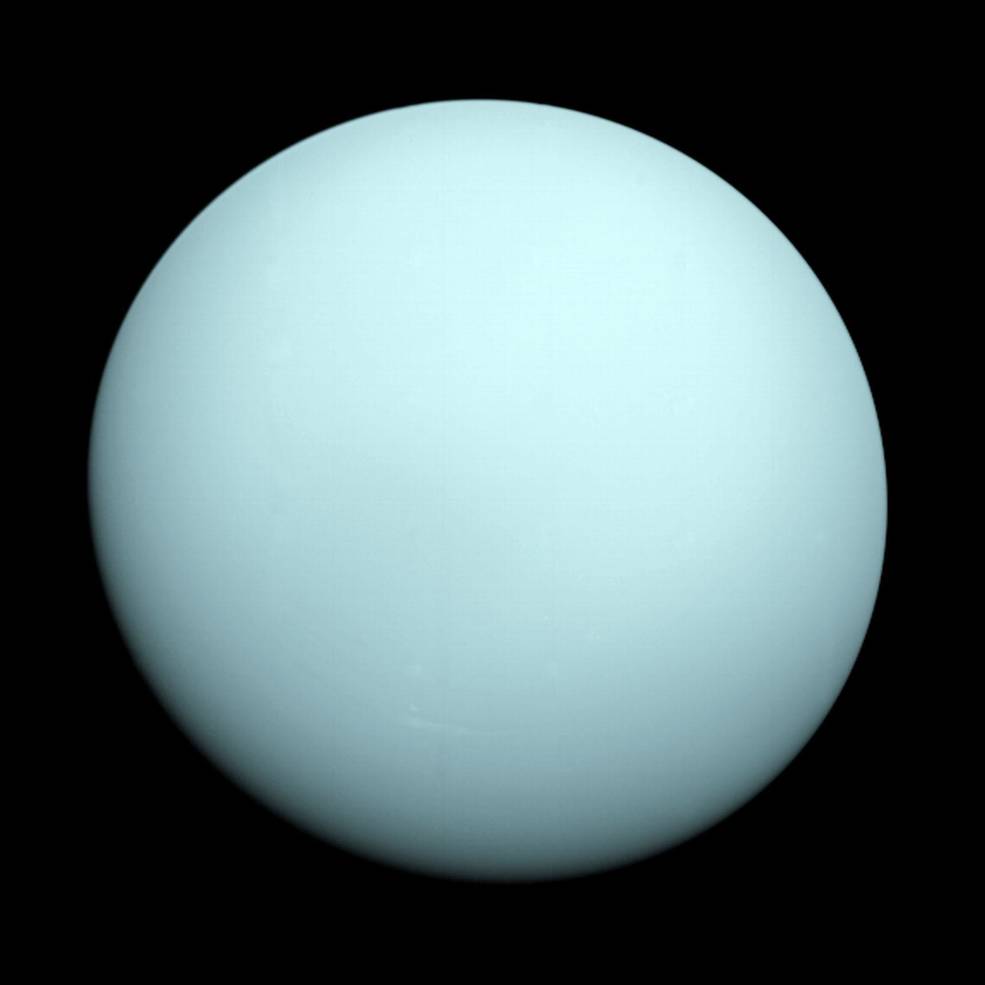

Voyager 2 carried out the first close-up observations of Uranus between Nov. 4, 1985, and Feb. 25, 1986, making its closest approach of 50,700 miles above the planet’s cloud tops on Jan. 24. It returned more than 7,000 photographs of the planet, its rings and moons, discovering two new rings and 11 new moons. The spacecraft’s instruments returned data about the planet’s atmosphere and its unusual magnetic field, tilted by 59 degrees compared to its rotational axis and offset from the planet’s center by about one-third of the planet’s radius. Voyager 2 took advantage of Uranus’ gravity to send it on to its last planetary destination, Neptune. The spacecraft conducted the first close-up observations of the eighth planet between June 5 and Oct. 2, 1989, making its flyby just 3,408 miles above its north pole on Aug. 25, its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth in 1977. This trajectory allowed Voyager 2 to observe Neptune’s large moon Triton, the last solid object it explored. During the encounter, it returned more than 9,000 images of the planet, its atmosphere, dark rings, and moons, discovering six new moons. Like Uranus, Voyager 2’s instruments revealed that Neptune has an unusual magnetic field, not only tilted 47 degrees from the planet’s axis but also significantly offset from the planet’s center.
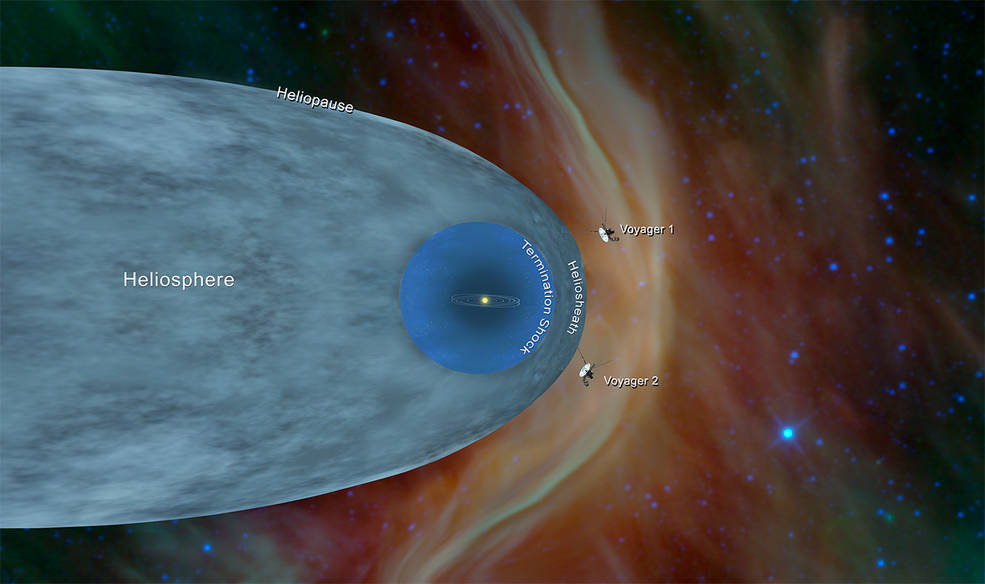
Following its reconnaissance of Neptune, Voyager 2 began its Interstellar Mission extension that continues to this day. Over the years, several of the spacecraft’s instruments have been turned off to conserve power, beginning with the imaging system in 1998, but it continues to return data about cosmic rays and the solar wind. On Nov. 5, 2018, six years after its twin, Voyager 2 crossed the heliopause, the boundary between the heliosphere – the bubble-like region of space created by the Sun – and the interstellar medium. Currently, Voyager 2 continues its mission, more than 12 billion miles from Earth, so distant that a signal from the spacecraft takes 18 hours to reach Earth, and just as long for a return signal to reach the craft. Engineers expect that Voyager 2 will continue to return data until about 2025. And just in case an alien intelligence finds it one day, Voyager 2 like its twin carries a gold-plated record that contains information about its home planet, including recordings of terrestrial sounds, music, and greetings in 55 languages. Engineers at NASA thoughtfully included Instructions on how to play the record.

For more on Voyagers 1 and 2, NASA’s longest-lived missions, please visit here , with thanks to our colleagues at JPL.
The voyage continues…

Voyager 1 and 2: The Interstellar Mission

An image of Neptune taken by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
NASA has beautiful photos of every planet in our solar system. We even have images of faraway Neptune , as you can see in the photo above.
Neptune is much too distant for an astronaut to travel there with a camera. So, how do we have pictures from distant locations in our solar system? Our photographers were two spacecraft, called Voyager 1 and Voyager 2!

An artist’s rendering of one of the Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before.
The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons. The pictures from Voyager 1 and 2 allowed us to see lots of things for the first time. For example, they captured detailed photos of Jupiter's clouds and storms, and the structure of Saturn's rings .

Image of storms on Jupiter taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
Voyager 1 and 2 also discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io , and much more. Voyager 2 also took pictures of Uranus and Neptune. Together, the Voyager missions discovered 22 moons.
Since then, these spacecraft have continued to travel farther away from us. Voyager 1 and 2 are now so far away that they are in interstellar space —the region between the stars. No other spacecraft have ever flown this far away.
Where will Voyager go next?
Watch this video to find out what's beyond our solar system!
Both spacecraft are still sending information back to Earth. This data will help us learn about conditions in the distant solar system and interstellar space.
The Voyagers have enough fuel and power to operate until 2025 and beyond. Sometime after this they will not be able to communicate with Earth anymore. Unless something stops them, they will continue to travel on and on, passing other stars after many thousands of years.
Each Voyager spacecraft also carries a message. Both spacecraft carry a golden record with scenes and sounds from Earth. The records also contain music and greetings in different languages. So, if intelligent life ever find these spacecraft, they may learn something about Earth and us as well!

A photo of the golden record that was sent into space on both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More about our universe!

Where does interstellar space begin?

Searching for other planets like ours

Play Galactic Explorer!
If you liked this, you may like:

NASA’s Voyager 2 Probe Enters Interstellar Space
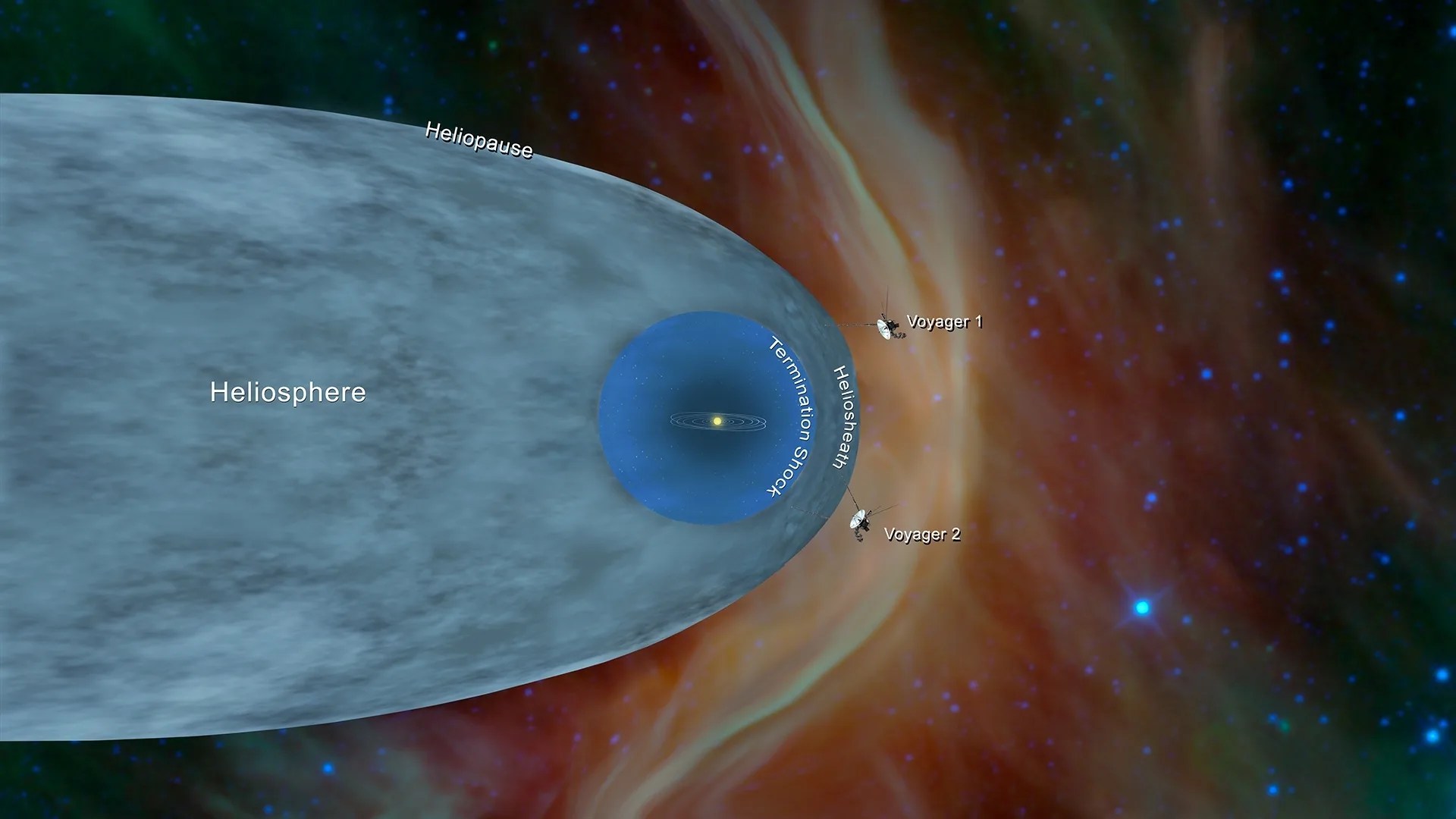
For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA’s Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere – the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.
Members of NASA’s Voyager team will discuss the findings at a news conference at 11 a.m. EST (8 a.m. PST) today at the meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) in Washington. The news conference will stream live on the agency’s website .
Comparing data from different instruments aboard the trailblazing spacecraft, mission scientists determined the probe crossed the outer edge of the heliosphere on Nov. 5. This boundary, called the heliopause, is where the tenuous, hot solar wind meets the cold, dense interstellar medium. Its twin, Voyager 1 , crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space.
Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as it enters this new phase of its journey, but information – moving at the speed of light – takes about 16.5 hours to travel from the spacecraft to Earth. By comparison, light traveling from the Sun takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.
The most compelling evidence of Voyager 2’s exit from the heliosphere came from its onboard Plasma Science Experiment ( PLS ), an instrument that stopped working on Voyager 1 in 1980, long before that probe crossed the heliopause. Until recently, the space surrounding Voyager 2 was filled predominantly with plasma flowing out from our Sun. This outflow, called the solar wind, creates a bubble – the heliosphere – that envelopes the planets in our solar system. The PLS uses the electrical current of the plasma to detect the speed, density, temperature, pressure and flux of the solar wind. The PLS aboard Voyager 2 observed a steep decline in the speed of the solar wind particles on Nov. 5. Since that date, the plasma instrument has observed no solar wind flow in the environment around Voyager 2, which makes mission scientists confident the probe has left the heliosphere.
“Working on Voyager makes me feel like an explorer, because everything we’re seeing is new,” said John Richardson, principal investigator for the PLS instrument and a principal research scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. “Even though Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause in 2012, it did so at a different place and a different time, and without the PLS data. So we’re still seeing things that no one has seen before.”
In addition to the plasma data, Voyager’s science team members have seen evidence from three other onboard instruments – the cosmic ray subsystem, the low energy charged particle instrument and the magnetometer – that is consistent with the conclusion that Voyager 2 has crossed the heliopause. Voyager’s team members are eager to continue to study the data from these other onboard instruments to get a clearer picture of the environment through which Voyager 2 is traveling.
“There is still a lot to learn about the region of interstellar space immediately beyond the heliopause,” said Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist based at Caltech in Pasadena, California.
Together, the two Voyagers provide a detailed glimpse of how our heliosphere interacts with the constant interstellar wind flowing from beyond. Their observations complement data from NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer ( IBEX ), a mission that is remotely sensing that boundary. NASA also is preparing an additional mission – the upcoming Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe ( IMAP ), due to launch in 2024 – to capitalize on the Voyagers’ observations.
“Voyager has a very special place for us in our heliophysics fleet,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters. “Our studies start at the Sun and extend out to everything the solar wind touches. To have the Voyagers sending back information about the edge of the Sun’s influence gives us an unprecedented glimpse of truly uncharted territory.”
While the probes have left the heliosphere, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have not yet left the solar system, and won’t be leaving anytime soon. The boundary of the solar system is considered to be beyond the outer edge of the Oort Cloud , a collection of small objects that are still under the influence of the Sun’s gravity. The width of the Oort Cloud is not known precisely, but it is estimated to begin at about 1,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun and to extend to about 100,000 AU. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth. It will take about 300 years for Voyager 2 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly 30,000 years to fly beyond it.
The Voyager probes are powered using heat from the decay of radioactive material, contained in a device called a radioisotope thermal generator ( RTG ). The power output of the RTGs diminishes by about four watts per year, which means that various parts of the Voyagers, including the cameras on both spacecraft, have been turned off over time to manage power.
“I think we’re all happy and relieved that the Voyager probes have both operated long enough to make it past this milestone,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. “This is what we've all been waiting for. Now we’re looking forward to what we’ll be able to learn from having both probes outside the heliopause.”
Voyager 2 launched in 1977, 16 days before Voyager 1, and both have traveled well beyond their original destinations. The spacecraft were built to last five years and conduct close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn. However, as the mission continued, additional flybys of the two outermost giant planets, Uranus and Neptune, proved possible. As the spacecraft flew across the solar system, remote-control reprogramming was used to endow the Voyagers with greater capabilities than they possessed when they left Earth. Their two-planet mission became a four-planet mission. Their five-year lifespans have stretched to 41 years, making Voyager 2 NASA’s longest running mission.
The Voyager story has impacted not only generations of current and future scientists and engineers, but also Earth's culture, including film, art and music. Each spacecraft carries a Golden Record of Earth sounds, pictures and messages. Since the spacecraft could last billions of years, these circular time capsules could one day be the only traces of human civilization.
Voyager’s mission controllers communicate with the probes using NASA’s Deep Space Network ( DSN ), a global system for communicating with interplanetary spacecraft. The DSN consists of three clusters of antennas in Goldstone, California; Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia.
The Voyager Interstellar Mission is a part of NASA’s Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. JPL built and operates the twin Voyager spacecraft. NASA’s DSN, managed by JPL, is an international network of antennas that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions and radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe. The network also supports selected Earth-orbiting missions. The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Australia’s national science agency, operates both the Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex, part of the DSN, and the Parkes Observatory, which NASA has been using to downlink data from Voyager 2 since Nov. 8.
For more information about the Voyager mission, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
More information about NASA’s Heliophysics missions is available online at:
https://www.nasa.gov/sunearth
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
Dwayne Brown / Karen Fox NASA Headquarters, Washington 202-358-1726 / 301-286-6284 [email protected] / [email protected]
Related Terms
- Voyager Program
Explore More

NASA’s Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters
The efforts should help extend the lifetimes of the agency’s interstellar explorers. Engineers for NASA’s Voyager mission are taking steps to help make sure both spacecraft, launched in 1977, continue to explore interstellar space for years to come. One effort addresses fuel residue that seems to be accumulating inside narrow tubes in some of the […]

NASA Mission Update: Voyager 2 Communications Pause
Once the spacecraft’s antenna is realigned with Earth, communications should resume.

NASA’s Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy
The plan will keep Voyager 2’s science instruments turned on a few years longer than previously anticipated, enabling yet more revelations from interstellar space.
Discover More Topics From NASA

Facts About Earth

Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
Kuiper Belt

Engineers Pinpoint Cause of Voyager 1 Issue, Are Working on Solution
Engineers have confirmed that a small portion of corrupted memory in one of the computers aboard NASA’s Voyager 1 has been causing the spacecraft to send unreadable science and engineering data to Earth since last November. Called the flight data subsystem (FDS), the computer is responsible for packaging the probe’s science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send the data to Earth.
In early March , the team issued a “poke” command to prompt the spacecraft to send back a readout of the FDS memory, which includes the computer’s software code as well as variables (values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status). Using the readout, the team has confirmed that about 3% of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations.
The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn’t working. Engineers can’t determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years.
Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again.
Launched in 1977 , the twin Voyager spacecraft flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune. They are both exploring interstellar space, outside the bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun, called the heliosphere. Voyager 2 continues to operate normally.
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
Engineers attempt to fix a computer glitch on Voyager 1
Voyager 1's system that sends data home is malfunctioning, preventing the computer from operating as it should.

Social Sharing
Last November, the Voyager 1 spacecraft began sending gibberish radio signals back to Earth. Engineers have now identified the problem, but trying to repair a 46-year-old device on a craft 24 billion kilometres from Earth is not easy.
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 were both launched in 1977 on a reconnaissance mission to Jupiter and Saturn. They were designed to fly past the giant planets to obtain closeup images of those distant worlds and their myriad of moons.
Both spacecraft performed beyond expectations, discovering many new moons — some covered in ice , one with active volcanoes , another with a thick atmosphere and closeup details of Saturn's rings .
Following the Saturn encounter, Voyager 1 was flung upwards by Saturn's gravity on a trajectory northward, above the orbital plane in which most of the planets orbit the Sun, out of our solar system. NASA extended its mission and from there it went on to become the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space in 2012.
Voyager 2, however, was aimed toward Uranus and Neptune, which were conveniently positioned in a rare alignment with Jupiter and Saturn making it the only spacecraft to visit those distant worlds.
Following the grand tour of the outer solar system, Voyager 2 was also tossed out toward interstellar space in 2018 when its mission was extended and where it continues on its journey today.
- After a 42-year journey, Voyager 2 goes interstellar
- Voyager 1 picks up the 'hum' of interstellar space
While their primary missions were over, both spacecraft were still in good health, thanks largely to their nuclear power sources or Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTG). These containers hold small amounts of plutonium which provide heat that is turned directly into electricity with no moving parts. They have an expected lifetime of around 50 years and have kept the Voyagers' instruments running.
Now, as both spacecraft continue their journey through the space between the stars, they are showing signs of their age.
For Voyager 1, the problem seems to be in the flight data subsystem (FDS) that packages data from the scientific instruments for transmission to Earth. The scientists don't know if the faulty module was corrupted by cosmic rays or just worn out, but they say they're optimistic they may be able to work around the problem, although it will take some time.
Engineers have confirmed that corrupted memory aboard my twin <a href="https://twitter.com/hashtag/Voyager1?src=hash&ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw">#Voyager1</a> has been causing it to send unreadable data to Earth. It may take months, but our team is optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally again: <a href="https://t.co/qe5iQUu4Oj">https://t.co/qe5iQUu4Oj</a> <a href="https://t.co/AGFBZFz53v">https://t.co/AGFBZFz53v</a> — @NASAVoyager
The challenge is that the computers were built in the 1970s using old code and send data very slowly by today's standards.
In addition, these computers are so deep in space, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal from Voyager 1 to reach Earth. That means the controllers on the ground have to wait 45 hours for each two-way communication with the spacecraft.
Given how very, very far they are from home, if something goes wrong with them, it's up to engineers on the ground to fix it by sending radio signals since reaching them for repair missions isn't possible. We're a long way from the fictional warp drive and sub-space communication that made life so easy on the Starship Enterprise of Star Trek fame.
The twin Voyagers are now the most distant objects ever sent from Earth; a demonstration of how vast space is and how slow our spacecraft are. In 1977, I attended the launch of Voyager 2 when my hair was black and skin was smooth. This one mission with Voyager 1 and 2 has occupied a good chunk of my lifetime.

In another few years, the RTGs on both Voyagers are expected to run down to the point where the spacecraft will no longer be able to communicate with Earth. They will just continue to drift in silence among the stars of the Milky Way for billions of years.
However, there is one item on both Voyagers that will continue to function, the Golden Record, which carries a message from Earth to anyone out there who may find the spacecraft in the future.
The chances of them being found are astronomically small, but they will become the longest running experiment in human history.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Bob McDonald is the host of CBC Radio's award-winning weekly science program, Quirks & Quarks. He is also a science commentator for CBC News Network and CBC TV's The National. He has received 12 honorary degrees and is an Officer of the Order of Canada.
- Quirks & Quarks
- Bob McDonald's recent columns
Scientists Thought They Knew What Uranus and Neptune Were Made Of. They Were Fooled.
New research unveils a surprising twist in the composition of our Solar System’s distant giants.

- Because Uranus and Neptune are so far away, scientists only have educated guesses about the combination of ices and gases that make up these ice giants.
- While the general understanding is that these planets both have large amounts of water ice, a new study posits that a significant portion of that ice is likely actually methane.
- It’s probable that organic-rich material found in planetesimals interacted with the planets’ hydrogen/helium atmosphere and high temps and pressures of the early planet development to develop a layer of methane ice that could account for as much as 10 percent of these planets’ masses.
However, the exact composition of that water is up for debate. Neptune, for example, has an atmosphere made of hydrogen and helium (with just a tinge of methane), and it doesn’t really have a surface—or, at least, not what we think of as a surface. NASA describes the “surface” of Neptune as “extend[ing] to great depths, gradually merging into water and other melted ices over a heavier, solid core with about the same mass as Earth.”
But scientists at the Technion–Israel Institute of Technology state in a new, not-yet-peer reviewed study that the planet could contain much more methane ice than previously believed. The results were published on the pre-print server arXiv in March .
To understand this overlooked composition means going back to Uranus and Neptune’s formation billions of years ago. To contain so much water, the planets must “accrete,” or gather under its immense gravity , ice-rich planetesimals during its formation. However, when analyzing planetesimals in the Kuiper belt—of which the notoriously demoted Pluto is a member—they’re mostly made of refractory materials, meaning they’re “ice poor.”
So, where exactly did all this ice come from?
“Uranus and Neptune are commonly considered ice giants, and it is often assumed that, in addition to a solar mix of hydrogen and helium, they contain roughly twice as much water as rock,” the study reads. “We show that chemical reactions between planetesimals dominated by organic-rich refractory materials and the hydrogen in gaseous atmospheres of protoplanets can form large amounts of methane ‘ice’. Uranus and Neptune could thus be compatible with having accreted refractory-dominated planetesimals, while still remaining icy.”
To figure out this mystery, scientists developed thousands of random statistical computer models of Uranus and Neptune’s interior, created a surface composition, and worked inward. When tested with several different chemicals and various water/rock compositions, the closest recreation of Uranus and Neptune’s radius and mass required vast amounts of methane ice formed through interactions with organic-rich (ice-poor) planetesimals and the planet’s hydrogen atmosphere. This formation was also helped by the high temperature, high pressure environment that occurs during the chaotic development of planets.
The paper states that this methane ice would likely be in a chunky, mushy layer between the hydrogen/helium atmosphere and the lower layer of water. According to Live Science , some models even showed that methane could make up as much as 10 percent of these planets’ masses.
“While the oxygen in rocky minerals and small amounts of CO ice will react with the hydrogen to form additional water, the carbon inside refractory organics will form very significant amounts of methane,” the paper reads. “Our random model generator shows that such methane-rich planets can fit the observed properties of Uranus and Neptune.”
Resolving many of these compositional mysteries requires sending a spacecraft to Uranus—the exploratory path for which was laid out by Voyager 2 in the 1980s. Luckily, NASA has recognized a mission to Uranus as of the “highest priority” as part of its Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey. Hopefully, when that mission finally arrives, we’ll learn for sure what really makes up these fascinating icy worlds.
Darren lives in Portland, has a cat, and writes/edits about sci-fi and how our world works. You can find his previous stuff at Gizmodo and Paste if you look hard enough.

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Solar System .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

This Is the Best Way to Exit Our Solar System

Stream the Great American Solar Eclipse

2 Dwarf Planets Are Hiding Something Incredible

Stars Passed in the Night—and Changed Our Climate

NASA Might As Well Be Walking on the Sun

NASA Finally Opened a Canister of Asteroid Dust

The 7 Greatest Cosmic Threats to Life on Earth

Crater Proves the Universe Has a Wicked Curveball

Voyager 1 Is Phoning Home Glitchy Nonsense Data

How Solar Storms Could Wreak Havoc on Railways

How Big Is the Sun? Well, It’s Complicated.

NASA spacecraft suddenly starts transmitting mysterious 'gibberish' 15 billion miles from Earth
It is not usual for a spacecraft that is sent into space to send out gibberish messages. However, it is always a mystery for scientists to find meaning behind these strange sounds and messages. That's what NASA's Voyager 1 craft was doing but in a breakthrough, NASA engineers have been finally able to figure out the reason, according to Indy100 . It had been happening since November last year. The craft was sending a stream of gibberish back to Earth that was completely unreadable.
According to the NASA website , the Voyager 1 has been exploring the solar system for more than 45 years. It is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the sun. It is the first spacecraft to cross the heliosphere. In March 2024, NASA engineers sent what is known as a "poke" to the probe to get information from the flight data subsystem (FDS). After it responded, they understood the problem and it was that the memory of the FDS had been corrupted.
A blog posted by NASA states that 3 percent of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations. They mentioned, "The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn't working. Engineers can't determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years."
Men over forty share 10 valuable tips for men in their 30s and it's good advice
They went on to say that it might take weeks or months but the engineers are optimistic that they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware. Then only Voyager 1 would be able to send science and engineering again. However, since its launch in 1977, the spacecraft has flown by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 has flown by Uranus and Neptune. Both the spacecraft are exploring interstellar space. Though there is an issue in Voyager 1, Voyager 2 has been working normally.
In other news, NASA was all set to launch three rockets to trace the path of the eclipse on April 8, 2024. The eclipse was said to be seen in various regions in North America for more than six hours. During this duration, the rockets were to "study how Earth's upper atmosphere is affected when sunlight momentarily dims over a portion of the planet, according to NASA''s website . The rockets were to be launched at three different times, one 45 minutes before, next during the eclipse and the last one 45 minutes after the eclipse.
The time intervals of the launches are to collect data on how the Sun's sudden disappearance affects the ionosphere or creates "potential disturbances" that can affect out communications. The launch would have taken place from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The rockets were earlier used during the annular solar eclipse in 2023, in Mexico and have been refurbished with new instruments to be launched in April 2024.


- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Galleries of Images Voyager Took
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft explored Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before starting their journey toward interstellar space. Here you'll find some of those iconic images, including "The Pale Blue Dot" - famously described by Carl Sagan - and what are still the only up-close images of Uranus and Neptune.

Photography of Jupiter began in January 1979, when images of the brightly banded planet already exceeded the best taken from Earth. Voyager 1 completed its Jupiter encounter in early April, after taking almost 19,000 pictures and many other scientific measurements. Voyager 2 picked up the baton in late April and its encounter continued into August. They took more than 33,000 pictures of Jupiter and its five major satellites.

The Voyager 1 and 2 Saturn encounters occurred nine months apart, in November 1980 and August 1981. Voyager 1 is leaving the solar system. Voyager 2 completed its encounter with Uranus in January 1986 and with Neptune in August 1989, and is now also en route out of the solar system.

NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft flew closely past distant Uranus, the seventh planet from the Sun, in January. At its closet, the spacecraft came within 81,800 kilometers (50,600 miles) of Uranus's cloudtops on Jan. 24, 1986. Voyager 2 radioed thousands of images and voluminous amounts of other scientific data on the planet, its moons, rings, atmosphere, interior and the magnetic environment surrounding Uranus.
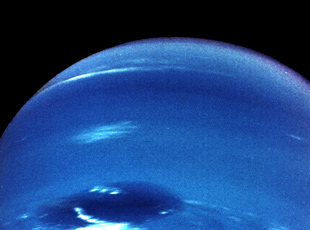
In the summer of 1989, NASA's Voyager 2 became the first spacecraft to observe the planet Neptune, its final planetary target. Passing about 4,950 kilometers (3,000 miles) above Neptune's north pole, Voyager 2 made its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth 12 years ago. Five hours later, Voyager 2 passed about 40,000 kilometers (25,000 miles) from Neptune's largest moon, Triton, the last solid body the spacecraft will have an opportunity to study.

This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed 'Pale Blue Dot', is a part of the first ever 'portrait' of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic. From Voyager's great distance Earth is a mere point of light, less than the size of a picture element even in the narrow-angle camera. Earth was a crescent only 0.12 pixel in size. Coincidentally, Earth lies right in the center of one of the scattered light rays resulting from taking the image so close to the sun. This blown-up image of the Earth was taken through three color filters -- violet, blue and green -- and recombined to produce the color image. The background features in the image are artifacts resulting from the magnification.

COMMENTS
Note: Because Earth moves around the Sun faster than Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 is traveling from Earth, the one-way light time between Earth and each spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of the year. Cosmic Ray Data: This meter depicts the dramatic changes in readings by Voyager's cosmic ray instrument. The instrument detected a dip in ...
When Voyager 2 passed behind Saturn, viewed from Earth, it utilized its radio link to investigate Saturn's upper atmosphere, gathering data on both temperature and pressure. In the highest regions of the atmosphere, where the pressure was measured at 70 mbar (1.0 psi), [42] Voyager 2 recorded a temperature of 82 K (−191.2 °C ; −312.1 °F ).
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to visit Uranus and Neptune. The probe is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the Sun. ... 1985, when signals took approximately 2.5 hours to reach Earth. Light conditions were 400 times less than terrestrial conditions ...
Voyager 2 Distance from the Earth This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 2's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 2 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at ...
Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as it enters this new phase of its journey, but information - moving at the speed of light - takes about 16.5 hours to travel from the spacecraft to Earth.
The space agency lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 when the mission team accidentally sent a command that pushed the spacecraft's antenna two degrees away from Earth. On Tuesday morning ...
A NASA image of one of the twin Voyager space probes. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after mistakenly pointing its antenna 2 degrees away from Earth.
Voyager 2 has reestablished communication with Earth and is operating normally. NASA's long-running Voyager 2 mission, which launched from Earth in 1977 and is currently about 12.4 billion miles ...
NASA. In the nearly 44 years since NASA launched Voyager 2, the spacecraft has gone beyond the frontiers of human exploration by visiting Uranus, Neptune and, eventually, interstellar space. Last ...
The call to Voyager 2 was a test of new hardware recently installed on Deep Space Station 43, the only dish in the world that can send commands to Voyager 2. Located in Canberra, Australia, it is part of NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN), a collection of radio antennas around the world used primarily to communicate with spacecraft operating ...
Article. Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 2 spacecraft left Earth to begin an epic journey that continues to this day. The first of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 2 lifted off on Aug. 20, 1977. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, manages the spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets and beyond.
Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as it enters this new phase of its journey, but information - moving at the speed of light - takes about 16.5 hours to travel from the spacecraft to Earth.
Voyager 2 is more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion km) from Earth, where it is hurtling at an estimated 34,390mph (55,346km/h) through interstellar space - the space between the stars.
As a result, Voyager 2 is currently unable to receive commands or transmit data back to Earth. Voyager 2 is located more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) from Earth, and this change has interrupted communication between Voyager 2 and the ground antennas of NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN). Data being sent by the spacecraft is ...
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before. The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons.
Its twin, Voyager 1, crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space. Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as ...
Engineers have confirmed that a small portion of corrupted memory in one of the computers aboard NASA's Voyager 1 has been causing the spacecraft to send unreadable science and engineering data to Earth since last November. Called the flight data subsystem (FDS), the computer is responsible for packaging the probe's science and engineering ...
Engineers have now identified the problem, but trying to repair a 46-year-old device on a craft 24 billion kilometres from Earth is not easy. Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 were both launched in ...
The ice giants Uranus and Neptune live up to their name. Although humans have only ever sent one spacecraft (Voyager 2) toward these far-flung worlds, scientists have a pretty good idea that these ...
Voyager 1 flew within 64,200 kilometers (40,000 miles) of the cloud tops, while Voyager 2 came within 41,000 kilometers (26,000 miles). Saturn is the second largest planet in the solar system. It takes 29.5 Earth years to complete one orbit of the Sun, and its day was clocked at 10 hours, 39 minutes.
Though there is an issue in Voyager 1, Voyager 2 has been working normally. In other news, NASA was all set to launch three rockets to trace the path of the eclipse on April 8, 2024.
In the summer of 1989, NASA's Voyager 2 became the first spacecraft to observe the planet Neptune, its final planetary target. Passing about 4,950 kilometers (3,000 miles) above Neptune's north pole, Voyager 2 made its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth 12 years ago.