

How to create a customer journey map
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 8 min
How to Make a Customer Journey Map
- Conduct persona research
- Define customer touchpoints
- Map current states
- Map future states
Steve Jobs, the genius behind Apple’s one-of-a-kind customer experience, said, “You’ve got to start with the customer experience and work back toward the technology, not the other way around.”
Nowadays, a clear vision and strategy for customer interactions is no longer an optional “nice-to-have”—it’s essential. As you refine your customer experience, a customer journey map is one of the most powerful ways to understand your current state and future state.
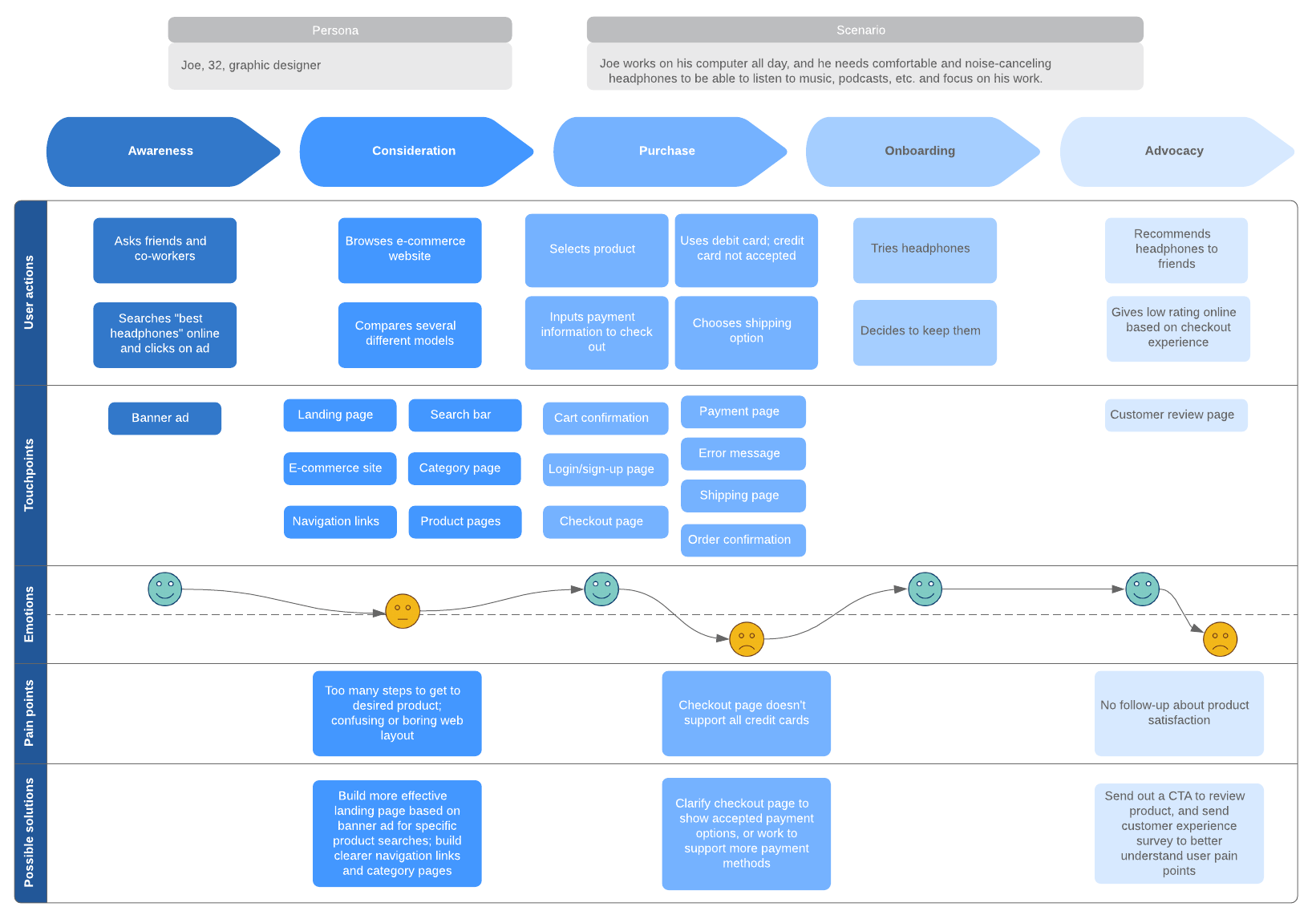
A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the process your customers go through in interacting with your business, such as an experience on the website, a brick and mortar experience, a service, a product, or a mix of those things.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with your brand. These visuals tell a story about how a customer moves through each phase of interaction and experiences each phase. Your customer journey map should include touchpoints and moments of truth, but also potential customer feelings, such as frustration or confusion, and any actions you want the customer to take.
Customer journey maps are often based on a timeline of events, such as a customer’s first visit on your website and the way they progress towards their first in-product experience, then purchase, onboarding emails, cancellation, etc.
Your customer journey maps may need to be tailored to your business or product, but the best way to identify and refine these phases is to actually talk to your customers. Research your target audiences to understand how they make decisions, decide to purchase, etc. Without an essential understanding of your customers and their needs, a customer map will not lead you to success. But, a well-constructed and researched customer journey map can give you the insights to drastically improve your business’s customer experience.
The benefits of customer journey mapping
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for uncovering insights into your customer experience, driving business goals, and building resilience in a changing market. In a 2022 report, Hanover Research found that 94% of businesses said their customer journey maps help them develop new products and services to match customer needs. Another 91% said their maps drove sales.
But understanding a customer’s journey across your entire organization does so much more than increase your revenue. It enables you to discover how to be consistent when it comes to providing a positive customer experience and retaining customer loyalty.
This was especially evident in recent years as top of improving marketing, customer journey maps emerged as a valuable way to understand evolving buyer behavior. In fact, 1 in 3 businesses used customer journey maps to help them navigate the changing landscape during the pandemic.
When done correctly, customer journey mapping helps to:
- Increase customer engagement through channel optimization.
- Identify and optimize moments of truth in the CX.
- Eliminate ineffective touchpoints.
- Shift from a company to a customer-focused perspective.
- Break down silos between departments and close interdepartmental gaps.
- Target specific customer personas with marketing campaigns relevant to their identity.
- Understand the circumstances that may have produced irregularities in existing quantitative data.
- Assign ownership of various customer touchpoints to increase employee accountability.
- Make it possible to assess the ROI of future UX/CX investments.
Following the process outlined above, customer mapping can put your organization on a new trajectory of success. Yet, according to Hanover Research, only 47% of companies currently have a process in place for mapping customer journeys. Making the investment to map your customer journey and solidify that process as part of your company’s DNA can result in significant advantages in your competitive landscape, making your solution the go-to option that customers love.
Customer journey maps can become complicated unless you keep them focused. Although you may target multiple personas, choose just one persona and one customer scenario to research and visualize at a time. If you aren’t sure what your personas or scenarios might be, gather some colleagues and try an affinity diagram in Lucidchart to generate ideas.
1. Set goals
Without a goal, it will be difficult to determine whether your customer journey map will translate to a tangible impact on your customers and your business. You will likely need to identify existing—and future—buyers so you can set goals specifically for those audiences at each stage of their experience.
Consider gathering the key stakeholders within your company—many of whom likely touch different points of the customer experience. To set a logical and attainable goal, cross-functional teamwork is essential. Gather unique perspectives and insights about each part of the existing customer journey and where improvements are needed, and how those improvements will be measured.
Pro Tip : If you don’t already have them in place, create buyer personas to help you focus your customer journey map on the specific types of buyers you’re optimizing for.
2. Conduct persona research
Flesh out as much information as possible about the persona your customer journey map is based on. Depending on the maturity of your business, you may only have a handful of records, reports, or other pre-existing data about the target persona. You can compile your preliminary findings to draft what you think the customer journey may look like. However, the most insightful data you can collect is from real customers or prospective customers—those who have actually interacted with your brand. Gather meaningful customer data in any of the following ways:
- Conduct interviews.
- Talk to employees who regularly interact with customers.
- Email a survey to existing users.
- Scour customer support and complaint logs.
- Pull clips from recorded call center conversations.
- Monitor discussions about your company that occur on social media.
- Leverage web analytics.
- Gather Net Promoter Score (NPS) data.
Look for information that references:
- How customers initially found your brand
- When/if customers purchase or cancel
- How easy or difficult they found your website to use
- What problems your brand did or didn’t solve
Collecting both qualitative and quantitative information throughout your research process ensures your business makes data-driven decisions based on the voice of real customers. To assist when conducting persona research, use one of our user persona templates .

Discover more ways to understand the Voice of the Customer
3. Define customer touchpoints
Customer touchpoints make up the majority of your customer journey map. They are how and where customers interact with and experience your brand. As you research and plot your touchpoints, be sure to include information addressing elements of action, emotion, and potential challenges.
The number and type of touchpoints on your customer journey map will depend on the type of business. For example, a customer’s journey with a SaaS company will be inherently different than that of a coffee shop experience. Simply choose the touchpoints which accurately reflect a customer’s journey with your brand.
After you define your touchpoints, you can then start arranging them on your customer journey map.
4. Map the current state
Create what you believe is your as-is state of the customer journey, the current customer experience. Use a visual workspace like Lucidchart, and start organizing your data and touchpoints. Prioritize the right content over aesthetics. Invite input from the stakeholders and build your customer journey map collaboratively to ensure accuracy.
Again, there is no “correct” way to format your customer journey map, but for each phase along the journey timeline, include the touchpoints, actions, channels, and assigned ownership of a touchpoint (sales, customer service, marketing, etc.). Then, customize your diagram design with images, color, and shape variation to better visualize the different actions, emotions, transitions, etc. at a glance.
Mapping your current state will also help you start to identify gaps or red flags in the experience. Collaborators can comment directly on different parts of your diagram in Lucidchart, so it’s clear exactly where there’s room for improvement.
5. Map future states
Now that you’ve visualized the current state of the customer journey, your map will probably show some gaps in your CX, information overlap, poor transitions between stages, and significant pain points or obstacles for customers.
Use hotspots and layers in Lucidchart to easily map out potential solutions and quickly compare the current state of the customer journey with the ideal future state. Present your findings company-wide to bring everyone up to speed on the areas that need to be improved, with a clear roadmap for expected change and how their roles will play a part in improving the customer journey.
Customer journey map templates
You have all the right information for a customer journey map, but it can be difficult to know exactly how to start arranging the information in a digestible, visually appealing way. These customer journey mapping examples can help you get started and gain some inspiration about what—and how much—to include and where.
Don’t let the possibility of a bad customer journey keep you up at night. Know the current state of the customer journey with you business, and make the changes you need to attract and keep customers happy.
Customer journey mapping is easy with Lucidchart.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
Send us an email
What is a customer journey map and how to make your own [examples included]
Written by by Kiran Shahid
Published on November 2, 2023
Reading time 12 minutes
Do you know what your customers see and do before they purchase from you?
They see your ads, interact with you on social media and explore your website before they buy. All these interactions—from the first ad impression to every “Please help” DM customers send—define your customer journey. To keep up with it all and better inform your social media marketing strategy , create a customer journey map as a blueprint to help you understand your customers at each stage.
Let’s explore what customer journey mapping is and how it helps your brand.

Social Customer Care by Sprout Social
What is customer journey mapping?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of each point of interaction your customers have with your company. You can style the map like a flowchart, timeline, table or even on sticky notes.
Creating the map is a great internal exercise. Along the way, you might find pain points or touchpoints you didn’t know existed. A basic customer journey map includes the buying stages (and support touchpoints) a customer goes through.

More detailed maps include:
- actions your customers take
- good and bad emotions your customers experienced
- departments involved in customer touchpoints
- content types you serve your customers
- solutions to pain points
What is a customer touchpoint?
A touchpoint on the customer journey map is the point of interaction a customer has with your brand. It doesn’t need to be a two-way interaction. Seeing a social media ad, getting a branded newsletter and asking a friend for a product recommendation are all touchpoints.
Customers may experience emotions and actions at touchpoints. When someone asks for product recommendations, people might mention your brand. You might not serve that recommendation to them directly but someone still introduces you to a potential customer.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
A customer journey map puts the customer first by giving you a deeper understanding of how your customers interact with your brand. This enable you to make better decisions and improve customer experiences.
When coupled with social media market research , they help brands:
- Provide an overview of the resources your customers use . This helps determine the ROI of customer-centric engagement and service. For example, if blogs are your highest traffic sources, investing more in those channels makes sense.
- Identify content gaps . Pain points without solutions are an excellent source for content ideation and development . If customers need help with a specific product issue, for example, but find limited guidance, create in-depth video tutorials to address this pain point.
- Identify inefficiencies . Maybe some processes are repetitive, or some solutions cause more friction. If your customers have trouble checking out due to a complicated form, for example, simplify it to reduce cart abandonment rates.
- Generate marketing campaign ideas . A clear understanding of customer motivations and journey stages creates targeted campaigns. You can provide them with relevant content and incentives to move them closer to a purchase.
- Guide multiple departments. Streamline content creation, social customer care strategy and messaging optimization across every touchpoint. Departments use the customer journey map as a central reference to ensure a consistent and customer-focused approach.
- Enhance customer communication . Customer journey maps reveal critical touchpoints, like social media interactions, for timely and meaningful engagement. In fact, The Sprout Social Index™ shows 51% of customers believe the most memorable brands on social respond to customers.
Every business and industry has its unique customer journey maps, but the fundamentals remain the same.
Recently, our social team talked about using social media for the customer journey in the auto industry. Watch the video below to hear their discussion on touchpoints, customer experience and how legacy brands are going beyond traditional tactics like targeted ads to tell their story.
It’s a great example of how industry-specific customer journey follows the fundamentals but also has touchpoints specific to them.
What’s included in a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is like a detailed travel itinerary for your customer’s experience with your brand. It includes elements like:
1. The buying process
The buying process is the step-by-step path a customer follows to make a purchase decision. It tells you where customers drop off or face obstacles during making purchases.
Use prospecting tools, content management systems (CMS) and behavior analytics tools to gather data. Facebook Shops, Instagram Shopping and TikTok Shop data also provide valuable insights into how customers find products and engage with content via social commerce .
Pro tip : Categorize the journey into stages like awareness, consideration and decision to map these steps horizontally on the customer journey map.
Don’t forget to integrate feedback mechanisms, such as customer surveys or user testing. These offer qualitative insights into the buying process. Understanding the “why” behind customer behavior can be as important as knowing the “what.”
2. Emotions
Emotions show how customers feel at different touchpoints in their interaction with your brand. Emotions heavily influence purchase decisions and brand loyalty which is exactly why it’s so important to include them.
Think about it: When someone has a great experience with your brand and feels happy, they’re more likely to buy from you again. On the flip side, if they feel frustrated or unhappy, they’ll knock on your competitor’s door.
Use surveys or feedback forms to ask customers how they felt during their experience. You might have come across these smileys during your own shopping experience:

These scales are a convenient way to gauge how your customers feel at any point.
Pay attention to what they say on social media and in reviews. You can tell if they’re happy or upset by their tone.
Tools like Sprout Social use AI-driven sentiment analysis to dig into social listening data to give you insights on what people think about your brand.

These insights are handy when creating emotional marketing campaigns . When you know how customers feel, take actionable steps to solve any negative experiences and encourage positive ones.
3. User actions
User actions are the steps customers take when they interact with your brand. They include steps like visiting your website, clicking on a product, adding items to their cart or signing up for your newsletter.
Actions highlight what people do at each stage. Each of these actions tells you something about what customers are interested in and how close they are to making a purchase.
Analytics tools for your website or app are your best bet for such data. These tools show you which pages customers visit, what they click on and where they drop off.
Once you have this information, tailor your marketing efforts and content to align with the actions customers take at each stage.
4. User research
User research examines what customers search for or where they turn for information during the buying process. This part of the customer journey map helps you understand how customers gather information.
For example, in the awareness stage, buyers often rely on search engines like Google to research solutions to their problems. But it’s not just about where they go—it’s about what they’re looking for. Knowing their specific research topics allows you to address their pain points.
What’s the trick? Keep an eye on what customers search for online. Tracking keywords and phrases they use on search engines, as well as social media market research are good places to start.
Also, monitor discussions and conversations to get a deeper understanding of the questions, concerns and topics that are top-of-mind for your potential customers.
The key is to use this information to provide potential customers with what they need at each stage. Targeted content delivery positions your brand as a valuable source of information.
5. Solutions
This section outlines the actions and strategies your brand implements to address customer pain points and improve their overall experience.
It documents the specific solutions or improvements applied at each stage of the customer journey. These include steps like changes to website design that resolve issues and improve the customer experience.
It visualizes how your brand responds to customer needs and challenges at different touchpoints. Besides that, it’s a good reference to ensure your team implements the solutions and refines them to increase customer satisfaction.
What are the 7 steps to map the customer journey?
A strategic approach to building a map ensures you capture every touchpoint, anticipate customer desires and address potential pain points. Here are seven steps to build a journey map unique to your customers and business needs.
1. Set your goals
What do you want to get out of this process? And why does it matter to your business? Knowing your goals sets the stage for how you assemble your map.
Some examples of goals include:
- Identify the top three customer pain points. Use these pain points to create content.
- Understand customer interests and motivations to develop better products and services.
- Total the cost of customer interactions to set a better social media budget .
2. Decide on a customer journey map type
There are several different customer journey maps and each one has its advantages. When you decide which map to work with, you know which details to focus on.
These are four of the most common types of customer journey maps: current state, future state, day in the life and service blueprint. We’ll go further into detail on each one later on.
Understanding your goals and where your brand stands in its evolution will guide you in selecting the appropriate map type.
3. Create and define your customer personas
Which customers will you focus on? It’s difficult to map a customer journey if you don’t have a customer in mind. Customer personas are fictional characters that represent each of your target customer groups. They’re detailed with everything from demographics to interests to buying behavior.

If you’ve already created social media personas to understand your audience, you’re more than halfway there. But if you haven’t, then our buyer persona template or Xtensio’s will be useful. To really get to know someone’s purchase decisions and shopping processes, interview existing customers.
Pro tip: If you have distinctively different personas—such as, if you serve both a B2C and B2B market—set up different customer journey maps.
4. Break it down: touchpoints and stages

The customer journey map is divided into stages that usually fit within the funnel illustrated above. List out the stages to begin. Next, list out the main customer touchpoints that exist for your company. When you’re done with both lists, place the touchpoints into the different stages.
To get even more detailed, assign department owners to each touchpoint. You can identify where certain social media channels fit into the mix. And, you can assign predicted customer sentiment or emotions to different stages of the journey. It’s up to you how detailed you want the map to be.
5. Gather data and customer feedback
You need rock-solid data on how customers interact with your brand to create an accurate customer journey map. Focus on these three aspects:
Analyze existing data
Jump into the data you already have—more specifically website performance, chats with customer support and sales records. This information can tell you loads about how customers act, what they like and what frustrates them.
This quantitative data offers a foundational perspective on how customers interact with your brand, helping you identify both strengths and areas of improvement.
Conduct customer interviews
Get personal with one-on-one chats with customers. Ask them about their experiences, what bugs them and what they expect when they deal with your brand. These talks reveal qualitative insights that numbers can’t, like understanding the emotional and psychological aspects of the customer journey.
Create surveys and questionnaires
Turn to surveys and questionnaires for a more structured and broader approach to gathering feedback. Send them out to a bunch of customers and get structured feedback. Ask questions about their journey with your brand, how happy they are and where they think things could get better.
A combination of these three aspects gives you a 360-degree view of what your customers really experience with your brand.
6. Test and identify pain points
To confirm your customer touchpoints, you probably checked in on various departments and spoke to customers. This is great work but you need to take another step further: test it yourself. Go through the customer journey from the viewpoint of the customer.
While you’re testing the journey, keep an eye out for challenges, confusion or any frustrating moments. For example, if the website takes forever to load, if instructions aren’t clear or if reaching customer support is a headache, make detailed notes of these issues.
It’s also a smart move to collect feedback from both colleagues and customers who’ve gone through the journey. This way, you double-check and confirm your findings for a more complete picture.
A hands-on approach ensures your customer journey map reflects the real-world experience and equips you to take targeted actions to improve the overall customer journey.
7. Make changes and find solutions
So your map is complete. What’s next? You need to find or create solutions to the pain points you identified in the previous step.
Now’s the time to check in on the goals you established in step one and make the moves to smooth out the journey. Give yourself time and space to implement some of the solutions, whether a quarter or six months, and check back on the map to update it.
As you put these changes into action, make sure to watch your customer journey map closely. Don’t forget to keep it up to date to show the improvements and how they affect the customer experience. This keeps your customer journey map fresh and super useful for steering your brand toward delivering an exceptional customer experience.
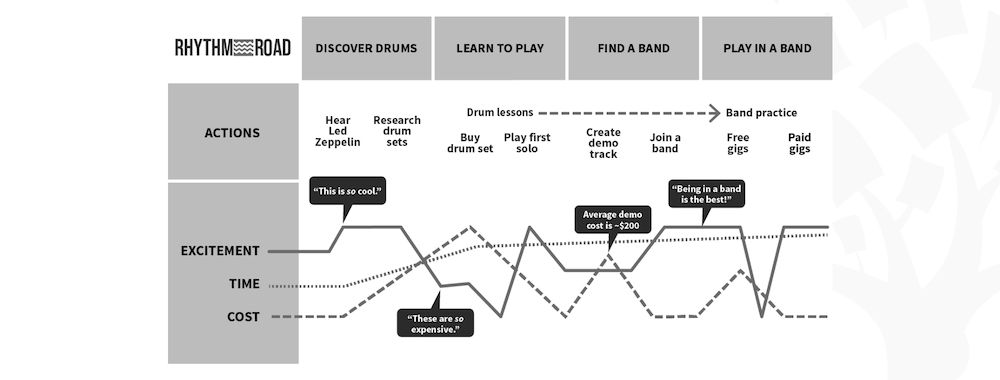
4 types of customer journey maps and examples
Let’s take a look at the four most common customer journey maps and examples of each.
1. Current state
Current state customer journey maps are like an audit. You document how your customers experience their buying and service paths in your company’s current state. These are especially helpful to establish a baseline for your customer service experience.
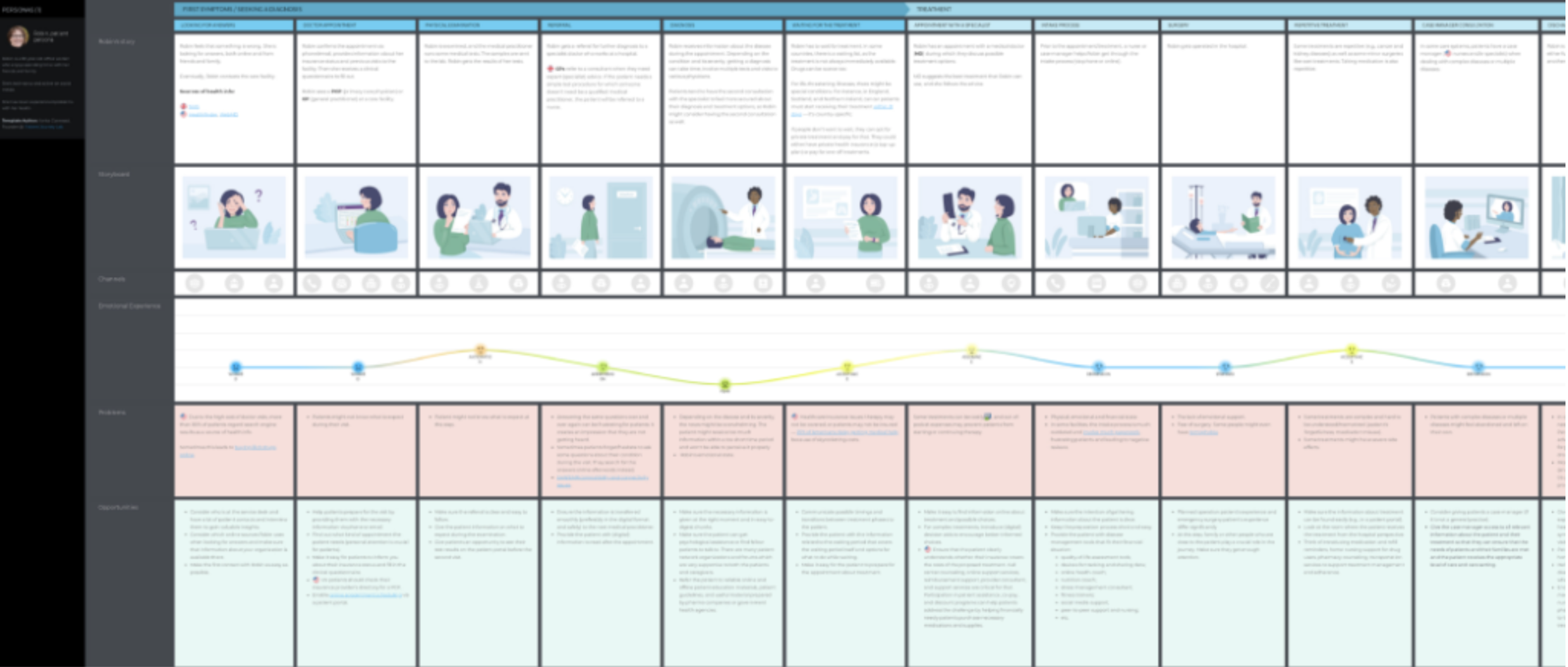
Take a look at this simplified current state customer journey map from Nielsen-Norman.

The map follows the journey of “Jumping Jamie” as they navigate the process of switching to a different mobile plan. The map defines the current journey into four stages. Apart from the journey, it also highlights opportunities and metrics to track.
Current state maps are fantastic for sharing user frustrations with all departments. This helps you get everyone on board with investing in solutions and brainstorming ways to address user pain points.
2. Future state
Future state customer journey maps follow the same format as current state maps except they represent the ideal journey. You can use them alongside your current state maps to identify painpoints and areas to improve.
Here’s an example of a future state journey map:

Why does this visual work? It covers different states, feelings and even touchpoints in a cohesive format.
The map visualizes the best-case scenario to create a north star vision for your brand. It aligns your efforts toward achieving the ideal customer journey.
3. Day-in-the-life
Day-in-the-life customer journey maps outline one of your persona’s schedules as they go about their day. The interactions may or may not involve your company. Creating one of these maps helps you identify the best times and areas to interact with your customer.
Here’s a “day-in-the-life” visual from Pipedrive.

The map doesn’t just highlight when the persona does something, but it also highlights different touchpoints and the different people they interact with throughout the day. And, notice those thumbs ups and downs? Those highlight how the child feels during different activities too.
4. Service blueprint

A service blueprint customer journey map focuses solely on when you provide customer service. It ignores components like ads that might exist in other maps.
Miro, a collaborative online whiteboard for teams, created the above map with a bank in mind. You’ll notice how this map is only about a customer’s visit to the bank. This type of map helps brands look at individual service areas and interactions. It’s a macro version of the current and future state maps.
Get started with customer journey map templates
Creating a customer journey map doesn’t have to be overwhelming. There are plenty of free and paid templates out there to help you create one. If you think you’ll need more guidance or many maps, some companies offer special software to design a custom map. Build your first journey map or improve your existing one with these options.
- Current state template , provided by Bright Vessel.

- Customer journey map template by Moqups, a design and collaboration tool.

- Service blueprint template by Miro

- Customer journey map template by Mural, a planning tool.

- UXPressia’s customer journey map online tool , made specifically to create presentation-ready customer journey maps.
Create a strong foundation with a well-integrated customer journey map
A customer journey map gives you the recipe for crafting personalized, impactful interactions that build customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When you know what they are and why they’re important, it’s time to make yours. Use data to create a solid customer journey map that exceeds customer expectations at every touchpoint.
Check out how you can turn your B2B social media data into a revenue-driving powerhouse and create a memorable brand.
- Customer Care
- Customer Experience
Customer service chatbots: How to create and use them for social media
- Marketing Disciplines
Grow your brand with customer-centric marketing
How a sentiment score improves your brand strategy
How to build customer relationships with social media
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
HOTSAUCE is back 🔥 We’re bringing the heat to CX Circle NYC on Sep 10 🗽 Get your ticket for the #1 DX event
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
The definitive 8-step customer journey mapping process
In business, as in life, it's the customer's journey that makes the company's destination worth all the trouble. No customer wants to jump through several different hoops to get to your product: they want it fast and they want it now.
Following certain customer journey mapping stages helps you improve your user's experience (UX) to create a product they love interacting with, ensures you stay ahead of key workflow tasks, and keeps stakeholders aligned. But a misaligned map can derail your plans—leading to dissatisfied users who don’t stick around long enough to convert or become loyal customers.
Last updated
Reading time.

This article walks you through the eight key stages of great customer journey mapping, and shows you how to adapt each to your unique business and product to optimize the customer experience from start to finish.
Learn how customers interact with your product and website
Hotjar's Observe and Ask tools let you go ‘behind the scenes’ to understand your users’ product experiences and improve their customer journey.
An 8-step process for effective customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a visualization of every point of interaction a user has with your company and product.
Mapping out the customer journey gives you insights into your buyers’ behavior to help you make changes that improve your website and the user flow between touchpoints. This helps you increase online sales and turn users into loyal customers and brand advocates.
Follow these eight proven steps to understand—and enhance—the customer experience.
Note: every business is distinct, so be sure to adapt these steps to your particular user and business needs.
1. Define your purpose
The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won’t know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
To define your purpose, consider your company’s mission statement and incorporate your specific user pain points as much as possible.
Make your purpose specific to your company’s needs and goals—for example, the purpose of an ecommerce brand looking to help users navigate several different products and make multiple purchases will differ from that of a SaaS company selling subscriptions for one core product.
2. Make sure your team is aligned and roles are clear
Cross-functional collaboration is essential when mapping out your brand's or product’s user journey. Get insights from different teams within your organization to find out exactly how users engage with key touchpoints to derive a holistic sense of the user experience (UX), which will help you improve every aspect of the customer experience.
Lisa Schuck , marketing lead at Airship , emphasizes the importance of keeping “anybody that has a touchpoint with a customer” involved. She advises teams to “figure out how to align your external marketing and sales with your internal operations and service.”
Although sales, product, and marketing departments are often the key players in customer journey mapping, also involve your operations and design teams that are responsible for creating the user flow.
If you have a SaaS company, for example, marketing creatives, sales teams, product owners and designers, and your customer experience department all need to participate in the process. Clearly define who’s responsible for different aspects of the map, and regularly check in to make sure your final map isn’t missing any important perspectives.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Highlights feature to collect and organize key product experience (PX) insights and data on user behavior from teams across your organization to help you build your customer journey map. Then use Hotjar’s Slack integration to quickly share learnings with your relevant stakeholders to get buy-in and ensure everyone is aligned.
Hotjar’s Slack integration Slack lets teams discuss insights in the moment, so they’re up to date with critical issues
3. Create user personas
Once you’ve defined your purpose and involved all relevant stakeholders, it’s time to design your user personas . Use resources like UXPressia and HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool to help you design various product personas .
Create a range of user personas to understand what each type of buyer needs to curate a journey that’s easy and enjoyable for every customer. This is an important early step in the customer journey mapping process—because if you don’t understand your users, you won’t be able to fully comprehend how they interact with your brand to better it.
Create user personas for all your product’s possible buyers—for example, to map out a B2B customer journey for a company in the hospitality business means developing personas for a range of different customers, from large chain hotel managers to small vacation rental owners.
4. Understand your user goals
Once you’ve designed your user personas, it’s time to define their jobs to be done . What do your users hope to accomplish when they search for your product or service? What do they want to do when they click on your website? Address and answer these questions to build a deep understanding of your users’ goals and pain points to inform your customer journey.
In a SaaS customer journey , perhaps users are looking for helpful comparisons of product features on your website, or want to easily sign up for a trial account in the hopes that your product will solve their problems. But you won’t know until you ask .
Once you have users or test users, get direct insights from them with Hotjar's Feedback tools and Surveys to ask buyers exactly what their goals are as they browse different pages of your website or interact with product features.
Since user goals are at the center of your customer journey map, define them early on—but keep speaking to your users throughout the entire process to make sure you’re up to date with their needs.
5. Identify customer touchpoints
After you understand your users and what their goals are, it’s time to identify the ways they interact with your company and your product.
"Touchpoints are the moments the customer interacts with your brand, be it through social media channels, your product, or customer support. The quality of these experiences affects the overall customer experience, which is why it’s important to be aware of them. Consider what happens before, during, and after a customer makes a purchase or uses your product."
Key customer journey touchpoints for a website or product include your homepage, landing pages, product pages, CTA buttons, sign-up forms, social media accounts, and paid ads.
Collaboration is key to identifying touchpoints throughout the entire customer journey. Include insights from different teams and stakeholders —your marketing and sales teams will have a strong understanding of the touchpoints involved pre-purchase, while the customer experience department can shed light on post-purchase touchpoints.
Post-purchase touchpoints can help turn users into loyal customers and even advocates for your brand.
In the words of Lisa Schuck, "When you create a raving fan, or a brand advocate, who goes out and tells the world how wonderful you are, you get social credibility and validity. It’s becoming more and more important to have advocates."
Pro tip : speak with your users regularly to get direct voice-of-the-customer (VoC) insights on what they love and what frustrates them on their journey. Place Hotjar Feedback widgets and Surveys at key website touchpoints like your homepage and landing pages to get valuable user insights on what you can improve. Use Hotjar’s survey templates to get inspiration for your survey questions.
An example of an on-site Hotjar Survey
6. Map out the customer journey
Once your user and product research are complete and all roles are distributed, it’s time to map out the full customer journey.
First, map out an overarching customer journey by putting your key touchpoints in order and identifying how your various user personas interact with them. Then, home in on the details, looking at how customers engage with specific aspects of your website, product, or social media accounts.
Breaking down the mapping process into smaller phases will ensure you don’t miss any key interactions.
Here’s how an ecommerce brand could lay out general touchpoints, then narrow each down into more specific actions:
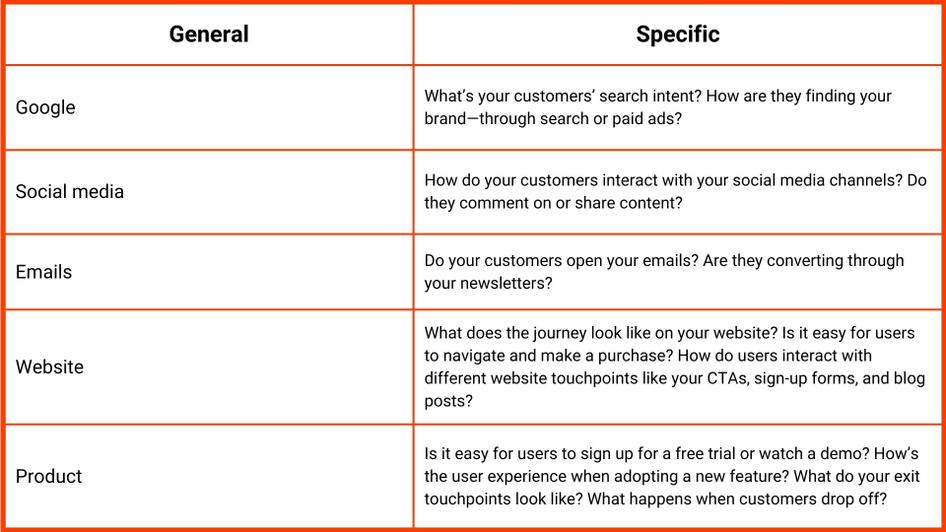
Pro tip : it’s helpful to think of the user journey in terms of different functions when mapping it out, like:
Connect: how are buyers connecting with your brand?
Attract: how are you convincing them to convert?
Serve: how are you serving customers when they want to purchase?
Retain: how are you promoting brand advocacy and customer retention ?
7. Test the customer journey
Once you’ve mapped out the customer journey, it’s time to take it for a spin. You can’t understand how your users move through customer touchpoints unless you test out the user flow yourself.
Start with an informational Google search, then visit your website, check out your social media pages, and simulate the purchase process. This will help you get a better sense of how users interact with each touchpoint and how easy it is to move between them.
Be sure to try out the journey from the standpoint of every relevant user persona. For an enterprise software company, this could mean looking at how decision-makers move through the user flow vs. the employees who’ll use your software day to day.
By walking through the customer journey yourself, you can identify issues and difficulties that users may have to address them proactively.
Try out the user flow with test users to get a realistic perspective of the user experience. Be sure to use focus groups that represent every one of your user personas.
8. Use continuous research to refine your map
Continuously map out, analyze, and evaluate the customer journey by observing users and getting their feedback. Hotjar Heatmaps and Recordings help you understand how your users are experiencing the customer journey on your website: create heatmaps to see whether users are clicking on CTAs or key buttons, and watch recordings to find out how they navigate once they reach your homepage.
Then, use Google Analytics to get an overview of your website traffic and understand how customers from different channels move through the user journey.
Finally, once you have these combined user insights, use them to make changes on your website and create a user journey that is more intuitive and enjoyable.
Pitfalls to avoid during the customer journey mapping stages
Jamie Irwin , director & search marketing expert at Straight Up Search , says companies should avoid these three common mistakes when mapping out the customer journey:
Don't map out the entire customer journey at once
Don't forget about the ‘hidden journeys’
Don't make assumptions about customer behavior
To sidestep these common pitfalls:
Start by mapping out the overall journey, and only drill down into more detail once you have a broader, higher-level overview of the customer journey
Factor in every way that customers interact with your brand, even the ones you don’t have as much visibility on, like ‘dark social’ communications about your brand shared in private channels. Talk to your users to find out what they’ve heard about your brand outside of public channels , and use sticky share buttons to keep track of when your content’s shared through email or social media messengers.
Take a data-informed approach: don’t assume you already know your users —test out your hypotheses with real users and qualitative and quantitative data.
Follow proven steps to successfully map out the customer journey
Take the time to understand your business goals and users, involve the right teams, and test frequently to consistently improve your customer journey and make the decisions that will help you map out an experience that will get you happy and loyal customers.
FAQs about customer journey mapping stages
What is the purpose of customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping helps you visualize how users interact with your business and product, from the moment they find it until long after they make their first purchase.
The purpose of customer journey mapping is to gain insights into the buyer's journey to create a more enjoyable, streamlined, and intuitive experience for your customers.
What are the benefits of following a customer journey mapping process?
The main benefits of a customer journey mapping process are: :
Building on tried-and-tested processes
Not missing any key steps
Considering all buyer personas
Keeping all relevant stakeholders involved
Creating a valuable customer journey map
Improving user experience
What happens if you don’t follow key steps in customer journey mapping?
If you don’t follow key steps when mapping out the customer journey, your map likely won’t give you the insights you need to enhance the experience users have with your most important touchpoints —like your homepage, landing pages, CTAs, and product pages.
This can result in high bounce rates, low conversion, and unsatisfied users who fail to become loyal customers.
CJM benefits
Previous chapter
CJM touchpoints
Next chapter
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Customer Journey Maps
What are customer journey maps.
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain points and opportunities to enhance customer experience and boost customer retention.
“ Data often fails to communicate the frustrations and experiences of customers. A story can do that, and one of the best storytelling tools in business is the customer journey map.” — Paul Boag, UX designer, service design consultant & digital transformation expert
In this video, Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, explains how you can include journey maps in your design process.
- Transcript loading…
Customer Journey Maps – Tell Customer Stories Over Time
Customer journey maps are research-based tools. They show common customer experiences over time To help brands learn more about their target audience.
Maps are incredibly effective communication tools. See how maps simplify complex spaces and create shared understanding.
Unlike navigation maps, customer journey maps have an extra dimension—time. Design teams examine tasks and questions (e.g., what-ifs) regarding how a design meets or fails to meet customers’ needs over time when encountering a product or service.
Customer journey maps should have comprehensive timelines that show the most essential sub-tasks and events. Over this timeline framework, you add insights into customers' thoughts and feelings when proceeding along the timeline. The map should include:
A timescale - A defined journey period (e.g., one week). This timeframe should include the entire journey, from awareness to conversion to retention.
Scenarios - The context and sequence of events where a user/customer must achieve a goal. An example could be a user who wants to buy a ticket on the phone. Scenarios are events from the first actions (recognizing a problem) to the last activities (e.g., subscription renewal).
Channels – Where do they perform actions (e.g., Facebook)?
Touchpoints – How does the customer interact with the product or service? What actions do they perform?
Thoughts and feelings – The customer's thoughts and feelings at each touchpoint.
A customer journey map helps you understand how customer experience evolves over time. It allows you to identify possible problems and improve the design. This enables you to design products that are more likely to exceed customers’ expectations in the future state.

How to Create a Customer Journey Map for Exceptional Experiences?
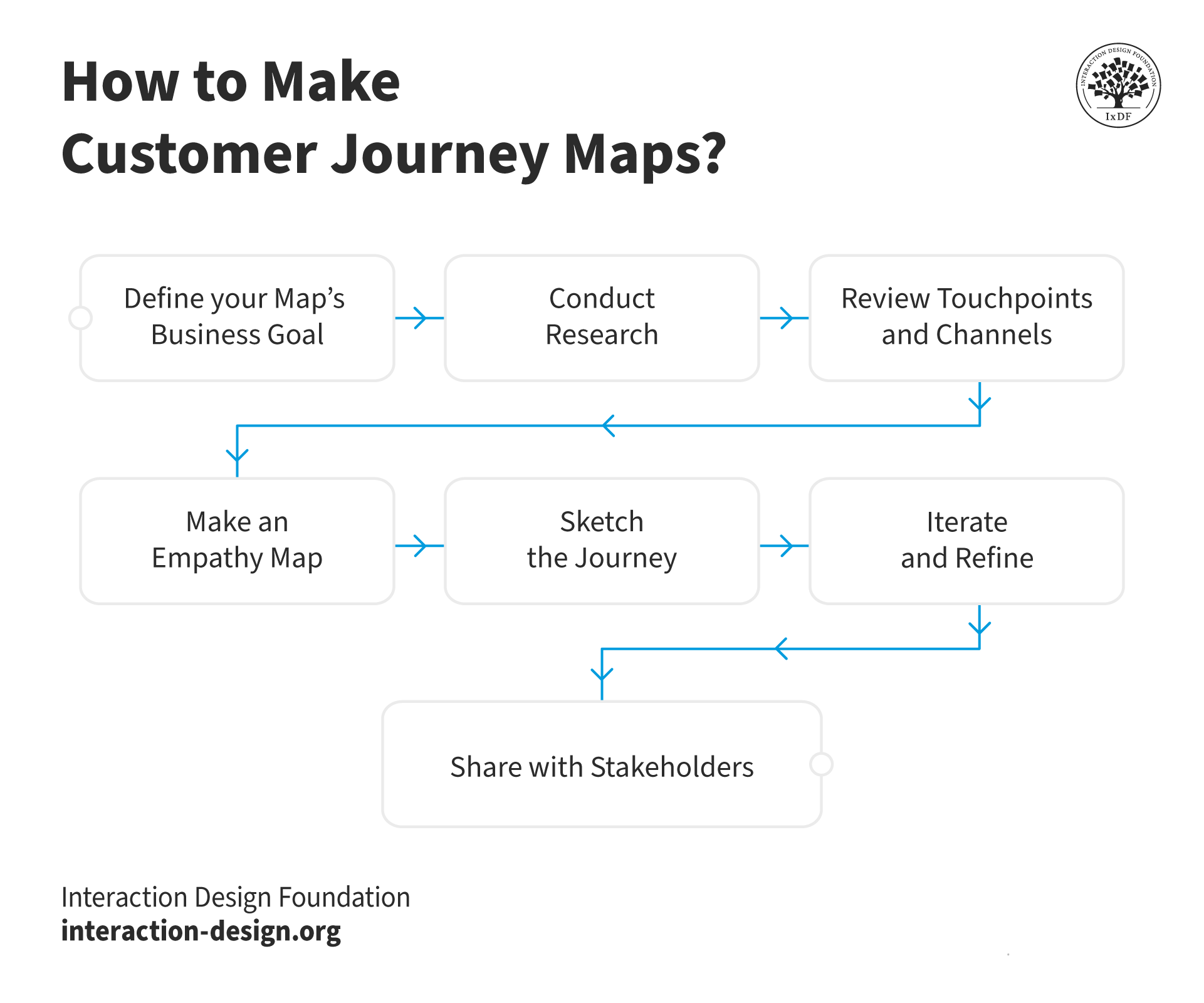
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Define Your Map’s Business Goal
Before creating a customer journey map, you must ask yourself why you're making one in the first place. Clarify who will use it and what user experience it will address.
Conduct Research
Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints. Get analytical/statistical data and anecdotal evidence. Leverage customer interviews, surveys, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
Watch user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen talk about how user research fits your design process and when you should do different studies.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Review Touchpoints and Channels
List customer touchpoints (e.g., paying a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for more touchpoints or channels to include.
Make an Empathy Map
Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc., in a given situation. Then, determine their needs and how they feel throughout the experience. Focus on barriers and sources of annoyance.
Sketch the Journey
Piece everything—touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.). Show a customer’s course of motion through touchpoints and channels across the timescale, including their feelings at every touchpoint.
Iterate and Refine
Revise and transform your sketch into the best-looking version of the ideal customer journey.
Share with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders understand your map and appreciate how its use will benefit customers and the organization.
Buyer Journey vs User Journey vs Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
You must know the differences between buyer, user, and customer journeys to optimize customer experiences. A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans.
Customer Journey
The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps:
1. Awareness : This is the first stage of the customer journey, where the customers realize they have a problem. The customer becomes aware of your brand or product at this stage, usually due to marketing efforts.
2. Consideration : Once customers know about your product or service, they start their research and compare brands.
3. Purchase : This is the stage where the customer has chosen a solution and is ready to buy your product or service.
4. Retention : After the purchase, it's about retaining that customer and nurturing a relationship. This is where good customer service comes in.
5. Advocacy : Also called the loyalty stage, this is when the customer not only continues to buy your product but also recommends it to others.
The journey doesn't end when the customer buys and recommends your solution to others. Customer journey strategies are cyclical and repetitive. After the advocacy stage, ideally, you continue to attract and retain the customers, keeping them in the cycle.
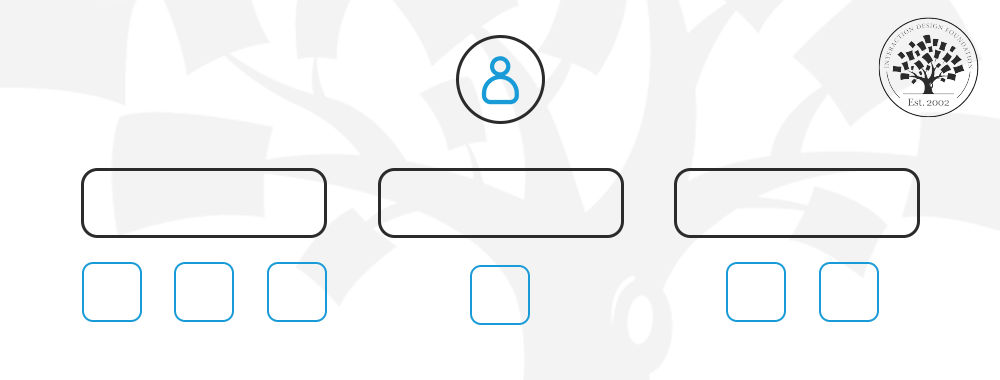
There is no standard format for a customer journey map. The key is to create one that works best for your team and product or service. Get started with customer journey mapping with our template:
This customer journey map template features three zones:
Top – persona and scenario.
Middle – thoughts, actions, and feelings.
Bottom – insights and progress barriers.
Buyer Journey
The buyer's journey involves the buyer's path towards purchasing. This includes some of the steps we saw in the customer journey but is specific to purchasing :
1. Awareness Stage : This is when a prospective buyer realizes they have a problem. However, they aren't yet fully aware of the solutions available to them.
2. Consideration Stage : After identifying their problem, the buyer researches and investigates different solutions with more intent. They compare different products, services, brands, or strategies here.
3. Decision Stage : The buyer then decides which solution will solve their problem at the right price. This is where the actual purchasing action takes place.
4. Post-Purchase Evaluation : Although not always included, this stage is critical. It's where the buyer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase. It includes customer service interactions, quality assessment, and attitudinal loyalty to the brand.
All these stages can involve many touchpoints, including online research, social media interactions, and even direct, in-person interactions. Different buyers may move through these stages at different speeds and through various channels, depending on a wide range of factors.
User Journey
The user journey focuses on people's experience with digital platforms like websites or software. Key stages include:
1. Discovery : In this stage, users become aware of your product, site, or service, often due to marketing efforts, word-of-mouth, or organic search. It also includes their initial reactions or first impressions.
2. Research/Consideration : Here, users dig deeper, exploring features, comparing with alternatives, and evaluating if your offering suits their needs and preferences.
3. Interaction/Use : Users actively engage with your product or service. They first-hand experience your solution's functionality, usability, and usefulness to achieve their goal.
4. Problem-solving : If they encounter any issues, how they seek help and resolve their issues fall into this stage. It covers user support, troubleshooting, and other assistance.
5. Retention/Loyalty : This stage involves how users stay engaged over time. Do they continue using your product, reduce usage, or stop altogether? It includes their repeated interactions, purchases, and long-term engagement over time.
6. Advocacy/Referral : This is when users are so satisfied they begin to advocate for your product, leaving positive reviews and referring others to your service.
Download this user journey map template featuring an example of a user’s routine.

Understanding these stages can help optimize the user experience, providing value at each stage and making the journey seamless and enjoyable.
Always remember the journey is as important as the destination. Customer relationships start from the first website visit or interaction with marketing materials. These initial touchpoints can influence the ongoing relationship with your customers.
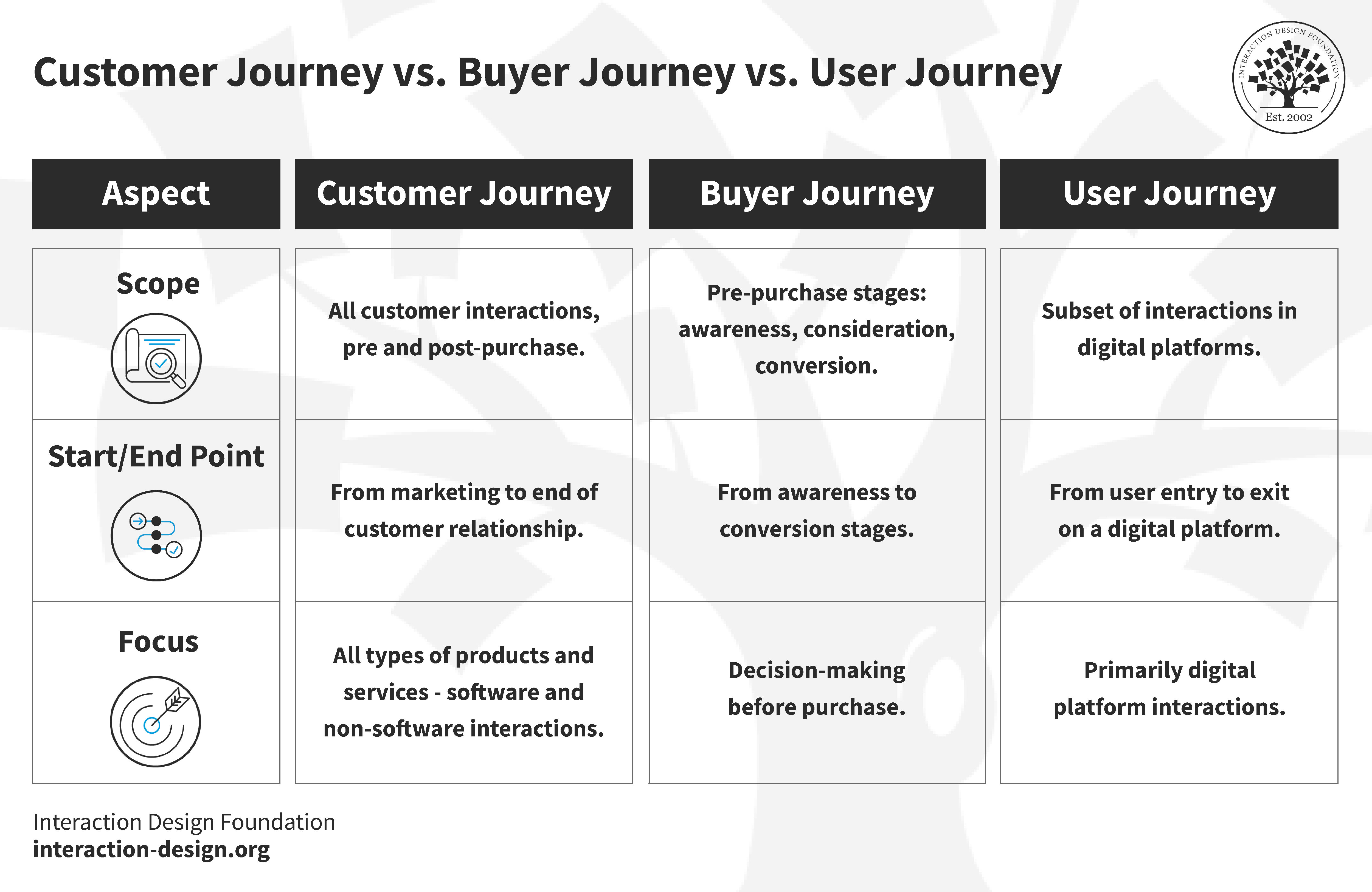
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
All customer interactions, pre and post-purchase.
Pre-purchase stages: awareness, consideration, conversion.
Subset of interactions in digital platforms.
Start/End Point
From marketing to end of customer relationship.
From awareness to conversion stages.
From user entry to exit on a digital platform.
All types of products and services—software and non—software interactions.
Decision-making before a purchase
Primarily digital platform interactions.
Drawbacks of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is valuable yet has limitations and potential drawbacks. Recognize these challenges and create more practical and realistic journey maps.
Over-simplification of Customer Experiences
Customer journey maps often risk simplifying complex customer experiences . They may depict varied and unpredictable customer behaviors as straightforward and linear. This simplification can lead to misunderstandings about your customers' needs and wants. As a result, you might overlook customers' diverse and unique paths.
Always remember that real customer experiences are more complex than any map. When you recognize this, you steer clear of decisions based on simple models.
Resource Intensity
Creating detailed customer journey maps requires a lot of resources and time. You must gather extensive data and update the maps to keep them relevant. This process can strain small businesses or those with limited resources.
You need to balance the need for comprehensive mapping with available resources. Efficient resource management and prioritization are crucial to maintaining effective journey maps.
Risk of Bias
Creating customer journey maps carries the inherent risk of biases . These biases can arise from various sources. They can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the maps.
Alan Dix, an expert in HCI, discusses bias in more detail in this video.
Common biases in customer journey mapping include:
Assumption Bias: When teams make decisions based on preconceived notions rather than customer data.
Selection Bias: When the data doesn’t represent the entire customer base..
Confirmation Bias : When you focus on information that supports existing beliefs and preferences. Simultaneously, you tend to ignore or dismiss data that contradicts those beliefs.
Anchoring Bias : Relying on the first information encountered (anchor) when making decisions.
Overconfidence Bias : Placing too much trust in the accuracy of the journey map. You may overlook its potential flaws.
These biases may misguide the team, and design decisions based on these maps might not be effective.
To address these biases, review and update journey maps with real user research data. Engage with different customer segments and gather a wide range of feedback to help create a more accurate and representative map. This approach ensures the journey map aligns with actual customer experiences and behaviors.
Evolving Customer Behaviors
Customer behaviors and preferences change with time. A journey map relevant today can become outdated. You need to update and adapt your maps to reflect these changes. This requires you to perform market research and stay updated with trends and customer feedback.
Getting fresh data ensures your journey map stays relevant and effective. You must adapt to evolving customer behaviors to maintain accurate and valuable customer journey maps.
Challenges in Capturing Emotions
Capturing emotions accurately in customer journey maps poses a significant challenge. Emotions influence customer decisions, yet you may find it difficult to quantify and represent them in maps. Most journey maps emphasize actions and touchpoints, often neglecting the emotional journey.
You must integrate emotional insights into these maps to understand customer experiences. This integration enhances the effectiveness of customer engagement strategies. You can include user quotes, symbols such as emojis, or even graphs to capture the ups and downs of the users’ emotions..
Misalignment with Customer Needs
Misalignments in customer journey maps can manifest in various ways. It can impact the effectiveness of your strategies. Common misalignments include:
Putting business aims first, not what customers need.
Not seeing or serving the varied needs of different customer types.
Not using customer feedback in the journey map.
Thinking every customer follows a simple, straight path.
Engage with your customers to understand their needs and preferences if you want to address these misalignments. Incorporate their direct feedback into the journey map. This approach leads to more effective customer engagement and satisfaction.
Over-Reliance on the Map
Relying too much on customer journey maps can lead to problems. These maps should serve as tools rather than definitive guides. Viewing them as perfect can restrict your responsiveness to customer feedback and market changes. Treat journey maps as evolving documents that complement direct customer interactions and feedback.
Make sure you get regular updates and maintain flexibility in your approach. Balance the insights from the map with ongoing customer engagement. This approach keeps your business agile and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Data Privacy Concerns
Collecting customer data for journey mapping poses significant privacy concerns. Thus, you need to create a balance. You must adhere to data protection laws and gather enough information for mapping.
You need a careful strategy to ensure customer data security. Stay vigilant to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and customer expectations. This vigilance helps maintain trust and compliance.
Learn More about Customer Journey Maps
Take our Journey Mapping course to gain insights into the how and why of journey mapping. Learn practical methods to create experience maps , customer journey maps, and service blueprints for immediate application.
Explore this eBook to discover customer journey mapping .
Find some additional insights in the Customer Journey Maps article.
Questions related to Customer Journey Maps
Creating a customer journey map requires visually representing the customer's experience with your product or company. Harness the strength of visual reasoning to understand and present this journey succinctly. Instead of detailing a lengthy narrative, like a book, a well-crafted map allows stakeholders, whether designers or not, to grasp the journey quickly. It's a democratized tool that disseminates information, unifies teams, and aids decision-making by illuminating previously unnoticed or misunderstood aspects of the customer's journey.
The customer journey encompasses five distinct stages that guide a customer's interaction with a brand or product:
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem.
Consideration: They research potential solutions or products.
Purchase: The customer decides on a solution and makes a purchase.
Retention: Post-purchase, the customer uses the product and forms an opinion.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences.
For a comprehensive understanding of these stages and how they intertwine with customer touchpoints, refer to Interaction-Design.org's in-depth article .
A perspective grid workshop is a activity that brings together stakeholders from various departments, such as product design, marketing, growth, and customer support, to align on a shared understanding of the customer's journey. These stakeholders contribute unique insights about customer needs and how they interact with a product or service. The workshop entails:
Creating a matrix to identify customers' jobs and requirements, not initially linked to specific features.
Identifying the gaps, barriers, pains, and risks associated with unmet needs, and constructing a narrative for the journey.
Highlighting the resulting value when these needs are met.
Discuss the implied technical and non-technical capabilities required to deliver this value.
Brainstorming possible solutions and eventually narrowing down to specific features.
The ultimate aim is to foster alignment within the organization and produce a user journey map based on shared knowledge.
Learn more from this insightful video:
Customer journey mapping is vital as it harnesses our visual reasoning capabilities to articulate a customer's broad, intricate journey with a brand. Such a depiction would otherwise require extensive documentation, like a book. This tool offers a cost-effective method to convey information succinctly, ensuring understanding of whether one is a designer or lacks the time for extensive reading. It also helps the team to develop a shared vision and to encourage collaboration. Businesses can better comprehend and address interaction points by using a journey map, facilitating informed decision-making and revealing insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Learn more about the power of visualizing the customer journey in this video.
Pain points in a customer journey map represent customers' challenges or frustrations while interacting with a product or service. They can arise from unmet needs, gaps in service, or barriers faced during the user experience. Identifying these pain points is crucial as they highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to enhance the customer experience and meet their needs more effectively. Pain points can relate to various aspects, including product usability, communication gaps, or post-purchase concerns. Explore the detailed article on customer journey maps at Interaction Design Foundation for a deeper understanding and real-world examples.
Customer journey mapping offers several key benefits:
It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting areas for improvement. This ensures that products or services meet users' needs effectively.
The process fosters team alignment, ensuring everyone understands and prioritizes the customer's perspective.
It helps identify pain points, revealing opportunities to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
This visualization allows businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring resources target the most impactful areas.
To delve deeper into the advantages and insights on journey mapping, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on key takeaways from the IXDF journey mapping course .
In design thinking, a customer journey map visually represents a user's interactions with a product or service over time. It provides a detailed look at a user's experience, from initial contact to long-term engagement. Focusing on the user's perspective highlights their needs, emotions, pain points, and moments of delight. This tool aids in understanding and empathizing with users, a core principle of design thinking. When used effectively, it bridges gaps between design thinking and marketing, ensuring user-centric solutions align with business goals. For a comprehensive understanding of how it fits within design thinking and its relation to marketing, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on resolving conflicts between design thinking and marketing .
A customer journey map and a user journey map are tools to understand the experience of users or customers with a product or service.
A customer journey map is a broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It considers physical and digital channels, multiple user personas, and emotional and qualitative aspects.
A user journey map is a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service. It only considers digital channels, one user persona, and functional and quantitative aspects.
Both are useful to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. However, they have different scopes, perspectives, and purposes. A customer journey map provides a holistic view of the entire customer experience across multiple channels and stages. A user journey map provides a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service.
While user journeys might emphasize specific tasks or pain points, customer journeys encapsulate the entire experience, from research and comparison to purchasing and retention.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience. It considers different user personas and emotional aspects.
A service blueprint shows how a service is delivered and operated by an organization. It focuses on the back stage of the service, which is what the customers do not see or experience. It considers one user persona and functional aspects. What are the steps that the customer takes to complete a specific task or goal within the service? What are the channels and devices that the customer interacts with at each step?
For an immersive dive into customer journey mapping, consider enrolling in the Interaction Design Foundation's specialized course . This course offers hands-on lessons, expert guidance, and actionable tools. Furthermore, to grasp the course's essence, the article “4 Takeaways from the IXDF Journey Mapping Course” sheds light on the core learnings, offering a snapshot of what to expect. These resources are tailored by industry leaders, ensuring you're equipped with the best knowledge to craft impactful customer journey maps.
Answer a Short Quiz to Earn a Gift
Why do designers create customer journey maps?
- To document internal company processes and designer feedback
- To replace other forms of customer feedback
- To visualize customer experiences and identify pain points
In which stage do customers first recognize they have a problem?
What element is essential in a customer journey map?
- Competitor analysis
- Customer's thoughts and feelings
- Empathy maps and user stories
Why are scenarios included in a customer journey map?
- To exemplify the design thinking process
- To list product features
- To show the context and sequence of events
Why should designers iterate and refine customer journey maps?
- To ensure it remains relevant and accurate
- To keep the map visually appealing
- To reduce the number of customer interactions
Better luck next time!
Do you want to improve your UX / UI Design skills? Join us now
Congratulations! You did amazing
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
Check Your Inbox
We’ve emailed your gift to [email protected] .
Literature on Customer Journey Maps
Here’s the entire UX literature on Customer Journey Maps by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Customer Journey Maps
Take a deep dive into Customer Journey Maps with our course Journey Mapping .
This course will show you how to use journey mapping to turn your own complex design challenges into simple, delightful user experiences . If you want to design a great shopping experience, an efficient signup flow or an app that brings users delight over time, journey mapping is a critical addition to your toolbox.
We will begin with a short introduction to mapping — why it is so powerful, and why it is so useful in UX. Then we will get familiar with the three most common types of journey map — experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints — and how to recognize, read and use each one. Then you will learn how to collect and analyze data as a part of a journey mapping process. Next you will learn how to create each type of journey map , and in the final lesson you will learn how to run a journey mapping workshop that will help to turn your journey mapping insights into actual products and services.
This course will provide you with practical methods that you can start using immediately in your own design projects, as well as downloadable templates that can give you a head start in your own journey mapping projects.
The “Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project” includes three practical exercises where you can practice the methods you learn, solidify your knowledge and if you choose, create a journey mapping case study that you can add to your portfolio to demonstrate your journey mapping skills to future employers, freelance customers and your peers.
Throughout the course you will learn from four industry experts.
Indi Young will provide wisdom on how to gather the right data as part of your journey mapping process. She has written two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models . Currently she conducts live online advanced courses about the importance of pushing the boundaries of your perspective. She was a founder of Adaptive Path, the pioneering UX agency that was an early innovator in journey mapping.
Kai Wang will walk us through his very practical process for creating a service blueprint, and share how he makes journey mapping a critical part of an organization’s success. Kai is a talented UX pro who has designed complex experiences for companies such as CarMax and CapitalOne.
Matt Snyder will help us think about journey mapping as a powerful and cost-effective tool for building successful products. He will also teach you how to use a tool called a perspective grid that can help a data-rich journey mapping process go more smoothly. In 2020 Matt left his role as the Sr. Director of Product Design at Lucid Software to become Head of Product & Design at Hivewire.
Christian Briggs will be your tour guide for this course. He is a Senior Product Designer and Design Educator at the Interaction Design Foundation. He has been designing digital products for many years, and has been using methods like journey mapping for most of those years.
All open-source articles on Customer Journey Maps
14 ux deliverables: what will i be making as a ux designer.

- 1.2k shares
What are Customer Touchpoints & Why Do They Matter?
- 4 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

- 3 years ago
How to Resolve Conflicts Between Design Thinking and Marketing

How to Create a Perspective Grid
4 Takeaways from the IxDF Journey Mapping Course
- 2 years ago
The Power of Mapping
User Story Mapping in Design
Start Your UX Journey: Essential Insights for Success

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
When and how to create customer journey maps.

July 31, 2016 2016-07-31
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
In This Article:
What is a customer journey map, deconstruction of a customer journey map, why do you need a journey map and when should you have one, key elements of customer journey maps, rules for creating successful journey maps.
In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user goals and actions into a timeline skeleton. Next, the skeleton is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative. Finally, that narrative is condensed into a visualization used to communicate insights that will inform design processes.
Storytelling and visualization are essential facets of journey mapping because they are effective mechanisms for conveying information in a way that is memorable, concise and that creates a shared vision. Fragmented understanding is chronic in organizations where KPIs are assigned and measured per individual department or group because many organizations do not ever piece together the entire experience from the user’s standpoint. This shared vision is a critical aim of journey mapping, because without it, agreement on how to improve customer experience would never take place.
Journey mapping creates a holistic view of customer experience, and it’s this process of bringing together and visualizing disparate data points that can engage otherwise disinterested stakeholders from across groups and spur collaborative conversation and change.

Zone A: The lens provides constraints for the map by assigning (1) a persona (“who”) and (2) the scenario to be examined (“what”).
Zone B: The heart of the map is the visualized experience, usually aligned across (3) chunkable phases of the journey. The (4) actions, (5) thoughts, and (6) emotional experience of the user has throughout the journey can be supplemented with quotes or videos from research.
Zone C: The output should vary based on the business goal the map supports, but it could describe the insights and pain points discovered, and the (7) opportunities to focus on going forward, as well as (8) internal ownership.
Journey maps should always be created to support a known business goal. Maps that do not align to a business goal will not result in applicable insight. The goal could be an external issue, such as learning about a specific persona’s purchasing behaviors, or an internal issue, such as addressing lack of ownership over certain parts of the customer experience. Some potential business goals that journey mapping could be applied toward are listed below.
Shift a company’s perspective from inside-out to outside-in. If an organization lets internal processes and systems drive decisions that affect customer experience, a journey map could help turn the culture of that organization by refocusing on the thoughts, actions and emotions of customers. Journey mapping sheds light on real human experiences that often organizations know very little about.
Break down silos to create one shared, organization-wide vision. Because journey maps create a vision of the entire customer journey, they become a tool for creating cross-department conversation and collaboration. Journey mapping could be the first step in building an organization-wide plan of action to invest in customer experience, as it helps answer the question, “Where do we start?” by highlighting areas of friction.
Assign ownership of key touchpoints to internal departments. Often, areas of inconsistencies and glitches in customer journeys exist simply because no internal team has been tasked with ownership of that element. Journey maps can create clarity around alignment of departments or groups with different stages or key touchpoints in the journey that need addressing.
Target specific customers. Journey maps can help teams focus in on specific personas or customers, whether that means understanding differences or similarities across the journeys of multiple personas, prioritizing a high-value persona or exploring ways to target a new type of customer.
Understand quantitative data. If you are aware through analytics or other quantitative data that something specific is happening—maybe online sales are plateauing or an online tool is being underutilized—journey mapping can help you find out why.
While journey maps can (and should) take a wide variety of forms, certain elements are generally included:
Point of view. First and foremost, choose the “actor” of the story. Who is this journey map about? For example, a university might choose either students or faculty members, both of which would result in very different journeys. “Actors” usually aligns with personas, if they exist. As a guideline, when creating a basic journey map, use one point of view per map in order to provide a strong, clear narrative.
Scenario. Next, determine the specific experience to map. This could be an existing journey, where mapping will uncover positive and negative moments within that current experience, or a “to-be” experience, where the mapper is designing a journey for a product or service that doesn’t exist yet. Make sure to clarify the user’s goal during this experience. Journey maps are best for scenarios that describe a sequence of events, such as purchasing behavior or taking a trip.
Actions, mindsets, and emotions. At the heart of a journey map’s narrative is what the user is doing, thinking, and feeling during the journey. These data points should be based on qualitative research, such as field studies, contextual inquiry, and diary studies . The granularity of representation can vary based on the purpose of the map. Is the purpose to evaluate or design an entire, broad purchasing cycle or a contained system?
Touchpoints and channels. The map should align touchpoints (times when the actor in the map actually interacts with the company) and channels (methods of communication or service delivery, such as the website or physical store) with user goals and actions. These elements deserve a special emphasis because they are often where brand inconsistencies and disconnected experiences are uncovered.
Insights and ownership. The entire point of the journey-mapping process is to uncover gaps in the user experience (which are particularly common in omnichannel journeys), and then take action to optimize the experience. Insights and ownership are critical elements that are often overlooked. Any insights that emerge from journey mapping should be explicitly listed. If politically possible, also assign ownership for different parts of the journey map, so that it’s clear who’s in charge of what aspect of the customer journey. Without ownership, no one has responsibility or empowerment to change anything.
Even with all the above critical elements included, two journey maps could look completely different, yet both be perfectly suitable for the context in which they were designed.Tradeoffs in scope, focus, and breadth vs. depth are required when deciding on what elements to include. To make informed decisions on those tradeoffs, consider the following:
- What level of detail is needed in order to tell the complete story?
- What elements (such as device, channel, encountered content) are also necessary in order to provide the most truthful narrative?
- Is the purpose of this journey map to diagnose issues with a current experience or to design a new experience?
- What’s the balance between external actions (on the customer side) and internal actions (on the organization side)?
- Who will be using this journey map?
Successful journey maps require more than just the inclusion of the “right” elements. Journey mapping should be a collaborative process informed by well-defined goals, and built from research. It requires hard work to keep the process on the right track and to build the buy-in needed to evangelize the insights it provides. Below are some tips for making sure that the process starts and stays in the right direction:
Establish the “why" and the “what.” First, identify the business goal that the journey map will support. Make sure there are clear answers to these basic key questions before you begin the process:
- What business goal does this journey map support?
- Who will use it?
- Who is it about and what experience does it address?
- How will it be shared?
Base it on truth. Journey maps should result in truthful narratives, not fairy tales. Start with gathering any existing research, but additional journey-based research is also needed to fill in the gaps that the existing research won’t cover. This is a qualitative-research process. While quantitative data can help support or validate (or aid in convincing stakeholders who may view qualitative data as “fuzzy”), quantitative data alone cannot build a story .
Collaborate with others. The activity of journey mapping (not the output itself) is often the most valuable part of the process, so involve others. Pull back the curtain and invite stakeholders from various groups to be a part of compiling the data and building the map.
Don’t jump to visualization. The temptation to create an aesthetic graphic or jump to design can lead to beautiful yet flawed journey maps. Make sure the synthesis of your data is complete and well-understood before moving to creating the visual.
Engage others with the end product. Don’t expect to get “buy-in” and foster interest in your journey map by simply sending a lovely graphic as an email attachment. Make it a living interactive document that people can be a part of. Bring up your story in meetings and conversations to promote a narrative that others believe in and begin to reference. One idea is to create a journey-mapping showroom where anyone not on the direct team can come experience the process and resulting artifacts.
Free Downloads
Related courses, journey mapping to understand customer needs.
Capture and communicate UX insights across complex interactions
Omnichannel Journeys and Customer Experience
Create a seamless, cohesive cross-channel experience
Interaction
Generating Big Ideas with Design Thinking
Unearth user pain points to drive breakthrough design concepts
Related Topics
- Customer Journeys Customer Journeys
- Design Process
- Research Methods
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2W13ext26kQ
Customer Journey Mapping 101

Interactive UX Maps 101
Megan Brown · 4 min

Journey Mapping: 2 Decisions to Make Before You Begin
Kate Kaplan · 3 min

Scenario Mapping for Design Exploration
Kim Flaherty · 3 min
Related Articles:
Journey Mapping 101
Sarah Gibbons · 7 min
Journey Mapping: 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Alita Joyce and Kate Kaplan · 7 min
Luxury Shopping User Groups and Journeys
Kate Moran · 14 min
User Experience vs. Customer Experience: What’s The Difference?
Kim Flaherty · 5 min
Seamlessness in the Omnichannel User Experience
Kim Flaherty · 12 min
How to Conduct Research for Customer Journey-Mapping
Kate Kaplan · 7 min
Collaborative customer journey mapping tools
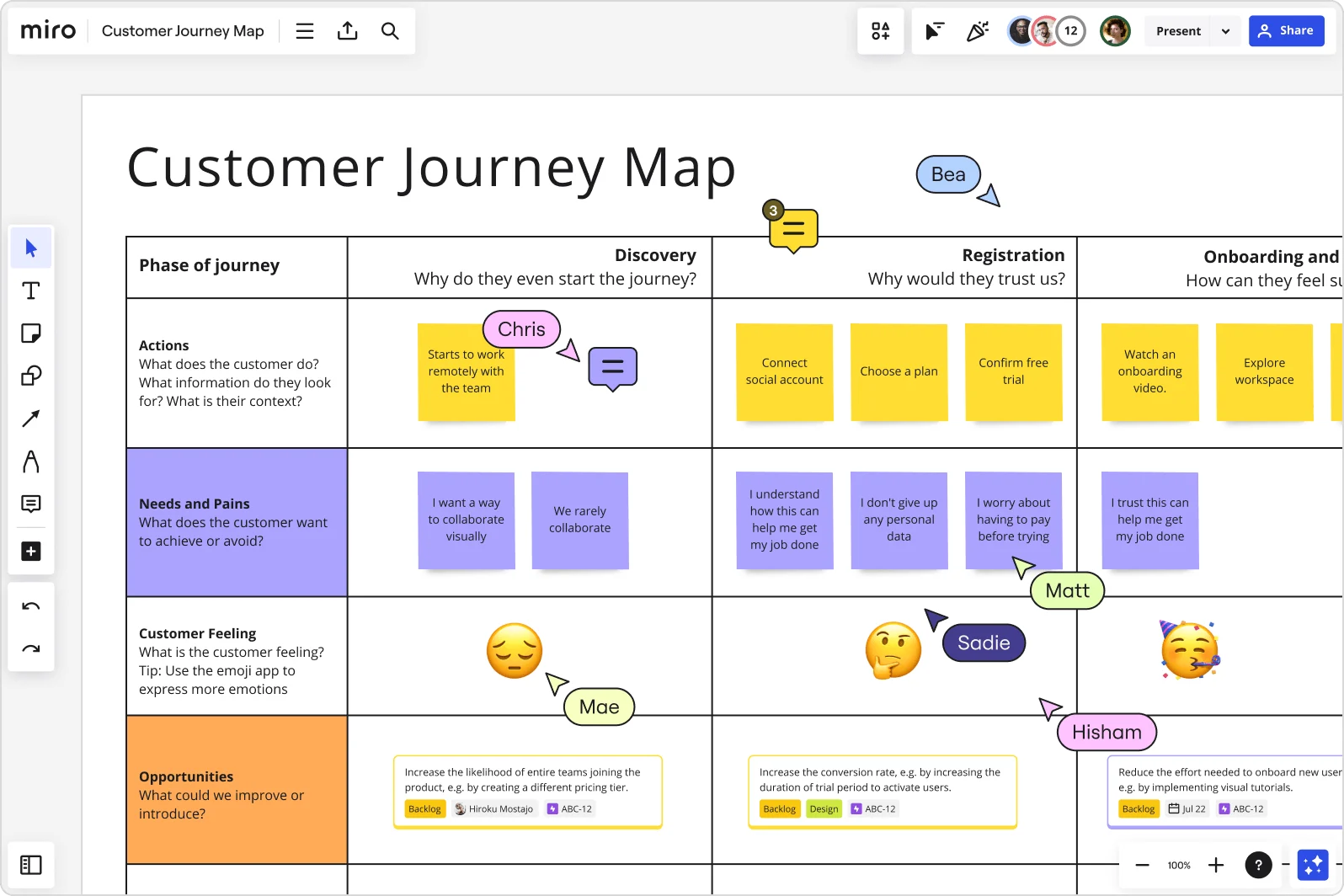
Gain a deep understanding of customer needs and business priorities
Ready-made customer journey map templates.
Design transformative customer journeys with templates for persona building, touchpoint maps, service blueprints, and more. Help your team quickly visualize, collaborate, and iterate on your customer experience, bringing in data and research to make the best-informed decisions.
Create a shared understanding, faster
Build highly visual and accurate maps that bring a customer’s humanity and experience to life with dynamically populated input, feedback, and data from various sources, like Amplitude, Looker, Blossom, Loom, and UserTesting. Record interactive walkthroughs with Talktrack so everyone can engage on their own time, with all the context on the board.
Easy to share and change
Give your team easy access to customer journey maps so they can leave feedback, ask questions, and make immediate changes as needed. Keep customer-centricity top of mind by embedding it everywhere your teams work (like Confluence) and it’ll always be synced to the latest version, or export your customer journey map as an image or PDF file for presentations.
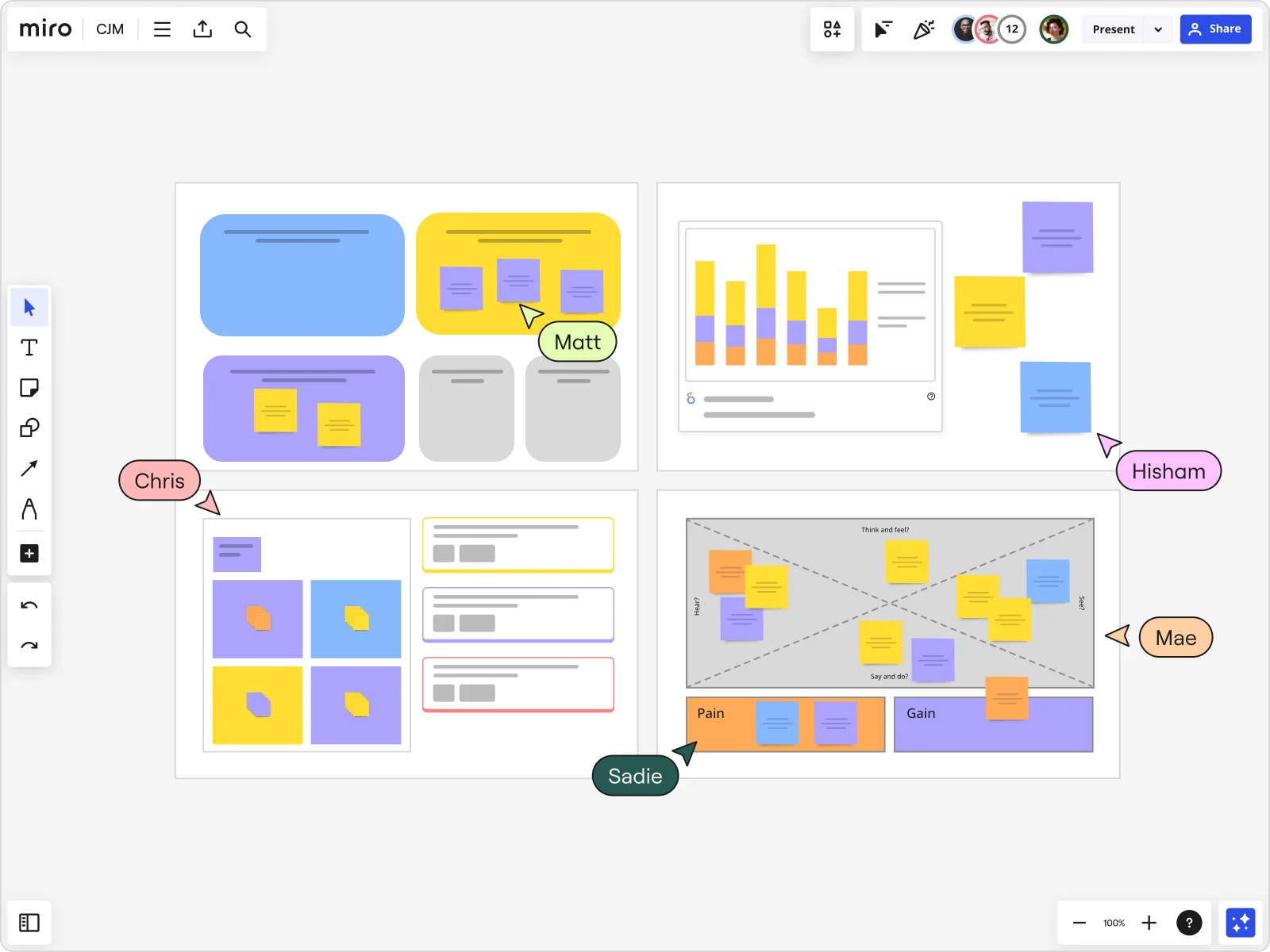
Watch how Product Designer Maureen designs and uses customer journey maps in Miro

Why people love Miro for customer journey mapping
Uncover possibilities.
Miro’s infinite canvas gives you the ability to collaborate across product teams and cross-functional stakeholders on customer journeys. It serves as a team hub for mapping and research, where you can plot your customer’s paths, visualize their journey, and gather insights all in one tool.
Empathy made easy
Make sure all voices are heard and tap into your team’s collective imagination to identify customer pain points, cultivate empathy, wireframe solutions, and ship innovative products — all with Miro’s customer journey map tools.
Be the voice of the customer
Map your user journey step-by-step and truly understand the people using your product. Bring your team with you in this process and share your customer journey map across your organization. Become the customer advocate and ensure you add value to your product.
Quickly get started
Miro’s customer journey map tool helps accelerate your team’s processes by clearly visualizing journeys, touchpoints, personas, and more. Save time by crafting your customer journey map using one of our pre-made frameworks, or build one from scratch with our many editing tools.
Deliver better results
Make better-informed decisions by getting instant feedback and craft experiences that people will remember. Tag team members, receive comments, and gain more insights with Miro’s collaborative customer journey mapping tool.
Share it with everyone
Share your insights and be proactive by running customer workshops inside your organization. Use Miro’s collaborative features, such as the timer and voting, to help lead interactive sessions and engage your team. Offer the space and tools needed for blue-sky thinking.
Related pages
Research and design.
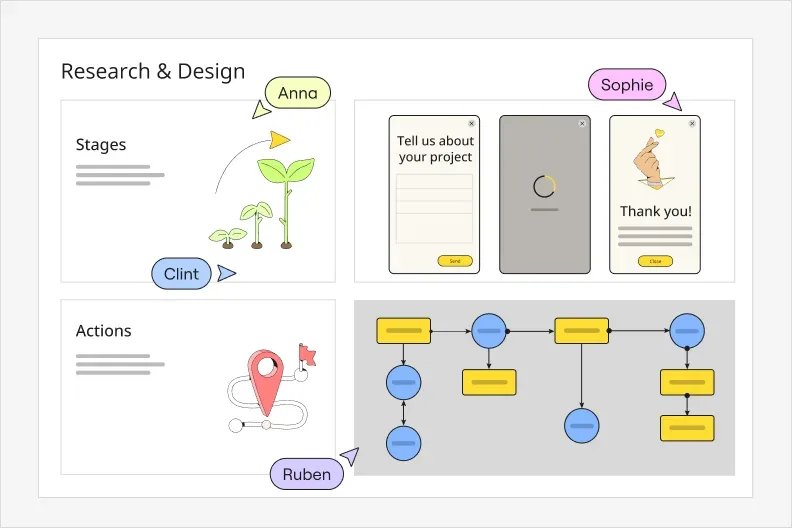
Strategy & planning
Product management
Content and data visualization
Related templates

Customer Journey Map Template
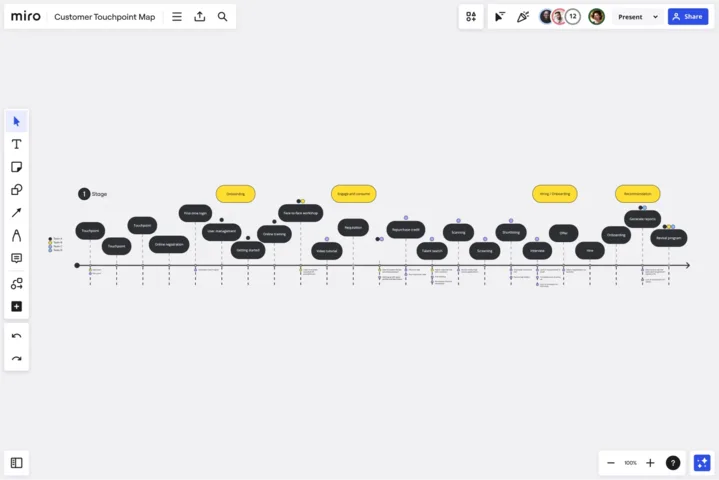
Customer Touchpoint Map Template
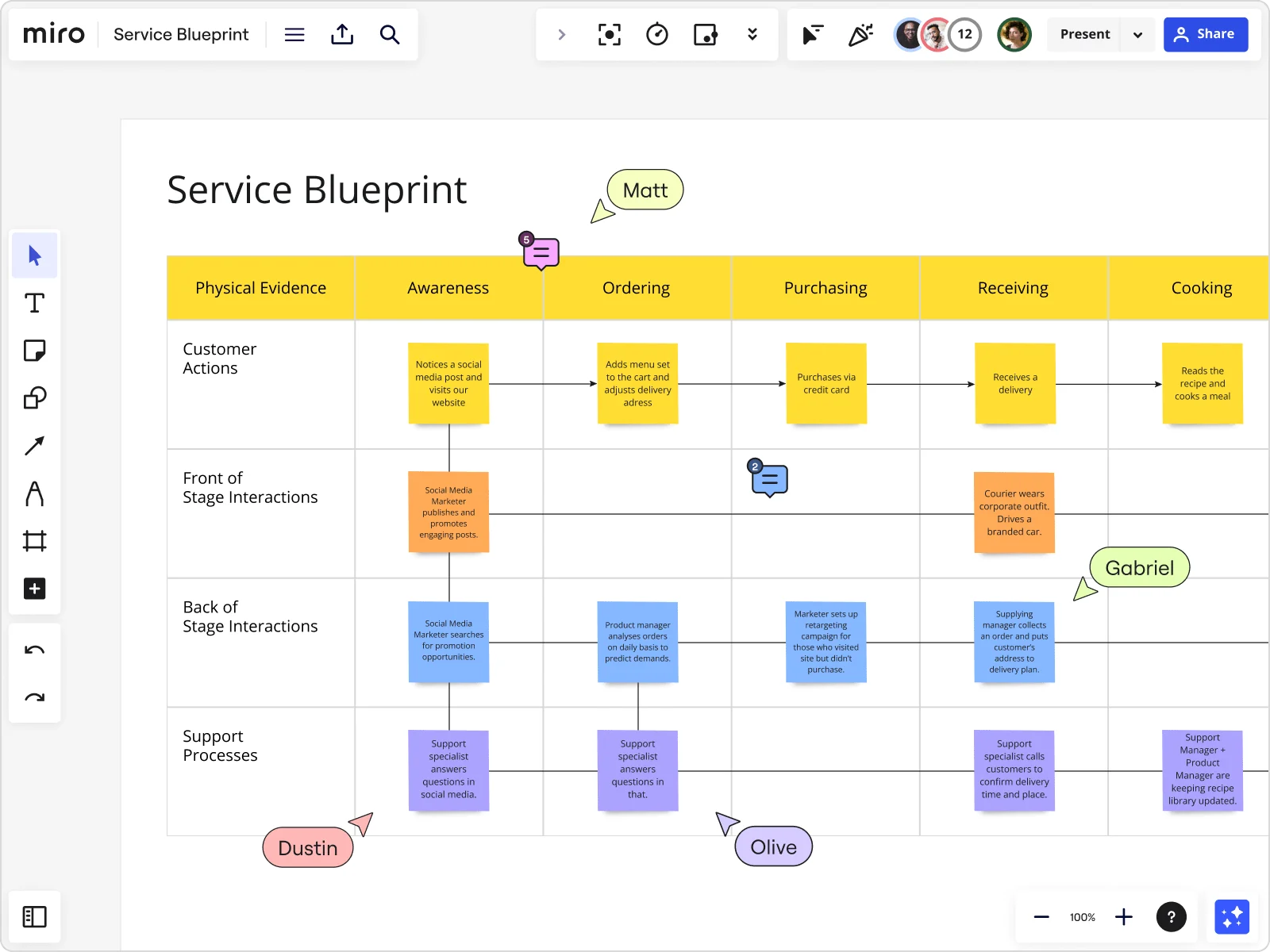
Service Blueprint Template

5E Service Blueprint

Customer Journey Map Workshop

Experience Mapping Template
Hyperact's Service Blueprint Template
How to create a customer journey map with miro.
1. Define personas
Determine which specific customer segments or personas you want to focus on. Collect data and insights about their needs, behaviors, and preferences.
2. Identify touchpoints
Identify key stages of the customer journey listing the touchpoints. Detail the specific actions, emotions, and pain points customers experience at each stage.
3. Add context and insights
Integrate data from customer surveys, interviews, analytics, and other sources to enrich your understanding of customer behaviors and preferences.
4. Share and find opportunities
Identify opportunities to improve the customer experience. When ready, share with stakeholders for feedback and collaboratively draft an action plan to implement the findings.
5. Iterate and update
Embed the map where teams and stakeholders can easily find it. Regularly review and evolve the customer journey map as you gain more data, insights, and feedback.
Customer journey mapping tools FAQs
What makes a good customer journey?
To create a good customer journey map, make sure you add all the stages your user goes through by mapping every customer touchpoint and the phases they belong to. After you map out your customer journey, to know more about who they are, you can create a storyboard or dig deeper with an empathy map. Miro’s customer journey mapping software makes it easy to add other artifacts and maps to your board, so you can have a great overview of your customer journey and what influences your customer's experiences. It can get messy, and it’s ok! Once you have all the information you need in one shared space, it’s easier to craft your customer journey or create a new user journey map.
What are the components of a customer journey map?
In Miro’s customer journey mapping tool, you have the flexibility to add as many components as you’d like. In our template, we use the following: actions, touchpoints, customer thoughts, customer feelings, process ownership, and opportunities. Each component belongs to a customer journey stage and is added to the board. Some folks also add user research data and other tools, such as empathy maps or timelines.
Can I download or share my customer journey map?
Yes, you can download your customer journey map as an image or PDF file or share your board link with others. Embed the map everywhere your teams work, like Confluence or Notion and it'll always be synced to the latest version. The customer journey map can be treated as a living document, evolving according to your product evolution and need.
The ultimate list of templates for understanding your customers
What is a customer journey map, 3 steps to go from customer interviews to a customer journey map, the difference between a service blueprint and a journey map, join our 70m+ users today, plans and pricing.
How to Create a Customer Experience Map [Free Templates]
Updated: June 15, 2021
Published: November 20, 2020
The customer journey is a long, winding, complex process.

Between hearing about your business from a friend, engaging with your content online, considering a sale, and becoming a customer — not to mention finally using your product and everything that comes afterward — each step is a different experience in its own right.
When a customer interacts with your business, their emotions might range from curiosity to indifference to excitement or even frustration. Because the customer experience is filled with various needs, touchpoints, and states of mind, it's beneficial for your business to map out its customer experience for one or many of the most common interactions users would have with your product, brand, website, or customer support team.
Making a customer experience map can help your team understand these peaks of joy and sorrow, when and why they occur, and what can be done to ensure a consistently positive customer experience.

What Is Customer Experience Mapping?
Customer experience mapping is the process of visually outlining the steps a customer takes during an interaction with your business. This map usually includes a description of each step, the emotions that a customer is feeling during that step, as well as additional insights on the design, intent, and/or implementation of that step from the business's side.
Unlike a holistic customer journey map , a customer experience map tends to narrow in one specific interaction with your business. For example, you might have individual customer experience maps for each of the following scenarios:
- Reading your blog or exploring your website
- Interacting with a customer support agent
- Visiting your store or your ecommerce site
- Using your product at home or at work
- Interacting with sales during the process of becoming a customer
How to Create an Experience Map
1. use a customer experience map template [featured tool].
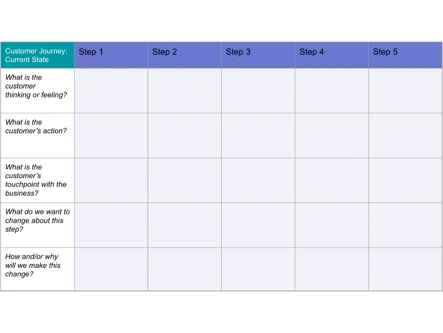
From there, use the following sections to identify what should be changed about your customer's experience and why.
2. Choose Your Experience.
Since a customer experience map usually focuses on one experience, your first step should be to choose an interaction of focus, which you will soon analyze for experience gaps and areas to improve.
While it's tempting to cover multiple experiences with your map, try to hone in on one specific experience which you'd like to improve for your customers. The rationale for choosing an experience can be anything from customer comments, to an employee observation, to a high traffic number, or even a part of your website that you want to make sure is fully optimized.
That said, we suggest prioritizing low-effort, high-impact opportunities with your customer experience mapping and improvement projects – those that can be addressed swiftly but will have a measurable positive impact on the customer experience.
3. List Your Touchpoints and Customer Actions.
After narrowing your scope, you should break the experience down into the actions that your customers will take, in addition to what the interaction with your business looks like during each action.
For example, let's say you're mapping out the process for a customer seeking support over the phone. The touchpoints might look something like this:
- Step 1: The customer experiences a pain point with your product or service and determines reaching out to support is the necessary next step.
- Step 2: Your customer visits your website, looking for (and eventually finding) your customer support phone number.
- Step 3: Your customer calls support and gets in touch with a support rep.
- Step 4: Your customer explains the pain point, and the support rep works to solve the problem.
- Step 5: The support rep solves the customer's issue over the phone, and the call is finished.
Like in the example above, touchpoints should be sequential and interconnected, but unique enough to be their own steps in the overall customer experience. This process makes it easier to identify what's going right or wrong in each individual step, in addition to what the customer might be feeling at each part of the process.
4. Determine Customer Thoughts or Feelings.
One of the key components of the customer experience map is to look beyond what customers are doing and attempt to understand their emotions during each step of their experience. For example, feelings of curiosity or excitement can easily be diminished by a broken link to your "About Us" page.
During your mapping process, tie your customers' mindset to the actions they're taking. There's no universal way to gauge these opinions, but below are a few common strategies.
User Testing
If your experience map is for a product or a website, you should consider conducting user tests regularly. These tests allow you to observe customers interacting with your product or website and help you make changes based on their actions.
During these tests, ask your customers to explain what they're doing, why they're doing it, and how they feel to add context to their actions as they're doing them.
Customer Feedback
If you're unable to observe customers in real-time, reach out to sales, support, and/or customer success employees to speak on any customer feedback pertaining to the experience in question. While the evidence might be more anecdotal, this path still provides you with the insights that you may otherwise have been unable to gather.
Educated Guess
If all else fails – or if you're building an experience for a new product, service, or business – employ your skills of empathy and critical thinking by making educated guesses on the feelings your experience may provoke. This extra step helps you take a second look at the work you're doing to help justify your actions.
5. Plan Out Improvements to the Customer Experience.
With all customer thoughts, actions, and touchpoints mapped out, the next step is to add potential improvements to your customer experience.
Based on your feedback, test results, and/or educated guesses, go through each step of the customer experience and ask yourself, "what can be done to improve the customer experience at this stage, and why?"
On top of your conversations with customers, consider doing some competitive analysis to see how the other players in your industry handle a similar customer experience.
It's understandable if you come into this step with attachment to the way things are, but remember that customer experience maps identify areas of improvement in your customer journey. If the data or feedback you've received are telling you something needs to change – then listen.
Customer Experience Map Templates

Mapping out your customer experiences is more organized, effective, and clear when using customer experience map templates .
Developed to capture seven different types of customer experiences and journeys, these templates will help you outline every part of the customer experience – and help you identify the biggest opportunities for improving it to delight and retain more customers.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![journey map customer experience Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-journey-map_13.webp)
Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]

How to Maximize Your Success with a Customer Experience Platform
![journey map customer experience How to Measure Customer Experience: 8 Metrics 1000+ Service Reps Prioritize [+Data]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/customerexperiencemetrics.webp)
How to Measure Customer Experience: 8 Metrics 1000+ Service Reps Prioritize [+Data]
![journey map customer experience How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![journey map customer experience How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![journey map customer experience Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
![journey map customer experience How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
- How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Is it time to rethink traditional journey mapping methods?
What is a customer journey map, why is a customer journey map important, components of a customer journey map, limitations of the traditional approach to journey mapping, meeting modern business challenges, evolving your customer journey maps, comparing approaches side-by-side, how to unlock behavioral-based, data-driven journey mapping, try qualtrics for free, how to create a customer journey map.
21 min read Customer journey mapping is a science, so it pays to think about the data that goes into the process. When you incorporate intelligent customer insights from the right tools and sources, your journey maps transform from static, outdated documentation into living, breathing resources that can guide business-wide strategies. Here’s how…
Author: Ray Gerber
In an era marked by rapid changes in consumer behavior and heightened expectations, traditional methods of customer journey mapping are, rightly, coming under scrutiny.
But what does that mean for the people looking to maximize each journey? Put simply: it’s time to adapt.
Traditionally, journey maps have been static – often created through time-consuming processes that involve extensive research and data collection. These methods, while thorough, tend to be resource-intensive and costly. More importantly, they lack the agility to adapt to fast-paced changes in customer behavior and preferences.
In a digital age where customer interactions and expectations evolve at an unprecedented rate, relying on these static maps can leave businesses trailing behind, operating on outdated assumptions and missing crucial opportunities for engagement and improvement.
All of this presents us with a pressing need: shifting towards more dynamic, data-driven journey mapping techniques. But it’s a shift that goes much further than simply keeping pace with change; it’s about embracing a more responsive, customer-centric approach that aligns closely with the ever-evolving journey of today’s consumers.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a visual interpretation of the overall relationship a customer has with an organization, service, product, or brand – over time and across different channels. It helps businesses step into their customers’ shoes and see their business from the customer’s perspective.
Crucially, a customer journey map also allows companies to gain insights into common customer pain points, how they interact with the brand, and the pathways they take from the first engagement to a long-term relationship.
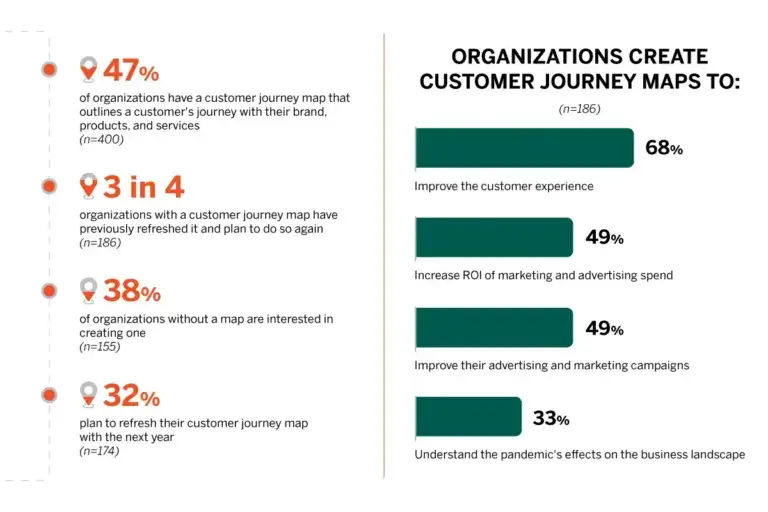
Image from: The Power of Customer Journey Mapping 2023 Hanover Research
How Businesses View Customer Journey maps
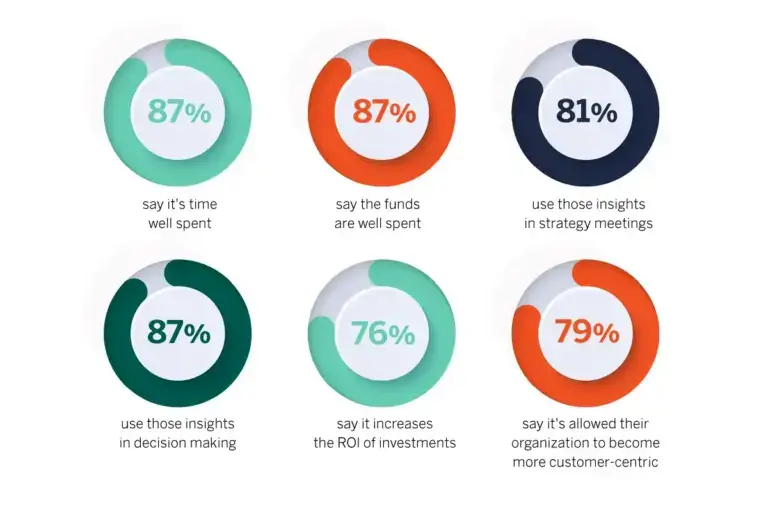
An accurate, adaptable customer journey map is a means to enable positive change. In an era where customer experience is a key differentiator, journey maps serve as crucial tools.
They help businesses:
- Understand and empathize with customers.
- Identify and address pain points and bottlenecks in the customer experience.
- Align internal teams around a shared understanding of customer needs and experiences.
- Optimize and personalize customer interactions at each touchpoint.
- Strategically plan enhancements to products, services, and processes.
But there’s a problem: not every company that creates customer journey maps knows how to put them to work. In 2019, Gartner reported that while some 82% of organizations have created customer journey maps, only 47% are using them effectively.
Worse still, in 2022, the Technology Services Industry Association found that only 29% of customer success teams who created a customer journey map actually used it at all.
Ok, so what actually goes into a successful, usable customer journey map?
A well-constructed map comprises a myriad component plays a distinct role in painting a complete picture of the customer’s journey, with valuable insights that can drive strategic improvements and foster deeper customer connections.
Here is an example of what a full customer journey map looks like with all this information collated:
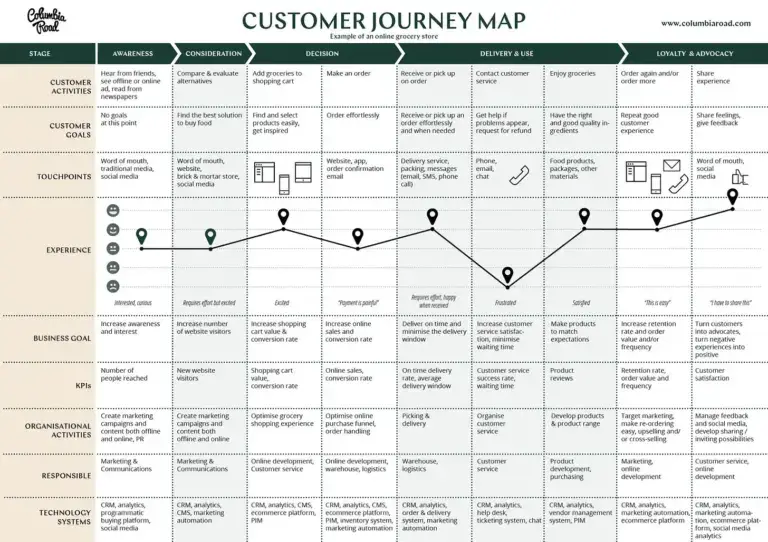
Image from: www.Columbiaroad.com
This customer journey map is a visual representation of the stages a customer goes through when interacting with an online grocery store, structured into six stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Delivery & Use, and Loyalty & Advocacy.
The customer learns about the store through word-of-mouth, media, or online. The goal is to increase awareness and interest, supported by marketing campaigns and social media.
Consideration:
The customer compares options and looks for the best solutions. The business aims to increase the number of website visitors through marketing and communications.
Adding items to the cart and making a purchase. The experience should be effortless, with the business goal of increasing sales and conversion rates, supported by an optimized online purchasing funnel.
Delivery & Use:
The customer receives their order. The goal is to deliver on time and ensure satisfaction , achieved by efficient logistics and customer service.
Loyalty & Advocacy:
Post-purchase, customers may reorder or share their experience. The business aims to increase retention and turn customers into advocates, managed by customer service and marketing.
Each stage lists customer activities, goals, touchpoints, experiences, business goals, KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) , organizational activities, and technology systems used. The map charts the emotional journey with peaks (excitement) and valleys (effort or frustration), aiming to provide insights into how to enhance the customer experience at each stage.
While traditional journey mapping has been a cornerstone for understanding and visualizing the customer’s path through various touchpoints with a brand, a static, one-time snapshot approach has its limitations.
Here are seven reasons why conventional mapping methods may no longer suffice in today’s dynamic market environment:
Static nature
Traditional journey maps are often static, representing a fixed snapshot of the customer journey. This rigidity fails to account for the fluid and ever-changing nature of customer interactions and preferences, leading to a map that quickly becomes outdated as market dynamics shift.
Time-consuming and resource-intensive
The creation of traditional journey maps typically involves extensive research, including customer interviews, surveys, and workshops. This process is not only time-consuming but also demands significant resources, both in terms of manpower and financial investment.
Lack of personalization
Traditional maps tend to generalize the customer experience, based on averaged data and broad customer personas. This approach overlooks the nuances and individual variations in customer behavior, resulting in a one-size-fits-all model that may not accurately reflect the experiences of different customer segments .
Limited real-time insights
The traditional journey mapping process does not incorporate real-time data. Consequently, businesses miss out on the opportunity to respond promptly to immediate changes in customer behavior or feedback, potentially leading to missed opportunities for engagement and improvement.
Over-reliance on assumptions
Often, these maps are created based on assumptions about customer behavior and preferences, rather than hard data. This can lead to a disconnect between what businesses perceive to be the customer journey and the actual experiences of their customers.
Inadequate measurement of impact
Traditional journey maps do not always include clear metrics or KPIs to measure the impact of various touchpoints on customer behavior. This lack of quantifiable measurement makes it challenging to assess the effectiveness of different aspects of the journey and to make data-driven improvements.
Difficulty in aligning cross-functional teams
Given their static nature, traditional maps can struggle to align different teams around a unified, evolving customer strategy . Different departments may interpret the journey map differently, leading to inconsistent customer experiences.
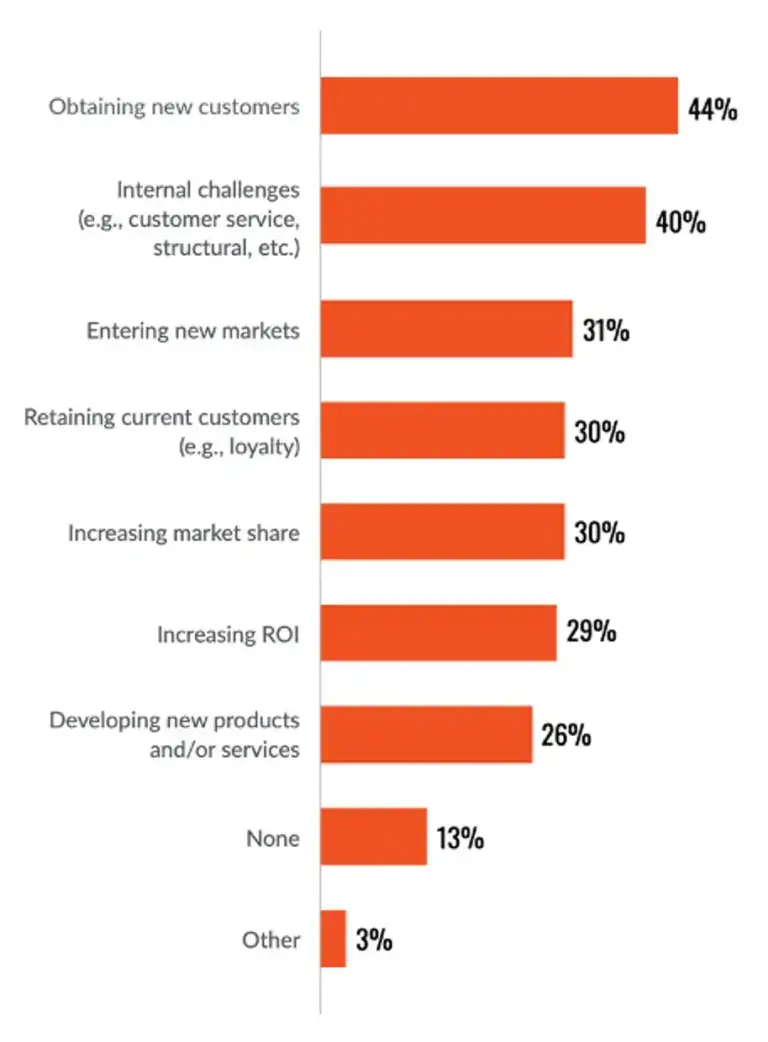
© 2023 Hanover Research CORWP0123
The image above lists several initiatives that have become more challenging for businesses: obtaining new customers, internal challenges, entering new markets, retaining current customers, increasing market share, increasing ROI , and developing new products/services.
These are universal challenges, and they all play a role in how journey mapping needs to evolve…
Obtaining new customers & entering new markets
Traditional journey maps may not account for the changing behaviors of different market segments – or the nuances of new market contexts. Dynamic journey maps that integrate behavioral data can provide a more accurate and adaptable model for understanding the customer journey in different markets.
Internal challenges
Static journey maps might not reflect the internal process changes quickly enough. A dynamic, behavior-based map offers real-time insights into operational issues that affect customer experience.
Retaining current customers
Traditional journey maps often lack the granularity to understand the shifting loyalty drivers. Dynamic mapping can highlight evolving customer needs and preferences, helping to tailor experiences that enhance loyalty .
Increasing market share & ROI
By focusing on actual behaviors rather than assumptions, dynamic journey maps can uncover opportunities for differentiation and value creation, directly influencing market share and return on investment.
Developing new products and services
Traditional maps might miss rapid changes in customer expectations and emerging trends. Behavioral-based mapping processes can identify new needs and opportunities for innovation, leading to more timely and relevant product development .
The challenges listed above all indicate a need for more sophisticated journey mapping that can adapt to the complex nature of customer behaviors and business environments.
So, with that in mind, let’s look at two ways that your journey maps can evolve…
1. Adding Voice of the Customer insights to journey maps
The integration of Voice of the Customer (VoC) data into journey maps marks the first significant evolution in the approach to understanding customer experiences.
VoC data transforms journey maps from static, assumption-based models into dynamic tools that reflect real customer feedback and sentiments. VoC data includes direct input from customers, such as survey responses, customer reviews, feedback forms, and social media comments. By integrating this data, journey maps become more aligned with the customer’s actual experiences and perceptions, providing a richer, more nuanced view of their journey.
Methodology for incorporating VoC data:
- Data collection: The first step involves gathering VoC data through various channels. This includes structured methods like surveys and feedback forms, as well as unstructured data from social media, customer reviews, and call center transcripts.
- Data analysis: The collected data is then analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This involves identifying common themes, sentiments, pain points, and moments of delight in the customer journey.
- Mapping VoC to journey stages : The insights are mapped to corresponding stages in the customer journey. This process helps in visualizing how customer sentiments and experiences vary across different touchpoints.
- Iterative refinement: The journey map is continuously updated with new VoC data, ensuring it remains relevant and reflective of the current customer experience.
The value of VoC-enhanced customer journey maps:
Customer-centricity
VoC-enhanced maps put the customer’s voice at the forefront, ensuring that strategies and improvements are directly aligned with customer needs and expectations.
Improved accuracy
These maps are more accurate in depicting the customer journey, as they are based on actual customer feedback rather than assumptions.
Enhanced engagement insights
VoC data provides deeper insights into why customers behave in certain ways, enabling businesses to understand the motivations behind customer actions.
Strategic decision making
Armed with precise customer feedback, businesses can make more informed decisions about product improvements, marketing strategies, and customer service enhancements.
Identifying pain points and opportunities
VoC data highlights specific areas where customers face challenges or where there are opportunities to enhance the experience, guiding targeted improvements.
Are there downsides of VoC-powered customer journey maps?
Integrating VoC data helps make these maps more reflective of the actual customer experience, but doing so is not without its limitations:
Subjectivity and bias
VoC data is inherently subjective, reflecting the perceptions and opinions of customers. This can introduce bias, as the feedback may not always represent the broader customer base or accurately reflect actual behaviors.
Lag in feedback
VoC data often captures customer sentiments after an experience has occurred. This delay can result in missed opportunities to address issues in real-time, reducing the ability to proactively enhance the customer experience.
Incomplete picture
Relying solely on VoC data can lead to gaps in understanding the customer journey. Customers may not accurately recall all their interactions or may only provide feedback on certain aspects of their experience, leaving out key touchpoints.
Challenges in quantification
Translating qualitative VoC data into actionable insights can be challenging. Quantifying sentiments and opinions for strategic decision-making requires sophisticated analysis, which can be resource-intensive.
Limited predictive power
While VoC data offers insights into past and present customer experiences, it has limited capability in predicting future behaviors or trends. This restricts the ability of businesses to anticipate customer needs proactively.
Understanding these limitations is important if we’re going to understand what’s still lacking from our customer journey maps – even with the added benefit of VoC data.
So what’s the solution here? Put simply: smarter insights on human behavior.
2. Adding behavioral insights to journey maps
The integration of actual customer behavioral data alongside Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights represents the second evolution in journey mapping.
That’s because this approach not only considers what customers say, but also what they actually do – providing a more holistic view of the customer experience. The result is a comprehensive view of the customer journey that encompasses both the tangible actions customers take and their perceptions and reactions to those experiences.
A key advantage of this integrated approach is its capacity for real-time responsiveness. Behavioral data, by its nature, offers insights as they happen, enabling businesses to swiftly adapt to emerging trends, shifts in customer behavior, and changing preferences. This agility is crucial in today’s fast-paced market, where customer expectations and behaviors can evolve rapidly.
Moreover, the inclusion of behavioral data opens the door to predictive analytics . By analyzing patterns and trends in customer behavior, businesses can move beyond reactive strategies to a more proactive stance. Predictive modeling, powered by this rich data integration, allows for the anticipation of future customer needs and trends. This forward-looking perspective is invaluable for businesses aiming to stay ahead of customer expectations and continuously refine their customer experience strategies.
How to collect behavioral data
Integrating behavioral and VoC Insights into journey maps begins with a comprehensive data collection phase, where behavioral data—encompassing website interactions, purchase history, and customer service engagements—is gathered alongside Voice of the Customer (VoC) feedback. This rich tapestry of information is typically sourced from digital analytics tools, CRM systems, and customer feedback platforms, providing a multifaceted view of customer interactions.
The subsequent phase involves a meticulous process of data analysis and synthesis. Here, advanced analytics and AI tools play a crucial role, sifting through large datasets to uncover patterns and correlations that might not be immediately apparent. This deep dive into the data helps in extracting meaningful insights that are crucial for the next step.
Once the data is analyzed, the integration process begins. The insights gleaned from both behavioral and VoC data are carefully mapped onto the customer journey.
This crucial step involves pinpointing how customer actions, as indicated by the behavioral data, and their feedback, as captured through VoC, align and interact at each stage of the journey. This mapping creates a more nuanced and comprehensive view of the customer experience, highlighting areas of alignment and divergence between what customers do and what they say.
Crucially, unlike traditional static journey maps, these dynamic maps are not set in stone. They are regularly updated with new data, ensuring they continuously evolve and remain reflective of the current customer experience. This ongoing process of renewal and adaptation ensures that the journey maps stay relevant, providing up-to-date insights that businesses can rely on for making informed decisions.
The enhanced value of journey maps that integrate both behavioral data and Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights is significant, offering a transformative impact on how businesses understand and interact with their customers:
- The accuracy of these integrated journey maps is markedly increased. By combining the objective data of customer behaviors with the subjective feedback from VoC, businesses can create a more precise and true-to-life representation of the customer journey. This approach minimizes the reliance on assumptions or potentially biased feedback , leading to a clearer and more factual understanding of customer experiences.
- Personalization is another critical area where these integrated maps excel. Armed with a deeper and more nuanced understanding of customer behaviors and preferences, businesses can tailor experiences to meet the individual needs of each customer more effectively. This level of personalization is key to creating more engaging and satisfying customer experiences.
- In terms of strategic decision-making, integrated journey maps are a goldmine of actionable insights. They provide a rich source of information that can inform a wide range of strategic decisions, from product development and innovation to targeted marketing strategies and customer service enhancements. This data-driven approach ensures that business strategies are closely aligned with actual customer needs and behaviors.
- The dynamic nature of these integrated journey maps facilitates proactive experience optimization. Unlike static maps, these dynamic versions can be continuously updated and adjusted in response to real-time data, allowing businesses to proactively enhance the customer experience. This agility not only improves customer satisfaction but also fosters stronger customer loyalty, as businesses can quickly adapt to meet and exceed customer expectations.
This table provides a clear comparison of traditional journey maps, VoC-enhanced maps, and behavioral data-driven maps, highlighting their respective data sources, strengths, limitations, adaptability, predictive power, personalization capabilities , and cost/resource intensity.
It illustrates how each method fits into the evolving landscape of customer journey mapping, with behavioral data-driven maps emerging as the most comprehensive and dynamic approach.
In comparing the three journey mapping methods, traditional maps offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness but lack dynamism and real-time insights.
VoC-enhanced maps bring customer feedback into the equation, providing richer insights into customer perceptions and experiences, yet they still struggle with real-time adaptability and objective behavioral analysis.
Behavioral data-driven maps, however, stand out for their comprehensive and dynamic nature. They integrate real-time behavioral data with VoC insights, offering a highly accurate, adaptable, and predictive view of the customer journey. This evolution underscores a shift towards more nuanced, data-informed strategies in journey mapping, essential for businesses to remain responsive and competitive in a rapidly changing customer landscape.
The evolution from traditional to behavioral-based, data-driven journey mapping is not just a shift in technique; it’s a fundamental transformation in how businesses understand and engage with their customers.
And, importantly, this transition to more agile, behaviorally informed, and data-driven methods is crucial in an era where customer behaviors and expectations are in constant flux.
Here’s a no-nonsense checklist for how to take the next step in your journey mapping evolution:
Assess your current journey mapping practices
Begin by evaluating your existing customer journey mapping methods. Understand their limitations and identify areas where incorporating VoC and behavioral data could make a significant impact.
Invest in the right tools and technologies
Embrace analytics tools, AI , and data management systems that can integrate and interpret both VoC and behavioral data . The right technology is crucial for making this transition successful.
Train your team
Ensure that your team has the skills and knowledge to leverage these new tools and insights. Consider workshops, training sessions, or partnering with experts in the field.
Start small and scale
Begin by applying these principles to a single customer journey or segment. Learn from this experience and gradually expand to other areas of your business.
Continuously gather and analyze data
Make data collection and analysis an ongoing process. The market and customer behaviors are constantly changing, and your journey maps should evolve accordingly.
Act on your insights
Use the insights gained from your enhanced journey maps to make informed decisions. Whether it’s refining your marketing strategy, improving customer service, or innovating your product line, let your customer insights guide you.
Measure and refine
Continuously measure the impact of the changes you make and be prepared to refine your strategies. Remember, journey mapping is an iterative process.
By adopting a behaviorally informed, data-driven approach to journey mapping, your business can gain a deeper understanding of your customers, anticipate their needs, and deliver experiences that not only meet but exceed their expectations.
Ultimately, this is your opportunity to be at the forefront of customer experience innovation.
Related resources
Customer Journey
B2B Customer Journey 13 min read
Customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, customer journey management 14 min read, customer journey stages 12 min read, buyer's journey 16 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica
Customer journey mapping: The path to loyalty
A version of this tutorial originally appeared in the free Primer app .
In an ideal world, the journey people take to become loyal customers would be a straight shot down a highway: See your product. Buy your product. Use your product. Repeat.
In reality, this journey is often more like a sightseeing tour with stops, exploration, and discussion along the way—all moments when you need to convince people to pick your brand and stick with it instead of switching to a competitor.
Staying on top of all of these moments might seem overwhelming, but mapping your customer’s journey can help. It can give you and your team a greater understanding of how your customers are currently interacting and engaging with your brand, and also help illustrate how your products and services fit into their lives, schedules, goals, and aspirations.
Let’s take a look at five steps your team can take to start journey mapping.
1. Find the sweet spot where your customers’ goals and your own align
Before you start journey mapping, nail down your business goals. Any marketing and communication you deliver during the customer journey should be focused on helping your brand reach those goals.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that your customers’ goals might be different from yours. For example, let’s say your goal is to sell more sunglasses with new, improved lenses that have a better profit margin. Meanwhile, your customers’ top concern might be getting sunglasses that match their personal style. Lens protection could be their second or even third priority.
Consider how your marketing and communication strategies can help your customers reach their goals while also getting you closer to yours.
2. Identify all of the communication touchpoints in your customer’s journey
When do you traditionally communicate or engage with customers? Make a list of these moments and group them based on when they happen during the journey: pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase.
Now find communication touchpoints you may have missed. Track what actions and interactions between your brand and your customers happen just before and after each of the pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase stages.
For example, you might decide that a major moment in your purchase stage is when your customers are guided through your website to buy an item in their shopping cart. But you might notice other communication touchpoints right before that purchase moment, like your website confirming to customers that an item has been added to their shopping cart, then suggesting related products.
Looking for all these touchpoints can quickly bog your team down in a lot of details and micro-interactions. To avoid that, prioritize the moments that get you closer to achieving your business goals.
3. Recognize pain points and moments of delight
How might your customers feel at the pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase stages as they attempt to achieve their goals? For example, could your customers be happy that your website makes browsing easy, but frustrated at how confusing it is to purchase a product?
Find the moments where your customers might have negative experiences. Who on your team is involved in those touchpoints? Your web designers? Your marketing team? Your copywriters? Are there other team members who could collaborate and improve the situation?
Say a customer likes how your online ad describes your product. But when they go to your store, salespeople present the product differently. That’s an opportunity for your copywriters and salespeople to better align their language and sales pitches.
4. Experience the customer journey yourself
Imagining how your customers might feel during their journey is valuable, but actually experiencing it for yourself can uncover much-needed insights.
If your business is run online, open a browser and experience what it’s like to be your customer. Similarly, if you have a brick-and-mortar store, go into a location that sells your product. Afterwards, ask yourself about the main communication touchpoints you encountered. Did they work well? Did they help you complete your journey? What was missing?
And don’t forget about the competition. Become one of their customers and experience the journey they’ve created. Then ask yourself all of the same questions.
5. Visualize your customer journey map
Go beyond just writing down your customer journey and communication touchpoints, and actually create a visual map of them. This doesn’t need to be a polished, heavily-designed visualization. Simply write each of your touchpoints down on individual sticky notes or papers, then pin them in order to a wall.
By doing this exercise, you’re helping your team take a bird’s eye view of the entire customer journey. You can organize your thoughts and collaboratively brainstorm new ideas for changing or adding to your communication at these touchpoints.
Make sure to create hypotheses around why new communication touchpoints will improve the customer journey, then implement and test them. If your hypotheses are wrong, go back to your journey map, reassess, tweak, and improve.
Yes, the journey mapping process can be fairly intensive, but it can have a big impact on your business. That’s why it shouldn’t be just a one-time event. Customer tastes can shift, new technology can become available, and your brand itself might evolve. So it’s important to do journey mapping at least once a year and evaluate what communication touchpoints are still working and what needs to be revisited.
Others are viewing
Marketers who view this are also viewing
Make it personal: Using marketing personas and empathy in your marketing
How to win travelers in the age of assistance, how hyundai changed course to improve the customer journey, how people decide what to buy lies in the ‘messy middle’ of the purchase journey, the ai handbook: resources and tools for marketers, better together: why integrating data strategy, teams, and technology leads to marketing success, stuart hogg.
Stuart Hogg is a marketing consultant who has worked with a number of Fortune 500 brands. He created “Journey Mapping: Connect the Customer Dots” for the Primer app.
Others are viewing Looking for something else?
Complete login.
To explore this content and receive communications from Google, please sign in with an existing Google account.
You're visiting our United States & Canada website.
Based on your location, we recommend you check out this version of the page instead:
8 Customer Journey Map Examples [+ Templates]
10 min read
![journey map customer experience 8 Customer Journey Map Examples [+ Templates] cover](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/8-customer-journey-map-examples-plus-templates_840d08c0e413d11d47ce1277afb8d529_2000.png)
According to Gartner , companies that properly use customer journey maps are twice as likely to outperform their competitors that don’t. But to unlock such effective results, first, you need to know how to create impactful maps—which is what these 8 customer journey map examples are for.
From Uber to Starbucks, all these examples share the same aim: to understand customer interactions, emotions, and pain points throughout their journey.
To enhance the customer experience and ultimately drive product engagement , let’s explore these 8 examples to help you achieve that goal!
- Customer or user journey maps come in many types, with the most beneficial formats being the current state, days in the life, future state map, and service blueprint.
- While there’s a lot to learn from successful customer journey map examples, here are 8 key insights from each map:
- Spotify : Effective journey maps help integrate features seamlessly by tracking user engagement and identifying areas for enhancement.
- Uber : Optimizing the first-time user experience requires focusing on critical touchpoints and user emotions to ensure a smooth onboarding process .
- Chatmate : Identifying and addressing user issues throughout their journey helps refine overall satisfaction and improve product usability .
- Starbucks : Enhancing repeat customer experiences involves analyzing interactions and emotions to build loyalty and manage ongoing engagement effectively.
- Rail Europe : Improving multi-channel interactions requires refining each touchpoint in the booking process and understanding customer sentiments to enhance overall service.
- Etsy : Detailed service blueprints are essential for perfecting complex actions and ensuring that touchpoints and processes align with customer needs .
- Amazon : Comprehensive journey maps are crucial for optimizing each stage of the e-commerce experience by tracking product metrics and addressing customer concerns.
- HubSpot : Detecting and resolving friction points across different user interactions can significantly improve engagement and satisfaction.
- The basic steps for designing comprehensive customer journey maps include:
- Defining your objectives.
- Creating user personas .
- Picking an appropriate template.
- Gathering relevant data and populating your map.
- Miro, Figma, and Canva each offer customizable customer journey map templates with unique collaboration features.
- To build insightful journey maps, you can also leverage data from behavioral analytics tools. Schedule a Userpilot demo to see how you can get started.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Customer Journey to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Types of customer journey maps
Every customer’s journey is unique. So there’s no universal customer journey mapping template for all companies to adopt. To help you pick the right type, here’s a look at the most commonly used map formats.
- Current state : Visualize the current customer experience based on actual interactions as of today. Useful for identifying customer pain points and setting the stage for future state mapping based on how you’d like the customer experience to be.
- Day in the life : Maps a customer’s entire daily routine chronologically to provide context and insights into when and where your product or service might be most valuable.
- Future state : Envisions how the customer journey should look in the future. It focuses on potential improvements, customer desires, and wants while aligning the changes with future goals.
- Service blueprint : Details behind-the-scenes processes and interactions performed by the company to support the customer journey. The service blueprint is the counterpart of a journey map since it focuses on the company’s view instead of the customer’s perspective.
Customer journey map examples
Customer journey mapping also helps reduce costs since you’re no longer making improvements on hunches alone. However, you only enjoy these benefits once you know how to create a solid journey map . Let’s learn how to do that with these successful customer journey map examples.
Spotify’s premium customer journey map
Spotify created a customer journey map to understand potential changes in user behavior and emotions once they became paid customers. You should use such a map when you need to learn how to boost conversion while keeping customers engaged for retention.
Let’s delve into the various elements tracked with this customer journey map:
- Customer journey stages and potential user interactions in each stage, from opening the mobile app until they engage with shared music from friends.
- Highlights various user touchpoints, such as app usage and music discovery.
- Includes multiple channels like Spotify’s mobile and desktop platforms.
- The map also captures users’ thoughts and emotions, from excitement to potential frustration, along different journey stages.

Uber’s first-time experience journey map
Uber’s experience map was created to understand and optimize the first-time user experience , starting from the initial moment they interacted with the app. So, use this map to improve the onboarding experience and refine the user experience for new customers.
Moving on to the elements, here’s everything the user journey map tracks:
- Details key user interactions from signing up and setting up payment information to requesting a ride and experiencing their first trip.
- Highlights multiple channels for potential touchpoints, including the mobile app and customer support interactions.
- Captures user emotions throughout the journey, ranging from anticipation to potential confusion.
- Breaks the experience into stages to highlight critical moments where users might need additional guidance.

Chatmate’s customer journey mapping example
Chatmate’s customer journey map pinpoints where users encounter problems , identifying customer pain points and opportunities throughout their interactions. This map is particularly valuable when launching new features .
Here are the various elements tracked with this experience map:
- Divides the user’s experience into customer journey stages.
- Highlights key user interactions for each stage, from initial discovery to ongoing engagement.
- Lists important touchpoints to drive engagement at each stage, such as digital ads during awareness or tutorials for onboarding.
- Includes various channels, such as mobile apps and web interfaces.
- Captures users’ emotions, ranging from initial curiosity and excitement to potential confusion or irritation at specific stages.


Starbuck’s repeat customer experience map example
Any list of the best customer journey mapping examples needs to include Starbucks. Starbucks developed a customer journey map to understand how repeat customers interact with the brand. Build this map when you want to manage repeat customer experiences to drive retention .
Here’s a detailed look at the elements tracked using this journey map example:
- Customer journey stages and potential interactions from the initial visit to ongoing use.
- Highlights journey touchpoints , such as mobile orders, in-store visits, and customer loyalty rewards.
- Includes multiple channels, like the app, physical store, and digital communications.
- Captures customers’ emotions through each stage of the experience, ranging from satisfaction to potential frustration.
- Differentiates between different customer experience types, i.e. poached, baseline, or enriched.

Rail Europe’s journey map with customer touchpoints by channels
Rail Europe created a journey map to enhance the travel booking experience. The purpose was to optimize how customers engage with Rail Europe’s services by refining customer journey touchpoints and their multiple channels throughout the booking process.
Let’s explore all the elements tracked with this customer journey map example:
- Customer journey stages and potential user interactions, from searching for train options to finalizing a booking.
- Highlights multiple channels for possible touchpoints, such as the website, mobile app, customer service , email communications, and beyond.
- Tracks customer sentiments at different stages, ranging from enthusiasm about trip planning to potential dissatisfaction if challenges arise during booking or travel.
Do note that due to the multi-channel approach, this customer journey map template is quite dense. So, only use it if you are comfortable undertaking such complexity.

Etsy’s service blueprint map
Etsy developed the service blueprint map with the main aim of perfecting its customer service and shopping experience. The purpose was to build up various touchpoints and processes that could enhance customer satisfaction and streamline complex support processes.

Let’s deep dive into the elements tracked with this blueprint map:
- Customer journey stages are divided into time stamps.
- Potential customer interactions , from browsing and purchasing items to post-purchase support and feedback.
- Highlights important touchpoints at the back end, such as the website interface, customer service activity, and order fulfillment.
- Includes multiple channels like online chat, email, and in-app notifications .
- Tracks user sentiments , ranging from enthusiasm during the discovery process to annoyance with order issues or support delays.

Amazon’s customer journey map
Customer journey map examples can’t be complete without mentioning Amazon. Amazon’s journey map was designed to improve its complex e-commerce experience and drive customer engagement .
This map is particularly helpful for identifying specific experience touchpoints and metrics—like conversion rates and purchase assists—crucial for optimizing processes.
Let’s explore the key elements captured in this customer journey map:
- Details user interactions across various touchpoints, from searching for products and adding items to the cart to completing a purchase.
- Includes multiple channels, like Amazon’s website, mobile app, and customer service .
- Captures customer emotions and concerns, ranging from anticipation during browsing to potential dissatisfaction if problems occur during checkout or delivery.
- Tracks success metrics across each stage of the customer journey.
Do note, Amazon’s customer journey map template is incredibly detailed and complicated. So, only use it if you’re comfortable with such complexities.

HubSpot’s customer journey map for identifying friction
Finally, there’s HubSpot’s simple customer journey map example, ideal for “a day in the life” mapping. The map was designed to identify friction points in the customer experience and solve problems customers encounter throughout their journey.
Building this type of map is especially useful when aiming to improve the success of customer engagement strategies .
Here are all the elements this customer journey map can track:
- Outlines customer interactions throughout various times of the day.
- Tracks touchpoints such as product discovery , engagement with customer support , and decision-making processes.
- Emphasizes different channels, including HubSpot’s website, email communications, and customer service .
- Captures customer sentiments , from initial enthusiasm during product exploration to potential disappointment when encountering obstacles or delays.

How to create customer journey maps?
Inspired to create your own customer journey maps? Here’s a concise guide to building effective maps, from initial planning to data collection for populating your map. Let’s get started!
Determine your customer journey mapping objectives
The first step is to set your goals for the customer journey map. Clearly define what you hope to achieve with the map. For instance, are you looking to uncover customer pain points , or is the objective to improve customer engagement ?
Also, define which stage of the customer journey you will focus on, such as onboarding, purchase, or retention.

Lastly, figure out who needs to be involved in the creation and utilization of the customer’s journey map. Consider involving key stakeholders, such as marketing, customer support, and product teams , to ensure a thorough and well-defined strategy.
Identify and build the customer personas
Creating accurate customer personas helps you understand your ideal customers by identifying their key characteristics and behaviors. You can build such personas by first gathering data through in-app surveys , interviews, and product analytics . Here’s an example:

To simplify persona creation, consider utilizing tools like the customer profile feature in Userpilot. The feature enables you to compile and analyze gathered information, ensuring your personas reflect the real needs and preferences of your target audience.

Use a suitable customer journey map template
There are several customer journey map formats and templates to choose from, each serving a different function.
So, pick a template or framework that aligns with your objectives and the specific stage of the customer journey you’re focusing on. Select one that provides clear visualizations , accommodates the data you will gather, and effectively highlights pain points and improvement areas.
Here’s a template from Miro:

Collect data to fill in your journey map
Before you start populating your customer journey map, you must first collect the relevant customer data . Some great sources for comprehensive data include customer interviews, surveys, and feedback collection .

You can also use analytics data to uncover behavioral patterns and drop-off points .
Templates for customer journey mapping process
Finally, it’s time to explore different templates for mapping various customer journeys. There are various tools available with their own templates, each offering unique features for brainstorming, collaboration, and customization. Let’s go over all the options to find the best fit for your needs.
Customer journey map templates in Miro
Considering the level of customizability they offer, Miro’s templates are suitable for creating journey maps for projects of all kinds.
You can adjust stages and paths, add notes or extra steps, and integrate visuals , ensuring a tailored approach to mapping your customer’s journey. The same template can be used to explore all customer journey stages, like the onboarding map below.
Miro aids collaboration by allowing teams to co-create simultaneously. Team members can also brainstorm in real-time by adding sticky notes and comments to the map.

Customer journey map templates in Figma
Use Figma’s template to visualize key interactions of a customer’s experience with your product, from initial contact to purchase and retention.
Figma supports collaboration with immediate updates, enabling team members to co-design together. Teams can also add comments within the design to aid the brainstorming process.
Lastly, you can adjust the template as needed by adding stages, updating content, managing connecting flows, and integrating feedback.

Customer journey map templates in Canva
Canva offers a variety of templates, most of which are useful for visually tracking and improving user experience interactions .
Canva facilitates collaboration with its real-time editing, comments, and reactions features, allowing team members to work together.
You can also customize the template by adjusting text, colors, and layout, as well as adding icons and graphics to align with your specific needs and branding. While Canva is a good option, its customizability features are simple and more suited for beginners.

The customer journey is not a linear path but an ongoing cycle of interactions and experiences. Nevertheless, we hope these customer journey map examples give you a starting point on how to build one. You can also try tools like Miro, Figma, and Canva, which provide great templates to build upon.
Looking to refine your customer journey map with data-driven insights? Get a Userpilot Demo and see how we can help you with effective user research.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
What is a user experience map and how to create one.
Aazar Ali Shad
Customer Segmentation Models: Ultimate Guide (Types, Strategy & Tools)
Customer Journey Map: Definition with Examples
Improved customer service, customer loyalty, and increased ROI; 3 things that every organization wishes they could achieve overnight. It’s possible, although not overnight, but with the right tools and the effort.
One such tool is the customer journey map and it’s there at the top with the other powerful tools that help drive customer-focused change effectively.
In this guide, we’ll explain the steps you need to take to create a customer journey map that drives the expected results while avoiding the common mistakes others make. Scroll down to learn:
- What is a Customer Journey Map?
- What Are the Benefits of Using a Customer Journey Map?
Factors to Consider Before Creating a Customer Journey Map
What are the components of a customer journey map, how to create a customer journey map in 6 steps, tips and best practices when creating a customer journey map, common mistakes to avoid when creating your customer journey map, customer journey map definition.
A customer journey map, also known as a customer experience map, is a visual representation that outlines the various steps and touchpoints a customer goes through when interacting with a company, product, or service. It chronologically represents each step of interaction the customer takes with your business. A customer journey map usually starts with the initial step of when the customer discovers your product/ service and depending on your goal it can extend as long as you want to.
Customer journey map is a tool used to understand and analyze the customer’s experience, from the initial awareness or consideration of a product or service through the purchase and post-purchase stages. It reveals customer actions, emotions, pain points and expectations along the customer journey. And it helps the business see things from the customer’s perspective which in turn helps the business gain a deep understanding of the needs of the customer.
At a glance, a customer journey map may look easy to make. But there are many details you need to pay attention to when creating one. In the following steps, we have simplified the process of creating a customer journey map.
One thing you need to keep in mind is that customer journey maps may differ from company to company based on the product/ service they offer and audience behavior.
It’s also important to have the right kind of people who know about your customer’s experience in the room when you are mapping the journey.
Here are 6 six easy steps that you can follow when creating a customer journey map.
- Build your buyer persona
- Map out the customer lifecycle stages and touchpoints
- Understand the goals of the customers
- Identify obstacles and customer pain points
- Identify the elements you want to focus on
- Fix the roadblocks
Let’s look at each step in more detail.
Step 1: Build Your Buyer Persona
Creating a customer journey map begins with defining your buyer persona, which profiles your target customer based on extensive research.
The buyer persona usually consists of demographic data such as age, gender, career, etc. in addition to other behavioral and psychographic details like customer goals, interests, lifestyle, challenges, etc.
Your business can have one or many buyer personas depending on how many audience segments you are targeting. And to avoid creating a customer journey map that is too generic, you need to create separate customer journey maps for each of the segments you identify.
You need to also be careful to rely on real data rather than assumptions to avoid creating an erroneous customer profile that won’t do much for you.
You can gather as much data as you want from online research, questionnaires, surveys, direct customer feedback, interviews and with tools like Google Analytics.
Here’s our guide on creating a buyer persona . Refer to it to create your own buyer persona in 4 simple steps. Start with a template to save time.
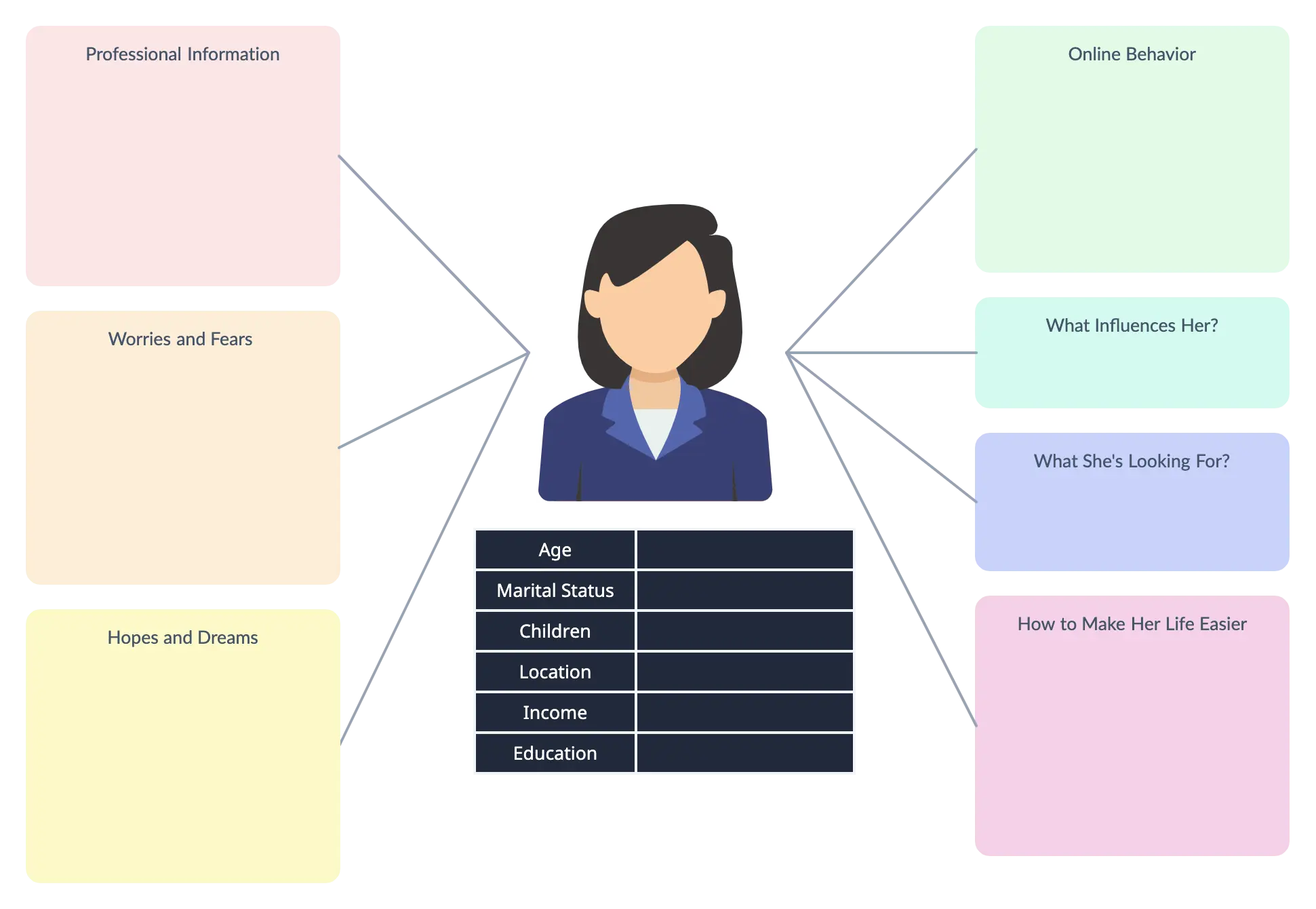
Creating the buyer persona will also shed light on the goals of the buyer, which is another thing you need to pay attention to when mapping your customer’s journey.
Step 2: Map Out the Customer LIfecycle Stages and Touchpoints
What are the stages your customer goes through to come into contact with your product/ service? Breaking down your customer journey map into various stages will make it easier to understand and refer to.
Now, these stages may vary depending on your business situation, sales funnel design, marketing strategies, etc. but usually, it would contain – Awareness, Consideration, Decision, and Retention.
Map out the touchpoints to clarify the customer lifecycle stages even better. A touchpoint refers to any moment in their journey when a customer comes into contact with your brand (i.e. website, social media, testimonials, advertisements, point of sale, billing, etc.).
The data you collected during your buyer persona research will give you a pretty good idea about the customer touchpoints along the lifecycle stages; these include the steps they take when they first discover your brand to purchasing your product and subsequent interactions.
Identifying all potential touchpoints may sound overwhelming, but you can always rely on tools like Google Analytics which will generate behavioral reports (which show the user path throughout your website) and goal flow reports (display the path a user takes to complete a goal conversion) for you to work with.
Or you can follow the traditional method and put yourself in the shoes of your customers and take yourself through the journey to identify the actions.
At the same time try to determine the emotional state (delighted/ frustrated) of the customer as they take each action. Knowing how they feel will help you understand whether they would go from one stage to the other in the journey.
Step 3: Understand the Goals of the Customers
This is where you need to focus your attention on understanding the goals your customers are trying to achieve at each stage. When it comes to optimizing your customer’s journey, it will help immensely if you know what your customers are trying to achieve.
Some methods you can use here include survey answers, interview transcripts, customer support emails, user testing, etc.
Once you know the goals your customers are trying to gain at each phase of the journey, you can align them with the touchpoints.
Step 4: Identify Obstacles and Customer Pain Points
By now you know what your customer is trying to achieve at each stage of the customer lifecycle, and each of the steps they take to get it done.
If your customer journey is perfect, then you won’t have your customers abandoning their purchases, leaving your landing pages without filling the forms, clicking the CTA only to close the tab, etc. If your journey didn’t have any roadblocks at all, then you wouldn’t be needing this user journey map in the first place.
But that’s not the case here, is it?
There might be many things that you are doing right to make your customer experience a smooth one, but there can still be many roadblocks that frustrate your users. In this step, you need to work on identifying what these roadblocks and pain points of customers are.
Maybe the product price is too high, or the shipping rates are unreasonable, or maybe the registration form is a few pages too long. Identifying such roadblocks will help you apply suitable solutions to improve your customer experience.
You can rely on the research data you gathered to create your buyer personas here as well.
Step 5: Identify the Elements You Want to Focus on
There are several types of customer journey maps and each focuses on a variety of elements. Based on your purpose, you can select one of them.
Current state: These maps show how your customers are interacting with your brand currently.
Future state: This type of map visualizes the actions that you assume or believe will be taken by your customers.
Day in the life: This type of map tries to capture what your current customers or prospects do in a day in their life. They will reveal more information about your customers, including pain points in real life.
Step 6: Fix the Roadblocks
Now that you know the issues/ roadblocks your customers come across as they interact with your brand, focus on prioritizing and fixing them to improve each touchpoint to retain customers at all stages of the journey.
Customers are constantly changing, and so should your customer journey maps. Test and update your customer journey maps as often as necessary to reflect the changes in your customers as well as in your products/ services.
Here are some templates you can start with right away.
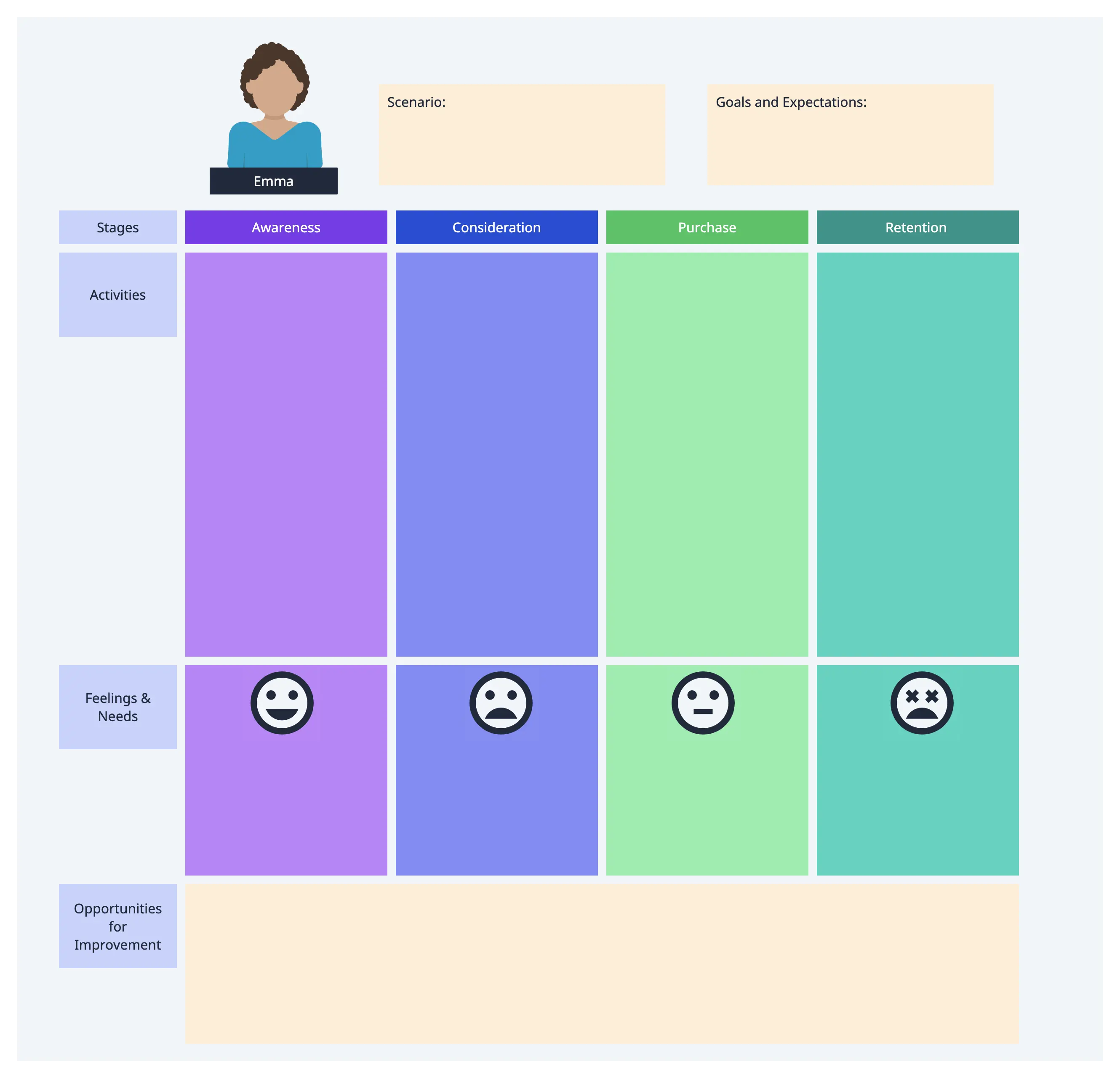
What are the Benefits of Using a Customer Journey Map?
There are many benefits to customer journey mapping. The customer journey map helps
- To enhance the customer experience. It helps businesses gain insights into customers' various touchpoints and interactions with the product or service.
- To reduce costs by identifying the areas the business should prioritize investing in and spending effort on. Customer journey mapping can help businesses identify and eliminate unnecessary touchpoints or processes that may not add value to the customer journey. Get valuable insight into what the customer is expecting from your brand, their internal motivations, and needs which will, in turn, help you improve your customer experience.
- To innovate and differentiate by discovering the gaps between customer expectations and current customer experience, unmet customer needs, pain points, and opportunities.
- To improve customer satisfaction by identifying severe customer experience issues and eliminating them effectively.
- To increase customer loyalty by helping to build strong customer relationships by understanding their needs, preferences, and emotions.
- To align teams by facilitating collaboration within organizations. This helps to provide a shared understanding of the customer’s journey, enabling different teams to align their efforts toward a common goal.
- Data-driven decision-making based on gathered insights from customer research, feedback, and analytics.
Before you delve into creating a customer journey map, it is important to consider several factors to ensure that the final outcome is accurate, effective and actionable.
- What is your team trying to achieve? Make sure to define your objective and purpose of creating the customer journey map, clearly.
- Identify the target customer segment as different customer segments may have different touchpoints, pain points and requirements leading to different journeys.
- Carry out a thorough research by gathering data and insights via customer research, feedback and analytics. Conduct customer interviews, surveys, feedback forms, social media and website analytics among others.
- Make the customer journey mapping a collaborative effort by involving cross-functional teams. Invite the marketing, sales, customer service, product, and design teams to work together to understand and align efforts.
- Consider including the emotional aspects of the customer journey such as feelings, motivations and perceptions at each touchpoint.
A customer journey map typically includes the following components:
- Touchpoints: All of the interactions and experiences a customer has with a company, including in-person, online, and mobile interactions.
- Customer personas: Representations of the target customer segments, including their demographics, behaviors, motivations, and pain points.
- Emotions: A visual representation of how the customer feels at different touchpoints during their journey.
- Channels: The ways in which a customer interacts with the company, such as website, phone, or in-person interactions.
- Data and insights: Customer behavior data and insights from surveys, analytics, or other sources.
- Pain points and opportunities: Identifications of areas where the customer experience can be improved, as well as opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
- Recommended actions: Specific recommendations for improving the customer experience, based on the journey map analysis.
- Alignment with company goals: A visual representation of how the customer journey aligns with the overall goals and strategy of the company.
Here are a few additional tips and best practices to ensure your customer journey map is accurate and effective.
- Use or create personas to better understand your customer and tailor your journey to specific customer segments. For example, if your business is fashion retail, you can develop personas such as ‘working professional,’ ‘fashionable mom,’ ‘teenage fashionista,’ etc.
- Use data and metrics to support your map and make it data-driven. Include data on customer satisfaction scores, conversion rates, or customer retention rates to identify areas for improvement. This can also help to prioritize actions and allocate resources effectively.
- Use multiple channels, both online and offline, to interact with customers. For example, a customer may discover your product or service on social media, then research more on your website, visit the store for a demo, and then make the final purchase.
- Go beyond existing touchpoints to include anticipated future customer needs as well. For example, if you are in the hospitality industry, you could include potential pain points and opportunities for pre-arrival, check-in, stay, check-out, and post-stay.
- Always keep the customer at the center of your customer journey map. Consider the customer’s emotions, preferences, and motivations at each touchpoint to create a more customer-centric experience. For example, a customer journey map for a subscription-based meal delivery service can include touchpoints for menu options, selecting meals, placing an order, receiving, and providing feedback.
- Customer journeys are dynamic and can evolve due to customer behavior, market trends, and business strategies. Therefore, continuously review and update by monitoring customer behavior, trends, and business strategies. Keep the customer journey map flexible and adaptable to changes.
- Create and present the journey map in a visually appealing and accessible format so stakeholders can easily understand it. Use visuals, diagrams, and infographics as required.
- A customer journey map is not a one-time exercise but a continuous process: test and iterate. Validate the map with real customers to ensure accuracy and relevance. Gather feedback, and conduct usability testing to gather additional insights to refine and make the map accurate.
- Keep it simple and accessible. Use clear and straightforward language and visual elements while avoiding jargon and cluttering. Make sure the customer journey map is easy to understand and accessible to all relevant stakeholders.
Creating a customer journey map can be a complex process. Here are a few mistakes you should be aware of and avoid at any cost.
Making assumptions without data
A common mistake is relying on assumptions without proper data or research. It would be best to put time into gathering data and insights from various sources. Make sure to carry out thorough research. Use a combination of qualitative and quantitative data to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Focusing on one touchpoint
Another mistake is focusing only on one touchpoint or a single interaction rather than considering the entire end-to-end journey. This can result in an incomplete or biased customer journey map. To avoid this, take a comprehensive approach and consider the whole customer journey from initial awareness to post-purchase stages. Include all relevant online and offline touchpoints, channels, and interactions.
Not involving cross-functional teams
Involve cross-functional teams in customer journey mapping to get diverse insights and a holistic view. Not involving different teams can result in biased views and missing valuable insights from different perspectives. Encourage team collaboration and communication to align the customer journey map and gather input from different stakeholders. This can help uncover blind spots and identify opportunities for improvements.
Failing to validate with real customers
Not validating the customer journey map with real customers can lead to inaccurate assumptions. Also, relying on internal assumptions or team perspectives will lead to skewed views and away from the reality of customer interactions. To avoid such a dilemma, validate the map through feedback loops, usability testing, and customer interviews. Gather input from actual customer experiences, preferences, and pain points.
Ready to Map Your Customer’s Journey?
Customer journey maps are a great way to gain deeper insight into your customers and their experience with your organization. Taking the time to understand how your customers interact with you, what they feel and what they want to achieve can go a long way toward retaining them.
Follow these 6 steps to get your customer journey map right. Use a template to save time.
And don’t forget to leave your feedback in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About Customer Journey Maps
Why is customer journey mapping important, how can customer journey maps improve customer experiences.
Customer journey maps can improve customer experiences by providing companies with a clear understanding of their customers' experiences with their products, and services. This information can be used to identify pain points and areas for improvement, allowing companies to better meet the needs and expectations of their customers. By using customer journey maps to optimize the customer experience, companies can:
- Align resources and efforts to meet customer needs better.
- Create a more personalized experience for customers.
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduce customer churn.
- Increase customer lifetime value.
- Enhance the overall customer experience.
- Improve operational efficiency.
- Facilitate cross-functional collaboration to improve the customer experience.
- Stay ahead of the competition by offering a differentiated and superior customer experience.
What tools are needed to create customer journey maps?
The tools needed to create a customer journey map vary depending on the complexity of the map and the size of the company, but some common tools include:
- Customer feedback: Surveys, customer interviews, and focus groups can be used to gather customer feedback and understand their experiences.
- Analytics tools: Data analytics tools, such as website analytics, customer behavior tracking, and customer relationship management systems, can provide insight into customer behavior and preferences.
- Customer journey map software: Tools like Creately that can be used to create visually appealing customer journey maps.
- Project management software: Tools like to manage the journey mapping process and keep track of progress.
- Collaboration tools: Tools like Creately, Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Google Workspace can be used to collaborate with team members and stakeholders.
What are some common use cases for customer journey maps?
- Identifying and resolving pain points in the customer journey
- Improving customer onboarding and retention
- Optimizing marketing and sales efforts
- Designing a customer-centric website or app
- Aligning cross-functional teams to deliver a cohesive customer experience
Can customer journey maps be used for different types of businesses or industries?
How can i use customer journey maps to drive customer-centric strategies in my organization.
- You can use customer journey maps to drive customer-centric strategies in your organization by Identifying pain points or gaps in the customer experience and developing targeted solutions
- Aligning cross-functional teams and processes to meet customer needs
- Optimizing touchpoints to deliver a seamless and satisfying customer experience
- Utilizing insights from the customer journey map to inform marketing, sales, and customer service strategies
More Related Articles
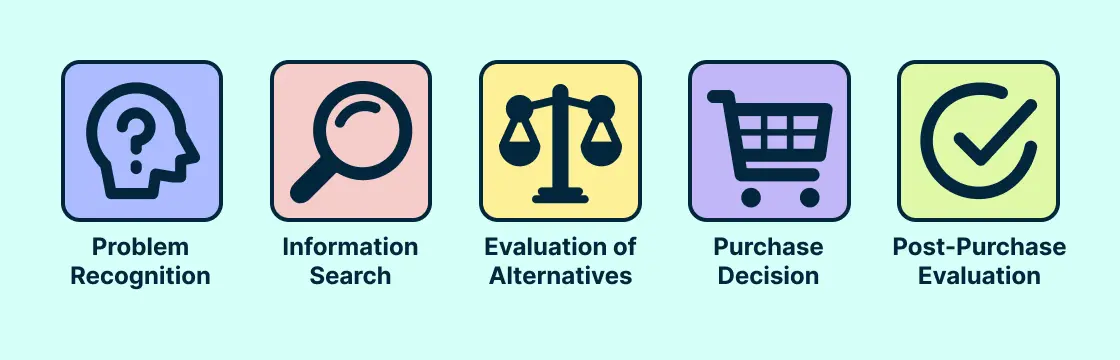
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.

- Contact sales
- Get started
- Customer Experience
- Customer Service
- Human Resources

- See all survey templates
- Resources Practical advice from the experts
- Help Center Get support and explore best practices
- Integrations Plug Delighted into your existing tech stack
- REST API Set up Delighted using our world-class API
- AI Enhancements Augment your program with built-in AI
- Case Studies Delighted customer case studies
- Blog Industry news and guidance
- Community Get support and explore best practices
- Product Roadmap See what innovations we have in store
Customer journey map: The key to understanding your customer
When you think of your customer, who comes to mind?
Can you name their intentions, motivations, and pain points? Better yet, do you know why they are choosing your company among competitors?

Defining customer needs, problems, and interactions with your company may seem overwhelming and at times, unnecessary. However, understanding every customer’s experience at each stage of the customer journey is crucial for turning business insights into long-term improvement strategies.
Creating a customer journey map can help you and your company visualize how customers feel at all brand touchpoints so you can avoid potential issues ahead of time, increase customer retention , and discover key information to make the best decisions for your business.
In this post, we will cover:
What is a customer journey map?
- How can customer journey maps improve customer experiences?
- Where do I start with my customer journey map?
- Why are surveys crucial for developing my customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual storyline of every engagement a customer has with a service, brand, or product. The customer journey mapping process puts the organization directly in the consumer’s mind to better understand the customer’s processes, needs, and perceptions.
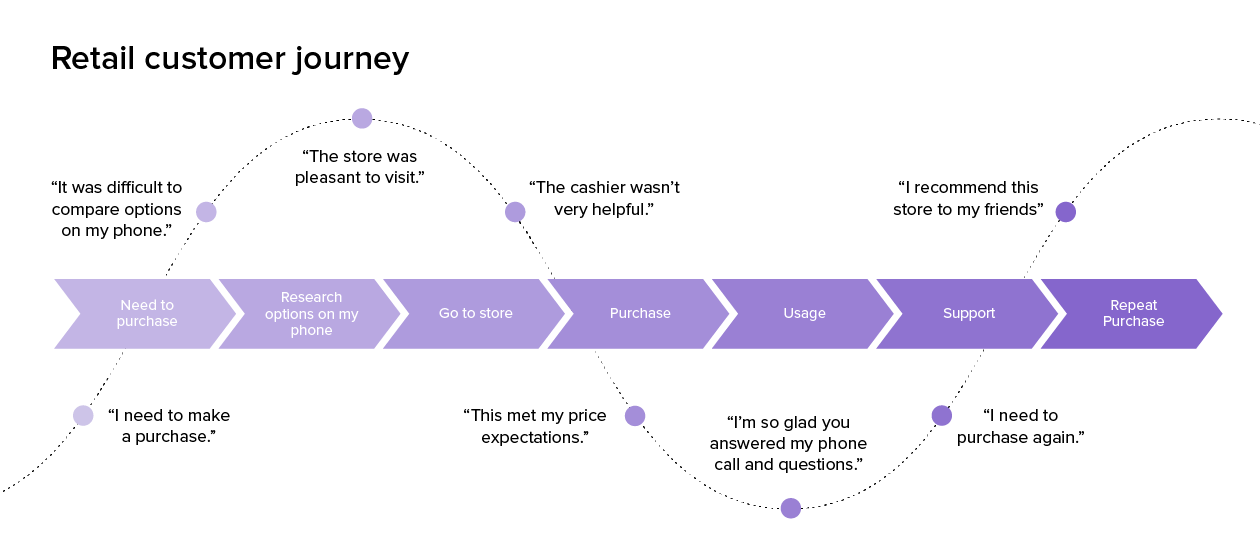
A journey map lays out all touchpoints that your customer may have with your brand – from how they first heard of you through social media or brand advertising, to their direct interactions with your product, website, or support team – and includes all of the actions your customer takes to complete an objective across a period of time.
A visual representation of the entire customer journey can provide valuable insights into the thoughts of your customers. This can then lay the groundwork for essential changes to your product or service, or overall customer experience, marketing, and business strategy.
Using a customer journey map to improve the customer experience
Outlining your current processes helps to visualize what the customer is experiencing in real time and may unveil common pain points that need to be addressed.
Through this mapping process, you’ll also be able to connect with your buyer and in turn, influence your organization to prioritize the customer experience ( CX ) through shared understanding.
Gaining a deeper understanding of your customer
“Experience maps look at a broader context of human behavior. They show how the organization fits into a person’s life.” -Jim Kalbach, author of Mapping Experiences
How does your customer feel when they can’t get in touch with customer service on an issue they’re experiencing? Or, if their package doesn’t arrive on time?
You may be imagining a situation where those instances happened to you outside of the workplace and can remember feelings of frustration. You assume this customer may feel the same and can relate to their sentiment.
The ability to establish empathy for your customers and identify how they’re feeling at every turn is what makes customer journey mapping, a powerful exercise.
A customer journey map – or customer experience map – expands that empathy on a broader level so you have a true understanding of their experience and can be meaningful in your organization’s customer experience improvement strategies. Utilizing this approach allows you to take your customer’s perspective and use it as an opportunity to find solutions to any problem they may face when interacting with your company.
Your map can help answer questions such as:
- Is my online interface user-friendly and matching customer expectations? Why is the user navigating away from the site so quickly?
- How often is my customer reaching out to customer support and is the team able to address the issues in a timely manner?
- How is the customer interacting with my brand before they decide to make a purchase? How are they feeling at this stage?
Understanding the customer journey from an empathetic, bird’s eye view will give you deeper insight into customer needs at every touchpoint so you can take the steps to meet their expectations.
Creating a customer-centric company
Aligning towards the same company objectives is essential for strategic customer experience goal planning and success tracking. When you build a journey map, you have a customer-centered tool to refer to and distribute across the company.
With your customer journey map, you can:
- Use your map to train team members on CX standards and best practices
- Present the visual diagram in company-wide meetings to map out customer-focused quarterly goals
- Include the sales team in your map assessment to improve onboarding flows
- Review the map with your customer service team to explore ways you can reduce obstacles throughout the customer lifecycle
Using visual mapping to tell a story to your company not only sets a united standard for exceptional customer care, but also benefits customer experience and customer retention in the long run.
Customer journey map design
There’s no correct or incorrect way to create a customer journey map. However, before you begin, consider aligning your map with a chosen customer persona and think through which journeys and stages make the most sense for your business to measure.
Creating a customer persona
A customer persona (or buyer persona ) is a fictional character that represents your average customer based on user and market research. Imagining this persona’s age, job function, personal goals, etc. can help you step into the customer’s shoes and thoroughly develop the customer journey story.
Start by creating three personas at most to help in narrowing your character and design focus.
Deciding what to measure
Next, you will need to decide what you want to measure and what goal you’re trying to achieve.
Perhaps you want to revisit current customer success processes or take a closer look at your prospect’s experience through the selling timeline. Whatever you choose, your customer journey map is customizable and should evolve over time to meet your business needs. You may also create multiple journey maps in the future as new opportunities shift your curiosities and goals.
Organizing with touchpoints and stages
As you begin your customer journey design, you may want to organize your map with touchpoints and stages:
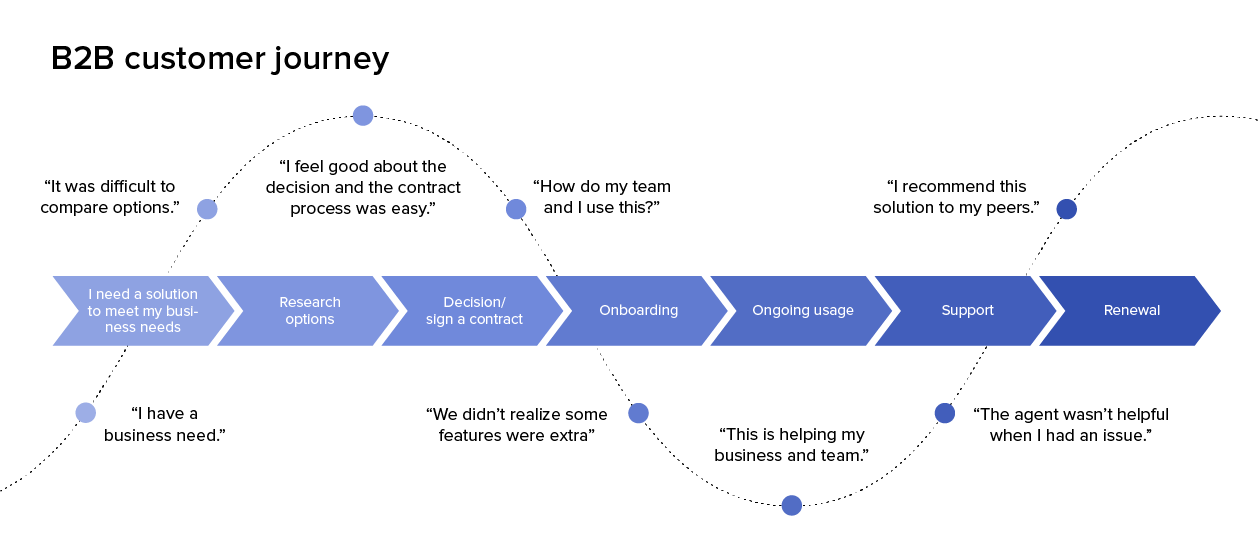
- Identify touchpoints : A touchpoint is any moment a customer interacts with your brand. From advertisements, to a thank you note they receive after a purchase, consider including these touchpoints within your map so you can collect feedback and identify patterns on how they’re feeling at each interaction.
- Write out the stages : Every time your customer engages with your brand, there is a goal-driven action behind it. Break down the customer journey in stages (or phases) based on the customer’s need throughout their journey.
Customer touchpoint mapping and journey mapping go hand in hand, but mapping out personas and defining specific customer touchpoints can seem time-consuming. Use Excel documents to organize your map or work from customer journey templates such as Qualtrics’ Journey Map Template to set a simple foundation for your diagram creation process.
Using survey data to boost your customer journey map
Research is crucial to learn your customer’s motivations, roadblocks, continued pain points, and successes. If you don’t have the survey data to answer these questions, you could be building your map from assumptions, leaving room for misguided strategic planning down the line.
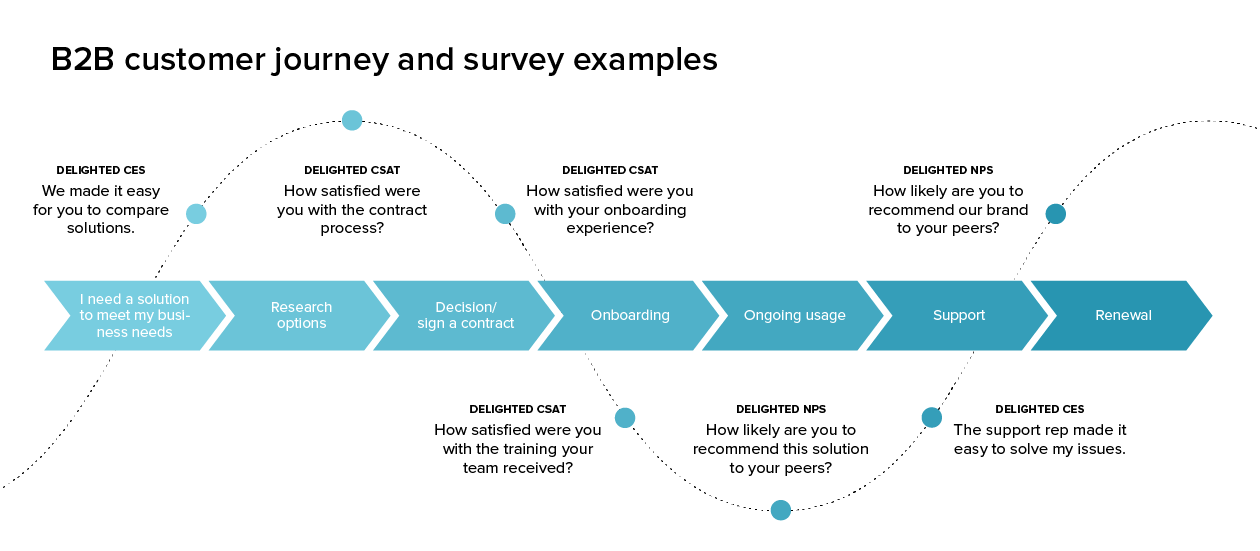
Consider using Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), or Customer Effort Score (CES) surveys to capture first-hand customer feedback to include within your customer journey map. Then, choose between a variety of surveying channels (Email, Web, Link, or SDK) to reach your audience wherever they are.
Here are some question examples to include in your survey:
- [CSAT]: How satisfied were you with your onboarding experience?
- [CSAT]: How satisfied were you with our checkout process?
- [NPS]: How likely are you to recommend this solution to your peers?
- [NPS]: How likely are you to recommend this store to your friends or family?
- [CES]: The website made it easy for me to compare options
- [CES]: The support reps made it easy to get my questions answered
After you select your survey, question, and channel, specify when and how often surveys are triggered throughout the customer lifecycle. Before you know it, your customer journey map includes up-to-date feedback for you to start analyzing and acting on CX feedback regularly.
TIP : To get greater context behind a customer experience at each journey stage, create customized follow-up questions after your initial survey question. From free response to multiple choice, craft up to 10 Additional Questions to ensure your journey map (and future state of customer experience) gets a boost with detailed verbatim feedback.
Delighted makes it easy to ask the right questions at the right time. Use Delighted’s customer experience solution to craft impactful, automated customer surveys or customize one of our survey templates .
Additional customer journey map resources
For additional resources, check out these articles on how to optimize your customer experience program , and the questions you can ask at each stage of the customer journey:
- 7 tips for an effective voice of the customer program
- 52 popular customer satisfaction survey questions by customer journey
- How to kickstart a customer experience program
- Your ultimate guide to customer journey mapping
Start collecting feedback from customers and employees today
- Free survey maker
- Survey templates
- CX solution
- NPS software
- CSAT software
- Email survey
- Delighted AI
- Testimonials
- Integrations
- What is NPS?
- NPS examples
- NPS calculator
- NPS benchmarks
- What is CSAT?
- What is CES?
- What is product/market fit?
- Employee experience management
- Customer experience metrics
- Sample size calculator
- Surveys Help
- Mobile apps
- Delighted + Qualtrics
© 2013–2024 Delighted, LLC
Security Terms Privacy Cookie Preferences Sitemap
NPS is a registered trademark, and Net Promoter Score is a service mark of Bain & Company, Inc., Satmetrix Systems, Inc. and Fred Reichheld.
Customer Journey Mapping: How to Create Perfect Maps
Zuzanna Bocian
A customer interacts with your brand multiple times before making a purchase. More than 63% of customers expect brands to know and understand their needs ( source ). But still, sometimes customers don’t feel the brands fulfill their needs. So, how do you attract a new customer?
Creating a meaningful connection with your customers is crucial for long-term business growth; customer journey marketing can help you achieve this. For instance, a customer may sign up for your website after reading an article, browsing your products, and purchasing. All of these interactions collectively form the customer journey.
What is digital customer journey mapping? How do you utilize it for your business? Let’s explore.
What is a customer journey map?
A company’s journey refers to a customer’s entire process when interacting with a brand, from initial awareness to purchase decisions. It encompasses all the touchpoints and experiences that a customer encounters along the way. Understanding the journey is crucial for businesses. Why?
It allows you to identify opportunities for improvement, optimize interactions, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. It also plays a significant role in customer retention strategies.

Throughout these customer journey stages, customers interact with various touchpoints, which are the contact points between the customer and the company. Touchpoints can include a company’s website, social media profiles, customer service interactions, and more.
Optimizing these touchpoints at each journey stage is essential to provide a seamless and satisfying customer experience.
The benefits of customer journey maps
Improved customer satisfaction.
You can identify pain points and areas for improvement by understanding the user journey’s various customer touchpoints and stages. Addressing these issues and providing solutions can lead to a smoother and more satisfying customer experience, ultimately enhancing overall satisfaction.
For example, a retail company maps its customer journey for online purchases. Through journey mapping, they identify that many buyers abandon their carts during checkout due to complicated forms and a lack of guest checkout options.
In response, the company simplifies the checkout process, adds a guest checkout option, and includes progress indicators to guide customers through each step. As a result, customer satisfaction improves, leading to higher completion rates for online purchases.
Take care of your customers better with a unique ticketing system. ✅ Join the HelpDesk trial and try all its features. 🚀
Higher conversion rates
A customer journey map is a helpful tool that identifies crucial moments in the customer journey where potential shoppers are most likely to make purchasing decisions. You can increase the likelihood of converting leads into customers by optimizing these touchpoints and providing relevant information or incentives.
For instance, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company can map the customer journey from trial sign-up to subscription. During this process, they may discover that many trial users drop off after the initial sign-up because they need clarification about how to get started. However, the company can improve user engagement and conversion rates from trial to paid subscription by providing personalized onboarding emails, tutorial videos, and live chat support during the trial period.
More effective marketing strategies
Nowadays, you must do more than just run ads to attract customers. The competition is very high. Mapping the customer journey provides insights into the customer’s mindset, preferences, and behaviors at each stage. With this knowledge, you can tailor their marketing strategies and messaging to better resonate with their target audience.
Consider an ecommerce company that plans to launch a new product. To ensure its success, they analyze the customer journey from the initial stage of product awareness to the final stage of purchase. They closely monitor customer behavior at each stage and identify the marketing channels and messages that resonate most with their target audience.
Based on this valuable insight, they tailor their marketing campaigns to better connect with their customers and increase the chances of a successful product launch.
Get a deeper understanding of customer needs
Customer journey mapping is a process that allows you to understand your customers’ journey by stepping into their shoes and seeing things from their perspective. This understanding helps uncover unmet needs, preferences, and pain points that may have gone unnoticed. By aligning products, services, and processes with customer needs, you can better meet and exceed customer expectations.
Identification of opportunities for innovation enhances the customer experience
How do you know which part of the product needs improvement? You can identify opportunities for innovation and differentiation through a customer’s journey map. You may discover new ways to enhance the customer experience, introduce new products or services, or differentiate themselves from competitors.
Essential elements of an effective customer journey map customer
A practical customer journey map comprises several crucial elements that provide valuable insights into the user’s perspective.
Customer personas
Customer personas represent fictional characters that embody the different segments of a business’s target audience. Each buyer persona typically includes demographic information, preferences, goals, and issues. Creating a detailed buyer persona allows you to empathize with their customers and tailor the customer journey map to specific audience segments. But to do that, you need to master customer communication.
Use HelpDesk to make things easier for you. Enhance your customer experience with a robust ticketing system. 🦸
Touchpoints
Touchpoints are customers’ interactions with the brand across different channels and platforms. These interactions can occur online (website, social media, email, etc.) or offline (in-store, customer service hotline, etc.).

Channels are the various mediums or platforms that customers use to interact with a brand. These can be online channels like websites, mobile apps, social media, and email or offline channels like physical stores, events, and customer service centers. Understanding customers’ different channels can help optimize the omnichannel strategy and deliver a seamless experience across all touchpoints.
Emotions play a significant role in shaping a customer’s marketing experience and can influence their purchasing decisions. When creating customer journey maps, it’s important to consider customers’ emotions at each stage, such as excitement, frustration, satisfaction, or disappointment.
To better understand these emotions, you can use sentiment analysis techniques. Analyzing customer feedback, reviews, and social media mentions using natural language processing (NLP) tools can identify and categorize emotional cues in customer interactions.
Pain points
Pain points are customers’ obstacles, challenges, or frustrations with the brand. These can include long wait times, confusing website navigation, product defects, or poor customer service. Improving customer experience and increasing satisfaction and loyalty requires identifying and addressing these difficulties.
Steps to create your customer journey map
Creating a customer journey map is a strategic process that requires careful research. You can use different customer mapping templates to gain valuable insights into their customer journey stage and identify opportunities for improvement by following structured steps.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to creating your customer journey map:
Step 1. Research and data collection: Gathering qualitative customer data is essential. You can use surveys, interviews, and analytics.
Step 2. Persona development: To create effective customer personas, it is important to include demographic information, goals, challenges, preferences, and key attributes for each persona.
Step 3. Identification of touchpoints and channels: List all possible touchpoints and channels that customers may interact with during their journey with your brand.
Step 4. Mapping the customer’s emotional journey: Understand and document the emotional highs and lows that customers experience.
Step 5. Identifying moments of truth: Pinpoint critical decision-making points or “moments of truth” in the customer journey.
Step 6. Customer action planning: Use the insights data to develop action plans to improve customer experience. Identify strategic interventions and initiatives that address pain points and enhance touchpoints.
Step 7. Prioritize improvements: Based on your analysis, prioritize improvements that will significantly impact the customer experience and align with your business objectives. Consider factors such as feasibility, impact, and resource requirements.
Step 8. Develop solutions: Brainstorm and develop solutions to address the identified pain points and capitalize on opportunities.
Step 9. Implement changes: Implement the proposed changes to the customer journey, whether updating website content, training customer support staff, or redesigning product packaging. Because not all customer journeys are the same, ensure all stakeholders are aligned and committed to the implementation plan.
Customer journey marketing strategies and ideas
Create proper awareness for your product or service .
Potential customers learn about a product, service, or brand during the awareness stage. They may see it through advertising, social media, word-of-mouth recommendations, or online searches.
To attract customers, create blog posts, videos, or social media content that addresses common pain points or questions in your industry. Provide valuable insights and solutions without promoting your products directly.
When introducing your brand through marketing efforts, send introductory emails and provide educational content to spark interest and encourage further exploration. Some educational content can be a game-changer for you.
Customer decision-making
In this stage, customers decide to purchase the product or service. This buying process could involve weighing price, features, quality, and brand reputation. They may also evaluate factors like shipping options, return policies, or customer support.
Use journey stage-specific retargeting strategies to re-engage customers who have shown interest but have yet to convert. Serve personalized ads highlighting specific products or promotions they’ve previously viewed. The content for this stage includes:
Free demos of your product.
Free sign-ups.
Product promotions (for example, sign up and get 30% off).
Delivery details and facilities.
Purchase stage
After becoming aware of the product or service, customers consider whether it meets their needs or solves their problems. They might research more information, compare it with alternatives, read reviews, or seek recommendations from friends or online communities.
Develop comparison guides, case studies, or product demonstrations that help customers evaluate your offerings against competitors.
Highlight key features and benefits to showcase your value proposition.
Send targeted emails with testimonials, reviews, or success stories to build trust and credibility.
Provide in-depth information about your products/services to help customers make informed decisions.
Promote it through different channels (search engines, social media, website, etc.) to get new customers.
Now, customers are deciding whether to purchase the product or not. This could involve weighing price, features, quality, and brand reputation. They may also evaluate factors like shipping options, return policies, or customer support.
You can use journey stage-specific retargeting strategies to re-engage customers who have shown interest but have yet to convert or serve personalized ads highlighting specific products or promotions they’ve previously viewed.
Customer retention
This is when the customer completes the transaction and acquires the product or service. Depending on the business, it could happen online, in-store, or through other channels. You have to provide top-notch services so they’ll return to you rather than go for another provider.
You can leverage customer data to provide personalized shopping experiences, product recommendations, and customer service. Use past purchase history and preferences to tailor communications and offers.
Then, mechanisms for collecting customer feedback at various stages should be incorporated to continuously refine and personalize the buyer journey.
Provide a dedicated manager to make things easier for the customer.
Make your team accessible to the customers.
Create a knowledge base to solve common issues.
Learn more about customer retention in the latest Learning Space guide. 🧑🚀 Discover the best strategies to improve your user experience now. 🎉
Loyalty and advocacy
Design loyalty programs that reward customers for repeat purchases and encourage them to become brand advocates to identify loyal users. Offer exclusive perks, discounts, or rewards through customer messaging to incentivize ongoing engagement and referrals.
Integrating customer journey mapping into marketing strategies
Segment your audience.
It’s important to understand that each customer is unique, and their journey toward purchasing your product or service may differ from one another. To cater to these differences, you should segment your audience based on demographics, behavior, and preferences. Doing so allows you to create personalized marketing strategies that resonate with customer segments at various stages of their journey. Conducting proper user research can significantly impact the success of your business.
Align content with each stage of the journey
Develop marketing content that caters to customers at each stage of the journey.
For example, create engaging content to raise awareness, informative content to aid the consideration stage, persuasive content to drive decision-making, and helpful content to encourage customer loyalty and advocacy.
Optimize channel mix
Analyze which channels are most effective at different stages of the customer journey.
For instance, social media might be great for raising awareness, while email marketing customer journeys might be more effective for nurturing leads. Allocate your marketing customer journey budget and resources accordingly to optimize channel performance. It would be best if you made a proper service blueprint.
Implement feedback loops
Continuously gather customer feedback at each touchpoint to understand their experiences and pain points. Use this feedback to refine your marketing strategies and improve the customer journey.
Monitor and analyze key metrics
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as conversion rates, engagement metrics, customer satisfaction scores, etc., to gauge the effectiveness of your marketing efforts across different channels. Use this data to iterate and optimize your strategies over time.
Stay agile and iterative
The customer journey is dynamic, so your marketing strategies should be different. Stay agile and be prepared to adapt your tactics based on evolving customer behavior, user research, market trends, and competitive landscape.
Challenges and solutions in customer journey mapping
Getting stuck from the inside-out perspective of the customer journey.
Businesses often create journey maps based solely on their internal processes and assumptions rather than the actual experiences of their customers.
Solution: To overcome this challenge, you should adopt an outside-in approach by gathering customer insights through surveys, real-life examples, interviews, and feedback mechanisms. It ensures that the journey map accurately reflects the customer’s perspective and identifies pain points and opportunities for improvement. Make a proper visual representation for better understanding.
Taking too narrow a view of the customer journey
Focusing on more than just specific touchpoints or channels within the customer journey can result in an incomplete understanding of the overall experience.
Solution: Take a holistic view of the customer journey, encompassing all stages, touchpoints, and channels. It can help you identify interactions and dependencies across various touchpoints, enabling them to deliver a seamless and consistent experience across the entire journey.
Overlooking all the participants in the customer journey
Businesses often concentrate solely on the customer’s interaction with their own company. They often need to pay more attention to the involvement of other stakeholders or influencers who may impact the customer’s experience.
Solution: Expand the scope of the journey map to include all relevant participants, such as influencers, partners, and third-party service providers. Consider how each participant contributes to or influences the customer’s experience at different journey stages. This comprehensive approach helps businesses identify collaboration opportunities and potential areas for partnership to enhance the overall positive customer experience.
Lack of data or data overload
A massive amount of data is needed to create accurate and actionable journey maps. Without this data, it’s difficult to target customers and create a marketing funnel.
Solution: Balance qualitative and quantitative data sources to understand the customer journey comprehensively. Use customer feedback, customer journey analytics, journey mapping tools, and other relevant data sources to uncover insights about customer behaviors, preferences, and obstacles. Focus on collecting data pertinent to the specific goals of the journey mapping exercise and prioritize quality over quantity.
Failure to iterate and update journey maps
Customer journeys are dynamic and evolve due to changes in customer behavior, market trends, and business strategies. Failing to update regularly and iterate journey maps can lead to outdated insights and missed opportunities for improvement.
Solution: Treat the entire customer journey as an ongoing rather than a one-time activity. Monitor customer feedback, analyze performance metrics, and incorporate new insights to refine and update journey maps regularly. Establish a feedback loop to capture changes in customer needs and expectations, ensuring that journey maps remain relevant and actionable.

Customer journey mapping is a precious tool for businesses looking to connect with their customers. With today’s fierce competition, using a well-crafted customer journey map template is more important than ever. By thoughtfully analyzing and planning, organizations can pinpoint areas for improvement and elevate customer satisfaction.
Creating a solid customer map is the key to unlocking increased sales and achieving your business goals. With enthusiasm and optimism, we encourage you to explore the benefits of customer mapping and take your customer experiences to the next level.

Get the cheat sheet for solving customer tickets
Join our newsletter to receive your cheat sheet and other amazing content directly in your inbox.
Success! You're one click away from the cheat sheet 👇
Share it with the world
- copy-button#copy track#send" data-controller="track" data-track-event="HelpDesk Blog" data-track-parameter1="Share" data-track-parameter2="Copy link" > Copy link Link copied to clipboard https://www.helpdesk.com/blog/customer-journey-mappping/
Keep all communication in one place
Free 14-day trial Simple setup
You'll be in good company
Discover our track#send">text| products
LiveChat Connect with customers
ChatBot Automate customer service with AI
KnowledgeBase Guide and educate customers
OpenWidget Enhance websites with widgets
Customer Journey Maps: The Top 10 Requirements

It’s hard to believe it’s been seven years since I launched my customer experience consultancy, Heart of the Customer, way back when CX was still in its infancy.
At that time, when I first wrote Customer Journey Maps – the Top 10 Requirements , I didn’t know the post would be viewed hundreds of thousands of times, and reposted around the world. But I did know that customer experience as a discipline – given its proven ability to boost customer loyalty and company results – was here to stay.
I enjoyed revisiting and updating the post back in 2015, but in the intervening years, the world has changed , the CX industry has evolved , research methodology has gotten more nimble, and technology has advanced . (And yet, somehow, none of us has aged a day – it’s uncanny!)
So it’s time once again to refresh the content. I am proud that the underlying philosophy and framework remains solid and consistent, but I’ve tweaked some terminology, techniques, guidelines, and examples.
In short, it’s an oldie, but a goodie, and I hope that regardless of whether you’re rereading it or encountering it for the first time, you will come away with something new and helpful.
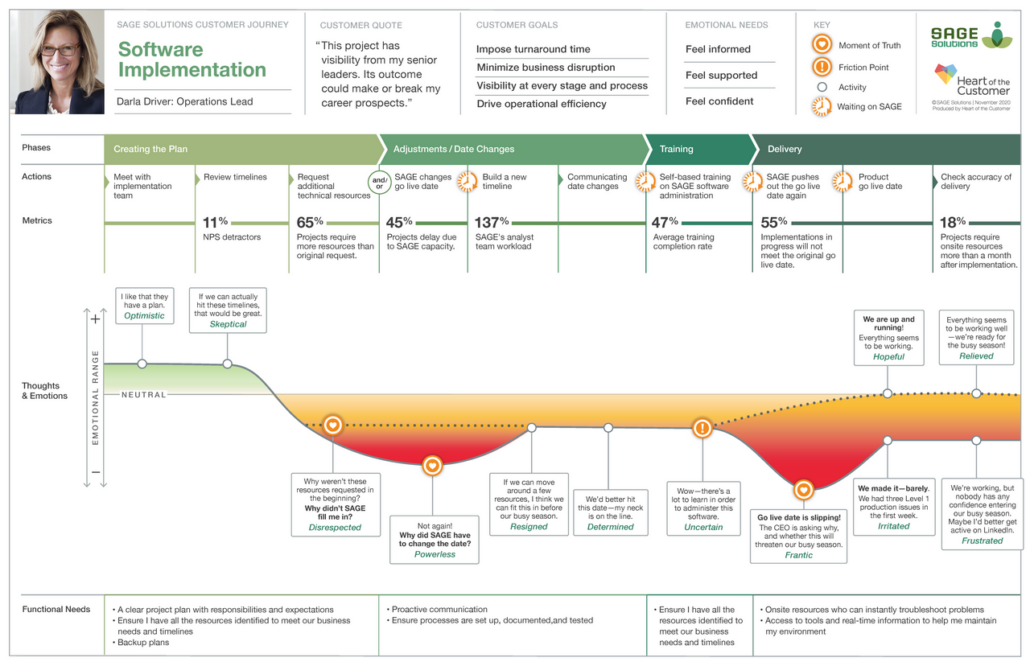
Understanding your customer experience is the key to improving it…and to reaping the financial rewards that go hand in hand with increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. And the best way to find out what customers do, think, and feel while interacting with your company is to create a customer journey map.
These visual representations show how a customer uses your product or service, or the decision-making process that turns a potential user into a customer. Undertaking the journey mapping process carries benefits that go way beyond the creation of a singular document, but here we will focus only on the maps themselves.
Guidelines are valuable because there is no “standard” map, since there is no “standard” customer experience. But not all journey maps are created equal. The best maps are highly customized, documenting your customer’s journey, as it is today, through your customer’s eyes. This allows you to easily identify where to focus your resources in the future, and the most cost-effective initiatives to implement to generate the greatest return on your investment (ROI) and the largest increase in customer loyalty.
The visual appeal of the document is extremely important, but the specific style is less so. You can build a map following high-quality design principles or use smiley faces. You can make it an engaging work of art or scribbles on a napkin. Ultimately, what is going to matter most is the content, and the integrity of the process used to compile it.
In this post, I’ll detail the criteria used to design and build the customer experiences and journey maps that can accelerate your customer experience program, focusing on the 10 critical components all great customer journey maps share. The examples we’ve peppered throughout the post show actual Heart of the Customer journey maps that incorporate these criteria.
Here’s what you need to include for an effective, actionable, customer-focused journey map:
Here are the top 10 requirements for creating a successful customer journey map
1. represent your customer’s perspective.

Customer’s Viewpoint
A great customer journey map must represent the experience as your customer sees it, not the way you think they see it. That means it will often include aspects out of your direct control, such as social media influences, web searches, and steps your customers take before you even enter the picture.
B2B Software Example
For example, while studying the software purchase process for a large B2B client, Heart of the Customer – much to our client’s surprise – discovered that the vast majority of clients and prospects relied extensively on their own networks to create their list of vendors, ignoring conference trade shows, Google searches, and other more traditional forms of marketing.
While those channels were employed later in the purchase process, our discovery revealed that if the company didn’t win at “ word of mouth ,” they lost before they even knew they were in the running. This invaluable insight allowed the company to avoid wasting resources on programs that weren’t really impacting their results – or their bottom line – and instead concentrate on more effective relationship-building efforts.
2. Do Your Research

Use Several Different Research Methods
You can’t rely on internal staff to build an accurate customer journey map. (Unless you employ a lot of mind-readers , in which case, go right ahead!) Depending on the scope of the customer journey map example, you’ll need interviews, ethnographies, surveys , and/or other types of customer research to figure out what’s really going on . Start with qualitative research, as your customer touchpoints often involve interactions and emotional responses that will be a surprise. We always begin there, then for some projects, follow up with quantitative surveys to confirm the results.
Talk to Customers
Talk to your customers. There is no substitute for having conversations with customers. Producing a map without talking to customers is what we call a hypothesis map. It is based on the hypotheses of the internal employees.
When I was at a large HSA company running the customer experience program, we led the nation in sales, but we also led the nation in churn. When I asked around, I found out that none of the people making decisions about the HSA product had ever talked to a customer to validate the customer’s journey. They said, “We are customers, so we do not have to talk with anyone else.” They were the strangest customers ever. They thought about HSAs all day, every day. No real customer experience matches that. When we talked to customers about their top pain points, we found the biggest driver of dissatisfaction was the inability to log in to the site. The internal group would never have considered this, as logging in was easy for them.
COCREATE WITH CUSTOMERS
Some companies bring in customers to work hand in hand with employees to build the customer journey map, but care must be taken in that scenario to avoid the bias that results from a small or tainted sample. This approach typically works best with B2B companies that want to focus on a specific journey, such as customer support. In most cases, it’s best to do customer research first, then build on the information gathered.
3. Recognize and Represent Customer Personas
The images show customer journey map examples
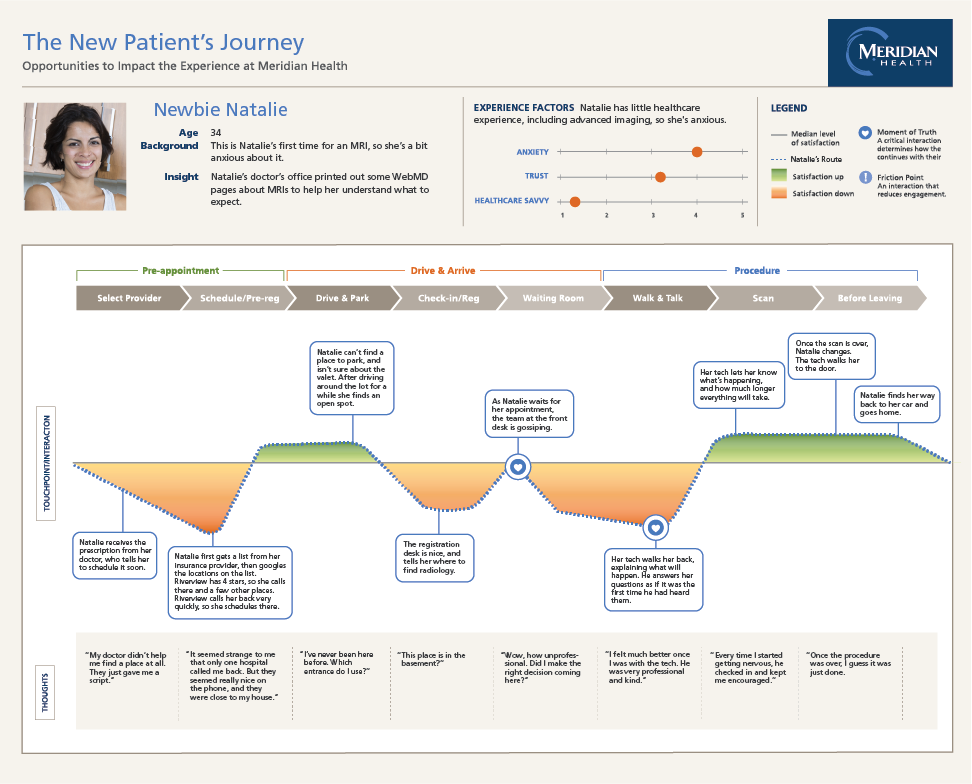
Health Insurance Example

Different customers have very different customer journeys. For instance, while mapping how consumers purchase health insurance, we found that while one segment of customers spent only a couple of hours on research, another invested six weeks and used completely different tools. A great customer journey map doesn’t lump those two segments together because the result wouldn’t accurately reflect the experience of either.
Retail Example

When doing customer journey mapping for a large retailer, we found that customers were segmented by need rather than by demographics. The average customer, coming in on the way back from work to grab a few things for the evening had unique needs and a different customer experience than one who had a sick child at home and needed medicine late at night. Other customers came each week to hunt for deals for their necessities. Each customer needed different things from their customer journey. To design the future state, you must uncover the differences so you can design to meet the specific customer needs.
Naming Drives Empathy

The solution is to identify the qualities and journey experiences of customers within a segment, and then use that data to build out a persona that represents that segment and brings their experiences to life. Naming the persona or personas allows employees to connect with their customer’s needs. Here are some examples of some personas, see if you can relate to any of them.
VP Vince — VP of Technology and Operations. He is tasked with implementing software that will transform the company’s business. He is focused on aggressive growth, modernization, automation, and innovation.
Cautious Carter — A buyer new to the Florida real estate market, relocating for a job and family. His goals are to find a realtor that is an expert in the Florida market to enable him to make a wise investment in the right property.
Security Driver Faye — A married woman in her 30s looking to purchase the right employee benefits. She wants to achieve peace of mind even if it costs a little more.
If you have already identified segments, use those in your research. If you haven’t, use your qualitative research to uncover different personas, which you can refine in the quantitative phase.
4. Include Customer Goals

Healthcare Customer journey goals
A great customer journey map illustrates what your customers are trying to accomplish at each stage of their experience and reflects whether those goals evolve as the journey progresses.
For example, when studying a healthcare journey for a hospital, we found that in the early stages, one persona focused extensively on understanding everything involved with the journey, whereas a different persona was just focused on getting through the process as quickly as possible. That revelation made designing cost-effective initiatives to meet the personas’ needs much easier.
Jobs to be done (JTBD) in a customer journey
The “jobs to be done” (JTBD) concept is a framework that helps businesses understand the underlying motivations and goals of customers when they “hire” a product or service to fulfill a specific job or task. It focuses on the progress a customer wants to achieve rather than the specific product or solution they are using. When applied to a customer journey map, the JTBD concept can provide valuable insights into understanding the customers’ goals at different stages of their journey.
5. Focus on Emotions

It’s impossible to overstate the importance emotions play in any customer experience, whether B2B or B2C, because emotions are the key motivator behind every decision we make. Even when it comes to the largest organizations, ultimately, every decision is still made by a human being.
The Science of customer emotions
In his book, Thinking, Fast and Slow, Nobel Laureate Daniel Kahneman identified that the overwhelming majority of decisions are made automatically, based on an emotional reaction.
This includes customers’ decisions to renew or abandon their ScoreSense® subscription. Those with a positive emotional experience are typically more likely to renew — and pay for — programs than those with a neutral or negative experience.
Qualtrics’ XM Institute reports that when an emotional experience is positive, 90% of customers are promoters, whereas when it is negative or neutral, only 22% survey customers are.
More importantly, when problems occur, 74% of those with a positive emotional experience will forgive you, whereas only 19% of those with a negative or neutral experience will.
Spotlight the emotions
Great customer journey maps spotlight these emotions. I’m not a fan of using the smiley and frowning emojis prevalent in many existing customer journey maps, but the information does need to be conveyed somehow. Heart of the Customer always uses professional designers , but there are now so many graphic tools and options readily accessible to anyone with an internet connection that using smiley faces seems needlessly inadequate and, frankly, a little lazy.
SAAS Software Customer Journey Design by Emotions
In our work with a large SAAS software company, we noticed a set of eight emotions customers kept expressing about their experiences. These included emotions such as pride, confidence, frustration, and exhaustion. These were laid out on the customer’s experience journey map at the different phases.
We helped the company tie these emotions to some specific customer behaviors. Customers that expressed confidence were 50% more likely to purchase additional modules. For customers that expressed exhaustion during the later stages of implementation, the likelihood of purchasing went to almost zero.
This software company redesigned the future state so that when customers expressed confidence, a sales rep would reach out to see how best to get the next sale. When a customer expressed exhaustion, the company provided ‘free’ professional services resources to help reduce the exhaustion and in-service of the customer purchasing more in the future.
Take advantage of color, style, and graphic elements to put viewers of your map in the shoes of your customer and convey how customers feel throughout the journey.
6. Indicate Touchpoints

One reason many clients choose to create a customer journey map is to better understand the order and type of each and every touchpoint – those times when your customer and your company interact – including those over which you have little direct control, such as the online research or referral from a friend that might lead a customer to your website early in their shopping journey.
“External” touchpoints are often some of the most important parts of the customer journey and are key to understanding the friction that occurs.
Types of Touchpoints
Advertising touchpoints : These include various channels such as TV commercials, radio ads, online banner ads, print ads, social media ads, and sponsored content.
Website touchpoints : Interactions that occur on the company’s website, such as landing pages, product pages, checkout process, customer support chat, and user account pages.
Social media touchpoints : Engagements that happen on social media platforms, such as Facebook posts, tweets, Instagram stories, YouTube videos, and customer comments or messages.
Physical store touchpoints : For businesses with physical locations, these touchpoints include in-store interactions, such as browsing products, talking to sales associates, making a purchase, or participating in events.
Customer service touchpoints : These touchpoints encompass interactions with the customer service team through support channels, including phone calls, live chat, email support, self-service portals, and support tickets.
Mobile app touchpoints : If the company has a mobile app, interactions within the app, such as signing up, navigating the app, making purchases, receiving push notifications, and using app-specific features.
Email touchpoints : Communication that occurs through email, including welcome emails, newsletters, transactional emails (order confirmations, shipping updates), and personalized offers.
Offline touchpoints : Any touchpoints that happen outside of digital channels, such as direct mail, brochures, catalogs, physical events or conferences, and product packaging. 60% of all customer touchpoints often occur in this group.
Word-of-mouth touchpoints : These include recommendations or referrals from friends, family, or colleagues, as well as online reviews and ratings on platforms like Yelp or Google.
Post-purchase touchpoints : Touchpoints occur after the customer purchases, such as post-purchase emails, product usage instructions, customer surveys, and loyalty programs.
Talk to Customers to get it right
Internal journey mapping done without capturing the voice of the customer is unlikely to take these customer steps into account – and therefore unlikely to be able to address and improve them – yet another reason involving real customers in your mapping efforts is so important.
7. Highlight Moments of Truth

Just as not all maps are created equal, not all interactions in the customer journey are equally important. Great journey maps reveal those Moments of Truth that have a disproportionate impact on a customer’s overall perception of the journey, and in doing so, pinpoint the key opportunities where your improvement efforts will provide the greatest return.
The outcome of these critical interactions might well determine whether a customer stops doing business with you or is so delighted they recommend you to their friends, family, and social media connections.
Healthcare Example
For one healthcare client, Heart of the Customer’s research revealed that problems during the hospital check-in process tainted the entire patient experience, even for patients that were otherwise quite satisfied with the care they subsequently received. In that circumstance, directly putting resources toward providing better care – a seemingly obvious way to improve customer satisfaction – would have little impact on loyalty. Removing the initial friction during the check-in process, however, increased customer loyalty and care ratings (for the same level of care) because it changed customers’ perception of the care received.
Manufacturing Example
Here is a two-part Moment of Truth from a manufacturing company. First, the customer changes the delivery date or quantity, thinking, “Things have changed. I need to adjust the quantity.” The customer is feeling anxious. Second, the manufacturer changes the delivery date. The customer is now thinking, “Not again! Why does the manufacturer keep changing the date?” The customer is feeling powerless. One or both could happen.
We had measures to show the first scenario, where the customer changed the date, occurred 25% of the time. The second scenario, where the manufacturer changed the delivery date, occurred 20% of the time. Do you think we needed to improve the journey around those experiences? I’ll give you a hint…they were both far below the emotion line.
The moments resonated with employees, but the data created urgency.
For the first moment, we obviously needed to be nimble with the shifting customer needs. But for the second moment, we were REALLY negative impacting customer satisfaction with unreliable delivery. (By the way, showing up early with shipments is almost just as bad as showing up late.)
8. Evaluate Your Brand Promise

Done right, journey mapping can reveal how your brand promise aligns with the actual customer experience you’re providing, as well as how to fix issues if you’re falling short.
Do you sell your process as being effortless ? Highly personalized? Affordable? A great customer journey map will show whether your customers believe you’re delivering – and if they think you’re not, how much their disappointment might be costing you in lost sales or increased expenses.
9. Measure Time

The length of a customer experience provides important context. Does a typical call last 30 seconds or 10 minutes? Did shoppers take an hour or a week to decide on a purchase? A great journey map recognizes that this information is essential and is built around it.
Financial Services Example
We mapped a journey for a financial services company. We mapped the onboarding journey for someone opening one of five different types of financial accounts.
The timing for each stage of the customer journey was important, like how the time between creating the account and signing the paperwork was negatively affected by the fact that 60% of customers needed to call customer service. The most crucial time was time to fund the account. If it took more than four days to fund the new account, the chance of funding went down by 75%. This outcome was bad for both the customer and the company.
10. Ditch the PowerPoint

The overarching themes of the story told by a journey map should be immediately obvious. But a great journey map is designed to be pored over and studied, with the nuances revealed in the details. Too many journey maps are created only for presentation on a screen, communicating basic information through concise bullet points. A great customer journey map defies those limitations.
Desktop Publishing Software
Use a desktop publishing application and a professional designer to create your own customer journey map, so you can dive deeper and more freely and effectively convey the richness of the customer experience. These tools allow each customer journey map to be bespoke and not rely on a generalized customer journey map template.
Customer Journey Mapping Software
The last few years have shown an explosion of software tools to help with customer journey map creation and customer journey management. Tools like Inspire Journey from Quadient and SuiteCX walk the line between being able to tell a story with powerful visualization and the need for advanced desktop publishing skills.
A Customer journey map template IS A no-go
Each journey is unique and has its own touchpoints, phases, and Moments of Truth. When you start with a customer journey map template, you lock in your expectations and often will miss a touchpoint because it does not fit the template being used.
Conclusion of the Top 10 Customer Journey Map Requirements
There you have it, as promised: 10 points that highlight the critical components of any great customer journey map. But we customer experience pros recognize the benefits of going above and beyond in our efforts to delight, right?
Four “bonus” criteria that you’ll also want to consider:
Break the experience into phases.
In longer journeys, customers are trying to accomplish different things, at different times, and in different ways. Document their mindset throughout, so you can tailor your customer experience to meet customer needs at every stage .
For example, it’s typical for preliminary steps in a shopping journey to revolve around finding out what questions to ask, but later steps in the journey are more transactional. Keep tabs on what your customer wants from you, and when they want it.
Weave in Their Words
Including customer quotes – what they’re actually saying during and about the experience – isn’t strictly necessary, but I’ve found it really adds dimension to the experience and helps employees relate to what the customer is going through.
3. Include Non-Customers
A pre-sales customer journey map should always include “the ones that got away,” i.e., the people who chose not to do business with you. Finding out where their experience differed from the people you successfully converted into customers is likely to shed a lot of light on the reasoning and emotions behind their decision-making process – and therefore illustrate where you should target your interventions .
For example, one Heart of the Customer journey map revealed that our client’s “non-customers” were typically people who relied on in-person meetings when making purchasing decisions – something our client didn’t offer at the time. That realization was critical to their improvement efforts, and yielded corresponding financial benefits.
Incorporate Your Other Voice of the Customer Components
Journey maps shouldn’t stand alone. Just as your maps can explain the findings from other methods of customer feedback, other methods of research can add richness to your journey maps.
Factor in operational data , such as the length of the journey, error rates, or the number of support calls, to add explanatory power and context to your journey maps, especially when presenting to executives.
Last Thoughts on Customer Journey Mapping
Keeping these 10 (plus four) components in mind during your customer journey mapping process will ensure you create a rich document that provides a solid foundation for your customer experience efforts. But make sure they don’t just gather dust on a shelf! Use what you’ve learned to drive action, manage your journey , and improve your business outcomes .
Our blog offers many more examples of how we apply these principles to benefit our clients . For additional details about our proprietary journey mapping process , download our journey mapping toolkit , watch our webinars , and peruse our authoritative journey mapping guidebook, How Hard Is It to Be Your Customer?
You might also find our recent white papers of interest:
CX for Skeptics: Showing the ROI of CX
Driving Change Through Journey Maps
FAQs about Customer Journey Mapping
At Heart of the Customer, we understand that the key to an exceptional Customer Experience (CX) is understanding the customer’s journey. In this FAQ, we’ll dive into the essentials of customer journey mapping to help you improve your CX strategy.
1. What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the entire experience a customer has with your company, from initial contact to long-term engagement. It’s designed to showcase the customer’s interactions, emotions, expectations, and pain points at each stage of their journey. By creating a customer journey map, you gain valuable insights into customer needs and preferences, helping you tailor your products, services, and communication to create the best possible CX.
2. What is the purpose of a customer journey map?
The primary goal of a customer journey map is to understand the customer’s perspective better, allowing you to improve the overall CX. It can help you identify areas of friction or dissatisfaction, discover opportunities for innovation, and streamline your processes. Ultimately, an effective customer journey map enables your organization to make more informed decisions, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
3. How do you structure a customer journey map?
Customer journey maps can vary in format and complexity, but they generally include these key components:
- Customer persona: This represents the target customer, including their demographics, goals, preferences, and motivations.
- Journey stages: The main phases a customer goes through when interacting with your business, such as awareness, consideration, purchase, and retention.
- Touchpoints: Specific moments of interaction between the customer and your company, like browsing your website, contacting support, or using your product.
- Emotions and sentiments: Indicate how the customer feels during each stage, revealing potential pain points and areas for improvement.
- Opportunities and actions: Identify areas where your organization can enhance the CX and outline the steps needed to implement these changes.
4. What are the three journey mapping techniques?
There are several methods for creating a customer journey map, but these three techniques are particularly popular:
– Workshop-based mapping: Involves collaborative brainstorming sessions with cross-functional teams, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the entire customer journey from multiple perspectives.
– Data-driven mapping of the buyer journey: Leverages quantitative and qualitative data (e.g., surveys, analytics, customer feedback) to build an evidence-based map of the customer’s journey.
– Diary study mapping: Customers record their experiences with your company over a certain period, providing first-hand insights into their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
By understanding the fundamentals of customer journey mapping, you’re better equipped to unlock the full potential of your CX strategy. Remember, a well-crafted customer journey map can illuminate opportunities for improvement and help drive your organization’s success. Happy mapping!
Keep reading .

What is a Customer Journey Map?
By Jared Tincher

The Maturity Model Advantage

The Secrets to AGCO’s CX Success

From Vision to Execution: Building Your Customer Experience Dream Team
Stay updated with our insights ..

- What is New
- Download Your Software
- Behavioral Research
- Software for Consumer Research
- Software for Human Factors R&D
- Request Live Demo
- Contact Sales
Sensor Hardware

We carry a range of biosensors from the top hardware producers. All compatible with iMotions
iMotions for Higher Education
Imotions for business.

How to Map and Analyze a Customer Journey
Consumer Behavioral Analysis
Morten Pedersen

Deciphering Consumer Motivation with Biosensors
Consumer Insights
News & Events
- iMotions Lab
- iMotions Online
Eye Tracking
- Eye Tracking Screen Based
- Eye Tracking VR
- Eye Tracking Glasses
- Eye Tracking Webcam
- FEA (Facial Expression Analysis)
- Voice Analysis
- EDA/GSR (Electrodermal Activity)
- EEG (Electroencephalography)
- ECG (Electrocardiography)
- EMG (Electromyography)
- Respiration
- iMotions Lab: New features
- iMotions Lab: Developers
- EEG sensors
- Sensory and Perceptual
- Consumer Inights
- Human Factors R&D
- Work Environments, Training and Safety
- Customer Stories
- Published Research Papers
- Document Library
- Customer Support Program
- Help Center
- Release Notes
- Contact Support
- Partnerships
- Mission Statement
- Ownership and Structure
- Executive Management
- Job Opportunities
Publications
- Newsletter Sign Up

A customer journey map visualizes the steps a user takes on a website, from entry to purchase or information acquisition. It identifies key touchpoints, user emotions, and pain points, providing insights into optimizing the user experience. Using tools like eye tracking and facial expression analysis enhances this understanding, offering deeper behavioral insights.
Table of Contents
Customer journey mapping with eye tracking and facial expression analysis on a website.
A Customer Journey is a person’s journey from A (entry) to B (purchase or correct information acquisition) on any given website. Understanding your customers’ experiences on your website is crucial for optimizing their journey and ensuring they find what they need with ease. Mapping out a customer journey helps you visualize and enhance these experiences. In this article, we’ll explore what a customer journey is, the importance of customer journey mapping, how you can gain deeper insights with biosensors, and how you can create an effective journey map to improve user experiences on your website.
What is a Customer Journey?
In a broad sense, a customer journey can be as long or as short as makes sense for your business case. In this instance, we are looking at it from a UX perspective as that is the most concise stimuli we have when later applying biosensors to our mapping.
As mentioned before, a customer journey refers to the complete sequence of interactions and experiences a customer has with your brand, from the moment they enter your website (and where you enter it from) to their eventual purchase of whatever that website is selling. This journey includes every step a customer takes, from initial contact through to purchasing, using, and advocating for your products or services. Understanding the customer journey helps businesses anticipate customer needs, remove barriers, and create a smoother path to conversion.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the steps and interactions a customer goes through during their journey from entry to exit on your website. It outlines key stages such as awareness, consideration, decision, and post-purchase, highlighting touchpoints, customer thoughts, emotions, and pain points. This map allows you to see the journey from the customer’s perspective, providing insights into how to improve their experience.
This example of a Customer Journey Map is a general representation of a person’s journey through a website, divided into the different phases the process goes through. The notes at the bottom are meant as checklists for features that are important to have in the different phases.
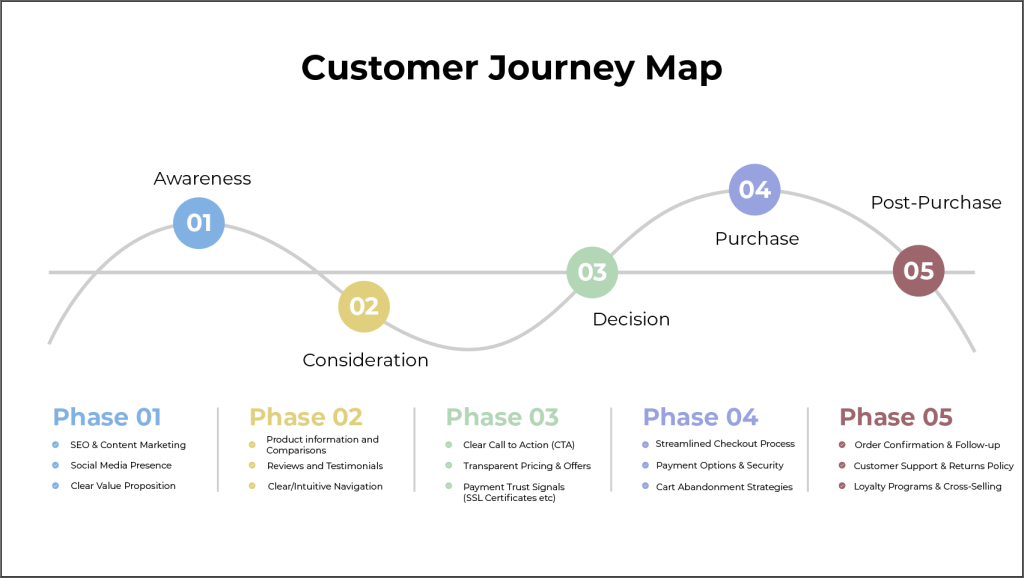
Increase Customer Journey insights with Eye Tracking and Facial Expression Analysis
Customer journeys are traditionally measured using session tracking software such as Google Analytics , Microsoft Clarity , Hotjar and many others. They work by recording user sessions, where mouse-clicks, scrolling and site navigation are merged to give an overview of customer behavior, drop-off points and session length.
While those metrics are very important for journey mapping, they do not tell you much about the customers themselves. By integrating biosensors, specifically eye tracking (either screen-based or webcam ) and facial expression analysis (FEA), you can gain insights on metrics such as, attention, frustration, joy and concentration among others. This helps you build a much better understanding of your users, and therefore a much more effective and robust customer journey map.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map Using Eye Tracking & FEA?
For those with a good understanding of customer journey mapping and interested in leveraging cutting-edge techniques like eye tracking and facial expression analysis, the following steps outline how to integrate these tools into your journey mapping process. These advanced methods provide deep insights into user behavior and emotions, enabling you to create a more accurate and empathetic customer journey map.
1. Define the Objectives and Hypotheses
- Objective Setting : Start by clearly defining what you want to achieve with eye tracking and facial expression analysis in your customer journey map. This could include understanding how users interact with specific elements on your website, identifying emotional responses at key touchpoints, or uncovering unconscious behaviors that impact decision-making.
- Formulate Hypotheses : Develop hypotheses about potential pain points, engagement triggers, or emotional responses that you believe are critical to the customer journey. This will guide the focus of your eye tracking and facial expression analysis.
2. Identify Key Touchpoints for Analysis
- Pinpoint Critical Touchpoints : Determine the specific touchpoints in the customer journey where visual attention and emotional reactions are most crucial. These could include landing pages, product pages, checkout processes, or customer support interactions.
- Prioritize Based on Impact : Prioritize touchpoints where small changes can lead to significant improvements in user experience or conversion rates.
3. Recruit Participants and Define Personas
- Select Target Personas : Recruit participants that represent your key customer personas. Ensure that these participants align with the segments you’re focusing on for the journey mapping.
- Ensure Diversity : Include a diverse group of participants to capture a wide range of behaviors and emotional responses, providing a comprehensive view of your customer journey.
4. Design the Study: Eye Tracking and Facial Expression Analysis
- Set Up Eye Tracking : Implement eye-tracking technology on your website or within a controlled environment to monitor where and how long users look at different elements. This could involve hardware-based eye trackers or software that uses webcams.
- Incorporate Facial Expression Analysis : Use facial expression analysis tools to capture real-time emotional reactions as users navigate through the journey. These tools can detect micro-expressions and emotional states such as frustration, confusion, satisfaction, or joy.
- Synchronize Data Collection : Ensure that eye tracking and facial expression data are collected simultaneously and synchronized with the user’s journey through the touchpoints. This will allow for a cohesive analysis of visual attention and emotional response.
5. Conduct the Usability Sessions
- Run Controlled Sessions : Have participants navigate through the key touch points while their eye movements and facial expressions are recorded. Provide tasks that align with typical user goals to mimic a real-world journey.
- Capture Behavioral Data : Alongside visual and emotional data, collect behavioral data such as click paths, time spent on tasks, and navigation patterns. This holistic approach will enrich your analysis.
6. Analyze Eye Tracking and Facial Expression Data
- Heatmaps and Gaze Plots : Use eye-tracking data to generate heatmaps and gaze plots that visualize where users look, the sequence of their visual attention, and areas that are ignored. Identify patterns that reveal how users interact with different elements at each touchpoint.
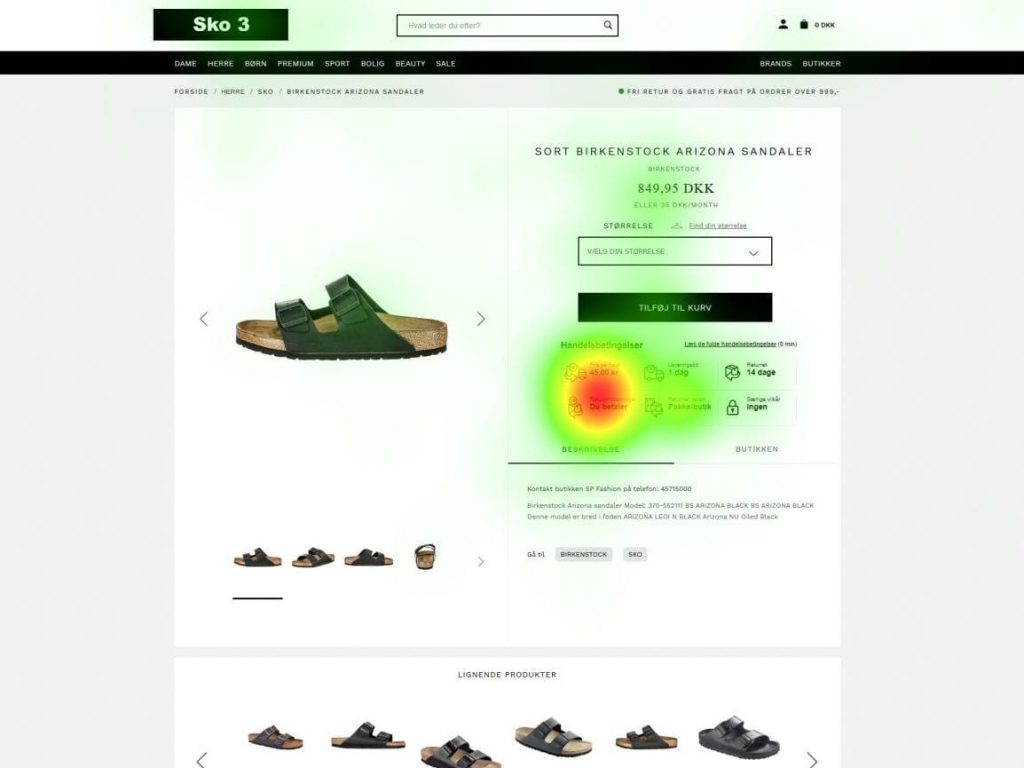
- Emotion Mapping : Analyze facial expression data to map emotional responses at each stage of the journey. Correlate these emotions with specific actions or inactions to understand the underlying causes.
- Combine Data Streams : Integrate eye tracking, facial expression, and behavioral data to create a detailed picture of the customer experience. Look for correlations, such as how prolonged focus on a specific area correlates with frustration or satisfaction.
7. Map Out the Journey with Insights
- Visualize the Journey : Create a customer journey map that incorporates insights from the eye tracking and facial expression analysis. Highlight the stages, key touchpoints, emotional responses, and areas of visual attention.
- Annotate with Findings : Annotate the journey map with key findings such as points of high frustration, elements that are frequently overlooked, or areas that elicit positive emotions.
8. Identify Optimization Opportunities
- Pinpoint Design Improvements : Use the insights to suggest specific design changes, such as repositioning elements that are frequently overlooked or simplifying areas that cause frustration.
- Emotion-Driven Enhancements : Propose enhancements that address emotional pain points or amplify positive experiences. For example, if users show confusion during the checkout process, simplify it to reduce cognitive load and frustration.
9. Test and Iterate
- Implement Changes : Make the suggested changes to the touchpoints and conduct follow-up studies to measure the impact.
- Continuous Improvement : Iterate on the process by periodically repeating eye tracking and facial expression analysis to ensure that the journey continues to meet user expectations and business goals.
What Are Touchpoints in Customer Journey Mapping?
Touchpoints in customer journey mapping refer to the specific moments where customers interact with your brand. These interactions could occur on your website, through social media, via email, or in-person. Mapping touchpoints helps you understand where customers engage with your brand, what their experiences are like at each interaction, and how these moments contribute to their overall journey. By identifying and optimizing touchpoints, you can create a seamless and positive customer experience.
Which Components Are Part of the Customer Journey?
The components of a customer journey typically include the following:
- Customer Stages: These include the phases of awareness, consideration, decision, retention, and advocacy.
- Touchpoints: Key interactions that customers have with your brand.
- Channels: The mediums through which touchpoints occur, such as websites, social media, or emails.
- Customer Actions: The specific actions customers take at each stage, such as clicking a link, reading a blog post, or making a purchase.
- Emotions and Motivations: Understanding how customers feel and what drives them at each stage.
- Pain Points: Identifying obstacles or frustrations that customers encounter during their journey.
- Opportunities: Areas where improvements can be made to enhance the customer experience.
What is Customer Journey Analytics?
Customer journey analytics involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to the customer journey. This data-driven approach allows businesses to track customer behavior, measure the effectiveness of different touchpoints, and understand how customers move through various stages of their journey. By leveraging customer journey analytics, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize the user experience, improve conversion rates, and increase customer satisfaction.
Analyzing Eye Tracking and Facial Expression Data
To effectively analyze eye tracking and facial expression data in your Customer Journey research, the checklist below covers the most important point you need to follow:
- Visual Data Analysis : Use heatmaps and gaze paths to visualize where users are focusing their attention on a webpage. Heatmaps provide a color-coded view of the most viewed areas, while gaze plots track the order in which users look at different elements. This helps identify which parts of the page are most engaging or distracting.

- Area of Interest (AOI) Analysis : Define specific areas of interest on the webpage, such as buttons, images, or forms, and measure how much time users spend looking at these areas. AOI analysis reveals which elements attract the most attention and whether they effectively guide users through their journey.

- Emotional Mapping : Map the emotions detected through facial expression analysis, such as joy, frustration, or surprise, at different points in the customer journey. This helps identify how users feel when interacting with various elements and content on the site.
- Correlate Attention and Emotion : Combine eye tracking and facial expression data to see how visual attention correlates with emotional responses. For instance, if users spend a lot of time on a product page but show signs of frustration, it may indicate confusing content or navigation issues that need to be addressed.
- Sequence Analysis : Examine the sequence of visual attention and corresponding emotional reactions to understand user navigation paths and potential friction points. This can help determine whether users are experiencing a smooth journey or encountering obstacles that cause negative emotions.
- Pattern Identification : Identify patterns such as high engagement with specific elements but low conversion rates or signs of frustration on particular pages. Recognizing these patterns helps pinpoint areas for improvement and enhance the overall user experience.
- Segmentation Analysis : Analyze data by different user segments (e.g., new vs. returning visitors, demographic groups) to understand how various customer types interact with the website. This enables tailored optimizations to better meet the needs of diverse audiences.
Mapping and analyzing the customer journey on a website is essential for enhancing the user experience. By examining each step of a customer’s interaction with your brand—from entry to purchase or information acquisition—you can identify key touchpoints, understand customer emotions, and pinpoint barriers to conversion. Traditional analytics tools provide valuable data on user behavior, but integrating advanced techniques like eye tracking and facial expression analysis offers much deeper insights.
Comprehensively analyzing customer journeys is about understanding not just what users do on your website, but why they do it and how they feel. Leveraging these insights allows businesses to enhance the customer experience, driving better engagement, conversion rates, and loyalty.
The Complete Pocket Guide
- 32 pages of comprehensive eye tracking material
- Valuable eye tracking research insights (with examples)
- Learn how to take your research to the next level
Free 42-page Facial Expression Analysis Guide
For Beginners and Intermediates
- Get a thorough understanding of all aspects
- Valuable facial expression analysis insights

Last edited
About the author
See what is next in human behavior research
Follow our newsletter to get the latest insights and events send to your inbox.
Related Posts
What is Structural Equation Modeling?

The Human Factors Dirty Dozen: From Aviation to Automotive
Human Factors
Jessica Justinussen

What is the Observer Effect?
You might also like these.

Neuroaesthetics: Decoding the Brain’s Love for Art and Beauty

Unlocking the Potential of VR Eye Trackers: How They Work and Their Applications
Exploring Mobile Eye Trackers: How Eye Tracking Glasses Work and Their Applications
Understanding Screen-Based Eye Trackers: How They Work and Their Applications
Product guides.
Case Stories
Explore Blog Categories
Best Practice
Collaboration, product news, research fundamentals, research insights, 🍪 use of cookies.
We are committed to protecting your privacy and only use cookies to improve the user experience.
Chose which third-party services that you will allow to drop cookies. You can always change your cookie settings via the Cookie Settings link in the footer of the website. For more information read our Privacy Policy.
- gtag This tag is from Google and is used to associate user actions with Google Ad campaigns to measure their effectiveness. Enabling this will load the gtag and allow for the website to share information with Google. This service is essential and can not be disabled.
- Livechat Livechat provides you with direct access to the experts in our office. The service tracks visitors to the website but does not store any information unless consent is given. This service is essential and can not be disabled.
- Pardot Collects information such as the IP address, browser type, and referring URL. This information is used to create reports on website traffic and track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Third-party iFrames Allows you to see thirdparty iFrames.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Cyara Customer Experience Assurance Platform
Blog / CX Assurance
August 29, 2024
The Impact of AI on Customer Journey Mapping
Danielle Marinis
It’s no secret that AI has disrupted the entire CX industry, empowering businesses to improve their customer experience offerings. And, with each passing day, it’s become increasingly clear that AI and chatbots aren’t going anywhere, with over 64% of CX leaders stating that they plan to increase their investments in AI and other related technology by the end of 2025.
Cyara’s conversational AI optimization platform helps leading businesses regain visibility and control throughout the entire chatbot development lifecycle.

But, while we often touch on the various risks and benefits of chatbots and other conversational AI-based tools, AI has transformed the CX space beyond these systems. By integrating AI into customer journey mapping, businesses have redefined the way they understand and interact with their customers, leading to improved customer experiences, higher customer satisfaction rates, and more effective business strategies.
While chatbots are integral to delivering high-quality CX, AI’s utility doesn’t end there. When optimized and used properly, AI-driven customer journey mapping can help you improve your CX pathways and forge long-lasting relationships with your customers.
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
Simply put, customer journey mapping is the process of tracking and understanding how customers are interacting with your brand and includes every touchpoint from when a customer first becomes aware of your business, to when they purchase one of your products or services. When it comes to improving your customer experiences, this process is integral to identifying trends in your customers’ needs and how you can further improve your CX offerings to maximize customer satisfaction, improve brand loyalty, and reduce churn.
For example, a customer journey map of a retail customer can track how a potential customer moves through the various stages of the decision-making process. The prospect may first hear about your clothing brand from a friend and visit your website to see if you’re offering clothes in the style that they prefer. From there, the customer will make the decision to place an order. But, when their order arrives, they realize that the clothing is the wrong size, so they call an agent to request an exchange. However, during the interaction, the customer has trouble due to a defect affecting call quality, leading to frustration, and leaving the customer dissatisfied, unlikely to recommend your brand.
In this example, the customer journey map shows the pathway your customer takes and identifies issues within your CX offerings. With these insights, you can better understand which improvements you can make, and how you can avoid these issues in the future.
The Benefits of AI for Customer Journey Mapping
While our example above highlights the importance of customer journey mapping to pinpoint areas of improvement and understand your customers better, it’s critical to recognize that customer journeys are often complicated, with many moving parts and potential blind spots. But that’s where AI can take your customer journey mapping to the next level.
With AI, businesses can take their customer journey mapping process to the next level, gaining better insights and creating a more nuanced understanding of exactly how customer preferences, needs, and the best way to improve your customer experience offerings to continue delighting customers.
By leveraging AI into customer journey mapping, your business can:
- Provide Personalized Customer Experiences: Compared to other methods of customer journey mapping, AI can track and analyze massive amounts of data such as trends in customer behavior and preferences. Based on this data analysis, brands can begin to tailor personalized journeys to meet an individual’s specific needs.
- Map Journeys in Real Time: One of the primary benefits of AI-powered CX is 24/7 availability and service, which translates to customer journey mapping as well. AI can continuously map journeys in real time, identify any potential issues as they occur, and seamlessly remediate defects to ensure that your customers are receiving the best experience possible.
- Predict Future Customer Behavior: Historically, customer journey mapping involves sorting through a lot of data, costing a team’s valuable time and resources. When you implement AI into the process, your system can analyze the data in a fraction of the time to identify trends, which can then be used to anticipate customer behavior. Using this predictive analysis, you can pinpoint areas of improvement to create a more efficient CX pathway.
- Make More Informed Business Decisions: It can often be difficult to understand exactly where you can improve your customer experiences, and where pain points exist throughout the customer journey. But AI’s ability to analyze and track data can help business and CX leaders visualize where their CX is failing and where they should be focusing efforts to delight customers.
Improve Customer Experiences with Cyara
Customer journey mapping is essential for any business that wants to ensure they’re meeting customer needs throughout the entire buyer’s journey. Within any single journey, there is plenty of room for errors to slip through the cracks and negatively impact your customers’ perception of your brand and offerings. But, when you implement AI-based systems into the customer journey mapping, you can efficiently analyze data and visualize where improvements need to be made.
Cyara’s AI-Led CX Transformation Platform helps leading enterprises take control over their entire CX development, including chatbot optimization, agent environment monitoring, and automated testing solutions. It’s critical to ensure that your CX journeys are always performing as designed, whether you’re gearing up to deploy a new pathway, or are updating an existing channel based on data from your customer journey mapping. And Cyara is here to help you every step of the way.
Contact us to schedule a demo and learn how Cyara helps leading companies improve customer experience and assure performance at scale or visit cyara.com to get started.
Read more about: Artificial Intelligence (AI) , Customer Experience (CX) , Customer Experience (CX) Monitoring , Customer Experience Issues , Customer Experience Management
Subscribe for Updates
Join our email list, and be among the first to learn about new product features, upcoming events, and innovations in AI-led CX transformation.

How to Transform Your Banking Customer Journey
Table of Contents
Digital banking is now the norm, with 90% of consumers and 86% of businesses using digital banking channels. Additionally, having 24/7 accessibility to financial information and services means that customers demand exceptional experiences in real time, everywhere. When digital services and customer service don’t measure up, customers may switch banks.
To enhance CX and retain bank customers, financial service organizations must undergo a digital transformation to deliver better banking customer journeys.
What Is a Banking Customer Journey?
A banking customer journey is a series of digital and non-digital interactions customers have with your bank to make a decision (e.g., open a new account?) or accomplish a specific task (e.g., apply for a credit card). Customers decide what actions to take at each step in the process, but the bank has an opportunity to influence those decisions and behaviors, improving the customer experience and increasing loyalty and lifetime value.
According to McKinsey, a typical regional bank has more than 1,500 customer journeys (across business units, product lines and customer interactions).
Here are some of the banking customer journeys that are particularly important, from onboarding and using bank products and services to resolving problems:
- Research account types, loans or credit cards
- Open a bank account
- Apply for a loan, mortgage or credit card
- Receive and activate card(s) (onboarding)
- Activate online banking
- Receive alerts about suspicious behavior on a credit card or other account
- Receive and pay bills
- Pay late fees
- Report a missing or stolen card
- Complain about transaction or fees
Why the Banking Customer Journey Matters
Customers rely on your bank to provide up-to-the-moment information to help them make wise financial decisions. They want real-time, easy and intuitive communications regarding important items like their mortgage loan application, alerts about fraudulent charges on their credit card account, reminders so they don’t miss a payment and even notifications about other financial service products they should be using.
Some banks are not meeting those expectations.
According to a global survey of 6,000 consumers, 25% of customers switched banks , and 39% of those who switched did so due to poor customer service. More than half (53%) would switch financial providers to get a better digital experience. An S&P global survey found that almost 40% of customers who switched banks between May 2021 and April 2022 switched to get a better mobile banking app experience (38.7%) or better customer service (37.9%).
To satisfy and retain customers, banks need to deliver better digital experiences and customer journeys.
Benefits of Improving Banking Customer Journeys
Making it easy and convenient to do business with your bank pays off in many ways.
Better customer satisfaction and CX: McKinsey research reveals that shopping, onboarding and problem resolution journeys “disproportionally drive the overall experience that a customer has with their bank.” According to Forrester research, organizations with better customer experiences tend to enjoy increased revenues, lower costs, reduced risk of customer attrition and the ability to charge premium prices for their products and services.
Greater loyalty: Satisfied customers are six times more likely (than dissatisfied customers) to say they’ll remain with a bank.
Higher revenue: Improving CX directly impacts the bottom line. For a large multichannel bank, a one-point improvement in its CX Index score can lead to an incremental $123 million in revenue. Customer satisfaction is positively correlated with purchasing decisions . Satisfied banking customers say they will purchase more of that bank’s products.
Better financial metrics : According to McKinsey research, banks excelling in customer satisfaction lead in several financial metrics:
- Increased growth
- Total shareholder return (TSR)
- Decreased costs
Focus on Three Forgotten Banking Customer Journeys
Many brands focus primarily on acquiring new customers—but not on keeping them happy. CX teams need to pay more attention to several “forgotten” banking customer journeys to reduce pain points, enhance CX and boost customer retention:
Receive proactive alerts about suspicious activity . When you’re at CostCo trying to pay for your new 75” Smart TV, you don’t want to discover that your credit card has been suspended due to suspicious activity. To eliminate this customer pain point, a customer journey management system delivers proactive fraud notifications:
- Detects suspicious behavior on a credit card account.
- Notifies customers that their card has been suspended due to suspicious activity.
- Allows customers to immediately verify the authenticity of the charges.
- Reactivates the card, allowing the customer to complete their purchase.
Receive notification of exceeding overdraft limit . Discovering on the last day of the month that you don’t have enough money in your account to cover your rent is extremely stressful. To eliminate this pain point, proactively notify customers when they are about to exceed their overdraft limit and indicate the charges they may incur if they exceed the limit. This gives them time to transfer money, avoiding the overdraft fees and the ding on their credit record for a late rent payment.
Pay late fees . Customers who miss several loan payments incur late fees, damage their credit score and face the embarrassment and hassle of dealing with a collection agency. To prevent these negative consequences (and eliminate the expense of using a collection agency), remind customers who have overdue payments to pay their late fees. Alert the customer that their account will be suspended and they will be handled by an external collection agency if payment is not made by a certain date.
Seven Tips to Improve CX
You must understand what your customers need and what pain points they’re experiencing to improve customer experience. Keep your customers front and center when developing your digital or CX transformation strategy and new processes. If you make assumptions about what needs fixing, you may waste a lot of time and money on a solution that doesn’t solve the real problem.
Some CX leaders don’t pay attention to the customer voice when they’re planning a CX transformation. For example, one payments provider was considering completely modifying its technology to reduce the processing time for resolving customer disputes. After collecting customer feedback, the company discovered that the major pain point was the lack of status updates—not processing time. By understanding what bothered customers, the company solved the problem more easily and effectively, with a higher likelihood of improving CX. Sending regular status updates by email or text is simpler and less expensive than overhauling technology.
Here are seven strategies to enhance CX:
1. Improve the digital experience.
Customers depend on your bank to deliver the information and communications they need, when they need them, wherever they are. To do that, you need efficient digital solutions such as:
- User-friendly website with self-service capabilities
- Interactive teller machines that offer expanded services such as real-time video conferencing and chat support
- Interactive voice response (IVR) system that helps customers resolve their issues without speaking with an agent
2. Help customers migrate to digital channels.
According to McKinsey research, customers who regularly use a bank’s mobile app or website (or both) have the highest average satisfaction compared to customers who use other interaction channels or infrequently use the digital channels. But offering fabulous digital tools doesn’t mean that customers will automatically use them. To encourage digital adoption:
- Streamline enrollment . Make it simple to set up an online account and mobile app.
- Educate customers about new digital offerings . “How-to” videos on the website—and printed instructions in paper statements—increase awareness and provide support for customers who are unfamiliar or uncomfortable with mobile apps and remote services.
- Redirect customers to digital channels . Use in-branch and call center or IVR intercepts to direct customers to digital solutions (e.g., ITM or website). Encourage customers to go digital through messages/reminders in statements and emails.
- Motivate customers and employees . Consider charging a fee for using non-digital channels or offering a discount for going paperless. Reward employees who redirect customers to digital channels.
3. Adopt an omnichannel approach.
Customers want to be able to get information and connect with your bank through their preferred channels, such as web, email, voice, live chat, SMS and/or mobile app. They may gather information about loan products and rates via your website, discuss their options with a banker via phone and then complete the transaction by phone, email or in-person. Then they may use a mobile app to check their loan application status or account balance and chat with support agents, if necessary. Bank customers expect consistent, secure experiences when accessing their financial information and seeking support, whatever channel they’re using—even if they are using more than one channel at a time. To provide this seamless omnichannel banking experience in your retail banking strategy, communication channels must work together. Maintaining the context of all customer interactions requires having real-time omnichannel customer data that is ingested across disparate systems and departments (e.g., billing, marketing, contact center).
4. Glean insights into your customers at the individual level.
Customers expect their banks to understand their specific needs and preferences and offer tailored products and services to meet those needs. According to Forrester’s 2022 U.S. Banking Customer Experience Index, the second-most important CX factor is “Offers the banking products/services that I need.” The number one CX factor is “Resolves problems/issues quickly.” According to a Bain & Company report, there’s a 123-point difference in Net Promoter Score between respondents who strongly agree that their bank interacts with them based on knowing who they are and those who strongly disagree. According to Deloitte , “ customers want interactions with their bank to be as sophisticated, immediate, and personalized as their experiences with other industries. As a result, financial services customers are willing to share data as long as they receive offerings tailored to their needs. Yet, 94% of banks cannot deliver on this hyper-personalization potential.” You can hyper-personalize customer experiences by analyzing real-time customer data, allowing you to deliver tailored messages about products, services and prices that are context-specific, timely and relevant to customers’ individual needs. For example, you could identify recent high school graduates and offer them checking accounts or credit cards geared toward college students.
5. Provide human touch as well as digital interactions.
While most bank customers use digital channels to do at least some of their banking, consumers expect assistance from a live representative—especially when they’re dealing with complicated issues. According to Citizens’ Banking Experience Survey , human interaction, delivered in person or virtually, is the preferred way to get financial advice and execute more complex transactions. Accenture’s Financial Services Global Consumer Study found that most consumers only use their bank’s digital channels for quick functional tasks. Nearly 63% of survey respondents said most of their mobile banking logins are simply to check their account balance. Almost half (44%) of consumers aged 18-44 had trouble getting human support when they needed it.According to Forrester’s UK Banking CX Index Rankings 2023 , digital-only experiences are ranked highest for ease and experience, while hybrid experiences (digital plus human interaction) win on emotion. Emotion strongly impacts customer loyalty, so it’s important to consider how to include hybrid experiences in customer journeys.
Use technology to enhance human interactions:
- Provide automated self-service . Self-service solutions should quickly solve basic customer problems, reducing call volume and freeing up live agents to assist customers with more complicated issues. Natural language processing analyzes customer responses to interactive voice response (IVR) prompts, identifying intent and needs. The decisioning system determines the most appropriate response or action based on customer information (intent, account information and behavioral patterns) and business rules or logic.
- Use technology to assist call center agents, not replace them . Intent-based call routing directs callers to the correct agent, reducing call transfers and customer frustration. Proactive agent guidance (e.g., real-time call transcripts, additional customer information) helps agents quickly assist customers.
6. Use customer journey analytics to understand each customer’s journey.
Customer journey analytics tracks and measures every interaction with your brand, across every channel and device the customer uses. Journey analytics helps you understand customer needs, desires and expectations, allowing you to deliver personalized experiences that meet those needs. Journey analytics combines individual channel analytics (e.g., website, email, call center) with customer intent indicators (e.g., intent to purchase or cancel, observed product preferences, switched channels) to provide insight into why customers are doing what they’re doing. Customer journey orchestration platforms then use this information to send the right messages at the right time to guide customers toward the next best action.
7. Use customer journey management (CJM) to deliver right-time and real-time journeys at the individual level.
CJM detects real-time signals (based on customer behavior) and determines the best next action to take—and when to take it. Journey orchestration analyzes interactions and customer behaviors from other technologies (e.g., customer relationship management, billing) to determine the next best action in the contact center. For example, when a customer calls to report fraudulent credit card charges, the system uses intent-based call routing to direct the customer to the fraud department and provides relevant information (e.g., the transcript from a chatbot session or previous calls) to the agent. The agent has access to the unified customer profile, enabling faster problem resolution.
Improve Your Banking Customer Experience With CSG Xponent Ignite
CSG Xponent , our industry-leading customer journey management solution, combines digital communication, customer journey analytics and decisioning to analyze customer behavior and deliver the right messages at the right time to guide customers to the next best action to achieve their desired outcome.
Improve Your Banking Customer Experience
Not sure where to start? Our CX experts will help you build a business case (based on projected return on investment) and identify high-impact journeys to achieve quick wins. Pre-templated journeys for financial services make it easier to deploy a few of your targeted journeys.

Forrester’s 2024 European Banking CX Index: UK Banks Provide The Highest-Quality Customer Experience
According to Forrester’s 2024 European Banking Customer Experience Index (CX Index™) rankings, CX quality has dropped significantly throughout the region. Compared to other countries, the UK provides the highest-quality customer experiences, with half of the top 10-ranking banks in Europe from the UK.
Based on a survey of more than18,000 customers in France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Spain, Sweden, and the UK, Forrester’s European Banking CX Index benchmarks the CX quality of 60 banks to evaluate customers’ banking experiences.
Key findings from the research include the following:
- Challenger and mutual banks outperform traditional banks. Eight of this year’s top 10 banks in Europe are smaller retail banks, known as challengers, or cooperative financial institutions, known as mutuals. Compared to customers of traditional banks, customers of mutuals and challengers rate their experiences as more emotionally positive.
- Nationwide Building Society secures the top spot. The UK bank performs particularly well in providing products and services that customers need and processing transactions quickly — two of the most important CX drivers for European banking customers.
- Hybrid CX creates the best experiences. A combination of digital and physical channels evokes the easiest, most effective, and most emotionally positive experiences for European banking customers.
To access this research or arrange an interview with a Forrester analyst, please contact [email protected] .
- customer experience
- customer experience index (CX Index)
Use Journey Maps To Kick-Start A CX Transformation
This complimentary guide will show you how to leverage customer journey maps to spur investment and interest in cx, as well as boost performance., forrester’s 2024 singapore customer experience index: financial services brands lack competitive differentiation, forrester announces full conference agenda for b2b summit emea 2024, help us improve.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products and Services

CCNP Enterprise certification
Demonstrate your expertise in enterprise infrastructure, assurance, security, and more. Configure, troubleshoot, and manage the networks of the largest companies in the world with the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Enterprise certification.
Empower the world's biggest networks

CCNP Enterprise
Earning a CCNP Enterprise certification demonstrates your ability to scale and maintain enterprise networks to meet growing demands. Showcase your expertise in enterprise infrastructure, virtualization, assurance, security, and automation to influential employers.
Dual stack architecture
Understand Cisco's solutions for managing networks, including configuring the quality of service settings, and switching between hardware and software.
Virtualization
Demonstrate your understanding of virtualization software, virtual machines, and virtual switches. Showcase your ability to divide and manage data paths and create virtual networks.
Infrastructure
Set up and troubleshoot communication protocols. Set up wireless networks and configure features like network time protocol and Network Address Translation/Port Address Translation (NAT/PAT).
Network assurance
Be able to diagnose and fix network problems. Configure and verify various networking features for optimal performance.
How it works
No formal prerequisites.
Learners often have three to five years of experience implementing enterprise network solutions.
Common learner profiles
Professional-level certifications expand on the foundations of associate-level certifications. They cover more advanced topics and allow candidates to hone in on a specific focus area of their choice. Many professional-level certification candidates are looking to prove they’re the best of the best in a specialized field.

Getting started
To earn this certification, you'll need to pass two exams:
- A core exam
- One of seven CCNP Enterprise concentration exams
You'll have access to many resources — from guided learning to self-study and a community forum — that are designed to help you pass your exams.

Unlock your career potential
Your CCNP Enterprise certification proves you can work with complex IT infrastructures - and that opens doors at some of the world’s largest companies.
Potential roles
Network automation engineer.
Use programming and automation tools to streamline network operations.
Systems engineer
Be the expert behind any project that optimizes systems for an organization.
Network support technician
Resolve connectivity issues, troubleshoot devices, and ensure networks are operating smoothly.
Alumni testimonials
Certifications give olivia credibility with employers.

"The knowledge that I’ve got from studying for those certifications gave me the confidence that I’ll always be able to get a job if I need to."
Olivia Wolf, Systems engineer
CCNA, CCNP Enterprise, DevNet Associate
Christoph's certifications earned him a salary boost

"Preparing for certification increased my knowledge and confidence, which ultimately translated to better work performance. As a result, I’ve received generous salary increases."
Christoph Neulinger, Senior network engineer
Getting certified has been a game-changer for AJ

"Cisco Certifications really helped to advance my career."
AJ Murray, Network engineer
Maintain your certification
Your certification is valid for three years. You can renew with Continuing Education credits or retake exams before they expire.
Professional-level Essentials Event: Enterprise
Watch our expert’s guidance and advice on planning your path towards your CCNP Enterprise certification success.
CCNP Enterprise summary
Get a quick primer on the CCNP Enterprise certification and exams.
The CCNP story
Learn why we created the CCNP certifications, and find out how you can use them to plan, support, and grow your career.
Enhance your learning journey
Stay up to date.
Get the latest news about Cisco certifications, plus tools and insights to help you get where you want to go.
Enterprise certifications community
Not sure where to begin? Head to the Cisco Enterprise certifications community to get advice and connect with experts.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A customer journey map is a chart that displays the stages your customers experience when interfacing with your business. ... and improve your product or service for a better user experience ...
The customer journey map template can also help you discover areas of improvement in your product, marketing, and support processes. Download a free, editable customer journey map template. Types of Customer Journey Maps and Examples. There are 4 types of customer journey maps, each with unique benefits. Pick the one that makes the most sense ...
Customer journey vs process flow. Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map - otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you're typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for uncovering insights into your customer experience, driving business goals, and building resilience in a changing market. In a 2022 report, Hanover Research found that 94% of businesses said their customer journey maps help them develop new products and services to match customer needs. Another 91% ...
Mapping the customer journey: narrow vs. wide focus. A customer journey map can have a very narrow focus and only look at a few, specific steps of the customer experience or buyer's journey (for example, a product-to-purchase flow on a website), or it can take into account all the touchpoints, online and offline, someone goes through before and after doing business with you.
This way, you double-check and confirm your findings for a more complete picture. A hands-on approach ensures your customer journey map reflects the real-world experience and equips you to take targeted actions to improve the overall customer journey. 7. Make changes and find solutions. So your map is complete.
Why make a customer journey map. Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for visualizing your customers' experience. It enables you to empathize with your customers and set them up for success. But for the uninitiated, customer journey mapping can seem intimidating, time-consuming, or even useless. We're here to tell you it's far from that.
1. Define your purpose. The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won't know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
ourney mapping process, start by making it.Of course there are many ways to build a jo. rney map that could work for your business. This guide covers the steps that we see customer experience (CX) innovator. using to drive measurable business impact. To see the best results you'll need to have the ability to collect and anal.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience.
See below for diagram annotations. Zone A: The lens provides constraints for the map by assigning (1) a persona ("who") and (2) the scenario to be examined ("what"). Zone B: The heart of the map is the visualized experience, usually aligned across (3) chunkable phases of the journey. The (4) actions, (5) thoughts, and (6) emotional ...
Map out every step of your customer's experience with a wide range of customer journey mapping tools. Better understanding your customers and their needs using Miro. 🗓️ Canvas '24 Save the date for Canvas '24 on Oct. 8 — our biggest user event of the year.
Step 1: The customer experiences a pain point with your product or service and determines reaching out to support is the necessary next step. Step 2: Your customer visits your website, looking for (and eventually finding) your customer support phone number. Step 3: Your customer calls support and gets in touch with a support rep.
So, with that in mind, let's look at two ways that your journey maps can evolve…. 1. Adding Voice of the Customer insights to journey maps. The integration of Voice of the Customer (VoC) data into journey maps marks the first significant evolution in the approach to understanding customer experiences.
What stands out about this journey map template is that it has a space for describing the specific stage of the customer, which you can also use to write associated actions. There's also a star rating row that can help sum up the customer experience at each stage. 6. Business Software Customer Journey Map Template.
Let's take a look at five steps your team can take to start journey mapping. 1. Find the sweet spot where your customers' goals and your own align. Before you start journey mapping, nail down your business goals. Any marketing and communication you deliver during the customer journey should be focused on helping your brand reach those goals.
HubSpot's customer journey map for identifying friction. Finally, there's HubSpot's simple customer journey map example, ideal for "a day in the life" mapping. The map was designed to identify friction points in the customer experience and solve problems customers encounter throughout their journey.
Customer Journey Map Definition. A customer journey map, also known as a customer experience map, is a visual representation that outlines the various steps and touchpoints a customer goes through when interacting with a company, product, or service. It chronologically represents each step of interaction the customer takes with your business.
A customer journey map is a visual storyline of every engagement a customer has with a service, brand, or product. The customer journey mapping process puts the organization directly in the consumer's mind to better understand the customer's processes, needs, and perceptions. ... A customer journey map - or customer experience map ...
Effective CX journey mapping is a team effort that requires collaboration across all departments. If you're a marketing or a communications leader looking to elevate your customer experience strategy, our comprehensive journey mapping approach is for you! Use the Gartner Buy/Own/Advocate framework to:
Step 4. Mapping the customer's emotional journey: Understand and document the emotional highs and lows that customers experience. Step 5. Identifying moments of truth: Pinpoint critical decision-making points or "moments of truth" in the customer journey.
Understanding your customer experience is the key to improving it…and to reaping the financial rewards that go hand in hand with increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. And the best way to find out what customers do, think, and feel while interacting with your company is to create a customer journey map.. These visual representations show how a customer uses your product or service, or ...
Mapping and analyzing the customer journey on a website is essential for enhancing the user experience. By examining each step of a customer's interaction with your brand—from entry to purchase or information acquisition—you can identify key touchpoints, understand customer emotions, and pinpoint barriers to conversion.
It's no secret that AI has disrupted the entire CX industry, empowering businesses to improve their customer experience offerings. And, with each passing day, it's become increasingly clear that AI and chatbots aren't going anywhere, with over 64% of CX leaders stating that they plan to increase their investments in AI and other related technology by the end of 2025.
Customer Communications & Operations - Communicate with customers on their channel of choice.; Network Solutions - Handle 5G data at scale.; Billing, Revenue Management & Monetization - Go from a telco leader to a digital leader.; Configure, Price, Quote - Spend less time hardcoding and more time closing.; Customer Experience - Drive customer loyalty with every interaction.
According to Forrester's 2024 European Banking Customer Experience Index (CX Index™) rankings, CX quality has dropped significantly throughout the region. Compared to other countries, the UK provides the highest-quality customer experiences, with half of the top 10-ranking banks in Europe from the UK. ... Use Journey Maps To Kick-Start A CX ...
Earning a CCNP Enterprise certification demonstrates your ability to scale and maintain enterprise networks to meet growing demands. Showcase your expertise in enterprise infrastructure, virtualization, assurance, security, and automation to influential employers.