/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/66094266/82_EatingLickingDrinking_HermanEckelmann_NAIC.0.0.0.0.jpg)
Filed under:

The 116 photos NASA picked to explain our world to aliens
Share this story.
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: The 116 photos NASA picked to explain our world to aliens
If any intelligent life in our galaxy intercepts the Voyager spacecraft, if they evolved the sense of vision, and if they can decode the instructions provided, these 116 images are all they will know about our species and our planet, which by then could be long gone:
When Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 launched into space in 1977, their mission was to explore the outer solar system, and over the following decade, they did so admirably.
With an 8-track tape memory system and onboard computers that are thousands of times weaker than the phone in your pocket, the two spacecraft sent back an immense amount of imagery and information about the four gas giants, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
But NASA knew that after the planetary tour was complete, the Voyagers would remain on a trajectory toward interstellar space, having gained enough velocity from Jupiter's gravity to eventually escape the grasp of the sun. Since they will orbit the Milky Way for the foreseeable future, the Voyagers should carry a message from their maker, NASA scientists decided.
The Voyager team tapped famous astronomer and science popularizer Carl Sagan to compose that message. Sagan's committee chose a copper phonograph LP as their medium, and over the course of six weeks they produced the "Golden Record": a collection of sounds and images that will probably outlast all human artifacts on Earth.
How would aliens know what to do with the Golden Record?
The records are mounted on the outside of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 and protected by an aluminum case. Etched on the cover of that case are symbols explaining how to decode the record. Put yourself in an extraterrestrial's shoes and try to guess what the etchings seek to communicate. Stumped? Hover over or click on the yellow circles for the intended meaning of these interstellar brain teasers:

What else is on the Golden Record?
Any aliens who come across the Golden Record are in for a treat. It contains:
- 116 images encoded in analog form depicting scientific knowledge, human anatomy, human endeavors, and the terrestrial environment. (These images appear in color in the video above, but on the record, all but 20 are black and white.)
- Spoken greetings in more than 50 languages.
- A compilation of sounds from Earth.
- Nearly 90 minutes of music from around the world. Notably missing are the Beatles, who reportedly wanted to contribute "Here Comes the Sun" but couldn't secure permission from their record company. For the video above, I chose to include "Dark Was the Night" by Blind Willie Johnson, a 1927 track Sagan described as "haunting and expressive of a kind of cosmic loneliness."
The committee also made space for a message from the president of the United States:
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/4249653/carter.0.jpg)
Where are they now?
Incredibly, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are still communicating with Earth — they aren't expected to lose power until the 2020s. That's how NASA knew that Voyager 1 became the first ever spacecraft to enter interstellar space in 2012: The probe detected high-density plasma characteristic of the space beyond the heliosphere (the bubble of solar wind created by the sun).
Voyager 2 is currently traveling through the outer layers of the heliosphere. It's moving southward relative to Earth's orbit, while Voyager 1 is moving northward. In more than 40,000 years, they will each pass closer to another star than they are to our sun. (Or, more accurately, stars will pass by them).
There are three other spacecraft headed toward interstellar space; two of them, Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11, are shown in this somewhat dated illustration:
NASA launched Pioneer 10 and 11 in 1972 and 1973, and has since lost communication with both. They aren't traveling as fast as the Voyagers, but they will eventually enter interstellar space as well.
They too, carry a message for extraterrestrial life, in the form of a 6-by-9-inch gold-anodized aluminum plaque, designed by Sagan and other members of the team that would go on to create the Voyager Golden Record five years later.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/4252067/GPN-2000-001621-x.0.jpg)
Like the Golden Record, the plaque features the pulsar map, uses hydrogen to define the binary units, and depicts humankind. NASA faced a backlash for the nudity of the human figures.
Another interstellar message
The fifth probe that will exit our solar system is New Horizons , the spacecraft that flew by Pluto in 2015. It is headed in a broadly similar direction as Voyager 2, but having launched in 2006, it's many years behind. It may not reach interstellar space for another 30 years.
New Horizons was sent into space without any message like the Golden Record, but it's not too late to add one. A group led by Jon Lomberg , a member of Sagan's Golden Record team, is trying to convince NASA to upload a crowdsourced message to the probe for any intelligent life that might come across it.
The spacecraft's memory system is similar to a flash drive, and it wouldn't be as durable as the copper records on Voyager. "The most conservative estimates are a lifetime of a few decades. Other physicists and engineers believe the message might remain for centuries or even millennia," says the website of the message initiative, adding, more hopefully, "Another unknown is the advanced technology possessed by any ETs who find the spacecraft. They might have ways of reading the faded memory we cannot yet imagine."
Will you support Vox today?
We believe that everyone deserves to understand the world that they live in. That kind of knowledge helps create better citizens, neighbors, friends, parents, and stewards of this planet. Producing deeply researched, explanatory journalism takes resources. You can support this mission by making a financial gift to Vox today. Will you join us?
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
The lies that sell fast fashion
Streaming got expensive. now what, why a total solar eclipse is a life-changing event, according to 8 eclipse chasers, sign up for the newsletter today, explained, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration
Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
The Voyager Golden Record
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
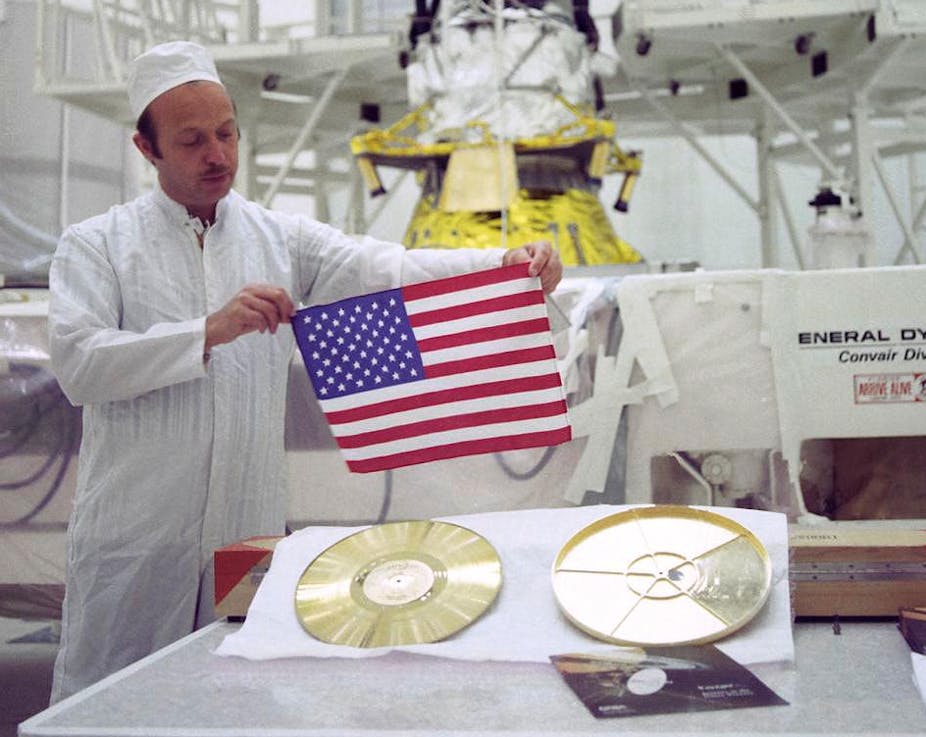
Voyager's Special Cargo: The Golden Record

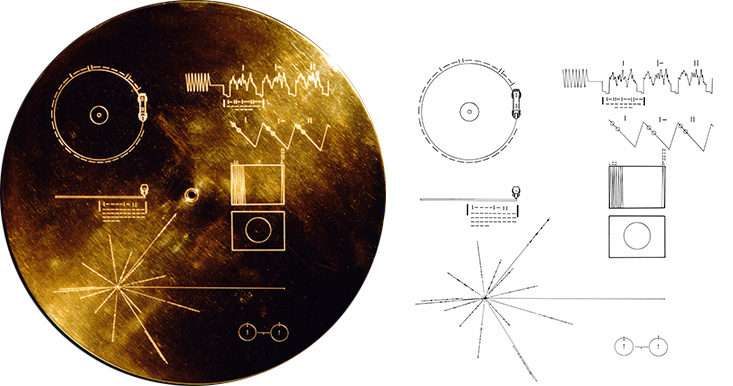
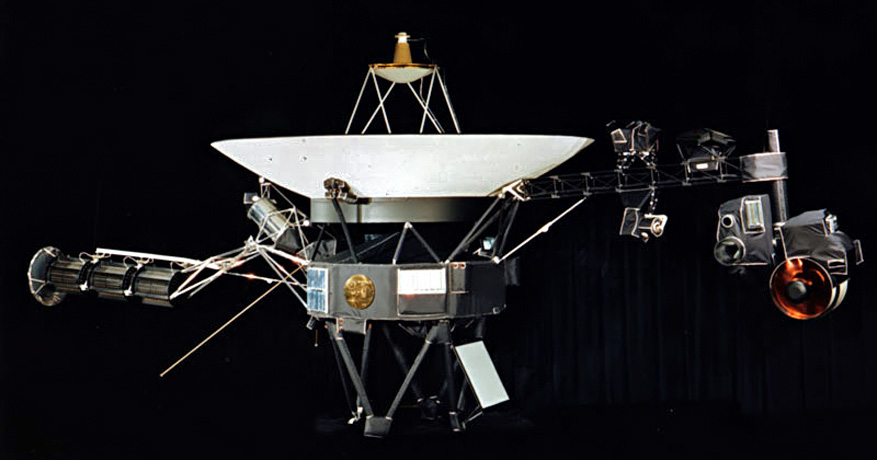
This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA's Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. An artist's rendering of the Voyager spacecraft is shown at bottom right, with a yellow circle denoting the location of the Golden Record. The cover of the Golden Record, shown on upper right, carries directions explaining how to play the record, a diagram showing the location of our sun and the two lowest states of the hydrogen atom as a fundamental clock reference. The larger image to the left is a magnified picture of the record inside.
The Voyagers were built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., which continues to operate both spacecraft. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit http://www.nasa.gov/voyager and http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .
Here’s What Humanity Wanted Aliens to Know About Us in 1977

I t was nearly 30 years ago—Jan. 24, 1986, nearly a decade after it had been launched—that the Voyager 2 spacecraft made its closest pass to Uranus and, as TIME phrased it, “taught scientists more about Uranus than they had learned in the entire 205 years since it was discovered.”
But the sophisticated equipment that sent information back to NASA wasn’t the only important thing on board the spacecraft. The Voyager 2, like the Voyager 1, carried with it a record, plated in gold, on which had been encoded sounds and images meant to “portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth,” according to NASA . The message from Earth was curated by a committee led by Carl Sagan and contained 115 images of “scenes from Earth.”
It was estimated in 1977, when the Voyagers launched, that it would take 40,000 years for them to reach a star system where there might be a being capable of deciphering the record. But, should that ever happen, what exactly could those photos say about humanity? Here’s a hint, from a few of the pictures on the golden record, and our best guesses at how hypothetical aliens might interpret them:
Cute young Earthlings and an image of their planet, or maybe giant Earthlings and a smaller planet under their control:
A fully grown earthling, or maybe a demonstration of the kinds of weapons available on earth:.

An Earth city building at sunset, or maybe the spacecraft with which a large number of Earthlings will come find you:

Earth traffic jam, or maybe why Earthlings will be fleeing to move to your home planet:

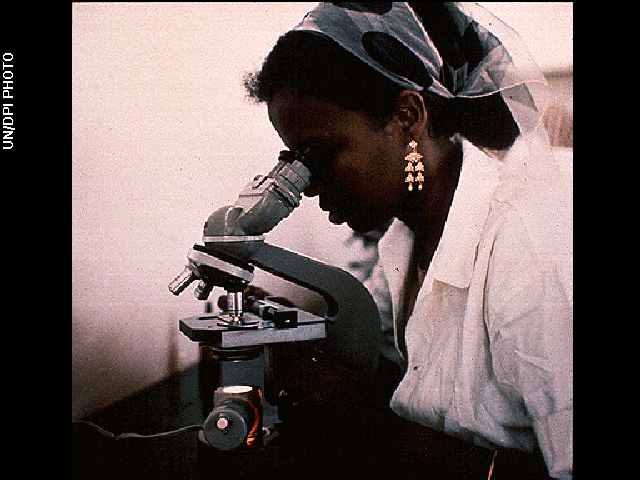
Earth scientist at work, or maybe an Earthling with goggles that can see you right now:
How this thing got to you, or maybe a missile:
An image of early Earth spaceflight, or a being we abandoned in space:
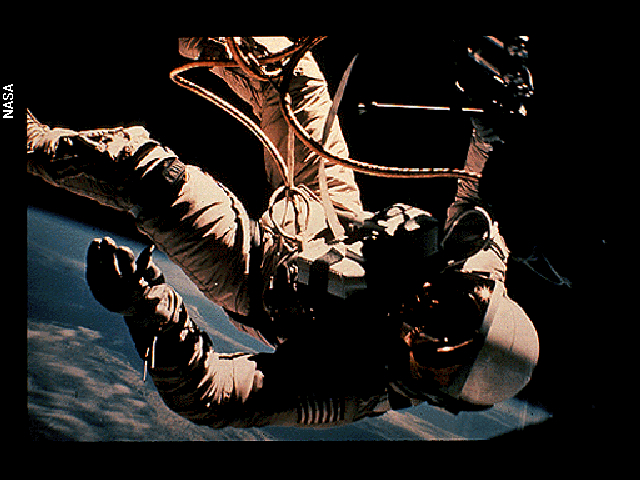

Celestial bodies near the Earth, Jupiter, Mercury and Mars, or maybe the places we’ve already conquered:
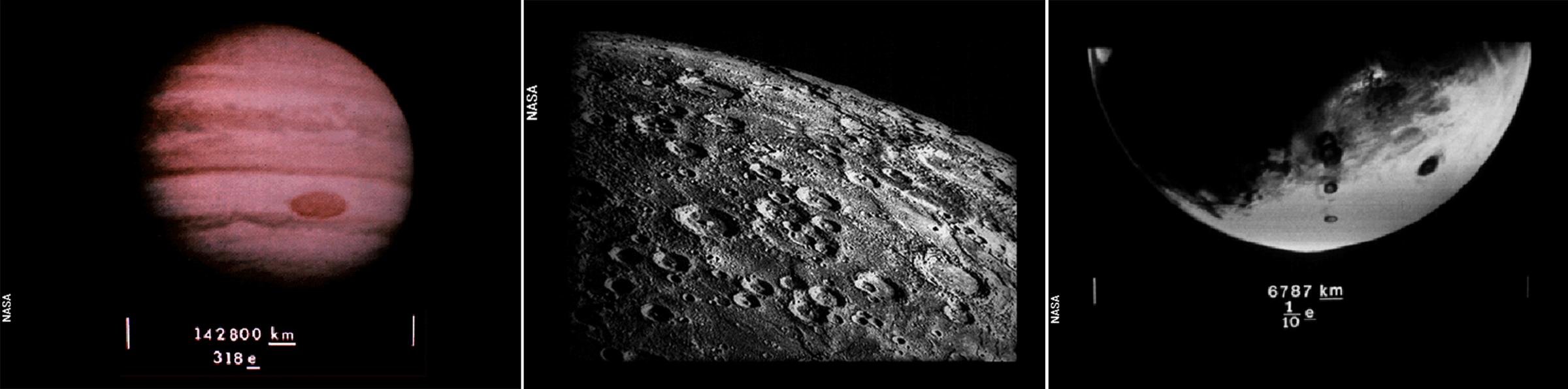

Where to find us, or maybe where to stay away from:

More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
What Is on Voyager’s Golden Record?
From a whale song to a kiss, the time capsule sent into space in 1977 had some interesting contents
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/megan.png)
Megan Gambino
Senior Editor
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/Voyager-records-631.jpg)
“I thought it was a brilliant idea from the beginning,” says Timothy Ferris. Produce a phonograph record containing the sounds and images of humankind and fling it out into the solar system.
By the 1970s, astronomers Carl Sagan and Frank Drake already had some experience with sending messages out into space. They had created two gold-anodized aluminum plaques that were affixed to the Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 spacecraft. Linda Salzman Sagan, an artist and Carl’s wife, etched an illustration onto them of a nude man and woman with an indication of the time and location of our civilization.
The “Golden Record” would be an upgrade to Pioneer’s plaques. Mounted on Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, twin probes launched in 1977, the two copies of the record would serve as time capsules and transmit much more information about life on Earth should extraterrestrials find it.
NASA approved the idea. So then it became a question of what should be on the record. What are humanity’s greatest hits? Curating the record’s contents was a gargantuan task, and one that fell to a team including the Sagans, Drake, author Ann Druyan, artist Jon Lomberg and Ferris, an esteemed science writer who was a friend of Sagan’s and a contributing editor to Rolling Stone .
The exercise, says Ferris, involved a considerable number of presuppositions about what aliens want to know about us and how they might interpret our selections. “I found myself increasingly playing the role of extraterrestrial,” recounts Lomberg in Murmurs of Earth , a 1978 book on the making of the record. When considering photographs to include, the panel was careful to try to eliminate those that could be misconstrued. Though war is a reality of human existence, images of it might send an aggressive message when the record was intended as a friendly gesture. The team veered from politics and religion in its efforts to be as inclusive as possible given a limited amount of space.
Over the course of ten months, a solid outline emerged. The Golden Record consists of 115 analog-encoded photographs, greetings in 55 languages, a 12-minute montage of sounds on Earth and 90 minutes of music. As producer of the record, Ferris was involved in each of its sections in some way. But his largest role was in selecting the musical tracks. “There are a thousand worthy pieces of music in the world for every one that is on the record,” says Ferris. I imagine the same could be said for the photographs and snippets of sounds.
The following is a selection of items on the record:
Silhouette of a Male and a Pregnant Female
The team felt it was important to convey information about human anatomy and culled diagrams from the 1978 edition of The World Book Encyclopedia. To explain reproduction, NASA approved a drawing of the human sex organs and images chronicling conception to birth. Photographer Wayne F. Miller’s famous photograph of his son’s birth, featured in Edward Steichen’s 1955 “Family of Man” exhibition, was used to depict childbirth. But as Lomberg notes in Murmurs of Earth , NASA vetoed a nude photograph of “a man and a pregnant woman quite unerotically holding hands.” The Golden Record experts and NASA struck a compromise that was less compromising— silhouettes of the two figures and the fetus positioned within the woman’s womb.
DNA Structure
At the risk of providing extraterrestrials, whose genetic material might well also be stored in DNA, with information they already knew, the experts mapped out DNA’s complex structure in a series of illustrations.
Demonstration of Eating, Licking and Drinking
When producers had trouble locating a specific image in picture libraries maintained by the National Geographic Society, the United Nations, NASA and Sports Illustrated , they composed their own. To show a mouth’s functions, for instance, they staged an odd but informative photograph of a woman licking an ice-cream cone, a man taking a bite out of a sandwich and a man drinking water cascading from a jug.
Olympic Sprinters
Images were selected for the record based not on aesthetics but on the amount of information they conveyed and the clarity with which they did so. It might seem strange, given the constraints on space, that a photograph of Olympic sprinters racing on a track made the cut. But the photograph shows various races of humans, the musculature of the human leg and a form of both competition and entertainment.
Photographs of huts, houses and cityscapes give an overview of the types of buildings seen on Earth. The Taj Mahal was chosen as an example of the more impressive architecture. The majestic mausoleum prevailed over cathedrals, Mayan pyramids and other structures in part because Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan built it in honor of his late wife, Mumtaz Mahal, and not a god.
Golden Gate Bridge
Three-quarters of the record was devoted to music, so visual art was less of a priority. A couple of photographs by the legendary landscape photographer Ansel Adams were selected, however, for the details captured within their frames. One, of the Golden Gate Bridge from nearby Baker Beach, was thought to clearly show how a suspension bridge connected two pieces of land separated by water. The hum of an automobile was included in the record’s sound montage, but the producers were not able to overlay the sounds and images.
A Page from a Book
An excerpt from a book would give extraterrestrials a glimpse of our written language, but deciding on a book and then a single page within that book was a massive task. For inspiration, Lomberg perused rare books, including a first-folio Shakespeare, an elaborate edition of Chaucer from the Renaissance and a centuries-old copy of Euclid’s Elements (on geometry), at the Cornell University Library. Ultimately, he took MIT astrophysicist Philip Morrison’s suggestion: a page from Sir Isaac Newton’s System of the World , where the means of launching an object into orbit is described for the very first time.
Greeting from Nick Sagan
To keep with the spirit of the project, says Ferris, the wordings of the 55 greetings were left up to the speakers of the languages. In Burmese , the message was a simple, “Are you well?” In Indonesian , it was, “Good night ladies and gentlemen. Goodbye and see you next time.” A woman speaking the Chinese dialect of Amoy uttered a welcoming, “Friends of space, how are you all? Have you eaten yet? Come visit us if you have time.” It is interesting to note that the final greeting, in English , came from then-6-year-old Nick Sagan, son of Carl and Linda Salzman Sagan. He said, “Hello from the children of planet Earth.”
Whale Greeting
Biologist Roger Payne provided a whale song (“the most beautiful whale greeting,” he said, and “the one that should last forever”) captured with hydrophones off the coast of Bermuda in 1970. Thinking that perhaps the whale song might make more sense to aliens than to humans, Ferris wanted to include more than a slice and so mixed some of the song behind the greetings in different languages. “That strikes some people as hilarious, but from a bandwidth standpoint, it worked quite well,” says Ferris. “It doesn’t interfere with the greetings, and if you are interested in the whale song, you can extract it.”
Reportedly, the trickiest sound to record was a kiss . Some were too quiet, others too loud, and at least one was too disingenuous for the team’s liking. Music producer Jimmy Iovine kissed his arm. In the end, the kiss that landed on the record was actually one that Ferris planted on Ann Druyan’s cheek.
Druyan had the idea to record a person’s brain waves, so that should extraterrestrials millions of years into the future have the technology, they could decode the individual’s thoughts. She was the guinea pig. In an hour-long session hooked to an EEG at New York University Medical Center, Druyan meditated on a series of prepared thoughts. In Murmurs of Earth , she admits that “a couple of irrepressible facts of my own life” slipped in. She and Carl Sagan had gotten engaged just days before, so a love story may very well be documented in her neurological signs. Compressed into a minute-long segment, the brain waves sound, writes Druyan, like a “string of exploding firecrackers.”
Georgian Chorus—“Tchakrulo”
The team discovered a beautiful recording of “Tchakrulo” by Radio Moscow and wanted to include it, particularly since Georgians are often credited with introducing polyphony, or music with two or more independent melodies, to the Western world. But before the team members signed off on the tune, they had the lyrics translated. “It was an old song, and for all we knew could have celebrated bear-baiting,” wrote Ferris in Murmurs of Earth . Sandro Baratheli, a Georgian speaker from Queens, came to the rescue. The word “tchakrulo” can mean either “bound up” or “hard” and “tough,” and the song’s narrative is about a peasant protest against a landowner.
Chuck Berry’s “Johnny B. Goode”
According to Ferris, Carl Sagan had to warm up to the idea of including Chuck Berry’s 1958 hit “Johnny B. Goode” on the record, but once he did, he defended it against others’ objections. Folklorist Alan Lomax was against it, arguing that rock music was adolescent. “And Carl’s brilliant response was, ‘There are a lot of adolescents on the planet,’” recalls Ferris.
On April 22, 1978, Saturday Night Live spoofed the Golden Record in a skit called “Next Week in Review.” Host Steve Martin played a psychic named Cocuwa, who predicted that Time magazine would reveal, on the following week’s cover, a four-word message from aliens. He held up a mock cover, which read, “Send More Chuck Berry.”
More than four decades later, Ferris has no regrets about what the team did or did not include on the record. “It means a lot to have had your hand in something that is going to last a billion years,” he says. “I recommend it to everybody. It is a healthy way of looking at the world.”
According to the writer, NASA approached him about producing another record but he declined. “I think we did a good job once, and it is better to let someone else take a shot,” he says.
So, what would you put on a record if one were being sent into space today?
Get the latest Science stories in your inbox.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/megan.png)
Megan Gambino | | READ MORE
Megan Gambino is a senior web editor for Smithsonian magazine.
Voyager Golden Records 40 years later: Real audience was always here on Earth
Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Penn State
Disclosure statement
Jason Wright acknowledges funding from NASA, the NSF, the Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Words at The Pennsylvania State University, and from Breakthrough Listen, part of the Breakthrough Initiatives sponsored by the Breakthrough Prize Foundation ( https://breakthroughinitiatives.org/ ).
Penn State provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners
Forty years ago, NASA launched Voyager I and II to explore the outer solar system. The twin spacecraft both visited Jupiter and Saturn; from there Voyager I explored the hazy moon Titan, while Voyager II became the first (and, to date, only) probe to explore Uranus and Neptune. Since they move too quickly and have too little propellant to stop themselves, both spacecraft are now on what NASA calls their Interstellar Mission , exploring the space between the stars as they head out into the galaxy.
Both craft carry Golden Records : 12-inch phonographic gold-plated copper records, along with needles and cartridges, all designed to last indefinitely in interstellar space. Inscribed on the records’ covers are instructions for their use and a sort of “map” designed to describe the Earth’s location in the galaxy in a way that extraterrestrials might understand.
The grooves of the records record both ordinary audio and 115 encoded images . A team led by astronomer Carl Sagan selected the contents, chosen to embody a message representative of all of humanity. They settled on elements such as audio greetings in 55 languages , the brain waves of “a young woman in love” (actually the project’s creative director Ann Druyan, days after falling in love with Carl Sagan ), a wide-ranging selection of musical excerpts from Blind Willie Johnson to honkyoku , technical drawings and images of people from around the world, including Saan Hunters, city traffic and a nursing mother and child.
Since we still have not detected any alien life, we cannot know to what degree the records would be properly interpreted. Researchers still debate what forms such messages should take . For instance, should they include a star map identifying Earth? Should we focus on ourselves, or all life on Earth? Should we present ourselves as we are, or as comics artist Jack Kirby would have had it, as “the exuberant, self-confident super visions with which we’ve clothed ourselves since time immemorial”?
But the records serve a broader purpose than spreading the word that we’re here on our blue marble. After all, given the vast distances between the stars, it’s not realistic to expect an answer to these messages within many human lifetimes. So why send them and does their content even matter? Referring to earlier, similar efforts with the Pioneer spacecraft , Carl Sagan wrote , “the greater significance of the Pioneer 10 plaque is not as a message to out there; it is as a message to back here.” The real audience of these kinds of messages is not ET, but humanity.
In this light, 40 years’ hindsight shows the experiment to be quite a success, as they continue to inspire research and reflection.
Only two years after the launch of these messages to the stars, “Star Trek: The Motion Picture” imagined the success of similar efforts by (the fictional) Voyager VI. Since then, there have been Ph.D. theses written on the records’ content , investigations into the identity of the person heard laughing and successful crowdfunded efforts to reissue the records themselves for home playback.
The choice to include music has inspired introspection on the nature of music as a human endeavor, and what it would (or even could) mean to an alien species. If an ET even has ears, it’s still far from clear whether it would or could appreciate rhythm, tones, vocal inflection, verbal language or even art of any kind. As music scholars Nelson and Polansky put it , “By imagining an Other listening, we reflect back upon ourselves, and open our selves and cultures to new musics and understandings, other possibilities, different worlds.”

The records also represent humanity’s deliberate effort to put artifacts among the stars. Unlike everything on Earth, which is subject to erosion and all but inevitable destruction (from the sun’s eventual demise, if nothing else), the Golden Records are essentially eternal, a permanent time capsule of humanity. And unlike the Voyager spacecraft themselves – which were designed to have finite lifespans and whose journey into interstellar space was incidental to their primary function of exploring the outer planets – the Golden Records’ only purpose is to serve as ambassadors of humanity to the stars.
Placing artifacts in interstellar space thus makes the galaxy subject to the social studies, in addition to astronomy. The Golden Records mark our claim to interstellar space as part of our cultural landscape and heritage , and once the Voyager spacecraft themselves are not functional any longer, they will become proper achaeological objects . They are, in a sense, how we as a species have planted our flag of exploration in space. Anthropologist Michael Oman-Reagan muses , “Has NASA been to interstellar space because this spacecraft has? Have we, as a human species, [now] been to interstellar space?”
I would argue we have, and we are a better species for it. Like the Pioneer plaques and the Arecibo Message before them, the Golden Records inspire us to broaden our minds about what it means to be human; what we value as humans; and about our place and role in the cosmos by having us imagine what we might, or might not, have in common with any alien species our Voyagers eventually encounter on their very long journeys.
- Extraterrestrial life
- Space exploration
- Golden Record

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Senior Disability Services Advisor

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

GRAINS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION CHAIRPERSON
- Featured Videos /
Decoding images from the Golden Record
It’s more complicated and less pretty than you’d expect.
By Cory Zapatka
Share this story
More than 11 billion miles away from Earth, two small discs are rocketing through space at speeds in excess of 37,200 miles per hour. Their journey started in 1977, when NASA sent the two Golden Records into space, bolted to the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft. The records contain a treasure trove of information about our home planet, including sounds, songs, and images from Earth.
At the moment, the records are just hangers-on to the Voyagers’ current mission , to document the outer limits of the Sun’s influence on the Solar System. By 2030, however, both Voyagers will cease communicating with NASA, but they will continue sailing through space. At that point, they will have only one mission: continue on with the Golden Records in hopes that another advanced civilization, somewhere in the galaxy, intercepts them.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13351619/voyager_gold_record_display_10_5_1977_30214218763_o.jpg)
The audio contained on the record should be fairly easy to decode — extraterrestrials will only need to figure out the correct speed and rotation of the disks, place the included stylus within the grooves of the record, and jam out to Chuck Berry, Mozart, and the sounds of the Earth.
Unscrambling the images contained on the record — that’s going to be a little bit harder.
You might think that the images were included in some printed or digital form, such as a .jpeg or .tiff. But back in 1977, there was no technology available to put images on analog disks. Voyager’s computer systems could only hold 69 kilobytes of information, barely enough for one image, let alone 115. So NASA invented a way to include image data on the LPs.
By projecting images onto a screen, recording them with a television camera, and then turning those video signals into audio waveforms, the images could be properly pressed onto the records. The reversal process — turning that image data back into images — is what any extraterrestrial (or curious human) would have to figure out how to do.
Luckily, NASA engineers included instructions on the cover of the record to help decode the data contained on the disks. And without access to 1970’s technology and expertise, the guidelines were tricky for us to follow. But after learning a lot from the DIY community, including from Ron Barry, who wrote his own in-depth guide to decoding the disks , we were able to see the data.
We tried two alternate methods using Microsoft Excel and Python — and were amazed to find that even 40 years later and with completely different technology, it was still possible to unravel images from the audio waves.
Maybe extraterrestrials will be able to figure this out after all.
Take a look at the video to see how we decoded the Golden Record — and maybe give it a try yourself.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13351939/humanbody_edited.jpg)
Verge Science on YouTube /
The home base for our explorations into the future of science.
The little smart home platform that could
How phish turned las vegas’ sphere into the ultimate music visualizer, the invisible seafaring industry that keeps the internet afloat, zack snyder’s rebel moon movies are a fandom menace, tesla recalls all 3,878 cybertrucks over faulty accelerator pedal.
More from Science
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23935561/acastro_STK103__04.jpg)
Amazon — like SpaceX — claims the labor board is unconstitutional
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25288452/246992_AI_at_Work_REAL_COST_ECarter.png)
How much electricity does AI consume?
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25287681/1371856480.jpg)
A Big Tech-backed campaign to plant trees might have taken a wrong turn
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25287408/2003731596.jpg)
SpaceX successfully launches Odysseus in bid to return US to the lunar surface

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

Join NASA in Celebrating Earth Day 2024 by Sharing a #GlobalSelfie

NASA Selects New Aircraft-Driven Studies of Earth and Climate Change


The Ocean Touches Everything: Celebrate Earth Day with NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Work Underway on Large Cargo Landers for NASA’s Artemis Moon Missions

Mars Science Laboratory: Curiosity Rover

NASA Open Science Initiative Expands OpenET Across Amazon Basin

NASA Motion Sickness Study Volunteers Needed!

Students Celebrate Rockets, Environment at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center

AI for Earth: How NASA’s Artificial Intelligence and Open Science Efforts Combat Climate Change

Sols 4159-4160: A Fully Loaded First Sol

NASA’s Juno Gives Aerial Views of Mountain, Lava Lake on Io

Hubble Captures a Bright Galactic and Stellar Duo

NASA’s TESS Returns to Science Operations

Astronauts To Patch Up NASA’s NICER Telescope

Hubble Goes Hunting for Small Main Belt Asteroids

NASA’s Near Space Network Enables PACE Climate Mission to ‘Phone Home’

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

ARMD Solicitations

Amendment 10: B.9 Heliophysics Low-Cost Access to Space Final Text and Proposal Due Date.

Tech Today: Taking Earth’s Pulse with NASA Satellites
Earth Day 2024: Posters and Virtual Backgrounds

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Voyager’s special cargo – the golden record.

This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA’s Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. An artist’s rendering of the Voyager spacecraft is shown at bottom right, with a yellow circle denoting the location of the Golden Record. The cover of the Golden Record, shown on upper right, carries directions explaining how to play the record, a diagram showing the location of our sun and the two lowest states of the hydrogen atom as a fundamental clock reference. The larger image to the left is a magnified picture of the record inside. The Voyagers were built by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., which continues to operate both spacecraft. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit https://www.nasa.gov/voyager and http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
11 Pieces of Media on the Voyager Golden Record
By michele debczak | apr 11, 2021.

At this moment, two gold-plated copper records are hurtling through space, speeding beyond our solar system. The Voyager 1 and 2 probes launched in 1977 , and they’ve since traveled billions of miles from Earth. They are currently the loneliest human-made objects in the universe—and they may stay that way forever—but they were built to make a connection.
The purpose of NASA ’s Voyager mission is to illustrate life on Earth to any intelligent aliens that come across the spacecraft. The records on board contain media selected by a committee chaired by scientist Carl Sagan. If extraterrestrials can use the instructions engraved on the disc's cover to access its contents, they’ll be exposed to animal noises, classical music, and photographs of people from around the world. Here are some pieces of media that were chosen to represent our planet.
1. Beethoven’s Fifth Symphony
Ludwig van Beethoven is one of many classical artists representing the music of Earth on the Voyager record. In addition to his Fifth Symphony , the composer’s String Quartet No. 13, Opus 130, is also included on the track list.
2. Chuck Berry’s “Johnny B. Goode”
Though there are many musical compositions on the Voyager Golden Record , the inclusion of “Johnny B. Goode” stirred controversy. Critics claimed rock n’ roll was too adolescent for a project of such significance. Carl Sagan responded by saying, “There are a lot of adolescents on the planet.”
3. A Mandarin Greeting and Invitation
The Voyager project recorded UN delegates from around the world saying greetings in 54 different languages. Most are straightforward, but the Mandarin message includes an invitation. Translated to English, it says: "Hope everyone's well. We are thinking about you all. Please come here to visit when you have time."
4. Humpback Whale Songs
The greetings section of the record features one language that doesn’t belong to humans. Interspersed between the spoken audio clips are the sounds of singing humpback whales . There’s a reason whales were included with the greetings rather than the other animal noises on the record—it was the committee’s way of acknowledging that humans aren’t the only intelligent life on Earth.
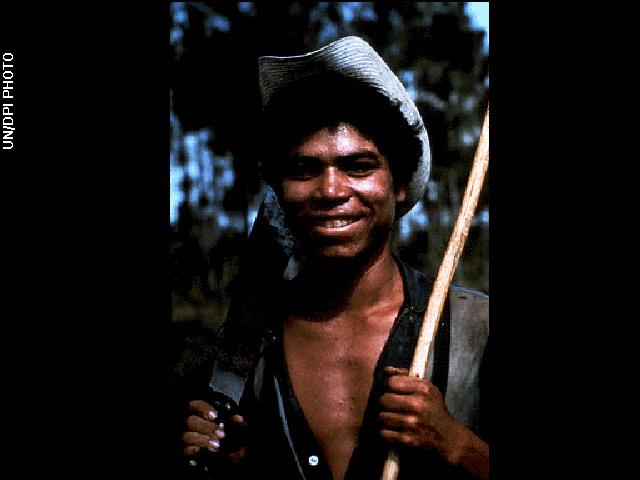
5. The UN Building
The Voyager committee chose the UN Building to represent modern urban architecture. The record includes two images of the New York City skyscraper, both taken at the same angle. One depicts the structure during the day and the other shows it at night .
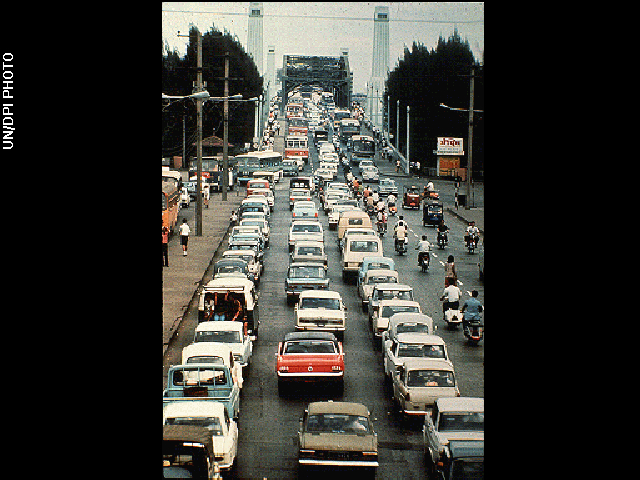
6. A Traffic Jam
The Voyager record highlights many technological marvels from the time it was made, including a rocket and an airplane. The photo of a traffic jam in Thailand that was included may seem less impressive, but it accurately depicts how we use cars on our planet.
7. A Bulgarian Folk Song
The Voyager committee wanted the record's music to represent a wide range of eras and cultures. One track, titled "Izlel je Delyo Hagdutin," is a traditional folk song from Bulgaria . Sung by Valya Balkanska, it’s about a famous rebel leader from the country’s history. Folk music from Azerbaijan, Georgia, and the Navajo people also made it onto the compilation.
8. Ann Druyan’s Brainwaves
While working on the Voyager committee, Ann Druyan had the idea to record her brainwaves, turn them into audio, and copy them onto the record. She spent an hour hooked up to electrical impulse-measuring systems while thinking various thoughts, including what it’s like to fall in love. She and Sagan—her collaborator on the Voyager record project—had recently gotten engaged.
9. A Map of the Solar System
The Voyager mission is designed to travel far, but it will always hold evidence of where it came from. One of the images on the record shows a picture of our solar system with a map illustrating Earth’s location.
10. People Eating
Some human behaviors are tricky to capture in one image. To show the different ways people consume food and drink, the Voyager committee included a photo of someone licking ice cream, someone else biting into a sandwich, and a third person pouring water into their mouth.
11. A Morse Code Message
Another type of communication represented on the Voyager record is Morse code . The message translates to the Latin saying ad astra per aspera , or “to the stars through hard work.”

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
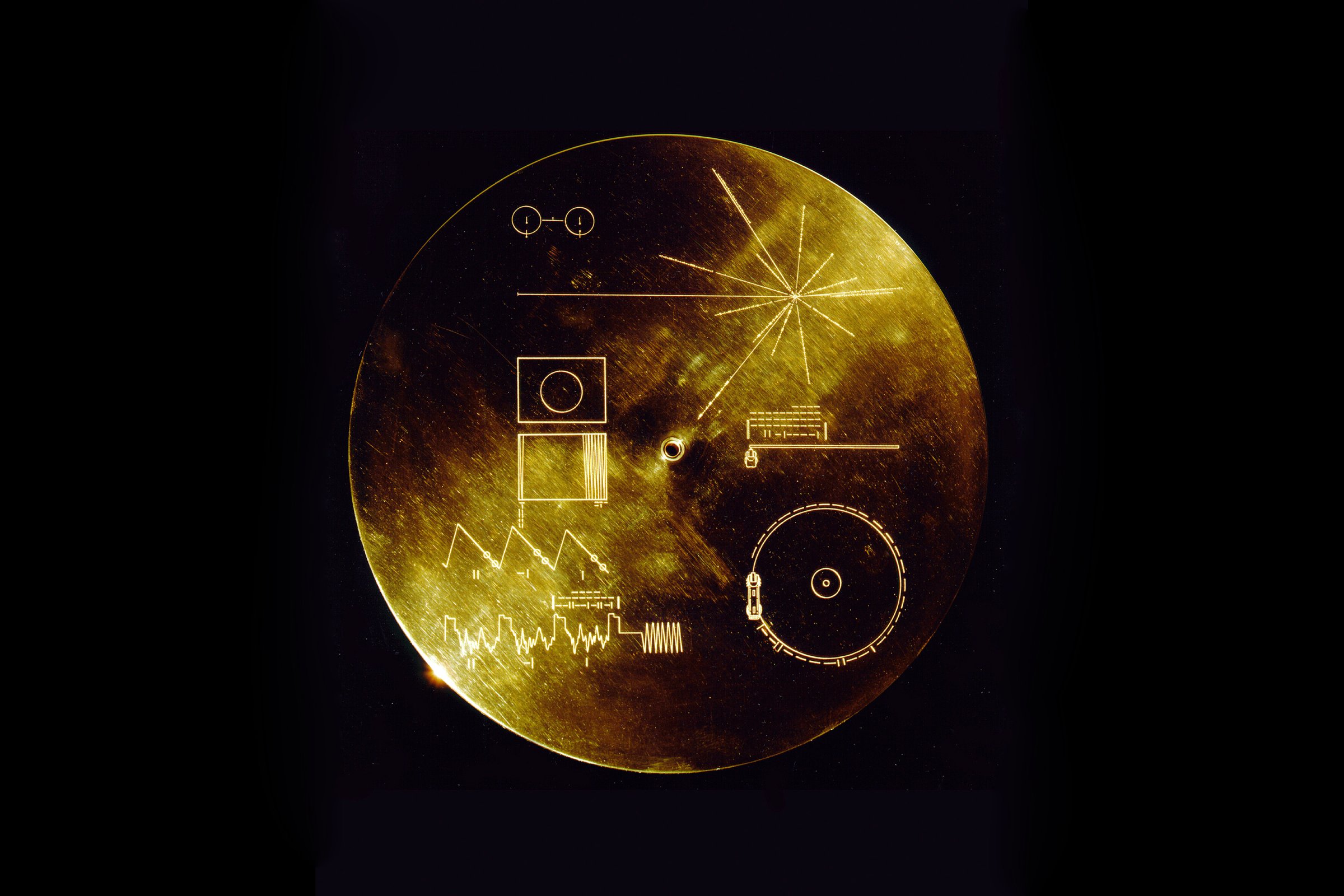
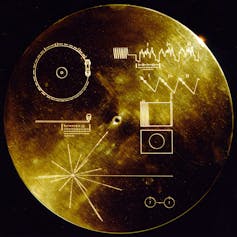
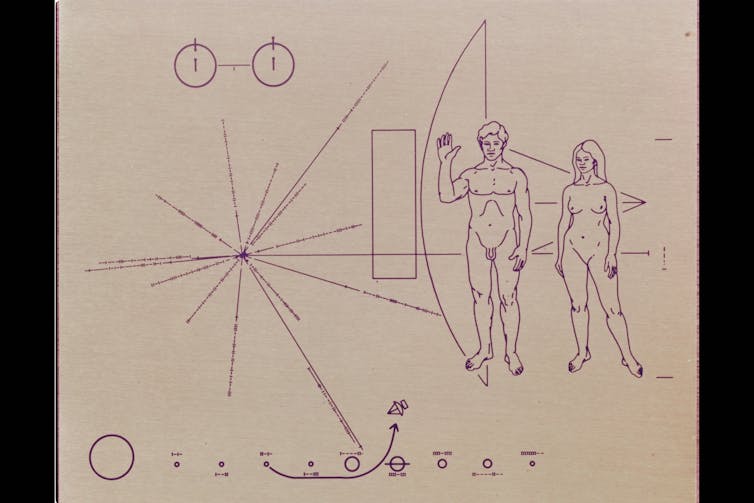
The Golden Record Cover
In the upper left-hand corner is an easily recognized drawing of the phonograph record and the stylus carried with it. The stylus is in the correct position to play the record from the beginning. Written around it in binary arithmetic is the correct time of one rotation of the record, 3.6 seconds, expressed in time units of 0,70 billionths of a second, the time period associated with a fundamental transition of the hydrogen atom. The drawing indicates that the record should be played from the outside in. Below this drawing is a side view of the record and stylus, with a binary number giving the time to play one side of the record - about an hour.
The information in the upper right-hand portion of the cover is designed to show how pictures are to be constructed from the recorded signals. The top drawing shows the typical signal that occurs at the start of a picture. The picture is made from this signal, which traces the picture as a series of vertical lines, similar to ordinary television (in which the picture is a series of horizontal lines). Picture lines 1, 2 and 3 are noted in binary numbers, and the duration of one of the "picture lines," about 8 milliseconds, is noted. The drawing immediately below shows how these lines are to be drawn vertically, with staggered "interlace" to give the correct picture rendition. Immediately below this is a drawing of an entire picture raster, showing that there are 512 vertical lines in a complete picture. Immediately below this is a replica of the first picture on the record to permit the recipients to verify that they are decoding the signals correctly. A circle was used in this picture to ensure that the recipients use the correct ratio of horizontal to vertical height in picture reconstruction.

The drawing in the lower left-hand corner of the cover is the pulsar map previously sent as part of the plaques on Pioneers 10 and 11. It shows the location of the solar system with respect to 14 pulsars, whose precise periods are given. The drawing containing two circles in the lower right-hand corner is a drawing of the hydrogen atom in its two lowest states, with a connecting line and digit 1 to indicate that the time interval associated with the transition from one state to the other is to be used as the fundamental time scale, both for the time given on the cover and in the decoded pictures.
Electroplated onto the record's cover is an ultra-pure source of uranium-238 with a radioactivity of about 0.00026 microcuries. The steady decay of the uranium source into its daughter isotopes makes it a kind of radioactive clock. Half of the uranium-238 will decay in 4.51 billion years. Thus, by examining this two-centimeter diameter area on the record plate and measuring the amount of daughter elements to the remaining uranium-238, an extraterrestrial recipient of the Voyager spacecraft could calculate the time elapsed since a spot of uranium was placed aboard the spacecraft. This should be a check on the epoch of launch, which is also described by the pulsar map on the record cover.
- Arts & Culture
Get Involved

Autumn 2023

Annual Gala Dinner

Internships
I voiced the Arabic greeting on Voyager’s Golden Record: International space cooperation offers a model for peace in today’s Middle East
Expert Commentary
Amahl Shakhashiri Drake

“ Tahiat li’asdiqayina fil alnujumi. Wanatamanaa ’an naltaqi bikum yawman ma. ”
“Greetings to our friends in the stars. We wish that we will meet you someday.”
This was the Arabic declaration I recorded, which NASA sent into the cosmos 47 years ago on the Voyager Golden Records, a collection of images, music, and language affixed to the twin probes of the same name, showcasing the diversity and triumph of life on Earth. My contribution, hopeful and welcoming, entertained the tantalizing possibility that the Voyager probes and their Golden Records could be intercepted by another intelligent civilization at some point in their interstellar journey.

Today, Voyagers 1 and 2 are 15 billion miles from their earthly origin, but the recorded expressions of hope they carry seem utterly misplaced against the daily images of devastation and heartbreak that dominate headlines from the region my greeting was intended to represent. From Israel-Gaza to Sudan and Yemen to Syria, war, looming famines, leveled hospitals, and missing hostages, stand in stark contrast to the images and spirit of optimism, comradery, and global communion etched into the twin gleaming disks speeding away from the center of our Solar System at more than 35,000 kilometers per second.
At a time of such ruinous conflict, how can we course-correct and create a future that reflects the values that informed the Golden Records’ creation? The answer, I believe, can be found in the history, and future, of space exploration itself.
Modern space exploration has regularly benefited from sustained international collaboration, even amidst some of the most trying of global circumstances. In 1975, at the height of tensions between the United States and the former Soviet Union, the two would-be rivals conducted their first jointly crewed space mission. Later, the US and Russia expanded their international collaboration in outer space to establish the International Space Station (ISS), alongside additional partners from Europe and Japan.
Even through relations between Russia and the US are today going through one of the sharpest downturns in their history, the two countries continue to find ways to collaborate in space. In December, NASA and Russia’s Roscosmos announced that joint shuttles to the ISS would continue through at least 2025. Last month, astronauts from Russia, Belarus, and the United States launched aboard a Soyuz rocket to the station.
Outer space’s suitability as a platform for international cooperation will only strengthen as new, previously excluded nations, governments, and voices are empowered to contribute to the field. Fortunately, many of these new actors are emerging in the Middle East itself. In 2020, the United Arab Emirates launched the indigenously developed Hope Probe, which successfully entered orbit around Mars to study the planet’s atmosphere in February 2021, the first for an Arab country. Emirati astronauts have also taken part in missions to the ISS. Most recently this included now-UAE Minister of State for Youth Affairs Sultan al-Neyadi, who, in September 2023, returned to Earth after a six-month stint, during which he became the first Arab astronaut to conduct a spacewalk.
They are not alone. From the Middle East region, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Bahrain, and Israel are among the 36 signatories of the Artemis Accord, a US-led multinational agreement that expresses a commitment to the civil use of outer space, alongside additional components related to international cooperation, research exchange, and interoperability. Within NASA’s Artemis program, the UAE has pledged to develop and provide an airlock for Gateway, a space station that will orbit the moon.
Almost five decades after my greeting became the first Arab woman’s voice in the stars, Arab women have now physically been in space. In May 2023, Saudi astronaut and biomedical researcher Rayyanah Barnawi broke the atmospheric glass ceiling by conducting stem cell and cancer research experiments aboard the ISS — work that may one day benefit us all. This past March, Emirati astronaut Norah al-Matroohsi became the first Emirati and Arab woman to graduate from NASA’s astronaut training program. I am thrilled that this week the Middle East Institute will honor the accomplishment of Ms. Barnawi and the path she has created for all Arab women as they present her with their “Visionary Award.” I hope more follow in her and Ms. Matrooshi’s footsteps.
The roots of the most pressing conflicts in today’s Middle East will undoubtedly require complex negotiations and painful compromises to reach lasting solutions. Space research alone will not fix them. What the history of space exploration does show us is that international collaboration can continue, and even thrive, at times of intense global tension. In outer space, rivals and friends alike continue to work together to explore the stars, advance technological and biomedical breakthroughs, and cure disease, even as division perpetuates conflict on the Earth below. The opening up of this sector to once overlooked voices, such as Arab women, only increases its potency as a model for international cooperation across differences. And for this reason, my hope only grows.
Amahl Shakhashiri Drake is a Lebanese-American who, while working at Cornell University in the prelude to the launch of the Voyager probes in 1977, was recruited by Carl Sagan to contribute an Arabic greeting to the Voyager Golden Record, a phonographic account of humanity accompanying the Voyager probes. Her voice was the first recording of an Arab woman in outer space. She is the wife of the late famed astrophysicist Frank Drake, developer of the namesake Drake Equation and founding figure in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Photo by GREGG NEWTON/AFP via Getty Images
The Middle East Institute (MEI) is an independent, non-partisan, non-for-profit, educational organization. It does not engage in advocacy and its scholars’ opinions are their own. MEI welcomes financial donations, but retains sole editorial control over its work and its publications reflect only the authors’ views. For a listing of MEI donors, please click her e .
Engineers attempt to fix a computer glitch on Voyager 1
Voyager 1's system that sends data home is malfunctioning, preventing the computer from operating as it should.

Social Sharing
Last November, the Voyager 1 spacecraft began sending gibberish radio signals back to Earth. Engineers have now identified the problem, but trying to repair a 46-year-old device on a craft 24 billion kilometres from Earth is not easy.
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 were both launched in 1977 on a reconnaissance mission to Jupiter and Saturn. They were designed to fly past the giant planets to obtain closeup images of those distant worlds and their myriad of moons.
Both spacecraft performed beyond expectations, discovering many new moons — some covered in ice , one with active volcanoes , another with a thick atmosphere and closeup details of Saturn's rings .
Following the Saturn encounter, Voyager 1 was flung upwards by Saturn's gravity on a trajectory northward, above the orbital plane in which most of the planets orbit the Sun, out of our solar system. NASA extended its mission and from there it went on to become the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space in 2012.
Voyager 2, however, was aimed toward Uranus and Neptune, which were conveniently positioned in a rare alignment with Jupiter and Saturn making it the only spacecraft to visit those distant worlds.
Following the grand tour of the outer solar system, Voyager 2 was also tossed out toward interstellar space in 2018 when its mission was extended and where it continues on its journey today.
- After a 42-year journey, Voyager 2 goes interstellar
- Voyager 1 picks up the 'hum' of interstellar space
While their primary missions were over, both spacecraft were still in good health, thanks largely to their nuclear power sources or Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTG). These containers hold small amounts of plutonium which provide heat that is turned directly into electricity with no moving parts. They have an expected lifetime of around 50 years and have kept the Voyagers' instruments running.
Now, as both spacecraft continue their journey through the space between the stars, they are showing signs of their age.
For Voyager 1, the problem seems to be in the flight data subsystem (FDS) that packages data from the scientific instruments for transmission to Earth. The scientists don't know if the faulty module was corrupted by cosmic rays or just worn out, but they say they're optimistic they may be able to work around the problem, although it will take some time.
Engineers have confirmed that corrupted memory aboard my twin <a href="https://twitter.com/hashtag/Voyager1?src=hash&ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw">#Voyager1</a> has been causing it to send unreadable data to Earth. It may take months, but our team is optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally again: <a href="https://t.co/qe5iQUu4Oj">https://t.co/qe5iQUu4Oj</a> <a href="https://t.co/AGFBZFz53v">https://t.co/AGFBZFz53v</a> — @NASAVoyager
The challenge is that the computers were built in the 1970s using old code and send data very slowly by today's standards.
In addition, these computers are so deep in space, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal from Voyager 1 to reach Earth. That means the controllers on the ground have to wait 45 hours for each two-way communication with the spacecraft.
Given how very, very far they are from home, if something goes wrong with them, it's up to engineers on the ground to fix it by sending radio signals since reaching them for repair missions isn't possible. We're a long way from the fictional warp drive and sub-space communication that made life so easy on the Starship Enterprise of Star Trek fame.
The twin Voyagers are now the most distant objects ever sent from Earth; a demonstration of how vast space is and how slow our spacecraft are. In 1977, I attended the launch of Voyager 2 when my hair was black and skin was smooth. This one mission with Voyager 1 and 2 has occupied a good chunk of my lifetime.

In another few years, the RTGs on both Voyagers are expected to run down to the point where the spacecraft will no longer be able to communicate with Earth. They will just continue to drift in silence among the stars of the Milky Way for billions of years.
However, there is one item on both Voyagers that will continue to function, the Golden Record, which carries a message from Earth to anyone out there who may find the spacecraft in the future.
The chances of them being found are astronomically small, but they will become the longest running experiment in human history.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Bob McDonald is the host of CBC Radio's award-winning weekly science program, Quirks & Quarks. He is also a science commentator for CBC News Network and CBC TV's The National. He has received 12 honorary degrees and is an Officer of the Order of Canada.
- Quirks & Quarks
- Bob McDonald's recent columns

Golden Record Sounds and Music
Sounds of earth.
The following is a listing of sounds electronically placed onboard the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft.
Music from Earth
The following music was included on the Voyager record.
Discover More Topics From NASA

Our Solar System


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Images on the Golden Record. The following is a listing of pictures electronically placed on the phonograph records which are carried onboard the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft. The contents of the record were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University, et. al. Dr. Sagan and his associates assembled 115 images and ...
The Voyager Golden Record contains 116 images and a variety of sounds. The items for the record, which is carried on both the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft, were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University.Included are natural sounds (including some made by animals), musical selections from different cultures and eras, spoken greetings in 59 languages ...
Any aliens who come across the Golden Record are in for a treat. It contains: 116 images encoded in analog form depicting scientific knowledge, human anatomy, human endeavors, and the terrestrial ...
The following is a listing of pictures electronically placed on the phonograph records which are carried onboard the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft. The contents of the record were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University, et. al. Dr. Sagan and his associates assembled 115 images and a variety […]
Watch videos and view images of Voyager 1 and 2 as they passed by Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune and get a glimpse into the images relating to the Golden Record. Videos. ... Many people were instrumental in the design, development and manufacturing of the golden record. Now you have the opportunity to see how it was made.
With this example before them, NASA placed a more ambitious message aboard Voyager 1 and 2, a kind of time capsule, intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and ...
The Voyager Golden Records are two identical phonograph records which were included aboard the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977. ... softcover book containing the images encoded on the record, images sent back by Voyager, commentary from Ferris, art print, turntable slipmat, and a collector's box. This edition was released in February ...
This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA's Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. ... revisit the well-known Voyager view while attempting to respect the original data and intent of those who planned ...
The Voyager Golden Record On board each Voyager spacecraft is a time capsule: a 12-inch, gold-plated copper disk carrying spoken greetings in 55 languages from Earth's peoples, along with 115 images and myriad sounds representing our home NASA/JPL. Most NASA images are in the public domain. Reuse of this image is governed by NASA's image use ...
April 29, 2011. Context Image. This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA's Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. An artist's rendering of the Voyager spacecraft is shown at bottom right, with a yellow ...
With this example before them, NASA placed a more ambitious message aboard Voyager 1 and 2, a kind of time capsule, intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and ...
Voyager Golden Record. December 4, 2017. Credit. NASA/JPL-Caltech. Language. english. Each Voyager spacecraft carries a copy of the Golden Record, which has been featured in several works of science fiction. The record's protective cover, with instructions for playing its contents, is shown at left.
January 22, 2016 4:56 PM EST. I t was nearly 30 years ago—Jan. 24, 1986, nearly a decade after it had been launched—that the Voyager 2 spacecraft made its closest pass to Uranus and, as TIME ...
The "Golden Record" would be an upgrade to Pioneer's plaques. Mounted on Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, twin probes launched in 1977, the two copies of the record would serve as time capsules and ...
The contents of the record were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University, et. al. Dr. Sagan and his associates assembled 115 images and a variety of natural sounds, such as those made by surf, wind and thunder, birds, whales, and other animals. To this they added musical selections from different cultures and eras, and spoken greetings from Earth-people in ...
The grooves of the records record both ordinary audio and 115 encoded images. A team led by astronomer Carl Sagan selected the contents, chosen to embody a message representative of all of humanity.
Welcome to our improved NASA website! If you don't find what you are looking for, please try searching above, give us feedback , or return to the main site . Watch videos and view images of Voyager 1 and 2 as they passed by Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune and get a glimpse into the images relating to the Golden Record.
The Golden Records have been sailing through space for over 40 years. They contain audio and images from Earth, but in order to decode the messages, you need a slight understanding of the universe ...
This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA's Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. An artist's rendering of the Voyager spacecraft is shown at bottom right, with a yellow circle denoting the ...
7. A Bulgarian Folk Song. The Voyager committee wanted the record's music to represent a wide range of eras and cultures. One track, titled "Izlel je Delyo Hagdutin," is a traditional folk song ...
The Voyager golden record commemorative edition, published by the Planetary Society in the early 1990's contains 2 CDs. One of them has an .exe file to display the 116 color images engraved on the original Voyager golden record. However I was never able to execute this file or to display the pictures...
The Voyager spacecraft showcasing where the Golden Record is mounted. Credit: NASA/JPL. The drawing in the lower left-hand corner of the cover is the pulsar map previously sent as part of the plaques on Pioneers 10 and 11. It shows the location of the solar system with respect to 14 pulsars, whose precise periods are given.
This was the Arabic declaration I recorded, which NASA sent into the cosmos 47 years ago on the Voyager Golden Records, a collection of images, music, and language affixed to the twin probes of the same name, showcasing the diversity and triumph of life on Earth. ... was recruited by Carl Sagan to contribute an Arabic greeting to the Voyager ...
Rockets aren't the only thing we launch. Welcome to our improved NASA website! If you don't find what you are looking for, please try searching above, give us feedback , or return to the main site . Images from the making of the Voyager Golden record in 1977.
The 12-inch, gold-plated copper disc records carried by both Voyager spacecraft contain sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth. (NASA) ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Sounds of Earth The following is a listing of sounds electronically placed onboard the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft. Music from Earth The following music was included on the Voyager record. Country of origin Composition Artist(s) Length Germany Bach, Brandenburg Concerto No. 2 in F. First Movement Munich Bach Orchestra, Karl Richter, conductor 4:40 Java […]