Indonesia Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status

Traveling from the United States to Indonesia
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces and enclosed environments.
Documents & Additional resources
Ready to travel, find flights to indonesia, find stays in indonesia, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Indonesia from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Indonesia.
Can I travel to Indonesia if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Indonesia without restrictions.
Can I travel to Indonesia without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Indonesia without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Indonesia?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Indonesia.
Can I travel to Indonesia without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Indonesia?
Mask usage in Indonesia is not required in public spaces and enclosed environments.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Indonesia?
Restaurants in Indonesia are open. Bars in Indonesia are .
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
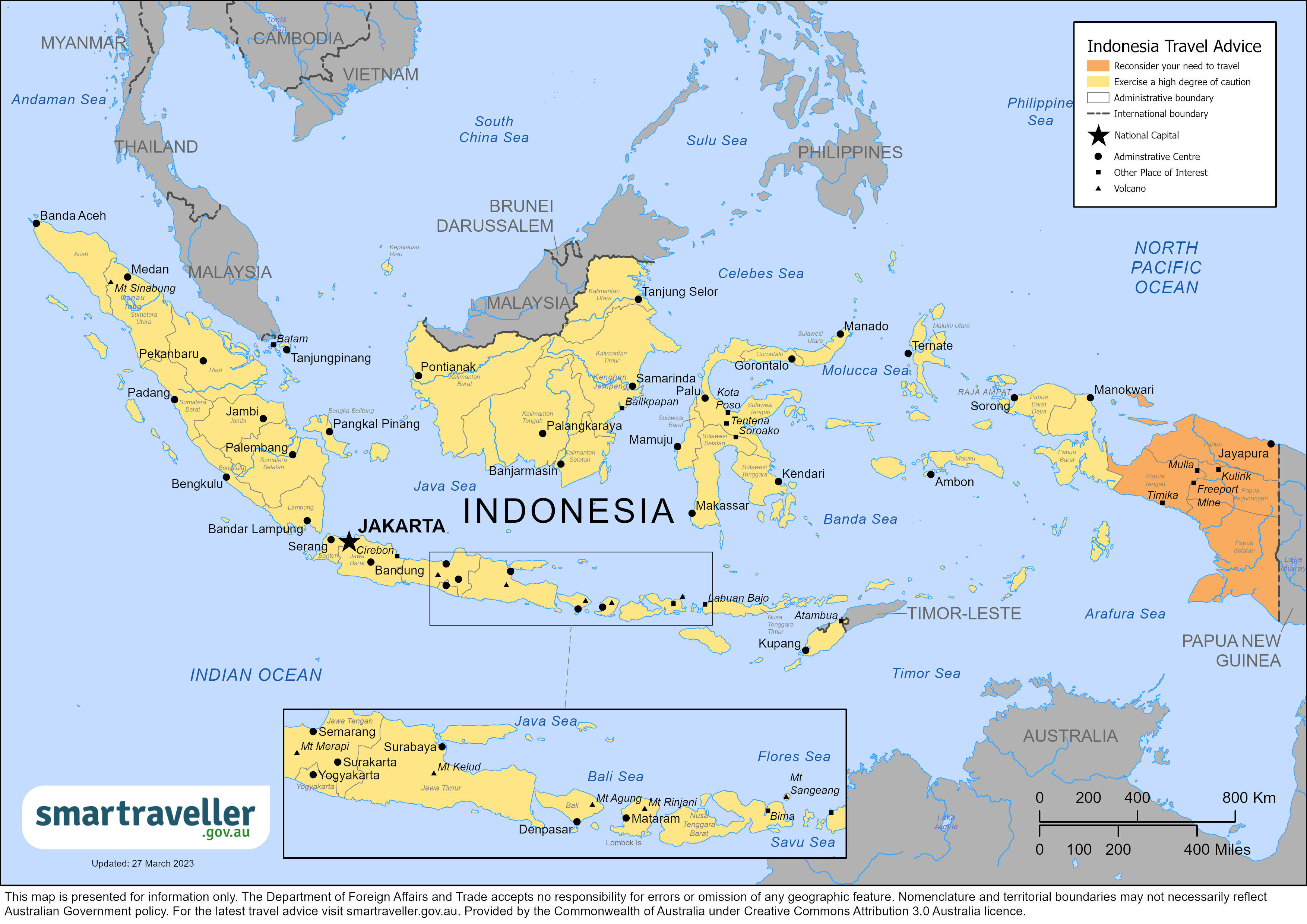
Indonesia Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 24, 2023, indonesia - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in Indonesia due to terrorism and natural disasters. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do Not travel to:
- The provinces of Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and Highland Papua (Papua Pegunungan) due to civil unrest.
Terrorists continue plotting possible attacks in Indonesia. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting police stations, places of worship, hotels, bars, nightclubs, markets/shopping malls, and restaurants.
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis or volcanic eruptions may result in disruptions to transportation, infrastructure, sanitation, and the availability of health services.
Demonstrations occur frequently and have the potential to become violent. Avoid demonstrations and crowds.
Indonesia’s revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. It is unclear how Indonesian authorities will implement the revised criminal code.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Indonesia.
If you decide to travel to Indonesia:
- Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to adjust your plans.
- Visit the websites for Badan Geologi (Indonesian Geological Agency, Indonesian language only) for the latest information from the Government of Indonesia on current natural disasters.
- Review the CDC’s suggestions on how to prepare for natural disasters.
- Be aware of your personal safety and security at all times.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Ensure your passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay.
- Follow the Department of State Facebook and Twitter . Follow the U.S. Embassy Jakarta on Facebook , Instagram , and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Indonesia.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Central Papua and Highland Papua– Level 4: Do Not Travel
In Central Papua and Highland Papua, violent demonstrations and conflict could result in injury or death to U.S. citizens. Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Armed separatists may kidnap foreign nationals.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Central Papua and Highland Papua as U.S. government employees must obtain special authorization before traveling to those areas.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, indonesia map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Indonesia travel advice
Latest updates: Health – editorial update
Last updated: May 6, 2024 14:57 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, indonesia - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia due to political and social tensions and the threat of terrorism throughout the country.
Indonesian Papua - Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid non-essential travel to all the provinces of Indonesia Papua due to the regular occurrence of violent incidents, threats made against foreigners by militant groups and risk of kidnapping.
Back to top
- Indonesian Papua
Political tension and regular violent incidents continue to occur in Indonesian Papua.
In February 2023, militant groups threatened to attack and take hostages, specifically referencing foreigners. You may also face increased threats of violence or kidnapping if you travel to Indonesian Papua.
Labour disputes at the Freeport-McMoRan mine near Timika have led to demonstrations, public transportation disruptions and violence.
Fatal attacks have occurred on roads near the mine. Foreigners have been targeted by local militants.
There is a heightened police and military presence in this area.
There is a threat of terrorism in Indonesia.
While effective counterterrorism measures by Indonesian authorities are in place, terrorist cells are active and have the capacity to carry out attacks throughout the country.
Attacks have targeted:
- military and government facilities
- tourist attractions and popular public places
- nightclubs and entertainment venues
- public transportation
Further attacks are likely, and terrorists may also target:
- crowded places
- places with high pedestrian traffic and where foreigners may gather
- commercial establishments
- local government offices
- public transit stations
- busy streets
- long lineups at tourist attractions
- places of worship
Stay at hotels that have robust security measures, including metal detectors, guards and security cameras. Keep in mind, however, that even the most secure locations cannot be considered completely free of risk.
Be particularly vigilant during religious holidays and other public celebrations, as terrorists have used such occasions to mount attacks.
- Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places and identify ways to leave the area in case of emergency
- Monitor local media
- Follow the instructions of the local authorities
Violent crime
Violent crime, such as armed robberies, occurs regularly. Be particularly cautious on the road from Banda Aceh to Medan, where armed robberies have occurred.
Foreigners travelling alone and those travelling at night are at particular risk.
Standards of police services differ considerably from those in Canada.
- Avoid showing signs of affluence
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- If you’re travelling by car, keep valuable belongings out of sight, windows closed and doors locked
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs throughout Indonesia, specifically in tourist areas, such as Bali and Lombok. Criminals sometimes force people to withdraw cash from ATMs.
Merchants don’t always honour pricing agreements. Use good judgment in engaging services of tourist guides, especially in places that tourists rarely visit.
There is a threat of kidnapping, particularly in the provinces of Indonesian Papua and Aceh province. Foreign travellers have been kidnapped and killed. Terrorist groups have also kidnapped tourists in East and West Kalimantan.
- Be extra vigilant if travelling in these areas
- Avoid travelling alone and after dusk
- Use varied routes and schedules when moving from one place to another
Women's safety
Women travelling alone may face some forms of harassment and verbal abuse.
Advice for women travellers
Demonstrations
Demonstrations take place from time to time. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Political and social tension
There are long-standing sectarian and social tensions throughout Indonesia, particularly in the provinces of:
- Central Sulawesi, in Palu, Poso and Tentena
- Maluku, especially in Ambon
Sectarian violence targeting civilians has occurred. The potential for violence remains, despite ongoing security operations efforts from local authorities. Be aware of your surroundings.
There is a very high rate of credit and debit card fraud in Indonesia, including online fraud.
When using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention if other people are handling your cards
- use ATMs located in public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Romance scams
If you’re travelling to Indonesia to meet someone you’ve only met online, keep it mind that you may be the victim of a scam. Be wary of unsolicited emails or requests for a wire transfer.
Don’t send money to someone you have never met in person.
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Even if the wrapping or container appears intact, snacks, beverages, gum and cigarettes may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
- Be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
- Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
People have died after drinking methanol-adulterated alcohol. Counterfeits of well-known alcohol brands often contain dangerous amounts of methanol. Poisoning incidents have happened at hotels, bars, and shops in tourist areas like Bali, Lombok, the Gili Islands and Sumatra.
- Be cautious if you choose to drink alcohol
- Be wary of lesser-known or illegal brands
- Avoid buying alcohol from individuals
- Seek medical assistance if you begin to feel sick
Alcohol, drugs and travel
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety vary greatly throughout the country. Driving conditions may be hazardous during the rainy season.
Road travel in Indonesia can be very challenging due to:
- reckless driving
- perilous road conditions
- inadequate lighting
- poor signage
- high traffic congestion
If you plan to rent a car, consider hiring a driver.
Avoid driving after dark outside of major cities or major roads as some drivers do not use lights.
You may face mob anger if you are involved in an accident that causes serious injury. In such cases, remain in your vehicle and wait for a police officer to arrive.
Motorcycles and scooters
Motorcycle and scooter accidents are the main cause of death and serious injury among foreigners visiting many parts of Indonesia, including Bali.
Rental motorcycles are also often targeted and stolen. In such cases, you may have to pay the replacement cost for a new motorcycle.
Public transport
Public transport can be crowded and safety standards are poor. Many remote parts of Indonesia have poor transportation networks.
Crashes involving overcrowded buses are common. Large buses are generally available only on Java. Minibuses are available elsewhere.
If you choose to travel by bus,
- keep in mind that minibus drivers may try to overcharge foreigners
- keep your belongings secure due to pickpocketing
The condition of taxis varies. Foreign travellers using taxis have been victims of armed robbery, either by the driver or other passengers.
- Pre-arrange transportation with a safe and reliable taxi company
- Only use a taxi company whose vehicles are equipped with a meter
- Never enter a cab if it already has one or more passengers
- Don’t hail taxis off the street and avoid using unmarked taxi services
Reliable taxis are available from Bluebird, Thunderbird and Express. Be careful of “lookalike” taxis from competitors.
Ferry accidents are common and are often caused by poor safety practices or extreme weather conditions.
If you choose to travel by ferry:
- make sure the vessel you are boarding is carrying appropriate safety equipment and that life jackets are provided for all passengers and accessible at all times
- don’t board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy
- verify the safety standards of ferries with your tour operator
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Indonesian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date of entry into Indonesia and must contain at least one blank page for the placement of the Indonesian visa or entry stamp.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Social-cultural visit visa: required
Indonesia strictly enforces its immigration and visa requirements. Foreign travellers have been detained in immigration detention centres for visa violations or overstays. Those in violation may be subject to substantial fines and deportation.
A round-trip or onward airline ticket is required to obtain all types of visas.
Tourist visa
If you are travelling for tourism with a regular Canadian passport, you may obtain a visa in advance or on arrival at select points of entry.
Business and social-cultural visas
If you are travelling to Indonesia for business or social-cultural purposes (e.g. volunteer work), you must obtain a visa prior to your arrival. You must provide a letter from both the sponsoring organization in Indonesia and the sending organization in Canada to obtain your visa.
A business or social-cultural single-entry visa is extendable from within Indonesia.
Aid workers
Aid workers must have a sponsor in Indonesia to obtain a visa. Those going to Aceh also require prior authorization from the Directorate General of Immigration in Aceh or Jakarta.
Journalists
Journalists visiting Indonesia for reporting and filming purposes must obtain authorization from the Directorate General of Immigration in Jakarta before applying for a visa.
Directorate General of Immigration – Ministry of Law and Human Rights of Indonesia
Restricted areas
You must obtain a permit to travel to Indonesian Papua.
Entry regulations and permission to remain in Indonesian Papua may change at any time.
Other entry requirements
Starting February 14, 2024, tourists entering Bali will be subject to a new tax, the Love Bali Tourist Levy. This fee will be in addition to the visa fees paid to enter Indonesia.
If your are travelling to Bali, you must pay directly though the Provincial Government of Bali website.
Levy for Foreign Tourists – Provincial Government of Bali
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Polio: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre
* It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Polio (poliomyelitis) is an infectious disease that can be prevented by vaccination. It is caused by poliovirus type 1, 2 or 3. Circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus 2 (cVDPV2) is present in this country. Polio is spread from person to person and through contaminated food and water. Infection with the polio virus can cause paralysis and death in individuals of any age who are not immune.
Recommendations:
- Be sure that your polio vaccinations are up to date before travelling. Polio is part of the routine vaccine schedule for children in Canada.
- One booster dose of the polio vaccine is recommended as an adult .
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Lymphatic filariasis , also known as elephantiasis, is caused by filariae (tiny worms) spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause a range of illnesses. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from mosquito bites. There is no vaccine available for lymphatic filariasis although drug treatments exist.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Human cases of avian influenza have been reported in this destination. Avian influenza is a viral infection that can spread quickly and easily among birds and in rare cases it can infect mammals, including people. The risk is low for most travellers.
Avoid contact with birds, including wild, farm, and backyard birds (alive or dead) and surfaces that may have bird droppings on them. Ensure all poultry dishes, including eggs and wild game, are properly cooked.
Travellers with a higher risk of exposure include those:
- visiting live bird/animal markets or poultry farms
- working with poultry (such as chickens, turkeys, domestic ducks)
- hunting, de-feathering, field dressing and butchering wild birds and wild mammals
- working with wild birds for activities such as research, conservation, or rehabilitation
- working with wild mammals, especially those that eat wild birds (e.g., foxes)
All eligible people are encouraged to get the seasonal influenza shot, which will protect them against human influenza viruses. While the seasonal influenza shot does not prevent infection with avian influenza, it can reduce the chance of getting sick with human and avian influenza viruses at the same time.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
Heath care is inadequate.
Most medical staff don’t speak English or French. You may have to pay in advance, in cash, to obtain medical services.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive and you may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Overview of the criminal law system in Indonesia
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences. They can also be detained for long periods, without the possibility of release on bail, while police conduct investigations prior to prosecution.
Police have arrested tourists after random drug testing throughout the country.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Some prescription and over-the-counter medications that are legal in Canada, such as those containing morphine and codeine, are classified as controlled substances in Indonesia. It’s illegal to bring them into the country, even in small quantities, without prior permission from the Indonesian Ministry of Health and the required documentation.
If you attempt to bring banned pharmaceuticals into Indonesia without prior authorization and proper documentation, Indonesian authorities may confiscate them. You may also be subject to fines and imprisonment.
In some areas, Islamic practices and beliefs closely adhere to local customs, laws and regulations.
Religious police enforce sharia law in Aceh. Specific applications of sharia may differ by region and apply to non-Muslims as well.
Be aware of the relevant provisions specifically related to the region, regardless of your religion.
Dress and behaviour
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
In 2025, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around February 28.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, be discreet when:
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Indonesian national law doesn’t criminalize sexual acts or relationships between persons of the same sex. However, they are prohibited and punishable under local laws in some provinces.
In Aceh, Sharia law is enforced and sexual acts between Muslim individuals of the same sex is punished by caning. They could also face arrest under charges related to immoral behaviour, prostitution or social ills.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or sex characteristics.
2SLGBTQI+ individuals should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Indonesia.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Indonesia.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Indonesia, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Indonesia allows minors to carry dual citizenship until the age of 18. After this time, they must choose between their Indonesian citizenship and foreign citizenship.
General information for travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Indonesia.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Indonesia by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Indonesia to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
Imports and exports
Local customs authorities may enforce strict regulations concerning temporary import or export of items such as audiovisual material.
Gambling is illegal in Indonesia.
Identification
You must carry adequate identification, such as your passport and your stay permit, at all times.
You may be detained and fined if you don’t have the original on you.
Traffic drives on the left.
You must carry an International Driving Permit along with your Canadian driver’s licence.
If you got your International Driving Permit outside of Indonesia, local authorities may ask to approve it.
If you’re involved in an accident, you must stop and exchange information with and provide assistance to other drivers.
- International Driving Permit registration – Traffic Police, Government of Indonesia (in Indonesian)
- More about the International Driving Permit
The currency is the rupiah (IDR).
Credit cards are not widely accepted outside of large urban centres and tourist areas.
Carry cash when visiting remote areas.
Climate change is affecting Indonesia. Extreme and unusual weather events are becoming more frequent. Indonesia is located in a very active seismic zone and is prone to natural disasters such as:
- earthquakes
- volcanic eruptions
Monitor local news to stay informed on the current situation.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
Each year, Indonesia experiences thousands of earthquakes. Some trigger tsunamis and cause significant damage. Deaths and injuries occasionally occur.
A tsunami can occur within minutes of a nearby earthquake. However, the risk of tsunami can remain for several hours following the first tremor. If you're staying on the coast, familiarize yourself with the region's evacuation plans in the event of a tsunami warning.
- Earthquakes - What to Do?
- Tsunami alerts - U.S. Tsunami Warning System
Indonesia has 129 active volcanoes and periodically experiences major volcanic events that can be dangerous, even life-threatening. Ash clouds can disrupt air travel, including on the island of Bali, and cause or worsen respiratory problems.
Active volcanoes are monitored to provide residents with an early warning should unusual activity occur. Local authorities can raise alert levels and order evacuations on short notice.
If you are near active volcanoes:
- take official warnings seriously and respect exclusion zones
- monitor local media to stay up-to-date on latest developments
- follow the advice of local authorities, including evacuation orders
- be prepared to modify your travel arrangements or even evacuate the area on short notice
- National Disaster Management Authority
- Map of active volcanoes in Indonesia – MAGMA Indonesia
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to March, but heavy rains are common throughout the year. Flooding and landslides can occur with little warning, especially in remote areas where extensive deforestation is common, but also in major cities, including Jakarta. Such incidents have led to fatalities and destruction of property.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
- Be aware of health risks associated with flood waters
- Keep informed of regional weather forecasts as well as road closures or detours
- Avoid disaster areas
- Follow the advice of local authorities
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Air pollution
Unrestricted burning in Sumatra and Kalimantan sometimes causes air pollution to rise to unhealthy levels, especially from June to October.
Monitor air pollution levels closely, as they change quickly.
During periods of high pollution:
- limit your activities outdoors
- monitor local media
- follow the instructions of local authorities
Local services
In case of emergency, dial 110 for police.
Research and carry contact information for local medical facilities.
Consular assistance
Timor-Leste
There is no Canadian government office in Bali. You can obtain consular assistance from the Australian Consulate General of Australia, in Bali, under the Canada-Australia Consular Services Sharing Agreement.
Sign up to receive email updates from the Australian government on situations and events that could affect your safety while in Bali.
Smartraveller - Australian travel advice
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Indonesia, in Jakarta, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall due to security risks.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
Indonesia (PDF 699.19 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire services, ambulance and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 110 or 112.
Tourist Police, Bali
Call (+0361) 759 687.
Tourist Police, Jakarta
Call (+201) 526 4073.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall.
Reconsider your need to travel to the provinces of Papua (Papua), Papua Highlands (Papua Pegunungan), Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and South Papua (Papua Selatan).
Reconsider your need to travel to the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan due to the risk of serious security incidents or demonstrations that may turn violent.
- There's an ongoing risk of terrorist attack in Indonesia. Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities. Popular tourist areas may be the target of terrorist attacks.
- Public protests and events that draw large groups of people occur regularly and can turn violent with little notice. Expect traffic delays and restricted access to locations if there are protests. Avoid protests and demonstrations and monitor local media for the latest updates.
- Many of Indonesia's volcanoes are active and can erupt without warning. Adhere to exclusion zones around volcanoes, which can change at short notice, and follow the advice of local authorities. Domestic and international flights can be disrupted. Monitor Indonesia's Volcano Observatory Notice for the latest volcanic activity (Bahasa Indonesia and English), Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System and the Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre for updates.
- There's been tension, including demonstrations and violence, in certain towns in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan in recent years. Armed groups have stated that they're targeting foreigners, including Australians. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited. Armed groups have shot at aircraft, including commercial planes, in remote airports in Papua Pegunungan and Papua Tengah provinces.
- Petty and violent crime occurs in Indonesia. Opportunistic crime, such as pickpocketing occurs. Drinks may be spiked or mixed with toxic substances. Crimes involving taxis and taxi drivers occur. Solo women are at higher risk. Be alert in taxis, public transport, crowds, bars and nightclubs.
- Legal disputes over real estate are common, including in Bali. Before entering into an agreement or providing financial details, do your research and get legal advice.
- Natural disasters such as severe weather, floods, landslides, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and tsunamis occur regularly. Weather conditions can change quickly during the wet season (October – April). Regularly check weather reports, monitor media and speak to your travel provider before continuing with planned activities. Follow the advice of local authorities.
- When undertaking adventure activities, ensure that functioning safety equipment is available, that you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for these activities.
Full travel advice: Safety
- The standard of medical facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than in Australia. Many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities.
- Some medications, including prescription medications, drugs for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), all cannabis-based products including medicinal cannabis, cannabis-based oils and creams, hemp-based products, CBD, THC, hash and edibles, are illegal in Indonesia. Harsh penalties, such as arrest and jail time, can apply even if you have a prescription. Make sure your medication is legal in Indonesia .
- Purchasing prescription medication online or over the counter in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller before your purchase.
Full travel advice: Health
- Indonesia has revised its criminal code, which includes penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions will not come into force until January 2026.
- Penalties for drug offences include heavy fines, long prison sentences and the death penalty. Police target tourist destinations.
- Some medications are illegal in Indonesia. Harsh penalties can apply even if you have a prescription. It is also illegal to purchase prescription medications online or over the counter without an Indonesian prescription. Ensure you have a valid Indonesian prescription. See ' Health '.
The death penalty exists for some crimes in Indonesia.
- Standards of dress and behaviour are conservative in many parts of Indonesia. Learn about local customs. Take care not to offend.
- Aceh province upholds aspects of sharia law. Sharia law applies to everyone, including travellers. Inform yourself about the laws, and be careful not to offend or break local laws. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the e-Visa on Arrival or the Visa on Arrival. Cashless payments can be made online prior to travel or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali's airport and seaport. See the Bali Provincial Government's official website and FAQs for further information.
- If you're travelling to Indonesia for tourism, official government duties or business meetings, you can apply for an e-Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) online at least 48 hours before your travel to Indonesia. This also applies if you're transiting through Indonesia at international airports, seaports and land crossings. You can get a Visa on Arrival (VOA) at some international airports, seaports or land crossings.
- To apply for the e-VOA or VOA, you must have an ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter (we also recommend having at least 6 months of passport validity from the date you plan to leave Indonesia, to avoid any issues for your departure or onward travel) and a return or onward flight booking to another country.
- You may need to apply for a visa in advance to enter Indonesia for purposes not covered by the e-VOA or VOA. Check the latest entry requirements with your travel provider or an Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before travel. Entry, exit and transit conditions can change at short notice. Monitor media for the latest updates.
- You'll be required to complete an e-customs declaration for arrival. You can complete this within 3 days of departure to Indonesia.
- Travel requirements may change at short notice, including travel to Bali and Jakarta by air, land or sea. Contact your travel provider and monitor media for up-to-date details.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter tells you what the Australian Government can and can't do to help when you're overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy, Jakarta , the Australian Consulate-General, Bali , the Australian Consulate-General, Makassar or the Australian Consulate-General, Surabaya .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
The terrorist threat in Indonesia is ongoing. Attacks could happen anywhere and anytime. This includes places that foreigners visit.
Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities. Remain respectful of religious and local customs.
Indonesian authorities continue to investigate and disrupt terrorist groups in Indonesia, including Bali.
Terrorist attacks are motivated by extreme beliefs. Both local grievances as well as events in other parts of the world could motivate extremists in Indonesia towards violence.
Recent terrorist attacks
In December 2022, an explosion occurred at a police station in Bandung, Jawa Barat, killing 2 and injuring 11.
In March 2021, 2 suicide bombers attacked a church in Makassar, injuring dozens.
In the past, police have said that terrorist suspects remain at large and may seek Western targets.
Indonesian security agencies continue to conduct operations against terrorist groups.
Terrorists in Indonesia may carry out small-scale violent attacks with little or no warning.
Be alert in places of worship, especially during periods of religious significance.
Terrorists have targeted places of worship in:
As well as places of worship, other possible targets by terrorists include:
- Indonesian government facilities, premises and symbols associated with the Indonesian Government
- police stations and checkpoints
- bars, nightclubs, cafes and restaurants
- cinemas and theatres
- shopping centres, public transport and transport hubs
- airports and airlines
- clubs, including sporting clubs
- tourist areas and attractions, tour buses and tour groups
- outdoor recreation events
Supporters have committed additional acts of violence in response to high-profile extremists being detained or killed.
To protect yourself during a terrorist attack:
- leave the area as soon as it's safe
- follow the advice of local authorities
- don't gather in a group after an attack
- don't gather in a group if you're evacuated from a building
Security remains at a high level at:
- the Australian Embassy in Jakarta
- the Consulates-General in Bali, Makassar and Surabaya
More information:
Civil unrest and political tension
Most events are announced before they happen; however, protests may occur with little or no notice.
Protests and events are often held near major government buildings and embassies in Jakarta, including the Australian Embassy.
Protests may also occur at any of Australia's Consulates-General in Surabaya, Bali and Makassar, at government buildings, or the offices of international organisations in Indonesia.
You can expect traffic delays and restricted access to locations if there are protests.
Phone or email ahead for an appointment before going to the Embassy or the Consulates-General (see Local contacts ).
Demonstrations and acts of violence can happen when courts try and sentence extremists.
Conflict between different communities can sometimes occur, including in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited.
Local violence can also be directed at minority groups in other parts of Indonesia, including in Java.
If you're found to endanger security or public order, you may be prosecuted under Indonesia's Immigration laws, which may result in imprisonment or deportation.
To protect yourself from possible violence:
- avoid protests and demonstrations
- monitor local media for the latest security updates
- plan your activities to avoid potential unrest on significant dates
- be prepared to change your travel plans
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Armed conflict
The provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan experience regular violent clashes involving armed groups, civilians, Indonesian police, and the military. Armed groups have stated that they are targeting foreigners, including Australians. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited.
Many people have been killed and injured in clashes. This includes members of security forces, armed groups and civilians. Violent attacks have occurred in several areas of these provinces, including in and around Jayapura. There's a risk of more attacks.
On 23 February 2023, a riot broke out in Wamena, Papua Pegunungan, when a crowd attacked Indonesian security personnel following the arrest of two people accused of child kidnapping. 12 civilians and rioters were killed.
Violent attacks have occurred around the Freeport Mine in Papua Tengah.
Armed groups have:
- taken a New Zealand pilot hostage in Paro, Papua Pegunungan
- shot at aircraft, including commercial planes, at Beoga airport in Pupua Tengah province and Nop Goliat Dekai airport in Papua Pegunungan province.
- killed people in attacks, including one Australian
- attacked vehicles using the road between Grasberg and Timika
- killed people in violent attacks in Puncak Jaya District, Papua Tengah
- more attacks are possible and could target infrastructure and national institutions.
A range of crimes, including violent crime, occur in Indonesia. Crimes can happen in popular tourist locations in Bali.
To protect yourself from crime:
- be aware of your surroundings
- be alert in crowds
- understand the potential crime risks
Theft, robbery and bag and phone snatching have occurred. These crimes can sometimes involve violence. Opportunistic crime such as pickpocketing occurs.
Be careful of thieves:
- on motorcycles targeting pedestrians
- in upmarket shopping malls
- in crowded public transport
- at traffic lights targeting people in stopped cars
- at bars and nightclubs
- when entering accommodation, including villas in Bali
Keep bags and valuables out of sight in vehicles.
If you're travelling on foot, walk:
- on footpaths
- away from the curb
- with your bag held away from traffic

Sexual assault
If you're a victim of sexual assault :
- get immediate medical assistance. If you have any doubts about seeking medical assistance after a sexual assault, contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate in Indonesia (see Local contacts ) as quickly as possible.
- make a full statement to local police, in person, so they can conduct a criminal investigation. You may wish to seek consular help before you visit the police station. Contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate (see Local contacts ).
Local police can only investigate a crime after you've left Indonesia if you've reported it.
Your sworn statement, or statements by witnesses, can be used as evidence in criminal court proceedings.
You don't always need to be in Indonesia for trial. Neither do witnesses who live outside of Indonesia.
Counselling support
Should you wish to speak to a counsellor, you can call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate (see Local contacts ). They can connect you to counselling hotlines and services.
- Reducing the risk of sexual assault
Bars and nightclubs
Be alert in bars and nightclubs. Drink-spiking and snatching of valuables may occur if you're not alert.
Drinks may be contaminated with drugs or toxic substances. See Health .
Don't leave your food or drinks unattended.
Never accept drinks, food, gum, cigarettes, vapes or e-cigarettes from people you've just met.
- Partying safely
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card, online banking and ATM fraud occurs in Indonesia.
Check your bank statements.
Make sure your bank doesn't block your cards. Tell your bank you'll be visiting Indonesia.
Never let your card out of your sight. This includes when you pay in restaurants.
Shield your PIN from sight.
Some vendors install hidden cameras and use card skimmers.
Don’t click on unknown links in WhatsApp or mobile phone text messages, particularly if your phone is linked to mobile banking.
Use ATMs at controlled and secure places, such as:
- shopping centres
Scams and confidence tricks
Beware of scams and confidence tricks.
Only exchange money at authorised money changers. Authorised money changers can also be found on the Bali Foreign Exchange website . Unauthorised money changers have been known to scam foreign tourists in Bali and elsewhere.
All types of gambling are illegal in Indonesia.
Australians have lost large sums of money in card game scams run by organised gambling gangs, particularly in Bali. See Local laws
Some tourists have been robbed or planted with drugs after taking new acquaintances back to their hotel rooms. In some cases, their drinks were spiked.
Legal disputes over the purchase of real estate are common, including in Bali, involving:
- holiday clubs and resorts
- timeshare schemes
Before entering into an agreement or providing financial details:
- thoroughly research the proposal
- get legal advice and know your rights, especially before you sign any documents
Using taxis
Only use licensed official metered taxis. Crimes involving unregistered taxis include:
- taxis departing before the passenger can take their baggage from the vehicle
- taxi drivers robbing or temporarily holding passengers, including in urban areas
- taxi drivers forcing passengers to withdraw money at ATMs before releasing them
Lone female travellers are at higher risk of crime.
If you're in an incident involving a taxi, leave the taxi and the immediate area if it's safe to do so.
To protect yourself from overcharging and scams:
- only travel in licensed taxis with signage, a "taxi" roof sign and meters working
- ensure the driver's identification card is visible
- book via your phone, on an official taxi company mobile app, from inside an airport, or at stands at major hotels
See Travel .
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas while travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including destinations that are typically at lower risk.
On 7 February 2023, a New Zealand pilot was taken hostage by an armed group in Paro, Papua Pegunungan.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Adventure activities
Many businesses don't follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes transport and tour operators, water sports providers, hotels, restaurants and shops.
It may affect adventure activities, such as:
- bungee jumping
- scuba diving and snorkelling
- chairlift or gondola rides
In the past, Australians have been seriously injured or died while participating in adventure activities. If you require intensive care medical treatment, emergency surgery or medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about safety, search and rescue procedures
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
- check with your travel provider on vessel capacity limits before embarking on sea, land or air travel
- check weather and ocean conditions, and whether the vessel has had any mechanical issues, on the day and before continuing with water activities or sea travel
- check where the nearest medical facilities are
If proper safety equipment isn't available or you're unsure of the provider's safety or maintenance procedures, use another provider.
Trekking and climbing
Some mountain treks suit only experienced climbers. Travel with a guide and check the level of difficulty beforehand.
Many trekking options may be on or around an active volcano. Many of Indonesia's volcanoes are active and can erupt without warning. Volcanic and seismic activity may continue for some time. Adhere to exclusion zones around volcanoes, which can change at short notice, and follow the advice of local authorities. If you're planning to travel to an area near an active volcano, check with local authorities before climbing and check:
- Bureau of Meteorology Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre
- MAGMA Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia) for daily updates on status and alert levels
- National Disaster Management Authority (BNPB) (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Swimming safety
People have drowned in coastal areas, including in Bali, due to rough seas, strong currents, or from swimming, snorkelling or scuba diving in areas where there is frequent passage of boats, resulting in collisions.
Local beach rescue services may not be of the same standard as in Australia.
Saltwater crocodiles are in rivers throughout Indonesia. Avoid swimming around river estuaries and seek local advice in other locations.
If you plan to spend time in or on the water:
- regularly check weather reports as sea conditions can change rapidly
- take warnings seriously
- check media and local sources for information about potential dangers
- speak to your travel provider about safety equipment and weather conditions before continuing with planned activities
- take a friend or family member with you when you undertake swimming or water activities
- be careful when swimming, snorkelling or scuba diving near motor-powered boats or where there is frequent passage of boats
- ensure you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for planned activities
Ensure you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for planned activities.
Climate and natural disasters
Indonesia experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- landslides and mudslides
- volcanic eruptions
- earthquakes
- storms resulting in turbulent sea conditions
- tsunamis and high wave events
If there's a natural disaster or severe weather:
- always carry your passport in a waterproof bag
- keep in contact with family and friends
- check the media and local sources for information
- don't undertake sea, land or air travel if it's not safe to do so
- Indonesian Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency (BMKG) (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
Floods and mudslides
Floods , landslides and mudslides occur regularly during the wet season from October to April, with some severe events resulting in injury, displacement, death or damaged infrastructure.
Heavy rains can cause significant flooding in urban areas, including the greater Jakarta region, causing disruption to transportation. Monitor the local media for updates.
Walking and driving in flooded areas can be dangerous. Flood waters may hide uncovered drainage ditches.
Volcanic activity may escalate with little or no notice, leading to flight disruptions and airport closures, including in surrounding provinces. Contact your airline for the latest flight information.
There are 147 volcanoes in Indonesia. 76 of them are active volcanoes and could erupt at any time.
Volcanic alert levels and exclusion zones may rise quickly. You may be ordered to evacuate at short notice. Volcanic activity can disrupt domestic and international flights. There are 4 volcano alert levels in Indonesia; 1 - normal, 2 - advisory, 3 - watch, 4 - warning.
Before you travel to areas that are prone to volcanic activity, monitor media and ensure you read the Indonesian Government's latest advice on current volcanic activity, including:
- Volcanic Activity Report by Indonesia's Multiplatform Application for Geohazard Mitigation and Assessment (MAGMA) (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Volcano Activity and Observatory Notices (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- MAGMA Indonesia Map of Latest Volcano Levels and Climate Information (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Bureau of Meteorology's Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre
If there's volcanic activity:
- avoid the area
- take official warnings seriously and adhere to exclusion zones
- follow the instructions and advice of local authorities
- follow evacuation orders
- read our advice on Volcanic eruptions while travelling
Volcanic ash can cause breathing difficulties. The risk is higher for people with chronic respiratory illnesses, including:
Recent and frequent volcanic activity has included:
- Mount Ile Lewetolok in East Nusa Tenggara (Nusa Tenggara Timur)
- Mount Lewotobi Laki Laki in East Flores Regency, Nusa Tenggara Timur
- Mount Marapi in West Sumatra
- Mount Anak Krakatau, to the south of Sumatra
- Mount Merapi, near Yogyakarta
- Mt Dukono in North Sulawesi
- Mount Semeru, near Malang, East Java
- Mount Agung in Bali
- Mount Sinabung in North Sumatra
Some trekking routes are on or near active volcanoes, including Mount Agung and Mount Batur in Bali, Mount Marapi in West Sumatra, Mount Merapi near Yogyakarta, Mount Rinjani in Lombok, Mount Bromo and Mount Ijen in East Java. See 'Trekking and climbing'.
If you're planning to travel to an area near an active volcano, make sure you have comprehensive travel insurance and check if any restrictions apply.
If a volcanic eruption occurs:
- make a backup plan in case you're affected
- contact your airline or travel insurer to confirm flight schedules and get help
- keep in touch with family and friends
- Learn more about volcanic eruptions (Geoscience Australia)
- See practical advice and information about volcanic eruptions (US CDC)
- See worldwide volcanic activity reports in real-time (GDACS)
Earthquakes
Indonesia is in an active earthquake region. It has a high level of earthquake activity, that sometimes triggers tsunamis.
There are approximately 4,000 earthquakes across Indonesia every year. Around 70 to 100 of these are over 5.5 magnitude.
Earthquakes can cause death, injury and significant damage to infrastructure.
Strong earthquakes can occur anywhere in Indonesia. They are less common in Kalimantan and south-west Sulawesi.
To stay safe during an earthquake:
- know the emergency plans at your accommodation
- take precautions to avoid exposure to debris and hazardous materials, including asbestos
- MAGMA Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Indonesia's Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency (Bahasa Indonesia) or BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Indonesia)
- Indonesia's Centre for Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation (Bahasa Indonesia)
- US Federal Emergency Management Agency advice on what to do before, during and after an earthquake (English)
Forest fires and smoke haze
During the dry season in April to November, widespread forest fires can cause smoke haze resulting in poor air quality across parts of Indonesia, particularly the Riau Islands, central Sumatra and Kalimantan.
Smoke haze could affect your health and travel plans.
Keep up to date with local information and seek medical advice on appropriate precautions.
- ASEAN Regional Haze Situation
- Smartraveller advice on Bushfires
Tsunamis and high wave events
The Indian and Pacific Oceans experience more frequent, large and destructive tsunamis than other parts of the world.
There are many large earthquakes along major tectonic plate boundaries and ocean trenches.
High wave events can happen throughout coastal regions and between islands. They're caused by strong weather conditions and storms.
If you plan to surf, undertake water activities or travel by sea, check local conditions regularly.
If there’s a tsunami or high wave event:
- don't travel by sea if it's not safe to do so
- Indonesia Tsunami Early Warning Centre issues warnings when a potential tsunami with significant impact is expected
- Indonesia's Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency with the latest list of earthquakes with a magnitude greater than 5.0 on the Richter scale (Bahasa Indonesia) or BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- US Federal Emergency Management Agency page on what to do before, during and after an earthquake
Piracy occurs in the coastal areas of Indonesia.
The International Maritime Bureau (IMB) issues weekly piracy reports.
If you decide to travel by boat in these regions:
- check IMB piracy reports
- get local advice
- arrange security measures
- Travelling by boat
- Going on a cruise
- International Maritime Bureau
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including emergency treatment and medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
Before you travel, confirm:
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away, including on all forms of transport you plan to take
- whether it covers medical evacuation in the event of hospitalisation or injury
- any exclusions to your policy
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some drugs used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are illegal in Indonesia.
If you plan to bring over-the-counter or prescription medication, check if it's legal in Indonesia by contacting the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra well in advance of your planned travel. Take enough legal medicine for your trip and carry it in its original packaging. Purchasing prescription medication online in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller prior to your purchase.
Carry a copy of your prescription and a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medicine is
- your required dosage
- that it's for medical treatment or use
If you're caught with illegal medicine, you could face detention, fines or harsher penalties. You could face charges even if an Australian doctor prescribed the medication.
Ask the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra for advice before you travel.
Medicinal cannabis and cannabis-based products
Cannabis-based products such as cannabis oil and creams, hemp, CBD, THC, hash and edibles remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation or the death penalty.
- Medications
Health Risks
Critical care for Australians who become seriously ill, including in Bali, is significantly below the standard available in Australia. Medical evacuation may not be possible.
The Australian Government cannot guarantee your access to hospitals and other health services in Indonesia.
Medical evacuation to Australia for medical conditions, is possible but is very expensive and may not be covered by travel insurance. Check your policy before you travel.
Ban on sale of liquid/syrup medication
The Indonesian Ministry of Health (MoH) has advised local health workers and pharmacists to stop selling liquid/syrup medication, including commonly used medications containing paracetamol and cough syrups. MoH and the Indonesian Paediatrician Association (IDAI) received reports of a sharp increase in cases of Atypical Progressive Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in children , especially under the age of 5 years.
Insect-borne illnesses
Insect-borne illnesses are common throughout the year.
To protect yourself from disease:
- research your destination
- ask locals for advice
- make sure your accommodation is mosquito-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Dengue occurs throughout Indonesia, including Bali, Jakarta and other major cities.
Dengue is common during the rainy season.
Australian health authorities have reported an increase in dengue infections in people returning from Bali in recent years.
Consult your travel doctor for further information on available vaccines and their suitability for your individual circumstances.
Zika virus can occur in Indonesia.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites.
The Australian Department of Health and Aged Care advises pregnant women to:
- discuss any travel plans with their doctor
- consider deferring non-essential travel to affected areas
Malaria , including chloroquine-resistant strains, is widespread in rural areas, particularly in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah, Papua Selatan, Papua Barat Daya, Papua Barat, Maluku and Nusa Tenggara Timur. There is no malaria transmission in Jakarta.
- Consider taking medicine to prevent malaria.
Japanese encephalitis and filariasis
Japanese encephalitis and filariasis occur in Indonesia, especially in rural agricultural areas.
Japanese encephalitis has been present in Australian travellers returning from Indonesia, including Bali.
Vaccination is recommended for certain groups of travellers.
- Infectious diseases
Drink poisoning
People have been poisoned by alcoholic drinks contaminated with harmful substances, including methanol and arak (a traditional rice-based spirit). Locals and foreigners, including Australians, have died or become seriously ill from poisoned drinks.
Cases of drink poisoning have been reported in Bali and Lombok.
Contaminated drinks have included:
- local spirits
- spirit-based drinks, such as cocktails
- brand name alcohol
To protect yourself from drink poisoning:
- consider the risks when drinking alcoholic beverages
- be careful drinking cocktails and drinks made with spirits
- drink only at reputable licensed premises
- avoid home-made alcoholic drinks
Labels on bottles aren't always accurate.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning can be similar to drinking too much. However, they are usually stronger.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning include:
- vision problems
Vision problems may include:
- blindness, blurred or snowfield vision
- changes in colour perception
- difficulty looking at bright lights
- dilated pupils
- flashes of light
- tunnel vision
If you suspect that you or someone you're travelling with may have been poisoned, act quickly. Urgent medical attention could save your life or save you from permanent disability.
Report suspected cases of methanol poisoning to the Indonesian police.
Magic mushrooms
Don't consume magic mushrooms. They're illegal.
Australians have become sick or injured after taking magic mushrooms.
Australians have been in trouble with local police after taking magic mushrooms, particularly in Bali.
Magic mushrooms can cause major health problems, including:
- erratic behaviour
- severe hallucinations
Rabies is a risk throughout Indonesia, especially in:
- Nusa Tenggara Timur, including Labuan Bajo
- South Sulawesi
- West Kalimantan
- Nias, off the west coast of Sumatra
To protect yourself from rabies:
- avoid direct contact with dogs
- don't feed or pat animals
- avoid contact with other animals, including bats and monkeys.
Talk to your doctor about getting a pre-exposure rabies vaccination.
If bitten or scratched by an animal:
- immediately use soap and water to wash the wound thoroughly for 15 minutes
- seek urgent medical attention.
Rabies treatment in Indonesia may be limited, including the rabies vaccine and immunoglobulin availability. If you're bitten, you may need to return to Australia or travel to another country for immediate treatment.
You're at risk of contracting rabies if you visit a market where live animals and fresh food are sold because:
- live rabies-positive dogs may be present
- rabies-positive dog meat may be sold as food
Selling dog meat for human consumption is a breach of government disease control regulations.
Avoid contact with monkeys, even in places where you're encouraged to interact with them. This includes:
- popular markets
- tourist destinations
- sanctuaries
Legionnaires' disease
Cases of Legionnaires' disease have been reported in people who have travelled to Bali. Travellers who are unwell with flu-like symptoms within 10 days of returning from Bali are advised to consult their GPs.
- Legionnaires' disease warning for Bali travellers (Western Australian Government Department of Health)
- Legionnaires’ disease (Better Health Channel, Victorian Government Department of Health)
- Legionnaires' disease (World Health Organization)
Cases of poliovirus (type 1) have been reported in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan. Poliovirus (type 2) cases have been reported in the provinces of Aceh, East, West and Central Java. There may be unreported cases in other provinces in Indonesia.
Ensure that you're vaccinated against polio.
- Factsheet on poliovirus types (World Health Organization)
- Health emergencies information for Indonesia (World Health Organization)
Periodic outbreaks of measles continue to be reported in Indonesia, including Bali.
You need 2 doses of vaccine 4 weeks apart to be fully vaccinated against measles.
If you have symptoms of measles, seek medical attention.
Measles is highly infectious. Call before attending a healthcare facility.
Nipah Virus and Yellow Fever
There are no cases of Nipah virus or Yellow Fever in Indonesia. You may be temperature checked on arrival at international and domestic airports. If you have fever symptoms, you may be referred to the airport clinic for further tests and asked to seek medical treatment. See your doctor or travel clinic before you travel to plan any vaccinations you need.
HIV/AIDS is a risk for travellers. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are widespread. These include:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- boil drinking water or drink bottled water
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw food, such as salads
To minimise the risk of food poisoning, only eat meat from reputable suppliers.
Seek urgent medical attention if you suspect food poisoning or have a fever or diarrhoea.
Seafood toxins
You can become sick from naturally occurring seafood toxins, including:
- ciguatera fish poisoning
- scombroid (histamine fish poisoning)
- toxins in shellfish
Avoid temporary black henna tattoos. The dye often causes serious skin reactions.
Before you get any tattoo, check the hygiene and safety of your tattoo provider.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than Australia. Many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities.
Hospitals expect families to provide support to patients, including all financial support.
Psychiatric and psychological services are limited in Indonesia. Hospital staff may use physical restraints on patients.
When diving in Indonesia, there is a risk that you may experience decompression illness. An illness may occur when a diver ascends to the water surface too quickly and may have severe consequences. Understand the risks before you dive.
Decompression chambers are available in various areas, including the following locations:
- Bali's Sanglah General Hospital
- Siloam Hospital in Labuan Bajo
- Hospitals in Jakarta, Balikpapan, Bintan, Medan, Makassar, Raja Ampat (Waisai), Maluku, Tual and Manado near popular dive sites
Before admitting patients, hospitals usually need:
- guarantee of payment from the patient or their next of kin (family or friend)
- confirmation of medical insurance
- deposit payment
There's no reciprocal healthcare agreement between Australia and Indonesia.
The Australian Government cannot provide guarantee of payment, confirmation of medical insurance or a deposit payment for services.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you may need to be evacuated to a place with better care. Medical evacuation can be very expensive. Check your insurance policy before you travel. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs. It's best to check with your travel provider on the location and functionality of decompression chambers and other medical facilities available in the area before undertaking remote travel.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
Indonesian Parliament has passed revisions to its criminal code, which includes penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions will not come into force until January 2026.
Indonesia has signed into law revisions to the Electronic and Information Transactions Law (ITE Law). Tough penalties apply for defamation, hate speech, spreading hoaxes and uploading immoral content to the Internet. The law applies both within and outside Indonesia.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
- Arrested or jailed
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
You may face heavy fines or jail for consuming or possessing even small amounts of drugs, including marijuana. Cannabis-based products such as cannabis oil and cream, hemp, CBD, THC, hash and edibles remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation or the death penalty.
Some prescription medications that are available in Australia are illegal in Indonesia. Purchasing prescription medication online or over the counter in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller before your purchase.
Magic mushrooms are illegal. Indonesian police work to prevent their distribution.
Police target illegal drug use and possession across Indonesia. Police often target popular places and venues in Bali, Lombok and Jakarta.
- Carrying or using drugs
Local labour laws can change at short notice. This can affect expatriate workers.
Under Indonesian law, you must always carry identification. For example, your:
- Australian passport; and
- Resident's Stay Permit (if applicable)
Gambling is illegal.
Property laws are strict, seek legal advice before acquiring property in Indonesia.
It's sometimes illegal to take photographs in Indonesia. Obey signs banning photography. If in doubt, get advice from local officials. See Safety .
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Local customs
Standards of dress and behaviour are conservative in many parts of Indonesia. Take care not to offend.
Find out what customs apply at your destination.
If in doubt, seek local advice.
LGBTQIA+ information
Same-sex relationships are legal in Indonesia, except in the province of Aceh. Same-sex relationships in Aceh may attract corporal punishment. Visible displays of same sex relationships could draw unwanted attention.
Some laws and regulations can be applied in a way that discriminates against the LGBTI community, including for pornography and prostitution.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
The Islamic holiday month of Ramadan is observed in Indonesia. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws at this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking and smoking may be illegal in public during this time. If you're not fasting, avoid these activities around people who are. Seek local advice to avoid offence and follow the advice of local authorities.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Aceh is governed as a special territory, not a province, and has a degree of special autonomy.
Some aspects of sharia law are upheld. This includes regulations and punishments that don't apply in other parts of Indonesia.
Local sharia police enforce sharia law.
Sharia law applies to anyone in Aceh, including:
- foreigners (expats and travellers)
- non-Muslims
Sharia law doesn't allow:
- drinking alcohol
- prostitution
- same-sex relationships
- extra-marital sex
- co-habitation before marriage
It also requires a conservative standard of dress.
Learn about the laws in Aceh. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Dual citizenship
Indonesia doesn't allow dual nationality for adults, and you may be prosecuted by Immigration authorities should you be found to hold valid passports of two nationalities. If you entered Indonesia on your non-Australian citizenship passport, Indonesian Immigration will require you to exit Indonesia on that nationality's passport.
A child of Indonesian and Australian parents can maintain citizenship of both countries until the age of 18 years. Before a dual Australian-Indonesian citizen minor travels from Indonesia, additional identity documentation may be required from Indonesian Immigration. Check with Indonesian Immigration or the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra well in advance of your planned travel.
- Embassy and Consulate of Indonesia
- Information on limited dual citizenship
- Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Bali Tourism Levy
The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the e-Visa on Arrival or the Visa on Arrival. Cashless payments can be made online prior to travel or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali's airport and seaport. Exemption from payment of the levy applies to transit passengers and certain visa holders. See the Bali Provincial Government's official website and FAQs for further information.
e-Visa on Arrival and Visa on Arrival
You can apply for an e-Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) no later than 48 hours prior to travelling to Indonesia if you are travelling for tourism, business meetings, purchasing goods or transiting only. Check the e-VOA requirements from Indonesian Immigration before applying.
You can still apply for a regular Visa on Arrival (VOA) at certain international airports, seaports and land crossings, including Jakarta, Bali, Surabaya, Makassar, Lombok, Batam, Medan, Manado, Aceh, Padang, Tanjung Pinang and Yogyakarta, if you do not apply for an e-VOA at least 48 hours in advance of your travel to Indonesia.
The e-VOA or VOA can be used for tourism, official government duties, business meetings, or to transit through Indonesia. You cannot transit in Indonesia without an e-VOA or VOA.
Additional requirements apply if you are travelling on government duties.
For the latest list of entry points for the e-VOA or VOA, refer to the Directorate General of Immigration's list of land border crossings, international airports, and international seaports .
The e-VOA and VOA cost IDR 500,000 (approximately $A 50), with the e-VOA charging a small online processing fee.
For the VOA, some airports, including Jakarta's international airport, are only accepting cash payment. Card payment facilities are available at Bali's international airport. ATM facilities may be in high demand. Be prepared to pay in cash if required.
The visa is valid for a 30 day stay and can be extended once (for a maximum of 30 days) by applying at an immigration office within Indonesia. Ensure you extend your visa within the initial 30 days to avoid an overstay fine and deportation.
To apply for a regular VOA, you must show:
- your ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter (we also recommend having at least 6 months passport validity from the date you plan to leave Indonesia, to avoid any issues for your departure or onward travel)
- a return flight booking to Australia or onward flight booking to another country
Contact your travel agent, airline, or your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia for details.
Other visas
If you're entering Indonesia from a port or airport that does not issue a visa on arrival, or you're visiting Indonesia for a purpose not allowed under the e-VOA or VOA conditions, you must apply for a visa in advance of travel. Check the Indonesian Immigration website for further information, or contact your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia .
Overstaying your permit may result in fines, detention and/or deportation.
- check your visa and permit, and contact the Directorate General of Immigration (DGI) for advice specific to your needs
- if you use an agent to extend your visa or stay permit, use only reputable companies
- if you have specific enquiries on visas or stay permits, contact DGI's Customer Service team via WhatsApp on +62 821 1295 3298
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest Embassy or Consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and entry rules.
You can't work or conduct research in Indonesia unless you have the appropriate visa. Fines of IDR1,000,000 (approx. $A 100) per day apply for the maximum 60 day overstay period.
If you breach Indonesian immigration regulations, you may face:
- deportation
- re-entry bans
You may not be allowed to enter Indonesia if you have a criminal record. This is regardless of how long ago the offence took place. If you're concerned, contact an Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before you travel.
Indonesian Immigration and visa decisions are final. The Australian Government can't help you.
- Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia
Border measures
You'll be required to complete an e-customs declaration for arrival . You can complete this within 3 days of departure to Indonesia.
Check entry requirements with your travel provider or the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before you travel.
You may be temperature checked on arrival at international and domestic airports. If you have fever symptoms, you may be referred to the airport clinic for further tests and asked to seek medical treatment. See your doctor or travel clinic before you travel to plan any vaccinations you need.
Departure from Indonesia
Indonesia, including Bali, currently has an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease affecting animals. In preparing to travel to Australia, read Smartraveller's advice on biosecurity and border controls . Measures include cleaning dirty shoes, clothing or equipment before boarding your flight to Australia and not packing meat or dairy products. On your Incoming Passenger Declaration, you must declare any meat, dairy or animal products and any of your travel in rural areas or near animals (e.g., farms, zoos, markets).
Other formalities
If you're staying in a private residence, not a hotel, register when you arrive with both:
- the local Rukun Tetangga Office
- local police
If you plan to be in Indonesia for more than 30 days:
- register with the local immigration office
- make sure you have the right visa
- Embassy of Indonesia in Canberra
Indonesia won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave Indonesia. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over. You can end up stranded or returned back to your previous port overseas at your own cost, if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months from the date you enter and the date you plan to leave Indonesia.
Indonesia does not accept entry with an emergency passport, even if it is valid for more than 6 months. Ensure you enter Indonesia on a valid ordinary, official, or diplomatic passport.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply these rules inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian Embassy, Consulate or High Commission.
Damaged Passports
Indonesian authorities have strict standards for damaged passports, and travellers have been refused entry into Indonesia with a damaged passport. Normal wear and tear, including water damage, minor tears or rips to the pages, can be considered damaged.
It's important that:
- there are no tears or cuts in the passport pages, especially the photo page
- everything on the photo page is legible and clear
- there are no marks across your photo or in the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) on the photo page
- no pages have been removed
- there is no alteration or tampering
If you're not sure about the condition of your passport, call the Australian Passport Office on 131 232 or contact your nearest Australian embassy or consulate overseas . We may need to see your passport to assess it.
- Passport Services
- Damaged and faulty passports
- Using and protecting your passport
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
More information:
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The local currency is the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR).
Declare cash in excess of IDR100,000,000 or equivalent when you arrive and leave. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
IDR100,000,000 is worth about $A10,000.
Local travel
Travel permits.
You may need a travel permit or Surat Keterangan Jalan to travel to some areas of the Papua provinces.
Check if you need a permit with the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia or with your travel provider.
Mobile Phone Reception and Wi-Fi
Mobile phone reception and Wi-Fi are not always available, including in remote areas and some resort islands.
If you plan to stay in Indonesia for more than 90 days and would like to use your mobile phone purchased overseas, you'll need to register your mobile phone IMEI number with Indonesian Customs within the first 60 days of your stay.
If you plan to stay in Indonesia for less than 90 days, you can visit the local cellular operator/provider booth at the airport to get an access period to use the Indonesian cellular network, which is only valid for 90 days and includes data roaming.
A customs payment may be required, or a tourist SIM card can be purchased for short-term stays. You can use Wi-Fi networks without registration.
To stay in communication and avoid mobile service interruptions:
- check mobile coverage with your service provider
- register your mobile device with Indonesian Customs on arrival if you plan to connect to the mobile network
Driving permit
To drive in Indonesia, you need either:
- an Indonesian licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Check that your licence or permit is appropriate for the type of vehicle you're driving.
Your Australian licence isn't enough.
Your travel insurer will deny any claims you make if:
- you're unlicensed
- you don't hold the correct class of licence
Road travel
Traffic can be extremely congested.
Road users are often unpredictable or undisciplined.
You're more likely to be killed in a motor vehicle accident in Indonesia than in Australia. Drive defensively. Some traffic incidents can escalate into violent disputes quickly.
Consider hiring a taxi or a driver who is familiar with local roads and traffic conditions.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Motorcycle accidents have killed and injured foreigners, including Australians. This includes in tourist areas, particularly Bali, Lombok and the Gili Islands.
If you're riding a motorbike and there's an accident, you'll often be assumed to be at fault. You may be expected to compensate all parties.
If you hire a motorbike:
- make sure your insurance policy covers you
- check if any policy restrictions apply, for example if you're not licensed to ride a motorcycle in Australia
Always wear a helmet.
Public transport
Buses, trains and the metro rail can be crowded, particularly:
- around public holidays
- during peak commute times
Safety standards may not be observed.
- Transport and getting around safely
Only use licensed official metered taxis.
- only travel in licensed taxis with signage, a "taxi" roof sign and meters
- book via phone or an official taxi company mobile app
You can book licensed official metered taxis
- on the taxi company's official mobile app
- from inside airports
- at stands at major hotels
Unofficial operators can have taxis that look similar to those run by reputable companies. Make sure the taxi meter is working before you get into the taxi.
See Safety .
Rail travel
Inter-city rail networks operate on the islands of Java, Sumatra and Sulawesi.
Commuter trains operate in Java, including Jakarta.
Trains can be crowded, particularly:
- during peak commuter times
Travel between islands
Travel by ferry or boat can be dangerous.
Passenger and luggage limits aren't always observed.
Equipment may not be properly maintained, and they may not have GPS or emergency communications equipment.
There may not be enough life jackets. It's unlikely that the crew will have life jackets for children.
In March 2024, a ferry sank in the Thousand Islands off the coast of Jakarta, resulting in one death, and a liveaboard boat caught fire and sank in Raja Ampat, Papua Barat Daya, requiring several passengers to be rescued.
In August 2023, two crew died after a boat carrying passengers sank in the Banyak Islands, Aceh, and three people went missing after a ship sank in the Thousand Islands off the coast of Jakarta.
In July 2023, 15 people died after a ferry sank off Sulawesi Island.
In January 2023, 23 passengers and 6 crew were rescued after an inter-island ferry sank while returning from Nusa Penida to Sanur Beach, Bali.
In May 2022, 19 people died after a ferry sank in the Makassar Strait.
In June 2018, a ferry sank on Lake Toba in Sumatra and 100s of people died.
If you plan to travel by sea between islands:
- make sure any ferry or boat you board has appropriate safety equipment, GPS and communication equipment, and life jackets
- wear a life jacket at all times
- take enough life jackets for all children travelling with you
- ask your tour operator or crew about safety standards before you travel
- check sea, weather conditions and forecasts before embarking on boat or ferry travel, and delay travel if conditions are not safe
If appropriate safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Avoid travelling by water after dark unless the vessel is properly equipped. Avoid travel during wet weather or storms.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Indonesia's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
The European Union (EU) has published a list of airlines that have operating bans or restrictions within the EU. See the EU list of banned airlines .
Australian travellers should make their own decisions on which airlines to travel with.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Search and rescue services
Medical emergencies and ambulance.
SMS 1717 for Jakarta Police
Police Stations in Bali
Refer to the Bali Tourism Board’s list of police stations in Bali
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australian Embassy, Jakarta
Jalan Patra Kuningan Raya Kav. 1-4 Jakarta Selatan 12950
Phone: (+62 21) 2550 5555 Email: [email protected] Website: indonesia.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australian Embassy Jakarta, Indonesia X: @DubesAustralia Instagram: @KeDubesAustralia
Make an appointment online or call (+62 21) 2550 5500 or (+62 21) 2550 5555.
Australian Consulate-General, Bali
Jalan Tantular 32 Renon Denpasar Bali 80234
Phone: (+62 361) 2000 100 Email: [email protected] Website: bali.indonesia.embassy.gov.au X: @KonJenBali Instagram: @konjenbali
Australian Consulate-General, Makassar
Wisma Kalla Lt. 7 Jalan Dr Sam Ratulangi No. 8 Makassar South Sulawesi 90125
Phone: (+62 411) 366 4100 Email: [email protected] Website: makassar.consulate.gov.au Facebook: Australian Consulate-General, Makassar, Sulawesi X: @KonJenMakassar Instagram: @konjenmakassar
Australian Consulate-General, Surabaya
Level 3 ESA Sampoerna Center Jl. Dokter.Ir. H. Soekarno No. 198 Klampis Ngasem, Sukolilo, Surabaya
Phone: (+62 31) 9920 3200 Email: [email protected] Website: surabaya.consulate.gov.au Instagram: @KonJenSurabaya
Check the websites for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Indonesia?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
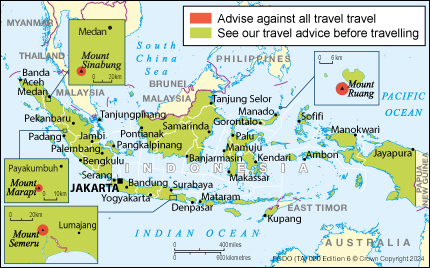
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) provides advice about risks of travel to support British nationals in making informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Areas where the FCDO advises against travel
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice. Consular support is also severely limited where FCDO advises against travel.
Mount Ruang, Northern Sulawesi
FCDO advises against all travel to within 7km of the crater of Mount Ruang in Northern Sulawesi. This is an exclusion zone put into place by the local authorities. Mount Ruang erupted on 16 April 2024.
Mount Marapi, Western Sumatra
FCDO advises against all travel to within 3km of the crater of Mount Marapi in West Sumatra.
Mount Sinabung area, Karo Regency
FCDO advises against all travel within 5 km of the Mount Sinabung crater in Karo Regency, North Sumatra.
Mount Semeru area, Lumajang Regency
FCDO advises against all travel within 5 km of the crater of Mount Semeru in Lumajang Regency, East Java. FCDO also advises against all travel to the southeast area of Mount Semeru along the Besuk Kobokan river (approximately 13 km from the crater). You should stay at least 500 m from the Besuk Kobokan riverbank.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide as well as support for British nationals abroad which includes:
- advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- information for women, LGBT and disabled travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and potential expenses in an emergency.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

- Countries & Regions
- International Organisations (IOs)
- Climate Change
- Counter Terrorism
- Disarmament
- Cybersecurity
- International Peacekeeping
- Singapore's Voluntary National Review
- Small States
- Sustainable Development
- Pedra Branca
- Singapore Universal Periodic Review
- Water Agreements
- Find A Singapore Overseas Mission
- Foreign Representatives To Singapore
- COVID-19 Information
- Travel Tips
- Visa Information
- I Need Help Overseas
- Passport Matters
- Legalisation of Documents
- Travel Advisories and Notices
- Useful links
- Press Statements, Transcripts & Photos
- Announcements and Highlights
- Experience Singapore
- Foreign Service Officer (Functional and Corporate)
- Foreign Service Officer (Political and Economic)
- Foreign Service Administration Specialist
- Job Opportunities
- Pre-University
- Undergraduate
- Foreign Service Scholarships
- Recruitment
- Scholarship
- Reach.gov.sg
Travel Notice: Mount Ruang's Eruption
18 April 2024
Since 17 April 2024, the Indonesian authorities have raised the alert level for Mount Ruang to Level IV (Warning). A tsunami alert has also been issued. Singaporeans are advised not to enter within a radius of 6km from the crater.
There are also reports of volcanic earthquakes at Mount Awu in Sangihe Islands Regency, North Sulawesi.
Following the eruptions, the Sam Ratulangi International Airport in Manado City has been temporarily closed. Singaporeans travelling to or from the Sam Ratulangi International Airport are advised to check with their airlines or tour operators for up-to-date flight schedules and updates on the airport closure.
Singaporeans in the proximity of the affected areas are advised to monitor the local news closely and take the necessary precautions for their personal safety. They should e-Register with MFA immediately at https://eregister.mfa.gov.sg/ if they have not done so. Those in need of consular assistance may contact the Singapore Embassy in Jakarta or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Duty office at:
Embassy of the Republic of Singapore in Jakarta
Tel: +62 (21) 2995 0400 during office hours, or the 24-hour hotline +62 811 863 348 for emergencies outside of office hours
Ministry of Foreign Affairs Duty Office (24-hours)
Tel: +65 6379 8800/6379 8855
Travel Notice: Mount Semeru's Eruption
16 February 2024
Since 4 December 2022, the Indonesian authorities have placed the alert-level for Mount Semeru at Level 3 (Siaga or Standby) and has advised residents to avoid Mount Semeru and its vicinity.
Given the volcanic activity of Mount Semeru as well as other active volcanoes in the region, Singaporeans should check on advisories issued by Indonesia’s Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation Agency (PVMBG) a t https://vsi.esdm.go.id/ before their travel. Singaporeans in Lumajang and Malang should monitor these developments closely and adhere to local advisories. They should take necessary precautions for their personal safety and e-Register with MFA immediately at https://eregister.mfa.gov.sg/ if they have not done so. Those in need of consular assistance may contact the Singapore Embassy in Jakarta or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Duty office at:
Embassy of the Republic of Singapore in Jakarta Tel: +62 (21) 2995 0400 during office hours, or the 24-hour hotline +62 811 863 348 for emergencies outside of office hours
Ministry of Foreign Affairs Duty Office (24-hours) Tel: +65 6379 8800/6379 8855
Expand All | Collapse All
Entry and Exit
Singaporeans travelling on their ordinary Singapore Passport can visit Indonesia for up to 30 days without a visa. Please visit the website of the Indonesian Directorate General of Immigration for details of the types of visit that fall under this category. Visa-free visits cannot be extended beyond the 30 days allotted. If you intend to travel to Indonesia for more than 30 days, you should apply for the appropriate visa before your travel. As visa requirements often change at short notice, we advise you to contact your travel agency, or the Embassy of Indonesia in Singapore for up-to-date information.
If you are visiting Indonesia for business purposes, you should apply for a business visa.
Holders of the APEC Business Travel Card (ABTC) are exempted from Indonesia’s Visit Visa requirements so long as they are not engaged in employment in Indonesia. They can remain in Indonesia for up to 60 days (which cannot be extended). Currently, there are 17 airports (4 with dedicated ABTC Gates and the other 13 without) as well as seaports, including Batam, in Indonesia, which holders of the ABTC who are travelling to Indonesia for business purposes can use.
If you are unsure of the type of visa you will need in Indonesia, please check the website of the Indonesian Directorate General of Immigration, with your local partner or representative in Indonesia, or the nearest Indonesian Embassy.
Overstaying is a serious offence in Indonesia. Overstayers must report to the local immigration authorities promptly. The penalties for overstaying can include, but are not limited to, a fine of up to IDR 1 million per day, detention and/or an entry ban. If you have overstayed, you may contact the Singapore Embassy in Jakarta or the Singapore Consulates-General in Batam or Medan for further assistance after you have reported to the local immigration authorities.
Safety and Security
You are advised to remain vigilant against possible crime and security threats while travelling. You should keep abreast of local developments and take the necessary precautions for your personal safety. You should avoid protest and demonstration sites. If you are planning to participate in potentially hazardous sports, you are advised to purchase comprehensive insurance.
All travellers are required to abide by Indonesia’s laws and regulations. The Singapore Government is unable to intervene in the enforcement of local laws and regulations by the host government.
Under Indonesian law, all residents and visitors are required to carry official documents of identification, including those issued by the Indonesian government, with them at all times.
Penalties for drug offences are severe and include the death penalty.
Additional Information
Indonesia is a large and diverse archipelagic country that lies in a seismically active region and has around 130 active volcanoes. Indonesia experiences various forms of natural disasters, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis, flash floods, and landslides.
You are advised to visit the following Indonesian official websites for information on weather, climate, air quality, and natural disasters:
Indonesian Agency for Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics (BMKG): www.bmkg.go.id
Centre for Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation (PVMBG): https://vsi.esdm.go.id
You should also monitor local developments closely, abide by the advice from local authorities, and take the necessary precautions for your personal safety.
General Travel Advice
Overseas Travel – Be Informed & Be Safe [Updated on 5 February 2024]
Singaporeans planning overseas travel are reminded to take the necessary precautions, including being prepared to deal with accidents, natural disasters or terrorist attacks. Singaporeans are also reminded to be familiar with your destination’s local laws, customs, and COVID-19 regulations.
Demonstrations do occur in major cities across the world. Such demonstrations can sometimes escalate into violence. It is important for Singaporeans to keep abreast of local news, avoid any protests or demonstrations and heed the advice of the local authorities.
When participating in outdoor leisure activities overseas, Singaporeans should be mindful that certain sporting activities, especially in open seas, may carry risks. Besides ensuring that one has the physical competencies and appropriate condition to undertake the activity, every effort should be made to ascertain if the trip organiser or guide is reliable and competent, and that appropriate safety and contingency plans are in place. When in doubt, Singaporeans should consult the relevant professional bodies or sporting associations for specific advice.
For those planning to travel, here are some tips:
Before travelling
- Familiarise yourself with our network of overseas missions.
- Purchase comprehensive travel insurance and be familiar with the terms and coverage.
- Equip yourself with research about your destination’s entry requirements, current situation, local laws and customs.
- eRegister with us on our website ( www.mfa.gov.sg ) so that we may reach out to you during an emergency.
While travelling
- Always take care of your personal safety, remain vigilant and monitor local weather news, advisories, and security developments.
- Exercise caution around large gatherings and avoid locations known for demonstrations or disturbances.
- Be prepared for possible delays and last-minute changes in travel plans especially during unforeseen events such as natural disasters, social unrest or terror attacks.
- Stay connected with your friends and family. Inform them of your whereabouts and provide them with your overseas contact details.
- In the event that you require consular assistance, please contact the nearest Singapore Overseas Mission or call the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Duty Office at +65 6379 8800/+65 6379 8855.
Advisory: Email Scams
There have been reports of individuals receiving scam emails/messages purportedly sent from friends in distress overseas. These emails/messages typically originate from an email address/social media known to the receiver bearing claims of the sender getting into trouble overseas and urgently requesting financial assistance. The sender would also claim to have approached a Singapore Embassy/Consulate and the local Police for help to no avail.
MFA takes the safety of all Singaporeans very seriously. Singaporeans in distress approaching our Overseas Missions for assistance will be rendered with all necessary consular assistance. If you receive such emails/messages from purported friends seeking funds transfers, we strongly advise you to call them first to verify the authenticity of the emails/messages before responding to their request. It is also not advisable to give out any personal information such as NRIC/passport numbers, address, telephone number, etc. Any form of reply, even one of non-interest, could result in more unsolicited emails. Members of the public who suspect that they have fallen prey to such scams should report the matter to the Police immediately. Should Singaporeans abroad require consular assistance, they can contact the nearest Singapore Overseas Mission or call the Ministry of Foreign Affairs 24-hr Duty Office at +65 6379 8800/+65 6379 8855.
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is a ministry of the Government of Singapore responsible for conducting and managing diplomatic relations between Singapore and other countries and regions.
Travel Page

COMMENTS
Accidents Happen. Get Travel Insurance Protection. Worldwide Coverage. Compare Plans. Expert Reviews & Analysis. Ratings Updated April. Trusted by Over 1,000,000 Customers
Plane Travel. Cheap Travel Deals. Search Cheapest, Quickest & Best Flights. Compare and Save on a Wide Choice of Cheap Flights Today with Cheapflights® Flight Search.
30 November 2023. New International Travel Regulations to Enter Indonesia as of 1 February 2022. As an immediate follow-up to prevent the spread of SARS-COV-2 B.1.1.529 from South Africa and some other countries in the world, COVID-19 Task Force issued the Circular of the Head of the COVID-19 Handling Task Force Number 4 of 2022 regarding International Travel Health Protocol during the Corona ...
RT-PCR tests will be conducted upon arrival in the Republic of Indonesia and upon completion of the 6th 24-hour period of the mandatory quarantine period. These new restrictions took effect 29 November 2021. The regulations to date are limited to international travel and will be re-adjusted according to global health developments.
Location: Indonesia Event: Government Announces New Travel Restrictions Effective September 19, 2021, the Government of Indonesia (GOI) introduced new Effective September 19, 2021, the Government of Indonesia (GOI) introduced new travel requirements and COVID-19 testing procedures which will affect all travelers arriving to or traveling within Indonesia.
1,861 Tourism Stakeholders in Bali are Targeted to Receive InDOnesia CARE Certification by the End of 2021. Read. . Covid 19 Travel Guide - Indonesia Travel.
Indonesia does not accept the 12-page U.S. emergency passport for entry into Indonesia. BLANK PASSPORT PAGES: Two blank visa pages required for entry stamp. TOURIST VISA REQUIRED: Yes, Visa or Visa on Arrival. VACCINATIONS: None. CURRENCY RESTRICTIONS FOR ENTRY: 100,000,000 Indonesian rupia (approx. $7,000 USD)
Restaurants in Indonesia are open. Bars in Indonesia are . Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Indonesia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
Suggested for you. JAKARTA, 23 November 2022 - As an immediate response to recover tourism industry and relaxing the international travel restrictions, COVID-19 Task Force issued the Circular Letter of the COVID-19 Task Force Number 25 of 2022 concerning Health Protocols for International Travels during the COVID-19 Pandemic.
Indonesia's revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. It is unclear how Indonesian authorities will implement the revised criminal code. Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Indonesia.
Please consult the Indonesia travel page at Travel.State.Gov for full information about travel to Indonesia. Entry Requirements: Starting on June 9, 2023, the Indonesian Government no longer requires proof of vaccination. It is still recommended by the Indonesian government to continue to be vaccinated against COVID-19 up to the second booster ...
Event. Authorities have tightened domestic intercity travel restrictions as of Aug. 28. Most people aged 18 and above who wish to travel intercity must now have received a booster COVID-19 dose. Individuals with medical conditions preventing them from receiving COVID-19 vaccines are exempt from the policy but must present a doctor's certificate ...
British nationals who visit Indonesia for the following reasons can also apply for a visa on arrival at a cost of 500,000 Indonesian rupiah: tourism official visit or government duties
U.S. Consular Agency in Bali, Indonesia. +62-361-233-605 or +62-21-5083-1000 after hours. [email protected]. For regular updates, follow the U.S. Consulate General in Surabaya on Twitter and Facebook and the U.S. Embassy in Jakarta at Twitter and Facebook. State Department - Consular Affairs.
Official travel. Passport with "X" gender identifier. While the Government of Canada issues passports with an "X" gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the "X" gender identifier.
Indonesia does not accept entry with an emergency passport, even if it is valid for more than 6 months. Ensure you enter Indonesia on a valid ordinary, official, or diplomatic passport. Some foreign governments and airlines apply these rules inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
Advisory on Coronavirus for Travelers to Indonesia. Tue, 17 Mar 2020. Due to the recent concern regarding the outbreak of COVID-19 in Indonesia, the Government of the Republic of Indonesia would be implementing the following measures in order to minimize the risk of the pandemic from spreading even further: 1| The Government continues to ...
consulate general of the republic of indonesia IN LOS ANGELES, UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 3457 Wilshire blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010.
Still current at: 4 May 2024 Updated: 2 May 2024 Latest update: FCDO now advises against all travel to within 7km of the crater of Mount Ruang in Northern Sulawesi ('Warnings and insurance' page).
Follow us on our Lab Indonesia Facebook Page Follow us on our Official Instagram Page Indonesia Travel Restrictions Updated on 5 April 2022 per National COVID-19 Task Force Circular Note No. 17/2022. In order to monitor, control, and evaluate for preventing an increase in the transmission of COVID-19 including the new and future variants … Continue reading "Indonesia Travel Restrictions"
Embassy of the Republic of Singapore in Jakarta. Tel: +62 (21) 2995 0400 during office hours, or the 24-hour hotline +62 811 863 348 for emergencies outside of office hours. Ministry of Foreign Affairs Duty Office (24-hours) Tel: +65 6379 8800/6379 8855. Travel Notice: Mount Semeru's Eruption.
Following the information about the emergence of a new variant of the 2019 novel coronavirus, the Indonesian government will impose a temporary entry restriction policy for foreign citizens from all countries to Indonesia in the period of 1- 8 February 2021. Based on Circular Letter No. 2 Year 2021 regarding International Travel Health ...