
- INSTITUTIONS

- Q&A on immigration, exit-entry during epidemic control
- 15 foreigners awarded for introducing China to world
- Notice of port visa application procedures for foreigners

Copyright© www.gov.cn | About us | Contact us
Website identification code bm01000001 registration number: 05070218, all rights reserved. the content (including but not limited to text, photo, multimedia information, etc) published in this site belongs to www.gov.cn., without written authorization from www.gov.cn, such content shall not be republished or used in any form., copyright© www.gov.cn | contact us, website identification code bm01000001, registration number: 05070218.

Business Services
Professional services.
Audit | Mergers & Acquisition | CFO Services | Due Diligence
Setup Services
Company Registration | Off-shore Setup
IT Services
Accounting System Setup | Software Selection | Software Implementation
Work Permit and Work Visa in China: The 2024 Guide
by Integra Group | Nov 16, 2023 | Legal
With the reopening of the Chinese market in the post-pandemic era, we saw a growing trend of expatriates seeking to obtain visas to work and reside in China. A thorough understanding of getting a work permit and work visa is essential for any expat planning to work in China. This guide provides an up-to-date overview of the application process, eligibility criteria, and necessary documentation for 2024.
An Introduction of China Work Permit
Basic eligibility for work permits.
To qualify for a Chinese work permit, both employer and employee (foreigner) must satisfy several criteria.
The employers must legally comply, offer roles of special necessity where domestic candidates are unavailable, ensure wages meet or exceed local standards, and secure any necessary industry-specific regulatory approvals for foreign employees.
The employees must be at least 18 years old and in good health, have no criminal record, and possess the required skills and a confirmed employer in China for their specific role.

Categories of Work Permits
The State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs (SAFEA) implemented a nationwide unified work permit system to assess foreign talents. This system uses market and international peer evaluations to emphasize abilities, achievements, and contributions. It integrates policy tools like points-based systems and guidance catalogs, dividing foreigners working in China into three groups: foreign high-end talents (Category A), foreign professionals (Category B), and ordinary foreign personnel (Category C).
- Category A: Foreign High-end Talents
Category A refers to individuals such as scientists, technology leaders, international entrepreneurs, and specialized talents. This category also includes those who qualify as foreign high-end talents based on a points system – with 85 or more points. There is no age, educational, or professional experience restrictions for these talents.
- Category B: Foreign Professionals
This category is for talents meeting specific educational, professional, or work criteria in China’s regulations. Typically, individuals with a bachelor’s degree and over two years of relevant work experience are eligible to apply for it. Foreign talents who have scored 60 or more in the scoring system also qualified.
- Category C: Ordinary Foreigners
Ordinary foreigners are classified as Category C when they align with the domestic labour market needs, are employed in temporary (no more than 90 days), seasonal, non-technical, or service positions that adhere to China’s policies and regulations.
Please visit the this link to view all the classification standards.
The Point-based Scoring System for China Work Permit
Following is the criterias for the point scoring system of the work permit:
积分要素计分赋值表(暂行版)
Integral Element Scoring Assignment Table (Provisional Version)
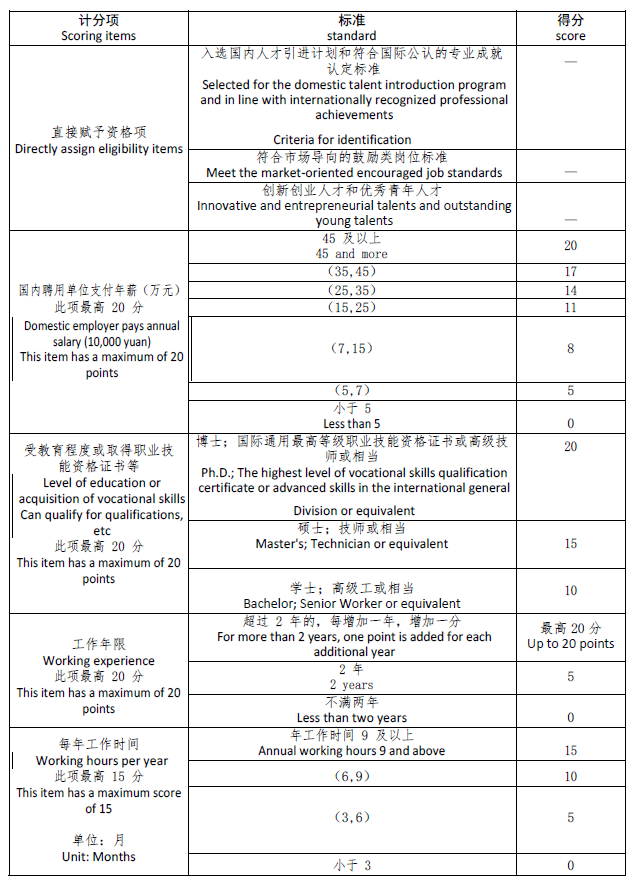
Source: Integra Group
Basic Handling Process
Online Application: Employers must log in to the designated system, submit information electronically, and provide necessary digital documents.
Online Preliminary Review: Within 5 working days, the acceptance authority reviews the submitted materials online. Incomplete or non-compliant applications will receive a one-time online notification for correction; otherwise, an online confirmation or an appointment for on-site material submission will be made.
Acceptance: The authority decides on the acceptance of the application. If the application is complete and falls under the agency’s jurisdiction, an acceptance receipt is issued immediately.
Review: The decision-making authority reviews the verified materials and makes a decision within 10 working days. Verification includes checking the original employment contract, work qualification certificate, no criminal record certificate, physical examination certificate, and highest degree certificate.
Decision: Where the requirements and criteria are met, the decision-making authority will decide to grant administrative permission, generate a Work Permit Notification online, and issue the Foreigner Work Permit within 10 days of the decision.
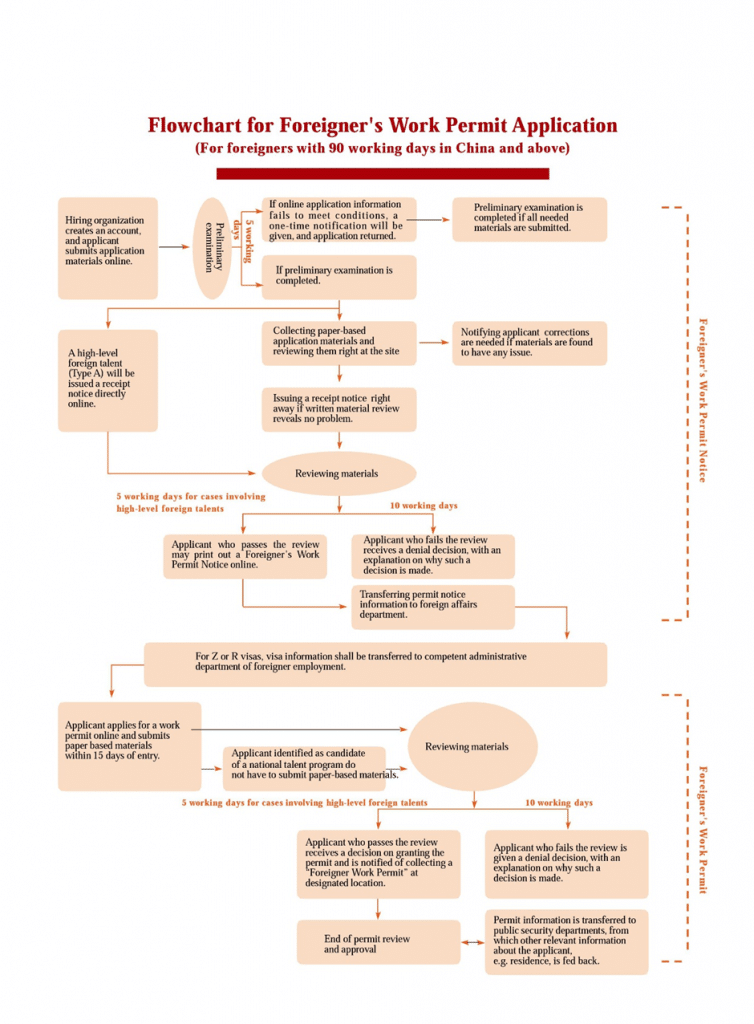
Source: Ministry of Science and Technology
In practical, for a new application, if all required documents are in order, it generally takes 15-20 working days from the submission of the application to receiving the work permit notice. Additionally, the actual situation can vary from city to city, so it is advisable to consult professional firms or the relevant authorities to obtain the most up-to-date information.
Obtaining a Work Visa (Z-Visa)for China
The Work Visa (Z-Visa) is granted to individuals who are employed, assume a professional post, or participate in commercial performances in China. After obtaining the Foreigner Work Permit Notification letter , applicants can proceed to apply for the China Work Visa at their local visa center or the nearest Chinese embassy.
The general process for obtaining a Chinese work permit and work visa involves:
Job Offer: Secure a job offer from an employer in China.
Work Permit Notification: The employer applies for a Work Permit Notification at the local labor bureau in China.
Visa Application: Apply for a Z Visa at the nearest Chinese embassy or consulate with the Work Permit Notification.
Entry into China: Enter China with the Z Visa.
Work Permit: Applicants must apply for the Work Permit within 15 days of entering China.
Residence Permit: If the duration of the work visa is more than 30 days, the holders of Z-Visa must apply for a residence permit from the immigration department of the local public security authority.
The standard documents required include:
Passport with at least six months of validity.
Completed visa application form with a passport-sized photo.
Official job offer from a Chinese employer.
Work Permit Notification.
Health certificate (if applicable).
No criminal record certificate.
For the most up-to-date information and specific guidelines, it’s advisable to consult the official websites .
Integra Group is a fully licensed asia-focused accounting, taxation, and business advisory firm – with dedicated offices in Shanghai, Beijing, Singapore and Taipei. We’ve helped companies ranging from Fortune 500 companies to small to medium sized businesses establish and grow their presence in Asia.
C ontact Us

Guide to Setting Up a Company in China: 2024 Edition
by Integra Group | Legal
Due to the latest changes in the China Company Law, we have updated this article to reflect the new regulations effective from July 1, 2024

New Policies to Enhance Travel Convenience in China
by Integra Group | Policy & News
China has recently introduced several new immigration policies aimed at facilitating travel and enhancing the convenience of immigration processes for both foreigners and residents.

China Eases Access for Foreign Investment in Service Sectors
On July 11, China has implemented regulatory adjustments in major cities to further open up the service sector and attract foreign investment.

Reminder for the 2023 Annual IIT Reconciliation
by Integra Group | Accounting & Tax
In China, the months from March to June are busy for the annual reconciliation of individual income tax (IIT). You will find key information for your reference in this article.

China Expands Foreign Access to Value-Added Telecom Services
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of China recently issued the Circular on the Pilot Scheme for the Further Opening of Value-Added Telecom Services to Foreign Investment (“Circular”).

Guide on Visa Extension, Change and Reissuance for Foreigners

I. Scope of Application
Applicable to foreigners applying for visa extension, change and reissuance after entry with a regular visa.
II. Legal Basis
Exit and Entry Administration Law of the People's Republic of China, Regulations of the People's Republic of China on Administration of the Entry and Exit of Foreigners.
III. Accepting Authorities
The National Immigration Administration (NIA) entrusts the exit-entry departments of public security organs at or above the prefecture-level cities (including counties and districts under the jurisdiction of municipalities directly under the central government) to accept the foreigners' visa affairs.
The exit-entry departments of public security organs at the county level, upon the request of the exit-entry departments of the provincial level public security organs and the approval of NIA, are authorized and may accept the visa application of foreigners.
IV. Conditions of Application
Foreigners who, after entering China with ordinary visas, need to stay in China for non-diplomatic or unofficial purposes may, in accordance with relevant regulations, apply to exit-entry departments of public security organs for visa extension, change and reissuance. The applicant shall go through the relevant formalities at exit-entry departments of public security organs. In any of the following cases, the inviting entity or relatives of the applicant may apply on behalf of the applicant:
1.The applicant is under the age of 16 or over the age of 60 or it would unduly inconvenience the applicant due to illness or other reasons;
2.The applicant's current entry is not his or her first entry into China and the applicant has good records of stay or residence in China;
3.The inviting entity or individual has guaranteed to cover the necessary expenses of the applicant incurred in China.
V. Application Materials
1. Applications for visa of foreigners may be accepted upon completion of relevant formalities and submission of relevant materials
a. Valid passport or other international travel documents
b. Fill out the Visa/ Stay Permit/ Residence Permit Application Form and submit a photo that complies with the Guide for Entry and Exit Document Photographs
c. Supporting materials related to reasons of application
d. Other formalities to be completed and supporting materials to be submitted
2. Documents required for visa extension
To apply for extension of a stay, a foreigner shall apply to the exit and entry departments of public security organs 7 days prior to the expiration date of the stay specified in the visa, and submit relevant supporting materials as required:
a. Holder of C visa shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the competent departments of the people's government at or above the county level or the local civil aviation, railway, road and port transportation companies. The stay may be extended for no more than 30 days.
b. Holder of F visa shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the inviting and receiving entities. The entities that have not filed for records shall also submit the registration certificate. The stay may be extended for no more than 180 days.
c. Holder of G visa shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the receiving entity and a connecting ticket (flight, bus or ship) to the destination country (region) with confirmed seat and date. The stay may be extended for no more than 30 days.
d. The holder of J2 visa shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the foreign affairs departments of the people's government at the provincial level. The stay may be extended for no more than 30 days.
e. Holder of L visa shall submit a travel plan and itinerary, and for a group tour, also a letter of certificate issued by the travel agency. The stay may be extended for no more 30 days.
f. Holder of M visa shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the local inviting and receiving entities or individuals, and the entities that have not filed the record shall also submit the registration certificate. The inviting individual shall put signature in the letter and submit local household registration or a certificate of the actual residence. The stay may be extended for no more than 180 days.
g. Holder of Q2 visa shall submit an invitation letter provided by the individuals to be visited, the identity certificate, and proof of family relationship. The stay may be extended for no more than 180 days.
h. Holder of R visa shall submit a certificate letter issued by the inviting and receiving entities, and the entities that have not filed for records shall also submit the registration certificate. The stay may be extended for no more than 180 days.
i. For the S2 visa holders, the visiting personnel shall submit an invitation letter provided by the individuals to be visited, a foreigner residence permit and proof of family relationship. Foreigners visiting for other purposes shall submit certificates stating the nature of the private affairs or humanitarian causes. The duration of stay may be extended to no more than 180 days for those visiting relatives, and no more than 90 days for those visiting for other purposes.
j. Holder of X2 visa shall submit a current study certificate issued by an education or training institution within the territory of China. The stay may be extended for no more than 180 days.
Note: The accumulated extension of stay shall not exceed the original duration of stay specified in the visa.
3. Documents required for visa change
Where a foreigner changes purpose of stay, is granted entry conveniences in accordance with relevant provisions of the State, starts using a new passport, or needs to stay separately from his or her tour group after entering China with a group visa due to objective reasons, the applicant may apply for a change of visa by submitting the following documents:
a. To apply for the change to F visa, the applicant shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the inviting entities, and may be issued the zero-entry, single-entry, double-entry or multiple-entry visa with a valid period upon entry no more than one year and a stay no more than 180 days.
b. To apply for the change to J2 visa, a letter of certificate issued by the foreign affairs department of the people's government at the provincial level shall be submitted. A zero-entry visa with a stay of no more than 30 days can be issued.
c. To apply for the change to M visa, the applicant shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the inviting entities, and may be issued the zero-entry, single-entry, double-entry or multiple-entry visa with a validity period of entry no more than one year and a stay not exceeding 180 days.
d. To apply for the change to Q2 visa, the applicant shall submit an inviting letter provided by the individual to be visited, identity certificates and proof of family relationship. And the zero-entry, single-entry, double-entry or multiple-entry visas with a validity period of entry no more than one year and a stay no more than 180 days may be issued.
e. To apply for the change to R visa, the applicant shall meet the qualifications and requirements set by the competent authorities of the Chinese government for inviting high-level foreign talents or urgently needed specialists, and submit relevant certificates and supporting materials in accordance with the provisions, as well as certification letter issued by the inviting and receiving entities. And the zero-entry, single-entry, double-entry or multiple-entry visas with a validity period of entry no more than five years and a stay no more than 180 days may be issued.
f. To apply for the change to S2 visa, the visiting individual shall submit an inviting letter provided by the person to be visited, foreigner's residence permit and proof of family relationship. Foreigners visiting for other purposes shall submit relevant supporting materials stating the nature of the humanitarian causes. And the zero-entry or single-entry visas with a validity period of entry no more than three months and a stay no more than 180 days may be issued.
g. To apply for the change to X2 visa, the applicant shall submit an official letter and a certificate of admission and enrollment issued by an education or training institution within Chinese territory, and may be issued a zero-entry, single-entry or double-entry visa with a validity period of no more than one year and a stay of no more than 180 days.
h. A foreigner who starts using a new passport because the original one is about to expire or is running out of visa pages may apply for a change of visa by submitting the original passport for the latest entry or relevant certificates issued by the embassy or consulate of the applicant's country in China specifying that the original passport has been withdrawn. A visa that is consistent with the original visas in type, validity period of entry, duration of stay and the remaining valid entry times may be issued. The entry times of the new visa will be decided in accordance with the remaining valid entry times of the original visa.
i. Foreigners who need to stay separately from the tour group after entering China with a group visa shall submit a letter of certificate issued by the hosting travel agency. The visa may be changed in accordance with the provisions in the preceding paragraph.
The accumulated stay period of the changed visas shall not exceed one year since the date of current entry.
4. Documents required for visa reissuance
Where a foreigner needs to apply for reissuance of visa because the original visa is lost, damaged, destroyed, stolen or robbed after entering China, the applicant shall submit the following supporting materials:
a. If the visa is lost, stolen or robbed, the applicant shall submit the certificate of reporting the loss of passport or the official note issued by the embassy or consulates of the applicant's country in China, and the new valid passport or other international travel documents.
b. If the visa is damaged, the applicant shall submit the damaged passport or the official note issued by the embassy or consulates of the applicant's country in China, and the new valid passport or other international travel documents.
c. If the group visa is lost, stolen, robbed or damaged, the applicant shall submit a certification letter issued by the hosting travel agency and a copy of the original group visa.
The applicant may be reissued a visa that is consistent in type, validity entry period, duration of stay and the remaining valid entry times with the original one.
VI. Facilitation Measures
1. Visa facilitation measures regarding the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
If foreign seafarers carrying out BRI maritime transport tasks need to leave the port city and change means of transport for exit, the time limit of issuance shall be shortened from 7 working days to 3 working days, and for emergency exits of the seafarers, visa may also be issued on the same day of acceptance.
2. Simplified formalities for visa extension

3. Expedited conveniences for foreigners in urgent needs
The exit and entry departments of public security organs shall provide convenience to the immediate acceptance and approval of visas for foreign nationals in the following three cases:
- For foreign nationals who have lost their passports and are in urgent need of reapplying for visas for departure, their application shall be accepted and examined in a timely manner by submitting the tickets (air, bus or ship) with confirmed seats and date as well as an explanation letter provided by the inviting entities;
- Foreign seamen and their accompanying family members who urgently need to apply for stay permits to leave the port cities for outbound flights shall be accepted for examination and approval in a timely manner by submitting the guarantee letter issued by the shipping agency and the tickets (air, ship or bus) with confirmed seats and date;
- Foreign tour group members who urgently need to apply for group visa separation to leave the country shall be accepted for examination in a timely manner by submitting the letter of explanation provided by the receiving travel agency and the tickets (air, bus or ship) with confirmed seats the date.
4. Visa and residence facilitation for Chinese of foreign nationality
For Chinese of foreign nationality who come to China to visit their relatives, for business talks, carry out exchanges in science, education, culture and health, or handle personal affairs, the exit and entry departments of public security organs may issue multiple-entry visas valid for five years. Residence permits valid for 5 years may be issued to Chinese of foreign nationality who need to stay for a long term to work, study, visit relatives or engage in private affairs in a local area.
5. High-level foreign talents
a. The foreign experts and scholars invited by key domestic institutions of higher learning, scientific research institutes and well-known enterprises, as well as the high-level foreign management talents and technical specialists identified by the competent talents authorities as well as the competent authorities for technology and innovation of the people's governments of the cities with subordinate districts or above, may apply for port visas for entry. After entering China, they may apply for multiple-entry visas or residence permits for private affairs with a validity period of no more than five years by presenting certificates and letters from the inviting entities. Those who are employed by enterprises or entities may apply for work-type residence permits with a validity period of no more than five years according to the regulations.
b. Foreign talents and members of innovation groups introduced to key sectors and industries in China may apply for work-type residence permits valid for no more than five years by presenting their work permits and certificate letters from their employers. A team member of innovation or entrepreneurship groups may apply for a residence permit for private matters valid for no more than five years (marked with "entrepreneurship") with a letter of guarantee from the leader of the team.
c. Foreigners with outstanding contributions and fit the special needs of China's development can recommend foreign members of their working team and research supporting personnel to apply for long-term visas or residence permits valid for no more than five years.
d. High-level foreign talents working in key domestic institutions of higher learning, scientific research institutes, and renowned enterprises are allowed to engage in part-time innovation and entrepreneurship after being approved by both the entities where they work full time and part time and filing for records to exit-entry departments.
6. International students
a. Outstanding foreign students who have obtained a bachelor's degree or above from a key Chinese institution of higher learning and engage in innovation and entrepreneurship in China after graduation can apply for a residence permit for private affairs valid for two to five years (marked with "entrepreneurship") by presenting their university graduation certificate and certificates for innovation and entrepreneurship. Those who are employed by enterprises and other entities may apply for a work-type residence permit in accordance with relevant regulations.
b. Foreign students who have graduated from internationally renowned universities and come to China for innovation and entrepreneurship within two years after graduation can apply for residence permit for private affairs valid for no more than two years (marked with "entrepreneurship") with the academic (degree) certificates. Those who are employed by enterprises and other entities may apply for a work-type residence permit in accordance with relevant regulations.
c. Foreign students from overseas institutions of higher learning who are invited to take internship in China by well-known Chinese enterprises and public institutions can apply for a visa for private affairs valid for one year (noting "internship") with a letter issued by the inviting entity and a study certificate issued by their institutions of higher learning. Foreign students from overseas institutions of higher learning who come to China for internship in accordance with intergovernmental agreements may apply for work-type residence permits in accordance with relevant regulations.
7. Employment of foreigners
If a foreigner has obtained a work permit but does not have enough time to go abroad to apply for a work-type visa, the applicant may directly apply for a work-type residence permit in China with relevant work permits. If the foreigner has applied for a work-type residence permit valid for more than one year twice consecutively, the applicant may apply for a work-type residence permit valid for five years at his or her third application in accordance with relevant regulations.
VII. Basic Process and Method of Handling
1. Application. Foreigners who apply for extension, change or reissuance of visa, shall go to exit-entry departments of public security organs in person to go through relevant formalities. For cases complying with relevant provisions, the inviting entities or individual, families or relatives of the applicant or specialized service agencies may file the application on behalf of the applicant.
2. Acceptance. The accepting authority decides whether to accept or not after examining the application. The applying matters shall fall within the functions and powers of the administrative authority. If the application materials are complete and meet the requirements, the application shall be accepted on the spot and a receipt of acceptance shall be issued. If the formalities or materials required for the application for a visa are incomplete, the applicant shall be notified regarding the formalities to be completed and the materials to be supplemented at one time.
3. Review and verification. The exit- and entry departments of public security organs shall strengthen verification. The authenticity of the application shall be confirmed through means of interviews, telephone inquiries, field investigations and others. Verification shall also be taken to confirm whether the applicant is of foreign nationality. If an applicant or relevant entity, individual is notified to take an interview but fails to do that at the agreed time without justifiable reasons, the application may be denied by law.
4. Decision-making. If the conditions and standards are met, the authority in charge shall make the decision on granting administrative permits and issue visas of corresponding categories.
VIII. Time Limit for Issuance
Upon examination and verification, if the foreigner's application complies with the conditions of acceptance, the application shall be accepted, and an acceptance receipt shall be provided. The decision on whether or not to issue a visa shall be made within the validity period of the acceptance receipt. The validity period of the acceptance receipt for visa application shall be no more than seven working days from the date of acceptance.
IX. Charging Basis and Standards
1. Charging Basis
Reply of the State Development Planning Commission and the Ministry of Finance on Approving the Adjustment to the Visa Charging Standards of Public Security Organs of the Mainland (Ji Jia Ge [2003] No. 392).
2. Charging Standards
Based on the Notice of Public Security Organs to Adjust Charging Standards to Foreigners' Visas (Gong Ming Fa [2011] No. 470)
Zero-entry Visa (of non-reciprocal countries): CNY 160 per person
Single-entry Visa (of non-reciprocal countries): CNY168 per person
Double-entry Visa (of non-reciprocal countries): CNY 252 per person
Multiple-entry Visa valid for no more than half a year (of non-reciprocal countries): CNY 420 per person
Multiple-entry Visa valid for no more than one year (of non-reciprocal countries): CNY 672 per person
Adding or reducing accompanying persons (non-reciprocal countries): CNY 160 per person
For reciprocal countries, the fees shall be charged in accordance with standards stipulated by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.

X. Results Delivery Issued Visas for foreigners after approval, shall be claimed by the applicants in person at relevant exit-entry departments of public security organs with the acceptance receipts.
XI. Circumstances in Which Visas Shall not be Issued According to Article 21 of the Exit and Entry Administration Law of the People's Republic of China, foreigners who fall under any of the following circumstances shall not be granted visas: 1. Those who were deported, or were repatriated upon decision, and the No-Entry-into-China period has not expired; 2. Those who are suffering from serious mental disorder, infectious tuberculosis, or any other infectious disease that may result in great harm to public health; 3. Those that may endanger China's national security and interests, disrupt public order or engage in other illegal or criminal activities; 4. Those who resort to deceit in the visa application process or fail to guarantee the expenses needed during their stay in China; 5. Those failing to submit relevant materials required by the visa authorities; 6. Other circumstances in which the visa authorities consider a visa should not be issued.
In the case of rejecting to issue a visa, the visa authority may not explain reasons. According to Article 31 of the Exit and Entry Administration Law of the People's Republic of China, foreigners who fall under any of the following circumstances shall not be granted residence permits: 1. The visa held does not belong to the type for which a foreigner’s residence permit should be issued; 2. Those who resort to deceit in the application process; 3. Those who fail to provide relevant supporting materials as required; 4. Those who are not eligible for residence in China due to violation of relevant Chinese laws and administrative regulations; 5. Other circumstances in which the issuing authorities consider a foreigner's residence permit should not be issued. Specialized talents and investors who meet the requirements of the State or other foreigners who need to change their stay to residence for humanitarian and other reasons, may apply for foreigners' residence permits upon the approval of the exit-entry departments of public security organs of the local people's governments of cities divided into districts at or above the prefectural level. According to Article 36 of the Exit and Entry Administration Law of the People's Republic of China, the decision made by the exit-entry departments of the public security organs on not granting extension, change, or reissuance of the foreigners' visa, or on rejecting issuing foreigners’ stay or residence permits, extending their duration of residence shall be final.
XII. Rights and Obligations of the Administrative Counterpart 1. In accordance with relevant laws and regulations, an applicant shall be entitled to the following rights: a. Those who meet the legal conditions and criteria are entitled to equal rights to obtain an administrative license in accordance with law; b. They shall have the right to make statements and defend against implementation of the administrative license by an administrative authority; c. Other rights stipulated by laws and regulations.
2. In accordance with relevant laws and regulations, an applicant shall perform the following obligations: a. Applicants shall submit relevant materials and reflect the reality truthfully to the administrative authority, and shall be held responsible for authenticity of substantive content of the application materials; b. Applicant shall cooperate with administrative authorities to verify the authenticity of the application materials through interviews, telephone inquiries, field investigations, etc.; c. Other obligations stipulated by laws and regulations.
XIII. Other Matters for Attention 1. Definition of family members: spouse, parents, spouse's parents, children, siblings, paternal grandparents, maternal grandparents, paternal grandchildren, maternal grandchildren, and children's spouses.
2. Proof of family relationship and kinship shall include marriage certificate, birth certificate, adoption certificate and other kinship certificate issued by competent authorities of relevant countries and related notary public authentication; or the marriage certificate, birth certificate, kinship certificate and certification on the change of name or other personal information issued by the embassy or consulates of the applicant's country in China.
3. Marriage certificates, birth certificates, kinship certificates, or certifications on the change of name or other personal information issued by the competent authorities or notary authorities of a foreign country shall be authenticated by the Chinese embassy or consulate in that country.
4. Identity certificates. Identity certificates of Chinese mainland residents refer to household register certificates or certificate of residence that prove the actual places of residence for over 6 months as well as resident ID cards. Overseas Chinese identity certificates refer to Chinese passports and certificates of overseas residence. Identity certificates of Hong Kong and Macao residents refer to the Mainland Travel Permit for Hong Kong and Macao Residents. Taiwan resident identity certificates refer to the Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents. Foreigner identity certificates refer to the Foreigner's Permanent Residence Card. Overseas Chinese as well as Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan residents shall also submit the certificate of residence that prove the actual places of residence for over 6 months. 5. Relevant supporting materials in foreign languages shall be translated into Chinese.
XIV. Flow Chart for Visa Extension, Change and Reissuance for Foreigners

LEAVE YOUR MESSAGE
*your e-mail address.
Copyright©2024 China Daily. All rights reserved.
京ICP备13028878号-6


- Document Authentication
- Login/Register
Login to eChinaCareers
Quick connect.

Email login:
How to transfer a work visa to a new employer in china.

Around this time each year, a lot of expats working in China start looking for new job opportunities. By changing to a new employer, there are important rules and processes that need to be kept in mind.
Firstly, the foundational case is that which requires applicants to apply for a “new” visa from scratch. This is the same process, whether in China or elsewhere. Candidates are treated as new applicants who need to freshly apply through the usual channels.
For those who are currently working in China and whose visas are still in date, the other option is to transfer your work permit so that it’s valid for working with the new employer.
- The only visa legally valid for employment in China is an employment visa.
- An employment visa grants the holder the right to work for the company that the work permit is registered with, NOT any other company.
- Do not work for employers that are not connected to your work permit. (See here for more information: Here’s How to Not Get Deported – Visa Laws and Scams in China )
- Make sure you are able to obtain all the relevant documents from the employer you want to leave
- To transfer your work permit to a new employer, you do not need to leave China
What to Do Below is a detailed summary outlining the steps that must be taken in order to transfer a work permit over to a new employer.
Firstly, it isn’t your visa that is transferred, it is your work permit!
Note that at this point you cannot start to work for them. This is simply an expression of desire to employ you; work cannot begin until the permit transfer process is completed satisfactorily.
Depending on how long you have been working, your resignation can be instant or it may be a few weeks before you work your final day. Check the details of your contract carefully to see what obligations you agreed to. We suggest you connect the HR representatives of the new employer and your current employer, so they can co-ordinate various paperwork aspects, for example agreeing on the dates at which your work permit transfer was completed.
Your current employer will have access to the online government system and access to the cancellation forms via their account.
You will be required to sign a document entitled ‘ APPLICATION FORM FOR CANCELLATION OF FOREIGNER’S WORK PERMIT ’, and another Chinese language document which states you have officially stopped working for your current employer.
Both forms must be signed and stamped, and must be original copies . A photocopy or scan is not okay.
Your current employer will then send the cancellation document for approval by the relevant authorities, after which you will be requested to submit your work permit for decommissioning.
After the work permit has been decommissioned, a document entitled ‘ FOREIGNER’S WORK PERMIT CANCELLATION CERTIFICATE ’ will be sent back to your current employer. This letter is required for your work permit transfer , so you must remember to obtain it. Your new employer requires the release certificate to start the application for your new work permit with the new company.
This stage of the process is very similar to a standard work permit application.
The process happens online and will most likely be handled by your new employer. Depending on the jurisdiction you are working in, may be required to provide copies of the documents you used during your previous work permit application. This includes legalized and notarized degree & criminal record certificates, and the health report which you completed the first time around.
You may also be required to provide a new passport style photo of yourself. It’s important to keep in mind that your new job must be similar to your old job . If you’re changing to a completely different role, this will quite likely cause an issue. To avoid this, try to make sure the job title on your new contract is quite similar to your old job title.
When the online part of the application process is completed, you will be required to go to the Entry and Exit Bureau or Labor Bureau to collect your new work permit card. This is often done on your behalf by your new employer. If not, you simply need to go to the Entry and Exit Bureau or Labor Bureau to collect it, with relevant evidence or receipts to prove who you are.
Your new work permit will be almost identical to your old one, indeed it may even be the same permit you handed in previously! The main difference is that if you scan the QR code on it to see your registered details, you’ll notice that the employer details have been updated to show your new employer.
Step 7 - The final step
In most cases, the final step is for your passport to have its visa updated so that its details (start and end date) are in line with those on the work permit. You will need to go to the Entry and Exit Bureau to do this.
There are some cases where people have complained that they were unable to obtain a release letter. This usually happens due to confusion or misunderstanding in the details of the employment contract.
In this unfortunate situation, if you are adamant that you want to leave regardless of having the release letter or not, the only option is to start again with a whole new visa application. This means surrendering your current visa and work permit, and in most cases you will have to leave China until the application is complete.
Transferring your work permit over to a new employer is a relatively easy process. Often everything is handled by your old employer, meaning you simply need to write your resignation then provide things as and when they are needed.
Remember – Do not start work for a new employer until the new work permit has been granted.
Popular Posts

FAQs for Foreigner’s Work Permit in China
1. What is Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: The Foreigner’s Work Permit in China is provided to integrate the former Foreign Expert Work Permit in China and the former Work License for Foreigners into the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners , which is developed in an electronic form. Employers and foreign applicants can print it directly online. The former Foreign Expert Certificate and Permit for Foreign Employees are integrated into the Foreigner’s Work Permit . The Foreigner’s Work Permit represents the legal document for foreigners to work in China. Each foreigner will be allocated with one unique number which remains unchanged forever.
2. What is the legal basis for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: Notice of the State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs on Issuing the Trial Implementation Plan of the Work Permit System for Foreigners in China (WZF [2016] No. 151), Notice on Issuing the Service Guide to the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China (for Trial Implementation) (WZF [2017] No. 36) and Notice on Comprehensively Implementing the Work Permit System for Foreigners in China [WZF [2017] No. 40].
3. Which examination subjects and application conditions are applicable to the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: Where an employer legally incorporated in the People’s Republic of China employs a foreigner to work in China and applies for the work permit, the employer employing the foreigner and the foreigner shall be subject to the examination.
(1) Basic conditions of the employer: The employer must be established in accordance with the law, have actual establishment of operation, perform its tax obligations and contribute to the social insurance funds, without any record of serious law-breaking and dishonesty. The post to be filled in by a foreigner shall be the one with special needs and temporarily short of appropriate choice in the country. In addition, it shall not be in contravention of the relevant national regulations. The salary and remunerations to be paid to the foreigner shall be no less than the minimum local salary standard. The post subject to the review and approval by the competent authorities in the industry pursuant to the laws and regulations shall be approved.
(2) The applicant shall at least reach the age of 18 years old, healthy, without any criminal record, confirmed by a domestic employer, and have the professional skills or appropriate knowledge required by the job. The applicant shall be an urgently-needed professional whose job is consistent with the demand of economic and social development in our country. If applicable laws and regulations specially provides for the foreigners working in China, such special provisions shall apply.
4. How do foreigners work lawfully in Shanghai?
Answer: (1) Foreigners who stay overseas shall follow the work visa and entry flowchart:
Permit notice - Work visa (Chinese embassies and consulates overseas) - Enter - Apply for the permit - Work-type residence permit (entry-exit)
(2) Foreigners who stay in China:
The foreigners who stay in China may apply for the work permit directly in China if they meet certain conditions:
Apply for the permit - Work-type residence permit (entry-exit)
Permit notice - Work-type residence permit (entry-exit) - Apply for the permit
5. What is the process of the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China
Answer: (1) Apply online. The employer logs in the system, files the application information online, and provide relevant electronic materials. The real name registration can be carried out online before the pre-review results come out. If a service agent is appointed for spot handling, the name of the service agent, its legal registration certificates (business license or organization code certificate, social insurance registration certificate or the registration certificate of the permanent representative office of the foreign enterprise), the name of the handling person, his identity certificate, phone number and other information shall be provided online, and both the employer and the service agent shall complete relevant real name registration procedures on the spot.
(2) Pre-review online. The accepting authority shall, within 5 working days after the submission of the materials (excluding the date of submission), carry out pre-review over the materials submitted online. The applicant shall, within 15 days after entry, apply for and get the Foreigner’s Work Permit . If the materials are not complete or standard, the accepting authority shall send the online notice to supplement or correct the materials. If the materials are complete and standard, the accepting authority shall send the online notice, or determine a reservation to submit the materials online.
(3) Accept. The accepting authority will decide to accept it or not after review. If the application matter is in the capacity of the administrative body and the materials are complete and standard, the accepting authority shall accept the application online, and issue the stamped and dated Acceptance Form of Application for Foreigner’s Work Permit ; if the application materials are not complete or in the legal form, the site notice of materials to be supplemented or corrected shall be sent immediately; after the materials are supplemented and corrected, the application will be accepted; if the application matter is not in the capacity of the administrative body, the accepting authority shall explain the reason and basis for the non-acceptance. If the foreigner is in China, all original materials shall be uploaded and examined.
(4) Review. After the materials are submitted for examination, the approval body shall carry out examining activities and make a decision within the required period.
(5) Decide. If the application complies with relevant conditions and standards, the approval body shall make the decision to give the administrative permit, generate the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners , and within 10 days after makingthe decision, deliver the for Foreigner’s Work Permit . If the application does not comply with relevant conditions or standards, the explanation shall be given.
The approval body may simplify the procedures for examining the hardcopy application materials for the extension of the Foreigner’s Work Permit .
6. What are the standards for classification of foreigners working in China?
Answer: According to the Notice on Comprehensively Implementing the Work Permit System for Foreigners in China [WZF [2017] No. 40], the foreigners working in China are divided into three categories, Category A, Category B and Category C. For the Foreign High-end Talents (Category A), there is not quantity limit; for the Foreign Professional Talents (Category B), the quantity limit is set according to the market demand; for the Other Foreigners (Category C), the quantity limit is set subject to relevant national regulations.
(1) Foreign High-end Talents (Category A) refer to the scientists, scientific & technological leading talents, international entrepreneurs and special talents who “have an advanced diploma, master the precision manufacturing technology and the sophisticated science knowledge and technology and are urgently-needed”, meet the market demand orientation and economic and social development requirements of China, and meet one of the following conditions, mainly including: ①are listed in the domestic talent introduction plan; ②meet the internationally recognized professional achievement affirmation standards; ③foreign talents meeting the market-oriented encouragement post demands; ④innovation and start-up talents; ⑤excellent youth talents; ⑥the points are more than 85. The Foreign High-end Talents are not restricted in terms of age and work experience.
(2) Foreign Professional Talents (Category B) refer to the foreign professional talents who meet the instruction directory of foreigners working in China and post demands, and are urgently needed by the economic and social cause development of China, and meet one of the following conditions, mainly including: ①foreign professional talents who have bachelor’s degree or above and relevant working experience for 2 years or more and are under the age of 60 years old; ②skilled talents who have the international universal occupational skill qualification certificate or urgently-needed skilled talents; ③foreign language teacher; ④foreign talents whose average wage income is not less than 4 times of social average wage income of last year in the region; ⑤special personnel and project implementation personnel meeting relevant departmental regulations of the State; ⑥professional personnel whose points are more than 60.
(3)Other Foreigners (Category C) refer to other foreigners who meet the domestic labor force market demand and policy regulations of the country, mainly including: ①foreigners meeting the current management regulations for foreigners working in China; ②foreigners who are engaged in the temporary and short-term (not more than 90 days) work; ③personnel subject to the quota system management, including the foreign youth who does practice in China according to the inter-governmental agreement, foreign student and foreign graduate of overseas colleges and universities meeting the specified conditions, and foreigners working in the long range fishing and other special fields.
7. Is there any facilitating measure when the Foreign High-end Talents (Category A) apply for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: (1) The accepting authority shall directly accept the application which has passed the online pre-review, and shall issue the electronic Confirmation Letter for Acceptance. The applicant is not required to submit hardcopy materials for review before enter.
(2)A Foreign High-end Talent who has been listed in a domestic talent plan can apply for the permit in the whole process, and no hardcopy material is required to be submitted for review.
(3) For the Foreign High-end Talents (Category A) defined in the Classification Standard for Foreigners Working in China, (I) who are listed in a domestic talent plan; (II) who meet the internationally recognized professional achievement affirmation standards, the commitment system shall apply to the certification of work qualification.
(4)For the Foreign High-end Talents (Category A) defined in the Classification Standard for Foreigners Working in China, (I) who are listed in a domestic talent plan; (II) who meet the internationally recognized professional achievement affirmation standards; (III) who are foreign talents meeting the market-oriented encouragement post demands; (IV) who are innovation and start-up talents, the commitment system shall apply to the certification of the highest degree certificate (diploma).
(5) The commitment system shall apply to the certification of crime-free record.
(6) For any foreigner who enters China by presenting other visa or valid residence certificate, the foreigner may apply for the work permit in China.
(7)Where a Foreign High-end Talent applies for the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners , or the application for the Foreigner’s Work Permit is filed by presenting the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners, or the Foreigner’s Work Permit is applied for directly, or the application for the extension or cancellation of the Foreigner’s Work Permit , the approval body shall, within 5 working days, carry out the review and make the decision.
(8) The Foreigner’s Work Permit may be granted for a period of up to 5 years.
8. What are the Scoring Items and Gained Points about the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: The scoring items and gained points include items for directly granting the permit (for example, being listed in the domestic talent introduction plan and meeting the internationally recognized professional achievement affirmation standards, meeting the market-oriented encouragement post demands, innovation and start-up talents, and outstanding young talents), annual salary paid by a domestic employer, education level or professional skill qualification certificate, work years, annual working hours, Chinese language level, work orientation, age, graduating from a high-level university outside the country (territory), or work experience in a Fortune Global 500 Company and other conditions (with patent and other intellectual property rights, having worked in China for 5 consecutive years or more), local incentive points, etc.
9. How long does it take to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: Online pre-review: 5 working days.
Accepting Window: After the online pre-review, the applicant shall submit the original document for review at the accepting window (except that the pre-review and acceptance will be processed at the same time) and make it accepted.
Online review and decision at the first level: Apply for the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners : 5 working days for the Foreign High-end Talents, and 10 working days for the Foreign Professional Talents and Other Foreigners.
Apply for the Foreigner’s Work Permit by presenting the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners : 5 working days for the Foreign High-end Talents, and 10 working days for the Foreign Professional Talents and Other Foreigners.
Directly apply for the Foreigner’s Work Permit : 5 working days for the Foreign High-end Talents, and 10 working days for the Foreign Professional Talents and Other Foreigners
Foreigner’s Work Permit (extension): 5 working days
Foreigner’s Work Permit (information change): 5 working days
Foreigner’s Work Permit (re-issuance): 5 working days
Foreigner’s Work Permit (cancellation): 5 working days
10. Where can we apply for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China?
Answer: The accepting authority is responsible for the pre-review, acceptance, first-level review and issuance.
The list of accepting points will be published online:
http://files.shafea.gov.cn/html/88b609df-a422-4e91-89d3-4cfd05cb02cc.htm
Please select one of the accepting points at the place where the registered address of the employer is or the place where the employer operates.
11. Are the employers allowed to appoint service agents to apply for the work permit?
Answer: Employers can appoint the service agents which have been registered in the “Service System for Foreigners Working in China” to process the work permit for them.
Those service agents authorized with the procedure of application, extension, changing, cancellation, or re-submission in respect of the work permit shall submit the Letter of Authorization issued by the employer, in which the authorized entity, the authorized person and his ID number and telephone number, and the authorized matters shall be clearly specified. That is, the service agent, the authorized person and the corresponding authorized matters shall be clearly specified.
12. Which materials are required for applying for the Notice for the Work Permit for Foreigners overseas ?
Answer: Application Form for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China; relevant work qualification certificates; the highest degree certificate (diploma) or relevant approval documents, occupational qualification certificates and certification materials; crime-free record certificates and certification materials; physical examination certificate; employment contract or office-taking certificate (dispatch letter); passport or international travel certificate of the applicant; front bareheaded picture of the applicant taken within 6 months; relevant evidentiary materials of accompanying family members; other materials (the accepting authority or the approval body may require the employer to provide other supplementary materials meeting the basic conditions for the applicant).
13 、 13. What are the circumstances for the applicant to apply in China for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China (to work in China for more than 90 days)? How about the processes?
Answer: (1) Foreign High-end Talents (Category A) enter China with other visa or valid residence permit; (2) A foreigner working in China changes his employer while the position (occupation) remains unchanged and his work-type residence permit is still valid; (3) The spouse or child of a Chinese citizen, or the spouse or child of a foreigner who resides or works in China permanently has a valid visa or a valid residence permit; (4) Relevant policies for FTZs and pilot innovative reform areas apply; (5) Employers are included in relevant policies which apply to headquarters of international companies incorporated in China; (8) The representatives of representative offices in China enter in China with work permits, and they have obtained the work permit for foreigners working in China (less than 90 working days) and are employed by other domestic employers during the effective period of the work permit; (9) Other conditions by approving authorities are met.
If the application for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China (to work in China for more than 90 days) is filed in China and is approved, the Foreigner’s Work Permit will be directly issued. Before the valid visa or residence permit expires, the work-type residence permit shall be processed at the exit-entry administrative body of the local public security organ in the jurisdiction where the employer is located.
14. Which materials are required for directly applying in China for the Foreigner’s Work Permit ?
Answer: Application Form for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China; relevant work qualification certificates; the highest degree certificate (diploma) or relevant approval documents, occupational qualification certificates and certification materials; crime-free record certificates and certification materials; physical examination certificate; employment contract or office-taking certificate (dispatch letter); passport or international travel certificate, visa or valid residence permit of the applicant; front bareheaded picture of the applicant taken within 6 months; relevant evidentiary materials of accompanying family members; other materials (the accepting authority or the approval body may require the employer to provide other supplementary materials meeting the basic conditions for the applicant).
15. If a foreigner newly entering China who has annual salary of 600,000 yuan and estimated tax obligation of 120,000 yuan per year takes an important or key position in a domestic company, but cannot meet the basic requirements for Category B Personnel (in terms of age or diploma), how can the foreigner apply for the work permit?
Answer: According to the contractual amount, the domestic employer can additionally submit a letter of undertakings and explain the employment reason and the position importance; the employer undertakes to pay for the salary according to the contractual amount, and the obligation of annual individual income tax shall be at least 120,000 yuan; the employer also undertakes to provide the slip of individual income tax after one year. Currently, the standards for pre-review and acceptance applicable to Category A Personnel shall apply, and the work permit shall be granted for 1 year. Foreigners from some countries who are engaged in certain works in China can enjoy tax exemption policies for 2 years, subject to the Notice of Several Issues on Tax Exemption for Introduced Foreign Experts in Respect of Individual Income Tax (HSW[1995] No. 105).
16. If a foreign professional technician newly entering China who does not meet the basic requirements of Category B Personnel but has gained 60 or more points, how can the technician apply for the work permit?
Answer: The employer shall give explanations, including the employment reason and the position importance as well as the basis for the gained points (as per the new-version scoring table), additionally upload relevant supporting materials. The standards for pre-review and acceptance applicable to Category A Personnel shall apply. However, the applicant may not exceed 65 years old.
17. Which people does the accepting standard of more than 4 times the social average wage income apply to?
Answer: These can apply to foreign talents whose average wage income is more than 4 times the social average wage income of last year in the region. After the professional qualifications or skill certificates are notarized or certified for relevant positions, the application shall be processed according to the standards for foreign professional talents (Category B).
18. Do offshore oil operators, artists engaged in commercial performances and foreign staff of consulates in Shanghai who are not required to process the Permit for Foreign Employees have to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit ?
Answer: No, they do not need to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit according to relevant provisions.
19. Does the foreigner who has obtained a Foreigner’s Permanent Residence Permit in China have to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit ?
Answer: According to relevant provisions, foreigners who have obtained the “green card of China” are not required to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit .
20. Does the foreigner studying in China who has obtained a Residence Permit (B) have to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit ?
Answer: According to relevant provisions, foreigners studying in China who have obtained the Residence Permit (B) are not required to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit .
21. Do the enterprise investor and legal representative have to process the Foreigner’s Work Permit ? How can they process the work permit?
Answer: (1) Subject to relevant regulations, if a foreigner who makes investment in China and the legal representative of the enterprise in China do not directly participate in the operation management of the enterprise, they may not process the formalities of working in China.
(2)If the legal representative of the enterprise directly participates in the operation management of the enterprise and relevant requirements are met, the age limit can be relaxed and a contract is required.
(3) If the educational background, working experience or age of the enterprise investor fails to meet the requirements, and the application is made for the first time, the application may be made per Category B Personnel, and the work permit with a 1-year valid term is given. In the application for work permit extension, the actual operation condition of the company shall be checked. If Category A Standards are met, the permit with more than 1-year valid term may be granted; if Category B Standards are met, the work permit with 1-year valid term may be granted.
22. Can the applicant apply for the work permit if he is over 60 years old?
Answer: if he is a Category A person, investor or legal entity, there is no age restriction. In other cases, the applicant who is over 60 years old will not be accepted generally; if he is over 60 years old, the system for scoring points shall apply, and the applicant who has gained 60 or more points may apply for the work permit, provided that he is not over 65 years old.
23. Except that a foreigner is directly employed by an employer, can a foreigner be dispatched overseas to work in China?
Answer: According to relevant provisions, foreigners dispatched overseas to work in China shall obtain the Foreigner’s Work Permit . If the case is covered by the Procedures for Foreigners Finishing Short-term Assignments in China (Trial Implementation) or the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of Procedures for Foreign Talents Coming to China for Short Time, relevant procedures shall apply.
24. Can the employer accept the dispatched foreigners?
Answer: No. According to relevant provisions, employers are not allowed to accept the foreigners dispatched overseas to work in China.
25. Does a foreigner sent to work in China need to sign employment contracts with the employer?
Answer: According to relevant provisions, if the foreigner sent to work in China has a labor contract with the overseas employer and the labor remuneration comes from overseas, the foreigner is not required to sign a labor contract with the domestic employer and relevant certificates for sending the foreigner to work in China shall be issued by the overseas employer.
26. Can I gain points for overseas salary income?
Answer: If you are mainly working in China, relevant taxes of China shall be imposed on your overseas salary income, so you can gain points for legal income from overseas salary.
27. For a Category B applicant, in which cases may the crime-free record certificate be waived?
Answer: (1) In principle, if the work-type residence permit is valid, the crime-free record certificate may be waived.
(2)Where a foreigner changes the employer, the entry-exit administrative body of the public security organ cancels the work-type residence permit and issues a stay visa, if the foreigner does not leave China, for one month after the work-type residence permit is canceled, the crime-free record certificate may be waived.
28. If the employment position on the original employment certificate and foreign expert certificate are the same as the current employment position, can the original foreign certificate and employment certificate replace the work qualification certificate?
Answer: Yes.
29. Can the original employer’s contract replace work qualification certificate?
Answer: No.
30. Can the certified work experience be part-time or internship experience?
Answer: No, it cannot be part-time or internship experience, and it must be full-time work experience. If you have both study and work experience in the same period of time, the work qualification certificate issued by the unit must indicate whether you work full-time.
31. With respect to the years of work in the new scoring table, does the years of relevant work experience count only?
Answer: No, all work experience counts.
32. If a Chinese person obtains a foreign nationality or a foreign student studies in China, and his or her highest educational certificate is granted by a domestic institution, does he or she still need certification?
33. If my degree certificate (diploma) is lost, what should I do?
Answer: If the degree certificate (diploma) is lost, please apply for the degree certificate (diploma) with your academic institution again. We will accept the certificate which has been certified.
34. If a foreigner has obtained relevant educational certification materials issued by the Ministry of Education of China, is there any other educational certification material to be submitted?
35. When an applicant who has been granted the Foreigner’s Work Permit files an application again, is it necessary to submit the highest degree certificate (diploma) again?
Answer: If relevant materials have been uploaded to the “Service System for Foreigners Working in China (V 2.0)”, it is not necessary to submit the highest degree certificate (diploma) and certification materials again.
36. In which cases may the educational certificates be waived or their submission be extended?
Answer: (1) For the Foreign High-end Talents (Category A) defined in the Classification Standard for Foreigners Working in China, (I) who are listed in a domestic talent plan; (II) who meet the internationally recognized professional achievement affirmation standard; (III) who are foreign talents meeting the market-oriented encouragement post demands; (IV) who are innovation and start-up talents, the commitment system shall apply to the certification of the highest degree certificate (diploma) and certification materials, and it is not required to provide a letter of undertakings. By signing the Application Form, the applicant shall be deemed to have made relevant undertakings.
(2)In case of internal transfer in a domestic group, the highest degree certificate (diploma) can be waived.
(3) If a Category B foreigner with “ Permit for Foreign Employees ” or “ Foreign Expert Certificate ” changes the employer in China, the foreigner shall meet basic conditions for foreigners working in China and provide the highest degree certificate (diploma). However, the highest degree certificate or relevant approval certificates and letter of undertakings for certifying professional qualification certificates are acceptable. The original certifying materials shall be provided within three months after the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China is granted. The accepting window will check the original materials and retain a copy thereof.
37. What are the requirements for employers to employ foreign language teachers?
Answer: When an employer registers for employing foreigner teachers, the public institution employer shall submit the certificate issued for the public institution, and the private non-enterprise school shall submit the “private non-enterprise” certificate and the valid “school operation permit”. The training institution shall meet two conditions to employ foreign teachers: I. the subject which the foreign teacher is employed to teach shall be one of those listed in the business license; and II. The “special account for tuition and miscellaneous fees” shall be provided.
38. What are the conditions required for foreign language teachers?
Answer: The foreign language teachers shall teach their native languages, obtain the bachelor or above degree in the subject of their native languages, and have more than 2 years of language teaching experience. If a foreign teacher has obtained the bachelor or above degree in the subject of education, language or normal school, or the teacher qualification certificate issued by the country of the foreign teacher, or the required international language teaching certificate (for example, TEFL, TESOL and CELTA shall be certified by embassies and consulates or notarized by notary office), the work experience condition may be waived.
39. With respect to TESOL or TEFL, what are the specific requirements?
Answer: It must be in class, and the online course is not accepted. Each certificate shall be obtained with 120 hours of studying and shall be certified or notarized.
40. How to decide the valid period of the Foreigner’s Work Permit ?
Answer: The expiry time of the permit shall be determined according to the valid period of the contract or passport of the foreigner or the valid period of the business license or industry permit, whichever expires earlier.
41. Is there any requirement on the remaining valid period of the passport when an application is filed for the Application Notice?
Answer: The remaining valid period of the passport shall be not less than 6 months. (from the time when the application is submitted for the first time)
42. Which positions are subject to the pre-approval by the industry competent authority or which positions are qualified for relevant accessible occupations?
Answer: The positions include chief representatives and representatives of representative offices of foreign enterprises in Shanghai, presidents of foreign-invested banks, foreign doctors and foreign pilots.
43. How can a foreigner change his employer when he works in China?
Answer: If a foreigner changes his employer during the valid period of the work-type residence permit of the foreigner, the original employer shall de-register the former work permit, and a new application for the Foreigner’s Work Permit shall be submitted directly. (Where the foreigner with a Permit for Foreign Employee s or a Foreign Expert Certificate changes his employer during the valid period of the work-type residence permit of the foreigner, the Permit for Foreign Employee s or the Foreign Expert Certificate shall be de-registered first, and a new application for the Foreigner’s Work Permit shall be submitted).
44. Will the valid Permit for Foreign Employee s or Foreign Expert Certificate remain effective and valid?
Answer: The valid Foreign Expert Work Permit in China , Work License for Foreigners , Foreign Expert Certificate and Permit for Foreign Employees will remain effective and valid.
45. Where can the application for de-registration, annual inspection or information change of the Permit for Foreign Employees be accepted?
Answer: Municipal Talent Service Center (1/F, No. 77, Meiyuan Road), Business service outlets of Talent Service Centers of Changning District, Huangpu District, Xuhui District, Minhang District, Pudong New Area (2/F, Building 3, No. 1158, Zhangdong Road) and FTZ (No. 55, Feila Road).
46. How to extend the valid Foreign Expert Certificate and Permit for Foreign Employees ? Which materials are required?
Answer: Where the employer intends to employ the applicant at the original position, the application shall be submitted thirty days before the expiry of the valid period of the work permit of the applicant.
Procedures for handling the extension
①After registering an account online (Service System for Foreigners Working in China: http://fwp.safea.gov.cn ), the employer shall submit the information and upload all original documents online, then take the original Employer Registration Form and copies of all the employer’s documents (stamped with the official seal) for real-name registration examination at the acceptance site selected (employers having processed the real-name registration and has opened an account can skip this step);
②The employer shall enter the account - select the option “Extend the former Foreign Expert Certificate or the Permit for Foreign Employees ” from the left menu - enter the application page.
③The employer shall truthfully fill in the applicant’s basic information, education background, work experience, application information, etc., and upload the original documents required.
④After uploading all the original documents, the employer can submit them for preliminary review; upon approval, the employer shall take all the original paper documents uploaded (all non-Chinese documents must be translated into Chinese and affixed with the official seal of the employer) to the window for verification and reception.
⑤After the approval decision shall be adopted, the operator of the employer shall receive the Foreigner’s Work Permit at the acceptance point with his or her identity card.
(2) Required Materials
Materials required for extension: Application Form for the Foreigner’s Work Permit in China; employment contract or office-taking certificate (contracts, appointment letters and dispatch letters in Chinese); the passport and valid residence permit of the applicant; the valid Foreign Expert Certificate or the Permit for Foreign Employees ; front bareheaded picture of the applicant taken within 6 months; and other materials.
47. What are the scope of information change of the Foreigner’s Work Permit ?
Answer: The procedures for information change of the Work Permit for Foreigners Working in China shall apply to changes about the name, passport number, position and category of the foreigner. If the foreigner changes the position (occupation) or the nationality, the current work permit shall be de-registered, and the new application for the Work Permit for Foreigners Working in China shall be submitted.

Modal title

Visas and Work Permits — 6 min
Work permits and visas in China: an employer’s guide
China has become a global hub for innovation and advanced industrialization, attracting more skilled workers from emerging and developed economies. To keep up, China has stepped up immigration efforts to incentivize best-in-market workers to come, work, and live in China.
International employers who wish to hire and pay workers in China should keep a few key considerations in mind. For instance, the visa or work permit application process is decided on a province-by-province basis. China is shifting to a platform economy (app-based, like rideshares) where gig work, freelancing, contracting, and similar forms of work are hardly protected by law.
Compliance is something every employer should consider. Failing to comply with national or provincial labor laws and regulations can lead to hefty fines, legal issues, and in extreme cases, civil or criminal offenses. Many companies find it easy and simple to hire international employees by working with an employer of record (EOR). An EOR like Remot e can handle legal compliance and all the processes involved in global hiring, including onboarding, benefits, taxes, and payroll.
The importance of immigration compliance in China
Which workers need a right-to-work check in china, do noncitizens need a work visa or work permit in china, what are the long-stay visa types in china, how do you get a work visa for china, what is the process for employee work visa sponsorship in china, what are the visa requirements for digital nomads in china, how remote makes compliance in china so much easier.
This definitive guide will be your go-to reference for all you need to know about visa requirements and work permits in China. But before you get started, here are a few words on why correct right-to-work checks and entitlements in China are important.
The correct right-to-work checks are requirements or criteria — set by the government or an organization — to ensure remote work is performed according to a set of standards. There are no specific laws or regulations governing how remote work should operate in China, so employers may risk facing regulatory penalties and fines or even civil or criminal offenses.
Choosing to go around the current gig economy situation in China by, for example, working on a tourist visa is not an option. If anything, working in China on a tourist visa is illegal, even when digital nomads and other remote workers are common.
There are many gray areas in China's labor laws, particularly in independent contracting and remote work, which is why the work visa and permit application process can be tricky. Always check local employment laws and regulations before hiring and paying remote workers or contractors in China and beyond.
Get your Remote Relocation Guide
Learn how to simplify your planned relocation with this walkthrough guide. We outline the key steps for you and your employer to enable a compliant, efficient, and hassle-free move.

China has specific visa categories for individuals wishing to work in China.
Two visa categories are generally issued for work purposes:
Category R , which is for high-skilled professionals whose skills are urgently needed in China.
Category Z , which is a general visa category for any eligible applicant who wants to work in China
Applying to work in China can also be classified according to an applicant's status as follows:
Permanent resident. This class of job applicants is free to work in China without any restrictions unless otherwise noted in one or more provinces or cities.
Temporary residents. This class of applicants may fall under any of China's many visa categories (e.g., C, F, and M) but may still need to apply for a Category R or Z visa to work in China.
Work permit holders. These are largely Category Z visa holders who may wish to extend their stay in China and may do so after getting the necessary approvals and employment contract renewal.
A residence permit is almost always required before foreign applicants can apply for a work visa. However, residence permits in China are province or city-specific, which could render one province's permit invalid in another. To give you a sense of how residence permits work in China, here is a list of documents required for a "stay permit" (long residence) in Shanghai.
Over recent years, China has introduced more restrictions to ensure foreigners live and work legally in China. Unlike visa arrangements in the European Union, for example, China is buckling down to squash backdoor channels for hiring foreigners without getting proper visas (most commonly Category Z) and work permits.
What are the eligibility requirements for a work visa in China?
As noted, work visas in China fall broadly into two main categories: Category R and Category Z. The eligibility requirements for each are as follows:
Category R:
Foreigners of or above 18 years old
Foreigners working in industries needed in China
Category A visa holders who hold additional visas or valid residence permits
Category Z:
Depends on employer, profession, province, and experience.
Generally, the Category D visa is China's premier long-stay visa is for individuals who wish to live permanently in China. The Ministry of Public Security in China is indispensable in deciding to grant a foreigner permanent residency or for work purposes. Typically, an official application form is required from the ministry.
A work permit or visa in China is issued on a province-by-province basis. For example, foreigners who want to work in Beijing are subject to general requirements (for all who apply to work in China) but may need to meet additional requirements specific to Beijing only.
There is no nationwide employee work visa sponsorship program in China. Instead, China follows what is akin to an invitation-only process to attract high-skilled foreign workers in specific industries under Category R visas. Chinese employers may also invite employees under a Category Z visa.
Managing "sponsorship" in China is daunting enough to deter many employers and workers from the employment process altogether.
As an employer, you need to focus on your growth, which only a world-class workforce can achieve. But to attract best-in-market candidates, you must always comply with local labor and tax laws. This egg-and-chicken situation is all too common in China. Unless you have strong legal and financial resources and enough business (and sometimes political) clout, you're simply left behind.
Luckily, you can work with an employer of record to make the hiring process and relocation a breeze. Learn more about how you can use an EOR in China to hire compliantly by reading our insightful article below.

How to use an Employer of Record in China
China does not have (so far) a digital nomad visa service or program per se. Instead, similar to remote workers, digital nomads can apply for a Category R or Z visa and follow all the required steps mentioned above to get a valid work permit in China.
Trying to work as a tourist in China is illegal, as previously noted. China is strict about enforcement, and if caught, you're at risk of fines or a ban on your business activities, and team members are at risk of deportation or imprisonment.
China’s growth as a platform economy makes it an attractive hub for remote employees as well as digital nomads. However, employers face challenges while hiring in the country. From having to navigate unfamiliar labor practices to keeping up with local regulations — hiring abroad can be a tricky process.
With Remote’s EOR, you’ll get all the advice and guidance you need to hire and pay your remote workforce in China compliantly. From understanding international taxation and permanent establishment risk to staying in compliance with immigration and local labor laws, partnering with Remote can make it easy for you to hire abroad.
Download Remote’s Relocation Guide to learn more about how you can manage the employee relocation process. Or contact our Mobility team for guidance and advice on local immigration and employment laws.
Hire, pay, and manage relocation for your global team
Create an account with G2’s top-ranked multi-country payroll software and start onboarding your first employees in minutes.

Subscribe to receive the latest Remote blog posts and updates in your inbox.
You may also like

Global HR — 20 min
How to prevent and manage work from home burnout

Contractor Management — 4 min
Independent contractor taxes in Michigan: freelancer tax management guide

Contractor Management — 6 min
Independent contractor taxes in Florida: freelancer tax management guide

Global HR — 11 min
HR document management: What it is, examples, benefits, and more

- Join the Chamber
- MEMBER DIRECTORY
- Membership Benefits
- Community Events
- Presentation
- Publication
- About the Chamber
- Shanghai Chapter Team and Board of Directors
- Our Sponsors
- Internships in China
- work visa vs work residence permit understanding difference and guidelines
Work Visa vs. Work Residence Permit: Understanding the Difference and Guidelines
Author: Benelux Chamber Shanghai
By Jonathan Xu Director of Business Operations and Marketing
Failure to comply with regulations can result in deportation, permanently barring your return to China. In response to the concerns raised by our esteemed members, we are pleased to share our comprehensive insights on the application process for work visas in Mainland China.
Eligibility for Employment
Drawing upon my personal experience as a former business owner, I had the privilege of delving into the reality of work visa applications for my foreign partners and employees. It is important to note that the only legal means to earn a salary and engage in employment within Mainland China is through a work residence permit , as opposed to a work visa. It is vital to distinguish between these two documents: visas are issued by the embassies of the People's Republic of China (PRC) located outside of China and typically allow for single or double entry. Residence permits are exclusively granted by the Public Bureau of Safety (PSB) and can only be obtained based on a valid visa. Unlike visas, residence permits provide multiple entries and various additional advantages, such as the ability to open a bank account and apply for social security status. While visas typically cover stays shorter than 180 days, residence permits are applicable to durations exceeding 180 days (multiple entry). To legally work and receive a salary in China, both a work residence permit (converted from a 30-day Z-visa, which is a working visa issued by a PRC embassy to enter China) and a work permit are mandatory.

Work Visa (Z-visa)

Work Residence Permit

Work Permit
Q2 visas , granted based on family reunion-related matters, obtained from a PRC embassy abroad, can be converted into a family reunion residence permit s . Conversely, Z visas, issued for work-related purposes, obtained from a PRC embassy abroad, must be converted into a work-based residence permit within 30 days of arrival in China. Tourist visas, business visas, and others cannot be converted into residence permits and are intended solely for short-term visits.
How does one apply for the work permit, work visa and the work residence permit?
The process commences with the employer, who must possess an operational entity within Mainland China. The entity should not be blacklisted and must demonstrate a valid justification for hiring a foreign employee. Given the current high unemployment rates among Chinese fresh graduates, which exceed 30%, it is vital to recognize the stringent regulations enforced by various authorities when applying for a work visa. In most cases, foreign candidates are supposed to hold a bachelor’s degree, must have a clean non-criminal record and must have at least 2 years of relevant working experience. Interesting note: the working experience does not count for graduates from Chinese universities.
Step 1 - The Employer
The employer's initial task is to register their company online with the Foreign Expert's Bureau, which, since 2021, has merged with the Government Service Platform of the Ministry of Science and Technology. Companies seeking to hire employees with foreign nationalities must complete the registration process, which typically takes 1 to 2 working days. The required information includes the legal representative's ID or passport, a scan of the business license, and details of an appointed contact person. To ensure accurate completion of this step, please follow the instructions provided in the following sections of the website: " 法人单位基本信息 " (Basic Information of Legal Entity), " 法人单位其他信息 " (Other Information of Legal Entity), and " 主代办人信息 " (Main Contact Person Information).
Once the registration process is approved, the designated contact person will receive a confirmation via text message, allowing them to proceed to the work permit application portal . It is crucial to note that this department operates separately from the PSB.
Step 2 - Work Permit Application
The work permit application is the most time-consuming yet vital step in the process. A work permit is a prerequisite for all foreign employees in China. Without a work permit, a work visa cannot be issued, and consequently, a work residence permit cannot be obtained. During the work permit application process, users must navigate the platform and follow the provided instructions.
The initial step entails determining the appropriate employee category: A, B, or C. These categories are mainly based on a point system. After reading the point system, we could conclude the following: c ategory A is typically designated for academics or high-level executives (CxO positions). Category B encompasses professionals in various fields, ranging from junior to senior positions. Category C is reserved for professionals engaged in labor-intensive industries, such as machine operators and heavy-industry workers. It is important to note that applications for Category C personnel are subject to more stringent scrutiny due to China's existing skilled labor force. Employment contracts generally have a minimum validity of one year. Throughout this article, we will focus on a one-year employment contract.
It is crucial to emphasize that, for the majority of job positions (approximately 90%), the minimum requirements consist of two crucial elements: a Bachelor's degree and a clear non-criminal record. These documents must also be legalized and translated by an authorized translation agency. The legalization process currently involves two steps: (i) legalization by the applicant's government, specifically the foreign affairs office, and (ii) legalization by the PRC embassy in the applicant's country. While the local apostille requirements may vary from country to country, the legalization performed by the PRC embassy always includes a green sticker. Scanned copies of these two documents must be uploaded to the system. Other necessary documents include :
Once the application successfully passes all inspection levels, the employer will receive a digital "NOTIFICATION LETTER OF FOREIGNER'S WORK PERMIT IN THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA." This document should be sent by the employer to the employee, granting them the right to apply for a Z-visa (30-day work visa) at a PRC embassy abroad. Applicants are advised to print the document in color and carry it during the work visa application.

Step 3 - Registration and Health Examination
All foreign visitors arriving in Mainland China who do not stay at a hotel are required to register at the local police station within 24 hours. Some cities offer online platforms to simplify this process. In Shanghai , foreign visitors can register by scanning the provided QR code. Failure to register may impede the conversion of a work visa into a residence permit.

Within the initial 30 days, foreign passport holders must also undergo a mandatory health examination if their intended stay in Mainland China exceeds 180 days. The health examination results, along with a scan of the entry stamp from Customs and the Z-visa, must be uploaded to the Work Permit system upon completion. After approximately four working days of further inspection, the work permit application can be considered finalized, and the employer must await further instructions from the Foreign Experts Bureau (FEB). The FEB will communicate a proposed date for the employer to visit their office. During this final step, the employer will need to bring the employee's original materials , as discussed in a previous step. No copies will be accepted.
Step 4 - Work Residence Permit
In the last step, the employer must accompany the employee to the Public Bureau of Safety (PSB), which handles all affairs related to the work residence permit. In certain Chinese cities, the employer may also need to obtain an additional certificate to issue the work residence permit. This certificate, known as the contact card ( 联系卡 ) , can only be granted after the local police station inspects the actual office. Acquiring this certificate may take up to 15 working days, so it is advisable to complete the process before the foreign employees' arrival in China, considering the initial 30-day stay limit.
In Shanghai, the contact card is not required. To conduct the final step at the PSB, the employer must bring the following documents:
Upon successful submission of all the aforementioned documents at the PSB, it generally takes up to 10 working days to receive the passport with the work residence permit, allowing multiple entries. If you have any questions or doubts, it is highly recommended to seek assistance from professionals. The Chamber is delighted to connect you with one of our Benelux members who can provide guidance.
Fortunately, the renewal process is much simpler and requires fewer documents. Remember to initiate the renewal process at least 30 days prior to the expiration of the work permit and work residence permit.
- How to Apply
- Application Requirements
- China Visa Fees
- Entries /Validity /Duration
- 10-year China Visa
- Tourist (L)
- Business (M)
- Student (X)
- Transit (G)
- Private Visit (S)
- Family Reunion (Q)
- Noncommercial Visit (F)
- Crew/ Resident/ Journalist
- 24-Hour Visa-Free Transit
- 72-Hour Visa-Free Transit
- 144-Hour Visa-Free Transit
- Hong Kong Visa Policy
- Macau Visa Policy
- Chinese Residence Permit
China Work Visa (Z)
Chinese work visa, or Z visa, is issued to foreigners who are going to China for a paid job offer or to undertake commercial entertainment performances in China.
How long is the duration of stay of Chinese Z visa?
This Z visa itself only allows a stay duration of 30 days from the date of arrival in China, during which time you and your employer must seek a Temporary Residence Permit for the duration of your contract, to a minimum of 90 days and a maximum of 5 years. Note that usually the work visa is a single entry, with the duration of stay being 000, which means the duration is to be determined by the Temporary Residence Permit you get after entering China.
What is the age limit for Z visa application?
The age limit is 18 - 60 for all applicants. However, there is some flexibility in these requirements, so if you are not in this age range and can find a willing employer, they may still be able to obtain approval for you.
China Work Visa Requirements & Documents
1. passport.
- Applicant's valid actual passport with at least six months before expiry and at least one blank page left in it.
2. Application Form
- One accurately and truthfully completed China Visa Application Form.
3. Recent Photo
- One recent passport standard photo affixed to the Application Form.

4. Work Permit
- Applicants need to submit one of the following work permits obtained through their employers in China: a. Foreigners Work Permit - issued by the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of the PRC. b. Registration Certificate of Resident Representative Offices of enterprises of foreign countries (regions) - issued by Chinese authorities of industrial and commercial administration. c. An approval document for commercial performances - issued by the Chinese government authorities for cultural affairs. d. Invitation Letter to Foreigners for Offshore Petroleum Operations - issued by National Offshore Oil Corporation.
5. Supporting Documents
Applicants might be required to submit supporting documents on a case-by-case basis. This could include a medical form and criminal history check, which has been notarized and authenticated. If you are not required to submit the medical form, you still need to take a medical check when applying for the Temporary Residence Permit in China. Download Physical Examination Record for Foreigner to check the tests you need to go through.
How to Apply for China Work Visa
You can go to the Chinese embassy, consulates, Chinese Visa Application Centers (CVASC) or other diplomatic missions in person for application. It's compulsory to make an appointment before going in most cases. Mailed applications are generally not acceptable.
China Employment Visa Fees
The fee is the same as the fee for other types of Chinese visa. Generally speaking, Chinese embassy or consulate only issue single entry Z visa to aliens, thus we only list single entry Z visa fees for some major countries here. For more details, please click China Visa Fees .
Processing Time
It usually takes 4 working days for processing. For example, you submit application on Monday and then you can pick up your visa on Thursday. An additional US$ 30 is charged for one working day processing, and US$ 20 for 2-3 working day processing.
Which visa applies to accompanying family members of Z visa applicants?
Accompanying family members should apply for an S visa by submitting invitation letter from the relative with work Z visa in China and a 'proof of relationship', i.e. their marriage certificate for a spouse, or birth certificate for a child.
Can foreign domestic helpers work legally in mainland China?
Foreign domestic helpers are not able to work in China, indicating that almost all domestic helpers currently working in China are illegal. Some agencies help them to apply for multiple entry tourist L visa or noncommercial visit F visa and then they use it to enter and exit regularly. Despite this, do not take a risk by working as a domestic helper or employing one to avoid being fined. Note: The most common employment in China for foreigners is teaching English for which the minimum qualifications are stated as having English as a first language and having at least a Bachelors degree and two year teaching experience.
Further Reading:
8 Tips for Filling Out Chinese Visa Application Form Top 8 Reasons Why Your China Visa Gets Rejected
Work Visa (Z) for China – The Complete Guide

Without a doubt, one of the motives that bring people to China is work. Today, the People’s Republic of China is a solid reality that isn’t as far off and exotic as our parents would have thought; it is present in many levels of our lives, and we know quite well that for some time it has already held the role of a superpower on a worldwide scale, whose growth seems to refuse to slow down.
For these reasons, moving to China for work is no longer an unusual step and the country continues to attract a growing international work force.
One of the most common jobs in China, at least for foreigners, is that of a foreign language teacher (English is first, but there’s also French, Spanish, and Italian) in universities, public or private schools and in language centers.
Besides teachers, growing numbers of interpreters are needed in the world of Chinese jobs, as are translators , entrepreneurs, etc.
In this article I will show you how to arrive in China with a type Z work visa .
In particular, we’ll look at the specifics of this type of visa, which documents you’ll need in order to apply for one, what are the conditions and prerequisites, where you can get one, what a Working Permit is, what you’ll need to apply for a residence permit when you get to China and what you need to do if you want to change jobs.
Chinese work visa – Index
What is a type z chinese work visa, where can i apply for a type z chinese work visa, what are the preliminary conditions for obtaining a type z chinese work visa, what documents are needed for a type z chinese work visa.
- How many and what are the classes for a “Foreigner’s Working Permit”
How much does a type Z Chinese work visa cost
How long does a type z chinese work visa last, how to read a type z chinese work visa, what to do after arriving in china, what to do if you want to change jobs while in china.
A type Z Chinese work visa is a category of visa designed for those looking to work in China, specifically as a “Foreign Expert Working in China”, “For Commercial Performance”, “Chief Representative or Representative of a Foreign Company”, “Offshore Oil Operations”, “Volunteering” (more than 90 days) and “Foreigner Working in China with a Work Permit Issued by the Chinese Government”.
As a result, a type Z visa is the only way to legally work in China.
Please note : in case you find yourself in China with a different type of visa than a work visa and want to work part-time (to supplement your scholarship, for example as a student with an X visa ), remember that it’s illegal.
Many companies, in fact, aren’t authorized to request a work visa for foreigners and will try to convince you that there’s no problem working with a different type of visa (in this case the most common is the student X visa).
If the authorities should discover that you don’t have a Z visa you risk a fine anywhere between 5,000 to 20,000 CNY (from more than 600 USD to more than about 2,500) and from five to fifteen days in a Chinese jail.
After this you’ll be “invited” to leave the country, or, depending on the specific conditions, deported to your country (at your own expense!). If this should happen, you’ll be prohibited to reenter China for a period of time ranging from one to ten years depending on the seriousness of your situation.
Nevertheless, the sneaky company also runs some risks: for every employee under their responsibility that works illegally, they’ll receive a fine of 10.000 CNY (a little more than 1,400 USD).
There are a few reasons that would move a company to illegally hire foreigners: the procedure that they have to follow to properly hire someone are many and at times complex, so much so that the bosses don’t know them; if they legally hire a foreigner, they are obligated to pay taxes, your insurance, etc; some simply just aren’t allowed to hire foreigners.
So think twice before accepting certain “job” offers.
Note that unlike the initial draft regulating a new work visa, there is no subdivision into a Z1 visa (for work periods more than 180 days) and Z2 visa (for work periods less than 180 days) as is the case for student visas. There is, in fact, just one work visa: the Z visa .
Lastly, there are age limits for those applying for a type Z Chinese work visa: a minimum of 18 years old and a maximum of 60 years. Nevertheless, if you surpass the maximum age limit but find an employer in China who wants to hire you, they may be able to get you a work permit and give you a chance. Age is just a number!
The type Z Chinese work visa can be applied for in one of the Chinese visa issuing centers in your country, either the embassy, consulate or the CVASC (China Visa Application Service Center) .
Pay attention : starting from April 10, 2019, these visa centers have inaugurated a new online application service and from May 10, 2019 they no longer accept handwritten visa applications; they will only accept forms filled out through the online platforms that you’ll find on their respective internet sites.
If you can’t apply for a visa in person, this procedure can also be handled by someone you know, so long as the proper section of the form is filled out.
If for some reason you don’t want to, or can’t personally go to the closest CVASC, embassy or consulate (and you don’t have anyone you can delegate it to), you can use an agency (which will obviously occur an additional cost). In this case, you’ll have to send your passport (and other necessary documents) to the agency and they’ll handle everything.
For a work visa though, I recommend that you do everything to go in person, given that it’s a more complex procedure compared to a tourist or student visa which you can more easily delegate to an agency.
According to Chinese law, you can only apply for a work visa in your home country. However, according to recent rumors, it would seem that you can also get a work visa in Hong Kong (so long as you have an Invitation Letter that clearly specifies that you intend to apply for a visa in that city).
In this case, there are two ways to apply for a visa:
- Apply at the CVASC (China Visa Application Service Center) in Hong Kong;
- Apply for a visa through a visa agency in Hong Kong.
In both cases, prepare all your necessary documents in advance.
In any event, I recommend that you apply for your Chinese work visa (of any type) within 90 days of the date of your proposed arrival in China.
The best time to do it is 30 to 60 days before your departure, so not before 90 days since the visa expires after 90 days (or in some cases, 180).
Before starting any procedure for getting a type Z Chinese work visa you have to be able to satisfy certain preliminary requirements.
First of all , obviously you have to find a Chinese employer who wants to hire you, and has the authorization to apply for a foreigner’s work permit.
If the employer doesn’t have such authorization, I recommend that you do not accept a “job”, otherwise you run the risks I mentioned in the first part of this article. Read it again!
Second , you must be an adult and in good health.
Third , you cannot have any type of criminal record.
Fourth , you must have a valid passport.
Fifth , you must have adequate professional ability in the field you are seeking a visa for.
There are many documents you’ll need to get a type Z Chinese work visa, so take good notes so that you don’t forget anything.
In this paragraph I’ll list all the documents that you need to prepare before leaving for China , which are different than the one’s you’ll need once you get there, which I’ll list later on.
Before leaving for China, you’ll need to prepare certain documents to present to the visa office or embassy/consulate closest to you. Before you go there, you should have ready:
- 1. Passport : the original, valid for more than 6 months with empty pages for the visa;
- 2. Copy of your passport : the first page with your information and photo;
- 3. Copy of your visa application : completely filled out, printed (you can fill it out online at the visa center’s site) and signed;
- 4. Passport photo : a recent, color passport photo sized 48mmx33mm, recente, showing a frontal view of your entire face, with a white background;
- 5. Privacy form : printed (you can download it on the visa center’s site), filled out and signed;
- 6. Self-declaration of countries you’ve visited : printed (you can download it on the visa center’s site), filled out and signed;
7. Work permit or other documentation : the majority of times this is a “Foreigner’s Working Permit” issued by Human Resources and Chinese Social Security (the original and a photocopy); otherwise it might be a:
a. “Foreign Expert Working in China” (the original and a photocopy) issued by the National Department for Foreign Experts, if you apply for a work visa as an expert, researcher, staff manager and nationally or locally organized staff
b. “Invitation letter for Foreigners that Run Offshore Activity in China” (the original and a photocopy) issued by the China National Offshore Oil Corporation if you’re looking to come to China for offshore activity
c. “Chinese certificate (regional) of registration of an representative office of a foreign company” (the original and a photocopy) issued by the administrative department for businesses and industry in the event that you are a representative of foreign offices in China
d. “Letter of approval” issued by the National or Regional Department for Chinese Culture (the original and a photocopy) or “Short term work permit” (the original and a photocopy) or Foreigner’s Work Permit (the original and a photocopy) if you’re in China for a commercial show
e. “Verbal Note” or “Official Act” (the original and a photocopy) issued by the firms of the boards of the foreign government and an “Invitation letter” (the original and a photocopy) issued by the International Section of the Chinese National Tourism Board if you belong to the foreign staff residing in China of the National or Regional Tourism Board;
- 8. Invitation letter : (if required) Consular functionaries could ask for an original format invitation letter, otherwise it could be sent as a fax, photocopy or print out;
9. Information about the family members that will accompany you : this type of visa can also be extended to your family for the entire length of the job (by family it means: spouses, parents, children, grandparents and in-laws). In this case, the family members have to apply for a S1 visa (a visa equal to or more than 180 days) or S2 visa (a visa for less than 180 days) specifically designed for families of foreign residents in China.
If you apply for a S1 visa at the same time as the relative applying for a type Z work visa (or X1 for students), you need to apply at the same time, provide a photocopy of the necessary material for a type Z (or X1) and an original and photocopy of a certificate legally documenting your relationship (marriage certificate, birth certificate, certificate of family relationship). If the S visa application is not applied for at the same time as the relative applying for the Z visa, you should follow the normal procedure for S visas.
Remember that the Consulate could ask you for additional supporting documents or call you in for an interview if they deem it necessary. In each case, the issuing or refusal of a visa (as well as validity, number of entrances and length of stay) is decided by the Consulate on the basis of the applicant, namely you.
Note that starting from November 1, 2019, you’ll be obligated to provide fingerprints at most of the visa centers at the time of applying for your Chinese visa.
What is a “Foreigner’s Working Permit”
As you have seen with the list of documents you need to have ready when applying for a type Z work visa before leaving for China, you absolutely need a work permit, better known as a “Foreigner’s Working Permit”.
When you decide to go work in China (unless it’s a particular job for which you have to provide other types of documents other than I’ve already mentioned for a “Foreigner’s Working Permit”) this is the most frequently required document.
Take note that this is a document (Notification Letter of Foreigner’s Work Permit in the People’s Republic of China) that you need to have before applying for a work visa, since it is one of the required documents for one to be issued and must be requested by your future boss in China (in fact it is issued by Human Resources of the Social Security of the People’s Republic of China).
Since the only document you’ll be sent will be a notice of work permit , when you arrive in China you’ll have to pick up the actual document. I’ll explain that more shortly.
In order for your employer to request a “Foreigner’s Working Permit” from the authorities, you’ll have to send the following documents:
- 1. Copy of your passport : the first page with all your information and photo;
- 2. Medical report : issued by an authorized clinic (if not provided in advance by your employer, ask them which exams are specifically needed or inquire of the Chinese consular officials in your country);
- 3. Passport photo : passport format;
- 4. Reference letter : serves to certify your number of years of experience in the field of your future job in China;
- 5. Certificate attesting to the absence of a criminal record : it must be valid for at least 6 months and be validated by a Chinese embassy or consulate;
- 6. School diploma or higher : validated by a Chinese embassy or consulate;
- 7. CV : if required. It should contain your email address, telephone number, address, schooling and work experience, preferably in English and Chinese.
Note that the majority of these documents should be authenticated by the respective authorities and validated by the Consular officers where you apply.
If you’re applying for a visa in a teaching position, you should also send a TEFL Certificate (Teaching English as a Foreign Language) or TESOL (Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages), validated at a Chinese embassy or consulate.
Keep in mind that your future employer might ask for further supporting documentation before issuing a work permit.
Once you’ve obtained these documents, the future employer can forward their request for the issue of a “Foreigner’s Working Permit” with the local authorities, sending: the company’s valid license and its relative codes, registration form, the employer’s, or the responsible person’s information and a copy of the work contract.
Note that the documents they ask you for can vary from those I listed depending on your specific situation. In each case you’ll be informed of the documents to send directly from your employer, because they’re the ones to request the work permit in enough time for you to request your type Z work visa.
Since the Chinese authorities are looking to attract highly qualified foreign workers, before issuing the work permit they will assign you a grade and classification attesting to your level of experience.
The classification system for foreigner’s work permits is rather complex, and since April 1, 2017 it is divided into three classes: class-A, class-B and class-C.
There is no limit on how many class-A work visas can be offered by the Chinese authorities, while there are restrictions for class-B and class-C.
How many and what are the classes for a “Foreigner’s Working Permit””
As was just specified, there are three “classes” of workers that can stay in China, divided into:
- Class-A (Elite foreign talent);
- Class-B (Professional foreign staff, the most common);
- Class-C (Foreigners who do not have technical ability or who are hired short term or seasonally).
The classification of the category you belong in is based on: salary, education, knowledge of the Chinese language, work experience, etc. The objective of the Chinese government is to encourage class-A foreign workers, control class-B foreign staff and limit class-C workers.
There are also two methods of classification for foreign employees:
1. They satisfy certain criteria to be directly qualified for a specific category; 2. They reach a sufficient point based on predefined criteria.
In the first case, class-A workers are those who meet the following criteria:
- They are the recipient of an internationally recognized prize or have been hired by an important organization as either a Manager or High Level Expert;
- Chosen by the Chinese Plan for Talent;
- They have demonstrated innovative business ability;
- They have been chosen for a job encouraged by the government;
- Chosen by the Project for Young Talent;
- They earn more than 600,000 CNY annually (a little more than 85,000 USD);
- They earned grades equal to or more than 85.
This is a more privileged class of worker than class-B or class-C, and for this reason, the procedure for issuing this type of permit will be quicker and less binding.
In fact, class A talent will have at their disposal a “Green Channel” for their documentation and will receive a work permit in 5 business days instead of 10 for the other two classes of workers. This category makes up about 17% of the total foreign workers in China.
Workers in the class-B category are those who meet the following criteria:
- Have a Bachelor’s degree or greater and at least two years of post-graduation experience in the field in which they are requesting a work permit;
- Belong to a “Technology Worker” category with experience (possessing an internationally accepted certificate indicating technical ability)
- For foreign language teachers, they must have a Bachelor’s degree or greater and no less than two years experience teaching the language (if your diploma is in the education, linguistic or teaching field, or you have a recognized TEFL/TESOL, the two years experience teaching is not necessary) as well as a TEFL or TESOL certificate;
- You have a salary equal to or more than 26,100 CNY a month (a little more than 3,500 USD);
- You have grade between 60 and 85.
This is a less privileged class of worker than class-A, and for this reason the issuing process will be slower. Despite this, this is the class of foreign workers that is most frequently granted work permits in China (in fact, it covers about 61% of the total number of foreign workers in China).
Those considered as class-C workers meet the following criteria:
- They are assistants of class-A employees;
- They have an internship in China thanks to a governmental agreement;
- They work short term (generally less than 90 days);
- They get a grade less than 60.
This is the most limited and restricted class of worker (though it does make up about 22% of the total number of foreign workers in China), since the Chinese government tends to attract higher levels of talent. For this reason, if you belong to this class it means you’ll work in China for a short period of time.
As I explained at the beginning of this section, a second method to be placed into a particular class is by getting a specific grade based on predefined criteria.
Class-A foreign workers will have a grade equal to or greater than 85, class-B foreign workers will have a grade between 60 and 85 and class-C workers will have a grade less than 60 according to the table you find in this article .
The notification of the “Foreigner’s Working Permit” will contain: your information, the name of the company that approved the issuance of the work permit, the class to which you belong, the work permit number, the name of your employer, the address of the place of work, the length of the job, the date the work permit was issued, the number of family members that will accompany you (with their names and surnames) and the period of the permit’s validity (this certificate is usually issued in two copies, one English and one Chinese).
When everything is ready and you’ve been evaluated, your future employer will send you a notification of your “Foreigner’s Working Permit” and you can then go to the visa center (along with all the other required documents) to start the necessary procedure to be issued your type Z work visa for China.
Remember : completing all these steps could take a few weeks if not months. In fact you’ll often have to go to different offices based on hours of operation and wait times, so I recommend that you start the process well in advance, keeping in mind that it will take a lot of time and much patience.
The cost of the Chinese visa will depenend on the place you apply and/or your nationality. If you apply for a type Z Chinese work visa in US, the Embassy or Consulate fees are the following:
- Single entry (valid up to three months): 140 USD (30 USD if you aren’t a US national);
- Double entry (valid from three to six months): 140 USD (45 USD if you aren’t a US national);
- Multiple entry (valid for six months): 140 USD (60 USD if you aren’t a US national);
- Multiple entry (valid for twelve months): 140 USD (90 USD if you aren’t a US national);
- Express visa supplement: 25 USD.
As was mentioned before, if you don’t apply for the visa in person you can do so through a visa agency, in which case you’ll have to pay for sending the passport and documents via a courier.
A Chinese type Z work visa is good for 30 days and allows a single entry. Note that like D, J1, Q1, S1 and X1 visas, normally on the type Z the validity will say “000” which means that you have 30 days starting from your entry into China, to transform it into a Resident Permit with multiple entries, and generally is the length of a work contract.
In the event that you don’t apply for the permit, your visa will expire automatically after 30 days of entry and you’ll be forced to leave the country.
If you don’t change your Z visa into a “Resident Permit” within that time of expiry you’ll be fined 500 CNY (a little more than 70 USD) for each additional day up to a maximum of 10,000 CNY (a little more than 1,400 USD), after which other actions will be taken (you could even wind up detained in a Chinese prison from 5 to 15 days).
Obviously, when your work permit expires (or residence permit) you can easily renew and extend it directly with the local authorities (generally it’s a Public Security Bureau Entry and Exit Administration Office), on the condition that your employer prearranges everything you need and is inclined to extend your work period and work contract at their firm.
Don’t worry : if the company is interested in renewing your work contract it will do everything it can to handle all necessary procedures quickly and easily. In this case it will be the company itself to indicate what steps to take and which office to turn to.
- Category : type of visa (Z);
- Entries : number of entries allowed (01, 02 or M, this last one indicates multiple entries);
- Enter before : validity of the visa (XX-XX-XXXX);
- Duration of each stay : length of stay for each entry (XX days after entry. In the case of a Z visa, a type of visa that requires it to be changed into a Residence Permit, you’ll see the writing “000”);
- Issue date : date of issue (XX-XX-XXXX);
- Issued at : place of issue;
- Full name : name of the visa holder often listed in abbreviated form (the name Mr. Mario Rossi, for example, could be written as M. Rossi. In any event, the full name is always listed in the last two lines of the visa’s text, called the “reading code”);
- Birth date : date of birth of the visa holder (XX-XX-XXXX);
- Passport number : the visa holder’s passport number (XXXXXX).
At this point, you’ve turned in all the required documents and have received your Chinese type Z work visa issued by the Consular Officials in your country.
You get on the plane (if you’re fortunate, your future employer will be the one covering the cost of the flight) and arrive in China.
Attention! Receiving a type Z visa doesn’t mean that you’re now totally free and legal to work in China. You should still take other fundamental steps to settle in at your position in the country.
First of all you should provide your registration with the local police within 24 hours after your arrival. Second, within 30 days of your entry into China, you should: submit to your medical visits, collect the actual “Foreigner’s Working Permit” and request your “Resident Permit”. After that you’ll be free to work with complete peace of mind.
So, armed with lots of patience, follow the procedures I’ll list in the next few paragraphs one at a time.
Register with the local authorities
Before moving on to change your type Z visa into a “Resident Permit” you have to go to the closest police station (generally you’ll be told where ahead of time by your future employer) within 24 hours of your arrival in China to register with the local authorities.
If you’re going to stay in a hotel when you arrive in China, the hotel staff should be able to carry out this task on their own; if, though, you’ll be staying in the apartment where you plan to live for the entire length of your job, you should show up in person at the closest police station.
This registration doesn’t cost anything, and if you have a boss that’s prepared, you’ll be accompanied by a colleague that will help you register. The only documents that you need are the following:
- 1. Original passport ;
- 2. Lodging contract where you’ll live;
- 3. A copy of the homeowners document and their telephone number . In fact the agents at the police station could contact them to confirm that you’ll be living in their apartment and that there won’t be any attempt at a scam on your part.
Once you finish registering, you’ll receive a temporary registration form (this is a simple piece of paper that will be issued to you even if you’re first staying at a hotel). This document will be essential for getting your “Resident Permit”. Moreover, if you change your residence address during your stay in China, you’ll have to give timely notice at the closest police station.
Let’s move on to the next step: the medical exams.
What do you need to handle medical exams after arriving in China
At this point you have 30 days to apply for a “Resident Permit” but first you still have to take two other important steps: submit to medical exams and collect the “Foreigner’s Working Permit” (the one that you’ll be sent, as I already said, is just a notice of a work permit). Note that these two steps are fundamental for obtaining a “Resident Permit”.
Let’s start with the doctor visits.
To undergo this type of visit you’ll have to go to International Travel Healthcare Centers which, generally, are found in any large Chinese city.
In principle, these centers don’t accept medical reports in English or they don’t fully correspond with their requests; so if at the company where you work there’s a translator who’s able to translate your medical report into Chinese, you can submit the translated version so long as it fulfills all the center’s requirements when it comes to physical tests.
In the opposite case, you’ll have to submit to specific medical visits that generally can be done in one day and can be assisted by the company itself. For this reason you’ll have to prepare the following materials:
- 1. A passport style photo in passport format;
- 2. A medical report from your country (if needed);
- 3. 600 CNY (a little more than 85 euro) to 1000 CNY in cash (a little more than 140 USD): generally covered by your employer and reimbursed with receipt of payment or direct payment.
Standard medical exams generally include: hearing and vision exams, a measuring of weight and height, blood pressure, ECG, chest X-ray and blood exams to verify that you’re not afflicted with AIDS or other sexually transmittable diseases.
Remember that the night before your medical exams you should not drink alcohol or coffee, while in the morning you shouldn’t eat or drink anything. Such medical visits are very important because if you test positive for certain illnesses or don’t pass the tests you will be denied a “Resident Permit”. So be healthy!
I recommend that you take these exams as soon as possible, so that you can start the remaining procedure calmly and unrushed.
When you pass the medical exams, you’ll be given a medical report that you’ll need to get a “Resident Permit”. It may be that the report will be given to you within 4 business days or even the same day as the visit.
Pick up your “Foreigner’s Working Permit”
After registering at the local police station and taking the medical exams, the next step that you have to complete is to pick up the “Foreigner’s Working Permit”. As we’ve already said before, the work permit will be issued by the Human Resources and Social Security of the People’s Republic of China, to which you’ll have to turn in the following documents:
- 1. Passport , the original copy;
- 2. A photo in passport format;
- 3. The document that attests to your temporary resident permit with the local police station;
- 4. A medical report from the International Travel Healthcare Centers ;
- 5. Other documentation required by your employer.
5 to 10 business days are needed to obtain the necessary documents. In this case too, if you’re fortunate, you might be helped by a member of the company where you’ll work.
On the “Foreigner’s Working Permit” there will be: photo, first and last name, sex, nationality, date of issue, name of the authority that issued the permit, the work permit number, class (A, B or C) and a QR Code.
What is a “Resident Permit”
If you’ve come to this point, it means that you’ve managed to complete all the earlier steps and are ready for the final act. Now you have to get what is perhaps the most important document, the “Resident Permit” which will allow you to stay in China for your entire time of stay without a limited number of entries. You can therefore travel with complete ease in and out of China.
It is, in fact, a sticker that, like the type Z visa that was issued to you before your departure for China, will be applied to one of your passport pages, thereby completing the conversion of your visa into a resident permit. In effect, it grants you the legal right to live in China.
In principle, resident permits are valid for no less than 90 days and no more than 5 years (however there is the chance of renewing them depending on the specific situation).
What are the documents and procedures to get a “Resident Permit”
To get the coveted “Resident Permit” you have to go in person to the Exit-Entry Administration Bureau in the area in which you live with the following documents:
- 2. A document attesting to the registration of your temporary residence with the local police;
- 3. “Resident Permit” application duly filled out (It will be given to you directly onsite or provided by the agency);
- 4. Photo in passport format;
- 5. Work permit , the original;
- 6. Medical report (if required);
- 7. Other documentation required by your employer.
Note that the Exit-Entry Administration Bureau will handle your passport for the necessary time to issue a “Resident Permit” (because they have to apply the sticker on the passport), generally between 7 and 15 business days.
Don’t worry, you’ll be given a temporary document as a substitution for your passport with the same validity, so as not to leave you deprived of a valid identification document for the Chinese authorities.
When the document is ready, you’ll be given back your passport with the “Resident Permit” inside, which will also include: first and last name, date of birth, passport number, date of issue, date of validity, place of issue, purpose of the residency and specific notes.
From that moment on you can sigh a breath of relief because the process for working in China is complete!
You’ll be a legal resident in China, you can be at peace and travel how and when you want within national borders or elsewhere.
Remember that after arriving in China with a work visa, you can’t leave the country without getting a residence permit.
If you leave the country, even just for one day, your type Z work visa will no longer be valid and obviously you’ll have to start the whole procedure from the beginning.
During your work experience in China you might want to change your type of work or employer, and in such cases you’ll have to go through the work permit process. Since each “Foreigner’s Working Permit” is connected to only one employer, if you change them you’re forced to apply for a new permit.
If you’ve already found a new job offer, the steps you have to take to change jobs are the following:
- Annul the work permit you already have;
- Request a new permit from your new employer.
In each case I strongly recommend that you carefully read the work contract that you signed to see if there are obligations tied to the cessation of the work.
Annul the work permit you already have
First, your old employer will be the one who, through a system they have access to which can handle work permits for foreign employees, will have to annul your work permit (which will take between 6 and 10 business days). To do this, along with your old employer you’ll have to prepare the following documents:
- 1. “Application Form for Cancellation of Foreign’s Work Permit” (provided by the old employer) signed by you and your former employer with the company’s stamp;
- 2. A “cessation of work” document (provided by the old employer) signed by you and your former employer with the company’s stamp;
- 3. Work permit , the original copy and a photocopy.
At this point all these signed and stamped documents will be sent by your employer to the appropriate authorities who, if everything goes well, will annul your work permit.
I recommend that you maintain a good relationship with your old boss, since they will be the one to request the cancellation of the old work permit needed to get a new one and change your job.
Note that the work permit could be cancelled for three reasons: at the request of the worker, if expired and not renewed, if revoked by the Chinese authorities.
In the end, you’ll receive the so-called “Foreigner’s Work Permit Cancellation Certificate” , essential for effectively changing jobs. Without this document, in fact, the new employer won’t be able to begin the process for your new work permit.
Attention : this document will include the reason for the cancellation of the work permit. So keeping a good relationship with the old employer could be essential so that the negative impact of this certificate doesn’t influence your new employer.
Request a new permit from your new employer
Now it’s time to address your future employer.
In this case too make sure that they have all the proper papers to hire foreign workers!
First of all you have to understand how to classify the new occupation. So, you have two options:
- A new employer but the same occupation : for this you can stay in China during the application for the new work permit without needing to leave and re-enter the country, so long as your “Resident Permit” is valid for the length of the process;
- A new employer and a new occupation : in this case you’ll be forced to leave the country and re-enter with a new work visa. For reasons we already mentioned before, the Chinese government will verify if you’re qualified for the job desired. So if you change from the job of a teacher to a director of a company, you’ll obviously have to prove that you are qualified. If you change your work position you’ll once again have to undergo the classification into Class-A, Class-B or Class-C and start all over again. In case of any doubts, I recommend that you contact the appropriate authorities (for example, the Entry/Exit Bureau or the Labor Bureau) for further clarification.
If you’re part of the first case (better for you!) you should prepare the following documents and provide them to your new employer:
- 1. “Application form for Foreigner’s Work Permit” , provided by the new employer, signed and stamped;
- 2. New work contract , provided by the new employer, signed and stamped;
- 3. Copy of your passport . In particular, the page with your personal information and photo;
- 4. Copy of the page in your passport that has the “Resident Permit” ;
- 5. Two photos in passport format;
- 6. Foreigner’s Work Permit Cancellation Certificate that you got from the last employer.
Note that if you request a transfer of your work permit within a month of its expiration, you won’t be required to present all those annoying documents you had to present the first time (criminal record, diploma, certificate that attests to your previous experience in the field, medical report, etc.) because it’s still valid.
In the opposite case, you should provide them again, prolonging the wait for the new work permit. In any case the new firm might ask you to undergo further medical exams according to the company’s guidelines.
It may take a few weeks to carry out this procedure (so long as you don’t belong to the class-A of foreign workers which provides a “Green Channel” to speed up times); as I suggested before, get going well in advance so as stay in the remaining period of validity of your “Resident Permit”.
When the work permit is ready, you’ll have to pick it up with the Entry/Exit Bureau or Labor Bureau of the area, but generally it will be the new company to do it for you.
Once you get a new work permit, you’ll note that it will be pretty much identical to the last one, but if you scan the QR Code, you’ll notice that now the information about the employer will have changed.
In many cases you’ll have to also update the “Resident Permit”, tied to the work permit. So go to the Entry/Exit Bureau and hand in all the required documents (they’re the same ones you turned in the first time, which you can find in this article under the heading “What are the documents and procedures for getting a ‘Resident Permit’”) .
For all procedures, from the beginning (notifying your desire to your old employer) to the end (the eventual updating of the “Resident Permit” with new information), will take about a month. If the new job isn’t too different from the last one, it’s a rather simple procedure that you can do right in China without having to leave the country.
All that’s left is to wish you a good stay in China and, as the Chinese often say, zhao cai jin bao 招财进宝, or “May health and prosperity enter into your dwelling”.
Photo Credits: Photo by Rudy and Peter Skitterians on Pixabay
About The Author
Manuel Recchia
Related posts.

Moving to China with Family

What’s it like to work for a Chinese boss?

Is it possible to improve your relationship with your Chinese colleagues?
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Get 3 Months FREE with EXPRESS VPN
+ Best VPN For China + 30-Day Money-Back Guarantee + 24/7 Live China Customer Support + 3 Months Free on 12 Months Package
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Liechtenstein
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- North Macedonia
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Switzerland
- United Arab Emirates

Chinese Work Visa for Foreigners
Foreigners, especially those that intend to work in China, often face the question of which visa type to apply for. Since the Chinese Central Government implemented new visa regulations in September 2013, the complexities of the application process for work visas have increased even further. The different visa categories should, therefore, be examined in detail.
Since 2013, the Administrative Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Entry and Exit of Aliens (as of September 1 st ), as well as The Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Administration of Exit and Entry (as of July 1 st ) regulate the entry requirements for foreigners into China. There are now twelve different visa categories instead of the previous eight.
If overseas or domestic companies wish to hire foreign workers in China , the first organisational obstacle is to solve this visa issue . Therefore, particularly those visa categories , which are relevant for foreigners with the intention to work in China, are illustrated below (see Figure 1). At this point, the new M , R, and S Visa categories, as well as recent changes with regard to the work visa (Z Visa) are most important (read here an analysis of the work visa new point system ) .
Figure 1: Overview of Visa Types according to activity in China
As companies in China may employ foreigners with valid work visas only , the most reasonable long-term solution for sending staff from Europe to China is the Z Visa . F oreigners planning to work in China should enter the country only when holding a valid Z Visa. H owever, the application process for such a work visa is more complicated than, for example, that of a business visa (M Visa) .
Before the actual start of the application process for a Z Visa, the foreign applicant must meet certain requirements (seeFigure 2 ): The employment agreement must already have been signed when applying for a Z Visa and the applicant must prove the qualifications needed for the desired job in China. Furthermore, the minimum age of 18 years and good physical health are required and the applicant must present a clean criminal record to prove no previous charges.
In some cases, a personal interview with the respective visa authorities may be necessary . This may be the case, for example , if you apply for a Permanent Residence Permit in China ; if you need to verify personal information and the reason for your application; or if you have been previously denied the entry into or exit out of China. Therefore, we advise companies in China to factor in enough time for the visa application procedure of their employees .
Upon arrival of the employee in China, expats need to obtain an Alien Employment Permit and a work-related Residence Permit first. These permits represent yet another step through Chinese bureaucracy. Figure 3 provides an overview of the lengthy process to a successful start of work in China – including responsibilities and timelines for the respective steps.
Alien Employment License
The prospective employer in China must provide certain documents in advance . Before hiring foreign employees, companies initially need to apply to the Beijing Administration of Foreign Expert Affairs for permission . The required documents for the application for an Alien Employment License are the following ( see Figure 4 ): CVs of the foreigners to be employed , confirmation of the employment , explanation of the planned employment relationship , certificates that demonstrate the employees’ qualifications for the respective position the necessary medical certificates and the completed visa application form with a recent coloured passport photo . The processing time for this step is generally 15 working days.
2. Ministerial Invitation Letter
Besides the Employment License , the company must also provide an original copy and a photocopy of the ministerial Invitation Letter to the foreign employee . The Invitation Letter is issued in China within three working days by the Beijing Municipal Commission of Commerce .
3. Work Visa
With the Employment License and the Invitation Letter, the actual application for the work visa can begin. This takes place in the Visa Centre of the respective Chinese embassy or Chinese consulate. In Germany, this may be the China Visa Centre of the Chinese Consulate in Munich, the Chinese Consulate in Frankfurt, the Chinese Consulate in Hamburg or the Chinese Embassy in Berlin. The authorities estimate the processing time at 4 working days.
4. and 5. Physical Examination and Employment Permit
The next step is to obtain an Alien Employment Permit for the applicant in China within 15 days after entering China . Therefore, the employee has to submit the health check report in duplicate. In addition, a photocopy of the labour contract , a photocopy of the Business License of the company and one original copy and a photocopy of the Registration Form of Temporary Residence and of the valid passport are needed for the application of the Employment Permit . The processing time of the application for a work permit is 5 working days .
6. Residence Permit
Once the new employee has obtained his Employment Permit, the expat has to apply for a Residence Permit at the Beijing Municipal Public Security Bureau Exit-Entry Administration within 30 days after entering China. The necessary documents for this purpose are a valid passport and all documents relevant to the purpose of the application as well as a scan of fingerprints. The Public Security Bureau will issue the residence permit within 15 working days. The validity of a work-related Residence Permit lasts for one year. For legal representatives a residence permit for the duration of two years is also possible. Recently, Chinese authorities have also started to issue permits with a longer validity.
According to Chinese law, foreigners contributing greatly to China’s economic and social growth or those that meet other conditions can apply for a Permanent Residence Permit. The Chinese Ministry of Social Security must recognize this application.
After completion of these steps, the foreign worker may begin the legal employment in China. If you need help, please contact our office for support during your application procedure.
If you have further questions about work visa in China, please contact [email protected] or visit the website of ECOVIS Beijing .
Contact person

- Asia Briefing
- China Briefing
- ASEAN Briefing
- India Briefing
- Vietnam Briefing
- Silk Road Briefing
- Russia Briefing
- Middle East Briefing
2024 Guidelines for Foreigners to Live and Work in China
The updated 2024 guidelines for foreign businesspersons living and working in China, released by the country’s Ministry of Commerce, outline essential procedures and considerations covering accommodations, visas, work permits, and emergency protocols.
On January 25, 2024, China’s Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) released the latest version of the Guidelines for Foreign Businessmen to Live and Work in China (hereinafter referred to as the “guidelines”).
The document is divided into four main sections, labeled as:
- Things to pay attention to;
- Daily living services;
- Services for stay and living in China; and
- Social services.
Each segment serves a specific purpose, aiming to highlight key considerations for foreign businesspersons residing in China. These cover essential aspects, such as the registration protocols for temporary accommodation, the validity duration of visas, stay permits, and work licenses, as well as the processes for acquiring and utilizing communication cards, bank cards, mobile payment options, foreign currency exchanges, transportation means, accommodation facilities, and other vital services.
Furthermore, the guidelines elucidate the regulatory framework governing foreign businessperson’s responsibilities concerning social security premiums and individual income tax obligations.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the guidelines, delving into their significance and implications for foreign businesspersons in China.
Overview of the 2024 guidelines
Things to pay attention to, temporary accommodation registration.
Upon arrival in China, prompt registration for temporary accommodation is required .
If staying in a hotel, registration can be facilitated by the hotel staff upon presentation of a valid passport or international travel documents.
For other accommodations, within urban areas, registration must be completed within 24 hours at the local police station; within rural areas, it should be done within 72 hours.
Visa and residence permit
Vigilance regarding visa and residence permit validity is crucial:
- Within 30 days of entry, visa holders planning to work or reside in China must convert their visa to a residence permit.
- Extensions require application 7 days prior to the permit’s expiration, with requisite documentation submitted to the local public security bureau’s exit-entry administration department.
- Holders must notify the exit-entry administration department within 10 days of any passport or residence document changes.
Work permits
Compliance with work permit regulations stands as a cornerstone for foreign businesspersons seeking to establish themselves in China’s dynamic business landscape. According to the guidelines:
- Holders of a Z-visa must adhere to the specified stay period indicated on the visa.
- Those exceeding a 90-day stay must apply for a “Foreigner’s Work Permit” within 30 days of entry, obtainable from the local foreigner’s work management department.
- Renewal applications must be submitted 30 days before permit expiration.
Noteworthy considerations and emergencies
In addition to the core considerations for living and working in China, several other essential guidelines demand attention to ensure a smooth experience:
- Adherence to Chinese laws and regulations is mandatory across all spheres, including engagement on social media platforms.
- Compliance with regulations governing pet ownership, encompassing dogs and cats, is expected to uphold local norms and standards.
- Photography of military facilities is strictly prohibited to maintain national security and safeguard sensitive areas.
In the event of emergencies, immediate action is crucial:
- Dial 110 for personal or property-related harm.
- Dial 119 in the event of a fire emergency.
- Dial 120 for medical emergencies.
- Report a lost passport promptly to the local police station to mitigate potential complications.
Daily living services
In this section, the guidelines introduce crucial procedures for accessing essential services in China, as illustrated in the table below:
Foreign currency exchange to Chinese Yuan (RMB) cash
Individuals entering China from abroad may exchange Chinese Yuan (RMB) cash in relevant countries or regions beforehand and carry it upon entry. The maximum amount of RMB cash each person can carry upon entry and exit is RMB 20,000 (US$2,812.95)
Upon arrival, individuals can exchange foreign currency for RMB cash at commercial bank counters, foreign exchange institutions, or self-service exchange machines located at international airports, land border checkpoints, ports, and other entry points.
Alternatively, individuals can use ATMs with overseas bank cards to withdraw RMB cash.
Means of transportation and stays
Navigating transportation systems in a foreign country can be daunting, especially for newcomers. In this section, the guidelines outline the step-by-step processes for utilizing different transportation options in China, including trains, planes, subways, buses, ride-hailing services, and car rentals.
Foreign travelers can make hotel reservations online using the Ctrip International version Trip.com APP or by contacting hotels via phone. It’s important to note that some hotels may have limitations and might not be able to accommodate foreign guests, so it’s advisable to inquire in advance about their policies regarding foreign guests.
Upon check-in at the hotel, guests are required to provide valid identification such as a passport or a foreigner’s permanent residence permit at the front desk.
Payment methods at the hotel include cash (RMB), credit/debit cards, Alipay, and WeChat Pay. For card payments, it’s recommended to inquire in advance whether international bank cards like Mastercard or Visa are accepted . Some hotels also support payment methods such as Apple Pay and PayPal, but it’s best to inquire about these options before making a payment.
Services for stay and living in China
Extending visa validity.
Foreign nationals holding visas can extend their stay if their original purpose of entry remains unresolved or for other legitimate reasons, without changing the visa type. Required documents for visa extension include:
- Valid passport or international travel documents;
- Completed Foreigner Visa Application Form with one recent passport-sized color photo against a white background;
- Relevant proof documents related to the application reasons; and
- Other necessary procedures and proof documents.
For specific requirements regarding visa extension, visit the Foreigner Visa Extension, Issuance, Replacement Approval Service Guide on the National Immigration Administration website.
Applying for a residence permit
Foreign nationals in China for non-diplomatic or official purposes must apply for residence permits within the country. Application for issuance, extension, replacement, and re-issuance of residence permits should be made at local public security exit-entry administration departments. Applicants must personally handle relevant procedures at the public security exit-entry administration department. Individuals meeting specific criteria may authorize others to apply on their behalf.
Required documents for residence permit application include:
Social services
Applying for a work permit.
Foreigners applying for a work permit need the following documents:
- Complete the “Foreigner’s Work Permit Application Form”;
- Proof of work qualifications;
- Additional certification (for countries that have joined the “Cancellation of Authentication of Foreign Public Documents” convention) or the highest degree (academic qualification) certificate certified by the Chinese embassy or consulate abroad, or related approval documents, professional qualification certificate;
- Certificate of no criminal record;
- Medical certificate;
- Employment contract or appointment certificate (including inter-company dispatch letter);
- Applicant’s passport or international travel document;
- Recent front-facing, bareheaded photo of the applicant taken within the last 6 months;
- Relevant proof of accompanying family members; and
- Other relevant documents.
The application is submitted online by the employing unit, and foreign workers’ service windows in various regions handle the process.
Applying for social insurance
Foreigners working in China should participate in social insurance according to the “Social Insurance Law of the People’s Republic of China” and the “Interim Measures for Foreigners Employed in China to Participate in Social Insurance.”
The social insurance covers the following three categories of foreign individuals in China:
- Holders of a valid “Foreigner’s Work Permit” and foreign residence documents, as well as foreign permanent residence permit holders;
- Individuals who have signed labor contracts with Chinese employers and receive salaries from them, or those dispatched to work in China by foreign companies and receive salaries from Chinese employers; and
- Individuals within the employment age range (men under 60 years old, women under 55 years old).
Newly insured individuals working in China start paying contributions from the month of employment. The payment base and rate for insured foreigners are based on the standards for Chinese nationals.
According to information on the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security website , China has signed social security agreements with countries including:
- South Korea;
- Switzerland;
- the Netherlands;
- Serbia; and
- Luxembourg.
Nationals of countries with such agreements are exempt from paying certain insurance obligations according to the agreements. More information is available on the website of the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security.
Individual Income Tax (IIT)
I ndividual Income Tax is imposed on all individuals, including Chinese and foreign nationals, residing in or deriving income from China.
The comprehensive income is subject to three to 45 percent of progressive rates on the whole.
The employer is responsible for accurately calculating and withholding IIT on employment income, including but not limited to wages and salaries, bonuses, stock options, and allowances, before paying a net amount to its employee.
About the Chinese tax residence status:
- Resident status : Foreigners with a residence in China or who have resided in China for a cumulative total of 183 days in a tax year are considered Chinese tax residents.
- Non-resident status: Foreigners who do not have a residence in China or who have not resided in China for a cumulative total of 183 days in a tax year are considered non-residents.
Chinese tax residents must declare and settle their comprehensive income within the period from March 1st to June 30th of the following year.
Individuals meeting specific conditions may be exempt from the settlement, such as meeting exemption criteria, prepaid tax equals payable amount, or eligible for refund but not applying.
Taxpayers can handle tax affairs at local government service halls, tax service halls, or through the Personal Income Tax APP or the Individual Electronic Tax Bureau webpage.
Moreover, China has Double Taxation Avoidance (DTA) agreements covering 114 countries (regions). Eligible foreigners can independently determine whether they meet the conditions for enjoying treaty benefits and apply them during declarations. Tax withholding agents can make declarations on behalf of foreigners eligible for treaty benefits. Relevant documents should be kept for future reference.
For details on the agreements, please refer to the tax treaty section of the State Administration of Taxation website .
The guidelines provided by China’s MOFCOM serve as a crucial resource for foreign businesspersons navigating life and work in China.
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates . The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at [email protected] .
Dezan Shira & Associates also has offices in Vietnam , Indonesia , Singapore , United States , Germany , Italy , India , and Dubai (UAE). We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines , Malaysia , Thailand , Bangladesh .
- Previous Article German Chamber’s Business Confidence Survey 2023/24: Key Findings
- Next Article AmCham China Business Climate Survey 2024: Key Takeaways
Our free webinars are packed full of useful information for doing business in China.

DEZAN SHIRA & ASSOCIATES
Meet the firm behind our content. Visit their website to see how their services can help your business succeed.
Want the Latest Sent to Your Inbox?
Subscribing grants you this, plus free access to our articles and magazines.
Get free access to our subscriptions and publications
Subscribe to receive weekly China Briefing news updates, our latest doing business publications, and access to our Asia archives.

Your trusted source for China business, regulatory and economy news, since 1999.

Subscribe now to receive our weekly China Edition newsletter. Its free with no strings attached.
Not convinced? Click here to see our last week's issue.
Search our guides, media and news archives
Type keyword to begin searching...
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
What’s It Like Traveling to China These Days?
China has been rolling out new visa-free programs and promising to make travel easier for foreigners. But challenges remain.

By Vivian Wang
Reporting from Shanghai
By some measures, visiting China has never been easier.
China has been making a huge push to attract foreign tourists in recent months. It has rolled out a visa-free program for dozens of countries, with the list still growing. It has pledged to make it easier for visitors to pay for things, book hotels and get around.
The goal is to signal that China is open for business — and fun! — again, after three years of pandemic controls made it literally impossible for most foreigners to enter. The government is especially keen to attract visitors as it tries to rev up growth .
China also wants to show that it is still connected to the world, despite tensions with the West and the growing reach of its security apparatus at home.
In a sign of its eagerness, Beijing has offered the visa waivers to countries that have not done the same in return — a rare move for a government that usually insists on reciprocity.
But actually traveling to China can still be a major challenge. Here’s what to know:
What’s new?
China is unilaterally offering visa-free entry for 15 days to citizens from a slew of countries, mostly Western European ones like France, Germany and Spain. The program began in December and has continued to expand; Australia, New Zealand and Poland were included last month. It is set to run through 2025.
In addition, citizens of more than 50 countries, including the United States, are now eligible for visa-free transit. They can enter China for 72 or 144 hours, depending on their port of entry, if they are continuing on to other destinations.
Transit travelers must stay within certain areas. For example, people flying into Shanghai can only visit the city and the neighboring provinces of Jiangsu and Zhejiang.
China has also promised to reduce logistical headaches for foreigners. WeChat and AliPay — the so-called super apps that most Chinese use for every aspect of daily life, from digital payments to ride hailing to ordering at restaurants — can now be linked to international credit cards, not just Chinese ones. (Most businesses do not accept credit cards directly.) And in May, the government told hotels not to refuse foreign guests, which was once a common practice.
Why is China doing all this?
Simply put: It needs money.
As China’s economy slows, its consumers have been hesitant to spend, fanning fears of deflation. The government also wants to win back foreign investment, after many overseas companies were spooked by China’s long Covid lockdowns and tightening political environment. Visitors on the 15-day visa-free program are allowed not only to sight-see, but to conduct business.
Attracting more visitors would also help the government rebut accusations from the United States and other Western countries that China has become more hostile to foreigners.
Beijing last year revised its counterespionage law to broaden the definition of spying, and state propaganda has warned that seemingly harmless foreigners might be trying to undermine China’s national security. Still, the government insists that reports of xenophobia and rising nationalism are just spin, orchestrated by countries trying to stop China’s rise.
Are more visitors coming?
In the first half of this year, there were 14.6 million arrivals from overseas, according to Chinese statistics. Most of them were visa-free.
That’s 2.5 times as many as China had during the same period last year, but well below the 24 million in the first half of 2019, before the pandemic.
China’s efforts to smooth out visitors’ experiences have also had mixed results.
On a recent Friday in Shanghai, Luka Lefevre, 24, and Charlotte Collet, 21, were cramming as much sightseeing as possible into a 10-hour layover between Paris and Vietnam. They had visited Yu Garden, a temple complex, and were taking photos on East Nanjing Road, a major shopping street.
But they’d had trouble using their phones to pay for things, and had to resort to cash, they said. They were also surprised by the ubiquitous surveillance cameras.
“For us, it’s a little bit too much, because we don’t have this in France,” Ms. Collet said. “But we know that it’s for safety.”
“For 10 hours, it’s O.K.,” Mr. Lefevre added.
Even visitors who’d figured out the Chinese apps said it had taken a while.
Walking along the Bund, Shanghai’s historic waterfront area, Maeline Lachaud and Nadia Hofmann, both Swiss university students, said they had linked their credit cards to AliPay while traveling through Xi’an, Chongqing and now Shanghai. The convenience was “amazing,” they said.
But Ms. Lachaud, a first-time visitor, said she had relied heavily upon Ms. Hofmann, who is minoring in Chinese studies and had visited once before. She hadn’t realized that AliPay had to be used not only to pay, but also to order at restaurants, and that the in-app menus were in Chinese.
Many major tourist attractions across China, such as the Forbidden City in Beijing, also require advance reservations through platforms like WeChat that are largely in Chinese. (Because of the super apps’ ubiquity, many websites in China are poorly maintained.)
“China’s not for beginners,” Ms. Hofmann said.
Vivian Wang is a China correspondent based in Beijing, where she writes about how the country’s global rise and ambitions are shaping the daily lives of its people. More about Vivian Wang

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A guide for foreigners applying for a work permit in China, detailing the process for those planning to work 90 days or more.
With the reopening of the Chinese market in the post-pandemic era, we saw a growing trend of expatriates seeking to obtain visas to work and reside in China. A thorough understanding of getting a work permit and work visa is essential for any expat planning to work in China. This guide provides an up-to-date overview of the application process, eligibility criteria, and necessary documentation ...
You should apply for a Z visa after you secure a work offer from your school. If you try to convert from a tourist visa while in China (mainland), there's a higher chance of rejection. Hello, I'm not able to find any concrete info on this so I'm hoping the minds of reddit can help! I'm wrapping up my TEFL certification, but I….
Foreigners who, after entering China with ordinary visas, need to stay in China for non-diplomatic or unofficial purposes may, in accordance with relevant regulations, apply to exit-entry departments of public security organs for visa extension, change and reissuance.
A "business visa" is for people who want to declare they are visiting for business - as opposed to tourism - and is not related to seeking employment. Changing visa types in-country is generally impossible, and many people get into trouble with dishonest employers that say it is ok to enter on a tourist or business visa and get a work permit ...
China's new work permit system for foreigners was rolled out nationwide on April 1 this year, introducing a three-tier talent grading system for expatriates. Here, we present a work permit calculator which can help employers and expats research tier category before applying.
China's new work permit system for foreigners introduces a point-based three tiered ranking system. Click to find out more about the tiered system.
Estonia is known for its high rate of accepted work visa applications, making it the easiest country to obtain a work visa. On the other hand, it receives a relatively small number of requests compared to other countries. Therefore, Estonia might be your best choice for working abroad. Applying for a D visa is beneficial if you wish to work on ...
When changing jobs in China, your work permit must be transferred from your old employer to your new one. Learn how to transfer work permits in China here.
This is the same process, whether in China or elsewhere. Candidates are treated as new applicants who need to freshly apply through the usual channels. For those who are currently working in China and whose visas are still in date, the other option is to transfer your work permit so that it's valid for working with the new employer.
Answer: (1) Foreigners who stay overseas shall follow the work visa and entry flowchart: Permit notice - Work visa (Chinese embassies and consulates overseas) - Enter - Apply for the permit - Work-type residence permit (entry-exit) (2) Foreigners who stay in China: The foreigners who stay in China may apply for the work permit directly in China ...
When the Work Permit would be issued, applicants will then have to apply for a working-purpose Residence Permit (in tier-1 cities, it is possible to convert a Tourist Visa, a Business Visa and a ...
Find out everything you need to know about work permits and visas in China, including the types, requirements, and documents needed.
Foreigners who have obtained a work permit and want to work in China can apply for a China work visa. The age limit for applicants is 18 to 60 years old. In addition, the applicant must: Be in good health. Have a clear criminal record. Have a valid job offer in China. Have valid travel documents. Have relevant skills and experience for the ...
Conversely, Z visas, issued for work-related purposes, obtained from a PRC embassy abroad, must be converted into a work-based residence permit within 30 days of arrival in China. Tourist visas, business visas, and others cannot be converted into residence permits and are intended solely for short-term visits.
How long is the duration of stay of Chinese Z visa? This Z visa itself only allows a stay duration of 30 days from the date of arrival in China, during which time you and your employer must seek a Temporary Residence Permit for the duration of your contract, to a minimum of 90 days and a maximum of 5 years. Note that usually the work visa is a single entry, with the duration of stay being 000 ...
Lastly, there are age limits for those applying for a type Z Chinese work visa: a minimum of 18 years old and a maximum of 60 years. Nevertheless, if you surpass the maximum age limit but find an employer in China who wants to hire you, they may be able to get you a work permit and give you a chance.
Foreign businesses will often face several challenges in the process of acquiring China work visas and permits. Explore our strategic approach today.
Foreigners, especially those that intend to work in China, often face the question of which visa type to apply for. Since the Chinese Central Government implemented new visa regulations in September 2013, the complexities of the application process for work visas have increased even further. The different visa categories should, therefore, be examined in detail.
I know many teachers who converted from M visa to Z visa in China, especially post-covid. It shouldn't a problem provided you have your university degree notarized / authenticated, plus 2 years work experience or a teaching degree (or TEFL certificate). You have to convert from M to Z within a certain timeframe (30 to 90 days).
The 2024 guidelines for foreign businesspersons living and working in China, cover accommodation, visas, permits, and emergency protocols.
Many people have gone for the option to get an M visa and then convert to work permit within the first 30-40 days upon arrival to China over the last year. So yes, it is possible if your visa centre is only giving out M visas right now.
Is it possible for a Russian national to convert a Chinese visitor (L) visa to a work (Z) visa while in China? The visitor visa expires in February.
China has been rolling out new visa-free programs and promising to make travel easier for foreigners. But challenges remain.
A short-term work visa shows the benefits of immigration America's J1 visa programme shows how open borders can build cultural links