NASA Voyager 1 Encounters New Region in Deep Space

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has entered a new region at the far reaches of our solar system that scientists feel is the final area the spacecraft has to cross before reaching interstellar space.
Scientists refer to this new region as a magnetic highway for charged particles because our sun's magnetic field lines are connected to interstellar magnetic field lines. This connection allows lower-energy charged particles that originate from inside our heliosphere -- or the bubble of charged particles the sun blows around itself -- to zoom out and allows higher-energy particles from outside to stream in. Before entering this region, the charged particles bounced around in all directions, as if trapped on local roads inside the heliosphere.
The Voyager team infers this region is still inside our solar bubble because the direction of the magnetic field lines has not changed. The direction of these magnetic field lines is predicted to change when Voyager breaks through to interstellar space. The new results were described at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco on Monday.
"Although Voyager 1 still is inside the sun's environment, we now can taste what it's like on the outside because the particles are zipping in and out on this magnetic highway," said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena. "We believe this is the last leg of our journey to interstellar space. Our best guess is it's likely just a few months to a couple years away. The new region isn't what we expected, but we've come to expect the unexpected from Voyager." Since December 2004, when Voyager 1 crossed a point in space called the termination shock, the spacecraft has been exploring the heliosphere's outer layer, called the heliosheath. In this region, the stream of charged particles from the sun, known as the solar wind, abruptly slowed down from supersonic speeds and became turbulent. Voyager 1's environment was consistent for about five and a half years. The spacecraft then detected that the outward speed of the solar wind slowed to zero. The intensity of the magnetic field also began to increase at that time. Voyager data from two onboard instruments that measure charged particles showed the spacecraft first entered this magnetic highway region on July 28, 2012. The region ebbed away and flowed toward Voyager 1 several times. The spacecraft entered the region again Aug. 25 and the environment has been stable since. "If we were judging by the charged particle data alone, I would have thought we were outside the heliosphere," said Stamatios Krimigis, principal investigator of the low-energy charged particle instrument, based at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Md. "But we need to look at what all the instruments are telling us and only time will tell whether our interpretations about this frontier are correct." Spacecraft data revealed the magnetic field became stronger each time Voyager entered the highway region; however, the direction of the magnetic field lines did not change. "We are in a magnetic region unlike any we've been in before -- about 10 times more intense than before the termination shock -- but the magnetic field data show no indication we're in interstellar space," said Leonard Burlaga, a Voyager magnetometer team member based at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The magnetic field data turned out to be the key to pinpointing when we crossed the termination shock. And we expect these data will tell us when we first reach interstellar space." Voyager 1 and 2 were launched 16 days apart in 1977. At least one of the spacecraft has visited Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 1 is the most distant human-made object, about 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) away from the sun. The signal from Voyager 1 takes approximately 17 hours to travel to Earth. Voyager 2, the longest continuously operated spacecraft, is about 9 billion miles (15 billion kilometers) away from our sun. While Voyager 2 has seen changes similar to those seen by Voyager 1, the changes are much more gradual. Scientists do not think Voyager 2 has reached the magnetic highway. The Voyager spacecraft were built and continue to be operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, Calif. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. The Voyager missions are a part of NASA's Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/voyager and http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .

News Media Contact
Jia-Rui Cook
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-0724
Dwayne Brown
202-358-1726

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA Wins 6 Webby Awards, 8 Webby People’s Voice Awards

NASA’s CloudSat Ends Mission Peering Into the Heart of Clouds

Hubble Celebrates 34th Anniversary with a Look at the Little Dumbbell Nebula
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

NASA’s Optical Comms Demo Transmits Data Over 140 Million Miles

Sols 4166-4167: A Garden Full of Rocks

European Service Module

NASA Shares Lessons of Human Systems Integration with Industry

Work Underway on Large Cargo Landers for NASA’s Artemis Moon Missions

NASA Open Science Initiative Expands OpenET Across Amazon Basin
Amendment 11: Physical Oceanography not solicited in ROSES-2024

NASA Data Helps Beavers Build Back Streams

Sols 4164-4165: What’s Around the Ridge-bend?

Sols 4161-4163: Double Contact Science
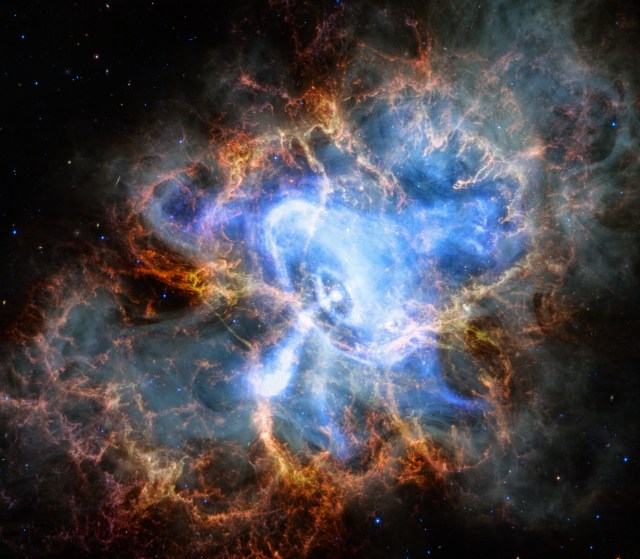

NASA’s Chandra Releases Doubleheader of Blockbuster Hits

Explore the Universe with the First E-Book from NASA’s Fermi

Dr. Douglas Hudgins

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Team Says Goodbye … for Now

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

NASA’s Near Space Network Enables PACE Climate Mission to ‘Phone Home’

Amendment 10: B.9 Heliophysics Low-Cost Access to Space Final Text and Proposal Due Date.

Washington State High Schooler Wins 2024 NASA Student Art Contest

NASA STEM Artemis Moon Trees

NASA Glenn Joins Big Hoopla STEM Challenge

First NASA Mars Analog Crew Nears End of Mission

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Nasa voyager 1 probe encounters new region in deep space.

WASHINGTON – NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has entered a new region at the far reaches of our solar system that scientists feel is the final area the spacecraft has to cross before reaching interstellar space. Scientists refer to this new region as a magnetic highway for charged particles because our sun’s magnetic field lines are connected to interstellar magnetic field lines. This connection allows lower-energy charged particles that originate from inside our heliosphere, or the bubble of charged particles the sun blows around itself, to zoom out and allows higher-energy particles from outside to stream in. Before entering this region, the charged particles bounced around in all directions, as if trapped on local roads inside the heliosphere. The Voyager team infers this region is still inside our solar bubble because the direction of the magnetic field lines has not changed. The direction is predicted to change when Voyager breaks through to interstellar space. The new results were described at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco on Monday. “Although Voyager 1 still is inside the sun’s environment, we now can taste what it’s like on the outside because the particles are zipping in and out on this magnetic highway,” said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena. “We believe this is the last leg of our journey to interstellar space. Our best guess is it’s likely just a few months to a couple years away. The new region isn’t what we expected, but we’ve come to expect the unexpected from Voyager.” Since December 2004 when Voyager 1 crossed a point in space called the termination shock, the spacecraft has been exploring the heliosphere’s outer layer, called the heliosheath. In this region, the stream of charged particles from the sun known as the solar wind abruptly slowed down from supersonic speeds and became turbulent. Voyager 1’s environment was consistent for about five and a half years. The spacecraft then detected that the outward speed of the solar wind slowed to zero. The intensity of the magnetic field also began to increase at that time. Voyager data from two onboard instruments that measure charged particles showed the spacecraft first entered this magnetic highway region on July 28, 2012. The region ebbed away and flowed toward Voyager 1 several times. The spacecraft entered the region again Aug. 25 and the environment has been stable since. “If we were judging by the charged particle data alone, I would have thought we were outside the heliosphere,” said Stamatios Krimigis, principal investigator of the low-energy charged particle instrument, based at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Md. “But we need to look at what all the instruments are telling us and only time will tell whether our interpretations about this frontier are correct.” Spacecraft data revealed the magnetic field became stronger each time Voyager entered the highway region; however, the direction of the magnetic field lines did not change. “We are in a magnetic region unlike any we’ve been in before – about 10 times more intense than before the termination shock – but the magnetic field data show no indication we’re in interstellar space,” said Leonard Burlaga, a Voyager magnetometer team member based at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. “The magnetic field data turned out to be the key to pinpointing when we crossed the termination shock. And we expect these data will tell us when we first reach interstellar space.” Voyager 1 and 2 were launched 16 days apart in 1977 and at least one of the spacecraft visited Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 1 is the most distant human-made object, about 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) away from the sun. The signal from Voyager 1 takes approximately 17 hours to travel to Earth. Voyager 2, the longest continuously operated spacecraft, is about 9 billion miles (15 billion kilometers) away from our sun. While Voyager 2 has seen changes similar to those seen by Voyager 1, the changes are much more gradual. Scientists do not think Voyager 2 has reached the magnetic highway. The Voyager spacecraft were built and continue to be operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, Calif. The Voyager missions are a part of NASA’s Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in NASA Headquarters in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
text-only version of this release
NASA press releases and other information are available automatically by sending a blank e-mail message to [email protected] . To unsubscribe from this mailing list, send a blank e-mail message to [email protected] .
Back to NASA Newsroom | Back to NASA Homepage
Dwayne Brown Headquarters, Washington 202-358-1726 [email protected] Jia-Rui C. Cook Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 818-354-0850 [email protected]
NASA's interstellar Voyager 1 spacecraft isn't doing so well — here's what we know
Since late 2023, engineers have been trying to get the Voyager spacecraft back online.

On Dec. 12, 2023, NASA shared some worrisome news about Voyager 1, the first probe to walk away from our solar system 's gravitational party and enter the isolation of interstellar space . Surrounded by darkness, Voyager 1 seems to be glitching.
It has been out there for more than 45 years, having supplied us with a bounty of treasure like the discovery of two new moons of Jupiter, another incredible ring of Saturn and the warm feeling that comes from knowing pieces of our lives will drift across the cosmos even after we're gone. (See: The Golden Record .) But now, Voyager 1 's fate seems to be uncertain.
As of Feb. 6, NASA said the team remains working on bringing the spacecraft back to proper health. "Engineers are still working to resolve a data issue on Voyager 1," NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory said in a post on X (formerly Twitter). "We can talk to the spacecraft, and it can hear us, but it's a slow process given the spacecraft's incredible distance from Earth."
Related: NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
So, on the bright side, even though Voyager 1 sits so utterly far away from us, ground control can actually communicate with it. In fact, last year, scientists beamed some software updates to the spacecraft as well as its counterpart, Voyager 2 , from billions of miles away. Though on the dimmer side, due to that distance, a single back-and-forth communication between Voyager 1 and anyone on Earth takes a total of 45 hours. If NASA finds a solution, it won't be for some time .
The issue, engineers realized, has to do with one of Voyager 1's onboard computers known as the Flight Data System, or FDS. (The backup FDS stopped working in 1981.)
"The FDS is not communicating properly with one of the probe's subsystems, called the telemetry modulation unit (TMU)," NASA said in a blog post. "As a result, no science or engineering data is being sent back to Earth." This is of course despite the fact that ground control can indeed send information to Voyager 1, which, at the time of writing this article , sits about 162 AU's from our planet. One AU is equal to the distance between the Earth and the sun , or 149,597,870.7 kilometers (92,955,807.3 miles).
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
From the beginning
Voyager 1's FDS dilemma was first noticed last year , after the probe's TMU stopped sending back clear data and started procuring a bunch of rubbish.
As NASA explains in the blog post, one of the FDS' core jobs is to collect information about the spacecraft itself, in terms of its health and general status. "It then combines that information into a single data 'package' to be sent back to Earth by the TMU," the post says. "The data is in the form of ones and zeros, or binary code."
However, the TMU seemed to be shuffling back a non-intelligible version of binary code recently. Or, as the team puts it, it seems like the system is "stuck." Yes, the engineers tried turning it off and on again.
That didn't work.
— SpaceX's Starship to launch 'Starlab' private space station in late 2020s
— Wonder what it's like to fall into Uranus? These scientists do, too
— Scientists' predictions for the long-term future of the Voyager Golden Records will blow your mind
Then, in early February, Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, told Ars Technica that the team might have pinpointed what's going on with the FDS at last. The theory is that the problem lies somewhere with the FDS' memory; there might be a computer bit that got corrupted. Unfortunately, though, because the FDS and TMU work together to relay information about the spacecraft's health, engineers are having a hard time figuring out where exactly the possible corruption may exist. The messenger is the one that needs a messenger.
They do know, however, that the spacecraft must be alive because they are receiving what's known as a "carrier tone." Carrier tone wavelengths don't carry information, but they are signals nonetheless, akin to a heartbeat. It's also worth considering that Voyager 1 has experienced problems before, such as in 2022 when the probe's "attitude articulation and control system" exhibited some blips that were ultimately patched up. Something similar happened to Voyager 2 during the summer of 2023, when Voyager 1's twin suffered some antenna complications before coming right back online again.
Still, Dodd says this situation has been the most serious since she began working on the historic Voyager mission.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Monisha Ravisetti is Space.com's Astronomy Editor. She covers black holes, star explosions, gravitational waves, exoplanet discoveries and other enigmas hidden across the fabric of space and time. Previously, she was a science writer at CNET, and before that, reported for The Academic Times. Prior to becoming a writer, she was an immunology researcher at Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York. She graduated from New York University in 2018 with a B.A. in philosophy, physics and chemistry. She spends too much time playing online chess. Her favorite planet is Earth.
NASA's Voyager 1 glitch has scientists sad yet hopeful: 'Voyager 2 is still going strong'
NASA's Voyager 1 probe in interstellar space can't phone home (again) due to glitch
Ancient rocks hold proof of Earth's magnetic field. Here's why that's puzzling
- Classical Motion There must be more to this story. Let me see if I have this right. They can receive a carrier. But the modulator gives them junk. Or possibly the processor's memory. And they can send new software. New instructions. So, why not simply use the packet data, to key the carrier on and off. OOK On and Off Keying. Telegraphy. Reply
Admin said: NASA's Voyager 1 deep space probe started glitching last year, and scientists aren't sure they can fix it. NASA's interstellar Voyager 1 spacecraft isn't doing so well — here's what we know : Read more
- Classical Motion I wish something would kick one of them back to us. I would love to see an analysis of every cubic cm of it. Reply
- billslugg Modulating the carrier wave would do no good unless the carrier knew what information to send us. The unit that failed takes the raw data and then tells the carrier what to say. Without the modulation unit there is no data to send. Reply
Classical Motion said: I wish something would kick one of them back to us. I would love to see an analysis of every cubic cm of it.
- Classical Motion I read that they were not sure if it was the modulator or the packet memory. The packet buffer. If they can send patch, it's easy to relocate that buffer into another section of memory. This can be done at several different memory locations to verify if it is a memory problem. If that works, then the modulator is ok. If the modulator fails with all those buffers, then it's the modulator. Turn off modulator. Just enable the carrier for a certain duration for a 1 bit. And turn it off for that certain duration for a 0 bit. One simply rotates that buffer string thru the accumulator at the duration rate, and use status flags to key the transmitter. Very simple and very short code. The packet is nothing more that a 128 BYTE or multiple size string of 1s and 0s. OOK is a very common wireless modulation. That's why I commented on more must be going on. And I would like to see what 30 years naked in space does to man molded matter. Reply
Classical Motion said: I read that they were not sure if it was the modulator or the packet memory. The packet buffer. If they can send patch, it's easy to relocate that buffer into another section of memory. This can be done at several different memory locations to verify if it is a memory problem. If that works, then the modulator is ok. If the modulator fails with all those buffers, then it's the modulator. Turn off modulator. Just enable the carrier for a certain duration for a 1 bit. And turn it off for that certain duration for a 0 bit. One simply rotates that buffer string thru the accumulator at the duration rate, and use status flags to key the transmitter. Very simple and very short code. The packet is nothing more that a 128 BYTE or multiple size string of 1s and 0s. OOK is a very common wireless modulation. That's why I commented on more must be going on. And I would like to see what 30 years naked in space does to man molded matter.
- damienassurre I think they should make another space craft and have it pick up voyager 1 and bring it back the info it went through would very valuable to stellar travel Reply
damienassurre said: I think they should make another space craft and have it pick up voyager 1 and bring it back the info it went through would very valuable to stellar travel
- billslugg The newer forms of memory can't be used easily in outer space as their feature size is too small and too easily corrupted by a cosmic ray. Very large, bulky features keep spacecraft memory far smaller than what earthbound computers can enjoy. As far as returning one of the Voyagers to Earth, it would take several thousand years using available technology. Better to wait for more advanced propulsion technologies. Reply
- View All 20 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Hubble telescope celebrates 34th anniversary with an iridescent Dumbbell Nebula (image)
- 3 The mystery of how strange cosmic objects called 'JuMBOs' went rogue
- 4 China's Tiangong space station damaged by debris strike: report
- 5 Space Force tests small satellite jammer to protect against 'space-enabled' attacks
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe
Engineers spent months working to repair link with Earth’s most distant spacecraft, says space agency
Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday , JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X . “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries , including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.

Cosmic cleaners: the scientists scouring English cathedral roofs for space dust

Russia acknowledges continuing air leak from its segment of space station

Uncontrolled European satellite falls to Earth after 30 years in orbit

Cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko sets world record for most time spent in space

‘Old smokers’: astronomers discover giant ancient stars in Milky Way

Nasa postpones plans to send humans to moon

What happened to the Peregrine lander and what does it mean for moon missions?

Peregrine 1 has ‘no chance’ of landing on moon due to fuel leak
Most viewed.
Voyager 1 had a problem. Here's how NASA fixed it from 15 billion miles away.
Working from more than 15 billion miles away, NASA engineers have solved a computer problem aboard Voyager 1 , allowing the probe to send readable data five months after a chip error made its transmissions impossible to decipher.
Voyager 1, along with its sister craft, Voyager 2, are robotic probes that were launched in 1977. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in 2012. It's now 15.1 billion miles away, the farthest from Earth a human-made object has ever traveled.
Learn more: Closer look at Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 .
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space − the space between the stars, starting at abou t 11 billion miles from our sun − in 2018. It's now 12.7 billion miles away.
Voyager 1's computer glitch garbled the science and engineering data the craft sends to Earth, which rendered it unreadable. That started on Nov. 14, 2023.
How did engineers fix Voyager's problem?
Engineers from NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered a single computer chip inside the spacecraft’s Flight Data Subsystem – which collects science and engineering information and transmits it to Earth – had malfunctioned.
Can't see our graphics? Click here .
The chip stored part of the Flight Data Subsystem's memory and software code. Engineers could still receive data from Voyager 1, but it was scrambled.
The chip could not be repaired. Instead, engineers moved software code from the chip into a different part of the subsystem's memory system.
The code was too large to to be stored in a single location in the spacecraft. Engineers divided the code into sections and stored them in different places within the subsystem. The code sections were adjusted to make sure they worked as a whole.
Engineers tested the fix by moving a code that transmits data about the spacecraft. They were rewarded with a transmission from Voyager that contained readable data about the craft's status.
All that took time. Voyager is moving about 38,000 mph. Because it's so far away, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach Voyager. It takes another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft’s reply to reach antenna networks on Earth.
What happens next?
Engineers will reposition and synchronize the other parts of the code. That should allow Voyager 1 to start sending readable data on what it finds as it moves farther away from Earth.
SOURCE USA TODAY Network reporting and research; NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology; Reuters
share this!
April 22, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth

For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft's three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it's sent to Earth.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory—including some of the FDS computer's software code—isn't working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.
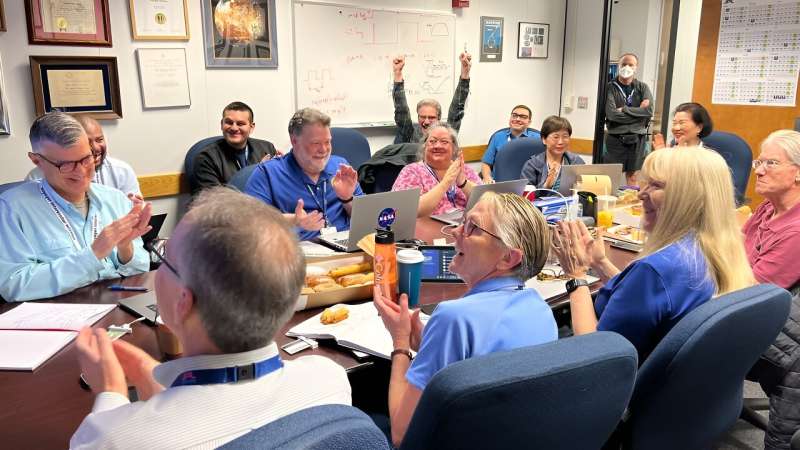

The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft's engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22.5 hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification had worked: For the first time in five months, they were able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago, the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Provided by NASA
Explore further
Feedback to editors

More efficient molecular motor widens potential applications

Managing meandering waterways in a changing world
14 hours ago


New dataset sheds light on relationship of far-red sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence to canopy-level photosynthesis
15 hours ago

How much trust do people have in different types of scientists?
16 hours ago

Scientists say voluntary corporate emissions targets not enough to create real climate action

Barley plants fine-tune their root microbial communities through sugary secretions

A shortcut for drug discovery: Novel method predicts on a large scale how small molecules interact with proteins

Yeast study offers possible answer to why some species are generalists and others specialists

Cichlid fishes' curiosity promotes biodiversity: How exploratory behavior aids in ecological adaptation

Climate change could become the main driver of biodiversity decline by mid-century, analysis suggests
Relevant physicsforums posts, our beautiful universe - photos and videos.
7 hours ago
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
13 hours ago
'Devil' comet visible tonight 21.04.24
Waves in space.
17 hours ago
Documenting the setup of my new telescope
Apr 24, 2024
What did I capture?
Apr 23, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Engineers working to resolve issue with Voyager 1 computer
Dec 13, 2023

NASA hears signal from Voyager 2 spacecraft after mistakenly cutting contact
Aug 1, 2023

NASA listens for Voyager 2 spacecraft after wrong command cuts contact
Jul 31, 2023

NASA's Voyager team focuses on software patch, thrusters
Oct 20, 2023

NASA's Voyager will do more science with new power strategy
Apr 27, 2023

Engineers investigating NASA's Voyager 1 telemetry data
May 18, 2022
Recommended for you

Japan's moon lander wasn't built to survive a weekslong lunar night. It's still going after 3

Simulated microgravity affects sleep and physiological rhythms, study finds
Apr 22, 2024

'Tube map' around planets and moons made possible by knot theory
Apr 17, 2024

NASA's Ingenuity Mars helicopter team says goodbye—for now

NASA confirms mystery object that crashed through roof of Florida home came from space station
Apr 16, 2024

NASA is seeking a faster, cheaper way to bring Mars samples to Earth
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission
NASA’s 1977-Vintage Voyager 1 Comes Back Online
NASA’s interstellar spacecraft, Voyager 1, is coming back online, the space agency announced on April 22.
After months of troubleshooting a glitch on Voyager 1 that caused the spacecraft to send home unusable data, the probe is working again and returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.
The next step, NASA said, is to enable the probe to begin returning science data.
NASA launched Voyager 1 — and later its twin Voyager 2 — in the summer of 1977 from Cape Canaveral, Fla., as part of a mission to explore interstellar space. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made its historic entry into interstellar space and beyond the influence of our Sun.
However, for the last year the probe has been experiencing several software and data glitches that could bring its mission to an end.
Engineers discovered a glitch on one of the probe ’ s three onboard computers , the flight data system (FDS). The FDS collects data – including engineering data about the health and status of the spacecraft. It then combines that information into a single data “package” which is sent back to Earth.
For the last year, the spacecraft has received and executed commands sent from Earth. However, the FDS was not communicating suitably with one of the probe’s subsystems – the telemetry modulation unit – and, as a result, it was returning distorted data.
The team attempted to fix the glitch by patching the software to prevent the recurrence of the glitch and prevent the issue from occurring again in Voyager 1 or arising in Voyager 2, but that that fix did not work.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally.
Unable to repair the chip, the team placed the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory because no single location was large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
According to NASA, the engineering team devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS.
For the plan to work, the team needed to adjust those code sections to ensure they still function, and the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated.
“The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft’s engineering data,” according to a NASA statement .
The team sent the code to the new location in the FDS memory on April 18. The mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, and the modification worked.
“For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft,” NASA said.
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
- DoD CIO Issues DevSecOps cATO Guidance
- Commerce Dept. Unveils $6.1B CHIPS Deal With Micron
- PCAST Report Argues Strong Use Cases for AI in Scientific Research
Privacy Overview
NASA's Voyager 1 sending readable data back to Earth for 1st time in 5 months
The problem stemmed from a corrupted chip in one of the spacecraft's computers.
After more than five months without contact, NASA has finally reconnected with Voyager 1, the farthest spacecraft from Earth.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) said Voyager 1 had not been sending readable data back to Earth since Nov. 14, 2023, despite the spacecraft still receiving mission controller commands.
In December 2023, the JPL announced the problem was with one of Voyager 1's onboard computers called the flight data subsystem (FDS). Engineers attempted to restart the computer, but the problem persisted, NASA said.
MORE: NASA asks for help studying Uranus and Neptune as it prepares to capture new images
However, the JPL announced this week that Voyager 1 had resumed sending engineering updates to Earth.
Engineers pinpointed the problem earlier this month, NASA said: A chip responsible for storing part of the computer's memory had become corrupted, making the data unreadable. The team was unable to repair the chip and decided the affected code needed to be stored elsewhere in the FDS memory, but no single location was large enough to do so, the JPL said in a release Monday.

The team "devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS," the release read. "To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole."
The code that packages Voyager 1's engineering data was the first to be sent to its new location on April 18. The JPL said it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach Voyager 1 and another 22.5 hours for the signal to come back to Earth. When the team heard from Voyager 1 on April 20, they knew the fix was a success, the JPL said.
"Hi, it's me. - V1," the X account for Voyager 1 posted on Monday afternoon.
Over the next few weeks, more portions of the FDS software will be relocated and the team will work to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again, the JPL said.
MORE: NASA says it's revising the Mars Sample Return mission due to cost, long wait time
Voyager 1 was launched in September 1977 under the Voyager program to study the farther planets of the solar system and interstellar space. Voyager 1 entered interstellar space in 2012 becoming the first man-made object to exit the solar system.
Meanwhile, its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, continues to "operate normally," according to the JPL. It reached interstellar space in 2018 and is the second-farthest spacecraft from Earth.
Related Topics
Top stories.

5 takeaways from historic Supreme Court arguments on Trump's immunity claim
- Apr 25, 4:06 PM

Could a president stage a coup? And 9 more key moments from Trump's immunity hearing
- Apr 25, 3:18 PM

Walmart US CEO talks inflation, self-checkout, and non-college degree workers
- Apr 25, 7:51 PM

Ex-official told investigators Trump had 'no standing declassification order'
- Apr 25, 6:55 PM

What witnesses said about Trump's handling of classified info while president
- Apr 24, 4:58 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
April 22, 2024
After Months of Gibberish, Voyager 1 Is Communicating Well Again
NASA scientists spent months coaxing the 46-year-old Voyager 1 spacecraft back into healthy communication
By Meghan Bartels

NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
NASA/JPL-Caltech
After months of nonsensical transmissions from humanity’s most distant emissary, NASA’s iconic Voyager 1 spacecraft is finally communicating intelligibly with Earth again.
Voyager 1 launched in 1977 , zipped past Jupiter and Saturn within just a few years and has been trekking farther from our sun ever since; the craft crossed into interstellar space in 2012. But in mid-November 2023 Voyager 1’s data transmissions became garbled , sending NASA engineers on a slow quest to troubleshoot the distant spacecraft. Finally, that work has paid off, and NASA has clear information on the probe’s health and status, the agency announced on April 22.
“It’s the most serious issue we’ve had since I’ve been the project manager, and it’s scary because you lose communication with the spacecraft,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in an interview with Scientific American when the team was still tracking down the issue.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The Voyager 1 spacecraft is a scientific legend : It discovered that Jupiter’s moon Io, far from being a dead world like our own companion, is instead a supervolcanic world . The craft’s data suggested that Saturn’s moon Titan might have liquid on its surface. And for more than a decade, Voyager 1 has given scientists a glimpse at what space looks like beyond the influence of our sun.
Yet its long years in the harsh environment of space have done a number on the probe, which was designed to last just four years. In particular, degraded performance and low power supplies have forced NASA to turn off six of its 10 instruments, and its communication has gotten even spottier than can be explained by the fact that cosmic mechanics mean a signal takes nearly one Earth day to travel between humans and the probe.
When the latest communications glitch occurred last fall, scientists could still send signals to the distant probe, and they could tell that the spacecraft was operating. But all they got from Voyager 1 was gibberish—what NASA described in December 2023 as “a repeating pattern of ones and zeros.” The team was able to trace the issue back to a part of the spacecraft’s computer system called the flight data subsystem, or FDS, and identified that a particular chip within that system had failed.
Mission personnel couldn’t repair the chip. They were, however, able to break the code held on the failed chip into pieces they could tuck into spare corners of the FDS’s memory, according to NASA. The first such fix was transmitted to Voyager 1 on April 18. With a total distance of 30 billion miles to cross from Earth to the spacecraft and back, the team had to wait nearly two full days for a response from the probe. But on April 20 NASA got confirmation that the initial fix worked. Additional commands to rewrite the rest of the FDS system’s lost code are scheduled for the coming weeks, according to the space agency, including commands that will restore the spacecraft’s ability to send home science data.
Although, for now, Voyager 1 appears to be on the mend, NASA scientists know it won’t last forever. Sooner or later, a glitch they can’t fix will occur, or the spacecraft’s ever dwindling fuel supply will run out for good. Until then NASA is determined to get as much data as possible out of the venerable spacecraft—and its twin, Voyager 2, which experienced its own communications glitch earlier in 2023 .
Voyager 1 talking to Earth again after NASA engineers 24 billion kilometres away devise software fix
NASA's Voyager 1 probe — the most distant man-made object in the universe — is returning usable information to ground control following months of spouting gibberish, the US space agency says.
The spaceship stopped sending readable data back to Earth on November 14, 2023, even though controllers could tell it was still receiving their commands.
In March, teams working at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered that a single malfunctioning chip was to blame.
They then had to devise a clever coding fix that worked within the tight memory constraints of its 46-year-old computer system.
"There was a section of the computer memory no longer working," project leader Dr Linda Spilker told the ABC.
"So we had to reprogram what was in that memory, move it to a different location, link everything back together and send everything up in a patch.
"And then on Saturday morning, we watched as Voyager 1 sent its first commands back and we knew we were back in communication once again."
Dr Spilker said they were receiving engineering data, so they knew the health and safety of the spacecraft.
"The next step is going to be to develop a patch so we can send back the science data," she said.
"That will really be exciting, to once again learn about interstellar space and what has been going on there that we've missed since November."
Dr Spilker said Voyager sent back data in real time, so the team had no facility to retrieve data covering the time since transmission was lost.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind's first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium , in 2012, and is currently more than 24 billion kilometres from Earth.
Messages sent from Earth take about 22.5 hours to reach the spacecraft.
Its twin, Voyager 2, also left the solar system in 2018 as it was tracked by Australia's Parkes radio telescope.
Australia was also vital to a 2023 search for Voyager 2 after signals were lost, with Canberra's Deep Space Communication Complex monitoring for signals and then sending a successful command to shift the spacecraft's antenna 2 degrees .
Both Voyager spacecraft carry " Golden Records ": 12-inch, gold-plated copper disks intended to convey the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
These include a map of our solar system, a piece of uranium that serves as a radioactive clock allowing recipients to date the spaceship's launch, and symbolic instructions that convey how to play the record.
The contents of the record, selected for NASA by a committee chaired by legendary astronomer Carl Sagan, include encoded images of life on Earth, as well as music and sounds that can be played using an included stylus.
Their power banks were expected to be depleted sometime after 2025, but Dr Spilker said several systems had been turned off, so they were hopeful the two spacecraft would function into the 2030s.
They will then continue to wander the Milky Way, potentially for eternity, in silence.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Nasa restores contact with missing voyager 2 spacecraft after weeks of silence.
How songs from tiny villages in the Pacific are now floating in outer space
Voyager 1 spacecraft enters interstellar space
- Astronomy (Space)
- Computer Science
- Space Exploration
- United States

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "Interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey through the Universe. In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
About the mission. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
Overview. The Cover. The Contents. The Making of. Galleries. Videos. Making of the Golden Record. Images on the Golden Record. Galleries of Images Voyager Took.
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018. Mission Type.
Phil Davis. PASADENA, Calif. -- NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has entered a new region at the far reaches of our solar system that scientists feel is the final area the spacecraft has to cross before reaching interstellar space. Scientists refer to this new region as a magnetic highway for charged particles because our sun's magnetic field lines ...
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
At approximately 2:10 p.m. Pacific time on February 17, 1998, Voyager 1, launched more than two decades ago, will cruise beyond the Pioneer 10 spacecraft and become the most distant human-created object in space at 10.4 billion kilometers (6.5 billion miles.) The two are headed in almost opposite directions away from the Sun.
On Saturday, April 5, Voyager 1 finally "phoned home" and updated its NASA operating team about its health. The interstellar explorer is back in touch after five months of sending back nonsense data.
Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 1 spacecraft began an epic journey that continues to this day. The second of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 1 lifted off on Sept. 5, 1977, 16 days after its twin left on a similar voyage. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, managed the two spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets.
In the SVG file, hover over a trajectory or orbit to highlight it and its associated launches and flybys. Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and the interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere.
This artist's concept shows NASA's two Voyager spacecraft exploring a turbulent region of space known as the heliosheath, the outer shell of the bubble of charged particles around our sun. Data from Voyager 1, now more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from the sun, suggest the spacecraft is closer to becoming the first human-made ...
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. In NASA's Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the actual spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers updated every five minutes.
In more common terms, Voyager 1 will be about 15 billion kilometers (9.3 billion miles) from the sun. Dr. Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist and the former director of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., says the Voyager team always predicted that the spacecraft would have enough power to last this long.
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 818-354-0724. [email protected]. Dwayne Brown. 202-358-1726. [email protected]. 2012-381. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has entered a new region at the far reaches of our solar system that scientists feel is the final area the spacecraft has to cross before reaching interstellar space.
NASA. Jun 06, 2013. RELEASE 12-416. WASHINGTON - NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has entered a new region at the far reaches of our solar system that scientists feel is the final area the spacecraft has to cross before reaching interstellar space. Scientists refer to this new region as a magnetic highway for charged particles because our sun ...
Since late 2023, engineers have been trying to get the Voyager spacecraft back online. On Dec. 12, 2023, NASA shared some worrisome news about Voyager 1, the first probe to walk away from our ...
Voyager 2 will make additional observations of the magnetic field in interstellar space and help scientists refine their estimates. Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were launched 16 days apart in 1977. Both spacecraft flew by Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 also flew by Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 2, launched before Voyager 1, is the longest continuously ...
Members of the Voyager flight team celebrate after receiving the first coherent data from Voyager 1 in five months at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on April 20. ... the Voyager 1 and its twin ...
Earth's most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.. Nasa's Jet Propulsion ...
NASA Voyager Status Update on Voyager 1 Location. Artist concept of NASA's Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech › larger image. "The Voyager team is aware of reports today that NASA's Voyager 1 has left the solar system," said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena ...
Learn more: Closer look at Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Voyager 2 entered interstellar space − the space between the stars, starting at about 11 billion miles from our sun − in 2018. It's now 12.7 ...
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and ...
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that ...
NASA's interstellar spacecraft, Voyager 1, is coming back online, the space agency announced on April 22. After months of troubleshooting a glitch on Voyager 1 that caused the spacecraft to send home unusable data, the probe is working again and returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) said Voyager 1 had not been sending readable data back to Earth since Nov. 14, 2023, despite the spacecraft still receiving mission controller commands.
But in mid-November 2023 Voyager 1's data transmissions became garbled, sending NASA engineers on a slow quest to troubleshoot the distant spacecraft. Finally, that work has paid off, and NASA ...
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind's first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium, in 2012, and is currently more than 24 billion kilometres from Earth.. Messages sent from Earth take ...