

Voyager 1 and 2: The Interstellar Mission

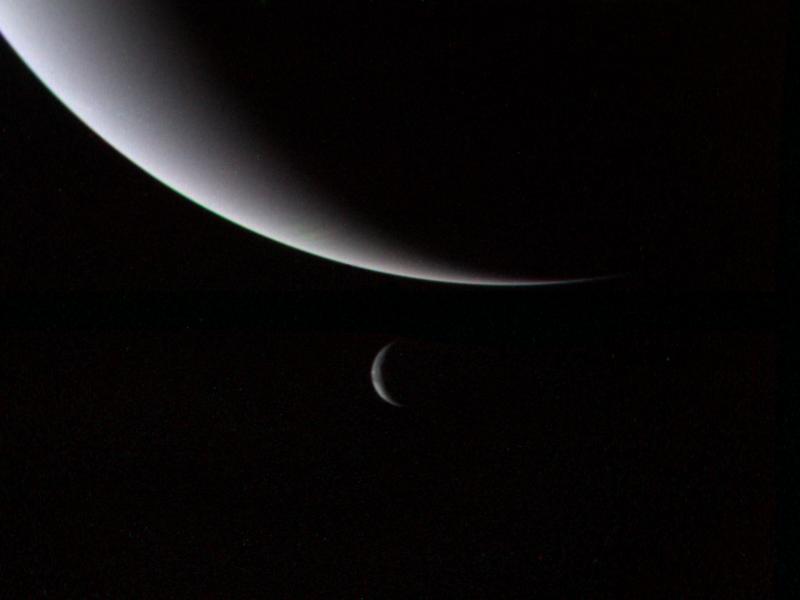
An image of Neptune taken by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
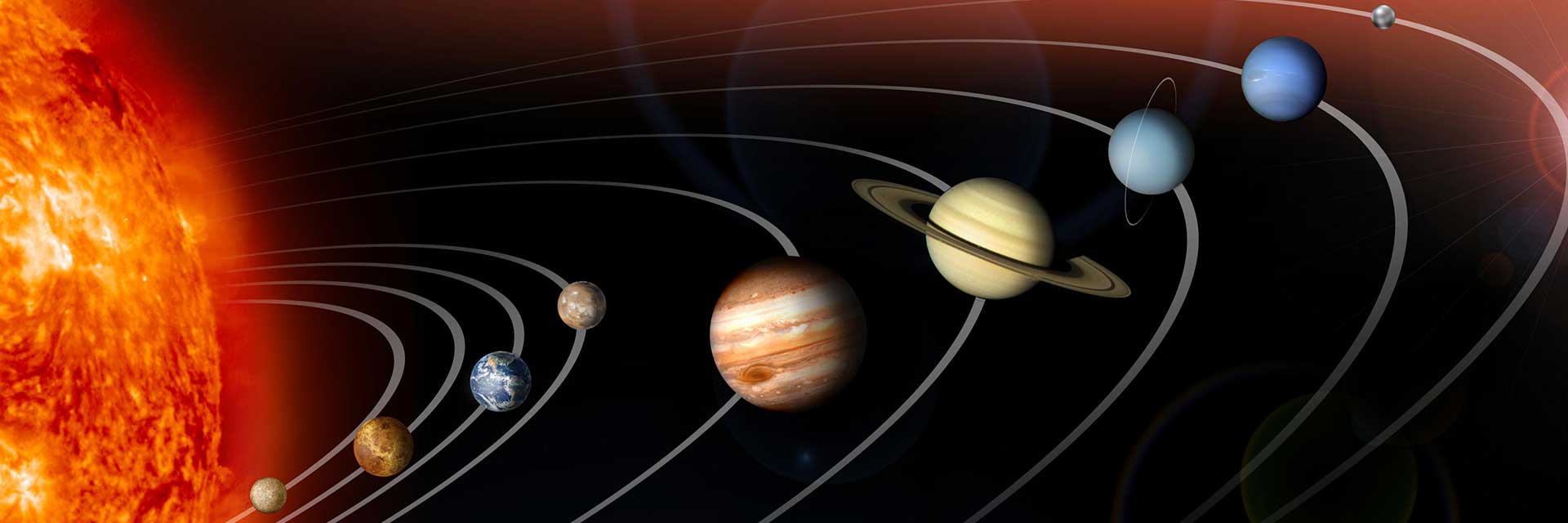
NASA has beautiful photos of every planet in our solar system. We even have images of faraway Neptune , as you can see in the photo above.
Neptune is much too distant for an astronaut to travel there with a camera. So, how do we have pictures from distant locations in our solar system? Our photographers were two spacecraft, called Voyager 1 and Voyager 2!

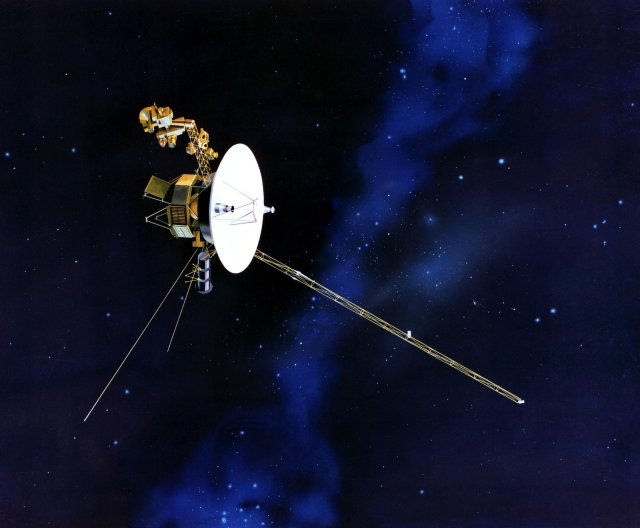
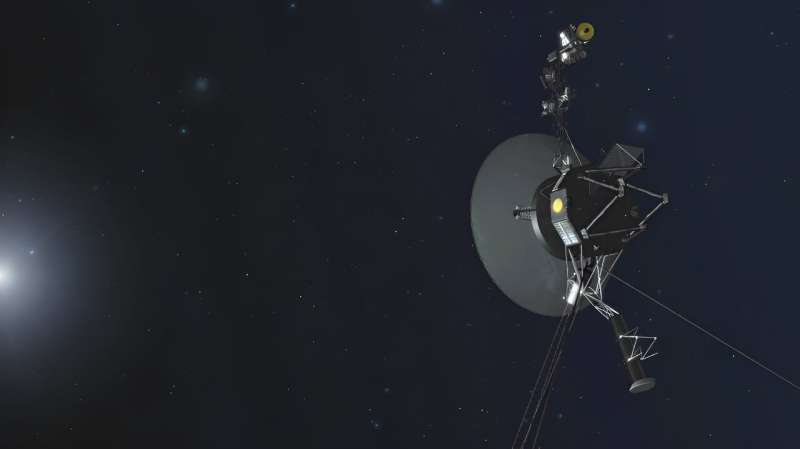
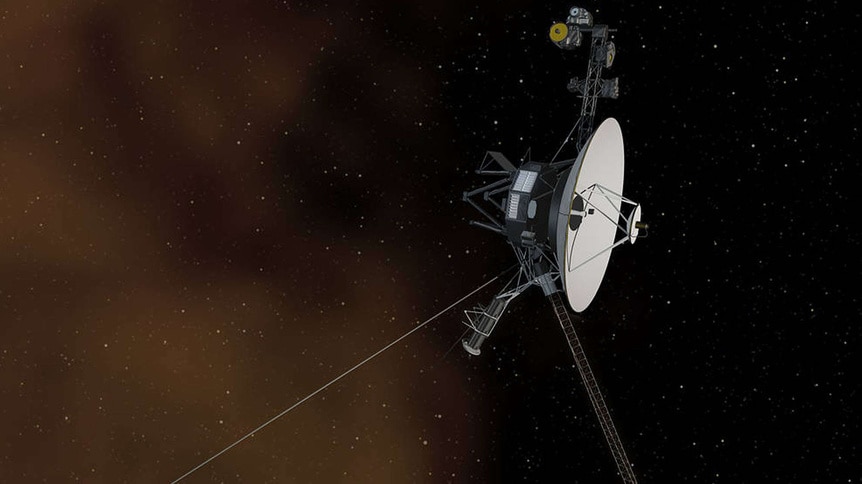
An artist’s rendering of one of the Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before.
The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons. The pictures from Voyager 1 and 2 allowed us to see lots of things for the first time. For example, they captured detailed photos of Jupiter's clouds and storms, and the structure of Saturn's rings .

Image of storms on Jupiter taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
Voyager 1 and 2 also discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io , and much more. Voyager 2 also took pictures of Uranus and Neptune. Together, the Voyager missions discovered 22 moons.
Since then, these spacecraft have continued to travel farther away from us. Voyager 1 and 2 are now so far away that they are in interstellar space —the region between the stars. No other spacecraft have ever flown this far away.
Where will Voyager go next?
Watch this video to find out what's beyond our solar system!
Both spacecraft are still sending information back to Earth. This data will help us learn about conditions in the distant solar system and interstellar space.
The Voyagers have enough fuel and power to operate until 2025 and beyond. Sometime after this they will not be able to communicate with Earth anymore. Unless something stops them, they will continue to travel on and on, passing other stars after many thousands of years.
Each Voyager spacecraft also carries a message. Both spacecraft carry a golden record with scenes and sounds from Earth. The records also contain music and greetings in different languages. So, if intelligent life ever find these spacecraft, they may learn something about Earth and us as well!

A photo of the golden record that was sent into space on both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More about our universe!

Where does interstellar space begin?

Searching for other planets like ours

Play Galactic Explorer!
If you liked this, you may like:

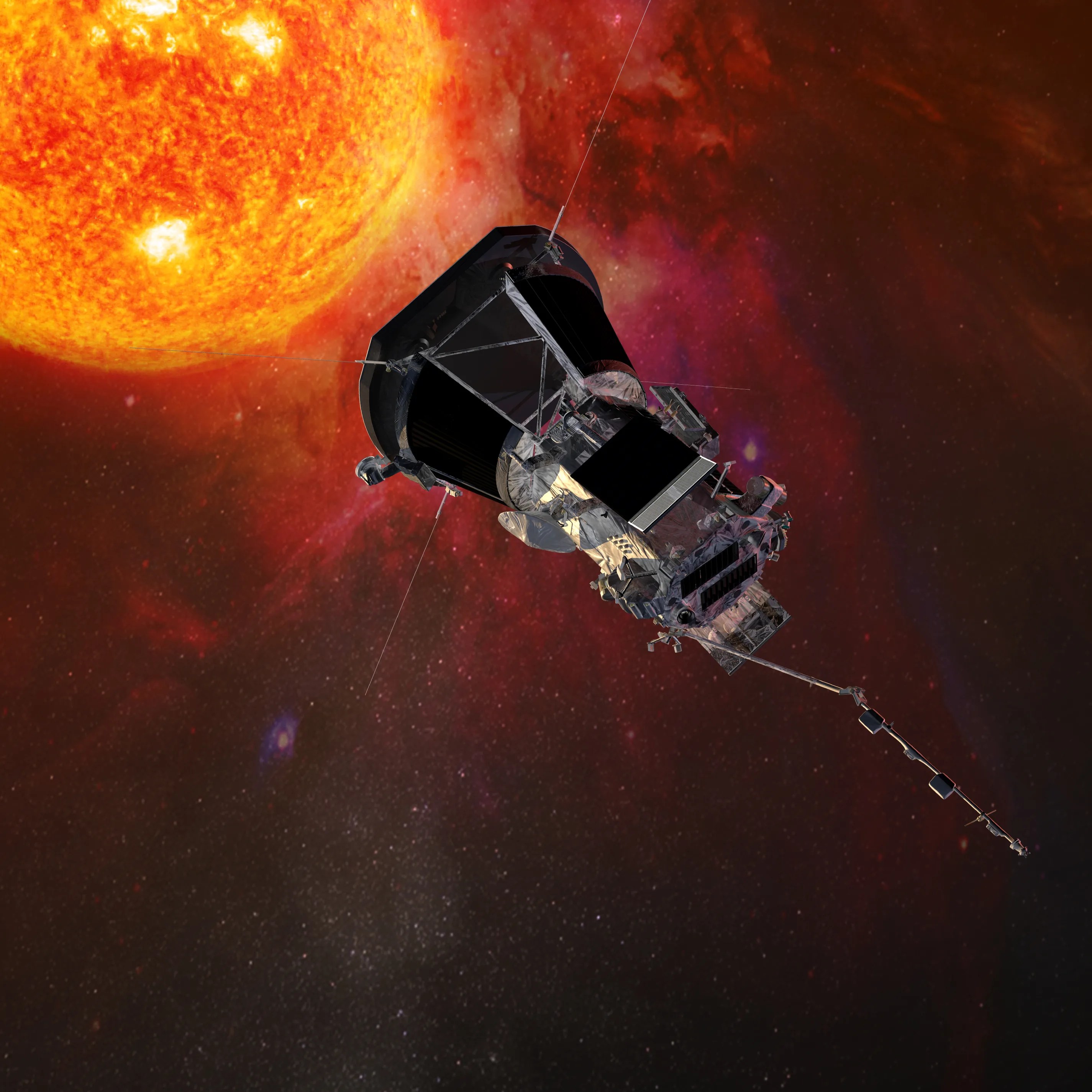
The remarkable twin Voyager spacecraft continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system decades after they completed their surveys of the Outer Planets. Launched in 1977 (September 5 for Voyager 1 (V1) and August 20 for Voyager 2 (V2), whose trajectory took it past Jupiter after Voyager 1), the spacecraft pair made many fundamental discoveries as they flew past Jupiter (March 1979 for V1, July 1979 for V2) and Saturn (November 1980 for V1, August 1981 for V2). The path of Voyager 2 past Saturn was targeted so that it continued within the plane of the solar system, allowing it to become the first spacecraft to visit Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). Following the Neptune encounter, both spacecraft started a new phase of exploration under the intriguing title of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.

Five instruments continue to collect important measurements of magnetic fields, plasmas, and charged particles as both spacecraft explore different portions of the solar system beyond the orbits of the planets. Voyager 1 is now more than 118 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the average orbital distance of Earth from the Sun) distant from the sun, traveling at a speed (relative to the sun) of 17.1 kilometers per second (10.6 miles per second). Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s.

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. The colors have been enhanced to bring out detail. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. The clouds travel around the planet in alternating eastward and westward belts at speeds of up to 540 kilometers per hour. Tremendous storms as big as Earthly continents surge around the planet. The Great Red Spot (oval shape toward the lower-left) is an enormous anticyclonic storm that drifts along its belt, eventually circling the entire planet.
As seen in the night sky at Earth, Voyager 1 is within the confines of the constellation Ophiuchus, only slightly above the celestial equator; no telescope can see it, but radio contact is expected to be maintained for at least the next ten years. Voyager 2 is within the bounds of the constellation Telescopium (which somehow sounds quite appropriate) in the far southern night sky.

Both spacecraft have already passed something called the Termination Shock † (December 2004 for V1, August 2007 for V2), where the solar wind slows as it starts to interact with the particles and fields present between the stars. It is expected that both spacecraft will encounter the Heliopause, where the solar wind ceases as true interstellar space begins, from 10 to 20 years after crossing the Termination Shock. Theories exist for what should be present in interstellar space, but the Voyagers will become the first man-made objects to go beyond the influences of the Sun, hopefully returning the first measurements of what it is like out there. Each spacecraft is carrying a metal record with encoded sounds and sights from Earth, along with the needle needed to read the recordings, and simplified instructions for where the spacecraft came from, in case they are eventually discovered by intelligent extra-terrestrials.

Keep track of the Voyager spacecraft on the official Voyager Interstellar Mission website or follow @NASAVoyager2 on Twitter. † The sun ejects a continuous stream of charged particles (electrons, protons, etc) that is collectively termed the solar wind. The particles are traveling extremely fast and are dense enough to form a very tenuous atmosphere; the heliosphere represents the volume of space where the effects of the solar wind dominate over those of particles in interstellar space. The solar wind particles are moving very much faster than the local speed of sound represented by their low volume density. When the particles begin to interact with interstellar particles and fields (the interaction can be either physically running into other particles or experiencing an electromagnetic force resulting from a charged particle moving within a magnetic field), then they start to slow down. The point at which they become subsonic (rather than their normal hypersonic speed) is the Termination Shock.
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event
Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use

Interstellar Mission
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence.

Mission Statistics
Launch Date
Sept. 5, 1977
About the mission
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
Voyagers 1 and 2 were designed to take advantage of a rare planetary alignment that occurs only once in 176 years and remain the most well traveled spacecraft in history. Both spacecraft carry a sort of time capsule called the Golden Record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
Instruments
- Imaging system
- Infrared interferometer spectrometer
- Ultraviolet spectrometer
- Triaxial fluxgate magnetometer
- Plasma spectrometer
- Low-energy charged particles detectors
- Cosmic Ray System (CRS)
- Photopolarimeter System (PPS)
- Plasma Wave System (PWS)
Mission Highlights
Sept. 1, 2013

Interactive 3D model of Voyager 1. View the full interactive experience at Eyes on the Solar System .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe
Engineers spent months working to repair link with Earth’s most distant spacecraft, says space agency
Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday , JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X . “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries , including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.

Cosmic cleaners: the scientists scouring English cathedral roofs for space dust

Russia acknowledges continuing air leak from its segment of space station

Uncontrolled European satellite falls to Earth after 30 years in orbit

Cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko sets world record for most time spent in space

‘Old smokers’: astronomers discover giant ancient stars in Milky Way

Nasa postpones plans to send humans to moon

What happened to the Peregrine lander and what does it mean for moon missions?

Peregrine 1 has ‘no chance’ of landing on moon due to fuel leak
Most viewed.

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.
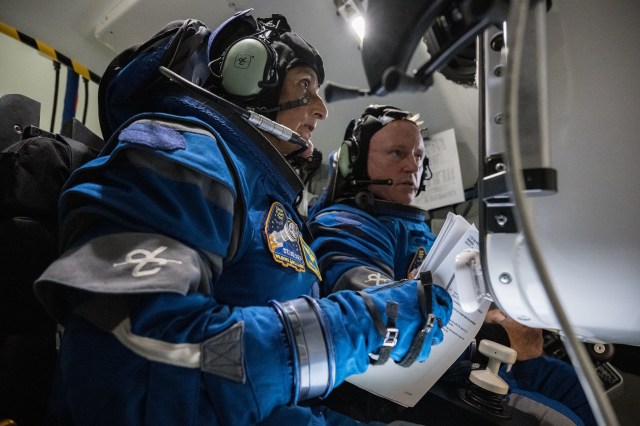

NASA’s Commercial Partners Deliver Cargo, Crew for Station Science
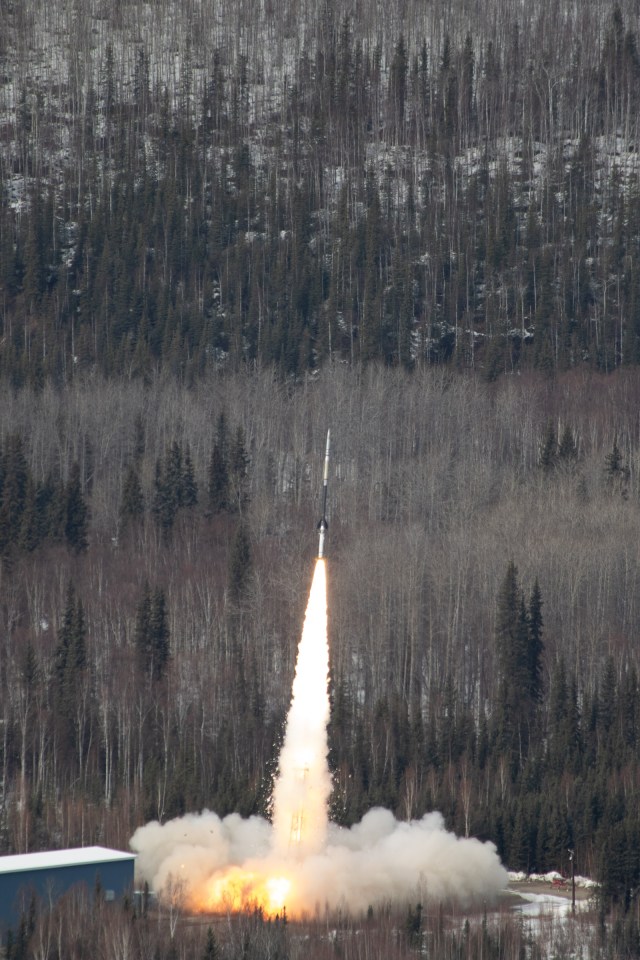

Hi-C Rocket Experiment Achieves Never-Before-Seen Look at Solar Flares
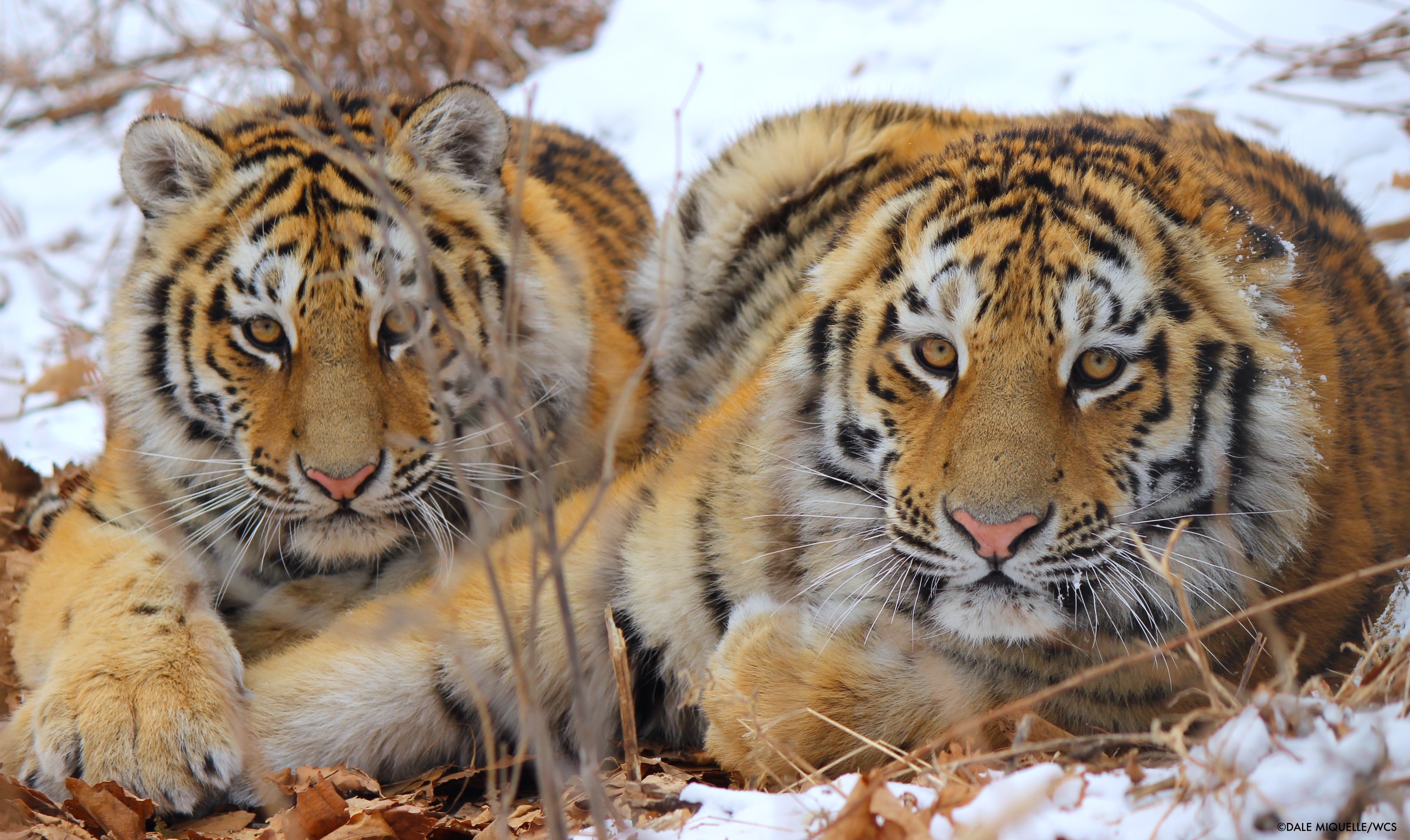

NASA Is Helping Protect Tigers, Jaguars, and Elephants. Here’s How.
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

C.26 Rapid Mission Design Studies for Mars Sample Return Correction and Other Documents Posted

Hubble Views a Galaxy with a Voracious Black Hole
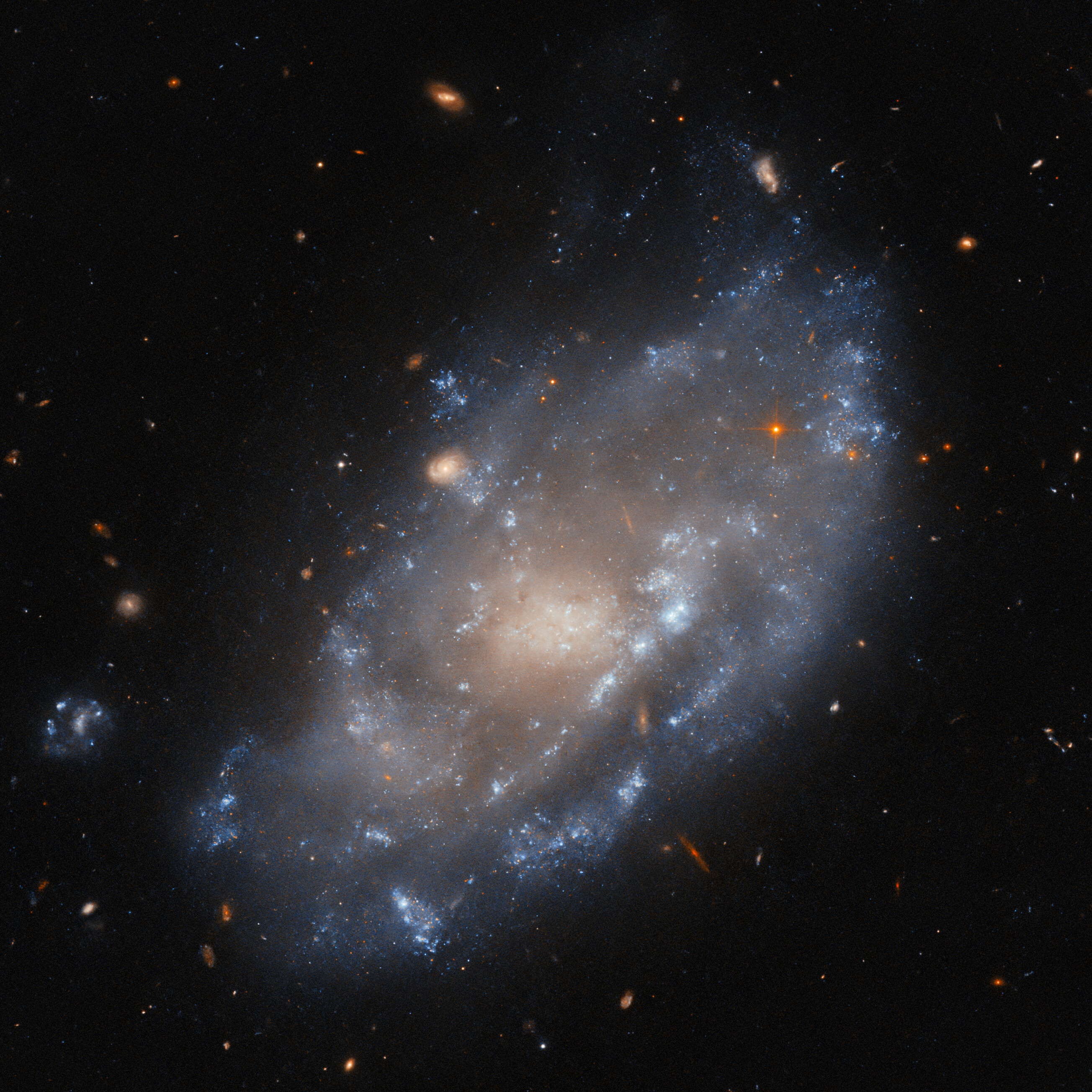

Hubble Hunts Visible Light Sources of X-Rays
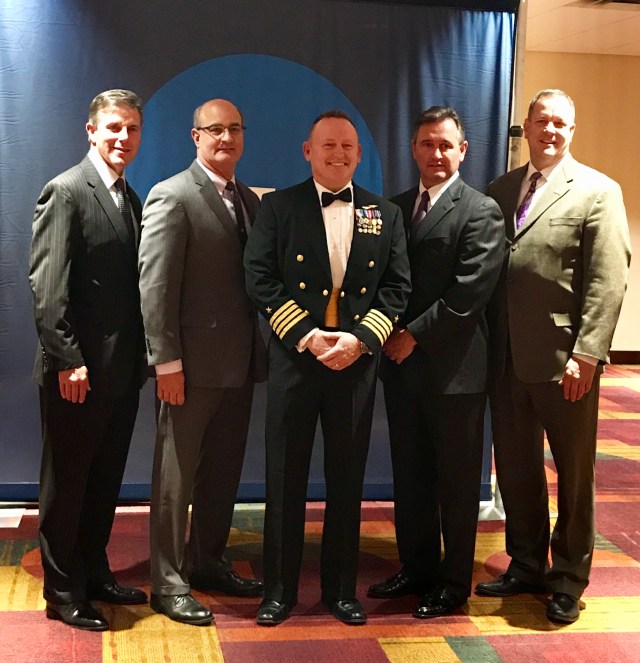

NASA Mission Strengthens 40-Year Friendship

NASA Selects Commercial Service Studies to Enable Mars Robotic Science

Two Small NASA Satellites Will Measure Soil Moisture, Volcanic Gases

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers

NASA Selects Students for Europa Clipper Intern Program
Orbits and Kepler’s Laws
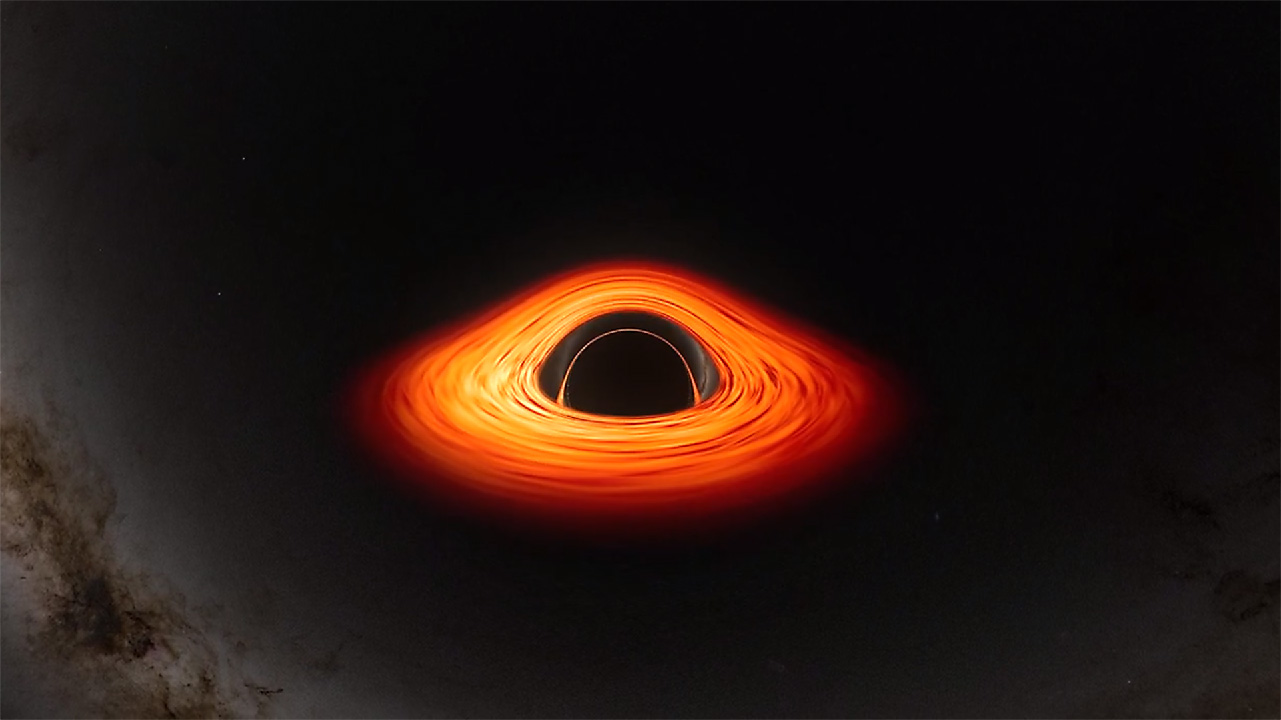

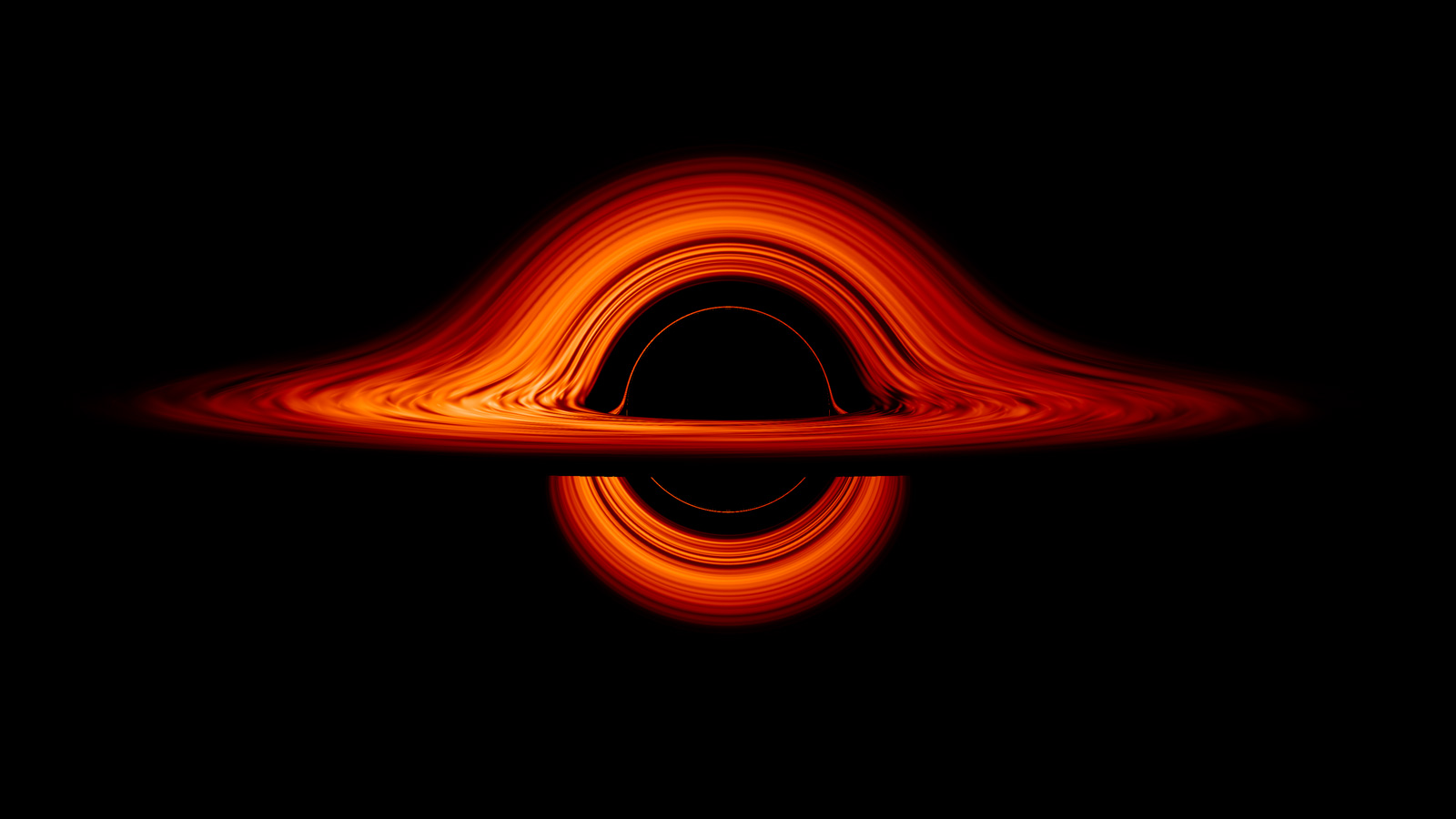
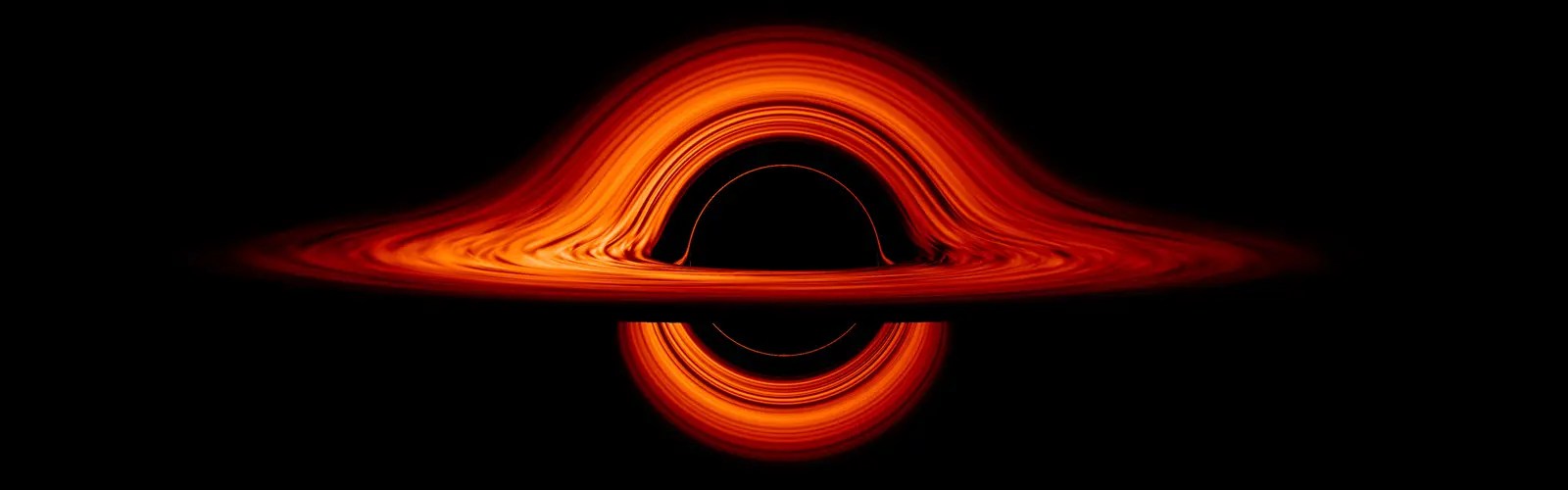
New NASA Black Hole Visualization Takes Viewers Beyond the Brink

Black Hole Week

The Big Event, 2024

ARMD Solicitations

NASA’s Commitment to Safety Starts with its Culture

NASA Uses Small Engine to Enhance Sustainable Jet Research
Tech Today: NASA’s Ion Thruster Knowhow Keeps Satellites Flying

Big Science Drives Wallops’ Upgrades for NASA Suborbital Missions

NASA Community College Aerospace Scholars

NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars

Asian-American and Native Hawaiian Pacific Islander Heritage Month

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
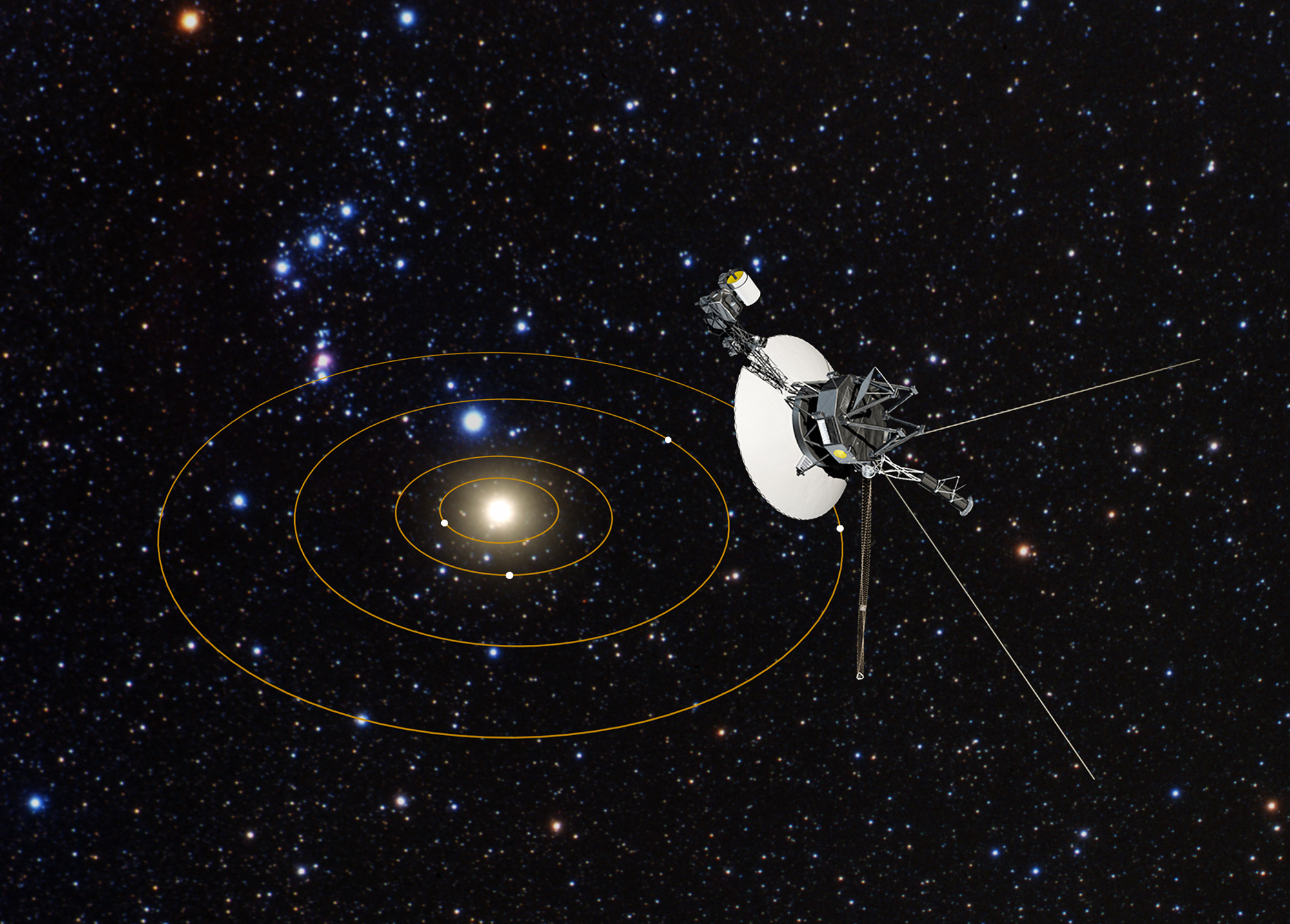
Voyager 1 and 2.

Voyager 1: Facts about Earth's farthest spacecraft
Voyager 1 continues to explore the cosmos along with its twin probe, Voyager 2.

The Grand Tour
Voyager 1 jupiter flyby, voyager 1 visits saturn and its moons, voyager 1 enters interstellar space, voyager 1's interstellar adventures, additional resources.
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space .
The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of August 2022 is approximately 14.6 billion miles (23.5 billion kilometers) away from our planet, making it Earth 's farthest spacecraft. Voyager 1 is currently zipping through space at around 38,000 mph (17 kilometers per second), according to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory .
When Voyager 1 launched a mission to explore the outer planets in our solar system nobody knew how important the probe would still be 45 years later The probe has remained operational long past expectations and continues to send information about its journeys back to Earth.
Related: Celebrate 45 years of Voyager with these amazing images of our solar system (gallery)

Elizabeth Howell, Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before that, since 2012. Elizabeth's on-site reporting includes two human spaceflight launches from Kazakhstan, three space shuttle missions in Florida, and embedded reporting from a simulated Mars mission in Utah.
Size: Voyager 1's body is about the size of a subcompact car. The boom for its magnetometer instrument extends 42.7 feet (13 meters). Weight (at launch): 1,797 pounds (815 kilograms). Launch date: Sept. 5, 1977
Jupiter flyby date: March 5, 1979
Saturn flyby date: Nov. 12, 1980.
Entered interstellar space: Aug. 25, 2012.
The spacecraft entered interstellar space in August 2012, almost 35 years after its voyage began. The discovery wasn't made official until 2013, however, when scientists had time to review the data sent back from Voyager 1.
Voyager 1 was the second of the twin spacecraft to launch, but it was the first to race by Jupiter and Saturn . The images Voyager 1 sent back have been used in schoolbooks and by many media outlets for a generation. The spacecraft also carries a special record — The Golden Record — that's designed to carry voices and music from Earth out into the cosmos.
According to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) , Voyager 1 has enough fuel to keep its instruments running until at least 2025. By then, the spacecraft will be approximately 13.8 billion miles (22.1 billion kilometers) away from the sun.
The Voyager missions took advantage of a special alignment of the outer planets that happens just once every 176 years. This alignment allows spacecraft to gravitationally "slingshot" from one planet to the next, making the most efficient use of their limited fuel.
NASA originally planned to send two spacecraft past Jupiter, Saturn and Pluto and two other probes past Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune . Budgetary reasons forced the agency to scale back its plans, but NASA still got a lot out of the two Voyagers it launched.
Voyager 2 flew past Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune , while Voyager 1 focused on Jupiter and Saturn.
Recognizing that the Voyagers would eventually fly to interstellar space, NASA authorized the production of two Golden Records to be placed on board the spacecraft. Sounds ranging from whale calls to the music of Chuck Berry were placed on board, as well as spoken greetings in 55 languages.
The 12-inch-wide (30 centimeters), gold-plated copper disks also included pictorials showing how to operate them and the position of the sun among nearby pulsars (a type of fast-spinning stellar corpse known as a neutron star ), in case extraterrestrials someday stumbled onto the spacecraft and wondered where they came from.
Both spacecraft are powered by three radioisotope thermoelectric generators , devices that convert the heat released by the radioactive decay of plutonium to electricity. Both probes were outfitted with 10 scientific instruments, including a two-camera imaging system, multiple spectrometers, a magnetometer and gear that detects low-energy charged particles and high-energy cosmic rays . Mission team members have also used the Voyagers' communications system to help them study planets and moons, bringing the total number of scientific investigations on each craft to 11.
Voyager 1 almost didn't get off the ground at its launch , as its rocket came within 3.5 seconds of running out of fuel on Sept. 5, 1977.
But the probe made it safely to space and raced past its twin after launch, getting beyond the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter before Voyager 2 did. Voyager 1's first pictures of Jupiter beamed back to Earth in April 1978, when the probe was 165 million miles (266 million kilometers) from home.
According to NASA , each voyager probe has about 3 million times less memory than a mobile phone and transmits data approximately 38,000 times slower than a 5g internet connection.
To NASA's surprise, in March 1979 Voyager 1 spotted a thin ring circling the giant planet. It found two new moons as well — Thebe and Metis. Additionally, Voyager 1 sent back detailed pictures of Jupiter's big Galilean moons ( Io , Europa , Ganymede and Callisto ) as well as Amalthea .
Like the Pioneer spacecraft before it , Voyager's look at Jupiter's moons revealed them to be active worlds of their own. And Voyager 1 made some intriguing discoveries about these natural satellites. For example, Io's many volcanoes and mottled yellow-brown-orange surface showed that, like planets, moons can have active interiors.
Additionally, Voyager 1 sent back photos of Europa showing a relatively smooth surface broken up by lines, hinting at ice and maybe even an ocean underneath. (Subsequent observations and analyses have revealed that Europa likely harbors a huge subsurface ocean of liquid water, which may even be able to support Earth-like life .)
Voyager 1's closest approach to Jupiter was on March 5, 1979, when it came within 174,000 miles (280,000 km) of the turbulent cloud tops. Then it was time for the probe to aim for Saturn.
Scientists only had to wait about a year, until 1980, to get close-up pictures of Saturn. Like Jupiter, the ringed planet turned out to be full of surprises.
One of Voyager 1's targets was the F ring, a thin structure discovered only the year previously by NASA's Pioneer 11 probe. Voyager's higher-resolution camera spotted two new moons, Prometheus and Pandora, whose orbits keep the icy material in the F ring in a defined orbit. It also discovered Atlas and a new ring, the G ring, and took images of several other Saturn moons.
One puzzle for astronomers was Titan , the second-largest moon in the solar system (after Jupiter's Ganymede). Close-up pictures of Titan showed nothing but orange haze, leading to years of speculation about what it was like underneath. It wouldn't be until the mid-2000s that humanity would find out, thanks to photos snapped from beneath the haze by the European Space Agency's Huygens atmospheric probe .
The Saturn encounter marked the end of Voyager 1's primary mission. The focus then shifted to tracking the 1,590-pound (720 kg) craft as it sped toward interstellar space.
Two decades before it notched that milestone, however, Voyager 1 took one of the most iconic photos in spaceflight history. On Feb. 14, 1990, the probe turned back toward Earth and snapped an image of its home planet from 3.7 billion miles (6 billion km) away. The photo shows Earth as a tiny dot suspended in a ray of sunlight.
Voyager 1 took dozens of other photos that day, capturing five other planets and the sun in a multi-image "solar system family portrait." But the Pale Blue Dot picture stands out, reminding us that Earth is a small outpost of life in an incomprehensibly vast universe.
Voyager 1 left the heliosphere — the giant bubble of charged particles that the sun blows around itself — in August 2012, popping free into interstellar space. The discovery was made public in a study published in the journal Science the following year.
The results came to light after a powerful solar eruption was recorded by Voyager 1's plasma wave instrument between April 9 and May 22, 2013. The eruption caused electrons near Voyager 1 to vibrate. From the oscillations, researchers discovered that Voyager 1's surroundings had a higher density than what is found just inside the heliosphere.
It seems contradictory that electron density is higher in interstellar space than it is in the sun's neighborhood. But researchers explained that, at the edge of the heliosphere, the electron density is dramatically low compared with locations near Earth.
Researchers then backtracked through Voyager 1's data and nailed down the official departure date to Aug. 25, 2012. The date was fixed not only by the electron oscillations but also by the spacecraft's measurements of charged solar particles.
On that fateful day — which was the same day that Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong died — the probe saw a 1,000-fold drop in these particles and a 9% increase in galactic cosmic rays that come from outside the solar system . At that point, Voyager 1 was 11.25 billion miles (18.11 billion km) from the sun, or about 121 astronomical units (AU).
One AU is the average Earth-sun distance — about 93 million miles (150 million km).
You can keep tabs on the Voyager 1's current distance and mission status on this NASA website .
Since flying into interstellar space, Voyager 1 has sent back a variety of valuable information about conditions in this zone of the universe . Its discoveries include showing that cosmic radiation out there is very intense, and demonstrating how charged particles from the sun interact with those emitted by other stars , mission project scientist Ed Stone, of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, told Space.com in September 2017 .
The spacecraft's capabilities continue to astound engineers. In December 2017, for example, NASA announced that Voyager 1 successfully used its backup thrusters to orient itself to "talk" with Earth . The trajectory correction maneuver (TCM) thrusters hadn't been used since November 1980, during Voyager 1's flyby of Saturn. Since then, the spacecraft had primarily used its standard attitude-control thrusters to swing the spacecraft in the right orientation to communicate with Earth.
As the performance of the attitude-control thrusters began to deteriorate, however, NASA decided to test the TCM thrusters — an idea that could extend Voyager 1's operational life. That test ultimately succeeded.
"With these thrusters that are still functional after 37 years without use, we will be able to extend the life of the Voyager 1 spacecraft by two to three years," Voyager project manager Suzanne Dodd, of NASA's Jet Propulsion, Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California, said in a statement in December 2017 .
Mission team members have taken other measures to extend Voyager 1's life as well. For example, they turned off the spacecraft's cameras shortly after the Pale Blue Dot photo was taken to help conserve Voyager 1's limited power supply. (The cameras wouldn't pick up much in the darkness of deep space anyway.) Over the years, the mission team has turned off five other scientific instruments as well, leaving Voyager 1 with four that are still functioning — the Cosmic Ray Subsystem, the Low-Energy Charged Particles instrument, the Magnetometer and the Plasma Wave Subsystem. (Similar measures have been taken with Voyager 2, which currently has five operational instruments .)
The Voyager spacecraft each celebrated 45 years in space in 2022, a monumental milestone for the twin probes.
"Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can," says Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, in a NASA statement .
"Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory," said Linda Spilker, Voyager's deputy project scientist at JPL in the same NASA statement.
"This is the first time we've been able to directly study how a star, our Sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere, helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars, upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions." Spilker continues.
Voyager 1's next big encounter will take place in 40,000 years when the probe comes within 1.7 light-years of the star AC +79 3888. (The star is roughly 17.5 light-years from Earth.) However, Voyager 1's falling power supply means it will probably stop collecting scientific data around 2025.
You can learn much more about both Voyagers' design, scientific instruments and mission goals at JPL's Voyager site . NASA has lots of in-depth information about the Pale Blue Dot photo, including Carl Sagan's large role in making it happen, here . And if you're interested in the Golden Record, check out this detailed New Yorker piece by Timothy Ferris, who produced the historic artifact. Explore the history of Voyager with this interactive timeline courtesy of NASA.
Bibliography
- Bell, Jim. " The Interstellar Age: Inside the Forty-Year Voyager Mission ," Dutton, 2015.
- Landau, Elizabeth. "The Voyagers in popular culture," Dec. 1, 2017. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/jpl/the-voyagers-in-popular-culture
- PBS, "Voyager: A history in photos." https://www.pbs.org/the-farthest/mission/voyager-history-photos/
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
- Daisy Dobrijevic Reference Editor
Virgin Galactic to launch 7th commercial spaceflight on June 8
China launches Chang'e 6 sample-return mission to moon's far side (video)
NASA astronaut and director Ellen Ochoa awarded Presidential Medal of Freedom
Most Popular
- 2 Happy National Astronaut Day 2024! Holiday's founder talks importance of honoring America's spaceflyers (exclusive)
- 3 After an 'emotional rollercoaster,' NASA astronauts are ready to fly on Boeing Starliner
- 4 Boeing Starliner 1st astronaut flight: Live updates
- 5 X-ray spacecraft reveals odd 'Cloverleaf' radio circle in new light (image)
share this!
April 27, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
NASA hears from Voyager 1, the most distant spacecraft from Earth, after months of quiet
by Marcia Dunn

NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 again in a way that makes sense.
The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data last November. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft's coding to work around the trouble.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California declared success after receiving good engineering updates late last week. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data.
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space . The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Contact was never lost, rather it was like making a phone call where you can't hear the person on the other end, a JPL spokeswoman said Tuesday.
Launched in 1977 to study Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 has been exploring interstellar space — the space between star systems — since 2012. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 12.6 billion miles (20 billion kilometers) away and still working fine.
© 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Loss of large herbivores affects interactions between plants and their natural enemies, study shows
17 minutes ago
Nanoparticle researchers develop microfluidic platform for better delivery of gene therapy for lung disease
35 minutes ago
Designing a novel substrate for myogenic differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells
46 minutes ago
Computer models show heat waves in north Pacific may be due to China reducing aerosols

Smart labs for bespoke synthesis of nanomaterials are emerging

Microbiome studies help explore treatments for genetic disorders
Fruit fly model identifies key regulators behind organ development
Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change

Research team discovers new property of light
Materials scientists reveal pathway for designing optical materials with specialized properties
Relevant physicsforums posts, documenting the setup of my new telescope.
9 hours ago
Our Beautiful Universe - Photos and Videos
11 hours ago
Why on Earth do we not see older stars close to us?
May 6, 2024
Retro/prograde flyby galaxies and their bar formation
May 5, 2024
Asteroid 2024 BX1 entered Earth's atmosphere over Germany 21 Jan 2024
May 4, 2024
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
May 3, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth
Apr 22, 2024

NASA hears signal from Voyager 2 spacecraft after mistakenly cutting contact
Aug 1, 2023

NASA listens for Voyager 2 spacecraft after wrong command cuts contact
Jul 31, 2023

Engineers working to resolve issue with Voyager 1 computer
Dec 13, 2023
As Voyager 1's mission draws to a close, one planetary scientist reflects on its legacy
Mar 18, 2024

NASA back in touch with Voyager 2 after 'interstellar shout'
Aug 4, 2023
Recommended for you

Scientists' research answers big question about our system's largest planet
23 hours ago


Compared to billions of years ago, Venus has almost no water: New study may reveal why
Study investigates a nearby M-dwarf binary system

TOI-837 b is a young Saturn-sized exoplanet with a massive core, observations find
May 2, 2024

Webb telescope probably didn't find life on an exoplanet—yet

New findings point to an Earth-like environment on ancient Mars
May 1, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration
Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
Bruce Murray Space Image Library
Voyager 1 and 2 Outside the Heliosphere
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
- Buying Guides
Inside NASA's 5-month fight to save the Voyager 1 mission in interstellar space
After working for five months to re-establish communication with the farthest-flung human-made object in existence, NASA announced this week that the Voyager 1 probe had finally phoned home.
For the engineers and scientists who work on NASA’s longest-operating mission in space, it was a moment of joy and intense relief.
“That Saturday morning, we all came in, we’re sitting around boxes of doughnuts and waiting for the data to come back from Voyager,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for the Voyager 1 mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “We knew exactly what time it was going to happen, and it got really quiet and everybody just sat there and they’re looking at the screen.”
When at long last the spacecraft returned the agency’s call, Spilker said the room erupted in celebration.
“There were cheers, people raising their hands,” she said. “And a sense of relief, too — that OK, after all this hard work and going from barely being able to have a signal coming from Voyager to being in communication again, that was a tremendous relief and a great feeling.”
The problem with Voyager 1 was first detected in November . At the time, NASA said it was still in contact with the spacecraft and could see that it was receiving signals from Earth. But what was being relayed back to mission controllers — including science data and information about the health of the probe and its various systems — was garbled and unreadable.
That kicked off a monthslong push to identify what had gone wrong and try to save the Voyager 1 mission.
Spilker said she and her colleagues stayed hopeful and optimistic, but the team faced enormous challenges. For one, engineers were trying to troubleshoot a spacecraft traveling in interstellar space , more than 15 billion miles away — the ultimate long-distance call.
“With Voyager 1, it takes 22 1/2 hours to get the signal up and 22 1/2 hours to get the signal back, so we’d get the commands ready, send them up, and then like two days later, you’d get the answer if it had worked or not,” Spilker said.
The team eventually determined that the issue stemmed from one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers. Spilker said a hardware failure, perhaps as a result of age or because it was hit by radiation, likely messed up a small section of code in the memory of the computer. The glitch meant Voyager 1 was unable to send coherent updates about its health and science observations.
NASA engineers determined that they would not be able to repair the chip where the mangled software is stored. And the bad code was also too large for Voyager 1's computer to store both it and any newly uploaded instructions. Because the technology aboard Voyager 1 dates back to the 1960s and 1970s, the computer’s memory pales in comparison to any modern smartphone. Spilker said it’s roughly equivalent to the amount of memory in an electronic car key.
The team found a workaround, however: They could divide up the code into smaller parts and store them in different areas of the computer’s memory. Then, they could reprogram the section that needed fixing while ensuring that the entire system still worked cohesively.
That was a feat, because the longevity of the Voyager mission means there are no working test beds or simulators here on Earth to test the new bits of code before they are sent to the spacecraft.
“There were three different people looking through line by line of the patch of the code we were going to send up, looking for anything that they had missed,” Spilker said. “And so it was sort of an eyes-only check of the software that we sent up.”
The hard work paid off.
NASA reported the happy development Monday, writing in a post on X : “Sounding a little more like yourself, #Voyager1.” The spacecraft’s own social media account responded , saying, “Hi, it’s me.”
So far, the team has determined that Voyager 1 is healthy and operating normally. Spilker said the probe’s scientific instruments are on and appear to be working, but it will take some time for Voyager 1 to resume sending back science data.
Voyager 1 and its twin, the Voyager 2 probe, each launched in 1977 on missions to study the outer solar system. As it sped through the cosmos, Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn, studying the planets’ moons up close and snapping images along the way.
Voyager 2, which is 12.6 billion miles away, had close encounters with Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and continues to operate as normal.
In 2012, Voyager 1 ventured beyond the solar system , becoming the first human-made object to enter interstellar space, or the space between stars. Voyager 2 followed suit in 2018.
Spilker, who first began working on the Voyager missions when she graduated college in 1977, said the missions could last into the 2030s. Eventually, though, the probes will run out of power or their components will simply be too old to continue operating.
Spilker said it will be tough to finally close out the missions someday, but Voyager 1 and 2 will live on as “our silent ambassadors.”
Both probes carry time capsules with them — messages on gold-plated copper disks that are collectively known as The Golden Record . The disks contain images and sounds that represent life on Earth and humanity’s culture, including snippets of music, animal sounds, laughter and recorded greetings in different languages. The idea is for the probes to carry the messages until they are possibly found by spacefarers in the distant future.
“Maybe in 40,000 years or so, they will be getting relatively close to another star,” Spilker said, “and they could be found at that point.”
This article was originally published on NBCNews.com
Recommended Stories
What boeing's delayed rocket launch means for the company, according to the intuitive machines ceo.
The delay of Boeing's Starliner launch, which was supposed to take two NASA astronauts to the International Space Station, marked the latest setback for a company already grappling with quality control and safety issues in its aviation business.
Starfish Space and D-Orbit complete orbital rendezvous, bringing Otter Pup mission to a close
Starfish Space’s ambitious first mission to demonstrate on-orbit rendezvous and docking tech has officially come to a close, with the startup managing to complete some of the objectives thanks to a little help from an unexpected partner: space logistics company D-Orbit. Starfish launched its first spacecraft, called Otter Pup, nearly a year ago with ambitious plans to use it to rendezvous and dock with another satellite on orbit. A docking maneuver was now off the table, but a rendezvous attempt might still be possible.
Apple's new Magic Keyboard for the iPad Pro gets a function row and haptic trackpad
Apple just announced a new Magic Keyboard intended specifically for the iPad Pro. It’s not available for the iPad Air.
'Cover without overheating': This No. 1 bestselling kimono cardigan is on sale for as low as $13
Score the stylish layering piece that over 43,000 Amazon shoppers adore.
Apple Pencil Pro adds squeeze, roll and haptic feedback to its bag of tricks
Apple's new Pencil brings squeeze and roll gestures to its iPad lineup.
Formula 1: Miami Grand Prix won by Lando Norris sets United States viewership record
Over 3 million people watched Norris get the first F1 win of his career.
Apple debuts iPad Pro with M4 chip, as company looks to turn around sales
Apple on Tuesday debuted its latest lineup of iPads complete with new chips and improved displays.
Team Penske suspends four crew members for Indianapolis 500 in wake of push to pass scandal
The suspensions come after two Team Penske drivers were disqualified from the season-opening race in St. Petersburg.
Disney stock falls as company attempts to make streaming business profitable
Disney reported its fiscal second quarter earnings before the bell on Tuesday. Here's what to know.
Rad AI, a startup that helps radiologists save time on report generation, raises $50M Series B from Khosla Ventures
In 2017, Vinod Khosla told CNBC that the job "of the radiologist will be obsolete in five years." While the founder of Khosla Ventures later revised that timeline to as long as 15 years, he maintained that AI image recognition could soon diagnose disease on scans better than human doctors. Seven years later, radiologists are still required to interpret most scans (even if AI software helps them); the more immediate challenge is the shortage of these doctors in the United States and around the world.
PGA Championship: Tiger Woods, LIV's Talor Gooch in the field at Valhalla
The PGA Championship will have a field stacked with stars from both the PGA Tour and LIV Golf.
Tubi calls on indie filmmakers and their fans to help beef up original content library
Notably, applicants will receive feedback directly from fans as well as one-on-one guidance from actress Issa Rae, the creator of “Insecure.” The streamer has previously bet on upcoming filmmakers, accepting five original scripts from emerging writers through a partnership with The Black List last year. Later this month, users will be able to follow creatives on the Tubi app and provide their opinions on greenlit projects, such as making suggestions about casting, the screenplay, trailer, key art and more.
Nintendo finally confirms the Switch 2 is on the way
In the most anticlimactic way possible, Nintendo on Tuesday confirmed years of rumors: the Nintendo Switch 2 console is on the way. "We will make an announcement about the successor to Nintendo Switch within this fiscal year," wrote Shuntaro Furukawa, the president of Nintendo, on X. Rather, Furukawa wanted to warn users not to expect the actual announcement in next month's Nintendo Direct livestream.
'Find a way': New York's state of mind powers Knicks past Pacers amid controversial ending
The Knicks came away with a Game 1 victory behind Donte DiVincenzo clutch bombs, Josh Hart lightning strikes and another historic performance by Jalen Brunson.
The UK's Ministry of Defence was hacked, and the country is reportedly blaming China
The UK's Ministry of Defence faced a hack of sensitive data and China is being blamed.
Return to Monkey Island comes to Apple Arcade in June
Where Cards Fall will also be available for the Apple Vision Pro on May 30.
'What my ears crave most': Grab Apple AirPods for $80 (their Black Friday price) — plus other deals of the day
Also on our cheat sheet: Spring savings from Kate Spade, Colgate, Crocs and more.
Akamai confirms acquisition of Noname for $450M
A couple of weeks ago, TechCrunch broke the news that Akamai was in discussions to acquire Noname Security, a specialist in API security, for around $500 million. Akamai on Tuesday said it has agreed to buy Noname in a $450 million deal. Noname was valued at $1 billion at its last private fundraise in December 2021, so it is selling for less than half that price tag.
Nintendo to announce Switch successor before March 2025
Nintendo will unveil a successor to the Switch sometime "within this fiscal year" ending March 2025.
CD rates today, May 7, 2024 (top rate at 5.15% APY)
CD rates available today are well above historical norms. Find out where to get the best cd rates.

Hubble Provides Interstellar Road Map for Voyagers’ Galactic Trek
NASA’s two Voyager spacecraft are hurtling through unexplored territory on their road trip beyond our solar system. Along the way, they are measuring the interstellar medium, the mysterious environment between stars. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope is providing the road map – by measuring the material along the probes’ future trajectories. Even after the Voyagers run out of electrical power and are unable to send back new data, which may happen in about a decade, astronomers can use Hubble observations to characterize the environment through which these silent ambassadors will glide.
A preliminary analysis of the Hubble observations reveals a rich, complex interstellar ecology, containing multiple clouds of hydrogen laced with other elements. Hubble data, combined with the Voyagers, have also provided new insights into how our sun travels through interstellar space.
“This is a great opportunity to compare data from in situ measurements of the space environment by the Voyager spacecraft and telescopic measurements by Hubble,” said study leader Seth Redfield of Wesleyan University in Middletown, Connecticut. “The Voyagers are sampling tiny regions as they plow through space at roughly 38,000 miles per hour. But we have no idea if these small areas are typical or rare. The Hubble observations give us a broader view because the telescope is looking along a longer and wider path. So Hubble gives context to what each Voyager is passing through.”
The astronomers hope that the Hubble observations will help them characterize the physical properties of the local interstellar medium. “Ideally, synthesizing these insights with in situ measurements from Voyager would provide an unprecedented overview of the local interstellar environment,” said Hubble team member Julia Zachary of Wesleyan University.
The team’s results will be presented Jan. 6 at the winter meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Grapevine, Texas.
NASA launched the twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft in 1977. Both explored the outer planets Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 went on to visit Uranus and Neptune.
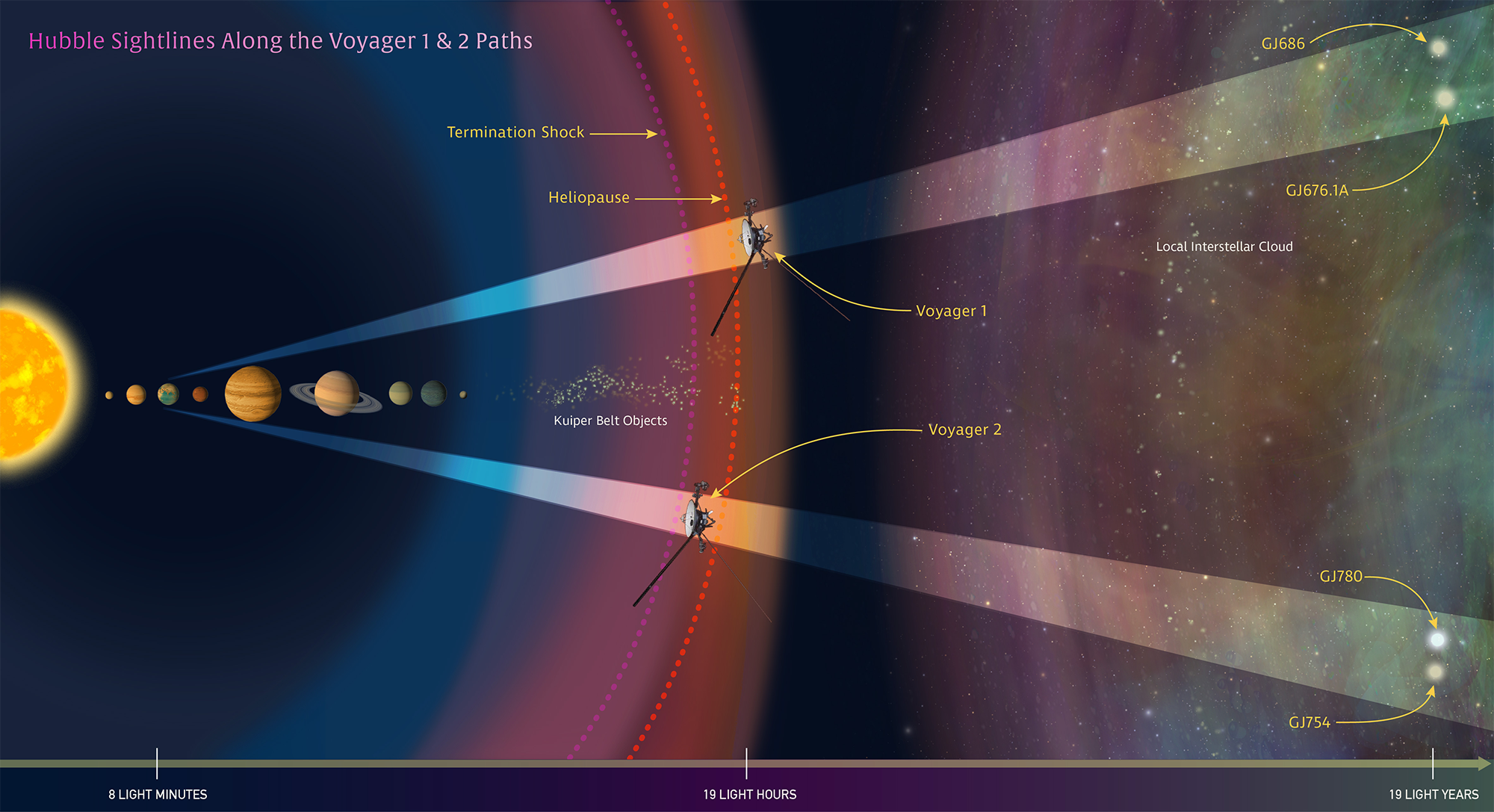
The pioneering Voyager spacecraft are currently exploring the outermost edge of the sun’s domain . Voyager 1 is now zooming through interstellar space, the region between the stars that is filled with gas, dust, and material recycled from dying stars.
Voyager 1 is 13 billion miles from Earth, making it the farthest human-made object ever built. In about 40,000 years, after the spacecraft will no longer be operational and will not be able to gather new data, it will pass within 1.6 light-years of the star Gliese 445, in the constellation Camelopardalis. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 10.5 billion miles from Earth, and will pass 1.7 light-years from the star Ross 248 in about 40,000 years.
For the next 10 years, the Voyagers will be making measurements of interstellar material, magnetic fields and cosmic rays along their trajectories. Hubble complements the Voyagers’ observations by gazing at two sight lines along each spacecraft’s path to map interstellar structure along their star-bound routes. Each sight line stretches several light-years to nearby stars. Sampling the light from those stars, Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph measures how interstellar material absorbs some of the starlight, leaving telltale spectral fingerprints.
Hubble found that Voyager 2 will move out of the interstellar cloud that surrounds the solar system in a couple thousand years. The astronomers, based on Hubble data, predict that the spacecraft will spend 90,000 years in a second cloud and pass into a third interstellar cloud.
An inventory of the clouds’ composition reveals slight variations in the abundances of the chemical elements contained in the structures. “These variations could mean the clouds formed in different ways, or from different areas, and then came together,” Redfield said.
An initial look at the Hubble data also suggests that the sun is passing through clumpier material in nearby space, which may affect the heliosphere, the large bubble containing our solar system that is produced by our sun’s powerful solar wind. At its boundary, called the heliopause, the solar wind pushes outward against the interstellar medium. Hubble and Voyager 1 made measurements of the interstellar environment beyond this boundary, where the wind comes from stars other than our sun.
“I’m really intrigued by the interaction between stars and the interstellar environment,” Redfield said. “These kinds of interactions are happening around most stars, and it is a dynamic process.”
The heliosphere is compressed when the sun moves through dense material, but it expands back out when the star passes through low-density matter. This expansion and contraction is caused by the interaction between the outward pressure of the stellar wind, composed of a stream of charged particles, and the pressure of the interstellar material surrounding a star.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. The Voyagers were built by JPL, which continues to operate both spacecraft. JPL is a division of Caltech.
For images and more information about the local interstellar medium and Hubble, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/hubble
For more information about the Voyager mission, visit: www.nasa.gov/voyager
For additional information, contact:
Felicia Chou NASA Headquarters, Washington, D.C. 202-358-0257 [email protected]
Donna Weaver / Ray Villard Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Maryland 410-338-4493 / 410-338-4514 [email protected] / [email protected]
Elizabeth Landau Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 818-354-6425 [email protected]
Seth Redfield Wesleyan University, Middletown, Connecticut 860-685-3669 [email protected]
Related Terms
- Astrophysics
- Goddard Space Flight Center
- Hubble Space Telescope
Explore More
Breaking the Scaling Limits: New Ultralow-noise Superconducting Camera for Exoplanet Searches
How nasa’s roman mission will hunt for primordial black holes.
Astronomers have discovered black holes ranging from a few times the Sun’s mass to tens of billions. Now a group of scientists has predicted that NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope could find a class of “featherweight” black holes that has so far eluded detection. Today, black holes form either when a massive star collapses […]

New NASA Black Hole Visualization Takes Viewers Beyond the Brink
Discover more topics from nasa.
James Webb Space Telescope

Perseverance Rover

Parker Solar Probe

Voyager 1 had a problem. Here's how NASA fixed it from 15 billion miles away.
Working from more than 15 billion miles away, NASA engineers have solved a computer problem aboard Voyager 1 , allowing the probe to send readable data five months after a chip error made its transmissions impossible to decipher.
Voyager 1, along with its sister craft, Voyager 2, are robotic probes that were launched in 1977. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in 2012. It's now 15.1 billion miles away, the farthest from Earth a human-made object has ever traveled.
Learn more: Closer look at Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 .
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space − the space between the stars, starting at abou t 11 billion miles from our sun − in 2018. It's now 12.7 billion miles away.
Voyager 1's computer glitch garbled the science and engineering data the craft sends to Earth, which rendered it unreadable. That started on Nov. 14, 2023.
How did engineers fix Voyager's problem?
Engineers from NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered a single computer chip inside the spacecraft’s Flight Data Subsystem – which collects science and engineering information and transmits it to Earth – had malfunctioned.
Can't see our graphics? Click here .
The chip stored part of the Flight Data Subsystem's memory and software code. Engineers could still receive data from Voyager 1, but it was scrambled.
The chip could not be repaired. Instead, engineers moved software code from the chip into a different part of the subsystem's memory system.
The code was too large to to be stored in a single location in the spacecraft. Engineers divided the code into sections and stored them in different places within the subsystem. The code sections were adjusted to make sure they worked as a whole.
Engineers tested the fix by moving a code that transmits data about the spacecraft. They were rewarded with a transmission from Voyager that contained readable data about the craft's status.
All that took time. Voyager is moving about 38,000 mph. Because it's so far away, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach Voyager. It takes another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft’s reply to reach antenna networks on Earth.
What happens next?
Engineers will reposition and synchronize the other parts of the code. That should allow Voyager 1 to start sending readable data on what it finds as it moves farther away from Earth.
SOURCE USA TODAY Network reporting and research; NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology; Reuters

golden record
- The Contents
- The Making of
where are they now
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone

Voyager 1 & 2
- Launched on September 5, 1977
- Surveyed the Jupiter and Saturn systems
- First spacecraft to reach interstellar space
- RTGs still operating
- Currently exploring beyond our solar system
- Launched on August 20, 1977
- Only spacecraft to visit Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
- Currently exploring the edge of the solar system
Each powered by:
- 3 Multi-Hundred Watt (MHW) RTGs stacked in a series on a boom, producing about 158 W e each, at launch.

As the electrical power decreases, power loads on the spacecraft must be turned off in order to avoid having demand exceed supply. As loads are turned off, some spacecraft capabilities are eliminated.
Voyager Goals & Accomplishments
Voyager 1 and 2 were designed to take advantage of a rare planetary alignment to explore the outer solar system. Voyager 1 targeted Jupiter and Saturn before continuing on to chart the far edges of our solar system. Voyager 2 targeted Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before joining its sister probe on their interstellar mission.
Voyager proved to be one of the greatest missions of discovery in history. Among their many revelations about the solar system are:
- Rings around Jupiter
- Volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io
- Moons of Saturn that shepherd its rings
- New moons around Uranus and Neptune
- Geysers of liquid nitrogen on Neptune's moon Triton
- Revealed and crossed the farthest boundary of our solar system
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to study all four of the solar system's giant planets at close range. The Voyagers are now exploring the outermost reaches of our sun's influence, where the solar wind mixes with the interstellar wind of our galaxy. Their long-lived power source has enabled these explorers to continue teaching us about our solar system for more than years after they left earth.
- Go to Voyager Homepage
- Go to Voyager Image Gallery
- Status: Where are the Voyagers?
Mission Elapsed Time
Create a free profile to get unlimited access to exclusive videos, sweepstakes, and more!
How NASA Fixed Voyager 1 from 15 Billion Miles Away
This is the most distant repair job in history.

When the crew of SYFY ’s The Ark jumped a ship to Proxima centauri (the star next door), they embarked upon the longest journey humanity had ever taken, either personally or through the use of machines. As it stands in the real world, the current deep space record holder is the distant spacecraft Voyager 1 . Launched in 1977, it’s presently at a distance of more than 15 billion miles from Earth .
Back in November of 2023, Voyager 1 started sending back nonsense in place of readable data. Now, engineers on Earth have figured out how to get Voyager talking again.
NASA Engineers Got Voyager 1 Talking Again!
Beginning November 14, 2023, the Voyager team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) started receiving a bunch of binary gibberish from deep space. They confirmed that Voyager was still receiving signals from Earth and otherwise operating normally, but when it tried to talk with us, everything came back garbled. In March of 2024 the team finally figured out the source of the problem.
For More on Voyager Why Did Voyager 1 Just Start Transmitting Gibberish from Deep Space? The Life and Eventual Death of Voyager 1 and 2 Voyager 1 is Now Rocking Out to Some Sweet Space Tunes Further Away Than Ever

The twin Voyager spacecraft have onboard computers called the flight data system (FDS) which takes information from the spacecraft’s other systems and health data from the craft itself and bundles it together to send to Earth. One of the chips in the FDS got busted, rendering that portion of the system and the code it housed unusable. Unfortunately, the team on Earth couldn’t replace it from 15 billion miles away so they had to find a remote fix.
To make matters worse, there was no one location in Voyager’s brain large enough to store the stuff on that chip. To work around that, engineers broke the contents into bits and stored them in various places, then they rewrote the associated code so Voyager knew how to use the bypass. Pulling that off was a laborious process in no small part because of the light-speed delay in communicating with Voyager. Every time the team wanted to test something, they had to send a signal and wait 22.5 hours for Voyager to receive it. Then they had to wait another 22.5 hours for Voyager’s answer to come back.
The team at JPL started by fixing the systems related to engineering data. That means Voyager can now tell the folks on Earth how it’s doing. Now, the team is working on implementing the same fix for the parts of Voyager responsible for sending back science data. If everything goes according to plan, Voyager 1 will soon resume sending observations from interstellar space, nearly 50 years after it left Earth.
For more things going wrong in deep space, catch The Ark when it returns for Season 2 on Peacock !
- Space Exploration
Related Stories

NASA is sending a Flying Dragonfly Rotorcraft to Explore Saturn's Moon Titan

NASA's ACS3 Spacecraft Will Soar with an 800-Square-Foot Solar Sail

NASA Prepares to Visit a Golden Asteroid Worth Up to $700 Quintillion

NASA Announces Update for Mars Sample Return Mission

NASA's APEP Mission to Fire Rockets at the Eclipse

NASA Proposes Moon Standard Time with Slightly Shorter Seconds

NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) Will Return Humans to the Moon

NASA Releases First Tabletop Roleplaying Game, The Lost Universe

Radiation Could Limit Mars Missions to Four Years

NASA Opens Up Applications for a New Astronaut Class

Odysseus Successfully Lands Near the Moon's South Pole

Retired NASA Telescope Detects Water on Asteroid's Surface
Recommended for you.

Linda Hamilton on Resident Alien Role: "I'm Not the Funny Girl, I'm the Straight Man"

The Classic Twilight Zone Episode That Inspired Jordan Peele's Us

Resident Alien's Alan Tudyk on Harry's New Love Interest, Edi Patterson's Blue Avian
Kentucky Derby post positions: Most wins from each spot at Churchill Downs starting gate

Over the course of an exhilarating two minutes on Saturday, horses will jockey (no pun intended) for position over 1 1/4 miles of Kentucky dirt, with the winner of that frenetic sprint earning a place in history as the champion of the world’s most storied race.
The winner of the 2024 Kentucky Derby , though, won’t just be determined by whoever crosses the finish line first at Churchill Downs . Historically speaking, it will be influenced by where the winning horse began the race.
Among the dozens of factors that go into prognosticating the Run for the Roses is the race’s post position — that is, where on the track’s 20-horse starting gate each competitor is before they take off.
For those who closely follow the sport and try to correctly bet on the winner of the race, last Saturday’s Kentucky Derby post position draw was an event of significant interest. Where a horse starts the race doesn’t foretell whether they’ll win it. But based on nearly a century’s worth of results, it can prevent even a top contender from galloping into the famed Winner’s Circle.
To get a better sense of what horses might be well-positioned to win the 2024 Derby, here’s a look at post positions of previous winners since the starting gate was first used in 1930, how many winners have come from each post position and more:
Kentucky Derby best post position
Post position No. 5 has produced the most Derby winners, with 10 wins in 94 starts, along with eight second-place finishes and four third-place showings.
The last winner from the No. 5 post position came in 2017, when Always Dreaming came in first by 2 3/4 lengths. For all of its historic success, however, the post position hasn’t had a top-three finisher since Audible came in third in 2018.
This year, Catalytic will occupy the No. 5 post position, though the horse isn’t among the race’s favorites. As of Thursday morning, Catalytic was at 42-1 odds to win.
REQUIRED READING: Who can beat the favorite in Kentucky Derby 2024? These are four horses to bet on
Kentucky Derby wins by post position
While the No. 5 post position has been the home to the most Derby winners, it doesn’t hold that distinction by a wide margin.
Post position Nos. 8 and 10 have each produced nine Derby winners, just one behind the lead. Mage, the 2023 Derby champion, came out of No. 8. Post position Nos. 1 and 7 have each been home to eight Derby victors.
Beyond post position No. 10, a horse’s chances of winning the Derby decrease noticeably. Only one gate from Nos. 11 through 20 has produced more than five Derby winners, while six of those 10 spots have been home to two or fewer champions, including post position No. 17, which has never been the starting spot for a Derby winner.
Here are the number of Derby champions that have come from each post position:
- Post No. 1 : 8 winners
- Post No. 2 : 7 winners
- Post No. 3 : 5 winners
- Post No. 4 : 5 winners
- Post No. 5 : 10 winners
- Post No. 6 : 2 winners
- Post No. 7 : 8 winners
- Post No. 8 : 9 winners
- Post No. 9 : 4 winners
- Post No. 10 : 9 winners
- Post No. 11 : 2 winners
- Post No. 12 : 3 winners
- Post No. 13 : 5 winners
- Post No. 14 : 2 winners
- Post No. 15 : 6 winners
- Post No. 16 : 4 winners
- Post No. 17 : 0 winners
- Post No. 18 : 2 winners
- No. 19 : 1 winner
- No. 20 : 2 winners
REQUIRED READING: Brown: Louisville trainers, with 5 horses in Kentucky Derby 150 field, out to make history
Kentucky Derby post positions 2024
What might that history of finishes from various spots on the starting gate mean for the 2024 Derby?
Here’s a look at which horse is starting from which post position:
- No. 1 : Dornoch
- No. 2 : Sierra Leone
- No. 3 : Mystik Dan
- No. 4 : Catching Freedom
- No. 5 : Catalytic
- No. 6 : Just Steel
- No. 7 : Honor Marie
- No. 8 : Just a Touch
- No. 9 : Encino (Scratched)
- No. 10 : T O Password
- No. 11: Forever Young
- No. 12: Track Phantom
- No. 13 : West Saratoga
- No. 14 : Endlessly
- No. 15 : Domestic Product
- No. 16 : Grand Mo the First
- No. 17 : Fierceness
- No. 18 : Stronghold
- No. 19 : Resilience
- No. 20 : Society Man
- No. 21 : Epic Ride

NASA back in communication with Voyager I, now 15 billion miles away | The Sky Guy
A fter five months NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is once again returning usable data to Earth. Voyager 1 stopped sending usable data in November last year though NASA scientists knew it was receiving data from them.
The space craft is the most distant manmade object in space having entered interstellar space 22 years ago. Voyager 1, and its twin Voyager 2, were launched 46 years ago.
According to NASA: “In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth.
“The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft’s engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22 ½ hours for a signal to come back to Earth.
When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.”
Morning sky: Mercury, Mars and Saturn will be visible in the east before sunrise. Mercury rises around 6 a.m. and will enter the Sun’s glare by the end of the month. Mars rises around 5 a.m. in early May and around 4 a.m. at month’s end. Saturn rises around 4:30 a.m. at the beginning of May and around 2:30 a.m. by end of month. Watch the Moon pass a couple of bright stars and planets, see below for dates.
Evening sky: Brilliant Jupiter has entered the Sun’s glare. Watch the Moon pass a couple of bright stars and planets, see below for dates.
1st: Last quarter Moon.
3rd: Moon, Saturn, and Mars form a big line in the east in the early morning sky.
4th : Crescent Moon between Saturn and Mars in the early morning sky.
4th : Tallahassee Astronomical Society’s free planetarium show, “May Skies over Tallahassee,” at the Downtown Digital Dome Theatre and Planetarium at the Challenger Learning Center (not recommended for children under 5). Doors close at 10 a.m. sharp.
5th : Crescent Moon between Mars and Mercury in the early morning sky.
8th : New Moon.
12th: Crescent Moon near bright star Pollux in Gemini in the early evening sky.
15th: First quarter Moon near bright star Regulus in Leo in the evening sky.
18th: Moon occults bright star Beta Virginis beginning at 1:53 a.m. and ends at 2:50 a.m.
23rd: Full Moon near bright star Antares in Scorpius in the evening sky.
31st: Moon near Saturn in morning sky.
Check out TAS’s events calendar at tallystargazers.org .
Ken Kopczynski is a former president of the Tallahassee Astronomical Society, a local group of amateur astronomers .
This article originally appeared on Tallahassee Democrat: NASA back in communication with Voyager I, now 15 billion miles away | The Sky Guy


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: Because Earth moves around the Sun faster than Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 is traveling from Earth, the one-way light time between Earth and each spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of the year. Cosmic Ray Data: This meter depicts the dramatic changes in readings by Voyager's cosmic ray instrument. The instrument detected a dip in ...
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. ... Voyager 2 Present Position. Voyager's Grand Tour Timeline. Mission Status. Voyager 1. Voyager 2. Launch Date. Monday, Sep 5, 1977 12:56:00 UTC. Saturday Aug 20, 1977
What have Voyager 1 and 2, Pioneer 10 and 11 and New Horizons been up to in 2022? ... Voyagers 1 and 2. ... New Horizons' unique position in the outer solar system provides new angles of looking ...
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
The Family Portrait of the Solar System acquired by Voyager 1 (February 14, 1990) Position of Voyager 1 above the plane of the ecliptic on ... Voyager 1 and 2 speed and distance from Sun The Pale Blue Dot image showing Earth from 6 billion kilometres (3.7 billion miles) appearing as a tiny dot (the bluish-white speck approximately halfway ...
The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars). Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally.
NOTE: values for the closest approach are computed with a sampling interval of 1 day. Visualization of Voyager 1 Orbit. This 3d orbit diagram is a feature of our 3D Solar System Simulator and shows the orbit of Voyager 1 with respect of the Sun and the orbits of the major planets.The position of Voyager 1 and the planets along their orbits in this diagram accurately represents the current ...
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018.
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before. The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons.
Voyager 1 live position and data. This page shows Voyager 1 location and other relevant astronomical data in real time. The celestial coordinates, magnitude, distances and speed are updated in real time and are computed using high quality data sets provided by the JPL Horizons ephemeris service (see acknowledgements for details). The sky map shown in the background represents a rectangular ...
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s. This processed color image of Jupiter was ...
Voyager 1 and 2 run 24 hours a day, seven days a week, but they were built to last," Stone said. The spacecraft have really been put to the test during their nearly 30 years of space travel, flying by the outer planets, and enduring such challenges as the harsh radiation environment around Jupiter.
About the mission. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first ...
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h). Hi, it's me.
Voyager 2, which is operating normally, has traveled more than 12.6 billion miles (20.3 billion kilometers) from our planet. Over time, both spacecraft have encountered unexpected issues and ...
This graphic provides some of the mission's key statistics from 2018, when NASA's Voyager 2 probe exited the heliosphere. This is Test--testTEST TEST UPDATED CAPTIONS This illustrated graphic was made to mark Voyager 1's entry into interstellar space in 2012.
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space . The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of ...
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Voyager 1 and 2 Outside the Heliosphere This illustration shows the position of NASA's Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes, outside of the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun that extends well past the orbit of Pluto. Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, or the edge of the heliosphere, in August 2012. Heading in a different direction, Voyager 2 crossed another part of the heliopause in ...
In 2012, Voyager 1 ventured beyond the solar system, becoming the first human-made object to enter interstellar space, or the space between stars. Voyager 2 followed suit in 2018. Voyager 2 ...
In about 40,000 years, after the spacecraft will no longer be operational and will not be able to gather new data, it will pass within 1.6 light-years of the star Gliese 445, in the constellation Camelopardalis. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 10.5 billion miles from Earth, and will pass 1.7 light-years from the star Ross 248 in about 40,000 years.
Learn more: Closer look at Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Voyager 2 entered interstellar space − the space between the stars, starting at about 11 billion miles from our sun − in 2018. It's now 12.7 ...
Overview. The Cover. The Contents. The Making of. Galleries. Videos. Making of the Golden Record. Images on the Golden Record. Galleries of Images Voyager Took.
Voyager Goals & Accomplishments. Voyager 1 and 2 were designed to take advantage of a rare planetary alignment to explore the outer solar system. Voyager 1 targeted Jupiter and Saturn before continuing on to chart the far edges of our solar system. Voyager 2 targeted Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before joining its sister probe on their ...
When the crew of SYFY's The Ark jumped a ship to Proxima centauri (the star next door), they embarked upon the longest journey humanity had ever taken, either personally or through the use of machines. As it stands in the real world, the current deep space record holder is the distant spacecraft Voyager 1.Launched in 1977, it's presently at a distance of more than 15 billion miles from Earth.
Here are the number of Derby champions that have come from each post position: Post No. 1: 8 winners; Post No. 2: 7 winners; Post No. 3: 5 winners; Post No. 4: 5 winners; Post No. 5: 10 winners;
They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and ...