- Corrections

What was the Great Trek?
The Great Trek was a perilous exodus of pioneers into the heart of South Africa, looking for a place to call home.

When the British took control of Cape Town and the Cape Colony in the early 1800s, tensions grew between the new colonizers of British stock, and the old colonizers, the Boers, descendants of the original Dutch settlers. From 1835, the Boers would lead numerous expeditions out of the Cape Colony, traversing towards the interior of South Africa. Escaping British rule would come with a host of deadly challenges, and the Boers, seeking their own lands, would find themselves in direct conflict with the people who resided in the interior, most notably the Ndebele and the Zulu.
The “Great Trek” is a story of resentment, displacement, murder, war, and hope, and it forms one of the bloodiest chapters of South Africa’s notoriously violent history.
Origins of the Great Trek

The Cape was first colonized by the Dutch , when they landed there in 1652, and Cape Town quickly grew into a vital refueling station between Europe and the East Indies. The colony prospered and grew, with Dutch settlers taking up both urban and rural posts. In 1795, Britain invaded and took control of the Cape Colony, as it was Dutch possession, and Holland was under the control of the French Revolutionary government . After the war, the colony was handed back to Holland (the Batavian Republic) which in 1806, fell under French rule again. The British responded by annexing the Cape completely.
Under British rule, the colony underwent major administrative changes. The language of administration became English, and liberal changes were made which designated non-white servants as citizens. Britain, at the time, was adamantly anti-slavery, and was enacting laws to end it.
Get the latest articles delivered to your inbox
Please check your inbox to activate your subscription.
Tensions grew between the British and the Boers (farmers). In 1815, a Boer was arrested for assaulting one of his servants. Many other Boers rose up in rebellion in solidarity, culminating in five being hanged for insurrection. In 1834, legislation passed that all slaves were to be freed. The vast majority of Boer farmers owned slaves, and although they were offered compensation, travel to Britain was required to receive it which was impossible for many. Eventually, the Boers had had enough of British rule and decided to leave the Cape Colony in search of self-governance and new lands to farm. The Great Trek was about to begin.
The Trek Begins

Not all Afrikaners endorsed the Great Trek. In fact, only a fifth of the Cape’s Dutch-speaking people decided to take part. Most of the urbanized Dutch were actually content with British rule. Nevertheless, many Boers decided to leave. Thousands of Boers loaded up their wagons and proceeded to venture into the interior and towards peril.
The first wave of voortrekkers (pioneers) met with disaster. After setting out in September 1835, they crossed the Vaal River in January, 1836, and decided to split up, following differences between their leaders. Hans van Rensburg led a party of 49 settlers who trekked north into what is now Mozambique. His party was slain by an impi (force of warriors) of Soshangane. For van Rensburg and his party, the Great Trek was over. Only two children survived who were saved by a Zulu warrior. The other party of settlers, led by Louis Tregardt, settled near Delagoa Bay in southern Mozambique, where most of them perished from fever.
A third group led by Hendrik Potgieter, consisting of about 200 people, also ran into serious trouble. In August 1836, a Matabele patrol attacked Potgieter’s group, killing six men, two women, and six children. King Mzilikazi of the Matabele in what is now Zimbabwe decided to attack the Voortrekkers again, this time sending out an impi of 5,000 men. Local bushmen warned the Voortrekkers of the impi , and Potgieter had two days to prepare. He decided to prepare for battle, although doing so would leave all the Voortrekker’s cattle vulnerable.

The Voortrekkers arranged the wagons into a laager (defensive circle) and placed thorn branches underneath the wagons and in the gaps. Another defensive square of four wagons was placed inside the laager and covered with animal skins. Here, the women and children would be safe from spears thrown into the camp. The defenders numbered just 33 men and seven boys, each armed with two muzzle-loader rifles. They were outnumbered 150 to one.
As the battle commenced, the Voortrekkers rode out on horseback to harry the impi . This proved largely ineffective, and they withdrew to the laager. The attack on the laager only lasted for about half an hour, in which time, two Voortrekkers lost their lives, and about 400 Matabele warriors were killed or wounded. The Matabele were far more interested in taking the cattle and eventually made off with 50,000 sheep and goats and 5,000 cattle. Despite surviving through the day, the Battle of Vegkop was not a happy victory for the Voortrekkers. Three months later, with the help of the Tswana people, a Voortrekker-led raid managed to take back 6,500 cattle, which included some of the cattle plundered at Vegkop.
The following months saw revenge attacks led by the Voortrekkers. About 15 Matabele settlements were destroyed, and 1,000 warriors lost their lives. The Matabele abandoned the region. The Great Trek would continue with several other parties pioneering the way into the South African hinterland.
The Battle of Blood River

In February 1838, the Voortrekkers led by Piet Retief met with absolute disaster. Retief and his delegation were invited to the Zulu King Dingane ’s kraal (village) to negotiate a land treaty; however, Dingane betrayed the Voortrekkers. He had them all taken out to a hill outside the village and clubbed to death. Piet Retief was killed last so that he could watch his delegation being killed. In total, about 100 were murdered, and their bodies were left for the vultures and other scavengers.
Following this betrayal, King Dingane directed further attacks on unsuspecting Voortrekker settlements. This included the Weenen Massacre, in which 534 men, women, and children were slaughtered. This number includes KhoiKhoi and Basuto tribe members who accompanied them. Against a hostile Zulu nation, the Great Trek was doomed to fail.
The Voortrekkers decided to lead a punitive expedition, and under the guidance of Andries Pretorius, 464 men, along with 200 servants and two small cannons, prepared to engage the Zulu. After several weeks of trekking, Pretorius set up his laager along the Ncome River, purposefully avoiding geographic traps that would have led to a disaster in battle. His site offered protection on two sides by the Ncome River to the rear and a deep ditch on the left flank. The approach was treeless and offered no protection from any advancing attackers. On the morning of December 16, the Voortrekkers were greeted by the sight of six regiments of Zulu impis , numbering approximately 20,000 men.

For two hours, the Zulus attacked the laager in four waves, and each time they were repulsed with great casualties. The Voortrekkers used grapeshot in their muskets and their two cannons in order to maximize damage to the Zulus. After two hours, Pretorius ordered his men to ride out and attempt to break up the Zulu formations. The Zulus held for a while, but high casualties eventually forced them to scatter. With their army breaking, the Voortrekkers chased down and killed the fleeing Zulus for three hours. By the end of the battle, 3,000 Zulu lay dead (although historians dispute this number). By contrast, the Voortrekkers suffered only three injuries, including Andries Pretorius taking an assegai (Zulu spear) to the hand.
December 16 has been observed as a public holiday in the Boer Republics and South Africa ever since. It was known as The Day of the Covenant, The Day of the Vow, or Dingane’s Day. In 1995, after the fall of apartheid , the day was rebranded as “Day of Reconciliation.” Today the site on the west side of the Ncome River is home to the Blood River Monument and Museum Complex, while on the east side of the river stands the Ncome River Monument and Museum Complex dedicated to the Zulu people. The former has gone through many variations, with the latest version of the monument being 64 wagons cast in bronze. When it was unveiled in 1998, The then Minister of Home Affairs and Zulu tribal leader, Mangosuthu Buthelezi , apologized on behalf of the Zulu people for the murder of Piet Retief and his party during the Great Trek, while he also stressed the suffering of Zulus during apartheid.

The Zulu defeat added to further divisions in the Zulu Kingdom, which was plunged into a civil war between Dingane and his brother Mpande. Mpande, supported by the Voortrekkers, won the civil war in January 1840. This led to a significant decrease in threats to the Voortrekkers. Andries Pretorius and his Voortrekkers were able to recover Piet Retief’s body, along with his retinue, and give them burials. On Retief’s body was found the original treaty offering the trekkers land, and Pretorius was able to successfully negotiate with the Zulu over the establishment of a territory for the Voortrekkers. The Republic of Natalia was established in 1839, south of the Zulu Kingdom. However, the new republic was short-lived and was annexed by the British in 1843.

Nevertheless, the Great Trek could continue, and thus the waves of Voortrekkers continued. In the 1850s, two substantial Boer republics were established: The Republic of the Transvaal and the Republic of the Orange Free State . These republics would later come into conflict with the expanding British Empire.
The Great Trek as a Cultural Symbol

In the 1940s, Afrikaner nationalists used the Great Trek as a symbol to unite the Afrikaans people and promote cultural unity among them. This move was primarily responsible for the National Party winning the 1948 election and, later on, imposing apartheid on the country.
South Africa is a highly diverse country, and while the Great Trek remains a symbol of Afrikaner culture and history, it is also seen as an important part of South African history with lessons to learn from for all South Africans.

6 Crazy Facts about Cape Town

By Greg Beyer BA History & Linguistics, Journalism Diploma Greg specializes in African History. He holds a BA in History & Linguistics and a Journalism Diploma from the University of Cape Town. A former English teacher, he now excels in academic writing and pursues his passion for art through drawing and painting in his free time.

Frequently Read Together

British History: The Formation of Great Britain and the United Kingdom
The French Revolution in 5 Iconic Paintings

Mandela & the 1995 Rugby World Cup: A Match that Redefined a Nation
The Great Trek

South African information – tourism, history, culture of South Africa
- South Africa
- Kwazulu-Natal
- African Tribes
- game reserves
- Sport and Culture
- Natural Resources
- Transportation
- Food and Recipes
- Neigbouring Countries
The Great Trek
The Great Trek was the emigration of the Cape of Good Hope colonists in the 1830’s. This followed previous isolated treks of Dutch colonists who moved inland almost from the beginning of European Settlement in South Africa .
There were a number of reasons that caused the colonists who were mainly of Dutch origin to leave their homes and settle themselves inland and away from British rule.
One of the causes was that the British Colonial Office and their representatives did not have any understanding of the difficulties and problems of the Frontier farmers . These farmers were also disgruntled by the inadequate compensation paid for the slaves that had been liberated under the Emancipation Law . They were also dissatisfied about the return to the local Native tribes of the buffer territory called the “Province of Queen Adelaide” and of course their dislike of the tax laws that had been set up. Many British settlers sympathized with the Voortrekkers protests symbolized by the bible presented to a Voortrekker leader Piet Retief by the British colonists of Grahamstown.
One of the first organized parties of Voortrekkers to leave the Cape was that of Louis Trichardt who led a party together with a group under Jan Van Rensburg (about 30 wagons in all), across the frontier and moved north. Along the way Van Rensburg’s party separated from the original group and moved east and disappeared. Louis Trichard’s party after many hardships reach Lourenco Marques in Mozambique but most died from fever and the survivors returned back to Natal by ship.
In spite of dire warnings by Dutch Reformed clergy and Government officials other groups also began the long Trek to find a new home in the hinterland of South Africa. Among the chief leaders was Andries Hendrik Potgieter who reached what is present day Potchefstroom. Other groups settled in what is now the Free State where they established the town of Winburg.
P ieter Retief and Gerrit Maritz were leaders of the most important groups. In April 1837 Retief reached Thaba N’chu where he was elected Commander of 1000 emigrants and 6 months later he led an advance party across the Drakensberg into what is now Kwazulu-Natal and signed a treaty with Dingaan the Zulu chief at the time. They were invited to Dingaan’s Kraal where his party were murdered and an attempt was made by the Zulu’s to kill the survivors of his party at Blaauwkranz.
In December of 1838 the Voortrekkers defeated the Zulu warriors at the Battle of Blood River when Andries Pretorius defeated a Zulu army of 10,000 with a force of 460 Boers. After that the Great Trek would have ended if it were not for the fact that the British dispatched a force from the Cape and asserted British authority which resulted in further treks being undertaken by the Boers which led them to establish independent republics in the Free State and Transvaal . When the British Colony of Natal was set up this marked the end of the Great Trek.
Read more about the history of South Africa
Back to home page.
- Society and Politics
- Art and Culture
- Biographies
- Publications

Great Trek Centenary Celebrations commence
Cameron, T. (ed) (1986) An Illustrated History of South Africa. Johannesburg, pp.258-259.|
Gilliomee, H. & Mbenga, B. (2007) New History of South Africa . Cape Town, pp.290-291.
Know something about this topic?
Towards a people's history
- Join - It's Free
Voortrekkers van Suid Afrika
« Back to Projects Dashboard
Project Tags
Related projects.
- Die Groot Trek / The Great Trek
- Familie/Family de Klerk
- Famous South Africans
- Voortrekker Begraafplaas - Pietermaritzburg
- Voortrekkers van Suid-Afrika - Doop van 58 Voortrekker kinders op 26 MEI 1844 te Valsch Revier, Winburg, Oranje Vrystaat, Suid-Afrika
- Women of the Great Trek - South Africa 1835 - 1845
Top Surnames

Hierdie is hoofsaaklik om die Voortrekkers te bespreek. This is mainly to discuss the Voortrekkers of South Africa. See Afrikaans version under the English.
The Voortrekkers (Afrikaans and Dutch for pioneers, literally "those who trek ahead", "fore-trekkers") were emigrants during the 1830s and 1840s who left the Cape Colony (British at the time, but founded by the Dutch) moving into the interior of what is now South Africa. The Great Trek consisted of a number of mass movements under a number of different leaders including Louis Tregardt, Hendrik Potgieter, Sarel Cilliers, Pieter Uys, Gerrit Maritz, Piet Retief and Andries Pretorius.
The Voortrekkers mainly came from the farming community of the Eastern Cape although some (such as Piet Retief) originally came from the Western Cape farming community while others (such as Gerrit Maritz) were successful tradesmen in the frontier towns. Some of them were wealthy men though most were not as they were from the poorer communities of the frontier. It was recorded that the 33 Voortrekker families at the Battle of Vegkop lost 100 horses, between 4,000 and 7,000 cattle, and between 40,000 and 50,000 sheep.[citation needed] These figures appear greatly exaggerated.[citation needed] Other members of the trekking parties were of Trekboer stock who came from a life of semi-nomadic herding; yet others were employees, many of whom had been slaves only a few years earlier.
The reasons for the mass emigration from the Cape Colony have been much discussed over the years. Afrikaner historiography has emphasized the hardships endured by the frontier farmers which they blamed on British policies of pacifying the Xhosa tribes. Other historians have emphasized the harshness of the life in the Eastern Cape (which suffered one of its regular periods of drought in the early 1830s) compared to the attractions of the fertile country of Natal, the Orange Free State and the Transvaal. Growing land shortages have also been cited as a contributing factor. The true reasons were obviously very complex and certainly consisted of both "push" factors (including the general dissatisfaction of life under British rule) and "pull" factors (including the desire for a better life in better country.)
The Voortrekkers were mainly of Trekboer (migrating farmer) descent living in the eastern frontiers of the Cape. Hence, their ancestors had long established a semi-nomadic existence of trekking into expanding frontiers.
*Battle of Blood River
Voortrekkers migrated into Natal and negotiated a land treaty with the Zulu King Dingane. Upon reconsideration, Dingane doublecrossed the Voortrekkers, killing their leader Piet Retief along with half of the Voortrekker settlers who had followed them to Natal. Other Voortrekkers migrated north to the Waterberg area, where some of them settled and began ranching operations, which activities enhanced the pressure placed on indigenous wildlife by pre-existing tribesmen, whose Bantu predecessors had previously initiated such grazing in the Waterberg region. These Voortrekkers arriving in the Waterberg area had believed they were in the Nile River area of Egypt based upon their understanding of the local topography
Andries Pretorius filled the leadership vacuum hoping to enter into negotiations for peace if Dingane would restore the land he had granted to Retief. When Dingane sent an impi (armed force) of around twelve thousand Zulu warriors to attack the local contingent of Voortrekkers in response, the Voortrekkers defended themselves at a battle at Nacome River (called the Battle of Blood River) on 16 December 1838 where the vastly outnumbered Voortrekker contingent defeated the Zulu warriors. This date has hence been known as the Day of the Vow as the Voortrekkers made a vow to God that they would honor the date if he were to deliver them from what they viewed as almost insurmountable odds. The victory of the besieged Voortrekkers at Nacome River was considered a turning point. The Natalia Republic was set up in 1839 but was annexed by Britain in 1843 whereupon most of the local Boers trekked further north joining other Voortrekkers who had established themselves in the region.
* Struggle against the Ndebele
Armed conflict, first with the Ndebele people under Mzilikazi in the area which was to become the Transvaal, then against the Zulus under Dingane, went the Voortrekkers' way, mostly because of their tactics, their horsemanship and the effectiveness of their muzzle-loading guns. This success led to the establishment of a number of small Boer republics, which slowly coalesced into the Orange Free State and the South African Republic. These two states would survive until their annexation in 1900 by United Kingdom during the Second Boer War.
The Voortrekkers are commemorated by the Voortrekker Monument located on Monument Hill overlooking Pretoria, the erstwhile capital of the South African Republic and the current and historic administrative capital of the Republic of South Africa. Pretoria was named after the Voortrekker leader Andries Pretorius.
Church of the Vow : In 1841 the victorious Trekkers built The Church of the Vow at Pietermaritzburg, and passed the obligation to keep the vow on to their descendants. ( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Day_of_the_Vow ) and ( http://www.voortrekkermuseum.co.za/exhibits/church-of-the-vow-2/ )
The Voortrekkers had a distinctive flag, used mainly by the Voortrekkers who followed Andries Hendrik Potgieter, which is why it was also known as the Potgieter Flag. This flag was used as the flag of the Zoutpansberg Republic until this republic was incorporated into the Transvaal Republic also known as the South African Republic. A version of this flag was used at Potchefstroom, one of the first independent Boer towns and republics established by local Voortrekkers.
*Die Voortrekkerleiers
Die Voortrekkers het tydens die Groot Trek vanaf 1836 vanuit die Kaapkolonie na die binneland van suidelike Afrika getrek. Meeste trekkers het met hulle hele gesin en al hulle besittings, vee en werkers ingesluit, vanuit die Oos-Kaap met ossewaens getrek. Die rede vir die massa-migrasie is steeds nie heeltemaal duidelik nie. Dit word gemeen dat die Frans-Nederduitse setlaars ongelukkig was oor die Britse regering se hardkoppigheid en hul streng beleid. Dit word ook gemeen dat die natuurlike wyding van die Transvaal en Natal meer aanloklik as die Kaap en die droë Karoo was.
Van die vernaamste leiers was Piet Retief, Gerrit Maritz, Andries Pretorius, Louis Tregardt, Hendrik Potgieter, Sarel Cilliers en Pieter Uys.
Onder leiding van Gerrit Maritz en Piet Retief het 'n groep voortrekkers na Natal getrek in die rigting van die huidige hoofstad, Pietermaritzburg. Hulle het onderhandel met die leier van die Zoeloes, die regerende stam in daardie gebied, om 'n stuk grond te verkry. Die leier van die Zoeloes, Dingaan, het die Voortrekkers toe om die bos gelei met die transaksie; 'n groot groep trekkers, waaronder Piet Retief, is deur Dingaan laat vermoor. Later is die oorlewendes deur 'n oorweldigende zoeloemag aangeval te Bloedrivier (vandag Nacome-rivier). Die Voortrekkers het egter die Slag van Bloedrivier gewen en later stig hulle die Republiek van Natalia. Dié is later deur die Britse Ryk oorgeneem.
Teenstrydig met algemene denke was die Voortrekkerbeweging in die 1840's/1850's nie 'n wit beweging nie, maar wel 'n wit-geleide beweging. Daar was menigte 'boere' wie se swart slawe na vryspraak vrywillig saamgetrek het a.g.v. die politieke ongerief in die Kaap.
More can be read on the following Wikipedia page.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voortrekkers
http://af.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lys_van_deelnemers_aan_die_Slag_van_Bl...
Add profiles to this project
Add collaborators to this project.
- © 2024 Geni.com
- US State Privacy Notice
- Code of Conduct
- World Family Tree

Subscription Offers
Give a Gift

The Great South African Trek
C.H.N. Routh records the travels and travails of the Boer pioneers
Heresies in history die hard; and the worst kind of school text-book, oversimplified and written down to the intelligence of the weakest pupils, helps to perpetuate popular errors. “Palmerston (we learn) fought the first Chinese War to force opium on to China,” or “The object of the Continental System was to starve out Great Britain. ...” A heresy that bears a charmed life teaches that the Great South African Trek was brought about by the abolition of slavery in 1833. The contention is that fury at the British government’s interference in the Boer way of life by this attack on their cherished system of slave labour, resentment at the financial losses incurred through inadequate compensation, and irritation at the inefficient machinery by which that compensation was to be paid, moved the frontier Boers to leave the colony in order to preserve slavery. Evidence is wholly against this reading. No doubt abolition increased the general irritation and added its quota to the growing resentment against the British government, but abolition itself would never have caused the Great Trek, and it cannot be regarded as the primary cause for the emigration.

To continue reading this article you will need to purchase access to the online archive.
Buy Online Access Buy Print & Archive Subscription
If you have already purchased access, or are a print & archive subscriber, please ensure you are logged in .
Please email [email protected] if you have any problems.
Popular articles

Was Portugal’s Carnation Revolution Inevitable?

Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape

The great treks : the transformation of Southern Africa, 1815-1854
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
obscured text back cover cut off text cover due to tight binding
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
5 Favorites
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station08.cebu on June 23, 2020
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis
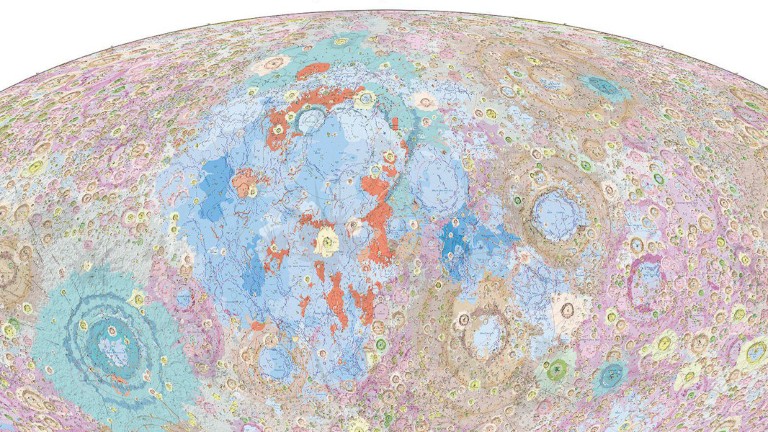
China's Moon atlas is the most detailed ever made
‘Shut up and calculate’: how Einstein lost the battle to explain quantum reality
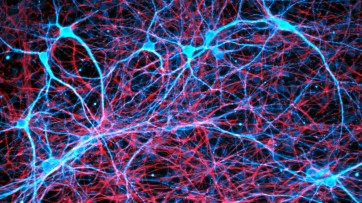
Rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell
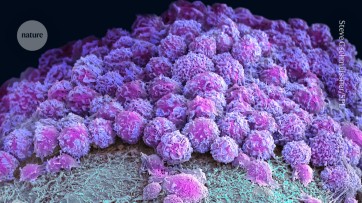
Mini-colon and brain 'organoids' shed light on cancer and other diseases
Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’, first glowing animals lit up the oceans half a billion years ago, plastic pollution: three numbers that support a crackdown, the maldives is racing to create new land. why are so many people concerned, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna.

Should the Maldives be creating new land?

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias

How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
Bird flu in us cows: is the milk supply safe, nato is boosting ai and climate research as scientific diplomacy remains on ice, hello puffins, goodbye belugas: changing arctic fjord hints at our climate future, nih pay raise for postdocs and phd students could have us ripple effect.
Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Citizenship privilege harms science
European ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner, will ai accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions, current issue.

Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species
Stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.

Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
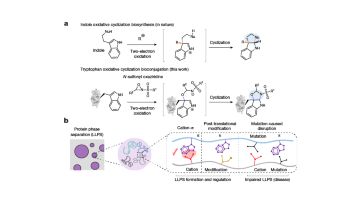
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
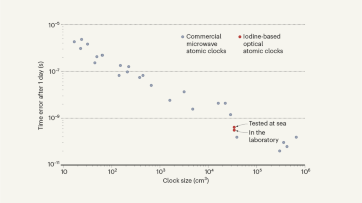
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
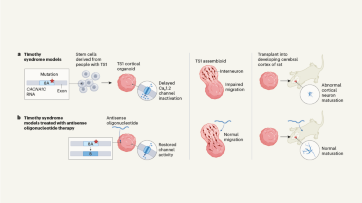
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, galaxy found napping in the primordial universe, tumours form without genetic mutations, marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved.

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill
How ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las borinqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Great Trek (Afrikaans: Die Groot Trek [di ˌχruət ˈtrɛk]; Dutch: De Grote Trek [də ˌɣroːtə ˈtrɛk]) was a northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of ...
Great Trek 1835-1846. The Great Trek was a movement of Dutch-speaking colonists up into the interior of southern Africa in search of land where they could establish their own homeland, independent of British rule. The determination and courage of these pioneers has become the single most important element in the folk memory of Afrikaner ...
Great Trek, the emigration of some 12,000 to 14,000 Boers from Cape Colony in South Africa between 1835 and the early 1840s, in rebellion against the policies of the British government and in search of fresh pasturelands. The Great Trek is regarded by Afrikaners as a central event of their 19th-century history and the origin of their nationhood.
The Great Trek was a perilous exodus of pioneers into the heart of South Africa, looking for a place to call home. When the British took control of Cape Town and the Cape Colony in the early 1800s, tensions grew between the new colonizers of British stock, and the old colonizers, the Boers, descendants of the original Dutch settlers. From 1835 ...
Great Trek. Afrikaners left the Cape Colony (in present-day South Africa) in large numbers during the second half of the 1830s, an act that became known as the "Great Trek" and that helped define white South Africans' ethnic, cultural, and political identity.In line with Afrikaners' belief in a separate existence, developing tensions between these settlers, British authorities, and African ...
The Great Trek was a very important event in the history of South Africa . It came about because of disagreements between British and Afrikaner settlers in the colony known as the Cape Colony. As a result of the disagreements, many Afrikaner farmers moved away from the Cape Colony and established their own colonies. This was a first step in ...
An event of prime importance in the history of South Africa is the Great Trek, a mass emigration of Boer farmers from the British-ruled Cape Colony between 1835 and the early 1840s. Several groups of the Boers trekked overland in a northward or northeastward direction. ... The Great Trek began in 1835. More than 12,000 farmers left the Cape ...
South Africa Table of Contents. Dutch speakers denounced these actions as striking at the heart of their labor and land needs. Those living in the eastern Cape, most of them among the poorer segment of the Dutch-speaking population, were particularly impassioned in their criticisms, and many decided to abandon their farms and to seek new lands beyond the reach of British rule.
Voortrekker, any of the Boers (Dutch settlers or their descendants), or, as they came to be called in the 20th century, Afrikaners, who left the British Cape Colony in Southern Africa after 1834 and migrated into the interior Highveld north of the Orange River.During the next 20 years, they founded new communities in the Southern African interior that evolved into the colony of Natal and the ...
The mass migration of the Boer farmers from Cape Colony to escape British domination in 1835-36 - the Great Trek - has always been a potent icon of Africaaner nationalism and identity. For African nationalists, the Mfecane - the vast movement of the Black populations in the interior following the emergence of a new Zulu kingdom as a major military force in the early 19th century - offers an ...
This war, fought between 1899 and 1902, had a profound impact on South Africa, ultimately leading to the formation of the Union of South Africa in 1910. Today, the Great Trek is remembered as a ...
Dutch colonists (Boers) load supply-filled wagons in preparation for their migration into the interior of South Africa in the 1830s. Dutch colonists (Boers) load supply-filled wagons in preparation for their migration into the interior of South Africa in the 1830s. ... The Great Trek The Great Trek Credit: James E. McConnell, painter, (1903 ...
The Great Trek was the emigration of the Cape of Good Hope colonists in the 1830's. This followed previous isolated treks of Dutch colonists who moved inland almost from the beginning of European Settlement in South Africa.. There were a number of reasons that caused the colonists who were mainly of Dutch origin to leave their homes and settle themselves inland and away from British rule.
The Great Trek led to several Boer republics, the South African Republic or Transvaal, the Orange Free State, and the Natalia Republic. Both the Cape Colony and these Boer republics became part of today's country of South Africa. The Great Trek was a mass migration of Boers from the British-run Cape Colony. Leaving the Cape, they travelled ...
The Great Trek was a northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Afri...
The Great Trek in South Africa between 1835 and 1840. The Great Trek in South Africa started in 1835 when over a time span of three years more then 12,000 Boers (farmers) left the Cape Colony. They trekked (moved) into the interior by ox wagon, in search of land where they would be free and beyond British control.
The Great Trek was a migration that took place between 1838 and the 1840s, and involved the Boers leaving the Cape Colony and settling in the interior of South Africa. White settlement led to the establishment of the republics of Natalia, the Orange Free State and the Transvaal. Among the reasons for the trek was the general dissatisfaction ...
Andries Pretorius (born Nov. 27, 1798, near Graaff-Reinet, Cape Colony [now in South Africa]—died July 23, 1853, Magaliesberg, Transvaal [now in South Africa]) was a Boer leader in the Great Trek from British-dominated Cape Colony, the dominant military and political figure in Natal and later in the Transvaal, and one of the major agents of white conquest in Southern Africa.
OORSIG. The Voortrekkers (Afrikaans and Dutch for pioneers, literally "those who trek ahead", "fore-trekkers") were emigrants during the 1830s and 1840s who left the Cape Colony (British at the time, but founded by the Dutch) moving into the interior of what is now South Africa. The Great Trek consisted of a number of mass movements under a ...
"Palmerston (we learn) fought the first Chinese War to force opium on to China," or "The object of the Continental System was to starve out Great Britain. ..." A heresy that bears a charmed life teaches that the Great South African Trek was brought about by the abolition of slavery in 1833.
The mass migration of the Boer farmers from Cape Colony to escape British domination in 1835-36 - the Great Trek - has always been a potent icon of Afrikaaner nationalism and identity. For African nationalists, the Mfecane - the vast movement of the Black populations in the interior following the emergence of a new Zulu kingdom as a major military force in the early 19th century - offers an ...
The term Afrikaners or Afrikaans people is generally used in modern-day South Africa for the white Afrikaans-speaking population of South Africa (the largest group of White South Africans) encompassing the descendants of both the Boers, and the Cape Dutch who did not embark on the Great Trek.
South Africa -- History -- Frontier Wars, 1811-1878, South Africa -- History -- Great Trek, 1836-1840 Publisher New York : Longman Collection printdisabled; internetarchivebooks Contributor Internet Archive Language English
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) says improvements in load shedding and energy availability in the country are coming quicker than previously projected - which is good news for South Africa ...
Employed South Africans could finally find some relief in 2024, with salary hikes in the country expected to outstrip inflation after two years of falling short. Salary hikes are expected to ...