Specialisaties
- Juridische vertalingen
- Contract laten vertalen
- SEO-vertalingen
- Webshop vertalen
- Alle specialisaties
Meestgekozen talen
- 🇮🇹 Italiaans
- Contactformulier
- Direct bellen
- Direct mailen
- Gratis SEO-audit
- Chat met ons

Een vraag over vertalingen? Neem dan contact op met Jouke.
SEO - Diensten
- SEO uitbesteden
- SEO-tekstschrijver
- Alle SEO diensten
Content diensten
- Contentmarketing uitbesteden
- Webteksten laten schrijven
- Blogs laten schrijven
- Bloggen uitbesteden
- Alles over content
- Offerte aanvragen
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit.

Customer journey: uitleg en voorbeeld

Een customer journey is onmisbaar voor iedere onderneming. Iedere fatsoenlijke online marketingstrategie heeft een goed uitgedachte customer journey nodig.
Ik vertel je wat een customer journey precies is en waarom je er een moet ontwikkelen. Ten slotte geef ik voorbeelden van hoe je een customer journey in kaart brengt.
Dit zijn de belangrijkste feiten over de klantreis:
- Customer journey: klantreis vanaf behoefte tot aankoop
- Touchpoints: contactmomenten met bedrijf
- Belang: verbeteren van customer experience
- Buyer persona’s: profiel van ideale klant
- Fasen: bewustzijn, overweging, aankoop, service, loyaliteit
Een customer journey is de route die een klant aflegt voor het kopen van een product/dienst. Het verbetert de klantervaring, verhoogt conversies en creëert loyaliteit.
Definitie customer journey
Customer journey – in het Nederlands klantreis – is de route die een klant aflegt voordat hij of zij je product of dienst koopt. De klant staat hier centraal, niet jouw bedrijf.
In iedere customer journey vind je touchpoints: contactmomenten waarbij de klant in aanraking komt met jouw bedrijf. Voorbeelden van touchpoints zijn je socialmediaberichten, reviews van andere klanten, je klantenservice of je webshop.
Waarom ontwikkel je een customer journey?
Het doel van een customer-journey-model is het verbeteren van de customer experience . Hoe tevredener een potentiële klant is, hoe groter de kans dat hij of zij jouw product of dienst uiteindelijk afneemt.
Door de klantreis in kaart te brengen, maak je het perspectief van je klant inzichtelijk en overzichtelijk. Zo zie je waar zwakke plekken en sterke punten liggen.
Door je customer journey te verbeteren, verhoog je de kans op conversies en fans. Oftewel: je krijgt meer nieuwe klanten, en je houdt bestaande klanten beter vast.
Hoe maak je een customer journey model?
Belangrijk om te weten: er zijn talloze customer journey-modellen. Het welbekende AIDA-model is een eenvoudige weergave van een klantreis tot en met de aankoop. Het AIDA-model bestaat uit de stappen Attention, Desire, Interest en Action.
Het in kaart brengen van customer journeys heeft zich de laatste jaren flink ontwikkeld. Meestal gaat customer-journey-mapping nog verder dan de vier stappen van AIDA. De klantreis stopt niet na de aankoop.
Er zijn online klantreizen te vinden van wel 10 stappen. Maar de meeste customer journeys hebben 4 of 5 fasen.
Optimale customer journey met buyer persona’s
We zeggen het wel vaker: een buyer persona is belangrijk voor een goede contentmarketingstrategie . Kortgezegd is een buyer persona (of customer avatar) een profiel van jouw ideale klant.
Als je een buyer persona opstelt, weet je wat er speelt bij je ideale klant. En zo kun je jouw customer journey naadloos laten aansluiten op zijn of haar behoeften.
Fasen customer journey
De meeste customer-journey-modellen hebben – ongeveer – de volgende fasen:
- overweging
In het Engels kom je deze fasen vaak tegen als awareness, consideration, purchase, service en loyalty. Afhankelijk van de branche of het bedrijf komen er stappen bij of verdwijnen stappen. Je kunt een customer journey zo compact of uitgebreid maken als je wilt.
Normaal gesproken begint de klantreis met bewustzijn. De potentiële klant ontwikkelt een behoefte aan jouw product of dienst. Het kan zijn dat de klant jouw bedrijf of jouw merk hier nog niet kent.
Dan komt de overweging. Hier oriënteert de potentiële klant zich online. Hij of zij ontdekt in deze fase wie het product of de dienst aanbiedt.
Het is belangrijk dat de klant er op dit moment achter komen dat jij bestaat. Zo kan de klant jou meenemen in zijn of haar overweging. Dit doe je bijvoorbeeld door met je SEO-geoptimaliseerde website zichtbaar te zijn op Google.
Tip : wat zijn SEO teksten eigenlijk?
De aankoop moet snel en soepel verlopen. Het bestelproces moet goed functioneren, anders kun je de conversie gedag zeggen.
De customer journey gaat na de aankoop verder. Als je klant een vervelende ervaring krijgt met je klantenservice, vergroot je de kans dat hij of zij de volgende keer niet terugkomt. Met goede nazorg is de klant blij en jij blij.
Dit is (hopelijk) een langdurige fase. Je wilt dat een klant loyaal aan je blijft. Dit kun je doen door nieuwsbrieven te e-mailen of door actief te zijn op social media. In deze fase probeer je de klant voor een langere periode aan je te binden. Het doel? Dat hij of zij de volgende keer direct (of in ieder geval eerder) bij jou uitkomt, zonder de hele customer journey opnieuw te doorlopen.
In het ideale geval is een customer journey geen trechter of lijn, maar een cirkel. In de cirkel komen eerdere klanten namelijk terug.
Sommige customer-journey-modellen voegen ook nog de stap ‘ambassadeurschap’ (advocacy) toe. In deze stap beveelt een klant jouw bedrijf actief aan bij bekenden.
Het is belangrijk om te benadrukken dat een goed uitgedachte customer journey essentieel is voor elke succesvolle marketingstrategie. Door de verschillende fasen en touchpoints van de klantreis te analyseren en optimaliseren, kun je een optimale ervaring bieden die leidt tot hogere conversies en klantloyaliteit.
Het creëren en onderhouden van buyer persona’s helpt je om de behoeften en verwachtingen van je ideale klanten beter te begrijpen, waardoor je beter in staat bent je content af te stemmen en een duurzame relatie met uw doelgroep op te bouwen.
- Wat is een Customer Journey Map [Betekenis & Uitleg]?
Customer Journey Voorbeeld
Hoe wordt een customer journey map gemaakt, conclusie: waarom is een customer journey map een waardevolle toevoeging voor jouw bedrijf, customer journey model betekenis; uitleg & bewezen modellen.
De Customer Journey of " klantreis " staat volledig centraal in dit artikel en zal van A tot Z worden uitgelegd. Het is als online ondernemer namelijk ontzettend belangrijk dat je weet wat je verkoopt; aan wie je het verkoopt ( doelgroep ) EN hoe je dat het beste kunt doen! Het maken van een customer journey kan dan ook een mooie kans zijn om inzichtelijk te maken door welke processen een klant heen gaat en WAT jij er als ondernemer aan kunt doen om binnen deze verschillende fases zichtbaar te zijn.
Hiermee kun je ook de Unique Selling Points extra aandacht geven en matchen aan de behoeften van de (potentiële) klant...
Wanneer je je gaat richten op het controleren en beïnvloeden van de klantenbeleving binnen de customer journey kun jij via slimme online marketing methodes meer klanten bereiken. Dus Heb jij jezelf wel eens afgevraagd hoe een klant het beste overtuigd zou kunnen worden om jouw aanbod te kopen en waar je deze klant kunt vinden? Dan kan het doen van een customer journey onderzoek en het maken van een customer Journey Map met touchpoints een mooie manier zijn om in het hoofd van jouw favoriete klant te kruipen en een beeld te schetsen van hoe (en waar) deze in de markt te vinden is!
Direct Meer Resultaten uit jouw online marketing strategie? Bekijk mijn webshop eens!
Vandaag ga ik je via dit artikel helpen om jouw eigen customer Journey in kaart te brengen via een Customer Journey Map! Heb jij meer begeleiding of informatie nodig om jouw online bedrijf te verbeteren? Bekijk dan dit online marketing boek en de bijbehorende cursus eens waarin het volledige online marketing proces uitgeschreven staat!
Wat is een Customer Journey Map [Betekenis & Uitleg]?
Hoe kan de Customer Journey aan online ondernemers worden uitgelegd?
Een customer journey map is een visuele weergave van hoe de klantervaring eruitziet vanaf het moment dat de eerste prikkels binnen komen die de klant laten realiseren dat ze een behoefte hebben tot aan het einde van het verkoopproces waarbij ze hun doel hebben bereikt. In online marketing is dat vaak een verkoop OF een serie verkopen die door allerlei verschillende zaken getriggerd kan worden, in veel gevallen zelfs door de SEO of SEA inspanningen van de verkopende partij...
Het maken van een customer journey map wordt ook wel customer journey mapping genoemd en hiermee kun jij als ondernemer een plan maken over hoe jouw klant de ontmoeting met jouw bedrijf ervaart. Je gaat dan een aantal stappen uitwerken en plannen die door jouw klant worden genomen vanaf de trigger die dingen in gang zet tot het daadwerkelijk doen van het onderzoekswerk en het aanschaffen van jouw product of dienst. Je wilt namelijk voorkomen dat je fouten maakt in dit proces en er de kantjes vanaf loopt, want je wilt in mijn optiek zo veel mogelijk aan lange termijn relaties met klanten bouwen. Door uitgebreid onderzoek naar de customer journey te doen kun je de conversie waarschijnlijk verhogen!
De Customer Journey vanuit de klant en het bedrijf gezien
Hoe denkt de klant na? Een klant is koning en heeft tegenwoordig veel keuze om van allerlei aanbieders te kopen. Maar toch is het in de tijd van social media marketing en advertising cruciaal om op de juiste manier te communiceren met je klant. Wanneer dit proces opgevat wordt als vermoeiend of vervelend, is het voor een bedrijf makkelijk om klanten te verliezen. Dit vertaalt zich natuurlijk in een lagere omzet en/of een negatief imago.
Dit is precies waar customer journey maps van pas komen. Niet alleen breng je hiermee in kaart op welke plekken je klant gaat zoeken naar informatie, maar je brengt ook in kaart hoe jij daar als bedrijf strategisch op in kunt spelen door "toevallig" aanwezig te zijn met een Google Adwords campagne of social media advertising. Customer journey maps zijn met name populair bij bedrijven die online actief zijn en bedrijven die software producten en platformen ontwikkelen.
Stel dat je op dit moment honger hebt en je wilt wat eten, maar je wilt niet de deur uit om het zelf te halen, wat doe je dan? Gelukkig zijn er tegenwoordig verschillende online winkels die eten verkopen en thuis laten bezorgen, zoals thuisbezorgd, maar je moet daar wel terecht komen! En als je Thuisbezorgd niet kent, zijn er manieren waarop jij als klant zou gaan zoeken.
Je gaat dan bijvoorbeeld kijken op je telefoon OF op het internet en dat biedt kansen voor online marketeers! Zo zou ik bijvoorbeeld een affiliate website kunnen maken met reclame / leads voor het platform en deze positioneren op slimme plekken. Aangezien het een behoefte is die uit de klant zelf komt, zul je op Facebook of Instagram geen koude advertenties tegenkomen op dat moment, tenzij het rond etenstijd is misschien. De kans is veel groter dat jij op Google iets intypt over eten + plaatsnaam OF zelfs direct naar de app gaat die al op je telefoon staat. Een customer journey map zou laten zien hoe jij als klant gaat zoeken naar informatie; doorklikt naar de verschillende categorieën en aanbieders bladert om te krijgen wat u wilt. U kunt ook de zoekknop gebruiken om te zien of een site iets heeft dat u zoekt. Zodra je hebt gekregen wat je wilt, ga je naar de afrekenpagina waar je de artikelen in je winkelwagentje bevestigt en vervolgens een betaalmethode kiest. eventueel online een bestelling doet; naar de applicatie gaat die eten aanbiedt om af te halen / bezorgen.
Dit is een relatief simpel te managen project, maar je kunt hier uiteraard nog allerlei andere bronnen bij betrekken, zoals een e-mail die je klaarzet wanneer mensen 2 weken niet meer bij Thuisbezorgd hebben bestelt, waarbij ze een korting krijgen van 10 euro op hun volgende bestelling van 40,- euro of meer. Er zijn verschillende manieren om Customer Journey Maps te maken, zowel offline als online. Welke manier kies jij om de customer journey in kaart te brengen?
Customer Journey Maps worden meestal gemaakt in de vroege stadia van het bedenken van een bedrijf. Om dit te realiseren zijn er framing-tools zoals Mockups of Figma die gebruikt kunnen worden om alles grafisch vorm te geven. Vaak starten ontwikkelaars met het maken van verschillende Buyer Persona 's, bijvoorbeeld een aantal mannelijke en vrouwelijke.
Wanneer ze hier verschillende eigenschappen in hebben gebouwd kunnen ze gaan kijken welke fases deze doorlopen en wat relevante touchpoints zijn waar deze personen zouden gaan zoeken. Sommige gebruiken bijvoorbeeld een mobiel; anderen een desktop of een verzamelsite van bezorgingsrestaurants.
Met welke fases hou je rekening tijdens het bepalen van een Customer Journey?
- Probleem Awareness
- Onderzoeksfase
- Selectie van mogelijkheden
- Afrekenproces
- Bezorgingsproces
- Eventuele Follow Up Marketing Wil jij echt weten waar je je klant allemaal tegen kunt komen? Zoek dan uit wat de pijnpunten en problemen zijn waar ze tegenaan lopen VOORDAT ze jouw product kopen; en dan kun jij precies uitzoeken hoe jij daar op in kunt spelen, bijvoorbeeld door op de juiste zoekwoorden te gaan adverteren om jouw bedrijf in de zoekmachine en op andere mediaplatformen bekender te maken! Misschien kom je heel snel laaghangend fruit of een volledig nieuw, briljant bedrijfsidee tegen.
Je kunt Customer Journey Maps maken om de touchpoints te bepalen van verschillende media kanalen, zoals:
- (E-Mail) Marketing Funnels;
- Social Media Kanalen ;
- Het normale internet;
- Offline Media;
- Het bestelproces en een eventuele garantie / retour procedure;
In dit artikel heb ik de Customer Journey Uitgelegd. Hopelijk heb jij er als online ondernemer iets aan gehad en kun jij er de volledige marketing funnel van je business OF andere onderdelen zoals je Sales Funnels mee optimaliseren. Om even een korte conclusie over Customer Journey mapping te geven wil ik zeggen dat een customer Journey precies laat waar klanten jouw content tegen zouden kunnen komen als hun behoefte getriggerd wordt...
Bij het bedenken en starten van een bedrijf is het erg belangrijk om in gedachten te houden hoe de customer journey map eruit ziet. Het helpt je ook om te begrijpen of je bedrijf daadwerkelijk een probleem oplost en het haalt de vervelende, storende processen uit het verkoopproces. Customer journey maps zijn ook belangrijk omdat ze het punt zijn waaruit innovaties op gebied van marketing of productontwikkeling komen. Je kunt het proces volledig blijven optimaliseren om de conversie te verhogen.
Customer Journey maps zijn handig om voor je bedrijf inzichtelijk te maken waar je winst op tafel laat liggen. Het helpt je niet alleen om er achter te komen hoeveel punten je nodig hebt om in het hele proces zichtbaar te zijn, maar ook om inzichtelijk te maken met welke bedrijven je samen moet werken om de doelgroep te bereiken. Door de Customer Journey van verschillende klantprofielen te maken krijg je antwoorden van de verschillende mensen die interactie hebben met je product.
Dit helpt je om alle verschillende klanten aan te spreken en potentiële klanten niet te missen wanneer je een nieuwe reclame campagne aan het plannen bent...
Heel veel succes met jouw groeiproces! Heb jij vragen of opmerkingen over dit artikel? Laat dan gerust een reactie achter!
Hopelijk heb jij iets gehad aan dit artikel uit mijn Eigen Bedrijf Starten Ideeën Kennisbank! Je bevindt je momenteel in mijn Internet Marketing Strategie Categorie. Wil jij meer leren over belangrijke online marketing Begrippen en waardevolle online marketing tools ? Bekijk dan mijn internet marketing unie kennismaterialen; mijn webshop en al mijn evergreen content zoals Internet Marketing voor Beginners !
Dan kun jij via persoonlijke ontwikkeling training aan de slag om zelf ook je resultaten te gaan verbeteren door te richten op meer autoriteit ; meer organisch bereik ; meer Web Verkeer; meer leads en meer omzet en winst! Voor jouw Side Hustle of een volwaardig eigen bedrijf!
Customer journey
Optimale klantbeleving creëren door de customer journey uitgebreid in kaart te brengen
Een succesvolle onderneming weet waar zijn klanten en prospects mee bezig zijn en hoe zij bediend willen worden. Om te kunnen voorspellen welke stappen klanten en prospects gaan nemen en hen te helpen bij hun keuzes, wordt de klantreis vastgelegd in een customer journey. In dit artikel leggen we gedetailleerd uit welke fasen je doorloopt bij het in kaart brengen van de customer journey en welke middelen ingezet kunnen worden om een optimale klantbeleving te realiseren.
Wat is een customer journey?
De customer journey is de ‘reis’ die een klant aflegt om tot de aankoop van een product of dienst over te gaan. De customer journey omvat het model waarbij deze ‘klantreis’ in kaart wordt gebracht. Ook potentiële klanten horen daarbij.
- Wat is een customer journey
Wat is een customer journey map?
Fasen van de customer journey, customer journey touchpoints.
- Risico’s inperken middels communicatie
- Net promotor score
Omnichannel marketing
Geen enkele customer journey is hetzelfde, customer journey in het strategisch marketingplan, sales funnel en marketing funnel.

Goede klantrelaties steeds grotere uitdaging
De uitdaging van (grotere) organisaties is om de klant niet uit het oog te verliezen en dicht bij hem te staan. Ondanks groei van het bedrijf en de aanwezigheid van veel verschillende medewerkers en afdelingen. Dat is een lastige taak; enerzijds zorgt het internet voor veel ontwikkelingen in de relatie tussen consument en bedrijf. Vergelijkingswebsites kunnen bijvoorbeeld zorgen voor een afnemende loyaliteit van de klant en de 24/7 online leefwijze van de consument schept hoge verwachtingen ten aanzien van online bereikbaarheid van organisaties. Tegelijk wil de consument persoonlijk worden aangesproken en weten met wie hij te maken heeft binnen het bedrijf.
Positieve klantbeleving realiseren
Onderzoeken waar klantcontact verbeteringen mogelijk zijn en de klantreis helder in kaart brengen, helpt om een positieve klantbeleving te realiseren en langdurige klantrelaties op te bouwen. Om het customer journey model in kaart te brengen, maak je gebruik van een customer journey map.
De customer journey of ‘klantreis’ wordt in kaart gebracht middels een customer journey map. Bij deze methode worden processen vanuit de klant bekeken en gevisualiseerd (‘mapping’). De customer journey map maakt inzichtelijk waar de klantbeleving verbeterd kan worden.
Waarom is customer journey mapping belangrijk?
Om als organisatie succesvol te zijn, dien je te weten waar de klant en prospects mee bezig zijn en goed naar hen te luisteren op elk moment in hun leven. Gelukkig is het met behulp van online en offline communicatiemiddelen, databronnen, statistieken en tools heel goed mogelijk om in kaart te brengen waar klanten en prospects zich bevinden in hun ‘journeys’. Zo is te voorspellen welke stappen ze vervolgens gaan nemen en kunnen ze geholpen worden in hun keuzes. Daarom is het in kaart brengen van de customer journey, oftewel customer journey mapping, een belangrijk onderdeel van de marketingstrategie van elke onderneming.
De klantreis bestaat uit meerdere fasen; van de nog onbekende latente behoefte of de reeds bekende concrete behoefte, tot het beslissingsmoment waarop de aankoop plaatsvindt. Maar ook na de afname van een dienst of product gaat de customer journey verder. De ideale klant worden uiteindelijk loyaal en zelfs een ambassadeur van het merk, product of de onderneming. Om te laten zien hoe een customer journey map gemaakt wordt, leggen we de verschillende fasen van de klantreis uit aan de hand van de indeling van Digital Marketing strateeg Bart van der Kooi.
Je moet daar zijn waar je doelgroep is, weten wat zij denken, hoe ze met je in aanraking komen of juist niet en beseffen waar ze in hun dagelijks leven mee bezig zijn. Niet alleen als ze hun portemonnee in de hand hebben om je product te kopen, maar ook daarvoor en daarna.
Marketing consultant en schrijver , 'De customer journey in kaart in 60 minuten'
- Latente behoefte en concrete behoefte
Bij de start van de klantreis is de vraag; is de doelgroep zich er al van bewust dat ze de producten of diensten van jouw organisatie nodig hebben? Of moeten ze hiervan nog overtuigd worden, wellicht omdat de producten of het merk nog niet bij hen bekend zijn?
Latente behoefte
Latente behoefte is een ‘verborgen behoefte’ waarbij een persoon nog niet weet dat hij iets nodig heeft. Dat komt bijvoorbeeld door onwetendheid; iemand wil een huis kopen, maar is nog niet bezig met de hypotheek die daarbij komt kijken. Als hypotheekverstrekker kun je inspelen op deze latente behoefte. Maar ook een veranderende situatie kan voor een latente behoefte zorgen, zoals gezinssamenstelling of leeftijd. Niet alleen bij potentiële nieuwe klanten maar ook bij huidige klanten kan sprake zijn van een latente behoefte, indien ze nog niet op de hoogte zijn van een nieuw product of nieuwe vorm van dienstverlening.
Hulpmiddelen bij onderzoek naar latente behoefte
Om te onderzoeken of een product of dienstverlening in een latente behoefte voorziet, kun je verschillende bronnen gebruiken, zoals zoekvolumes in Google Trends of Google Keyword Planner, openbare datasets (bijvoorbeeld; hoeveel woningen worden er verkocht in een bepaalde regio en hoeveel potentiële hypotheek afnemers horen daarbij), actuele cijfers en voorspellingen of data afkomstig van de eigen klanten.
Concrete behoefte
Na de latente behoefte komt de concrete behoefte; dit is de fase van de klantreis waarin de doelgroep daadwerkelijk bereikt moet worden om de latente behoefte om te kunnen zetten in een concrete behoefte. Deze fase van de customer journey gaat om zichtbaarheid op plekken waar de doelgroep zich bevindt of in de toekomst gaat bevinden. Overigens is het ook mogelijk dat een persoon zich al direct in een staat van concrete behoefte bevindt zonder dat er eerst sprake is geweest van een latente behoefte. Daarom zien wij latente behoefte en concrete behoefte in dit geval als één fase van de customer journey, maar ze kunnen ook opgesplitst worden in twee fasen.
Voorbeelden concrete behoefte
Voorbeelden van een concrete behoefte zijn de zomervakantie (behoefte aan een gezinsvakantie), veranderingen in iemands leven (nieuwe baan, verbouwing), geplande momenten (het aflopen van een abonnement) of speciale momenten zoals verjaardagen, geboortes en huwelijken.
Inspelen op de concrete behoefte middels zichtbaarheid
Zichtbaarheid voor een onderneming, product, dienst of merk is op diverse manieren te creëren, bijvoorbeeld middels display advertising, bannering of video advertenties op websites van anderen, affiliate marketing, offline adverteren, contentmarketing, adverteren op social media of via de eigen nieuwsbrief, website en social media kanalen. Succes in deze fase houdt in dat de doelgroep weet wat je doet, wie je bent en waarom men bij jouw onderneming moet zijn voor een bepaald product of specifieke dienstverlening.
De latente en concrete behoeften zorgen voor de eerste customer journey touchpoints; het moment en de manier waarop een persoon en een merk elkaar tegenkomen. Verschillende customer touchpoints bij elkaar vormen een totale klantbeleving. Er komen daarom meerdere belangrijke touchpoints voor in de customer journey.
Latente en concrete behoeften belangrijke fasen van de customer journey
- De concrete behoefte is voor de (potentiële) klant het startpunt om zich te oriënteren op een soort product of dienstverlening, het merk en de mogelijke aanbieders. Daarom zijn de fasen van latente en concrete behoefte erg belangrijke momenten om in te spelen op de klantreis. Hiervoor moet achterhaald worden; Vanaf welk moment in het leven van de doelgroep de concrete behoefte voor een product of dienst ontstaat.
- Of huidige klanten een concrete behoefte hebben aan andere producten of diensten in het assortiment.
- Of er verschillende momenten zijn waarop een concrete behoefte ontstaat voor de diverse producten of diensten in het assortiment.
- Welke trends en ontwikkelingen in de markt de concrete behoefte stimuleren.
- Oriëntatiefase
- Overwegingsfase
- Beslismoment
- Leveringsfase
- Gebruiksfase
- Loyaliteitsfase
- Ambassadeursfase
The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well, the product or service fits him and sells itself.
Auteur en management professor , diverse hooggewaardeerde Amerikaanse business schools
De manier waarop (potentiële) klanten zich oriënteren op de aanschaf van producten of diensten heeft zich sterk ontwikkeld de afgelopen decennia. Dankzij de online wereld is oriëntatie nu mogelijk vanaf elk apparaat, op elk moment van de dag en zelfs landsgrensoverschrijdend. Belangrijk in deze fase is te onderzoeken op welke momenten je in het oriëntatieproces in beeld kunt komen als merk en hoe je daarin waarde kunt toevoegen voor de doelgroep die zich aan het oriënteren is. Goed in beeld komen middels objectief advies is daarbij belangrijk.
Oriëntatieproces in de klantreis
Hoe identificeer je personen die in een oriënterende fase zitten? Er zijn verschillende wegen die men kan bewandelen, zoals;
- Concreet zoekgedrag via zoekmachines.
- Bepaalde producten worden opgeslagen en verzameld op digitale prikborden zoals Pinterest of WeHeartIt.
- Sociale media worden gebruikt om familie, vrienden en andere bekenden om meningen en ervaringen met producten en diensten te vragen.
- Fora en discussiegroepen worden gebruikt om ervaringen uit te wisselen.
- Onafhankelijke websites en blogs die producten met elkaar vergelijken en reviews schrijven worden gebruikt. Hieronder vallen ook video’s waar bepaalde soorten producten tegen elkaar worden afgezet.
- Kieswijzers en vergelijkingssites helpen bij het maken van een keuze, denk bijvoorbeeld aan websites die zorgverzekeraars of energiemaatschappijen met elkaar vergelijken.
- Huidige klanten bezoeken de website van jouw onderneming en die van concurrenten voor extra informatie.
Inzicht verkrijgen in het oriëntatieproces
Het gedrag van de oriënterende potentiële klant is te monitoren door naar de zoekvraag te kijken met behulp van monitoring tools zoals AdWords Keyword Planner en Google Trends. Huidige klanten zijn te monitoren door te kijken naar Google Analytics, klikgedrag vanuit e-mailmarketing, social media kanalen of polls.
Doelgroep bereiken in oriëntatiefase
Het oriëntatieproces is het uitgelezen moment om de doelgroep zo goed mogelijk te bereiken of te helpen; een goed touchpoint in de klantreis. Er zijn verschillende marketingmiddelen die je daarbij kunt inzetten:
- Contentmarketing: via blogs, video’s, whitepapers, ebooks, infographics, etcetera.
- SEO (zoekmachine optimalisatie): zorgt voor vindbaarheid van jouw content via zoekmachines.
- SEA (zoekmachine adverteren): om op te vallen via de betaalde weg.
- Social media: waar meningen worden gevraagd van bekenden.
- Fora of discussiegroepen: waar meningen worden gevraagd van onbekenden. Door op deze plekken proactief service aan te bieden en door vragen objectief te beantwoorden kan de doelgroep bereikt worden.
- Webcare en proactief advies: in deze fase stellen mensen vragen over een product of dienst via de eigen website, bijvoorbeeld middels live chatting.
- Prikbordmarketing: kanalen zoals Pinterest worden gebruikt om wensenlijstjes te maken van producten of activiteiten. Na het ‘pinnen’ is de kans groot dat men het gepinde product wil aanschaffen of de vakantie wil boeken.
- Offline: ook tijdens beurzen en events waar liefhebbers bij elkaar komen, kun je als onderneming aanwezig zijn en in het oog springen. Denk bijvoorbeeld aan de jaarlijkse Vakantiebeurs.
A brand is no longer what we tell the consumer it is, it is what consumers tell each other it is.
Co-founder , Softwarebedrijf Intuit
In de overwegingsfase wordt de keuze van de doelgroep voor een merk of aanbieder van producten en diensten bekeken. Merkvoorkeur is tegenwoordig vrij instabiel doordat het voor de consument heel makkelijk is om producten of diensten te vergelijken op vergelijkingsplatforms; men 24/7 kan zoeken naar aanbieders en de hele wereld is bereikbaar. Om succesvol te zijn in deze fase moet een onderneming deze bedreigingen kunnen tegengaan en de kansen benutten.
Welke factoren spelen een rol in de overwegingsfase?
De keuze van merk en aanbieder wordt onder andere gebaseerd op de volgende factoren:
- Merkbekendheid
- Ervaringen van bekenden en onbekenden
- Serviceniveau
Per branche en per doelgroep kunnen natuurlijk extra factoren een rol spelen, zoals bepaalde apps die worden gebruikt in de dienstverlening.
Doelgroep herkennen in overwegingsfase
Een onderneming kan de mensen herkennen die in de overwegingsfase diverse aanbieders of merken met elkaar vergelijken. Dat is belangrijk om hierop in te kunnen spelen. De doelgroep is als volgt te identificeren:
- Zoekt naar merken/aanbieders in online zoekmachines.
- Raadpleegt vergelijkingssites en reviewsites.
- Vraagt naar ervaringen van onbekenden op fora of in discussiegroepen.
- Zoekt ervaringen van bekenden op social media.
- Bekijkt productdemonstraties op YouTube.
- Bezoekt websites van aanbieders voor extra informatie.
- Stelt vragen op de website van de onderneming via de chatfunctie op WhatsApp.
Inzicht verkrijgen in de overwegingsfase
Doelgroep bereiken in de overwegingsfase.
- SEO (zoekmachine optimalisatie): inspelen op branded zoektrends (waarbij specifiek naar jouw merk wordt gezocht) en op non-branded zoektrends (waarbij op producten, diensten of informatie wordt gezocht).
- SEA (zoekmachine adverteren): scoren middels betaalde advertenties.
- Conversie optimalisatie: websitebezoeker naar de juiste handeling leiden middels een goede sales funnel.
- Remarketing: eerdere websitebezoekers achtervolgen met advertenties om jouw merk opnieuw onder de aandacht te brengen.
- Vergelijkingswebsites: aanwezig zijn op de belangrijke vergelijkingssites in jouw branche.
- Reviewmarketing: stimuleer huidige tevreden klanten om een review achter te laten op belangrijke websites in jouw branche en reageer altijd begripvol en correct bij negatieve reviews.
- Webcare: snel en correct advies geven bij vragen op social media en op de websitechat.
- Mobile marketing: website optimaliseren voor mobiel gebruik en geo-targetting (gericht plaatsen van online advertenties op basis van de geografische locatie van de gebruiker).
Customers buy for their reasons, not yours.
Sales & marketing expert , spreker en auteur

Afhaakmomenten voorkomen
Bij ieder aankoopproces, zowel offline als online, is het belangrijk om afhaakmomenten te voorkomen. Met ‘aankoop’ wordt dan gedoeld op het aanschaffen van een product of dienst, inschrijven voor een cursus, het boeken van een vakantie, etc. Op je website, in de winkel of in de app. Omdat de koopfase op veel verschillende manieren kan plaatsvinden en het proces bij elke onderneming en voor elke klant anders is, is het reduceren en het liefst elimineren van afhaakmomenten niet eenduidig. De koopervaring kan voor elke klant anders zijn en bestaat online vaak uit veel handelingen; gegevens invullen, eventueel een account aanmaken, producten toevoegen, levermoment kiezen en afrekenen. In het proces zitten meerdere momenten waarop de consument kan afhaken.
Mogelijke afhaakmomenten voor de consument
- Bijkomende kosten: bijvoorbeeld extra leveringskosten.
- Niet tevreden met betalingsmogelijkheden: bijvoorbeeld alleen betalen via creditcard of juist niet via paypal.
- Niet tevreden met levertijd: bijvoorbeeld bij levering volgende week, maar de klant wil het product morgen in huis.
- Tijdelijk afbreken of pauzeren van de online aankoop: bijvoorbeeld door ontbrekende informatie, geen tijd, langer willen nadenken.
- Annuleren van het aankoopproces door nieuwe omstandigheden: bijvoorbeeld aankoop huis gaat niet door want de hypotheek komt niet rond.
- Onduidelijke of onvolledige productinformatie: bijvoorbeeld online koffie willen kopen maar bij het toevoegen aan het winkelmandje staat niet vermeld of het om bonen, gemalen koffie, cups of pads gaat.
- Andere obstakels in de sales funnel .
Aankoopproces optimaliseren met handige tools
- Google Analytics: richt Analytics zo in dat duidelijk is wanneer men teruggaat naar een vorige stap, wanneer men afhaakt, of er verschil is tussen afhaakmomenten op desktop en mobiel, etc.
- Heatmaps: deze software meet muisbewegingen op de website en biedt inzicht in verbeteringen. Een bekende heatmap tool is Hotjar .
- A/B testen: voer tests uit op je website met verschillende versies van dezelfde pagina waarbij je inzicht krijgt in welke pagina (A of B) beter presteert.
- Gebruikersonderzoeken: onder leiding van een expert worden personen uit de doelgroep gevraagd om bepaalde handelingen te verrichten op de website met als doel te achterhalen of dit lukt en hoe de gebruiker het ervaart. Hierbij kan ook eye-tracking aan bod komen; een analyse op basis van oogbewegingen.
Doelgroep faciliteren in de koopfase
- Conversie optimalisatie: de sales funnel zo optimaal mogelijk maken met behulp van bovengenoemde tools.
- E-mailmarketing: klanten die hun aankoop niet hebben afgemaakt een mail sturen om de bestelling af te kunnen maken of een notificatie mogelijkheid bieden bij tijdelijk niet leverbare producten, voor nieuwe cursussen, etc.
- Affiliate marketing: samenwerkingen tussen relevante publishers en advertisers.
- Remarketing: retargeting van websitebezoekers die hun aankoop niet hebben afgemaakt of nog iets in hun online winkelmandje hebben zitten.
- Social sharing: enthousiaste kopers delen de aankoop direct middels een button op de bedankt-pagina of in de bevestigingsemail.
Klantgegevens verzamelen
In de koopfase verkrijgt de onderneming vaak veel gegevens van de klant; naam, adres, e-mailadres, telefoonnummer, etc. Een goed CRM-systeem zorgt ervoor dat deze klanten ook een positieve ervaring krijgen in de nog komende fasen van de customer journey.
De levering van een dienst of product bestaat uit meer varianten dan enkel de pakketbezorger die een bestelling uit een online webshop komt afleveren. Afhankelijk van wat er geleverd wordt, kan een ‘levering’ er onder meer als volgt uit zien:
- Een product kopen in een fysieke winkel.
- De genoemde levering aan huis vanuit een webshop.
- Start van een dienstverlening voor langere tijd (bijvoorbeeld energie, internet, telefoon abonnement, online marketing abonnement).
- Start van een dienstverlening voor kortere tijd (bijvoorbeeld een vlucht, dienst van een loodgieter of elektricien).
- Downloaden van e-tickets (bijvoorbeeld voor een concert, festival of theatershow).
Ook voor diensten, die niet letterlijk bij de koper thuis worden gebracht, kan de leveringsfase benadrukt worden door bijvoorbeeld aan te kondigen; ‘vanaf nu maakt u gebruik van de online marketing diensten van bedrijf X’. Er zijn veel kansen voor een onderneming die de leveringsfase van een saai moment in de klantreis weet om te zetten naar een positieve klantervaring en klanten zelfs weet te enthousiasmeren.
The key is to set realistic customer expectations, and then not to just meet them, but to exceed them – preferably in unexpected and helpful ways.
Succesvolle Britse zakenman en oprichter , Virgin Group
Klantreis risico’s in de leveringsfase
De leveringsfase brengt verschillende risico’s met zich mee wat betreft de klantreis; momenten waarop de klant alsnog kan afhaken. Dat risico is groter als er enige tijd zit tussen de aankoop en het moment van de levering:
- De klant kan een bestelling annuleren na de aankoop maar nog voor de levering.
- De klant kan een bestelling retour zenden na levering bij ontevredenheid of indien er iets niet klopt.
Risico’s inperken middels communicatie
De risico’s in de leveringsfase kunnen worden ingeperkt door in de overbruggingsperiode goed te blijven communiceren met de klant. Zo kan er in de periode tussen aankoop en levering content worden gecommuniceerd waardoor de klant enthousiast wordt gemaakt en waardoor annuleringen worden voorkomen. Bijvoorbeeld gebruikstips, previews en een kennismaking met het merk of het product. In de periode tussen levering en gebruik kan het risico op retourzendingen worden verkleind met communicatie tijdens of direct na de levering. Bijvoorbeeld met een enquête over de levering, de kwaliteit van de zending, etc. Zo kan ontevredenheid beperkt of voorkomen worden.
Customer journey touchpoint in de leveringsfase
De levering van het product of de aanvang van een dienstverlening is een belangrijk customer journey touchpoint waarop de doelgroep geïnformeerd en enthousiast gemaakt kan worden. Bijvoorbeeld middels:
- E-mailmarketing: verstuur e-mails waarin de klant op de hoogte wordt gehouden van de status van de levering. Ook enquêtes en vragenlijsten over tevredenheid kunnen per e-mail worden verstuurd, zodat de klant ervaringen kan delen voordat hij dit bijvoorbeeld openbaar doet.
- Content marketing: content met gebruikerstips of installatietips kunnen tijdens het wachten op de levering verstuurd worden naar de klant middels e-mailmarketing, maar ook gedeeld worden op de site, een blog, via sms of in een persoonlijke klantomgeving op de website.
- Sms-marketing: houd de klant op de hoogte via sms. Sms is op dit moment toegankelijker dan WhatsApp, omdat hiervoor toestemming nodig is van de ontvanger van de apps.
- Chatbots: een chatbot is een voorgeprogrammeerde gesprekspartner die op websites en Instant Messenger programma’s ingezet wordt om veelgestelde vragen goed, snel en 24/7 te beantwoorden. Vragen over de status van een bestelling en het wijzigen van een bezorgdatum kunnen hierdoor eenvoudig worden afgevangen.
- Webcare en klantenservice: vragen die ‘niet standaard’ zijn, of bij het ontbreken van een chatbot, kunnen worden beantwoord door webcare medewerkers en klantenservice medewerkers.
De fase waarin een product of dienst gebruikt wordt biedt veel aanknopingspunten die inzicht geven in de klant en momenten waarop met de klant gecommuniceerd kan worden. Dit is een belangrijk moment in de klantreis, omdat er zo waardevolle informatie vrijkomt voor het optimaliseren van toekomstige producten en processen, om in te spelen op eventuele ontevredenheid en om klanten te kunnen binden aan jouw merk of product.
Klantinformatie verkrijgen in de gebruiksfase
Gebruiksinformatie kan achterhaald worden op verschillende manieren, afhankelijk van de kanalen die de doelgroep gebruikt om informatie te vinden en (on)tevredenheid te delen. Bijvoorbeeld:
- Klachten of vragen die binnenkomen via e-mail, telefoon of chat.
- Informatie analyseren uit de persoonlijke klantomgeving op de website, mits deze ‘mijn omgeving’ meerwaarde biedt voor de klant.
- Online monitoringtools inzetten om het internet te scannen op gebruik van merk- en productnamen, bijvoorbeeld op social media en op online fora.
- Proactief inspelen op openbare berichten om negativiteit om te buigen, oplossingen aan te bieden en ervan te leren.
- Gebruiksgegevens analyseren uit producten of diensten waarbij online ingelogd moet worden.
- Zoekresultaten analyseren op Google en YouTube (trefwoorden analyseren, zoekresultaten van handleiding-video’s analyseren).
- Google Analytics inzetten om te achterhalen of klanten op de eigen website zoeken naar productinformatie of handleidingen.
- Indien het gebruik niet online geanalyseerd kan worden, zoals in een pretpark of een museum, kan het gedrag bekeken worden met behulp van tracking op looppaden of beacons om te zien waar de bezoeker zich bevindt.
Customer journey touchpoints in de gebruiksfase
In de gebruiksfase is het doel de klant tevreden houden middels communicatie en kansen benutten voor cross selling en upselling middels marketing. Om deze redenen is de gebruiksfase een belangrijk customer journey touchpoint in de klantreis. De doelgroep is in deze fase als volgt te bereiken:
- E-mailmarketing: klant informeren met persoonlijke en relevante e-mails die inspelen op het aankoopgedrag van de klant (bijvoorbeeld; klant heeft een reis naar Thailand geboekt, dan dient de e-mailmarketing toegespitst te zijn op Thailand i.p.v. algemene mails over wereldwijde vakanties).
- Contentmarketing: blogs en social media kanalen inzetten om de klant nuttige informatie te geven over productgebruik of dienstverlening. De mogelijkheid voor de klant om te reageren bevordert klanttevredenheid.
- Videomarketing: YouTube is na Google de grootste zoekmachine ter wereld. Handleidingen en infographics kunnen middels video gecommuniceerd worden.
- Website optimalisatie: een duidelijk onderscheid tussen informatie voor prospects en informatie voor klanten op de website van de onderneming zorgt voor een goed touchpoint. SEO (zoekmachine optimalisatie) en conversie optimalisatie zorgen ervoor dat de klant deze info ook kan vinden.
- Online monitoring: online monitoringtools helpen berichten van klanten te onderscheppen die vragen hebben of hulp zoeken bij een product of dienst, bijvoorbeeld op social media of online fora. Met proactieve webcare kan hier vervolgens op ingespeeld worden.
- Chat: online contact middels een chatfunctie of app zorgt voor snelle oplossingen bij vragen of problemen van de klant.
There is a big difference between a satisfied customer and a loyal customer
Auteur en spreker , Amerikaanse customer service expert
Transactionele loyaliteit
Emotionele loyaliteit.
Een duurzamere vorm van merkloyaliteit is daarom ‘emotionele loyaliteit’. Deze klanten zijn aan het merk gehecht en voelen een emotionele verbondenheid. Het zijn ‘fans’ van je merk en zij zullen hun positieve totaalervaring bij het merk niet willen inruilen voor de korting van de concurrent. Emotionele loyaliteit komt veel voor bij ‘likeable’ merken zoals Nike, Harley Davidson of Apple, bij bepaalde populaire modemerken en natuurlijk bij veel sportclubs.
Customer Decision Journey en Loyalty Loop van McKinsey

Customer intimacy voor hoge merkloyaliteit
If people believe they share values with a company, they will stay loyal to the brand.
Oprichter en executive chairman , Starbucks
Loyale klanten herkennen
Tevreden klanten zijn niet per definitie ook loyale klanten. Om loyale klanten te identificeren moet er daarom gemeten worden. De mate van klantentrouw kan het beste afgemeten worden aan het gedrag van de klant. Klantentrouw blijkt uit het koopgedrag van de klant en uit de emotionele band van de klant met het merk of de onderneming en zijn positieve houding ten opzichte van het merk of de onderneming (loyaliteit).
Net Promotor Score
- Promotors: hebben een score van 9-10 gegeven.
- Passief tevredenen / Neutralen: hebben een score van 7-8 gegeven.
- Criticasters: hebben een score van 0-6 gegeven.
Net Promotor Score berekenen
Voordelen en nadelen van de net promotor score.
Volgens onderzoek zijn Promotors trouwere klanten die meer producten of diensten afnemen, hun leverancier vaker aanbevelen aan een bekende en zo autonome bedrijfsgroei creëren. Het doel van de onderneming is dus het creëren van zoveel mogelijk Promotors en zo weinig mogelijk Criticasters. Een belangrijk kritiekpunt op de NPS methode is dat de intentie om een bedrijf aan te raden alleen onvoldoende is om het loyaliteitsgedrag van klanten in de toekomst te kunnen voorspellen. Het meet alleen het voorgenomen bedrag (zou u ons aanbevelen), niet het daadwerkelijke gedrag (heeft hij ons aanbevolen en blijft het zelf ook klant).
Meten in Google Analytics en CRM-systeem
Eerst zelf aan de slag met de data uit Google Analytics en het CRM-systeem of de administratie is natuurlijk ook een goede optie. Hierdoor zijn bijvoorbeeld de volgende zaken te meten:
- Hoe lang zijn personen al klant.
- In welke leeftijdscategorie blijven klanten langer klant.
- In welke regio wonen de meest loyale klanten.
- Data over het bezoek aan de ‘opzeggen’ pagina.
- Hoe vaak er wordt gezocht naar voorwaarden om een contract te beëindigen, naar opzegtermijnen of andere afmeldingsmogelijkheden.
- Hoe vaak er wordt gezocht naar de optie om een klacht in te dienen.
Met deze data krijg je inzage in de succes-KPI’s (Kritieke Prestatie Indicatoren) maar ook de mogelijkheid om de doelgroep te bereiken alvorens ze opzeggen en ze zo uiteindelijk om te vormen naar loyale klanten.
Customer journey touchpoints in de loyaliteitsfase
Voor het creëren en behouden van loyale klanten zijn enkele marketingmiddelen in te zetten. Daarbij is het belangrijk de juiste boodschap naar de juiste klant (of niet-klant) te communiceren, in de juiste fase van de customer journey. De volgende middelen kunnen daarbij helpen:
- Data/statistieken: inloggegevens uit de klantomgeving op de website, bezoekers aan de ‘opzeggen’-pagina en gegevens over de periode die verstrijkt tussen aankopen geven o.a. inzage in klantloyaliteit.
- Webcare en appcare: online aanwezigheid op de juiste social media kanalen en natuurlijk op WhatsApp of Messenger zorgt voor kortere lijnen met klanten.
- Live chat: live chat op de eigen website is een goede manier om klanten met vragen direct te bedienen en om mensen die willen opzeggen te behouden of naar hun redenen te vragen.
- Enquêtes: vragen stellen over tevredenheid geeft inzichten en biedt de klant de gelegenheid zijn hart te luchten.
- E-mailmarketing: relevante malingen met specifieke inhoud (gepersonaliseerd en gesegmenteerd) zorgen voor betrokkenheid van de klant.
- Contentmarketing: diverse vormen van content (tekstueel, video of beeld) verspreiden op de juiste kanalen (zoals de eigen website of social media) waarbij duidelijk onderscheid gemaakt wordt tussen verschillende doelgroepen (bestaande klanten en prospects of niet-klanten).
- Adverteren via remarketing: mensen die de bedrijfswebsite hebben bezocht kunnen via remarketing met advertenties achtervolgd worden waarbij ze heel specifiek producten te zien krijgen waarin ze interesse hebben getoond op je website.
- Monitoring: het monitoren van social media (bijvoorbeeld specifieke Facebook groepen binnen jouw branche), fora en discussiegroepen leidt tot het opsporen van trends en de mogelijkheid gepast te reageren op vragen die niet direct aan de organisatie waren gericht.
Ook omnichannel is een belangrijke strategie als het gaat om klantloyaliteit. Klanten verwachten dat ze hun verhaal slechts eenmaal hoeven te vertellen als ze contact opnemen met de organisatie. Mochten ze hun probleem of vraag al voorgelegd hebben aan de telefonische klantenservice, dan zorgt een goede omnichannel ervoor dat de klant niet de volgende dag het verhaal nogmaals hoeft te vertellen aan webcare afdeling. Ook consistentie in de manier waarop klanten behandeld en aangesproken worden is belangrijk. Omnichannel omvat dus zowel technische componenten als mindset componenten. Omnichannel leidt tot een betere klantrelatie waardoor klantloyaliteit kan toenemen.

Every contact we have with a customer influences whether or not they’ll come back. We have to be great every time or we’ll lose them.
Internetmarketing expert en auteur , More Loyal Customers & Marketing for Smart People
Naast loyale klanten is er natuurlijk nog een overtreffende trap; de ambassadeurs. Ambassadeurs zijn niet alleen tevreden en loyaal aan het merk of de onderneming, ze brengen ook nog eens nieuwe klanten aan.
Wat is een ambassadeur?
Ambassadeurs zijn klanten die zo blij met het merk of product, dat ze bereid zijn om uit zichzelf reclame te maken. Daarbij zijn er ambassadeurs die een zetje in de rug nodig hebben en aan wie gevraagd moet worden of ze bijvoorbeeld een review willen schrijven. En er zijn spontane ambassadeurs die hun enthousiasme gevraagd en ongevraagd delen met bekenden en onbekenden.
Hoe wordt een ambassadeur herkend?
Offline ambassadeurs die je product of merk aanbevelen aan vrienden en familie zijn lastig te achterhalen. Maar er is een grote groep ambassadeurs die online actief is, en dat valt te monitoren:
- Monitoringstools kunnen achterhalen hoeveel en welke fans hun boodschap verspreiden op social media, fora en in discussiegroepen. En ook of bijvoorbeeld YouTube wordt gebruikt om producten te testen of gebruiksvideo’s te delen.
- Echte fans vertellen niet alleen op online platformen dat ze enthousiast zijn, maar beantwoorden vragen van prospects en verdedigen het merk of product als er negatieve reacties zijn.
- E-mails van klanten die meedenken of tips geven voor verbeteringen zijn bedoeld om te helpen en kunnen afkomstig zijn van ambassadeurs.
- Ambassadeurs zijn binnen e-mailmarketing ook te herkennen aan hoe vaak ze doorklikken binnen een nieuwsbrief en hoe vaak ze content delen of doorsturen. Dit is allemaal te meten binnen e-mailmarketing platformen.
The way to a customer’s heart is much more than a loyalty program. Making customer evangelists is about creating experiences worth talking about.
Customer experience strateeg , Diverse Fortune 500 bedrijven en auteur
Ambassadeurs bereiken en faciliteren
Ambassadeurs van je merk of product moeten niet alleen gekoesterd worden maar ook gefaciliteerd worden om hun positiviteit over het merk gemakkelijk te kunnen verspreiden. Het bereiken van deze doelgroep is daarom een belangrijke stap in de customer journey. Dat kan als volgt:
- Delen: maak het mogelijk om content, aankopen of productpagina’s te delen op social media, via e-mail en WhatsApp.
- Reviews en aanbevelingen: vraag klanten een review achter te laten op belangrijke review websites, je Facebook pagina en in Google en vraag hen ook om een review om op de eigen website te plaatsen.
- E-mailmarketing: zorg dat fans en ambassadeurs andere content krijgen aangeboden in nieuwsbrieven dan ‘gewone klanten’ of prospects. Ze hebben andere behoeften en verwachtingen.
- WhatsApp: communicatie via messaging-apps zoals WhatsApp bewerkstelligt een meer directe band met ambassadeurs.
- Monitoring van online media: identificeer je trouwe achterban door fora, discussieplatforms en social media te monitoren. Mensen die hier veel over je merk praten en een groot bereik hebben, zijn ideale ambassadeurs.
- Member acties: faciliteer ambassadeurs met de juiste tools zodat ze anderen kunnen aansporen om klant te worden.
- Contentmarketing: merkambassadeurs kunnen een blog, nieuwsbrief of artikel schrijven of een video maken zodat contentmarketing heel persoonlijk wordt.
- Custom audiences: custom audiences is een optie voor advertentie targeting waarmee adverteerders een doelgroep kunnen targeten vanuit een geüploade klantenlijst. Target je lijst met ambassadeurs zodat ze positieve berichten over je merk blijven verspreiden.
The purpose of a business is to create a customer who creates customers.
Global Head of Innovation , United Rentals
- Het in kaart brengen van de klantreis helpt bij het identificeren van groeikansen en mogelijk te behalen voordelen tussen verschillende kanalen.
- De customer journey helpt bij het ontwikkelen van nieuwe producten of diensten.
- Bij veranderingen in de organisatie helpt de customer journey map te onderbouwen waarom delen van de organisatie anders moeten worden ingedeeld.
- Op operationeel niveau zorgt de customer journey map ervoor dat de organisatie zichzelf bekijkt vanuit het klantperspectief en zo inzicht krijgt in mogelijkheden voor verbetering en verandering.
- De customer journey biedt aanknopingspunten voor het indelen van de marketingmix. Met behulp van de marketingmix (de 4P’s, maar vooral het klantgerichte 4C-model en het SIVA model ) vult de organisatie zijn marketingstrategie in. De in kaart gebrachte klantreis helpt te bepalen hoe de verschillende marketinginstrumenten ingezet moeten worden en welke onderlinge wisselwerking gewenst is, gezien vanuit het klantperspectief.
- Het customer journey model geeft inzicht in de klantbeleving en is erg waardevol als basis om de totale customer experience te optimaliseren.
- De fase van latente of concrete behoefte valt samen met Suspects in de sales funnel.
- De oriëntatiefase richt zich op Leads .
- Prospects zitten in de overwegingsfase en zijn dicht bij het beslismoment.
- Klanten bevinden zich in de koopfase, leveringsfase of gebruiksfase.
- De loyaliteitsfase en de ambassadeursfase richten zich op Terugkerende klanten uit de sales funnel.
TED Talk ‘What Consumers Want’ door Joseph Pine
De TED Talk van Joseph Pine, business consultant en schrijver van ‘Mass Customization’, stamt uit 2004 maar is nog steeds erg actueel. Volgens Pine willen mensen die aankopen doen meer dan alleen het product in hun winkelwagentjes. Pine beweert dat een authentieke klantervaring net zo waardevol is als een kwalitatief hoogstaand product dat te koop is. In deze tijd, wanneer klanten hun mening geven op openbare platforms, is het belangrijker dan ooit om hen te geven wat ze willen.
Een interessante TED Talk die inspiratie biedt voor het uitbreiden en perfectioneren van de customer journey.
Literatuur: Van der Kooi, B. (2017). De customer journey in kaart in 60 minuten . Zaltbommel, Nederland: Haystack.
APA bronvermelding voor dit artikel: ‘Van der Linde, M. (2018, 20 maart). Customer journey. Geraadpleegd van https://www.marketingbright.nl/customer-journey/’
Meer over dit onderwerp: Customer journey map , Customer journey model , Klantreis

Monique van der Linde
Journalist marketing en commercie
Monique is een gedreven onderneemster en heeft in de combinatie van haar commerciële en journalistieke achtergrond, de uitdaging gevonden om complexe marketing onderwerpen in jip-en-janneke taal uit te leggen. Daarmee maakt ze marketing toegankelijk voor een groot publiek.
12 Reacties
Beste Monique,
Op dit moment ben ik bezig met het schrijven van een ontwerpgericht onderzoek waarbij mijn ontwerpvraag het volgende is: ““Wat voor onderscheidende marketingcommunicatiestrategie kan ingezet worden om potentiële klanten van dtevents te bereiken en behouden?”
Ik ben nu bezig met het zoeken naar een theoretisch kader om mijn onderzoek op te kunnen baseren en vroeg mij af of de customer journey hiervoor geschikt zou kunnen zijn? Deze zou ik toch eventueel ook kunnen inzetten bij een doelgroepanalyse of concurrentie?
Heb je eventueel nog andere suggesties voor modellen?
Bedankt alvast!
Hallo Romy, kijk ook even naar dit artikel over het Communicatieplan 😉
Ik ben bezig met mijn scriptie, en doe hierbij interviews over de customer journey. Graag zou ik u willen interviewen gezien de kennis die u hierover heeft.
Ik hoor graag van u !
Hoi Gaby, zou je je vraag via het contact formulier willen insturen? Dankje!
Hallo Jerome, ik heb een korte vraag. Ik ben momenteel bezig met mijn afstudeerscriptie en ben aan het onderzoeken hoe je de afnemers van tele-sales richting de webshop kan krijgen.. Dit is een vrij lastige insteek aangezien ik mij afvraag of ik a. überhaupt een model nodig heb, b. twijfel ik tussen het Servqual-model en bijv. de customer journey..
Zou jij misschien kunnen helpen met dit dilemma?
Groet Ramon
Hi, momenteel ben ik bezig met een onderzoek. Mijn communicatievraagstuk is: ”Op welke wijze kan de customer journey geoptimaliseerd worden om de klantbeleving en daarmee inschrijvingen van bedrijf X te bevorderen?” In de eerste instantie wilde ik een DESTEP-analyse (macro-analyse) maken en ook het 5 krachten model van porter (meso-analyse) gebruiken. Nu ik me meer heb verdiept in de andere marketingmodellen m.b.v. jullie site, ben ik aan het twijfelen. Is dit wel relevant? Of kan ik beter beginnen met het maken van een customer journey map? Alvast bedankt!
hoi, ligt er een beetje aan of je je onderzoek strategisch wilt insteken of dat je je voornamelijk concentreert op de tactische inrichting (het communicatievraagstuk).
Ik adviseer je om de SMP-methode eens te bekijken, daar zijn DESTEP-analyse en het vijfkrachtenmodel van Porter onderdeel van, en vervolgens bij het tactische deel (stap 6) de Customer journey vorm te geven bij het samenstellen van je marketingmix. Klinkt dit logisch voor je?
Goedendag Jerome,
Momenteel ben ik bezig met mijn scriptie. Mijn onderzoek gaat over het optimaliseren van de verkoopkanalen en de communicatiemiddelen binnen de organisatie. Hiervoor ben ik opzoek naar bepaalde modellen die mij handvatten kunnen geven tijdens het schrijven. Lastiger dan gedacht…
Welke modellen zou ik hiervoor kunnen raadplegen? Alvast bedankt.
Je maakt in elk geval een goede start door de customer journey te bekijken. Ik weet niet precies wat de hoofdvraag van je scriptie is, maar ga je de customer journey ook in kaart brengen voor de organisatie? Dan kunnen ook de verdiepende artikelen customer journey map , customer journey model en klantreis je helpen. Ook belangrijk voor het optimaliseren van de verkoopkanalen is kijken naar de salesfunnel . Maak daarbij goed onderscheid tussen de salesfunnel en de marketingfunnel . In deze artikelen kom je weer modellen tegen die je verdere verdieping bieden, afhankelijk van de kant die je onderzoek moet opgaan.
Veel succes met je scriptie en laat het gerust weten als je tegen specifieke vragen aanloopt tijdens je onderzoek.
Beste Monique van der Linde,
Ik zou graag weten wanneer dit artikel geschreven is? Ik wil hem graag gebruiken voor mijn scriptie en het jaar waarin een artikel geschreven is, is van belang.
Hoi Bob, Helemaal onderaan alle artikelen kun je de publicatiedatum vinden (in dit geval: 20 maart 2018) alsmede de APA bronvermelding. Succes gewenst met je scriptie!
Super dankjewel!
Een reactie versturen Reactie annuleren
Het e-mailadres wordt niet gepubliceerd. Vereiste velden zijn gemarkeerd met *
Reactie versturen

Jouw marketingplan in 7 stappen
Met deze gratis PDF...
Controleer je e-mail inbox!
36.652 mensen hebben het ebook inmiddels al gedownload.
- Gratis e-learning
- Al onze 84 blogs >>
- Missie en visie formuleren
- Storytelling
- Greenwashing
- Marketingstrategie
- Duurzaam consumentengedrag
- Marketing 3.0
- Kernwaarden bedrijf bepalen
- Duurzaam ondernemen

"Te klein om impact te maken? Ga eens met een mug slapen"

De customer journey – alles wat je moet weten .
Customer journey, de reis die jouw klanten afleggen. zorg jij voor een happy ending.
Als organisatie wil je jouw (potentiële) klanten een optimale klantbeleving bieden. Maar dit gaat niet zonder slag of stoot. Door de vele aanbieders en 24/7 economie hebben consumenten hoge verwachtingen en weinig geduld. Daarom is het niet gek als je soms wakker ligt van vragen als:
- Waar hebben mijn (potentiële) klanten behoefte aan?
- Ben ik wel relevant voor deze doelgroep?
- Geef ik hen de juiste informatie, op het juiste moment, via het juiste kanaal?
- En sluit deze informatie aan bij wat ze van mijn bedrijf verwachten?
Kortom, je denkt na over de beleving die de klant heeft van jouw organisatie.
Om op te vallen tussen de massa moet je relevant zijn. Je moet weten waar je doelgroep naar op zoek is en hoe ze hierbij geholpen willen worden. Dit is essentieel voor een goede klantbeleving. Een goed startpunt hiervoor, is door te kijken naar de zogeheten ‘customer journey’ die de doelgroep doorloopt. Dit is een strategisch model waarmee je de stappen van de (potentiële) klant voorspelt, nagaat waar ze op dat moment behoefte aan zouden hebben en kijkt hoe je ze gaat helpen bij hun keuzes.
Lastig? Dat snappen we. Maar no worries. In deze blog geven we jou praktische handvatten om hiermee aan de slag te gaan.
Wat is een customer journey?
Het belang van een customer journey.
- Fasen customer journey
Customer journey mapping
- Voorbeeld customer journey
Een customer journey (of in regulier Nederlands: een klantreis) is de reis die een klant aflegt naar een bepaald doel. Deze begint vaak bij oriëntatie en gaat door tot ver na de aankoop. Tijdens deze reis komt de klant op verschillende momenten en op verschillende manieren, in aanraking met jouw bedrijf. Deze momenten worden ook wel touchpoints genoemd. Denk bijvoorbeeld aan advertenties, blogs, reviews of reclamevideo’s.

Je hebt nu waarschijnlijk al een beetje door dat een potentiële klant niet pas met jouw organisatie in contact komt als hij of zij voor je neus staat. Vóór dit moment zijn er al veel punten geweest waarop het pad van de klant kruist met dat van jouw bedrijf. Ook op deze punten wil je er voor de klant zijn, om ze te begeleiden en voorzien in hun behoeftes. Want als jij het niet doet, doet iemand anders het wel.
Tegenwoordig zijn consumenten namelijk niet meer zo loyaal aan bepaalde merken als voorheen. Er zijn veel aanbieders en daarmee hoge verwachtingen vanuit de klant. De kleinste afleiding of drempel (denk bijvoorbeeld aan een niet werkend linkje) kan al een reden zijn om van het pad af te dwalen. Ook zijn klanten zich erg bewust van de alternatieven, waardoor een kleine inconsistentie in je verhaal al de reden kan zijn dat een consument voor een andere aanbieder kiest. Het gras lijkt namelijk altijd groener aan de overkant.
Daarom is het belangrijk om de customer journey in kaart te brengen, zodat je weet op welke momenten je aanwezig bent en welke klantbehoeftes je vervult. Met deze inzichten optimaliseer je de klantbeleving en pluk je er meteen de vruchten van.
De fasen van een customer journey
Om te voorkomen dat je in de content overload van alle andere aanbieders verzuipt, wil je op het juiste moment met de juiste content aanwezig zijn. Door de klantreis op te delen in verschillende fases met een bijbehorende klantbehoefte, kun je content maken die relevant is voor de doelgroep op dat specifieke moment in hun reis.
Er zijn veel verschillende modellen voor klantreizen. Bij Ten Stripes gebruiken wij voor de customer journey het populaire model van Google – de vier fasen: SEE, THINK, DO en CARE. Wij hebben hier nog een vijfde aan toegevoegd, namelijk de LOVE-fase.
Waarom? Omdat we nog een fase misten waarin je van jouw trouwe klanten echte fans maakt.

De SEE-fase
Dit is de fase waarin je voor het eerst in contact komt met potentiële klanten, welke een latente of concrete behoefte heeft. Een latente behoefte is wanneer iemand bijvoorbeeld op vakantie gaat, maar nog niet heeft nagedacht over een huurauto. Een concrete behoefte is wanneer iemand op vakantie gaat en weet dat hij of zijn een huurauto nodig zal hebben. Beide behoeftes zijn de start van de SEE-fase.
In deze fase is de communicatie gericht op het genereren van merkbekendheid en bereik. Dit doe je door zichtbaar te zijn op plekken waar de doelgroep zich bevindt. Wanneer je bijvoorbeeld online bent, tv kijkt of billboards langs de weg ziet kom je meestal in aanraking met boodschappen die passen bij de SEE-fase.
De THINK-fase
Na de SEE-fase komt de THINK-fase. Hier zit de doelgroep die interesse heeft getoond in de vorige fase. Bijvoorbeeld wanneer ze op de website zijn geweest of interactie hebben gehad met je sociale kanalen. De consumenten in deze fase zijn zich aan het oriënteren en aanbieders met elkaar aan het vergelijken op basis van onder andere prijs, merkbekendheid en reviews. Wat dankzij de online economie nu op elk moment van de dag via elk apparaat mogelijk is.
Deze fase is daarom gericht op informeren met relevante informatie, zodat je op het juiste moment in het oriëntatieproces aanwezig bent om de klant zo goed mogelijk te helpen.
Whitepapers, SEO blogs, reviews, betaalde campagnes en webcare zijn middelen die je hiervoor kunt inzetten.
Gefeliciteerd! Je hebt nu mensen in jouw DO-doelgroep weten te krijgen. Nu is het tijd om de doelgroep te overtuigen om tot actie over te gaan. Communicatie in deze fase is daarom gericht op het behalen van conversies. De ‘conversie’ kan van alles zijn: het aanschaffen van een product, het inschrijven voor een nieuwsbrief of het invullen van een contactformulier.
In deze fase heeft de consument alle alternatieven afgewogen en heeft hij voor jouw organisatie gekozen. Toch kunnen er na dit besluit nog afhaakmomenten plaatsvinden. Consumenten zijn snel afgeleid, weet je nog? Bijkomende kosten, beperkte betalingsmogelijkheden, onduidelijke productinformatie en andere obstakels in het aankoopproces zijn allemaal drempels die tot afhaakmomenten kunnen leiden.
Daarom wil je ervoor zorgen dat de doelgroep in deze fase zo goed mogelijk begeleid wordt, in plaats van afgeleid. Om afhaakmomenten en drempels inzichtelijk te maken, kun je conversie-optimalisatie tools gebruiken zoals Google Analytics en Heatmaps. Een andere manier om mensen door de funnel te krijgen is door e-mailmarketing of remarketing (”Er ligt nog een product in je winkelmandje!”).
De CARE-fase
Wanneer een klant een aankoop heeft gedaan, zijn de doelen van de voorgaande fases geslaagd. Maar we zijn natuurlijk niet op zoek naar een eenmalige klant. Daarom is het belangrijk om na een conversie goed voor je klanten te zorgen. Daarom komt nu de CARE-fase in het vizier.
In deze fase gaat de klant jouw product of dienst daadwerkelijk gebruiken. Maar voor dat zover is, komt de klant eerst in de leveringsfase van het product of de aanvang van een dienst. Dit is een belangrijk punt in de klantreis, waarin de doelgroep geïnformeerd moet worden over de status van de aankoop en enthousiast gemaakt moet worden voor de gebruiksfase. Middelen om hiervoor in te zetten zijn bijvoorbeeld e-mailmarketing (statusupdates, wacht-tips, previews) en SMS-marketing (updates, kortingsactie voor de volgende aankoop).
Als het product binnen is of de dienst is gestart, begint ook de gebruiksfase. Hierbij is het voornaamste doel om de klant tevreden te houden en kansen voor upselling te benutten. Het tevreden houden kan worden gedaan door het monitoren van vragen en klachten (via webcare of op forums) en hier proactief op in te spelen of door het publiceren van blogs en video’s met nuttige informatie over het product of de dienst. Upselling kan worden gedaan via bijvoorbeeld e-mailmarketing (gerelateerde producten).
De LOVE-fase
We zijn nu aangekomen in de laatste fase van de customer journey. In deze fase maak je van je vaste klanten echte fans of ambassadeurs. Dit zijn loyale klanten die zich aan jouw organisatie binden en jouw verhaal proactief doorvertellen. Er zijn verschillende vormen van loyaliteit. Zo kun je bijvoorbeeld jouw klanten allemaal cadeautjes en kortingen aanbieden. Maar doet jouw concurrent dit ook en geeft die meer? Dan stappen deze klanten zonder twijfelen over. Er is geen gevoel van binding bij die klant. Dus hoe loyaal zijn die klanten dan eigenlijk?
Daarom is er een diepere en emotionele connectie nodig met jouw merk, want dat werkt op de lange termijn. Deze klanten zijn gehecht aan je merk en voelen zich ermee verbonden. Dit zijn klanten die je echte fans mag noemen en waar jij ook fan van mag zijn. Om dit voor elkaar te krijgen kun je bijvoorbeeld een aantal van de overtuigingsprincipes van Cialdini inzetten, zoals: liking, authority, sympathie en community.
In deze video legt Tamara uit hoe de klantreis werkt
Deze video maakt deel uit van de kosteloze e-learning the impact project.
Je weet nu wat touchpoints zijn, welke fases er in de customer journey zitten en hoe je de doelgroep hierin bedient. Nu is het tijd om deze informatie overzichtelijk weer te geven zodat je er uiteindelijk voor zorgt dat je op de juiste momenten, met de juiste informatie, via de juiste kanalen aanwezig bent voor de klant. Want als je weet waar de klant zich in de reis bevindt en waar deze op dat moment behoefte aan heeft, kun je daarop inspelen en de klant voor je winnen.

Om de klantreis in kaart te brengen, maak je gebruik van customer journey mapping . Dit is simpelweg het volgende: je bedenkt via welke punten de potentiële klant met jouw merk in aanraking kan komen en welke behoeftes ze hier hebben. Door alle touchpoints te visualiseren, maak je zichtbaar hoe een consument interactie heeft met jouw merk in zijn of haar klantreis. Op deze manier zie je waar kansen liggen en waar je kunt verbeteren om een optimale klantbeleving te bieden.
Het belangrijkste bij customer journey mapping is dat de touchpoints onderdeel zijn van een consistent en samenhangend verhaal . In plaats van losse boodschappen, zorg je hiermee voor betekenisvolle informatie die de doelgroep echt raakt.
Positieve en negatieve momenten
Het inzichtelijk maken van je touchpoints is zeer belangrijk voor customer journey mapping. Als je alles in kaart hebt gebracht weet je namelijk op welke punten je voor positieve klantbelevingen zorgt (zoals inspirerende klantcases) en op welke punten je voor negatieve klantbelevingen zorgt (zoals een niet-werkende betaalpagina) en hoe deze elkaar af wisselen. Zie je ergens in de journey een punt waarop veel negatieve momenten zijn, dan kun je dit optimaliseren door er een kleine stimulans achteraan te geven, zoals korting bij de volgende aankoop of een leuke bedankpagina.
Door het inbouwen van zulke positieve momenten in de klantreis kun je jouw klanten verrassen of enthousiasmeren. Zoek hier wel een balans in. Sommige punten zijn ‘slechts’ hygiëne factoren, ondersteunend aan de klantreis, en hebben geen toeters en bellen nodig. Het belangrijkste is dat de touchpoints op elkaar aansluiten en de klant goed begeleiden bij elke belangrijke keuze die hij maakt.
Om dit uit te leggen geven we je graag een voorbeeld

Stel, je bent een parkeigenaar van een ontzettend mooi en groot bos. Aan het einde van het bos heb je een restaurant neergezet, als bezoekers trek krijgen na het wandelen. Ook heb je routes uitgezet voor lange en korte wandeltochten. Lekker bezig!
Naast het voldoen aan een behoefte, is het ook belangrijk om te bedenken hoe je deze behoefte gaat vervullen. Ga je de aandacht sparen? Of wil je deze juist grijpen? Als de bezoeker een brug over gaat, wil je hem dan simpelweg van A naar B brengen? Of wil je op dit punt een onvergetelijke ervaring creëren? Bedenk ook hoe belangrijk dat punt is voor de rest van de klantreis. Is het wel nodig om hier te pieken met een extravagante brug? Of is een simpele houten brug ook voldoende?
Dit is meteen een goede brug (pun intended) naar het volgende punt. Want het inrichten van je touchpoints is één, maar het is ook belangrijk dat deze goed op elkaar aansluiten. Je kunt nog zo’n mooie brug bouwen, maar als hij nergens naartoe leidt heeft de bezoeker er ook niks aan… en haakt hij dus af. Dat is zeker niet de bedoeling.
Voorbeeld customer journey mapping
We horen je denken: ‘’verdiepende boodschappen, fans maken… allemaal leuk en aardig, maar hoe doe ik dit dan?’’. Een voorbeeld geeft vaak meer context. Daarom hierbij een voorbeeld van een klantreis die je vast weleens hebt doorlopen: schoenen kopen!

Customer experience vroeger
‘’Vroeger was alles anders’’. Die uitspraak klopt vaak, en zeker in het geval van customer journeys. Kijk maar eens mee.
- SEE Vroeger kreeg jij folders in de brievenbus, bijvoorbeeld van schoenenwinkels. Zo zag je de laatste trends op schoenenvlak en welke nieuwe boots in de aanbiedingen waren.
- THINK Vervolgens ging je een lekker dagje shoppen in de dichtstbijzijnde stad en liep je van de ene schoenenzaak naar de andere om de balans op te maken wat je wilde hebben. Vaak kwam je dan aan het einde van de middag weer terug in één van de eerste winkels die je had bezocht. Herkenbaar toch? 😉
- DO Na deze analyse en het passen van je nieuwe boots in de winkel besloot je uiteindelijk welke schoenen het moesten gaan worden. Of je kon niet kiezen en nam ze allemaal mee?
- CARE Doordat de shop regio kleiner was, kwam je vaak bij dezelfde winkels en maakte je in het algemeen snel gebruik van een spaarkaart voor korting (loyaliteitsprogramma).
- LOVE Door goede ervaring (en jouw loyaliteitspas) was je sneller geneigd om bij toekomstige aankopen dezelfde winkel mee te nemen tijdens jouw dagje shoppen. En deze te promoten bij jouw vrienden.

Customer experience nu
Even fast forward naar vandaag. Hoe kopen veel mensen op dit moment schoenen?
- SEE “Folders in de brievenbus? Wat is dat?” Tegenwoordig check je online wat de trends zijn op schoenengebied, bijvoorbeeld via bekende personen op Instagram.
- THINK Daarna klik je op de link of google je de specifieke schoen en krijg je direct alle online shops die je met elkaar kunt vergelijken te zien.
- DO Als je de schoenen hebt gevonden met de beste deal maak je een keuze. Ga je voor de beste prijs/kwaliteit of haalt de gratis retournering jou over de streep?
- CARE De volgende keer dat jij een nieuwe schoenen wilt kopen, is de kans groot dat je weer gaat googelen en uit de beste deals een nieuw paar kiest.
Zoals je ziet, is loyaliteit vaak niet meer een stimulans om een aankoop te doen. Elke keer als je schoenen wilt kopen, kan er een andere winkel uitkomen. De deal is dus belangrijker geworden dan loyaliteit. Hierdoor worstelen bijvoorbeeld schoenenzaken met hun CARE-fase. En dan hebben we het nog niet eens over de LOVE-fase gehad…
Walk a mile in the “customers” boots
De wijziging in de contactmomenten tijdens de klantreis zorgen voor andere behoeften voor de klant, en daarmee voor andere marketingtactieken voor schoenenzaken. Zij moeten dus opstaan en proberen op stoel van de klant te gaan zitten, of liever gezegd: eens in de schoenen van de klant gaan lopen. Zo kun je stapsgewijs de customer journey opnieuw in kaart brengen.

Ga in gesprek* met onze gedreven marketingstrateeg en dan gaan we ons lekker uitleven.
- Straalt je bedrijf uit wat je denkt wat het waard is?
- Zit er voldoende intrinsieke motivatie in het bedrijf?
- Vertel je je verhaal eigenlijk wel goed genoeg?
Na dit gesprek ben je overtuigd van onze gedrevenheid en onze skills. Een week later heb je een concreet voorstel in de mail, zodat we jouw verhaal ijzersterk en oprecht kunnen vertellen.
*no strings attached
Benieuwd hoe we jou kunnen helpen?
Gratis advies en geen verplichtingen.
Meer weten over De customer journey – alles wat je moet weten ?
- E-mail: [email protected]
Bart Joling
Missie gedreven marketingbureau
Bekijk ook deze goede verhalen .
We kunnen jou alleen goed helpen als we zelf op de hoogte zijn van de laatste ontwikkelingen op marketinggebied. Daarom duiken we regelmatig de boeken weer in, steeds op zoek naar nieuwe ontwikkelingen in marketingland. De theorie maken we ons eigen. En dat kun jij vervolgens weer lezen in onze blogs.
Terug naar alle b logs
Duurzaam ondernemen met B Corp .
Ten stripes gpt’s ., de kracht van verhalen ., van b2b en b2c naar h2h (human to human) ., de kunst van duurzaamheidscommunicatie ., voor- en nadelen van een gedragsprotocol ., interview guido & bart: de kracht van kernwaarden ., copywriting ., directe download, zonder mailadres..
- Algemene voorwaarden
- Privacybeleid
- Cookiebeleid
Hé, jij daar! Wat leuk dat je op onze fanpagina kijkt. Wil je weten wat fan zijn inhoudt? Zit je erover na te denken om officieel Ten Stripes fan te worden? Of ben je gewoon nieuwsgierig wie onze fans zijn?
Waarom fan worden?
- Je word lid van onze community
- Mee sparren over de ontwikkelingen binnen Ten Stripes
- Een extra nieuwsbrief, speciaal voor onze fans
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
What is customer journey mapping?
Customer journey map template, the customer journey mapping process, data inputs for your customer journey map, why should you use customer journey maps, the uses of customer journey mapping, how to improve a customer journey, tools to help you with your journey mapping, see how xm for customer frontlines works, customer journey mapping 101: definition, template & tips.
22 min read Find out about how to start customer journey mapping, and how to improve it for the benefit of your customers and the business.
If you want to improve your customer experience you need to be able to understand and adapt the customer journey you offer when someone interacts with your organization. Whether their journey is entirely online , offline, or a blend of both, there are multiple journeys a customer might undergo.
Understanding the customer journey in depth helps you identify and take action on customer pain points and repeat what’s working. By doing this, you will improve the overall experience that your customers have, which will have better outcomes for your business.
Outlining the potential customer journeys your audience might go through requires a process called customer journey mapping.
Free Course: Customer journey management & improvement
Creating a customer journey map is the process of forming a visual representation of customers’ processes, needs , and perceptions throughout their interactions and relationship with an organization. It helps you understand the steps customers take – the ones you see, and don’t – when they interact with your business.
It enables you to assess:
- Insights – from your existing customer journey, how to understand it better
- Impact – how to optimize budgets and effort for changes we want to make to the customer experiences
- Issues/opportunities – Diagnose the existing customer journey
- Innovation – where you might want to completely change the existing customer experience
A customer journey map gives you deeper insight into the customer, so you can go beyond what you already know. Many brands see the customer journey as something that is visible – where the customer interacts with the brand. But in reality, this is not true, and only accounts for a percentage of the entire customer journey. Creating a customer journey map gets you thinking about the aspects of the journey you don’t see, but have equal weight and importance to the entire experience.
When mapping out the customer journey, you are looking for the moments that matter – where there is the greatest emotional load.
If you’re buying a car, then the greatest moment of emotional load is when you go to pick the car up because it’s yours , after picking the color, choosing the model, and waiting for it to be ready.
Ensuring these moments match your customers’ expectations of your product, brand and service teams are key to helping you reach your business goals. But you can only do that by understanding the journey your customers go on in order to get there, what they’re thinking and needing from you at that time. Developing a customer journey map puts you in their shoes so you can understand them better than ever before.
Getting started when creating a customer journey map template doesn’t have to be difficult. However, your customer journey map template will need to cover several elements in order to be effective.
There are several ingredients that make up the anatomy of a customer journey, all of which should be looked at carefully so that you can find out where the customer journey runs smoothly and meets customer needs at that moment in time – and where the experience does not, and needs some improvement.
Understanding their behaviors and attitudes also means you can fix bad experiences more effectively too because you know why you haven’t met your customers’ expectations and what you need to do to make amends. There may be times when things go wrong, but it’s how you adapt and what you do to fix these experiences that separates the best. Knowing how the customer will be feeling makes taking that decisive action much easier.
When exploring and visualizing the customer journey we are assessing:
- Customer behavior What is your customer trying to do?
- Customer attitudes What is your customer feeling/saying?
- The on-stage experience Who/what is your customer directly interacting with? (This includes various channels, such as TV ads or social media)
- The off-stage experience Who/what needs to be in place but which your customer is NOT directly aware of?
So what could the customer journey map examples look like when starting the process of buying a car?
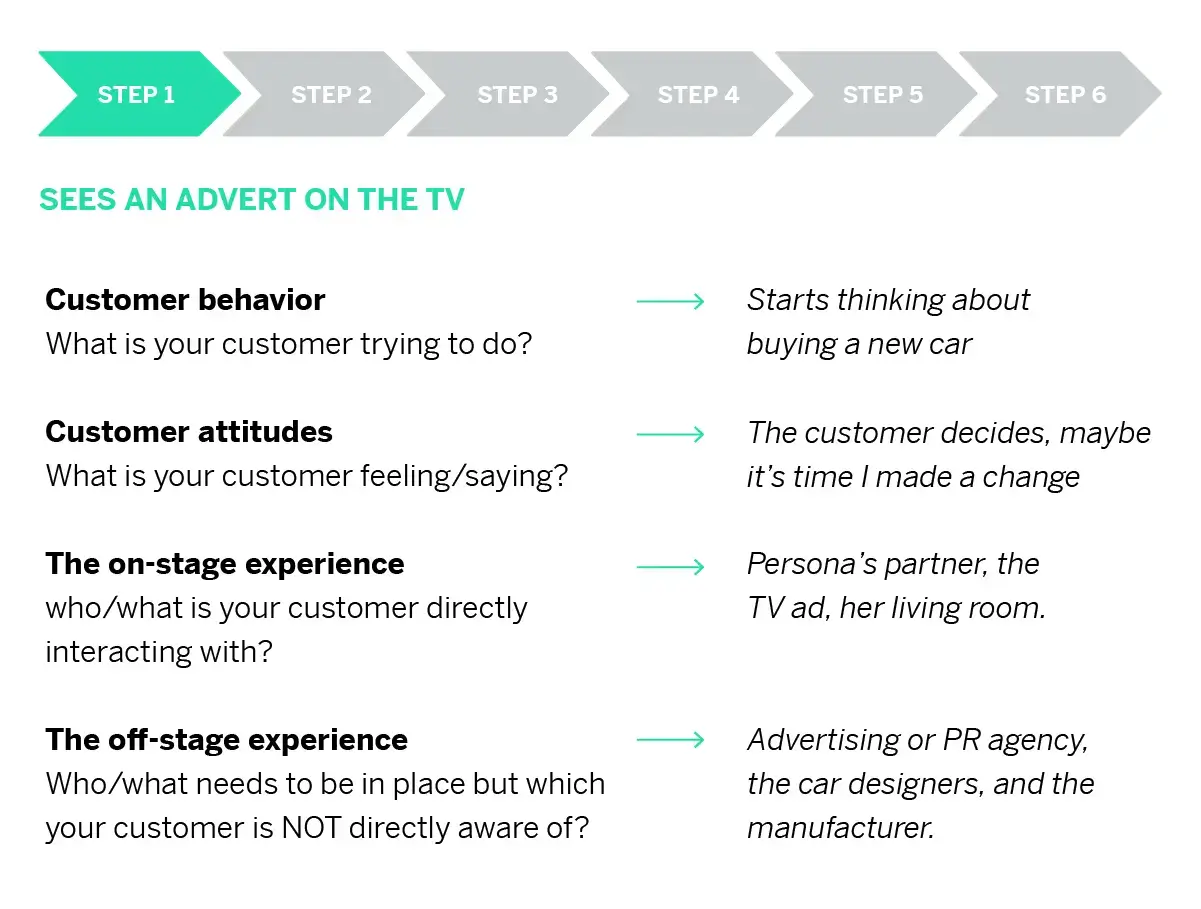
Customer journey vs process flow
Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map – otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you’re typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
There is no single customer journey. In fact, there are multiple. The best experiences combine multiple journeys in a seamless way to create a continuous customer lifecycle as outlined below.
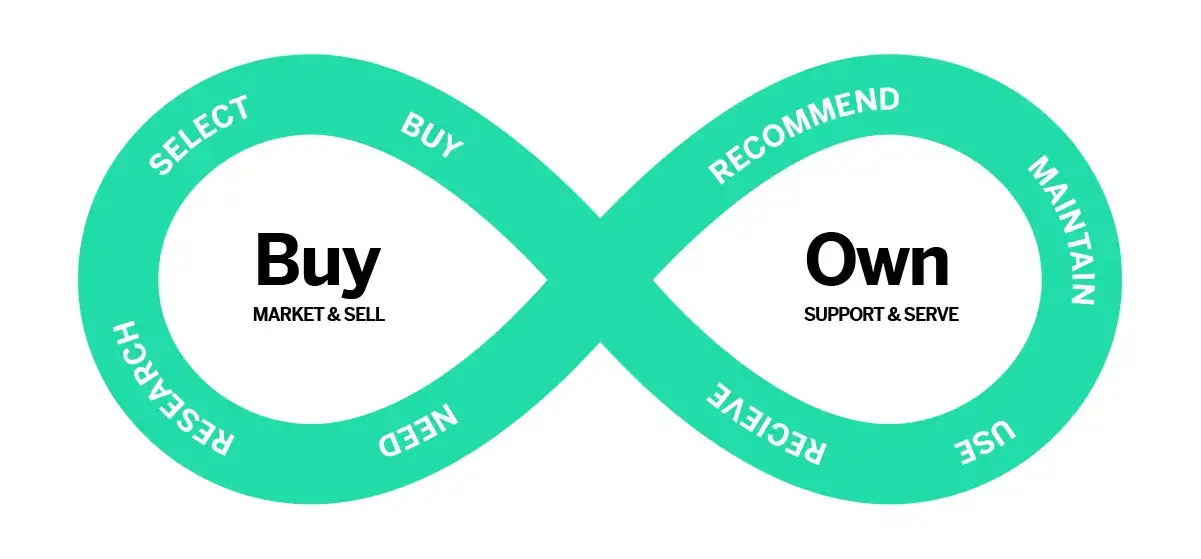
Getting started with customer journey map templates
To begin, start by choosing a journey that you would like to create a customer journey map for and outline the first step that customers will take.
You can use this customer journey map template below to work out the customer behaviors, attitudes, the on-stage and off-stage processes – and the KPIs attached to measuring the success of this experience.
Download our free journey mapping template here
The step-by-step process of mapping the customer journey begins with the buyer persona .
Step 1 – Create a customer persona to test
In order to effectively understand the customer journey, you need to understand the customer – and this is where creating a persona really helps. You may base this around the most common or regular customers, big spend, or new customers you haven’t worked with before. This persona is beyond a marketing segment , but that can be a great place to begin if you’re just starting out on the mapping process for your organization.
What do you include? Start with these characteristics.
- Family status
- Professional goals
- Personal goals
These personas help you gain a deeper understanding of your customers and can be derived from insights and demographic data , or even customer interviews . This works for both B2B and B2C business models, but in B2B especially you’ll have multiple customers for each opportunity so it’s recommended you build out multiple personas.
To begin, start with no more than three personas to keep things simple.
Create a diverse team
When creating a customer journey map, you also need to build out a diverse mapping team to represent the whole business. Include frontline staff , day-to-day management, corporate teams, HR, and business support functions. They will give you vital feedback, advice, and perspectives you hadn’t thought of.
Step 2 – Choose a customer journey for mapping
Select a customer journey map to construct, then build a behavior line. This might be a new customer journey, renewal, or fixing a product issue. You might also choose this based on the most frequent customer journeys taken, or the most profitable.
Step 3 – Work through the mapping process
Ask yourself the following:
- Who are the people involved in this journey? E.g. if you’re in a car dealership, that might be the customer, the sales rep, and front-of-house staff.
- What are the processes or the things that happen during this journey?
- What are the customer attitudes ? What are they feeling at this time? Go beyond excitement or frustration. Bring these feelings to life. This car is my dream come true!
- What is the moment that matters? Identify the greatest moment of emotional load. The make or break where everything could be good up until that point, but if you get that moment of maximum impact wrong, then all that’s good is forgotten. The best experience brands get this moment right and identifying it is an important first step to achieving that. In that moment, ask yourself what are the things/people/processes involved? Think about this for the whole business – across your product , brand , and service teams.
- But beyond identifying this moment, you need to establish what your customers’ needs are. What are they getting out of this moment? How do their needs change if this experience goes badly? Knowing the answer to these questions can help you deliver experiences that will resonate , and respond quickly to unforeseen circumstances or issues.
- And finally, how do you measure how effectively you are meeting customer needs throughout the journey? Set KPIs to put benchmarks in place for your customer journey map and customer experience and track your progress.
Step 4 – Innovate
When you are mapping out your customer journey, brainstorm ideas for how to improve that moment that really matters . These ideas don’t need to be practical, but by putting together a diverse mapping team from around the business you can begin to filter through these ideas.
Then, test it.
Ask yourself: Is it feasible? Is it viable? Is it desirable? Don’t ask can we do it, ask should we do it? Then you can start to differentiate yourself from your competitors.
Step 5 – Measure
Use the customer journey map to decide on your measurement framework.
Who are you measuring? What are you measuring? When on the journey are you measuring it? And why? And finally, what metrics and KPI’s are in place to measure this?
Your customer journey map process will require you to use several different data inputs to get an accurate picture of how your customers behave and where you can improve their experience.
A customer journey map is often developed using data gleaned from customer feedback you’ve requested . While this type of market research is useful, your research process needs to be deeper to gain a richer, more accurate understanding of your customer’s behavior.
To create a customer journey map that accurately reflects the truth of customer actions and intentions, you need to take into account both solicited and unsolicited data.
Use solicited data to understand the voice of the customer
Solicited data includes the customer feedback you gain when you conduct research through surveys such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) or ask customers for feedback on social media. This approach can be very useful for understanding your customer’s point of view , rather than just making assumptions about how they think and behave.
However, your target audiences won’t tell you everything about what they plan to do when undergoing their customer journey. Though they might tell you that they’ve had a great experience in a particular part of their customer journey, this type of feedback presents a few issues:
- You have to know when to ask for feedback : You might already have a customer journey in mind when asking for feedback – but do you know all the routes a customer might take in your customer journey map?
- It’s a snapshot: When you survey customers, you’ll likely only get insights into their experience at that particular moment about a specific touchpoint
- It’s what customers say they think/will do, not what they actually think/will do: You’re relying on your customers to accurately reflect their sentiment and intentions in their responses, which isn’t always the case. For your customer journey map to be effective, you need to find the truth
- Your sample size might be too small : If you’re trying to understand how a relatively niche customer journey is doing, you might find that the number of customers who have not only taken the customer journey but are willing to respond with feedback is very limited. You can’t risk survey fatigue by polling the same audience several times, so your insights are limited
- You’re only getting part of the picture : You will likely have several types of useful customer data on file, but these are often not considered as part of the process when creating a customer journey design because solicited data takes precedence
You’ll need to infer how customers feel to be able to accurately predict the actions a customer takes. To do so, you’ll need to look at unsolicited data.
Unsolicited data
Unsolicited data covers everything your customers aren’t telling you directly when you ask them and contextual data that you likely already collect on them, such as purchase history. It can be taken from various sources, such as your website and social channels, third-party sites, customer calls, chat transcripts, frontline employee feedback , operational sources, and more.
This type of data is nuanced, but it allows you to establish the truth of your customers’ experience. The ability to gather unsolicited customer feedback from every channel enables you to see more than just what a customer tells you directly. Using real-time feedback gathering and natural language understanding (NLU) models that can detect emotion, intent, and effort, you’ll be able to understand your customers’ actions in a more profound way. Unsolicited data offers you a 100% response rate that better indicates what your customers actually think of each step in their customer journey.
Rather than be limited to a small sample size of customers who respond to surveys, you’ll be able to build an accurate picture of the average customer on each step of the customer journey map by using this richer insight data with your own operational data.
Why using solicited and unsolicited data is important data
With solicited data, you don’t always see why a customer behaves or thinks as they do. For example, a customer might tell you that they would recommend you to a friend or family – but they don’t renew their subscription with you. A customer might be an ideal candidate for a particular journey, but they abandon their basket when prompted to give their personal details. Understanding the why behind customer actions is key for designing a great customer journey, and that’s why both solicited and unsolicited data collection and evaluation are necessary for creating great customer journey maps.
Of course, knowing how customers will actually respond to your customer touchpoints is only part of the process. You may need to develop more than one customer journey map and create sub-audiences for your customer personas to accurately see where you can rectify pain points and improve outcomes. You will need to collect and analyze contextual data across all customer journey touchpoints and develop a highly detailed journey map that can unveil routes your customers might be taking without your knowledge.
Qualtrics’ Experience ID platform can overlay solicited and unsolicited data to provide an all-encompassing picture of your customer journey map, no matter how complex. Creating an effective customer journey map is easier with all your data collated and analyzed together, with actionable insights created automatically.
A customer journey map creates a common understanding for the organization of how a customer interacts during different stages of the customer lifecycle, and the roles and responsibilities of the different teams in charge of fulfilling that experience.
It will also bring an organization together, and foster empathy and collaboration between teams because people will know what is required from everyone in the business to deliver the experiences that customers expect. This will help you to develop a shared sense of ownership of the customer relationship, which ultimately drives a customer-centric culture . With everyone working towards a common goal, communication of what you learn about the customer and the journey they go through is vital in order to drive best practices throughout the organization.
Creating an accurate customer journey map will help your customer service team to focus on more specific issues, rather than handling problems generated by a less-tailored customer journey. Your customer experience will be improved with a customer journey that’s personalized to the specific personas you have generated. You’ll have put yourself in your customer’s shoes and adapted your strategy to reflect your customer’s perspective – which in turn will create more memorable experiences.
Creating a customer journey map will influence your journey analytics across the business. So for example, it will determine what you ask, who you ask, when you ask, why you ask it and how you ask questions in your Voice of the Customer Program .
So when should you use customer journey mapping?
There are four main uses:
- Assess the current state of your customer journey Understand and diagnose the specific issues in current experiences
- Understand what the future state of your customer journey should look like Design, redesign and create new experiences
- Blueprints For implementing change
- Communication Bringing teams together to train and scale up best practices.
Take stock and take action
To improve the customer journey you need a clear vision of what you want to achieve and you need to make a distinction between the present and the future.
- What is your customer journey right now?
- What does the future state of your customer journey look like?
This is why organizations blueprint their customer journey because they can see what works and act accordingly. By understanding your customers’ attitudes and needs at critical times in the journey, you can make amends to better meet them – and develop contingencies to cope when these needs aren’t or can’t be met. For example, during a sudden, unexpected surge in demand.
Orchestrate your customer journey
To offer your customers truly optimized experiences, you’ll need to go further than just creating a customer journey map. You’ll also need to orchestrate journeys using real-time customer behavior to adapt your strategy as your customers make choices. Orchestrating a journey means taking dynamic action towards optimizing your customer’s experience, using real-time customer behavior as informative data.
Improve your employee experience
Use your diverse mapping team to come up with ideas that incorporate experience from all aspects of the business to improve the customer journey – and remember that this has a significant payoff for your employees too. Improving the employee journey – by giving teams the tools to make a difference – can have a positive knock-on effect for the customer and improve their experience in those key moments. This is because employees have the autonomy and motivation in their roles to help their customers, and realize their own potential.
Your customer journey map isn’t just designed to improve the customer experience. Creating an accurate customer journey map can help you to improve your business outcomes.
Being able to link operational data to key touchpoints in a customer journey is transformative for organizations. This is because improving segments of the customer journey will see a direct impact on your business. The Qualtrics Journey Optimizer helps you do just that. By analyzing areas for improvement as outlined by your customer journey map, organizations can take actions that will have maximum benefit for their customers, and the business too.
With Qualtrics CustomerXM , you’ll:
- Create a common understanding throughout your workforce of how a customer interacts with your organization, and you’ll know the roles and responsibilities of your different teams
- Develop empathy and collaboration between teams, working together to achieve the same outcome
- Develop a shared sense of ownership of the customer relationship which ultimately drives a customer-centric culture
Free course: Customer journey management & improvement
Related resources
Customer Journey
B2B Customer Journey 13 min read
Customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, customer journey management 14 min read, customer journey stages 12 min read, buyer's journey 16 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Brochure aanvragen
Wat is de customer journey en hoe breng je hem in kaart?
De term ‘customer journey’ staat voor de reis die jouw klant aflegt om tot de aankoop van jouw product of dienst te komen. Door dit visueel weer te geven, krijg je inzicht in hoe je de beleving van jouw klant kunt verbeteren. In dit artikel lees je alles wat je moet weten over customer journeys en het in kaart brengen ervan: customer journey mapping.
Wat is de customer journey?
De customer journey is een visuele representatie van de klantreis waarin je alle contactmomenten vastlegt die jouw potentiële klant heeft met jouw organisatie. Dit proces begint bij de oriëntatie van jouw klant tot ná de aankoop van een product of dienst. Het vastleggen van de customer journey helpt je namelijk ook te onderzoeken hoe je waardevolle klantrelaties behoudt.
De contactmomenten met jouw bedrijf, product en service in de customer journey noemen we ook wel brand touchpoints . Deze brand touchpoints ontstaan iedere keer wanneer een klant een interactie heeft met jouw merk. Door deze touchpoints te identificeren en prioriteren zie je welke van deze niet geheel in lijn zijn met jouw merkboodschap en heb je de mogelijkheid om ze te verbeteren. Hieronder zie je een voorbeeld van een customer journey visualisatie.

Fases van de customer journey
Het customer journey model bestaat uit verschillende fases. Deze vijf fases zijn verdeeld over het gehele koopproces. Iedere fase roept verschillende emoties en gevoelens op bij de klant. Door deze emoties in kaart te brengen leer je beter inspelen op de wensen van je klant. Hieronder staan ze voor je op een rijtje.
Breng de klantreis in kaart met customer journey mapping
Bij het maken van een customer journey map koppel je de verschillende brand touchpoints aan de juiste fase in de customer journey. Het doel is om al deze touchpoints overeen te laten komen met de boodschap van jouw merk. Door de touchpoints in de juiste fase van de customer journey te plaatsen, zie je in welke fase van de reis de klant zich bevindt bij ieder touchpoint. Je ziet hierdoor ook welke kanalen de klant gebruikt en welke touchpoints je liever niet gebruikt. Op deze manier verbeter je de kanalen in de klantreis en zet je deze efficiënter in.
In 5 praktische stappen naar de customer journey map
Voordat je aan de slag gaat met je touchpoints, is het van belang om vast te leggen wat je wil uitstralen als bedrijf. Waarom zouden klanten kiezen voor jouw merk ten opzichte van een ander merk? De ‘waarom’ is hier de basis. Vraag jezelf waar je bedrijf voor staat en denk vervolgens na over hoe jullie te werk gaan. Wat maakt jouw bedrijf sterk en uniek? Zet op papier wat jouw brand essence is.
2. Creëer complexe persona’s voor je doelgroep
Een persona weergeeft een karakterisering van jouw potentiële klant. Hoe zit deze klant eruit? Wat zijn diens hobby’s? Welke kanalen gebruikt deze klant? Door een fictief, maar concreet karakter te bouwen rondom je persona krijg je meer inzicht in wie jouw ideale klant is. Via deze website bouw je via een template gemakkelijk je eigen persona. Door persona’s te gebruiken leer je je doelgroep beter begrijpen en verzeker je een solide basis voor je marketing-uitingen.

Voorbeeld van een persona
3. Identificeer alle touchpoints in de klantreis
Nu je weet wie je ideale doelgroep is en welke boodschap je wil uitdragen als bedrijf is het tijd om je touchpoints te identificeren. Je kunt hierbij denken aan zoekresultaten op Google of het zien van advertenties. Een methode om dit als team te doen is bijvoorbeeld door alle touchpoints op te schrijven op een memoblaadje. Schrijf de vijf fases vervolgens op een whiteboard en ga aan de slag met het categoriseren van de touchpoints door ze op de juiste plek te hangen.
Je kunt de touchpoints ook categoriseren in handige templates zoals de afbeelding hieronder. Dit doe je bijvoorbeeld via deze website.

4. Analyseer en beoordeel je touchpoints
Doordat je duidelijk inzicht hebt in alle contactpunten tussen je klant en je bedrijf zie je eenvoudig welke touchpoints verbetering nodig hebben. Koppel je touchpoints terug aan je brand essence uit stap 1 en zie of ze overeenkomen. Het doel is niet om zoveel mogelijk touchpoints te realiseren, maar om deze zo waardevol en effectief mogelijk in te zetten. Een tip is om tijdens deze stap in contact te komen met je doelgroep. Vraag na een contactmoment bijvoorbeeld wat je klant van de ervaring vond of maak een vragenlijst en stuur deze rond naar je doelgroep. Heb je de wensen van je klant duidelijk voor ogen, dan is het eenvoudiger om deze om te verbeteren en de klant centraal te stellen.
5. Start met verbeteren
Je klantreis is in kaart gebracht. Nu is het tijd voor verandering! Maak een strategisch plan om touchpoints te verbeteren en kijk waar je terrein kan winnen. Zorg ervoor dat je altijd vanuit het perspectief van de klant blijft denken bij het maken van deze verbeterslagen.
Ben je marketing- of communicatieprofessional en wil je de customer journey-methodiek compleet beheersen? Wil je diepgaand onderzoeken wat een klant drijft, zodat je hem een onvergetelijke ervaring kunt meegeven? In de training Customer Journey van ICM leer je de klantreis in kaart te brengen en momenten van de waarheid te herkennen. Vervolgens maak je een plan om op die belangrijke momenten klantervaringen te optimaliseren. Ben je benieuwd naar meer? Bekijk hier de training en start gelijk met het verbeteren van de klantreis .
Ook interessant voor jou
- Vragen over dit onderwerp? We helpen je graag met een persoonlijk advies over welke opleiding of training het beste bij je past. Maar ook voor praktische vragen kun je terecht bij onze adviseurs. Wij zijn te bereiken op Telefoon 030 - 29 19 888 van maandag t/m vrijdag van 08.30 tot 17.30 uur. Stel jouw vraag via mail Voor meer informatie kan je ook de ICM Brochure bestellen Bestel nu ICM - Je kunt meer dan je denkt Voorwaarden
Customer journey
De customer journey is iets dat je als ondernemer vandaag de dag niet meer kan overslaan. Het is een ontzettend belangrijk onderdeel van online succes. De customer journey is veel meer dan alleen een reeks van interacties tussen klanten en een bedrijf. Het is een complex en dynamisch proces waarin potentiële klanten in contact komen met je merk, onderzoek doen, beslissingen nemen en uiteindelijk actie ondernemen. Het begrijpen van deze reis zorgt ervoor dat je de behoeften, verwachtingen en pijnpunten van je doelgroep kunt identificeren en daarop kunt inspelen.
- Hoe kom jij in de top 3?
- Waarom sta je er nu nog niet?
- Wat doet jouw concurrentie wél goed?
Wat is een customer journey?
Een customer journey is een belangrijk concept in de moderne marketingwereld. Het is de reis die een potentiële klant aflegt, vanaf het allereerste contactmoment met je bedrijf tot en met de uiteindelijke aankoopbeslissing en eventuele vervolg interacties. De customer journey kan worden opgedeeld in verschillende fasen, waarbij elke fase everschillende uitdagingen en kansen met zich meebrengt. De typische fasen omvatten bewustwording, overweging, aankoop en nazorg. Tijdens elke fase kan een potentiële klant verschillende kanalen en touchpoints gebruiken om informatie te verzamelen, beslissingen te nemen en interacties te hebben met jouw merk.
Het begrijpen van de customer journey stelt bedrijven in staat om beter in te spelen op de behoeften en verwachtingen van hun doelgroep. Door te anticiperen op wat klanten nodig hebben in elke fase van hun reis, kun je gerichte marketinginspanningen en klantgerichte strategieën ontwikkelen. Dit resulteert in een verbeterde klanttevredenheid, verhoogde loyaliteit en uiteindelijk een hogere omzet.
Bij SAM Online Marketing geloven we in de kracht van de customer journey en helpen we bedrijven deze te begrijpen en te optimaliseren. We combineren gegevensanalyse, strategische planning en creatieve uitvoering om ervoor te zorgen dat jouw potentiële klanten een naadloze en bevredigende reis ervaren op weg naar het worden van waardevolle klanten voor je bedrijf.
Ontdek hoe jij succes behaalt met SEO
Waarom is je customer journey belangrijk.
Je customer journey is van vitaal belang omdat het je in staat stelt om de ervaring van je klanten te begrijpen en te optimaliseren. Het verbeteren van de customer journey resulteert in hogere klanttevredenheid, betere klantenbinding en verhoogde omzet. Het helpt ook om klantgedrag te voorspellen en biedt waardevolle inzichten voor het ontwikkelen van effectieve marketingstrategieën. Als consultants in conversie optimalisatie begrijpen we de cruciale rol van de customer journey en helpen we bedrijven deze te verbeteren voor groei en succes.
Wat zijn customer journey touchpoints?
Customer journey touchpoints zijn de contactpunten waar klanten in aanraking komen met je merk gedurende hun reis. Dit kunnen je website, sociale media, e-mailmarketing, fysieke winkels, klantenservice kanalen en meer zijn. Het identificeren en begrijpen van deze touchpoints is cruciaal, omdat ze kritieke momenten vertegenwoordigen waarop je invloed kan uitoefenen op de ervaring van je klanten en hun besluitvorming. Hulp en advies nodig bij het optimaliseren van deze touchpoints om de customer journey te verbeteren en te personaliseren? Bij SAM Online Marketing ben je aan het juiste adres!
Wat is het verschil tussen de customer journey en de buyer’s journey?
Het verschil tussen de customer journey en de buyer’s journey ligt in de focus en timing. De buyer’s journey richt zich op het proces dat een potentiële klant doorloopt vanaf het moment van bewustwording tot de aankoopbeslissing. De customer journey daarentegen omvat de gehele ervaring van klanten met je merk, inclusief de periode voorafgaand aan de aankoop, de aankoop zelf en de nazorg. Beide reizen zijn belangrijk om te begrijpen en te optimaliseren voor succes in marketing.
Breng je customer journey in 5 stappen in kaart
Het begrijpen van de customer journey is van onschatbare waarde voor moderne bedrijven. Het stelt je in staat om de behoeften en verwachtingen van je klanten beter te begrijpen en te anticiperen op hun verlangens gedurende hun interactie met jouw merk. Bij SAM Online Marketing geloven we dat het in kaart brengen van de customer journey een essentiële stap is in het creëren van succesvolle marketingstrategieën. Hier zijn vijf stappen om je te helpen deze reis te begrijpen en te optimaliseren.
Stap 1: Bepaal wie je doelgroep is
Voordat je de customer journey in kaart kunt brengen, moet je eerst je doelgroep duidelijk definiëren. Dit omvat het identificeren van je ideale klanten, hun behoeften, demografische gegevens en gedrag. Het begrijpen van wie jouw klanten zijn, is essentieel om een effectieve customer journey te creëren die hen aanspreekt en boeit. Gebruik gegevensanalyse en klantonderzoek om inzicht te krijgen in jouw doelgroep.
Stap 2: Identificeer customer touchpoints
Een customer journey omvat verschillende touchpoints of contactmomenten waarop klanten in aanraking komen met je merk. Dit kunnen je website, sociale media, e-mailmarketing, fysieke winkels en klantenservice kanalen zijn, om er maar een paar te noemen. Identificeer alle mogelijke touchpoints waar klanten met jouw merk in contact komen. Het is belangrijk om te onthouden dat deze touchpoints kunnen variëren afhankelijk van jouw branche en doelgroep.
Stap 3: Analyseer klantinteracties
Met de touchpoints in kaart gebracht, is het tijd om de daadwerkelijke interacties van klanten te analyseren. Dit omvat het onderzoeken van hoe klanten omgaan met elk touchpoint en welke acties ze ondernemen. Analyseer bijvoorbeeld hoe klanten je website navigeren, welke pagina’s ze bezoeken en waar ze afhaken. Gebruik ook gegevens zoals klik frequenties, conversieratio’s en bouncepercentages om inzicht te krijgen in het gedrag van klanten.
Stap 4: Creëer klantpersona’s
Een effectieve manier om de customer journey te begrijpen, is door klant persona’s te creëren. Klantpersona’s zijn fictieve representaties van jouw ideale klanten, gebaseerd op demografische gegevens, gedrag en behoeften. Deze persona’s helpen je om je klanten beter te begrijpen en hun reis te personaliseren. Geef elke persona een naam, leeftijd, beroep en andere relevante details, en beschrijf hun specifieke behoeften en pijnpunten.
Stap 5: Maak Customer journey maps
Nu kun je beginnen met het daadwerkelijk in kaart brengen van de customer journey. Customer journey maps zijn visuele representaties van de reis die klanten afleggen, van bewustwording tot aankoop en nazorg. Gebruik de informatie die je heeft verzameld over doelgroepen, touchpoints en klantinteracties om deze kaarten te maken. Markeer de belangrijkste momenten en touchpoints in de reis en identificeer kansen voor verbetering.
Voor elk touchpoint en elke fase in de customer journey, overweeg de volgende aspecten:
- Klantdoelen: Wat proberen klanten te bereiken op dit touchpoint?
- Pijnpunten: Welke obstakels ervaren klanten op dit moment?
- Emoties: Hoe voelen klanten zich tijdens deze interactie?
- Kansen: Welke mogelijkheden zijn er om de ervaring te verbeteren?
Een customer journey map biedt je een holistisch overzicht van hoe klanten je merk ervaren en helpt je om strategieën te ontwikkelen om de klanttevredenheid te vergroten.
Het begrijpen van de customer journey is een doorlopend proces. Na het in kaart brengen van de reis is het belangrijk om deze regelmatig te herzien en aan te passen aan veranderende klantbehoeften en marktomstandigheden. Het stelt je in staat om voortdurend te evolueren en te blijven voldoen aan de verwachtingen van jouw klanten.
Bij SAM Online Marketing hebben we uitgebreide ervaring in het helpen van bedrijven bij het begrijpen en optimaliseren van hun customer journey. Onze aanpak is gebaseerd op gegevensanalyse, strategische planning en creatieve uitvoering om ervoor te zorgen dat je klanten een naadloze en bevredigende reis ervaren op weg naar het worden van waardevolle klanten voor je bedrijf. Neem vandaag nog contact met ons op om te ontdekken hoe wij je kunnen helpen jouw customer journey te optimaliseren en jouw bedrijf naar nieuwe hoogten te tillen.
Een greep uit onze kennisbank
In de top 3 van Google staat, doe je niet zomaar. Benieuwd naar alle ins en outs over SEO? Klik op een van de items hieronder!
Wat is seo?
SEO is de afkorting voor Search Engine Optimization.
Hoe werkt Google Ads?
Wil je beginnen met SEA, als bijvoorbeeld aanvulling op jouw SEO
Wat is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is gratis software van Google waarmee je uitgebreide…
Wat is conversie optimalisatie?
Conversie optimalisatie is één van de belangrijkste tactieken binnen…
Wat is online marketing?
Bij online marketing kies je ervoor om jouw product of dienst te promoten via het…
Wat is de customer journey?
Een customer journey is in het Nederlands een klantreis. Het is de reis de klant..

Hoe kan ik klantfeedback gebruiken om de customer journey te verbeteren?
Klantfeedback is een waardevolle bron om de customer journey te verbeteren. Door naar de stem van de klant te luisteren, kun je inzicht krijgen in hun ervaringen en pijnpunten tijdens hun interactie met jouw merk. Analyseer feedback uit enquêtes, beoordelingen en sociale media om knelpunten te identificeren en verbeteringen door te voeren. Door proactief te reageren op klantfeedback en hun behoeften aan te pakken, kun je de klanttevredenheid vergroten en de customer journey optimaliseren.
Is de customer journey een continu proces?
Ja, de customer journey is een voortdurend evoluerend proces. Klantgedrag en verwachtingen veranderen in de loop der tijd, evenals de technologie en kanalen die beschikbaar zijn. Het is essentieel om de customer journey regelmatig te monitoren en aan te passen om relevant te blijven en effectief in te spelen op veranderende behoeften. Bij SAM Online Marketing begrijpen we het belang van voortdurende optimalisatie en helpen we bedrijven om hun customer journey aan te passen aan de steeds veranderende omgeving.
Het verbeteren van je customer journey uitbesteden aan SAM Online Marketing
Het uitbesteden van het verbeteren van je customer journey aan SAM Online Marketing is een strategische zet die je bedrijf aanzienlijk kan versterken. Wij begrijpen dat de customer journey niet alleen een reeks interacties is, maar eerder een cruciale reis waarop klanten in aanraking komen met je merk, beslissingen nemen en uiteindelijk actie ondernemen. Ons ervaren team van professionals heeft bewezen expertise in het begrijpen van klantgedrag en het identificeren van de meest kritieke touchpoints in de customer journey.
Met een data-gedreven aanpak analyseren we gedetailleerde gegevens om inzicht te krijgen in het gedrag van je klanten en hun behoeften. We geloven in feiten en cijfers om gefundeerde beslissingen te nemen en de best mogelijke resultaten te behalen. Ons bureau biedt maatwerk oplossingen, afgestemd op de specifieke behoeften en doelen van jouw bedrijf, ongeacht de omvang of de branche waarin je actief bent. Onze toewijding aan voortdurende verbetering betekent dat we de customer journey blijven monitoren en aanpassen aan veranderende marktomstandigheden en klantbehoeften, zodat je altijd relevant blijft. We zijn resultaatgericht en hebben een bewezen staat van dienst in het vergroten van klanttevredenheid, conversieratio’s en omzet voor onze klanten. Het verbeteren van je customer journey is een strategische investering in de groei en het succes van je bedrijf. SAM Online Marketing staat klaar om je te helpen bij het creëren van een boeiende en bevredigende ervaring voor je klanten. Neem vandaag nog contact met ons op om te ontdekken hoe wij je hulp en advies kunnen geven bij het optimaliseren van je customer journey en het behalen van je bedrijfsdoelen. Samen bouwen we aan een betere klantenervaring en een sterker bedrijf.
Wat maakt ons uniek?
Waarom jij met SAM wél wint
We zetten de extra stap
Waar andere marketeers het houden bij tools, denken wij verder dan dat om resultaten voor jou te halen.
Super resultaat gericht!
Door onze holistische aanpak behalen wij consistent resultaten voor al onze klanten!
Alle online expertise in-house
Vanuit jouw budget maken we een strategisch plan met de kortste weg naar resultaat

Hoe kan ik de customer journey optimaliseren?
Het optimaliseren van de customer journey begint met het begrijpen van je klanten. Verzamel gegevens en feedback om knelpunten te identificeren en te begrijpen waar verbeteringen nodig zijn. Personaliseer de interacties op basis van klantvoorkeuren en behoeften. Zorg voor een naadloze overgang tussen verschillende touchpoints en fases in de reis. Blijf de customer journey monitoren en aanpassen aan veranderende behoeften en technologische ontwikkelingen om ervoor te zorgen dat klanten een bevredigende en boeiende ervaring hebben bij elk contact met je merk.

Meer dan 17.000 maandelijkse bezoekers!
Wat begon als een aanvraag voor een conversiegerichte website, werd een tijd een langdurige SEO samenwerking. Benieuwd naar deze resultaten? Lees verder!
#SEO #conversie #landelijk #webshop #Speedcube
Ontdek jouw SEO score
Doe de GRATIS SEO scan
Laat ons je website analyseren en zet stappen in de juiste richting.

SEO specialist
Wat andere ondernemers zeggen…
#SEO #website
Professionele Team die hart heeft voor jou zaak en er voor zorgt dat jij moet goed gevoel je werk kan doen!
Brahim Vlogs
Ik kan niet anders zeggen dan dat ik zeer tevreden ben, alle afspraken zijn tot nu nagekomen. Wat ik zeer belangrijk vindt is dat als er een verandering plaats moet vinden dat het snel gedaan wordt, en dat is hier zeer zeker het geval!
Van Vleuten Marketing
Wij hebben een hele prettige samenwerking met SAM Online Marketing. De werkwijze en communicatie is altijd helder. Beide partijen weten wat we van elkaar kunnen verwachten. Dit is zeker een aanrader.

Expertise nodig voor jouw online marketing?
Onze specialisten geven je advies op maat waarmee jij boven jouw concurrenten uit stijgt!
- Nauw contact met onze specialisten
- Altijd gericht op conversie
- Transparant in wat wij voor jou doen
Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Updated: April 17, 2024
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2022? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map at the last second?

The thing is — understanding your customer base can be very challenging. Even when you think you’ve got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

While it isn’t possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a convenient tool for keeping track of critical milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents
What is the customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, benefits of customer journey mapping, customer journey stages.
- What’s included in a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Customer Journey Design
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer’s journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I’ve worked with were confused about the differences between the customer’s journey and the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don’t wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process of considering, evaluating, and purchasing a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand’s place within the buyer’s journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer’s journey. When you create a customer journey map, you’re taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey instead of leaving it up to chance.
For example, at HubSpot, our customer’s journey is divided into three stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
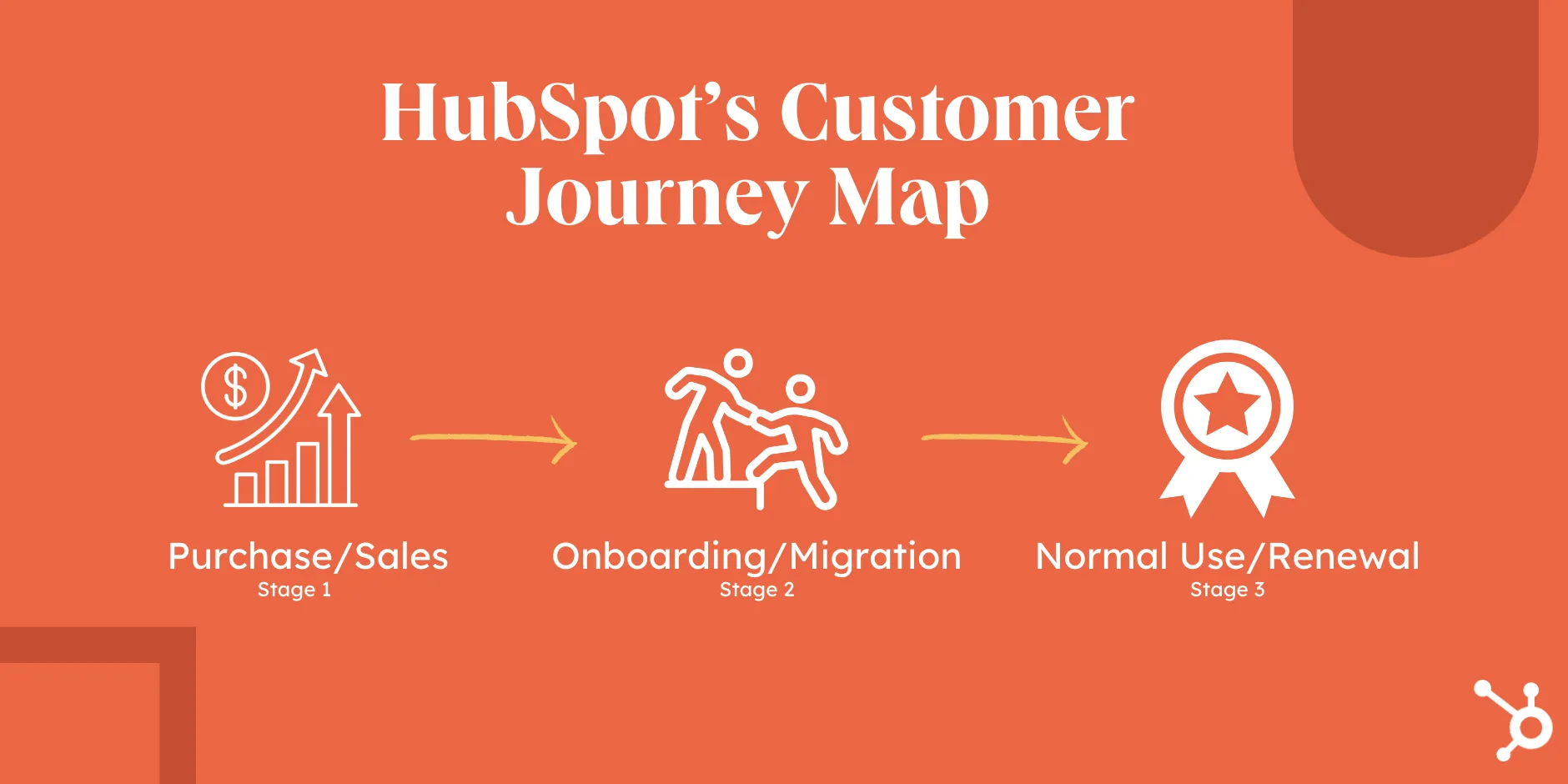
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot’s free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer’s journey, a day in your customer’s life, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company’s buyer persona. This will improve your product and customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you’re creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don’t have one, I recommend creating a buyer persona . This persona is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics of your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics ready.
Don’t have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot’s Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Questionnaires and user testing are great ways to obtain valuable customer feedback. The important thing is to only contact actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you’ve learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a customer journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company. If you group too many personas into one journey, your map won’t accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it’s best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don’t worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
What is a touchpoint in a customer journey map?
A touchpoint in a customer journey map is an instance where your customer can form an opinion of your business. You can find touchpoints in places where your business comes in direct contact with a potential or existing customer.
For example, if I were to view a display ad, interact with an employee, reach a 404 error, or leave a Google review, all of those interactions would be considered a customer touchpoint.
Your brand exists beyond your website and marketing materials, so you must consider the different types of touchpoints in your customer journey map. These touchpoints can help uncover opportunities for improvement in the buying journey.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there’s no overlap.
This is essential in creating a customer journey map because it provides insight into your customers’ actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they’re quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you must also look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels.
- Email marketing.
- Third-party review sites or mentions.
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding — you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![customer journey model uitleg How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey model uitleg How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey model uitleg Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![customer journey model uitleg How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
![customer journey model uitleg Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-experience-vs-user-experience_2.webp)
Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
The definitive 8-step customer journey mapping process
In business, as in life, it's the customer's journey that makes the company's destination worth all the trouble. No customer wants to jump through several different hoops to get to your product: they want it fast and they want it now.
Following certain customer journey mapping stages helps you improve your user's experience (UX) to create a product they love interacting with, ensures you stay ahead of key workflow tasks, and keeps stakeholders aligned. But a misaligned map can derail your plans—leading to dissatisfied users who don’t stick around long enough to convert or become loyal customers.
Last updated
Reading time.

This article walks you through the eight key stages of great customer journey mapping, and shows you how to adapt each to your unique business and product to optimize the customer experience from start to finish.
Learn how customers interact with your product and website
Hotjar's Observe and Ask tools let you go ‘behind the scenes’ to understand your users’ product experiences and improve their customer journey.
An 8-step process for effective customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a visualization of every point of interaction a user has with your company and product.
Mapping out the customer journey gives you insights into your buyers’ behavior to help you make changes that improve your website and the user flow between touchpoints. This helps you increase online sales and turn users into loyal customers and brand advocates.
Follow these eight proven steps to understand—and enhance—the customer experience.
Note: every business is distinct, so be sure to adapt these steps to your particular user and business needs.
1. Define your purpose
The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won’t know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
To define your purpose, consider your company’s mission statement and incorporate your specific user pain points as much as possible.
Make your purpose specific to your company’s needs and goals—for example, the purpose of an ecommerce brand looking to help users navigate several different products and make multiple purchases will differ from that of a SaaS company selling subscriptions for one core product.
2. Make sure your team is aligned and roles are clear
Cross-functional collaboration is essential when mapping out your brand's or product’s user journey. Get insights from different teams within your organization to find out exactly how users engage with key touchpoints to derive a holistic sense of the user experience (UX), which will help you improve every aspect of the customer experience.
Lisa Schuck , marketing lead at Airship , emphasizes the importance of keeping “anybody that has a touchpoint with a customer” involved. She advises teams to “figure out how to align your external marketing and sales with your internal operations and service.”
Although sales, product, and marketing departments are often the key players in customer journey mapping, also involve your operations and design teams that are responsible for creating the user flow.
If you have a SaaS company, for example, marketing creatives, sales teams, product owners and designers, and your customer experience department all need to participate in the process. Clearly define who’s responsible for different aspects of the map, and regularly check in to make sure your final map isn’t missing any important perspectives.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Highlights feature to collect and organize key product experience (PX) insights and data on user behavior from teams across your organization to help you build your customer journey map. Then use Hotjar’s Slack integration to quickly share learnings with your relevant stakeholders to get buy-in and ensure everyone is aligned.
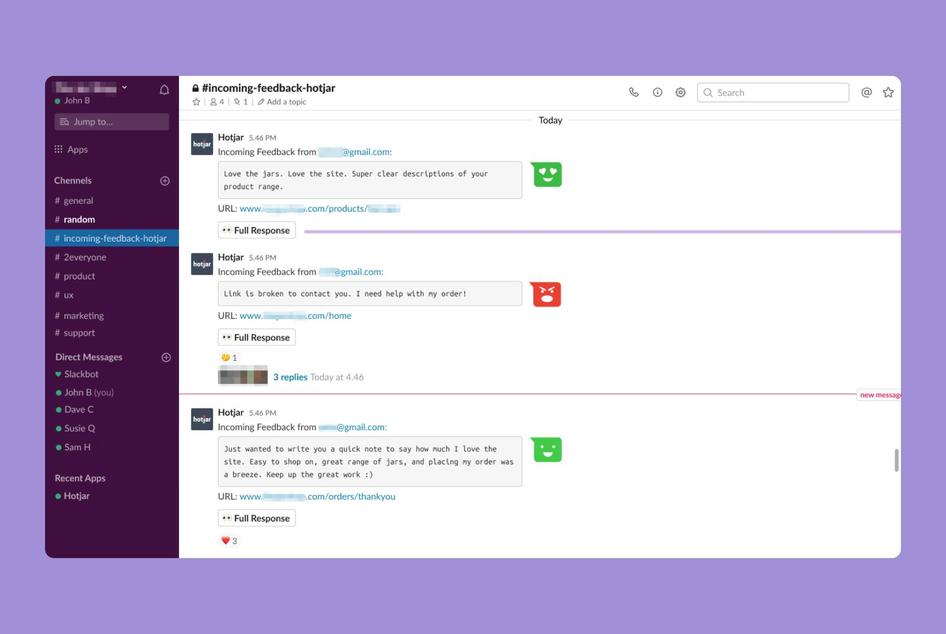
Hotjar’s Slack integration Slack lets teams discuss insights in the moment, so they’re up to date with critical issues
3. Create user personas
Once you’ve defined your purpose and involved all relevant stakeholders, it’s time to design your user personas . Use resources like UXPressia and HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool to help you design various product personas .
Create a range of user personas to understand what each type of buyer needs to curate a journey that’s easy and enjoyable for every customer. This is an important early step in the customer journey mapping process—because if you don’t understand your users, you won’t be able to fully comprehend how they interact with your brand to better it.
Create user personas for all your product’s possible buyers—for example, to map out a B2B customer journey for a company in the hospitality business means developing personas for a range of different customers, from large chain hotel managers to small vacation rental owners.
4. Understand your user goals
Once you’ve designed your user personas, it’s time to define their jobs to be done . What do your users hope to accomplish when they search for your product or service? What do they want to do when they click on your website? Address and answer these questions to build a deep understanding of your users’ goals and pain points to inform your customer journey.
In a SaaS customer journey , perhaps users are looking for helpful comparisons of product features on your website, or want to easily sign up for a trial account in the hopes that your product will solve their problems. But you won’t know until you ask .
Once you have users or test users, get direct insights from them with Hotjar's Feedback tools and Surveys to ask buyers exactly what their goals are as they browse different pages of your website or interact with product features.
Since user goals are at the center of your customer journey map, define them early on—but keep speaking to your users throughout the entire process to make sure you’re up to date with their needs.
5. Identify customer touchpoints
After you understand your users and what their goals are, it’s time to identify the ways they interact with your company and your product.
"Touchpoints are the moments the customer interacts with your brand, be it through social media channels, your product, or customer support. The quality of these experiences affects the overall customer experience, which is why it’s important to be aware of them. Consider what happens before, during, and after a customer makes a purchase or uses your product."
Key customer journey touchpoints for a website or product include your homepage, landing pages, product pages, CTA buttons, sign-up forms, social media accounts, and paid ads.
Collaboration is key to identifying touchpoints throughout the entire customer journey. Include insights from different teams and stakeholders —your marketing and sales teams will have a strong understanding of the touchpoints involved pre-purchase, while the customer experience department can shed light on post-purchase touchpoints.
Post-purchase touchpoints can help turn users into loyal customers and even advocates for your brand.
In the words of Lisa Schuck, "When you create a raving fan, or a brand advocate, who goes out and tells the world how wonderful you are, you get social credibility and validity. It’s becoming more and more important to have advocates."
Pro tip : speak with your users regularly to get direct voice-of-the-customer (VoC) insights on what they love and what frustrates them on their journey. Place Hotjar Feedback widgets and Surveys at key website touchpoints like your homepage and landing pages to get valuable user insights on what you can improve. Use Hotjar’s survey templates to get inspiration for your survey questions.
An example of an on-site Hotjar Survey
6. Map out the customer journey
Once your user and product research are complete and all roles are distributed, it’s time to map out the full customer journey.
First, map out an overarching customer journey by putting your key touchpoints in order and identifying how your various user personas interact with them. Then, home in on the details, looking at how customers engage with specific aspects of your website, product, or social media accounts.
Breaking down the mapping process into smaller phases will ensure you don’t miss any key interactions.
Here’s how an ecommerce brand could lay out general touchpoints, then narrow each down into more specific actions:
Pro tip : it’s helpful to think of the user journey in terms of different functions when mapping it out, like:
Connect: how are buyers connecting with your brand?
Attract: how are you convincing them to convert?
Serve: how are you serving customers when they want to purchase?
Retain: how are you promoting brand advocacy and customer retention ?
7. Test the customer journey
Once you’ve mapped out the customer journey, it’s time to take it for a spin. You can’t understand how your users move through customer touchpoints unless you test out the user flow yourself.
Start with an informational Google search, then visit your website, check out your social media pages, and simulate the purchase process. This will help you get a better sense of how users interact with each touchpoint and how easy it is to move between them.
Be sure to try out the journey from the standpoint of every relevant user persona. For an enterprise software company, this could mean looking at how decision-makers move through the user flow vs. the employees who’ll use your software day to day.
By walking through the customer journey yourself, you can identify issues and difficulties that users may have to address them proactively.
Try out the user flow with test users to get a realistic perspective of the user experience. Be sure to use focus groups that represent every one of your user personas.
8. Use continuous research to refine your map
Continuously map out, analyze, and evaluate the customer journey by observing users and getting their feedback. Hotjar Heatmaps and Recordings help you understand how your users are experiencing the customer journey on your website: create heatmaps to see whether users are clicking on CTAs or key buttons, and watch recordings to find out how they navigate once they reach your homepage.
Then, use Google Analytics to get an overview of your website traffic and understand how customers from different channels move through the user journey.
Finally, once you have these combined user insights, use them to make changes on your website and create a user journey that is more intuitive and enjoyable.
Pitfalls to avoid during the customer journey mapping stages
Jamie Irwin , director & search marketing expert at Straight Up Search , says companies should avoid these three common mistakes when mapping out the customer journey:
Don't map out the entire customer journey at once
Don't forget about the ‘hidden journeys’
Don't make assumptions about customer behavior
To sidestep these common pitfalls:
Start by mapping out the overall journey, and only drill down into more detail once you have a broader, higher-level overview of the customer journey
Factor in every way that customers interact with your brand, even the ones you don’t have as much visibility on, like ‘dark social’ communications about your brand shared in private channels. Talk to your users to find out what they’ve heard about your brand outside of public channels , and use sticky share buttons to keep track of when your content’s shared through email or social media messengers.
Take a data-informed approach: don’t assume you already know your users —test out your hypotheses with real users and qualitative and quantitative data.
Follow proven steps to successfully map out the customer journey
Take the time to understand your business goals and users, involve the right teams, and test frequently to consistently improve your customer journey and make the decisions that will help you map out an experience that will get you happy and loyal customers.
FAQs about customer journey mapping stages
What is the purpose of customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping helps you visualize how users interact with your business and product, from the moment they find it until long after they make their first purchase.
The purpose of customer journey mapping is to gain insights into the buyer's journey to create a more enjoyable, streamlined, and intuitive experience for your customers.
What are the benefits of following a customer journey mapping process?
The main benefits of a customer journey mapping process are: :
Building on tried-and-tested processes
Not missing any key steps
Considering all buyer personas
Keeping all relevant stakeholders involved
Creating a valuable customer journey map
Improving user experience
What happens if you don’t follow key steps in customer journey mapping?
If you don’t follow key steps when mapping out the customer journey, your map likely won’t give you the insights you need to enhance the experience users have with your most important touchpoints —like your homepage, landing pages, CTAs, and product pages.
This can result in high bounce rates, low conversion, and unsatisfied users who fail to become loyal customers.
CJM benefits
Previous chapter
CJM touchpoints
Next chapter

23 dec Het Geheim: De Customer Journey
Update 2023:.
Het mappen van de customer journey helpt jou na te denken over wanneer je nu wat moet vertellen en met welke boodschap. We zien heel vaak dat heel veel boodschappen door elkaar lopen op de verkeerde kanalen op het verkeerde moment. Ervaar jij dit ook zo en weet je niet precies wanneer je wat moet vertellen. Dan is het gebruik maken van Het Kijk-, Kies-, Koop-, Krijg-, Koestermodel van MijnMarketing.com een uitkomst. Customer journey mappen in 2023, lees het hier .
———————————-
In dit artikel lees je over de 5 fases binnen de customer journey en geven we 5 tips weg. Dit is pas het topje van de ijsberg, want er is veel meer te vertellen over dit thema. In de volgende blog-items zullen we verder inzoomen op de specifieke onderdelen van de customer journey.
5 fases binnen de customer journey
Fase 1: awareness.
Awareness is de beginfase van de customer journey. In deze fase zijn klanten passief. Ze horen misschien wel iets over je merk, maar doen niet actief iets met deze kennis. Ze gaan bijvoorbeeld niet meteen je website bezoeken of reviews checken. In deze fase ga je dus je klanten triggeren om een actieve houding aan te nemen. Dit kan bijvoorbeeld door middel van online Display advertising, Facebook advertising, print media, of mond-tot-mond reclame.
Fase 2: Consideration
In deze fase zijn je klanten getriggerd en gaan ze een keuze maken. Hoewel ze misschien inmiddels wel al wat kennis hebben zullen ze zich tijdens deze oriëntatiefase verder gaan verdiepen om meer te ontdekken. Ja, ze ontdekken dan ook de concurrent. Het is belangrijk om in deze fase ervoor te zorgen dat bezoekers niet meteen afhaken. Stel je bijvoorbeeld voor dat een klant gaat zoeken naar de beste wijn die je online kunt kopen. Wanneer je als merk niet op de eerste pagina staat op Google is de kans dat een klant afhaakt heel groot. SEO en SEA zijn middelen die dit voorkomen.
Fase 3: Purchase
Tijdens ‘purchase’ gaat de klant over tot aankoop. In deze fase is het belangrijk dat het aankoopproces goed, snel en makkelijk verloopt. Het bezoek aan jouw winkel, de verkoop afspraak of een online aankoop. Als er veel problemen ontstaan in bijvoorbeeld een online bestelproces kan de klant afhaken. Daarnaast geeft onvriendelijk personeel of te veel clicks op je website ook een negatief gevoel af. Klantvriendelijkheid & gebruiksgemak staan in deze fase centraal. Veel van deze mogelijke problemen kun je oplossen middels conversie optimalisatie. Heb je een mooie, gebruiksvriendelijke website met de juiste call-to-actions?
Fase 4: Retention / service
Waar het bij de vorige fases voornamelijk om gebruiksvriendelijkheid gaat, is het in deze fase belangrijk om de klant een positieve ervaring mee te geven. De customer journey houdt namelijk niet op na de aankoop. Het is een continue cyclus. Webcare & service zijn in deze fase belangrijke touchpoints. Grote merken zijn zeer actief op het gebied van webcare . De customer journey houdt niet op na de aankoop
Fase 5: Loyalty
In deze fase kun je een loyalty loop creëren: een lus die klanten een verkorte customer journey laat ervaren. De loyalty fase staat geheel in het teken van nazorg. Denk bijvoorbeeld aan het versturen van een nieuwsbrief , Social Media , een App en CRM. Wanneer je middels deze kanalen een goede relatie krijgt met jouw klant dan zal deze sneller de ‘consideration’ fase overslaan. Je klant weet dat wat jij doet goed is en kiest voor jouw merk.
5 tips voor jouw customer journey
We kunnen stellen dat er niet één customer journey is, maar dat deze per klant verschilt, het instap- en vertrekkanaal per klant anders is, de customer journey gaandeweg verandert en niet volledig gecontroleerd kan worden door bedrijven. Maar hoe kun jij de customer journey bepalen voor jouw merk? We geven 5 tips weg.
Tip 1: Less is more
Laat onnodige kanalen vallen en wees aanwezig op de juiste kanalen. Hiervoor moet je eerst analyseren wat de voorkeur van jouw doelgroep heeft.
Tip 2: Hit the right moment
Elimineer alle overbodige klantcontactmomenten. Maak geen gebruik van massacommunicatie en bijvoorbeeld onnodige stappen in het bestelproces. Think small: een bevestigingsmailtje na een bestelproces wordt zeer op prijs gesteld.
Tip 3: Mobile first
Het principe “design mobile first” dwingt je om je communicatie terug te brengen tot de kern: wat is er echt nodig?
Tip 4: Be there
Wees er op het juiste moment, op de juiste plaats, via het juiste kanaal en op de juiste manier. Het draait allemaal om relevantie op het moment dat de klant er behoefte aan heeft. Wees er op het juiste moment, op de juiste plaats, via het juiste kanaal en op de juiste manier
Tip 5: Become friends
Als merk wil je maar één ding: vrienden worden met je klanten. Dit kun je realiseren door op individueel niveau te communiceren met je klanten.
Hoe ziet jouw customer journey er uit?
Marketeers die het verschil willen maken richten zich op de hele customer journey van de klant op weg naar zijn doel(en) en niet alleen tot het moment dat de verkoop is gerealiseerd. De hedendaagse marketeer onderzoekt, ontwerpt, integreert, kanaliseert en optimaliseert de customer journey en zijn touchpoints. Hulp nodig? Bij MijnMarketing.com zijn er specialisten op het gebied van customer journey, die graag in de huid van jouw merk en klant kruipen!
See author's posts
About The Author

Customer journey map: de klantreis in kaart brengen
Lucid Content
Leestijd: ongeveer 9 min
Onderwerpen:
Een customer journey map maken
- Stel doelen - Door de juiste doelen te stellen heeft je customer journey de gewenste impact.
- Doe onderzoek naar persona - Verzamel zoveel mogelijk info over de wensen en behoeften van je klanten.
- Definieer contactpunten voor klanten - Breng alle interacties tussen de klant en je merk in kaart
- Breng huidige situaties in kaart - Visualiseer je huidige staat. Pro tip: Gebruik Lucidchart !
- Breng toekomstige situaties in kaart - Deel de resultaten van je onderzoek met relevante stakeholders en ga samen op zoek naar verbeteringen.
Steve Jobs, het brein achter de unieke klantervaring van Apple, zei: "Je moet beginnen met de klantervaring en dan naar de technologie toe werken, niet andersom."
Tegenwoordig is een duidelijke visie en strategie voor interacties met klanten niet langer een optionele "nice-to-have"—het is essentieel. Terwijl je je customer experience verfijnt, is een customer journey map één van de krachtigste manieren om inzicht te krijgen in je huidige situatie en toekomstige situaties.
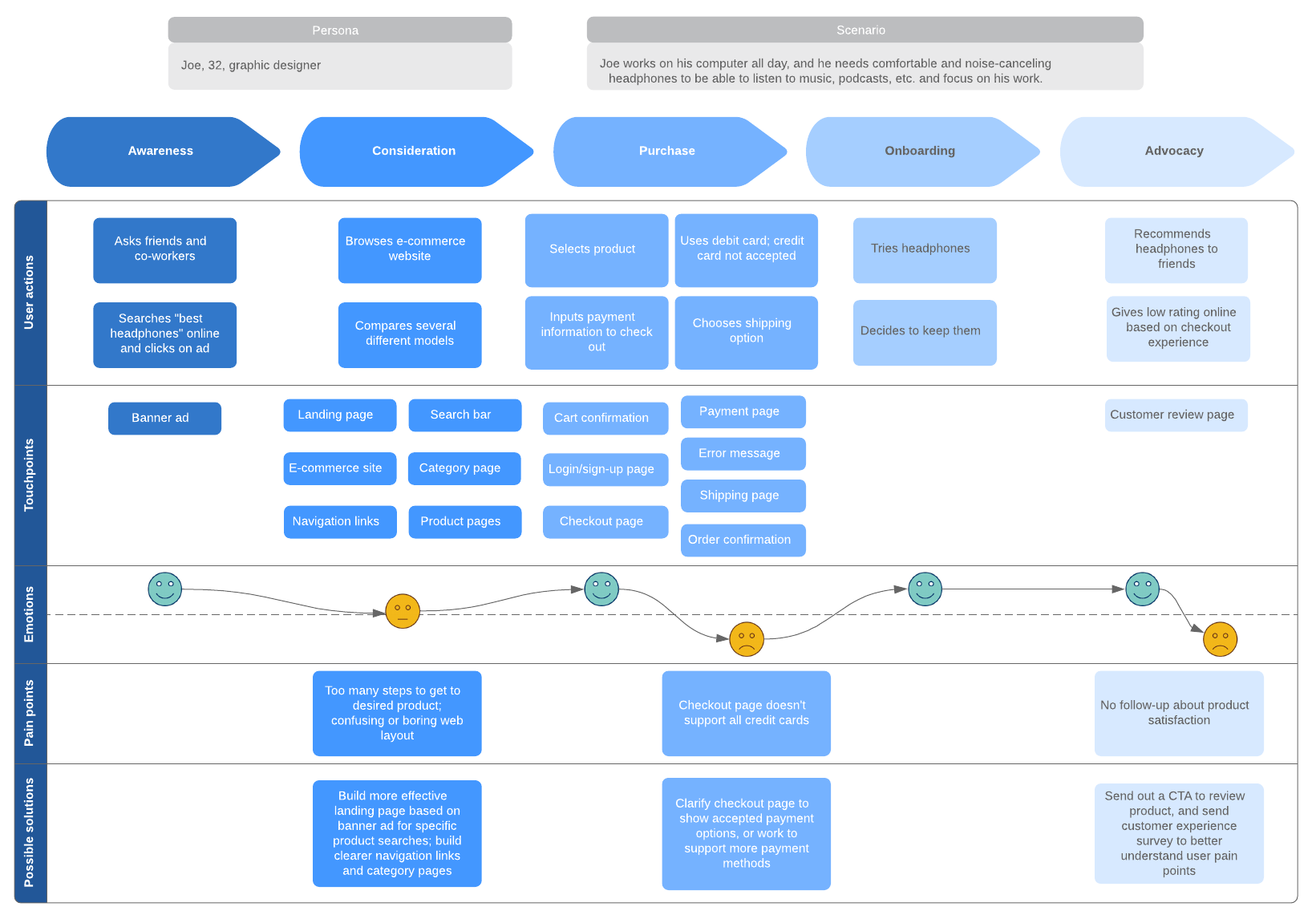
Een customer journey map is een diagram die het proces weergeeft waar je klanten doorheen gaan bij interactie met jouw bedrijf, zoals de ervaring op de website, de ervaring in de winkel, de service, een product of een mix van deze dingen.
Wat is een customer journey?
Een customer journey, ofwel klantreis, is een visuele weergave van de ervaring van een klant met jouw merk. Deze beelden vertellen een verhaal over hoe een klant zich door elke fase van interactie beweegt en elke fase ervaart. Je customer journey map moet contactpunten en momenten van waarheid bevatten, maar ook potentiële gevoelens van de klant, zoals frustratie of verwarring, en eventuele acties die je wilt dat de klant onderneemt.
Customer journey maps zijn vaak gebaseerd op een tijdlijn van gebeurtenissen, zoals het eerste bezoek van een klant op je website en de manier waarop ze evolueren naar hun eerste productervaring, daarna de aankoop, onboardingmails, annulering, enz.
Je customer journey maps moeten misschien worden afgestemd op je bedrijf of product, maar de beste manier om deze fasen te identificeren en te verfijnen is door daadwerkelijk met je klanten te praten. Doe onderzoek naar je doelgroepen om te begrijpen hoe ze beslissingen nemen, overgaan tot aankoop, enz. Zonder een essentieel inzicht in je klanten en hun behoeften, zal een customer map je niet naar succes leiden. Toch kan een goed geconstrueerde en onderzochte customer journey map je de nodige inzichten geven om de customer experience van je bedrijf drastisch te verbeteren.
De voordelen van het in kaart brengen van customer journeys
Het in kaart brengen van de customer journey is een krachtig hulpmiddel om inzicht te krijgen in de klantervaring, zakelijke doelen te stimuleren en veerkracht op te bouwen in een veranderende markt. In een rapport uit 2022 ontdekte Hanover Research dat 94% van de bedrijven zei dat hun customer journey maps hen helpen nieuwe producten en diensten te ontwikkelen die aansluiten bij de behoeften van de klant. Nog eens 91% zei dat hun maps de verkoop stimuleerden.
Het begrijpen van een customer journey door je hele organisatie doet echter zo veel meer dan je inkomsten uit marketingcampagnes verhogen, je servicekosten verlagen en je verkoopcyclus verkorten. Het stelt je in staat te ontdekken hoe je consistent kunt zijn als het gaat om het bieden van een positieve customer experience en het behouden van klantloyaliteit. Dit was vooral duidelijk in de afgelopen jaren, aangezien naast het verbeteren van marketing, customer journey maps naar voren kwamen als een waardevolle manier om evoluerend kopersgedrag te begrijpen. Sterker nog, 1 op de 3 bedrijven gebruikte klantreiskaarten om hen te helpen navigeren door het veranderende landschap tijdens de pandemie.
Wanneer het goed is uitgevoerd, helpt het in kaart brengen van de customer journey om:
- De betrokkenheid van klanten te verhogen door kanalen te optimaliseren.
- Momenten van waarheid in de CX te identificeren en optimaliseren.
- Ineffectieve contactpunten te elimineren.
- Van een bedrijfsgericht naar een klantgericht perspectief over te stappen.
- Silo's tussen afdelingen te doorbreken en interdepartementale kloven te dichten.
- Je te richten op specifieke buyepersona's met marketingcampagnes die relevant zijn voor hun identiteit.
- De omstandigheden te begrijpen die eventueel tot onregelmatigheden in bestaande kwantitatieve gegevens hebben geleid.
- Eigendom toe te kennen aan verschillende contactpunten voor klanten om de verantwoordelijkheid van de werknemers te vergroten.
- Het mogelijk te maken om de ROI van toekomstige UX/CX-investeringen te beoordelen.
Door het proces te volgen dat we hierboven hebben geschetst, kan het in kaart brengen van klanten je organisatie op een heel nieuw succesvol traject zetten. Volgens onderzoek van HAnover Reasearch beschikt slechts 47% van de bedrijven momenteel over een proces om customer journeys in kaart te brengen. De investering om je customer journey in kaart te brengen en dat proces te versterken als onderdeel van het DNA van je bedrijf, kan resulteren in aanzienlijke voordelen in het competitieve landschap, waardoor jouw oplossing de beste optie wordt waar klanten van houden.
Customer journey map maken
Customer journey maps kunnen ingewikkeld worden als je ze niet overzichtelijk houdt. Hoewel je je op meerdere persona's kunt richten, kies je toch maar één persona en één klantenscenario per keer om te onderzoeken en te visualiseren. Als je niet zeker weet wat je persona's of scenario's zouden kunnen zijn, verzamel dan een aantal collega's en probeer een affiniteitsdiagram in Lucidchart uit om ideeën op te doen.
1. Stel doelen
Zonder een doel zal het moeilijk zijn om te bepalen of je customer journey map zich zal vertalen in een tastbare impact voor je klanten en je bedrijf. Je zult wellicht bestaande en toekomstige kopers moeten identificeren, zodat je specifieke doelen kunt stellen voor die doelgroepen in elke fase van hun ervaring.
Breng de belangrijkste stakeholders van je bedrijf samen — van wie velen wellicht te maken hebben met verschillende punten van de customer experience. Om een logisch en haalbaar doel te stellen, is functieoverschrijdend teamwork essentieel. Verzamel unieke perspectieven en inzichten over elk onderdeel van de huidige customer journey, waar verbeteringen nodig zijn en hoe die verbeteringen gemeten zullen worden.
Pro Tip : Creëer buyer personas, als je deze nog niet hebt, ze helpen je om je customer journeys te focussen op de specifieke kopers waar je voor optimaliseert.
2. Doe klantonderzoek
Geef zoveel mogelijk informatie over de persona waarop je customer journey map is gebaseerd. Afhankelijk van de maturiteit van je bedrijf, heb je misschien maar een handvol dossiers, rapporten, of andere bestaande gegevens over de doelpersoon. Je kunt je voorlopige bevindingen samenvoegen tot een schets van hoe de customer journey er volgens jou uit zou kunnen zien. De belangrijkste gegevens die je kunt verzamelen, zijn die van echte klanten of potentiële klanten, van degenen die daadwerkelijk ervaring hebben met je merk. Verzamel nuttige klantgegevens op een van de volgende manieren:
- Doe interviews.
- Praat met werknemers die regelmatig met klanten communiceren.
- E-mail een enquête naar bestaande gebruikers.
- Doorzoek de logboeken van de klantenservice en klachten.
- Haal fragmenten uit opgenomen telefoongesprekken van het callcenter.
- Volg discussies over je bedrijf die op sociale media plaatsvinden.
- Maak gebruik van webanalyses.
- Verzamel gegevens over de Net Promoter Score (NPS).
Zoek naar informatie die verwijst naar:
- Hoe klanten je merk hebben gevonden
- Wanneer/of klanten kopen of annuleren
- Hoe eenvoudig of moeilijk ze je website vonden om te gebruiken
- Welke problemen je merk wel of niet heeft opgelost
Door tijdens het onderzoeksproces zowel kwalitatieve als kwantitatieve informatie te verzamelen, zorg je ervoor dat je bedrijf datagestuurde beslissingen neemt op basis van de mening van echte klanten.

Ontdek meer manieren om de Voice of the Customer te begrijpen
3. Definieer contactpunten voor klanten
Contactpunten voor klanten vormen het leeuwendeel van je customer journey map. Zij zijn de manier waarop en de plaats waar klanten met je merk in aanraking komen en het ervaren. Wanneer je onderzoek doet en je contactpunten uitstippelt, zorg er dan voor dat je informatie opneemt die elementen van actie, emotie en potentiële uitdagingen aanpakt.
Het aantal en het soort contactpunten op je customer journey map hangt af van het soort bedrijf. Zo zal de customer journey bij een SaaS-bedrijf inherent anders zijn dan die van een koffiehuis. Kies de contactpunten die de customer journey met je merk nauwkeurig weergeven.
Nadat je je contactpunten hebt gedefinieerd, kun je ze gaan ordenen op je customer journey map.
4. Breng de huidige situatie in kaart
Schets wat volgens jou de huidige status is van de customer journey, de huidige customer experience. Gebruik een visuele werkruimte zoals Lucidchart, en begin met het organiseren van je gegevens en contactpunten. Geef voorrang aan de juiste inhoud boven esthetiek. Vraag de stakeholders om input en maak samen een customer journey map om de nauwkeurigheid te garanderen.
Nogmaals, er is geen "juiste" manier om je customer journey map op te stellen, maar vermeld voor elke fase van de journey de contactpunten, acties, kanalen, en toegewezen verantwoordelijkheid van een contactpunt (verkoop, klantenservice, marketing, enz.). Pas vervolgens het ontwerp van je diagram aan met afbeeldingen en kleur- en vormvariaties om de verschillende acties, emoties, overgangen, enz. beter te visualiseren in één oogopslag.
Door je huidige situatie in kaart te brengen, kun je ook beginnen met het identificeren van tekortkomingen of rode vlaggen in de ervaring. Bijdragers kunnen direct commentaar geven op verschillende delen van je diagram in Lucidchart, zodat het precies duidelijk is waar er ruimte is voor verbetering.
5. Breng de toekomstige situatie in kaart
Nu je de huidige situatie van de customer journey hebt gevisualiseerd, zal je map waarschijnlijk enkele tekortkomingen in je CX laten zien, overlappende informatie, slechte overgangen tussen fases, en belangrijke pijnpunten of obstakels voor klanten.
Gebruik hotspots en lagen in Lucidchart om gemakkelijk potentiële oplossingen in kaart te brengen en vergelijk snel de huidige situatie van de customer journey met de ideale, toekomstige situatie. Presenteer je bevindingen aan het hele bedrijf om iedereen op de hoogte te brengen van de verbeterpunten, met een duidelijk stappenplan voor verwachte veranderingen en hoe hun rol kan bijdragen aan het verbeteren van de customer journey.
Sjablonen voor customer journey mapping
Je beschikt over alle juiste informatie voor een customer journey map, maar het kan moeilijk zijn om precies te weten hoe je de informatie moet rangschikken op een leesbare en visueel aantrekkelijke manier. Deze voorbeelden van customer journey mapping kunnen je op weg helpen en je inspiratie geven over wat en hoeveel je waar in kaart moet brengen.

Laat de mogelijkheid van een slechte customer journey je geen slapeloze nachten bezorgen. Ken de huidige status van de customer journey met je bedrijf, en breng de veranderingen aan die je nodig hebt om klanten aan te trekken en tevreden te houden.

Customer journeys in kaart brengen is gemakkelijk met Lucidchart.
Over Lucidchart
Lucidchart, een slimme diagramapplicatie in de cloud, is een kernonderdeel van Lucid Software's pakket voor visuele samenwerking. Met deze intuïtieve cloudgebaseerde oplossing kunnen teams in realtime samenwerken om flowcharts, mockups, UML-diagrammen, kaarten van customer journeys en meer te maken. Lucidchart stuwt teams vooruit om sneller aan de toekomst te bouwen. Lucid is trots op zijn diensten aan belangrijke bedrijven over de hele wereld, waaronder klanten als Google, GE en NBC Universal, en 99% van de Fortune 500. Lucid werkt samen met brancheleiders, waaronder Google, Atlassian en Microsoft. Sinds de oprichting heeft Lucid talrijke onderscheidingen ontvangen voor zijn producten, bedrijfsvoering en werkcultuur. Ga voor meer informatie naar lucidchart.com.
Begin vandaag nog met diagrammen maken met Lucidchart - probeer het gratis!
of verdergaan met
Customer Journey Map (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]
Home » Customer Journey Map | 🕑
Gust de Backer
November 10, 2023.
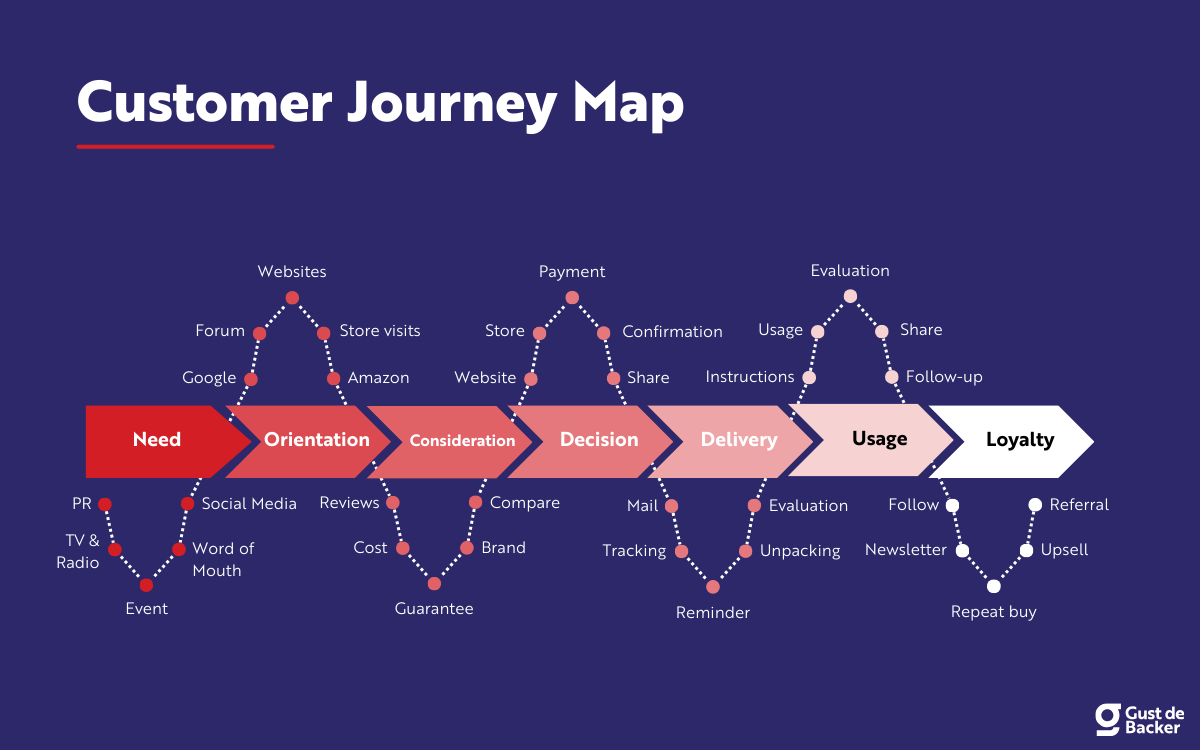
The Customer Journey is the process your customers go through with your company. This then covers the first to last interaction someone has with your company.
Many companies do not have a map of how their customers orient, what they care about or when the company comes into the potential buyer’s mind.
Not having enough mapping of the Customer Journey puts you at risk of having, perhaps unknowingly, negative touchpoints with your (potential) customer.
I’m going to show you:
- What the Customer Journey is
- How to create your Customer Journey
- And what good examples of a Customer Journey are
Let’s get started…
Table of Contents
What is the Customer Journey?
The Customer Journey is the process that maps every interaction with your brand:

The first interaction someone has with your brand is the beginning of the Customer Journey. If you find yourself in a niche market, it can also be interesting to map interactions with your niche.
The Customer Journey for B2B and B2C often looks quite different:
The Customer Journey is relevant to any business, but particularly important for companies that:
- Are customer-centric
- Want to improve customer satisfaction
- Want to increase sales
In general, you often see in companies that the marketing department is responsible for ensuring that (potential) customers have a positive experience with the brand.
A nice trend you see is that marketing/growth teams are becoming more responsible for the entire funnel rather than just reaching and bringing in new customers.
7 Stages of the Customer Journey
There are different models you can use to map out the Customer Journey, but in the end they all boil down to the same thing:

Keep in mind the different roles of the Decision-making Unit , but essentially there are 7 steps you can include in the Customer Journey….
Your (potential) customer can have 2 types of needs:
- Latent need : the person does not yet know he needs something. If you are going to buy a car you are not yet directly concerned with insurance.
- Concrete need : the person knows they have a certain need, here it is important to be visible with your brand. For example, think of buying a phone when your old one is broken.
Every Customer Journey basically starts with a certain need.
In practice, you can encounter 5 types of customers in this:
- Unaware : don’t realize they have a problem or need.
- Problem Aware : realize they have a problem or need.
- Solution Aware : they know there are solutions to their problem or need, but they don’t know you.
- Product Aware : they know you, but haven’t bought you yet.
- Most Aware : brand ambassadors.
2. Orientation
The orientation process has changed a lot in recent years thanks to digitalization, which makes it extra important to map it out using research.
You want to be visible with your brand at least in the orientation phase so that you will eventually be included in the consideration phase .
Some examples of behavior in the orientation phase:
- Concrete keywords in search engines
- Asking acquaintances for their opinions
- Checking out inspiration platforms such as Pinterest, TikTok or Instagram
3. Consideration
In the consideration phase, we examine which option from the orientation phase best meets the customer’s wishes and needs.
Here it is important to know which decision criteria weigh most heavily for the customer; this should be properly researched.
Some examples of decision criteria:
- Brand awareness
4. Decision
In the decision phase, a product or service from a specific vendor is actually chosen.
There are a number of things that make it easier for the customer to choose your product or service:
- Make it easy to compare
- Provide a good selection in different options
- Offer a good deal, make sure your customer can’t say no
- Provide a smooth payment process
- Increase engagement in your brand by providing valuable content, offers and support
Provide as few distractions as possible during the decision phase, people who are still Googling “[company name] discount code” from the checkout want to be convinced to convert.
5. Delivery
After someone has become a customer, a product or service will need to be delivered.
Here the first moments of evaluation will be whether someone actually made the right choice to choose your company, product or service.
- Make sure you deliver on time and that your product arrives in the right condition or that your service is of high quality.
- Give clear instructions on how to use or what the added value of the service is.
- Provide good support if the customer experiences problems in using your product or service.
In the use phase it is important that customers get the most out of your product or service and that they really see the added value .
You can stimulate this in a number of ways:
- Include tutorials
- Measuring and communicating impact
- Aftersales phone call
This is the ultimate evaluation moment ; if your product or service did not help the customer well, there is little chance that they will make a repeat purchase or become a brand ambassador .
In any case, it is important to prevent people from talking badly about your brand, so make sure that in the earlier stages you already make sure that people who are not ideal customers for you are excluded and that you make sure that customers see the added value of your product or service.
It is 5 to 7 times cheaper to retain a customer than to bring in a new customer. This is precisely why it is so important to encourage loyalty.
Loyalty can be expressed in the number of repeat purchases or upsells a customer eventually makes with you. You can encourage this by offering valuable content, offers and support.
The goal is for people to remain loyal to your brand and not switch to a competitor or go out of business in the first place.
There are different forms of loyalty:
- Transactional Loyalty : getting customers to make repeat purchases by giving offers.
- Social Loyalty : interacting with your customers on social media, for example.
- Engagement Loyalty : you reward people who engage with you where you can receive points for subscribing to a newsletter, for example.
- Emotional Loyalty : if your brand is positively aligned with your customer’s emotions, you can’t get this kind of loyalty with offers. In this, you want to make people feel part of something.
- Behavioral Loyalty : a level of loyalty in which you want to make customers do something like buy higher volumes where you give a third product for free after buying 2 products.
- Advocacy Loyalty : you are going to reward people who recommend others to become customers of your brand.
Customer Journey Mapping
Download the Customer Journey Canvas:

Good choice! Check your e-mail for the resources...
How do you complete the Customer Journey Canvas?

Once you know who all is in your Decision-making Unit, you can start creating personas and empathy maps so you can better understand the behaviors, needs, problems and wants of those individuals.
Determine what questions you would like to have answered after doing your Customer Journey Mapping research. Some common questions are: – When do you experience X? – On a scale of 1 – 10, how much would you like a solution to X? – How much are you willing to pay for a solution on X? – How would you orient yourself to a solution for X? – What brands would you consider in a solution for X? – What should a solution for X satisfy you in? – How would you go about determining if the solution was effective?
The threshold in terms of time and cost is often somewhat lower for quantitative research than for qualitative research. In it, you can gather good insights about your target audience from a helicopter perspective. Consider, for example: – Questionnaire – Post-purchase survey – Exit-intent Survey – Search volume
Once you have a high-level validated understanding of your target audience, you can begin to supplement your findings at a detailed level using qualitative research. Consider: – Customer interviews – User tests – Screen recordings
If you have made your Customer Journey Map comprehensible, you have gathered many insights on which you can improve your Customer Journey. To prevent it from becoming a dusty document that is no longer looked at, it is important to determine follow-up actions and evaluate them accordingly.
Common mistakes
There are a number of mistakes that you often see passed in Customer Journey Mapping:
- Based on assumptions : often you see that a Customer Journey is completely based on assumptions and not on validated research.
- Wrong scope : critically determine in advance where you want your Customer Journey to begin and end otherwise you quickly lose focus and overview.
- No customer perspective : reason the Customer Journey from your persona or customer and not from your company.
- Inside-out : if you start from how you do it as a company you are not customer-centric and there is going to be a mismatch in how the customer experiences something and how your company does it. Make sure your Customer Journey is actually completed from the customer’s perspective.
- Stakeholders : it is important to involve all relevant stakeholders so that you start creating support for the Customer Journey.
- End goal : the Customer Journey is not an end goal, but a starting point. It is something that will continuously play out and needs to be changed.
And now you…
Now you’re armed with enough knowledge to start visualizing your Customer Journey.
I’m curious, what has been the biggest insight for you in understanding your target audience?
Let me know in a comment.
P.S. if you would like additional help you can email me at [email protected]
Frequently Asked Questions
The 7 steps of the Customer Journey are: need, orientation, consideration, decision, delivery, use and loyalty.
A customer journey is a term used in marketing and customer experience management to describe the path a customer takes through the stages of awareness, consideration, purchase and use of a product or service. The term can also be used to describe the path a potential customer takes.
A customer journey map is a visualization of a customer’s experience with a company, product or service. It begins when the customer first becomes aware of a need and ends at the level of loyalty. The map tracks all the contact moments the customer has with a brand, both online and offline. Customer journey maps can help companies understand where they need to make improvements to provide a better experience for their customers.
The Customer Journey for every business is different. It is important to research for your business what the most ideal customer journey is, in doing so you want to validate all assumptions.
I try to help business surpass their growth ceiling with my content.
Sounds interesting?
Let’s connect on LinkedIn!
Account-Based Marketing | Business Strategy | Customer Development Process | Customer Journey | Decision-Making Unit | Digital Marketing | Lead Generation | Market Research | Marketing and Sales | Marketing Strategy
Gust’s Must-Reads 👇🏼
- TAM SAM SOM
- Value Proposition
- Brainstorming
- Decision Making Unit
- Product-Market Fit
- North Star Metric
- Market Research
- Customer Development
- Growth Hacking
- Brand Identity
- Customer Journey
- Account-Based Marketing
![customer journey model uitleg OGSM Model (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/OGSM-Model.png)
OGSM Model (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]
OGSM Model: a solution that helps with strategic planning and goal setting. You know where you want to go, but you don't have a clear picture of how you're going to get there. Ideas and goals are often not realized because there is no clear planning associated with...
Rapid Experimentation: The Road To Innovation (Complete Guide)
You read it left and right, companies that owe much of their success to experimentation.... Of course, experimentation can be understood in a hugely broad way, so in this article I'm going to get you started with: Understanding why experimentation is important...
![customer journey model uitleg Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/151-Cognitive-Biases.png)
Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]
Cognitive biases, there are so many of them... Decisions we make based on emotion, cognitive biases are irrational 'errors' that are programmed into people's brains and affect the decision-making process. Plenty of different articles have been written and an entire...
Ziet er zeer volledig en praktisch uit.
Bedankt Nicole!
Thanks! I’m trying to understand how to explain this approach in simple words, and your material is one of the best so far.
Thank you, Marie!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Customer Journey Map
You have successfully subscribed.
Customer journey (klantreis)
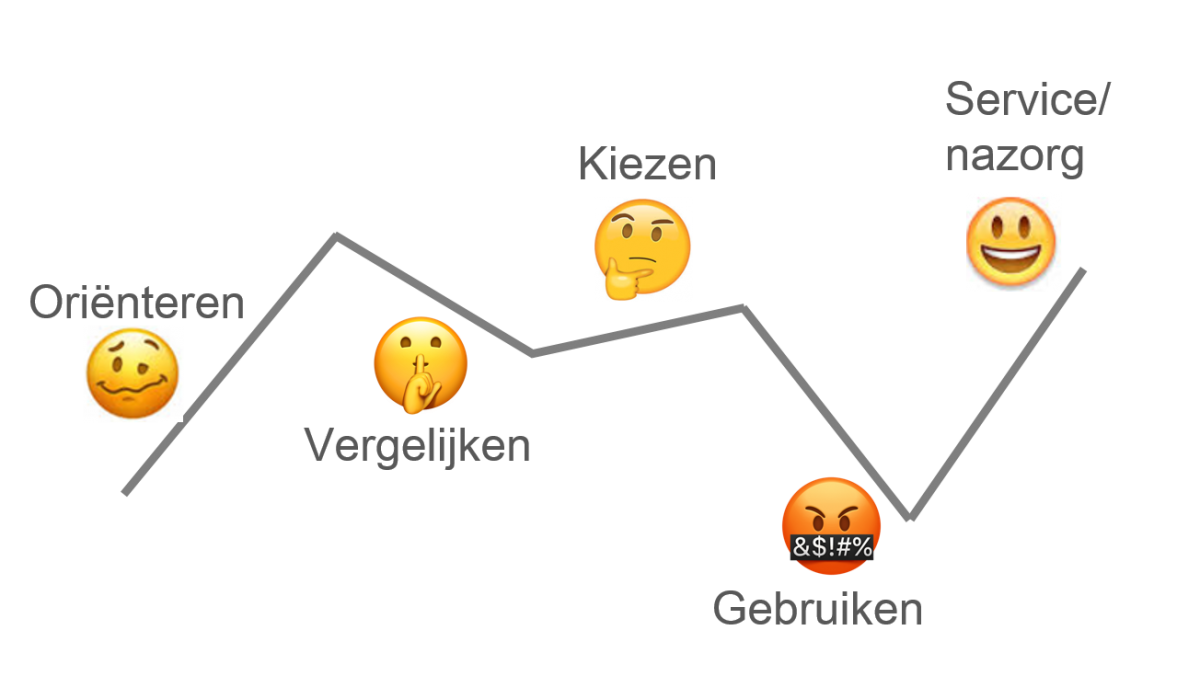
Een klantreis begint meestal ruim voordat een organisatie zich daarvan bewust is. Een potentiele klant zoekt op internet naar informatie, leest iets over een nieuw product, gaat naar een vergelijkingssite, vraagt vrienden om hun mening etc. Allemaal zaken die zich waarschijnlijk grotendeels aan het zicht van de organisatie onttrekken. Bij het maken van een klantreis begin je dus helemaal aan het begin.
Door te analyseren en te gaan snappen hoe klanten met jouw bedrijf en aanbod in contact komen, ontstaat de mogelijkheid hier invloed op uit te gaan oefenen; bijvoorbeeld door banners te plaatsen op websites die door je doelgroep bezocht worden, advertenties in bladen die suspects lezen en marketing- en promotieactiviteiten te ontplooien in forums of vergelijkingssites die in het voortraject een rol spelen.
Vanaf het moment dat een klant voor het eerst in contact komt tot en met het moment van afscheid zijn er meerdere zg. touchpoints – of contactmomenten -, waar de klant direct met de organisatie in contact staat. De klant stuurt bijvoorbeeld een e-mail en krijgt een reactie, belt met de verkoopondersteuning of servicedesk, plaatst een order of ontvangt een pakje.
Touchpoints zijn momenten waarop een organisatie een goede indruk op de prospect of klant kan maken (of juist niet) en die zijn dus heel belangrijk voor het managen van de klantbeleving. Naast het in kaart brengen van het voortraject, valt dus vaak veel te winnen met het benoemen en analyseren van de contactmomenten.
Tevreden klanten kunnen zichzelf als ambassadeur opwerpen en je product actief bij anderen aanbevelen. Je kunt dit meten met een loyaliteitsmeting, zoals de Netpromoter score (NPS score). Ontevreden klanten daarentegen, kunnen online klagen, hun netwerk adviseren jouw product of dienst vooral niet te kopen of op andere manier negatieve publiciteit opleveren. De klantreis loopt daarom door tot en met nazorg en afscheid van elkaar nemen.

Aanpak Een customer journey ontwerp je in een aantal stappen. Deze liggen min of meer vast, maar kunnen per situatie verschillen. Het maken van een customer journey is bijna altijd een groepsproces. De groep doorloopt gezamenlijk een aantal logische stappen:
- Vorm een team . Een goede customer journey vereist input van verschillende stakeholders. Het gebeurt zelden dat een enkele persoon alleen een goed beeld van de klant kan vormen. Denk goed na over wie je moet betrekken, om een betrouwbaar en min of meer volledig beeld van je klanten te kunnen vormen. Denk bijvoorbeeld aan webbeheer, marketeers, verkoop buitendienst, servicedesk en productmanagement. Denk ook aan externe stakeholders, zoals vertegenwoordigers van een belangenvereniging of de klant zelf.
- marketingstudies naar het aankoopgedrag te raadplegen
- nieuwe klanten systematisch te vragen hoe ze je organisatie/product hebben gevonden
- verslagen van klantbezoeken te analyseren
- klachten en serviceverzoeken te evalueren
- klantenquêtes en tevredenheidsonderzoeken te houden
- te analyseren om welke redenen klanten afhaken
- Bepaal de logische stappen van de klantreis. De tweede stap bestaat uit het bepalen van de verschillende stappen of fasen die de klant doorloopt. Veelal doorloopt deze een aantal vaste fasen: oriëntatie, vooronderzoek, vergelijking met andere organisaties/producten, selectie, aankoop, aflevering, gebruik, onderhoud/nazorg en afdanken/afscheid nemen. Maak deze specifiek voor de eigen organisatie en het eigen aanbod.
- Bepaal touchpoints . Gedurende de reis zijn er allerlei contactpunten. Dit kunnen echte contactmomenten zijn, maar ook momenten waarbij een klant communicatie van je organisatie ervaart die je kunt meten en beïnvloeden, zoals het ervaren van een reclame-uiting op een belangrijke vergelijkingssite of het eerste bezoek aan de eigen website. Breng de touchpoints systematisch in kaart.
- Ontwerp de klantreis . Er zijn allerlei manieren om een customer journey weer te geven. Belangrijk is dat niet alleen de stappen en touchpoints op een rijtje staan, maar dat je de activiteiten die de klant moet verrichten, de ervaring die hij hierbij heeft en de emoties die worden ervaren duidelijk maakt. Denk vanuit het perspectief van je klant en weet dat de activiteiten die de klant moet verrichten en de emoties die hierbij worden ervaren bepalend zijn voor het al dan niet doorzetten van de reis.
- Werk de klantreis grafisch uit . Met een klantreis maak je niet alleen de rationele stappen, activiteiten en beslispunten duidelijk, maar maak je vooral ook ervaringen en emoties zichtbaar. Dit lukt beter, als je niet alleen tabellen en teksten gebruikt, maar slim gebruik maakt van visualisaties, emoticons, kleuren en andere beelden. Goede klantreizen steken logisch in elkaar, maar stimuleren ook de minder rationele kant van ons brein met een pakkende vormgeving en grafische accenten.
- Gebruik, evalueer en stel bij . Een klantreis wordt beter naarmate deze wordt geëvalueerd en waar nodig verduidelijkt of bijgesteld. Een klantreis is een ‘groeidocument’. Er valt altijd meer te leren over de klant, eisen en wensen ontwikkelen, communicatiekanalen veranderen. Een klantreis is dus nooit klaar.

- Een customer journey in kaart brengen helpt je, je in te leven in de wereld van je klant. Door je te verdiepen in diens ervaring, activiteiten en emoties ga je niet uit van wat je zelf te bieden hebt, maar kijk je door de ogen van de klant en beleef je jouw dienstverlening vanuit zijn of haar perspectief.
- Met een customer journey kun je systematisch evalueren of vooronderstellingen over klanten kloppen. Je kunt per logische stap controleren of je aannames kloppen, bijvoorbeeld door registratie te raadplegen, klantonderzoek uit te voeren of het je klanten direct te vragen.
- Een customer journey biedt de mogelijkheid om je contactmomenten te optimaliseren. Zorg dat je weet wat een klant op dat moment van je verwacht en anticipeer daarop, bijvoorbeeld door proactief de juiste informatie te verschaffen, of een passende aanbieding te doen.
- Door in te zoomen op het traject dat de klant voorafgaand aan het eerste contact aflegt, verkrijg je informatie die je helpt hier bewust invloed op te gaan uitoefenen. Het biedt bijvoorbeeld de mogelijkheid de content van je website af te stemmen op de zoektermen die je klanten gebruiken (Search Engine Optimization), via de juiste media te adverteren en je tijdens de juiste evenementen (bv. beurzen) te profileren.
- Door in kaart te brengen waarom mensen afhaken, kun je hierop anticiperen en mocht de klant desondanks vertrekken, dan kun je de schade minimaliseren. Denk bijvoorbeeld aan een bedankje voor de samenwerking, zodat een ontevreden klant minder de neiging heeft zich over je dienstverlening te beklagen.
- Een customer journey helpt bij het inrichten en verbeteren van je informatiesysteem. Zodra je je bewust wordt van wat je over je klanten wilt weten, kun je dit systematisch gaan verzamelen en rapporteren.
Customer journey beluisteren als podcast

Klik op de afspeelknop en beluister de podcast over de customer journey.
Managementmodellensite
Wie zijn we, wat kunnen we voor je betekenen.
Sales CRM Terms
What is the Customer Journey? (Explained With Examples)
Oct 11, 2023

The customer journey is a concept that refers to the process that a customer goes through when interacting with a company or brand. It encompasses all the touchpoints and interactions that a customer has, from the moment they become aware of a product or service, to the point of making a purchase and beyond
1°) What is the Customer Journey?
1.1 - definition of the customer journey.
The customer journey can be defined as the series of steps or stages that a customer goes through during their engagement with a company. It typically starts with the initial awareness of a product or service, followed by consideration, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase experiences.
The customer journey is not always linear and can vary depending on the individual and the specific product or service. It can involve multiple touchpoints, such as online research, social media interactions, in-store visits, customer service interactions, and more.
Let's dive deeper into each stage of the customer journey to understand the significance and impact of each step.
1.2 - Advantages of the Customer Journey
Understanding the customer journey can provide several benefits for a company. By mapping out the customer journey, businesses can gain insights into the different stages and touchpoints that customers go through. This knowledge can help identify areas for improvement, optimize marketing efforts, and enhance the overall customer experience.
For example, during the initial awareness stage, companies can focus on creating impactful marketing campaigns to generate interest and capture the attention of potential customers. By understanding the specific touchpoints that lead to consideration and evaluation, businesses can tailor their messaging and content to address customer pain points and showcase the unique value proposition of their products or services.
By understanding how customers move through each stage of the journey, companies can tailor their strategies and communications to provide relevant and personalized experiences. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, higher conversions and revenue.
Let's explore some real-life examples of how companies have leveraged the customer journey to their advantage.
1.3 - Disadvantages of the Customer Journey
While the customer journey concept can be valuable, it also has some limitations. One limitation is that it is difficult to accurately capture every touchpoint and step that a customer goes through. Customer journeys can be complex and unique to each individual, making it challenging to create a one-size-fits-all model.
However, companies can overcome this limitation by conducting thorough customer research and utilizing data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. By continuously monitoring and analyzing customer interactions, companies can refine their understanding of the customer journey and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Additionally, customer journeys can change over time, influenced by factors such as changing consumer preferences, advancements in technology, or shifts in industry trends. This means that companies need to regularly review and update their understanding of the customer journey to stay relevant and effectively meet customers' evolving needs.
By staying agile and responsive to changing customer behaviors, companies can ensure that their customer journey remains effective and aligned with customer expectations.
Now that we have explored the advantages and disadvantages of the customer journey, let's move on to the next section to understand how companies can effectively map and analyze the customer journey.
2°) Examples of the Customer Journey
2.1 - example in a startup context.
Let's consider a hypothetical startup that has developed a new mobile productivity app. In this example, the customer journey begins with the app appearing on the user's radar, perhaps through an advertisement or a recommendation from a friend. The customer then explores the app's website and reads reviews to gather more information.
As they delve deeper into their research, the customer discovers the unique features and benefits of the app. They learn about how it can help them streamline their daily tasks, increase their productivity, and stay organized. The customer also comes across testimonials from other users who have experienced positive results after using the app.
After considering their options, the customer decides to download and install the app. Excitement builds as they anticipate the potential impact it can have on their work and personal life. They eagerly open the app for the first time and begin exploring its functionalities.
As the customer starts using the app, they quickly realize its value. They find themselves effortlessly managing their tasks, setting reminders, and accessing important information on the go. The app becomes an indispensable tool in their daily routine, helping them stay on top of their responsibilities and achieve their goals.
However, no product is perfect, and the customer may encounter some issues or have questions along the way. In such situations, they reach out to the app's support team for assistance. The support team promptly responds, providing helpful guidance and resolving any concerns the customer may have.
Over time, the customer becomes a loyal user of the app. They appreciate the continuous updates and improvements made by the startup, which further enhance their experience. The customer becomes an advocate for the brand, recommending the app to friends, family, and colleagues who may benefit from its features.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In the consulting industry, the customer journey can be more complex. A potential client might first become aware of a consulting firm through a referral or by reading thought leadership content online. Intrigued by the firm's expertise and reputation, they decide to explore further.
Upon visiting the firm's website, the potential client is greeted with a wealth of information about the services offered. They discover case studies showcasing successful client engagements, demonstrating the firm's ability to deliver results. The client also comes across testimonials from satisfied clients, reinforcing the firm's credibility.
Impressed by what they have seen, the client decides to take the next step and contact the firm to schedule an initial consultation. The firm's consultant, well-versed in understanding client needs, conducts a thorough discussion to gather information about the client's pain points and challenges.
Based on the information gathered during the consultation, the consultant develops a customized proposal tailored to address the client's specific needs. The proposal outlines the recommended approach, the expected outcomes, and the timeline for the engagement.
Excitement builds as the client reviews the proposal. They see the potential for positive change and growth that the consulting firm can bring to their organization. After careful consideration, the client decides to move forward with the engagement, signaling the start of a collaborative partnership.
The consulting engagement involves regular meetings between the client and the consultant. Progress updates are shared, and any adjustments to the strategy are discussed and implemented as needed. The consultant provides guidance, expertise, and support throughout the journey, ensuring the client's objectives are met.
Finally, the consulting engagement reaches its conclusion with the successful delivery of the agreed-upon solutions. The client experiences the desired outcomes, witnessing the positive impact on their organization. They express their satisfaction with the consulting firm's services and may choose to engage them again in the future for additional projects or recommend them to other businesses in need of similar expertise.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
A digital marketing agency's customer journey often starts with the client expressing interest in improving their online presence. The agency may offer a range of services, such as search engine optimization, social media management, and content marketing.
Upon expressing interest, the agency's team conducts a thorough analysis of the client's current digital presence. They examine the client's website, social media accounts, and online reputation. Through this analysis, they identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth.
Based on the findings of the analysis, the agency develops a tailored strategy to address the client's specific goals and objectives. The strategy may include recommendations for optimizing the client's website, creating engaging content, and implementing targeted advertising campaigns.
The agency presents the strategy to the client, explaining the rationale behind each recommendation and the expected outcomes. The client reviews the strategy and provides feedback, ensuring that it aligns with their vision and objectives.
Once the strategy is agreed upon, the agency begins implementing various tactics to execute the plan. They optimize the client's website for search engines, create compelling content to engage the target audience, and launch targeted advertising campaigns to increase brand visibility.
Throughout the implementation phase, the agency monitors the performance of the various tactics. They analyze data, measure key performance indicators, and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal results. Regular reports and updates are provided to the client, keeping them informed of the progress being made.
The final stage of the customer journey involves evaluating the results achieved through the agency's efforts. The agency and the client review the impact of the implemented strategies and tactics, examining key metrics such as website traffic, conversion rates, and social media engagement.
Based on the evaluation, the agency and the client collaborate to make any necessary adjustments to the strategy. This iterative process ensures that the client's online presence continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing digital landscape, maximizing their return on investment.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
To help illustrate the concept further, let's consider some analogies for the customer journey. Imagine you are planning a vacation. The journey begins with the initial inspiration and research for destinations and accommodations.
You spend hours browsing travel websites, reading reviews, and comparing prices. You envision yourself relaxing on a pristine beach or exploring a vibrant city. The anticipation builds as you imagine the experiences that await you.
Once you've chosen a destination, you move into the consideration stage. You carefully weigh the pros and cons of different accommodations, comparing amenities, locations, and prices. You read more reviews, seeking reassurance that you are making the right choice.
Finally, you make your purchase, book your flights and accommodations, and embark on your trip. The excitement is palpable as you board the plane and begin your journey to your chosen destination.
During your vacation, you have experiences that can impact your overall satisfaction and potentially influence your future travel decisions. The quality of service at your hotel, the local attractions you visit, and the interactions with locals all contribute to your experience.
Upon returning home, you reflect on your trip, share your experiences with friends and family, and may decide to visit the same destination again or choose a different one for your next vacation. This process mirrors the stages and interactions of the customer journey.
The customer journey is a vital concept for businesses to understand and optimize. By mapping out the different stages and touchpoints, companies can gain insights into their customers' experiences and tailor their strategies and communications accordingly.
While the customer journey may have some limitations and variations, it provides a valuable framework for companies to enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately drive business growth.
About the author

Arnaud Belinga

Close deals x2 faster with
Breakcold sales crm.
SEE PRICING
*No credit card required

Related Articles

What is the 80-20 rule? (Explained With Examples)

What is the ABCD Sales Method? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Accelerated Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Marketing (ABM)? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Account Manager? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ad Targeting? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Addressable Market? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Adoption Curve? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AE (Account Executive)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Affiliate Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is AI in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AI-Powered CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Alternative Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Annual Contract Value? (ACV - Explained With Examples)

What are Appointments Set? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Assumptive Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Automated Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2B (Business-to-Business)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2G (Business-to-Government)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2P (Business-to-Partner)? (Explained With Examples)

What is BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Behavioral Economics in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benchmark Data? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What are Benefit Statements? (Explained With Examples)

What is Beyond the Obvious? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Bootstrapped Startup? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Bounce Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Brand Awareness? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Break-Even Point? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Breakup Email? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Development? (Explained With Examples)

What are Business Insights? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Process Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buyer Persona? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buyer's Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buying Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Signal? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Team? (Explained With Examples)

What is a C-Level Executive? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Logging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Recording? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Call-to-Action (CTA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Case Study Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Challenger Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Chasing Lost Deals? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Prevention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Client Acquisition? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Closing Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Ben Franklin Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Bias in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Dissonance in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Calling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Advantage? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Competitive Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conceptual Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Closing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Syndication? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Optimization? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Path? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cost-Per-Click (CPC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Cultural Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Cross-Sell Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Journey Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Profiling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Retention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dark Social? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Database Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What are Decision Criteria? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision Maker? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision-Making Unit (DMU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Demand Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Digital Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Direct Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Call? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Meeting? (Explained With Examples)

What are Discovery Questions? (Explained With Examples)

What is Door-to-Door Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Drip Campaign? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dunning? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Early Adopter? (Explained With Examples)

What is Elevator Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Hygiene? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Emotional Intelligence Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Feature-Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Field Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Follow-Up? (Explained With Examples)

What is Forecast Accuracy? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gamification in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Go-to Market Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Hacking? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Guerrilla Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is High-Ticket Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Holistic Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Inbound Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Influencer Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales Representative? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Insight Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Account? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Landing Page? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Database? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Lead Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Nurturing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Qualification? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What are LinkedIn InMails? (Explained With Examples)

What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lost Opportunity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Research? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is MEDDIC? (Explained With Examples)

What is Middle Of The Funnel (MOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Motivational Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead)? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)? (Explained With Examples)

What is N.E.A.T. Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Neil Rackham's Sales Tactics? (Explained With Examples)

What is Networking? (Explained With Examples)

What is NLP Sales Techniques? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Net Promotion Score? (NPS - Explained With Examples)

What is Objection Handling Framework? (Explained With Examples)

What is On-Hold Messaging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Onboarding in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Online Advertising? (Explained With Examples)

What is Outbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Permission Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Personality-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Persuasion Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Management? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Velocity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Predictive Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Objection? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Sensitivity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Problem-Solution Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product Knowledge? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product-Led-Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Qualified Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Question-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Referral Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Relationship Building? (Explained With Examples)

What is Revenue Forecast? (Explained With Examples)

What is a ROI? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Bonus Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Champion? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Collateral? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Commission Structure Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Demo? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Enablement? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Flywheel? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What are Sales KPIs? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Meetup? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pipeline? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Playbook? (Explained With Examples)
Try breakcold now, are you ready to accelerate your sales pipeline.
Join over +1000 agencies, startups & consultants closing deals with Breakcold Sales CRM
Get Started for free
Sales CRM Features
Sales CRM Software
Sales Pipeline
Sales Lead Tracking
CRM with social media integrations
Social Selling Software
Contact Management
CRM Unified Email LinkedIn Inbox
Breakcold works for many industries
CRM for Agencies
CRM for Startups
CRM for Consultants
CRM for Small Business
CRM for LinkedIn
CRM for Coaches
Sales CRM & Sales Pipeline Tutorials
The 8 Sales Pipeline Stages
The Best CRMs for Agencies
The Best CRMs for Consultants
The Best LinkedIn CRMs
How to close deals in 2024, not in 2010
CRM automation: from 0 to PRO in 5 minutes
LinkedIn Inbox Management
LinkedIn Account-Based Marketing (2024 Tutorial with video)
Tools & more
Sales Pipeline Templates
Alternatives
Integrations
CRM integration with LinkedIn
© 2024 Breakcold
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
The customer journey — definition, stages, and benefits

Businesses need to understand their customers to increase engagement, sales, and retention. But building an understanding with your customers isn’t easy.
The customer journey is the road a person takes to convert, but this journey isn’t always obvious to business owners. Understanding every step of that journey is key to business success. After reading this article, you’ll understand the customer journey better and how to use it to improve the customer experience while achieving your business goals.
This post will discuss:
- What a customer journey is
Customer journey stages
Benefits of knowing the customer journey.
- What a customer journey map is
How to create a customer journey map
Use the customer journey map to optimize the customer experience, what is a customer journey.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. Businesses use the customer journey to better understand their customers’ experience, with the goal of optimizing that experience at every touchpoint.
Giving customers a positive customer experience is important for getting customers to trust a business, so optimizing the customer journey has never mattered more. By mastering the customer journey, you can design customer experiences that will lead to better customer relationships, loyalty, and long-term retention .
Customer journey vs. the buyer journey
The stages of the customer’s journey are different from the stages of the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey follows the customer experience from initial awareness of a brand to buying a product. The customer journey extends beyond the purchase and follows how customers interact with your product and how they share it with others.
Every lead goes through several stages to become a loyal customer. The better this experience is for customers at each stage, the more likely your leads are to stick around.
Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey:

1. Awareness
In the awareness phase, your target audience is just becoming aware of your brand and products. They need information or a solution to a problem, so they search for that information via social media and search engines.
For example, if someone searches on Google for pens for left-handed people, their customer journey begins when they’re first aware of your brand’s left-handed pen.
At this stage, potential customers learn about your business via web content, social media, influencers, and even their friends and family. However, this isn’t the time for hard sells. Customers are simply gathering information at this stage, so you should focus first on answering their questions and building trust.
2. Consideration
In the consideration phase, customers begin to consider your brand as a solution to their problem. They’re comparing your products to other businesses and alternative solutions, so you need to give these shoppers a reason to stick around.
Consideration-stage customers want to see product features that lean heavily toward solving problems and content that doesn’t necessarily push a sale. At this stage, businesses need to position their solution as a better alternative. For example, a nutrition coaching app might create content explaining the differences between using the app and working with an in-person nutritionist — while subtly promoting the benefits of choosing the app.
3. Purchase
The purchase stage is also called the decision stage because at this stage customers are ready to make a buying decision. Keep in mind that their decision might be to go with a competing solution, so purchase-stage buyers won’t always convert to your brand.
As a business, it’s your job to persuade shoppers at this stage to buy from you. Provide information on pricing, share comparison guides to showcase why you’re the superior option, and set up abandoned cart email sequences.
4. Retention
The customer journey doesn’t end once a shopper makes their first purchase. Once you’ve converted a customer, you need to focus on keeping them around and driving repeat business. Sourcing new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing clients, so this strategy can help you cut down on marketing costs and increase profits.
The key to the retention stage is to maintain positive, engaging relationships between your brand and its customers. Try strategies like regular email outreach, coupons and sales, or exclusive communities to encourage customer loyalty.
5. Advocacy
In the advocacy stage, customers are so delighted with your products and services that they spread the word to their friends and family. This goes a step beyond retention because the customer is actively encouraging other people to make purchases.
Customer journeys don’t have a distinct end because brands should always aim to please even their most loyal customers. In the advocacy stage of the customer journey, you can offer referral bonuses, loyalty programs, and special deals for your most active customers to encourage further advocacy.
Being aware of the customer journey helps shed more light on your target audience’s expectations and needs. In fact, 80% of companies compete primarily on customer experience. This means optimizing the customer journey will not only encourage your current customers to remain loyal but will also make you more competitive in acquiring new business.
More specifically, acknowledging the customer journey can help you:

- Understand customer behavior. Classifying every action your customers take will help you figure out why they do what they do. When you understand a shopper’s “why,” you’re better positioned to support their needs.
- Identify touchpoints to reach the customer. Many businesses invest in multichannel marketing, but not all of these touchpoints are valuable. By focusing on the customer journey, you’ll learn which of these channels are the most effective for generating sales. This helps businesses save time and money by focusing on only the most effective channels.
- Analyze the stumbling blocks in products or services. If leads frequently bail before buying, that could be a sign that something is wrong with your product or buying experience. Being conscious of the customer journey can help you fix issues with your products or services before they become a more expensive problem.
- Support your marketing efforts. Marketing requires a deep familiarity with your target audience. Documenting the customer journey makes it easier for your marketing team to meet shoppers’ expectations and solve their pain points.
- Increase customer engagement. Seeing the customer journey helps your business target the most relevant audience for your product or service. Plus, it improves the customer experience and increases engagement. In fact, 29.6% of customers will refuse to embrace branded digital channels if they have a poor experience, so increasing positive customer touchpoints has never been more important.
- Achieve more conversions. Mapping your customers’ journey can help you increase conversions by tailoring and personalizing your approach and messages to give your audience exactly what they want.
- Generate more ROI. You need to see a tangible return on your marketing efforts. Fortunately, investing in the customer journey improves ROI across the board. For example, brands with a good customer experience can increase revenue by 2–7% .
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Today, 94% of customers say a positive experience motivates them to make future purchases. Optimizing the customer journey helps you meet shopper expectations, which increases satisfaction and loyalty.

What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every step your customer takes from being a lead to eventually becoming an advocate for your brand. The goal of customer journey mapping is to simplify the complex process of how customers interact with your brand at every stage of their journey.
Businesses shouldn’t use a rigid, one-size-fits-all customer journey map. Instead, they should plan flexible, individual types of customer journeys — whether they’re based on a certain demographic or on individual customer personas. To design the most effective customer journey map, your brand needs to understand a customer’s:
- Actions. Learn which actions your customer takes at every stage. Look for common patterns. For example, you might see that consideration-stage shoppers commonly look for reviews.
- Motivations. Customer intent matters. A person’s motivations change at every stage of the customer journey, and your map needs to account for that. Include visual representation of the shopper’s motivations at each stage. At the awareness stage, their motivation might be to gather information to solve their problem. At the purchase stage, it might be to get the lowest price possible.
- Questions. Brands can take customers’ common questions at every stage of the customer journey and reverse-engineer them into useful content. For example, shoppers at the consideration stage might ask, “What’s the difference between a DIY car wash and hiring a professional detailer?” You can offer content that answers their question while subtly promoting your car detailing business.
- Pain points. Everybody has a problem that they’re trying to solve, whether by just gathering intel or by purchasing products. Recognizing your leads’ pain points will help you craft proactive, helpful marketing campaigns that solve their biggest problems.
Customer journey touchpoints
Every stage of the customer journey should also include touchpoints. Customer touchpoints are the series of interactions with your brand — such as an ad on Facebook, an email, or a website chatbot — that occur at the various stages of the customer journey across multiple channels. A customer’s actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will differ at each stage and at each touchpoint.
For example, a customer searching for a fishing rod and reading posts about how they’re made will have very different motivations and questions from when later comparing specs and trying to stay within budget. Likewise, that same customer will have different pain points when calling customer service after buying a particular rod.

It might sound like more work, but mapping the entire customer journey helps businesses create a better customer experience throughout the entire lifecycle of a customer’s interaction with your brand.
Before jumping into the steps of how to create the customer journey map, first be clear that your customer journey map needs to illustrate the following:
- Customer journey stages. Ensure that your customer journey map includes every stage of the customer journey. Don’t just focus on the stages approaching the purchase — focus on the retention and advocacy stages as well.
- Touchpoints. Log the most common touchpoints customers have at every stage. For example, awareness-stage touchpoints might include your blog, social media, or search engines. Consideration-stage touchpoints could include reviews or demo videos on YouTube. You don’t need to list all potential touchpoints. Only list the most common or relevant touchpoints at each stage.
- The full customer experience. Customers’ actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will change at every stage — and every touchpoint — during the customer journey. Ensure your customer journey map touches on the full experience for each touchpoint.
- Your brand’s solutions. Finally, the customer journey map needs to include a branded solution for each stage and touchpoint. This doesn’t necessarily mean paid products. For example, awareness-stage buyers aren’t ready to make a purchase, so your brand’s solution at this stage might be a piece of gated content. With these necessary elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map is a simple three-step process.
1. Create buyer personas
A buyer persona is a fictitious representation of your target audience. It’s a helpful internal tool that businesses use to better understand their audience’s background, assumptions, pain points, and needs. Each persona differs in terms of actions, motivations, questions, and pain points, which is why businesses need to create buyer personas before they map the customer journey.
To create a buyer persona, you will need to:
- Gather and analyze customer data. Collect information on your customers through analytics, surveys, and market research.
- Segment customers into specific buying groups. Categorize customers into buying groups based on shared characteristics — such as demographics or location. This will give you multiple customer segments to choose from.
- Build the personas. Select the segment you want to target and build a persona for that segment. At a minimum, the buyer persona needs to define the customers’ basic traits, such as their personal background, as well as their motivations and pain points.

For example, ClearVoice created a buyer persona called “John The Marketing Manager.” The in-depth persona details the target customer’s pain points, pet peeves, and potential reactions to help ClearVoice marketers create more customer-focused experiences.
2. List the touchpoints at each customer journey stage
Now that you’ve created your buyer personas, you need to sketch out each of the five stages of the customer journey and then list all of the potential touchpoints each buyer persona has with your brand at every one of these five stages. This includes listing the most common marketing channels where customers can interact with you. Remember, touchpoints differ by stage, so it’s critical to list which touchpoints happen at every stage so you can optimize your approach for every buyer persona.
Every customer’s experience is different, but these touchpoints most commonly line up with each stage of the customer journey:
- Awareness. Advertising, social media, company blog, referrals from friends and family, how-to videos, streaming ads, and brand activation events.
- Consideration. Email, sales calls, SMS, landing pages, and reviews.
- Purchase. Live chat, chatbots, cart abandonment emails, retargeting ads, and product print inserts.
- Retention. Thank you emails, product walkthroughs, sales follow-ups, and online communities.
- Advocacy. Surveys, loyalty programs, and in-person events.
Leave no stone unturned. Logging the most relevant touchpoints at each stage eliminates blind spots and ensures your brand is there for its customers, wherever they choose to connect with you.
3. Map the customer experience at each touchpoint
Now that you’ve defined each touchpoint at every stage of the customer journey, it’s time to detail the exact experience you need to create for each touchpoint. Every touchpoint needs to consider the customer’s:
- Actions. Describe how the customer got to this touchpoint and what they’re going to do now that they’re here.
- Motivations. Specify how the customer feels at this moment. Are they frustrated, confused, curious, or excited? Explain why they feel this way.
- Questions. Every customer has questions. Anticipate the questions someone at this stage and touchpoint would have — and how your brand can answer those questions.
- Pain points. Define the problem the customer has — and how you can solve that problem at this stage. For example, imagine you sell women’s dress shoes. You’re focusing on the buyer persona of a 36-year-old Canadian woman who works in human resources. Her touchpoints might include clicking on your Facebook ad, exploring your online shop, but then abandoning her cart. After receiving a coupon from you, she finally buys. Later, she decides to exchange the shoes for a different color. After the exchange, she leaves a review. Note how she acts at each of these touchpoints and detail her likely pain points, motivations, and questions, for each scenario. Note on the map where you intend to respond to the customer’s motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions. If you can create custom-tailored solutions for every stage of the funnel, that’s even better.
A positive customer experience is the direct result of offering customers personalized, relevant, or meaningful content and other brand interactions. By mapping your customers’ motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions, you’ll find opportunities to improve the customer experience. When you truly address their deepest needs, you’ll increase engagement and generate more positive reviews.
Follow these strategies to improve the customer experience with your customer journey map:
- Prioritize objectives. Identify the stages of the customer journey where your brand has the strongest presence and take advantage of those points. For example, if leads at the consideration stage frequently subscribe to your YouTube channel, that gives you more opportunities to connect with loyal followers.
- Use an omnichannel approach to engage customers. Omnichannel marketing allows businesses to gather information and create a more holistic view of the customer journey. This allows you to personalize the customer experience on another level entirely. Use an omnichannel analytics solution that allows you to capture and analyze the true cross-channel experience.
- Personalize interactions at every stage. The goal of mapping the customer journey is to create more personalized, helpful experiences for your audience at every stage and touchpoint. For example, with the right data you can personalize the retail shopping experience and customer’s website experience.
- Cultivate a mutually trusting relationship. When consumer trust is low, brands have to work even harder to earn their customers’ trust. Back up your marketing promises with good customer service, personalized incentives, and loyalty programs.
Getting started with customer journeys
Customer journeys are complicated in an omnichannel environment, but mapping these journeys can help businesses better understand their customers. Customer journey maps help you deliver the exact experience your customers expect from your business while increasing engagement and sales.
When you’re ready to get started, trace the interactions your customers have at each stage of their journey with your brand. Adobe Customer Journey Analytics — a service built on Adobe Experience Platform — can break down, filter, and query years’ worth of data and combine it from every channel into a single interface. Real-time, omnichannel analysis and visualization let companies make better decisions with a holistic view of their business and the context behind every customer action.
Learn more about Customer Journey Analytics by watching the overview video .
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/introducing-adobes-customer-journey-maturity-model
https://business.adobe.com/blog/how-to/create-customer-journey-maps
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-customer-journey-map

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Customer Journey: What it is & Examples [Free Template]

Have you ever thought that all the purchases we make involve a buying process before the time of the transaction? We call this process the customer journey, which encompasses all the phases a person/buyer persona goes through from the moment they identify their need until they acquire a product or service to satisfy it.
This process can be as short as a few minutes in the case of low-cost products that we buy impulsively (food in a supermarket, for example). The purchasing process may also last for months or more than a year (for instance, when acquiring a car or purchasing a customer experience management software).
This article will cover the customer journey, its phases, and how we can define it in our customer experience strategy.
Don’t forget to download the free template, Customer Journey Map , available toward the end of this guide!
What is a Customer Journey?
By book definition, a customer journey is the set of interactions that a customer has with a brand in buying a service or product. Put plainly, and It considers the complete interaction roadmap – from brand discovery to purchasing and beyond.
The focus isn’t only on transactions and how the customer feels after every interaction with the brand. In other words, the customer journey can be used as a strategy to gain insights into the customer’s experience throughout their buying process.
The objective of these journeys is, on the one hand, to measure and evaluate how you are taking care of your customers and, on the other. In this way, you can enhance and bring further delight to their experience with your brand measurement .
Excellent products, a praiseworthy website, and an on-call customer service team may seem like the perfect mix to capture prospective clients. However, when customers feel something is off in your communication, they’re more likely to seek competitors.
By improving the customer experience at each touchpoint in the customer journey, you focus your business on your customers, putting them at the heart of all. This builds a loyal fan base and keeps customers coming back time and again, fostering a strong connection throughout the entire customer journey. This builds brand loyalty as a positive outcome, leading to having satisfied customers and an influence over their lives, choosing your brand above others.
The brands that gain the most loyalty are the ones that influence their clients’ lives. It is the outcome of so many variables —some of which we can control and others we cannot— and understanding how those variables play out in our markets is a crucial first step to understanding what causes brand loyalty.
Customer Journey Stages
Now that you know what a customer journey is, it’s time to look more closely at what you can do to commit to your present and potential clients. Various stages make up the complete journey.
These three steps generally make up most journeys: Awareness, Consideration, and Conversion . These customer journey stages are most suitable for offline purchases.
With the progress of digital platforms, two critical additions appear in the customer experience: Retention and Advocacy . These new stages of the customer journey explore brand touchpoints with online shoppers.
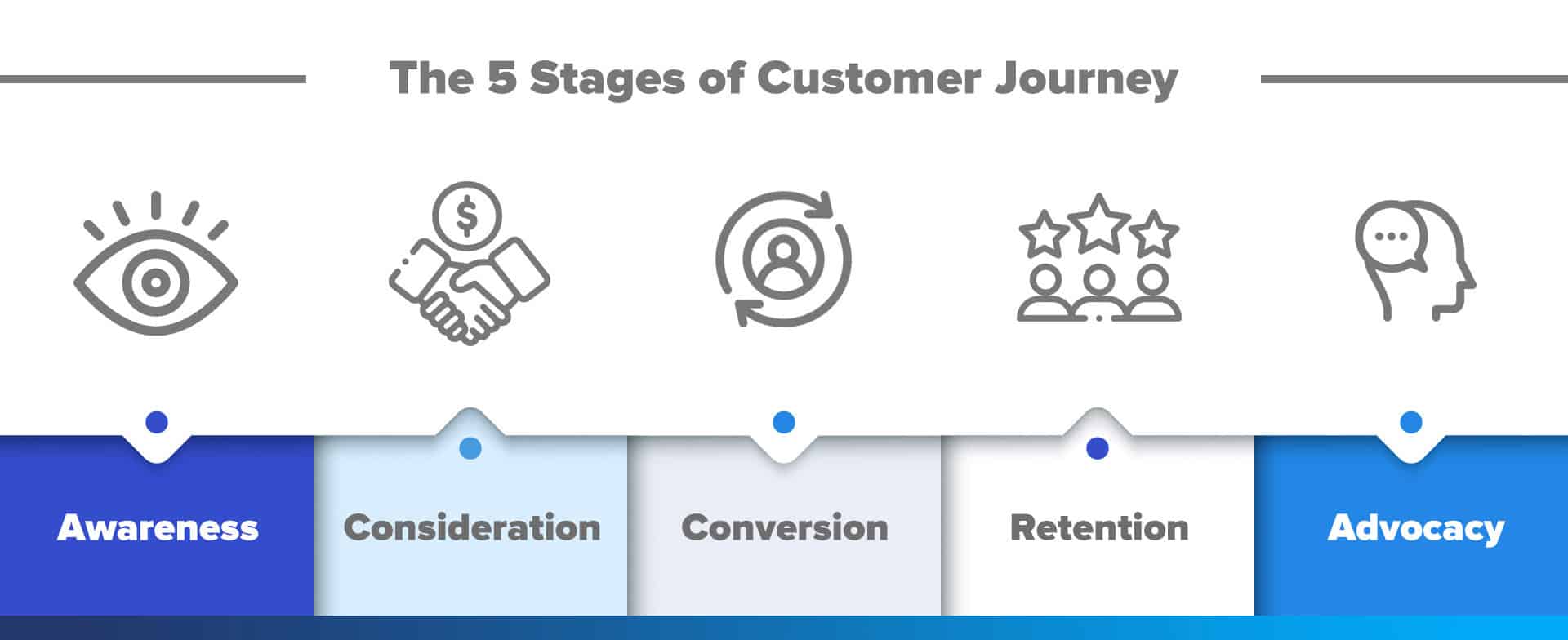
1. Awareness: The first stage
Awareness involves spreading general information about your products and services to your target audience (s).
During the customer awareness stage of the customer journey, consumers search for solutions and encounter multiple brands and products. Hint: This is the time to shine if you want to make a good first impression.
What consumers are doing : During this customer journey step, consumers are likely conducting research. This can include searching online for solutions to keyword problems, reading blog posts and news articles, browsing online forums, and first meeting brands.
What brands can do : You might think consumers are doing all the heavy lifting at this stage of the customer journey because they’re asking questions and browsing content.
However, you don’t want to approach brand awareness passively. You have to be there already, where the consumer is looking at alternatives. By “being there,” we mean taking the form of an educational blog post or video, providing the solution or information they want. Bringing valuable resources to the consumer is vital in this initial customer journey phase.
Read about the consumer decision journey .
2. Consideration: The second stage
Brands focus on promotion during the consideration stage of the customer journey. This is where customers begin to look for alternatives to past purchases. During this journey phase, your business strives to convince potential buyers to include you on the list of available options.
Your brand will most likely be considered alongside others, so make sure every impression you make counts.
At this point, consumers are directly interacting with your brand, and you want them to stick around for the next step in the customer journey.
What consumers do : Research specific brands and products, compare competitors, and evaluate your priorities. This could include looking closely at your product and service specifications and features, examining customer support policies, and turning to direct comparison reviews.
The consideration phase of the journey varies because consumer-centric channels can come in many forms.
What brands can do : Value the importance of the user experience (UX). Continuously optimize the UX across all your touchpoints, including e-commerce transaction and description pages.
Little things like making sure the descriptions and processes are clear and that all the buttons work correctly go a long way when someone considers you against a competitor on their customer journey.
For instance, a person becomes aware they’re hungry and could be scouting for a place to eat on an app like Google Maps.
Suppose your business has a strong presence there, i.e. , with information about what kind of food you sell, the menu, photos of the place and the food, phone number, and truthful, positive customer reviews. In that case, you might make them consider that you could be an excellent alternative to what they’re looking for.
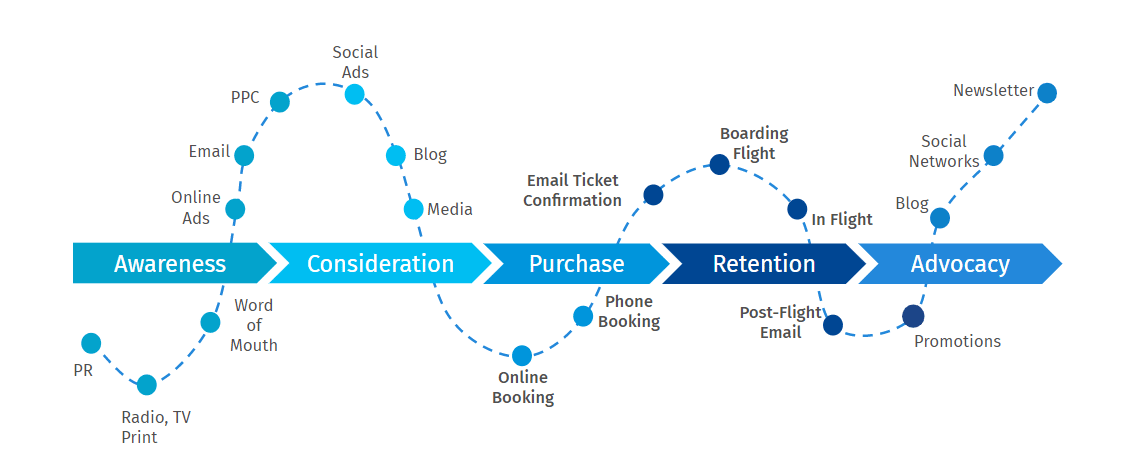
3. Conversion: The third stage
This stage of the customer journey prompts visitors to take a particular action. Using a dedicated call-to-action (CTA), you encourage customers to make a purchase, subscribe to a mailing list, or sign up for services. You should use this phase to sell your product as the best fit to solve a visitor’s problem.
It is your moment to make or break during the Customer Journey. Once potential customers are satisfied with researching and comparing their options, they will eventually decide.
Sometimes, they find that none of the brands they’ve been considering offer what they’re looking for. If they make a favorable decision, they want to make the process easier by choosing their trusted products.
What consumers are doing : They are considering factors like price vs. value, customer service responsiveness, company values, and policies as part of the existing customer journey. When they’re in the decision phase, it’s not just about product specifications or the shopping experience but how these elements fit into their customer journey design.
Consumers want to support a brand they trust to provide a quality solution to their problems, ensuring a positive customer journey begins and continues throughout their interaction with the company.
What brands can do : To anticipate this customer journey step, you must go further. This could include marketing strategies where you offer incentives to potential customers who have already visited your website or engaged with your business.
Ensure your return and refund policies are easy to find and train your customer support team to answer key decision-making questions.
Note that the following two customer journey stages, Retention and advocacy, were optional in previous business models. Nevertheless, the increase in online purchases makes these stages of the customer journey as significant as the others.
Read about the customer value journey and what it is.
4. Retention: The fourth stage
At this point in the customer journey, you already have a new customer – Congratulations! All that planning and asset building is paying off when they get to this phase. The journey refers to the consumer’s path from initial awareness to making a purchase, and in this phase, they have decided to navigate their purchase journey with you. But don’t assume it’s a done deal.
A loyal customer brings an organization consistent business and costs less than the effort to bring in new customers. A study by Bain & Company discovered that loyal customers are 50% more likely to try new products and spend 31% more than new customers. This demonstrates the value of nurturing and maintaining relationships with customers throughout their customer journey.
Retention includes keeping customers happy with a relationship management/customer success team to stop them from leaving and take them as many as possible to the next and final stage of the customer journey- make them so loyal to your brand that they want to advocate for your product and service.
What consumers are doing : Depending on your business model, customers are taking advantage of this moment to buy your products online, with a physical retailer, or are booking a service they plan to experience soon.
Once they have the product or service as a part of their consumer journey, they will start to implement their purchase, and if they go through the phase successfully, you will earn their customer loyalty.
What brands can do : Optimize the transaction experience in the Journey. Ensure the quality of your e-commerce site or physical store, and regularly review how your competition optimizes customers’ experience for each customer touchpoint .
5. Advocacy: The fifth stage of customer journey
Most organizations acknowledge the benefits of word-of-mouth. However, few companies commit to a plan for boosting customer advocacy . Encouraging each customer to share reviews can take time and money. Reaching out to influencers or guest bloggers is an effective alternative to traditional word-of-mouth.
Enthusiastic customers are more likely to recommend your brand and products to a friend, which can be a deal-breaker for many as it enhances the entire customer journey.
When you keep your customers happy and exceed their expectations with innovation and excellent customer service, the customer journey shortens, and transaction costs decrease.
What consumers are doing : At this point in the customer journey, customers are using your offerings to address their needs. The better the results and experience they get with your product, the more likely they will buy again and recommend you.
They can also begin to engage with your brand more casually on social media and plan their next purchase.
What brands can do : Take the initiative to contact customers in a friendly and supportive manner during their journey. A short customer experience survey is an excellent way to let them know you care about their feedback.
Consider starting a loyalty program for referrals and future transactions. This is also an excellent opportunity to keep consumers returning to some relevant assets you create to build brand awareness.
This could include blog content with tips to enrich your product experience, a newsletter with updates, promotions, and occasional opportunities to provide further feedback.
Benefits of Understanding the Customer Journey
Identifying customer journeys allows us to understand better how they buy to meet their needs and expectations and what role a specific business plays in this process.
Furthermore, being aware of all their journey interactions (customer touchpoints) through any channel, such as email or social networks, allows for a better shopping experience while delivering a consistent message across all communication channels.
Next, we will explain the benefits of implementing a customer journey strategy in your business.
A better understanding of customer emotions.
Building a customer journey framework puts you directly in the mind of the consumer. Understanding why a customer makes a particular choice sets your business up for success.
Knowing how customers feel encourages you to improve how the organization functions because it allows you to identify the friction points throughout their customer journey, making them easier to fix.
Analyze the stumbling blocks in products/services.
Mapping the journey gives your organization insights into where your customer communications fall short. For instance, if your support staff is undermanned, customers don’t receive help when needed. Your customers become angry because they expect prompt replies. You resolve the issue by hiring another support team member to tackle more customer questions.
Creating a customer journey map provides the customers’ viewpoint of a business. The map is a visual representation of the transactions and emotions that lead through each touchpoint with customers that helps to identify weak points in your messaging.
Improve employee and customer satisfaction.
As issues are resolved, confidence levels among customers and employees alike increase, leading to a more positive customer journey. Employees are encouraged to continue doing great work, increasing overall customer satisfaction.
Create a united team.
To develop unique customer experiences, the teams in your organization need to be on the same page. Marketing, product development, sales, and customer service must work together to improve customer journey processes within the organization. As the teams work together, the efficiency and effectiveness of each team increase, positively impacting the customer journey mapping process.
Make sure to check these 10 customer journey benefits for mapping
Customer Journey Analysis
Understanding the organization from the customer’s point of view brings new ideas and opinions to the table. Customer Journey Analytics does precisely that – it analyzes customer viewpoints about products so that you can make appropriate changes to keep customers loyal to your brand. Use data from customers to implement improved marketing strategies.
The analysis involves three stages: gathering accurate information, developing customer personas , and analyzing customer interactions.
Here is how customer journey analysis is beneficial in gathering information:
- Clearly defines all customer interaction points.
- Evaluates how the customer journey progresses from beginning to end.
- Analyzes the impact on customer loyalty and brand shareability according to customer interaction points.
- Highlights areas that waste a customer’s time to improve efficiency.
- Generalize the customer journey of similar audiences to make improvements and keep customers satisfied.
Learn what Customer Journey Monitoring is and the benefits of implementing this systematic activity.
Customer Journey Communication Channels
Your map is a 360-degree view of customer feedback from each step in their journey. Customer journey mapping is a proven model for understanding how, when, and where your customers experience your brand.
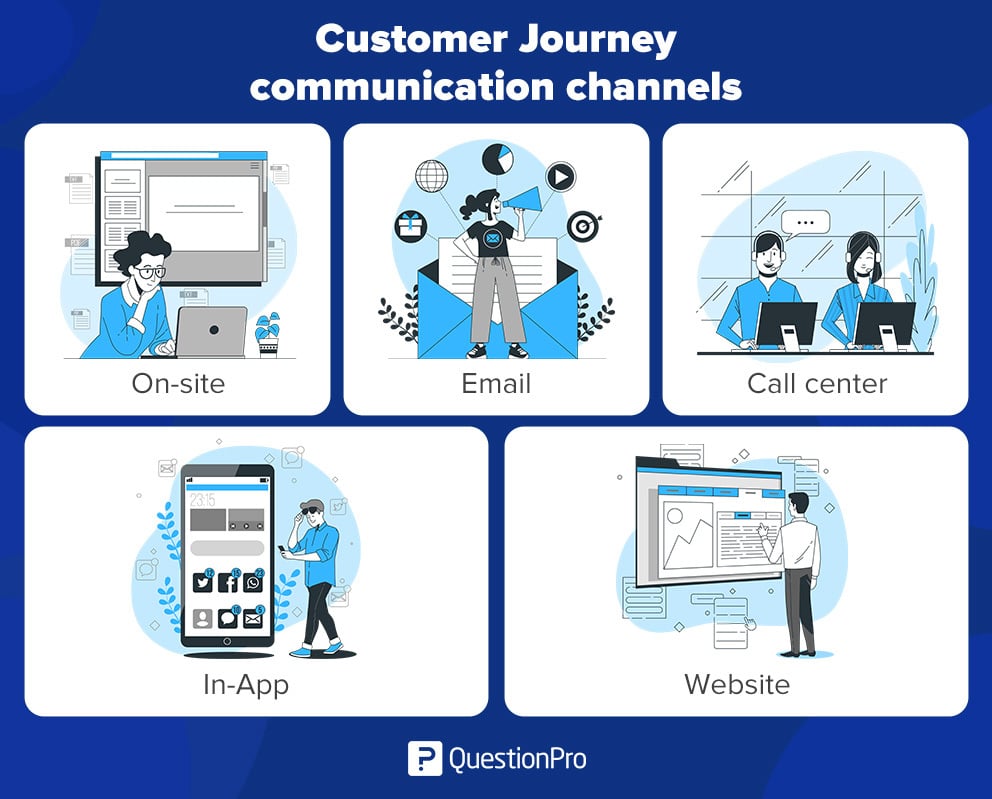
To start, here are some places to measure experience on an ongoing basis:
- On-site: Capture feedback at the moment customers visit businesses with physical locations. For example, let’s say you run a restaurant. Give diners a short survey to complete along with their bill at the end of their meal, allowing you to gather valuable insights into their customer journey.
- Email: Sending emails is one of the easiest ways to get customer feedback. Set up your sales system to trigger an email after a customer completes a purchase.
- Call center: After every customer interaction, you can collect feedback via email or phone-based survey.
- In-App: For app developers, collecting responses without leaving the app is ideal. An in-app survey allows users to continue enjoying the app while still providing you with feedback, contributing to a seamless customer journey.
- Website: Your prospects browse your site to consider becoming customers. Once customers continue visiting for support and account access, gathering feedback on your website is essential to a holistic customer experience approach.
If you like reading about what the customer journey is, you might find it interesting to learn about the in-store customer journey: definition, importance and stages .
Elements of the Customer Journey
There are various elements that are essential when creating your Customer Journey and that will help you have a better customer analysis.
Each of these elements will help you identify the points that you should improve on your journey:
Buyer persona
Buyer personas are iconic representations of your ideal customer. They are based on research, data, facts, and real interviews with recent buyers (and may even include perspectives from people who postponed a purchasing decision or purchased a competitive solution).
By creating a buyer persona correctly, marketing managers will be able to segment their messages better, targeting different people with the most appropriate content and offers; develop new products/services based on the needs and wants of its key customers; and reach the right people, thus pre-qualifying potential customers by attracting them.
Let’s remember that the journey of a customer is the story of a customer’s experience, and it helps you explain what happens along the way, to whom, and how it happens. Therefore, it is necessary to know who makes the trip to tell the story. The buyer persona represents the customers whose journey you are mapping.
Contact points or touchpoints
Where are the customer contact points? Touchpoints encompass all interactions between a brand and a customer at any point in the customer journey.
These individual touchpoints can influence how a customer perceives your overall brand experience. Every touchpoint represents an opportunity to guide and delight the customer. Touchpoints can occur through web and offline channels and may or may not be controlled by the brand.
These are some channels you can use to stay in touch during the journey:
- In the place
- Via telephone
- Social networks
- Word-of-mouth recommendations
- Evaluation sites
The number of customer touchpoints and the time it takes to complete each step can vary depending on multiple factors, including:
- Customer preferences (i.e., preferred mode of searching, purchasing, support, etc.).
- Relevance and importance of the goal (for example, buying a car compared to buying food for your dog)
- The channels chosen by companies to interact with their customers.
Performance indicators
A key role is to identify critical opportunity areas based on understanding your customers’ perceptions of the experiences.
You can use common indicators that indicate positive/neutral/negative or exceeds/meets/does not meet expectations. This generalized approach to performance indicators can be used effectively to identify and evaluate areas of opportunity.
Because qualitative research is typically conducted with smaller sample sizes, quantitative research with a large sample size can strengthen confidence in qualitative insights.
Quantitative research provides an opportunity to capture customer experience metrics for specific journey stages or touchpoints. By integrating metrics into the customer journey map, they become a useful tool for measuring customer experience initiatives over time. Some useful metrics you can include are:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) or other customer loyalty measures
- Customer satisfaction metrics
- Quantitative assessments of the primary emotions customers are experiencing at specific stages or touchpoints in their journey
- Effort metrics
- Measures of importance, usefulness, etc. from a specific point of contact
The metrics collected and included in the Customer Journey will help you measure the health of the customer experience, now and in the future. And in doing so, there must be a commitment to making value decisions based on customer experience performance.
Customer experience map
The customer experience map helps you list the following elements that will help satisfy users and compel them to move forward. Consider these examples:
- Consumer activities and questions
- Touchpoints such as websites, forums, and advertisements
- Assets such as paid media, blog posts, videos, and webinars (some assets are customer touchpoints)
- Strategies such as SEO, social networks, managing virtual communities, and creating referral programs
- Tools like engagement reports and online surveys.
How to Define a Customer Journey Effectively?
After learning what Customer Journey is and the elements that make it up, it is time to build a journey map that converts prospects into loyal customers and creates the best strategy.
Follow these 5 steps to ensure your customers get the products they need for their needs and enjoy a customer experience that will keep them coming back to your business.
1.- Understand what you have to offer and who benefits from it
Each member of your team should know how to communicate the benefits of your products and services. You can’t share something when you don’t know what it is! In the same way, you need to know who your ideal client is.
Ask yourself, “Who needs this solution most?” This is a good opportunity to take advantage of online surveys, which allow you to identify your target audience, their primary needs related to your offers, and any other considerations you need to make to attract them.
2.- Create your ideal client
Once you have a general idea of who your target audience is, create a few profiles to give them a name and a face. When you have a well-developed sense of who to include in your demographic segmentation, you’ll have a clear understanding of the variations in your customers’ journeys.
For example, you may discover that your reusable water bottles will solve problems for athletes of all ages, sustainability-conscious millennials, and adults with limited mobility. Avoid expanding your market too much because that can blur your focus and make your market strategies less efficient.
Create a customer archetype for each of these groups within your target audience, taking into account these imaginary but realistic variables:
- Economic situation/income range
- Interests and hobbies
- Main sources to communicate and obtain information
- Consistent touchpoints
- Favorite brands and products
- Consumption habits
3.- Identify any specific details of your industry
The next strategy to create an effective Customer Journey is to obtain details of your industry. Generally, customers’ stops along their journey will be similar. However, their specific needs should influence your value propositions and the assets you create to market your product.
4.- Optimize your value propositions
The Customer Journey is personal, and your value propositions must be consistent in each encounter with consumers.
As you become familiar with your target market, refine your value propositions to be inclusive, communicative, and aspirational. Use these statements as a guide in your customer journey map and your company’s marketing assets.
It’s time to put your customer experience map into practice. Consider what each of your customers would need and do so throughout the entire process while assigning these elements to each phase of the customer journey map.
5.- Build assets for each touchpoint in the Customer Journey
By mapping out the customer journey, you’ll have a clearer idea of what your ideal consumers will ask of you, the brands they might be considering, and the types of content they’re likely to consume to move from one phase to the next.
Depending on your industry, customer touchpoint content may include the following asset types:
- Associated or influential content
- Print or email newsletters
- Infographics
- Information on social networks
- Videos (ads, tutorials, webinars)
- Promotional flyers
- Sample kits or demos
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) tells the story of your customer’s experiences with your brand across every touchpoint – all on the same canvas. Or Customer Journey Map (CJM) as a key tool to improve the customer experience. Depending on the objective of the CJM, it can be more or less complex.
The things your customer feels, sees, and hears as they interact with your business, builds the foundation for their experience.
Understanding these experiences allows you to map and control the customer journey accurately.
Example of Customer Journey Mapping
Starbucks, for example, masters the concept of customer intimacy and uses customer journey maps to control the experience. The customer journey is calculated from the moment you step in the door.
Imagine a trip to your local Starbucks. As you walk inside, you smell the aroma of roasted coffee beans. The barista behind the counter greets you with a smile. As the muffled chit-chat disappears into the tranquil background music, you feel the coziness around you.
When you receive your coffee, you see your name handwritten by one of the friendly baristas, a personalized moment clearly indicated on the customer journey map. If you’re a regular, the staff knows you by name and can make your order from memory.
The coffee giant doesn’t just sell a product. It sells what people are best at remembering – the experience. The company retains loyal customers by packaging the product with an unforgettable experience. They’re also able to charge up to 10 times more than their competitors. Starbucks clearly understands customer experience and infuses that into the core of its business strategy.
Learn More: Click here if you’d like to review 7 more Customer Journey Examples.
Below, you will find a customer journey map template in case you need a reference to create your own. If you’d like to download the customer journey map template, keep reading! Or scroll down a little bit more 😉
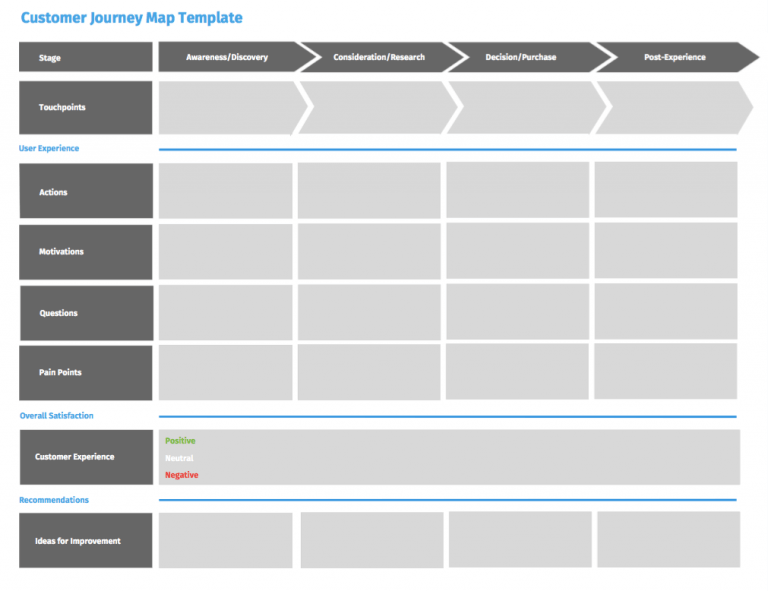
Your customer journey could take place over a few hours or more than several weeks. The simplest way to start is to create a timeline. Using your customer knowledge, fill in what’s happening with your customer at each stage of your customer journey timeline.
The customer journey mapping framework includes the following alongside the timeline:
- Actions: What is your customer doing? What are the key actions a customer takes to move to the next customer journey stage? What actions does a person take when they don’t move on?
- Motivations: What drives the customer to proceed to the next stage of the customer journey? What is the goal? Are they trying to solve a problem? What are they feeling?
- Questions: What are the customer’s uncertainties? Are they looking for something specific? Are they confused? Identify which stage of the journey customers have the most questions and quickly address them.
- Pain points: What obstacles prevent your customers from moving to the next stage? Is it the process? Price?
Direct customer opinions are the most effective way to get answers. Send surveys or conduct interviews to learn more about your customers and their needs. Input the data you receive into the framework above so you can see your company from your customer’s perspective.
Free eBook: The Hacker’s Guide to Customer Experience – CX= Emotion x Value
Halfway there? Congratulations! Luckily, you’ve learned a bit more about what Customer Journey is and its interconnection with customer experience. If you’d like to go the extra mile and learn more about how customer experience can help you gain happier , loyal customers and increase your business growth, download our free eBook: The Hacker’s Guide to Customer Experience – CX= Emotion x Value.
DOWNLOAD EBOOK FOR FREE
Tips for Conducting a Customer Journey Mapping
If you’ve made it this far, you would probably agree that knowing your customer’s journey is critical to creating a great customer experience. But how do you make the most out of it?
Let’s take a look at some of the following tips to create an effective Customer Journey Map:
Tip #1: Building a customer journey map is a team effort
It is not easy to reflect on the Customer Journey Map of all the interactions a customer goes through. The task can be further complicated when the people responsible for interaction cannot be found in the different departments.
This takes for granted the phases or interactions the client goes through with the company. What’s worse, it sometimes leads to mapping a Customer Journey Map that has more emphasis on departmental silos than the overall customer journey.
Remember, your team cannot forget the goal. It seeks to map the Customer Experience from its perspective. This is most effectively achieved when different company profiles are brought together. Only in this way will the final result reflect the knowledge that each one has of the client.
The idea is to dedicate a workspace with the different professionals, with and without client contact. If this is impossible, performing at least one validation with each department is vital. This will allow you to turn your Customer Journey Map into a shared responsibility tool.
Tip #2: Know your customer thoroughly
Understanding your customers at each intersection or checkpoint in their customer journey is critical. This allows you to develop content, products, and services that meet their needs. Rather than gathering occasional data from customers, employ continuous surveys to collect information.
You’ll enjoy the ability to adjust your marketing or product development in real-time to meet customer needs as the market changes.
Tip #3: Obtain a comprehensive view
The customer journey starts before potential customers purchase or sign up for services. Prospects begin their customer journey as they learn about offerings on your website, online review sites, or advertisements. After the awareness and discovery stages of the customer journey, consumers enter the purchase process. Customers experience your products and services when making a purchase and then form opinions.
Throughout these stages of the customer journey, you must know how customers feel about your business and products. For example, do you know what factors cause customers to choose you over the competition? How do customers perceive your sales staff? What do customers like about your products? Is your support team answering customer questions with accuracy?
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
There are six main steps to creating a customer journey map :
Step 01: Understand the target buyer’s persona: An organization must define its ideal buyer’s persona before journey mapping.
Step 02: Acknowledge the target audience’s intent: What does a buyer hope to achieve by interacting with a brand? What are their expectations?
Answer these questions by:
- Sending out online surveys to all the customers
- Organizing focus groups or one-on-one interviews
Then, develop action plans using the results of your research to meet buyer expectations.
Step 03: Note the touchpoints: Map all interaction touchpoints every time new customers visit your website or contact a sales team member. Include interactions before, during, and after purchase in your customer journey map.
Your organization should understand:
- Where customers obtain information about your website – Google search, social media, or Google ads.
- Which pages do most customers visit? What’s the average time spent on each?
- Did the customers enjoy shopping with the organization? Did they face any difficulties, and how helpful was the customer service team?
Step 04: Ask crucial questions: It’s essential to ask questions such as:
- Does my organization satisfy all the requirements of my target audience?
- In which stages of the customer journey do customers face common problems?
- Which website pages have higher bounce rates than what is acceptable?
If you interact directly with customers, be sure to ask them:
- How did you know about our organization?
- What were your expectations from our organization’s website?
- Were your expectations satisfied?
- What prompted you to purchase from our organization?
Step 05: Make a list of priorities: You can optimize customer journey mapping by identifying the areas that need immediate attention. Once you know common problems, you can take steps to limit their impact on customer loyalty.
Step 06: Put all ideas to paper: Most marketers prefer drawing the entire map on a whiteboard or using customer journey mapping tools to create a digital customer journey . Refer to your copy when you need to make decisions to improve customer experience.
Learn: What is the buyer’s journey , and what is its difference from the customer journey?
Free Customer Journey Map Template
At QuestionPro, we know that all this information can be overwhelming, and starting to create your Customer Journey without help can be intimidating.
That is why we have created a Customer Journey Map Template that we hope can help you start sketching the stages, UX, and overall satisfaction of your customers with your brand.
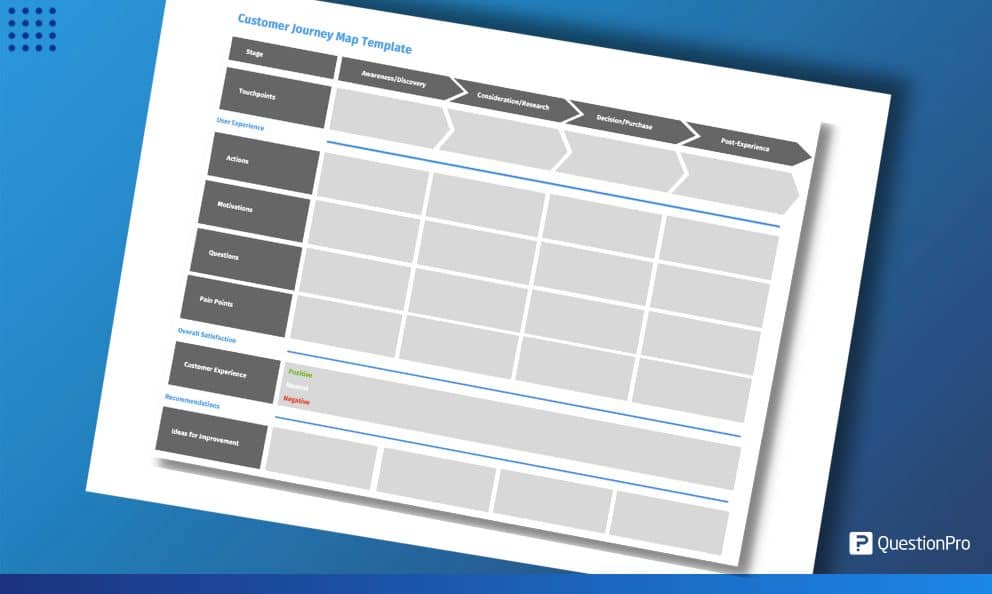
DOWNLOAD CUSTOMER JOURNEY MAP TEMPLATE (PDF)
How to Use Customer Journey to Improve Your Customer Experience?
Customers expect every exchange with a brand to be seamless from the start. Understanding the interactions at each customer journey touchpoint helps you satisfy customer needs and improves your business’s efficiency.
“Customer-centric companies are 60% more profitable than those not focused on the customer.” – Deloitte and Touche
To accurately map the customer journey, consider each stage of buying a product. At each customer journey stage, write down what a customer feels and the actions they must take to move forward.
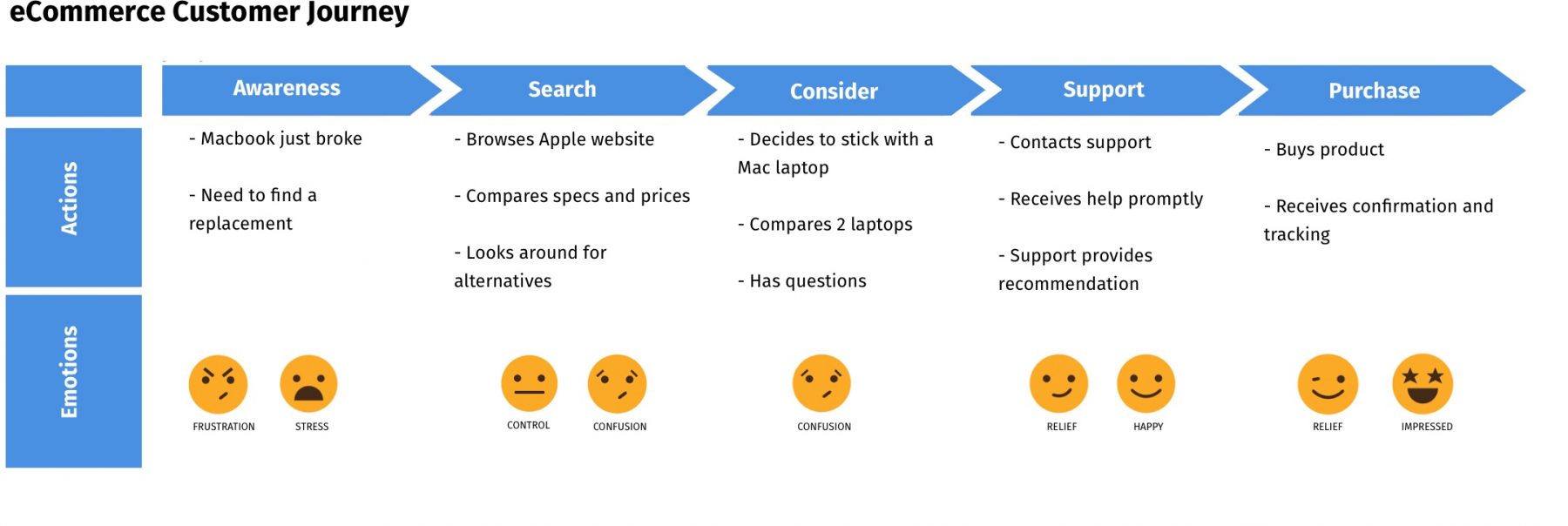
Examine the emotions at each touchpoint and rate the experiences. Is it positive or negative?
Begin to connect the dots and identify which gaps are falling short of your customer’s expectations. This exercise will help you formulate and decipher where you can have the most significant impact on improving the experience.
Learn more about the Customer Journey Canvas
Collect customer satisfaction feedback for more accurate results
Include your customer satisfaction scores as you map out your customer journey template. This additional information helps validate gaps or assumptions you make from mapping.
For example, your customer rates a CSAT score of 3 at their point of purchase and gives a score of 8 post-purchase. You immediately know that your point of sale requires attention.
Look at multiple customer satisfaction scores to find the most crucial pain points. If there is a customer journey touchpoint that ranks poorly for most customers, start your improvements there.
Start following your customer’s journey and create a detailed customer journey map. QuestionPro offers some of the most advanced customer experience tools available. Gain valuable insights into your customers’ thoughts and emotions using QuestionPro CX today.
MORE LIKE THIS

Like Never Seen Before: QuestionPro CX Product Updates – Quarter 1, 2024
Apr 29, 2024

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Let's chat! When’s a good time?

5 Stages Of The Customer Journey

Customer centricity is at the heart of successful business. Delivering value to buyers at every stage of the customer journey drives sales conversions and retention. This, however, is easier said than done — especially in the case of B2B customer journeys.
The B2B customer journey consists of several touchpoints — each with its unique influence on customer experience. These touchpoints can be divided into 5 broad customer journey stages . This blog explores each of these customer journey stages to eliminate any friction or pain points that may be limiting conversions.
- Customer journeys map out various buyer interactions in order to track how and why prospects become paying customers.
- The customer journey consists of 5 broad stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy.
- Delivering relevant material along each stage ensures that prospects feel understood and valued. This in turn contributes to successful journeys.
- Factors.ai connects the dots across campaigns, website and CRM to map out the customer journey with path analysis and account timelines
But first, a brief introduction to the customer journey:
The B2B sales cycle involves several stakeholders and touchpoints across campaigns, social media, organic efforts, offline events, and more. A customer journey maps out these various interactions to track how and why prospects become paying customers.
Given that B2B sales cycles tend to be lengthy, non-linear experiences, it can be challenging to accurately map without the right tools and frameworks. Learn more about customer journey mapping here: The Complete Guide To Customer Journey Mapping .
What are the 5 stages of the customer journey?
As previously mentioned, customer journeys can be broken down into five broad stages.
The 5 stages of the customer journey are:
- Consideration
According to Gartner , only 17% of a customer journey is spent in direct conversation with the vendor. The remaining 83% takes place through independent research and internal deliberation. Hence, it’s important for businesses to distribute relevant value at each stage of the journey — even outside discovery sessions and demo calls.
For example, at the Awareness stage of the customer journey, buyers are starting to learn more about their pain-points and the use-cases they’re looking to address. It wouldn't make sense to target this set of audience with bottom of the funnel assets like comparison articles because they’re only just growing awareness about their problem and possible solutions. Instead, this material may be more relevant to buyers at the Consideration stage as a comparison article will help weigh the pros and cons between alternate solutions.
The following sections explore each of these customer journey stages — and highlights what content assets are likely to resonate best with audiences at different stages.
#1 Awareness
The Awareness stage of the customer journey is when prospects discover your brand and product . This can take place through various channels — social media, brand campaigns, SEO, word of mouth, etc.
At this stage, these potential buyers know little about your work. Hence, it’s important to share educational information about what you do and how you do it. The objective here is to capture the interest of ideal clients by showcasing that in fact, your business understands the pain-points and provides the right solutions.
A few great assets to use during the Awareness stage are ToFu blogs, e-books, and podcasts. For one, this provides helpful information about the pain points your audience is looking to address. For another, it helps your brand stand out as an authoritative source in this field.

#2 Consideration
Once high-intent prospects conduct their preliminarily internal research, they shortlist a handful of solutions to pick from. Unlike B2C or D2C transactions, B2B deals involve buying committees with professionals from a wide range of departments. Hence, a successful deal involves ticking the right boxes for several stakeholders. Your product needs to be budget-friendly, user-friendly, and tech-friendly in order to close the deal.
Accordingly, the Consideration stage of the customer journey is where competition starts to heat up. Prospects are weighing your offering against that of alternatives in the market. Prices, reviews, features, and limitations are pit against each other to see which solution comes out on top.
This is the make or break stage for most deals. Companies need to showcase why they’re stronger options with more value to add to customers than their competitors. It’s vital to step back and assess whether you’re positioned in a favorable manner.
A few questions to ask here would be:
- Is the value of my product easy to grasp?
- Can people find my business without hassle?
- How does my product compare against competitors in terms of pricing and features?
- What is my unique selling point to convince buyers to pick me over the competition?
At this stage, it’s important to highlight why your product outshines the others with relevant case studies, product webinars, FAQ documentation, and more.

#3 Decision
To buy or not to buy? This is the question in the Decision stage of the customer journey.
After the awareness and consideration stage, prospects will narrow their search down to a couple of options. Here, most B2B SaaS companies offer two approaches to help buyers make their purchase decision:
- Risk-free trial
- Personalized demo
This is the real deal. Prospects have the opportunity to interact with the product and sales reps to reinforce their learnings from previous stages of the customer journey.
Apart from demos and trials, social proof is crucial to conversions at this stage. Peer-to-peer recommendations, case-studies, and customer reviews help prospects answer the “why you over the others?” question before finally choosing to either purchase or skip a product.

#4 Retention
If you customers have made it this far, you’re definitely doing something right. Still, a number of marketers and sales folk believe that the job is done once the deal is won. Customer retention, however, is just as important in the long run as bringing in new revenue. In fact, retaining customers works out to 5-10 times less expensive than acquiring new ones.

The customer journey continues long after the contract is signed. To ensure sustained renewal, companies must ensure that customers receive constant support and value from what they’re paying for.
The product itself is one of the most important, albeit overlooked, touchpoints along the customer journey. Building loyalty through excellent customer service and product development is key to customer satisfaction. This can be measured through surveys and customer interviews.
#5 Advocacy
Finally, we arrive at the fifth, and arguably most challenging stage of the customer journey. There’s no better endorsement than happy customers who are willing to advocate the value that the product brings to the table. However, customers will voice their satisfaction only if they’re truly convinced and satisfied.

A few touchpoints to lay along this final stage of the customer journey include:
- Referral programs
- Loyalty programs
- Testimonial requests
- Excellent customer support
- Qualified product roadmaps
Before exploring how Factors.ai helps track and optimize the customer journey from awareness to advocacy, let’s highlight a common point of confusion for marketing teams.
What’s the difference between customer journeys and sales funnels?
Often, sales and marketing teams conflate customer journeys and sales funnels. Sales funnels involve objective steps of conversions from awareness to deal won. For example, a common sales funnel in SaaS involves steps from web sessions to demo booking to opportunity creator to deal created to deal won:

Customer journeys, on the other hand, aren’t as clear-cut. Different buyers behave differently along each stage of the journey. Some may spend several weeks researching different products in the awareness or consideration stage. Others may simply jump ahead to a demo call without any research at all. Hence, customer journey stages provide a rough framework to classify the average behavior as they progress from visitors to prospects to paying customers.
How to track customer journey maps with Factors.ai
Mapping out the B2B customer journey is no easy task. Given the wide range of touchpoints across online and offline channels, it helps to use a tool that tracks and analyzes journeys automatically.
Factors.ai connects data across several sources including ad platforms, website, and CRMs to deliver a complete view of the customer journey. Users can track and analyze how prospects are interacting with campaigns, email outreach , webinars, website assets, and more before finally converting to customers.
Additionally, Factors connects the dots between marketing initiatives and pipeline to prove which efforts are driving bottom line metrics. For one, this helps improve resource allocation towards what drives results. For another, this helps marketing teams quantify their ROI and impact on revenue.
There are two key ways in which Factors.ai helps track the customer journey across campaigns, website, and CRM:
1. Account timelines
Account timelines map out account and user-level touchpoints in an intuitive, interactive timeline. This provides deep insight into how target accounts are interacting with your brand. Here are a few questions you can answer with account timeline:
- How are decision makers from a particular account engaging with ungated content?
- How much intent does a particular account show based on their website engagement?
- How are different leads from the same account behaving/interacting with your brand?

2. Path analysis
Path analysis is similar to account timelines in that it provides an intuitive overview of buyer behavior across the customer journey. The difference is that path analysis provides this visualization at an aggregated user level to see high-level patterns and trends. Here are a few questions you can answer with path analysis
- What sources are high-intent leads coming from?
- What website content are they interacting with most?
- Where are users dropping off most along the customer journey?

These analysis techniques in turn help with retargeting campaigns, personalizing sales pitches, and optimizing marketing efforts based on what’s driving results. Ultimately, this results in friction-free customer journeys that drive conversions and pipeline.
And there you have it! A brief overview of customer journey stages — and how Factors.ai can help track each stage from awareness to advocacy. If you’d like to see Factors.ai in action, book a personalized demo here !
Related Articles

Google Ads: Better Audience Segments with Factors.ai

LinkedIn Sales Navigator Cost: Is It Really Worth it?
Want to learn more about factors.
See how we can help your team over a quick call or an interactive product tour
Want to make the most of your LinkedIn ads?
See how Factors can help
Join our mailing list
Get the latest best practices in Marketing Analytics delivered to your inbox. You don't want to miss this!!
Customer journey: know where the customer is
The paths a customer takes can be followed. Job Wizards explains how companies benefit from knowledge of customer journeys.
Ten per cent more sales, and advertising that reaches customers at the right time. Sounds good? The customer journey makes it possible. In this article you can read how it works and how you can profit from the advantages.
Definition of the customer journey
Every purchase begins with an unfulfilled desire or unsolved problem: it could be a book that satisfies your crime novel craving. A new laptop that speeds up working from home. Or a bigger car to finally provide enough space for the whole family to sit comfortably. And your products, too, could be the solution when customers find out about them.
The customer journey, also known as the user journey or buyer’s journey, can help you, because all potential customers take a journey to a product. That journey may only take a few minutes, but it could also last weeks or even years. In that period, the users are looking for information to help them decide for or against a certain product.
The five phases of the customer journey
Customers go through certain phases in their customer journey where the awareness of the product is awakened and heightened. There are various models, describing three to seven phases. The most common model has five phases.
Direct and indirect touchpoints show the way along the customer journey. Customers find direct ones in magazines or on websites: this category includes price comparisons, test reports, recommendations and offers. Indirect touchpoints are advertisements placed by you, such as posters, TV advertising, advertising banners and social media ads.
- Awareness: A problem or requirement exists. A product could be the solution. Interest is awakened.
- Favourability : Initial information about the product and its alternatives increases interest. Those interested are aware of their favourites.
- Consideration: Customers consider purchasing a product. They compare prices and weigh up pros and cons.
- Purchase intent: The intention to purchase becomes more concrete. All that is missing is a little encouragement: an offer, a discount or fast delivery.
- Conversion: The decision is made and the purchase is completed.
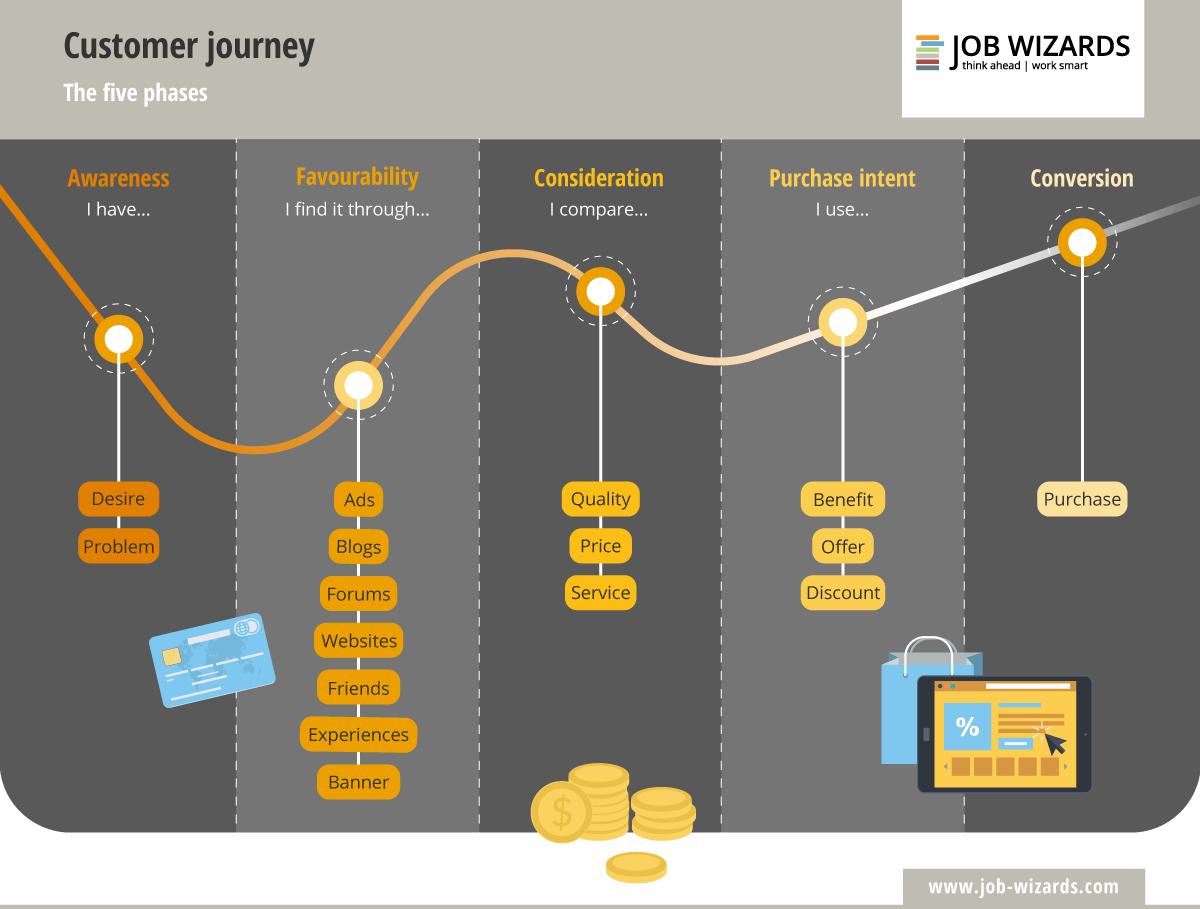
The five phases of customer journey
What opportunities does the customer journey offer?
A study by McKinsey has shown that companies who understand the customer journey generate an average of 10 per cent more turnover, and their customer satisfaction is 20 per cent higher. The numbers are impressive. But what makes knowledge of the customer journey so valuable?
A few years ago, companies would spread their advertising materials as widely as possible. The scatter loss was correspondingly high. With knowledge of the customer journey, you can make your advertising far more targeted – exactly where your customers most often stop.
These places are called touchpoints. If you only advertise your product there, you will reach potential customers much more often. That increases customer awareness of the product and increases the chances that the purchase decision will go your way. In other words, you inevitably increase the conversion rate and reduce advertising costs.
Analysis of the customer journey also captures previously unknown sales channels, such as hitherto unused online channels or product placement opportunities. At the same time, you make new discoveries: about customer desires, customer aims and possibly even weaknesses of your own products. Online tools can help you filter these findings. Read more about that at the end of this article.
Touchpoints: there is not just one customer journey
The greatest challenge in the analysis of the user journey is in comprehending the inconsistent user behaviour, because everyone starts at a different point with different destinations.
Some already know the product they want. Some have even used it already. If you find the touchpoints such as websites, influencers or discussion platforms, you can influence the customer journey and purchase decision.
However, there are more and more routes to the product these days: some users are initially just looking for inspiration. They have a desire or something in mind, but no solution yet. Their entry point to the user journey begins with a Google search or social media channels like Pinterest, Twitter or Instagram. Other customers look for specific information and opinions in tests and articles on blogs and specialist sites.
No two touchpoints are the same
Every touchpoint works differently and requires different measures. However, those that are highly frequented and particularly valuable are the ones that are most lucrative. While some touchpoints guarantee reach, others are qualitative lead generators. Depending on what your aims are, the focus of your advertising strategy might be on other touchpoints. Placement of banner advertising or individualised content such as sponsored posts and testimonials are measures that would reach customers but could fulfil other aims.
In addition, the journey is not linear and has shifted ever further into the digital world. Users continue their journey at different points and visit websites several times, often changing back and forth between their computer, tablet and smartphone. This behaviour makes it more difficult to seamlessly follow the customer journey.
An additional difficulty is that people also gather information offline: friends, family and work colleagues can influence the purchase, just as advertising posters, brochures, adverts and magazines can. All these entry points, routes and destinations are what make the customer journey so exciting – and hard to grasp.
How do you identify the customer journey?
The internet has fundamentally changed the customer journey. It has become more complex, but it is also easier to measure than ever. Modern tracking makes that possible: every website click, every dwell time and even users’ devices and their current locations can be tracked using cookies.
Online users interact with companies via various channels, such as social media ads, newsletters or banner clicks. Each interaction leads to valuable information about the target group and its interests. For example, the journey analysis reveals important indications about product desires or expected prices to you. The information and indications gathered can be summarised in a digital customer journey map .
Important factors when mapping:
- Customer types: which target groups are interested in the product?
- Touchpoints: what destinations does the journey go through?
- Funnel: what direction do the target groups go in which phase?
- Conversion: which measures can encourage the customer to complete the purchase?
Customer journey mapping: the analysis of the customer journey
Web-based tools help collate and evaluate the gathered data: they identify potential customers on their complex journey and analyse the advertising potential of touchpoints. Digital maps make the results visible and the customer journey thus becomes comprehensible at a glance.
Three proven tools for customer journey mapping:
- Canvanizer is a clear mapping tool that can put together information quickly and vividly in prepared templates. The team function also makes it possible to create tasks and exchange ideas.
- Smaply has three main elements: mapping, persona and stakeholder maps. Personas simulate customer types – users verify the results of their mapping and optimise the identified customer journey with these stored target groups. The stakeholder maps analyse the product placement environment in the touchpoints.
- The aim of Touchpoints Dashboard is to improve all user touchpoints. To do so, it includes a comprehensive area for teams to define tasks or create informative reports.
Your journey is just beginning …
New sales channels, specific touchpoints for customer interaction and an ensured increase in conversion rate: the customer journey has great potential for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Even a Google Analytics evaluation alone can provide initial information about touchpoints that are already highly frequented. Taking a look at the statistics of your Facebook ads makes the target group that has already been reached clearer. Digital monitoring tools like these are numerous and in some cases free to use. That makes getting into your customers’ journey possible for anyone – but the results can be extremely lucrative.
Share this article:
Rate this article:
Related topics:
Smart Windows: Digital innovation from Poland
Glass is rarely the first product that people associate with digitisation...
Digital competence – improve step by step. (Part 2 of 3)
If you want to be active professionally in the ‘digital ocean’, you should...
Digital competence – improve step by step (Part 1 of 3)
Digital competence is increasingly in demand, but what exactly does it mean...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Customer Journey (2024): Uitleg en Voorbeelden [+ Template] De Customer Journey is het proces dat je klanten doorlopen met jouw bedrijf. Dat gaat dan over de eerste tot en met de laatste interactie die iemand met jouw bedrijf heeft. Veel bedrijven hebben niet in kaart hoe hun klanten oriënteren, wat ze belangrijk vinden of wanneer het bedrijf ...
Definitie customer journey. Customer journey - in het Nederlands klantreis - is de route die een klant aflegt voordat hij of zij je product of dienst koopt. De klant staat hier centraal, niet jouw bedrijf. In iedere customer journey vind je touchpoints: contactmomenten waarbij de klant in aanraking komt met jouw bedrijf.
Customer journey model maken met behulp van customer journey mapping. Een customer journey maken kan met behulp van 5 stappen, zoals we uitgebreid bespreken en uitleggen in het artikel over de customer journey map : Bepaal het doel van de customer journey. Klantpersona's maken. Vul voor iedere klantpersona de klantreis en customer journey ...
McKinsey's consumer decision journey model helps you identify the moment of purchase, while the RACE Framework helps you build a strategy to get there. Use these customer journey models to win more customers. Based on empirical research, in 2009, McKinsey & Company suggested dramatic alternative customer journey models to the traditional ...
Dit is precies waar customer journey maps van pas komen. Niet alleen breng je hiermee in kaart op welke plekken je klant gaat zoeken naar informatie, maar je brengt ook in kaart hoe jij daar als bedrijf strategisch op in kunt spelen door "toevallig" aanwezig te zijn met een Google Adwords campagne of social media advertising.
De customer journey is de 'reis' die een klant aflegt om tot de aankoop van een product of dienst over te gaan. De customer journey omvat het model waarbij deze 'klantreis' in kaart wordt gebracht. Ook potentiële klanten horen daarbij. Wat is een customer journey.
Je moet weten waar je doelgroep naar op zoek is en hoe ze hierbij geholpen willen worden. Dit is essentieel voor een goede klantbeleving. Een goed startpunt hiervoor, is door te kijken naar de zogeheten 'customer journey' die de doelgroep doorloopt. Dit is een strategisch model waarmee je de stappen van de (potentiële) klant voorspelt ...
Customer journey vs process flow. Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map - otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you're typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
De term 'customer journey' staat voor de reis die jouw klant aflegt om tot de aankoop van jouw product of dienst te komen. Door dit visueel weer te geven, krijg je inzicht in hoe je de beleving van jouw klant kunt verbeteren. In dit artikel lees je alles wat je moet weten over customer journeys en het in kaart brengen ervan: customer ...
Hier zijn vijf stappen om je te helpen deze reis te begrijpen en te optimaliseren. Stap 1: Bepaal wie je doelgroep is. Voordat je de customer journey in kaart kunt brengen, moet je eerst je doelgroep duidelijk definiëren. Dit omvat het identificeren van je ideale klanten, hun behoeften, demografische gegevens en gedrag.
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams. Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is convenient for cross-functional teams to provide feedback. Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team so they always keep the customer in mind.
1. Define your purpose. The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won't know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
Fase 1: Awareness. Awareness is de beginfase van de customer journey. In deze fase zijn klanten passief. Ze horen misschien wel iets over je merk, maar doen niet actief iets met deze kennis. Ze gaan bijvoorbeeld niet meteen je website bezoeken of reviews checken. In deze fase ga je dus je klanten triggeren om een actieve houding aan te nemen.
Kies de contactpunten die de customer journey met je merk nauwkeurig weergeven. Nadat je je contactpunten hebt gedefinieerd, kun je ze gaan ordenen op je customer journey map. 4. Breng de huidige situatie in kaart. Schets wat volgens jou de huidige status is van de customer journey, de huidige customer experience.
The Customer Journey is the process your customers go through with your company. This then covers the first to last interaction someone has with your company. Many companies do not have a map of how their customers orient, what they care about or when the company comes into the potential buyer's mind. Not having enough mapping of the Customer ...
Een customer journey - of klantreis - is een manier om de klantbeleving in kaart te brengen. Je beschrijft hiermee de verschillende activiteiten, ervaringen en emoties die een klant met je organisatie, producten en/of diensten ervaart. Een klantreis begin op het eerste moment dat een klant zich bewust wordt van het aanbod en loopt via ...
1.1 - Definition of the Customer Journey. The customer journey can be defined as the series of steps or stages that a customer goes through during their engagement with a company. It typically starts with the initial awareness of a product or service, followed by consideration, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase experiences.
Every lead goes through several stages to become a loyal customer. The better this experience is for customers at each stage, the more likely your leads are to stick around. Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey: 1. Awareness.
Customer journey mapping is a proven model for understanding how, when, and where your customers experience your brand. To start, here are some places to measure experience on an ongoing basis: On-site: Capture feedback at the moment customers visit businesses with physical locations. For example, let's say you run a restaurant.
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
Customer journeys map out various buyer interactions in order to track how and why prospects become paying customers. The customer journey consists of 5 broad stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy. Delivering relevant material along each stage ensures that prospects feel understood and valued.
The customer journey, also known as the user journey or buyer's journey, can help you, because all potential customers take a journey to a product. That journey may only take a few minutes, but it could also last weeks or even years. In that period, the users are looking for information to help them decide for or against a certain product.
Definition Abbreviated as CDJ, customer decision journey is a model that describes the process customers undergo before making any purchase decisions. It is believed that there is no such thing as an impulse buy. New businesses always develop marketing strategies without considering the decision-making process by assuming that customers are always prepared to make a purchase.