Header Text
Footer Text
- The Landscapes of Palestine
- The Rulers of Palestine
- The Climate of Palestine
- Major Jewish Religious Festivals
- What is the New Testament?
- Who wrote the Gospels?
- English Translations of the New Testament
- John's mission foretold
- The birth of John
- John's message
- John begins baptising
- John criticises Herod
- Was John the promised Elijah?
- Jesus's birth announced
- Mary & Joseph go to Bethlehem
- The birth of Jesus
- Shepherds visit the infant
- Jewish religious rituals
- Wise men visit Jerusalem
- The holy family flees to Egypt
- The holy family returns to Nazareth
- Jesus grows up
- Jesus starts his ministry
- Jesus is tempted
- Jesus returns to Galilee
- Jesus goes back to Nazareth
- Jesus travels to Jerusalem
- Jesus passes through Samaria
- Jesus performs healing miracles
- Jesus teaches in Capernaum
- Jesus's teachings on a hillside
- Jesus upsets the Pharisees
- Jesus crosses the Sea of Galilee
- Jesus heals & teaches in Jerusalem
- Jesus teaches how to receive the Holy Spirit
- Jesus journeys among the Gentiles
- Jesus walks on the Sea of Galilee
- Jesus in Tyre and Sidon
- Who is Jesus?
- Jesus is changed on the slopes of Mount Hermon
- Jesus pays the Temple Tax
- Jesus claims God's personal name
- The Parable of the Good Samaritan
- The Parable of the Prodigal Son
- Lazarus, Come out!
- Jesus's entry into Jerusalem
- Jesus curses a fig tree
- Jesus heralds the end of the sacrificial system
- Jesus in Jerusalem during Passover week
- The Parable of the Sheep & the Goats
- Paying taxes to Caesar
- Jesus is betrayed
- The Last Supper
- Jesus crosses the Kidron Valley
- Jesus is arrested
- Jesus is taken to the Praetorium
- Jesus is tried by Pilate
- The death of Judas
- Jesus is executed by crucifixion
- The Pharisees mount a guard on the tomb
- Jesus rises from the tomb
- Jesus appears to his followers
- Jesus is taken into God's presence
- Jesus appears to Peter, James & Paul
- Who were Jesus's followers?
- The believers are filled with the Holy Spirit
- Peter & John heal a crippled man
- The believers share their possessions
- Opposition in Jerusalem
- Stephen is killed & the believers are scattered
- Philip's Journeys
- Peter's Journeys
- Peter hands over the leadership to James
- The Gentile Church at Antioch
- Saul's Early Life
- Saul persecutes the believers
- The beginning of Saul's ministry
- Saul & Barnabas in Antioch & Jerusalem
- Paul starts his 1st Missionary Journey
- Paul, Barnabas & Mark in Cyprus
- Paul, Barnabas & Mark sail to Pamphylia
- Paul & Barnabas travel inland
- Paul & Barnabas in Iconium
- Paul & Barnabas in Lystra
- Paul & Barnabas return to Perga
- Paul & Barnabas return to Antioch in Syria
- Paul & Barnabas attend the Council of Jerusalem
- Paul & Barnabas take the decision to Antioch
- Paul starts his 2nd Missionary Journey
- Paul travels to Troas
- Paul sails across to Europe
- Paul arrives in Philippi
- Paul travels to Amphipolis & Apollonia
- Paul in Thessalonica
- Paul in Berea
- Paul in Athens
- Paul in Corinth
- Paul returns to Jerusalem
- Paul starts his 3rd Missionary Journey
- The Ephesians are filled with the Holy Spirit
- The silversmiths riot in Ephesus
- Paul travels to Corinth
- Paul returns to Macedonia
- Eutychus falls from a window in Troas
- Paul leaves for Assos
- Paul sails to Miletus
- Paul visits Cos and Rhodes
- Paul visits Philip in Caesarea
- Paul meets violent opposition in Jerusalem
- Paul addresses the crowds
- Paul in Caesarea
- Paul appeals to Emperor Nero
- Paul sets sail for Rome
- Paul is shipwrecked
- Paul in Malta
- Paul heads for Rome
- An Introduction to Paul's Letters
- Paul's Letter to Galatia
- Paul explains his personal background
- Alive in Christ
- Set free from Slavery
- The Fruit of the Spirit
- Paul's 1st Letter to Thessalonica
- Paul hopes to visit Thessalonica
- The Day of the Lord
- How Christians should behave
- Paul's 2nd Letter to Thessalonica
- The coming Day of the Lord
- Saved by the power of the Holy Spirit
- Paul's 1st Letter to Corinth
- The Holy Spirit helps us understand
- Temples of the Holy Spirit
- Advice on Marriage & Relationships
- Running the Race of Life
- The Lord's Supper
- Spiritual Gifts
- Worship in the early church
- The risen Lord Jesus appears to his followers
- Paul's 2nd Letter to Corinth
- Paul explains his revised plans
- Christ's Victory Parade & the New Covenant
- How God changes lives
- Paul's plans for the future
- Paul defends himself against criticism
- Paul's weaknesses
- Paul's Letter to Rome
- How to be put right with God
- God's covenant promise fulfilled
- New life in the power of the Holy Spirit
- Persecution by the Jews
- Paul's mission
- Paul's Letter to Ephesus
- God's secret plan
- The new life
- The armour of God
- Paul's Letter to Colossae
- Jesus is exactly like God
- Saved by Christ's death
- Practical advice for believers
- Paul's Letter to Philemon at Colossae
- Paul's Letter to Philippi
- To live is Christ
- Warnings about the Jewish Law
- Introduction to Paul's Pastoral Letters
- Paul's 4th Missionary Journey
- Paul's 1st Letter to Timothy in Ephesus
- Worship among the believers
- Holding onto the truth
- Paul's Letter to Titus in Crete
- Appointing Church Leaders
- Paul's 2nd Letter to Timothy at Ephesus
- The 'last days'
- Paul's Final Sacrifice
- The Letter to the Jewish believers
- God speaks through the prophets & Jesus
- Jesus is greater than Moses
- Jesus speaks to God for believers
- Jesus - a priest like Melchizedek
- The New Covenant agreement
- God does not want animal sacrifices
- Having faith
- Looking forwards, not backwards
- The General Letters: James, Jude, Peter & John
- The Letter of James to the Jewish believers
- Faith without actions is worthless
- The power of words
- The Letter of Jude to the Jewish believers
- Signs of 'the last days'
- The 1st Letter of Peter to the Jewish believers
- The living hope
- Living stones
- Baptism & the flood
- The 2nd Letter of Peter to the Jewish believers
- Peter speaks out against immorality
- The 'Last Days' & The 'Day of the Lord'
- Introduction to John & his 3 Letters
- The 1st Letter of John
- The 'logos' of God
- The 'new' commandment
- The last days
- Filled with the Holy Spirit
- Love one another
- God's love drives away fear
- The 2nd Letter of John
- The 3rd Letter of John
- Introduction to the Revelation of John
- John's Letter to the 7 Churches of Asia Minor
- The messages to the believers on the coastal plain
- The messages to the believers living inland
- John's vision of God's heavenly rule
- The satan's rebellion against God
- The downfall of Rome & it's empire
- The resurrection of the dead
- The final judgement
- The new heaven & the new earth
- Introduction to the Romano-Jewish world
- Roman Emperors in the New Testament
- Jewish Religious Leaders
- New Testament Languages
- Jewish & Greek Names
- Jewish & Roman Currency
- Jewish Nationalists
- The Romano-Jewish War
- Constantine & the Helena Churches
- Ecumenical Church Councils
- Palestine - A Land Bridge
- Routes across Palestine
- The River Jordan
- Ancient Israel
- The Message of the Old Testament
- Who wrote the Old Testament?
- Dating events in the Old Testament
- The Biblical account of Creation
- Adam's Journey from the Garden of Eden
- Cain is sent on a journey to the east of Eden
- Enoch founds a city in Mesopotamia
- Noah journeys to Aratta on the flood
- The Colonisation of the Ancient World
- The Tower of Babylonia

Abram's Journey to Canaan
- Abram settles in Canaan
- Abram travels north to rescue Lot
- The birth of Ishmael
- Sodom and Gomorrah are destroyed
- Abraham journeys south and Isaac is born
- Abraham's sacrifice on Mount Moriah
- Abraham's wife dies at Hebron
- Abraham seeks a wife for Isaac
- Abraham dies at Hebron
- Isaac moves to Beersheba
- Jacob cheats Esau and flees to Mesopotamia
- Jacob returns to Canaan and meets Esau
- God blesses Jacob at Bethel
- Joseph is sold into slavery in Egypt
- Joseph becomes Vizier of Egypt
- Jacob's family joins Joseph in Egypt
- The Israelites in Egypt
- Prince Moses escapes to Midian
- Moses is called by God at Mt Sinai
- Egypt suffers ten plagues
- The Israelites flee from Egypt
- The Israelites cross the Sea of Reeds
- Moses receives the Ten Commandments
- Moses constructs the Ark of the Covenant
- The Israelites rebel against God
- The Israelites are counted
- Hardships encountered in the desert
- Moses sends spies into Canaan
- Korah leads a rebellion against Moses
- The Israelites remain at Kadesh Barnea
- The Israelites attempt to enter Canaan
- The Israelites journey north to Moab
- The Israelites defeat King Sihon and King Og
- Balaam blesses the Israelites
- The Israelites defeat the kings of Midian
- The boundaries of Canaan are agreed
- More laws and religious practices
- Moses dies at Mount Nebo
- The Israelites cross the River Jordan
- The Israelites conquer Jericho and Ai
- Joshua builds an altar at Mt Ebal
- Joshua is deceived by the Hivites
- Joshua conquers the Southern Cities
- Joshua embarks on the Northern Campaign
- Canaan is divided among the twelve tribes
- Six Cities of Refuge are set up
- Joshua says farewell
- The Israelites fight the remaining Canaanites
- God appoints inspirational leaders
- Israel under the 'judges': Othniel and Ehud
- Deborah and Barak defeat Sisera
- Gideon defeats the Midianites
- Abimelech becomes king
- Jephthah defeats the Ammonites
- Samson challenges the Philistines
- The conquest of Laish
- Gibeah is destroyed & the Benjamites punished
- Job is faced with adversity
- Ruth's journey to Bethlehem
- Samuel is taken to Shiloh
- The Ark of the Covenant is captured at Aphek
- The Ark is taken to Ashdod
- The Ark is moved to Ekron
- The Ark is returned to the Israelites
- Samuel administers justice from Ramah
- Saul's Journey to Kingship
- Jonathan demolishes the Philistine pillar at Geba
- Samuel condemns Saul at Gilgal
- David defeats Goliath of Gath
- Saul becomes jealous of David
- Samuel dies and is buried at Ramah
- David marries Abigail
- Saul is killed by the Philistines at Mt Gilboa
- David becomes King of Judah and Israel
- David captures Jerusalem
- The Ark of the Covenant is brought to Jerusalem
- David's victories over Israel's neighbours
- David's affair with Bathsheba
- Absalom's flight & his rebellion against David
- Further events during David's reign
- Solomon succeeds his father David
- Solomon's alliance with Egypt
- Solomon builds the Temple in Jerusalem
- Solomon builds a palace and furnishes the Temple
- The Ark of the Covenant is installed in the Temple
- Solomon rebuilds the cities of Israel
- Solomon's overseas trading expeditions
- The Queen of Sheba travels to Jerusalem
- Solomon builds a network of chariot cities
- Solomon turns away from God
- Solomon dies and the kingdom is divided
- Jeroboam builds temples to worship Baal
- Israel and Judah fight each other
- Israel descends into civil war
- Jezebel kills the prophets & Elijah escapes
- Elijah challenges the prophets of Baal
- Elijah organises the opposition to King Ahab
- King Ahab seizes Naboth's vineyard
- Elijah is taken up to heaven
- Elisha performs miracles and healings
- Elisha displays spiritual gifts
- Jehu races to Jezreel to depose King Joram
- King Joash repairs the Temple in Jerusalem
- Pharaoh Shoshenk I rescues Israel
- Jeroboam II restores the boundaries of Israel
- Tiglath-Pileser of Assyria invades Israel
- Israel falls & the exiles are led to Assyria
- Assyrians settle in Samaria
- King Hezekiah of Judah rebels against Assyria
- Sennacherib attacks and destroys Lachish
- Isaiah prophesies the destruction of Judah
- King Josiah ushers in religious reforms
- Assyria is conquered by the Babylonians
- King Nebuchadnezzar of Babylon invades Judah
- Jerusalem falls and the exile in Babylon begins
- Biblical sources relating to Judah in exile
- The middle years of exile (586-539BC)
- Daniel interprets dreams and riddles
- Daniel's vision of the 'Son of Man'
- Daniel's vision of the 'end times'
- The later years of exile & the return to Judah
- The completion of the Second Temple in Jerusalem
- A third group of exiles returns with Ezra
- A fourth group of exiles returns with Nehemiah
- Nehemiah becomes Governor of Judah
- The people renew their covenant with God
- Jerusalem's new walls are dedicated
- Esther becomes Queen of Persia
- Mordecai uncovers a plot to kill the king
- The origin of the Jewish festival of Purim
- What are the Psalms?
- Some psalms of King David
- Songs of Praise and Despair
- Later psalms ... and the earliest
- Some Memorable Sayings
- The wisdom of Solomon's words
- The Ways of the LORD
- Quarrelling, drinking & gossiping
- The Philosopher
- More wise words from the Philosopher
- More from the Lovers
- Love is as strong as death
- The Mourner
- The LORD's love and mercy continue
- Introduction to the Old Testament Prophets
- Introduction to the Book of Amos
- Amos denounces social injustice in Israel
- Introduction to Hosea's prophesy
- Hosea laments the unfaithfulness of Israel
- The Lord promises to punish Israel
- Introduction to Micah's prophesy
- Micah decries social injustice in Israel and Judah
- Introduction to the Book of Isaiah
- Prophecies written before the fall of Jerusalem
- Isaiah predicts a future golden age
- Isaiah reassures King Ahaz of God's support
- Troubled times and a glorious future kingdom
- Isaiah foresees the return of the exiles
- Isaiah warns of six catastrophes
- The final years before the fall of Judah
- Words of comfort after the fall of Jerusalem
- The LORD will help Israel
- God chooses Cyrus to save his people
- The suffering servant of the LORD
- Encouragement for those in exile
- Those returning are encouraged to follow the LORD
- The LORD's blessing will rest on Jerusalem
- Introduction to the Book of Jonah
- Jonah is thrown overboard to appease the gods
- Jonah arrives at Nineveh
- Introduction to the Book of Nahum
- Nahum predicts the fall of Nineveh
- Introduction to the Book of Jeremiah
- Jeremiah says idolatry will bring Judah's fall
- Jeremiah prophesies the destruction of Jerusalem
- Jeremiah calls for repentance
- Plots are hatched against Jeremiah
- Jeremiah is beaten and arrested
- Jeremiah is charged with treason
- Words of hope and consolation
- Miscellaneous flashbacks to earlier times
- Jeremiah attempts to leave Jerusalem
- Jerusalem falls to the Babylonians
- Gedeliah is murdered & Jeremiah goes to Egypt
- Jeremiah sees disaster in Egypt
- Messages to the surrounding nations
- Introduction to the Book of Zephaniah
- Zephaniah warns of the punishment of Judah
- Introduction to the Book of Habakkuk
- Habakkuk asks why the cruel Babylonians succeed
- Introduction to the Book of Ezekiel
- Ezekiel is called to be a prophet
- Ezekiel's vision of idolatry in the Temple
- Ezekiel speaks through prophesies and parables
- Ezekiel's message of impending doom
- Further prophecies & the fall of Jerusalem
- Hope for the future - New life for Israel
- The defeat of Gog and Magog
- Ezekiel's vision of the New Jerusalem
- Ezekiel sees the glory of the LORD
- The restored land of Israel
- Introduction to the prophecy of Obadiah
- Obadiah prophesies the resurgence of Israel
- Introduction to the Book of Haggai
- Haggai urges the exiles to re-build the Temple
- Introduction to the Book of Zechariah
- Zechariah has visions of horses & horns
- The vision of the measuring line
- Further visions about Jerusalem
- The LORD promises to restore Jerusalem
- Prophesies about the coming of the Messiah
- Prophesies about the Last Days
- An Introduction to the Book of Malachi
- Malachi announces the Day of the LORD
- God promises to send Elijah
- Introduction to the Book of Joel
- Joel foresees the Day of the LORD
- The Names of the God of Israel
- Foreign gods
- Pharaohs of the Old Testament
- The Old Testament & the Jewish Tanakh
- Sources of the History of Israel and Judah
- The Dead Sea Scrolls
- Between the Old and the New Testaments
- The Old Covenant & The New Covenant
- Who is my neighbour?
- Seeking revenge or Offering forgiveness?
- The Commandments - Impossible to keep?
- Was Jesus the Jewish Messiah?
- Was Jesus an outspoken rabbi or was he God?
- How to get right with God: Sacrifice or Faith?
- How to get right with God: By water or the Spirit?
- The power of the Holy Spirit - for everyone?
- A new nation? Or eternal life in God's kingdom?
- 1. From Cain & Abel to the Judges
- 2. From the Kingdom of Israel to the Exile
- 3. From the Exile to the Birth of Jesus
- 4. From the Birth to the Death of Jesus
- 5. From Acts of the Apostles to John's Revelation
- Find People
- Find Places
- Find Feature Articles
- Find Maps & Diagrams
- Find Photos
- What people are saying
- Privacy Statement
- 1 Jan. John 2:1-11
- 2 Jan. Luke 4:14-30
- 3 Jan. Luke 4:31-37
- 4 Jan. John 3:1-7
- 5 Jan. John 3:9-19
- 6 Jan. John 4:1-9
- 7 Jan. John 4:7-13
- 8 Jan. John 4:15-26
- 9 Jan. Mark 1:14-15
- 10 Jan. John 4:43-53
- 11 Jan. Luke 7:11-17
- 12 Jan. Mark 1:16-20
- 13 Jan. Mark 1:21-27
- 14 Jan. Mark 1:29-34
- 15 Jan. Mark 1:35-42
- 16 Jan. Matthew 4:25 - 5:10
- 17 Jan. Matthew 5:13
- 18 Jan. Matthew 5:14-16
- 19 Jan. Matthew 5:38-48
- 20 Jan. Matthew 6:5-13
- 21 Jan. Matthew 6:19-24
- 22 Jan. Matthew 7:1-5
- 23 Jan. Matthew 7:7-12
- 24 Jan. Matthew 7:13-14
- 25 Jan. Matthew 7:24-29
- 26 Jan. Mark 2:1-6
- 27 Jan. Mark 2:13-17
- 28 Jan. Mark 2:21-22
- 29 Jan. Mark 2:23-27
- 30 Jan. Mark 3:7-12
- 31 Jan. Mark 3:13-19
- 1 Feb. Mark 3:20-30
- 2 Feb. Mark 4:1-8
- 3 Feb. Mark 4:30-34
- 4 Feb. Mark 4:35-41
- 5 Feb. Mark 5:1-15
- 6 Feb. Mark 5:21-43
- 7 Feb. Mark 6:1-6
- 8 Feb. Mark 6:6-13
- 9 Feb. Mark 6:14-16
- 10 Feb. John 5:1-18
- 11 Feb. Luke 11:1-4
- 12 Feb. Luke 11:5-13
- 13 Feb. Luke 12:13-21
- 14 Feb. Mark 6:31-44
- 15 Feb. Mark 6:45-52
- 16 Feb. Mark 7:1-13
- 17 Feb. Mark 7:24-30
- 18 Feb. Mark 7:31-36
- 19 Feb. Mark 8:11-21
- 20 Feb. Mark 8:22-29
- 21 Feb. Mark 8:31-33
- 22 Feb. Mark 8:34-9:1
- 23 Feb. Mark 9:2-9
- 24 Feb. Mark 9:11-13
- 25 Feb. Mark 9:14-27
- 26 Feb. Mark 9:33-37
- 27 Feb. Matthew 17:24-27
- 28 Feb. Luke 17:11-19
- 1 Mar. John 7:14-24
- 2 Mar. John 7:37-44
- 3 Mar. John 7:44-52
- 4 Mar. John 8:12-20
- 5 Mar. John 8:21-59
- 6 Mar. John 9:1-34
- 7 Mar. Mark 9:42-43
- 8 Mar. Luke 10:25-37
- 9 Mar. Luke 15:11-24
- 10 Mar. Luke 15:25-32
- 11 Mar. Luke 17:20-21
- 12 Mar. John 10:1-10
- 13 Mar. John 10:11-18
- 14 Mar. John 10:22-33
- 15 Mar. John 10:40-11:11
- 16 Mar. John 11:17-44
- 17 Mar. John 11:45-54
- 18 Mar. Luke 19:1-10
- 19 Mar. Mark 11:1-7
- 20 Mar. Luke 19:28,35-40
- 21 Mar. Luke 19:41-44
- 22 Mar. John 12:12-19
- 23 Mar. Mark 11:12-14,20-24
- 24 Mar. Mark 11:15-19
- 25 Mar. Mark 11:27-33
- 26 Mar. Matthew 23:1-28
- 27 Mar. Matthew 25:31-46
- 28 Mar. Mark 12:1-12
- 29 Mar. Mark 12:13-17
- 30 Mar. Mark 12:18-27
- 31 Mar. Mark 12:28-34
- 1 Apr. Mark 12:41-44
- 2 Apr. Mark 14:1-9
- 3 Apr. Mark 14:12-16
- 4 Apr. John 13:1-15
- 5 Apr. John 13:21-30
- 6 Apr. John 14:1-11
- 7 Apr. John 14:15-26
- 8 Apr. John 15:1-11
- 9 Apr. Mark 14:22-25
- 10 Apr. Mark 14:26-31
- 11 Apr. Mark 14:32-42
- 12 Apr. Mark 14:43-52
- 13 Apr. John 18:12-14,19-24
- 14 Apr. Mark 14:53-59
- 15 Apr. Mark 14:60-65
- 16 Apr. Mark 14:66-72
- 17 Apr. Luke 23:1-11
- 18 Apr. John 18:28-40
- 19 Apr. Matthew 27:27-40
- 20 Apr. Matthew 27:62-66
- 21 Apr. Matthew 28:1-10
- 22 Apr. Luke 24:35-43
- 23 Apr. John 20:24-29
- 24 Apr. John 21:1-13
- 25 Apr. Matthew 28:16-20
- 26 Apr. Luke 24:45-53
- 27 Apr. 1 Corinthians 15:1-9
- 28 Apr. John 21:20-25
- 29 Apr. Acts 1:1-5
- 30 Apr. Acts 1:15-26
- 1 May. Acts 2:1-4
- 2 May. Acts 2:5-13
- 3 May. Acts 2:14-42
- 4 May. Acts 2:43-47
- 5 May. Acts 3:1-10
- 6 May. Acts 3:11-26
- 7 May. Acts 4:1-31
- 8 May. Acts 4:32-5:11
- 9 May. Acts 5:12-16
- 10 May. Acts 5:17-42
- 11 May. Acts 6:1-7
- 12 May. Acts 6:8-15
- 13 May. Acts 7:1-60
- 14 May. Acts 8:1,11:19-21
- 15 May. Acts 8:5-8
- 16 May. Acts 8:9-13
- 17 May. Acts 8:14-25
- 18 May. Acts 8:26-40
- 19 May. Acts 2:1-2,3:1-2,5:1-3,8:14-17
- 20 May. Acts 9:32-43
- 21 May. Acts 10:1-23
- 22 May. Acts 10:23-48
- 23 May. Acts 11:1-18
- 24 May. Acts 12:1-19
- 25 May. Acts 7:58-8:3,9:1-9
- 26 May. Acts 9:10-19
- 27 May. Galatians 1:11-2:2
- 28 May. Acts 11:19-26
- 29 May. Acts 11:27-13:3
- 30 May. Acts 13:1-5
- 31 May. Acts 13:4-12
- 1 June Acts 13:13
- 2 June. Acts 13:14-52
- 3 June. Acts 14:1-7
- 4 June. Acts 14:8-20
- 5 June. Acts 14:21-28
- 6 June. Acts 15:1-20
- 7 June. Acts 15:22-35
- 8 June. Acts 15:36-16:5
- 9 June. Acts 16:6-8
- 10 June. Acts 16:9-10
- 11 June. Acts 16:13-15
- 12 June. Acts 16:16-24
- 13 June. Acts 16:25-34
- 14 June. Acts 16:35-40
- 15 June. Acts 17:1
- 16 June. Acts 17:1-9
- 17 June. Acts 17:10-15
- 18 June. Acts 17:16-33
- 19 June. Acts 18:1-11
- 20 June. Acts 18:12-17
- 21 June. Acts 18:18-23
- 22 June. Acts 18:24-28
- 23 June. Acts 19:1-7
- 24 June. Acts 19:8-10
- 25 June. Acts 19:11-20
- 26 June. Acts 19:23-20:1
- 27 June. Acts 20:1-3
- 28 June. Acts 20:3-6
- 29 June. Acts 20:7-12
- 30 June. Acts 20:13-38
- 1 July Acts 21:1-7
- 2 July Acts 21:7-15
- 3 July Acts 21:17-26
- 4 July Acts 21:27-40
- 5 July Acts 22:1-29
- 6 July Acts 22:30-23:11
- 7 July Acts 23:12-32
- 8 July Acts 24:1-26
- 9 July Acts 24:27-25:12
- 10 July Acts 25:13-27
- 11 July Acts 26:1-32
- 12 July Acts 27:1-6
- 13 July Acts 27:7-20
- 14 July Acts 27:21-44
- 15 July Acts 28:1-10
- 16 July Acts 28:11-31
- 17 July Colossians 4:2-17
- 18 July 2 Peter 1:1-2,3:1-16
- 19 July Galatians 1:1-24
- 20 July Galatians 2:1-10
- 21 July Galatians 3:1-14
- 22 July Galatians 3:19-29
- 23 July Galatians 4:1-31
- 24 July Galatians 5:16-25,6:1-18
- 25 July 1 Thessalonians 1:1-10
- 26 July 1 Thessalonians 2:1-16
- 27 July 1 Thessalonians 2:17-3:13
- 28 July 1 Thessalonians 4:1-12
- 29 July 1 Thessalonians 4:13-5:11
- 30 July 1 Thessalonians 5:12-28
- 31 July 2 Thessalonians 1:1-12
- 1 Aug. 2 Thessalonians 2:1-15
- 2 Aug. 2 Thessalonians 3:1-18
- 3 Aug. 1 Corinthians 1:1-9
- 4 Aug. 1 Corinthians 1:10-17
- 5 Aug. 1 Corinthians 1:18-31
- 6 Aug. 1 Corinthians 2:1-16
- 7 Aug. 1 Corinthians 3:1-23
- 8 Aug. 1 Corinthians 4:1-17
- 9 Aug. 1 Corinthians 6:1-11
- 10 Aug. 1 Corinthians 7:1-16
- 11 Aug. 1 Corinthians 9:1-27
- 12 Aug. 1 Corinthians 10:16-17,11:20-34
- 13 Aug. 1 Corinthians 12:1-11
- 14 Aug. 1 Corinthians 12:12-31
- 15 Aug. 1 Corinthians 13:1-13
- 16 Aug. 1 Corinthians 14:1-25
- 17 Aug. 1 Corinthians 14:26-40
- 18 Aug. 1 Corinthians 15:1-26
- 19 Aug. 1 Corinthians 15:35-55
- 20 Aug. 1 Corinthians 16:1-24
- 21 Aug. 2 Corinthians 1:1-11
- 22 Aug. 2 Corinthians 2:12-17
- 23 Aug. 2 Corinthians 3:5-18
- 24 Aug. 2 Corinthians 4:1-6
- 25 Aug. 2 Corinthians 4:7-18
- 26 Aug. 2 Corinthians 5:1-10
- 27 Aug. 2 Corinthians 5:14-21
- 28 Aug. 2 Corinthians 6:1-18,7:1
- 29 Aug. 2 Corinthians 8:1-12
- 30 Aug. 2 Corinthians 11:16-33
- 31 Aug. 2 Corinthians 12:1-10
- 1 Sept. 2 Corinthians 13:5-14
- 2 Sept. Romans 1:1-7
- 3 Sept. Romans 1:18-32
- 4 Sept. Romans 2:1-11
- 5 Sept. Romans 3:19-31
- 6 Sept. Romans 4:1-16
- 7 Sept. Romans 5:1-11
- 8 Sept. Romans 6:1-14
- 9 Sept. Romans 7:1-6
- 10 Sept. Romans 8:5-17
- 11 Sept. Romans 8:18-30
- 12 Sept. Romans 8:31-39
- 13 Sept. Romans 10:1-13
- 14 Sept. Romans 12:1-21
- 15 Sept. Romans 13:1-10
- 16 Sept. Romans 14:1-12
- 17 Sept. Romans 15:1-33
- 18 Sept. Romans 16:1-27
- 19 Sept. Ephesians 1:1-10
- 20 Sept. Ephesians 1:11-22
- 21 Sept. Ephesians 2:1-10
- 22 Sept. Ephesians 2:11-22
- 23 Sept. Ephesians 3:1-13
- 24 Sept. Ephesians 3:14-21
- 25 Sept. Ephesians 4:1-16
- 26 Sept. Ephesians 4:17-32
- 27 Sept. Ephesians 5:1-20
- 28 Sept. Ephesians 5:21-33
- 29 Sept. Ephesians 6:1-9
- 30 Sept. Ephesians 6:10-18
- 1 Oct. Ephesians 6:18-24
- 2 Oct. Colossians 1:1-14
- 3 Oct. Colossians 1:15-23
- 4 Oct. Colossians 2:1-15
- 5 Oct. Colossians 2:16-23
- 6 Oct. Colossians 3:1-17
- 7 Oct. Colossians 3:18-4:6
- 8 Oct. Colossians 4:7-18
- 9 Oct. Philemon 1:1-7
- 10 Oct. Philemon 1:7-25
- 11 Oct. Philippians 1:1-11
- 12 Oct. Philippians 1:12-26
- 13 Oct. Philippians 2:1-18
- 14 Oct. Philippians 3:1-21
- 15 Oct. Philippians 4:1-23
- 16 Oct. 1 Timothy 1:1-7
- 17 Oct. 1 Timothy 1:12-20
- 18 Oct. 1 Timothy 2:1-15
- 19 Oct. 1 Timothy 3:1-13
- 20 Oct. 1 Timothy 4:1-16
- 21 Oct. 1 Timothy 5:1-22
- 22 Oct. 1 Timothy 6:3-21
- 23 Oct. Titus 1:1-14
- 24 Oct. Titus 2:1-15
- 25 Oct. Titus 3:1-15
- 26 Oct. 2 Timothy 1:1-18
- 27 Oct. 2 Timothy 2:1-26
- 28 Oct. 2 Timothy 3:1-17
- 29 Oct. 2 Timothy 4:6-22
- 30 Oct. James 1:1-21
- 31 Oct. James 2:14-19,4:11-12
- 1 Nov. Jude 1:1-24
- 2 Nov. 1 Peter 1:1-11
- 3 Nov. 1 Peter 2:1-10
- 4 Nov. 2 Peter 1:1-19
- 5 Nov. 2 Peter 3:1-16
- 6 Nov. 1 John 1:5-9
- 7 Nov. 1 John 1:1-4
- 8 Nov. 1 John 2:7-17
- 9 Nov. 1 John 2:18-19
- 10 Nov. 1 John 2:20-29
- 11 Nov. 1 John 3:11-24
- 12 Nov. 1 John 4:7-20
- 13 Nov. 2 John 1:1-13
- 14 Nov. 3 John 1:1-15
- 15 Nov. Revelation 1:1-11
- 16 Nov. Revelation 2:1-7
- 17 Nov. Revelation 2:8-11
- 18 Nov. Revelation 2:12-17
- 19 Nov. Revelation 2:18-27
- 20 Nov. Revelation 3:1-6
- 21 Nov. Revelation 3:7-13
- 22 Nov. Revelation 3:14-22
- 23 Nov. Revelation 4:1-11
- 24 Nov. Revelation 5:1-14
- 25 Nov. Revelation 6:1-17
- 26 Nov. Revelation 7:1-17
- 27 Nov. Revelation 12:1-9
- 28 Nov. Revelation 17:1-18:19
- 29 Nov. Revelation 20:1-15
- 30 Nov. Revelation 21:1-27
- 1 Dec. Luke 1:5-20
- 2 Dec. Luke 1:26,39-56
- 3 Dec. Luke 1:57-80
- 4 Dec. Luke 3:1-16
- 5 Dec. Luke 3:15-20
- 6 Dec. Mark 1:1-8
- 7 Dec. Matt 3:13-17, John 1:28-34
- 8 Dec. Mark 6:14-29
- 9 Dec. Matthew 11:2-15
- 10 Dec. Luke 1:26-38
- 11 Dec. Luke 2:1-5
- 12 Dec. Luke 2:6-7
- 13 Dec. Matthew 1:1-17,22-23
- 14 Dec. Luke 2:8-14
- 15 Dec. Luke 2:15-20
- 16 Dec. Luke 2:21-24
- 17 Dec. Luke 2:25-35
- 18 Dec. Matthew 2:1-6
- 19 Dec. Matthew 2:7-9
- 20 Dec. Matthew 2:10-12
- 21 Dec. Matthew 2:13-14
- 22 Dec. Matthew 2:14-15
- 23 Dec. Matthew 2:16-18
- 24 Dec. Matthew 2:19-23
- 25 Dec. John 1:1-14
- 26 Dec. Luke 2:40-43
- 27 Dec. Luke 2:43-52
- 28 Dec. Hebrews 1:1-4
- 29 Dec. Hebrews 3:1-4:1
- 30 Dec. Hebrews 4:14-5:6
- 31 Dec. Hebrews 9:1-5,11-15
- 1 Jan. Genesis 1:1 - 2:3
- 2 Jan. Genesis 2:4-24
- 3 Jan. Genesis 2:8-17
- 4 Jan. Genesis 3:1-23
- 5 Jan. Genesis 4:1-16
- 6 Jan. Genesis 4:17-26
- 7 Jan. Genesis 6:5-22
- 8 Jan. Genesis 7:11-24
- 9 Jan. Genesis 8:1-17
- 10 Jan. Genesis 9:1-16
- 11 Jan. Genesis 10:11-12,32
- 12 Jan. Genesis 11:1-9
- 13 Jan. Genesis 11:27&37,12:1-7
- 14 Jan. Genesis 12:6,8-20
- 15 Jan. Genesis 13:1-18
- 16 Jan. Genesis 14:8-20
- 17 Jan. Genesis 15:1-11,17-21
- 18 Jan. Genesis 16:1-16
- 19 Jan. Genesis 17:1-16
- 20 Jan. Genesis 18:1-16
- 21 Jan. Genesis 19:1-26
- 22 Jan. Genesis 21:1-21
- 23 Jan. Genesis 22:1-18
- 24 Jan. Genesis 23:1-19
- 25 Jan. Genesis 24:1-61
- 26 Jan. Genesis 24:61-67
- 27 Jan. Genesis 25:1-11
- 28 Jan. Genesis 25:19-21,24-34
- 29 Jan. Genesis 26:1-9,12-15,23-25
- 30 Jan. Genesis 27:1-23,30-33,42-45
- 31 Jan. Genesis 28:10-22
- 1 Feb. Genesis 29:1-30
- 2 Feb. Genesis 29:31-35,30:1-12,17-24
- 3 Feb. Genesis 30:25-43
- 4 Feb. Genesis 31:1-21
- 5 Feb. Genesis 31:25-55
- 6 Feb. Genesis 32:1-8,13,22-30
- 7 Feb. Genesis 33:1-11
- 8 Feb. Genesis 33:12-20
- 9 Feb. Genesis 35:1-7
- 10 Feb. Genesis 35:9-15
- 11 Feb. Genesis 35:16-21,27-29
- 12 Feb. Genesis 37:1-11
- 13 Feb. Genesis 37:12-24
- 14 Feb. Genesis 37:25-34
- 15 Feb. Genesis 39:1-6
- 16 Feb. Genesis 39:6-22
- 17 Feb. Genesis 40:1-23
- 18 Feb. Genesis 41:1-14
- 19 Feb. Genesis 41:15-37
- 20 Feb. Genesis 41:39-57
- 21 Feb. Genesis 42:1-38
- 22 Feb. Genesis 43:1-33
- 23 Feb. Genesis 45:1-28
- 24 Feb. Genesis 46:1-7,28-30
- 25 Feb. Genesis 47:1-7,11-12,27-31
- 26 Feb. Genesis 50:1-26
- 27 Feb. Exodus 1:1-14
- 28 Feb. Exodus 1:15-22
- 1 Mar. Exodus 2:1-10
- 2 Mar. Exodus 2:11-15
- 3 Mar. Exodus 2:16-22
- 4 Mar. Exodus 3:1-10
- 5 Mar. Exodus 3:11-20
- 6 Mar. Exodus 4:1-17
- 7 Mar. Exodus 4:18-31
- 8 Mar. Exodus 5:1-21
- 9 Mar. Exodus 5:22-6:9
- 10 Mar. Exodus 7:14-21
- 11 Mar. Exodus 11:1-10
- 12 Mar. Exodus 12:1-17
- 13 Mar. Exodus 12:21-30
- 14 Mar. Exodus 12:29-40
- 15 Mar. Exodus 13:17-14:4
- 16 Mar. Exodus 14:5-31
- 17 Mar. Exodus 15:1-27
- 18 Mar. Exodus 16:1-18,31
- 19 Mar. Exodus 17:1-7
- 20 Mar. Exodus 17:8-16
- 21 Mar. Exodus 18:1-27
- 22 Mar. Exodus 19:1-11,14-19
- 23 Mar. Exodus 20:1-20
- 24 Mar. Exodus 21:1-23:17
- 25 Mar. Exodus 24:12-18
- 26 Mar. Exodus 25:1-26,33
- 27 Mar. Exodus 32:1-20
- 28 Mar. Exodus 32:21-35
- 29 Mar. Exodus 34:1-22,27-29
- 30 Mar. Exodus 40:1-21,33-36
- 31 Mar. Leviticus 1;1-14:4
- 1 Apr. Numbers 1:1-2:34
- 2 Apr. Numbers 10:11-11:35
- 3 Apr. Numbers 12:1-16
- 4 Apr. Numbers 13:1-33
- 5 Apr. Numbers 14:1-38
- 6 Apr. Numbers 14:41-45
- 7 Apr. Numbers 16:1-40
- 8 Apr. Numbers 16:41-17:11
- 9 Apr. Numbers 20:1-13
- 10 Apr. Numbers 20:14-21:4
- 11 Apr. Numbers 21:4-9
- 12 Apr. Numbers 21:10-20
- 13 Apr. Numbers 21:21-35
- 14 Apr. Numbers 22:1-24:25
- 15 Apr. Numbers 25:1-18
- 16 Apr. Numbers 26:1-65
- 17 Apr. Numbers 27:12-23
- 18 Apr. Numbers 31:1-16,25-31
- 19 Apr. Numbers 32:1-38
- 20 Apr. Numbers 34:1-18,35:1-12
- 21 Apr. Deuteronomy 8:1-11
- 22 Apr. Deuteronomy 34:1-12
- 23 Apr. Joshua 1:1-18
- 24 Apr. Joshua 2:1-24
- 25 Apr. Joshua 3:1-17
- 26 Apr. Joshua 4:1-24,5:1
- 27 Apr. Joshua 6:1-27
- 28 Apr. Joshua 7:1-26
- 29 Apr. Joshua 8:1-29
- 30 Apr. Joshua 8:30-35
- 1 May. Joshua 9:1-27
- 2 May. Joshua 10:1-28
- 3 May. Joshua 10:29-43
- 4 May. Joshua 11:1-14
- 5 May. Joshua 13:1-8,14:1-4,18:1
- 6 May. Joshua 20:1-9
- 7 May. Joshua 22:1-16,21,28,30-34
- 8 May. Joshua 23:1-16,24:14-16,22-27
- 9 May. Joshua 24:29-33
- 10 May. Judges 1:1-11,17-19
- 11 May. Judges 2:1-5,10-15
- 12 May. Judges 2:16-23
- 13 May. Judges 3:5-11
- 14 May. Judges 3:12-30
- 15 May. Judges 4:1-24,5:31
- 16 May. Judges 6:1-27
- 17 May. Judges 6:33-40
- 18 May. Judges 7:1-25
- 19 May. Judges 8:4-28
- 20 May. Judges 8:29-9:21
- 21 May. Judges 9:22-49
- 22 May. Judges 9:50-57
- 23 May. Judges 10:1-16
- 24 May. Judges 10:17-11:33
- 25 May. Judges 11:30-31,34-40
- 26 May. Judges 12:1-6
- 27 May. Judges 12:7-15,13:1
- 28 May. Judges 13:2-25
- 29 May. Judges 14:1-11
- 30 May. Judges 14:12-20
- 31 May. Judges 15:1-8
- 1 June Judges 15:9-20
- 2 June Judges 16:1-3
- 3 June Judges 16:4-15
- 4 June Judges 16:16-31
- 5 June Judges 17:1-13
- 6 June Judges 18:1-31
- 7 June Judges 19:1-30
- 8 June Judges 20:1-48
- 9 June Judges 21:1-23
- 10 June Job 1:1-22
- 11 June Job 2:1-13
- 12 June Job 3:11-13:8
- 13 June Job 38:1-42:17
- 14 June Ruth 1:1-22
- 15 June Ruth 2:1-23
- 16 June Ruth 3:1-18
- 17 June Ruth 4:1-17
- 18 June 1 Samuel 1:1-20
- 19 June 1 Samuel 1:21-2:2
- 20 June 1 Samuel 2:11-12,18-26
- 21 June 1 Samuel 3:1-21
- 22 June 1 Samuel 4:1-18
- 23 June 1 Samuel 5:1-12
- 24 June 1 Samuel 6:1-21,7:1
- 25 June 1 Samuel 7:2-17
- 26 June 1 Samuel 8:1-22
- 27 June 1 Samuel 9:1-27,10:1
- 28 June 1 Samuel 10:1-11
- 29 June 1 Samuel 10:13-25
- 30 June 1 Samuel 11:1-15
- 1 July 1 Samuel 12:1-25
- 2 July 1 Samuel 13:2-7
- 3 July 1 Samuel 13:8-15
- 4 July 1 Samuel 14:1-23
- 5 July 1 Samuel 14:24-46
- 6 July 1 Samuel 14:47-15:9
- 7 July 1 Samuel 15:10-31
- 8 July 1 Samuel 16:1-13
- 9 July 1 Samuel 16:14-23
- 10 July 1 Samuel 17:1-52
- 11 July 1 Samuel 17:57-58,18:1-16
- 12 July 1 Samuel 18:17-29
- 13 July 1 Samuel 19:1-18
- 14 July 1 Samuel 20:1-47
- 15 July 1 Samuel 21:1-9
- 16 July 1 Samuel 21:10-11,22:1-5
- 17 July 1 Samuel 22:6-19
- 18 July 1 Samuel 23:1-13
- 19 July 1 Samuel 24:1-22
- 20 July 1 Samuel 25:1-44
- 21 July 1 Samuel 26:1-25
- 22 July 1 Samuel 27:1-12
- 23 July 1 Samuel 28:1-20
- 24 July 1 Samuel 29:1-11
- 25 July 1 Samuel 30:1-31
- 26 July 1 Samuel 31:1-13
- 27 July 2 Samuel 1:1-16
- 28 July 2 Samuel 2:1-7
- 29 July 2 Samuel 2:8-17
- 30 July 2 Samuel 3:1,6-21
- 31 July 2 Samuel 3:22-32
- 1 Aug. 2 Samuel 4:1-12
- 2 Aug. 2 Samuel 5:1-12
- 3 Aug. 2 Samuel 5:17-25
- 4 Aug. 2 Samuel 6:1-23
- 5 Aug. 2 Samuel 7:1-17
- 6 Aug. 2 Samuel 8:1-14
- 7 Aug. 2 Samuel 9:1-13
- 8 Aug. 2 Samuel 10:1-14
- 9 Aug. 2 Samuel 11:1-17,26-27
- 10 Aug. 2 Samuel 12:1-18
- 11 Aug. 2 Samuel 12:24-31
- 12 Aug. 2 Samuel 13:1-39
- 13 Aug. 2 Samuel 14:21-33
- 14 Aug. 2 Samuel 15:1-12
- 15 Aug. 2 Samuel 15:13-37
- 16 Aug. 2 Samuel 16:1-22
- 17 Aug. 2 Samuel 17:1-29
- 18 Aug. 2 Samuel 18:1-33
- 19 Aug. 2 Samuel 19:1-18
- 20 Aug. 1 Kings 1:5-27
- 21 Aug. 1 Kings 1:28-53
- 22 Aug. 1 Kings 2:1-12
- 23 Aug. 1 Kings 2:13-46
- 24 Aug. 1 Kings 3:1-15
- 25 Aug. 1 Kings 3:16-28
- 26 Aug. 1 Kings 4:7,20-34
- 27 Aug. 1 Kings 5:1-18
- 28 Aug. 1 Kings 6:1-22,38
- 29 Aug. 1 Kings 7:1-12
- 30 Aug. 1 Kings 7:13-30,37-38,45-46
- 31 Aug. 1 Kings 8:1-11
- 1 Sept. 1 Kings 8:22-34,54-57,62-63
- 2 Sept. 1 Kings 9:1-9
- 3 Sept. 1 Kings 10:1-10,13
- 4 Sept. 1 Kings 11:1-13
- 5 Sept. 1 Kings 11:14-40
- 6 Sept. 1 Kings 11:42-12:20
- 7 Sept. 1 Kings 12:25-33
- 8 Sept. 1 Kings 14:1-20
- 9 Sept. 1 Kings 14:21-31
- 10 Sept. 1 Kings 15:1-16
- 11 Sept. 1 Kings 15:25-29,17-24
- 12 Sept. 1 Kings 16:1-22
- 13 Sept. 1 Kings 16:23-28
- 14 Sept. 1 Kings 16:29-33
- 15 Sept. 1 Kings 17:1-16
- 16 Sept. 1 Kings 17:17-24
- 17 Sept. 1 Kings 18:1-9,15-21
- 18 Sept. 1 Kings 18:22-40
- 19 Sept. 1 Kings 18:41-46
- 20 Sept. 1 Kings 19:1-18
- 21 Sept. 1 Kings 19:19-21
- 22 Sept. 1 Kings 20:1-22
- 23 Sept. 1 Kings 21:1-16
- 24 Sept. 1 Kings 21:17-29
- 25 Sept. 1 Kings 22:1-40
- 26 Sept. 2 Kings 1:1-18
- 27 Sept. 2 Kings 2:1-15
- 28 Sept. 2 Kings 3:1-27
- 29 Sept. 2 Kings 2:19-22,4:1-7
- 30 Sept. 2 Kings 4:8-37
- 1 Oct. 2 Kings 4:38-44
- 2 Oct. 2 Kings 5:1-15
- 3 Oct. 2 Kings 6:8-23
- 4 Oct. 2 Kings 8:7-15
- 5 Oct. 2 Kings 9:1-25
- 6 Oct. 2 Kings 9:30-37
- 7 Oct. 2 Kings 12:1-12
- 8 Oct. 2 Kings 13:1-9
- 9 Oct. 2 Kings 13:14-21
- 10 Oct. 2 Kings 14:23-29
- 11 Oct. 2 Kings 15:19-20,16:15-18
- 12 Oct. 2 Kings 17:1-18
- 13 Oct. 2 Kings 17:24-34
- 14 Oct. 2 Kings 18:1-8
- 15 Oct. 2 Kings 18:13-21,28-31,36
- 16 Oct. 2 Kings 19:1-10,19-20,32-36
- 17 Oct. 2 Kings 20:1-11
- 18 Oct. 2 Kings 20:12-21
- 19 Oct. 2 Kings 22:1-13
- 20 Oct. 2 Kings 23:1-4,8-11,21-25
- 21 Oct. 2 Kings 23:29-37
- 22 Oct. 2 Kings 24:1-7
- 23 Oct. 2 Kings 24:8-18
- 24 Oct. 2 Kings 25:1-21
- 25 Oct. Daniel 1:1-17
- 26 Oct. Daniel 3:9-15,19-20,24-30
- 27 Oct. Daniel 5:1-13,16-18,20-31
- 28 Oct. Daniel 6:1-11,16-17,19-23
- 29 Oct. Daniel 7:1-9,11-14,16-18
- 30 Oct. Daniel 11:1-9
- 31 Oct. Daniel 12:1-13
- 1 Nov. Ezra 1:1-11
- 2 Nov. Ezra 2:1-70
- 3 Nov. Ezra 3:1-13
- 4 Nov. Ezra 4:1-13,19-21
- 5 Nov. Ezra 5:1-9,6:1-4.13-22
- 6 Nov. Ezra 7:1-6,11-23,8:31-36
- 7 Nov. Nehemiah 1:1-4,2:1-10
- 8 Nov. Nehemiah 2:11-20
- 9 Nov. Nehemiah 4:1-23
- 10 Nov. Nehemiah 5:1-16,6:1-3,15-16
- 11 Nov. Nehemiah 8:1-12
- 12 Nov. Nehemiah 12:27-43
- 13 Nov. Esther 2:1-18
- 14 Nov. Esther 2:19-23
- 15 Nov. Esther 3:1-13
- 16 Nov. Esther 4:1-16
- 17 Nov. Esther 5:1-14
- 18 Nov. Esther 6:1-14
- 19 Nov. Esther 7:1-10
- 20 Nov. Esther 8:1-14
- 21 Nov. Esther 9:1-17,24-28
- 22 Nov. Amos 1:1-15,2:1-2
- 23 Nov. Amos 5:1-7,10-15
- 24 Nov. Hosea 1:1-11
- 25 Nov. Hosea 9:1-9
- 26 Nov. Micah 1:1-9
- 27 Nov. Micah 4:1-5,5:1-5
- 28 Nov. Isaiah 1:1-7,11-20
- 29 Nov. Isaiah 7:1-17,8:3-4
- 30 Nov. Isaiah 9:1-7
- 1 Dec. Isaiah 10:28-34,11:1-10
- 2 Dec. Isaiah 40:1-11
- 3 Dec. Isaiah 44:1-11
- 4 Dec. Isaiah 45:1-7,13-17
- 5 Dec. Isaiah 52:13-15,53:1-12
- 6 Dec. Isaiah 60:1-14
- 7 Dec. Nahum 2:1-13
- 8 Dec. Jeremiah 6:1-8,13-23
- 9 Dec. Jeremiah 7:1-11
- 10 Dec. Jeremiah 18:1-12
- 11 Dec. Jeremiah 19:1-13
- 12 Dec. Jeremiah 23:1-8
- 13 Dec. Jeremiah 26:1-15
- 14 Dec. Jeremiah 29:1-12
- 15 Dec. Zephaniah 1:1-13
- 16 Dec. Habakkuk 1:1-13
- 17 Dec. Ezekiel 1:1-17,22-28
- 18 Dec. Ezekiel 10:1-19,11:22-24
- 19 Dec. Ezekiel 17:1-10
- 20 Dec. Ezekiel 33:21-26,34:1-24
- 21 Dec. Ezekiel 37:1-14
- 22 Dec. Ezekiel 40:1-31
- 23 Dec. Ezekiel 43:1-12
- 24 Dec. Obadiah 1:1-11
- 25 Dec. Haggai 1:1-15
- 26 Dec. Zechariah 1:1-6
- 27 Dec. Zechariah 9:9-17
- 28 Dec. Zechariah 14:1-11
- 29 Dec. Malachi 3:1-5,4:1-6
- 30 Dec. Joel 2:1-11
- 31 Dec. Joel 2:25-32
- Bible Journey 2
- 22. The World of the Old Testament Journeys
- 23.The Journeys of Adam, Enoch, Noah & Abraham
- 24. The Journeys of Isaac, Jacob & Joseph
- 25. The Israelites journey from Egypt to Mt Sinai
- 26. The Journey continues from Sinai to Moab
- 27. The Israelites move into Canaan
- 28. The Israelites face continuing opposition
- 29. The Journeys of Ruth and Samuel
- 30. Israel becomes a kingdom under Saul and David
- 31. The Golden Age of Israel under King Solomon
- 32. The Divided Kingdom & Journey into Exile
- 33. Judah after the fall of Israel
- 34. Judah in exile in Babylonia
- 35. The Exiles return to Judah
- 36. Songs, Prayers & Memorable Sayings
- 37. The Philosopher, the Lover & the Mourner
- 38. Amos, Hosea & Micah criticize Israel
- 39. Isaiah predicts the fall of Israel & Judah
- 40. Isaiah offers comfort to those in exile
- 41. Jonah goes to Nineveh & Nahum condemns it
- 42. Jeremiah warns of the destruction of Jerusalem
- 43. Zephaniah & Habakkuk foretell Judah's fall
- 44. Ezekiel warns of the conquest of Jerusalem
- 45. Obadiah foretells the punishment of Edom
- 46. Haggai & Zechariah encourage re-building
- 47. Malachi & Joel await the Day of the LORD
- 48. The Jewish World of the Old Testament
- 49. Judaism and Christianity compared
Gen 11:10-26 The Book of Genesis lists many generations of Shem’s descendants including Terah and Abram (later called Abraham).
The story then recommences nearly a thousand years after the building of the Tower of Babylonia when Abram is born in the Amorite kingdom of Mesopotamia , in c.1900BC.
Gen 11:28 Terah and his family (including his sons Abram and Nahor, and his grandson Lot) live at Ur in Mesopotamia (see Map 38 ).
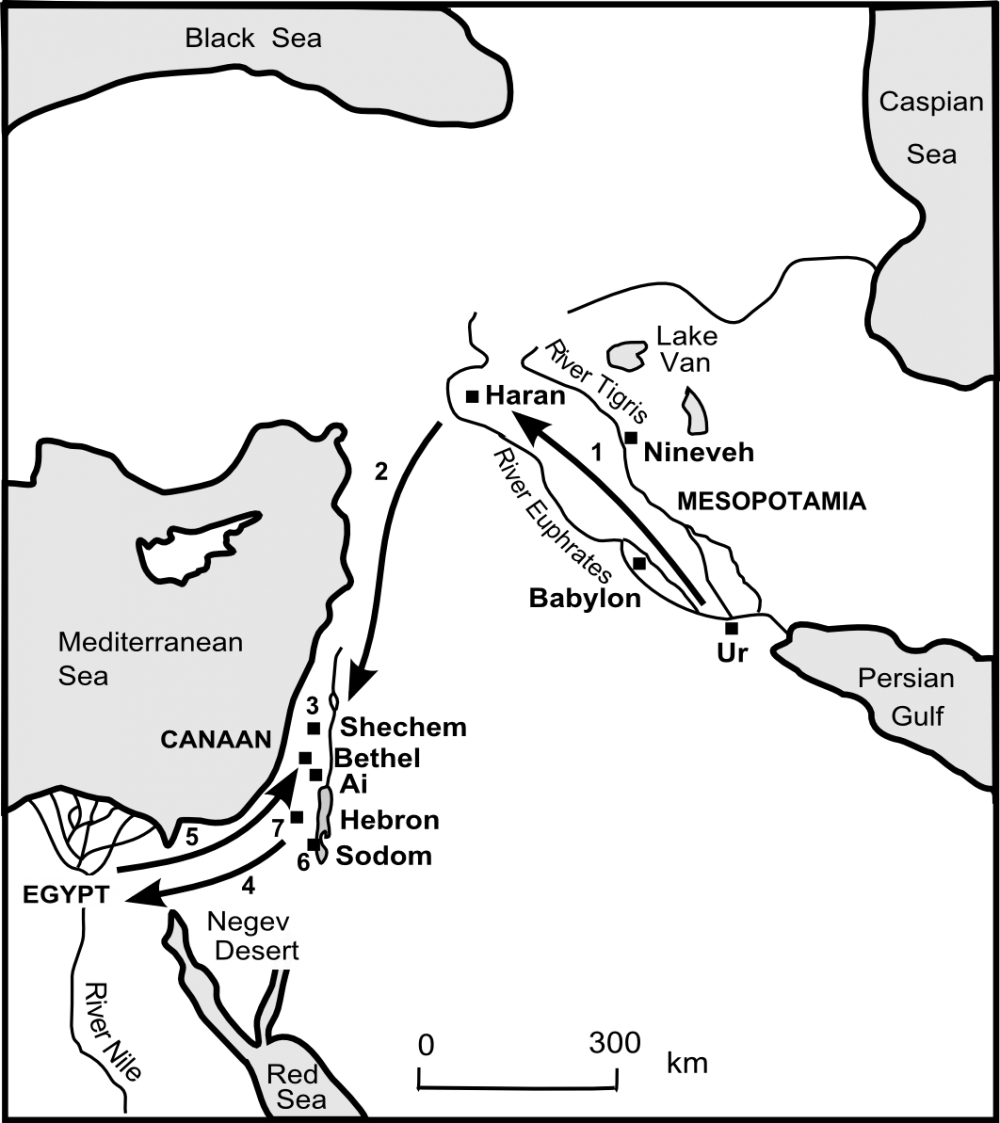
Map 38 Abram's Journey to Canaan
Ur developed during the reign of the Sumerian kings (c.3000 – 2300BC) and had been a major city for hundreds of years when Abram was born. A ‘ziggurat’ (a stepped temple platform) about 70 feet / 21 metres high, surmounted by a temple and shrine to the Akkadian moon god Sin, was built by King Ur-Nammu in c.2100BC, using a solid mud brick core covered with waterproof baked mud bricks.
Archaeologists in the 1920s discovered thousands of graves dating back to the first dynasty of the Sumerian kings, including several so-called ‘death-pits’ where royal harpists and members of the royal court had taken poison before being buried above the tomb of their dead monarch. One of these ‘Royal Tombs’, contained the queen’s exquisite jewellery as well as a harp, a lyre, gold bowls and silver jugs.
Modern-day travellers to the site of Ur in southern Mesopotamia (near Basra in modern-day southern Iraq ) can visit the archaeological remains of the Royal Tombs of the Sumerian Kings (dating from c.2600BC), excavated by Leonard Woolley in the 1920s, together with the partially reconstructed remains of the Ziggurat of Ur . Many items from the tombs are on display at the British Museum in London .
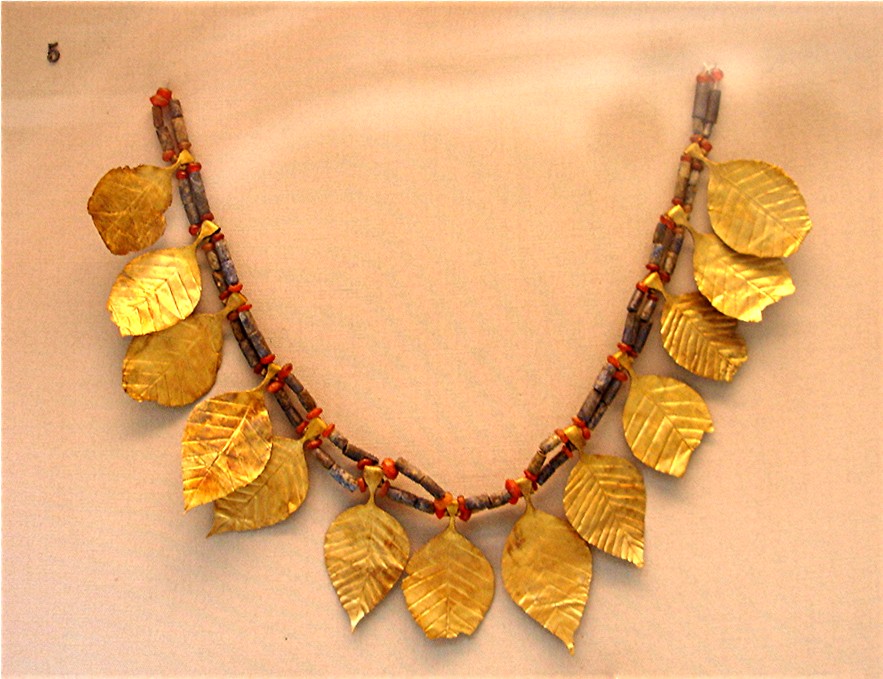

Queen Pu-abi's gold pendant from the Royal Tombs of Ur
Gen 11:31-32 Terah and his family decide to move from Ur and follow the River Euphrates upstream for about 600 miles / 950km to Haran (see 1 on Map 38 ). Haran is the name of Abram's brother (see Genesis 11:27) so Terah apparently re-named the place Haran in memory of his son, Lot's father, who had died before the family left Ur (Genesis 11:28).
Haran is one of the oldest cities on earth that is still inhabited today. Founded by settlers migrating west from Mesopotamia in the 18 th century BC, the city was at its peak during the Hittite Empire, based on Central Anatolia in the 12 th century BC. It was already centuries old when the Hittites fought Ramesses II of Egypt at the Battle of Kadesh in 939 BC.
Modern travellers to Harran ( Haran ), near AltinbaÅŸak in eastern Turkey , can sense the antiquity of the settlement when they encounter its decaying walls, the ruins of the ancient 11 th century citadel, and the remains of the Old Mosque. Haran is famous for its unique beehive-shaped mudbrick houses that originated in the 3 rd century BC and which have been rebuilt in the same style many times during the intervening centuries.
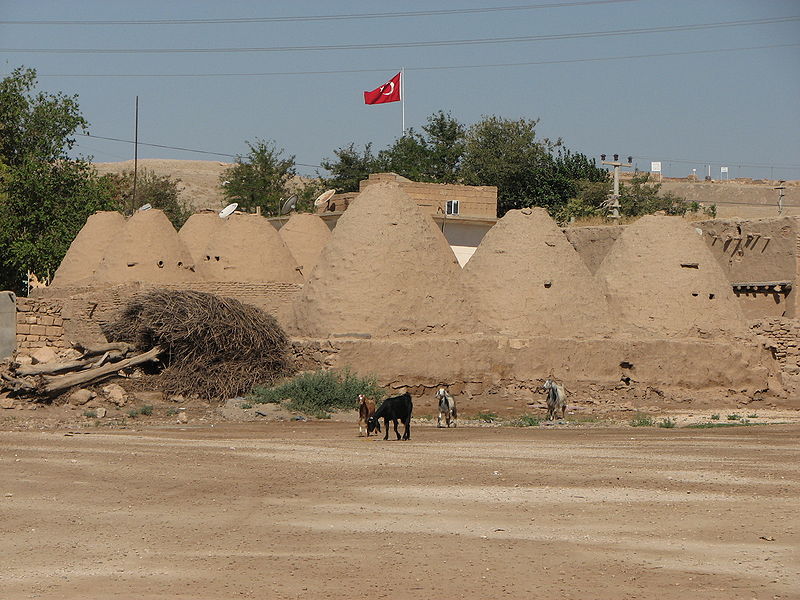

Traditional bee-hive shaped houses at Harran (Glumik)
Gen 12:1-3 God calls Terah’s son Abram to “Leave your country… and go to the land I will show you.” God establishes a covenant agreement with Abram to give his family the ‘promised land’ of Canaan (later called Palestine ). This solemn agreement – which is renewed on many occasions – becomes the recurring theme of the Old Testament (‘testament’ means ‘covenant’ or solemn agreement).
Gen 12:4-5 In c.1855BC, Abram and his nephew Lot set out for Canaan , about 400 miles / 640km away, with their tents and flocks (see 2 on Map 38 ).
Go to next page
The Exodus Route: Travel times, distances, rates of travel, days of the week
Buy “Exodus Route Restored” from Amazon by Steven Rudd
Buy Discounted copy: Email Steven Rudd to order: Order discounted copy direct from author by email
Overview of the Exodus and Conquest:
In 1446 BC, the 700 km trip from Goshen (Tell el-Dab’a) to Mt. Sinai took a total of took 47 days. After travelling day and night 500 km from Goshen, Israel made the 19 km crossing of the Red Sea at the Straits of Tiran on day 25 then took 22 days to travel 200 km from the Red Sea Crossing to Mt. Sinai. Travel was easy for the 2-3 million Hebrews because there was a 20 km wide, flat coastal plain that hugged the eastern shore of the Gulf of Suez from Goshen to the Strait of Tiran, which the author calls, “The Exodus Highway”. On day 9 after leaving Goshen, they arrived at Succoth, adjacent to the turquoise mines of Serabit el-Khadim and waited for the Hebrew mining slaves to join the main group. On day 15 they reach the Straits of Tiran and pass the Egyptian Migdol watchtower stationed above the final Red Sea crossing point and on day 16 they reached the dead-end at Etham. God orders them to backtrack to the final Red Sea crossing camp beside the Migdol where God used Israel to bait Pharaoh to attack. On day 17, as Israel leaves Etham, it would take 4 hours for a passenger pigeon (cf. Eccl 10:20) to fly 400 km from the Egyptian watchtower (Migdol) back to Egypt with the message that Israel was trapped and wandering aimlessly. (If a passenger pigeon was not used, Israel travelled day and night arriving on day 7, leaving plenty of time for a message to get back to Egypt by horseback in 7 days and pharaoh to return in 7 days, maintaining a Red Sea crossing on Day 25.) For 8 days Israel camped at the Red Sea crossing point (days 17-24) while Pharaoh's army pursued them with 600 choice horse-drawn chariots (Exodus 14:6-9). On day 18 Pharaoh's army easily traveled the 400 km from Goshen to the Red Sea crossing in 7 days (days 17-24), at a rate of 57 km/day with horse-drawn chariots and arrived on day 24. The Egyptians were stopped on the eastern shore of the Gulf of Suez by an angel, about 36 km short of Israel’s camp. After crossing the Red Sea at the Straits of Tiran via the natural underwater land bridge on day 25, Israel travelled 3 days (day 25-27) on “The Exodus Highway” through the Wilderness of Shur and the land of Midian, then travelled 3 more days (day 28-30) and arrived at the second Red Sea camp, then one more day to reach the wilderness of Sin. The only difficult portion of the trip was the canyons between the Wilderness of Sin through Dophkah to Alush. Amazingly Scripture notes that only during this portion of the journey, they “travelled in stages” (Ex 17:1) because the terrain was narrow and difficult. Exactly 31 days after leaving Goshen they enter the Wilderness of Sin (Nisan 15 - Iyar 15: Ex 16:1). In the Wilderness of Sin Israel camped 8 days (day 31-38) to learn about the Manna/Sabbath day cycle. Leaving the Wilderness of Sin as a single group of 2-3 million, Israel arrived at Dophkah on day 39. Between Dophkah and Alush Israel travelled in small groups by “stages” through the 23 kilometers of mountain canyons to Alush on days 40-41. On days 41-42 Israel arrived in stages at Rephidim and complained about having no water. God told Moses that when he finally arrived at Mt. Horeb, he is to bring water out of the “split rock” as the main water supply for the 11 months stay camped at the foot of Mt. Sinai. On the night of day 42 the Amalekites attack and the next morning Moses assembles an army, and his hands are held up high on a hilltop on day 43. That night Jethro arrives, and watches Moses judge the people all day long on day 44. Day 45 is the second sabbath and Jethro gives Moses his advice about delegating the judging duties to others. Day 46 Jethro returns home to Midian while Moses departs for Mt. Sinai arriving after dark on day 47 which is Sivan 1 (Ex 19:1). In the morning of day 47 Moses strikes and splits the rock at Mt. Horeb for a massive water supply for 3 million Hebrews. On day 48 Moses ascends Mt. Sinai for the first time and God recites the Ten Commandments orally. Moses descends and tells the people to take an oath to obey the laws of YHWH (Ex 19:3-8). On day 50 (Thursday, Sivan 4), God tells Israel to prepare for three days (Friday – Sunday) at the end of which God will descend upon Mt. Sinai. (Ex 19:10-11). On Pentecost Sunday (Sivan 7), day 53 from leaving Egypt, Mt. Sinai explodes (Heb 12:18) when God gives the law to Moses over a period of 40 days. Israel spent 343 days (11 lunar months and 19 days) camped in the Wilderness of Sinai (Num 10:11) while Moses received the law and Israel built the Tabernacle tent. The journey from Mt. Sinai through Ezion Geber (Numbers 33:35-36) to Kadesh Barnea, was 20 stops over a period of about 11 months. Israel spends 38 years camped at Kadesh Barnea located at modern Petra. Aaron died on the 1st day of the 5th month of the 40th year of the wilderness wandering (summer 1407 BC). Shortly after mourning Aaron for 30 days, the people left Mount Hor which was beside Petra (Kadesh) and moved south to the Red Sea (“Yam Suph”- Deut 1:40 – Gulf of Aqaba) passing a second time through Ezion Geber (Deut 2:8). They journeyed east to avoid the Edomites living in the mountains and began moving north. Before they crossed the Wadi Zered, Israel rebelled again with the result that God sends poisonous snakes to kill the people. In obedience to God, Moses sets up a pole with a snake to heal them. Those who had been bitten could look at the snake and be healed as a type of the crucifixion of Christ (Jn 3:14). They crossed the Wadi Zered at the south end of the Salt Sea and Moses spoke the words of the book of Deuteronomy at Iye-abarim. The conquest began and Israel passed directly through Dibon-gad and commenced the defeat of the Transjordan nations. While camped at Shittim (Tel Hammam) Israel mourned Moses for 30 days. In 1406 BC Israel crossed the Jordan on the 10th day of the 1st month of the 41st year (spring, 1406 BC), four days before the 41st Passover, which was exactly 40 years from when they left Goshen. They started counting sabbatical years and Jubilees after crossing the Jordan. (Num 33:38; 20:28; Deut 34:8; Josh 4:19; 5:10). Israel camped at Gilgal then defeated Jericho and Ai. They traveled to Shechem and built Joshua’s Altar. The Ark of the Covenant was positioned in the valley between Mt Gerizim and Mt. Ebal with half the tribes on each of the two mountain sides. The echo-ritual “curses and blessings ceremony” of Deut 27-28 were spoken across the valley to each of the six tribes on each side. From 1406-1400 BC Israel first defeated the northern Amorite Pentapolis, then second, the southern Amorite Pentapolis. They were unable to defeat the five Philistine Pentapolis cities (Ex 13:17-18; Deut 2:23; Josh 11:22; 13:2-3; Jud 1:18-19; 3:1-3) until the time of David. The Philistines had restricted Israel’s possession of the promised land to the central hill country until 1003 BC. After 6 years of conquest war, on the first Sabbatical year of 1399 BC, Israel moved the tabernacle from Gilgal to Shiloh which served as Israel’s first capital city for 305 years until the Philistines burned the city in 1094 BC.
Introduction:
1. Many Christians falsely assume there is little information contained in scripture about the 50 locations of the Exodus, much less the timing. Many preachers never give this subject a look stating that we don't even know for certain any more than 4 of the 50 Exodus stops.
2. Scripture specifically tells us the total number of days it took to travel from Goshen to Sinai: 47
a. The day they left Goshen: Nisan 15 (Num 33:3)
b. The day they entered the Wilderness of Sin: Iyar 15 = Day 31 (Ex 16:1)
a. The day they arrived at the final Sinai camp in the Wilderness of Sinai : Sivan 1 = day 47 (Ex 19:1)
2. There is a wealth of information in scripture about many of the 50 Exodus locations. We know four locations for certain and using key clues in scripture, we are able to discern several others.
a. Goshen
b. Wilderness of Shur near el Bad in Midian, modern Saudi Arabia
c. Ezion Geber near Elat on the Gulf of Aqaba
d. Kadesh Barnea at modern Petra
e. Dibon
f. Shittim
g. Mt. Nebo
h. The location of the Jordan crossing in 1406 BC
3. Using careful analysis, we have calculated the distances between each of the stops. We have calculated total distances as well as daily average travel rates.
4. Miracles of red sea: there is a lot of detail in here about the canopy that protected from sun and rain and provided light to travel at night.
a. Guidance: Exodus 13:21
b. Shelter canopy from Sunlight and Rain: Isaiah 4:4-6; Psalm 105:39
c. Protection from pharaoh's armies: Exodus 14:19, 24.
5. Two verses say that God gave them supernatural help crossing the depths of the Red Sea:
a. "Like the horse in the wilderness, they did not stumble ; As the cattle which go down into the valley (red sea), The Spirit of the Lord gave them rest." Isaiah 63:11-13
- "Then He brought them out with silver and gold, And among His tribes there was not one who stumbled . " Psalm 105:37
6. Two verses say they travelled day and night with miraculous light for night travel. Standard daily travel rates in ancient times are therefore irrelevant.
a. "The Lord was going before them in a pillar of cloud by day to lead them on the way, and in a pillar of fire by night to give them light, that they might travel by day and by night. He did not take away the pillar of cloud by day, nor the pillar of fire by night, from before the people." Exodus 13:21-22
b. "“And with a pillar of cloud You led them by day, and with a pillar of fire by night to light for them the way in which they were to go ." (Nehemiah 9:12)
I. Exodus Route Travel Calendar by Steven Rudd: March 2020
A. Bible timing from Ramses to Mt. Sinai is 47 days:
1. The Bible tells us that it was a 47-day journey from Goshen to Sinai .
a. They left Goshen on Passover (15 th day of the first month) and arrived at the Wilderness of Sin on the 15th day of the second month and arrived at the Wilderness of Sinai on the 1st day of the third month. This equals 47 days.
b. It took 24 days to travel 500 km to the Red Sea and they spent 8 days camped there waiting for Pharaoh's army to come. It took 22 days to travel 200 km to Sinai after the Red Sea including 8 days camping in the wilderness of Sin and 3 days battling the Amalekites at Rephidim.
2. Num 33:3 and Exodus 12:51 tells us Israel was driven out of Egypt by Pharaoh the day after Passover night (Nisan 15)
a. "In the first month, on the fourteenth day of the month at twilight is the Lord's Passover." Leviticus 23:5.
b. "They journeyed from Rameses in the first month, on the fifteenth day of the first month; on the next day after the Passover the sons of Israel started out boldly in the sight of all the Egyptians," (Numbers 33:3)
c. "Then Pharaoh called for Moses and Aaron at night and said, "Rise up, get out from among my people, both you and the sons of Israel; and go, worship the Lord, as you have said." Exodus 12:31.
d. "And on that same day (Nisan 15) the Lord brought the sons of Israel out of the land of Egypt by their hosts." Exodus 12:51
3. Exodus 19:1 tells us they ended the trip when they reached the Wilderness of Sinai on the 1st day of the third month (Sivan 1) "In the third month (Sivan 1) after the sons of Israel had gone out of the land of Egypt, on that very day they came into the wilderness of Sinai." Exodus 19:1
a. Since the Law of Moses was given on Pentecost, this means that they arrived on the first day of the third month, not the 15 th day of the third month.
b. “ On that very day (19:1b) points emphatically to the day of the new moon, the first day of the new lunar month, and not the whole first month (as NIV has it). This expression also recalls the time designations on this very day (12:17) and that very day (12:51), expressions almost identical to the one here.” (Believers Church Bible Commentary, Waldemar Janzen, Exodus 19:1, 2000 AD)
c. “ On the third new moon the closer definition “on that very day” shows that Hebrew ḥodesh, usually “month,” is here used in its original sense of “new moon.”” (Exodus, Jewish Publication Society, Nahum M. Sarna, Ex 19:1, 1991 AD)
d. If they arrived on the 15 th day of the third month, they arrived after Pentecost, missing an important messianic synchronism of where both the Law of Moses and the Law of Christ were revealed on Pentecost Sunday (Isa 2:2-5; Acts 2)
e. While the Tiran Red Sea crossing has time to spare in arriving at Sinai well in advance of Pentecost on day 47, the Nuweiba crossing forces them to arrive after Pentecost in a full 61-day journey from Goshen.
4. Exodus 16:1 tells us that when they entered the Wilderness of Sin on the 15th day of the second month (Iyar 15)
a. Nisan 15 to Iyar 15 is exactly 31 days after leaving Goshen with a 30-day month.
b. "Then they set out from Elim, and all the congregation of the sons of Israel came to the wilderness of Sin, which is between Elim and Sinai, on the fifteenth day of the second month (Iyar 15) after their departure from the land of Egypt." Exodus 16:1
c. Since the total trip was 47 days, arriving at the Wilderness of Sin on day 31 means they were only 22 days away from reaching the Mt. Sinai.
5. Exodus 16:1: In 1446 BC Nisan and Iyar both had 30 days not 29 days .
a. A 30-day Hebrew month is confirmed by Josephus in Antiquities 2.316 when he say they had 30 days of food, meaning they ran out on the 31 st day when they entered the Wilderness of Sin.
b. “The lunar calendar measured time by lunations; a lunation is the interval of time, expressed in days, between two successive new moons. Each lunar month, beginning when the thin crescent of the new moon first becomes visible at dusk, averages just over 29½ days. The moon actually orbits the earth in about 27⅓ days; because the earth is meanwhile moving around the sun, it takes the moon 2 extra days to come to the same position between the sun and earth and produce a “new moon.”” (Baker Encyclopedia of the Bible, Calendars, p 400)
c. It is also possible to have up to 4 consecutive 30 day lunar months:
i. Nisan, Iyar and Sivan were 30 day lunar months: “the lunar year is divided into twelve months: 1–3, 7–9 have 30 days; 4–6, 10–12 have 29” (AYBD, Calendars, vol 1, p 818)
ii. “Now, I want to assume that every month thereafter is 30 days long. (That is what we are looking for – can there be 5, consecutive, 30-day months?) So looking at the data, we see everything is fine – as annotated by “OK” in the far-right column till we see that the 5th consecutive 30-day month has added up to 150 days, yet the “real” moon has added up only to 148.753 days (that is, the real months can be no more than 149 days when rounded to whole days for calendar purposes), so our calendar is 1 day ahead if we insist on a 30-day month that last lunation (the red one – 30 days). But what we see is that that last calendar month must instead be 29 days so our calendar total is 149 to match the “real” moon of 148.753 days (rounded to 149) in 5 months. This illustrates that it is possible only to have 4 consecutive 30-day months and the calendar still works. … The conclusion: That no, five, consecutive lunations can exceed 148.88 days. So if the month you stared with was itself a 30-day month, then the 5th lunation including that starting 30-day month, will end up no greater than 148.88 days long, thus, you’d find that only 3 months after the 30-day month in which you began, you’d be forced to follow it with a 29 day, 5th month, to keep the calendar in-sync with the real moon .” (On the possibility of 5 consecutive 30-day months, William J. Welker, 2015 AD)
6. The Red Sea crossing was on day 25 from Goshen: (Iyar 9)
a. The author noticed an important fact that the Bible begins counting days after crossing the Red Sea but not before. For the first time in the route itinerary, Moses indicates Israel travelled 3 days to Marah in the Wilderness of Shur. There are only two stops to reach the hard calendar marker of day 31 at the Wilderness of Sin.
b. Israel travelled three days in the Wilderness of Shur (days 26-28) and arrived at Marah. They travelled one day and arrived at Elim on day 29. They travelled another day and arrived at 2 nd Red Sea camp on day 30. Finally, on day six after crossing the Red Sea, the entire 3 million Hebrews arrived at the Wilderness of Sin on day 31 which was Iyar 15 (Ex 16:1). Scripture tells us they travelled “3 days” from the Red Sea to Marah and that Moses arrived on day 31.
c. This is a total of six travel days after crossing the Red Sea to reach the Wilderness of Sin on day 31 from Goshen.
d. Counting six travel days back from day 31 (Iyar 15) we can be certain the Red Sea crossing was on day 25 (Iyar 9).
e. A Red Sea crossing at the Straits of Tiran on day 25 is a perfect fit for the timing and topography. No other candidate Red Sea crossing location is a perfect fit for a day 25 Red Sea crossing.
B. Ancient literary Sources confirm a 47-day journey from Goshen to Sinai:
1. The 47-day exodus itinerary alone refutes the Nuweiba exodus route of Glen Fritz because even he admits his 555-mile (888 km) route cannot be travelled in less than 53 days. Fritz calculates Israel arrived at Mt. Sinai on day 64-65 and he added 12 “arbitrary” filler days to delay the arrival from day 53 to day 65.
2. The 47-day journey predated Christianity by 200 years and is not a “late Rabbinic tradition” as Fritz and other commentators commonly suggest:
a. “The biblical timing of Pentecost 50 days after Passover is not being disputed here. What is disputable is the late rabbinic tradition that Pentecost also commemorated "the giving of the law” . … It must be recalled that the 2nd century AD development of Rabbinic Judaism occurred after the AD 70 destruction of the Jewish temple in Jerusalem, which caused the rabbis to face the reality of a Judaism without sacrificial worship. This situation catalyzed an emphasis on the oral traditions of the Torah, which were recorded in the Mishnah ca. AD 200 , and subsequently expanded in the Gemara." (Exodus Mysteries, Glen Fritz, p450, 2019 AD)
b. For Fritz to call oral traditions that were recorded in the Mishna in AD 200 a “late tradition” is puzzling since the Mishna represents one of the earliest written Jewish traditions extant today. Although the Babylonian Talmud could be considered a later tradition must of its content merely echoes the Mishna (AD 200) and the Tosefta (AD 250) and other traditions that predate Christianity by hundreds of years.
c. It is well documented that the oral traditions in the Mishna predate Christianity by hundreds of years.
d. The correct scholarly approach would be to say the earliest known written Jewish sources all unanimously confirm the 47-day journey where the Law was given on Pentecost and none of them provide any evidence for a 61-day journey.
e. The correct scholarly approach would be to say that the 61-day exodus itinerary is without any confirmation from the earliest literary sources or traditions.
f. The correct scholarly approach would be to say that the 61-day exodus itinerary is in fact a very late tradition.
3. 170 BC: book of Jubilees : Ex 24:12-18, Moses’ 6 th ascension
a. “In the first year of the Exodus of the children of Israel from Egypt, in the third month on the sixteenth day of that month (Sivan 16) , the LORD spoke to Moses, saying, “Come up to me on the mountain, and I shall give you two stone tablets of the Law and the commandment, which I have written, so that you may teach them. ( Ex 24:12-18 )” (Book of Jubilees 1:1, 170 BC)
b. The book of Jubilees confirms arrival before Pentecost: Day 60 was Moses 6 th Ascension: Ex 24:12-18
c. The Book of Jubilees is referring to the 6 th ascension of Moses when he physically got the stone tablets. Moses orally heard the Ten Commandments on his third ascension but did not get the two tablets of stone until his 6 th ascension.
d. Some misread the Book of Jubilees to say that Israel arrived on day 60 (14 th day of 3 rd month, Sivan 14) and then three days later, on day 62 (16 th day of 3 rd month, Sivan 16) God ascended Mt. Sinai with trumpet blasts, fire and thunder and gave the Law to Moses.
e. The Jubilees specifies that the two tablets of stone were given on Moses’ 6 th Ascension up Mt. Sinai not his 1 st ascension: Ex 24:12-18
i. Sivan 1: Israel arrives at Sinai. (Ex 19:1)
ii. Sivan 2: On Moses’ 1 st ascension he returned to the camp with an oath for people: Ex 19:3-8.
iii. Sivan 4: On Moses’ 2 nd ascension God said to get ready for the third day: Ex 19:8-14.
iv. Sivan 7: On Pentecost Moses’ made his 3 rd ascension and the mountain exploded with trumpet blasts, fire and thunder and gave orally the Law to Moses: Ex 19:18-25, 20:1-26 .
v. Sivan 14: It was Moses’ 6 th (sixth) ascension that God gave the two tablets of stone of the Ten Commandments during Moses’ 40 days at the summit: Law to Moses: Ex 24:12-18
f. The book of Jubilees proves a 47-day journey not 60 days because it says that Moses got the tablets of stone on Sivan 16 which would be day 63. Although we time the events of Ex 24:12-18 to Sunday Sivan 14, it doesn’t make any difference. We could easily shift the 6 th ascension to Sivan 16 (day 62) and it would make no difference because in either case, it would be impossible for Israel to arrive on day 60, have Moses ascend the mountain 5 times in two days before Moses Got the two tables of stone on the 6 th ascension as per Ex 24:12-18.
4. AD 70: Josephus : Three months: 90 days or three inclusive months
a. “And going gradually on, he came to Mount Sinai, in three months’ time after they were removed out of Egypt” (Josephus Antiquities 3.62)
b. Jewish inclusive counting is well documented in the three days (Friday to Sunday) in both the triumphal entry and the crucifixion and resurrection of Christ (Luke 13:32). Several other examples of three day periods being less than 72 hours are Queen Esther (Esther 4:16 + 5:1), faithless Jews: (Matthew 27:63-64), starving servant: (1 Samuel 30:12-13). Most notably is the fact that 72 literal hours (three days and three nights) was called four days by Cornelius (Acts 10:3+9+23+24+30).
c. In non-inclusive counting, three months means 90 days, which contradicts both those who say the journey took 60 days. Using this reasoning, if Josephus wanted to say 60 days, he would have said two months. So either Josephus was wrong or he was using inclusive counting.
d. Josephus used standard inclusive counting because the exodus spanned parts of three months but literally 47 days, the same way Jesus was in the tomb parts of three days but literally 38 hours.
e. The three months of Josephus are counted as 47 days: Nisan 15-30 (15 days); Iyar 1-30 (30 days); Sivan 1 (1 days).
f. Josephus therefore actually confirms the earliest written Jewish traditions.
g. Anybody who objects that Josephus confirms the 47-day exodus itinerary are forced to say Josephus actually recorded a 90-day journey, which contradicts their own 60-day exodus itinerary.
h. The only two options in interpreting Josephus’ “three months” are to reject the 90 days as an error he made or confirmation of the 47-day itinerary.
i. Josephus’ statement therefore agrees with all the other earliest literary sources that all confirm a 47-day exodus journey.
5. AD 160: Seder Olam Rabbah : Ten commandments given day 47 on Pentecost: Sivan 6
a. “For the next five days Moses ascended the mountain, descended, told the people the words of the Omnipresent, and returned their answer to the Omnipresent. In the Third month, on the Sixth of the month , the Ten Commandments were given to them on a Sabbath day.” ( Seder Olam Rabbah 5:31 , Rabbi Yose ben Halafta, 160 AD)
b. In a stunning confirmation of our exodus calendar, Sivan 6 falls on a Sabbath in both our chronology and Sedar Olam Rabbah’s chronology confirming a 47-day journey.
c. Seder Olam dates Pentecost to Sabbath Sivan 6 (day 52) and we date Pentecost to Sunday Sivan 7 (day 53). This proves they arrived in Sivan 1 not Sivan 15.
d. Rabbi Yose ben Halafta follows the first century tradition that Pentecost fell on different days as opposed the the Sadducees Moses and the New Testament that teaches Pentecost always fell on a Sunday. Seder Olam therefore is in error by saying Pentecost occurred on a Sabbath rather than a Sunday. This is just another in series of revisions where Jews in AD 160 at Zippori changed Masoretic Text and key chronological events in the Old Testament to disconnect Jesus Christ as the Messiah. In truth, Pentecost always fell on a Sunday and although they could not break the well-known synchronism between the Law of Moses and Christian Pentecost in Acts 2, they wanted to disconnect the day of the week for both event falling on the day Jesus rose from the dead.
6. AD 400: Augustine : Calculates a 47-day journey and the synchronism of both laws given on Pentecost:
a. In a stunning confirmation of our exodus Chronology, Augustine specifically states that the journey between Goshen and Sinai was 47 days.
b. Augustine emphasized the direct messianic connection between both the Law of Moses and the Law Christ were given on Pentecost. This proves the journey was 47 days.
c. “The Pentecost too we observe, that is, the fiftieth day from the passion and resurrection of the Lord, for on that day he sent to us the Holy Paraclete whom he had promised. This was prefigured in the Jewish Passover, for on the fiftieth day after the slaying of the lamb, Moses on the mount received the law written with the finger of God .” (Augustine, Against Faustus the Manichaean 32.12, 400 AD)
d. “But, the fifty-day period is also praised in Scripture, not only in the Gospel, because the Holy Spirit came on the fiftieth day, but even in the Old Testament. Therein, fifty days are numbered from the celebration of the pasch by the killing of a lamb, to the day on which the law was given on Mount Sinai to the servant of God, Moses .’ This law was ‘written with the finger of God,’ and this finger of God the New Testament explicitly identifies with the Holy Spirit. For, when one Evangelist has: ‘By the finger of God, I cast out devils,’ another says this same thing thus: ‘By the spirit of God, I cast out devils.’ Who would not have this joy in the divine mysteries, when the redemptive doctrine shines with so clear a light, rather than all the powers of this world though they be infused with unwonted peace and happiness? Do not the Seraphim cry to each other, singing the praises of the Most High: ‘Holy, holy, holy, the Lord God of hosts’? Thus the two Testaments agree faithfully in proclaiming the sacred truth. A lamb is slain, the pasch is celebrated, and after fifty days the law, written with the finger of God , is given in fear: Christ is slain, who was led ‘as a sheep to the slaughter,’ as the Prophet Isaias testifies, the true pasch is celebrated, and after fifty days the Holy Spirit, who is the finger of God, is given in love.” (Augustine to Januarius , Book 2, Letter 55, 400 AD)
e. “ The law was given on the day of Pentecost, and the Holy Spirit came on the day of Pentecost . But I said I was going to prove that the Jews received the law on the fiftieth day from the Passover, or Pasch, which we both celebrate. You have it that they were commanded to kill the lamb on the fourteenth day of the first month, and to celebrate the Passover. Of that month there are seventeen days left, if you include the fourteenth day itself, on which the Passover begins. We come now to the desert, where the law was given, and this is what scripture says: But in the third month from when the people was brought out of Egypt (Ex 19:1) the Lord spoke to Moses that those who were going to receive the law should purify themselves in readiness for the third day, on which the law was to be given. So at the beginning of the third month a purification is commanded in readiness for the third day. And Passover begins ... —Pay close attention, please, or the numbers may set your heads spinning, and bring a fog down upon your understanding. I am opening the thing up as best I can, with the Lord's approval. If you help me with your attention, you will soon grasp what is being said; but if that's lacking, whatever I say will remain obscure, even if it is said ever so plainly ... — So the Passover is announced for the fourteenth day of the month; and a purification is ordered, so that the law may be given on the mountain, written by the finger of God; and the finger of God is the Holy Spirit. Remember, we proved this from the gospel. So a purification is proclaimed, in readiness for the third day of the third month. So from the first month deduct thirteen, and seventeen are left, as you begin from the fourteenth. Add the whole second month; it makes forty-seven days; from that day of purification to the third day, it makes fifty days . Nothing could be plainer, nothing more obvious, than that the Jews received the law on the day of Pentecost.” (Augustine Sermon 272B, On the Day of Pentecost, 417 AD)
7. AD 500: Babylonian Talmud : Moses received the Torah on Pentecost proves a 47-day journey :
a. “Said R. Eleazar, “All concur with respect to Pentecost that we do require ‘for you’ as well. How come? It is the day on which the Torah was given.” (Babylonian Talmud, Pesahim 68A , 500 AD)
8. AD 810: George Syncellus: Arrived on new moon of third month = Sivan 1, Day 47
a. “And on the third new moon of the Exodus of the sons of Israel from the land of Egypt, on this very day they came into the wilderness of Sinai.” (Chronography of George Synkellos 151, William Adler, Paul Tuffin, p189, 2002 AD)
9. AD 1735: Midrash, Tanḥuma : Moses received the Torah on Pentecost proves a 47-day journey:
a. “And in the same manner, the holiday of Pentecost (Shavuot) for the giving of the Torah” ( Midrash, Tanḥuma C , Derech Hashem, Part Four, On Divine Service and the Calendar, Manuscript C, 1735 AD)
C. Calendar of events from Goshen to Sinai: Days 1-47
D. Calendar of events at Sinai from arrival to departure: Days 47 – 382
Detailed outline on the Eight Ascensions of Moses up Mt. Sinai: click here
E. The Eight Ascensions of Moses up Mt. Sinai:
- 1 st Ascension: Tuesday Sivan 2, Day 48 from Goshen: Ex 1 9:3-8
- Moses Ascends Mt. Sinai and returns with oath for people to obey the Law soon to be revealed.
- Moses returns to the camp and asks the people if they will keep the law soon to be revealed. The people reply yes.
- 2 nd Ascension: Friday Sivan 4, Day 50: Ex 19:7-14
- Moses ascends Mt. Sinai to give God the people's "yes" answer. God says to be ready on the third day (Sunday Sivan 7, day 53 from Goshen) when he will descend on the Mountain in fire: Ex 19:7-14. The people are told to walk to the base of the mountain from their camp and be ready for God's coming. God tells Moses to set up boundaries around the mountain so the people cannot break through, climb the mountain and die.
- The third day = Friday to Sunday: There is a direct triple correspondence between the Sinai, the Triumphal entry and the crucifixion since all were periods of three days between Friday and Sunday: Luke 13:32.
- As the Israelites waited as instructed the third day, for God to descend on Mt. Sinai, they suddenly looked due north 100 km and saw God in the wilderness of Paran. God " dawns from Seir " like a sunrise in its glory, until He is hovering directly over Mt. Sinai. The Israelites watched in wonder and were amazed at the beauty and splendor of God as He came closer and closer to them where they stood. One of the most interesting facts about the Wilderness of Paran, is its connection with God's appearing at Mt. Sinai. When Israel was encamped at the foot of Mt. Sinai (Mt. Al-Lawz), God thundered, in a volcanic level display that terrified the Israelites. But three verses explicitly tell us that God dawned from the north like a sunrise, or like Elijah's small cloud the size of a man's fist in the distance that became a storm (1 Kings 18:44). God dawned from Mt. Seir until he came to Mt. Sinai and made the mountain turn to fire before Israel. They were terrified. The four key verses that describe "dawning from the north" are: Deut 33:2; Isa 63:1-2; Judg 5:4; Hab 3:3-7. 40 years later, when Israel was at Mt. Seir, God gave the "go ahead" to finally start their way to the promised land by the command, "Now turn North". In fact Mount Seir is absolute due south of Jerusalem and absolute due north of Mt. Sinai in modern Saudi Arabia. There are several passages that repeat this pattern of God coming "from the North". Most notably is Ezekiel's vision where God came from a distant storm in the North finally to overshadow him. (Ezekiel 1:4) Job describes God as coming from the North in golden splendor. (Job 37:22-23) Lucifer, the king of Babylon describes God's throne as being in the far north. (Isaiah 14:13-14) Psalm 48:1-2 describes Jerusalem as being located in the "far north". Further detailed study .
- 3 rd Ascension: Pentecost Sunday, Sivan 7, Day 53: Ex 20:18-25; 20:1-26
a. God descends on Mt. Sinai in fire and He calls Moses to climb the mountain. Ex 19:20
b. Moses hears the Ten Commandments and other laws including building altars.
c. God tells Moses to go back down and warn the people again to stay away from the mountain so they will not die, then come up again ( 4th ) with Aaron. Ex 19:21
- 4 th Ascension: Ex 19:24, Sivan 9, Day 55
a. Moses ascends with Aaron only where Ten Commandments and other laws are repeated for Aaron who hears the Ten Commandments and various other laws found in Exodus chapters 20-23
b. Moses and Aaron. God tells Moses to descend and return with Aaron, Nadab and Abihu, and 70 elders of Israel. Moses goes back down and tells the people what God has said. Deut 24:1-3
c. Moses descends and writes down the words in the Book of the Law, which will eventually be placed on the side of the ark. Ex 24:1-4
d. Moses builds an alter with 12 pillars at the foot of the mountain for the twelve tribes. He then sprinkles the alter with blood. Ex 24:4-6
e. Moses read the book of the law to the people and after they agreed, he sprinkled the people with blood of the covenant. Ex 24:7-8
- 5 th Ascension: Ex 24:1; 9-11 Sivan 11, day 57
- Moses now returns to the mountain with Aaron, Nadab and Abihu, and 70 elders of Israel. After seeing God and eating the group descend to the foot of the mountain. Ex 24:9-11
- 6th Ascension: Sunday Sivan 14, day 60-99: Ex 24:12-18
- Moses begins 40 days on the Mountain and receives two tables of stone:
- Day 60-99 inclusive counting equals 40 days ending on day 99 after leaving Egypt
- God calls Moses up with Joshua to the mountain to receive the two tablets of stone with the ten commandments written by the finger of God. Ex 24:12
- Moses spends 40 days on the mountain ( 6th ) where God reveals the plan for the tabernacle. Exodus chapters 25-31
- After 40 days, Aaron makes the golden calf as Moses was on the mountain for 40 days. In one of the most fascinating interaction between a man and God in the Bible , God tells Moses He will kill all the Hebrews who sinned and make Moses into a great nation. Moses pleads for the people. Then God changes his mind and says he won't kill them. Moses physically throws 10 commandments at the people who had made the golden calf, rebukes Aaron. Moses grinds up the golden calf and makes them drink the gold dust. Then Moses commanded the Levites to kill about 3000 of the idol worshippers. Ex 32:7-29
- 7th Ascension: Day 100 from leaving Goshen: Ex 32:30-33:23
- The next day, Moses climbed Mt. Sinai ( 7th ). God tells Moses is to take them into the promised land with God's angel as protection, but God himself will not go with them. Moses goes down the mountain. God strikes down a number of the Hebrews who sinned. Ex 32:30-35
- When the people hear that God's angel will lead them but God himself will not go with them, the people get sad and they remove all their jewelry. Ex 33:2-6
- Moses continues to plead with God for the people and says, "I pray You, show me Your glory!" God says He will show Moses his Glory on the Mountain. Ex 33:18-23
- 8th Ascension: Days 102 - 141 days from Goshen (40 days inclusive): Ex 34:1-9; 2 Cor 3.
- God tells Moses to cut out two replacement tablets and God calls Moses back up to Mt. Sinai ( 8th ), where God passes by while Moses was in the cleft of the rock.
- Again Moses asks God to join them on the journey to the promised land. God changes his mind finally and tells Moses he will lead them to the promised land.
- Moses spends forty more days on the mountain, then returns.
- God said he would perform new miracles and Moses face is shining in view of the people so he puts a veil over his face. Ex 34:1-9; 2 Cor 3.
F. Calendar of events between Sinai and Kadesh Barnea: about 11 months
1. Israel departed Sinai on Day 382 after leaving Goshen
a. "Now in the second year, in the second month, on the twentieth of the month, the cloud was lifted from over the tabernacle of the testimony;" Numbers 10:11
b. Israel departs from Sinai for promised land after spending 11 months, 5 days at Sinai.
c. Since they left on the 14th day of the first month, this means they had been traveling one year, one month and one week, since leaving Egypt.
d. Using the syntax of “year:month:week” for the amount of time they spent at Sinai we get: 1:1:1 = 1 month:1 week:1 day.
2. They navigated about 20 stops over a period of between 10.5 and 11 months between Sinai and Kadesh Barnea
a. "Then the sons of Israel, the whole congregation, came to the wilderness of Zin in the first month; and the people stayed at Kadesh." Numbers 20:1
b. They arrived at Kadesh Barnea in the first of the month of the third year or exactly 24 months after leaving Egypt.
c. They celebrated their second Passover at Sinai, then leave almost immediately afterwards for Kadesh. They arrived at Kadesh and immediately celebrated their third Passover.
3. They spend 38 continuous years at Kadesh Barnea (they do not leave and come back), then depart for the Jordan in the 40th year.
a. Many commentators mistakenly believe Num 20:1 was the 40th year , but they are wrong.
b. The verse tells us they arrived at Kadesh in the first month, but does not tell us the year!
c. It does not say, "the first month in the 40th year".
d. Since Israel left Sinai in the second month of the second year after leaving Egypt (14 months), this means they arrived at Kadesh in the first month of the third year after leaving Egypt or 24 months.
e. More details: Israel spent 38 continuous years at Kadesh Barnea
G. Calendar of events between Kadesh Barnea and the Jordan River: about 9 months
1. Israel Crossed the Jordan exactly 40 years after leaving Goshen to the day:
a. Aaron died on the 1st day of the 5th month of the 40th year of the wilderness wandering (summer 1407 BC).
b. Shortly after mourning Aaron for 30 days, the people left Mount Hor, defeated the Transjordan nations, and then mourned for Moses 30 days.
2. They crossed the Jordan on the 10th day of the 1st month of the 41st year (spring, 1406 BC), four days before the 41st Passover, which was exactly 40 years to the day they left Goshen.
3. They started counting sabbatical years and Jubilee after crossing the Jordan. (Num 33:38; 20:28; Deut 34:8; Josh 4:19; 5:10)
III. Understanding Jewish dating and times:
A. Jewish days started at sundown not midnight:
- The entire world today uses the Roman method of reckoning days from Midnight to Midnight.
- Jewish days began at sundown. This means that if it is 5 pm on a Friday night and you are just getting off work, two hours later (Roman time 7 PM) would actually be Saturday.
- This is helpful to know because in the Wilderness of Sin they arrived on a Saturday, and after sunset, that evening while they were in the camp, God revealed the Sabbath for the first time using manna as an instructor. So from Roman time, God revealed the Sabbath on Saturday evening 8 PM, but to the Jews, it was a the 1st day of the week (Sunday).
- We are very glad because the Jewish method of time keeping would be awkward to implement today.
B. Jewish inclusive reckoning method of counting days:
- Biblical Jews counted days differently from how we count today. Jews used the inclusive counting system .
- Jesus was crucified on a Friday and rose from the dead on the first day (Sunday) Three days and three nights: Friday crucifixion - Sunday resurrection. For us this would only be two days, but for Jews it was three days.
- On the Friday before "Palm Sunday", exactly one week before Jesus died, Jesus said: Luke 13:32 "Behold, I cast out demons and perform cures today [Fri] and tomorrow [Sat] , and the third day [Sun] I reach My goal."
- Even during the Exodus there is an excellent example of Jewish inclusive time keeping. The Bible says: "The Lord also said to Moses, "Go to the people and consecrate them today and tomorrow , and let them wash their garments; and let them be ready for the third day , for on the third day the Lord will come down on Mount Sinai in the sight of all the people." Exodus 19:10-11
- Notice that even Jesus counted three days as a duration from Friday to Sunday. He started counting today as day one.
- We don't count this way. Today is day 0. For the Jews today is day 1.
- We need to keep this in mind when calculating days the way the Jews did.
- For example, when it says they went three days into the wilderness of Shur after crossing the Red Sea, this would be a Monday to Wednesday duration for the Jews.
- They counted a day even if there was only one hour left in that day.
- For a full discussion about Jewish time keeping see this .
IV. Calculating Exodus dates and times:
A. Calculating the days of the week at the Wilderness of Sin: Day 31 from Goshen
- The primary way we have used to calculate the days of the week for the Exodus journey is based solely on their visit to the Wilderness of Sin. It is there God first revealed the Sabbath.
- We believe with some level of confidence, that we have enough information to actually calculate the days of the week for the journey between the Red Sea and Mt. Sinai.
- In Ex 16:1 God revealed the Sabbath for the very first time in world history. Contrary to the unbiblical ravings of Seventh-day Adventists, Adam and Abraham never kept the weekly seventh day Sabbath (Saturday). In fact the word Sabbath is never even used once in the book of Genesis. The Sabbath was a Jewish holy day that was abolished by God when he nailed the first covenant to the cross. Col 2:14-17 clearly teaches that the Law of Moses, including the 10 commandments , were nailed to the cross. The New Testament passage specifically states that Christians are free to eat "unclean foods" (pork) and that all the system of Jewish holy days, yearly (Passover), monthly (new moon) and weekly (7th day Sabbath) are all nailed to the cross . Christians do not keep the Jewish Sabbath, but worship on the first day of the week: Sunday. Christians assembled every 1st day (Sunday) for the Lord's Supper: Acts 20:7 and are commanded to give every Sunday: 1 Cor 16:2.
- In Ex 16, It was the 7 th day of the week when Moses revealed the sabbath cycle. We know this because the day after was the first day of work, namely Sunday or the 1 st day of the week. In other words, when God said to Moses on the 7 th day these words: "Behold, I will rain bread from heaven for you; and the people shall go out and gather a day's portion every day, that I may test them, whether or not they will walk in My instruction. On the sixth day, when they prepare what they bring in, it will be twice as much as they gather daily." Exodus 16:4-5. These words would have been spoken on the Sabbath they arrived and grumbled about having no food. The very next day had to be a Sunday, or the 1st day of the week.
- What is clear, is that God used Manna to teach them, for the first time, about the weekly Sabbath day. In order to do this, it would mean that they are camped in the Wilderness of Sin for the full week (Sunday - Saturday).
- Since manna fell in the early morning and melted by mid-day, this also proves that God instructed Moses the words of Exodus 16:4-5 on the day before the first morning Manna fell: Saturday.
- From this, we can quite safely determine that they arrived in the Wilderness of Sin on a Saturday and grumbled about being hungry. God gave them Manna for 6 days, then on the Sabbath they rested for the first time in world history. Then they departed early Monday morning to continue the journey in stages, since the terrain ahead was difficult and narrow.
- The Holy Spirit has told us in Exodus 16:1, that they arrived in the Wilderness of Sin on day 31 after leaving Goshen which was the 15 th day of the second month and left the wilderness of Sin on day 39. This leaves 8 days to travel from the Wilderness of Sin till they arrived on day 47 at Mt. Sinai. We know this because we are told they arrived in Sinai on the 1st day of the third month or day 47 after leaving Goshen. They might have even traveled at night. The Bible says that they travel by night by the pillar of fire.
- Now that we have determined the day they arrived and left the Wilderness of Sin, we can use this as a benchmark to determine the days of the week before and afterwards.
B. Calculating the day of the week they crossed the Red Sea: Sunday day 25
- In a most natural calculation backwards from the wilderness of Sin, we discover something incredible, that they crossed the Red Sea on Sunday, Iyar 9. This is a shadow of the fulfillment of the day of First Fruits (Lev 23:10-12) which always fell on a Sunday. Israel was "saved" by coming through the Red Sea. This would fit the New Testament antitype of water baptism very well. Paul tells us in 1 Cor 10:1-4 that passing through the Red Sea with the wall of water on either side and the cloud over head was an antitype of our full immersion into Christ for the remission of our sins. Israel was "baptized into Moses" and Christians are Baptized into Christ. The Hebrews were saved from the slavery of Egyptian bondage, Christians are saved from the slavery to sin. Any Hebrew who refused to cross the Red Sea and be Baptized into Moses would be killed the Egyptian army. Likewise anybody today who is not water baptized will be lost in hell because their sins are not forgiven. See these verses: Mk 16:16; Acts 2:28; 22:16; Rom 6:2-4; 1 Pet 3:21 and take this on line interactive study on water baptism .
- Rom 6:3-4 tells us that our baptism is a symbol of the death burial and resurrection of Christ and that we are raised from the dead to new life when we rise from the waters of Baptism. Since Christ was raised from the dead on a Sunday and since water baptism is a symbol of this resurrection and since the crossing of the Red Sea was an antitype of water baptism, it is most natural to expect that God would orchestrate, through his power and providence, that Israel would be baptized into Moses on a Sunday.
- Israel crossed the Red Sea on a Sunday, Iyar 9, on day 25 after leaving Goshen.
C. Calculating the day of the week of Passover: Wednesday
- Since the Bible tells us the fact that the entire trip was 47 days from Goshen to Sinai, we can now calculate the day of the week that Passover fell upon when they left Goshen.
- This is done by knowing they arrived on a Saturday at the Wilderness of Sin, which the Bible tells us is day 31 after leaving Goshen (Ex 16:1)
- Passover (Nisan 14) was 32 days before they arrived at the Wilderness of Sin.
- Counting back the days of the week makes Nisan 14 a Wednesday.
- They killed the lamb on Wednesday during the day, ate it after sunset on Nisan 15 (Wed night) and departed the following day (Thursday) during daylight hours.
D. Calculating the day of the week of Pentecost: Sunday day 53
- Pentecost means "the 50th day" after Passover. But the counting did not always start immediately after Passover as we will see.
- Recent Jewish tradition states that the Law was given on Pentecost, which is 50 days after the first Sabbath following Passover. Although we cannot trace this Jewish tradition very far back in history, it is very likely correct. On the other hand even the Jews of Jesus' time were notorious at adding to or changing God's Law.
- Pentecost always fell on a Sunday . Pentecost was calculated by counting 50 days, where day #1 is the first Sabbath after Passover. Since Passover could fall on any day of the week, sometimes there was up to a 6 day wait until the first Sabbath came by and you started counting the 50 days. When that Sabbath came, it was day one, then you would count seven additional Sabbath days for a total of 49 days. They next day after the seventh Sabbath was Pentecost.
- This means that if Passover fell on a Sunday, for example, they would not start counting the fifty days until the next Sabbath 6 days later.
- The actual number of days between Passover and Pentecost could vary from exactly 50 days if Passover fell on a Friday to as many as 56 days if Passover fell on a Sunday.
- On day 47 from Goshen, they arrived in the Wilderness of Sinai on a Monday.
- Pentecost fell on the Sunday after the next Sabbath day. This was day 53 after leaving Goshen.
- On Pentecost, Moses ascended ascends Mt. Sinai and returns with law (Ex 19:3-6). Jewish tradition fits very nicely into this time scale.
E. God "Dawned from Seir on Mt. Sinai" on Pentecost Sunday 1446 BC
1. Day 47 (Sivan 1) On Monday Israel arrives at Sinai and Moses gave them water out of the Rock at Mt. Sinai that was promised several days earlier at Rephidim (Meribah) .
1. Day 48: (Sivan 2) 1 st ascension of Moses: Ex 19:3-8. Moses ascends Mt. Sinai and returns with oath for people to obey the Law soon to be revealed (Ex 19:3-6)
2. On Friday Sivan 4, (day 50) Moses ascends Mt. Sinai 2 nd time. God says be ready on the third day which was Pentecost Sunday (Ex 19:8-14). Moses told them that God would descend on Mt. Sinai three days later and to prepare themselves during these three days. Friday was the only day they had to wash their clothes because the next day was the Sabbath. This may be where the first century tradition that “preparation day” was their word for “Friday” because on Friday they prepared for God on Pentecost.
a. The Bible says: "The Lord also said to Moses, "Go to the people and consecrate them today and tomorrow , and let them wash their garments; and let them be ready for the third day , for on the third day the Lord will come down on Mount Sinai in the sight of all the people." Exodus 19:10-11
b. This means the duration would be a Friday - Sunday. This method of counting is typical of the inclusive counting system of the Jews. This further illustrates how Jesus was in the tomb three days, yet it was a duration of Friday 3 PM to Sunday 6 AM.
c. This matches the three day sequence of the Triumphal entry: "And He said to them, “Go and tell that fox, ‘Behold, I cast out demons and perform cures today [Friday] and tomorrow [Saturday], and the third day [Sunday] I reach My goal.’" (Luke 13:32)
d. This matches the three day sequence of Friday crucifixion being raised the third day on Sunday.
3. Counting the day after the 7 th sabbath makes Pentecost day 53 after leaving Goshen on Thursday Nisan 15.
4. God dawned from Seir and descend upon Mt. Sinai on Pentecost Sunday (day 53, Sivan 7) as described in Hebrews 12.
IV. Calculating distances between stops: Red Sea to Sinai
V. Calculating rates of travel from Goshen to Sinai: 700 km in 47 days
A. Examples of historic rates of travel:
1. Israel miraculously travelled day AND NIGHT and therefore walked far greater daily distances than under normal human conditions. This means that traditional rates of travel are no applicable to the Exodus itinerary: Exodus 13:21; Num 9:21; 14:14; Deut 1:33; Neh 9:12; Ps 78:14
a. "The Lord was going before them in a pillar of cloud by day to lead them on the way, and in a pillar of fire by night to give them light, that they might travel by day and by night ." (Exodus 13:21)
b. "If sometimes the cloud remained from evening until morning, when the cloud was lifted in the morning, they would move out; or in the daytime and at night, whenever the cloud was lifted, they would set out ." (Numbers 9:21)
c. “You go before them in a pillar of cloud by day and in a pillar of fire by night ” Num 14:14.
d. "who goes before you on your way, to seek out a place for you to encamp, in fire by night and cloud by day, to show you the way in which you should go ." (Deuteronomy 1:33)
e. “To light for them the way in which they were to go ” Neh 9:12.
f. “He led them with the cloud by day and all the night with a light of fire ” Ps 78:14.
2. Scripture gives us a daily travel rate of 22 km per day:
a. "It is eleven days’ journey from Horeb by the way of Mount Seir to Kadesh-barnea." (Deut 1:2)
b. A direct route from Mt. Maqla/Lawz to Kadesh Barnea at Petra via Ezion Geber is 250 km which calculates a daily travel rate of 22 km per day. This is likely the time caravans would take to make the journey on camels. Camels and humans walk at the same rate of 5 km per hour. This allows for only 5 hours of travel a day. The Hebrews likely travelled most of the day and even during the night.
3. 800 km in 21 days from Riblah to Babylon = 53 km per day
a. "For twenty-one years Nabopolassar had been king of Babylon, when on 8 Abu [15 August 605 BC] he went to his destiny; in the month of Ululu Nebuchadnezzar returned to Babylon and on 1 Ululu [7 September 605 BC] he sat on the royal throne in Babylon." (Nebuchadnezzar Babylonian Chronicles cuneiform tablet lines 9-11)
b. From the time news of Nabopolassar’s death in Babylon reached Nebuchadnezzar in Judea and then for Nebuchadnezzar to travel to Babylon to claim the throne was only 3 weeks (21 days).
c. Nebuchadnezzar set up his military headquarters at Riblah: "Nebuzaradan the captain of the guard took them and brought them to the king of Babylon at Riblah ." (2 Kings 25:20)
d. Within a three-week window, news of Nabopolassar’s death had to travel from Babylon to Riblah AND Nebuchadnezzar then had to travel from Riblah to Babylon. The use of passenger pigeons would be impossible to get a message from Babylon to Riblah, given it was a temporary outpost and Pigeons needed to be raised at Riblah and transported to Babylon to be useful as messengers back to Riblah.
e. If we assume that Nebuchadnezzar took a direct easterly route through Palmyra/Tadmor (2 Chron 8:4) to the Euphrates, then south to Babylon, this journey was 800 km one way. This is the most likely route.
f. A message that Nabopolassar had died could easily arrive from Babylon in about 7 days on horseback at a rate of 110 km per day if the horse was in top shape.
4. In AD 1814, Sam Dale (1772-1841), traveled on horseback 670 miles (1072 km) in eight days from Georgia to New Orleans in winter to deliver instructions from Washington D.C. to General Jackson during the War of 1812. This computes to a daily travel rate of 134 km per day on horseback.
5. In AD 1893, John Berry won the 1,000-mile (1600 km) race from Chaldron, Nebraska to the Chicago World’s Fair in a time of 13 days and 16 hours. Berry and his horse “Poison” covered the final 130 miles in 24 hours. Veterinarians examined Poison after the race and pronounced that the horse was in good condition. This computes to a horseback travel rate on of 114 km per day for 14 days to make the 1600 km trip.
7. These seemingly impossible travel rates very much echo the fact that during the Exodus, news Israel was “trapped in the wilderness at Etham” 430 km to Egypt and then Pharaoh had to return 430 km to the Straits of Tiran where Israel was camped at the Red Sea. Passenger Pigeons flew back to Egypt in 5 hours that were sent from the Migdol overlooking the Hebrew camp at the Red Sea. This gave Pharaoh 7 days to easily travel the 430 km. A horseback rider could travel 430 km from the Straits of Tiran back to Egypt in only 4 days.
B. Daily travel rates from Goshen to Sinai: 700 km in 47 days
1. You must also keep in mind the supernatural help that God gave the Hebrews during the Exodus.
a. Nehemiah 9:12 and Exodus 13:21 says they traveled day and night by the light of the pillar of fire.
b. Isaiah 63:11-13 and Psalm 105:37 say God miraculously prevented any of the 3.5 million from tripping during the Red Sea crossing. Young, old or crippled did not stumble once.
2. There are only a 3-stops mentioned in the Bible between Goshen and the Red Sea: Succoth, Etham and the final the Red Sea camp before crossing. This has led many to wrongly assume it took only three day from Goshen to the Red Sea.
3. Some people falsely assume the trip took only seven days. This assumption is based upon an inference about the 7 days of unleavened bread which was a memorial of when Israel left Egypt so quickly, that they did not have time for their bread to rise.
a. But nowhere does the Bible say they ate unleavened bread for 7 days, only that there would be a seven-day period to remember that first day they left with unleavened bread. Day two, they ate leavened bread again.
b. The Bible does not say, "Because you ate unleavened bread for 7 days after leaving Egypt, you will east unleavened bread for 7 days each year as a memorial."
c. Instead the Bible says, (paraphrased) "You will not eat leaven for 7 days in remembrance of that one day you ate unleavened bread, when you first left Egypt.
4. The Bible does tell us that the entire 700 km trip from Egypt to Mt. Sinai took 47 days.
a. It was day 25 when they crossed the Red Sea and day 47 when they reached Sinai.
b. It took 17 days to travel 500 km to the Red Sea and they spent 8 days camped there waiting for Pharaoh's army to come. We included the 16 km Red Sea crossing in the 500 km.
c. It took 22 days to travel 200 km to Sinai after the Red Sea including 7 days camping in the wilderness of Sin and 2 days battling the Amalekites at Rephidim 3 days for the visit of Jethro at Rephidim including a second Sabbath day before reaching Sinai.
5. Distance traveled from Egypt to Jebel Al-Lawz based upon actual route is 700 Km. It is 400 km line of sight as the bird flies.
a. From Goshen to the crossing point of the Red Sea is 500 KM. Israel passed the Red Sea camp under the Migdol at 436 km from Goshen, then travelled 24 km to Etham at 460 km, then 24 km back to the Red Sea camp at 484 km and crossed the Red Sea (16 km) for a total of 500 km.
b. These distances include the Etham and back the way they came, to the camp at the Red Sea before they crossed.
c. Etham was 24 km past the point where they crossed, so the round trip was 48 km extra.
d. The distance Pharaoh's army traveled from Goshen to where the pillar of cloud stopped them is 400 km. The angel stopped the Egyptian army on the coast of the Gulf of Suez 36 km short of reaching the Hebrew Red Sea camp which was 436 km from Egypt.
e. It was 16 km (10miles) across the Straits of Tiran. The straight-line diagonal track ran north of the Enterprise Passage, not through it, to the shores of Arabia in the Wilderness of Shur.
f. After they crossed into the wilderness of Shur, the distance to the camp in the wilderness of Sinai was 200 km.
6. Average rates of travel must be based upon the total distance and the actual days they were moving. The total distance is 700 km and the total number of actual travel days is 29.
7. Between Goshen and Sinai there were 18 rest days:
a. 7 rest days at the Red Sea before crossing waiting for pharaoh to arrive.
b. 7 rest days in wilderness of Sin.
c. 3 stationary days battling the Amalekites in Rephidim.
d. 1 rest day for the second sabbath.
8. 700 km between Goshen and Sinai their daily rate of travel was 24 km (14 miles) per day.
a. Total distance Goshen to Sinai is 700 km.
b. 47 total days between Goshen and Sinai.
c. 18 rest days between Goshen to Sinai.
d. 29 travel days between Goshen and Sinai.
e. 700 km / 29 travel days = 24 km per day (14 miles per day).
9. 500 km between Goshen and the Red Sea crossing their daily rate of travel was 29 km (17 miles) per day.
a. Total distance is 500 km in 24 total days but only 17 travel days = 29 km (17 miles) per travel day.
b. There were 7 rest days while camped as bait at the Red Sea waiting for Pharaoh to arrive.
c. Israel travelled 17 days and arrived at the Red Sea on day 17, which includes a night camp (day 9) at Succoth to collect the Hebrew slaves at the local turquoise mines at Serabit el-Khadim and Wadi Nasb. Messengers could be sent ahead of the main group to the miners in order to bring the Hebrew miner to the shoreline camp at Succoth.
d. As Israel began to backtrack from Etham on day 17 it took only 4 hours for a passenger pigeon to travel the 400 km back to Egypt at 100 km per hour from the Migdol military watchtower which directly overlooked the Hebrew camp. (5 hours at 80 km per hour). Pharaoh would understand the topography of the area that he could arrive before Israel came back up the coast towards Egypt just past Succoth before they would have an eastern escape route. Pharaoh was triggered by the dead end and backtrack at Etham even before Israel reached the final Red Sea camp on day 17.
e. Pharaoh easily travelled the 400 km in 7 days with 600 horse drawn chariots at a rate of 57 km per day (34 miles per day) and arrived on day 24 or sooner if he drove faster or longer each day. Navel support of supplies down the coast of the Gulf of Suez by ship would have made the trip even faster.
f. Israel crossed the Red Sea on day 25.
10. 200 km between the Red Sea crossing and Sinai there were 11 rest days:
a. 22 total days between Red Sea and Sinai.
11. 200 km between the Red Sea and Sinai their daily rate of travel was 18 km per day.
a. 22 total days between the Red Sea crossing and Sinai.
b. 11 rest days between the Red Sea crossing and Sinai.
c. 11 travel days between the Red Sea crossing and Sinai
d. The average daily rate from the red sea to Sinai was 200 km / 11 actual travel days = 18 km (11 miles) per day.
12. We would predict that their rate of travel would be lower after crossing the Red Sea, given the urgency of fleeing Egypt was gone. The rates of travel figures are realistic easily possible for a large crowd. Keep in mind that God gave them miraculous help and they traveled day and night and Israel could have arrived at the Red sea in 7 days.
a. Daily travel rate before crossing is 29 km per day.
b. Daily travel rate after crossing is 18 km per day.
13. Herodotus said that the same basic area was traveled at a rate of 38 km per day.
a. Herodotus (450 BC) said that the 150 km trip from the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea (north tip of the Gulf of Suez) was a four days journey.
b. This means they traveled 38 km (23 miles) per day.
c. "Psammetichus left a son called Necos, who succeeded him upon the throne. This prince was the first to attempt the construction of the canal to the Red Sea - a work completed afterwards by Darius the Persian - the length of which is four days' journey , and the width such as to admit of two triremes being rowed along it abreast. (Herodotus 2.158)
d. Considering they miraculously travelled day and night, the 3.5 million Hebrews travelled much slower Herodotus indicates was possible.
VI. Chronological markers of the Exodus
2. In 1446 BC Israel left Egypt exactly 430 years after Jacob entered Egypt “to the day”:
a. "And at the end of four hundred and thirty years, to the very day, all the hosts of the Lord went out from the land of Egypt." (Exodus 12:41)
3. In 1406 BC Israel crossed the Jordan River 40 years “to the day”:
a. "While the sons of Israel camped at Gilgal they observed the Passover on the evening of the fourteenth day of the month on the desert plains of Jericho. On the day after the Passover, on that very day, they ate some of the produce of the land, unleavened cakes and parched grain." (Joshua 5:10-11)
By Steve Rudd: Contact the author for comments, input or corrections .
Go To Start: WWW.BIBLE.CA
The Journey to Canaan
After many years of wandering in the wilderness as a consequence of their sin, the Israelites set out from Kadesh-barnea toward the Promised Land. It is difficult to know for certain the exact route they took from Kadesh-barnea to the plains of Moab, but it is possible that they followed a course that went around the lands of Edom and Moab along a desert route, after being refused passage through those lands—or they may have taken another route, through the heart of Edom and Moab along the King’s Highway.

- Accessibility decleration
Israel and You Spaces and Places in Israel
Major routes in the land of the bible *.
Israel and You June 17, 2020 History
Major routes in the Land of the Bible including the Via Maris (International Coastal Highway), the Way of the Patriarchs , the Jordan Rift Valley Route , the King’s Highway , and the Jezreel Valley . Routes are important since many biblical, historical events occurred at locations and towns along the routes.
Via Maris (International Coastal Highway) is the name for an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia. In Latin, Via Maris means “way of the sea” – דֶּרֶךְ הַיָּם. See Isaiah 8:23 in the Bible. It is a historic road that runs in part along the Israeli Mediterranean coast. It was the most important route from Egypt to the Fertile Crescent which followed the coastal plain before crossing over into the plain of Jezreel and the Jordan valley.

Way of the Patriarchs
Way of the Patriarchs is an ancient north south route traversing the land of Israel. The name refers to mentions in biblical narratives that it was frequently travelled by Abraham, Isaac and Jacob.

The Way of the Patriarchs follows the watershed ridge line of the Samarian and Judaean Mountains, running south through: Megiddo, Hazor, Shechem, Bethel, Jerusalem, Ephrath and Hebron to Beersheba .
Unlike the Via Maris and the King’s Highway which were international roads crossing the territories of many peoples, the Way of the Patriarchs was wholly within the territory of ancient Israel.
The ancient road of the patriarchs is now known as Highway 60. Highway 60 runs from north to south through Israel and passes through some of the most notable biblical sights including: Shiloh, Bethel, Elon Moreh, Jerusalem , and Hebron .
The Jordan Rift Valley Route
The Jordan Valley is part of the Levantine corridor and constitutes a route for animal migration, including in the past for the developing human species. The Jordan Valley still is an essential part of one of the main migration routes for birds in the world allow an estimated 500 million birds belonging 200 species to fly across Israel twice a year.
The Jordan Rift Valley is a significant topographic feature over which a few narrow paved roads and difficult mountain tracks lead. Even so, the Jordan Rift Valley has traditionally been a North-South transport corridor, and is crossed by important land routes in the East-West direction.
King’s Highway
The King’s Highway was a trade route of vital importance connecting Africa with Mesopotamia. It ran from Egypt across the Sinai Peninsula to Aqaba, then turned northward across Transjordan, to Damascus and the Euphrates River.
After the Muslim conquest of the Fertile Crescent in the 7th century CE it was the darb al-hajj or pilgrimage road for Muslims from Syria, Iraq, and beyond heading to the holy city of Mecca.

Driving the King’s Highway in Jordan
Jezreel Valley
The valley formed an easier route through the Levant than crossing the mountains on either side, and so saw a large amount of traffic, and was the site of many historic battles. Via Maris passed through Megiddo and the Jezreel Valley until it reached Tiberias on the Sea of Galilee.
The Jezreel Valley is located at the southern end of the Lower Galilee bordered to the south by the Samarian Highlands, the south east by Mount Gilboa, the west by Mount Carmel, and the country of Jordan to the east. The valley’s strategic location meant that throughout history, armies and travelers along the Via Maris would pass through the valley.
The valley once was the channel by which the Mediterranean Sea, at the north-western end of the valley, connected to the Sea of Galilee, the Jordan Valley and ultimately to the Dead Sea. About two million years ago, as the land between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan Rift Valley rose, this connection was lost, and the periodic floods from the Mediterranean Sea ceased.
This resulted in the Dead Sea no longer having a connection to the ocean, and over time, due to greater evaporation than precipitation plus surface water inflow, it has become heavily saline. The Sea of Galilee, on the other hand, consists of fresh water.
Land of the Bible Routes
The lay of the land (avoiding steep hillsides and deserts) determines where roads run. Roads transmitted wealth, knowledge and power. These factors determine where cities were built and where armies campaigned. Though there are few descriptions of roads in the Bible their location shapes the story of Scripture.
Share this:
About israel and you, related articles, the siege of jerusalem (70 ad).
November 23, 2022

Judaism and Zoroastrianism *
June 8, 2022

The expulsion of Jews from Arab and Muslim countries *
June 2, 2022

Judaism and Buddhism *
March 14, 2022

Conversos – Crypto Jews – Marranos *
December 27, 2021

Judaism and Astrology *
November 14, 2021
Bible Odyssey
Search the Site
Trade Routes of Palestine Map
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter

Search the Bible
Results from new revised standard version updated edition.
The land of Canaan has been called the “sacred bridge,” a strip of land that connects two worlds. In ancient times it was the only way to travel between Egypt and Mesopotamia, since a more direct route through the Arabian Desert was impractical if not impossible. There were two major arteries for international trade that traversed the land. The coastal highway, or Via Maris, followed along the coast of the Mediterranean and cut through the Jezreel Valley and along the shore of the Sea of Galilee before heading north into Damascus. (Some historical geographers argue that Via Maris was not the coastal highway, but rather an east-west artery in northern Israel.) The other major route, the King’s Highway, was located to the east along the high fertile plain beyond the Dead Sea and the Jordan River. The two routes converged on Damascus, where the route splits toward Antioch to the north, and towards Mesopotamia to the east.
A regional route worth noting, though of less importance for international commerce, is known as the Ridge Route, which traveled through the hills of Judea and Samaria, passing by the city of Jerusalem.
The impact these international trade routes had on the cultures and societies of ancient Canaan cannot be underestimated. The strategic importance of this land bridge for gaining and maintaining power and wealth in antiquity is reflected in the constant struggle that went on between regional and imperial powers to control the region for centuries.

Antioch to Jerusalem
- Warren Carter
Search a pre-defined list
The Whole Bible The Old Testament The New Testament ────────────── Pentateuch Historical Books Poetical Books Wisdom Literature Prophets Major Prophets Minor Prophets ────────────── The Gospels Luke-Acts Pauline Epistles General Epistles Johannine Writings ────────────── Genesis Exodus Leviticus Numbers Deuteronomy Joshua Judges Ruth 1 Samuel 2 Samuel 1 Kings 2 Kings 1 Chronicles 2 Chronicles Ezra Nehemiah Esther Job Psalms Proverbs Ecclesiastes Song of Songs Isaiah Jeremiah Lamentations Ezekiel Daniel Hosea Joel Amos Obadiah Jonah Micah Nahum Habakkuk Zephaniah Haggai Zechariah Malachi Matthew Mark Luke John Acts Romans 1 Corinthians 2 Corinthians Galatians Ephesians Philippians Colossians 1 Thessalonians 2 Thessalonians 1 Timothy 2 Timothy Titus Philemon Hebrews James 1 Peter 2 Peter 1 John 2 John 3 John Jude Revelation
OR Select a range of biblical books
Select a Beginning Point Genesis Exodus Leviticus Numbers Deuteronomy Joshua Judges Ruth 1 Samuel 2 Samuel 1 Kings 2 Kings 1 Chronicles 2 Chronicles Ezra Nehemiah Esther Job Psalms Proverbs Ecclesiastes Song of Songs Isaiah Jeremiah Lamentations Ezekiel Daniel Hosea Joel Amos Obadiah Jonah Micah Nahum Habakkuk Zephaniah Haggai Zechariah Malachi Matthew Mark Luke John Acts Romans 1 Corinthians 2 Corinthians Galatians Ephesians Philippians Colossians 1 Thessalonians 2 Thessalonians 1 Timothy 2 Timothy Titus Philemon Hebrews James 1 Peter 2 Peter 1 John 2 John 3 John Jude Revelation
Select an Ending Point Genesis Exodus Leviticus Numbers Deuteronomy Joshua Judges Ruth 1 Samuel 2 Samuel 1 Kings 2 Kings 1 Chronicles 2 Chronicles Ezra Nehemiah Esther Job Psalms Proverbs Ecclesiastes Song of Songs Isaiah Jeremiah Lamentations Ezekiel Daniel Hosea Joel Amos Obadiah Jonah Micah Nahum Habakkuk Zephaniah Haggai Zechariah Malachi Matthew Mark Luke John Acts Romans 1 Corinthians 2 Corinthians Galatians Ephesians Philippians Colossians 1 Thessalonians 2 Thessalonians 1 Timothy 2 Timothy Titus Philemon Hebrews James 1 Peter 2 Peter 1 John 2 John 3 John Jude Revelation
OR Custom Selection:
Use semicolons to separate groups: 'Gen;Jdg;Psa-Mal' or 'Rom 3-12;Mat 1:15;Mat 5:12-22'

Click to Change
Return to Top

ESV Global Study Bible :: Abram Travels to Canaan

Abram Travels to Canaan
C. 2091 b.c..
Abram was born in Ur, a powerful city in southern Babylonia. Abram's father, Terah, eventually led the family toward the land of Canaan but decided to settle in Haran (see Gen. 11:27-31 ). After Terah's death, the Lord called Abram to go "to the land that I will show you" (Canaan), which he promises to give to Abram's descendants.
The ESV Global Study Bible Copyright © 2012 by Crossway . All rights reserved. Used by permission.
Search Results in Other Versions
Search results by book, blb searches, search the bible.
Advanced Options
There are options set in 'Advanced Options'
Theological FAQs
Other Searches
Multi-Verse Retrieval
* 'Number Delimiters' only apply to 'Paragraph Order'
Let's Connect
Daily devotionals.
Blue Letter Bible offers several daily devotional readings in order to help you refocus on Christ and the Gospel of His peace and righteousness.
- BLB Daily Promises
- Day by Day by Grace
- Morning and Evening
- Faith's Checkbook
- Daily Bible Reading
Daily Bible Reading Plans
Recognizing the value of consistent reflection upon the Word of God in order to refocus one's mind and heart upon Christ and His Gospel of peace, we provide several reading plans designed to cover the entire Bible in a year.
One-Year Plans
- Chronological
- Old Testament and New Testament Together
Two-Year Plan
- Canonical Five Day Plan
Recently Popular Pages
- H3068 - Yᵊhōvâ - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv)
- Hoekstra's Day by Day by Grace
- O.T. Names of God - Study Resources
- Fear Only God by C. H. Spurgeon
- David Guzik :: Hechos 9 – La Conversión de Saulo de Tarso
- David Guzik :: Apocalipsis 11 – Los Dos Testigos
- David Guzik :: Apocalipsis 12 – La Mujer, el Niño, y el Dragón
- David Guzik :: Génesis 3 – La tentación y caída del hombre
- David Guzik :: 1 Samuel 22 – David en la Cueva de Adulam, Saúl Asesina a los Sacerdotes
Recently Popular Media
- Who Is Jesus Christ? (Tony Clark)
- Jehovah's Witnesses, Jesus and the Holy Trinity (Walter Martin)
- Judges 1 (Bob Davis)
- How Jesus Handled Anger Pt. 1 (Tony Clark)
- Matthew 8-9 (1982-85 Audio) (Chuck Smith)
- Joseph Glorified (Chuck Missler)
- Daniel Intro [1990s] (Chuck Missler)
- Romans 11-12 (1982-85 Audio) (Chuck Smith)
- Genesis 4-5 (1979-82 Audio) (Chuck Smith)
- 1 Timothy 5-6 (1982-85 Audio) (Chuck Smith)
CONTENT DISCLAIMER:
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.

Blue Letter Bible
Login to your account.
Email / username or password was incorrect!
Check your email for password retrieval
Keep me logged in!
Did you forget your password?
Register a new BLB account
Complete the form below to register [?]
Error: That Email is already registered
Error: Please provide a valid Email
Error: Passwords should have at least 6 characters
Error: Passwords do not match
Error: Please provide a valid first name
Error: That username is already taken
Error: Usernames should only contain letters, numbers, dots, dashes, or underscores
← Login to Your Account
Passwords should have at least 6 characters. Usernames should only contain letters, numbers, dots, dashes, or underscores.
Thank you for registering. A verification email has been sent to the address you provided.
Did You Know BLB Is User Supported?
Your partnership makes all we do possible. Would you prayerfully consider a gift of support today?
Cookie Notice: Our website uses cookies to store user preferences. By proceeding, you consent to our cookie usage. Please see Blue Letter Bible's Privacy Policy for cookie usage details.
Old Testament
New testament.
The Geography of the Exodus: A Journey from Egypt to Canaan
The Exodus is one of the most significant events in the history of the Israelites. It is the story of their escape from slavery in Egypt and their journey to the land of Canaan, which God had promised to them. The geography of the Exodus played a crucial role in shaping the experiences and beliefs of the Israelites. Here's a closer look at the journey from Egypt to Canaan.
- Egypt: The Exodus began in Egypt, where the Israelites had been living in slavery for over 400 years. According to the Bible, Moses led the Israelites out of Egypt and across the Red Sea, which God miraculously parted to allow them to pass.
- Sinai Peninsula: After crossing the Red Sea, the Israelites traveled through the Sinai Peninsula, a barren and desolate region that was difficult to navigate. It was at Mount Sinai that Moses received the Ten Commandments and established the covenant between God and the Israelites.
- Wilderness: The Israelites spent 40 years wandering in the wilderness, a harsh and unforgiving landscape that was marked by sand dunes, rocky terrain, and extreme temperatures. They relied on God's provision of manna and water to sustain them during their journey.
- Jordan River: The Israelites eventually arrived at the Jordan River, which they crossed into the land of Canaan, the promised land. The crossing of the Jordan River is seen as a symbol of the Israelites' transition from slavery to freedom.
- Canaan: The land of Canaan was a region that was rich in resources and had fertile soil, making it an ideal location for settlement. The Israelites faced many challenges as they established themselves in the land, including conflicts with other tribes and struggles to maintain their religious beliefs.
The geography of the Exodus provides us with a greater understanding of the challenges and triumphs of the Israelites as they journeyed from slavery in Egypt to freedom in the promised land. The landscape of the region played a significant role in shaping their experiences and beliefs, and continues to be an important part of their cultural and religious heritage.
Related Posts


The Reign of Otho: A Brief Yet Impactful Chapter in Roman History
In the annals of ancient Rome, the name Otho stands as a reminder of the tumultuous nature of imperial politics... Read More

The Land of Milk and Honey: Understanding the Geography of Israel in the Bible
The land of Israel, also known as the Holy Land, has a rich history and plays a prominent role in... Read More

The Role of Geography in the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is one of the most intriguing and controversial books in the Bible. It is a prophetic... Read More
The Exodus is one of the most significant events in the history of the Israelites. It is the story of... Read More
2. Israel’s Exodus from Egypt and Entry into Canaan
Possible route of the Exodus
Jordan River
Salt Sea (Dead Sea)
Great Sea (Mediterranean Sea)
Philistines
River of Egypt
Wilderness of Zin
Rameses (Tanis)
Wilderness of Shur
Kadesh-barnea
Wilderness of Paran
Arabah (Rift Valley)
Eastern Wilderness
On (Heliopolis)
Pi-hahiroth?
Wilderness of Etham
Sinai Peninsula
Ezion-geber
Noph (Memphis)
Gulf of Suez
Wilderness of Sin
Sinai Wilderness
Wilderness Camps
Gulf of Aqaba
Mt. Sinai? (Horeb)
0 40 80 120
Rameses Israel was thrust out of Egypt ( Ex. 12 ; Num. 33:5 ).
Succoth After the Hebrews left this first campsite, the Lord attended them in a cloud by day and in a pillar of fire by night ( Ex. 13:20–22 ).
Pi-hahiroth Israel passed through the Red Sea ( Ex. 14 ; Num. 33:8 ).
Marah The Lord healed the waters of Marah ( Ex. 15:23–26 ).
Elim Israel camped by 12 springs ( Ex. 15:27 ).
Wilderness of Sin The Lord sent manna and quail to feed Israel ( Ex. 16 ).
Rephidim Israel fought with Amalek ( Ex. 17:8–16 ).
Mount Sinai (Mount Horeb or Jebel Musa) The Lord revealed the Ten Commandments ( Ex. 19–20 ).
Sinai Wilderness Israel constructed the tabernacle ( Ex. 25–30 ).
Wilderness Camps Seventy elders were called to help Moses govern the people ( Num. 11:16–17 ).
Ezion-geber Israel passed through the lands of Esau and Ammon in peace ( Deut. 2 ).
Kadesh-barnea Moses sent spies into the promised land; Israel rebelled and failed to enter the land; Kadesh served as the main camp of Israel for many years ( Num. 13:1–3, 17–33 ; 14 ; 32:8 ; Deut. 2:14 ).
Eastern Wilderness Israel avoided conflict with Edom and Moab ( Num. 20:14–21 ; 22–24 ).
Arnon River Israel destroyed the Amorites who fought against them ( Deut. 2:24–37 ).
Mount Nebo Moses viewed the promised land ( Deut. 34:1–4 ). Moses delivered his last three sermons ( Deut. 1–32 ).
Plains of Moab The Lord told Israel to divide the land and dispossess the inhabitants ( Num. 33:50–56 ).
Jordan River Israel crossed the Jordan River on dry ground. Near Gilgal, stones from the bottom of the Jordan River were placed as a monument of Jordan’s waters being divided ( Josh. 3:1–5:1 ).
Jericho The children of Israel captured and destroyed the city ( Josh. 6 ).
The Israelites’ Wandering: A Map of Their 40-Year Journey in the Wilderness

The story of the Israelites' wandering in the wilderness is one of the most well-known and powerful stories in the Bible. According to the Book of Exodus, after being led out of Egypt by Moses, the Israelites spent 40 years wandering in the wilderness before finally reaching the Promised Land. But have you ever wondered exactly where they traveled during this time? By using maps, we can trace their journey through the wilderness and gain a deeper understanding of this powerful story.
The journey of the Israelites began at the Red Sea, where they crossed on dry ground after God parted the waters. From there, they traveled south to the area of Marah, where they found bitter water that was made sweet by a miracle from God. They then continued eastward to the desert of Sin, where they were provided with manna from heaven and quail to eat.
The Israelites then traveled to Mount Sinai, where they received the Ten Commandments and other laws from God. After spending several months at Sinai, they continued their journey northward towards the Promised Land, but their progress was slowed by their disobedience and lack of faith in God.
The Israelites continued to wander in the wilderness for another 38 years, traveling back and forth across the desert and encountering many challenges and trials along the way. They fought battles against other nations, complained about their lack of food and water, and even rebelled against Moses and God on several occasions.
Finally, after 40 years of wandering, the Israelites reached the Promised Land, which was located on the eastern shores of the Jordan River. By using maps, we can see the locations of the places where they camped, the routes they took, and the challenges they faced during their journey.
In conclusion, a map of the Israelites' 40-year journey in the wilderness can help us to better understand this powerful story and the faith and perseverance of the Israelites. By tracing their journey, we can see the locations of the places where they camped and the routes they took, and gain a deeper appreciation for their struggles and ultimate triumph. So why not take a journey through the wilderness with the Israelites and discover the power of their story?
Related Posts

Brow Lamination Toronto & Beauty Through the Ages: A Fascinating Journey
The Art of Beauty: From Ancient Egyptians to brow lamination Toronto Have you ever wondered how our ideas approximately beauty have... Read More
Unveiling the Majesty of Augustus Caesar: Exploring Statues, Busts, and Symbols of the Iconic Emperor
In the annals of history, few figures loom as large as Augustus Caesar. Known for his transformative reign and lasting... Read More

The Enchanting History of Cameo Jewelry
Step into the enthralling global of cameo rings, wherein historic craftsmanship meets timeless elegance in a enchanting display of artistry... Read More

Abraham’s Obedience: Lessons in Trusting God
Abraham, often referred to as the "father of faith," is a key figure in the biblical narrative renowned for his... Read More
- Skip to main content
- Skip to header right navigation
- Skip to site footer

Casual English Bible
By Stephen M. Miller
Map of Canaan, Promised Land

Hill people
Powerful philistine enemy, israel’s many enemies, related to bible books:.
- Deuteronomy
Showing Locations:
- Caesarea Philippi
- Jordan River
- Judean hills
- Mount Hermon
- Mount Tabor
- Samaria the city
- All Bible Maps
- Heart Messages
- Roman Roads
- Archaeology
Map of the Roads in Israel
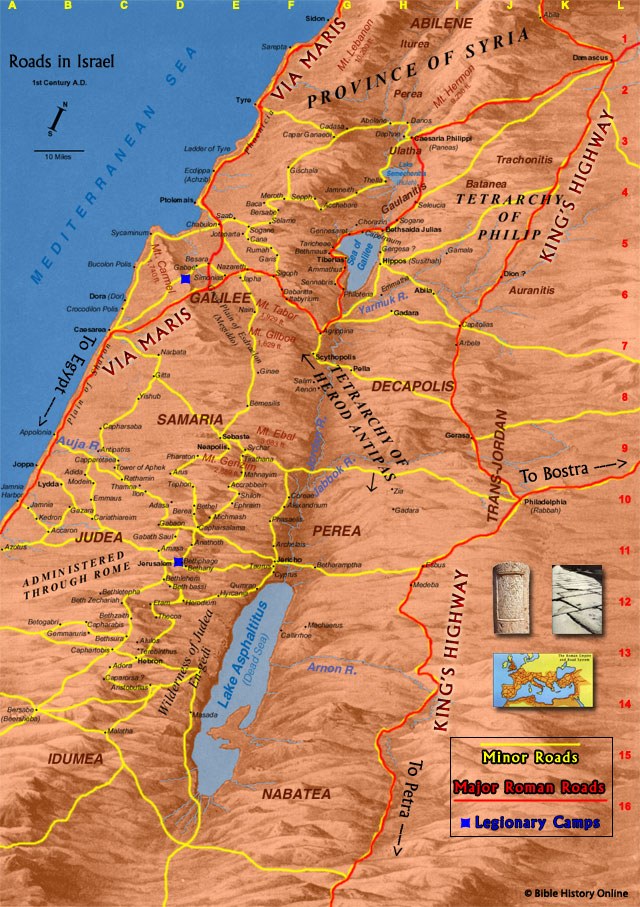
( Enlarge ) ( PDF for Print ) (Freely Distributed)
Map of the Roads in First Century Israel
This map includes general roads and Roman paved roads in ancient Israel. You can see the major and minor roads and highways, and the Roman Legionary Camps in the land of Israel during the first century AD. The Via Maris, the King's Highway, the Way of the Sea, and other small roads can be seen on this map.
Proverbs 16:17 - The highway of the upright is to depart from evil: he that keepeth his way preserveth his soul.
Highways in Ancient Israel In ancient Israel most people traveled on foot and israel was a difficult place to travel. The highways and roads connected travelers to the 6 parallel divisions in the topography, Israel's cities and villages, the Dead Sea, and the Negev. The Hebrews generally followed their small roads but they were not into major road construction as the Romans were. In fact the Hebrew word for road means a beaten worn out path. Road construction would have been difficult for any skillful engineer because of the topography of the land. When Jesus journeyed from Jerusalem through the land of Samaria (John 4) there were no special roads but large dirt paths with some stone. As He journeyed around Nazareth and the surrounding villages in Galilee He was following beaten dirt tracks, with little road making.
The Romans were skillful road makers who made the great highways of the Empire, so that soldiers and horses could travel on them. Most of the travelers along Roman highways were caravans, camels, horses, and donkeys.
The roads in first century Israel in the time of Jesus were as follows: 1. The road that passed northward up the coastal plain from Gaza, (the port of the Egyptian desert), past Joppa and Caesarea round the nose of Mount Carmel up to Tyre, and Sidon. This road, at a point due west of Jerusalem, had a fork running north-eastward, climbing the foothills of Samaria and going through the valleys of Samaria (including that in which Joseph was sold to the Egyptians) to the plain of Esdraelon. Crossing that plain it climbed the Galilean hills and passed between two strange rocky peaks called the Horns of Hattin down a ravine in which dwelt thousands of pigeons that were captured in Jesus' day to be sold in the Temple for the poor to use as sacrificial offerings. Then to the Plain of Gennesaret which the road then crossed, and north through Capernaum and crossing the Jordan with Mount Hermon on it's left, eastward to Damascus. 2. Starting in the south from Beersheba (the other port of Palestine on the Egyptian desert), a very ancient road climbed northward up the Judean hills to Hebron and through Bethlehem to Jerusalem. The Flight into Egypt from Bethlehem with the infant Jesus would probably take this route. From Jerusalem the road forked in three directions. One ran to the left down the steep ravines of the Judean hills to the coastal plain and to Joppa. It is down this road that Peter would go in the journey described in Acts. The road to the east ran even more steeply down past Bethany to the deep trench of the Jordan valley. This is the road from Jerusalem to Jericho (a descent of 3500 feet in 14 miles) that is the scene of the story of the Good Samaritan; and up its steep slopes Jesus came from Transjordania, the Jordan Valley, and Jericho, to face trial and death at Jerusalem. 3. Another road from Jerusalem ran directly northward over the hills of Judea, passing by the site of Bethel and descending into a small plain before lifting again to the hills of Samaria under the shadow of Mount Gerizim and Mount Ebal. Through Samaria it runs past the foot of Mount Gilboa across the Plain of Esdraelon, where one fork runs north-westward to Nazareth and another north-eastward by the foot of Mount Tabor and the north end of the Lake of Galilee, where it joins up with the great Way of the Sea. It will be seen that none of these roads to and from Jerusalem is a great international highway. The roads or tracks are there because Jerusalem exists; and they simply lead to and from the Holy City. 4. Moving still farther east we come upon another series of routes important in the life of Jesus. The Gospels tell us that He took the road from Galilee to Jerusalem through Samaria on at least one occasion. The fierce hostility of the Samaritans to the Jews, however, led Jews when traveling from the north to Jerusalem to turn eastward at Jezreel (the eastern gap from the Plain of Esdraelon into the Jordan Valley), and go down into that valley to join a road running southward on the western side of the river to Jericho. There the pilgrims to Jerusalem would turn west again to climb up to Jerusalem, having avoided Samaria. 5. Still farther east, on the Transjordania side of the Jordan River, roads ran in Jesus' time between the Graeco-Roman cities of Decapolis. It is highly probable that in His last journey (associated in Luke with the parables of the lost money, the lost sheep, and the prodigal son) Jesus walked upon these roads, which ran through Philadelphia, Gerasa, Gadara and up to Damascus. The road from Amman also ran southward. Jesus did not take this road; but as it ran near to the Castle of Machaerus, in which Herod Antipas imprisoned John the Baptist, John himself may have been led in chains along that route.
Merchants and Trade
During the first century A.D. the East and West were making a solid connection, especially with the Jews. By the time of Jesus the Jews were living in a commercial Greek world, due to the achievements of Alexander the Great. The Romans built even more and established additional trade in all of its provinces, linking the major centers of population and uniting the provinces. The Mediterranean world had become a Greco-Roman world and it had become like one big marketplace, attracting trade goods from distant lands as far as India and China. The Roman army and navy protected the boundaries of the Empire from barbarians and pirates. The Jews had become very familiar with trade and the art of international commerce. They became very wealthy and it was all controlled by a select few. Most of the common Israelites bought and sold in the local marketplace without ever realizing how all the goods from around the world had arrived there. How many of the goods had arrived there on the backs of camels and donkeys, passing through countless cities and villages upon roads and footpaths that were all but washed away by the heavy rains. There were many roads that criss-crossed all of Israel, roads that had been there for hundreds of years and when the legions of Rome came they had built up certain highways to march their mighty chariots and soldiers. The main roads contained 3-foot deep bed, paved with gravel, stones and concrete. They were built to last and made life much easier for the many caravans of merchants in the ancient world. Some of these roads can still be seen today. Milestones marked the roads with their drainage ditches and curbs. By the end of the first century 50,000 miles of roads linked the Roman Empire with the whole Mediterranean world. The network of roads made it safe to trade, for the first time in the history of the world.
The ancient Jews learned the art of commerce very quickly. They became renown throughout the world as successful traders within and without the borders of their country.
The Provinces - The Roman Empire beyond Italy was divided into about 40 provinces, or territories. Each province had its own governor, who was appointed by the emperor or named by the Senate. The governors' work mainly included keeping order and collecting taxes. Augustus and the emperors who followed him expanded the empire by conquering new territories. By the end of the first century A.D. the Roman Empire had a population of about 60 million. This was more than one-fifth of the total population of the world at that time.
The Pax Romana - Augustus's reign marked the beginning of a remarkable period in Rome's history. For more than 200 years, the vast Roman Empire was united and, for the most part, peaceful. This period from 27 B.C. to 180 A.D. is called the Pax Romana, or "Peace of Rome." Roman Roads By the time of Jesus the Romans had brought peace throughout their Empire. The Mediterranean world had become a place of opportunity for traders and merchants. The Romans developed a massive network of roads that stretched over 50,000 miles throughout the Mediterranean world. This made it relatively easy for the Roman army to move quickly to defend its borders. Supplies could also be sent to the troops over long distances. Along the roads were inns, restaurants and hotels; places where horses were changed, or where weary travelers could rest for the night and get food. The Via Appia was the first of the marvelous Roman roads. It began to be built in 312 B.C. and reached as far from Rome as Brundisium, an Adriatic port. In Israel there were 3 main roads, one of which was the Via Maris. Paved Roads Roman were experts at surveying and building roads. They would plan out a strategic route and remove any obstacles in its path. Then they would dig a trench about 3 feet deep and 10-25 feet wide, depending upon the importance of the road.
Illustration of a Roman Paved Road The 4 Layers The deepest portion of the trench was filled in with a layer of large stones tightly fitted together. This was strategic in preventing puddles and keeping the roads from freezing, which caused cracks. The second layer was filled with smaller stones compressed together and filled with concrete. The third layer was filled with gravel and flattened out smoothly. The fourth and last layer was a pavement of large smooth stone slabs. Every major road had curbs and drainage ditches. The largest roads were in Rome and on its borders, to bring a sense of awe to anyone from the outside. They sometimes reached 50 feet wide.

Photo of a Roman Road
Network of Roads in the Roman Empire
Robbers and Thugs During the time of Jesus it was very dangerous to travel in certain parts of Israel. Even though there was added security in various parts of the Empire, there were bandits that would lie in wait and attack unsuspecting merchants. The wealthy merchants could be noticed easily because their goods were packed high on the backs of their donkeys and camels. Robbers were known to hide in the hills, make their attack, and return to caves and other hiding places. The ancient Jews learned the art of commerce very quickly. They became renown throughout the world as successful traders within and without the borders of their country. The Land of Israel The Province of Syria Via Maris One of the most important trade routes in the Middle East during ancient times was the Via Maris. The Latin term, meaning "Way of the Sea" is referenced in Isaiah 8:23 in the Tanakh (in the Christian Old Testament it is Isaiah 9:1) as "Derech HaYam" or "Way of the Sea." The Latin name comes from the Vulgate, the Latin translation of the New Testament, in Matthew 4:15. The term "Via Maris" comes from the Romans and hence the terminology "Via Maris" tends to be an exclusively Christian reference to the Sea Road. Other names for the Derech HaYam/Via Maris include "Coastal Road" and "Way of the Philistines." From the coast to Damascus, the route is called the Trunk Road. The Via Maris travels and is also known as the International Coastal Highway. The International Coastal Highway is still a major route in modern-day Israel. The "Way of the Sea" is one of three major trade routes in ancient Israel – the Via Maris, Ridge Route, and the King's Highway. It is situated from the Galilee to the North to Samaria to the South, running through the Jezreel Valley. At the Philistine Plain, the Way broke into two branches, one on the coast and one inland (through the Jezreel Valley, the Sea of Galilee, and Dan), which unites at Megiddo ("Armageddon"). The location of Megiddo vis a vis the Via Maris explains why Megiddo was a very important route for travel and trading city in ancient Israel. The Way of the Sea connected the major routes from the Fertile Cresent to Mesopotamia (from Egypt to modern day Iran, Iraq, Turkey and Syria).The road was the main thoroughfare running north/south from the Sinai along the coastal plain through the Jezreel valley, Beit Shean and on until Damascus Throughout the centuries, once the Jews were exiled from Israel, the Jezreel Valley, in which the route traverses, became abandoned and the area became an infested swamp. Zionist pioneers, however, drained the swamp from the time of the first land acquisition in 1921, and the valley has been transformed into a fertile, fruit-bearing plain.
King's Highway
The King’s Highway was a very ancient trade route that was important in Biblical times. The highway started in Egypt and went up through the Sinai Peninsula over to Aqaba and up the eastern side of the Jordan River to Damascus and the Euphrates River.
The King's Highway is mentioned in the Bible in Numbers 20:17-21: "Please let us pass through your country. We will not pass through fields or vineyards, nor will we drink water from wells; we will go along the King's Highway; we will not turn aside to the right hand or to the left until we have passed through your territory.'" Then Edom said to him, "You shall not pass through my land, lest I come out against you with the sword." So the children of Israel said to him, "We will go by the Highway, and if I or my livestock drink any of your water, then I will pay for it; let me only pass through on foot, nothing more." Then he said,"You shall not pass through." So Edom came out against them with many men and with a strong hand. Thus Edom refused to give Israel passage through his territory; so Israel turned away from him. "
"Numerous ancient states, including Edom, Moab, Ammon, and various Aramaean polities depended largely on the King's Highway for trade. The Highway began in Heliopolis, Egypt and from there went eastward to Clysma (modern Suez), through the Mitla Pass and the Egyptian forts of Nekhl and Themed in the Sinai desert to Eilat and Aqaba. From there the Highway turned northward through the Arabah, past Petra and Ma'an to Udruh, Sela, and Shaubak. It passed through Kerak and the land of Moab to Madaba, Rabbah Ammon/Philadelphia (modern Amman), Gerasa, Bosra, Damascus, and Tadmor, ending at Resafa on the upper Euphrates...The Nabataeans used this road as a trade route for luxury goods such as frankincense and spices from southern Arabia. During the Roman period, the King's Highway was rebuilt by Trajan and called the Via Traiana Nova." - Wikipedia
Judea It was King Herod’s goal to make Jerusalem the most impressive city in the world. He would go to any means to impress the world with his Hellenized buildings and magnificent Greek architecture.
Legionary Camps in Israel and the Province of Syria
"Tiles found in Caesarea Maritima, built in the second decade BC, suggest that the legion was at that time based in Judaea. Later X Fretensis moved to Syria. In 6 AD it was stationed in that province together with legions III Gallica, VI Ferrata, and XII Fulminata. In the same year, Publius Sulpicius Quirinus, governor of Syria, led these legions in the suppression of the revolt that sprung out after the deposition of Herod Archelaus. Under Nero, in 58-63 AD, X Fretensis participated in the campaigns of Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo against the Parthians. First Jewish-Roman War. Ruins of the city of Gamla, conquered by X Fretensis in 68 AD. X Fretensis was centrally involved in the First Jewish-Roman War (66–73 AD), under the supreme command of Vespasian. In 66 AD, the X Fretensis and V Macedonica went to Alexandria for an invasion of Ethiopia planned by Nero. However, the two legions were needed in Judaea to suppress a revolt. After spending the winter in Ptolemais Ace (modern Acre, Israel), X Fretensis and V Macedonica relocated in the coastal city of Caesarea Maritima (67/68). This was due to the large number of legions being mobilized in Ptolemais, under Marcus Ulpius Traianus, future governor of Syria and father of the emperor Trajan. During that same winter, the Caesarea camp of Xth and Vth hosted Vespasian, who was forced to go to Rome the following year, where he seized power. Vespasian's son, Titus finished the suppression of the revolt.
By 70, the rebellion in all of Iudaea had been crushed, except for Jerusalem and a few fortresses, including Masada. In that year X Fretensis, in conjunction with V Macedonica, XII Fulminata, and XV Apollinaris, began the siege of Jerusalem, stronghold of the rebellion. The Xth camped on the Mount of Olives. During the siege, Legio X gained fame in the effective use of their various war machines. It was noted that they were able to hurl stones that weighted a talent (about 25 kg) a distance of two furlongs (400 m) or further. The projectiles of their ballistae caused heavy damage to the ramparts. According to Josephus (vol. III of his history of Judaean war) Larcius Lepidus was the commanding officer of the X Legion. The siege of Jerusalem lasted five months and the besieged population experienced all the terrible rigors of starvation. Finally, the combined assaults of the legions succeeded in taking the city, which was then subjected to destruction." - Wikipedia Ancient Roman Roads "When the fullness of time came, God brought forth His Son, born of a woman, born under the law." (Gal 4:4) The Roman road was the bloodstream of the empire. Merchants paid taxes to Rome on all their transactions, and they needed the roads to carry their goods to an ever-widening market. Legionnaires marched upon them swiftly gaining efficient access to battle. In a sense, the roads were funding and facilitating Roman expansion. Yet God had a higher purpose. A new kind of merchant would soon be traversing the entire Mediterranean area, not one who transports his treasure to the city marketplace, but one who is a treasure, and who carries true riches, - not to sell, but to give away freely. The transforming good news of God’s forgiveness through Jesus the Messiah was imbedded into the hearts of the Apostles and early believers, and God prepared those roads for them to walk upon and lead others into His path. A new kind of soldier would be running these well built thoroughfares to fight, - not flesh and blood, but a spiritual warfare that would liberate entire civilizations from the bondage of Satan’s tyrannical oppression and coercion, to a Kingdom ruled by love, service and willing devotion. Throughout history ‘the road’ has provided an excellent metaphor for life’s journey. With amazement, we can look back over the winding grades of difficulty, the narrow pass of opportunity, the choice between security or adventure, when our road divided and we had to make the call. Yes, all roads led to Rome, specifically the Forum, in the ancient empire of old, where an Emperor judged the players in the arena for their conduct before him. Our personal road will eventually and inevitably cease at the throne of Almighty God. It is He who must judge our travel upon this earth, in the blinding glory of His eternal justice. Compelled by His love, He placed sin’s damning penalty upon His Own Son, instead of us, so that we could freely receive the "thumbs up!" from Him who loves us beyond all measure.

Painting of a Roman Highway
Highways in Smith's Bible Dictionary
Highways Though during the sway of the Romans over Israel they made a few substantial roads for their carts and chariots, yet for the most of the time, as today, the Jews had nothing such as we call roads, but only footpaths through which animals walk in single file. These are never cared for, no repairs are made or obstacles removed. This fact brings into striking prominence the figure of repairing a highway for the return Of the captives, or the coming of the great King. On special occasions kings had roads prepared for the progress of their armies, or their own going from place to place. Full Article
Roman Roads in the Bible Encyclopedia - ISBE 7. Cities of Galilee: In material ways too Rome opened the way for Christianity by building the great highways for the gospel. The great system of roads that knit then civilized world together served not only the legions and the imperial escorts, but were of equal service to the early missionaries, and when churches began to spring up over the empire, these roads greatly facilitated that church organization and brotherhood which strengthened the church to overcome the empire. With the dawn of the pax Romana all these roads became alive once more with a galaxy of caravans and traders. Commerce revived and was carried on under circumstances more favorable than any that obtained till the past century. Men exchanged not only material things, but also spiritual things. Many of these early traders and artisans were Christians, and while they bought and sold the things that perish, they did not lose an opportunity of spreading the gospel. For an empire which embraced the Mediterranean shores, the sea was an important means of intercommunication; and the Mediterranean routes were safer for commerce and travel at that period than during any previous one. Pompey the Great had driven the pirates off the sea, and with the fall of Sextus Pompey no hostile maritime forces remained. The ships which plied in countless numbers from point to point of this great inland sea offered splendid advantages and opportunity for early Christian missionary enthusiasm. Full Article
Highways in Easton's Bible Dictionary
Highway. a raised road for public use. Such roads were not found in Israel; hence the force of the language used to describe the return of the captives and the advent of the Messiah (Isa. 11:16; 35:8; 40:3; 62:10) under the figure of the preparation of a grand thoroughfare for their march. During their possession of Israel the Romans constructed several important highways, as they did in all countries which they ruled. Full Article
The Bible Mentions the "Highway" Often
2 Kings 18:17 - And the king of Assyria sent Tartan and Rabsaris and Rabshakeh from Lachish to king Hezekiah with a great host against Jerusalem. And they went up and came to Jerusalem. And when they were come up, they came and stood by the conduit of the upper pool, which [is] in the highway of the fuller's field. Isaiah 19:23 - In that day shall there be a highway out of Egypt to Assyria, and the Assyrian shall come into Egypt, and the Egyptian into Assyria, and the Egyptians shall serve with the Assyrians. Judges 21:19 - Then they said, Behold, [there is] a feast of the LORD in Shiloh yearly [in a place] which [is] on the north side of Bethel, on the east side of the highway that goeth up from Bethel to Shechem, and on the south of Lebonah. Jeremiah 31:21 - Set thee up waymarks, make thee high heaps: set thine heart toward the highway , [even] the way [which] thou wentest: turn again, O virgin of Israel, turn again to these thy cities. Isaiah 62:10 - Go through, go through the gates; prepare ye the way of the people; cast up, cast up the highway ; gather out the stones; lift up a standard for the people. Isaiah 36:2 - And the king of Assyria sent Rabshakeh from Lachish to Jerusalem unto king Hezekiah with a great army. And he stood by the conduit of the upper pool in the highway of the fuller's field. 1 Samuel 6:12 - And the kine took the straight way to the way of Bethshemesh, [and] went along the highway , lowing as they went, and turned not aside [to] the right hand or [to] the left; and the lords of the Philistines went after them unto the border of Bethshemesh. Mark 10:46 - And they came to Jericho: and as he went out of Jericho with his disciples and a great number of people, blind Bartimaeus, the son of Timaeus, sat by the highway side begging. Isaiah 7:3 - Then said the LORD unto Isaiah, Go forth now to meet Ahaz, thou, and Shearjashub thy son, at the end of the conduit of the upper pool in the highway of the fuller's field; Isaiah 40:3 - The voice of him that crieth in the wilderness, Prepare ye the way of the LORD, make straight in the desert a highway for our God. Isaiah 11:16 - And there shall be an highway for the remnant of his people, which shall be left, from Assyria; like as it was to Israel in the day that he came up out of the land of Egypt. 2 Samuel 20:13 - When he was removed out of the highway , all the people went on after Joab, to pursue after Sheba the son of Bichri. Proverbs 16:17 - The highway of the upright [is] to depart from evil: he that keepeth his way preserveth his soul. Isaiah 35:8 - And an highway shall be there, and a way, and it shall be called The way of holiness; the unclean shall not pass over it; but it [shall be] for those: the wayfaring men, though fools, shall not err [therein]. 2 Samuel 20:12 - And Amasa wallowed in blood in the midst of the highway . And when the man saw that all the people stood still, he removed Amasa out of the highway into the field, and cast a cloth upon him, when he saw that every one that came by him stood still.

Explore the Bible Like Never Before!
Unearth the rich tapestry of biblical history with our extensive collection of over 1000 meticulously curated Bible Maps and Images . Enhance your understanding of scripture and embark on a journey through the lands and events of the Bible.
- Ancient city layouts
- Historic routes of biblical figures
- Architectural wonders of the Holy Land
- Key moments in biblical history
Start Your Journey Today!
Click here to access our Bible Maps and Images
Table of Contents
About bible geography, about bible maps, ancient empire maps, bible map collections, bible map series, biblical map projects, geographical maps, interactive bible maps, intertestamental color maps, new testament color maps, new testament maps, old testament color maps, old testament maps.
Map of Ancient Canaan
Podcast Episodes: Season One.
Back to Show Notes Contents.
This map shows most of the place names I refer to in season one. The brown-shaded area is the crucial central highlands area.
For more maps, see my page on The Geopolitics of the Bible .
Reference map of Ancient Canaan
Click the map to enlarge.
Ancient Canaan. Most of the places you need to know about to follow the tricky bits in the first season of the podcast. Click the map to enlarge.
- Daily Tours Jerusalem Day Tours Tel Aviv Tours Dead Sea Day Tours Galilee & Golan Day Tours Bethlehem & Jericho Christian Day Tours Tours from Tel Aviv Tours from Jerusalem
- Tour Packages Mini Packages, 2-3 Days Classical Tour Package Christian Tour Package Jewish Tour Package Galilee & Golan Package Israel and Jordan
- Private Tours Jerusalem Private Tours Dead Sea Private Tours Galilee Private Tours Israel Shore Excursions Airport Transfers
- Destination Jerusalem Tours Dead Sea Tours Masada Tours Nazareth Tours Galilee & Golan Tours Tel Aviv Tours Caesarea Tours West Bank Tours Bethlehem Tours Jericho Tours Petra & Jordan Tours
- Petra Tours Petra from Jerusalem Petra from Tel Aviv Petra from Eilat Petra 1-Day Tours Petra 2-Day Tours Jordan Tours from Israel Israel and Jordan
- Shore Excursions Haifa Shore Excursions Ashdod Shore Excursions
- Blog Activities in Israel Israel Culture Practical Travel Info Jordan Travel Guide

- Bein Harim Israel Tours
- Historical Sites in Israel
Ancient Routes of Israel
When reading about the history of the Middle East and, in particular, the Holy Land, you’ll often hear references to the term ‘‘ancient Israel’. But what does that really mean? Well, in large part it is to do with the tribes and kingdoms that were formed by the Jewish people in the Levant in ancient times. (The Levant is an area that, today, is made up of Lebanon, Jordan, Syria, Israel and Palestine)

A camel rests between trips, Negev Desert, Israel. Photo by Cole Keister on Unsplash
Ancient Israel's main agricultural products were grapes, olives, lentils, dates and grains (usually wheat or barley). Over time, they developed a thriving trade with Egypt, Greece and Cyprus (using their ports on the Mediterranean). But how did they travel further afield? By creating different routes, some which ran by the sea and others which ran over hilly terrain.
Below we’ll be taking a look at certain ancient routes in Israel - some no longer exist, and others have been ‘modernised’ to give tourists a sense of what life was like thousands of years ago when people travelled by foot and with camels to explore new lands and trade their wares...
The Via Maris
The Via Maris was, for sure, one of the most significant ancient Israel trade routes. Both In Hebrew (‘Derech haYam’) and Latin, this means ‘ Way of the Sea’ and references to it can be found both in Isaiah (in the Hebrew Bible) and Matthew (in the Christian Bible). It dates back to the early Bronze Age and was a route linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Mesopotamia and Anatolia. ‘Via Maris’ is a Roman term and the reference to the sea is, of course, the Mediterranean Sea - the stretch of coast through which the route passed. It is also known by other names - the ‘Coastal Road’ and ‘the way of the Philistines’ and in modern-day Israel, it is referred to as the ‘International Coastal Highway.’
Tel Aviv Port, Israel. Photo by Shai Pal on Unsplash
Sea of Galilee, Israel. Photo by Chris Gallimore on Unsplash
Nachsholim Beach, Nahsholim, Israel. Photo by Ben Michel on Unsplash
The King’s Highway
The Kings Highway (also referred to as the ‘Via Nova Traiana’ was an ancient thoroughfare that connected the Gulf of Aqaba and Syria through the area that we now know as Jordan. One of the world’s oldest continually used routes of communication, it is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. The King’s Highway was a crucial passage for ancient trade, running from north to south of this part of the Levant. The Roman Emperor Trajan (who reigned from 98-1117 CE) actually renovated the road, in his desire to improve communications and transport between Aqaba and Bostra. Once ‘modernised’ the road was then referred to as the ‘Via Nova Traiana’ (as opposed to another road, in Italy, that had been built by the same Emperor, named ‘Via Traiana’. The King’s Highway was a crucial artery for Crusaders, journeying from Europe via Syria to Jerusalem on their military pilgrimages and for the interested visitor, there are many fortified castles to be explored on its route, even today. Today, the King’s Highway is still promoted as a tourist attraction with more rural parts of Jordan. It links up important historical sites such as Al Karak, Al Tafilah and, most notably, Petra , as well as beautiful natural sites such as Wadi Al Mujib.
Wadi Rum, Aqaba, Jordan. Photo by Rinaldo Vadi on Unsplash
The Ridge Route
This path was of less importance for international trade than either the Via Maris or the King’s Highway but, nevertheless, travellers used this route. They would travel through the hills of Judea and Samaria, passing by the city of Jerusalem. It was called the Ridge Route (or sometimes the Hill Route) because it followed the watershed ridgeline of the surrounding mountains.
The Way of the Patriarchs
This ancient north-south route crisscrossed the land of Israel. It was given this name by biblical scholars because of its having been mentioned in biblical narratives. This, you see, was the route often travelled by Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, the three founding fathers of Judaism. Also known as Derech ha Avot (the Hebrew term), it linked Jerusalem and Hebron and today can be found between the communities of Alon Shvut and Neve Daniel in the Gush Etzion part of Judea. Unlike the Via Maris and the King’s Highway, which were ancient roads that ran international borders and passed through the territory of many different peoples, this route was entirely within the territory of ancient Israel.

Snow in Kings Highway, Jordan. Photo by Thales Botelho de Sousa on Unsplash
The Incense Route
The Incense Route was an ancient trade network of important land and sea trading routes. It connected the Eastern world with the Mediterranean and involved ports all across Egypt and the Levant, as well as northeastern Africa, Arabia, India and the Far East. From the 3rd century BCE until 2 CE, the Nabateans were transporting incense across the desert, from Arabia to the Mediterranean and, from then on, demand for other luxury goods in the Roman world flourished. The Incense Route was a way to trade all kinds of articles, including Arabian frankincense and myrrh. Gold, rare woods and feathers came from Africa whilst precious stones, pearls, silk and spices arrived from India and further east. The Incense Trade Route was, in the main, controlled by the Arabs, who transported goods by camel caravans and for almost 700 years, this hazardous but very profitable trade was carried on.

Mamshit, Nabatean city, part of the Incense Road, Israel. Photo credit: Jenny Ehrlich
Mitzpe Ramon, Israel. Photo by Dmitry Shamis on Unsplash
The Gospel Trail
The Gospel Trail was established by Israel’s Ministry of Tourism in November 2011, giving Christian pilgrims (and indeed anyone else interested in this period of history) the opportunity to walk in the footsteps of Jesus. Consisting of over 60 km of paths and roads with special signposts, tourists can walk, hike or cycle as little or as much of the route as they choose. The route itself runs through Galilee, beginning at Nazareth (where Jesus spent many of his formative years) and ending at Capernaum , on the edge of the Sea of Galilee. It follows the route Jesus was supposed to have taken (referenced in the Book of Matthew, in the Christian Bible) when he left his hometown and set off for Galilee, where he would begin his ministry . The main part of the route begins, as stated above, in Nazareth, and visitors can walk along the Nazareth range, affording panoramic views of Mount Tabor , the Church of the Transfiguration , Kfar Kanna , and the Turan Valley.
Column in the synagogue, Capernaum, Israel. Photo by Phil Goodwin on Unsplash
The path then slopes down through the Arbel cliffs towards the sea of Galilee, until it reaches ancient Magdala (the home of Mary Magdalene). From Magdala, it continues north along the Sea of Galilee until it reaches what is known as the ‘Holy Triangle’ - the places that are the Mount of Beatitudes , Tabgha , and Capernaum. From there, visitors can walk the length of the Sea of Galilee on the promenade (or bike around it, if they are fit!) and stop along the way to see all kinds of attractions, including national parks, churches and the baptismal site of Yardenit .
Israel National Trail (Shvil Israel)
This hiking trail traverses the length of the country, stretching approximately 1000 km from Kibbutz Dan in the far north (near the Lebanon border) all the way down to Eilat , on the Red Sea . Loved by nature enthusiasts, biblical scholars, and adventurers alike, it's the perfect way to see Israel’s natural beauty. The Israel National Trail was the idea of Abraham Tamir and Ori Dvir, who were avid Israeli hikers. Inaugurated in 1995, it has given thousands of locals and tourists the opportunity to experience Israel’s varied landscapes up close and personal - from mountains and hills to deserts and wadis. A continuous footpath across the country, it has been lauded by nature enthusiasts, ramblers, hikers, and even National Geographic.
Mountains near Eilat, Israel. Photo by Josh Appel on Unsplash

Thank you for subscribing
Keep in Touch
Customer Care
Get to Know Israel
Popular Destinations
Our Services

Israel Comes to Canaan
Is the biblical account of the israelite conquest of canaan historically reliable.
By Yigael Yadin

There are essentially two views of the Israelite occupation of Canaan. The first conforms in its main outlines to the Biblical view; that is, the Israelite occupation was initiated by several lightning military attacks on major Canaanite cities and was followed after some time by Israelite occupation of adjacent areas thus subdued. (The Bible also recognizes that certain Canaanite enclaves like Jerusalem held out much longer, even to David’s time.)
The other view is that the occupation was initiated by peaceful Israelite infiltration of largely unoccupied hill country. Then increasing Israelite pressure led to the collapse of the main Canaanite cities.
The first view is associated especially with the great American archaeologist, William Foxwell Albright, who pioneered in the use of archaeological materials to elucidate the Bible. The second view is associated with scholars of the so-called German school: Albrecht Alt and his follower Martin Noth, who based their views principally on a study of the literary traditions contained in the Bible, and, more recently, Manfred Weippert who attempts to conform archaeological evidence to this interpretation of the literary traditions.
Since I disagree with the Alt school, I shall let Professor Weippert summarize its views. In a recent book entitled The Settlement of the Israelite Tribes in Palestine , Weippert states:
“The tribal confederacy did not exist at the time when those who later became the Israelites entered Palestine. It is extremely doubtful whether in that period one can speak at all of ‘Israelite’ tribes in the later sense. According to Alt, one must suppose, rather, that it was a question of individual clans or confederacies of clans of nomads with small cattle who, during the winter rainy season and the spring, lived with their herds in the border territory between the desert and the cultivated land and who were forced, when the vegetation in that area ceased in summer, to penetrate further into the cultivated land and to come to an understanding with the owners of the land about summer pasturage in the harvested fields and in the woods.” 1
Again quoting Weippert, according to Alt:
“The clans who entered the country in this way in the course of a regular change of pasture then gradually 018 settled in the relatively thinly populated wooded areas of the uplands, areas which were not directly exposed to the reach either of the Canaanite city-states or of Egyptian sovereignty, and began to practice agriculture once they had turned these wooded areas into arable land. This peaceful process of transition on the part of nomads to a sedentary life was, according to Alt, the real process of settlement and it was, in the nature of things, a peaceful development since the interest of any landowner in the area would not be harmed. Only gradually, at a second stage, did the ‘Israelites’ expand also into the fruitful plains and valleys which had long been occupied by closely packed groups of Canaanite cities. In this way there occurred isolated military encounters in which the ‘Israelites’ were not always the victors … but in which they nevertheless succeeded from time to time in taking a fortified city, massacring or driving away its inhabitants and themselves taking over the cultivation of its arable land. Alt called this second stage of ‘Israelite’ settlement in Palestine ‘territorial expansion.’” 2
Weippert’s analysis of the archaeological evidence led him to conclude that this evidence is “essentially silent.” 3 According to Weippert, we must rely basically on Alt’s literary analysis because the archaeological evidence simply does not speak to the problem. “Where definite statements are possible,” Weippert tells us, “these support the settlement theories of Alt and Noth rather than those of Albright and his followers.” 4
I find this conclusion that the archaeological evidence is “silent” rather astounding. I submit that the archaeological evidence Weippert calls “silent” is, in fact, resounding. I shall now try to explain why.
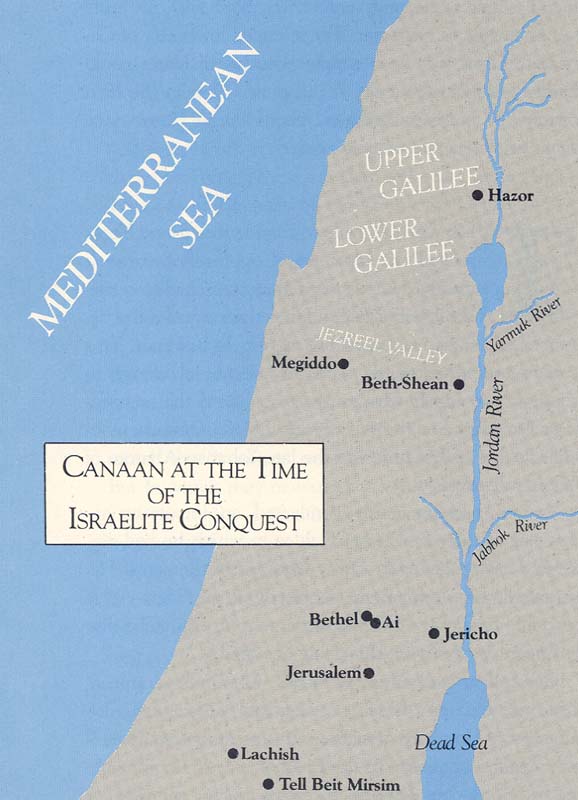
All archaeologists agree that at the end of the Late Bronze Age (the Late Bronze Age is generally dated from about 1,550 B.C. to 1,200 B.C.), the material culture we associate with this period abruptly stopped. Late Bronze agriculture was based on fortified city-states. At the end of the period, many of these cities were destroyed. The archaeological evidence shows conflagrations and distinctions which cannot be attributed to famine or earthquakes. Sometime later (that is, in a later archaeological stratum), a new and completely different culture developed, sometimes on the destroyed site and sometimes on a new site. This new culture (Iron Age culture) was initially rather poor architecturally, so poor it can hardly be called urban. This culture appears to reflect the first efforts at settlement by a semi-nomadic people. While this is the general pattern, certain destroyed sites were rebuilt immediately with fortifications and the attributes of a proper city.
Suppose we were excavating not in Israel, which is so intimately bound up with historical sources in the Bible, but in some terra incognita . Surely, in that context, no one would regard this evidence as “silent.” I submit that the archaeological evidence can be regarded as silent only if one has an a priori commitment to the Alt school which thoroughly rejects the historical value of the Biblical text.
Suppose the archaeological evidence were different. Suppose that no Late Bronze Age cities had been destroyed. Suppose that the destruction of these cities had occurred in the Iron Age (say about 1,050 B.C.). Suppose that only then was the older culture replaced by a semi-nomadic culture. If those were the facts, you may be sure the followers of the Alt school would not regard this evidence as “silent.” They would instead have pointed to the remarkable archaeological support for their view of the Israelite settlement.
The fact is, however, that excavation results from the last 50 years or so support in a most amazing way (except in some cases to be mentioned later) the basic historicity of the Biblical account.
The Biblical narrative in broad outline tells us that at a certain period nomadic Israelites attacked the city-state organization of the Holy Land, destroying many cities and setting them on fire. Then, slowly but surely, the Israelites 019 replaced these cities with new, unfortified cities or settlements. At the same time, they attempted to occupy certain cities but were unsuccessful. The residents of those cities continued to live side by side with the new invaders. As already indicated, this description—leaving out the words “Canaanite” or “Israelite”—is exactly the picture which the archaeological finds present to us: a complete system of fortified cities collapsed and was replaced by a new culture whose material aspect can be defined as the first efforts of semi-nomads to settle down.
I do not wish to be misunderstood as arguing that the archaeological record is absolutely consistent with the Biblical record and that excavation results raise no problem whatever. What I am saying is that in its broad outline the archaeological record supports the narrative in Joshua and Judges, as Albright said.
I think it would be a mistake to argue either that the entire conquest account in Joshua and Judges is historically accurate in every detail or that it is historically worthless.
I believe that Albright’s approach is correct in its broad outline—although not necessarily in its details and, again with Albright, we must examine Biblical evidence open-mindedly and compare it with the archaeological evidence in each case, without prejudice or bias or any preconceived notion. Where we find agreement between the Biblical narrative and the archaeological evidence, there is no reason to doubt the historicity of that particular Biblical source. On the other hand, where the archaeological evidence bluntly contradicts the Biblical narrative—as it sometimes does—we should examine the possibility that that particular chapter in the Bible is either etiological, a a later interpolation, or an editor’s misunderstanding. Let us not be dogmatic. Let us not try to find a solution which will satisfy or reconcile all the sources in the Bible; yet at the same time let us not dismiss a priori the basic historiographic approach of the Bible—(which I believe is fully confirmed by archaeological excavations)—that there was a phase in the Late Bronze Age in which Israelite nomads, like nomads from other parts of the country, managed to attack the decadent Canaanite settlements; these nomads then slowly but surely moved into the next phase in Israel’s history, the sedentary settlement of the tribes in the country on the ruins of earlier Canaanite cities.
With this approach in mind, let us examine some of the archaeological evidence which, I think readers will agree, is far from “silent.”
Let me begin by considering Hazor, not simply because I excavated it, but because it has been regarded by both sides in the debate as a key site, especially in the north, and also because it illustrates the attempts made by followers of the Alt school to conform the archaeological evidence to preconceived notions.
Hazor is mentioned in the conquest narrative primarily in Joshua 11 , which describes how Joshua defeated a Canaanite league headed by Jabin, king of Hazor. Joshua then captured Hazor, smote its king, and burned the city. The Biblical description is vivid:
“At this point Joshua turned his forces against Hazor, formerly the head of all these kingdoms. He captured the city and put its king to death with the sword. They killed every living thing in it and wiped them all out. They spared nothing that drew breath, and Hazor itself they destroyed by fire … The other cities whose ruined mounds are still standing were not burned by the Israelites. It was Hazor alone that Joshua burnt.” Joshua 11:10–15
Our very extensive excavations at Hazor clearly demonstrated that a large Canaanite city was suddenly destroyed and set on fire in the 13th century B.C. (end of the Late Bronze Age), no later than about 1,230 B.C. On the thick debris of the mound of the destroyed Canaanite city, we found a new settlement, unfortified, poor and obviously semi-nomadic in character. The so-called lower city of Canaanite Hazor had been simply abandoned. Hazor could hardly be considered a city at this point. Only in the 10th century B.C. when Solomon rebuilt it did Hazor once again become a major urban center.
This very “unsilent” evidence from Hazor rocked the basic “Alt” approach because it clearly demonstrated that the Israelite settlement had followed rather than preceded the destruction of the great Canaanite metropolis of Hazor. This conclusion presented an especially serious challenge to those archaeologists who sought to conform the archaeological evidence to the Alt theory. Chief among these archaeologists at that time was the late Yohanan Aharoni of Tel Aviv University.
Aharoni had previously conducted an important archaeological survey of upper Galilee in which he had discovered a large number of tiny Iron Age settlements. He attributed these settlements—correctly, in my view—to a peaceful phase of the Israelite settlement process. (The disagreement is over when this phase occurred.)
Prior to our excavation at Hazor, Aharoni had argued that these Iron Age Israelite settlements preceded the destruction of Hazor. At that time, this argument was based on a reading of a verse in the book of Judges. (In general, the book of Judges describes the era following the time of 020 Joshua.) In Judges 4 a prose narrative describes the famous battle in which the prophetess Deborah and her general Barak led a group of Israelite tribes against Sisera, commander-in-chief of the forces of Jabin, king of Hazor. (This same battle is described in a poem in Judges 5 , but no mention is made of Jabin in that account.)
According to the Alt school, the mention of King Jabin of Hazor in Judges 4 must mean that the destruction of Hazor described in Joshua 11 occurred quite late in the Israelite settlement process, permitting Jabin, the king of Hazor, to still be on the scene in the period of the Judges.
Albright explained the discrepancy between the destruction of Hazor in the book of Joshua and the later battle between Jabin of Hazor and Deborah in Judges by concluding that the battle of Deborah had been fought in the late 12th century but that it had nothing to do with Hazor.
Professor Benjamin Mazar of Hebrew University, in a penetrating analysis, concluded that the chronological order of the events in Joshua and Judges must be reversed—that the battle of Deborah (in Judges) in fact preceded the destruction of Hazor (described in Joshua 11 ) Aharoni accepting Alt’s basic approach, as well as Albright’s date for the battle of Deborah and Mazar’s chronological reversal of the events described in Joshua and Judges, concluded, quite naturally, that the great Canaanite city of Hazor had been destroyed by the Israelites at the end of the 12th century, that is, a generation or so after the date of the Israelite settlements he had found in his archaeological survey of Upper Galilee.
Aharoni was a member of the staff at our excavations at Hazor, and if I may say so, he was at the time the only staff member who was committed to a clear-cut sequence of historical events. When we discovered that the major Canaanite city at Hazor had been destroyed in the Late Bronze Age, Aharoni’s first reaction was that this was not necessarily the last urban center that existed at Hazor, that a later destroyed city might represent the Israelite destruction of the city described in Joshua 11 . When further excavation proved beyond doubt that there was no later city which the Israelites could have destroyed, Aharoni began to challenge the dating of the destruction of the Late Bronze Age city.
The key to the dating of this destruction layer at Hazor is the so-called Mycenean IIIB pottery which was found in the destruction layer. According to the authoritative and universally accepted dating of this pottery by the distinguished Swedish archaeologist Arne Furumark, it was not used after about 1,230 B.C. b Therefore, this destruction must have occurred sometime before 1,230 B.C.

For a while, Aharoni argued that Mycenean III B might well have been used as late as the first half of the 12th century B.C. If that was the case, he continued, the archaeological evidence did not contradict the theory that the city of Hazor had been destroyed in the 12th century, after the initial peaceful infiltration phase in the early days of the Iron Age.
After considerable time, however, Aharoni was forced to face the bitter but unchallengeable fact—as everyone now agrees—that Mycenean IIIB pottery must be basically 13th century and therefore the Canaanite city of Hazor must have been destroyed in the 13th century.
Still adhering to the basic theory of the Alt school of a peaceful Israelite infiltration preceding the expansion phase, and still believing that the Iron Age settlements he had discovered in Upper Galilee were indicative of this earlier phase, Aharoni then decided that these Iron Age settlements dated to the 14th–13th century! His assertion was based on a flimsy and unsound argument concerning the so-called collar-rim jar. The collar-rim jar is a storage jar which has a ridge around the neck, thus giving the appearance of a collar. Albright first alerted the archaeological world to the importance of this storage jar for purposes of Iron Age dating and identification of ethnic groups.
In his effort to date his Israelite settlements in the upper Galilee prior to the destruction of Canaanite Hazor, Aharoni decided that collar-rim jars first made their appearance in the 14th century. This time his evidence comes from Megiddo, excavated by a University of Chicago team in the 1930’s. In their final report, the Chicago excavators published fragments of two collar-rim jars which they ascribe to a Late Bronze Age stratum. However, a careful examination of the locus in which the two fragments were found clearly shows that these fragments were intrusive and in fact belong to a later period. The excavation report states that much of the construction in this locus was “interwoven with” buildings which were clearly from the Iron Age. 5 An examination of the plans of this area published in the final report clearly shows the area to be disturbed; sherds found there could theoretically belong to any of five different strata.
In any event it is somewhat amazing that Aharoni would base a whole system of chronology on two isolated sherds. This is wholly contrary to Aharoni’s basic approach (shared by most archaeologists) of not dating strata on the basis of isolated sherds. He himself has written “that sherds are stratigraphically not reliable, even if found in clear stratigraphical context.” 6 The dating of a stratum should be determined, he has emphasized, “on the reconstruction of vessels found in situ.” c 7
In short, there is no archaeological proof that the Iron Age collar-rim pottery goes back to the 14th or early 13th century. This negative in fact one of the strongest arguments against accepting a theory of coexistence of the Late Bronze Age Canaanite culture and the early Israelite culture in the 14th and early 13th centuries B.C. The complete absence of both cultures together is strong—not “silent”—archaeological evidence fundamentally indicating a sequence of cultures, not contemporaneous ones.
Perhaps I should also mention a very recent—and I may add, desperate—theory advanced by Volkmar Fritz of the University of Mainz to conform our findings at Hazor with Alt’s theory that peaceful Israelite settlements preceded the fall of Canaan’s principal cities to the Israelites. Fritz concedes that Canaanite Hazor fell in the 13th century. But he suggests that its destruction is attributable to the Sea People! This suggestion is unwarranted by any source. Fritz is simply unable to accept the possibility that the Israelites may have conquered Hazor.
Imagine that, instead of the Bible, we possessed an external document describing the Israelites as the Desert Peoples just as the Philistines are referred to in Egyptian documents as one of the Sea Peoples. Perhaps it would then have been easier for scholars to accept the possibility that, just as the Sea Peoples managed to destroy some of the Canaanite cities in western Syria and Palestine, so the Desert Peoples could have destroyed the Canaanite cities to the east.
It should not be surprising that semi-nomadic Israelites were able to conquer fortified cities like Hazor. As all scholars, including Weippert, recognize, there was a marked decline in political and economic stability in Canaan at the end of the Late Bronze Age. The city-states system had, in effect, dissolved. Weippert argues that this 022 state of affairs allowed the peaceful infiltration of the semi-nomadic Israelites. Later, when they had become sedentary, the Israelites founded their twelve-tribe confederacy.
I would make a somewhat different argument. The city-state system had declined not only because of internal problems but also as a result of the hammering and destruction wrought in Palestine by the Egyptian pharaohs during the 14th and 13th centuries. The city-state system had weakened to a degree that enabled even the semi-nomadic Israelites not only to infiltrate into the country but also to capture and give it the coup de grace . We do not have to visualize impregnable, strongly fortified Canaanite bastions, but rather degenerated cities with weak fortifications. Faced with a series of brilliant Israelite military stratagems, these cities fell.
I mentioned earlier that the general historicity of the Biblical account does not exclude the possibility that the account of Israelite conquest of some cities may be etiological or that some details in the conquest narratives may be late inaccurate glosses.
One of the best known cruxes in connection with the Israelite conquest is the apparent conflict between the Biblical account of the conquest of Jericho on the one hand, and the archaeological evidence, on the other. Dame Kathleen Kenyon’s meticulous excavation of the site in the 1950’s uncovered a Middle Bronze Age city fortified by a glacis. At the base of the glacis was a revetment wall and on top of the glacis another wall to give it added height. The city that this wall had enclosed was violently destroyed at the very end of the Middle Bronze Age. Kenyon dates this destruction to about 1,560 B.C.
Evidence of a Late Bronze Age town was also found but Kenyon could not find even a trace of a Late Bronze Age wall. How could the walls of Jericho come tumbling down during the Late Bronze Age if there was no Late Bronze Age wall around the town. There may be an explanation.
In many cases the Late Bronze Age people did not actually build new fortifications but, rather, reused Middle Bronze fortifications, strengthening them where necessary Interpreters often overlook this fact, and it may have an important bearing on the case of Jericho. It may well be that the Late Bronze Age settlement at Jericho reused the city wall from the Middle Bronze Age. If I am correct in this theory, the first Israelite attack on a Canaanite city in the promised land may have occurred in the 14th or 13th century The attack could have been against Jericho, a Late Bronze Age settlement fortified by the still standing Middle Bronze Age city wall.
Ai, the second city on Joshua’s conquest route ( Joshua 7–8 ), presents another problem. The late Judith Marquet-Krause excavated at Ai in the 1930’s and concluded that there was no Late Bronze Age city there. Joseph A. Callaway of the southern Baptist Theological Seminary conducted extensive excavations at Ai in the 1960’s; he too uncovered no remains whatever from the Late Bronze Age. Faced with the conflict between the evidence of Marquet Krause and Callaway, on the one hand, and the Biblical account of Ai’s destruction on the other, Albright suggested that the Biblical description referred not to the conquest of Ai, but to the conquest of nearby Bethel. No destruction of Bethel is referred to in the Bible, but a Late Bronze Age city was destroyed there. Others argued that the Biblical description of Ai was purely etiological, that a late Biblical author had attributed an earlier conquest to the Israelites in order to glorify Israelite history.
Callaway found Albright’s solution to the Ai problem—that the destruction of Ai referred to the destruction of nearby Bethel—unconvincing. Approaching the problem with a more fundamentalistic approach, Callaway was equally unwilling to accept the etiological solution of the Alt school. Callaway suggested a new answer. Because he had discovered two phases of occupation at Ai, each having a slightly different type of collar-rim pottery, Callaway suggested that there were two cities at Ai. The first, he suggests, was a Hivite city. This is the settlement, he says, that the Israelites conquered. Despite the presence of collar-rim pottery associated with this “Hivite” settlement, Callaway says the date of this settlement could be “before some of the last Late Bronze cities fell.” 8 Callaway offers the Khirbet Raddana sherd mentioned by Aharoni, as well as another type of jar found at Megiddo as proof for the existence of this type of collar-rim pottery in a Late Bronze context. But the excavators of all the loci in which this type of collar-rim jar was found at Megiddo ascribed these materials, without exception, to the Iron Age. Apparently Callaway recognized that the evidence was being stretched and that the destruction of Ai had occurred at most at the very end of the late Bronze Age, which would place it after the Late Bronze Age destructions of central Canaan.

Callaway thus concluded, “I think we can no longer take for granted that the conquest of Canaan by invading Israelites accounts for the Late Bronze Age destructions of Bethel, Lachish, Tell Beit Mirsim, or Hazor.” 9 Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research , No. 201, pp. 19–22 (1971)--> In other words, Callaway concluded that the Israelite conquest had occurred in the Iron Age and that not all the cities captured by the Israelites had been fortified. Some may have been simply villages or hamlets so characteristic of the early phase of the Iron Age. Other places such as Megiddo and 023 Beth-Shean were not conquered at all, says Callaway Biblical tradition says explicitly that they were not captured by the Israelites.
Callaway’s analysis is, in my opinion, untenable. He misdates his so-called “Hivite” settlement; he wrongly rejects the archaeological evidence of Late Bronze Age destruction of major fortified cities at Bethel, Lachish, Tell Beit Mirsim and Hazor and elsewhere; and he ignores the Biblical descriptions of the Israelite capture of large fortified Canaanite cities.
In the case of Ai, therefore, we are left with Albright’s solution or the Alt-school’s etiological solution. My own view is that here the archaeological evidence contradicts the Biblical narrative and we must interpret the Biblical account as etiological.
One final example illustrates a case where I think we must conclude that a late editorial gloss was added to a basically authentic historic text. In the Biblical chronology, the Israelite destruction and burning of Hazor is described in Joshua 11 . Later, in the prose description of the Battle of Deborah ( Judges 4 ), we find Deborah and her general Barak fighting against “Jabin king of Hazor.” If Hazor had already been destroyed in Joshua 11 , how could Deborah and Barak be fighting against its king in Judges 4 ? A number of solutions have been proposed. One, mentioned above, proposed by Professor Benjamin Mazar, is to reverse the chronology. He places the battle of Deborah in Judges 4 before the conquest of Hazor in Joshua 11 . Recognizing that the archaeological evidence clearly establishes that Hazor was destroyed in the 13th century, Mazar suggests that Deborah lived and fought earlier in the 13th century, rather than in the 12th century, as had previously been supposed. This is possible—at least it tallies with the archaeological evidence from Hazor—but I personally do not believe it. As we have seen, Aharoni’s solution is archaeologically impossible.
Before my excavation at Hazor, Alt himself, who in this case agrees that an historical event lies behind the Biblical narrative, had argued that the mention of “Jabin king of Hazor” in the battle of Deborah required us to place Hazor’s destruction (as described in Joshua 11 ) at a fairly late date. The Hazor excavations have now rendered this solution untenable.
My own solution, as I indicated above and as Albright already suggested, is that the reference to “Jabin king of Hazor” in Judges 4 is an editorial gloss by a later editor. This suggestion finds support in the fact that the poetic account of this same battle (in Judges 5 ) makes no mention of Hazor or Jabin.
My basic point in this article is that we should not be dogmatic. We can pick and choose based on the evidence in each case. It is not necessary either to accept each detail of the Biblical account, on the one hand, or to reject the basic historicity of the Conquest, on the other. Examined in this light, archaeology broadly confirms that at the end of the Late Bronze Age, semi-nomadic Israelites destroyed a number of major Canaanite cities; then, gradually and slowly, they built their own sedentary settlements on the ruins, and occupied the remainder of the country.
(For further details, see Yigael Yadin, “The Transition from a Semi-Nomadic to a Sedentary Society in the Twelfth Century B.C.E.,” in Symposia , edited by Frank Moore Gross (American Schools of Oriental Research, 1979).)
There are essentially two views of the Israelite occupation of Canaan. The first conforms in its main outlines to the Biblical view; that is, the Israelite occupation was initiated by several lightning military attacks on major Canaanite cities and was followed after some time by Israelite occupation of adjacent areas thus subdued. (The Bible also recognizes that certain Canaanite enclaves like Jerusalem held out much longer, even to David’s time.) The other view is that the occupation was initiated by peaceful Israelite infiltration of largely unoccupied hill country. Then increasing Israelite pressure led to the collapse of the […]
You have already read your free article for this month. Please join the BAS Library or become an All Access member of BAS to gain full access to this article and so much more.
Join the BAS Library!
Already a library member? Log in here.
Institution user? Log in with your IP address or Username
that is, not historical, but intended to explain or justify a later historical situation.
Mycenean pottery is an easily recognized type which originated in mainland Greece and was found all over the Aegean, as well as in Egypt and the eastern Mediterranean coasts. It is subdivided into Mycenean I, II and III. Mycenean I and II are characteristic of 16th and 15th-century B.C. sites.
The Mycenean III type serves as evidence—nearly the only firm testimony available to archaeologists—for absolute dating of strata to the 14th and 13th centuries B.C. A great quantity of Mycenean III pottery was discovered in the short-lived city of el-Amarna in Middle Egypt. Artifacts discovered there are of tremendous importance because they can be absolutely dated to the reign of Amenophis IV (1,364–47 B.C.); the fact that a certain type of Mycenean III pottery, primarily III A, was discovered at el-Amarna makes it a sure peg for absolute chronology throughout the Near East. Another type, Mycenean III B, is associated at Egyptian archaeological sites and other places with the second third of the 13th century B.C., or roughly with the reign of Ramses II.—Ed.
Aharoni also relies on a two-and-a-half letter inscription found on a collar-rim jar at Khirbet Raddana. Aharoni dates the letters—and therefore the jar—to 1,300 B.C. at the latest. Thus, he argues, the collar-rim jar was in use in the Late Bronze Age. Two of the world’s most skilled epigraphists, Frank Moore Cross of Harvard and David Noel Freedman of the University of Michigan date this inscription, on epigraphic grounds, 100 years later, to the Iron Age. Moreover, as Moshe Dothan has pointed out, several iron implements were found with the collar-rim jar at Khirbet Raddana, also indicating a later date.
Similarly, we must reject the argument recently put forward by Aharon Kempinski that a single scarab found on the surface of Tell Masos dates the earliest settlement there to the Late Bronze Age. The dating of the scarab to the reign of Ramses II or Seti II is unconvincing. The whole repertoire of pottery found at the settlement is typical Iron Age and to date has not been found in any context of Late Bronze Age cultures. Moreover, the Pharaoh on the scarab holds a straight sword rather than a sickle-shaped sword, indicating that it probably dates to the Iron Age. In any event, this surface find could well be an heirloom from an earlier period, so it is a thoroughly unreliable basis for dating the Tel Masos settlement.
Manfred Weippert, The Settlement of the Israelite Tribes in Palestine: A Critical Survey of the Recent Scholarly Debate , translated from the German by James D. Martin (London, 1971), p. 5.
Weippert, p. 6.
Weippert, pp. 128–129.
Weippert, p. 135.
Megiddo , Volume II, University of Chicago Press (1948) p. 105.
Israel Exploration Journal , Vol. 21, p. 135. (The article begins on p. 130.)
Journal of Biblical Literature , Vol. 87, (1968) pp. 316 ff.
Ibid. , p. 320.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

“A highway out of Egypt”: The main road from Egypt to Canaan

2013, 27 Africa Prahistoria
Related Papers
Pp. 155-189 in: S.Bar, D.Kahn and JJ Shirley (editors) Egypt, Canaan and Israel: History, Imperialism, Ideology and Literature: Proceedings of a Conference at the University of Haifa, 3-7 May 2009. Leiden, Brill 2011.
Amihai Mazar
Nadav Na'aman
Aula Orientalis 30: 359-367.
Andrés Diego Espinel
The Power of Walls
James Hoffmeier
Rameside Studies in Honour of K.A. Kitchen
Cambridge Archaeological Journal
Alison L Gascoigne
Elsayed Abd el-Alim
The "Way(s) of Horus" represented an active route and part of Egypt's eastern frontier; it is known during the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms, and continued to be maintained and controlled by Saite kings (Dynasty 26: 664-525 B. C.). Tell el-Kedwa formed part of a series of Saite fortresses guarding Egypt's East frontier, and lies on the eastern edge of an ancient lagoon, guarding a northern access point to Egypt. n 2007, investigations at Kedwa uncovered a succession of two massive Saite forts, and constitute an important factor in clarifying Tell el-Kedwa 's role as a key control point for access to Egypt during the Late Period. Excavations have continued in 2008 along the south wall of the successive fortresses, and these results will be published in due course. However, the initial excavation results from 2007 have confirmed the role of this fortress as a significant Egyptian garrison defending Egypt's eastern gateway.
Ägypten und Altes Testament (121). Proceedings of the International Conference Held at the Institute for Egyptology and Coptology of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Munich, 10–11 December, 2021
SOMA 2012. Identity and Connectivity: Proceedings of the 16th Symposium on Mediterranean Archaeology, Florence, Italy
Angela Massafra
Set in a flourishing oasis near the Jordan River, of Tell es-Sultan, the Biblical Jericho, is one of the most unique cases of archaeological site which undergoes a continued and systematic study. During the first half of the 2nd millennium, the site provides clues for the existence of an elite class with strong links with Egypt. A relevant element is given by the built-up tombs on the tell itself: these burials were found in the Middle Bronze age levels of the Spring Hill and belongs to a very rare type in the funerary architecture of Palestine. The position of these mudbrick tombs, probably located under the Middle Bronze age palace, denotes the high status of the buried. But another significant element is given by the structural typology of these graves: mudbrick built-up tombs are mostly unknown in Palestine, while they are widely used in the ‘hyksos’ capital of Avaris, modern Tell el-Dabᶜa, located in the eastern Nile delta. The analysis of these structures and of the related finds could give a precious hint for the study of the interactions between Jericho and Egypt at the beginning of the Middle Bronze age.
Bettina Bader
RELATED PAPERS
Moises Sastre
Kristi Philips
Public Management Researches
Camilo Romero
Seongman Moon
Israel Journal of Health Policy Research
Hila Elinav
Marine Biology
Y. Benayahu
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
Kurosh Gharagozli
Journal of Applied Polymer Science
Thambusamy Stalin
adam kurland
Jurnal Penelitian Ekonomi Manajemen dan Bisnis
Yesika ade Noviyani
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta
Sapere Aude
Pedro Véras
florence soutric
Clinical cardiology
Verlin Joseph
Physical Review Fluids
Evgeny Ermanyuk
Intensive Journal
Faida Azhimia
Il Nuovo Cimento C
Antonio Meloni
Photosynthetica
Nathalie Vaillant-gaveau
Pedro Eiras
hyutrTT hytutr
Journal of Functional Biomaterials
Vipuil Kishore
Manouchehr Soltani
Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis
British Journal of Ophthalmology
MUHAMMAD JAVED KHAN JADOON
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

JetBlue to Cut Routes Across the U.S., UK, in Major Change Up
The changes will take place in October.
JetBlue is making major changes to its network for this summer and fall following the U.S. government’s breakup of its planned merger with Spirit Airlines earlier this year.
Travelers in the New York, Boston, and Los Angeles area will be most affected, with a handful of route cuts and reduced transatlantic service to Europe during the winter months. However, there will also be a boost in service on JetBlue’s popular lie-flat business class cabin, Mint, to hot spots like Phoenix and Vancouver (along with new San Juan and Caribbean flights ).
Route Cuts and Reductions
While JetBlue only started flying to Europe in recent years JetBlue will slightly scale back its transatlantic operation during the slower winter season this year. It’s not unusual for major U.S. airlines to deploy their aircraft more efficiently during this time period (more on that below).
Starting Oct. 27, JetBlue will cut Boston (BOS) and JFK service to London-Gatwick (LGW) and reduce service between JFK and Paris (CDG) to once daily, from twice daily. The airline will continue to fly daily to London-Heathrow (LHR) from both JFK and BOS. JetBlue also intends to bring back these flights later in 2025 when the warmer months return—and along with it, the crowds to Europe.
The New York City-based airline will cut service on select North American routes entirely starting on Oct. 27 — with the hardest hit being New York LaGuardia (LGA) — including:
- LGA to Atlanta (ATL)
- LGA to New Orleans (MSY)
- LGA to Nassau, Bahamas (NAS)
- LGA to Fort Myers (RSW)
- Los Angeles (LAX) to Orlando (MCO)
- Los Angeles (LAX) to Newark (EWR)
- JFK to Puerto Vallarta (PVR)
More Lie-Flat Seats in the Americas
JetBlue’s much-beloved premium Mint cabin , which is only found on select JetBlue aircraft, will make its debut on several routes. That includes a once-daily service beginning in July between JFK and Vancouver (YVR); and JFK and San Juan (SJU).
Starting in late October, travel to Phoenix (PHX) will be getting a major upgrade with the airport’s only dedicated lie-flat business class service domestically. JetBlue will launch Mint seasonal flights from PHX to Fort Lauderdale (FLL), JFK, and BOS. In addition, Mint-equipped planes will also operate between FLL and Las Vegas (LAS).
All of these new Mint flights mean more opportunities to travel in style within North America.
For more Travel & Leisure news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Travel & Leisure .


COMMENTS
Map 38 Abram's Journey to Canaan . Ur. Ur developed during the reign of the Sumerian kings (c.3000 - 2300BC) and had been a major city for hundreds of years when Abram was born. A 'ziggurat' (a stepped temple platform) about 70 feet / 21 metres high, surmounted by a temple and shrine to the Akkadian moon god Sin, was built by King Ur ...
1. The 47-day exodus itinerary alone refutes the Nuweiba exodus route of Glen Fritz because even he admits his 555-mile (888 km) route cannot be travelled in less than 53 days. Fritz calculates Israel arrived at Mt. Sinai on day 64-65 and he added 12 "arbitrary" filler days to delay the arrival from day 53 to day 65. 2.
The Journey to Canaan. After many years of wandering in the wilderness as a consequence of their sin, the Israelites set out from Kadesh-barnea toward the Promised Land. It is difficult to know for certain the exact route they took from Kadesh-barnea to the plains of Moab, but it is possible that they followed a course that went around the ...
Via Maris. Via Maris (International Coastal Highway) is the name for an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia.In Latin, Via Maris means "way of the sea" - דֶּרֶךְ הַיָּם.See Isaiah 8:23 in the Bible. It is a historic road that runs in part along the Israeli Mediterranean coast.
The land of Canaan has been called the "sacred bridge," a strip of land that connects two worlds. In ancient times it was the only way to travel between Egypt and Mesopotamia, since a more direct route through the Arabian Desert was impractical if not impossible. There were two major arteries for international trade that traversed the land ...
Abram Travels to Canaan c. 2091 b.c. Abram was born in Ur, a powerful city in southern Babylonia. Abram's father, Terah, eventually led the family toward the land of Canaan but decided to settle in Haran (see Gen. 11:27-31). After Terah's death, the Lord called Abram to go "to the land that I will show you" (Canaan), which he promises to give ...
Here's a closer look at the journey from Egypt to Canaan. Egypt: The Exodus began in Egypt, where the Israelites had been living in slavery for over 400 years. According to the Bible, Moses led the Israelites out of Egypt and across the Red Sea, which God miraculously parted to allow them to pass. Sinai Peninsula: After crossing the Red Sea ...
2. Israel's Exodus from Egypt and Entry into Canaan. Image. Bible map 2. Rameses Israel was thrust out of Egypt ( Ex. 12; Num. 33:5 ). Succoth After the Hebrews left this first campsite, the Lord attended them in a cloud by day and in a pillar of fire by night ( Ex. 13:20-22 ). Pi-hahiroth Israel passed through the Red Sea ( Ex. 14; Num. 33 ...
Canaan, area variously defined in historical and biblical literature, but always centred on Palestine.Its original pre-Israelite inhabitants were called Canaanites. The names Canaan and Canaanite occur in cuneiform, Egyptian, and Phoenician writings from about the 15th century bce as well as in the Old Testament.In these sources, "Canaan" refers sometimes to an area encompassing all of ...
Canaan was the name of a large and prosperous ancient country (at times independent, at others a tributary to Egypt) located in the Levant region of present-day Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Israel.It was also known as Phoenicia.The origin of the name 'Canaan' comes from various ancient texts and there is no scholarly consensus on precisely where the name originated nor what it meant.
The Israelites continued to wander in the wilderness for another 38 years, traveling back and forth across the desert and encountering many challenges and trials along the way. They fought battles against other nations, complained about their lack of food and water, and even rebelled against Moses and God on several occasions.
Map of Canaan, Promised Land. Ancient Israel, known as Canaan, was located in the eastern Mediterranean region on a plug of ground with diverse geography: seacoast, mountains, river valley, desert. There's also some wasteland that's something of a cross between desert, Mars, and the floormat in a '91 Buick Skylark.
The "Way of the Sea" is one of three major trade routes in ancient Israel - the Via Maris, Ridge Route, and the King's Highway. It is situated from the Galilee to the North to Samaria to the South, running through the Jezreel Valley. At the Philistine Plain, the Way broke into two branches, one on the coast and one inland (through the Jezreel ...
Map of the Route of the Hebrews from Egypt. This map shows the Exodus of the Israelites from Egypt to the Promised Land under the leadership of Moses. The Nile Delta was a triangular area of marshland about 150 miles from north to south, from Memphis to the Mediterranean, and about 150 - 200 miles wide. Upper Egypt was a bit further south from ...
The John Speed map of Canaan, formally titled "Canaan as it was possessed both in Abraham and Israels dayes with the stations and bordering nations," is an ancient wall map of the Land of Israel drawn by the English historian and cartographer John Speed in 1595. It is the first map to be drawn by Speed. Today the only copy of the map is found ...
The Via Maris was crossed by other trading routes, so that one could travel from Africa to Europe or from Asia to Africa. ... Way of the Patriarchs - the biblical north-to-south route through the mountains of Canaan; Grand Trunk Road - one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads linking South Asia and Central Asia. Sites along Via Maris
This map includes general roads and Roman paved roads in ancient Israel. You can see the major and minor roads and highways, and the Roman Legionary Camps in the land of Israel during the first century AD. The Via Maris, the King's Highway, the Way of the Sea, and other small roads can be seen on this map. Proverbs 16:17 - The highway of the ...
The musical theme in season one of the podcast is Five Armies, and in season two is Take a Chance, both by Kevin MacLeod. Licensed under Creative Commons 3.0: By Attribution licence. In season three I used Inspiring Teaser by Rafael Krux, licensed under the Filmmusic.io Standard license. Map of Ancient Canaan.
Bible Atlas
Kingdom of David and Solomon. Kingdom of Herod (30 BCE to 70 CE) The Kingdom of Israel under David and Solomon. Mesopotamia to 2500 BCE. Palaestina. The Persian Empire (Atlas) Principal Trade Routes. Sea Peoples in the Late Bronze Age. Sumer, Elam and Subartu.
The Via Maris. The Via Maris was, for sure, one of the most significant ancient Israel trade routes. Both In Hebrew ('Derech haYam') and Latin, this means ' Way of the Sea' and references to it can be found both in Isaiah (in the Hebrew Bible) and Matthew (in the Christian Bible). It dates back to the early Bronze Age and was a route ...
There are essentially two views of the Israelite occupation of Canaan. The first conforms in its main outlines to the Biblical view; that is, the Israelite occupation was initiated by several lightning military attacks on major Canaanite cities and was followed after some time by Israelite occupation of adjacent areas thus subdued.
Since the archaeological sites from the earlier periods were discovered first in the Canaan end of the route, we will move in our investigation from east to west. ... and the decorative schemes used suggest to the excavators that the site was some sort of royal residence used in travel between Egypt and Canaan, but was related to a nearby ...
The changes will take place in October. JetBlue is making major changes to its network for this summer and fall following the U.S. government's breakup of its planned merger with Spirit Airlines ...
SFGATE contributor Jim Glab rounds up air travel and airport news for our weekly column Routes By Jim Glab May 4, 2024 United Airlines resumes flying this summer from SFO to St. Louis with 13 ...