- Do Not Sell My Personal Info

- ⋅
- Web Dev SEO

How to Change User Agents in Chrome, Edge, Safari & Firefox
SEO professionals can change their browser's user-agent to identify issues with cloaking or audit websites on different devices. Learn the process here.

Whether you are an SEO, marketer, or web developer, often you might need to change your browser’s user-agent to test different things.
For example, you’re running a MAC-OS-specific campaign. To find out if your campaign is running properly and not targeting Linux users, changing the user-agent of your browser can help you test.
For web developers, changing user-agents is almost a daily task in order to test how websites behave in different browsers and devices.
What Is a User-Agent?
A user-agent is an HTTP request header string identifying browsers, applications, or operating systems that connect to the server.
Not only browsers have user-agents, but also bots, crawlers such as search engines Googlebot , Google AdSense, etc.
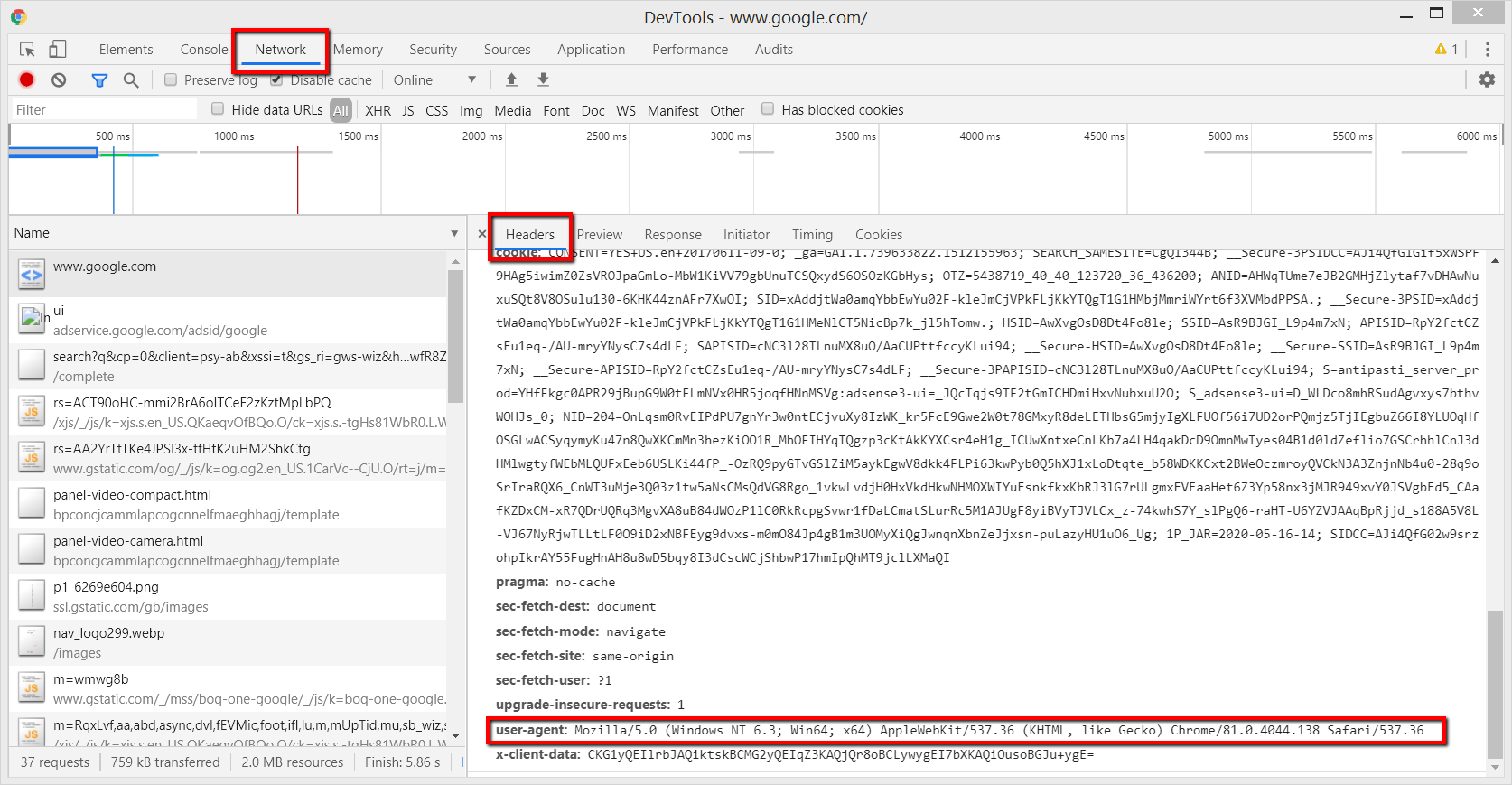
Here we are going to learn how to change the user-agent of your browser.
The process is called user-agent spoofing .
Yes, when a browser or any client sends a different user-agent HTTP header from what they are and fake it that is called spoofing.
While the term may be alarming, this is not a dangerous activity and will not cause any problems for you. (So feel free to spoof your user-agent as much as you want. 🙂)
How to Change Your User-Agent on Chrome & Edge
Since Microsoft Edge is now using Chromium , the settings for both Chrome and Edge are the same.
1. Right Click Anywhere in Webpage > Inspect
Alternatively, you can use CTR+Shift+I on Windows, Cmd + Opt +J on Mac.
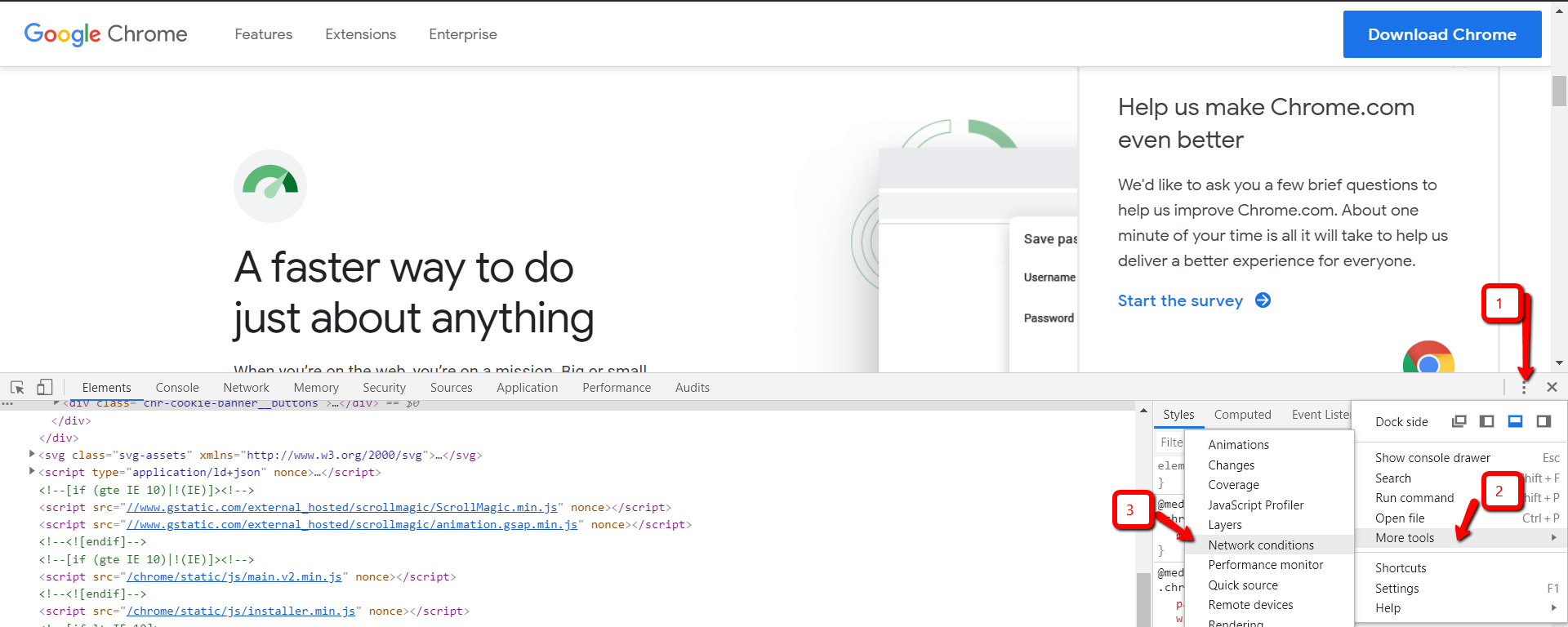
2. Choose More Tools > Network Conditions
Click on the three vertical dots on the upper right corner.
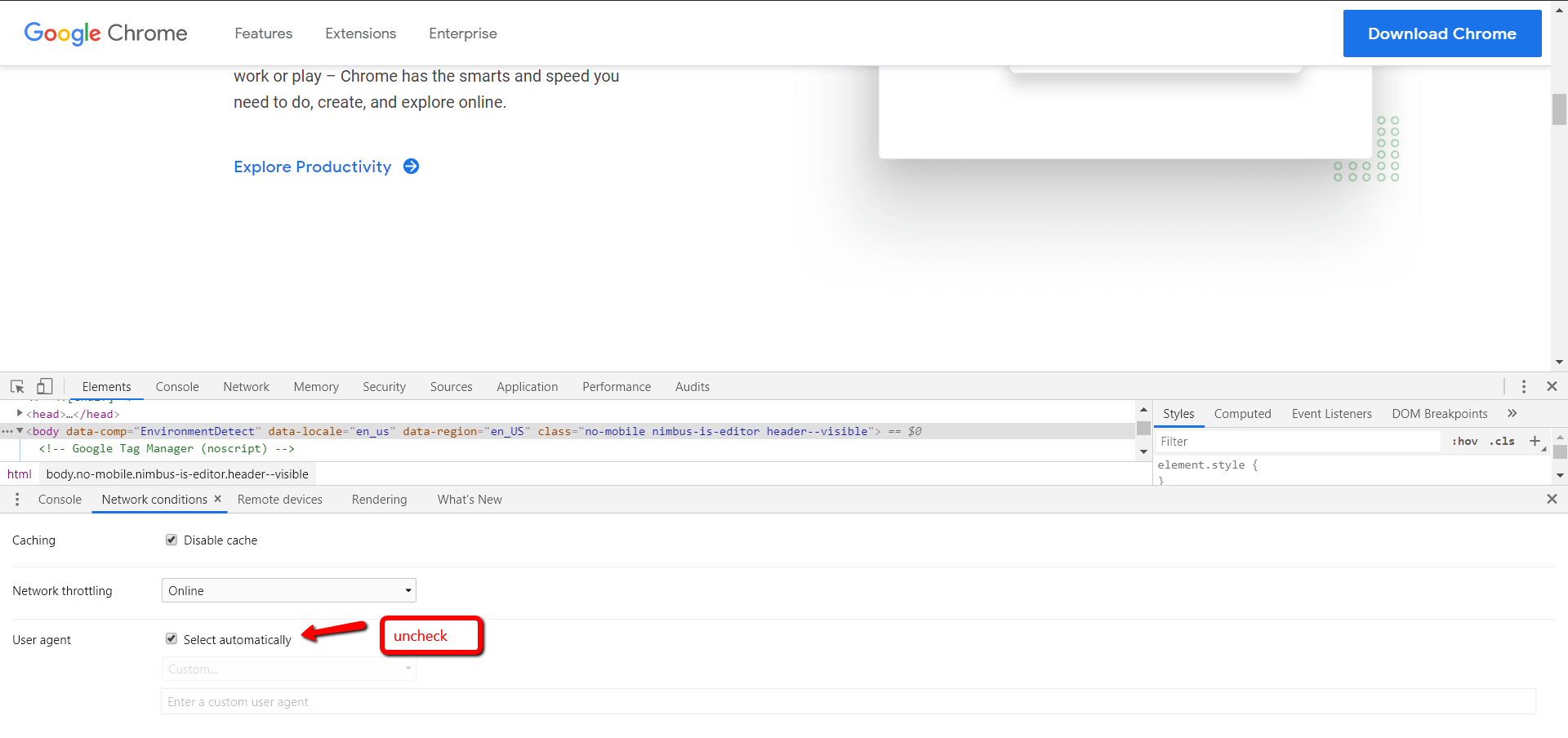
3. Uncheck Select Automatically Checkbox
4. Choose One Among the Built-In User-Agents List
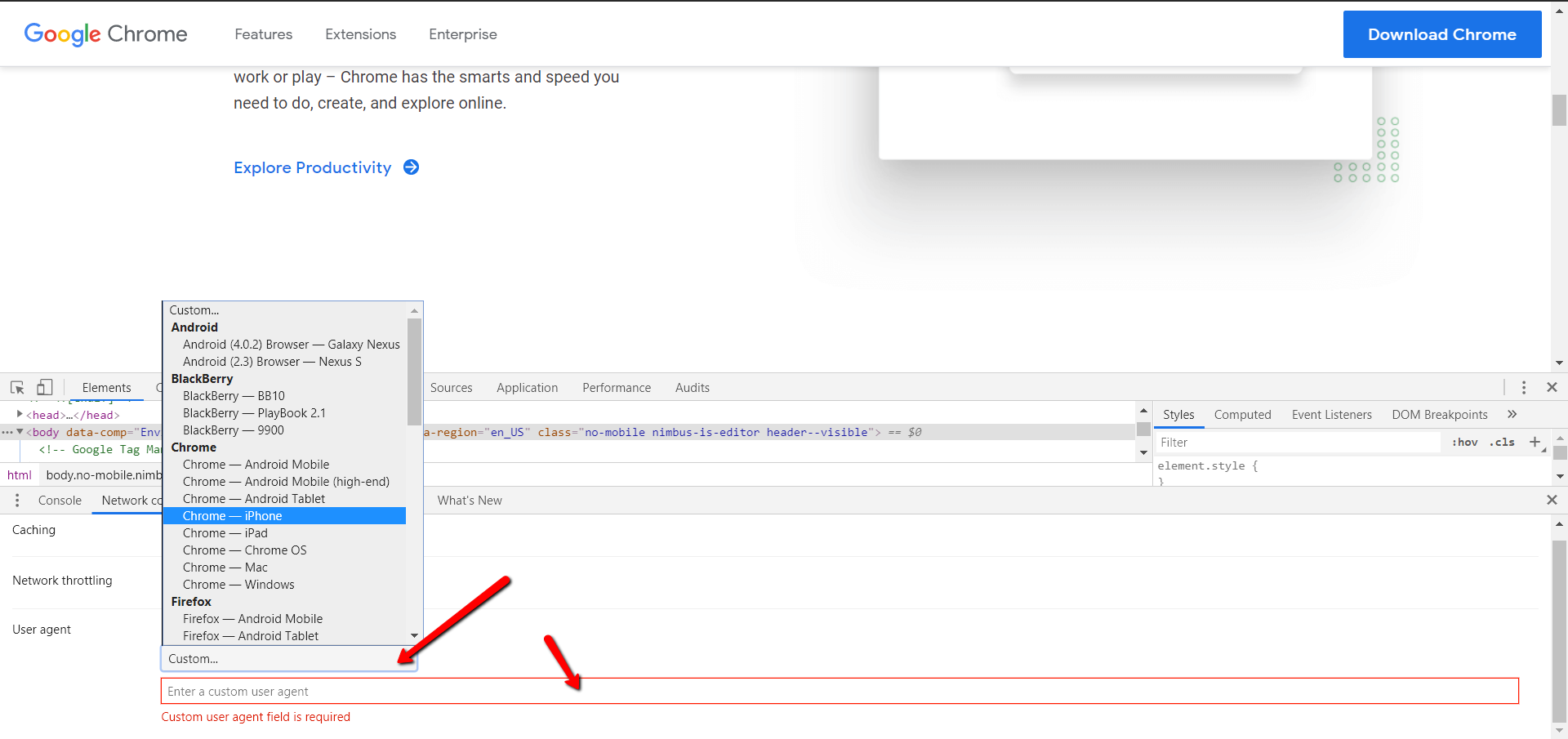
If the user-agent you want doesn’t exist, you can enter any string you want on the field below the list.
For example, you can enter the following (Googlebot’s user-agent) into the custom field.
This may be useful for SEO professionals to identify if there is a cloaking on the website when the webpage shows different content to Googlebot and another to website visitors.
Alternatively, you can use the Chrome extension User-Agent Switcher and Manager .
That said, I try not to use browser extensions when the browser can actually do the action I want. This is to avoid overloading the browser with tons of add-ons.
Also, extensions have a habit to break websites unexpectedly sometimes.
While you might think the website you visited has an issue, the root cause can be one of the add-ons you’re using.
How to Change User-Agent on Safari
1. go to preferences.
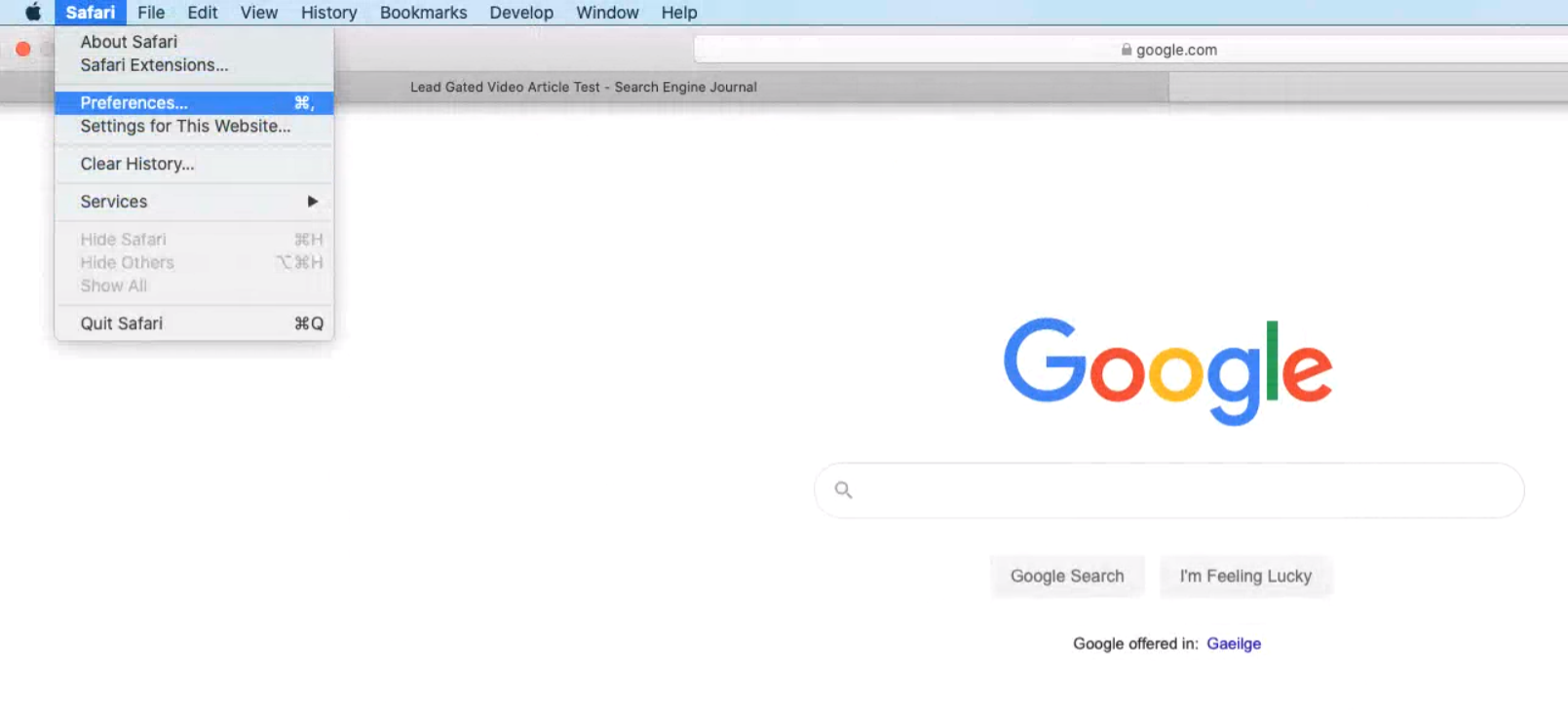
2. Enable Develop Menu Bar
Go to Advanced and check Show Develop menu in menu bar .
3. Navigate to Develop > User-Agent
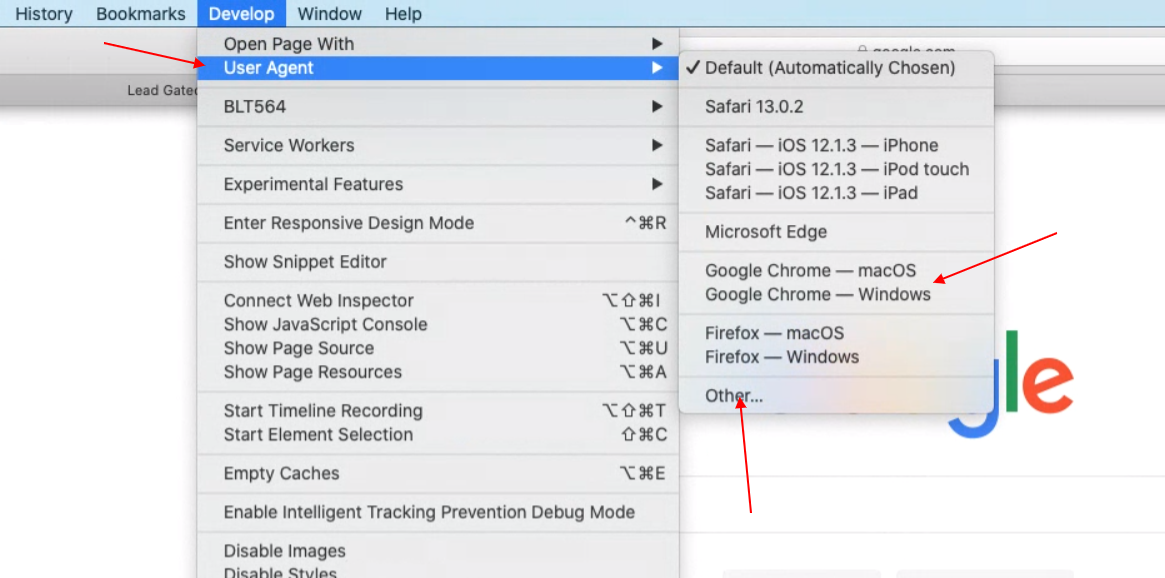
You can again select from a predefined list or enter custom user-agent string by choosing “Other…”
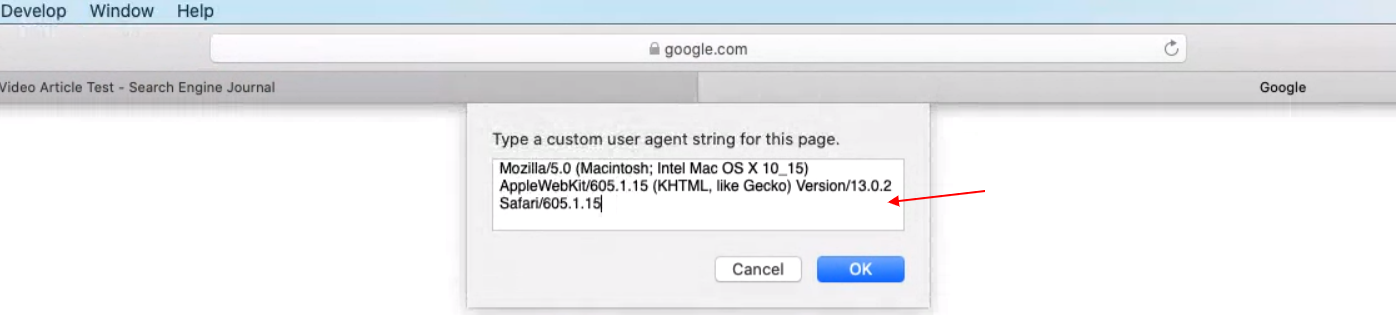
How to Change User-Agent in Firefox
In Firefox, it is possible to change user-agents via the browser’s built-in settings.
However, it is not as user-friendly as on Chrome or Safari.
It is a real pain to use the browser’s built-in feature.
Instead, we will use a Firefox add-on called User-Agent Switcher .
After installing the add-on, you will see an icon in the upper right corner.
You can select one of the predefined user-agents or enter a custom user-agent by clicking on the pen icon below.
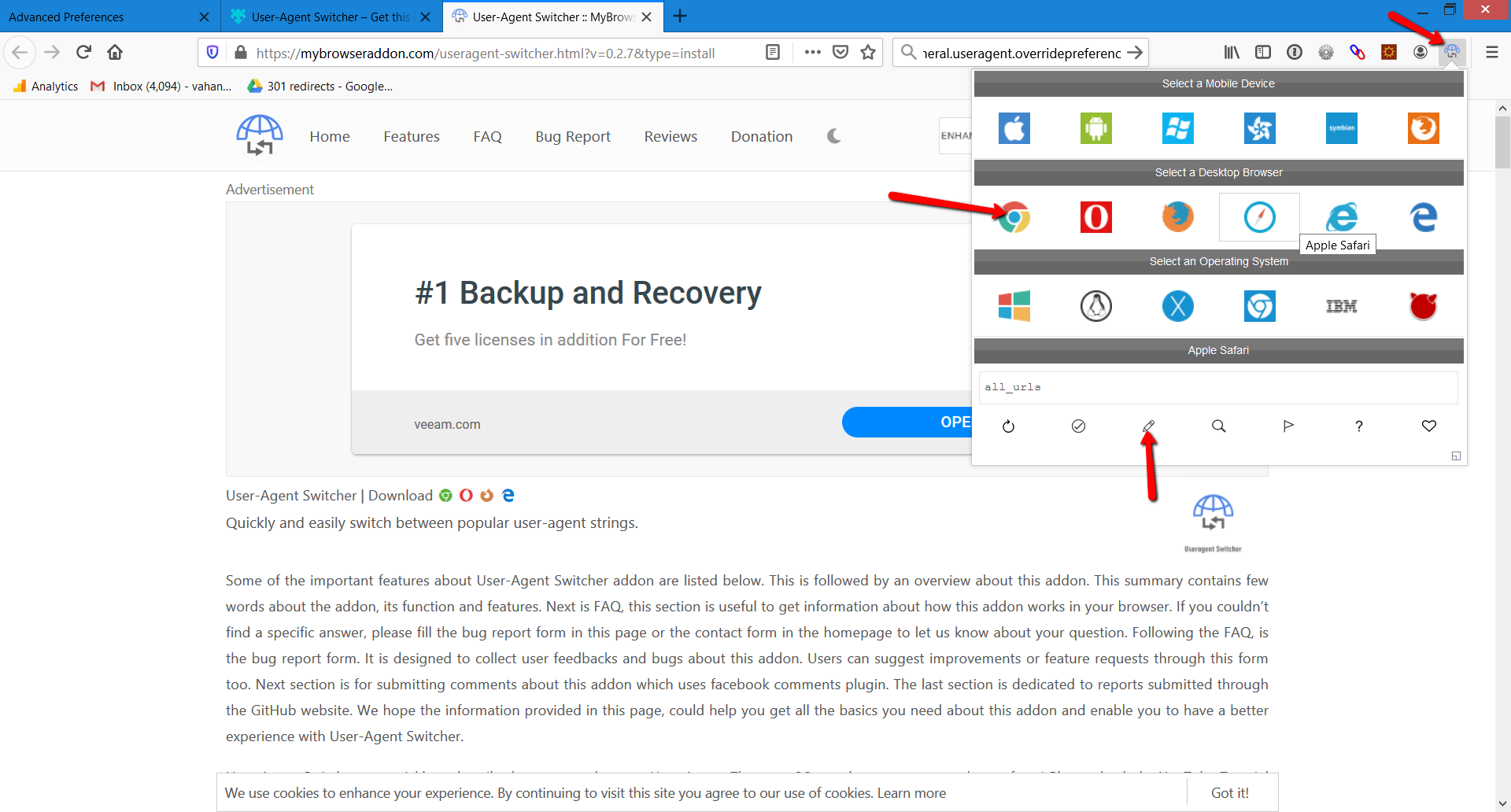
Another extension you can use is User-Agent Switcher and Manager .
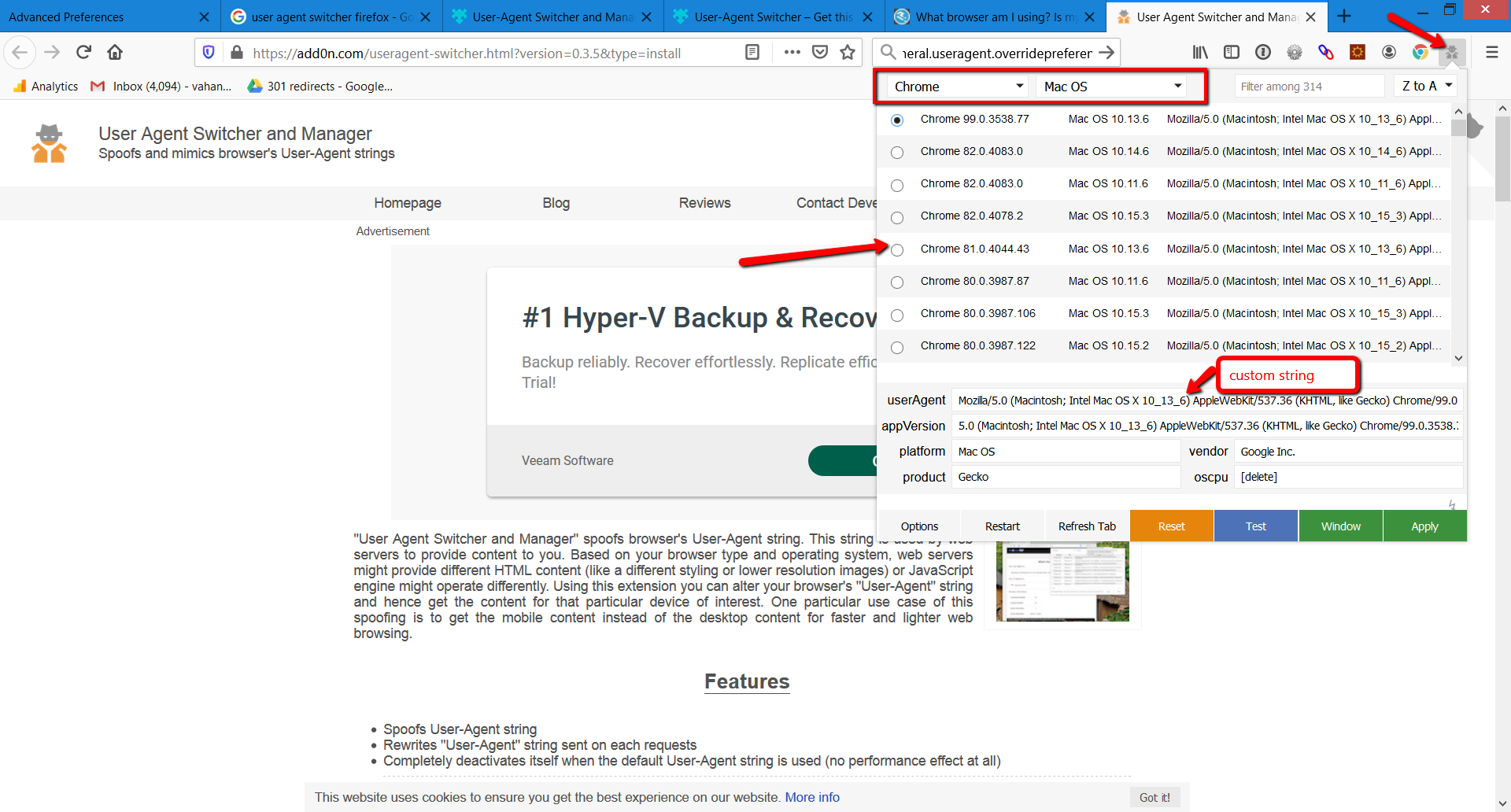
The user-agents are easy to spoof and anyone can use these easy tricks to alter it.
This feature is useful for testing web apps against various devices especially when one has different HTML for mobile or tablet devices.
One doesn’t need to have many physical devices to be able to test.
This feature is useful for SEO professionals, for example, to identify issues with cloaking which is against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines or auditing websites which has different look depending on the device.
More Resources:
- Crawl-First SEO: A 12-Step Guide to Follow Before Crawling
- New Bingbot User Agents Will Streamline SEO
- 7 Essential SEO Browser Extensions & Plugins
Image Credits
All screenshots taken by author, May 2020
What is a user agent?
User agent is a HTTP request header string identifying browser, application, operating system which connects to the server. Not only browsers have user agent but also bots, search engines crawlers such as Googlebot, Google Adsense etc. which are not browsers.
What is user-agent spoofing?
When browser or any client sends different user-agent HTTP header from what they are and fakes it that is called spoofing .
I am dedicated to ensuring the smooth and uninterrupted operation of Search Engine Journal. As the Director of Technology, I ...
Subscribe To Our Newsletter.
Conquer your day with daily search marketing news.

Home » Tech Tips » Browsers » How to Change User Agent in Mac Safari Browser?
How to Change User Agent in Mac Safari Browser?
Mac comes with Safari as a default web browser app. Though Safari works well for visiting website, many prefer Chrome for development and integration purposes. If you are using Safari, did you anytime wonder how a website you see in Safari will look like in Chrome on Mac? You will probably install Chrome and check the site. However, what will you do if you want to test in Chrome Windows version or Microsoft Edge Windows version? Good thing is that it is not necessary to install Chrome and you can change the user agent in Safari as Chrome and test the sites easily.
User Agents
Each browser has its own user agent string so that the website owner can identify how the site is being accessed. The string will change based on the device, operating system and browser version you use. For example, below is the user agent for Chrome in Mac. You can use this free tool to check your browser’s user agent.
From this information, you can find the device is Macintosh and Chrome version 114 is used to access your website. For mere testing purposes, you do not need to install Chrome, Edge or Firefox in your Mac for checking the websites on those browsers. All you need is to simply switch the user agent string in Safari and test the site’s appearance.
Changing User Agent in Safari Mac
Since user agent is kind of developer stuff, Safari by default will disable this feature. You need to first enable “Develop” menu to reveal the feature in Safari.
- Open Safari app in Mac and go to “Safari > Settings…” menu.

- Go to “Advanced” tab and enable “Show features for web developers” option showing at the bottom.

- Close Safari Settings pop-up and now you will see a “Develop” menu added to the browser.
- Click on “Develop” menu and hover over “User Agent” to view a list of items.
- By default, Safari automatically chooses the user agent and you can switch to one of the available agents from the list.
- If you want to check the string, just hover over any item and Safari will show the full string as a tooltip for you to check.

Available and Custom User Agents
As of Safari 17.0, below are the available user agents showing in the menu items for the latest OS/browser versions. User agent string will be automatically updated in Safari when the OS/browser gets new version.
- Safari – Mac, iPhone, iPad Mini and iPad.
- Microsoft Edge – macOS and Windows
- Google Chrome – macOS and Windows
- Firefox – macOS and Windows
You can switch the user agent to any of these browsers and test the site. If you want to use custom string, then click on “Custom” menu showing as a last option in the menu. This will show a text box in the pop-up where you can enter your custom user agent string and click “OK” button.

Testing Websites
After choosing the user agent, open the site that you want to test. Now, Safari will load the site as if you are seeing on different browser or device.

You can switch the user agent any time and Safari will reload the page using the new user agent. This way you can test whether the site is loading properly on different browsers without installing them on your Mac.
If you are using Chrome, learn more on how to change user agent in Google Chrome .
About Nagasundaram Arumugham
Naga is the founder and chief content editor of WebNots. He has over 20 years of experience in technology field and published more than 2000 articles.
You also might be interested in

Fix Google Chrome Slow Page Loading Issue
Google Chrome is undoubtedly the popular browser with more than 60%[...]

How to Reopen Closed Tabs in Browsers?
it is common to work on multiple tabs on a[...]

How to Use Stickies App in Mac Like a Pro?
Sticky notes are useful to note down important tasks and[...]
DOWNLOAD EBOOKS
- SEO Guide for Beginners
- WordPress SEO PDF Guide
- Weebly SEO PDF Guide
- Alt Code Emoji Shortcuts PDF
- Free ALT Code Shortcuts PDF
- View All eBooks
TRENDING TECH ARTICLES
- 600+ Windows Alt Codes for Symbols
- Fix Chrome Resolving Host Problem
- Fix Slow Page Loading Issue in Google Chrome
- View Webpage Source CSS and HTML in Google Chrome
- Fix Safari Slow Loading Pages in macOS
- Fix Windows WiFi Connection Issue
- ROYGBIV or VIBGYOR Rainbow Color Codes
- Fix I’m Not A Robot reCAPTCHA Issue in Google Search
- Structure of HTTP Request and Response
POPULAR WEB TUTORIALS
- Move WordPress Localhost Site to Live Server
- Move Live WordPress Site to Localhost
- Move WordPress Media Folder to Subdomain
- Fix WooCommerce Ajax Loading Issue
- Create a Free Weebly Blog
- Edit Weebly Source Code HTML and CSS
- Add Scroll To Top Button in Weebly
- Add Table in Weebly Site
- How to Add Advanced Data Table Widget in Weebly?
- Up to $500 Free Google Ads Coupon Codes
FREE SEO TOOLS
- Webpage Source Code Viewer
- HTTP Header Checker
- What is My IP Address?
- Google Cache Checker
- Domain Age Checker Tool
- View All Free Web and SEO Tools
© 2024 · WebNots · All Rights Reserved.
Type and press Enter to search
Sign up for our daily newsletter
- Privacy Policy
- Advertise with Us
How to Change the User Agent in Safari for Mac
In order to let websites serve browser-specific settings and pages, your browser sends a string called user agent to the websites that you visit on your computer. That way the target website gets to know what browser you are using and serves the pages accordingly. While most websites look the same in every browser, some have specific files that are only rendered when using a specific browser, Safari, for example. If you wish to see how a site looks in a specific browser, you can change the user agent in Safari on your Mac and pretend to be another browser.
When you change the user agent string, it technically changes the way websites interact with your browser. For example, if a site has a file that only renders when you’re using Chrome for Android, you can change the user agent to Chrome for Android in Safari and see that site as if you’re viewing it for real on your Android device.
Here’s how you can go about doing that.
Changing the User Agent in Safari for Mac
Fire up Safari on your Mac from the dock.
Click on “Safari” in the top left corner and select “Preferences…” You will be taken to the preferences panel for your browser.

Once in the “Preferences” panel, click on the “Advanced” tab located in the top bar. It should open the advanced settings for your browser.

In the “Advanced” tab, you should see an option that says “Show Develop menu in menu bar.” Tick mark it, and it will add a new menu in the menu bar for you to change the user agent.

Pull down the new menu by clicking on “Develop” in the menu bar. Then select “User Agent,” and you should see a list of the predefined user agents that you can use right away with your browser. Click on any and it will be selected.

If you can’t find the user agent you want to use, click on “Other” in the menu, and it will let you manually specify one.

You should see a prompt asking you to enter a user agent string that you wish to use in Safari on your Mac. This part is usually used by the geeks or developers who know what a user agent looks like and how to write one. If you are unsure, you can use the help of the User Agent String website to try out various agents in your browser.
When you are done entering the string, click on “OK,” and it will save it for you.

To check whether the new user agent works or not, just visit any site that lets you check what browser you are using, and it will tell you the name of the browser depending on what user agent you provided in the previous step. I have provided the Opera Mini user agent thus the browser check site says I’m using Opera Mini, although my actual browser is Safari.

The user agent has been changed in Safari on your Mac, and you are now telling websites that you don’t use Safari but use another browser because the user agent string says so.
If you are looking to see how a website looks like in another browser without actually downloading it, you can use the above method and have Safari pretend to be the browser you want.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox
Mahesh Makvana is a freelance tech writer who's written thousands of posts about various tech topics on various sites. He specializes in writing about Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android tech posts. He's been into the field for last eight years and hasn't spent a single day without tinkering around his devices.

How-To Geek
How to change safari's user agent on os x.
User agent "spoofing" is not a new thing.
Quick Links
What is a user agent anyway.
You've probably been annoyed at one time or another when visiting a website that requires a specific browser. Luckily, you can fool a website into thinking you're using a different browser and you can do this with most, including Safari.
User agent "spoofing" is not a new thing. It was sometimes necessary when there was a so-called browser war. Website designers would often design pages to render and deliver different content depending on the user's browser. The solution to this was often to send a false "user agent string," which would fool the web server into delivering you the preferred content.
Today, users are less likely to have a problem since websites and browsers are better at adhering to web standards. That's not to say you won't still encounter one every now and then.
If you use Apple OS X's Safari, here's how you change the user agent, and even create custom ones as well.
When Safari visits a website, it will send a string of text such as this:
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_2) AppleWebKit/600.3.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/8.0.3 Safari/600.3.18
This tells the web server that this particular user is running Safari 8 on a Mac running OS X 10.10.2.
It will obviously be different per the operating system and web browser. A computer running Windows 7 and Internet Explorer 10 would appear as such:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 10.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/6.0)
The list of user agent strings is quite extensive because there are so many browsers on different operating systems. By the way, it's possible to see what information your browser reveals about you , which includes your screen resolution, IP address, and more.
Changing Your User Agent on Safari
We've discussed the ways you can change the user agent on Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, and Firefox . Let's discuss now how to change it on Apple OS X's Safari.
First, open Safari's preferences from the "Safari" menu or with "Command + ,".
With the preferences open, click on the "Advanced" tab. At the very bottom, you want to check the box next to "Show Develop menu in the menu bar" and then exit out of the preferences.
Now Safari will have a new menu devoted solely to development tools.
The "User Agent" menu is at the top. There's already quite a few options available including preceding versions of Safari on OS X and iOS, Chrome on Mac and Windows, as well as an "Other..." option.
The "Other..." option allows you to specify a user agent other than those listed, such as if you're curious to see how Google Chrome on an iPad running iOS 8.2 renders, you'd use the appropriate string.
When you open the "Other..." option from the User Agent menu then, you'd simply type of copy the user agent string for the browser you want to test.
Afterwards, the new user agent will appear in the User Agent menu. Note, however, you can only have one "other" user agent at a time.
As we suggested in the introduction, it's unusual to have to change your user agent because most browsers are fairly good now at adhering to standards, and most websites are browser agnostic (though some browsers work better on some sites than others).
On a related note, if you're curious to see how your browser does with regard to web standards, you can always try the Acid Tests developed by the Web Standards Project .
That said, we hope you've found this article useful. If you have anything you'd like to add, such as a question or a comment, please provide feedback in our discussion forum.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Português (do Brasil)
The User-Agent request header is a characteristic string that lets servers and network peers identify the application, operating system, vendor, and/or version of the requesting user agent .
Warning: Please read Browser detection using the user agent for why serving different Web pages or services to different browsers is usually a bad idea.
Common format for web browsers:
A product identifier — its name or development codename.
Version number of the product.
Zero or more comments containing more details. For example, sub-product information.
Firefox UA string
For more on Firefox- and Gecko-based user agent strings, see the Firefox user agent string reference . The UA string of Firefox is broken down into 4 components:
- Mozilla/5.0 is the general token that says that the browser is Mozilla-compatible. For historical reasons, almost every browser today sends it.
- platform describes the native platform that the browser is running on (Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, etc.) and if it is a mobile phone. Firefox OS phones say Mobile — the web is the platform. Note that platform can consist of multiple " ; "-separated tokens. See below for further details and examples.
- rv: geckoversion indicates the release version of Gecko (such as " 17.0 "). In recent browsers, geckoversion is the same as firefoxversion .
- Gecko/geckotrail indicates that the browser is based on Gecko. (On the desktop, geckotrail is always the fixed string 20100101 .)
- Firefox/firefoxversion indicates that the browser is Firefox and provides the version (such as " 17.0 ").
Chrome UA string
The Chrome (or Chromium/Blink-based engines) user agent string is similar to Firefox's. For compatibility, it adds strings like KHTML, like Gecko and Safari .
Opera UA string
The Opera browser is also based on the Blink engine, which is why it almost looks the same as the Chrome UA string, but adds "OPR/<version>" .
Older, Presto-based Opera releases used:
Microsoft Edge UA string
The Edge browser is also based on the Blink engine. It adds "Edg/<version>" .
Safari UA string
In this example, the user agent string is mobile Safari's version. It contains the word "Mobile" .
Crawler and bot UA strings
Library and net tool ua strings, specifications, browser compatibility.
BCD tables only load in the browser with JavaScript enabled. Enable JavaScript to view data.
- User-Agent detection, history and checklist
- Firefox user agent string reference
- Browser detection using the user agent
- Client hints

How To Change Your Browser’s User Agent Without Installing An Extension
Get rid of bloat and enhance security
The user-agent string is a little-known line of information with a very big impact on how browsers see the web. We recently discussed the benefits of a user-agent switcher and how it can enhance your browsing experience.
However, switching your browser’s user agent no longer requires that you install third-party software, such as extensions. Over the past few years, mainstream browsers have all started including such functionality as a part of their developer console or within standard menus.

Although uncommon, there is a chance for browser extensions to become hijacked for malicious purposes, which could be a risk to your security. They can also add unnecessary bloat to the browser and eventually cause it to slow down.
In this article, let’s go over how you can change your user agent in today’s most popular browsers without an extension.
How To Change Your User Agent In Google Chrome
- First, you’ll need to open Chrome’s developer console. To do so, press the Ctrl + Shift + I keys. A panel should open up on the right side of your Chrome window.
- Click on the icon of the three vertical dots (top-right corner).
- In this menu, hover over More tools and then select Network conditions .
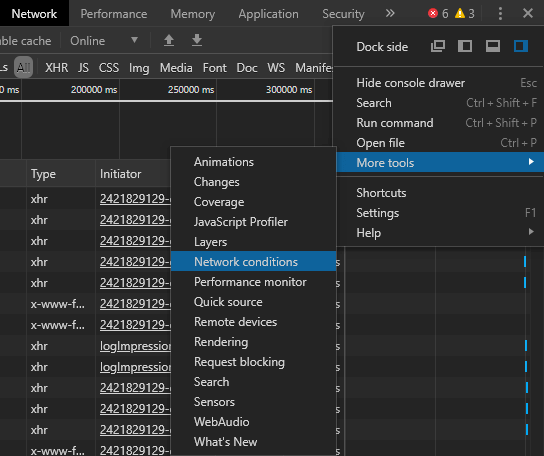
- A new panel should open at the bottom of the current one. If you look or scroll down towards the bottom of this panel, you should see a User agent label, which includes a respective set of options.
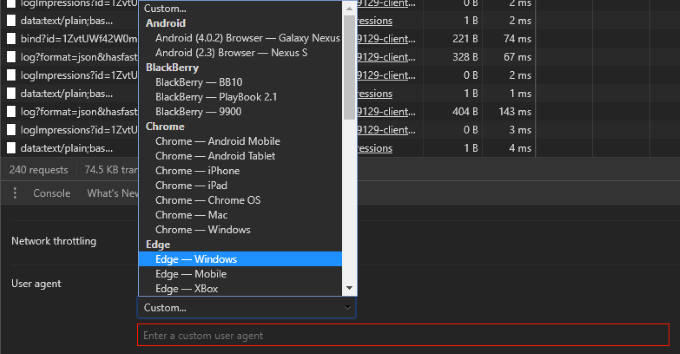
Here, you can select from a set of defined user agents or even enter your own custom user agent string . It’s that simple.
How To Change Your User Agent In Mozilla Firefox Or Opera
Without using a browser add-on, changing Firefox’s user agent is a tricky task that requires you to delve deep into the browser’s configuration. For Opera users, you can follow these same instructions – the process is identical.
- The first step is to type about:config in the address bar and hit Enter . If it’s your first time doing so, you should see a disclaimer stating that you’re entering risky territory that’s for advanced users only. Proceed past this warning.
- Next, in the Search field at the top of this screen, type in general.useragent.override . You’ll likely be met with a blank screen. If your search finds a preference though, skip further down this page to where we’re modifying the value of it.
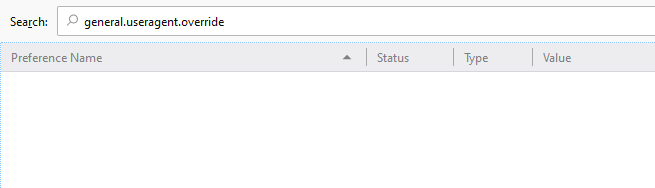
- If the preference isn’t there, right-click on a blank area of the page, hover New , and select the String option. Here, enter the same string that we searched for: general.useragent.override .
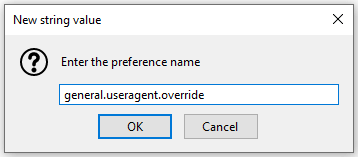
- After hitting Enter , the next prompt will ask for the new string’s value. The value has to be the exact name of the user-agent string you wish to use. You can use something completely custom or find millions of valid user-agent strings from WhatIsMyBrowser.com .
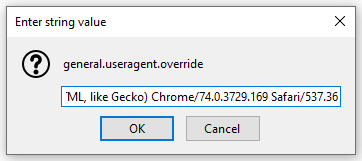
- Once you’ve input a user-agent string, hit Enter , and that’s it. This setting will remain persistent each time you restart your browser. If you’d ever like to reset this setting to its default value, just right-click on the preference name and select Reset .
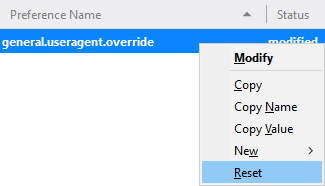
The string will remain in your settings, but setting it to a blank value has the same effect as deleting it.
How To Change Your User Agent In Microsoft Edge
Edge is the new browser that Microsoft has been trying to shine a spotlight on lately, but if you still prefer Internet Explorer, the process to change your user agent is the same.
- First, open Edge and press the F12 key on your keyboard.
- In the right-side panel that opens, look for Emulation across the top. Depending on your resolution size, you may not be able to find it at first, but if you click on the arrow pointing downwards with the More tools tooltip, you’ll find it.
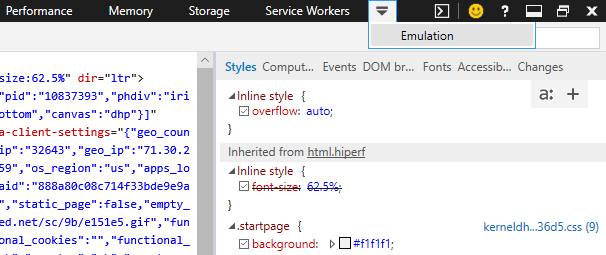
Edge’s emulation options are quite robust, allowing you to change your device, display orientation/resolution, geolocation, and user-agent string.
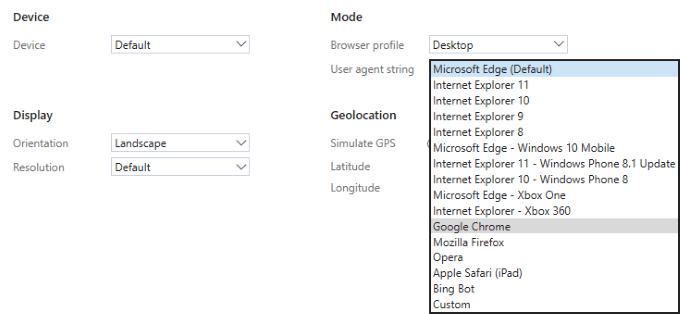
Like many other browsers, Edge supports custom user-agent strings .
How To Change Your User Agent In Safari
Safari allows you to change your user agent from the menu bar, but you’ll first need to enable the developer menu.
- To do so, go into the Preferences… menu (either by clicking on Safari or the far-right cog icon , depending on your version).
- On the window that pops up, click on the Advanced tab and then tick the checkbox of the bottommost option, Show Develop menu in menu bar .
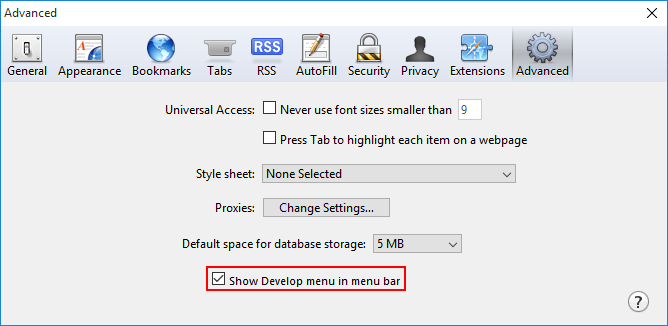
- Close this window and look for the Develop menu across your top menu bar, in the same place you see the File, Edit, View , and other menu options.
- If you don’t see this row of options, you may need to click again on either the Safari menu option or cog icon and click on Show Menu Bar .
- Next, click on the Develop menu option, hover User Agent , and you’ll see a list of user agents you can switch to.
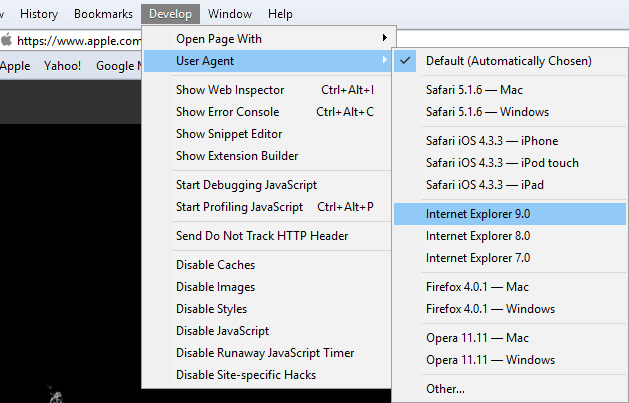
- While the preset list isn’t very extensive, clicking on Other… will give you the option to enter your own custom user-agent string .
If you’re not afraid to go under the hood, changing the user-agent string via the preferences or developer console of your browser is a great way to skip out on one extra browser extension. There are millions of valid user-agent strings out there, so keep in mind that using a custom string is usually an option in the case that the presets don’t offer what you’re looking for.
Also, remember to clear or undo all changes made to your user-agent string if you want to browse the internet as intended. Many websites will alter the way content is delivered to you based on your user agent, so forgetting this can cause you to view websites in a suboptimal way.
Craig is a long-time writer, coder, and marketer with years of experience in the technology and gaming spaces. Since 2008, he's worked remotely with some of the most notable publications in these industries, specializing in Windows, PC hardware and software, automation, and the like. Read Craig's Full Bio
Read More Posts:

User Agent String.Com
Safari user agent strings, safari 7.0.3.
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_3) AppleWebKit/537.75.14 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/7.0.3 Safari/7046A194A
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; CPU OS 6_0 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/536.26 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/6.0 Mobile/10A5355d Safari/8536.25
Safari 5.1.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8) AppleWebKit/537.13+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1.7 Safari/534.57.2
Safari 5.1.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_7_3) AppleWebKit/534.55.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1.3 Safari/534.53.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; CPU OS 5_1 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/534.46 (KHTML, like Gecko ) Version/5.1 Mobile/9B176 Safari/7534.48.3
Safari 5.0.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; de-at) AppleWebKit/533.21.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.5 Safari/533.21.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_7; da-dk) AppleWebKit/533.21.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.5 Safari/533.21.1
Safari 5.0.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; tr-TR) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; ko-KR) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; cs-CZ) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; zh-cn) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_7; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; zh-cn) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; sv-se) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; ko-kr) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; it-it) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; es-es) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; en-gb) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; de-de) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.4 Safari/533.20.27
Safari 5.0.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; sv-SE) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; de-DE) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; hu-HU) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; de-DE) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; it-IT) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.20.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_7; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.16+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_6; fr-ch) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_5; de-de) AppleWebKit/534.15+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_5; ar) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Android 2.2; Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.3 Safari/533.19.4
Safari 5.0.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; zh-HK) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; tr-TR) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; nb-NO) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; zh-cn) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPod; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_3_3 like Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8J2 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPod; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_3_1 like Mac OS X; zh-cn) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8G4 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPod; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_2_1 like Mac OS X; he-il) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8C148 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; ru; CPU iPhone OS 4_2_1 like Mac OS X; ru) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8C148a Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; ru; CPU iPhone OS 4_2_1 like Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8C148a Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; fr; CPU iPhone OS 4_2_1 like Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8C148a Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_3_1 like Mac OS X; zh-tw) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8G4 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_3 like Mac OS X; pl-pl) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8F190 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_3 like Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8F190 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_3 like Mac OS X; en-gb) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8F190 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_2_1 like Mac OS X; ru-ru) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8C148 Safari/6533.18.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_2_1 like Mac OS X; nb-no) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8C148a Safari/6533.18.5
Safari 5.0.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.17.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.1 Safari/533.17.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_4; th-th) AppleWebKit/533.17.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.1 Safari/533.17.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux x86_64; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.2+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/531.2+
- Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux x86_64; en-ca) AppleWebKit/531.2+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/531.2+
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; es-ES) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; fr) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; zh-cn) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; ru-ru) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; ko-kr) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; it-it) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; HTC-P715a; en-ca) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; en-au) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; el-gr) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; ca-es) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; zh-tw) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; it-it) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.0; en-en) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.1 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.1 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.1 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; de-de) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.1 Safari/533.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_7; en-us) AppleWebKit/533.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.1 Safari/533.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_2; nb-no) AppleWebKit/533.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.1 Safari/533.16
Safari 4.0dp1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en) AppleWebKit/526.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; tr) AppleWebKit/528.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.11.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; en) AppleWebKit/528.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.11.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; de) AppleWebKit/528.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.11.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10.5; en-US; rv:1.9.1b3pre) Gecko/20081212 Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en) AppleWebKit/526.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-gb) AppleWebKit/528.10+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.11.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_4; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.11.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_4; en-gb) AppleWebKit/528.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0dp1 Safari/526.11.2
Safari 4.0.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; es-ES) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-gb) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; cs-CZ) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; da-dk) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; en-us) AppleWebKit/533.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; de-de) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_2; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8) AppleWebKit/534.57.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Safari/531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_1 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/532.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Mobile/8B5097d Safari/6531.22.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_1 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/532.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Mobile/8B117 Safari/6531.22.7
Safari 4.0.4
- Mozilla/5.0(iPad; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B314 Safari/531.21.10gin_lib.cc
- Mozilla/5.0(iPad; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B314 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0(iPad; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B314 Safari/123
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; ko-KR) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/533.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; en-US) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; de-DE) AppleWebKit/532+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_6_1; en_GB, en_US) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; hu-hu) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_2; ru-ru) AppleWebKit/533.2+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_2; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_2; de-at) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B334b Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone Simulator; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7D11 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPad;U;CPU OS 3_2_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B500 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; U; CPU OS 3_2_2 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B500 Safari/53
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; U; CPU OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; es-es) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B367 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; U; CPU OS 3_2 like Mac OS X; es-es) AppleWebKit/531.21.10 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.4 Mobile/7B360 Safari/531.21.10
Safari 4.0.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; fr-ch) AppleWebKit/531.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/532.0+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.9.2009
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/532.0+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_1; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/532.3+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; fi-fi) AppleWebKit/531.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.21.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.21.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_6) AppleWebKit/531.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.3 Safari/531.4
Safari 4.0.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/532+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; pl-PL) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; de-DE) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_7; en-us) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_7; en-us) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.2 Safari/530.19
Safari 4.0.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_7; en-us) AppleWebKit/531.2+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.1 Safari/530.18
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_7; en-us) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.1 Safari/530.18
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; hu-HU) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; he-IL) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; he-IL) AppleWebKit/528+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; es-es) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; de-DE) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; sv-SE) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pt-PT) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pt-BR) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; nb-NO) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; hu-HU) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; fi-FI) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/528.16
Safari 3.2.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; cs-CZ) AppleWebKit/525.28.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.3 Safari/525.29
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/530.19.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.3 Safari/525.28.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_7; de-de) AppleWebKit/525.28.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.3 Safari/525.28.3
Safari 3.2.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; de-DE) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; en-US) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; de-DE) AppleWebKit/528+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; nb-NO) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ko-KR) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; es-ES) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/525.28 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.2 Safari/525.28.1
Safari 3.2.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; sv-SE) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; de-DE) AppleWebKit/528+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ja-JP) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_8; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_6; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/530.0+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_6; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/530.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; sv-se) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; pl-pl) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; it-it) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; es-es) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; zh-tw) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; ru-ru) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; nb-no) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; ko-kr) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; it-it) AppleWebKit/528.8+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; it-it) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; hr-hr) AppleWebKit/530.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2.1 Safari/525.27.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; hu-HU) AppleWebKit/525.26.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.26.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/525.26.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.26.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_5; fi-fi) AppleWebKit/525.26.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.26.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_5; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.26.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.26.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_5; sv-se) AppleWebKit/525.26.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.26.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_5; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/525.26.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.26.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_5; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.2 Safari/525.25
Safari 3.1.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; pl-PL) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; pt-BR) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pl-PL) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; it-IT) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; it-IT) AppleWebKit/525+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-GB) AppleWebKit/525.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; en) AppleWebKit/420+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.21
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_5; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_4; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; sv-se) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.22
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; fr) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.22
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/530.6+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.7+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.4+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-gb) AppleWebKit/525.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.2 Safari/525.20.1
Safari 3.1.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.17
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pl-PL) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.17
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.17
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/525+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.17
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ca-es) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 2_0_1 like Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Mobile/5G77 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_3; sv-se) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_3; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_3; en) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_2; en) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.18
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.18
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; en) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.18
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_7; de-de) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.18.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_3; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/527+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_3; nb-no) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_3; hu-hu) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_3; es-es) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_3; en-ca) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.20
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1.1 Safari/525.18
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; ru-RU) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; es-ES) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; da-DK) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_4; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-gb) AppleWebKit/526+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-gb) AppleWebKit/526+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 iPhone
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; zh-tw) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.27.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; pt-br) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; it-it) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; es-es) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-us) AppleWebKit/526.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-gb) AppleWebKit/525.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_2; en-au) AppleWebKit/525.8+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.1 Safari/525.6
Safari 3.0.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en) AppleWebKit/525+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.11
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; da-dk) AppleWebKit/523.15.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/523.12.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/523.10.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/523.10.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_4; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_4_11; en) AppleWebKit/525.3+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/523.12.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/523.10.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/523.10.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; ko-kr) AppleWebKit/523.15.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/523.12.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/523.10.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/523.12.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/523.10.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/525.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/523.10.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/523.12.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; es-es) AppleWebKit/523.15.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/525.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.4 Safari/523.10
Safari 3.0.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; cs) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; sv) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; fr) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; de) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; da-DK) AppleWebKit/523.11.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; da) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; cs) AppleWebKit/522.15.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.15.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/523.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/523.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/523.3+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ca-es) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; ru-ru) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/523.9+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/523.5+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/523.2+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.3 Safari/522.12.1
Safari 3.0.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; nl) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; zh) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; en) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; nl) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; it) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; el) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; cs) AppleWebKit/522.13.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.13.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/522.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/522+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/522.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/522.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/522.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/522+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.2 Safari/522.12
Safari 3.0.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; fi) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; th) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; sv) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; nl) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en) AppleWebKit/522.4.1+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.0; en) AppleWebKit/522.12.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0.1 Safari/522.12.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; sv-SE) AppleWebKit/523.13 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; nl) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; en-US) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0; da-DK) AppleWebKit/523.12.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.12.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; pt) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2; nl) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; tr-TR) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; sv) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; ru) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pt-BR) AppleWebKit/525+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pt-BR) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pl-PL) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; pl-PL) AppleWebKit/523.12.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.12.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; nl) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; nb) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; id) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; hr) AppleWebKit/522.11.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/522.11.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; fr-FR) AppleWebKit/523.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/3.0 Safari/523.15
Safari 2.0.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/419 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/418.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/418.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; pt-pt) AppleWebKit/418.9.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/418.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/418.9.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/418.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/419 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/418.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/418.9.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fi-fi) AppleWebKit/418.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es-es) AppleWebKit/418.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es) AppleWebKit/419 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en_CA) AppleWebKit/419 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/419 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/418.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/418.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/419 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/418.9.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/418.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
Safari 2.0.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; tr-tr) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nb-no) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nb-no) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/417.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/418 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/417.9.2
Safari 2.0.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nl-nl) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; nb-no) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-ca) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/416.11 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/416.12 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/416.13
Safari 2.0.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS; pl-pl) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS; en-en) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es-ES) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en_US) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412 Privoxy/3.0
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/412.6.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/412.6.2 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412.6.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412.6 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/412 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/412
Safari 1.3.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.8.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.8.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.8 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.5
Safari 1.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/312.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es-es) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.5.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.5.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.1.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-ch) AppleWebKit/312.1.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-ca) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.1.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.1.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.3.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-ch) AppleWebKit/312.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312

Safari 1.2.4
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/125.5.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.11
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-ch) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-ch) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.11
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/125.5.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/125.5.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.11
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.5.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.11
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.5.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.5.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.5.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12_Adobe
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.5.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.12
Safari 1.2.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/125.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en_CA) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-au) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/100
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.9
Safari 1.2.2
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; es-es) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-gb) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/125.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; it-it) AppleWebKit/124 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/124 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/124 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/124 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/124 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/124 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/125
Safari 1.0.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/85.8.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-gb) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/85.8.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/85.8.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/85.8.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.8
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; sv-se) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; ja-jp) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr-fr) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fr) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.7
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/85.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85.5
- Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux i686; en-US; rv:1.9.0.3) Gecko/2008092816 Mobile Safari 1.1.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; zh-CN) AppleWebKit/533+ (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US) AppleWebKit/528.8 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) Dooble/1.40 Safari/534.34
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; fi-fi) AppleWebKit/420+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/312.8.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/312.6
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/419.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-de) AppleWebKit/418.9.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-ch) AppleWebKit/85 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/85
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; de-CH) AppleWebKit/419.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X; da-dk) AppleWebKit/522+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; PPC Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; it-IT) AppleWebKit/521.25 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/521.24
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/419.2.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/522.11.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/419.3
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit/521.32.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/521.32.1
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X; en) AppleWebKit (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_3; es-es) AppleWebKit/531.22.7 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_6; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.16 (KHTML, like Gecko)
- Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_5_5; it-it) AppleWebKit/525.18 (KHTML, like Gecko)
Looks like no one’s replied in a while. To start the conversation again, simply ask a new question.
internet Explorer user agent
I want to use the Internet Explorer user agent from the Develop tab to use a specific website. However on my version of Safari (13.0.3) none of the IE versions are shown - only Edge. I have tried searching for the user agent strings but cannot find them.
Can anyone help how to install those user agents into Safari ?
MacBook Pro 13", macOS 10.14
Posted on Nov 14, 2019 2:37 PM
Loading page content
Page content loaded
Nov 15, 2019 4:07 AM in response to dominic23
We have been told Edge will not work on this website - IE only. I would put a string into the other filed if I could find one for IE. I have searched the Web and find all sorts for Chrome etc but I cannot find a string to paste for IE of any version to run on Safari 13
Nov 15, 2019 10:27 AM in response to Satcom_Eng
I couldn't find Safari 13 specific IE user agent string either.
If Apple don't provide one, it is going to be tough to get IE user agent string working.
Do you have clone backup with previous version of Safari installed?
Nov 18, 2019 6:10 AM in response to Satcom_Eng
im having the exact same problem . there was a IE extension that used to be free on chrome as well and now they want to charge u for it . I usually use the developer tab but my computer auto updated itself to 13.0.3 and not IE is gone ...
Nov 22, 2019 9:12 AM in response to Satcom_Eng
There has not been an Internet Explorer version for Mac in 16 years. There is no user Agent String that would Identify a current Internet Explorer version on a Mac.
But not sure why you need that. If you just want to trick the website into thinking you are using Internet Explorer, then any current version of Internet Explorer you would be using would have to be on Windows, so those strings should work.
Jan 12, 2020 11:44 AM in response to Da-Kang
HI Da-Kang - I was wondering what it was that you found that WORKS!!
I am too trying to "use" IE and EDGE does not work - Please advise what did it for you!
Best regards
PS I see the DEFAULT string showing on my MAC under Develop/User Agent/other is:
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_2) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/13.0.4 Safari/605.1.15
Is this for Internet explorer?
Jan 30, 2020 3:05 PM in response to aofrombeaconsfield
This will work I have a website that only will run on ie 8-11 this following string run the website when used in the agent string.
Unfortunately, you have to do this step each time you want to use the in question website..
Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0)
Apr 6, 2020 6:51 AM in response to felippemagoo
felippemagoo wrote:
I think these user agents don’t work for Mac.
They do. User Agents are platform agnostic, they'll work anywhere. On Mac, on Pc, even on Linux.
As I said before, there are no user agents that will identify your browser as Internet Explorer on Mac because there has been no Internet Explorer on Mac for 16 years. So no user agent either.
If the website is expecting Internet Explorer, then its expecting Internet Explorer on Windows which is what these user agents would make it think you have.
May 9, 2020 5:16 AM in response to Phil0124
I have the same problem now and good thing I've stumbled in this discussion. I have tried the link you provided and used all the strings but none is working too. Not sure what needs to be done next. :-(
May 9, 2020 8:52 AM in response to ProvinceBoy
Define “not working”. What does the website do when using the user agent strings?
There’s also the possibility, the website you are trying to access is not using the user agent to identify the browser. It may be looking for support of a particular Javascript function, or some other mechanism of identifying the browser.
May 10, 2020 6:34 AM in response to Kurt Lang
I guess I was able to figure this one out on how to make it work. At least from what I have experienced. Downloaded chrome for Mac, then added an ie extension.
From that ie extension's options and settings, I have chosen IE 10 Forced Standard Mode.
Nov 22, 2019 2:38 PM in response to VikingOSX
i take it back Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0) this works perfectly
thanks again ...
Nov 15, 2019 3:27 AM in response to Satcom_Eng
- Have you tried Microsoft Edge as the User Agent?
- Try 'Other" at the bottom of the pop-up, enter the user agent string and "OK".
Nov 18, 2019 6:44 AM in response to Satcom_Eng
Latest user agents for Internet Explorer .
Nov 22, 2019 9:00 AM in response to VikingOSX
Thanks for the link but they all seem to be for Windows machines. I need the string for IE on OS X 13 ? Unless I am reading those incorrectly.
it works !!!!!
- Privacy Sandbox
- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
- Tiếng Việt
- Protections APIs and proposals
- Protections
- Limit passive fingerprinting
What is User-Agent reduction?
User-Agent (UA) reduction minimizes the identifying information shared in the User-Agent string, which may be used for passive fingerprinting . Now that these changes have been rolled out for general availability, all resource requests have a reduced User-Agent header. As a result, the return values from certain Navigator interfaces are reduced, including: navigator.userAgent , navigator.appVersion , and navigator.platform .
Web developers should review their site code for usage of the User-Agent string. If your site relies on parsing the User-Agent string to read the device model, platform version, or full browser version, you'll need to implement the User-Agent Client Hints API .
User-Agent Client Hints (UA-CH)
User-Agent Client Hints allow access to the full set of User-Agent data, but only when servers actively declare an explicit need for specific pieces of data.
By removing passively exposed user data, we better measure and reduce the amount of information that is intentionally exposed by request headers, JavaScript APIs, and other mechanisms.
Why do we need reduced UA and UA-CH?
Historically, the User-Agent string would broadcast a large string of data about a user's browser, operating system, and version with every HTTP request. This was problematic for two reasons:
- The granularity and abundance of detail can lead to user identification.
- The default availability of this information can lead to covert tracking.
Reduced UA and UA-CH improve user privacy by sharing only basic information by default.
The reduced User-Agent includes the browser's brand and a significant version, where the request came from (desktop or mobile), and the platform. To access more data, User-Agent Client Hints allow you to request specific information about the user's device or conditions.
Further, over time the User-Agent string grew longer and more complex, which led to error-prone string parsing. UA-CH provides structured and reliable data that is easier to interpret. Existing code that parses the UA string shouldn't break (though it will return less data), and you'll need to migrate to UA-CH if your site needs specific client information .
How does the reduced UA and UA-CH work?
Here is a brief example of how the reduced User-Agent string and UA-CH work. For a more in-depth example, review Improving user privacy and developer experience with User-Agent Client Hints .
A user opens the browser and enters example.com into the address bar:
The browser sends a request to load the webpage.
- The browser includes the User-Agent header with the reduced User-Agent string. For example: User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 10; K) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/98.0.0.0 Mobile Safari/537.36
The browser includes that same information in the default User-Agent Client Hint headers. For example:
The server can ask the browser to send additional client hints, such as the device model, with the Accept-CH response header. For example: Accept-CH: Sec-CH-UA, Sec-CH-UA-Mobile, Sec-CH-UA-Platform, Sec-CH-UA-Model
The browser applies policies and user configuration to determine what data is allowed to return to the server in subsequent request headers. For example:
Critical Client Hints
If you need a specific set of Client Hints in your initial request, you can use the Critical-CH response header. Critical-CH values must be a subset of the values requested by Accept-CH .
For example, the initial request may include a request for Device-Memory and Viewport-Width , where Device-Memory is considered critical.
If the browser requires a critical hint ( Critical-CH ) to properly render the webpage, then the server can ask for this additional information with the Accept-CH header. Then, the browser can send a new request for the page, including the critical hint.
In summary, Accept-CH requests all values you'd like for the page, while Critical-CH requests only the subset of values you must have on-load to properly load the page. Refer to the Client Hints Reliability specification for more information.
Detect tablet devices with the UA-CH API
As the line between mobile, tablet, and desktop devices continues to become less distinct and dynamic form factors are more common (folding screens, switching between laptop and tablet mode), it's advisable to use responsive design and feature detection to present an appropriate user interface.
However, information provided by the browser for both the User-Agent string and User-Agent Client Hints comes from the same source, so the same forms of logic should work.
For example, if this pattern is checked on the UA string:
- Phone pattern: 'Android' + 'Chrome/[.0-9]* Mobile'
- Tablet pattern: 'Android' + 'Chrome/[.0-9]* (?!Mobile)'
The matching default UA-CH headers interface may be checked:
- Phone pattern: Sec-CH-UA-Platform: "Android" , Sec-CH-UA-Mobile: ?1
- Tablet pattern: Sec-CH-UA-Platform: "Android" , Sec-CH-UA-Mobile: ?0
Or the equivalent JavaScript interface:
- Phone pattern: navigator.userAgentData.platform === 'Android' && navigator.userAgentData.mobile === true
- Tablet pattern: navigator.userAgentData.platform === 'Android' && navigator.userAgentData.mobile === false
For hardware-specific use cases, the device model name can be requested via the high-entropy Sec-CH-UA-Model hint.
How do I use and test reduced UA?
To begin, review your site code for instances and uses of the User-Agent string. If your site relies on parsing the User-Agent string to read the device model, platform version, or full browser version, you'll need to implement the UA-CH API .
Once you've updated to the UA-CH API, you should test to ensure you get the data you expect from the User-Agent. There are three ways to test, each increasing in complexity.
Scaled availability for User-Agent reduction means the fully reduced UA string shipped on all Chrome devices. Reduction began with a Chrome minor release in Q2 of 2022.
Test custom strings locally
If you want to test your site using custom User-Agent strings to simulate different devices, launch Chrome with the --user-agent="Custom string here" command-line flag. Find more on command-line flags here.
Alternatively, use the device emulator in Chrome DevTools.
Transform the string in your site's code
If you process the existing Chrome user-agent string in your client-side or server-side code, you can transform that string to the new format to test compatibility. You can test by either overriding and replacing the string, or generating the new version and test side by side.
Support for Client Hints and critical hints
There are three default Client Hints returned to the server, including browser name and major version, a boolean that indicates if the browser is on a mobile device, and the operating system name. These are sent after the Transport Layer Security protocol (TLS) handshake. These are already available and supported in your browser.
However, there may be times when you need to retrieve critical information for your site to render.
Optimize critical hints
A TLS handshake is the first step to create a secure connection between the browser and web server. Without an intervention, the Critical-CH response header was designed to tell the browser to immediately retry the request if the first one was sent without a critical hint.
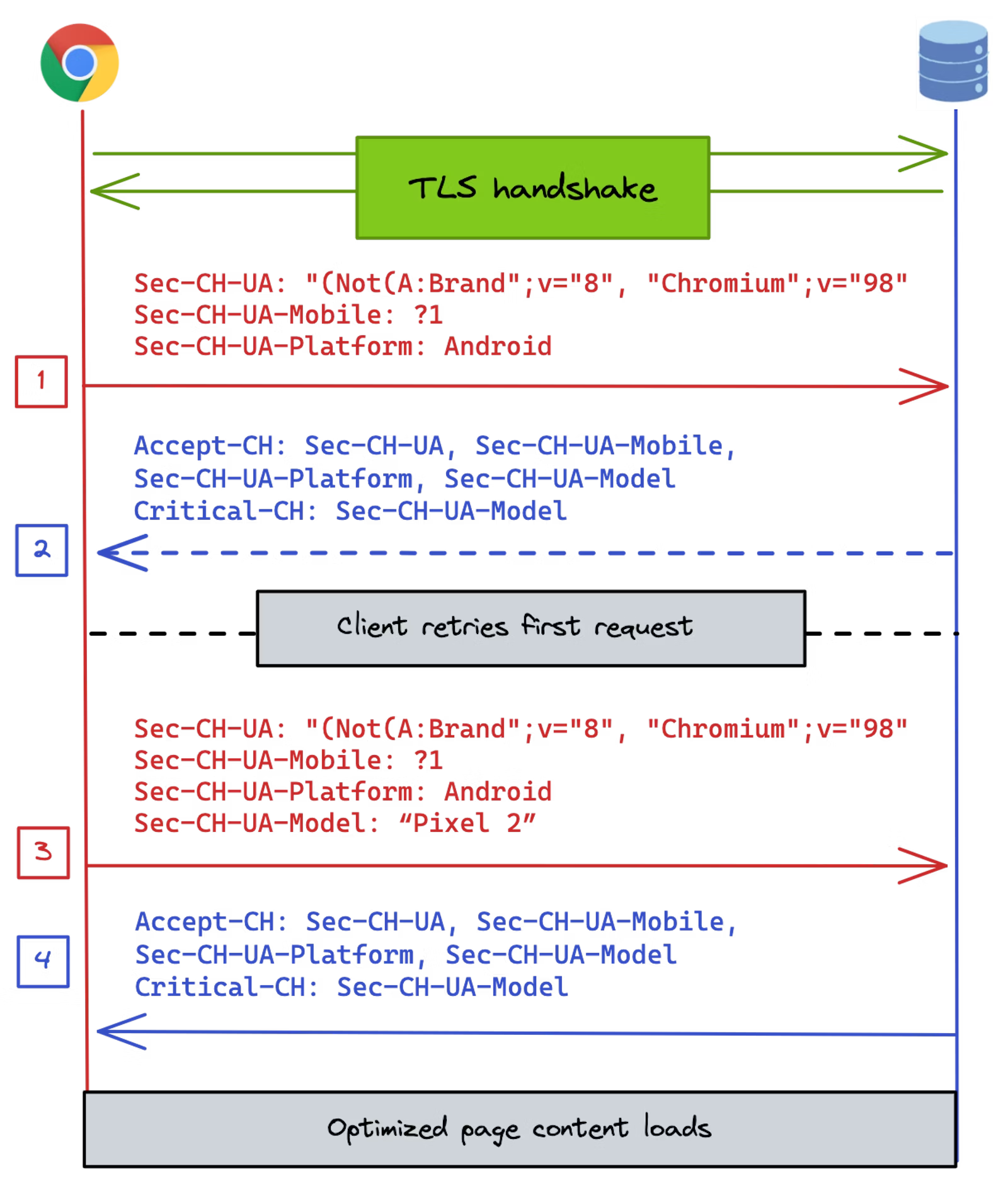
To optimize critical hints ( Critical-CH header ), you must intercept this handshake and provide a model for Client Hints. These steps may be complex, and require advanced knowledge.
The ACCEPT_CH HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 frames , combined with the TLS ALPS extension , is a connection-level optimization to deliver the server's Client Hint preferences in time for the first HTTP request. These require complex configuration, and we recommend only using this for truly critical information.
BoringSSL (a fork of OpenSSL) helps you work with Google's experimental features in Chromium. At this time, ALPS is only implemented in BoringSSL .
If you need to use critical hints, refer to our guide on critical hints reliability and optimization .
How long will hints specified via the Accept-CH header be sent?
Hints specified via the Accept-CH header will be sent for the duration of the browser session or until a different set of hints is specified.
Does UA-CH work with HTTP/2 and HTTP/3?
UA-CH works with both HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 connections.
Do subdomains (and CNAMEs) require a top-level page Permissions-Policy to access high-entropy UA-CH?
High-entropy UA-CH on request headers are restricted on cross-origin requests regardless of how that origin is defined on the DNS side. Delegation must be handled via Permissions-Policy for any cross-origin subresource or obtained via JavaScript that executes in the cross-origin context.
How does User-Agent reduction affect bot detection?
Chrome's change to its User-Agent string does not directly impact the User-Agent string that a bot chooses to send.
Bots may choose to update their own strings to reflect the reduced information Chrome sends, but that is entirely their implementation choice. Chrome is still sending the same User-Agent format, and bots that append their own identifier to the end of a Chrome User-Agent string can continue to do so.
For any concerns with specific bots, it may be worth reaching out directly to the owners to ask if they have any plans to change their User-Agent string.
Engage and share feedback
- Origin trial : Share your feedback on previous origin trials .
- Demo : Try our demo of User-Agent reduction .
- GitHub : Read the UA-CH explainer , raise questions and follow discussion .
- Developer support : Ask questions and join discussions on the Privacy Sandbox Developer Support repo .
Find out more
- Improving user privacy and developer experience : an overview for web developers
- Migrate from UA string to UA-CH : a tutorial for web developers
- Digging into the Privacy Sandbox
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License , and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License . For details, see the Google Developers Site Policies . Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2024-04-19 UTC.

Understanding the User-Agent string
Marketing & Data Team
11/24/2021 4:30 PM
These strings hold more insight than you may realize
As we browse the web, we've come to expect a seamlessly smooth experience from the websites we visit. And as website owners, we strive to improve the performance and engagement of our websites by understanding our visitors. We need to understand their different characteristics, from their location to the browser, operating system, and hardware of the device they are using to access our site.
This information supports a multitude of use cases, including website analytics and optimization, security features if your user logs in to your site with a new device, or content adaption tailored specifically to the device used (such as a mobile phone). These use cases all require knowledge of your user's device, browser, or operating system.
One way to gather this information is via the User-Agent – a type of HTTP request header. For nearly thirty years, the User-Agent has been a well-established part of the web experience. However, a new HTTP header has been created by Google to replace the User-Agent: User-Agent Client Hints (UA-CH).
We've got more information on User-Agent Client Hints later in this blog . In the meantime, let's dissect the User-Agent for more detail.
Table of contents
Unpacking the user-agent string, other user-agent strings, why are user-agent strings like this, software/operating systems, the web browser, device hardware, changing your user-agent string, the future of the user-agent string, user-agent device detection.
The information contained within a User-Agent HTTP request header is also known as the User-Agent (UA) string. This string contains information on the device. For example, if you browse the web on your smartphone, your device will send a HTTP request header to the web server, saying that it is a mobile device. The website will then respond and show you the mobile version of the page.
We could just give you a list of User-Agent strings and be done with it. But that’s not particularly good for developing your learning, is it?
Instead, let’s dissect some example User-Agent strings:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 12; Pixel 6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/93.0.4577.62 Mobile Safari/537.36
Mozilla/5.0 appears at the start of most UA strings. It can largely be ignored as it has no relevance to the associated device. Historically, it was used to indicate compatibility with the Mozilla rendering engine, a piece of software that draws text and images on the screen.
Linux; Android 12 tells us details about the operating system. In this case, the device is running the Android operating system, which is based on Linux.
For mobile User-Agent strings, the Pixel 6 section of the string tells us the device name or device model number. In this case, this User-Agent came from a Google Pixel 6 phone. In other instances (such as for a Windows desktop device), this element of the string may define the device architecture.
AppleWebKit/537.36 indicates what browser rendering engine is used. A rendering engine is what transforms HTML into an interactive webpage on the user’s screen. The WebKit browser engine was developed by Apple and is primarily used by Safari, Chromium, and all other WebKit-based browsers.
(KHTML, like Gecko) . This section of the string doesn’t necessarily provide more detail on the device but ensures compatibility for historical reasons. Check out the history of the User Agent string guide from Human Who Codes for more details.
And finally, Chrome/93.0.4577.62 Mobile Safari/537.36 has more detail on the browser and its version number. In this example, the device is using a mobile version of Chrome, version 93.
So, the different sections of this Chrome User-Agent string are:
Let’s look at another example, this time it’s a Firefox User-Agent:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:94.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/94.0
Firefox User Agent strings tend to follow a four-component format, whereas Chrome User Agent strings may include more elements. In the above case, the rendering engine is Gecko, and rv:94.0 is its version number. Win64; x64 indicates that the device is using the 64-bit version of Windows with x64 computer architecture.
The Mozilla/5.0 and (KHTML, like Gecko) parts of a User-Agent string can largely be ignored, but why were they included in the first place?
Originally, the User-Agent string wasn't designed to be confusing, but it was a necessary evil to ensure compatibility between new and old browsers. For new browsers to ensure they got a slice of the browser market share pie, they need to make sure that they're not excluded because they're new.
As an example, there's a new browser on the block called "VeryNewBrowser". Your User-Agent contains information that you are using VeryNewBrowser to access a website. Many sites will (incorrectly!) see that VeryNewBrowser is not PopularBrowser, so will serve you a crappy version of the website.
To counteract this, the User-Agent could contain "PopularBrowser (actually VeryNewBrowser)" which fools the web server into thinking that you are using PopularBrowser.
This addition to the User-Agent string continues for many many years, until eventually you end up where we are today. Everyone claims to be Mozilla 5.0; Android Chrome claims to be Mobile Safari; Mobile Safari claims to be Gecko. It can get very confusing, very quickly. Check out WebAIM's blog for more information on the compatibility history of the User Agent string .
User-Agent strings don't necessarily follow the same format. You may see a string that looks like the following:
Dalvik/2.1.0 (Linux; U; Android 9.0; ZTE BA520 Build/MRA58K)
Looks scary, right? But when you start to look deeper, you can see that this is a ZTE Android phone. To gather more insight, you can run the UA string through our User-Agent parser and it’ll decode the rest!
It’s important to note that it’s not always easy to detect a device. For example, iPad or iPhone User-Agent strings don’t always contain a lot of information on the device. Additionally, with each new Apple device that is released, it gets harder to identify between the latest devices.
With the release of iOS 12.2 , Apple have altered the values returned from WebGL to prevent the precise iPhone or iPad model of an iOS device being obtained in JavaScript.
In the following User-Agent string, we can only identify that this is an iPhone device – we can’t determine the exact device model.
Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 12_1 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/12.1 Mobile/15E148 Safari/604.1
Our Device Detection takes the pain out of identifying devices from the User-Agent. Since the release of iOS 12.2, we upgraded our device detection with a two-part solution to identifying Apple devices : Image Hashing and Benchmarking.
Put our device identification to the test below with an iPhone User-Agent string. We’ll take the string and show you what information we can parse from it.

Let’s talk about the operating systems (OS) section of the UA string. Some of the main OS software used by various devices are Android, Windows, and Chrome OS (a Linux-based desktop OS developed by Google).
For Apple devices, we have iOS, iPadOS, macOS (previously Mac OS X and later OS X), tvOS, and watchOS. You could also include Darwin in this list, as it is an open-source Unix-like operating system first released by Apple in 2000. (Fun fact: Darwin forms the core set of components upon which the other Apple OS software are built upon.)
Within a UA string, you might find information on both the operating system and its version number. Each software vendor determines their own numbering system, as well as whether each release is a minor or major increment.
Seems simple, but don’t assume a software vendor will always follow the same pattern for a new release – sometimes conventions can change, or version numbers are skipped. And if that wasn’t enough, the User-Agent doesn’t always present the browser name and version number in a consistent manner.
To keep our User-Agent string database healthy, we regularly map new User-Agents, especially when there are new OS versions that have recently been released. It’s imperative that we provide our customers with the most accurate and up-to-date User-Agent database available.
The UA string also contains information on the type of web browser that is used by the device. Some of the more commonly known web browsers are Chrome, Safari, Edge, Firefox, and Opera.
Like software vendors, each browser vendor (think Google for Chrome, and Mozilla for Firefox) determines their own numbering system. Browser versions can be represented in the string at various stages of the development cycle. For example, a UA string might contain a browser that is in beta, canary, or developer stage.
Again, the browser name and version number aren’t always presented in a consistent manner. For example, let’s look at this common Android User-Agent string:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 10; POT-LX1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/95.0.4621.2 Mobile Safari/537.36
At first glance, you may look at this UA string and assume the browser vendor is Mozilla, or even Safari on mobile (thanks to the Mozilla/5.0’ and Mobile Safari/537.36 portions of the string). In fact, for this string, the browser is Chrome version 95.0.4621.2. It pays to slow down and carefully analyze a UA string!
If you are ever in doubt about what information is contained within a UA string, we recommend referring to our User-Agent tester to do all the hard analysis for you.

Within the UA string, there is a key element present that can be used to detect the device. This element details whether the physical device that is accessing the website is a mobile phone, tablet, e-reader, smart TV, or games console (to name but a few).
For example, the UA string below tells us that the device is a 2018 model Samsung Galaxy J7:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 8.0.0; SAMSUNG SM-J737F ) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) SamsungBrowser/14.0 Chrome/87.0.4280.141 Mobile Safari/537.36
Sometimes, it’s difficult to be certain of a device’s hardware. The biggest reason for this is because the UA string is lacking information, or the device could belong to multiple vendors.
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 9; S20_EEA Build/PPR1.180610.011; wv) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Chrome/95.0.4638.74 Safari/537.36
In this UA string, the only supplied information on the device is ‘S20’. That could refer to any of these hardware vendors:
Samsung Galaxy S20
CONQUEST S20
A User-Agent isn’t always associated with a physical device. Sometimes they represent something called a crawler.
A crawler is a type of web traffic that operates without human interaction. Its purpose is to monitor the availability or performance of a website, retrieving information to be included into search engines or monitoring services.
Crawlers go by many names – bots, robots, spiders, probes, monitors – but they are typically easy to spot and not necessarily harmful to your website.
A good crawler will proudly identify itself as a crawler, often including “bot” at some point within their UA string:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; bingbot/2.0; +http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm)
However, bad crawlers may crawl your website to find email addresses to send spam to, or to try and gain access to your website development login page. Since these bad crawlers will actively try to hide their intentions, they may spoof their User-Agent to look like a bog-standard device.
We recently created a method to filter out these bad crawlers from our website analytic reports. Find out how you can utilize User Agent string information to find these malicious crawlers .

Let’s talk more about User-Agent spoofing, as mentioned above. User-Agent spoofing can be boiled down to replacing characters in your User-Agent string with anything from a few characters to the whole string.
It’s surprisingly easy to change your UA string – you can change your browser User-Agent by pressing F12 on your keyboard to open your browser’s debug tool . Alternatively, most major browsers have plugins that can spoof the UA for you. Search for “User-Agent changer” or “User-Agent switcher” in your browser’s plugins and add-ons to see what’s available.
One benefit of spoofing your User-Agent is that you can test your website for various devices. It’s easy to change the string from a desktop to a mobile. However, there are more reliable ways to test your website for its mobile friendliness (check out our article on mobile emulators to learn more).
The accessibility of User-Agent spoofing is great for the humble user who just wants to test their website on a different device. But in the hands of a malicious crawler, having a fake User-Agent can alter the accuracy of device detection.
When the whole string is changed, it can be near-impossible to detect whether the string belongs to a real device or not. However, when only part of the string is changed, it is still possible to detect the device with a fair level of accuracy.
For example, let’s take this spoofed User-Agent string:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux;Android 3.1ipad 4 Build/AppleWebKit Gecko) Version/4.0 Safari/534
There is conflicting information in this string, as it contains both Android and iPad. An iPad User-Agent tends to follow the format Mozilla/5.0 (iPad... , which isn’t the case here. Therefore, you can deduce that this is an Android device, not iPad.
You can see from this article that we know our onions when it comes to detecting information from a User-Agent HTTP request header.
However, change is on the horizon. Google's alternative to the User-Agent HTTP header, User-Agent Client Hints (UA-CH) , are due to reduce the UA string on all Chrome devices in the first half of 2023.
User-Agent Client Hints dissect device information in a similar way to the User-Agent, but often includes additional information in the response, such as Sec-CH-UA-Platform or Sec-CH-UA-Mobile.
This unilateral change pushed by only the one company has forced others to adapt, regardless of whether they want to or not. Not all the User-Agent Client Hints are sent by default, so website owners will need to undertake extra work to adapt to the change. Some will inevitably drag their heels, which could cause their website to break.
The best way to prepare in the next few months is to upgrade your services to support UA-CH. Version 4 of our Device Detection has been upgraded to support UA-CH detection .
Don’t get caught short when the User-Agent is reduced in favor of User-Agent Client Hints – sign up to version 4 of our solution today.
The purpose of gathering User-Agent data from your users allows you to gain further insights into their characteristics. If you find that 80% of your website visitors use mobile, you should probably look into mobile optimization of your website .
There are so many reasons to use User-Agents for device detection in industries such as AdTech , E-commerce , and Digital publishing . Find out how businesses like yours have excelled with our real-time data services .

Try us for free
The question isn't "why should you?", it's "why on earth wouldn't you?".
Useragents.me
Last updated: 15 may, 2024.
A self-updating list of the latest and most common useragents seen on the web across all device types, operating systems, and browsers. Data is always fresh, updating weekly.
This user agent list is perfect for web scrapers looking to blend in, developers, website administrators, and researchers.
The most common useragents list is compiled from the user logs data of a number of popular sites across niches and geography, cleansed (bots removed), and enriched with information about the device and browser.
Most Common Desktop Useragents
Most common mobile useragents, latest windows desktop useragents.
- Latest Mac Desktop Useragents
Latest Linux Desktop Useragents
Latest iphone useragents, latest ipod useragents, latest ipad useragents, latest android mobile useragents, latest tablet useragents.
- Smartproxy: Fast, Reliable Proxies
- Free Proxy Checker
An updated list of the most common useragents on the web, specifically the most common desktop useragents. You can see the relative share of each useragent included in the data table below. Hint: scroll sideways if you're viewing this page on a mobile device.
Get useragent list as JSON or TSV
Get the most common desktop useragents list conveniently in JSON format
Get the most common desktop useragents list conveniently in TSV (tab separated values) format
An updated list of the most common useragents on the web, specifically the most common mobile useragents. You can see the relative share of each useragent included in the data table below. Hint: scroll sideways if you're viewing this page on a mobile device.
Get the most common mobile useragents list conveniently in JSON format
Get the most common mobile useragents list conveniently in TSV (tab separated values) format
A complete list of the absolute latest Windows (desktop) useragents.
Latest Mac OS X Desktop Useragents
A complete list of the absolute latest Mac OS X (desktop) useragents.
A complete list of the absolute latest Linux (desktop) useragents.
A complete list of the absolute latest iPhone (mobile) useragents.
A complete list of the absolute latest iPod (touch mp3 player) useragents.
A complete list of the absolute latest iPad (tablet) useragents.
A complete list of the absolute latest android (mobile) useragents.
A complete list of the absolute latest tablet useragents.
About useragents.me
Useragents.me was created for web scrapers to give them quick and easy access to a list of the latest and most commmon useragents. Many similar lists have appeared in the past before us, but which have been quickly forgotten about and left to die.
Useragents.me is run and developed by someone working directly in the business of web scraping and who uses the site himself daily. Furthermore it's designed to be self-sustaining, self-updating, and low mantinence — meaning it will be a resource you can trustfully rely on for years.
What can I do with the useragents listed here?
The useragents listed here are most commonly used by web crawlers and web scrapers who want to mask their requests.
How often is the list of most common user agents updated?
The list of most common useragents (both desktop and mobile) is updated every week (specifically, on Sunday nights).
What is my current useragent?
As far as we can see, it's:
What is the difference between the most common and latest useragents listed here?
- The most common useragents list is a list of useragents that were observed accessing a set of sites in a given period of time. If you need to scrape a large number of pages and want your scraping requests to 'blend in', you can likely safely use this list in rotation to be successful.
- The latest useragents list is a list of the absolute latest useragents for a specific browser and device type. If you don't have a large scraping task (and so don't need to rotate useragents), you can likely safely use just one of these.
When should I use a mobile or desktop useragent?
Some sites will give you different content depending on the device you're using, so you should select the user agent with the correct device type for the task.
Node.js API Wrapper
useragents-me-api (by Davide Violante)
Built something with our API and want it featured here? — DM me @_stayml .
Useragents.me has been featured in...
- latenightlinux
- stackoverflow
- infoextreme
- Softantenna
- 阮一峰的网络日志 (Ruan Yifeng's weblog)
© 2022 - 2024 Useragents.me
How to change your user agent in Firefox
Updated at: Jul 13, 2022
Changing your user agent in Firefox takes a few simple steps.
Open a new tab
While Firefox has a standard settings interface for changing common settings, the interface for changing advanced settings such as the user agent in Firefox is done via the browser itself. Please open a blank window or tab.
Browse to "about:config"
In the address bar, type in about:config and press the Enter button on your keyboard.
Dismiss the warning
The "about:config" system will give you access to change special settings which might make your Firefox unusable or behave strangely. Firefox will normally give you a warning about this to make you aware of it.
As long as you follow the instructions here, you should be fine.
Create a new preference item
Firefox's settings are stored as a series of Preference Names and Values.
The setting to change your user agent doesn't exist in a default installation of Firefox; you need to create it yourself and then set it to the new user agent value you want to use.
To create the new preference value:

- You will then see an input box, where you can type or paste a new user agent (You could choose one from our list of user agents !)
- When you've done that, simple press the Enter button on your keyboard to save the new value
Congratulations, you have just set a custom user agent for Firefox. You can test out your new user agent by visiting our My Browser page and setting what we detect it as!
Close the Preferences tab
You can simply close the Advanced Preferences tab and resume browsing the internet.
Resetting your user agent in Firefox
Firefox will continue to use this user agent you've set until you delete the preference you've created.
To do remove that preference, search again for the general.useragent.override preference in the "about:config" window. Once you have found the preference that is overriding your user agent, get rid of it by clicking the Trash Can icon next to it.
Firefox will resume using its default user agent.
You have now changed (or reset!) your user agent string in Firefox. We hope this guide was useful.
If you are a software developer who needs to parse user agents in your system, please check out our User Agent Parsing API . It will make your life much easier!
More guides and help for Firefox
Need more help with Firefox? Read our other Firefox guides .
Clear cache & history
Do i need to clear my cache.
Not sure why you've been asked to clear your cache? We can explain. Why you need to clear your cache
What is a cache?
Before you consider clearing your browser cache, you should know what it is! Learn a little bit about browser caches
Is it safe to clear my cache?
Are there any risks to clearing your cache? Find out if it's ok to clear your cache
Update my web browser
Do i need to update my browser.
Find out if your browser is out of date Is my browser out of date?
Why should I update my browser?
There are very good reasons to, find out here! Why update your browser?
Is it free to update Chrome?
Find out about the cost of updating Chrome... Does Chrome cost anything?
What does "Update browser" mean?
What does it actually mean? What does it mean to update your browser
Get help with our guides
How to enable javascript.
Change your JavaScript settings Guide to enabling Javascript
How to enable Cookies
Configure your cookie settings for privacy Guide to enabling cookies
Related articles
I can't log in to a website..
We've got a detailed guide to help you solve login problems How to fix website log in problems
Why do websites use cookies?
Why are cookies useful? Do you need them? What's the deal with cookies?
How to update your browser
Old software puts you at risk. Keep your browser fresh and up to date
Clear Cache, Cookies and History
How to reset your browsing history How to reset your browser
Try a different web browser
Different web browsers have different features - try a different one to see if you prefer it. Experiment a bit!
Use a VPN to hide your IP address
We recommend NordVPN to hide your IP address or to unblock websites. Hide your IP Address
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Override the user agent string
- 6 contributors
To override the user agent string from Microsoft Edge DevTools:
Press Ctrl+Shift+P (Windows, Linux) or Command+Shift+P (macOS) to open the Command Menu .

Type network conditions , select Show Network conditions , and then press Enter to open the Network conditions tool.

In the User agent section, clear the Use browser default checkbox.

Select a user agent from the dropdown list, or enter a custom user agent.
Click User agent client hints to view and change these values as described in Network features reference .
- Set the user agent string in Emulate mobile devices (Device Emulation)
Portions of this page are modifications based on work created and shared by Google and used according to terms described in the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License . The original page is found here and is authored by Kayce Basques (Technical Writer, Chrome DevTools & Lighthouse).

Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources

Custom User Agent String
Feature supported in:.

Some websites use a method called user-agent sniffing to determine which browser visitors are using. This method is generally considered to be a bad practice since it can lead to errors being shown on unknown browsers.
If necessary, you can use this setting to provide a custom user agent string for Kiosk Pro to identify as, such as mobile Safari.
Default: blank, defaulting to the user agent string for the current version of WKWebView
If the website you're displaying in Kiosk Pro is showing different content or an error, you can try setting a custom user-agent string to resolve the problem. User-agent strings are pretty long, so instead of manually typing in the string, you can use a sample file on our website to update the setting.
To do this:
- In Kiosk Pro settings scroll down to the "Remote Management & Notifications" category
- Tap "Remote Settings Control"
- Enable Remote Settings Control = On
- Settings XML File Location = "https://docs.kioskgroup.com/mobile.xml" (for mobile Safari) or "https://docs.kioskgroup.com/desktop.xml" (for desktop Safari)
- Go back to the main menu and run the kiosk presentation
The file will update the Custom User Agent String setting and reset the Remote Settings Control settings to the default.
Values for Remote Settings Control & Managed App Configuration
- Included in version 6.0
Related Articles
- How to Set a Custom User Agent String with Remote Settings Control
Still stuck? How can we help? How can we help?
- PC & Mobile
How to Change the User-Agent String in Google Chrome
Evan Gower With over a decade of experience in digital publishing. Evan leads our team with a keen eye for emerging tech trends. Read more February 19, 2021
As we tend to spend more time on our phones than our PCs, most of today’s web content is optimized for mobile users. But have you ever wondered how your browser knows when to show you the mobile-friendly version of a website? How does it know what device you’re using to access a web page? Meet user-agent strings!

Every HTTP header contains, among other data, the user-agent string, which helps the server to identify where you’re accessing a site from. That’s is how it’s capable of delivering the right content format for every popular platform, such as games consoles, tablets, iPhones, Androids, etc.
How User-Agent Strings Work
User-Agent strings are part of web architecture and can provide useful information about the device asking to access a web server. It can help handle a website’s traffic better because it reveals what kind of device it is, what software and browser it uses, etc.
These strings are essential in marketing as they help you target your ads, optimize your website for different devices, analyze web traffics, and more.
Can I Change the User-Agent String Manually?
Sometimes, you’ll need to access a mobile website from your desktop. It may be out of curiosity or for professional reasons. However, to do so, you need to change the user-agent string. Is it possible? Absolutely.
If you’re testing your new website, you can do it all directly from your PC, just by changing the user-agent string. It takes a couple of easy steps.
User-Agent Strings in Google Chrome
Google Chrome is the most used browser worldwide, and, naturally, it has many user-agent strings. That’s because it needs to cover a large number of different devices and provide the user with the best possible experience.
If you’re building a website and you want to make sure it’s optimized for all the devices your target audience may use, here are two simple ways to change the user-agent string and test your product.
1. Built-In User-Agent Switcher
There’s a way to change the user-agent string in Chrome without installing additional programs. Here’s how to do it.
- Launch Google Chrome on your PC.
- Click on the three-dot icon in the top right corner of the window.

- In the Network conditions tab, you’ll see that the Select automatically option is ticked. Disable it.
- There’s a Custom list button underneath, so click on it and choose a device from the list to see how the website would look on that device.
2. Installing User-Agent Switcher
The other way to change the user-agent string in Google Chrome is to install a dedicated program. It’s an extension for Chrome, and it’s super-simple to add it to your browser.

- Click on the Add to Chrome blue button next to the name of the extension.

- If you don’t see the device you want in this menu, click on Other and create the one you want. You can later add this custom user-agent to the menu.
For Safari and Firefox Users
You can also change the user-agent switcher if you use Safari or Firefox as your default browsers. Here’s how.
When you launch Safari on your computer, do the following to change the user-agent string.

- Select a browser and a device, or click on Other… if the device you need is not on the list.
You can change the user-agent string in your Firefox browser, as well. There’s a built-in way to do this, but using an extension is more recommended. That’s because it makes the process quicker and less complicated.

- Open your Firefox browser and go to the official Firefox Store to search for add-ons.
- Search for the User-Agent Switcher.
- Click on the blue +Add to Firefox button.
- You’ll see that a new menu and toolbar have been added to your browser, meaning you can start using the extension.

- Select one of the options from the drop-down menu and enjoy viewing the webpage in the version of your choice.
Note: The Firefox store has a lot of options available from third-party developers. Be sure to read the reviews before installing. This ensures that you are using an extension that is safe and reliable.
Extensions Save Your Time
Installing an extension is certainly a good choice if you have to switch the user-agent string often. If you don’t, we also recommend doing so, as they’re very convenient and easy to use.
Have you tried to switch the user-agent string in Google Chrome or other browsers? Tell us in the comments section below!
Related Posts

Disclaimer: Some pages on this site may include an affiliate link. This does not effect our editorial in any way.

Dave Johnson May 11, 2024

Lee Stanton April 24, 2024

Paras Rastogi March 15, 2024
Send To Someone
Missing device.
Please enable JavaScript to submit this form.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Alternatively, you can just open the Safari app and then hit the hotkey Command + comma (,) to bring up Safari Preferences. Go to the Advanced tab from the General tab. The Safari Preferences menu Advanced tab. At the bottom of the Advanced tab, checkmark the checkbox for the setting Show Develop menu in menu bar. 2.
The latest user agents for Safari. Apple's Safari web browser runs on mobile devices (iPhones, iPads and iPod Touches) and macOS computers. Depending on which platform you're using (or want to pretend you're using!) the user agent will be a bit different. Here we have the latest user agents for Safari on mobile and computer platforms.
How to Change User-Agent on Safari. 1. Go to Preferences. 2. Enable Develop Menu Bar. Go to Advanced and check Show Develop menu in menu bar. 3. Navigate to Develop > User-Agent. You can again ...
Open Safari Settings. Go to "Advanced" tab and enable "Show features for web developers" option showing at the bottom. Advanced Safari Settings. Close Safari Settings pop-up and now you will see a "Develop" menu added to the browser. Click on "Develop" menu and hover over "User Agent" to view a list of items.
Here's how: Go to Preferences from the Safari menu. Here move to the Advanced tab and check the checkbox next to the Show Develop menu in the menu bar option. A new Develop menu will appear on the menu bar next to Bookmarks; click on it and hover the mouse cursor over the User Agent option.
3. I need help with changing Safari's user agent permanently by editing the plist file. Usually one would go to Preferences > Advanced > Show Developer mode in menu bar. Then Develop > User Agent > Chrome - Windows for example. However, when you open a new tab or window, this goes back to Default (Safari). This is expected behaviour.
Another way is from the More actions menu (…) > F12 Developer Tools. Select the Emulation tab, then click in the User agent string list box. Choose an appropriate web browser you would like to ...
In the "Advanced" tab, you should see an option that says "Show Develop menu in menu bar.". Tick mark it, and it will add a new menu in the menu bar for you to change the user agent. Pull down the new menu by clicking on "Develop" in the menu bar. Then select "User Agent," and you should see a list of the predefined user agents ...
Click Develop > User Agent and select the user agent you want to use in the list. If the user agent you want to use isn't shown here, select "Other" and you can provide a custom user agent. You can find extensive lists of user agents on various websites, such as this one . This option only applies to the current tab.
First, open Safari's preferences from the "Safari" menu or with "Command + ,". With the preferences open, click on the "Advanced" tab. At the very bottom, you want to check the box next to "Show Develop menu in the menu bar" and then exit out of the preferences. Now Safari will have a new menu devoted solely to development tools.
For more on Firefox- and Gecko-based user agent strings, see the Firefox user agent string reference. The UA string of Firefox is broken down into 4 components: Mozilla/5.0 (platform; rv:geckoversion) Gecko/geckotrail Firefox/firefoxversion Mozilla/5.0 is the general token that says that the browser is Mozilla-compatible. For historical reasons ...
How To Change Your User Agent In Google Chrome. First, you'll need to open Chrome's developer console. To do so, press the Ctrl + Shift + I keys. A panel should open up on the right side of your Chrome window. Click on the icon of the three vertical dots (top-right corner).
More Safari user agents strings -->>. Understand what information is contained in a user agent string. Get an analysis of your or any other user agent string. Find lists of user agent strings from browsers, crawlers, spiders, bots, validators and others..
I've been getting page errors on a variety of sites when using both safari and edge browsers. This one came from my school account when I was trying to open a different page and was dumped out: • ... The paid web browser iCab lets you change the user agent string.
This will present a 'Mac' Safari user-agent. Share. Improve this answer. Follow answered Jul 21, 2022 at 17:17. alec alec. 123 1 1 silver badge 3 3 bronze badges. 1. 1. ... Custom Arduino MEGA crashes ONLY on a specific command when plugging UART-USB converter before main power. Phantom power leaking through UARTs pins
User Agents are platform agnostic, they'll work anywhere. On Mac, on Pc, even on Linux. As I said before, there are no user agents that will identify your browser as Internet Explorer on Mac because there has been no Internet Explorer on Mac for 16 years. So no user agent either. If the website is expecting Internet Explorer, then its expecting ...
Test custom strings locally. If you want to test your site using custom User-Agent strings to simulate different devices, launch Chrome with the --user-agent="Custom string here" command-line flag. Find more on command-line flags here. Alternatively, use the device emulator in Chrome DevTools. Transform the string in your site's code
Everyone claims to be Mozilla 5.0; Android Chrome claims to be Mobile Safari; Mobile Safari claims to be Gecko. It can get very confusing, very quickly. Check out WebAIM's blog for more information on the compatibility history of the User Agent string. Other User-Agent strings. User-Agent strings don't necessarily follow the same format.
The Latest and Most Common User Agents List (Updated Weekly) Last Updated: 30 April, 2024. A self-updating list of the latest and most common useragents seen on the web across all device types, operating systems, and browsers. Data is always fresh, updating weekly. This user agent list is perfect for web scrapers looking to blend in, developers ...
into the search box at the top of the Preferences tab. From the three choices: Boolean, Number, and String, select String and then press the button. You will then see an input box, where you can type or paste a new user agent (You could choose one from our list of user agents !) When you've done that, simple press the Enter button on your ...
In the User agent section, clear the Use browser default checkbox. Select a user agent from the dropdown list, or enter a custom user agent. Click User agent client hints to view and change these values as described in Network features reference. See also. Set the user agent string in Emulate mobile devices (Device Emulation)
Some websites use a method called user-agent sniffing to determine which browser visitors are using. This method is generally considered to be a bad practice since it can lead to errors being shown on unknown browsers. If necessary, you can use this setting to provide a custom user agent string for Kiosk Pro to identify as, such as mobile Safari.
Open the Safari menu and click on Preferences. Select the Advanced tab and tick the Show Develop menu in the menu bar option. Close Preferences and open the Develop menu. Choose User Agent from ...
User agent. On the Web, a user agent is a software agent responsible for retrieving and facilitating end-user interaction with Web content. [1] This includes all web browsers, such as Google Chrome and Safari, some email clients, standalone download managers like youtube-dl, and other command-line utilities like cURL . The user agent is the ...