THE BEST Landmarks in Sion (Mumbai)
Sights in sion.
- Points of Interest & Landmarks
- Historic Sites
- Lighthouses
- 4.0 of 5 bubbles & up
- South Mumbai
- Western Suburbs
- Eastern Suburbs
- Malabar Hill/Peddar Road
- Good for Kids
- Good for Big Groups
- Adventurous
- Budget-friendly
- Good for a Rainy Day
- Hidden Gems
- Good for Couples
- Honeymoon spot
- Good for Adrenaline Seekers
- Things to do ranked using Tripadvisor data including reviews, ratings, photos, and popularity.


1. Sion Hillock Fort

2. Astrologer House
Recommended Sightseeing Experiences (655)

3. Bhakti Dham Mandir
What travelers are saying.

Hello, we are currently not providing access or use of our website/mobile application to our users in Europe.

COPYRIGHT © TIMES INTERNET LIMITED. POWERED BY INDIATIMES LIFESTYLE NETWORK. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
- Group Enquiry? NEW
Places to Visit in Sion
- Places To Visit
Popular Nearby Places Around Sion
Best domestic packages, best international packages, domestic honeymoon packages, international honeymoon packages, places to visit in india, international places to visit, things to do in india, international things to do, popular on thrillophilia.
- We assure the privacy of your contact data.
- This data will only be used by our team to contact you and no other purposes.
Your enquiry has been received successfully. Our destination expert will reach out to you soon!
Best time to visit Sion
Opening time of sion, things to do at sion, places to visit near sion.

Trips near Sion

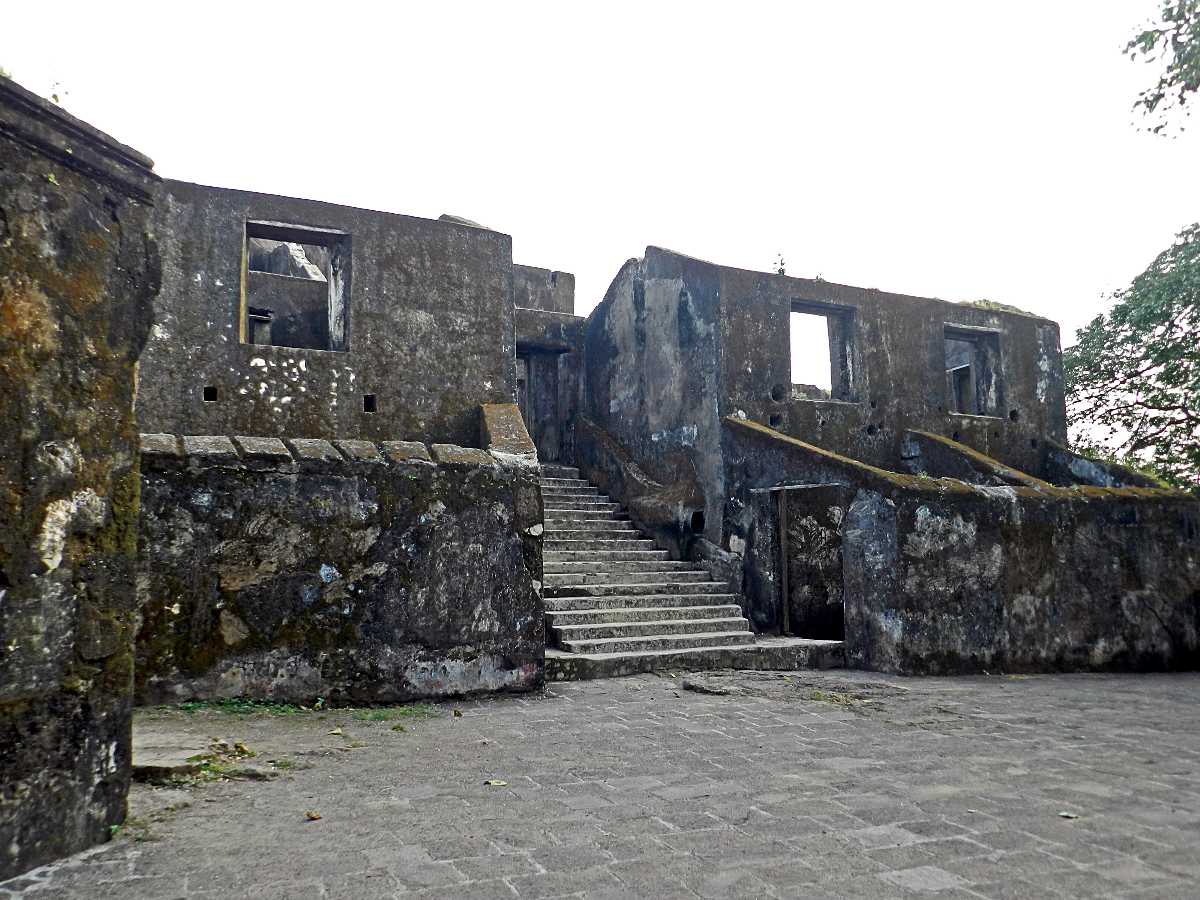
You Need To Visit This Hidden Fort in Mumbai for the Best Views
Top hotel collections.

Near Airport
5 Star Hotels
Nearby Resorts
Significance of Sion Fort
Fort Timings - 6:00 AM to 12:00 PM and 4:00 PM to 8:30 PM
The History of Sion Fort - From Then to Now

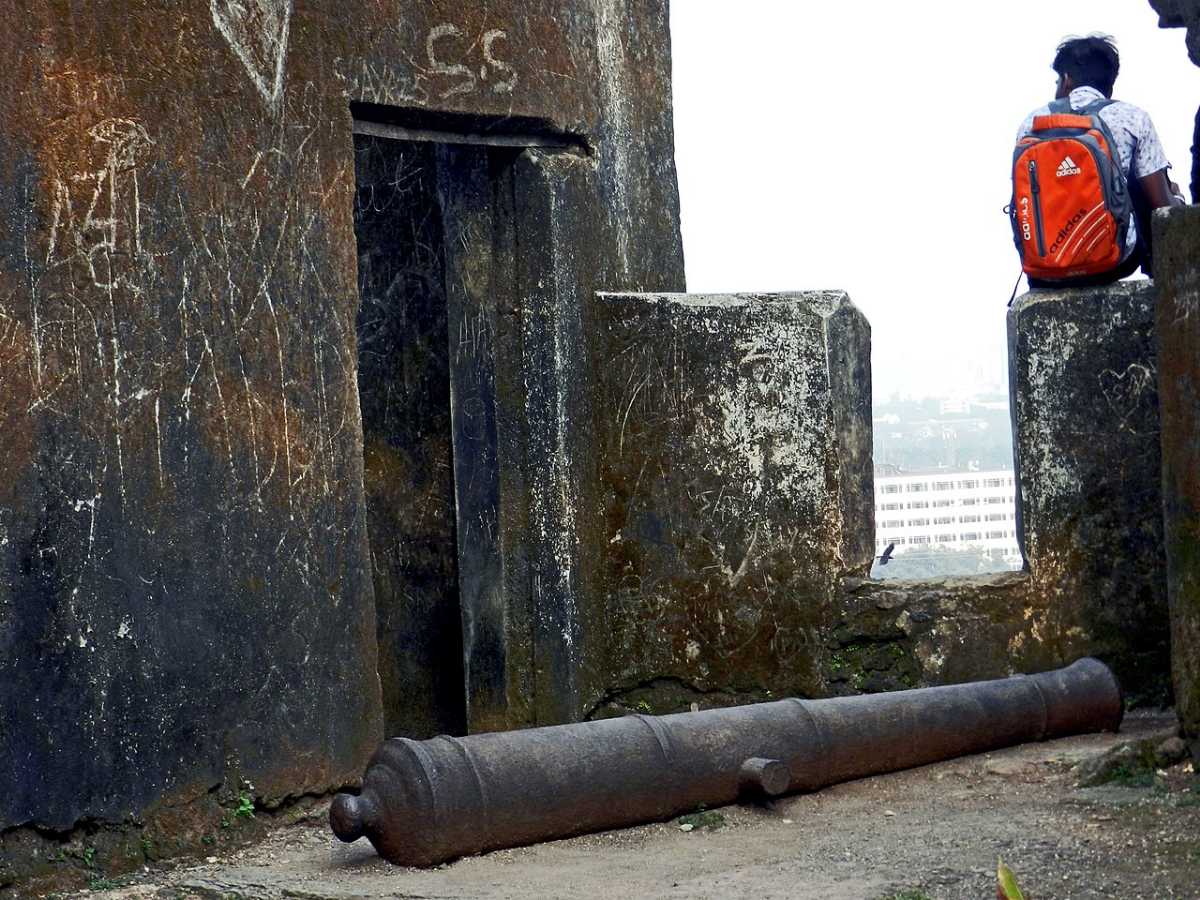
Attractions At Sion Fort

How to Reach The Fort
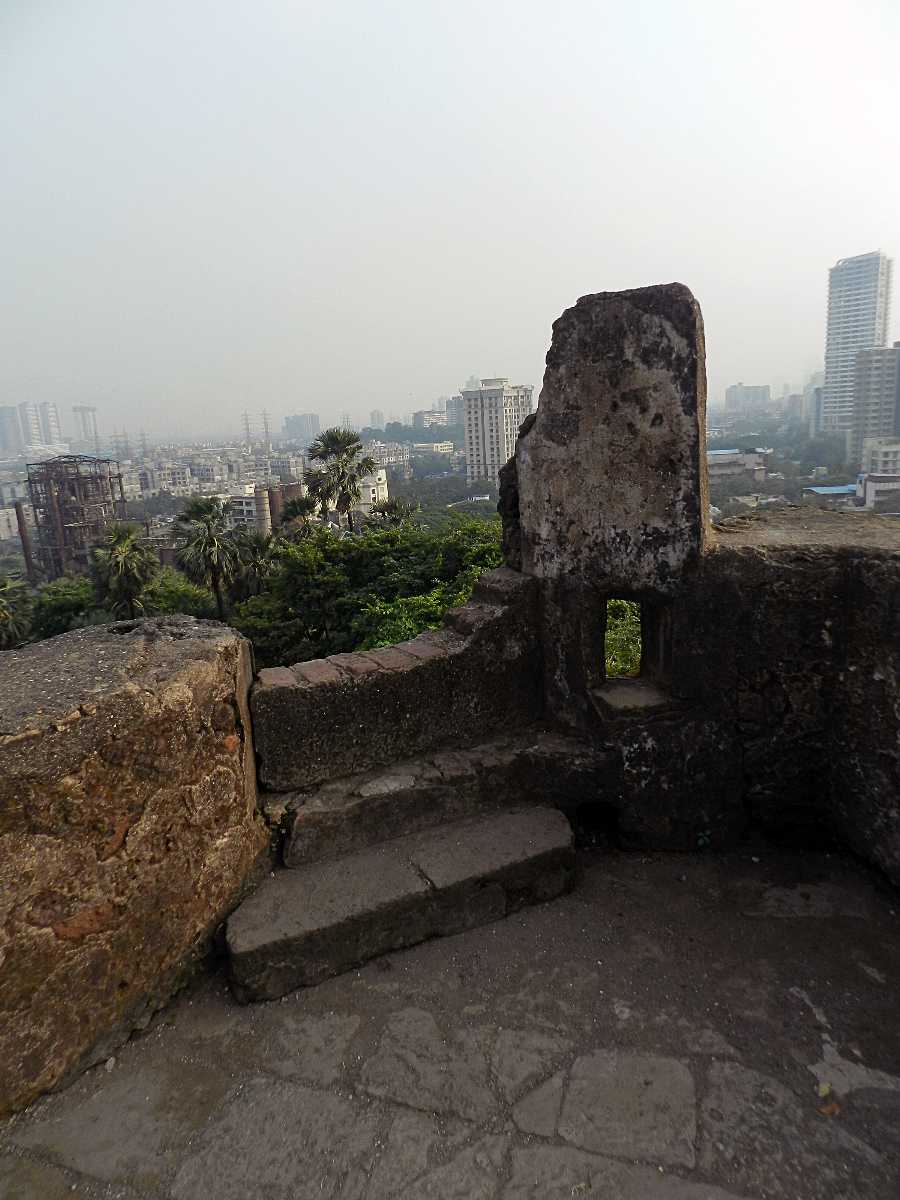

By Train: To get to Sion Fort, take a train to Sion railway station and then walk up to the fort. The distance from Sion railway station is about 7 kilometres. By Bus: You can take a bus from different points of the city to get to the fort. The bus lines which stop near the fort are 180, 22 LTD, 305, 348 LTD, 351, 354. Taxi: You can take a cab from anywhere in the city to get to the fort directly. It is a convenient way, but it is time-consuming considering heavy traffic.
This post was published by Sony Punjabi
Share this post on social media Facebook Twitter
Top Hotels In Mumbai
₹ 10,500 onwards
₹ 741 onwards
₹ 6,750 onwards
₹ 2,127 onwards
₹ 599 onwards
₹ 1,699 onwards
Related Articles

Experiences
Sassoon Docks Mumbai - A Walk Through The City's Oldest Dock Open to Public
Top 18 Places To Enjoy Live Music in Mumbai!
Golf Courses in Mumbai For A Hole-in-One Experience
Mumbai-Pune Hyperloop Fast Approaching!
Mumbai To Swank An Identical Bangkok-Style Aquarium Soon
After 24x7 Nightlife Policy, BMC Now Plans to Plant Food Trucks Across Mumbai!

Amazing Amusement Parks in Mumbai for a Fun-filled Day-out

Historical & Heritage
Forts in Mumbai
Treks in Mumbai For An Adventurous Wildlife Experience

This Train Will Change The Way Of Travelling Between Mumbai and Goa
12 Best Water Parks in Mumbai for a Summer Retreat

Art & Culture
Art Galleries in Mumbai - Where Art Comes Alive!

Sightseeing
Mumbai Darshan - Buses, Places, Packages and All You Need To Know

Mulling Over Malls in Mumbai? Check Out The List of Best Shopping Malls in Mumbai

Romantic & Honeymoon
Romantic Places In Mumbai - Perfect Places in Mumbai for Couples to have the Perfect Date!
Chota Kashmir - Aamchi Mumbai's Kashmir Connection

Travel Tips
Bike On Rent In Mumbai - Your Guide To Riding Out
Shopping in Mumbai - Best Places for Street Shopping in Mumbai
Ro-Ro Your Way from Mumbai To Alibaug In Less Than 30 Minutes!

Bike Rental In Mumbai - Best Operators, Prices & Documents Required

18 Best Places to Visit in Mumbai for Kids

Food & Drink
20 Cafes in Bandra That Are Perfect Hangout Spots In The City

Visiting Elephanta Caves with my Mother #TWC
From the Financial Capital to the National on Royal Enfield #TWC
Of the blue tiger and the flame of the forest : A travelogue
Cycling from Mumbai to Goa (Partially On A Solar Powered Bicycle)

Nightlife in Mumbai: 30 Best Places to Party the Night Away

The 83 Year Old Worli Sea-Face Walkway To Be Remade
Uber Sets Foot In The Sea: UberBOAT Services To Start In Mumbai From February 1st

Fairs & Festivals
Kala Ghoda Arts Festival 2024 - Dates, Venue, Events
Comments on this post
Browse hotel collections, by hotel type.
Best Hotels in Mumbai
Best Villas Near Mumbai
Best Beach Resorts in Mumbai
Homestays In Mumbai for a Pocket-Friendly Stay
Best Backpacker Hostels In Mumbai
Best Places To Stay In Mumbai for an Urban Retreat
Boutique Hotels in Mumbai
Heritage Hotels in Mumbai
Business Hotels In Mumbai That Are Perfect for a Business Outing
By Budget Category
Taj Hotels In Mumbai
Cheap Hotels In Mumbai
ITC Hotels In Mumbai
Best Luxury Hotels In Mumbai
Hotels In Ghatkopar
Lodges In Mumbai
By Star Category
Best 5 Star Hotels in Mumbai
3 Star Hotels In Mumbai
4-star Hotels in Mumbai
Cheapest 5-Star Hotels in Mumbai for a Pocket-Friendly Affluent Vacay
Best 5-Star Resorts in Mumbai for an Affluent Stay
With Specific Facilities
Mumbai Hotels Near Airport
Hotels In Bandra
Hotels In Andheri East
Hotels In Dadar
Hotels In Vashi
Hotels In Andheri West
Hotels In Bandra (West)
Hotels in Colaba
Hotels In Malad
Hotels In Mumbai Central
Hotels In Goregaon
Near Landmarks
Resorts Near Gorai Beach
Hotels Near Aksa Beach
Resorts Near Madh Island
Hotels Near Madh Island
Villas Near Gorai Beach
Hotels Near Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus
Hotels Near Lokhandwala Market
Hotels Near Palladium Mall
Hotels Near Worli Sea Face
Hotels Near Versova Beach
Hotels Near Powai Lake
For Special Purposes
Best Resorts Near Mumbai For An Urban Getaway
Best Resorts near Mumbai for Family
Pet Friendly Hotels In Mumbai
Best Wedding Resorts In Mumbai for a Big Fat Indian Wedding
Romantic Resorts near Mumbai
Workations in Mumbai
Top Places in Mumbai

Get the best offers on Travel Packages
Compare package quotes from top travel agents
- India (+91)
*Final prices will be shared by our partner agents based on your requirements.
Log in to your account
Welcome to holidify.
Forget Password?
Share this page
Mumbai's Most Iconic Architecture
Best Day Trips
Best Tours to Take
48 Hours in Mumbai
One Week in Mumbai
Best Restaurants
Nightlife in Mumbai
Best Time to Visit
Weather & Climate
Mumbai Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport G...
How to Ride the Mumbai Local Train
Places to Visit
Things to Do in Mumbai
Neighborhoods to Explore
Mumbai's Best Markets
14 Best Mumbai Markets for Shopping and Sightseeing
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/10947453_10153084623948270_8191342691038933499_o-591d1e8d3df78cf5fa731909.jpg)
Paul Harris/Getty Images
These days, Mumbai is known more for its designer shops and malls than its markets. However, if you're after a bargain, fabulous photo opportunities or some interesting souvenirs to take back home, you won't be disappointed. Check out these top Mumbai markets for the best shopping and sightseeing. Be warned though, that many of them are located in crowded areas that are difficult to navigate. If you think you may be daunted or overwhelmed, consider taking this guided Mumbai bazaar walking tour .
Interested in handicrafts? Also check out these top places buy Indian handicrafts in Mumbai.
Colaba Causeway
TripSavvy / Shraddha Gosavi
The everyday carnival of the Colaba Causeway market is a shopping experience like no other in Mumbai. Geared especially towards tourists, that infamous Indian saying of " sab kuch milega " (everything is possible) certainly applies at this market. Dodge persistent balloon and map sellers, as you meander along the sidewalk and peruse the stalls. Want your name written on a grain of rice? That's possible too. If you need a break from shopping, pop into Leopold's Cafe or Cafe Mondegar, two well known Mumbai hangouts.
- Location: Colaba Causeway, south Mumbai.
- Opening Hours: Daily from morning until night.
- What to Buy: Handicrafts, books, junk jewelry, crystals, brass items, incense, clothes.
Chor Bazaar
Vatsal Shah / TripSavvy
Chor Bazaar is nestled in the heart of Mumbai's main Muslim district. This iconic market has a history spanning more than 150 years. Its name means "thieves market", but this was derived from the British mispronunciation of the its original name of Shor Bazaar, "noisy market". Eventually stolen goods started finding their way into the market, resulting in it living up to its new name! Read more about Chor Bazaar and what's up for grabs.
- Location: Mutton Street, between SV Patel and Moulana Shaukat Ali Roads, near Mohammad Ali Road in south Mumbai.
- Opening Hours: Daily 11 a.m. until 7.30 p.m., except Friday. The Juma Market is held there on Fridays.
- What to Buy: Antiques, bronze items, vintage items, trash and treasure.
Crawford Market
Hectic Crawford Market (officially renamed Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Mandai) is an old-style market, housed in an historic colonial building. It specializes in wholesale fruit and vegetables but sells an array of other items, including imported food and toys. It's also got an entire section devoted to pets of all shapes, sizes and breeds.
- Location: Lokmanya Tilak Marg, Dhobi Talao, Fort area, south Mumbai. It's near Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (Victoria Terminus) railway station.
- Opening Hours: Daily from morning until night, except Sunday. Open mornings only on Sundays.
- What to Buy: Fruit, vegetables, spices, food, flowers, birds, fish, and other pets.
Zaveri Bazaar
Zaveri Bazaar, Mumbai's renowned gold market, is one of the oldest and largest gold markets in India. It accounts for more than half of the country's gold trade and has thousands of shops, some of which are centuries old. Many of the buildings look dilapidated and outdated but they're full of riches. Read up on how to buy gold in India and how to buy gemstones in India before going there. In addition, be aware that some shops do sell fake items.
- Location: Between Crawford Market and Mumbadevi temple. From Crawford Market, walk along Sheik Memon Street leading to Jama Masjid.
- Opening Hours: Daily from morning until night, except Sundays.
- What to Buy: Indian-style gold, platinum and diamond jewelry. Silver and imitation jewelry are also available.
Mangaldas Market and Mulji Jetha Market
If you're after cloth by the meter or un-stitched dress material to make Indian outfits, Mangaldas Market and Mulji Jetha Market (also called M.J. Market) are where you should head. Located close to each other, these sprawling wholesale markets are among the largest textile markets in Asia. Rows and rows of stalls are filled to the brim with a diverse assortment of fabrics, from bling to block prints!
- Location: Near Zaveri Bazaar, Kalbadevi, south Mumbai. Also in this area is the iconic Mumbadevi temple , which the city was named after.
- Opening Hours: Daily from 11 a.m. until 8 p.m., except Sundays.
- What to Buy: Textiles and shawls.
The area around C.P. Tank (Cawasji Patel Tank) is notable for its exquisite bangles. Try TipTop Point for something special. If you want bangles to go with a sari or other outfit, be sure to bring it with you so the seller can match the colors perfectly.
- Location: Bhuleshwar Road, Bhuleshwar, south Mumbai. It's northwest of Mumbadevi temple. You may also wish to visit Bombay Panjrapole cow shelter, which is tucked away in this area.
- What to Buy: Bangles and imitation jewelry.
Kala Ghoda Art Plaza Pavement Gallery
The leafy pavement on either side of the Jehangir Art Gallery in Mumbai's Kala Ghoda (Black Horse) Arts Precinct is bordered with the works of promising young artists, who gather there to exhibit and sell them. The great thing about the Kala Ghoda pavement gallery is that you can interact with the artists to learn about their techniques, and even see them in action.
- Location: MG Road, Fort, south Mumbai.
- Opening Hours: Daily from around 11 a.m. until 7 p.m.
- What to Buy: Everything from portraits to religious paintings.
Book Street
Dan Herrick/Getty Images
Love reading? Don't miss visiting Book Street, as it's fondly called by locals, where street vendors pile new and secondhand books along the pavement. There's everything from academic texts to poetry, including rare publications and commercial paperback novels. The vendors are very knowledgeable and well-informed too. Don't be afraid to ask them if you have certain interests or favorite authors. A lot of the books are sourced from bookstores that want to get rid of old stock, so they're bargain priced.
- Location: Between Flora Fountain and Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (Victoria Terminus) railway station, Fort, south Mumbai.
- Opening Hours: 10 a.m. to 8.30 p.m.
- What to Buy: Books.
Sassoon Docks Fish Market
TripSavvy / Ivey Redding
If you don't mind getting up really early, Sassoon Docks is a fascinating place to experience local life in the morning when fishing trawlers return and get unloaded. Mumbai's indigenous fishing community, the Kolis , were the original inhabitants of the city long before it was developed. About 1,500 trawlers operate from the docks and they bring in about 20 tonnes of fish daily! It's sold in spirited wholesale fish auctions. This No Footprints' Mumbai by Dawn tour is highly recommended and includes the fish market.
- Location: Azad Nagar, Colaba, south Mumbai. Follow Colaba Causeway (Shahid Bhagat Singh Road) and you'll come across it.
- Opening Hours: From about 5 a.m. to 9.30 a.m.
- What to Buy: Fish.
Dadar Flower Market
Another attraction for early risers and an important part of Mumbai's infrastructure , Dadar flower market is the largest wholesale flower market in the city. Its hundreds of stalls sell flowers to local street vendors who use them to make garlands used in worship, as well as to wedding decorators and event managers. The market comes alive before sunrise when delivery trucks from all over the state arrive laden with an abundance of beautiful blooms. Mumbai Magic includes Dadar flower market on this Good Morning Mumbai tour.
- Location: Next to Dadar railway station. Tulsi Pipe Road, between Dadar and Parel, in central south Mumbai.
- Opening Hours: Most of the action happens from about 4 a.m. to 9 a.m., although the market is open all day. It's particularly busy during festivals, especially Dussehra.
- What to Buy: Fresh flowers.
Lalbaug Market
Plump sacks of dried red chilies line Mirchi Galli (chili lane) in Lalbaug Market. Unlike Crawford Market, which is frequented by foreign tourists, this market provides an authentic local atmosphere. Sheets of chilies can also be seen drying in the street under the sun. Try the fiery Guntur Sannam from Andhra Pradesh if you don't mind a lot of burn. You can choose your own spices and have them freshly roasted, ground and mixed into a customized blend. Be prepared to sneeze during the process though! Khamkar Spices has been in business since 1933 and is popular. Perpendicular lanes sell Maharashtrian chivda snacks and pickles.
- Location: Under the Lalbaug flyover, Dinshaw Petit Road, Lalbaug, central south Mumbai. It's a short distance south of Dadar flower market.
- Opening Hours: 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. except for Mondays (closed).
- What to Buy: Spices from all over India.
Linking Road
A fusion of modern and traditional, and East meets West, in one of Mumbai's hippest suburbs. Here streets stalls contrast with brand name shops, and you'll find a local Indian roadside food vendor on one side of the road and a Kentucky Fried Chicken outlet on the other. The street stalls tend to be grouped together according to the type of goods they sell. If you visit this market on a Sunday, be prepared for the crowds! See what's up for grabs on Linking Road .
- Location: Linking Road, Bandra West (starts from Waterfield Road intersection).
- Opening Hours: Daily from 10 a.m. until 10 p.m.
- What to Buy: Indian traditional clothes, children's clothes, shoes, bags, belts, fashion accessories.
Dharavi Leather Market
A lot of people automatically associate Mumbai's notorious Dharavi slum with poverty and misery. However, this is actually very ignorant and insulting. While the conditions are poor, Dharavi is in fact home to many flourishing small-scale industries . The leather industry is the most dominant. It's the second largest of its kind in India and it exports across the world. Quality genuine leather goods can be purchased from more than 200 shops at Dharavi and the prices are attractive. High Design is a leading store. Do bargain to get the best price.
- Location: 90 Feet Road and adjoining Sion-Bandra Link Road, Dharavi, Sion, central Mumbai.
- Opening Hours: Daily from 11 a.m. to 9 p.m.
- What to Buy: Leather jackets, bags, backpacks, wallets, belts, shoes.
Fashion Street
Fashion Street is literally just that -- a street lined with fashion! There are about 150 stalls there. The market mainly attracts teenagers and college students, who come to grab the latest western clothes and fake brand names at cheap prices.
- Location: MG Road, south Mumbai. Near Metro Cinema and Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (Victoria Terminus) railway station, opposite Azad Maidan.
- What to Buy: Clothes, shoes, belts.
Top 12 Attractions and Places to Visit in Mumbai
101 Places to Visit in Mumbai
One Week in Mumbai: The Perfect Itinerary
Top 18 Things to Do in Mumbai
15 Best Mumbai Tours to Really Get to Know the City
11 Free Things to Do in India
Top 15 Markets in Delhi and What You Can Buy
Essential Guide to Walking Tours in India
48 Hours in Mumbai: The Perfect Itinerary
9 Best Luxury Day Spas in Mumbai to Relax and Rejuvenate
One Week in Delhi: The Perfect Itinerary
18 Best Places to Visit in Kolkata to Discover the City
The 9 Top Things to Do in Mumbai's Fort Neighborhood
Mumbai's Kala Ghoda Art Precinct: Self-Guided Walking Tour
Mumbai Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport Guide
How to Travel From Mumbai to Goa by Train, Bus, Plane, and Car
types of interviews in research guide and examples
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Types of Interviews in Research and Methods

There are more types of interviews than most people think. An interview is generally a qualitative research technique that involves asking open-ended questions to converse with respondents and collect elicit data about a subject.
The interviewer, in most cases, is the subject matter expert who intends to understand respondent opinions in a well-planned and executed series of star questions and answers .
Interviews are similar to focus groups and surveys for garnering information from the target market but are entirely different in their operation – focus groups are restricted to a small group of 6-10 individuals, whereas surveys are quantitative.
Interviews are conducted with a sample from a population, and the key characteristic they exhibit is their conversational tone.
LEARN ABOUT: telephone survey
Content Index
What is An Interview?
Fundamental types of interviews in research, other types of interviews.
- Methods of Research Interviews
What to Avoid in Different Types of Interviews
- Interview-Related Questions
An interview is a way to get information from a person by asking questions and hearing their answers.
An interview is a question-and-answer session where one person asks questions, and the other person answers those questions. It can be a one-on-one, two-way conversation, or there can be more than one interviewer and more than one participant.
The interview is the most important part of the whole selection bias process. It is used to decide if a person should be interviewed further, hired, or taken out of consideration. It is the main way to learn more about applicants and the basis for judging their job-related knowledge, research skills , and abilities.
A researcher has to conduct interviews with a group of participants at a juncture in the research where information can only be obtained by meeting and personally connecting with a section of their target audience. Interviews offer the researchers a platform to prompt their participants and obtain inputs in the desired detail. There are three fundamental types of interviews in research:
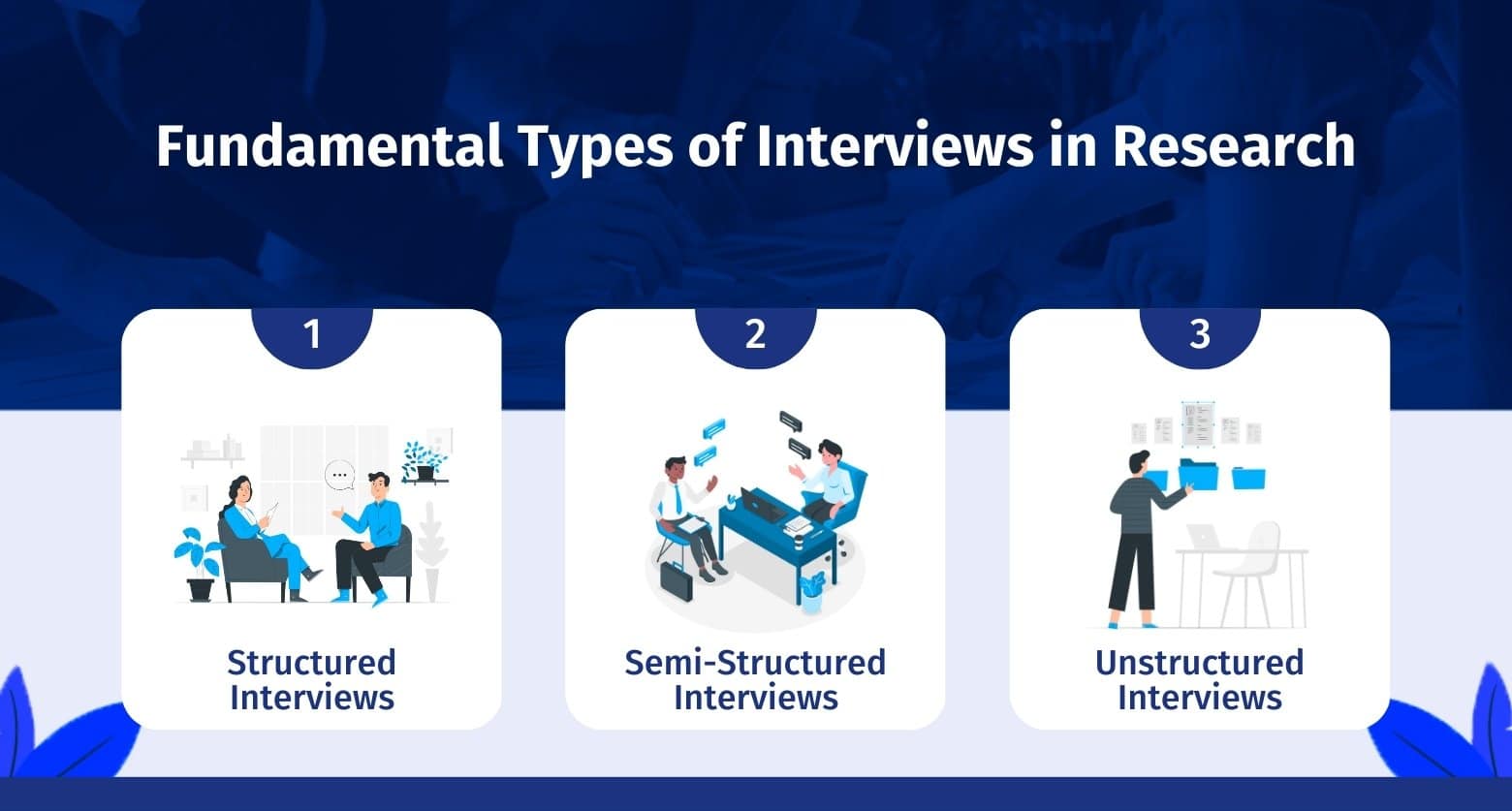
1. Structured Interviews:
Structured interviews are defined as research tools that could be more flexible in their operations are allow more or no scope of prompting the participants to obtain and analyze results. It is thus also known as a standardized interview and is significantly quantitative in its approach.
Questions in this interview are pre-decided according to the required detail of information. This can be used in a focus group interview and an in-person interview.
These interviews are excessively used in survey research with the intention of maintaining uniformity throughout all the interview sessions.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
They can be closed-ended and open-ended – according to the type of target population. Closed-ended questions can be included to understand user preferences from a collection of answer options. In contrast, open-ended ones can be included to gain details about a particular section in the interview.
Example of a structured interview question:
Here’s an example of a structured question for a job interview for a customer service job:
- Can you talk about what it was like to work in customer service?
- How do you deal with an angry or upset customer?
- How do you ensure that the information you give customers is correct?
- Tell us about when you went out of your way to help a customer.
- How do you handle a lot of customers or tasks at once?
- Can you talk about how you’ve used software or tools for customer service?
- How do you set priorities and use your time well while giving good customer service?
- Can you tell us about when you had to get a customer to calm down?
- How do you deal with a customer who wants something that goes against your company’s rules?
- Tell me about a time when you had to deal with a hard customer or coworker.
Advantages of structured interviews:
- It focuses on the accuracy of different responses, due to which extremely organized data can be collected. Different respondents have different types of answers to the same structure of questions – answers obtained can be collectively analyzed.
- They can be used to get in touch with a large sample of the target population.
- The interview procedure is made easy due to the standardization offered by it.
- Replication across multiple samples becomes easy due to the same structure of the interview.
- As the scope of detail is already considered while designing the interview questions, better information can be obtained. The researcher can analyze the research problem comprehensively by asking accurate research questions .
- Since the structure of the interview is fixed, it often generates reliable results and is quick to execute.
- The relationship between the researcher and the respondent is not formal, due to which the researcher can clearly understand the margin of error in case the respondent either degree to be a part of the survey or is just not interested in providing the right information.
Disadvantages of structured interviews:
- The limited scope of assessment of obtained results.
- The accuracy of information overpowers the detail of information.
- Respondents are forced to select from the provided answer options.
- The researcher is expected to always adhere to the list of decided questions, irrespective of how interesting the conversation is turning out to be with the participants.
- A significant amount of time is required for a structured interview.
Learn more: Market Research
2. Semi-Structured Types of Interviews:
Semi-structured interviews offer a considerable amount of leeway to the researcher to probe the respondents, along with maintaining a basic interview structure. Even if it is a guided conversation between researchers and interviewees – appreciable flexibility is offered to the researchers. A researcher can be assured that multiple interview rounds will not be required in the presence of structure in this type of research interview.
Keeping the structure in mind, the researcher can follow any idea or take creative advantage of the entire interview. Additional respondent probing is always necessary to garner information for a research study. The best application of semi-structured interviews is when the researcher doesn’t have time to conduct research and requires detailed information about the topic.
Example of a semi-structured interview question:
Here’s an example of a semi-structured marketing job interviews question:
- Can you tell us about the marketing work you’ve done?
- What do you think are the most important parts of a marketing campaign that works?
- Tell me about a campaign you worked on that you’re very proud of.
- How do you do research on the market and look at data to help you make marketing decisions?
- Can you tell us about a time when you had to change your marketing plan because of something that didn’t go as planned?
- How do you figure out if a marketing campaign worked?
- Can you talk about how you’ve used social media to market?
- How do you ensure your marketing message gets through to the people you want to hear it?
- Can you tell us about a time when you had to run a marketing campaign on a small budget?
- How do you keep up with changes and trends in marketing?
Advantages of semi-structured interviews:
- Questions from semi-structured interview questions are prepared before the scheduled interview, giving the researcher time to prepare and analyze the questions.
- It is flexible to an extent while maintaining the research guidelines.
- Unlike a structured interview, researchers can express the interview questions in the preferred format.
- Reliable qualitative data can be collected via these interviews.
- The flexible structure of the interview.
Learn more: Quantitative Data
Disadvantages of semi-structured interviews:
- Participants may question the reliability factor of these interviews due to the flexibility offered.
- Comparing two different answers becomes difficult as the guideline for conducting interviews is not entirely followed. No two questions will have the exact same structure, and the result will be an inability to compare are infer results.
3. Unstructured Interviews:
Also called in-depth interviews , unstructured interviews are usually described as conversations held with a purpose in mind – to gather data about the research study. These interviews have the least number of questions as they lean more towards a normal conversation but with an underlying subject.
The main objective of most researchers using unstructured interviews is to build a bond with the respondents, due to which there is a high chance that the respondents will be 100% truthful with their answers. There are no guidelines for the researchers to follow. So they can approach the participants ethically to gain as much information as possible about their research topic.
Since there are no guidelines for these interviews, a researcher is expected to keep their approach in check so that the respondents do not sway away from the main research motive.
For a researcher to obtain the desired outcome, he/she must keep the following factors in mind:
- The intent of the interview.
- The interview should primarily take into consideration the participant’s interests and skills.
- All the conversations should be conducted within the permissible limits of research, and the researcher should try and stick by these limits.
- The researcher’s skills and knowledge should match the interview’s purpose.
- Researchers should understand the dos and don’ts of it.
Example of an unstructured interview question:
Here’s an example of a question asked in an unstructured interview:
- Can you tell me about when you had to deal with something hard and how you did it?
- What are some of the things you’re most proud of, and what did you learn from them?
- How do you deal with ambiguity or not knowing what to do at work?
- Can you describe how you lead and how you get your team going?
- Tell me about a time when you had to take a chance and how it turned out.
- What do you think are the most important qualities for success in this role?
- How do you deal with setbacks or failures, and what do you learn from them?
- Can you tell me about a time when you had to solve a problem by thinking outside the box?
- What do you think makes you different from the other people who want this job?
- Can you tell me about a time when you had to make a hard choice and how you made that choice?
Advantages of Unstructured Interviews:
- Due to this type of interview’s informal nature, it becomes extremely easy for researchers to try and develop a friendly rapport with the participants. This leads to gaining insights in extreme detail without much conscious effort.
- The participants can clarify all their doubts about the questions, and the researcher can take each opportunity to explain his/her intention for better answers.
- There are no questions that the researcher has to abide by, and this usually increases the flexibility of the entire research process.
Disadvantages of Unstructured Interviews:
- Researchers take time to execute these interviews because there is no structure to the interview process.
- The absence of a standardized set of questions and guidelines indicates that its reliability of it is questionable.
- The ethics involved in these interviews are often considered borderline upsetting.
Learn more: Qualitative Market Research & Qualitative Data Collection
Besides the 3 basic interview types, we have already mentioned there are more. Here are some other interview types that are commonly used in a job interview:
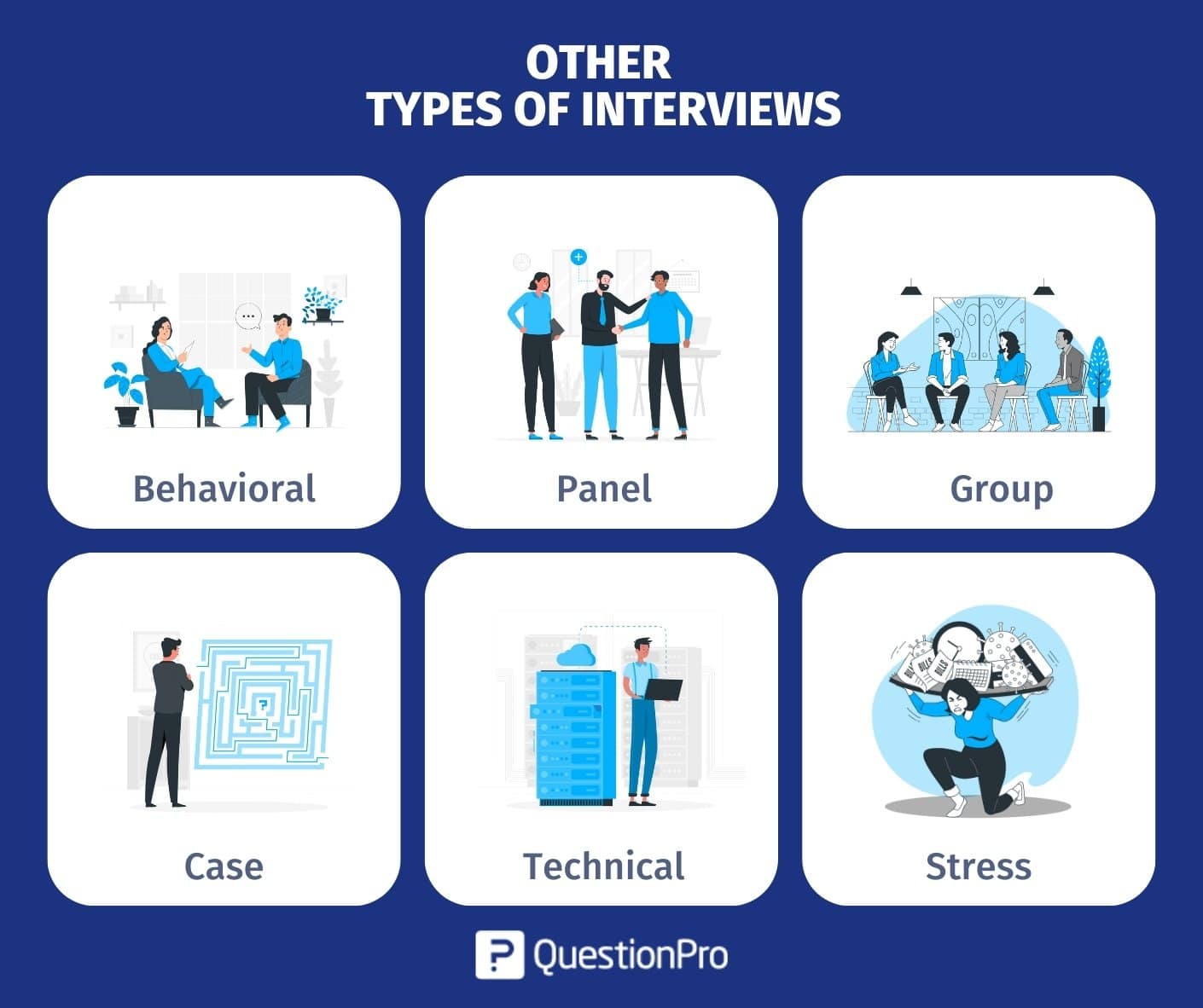
Behavioral Interview
During this type of interview, candidates are asked to give specific examples of how they have acted in the past. The idea behind this kind of interview is that what someone did in the past can be a sign of how they will act in the future. And by this interview, the company can also understand the interviewee’s behavior through body language.
Panel Interview
During a panel interview, three or more interviewers usually ask questions and evaluate the candidate’s answers as a group. This is a good way to get a full picture of a candidate’s skills and suitability for the job.
Group Types of Interviews
Multiple people are interviewed at the same time in group interviews. This form of interview often focus groups that are utilized on entry-level positions or employment in customer service to examine how well candidates get along with others and function as a team.
Case Interview
During a case interview, candidates are given a business problem or scenario and asked to think about how to solve it. In the consulting and finance fields, this kind of interview is common.
Technical Interview
A candidate’s technical skills and knowledge are tested during a technical interview, usually in fields like engineering or software development. Most of the time, candidates are asked to solve problems or complete technical tasks.
Stress Interview
During a stress interview, candidates are put under pressure or asked difficult or confrontational questions on purpose to see how they react in stressful situations. This kind of interview is used to see how well a candidate can deal with stress and hard situations.
Methods of Research Interviews:
There are four methods to conduct research interviews, each of which is peculiar in its application and can be used according to the research study requirement.
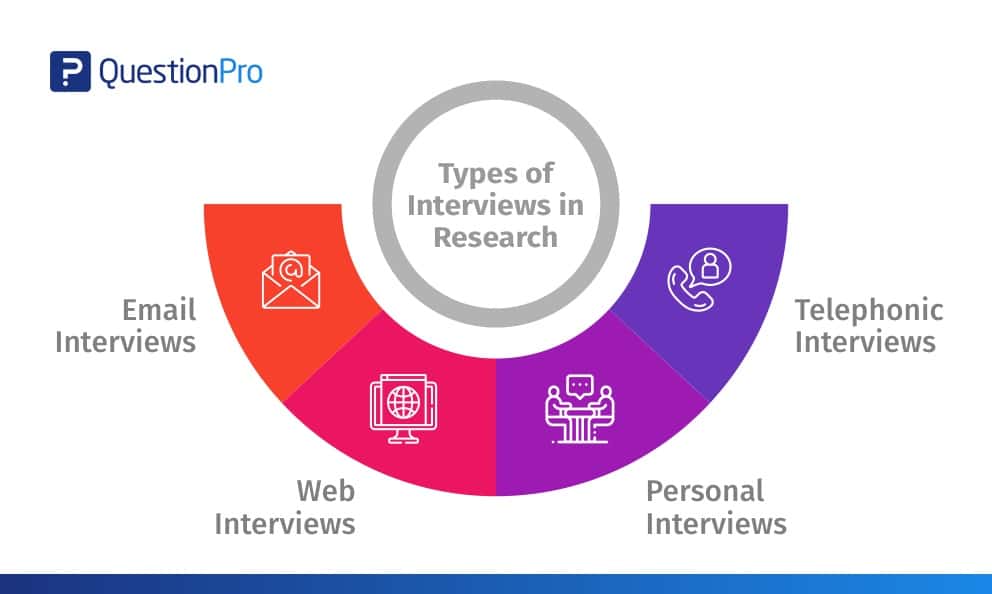
Personal Interviews:
Personal interviews are one of the most used types of interviews, where the questions are asked personally directly to the respondent as a form of an individual interview. One of the many in-person interviews is a lunch interview, which is frequently better suited for casual inquiries and discussions.
For this, a researcher can have a guide to online surveys to take note of the answers. A researcher can design his/her survey in such a way that they take notes of the comments or points of view that stands out from the interviewee. It can be a one-on-one interview as well.
- Higher response rate.
- When the interviewees and respondents are face-to-face, there is a way to adapt the questions if this is not understood.
- More complete answers can be obtained if there is doubt on both sides or a remarkable piece of information is detected.
- The researcher has an opportunity to detect and analyze the interviewee’s body language at the time of asking the questions and taking notes about it.
Disadvantages:
- They are time-consuming and extremely expensive.
- They can generate distrust on the part of the interviewee since they may be self-conscious and not answer truthfully.
- Contacting the interviewees can be a real headache, either scheduling an appointment in workplaces or going from house to house and not finding anyone.
- Therefore, many interviews are conducted in public places like shopping centers or parks. Even consumer studies take advantage of these sites to conduct interviews or surveys and give incentives, gifts, and coupons. In short, There are great opportunities for online research in shopping centers.
- Among the advantages of conducting such types of interviews is that the respondents will have more fresh information if the interview is conducted in the context and with the appropriate stimuli so that researchers can have data from their experience at the scene of the events immediately and first hand. The interviewer can use an online survey through a mobile device that will undoubtedly facilitate the entire process.
Telephonic Type of Interviews:
Phonic interviews are widely used and easily combined with online surveys to conduct research effectively.
Advantages:
- To find the interviewees, it is enough to have their phone numbers on hand.
- They are usually lower cost.
- The information is collected quickly.
- Having a personal contact can also clarify doubts or give more details of the questions.
- Many times researchers observe that people do not answer phone calls because it is an unknown number for the respondent or simply already changed their place of residence and they cannot locate it, which causes a bias in the interview.
- Researchers also face that they simply do not want to answer and resort to pretexts such as they are busy to answer, they are sick, they do not have the authority to answer the questions asked, they have no interest in answering, or they are afraid of putting their security at risk.
- One of the aspects that should be taken care of in these types of interviews is the kindness with which the interviewers address the respondents in order to get them to cooperate more easily with their answers. Good communication is vital for the generation of better answers.
Email or Web Page Types of Interviews:
Online research is growing more and more because consumers are migrating to a more virtual world, and it is best for each researcher to adapt to this change.
The increase in people with Internet access has made it popular that interviews via email or web page stand out among the types of interviews most used today. For this nothing better than an online survey.
More and more consumers are turning to online shopping, which is why they are a great niche to be able to carry out an interview that will generate information for the correct decision-making.
Advantages of email surveys:
- Speed in obtaining data
- The respondents respond according to their time, when they want, and where they decide.
- Online surveys can be mixed with other research methods or using some of the previous interview models. They are tools that can perfectly complement and pay for the project.
- A researcher can use a variety of questions and logic to create graphs and reports immediately.
Disadvantages of email survey:
- Low response rates
- Limited access to certain populations
- Potential for spam filters
- Lack of personal touch
Try not to do any of the following things when you’re in an interview:
- Don’t blame your previous managers, coworkers, or companies. This will make a bad impression on the interviewer and show that you are not accountable.
- Do not go to the interview without knowing anything about the company you are interviewing for. Interviewers will think you don’t care about learning about the company if you don’t know anything.
- Don’t fidget with things because that shows you lack self-confidence and focus.
- Stop checking the time because it shows that you have something more important to do and that you don’t give the interview much importance.
Related Questions of Interviews
After the interview is over, you might also get a chance to ask some questions. You should make the most of this chance to learn useful things from the interviewer. Based on what you’ve learned, you can then decide if the company and the job are a good fit for you. You can ask the interviewer questions about the company or about the job role.
Here are some common but important questions to ask in an interview:
- What do you anticipate from team members in this role?
- What does a typical day look like for an employee in this role?
- What qualities are essential for success in this position?
- How is success measured for this position?
- How does this job profile relate to the organization’s overarching objectives?
- What are your company’s guiding principles?
- Which departments will I work closely with throughout my time in this profile?
Learn more: Quantitative Research
To summarize the discussion, an effective interview will be one that provides researchers with the necessary data to know the object of study and that this information is applicable to the decisions researchers make.
Undoubtedly, the objective of the research will set the pattern of what types of interviews are best for data collection. Based on the research design , a researcher can plan and test the questions, for instance, if the questions are correct and if the survey flows in the best way.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
In addition, other types of research can be used under specific circumstances.
For example, there are no connections or adverse situations to carry out surveyors. In these types of occasions, it is necessary to conduct field research, which can not be considered an interview if not rather a completely different methodology.
QuestionPro is a flexible online survey platform that can help researchers do different kinds of interviews, like structured, semi-structured, unstructured, phone interview, group interview, etc. It gives researchers a flexible platform that can be changed to fit their needs and the needs of their research project.
QuestionPro can help researchers get detailed and useful information from participants using features like skip logic, piping, and live chat. Also, the platform is easy to use and get to, making it a useful tool for researchers to use in their work.
LEARN ABOUT: Candidate Experience Survey
Overall, QuestionPro can be helpful for researchers who want to do good interviews and collect good project data.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
The 3 main types of interviews are 1. Structured interviews 2. Semi-structured interviews 3. Unstructured interviews
There are different ways to conduct an interview, and each one can add depth and substance to the information the interviewer gathers by asking questions. We discuss four interview methods: situational, professional behavior profiling, stress, and behavioral.
Face-to-face means in-person interviews are the most common type of interview. It’s about getting a good sense of the candidate by focusing on them directly. But it also allows the person interviewed to talk freely and ask questions.
Personal interviews, phone interviews, email or web page interviews, and a combination of these methods are the four types of research interviews.
MORE LIKE THIS

9 Best Word Cloud Generator Uses, Pros & Cons
Mar 15, 2024

Top 8 Best Digital Experience Platforms in 2024

Top 10 Patient Experience Software to Shape Modern Healthcare
Mar 14, 2024

Email List Building Tool: Choose The Best From These 9 Tools
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Chapter 11. Interviewing
Introduction.
Interviewing people is at the heart of qualitative research. It is not merely a way to collect data but an intrinsically rewarding activity—an interaction between two people that holds the potential for greater understanding and interpersonal development. Unlike many of our daily interactions with others that are fairly shallow and mundane, sitting down with a person for an hour or two and really listening to what they have to say is a profound and deep enterprise, one that can provide not only “data” for you, the interviewer, but also self-understanding and a feeling of being heard for the interviewee. I always approach interviewing with a deep appreciation for the opportunity it gives me to understand how other people experience the world. That said, there is not one kind of interview but many, and some of these are shallower than others. This chapter will provide you with an overview of interview techniques but with a special focus on the in-depth semistructured interview guide approach, which is the approach most widely used in social science research.
An interview can be variously defined as “a conversation with a purpose” ( Lune and Berg 2018 ) and an attempt to understand the world from the point of view of the person being interviewed: “to unfold the meaning of peoples’ experiences, to uncover their lived world prior to scientific explanations” ( Kvale 2007 ). It is a form of active listening in which the interviewer steers the conversation to subjects and topics of interest to their research but also manages to leave enough space for those interviewed to say surprising things. Achieving that balance is a tricky thing, which is why most practitioners believe interviewing is both an art and a science. In my experience as a teacher, there are some students who are “natural” interviewers (often they are introverts), but anyone can learn to conduct interviews, and everyone, even those of us who have been doing this for years, can improve their interviewing skills. This might be a good time to highlight the fact that the interview is a product between interviewer and interviewee and that this product is only as good as the rapport established between the two participants. Active listening is the key to establishing this necessary rapport.
Patton ( 2002 ) makes the argument that we use interviews because there are certain things that are not observable. In particular, “we cannot observe feelings, thoughts, and intentions. We cannot observe behaviors that took place at some previous point in time. We cannot observe situations that preclude the presence of an observer. We cannot observe how people have organized the world and the meanings they attach to what goes on in the world. We have to ask people questions about those things” ( 341 ).
Types of Interviews
There are several distinct types of interviews. Imagine a continuum (figure 11.1). On one side are unstructured conversations—the kind you have with your friends. No one is in control of those conversations, and what you talk about is often random—whatever pops into your head. There is no secret, underlying purpose to your talking—if anything, the purpose is to talk to and engage with each other, and the words you use and the things you talk about are a little beside the point. An unstructured interview is a little like this informal conversation, except that one of the parties to the conversation (you, the researcher) does have an underlying purpose, and that is to understand the other person. You are not friends speaking for no purpose, but it might feel just as unstructured to the “interviewee” in this scenario. That is one side of the continuum. On the other side are fully structured and standardized survey-type questions asked face-to-face. Here it is very clear who is asking the questions and who is answering them. This doesn’t feel like a conversation at all! A lot of people new to interviewing have this ( erroneously !) in mind when they think about interviews as data collection. Somewhere in the middle of these two extreme cases is the “ semistructured” interview , in which the researcher uses an “interview guide” to gently move the conversation to certain topics and issues. This is the primary form of interviewing for qualitative social scientists and will be what I refer to as interviewing for the rest of this chapter, unless otherwise specified.
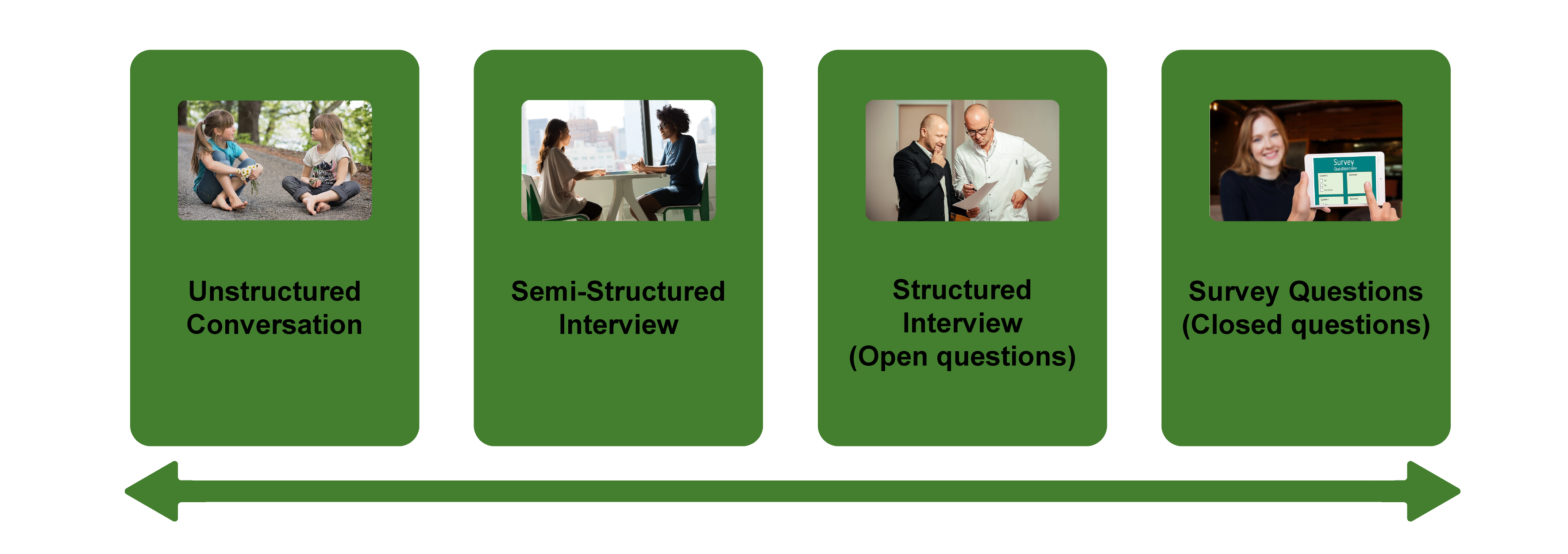
Informal (unstructured conversations). This is the most “open-ended” approach to interviewing. It is particularly useful in conjunction with observational methods (see chapters 13 and 14). There are no predetermined questions. Each interview will be different. Imagine you are researching the Oregon Country Fair, an annual event in Veneta, Oregon, that includes live music, artisan craft booths, face painting, and a lot of people walking through forest paths. It’s unlikely that you will be able to get a person to sit down with you and talk intensely about a set of questions for an hour and a half. But you might be able to sidle up to several people and engage with them about their experiences at the fair. You might have a general interest in what attracts people to these events, so you could start a conversation by asking strangers why they are here or why they come back every year. That’s it. Then you have a conversation that may lead you anywhere. Maybe one person tells a long story about how their parents brought them here when they were a kid. A second person talks about how this is better than Burning Man. A third person shares their favorite traveling band. And yet another enthuses about the public library in the woods. During your conversations, you also talk about a lot of other things—the weather, the utilikilts for sale, the fact that a favorite food booth has disappeared. It’s all good. You may not be able to record these conversations. Instead, you might jot down notes on the spot and then, when you have the time, write down as much as you can remember about the conversations in long fieldnotes. Later, you will have to sit down with these fieldnotes and try to make sense of all the information (see chapters 18 and 19).
Interview guide ( semistructured interview ). This is the primary type employed by social science qualitative researchers. The researcher creates an “interview guide” in advance, which she uses in every interview. In theory, every person interviewed is asked the same questions. In practice, every person interviewed is asked mostly the same topics but not always the same questions, as the whole point of a “guide” is that it guides the direction of the conversation but does not command it. The guide is typically between five and ten questions or question areas, sometimes with suggested follow-ups or prompts . For example, one question might be “What was it like growing up in Eastern Oregon?” with prompts such as “Did you live in a rural area? What kind of high school did you attend?” to help the conversation develop. These interviews generally take place in a quiet place (not a busy walkway during a festival) and are recorded. The recordings are transcribed, and those transcriptions then become the “data” that is analyzed (see chapters 18 and 19). The conventional length of one of these types of interviews is between one hour and two hours, optimally ninety minutes. Less than one hour doesn’t allow for much development of questions and thoughts, and two hours (or more) is a lot of time to ask someone to sit still and answer questions. If you have a lot of ground to cover, and the person is willing, I highly recommend two separate interview sessions, with the second session being slightly shorter than the first (e.g., ninety minutes the first day, sixty minutes the second). There are lots of good reasons for this, but the most compelling one is that this allows you to listen to the first day’s recording and catch anything interesting you might have missed in the moment and so develop follow-up questions that can probe further. This also allows the person being interviewed to have some time to think about the issues raised in the interview and go a little deeper with their answers.
Standardized questionnaire with open responses ( structured interview ). This is the type of interview a lot of people have in mind when they hear “interview”: a researcher comes to your door with a clipboard and proceeds to ask you a series of questions. These questions are all the same whoever answers the door; they are “standardized.” Both the wording and the exact order are important, as people’s responses may vary depending on how and when a question is asked. These are qualitative only in that the questions allow for “open-ended responses”: people can say whatever they want rather than select from a predetermined menu of responses. For example, a survey I collaborated on included this open-ended response question: “How does class affect one’s career success in sociology?” Some of the answers were simply one word long (e.g., “debt”), and others were long statements with stories and personal anecdotes. It is possible to be surprised by the responses. Although it’s a stretch to call this kind of questioning a conversation, it does allow the person answering the question some degree of freedom in how they answer.
Survey questionnaire with closed responses (not an interview!). Standardized survey questions with specific answer options (e.g., closed responses) are not really interviews at all, and they do not generate qualitative data. For example, if we included five options for the question “How does class affect one’s career success in sociology?”—(1) debt, (2) social networks, (3) alienation, (4) family doesn’t understand, (5) type of grad program—we leave no room for surprises at all. Instead, we would most likely look at patterns around these responses, thinking quantitatively rather than qualitatively (e.g., using regression analysis techniques, we might find that working-class sociologists were twice as likely to bring up alienation). It can sometimes be confusing for new students because the very same survey can include both closed-ended and open-ended questions. The key is to think about how these will be analyzed and to what level surprises are possible. If your plan is to turn all responses into a number and make predictions about correlations and relationships, you are no longer conducting qualitative research. This is true even if you are conducting this survey face-to-face with a real live human. Closed-response questions are not conversations of any kind, purposeful or not.
In summary, the semistructured interview guide approach is the predominant form of interviewing for social science qualitative researchers because it allows a high degree of freedom of responses from those interviewed (thus allowing for novel discoveries) while still maintaining some connection to a research question area or topic of interest. The rest of the chapter assumes the employment of this form.
Creating an Interview Guide
Your interview guide is the instrument used to bridge your research question(s) and what the people you are interviewing want to tell you. Unlike a standardized questionnaire, the questions actually asked do not need to be exactly what you have written down in your guide. The guide is meant to create space for those you are interviewing to talk about the phenomenon of interest, but sometimes you are not even sure what that phenomenon is until you start asking questions. A priority in creating an interview guide is to ensure it offers space. One of the worst mistakes is to create questions that are so specific that the person answering them will not stray. Relatedly, questions that sound “academic” will shut down a lot of respondents. A good interview guide invites respondents to talk about what is important to them, not feel like they are performing or being evaluated by you.
Good interview questions should not sound like your “research question” at all. For example, let’s say your research question is “How do patriarchal assumptions influence men’s understanding of climate change and responses to climate change?” It would be worse than unhelpful to ask a respondent, “How do your assumptions about the role of men affect your understanding of climate change?” You need to unpack this into manageable nuggets that pull your respondent into the area of interest without leading him anywhere. You could start by asking him what he thinks about climate change in general. Or, even better, whether he has any concerns about heatwaves or increased tornadoes or polar icecaps melting. Once he starts talking about that, you can ask follow-up questions that bring in issues around gendered roles, perhaps asking if he is married (to a woman) and whether his wife shares his thoughts and, if not, how they negotiate that difference. The fact is, you won’t really know the right questions to ask until he starts talking.
There are several distinct types of questions that can be used in your interview guide, either as main questions or as follow-up probes. If you remember that the point is to leave space for the respondent, you will craft a much more effective interview guide! You will also want to think about the place of time in both the questions themselves (past, present, future orientations) and the sequencing of the questions.
Researcher Note
Suggestion : As you read the next three sections (types of questions, temporality, question sequence), have in mind a particular research question, and try to draft questions and sequence them in a way that opens space for a discussion that helps you answer your research question.
Type of Questions
Experience and behavior questions ask about what a respondent does regularly (their behavior) or has done (their experience). These are relatively easy questions for people to answer because they appear more “factual” and less subjective. This makes them good opening questions. For the study on climate change above, you might ask, “Have you ever experienced an unusual weather event? What happened?” Or “You said you work outside? What is a typical summer workday like for you? How do you protect yourself from the heat?”
Opinion and values questions , in contrast, ask questions that get inside the minds of those you are interviewing. “Do you think climate change is real? Who or what is responsible for it?” are two such questions. Note that you don’t have to literally ask, “What is your opinion of X?” but you can find a way to ask the specific question relevant to the conversation you are having. These questions are a bit trickier to ask because the answers you get may depend in part on how your respondent perceives you and whether they want to please you or not. We’ve talked a fair amount about being reflective. Here is another place where this comes into play. You need to be aware of the effect your presence might have on the answers you are receiving and adjust accordingly. If you are a woman who is perceived as liberal asking a man who identifies as conservative about climate change, there is a lot of subtext that can be going on in the interview. There is no one right way to resolve this, but you must at least be aware of it.
Feeling questions are questions that ask respondents to draw on their emotional responses. It’s pretty common for academic researchers to forget that we have bodies and emotions, but people’s understandings of the world often operate at this affective level, sometimes unconsciously or barely consciously. It is a good idea to include questions that leave space for respondents to remember, imagine, or relive emotional responses to particular phenomena. “What was it like when you heard your cousin’s house burned down in that wildfire?” doesn’t explicitly use any emotion words, but it allows your respondent to remember what was probably a pretty emotional day. And if they respond emotionally neutral, that is pretty interesting data too. Note that asking someone “How do you feel about X” is not always going to evoke an emotional response, as they might simply turn around and respond with “I think that…” It is better to craft a question that actually pushes the respondent into the affective category. This might be a specific follow-up to an experience and behavior question —for example, “You just told me about your daily routine during the summer heat. Do you worry it is going to get worse?” or “Have you ever been afraid it will be too hot to get your work accomplished?”
Knowledge questions ask respondents what they actually know about something factual. We have to be careful when we ask these types of questions so that respondents do not feel like we are evaluating them (which would shut them down), but, for example, it is helpful to know when you are having a conversation about climate change that your respondent does in fact know that unusual weather events have increased and that these have been attributed to climate change! Asking these questions can set the stage for deeper questions and can ensure that the conversation makes the same kind of sense to both participants. For example, a conversation about political polarization can be put back on track once you realize that the respondent doesn’t really have a clear understanding that there are two parties in the US. Instead of asking a series of questions about Republicans and Democrats, you might shift your questions to talk more generally about political disagreements (e.g., “people against abortion”). And sometimes what you do want to know is the level of knowledge about a particular program or event (e.g., “Are you aware you can discharge your student loans through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program?”).
Sensory questions call on all senses of the respondent to capture deeper responses. These are particularly helpful in sparking memory. “Think back to your childhood in Eastern Oregon. Describe the smells, the sounds…” Or you could use these questions to help a person access the full experience of a setting they customarily inhabit: “When you walk through the doors to your office building, what do you see? Hear? Smell?” As with feeling questions , these questions often supplement experience and behavior questions . They are another way of allowing your respondent to report fully and deeply rather than remain on the surface.
Creative questions employ illustrative examples, suggested scenarios, or simulations to get respondents to think more deeply about an issue, topic, or experience. There are many options here. In The Trouble with Passion , Erin Cech ( 2021 ) provides a scenario in which “Joe” is trying to decide whether to stay at his decent but boring computer job or follow his passion by opening a restaurant. She asks respondents, “What should Joe do?” Their answers illuminate the attraction of “passion” in job selection. In my own work, I have used a news story about an upwardly mobile young man who no longer has time to see his mother and sisters to probe respondents’ feelings about the costs of social mobility. Jessi Streib and Betsy Leondar-Wright have used single-page cartoon “scenes” to elicit evaluations of potential racial discrimination, sexual harassment, and classism. Barbara Sutton ( 2010 ) has employed lists of words (“strong,” “mother,” “victim”) on notecards she fans out and asks her female respondents to select and discuss.
Background/Demographic Questions
You most definitely will want to know more about the person you are interviewing in terms of conventional demographic information, such as age, race, gender identity, occupation, and educational attainment. These are not questions that normally open up inquiry. [1] For this reason, my practice has been to include a separate “demographic questionnaire” sheet that I ask each respondent to fill out at the conclusion of the interview. Only include those aspects that are relevant to your study. For example, if you are not exploring religion or religious affiliation, do not include questions about a person’s religion on the demographic sheet. See the example provided at the end of this chapter.
Temporality
Any type of question can have a past, present, or future orientation. For example, if you are asking a behavior question about workplace routine, you might ask the respondent to talk about past work, present work, and ideal (future) work. Similarly, if you want to understand how people cope with natural disasters, you might ask your respondent how they felt then during the wildfire and now in retrospect and whether and to what extent they have concerns for future wildfire disasters. It’s a relatively simple suggestion—don’t forget to ask about past, present, and future—but it can have a big impact on the quality of the responses you receive.
Question Sequence
Having a list of good questions or good question areas is not enough to make a good interview guide. You will want to pay attention to the order in which you ask your questions. Even though any one respondent can derail this order (perhaps by jumping to answer a question you haven’t yet asked), a good advance plan is always helpful. When thinking about sequence, remember that your goal is to get your respondent to open up to you and to say things that might surprise you. To establish rapport, it is best to start with nonthreatening questions. Asking about the present is often the safest place to begin, followed by the past (they have to know you a little bit to get there), and lastly, the future (talking about hopes and fears requires the most rapport). To allow for surprises, it is best to move from very general questions to more particular questions only later in the interview. This ensures that respondents have the freedom to bring up the topics that are relevant to them rather than feel like they are constrained to answer you narrowly. For example, refrain from asking about particular emotions until these have come up previously—don’t lead with them. Often, your more particular questions will emerge only during the course of the interview, tailored to what is emerging in conversation.
Once you have a set of questions, read through them aloud and imagine you are being asked the same questions. Does the set of questions have a natural flow? Would you be willing to answer the very first question to a total stranger? Does your sequence establish facts and experiences before moving on to opinions and values? Did you include prefatory statements, where necessary; transitions; and other announcements? These can be as simple as “Hey, we talked a lot about your experiences as a barista while in college.… Now I am turning to something completely different: how you managed friendships in college.” That is an abrupt transition, but it has been softened by your acknowledgment of that.
Probes and Flexibility
Once you have the interview guide, you will also want to leave room for probes and follow-up questions. As in the sample probe included here, you can write out the obvious probes and follow-up questions in advance. You might not need them, as your respondent might anticipate them and include full responses to the original question. Or you might need to tailor them to how your respondent answered the question. Some common probes and follow-up questions include asking for more details (When did that happen? Who else was there?), asking for elaboration (Could you say more about that?), asking for clarification (Does that mean what I think it means or something else? I understand what you mean, but someone else reading the transcript might not), and asking for contrast or comparison (How did this experience compare with last year’s event?). “Probing is a skill that comes from knowing what to look for in the interview, listening carefully to what is being said and what is not said, and being sensitive to the feedback needs of the person being interviewed” ( Patton 2002:374 ). It takes work! And energy. I and many other interviewers I know report feeling emotionally and even physically drained after conducting an interview. You are tasked with active listening and rearranging your interview guide as needed on the fly. If you only ask the questions written down in your interview guide with no deviations, you are doing it wrong. [2]
The Final Question
Every interview guide should include a very open-ended final question that allows for the respondent to say whatever it is they have been dying to tell you but you’ve forgotten to ask. About half the time they are tired too and will tell you they have nothing else to say. But incredibly, some of the most honest and complete responses take place here, at the end of a long interview. You have to realize that the person being interviewed is often discovering things about themselves as they talk to you and that this process of discovery can lead to new insights for them. Making space at the end is therefore crucial. Be sure you convey that you actually do want them to tell you more, that the offer of “anything else?” is not read as an empty convention where the polite response is no. Here is where you can pull from that active listening and tailor the final question to the particular person. For example, “I’ve asked you a lot of questions about what it was like to live through that wildfire. I’m wondering if there is anything I’ve forgotten to ask, especially because I haven’t had that experience myself” is a much more inviting final question than “Great. Anything you want to add?” It’s also helpful to convey to the person that you have the time to listen to their full answer, even if the allotted time is at the end. After all, there are no more questions to ask, so the respondent knows exactly how much time is left. Do them the courtesy of listening to them!
Conducting the Interview
Once you have your interview guide, you are on your way to conducting your first interview. I always practice my interview guide with a friend or family member. I do this even when the questions don’t make perfect sense for them, as it still helps me realize which questions make no sense, are poorly worded (too academic), or don’t follow sequentially. I also practice the routine I will use for interviewing, which goes something like this:
- Introduce myself and reintroduce the study
- Provide consent form and ask them to sign and retain/return copy
- Ask if they have any questions about the study before we begin
- Ask if I can begin recording
- Ask questions (from interview guide)
- Turn off the recording device
- Ask if they are willing to fill out my demographic questionnaire
- Collect questionnaire and, without looking at the answers, place in same folder as signed consent form
- Thank them and depart
A note on remote interviewing: Interviews have traditionally been conducted face-to-face in a private or quiet public setting. You don’t want a lot of background noise, as this will make transcriptions difficult. During the recent global pandemic, many interviewers, myself included, learned the benefits of interviewing remotely. Although face-to-face is still preferable for many reasons, Zoom interviewing is not a bad alternative, and it does allow more interviews across great distances. Zoom also includes automatic transcription, which significantly cuts down on the time it normally takes to convert our conversations into “data” to be analyzed. These automatic transcriptions are not perfect, however, and you will still need to listen to the recording and clarify and clean up the transcription. Nor do automatic transcriptions include notations of body language or change of tone, which you may want to include. When interviewing remotely, you will want to collect the consent form before you meet: ask them to read, sign, and return it as an email attachment. I think it is better to ask for the demographic questionnaire after the interview, but because some respondents may never return it then, it is probably best to ask for this at the same time as the consent form, in advance of the interview.
What should you bring to the interview? I would recommend bringing two copies of the consent form (one for you and one for the respondent), a demographic questionnaire, a manila folder in which to place the signed consent form and filled-out demographic questionnaire, a printed copy of your interview guide (I print with three-inch right margins so I can jot down notes on the page next to relevant questions), a pen, a recording device, and water.
After the interview, you will want to secure the signed consent form in a locked filing cabinet (if in print) or a password-protected folder on your computer. Using Excel or a similar program that allows tables/spreadsheets, create an identifying number for your interview that links to the consent form without using the name of your respondent. For example, let’s say that I conduct interviews with US politicians, and the first person I meet with is George W. Bush. I will assign the transcription the number “INT#001” and add it to the signed consent form. [3] The signed consent form goes into a locked filing cabinet, and I never use the name “George W. Bush” again. I take the information from the demographic sheet, open my Excel spreadsheet, and add the relevant information in separate columns for the row INT#001: White, male, Republican. When I interview Bill Clinton as my second interview, I include a second row: INT#002: White, male, Democrat. And so on. The only link to the actual name of the respondent and this information is the fact that the consent form (unavailable to anyone but me) has stamped on it the interview number.
Many students get very nervous before their first interview. Actually, many of us are always nervous before the interview! But do not worry—this is normal, and it does pass. Chances are, you will be pleasantly surprised at how comfortable it begins to feel. These “purposeful conversations” are often a delight for both participants. This is not to say that sometimes things go wrong. I often have my students practice several “bad scenarios” (e.g., a respondent that you cannot get to open up; a respondent who is too talkative and dominates the conversation, steering it away from the topics you are interested in; emotions that completely take over; or shocking disclosures you are ill-prepared to handle), but most of the time, things go quite well. Be prepared for the unexpected, but know that the reason interviews are so popular as a technique of data collection is that they are usually richly rewarding for both participants.
One thing that I stress to my methods students and remind myself about is that interviews are still conversations between people. If there’s something you might feel uncomfortable asking someone about in a “normal” conversation, you will likely also feel a bit of discomfort asking it in an interview. Maybe more importantly, your respondent may feel uncomfortable. Social research—especially about inequality—can be uncomfortable. And it’s easy to slip into an abstract, intellectualized, or removed perspective as an interviewer. This is one reason trying out interview questions is important. Another is that sometimes the question sounds good in your head but doesn’t work as well out loud in practice. I learned this the hard way when a respondent asked me how I would answer the question I had just posed, and I realized that not only did I not really know how I would answer it, but I also wasn’t quite as sure I knew what I was asking as I had thought.
—Elizabeth M. Lee, Associate Professor of Sociology at Saint Joseph’s University, author of Class and Campus Life , and co-author of Geographies of Campus Inequality
How Many Interviews?
Your research design has included a targeted number of interviews and a recruitment plan (see chapter 5). Follow your plan, but remember that “ saturation ” is your goal. You interview as many people as you can until you reach a point at which you are no longer surprised by what they tell you. This means not that no one after your first twenty interviews will have surprising, interesting stories to tell you but rather that the picture you are forming about the phenomenon of interest to you from a research perspective has come into focus, and none of the interviews are substantially refocusing that picture. That is when you should stop collecting interviews. Note that to know when you have reached this, you will need to read your transcripts as you go. More about this in chapters 18 and 19.
Your Final Product: The Ideal Interview Transcript
A good interview transcript will demonstrate a subtly controlled conversation by the skillful interviewer. In general, you want to see replies that are about one paragraph long, not short sentences and not running on for several pages. Although it is sometimes necessary to follow respondents down tangents, it is also often necessary to pull them back to the questions that form the basis of your research study. This is not really a free conversation, although it may feel like that to the person you are interviewing.
Final Tips from an Interview Master
Annette Lareau is arguably one of the masters of the trade. In Listening to People , she provides several guidelines for good interviews and then offers a detailed example of an interview gone wrong and how it could be addressed (please see the “Further Readings” at the end of this chapter). Here is an abbreviated version of her set of guidelines: (1) interview respondents who are experts on the subjects of most interest to you (as a corollary, don’t ask people about things they don’t know); (2) listen carefully and talk as little as possible; (3) keep in mind what you want to know and why you want to know it; (4) be a proactive interviewer (subtly guide the conversation); (5) assure respondents that there aren’t any right or wrong answers; (6) use the respondent’s own words to probe further (this both allows you to accurately identify what you heard and pushes the respondent to explain further); (7) reuse effective probes (don’t reinvent the wheel as you go—if repeating the words back works, do it again and again); (8) focus on learning the subjective meanings that events or experiences have for a respondent; (9) don’t be afraid to ask a question that draws on your own knowledge (unlike trial lawyers who are trained never to ask a question for which they don’t already know the answer, sometimes it’s worth it to ask risky questions based on your hypotheses or just plain hunches); (10) keep thinking while you are listening (so difficult…and important); (11) return to a theme raised by a respondent if you want further information; (12) be mindful of power inequalities (and never ever coerce a respondent to continue the interview if they want out); (13) take control with overly talkative respondents; (14) expect overly succinct responses, and develop strategies for probing further; (15) balance digging deep and moving on; (16) develop a plan to deflect questions (e.g., let them know you are happy to answer any questions at the end of the interview, but you don’t want to take time away from them now); and at the end, (17) check to see whether you have asked all your questions. You don’t always have to ask everyone the same set of questions, but if there is a big area you have forgotten to cover, now is the time to recover ( Lareau 2021:93–103 ).
Sample: Demographic Questionnaire
ASA Taskforce on First-Generation and Working-Class Persons in Sociology – Class Effects on Career Success
Supplementary Demographic Questionnaire
Thank you for your participation in this interview project. We would like to collect a few pieces of key demographic information from you to supplement our analyses. Your answers to these questions will be kept confidential and stored by ID number. All of your responses here are entirely voluntary!
What best captures your race/ethnicity? (please check any/all that apply)
- White (Non Hispanic/Latina/o/x)
- Black or African American
- Hispanic, Latino/a/x of Spanish
- Asian or Asian American
- American Indian or Alaska Native
- Middle Eastern or North African
- Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
- Other : (Please write in: ________________)
What is your current position?
- Grad Student
- Full Professor
Please check any and all of the following that apply to you:
- I identify as a working-class academic
- I was the first in my family to graduate from college
- I grew up poor
What best reflects your gender?
- Transgender female/Transgender woman
- Transgender male/Transgender man
- Gender queer/ Gender nonconforming
Anything else you would like us to know about you?
Example: Interview Guide
In this example, follow-up prompts are italicized. Note the sequence of questions. That second question often elicits an entire life history , answering several later questions in advance.
Introduction Script/Question
Thank you for participating in our survey of ASA members who identify as first-generation or working-class. As you may have heard, ASA has sponsored a taskforce on first-generation and working-class persons in sociology and we are interested in hearing from those who so identify. Your participation in this interview will help advance our knowledge in this area.
- The first thing we would like to as you is why you have volunteered to be part of this study? What does it mean to you be first-gen or working class? Why were you willing to be interviewed?
- How did you decide to become a sociologist?
- Can you tell me a little bit about where you grew up? ( prompts: what did your parent(s) do for a living? What kind of high school did you attend?)
- Has this identity been salient to your experience? (how? How much?)
- How welcoming was your grad program? Your first academic employer?
- Why did you decide to pursue sociology at the graduate level?
- Did you experience culture shock in college? In graduate school?
- Has your FGWC status shaped how you’ve thought about where you went to school? debt? etc?
- Were you mentored? How did this work (not work)? How might it?
- What did you consider when deciding where to go to grad school? Where to apply for your first position?
- What, to you, is a mark of career success? Have you achieved that success? What has helped or hindered your pursuit of success?
- Do you think sociology, as a field, cares about prestige?
- Let’s talk a little bit about intersectionality. How does being first-gen/working class work alongside other identities that are important to you?
- What do your friends and family think about your career? Have you had any difficulty relating to family members or past friends since becoming highly educated?
- Do you have any debt from college/grad school? Are you concerned about this? Could you explain more about how you paid for college/grad school? (here, include assistance from family, fellowships, scholarships, etc.)
- (You’ve mentioned issues or obstacles you had because of your background.) What could have helped? Or, who or what did? Can you think of fortuitous moments in your career?
- Do you have any regrets about the path you took?
- Is there anything else you would like to add? Anything that the Taskforce should take note of, that we did not ask you about here?
Further Readings
Britten, Nicky. 1995. “Qualitative Interviews in Medical Research.” BMJ: British Medical Journal 31(6999):251–253. A good basic overview of interviewing particularly useful for students of public health and medical research generally.
Corbin, Juliet, and Janice M. Morse. 2003. “The Unstructured Interactive Interview: Issues of Reciprocity and Risks When Dealing with Sensitive Topics.” Qualitative Inquiry 9(3):335–354. Weighs the potential benefits and harms of conducting interviews on topics that may cause emotional distress. Argues that the researcher’s skills and code of ethics should ensure that the interviewing process provides more of a benefit to both participant and researcher than a harm to the former.
Gerson, Kathleen, and Sarah Damaske. 2020. The Science and Art of Interviewing . New York: Oxford University Press. A useful guidebook/textbook for both undergraduates and graduate students, written by sociologists.
Kvale, Steiner. 2007. Doing Interviews . London: SAGE. An easy-to-follow guide to conducting and analyzing interviews by psychologists.
Lamont, Michèle, and Ann Swidler. 2014. “Methodological Pluralism and the Possibilities and Limits of Interviewing.” Qualitative Sociology 37(2):153–171. Written as a response to various debates surrounding the relative value of interview-based studies and ethnographic studies defending the particular strengths of interviewing. This is a must-read article for anyone seriously engaging in qualitative research!
Pugh, Allison J. 2013. “What Good Are Interviews for Thinking about Culture? Demystifying Interpretive Analysis.” American Journal of Cultural Sociology 1(1):42–68. Another defense of interviewing written against those who champion ethnographic methods as superior, particularly in the area of studying culture. A classic.
Rapley, Timothy John. 2001. “The ‘Artfulness’ of Open-Ended Interviewing: Some considerations in analyzing interviews.” Qualitative Research 1(3):303–323. Argues for the importance of “local context” of data production (the relationship built between interviewer and interviewee, for example) in properly analyzing interview data.
Weiss, Robert S. 1995. Learning from Strangers: The Art and Method of Qualitative Interview Studies . New York: Simon and Schuster. A classic and well-regarded textbook on interviewing. Because Weiss has extensive experience conducting surveys, he contrasts the qualitative interview with the survey questionnaire well; particularly useful for those trained in the latter.
- I say “normally” because how people understand their various identities can itself be an expansive topic of inquiry. Here, I am merely talking about collecting otherwise unexamined demographic data, similar to how we ask people to check boxes on surveys. ↵
- Again, this applies to “semistructured in-depth interviewing.” When conducting standardized questionnaires, you will want to ask each question exactly as written, without deviations! ↵
- I always include “INT” in the number because I sometimes have other kinds of data with their own numbering: FG#001 would mean the first focus group, for example. I also always include three-digit spaces, as this allows for up to 999 interviews (or, more realistically, allows for me to interview up to one hundred persons without having to reset my numbering system). ↵
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
A document listing key questions and question areas for use during an interview. It is used most often for semi-structured interviews. A good interview guide may have no more than ten primary questions for two hours of interviewing, but these ten questions will be supplemented by probes and relevant follow-ups throughout the interview. Most IRBs require the inclusion of the interview guide in applications for review. See also interview and semi-structured interview .
A data-collection method that relies on casual, conversational, and informal interviewing. Despite its apparent conversational nature, the researcher usually has a set of particular questions or question areas in mind but allows the interview to unfold spontaneously. This is a common data-collection technique among ethnographers. Compare to the semi-structured or in-depth interview .
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Follow-up questions used in a semi-structured interview to elicit further elaboration. Suggested prompts can be included in the interview guide to be used/deployed depending on how the initial question was answered or if the topic of the prompt does not emerge spontaneously.
A form of interview that follows a strict set of questions, asked in a particular order, for all interview subjects. The questions are also the kind that elicits short answers, and the data is more “informative” than probing. This is often used in mixed-methods studies, accompanying a survey instrument. Because there is no room for nuance or the exploration of meaning in structured interviews, qualitative researchers tend to employ semi-structured interviews instead. See also interview.
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
An interview variant in which a person’s life story is elicited in a narrative form. Turning points and key themes are established by the researcher and used as data points for further analysis.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Types of Interviews – A Simple Guide & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The methodology of employing different types of interviews plays a pivotal role in research, allowing for deep, qualitative insight into subjects’ experiences and perspectives. From structured to semi-structured and unstructured interviews, each type provides unique and invaluable information to meet diverse research objectives. In this guide, we will learn about the different types of interviews and where they are best applied.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Types of Interviews – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Types of interviews
- 3 Types of interviews – Structured interview
- 4 Types of interviews – Semi-structured interview
- 5 Types of interviews – Unstructured interview
- 6 Types of interviews – Focus group
- 7 Types of interviews – Examples of interview questions
- 8 Pros and Cons of different types of interviews
Types of Interviews – In a Nutshell
- The types of interviews you can use in research are structured interviews, unstructured interviews, semi-structured interviews, and focus group interviews.
- The interviewer effect is a bias that arises when the characteristics of the researcher influence the responses of the interviewees.
- A focus group is a research method that involves asking interview questions to a small group of people.
Definition: Types of interviews
There are three types of interviews, and these differ in the structure of the questions. The types of interviews are structured interviews, semi-structured interviews, and unstructured interviews. Structured interviews involve the use of set questions, and these must be asked in a given order. On the other hand, unstructured interviews are flexible and feature open-ended questions. Semi-structured interviews have elements of both structured and unstructured interviews.
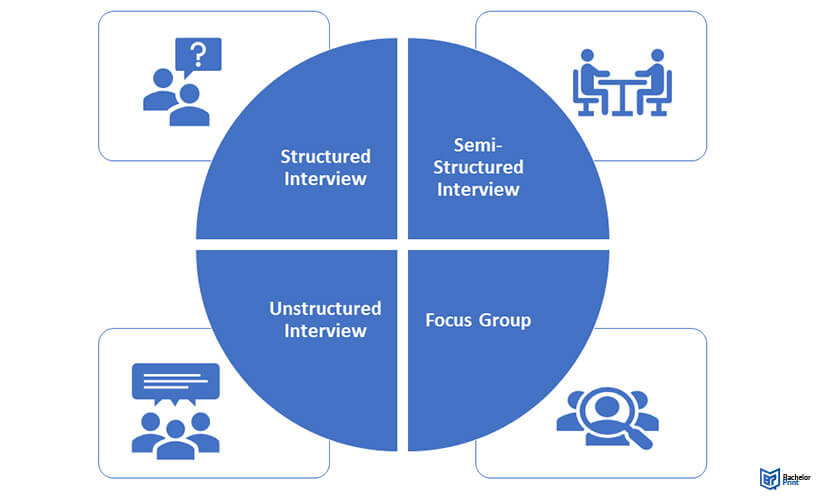
Types of interviews – Structured interview
A structured interview is one where the questions are predetermined and set in a particular order. Typically, the questions will be closed-ended and will offer multiple choices. Since the questions are asked in a set order, it is easy for the researcher to compare responses and determine the patterns. Structured interviews help to mitigate biases and offer higher levels of validity and reliability. You can use this type of interview in the following cases:
- You understand the subject thoroughly and can design excellent questions
- You don’t have sufficient time and resources to carry out the research
- Your research question depends on a strong parity between the respondents

Types of interviews – Semi-structured interview
Semi-structured interviews have elements of both structured and unstructured interviews. With these interviews, the researcher will have an idea of the questions to ask, but the phrasing and order of the questions will not be set. Since they are often open-ended, the researcher will enjoy high levels of flexibility, and they will still be able to compare the responses fairly easily. These types of interviews are ideal in these situations:
- The researcher has a lot of experience in interviews
- The research question is exploratory in nature
Types of interviews – Unstructured interview
Unstructured interviews are also known as non-directive interviewing, and they don’t have a set pattern. Also, questions are not arranged in advance. These interviews are used as exploratory research tools and are commonly used in social sciences and humanities. Here are some occasions when an unstructured interview will be a great fit:
- If the research question is exploratory in nature
- If the research requires you to form a connection with your respondents
Types of interviews – Focus group
With focus group interviews, the researcher will present the questions to a group instead of an individual. These types of interviews don’t just study the responses of the interviewees; they also study the group dynamic and body language. The main issue with focus group interviews is that they have low external validity, and the interviewer may be biased when choosing the responses to include. Here are a few cases where focus group interviews can be suitable:
- If the study depends on group discussion dynamics
- If the questions are complex and can’t be answered with multiple choices
- If the study is open to uncovering new ideas and questions
Types of interviews – Examples of interview questions
The types of interview questions will vary depending on the type of interview. With structured interviews, the questions are set and precise, but the other types of interviews allow for flexible and open-ended questions.
Pros and Cons of different types of interviews
Interviews can help you collect useful information, but the types of interviews come with different pros and cons.
What is an interviewer effect?
This is a type of bias that emerges when the characteristics of an interviewer affect the responses given by the respondents.
When should you use unstructured interviews?
Unstructured interviews are great for building a bond with the respondent, and they can be used in cases where the interviewer needs the interviewee to be 100% honest.
When should you use structured interviews?
Structured interviews will be a good option for your research if you have limited time and resources. This is because they are easy to analyze.
What are the three types of interviews in research?
The three types of interviews in research are structured interviews, semi-structured interviews, and unstructured interviews.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads
Product updates
Dovetail retro: our biggest releases from the past year
Tips and tricks
How to affinity map using the canvas

Dovetail in the Details: 21 improvements to influence, transcribe, and store
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
Structured vs. unstructured interviews: A complete guide
Last updated
7 March 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Interviews can help you understand the context of a subject, eyewitness accounts of an event, people's perceptions of a product, and more.
In some instances, semi-structured or unstructured interviews can be more helpful; in others, structured interviews are the right choice to obtain the information you seek.
In some cases, structured interviews can save time, making your research more efficient. Let’s dive into everything you need to know about structured interviews.
Analyze all kinds of interviews
Bring all your interviews into one place to analyze and understand
- What are structured interviews?
Structured interviews are also known as standardized interviews, patterned interviews, or planned interviews. They’re a research instrument that uses a standard sequence of questions to collect information about the research subject.
Often, you’ll use structured interviews when you need data that’s easy to categorize and quantify for a statistical analysis of responses.
Structured interviews are incredibly effective at helping researchers identify patterns and trends in response data. They’re great at minimizing the time and resources necessary for data collection and analysis.
What types of questions suit structured interviews?
Often, researchers use structured interviews for quantitative research . In these cases, they usually employ close-ended questions.
Close-ended questions have a fixed set of responses from which the interviewer can choose. Because of the limited response selection set, response data from close-ended questions is easy to aggregate and analyze.
Researchers often employ multiple-choice or dichotomous close-ended questions in interviews.
For multiple-choice questions, interviewees may choose between three or more possible answers. The interviewer will often restrict the response to four or five possible options. An interviewee will likely need help recalling more, which can slow down and complicate the interview process.
For dichotomous questions, the interviewee may choose between two possible options. Yes or no and true or false questions are examples of dichotomous questions.
Open-ended questions are common in structured interviews. However, researchers use them when conducting qualitative research and looking for in-depth information about the interviewee's perceptions or experiences.
These questions take longer for the interviewee to answer, and the answers take longer for the researcher to analyze. There's also a higher possibility of the researcher collecting irrelevant data. However, open-ended questions are more effective than close-ended questions in gathering in-depth information.
Sometimes, researchers use structured interviews in qualitative research. In this case, the research instrument contains open-ended questions in the same sequence. This usage is less common because it can be hard to compare feedback, especially with large sample sizes.
- What types of structured interviews are there?
Researchers conduct structured interviews face-to-face, via telephone or videoconference, or through a survey instrument.
Face-to-face interviews help researchers collect data and gather more detailed information. They can collect and analyze facial expressions, body language, tone, and inflection easier than they might through other interview methods .
However, face-to-face interviews are the most resource-intensive to arrange. You'll likely need to assume travel and other related logistical costs for a face-to-face interview.
These interviews also take more time and are more vulnerable to bias than some other formats. For these reasons, face-to-face interviews are best with a small sample size.
You can conduct interviews via an audio or video call. They are less resource-intensive than face-to-face interviews and can use a larger sample size.
However, it can be difficult for the interviewer to engage effectively with the interviewee within this format, which can inject bias or ambiguity into the responses. This is particularly true for audio calls, especially if the interviewer and interviewee have not met before the interview.
A video call can help the interviewer capture some data from body language and facial expressions, but less so than in a face-to-face interview. Technical issues are another thing to consider. If you’re studying a group of people that live in an area with limited Internet connectivity, this can make a video call challenging.
Survey questionnaires mirror the essential elements of structured interviews by containing a consistent sequence of standard questions. Surveys in quantitative research usually include close-ended questions. This data collection method can be beneficial if you need feedback from a large sample size.
Surveys are resource-efficient from a data administration standpoint but are more limited in the data they can gather. Further, if a survey question is ambiguous, you can’t clear up the ambiguity before someone responds.
By contrast, in a face-to-face or tele-interview, an interviewee may ask clarifying questions or exhibit confusion when asked an unclear question, allowing the interviewer to clarify.
- What are some common examples of structured interviews?
Structured interviews are relevant in many fields. You can find structured interviews in human resources, marketing, political science, psychology, and more.
Academic and applied researchers commonly use them to verify insights from analyzing academic literature or responses from other interview types.
However, one of the most common structured interview applications lies outside the research realm: Human resource professionals and hiring managers commonly use these interviews to hire employees.
A hiring manager can easily compare responses and whittle down the applicant pool by posing a standard set of closed-ended interview questions to multiple applicants.
Further, standard close-ended or open-ended questions can reduce bias and add objectivity and credibility to the hiring process.
Structured interviews are common in political polling. Candidates and political parties may conduct structured interviews with relatively small voter groups to obtain feedback. They ask questions about issues, messaging, and voting intentions to craft policies and campaigns.
- What do you need to conduct a structured interview?
The tools you need to conduct a structured interview vary by format. But fundamentally, you will need:
A participant
An interviewer
A pen and pad (or other note-taking tools)
A recording device
A consent form
A list of interview questions
While some interviewees may express qualms about you recording the interview, it’s challenging to conduct quality interviews while taking detailed notes. Even if you have a note-taker in the room, note-taking may introduce bias and can’t capture body language or facial expressions.
Depending on the nature of your study, others may wish to review your sources. If they call your conclusions into question, audio recordings are additional evidence in your favor.
To record, you should ask the interviewee to sign a consent form. Check with your employer's legal counsel or institutional review board at your academic institution for guidance about obtaining consent legally in your state.
If you're conducting a face-to-face interview, a camcorder, digital camera, or even some smartphones are sufficient for recording.
For a tele-interview, you'll find that today's leading video conferencing software applications feature a convenient recording function for data collection.
If a survey is your method of choice, you'll need the survey and a distribution and collection method. Online survey software applications allow you to create surveys by inputting the questions and distributing your survey via text or email.
In some cases, survey companies even offer packages in which they will call those who do not respond via email or text and conduct the survey over the phone.
- How to conduct a structured interview
If you're planning a face-to-face interview, you'll need to take a few steps to do it efficiently.
First, prepare your questions and double-check that the structured interview format is best for your study. Make sure that they are neutral, unbiased, and close-ended. Ask a friend or colleague to test your questions pre-interview to ensure they are clear and straightforward.
Choose the setting for your interviews. Ideally, you'll select a location that is easy to get to. If you live in a city, consider addresses accessible via public transportation.
The room where your interview takes place should be comfortable, without distraction, and quiet, so your recording device clearly captures your interviewee's audio.
If you're looking to interview people with specific characteristics, you'll need to recruit them. Some companies specialize in interview recruitment. You provide the attributes you need, and they identify a pool of candidates for a fee. Alternatively, you can advertise to participants on social media and other relevant avenues.
If you're looking for college students in a specific region, look at student newspaper ads or affiliated social media pages.
You'll also want to incentivize participation, as recruiting interview respondents without compensation is exceedingly difficult. It’s best to include a line or two about requiring written consent for participation and how you’ll use the interview audio.
When you have an interview participant, discuss the intent of your research and acquire their consent. Ensure your recording tools are working well, and begin your interview.
Don't rely on the recordings alone: Note the most significant insights from your participant, as you could easily forget them when it's time to analyze your data.
You'll want to transcribe your audio at the data analysis stage. Some recording applications use AI to generate transcripts. Remove filler words and other sounds to generate a clear transcript for the best results.
A written transcript will help you analyze data and pull quotes from your audio to include in your final research paper.
- What are other common types of interviews?
Typically, you'll find researchers using at least one of these other common interview types:
Semi-structured interviews
As the name suggests, semi-structured interviews include some elements of a structured interview. You’ll include preplanned questions, but you can deviate from those questions to explore the interviewee's answers in greater depth.
Typically, a researcher will conduct a semi-structured interview with preplanned questions and an interview guide. The guide will include topics and potential questions to ask. Sometimes, the guide may also include areas or questions to avoid asking.
Unstructured interviews
In an unstructured interview , the researchers approach the interview subjects without predetermined questions. Researchers often use this qualitative instrument to probe into personal experiences and testimony, typically toward the beginning of a research study.
Often, you’ll validate the insights you gather during unstructured and semi-structured interviews with structured interviews, surveys, and similar quantitative research tools.
Focus group interviews
Focus group interviews differ from the other three types of interviews as you pose the questions to a small group. Focus groups are typically either structured or semi-structured. When researchers employ structured interview questions, they are typically confident in the areas they wish to explore.
Semi-structured interviews are perfect for a researcher seeking to explore broad issues. However, you must be careful that unplanned questions are unambiguous and neutral. Otherwise, you could wind up with biased results.
What is a structured vs. an unstructured interview?
A structured interview consists of standard preplanned questions for data collection. These questions may be close-ended, open-ended, or a combination.
By contrast, an unstructured interview includes unplanned questions. In these interviews, you’ll usually equip facilitators with an interview guide. This includes guidelines for asking questions and samples that can help them ask relevant questions.
What are the advantages of a structured interview?
Relative to other interview formats, a structured interview is usually more time-efficient. With a preplanned set of questions, your interview is less likely to go into tangents, especially if you use close-ended questions.
The more structure you provide to the interview, the more likely you are to generate responses that are easy to analyze. By contrast, an unstructured interview may involve a freewheeling conversation with off-topic and irrelevant feedback that lasts a long time.
What is an example of a structured question?
A structured question is any question you ask in an interview that you’ve preplanned and standardized.
For example, if you conduct five interviews and the first question you ask each one is, "Do you believe the world is round, yes or no?" you have asked them a structured question. This is also a close-ended dichotomous question.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 September 2023
Last updated: 14 February 2024
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2024
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Interview Research
Research Methods Guide: Interview Research
- Introduction
- Research Design & Method
- Survey Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Interview Method
Interview as a Method for Qualitative Research

Goals of Interview Research
- Preferences
- They help you explain, better understand, and explore research subjects' opinions, behavior, experiences, phenomenon, etc.
- Interview questions are usually open-ended questions so that in-depth information will be collected.
Mode of Data Collection
There are several types of interviews, including:
- Face-to-Face
- Online (e.g. Skype, Googlehangout, etc)
FAQ: Conducting Interview Research
What are the important steps involved in interviews?
- Think about who you will interview
- Think about what kind of information you want to obtain from interviews
- Think about why you want to pursue in-depth information around your research topic
- Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview
- Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question
- Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes
- Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics
- Make sure your questions are clear and easy to understand
- Do not ask leading questions
- Do you want to bring a second interviewer with you?
- Do you want to bring a notetaker?
- Do you want to record interviews? If so, do you have time to transcribe interview recordings?
- Where will you interview people? Where is the setting with the least distraction?
- How long will each interview take?
- Do you need to address terms of confidentiality?
Do I have to choose either a survey or interviewing method?
No. In fact, many researchers use a mixed method - interviews can be useful as follow-up to certain respondents to surveys, e.g., to further investigate their responses.
Is training an interviewer important?
Yes, since the interviewer can control the quality of the result, training the interviewer becomes crucial. If more than one interviewers are involved in your study, it is important to have every interviewer understand the interviewing procedure and rehearse the interviewing process before beginning the formal study.
- << Previous: Survey Research
- Next: Data Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM

Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional endeavors. They provide researchers with an opportunity to delve deep into the thoughts, experiences, and perspectives of an individual, thus enabling a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. It is important for researchers to design an effective and insightful method of data collection on a particular topic. A research interview is typically a two-person meeting conducted to collect information on a certain topic. It is a qualitative data collection method to gain primary information.
The three key features of a research interview are as follows:
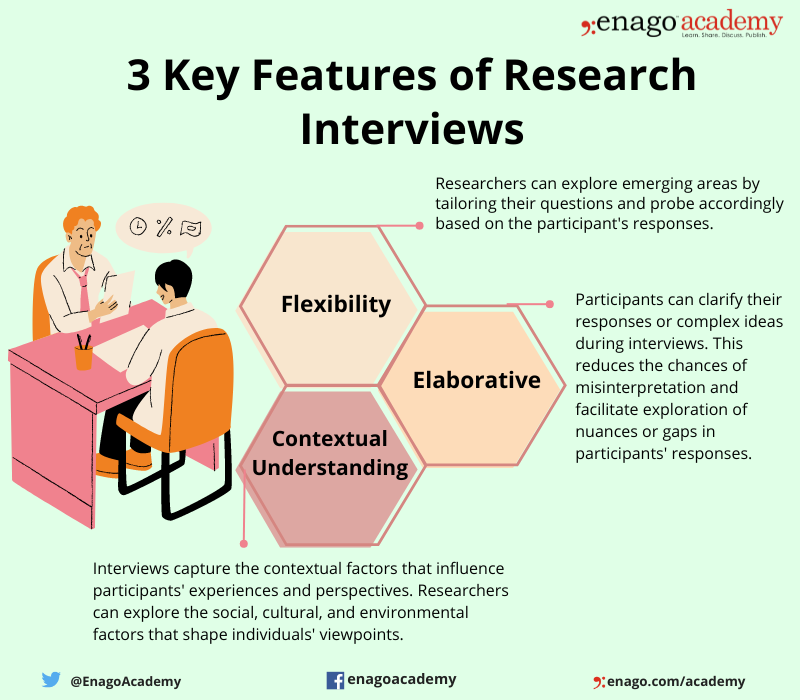
Table of Contents
The Significance of Research Interviews in Gathering Primary Data
The role of research interviews in gathering first-hand information is invaluable. Additionally, they allow researchers to interact directly with participants, enabling them to collect unfiltered primary data.
1. Subjective Experience
Research interviews facilitate in-depth exploration of a research topic. Thus, by engaging in one-to-one conversation with participants, researchers can delve into the nuances and complexities of their experiences, perspectives, and opinions. This allows comprehensive understanding of the research subject that may not be possible through other methods. Also, research interviews offer the unique advantage of capturing subjective experiences through personal narratives. Moreover, participants can express their thoughts, feelings, and beliefs, which add depth to the findings.
2. Personal Insights
Research interviews offer an opportunity for participants to share their views and opinions on the objective they are being interviewed for. Furthermore, participants can express their thoughts and experiences, providing rich qualitative data . Consequently, these personal narratives add a human element to the research, thus enhancing the understanding of the topic from the participants’ perspectives. Research interviews offer the opportunity to uncover unanticipated insights or emerging themes. Additionally, open-ended questions and active listening can help the researchers to identify new perspectives, ideas, or patterns that may not have been initially considered. As a result, these factors can lead to new avenues for exploration.
3. Clarification and Validation
Researchers can clarify participants’ responses and validate their understanding during an interview. This ensures accurate data collection and interpretation. Additionally, researchers can probe deeper into participants’ statements and seek clarification on any ambiguity in the information.
4. Contextual Information
Research interviews allow researchers to gather contextual information that offers a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Additionally, participants can provide insights into the social, cultural, or environmental factors that shape their experiences, behaviors, and beliefs. This contextual information helps researchers place the data in a broader context and facilitates a more nuanced analysis.
5. Non-verbal Cues
In addition to verbal responses, research interviews allow researchers to observe non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Additionally, non-verbal cues can convey information, such as emotions, attitudes, or levels of comfort. Furthermore, integrating non-verbal cues with verbal responses provides a more holistic understanding of participants’ experiences and enriches the data collection process.
Research interviews offer several advantages, making them a reliable tool for collecting information. However, choosing the right type of research interview is essential for collecting useful data.
Types of Research Interviews
There are several types of research interviews that researchers can use based on their research goals , the nature of their study, and the data they aim to collect. Here are some common types of research interviews:
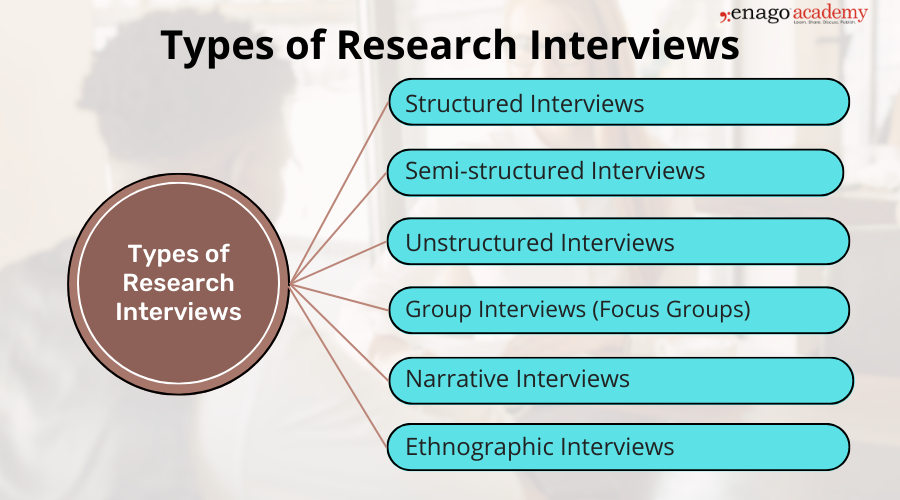
1. Structured Interviews
- Structured interviews are standardized and follow a fixed format.
- Therefore, these interviews have a pre-determined set of questions.
- All the participants are asked the same set of questions in the same order.
- Therefore, this type of interview facilitates standardization and allows easy comparison and quantitative analysis of responses.
- As a result, structured interviews are used in surveys or studies which aims for a high level of standardization and comparability.
2. Semi-structured Interviews
- Semi-structured interviews offer a flexible framework by combining pre-determined questions.
- So, this gives an opportunity for follow-up questions and open-ended discussions.
- Researchers have a list of core questions but can adapt the interview depending on the participant’s responses.
- Consequently, this allows for in-depth exploration while maintaining some level of consistency across interviews.
- As a result, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research, where content-rich data is desired.
3. Unstructured Interviews
- Unstructured interviews provide the greatest flexibility and freedom in the interview process.
- This type do not have a pre-determined set of questions.
- Thus, the conversation flows naturally based on the participant’s responses and the researcher’s interests.
- Moreover, this type of interview allows for open-ended exploration and encourages participants to share their experiences, thoughts, and perspectives freely.
- Unstructured interviews useful to explore new or complex research topics, with limited preconceived questions.
4. Group Interviews (Focus Groups)
- Group interviews involve multiple participants who engage in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic.
- This format allows the interaction and exchange of ideas among participants, generating a group dynamic.
- Therefore, group interviews are beneficial for capturing diverse perspectives, and generating collective insights.
- They are often used in market research, social sciences, or studies demanding shared experiences.
5. Narrative Interviews
- Narrative interviews focus on eliciting participants’ personal stories, views, experiences, and narratives. Researchers aim to look into the individual’s life journey.
- As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data.
- Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews.
6. Ethnographic Interviews
- Ethnographic interviews are conducted within the context of ethnographic research, where researchers immerse themselves in a specific social or cultural setting.
- These interviews aim to understand participants’ experiences, beliefs, and practices within their cultural context, thereby understanding diversity in different ethnic groups.
- Furthermore, ethnographic interviews involve building rapport, observing the participants’ daily lives, and engaging in conversations that capture the nuances of the culture under study.
It must be noted that these interview types are not mutually exclusive. Therefore, researchers often employ a combination of approaches to gather the most comprehensive data for their research. The choice of interview type depends on the research objectives and the nature of the research topic.
Steps of Conducting a Research Interview
Research interviews offer several benefits, and thus careful planning and execution of the entire process are important to gather in-depth information from the participants. While conducting an interview, it is essential to know the necessary steps to follow for ensuring success. The steps to conduct a research interview are as follows:
- Identify the objectives and understand the goals
- Select an appropriate interview format
- Organize the necessary materials for the interview
- Understand the questions to be addressed
- Analyze the demographics of interviewees
- Select the interviewees
- Design the interview questions to gather sufficient information
- Schedule the interview
- Explain the purpose of the interview
- Analyze the interviewee based on his/her responses
Considerations for Research Interviews
Since the flexible nature of research interviews makes them an invaluable tool for data collection, researchers must consider certain factors to make the process effective. They should avoid bias and preconceived notion against the participants. Furthermore, researchers must comply with ethical considerations and respect the cultural differences between them and the participants. Also, they should ensure careful tailoring of the questions to avoid making them offensive or derogatory. The interviewers must respect the privacy of the participants and ensure the confidentiality of their details.

By ensuring due diligence of these considerations associated with research interviews, researchers can maximize the validity and reliability of the collected data, leading to robust and meaningful research outcomes.
Have you ever conducted a research interview? What was your experience? What factors did you consider when conducting a research interview? Share it with researchers worldwide by submitting your thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform .
Frequently Asked Questions
• Identify the objectives of the interview • State and explain the purpose of the interview • Select an appropriate interview format • Organize the necessary materials for the Interview • Check the demographics of the participants • Select the Interviewees or the participants • Prepare the list of questions to gather maximum useful data from the participants • Schedule the Interview • Analyze the participant based on his/ her Responses
Interviews are important in research as it helps to gather elaborative first-hand information. It helps to draw conclusions from the non-verbal views and personal experiences. It reduces the ambiguity of data through detailed discussions.
The advantages of research interviews are: • It offers first-hand information • Offers detailed assessment which can result in elaborate conclusions • It is easy to conduct • Provides non-verbal cues The disadvantages of research interviews are: • There is a risk of personal bias • It can be time consuming • The outcomes might be unpredictable
The difference between structured and unstructured interview are: • Structured interviews have well-structured questions in a pre-determined order; while unstructured interviews are flexible and do not have a pre-planned set of questions. • Structured interview is more detailed; while unstructured interviews are exploratory in nature. • Structured interview is easier to replicate as compared to unstructured interview.
Focus groups is a group of multiple participants engaging in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic. This format allows for interaction and exchange of ideas among participants.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Industry News
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research
Language as a Bridge, Not a Barrier: ESL researchers’ path to successful…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

When should AI tools be used in university labs?
- Harvard Library
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries
Library Support for Qualitative Research
- Resources for Methodology
- Remote Research & Virtual Fieldwork
Resources for Research Interviewing
Nih-funded qualitative research.
- Oral History
- Data Management & Repositories
- Campus Access
- Engaging Participants
Interview Questions
- Conducting Interviews
- Transcription
- Coding and Analysis
- Managing & Finding Interview Data
- UX & Market Research Interviews
Textbooks, Guidebooks, and Handbooks
- The Ethnographic Interview by James P. Spradley “Spradley wrote this book for the professional and student who have never done ethnographic fieldwork (p. 231) and for the professional ethnographer who is interested in adapting the author’s procedures (p. iv). Part 1 outlines in 3 chapters Spradley’s version of ethnographic research, and it provides the background for Part 2 which consists of 12 guided steps (chapters) ranging from locating and interviewing an informant to writing an ethnography. Most of the examples come from the author’s own fieldwork among U.S. subcultures . . . Steps 6 and 8 explain lucidly how to construct a domain and a taxonomic analysis” (excerpted from book review by James D. Sexton, 1980).
- Fundamentals of Qualitative Research by Johnny Saldana (Series edited by Patricia Leavy) Provides a soup-to-nuts overview of the qualitative data collection process, including interviewing, participant observation, and other methods.
- InterViews by Steinar Kvale Interviewing is an essential tool in qualitative research and this introduction to interviewing outlines both the theoretical underpinnings and the practical aspects of the process. After examining the role of the interview in the research process, Steinar Kvale considers some of the key philosophical issues relating to interviewing: the interview as conversation, hermeneutics, phenomenology, concerns about ethics as well as validity, and postmodernism. Having established this framework, the author then analyzes the seven stages of the interview process - from designing a study to writing it up.
- Practical Evaluation by Michael Quinn Patton Surveys different interviewing strategies, from, a) informal/conversational, to b) interview guide approach, to c) standardized and open-ended, to d) closed/quantitative. Also discusses strategies for wording questions that are open-ended, clear, sensitive, and neutral, while supporting the speaker. Provides suggestions for probing and maintaining control of the interview process, as well as suggestions for recording and transcription.
- The SAGE Handbook of Interview Research by Amir B. Marvasti (Editor); James A. Holstein (Editor); Jaber F. Gubrium (Editor); Karyn D. McKinney (Editor) The new edition of this landmark volume emphasizes the dynamic, interactional, and reflexive dimensions of the research interview. Contributors highlight the myriad dimensions of complexity that are emerging as researchers increasingly frame the interview as a communicative opportunity as much as a data-gathering format. The book begins with the history and conceptual transformations of the interview, which is followed by chapters that discuss the main components of interview practice. Taken together, the contributions to The SAGE Handbook of Interview Research: The Complexity of the Craft encourage readers simultaneously to learn the frameworks and technologies of interviewing and to reflect on the epistemological foundations of the interview craft.
- The SAGE Handbook of Online Research Methods by Nigel G. Fielding, Raymond M. Lee and Grant Blank (Editors) Bringing together the leading names in both qualitative and quantitative online research, this new edition is organised into nine sections: 1. Online Research Methods 2. Designing Online Research 3. Online Data Capture and Data Collection 4. The Online Survey 5. Digital Quantitative Analysis 6. Digital Text Analysis 7. Virtual Ethnography 8. Online Secondary Analysis: Resources and Methods 9. The Future of Online Social Research
ONLINE RESOURCES, COMMUNITIES, AND DATABASES
- Interviews as a Method for Qualitative Research (video) This short video summarizes why interviews can serve as useful data in qualitative research.
- Companion website to Bloomberg and Volpe's Completing Your Qualitative Dissertation: A Road Map from Beginning to End, 4th ed Provides helpful templates and appendices featured in the book, as well as links to other useful dissertation resources.
- International Congress of Qualitative Inquiry Annual conference hosted by the International Center for Qualitative Inquiry at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, which aims to facilitate the development of qualitative research methods across a wide variety of academic disciplines, among other initiatives.
- METHODSPACE An online home of the research methods community, where practicing researchers share how to make research easier.
- SAGE researchmethods Researchers can explore methods concepts to help them design research projects, understand particular methods or identify a new method, conduct their research, and write up their findings. A "methods map" facilitates finding content on methods.
The decision to conduct interviews, and the type of interviewing to use, should flow from, or align with, the methodological paradigm chosen for your study, whether that paradigm is interpretivist, critical, positivist, or participative in nature (or a combination of these).
Structured:
- Structured Interview. Entry in The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methodsby Floyd J. Fowler Jr., Editors: Michael S. Lewis-Beck; Alan E. Bryman; Tim Futing Liao (Editor) A concise article noting standards, procedures, and recommendations for developing and testing structured interviews. For an example of structured interview questions, you may view the Current Population Survey, May 2008: Public Participation in the Arts Supplement (ICPSR 29641), Apr 15, 2011 at https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR29641.v1 (To see the survey questions, preview the user guide, which can be found under the "Data and Documentation" tab. Then, look for page 177 (attachment 8).
Semi-Structured:
- Semi-Structured Interview. Entry in The SAGE Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methodsby Lioness Ayres; Editor: Lisa M. Given The semi-structured interview is a qualitative data collection strategy in which the researcher asks informants a series of predetermined but open-ended questions. The researcher has more control over the topics of the interview than in unstructured interviews, but in contrast to structured interviews or questionnaires that use closed questions, there is no fixed range of responses to each question.
Unstructured:
- Unstructured Interview. Entry in The SAGE Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methodsby Michael W. Firmin; Editor: Lisa M. Given Unstructured interviews in qualitative research involve asking relatively open-ended questions of research participants in order to discover their percepts on the topic of interest. Interviews, in general, are a foundational means of collecting data when using qualitative research methods. They are designed to draw from the interviewee constructs embedded in his or her thinking and rationale for decision making. The researcher uses an inductive method in data gathering, regardless of whether the interview method is open, structured, or semi-structured. That is, the researcher does not wish to superimpose his or her own viewpoints onto the person being interviewed. Rather, inductively, the researcher wishes to understand the participant's perceptions, helping him or her to articulate percepts such that they will be understood clearly by the journal reader.
Genres and Uses
Focus groups:.
- "Focus Groups." Annual Review of Sociology 22 (1996): 129-1524.by David L. Morgan Discusses the use of focus groups and group interviews as methods for gathering qualitative data used by sociologists and other academic and applied researchers. Focus groups are recommended for giving voice to marginalized groups and revealing the group effect on opinion formation.
- Qualitative Research Methods: A Data Collector's Field Guide (See Module 4: "Focus Groups")by Mack, N., et al. This field guide is based on an approach to doing team-based, collaborative qualitative research that has repeatedly proven successful in research projects sponsored by Family Health International (FHI) throughout the developing world. With its straightforward delivery of information on the main qualitative methods being used in public health research today, the guide speaks to the need for simple yet effective instruction on how to do systematic and ethically sound qualitative research. The aim of the guide is thus practical. In bypassing extensive discussion on the theoretical underpinnings of qualitative research, it distinguishes itself as a how-to guide to be used in the field.
In-Depth (typically One-on-One):
- A Practical Introduction to in-Depth Interviewingby Alan Morris Are you new to qualitative research or a bit rusty and in need of some inspiration? Are you doing a research project involving in-depth interviews? Are you nervous about carrying out your interviews? This book will help you complete your qualitative research project by providing a nuts and bolts introduction to interviewing. With coverage of ethics, preparation strategies and advice for handling the unexpected in the field, this handy guide will help you get to grips with the basics of interviewing before embarking on your research. While recognising that your research question and the context of your research will drive your approach to interviewing, this book provides practical advice often skipped in traditional methods textbooks.
- Qualitative Research Methods: A Data Collector's Field Guide (See Module 3: "In-Depth Interviews")by Mack, N., et al. This field guide is based on an approach to doing team-based, collaborative qualitative research that has repeatedly proven successful in research projects sponsored by Family Health International (FHI) throughout the developing world. With its straightforward delivery of information on the main qualitative methods being used in public health research today, the guide speaks to the need for simple yet effective instruction on how to do systematic and ethically sound qualitative research. The aim of the guide is thus practical. In bypassing extensive discussion on the theoretical underpinnings of qualitative research, it distinguishes itself as a how-to guide to be used in the field.
Folklore Research and Oral Histories:
In addition to the following resource, see the Oral History page of this guide for helpful resources on Oral History interviewing.
American Folklife Center at the Library of Congress. Folklife and Fieldwork: A Layman’s Introduction to Field Techniques Interviews gathered for purposes of folklore research are similar to standard social science interviews in some ways, but also have a good deal in common with oral history approaches to interviewing. The focus in a folklore research interview is on documenting and trying to understand the interviewee's way of life relative to a culture or subculture you are studying. This guide includes helpful advice and tips for conducting fieldwork in folklore, such as tips for planning, conducting, recording, and archiving interviews.
An interdisciplinary scientific program within the Institute for Quantitative Social Science which encourages and facilitates research and instruction in the theory and practice of survey research. The primary mission of PSR is to provide survey research resources to enhance the quality of teaching and research at Harvard.
- Internet, Phone, Mail, and Mixed-Mode Surveysby Don A. Dillman; Jolene D. Smyth; Leah Melani Christian The classic survey design reference, updated for the digital age. The new edition is thoroughly updated and revised, and covers all aspects of survey research. It features expanded coverage of mobile phones, tablets, and the use of do-it-yourself surveys, and Dillman's unique Tailored Design Method is also thoroughly explained. This new edition is complemented by copious examples within the text and accompanying website. It includes: Strategies and tactics for determining the needs of a given survey, how to design it, and how to effectively administer it. How and when to use mail, telephone, and Internet surveys to maximum advantage. Proven techniques to increase response rates. Guidance on how to obtain high-quality feedback from mail, electronic, and other self-administered surveys. Direction on how to construct effective questionnaires, including considerations of layout. The effects of sponsorship on the response rates of surveys. Use of capabilities provided by newly mass-used media: interactivity, presentation of aural and visual stimuli. The Fourth Edition reintroduces the telephone--including coordinating land and mobile.
User Experience (UX) and Marketing:
- See the "UX & Market Research Interviews" tab on this guide, above. May include Focus Groups, above.
Screening for Research Site Selection:
- Research interviews are used not only to furnish research data for theoretical analysis in the social sciences, but also to plan other kinds of studies. For example, interviews may allow researchers to screen appropriate research sites to conduct empirical studies (such as randomized controlled trials) in a variety of fields, from medicine to law. In contrast to interviews conducted in the course of social research, such interviews do not typically serve as the data for final analysis and publication.
ENGAGING PARTICIPANTS
Research ethics .
- Human Subjects (IRB) The Committee on the Use of Human Subjects (CUHS) serves as the Institutional Review Board for the University area which includes the Cambridge and Allston campuses at Harvard. Find your IRB contact person , or learn about required ethics training. You may also find the IRB Lifecycle Guide helpful. This is the preferred IRB portal for Harvard graduate students and other researchers. IRB forms can be downloaded via the ESTR Library (click on the "Templates and Forms" tab, then navigate to pages 2 and 3 to find the documents labelled with “HUA” for the Harvard University Area IRB. Nota bene: You may use these forms only if you submit your study to the Harvard University IRB). The IRB office can be reached through email at [email protected] or by telephone at (617) 496-2847.
- Undergraduate Research Training Program (URTP) Portal The URTP at Harvard University is a comprehensive platform to create better prepared undergraduate researchers. The URTP is comprised of research ethics training sessions, a student-focused curriculum, and an online decision form that will assist students in determining whether their project requires IRB review. Students should examine the URTP's guide for student researchers: Introduction to Human Subjects Research Protection.
- Ethics reports From the Association of Internet Researchers (AoIR)
- Respect, Beneficence, and Justice: QDR General Guidance for Human Participants If you are hoping to share your qualitative interview data in a repository after it has been collected, you will need to plan accordingly via informed consent, careful de-identification procedures, and data access controls. Consider consulting with the Qualitative Research Support Group at Harvard Library and consulting with Harvard's Dataverse contacts to help you think through all of the contingencies and processes.
- "Conducting a Qualitative Child Interview: Methodological Considerations." Journal of Advanced Nursing 42/5 (2003): 434-441 by Kortesluoma, R., et al. The purpose of this article is to illustrate the theoretical premises of child interviewing, as well as to describe some practical methodological solutions used during interviews. Factors that influence data gathered from children and strategies for taking these factors into consideration during the interview are also described.
- "Crossing Cultural Barriers in Research Interviewing." Qualitative Social Work 63/3 (2007): 353-372 by Sands, R., et al. This article critically examines a qualitative research interview in which cultural barriers between a white non-Muslim female interviewer and an African American Muslim interviewee, both from the USA, became evident and were overcome within the same interview.
- Decolonizing Methodologies: Research and Indigenous Peoples by Linda Tuhiwai Smith This essential volume explores intersections of imperialism and research - specifically, the ways in which imperialism is embedded in disciplines of knowledge and tradition as 'regimes of truth.' Concepts such as 'discovery' and 'claiming' are discussed and an argument presented that the decolonization of research methods will help to reclaim control over indigenous ways of knowing and being. The text includes case-studies and examples, and sections on new indigenous literature and the role of research in indigenous struggles for social justice.
This resource, sponsored by University of Oregon Libraries, exemplifies the use of interviewing methodologies in research that foregrounds traditional knowledge. The methodology page summarizes the approach.
- Ethics: The Need to Tread Carefully. Chapter in A Practical Introduction to in-Depth Interviewing by Alan Morris Pay special attention to the sections in chapter 2 on "How to prevent and respond to ethical issues arising in the course of the interview," "Ethics in the writing up of your interviews," and "The Ethics of Care."
- Handbook on Ethical Issues in Anthropology by Joan Cassell (Editor); Sue-Ellen Jacobs (Editor) This publication of the American Anthropological Association presents and discusses issues and sources on ethics in anthropology, as well as realistic case studies of ethical dilemmas. It is meant to help social science faculty introduce discussions of ethics in their courses. Some of the topics are relevant to interviews, or at least to studies of which interviews are a part. See chapters 3 and 4 for cases, with solutions and commentary, respectively.
- Research Ethics from the Chanie Wenjack School for Indigenous Studies, Trent University (Open Access) An overview of Indigenous research ethics and protocols from the across the globe.
- Resources for Equity in Research Consult these resources for guidance on creating and incorporating equitable materials into public health research studies that entail community engagement.
The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research Ethics by Ron Iphofen (Editor); Martin Tolich (Editor) This handbook is a much-needed and in-depth review of the distinctive set of ethical considerations which accompanies qualitative research. This is particularly crucial given the emergent, dynamic and interactional nature of most qualitative research, which too often allows little time for reflection on the important ethical responsibilities and obligations. Contributions from leading international researchers have been carefully organized into six key thematic sections: Part One: Thick Descriptions Of Qualitative Research Ethics; Part Two: Qualitative Research Ethics By Technique; Part Three: Ethics As Politics; Part Four: Qualitative Research Ethics With Vulnerable Groups; Part Five: Relational Research Ethics; Part Six: Researching Digitally. This Handbook is a one-stop resource on qualitative research ethics across the social sciences that draws on the lessons learned and the successful methods for surmounting problems - the tried and true, and the new.
RESEARCH COMPLIANCE AND PRIVACY LAWS
Research Compliance Program for FAS/SEAS at Harvard : The Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS), including the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), and the Office of the Vice Provost for Research (OVPR) have established a shared Research Compliance Program (RCP). An area of common concern for interview studies is international projects and collaboration . RCP is a resource to provide guidance on which international activities may be impacted by US sanctions on countries, individuals, or entities and whether licenses or other disclosure are required to ship or otherwise share items, technology, or data with foreign collaborators.
- Harvard Global Support Services (GSS) is for students, faculty, staff, and researchers who are studying, researching, or working abroad. Their services span safety and security, health, culture, outbound immigration, employment, financial and legal matters, and research center operations. These include travel briefings and registration, emergency response, guidance on international projects, and managing in-country operations.
Generative AI: Harvard-affiliated researchers should not enter data classified as confidential ( Level 2 and above ), including non-public research data, into publicly-available generative AI tools, in accordance with the University’s Information Security Policy. Information shared with generative AI tools using default settings is not private and could expose proprietary or sensitive information to unauthorized parties.
Privacy Laws: Be mindful of any potential privacy laws that may apply wherever you conduct your interviews. The General Data Protection Regulation is a high-profile example (see below):
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) This Regulation lays down rules relating to the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and rules relating to the free movement of personal data. It protects fundamental rights and freedoms of natural persons and in particular their right to the protection of personal data. The free movement of personal data within the Union shall be neither restricted nor prohibited for reasons connected with the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data. For a nice summary of what the GDPR requires, check out the GDPR "crash course" here .
SEEKING CONSENT
If you would like to see examples of consent forms, ask your local IRB, or take a look at these resources:
- Model consent forms for oral history, suggested by the Centre for Oral History and Digital Storytelling at Concordia University
- For NIH-funded research, see this resource for developing informed consent language in research studies where data and/or biospecimens will be stored and shared for future use.
POPULATION SAMPLING
If you wish to assemble resources to aid in sampling, such as the USPS Delivery Sequence File, telephone books, or directories of organizations and listservs, please contact our data librarian or write to [email protected] .
- Research Randomizer A free web-based service that permits instant random sampling and random assignment. It also contains an interactive tutorial perfect for students taking courses in research methods.
- Practical Tools for Designing and Weighting Survey Samples by Richard Valliant; Jill A. Dever; Frauke Kreuter Survey sampling is fundamentally an applied field. The goal in this book is to put an array of tools at the fingertips of practitioners by explaining approaches long used by survey statisticians, illustrating how existing software can be used to solve survey problems, and developing some specialized software where needed. This book serves at least three audiences: (1) Students seeking a more in-depth understanding of applied sampling either through a second semester-long course or by way of a supplementary reference; (2) Survey statisticians searching for practical guidance on how to apply concepts learned in theoretical or applied sampling courses; and (3) Social scientists and other survey practitioners who desire insight into the statistical thinking and steps taken to design, select, and weight random survey samples. Several survey data sets are used to illustrate how to design samples, to make estimates from complex surveys for use in optimizing the sample allocation, and to calculate weights. Realistic survey projects are used to demonstrate the challenges and provide a context for the solutions. The book covers several topics that either are not included or are dealt with in a limited way in other texts. These areas include: sample size computations for multistage designs; power calculations related to surveys; mathematical programming for sample allocation in a multi-criteria optimization setting; nuts and bolts of area probability sampling; multiphase designs; quality control of survey operations; and statistical software for survey sampling and estimation. An associated R package, PracTools, contains a number of specialized functions for sample size and other calculations. The data sets used in the book are also available in PracTools, so that the reader may replicate the examples or perform further analyses.
- Sampling: Design and Analysis by Sharon L. Lohr Provides a modern introduction to the field of sampling. With a multitude of applications from a variety of disciplines, the book concentrates on the statistical aspects of taking and analyzing a sample. Overall, the book gives guidance on how to tell when a sample is valid or not, and how to design and analyze many different forms of sample surveys.
- Sampling Techniques by William G. Cochran Clearly demonstrates a wide range of sampling methods now in use by governments, in business, market and operations research, social science, medicine, public health, agriculture, and accounting. Gives proofs of all the theoretical results used in modern sampling practice. New topics in this edition include the approximate methods developed for the problem of attaching standard errors or confidence limits to nonlinear estimates made from the results of surveys with complex plans.
- "Understanding the Process of Qualitative Data Collection" in Chapter 13 (pp. 103–1162) of 30 Essential Skills for the Qualitative Researcher by John W. Creswell Provides practical "how-to" information for beginning researchers in the social, behavioral, and health sciences with many applied examples from research design, qualitative inquiry, and mixed methods.The skills presented in this book are crucial for a new qualitative researcher starting a qualitative project.
- Survey Methodology by Robert M. Groves; Floyd J. Fowler; Mick P. Couper; James M. Lepkowski; Eleanor Singer; Roger Tourangeau; Floyd J. Fowler coverage includes sampling frame evaluation, sample design, development of questionnaires, evaluation of questions, alternative modes of data collection, interviewing, nonresponse, post-collection processing of survey data, and practices for maintaining scientific integrity.
The way a qualitative researcher constructs and approaches interview questions should flow from, or align with, the methodological paradigm chosen for the study, whether that paradigm is interpretivist, critical, positivist, or participative in nature (or a combination of these).
Constructing Your Questions
Helpful texts:.
- "Developing Questions" in Chapter 4 (pp. 98–108) of Becoming Qualitative Researchers by Corrine Glesne Ideal for introducing the novice researcher to the theory and practice of qualitative research, this text opens students to the diverse possibilities within this inquiry approach, while helping them understand how to design and implement specific research methods.
- "Learning to Interview in the Social Sciences" Qualitative Inquiry, 9(4) 2003, 643–668 by Roulston, K., deMarrais, K., & Lewis, J. B. See especially the section on "Phrasing and Negotiating Questions" on pages 653-655 and common problems with framing questions noted on pages 659 - 660.
- Qualitative Research Interviewing: Biographic Narrative and Semi-Structured Methods (See sections on “Lightly and Heavily Structured Depth Interviewing: Theory-Questions and Interviewer-Questions” and “Preparing for any Interviewing Sequence") by Tom Wengraf Unique in its conceptual coherence and the level of practical detail, this book provides a comprehensive resource for those concerned with the practice of semi-structured interviewing, the most commonly used interview approach in social research, and in particular for in-depth, biographic narrative interviewing. It covers the full range of practices from the identification of topics through to strategies for writing up research findings in diverse ways.
- "Scripting a Qualitative Purpose Statement and Research Questions" in Chapter 12 (pp. 93–102) of 30 Essential Skills for the Qualitative Researcher by John W. Creswell Provides practical "how-to" information for beginning researchers in the social, behavioral, and health sciences with many applied examples from research design, qualitative inquiry, and mixed methods.The skills presented in this book are crucial for a new qualitative researcher starting a qualitative project.
- Some Strategies for Developing Interview Guides for Qualitative Interviews by Sociology Department, Harvard University Includes general advice for conducting qualitative interviews, pros and cons of recording and transcription, guidelines for success, and tips for developing and phrasing effective interview questions.
- Tip Sheet on Question Wording by Harvard University Program on Survey Research
Let Theory Guide You:
The quality of your questions depends on how you situate them within a wider body of knowledge. Consider the following advice:
A good literature review has many obvious virtues. It enables the investigator to define problems and assess data. It provides the concepts on which percepts depend. But the literature review has a special importance for the qualitative researcher. This consists of its ability to sharpen his or her capacity for surprise (Lazarsfeld, 1972b). The investigator who is well versed in the literature now has a set of expectations the data can defy. Counterexpectational data are conspicuous, readable, and highly provocative data. They signal the existence of unfulfilled theoretical assumptions, and these are, as Kuhn (1962) has noted, the very origins of intellectual innovation. A thorough review of the literature is, to this extent, a way to manufacture distance. It is a way to let the data of one's research project take issue with the theory of one's field.
McCracken, G. (1988), The Long Interview, Sage: Newbury Park, CA, p. 31
When drafting your interview questions, remember that everything follows from your central research question. Also, on the way to writing your "operationalized" interview questions, it's helpful to draft broader, intermediate questions, couched in theory. Nota bene: While it is important to know the literature well before conducting your interview(s), be careful not to present yourself to your research participant(s) as "the expert," which would be presumptuous and could be intimidating. Rather, the purpose of your knowledge is to make you a better, keener listener.
If you'd like to supplement what you learned about relevant theories through your coursework and literature review, try these sources:
- Annual Reviews Review articles sum up the latest research in many fields, including social sciences, biomedicine, life sciences, and physical sciences. These are timely collections of critical reviews written by leading scientists.
- HOLLIS - search for resources on theories in your field Modify this example search by entering the name of your field in place of "your discipline," then hit search.
- Oxford Bibliographies Written and reviewed by academic experts, every article in this database is an authoritative guide to the current scholarship in a variety of fields, containing original commentary and annotations.
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses (PQDT) Indexes dissertations and masters' theses from most North American graduate schools as well as some European universities. Provides full text for most indexed dissertations from 1990-present.
- Very Short Introductions Launched by Oxford University Press in 1995, Very Short Introductions offer concise introductions to a diverse range of subjects from Climate to Consciousness, Game Theory to Ancient Warfare, Privacy to Islamic History, Economics to Literary Theory.
CONDUCTING INTERVIEWS
Equipment and software: .
- Lamont Library loans microphones and podcast starter kits, which will allow you to capture audio (and you may record with software, such as Garage Band).
- Cabot Library loans digital recording devices, as well as USB microphones.
If you prefer to use your own device, you may purchase a small handheld audio recorder, or use your cell phone.
- Audio Capture Basics (PDF) - Helpful instructions, courtesy of the Lamont Library Multimedia Lab.
- Getting Started with Podcasting/Audio: Guidelines from Harvard Library's Virtual Media Lab for preparing your interviewee for a web-based recording (e.g., podcast, interview)
- Camtasia Screen Recorder and Video Editor
- Zoom: Video Conferencing, Web Conferencing
- Visit the Multimedia Production Resources guide! Consult it to find and learn how to use audiovisual production tools, including: cameras, microphones, studio spaces, and other equipment at Cabot Science Library and Lamont Library.
- Try the virtual office hours offered by the Lamont Multimedia Lab!
TIPS FOR CONDUCTING INTERVIEWS
Quick handout: .
- Research Interviewing Tips (Courtesy of Dr. Suzanne Spreadbury)
Remote Interviews:
- For Online or Distant Interviews, See "Remote Research & Virtual Fieldwork" on this guide .
- Deborah Lupton's Bibliography: Doing Fieldwork in a Pandemic
Seeking Consent:
Books and articles: .
- "App-Based Textual Interviews: Interacting With Younger Generations in a Digitalized Social Reallity."International Journal of Social Research Methodology (12 June 2022). Discusses the use of texting platforms as a means to reach young people. Recommends useful question formulations for this medium.
- "Learning to Interview in the Social Sciences." Qualitative Inquiry, 9(4) 2003, 643–668 by Roulston, K., deMarrais, K., & Lewis, J. B. See especially the section on "Phrasing and Negotiating Questions" on pages 653-655 and common problems with framing questions noted on pages 659-660.
- "Slowing Down and Digging Deep: Teaching Students to Examine Interview Interaction in Depth." LEARNing Landscapes, Spring 2021 14(1) 153-169 by Herron, Brigette A. and Kathryn Roulston. Suggests analysis of videorecorded interviews as a precursor to formulating one's own questions. Includes helpful types of probes.
- Using Interviews in a Research Project by Nigel Joseph Mathers; Nicholas J Fox; Amanda Hunn; Trent Focus Group. A work pack to guide researchers in developing interviews in the healthcare field. Describes interview structures, compares face-to-face and telephone interviews. Outlines the ways in which different types of interview data can be analysed.
- “Working through Challenges in Doing Interview Research.” International Journal of Qualitative Methods, (December 2011), 348–66 by Roulston, Kathryn. The article explores (1) how problematic interactions identified in the analysis of focus group data can lead to modifications in research design, (2) an approach to dealing with reported data in representations of findings, and (3) how data analysis can inform question formulation in successive rounds of data generation. Findings from these types of examinations of interview data generation and analysis are valuable for informing both interview practice as well as research design.
Videos:

The way a qualitative researcher transcribes interviews should flow from, or align with, the methodological paradigm chosen for the study, whether that paradigm is interpretivist, critical, positivist, or participative in nature (or a combination of these).
TRANSCRIPTION
Before embarking on a transcription project, it's worthwhile to invest in the time and effort necessary to capture good audio, which will make the transcription process much easier. If you haven't already done so, check out the audio capture guidelines from Harvard Library's Virtual Media Lab , or contact a media staff member for customized recommendations. First and foremost, be mindful of common pitfalls by watching this short video that identifies the most common errors to avoid!
SOFTWARE:
- Adobe Premiere Pro Speech-To-Text automatically generates transcripts and adds captions to your videos. Harvard affiliates can download Adobe Premiere in the Creative Cloud Suite.
- GoTranscript provides cost-effective human-generated transcriptions.
- pyTranscriber is an app for generating automatic transcription and/or subtitles for audio and video files. It uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text service, has a friendly graphical user interface, and is purported to work nicely with Chinese.
- Otter provides a new way to capture, store, search and share voice conversations, lectures, presentations, meetings, and interviews. The startup is based in Silicon Valley with a team of experienced Ph.Ds and engineers from Google, Facebook, Yahoo and Nuance (à la Dragon). Free accounts available. This is the software that Zoom uses to generate automated transcripts, so if you have access to a Zoom subscription, you have access to Otter transcriptions with it (applicable in several languages ). As with any automated approach, be prepared to correct any errors after the fact, by hand.
- Panopto is available to Harvard affiliates and generates ASR (automated speech recognition) captions . You may upload compatible audio files into it. As with any automatically generated transcription, you will need to make manual revisions. ASR captioning is available in several languages . Panopto maintains robust security practices, including strong authentication measures and end-to-end encryption, ensuring your content remains private and protected.
- REV.Com allows you to record and transcribe any calls on the iPhone, both outgoing and incoming. It may be useful for recording phone interviews. Rev lets you choose whether you want an AI- or human-generated transcription, with a fast turnaround. Rev has Service Organization Controls Type II (SOC2) certification (a SOC2 cert looks at and verifies an organization’s processing integrity, privacy practices, and security safeguards).
- Scribie Audio/Video Transcription provides automated or manual transcriptions for a small fee. As with any transcription service, some revisions will be necessary after the fact, particularly for its automated transcripts.
- Sonix automatically transcribes, translates, and helps to organize audio and video files in over 40 languages. It's fast and affordable, with good accuracy. The free trial includes 30 minutes of free transcription.
- TranscriptionWing uses a human touch process to clean up machine-generated transcripts so that the content will far more accurately reflect your audio recording.
- Whisper is a tool from OpenAI that facilitates transcription of sensitive audiovisual recordings (e.g., of research interviews) on your own device. Installation and use depends on your operating system and which version you install. Important Note: The Whisper API, where audio is sent to OpenAI to be processed by them and then sent back (usually through a programming language like Python) is NOT appropriate for sensitive data. The model should be downloaded with tools such as those described in this FAQ , so that audio is kept to your local machine. For assistance, contact James Capobianco .
EQUIPMENT:
- Transcription pedals are in circulation and available to borrow from the Circulation desk at Lamont, or use at Lamont Library's Media Lab on level B. For hand-transcribing your interviews, they work in conjunction with software such as Express Scribe , which is loaded on Media Lab computers, or you may download for free on your own machine (Mac or PC versions; scroll down the downloads page for the latter). The pedals are plug-and-play USB, allow a wide range of playback speeds, and have 3 programmable buttons, which are typically set to rewind/play/fast-forward. Instructions are included in the bag that covers installation and set-up of the software, and basic use of the pedals.
NEED HELP?
- Try the virtual office hours offered by the Lamont Multimedia Lab!
- If you're creating podcasts, login to Canvas and check out the Podcasting/Audio guide .
Helpful Texts:
- "Transcription as a Crucial Step of Data Analysis" in Chapter 5 of The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysisby Uwe Flick (Editor) Covers basic terminology for transcription, shares caveats for transcribers, and identifies components of vocal behavior. Provides notation systems for transcription, suggestions for transcribing turn-taking, and discusses new technologies and perspectives. Includes a bibliography for further reading.
- "Transcribing the Oral Interview: Part Art, Part Science " on p. 10 of the Centre for Community Knowledge (CCK) newsletter: TIMESTAMPby Mishika Chauhan and Saransh Srivastav
QUALITATIVE DATA ANALYSIS
Software .
- Free download available for Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS) affiliates
- Desktop access at Lamont Library Media Lab, 3rd floor
- Desktop access at Harvard Kennedy School Library (with HKS ID)
- Remote desktop access for Harvard affiliates from IQSS Computer Labs . Email them at [email protected] and ask for a new lab account and remote desktop access to NVivo.
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) access available to Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health affiliates
CODING AND THEMEING YOUR DATA
Data analysis methods should flow from, or align with, the methodological paradigm chosen for your study, whether that paradigm is interpretivist, critical, positivist, or participative in nature (or a combination of these). Some established methods include Content Analysis, Critical Analysis, Discourse Analysis, Gestalt Analysis, Grounded Theory Analysis, Interpretive Analysis, Narrative Analysis, Normative Analysis, Phenomenological Analysis, Rhetorical Analysis, and Semiotic Analysis, among others. The following resources should help you navigate your methodological options and put into practice methods for coding, themeing, interpreting, and presenting your data.
- Users can browse content by topic, discipline, or format type (reference works, book chapters, definitions, etc.). SRM offers several research tools as well: a methods map, user-created reading lists, a project planner, and advice on choosing statistical tests.
- Abductive Coding: Theory Building and Qualitative (Re)Analysis by Vila-Henninger, et al. The authors recommend an abductive approach to guide qualitative researchers who are oriented towards theory-building. They outline a set of tactics for abductive analysis, including the generation of an abductive codebook, abductive data reduction through code equations, and in-depth abductive qualitative analysis.
- Analyzing and Interpreting Qualitative Research: After the Interview by Charles F. Vanover, Paul A. Mihas, and Johnny Saldana (Editors) Providing insight into the wide range of approaches available to the qualitative researcher and covering all steps in the research process, the authors utilize a consistent chapter structure that provides novice and seasoned researchers with pragmatic, "how-to" strategies. Each chapter author introduces the method, uses one of their own research projects as a case study of the method described, shows how the specific analytic method can be used in other types of studies, and concludes with three questions/activities to prompt class discussion or personal study.
- "Analyzing Qualitative Data." Theory Into Practice 39, no. 3 (2000): 146-54 by Margaret D. LeCompte This article walks readers though rules for unbiased data analysis and provides guidance for getting organized, finding items, creating stable sets of items, creating patterns, assembling structures, and conducting data validity checks.
- "Coding is Not a Dirty Word" in Chapter 1 (pp. 1–30) of Enhancing Qualitative and Mixed Methods Research with Technology by Shalin Hai-Jew (Editor) Current discourses in qualitative research, especially those situated in postmodernism, represent coding and the technology that assists with coding as reductive, lacking complexity, and detached from theory. In this chapter, the author presents a counter-narrative to this dominant discourse in qualitative research. The author argues that coding is not necessarily devoid of theory, nor does the use of software for data management and analysis automatically render scholarship theoretically lightweight or barren. A lack of deep analytical insight is a consequence not of software but of epistemology. Using examples informed by interpretive and critical approaches, the author demonstrates how NVivo can provide an effective tool for data management and analysis. The author also highlights ideas for critical and deconstructive approaches in qualitative inquiry while using NVivo. By troubling the positivist discourse of coding, the author seeks to create dialogic spaces that integrate theory with technology-driven data management and analysis, while maintaining the depth and rigor of qualitative research.
- The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers by Johnny Saldana An in-depth guide to the multiple approaches available for coding qualitative data. Clear, practical and authoritative, the book profiles 32 coding methods that can be applied to a range of research genres from grounded theory to phenomenology to narrative inquiry. For each approach, Saldaña discusses the methods, origins, a description of the method, practical applications, and a clearly illustrated example with analytic follow-up. Essential reading across the social sciences.
- Flexible Coding of In-depth Interviews: A Twenty-first-century Approach by Nicole M. Deterding and Mary C. Waters The authors suggest steps in data organization and analysis to better utilize qualitative data analysis technologies and support rigorous, transparent, and flexible analysis of in-depth interview data.
- From the Editors: What Grounded Theory is Not by Roy Suddaby Walks readers through common misconceptions that hinder grounded theory studies, reinforcing the two key concepts of the grounded theory approach: (1) constant comparison of data gathered throughout the data collection process and (2) the determination of which kinds of data to sample in succession based on emergent themes (i.e., "theoretical sampling").
- “Good enough” methods for life-story analysis, by Wendy Luttrell. In Quinn N. (Ed.), Finding culture in talk (pp. 243–268). Demonstrates for researchers of culture and consciousness who use narrative how to concretely document reflexive processes in terms of where, how and why particular decisions are made at particular stages of the research process.
- Presentation slides on coding and themeing your data, derived from Saldana, Spradley, and LeCompte Click to request access.
- Qualitative Data Analysis by Matthew B. Miles; A. Michael Huberman A practical sourcebook for researchers who make use of qualitative data, presenting the current state of the craft in the design, testing, and use of qualitative analysis methods. Strong emphasis is placed on data displays matrices and networks that go beyond ordinary narrative text. Each method of data display and analysis is described and illustrated.
- "A Survey of Qualitative Data Analytic Methods" in Chapter 4 (pp. 89–138) of Fundamentals of Qualitative Research by Johnny Saldana Provides an in-depth introduction to coding as a heuristic, particularly focusing on process coding, in vivo coding, descriptive coding, values coding, dramaturgical coding, and versus coding. Includes advice on writing analytic memos, developing categories, and themeing data.
- "Thematic Networks: An Analytic Tool for Qualitative Research." Qualitative Research : QR, 1(3), 385–405 by Jennifer Attride-Stirling Details a technique for conducting thematic analysis of qualitative material, presenting a step-by-step guide of the analytic process, with the aid of an empirical example. The analytic method presented employs established, well-known techniques; the article proposes that thematic analyses can be usefully aided by and presented as thematic networks.
- Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clark Walks readers through the process of reflexive thematic analysis, step by step. The method may be adapted in fields outside of psychology as relevant. Pair this with One Size Fits All? What Counts as Quality Practice in Reflexive Thematic Analysis? by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clark
TESTING OR GENERATING THEORIES
The quality of your data analysis depends on how you situate what you learn within a wider body of knowledge. Consider the following advice:
Once you have coalesced around a theory, realize that a theory should reveal rather than color your discoveries. Allow your data to guide you to what's most suitable. Grounded theory researchers may develop their own theory where current theories fail to provide insight. This guide on Theoretical Models from Alfaisal University Library provides a helpful overview on using theory.
MANAGING & FINDING INTERVIEW DATA
Managing your elicited interview data, general guidance: .
- Research Data Management @ Harvard A reference guide with information and resources to help you manage your research data. See also: Harvard Research Data Security Policy , on the Harvard University Research Data Management website.
- Data Management For Researchers: Organize, Maintain and Share Your Data for Research Success by Kristin Briney. A comprehensive guide for scientific researchers providing everything they need to know about data management and how to organize, document, use and reuse their data.
- Open Science Framework (OSF) An open-source project management tool that makes it easy to collaborate within and beyond Harvard throughout a project's lifecycle. With OSF you can manage, store, and share documents, datasets, and other information with your research team. You can also publish your work to share it with a wider audience. Although data can be stored privately, because this platform is hosted on the Internet and designed with open access in mind, it is not a good choice for highly sensitive data.
- Free cloud storage solutions for Harvard affiliates to consider include: Google Drive , DropBox , or OneDrive ( up to DSL3 )
Data Confidentiality and Secure Handling:
- Data Security Levels at Harvard - Research Data Examples This resource provided by Harvard Data Security helps you determine what level of access is appropriate for your data. Determine whether it should be made available for public use, limited to the Harvard community, or be protected as either "confidential and sensitive," "high risk," or "extremely sensitive." See also: Harvard Data Classification Table
- Harvard's Best Practices for Protecting Privacy and Harvard Information Security Collaboration Tools Matrix Follow the nuts-and-bolts advice for privacy best practices at Harvard. The latter resource reveals the level of security that can be relied upon for a large number of technological tools and platforms used at Harvard to conduct business, such as email, Slack, Accellion Kiteworks, OneDrive/SharePoint, etc.
- “Protecting Participant Privacy While Maintaining Content and Context: Challenges in Qualitative Data De‐identification and Sharing.” Proceedings of the ASIST Annual Meeting 57 (1) (2020): e415-420 by Myers, Long, and Polasek Presents an informed and tested protocol, based on the De-Identification guidelines published by the Qualitative Data Repository (QDR) at Syracuse University. Qualitative researchers may consult it to guide their data de-identification efforts.
- QDS Qualitative Data Sharing Toolkit The Qualitative Data Sharing (QDS) project and its toolkit was funded by the NIH National Human Genome Research Institute (R01HG009351). It provides tools and resources to help researchers, especially those in the health sciences, share qualitative research data while protecting privacy and confidentiality. It offers guidance on preparing data for sharing through de-identification and access control. These health sciences research datasets in ICPSR's Qualitative Data Sharing (QDS) Project Series were de-identified using the QuaDS Software and the project’s QDS guidelines.
- Table of De-Identification Techniques
- Generative AI Harvard-affiliated researchers should not enter data classified as confidential ( Level 2 and above ), including non-public research data, into publicly-available generative AI tools, in accordance with the University’s Information Security Policy. Information shared with generative AI tools using default settings is not private and could expose proprietary or sensitive information to unauthorized parties.
- Harvard Information Security Quick Reference Guide Storage guidelines, based on the data's security classification level (according to its IRB classification) is displayed on page 2, under "handling."
- Email Encryption Harvard Microsoft 365 users can now send encrypted messages and files directly from the Outlook web or desktop apps. Encrypting an email adds an extra layer of security to the message and its attachments (up to 150MB), and means only the intended recipient (and their inbox delegates with full access) can view it. Message encryption in Outlook is approved for sending high risk ( level 4 ) data and below.

Sharing Qualitative Data:
- Repositories for Qualitative Data If you have cleared this intention with your IRB, secured consent from participants, and properly de-identified your data, consider sharing your interviews in one of the data repositories included in the link above. Depending on the nature of your research and the level of risk it may present to participants, sharing your interview data may not be appropriate. If there is any chance that sharing such data will be desirable, you will be much better off if you build this expectation into your plans from the beginning.
- Guide for Sharing Qualitative Data at ICPSR The Inter-university Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPSR) has created this resource for investigators planning to share qualitative data at ICPSR. This guide provides an overview of elements and considerations for archiving qualitative data, identifies steps for investigators to follow during the research life cycle to ensure that others can share and reuse qualitative data, and provides information about exemplars of qualitative data
International Projects:
- Research Compliance Program for FAS/SEAS at Harvard The Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS), including the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), and the Office of the Vice Provost for Research (OVPR) have established a shared Research Compliance Program (RCP). An area of common concern for interview studies is international projects and collaboration . RCP is a resource to provide guidance on which international activities may be impacted by US sanctions on countries, individuals, or entities and whether licenses or other disclosure are required to ship or otherwise share items, technology, or data with foreign collaborators.
Finding Extant Interview Data
Finding journalistic interviews: .
- Academic Search Premier This all-purpose database is great for finding articles from magazines and newspapers. In the Advanced Search, it allows you to specify "Document Type": Interview.
- Guide to Newspapers and Newspaper Indexes Use this guide created to Harvard Librarians to identify newspapers collections you'd like to search. To locate interviews, try adding the term "interview" to your search, or explore a database's search interface for options to limit your search to interviews. Nexis Uni and Factiva are the two main databases for current news.
- Listen Notes Search for podcast episodes at this podcast aggregator, and look for podcasts that include interviews. Make sure to vet the podcaster for accuracy and quality! (Listen Notes does not do much vetting.)
- NPR and ProPublica are two sites that offer high-quality long-form reporting, including journalistic interviews, for free.
Finding Oral History and Social Research Interviews:
- To find oral histories, see the Oral History page of this guide for helpful resources on Oral History interviewing.
- Repositories for Qualitative Data It has not been a customary practice among qualitative researchers in the social sciences to share raw interview data, but some have made this data available in repositories, such as the ones listed on the page linked above. You may find published data from structured interview surveys (e.g., questionnaire-based computer-assisted telephone interview data), as well as some semi-structured and unstructured interviews.
- If you are merely interested in studies interpreting data collected using interviews, rather than finding raw interview data, try databases like PsycInfo , Sociological Abstracts , or Anthropology Plus , among others.
Finding Interviews in Archival Collections at Harvard Library:
In addition to the databases and search strategies mentioned under the "Finding Oral History and Social Research Interviews" category above, you may search for interviews and oral histories (whether in textual or audiovisual formats) held in archival collections at Harvard Library.
- HOLLIS searches all documented collections at Harvard, whereas HOLLIS for Archival Discovery searches only those with finding aids. Although HOLLIS for Archival Discovery covers less material, you may find it easier to parse your search results, especially when you wish to view results at the item level (within collections). Try these approaches:
Search in HOLLIS :
- To retrieve items available online, do an Advanced Search for interview* OR "oral histor*" (in Subject), with Resource Type "Archives/Manuscripts," then refine your search by selecting "Online" under "Show Only" on the right of your initial result list. Revise the search above by adding your topic in the Keywords or Subject field (for example: African Americans ) and resubmitting the search.
- To enlarge your results set, you may also leave out the "Online" refinement; if you'd like to limit your search to a specific repository, try the technique of searching for Code: Library + Collection on the "Advanced Search" page .
Search in HOLLIS for Archival Discovery :
- To retrieve items available online, search for interview* OR "oral histor*" limited to digital materials . Revise the search above by adding your topic (for example: artist* ) in the second search box (if you don't see the box, click +).
- To preview results by collection, search for interview* OR "oral histor*" limited to collections . Revise the search above by adding your topic (for example: artist* ) in the second search box (if you don't see the box, click +). Although this method does not allow you to isolate digitized content, you may find the refinement options on the right side of the screen (refine by repository, subject or names) helpful. Once your select a given collection, you may search within it (e.g., for your topic or the term interview).
UX & MARKET RESEARCH INTERVIEWS
Ux at harvard library .
- User Experience and Market Research interviews can inform the design of tangible products and services through responsive, outcome-driven insights. The User Research Center at Harvard Library specializes in this kind of user-centered design, digital accessibility, and testing. They also offer guidance and resources to members of the Harvard Community who are interested in learning more about UX methods. Contact [email protected] or consult the URC website for more information.
Websites
- User Interviews: The Beginner’s Guide (Chris Mears)
- Interviewing Users (Jakob Nielsen)
Books
- Interviewing Users: How to Uncover Compelling Insights by Steve Portigal; Grant McCracken (Foreword by) Interviewing is a foundational user research tool that people assume they already possess. Everyone can ask questions, right? Unfortunately, that's not the case. Interviewing Users provides invaluable interviewing techniques and tools that enable you to conduct informative interviews with anyone. You'll move from simply gathering data to uncovering powerful insights about people.
- Rapid Contextual Design by Jessamyn Wendell; Karen Holtzblatt; Shelley Wood This handbook introduces Rapid CD, a fast-paced, adaptive form of Contextual Design. Rapid CD is a hands-on guide for anyone who needs practical guidance on how to use the Contextual Design process and adapt it to tactical projects with tight timelines and resources. Rapid Contextual Design provides detailed suggestions on structuring the project and customer interviews, conducting interviews, and running interpretation sessions. The handbook walks you step-by-step through organizing the data so you can see your key issues, along with visioning new solutions, storyboarding to work out the details, and paper prototype interviewing to iterate the design all with as little as a two-person team with only a few weeks to spare *Includes real project examples with actual customer data that illustrate how a CD project actually works.
Videos

Instructional Presentations on Interview Skills
- Interview/Oral History Research for RSRA 298B: Master's Thesis Reading and Research (Spring 2023) Slideshow covers: Why Interviews?, Getting Context, Engaging Participants, Conducting the Interview, The Interview Guide, Note Taking, Transcription, File management, and Data Analysis.
- Interview Skills From an online class on February 13, 2023: Get set up for interview research. You will leave prepared to choose among the three types of interviewing methods, equipped to develop an interview schedule, aware of data management options and their ethical implications, and knowledgeable of technologies you can use to record and transcribe your interviews. This workshop complements Intro to NVivo, a qualitative data analysis tool useful for coding interview data.
NIH Data Management & Sharing Policy (DMSP) This policy, effective January 25, 2023, applies to all research, funded or conducted in whole or in part by NIH, that results in the generation of scientific data , including NIH-funded qualitative research. Click here to see some examples of how the DMSP policy has been applied in qualitative research studies featured in the 2021 Qualitative Data Management Plan (DMP) Competition . As a resource for the community, NIH has developed a resource for developing informed consent language in research studies where data and/or biospecimens will be stored and shared for future use. It is important to note that the DMS Policy does NOT require that informed consent obtained from research participants must allow for broad sharing and the future use of data (either with or without identifiable private information). See the FAQ for more information.
- << Previous: Remote Research & Virtual Fieldwork
- Next: Oral History >>
Except where otherwise noted, this work is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which allows anyone to share and adapt our material as long as proper attribution is given. For details and exceptions, see the Harvard Library Copyright Policy ©2021 Presidents and Fellows of Harvard College.

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
What is an interview and its purpose in qualitative research?
What are some examples of interviews in research, how to carry out great interviews in qualitative research, fundamental types of interviews, process of conducting an interview.
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Interviews: Research methods and approaches
As a qualitative research method, interviewing is widely used to gather in-depth information from participants about their experiences, opinions, and perspectives on a specific topic. There are various qualitative research techniques for interviews available to researchers to achieve the greatest potential in data collection .

This section will provide an overview of the importance of interviews, the different types of interviews, tools for conducting interviews, analysis of interview data , and ethical considerations in this research method. Note that the focus group interview is a related concept but will be discussed in greater detail in the next section of this guide, as focus groups have slightly different dynamics to consider.
Interviews, as a qualitative research method , play a pivotal role in uncovering complexities in human behavior and decision-making. Researchers can observe behavior, on the one hand, or they can investigate the perspectives and values informing that behavior by interviewing research participants.
Purpose and importance
Interviews allow researchers to delve into the subjective experiences of individuals, providing insights that may not be accessible through other research methods. They illuminate people's perceptions, thoughts, feelings, and understandings about a particular phenomenon.
Unlike quantitative methods, which typically collect numerical data that can be statistically analyzed, interviews capture rich, detailed data in the form of words, ideas, and themes. They allow researchers to collect data on people's experiences in a manner that is sensitive to the context and the individual's perspective. Through interviews, researchers can explore the meanings people attribute to their experiences and gain a deeper understanding of the phenomena being studied.
Interviews also empower participants by giving them a voice. The interviewee has the opportunity to express their views, feelings, and experiences in their own words. This participatory aspect of interviews underscores the respect for individual experiences and perspectives, which is a central tenet of qualitative research.
Comparing interviews with other methods
While interviews share many similarities with other qualitative methods, they also have unique features that set them apart. Unlike interviews, methods like observations are more passive and rely more on the researcher's interpretation of events.
On the other hand, interviews actively involve participants in the data generation process. Compared to surveys , which may limit responses to predetermined choices or word limits, interviews allow for open-ended responses and the flexibility to explore topics in depth.
However, it's worth noting that interviews do not have to be a stand-alone method. They are often used with other methods, such as observation or document analysis , in a multi-method or mixed-methods research design . This combination of methods can enhance the richness and credibility of the data collected, providing a more holistic understanding of the research problem.
The qualitative research interview can be conducted in various formats, each with its own strengths and limitations. Choosing the appropriate type of interview to use largely depends on the research question, the nature of the topic, the characteristics of the participants, and the resources available to the researcher.
Face-to-face interviews
In-person interviews are often considered the traditional form of interviewing. They involve a direct conversation between the interviewer and the interviewee. This form allows for comprehensive communication as it includes verbal and non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice.

This type of interview allows for immediate clarification of responses and can help foster rapport between the interviewer and interviewee, which may lead to richer, more nuanced data. However, these kinds of interviews can be time-consuming, expensive, and limited by geographic location.
Telephone interviews
Telephone interviews can be a practical alternative when face-to-face interviews are not feasible due to distance, time, or budget constraints. Phone interviews allow researchers to reach participants who may be geographically dispersed and offer a level of anonymity that may encourage candid responses, particularly on sensitive topics.
However, they might lack non-verbal cues that can provide additional context to a participant's responses. A phone interview may differ from a conversation in person in that you can't see someone's face, gestures, or other body language, which might be useful for contextualizing detailed information.
Online/internet-based interviews
Online or internet-based interviews conducted through platforms such as Zoom, Skype, or email have become increasingly popular in recent years. They can be synchronous (occurring in real-time, like video calls) or asynchronous (participants respond in their own time, such as email interviews).
These interviews can reach participants globally, are often cost-effective, and can be more convenient for both the researcher and the participant. However, they rely on technology and internet access, which may not be available to all potential participants.
Effective interview research with ATLAS.ti
Get key insights from insightful analysis with ATLAS.ti. Try a free trial today.
Qualitative interviews are more than just casual conversations. Some qualitative research interviews may not follow a strict structure and allow the researcher to explore any topics in the moment. In contrast, other interviews may be highly structured and aim to collect the same kind of information across participants. As a matter of empirical research, research interviews require careful planning, execution, and reflection to ensure they yield valuable and trustworthy data. Here are some key components to consider:
Developing appropriate interview questions
The foundation of any successful interview lies in its questions. Good interview questions are open-ended, clear, and directly related to the research objectives. They should allow participants to share their experiences, opinions, and feelings without leading them toward certain answers. In qualitative research, it's often useful to have a mix of more and less structured questions, allowing for both depth and breadth in responses.
Building rapport with participants
Establishing rapport with interviewees is crucial to encourage open and honest responses. In-depth interviews can be challenging if the interviewer doesn't know the interviewee in detail or hasn't established the necessary trust.

Researchers establish rapport with interviewees by displaying empathy, active listening, and respect. Clarifying the purpose of the interview, ensuring confidentiality, and asking for consent before beginning can also help in building trust.
Note-taking and recording
Accurate and comprehensive documentation of interview data is critical. While audio or video recording is highly recommended for completeness and accuracy, it's also beneficial to take notes during or immediately after the interview. These notes can capture non-verbal cues, the interviewer's impressions, and any issues or incidents that occur during the interview.
Ethical considerations are paramount in any research involving human participants. Researchers must obtain informed consent , respect participants' privacy and confidentiality , and ensure participants understand their right to withdraw from the study at any time without any negative consequences. It's also important to be aware of power dynamics and strive for a respectful and equitable researcher-participant relationship.
The effectiveness of a qualitative interview largely depends on the thoughtfulness and rigor with which these components are addressed. Interviews are not just a data collection tool; they are a way of acknowledging and respecting participants' lived experiences and perspectives. Therefore, each component should be handled with utmost care and consideration.
Organize your data all in one place.
Text files, PDFs, videos, and pictures. ATLAS.ti helps you analyze them all. See how with a free trial.
The structure of an interview can greatly influence the data collected. The level of structure varies along a continuum, with structured and unstructured interviews occupying opposite ends of that spectrum.
Unstructured interviews are characterized by their flexibility. The researcher usually only has a list of topics or themes to be covered, known as an interview guide, but the conversation does not follow a predetermined set of questions. Instead, the interviewer allows the conversation to flow naturally, following leads provided by the interviewee. An unstructured interview is particularly useful when the researcher is exploring a new area of study and aims to gather as much information as possible without preconceived notions.
Semi-structured interviews strike a balance between flexibility and structure. The researcher has a list of predetermined questions to conduct interviews but is free to ask additional open-ended questions or to deviate from the list based on the interviewee's responses. The semi-structured interview is the most common form of interview in qualitative research, as it provides deep, rich data while still ensuring that all necessary topics are covered.

Structured interviews
Structured interviews , sometimes called standardized interviews, are the most rigid form of interview. The researcher asks the same set of predetermined questions in the same order to all participants, with little to no deviation.
While a structured interview may limit the depth of data collected, it allows for greater consistency across interviews. This can be helpful for keeping responses confined to the research topic and comparing responses between participants.
In determining the level of structure for an interview, researchers should consider their research objectives, the nature of the topic, and the characteristics of the participants. Different structures lend themselves to different research goals, and the most effective interviewers are those who can adapt their approach based on the needs of their study.
Conducting an interview in qualitative research involves a series of well-planned steps before, during, and after the interview. These steps ensure that the process is systematic, ethical, and capable of yielding high-quality data.
Pre-interview preparation and research
Before conducting the interview, the researcher needs to thoroughly understand the research topic, define the purpose of the interview, and identify potential interviewees. Preparing an interview guide with key themes or questions is essential, though the level of detail will depend on the interview structure. Logistics, such as scheduling the interview at a convenient time and place for the participant and ensuring necessary equipment is available and working, also need to be addressed.
Conducting the interview
The interview begins with an introduction in which the interviewer explains the purpose of the interview, assures confidentiality, and obtains consent from the participant. Throughout the interview, the researcher should aim to build rapport, listen attentively, and adapt their questioning based on the interviewee's responses. Non-verbal cues should also be observed and noted, as they can provide additional insights.
Post-interview activities
After the interview, it is important to thank the participant for their time and contribution. Researchers should then promptly transcribe the interview while the details are still fresh. Reflections and observations about the interview should also be noted, including the context, the behavior of the participant, and any unexpected occurrences. These notes can provide valuable context during data analysis.
Executing each of these stages effectively requires not only good planning and organization but also interpersonal skills, flexibility, and respect for the participant. The quality of the data collected during an interview is largely dependent on how well the interview process is managed.
Transcribing interviews
The transcription of interview data is a critical step in the qualitative research process. This involves converting the recorded audio or video interviews into written text, providing a detailed account of the dialogues that took place during the interviews.

Transcriptions allow for more detailed examination, analysis, and reporting of the data. However, making transcriptions can be arduous and time-consuming. Here are some key considerations in the transcription process:
Types of transcription
There are two main types of transcription: verbatim and clean. Verbatim transcription involves writing down every single word, pause, and utterance made during the interview. This is a very detailed and time-consuming process, but it can be useful when the researcher needs to analyze not just the content of the interview but also the way it was expressed. On the other hand, clean transcription omits irrelevant elements like stutters, repetitions, and filler words, focusing instead on the core content of the conversation.
Manual vs. automated transcription
Researchers may choose to transcribe interviews manually or use transcription software. Manual transcription, while time-consuming, allows researchers to become intimately familiar with the data and can be more accurate, especially for complex or nuanced dialogues.
Automated transcription software, however, can save time and effort, particularly for large volumes of data, although it may require manual checking and correction for errors. Some researchers choose a hybrid approach, using software for the initial transcription and then manually checking and correcting the output.
Formatting and anonymizing transcripts
To facilitate analysis, transcripts should be formatted consistently, with clear identifiers for different speakers and timestamps for reference. If there are multiple interviewers or participants, each individual's speech should be clearly marked. Additionally, to ensure confidentiality, any personally identifiable information should be removed or anonymized in the transcript. This is especially important to consider in qualitative data, because participants may talk about aspects of their lives through which they could be identified, for instance if they mention specific names, their neighborhood, or place of work.
Quality checks
Finally, it's important to check the quality of the transcript. This could involve a second person checking the transcription against the audio or the researcher re-listening to portions of the recording to confirm accuracy. Any unclear or inaudible sections should be marked in the transcript.

Get the most out of interviews with ATLAS.ti
Collect, transcribe, and analyze interviews with our intuitive interface. Try it out with a free trial.
The Interview Method In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, Ph.D., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years experience of working in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Interviews involve a conversation with a purpose, but have some distinct features compared to ordinary conversation, such as being scheduled in advance, having an asymmetry in outcome goals between interviewer and interviewee, and often following a question-answer format.
Interviews are different from questionnaires as they involve social interaction. Unlike questionnaire methods, researchers need training in interviewing (which costs money).

How Do Interviews Work?
Researchers can ask different types of questions, generating different types of data . For example, closed questions provide people with a fixed set of responses, whereas open questions allow people to express what they think in their own words.
The researcher will often record interviews, and the data will be written up as a transcript (a written account of interview questions and answers) which can be analyzed later.
It should be noted that interviews may not be the best method for researching sensitive topics (e.g., truancy in schools, discrimination, etc.) as people may feel more comfortable completing a questionnaire in private.
There are different types of interviews, with a key distinction being the extent of structure. Semi-structured is most common in psychology research. Unstructured interviews have a free-flowing style, while structured interviews involve preset questions asked in a particular order.
Structured Interview
A structured interview is a quantitative research method where the interviewer a set of prepared closed-ended questions in the form of an interview schedule, which he/she reads out exactly as worded.
Interviews schedules have a standardized format, meaning the same questions are asked to each interviewee in the same order (see Fig. 1).

Figure 1. An example of an interview schedule
The interviewer will not deviate from the interview schedule (except to clarify the meaning of the question) or probe beyond the answers received. Replies are recorded on a questionnaire, and the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers, is preset by the researcher.
A structured interview is also known as a formal interview (like a job interview).
- Structured interviews are easy to replicate as a fixed set of closed questions are used, which are easy to quantify – this means it is easy to test for reliability .
- Structured interviews are fairly quick to conduct which means that many interviews can take place within a short amount of time. This means a large sample can be obtained, resulting in the findings being representative and having the ability to be generalized to a large population.
Limitations
- Structured interviews are not flexible. This means new questions cannot be asked impromptu (i.e., during the interview), as an interview schedule must be followed.
- The answers from structured interviews lack detail as only closed questions are asked, which generates quantitative data . This means a researcher won’t know why a person behaves a certain way.
Unstructured Interview
Unstructured interviews do not use any set questions, instead, the interviewer asks open-ended questions based on a specific research topic, and will try to let the interview flow like a natural conversation. The interviewer modifies his or her questions to suit the candidate’s specific experiences.
Unstructured interviews are sometimes referred to as ‘discovery interviews’ and are more like a ‘guided conservation’ than a strictly structured interview. They are sometimes called informal interviews.
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values. Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective points of view.
Interviewer Self-Disclosure
Interviewer self-disclosure involves the interviewer revealing personal information or opinions during the research interview. This may increase rapport but risks changing dynamics away from a focus on facilitating the interviewee’s account.
In unstructured interviews, the informal conversational style may deliberately include elements of interviewer self-disclosure, mirroring ordinary conversation dynamics.
Interviewer self-disclosure risks changing the dynamics away from facilitation of interviewee accounts. It should not be ruled out entirely but requires skillful handling informed by reflection.
- An informal interviewing style with some interviewer self-disclosure may increase rapport and participant openness. However, it also increases the chance of the participant converging opinions with the interviewer.
- Complete interviewer neutrality is unlikely. However, excessive informality and self-disclosure risk the interview becoming more of an ordinary conversation and producing consensus accounts.
- Overly personal disclosures could also be seen as irrelevant and intrusive by participants. They may invite increased intimacy on uncomfortable topics.
- The safest approach seems to be to avoid interviewer self-disclosures in most cases. Where an informal style is used, disclosures require careful judgment and substantial interviewing experience.
- If asked for personal opinions during an interview, the interviewer could highlight the defined roles and defer that discussion until after the interview.
- Unstructured interviews are more flexible as questions can be adapted and changed depending on the respondents’ answers. The interview can deviate from the interview schedule.
- Unstructured interviews generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
- They also have increased validity because it gives the interviewer the opportunity to probe for a deeper understanding, ask for clarification & allow the interviewee to steer the direction of the interview, etc. Interviewers have the chance to clarify any questions of participants during the interview.
- It can be time-consuming to conduct an unstructured interview and analyze the qualitative data (using methods such as thematic analysis).
- Employing and training interviewers is expensive and not as cheap as collecting data via questionnaires . For example, certain skills may be needed by the interviewer. These include the ability to establish rapport and knowing when to probe.
- Interviews inevitably co-construct data through researchers’ agenda-setting and question-framing. Techniques like open questions provide only limited remedies.
Focus Group Interview
Focus group interview is a qualitative approach where a group of respondents are interviewed together, used to gain an in‐depth understanding of social issues.
This type of interview is often referred to as a focus group because the job of the interviewer ( or moderator ) is to bring the group to focus on the issue at hand. Initially, the goal was to reach a consensus among the group, but with the development of techniques for analyzing group qualitative data, there is less emphasis on consensus building.
The method aims to obtain data from a purposely selected group of individuals rather than from a statistically representative sample of a broader population.
The role of the interview moderator is to make sure the group interacts with each other and do not drift off-topic. Ideally, the moderator will be similar to the participants in terms of appearance, have adequate knowledge of the topic being discussed, and exercise mild unobtrusive control over dominant talkers and shy participants.
A researcher must be highly skilled to conduct a focus group interview. For example, the moderator may need certain skills, including the ability to establish rapport and know when to probe.
- Group interviews generate qualitative narrative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondents to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation. Qualitative data also includes observational data, such as body language and facial expressions.
- Group responses are helpful when you want to elicit perspectives on a collective experience, encourage diversity of thought, reduce researcher bias, and gather a wider range of contextualized views.
- They also have increased validity because some participants may feel more comfortable being with others as they are used to talking in groups in real life (i.e., it’s more natural).
- When participants have common experiences, focus groups allow them to build on each other’s comments to provide richer contextual data representing a wider range of views than individual interviews.
- Focus groups are a type of group interview method used in market research and consumer psychology that are cost – effective for gathering the views of consumers .
- The researcher must ensure that they keep all the interviewees” details confidential and respect their privacy. This is difficult when using a group interview. For example, the researcher cannot guarantee that the other people in the group will keep information private.
- Group interviews are less reliable as they use open questions and may deviate from the interview schedule, making them difficult to repeat.
- It is important to note that there are some potential pitfalls of focus groups, such as conformity, social desirability, and oppositional behavior, that can reduce the usefulness of the data collected.
For example, group interviews may sometimes lack validity as participants may lie to impress the other group members. They may conform to peer pressure and give false answers.
To avoid these pitfalls, the interviewer needs to have a good understanding of how people function in groups as well as how to lead the group in a productive discussion.
Semi-Structured Interview
Semi-structured interviews lie between structured and unstructured interviews. The interviewer prepares a set of same questions to be answered by all interviewees. Additional questions might be asked during the interview to clarify or expand certain issues.
In semi-structured interviews, the interviewer has more freedom to digress and probe beyond the answers. The interview guide contains a list of questions and topics that need to be covered during the conversation, usually in a particular order.
Semi-structured interviews are most useful to address the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘why’ research questions. Both qualitative and quantitative analyses can be performed on data collected during semi-structured interviews.
- Semi-structured interviews allow respondents to answer more on their terms in an informal setting yet provide uniform information making them ideal for qualitative analysis.
- The flexible nature of semi-structured interviews allows ideas to be introduced and explored during the interview based on the respondents’ answers.
- Semi-structured interviews can provide reliable and comparable qualitative data. Allows the interviewer to probe answers, where the interviewee is asked to clarify or expand on the answers provided.
- The data generated remain fundamentally shaped by the interview context itself. Analysis rarely acknowledges this endemic co-construction.
- They are more time-consuming (to conduct, transcribe, and analyze) than structured interviews.
- The quality of findings is more dependent on the individual skills of the interviewer than in structured interviews. Skill is required to probe effectively while avoiding biasing responses.
The Interviewer Effect
Face-to-face interviews raise methodological problems. These stem from the fact that interviewers are themselves role players, and their perceived status may influence the replies of the respondents.
Because an interview is a social interaction, the interviewer’s appearance or behavior may influence the respondent’s answers. This is a problem as it can bias the results of the study and make them invalid.
For example, the gender, ethnicity, body language, age, and social status of the interview can all create an interviewer effect. If there is a perceived status disparity between the interviewer and the interviewee, the results of interviews have to be interpreted with care. This is pertinent for sensitive topics such as health.
For example, if a researcher was investigating sexism amongst males, would a female interview be preferable to a male? It is possible that if a female interviewer was used, male participants might lie (i.e., pretend they are not sexist) to impress the interviewer, thus creating an interviewer effect.
Flooding interviews with researcher’s agenda
The interactional nature of interviews means the researcher fundamentally shapes the discourse, rather than just neutrally collecting it. This shapes what is talked about and how participants can respond.
- The interviewer’s assumptions, interests, and categories don’t just shape the specific interview questions asked. They also shape the framing, task instructions, recruitment, and ongoing responses/prompts.
- This flooding of the interview interaction with the researcher’s agenda makes it very difficult to separate out what comes from the participant vs. what is aligned with the interviewer’s concerns.
- So the participant’s talk ends up being fundamentally shaped by the interviewer rather than being a more natural reflection of the participant’s own orientations or practices.
- This effect is hard to avoid because interviews inherently involve the researcher setting an agenda. But it does mean the talk extracted may say more about the interview process than the reality it is supposed to reflect.
Interview Design
First, you must choose whether to use a structured or non-structured interview.
Characteristics of Interviewers
Next, you must consider who will be the interviewer, and this will depend on what type of person is being interviewed. There are several variables to consider:
- Gender and age : This can greatly affect respondents’ answers, particularly on personal issues.
- Personal characteristics : Some people are easier to get on with than others. Also, the interviewer’s accent and appearance (e.g., clothing) can affect the rapport between the interviewer and interviewee.
- Language : The interviewer’s language should be appropriate to the vocabulary of the group of people being studied. For example, the researcher must change the questions’ language to match the respondents’ social background” age / educational level / social class/ethnicity, etc.
- Ethnicity : People may have difficulty interviewing people from different ethnic groups.
- Interviewer expertise should match research sensitivity – inexperienced students should avoid interviewing highly vulnerable groups.
Interview Location
The location of a research interview can influence the way in which the interviewer and interviewee relate and may exaggerate a power dynamic in one direction or another. It is usual to offer interviewees a choice of location as part of facilitating their comfort and encouraging participation.
However, the safety of the interviewer is an overriding consideration and, as mentioned, a minimal requirement should be that a responsible person knows where the interviewer has gone and when they are due back.
Remote Interviews
The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated remote interviewing for research continuity. However online interview platforms provide increased flexibility even under normal conditions.
They enable access to participant groups across geographical distances without travel costs or arrangements. Online interviews can be efficiently scheduled to align with researcher and interviewee availability.
There are practical considerations in setting up remote interviews. Interviewees require access to internet and an online platform such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams or Skype through which to connect.
Certain modifications help build initial rapport in the remote format. Allowing time at the start of the interview for casual conversation while testing audio/video quality helps participants settle in. Minor delays can disrupt turn-taking flow, so alerting participants to speak slightly slower than usual minimizes accidental interruptions.
Keeping remote interviews under an hour avoids fatigue for stare at a screen. Seeking advanced ethical clearance for verbal consent at the interview start saves participant time. Adapting to the remote context shows care for interviewees and aids rich discussion.
However, it remains important to critically reflect on how removing in-person dynamics may shape the co-created data. Perhaps some nuances of trust and disclosure differ over video.
Vulnerable Groups
The interviewer must ensure that they take special care when interviewing vulnerable groups, such as children. For example, children have a limited attention span, so lengthy interviews should be avoided.
Developing an Interview Schedule
An interview schedule is a list of pre-planned, structured questions that have been prepared, to serve as a guide for interviewers, researchers and investigators in collecting information or data about a specific topic or issue.
- List the key themes or topics that must be covered to address your research questions. This will form the basic content.
- Organize the content logically, such as chronologically following the interviewee’s experiences. Place more sensitive topics later in the interview.
- Develop the list of content into actual questions and prompts. Carefully word each question – keep them open-ended, non-leading, and focused on examples.
- Add prompts to remind you to cover areas of interest.
- Pilot test the interview schedule to check it generates useful data and revise as needed.
- Be prepared to refine the schedule throughout data collection as you learn which questions work better.
- Practice skills like asking follow-up questions to get depth and detail. Stay flexible to depart from the schedule when needed.
- Keep questions brief and clear. Avoid multi-part questions that risk confusing interviewees.
- Listen actively during interviews to determine which pre-planned questions can be skipped based on information the participant has already provided.
The key is balancing preparation with the flexibility to adapt questions based on each interview interaction. With practice, you’ll gain skills to conduct productive interviews that obtain rich qualitative data.
The Power of Silence
Strategic use of silence is a key technique to generate interviewee-led data, but it requires judgment about appropriate timing and duration to maintain mutual understanding.
- Unlike ordinary conversation, the interviewer aims to facilitate the interviewee’s contribution without interrupting. This often means resisting the urge to speak at the end of the interviewee’s turn construction units (TCUs).
- Leaving a silence after a TCU encourages the interviewee to provide more material without being led by the interviewer. However, this simple technique requires confidence, as silence can feel socially awkward.
- Allowing longer silences (e.g. 24 seconds) later in interviews can work well, but early on even short silences may disrupt rapport if they cause misalignment between speakers.
- Silence also allows interviewees time to think before answering. Rushing to re-ask or amend questions can limit responses.
- Blunt backchannels like “mm hm” also avoid interrupting flow. Interruptions, especially to finish an interviewee’s turn, are problematic as they make the ownership of perspectives unclear.
- If interviewers incorrectly complete turns, an upside is it can produce extended interviewee narratives correcting the record. However, silence would have been better to let interviewees shape their own accounts.
Recording & Transcription
Design choices.
Design choices around recording and engaging closely with transcripts influence analytic insights, as well as practical feasibility. Weighing up relevant tradeoffs is key.
- Audio recording is standard, but video better captures contextual details, which is useful for some topics/analysis approaches. Participants may find video invasive for sensitive research.
- Digital formats enable the sharing of anonymized clips. Additional microphones reduce audio issues.
- Doing all transcription is time-consuming. Outsourcing can save researcher effort but needs confidentiality assurances. Always carefully check outsourced transcripts.
- Online platform auto-captioning can facilitate rapid analysis, but accuracy limitations mean full transcripts remain ideal. Software cleans up caption file formatting.
- Verbatim transcripts best capture nuanced meaning, but the level of detail needed depends on the analysis approach. Referring back to recordings is still advisable during analysis.
- Transcripts versus recordings highlight different interaction elements. Transcripts make overt disagreements clearer through the wording itself. Recordings better convey tone affiliativeness.
Transcribing Interviews & Focus Groups
Here are the steps for transcribing interviews:
- Play back audio/video files to develop an overall understanding of the interview
- Format the transcription document:
- Add line numbers
- Separate interviewer questions and interviewee responses
- Use formatting like bold, italics, etc. to highlight key passages
- Provide sentence-level clarity in the interviewee’s responses while preserving their authentic voice and word choices
- Break longer passages into smaller paragraphs to help with coding
- If translating the interview to another language, use qualified translators and back-translate where possible
- Select a notation system to indicate pauses, emphasis, laughter, interruptions, etc., and adapt it as needed for your data
- Insert screenshots, photos, or documents discussed in the interview at the relevant point in the transcript
- Read through multiple times, revising formatting and notations
- Double-check the accuracy of transcription against audio/videos
- De-identify transcript by removing identifying participant details
The goal is to produce a formatted written record of the verbal interview exchange that captures the meaning and highlights important passages ready for the coding process. Careful transcription is the vital first step in analysis.
Coding Transcripts
The goal of transcription and coding is to systematically transform interview responses into a set of codes and themes that capture key concepts, experiences and beliefs expressed by participants. Taking care with transcription and coding procedures enhances the validity of qualitative analysis .
- Read through the transcript multiple times to become immersed in the details
- Identify manifest/obvious codes and latent/underlying meaning codes
- Highlight insightful participant quotes that capture key concepts (in vivo codes)
- Create a codebook to organize and define codes with examples
- Use an iterative cycle of inductive (data-driven) coding and deductive (theory-driven) coding
- Refine codebook with clear definitions and examples as you code more transcripts
- Collaborate with other coders to establish the reliability of codes
Ethical Issues
Informed consent.
The participant information sheet must give potential interviewees a good idea of what is involved if taking part in the research.
This will include the general topics covered in the interview, where the interview might take place, how long it is expected to last, how it will be recorded, the ways in which participants’ anonymity will be managed, and incentives offered.
It might be considered good practice to consider true informed consent in interview research to require two distinguishable stages:
- Consent to undertake and record the interview and
- Consent to use the material in research after the interview has been conducted and the content known, or even after the interviewee has seen a copy of the transcript and has had a chance to remove sections, if desired.
Power and Vulnerability
- Early feminist views that sensitivity could equalize power differences are likely naive. The interviewer and interviewee inhabit different knowledge spheres and social categories, indicating structural disparities.
- Power fluctuates within interviews. Researchers rely on participation, yet interviewees control openness and can undermine data collection. Assumptions should be avoided.
- Interviews on sensitive topics may feel like quasi-counseling. Interviewers must refrain from dual roles, instead supplying support service details to all participants.
- Interviewees recruited for trauma experiences may reveal more than anticipated. While generating analytic insights, this risks leaving them feeling exposed.
- Ultimately, power balances resist reconciliation. But reflexively analyzing operations of power serves to qualify rather than nullify situtated qualitative accounts.
Some groups, like those with mental health issues, extreme views, or criminal backgrounds, risk being discredited – treated skeptically by researchers.
This creates tensions with qualitative approaches, often having an empathetic ethos seeking to center subjective perspectives. Analysis should balance openness to offered accounts with critically examining stakes and motivations behind them.
Potter, J., & Hepburn, A. (2005). Qualitative interviews in psychology: Problems and possibilities. Qualitative research in Psychology , 2 (4), 281-307.
Houtkoop-Steenstra, H. (2000). Interaction and the standardized survey interview: The living questionnaire . Cambridge University Press
Madill, A. (2011). Interaction in the semi-structured interview: A comparative analysis of the use of and response to indirect complaints. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 8 (4), 333–353.
Maryudi, A., & Fisher, M. (2020). The power in the interview: A practical guide for identifying the critical role of actor interests in environment research. Forest and Society, 4 (1), 142–150
O’Key, V., Hugh-Jones, S., & Madill, A. (2009). Recruiting and engaging with people in deprived locales: Interviewing families about their eating patterns. Social Psychological Review, 11 (20), 30–35.
Puchta, C., & Potter, J. (2004). Focus group practice . Sage.
Schaeffer, N. C. (1991). Conversation with a purpose— Or conversation? Interaction in the standardized interview. In P. P. Biemer, R. M. Groves, L. E. Lyberg, & N. A. Mathiowetz (Eds.), Measurement errors in surveys (pp. 367–391). Wiley.
Silverman, D. (1973). Interview talk: Bringing off a research instrument. Sociology, 7 (1), 31–48.
404 Not found
Have a language expert improve your writing.
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
Published on 4 May 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 26 August 2022.
A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. It is one of four types of interviews .
In research, structured interviews are often quantitative in nature. They can also be used in qualitative research if the questions are open-ended, but this is less common.
While structured interviews are often associated with job interviews, they are also common in marketing, social science, survey methodology, and other research fields.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, whereas the other questions aren’t planned.
- Unstructured interviews : None of the questions are predetermined.
- Focus group interviews : The questions are presented to a group instead of one individual.
Table of contents
What is a structured interview, when to use a structured interview, advantages of structured interviews, disadvantages of structured interviews, structured interview questions, how to conduct a structured interview, how to analyse a structured interview, presenting your results, frequently asked questions about structured interviews.
Structured interviews are the most systematised type of interview. In contrast to semi-structured or unstructured interviews, the interviewer uses predetermined questions in a set order.
Structured interviews are often closed-ended. They can be dichotomous, which means asking participants to answer ‘yes’ or ‘no’ to each question, or multiple-choice. While open-ended structured interviews do exist, they are less common.
Asking set questions in a set order allows you to easily compare responses between participants in a uniform context. This can help you see patterns and highlight areas for further research, and it can be a useful explanatory or exploratory research tool.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Structured interviews are best used when:
- You already have a very clear understanding of your topic, so you possess a baseline for designing strong structured questions
- You are constrained in terms of time or resources and need to analyse your data efficiently
- Your research question depends on strong parity between participants, with environmental conditions held constant
A structured interview is straightforward to conduct and analyse. Asking the same set of questions mitigates potential biases and leads to fewer ambiguities in analysis. It is an undertaking you can likely handle as an individual, provided you remain organised.
Differences between different types of interviews
Make sure to choose the type of interview that suits your research best. This table shows the most important differences between the four types.
Reduced bias
Increased credibility, reliability, and validity, simple, cost-effective, and efficient, formal in nature, limited flexibility, limited scope.
It can be difficult to write structured interview questions that approximate exactly what you are seeking to measure. Here are a few tips for writing questions that contribute to high internal validity :
- Define exactly what you want to discover prior to drafting your questions. This will help you write questions that really zero in on participant responses.
- Avoid jargon, compound sentences, and complicated constructions.
- Be as clear and concise as possible, so that participants can answer your question immediately.
- Do you think that employers should provide free gym memberships?
- Did any of your previous employers provide free memberships?
- Does your current employer provide a free membership?
- a) 1 time; b) 2 times; c) 3 times; d) 4 or more times
- Do you enjoy going to the gym?
Structured interviews are among the most straightforward research methods to conduct and analyse. Once you’ve determined that they’re the right fit for your research topic , you can proceed with the following steps.
Step 1: Set your goals and objectives
Start by brainstorming some guiding questions to help you conceptualise your research question, such as:
- What are you trying to learn or achieve from a structured interview?
- Why are you choosing a structured interview as opposed to a different type of interview, or another research method?
If you have satisfying reasoning for proceeding with a structured interview, you can move on to designing your questions.
Step 2: Design your questions
Pay special attention to the order and wording of your structured interview questions . Remember that in a structured interview they must remain the same. Stick to closed-ended or very simple open-ended questions.
Step 3: Assemble your participants
Depending on your topic, there are a few sampling methods you can use, such as:
- Voluntary response sampling : For example, posting a flyer on campus and finding participants based on responses
- Convenience sampling of those who are most readily accessible to you, such as fellow students at your university
- Stratified sampling of a particular age, race, ethnicity, gender identity, or other characteristic of interest to you
- Judgement sampling of a specific set of participants that you already know you want to include
Step 4: Decide on your medium
Determine whether you will be conducting your interviews in person or whether your interview will take pen-and-paper format. If conducted live, you need to decide if you prefer to talk with participants in person, over the phone, or via video conferencing.
Step 5: Conduct your interviews
As you conduct your interviews, be very careful that all conditions remain as constant as possible.
- Ask your questions in the same order, and try to moderate your tone of voice and any responses to participants as much as you can.
- Pay special attention to your body language (e.g., nodding, raising eyebrows), as this can bias responses.
After you’re finished conducting your interviews, it’s time to analyse your results.
- Assign each of your participants a number or pseudonym for organizational purposes.
- Transcribe the recordings manually or with the help of transcription software.
- Conduct a content or thematic analysis to look for categories or patterns of responses. In most cases, it’s also possible to conduct a statistical analysis to test your hypotheses .
If you have audio-recorded your interviews, you will likely have to transcribe them prior to conducting your analysis. In some cases, your supervisor might ask you to add the transcriptions in the appendix of your paper.
First, you will have to decide whether to conduct verbatim transcription or intelligent verbatim transcription. Do pauses, laughter, or filler words like ‘umm’ or ‘like’ affect your analysis and research conclusions?
- If so, conduct verbatim transcription and include them.
- If not, conduct intelligent verbatim transcription, which excludes fillers and fixes any grammar issues, and is often easier to analyse.
The transcription process is a great opportunity for you to clean your data as well, spotting and resolving any inconsistencies or errors that come up as you listen.
Coding and analysing structured interviews
After transcribing, it’s time to conduct your thematic or content analysis . This often involves ‘coding’ words, patterns, or themes, separating them into categories for more robust analysis.
Due to the closed-ended nature of many structured interviews, you will most likely be conducting content analysis, rather than thematic analysis.
- You quantify the categories you chose in the coding stage by counting the occurrence of the words, phrases, subjects, or concepts you selected.
- After coding, you can organise and summarise the data using descriptive statistics .
- Next, inferential statistics allows you to come to conclusions about your hypotheses and make predictions for future research.
When conducting content analysis, you can take an inductive or a deductive approach. With an inductive approach, you allow the data to determine your themes. A deductive approach is the opposite: it involves investigating whether your data confirm preconceived themes or ideas.
Content analysis has a systematic procedure that can easily be replicated , yielding high reliability to your results. However, keep in mind that while this approach reduces bias, it doesn’t eliminate it. Be vigilant about remaining objective here, even if your analysis does not confirm your hypotheses .
After your data analysis, the next step is to combine your findings into a research paper .
- Your methodology section describes how you collected the data (in this case, describing your structured interview process) and explains how you justify or conceptualise your analysis.
- Your discussion and results sections usually address each of your coded categories, describing each in turn, as well as how often they occurred.
If you conducted inferential statistics in addition to descriptive statistics, you would generally report the test statistic , p value , and effect size in your results section. These values explain whether your results justify rejecting your null hypothesis and whether the result is practically significant .
You can then conclude with the main takeaways and avenues for further research.
Example of interview methodology for a research paper
Let’s say you are interested in healthcare on your campus. You study abroad in the US with a lot of international students, and you think there may be a difference in perceptions based on country of origin.
Specifically, you hypothesise that students coming from countries with single-payer or socialised healthcare will find US options less satisfying.
There is a large body of research available on this topic, so you decide to conduct structured interviews of your peers to see if there’s a difference between international students and local students.
You are a member of a large campus club that brings together international students and local students, and you send a message to the club to ask for volunteers.
Here are some questions you could ask:
- Do you find healthcare options on campus to be: excellent; good; fair; average; poor?
- Does your home country have socialised healthcare? Yes/No
- Are you on the campus healthcare plan? Yes/No
- Have you ever worried about your health insurance? Yes/No
- Have you ever had a serious health condition that insurance did not cover? Yes/No
- Have you ever been surprised or shocked by a medical bill? Yes/No
After conducting your interviews and transcribing your data, you can then conduct content analysis, coding responses into different categories. Since you began your research with the theory that international students may find US healthcare lacking, you would use the deductive approach to see if your hypotheses seem to hold true.
A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. They are often quantitative in nature. Structured interviews are best used when:
- You already have a very clear understanding of your topic. Perhaps significant research has already been conducted, or you have done some prior research yourself, but you already possess a baseline for designing strong structured questions.
- You are constrained in terms of time or resources and need to analyse your data quickly and efficiently
More flexible interview options include semi-structured interviews , unstructured interviews , and focus groups .
The four most common types of interviews are:
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, but other questions aren’t planned.
The interviewer effect is a type of bias that emerges when a characteristic of an interviewer (race, age, gender identity, etc.) influences the responses given by the interviewee.
There is a risk of an interviewer effect in all types of interviews , but it can be mitigated by writing really high-quality interview questions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, August 26). Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 12 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/structured-interviews/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, types of interviews in research | guide & examples, data collection methods | step-by-step guide & examples, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods.

*Education Research Guide: APA Style
- Search for Information
- Research Tips
- Teaching Resources
- Psychological Testing
APA Style Guide
- Reference Examples: APA Style Website
Citing Personal Communications--Emails, Interviews, Lectures, etc. in APA Format
Emails, letters, memos, telephone conversations, lectures, course materials handed out in class or provided via Blackboard, and personal interviews are considered personal communications in APA. This type of communication can be difficult to provide recoverable data; therefore, these types of communication are not included in the Reference list. Cite personal communications within the body of your paper only. Information on citing communications .
In an interview, Sally Shoefeld explained the treatment for an accident victim (personal communication, December 18, 2023).
Note: For more information about interviews, https://apastyle.apa.org/learn/faqs/cite-interview
Citing Government Websites
APA Citation Style does not have a separate category for government publications. According to APA, government documents can be considered Books, Technical/Research Reports, or Brochures.
Helpful Tips:
- Treat a government document as a book, report, or brochure.
- If a person is named on the title page, use her or him as author.
- If no person is named, use the government agency, department, or branch as a group author.
- Give the name of the group author exactly as it appears on the title page. If the branch or agency is not well known, include its higher department first.
- If the group author is also the publisher, just use the word Author after the location.
- If there is a series or report number, include it after the title.
- The manual refers to the GPO (U.S. Gov. Printing Office).
General Format
In-Text Citation (Paraphrase):
(Author Surname OR Name of Government Organization, Year)
In-Text Citation (Quotation):
(Author Surname OR Name of Government Organization, Year, page number)
References:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. OR Government Name. Name of Government Agency. (Year). Title: Subtitle (Report No. xxx [if available]). Publisher.
(Gilmore et al., 1999)
(Gilmore et al., 1999, p. 5)
Gilmore, J., Woollam, P., Campbell, T., McLean, B., Roch, J., & Stephens, T. (1999). Statistical report on the health of Canadians: Prepared by the Federal, Provincial and Territorial Advisory Committee on Population Health . Health Canada, Statistics Canada, Canadian Institute for Health Information.
(Edwards, et al., 1997)
(Edwards, et al., 1997, p. 2)
Edwards, N., Sims-Jones, N., Hotz, S., & Cushman, R. (1997). Development and testing components of a multifaceted intervention program to reduce the incidence of smoking relapse during pregnancy and post-partum of both women and their partners . Report prepared for Health Canada at the Community Health Research Unit, University of Ottawa, Canada.
(Ontario Ministry of Health, 1994)
(Ontario Ministry of Health, 1994, p. 7)
Ontario Ministry of Health. (1994). Selected findings from the mental health supplement of the Ontario Health Survey . Queen's Printer for Ontario.
(U. S. Food and Drug Administration, 2004)
(U. S. Food and Drug Administration, 2004, p. 8)
U. S. Food and Drug Administration/Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. (2004). Worsening depression and suicidality in patients being treated with antidepressant medications: FDA public health advisory . Author.
text adapted from https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/APA/book-government-publication#:~:text=Name%20of%20Government%20Agency.,xxx%20%5Bif%20available%5D).
Citing ERIC documents

The ERIC databases adds Education document numbers to the records. Make sure to include these and when in doubt always give your reader the trail to find the document you are referencing.
https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/eric-database-references
Instructional Pedagogy and Curriculum Materials Librarian

- << Previous: Psychological Testing
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 3:36 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.campbell.edu/education
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

What’s Your Interviewing Style?
A conversation with author Anna Papalia on a new way to approach interviews.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
There’s a lot of advice out there on how to get job interviews right, whether you’re the one trying to get hired or the one evaluating the candidates. But the dos and don’ts aren’t always applicable to every person. In fact, author Anna Papalia thinks we’re better served by understanding and leveraging our own natural interviewing style. Having spent years as a corporate recruiter, organizational consultant, and coach to students and professions, she’s conducted thousands of real and mock interviews and noticed that people tend to fall into one of four categories: charmer, examiner, challenger, or harmonizer. She outlines the strengths and weaknesses of each and explains how this framework can help us get better from both sides of the desks. Papalia wrote the book Interviewology: The New Science of Interviewing .
ALISON BEARD: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Alison Beard.
Most advice about job interviews, whether you’re the one trying to get hired or the one evaluating the candidates, focuses on things we should or shouldn’t do. Interviewers should ask uniform questions, focused on skills and experience. They shouldn’t make snap judgements. Interviewees should come prepared to talk about their achievements. They shouldn’t seem demanding.
I’ll bet most of you listening know all these do’s and don’ts, and yet interviews are still so hard to get right. We flub them and miss a great opportunity. We think we found the right person for a job, but really haven’t.
Today’s guest has spent years on all sides of this challenge. She’s been a job hunter herself, a corporate recruiter, a consultant to organizations trying to get better at hiring, and a teacher and coach to students and professionals trying to land their dream jobs. In interviewing thousands of people and studying relevant research, she’s identified a new way to get better at this important aspect of career and organizational growth.
The key, she says, is to understand and leverage your natural interviewing style. Anna Papalia is the author of the book, Interviewology: The New Science of Interviewing. Anna, welcome.
ANNA PAPALIA: Hi Alison. Thanks so much for having me.
ALISON BEARD: Before we dig into the four interviewing styles that you’ve identified, let me first ask: why is it still so hard to do well in interviews, given all the good advice out there?
ANNA PAPALIA: I think mainly it comes down to the fact that job interviewing is still very new. We have all grown up with this thing that we have to do to get a job, but when you think about it in historical context, we’ve only been interviewing for jobs for less than 100 years. And we don’t really know exactly how to do this. It’s a pretty difficult process to make complex decisions about people, and we have to figure out how to get through our own biases and how to present ourselves well in a job interview.
ALISON BEARD: You point out that most job seekers and hiring managers aren’t really trained on this. You might read some articles or read some books, but it’s not something that you study in school or get in your development programs. And part of the problem is that people think of it as a conversation and that it’s something that they can trust their instincts on, rather than following the pat advice that they do find?
ANNA PAPALIA: It’s this very strange thing that we think that interviewing is somewhat like a date. I’ve heard hundreds of hiring managers say that, “I just want to click with the person,” or, “I need to like them.” Why is that a prerequisite to hiring someone to do a job? And unpacking some of that is what led me to discover interview styles.
ALISON BEARD: Tell me more about what prompted you to start this research and develop this framework.
ANNA PAPALIA: So I was previously a director of talent acquisition in the corporate world, and I had hired lots of people. I came up to the end of my time and I realized that I wanted to teach both job seekers and hiring managers how to do this better because I didn’t have any tools backed in research or science to do this. I thought that was very weird. Some of the most important business decisions are made in job interviews. Who you hire changes your business. Who you hire changes the effectiveness of your team. It is so impactful, yet we don’t have any training on how to do this.
Then I started teaching at the college level. I was teaching thousands of students at the Fox School of Business at Temple University. And as most good teachers, I think all good teachers get to this point where you start to wrestle with, why are some of my students getting this and other students really aren’t? Is it about me? Is it how I’m teaching it? What’s going on?
And I looked out onto the classrooms of students, I was teaching three three-hour interview skills workshops a week, and I got to see how lots of people were interviewing. And when I took a deeper look into all of this, I realized that: What if we don’t all do this the same way?
So I wrote a personality assessment, and I collected lots of research, and I talked to 280 of my students to really get in and figure out, what do you prioritize in an interview? What are you thinking when you are interviewing? What’s important to you? And I have to confess, I assumed since I was so great at interviewing, I had spent over a decade in HR and I was the corporate gatekeeper. I thought to myself, “I’m going to discover interview styles, and of course the best style was going to be my style.”
And I discovered these four unique interview styles. We all interview as charmers, challengers, examiners, or harmonizers. And I think one of the best things I learned in this entire process is that I was dead wrong, that there isn’t one style that’s better at interviewing than others. There was an equal distribution. I realized that we all have a capacity to nail the job interview, but we all do it differently. And to be better understood in job interviews means understanding where we’re all coming from because we have entirely unique ways of doing this.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. So there’s no one correct way to interview someone or be interviewed. So let’s talk about each of those four styles that you identified.
ANNA PAPALIA: There can be some variation, but there are four primary styles. Charmers want to be liked, challengers want to be heard, examiners want to get it right, and harmonizers want to adapt. So charmers go into an interview wanting to make a connection. They really don’t think so much about, are they going to see me as qualified? They think that they can win over the interview by using the force of their personality. They’ll even pay a compliment or tell a joke, which is much different than the other interview styles.
ALISON BEARD: And so what would the downside of a charmer be?
ANNA PAPALIA: I can speak from personal experience that charmers have a tendency to overemphasize that connection. And while they might get the person to like them, they may forget to talk about some of their successes, using some examples, answering those behavioral questions with some hard facts and data, and giving some real examples of what they’ve done can be something that they just really forget about. It can be kind of like the second thought because they’re always focused on being liked.
ALISON BEARD: And if I’m the hiring manager, what would charmer tendencies be?
ANNA PAPALIA: Well, they’re so interested in getting along, they forget to test the candidate. They forget that they need to make sure that this person can do the job. Are they technically qualified? And if you want a charmer hiring manager to like you, it’s really basic. You tell them that you like them.
ALISON BEARD: What about challengers?
ANNA PAPALIA: Challengers are more steadfast than charmers, and they are not as accommodating. If charmers look at an interview like a performance and they’re the star of the show, challengers look at an interview like a cross examination, and they’re going to figure something out. They’re highly skeptical, and they show that they’re qualified and they show their value by asking a lot of tough questions. Challengers are thought-provoking, they’re undaunted, they’re pretty strong, and they’re often long-winded.
ALISON BEARD: Okay, so I can see how challengers would work on both sides of the table – what about examiners?
ANNA PAPALIA: Examiners go into an interview seeing it as a test that they’re either going to pass or fail. Examiners don’t look at interviews like an opportunity to be liked; they look at it as a business opportunity. They are more private and very professional in their approach. But they also hold back quite a lot, and their answers can be much shorter.
Your interview style doesn’t change whether you’re a job seeker or a hiring manager. So if you’re an examiner hiring manager, you’re treating this like a test. You’re going to ask questions. You’re not going to elaborate, you’re not going to tell stories, you’re not prioritizing making a connection. You’re just making sure that this person can do the job.
ALISON BEARD: And finally, the fourth style, harmonizer.
ANNA PAPALIA: Harmonizers look at an interview like a tryout for a team that they want to join. They’re always talking about the collective, we, us. They talk about that as hiring managers or job seekers as what we accomplished and how we did this. They have a hard time owning their successes. They look at an interview as this opportunity to adapt to something that’s bigger than themselves. And you can see how this plays out, how they’re the polar opposite of a challenger. Challengers put a stake in the ground and say, “This is me.” They want to be respected and heard. And harmonizers are the opposite of that. “I want to get along. I’m collaborative. I want to adapt.”
ALISON BEARD: And I guess it’s also really important to quickly suss out what kind of person you’re facing across the table, whether you’re the interviewer trying to figure out what the interviewee is like, or you’re the interviewee trying to figure out what the interviewer is like. So how do you do that quickly?
ANNA PAPALIA: I think the old interviewing advice tells us that you should tell them what they want to hear. You should mirror the other person on the other side of the table. It doesn’t really work. I don’t tell people, “Figure this out so you can pretend to be something that you’re not.” I think understanding your interview style is more about how you can be more authentic, how you can better understand yourself, so you in turn can be better understood. I think everyone has left a job interview and you’ve thought, “Man, I hope I came across the way I intended. I hope I made the impression I was hoping to make.”
And here’s the thing. In researching interview styles, I found that this is connected to your personality. It’s like telling someone to go into an interview and change their eye color. And I think that’s one of the biggest problems with some of the advice that’s out there, and historically the advice that we’ve been given: “Just say whatever they want to hear to get the job.” That isn’t going to get you the job. An interview in the most basic sense is a set of questions about you. The more you know yourself, the better you’ll do.
And while I think it’s important that we use our emotional intelligence, and I’m a charmer, for example, if I’m in an interview and I realize that this person is my opposite because they are really drilling down on some questions and they are testing me, sure, I’m going to not tell as many stories and I’m going to shift my energy a bit. I can’t become an examiner, but I can become a softer version of a charmer to meet that person where they are.
ALISON BEARD: Got it. Almost a harder version of a charmer actually, more serious.
ANNA PAPALIA: Touche. Absolutely.
ALISON BEARD: That seems though hard to do on the fly if it’s this really innate sort of way of being driven by your personality. How exactly do you make those subtle adaptations so they still feel authentic, but you’re moving in the direction of your counterpart?
ANNA PAPALIA: It’s an excellent point. It’s actually harder to pretend to be something that you’re not. It’s actually much easier to be yourself and to be authentic. If you pretend to be something that you’re not in a job interview, how long are you going to pretend? You’re hoping that you get this job and then you work there for two or three or four years. When does the mask come off?
And this is the hardest thing, especially for some interview styles that are very accommodating like charmers and harmonizers. It’s really hard to put a stake in the ground and say who you are and be authentic in yourself. It’s a lifelong practice. It is a difficult thing to learn how to not be overly accommodating or have some hard boundaries around who you are and what you need. That’s a lifelong practice in so many things, but especially in how you perform in this artificial event that is an interview. Someone has this power over you, and what happens to you? What do you do? Do you turn up the volume? Do you turn on the charm? I think if you start there and understand what your style is, you know how to shift comfortably from your baseline.
ALISON BEARD: Is part of it that if your hiring manager isn’t looking for someone with the qualities of a charmer, then it’s probably not the right job for you?
ANNA PAPALIA: Well we could get deeply into the biases of hiring managers. We all believe our interview style is the best one. So whether you’re a charmer, challenger, examiner, or harmonizer, you will prefer the other charmer. I will always prefer and it will always be easier for me to be in an interview with another charmer. It’s difficult for me to interview an examiner who’s my polar opposite, and for challengers and harmonizers, the same thing. That’s what I hope this research and this framework helps us do is to be more open-minded in the interview process. Because right now we’re not, and that’s what creates a lot of problems.
ALISON BEARD: So when you introduce these ideas to either people looking for jobs or people hiring, what sort of changes have you seen once they understand their own style and the style of their counterparts? Is it less biased decisions, more success at getting the job, better person job fit?
ANNA PAPALIA: Well, I think with everything, it starts with acceptance. I remember when I first launched this and was studying my students’ reactions and asking them deep questions about how they felt when they received their interview style. It was an overwhelming response of feeling validated and understood.
I think if we start there and understand that we have a style and we have preferences and it’s born somewhere in our personality, that’s an excellent place to start to help people understand that we have strengths, and what I like to call overused strengths instead of weaknesses.
So as charmers, you’re very friendly. You’re always going to be warm and accommodating. But what is that as an overused strength? It means that you can come across sometimes as vapid, or maybe a chameleon. Maybe you’re just telling people what they want to hear to make them feel good. And there’s no their there. So understanding what your strengths is, you can therefore pull out how that can be seen as a negative, especially to your polar opposite.
ALISON BEARD: Do you find that some styles are more common or accepted in certain functions or industries or geographies? I can think of examiners in the tech industry and harmonizers in the healthcare industry.
ANNA PAPALIA: Yeah, so we have these stereotypes. We think that all realtors are charmers, all accountants are examiners. And I was curious about this. Our interview style assessment is scientifically validated, which means that a third party looked at our numbers and means that there’s a normal distribution of the data, which is also another surprising and interesting thing, that not all accountants are examiners. And not everyone in healthcare is a harmonizer. This is a stereotype that we believe.
What I found very interesting is there are an equal amount of harmonizers and charmers and challengers as accountants, but we have a tendency to believe that certain people are certain ways. And as hiring managers, it absolutely limits us.
ALISON BEARD: How does corporate culture play into all of this?
ANNA PAPALIA: For example, I have been consulting with a large organization for years to teach all of their hiring managers how to interview better. And the first time we went around and collected 176 of their respondents, of their hiring managers’ interview styles, and an overwhelming amount of the hiring managers were challengers. In fact, my data analyst was like, “This has to be a mistake. This has to be broken. There’s no way this is true.” But it was true.
What we realized is, is that an interview is you going out into the world and positively reinforcing one style or one way of doing things in an interview. Who you hire at your organization is you showing the world what your preferences are. We’ve all worked at companies where there are a lot more charmers than there are anyone else, or examiners or whatever. And that’s what company cultures are. Companies are just groups of people, 100 or 100,000 people, but they’ve been chosen somehow, usually by hiring managers in an interview process, and those hiring managers have biases. If you want to check to see how biased your organization is, it happens at the interview table.
ALISON BEARD: Give me an example of how you as a charmer, let’s first do it from the interviewee perspective. So you’re a charmer, you go into an interview with an examiner. How do you react in a way that maintains your charm but gives them what they need? So very specifically, if you come in and rather than me asking, “Hey, tell me about yourself,” I say, “How many balloons would it take to fit into this room?”
ANNA PAPALIA: I think in order to maintain your charmer style and to be true to your personality and to have integrity is to formulate the answer in a story form, because that feels very natural and comfortable to charmers. They also ask questions to make a connection, and they prioritize building that rapport. And in that way, it will be challenging for them because they’re not going to get that rapport to build off of. Examiners don’t need that in a way a charmer does.
So it would be a couple things. It would be moderating your own personal need for that rapport and not having it, and have faith that you can do it, and making sure that you’re paying attention to answering their interview question by giving facts and data and sharing examples from your work experience. You can put that into story form, and you can be charming while you do that.
ALISON BEARD: So I could talk about how I would do the calculations of the size of each balloon and the size of the room, et cetera.
ANNA PAPALIA: And a charmer, they would tell the story about why weren’t they in a room with balloons, or they would talk about their thought process. I’ll put it this way. Extroverts who are charmers and challengers, they talk to think, which means they’re more long-winded. They have to talk in order to figure out the answer. Examiners and harmonizers, on the other hand, they think before they speak. So they require some time to collect themselves before they go and give an answer. And that changes the impression that you make in an interview greatly. If you ask someone a question, “Tell me about yourself,” and they’re raring to go and they can talk for 20 minutes about themselves, or if you ask someone who’s highly introverted, it’s different. Introverts don’t love talking about themselves, let alone a perfect stranger about a job.
ALISON BEARD: It sounds like from the hiring manager’s perspective, the main thing is to just be aware that the person might respond differently, might need a moment, might be more long-winded than you expect them to be. But are there any sort of specific techniques, for example, that you would give a charmer interviewer who’s talking to an examiner interviewee?
ANNA PAPALIA: I think one of the techniques that I train hiring managers on, which is so important no matter what your interview style, is to write down what you want ahead of time. As a hiring manager, lots of biases creep in when there’s ambiguity. There’s lots of research on this.
If you go into an interview not really clear what you want, you’ll be swayed by so many things. Beauty, someone’s success in a different part of their career. I have seen so many hiring managers tell me, “We want to hire someone who was successful in sports.” Why? Just because someone ran a triathlon doesn’t mean that they’re going to be great at this job. So writing down what you want ahead of time limits and decreases the likelihood that you’re going to be swayed by something in the interview process. That’s really important. That’s why job descriptions are so important. If you write your job description out, if you know intimately what you need, and then thinking deeply about what your department needs, what the team needs, what the company needs, that’s huge.
And then, take it one step further and recruit an accountability partner. So it’s fine and good if you have this written down in your desk drawer, but it’s even better if you tell someone. And you get extra points if that accountability partner is your opposite. My accountability partner in my head and in my life is an examiner who couldn’t be more different than me. And sometimes I ask myself, “What would David do? How can I tap into that examiner part of me?” Because we all have this capability within us. We just prioritize being a charmer challenger examiner or harmonizer. And for hiring managers, having an accountability partner really helps us reflect on the things that excite us in interviews.
ALISON BEARD: What happens if you are the interviewer and you’re asking various kinds of questions, but because of the interviewee’s style, you’re not totally getting what you need? Maybe it’s a charmer who’s too long-winded and going on and on. Or a challenger who’s asking you questions back instead of answering the question. Or an examiner who’s just very short and to the point but not giving you any detail. Or a harmonizer who just seems to be like, “Whatever you think,” and, “Believe in the team.”
ANNA PAPALIA: I’ve been in this situation so many times, and this is the critical mistake a lot of people make. Some hiring managers who are overly accommodating jump in and try to help that person. “Well, what I’m looking for here is.” “What I hope your answer was.” Really? If an interview is a test, what you’ve just done is walked around, tapped someone on the shoulder and said, “Ah, the answer is D.” You’re not testing that person. If a candidate in an interview isn’t giving you what you want, that’s your answer.
Let’s say you’re asking someone a behavioral question, “Tell me about a time you dealt with a tough customer,” and they’re just not getting there and they’re not giving you the information that you need, I suppose you could ask a follow-up question, but I’ve very rarely ever seen that work in interviews. If they’re not giving it to you, they don’t have it to give. Sometimes it’s a lack of preparation, but often it’s just a misalignment.
ALISON BEARD: I guess my point is, as a hiring manager, I don’t want to miss out on good candidates because they’re letting their charming tendencies overwhelm them or their examiner tendencies overwhelm them.
ANNA PAPALIA: So as someone who coaches both job seekers and hiring managers, if a client came to me and they were having issues getting passed on to different rounds, I would dig in and help them prepare better. It sounds to me in this example that that candidate wasn’t prepared or didn’t practice enough in the interviews. And like I said before, this baseline, their interview style became an overused strength, and it was more lack of preparation and practice.
ALISON BEARD: Tell me a little bit about your view on preparation. How much preparation should an interviewee do to have pat answers versus go with the flow? And how much preparation should an interviewer do apart from knowing what questions they’re going to ask?
ANNA PAPALIA: I always say for job seekers specifically, “An interview is a set of questions about you.” So the more you know yourself, the better you’ll do. You build up yourself knowledge, you really get to know who you are, and practice those questions. You’re going to be more prepared. Challengers hate this. They’ve told me before, “I don’t want to go in scripted.” This is sort of an excuse some people tell themselves not to do the hard work. Everyone gets better at doing things the more you do it. Practice truly does make perfect, and interviewing is no exception. I have coached over 10,000 people. I have never seen anyone get worse. Everyone gets better the more they do this.
Now, there is a question about how you do it, right? I always ask clients that come to me for interview coaching, and I ask them, “What’s your prep like?” If you’re spending 80% of your interview prep focused on the company, reading the company’s website, and going onto the company’s information about their third quarter numbers, the company knows that information. They don’t know you. They want to know about you.
So you need to be prepared to answer questions like all the ones we talked about. “Tell me about yourself.” “Where do you see yourself in five years?” “What are your strengths and weaknesses?” You don’t get better at doing that by not practicing those questions or thinking deeply about that. And I learned that really early on when I was collecting my research. What made some of my students better at interviewing? It was the ones that had the self-awareness, that understood who they were; charmer, challenger, examiner or harmonizer.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. It’s not a test on how much you know about the company; it’s a test on what you can do for the company.
ANNA PAPALIA: Absolutely. And for hiring managers, because they’re in this position of power, they have a tendency sometimes to not do the work and to rely on this thing that’s so bad, which is, “I just want to like them. I’m just going to have a conversation and see how I feel.” And we know that ambiguity leads to bias, like I said before.
We want to make sure that ahead of a job interview, you’re doing a couple of things. You’re really understanding exactly what you want, writing it down ahead of time, thinking deeply about your own biases, getting to know your interview style so you’ll also know what your bias is. I’m a charmer, I know I’m going to like other charmers. I’m just going to know that. I know I’m going to be swayed by some of these people. I know that sometimes some people’s interview styles are going to rub me the wrong way, and I have to practice looking past that and knowing that their interview performance doesn’t have a great predictor on whether or not they can do the job.
Hiring managers very seldom do this deep work because partly it didn’t exist, and they’re busy. We’re really busy. You have a team of eight. Now you have a job opening. That means you’re even busier. The work’s piling up. Looking for a job and hiring is sort of a part-time job. So I get it, it’s a lot to do. But if you take your time, you’ll make better decisions than winging it. Winging it never works.
ALISON BEARD: Terrific. Well, all great advice. Hopefully this will help our listeners be better interviewees and interviewers. Anna, thanks so much for being with me.
ANNA PAPALIA: Thank you. This was great. Thanks so much.
ALISON BEARD: That’s Anna Papalia, author of the book Interviewology: The New Science of Interviewing.
We have more episodes and more podcasts to help you manage your team, your organization, and your career. Find them at hbr.org/podcasts or search HBR on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen. Thanks to our team: senior producer Mary Dooe, associate producer Hannah Bates, audio product manager Ian Fox, and senior production specialist Rob Eckhardt. And thanks to you for listening to the HBR IdeaCast . We’ll be back with a new episode on Tuesday. I’m Alison Beard.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about job interviews.
- Hiring and recruitment
- Managing yourself
- Talent management
Partner Center
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design , you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.
There are many ways to categorize different types of research. The words you use to describe your research depend on your discipline and field. In general, though, the form your research design takes will be shaped by:
- The type of knowledge you aim to produce
- The type of data you will collect and analyze
- The sampling methods , timescale and location of the research
This article takes a look at some common distinctions made between different types of research and outlines the key differences between them.
Types of research aims, types of research data, types of sampling, timescale, and location, other interesting articles.
The first thing to consider is what kind of knowledge your research aims to contribute.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The next thing to consider is what type of data you will collect. Each kind of data is associated with a range of specific research methods and procedures.
Finally, you have to consider three closely related questions: how will you select the subjects or participants of the research? When and how often will you collect data from your subjects? And where will the research take place?
Keep in mind that the methods that you choose bring with them different risk factors and types of research bias . Biases aren’t completely avoidable, but can heavily impact the validity and reliability of your findings if left unchecked.
Choosing between all these different research types is part of the process of creating your research design , which determines exactly how your research will be conducted. But the type of research is only the first step: next, you have to make more concrete decisions about your research methods and the details of the study.
Read more about creating a research design
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/types-of-research/
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is your plagiarism score.
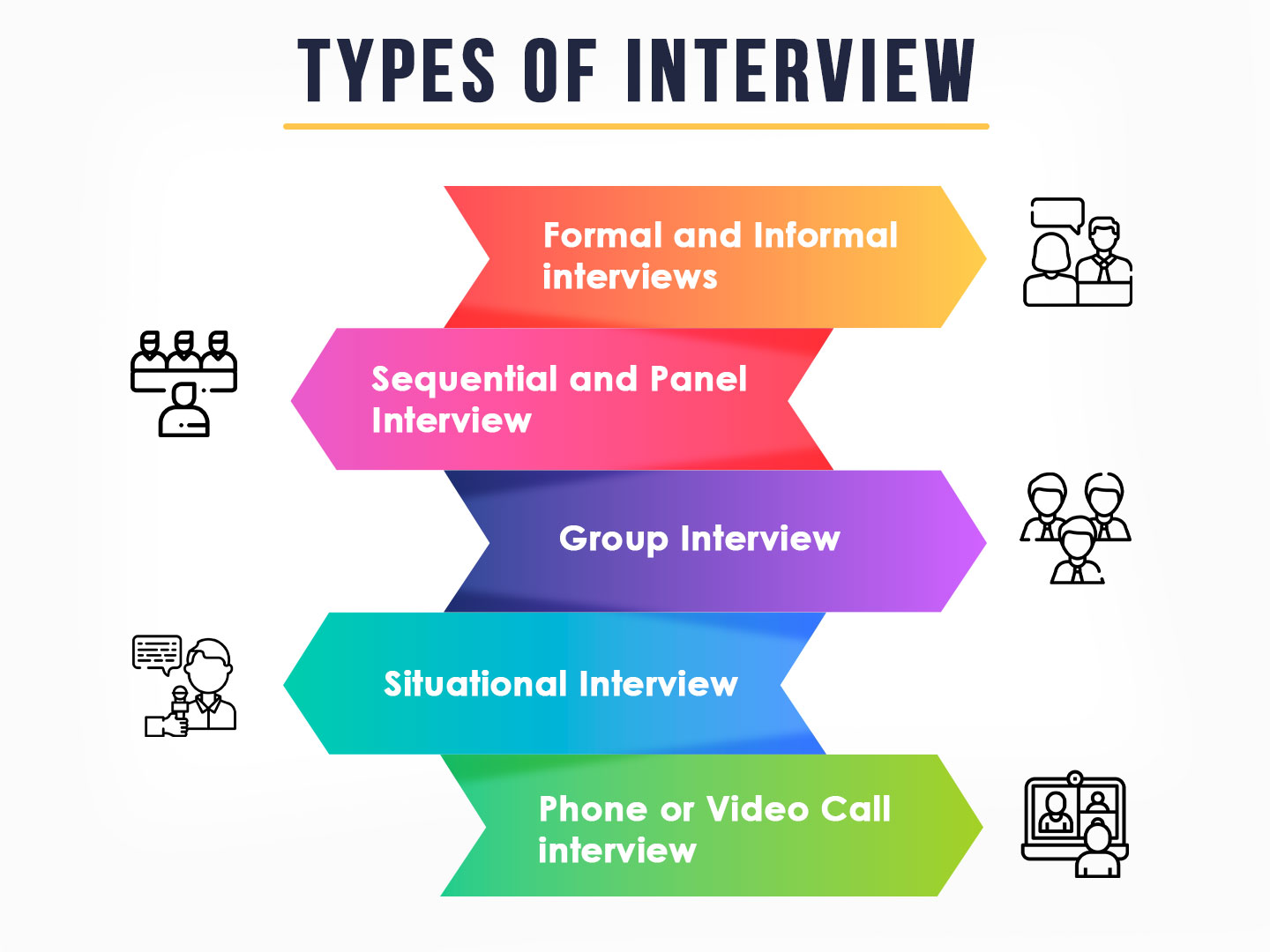
There are several types of interviews, often differentiated by their level of structure. Structured interviews have predetermined questions asked in a predetermined order. Unstructured interviews are more free-flowing. Semi-structured interviews fall in between. Interviews are commonly used in market research, social science, and ethnographic ...
There are more types of interviews than most people think. An interview is generally a qualitative research technique that involves asking open-ended questions to converse with respondents and collect elicit data about a subject.. The interviewer, in most cases, is the subject matter expert who intends to understand respondent opinions in a well-planned and executed series of star questions ...
Introduction. Interviewing people is at the heart of qualitative research. It is not merely a way to collect data but an intrinsically rewarding activity—an interaction between two people that holds the potential for greater understanding and interpersonal development. Unlike many of our daily interactions with others that are fairly shallow ...
Types of Interviews - In a Nutshell. The types of interviews you can use in research are structured interviews, unstructured interviews, semi-structured interviews, and focus group interviews. The interviewer effect is a bias that arises when the characteristics of the researcher influence the responses of the interviewees.
Interviews are one of the most promising ways of collecting qualitative data through establishment of a communication between researcher and the interviewee. Researcher in a face to face, phone or ...
What are the different types of Interviews? There are three main kinds of research interviews. 1. Structured Interview. This interview type only includes predetermined questions. The interviewer prepares a set of questions to ask during the interview and strictly follows them. There are no follow-up or on-the-spot questions.
Yes or no and true or false questions are examples of dichotomous questions. Open-ended questions are common in structured interviews. However, researchers use them when conducting qualitative research and looking for in-depth information about the interviewee's perceptions or experiences. These questions take longer for the interviewee to ...
Develop an interview guide. Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview. Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question. Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes. Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics. Make sure your questions are clear and ...
Researchers aim to look into the individual's life journey. As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data. Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews. 6.
A semi-structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions within a predetermined thematic framework. However, the questions are not set in order or in phrasing. In research, semi-structured interviews are often qualitative in nature. They are generally used as an exploratory tool in marketing, social science ...
3. People's espoused theories differ from their theories-in-practice. Get them to tell a story. Ask "how" questions not "do". Use "tell me about" and "tell me more about that". Use open-ended questions. Approach your topic sideways. Don't take the first answer as a final answer. Ask for elaboration.
There are several types of interviews, often differentiated by their level of structure. Structured interviews have predetermined questions asked in a predetermined order. Unstructured interviews are more free-flowing, and semi-structured interviews fall in between. Interviews are commonly used in market research, social science, and ...
InterViews by Steinar Kvale Interviewing is an essential tool in qualitative research and this introduction to interviewing outlines both the theoretical underpinnings and the practical aspects of the process. After examining the role of the interview in the research process, Steinar Kvale considers some of the key philosophical issues relating ...
Pre-interview preparation and research. Before conducting the interview, the researcher needs to thoroughly understand the research topic, define the purpose of the interview, and identify potential interviewees. Preparing an interview guide with key themes or questions is essential, though the level of detail will depend on the interview ...
The interview method in psychology is a data collection technique where a researcher engages in direct conversation with individuals to gather information about their thoughts, experiences, and behaviors. It involves asking structured or open-ended questions to elicit responses that can provide insights into various psychological phenomena.
result, the structure of interviews can range from loose conversations to structured exchanges in which all interviewees are asked the exact same set of questions. Your choice of interview structure should reflect the goals and stage of your research. Less structured interviews are most appropriate for early stages of research because they
7 interview methods in research. Here's a list of seven major interview methods that you can use in your research: 1. Focus group. One popular research interview method is conducting a focus group interview, which involves a group of individuals interviewed at the same time.
Kinds of qualitative interviews - we will discuss each, in turn. Unstructured interviews can help a researcher LEARN MORE about an entire phenomenon set - to THEN go back and refine his/her research. • unstructured interview is a type of interview that does not make use of a set of standardized questions.
An interview remains a qualitative investigate manner that depend on asking questions in order to collect data. Interviews including two or more people, one of whom
Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples. Published on 4 May 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on 26 August 2022. A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. It is one of four types of interviews.. In research, structured interviews are often quantitative in nature.
Revised on June 22, 2023. An unstructured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking participants questions to collect data on a topic. Also known as non-directive interviewing, unstructured interviews do not have a set pattern and questions are not arranged in advance. In research, unstructured interviews are usually ...
Emails, letters, memos, telephone conversations, lectures, course materials handed out in class or provided via Blackboard, and personal interviews are considered personal communications in APA. This type of communication can be difficult to provide recoverable data; therefore, these types of communication are not included in the Reference list.
In interviewing thousands of people and studying relevant research, she's identified a new way to get better at this important aspect of career and organizational growth.
Evidence-based practice in nursing involves providing holistic, quality care based on the most up-to-date research and knowledge rather than traditional methods, advice from colleagues, or personal beliefs. Nurses can expand their knowledge and improve their clinical practice experience by collecting, processing, and implementing research findings.
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
36 Hours in Mumbai
By Saumya Roy Updated March 26, 2024
- Share full article

By Saumya Roy Photographs by Atul Loke
Saumya Roy, a Mumbai-based author, has written a book about the city’s wealth, poverty and the waste pickers who make their living in its landfill.
Mumbai appears as much a dream as a city. Sprinkled with the stardust of Bollywood, the Hindi-language film industry that bases itself here, and studded with billionaires , India’s hyperkinetic metropolis, known as Bombay until 1995, feels like a place where anything is possible. But over the years, the city’s reality has been one of crumbling infrastructure, unmoving traffic and unending slums. Amid tight pandemic lockdowns, Mumbai turned into one of the world’s great construction sites , trying to remake itself with new towers, subway lines and bridges . Take in the dizzying juxtapositions — while discovering experimental performances in former textile mills and serene, ancient caves a short drive from the urban chaos — in a city guaranteed to look different again the next time you visit.
Recommendations
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya , a sprawling and immaculately kept museum, houses a trove of Hindu, Jain and Buddhist sculptures.
- The Bombay Poetry Crawl offers a walking tour through one of Mumbai’s most rapidly gentrifying areas and traces the city’s working-class roots through poetry.
- The Kanheri Caves are an ancient Buddhist complex of more than 100 caves, some dating back as far as 2,000 years, in Sanjay Gandhi National Park . Some of the caves have pillared prayer halls and serene, carved Buddhist deities.
- G5A , an arts center housed in part of a former textile mill, hosts music, film screenings, poetry readings and performances.
- The Afghan Church , formally known as the Church of St. John the Evangelist, is a newly restored 19th-century house of worship that serves as a poignant memorial for fallen Indian and British soldiers.
- Mani Bhavan , the former home of Mohandas K. Gandhi, is now a museum that preserves details of his spartan life, underscoring his emphasis on self-reliance.
- Moghal Masjid , a Shiite mosque built in 1860, is known for its intricate blue tile work.
- Hasnabad Dargah , known as Mumbai’s Taj Mahal for its resemblance to that celebrated monument, is a milky-white mausoleum that evokes calm in the middle of the city.
- Magen David Synagogue is a large historic temple, painted sky blue, in the Byculla neighborhood.
- Stroll by murals of Bollywood stars in Bandra , a coastal neighborhood of old Portuguese bungalows and celebrity homes.
- Masque is a high-end restaurant that reinvents traditional Indian dishes in modern, surprising ways over a nine-course tasting menu.
- Kala Ghoda Cafe serves healthy breakfasts, including spicy egg dishes.
- Swati Snacks , a Mumbai institution, offers street-food classics and traditional favorites in a bright, clean setting.
- Aaswad Upahar and Mithai Griha is a popular, no-frills restaurant in the Dadar neighborhood that offers a mango-themed thali (a platter filled with various small dishes) in April and May, when the fruit is in season.
- Bastian at the Top , a sceney rooftop restaurant with lavish décor that includes an indoor swimming pool, is worth a stop to take in the views of the bay over a drink.
- Moonray , a newly opened women’s wear store, brings together immaculate European cuts and handmade embroidery from Mumbai.
- Payal Khandwala sells silk tops, sharply cut suits and trench coats in bold-colored Indian fabric.
- Ogaan showcases a range of local designers whose garments include ornate Indian wedding wear and silk shirts.
- Kitab Khana has a large and well-curated selection of books on Indian literature, politics and Gandhian thought, set in a building that is more than a century old.
- Induri Saree Centre sells glittering, traditional saris in a candy-box-size store.
- The Taj Mahal Palace , an ornate hotel open since 1903, looks over the Arabian Sea and the historic Gateway of India arch. A memorial in the lobby commemorates the terror attack at the hotel in 2008. Rooms start at 23,550 rupees, or about $282.
- Sea Green Hotel , on the curved, lit-up shoreline called the Queen’s Necklace, has basic rooms with gorgeous bay views. Rooms start at around 9,000 rupees.
- The Grand Hotel is a century-old establishment in the city’s historic Ballard Estate district, an area that is also home to one of Mumbai’s best-known Parsi restaurants, Britannia & Co. You can also walk to many of the city’s well-known attractions. Rooms start at around 6,850 rupees.
- Traveling in Mumbai’s packed trains is fast, efficient and an experience like no other. Millions travel on the local trains every year, and vendors and singers walk through compartments (25 rupees for a first-class single ticket). Black-and-yellow cabs , which use meters with fixed rates, and ride-hailing apps like Uber are readily available. Mumbai’s red buses also offer a breezy, scenic and cheap way to get around the city (from 5 rupees per trip).

See spindly chimneys rising amid luxury hotels and condos in the jagged skyline of Lower Parel, a rapidly gentrifying precinct in central Mumbai. The chimneys are relics of the area’s former textile mills, which began slowly being redeveloped into malls after a worker strike in the 1980s. Trace Mumbai’s working-class roots here with the writer Saranya Subramanian, who leads the Bombay Poetry Crawl (600 rupees, or about $7), a series of walking tours conducted through the lens of poetry and local history. During the tour, Ms. Subramanian reads poetry by workers and encourages participants to read, too. She leads the tour monthly and also hosts a range of other poetry walks in the city, including one on a local train. Check her Instagram page, @thebombaypoetrycrawl , for scheduling.

Take a car to the nearby G5A , a cultural center housed in a repurposed textile mill compound. Trees grow out of the stone walls of a neighboring former mill , and skyscrapers rise, seemingly by the minute, on the other side. Catch a show at G5A, which hosts edgy art performances, movie screenings and discussions in its small theater, or on its terrace, with the moon glowing through the Mumbai haze. Recent shows include a poetry reading by the Pulitzer Prize-winning author Forrest Gander, along with the celebrated Indian poet Arvind Krishna Mehrotra; Norwegian and Bangalorean jazz bands; and a Kashmiri film. Tickets from 250 to 700 rupees.

Walk next door, still within the mill compound, to the high-ceilinged and warmly lit Masque , a restaurant that reinvents traditional Indian dishes across a nine-course tasting menu (5,200 rupees per person). It takes puran poli and amti, for instance, a sweet, lentil-filled flatbread and side of spicy coconut dal that is often eaten during Mumbai festivals, and remixes it as a bite-size chickpea tart with a hint of jaggery (Indian raw sugar), filled with green peas or crab and topped with coconut foam. Pav, a ubiquitous Mumbai bread bun with a crackly top and slightly sweet, dense interior, acquires a croissant-like, buttery texture here — dip it into a silky morel or lamb curry. Cap off the meal with a popsicle made with unlikely layers of Indian pickle, mulberry and white chocolate. Vegetarian menus available.

Trace Mumbai’s working-class roots in Lower Parel with the Bombay Poetry Crawl, a series of walking tours conducted through the lens of poetry and local history.

Walk through the soft-colored shadows cast by stained-glass windows in the Church of St. John the Evangelist, more commonly known as the Afghan Church , which reopened in March after a two-year renovation. The building, in the leafy Navy Nagar, a naval area at the southern tip of Mumbai, was completed in 1858 and commemorates the more than 4,500 Indian and British soldiers who died during the first Anglo-Afghan war, including in its disastrous retreat from Kabul. The church is also known for multifaith prayers, Indian classical music concerts and a midnight Mass at Christmas. Entry is free.

Kala Ghoda Cafe
Dig into a breakfast of akuri, a spicy scrambled egg dish (345 rupees) that is traditional in India’s Parsi community, at Kala Ghoda Cafe , in the Kala Ghoda neighborhood. Then walk to the sprawling Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya , a museum with manicured lawns and a Gothic-style building topped with a bulbous dome. As part of “ Ancient Sculptures ,” showing through October, chiseled Greek gods and Egyptian deities from the British Museum and the J. Paul Getty Museum share space with Assyrian gods from CSMVS’s permanent collection. The museum’s permanent galleries are a trove of Hindu, Buddhist and Jain sculptures and also feature artifacts from the ancient Indus Valley civilization. Tickets, 150 rupees for Indian nationals; 700 rupees for foreigners.

Stroll the Kala Ghoda neighborhood, starting with Artisans ’, a gallery and shop in a graffiti-covered building that showcases traditional Indian crafts. In the area’s ever-expanding fashion district, browse crisp white shirts with handmade lace collars (from around 9,500 rupees) at Moonray , a women’s fashion label and shop (its co-founder also runs the Chanakya School of Craft , which teaches women embroidery and collaborates with Dior). Also check out Payal Khandwala , which has silk tops (14,000 rupees), sharply cut suits and trench coats in bold-colored Indian fabric, and Ogaan , with heavily embellished wedding dresses, pleated dresses and more. Then walk to Kitab Khana , an independent bookstore in a more-than-century-old building with Corinthian columns in the nearby Fort district. Browse the well-curated selection of Indian literature and the books on history and Gandhian thought that line the high shelves.

Swati Snacks
A dizzying range of delicacies can be found on Mumbai’s khao gallis, a Hindi term for “food streets.” The safest way to try them all (and avoid tummy trouble) might be at Swati Snacks , a six-decade-old restaurant in the Tardeo area. Have the vada pav (175 rupees), like garlicky potato sliders, and the signature panki (230 rupees), a wispy rice pancake flavored with mint or dill that arrives steaming in a banana-leaf parcel. Then visit the nearby Mani Bhavan , a three-story building where Mohandas K. Gandhi, known as the father of the nation, often stayed; it is now a museum. Spinning wheels and floor seating in his preserved, spartan bedroom provide a window to his belief that the route to Indian independence could come only through discipline and self-reliance. Entry, 20 rupees.

Moghal Masjid
Take a car to Byculla, the chaotic old quarter of Mumbai. Get a coffee (Americano, 228 rupees) at the Craftery by Subko , a new Mumbai cafe and roastery chain bringing hipsters to this part of the city. Then drive through the busy, narrow streets to see some of Mumbai’s diverse and beautiful religious monuments. Visit the nearby Moghal Masjid , a jewel-like, Iranian-style Shiite mosque built in 1860, with intricate blue tiling adorning a curved entrance. Women cannot pray inside the mosque but can enter the compound, which has a pool for ablution. Take in the facade of Hasnabad Dargah , a pristine, ivory-colored mausoleum, known as Mumbai’s Taj Mahal for its resemblance to the original (entry only for Shia Ismaili Muslims). Not far from there is the Magen David Synagogue (entry, 300 rupees), recognizable by its sky blue clock tower, built in the 1860s to serve Mumbai’s once wealthy and influential, but now vanishing , Jewish community.

Bastian at the Top
In the Dadar neighborhood, shop for handwoven saris (from 2,000 rupees) and scarves at Induri Saree Centre , a candy-box-size store. Then line up at Aaswad Upahar and Mithai Griha , a no-frills Dadar institution best visited in April and May with the arrival of fragrant and luscious Alphonso mangoes. Aaswad does a seasonal mango-themed thali (a platter of various small dishes; 470 rupees) that includes a saffron, mango and cardamom drink; a mango dal; and chilled mango pulp called aamras that is the taste of a Mumbai summer in a bowl. Then cross the street to the gleaming, new Kohinoor Square mall and take the elevator 48 floors to Bastian at the Top . With a tree-lined plunge pool and glowing figurines carved into giant pillars, it can feel more like a theme park than a restaurant (it often attracts Bollywood celebrities). It’s worth a cocktail (1,295 rupees) just to take in the sweeping views of the bay.

Catch a show at G5A, a cultural center housed in a repurposed textile mill compound.

A mural by Ranjit Dahiya
The laid-back suburb of Bandra has Portuguese bungalows, Bollywood studios and the full wattage of star homes along with fans hoping for a glimpse. The best bet for encountering Bollywood stars is on the Technicolor, larger-than-life murals in the area’s charming lanes. See a pistol-wielding Dharmendra, from the iconic 1975 movie “Sholay,” opposite the Subko cafe on Chapel Road. Next to it is a triptych of Bollywood’s dancing divas — a feathered Helen and a bejeweled Waheeda Rehman and Asha Parekh. (Ranjit Dahiya, the artist behind many of these murals, also teaches workshops .) Stroll on to Waroda Road (past a moody depiction of the celebrated actor Irrfan Khan) to reach the brightly colored Veronica’s , an all-day cafe that has become something of a living room for Bandra’s young set, who come for creative bites like chicken-and-cheese-filled breakfast momos (395 rupees), potato waffles (350 rupees) and babka stuffed with chorizo (275 rupees).
Leave the chaos of the city behind, driving north to reach the entrance of Sanjay Gandhi National Park , a 40-square-mile preserve where deer, monkeys and the occasional leopard roam. From inside the park, minivans drive visitors about 10 minutes through the forest (1,000 rupees round-trip) to the bottom of a hill. From there, walk up to the Kanheri Caves, a Buddhist complex of more than 100 caves, the oldest dating back 2,000 years, carved into basalt. Some form large, pillared prayer halls, while others feature carved serene Buddhist deities in prayer. Also see the waterways, loosely cut into the hills, that provided water to the monks who lived and meditated there many centuries ago. Park entry, 95 rupees; caves entry, 25 rupees.
Advertisement
Best Restaurants in Sion (Mumbai), Maharashtra
Sion restaurants, establishment type, traveller rating, dietary restrictions, restaurant features, neighbourhood.


The 49 best parks and gardens in Mumbai
Navigate forward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.
Navigate backward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.

1 Sanjay Gandhi National Park
2 Kamala Nehru Park

3 Hanging Gardens
4 shivaji park, 5 priyadarshini park.
Track your travel spending and split costs with friends
Plan your trip. Keep your budget organized. Split the cost between tripmates. Wanderlog does it all.

6 Horniman Circle Garden
7 maharashtra nature park, 8 esselworld, 9 snow world, 10 joggers park, 11 water kingdom, 12 kidzania mumbai, 13 cross maidan garden, 14 bmc nirvana park, 15 mumbai zoo park.

Don’t forget to pack anything
Stay organized with a to-do list, packing list, shopping list, any kind of list.

16 Gateway Of India Mumbai
18 elephanta caves, 19 chatrapati shivaji maharaj park, 20 dr. bhau daji lad museum, 21 suraj water park, 22 jogger's park, 23 smaaash utopia city, 24 amarsons garden, 25 vardhman fantasy.
All travel reservations in 1 place
Never dig through your emails again — access all your flights, lodging, and any reservations in 1 place.

26 Lions Juhu Children's Municipal Park
27 nanalal d mehta garden, 28 bmc forest theme garden, 29 joggers' park, 30 chhatrapati shivaji maharaj vastu sangrahalaya, 31 nehru planetarium, 32 tikuji-ni-wadi, 33 kamala nehru park, 34 snow kingdom (mumbai), 35 aarey colony.

Perfect for road trips
See time and distance between places, and optimize your route to get the most of your day.
36 Ovalekar Wadi Butterfly Garden
37 sagar upvan garden, 38 raj bhavan, 39 city park, 40 veer baji prabhu udyan, 41 tata garden park, 42 pushpa narsee park, 43 chhota kashmir park., 44 borivali national park, 45 jiogarden.
Collaborate with friends in real time
Plan along with your friends with live syncing and collaborative editing.

46 Mani Bhavan
47 h2o water, 48 veer savarkar garden, 49 bhakti park, top searches in mumbai, popular road trips from mumbai, what's the weather like in mumbai.
It depends on when you visit! We've compiled data from NASA on what the weather is like in Mumbai for each month of the year: see the links below for more information.
- Weather in Mumbai in January
- Weather in Mumbai in February
- Weather in Mumbai in March
- Weather in Mumbai in April
- Weather in Mumbai in May
- Weather in Mumbai in June
- Weather in Mumbai in July
- Weather in Mumbai in August
- Weather in Mumbai in September
- Weather in Mumbai in October
- Weather in Mumbai in November
- Weather in Mumbai in December
All road trips from Mumbai
- Mumbai to Pune drive
- Mumbai to New Delhi drive
- Mumbai to Jaipur drive
- Mumbai to Hyderabad drive
- Mumbai to Bengaluru drive
- Mumbai to Udaipur drive
- Mumbai to Agra drive
- Mumbai to Ahmedabad drive
- Mumbai to Mahabaleshwar drive
- Mumbai to Nashik drive
- Mumbai to Mysuru (Mysore) drive
- Mumbai to Kathmandu drive
- Mumbai to Chennai (Madras) drive
- Mumbai to Aurangabad drive
- Mumbai to Panjim drive
- Mumbai to Jodhpur drive
- Mumbai to Kochi (Cochin) drive
- Mumbai to Kolkata (Calcutta) drive
- Mumbai to Shirdi drive
- Mumbai to Ooty (Udhagamandalam) drive
- Mumbai to Munnar drive
- Mumbai to Vadodara drive
- Mumbai to Jaisalmer drive
- Mumbai to Varanasi drive
- Mumbai to Daman drive
- Mumbai to Hampi drive
- Mumbai to Pondicherry drive
- Mumbai to Surat drive
- Mumbai to Alibaug drive
- Mumbai to Amritsar drive
Explore nearby places
- Navi Mumbai
- Mulund West
- Mira Bhayandar
All related maps of Mumbai
- Map of Mumbai
- Map of Ghatkopar
- Map of Navi Mumbai
- Map of Mulund West
- Map of Karnala
- Map of Panvel
- Map of Alibaug
- Map of Nagaon
- Map of Mira Bhayandar
- Map of Dombivli
- Map of Thane
- Map of Revdanda
- Map of Bhiwandi
- Map of Kalyan
- Map of Matheran
- Map of Vasai
- Map of Ambarnath
- Map of Ulhasnagar
- Map of Khalapur
- Map of Badlapur
- Map of Karjat
- Map of Neral
- Map of Chinchoti
- Map of Kashid
- Map of Khopoli
- Map of Tembhi
- Map of Titwala
- Map of Virar
- Map of Raigad
- Map of Khandala
- Map of Rajmachi
Mumbai throughout the year
- Mumbai in January
- Mumbai in February
- Mumbai in March
- Mumbai in April
- Mumbai in May
- Mumbai in June
- Mumbai in July
- Mumbai in August
- Mumbai in September
- Mumbai in October
- Mumbai in November
- Mumbai in December
Looking for day-by-day itineraries in Mumbai?
Get inspired for your trip to Mumbai with our curated itineraries that are jam-packed with popular attractions everyday! Check them out here:
- 1-Day Mumbai Itinerary
- 2-Day Mumbai Itinerary
- 3-Day Mumbai Itinerary
- 4-Day Mumbai Itinerary
- 5-Day Mumbai Itinerary
Best attractions in nearby cities
- Top things to do and attractions in Navi Mumbai
- Top things to do and attractions in Alibaug
- Top things to do and attractions in Matheran
- Top things to do and attractions in Khandala
Best restaurants in nearby cities
- Where to eat: the best restaurants in Navi Mumbai
- Where to eat: the best restaurants in Thane
- Where to eat: the best restaurants in Alibaug
- Where to eat: the best restaurants in Khopoli

- Itinerary + map in one view
- Live collaboration
- Auto-import hotels and reservations
- Optimize your route
- Offline access on mobile
- See time and distance between all your places
THE 5 BEST Things to Do in Sion, Mumbai
Top things to do in sion.
- 5.0 of 5 bubbles
- 4.0 of 5 bubbles & up
- South Mumbai
- Western Suburbs
- Eastern Suburbs
- Bandra West
- Good for a Rainy Day
- Good for Kids
- Budget-friendly
- Good for Big Groups
- Adventurous
- Hidden Gems
- Good for Couples
- Honeymoon spot
- Good for Adrenaline Seekers
- Things to do ranked using Tripadvisor data including reviews, ratings, photos, and popularity.

1. Sion Hillock Fort

2. LInda Tours Mumbai
3. Astrologer House
4. Bhakti Dham Mandir
5. rupam shopping centre.

6. Alliggo Group
What travellers are saying.

33 Incredible Tourist Places to Visit in Mumbai

Aptly known as 'City of Dreams', Mumbai is the capital city of Maharashtra located on the west coast of the Indian peninsula. Named after Goddess Mumba Devi, Mumbai is a diverse city that offers a variety of choices to spend some quality time with your loved ones. From beaches to theme parks, from historical sites to religious spots, from shopping centres to wide array of eateries, Mumbai offers something for everyone. Mumbai Tourism is ideal for all kinds of holiday, be it a long break or a weekend getaway or a one day trip to the happening city.
Here is a list of Top places to visit in Mumbai
1. Nariman Point

Nariman Point is known as the Manhattan of Mumbai. It is near the southern end of Marine Drive, and it forms a part of the majestic skyline of Mumbai. This place is the business hub of Mumbai, and here you'll find corporate offices of many renowned multinational companies.
At Nariman Point, you'll also come across grand hotels, lavish restaurants and classy pubs. The area is known for its branded showrooms and shopping malls too.
Nariman Point has been developed on land reclaimed from the sea. And from here, you can enjoy a panoramic view of Marine Drive and the endless sea. Many Bollywood movies, like Munnabhai MBBS and Wake Up Sid, have scenes from that sea-facing promenade.
This area also has a lively nightlife, and it’s among the best places to visit in Mumbai at night.
2. Churchgate
Churchgate is the business district of Mumbai. It has offices of many banks and business organisations. And it also has the High Court of Bombay and many reputed educational institutions.
The area is known as Churchgate because the Church Gate of the old, walled-city Mumbai used to be here. It was demolished in 1860.
The neighbourhood has the historical Churchgate station and many prominent tourist spots of Mumbai. Some well-known places to visit like Gateway of India, Marine Drive and Elephanta Caves lie close to Churchgate area. Nariman Point is a part of the Churchgate area too.
And here, you can also enjoy shopping. From low-priced street-side stalls to luxury showrooms, and retail stores to wholesale counters, you have got plenty to choose from.
3. Gateway of India

About Gateway of India
One of the most popular places to see in Mumbai is the Gateway of India which was built during the colonial era. Built to commemorate the visit of King George V in 1911, it was the first structure that a visitor would see while arriving to Mumbai via sea. Its magnificent architecture still allures everyone. Overlooking the Arabian Sea, Gateway of India presents an impressive sight that is impossible to miss when in Mumbai. Gateway of India not only presents historical significance but also a captivating architecture which was designed by George Wittet.
Now a popular place to hangout, Gateway of India buzzes with hordes of visitors every day. Various local vendors selling snacks, balloons and other items, stalls and photographers make this place vibrant with activities.
History of Gateway of India
Gateway of India was built to mark the royal visit of King George V and Queen Mary to Mumbai (Bombay) in 1911. Foundation of the monument was laid out by the then Governor of Bombay, Sir George Sydenham Clarke in March 1911. The construction of this monument was completed in 1924.
Once representing the grandeur of British era, it was also the place from where the last troop of British regiment marched at the time of independence. A ceremony on the passing of the 'First Battalion of the Somerset Light Infantry' was conducted here for the same in 1948.
Architecture of Gateway of India
The monument, Gateway of India stands majestic with an arch of height of 26 meter. It is designed by the then renowned architect George Wittet. It has been built in the architectural style of Indo-Saracenic and has a touch of Islamic architectural styles too. Constructed in yellow basalt and binding concrete, it consists of exquisite lattice work. Its central dome with a height of 83 feet with a diameter of 48 feet makes the monument even more imposing. The four pillars are another prominent feature of Gateway of India. Behind its arch, steps have been built that lead visitors to the Arabian Sea.
Nearby Attractions
Gateway of India is located quite close to Elephanta caves and Taj Mahal Palace Hotel, which are two other prominent tourist attractions of Mumbai. Hence, you can club together visit to all these three places on the same day.
Timings of Gateway of India
Gateway of India is open throughout the day and night and on all days of the week.
How to reach Gateway of India
As it is a popular landmark of the city, you will not find any difficulty in reaching here. One can hire an autorickshaw or a private taxi from any part of the city to Gateway of India. If you are travelling by local trains, then you can get down at the nearest stations which are Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus station (2.5 km away) and Churchgate station (2.4 km away). From here you can hire a locally run auto-rickshaw.
4. Flora Fountain

Flora Fountain is one of the tourist places within Churchgate. It stands at the same place where the destroyed ChurchGate of Mumbai used to be.
The fountain was designed by R. Norman Shaw, and it has a mix of Neo-Gothic and Indo-Saracenic styles. It was built in 1864, by Engineer James Forsythe.
This Portland stone structure has fine carvings and sculptures. Its four corners are decorated with different statues. And the water basin below has stone fish figures and lion heads.
A magnificent 7 feet high statue of Roman Goddess Flora adorns the fountain top. And you can enjoy a spectacular view of Flora Fountain in the evening; when it's illuminated by lights.
5. Jehangir Art Gallery
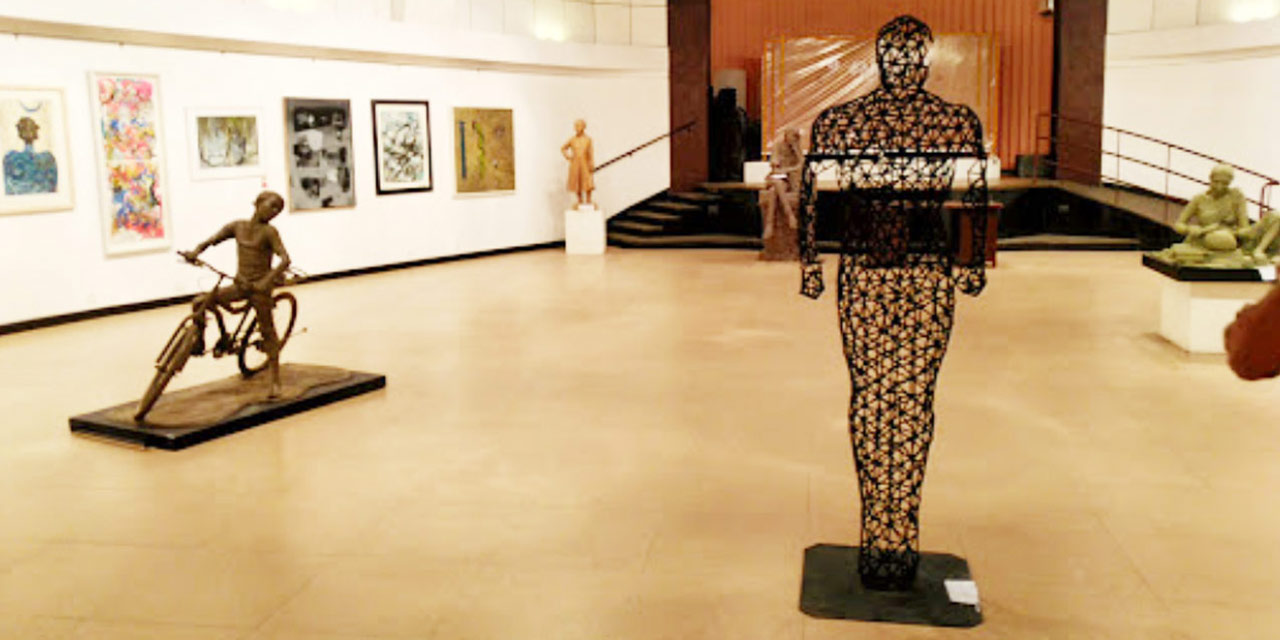

Jehangir Art Gallery has played a prominent role in the evolution of contemporary Indian art. It was established in 1952 with the help of Sir Cowasji Jehangir’s donations. And since then, this art gallery has hosted numerous exhibitions for painters, sculptors, and other artists.
But it’s more than a venue for art exhibitions. Jehangir Art Gallery conducts workshops and other art programmes. And it’s a must-visit place for aspiring artists and art connoisseurs.
You can also buy a range of antique items and artefacts from the shop here.
Jehangir Art Gallery is in the Kala Ghoda area, the art district of Mumbai. And this area has several other art galleries and designer boutiques with some of the finest arts in the city.
6. Marine Drive
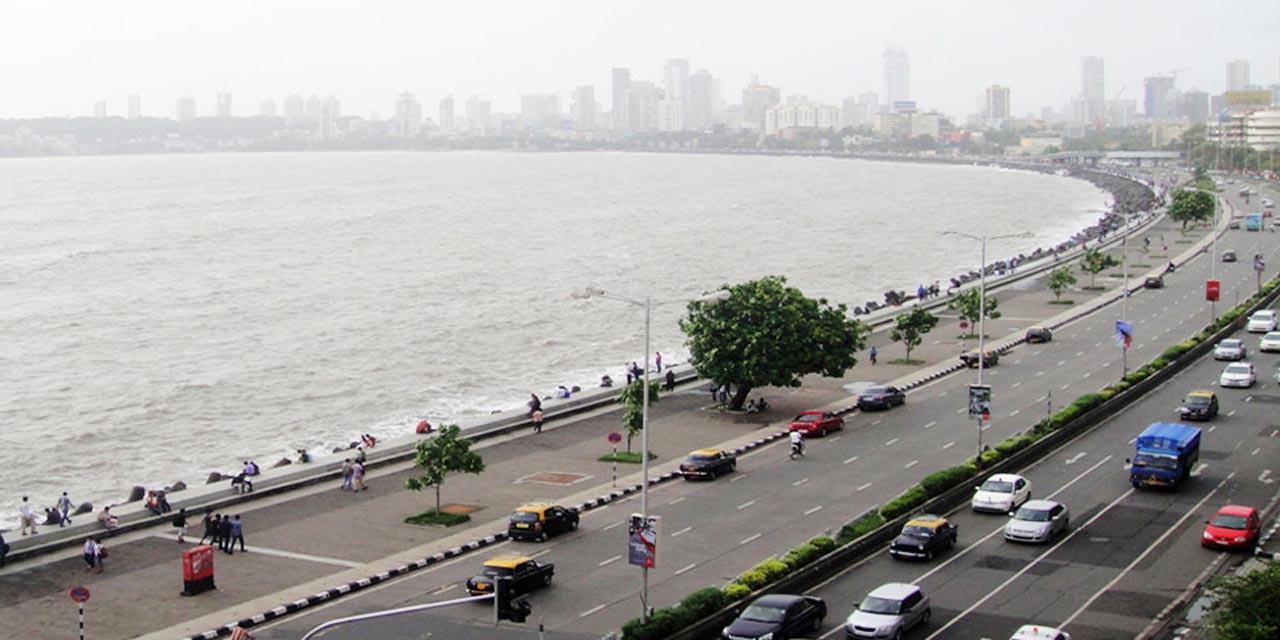

Another place to visit in Mumbai is the Marine Drive. Officially named as Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Road, this is a 3 km long stretch with six lanes that runs by the coastline. It is located in the southern Mumbai while it runs towards the north of the city. Marine Drive forms a natural bay, which hypnotizes every visitor with its serene scenic beauty.
Marine Drive is a C- shaped road which is a place to must visit when in Mumbai. The palm trees lined on the side make the pathway even more alluring. Its beauty is enhanced in night when wide stretch of street lights is lit up, giving it a look of necklace. The view is especially breath-taking when seen from an elevated point. Owing to this, it is often referred with the name of Queen’s Necklace. Marine Drive also links Nariman Point, which is also a popular place to visit in Mumbai to Babulnath.
Things to do at Marine Drive
Evening Walk - One of the best places for a walk, Marine Drive is visited by hordes of tourists as well as residents in evenings and mornings. The view of vast spread of Arabian Sea which is accompanied by refreshing breeze creates calming atmosphere. At the same time, umpteen number of stalls and restaurants give the place a lively touch. With best of both, Marine Drive promises a unique experience. It is a place for all age groups offering a soothing break from day to day monotony.
Events - Marine Drive is a popular venue for various events such as Bombay Marathon, French Festival, IAF Airshow, International Fleet Review, etc. So when in Mumbai, if lucky you might be able to be a part of one of these events. An open air gallery is also located close by.
Chowpatty Beach - On the northern end of Marine Drive is the Chowpatty beach, which is another popular place to visit in Mumbai. This place is an ideal place to experience the best of Mumbai’s night life. The place takes a form of a lively fair in night with food stalls and hawkers, restaurants and various other entertaining choices like merry-go-round, ferris wheels, etc. From Marine Drive, it is a must to visit Chowpatty beach.
Timings of Marine Drive
Marine Drive is open 24 hours a day. You can visit it at any time of the day. However, the best time to visit Marine drive is in evening. It is enthralling sight to watch the sunset over the shimmering waters of the Arabian Sea and then stroll with the cool refreshing air caressing you.
There is no entry fee at Marine Drive.
How to reach Marine Drive
As Marine Drive is centrally located, it is easily accessible. It is situated at the bottom of Malabar hills. Tourists can reach by all means of local transportation. As it is a popular landmark of Mumbai, tourists will not face any difficulty in finding it.
7. Rajabai Clock Tower

Rajabai Clock Tower is an 85-metre tall tower in the Fort Campus of the University of Mumbai. Premchand Roychand, a businessman and a stockbroker, financed its construction. And Sir George Gilbert Scott designed it.
The tower resembles London’s Big Ben, and it is among the tallest structures in the area. It chimes every fifteen minutes. The construction began in 1869, and it was completed by 1878.
The access to the inside of the tower is closed to visitors, but you can admire the architecture and detailed stonework from outside. The tower has one of the best stained-glass works in the city. And the architecture is a blend of Venetian-Gothic style. The tower also has 24 small statues, portraying the life of common people during the British rule.
8. Bombay High Court

Bombay High Court is one of the oldest High Courts in India, and it’s a UNESCO-recognised site. It was built in the 19th century, in the grand Gothic Revival architectural style. And you'll find traces of Victorian style too.
Here, you can click photographs of this heritage building and visit the museum within the premises. The museum of Bombay High Court provides plenty of information about the Indian judicial system and Indo-British legal history. It has preserved many historical documents too.
And while you're here, you can also be a part of the ongoing hearings. The court looks after the events in Maharashtra and Goa. And two Union Territories – Daman and Diu, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli, also fall under the jurisdiction of this court.
9. Siddhivinayak Temple

Shree Siddhivinayak temple is undeniably one of the most popular temples not only in Mumbai but also in India. With lakhs of devotees visiting every day, it is also one of the richest temples in Mumbai. Dedicated to Lord Ganesha, Shree Siddhivinayak Temple was built in the year 1801. Since then it has been attracting devotees from all over the country. Tuesday is one of the most important days of the temple. Celebrities and lay person both flock to the temple alike to seek blessings. Its architectural excellence and divine statue of Lord Ganesha adds to the splendor of the temple. More than two centuries old, Shree Siddhivinayak Ganapati Temple is believed to fulfil wishes and desires of everyone who pray with utmost devotion to the lord.
Story of Shree Siddhivinayak temple
There is a story behind the temple as per which its construction was funded by rich woman named Deubai Patil. As she was childless, she wished to create a temple where childless couples can come and worship the lord for children. Later an ardent disciple of Saint Akkalkot Swami Samarth, Ramakrishna Jambhekar Maharaj, on instruction of his guru, buried two divine idols in front of the temple. Later, after 21 years, as prophesied by the saint, a tree grew on the same spot bearing a svayambhu Ganesha.
Architecture of Shree Siddhivinayak temple
Shree Siddhivinayak temple was first built in the year 1801. Laxman Vithu and Deubai Patil are the brains behind its construction. Later the temple was rebuilt so as to accommodate more number of devotees.
Although small, the initial architecture of the temple was equally captivating. It consisted of a hall, a sanctum sanctorum and water tank. An administrative office of the temple was also built on its right side.
Lord Ganesha idol at the temple is as alluring as its excellent architecture. The idol of Lord Ganesha is carved out of a single black stone. It has a height of 2.5 feet and width of 2 feet. The unique feature of this idol is that the trunk of the Lord Ganesha is tilted towards right side. The idol of Lord Ganesha is Chaturbhuj, meaning it has four hands. The upper right hand of the deity holds a lotus flower while the lower right hand holds a rosary. The upper left hand holds an axe and the lower left hand of the Lord holds a modaka, which is considered to be lord’s favourite sweet. There is a snake that hangs like threat on the deity’s neck. On to the sides of the main deity, idols of Goddess Riddhi and Siddhi are placed.
The current structure of Shree Siddhivinayak temple is a result of the determinations of Shri Sharad Athale from SK Athale & Associates. Apart from the idol of the main deity that was kept intact, the temple was reconstructed into its present architecture.
The sanctum sanctorum has wooden doors that are intricately carved with images of eight forms of Lord Ganesha, called as Ashtavinayaka and the interior roof is plated in gold. Shree Siddhivinayak temple Mumbai has three entrances. Its current structure is nothing less than a palace, giving it an unparalleled grandeur.
How to reach Shree Siddhivinayak Temple
Shree Siddhivinayak Temple is located at Prabhadevi, which is easily accessible from all parts of Mumbai. Tourists can hire a taxi or an auto-rickshaw and reach this temple. If travelling by train, then you can get down at Dadar, which is the nearest railway station to the temple. Local trains can be boarded from Lower Parel, Mahalaxmi and Elphinstone Road.
After darshan at the temple, tourists can also visit other popular tourist attractions that are located close by such as Worli Sea-Link and the Shivaji Park Beach. Visit to all these places can be clubbed together.
10. Taraporewala Aquarium
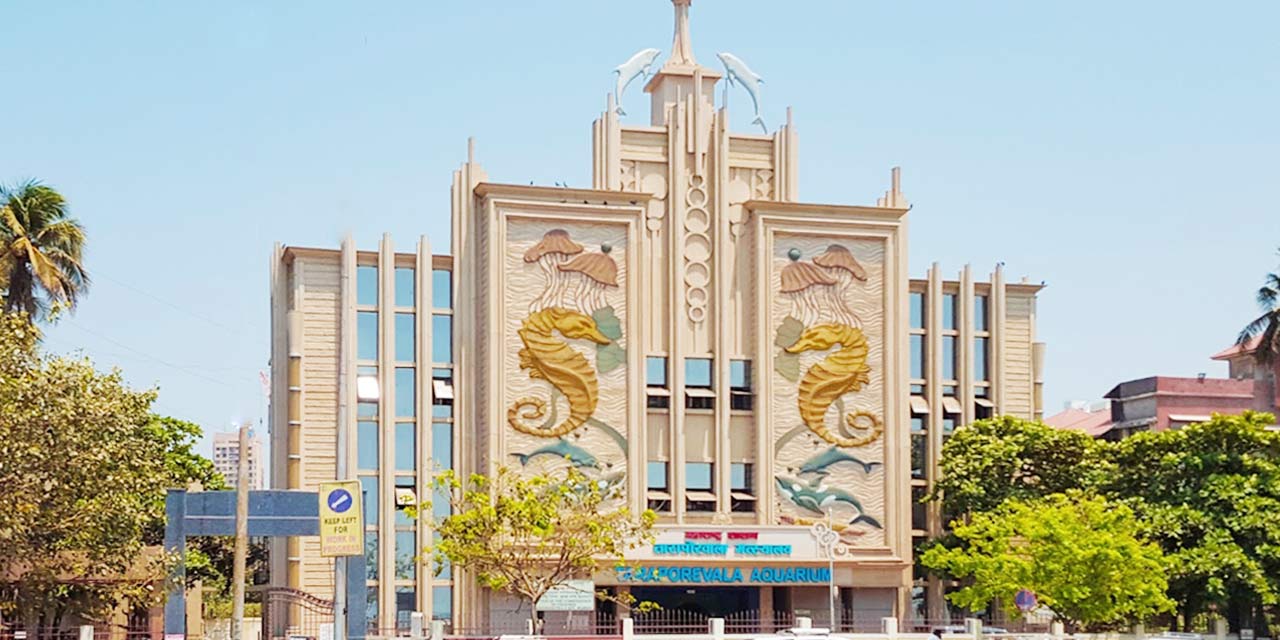

Taraporewala Aquarium is the oldest aquarium of India and it has over 100 species of fish and other aquatic animals.
At the entrance, there’s a glass tunnel around which various fishes and water plants are on display. Then, in the main gallery, you’ll see the water tanks where other fishes are.
Among the fish species, the aquarium has Alligator fishes, Puffer fishes and Moray eels among others. Angelfishes, Groupers and a variety of Tangs too are here. And you will also see a Jellyfish. The aquarium has 16 tanks for marine fishes and 9 tanks for the freshwater species.
It has a small museum too, where you'll find preserved corals, seashells and other marine life species.
11. Girgaon Chowpatty

Girgaon Chowpatty is among the most popular beaches of Mumbai. And it is also one of the most crowded places to visit in Mumbai. But it’s a lively tourist spot.
In the morning, you’ll find various people coming for a walk along the shore, carrying out their daily exercises or doing yoga. And during the day, people come here with friends and family to relax and get entertained. Numerous magicians and street artists put up their show throughout the day.
Girgaon Chowpatty is not known for sunbathing and other water activities. Instead, it’s visited for the street food varieties. From spicy bhel puri to piping hot pav-bhaji, the food vendors offer a plethora of options.
And this beach is also a renowned shooting spot.
12. Elephanta Caves
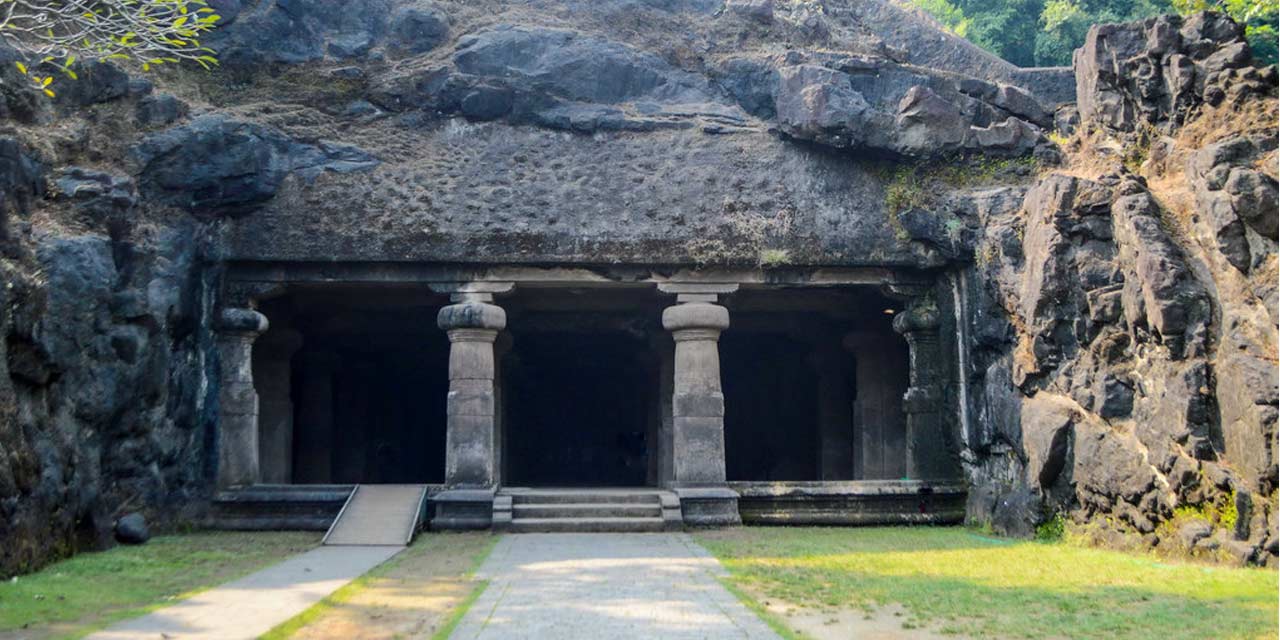

A Mumbai tour is incomplete without a visit to the majestic Elephanta Caves. These are located on the islands in the Arabian Sea, which are named after the gigantic elephant that was found here. It is also called as Gharapuri. Elephanta caves are one of the finest examples of rock-cut architecture and offer a glimpse into the lives of pre-medieval India. Although it suffered during colonial era, it still presents a stunning sight with enviably sturdy and intricate structure.
The island is consisted of two set of caves; the first set is of five caves that are related to Hindu religion, dedicated to Lord Shiva and the second set is of two Buddhist caves. These caves are a place to visit not only for their historical importance but also for the natural beauty that they present.
History of Elephanta Caves
According to the most popular theories, Elephanta Caves date back to 5th – 8th century, however the exact period when these were built and its creators are still a mystery. As per some theories, these caves were excavated during 450 to 750 AD, while later it came under various dynasties. From Chalukyas of Badami Dynasty, Mauryas of Konkan, Trikutakas, Silaharas, Rashtrakutas, Yadavas of Deogiri, Kalyani Chalukyas, Shahi dynasty of Gujarat, Marathas to Portuguese and British, Elephanta Island and the caves saw many reigns.
The main cave of the Elephanta caves was a religious shrine for Hindus which later suffered huge damages during the rule of Portuguese since 1953. In 1970s, the cave was renovated. In 1987, it was recognized as the UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is now maintained by the ASI (Archaeological Survey of India).
Architecture of Elephanta Caves
Elephanta Caves were built by carving the rocks. Its rock-cut architecture presents an alluring sight. Spread over an area of 6000 sq. feet, the entire cave complex is consisted of a main chamber, two side chambers, various small shrines and courtyards. The columns, spaces and images have been carved out aesthetically in the caves.
The cave 1, which has been built in Brahmanical rock-cut architecture, is the most captivating cave, with brilliant sculptures. There are three entrances to the cave temple- the main entrance on the north while one opening on the west and another on the east. A huge hall in the centre consisting of six rows of pillared columns adds on to the impressive structure of the caves. Each row consists of six pillars except the row on the western corner where a lingam of Lord Shiva is located.
There are three indentations on the walls, each with a massive image of dvarapala. On the east side, there is an Ardhanarishvara figure, which is a form of Lord Shiva where energies of male and female amalgamated while to the west, there are figures of Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati. While the central part showcases an impressive figure of Mahesa-murti. There are many other sections in the cave, each presenting beautiful carvings. Andhakasura Vada murti, Kalyanasundara murti; Lord Shiva as Lakulisa, Gangadhara murti and Ravana shaking Kailasa are few other worth noticing figures here.
Elephanta Cave Timings and Entry Fee
Timings of Elephanta Caves are from 9:30 AM to 5:30 PM. It is open on all days of the week except on Mondays.
The entry fee of Elephanta caves is Rs.40 per person for Indian citizens as well as visitors from countries like Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, Maldives, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Afghanistan while it is Rs.600 for tourists from other countries.
There is a minimal charge for videography at the caves while photography is free of cost. A toy train also runs on the Elephanta pier, between the ferry point and the caves. The ticket cost for the toy train is Rs.10 per person.
Boat Timings to Elephanta Caves : The ferry boat to Elephanta caves starts at 9 AM from Gateway of India while the first boat to return from elephanta caves starts at 12 in noon. The last boat that leaves the Elephanta caves is at 5.30 PM.
Location of Elephanta Caves
Elephanta Caves are located on the island hills which are around 7 km away from the mainland and around 11 km from Apollo Bandar of Mumbai.
How to reach Elephanta Caves
Reaching Elephanta caves is not at all a difficult task. Tourists are required to reach Gateway of India , which is another prominent landmark in the city. From there you can take a ferry that takes around 1 hour to reach Elephanta caves.
One can hire a taxi or city bus to reach Gateway of India. If travelling by local trains, then you can get down at the Church gate station, which is located nearby. You can also get down at Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus which is a UNESCO world heritage site and a popular place to see in Mumbai. CST (Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus) is also located quite close to Gateway of India; it is at a distance of around 10 minutes by taxi and 30 minutes by walk.
13. Raj Bhavan
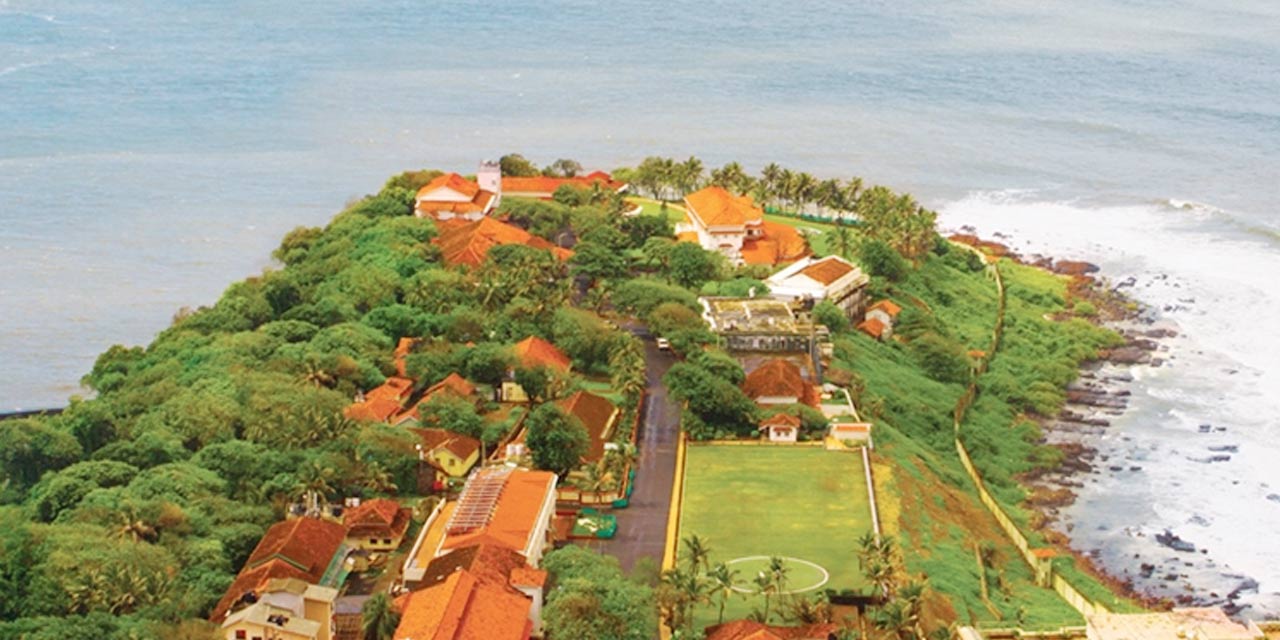

Raj Bhavan is the official residence of the Governor of Maharashtra. And you can visit it during your Mumbai tour.
It has lush green lawns, conserved forest areas and heritage buildings in the complex. The place is spread over an area of around 50 acres in the picturesque Malabar Hill, and the sea surrounds it on three sides.
The buildings are built in varied architectural styles: from British colonial style to Maratha style and modern Indian style of architecture. And the complex also has a British-era bunker, which has been turned into a museum.
During your tour, you can watch the sun rising over the sea. And you might also be able to enjoy a cup of tea with the Governor.
14. Kamala Nehru Park
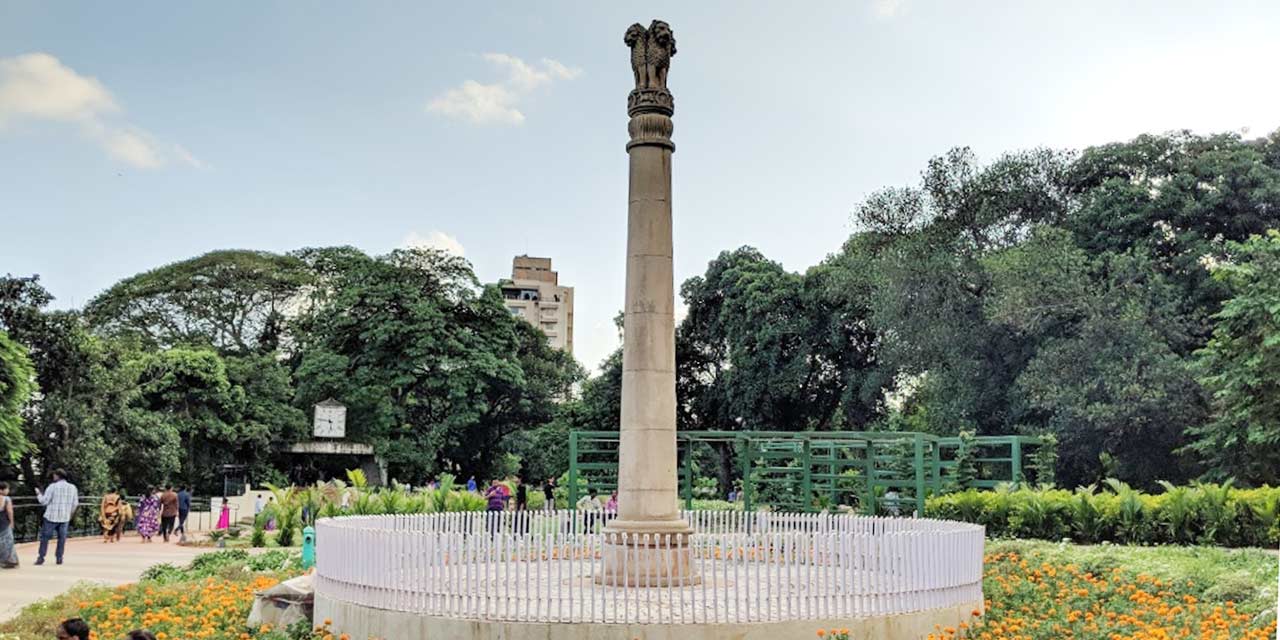

Kamala Nehru Park is a popular recreational spot, and among the best places to visit in Mumbai with toddlers. Many people come here to stroll around, to meditate and to hang out with friends.
People come here to get a scenic view of the famed Marine Drive too, looking over the Arabian Sea. Also, you can sit on the lawn or on the wooden cane benches, and munch at a variety of snacks being sold by vendors.
Kids love the colourful theme park here. And they can play in and around the Boot House.
Kamala Nehru Park also has a small open-air amphitheatre. And you'll also find selfie-points decorated with painted rhymes and other kid-themed designs.
15. Mahalakshmi Temple

Mahalakshmi Temple is one of the oldest temples in Mumbai. The temple is dedicated to Goddess Mahalakshmi – the Goddess of Wealth, and it is built along the seashore.
The temple also has the idols of Goddess Mahakali and Mahasaraswati. And devotees come here, throughout the year, for blessings.
And the charm of Shree Mahalakshmi Temple increases manifold during festivals and other special occasions. The entire complex is decorated with lights and flowers. Arrangements are also made for the devotees to get a proper darshan and pass the offerings.
You'll find many shops within the temple complex to buy coconuts, sweets and fresh flowers among other required items.
16. Haji Ali Dargah

Haji Ali Dargah is a mosque built on an islet, only a few hundred metres away from Shree Mahalakshmi Temple. And a narrow, pebbled walkway connects it to the mainland. Haji Ali is also the shrine of a Sufi saint, Haji Ali Shah Bukhari.
This mosque was built in 1431, in the Indo-Islamic style. The central courtyard of the complex is made of marble. And the ceiling in the main hall is also of marble. It has been decorated with various coloured mirror patterns and Arabic inscriptions. You'll also notice Quran verses on the ceilings and the walls.
The tallest minaret of Haji Ali Dargah is 85 feet high. And from that minaret, namaz calls are made at the five designated times of the day.
17. Juhu Beach

Juhu Beach is among the well-known beaches in India. It is popular for the mesmerising views of the sunset and the street food corners in the area.
Apart from enjoying the food, you can also check out activities like camel riding and horse riding on the beach. Many street artists like monkey trainers, snake charmers and tarot card readers also show off their skills at Juhu Beach. And on some days, you might also catch an artist carving out art from sand.
The beach is a favourite among the film-makers too. Celebrity photo sessions and movie shoots are regular events here. Also, many actors and actresses stay in the locality. And you might get to meet them during your visit.
The area is known for its nightlife too. You'll find many bars, pubs and nightclubs to spend your evenings.
18. ISKCON Temple
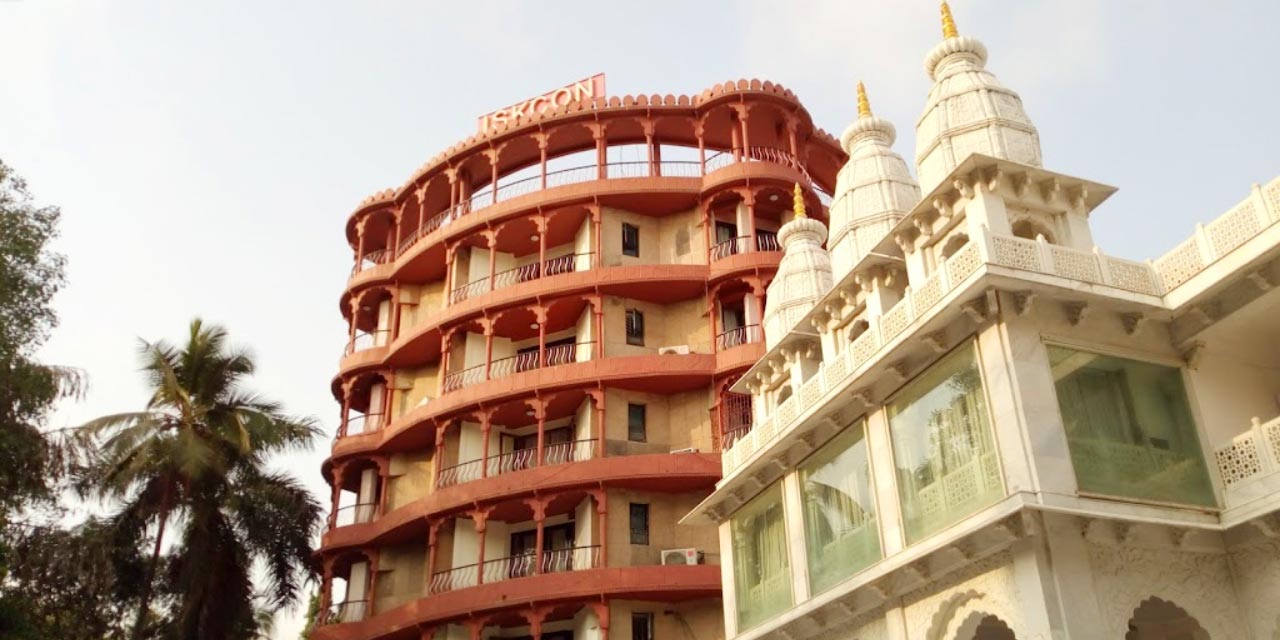

ISKCON Temple is a magnificent Hindu temple near Juhu Beach. It’s a revered temple, especially among the devotees of Lord Krishna. But it also houses idols of Radha, Lord Rama, and Sita among others.
The temple is also known as Radha Rasabihari Temple and Hare Rama Hare Krishna Temple. And it’s an ideal place to pray, meditate and gain knowledge. The temple offers various lessons ranging from Vedic education to meditation and spirituality.
Apart from the main temple, you'll also find a restaurant, a library and a guesthouse here.
Thousands of devotees visit ISKCON temple throughout the year. And the grand celebrations during Janmashtami, Jagannath Rath Yatra, Radhastami and many other festivals is worth the experience.
19. Castella De Aguada (Bandra Fort)
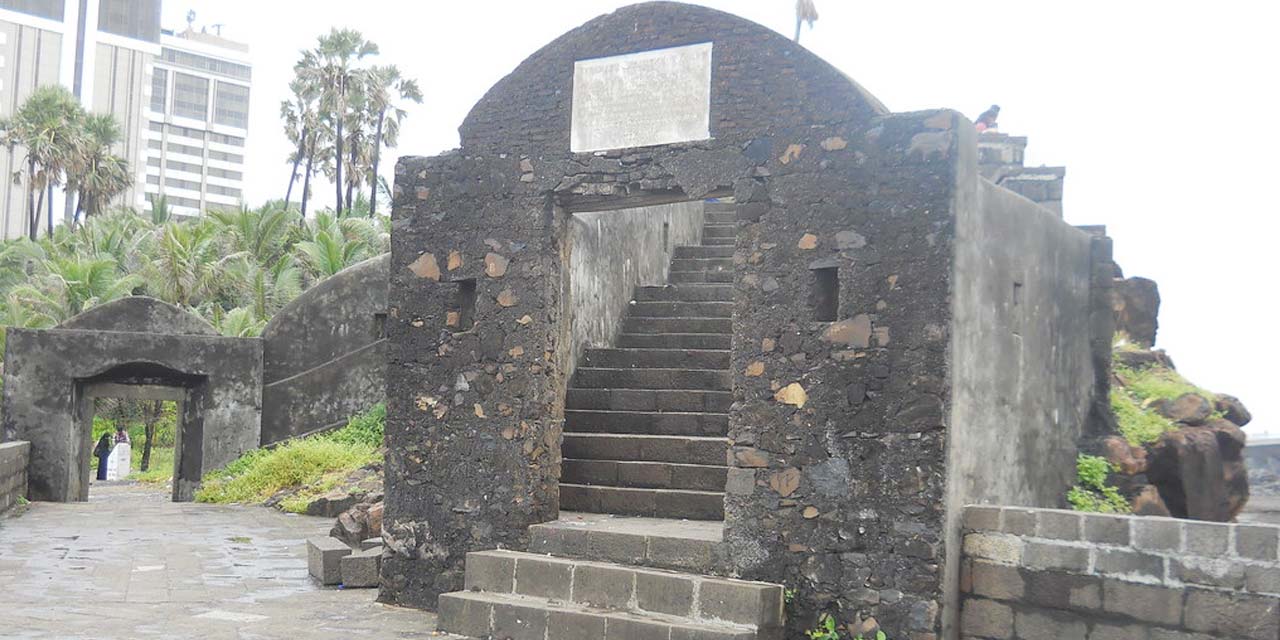

Castella de Aguada (or Bandra Fort) was built by the Portuguese to guard the sea route and fortify the area around. It is built in the European style, with granite blocks, and it offers a panoramic view of the Arabian Sea.
Much of the fort is in ruins today, but the view captivates many tourists. It is also a preferred hangout spot for the youths, and among the most popular places to visit in Mumbai for couples.
An evening walk on the walkway to the sea is de-stressing. And the fort also has a seating area for you to spend the evening.
Bandra Fort offers a majestic view of the Bandra Worli Sea Link too.
20. Bandra Worli Sea Link

Bandra Worli Sea Link is a 5 km long bridge built on the Arabian Sea; it connects Bandra and Worli. The bridge is known for its architectural magnificence, and it is the first cable-stayed bridge built on the open sea in India. It is also one of the prominent landmarks of Mumbai.
This sea bridge saves considerable time for the daily commuters. But it has also turned out to be among the best places to visit in Mumbai for photography. The bridge looks even more glamorous when it comes alive with lights in the evening.
The adjacent Worli Sea Face is another popular spot. You can spend your evenings there, munching on local snacks.
21. Mount Mary Church

Mount Mary Church, or Basilica of Our Lady of the Mount, is among the beautiful churches in Mumbai. It is dedicated to Virgin Mary and it has been built in the Gothic architectural style. And the walls are covered with colourful fibreglass murals depicting stories from the life of Mother Mary.
The peaceful environment and the view from the church also attract many people to spend time here. The church stands on a hillock overlooking the Arabian Sea. And from the backyard, you get a view of the spectacular Mumbai skyline.
Mount Mary Church is also famous for the annual Bandra Fair. It is celebrated in September on the birthday of Mother Mary. The church holds a feast on the day, and the area surrounding it experiences a week-long carnival-like celebration.
22. Fort Bassein (Vasai Fort)
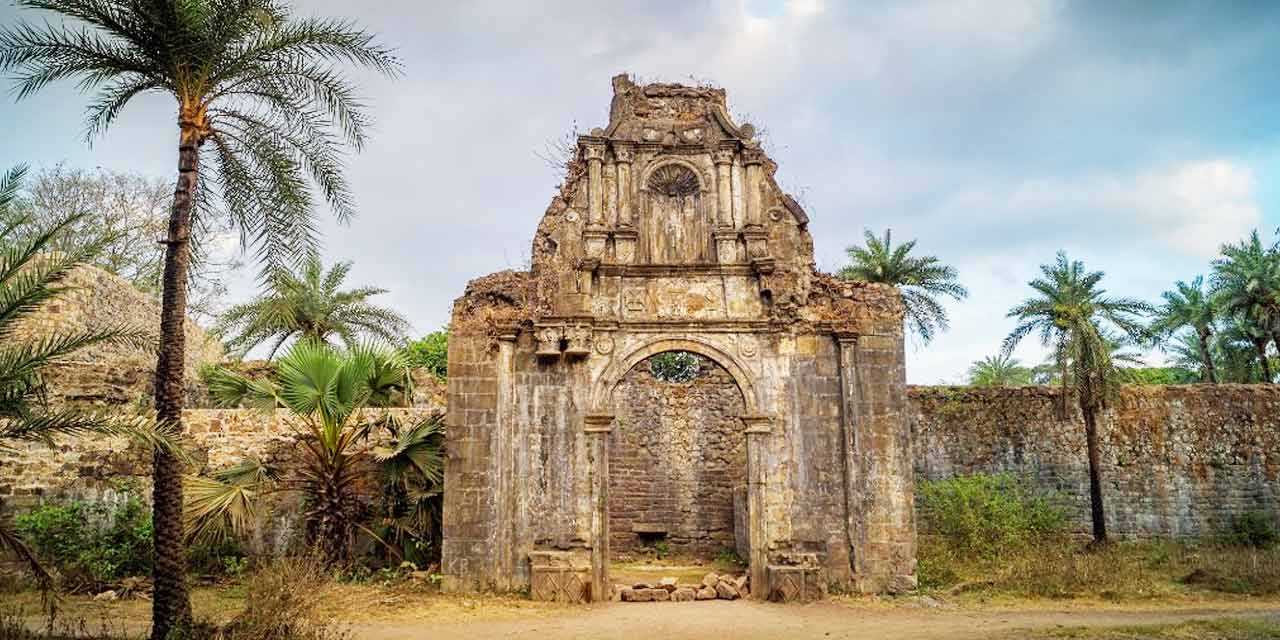

Fort Bassein (or Vasai Fort) is a 500-year old Portuguese fort near Vasai-Virar. And it is among the most popular places to visit in Mumbai outskirts.
At its prime, Fort Bassein was a complete city. It had administrative blocks, churches, hospitals, and the Portuguese used it as their base to control the region. The fort also used to be the official residence of the Portuguese governor when he was here.
Today, the fort is in ruins, but it is a part of the heritage tour of the area. The watchtowers allow you to observe the surrounding Vasai village and the extended skyline of Mumbai. And the fort is also a popular spot for movie shoots and pre-wedding photoshoots.
23. Kanheri Caves
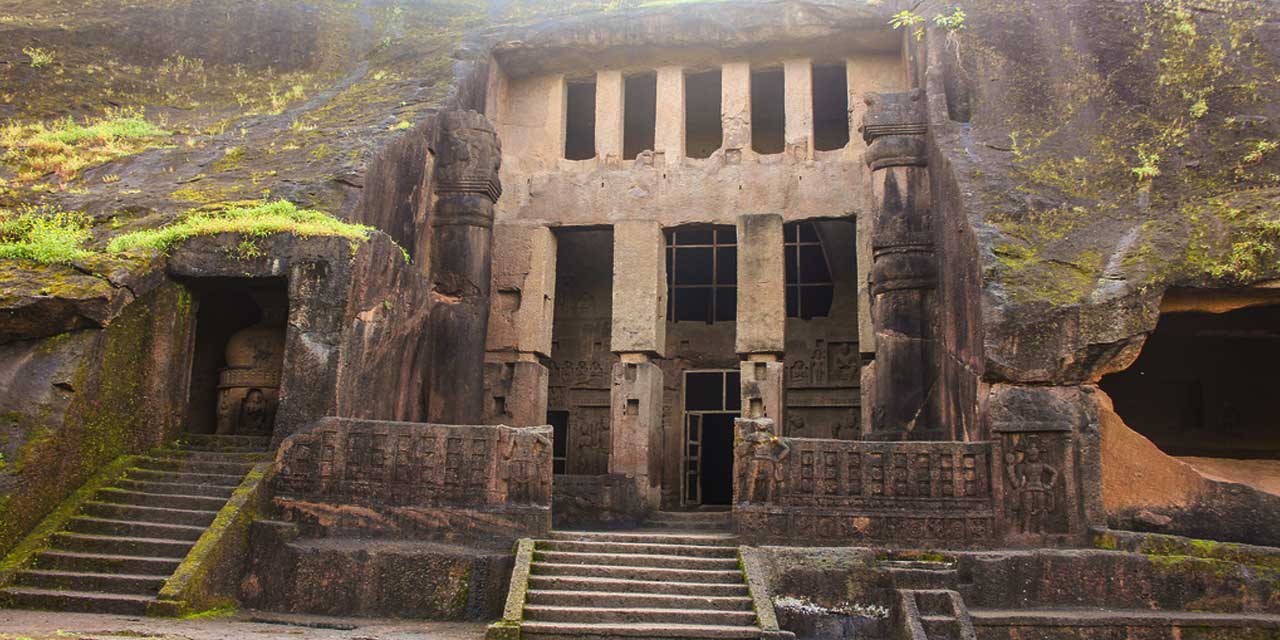

Kanheri Caves are a collection of 109 Buddhist caves. These caves used to be a Buddhist monastery, and they’ve been built over a long period. The earliest caves are from the 1st century BCE, while the most recent ones are from the 11th century CE.
Paintings and stone sculptures adorn the walls of the caves. Statues of Buddha in various postures and sizes are in the caves. And you'll also find numerous inscriptions in Brahmi and Devanagari, and some epigraphs in Pahlavi, on the walls.
These caves served as a place for worship, study and meditation. Cave 3 is the largest among the Kanheri Caves, and the most remarkable.
This serene cave complex is situated on a hillside, and it takes a long trek through lush green bushes and rocks to reach here. This site has numerous small streams and waterfalls too. And it also offers a view of the sprawling Mumbai city.
24. Film City

Film City of Mumbai is where much of the action of Indian movies and TV shows take place.
With 10+ indoor studios and around 50 outdoor shooting locations, you might also catch a live movie shoot. From temples to playgrounds and open roads to bungalows, various setups are available to help in shooting an entire movie.
It is an iconic landmark of the city and your Mumbai tour would remain incomplete without visiting it.
The official name of Film City is Dadasaheb Phalke Chitra Nagari, and here you get a chance to witness all the hard work that goes behind the scenes. Various TV commercials are also shot here.
25. Global Vipassana Pagoda

Global Vipassana Pagoda is a meditation dome on the outskirts of Mumbai. The dome is built as a tribute to a Vipassana teacher – Sayagyi U Ba Khin, and it resembles the Shwedagon Pagoda of Myanmar.
The dome of the pagoda is the world’s largest stone dome standing without any supporting pillars. And 8000 people can meditate at a time here.
The architectural pagoda and the intricately carved gates are among the major points of tourist interests. But there also are other structures like the 21.5 feet high statue of Gautam Buddha, the Bell Tower and the Gong Tower. The pagoda complex also has a park, a small waterfall and a replica of the Ashoka Pillar of Sarnath.
Global Vipassana Pagoda spreads the values of Gautam Buddha through its meditation and relaxation sessions. And you can also take meditation courses. The campus has a library and a museum too.
26. Essel World

Essel World is an amusement park, only a few metres from Global Vipassana Pagoda. It’s a popular getaway for relaxation for local people, and it is also among the famous amusement parks in India.
This amusement park has got over 50 amusement rides, adventure activities and fun points to check. There are different rides for adults and kids. And you'll find group rides too. Apart from the rides, you can enjoy in the bowling alley, ice-skating rink, discotheque and many other places.
Essel World has numerous food courts serving a variety of cuisines. And it also has a small merchandise shop. And while you're at Essel World, visit Water Kingdom too.
27. Water Kingdom
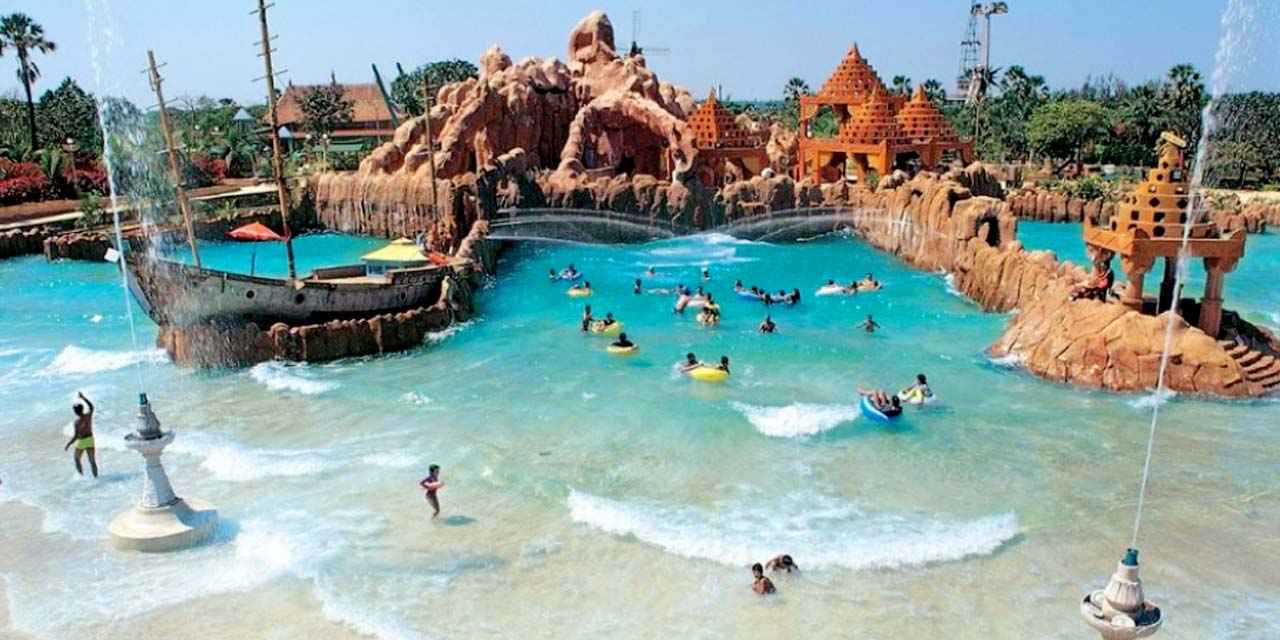

Water Kingdom is a water-themed amusement park right next to Essel World. It has various wet adventure rides, fun-filled water slides and numerous pools to play together. And many people visit Essel World and Water Kingdom together.
This park also has a large wave pool and over 30 water activities, including a rain dance floor.
And if you aren’t interested in the water games, you can relax beside the pools with some cold drinks and snacks. Water Kingdom has a couple of restaurants and snacks parlours serving a variety of delicacies.
Apart from those fun rides and water slides, a fish spa and pedicure zone are also here.
28. Powai Lake

Powai Lake is an artificial lake known for its charming evenings. The lake is surrounded by trees and bushes, and you will find many birds like kingfishers, herons and falcons. Bees and various colourful butterflies can also be seen near Powai Lake.
And the lake also has many fishes and a few crocodiles.
People come to Powai Lake to spend their evenings after work. A small play area is also near the lake. You can buy some local snacks and munch at them while admiring the golden hues of the sky and the setting sun.
And while you're here, you can also check out the Nirvana Park across the road in the Hiranandani complex. It is a beautiful garden furnished with wooden walkways, kids’ slides and benches. You'll also find grass lawns, ponds and tiny flowers around this park.
29. Nehru Science Centre

Nehru Science Centre is the largest interactive science centre in India.
It was opened to the public in 1985, and it has around 500 varieties of exhibits and interactive science games. This science centre also has a museum showcasing various models to tell you about the developments in science and technology. And it has a library too, with scientific books and movies.
The science centre offers practical experience with laws of physics, human anatomy, and many other facets of science. The available activities also include regular shows, films, and documentaries.
A sky observatory – Nehru Planetarium, is also within the complex. Multiple telescopes are available here for stargazing and studying planetary motions and Solar/Lunar eclipses.
30. Mumbai Zoo

Mumbai Zoo, or Veermata Jijabai Bhosale Udyan, is one of the oldest zoos in India. It was established in 1861.
The zoo has many common animal species of India and other lesser-known animals. You'll find jackals, sloth bears and swamp deers here. Hyenas, tigers and crocodiles are also in the zoo. And you can meet with penguins too.
Mumbai zoo also has an aviary for aquatic birds. You can interact with birds like pelicans, flamingos and albino crows. And you can also have selfies with cranes, herons and storks among other birds.
The place is known for its range of fauna too. The botanical garden here has more than 3000 trees, herbs and flowering plants.
31. Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum
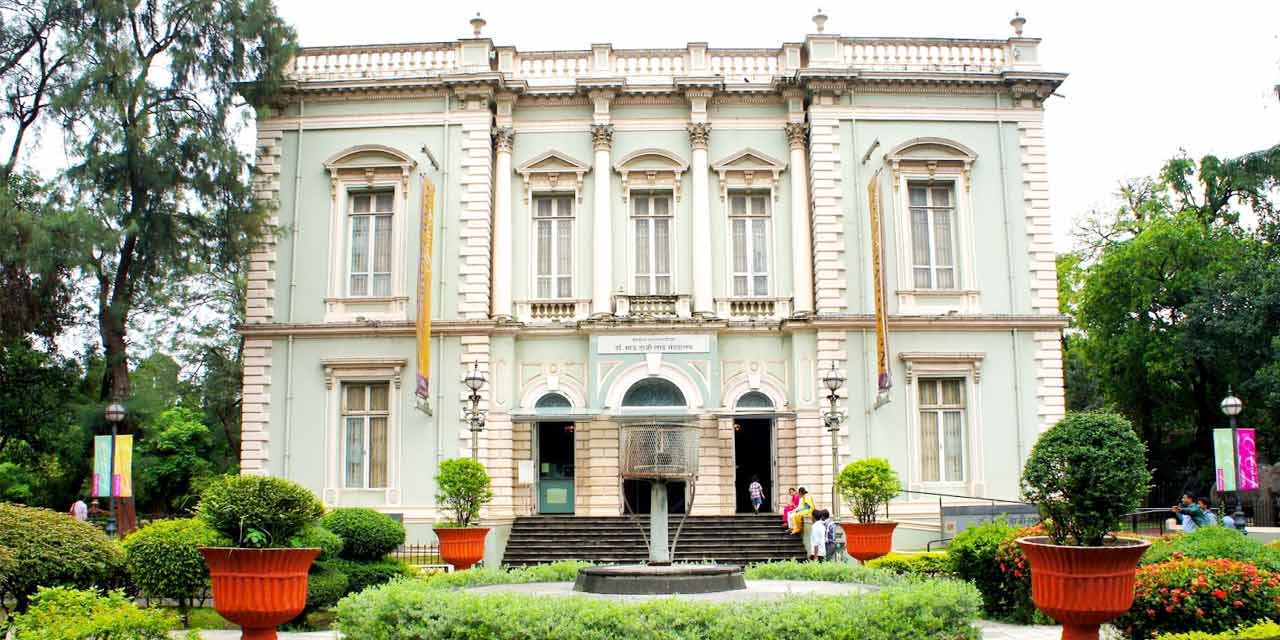

Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum is a place for entertainment, knowledge and relaxation. It is near Mumbai Zoo, and it is the oldest museum in the city. In the museum, you'll find artefacts, maps and manuscripts showcasing the rich history and cultural heritage of Mumbai.
The museum also displays clay models and has a plethora of photographs and books narrating the story of the city. And it also organises art workshops, cultural performances and lectures from time to time.
Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum was opened to the public in 1872. And the place has been known for its magnificence too. The grand metal palisades, staircase railings and the arched supports were all imported from England. And the etched glass designs are reminiscence of the glorious 19th-century architectural style.
It has been among the underrated places to visit in Mumbai for a long time. And history buffs or knowledge seekers must visit this museum.
32. Mumba Devi Temple
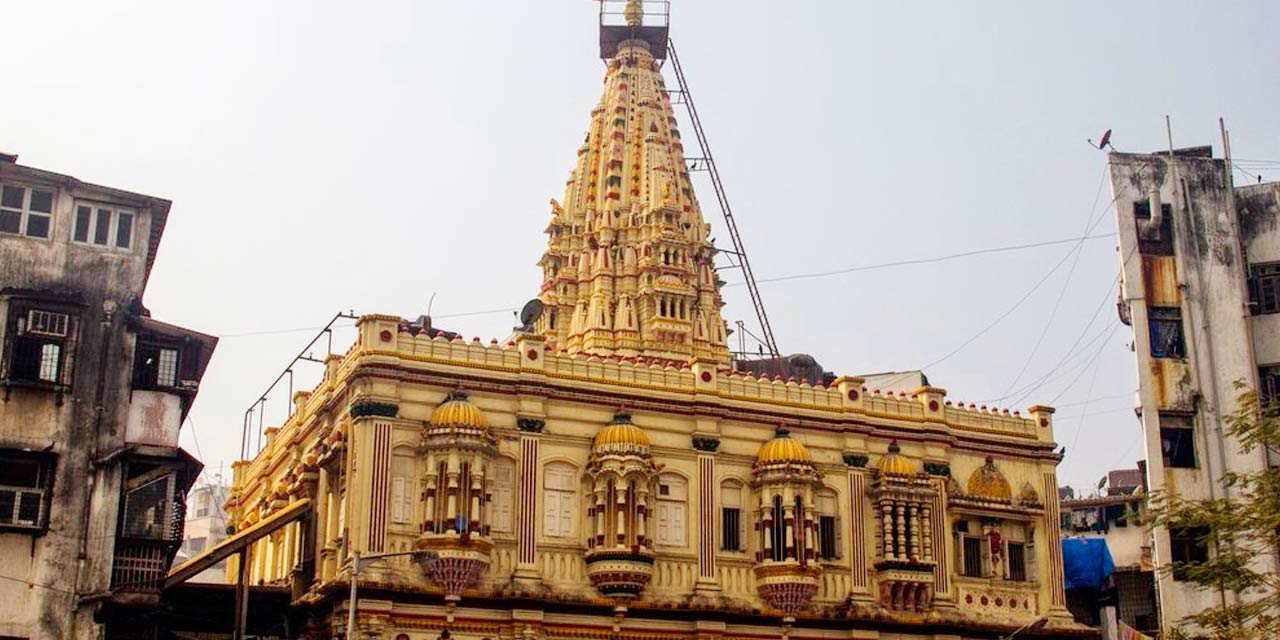

Mumba Devi Temple is among the oldest temples of Mumbai. It is dedicated to Goddess Mumba, after which Mumbai is named. She is considered the guardian goddess of the city.
Local people come to the temple for the daily aarti in the evening and morning. Devotees also come from nearby places to take blessings from Mumba Devi.
The temple is built in the classic ancient Hindu temple style. It has one high spire, with a red flag flying on its top. And the walls are etched with religious mantras and shlokas prominent in the Hindu temples.
During festivals like Navratri, it is decorated with flowers and lights, and the celebrations go on for 10 days. People come from many places to be a part of the religious ceremonies and enjoy the ongoing fair.
33. Crawford Market
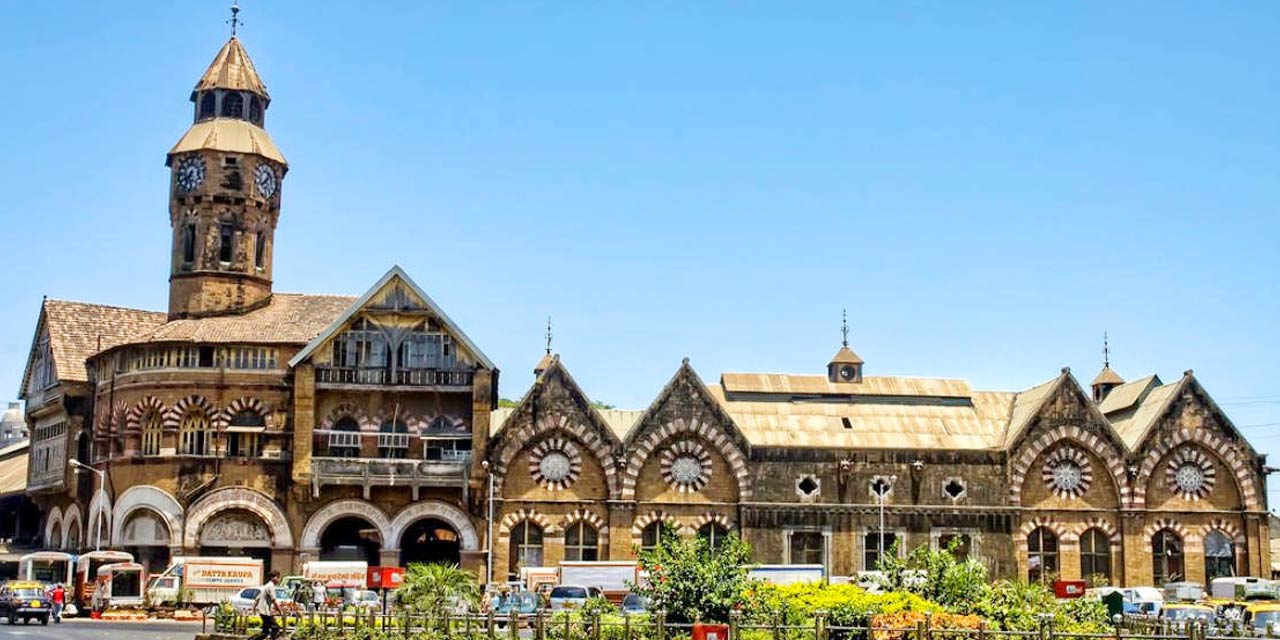

Crawford Market (officially named Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Mandai) is the largest market in the southern Mumbai. From gifts to groceries and from toys to pets, the market has everything. And it is the best place to visit in Mumbai for shopping.
During British rule, it was a source to buy daily fresh produce. And it’s still a popular place to get good deals on various household goods and fresh fruits and vegetables.
Crawford Market is known for its striking architecture too.
It has a blend of Norman and Flemish architectural styles, and it is decorated with paintings and murals. The clock tower is adorned with carvings that resemble Victorian style. And in some parts of the building, you will find glimpses of the Gothic architecture style too.
34. Dhobi Ghat
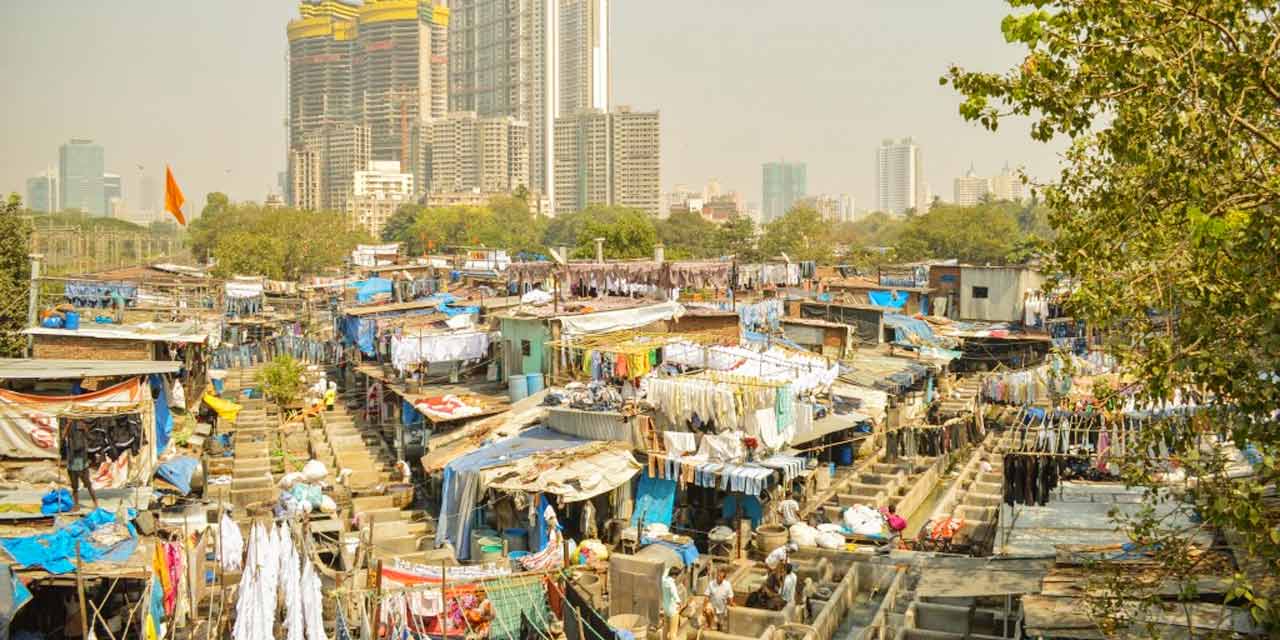

Dhobi Ghat is the world's largest open-air laundry. Here, hundreds of washermen and women – dhobis, work their shifts through the day to wash clothes. Porters bring dirty clothes from all over Mumbai and they take them back in their fresh, crisp and spotless state.
The system is well-optimised, and each cloth is coded to be traced back to the client.
This laundry was set up by an association of 50 washers in 1890. And today, around 700 washer families live here. And although some have installed washing and drying machines, most still carry on their work manually.
Dhobi Ghat has maintained much of its old charm and washing methods.
Other Popular Places to visit in Mumbai
Apart from the above 34 tourist spots, you’ve many other places to visit in Mumbai and around. You can visit beaches like Aksa Beach , Gorai Beach and Versova Beach here. These are known for their sunset views, horse rides and street food stalls. Gorai Beach is also popular among the local people for weekend getaways and parties.
Then, you can also enjoy various gardens spread throughout the city. Chhota Kashmir and Hanging Garden are among the most popular of them. And if you love trekking, animal-spotting or bird-watching, you must visit Sanjay Gandhi National Park .
Also, if you're looking for places to visit in Mumbai for fun, plenty of amusement parks are there in and around the city. Snow World , Tikuji-ni-Wadi and Yazoo Park are popular.
You can also enjoy in themed water parks like Anand Sagar Water Park , Royal Garden Water Park and The Great Escape Water Park . These water parks are away from the hustle-bustle of the city. And they provide accommodation facilities if you want to stay for a night or two.
If you’re interested in cricket, you can buy a ticket for a game in Wankhede Stadium . And if you like theatres and plays, you can check out Prithvi Theatre . The theatre also hosts workshops, performing art programmes and other events.
And while you're in Mumbai, also visit Babulnath Temple . It has a special place among the devotees of Shiva, and the celebrations during Mahashivaratri festival are full of excitement.
Mumbai is a mix of art, culture and entertainment, and it should be in the bucket list of every traveller. Whether you're looking for places to visit in Mumbai with family and friends or you want quiet corners to spend time with yourself, you'll find them here.
The city will be a memorable holiday destination for adults and youngsters alike. From religious sites to beautiful beaches and historical caves to magnificent architectural monuments, you'll find a variety of places to visit in Mumbai.
Whether you want to go on a solo tour or want to book a honeymoon holiday, Mumbai won't disappoint you. Here you can be a part of the modern lifestyle, or enjoy a laid-back holiday in the lap of nature.
Excited About Mumbai?
Request A Call Back!
Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Shirdi Tour Packages from Mumbai (Shani Shingnapur)
- Lonavala & Khandala Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Malshej Ghat Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Igatpuri Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Alibaug Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Raigad Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Lavasa Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Pune Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Mahabaleshwar Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Bhimashankar Tour Packages from Mumbai
- Matheran Tour Packages from Mumbai
Top Tourism Places to Visit in Mumbai
- Gateway of India, Mumbai
- Elephanta Caves, Mumbai
- Marine Drive, Mumbai
- Shree Siddhivinayak Temple, Mumbai
- Haji Ali Dargah, Mumbai
- Bandra-Worli Sea Link, Mumbai
- Essel World, Mumbai
- Nariman Point, Mumbai
- Juhu beach, Mumbai
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus, Mumbai
- Asiatic Society, Town Hall in Mumbai
- Colaba Causeway, Mumbai
- Nehru Planetarium, Mumbai
- Girgaon Chowpatty, Mumbai
- Chor Bazaar, Mumbai
- Mount Mary Church, Mumbai
- Sanjay Gandhi National Park, Mumbai
- Kanheri Caves, Mumbai
- Raj Bhavan, Mumbai
- Jehangir Art Gallery, Mumbai
- Taraporewala Aquarium, Mumbai
- Bombay High Court
- Bandra Bandstand, Mumbai
- Versova beach, Mumbai
- Churchgate, Mumbai
- Aksa Beach, Mumbai
- Worli Sea Face, Mumbai
- Chhota Kashmir, Mumbai
- Malabar Hill, Mumbai
- Prithvi Theatre, Mumbai
- ISKCON Temple, Mumbai
- Wankhede Stadium, Mumbai
- St. Michael's Church, Mumbai
- St. Thomas Cathedral, Mumbai
- Hanging Gardens, Mumbai
- Mani Bhavan, Mumbai
- Elephanta Island, Mumbai
- Dhobi Ghat, Mumbai
- Babulnath Temple, Mumbai
- Global Vipassana Pagoda, Mumbai
- Flora Fountain, Mumbai
- Water Kingdom, Mumbai
- Powai Lake, Mumbai
- Mahalakshmi Temple, Mumbai
- Dr. Bhau Daji Lad Museum, Mumbai
- Marve Beach, Mumbai
- Gorai Beach, Mumbai
- Mumba Devi Temple, Mumbai
- Nehru Science Centre, Mumbai
- Kamala Nehru Park, Mumbai
- Fort Bassein / Vasai Fort, Mumbai
- Rajabai Clock Tower, Mumbai
- Suraj Water Park, Mumbai
- Shangrila Water Park, Mumbai
- Snow World, Mumbai
- Yazoo Park, Mumbai
- Tikuji-ni-Wadi, Mumbai
- Ammu Water Park, Mumbai
- Shivganga Water Park, Mumbai
- Sargam Water Park, Thane
- Paradise Funland, Mumbai
- Mati Hill County Resort, Mumbai
- Snow Kingdom, Mumbai
- Imagicaa Theme Park, Mumbai
- Imagicaa Water Park, Mumbai
- Snow Park at Imagicaa, Mumbai
- Eyelusion at Imagicaa, Mumbai
- House of Stars at Imagicaa, Mumbai
- Rainy Resort & Water Park, Mumbai
- The Great Escape Water Park, Mumbai
- Pali Beach Resort & Water Park, Mumbai
- Bandra Fort Mumbai / Castella de Aguada
- Royal Garden Resort & Water Park, Mumbai
- Anand Sagar Resort & Water Park, Mumbai
- Panoramic Resort and Water Park, Mumbai
- Shanti Sagar Resort & Water Park, Mumbai
- Magic Mountain Amusement Park, Lonavala
- Vardhman Fantasy Amusement Park, Mumbai
- Wet N Joy Water & Amusement Park, Lonavala
- Mumbai Film City / Dadasaheb Phalke Chitranagri
- Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Mandai / Crawford Market, Mumbai
- Mumbai Zoo / Veer Mata Jijabai Bhonsale Park / Byculla Mumbai
- Prince of Wales Museum, Mumbai
- Glowmagica at Imagicaa Mumbai

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kulture Shop. 95 Reviews. 30th Road, Off Linking Road, Opp. Amarsons Next To Royal Enfield, Mumbai 400050 India. LInda Tours Mumbai. 754 Reviews. Sion Trombe Road, Mumbai 400022 India. Experiences from ₹1,026. See 13 Experiences. Bhimnath Temple.
Best Time To Visit Sion Mumbai. The best time to visit Sion Mumbai is during the winter months of November to February.During this time, the weather is pleasant and cool, with temperatures ranging from 15 to 30 degrees Celsius.It is also the driest period of the year, with minimal rainfall. This makes it ideal for exploring the city's attractions and outdoor activities.
Places to visit in Mumbai. Places to visit in Sion. Top Things to Do in Sion. THE 5 BEST Things to Do in Sion, Mumbai. Top Things to Do in Sion. Enter dates. Attractions. Filters • 1. Sort. Map. All things to do. Category types. Attractions. Tours.
Top 5 Things to Do in Sion: See reviews and photos of Sion, Mumbai (India) on Tripadvisor.
from ₹2,966 per adult. 3. Bhakti Dham Mandir. 3. Points of Interest & Landmarks. South Mumbai. By manipra342. The place is the nice venue for meditation with the good seating arrangement and also calm environment....
Bhagwan Collection, Sion, Mumbai. See On Map. +919820210263. Located right next to Gandhi Market, Bhagwan Collection is a large fabric store. You'll find fabrics for any occasion, and in a price range for varying budgets. They have bandhani, leheriya, phulkari, digitally-printed fabrics and more.
3 places sorted by traveler favorites. Clear all filters. 1. Sion Hillock Fort. 19. Historic Sites. South Mumbai. By sagarmoya. It has ruins of a fort, a maze, a fountain, and the garden in the entrance , Entry is free, Lot of college crowds you...
Places to visit in Sion, Mumbai. 1. Sion Fort. Sion Fort is a short walk from Sion railway station. It was built during British rule and sits on top of a hillock. Here you will forget you are in the city as you hear the sounds of birds and see the beautiful view around. There are beautiful gardens in this area filled with lush greenery.
1. Trek Up Sion Fort. This fort is one of the biggest secrets of Mumbai and is hidden in plain sight. Sion Fort was built in the 17th Century by the Governor of Bombay, Gerald Aungier. It was built to mark the boundary between the British-held Mumbai and the Portugese-held Salsette land. While there is a very rich history behind the fort, sadly ...
Places to Visit in Sion: Find best tourist places in Sion, attractions, sightseeing tours, & traveler reviews for a perfect holiday ... Camping Chadar Trek Everest Base Camp Trek Treks in India Camps in Rishikesh Jaisalmer Camps Weekend Getaways from Bangalore Places to Visit near Mumbai Weekend Getaways from Delhi Weekend Getaways from Pune ...
Sion (/ˈsaːjən/; IAST: Śīv) is a neighbourhood of Mumbai.In the 17th century the village formed the boundary between Mumbai and Salsette Island.The British named it marking the end of the city. The name remained even after Mumbai was joined to the Salsette and extended up to Mulund.One of the local historical places in Sion is a hilltop garden commonly known as Sion Fort or Sheevon Killa ...
About Sion Mumbai India, opening hours, entry fee, approx trip budget, activities to do at Sion, Itineraries, how to reach, nearby hotels, reviews, best time to visit.
By Train: To get to Sion Fort, take a train to Sion railway station and then walk up to the fort. The distance from Sion railway station is about 7 kilometres. By Bus: You can take a bus from different points of the city to get to the fort. The bus lines which stop near the fort are 180, 22 LTD, 305, 348 LTD, 351, 354.
The Garlic Bread At Cafe Istaa In Sion Is The Cheesiest Way To…. 18477 Views. Discover Sion in Mumbai with curated reviews and recommendations on top places to see, best shops, best cafes, restaurants, & bars, and markets & other tourist attractions. Explore Sion with LBB.
View Map. Address. 159-161, Mahatma Gandhi Road, Lion Gate, Fort, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400001, India. Phone +91 22 6958 4400. Web Visit website. Originally called the Prince of Wales Museum, Mumbai's main museum was renamed after legendary Maratha warrior Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj in 1998. (King Shivaji Museum is simpler to say, if you're ...
Location: 90 Feet Road and adjoining Sion-Bandra Link Road, Dharavi, Sion, central Mumbai. Opening Hours: Daily from 11 a.m. to 9 p.m. ... 101 Places to Visit in Mumbai One Week in Mumbai: The Perfect Itinerary Top 18 Things to Do in Mumbai 15 Best Mumbai Tours to Really Get to Know the City
Visit nearby attractions: The Sion Fort is located near several other attractions in Mumbai. You can visit the Bandra-Worli Sea Link, the... Source The fort requires some excavation as it is no fun from just taking a view from the outside.
Entry is free. Kala Ghoda Cafe. 10:30 a.m. Savor a spicy breakfast then head to an ancient world. Dig into a breakfast of akuri, a spicy scrambled egg dish (345 rupees) that is traditional in ...
Hira Misthan. The owner was very kind and took time to explain to us the difference and the... 30. Amore Gourmet Gelato. Amore Gelato is what you need! Sion Restaurants - Mumbai, Maharashtra: See 588 Tripadvisor traveler reviews of 588 restaurants in Mumbai Sion and search by cuisine, price, and more.
Nature & Parks. Sanjay Gandhi National Park, formerly known as Borivali National Park, is a sprawling forested park located in Mumbai. It is one of the largest and most popular nature reserves in India. The park is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including tigers and leopards.
Mani Bhavan Gandhi Sangrahalaya, Mumbai. See On Map. +912223805864. The focal point of Mahatma Gandhi's political activities in Mumbai, Mani Bhavan is now a museum and historical building. Owned by a friend of Gandhi's, from 1917 to 1934 Mani Bhavan posed as Gandhi's Mumbai headquarters for 17 years.
2. Self-equipped rental in the heart of Sion (from USD 52) Show all photos. Offering fantastic access, handy essentials, and well-furnished rooms, this suite for rent sits right next to the Sion Circle in Mumbai. This busy thoroughfare hosts a diverse offering of shops, boutiques, eateries, and even green spaces.
Mumbai Tourism Mumbai Hotels Mumbai Bed and Breakfast Mumbai Vacation Rentals Flights to Mumbai Mumbai Restaurants Mumbai Attractions Mumbai Travel Forum Mumbai ... and the garden in the entrance , Entry is free, Lot of college crowds you will see . The Sion Fort was built sometime in the late 17th century I guess not a expert on this , A canon ...
This area also has a lively nightlife, and it's among the best places to visit in Mumbai at night. 2. Churchgate. Churchgate is the business district of Mumbai. It has offices of many banks and business organisations. And it also has the High Court of Bombay and many reputed educational institutions.