Language selection
- Français fr

Latest border and travel measures
This news release may not reflect the current border and travel measures. Check COVID-19: Travel, testing and borders for the latest requirements to enter Canada.
Important notice
Note that information and resources on the coronavirus (COVID-19) are available on Canada.ca. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/coronavirus-disease-covid-19.html
Government of Canada expands restrictions to international travel by land and air
From: Public Health Agency of Canada
News release
The Government of Canada is announcing today further testing and quarantine requirements for international travellers arriving to Canada’s air and land ports of entry. These new measures will help prevent variants of concern from reaccelerating the pandemic and making it more difficult to contain.
February 12, 2021 | Ottawa, ON | Government of Canada
Canada has some of the strictest travel and border measures in the world, including a mandatory 14-day quarantine for everyone returning to the country. With new COVID-19 variant detections increasing in the country, the Government of Canada is announcing today further testing and quarantine requirements for international travellers arriving to Canada’s air and land ports of entry. These new measures will help prevent variants of concern from reaccelerating the pandemic and making it more difficult to contain.
For travellers arriving to Canada by land, as of February 15, 2021, all travellers, with some exceptions, will be required to provide proof of a negative COVID-19 molecular test result taken in the United States within 72 hours of pre-arrival, or a positive test taken 14 to 90 days prior to arrival. In addition, as of February 22, 2021, travellers entering Canada at the land border will be required to take a COVID-19 molecular test on arrival as well as toward the end of their 14-day quarantine.
All travellers arriving to Canada by air, as of February 22, 2021, with some exceptions, will be required to take a COVID-19 molecular test when they arrive in Canada before exiting the airport, and another toward the end of their 14-day quarantine period. With limited exceptions, air travellers, will also be required to reserve, prior to departure to Canada, a 3-night stay in a government-authorized hotel. Travellers will be able to book their government-authorized stay starting February 18, 2021. These new measures are in addition to existing mandatory pre-boarding and health requirements for air travellers.
Finally, at the same time on February 22, 2021, all travellers, whether arriving by land or air will be required to submit their travel and contact information, including a suitable quarantine plan, electronically via ArriveCAN before crossing the border or boarding a flight.
The Government of Canada continues to strongly advise Canadians to cancel or postpone any non-essential travel, including vacation plans, outside Canada. Foreign nationals should likewise postpone or cancel travel plans to Canada. Now is not the time to travel.
“I want to thank Canadians who continue to make sacrifices to protect each other from COVID-19. We continue to detect variants of concerns, and this is why we are putting these additional measures in place. Now is not the time to travel, so please cancel any plans you might have." The Honourable Patty Hajdu Minister of Health
“With these additional COVID testing requirements and safety measures at the land border we are taking extra steps to help prevent the spread of COVID-19 and its variants. As we do for air travel, we are now also requiring travellers by land to provide information using ArriveCAN to facilitate processing and limit points of contacts between border services officers and travellers. We’ll always prioritize the health and safety of Canadians as we make decisions.” The Honourable Bill Blair Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness
“We’re moving forward with these critical measures to help prevent the spread of COVID-19 and the introduction of new variants of the virus into Canada. At the same time, we recognize the importance of the continued movement of goods and the ongoing delivery of essential services in Canada. Our government’s response to this pandemic includes necessary measures to protect the health and safety of Canadians while keeping our economy going.” The Honourable Omar Alghabra Minister of Transport
Quick facts
Canadians citizens, persons registered under the Indian Act and permanent residents arriving by land to Canada, who do not present a valid COVID-19 molecular test, will be allowed entry, but may be subject to a fine of up to $3,000 per day or face criminal prosecution. Travellers may also be required to go to a designated quarantine facility if they are symptomatic on arrival at the border, or do not have a suitable quarantine plan.
Foreign nationals who have obtained an exemption to enter Canada, will be refused entry, with limited exceptions, if they do not have a valid COVID-19 molecular test result.
Failure to provide accurate information is an offence under the Quarantine Act . In addition, violating any quarantine or isolation instructions provided to travellers by a screening officer or quarantine officer when entering Canada is an offence under the Quarantine Act and could lead to serious penalties, including 6 months in prison and/or $750,000 in fines.
Exemptions continue to be in place to ensure that economic supply chains continue between Canada and the U.S. The Government of Canada is closely engaging the Biden Administration on our respective border measures and we continue to keep the lines of communication open.
Associated links
- Infographic for travellers arriving by air
- Infographic for travellers arriving by land
- Backgrounder - Additional testing and more stringent quarantine requirements for travel to Canada
- COVID-19: Travel, quarantine and borders
- COVID-19 measures, updates, and guidance issued by Transport Canada
- Group Exemption from Quarantine under 6(e) of the Order
Media Relations Public Health Agency of Canada 613-957-2983 [email protected]
Page details

GHANA TRAVEL REQUIREMENTS
Individuals traveling to Ghana are required to strictly adhere to the following new directives as stated by Ghana’s President during his 16 th address to the Nation on Measures Taken Against the Spread of the Coronavirus:
- All passengers arriving in Ghana must be in possession of a negative COVID-19 PCR test result from an accredited laboratory in the country of origin and the test must have been done not more than seventy-two (72) hours before the scheduled arrival in the country. All airlines have been instructed to ensure compliance with this directive for all passengers traveling to Ghana;
- All passengers would be required to undergo a mandatory COVID-19 test at the airport terminal upon arrival in Ghana at a fee of one hundred and fifty dollars ($150.00) to be borne by the passenger. The test result will be available within thirty (30) minutes;
- Children under the age of five (5) will not be required to undergo testing at the airport;
- Passengers who test positive for COVID-19 will be handled by the health authorities for further clinical assessment and management; and
- Passengers who test negative will be admitted into the country and will be advised to continue to observe COVID-19 safety precautions during their stay in Ghana.
Ministry of Health / Ghana Health Service Guidelines
INTRODUCTION
Following the declaration of the novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a global Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30th January 2020, several countries instituted measures to curb the spread of the disease. In Ghana, similar measures were instituted in addition to the Executive Instrument (EI) 61 requiring some practices to be enforced.
As part of plans to reopen the Kotoka International Airport (KIA) on Tuesday, September 1, 2020, the Ghana Health Service/Ministry of Health has instituted measures to prevent and control the spread of COVID 19 in Ghana related to international travel. The outlined measures below are applicable to flight crew and passengers arriving and/or departing KIA within the period of reopening the airport to international travel until further advised.
The Ghana Health Service in collaboration with other partners will provide Port Health Services to ensure safety of flight crew, passengers and users of the airport. Port Health Services at the airport includes all health-related activities within the terminal including laboratory testing, inspection of relevant health documents, screening and triaging of passengers and the management of ill persons including transfer to appropriate health facilities; environmental inspections, supervision of cleaning and disinfection of aircraft and the entire airport terminal among others.
COVID-19 PROTOCOLS FOR DEPARTING AND ARRIVING PASSENGERS
All passengers departing or arriving on international flights at KIA including those from the ECOWAS region will be required to meet the health requirements outlined below prior to admission into Ghana by the Ghana Immigration Service.
- Departing Passengers
All passengers on international flights departing KIA will be required to adhere to COVID-19 testing requirements for the destination countries. All persons must be wearing a face mask appropriately (extending from the middle of the nasal bridge to halfway between the chin and the neck) and adhere to social distancing and hygiene protocols. Departing passengers will under g o COVID-19 screening including the checking of temperature.
- Arriving Passengers
All arriving passengers must not have any symptoms suggestive of COVID-19 including body temperature >38°C. They must be in possession of a COVID-19 negative PCR test result from an accredited laboratory in the country of origin. The test should have been done not more than 72 hours before the scheduled departure time from the country of origin. For passengers who transit through other countries before arriving in Ghana, the first country of departure will be the reference point. For passengers who depart Ghana and return within one (1) week, the passengers will not be required to present a COVID-19 test result from the country of departure. A negative COVID-19 test from Ghana used on departure will serve as evidence of meeting the COVID-19 test criteria for arriving in Ghana. In addition, all persons must be wearing face masks appropriately upon arrival (extending from the middle of the nasal bridge to halfway between the chin and the neck). All passengers will be subjected to a mandatory COVID-19 test at the airport terminal at the cost to the passenger. All persons testing positive will receive further clinical assessment and treatment. All persons testing negative will be advised to continue to observe COVID-19 safety precautions following arrival in Ghana.
- 5 . Exemptions
The following categories of passengers and crew are exempt from COVID-19 PCR test Testing:
- Children under-5 years of age will not be required to undergo testing at the airport;
- Persons who arrive under emergency circumstances such as diverted flights will not be required to undergo testing if they do not leave the airport or if they remain in transit such that they do not leave the hotel; and
- Airline crew are exempt from the pre-departure and arrival testing and should follow airline policy for testing.
MANAGEMENT OF CONFIRMED COVID-19 CASES
All persons testing positive will receive further clinical assessment and treatment. Confirmed COVID 19 positive will be handled by the Port Health Unit for the remainder of their arrival processes. Following completion of the arrival procedures, they will be sent to the Ga East Municipal Hospital for further clinical assessment and management. All persons testing negative will be advised to continue to observe COVID-19 safety precautions following arrival in Ghana.
CLICK HERE TO READ MORE
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Ghana Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Ghana. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Measles April 26, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Timor-Leste (East Timor), Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
There is no longer active cholera transmission and vaccine is not recommended.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Ghana.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Ghana.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to Ghana take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Ghana.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Meningitis (Meningococcal disease)
Recommended for travelers 2 months old or older traveling to areas of Ghana that are part of the meningitis belt during the dry season.
Meningococcal disease - CDC Yellow Book
Meningitis Belt Map
In Ghana poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Travelers to Ghana are at increased risk of exposure to poliovirus.
Vaccine recommendations : Adults traveling to Ghana who received a complete polio vaccination series as children may receive a single lifetime booster dose of inactivated polio vaccine; travelers who are unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated should receive a complete polio vaccination series before travel. Children who are not fully vaccinated will be considered for an accelerated vaccination schedule .
Polio - CDC Yellow Book
Polio: For Travelers
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Ghana. If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Ghana, there may be limited or no rabies treatment available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Ghana.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for all arriving travelers ≥9 months old.
Recommended for all travelers ≥9 months old.
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
African tick-bite fever.
- Avoid Bug Bites
African Tick-bite fever
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Lassa Fever
- Breathe in air or eat food contaminated with the urine or droppings of infected rats
- Touch the body fluids of a person infected with Lassa virus or objects contaminated with infected body fluids
Lassa fever
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Ghana, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Ghana. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Ghana—such as dengue, leishmaniasis, and African sleeping sickness—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Ghana include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Ghana. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Ghana’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in Ghana. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Ghana may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Ghana, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Ghana, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Ghana .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Ghana, dial 193 for an ambulance, 192 for the fire department, and 191 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you during your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Ghana before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Ghana from the US Department of State.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Ghana for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Language selection
Information by country and territory.
Canada's presence abroad includes embassies, consulates, high commissions and trade offices . Canada also maintains a number of permanent missions to international organizations.
The information below offers a comprehensive view of Canada's travel advice and advisories, basic country information, the name of Canada's representative at the relevant Canadian government office abroad, the location of relevant trade offices and information for Canadians abroad requiring assistance, and information about Canada's international development assistance in that country.
Countries and territories starting with the letter A
- Doing business in Afghanistan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Afghanistan
- Doing business in Albania (served by Rome, Italy)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Albania
- Doing business in Algeria
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Algeria
- Doing business in American Samoa (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - American Samoa
- Doing business in Andorra (served by Madrid, Spain)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Andorra
- Doing business in Angola (served by Maputo, Mozambique)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Angola
- Doing business in Anguilla (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Anguilla
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Antarctica
- Doing business in Antigua and Barbuda (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Antigua and Barbuda
- Doing business in Argentina
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Argentina
- Doing business in Armenia (served by Moscow, Russia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Armenia
- Doing business in Aruba (served by Bogota, Colombia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Aruba
- Doing business in Australia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Australia
- Doing business in Austria
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Austria
- Doing business in Azerbaijan (served by Ankara, Türkiye)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Azerbaijan
- Doing business in Azores (served by Lisbon, Portugal)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Azores
Countries and territories starting with the letter B
- Doing business in Bahamas (served by Kingston, Jamaica)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bahamas
- Doing business in Bahrain (served by Riyadh, Saudi Arabia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bahrain
- Doing business in Bangladesh
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bangladesh
- Doing business in Barbados
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Barbados
- Doing business in Belarus (served by Warsaw, Poland)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Belarus
- Doing business in Belgium
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Belgium
- Doing business in Belize (served by Guatemala City, Guatemala)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Belize
- Doing business in Benin (served by Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Benin
- Doing business in Bermuda (served by New York, U.S.A)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bermuda
- Doing business in Bhutan (served by New Delhi, India)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bhutan
- Doing business in Bolivia (served by Lima, Peru)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bolivia
- Doing business in Bonaire (served by Bogota, Colombia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bonaire
- Doing business in Bosnia and Herzegovina (served by Budapest, Hungary)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Doing business in Botswana (served by Harare, Zimbabwe)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Botswana
- Doing business in Brazil
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Brazil
- Doing business in British Virgin Islands (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - British Virgin Islands
- Doing business in Brunei Darussalam
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Brunei Darussalam
- Doing business in Bulgaria (served by Bucharest, Romania)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Bulgaria
- Doing business in Burkina Faso
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Burkina Faso
- Doing business in Burundi (served by Nairobi, Kenya)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Burundi
Countries and territories starting with the letter C
- Doing business in Cabo Verde (served by Dakar, Senegal)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cabo Verde
- Doing business in Cambodia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cambodia
- Doing business in Cameroon
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cameroon
- Doing business in Canary Islands (served by Madrid, Spain)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Canary Islands
- Doing business in Cayman Islands (served by Kingston, Jamaica)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cayman Islands
- Doing business in Central African Republic (served by Yaoundé, Cameroon)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Central African Republic
- Doing business in Chad (served by Yaoundé, Cameroon)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Chad
- Doing business in Chile
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Chile
- Doing business in China
- Travel Advice and Advisories - China
- Doing business in Colombia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Colombia
- Doing business in Comoros (served by Dar es Salaam, Tanzania)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Comoros
- Doing business in Cook Islands (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cook Islands
- Doing business in Costa Rica
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Costa Rica
- Doing business in Côte d'Ivoire
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Côte d'Ivoire
- Doing business in Croatia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Croatia
- Doing business in Cuba
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cuba
- Doing business in Curaçao (served by Bogota, Colombia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Curaçao
- Doing business in Cyprus (served by Athens, Greece)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Cyprus
- Doing business in Czechia (Czech Republic)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Czechia
Countries and territories starting with the letter D
- Doing business in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (served by Seoul, Republic of Korea)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
- Doing business in Democratic Republic of Congo
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Democratic Republic of Congo
- Doing business in Denmark
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Denmark
- Doing business in Djibouti (served by Addis Ababa, Ethiopia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Djibouti
- Doing business in Dominica (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Dominica
- Doing business in Dominican Republic
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Dominican Republic
Countries and territories starting with the letter E
- Doing business in Ecuador
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Ecuador
- Doing business in Egypt
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Egypt
- Doing business in El Salvador
- Travel Advice and Advisories - El Salvador
- Doing business in Equatorial Guinea (served by Lagos, Nigeria)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Equatorial Guinea
- Doing business in Eritrea (served by Nairobi, Kenya)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Eritrea
- Doing business in Estonia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Estonia
- Doing business in Eswatini (served by Maputo, Mozambique)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Eswatini
- Doing business in Ethiopia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Ethiopia
Countries and territories starting with the letter F
- Doing business in Falkland Islands (served by London, United Kingdom)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Falkland Islands
- Doing business in Fiji (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Fiji
- Doing business in Finland
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Finland
- Doing business in France
- Travel Advice and Advisories - France
- Doing business in French Guiana (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - French Guiana
- Doing business in French Polynesia (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - French Polynesia
Countries and territories starting with the letter G
- Doing business in Gabon (served by Yaoundé, Cameroon)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Gabon
- Doing business in Gambia (served by Dakar, Senegal)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Gambia
- Doing business in Georgia (served by Ankara, Türkiye)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Georgia
- Doing business in Germany
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Germany
- Doing business in Ghana
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Ghana
- Doing business in Gibraltar (served by London, United Kingdom)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Gibraltar
- Doing business in Greece
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Greece
- Doing business in Greenland (served by Copenhagen, Denmark)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Greenland
- Doing business in Grenada (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Grenada
- Doing business in Guadeloupe (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Guadeloupe
- Doing business in Guam (served by Makati City, Philippines)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Guam
- Doing business in Guatemala
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Guatemala
- Doing business in Guinea (served by Dakar, Senegal)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Guinea
- Doing business in Guinea-Bissau (served by Dakar, Senegal)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Guinea-Bissau
- Doing business in Guyana
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Guyana
Countries and territories starting with the letter H
- Doing business in Haiti
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Haiti
- Doing business in Honduras (served by San Jose, Costa Rica)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Honduras
- Doing business in Hong Kong
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Hong Kong
- Doing business in Hungary
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Hungary
Countries and territories starting with the letter I
- Doing business in Iceland
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Iceland
- Doing business in India
- Travel Advice and Advisories - India
- Doing business in Indonesia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Indonesia
- Canadian Sanctions Related to Iran
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Iran
- Doing business in Iraq
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Iraq
- Doing business in Ireland
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Ireland
- Doing business in Israel
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Israel
- Doing business in Italy
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Italy
Countries and territories starting with the letter J
- Doing business in Jamaica
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Jamaica
- Doing business in Japan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Japan
- Doing business in Jordan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Jordan
Countries and territories starting with the letter K
- Doing business in Kazakhstan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Kazakhstan
- Doing business in Kenya
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Kenya
- Doing business in Kiribati (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Kiribati
- Doing business in Kosovo (served by Zagreb, Croatia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Kosovo
- Doing business in Kuwait
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Kuwait
- Doing business in Kyrgyzstan (served by Astana, Kazakhstan)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Kyrgyzstan
Countries and territories starting with the letter L
- Doing business in Laos
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Laos
- Doing business in Latvia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Latvia
- Doing business in Lebanon
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Lebanon
- Doing business in Lesotho (served by Johannesburg, South Africa)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Lesotho
- Doing business in Liberia (served by Plateau, Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Liberia
- Doing business in Libya
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Libya
- Doing business in Liechtenstein (served by Bern, Switzerland)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Liechtenstein
- Doing business in Lithuania
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Lithuania
- Doing business in Luxembourg (served by Brussels, Belgium)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Luxembourg
Countries and territories starting with the letter M
- Doing business in Macao (served by Hong Kong)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Macao
- Doing business in Madagascar (served by Johannesburg, South Africa)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Madagascar
- Doing business in Malawi (served by Maputo, Mozambique)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Malawi
- Doing business in Malaysia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Malaysia
- Doing business in Maldives (served by Colombo, Sri Lanka)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Maldives
- Doing business in Mali
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mali
- Doing business in Malta (served by Rome, Italy)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Malta
- Doing business in Marshall Islands (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Marshall Islands
- Doing business in Martinique (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Martinique
- Doing business in Mauritania (served by Rabat, Morocco)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mauritania
- Doing business in Mauritius (served by Johannesburg, South Africa)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mauritius
- Doing business in Mayotte (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mayotte
- Doing business in Mexico
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mexico
- Doing business in Micronesia (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Micronesia
- Doing business in Moldova (served by Bucharest, Romania)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Moldova
- Doing business in Monaco (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Monaco
- Doing business in Mongolia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mongolia
- Doing business in Montenegro (served by Belgrade, Serbia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Montenegro
- Doing business in Montserrat (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Montserrat
- Doing business in Morocco
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Morocco
- Doing business in Mozambique
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Mozambique
- Doing business in Myanmar
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Myanmar
Countries and territories starting with the letter N
- Doing business in Namibia (served by Johannesburg, South Africa)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Namibia
- Doing business in Nauru (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Nauru
- Doing business in Nepal (served by New Delhi, India)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Nepal
- Doing business in Netherlands
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Netherlands
- Doing business in New Caledonia (served by Sydney, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - New Caledonia
- Doing business in New Zealand
- Travel Advice and Advisories - New Zealand
- Doing business in Nicaragua (served by San Jose, Costa Rica)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Nicaragua
- Doing business in Niger (served by Bamako, Mali)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Niger
- Doing business in Nigeria
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Nigeria
- Doing business in Niue (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Niue
- Doing business in North Macedonia (served by Belgrade, Serbia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - North Macedonia
- Doing business in Northern Marianas (served by Makati City, Philippines)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Northern Marianas
- Doing business in Norway
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Norway
Countries and territories starting with the letter O
- Doing business in Oman (served by Riyadh, Saudi Arabia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Oman
Countries and territories starting with the letter P
- Doing business in Pakistan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Pakistan
- Doing business in Palau (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Palau
- Doing business in Panama
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Panama
- Doing business in Papua New Guinea (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Papua New Guinea
- Doing business in Paraguay (served by Buenos Aires, Argentina)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Paraguay
- Doing business in Peru
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Peru
- Doing business in Philippines
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Philippines
- Doing business in Poland
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Poland
- Doing business in Portugal
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Portugal
- Doing business in Puerto Rico (served by Miami, U.S.A)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Puerto Rico
Countries and territories starting with the letter Q
- Doing business in Qatar
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Qatar
Countries and territories starting with the letter R
- Doing business in Republic of Congo (served by Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Republic of Congo
- Doing business in Republic of Korea
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Republic of Korea
- Doing business in Réunion (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Réunion
- Doing business in Romania
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Romania
- Doing business in Russia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Russia
- Doing business in Rwanda
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Rwanda
Countries and territories starting with the letter S
- Doing business in Saint Kitts and Nevis (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Doing business in Saint Lucia (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saint Lucia
- Doing business in Saint Martin (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saint Martin
- Doing business in Saint Vincent & the Grenadines (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saint Vincent & the Grenadines
- Doing business in Saint-Barthélemy (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saint-Barthélemy
- Doing business in Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon (served by Paris, France)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Doing business in Samoa (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Samoa
- Doing business in San Marino (served by Rome, Italy)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - San Marino
- Doing business in Sao Tome and Principe (served by Lagos, Nigeria)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Sao Tome and Principe
- Doing business in Saudi Arabia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Saudi Arabia
- Doing business in Senegal
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Senegal
- Doing business in Serbia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Serbia
- Doing business in Seychelles (served by Dar es Salaam, Tanzania)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Seychelles
- Doing business in Sierra Leone (served by Accra, Ghana)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Sierra Leone
- Doing business in Singapore
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Singapore
- Doing business in Sint Maarten (served by Bridgetown, Barbados)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Sint Maarten
- Doing business in Slovakia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Slovakia
- Doing business in Slovenia (served by Budapest, Hungary)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Slovenia
- Doing business in Solomon Islands (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Solomon Islands
- Doing business in Somalia (served by Nairobi, Kenya)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Somalia
- Doing business in South Africa
- Travel Advice and Advisories - South Africa
- Doing business in South Sudan (served by Nairobi, Kenya)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - South Sudan
- Doing business in Spain
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Spain
- Doing business in Sri Lanka
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Sri Lanka
- Doing business in Sudan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Sudan
- Doing business in Suriname (served by Georgetown, Guyana)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Suriname
- Doing business in Sweden
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Sweden
- Doing business in Switzerland
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Switzerland
- Doing business in Syria (served by Amman, Jordan)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Syria
Countries and territories starting with the letter T
- Doing business in Taiwan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Taiwan
- Doing business in Tajikistan (served by Astana, Kazakhstan)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Tajikistan
- Doing business in Tanzania
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Tanzania
- Doing business in Thailand
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Thailand
- Doing business in Timor-Leste (served by Jarkarta, Indonesia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Timor-Leste
- Doing business in Togo (served by Accra, Ghana)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Togo
- Doing business in Tokelau (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Tokelau
- Doing business in Tonga (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Tonga
- Doing business in Trinidad and Tobago
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Trinidad and Tobago
- Doing business in Tunisia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Tunisia
- Doing business in Türkiye
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Türkiye
- Doing business in Turkmenistan (served by Ankara, Türkiye)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Turkmenistan
- Doing business in Turks and Caicos Islands (served by Kingston, Jamaica)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Turks and Caicos Islands
- Doing business in Tuvalu (served by Auckland, New Zealand)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Tuvalu
Countries and territories starting with the letter U
- Doing business in Uganda (served by Nairobi, Kenya)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Uganda
- Doing business in Ukraine
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Ukraine
- Doing business in United Arab Emirates
- Travel Advice and Advisories - United Arab Emirates
- Doing business in United Kingdom
- Travel Advice and Advisories - United Kingdom
- Doing business in United States
- Travel Advice and Advisories - United States
- Doing business in US Virgin Islands (served by New York, U.S.A)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - US Virgin Islands
- Doing business in Uruguay
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Uruguay
- Doing business in Uzbekistan
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Uzbekistan
Countries and territories starting with the letter V
- Doing business in Vanuatu (served by Canberra, Australia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Vanuatu
- Doing business in Venezuela (Served by Bogota, Colombia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Venezuela
- Doing business in Vietnam
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Vietnam
Countries and territories starting with the letter W
- Doing business in West Bank and the Gaza Strip
- Travel Advice and Advisories - West Bank and the Gaza Strip
Countries and territories starting with the letter Y
- Doing business in Yemen (served by Riyadh, Saudi Arabia)
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Yemen
Countries and territories starting with the letter Z
- Doing business in Zambia
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Zambia
- Doing business in Zimbabwe
- Travel Advice and Advisories - Zimbabwe
Thank you for your help!
You will not receive a reply. For enquiries, please contact us .

Last verified: Monday, 6. May 2024 at 08:04 AM
Ghana Travel Advisory
- Western Africa
- Ghana Travel Advice
We advise caution when travelling to Ghana
Local situation: 3.4 / 5.
We advise caution when travelling to Ghana. We detected travel advisories from 5 sources for this specific country.
Regional Situation: 3.3 / 5
Ghana shares a land border with 3 neighbouring states. For this region of countries (including Ghana), the Advisory Index is 3.3 (average value over all countries). All countries have some reported advisories: Burkina Faso (4.1), Ivory Coast with 3.3 and Togo with 2.3 (of 5).
Current informationen on Covid-19 in Ghana
There are currently no officially reported cases of infections with SARS-CoV-2 (or Coronavirus) in Ghana. As reported by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control this morning (~8:30am CET).
There are currently no officially reported deaths related to this disease in Ghana.
Source: www.ecdc.europa.eu
Advice scoring history for Ghana
Chart of the risk level over that last 200 days. This is the daily calculated travel risk for Ghana.
Chart of the number of sources over that last 200 days. This is the daily number of advisory sources (of any rating) that have been active on that day.
Note: Changes happening on the 28th/29th of July 2019 are related to a change in the software and number of sources processed.
Rating Details (single travel warnings)
These are the individual advisories published by other countries about the destination Ghana from a travellers perspective. The scoring of all messages combined is the foundation for the current rating 3.4 out of 5.0 .
This is the general advisory usually covering the country as a whole.
Advisory issued by: New Zealand

Exercise increased caution in Ghana due to crime (level 2 of 4).
Source: https://www.safetravel.govt.nz/ghana
Advisory issued by: United States

Updated to reflect threats against LGBTQI+ travelers. Exercise increased caution in Ghana due to crime and violence against members of the LGBTQI+ community. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory. Exercise increased caution in: Parts of the Bono East, Bono, Savannah, Northern, North East, and Upper East regions due to civil unrest. Country ...
Source: http://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/traveladvisories/traveladvisories/ghana-travel-advisory.html
Advisory issued by: Canada

The Canadian goverment suggests: Exercise a high degree of caution.
Source: https://travel.gc.ca/destinations/ghana
Individual rating changes for Ghana
This is the recent history of individual changes of travel advices that affected the total asessment of Ghana. Most recent events first.
Changes from August 7th 2020
The total rating for Ghana changed from 3.6 to 4.2 . Here are the influencing details:

The United States government increased their existing warning for Ghana to 4.0 (of 5.0) from the previous rating of 1.0 (by +3.0).
Changes from March 22nd 2020
The total rating for Ghana changed from 3.4 to 3.6 . Here are the influencing details:

The Canadian government increased their existing warning for Ghana to 4.0 (of 5.0) from the previous rating of 3.0 (by +1.0).
Changes from March 18th 2020
The total rating for Ghana changed from 3.0 to 3.4 . Here are the influencing details:

The Australian government increased their existing warning for Ghana to 5.0 (of 5.0) from the previous rating of 4.0 (by +1.0).
The Irish government increased their existing warning for Ghana to 4.0 (of 5.0) from the previous rating of 3.0 (by +1.0).
Changes from March 16th 2020
The total rating for Ghana changed from 2.8 to 3.0 . Here are the influencing details:
The Australian government issued a new warning for Ghana with a rating of 4.0.
Changes from March 14th 2020
The total rating for Ghana changed from 2.5 to 2.8 . Here are the influencing details:
The Danish government increased their existing warning for Ghana to 4.0 (of 5.0) from the previous rating of 3.0 (by +1.0).
Changes from September 25th 2019
The total rating for Ghana changed from 0.0 to 0.0 . Here are the influencing details:
The United States government issued a new warning for Ghana with a rating of 1.0.
The Canadian government issued a new warning for Ghana with a rating of 3.0.
The Irish government issued a new warning for Ghana with a rating of 3.0.
The Danish government issued a new warning for Ghana with a rating of 3.0.
About Ghana
Ghana with its capital Accra is a country in Africa (Western Africa), slightly smaller than Oregon (239,460 km²). The country is located Western Africa, bordering the Gulf of Guinea, between Cote d'Ivoire and Togo. The climate can be described as tropical; warm and comparatively dry along southeast coast; hot and humid in southwest; hot and dry in north. The landscape is mostly low plains with dissected plateau in south-central area. With a population of about 23.38 million citizens.
Ghanaian flag

Introduction Video
Basic Statistics and Facts
Environmental problems and natural hazzards.
These are problems Ghana is facing. Environmental issues refer to damages of the nature due to industry and society. Natural hazzards refer to potential dangers originating in nature.
Environmental problems
- deforestation
- inadequate supplies of potable water
- overgrazing
- poaching and habitat destruction threatens wildlife populations
- recurrent drought in north severely affects agricultural activities
- soil erosion
- water pollution
Natural hazzards
- dry, dusty, northeastern harmattan winds from January to March
Top Industries and Agricultural Products
These are the main product industries and agricultural products of Ghana. This list indicates what this country is good at producing.
- aluminum smelting
- food processing
- light manufacturing
- small commercial ship building
Agriculture products

Ghanaian Imports and Exports
These are the main product categories of imports and exports to and from Ghana.
Export products
- horticultural products
- manganese ore
Import products
- capital equipment
- refined petroleum
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current travel advisory for ghana.
Ghana is currently rated at 3,4 out of a possible 5.0. Collected from 5 official sources. We advise caution when travelling to Ghana.
Is it safe to travel Ghana in 2024?
Visiting the country Ghana is usually fine. The score is at 3,4 Just keep an eye open, obey local rules and you'll most likely be fine.
How many travel advisories do you know for Ghana?
We currently evaluate 11 official sources each morning. Today, we know of active advisories from 5 individual sources for Ghana.
What is the current Corona virus situation in Ghana?
There are currently no officially reported cases of infections with SARS-CoV-2 (or Coronavirus) in Ghana. As reported by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control this morning (~8:30am CET). There are currently no officially reported deaths related to this disease in Ghana.
What is the size of Ghana?
Ghana has a size of 239,460 km² or 92,456 mi² which is slightly smaller than Oregon.
Common Frequently Asked Questions
For non-country specific questions, please check our global F.A.Q.
Travel safety map for Ghana and bordering countries.
If you want to embed Ghana travel warning information into your website or application, check out these tools.
- Is Ghana safe to travel?
- What's the safety situation in Ghana?
- Are there security warnings for Ghana?

2020-03-10: Integrated data from European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (COVID-19/ SARS-CoV-2/ Coronavirus).
2019-09-01: Added timeline charts for risk level and number of advisories.
2019-07-29: Added two more sources (Finland and Denmark). Affects country ratings.
2019-07-15: South-Sudan was missing and was added today.
2019-05-18: Performance improvements for API users.
2019-03-23: Introduced professional API with more data.
2019-02-13: Added three more sources (Cyprus, Ireland and Malta). Affects country ratings.

- Entertainment
- GhanaWeb TV
- Latest News
- What is Coronavirus
- Symptoms of Coronavirus
- Facts vs Fiction
Travel Advisory
- Emergency Guide
- National Reactions
- Send your Stories
All travellers should be aware of the virus, pay close attention to travel advisories and health guidance, steer clear of heavily impacted areas and exercise preventive measures. Travel advisories have been issued by countries around the world. Make sure that your destination has not restricted your arrival before embarking on an international trip.
Here is the travel advisory issued by the Government of Ghana.
- All travel to Ghana is strongly discouraged until further notice.
- Any traveller, except for Ghanaian citizens and persons with Ghana residence permits, who within the last 14 days, has been to a country that has recorded at least 200 cases of COVID-19, will not be admitted into the Ghanaian jurisdiction. Airlines are instructed not to allow such persons to embark. Border posts are instructed not to allow such persons into the jurisdiction.
- There will be a mandatory 14-day self-quarantine for persons who are otherwise allowed to enter the Ghanaian jurisdiction. Guidelines for self-quarantine will be available at the various Ghanaian ports of entry. Enforcement protocols are being deployed in collaboration with state security and health authorities. Persons determined to be unable to satisfactorily self-quarantine will be quarantined by the State.
- Any admissible traveller, who exhibits symptoms of COVID-19 will be quarantined and tested upon reaching Ghana.
- Item one of this statement takes immediate effect.
- Items 2,3 & 4 take effect at 1 pm on Tuesday, March 17th 2020. All travellers should be aware of the virus, pay close attention to travel advisories and health guidance, steer clear of heavily impacted areas and exercise preventive measures. Travel advisories have been issued by countries around the world. Make sure that your destination has not restricted your arrival before embarking on an international trip.
Items 2,3 & 4 take effect at 1 pm on Tuesday, March 17th 2020.

- Advertising
- Privacy Policy
Travel Advice for Ghana
Going to Ghana and need to know about the latest government travel advice for Ghana? Find the updated travel advice and travel warnings for Ghana from governments around the world, here.
General Travel Advice and Warnings for Ghana
The decision to take a trip to Ghana is your decision and you are accountable for your personal safety whilst in Ghana.
The web content on this page is given information only and collected from travel advice and warnings for Ghana by authorities all over the world to their citizens.
While we make every effort to provide you most recent travel advice details, it is given on an “as is” basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied.
This operators of this website does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information offered.
Standard Cautions You Need to Bear In Mind Whilst Taking a Trip in Ghana
Crime – Petty criminal activities such as pick pocketing in a jampacked environment to sexual assault and muggings do take place in larger cities of Ghana. Ensure that all your personal possessions, such as passports and other traveling documents, are safe at all times.
Terrorism – Always be aware of your surroundings whenever in public locations. Be particularly vigilant if going to sporting occasions and throughout religious holidays and other public occasions, as terrorists frequently make use of such events to mount attacks.
Demonstrations and Protests – Demonstrations might occur. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent any time. They can also result in disruptions to traffic and public transportation. It is in your interest of safety to stay away from locations where demonstrations and large gatherings are occurring and follow the instructions of local authorities. Monitor local media in Ghana for information on on-going demonstrations in Ghana.
Scams – Exercise care in crowded tourist areas in Ghana, where scammers target foreigners. If you’ve been scammed in Ghana, get to a safe area right away; make note, as soon as possible of the name and address of the facility where you were held; alert the authorities in Ghana and get a report and if your credit card is used by the scammer call your credit card provider to report the scam; they will likely ask for a copy of the police report to cancel the financial transaction.
Spiked Food and Drinks – Never ever leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of complete strangers when taking a trip in Ghana or anywhere else. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from unknown acquaintances. These items might have drugs that can put you at risk of sexual assault and mugging.
What is the entry/exit conditions for Ghana?
Every nation or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders, in the same manner Ghana chooses who enter its borders. The Government of your home country cannot step in on your behalf if you do not satisfy your Ghana’s entry or exit requirements.
For more information regarding the entry/exit requirement for Ghana go to visa requirements for Ghana or get the current info with the visa office at the Ghanaian embassy in your home country.
Travel insurance coverage for Ghana
Travel health cover is one of the primary factors travellers get travel insurance. It will not stop you getting ill or injured, though it can stop you being affected financially. Medical aid overseas can be really expensive.
You must shell out for all healthcare you receive overseas. You can not expect to get free or subsidised treatment through your Ghana’s public health system, like you would in your home country.
If you can not pay, local authorities can detain you. The government from your home country can’t pay you medical costs for you, loan you money or get you out of jail.
You need travel insurance coverage for travelling to Ghana . You also need to ensure you select a plan that is right for you.
Read through the fine print of your travel insurance policy.
Declare all pre-existing conditions to your travel insurance provider upfront. If you don’t, you may void your travel insurance policy.
Inform your travel insurance company the activities you plan to do, prior to you go. Many common activities like skiing are left out in basic plans. You may need to pay added.
Check if you have free credit card travel insurance coverage. Some cards include travel insurance coverage cover. Nevertheless, they typically have different conditions than paid plans. Understand the differences.
If you’re visiting Ghana from a country that has a reciprocal healthcare arrangement, you still need travel medical insurance. Agreements are limited in what they’ll will cover.
If you have an incurable ailment, you may not be able to obtain standard travel insurance policy. Nevertheless you might be able to get a specialised insurance provider that covers you for health, accidents or property troubles unconnected to your illness. Speak with your insurer to find out.
Learn more about getting global travel insurance coverage for Ghana before you go.
© 2021 Government Travel Advice
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against advice from the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO).
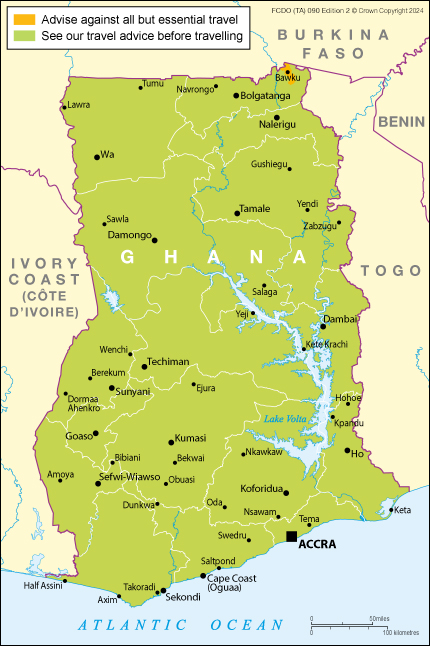
Areas where FCDO advises against all but essential travel
Bawku municipality.
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to the Bawku Municipal area in the Upper East region of Ghana.
Find out why FCDO advises against travel to Bawku Municipality .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and any specific travel advice that applies to you:
- women travellers
- disabled travellers
- LGBT+ travellers
- solo and independent travel
- volunteering and adventure travel
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
About FCDO travel advice
FCDO provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Ethiopia travel advice
Latest updates: Risk levels – changes to regional advisories for Afar, Oromia, Tigray and Somali region; Safety and security – updated information on Afar and Oromia regions
Last updated: April 22, 2024 09:09 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, ethiopia - avoid non-essential travel.
This advisory excludes Addis Ababa where you should exercise a high degree of caution.
Additional regional advice and advisories are in effect. Our ability to provide consular assistance is limited in some regions.
Addis Ababa - Exercise a high degree of caution
Exercise a high degree of caution in Addis Ababa due to the high crime rate and the risk of spontaneous demonstrations becoming violent. Ongoing armed conflict and civil unrest in other parts of the country could spread to major cities without warning.
Northern regions - Avoid all travel
- Benishangul-Gumuz
- northward to Adigrat along road A2
- west and northwest to Abiy Addi, Adwa and Shire along B30 and C23
- soutward to Maychew along road A2
Central regions - Avoid all travel
- North Shewa
- West Shewa, except the A4 highway, from Addis to and including Ambo where you should avoid non-essential travel
- West Wollega
- East Wollega
- Kellem Wollega
- Horo Gudru Wollega
Border areas - Avoid all travel
- 10 km of the border with Eritrea
- 100 km of the Somali region border with Somalia and Kenya
- 30 km of the border with Somalia in Fafan zone, except for road C104, the town of Wajale and its border crossing where you should avoid non-essential travel
- 10 km of the border with Somalia in the Sitti zone
- 20 km of the border with Kenya, South Sudan and Sudan
Back to top
The situation is volatile and unpredictable in several areas throughout the country due to ethnic conflicts. Violent clashes occur, especially near regional borders.
Frequent incidents of civil unrest can lead to violence. Sporadic roadblocks, curfews and disruptions to telecommunications services are possible throughout the country.
If you travel to Ethiopia:
- expect a heightened security presence
- ensure that your travel documents are up to date
- carry identification documents at all times
- make sure to stop at all checkpoints and roadblocks, even if they appear unattended
- if you are stopped by security forces, stay calm and follow instructions
Amhara region
The state of emergency, declared by the Ethiopian authorities on August 14, 2023, remains in effect in the Amhara region due to continued clashes between armed groups and security forces.
While a state of emergency is in effect, police and military have the power to:
- restrict freedom of movement and assembly
- enter private properties to conduct searches
- detain persons of interest
There is increasing and spreading violence in the Amhara region. The majority of the instability is taking place in towns and villages along the A2 and B22 highways, as well as along the southern part of the A3 highway. The cities of Lalibela, Bahir Dar and Gondar have also been affected. The safety and security situation is changing rapidly and includes violent clashes between armed groups in and around cities, towns and airports. Road blocks and curfews are also being used to restrict movements.
Due to the potential for violence to increase and spread in this region, you are at high risk of encountering movement restrictions and having no access to communications.
If you are in the Amhara region affected by the armed conflict:
- monitor local media to stay informed on the evolving situation
- follow the instructions of local authorities
- shelter-in-place until the situation stabilizes and until it is safe to leave the region (flights and land transportation may be disrupted)
- register with ROCA ( https://travel.gc.ca/travelling/registration ) to receive important safety updates from the Government of Canada
- contact the Embassy of Canada in Addis Ababa by email if you require consular assistance: [email protected]
Violent clashes between armed groups occur. Inter-ethnic disputes in Amhara have resulted in casualties, including civilians. Although foreigners are generally not targeted, there is a risk that you could be caught up in violence.
Tigray region
A cessation of hostilities agreement was signed on November 2, 2022 between the Government of Ethiopia and the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF), after two years of armed conflict. The agreement has yet to be fully implemented and there remains uncertainty regarding its implications for security in the region.
Travel in and out of the Tigray region can be restricted without notice and food insecurity remains a major concern. Heightened security measures are in place.
Danakil Depression (Afar region)
Foreign tourists were targeted by armed groups in the past.
If you decide to travel to the Danakil Depression:
- always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company escorted by official security forces
- be aware of excessive heat and difficult terrain
- maintain a full tank of gas
- keep a supply of water and non-perishable snacks
Border areas
Border areas, including regional borders, often see higher criminal activity and violence, including in rural areas. Confrontations between organized criminal groups, ethnic groups, and Ethiopian authorities pose a risk.
The border with Eritrea is still a heavily militarized security corridor despite the peace agreement signed in 2018. Armed conflict could erupt without notice. Due to the conflict in Tigray, border roads and border crossings with Eritrea are closed. Conditions at the border may change without notice. Landmines pose a risk.
Inter-ethnic conflicts and banditry are frequent near the border with Kenya. Security forces regularly carry out military operations, which periodically raises tensions.
Cross-border violence also occurs. Armed groups hostile to the Government of Ethiopia operate in several areas near the border.
Terrorists maintain a presence in this area, and ethnic conflict has been reported. This includes but is not limited to the Konso Zone and surrounding areas. Kidnapping also poses a risk in this area.
Sporadic armed clashes over disputed land occur. The risk of terrorism and kidnapping is high in this area. Landmines pose a threat to safety.
South Sudan
Ethnic tensions and sporadic violence are common. Ethnic militias from South Sudan have crossed into Ethiopia to attack rival communities. The security situation is extremely unstable. The threat of violent crime, civil unrest and tribal clashes is high. Kidnapping and landmines pose a threat to safety.
Gambella region
Ethnic conflict, violent crime and sporadic violence are of concern in the city of Gambella and its surrounding areas. Armed clashes have caused casualties and damage to foreign companies’ installations in the area.
Somali region
Terrorist groups maintain a presence in Somali towns near the Ethiopian border, presenting a risk for cross-border attacks and kidnappings. Violent crime, including armed robbery, occurs. Violent clashes between armed groups and security forces, as well as ethnic violent, are common. Landmines pose a threat to safety.
Oromia region
Demonstrations, civil unrest, violent crime, armed conflicts, and clashes between security forces and armed groups occur in Oromia, including in areas bordering Amhara. There is a threat of kidnapping. Roadside attacks have also taken place. These incidents are particularly prevalent in the following zones:
- West Wellega and the main Addis Ababa to Gambella road (A4 highway)
- East Wellega
- Kellem Wellega
- Horro-Guduru Wellega
The security situation could deteriorate without warning. A heightened security presence remains throughout these areas. Local authorities may impose curfews without notice. Internet and cellular data outages could occur.
- avoid military, police and security installations
- exercise extreme caution
- follow the advice of local authorities
Benishangul Gumuz region
Civil unrest, including armed conflicts, has resulted in deaths. Violent clashes can occur without warning due to local ethnic tensions.
Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples region
Armed conflicts and civil unrest have occurred sporadically across the region. These have led to casualties and mass arrests. Residents have also randomly attacked cars and disrupted road travel. Militia attacks have also occurred.
The security situation could deteriorate without warning. A heightened security presence remains throughout these areas. Local authorities may impose curfews without notice. Internet and cellular data outages could occur.
Kidnapping occurs, especially in the Somali, Gambella and Oromia regions, as well as in the border areas with Kenya, Somalia, South Sudan and Eritrea (Danakil Depression).
If you are travelling in a region prone to kidnapping:
- get professional security advice
- arrange for personal security
- change your travel patterns regularly
- be aware of your surroundings
- avoid displaying signs of affluence
- don’t travel alone
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing, purse snatching and mugging, occurs, especially in Addis Ababa. Incidents are mostly opportunistic. However, they have been increasingly reported in the following areas:
- the Bole Medhanealem
- the Bole Atlas
- the Meskel Square
- the Merkato
Theft from parked cars and burglaries in vacant residences also occur, especially in rural areas, where the police response is limited.
Crime significantly increases after dark.
- Be aware of your surroundings at all times, especially in crowded areas
- Avoid displaying any signs of affluence in public
- Avoid walking alone after sundown
- Choose living accommodations that have good security measures
- Keep car doors locked while you’re in your vehicle
- Park your car in a well-lit and guarded area
- Be vigilant if approached by strangers seeking assistance
- If threatened, hand over valuables without resistance
- Ensure that your belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
Violent crime
Violent crime is rare in Addis Ababa, but happens. Westerners have been victims of armed assaults and muggings.
If threatened:
- stay calm and don’t resist
- comply with the robbers’ requests
Demonstrations and civil unrest
Demonstrations take place regularly, especially across the Oromia region and Addis Ababa. They can occur without warning. Ethnic tensions and territorial disputes in this area have led to demonstrations and civil unrest near the regional state borders.
Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
There is a threat of terrorism. Regional terror groups continue to threaten Western interests and other potential targets in Ethiopia, including in Addis Ababa. Domestic terror groups also pose an increased threat in some regions, like the Somali region.
Targets could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as tourist attractions, restaurants, bars, coffee shops, shopping centres, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places.
Ethiopia is primarily a cash-based economy but credit card and ATM fraud may sometimes occur, especially in large cities. There have been reports of unauthorized charges. Connectivity issues may also be a problem.
Be cautious when using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Overseas fraud
Outages and shortages
Power outages are frequent nationwide, particularly during the dry season from November to June. Local authorities may impose power rationing.
Not all buildings have generators. Outages can result in lack of street lighting, restaurants and supermarkets without adequate refrigeration, and gas stations unable to supply fuel.
Communications
Although there are some plans to improve the network, cellular coverage is unreliable and connectivity remains an issue in several parts of the country.
Local authorities also control telecommunications and may shut down both cell phone and internet systems during periods of civil unrest or ahead of a large planned protest.
You should not rely on your cell phone in case of emergency, especially outside major cities.
- Avoid travelling alone
- Inform relatives of your itinerary
Fuel and food
Periodic fuel and food shortages occur. This may create social tensions and increase food prices.
- Carry flashlights
- Plan to have adequate water, food and fuel supplies
Road safety
Driving standards, vehicle maintenance and road conditions are often poor throughout the country. Traffic accidents are a regular occurrence, especially in Addis Ababa and on the Addis Ababa–Djibouti road.
Apart from major arteries, roads are generally unpaved. They often lack markings and signage, reflectors and shoulders, even in urban areas. They are poorly lit and maintained.
Drivers often drive at excessive speed and don’t respect traffic laws. They may be reckless. Poorly maintained vehicles, roaming animals and pedestrians pose further hazards. Armed robbery, carjacking and landmines also pose a threat, especially in border areas
There is no road assistance and emergency services are limited to nonexistent in several areas. Although improving, the cellular coverage remains unstable outside main cities.
- Avoid driving after dark
- Always keep your gas tank full when in remote areas
- Always carry a first-aid kit, as medical facilities are often undersupplied
- Advise a relative of your anticipated itinerary and route
- If you encounter a roadblock, turn around and don’t attempt to pass it
- Don’t rely on your phone for navigation or emergency contacts
Traffic accidents occur regularly throughout Ethiopia. Traffic often moves unpredictably.
Under Ethiopian law, it is illegal to move your vehicle before a police officer arrives if an accident occurs. Large crowd may gather and could become hostile and aggressive.
If involved in an accident:
- avoid confrontation
- call the local police and remain at the scene of the accident until they arrive
- should you feel unsafe, leave immediately and report the incident to the nearest police station
Public transportation
Most public transport is unregulated and unsafe. Hire private transport from a reliable source or use transportation provided by your hotel.
Minibuses and large buses are often old, poorly maintained and overcrowded.
Some buses have been attacked on their way from one region to another.
Only use buses from the airport that have been organised by your hotel or your tour operator.
Rail services are limited and trains are poorly maintained. Avoid travelling by train.
Taxis are generally unsafe.
If travelling by taxi:
- only use metered taxis
- choose yellow taxis rather than white or blue ones
- make sure you are the only passenger in the vehicle
Hiking in the Danakil Depression
Weather conditions in the Danakil depression area can be fairly arid. Facilities are basic. There is no running water and medical options are very limited.
You should prepare for excessive heat and difficult terrain, namely around the Erta Ale Volcano.
If you intend on hiking in this area despite the advisory in place:
- never do so alone and always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you’re properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back to camp
- know the symptoms of acute altitude sickness, which can be fatal
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes before setting out and do not venture off marked trails
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to harassment and verbal abuse.
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from Ethiopian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Ethiopia.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Transit visa: required
Canadians must have a valid visa to enter the country. You may obtain a visa online. If you overstay your visa, you may face daily fines and imprisonment.
You need the proper visa if you want to conduct a business or volunteering activity. If you fail to do so, you may be fined or detained.
- Obtain a visa online before arrival
- Verify carefully that your visa is valid
- Ensure that your activities in the country adhere to the type of visa you have obtained
Ethiopian e-Visa – Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
Other entry requirements
Authorities may request additional documents if you attempt to enter Ethiopia by vehicle at certain border crossings.
Contact the Embassy of Canada to Ethiopia, in Addis Ababa, to determine specific entry requirements at land borders.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 8 April, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is a risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are arriving from Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, or Venezuela or have transited through an airport in one of these countries.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites .
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
This destination is in the African Meningitis Belt, an area which has the highest rates of meningococcal disease in the world. Meningococcal disease is a serious and sometimes fatal infection.
Travellers who are at higher risk should discuss vaccination with a health care provider. High-risk travellers include those living or working with the local population (e.g., health care workers) or those travelling to crowded areas or taking part in large gatherings.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified this country as no longer poliovirus-infected but at high risk of an outbreak . Polio can be prevented by vaccination.
Recommendations:
- Be sure that your polio vaccinations are up to date before travelling. Polio is part of the routine vaccine schedule for children in Canada.
- One booster dose of the polio vaccine is recommended as an adult .
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Visceral leishmaniasis (or kala azar) affects the bone marrow and internal organs. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly. It can also be transmitted by blood transfusion or sharing contaminated needles. If left untreated it can cause death. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Onchocerciasis (river blindness) is an eye and skin disease caused by a parasite spread through the bite of an infected female blackfly. Onchocerciasis often leads to blindness if left untreated. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from blackfly bites, which are most common close to fast-flowing rivers and streams. There is no vaccine available for onchocerciasis although drug treatments exist.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Rift Valley fever is a viral disease that can cause severe flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can be fatal. It is spread to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, from the bite of an infected mosquito, or eating or drinking unpasteurized dairy. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from insect bites and avoid animals, particularly livestock, and unpasteurized dairy. There is no vaccine available for Rift Valley fever.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Anthrax is a serious infectious disease caused by bacteria. People can get sick with anthrax if they come into contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products. Anthrax can cause severe illness in both humans and animals. Travellers to areas where anthrax is common or where an outbreak is occurring in animals can get sick with anthrax if:
- they have contact with infected animal carcasses or eat meat from animals that were sick when slaughtered
- they handle animal parts, such as hides, wool or hair, or products made from those animal parts, such as animal hide drums.
If you are visiting these areas, do not eat raw or undercooked meat and avoid contact with livestock, wildlife, animal products, and animal carcasses.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and impairs the immune system, resulting in a chronic, progressive illness known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
High risk activities include anything which puts you in contact with blood or body fluids, such as unprotected sex and exposure to unsterilized needles for medications or other substances (for example, steroids and drugs), tattooing, body-piercing or acupuncture.
Medical services and facilities
Health care is inadequate, except in private hospitals of Addis Ababa where you can expect reasonable standard of basic care for minor health problems. Otherwise, health facilities are not up to Canadian standards. They lack of personnel, equipment, supplies and medications.
Ambulance services are extremely limited and unreliable.
Ensure that you always carry a comprehensive medical pack when travelling.
You will likely need medical evacuation in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Altitude sickness
Addis Ababa is located about 2500 metres above sea level. Acute mountain sickness may occur at high altitudes.
Be well informed about the potential health hazards at high altitudes.
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Death penalty
Ethiopian authorities may apply the death penalty for serious offences.
All illicit drugs are illegal except khat, a local stimulant. Khat is illegal in several countries. Don’t attempt to export it.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy jail sentences and heavy fines.
Ethiopia is used as a drug trafficking hub between Western markets and southern Asia for heroin.
- Carry only your personal belongings, and don’t leave them unattended
- Don’t agree to carry packages that are not your own
Drugs, alcohol and travel
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Ethiopian law prohibits sexual acts between individuals of the same sex. Those convicted can face up to 15 years in prison.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Ethiopia.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Ethiopia.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Ethiopia, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Ethiopia.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Ethiopia by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Ethiopia to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
Identification
You must carry photo ID with you at all times, as local authorities can ask you to prove your identity.
Keep a photocopy of your passport in a safe place, in case it is lost or confiscated.
It’s illegal to carry a firearm in Ethiopia.
It’s illegal to own any quantity of ivory, including in jewellery.
Antiques or religious paraphernalia
You may not export real antiques or religious items.
Tourist souvenirs are often copies of Ethiopian antiques or religious paraphernalia.
If buying such items, ensure that you have a receipt, clearly indicating that it’s a souvenir and not authentic. However, be aware that authorities may confiscate items purchased for export or for personal use, especially ceremonial knives, even if you present a receipt.
Photography
It’s strictly prohibited to photograph:
- military installations
- police and military personnel
- industrial facilities
- government buildings and infrastructure, including roads, bridges, dams and airfields
Never stop near a restricted area, no matter the reason, on foot or in a vehicle.
Street vendors
It is illegal to give money to, or purchase something from, people who approach vehicles stopped in traffic, including children.
If caught, both the beggar/vendor and the vehicle operator face fines.
Social media
Writing on blogs or social media about political subjects could lead to detention and arrest.
Cell phones
You can use one cell phone or tablet on the network of the sole, state-owned telecommunications provider, Ethio Telecom.
Additional devices are subject to a customs fee of 10% of the total cost of the device, as well as the activation fee.
Other electronic devices
You must declare all laptop computers and video equipment other than those for personal use upon arrival and departure. Some recording devices may require special customs permits.
If you will be using these items for work, obtain permission to bring them into the country from the Embassy of Ethiopia in Ottawa or the Consulate of Ethiopia in Toronto.
Foreign representatives in Canada
In 2025, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around February 28.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, be discreet when:
Orthodox Christian
The Ethiopian highlands population is predominantly Orthodox Christian. There is fasting in this region every Wednesday and Friday, and during Lent.
- Always obtain permission from religious authorities before visiting churches
- Dress conservatively, behave discreetly, and respect religious traditions to avoid offending local sensitivities
Time of day
Many people in Ethiopia use the Ethiopian clock.
According to the Ethiopian clock, unlike the convention in most countries, the start of the day is dawn rather than midnight. As a result, daytime hours are counted beginning from what would be 6 a.m. For instance, the time at one hour after dawn – 7 a.m. – would be 1 a.m. on the Ethiopian clock.
Most hotels and larger organisations, including all airlines, use the global clock. However, many individuals or smaller organisations continue to use the Ethiopian clock.
Check with your host if you are unsure which clock is being used for a meeting or an event.
You must have a local driver’s licence to drive in Ethiopia. You must present your valid Canadian driver’s licence or an International Driving Permit to obtain one.
If you're involved in an accident, don’t move your vehicle before a police officer arrives. It's illegal to do so.
International Driving Permit
The currency of Ethiopia is the birr (ETB).
Credit cards are not widely accepted except by large hotels, travel agencies and a few shops and restaurants in Addis Ababa. ATMs are very limited outside urban areas and may run out of cash without notice.
Make sure you have access to hard-currency cash in case of emergency.
It is illegal to enter or exit Ethiopia with more than 1,000 birr.
You may enter or exit Ethiopia with up to US$3,000 or its equivalent in any convertible foreign currency. This doesn’t include birr. However:
- if you enter with more, you must declare the funds upon arrival
- a bank document certifying the purchase of the foreign currency and approving travel with the funds or
- a customs declaration form made upon entry
Be aware that even the provision of such documents may not safeguard you against confiscation of the extra funds, imprisonment or fines. Policies may change at any time without notice.
Exchanging money on the black market is illegal. Exchange foreign currency at banks or official foreign exchange offices only as you may face heavy fines or detention.
Due to below-average rainfall for several years in a row, Ethiopia is experiencing severe drought.
Local services and the availability of water and basic food may be affected.
You may encounter difficulties travelling overland.
Rainy season
The rainy season normally extends from June to September. Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable due to mudslides and landslides.
- Monitor local media for the latest updates, including road conditions
- Stay away from flooded areas
- Follow instructions from local authorities, including evacuation orders
Earthquakes
Ethiopia is located in an active seismic zone. Earthquakes may occur.
Earthquakes - What to Do?
Local services
In case of emergency, dial 991.
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Ethiopia, in Addis Ababa, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

COMMENTS
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Ghana. If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Ghana, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. ... IMPORTANT:The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or ...
Safety and security Border areas. Border areas often see higher criminal activity and violence. There is a heightened risk of terrorist attacks in the northern areas of Ghana bordering Côte d'Ivoire, Togo and Benin, and more specifically, Burkina Faso, where armed groups and militias are active.
If you decide to travel to Ghana: See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights Report for further details. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program to receive alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency. Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter. Review the Country Security Report for ...
Canada and Ghana. Services for Canadians if you're visiting, studying, working or doing business in Ghana. ... Ghana. Includes information about coming to Canada. Travel advice and advisories - Ghana. Exercise a high degree of caution. Travel advice, passport and entry requirements, health and safety information, and more. ... Find a Government ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Government of Canada. All contacts; Departments and agencies; About government; Themes and topics. Jobs and the workplace; Immigration and citizenship; Travel and tourism; Business and industry; Benefits; Health; Taxes; Environment and natural resources; National security and defence; Culture, history and sport; Policing, justice and ...
2021-02-12. The Government of Canada is announcing today further testing and quarantine requirements for international travellers arriving to Canada's air and land ports of entry. These new measures will help prevent variants of concern from reaccelerating the pandemic and making it more difficult to contain.
Read the Department of State's COVID-19 page before you plan any international travel. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued a Level 3 Travel Health Notice for Ghana due to COVID-19. While the country's land, air, and sea borders remain closed, Ghana has lifted stay at home orders and resumed many internal ...
GHANA TRAVEL REQUIREMENTS. Individuals traveling to Ghana are required to strictly adhere to the following new directives as stated by Ghana's President during his 16 th address to the Nation on Measures Taken Against the Spread of the Coronavirus:. All passengers arriving in Ghana must be in possession of a negative COVID-19 PCR test result from an accredited laboratory in the country of ...
To call for emergency services while in Ghana, dial 193 for an ambulance, 192 for the fire department, and 191 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you during your trip. Learn as much as you can about Ghana before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Ghana from the US Department of ...
Information by country and territory. Canada's presence abroad includes embassies, consulates, high commissions and trade offices. Canada also maintains a number of permanent missions to international organizations. The information below offers a comprehensive view of Canada's travel advice and advisories, basic country information, the name of ...
Comply with all police and security service instructions. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security, travel, and health updates. Assistance: U.S. Embassy Accra, Ghana. + (233) 30-27-41-000 24/7 for a recorded message. No. 24, Fourth Circular Rd., Cantonments, Accra.
Rating Details (single travel warnings) These are the individual advisories published by other countries about the destination Ghana from a travellers perspective. The scoring of all messages combined is the foundation for the current rating 3.4 out of 5.0. Danger level: 2 - Travel is usually safe. This is the general advisory usually covering ...
Travel Advisory. All travellers should be aware of the virus, pay close attention to travel advisories and health guidance, steer clear of heavily impacted areas and exercise preventive measures.
The web content on this page is given information only and collected from travel advice and warnings for Ghana by authorities all over the world to their citizens. While we make every effort to provide you most recent travel advice details, it is given on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied.
US State Dept Travel Advisory. The US Department of State currently recommends US citizens exercise increased caution in Ghana due to crime and violence against members of the LGBTQI+ community. ... US State Dept Travel Information - Overall information about foreign travel for US citizens.
Travelling to Ghana. FCDO travel advice for Ghana. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
U.S. Embassy Accra, Ghana. Follow us on Facebook and Twitter. [email protected]. U.S. Embassy Ghana Website. Country Information Page for Ghana. State Department - Consular Affairs. 888-407-4747 or 202-501-4444. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP)
Regular Canadian passport. Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Côte d'Ivoire. ... IMPORTANT:The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk. Avoid non ...
Ghana Travel Advisory: Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution: November 20, 2023: Democratic Republic of the Congo Travel Advisory : Level 3: Reconsider Travel: ... entities on this page are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as the U.S. Department of State or U.S. government endorsement of the entity, its views, the products or ...
Regular Canadian passport. Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Ethiopia. ... IMPORTANT:The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk. Avoid non ...