Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2021? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map right at the last second?

The thing is -- understanding your customer base can be extremely challenging. And even when you think you've got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

Download Now
While it isn't possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a very handy tool for keeping track of important milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I'll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents

What is the customer journey?
Customer journey stages.
- What is a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
What's included in a customer journey map, steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
- Customer Journey Map Best Practices
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer's journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I've worked with were confused about the differences between the customer's journey and the buyer's journey. The buyer's journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don't wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process to consider, evaluate, and decide to purchase a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand's place within the buyer's journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer's journey. When you create a customer journey map, you're taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey, instead of leaving it up to chance.
Free Customer Journey Map Template
Fill out this form to access the free templates..
For example, at HubSpot, our customer's journey is divided into 3 stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
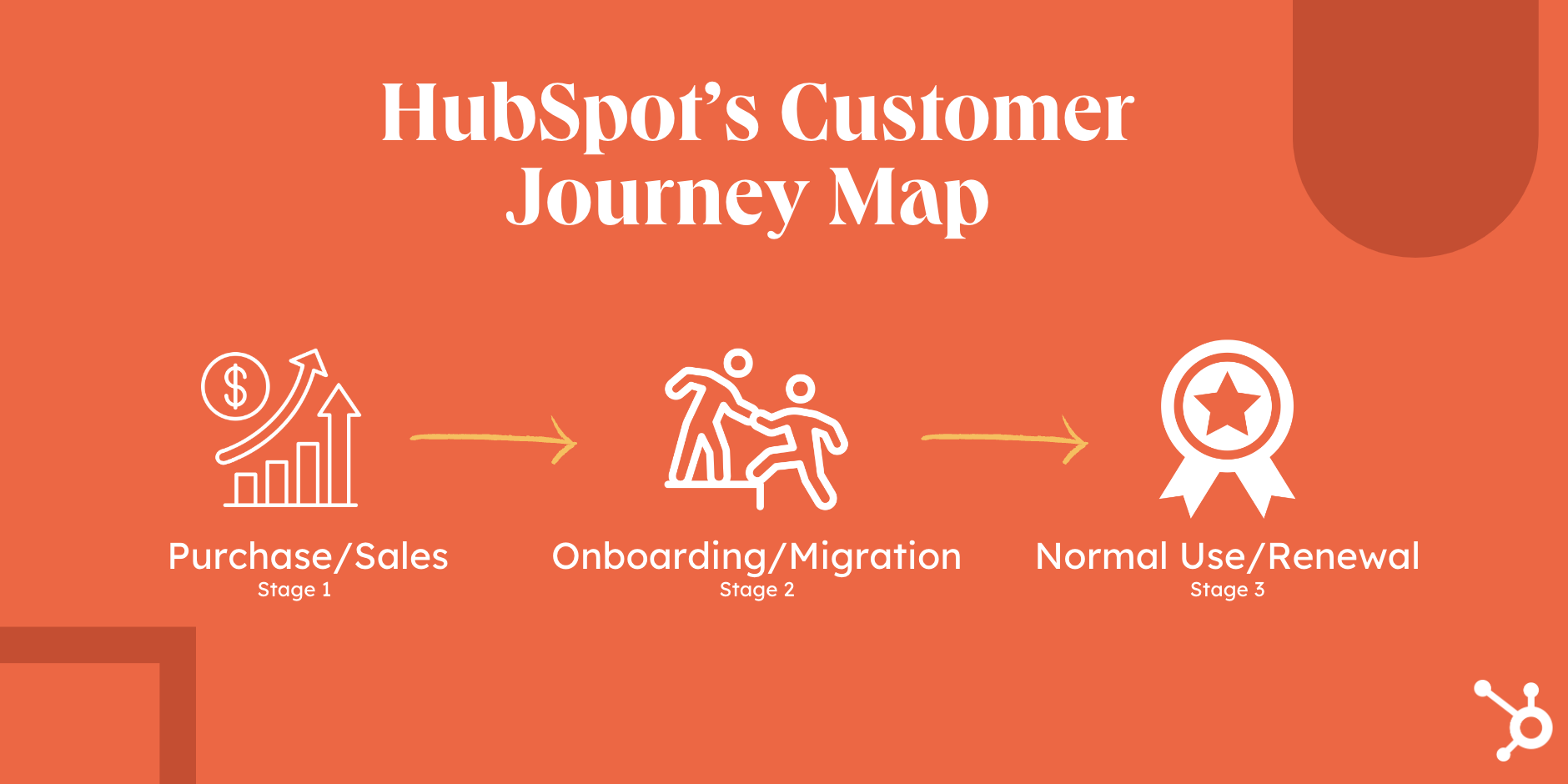
The stages may not be the same for you — in fact, your brand will likely come up with a set of unique stages of the customer journey. But where do you start? Let's take a look.
Generally, there are 5 phases that customers go through when interacting with a brand or a product: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Loyalty.
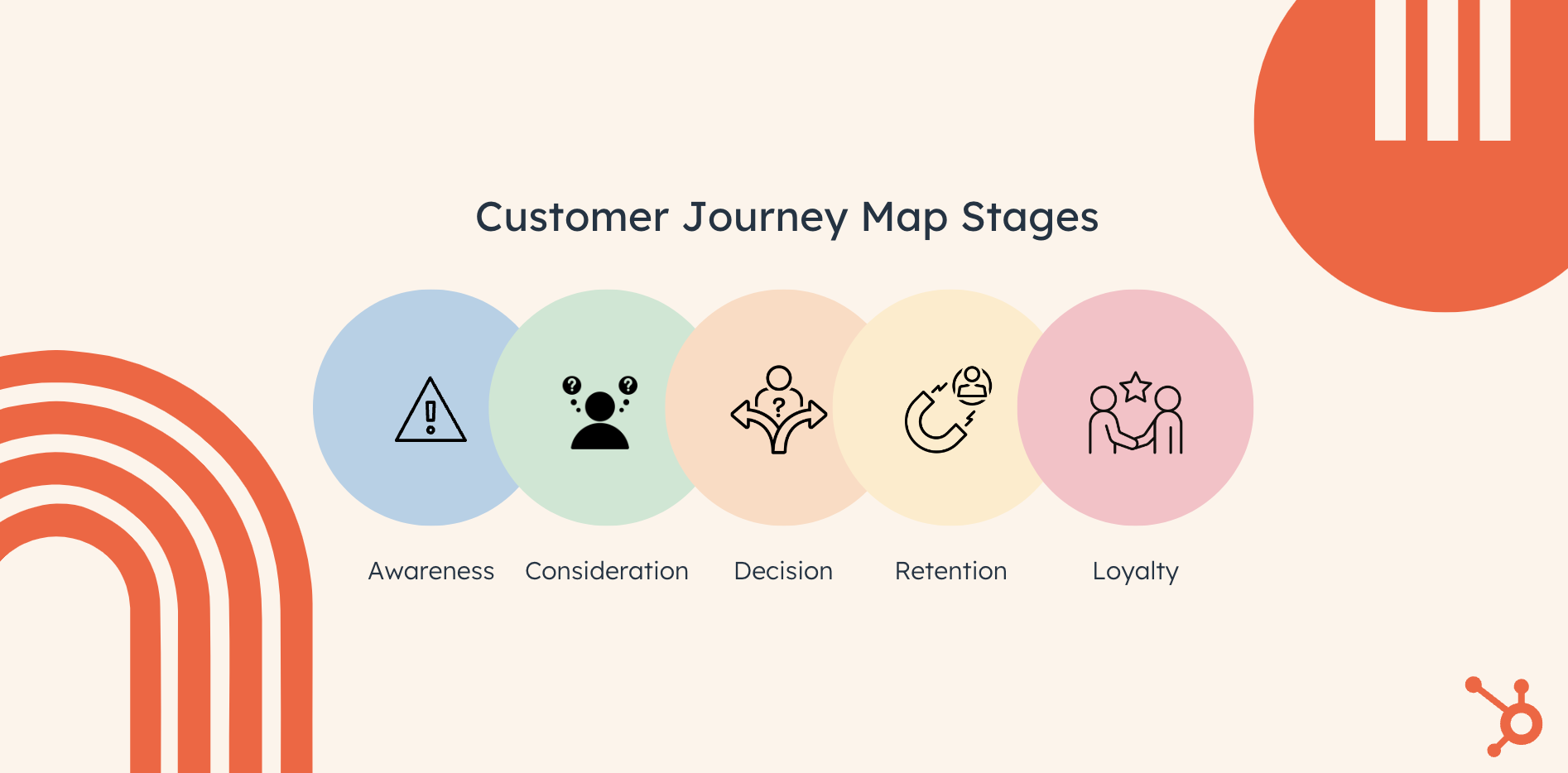
1. Awareness Stage
In the awareness stage, customers realize they have a problem. At this point, they may not know that they need a product or service, but they will begin doing research either way.
During this stage of the customer journey, brands should deliver educational content to help customers diagnose a problem and offer potential solutions. Your aim should be to help customers alleviate their pain point, not encourage a purchase.
Some educational content that I've created in the past are:
- How-to articles and guides
- General whitepapers
- General ebooks
- Free courses
Educational content may also be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Social media
- Search engines
2. Consideration
In the consideration stage, customers have done enough research to realize that they need a product or service. At this point, they begin to compare brands and offerings.
During this stage, brands should deliver product marketing content to help customers compare different offerings and, eventually, choose their product or service. The aim is to help customers navigate a crowded marketplace and move them toward a purchase decision.
Product marketing content may include:
- Product listicles
- Product comparison guides and charts
- Product-focused white papers
- Customer success stories or case studies
Product marketing content may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Your website
- Conferences
3. Decision Stage
In the decision stage, customers have chosen a solution and are ready to buy.
During this stage, your brand should deliver a seamless purchase process to make buying products as easy as possible. I wouldn't recommend any more educational or product content at this stage — it's all about getting customers to make a purchase. That means you can be more direct about wanting customers to buy from you.
Decision-stage content may include:
- Free consultations
- Product sign-up pages
- Pricing pages
- Product promotions (i.e "Sign up now and save 30%")
Decision-stage content may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
4. Retention Stage
In the retention stage, customers have now purchased a solution and stay with the company they purchased from, as opposed to leaving for another provider.
During this stage, brands provide an excellent onboarding experience and ongoing customer service to ensure that customers don't churn.
Retention-stage strategies may include:
- Providing a dedicated customer success manager
- Making your customer service team easily accessible
- Creating a knowledge base in case customers ever run into a roadblock
Retention-stage strategies may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
5. Loyalty Stage
In the loyalty stage, customers not only choose to stay with a company — they actively promote it to family, friends, and colleagues. The loyalty stage can also be called the advocacy stage.
During this phase, brands should focus on providing a fantastic end-to-end customer experience. This should span from your website content to your sales reps all the way to your social media team and your product's UX.
Most importantly, customers become loyal when they've achieved success with your product — if it works, they're more likely to recommend your brand to others.
Loyalty-stage strategies may include:
- Having an easy-to-navigate website
- Investing in your product team to ensure your product exceeds customer expectations
- Making it easy to share your brand with others via a loyalty or referral program
- Providing perks to continued customers, such as discounts
Loyalty-stage strategies may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Your products
To find out whether your customers have reached the loyalty stage, try a Net Promoter Score survey , which asks one simple question: "On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend us to a friend?" To deliver this survey, you can use customer feedback software like Service Hub .
Now, let's get to the good stuff. Let's talk about creating your customer journey map.
What is the customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer's experience with a company. It also provides insight into the needs of potential customers at every stage of this journey and the factors that directly or indirectly motivate or inhibit their progress.
The business can then use this information to improve the customer's experience, increase conversions, and boost customer retention.
Now, the customer journey map is not to be confused with a UX journey map. But, for clarity, let's distinguish these two below.
What is UX journey mapping?
A UX journey map represents how a customer experiences their journey toward achieving a specific goal or completing a particular action.
For example, the term "UX journey mapping" can be used interchangeably with the term "customer journey mapping" if the goal being tracked is the user's journey toward purchasing a product or service.
However, UX journey mapping can also be used to map the journey (i.e., actions taken) towards other goals, such as using a specific product feature.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
While the customer journey might seem straightforward — the company offers a product or service, and customers buy it — for most businesses, it typically isn't.
In reality, it's a complex journey that begins when the customer becomes problem-aware (which might be long before they become product-aware) and then moves through an intricate process of further awareness, consideration, and decision-making.
The customer is also exposed to multiple external factors (competitor ads, reviews, etc.) and touchpoints with the company (conversations with sales reps, interacting with content, viewing product demos, etc.).
Keep in mind that 80% of customers consider their experience with a company to be as important as its products.
By mapping this journey, your marketing, sales, and service teams can understand, visualize, and gain insight into each stage of the process.
You can then decrease any friction along the way and make the journey as helpful and delightful as possible for your leads and customers.
Customer journey mapping is the process of creating a customer journey map — the visual representation of a company's customer experience. It compiles a customer's experience as they interact with a business and combines the information into a visual map.
The goal of this process is to draw insights that help you understand how your customers experience their journeys and identify the potential bottlenecks along the way.
It's also important to note that most customer journeys aren't linear. Instead, buyers often experience a back-and-forth, cyclical, multi-channel journey.
Let's look at the stages that you should include in any customer journey.
- The Buying Process
- User Actions
- User Research
1. The Buying Process
To determine your customers' buying process, you'll want to pull data from all relevant sources (prospecting tools, CMS, behavior analytics tools, etc.) to accurately chart your customer's path from first to last contact.
However, you can keep it simple by creating broad categories using the typical buying journey process stages — awareness, consideration, and decision — and mapping them horizontally.
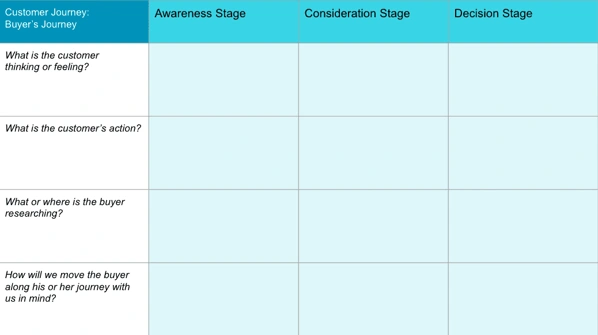
2. Emotions
Whether the goal is big or small, remember your customers are solving a problem. That means they're probably feeling some emotion — whether that's relief, happiness, excitement, or worry.
Adding these emotions to the journey map will help you identify and mitigate negative emotions and the pain points that cause them.
On HubSpot's journey map , we use emojis to represent potential emotions at different stages of the customer journey.
3. User Actions
This element details what a customer does in each stage of the buying process. For example, during the problem-awareness stage, customers might download ebooks or join educational webinars.
Essentially, you're exploring how your customers move through and behave at each stage of their journey.
4. User Research
Similar to the last section, this element describes what or where the buyer researches when they are taking action.
More than likely, the buyer will turn to search engines, like Google, to research solutions during the awareness stage. However, it's important to pay attention to what they're researching so you can best address their pain points.
5. Solutions
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot's free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer's journey, a day in the life of your customer, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company's buyer persona. Not only will this lead to improvements to your product, but also a better customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you're creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don't have one, I would recommend creating a buyer persona . This is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics representing your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics at the ready.
Don't have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot's Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Some great ways to get valuable customer feedback are questionnaires and user testing. The important thing is to only reach out to actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services and who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you've learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I would recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a UX journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company — so if you group too many personas into one journey, your map won't accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it's best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don't worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there's no overlap.
This is essential in creating a UX journey map because it provides insight into your customers' actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they're quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you also need to look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels
- Email marketing
- Third-party review sites or mentions
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
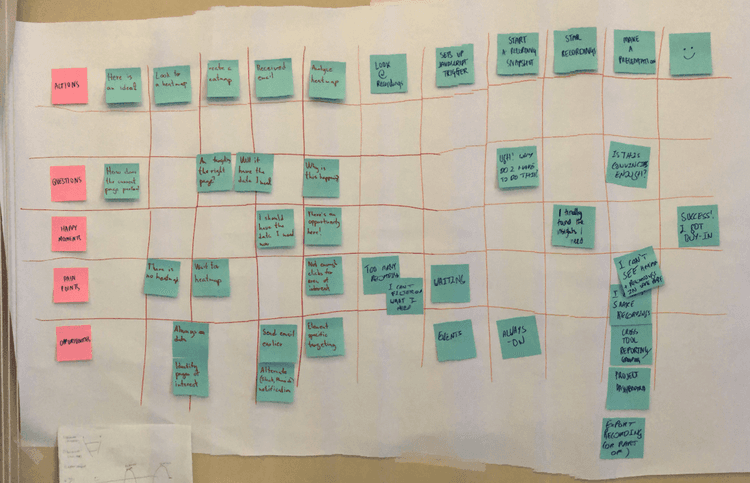
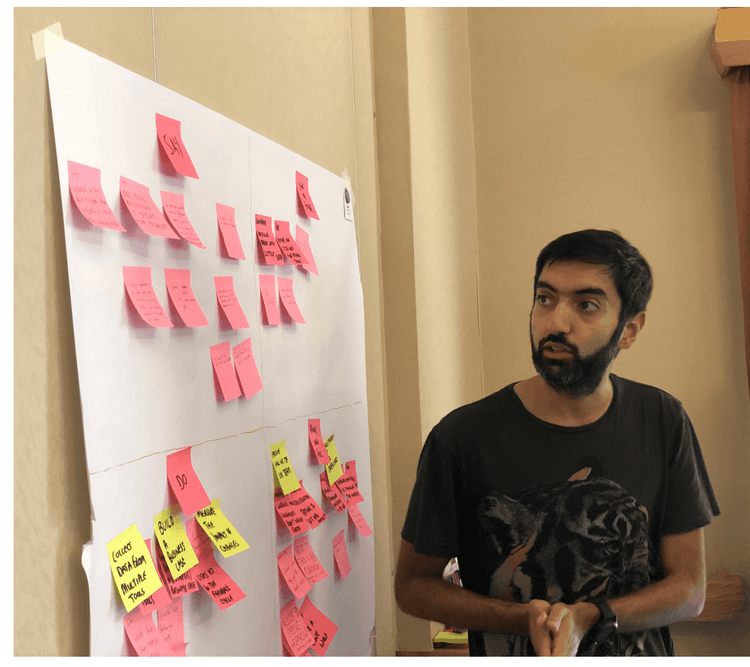
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand, impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding -- you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

HubSpot's free customer journey map template makes it easier than ever to visualize the buyer's journey. It saved me some time organizing and outlining my customer experience and it made it clear how a website could impact my user's lives.
The customer journey map template can also help you discover areas of improvement in your product, marketing, and support processes.
Download a free, editable customer journey map template.
Types of Customer Journey Maps and Examples
There are four types of customer journey maps , each with unique benefits. Pick the one that makes the most sense for your company.
Current State
These customer journey maps are the most widely used type. They visualize the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers currently experience while interacting with your company. They're best used for continually improving the customer journey.
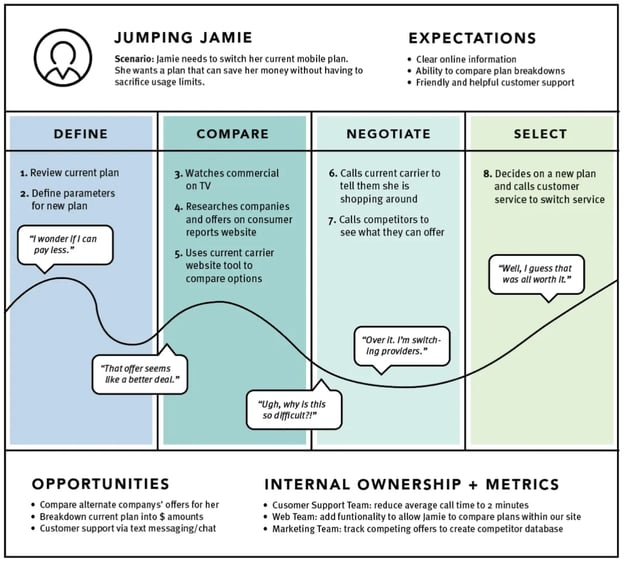
Image Source
Day in the Life
These customer journey maps visualize the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers currently experience in their daily activities, whether or not that includes your company.
This type gives a broader lens into your customers' lives and what their pain points are in real life.
Day-in-the-life maps are best used for addressing unmet customer needs before customers even know they exist. Your company may use this type of customer journey map when exploring new market development strategies .

Future State
These customer journey maps visualize what actions, thoughts, and emotions that your customers will experience in future interactions with your company. Based on their current interaction with your company, you'll have a clear picture of where your business fits in later down the road.
These maps are best for illustrating your vision and setting clear, strategic goals.
Service Blueprint
These customer journey maps begin with a simplified version of one of the above map styles. Then, they layer on the factors responsible for delivering that experience, including people, policies, technologies, and processes.
Service blueprints are best used to identify the root causes of current customer journeys or the steps needed to attain desired future customer journeys.
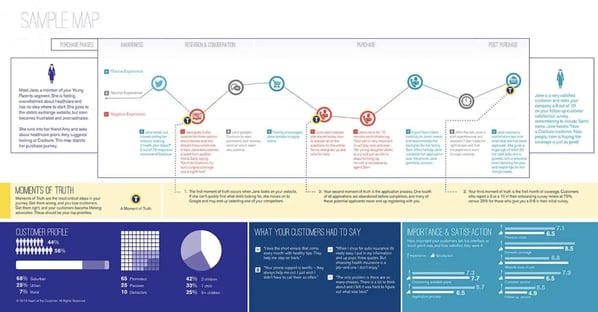
If you want a look at a real customer journey map that HubSpot has used recently, check out this interview we conducted with Sarah Flint, Director of System Operations at HubSpot. We asked her how her team put together their map (below) as well as what advice she would give to businesses starting from scratch.

Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Set a goal for the journey map.
- Survey customers to understand their buying journey.
- Ask customer service reps about the questions they receive most frequently.
- Consider UX journey mapping for each buyer persona.
- Review and update each journey map after every major product release.
- Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams.
1. Set a goal for the journey map.
Determine whether you aim to improve the buying experience or launch a new product. Knowing what the journey map needs to tell you can prevent scope creep on a large project like this.
2. Survey customers to understand their buying journey.
What you think you know about the customer experience and what they actually experience can be very different. Speak to your customers directly, so you have an accurate snapshot of the customer's journey.
3. Ask customer service reps about the questions they receive most frequently.
Sometimes, customers aren't aware of their specific pain points, and that's where your customer service reps come in.
They can help fill in the gaps and translate customer pain points into business terms you and your team can understand and act on.
4. Consider UX journey mapping for each buyer persona.
It's easy to assume each customer operates the same way, but that couldn't be further from the truth.
Demographics, psychographics, and even how long someone has been a customer can determine how a person interacts with your business and makes purchasing decisions.
Group overarching themes into buyer personas and create a UX journey map for each.
5. Review and update each journey map after every major product release.
Every time your product or service changes, the customer's buying process changes. Even slight tweaks, like adding an extra field to a form, can become a significant roadblock.
So, reviewing the customer journey map before and after implementing changes is essential.
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams.
Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is a convenient way for cross-functional teams to provide feedback.
Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team, so they always keep the customer top of mind.
Breaking down the customer journey, phase by phase, aligning each step with a goal, and restructuring your touchpoints accordingly are essential steps for maximizing customer success .
Here are a few more benefits to gain from customer journey mapping.
1. You can refocus your company with an inbound perspective.
Rather than discovering customers through outbound marketing, you can have your customers find you with the help of inbound marketing.
Outbound marketing involves tactics targeted at generalized or uninterested audiences and seeks to interrupt the customers' daily lives. Outbound marketing is costly and inefficient. It annoys and deters customers and prospects.
Inbound marketing involves creating helpful content that customers are already looking for. You grab their attention first and focus on the sales later.
By mapping out the customer journey, you can understand what's interesting and helpful to your customers and what's turning them away.
2. You can create a new target customer base.
You need to understand the customer journey properly to understand your customers' demographics and psychographics.
It's a waste of time and money to repeatedly target too broad of an audience rather than people who are actually interested in your offering.
Researching the needs and pain points of your typical customers will give you a good picture of the kinds of people who are trying to achieve a goal with your company. Thus, you can hone your marketing to that specific audience.
3. You can implement proactive customer service.
A customer journey map is like a roadmap to the customer's experience.
It highlights moments where people experience delight and situations where they might face friction. Knowing this ahead of time allows you to plan your customer service strategy and intervene at ideal times.
Proactive customer service also makes your brand appear more reliable. For example, when I worked in customer support, we would anticipate a surge in tickets around the holidays. To be proactive, we'd send out a message to customers letting them know about our team's adjusted holiday hours. We would aalso tell them about additional support options if we were unavailable and what to do if an urgent problem needed immediate attention.
With expectations set, customers won't feel surprised if they're waiting on hold a little longer than usual. They'll even have alternative options to choose from — like a chatbot or knowledge base — if they need to find a faster solution.
4. You can improve your customer retention rate.
When you have a complete view of the customer journey, it's easier to pick out areas where you can improve it. When you do, customers experience fewer pain points, leading to fewer people leaving your brand for competitors.
After all, 33% of customers will consider switching brands after just one poor experience.
UX journey mapping can point out individuals on the path to churn. If you log the common behaviors of these customers, you can start to spot them before they leave your business.
While you might not save them all, it's worth the try. Increasing customer retention rates by just 5% can increase profits by 25%-95%.
5. You can create a customer-focused mentality throughout the company.
As your company grows, it can be tricky to coordinate all your departments to be as customer-focused as your customer service, support, and success teams are. That's because each department has varying goals, meaning they might not be prioritizing customer needs -- they might focusing on website traffic, leads, product signups, etc.
One way to overcome this data silo is to share a clear customer journey map with your entire organization. The great thing about these maps is that they map out every single step of the customer journey, from initial attraction to post-purchase support. And, yes, this concerns marketing, sales, and service.
For more examples of customer journey maps, read on to the next section for a few templates you can use as a baseline for your company's map.
Customer Journey Mapping Examples
To help guide your business in its direction, here are examples to draw inspiration from for building out your customer journey map.
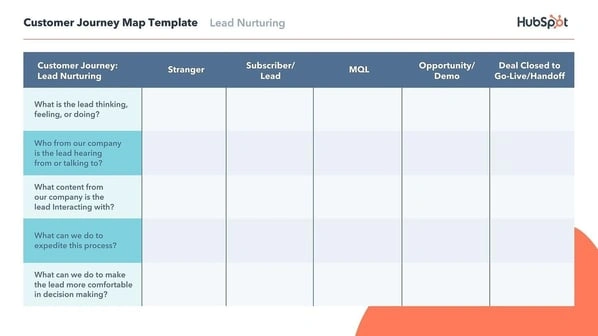
1. HubSpot's Customer Journey Map Templates
HubSpot's free Customer Journey Map Templates provide an outline for companies to understand their customers' experiences.
The offer includes the following:
- Current State Template
- Lead Nurturing Mapping Template
- A Day in the Customer's Life Template
- Customer Churn Mapping Template
- Customer Support Blueprint Template
Each of these templates helps organizations gain new insights into their customer base and help make improvements to product, marketing, and customer support processes.
Download them today to start working on your customer journey map.
2. B2B Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map clearly outlines the five steps Dapper Apps believes customers go through when interacting with them.
As you can see, it goes beyond the actual purchasing phase by incorporating initial research and post-purchase needs.
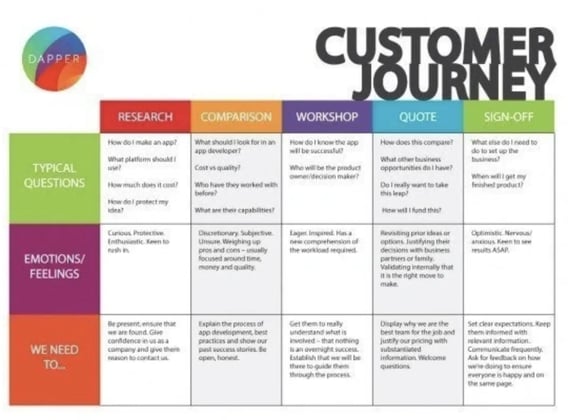
This map is effective because it helps employees get into the customers' minds by understanding the typical questions they have and the emotions they're feeling.
There are incremental action steps that Dapper Apps can take in response to these questions and feelings that will help it solve all the current problems customers are having.
3. Ecommerce Customer Journey Map Example
This fictitious customer journey map is a clear example of a day-in-the-life map.
Rather than just focusing on the actions and emotions involved in the customer's interaction with the company, this map outlines all the actions and emotions the customer experiences on a typical day.
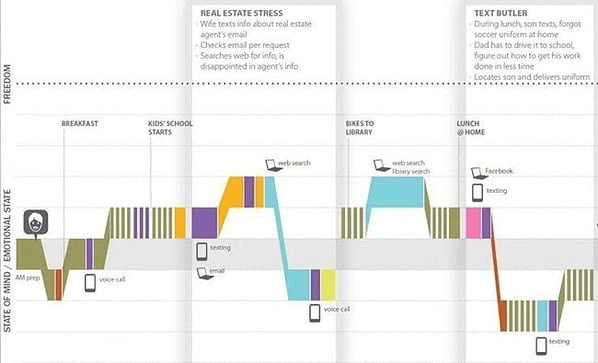
This map is helpful because it measures a customer's state of mind based on the level of freedom they get from certain stimuli.
This is helpful for a company that wants to understand what its target customers are stressed about and what problems may need solving.
4. Future B2C Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map, designed for Carnegie Mellon University, exemplifies the usefulness of a future state customer journey map. It outlines the thoughts, feelings, and actions the university wants its students to have.
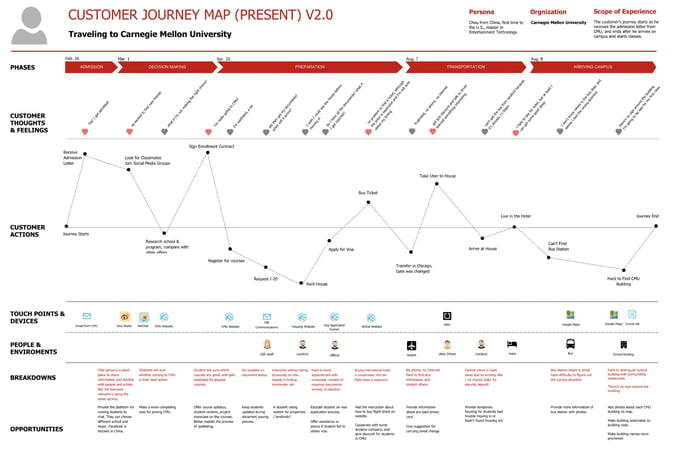
Based on these goals, CMU chose specific proposed changes for each phase and even wrote out example scenarios for each phase.
This clear diagram can visualize the company vision and help any department understand where they will fit into building a better user experience.
5. Retail Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map shows an in-depth customer journey map of a customer interacting with a fictitious restaurant.
It's clear that this style of map is more comprehensive than the others. It includes the front-of-stage (direct) and back-of-stage (non-direct or invisible) interactions a customer has with the company, as well as the support processes.
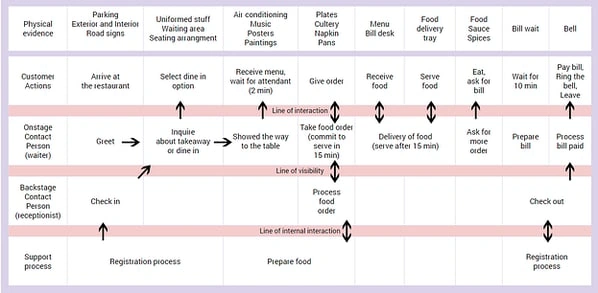
This map lays out every action involved in the customer experience, including those of the customer, employees directly serving diners, and employees working behind the scenes.
By analyzing how each of these factors influences the customer journey, a company can find the root cause of mishaps and problem-solve this for the future.
To get your business from point A — deciding to focus on customer journeys — to point B — having a journey map — a critical step to the process is selecting which customer mindset your business will focus on.
This mindset will determine which of the following templates you'll use.
1. Current State Template
If you're using this template for a B2B product, the phases may reflect the search, awareness, consideration of options, purchasing decision, and post-purchase support processes.
For instance, in our Dapper Apps example, its phases were research, comparison, workshop, quote, and sign-off.
2. Day in the Life Template
Since this template reflects all the thoughts, feelings, actions, needs, and pain points a customer has in their entire daily routine — whether or not that includes your company — you'll want to map out this template in a chronological structure.
This way, you can highlight the times of day at which you can offer the best support.
Get an interactive day in the life template.
3. Future State Template
Similar to the current state template, these phases may also reflect the predicted or desired search, awareness, consideration of options, purchasing decision, and post-purchase support processes.
Since this takes place in the future, you can tailor these phases based on what you'd like the customer journey to look like rather than what it currently looks like.
Get an interactive future state template.

4. Service Blueprint Template
Since this template is more in-depth, it doesn't follow certain phases in the customer journey.
Instead, it's based on physical evidence — the tangible factors that can create impressions about the quality and prices of the service — that often come in sets of multiple people, places, or objects at a time.
For instance, with our fictitious restaurant example above, the physical evidence includes all the staff, tables, decorations, cutlery, menus, food, and anything else a customer comes into contact with.
You would then list the appropriate customer actions and employee interactions to correspond with each physical evidence.
For example, when the physical evidence is plates, cutlery, napkins, and pans, the customer gives their order, the front-of-stage employee (waiter) takes the order, the back-of-stage employee (receptionist) processes the order, and the support processes (chefs) prepare the food.
Get an interactive service blueprint template.

5. Buyer's Journey Template
You can also use the classic buyer's journey — awareness, consideration, and decision — to design your customer journey map.
Get an interactive buyer's journey template.
Charter the Path to Customer Success
Once you fully understand your customer's experience with your business, you can delight them at every stage of their buying journey. Remember, many factors can affect this journey, including customer pain points, emotions, and your company's touchpoints and processes.
A customer journey map is the most effective way to visualize this information, whether you're optimizing the customer experience or exploring a new business opportunity to serve a customer's unrecognized needs.
Use the free templates in this article to start mapping the future of customer success at your business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August, 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![create a customer journey map How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![create a customer journey map How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![create a customer journey map Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]
![create a customer journey map How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-journey-map_13.webp)
How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![create a customer journey map How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
Customer journey mapping in 2 and 1/2 days
How to create a customer journey map that improves customer success.
Last updated
Reading time.
There’s a common saying that you can’t understand someone until you’ve walked a mile in their shoes—and that’s exactly what customer journey maps do: they help you put yourself in different customers’ shoes and understand your business from their point of view.
Why should you do it? How should you do it? Find the answers in this guide, which we wrote after interviewing 10+ customer journey experts who shared methodologies, dos and don’ts, and pro tips with us.
On this page:
What is a customer journey map?
How to create a customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
4 benefits of customer journey mapping for your business
In later chapters, we dive deeper into customer journey analytics, workshops, and real-life examples.
Start mapping your customer journey
Hotjar lets you experience the customer journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of how customers interact with and experience your website, products, or business across multiple touchpoints.
By visualizing the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience, a customer journey map helps you better understand them and identify the pain points they encounter. This is essential if you want to implement informed, customer-focused optimizations on your site.
Mapping the customer journey: narrow vs. wide focus
A customer journey map can have a very narrow focus and only look at a few, specific steps of the customer experience or buyer’s journey (for example, a product-to-purchase flow on a website), or it can take into account all the touchpoints, online and offline, someone goes through before and after doing business with you.
Each type of customer journey map has its advantages:
A CJM with a narrow focus allows you to zero in on an issue and effectively problem-solve
A CJM with a wide focus gives you a broader, holistic understanding of how customers experience your business
Regardless of their focus, the best customer journey maps have one thing in common: they are created with real customer data that you collect and analyze . The insights are usually organized into a map (hence the name), diagram, or flowchart during a group workshop, which is later shared across the entire business so everyone gets a clear and comprehensive overview of a customer’s journey.
How to create your first customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
The process of creating a customer journey map can be as long or short as you need. Depending on how many people and stakeholders you involve, how much data you collect and analyze, and how many touchpoints there are across the business, you could be looking at days or even weeks and months of work.
If you’re new to customer journey mapping, start from a narrower scope before moving on to mapping every single customer touchpoint .
Here’s our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days:
Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work
Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop.
Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results
Download your free customer journey map checklist (as seen below), to mark off your tasks as you complete them.
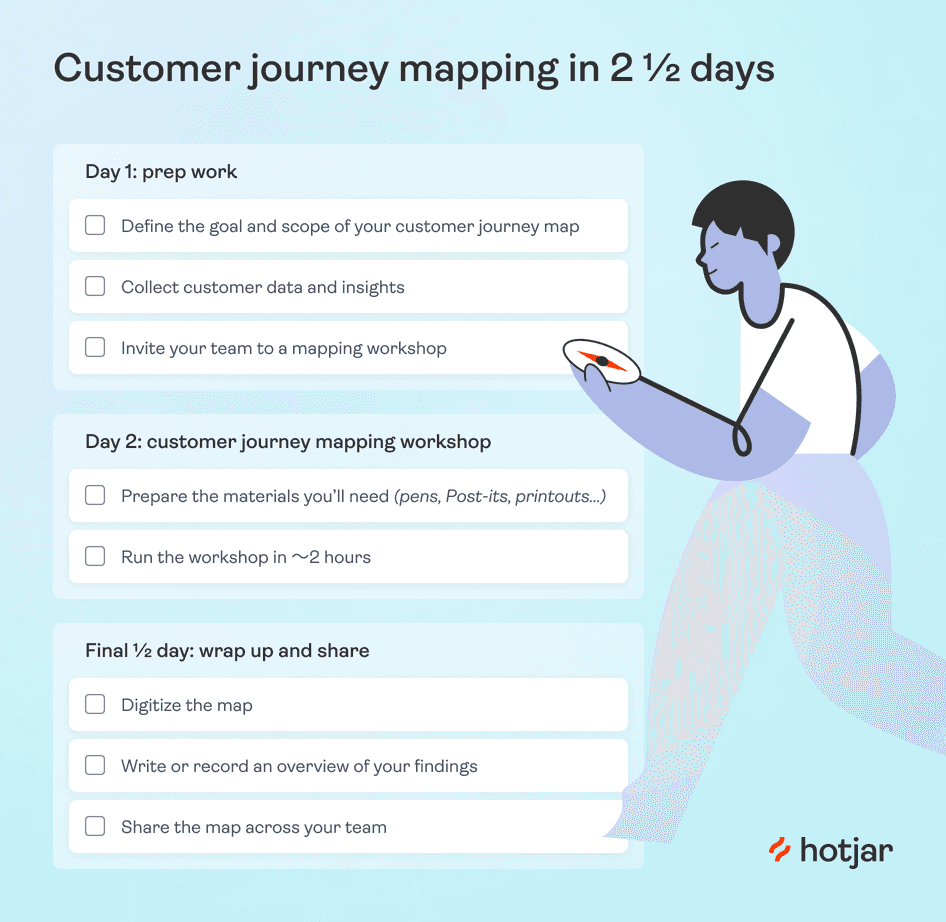
On your first day, you have three essential tasks:
Define the goal and scope of your CJM
Collect customer data and insights
Invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
Step 1: define the goal and scope of your CJM
Clarifying what part(s) of the journey you're looking at, and why, helps you stay focused throughout the mapping process.
If this is your first map, start from a known issue or problematic area of your website. Keep the scope small, and focus on anything you can break down into four or five steps. For example:
If you have a high drop-off on a pricing page with five calls-to-action, each of which takes users to a different page, that’s enough for a mappable journey
If your purchase flow is made of five self-contained pages, each of which loses you potential customers, that’s a good candidate for mapping
✅ The output: a one- or two-sentence description of what your map will cover, and why, you can use whenever you need to explain what the process is about. For example: this map looks at the purchase flow on our website, and helps us understand how customers go through each step and the issues or obstacles they encounter. The map starts after users click ‘proceed to checkout’ and ends when they reach the 'Thank You' page .
Step 2: collect customer data and insights
Once you identify your goal and scope, the bulk of your first day should be spent collecting data and insights you’ll analyze as part of your mapping process. Because your map is narrow in focus, don’t get distracted by wide-scale demographics or data points that are interesting and nice to know, but ultimately irrelevant.
Get your hands on as much of the following information as you can:
Metrics from traditional analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) that give you insight into what’s happening, across the pages and stages your customer journey map covers
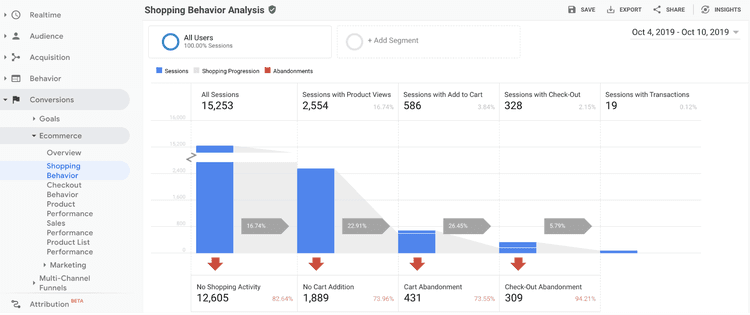
Data from analyzing your conversion ‘funnels’ , which record how many visitors end up at each stage of the user journey, so you can optimize those steps for potential customers and increase conversions
Behavior analytics data (from platforms like Hotjar) that show you how people interact with your site. For example, heatmaps give you an aggregate view of how users click, move and scroll on specific pages, and session recordings capture a user’s entire journey as they navigate your site
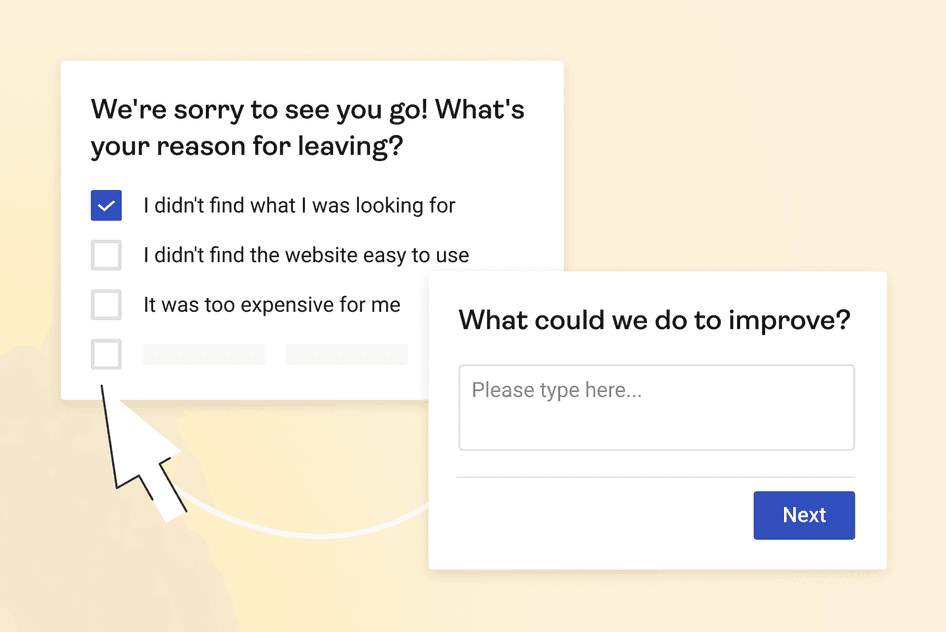
Quantitative and qualitative answers to on-site surveys relevant to the pages you’re going to investigate, as customer feedback will ultimately guide your roadmap of changes to make to improve the journey
Any demographic information about existing user and customer personas that helps you map the journey from the perspective of a real type of customer, rather than that of any hypothetical visitor, ensuring the journey makes sense for your target audience
Any relevant data from customer service chat logs, emails, or even anecdotal information from support, success, and sales teams about the issues customers usually experience
✅ The output: quantitative and qualitative data about your customers' interactions and their experiences across various touchpoints. For example, you’ll know how many people drop off at each individual stage, which page elements they interact with or ignore, and what stops them from converting.
💡Pro tip: as you read this guide, you may not yet have most of this data, particularly when it comes to heatmaps, recordings, and survey results. That’s ok.
Unless you’re running your CJM workshop in the next 12 hours, you have enough time to set up Hotjar on your website and start collecting insights right now. The platform helps you:
Learn where and why users drop off with Funnels
Visualize interactions on key pages with Heatmaps
Capture visitor sessions across your website with Recordings
Run on-site polls with Surveys
When the time comes for you to start your customer journey mapping process, this data will be invaluable.
Step 3: invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
In our experience, the most effective way to get buy-in is not to try and convince people after things are done—include them in the process from the start. So while you can easily create a customer journey map on your own, it won’t be nearly as powerful as one you create with team members from different areas of expertise .
For example, if you’re looking at the purchase flow, you need to work with:
Someone from the UX team, who knows about the usability of the flow and can advocate for design changes
Someone from dev or engineering, who knows how things work in the back end, and will be able to push forward any changes that result from the map
Someone from success or support, who has first-hand experience talking to customers and resolving any issues they experience
✅ The output: you’ve set a date, booked a meeting space, and invited a group of four to six participants to your customer journey mapping workshop.
💡Pro tip: for your first map, stay small. Keep it limited to four to six people, and no main stakeholders . This may be unpopular advice, especially since many guides out there mention the importance of having stakeholders present from the start.
However, when you’re not yet very familiar with the process, including too many people early on can discourage them from re-investing their time into future CJM tasks. At this stage, it’s more helpful to brainstorm with a small team, get feedback on how to improve, and iterate a few times. Once you have a firm handle on the process, then start looping in your stakeholders.
On workshop day, you’ll spend half your time prepping and the other half running the actual session.
Step 1: prepare all your materials
To run a smooth workshop, ensure you do the following:
Bring stationery: for an interactive workshop, you’ll need basic materials such as pens, different colored Post-its, masking tape, and large sheets of paper to hang on the wall
Collect and print out the data: use the data you collected on Day 1. It’s good to have digital copies on a laptop or tablet for everybody to access, but print-outs could be the better alternative as people can take notes and scribble on them.
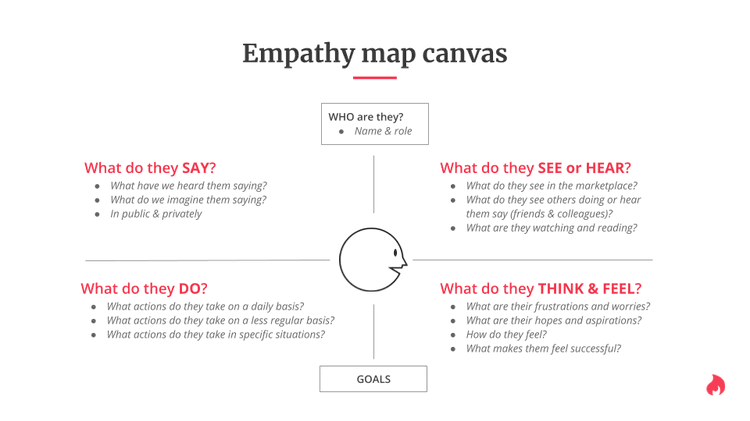
Print out an empathy map canvas for each participant: start the workshop with an empathy mapping exercise (more on this in Step 2). For this, hand each participant an empty empathy map canvas you can recreate from the template below.
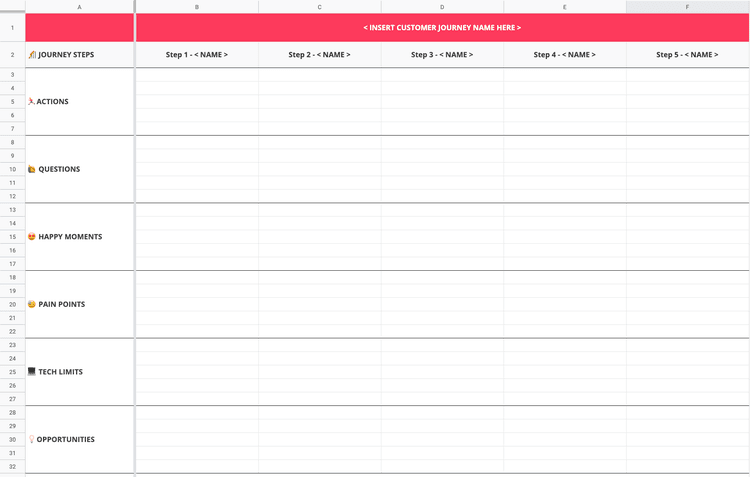
Set up a customer journey map template on the wall: use a large sheet of paper to create a grid you'll stick to the wall and fill in as part of the workshop. On the horizontal axis, write the customer journey steps you identified during your Day 1 prep work; on the vertical axis, list the themes you want to analyze for each step. For example:
Actions your customers take
Questions they might have
Happy moments they experience
Pain points they experience
Tech limits they might encounter
Opportunities that arise
Step 2: run the workshop
This is the most interactive (and fun) part of the process. Follow the framework below to go from zero to a completed draft of a map in just under 2 hours .
Introduction [🕒 5–10 min]
Introduce yourself and your participants to one another
Using the one-two sentence description you defined on Day 1, explain the goal and scope of the workshop and the activities it will involve
Offer a quick summary of the customer persona you’ll be referring to throughout the session
Empathy mapping exercise [🕒 30 min]
Using the personas and data available, have each team member map their observations onto sticky notes and paste them on the relevant section of the empathy mapping canvas
Have all participants take turns presenting their empathy map
Facilitate group discussions where interesting points of agreement or disagreement appear
Customer journey mapping [🕒 60 min]
Using Post-its, ask each participant to fill in parts of the map grid with available information. Start by filling in the first row together, so everybody understands the process, then do each row individually (15–20 min). At the end of the process, you should have something like this:

Looking at the completed map, encourage your team to discuss and align on core observations (and take notes: they’ll come in handy on your final half day). At this point, customer pain points and opportunities should become evident for everybody involved. Having a cross-functional team means people will naturally start discussing what can, or cannot, immediately be done to address them (35–40 min).
Wrap up [🕒 5 min]
Congratulations! Your first customer journey map is complete. Finish the session by thanking your participants and letting them know the next steps.
Final half-day: wrap up and share
Once you’ve gone through the entire customer journey mapping workshop, the number one thing you want to avoid is for all this effort to go to waste. Instead of leaving the map hanging on the wall (or worse: taking it down, folding it, and forgetting about it), the final step is to wrap the process up and communicate the results to the larger team.
Digitize the map so you can easily update and share it with team members: it may be tempting to use dedicated software or invest time into a beautiful design, but for the first few iterations, it’s enough to add the map to your team’s existing workflows (for example, our team digitized our map and added it straight into Jira, where it’s easily accessible)
Offer a quick write-up or a 5-minute video introduction of the activity: re-use the description you came up with on Day 1, including who was involved and the top three outcomes
Clearly state the follow-up actions: if you’ve found obvious issues that need fixing, that’s a likely next step. If you’ve identified opportunities for change and improvement, you may want to validate these findings via customer interviews and usability testing.
4 benefits of customer journey mapping
In 2023, it’s almost a given that great customer experience (CX) provides any business or ecommerce site with a competitive advantage. But just how you’re supposed to deliver on the concept and create wow-worthy experiences is often left unsaid, implied, or glossed over.
Customer journey maps help you find answers to this ‘How?’ question, enabling you to:
Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
Create cross-team alignment around the business
Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
We’ve done a lot of customer journey work here at Hotjar, so we know that the above is true—but don’t just take our word for it: all the people we interviewed for this guide confirmed the benefits of journey mapping. Let’s take a look at what they shared.
1. Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
It’s one thing to present your entire team with charts, graphs, and trends about your customers, and quite another to put the same team in front of ONE map that highlights what customers think, want, and do at each step of their journey.
I did my first customer journey map at MADE.COM within the first three months of joining the company. I was trying to map the journey to understand where the pain points were.
For example, people who want to buy a sofa from us will be coming back to the site 8+ times over several weeks before making a purchase. In that time, they may also visit a showroom. So now I look at that journey, at a customer’s motivation for going to the website versus a physical store, and I need to make sure that the experience in the showroom complements what they're doing on-site, and vice-versa, and that it all kind of comes together.
The map helps in seeing that journey progress right up to the time someone becomes a customer. And it also continues after: we see the next touchpoints and how we're looking to retain them as a customer, so that they come back and purchase again.
A customer journey map is particularly powerful when you incorporate empathy into it, bringing to light specific emotions that customers experience throughout the journey.

2. Create cross-team alignment around the business
The best, most effective customer journey maps are not the solo project of the user experience (UX) or marketing team (though they may originate there).
Customer journey maps are a quick, easy, and powerful way to help everybody in your business get a clearer understanding of how things work from a customers’ perspective and what the customers’ needs are—which is the first step in your quest towards creating a better experience for them.
Our first goal for preparing a customer journey map was to improve understanding customers across the company, so that every employee could understand the entire process our clients go through.
For example, people from the shipping department didn't know how the process works online; people from marketing didn't know how customers behave after filing a complaint. Everything seems obvious, but when we shared these details, we saw that a lot of people didn't know how the company itself works—this map made us realize that there were still gaps we needed to fill.

If we discover that customers have a pain point in a specific section of the map, different teams can look at the same section from several angles; customer support can communicate why something is not possible, and engineering can explain why it’s going to take X amount of effort to get it done. Especially in cross-functional teams where we all come from really different disciplines, I find these maps to be an incredible way for us all to speak the same language.
3. Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
As a company grows in size and complexity, the lines of ownership occasionally become blurry. Without clarity, a customer might get bounced like a ping pong ball across Sales, Success, and Support departments—not great for the seamless and frictionless customer experience we all want to offer.
A central source of ‘truth’ in the form of a customer journey map that everybody can refer to helps clarify areas of ownership and handover points.
We were growing as a team, and we realized we needed to operationalize a lot of the processes that, before then, had just been manually communicated. We did it through a customer journey map. Our goal was to better understand where these hand-off points were and how to create a more seamless experience for our customers, because they were kind of being punted from team to team, from person to person—and often, it was really hard to keep tabs on exactly where the customer was in that entire journey.
4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
A customer journey map will take your team from 'It appears that 30% of people leave the website at this stage' to 'Wow, people are leaving because the info is incomplete and the links are broken.' Once everyone is aligned on the roadblocks that need to be addressed, changes that have a positive impact on the customer experience and customer satisfaction will happen faster.
The customer journey map brings it all together: it doesn't matter who you've got in the room. If you’re doing a proper journey map, they always get enlightened in terms of ‘Oh, my word. I did not know the customer's actually experiencing this.’ And when I walk out of the session, we have often solved issues in the business. Accountability and responsibilities have been assigned, and I find that it just works well.
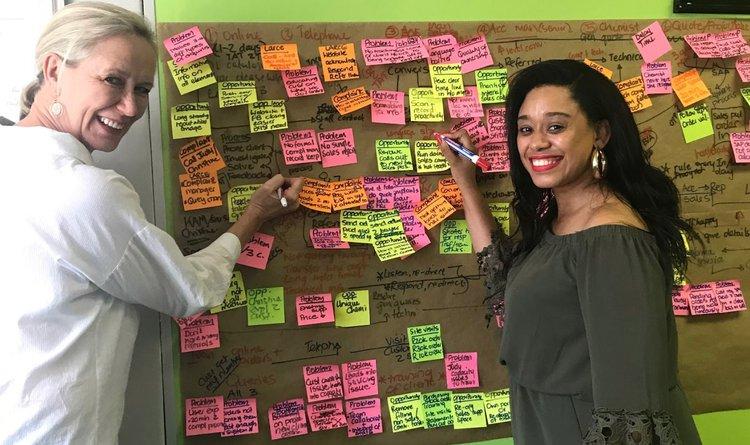

Shaheema (right) working on a customer journey map
Collect the right data to create an effective customer journey map
The secret of getting value from customer journey mapping is not just building the map itself: it's taking action on your findings. Having a list of changes to prioritize means you can also measure their effect once implemented, and keep improving your customers' experience.
This all starts with collecting customer-centric data—the sooner you begin, the more information you’ll have when the time comes to make a decision.
Start mapping your customer journey today
Hotjar lets you experience your customer’s journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
FAQs about customer journey mapping
How do i create a customer journey map.
To create a useful customer journey map, you first need to define your objectives, buyer personas, and the goals of your customers (direct customer feedback and market research will help you here). Then, identify all the distinct touchpoints the customer has with your product or service in chronological order, and visualize the completion of these steps in a map format.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping provides different teams in your company with a simple, easily understandable visualization that captures your customers’ perspective and needs, and the steps they’ll take to successfully use your product or service.
Consider customer journey mapping if you want to accomplish a specific objective (like testing a new product’s purchase flow) or work towards a much broader goal (like increasing overall customer retention or customer loyalty).
What is the difference between a customer journey map and an experience map?
The main difference between an experience map and a customer journey map is that customer journey maps are geared specifically toward business goals and the successful use of a product or service, while experience maps visualize an individual’s journey and experience through the completion of any task or goal that may not be related to business.
What is a Customer Journey Map? [Free Templates]
Learn what the customer journey mapping process is and download a free template that you can use to create your own customer journey map.
Table of Contents
Mapping the customer journey can give you a way to better understand your customers and their needs. As a tool, it allows you to visualize the different stages that a customer goes through when interacting with your business; their thoughts, feelings, and pain points.
And, it’s shown that the friction from those pain points costs big: in 2019, ecommerce friction totaled an estimated 213 billion in lost US revenue .
Customer journey maps can help you to identify any problems or areas where you could improve your customer experience . In this article, we’ll explain what the customer journey mapping process is and provide a free template that you can use to create your own map. Let’s get started!
Bonus: Get our free, fully customizable Customer Experience Strategy Template that will help you understand your customers and reach your business goals.
What is a customer journey map?
So, what is customer journey mapping? Essentially, customer journey maps are a tool that you can use to understand the customer experience. Customer journey maps are often visual representations showing you the customer’s journey from beginning to end. They include all the touchpoints along the way.
There are often four main stages in your sales funnel, and knowing these can help you create your customer journey maps:
- Inquiry or awareness
- Interest, comparison, or decision-making
- Purchase or preparation
- Installation, activation, or feedback
Customer journey maps are used to track customer behavior and pinpoint areas where the customer experiences pain points. With this information uncovered, you can improve the customer experience, giving your customers a positive experience with your company.
You can use customer journey mapping software like Excel or Google sheets, Google Decks, infographics, illustrations, or diagrams to create your maps. But you don’t actually need customer journey mapping tools. You can create these maps with a blank wall and a pack of sticky notes.
Though they can be scribbled on a sticky note, it’s often easier to create these journeys digitally. That way, you have a record of your journey map, and you can share it with colleagues. We’ve provided free customer journey mapping templates at the end of this article to make your life a little easier.
The benefits of using customer journey maps
The main benefit of customer journey mapping is a better understanding of how your customers feel and interact with your business touchpoints. With this knowledge, you can create strategies that better serve your customer at each touchpoint.
Give them what they want and make it easy to use, and they’ll keep coming back. But, there are a couple of other great knock-on benefits too.
Improved customer support
Your customer journey map will highlight moments where you can add some fun to a customer’s day. And it will also highlight the pain points of your customer’s experience. Knowing where these moments are will let you address them before your customer gets there. Then, watch your customer service metrics spike!
Effective marketing tactics
A greater understanding of who your customers are and what motivates them will help you to advertise to them.
Let’s say you sell a sleep aid product or service. A potential target market for your customer base is young, working mothers who are strapped for time.
The tone of your marketing material can empathize with their struggles, saying, “The last thing you need is someone asking if you’re tired. But we know that over half of working moms get less than 6 hours of sleep at night. While we can’t give you more time, we know how you can make the most of those 6 hours. Try our Sleep Aid today and sleep better tonight.”
Building out customer personas will show potential target audiences and their motivation, like working moms who want to make the most of their hours asleep.
Product advancements or service improvements
By mapping your customer’s journey, you’ll gain insights into what motivates them to make a purchase or prevents them from doing so. You’ll have clarity on when or why they return items and which items they buy next. With this information and more, you’ll be able to identify opportunities to upsell or cross-sell products.
A more enjoyable and efficient user experience
Customer journey mapping will show you where customers get stuck and bounce off your site. You can work your way through the map, fixing any friction points as you go. The end result will be a smoothly-running, logical website or app.
A customer-focused mindset
Instead of operating with the motivation of business success, a customer journey map can shift your focus to the customer. Instead of asking yourself, “how can I increase profits?” ask yourself, “what would better serve my customer?” The profits will come when you put your customer first.
At the end of the day, customer journey maps help you to improve your customer experience and boost sales. They’re a useful tool in your customer experience strategy .
How to create a customer journey map
There are many different ways to create a customer journey map. But, there are a few steps you’ll want to take regardless of how you go about mapping your customer’s journey.
Step 1. Set your focus
Are you looking to drive the adoption of a new product? Or perhaps you’ve noticed issues with your customer experience. Maybe you’re looking for new areas of opportunity for your business. Whatever it is, be sure to set your goals before you begin mapping the customer journey.
Step 2. Choose your buyer personas
To create a customer journey map, you’ll first need to identify your customers and understand their needs. To do this, you will want to access your buyer personas.
Buyer personas are caricatures or representations of someone who represents your target audience. These personas are created from real-world data and strategic goals.
If you don’t already have them, create your own buyer personas with our easy step-by-step guide and free template.
Choose one or two of your personas to be the focus of your customer journey map. You can always go back and create maps for your remaining personas.
Step 3. Perform user research
Interview prospective or past customers in your target market. You do not want to gamble your entire customer journey on assumptions you’ve made. Find out directly from the source what their pathways are like, where their pain points are, and what they love about your brand.
You can do this by sending out surveys, setting up interviews, and examining data from your business chatbot . Be sure to look at what the most frequently asked questions are. If you don’t have a FAQ chatbot like Heyday , that automates customer service and pulls data for you, you’re missing out!
Get a free Heyday demo
You will also want to speak with your sales team, your customer service team, and any other team member who may have insight into interacting with your customers.
Step 4. List customer touchpoints
Your next step is to track and list the customer’s interactions with the company, both online and offline.
A customer touchpoint means anywhere your customer interacts with your brand. This could be your social media posts , anywhere they might find themselves on your website, your brick-and-mortar store, ratings and reviews, or out-of-home advertising.
Write as many as you can down, then put on your customer shoes and go through the process yourself. Track the touchpoints, of course, but also write down how you felt at each juncture and why. This data will eventually serve as a guide for your map.
Step 5. Build your customer journey map
You’ve done your research and gathered as much information as possible, now it’s time for the fun stuff. Compile all of the information you’ve collected into one place. Then, start mapping out your customer journey! You can use the templates we’ve created below for an easy plug-and-play execution.
Step 6. Analyze your customer journey map
Once the customer journey has been mapped out, you will want to go through it yourself. You need to experience first-hand what your customers do to fully understand their experience.
As you journey through your sales funnel, look for ways to improve your customer experience. By analyzing your customer’s needs and pain points, you can see areas where they might bounce off your site or get frustrated with your app. Then, you can take action to improve it. List these out in your customer journey map as “Opportunities” and “Action plan items”.
Types of customer journey maps
There are many different types of customer journey maps. We’ll take you through four to get started: current state, future state, a day in the life, and empathy maps. We’ll break down each of them and explain what they can do for your business.
Current state
This customer journey map focuses on your business as it is today. With it, you will visualize the experience a customer has when attempting to accomplish their goal with your business or product. A current state customer journey uncovers and offers solutions for pain points.
Future state
This customer journey map focuses on how you want your business to be. This is an ideal future state. With it, you will visualize a customer’s best-case experience when attempting to accomplish their goal with your business or product.
Once you have your future state customer journey mapped out, you’ll be able to see where you want to go and how to get there.
Day-in-the-life
A day-in-the-life customer journey is a lot like the current state customer journey, but it aims to highlight aspects of a customer’s daily life outside of how they interact with your brand.
Day-in-the-life mapping looks at everything that the consumer does during their day. It shows what they think and feel within an area of focus with or without your company.
When you know how a consumer spends their day, you can more accurately strategize where your brand communication can meet them. Are they checking Instagram on their lunch break, feeling open and optimistic about finding new products? If so, you’ll want to target ads on that platform to them at that time.
Day-in-the-life customer journey examples can look vastly different depending on your target demographic.
Empathy maps
Empathy maps don’t follow a particular sequence of events along the user journey. Instead, these are divided into four sections and track what someone says about their experience with your product when it’s in use.
You should create empathy maps after user research and testing. You can think of them as an account of all that was observed during research or testing when you asked questions directly regarding how people feel while using products. Empathy maps can give you unexpected insights into your users’ needs and wants.
Customer journey map templates
Use these templates to inspire your own customer journey map creation.
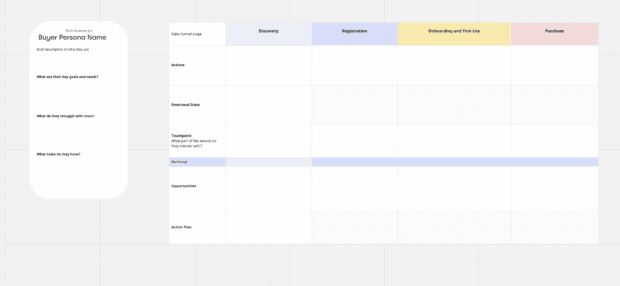
Customer journey map template for the current state:
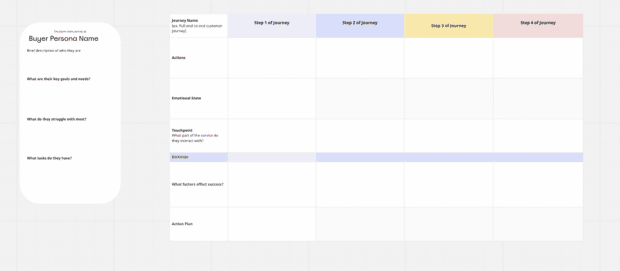
The future state customer journey mapping template:
A day-in-the-life customer journey map template:

An empathy map template:
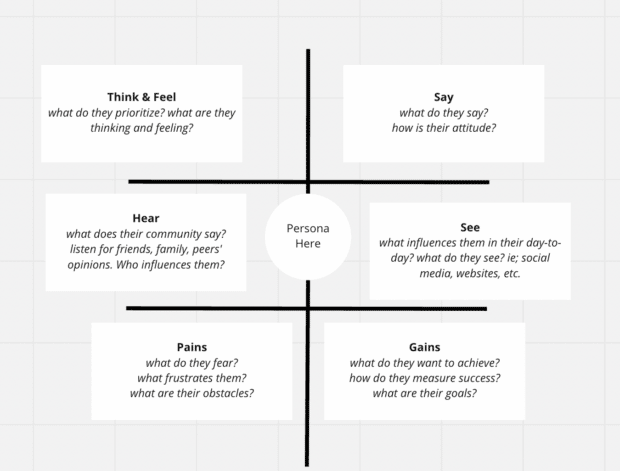
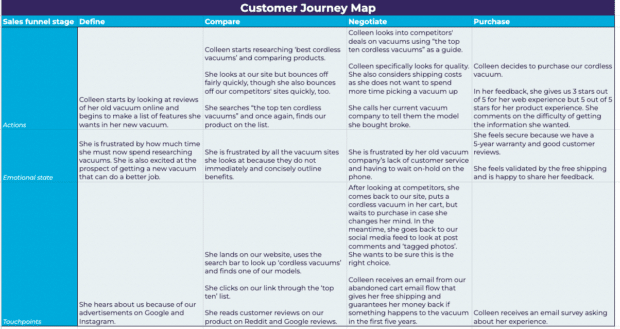
A customer journey map example
It can be helpful to see customer journey mapping examples. To give you some perspective on what these look like executed, we’ve created a customer journey mapping example of the current state.
Buyer Persona:
Curious Colleen, a 32-year-old female, is in a double-income no-kids marriage. Colleen and her partner work for themselves; while they have research skills, they lack time. She is motivated by quality products and frustrated by having to sift through content to get the information she needs.
What are their key goals and needs? Colleen needs a new vacuum. Her key goal is to find one that will not break again.
What are their struggles?
She is frustrated that her old vacuum broke and that she has to spend time finding a new one. Colleen feels as though this problem occurred because the vacuum she bought previously was of poor quality.
What tasks do they have?
Colleen must research vacuums to find one that will not break. She must then purchase a vacuum and have it delivered to her house.
Opportunities:
Colleen wants to understand quickly and immediately the benefits our product offers; how can we make this easier? Colleen upholds social proof as a decision-making factor. How can we better show our happy customers? There is an opportunity here to restructure our website information hierarchy or implement customer service tools to give Colleen the information she needs faster. We can create comparison charts with competitors, have benefits immediately and clearly stated, and create social campaigns.
Action Plan:
- Implement a chatbot so customers like Colleen can get the answers they want quickly and easily.
- Create a comparison tool for competitors and us, showing benefits and costs.
- Implement benefit-forward statements on all landing pages.
- Create a social campaign dedicated to UGC to foster social proof.
- Send out surveys dedicated to gathering customer feedback. Pull out testimonial quotes from here when possible.
Now that you know what the customer journey mapping process is, you can take these tactics and apply them to your own business strategy. By tracking customer behavior and pinpointing areas where your customers experience pain points, you’ll be able to alleviate stress for customers and your team in no time.
Turn customer conversations and inquiries into sales with Heyday, our dedicated conversational AI chatbot for social commerce retailers. Deliver 5-star customer experiences — at scale.
Turn customer service conversations into sales with Heyday . Improve response times and sell more products. See it in action.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Colleen Christison is a freelance copywriter, copy editor, and brand communications specialist. She spent the first six years of her career in award-winning agencies like Major Tom, writing for social media and websites and developing branding campaigns. Following her agency career, Colleen built her own writing practice, working with brands like Mission Hill Winery, The Prevail Project, and AntiSocial Media.
Related Articles
FAQ Chatbot: The Best Way to Save Time on Customer Service
FAQ chatbots are bots designed to answer common questions people have about a product or service. They are used on websites or in customer service applications.

Customer Service Metrics: 2024 Guide + Free Template
Customers expect to get support wherever they look for and they expect it fast. To keep up, track the customer service metrics that matter.

Create a Customer Experience Strategy [FREE TEMPLATE]
This step-by-step template makes it easy to deliver a well-laid-out customer experience strategy that can give you planned, targeted growth.

Customer Experience Management Explained [11 Top Tips]
Turn that frown upside down! Keep your customers smiling with a strong customer experience management strategy.


How to create a customer journey map
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 8 min
How to Make a Customer Journey Map
- Conduct persona research
- Define customer touchpoints
- Map current states
- Map future states
Steve Jobs, the genius behind Apple’s one-of-a-kind customer experience, said, “You’ve got to start with the customer experience and work back toward the technology, not the other way around.”
Nowadays, a clear vision and strategy for customer interactions is no longer an optional “nice-to-have”—it’s essential. As you refine your customer experience, a customer journey map is one of the most powerful ways to understand your current state and future state.

A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the process your customers go through in interacting with your business, such as an experience on the website, a brick and mortar experience, a service, a product, or a mix of those things.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with your brand. These visuals tell a story about how a customer moves through each phase of interaction and experiences each phase. Your customer journey map should include touchpoints and moments of truth, but also potential customer feelings, such as frustration or confusion, and any actions you want the customer to take.
Customer journey maps are often based on a timeline of events, such as a customer’s first visit on your website and the way they progress towards their first in-product experience, then purchase, onboarding emails, cancellation, etc.
Your customer journey maps may need to be tailored to your business or product, but the best way to identify and refine these phases is to actually talk to your customers. Research your target audiences to understand how they make decisions, decide to purchase, etc. Without an essential understanding of your customers and their needs, a customer map will not lead you to success. But, a well-constructed and researched customer journey map can give you the insights to drastically improve your business’s customer experience.
The benefits of customer journey mapping
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for uncovering insights into your customer experience, driving business goals, and building resilience in a changing market. In a 2022 report, Hanover Research found that 94% of businesses said their customer journey maps help them develop new products and services to match customer needs. Another 91% said their maps drove sales.
But understanding a customer’s journey across your entire organization does so much more than increase your revenue. It enables you to discover how to be consistent when it comes to providing a positive customer experience and retaining customer loyalty.
This was especially evident in recent years as top of improving marketing, customer journey maps emerged as a valuable way to understand evolving buyer behavior. In fact, 1 in 3 businesses used customer journey maps to help them navigate the changing landscape during the pandemic.
When done correctly, customer journey mapping helps to:
- Increase customer engagement through channel optimization.
- Identify and optimize moments of truth in the CX.
- Eliminate ineffective touchpoints.
- Shift from a company to a customer-focused perspective.
- Break down silos between departments and close interdepartmental gaps.
- Target specific customer personas with marketing campaigns relevant to their identity.
- Understand the circumstances that may have produced irregularities in existing quantitative data.
- Assign ownership of various customer touchpoints to increase employee accountability.
- Make it possible to assess the ROI of future UX/CX investments.
Following the process outlined above, customer mapping can put your organization on a new trajectory of success. Yet, according to Hanover Research, only 47% of companies currently have a process in place for mapping customer journeys. Making the investment to map your customer journey and solidify that process as part of your company’s DNA can result in significant advantages in your competitive landscape, making your solution the go-to option that customers love.
Customer journey maps can become complicated unless you keep them focused. Although you may target multiple personas, choose just one persona and one customer scenario to research and visualize at a time. If you aren’t sure what your personas or scenarios might be, gather some colleagues and try an affinity diagram in Lucidchart to generate ideas.
1. Set goals
Without a goal, it will be difficult to determine whether your customer journey map will translate to a tangible impact on your customers and your business. You will likely need to identify existing—and future—buyers so you can set goals specifically for those audiences at each stage of their experience.
Consider gathering the key stakeholders within your company—many of whom likely touch different points of the customer experience. To set a logical and attainable goal, cross-functional teamwork is essential. Gather unique perspectives and insights about each part of the existing customer journey and where improvements are needed, and how those improvements will be measured.
Pro Tip : If you don’t already have them in place, create buyer personas to help you focus your customer journey map on the specific types of buyers you’re optimizing for.
2. Conduct persona research
Flesh out as much information as possible about the persona your customer journey map is based on. Depending on the maturity of your business, you may only have a handful of records, reports, or other pre-existing data about the target persona. You can compile your preliminary findings to draft what you think the customer journey may look like. However, the most insightful data you can collect is from real customers or prospective customers—those who have actually interacted with your brand. Gather meaningful customer data in any of the following ways:
- Conduct interviews.
- Talk to employees who regularly interact with customers.
- Email a survey to existing users.
- Scour customer support and complaint logs.
- Pull clips from recorded call center conversations.
- Monitor discussions about your company that occur on social media.
- Leverage web analytics.
- Gather Net Promoter Score (NPS) data.
Look for information that references:
- How customers initially found your brand
- When/if customers purchase or cancel
- How easy or difficult they found your website to use
- What problems your brand did or didn’t solve
Collecting both qualitative and quantitative information throughout your research process ensures your business makes data-driven decisions based on the voice of real customers. To assist when conducting persona research, use one of our user persona templates .

Discover more ways to understand the Voice of the Customer
3. Define customer touchpoints
Customer touchpoints make up the majority of your customer journey map. They are how and where customers interact with and experience your brand. As you research and plot your touchpoints, be sure to include information addressing elements of action, emotion, and potential challenges.
The number and type of touchpoints on your customer journey map will depend on the type of business. For example, a customer’s journey with a SaaS company will be inherently different than that of a coffee shop experience. Simply choose the touchpoints which accurately reflect a customer’s journey with your brand.
After you define your touchpoints, you can then start arranging them on your customer journey map.
4. Map the current state
Create what you believe is your as-is state of the customer journey, the current customer experience. Use a visual workspace like Lucidchart, and start organizing your data and touchpoints. Prioritize the right content over aesthetics. Invite input from the stakeholders and build your customer journey map collaboratively to ensure accuracy.
Again, there is no “correct” way to format your customer journey map, but for each phase along the journey timeline, include the touchpoints, actions, channels, and assigned ownership of a touchpoint (sales, customer service, marketing, etc.). Then, customize your diagram design with images, color, and shape variation to better visualize the different actions, emotions, transitions, etc. at a glance.
Mapping your current state will also help you start to identify gaps or red flags in the experience. Collaborators can comment directly on different parts of your diagram in Lucidchart, so it’s clear exactly where there’s room for improvement.
5. Map future states
Now that you’ve visualized the current state of the customer journey, your map will probably show some gaps in your CX, information overlap, poor transitions between stages, and significant pain points or obstacles for customers.
Use hotspots and layers in Lucidchart to easily map out potential solutions and quickly compare the current state of the customer journey with the ideal future state. Present your findings company-wide to bring everyone up to speed on the areas that need to be improved, with a clear roadmap for expected change and how their roles will play a part in improving the customer journey.
Customer journey map templates
You have all the right information for a customer journey map, but it can be difficult to know exactly how to start arranging the information in a digestible, visually appealing way. These customer journey mapping examples can help you get started and gain some inspiration about what—and how much—to include and where.

Don’t let the possibility of a bad customer journey keep you up at night. Know the current state of the customer journey with you business, and make the changes you need to attract and keep customers happy.

Customer journey mapping is easy with Lucidchart.
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
- How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Is it time to rethink traditional journey mapping methods?
What is a customer journey map, why is a customer journey map important, components of a customer journey map, limitations of the traditional approach to journey mapping, meeting modern business challenges, evolving your customer journey maps, comparing approaches side-by-side, how to unlock behavioral-based, data-driven journey mapping, see how xm for customer frontlines works, how to create a customer journey map.
22 min read Customer journey mapping is a science, so it pays to think about the data that goes into the process. When you incorporate intelligent customer insights from the right tools and sources, your journey maps transform from static, outdated documentation into living, breathing resources that can guide business-wide strategies. Here’s how…
Author: Ray Gerber
In an era marked by rapid changes in consumer behavior and heightened expectations, traditional methods of customer journey mapping are, rightly, coming under scrutiny.
But what does that mean for the people looking to maximize each journey? Put simply: it’s time to adapt.
Traditionally, journey maps have been static – often created through time-consuming processes that involve extensive research and data collection. These methods, while thorough, tend to be resource-intensive and costly. More importantly, they lack the agility to adapt to fast-paced changes in customer behavior and preferences.
In a digital age where customer interactions and expectations evolve at an unprecedented rate, relying on these static maps can leave businesses trailing behind, operating on outdated assumptions and missing crucial opportunities for engagement and improvement.
All of this presents us with a pressing need: shifting towards more dynamic, data-driven journey mapping techniques. But it’s a shift that goes much further than simply keeping pace with change; it’s about embracing a more responsive, customer-centric approach that aligns closely with the ever-evolving journey of today’s consumers.
And that’s exactly what we’ll be covering in this article – starting with some of the basics…
A customer journey map is a visual interpretation of the overall relationship a customer has with an organization, service, product, or brand – over time and across different channels. It helps businesses step into their customers’ shoes and see their business from the customer’s perspective.
Crucially, a customer journey map also allows companies to gain insights into common customer pain points, how they interact with the brand, and the pathways they take from the first engagement to a long-term relationship.
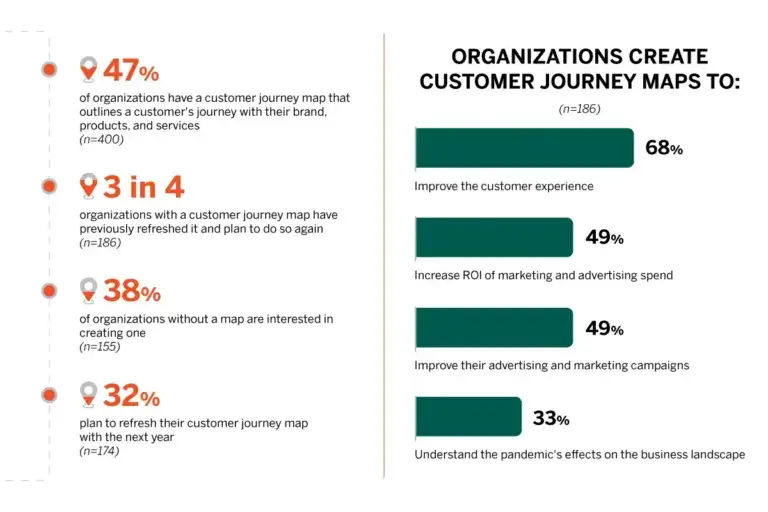
Image from: The Power of Customer Journey Mapping 2023 Hanover Research
How Businesses View Customer Journey maps
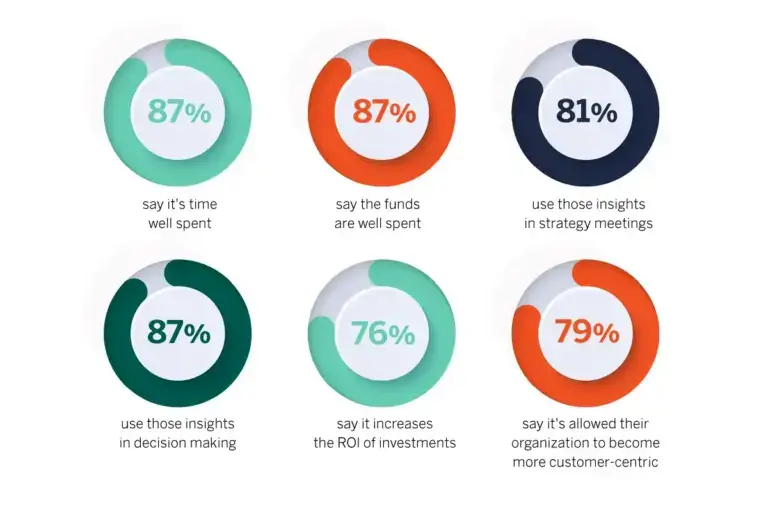
An accurate, adaptable customer journey map is a means to enable positive change. In an era where customer experience is a key differentiator, journey maps serve as crucial tools.
They help businesses:
- Understand and empathize with customers.
- Identify and address pain points and bottlenecks in the customer experience.
- Align internal teams around a shared understanding of customer needs and experiences.
- Optimize and personalize customer interactions at each touchpoint.
- Strategically plan enhancements to products, services, and processes.
But there’s a problem: not every company that creates customer journey maps knows how to put them to work. In 2019, Gartner reported that while some 82% of organizations have created customer journey maps, only 47% are using them effectively.
Worse still, in 2022, the Technology Services Industry Association found that only 29% of customer success teams who created a customer journey map actually used it at all.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to customer journey mapping
Ok, so what actually goes into a successful, usable customer journey map?
A well-constructed map comprises a myriad component plays a distinct role in painting a complete picture of the customer’s journey, with valuable insights that can drive strategic improvements and foster deeper customer connections.
Here is an example of what a full customer journey map looks like with all this information collated:
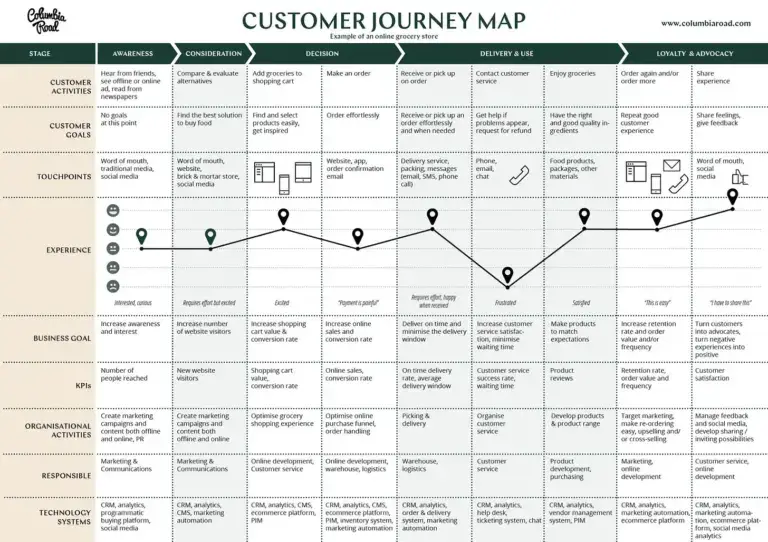
Image from: www.Columbiaroad.com
This customer journey map is a visual representation of the stages a customer goes through when interacting with an online grocery store, structured into six stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Delivery & Use, and Loyalty & Advocacy.
The customer learns about the store through word-of-mouth, media, or online. The goal is to increase awareness and interest, supported by marketing campaigns and social media.
Consideration:
The customer compares options and looks for the best solutions. The business aims to increase the number of website visitors through marketing and communications.
Adding items to the cart and making a purchase. The experience should be effortless, with the business goal of increasing sales and conversion rates, supported by an optimized online purchasing funnel.
Delivery & Use:
The customer receives their order. The goal is to deliver on time and ensure satisfaction , achieved by efficient logistics and customer service.
Loyalty & Advocacy:
Post-purchase, customers may reorder or share their experience. The business aims to increase retention and turn customers into advocates, managed by customer service and marketing.
Each stage lists customer activities, goals, touchpoints, experiences, business goals, KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) , organizational activities, and technology systems used. The map charts the emotional journey with peaks (excitement) and valleys (effort or frustration), aiming to provide insights into how to enhance the customer experience at each stage.
While traditional journey mapping has been a cornerstone for understanding and visualizing the customer’s path through various touchpoints with a brand, a static, one-time snapshot approach has its limitations.
Here are seven reasons why conventional mapping methods may no longer suffice in today’s dynamic market environment:
Static nature
Traditional journey maps are often static, representing a fixed snapshot of the customer journey. This rigidity fails to account for the fluid and ever-changing nature of customer interactions and preferences, leading to a map that quickly becomes outdated as market dynamics shift.
Time-consuming and resource-intensive
The creation of traditional journey maps typically involves extensive research, including customer interviews, surveys, and workshops. This process is not only time-consuming but also demands significant resources, both in terms of manpower and financial investment.
Lack of personalization
Traditional maps tend to generalize the customer experience, based on averaged data and broad customer personas. This approach overlooks the nuances and individual variations in customer behavior, resulting in a one-size-fits-all model that may not accurately reflect the experiences of different customer segments .
Limited real-time insights
The traditional journey mapping process does not incorporate real-time data. Consequently, businesses miss out on the opportunity to respond promptly to immediate changes in customer behavior or feedback, potentially leading to missed opportunities for engagement and improvement.
Over-reliance on assumptions
Often, these maps are created based on assumptions about customer behavior and preferences, rather than hard data. This can lead to a disconnect between what businesses perceive to be the customer journey and the actual experiences of their customers.
Inadequate measurement of impact
Traditional journey maps do not always include clear metrics or KPIs to measure the impact of various touchpoints on customer behavior. This lack of quantifiable measurement makes it challenging to assess the effectiveness of different aspects of the journey and to make data-driven improvements.
Difficulty in aligning cross-functional teams
Given their static nature, traditional maps can struggle to align different teams around a unified, evolving customer strategy . Different departments may interpret the journey map differently, leading to inconsistent customer experiences.
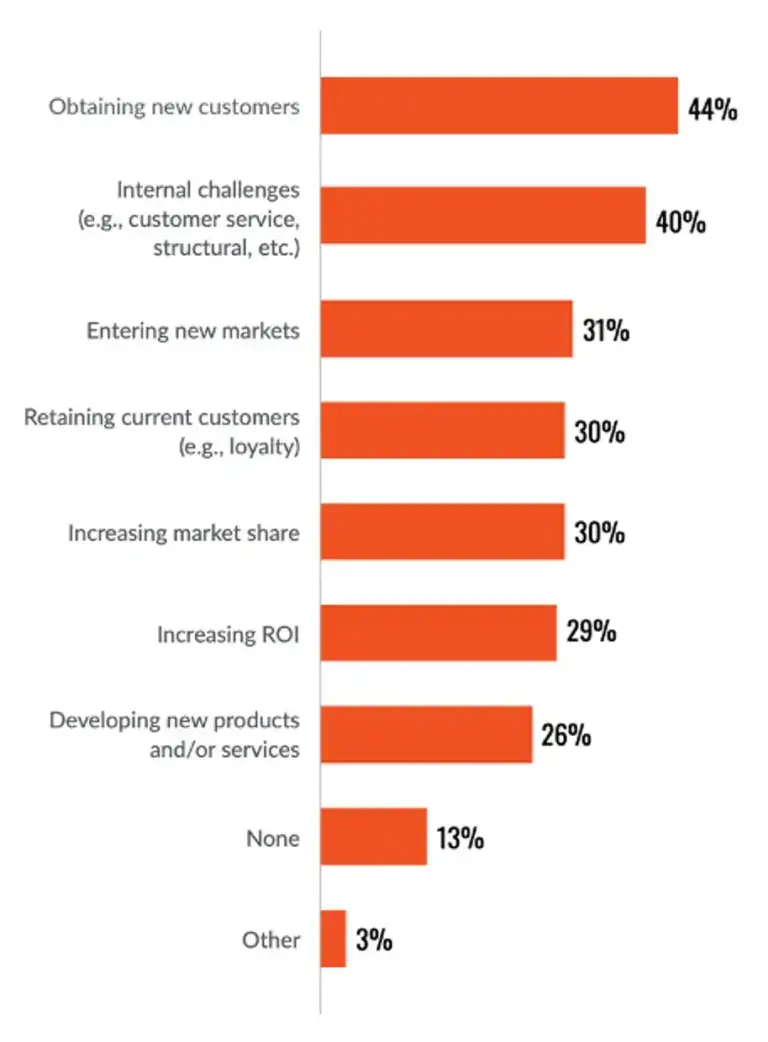
© 2023 Hanover Research CORWP0123
The image above lists several initiatives that have become more challenging for businesses: obtaining new customers, internal challenges, entering new markets, retaining current customers, increasing market share, increasing ROI , and developing new products/services.
These are universal challenges, and they all play a role in how journey mapping needs to evolve…
Obtaining new customers & entering new markets
Traditional journey maps may not account for the changing behaviors of different market segments – or the nuances of new market contexts. Dynamic journey maps that integrate behavioral data can provide a more accurate and adaptable model for understanding the customer journey in different markets.
Internal challenges
Static journey maps might not reflect the internal process changes quickly enough. A dynamic, behavior-based map offers real-time insights into operational issues that affect customer experience.
Retaining current customers
Traditional journey maps often lack the granularity to understand the shifting loyalty drivers. Dynamic mapping can highlight evolving customer needs and preferences, helping to tailor experiences that enhance loyalty .
Increasing market share & ROI
By focusing on actual behaviors rather than assumptions, dynamic journey maps can uncover opportunities for differentiation and value creation, directly influencing market share and return on investment.
Developing new products and services
Traditional maps might miss rapid changes in customer expectations and emerging trends. Behavioral-based mapping processes can identify new needs and opportunities for innovation, leading to more timely and relevant product development .
The challenges listed above all indicate a need for more sophisticated journey mapping that can adapt to the complex nature of customer behaviors and business environments.
So, with that in mind, let’s look at two ways that your journey maps can evolve…
1. Adding Voice of the Customer insights to journey maps
The integration of Voice of the Customer (VoC) data into journey maps marks the first significant evolution in the approach to understanding customer experiences.
VoC data transforms journey maps from static, assumption-based models into dynamic tools that reflect real customer feedback and sentiments. VoC data includes direct input from customers, such as survey responses, customer reviews, feedback forms, and social media comments. By integrating this data, journey maps become more aligned with the customer’s actual experiences and perceptions, providing a richer, more nuanced view of their journey.
Methodology for incorporating VoC data:
- Data collection: The first step involves gathering VoC data through various channels. This includes structured methods like surveys and feedback forms, as well as unstructured data from social media, customer reviews, and call center transcripts.
- Data analysis: The collected data is then analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This involves identifying common themes, sentiments, pain points, and moments of delight in the customer journey.
- Mapping VoC to journey stages : The insights are mapped to corresponding stages in the customer journey. This process helps in visualizing how customer sentiments and experiences vary across different touchpoints.
- Iterative refinement: The journey map is continuously updated with new VoC data, ensuring it remains relevant and reflective of the current customer experience.
The value of VoC-enhanced customer journey maps:
Customer-centricity
VoC-enhanced maps put the customer’s voice at the forefront, ensuring that strategies and improvements are directly aligned with customer needs and expectations.
Improved accuracy
These maps are more accurate in depicting the customer journey, as they are based on actual customer feedback rather than assumptions.
Enhanced engagement insights
VoC data provides deeper insights into why customers behave in certain ways, enabling businesses to understand the motivations behind customer actions.
Strategic decision making
Armed with precise customer feedback, businesses can make more informed decisions about product improvements, marketing strategies, and customer service enhancements.
Identifying pain points and opportunities
VoC data highlights specific areas where customers face challenges or where there are opportunities to enhance the experience, guiding targeted improvements.
Are there downsides of VoC-powered customer journey maps?
Integrating VoC data helps make these maps more reflective of the actual customer experience, but doing so is not without its limitations:
Subjectivity and bias
VoC data is inherently subjective, reflecting the perceptions and opinions of customers. This can introduce bias, as the feedback may not always represent the broader customer base or accurately reflect actual behaviors.
Lag in feedback
VoC data often captures customer sentiments after an experience has occurred. This delay can result in missed opportunities to address issues in real-time, reducing the ability to proactively enhance the customer experience.
Incomplete picture
Relying solely on VoC data can lead to gaps in understanding the customer journey. Customers may not accurately recall all their interactions or may only provide feedback on certain aspects of their experience, leaving out key touchpoints.
Challenges in quantification
Translating qualitative VoC data into actionable insights can be challenging. Quantifying sentiments and opinions for strategic decision-making requires sophisticated analysis, which can be resource-intensive.
Limited predictive power
While VoC data offers insights into past and present customer experiences, it has limited capability in predicting future behaviors or trends. This restricts the ability of businesses to anticipate customer needs proactively.
Understanding these limitations is important if we’re going to understand what’s still lacking from our customer journey maps – even with the added benefit of VoC data.
So what’s the solution here? Put simply: smarter insights on human behavior.
2. Adding behavioral insights to journey maps
The integration of actual customer behavioral data alongside Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights represents the second evolution in journey mapping.
That’s because this approach not only considers what customers say, but also what they actually do – providing a more holistic view of the customer experience. The result is a comprehensive view of the customer journey that encompasses both the tangible actions customers take and their perceptions and reactions to those experiences.
A key advantage of this integrated approach is its capacity for real-time responsiveness. Behavioral data, by its nature, offers insights as they happen, enabling businesses to swiftly adapt to emerging trends, shifts in customer behavior, and changing preferences. This agility is crucial in today’s fast-paced market, where customer expectations and behaviors can evolve rapidly.
Moreover, the inclusion of behavioral data opens the door to predictive analytics . By analyzing patterns and trends in customer behavior, businesses can move beyond reactive strategies to a more proactive stance. Predictive modeling, powered by this rich data integration, allows for the anticipation of future customer needs and trends. This forward-looking perspective is invaluable for businesses aiming to stay ahead of customer expectations and continuously refine their customer experience strategies.
How to collect behavioral data
Integrating behavioral and VoC Insights into journey maps begins with a comprehensive data collection phase, where behavioral data—encompassing website interactions, purchase history, and customer service engagements—is gathered alongside Voice of the Customer (VoC) feedback. This rich tapestry of information is typically sourced from digital analytics tools, CRM systems, and customer feedback platforms, providing a multifaceted view of customer interactions.
The subsequent phase involves a meticulous process of data analysis and synthesis. Here, advanced analytics and AI tools play a crucial role, sifting through large datasets to uncover patterns and correlations that might not be immediately apparent. This deep dive into the data helps in extracting meaningful insights that are crucial for the next step.
Once the data is analyzed, the integration process begins. The insights gleaned from both behavioral and VoC data are carefully mapped onto the customer journey.
This crucial step involves pinpointing how customer actions, as indicated by the behavioral data, and their feedback, as captured through VoC, align and interact at each stage of the journey. This mapping creates a more nuanced and comprehensive view of the customer experience, highlighting areas of alignment and divergence between what customers do and what they say.
Crucially, unlike traditional static journey maps, these dynamic maps are not set in stone. They are regularly updated with new data, ensuring they continuously evolve and remain reflective of the current customer experience. This ongoing process of renewal and adaptation ensures that the journey maps stay relevant, providing up-to-date insights that businesses can rely on for making informed decisions.
The enhanced value of journey maps that integrate both behavioral data and Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights is significant, offering a transformative impact on how businesses understand and interact with their customers:
- The accuracy of these integrated journey maps is markedly increased. By combining the objective data of customer behaviors with the subjective feedback from VoC, businesses can create a more precise and true-to-life representation of the customer journey. This approach minimizes the reliance on assumptions or potentially biased feedback , leading to a clearer and more factual understanding of customer experiences.
- Personalization is another critical area where these integrated maps excel. Armed with a deeper and more nuanced understanding of customer behaviors and preferences, businesses can tailor experiences to meet the individual needs of each customer more effectively. This level of personalization is key to creating more engaging and satisfying customer experiences.
- In terms of strategic decision-making, integrated journey maps are a goldmine of actionable insights. They provide a rich source of information that can inform a wide range of strategic decisions, from product development and innovation to targeted marketing strategies and customer service enhancements. This data-driven approach ensures that business strategies are closely aligned with actual customer needs and behaviors.
- The dynamic nature of these integrated journey maps facilitates proactive experience optimization. Unlike static maps, these dynamic versions can be continuously updated and adjusted in response to real-time data, allowing businesses to proactively enhance the customer experience. This agility not only improves customer satisfaction but also fosters stronger customer loyalty, as businesses can quickly adapt to meet and exceed customer expectations.
This table provides a clear comparison of traditional journey maps, VoC-enhanced maps, and behavioral data-driven maps, highlighting their respective data sources, strengths, limitations, adaptability, predictive power, personalization capabilities , and cost/resource intensity.
It illustrates how each method fits into the evolving landscape of customer journey mapping, with behavioral data-driven maps emerging as the most comprehensive and dynamic approach.
In comparing the three journey mapping methods, traditional maps offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness but lack dynamism and real-time insights.
VoC-enhanced maps bring customer feedback into the equation, providing richer insights into customer perceptions and experiences, yet they still struggle with real-time adaptability and objective behavioral analysis.
Behavioral data-driven maps, however, stand out for their comprehensive and dynamic nature. They integrate real-time behavioral data with VoC insights, offering a highly accurate, adaptable, and predictive view of the customer journey. This evolution underscores a shift towards more nuanced, data-informed strategies in journey mapping, essential for businesses to remain responsive and competitive in a rapidly changing customer landscape.
The evolution from traditional to behavioral-based, data-driven journey mapping is not just a shift in technique; it’s a fundamental transformation in how businesses understand and engage with their customers.
And, importantly, this transition to more agile, behaviorally informed, and data-driven methods is crucial in an era where customer behaviors and expectations are in constant flux.
Here’s a no-nonsense checklist for how to take the next step in your journey mapping evolution:
Assess your current journey mapping practices
Begin by evaluating your existing customer journey mapping methods. Understand their limitations and identify areas where incorporating VoC and behavioral data could make a significant impact.
Invest in the right tools and technologies
Embrace analytics tools, AI , and data management systems that can integrate and interpret both VoC and behavioral data . The right technology is crucial for making this transition successful.
Train your team
Ensure that your team has the skills and knowledge to leverage these new tools and insights. Consider workshops, training sessions, or partnering with experts in the field.
Start small and scale
Begin by applying these principles to a single customer journey or segment. Learn from this experience and gradually expand to other areas of your business.
Continuously gather and analyze data
Make data collection and analysis an ongoing process. The market and customer behaviors are constantly changing, and your journey maps should evolve accordingly.
Act on your insights
Use the insights gained from your enhanced journey maps to make informed decisions. Whether it’s refining your marketing strategy, improving customer service, or innovating your product line, let your customer insights guide you.
Measure and refine
Continuously measure the impact of the changes you make and be prepared to refine your strategies. Remember, journey mapping is an iterative process.
By adopting a behaviorally informed, data-driven approach to journey mapping, your business can gain a deeper understanding of your customers, anticipate their needs, and deliver experiences that not only meet but exceed their expectations.
Ultimately, this is your opportunity to be at the forefront of customer experience innovation.
Related resources
Customer Journey
B2B Customer Journey 13 min read
Customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, customer journey management 14 min read, customer journey stages 12 min read, buyer's journey 16 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
How to make a customer journey map?
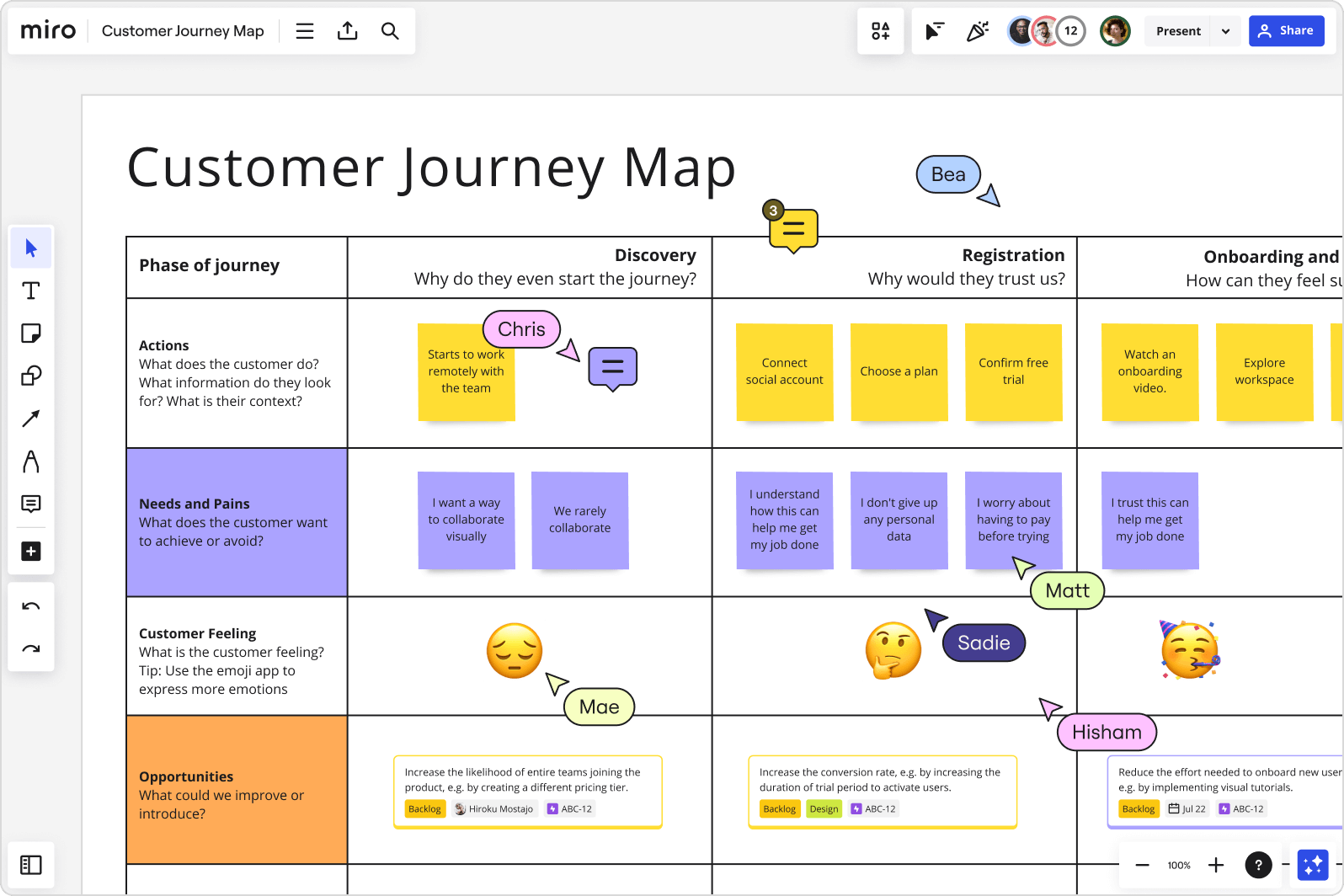
Why make a customer journey map
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for visualizing your customers' experience. It enables you to empathize with your customers and set them up for success. But for the uninitiated, customer journey mapping can seem intimidating, time-consuming, or even useless. We’re here to tell you it’s far from that. With the right guidance, you can use customer journey map tools to form a foundational part of your business.
Let’s be real: modern customers expect a guaranteed high-quality experience. According to a study conducted by customer strategist and researcher Esteban Kolsky, only 1 in 26 unhappy customers regularly complains – and the rest simply stop doing business with the company altogether. Ultimately, around 91% of unhappy customers will simply leave without a complaint. That means your business can be missing out on the valuable feedback you need to correct mistakes that are costing you customers.
This finding underlines just how crucial it is for companies to map their customer journeys. Simply put, by creating a CJM , you are likely to unearth issues you might not hear about directly from the customers themselves. That kind of information can be beneficial to your company’s bottom line. Let’s talk about how to make a customer journey map that’s valuable to your organization – and not a waste of time.
Before you get started
If you’re thinking about creating a customer journey map without a specific, measurable goal in mind ... stop. Back up and pause a minute. Consider the reason you need a CJM at all. You’re going to need to spend some time articulating the challenges your team faces, so you can more efficiently seek answers in your CJM.
CJMs are especially useful in scenarios like these:
You have a customer churn problem you’re looking to understand and solve.
You’re trying to understand the buying patterns of different personas.
Your company is shifting approaches (e.g. from a bottoms-up to top-down, inside-out to outside-in, etc.).
You’re about to release a new product or service.
You’re looking to assign team resources to specific touchpoints within the journey.
Write down the problem or reason you need a CJM first, then consider what kind of business goal you’re looking to achieve.
Customer journey maps are great for:
Identifying ways to engage or reach customers
Unearthing and addressing internal inefficiencies
Increasing conversions and ROI
We recommend making sure you’re setting measurable goals for your map before you get started. You can always adjust as you learn new things from your map, but it’s important to have an actual objective and KPI.
Common business KPIs to consider are:
Customer satisfaction scores
Retention or churn rates
Preliminary Customer Journey Mapping Work
Before you host a customer journey mapping workshop, it’s important to understand who needs to be involved, what tools you’ll be using to make your map, and what technology you’ll need to host your workshop. Here are a few important steps to take before making your customer journey map.
Map out your stakeholders
Your internal stakeholders are the people who will be impacted by the results of your customer journey map the most. Be sure to identify them before you get started, so you know who should be invited to your mapping workshop. Learn more in The Complete Stakeholder Mapping Guide .
Set up your CJM Canvas
Many teams prefer to use pen and paper to create their journey map, and remote teams need digital tools. Regardless of how you host your workshop, you’re going to need to digitize your map at some point to share it across your organization. Miro is a perfect visual canvas to use for your map – and a great tool when you don’t have the luxury of being in the same place as your team. Get started by opening up a board, and adding the templates you’ll need for your mapping exercise.
Now, with your digital canvas open, write down your goals and objectives on the board for the team to review during your workshop. You can even create a quick introductory presentation on a few slides to talk through at the beginning of your workshop.
Decide which CJM angle to take
There are different ways to structure your map, depending on your goal. Here are four common ways you can map your customer journey.
Current state : When you think of a CJM, you’re probably thinking of a current state map. These maps articulate the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience while interacting with your brand. Use current state maps to improve the customer journey.
Day-in-the-life : These maps illustrate the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience during their daily activities – regardless of whether they involve your brand. Use these types of maps to gain a broader understanding of who your customers are and to expand possible applications of your product.
Future state : As the name suggests, future state maps allow you to visualize how your customers will experience future actions, thoughts, and emotions when interacting with your brand. Use these aspirational maps to illustrate your vision for your organization’s future.
Service blueprint : To create a service blueprint, start with a simplified version of one of the other types of maps. Then add in the factors that contribute to the customer’s experience of your brand—including people, technologies, processes, and policies. Use service blueprints to identify concrete steps you must take to achieve your desired customer journey in the future. For this, you may want to consider adding another template to your board.
Once you’re ready to get started, share the Miro board with your stakeholder team and get ready for your kickoff meeting.
Running your CJM workshop
Now that you’ve invited your stakeholders and shared your workshop board, it’s time to get started. When running a customer journey mapping workshop, we recommend breaking it out into a few specific chunks:
The setup. Kick the meeting off by engaging your team with ice breakers, then present the goals and objectives of the session.
The persona exercise. First, start by identifying your target customer and understanding their point of view. This is about building empathy.
Mapping the customer journey. Now’s when you list out the touchpoints of your customer’s experience with your company.
Testing. Once you’ve mapped out the journey, go through it yourself to better empathize with the customer and understand the hurdles they may face/
Iterate on the map. Once you start to notice gaps, or opportunities for improvement, test out ways you can iterate on and improve the map.
After the session, make sure you gather the key insights you found during the exercise and share them with the team. This will help you form plans and align on next steps.
Now let’s dive into each of these areas.
Start the meeting with an icebreaker
Ice breakers are a great way to get everyone involved feeling loosened up, engaged, and ready to go. Try this Ice Breaker Template for a quick, fun exercise at the beginning of the meeting.
Present the CJM’s purpose & goals
Now it’s time to kick off the customer journey map exercise. Start by speaking to the purpose and goals you’ve identified for the map. It’s important to make sure your team understands what you’re trying to accomplish, or else you run the risk of the session getting off track.
Create personas
Now for your first official team exercise. Drawing on your objectives, start to create personas. Personas are snapshots of ideal customers. They allow you to visualize the individuals who benefit from your products or services. When you’re mapping out your customer journey, it’s important to visualize who the customer is – and that’s where personas can help.
Try to build as exhaustive a picture of your customer as you can. If you have demographic and psychographic data, include that in your personas. You might find it useful to send out a questionnaire to customers or prospects ahead of time to get their feedback on your products or services. Include questions like:
How did you hear about our company?
What comes to mind when you think of our brand?
How do you use our product?
How often do you use our product?
What goals do you want to achieve with our company?
Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, why did you decide to purchase?
Have you ever interacted with our site intending to make a purchase but did not follow through? If so, what stopped you?
What can we do to improve your experience with our site?
How can we make it easier for you to purchase and use our products?
Remember, the goal of customer journey mapping is to center on the customer’s perspective and empathize with their experience of your product. The more complete your persona is, the more useful a tool your customer journey map will be.
List customer touchpoints
Touchpoints are all the places where your customers can interact with your brand. Think of them as signposts along a road. Drawing on your research, list all the touchpoints your customers and prospects use when visiting your site, as well as those you think they should be using.
It’s important to document the gap between touchpoints they are using and touchpoints you intend for them to use, because that helps you draw conclusions about the actions of your customers. Are they using fewer touchpoints than expected? More? This could mean your site is too complicated, or some obstacle is causing them to leave earlier than you might want.
When you’re building a list of touchpoints, be sure to include paid ads, email marketing, and third-party review sites or mentions. You can also access your Google Analytics and look at the Behavior Flow report which shows how users navigate between different pages on your site.
Test the customer journey
You’re not quite done! Next, test-drive the map yourself. Work through the CJM and see if you can start answering some questions you posed before you started mapping. How can you make it easier for customers to buy your product? How many people bounce once they click onto your site? If you’ve thoroughly built out the map, you should be able to answer these questions.
Test driving the map is important for a few reasons: For one, you want to make sure it accurately represents the customer’s journey. That ensures you’re in a good place to start making decisions based on your analysis of the map. Moreover, you want anyone from the organization to be able to use your map to perform their own analyses. Testing out the CJM transforms your map from a thought experiment into a practical tool.
Map resources you have and those you’ll need
As you’re mapping, you’ll become aware of missing pieces in the customer journey. Since your map touches on nearly every aspect of your business, you’ll quickly be able to take stock of what you’re missing. As you develop the map and get clarity on those missing parts, keep a running list of resources you have and those you’ll need to improve the customer’s journey.
Like many teams, your team might like to add those resources and tools into the map to predict how they might impact your business and drive revenue. Fleshing out the map with these added components will make it easier to get buy-in and augment parts of the customer’s journey.
Iterate on your map
After you’ve tested the map, you can start to make changes to your customer journey. And each time you do, you can also adjust the map. A customer journey map is powerful partly because it’s a living document. Review it on a monthly or quarterly basis to keep up the momentum, identify gaps as they arise, and further streamline and improve your customer journey.
Gathering and sharing insights
Now that you’ve completed your mapping exercise, make sure to list out key insights and takeaways so your team can align on what to do next. You can create a specific section on your board, or send takeaways out via email after the meeting.
Discover more
Service blueprint vs. journey map
Benefits of customer journey mapping
Customer experience vs. customer journey map
What is consumer decision-making process?
Buyer journey vs customer journey
The 7 steps of the customer journey
What is service blueprint?
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Hey there! Free trials are available for Standard and Essentials plans. Start for free today.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map (With Examples)
Learn how to create a customer journey map to optimize your company's customer experience.
As a business owner, there tends to be a lot of work that goes into getting a customer to buy your product. Several interactions lie between the moment a potential customer first discovers your brand and the moment they make a purchase. The steps that the customer takes on their way to making a purchase is commonly referred to as the customer journey.
Understanding the stages of the customer journey and building a customer journey that leads to conversions are essential as you attempt to grow your brand and build relationships with clients. You want to facilitate positive interactions with your brand at every step of the journey, which means optimizing the customer experience and providing excellent customer service.
While the customer journey is an important element for any company to consider, it may seem somewhat abstract or difficult when it comes down to the details. This is where a customer journey map comes in.
With a customer journey map, you can begin to better understand the customer journey, build out a better customer experience for your business, and keep customers happy. A customer journey map can also help you set short- and long-term goals and optimize certain business processes.
In this article, we go into detail about what customer journey maps are and why they’re so important. Read on to learn more about how customer journey maps can help your business or navigate the article using the links below.

What is a customer journey?
The customer journey refers to the series of interactions a customer has with a business before taking a particular action.
Essentially, the customer journey identifies all of your touchpoints—or, in other words, interactions that take place during the customer lifecycle—and organizes them into defined stages. This can help you better understand the customer lifecycle and identify points along the journey that can be improved or adjusted.
So, why should you create a customer journey ? Creating a defined customer experience allows you to better understand the customer experience and collect valuable insights about how customers interact with your brand. You can use those insights to boost engagement, improve customer service, and increase conversions.
Thus, in addition to helping the customer have as smooth of an experience as possible, building out a customer journey can benefit your business and increase your bottom line.
That brings us to customer journey mapping. Creating a customer journey map is one way to visualize the customer journey and clearly identify touchpoints. But what, exactly, is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual tool that allows you to see a step-by-step representation of a customer experience. Using a customer journey map, you can visualize the customer journey from start to finish and view touchpoints that may span across different channels or departments.
By allowing you to visualize customer journeys, a customer journey map turns a somewhat abstract concept into something much more concrete. Viewing a diagram representing your customer experience can make it easier to recognize customer pain points and find areas for improvement in all departments of your business.
Additionally, a visual tool like a customer journey map can be distributed as a resource to employees that helps them better serve customers. Whether they work in customer service or sales, a customer journey map can be an invaluable resource for employees seeking to better understand clients and provide excellent service every step of the way.
What elements should be included in a customer journey map?
As you create a customer journey map, there are a few things you should keep in mind. Customer journey maps may vary in their goals and scope. However, there are some essential elements that every customer journey map can benefit from.
By including certain elements in your customer journey map, you can design a customer journey that effectively allows you to reach your business goals. Below, we’ve listed a few elements that you should consider adding to your customer journey map.
Buyer personas
Buyer personas—also known as user personas or customer personas—are general representations of your average customer based on market research and your own experiences with your client base.
The primary purpose of a buyer persona is to show the characteristics, behavioral traits, values, and customer expectations demonstrated by your target audience. This allows you to better understand your customers and, in turn, design a customer journey that’s tailored to your specific client base.
When it comes to developing buyer personas, there are several approaches you can take. From reviewing hard data to speaking with customers, there are a variety of ways to identify your ideal customer. Below are some of the ways in which you might collect customer data and conduct persona research:
- Send out customer surveys
- Review audience demographic data
- Interview customer-facing employees
- Review customer complaints and inquiries
- Monitor company social media channels
Overall, the goal of creating a buyer persona is to better empathize with your customers and understand what they’re looking for.
As you begin creating buyer personas, keep it simple by crafting only one or two. This will keep you focused on your target customer—as your business grows and your customer base becomes larger and more diverse, you can consider creating more buyer personas to further segment your audience.
Buyer’s journey
Every customer journey map should thoroughly outline the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the ideal route that you would like the customer to follow in order to take a specific action.
In order to map out the buying process, you will need to set goals, identify key touchpoints, and organize the stages of the customer journey. Mapping out the buyer’s journey will allow you to better understand the steps customers take from their first interaction with your company to finally making a purchase.
Customer touch points
Identifying touchpoints is one of the most crucial steps when creating a customer journey map. Customer touchpoints represent any interaction that a customer has with your business and they can occur on any type of channel. For instance, customers may interact with:
- Your website
- Your online store
- Your company’s social media channels
- Customer service representatives
- Your physical storefront
- Digital ads
- Company events
Touchpoints can even encapsulate indirect interactions that customers have with your brand.
For instance, a customer may look on an industry review site and see reviews of your company, or they may read a blog that includes an outbound link to your company website. These are all examples of potential touchpoints.
Every touchpoint presents a customer with an opportunity to make a judgment or form an opinion about your business.
This is why customer touchpoints are so important. By optimizing as many touch points as you can along the customer journey, you can improve the reputation of your business, facilitate a positive customer experience, generate leads , nurture leads , and ultimately increase conversions by guiding customers towards a desired action or goal.

Customer journey stages
You can effectively structure your customer journey by dividing it up into stages. The stages of a customer journey map help break up the timeline by defining distinct stages.
Depending on the industry you’re in, your customer journey map may include just a few stages or you may have many. In some cases, you may be able to adapt the AIDA model to your customer journey stages, while in other cases you may require more stages.
As a starting point, you might divide the customer journey into five general stages:
During the initial stage of the customer journey, consumers have want or need and they’re researching products and services that can provide them with a solution. At this step in the process, your job is to reach the customer as they’re researching their options and position your company as a potential solution.
Consideration
Once consumers conduct some initial research, they will begin to seriously consider their options. Most consumers will compare brands that offer similar products and services to see which option best meets their needs. Optimizing the customer experience and emphasizing your company’s unique selling proposition (USP) is crucial during this stage.
After conducting research, a consumer will take action by making a purchase, signing up for a subscription, or opting into a mailing list. In order for consumers to take a desired action, brands must present a call to action and streamline the purchasing process.
Converting a new customer is a success in and of itself, but maximizing customer retention is key to generating consistent profits. As a business owner, you want to ensure that everyone has a great customer experience at every touchpoint and make the transaction process as easy as possible. When customers have a positive customer experience with your business, they will be more likely to return in the future.
Word of mouth is one of the best ways you can promote your business. Satisfied customers may refer friends, family members, and colleagues to your business, helping to generate more customers and drum up more business.
By consistently providing an excellent customer experience and perhaps even implementing a loyalty program, you can build strong relationships with your customers and turn them into advocates for your business.
Thoughts and emotions
It’s important to take your customers’ thoughts and emotions into account at every step of the customer experience.
Consider how a customer feels at each stage of the journey and brainstorm methods for appealing to these emotions. If you can create a positive emotional association between a customer and your brand, this will often translate to strong relationships and increased customer loyalty.
No matter what a customer purchases, they want to feel good in the process. As you create your customer journey map, consider listing emotions that your customers may be feeling at each touchpoint. Try to find opportunities to resolve negative emotions in order to forge a positive emotional bond between the customer and your brand.
Pain points
Customer pain points are the specific problems that your customers are dealing with and may be actively seeking out a solution for.
Identifying customer pain points is important because it opens up a window of opportunity for your business: you can provide a solution to their problem, meet their needs, and profit in the process.
Identifying customer pain points is also helpful as you seek to optimize your customer experience. With a better understanding of the pain points involved in your own buying process, you can find streamlined solutions that make purchasing easier.
So, as you create your customer journey map, list out pain points that customers may experience at each step in their journey. Appealing to these pain points and providing convenient solutions can help you convert leads.

4 reasons you should prioritize customer journey mapping
When used properly, customer journey mapping can be a valuable tool that enables you to achieve even your most ambitious business goals. Below, we go over four reasons why you should prioritize customer journey mapping for your own business.
Optimize customer experience
Ultimately, creating a customer journey map is centered around improving the average customer experience when interacting with your business. Customer journey maps enable you to be a more customer-centric business that sees things from the customer’s perspective and acts accordingly.
By creating a customer journey map, you can provide customers with an excellent experience every time they interact with you, which can increase sales, bolster your customer retention strategy , and improve your brand’s reputation.
Better understand customer behavior
Many of the world’s most successful brands use behavior-based marketing to reach their audience. With a better understanding of customer behavior, you can effectively segment your audience and lead customers down the marketing funnel .
Build strong customer relationships
A customer journey map helps to create positive customer experiences, which in turn leads to strong customer relationships. Customers with a strong connection to your brand will not only continue to make purchases, they will also recommend your brand to others. By connecting on a personal level, you can cultivate a devoted customer base that enables your business to grow.
Streamline the buying process
Using a customer journey map, you can identify steps in the buying process that may be unnecessary or frustrating to customers. If certain steps in the buying process irritate your customers or make them abandon their cart, this leads to lost opportunities for your business. Overall, you want to make the purchasing process as easy and convenient as possible.
How to create a customer journey map with examples
Now that you understand what a customer journey map is and why it’s important, you may be wondering how to create one. Below, we go over the basic steps involved in creating a customer journey map.
Set clear goals
The first step in creating a customer journey map is setting clear goals and objectives. What do you hope to gain from this customer journey map? Who are you targeting and why?
Once you have set clear goals, you can identify key metrics to track that will help you measure progress. For example, if your goal is related to building stronger customer relationships, then you may want to pay attention to KPIs such as your customer retention rate and referrals per user.
Research and build buyer personas
As we mentioned above, buyer personas are essentially profiles highlighting common characteristics that your average customers share. Conducting research and building out these buyer personas are essential when it comes to creating a customer journey map.
A typical buyer persona may contain the following information about your target audience:
- Education level
- Geographic location
- Income level
- Challenges faced
Essentially, with a buyer persona, you’re creating a profile of your ideal target customer. This helps you understand your audience and, thus, enables you to build a more effective customer journey map that caters to their wants and needs.
Identify customer touch points
Customer touchpoints occur during the customer journey. Touchpoints refer to moments when the customer interacts with your company and they can take all kinds of forms. By identifying significant touchpoints and milestones on your customer journey map, you can more easily pinpoint opportunities to boost engagement and make a good impression.
Some customer touchpoints might include:
- Social media
- In-person conversations
- Product ratings and reviews
- Point of sale
- Follow-up emails
- Customer service tickets
- Transactional emails
Map the current customer journey
Once you have your goals, buyer personas, and touchpoints, all that’s left to do is to map the customer journey. To get started with mapping the customer experience, you can create a draft by hand or use an online visualization tool to help you build a more in-depth graphic.
From there, put yourself in the customer’s shoes and imagine the customer journey from start to finish. Make sure to keep in mind the key touchpoints you identified and add those touch points along the way. At each step or stage of the customer journey, note any crucial data or considerations that you would like to remember going forward.
Test the journey and make adjustments
Once you have mapped out the customer journey, make sure to test it by taking the journey yourself. By following the journey yourself, you can better understand what your customers go through and empathize with their experience.
This allows you to identify gaps in your customer journey and find areas that could use improvement. As you test your customer journey and as time goes on, don’t hesitate to make any changes that can help optimize the customer experience and convert website leads into devoted customers.
Connect with customers throughout their customer journey
Optimizing your customer's experience can help to increase engagement, improve the customer experience, and boost sales. Mapping out the customer journey is one effective method for visualizing and organizing all of the elements of the customer journey so that you can keep your clients happy.
Mailchimp makes it easy to map the customer journey, allowing you to personalize everything from the customer onboarding process to post-purchase interactions. Use Mailchimp’s customer journey builder and our suite of tools to create a visual representation of the customer journey, and then capitalize on key touch points across marketing channels.
Related Topics
- Email Automations
- CRM Automations
- Transactional Email
- Map Customer Journeys

How to Create a Customer Journey Map
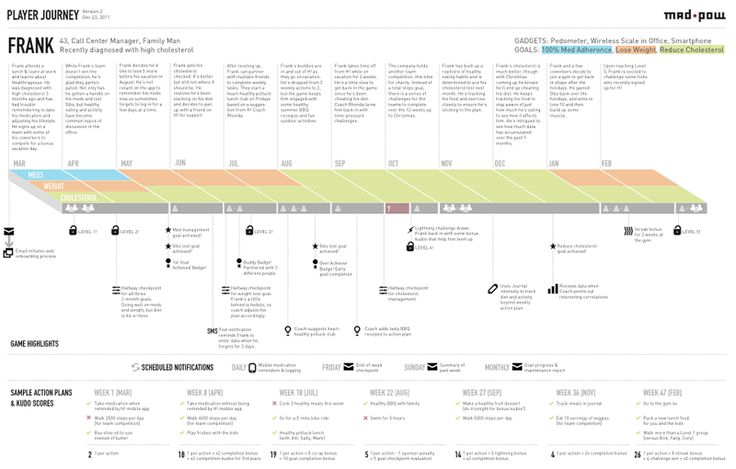
Customer Journey maps are a visual interpretation from an individual’s perspective of their relationship with an organization, service, product or brand.
This whiteboard animation (and article) shows you how to create a Customer Journey Map.
Despite best intentions and mountains of data, many organizations continue to offer lackluster experiences for their customers.
Many organizations function with an internal focus, and that becomes apparent when customers interact with their various products, services and employees. Every interaction a customer has with an organization has an effect on satisfaction, loyalty, and the bottom line. Plotting out a customer’s emotional landscape by way of a Customer Journey Map, or Experience Map, along their path sheds light on key opportunities for deepening those relationships.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
A Customer Journey map is a visual or graphic interpretation of the overall story from an individual’s perspective of their relationship with an organization, service, product or brand, over time and across channels. Occasionally, a more narrative, text-based approach is needed to describe nuances and details associated with a customer experience. The story is told from the customer’s perspective, but also emphasizes the important intersections between user expectations and business requirements.
Inspired by user research , no two journey maps are alike, and regardless of format they allow organizations to consider interactions from their customers’ points of view, instead of taking an inside-out approach. They are one tool that can help organizations evolve from a transactional approach to one that focuses on long term relationships with customers built on respect, consistency and trust.
All organizations have business goals but leveraging customer journeys as a supporting component of an experience strategy keeps customers (or members, patients, employees, students, donors etc.) at the forefront when making design decisions. They can be used in both current state review and future state visioning to examine the present, highlight pain points and uncover the most significant opportunities for building a better experience for customers.
How Do We Use Them?
Customer engagement is not simply a series of interactions, or getting people to visit a website, “Like” something on FaceBook, or download a mobile app. Genuine engagement centers on compatibility, and identifying how and where individuals and organizations can exist harmoniously together. Giving thought to how your organization/product/service/brand fits into customers’ lives is crucial.
I also use journey maps to gain internal consensus on how customers should be treated across distinct channels. Holding collaborative workshops with cross-disciplinary teams mixing people who otherwise never communicate with each other can be extremely valuable in large organizations in particular.
Illustrating or describing how the customer experience could be brought to life across channels allows all stakeholders from all areas of the business to better understand the essence of the whole experience from the customer’s perspective. How do they want to be spoken to, what are they thinking, feeling, seeing, hearing, and doing? Journey maps help us explore answers to the “what ifs” that arise during research and conceptual design.
What Components Does a Journey Map Include?
- Personas : the main characters that illustrate the needs, goals, thoughts, feelings, opinions, expectations, and pain points of the user;
- Timeline : a finite amount of time (e.g. 1 week or 1 year) or variable phases (e.g. awareness, decision-making, purchase, renewal);
- Emotion: peaks and valleys illustrating frustration, anxiety, happiness etc.;
- Touchpoints : customer actions and interactions with the organization. This is the WHAT the customer is doing; and
- Channels : where interaction takes place and the context of use (e.g. website, native app, call center, in-store). This is the WHERE they are interacting.
Nice-to-haves
- Moments of truth : A positive interaction that leaves a lasting impression, often planned for a touchpoint known to generate anxiety or frustration; and
- Supporting characters: peripheral individuals (caregivers, friends, colleagues) who may contribute to the experience.
The Process
1. review goals.
Consider organizational goals for the product or service at large, and specific goals for a customer journey mapping initiative.
2. Gather Research
Review all relevant user research, which includes both qualitative and quantitative findings to provide insights into the customer experience . If more research is needed, get those research activities in the books. Some of my favorite research methods include customer interviews, ethnography & contextual inquiry, customer surveys, customer support/complaint logs, web analytics, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
3. Touchpoint and Channel brainstorms
As a team, generate a list of the customer touchpoints and the channels on which those touchpoints occur today. Then brainstorm additional touchpoints and/or channels that can be incorporated in the future journeys you will be mapping. For example, the touchpoint could be “pay a bill”, and the channels associated with that touchpoint could be “pay online”, “pay via mail” or “pay in person”.
4. Empathy map
Empathy maps are a depiction of the various facets of a persona and his or her experiences in a given scenario. This exercise helps me organize my observations, build a deeper understanding of customers’ experiences, and draw out surprising insights into what customers need. Empathy maps also provide a foundation of material to fuel journey mapping. The goal is to get a well-rounded sense of how it feels to be that persona in this experience, specifically focusing on what they’re thinking, feeling, seeing, hearing, saying and doing.
5. Brainstorm with lenses
The goal of lensed brainstorming is to generate as many ideas as possible in a short period of time. To gain focus as I generate ideas I use “lenses”—words representing key concepts, brand attributes or mindsets that help us look at a problem or scenario in a different way. For this exercise I recommend that the team agree on 3-5 lens words (for example: accessible, social, comforting), then set the clock for 2 minutes per lens word. Each person individually writes down as many ideas as they can think of in that time. After 2 minutes switch to the next lens word until all lens words have been used as idea inspiration. This ensures that every voice on the team is heard and generates a huge inventory of ideas.
6. Affinity diagram
This is a method to visually organize ideas and find cohesion in the team’s concepts. Affinity diagramming helps us shift from casting a wide net in exploring many possibilities, to gaining focus on the right solutions for this audience. All team members should put their ideas generated in the lensed brainstorming activity up on the wall. Have someone sort the ideas into categories and label them. As a group, begin to consider where you might combine, refine, and remove ideas to form a cohesive vision of the future customer experience.
7. Sketch the journey
Drumroll, please. This is the part you’ve been waiting for! It’s now time to put together all the pieces: timeline, touchpoints, channels, emotional highs and lows, and all the wonderful new ideas the team generated for how to improve the future customer journey. Get creative with how you lay it out—it doesn’t have to be a standard left to right timeline. It could be circular or helical. It could be one large map or it could be an interactive, clickable piece with embedded video. There are no templates, and there are infinite possibilities.
8. Refine and digitize
Journeys don’t always become a sophisticated deliverable—sometimes they begin and end as sticky notes on a wall or sketches on a whiteboard. But most of the time, when you go through the activities to arrive at a solid customer journey map, you want to polish it, leverage it in your work and share it with colleagues across the organization. If visual design isn’t your strong suit, consider collaborating closely with a visual designer who can transform the journey map sketch into an impressive artefact.
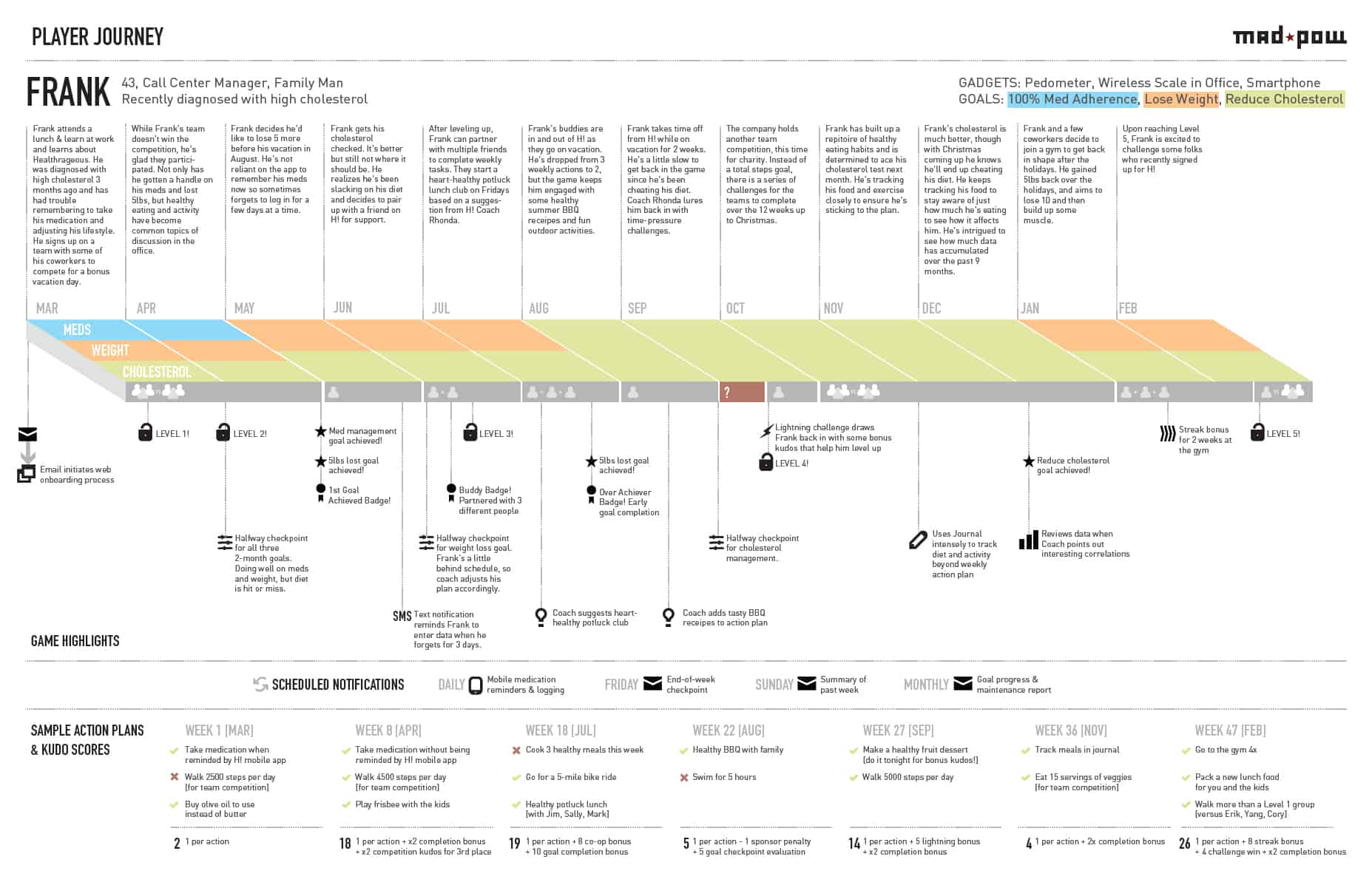
While journey maps are usually a tangible deliverable, like the one above, the process of journey mapping is what’s most important – it pushes us to think deeply about how we can use experience design to have a positive impact on our customers.
9. Share and use
It can be beneficial to maintain journey maps over time. For example, you could set a time each quarter or year to evaluate how your current customer experience matches your documented vision journeys. If your organization tracks quantitative KPIs, you can integrate these into a journey benchmarking process. Socializing journeys among stakeholders is critical in moving your organization toward action.
In addition to prioritization, the output of a journey map can serve as a backbone for strategic recommendations and more tactical initiatives.
For example, if you’re a mortgage company and you identify the closing process as a key area of frustration, anxiety and opportunity for engaging with the customer and designing for the “moment of truth”, then mark this as a high priority and get that on your strategic roadmap.
Schedule enough time to properly go through the recommended process. I’ve found that you can document a current state journey in about 3 hours, and a future state journey in about 5 hours. This makes for a full day to do both for one persona.
Make sure a good mix of people are involved in the journey map creation. It’s helpful to have stakeholder participants from many areas of the organization, as well as people of varying levels of seniority.
Once the journey maps are created, share them with zeal. Shout them from the rooftops and display them prominently in common areas.
Megan Grocki
Megan Grocki is an experience strategy director at Mad*Pow. With over 15 years of experience in research, experience design and strategy, she helps clients discover the expectations and behaviors of their audiences and identify opportunities for engagement. She has presented and led workshops at several UX, healthcare, and strategy industry events. In her spare time she is earning her master's degree in gastronomy with a concentration in food policy at Boston University. She hopes to leverage her design and strategy chops to educate the public about the connections between their health and what they eat, and use design to help affect changes in food policy at local, national and global levels.

Join the discussion Cancel reply
49 comments.
The post is incredibly good and very well explained. Well done Megan. Thanks UX Mastery for gathering this content and people.
Thanks Justin—I agree Megan did a great job explaining it, and we’re pretty proud of the resulting animation!
Keep an eye on the site as we tackle other UX techniques .
Megan – can you kindly post a better quality image to your final visual please – it certainly seems it will be worth reading your output. Good work!
That’s been done, Max.
Excellent Post Megan! Your process and explanations are easy to follow and very useful. I love the video too. I help people & groups as they through change and an early step in creating a compelling future is gaining a shared understanding of where we actually want to go. Techniques like the ones you’ve described here are so important to structuring the kind of dialogue needed to build that understanding! Thanks for sharing! -Steve
Great article, I agree with everything you’ve written. In my daily workflow, I use Mediatoolkit.com for media listening activities and I highly recommend it, because it enables me to be careful around the challenges you mentioned. :)
Great article Megan! As a Customer Journey Research provider from The Netherlands, it’s very interesting to read. The process and examples are well explained!
This is a really great article. It is well written and a step-by-step tool for mapping and exploring user journeys. The video is also excellent! Thanks!
Hey Megan!!
Just doing a little bit of research on customer journey maps for a talk and boom!! here you are!! This is very helpful information!!!
Great work. Thanks for sharing your methods.
Thanks for this article! However, several points are still unclear. For example – step 5) Brainstorm with Lenses. What exactly is the team brainstorming for? What ideas are we looking for? Shouldn’t the customer journey map be based on observing what frustrations and triumphs people have at each stage in the journey?
Similarly, I didn’t understand clearly how affinity diagramming fit into this process. Is it simply gathering and organizing all the data from research into potential steps in the customer journey?
Hope to hear from you soon! :) And thanks again!
Best wishes, Eureka UX Researcher at Piktochart
I had the same thought. I assume these are the steps for creating a future state journey map, not a current state.
Great post Megan! Thank you for the explanation and process mapping.
Thank you for your post and the video! We use it sometimes to explain our students in just several minutes how to build CJM. On step 4 we also try to identify mood (experience). And on step 10 we usually say “Iterate!” (: We also created a tool to create customer journey maps online – http://uxpressia.com .
Beautifully explained…Amazing how relevant this is for transporting your customer to a virtual world during a sales demo!
Hello Megan,
Very nice article & informative vide, ths for the share.
Regards, Ayman
Thanks for the great information. Very helpful and well-outlined. Much appreciated!
Love the intelligence and delivery. Off to put to good use hopefully! Thank you Megan.
Thank you for your thoughtful post. I’m finding that different groups in my company (engineers, sales, client services) all want and could benefit from user research assets such as personas and journey maps. However, they each prioritize different content. Do you happen to know of a tool that enables storing and maintaining a lot of content pieces (modules) about a persona and enables dynamic updating of “child” content? For example, if I tweaked the empathy map in the master, all the child artifacts that included the empathy map would be updated. I’d be happy to pay for a good solution, but have not found any. I also work on a mac… Thanks in advance for your help!
hi Megan thanks for your post being a student I have to create an assignment of a customer journey map of any service or any product can you tell me which software is to be used for this purpose.
Hello Megan for sharing extreamly good idea about customer journey map.Really Great Work.Keep it up
Thanks for brilliantly mapping the steps in visual form!
Excellent Megam, process mapping really well done.
Hey guys, what tool do you use Megan for the journey map? Can people recommend good free alternatives?
Great stuff… very helpful video.
1+1=3 Ger dig snabbt en bild av värdet i kundresan ur kundens perspektiv. vilka tjänster skall jag erbjuda med utgångspunkt från kundens resa
Well Done Megan! Great video.
One thing I’d maybe add for what it’s worth is the idea of interviewing Stakeholders as you begin the process. They can add some great ideas into what they perceive the customer pain points and relevant journeys to be. But more important than that, is that the Stakeholders will be more “bought-in” to your feedback when you present the final Journey Map product. That part is priceless.
Thank you for putting this together!
Hi, thanks for such an a valuable and insightful article. I’m just curious to understand more about affinity diagram. Could you elaborate more? From my understanding, I gathered that affinity diagraming is more of an activity than a documentation that requires a team discussion to gain consensus and categorize the deliverables from the preceding procedures into something more visual/documented? Could you elaborate more and point me in the right direction?
Trying to get in touch with Mad Pow Megan Grocki, does someone have her direct email address?
Thanks, Paul L
Some time has passed since we did that, but I think it’s still actual for the community. This year we’ve published a list of free customer journey maps templates here – https://uxpressia.com/templates . It is a pretty bunch of customer journey maps templates created for different business domains (including Healthcare, Travel, Banking, Telecom, etc.). All of them are based on the actual experience. You can download the template as PDF or start creating online map inside our tool based on that template.
All perfect and fine, but what I am always missing in discussions about user journeys is an overview of what we are ‘competing’ with. To achieve a touchpoint (meaning the client or user gives his or her attention to my app, or my service, or simply to me), what else is screaming for attention that the user then has to ignore.
I tried to discuss this here: http://www.expressiveproductdesign.com/competing-for-attention/
And did an attempt to create a template to help uncover the competition here: http://www.expressiveproductdesign.com/stickiness-creating-products-services-make-people-come-back/
Not sure if I am there yet. What do you think? Is ‘competition’ an issue in user journey mapping, and how do we best deal with this?
Great article!! In addition to all the pointers mentioned, would like to add the importance of CRM in regards to customer journey mapping. Traditionally retail stores, call centers, social media, and other channels were separately managed. However, now businesses cannot take the risk of handling these channels separately as it will result in a disjointed customer service.
Today the objective should be to have a broad single channel with multiple touch points. And that is only possible when all channels are merged.
Buisnesses who use a robust CRM software like ConvergeHub, Zoho or Infusionsoft are able to combine all communication channels to have a consolidated view of the customers and deliver consistent experience across all channels. So whether customers want to make a purchase, renew a service, or resolve a problem, they can do so in any of their preferred channels.
As the customers move across physical store, online e-commerce, social media and call centers, businesses can map the entire customer journey to provide a unified experience.
I dont see the highs and lows in the CJM?
This post illustrates well on this concept, thanks Megan, hope I have chance to translate the article into Chinese soon.
This is an awesome and very helpful post! Thanks for sharing these tidbits! I’d love to learn more.
This is immensely resourceful and precise. The nuances of user journey and the process explained in a lucid manner, keeping in mind the user journey of the reader. That’s a story within a story, using your technique to explain your technique. Thanks a ton, Megan. God bless!
Ditto. Very helpful, clear process to follow and great sample of the outcome. A watershed moment for me in documenting my own businesses CJM
Great post and video, thanks.
Wonderful post Megan
Great work, thank you very much!
Thanks for sharing, very useful post.
Thanks Kevin.
This is a really great article…concise with a great visual that really ties everything together well.
However, I struggle making these types of documents because of the abstraction. Frank isn’t real and the behavior pattern (the “journey”) has never happened. I know you pulled this from real data, but since I can’t tell what is real and what isn’t from this doc I am treating real behavior with equal weight to behavior you made up.
In fact searching for Healthrageous reveals a postmortem that admits they overbuilt and didn’t focus enough on market fit. This document fully embraces that admittedly flawed business approach…almost celebrates it. Do you think this document contributed to a false sense of security? Do you think it would have helped to surface more about what was real and what wasn’t, or is this document format more a symptom of this client’s approach than a cause?
Hi, I’am a trainee from Huawei Tunisia, i want to create a customer journey map and i’m looking for some examples of customer journey map for a telecom operator. Can you help me please with some design examples? I will be very grateful. Thank you.
This is a very informative document. I can’t wait to apply them. Thank you for sharing!
Thank you so much!!! Loved it:) Simple language & full of quality information:) Good job :)
Thank you so much its good
Hi, how to write the customer journey as a critical narrative. can u guide
Gorgeous 3-D Journey Map concept. Wish it was just a little less blurry!
Further reading

The Ethical Considerations, Trust, and Responsibility in Designing Voice UI
When it comes to creating Voice UI there’s a lot of conversation around voices, but very little around personality. How trustworthy should that...
Success in ResearchOps: An indicator of UX maturity
User research is not just an integrated part of business, but rather teams of people supporting the research process with the practice of ResearchOps...

How to Organize and Reuse Research Insights
Have you ever wondered what life would be like if we reused research insights? Lucky for you - it's easy! Zack Naylor from Aurelius teaches us how.
Follow @uxmastery

How to Create a Customer Journey Map
%20(3).jpg)
Creating a customer journey map can help you gain a deeper understanding of the steps, interactions, and emotions that a customer experiences as they move through their journey.
In this blog post, we’ll cover what we mean by a journey map, the benefits and challenges, and provide a step-by-step guide to building your own, including free (and editable) templates you can share with your team.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the steps and experiences a customer has as they interact with a business, product, or service. It can be used to identify areas of friction, understand customer preferences, and create a personalized experience for each customer.
By creating a customer journey map, businesses can gain insight into how customers move from awareness to purchase, and build meaningful relationships with them.
Why is it important to map the customer journey?
- Customer journey maps provide businesses with an in-depth understanding of the steps and experiences of their customers.
- They can help identify pain points in the customer experience and identify areas for improvement.
- Customer journey maps can be used to personalize the customer experience, creating a more meaningful relationship with customers.
- They can help businesses identify new opportunities and growth areas.
- Customer journey maps can help teams create and manage customer-centric strategies.
Benefits and challenges of customer journey mapping
Creating a customer journey map can provide businesses with invaluable insights into their customers' experiences, while also presenting some challenges in terms of gathering customer data and creating a strategy to address customer pain points.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
Creating a customer journey map can provide businesses with invaluable insights into their customers' experiences. It can help identify pain points in the customer experience, understand customer preferences, create a personalized experience for each customer across different touch points, and identify new opportunities and growth areas. It also helps teams create and manage customer-centric strategies, which can help businesses stay ahead of the competition.
Challenges of customer journey mapping
Creating an accurate customer journey map can be challenging, as it requires gathering customer data from multiple sources and understanding customer needs and preferences. It can also be difficult to create an actionable strategy to address customer pain points, as different customers may have different needs and preferences. Additionally, customer journey maps can quickly become outdated, making it important for businesses to stay up-to-date on customer trends and preferences.
How to create a customer journey map
To build your customer journey map, you’ll need to follow the seven steps below. Each of these steps has multiple components that require cross-functional teamwork, making having a shared, digital space key to your success.
Duration: 2 hours
Participants: 2-10 people
1. Gather customer data from multiple sources, such as surveys, interviews, online reviews, and analytics.
The first step in creating an actionable customer journey map is to ensure that you have a very solid understanding of your customers. Without a deep appreciation for their experience and a holistic view of your interactions, it’s impossible to capture accurate insights or make informed decisions.
2. Analyze the data to understand customer needs and preferences.
It is essential to thoroughly analyze customer needs and preferences in order to create an effective customer journey map that accurately reflects the customer experience. This is where you’ll be challenging any assumptions you may have had and beginning to look for patterns or insights that can be drawn from the data impact the overall experience.
3. Identify key customer touchpoints and create a timeline of the customer journey.

Once you’ve done your analysis, it’s time to start mapping your customer journey. To map the experience, you should:
- Narrow your focus to a facet of your customer experience (for example, when building solutions for Agile teams, you may want to focus on a particular ritual, like a retrospective )
- Decide on a single user, customer, or persona whose experience your diagram will represent
- Using sticky notes, have your team collect all the places, people, and items your persona will interact with (be as comprehensive as possible)
- Make sure you include instances where you have less control (e.g., the timing of a meeting vs. the structure)
- Consider the aspects of the experience that may be connected, even — especially — where those connections may not be immediately obvious
For this, a visual, collaborative platform like Mural can be a huge help, allowing you to connect what may seem like disparate elements of an overall experience, painting an accurate picture of your customers’ experience as a whole.
4. Identify areas of friction and opportunities for improvement.

After documenting the existing state of a person’s experience, it’s time to focus on key moments to deepen your understanding. Visualize the journey as pain points, bright spots, and opportunities to create a clear picture of how to improve the product or service experience, overall.
Things to do:
- Bring together the team that created the Experience Diagram(s) or people who are familiar with the experience
- Review your notes and any other artifacts collected during diagramming or early research (notes, photos, audio or video files, etc.)
- Select three colors of sticky notes (physical or digital) to capture Roses, Thorns, and Buds — we recommend Pink (Roses), Blue (Thorns), and Green (Buds) — to capture what is going well, what needs improvement, and any opportunities to expand upon in the future
5. Create an actionable strategy to address customer pain points.
Now that you’ve conducted your analysis and brainstormed ways to improve, it’s time to turn all that good information into actionable next steps.
Once you’ve organized all the information into categories, you can assign teammates to specific tasks all within the same visual platform, so everyone knows who is working on what, and expectations are transparent for every team member.
6. Test and refine the customer journey map.
Once you have a prototype of your customer journey map, you can begin to test it. You might start by applying your changes to a segment of your audience’s experience, and seeing what the preliminary results tell you. If it works, do more of it. If it’s not working so well, gather your team again to analyze performance and see what might be negatively affecting the experience.
7. Monitor customer trends and preferences to ensure the customer journey map stays up-to-date.
Iterate, iterate, iterate. Just because you’ve successfully created a customer journey map doesn’t mean the work is finished. As you begin to implement your changes, you’ll also be collecting new feedback — use that data loop to continuously improve your customer experience by returning to check in and reflect on progress with your team at regular intervals.
Customer journey mapping templates
Mural offers free, customizable customer journey mapping templates that you can share with unlimited members, so your whole team can get engaged.
Customer journey map template
The Mural customer journey map template, built by the Product School, has five components: entice , enter , engage , exit , and extend. Each of these steps includes a breakdown of interactions, goals and motivations, positive and negative moments, and opportunities for improvement.

Experience diagramming template
With the Mural experience diagramming template, you can pull back and come to grips with an individual experience for a customer, allowing you to consider each interaction in a more open, but also more granular way.

Rose, thorn, bud and affinity clusters template
The Mural rose, thorn, bud & affinity clusters template, built by the experts at the LUMA Institute (part of Mural’s Collaboration Design Institute), is a great brainstorming tool that allows your team to identify as many positive and negative aspects of a customer journey, while also providing space to investigate opportunities and organize feedback.
Use this template after the experience diagramming template to effectively map the interactions and emotions in a customer’s journey.

Customer journey maps are a stepping-stone to a better experience
Creating an actionable customer journey map is essential for businesses to stay ahead of the competition and provide a meaningful customer experience. By turning the customer journey map into actionable next steps, businesses can identify areas of friction in the customer experience, understand customer needs and preferences, create a personalized experience for each customer, and identify new opportunities for growth.
Mural makes extraordinary teamwork simple . Get started building your customer journey map today with a Mural Free Forever plan , and invite unlimited team members, so that you can ensure broad engagement and valuable insights that can be easily lost in traditional meetings, or with traditional brainstorming methods.
{{mural-luma-system="/cta-components"}}
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts

4 steps to creating digital customer & employee journey maps

Mural cited as a strong performer in Forrester’s Q2 2022 Forrester Wave™: journey mapping platforms
.webp)
Win, wow, and retain customers: Mural features and templates for sales and success teams
Related blog posts.
%20(1).jpg)
How to make a digital vision board: A complete guide
%20(1).jpg)
5 ways visual task management benefits your team
%20(1).jpg)
11 top tips for facilitating strategic planning sessions
Get the free 2023 collaboration trends report.
Extraordinary teamwork isn't an accident
Product Design Bundle and save
User Research New
Content Design
UX Design Fundamentals
Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
- UX training for teams
- Hire our alumni
- Journal of UX Leadership
- Our mission
- Advisory Council
Education for every phase of your UX career
Professional Diploma
Learn the full user experience (UX) process from research to interaction design to prototyping.
Combine the UX Diploma with the UI Certificate to pursue a career as a product designer.
Professional Certificates
Learn how to plan, execute, analyse and communicate user research effectively.
Learn the principles of content design, from mastering tone and style, to writing for interfaces.
Understand the fundamentals of UI elements and design systems, as well as the role of UI in UX.
Short Courses
Gain a solid foundation in the philosophy, principles and methods of user experience design.
Learn the essentials of software development so you can work more effectively with developers.
Give your team the skills, knowledge and mindset to create great digital products
Join our hiring programme and access our list of certified professionals.
Learn about our mission to set the global standard in UX education
Meet our leadership team with UX and education expertise
Members of the council connect us to the wider UX industry
Our team are available to answer any of your questions
Fresh insights from experts, alumni and the wider design community
Read stories from our students who have made successful careers in UX after completing our course
How to design a customer journey map (A step-by-step guide)
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how a user interacts with your product. Learn how to create a customer journey map in this practical step-by-step guide.
Free course: Introduction to UX Design
What is UX? Why has it become so important? Could it be a career for you? Learn the answers, and more, with a free 7-lesson video course.
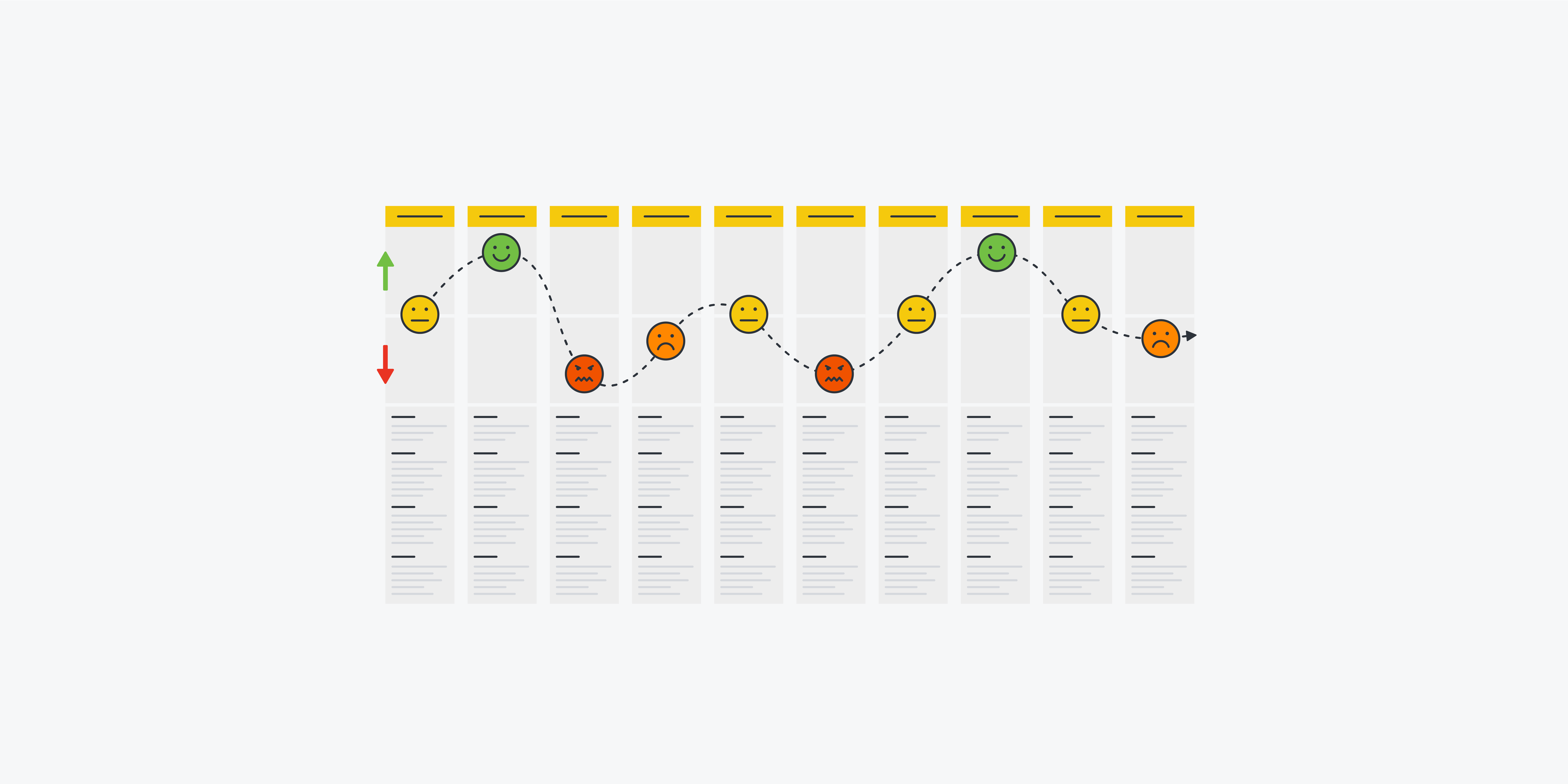
Successful UX design is rooted in empathy. The best designers are able to step into their users’ shoes and imagine what they think, feel, and experience as they interact with a product or service.
One of the most effective ways to foster user empathy and consider different perspectives is to create customer journey maps—otherwise known as customer journey maps.
If you’re new to journey mapping, look no further than this guide. We’ll explain:
- What is a customer journey map?
Why create customer journey maps?
When to create customer journey maps, what are the elements of a customer journey map, how to create a customer journey map (step-by-step).
If you want to skip straight to the how-to guide, just use the clickable menu to jump ahead. Otherwise, let’s begin with a definition.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UX]
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map (otherwise known as a user journey map) is a visual representation of how a user or customer interacts with your product. It maps out the steps they go through to complete a specific task or to achieve a particular goal—for example, purchasing a product from an e-commerce website or creating a profile on a dating app.
Where does their journey begin? What’s their first point of interaction with the product? What actions and steps do they take to reach their end goal? How do they feel at each stage?
You can answer all of those questions with a user journey map.
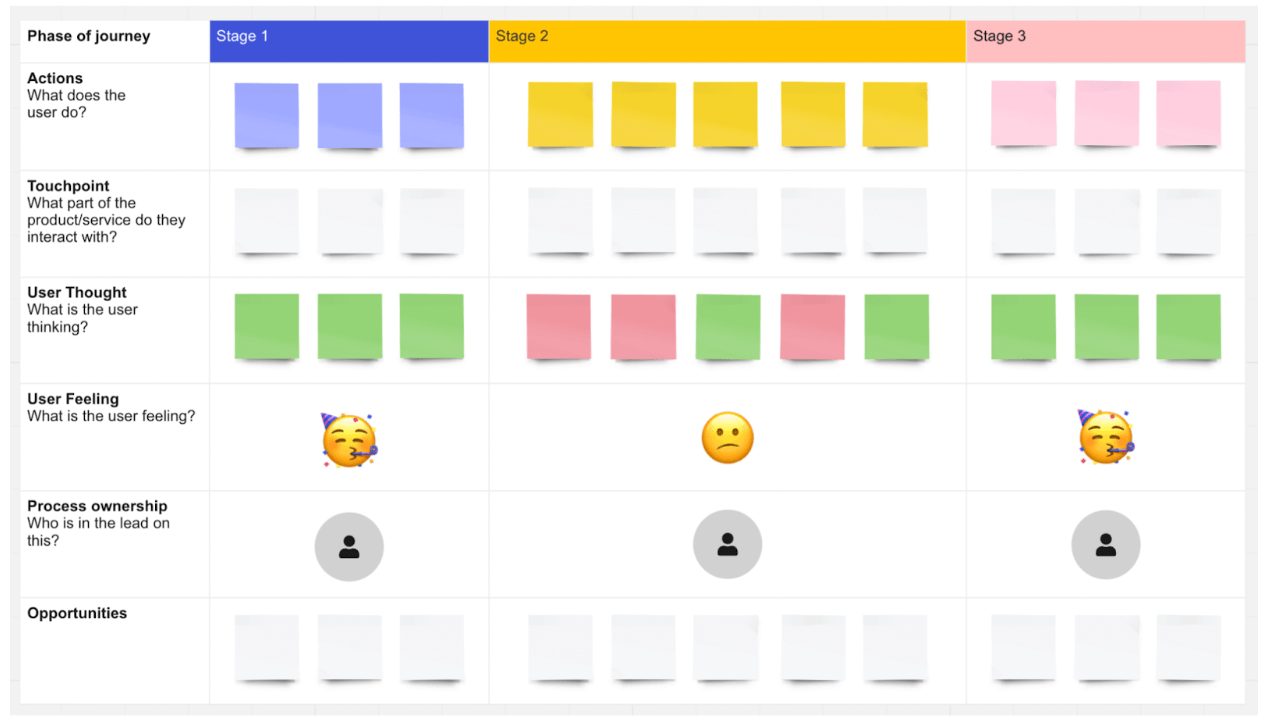
A user journey map template from Miro .
Creating customer journey maps helps to:
- Centre the end user and foster empathy. Creating a user/customer journey map requires you to step into the end user’s shoes and experience the product from their perspective. This reminds you to consider the user at all times and fosters empathy.
- Expose pain-points in the user experience. By viewing the product from the user’s perspective, you quickly become aware of pain-points or stumbling blocks within the user experience. Based on this insight, you can improve the product accordingly.
- Uncover design opportunities. User journey maps don’t just highlight pain-points; they can also inspire new ideas and opportunities. As you walk in your end user’s shoes, you might think “Ah! An [X] feature would be great here!”
- Get all key stakeholders aligned. User journey maps are both visual and concise, making them an effective communication tool. Anybody can look at a user journey map and instantly understand how the user interacts with the product. This helps to create a shared understanding of the user experience, building alignment among multiple stakeholders.
Ultimately, user journey maps are a great way to focus on the end user and understand how they experience your product. This helps you to create better user experiences that meet your users’ needs.
User journey maps can be useful at different stages of the product design process.
Perhaps you’ve got a fully-fledged product that you want to review and optimise, or completely redesign. You can create journey maps to visualise how your users currently interact with the product, helping you to identify pain-points and inform the next iteration of the product.
You can also create user journey maps at the ideation stage. Before developing new ideas, you might want to visualise them in action, mapping out potential user journeys to test their validity.
And, once you’ve created user journey maps, you can use them to guide you in the creation of wireframes and prototypes . Based on the steps mapped out in the user journey, you can see what touchpoints need to be included in the product and where.
No two user journey maps are the same—you can adapt the structure and content of your maps to suit your needs. But, as a rule, user journey maps should include the following:
- A user persona. Each user journey map represents the perspective of just one user persona. Ideally, you’ll base your journey maps on UX personas that have been created using real user research data.
- A specific scenario. This describes the goal or task the journey map is conveying—in other words, the scenario in which the user finds themselves. For example, finding a language exchange partner on an app or returning a pair of shoes to an e-commerce company.
- User expectations. The goal of a user journey map is to see things from your end user’s perspective, so it’s useful to define what their expectations are as they complete the task you’re depicting.
- High-level stages or phases. You’ll divide the user journey into all the broad, high-level stages a user goes through. Imagine you’re creating a user journey map for the task of booking a hotel via your website. The stages in the user’s journey might be: Discover (the user discovers your website), Research (the user browses different hotel options), Compare (the user weighs up different options), Purchase (the user books a hotel).
- Touchpoints. Within each high-level phase, you’ll note down all the touchpoints the user comes across and interacts with. For example: the website homepage, a customer service agent, the checkout page.
- Actions. For each stage, you’ll also map out the individual actions the user takes. This includes things like applying filters, filling out user details, and submitting payment information.
- Thoughts. What is the user thinking at each stage? What questions do they have? For example: “I wonder if I can get a student discount” or “Why can’t I filter by location?”
- Emotions. How does the user feel at each stage? What emotions do they go through? This includes things like frustration, confusion, uncertainty, excitement, and joy.
- Pain-points. A brief note on any hurdles and points of friction the user encounters at each stage.
- Opportunities. Based on everything you’ve captured in your user journey map so far, what opportunities for improvement have you uncovered? How can you act upon your insights and who is responsible for leading those changes? The “opportunities” section turns your user journey map into something actionable.
Here’s how to create a user journey map in 6 steps:
- Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
- Define your persona and scenario
- Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions
- Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
- Identify opportunities
- Define action points and next steps
Let’s take a closer look.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UI DESIGN]
1. Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
The easiest way to create a user journey map is to fill in a ready-made template. Tools like Miro , Lucidchart , and Canva all offer user/customer journey map templates that you can fill in directly or customise to make your own.
Here’s an example of a user journey map template from Canva:
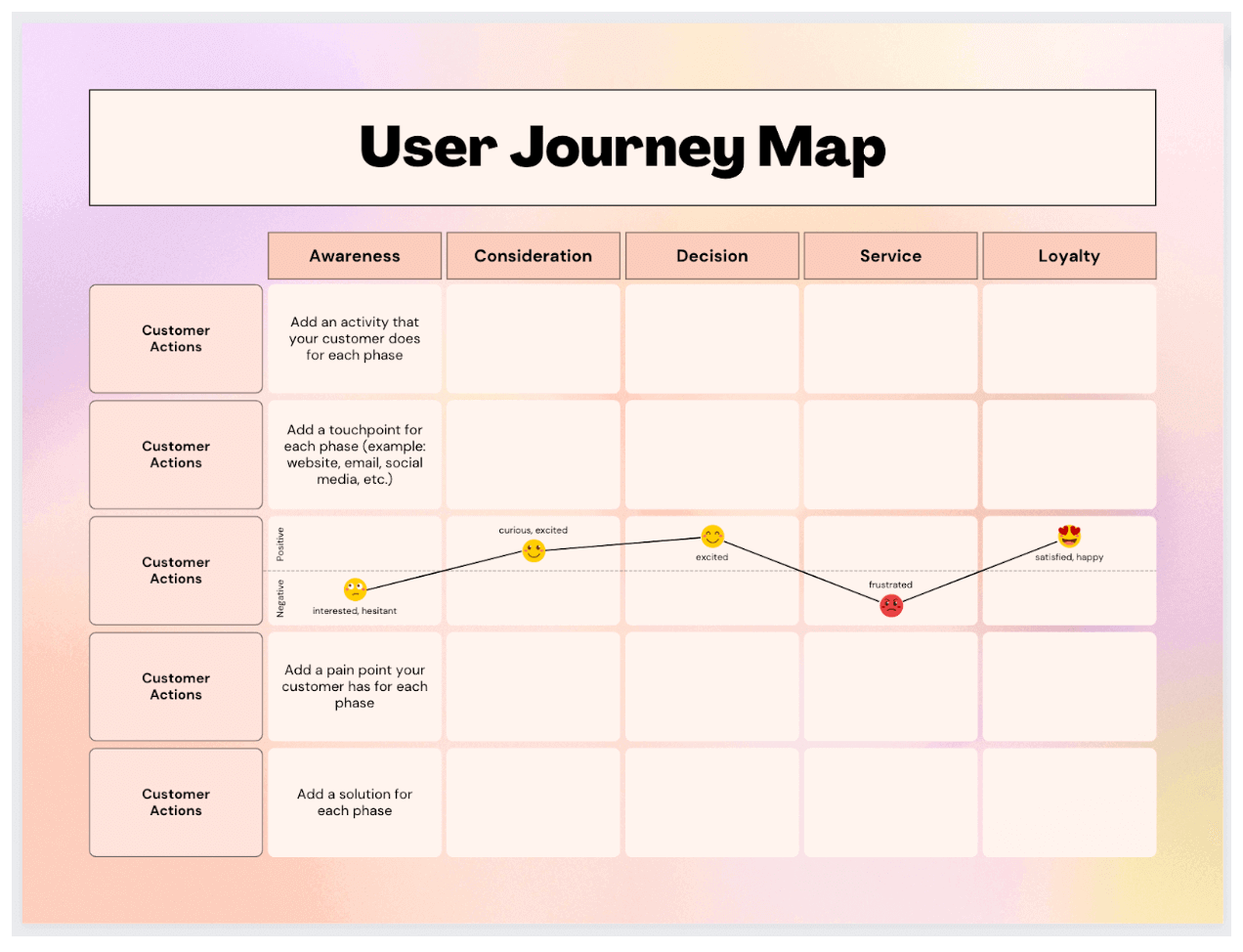
2. Define your persona and scenario
Each user journey map you create should represent a specific user journey from the perspective of a specific user persona. So: determine which UX persona will feature in your journey map, and what scenario they’re in. In other words, what goal or task are they trying to complete?
Add details of your persona and scenario at the top of your user journey map.
3. Outline key stages, actions, and touchpoints
Now it’s time to flesh out the user journey itself. First, consider the user scenario you’re conveying and think about how you can divide it into high-level phases.
Within each phase, identify the actions the user takes and the touchpoints they interact with.
Take, for example, the scenario of signing up for a dating app. You might divide the process into the following key phases: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Service, and Advocacy .
Within the Awareness phase, possible user actions might be: Hears about the dating app from friends, Sees an Instagram advert for the app, Looks for blog articles and reviews online.
4. Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
Next, step even further into your user’s shoes to imagine what they may be thinking and feeling at each stage, as well as what pain-points might get in their way.
To continue with our dating app example, the user’s thoughts during the Awareness phase might be: “ I’ve never used online dating before but maybe I should give this app a try…”
As they’re new to online dating, they may be feeling both interested and hesitant.
While looking for blog articles and reviews, the user struggles to find anything helpful or credible. This can be added to your user journey map under “pain-points”.
5. Identify opportunities
Now it’s time to turn your user pain-points into opportunities. In our dating app example, we identified that the user wanted to learn more about the app before signing up but couldn’t find any useful articles or reviews online.
How could you turn this into an opportunity? You might start to feature more dating app success stories on the company blog.
Frame your opportunities as action points and state who will be responsible for implementing them.
Here we’ve started to fill out the user journey map template for our dating app scenario:
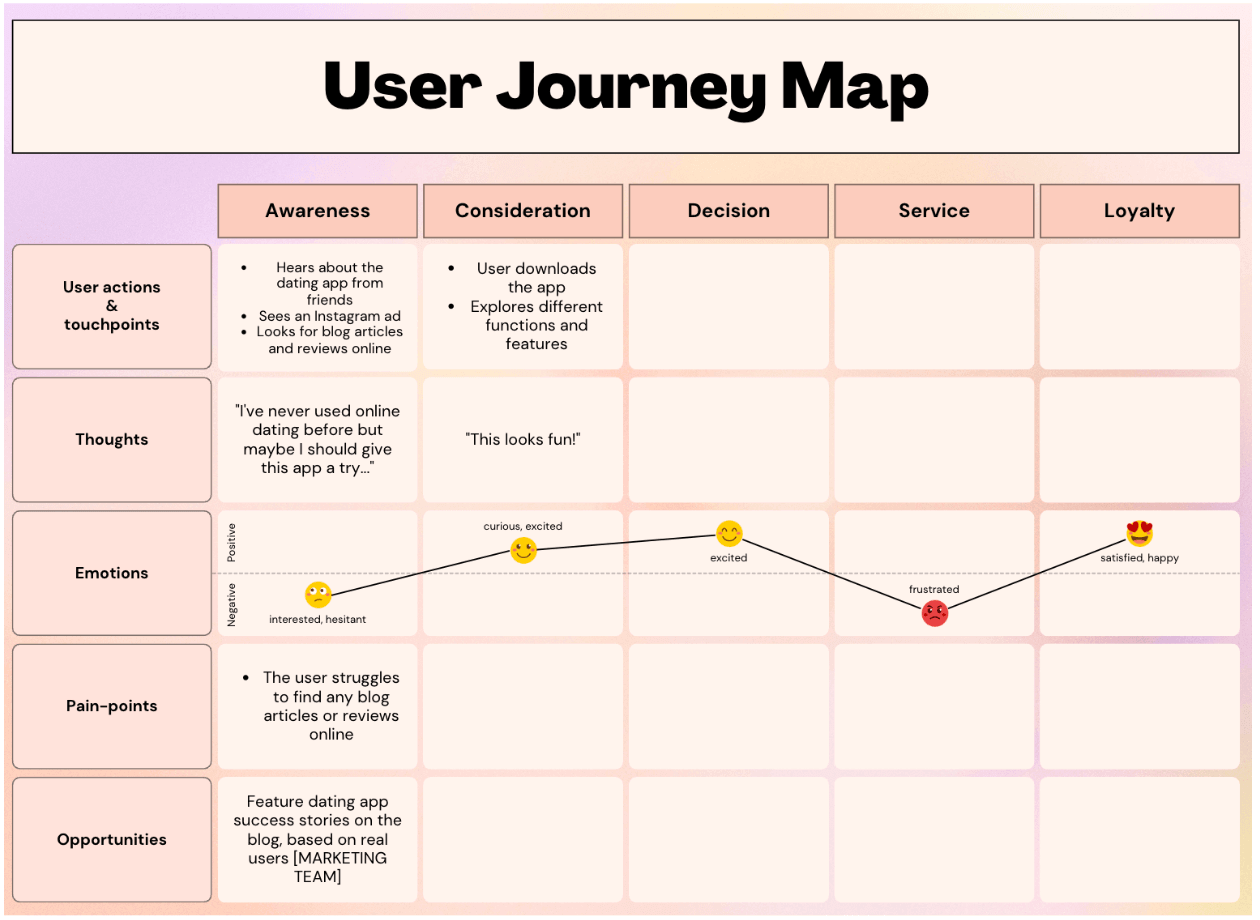
Repeat the process for each phase in the user journey until your map is complete.
6. Define action points and next steps
User journey maps are great for building empathy and getting you to see things from your user’s perspective. They’re also an excellent tool for communicating with stakeholders and creating a shared understanding around how different users experience your product.
Once your user journey map is complete, be sure to share it with all key stakeholders and talk them through the most relevant insights.
And, most importantly, turn those insights into clear action points. Which opportunities will you tap into and who will be involved? How will your user journey maps inform the evolution of your product? What are your next steps?
Customer journey maps in UX: the takeaway
That’s a wrap for user journey maps! With a user journey map template and our step-by-step guide, you can easily create your own maps and use them to inspire and inform your product design process.
For more how-to guides, check out:
- The Ultimate Guide to Storyboarding in UX
- How to Design Effective User Surveys for UX Research
- How to Conduct User Interviews
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the best UX insights and career advice direct to your inbox each month.
Thanks for subscribing to our newsletter
You'll now get the best career advice, industry insights and UX community content, direct to your inbox every month.
Upcoming courses
Professional diploma in ux design.
Learn the full UX process, from research to design to prototyping.
Professional Certificate in UI Design
Master key concepts and techniques of UI design.
Certificate in Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
Collaborate effectively with software developers.
Certificate in UX Design Fundamentals
Get a comprehensive introduction to UX design.
Professional Certificate in Content Design
Learn the skills you need to start a career in content design.
Professional Certificate in User Research
Master the research skills that make UX professionals so valuable.
Upcoming course
Build your UX career with a globally-recognised, industry-approved certification. Get the mindset, the skills and the confidence of UX designers.
You may also like

The ultimate guide to mobile app design: Follow these UI principles & best practices
The best online survey tools to use in 2024

What is colour theory? A complete introductory guide
Build your UX career with a globally recognised, industry-approved qualification. Get the mindset, the confidence and the skills that make UX designers so valuable.
- Case studies
- Expert advice
How to create a customer journey map — a step-by-step guide with examples
Learning more about client experience is the best way to understand and improve it. As you are reading this article, you already know that 😉
Here, you will find a detailed step-by-step guide on making a customer journey map (CJM), examples, expert tips, templates, and a PDF guide to download and save for later.
- 1 What is a customer journey map?
- 2 Benefits of client journey mapping
- 3.1 Step 1: Define your persona
- 3.2 Step 2: Set customer journey stages
- 3.3 Step 3: Define journey map sections
- 3.4 Step 4: Set customer goals
- 3.5 Step 5: Define touchpoints
- 3.6 Step 6: Processes and channels
- 3.7 Step 7: Problems and ideas
- 3.8 Step 8: Emotional graph
- 3.9 Step ?: Be Creative!
- 4 Customer journey map examples
- 5 A customer journey mapping checklist
- 6 The free guide to download
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is the final output of the collaborative visualization process called customer journey mapping. This process lets you reveal typical experiences the customers have over time when interacting with your organization, service, or product. A finished map provides insights into their actions, processes, goals, needs, channels, emotions, and many other aspects shaping the customer experience.
Journey maps can be of different scopes. For example, a broad-scope map would include multiple customer journey stages like ‘Awareness’, ‘Decision’, ‘Purchase’, ‘Support’, and ‘Renewal’. In contrast, a map with a narrower focus would look at a few specific stages like ‘Decision’ and ‘Purchase’.
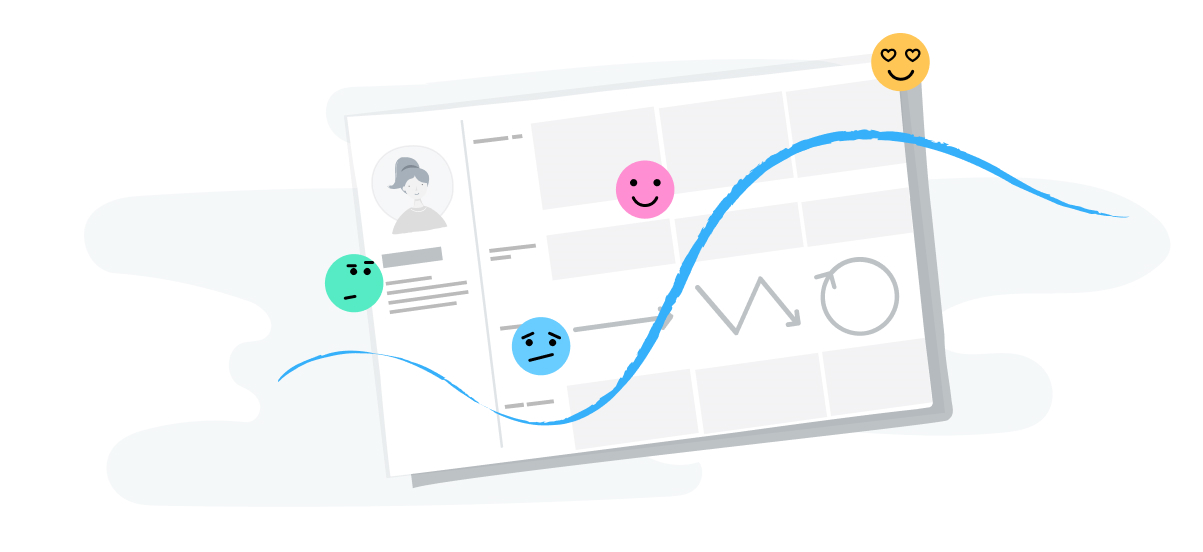

CJMs focusing on the current experience are AS-IS maps, while journey maps visualizing the future, desired, state of the experience are called TO-BE maps.
There’s also a similar technique, customer experience mapping, which is often used interchangeably with journey mapping. Experience maps are variations of CJMs, but they typically cover a wider range of interactions and contexts beyond a specific consumer-business relationship.
Benefits of client journey mapping
Why make journey mapping your tool of choice? There are plenty of reasons, the major of which include:
- Gaining a deeper understanding of your customers
For instance, a high-end fashion retailer may discover that its younger customers prefer online shopping, while older customers enjoy the in-store experience.
- Getting a single view of your customer within the organization
Journey mapping will help you turn a fragmented vision of the customer experience into a unified, organization-wide one. It will have a massive impact on the decision-making process, encouraging you to consider how your actions will affect your clients and become customer-focused.
- Breaking corporate and cross-department silos
To make the way toward delivering a great customer experience, you will need to collaborate with others. Understanding why this collaboration is essential, departments and employees will be more inclined to participate in conversations and collaborate.

- Improving customer experience, retention, and loyalty
While working on a map, you will discover customer pain points at different stages of their journey with you. Fixing the most crucial one as quickly as possible will do you a good turn by eliminating the reasons for leaving you. If fixes take much time, look for quick wins first.
For instance, adding details about your shipping policy on the website will take a developer half an hour, while it will set the right expectations among customers. They won’t be expecting the delivery the next day anymore, bombarding your customer support team with frustrated messages. Another example is a subscription-based video streaming service that can personalize content recommendations to keep subscribers engaged and less likely to cancel their subscriptions.
- Better conversion and targeting of your target customers
Sometimes, it makes sense to focus on a specific segment or, talking journey mapping terms, specific personas. Customer journey insights will help you with this endeavor by giving you a glimpse into these people’s minds and ensuring the higher effectiveness of your marketing.

How to build a customer journey map
Although there is no gold standard for creating a customer journey map, we’ll try to create a somewhat generalized map. So that you can use it as a reference when making maps of your own.
We’ll be using our CJM Online tool along the way for two reasons. Because it’s easy to use and lets you create a CJM fairly quickly without wasting time setting up the environment. Oh, and there's a Personas building tool that comes with it 😉

We’ll take a pizza restaurant as an example of business and learn how to make a customer journey map together.
Step 1: Define your persona
Creating personas is a crucial part of customer experience service and journey mapping in particular. We won’t go into details — you can find them in this post about defining personas .
Let’s just say that our persona’s name will be Eva Moline — 29, works as a journalist and loves pizza. Eva is not really tech-savvy, and she tries to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
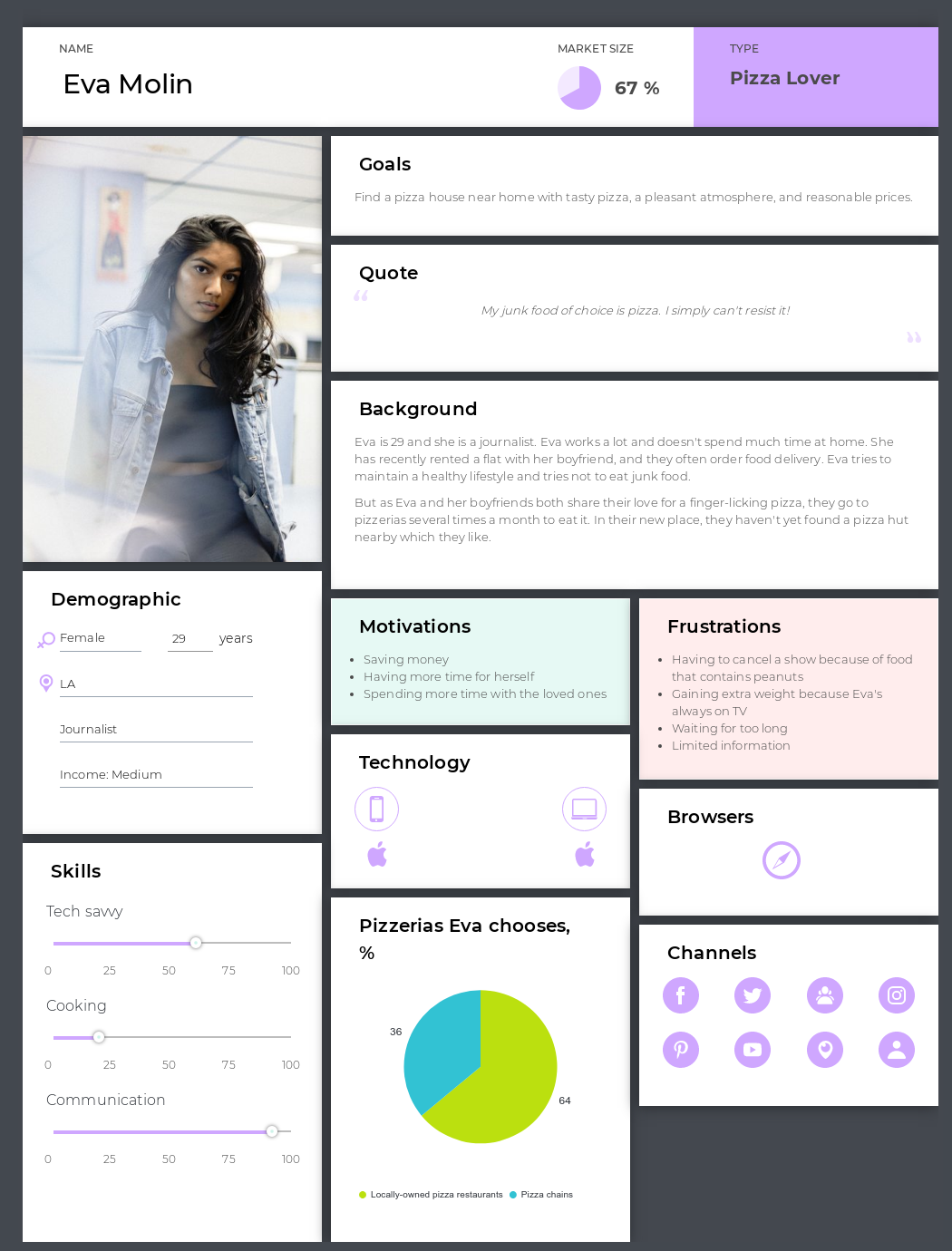
Step 2: Set customer journey stages
Stages are the steps customers take when interacting with a business. The easiest way to identify them is to think of all the actions the person has to take throughout their journey, organize them into logical groups, and name these groups. These will be your map stages.
The number of stages varies from business to business, but we’ll take 8 for this example:
💡 Expert tips:
- If you’re unsure about the order or names of the stages, don’t worry about that. You can change both at any time when working on the map.
- If your stages are complex, you can break them into smaller ones. Read this blog post about defining customer journey stages to learn more.
Step 3: Define journey map sections
Sections are horizontal rows with data that, together with the stages you defined, make up a customer journey map.
When picking sections for a map, your choice will depend on your journey’s type and purpose.
As for UXPressia’s Journey Map tool, it offers a set of more or less universal sections for all kinds of maps.
We’ll use some of the sections in the current example.
Step 4: Set customer goals
Setting customer goals at each stage is great for multiple reasons:
- It helps you understand how your business goals align with the goals of your customers.
- You can meet your customers’ needs better, gaining their loyalty by helping them achieve their goals at each stage.

Above, you can see some of the goals we set for Eva. They are self-explanatory, so there’s no need for extra details.
Step 5: Define touchpoints
Touchpoints are encounters that happen between your business and customers. In the pizza restaurant example, touchpoints happen:
- At the Awareness phase, when Eva is actively looking for a pizza place nearby. She is asking around, searching locations on Google Maps, etc.
- At the Research phase, when she is trying to find out what people say about the place by asking her friends and reading online reviews.
- At the Arrival stage, when Eva searches for a parking spot and enters the restaurant to get seated after parking the car.
- At the Order stage, when she makes an order and waits for it.
- Time to eat! At this stage, touchpoints occur when Eva is being served and when she is eating her meal.
- At the Leave stage, Eva interacts with the waiter, pays for the meal, etc.
- At the Feedback stage, she goes to the pizzeria’s website and drops a few lines on Instagram.
- At the last stage, Eva gets a promo email from the restaurant with discounts or other special offers.
Defining all the touchpoints is critical because each touchpoint leaves some impression, and your main goal is to keep it up to the mark.
You can also have a separate section to describe the actions your persona takes:
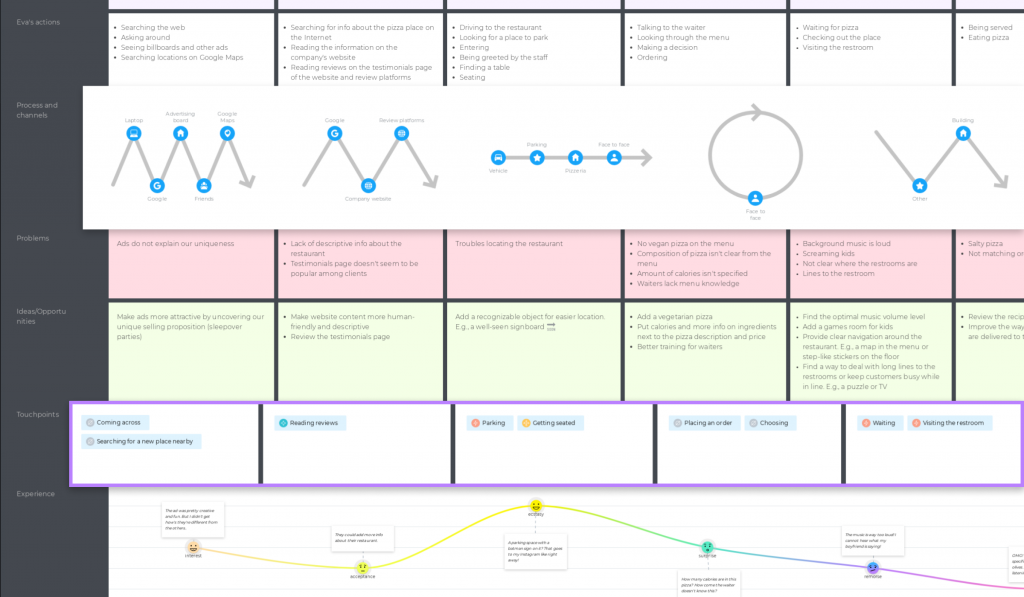
Step 6: Processes and channels
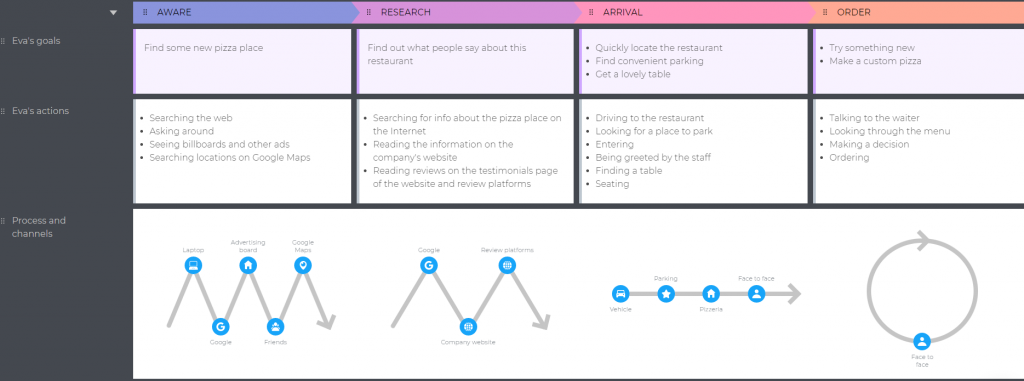
Now, you may want to add some processes and channels to the map. Just to see what channels your persona uses and what types of processes are in their journey. Luckily, our tool lets you do it in the most awesome way. Processes can be linear, non-linear & time-based, cyclic, or bi-directional. In UXPressia, you can specify up to 10 channels per process.
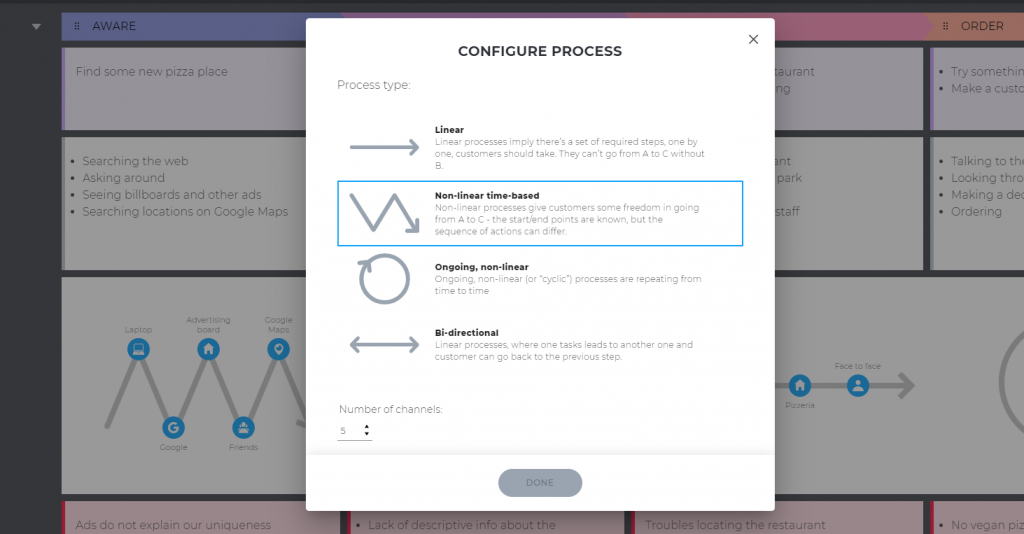
Step 7: Problems and ideas
It’s time to explore problems Eva might have when using our service. It could be a lack of info about the pizza house. Few reviews and ads do not show how our pizza differs from others.
Upon arriving, Eva may struggle with locating the place due to unclear information on signboards or just because of a hard-to-find location.
When making her order, Eva may look for detailed info on dish ingredients to learn whether it contains peanuts she’s allergic to. Descriptions may not be as detailed as she’d want them to be.
While waiting for the pizza, Eva may want to check out the place. Finding a restroom can turn into a nightmare if you don’t have clear signs showing what’s where in the restaurant.
Once you’re done with problems, it’s time to find solutions to these problems. Brainstorm for some ideas on how this or that problem can be solved. Here’s what we brainstormed for Eva’s case:

Step 8: Emotional graph
Never underestimate the power of visualization. And our Customer Journey tool is all about it. We added an emotional graph to see where our service example shines and where it stinks. Plus, we filled text boxes with Eva’s thoughts:
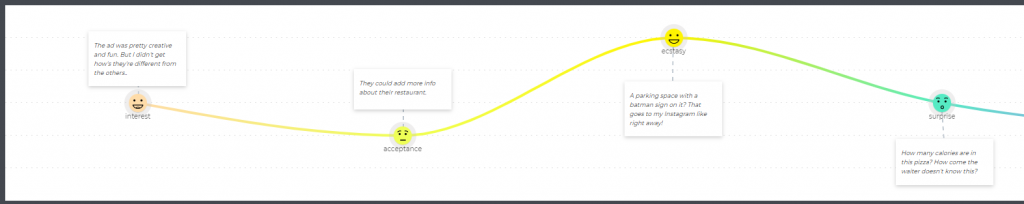
There’s also a special section ( “Think & feel” ) to put personas’ thoughts.
Step ?: Be Creative!
This is a good start, but the map is far from being complete. So, keep exploring Eva’s journey to find more insights and then add all of them to the map.
If you use our tool (which we highly recommend you to do), check out other CJM sections:
- Image section for screenshots, photos, or any other relevant imagery. You can even turn it into a storyboard , describing the journey from beginning to end with your images or those from our library.
- Charts section for communicating data in a visual and meaningful way, just like we did it in the persona:
- Video and document sections for journey-related videos and documentation (e.g., an annual marketing report).
- Personas section for visualizing different personas’ interactions within the same journey.
💡 Expert tip: The section with the persona’s questions works like a charm for marketing and content purposes. So be sure to add one 😉
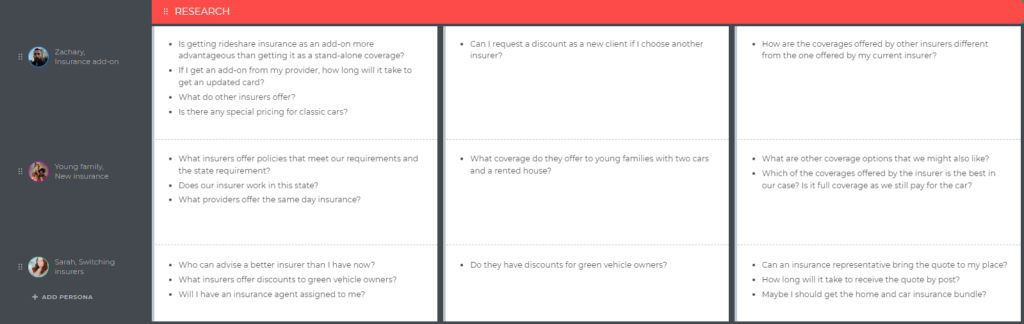
Customer journey map examples
There are also a whole lot of free CJM templates for all sorts of journeys in our library. Here are three examples we picked for you.
- Example 1: a mobile user journey
This user journey map template covers the digital experience of the persona who discovers a new mobile app, installs it, and uses the app for some time before deleting it.
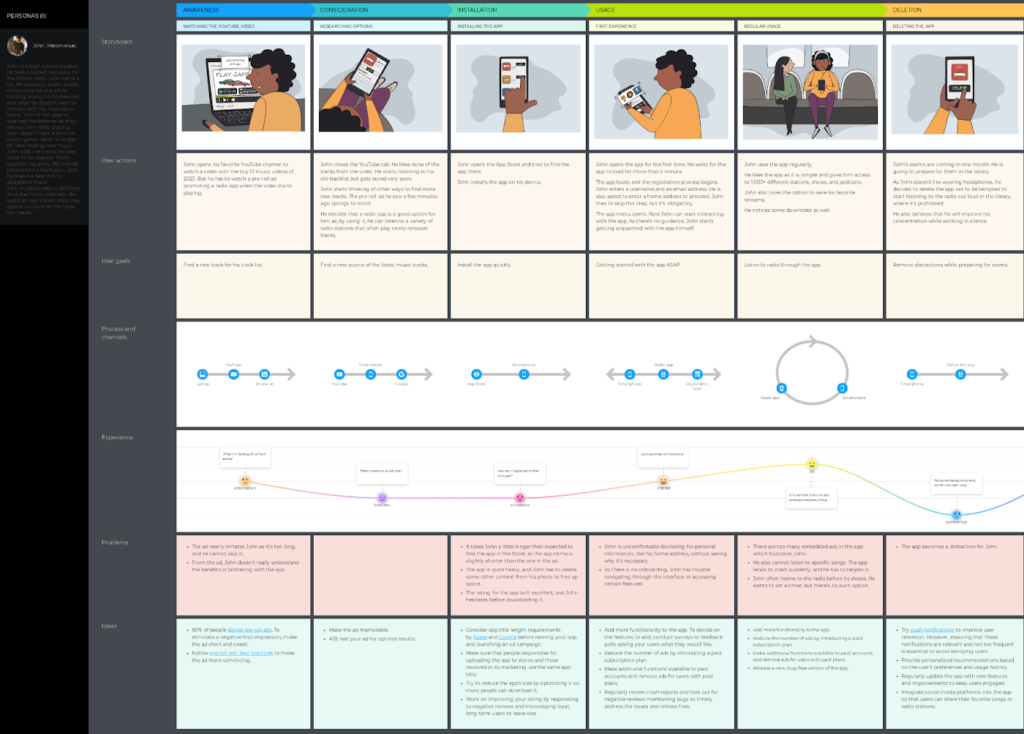
- Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank
This free template is an example of a multi-persona, B2B customer journey. The key persona is a newly opened company looking for a bank to run their business. The CJM also visualizes interactions between the personas involved.
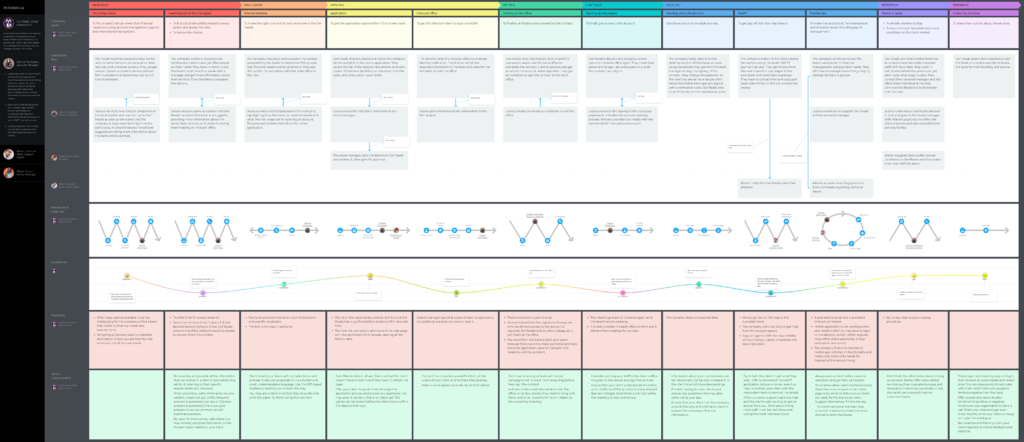
- Example 3: a digital customer journey
This customer journey map example shows the digital journey of three customer personas who want to buy a new pair of sneakers online. They go through the same stages, but if you look at the map, you will be able to see the differences in customer behavior, goals, and actions. It’s also a multi-persona journey map .
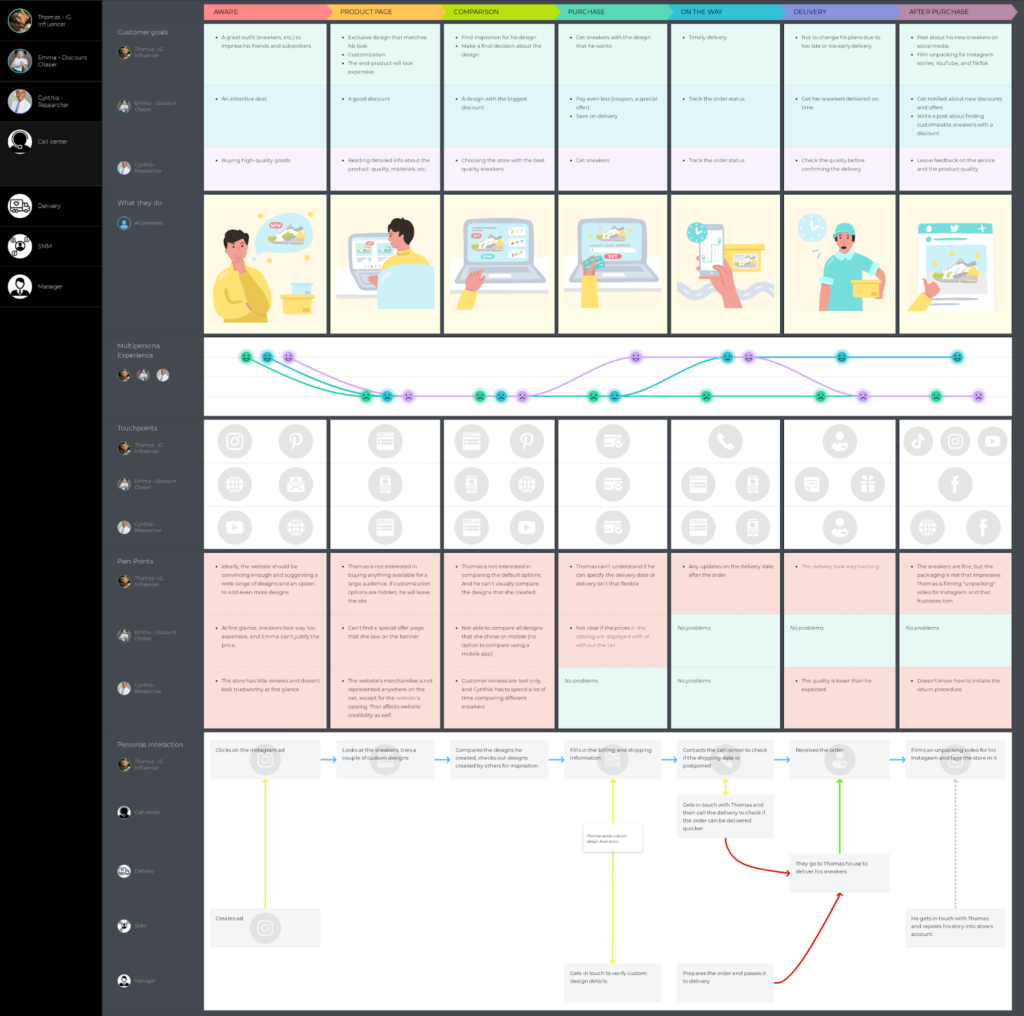
A customer journey mapping checklist
As a quick recap, here is a checklist with key steps to follow when creating a customer journey map:
- Do research
To represent real people, your real customers, and visualize their journeys, you must base your personas and journey maps upon actual data.
- Define your customer persona(s)
Identify your target personas. Create detailed profiles focusing on information relevant to your journey mapping initiative. Include such details as background, customer needs, motivations, channels, etc.
- Specify journey map stages
Determine the stages you want to have on your map and come up with their names.
- Decide on the map sections
Determine which sections to include in your map (e.g., actions, touchpoints, emotions, channels).
- Set customer goals for each stage
Make sure that it is your customers’ goals, not your business goals.
- Identify touchpoints between the persona(s) and your organization, product, or service
Consider both online and offline interactions.
- Map out processes and channels
Visualize the journey-specific processes and the channels your customers use at each stage. Include both digital and physical channels.
- Highlight problems and look for opportunities
Identify any pain points and issues customers might encounter. Brainstorm potential solutions and quick wins to improve the experience.
- Add details about the emotional experience
Visualize the persona’s emotional journey. Include thoughts and feelings where it’s relevant.
- Use more sections
Include illustrations, images, and charts to make the map visually engaging and easy to understand. Enrich your journey map with more data, like KPIs related to journey stages.
Feel free to tailor this checklist to the specific context of your business and your project's needs.
The free guide to download
As a bonus, download our free customer journey mapping guide. Fill in the form below to get a PDF file as an email.
Related posts
The post was originally written in 2017.
Rate this post
first of all, excellent example and I’m very happy to I could understand how to create user journey map, due to for a long time I can’t understand it and how, many thanks for your efforts 🙂 I have some question about ser journey map. I hope to open your chest for me,
1-no there are rules for user journey map? 2-I need another example ?(for example Uber)?further understand 3-have I create user journey map without customer?
Hello, Karim!
I am very glad that this article helped you understand customer journey mapping 🙂
In regards to your first question, I would say that journey maps differ from business to business. However, they tend to have the same structure give or take. So no matter what industry you make a CJM for, you will end up having several stages and a bunch of sections we mentioned in this post.
If you’re looking for CJM examples of Uber customers, here is one: https://www.mindomo.com/doc.htm?d=92be818b774d422bad7eab790957ebc0&m=7d286174ccf1450bbb77c921a609ff65 Plus we have a lot more on our template page: https://uxpressia.com/templates
As for your last question, yes. You may have a journey map without a customer (persona) and use target audience segments instead (or have a generic map without personas at all, though I don’t recommend the latter as in this case it will be hard to empathize with real people). So you will certainly have to introduce a customer down the road to gain a deeper understanding of the journey.
many thanks for your reply to me and again I have some questions
1-why you don’t use in your example? user experience, empathy maps such as use goal touch point, and how to create it 2-As for the previous example (Uber) very confuse for me not as your example
Could you please rephrase your first question? And as for the Uber map, well, that’s all I managed to find. 🙂 But again, here you can find a hundred of map examples of all stripes and colors: https://uxpressia.com/templates
welcome again, my question is? what’s different between Aware and Research
The differences come from the names.
At the aware stage your client realizes that there’s a need for a service/product. Or they find out that your company exists and offer a desired service.
While at the research stage they either do research on your business (e.g. visit your website or ask their friends if they used your service) or they research what is out there on the market that can help them.
Makes sense? 🙂
Thank you for this,
I am wondering , Have you done examples on B2B services. I work in Accreditation & Certification, this seems to be the least visited topic in marketing platforms and blog sites.
We have some B2B templates in our Template Library . Type B2B tag in the search placeholder and you will see all categories with the fitting templates. You can also explore the B2B mapping guide here .
Good luck and happy customers!
Great article, well articulated and detailed. I am starting off with service design and was wondering if I could get some advice mapping out a customer journey for a specific project. I was mapping out how do one approach to repair services?
Hi Shreya, glad you liked the article!
If you’re dealing with home repair, I might suggest our pre-filled template for an interior design agency customer journey: https://uxpressia.com/templates/real-estate . Templates can be a great starting point even if they’re not a 100% match to your use case.
Other than that, you will need to create a persona. If you don’t have any research data yet, do it based on your assumptions. Then, try to visualize what their experience across all stages and interactions with the repair service might be. Once you have the first draft, you can proceed with validating it and adding more data as it comes in.
If you have more context on the project, I can look into it and come up with specific tips 🙂
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Thank you for sharing, it was something I researched.
Hi Rok! Happy mapping 🙂
- Woopra Logo
- Platform Customers Pricing Resources Company
- Log in Start For Free
- Automations
- Integrations
- Documentation
How to Create a Customer Journey Map: A Step-By-Step Breakdown

There are often a lot of twists and turns in the customer journey, with each individual experience being unique.
That said, there is a predictable sequence of touchpoints throughout the sales funnel.
Mapping each customer touchpoint out effectively helps enhance the user experience and increases the chances of customer success.
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
Simply put, a customer journey map is a visualization of the process someone undertakes as they move through the various touchpoints of the customer journey.
It typically starts with the initial interaction they have, like visiting your website for the first time when gaining brand awareness, and then moves through the subsequent stages of consideration, purchase, retention, and advocacy.
Here’s an example of what a typical customer journey map may look like.
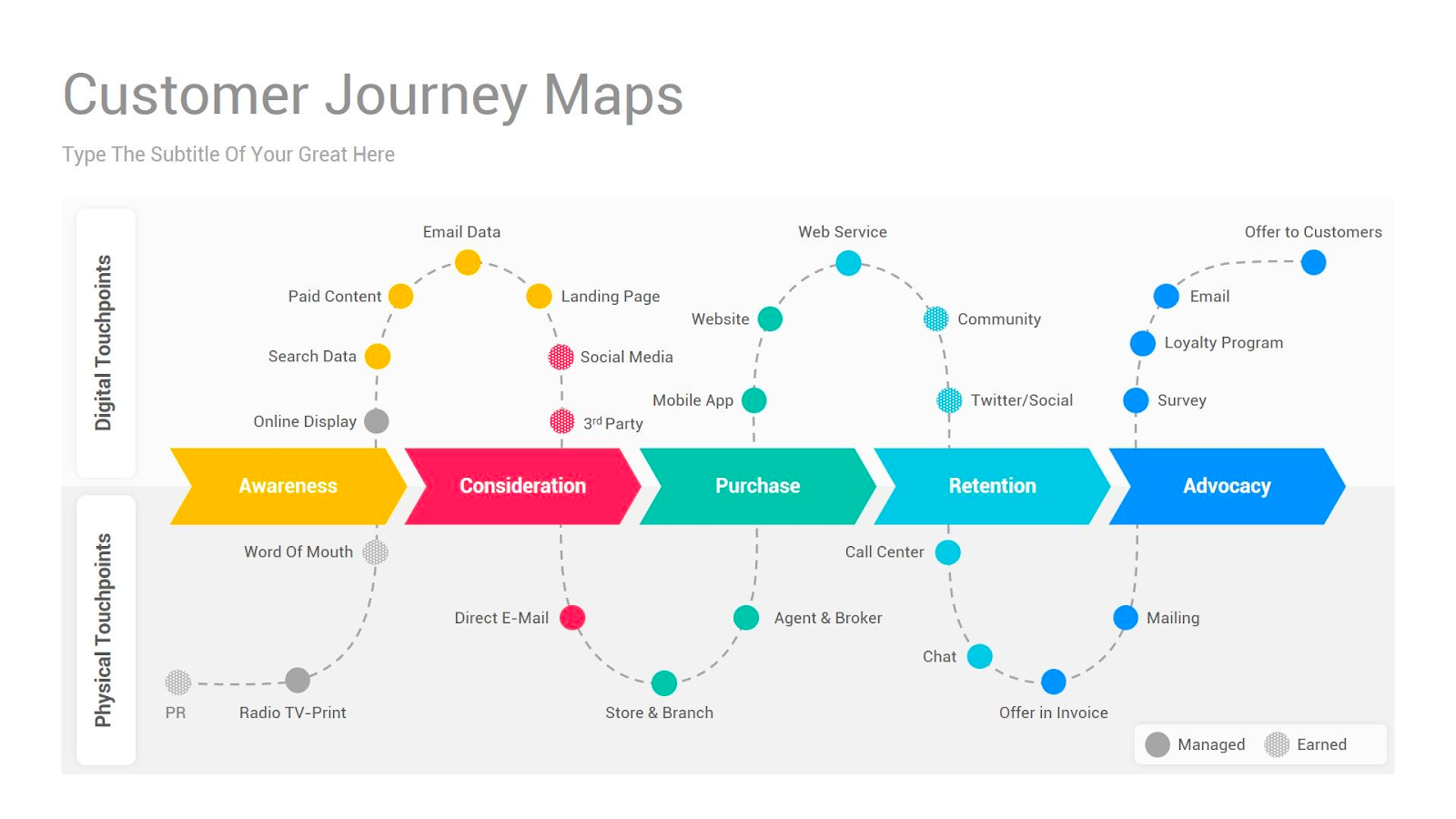
Notice how it concisely outlines the touchpoints customers take as they move throughout the customer journey.
It starts in the awareness stage with touchpoints like search results or paid content, moves on to the consideration stage with social media or email, then to the purchase stage, and so on.
There are four main purposes of customer journey mapping.
- Flesh out the step-by-step process someone takes from being a potential customer to a lead to an actual customer and ideally, a loyal advocate
- Understand the customer’s perspective
- Identify friction points that are causing issues with customer engagement
- Discover opportunities to reduce pain points and improve the overall customer experience
By doing so, you set the stage for better product design, more effective customer journey marketing, increased customer satisfaction, better customer retention, and ultimately, greater customer success.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
1. define business goals.
Before doing anything else, you’ll want to pinpoint exactly what you’re looking to accomplish with customer journey mapping.
Some common examples include:
- Optimizing each touchpoint in the customer experience
- Identifying areas with higher than average dropoff
- Resolving issues that are leading to excessive dropoff
- Improving the overall customer experience both during the buyer journey and post-purchase
Clearly articulating what you’re trying to achieve is essential because it will direct the path you take for subsequent steps of customer journey mapping.
Note that a big part of effectively defining business goals is getting input from multiple key stakeholders in your company who are responsible for different aspects of the customer experience.
For instance, you may want to get input from your marketing leaders when developing the awareness and consideration stages of your customer journey map, input from your sales leaders when ironing out the purchase stage, and input from your customer service leaders when constructing the retention and advocacy stages.
It’s also smart to perform extensive user research and incorporate customer feedback to ensure you address the right pain points and tackle the issues that are most pressing for creating a positive user experience and long-term customer loyalty.
This should make for cohesive CX journey mapping where touch points flow smoothly from one to the next.
2. Identify Key Stages in the Customer Journey
Next, you’ll want to pinpoint the exact sales funnel stages involved with the customer journey.
The sales funnel stages can vary slightly from company to company, but as we mentioned earlier, some common ones include:
- Consideration
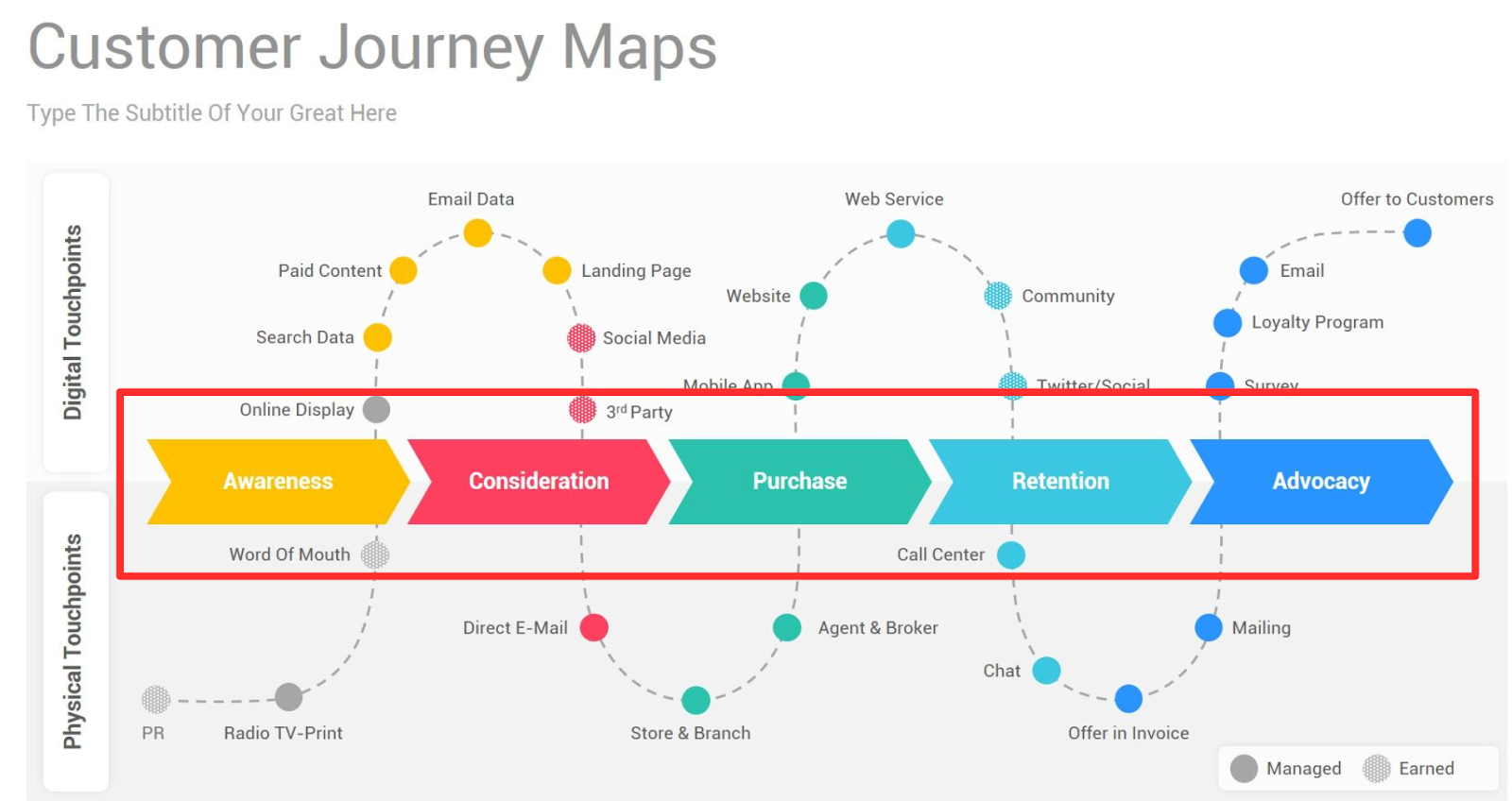
Fleshing the key stages out like this will show you the path users take as they go from being a prospect to a lead to a customer to an advocate.
By visualizing the key stages like this, you’ll see how each stage flows into the next — something that’s vital for making the customer journey as seamless as possible, meeting customer needs, and improving overall customer experience quality.
This is also what the next step in constructing customer journey maps is built on, which brings us to our next point.
3. Define Customer Touchpoints
You can think of the key stages in the customer journey on the macro level and the next step in the process — defining customer touchpoints — on the micro level.
These are the smaller interactions that customers take as they move from stage to stage in the user journey.
This can include digital touchpoints like becoming aware of your brand through an online ad, a search engine, paid content, and so on.
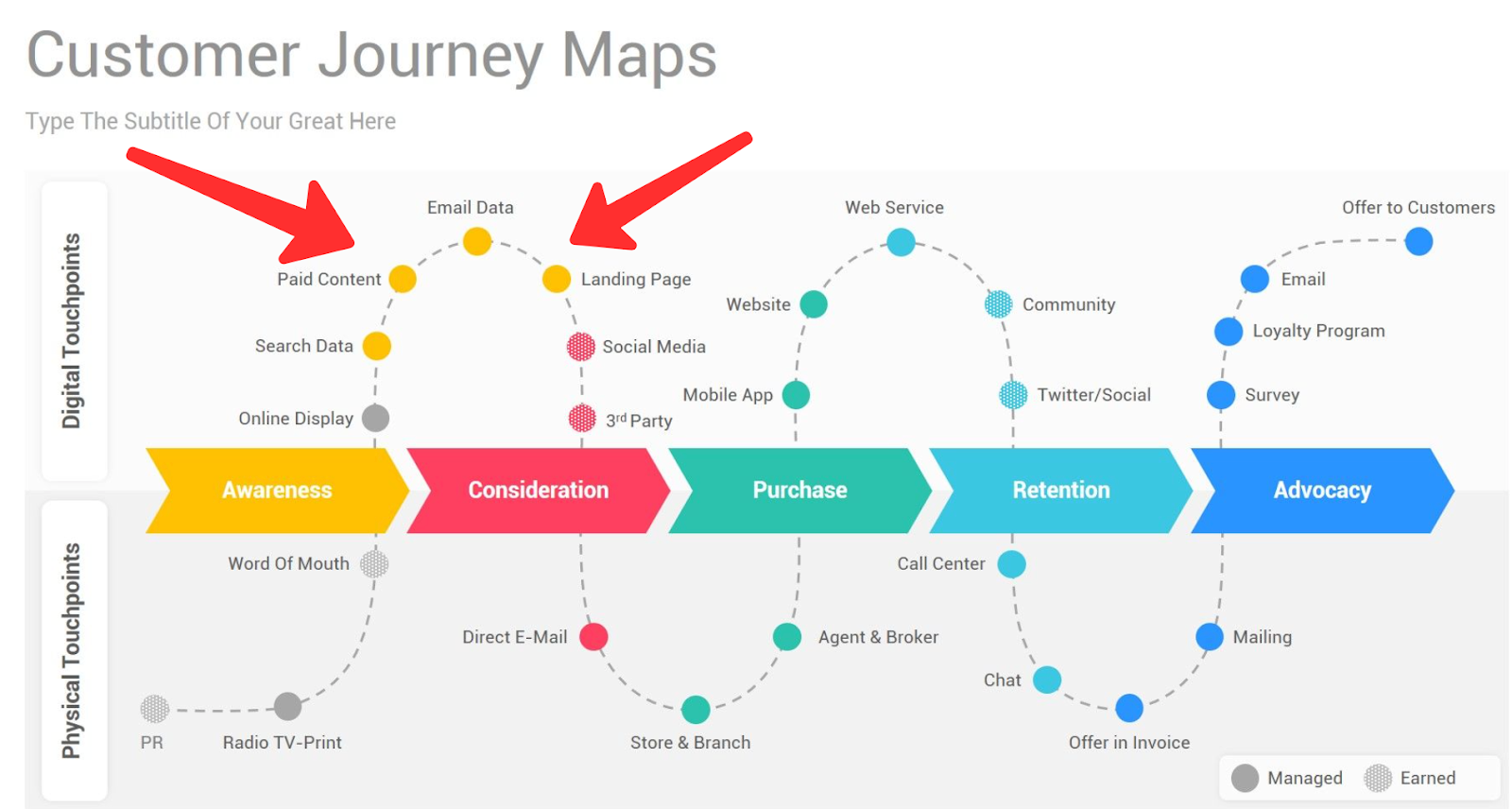
It can also include physical touchpoints like word-of-mouth.
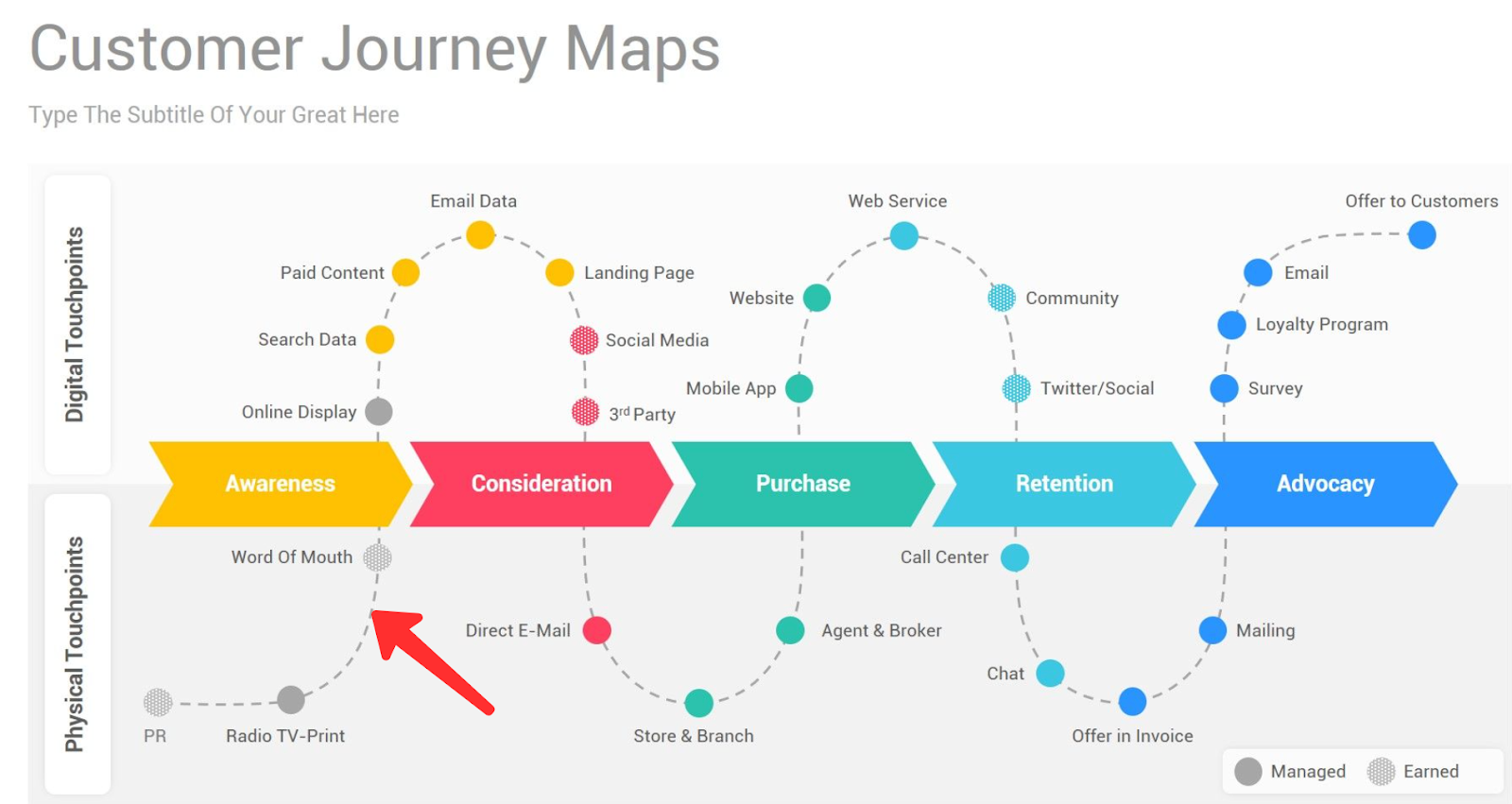
Customer touchpoints will account for the majority of your customer journey map and help you visualize how people interact with your brand.
The exact number of touchpoints can vary considerably, so defining them is highly individualistic.
When identifying them, you’ll want to carefully consider the typical customer journey and write down every step involved. Then, arrange each touchpoint sequentially so you can see the big picture.
4. Design a Visual Representation of the Customer Journey
After defining business goals, identifying key stages in the customer journey, and defining customer touchpoints, it’s time to actually create your customer journey map.
Here, you’ll create a visual representation of what your business’s specific customer journey looks like for a bird’s-eye view.
To do this effectively, it’s helpful to use strong visual elements like different colors, symbols, bullets, and emojis so you can easily see everything at a glance.
Here’s an example of what an online shopping customer journey map could look like.
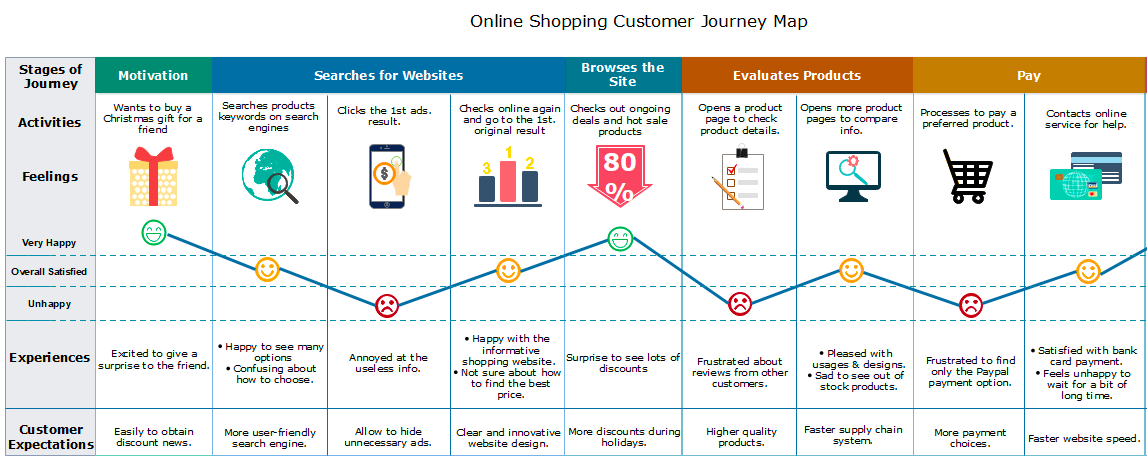
When it comes to customer journey mapping tools, there are several options available.
If you’re looking for something bare-bones and simple, you can use Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
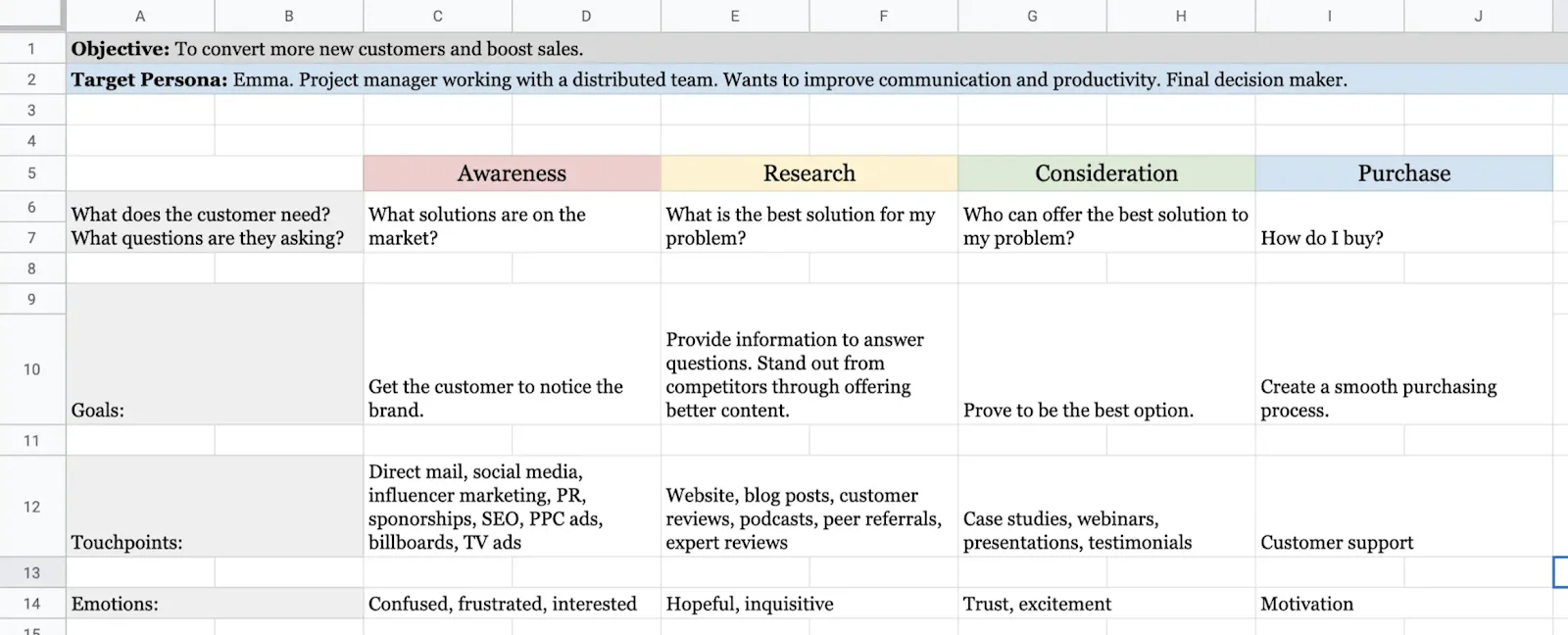
If you want something a bit more advanced, you can use HubSpot’s Customer Journey Map Template , which includes seven free templates (more on this later).

Or, if you want software with extensive features that are specifically designed for creating customer journey maps, you can find a list of the top 10 products here .
Note that most companies have more than one customer persona. Therefore, you may need to create multiple customer journey maps while targeting each individual buyer persona.
Customer Journey Map Templates
When most people think of customer journey mapping, they think of the classic buyer’s journey.
And they wouldn’t be wrong.
Generally, that’s the most commonly used customer journey map and the type of mapping we used in the customer journey map examples above.
But it’s certainly not the only type of mapping you can use.
As we’ll learn in a moment, there are also customer journey maps that target specific segments of the buyer’s journey and customer journey maps that focus on what you want your ideal journey to be like.
For the rest of this post, we’ll cover four of the most popular customer journey map templates you can use for different situations.
That way you can cover all the angles and increase the chances of customer success every step of the way.
Buyer’s Journey
As we just mentioned, this is widely considered the most classic type of customer journey mapping.
When mapping the buyer’s journey, you follow the key stages in the customer journey (awareness, consideration, purchase, etc.) like we outlined above, along with customer touchpoints.
Here’s a simple template journey map example for the buyer’s journey from HubSpot, which you can find for free here .
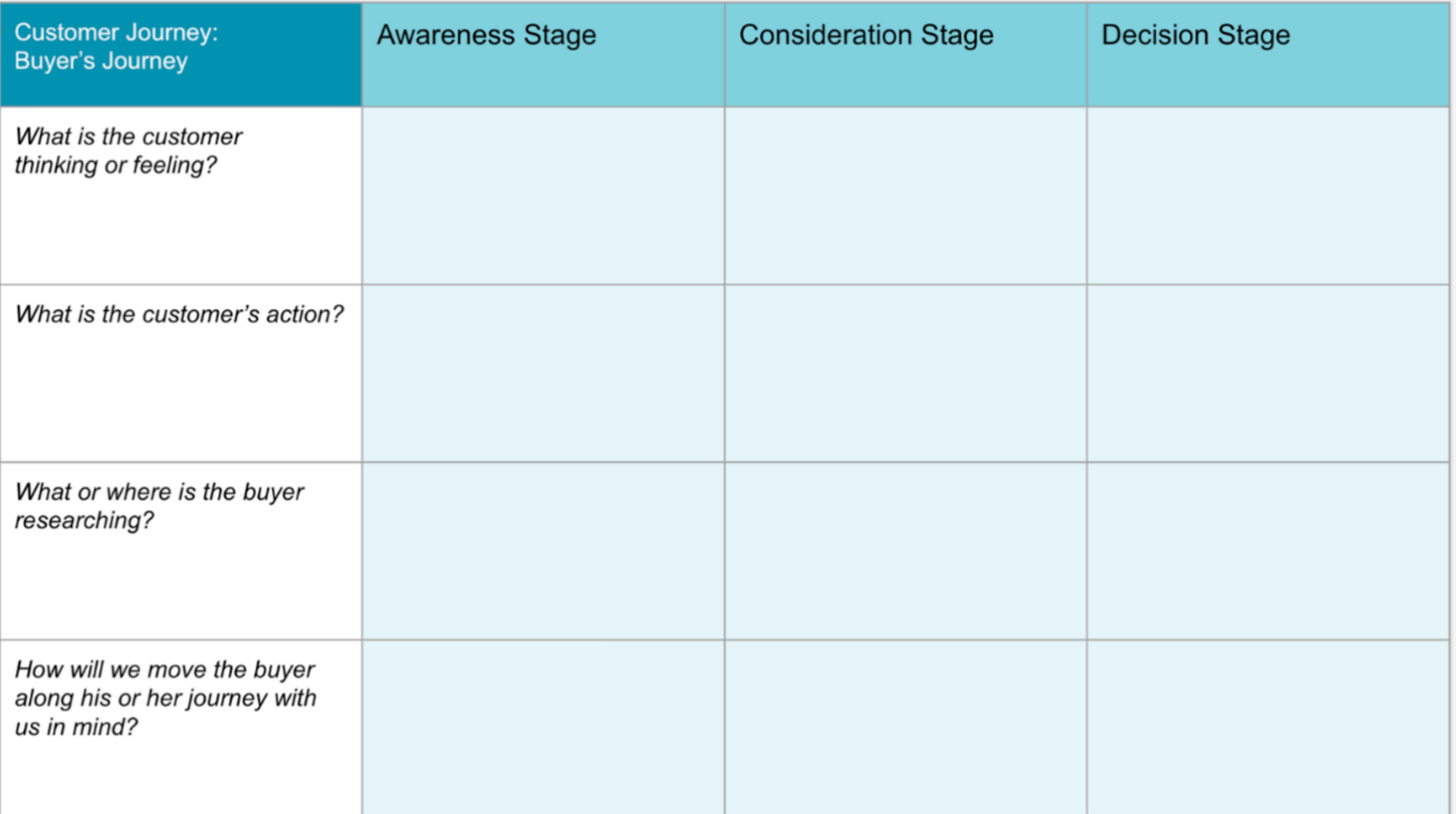
The default starting point is extremely simple. It includes just three stages and a handful of questions to understand customer interaction.
However, you can easily add more stages, questions, and additional information to fully customize the buyer’s journey so that it’s specific to your business.

This template, admittedly, won’t provide the same depth as some of the more advanced tools for creating customer journey maps, but it should be adequate for many business owners.
If you don’t need anything fancy and are testing out customer journey maps for the first time, HubSpot should be more than sufficient.
Whatever template you use, buyer’s journey mapping tends to be a good starting point as it helps you visualize the entire process from someone entering your sales funnel to converting to becoming a loyal customer.
This is integral for optimizing every aspect of the customer experience end-to-end, and from a product standpoint, is essential for achieving UX mastery.
It’s also worth mentioning that if you’re looking to improve your UX design skills, The Interaction Design Foundation is an excellent resource for doing so. They offer a wide variety of courses from the beginner to expert level and only charge a flat monthly fee for access to all courses.
Now that we’ve tackled buyer journey mapping, let’s look at three other popular types of customer journey map template options that are also available.
Future State
In most cases, the buyer’s journey is the current journey customers are taking.
While there will likely be several areas you’re satisfied with, your existing customer journey probably won’t be ideal and likely isn’t meeting customer expectations 100%.
For example, there may be friction points along the way where customers are attempting to accomplish a goal. Or, there may be higher than acceptable dropoff in a particular area like using core features or becoming a paid customer after using a free product version.
By the way, if you want to holistically understand the customer journey and generate objective customer data, you can use a customer journey analytics platform like Woopra . This enables you to analyze essential customer journey metrics so you can see what it looks like end-to-end.
With future state customer journey mapping, you design a new map with new touchpoints and engagements based on your ideal vision.
That way, you’ll know what needs to be done to create the optimal customer journey.
If you’ve already experimented with creating customer journey maps and are looking to take the next step to refine the customer experience, you’ll likely be interested in future state mapping.
HubSpot offers a free future state template as well, which allows you to outline the series of steps that need to be taken to make the customer journey as perfect as possible. And it’s completely customizable.
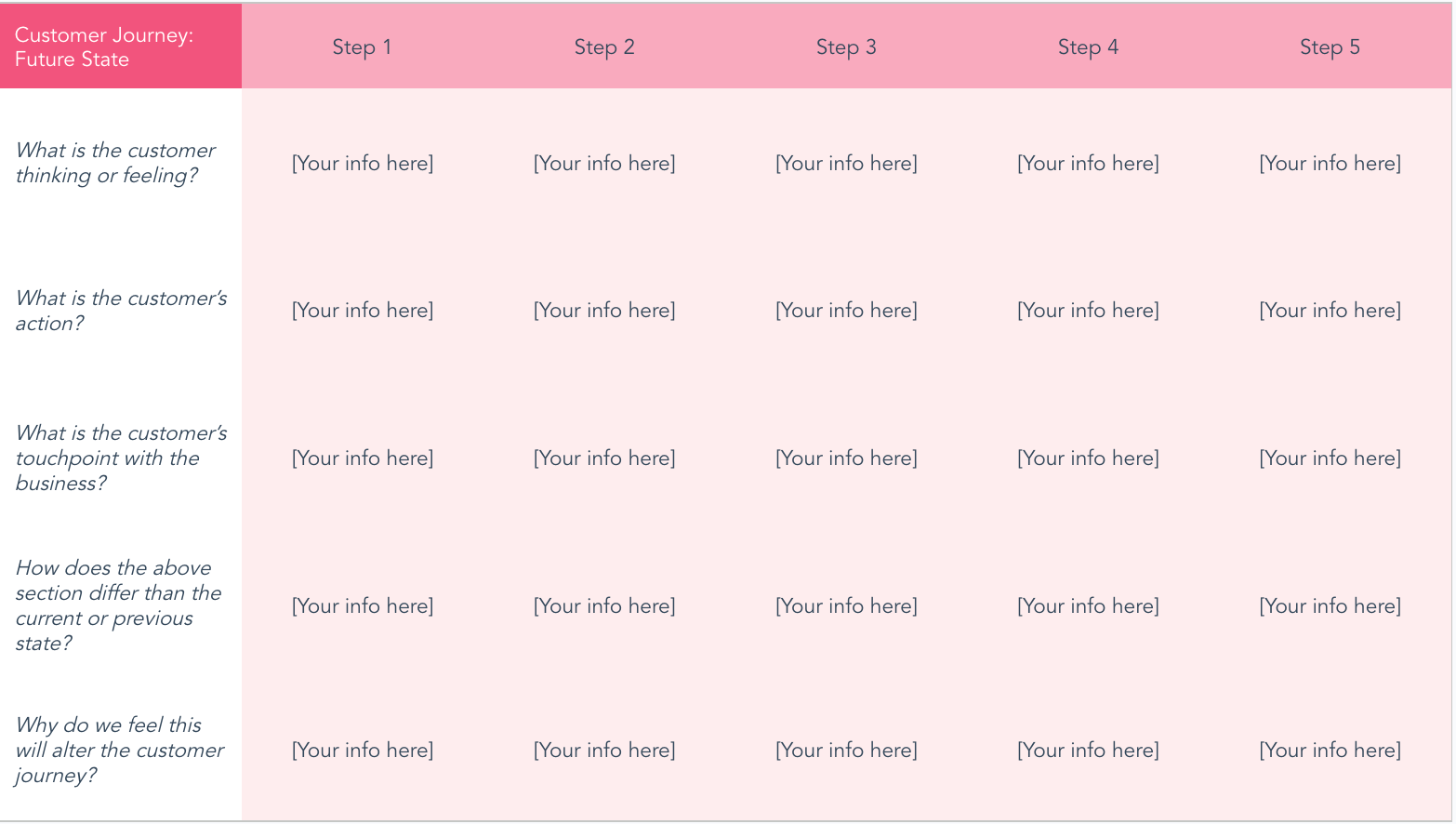
You simply list the steps you want to take to create an amazing customer experience and ask key questions regarding customer behavior.
It’s nothing over the top, but it should get the job done for many business owners.
Lead Nurturing
Although technically part of the buyer’s journey, some marketers choose to create a lead nurturing customer journey map because of the extreme importance of lead nurturing.
After all, any major holes in the lead nurturing process can disrupt sales as a whole. And no matter how good your marketing team is at generating leads, the impact will be negated if you can’t successfully nurture them.
To optimize this area of sales, you can create a lead nurturing map using a template like this one.
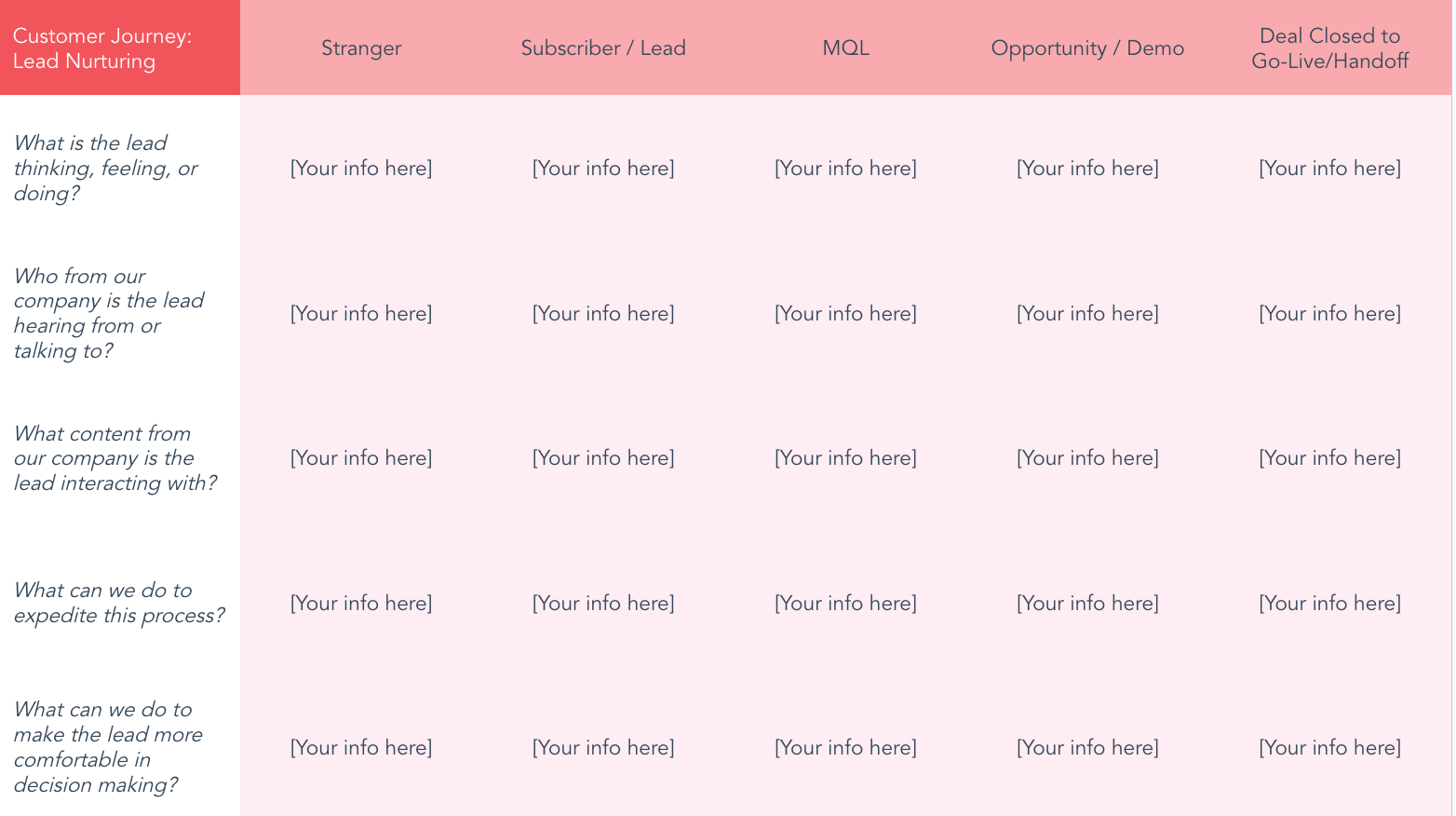
Here, the default starts with someone being a stranger, then moves on to them being a subscriber/lead, then a marketing qualified lead (MQL), a sales opportunity/demo, then a deal closed/handoff.
Again, everything is customizable, so you can adjust the lead nurturing customer journey to your exact specifications. And, it too, is available for free from HubSpot .
Customer Service and Support
Once again, a truly rewarding user experience goes beyond the purchase and ensures a customer is satisfied well after they’ve bought a product.
Like lead nurturing, customer service and support are also technically part of the buyer’s customer journey map.
However, it dives deeper into this area of the sales funnel with the intention of increasing customer retention and advocacy.
And I think we can all agree that this is incredibly important given that “Happy and satisfied customers are 87% more likely to purchase upgrades and new services.”
Here’s yet another free customer journey map template you can get from HubSpot that focuses specifically on customer service and support.

With it, you can follow how a customer goes from engaging in the normal use of a product to noticing an issue/having a complaint to asking for help/contacting customer support to speaking with support to conflict resolution.
Having a clear overview of the touchpoints involved with this process should help you fully understand the flow so you can 1) see things from a customer’s point of view and 2) identify issues that may be detrimental to customer support.
For inspiration from real-life major brands like Spotify, TurboTax, and Amazon, here’s a list of customer journey map examples you can learn from.
Crafting an Exceptional User Experience with Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is a simple yet effective way to visualize each touchpoint in the user journey holistically for each buyer persona.
From the initial moment someone becomes aware of your brand to the time of purchase and beyond, customer journey maps allow you to see how users move throughout the entire lifecycle.
And as we’ve learned, this serves several important purposes, including seeing the buying process from a customer’s point of view, identifying customer pain points, and unearthing opportunities to improve the customer experience end-to-end.
It’s just a matter of following the correct customer journey mapping guidelines and using the appropriate template to outline the buying process.
Then, tracking key customer journey metrics like engagement, churn rate, and customer satisfaction with an analytics platform like Woopra or Google Analytics should help you refine your customer journey mapping to fully optimize the customer experience.
Full insight into the customer journey. No SQL required.
Get started with Woopra for free to see who your customers are, what they do and what keeps them coming back.
Related Articles
The beginner’s guide to behavioral targeting to increase conversions.

How to get Started with Analytics

From Emails to Customers — Woopra Campaign Tracking
5 actionable methods to engage mobile customers, explore topics.
© Woopra, Inc. 600 California St 11th Floor San Francisco, CA 94108
- Request a demo
- Product Analytics
- Customer Analytics
- Customer Journey Analytics
- Google Analytics F.A.Q.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of service
How to Create a Customer Journey Map with Templates and Examples

Using data gathered from feedback surveys , online reviews, and other customer satisfaction metrics , a customer journey map is used to tell the story of a customer’s lifetime relationship with a company. Depending on the customer persona, this relationship can be as short as a few minutes or as long as many years. Customer journey maps are useful tools for visualizing the quality of each interaction and the customer’s reaction to that touchpoint as they move up the brand equity pyramid .
You can download our customer journey map template, or continue reading to learn more about creating your own.
Table of Contents:
Customer Journey Map: Understanding the Basics
- How to Create a Customer Journey Map in 7 Steps:
- Determine Target Personas
- Define Your Customer Touchpoints, Actions, and Reactions
- Break Out Touchpoints and Actions Into Phases
- Test the Customer Journey Map
- Complete the Customer Journey Map with Persona Data
- Identify Areas of Improvement
- Create a Corresponding “Business Actions” Map
Customer Journey Map Examples
- Customer Journey Map Downloadable Template
Before we dive into creating your own customer journey map, it’s important to cover the basic ideas behind these types of visualizations and why they’re helpful for businesses.
How Journey Map Tracking Helps Businesses Understand Customers
As we briefly mentioned earlier, customer journey maps are tools that help you visualize the specific steps customers go through when interacting with your business. Using buyer personas (a semi-fictional representation of a type of customer based on market research and real customer data, as defined by Hubspot ) you can track the path different customers take on the road to conversion and pinpoint failed or successful interactions. This ultimately helps you do things like:
- Allocate advertising budgets to channels that produce the most positive responses
- Collaborate across teams to improve touchpoints that continuously produce a negative reaction
- Retain and satisfy existing customers by improving previous customers’ churn points
What Are Customer “Touchpoints”?
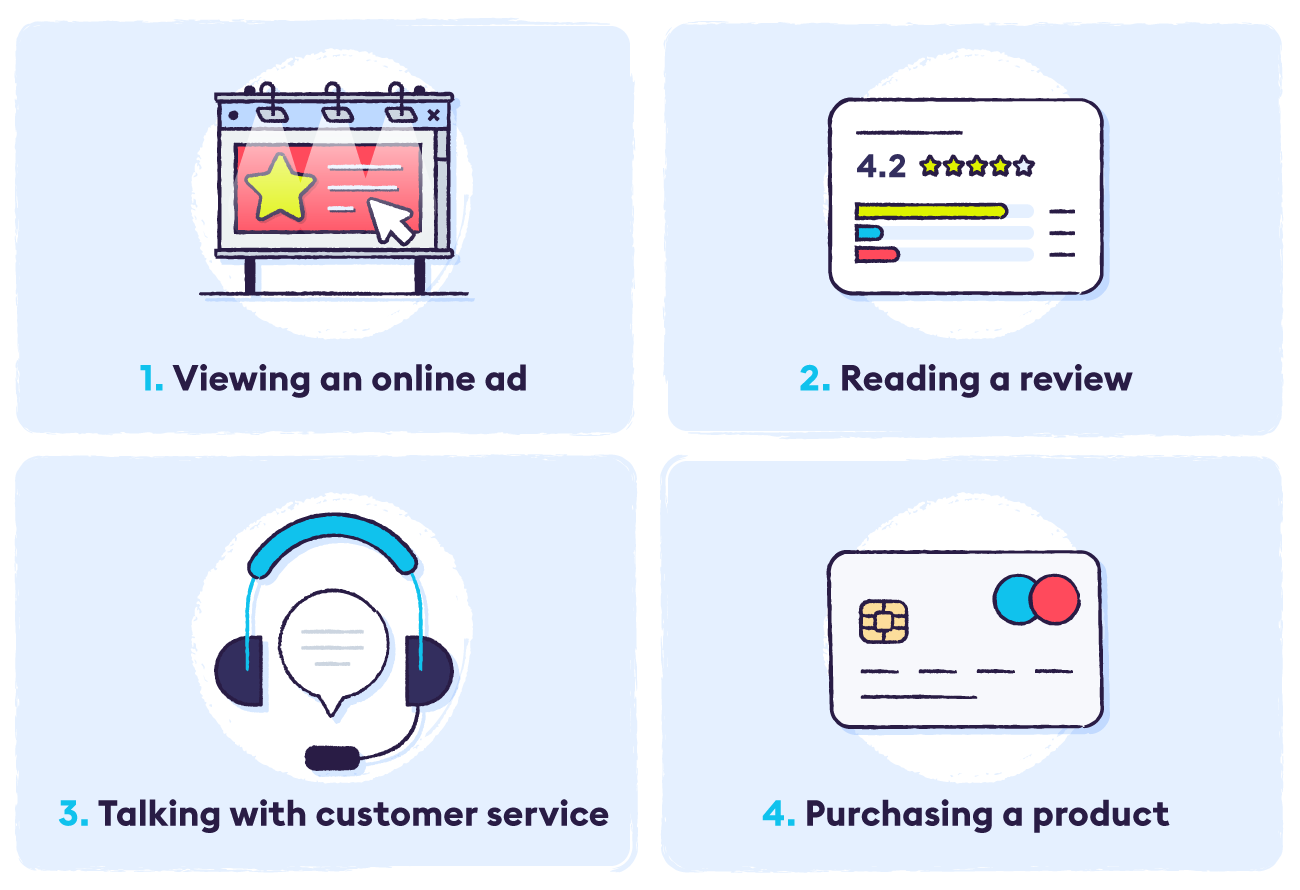
Customer touchpoints are any interaction someone has with your brand. These could be awareness-based touchpoints, where a potential customer learns about your company for the first time through things like:
- Social media ads
- Reading an online review
- Finding your site through organic search
Or, touchpoints can be more direct interactions such as:
- Clicking a product and reading the description
- Adding a product to their shopping cart
- Making a call to your customer service center
- Signing up for an email newsletter
Depending on the structure of your business, your customer journey map can cover just the main customer touchpoints on your buyer journey, or it can encompass any small interaction that can occur as well. Your ability to create a broad or detailed customer journey map will also depend on the customer data available to you.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map in 7 Steps
Though there are many customer journey map templates available online (including ours at the end of this article) it’s still good to understand the fundamental ideas behind how these maps are created so you can learn to customize each to suit your needs.
Step 1: Determine Target Personas

Each customer journey map is meant to demonstrate just one segment of your customer base, so it should be built specifically for each persona. Many businesses already have personas built for other purposes such as targeted ad campaigns, but if you haven’t, they aren’t too hard to construct. Utilizing your existing user data, create mock customers based on factors like:
- Demographic data (age, gender, location, etc.)
- How they first learned about your company
- Their budget
- What their goals are when purchasing from you
- What’s most important to them when buying
- Pain points that your company either does or could address
Then, decide which persona you’re going to target for this iteration of your customer journey map. For example, you could focus on the “tech-forward business executive” or the “Millennial startup owner,” whichever customer type you want to learn more about and improve the customer experience for.
Step 2: Define Your Customer Touchpoints, Actions, and Reactions
Once you’ve decided on your target persona, the next step is to define the customer touchpoints you want to track. As we talked about earlier, customer journey maps can be used to paint a broad picture of the buyer journey or track every little interaction possible. It’s up to you to determine what the most useful route will be for your project and where you want to focus your efforts.
It can be helpful at this step to list out every touchpoint you can think of, and then narrow down as needed. You’ll likely need to collaborate across teams to make sure you’re covering every type of customer interaction.
When you have your list of touchpoints compiled, it’s then easy to construct a corresponding list of customer actions. For example, if the touchpoint is “reads online review,” then the logical action would be “searches for company/product online.” After that, the next touchpoint would be “homepage/landing page” and the action would be “reads about product details.” You can see how building your customer journey map becomes easier once you get started.
In addition to touchpoints and actions, the third metric you will need to track in your journey map is customer reactions. These can be as basic as “positive and negative,” or be broken down further into numerical scales or other ratings. Customers take each action based on their reaction to the previous touchpoint. For example, a progression could look something like:
Touchpoint: targeted ad, Reaction: positive, Action: clicks ad > Touchpoint: ad landing page, Reaction: neutral, Action: reviews additional competitor options
It’s important to track each of these points concurrently to understand where customer pain points come from.
Step 3: Break Out Touchpoints and Actions Into Phases

Once you have all of your touchpoints, actions, and reactions listed, put them in a logical order that follows the actual buyer journey. At this point, it can be helpful to break out the list into overall phases in order to get a clearer visualization of the process. Again, these phases can be named whatever makes the most sense for your business. If you want to keep things general, you could follow a specific model, for example, the brand equity pyramid, and use the related phases of “brand salience,” “brand meaning,” “brand response,” and “brand resonance.”
It may be more helpful to name your phases something more specific, however, so you could also structure the map into sections labeled “Discovery,” “Exploration,” “Comparison,” “Conversion,” and “Retention” in order to better represent the customer’s thought processes. Though this step is optional, it’s easier to look at a chart that is broken down into larger phases vs a timeline that just details every specific interaction.
Step 4: Test the Customer Journey Map
Now that you’ve established the basic structure of your map via touchpoints grouped into phases, you should have a few different people run through the map to make sure your model is sound. Put yourself into the shoes of your target persona and pretend you are going through each touchpoint as that type of customer. At each point, stop and ask yourself “What would the customer do next?” The point of this exercise is just to ensure that you’re not leaving out any vital steps in the customer journey and that the map follows a logical progression.
Step 5: Complete the Customer Journey Map with Persona Data

Now that you’ve properly set up your customer journey map and tested it for any missing pieces, all that’s left to do is fill in the persona data. From your persona creation process, you should already have a good understanding of each type’s reasons for interacting with your business and what their specific pain points are. Using customer feedback data, abandoned cart data, advertising data, page bounce rate data, and other sources of customer information, you can reconstruct what the typical buyer’s journey looks like for this segment, including their unique actions and reactions at each step.
Step 6: Identify Areas of Improvement
The main purpose of creating customer journey maps is to display your data in a way that’s easier to visualize than numbers in a spreadsheet. If you’ve displayed your persona data accurately, then it should be simple enough to determine where customers are dropping out of the buyer’s journey. Look for places with negative reaction scores, especially scores that lead to customers bouncing from your site, and identify why this is.
At this point in your analysis, it can be helpful to add a new section to your customer journey map called something like “Pain Points,” “Reaction Explanations,” or simply “Why?” In this section, you can add notes or theories about why those negative reactions are occurring. Sometimes figuring out the issue can be a simple matter of walking through the buyer’s journey yourself (perhaps you discover something like an ad pointing to an unrelated landing page) or running additional customer feedback surveys to gather more data about a particular touchpoint.
Step 7: Create a Corresponding “Business Actions” Map

Now that you’ve pinpointed steps on the customer journey that are causing negative reactions, you should be able to identify what your company needs to do to improve these interactions. However, when you aren’t able to determine exactly what is causing these negative reactions, it’s hard to know what to do to fix them. As mentioned, you can always run additional customer feedback surveys to try to shed some light on the issue, but you may be able to discover more immediate fixes by creating a “business actions” map that corresponds to your customer journey map.
While a customer journey map is structured from the customer’s point of view, this reverse map would look at the same touchpoints and actions but from the business’s point of view. For example, if a customer submits a return request, what actions does the returns team take in response? Having each step detailed like this helps you paint a more holistic picture of your business processes to find unexpected areas of customer friction where things may be slipping through the cracks.
Just like customer data in a spreadsheet, there’s only so much you can explain with words on a page. Take a look at the customer journey map examples below to better visualize how these tools can help your business operations.
Hubspot’s simple example helps you understand customer motivations on a basic level, and is most useful for companies without in-depth persona data.

Bright Vessel’s customer journey map is color-coordinated so each department can easily see which touchpoints and actions they are responsible for.

Digital.gov’s example allows for more in-depth customer details, helping you better visualize your personas.

Customer Journey Map Template
Below is a customer journey map template that you can download, edit, and customize to represent your business’s needs.

Customer journey maps are an essential tool for any business looking to learn more about customer pain points on the buyer’s journey. But in order to create these maps, you first need to gather customer data. Chattermill can help you collect, manage, and analyze your customer feedback with our AI-powered software. Contact us to learn more.
Related Articles

Customer Experience Intelligence: The Top 6 Use Cases for Travel
In this guide, you will learn about the top customer experience intelligence use cases for travel businesses. Read on to find out all you need to know.

Customer Experience Intelligence: The Top 6 Use Cases for Retail
In this guide, you will learn about the top retail use cases for customer experience intelligence. Read on to find out how you can benefit.

The 3 big challenges CX is facing in 2024
We look at the biggest challenges CX is facing in 2024...and what you can do about them now.
See Chattermill in action
Understand the voice of your customers in realtime with Customer Feedback Analytics from Chattermill.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map? Template, Examples
Appinio Research · 01.11.2023 · 32min read

Are your customers truly at the heart of your business strategy? Understanding their experiences and interactions is key to success. In this guide, we'll navigate the intricate landscape of customer journey mapping, equipping you with the tools and insights needed to create exceptional customer experiences. From deciphering customer touchpoints to harnessing the power of emotions, we'll dive deep into every aspect of crafting an effective customer journey map. Let's explore how to transform your customer relationships and elevate your brand.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map is a powerful tool used by businesses to gain a holistic understanding of their customers' experiences throughout their interactions with the brand. It is a visual representation that illustrates the entire journey, from the initial awareness stage to post-purchase engagement.
Components of a Customer Journey Map
- Stages: A typical customer journey is divided into stages, including awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase phases. These stages represent the key milestones in a customer's interaction with your brand.
- Customer Actions: Within each stage, customer actions are documented. These actions can include visiting your website, researching products, making a purchase, seeking customer support, and providing feedback.
- Touchpoints: Customer touchpoints are the points of contact where interactions occur. These can be digital, such as website visits and social media interactions, or physical, like in-store visits and phone calls.
- Emotions and Pain Points: Effective journey maps also incorporate the emotional aspects of the customer experience. They highlight where customers may feel frustration, delight, confusion, or satisfaction.
- Moments of Truth: These are pivotal moments in the journey that significantly influence a customer's perception of your brand. Moments of truth can be positive, such as exceptional customer service, or negative, like unresolved issues.
Importance of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is more than just a visual representation; it is a strategic tool with significant business implications. Here's why it's essential:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: By understanding the customer journey, businesses can identify pain points and areas for improvement, leading to a smoother and more enjoyable experience for customers.
- Improved Customer Retention: Identifying moments of truth and addressing pain points can foster customer loyalty and increase retention rates.
- Higher Conversion Rates: A well-optimized customer journey can boost conversion rates at critical stages, such as during the consideration and purchase phases.
- Data-Driven Insights: Customer journey maps are grounded in data and feedback, providing actionable insights that guide decision-making and strategic planning.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: The process of creating a customer journey map encourages collaboration among different departments within a company, ensuring a unified focus on the customer.
- Competitive Advantage: A thorough understanding of the customer journey can differentiate your brand from competitors by delivering a superior and personalized experience.
In summary, customer journey mapping is a vital tool for businesses looking to deliver exceptional customer experiences, enhance brand loyalty, and remain competitive in today's market. It provides valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and continuous improvement efforts.
How to Prepare for Customer Journey Mapping?
Once you've recognized the importance of customer journey mapping, it's time to prepare for the process ahead. Proper preparation lays the foundation for a successful journey mapping endeavor.
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before diving into customer journey mapping, you must be clear about what you aim to achieve. Your goals and objectives should drive the entire process. Consider these questions:
- What specific insights do you hope to gain from the journey mapping process?
- Are you looking to improve specific touchpoints, reduce customer churn, or enhance the overall customer experience?
- How will you measure the success of your journey mapping efforts?
By defining your goals upfront, you can focus your efforts and ensure that the resulting map aligns with your business objectives.
2. Identify Your Target Audience
Understanding your audience is at the core of effective customer journey mapping. Your customers are unique, and their experiences may vary widely. To create a customer journey map that resonates, you must define your target audience . Consider factors such as:
- Demographics : Who are your typical customers in terms of age, gender, location, and income?
- Behavior: What actions do they take when interacting with your brand?
- Preferences: What are their communication preferences and channels of choice?
The more detailed your understanding of your audience, the more accurate and actionable your customer journey map will be.
3. Gather Relevant Data and Information
Data is the lifeblood of customer journey mapping. To create a comprehensive map, you need to gather as much relevant data as possible. Sources of data may include:
- Customer Surveys: Collect customer feedback to understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations.
- Customer Support Tickets: Analyze support tickets to identify common issues and areas for improvement.
- Website Analytics: Dive into website data to see how customers navigate and interact with your online presence.
- Sales Data: Examine sales data to gain insights into the customer buying process.
Effective data collection is essential for a successful customer journey mapping initiative, and Appinio can be your trusted ally in this endeavor. Appinio empowers you to gather valuable customer insights swiftly and efficiently. With access to a diverse pool of respondents, you can tailor your surveys to target specific audience segments, ensuring that you capture a comprehensive range of perspectives.
Harness the power of data-driven decision-making with Appinio, and transform your customer journey mapping into a dynamic and responsive strategy. Dive into the world of insights – book a demo today!
Book a Demo
The depth and quality of your data collection will significantly impact the accuracy of your customer journey map. Remember to maintain data privacy and security throughout this process.
4. Assemble Your Team
Customer journey mapping is not a solo venture. It requires a cross-functional team with diverse perspectives and expertise. Assemble a team that may include members from:
- Marketing: Marketers can provide insights into customer segmentation and messaging strategies.
- Sales: Sales teams can shed light on the buying process and customer interactions.
- Customer Support: Customer support representatives can share knowledge about common customer issues and pain points.
- Product Development : Product teams can contribute insights into product-related touchpoints and improvements.
Collaboration across these functions ensures a holistic view of the customer journey. Remember that each team member brings a unique perspective that can lead to valuable insights.
With your preparations complete, you're now ready to embark on the journey mapping process.
What is the Customer Journey?
Now that you've laid the groundwork for your customer journey mapping project, it's time to delve into the core concepts that will enable you to create a comprehensive and effective customer journey map.
Customer Touchpoints
Customer touchpoints are the various interactions and moments of contact that customers have with your brand throughout their journey. These touchpoints can occur across multiple channels, both online and offline.
To effectively map the customer journey, it's essential to identify and analyze these touchpoints:
- Website Visits: Consider how customers navigate your website, which pages they visit, and where they drop off.
- Social Media Engagement: Examine how customers interact with your brand on social media platforms and the sentiment of their interactions.
- Email Communication: Evaluate the effectiveness of your email campaigns and the responses they generate.
- In-Person Interactions: If you have physical locations or provide face-to-face services, assess the customer experience during in-person interactions.
By mapping customer touchpoints, you gain insights into the various channels customers use to engage with your brand. This insight is invaluable for improving the overall customer experience.
Customer Emotions and Pain Points
Understanding customer emotions and identifying pain points are central to creating a customer journey map that resonates with your audience. Emotions play a significant role in shaping the customer experience, so consider the following:
- Emotional Highs and Lows: At which touchpoints do customers experience high levels of satisfaction, delight, or frustration?
- Moments of Confusion: Identify areas where customers might feel lost or encounter difficulties.
- Customer Feedback: Analyze customer feedback, reviews, and surveys to uncover recurring emotional themes.
By acknowledging and addressing these emotional aspects of the journey, you can take steps to enhance the overall experience and create more positive interactions.
Customer Needs and Expectations
To create a customer journey map that genuinely aligns with your audience, you must pinpoint your customers' specific needs and expectations at each stage of their journey.
Consider the following questions:
- Desired Outcomes: What are customers trying to achieve at each stage of their journey?
- Expectations: What do customers expect from your brand at different touchpoints?
- Information Needs: What kind of information are customers seeking, and where do they expect to find it?
Understanding customer needs and expectations allows you to tailor your map to meet those requirements effectively. It also helps you identify opportunities for proactive engagement and value delivery.
As you move forward with customer journey mapping, keep these three fundamental elements in mind. They will serve as the building blocks for creating a detailed and actionable map that will help you enhance the overall customer experience.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
Now that you've gained a solid understanding of the customer journey and its key components, it's time to roll up your sleeves and start crafting your customer journey map. We will guide you through the critical steps involved in the creation process.
1. Select the Right Template or Format
Choosing the appropriate template or format for your customer journey map is the first crucial step. The choice depends on factors such as the complexity of your customer journey and the level of detail you wish to include. Common formats include:
- Visual Diagrams: These are graphical representations of the journey, often resembling flowcharts. They provide a visual overview of the customer's path.
- Spreadsheets: Spreadsheets can be used to create detailed, data-driven customer journey maps. They allow you to input specific metrics, timelines, and customer actions.
- Specialized Software: Various software tools are available specifically designed for customer journey mapping. These tools often come with pre-built templates and features for collaboration.
Consider your team's familiarity with the chosen format and ensure it aligns with your objectives. The chosen format should facilitate the clear communication of insights.
2. Map the Customer Stages
To create an effective customer journey map, you need to identify and define the stages your customers go through when interacting with your brand. These stages typically include:
- Awareness: The initial stage where customers become aware of your brand or product.
- Consideration: Customers evaluate your offerings, comparing them with alternatives.
- Purchase: The stage where customers make a buying decision and complete a transaction.
- Post-Purchase Experience: After the purchase, customers assess their experience with your product or service.
Understanding these stages helps you structure your map and align it with the customer's journey from discovery to satisfaction.
3. Document Customer Actions
At each stage of the customer journey, document the specific actions customers take.
- Visiting your website: Track the pages they view and interactions they make.
- Engaging on social media: Note the types of engagement, such as likes, comments, or shares.
- Making a purchase: Record the product or service bought and the transaction details.
- Providing feedback: Document instances where customers offer feedback, whether positive or negative.
By documenting these actions, you create a roadmap illustrating how customers engage with your brand throughout their journey.
4. Identify Key Touchpoints
Key touchpoints are the critical moments of interaction between your brand and the customer. These touchpoints significantly influence the customer's perception of your brand. Examples of critical touchpoints might include:
- Homepage visit: The first impression customers have of your website.
- Customer support interaction: How effectively and empathetically your support team handles inquiries.
- Checkout process: The ease and efficiency of the purchasing process.
- Product delivery or service fulfillment: The customer's experience after making a purchase.
Identifying these touchpoints allows you to prioritize them when making improvements to the customer journey.
5. Incorporate Customer Emotions and Pain Points
As mentioned earlier, emotions and pain points are integral to understanding the customer journey fully. When creating your map, consider:
- Emotional Impact: Include icons or indicators that represent the emotional highs and lows experienced by customers at different stages and touchpoints.
- Pain Points: Highlight areas where customers might feel frustration, confusion, or dissatisfaction.
By visualizing these emotional aspects, your map becomes more empathetic and actionable.
6. Highlight Key Moments of Truth
Moments of truth are pivotal points in the customer journey that significantly impact the overall experience. These moments can be both positive and negative. Examples of moments of truth include:
- Resolution of a customer issue: How effectively a problem is resolved can create a lasting impression.
- Personalized recommendations: Providing tailored suggestions can enhance the buying experience.
- Timely communication: Prompt responses to inquiries or order updates can boost customer satisfaction.
Identifying and emphasizing these key moments on your map helps ensure they are addressed and optimized.
With these steps, you're well on your way to creating a detailed and insightful customer journey map that will serve as a valuable tool for enhancing the customer experience.
Customer Journey Map Template
Creating a customer journey map begins with a well-structured template that serves as the foundation for your visualization. While every map should be customized to fit your specific business and industry , here's a basic template to get you started. You can adapt and expand upon it as needed.
1. Customer Persona
- Name: Give your customer persona a fictional name to humanize the journey.
- Demographics: Include details such as age, gender, location, and occupation.
- Goals: Outline the main objectives and needs of this persona in their interactions with your brand.
2. Stages of the Journey
- Awareness: Describe how the customer becomes aware of your brand or product.
- Consideration: Detail the process of the customer evaluating your offerings.
- Purchase: Explain the steps leading to a successful transaction.
- Post-Purchase: Highlight the experiences and interactions that occur after the purchase is made.
3. Customer Actions
- List the actions: Within each stage, enumerate the specific actions the customer takes. This could include visiting your website, subscribing to your newsletter, or contacting customer support.
- Timeline: Create a timeline for each action to show the sequence of interactions.
4. Touchpoints
- Identify touchpoints: For each action, identify where the interaction takes place. It could be your website, social media, email, phone, or in-person.
- Channels: Specify the channels used, such as website, mobile app, social platforms, or physical locations.
5. Emotions and Pain Points
- Emotions: Capture the emotional state of the customer at each touchpoint, whether it's frustration, delight, or satisfaction.
- Pain Points: Document areas where the customer might encounter difficulties or experience frustration.
6. Moments of Truth
- Highlight moments: Identify the pivotal moments that significantly impact the customer's perception of your brand, both positive and negative.
- Importance: Indicate the level of significance or influence each moment holds.
7. Opportunities for Improvement
- Actionable insights: Based on the journey map, list potential improvements and opportunities to enhance the customer experience.
- Responsible Parties: Assign responsibility for each improvement to relevant departments or team members.
8. Monitoring and Measurement
- Key Metrics: Define the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help you measure the success of your journey map.
- Frequency: Specify how often you will revisit the map and update it based on new data and insights.
Remember that this template is a starting point. You can customize it to align with your specific industry, customer segments, and objectives. As you gather data, engage with customers, and analyze feedback, your customer journey map will evolve and become a dynamic tool for improving the overall customer experience.
How to Interpret the Customer Journey Map?
With your customer journey map in hand, it's time to roll up your sleeves and extract valuable insights. Let's explore how you can analyze and interpret your map effectively.
1. Identify Opportunities for Improvement
Your customer journey map is a treasure trove of insights waiting to be uncovered. Start by closely examining the map and identifying areas where improvements can be made. These opportunities might include:
- Pain Points: Pinpoint where customers encounter frustration, delays, or roadblocks. These are prime areas for improvement.
- Communication Gaps: Identify instances where customers may not receive clear or timely information.
- Missing Touchpoints: Check for stages in the journey where there might be gaps in engagement or opportunities to connect with customers.
By identifying these opportunities, you set the stage for enhancing the overall customer experience and increasing customer satisfaction.
2. Address Pain Points and Friction
Once you've identified pain points in the customer journey, it's essential to take action to address them. Consider implementing the following strategies:
- Streamlining Processes: Simplify and optimize processes to reduce friction and make interactions smoother.
- Improving Communication: Enhance communication channels to ensure customers receive timely and relevant information.
- Offering Solutions: Develop solutions that directly address the specific pain points identified in the map.
Addressing pain points and friction not only improves the customer experience but also contributes to customer loyalty and retention.
3. Leverage Positive Touchpoints
Your customer journey map is not just about identifying issues—it's also about recognizing what's working well. Leverage the positive touchpoints to your advantage by:
- Replicating Success: Identify elements of these positive interactions that can be applied to other stages or touchpoints in the journey.
- Enhancing Personalization: Use insights from positive touchpoints to tailor your messaging and offerings to individual customer preferences.
- Fostering Engagement: Encourage more frequent and positive interactions by amplifying the aspects customers enjoy.
By amplifying positive touchpoints, you can create a consistently delightful customer journey that strengthens brand loyalty.
4. Align with Customer Needs and Expectations
Your customer journey map should be a reflection of your customer's needs and expectations. To ensure alignment, take the following steps:
- Regularly Review and Update: Keep your map current by revisiting it periodically to account for changes in customer behavior and market trends.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Continuously gather and incorporate customer feedback to adjust your map as necessary.
- Measure Performance: Use key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), and Conversion Rates to evaluate how well your map aligns with customer needs and expectations.
Alignment with customer needs and expectations is the cornerstone of a successful customer journey map. It ensures that your efforts are customer-centric and result in a more satisfying experience.
With your insights gained and improvements identified, it's time to move on to the next step: implementing changes based on the customer journey map.
How to Implement Changes Based on the Customer Journey Map?
After thoroughly analyzing and interpreting your customer journey map, it's time to put your insights into action. Implementing changes based on your map is critical to enhancing the customer experience and achieving your goals.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Collaborate across departments, including marketing, sales, customer support, and product development. Effective communication and teamwork are essential for successful implementation.
- Prioritize Actionable Insights: Not all insights from your map may be equally actionable or impactful. Prioritize changes that align with your objectives and have the potential to make the most significant difference in the customer journey.
- Develop an Action Plan: Create a detailed action plan that outlines the specific changes, responsibilities, timelines, and resources needed for implementation. This plan will serve as your roadmap for executing improvements.
- Test and Iterate: Before making broad changes, consider conducting pilot tests or small-scale implementations to assess their effectiveness. Continuously gather feedback and refine your approach based on results.
- Monitor and Measure Impact: Implement key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of your changes. Monitor metrics such as Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), Net Promoter Score ( NPS ), and Conversion Rates to gauge success.
- Feedback Loop: Maintain an open feedback loop with customers to gather their thoughts and reactions to the implemented changes. Customer feedback is invaluable for fine-tuning your efforts.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of all changes made based on your customer journey map. This documentation helps track progress and serves as a reference for future initiatives.
Examples of Effective Customer Journey Maps
To gain a deeper understanding of how customer journey mapping can be applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore some examples of companies that have successfully leveraged this strategy to enhance their customer experiences.
Example 1: Airbnb
Airbnb, the global vacation rental platform, excels at using customer journey mapping to create a seamless user experience. Their journey map spans from the moment a traveler starts searching for accommodation to the post-stay phase. Airbnb identified vital touchpoints, including website navigation, host communication, the booking process, and the stay itself.
How Airbnb Uses Journey Mapping:
- Personalization: Airbnb tailors its website content based on user preferences and search history, ensuring a personalized experience.
- Clear Communication: Hosts and guests can communicate through the platform, streamlining interactions and reducing friction.
- Post-Stay Engagement: After a stay, Airbnb encourages guests to leave reviews, fostering trust and transparency.
By mapping the entire journey and optimizing each touchpoint, Airbnb has become a customer-centric platform known for its user-friendly experience.
Example 2: Disney
Disney, a pioneer in the realm of customer experience, utilizes customer journey mapping extensively to create magical moments for visitors at their theme parks and resorts. Their journey map covers everything from planning a trip to the actual park experience and beyond.
How Disney Uses Journey Mapping:
- Pre-Visit Engagement: Disney engages customers even before they arrive by providing tools like the "My Disney Experience" app for planning and reservations.
- In-Park Experience: The company uses RFID technology for seamless entry, mobile food ordering, and interactive experiences within the park.
- Post-Visit Connection: Disney continues to engage with customers through personalized emails, offers, and surveys to gather feedback.
Disney's commitment to understanding and optimizing every stage of the customer journey contributes to its reputation as a world-class destination for families.
Example 3: Amazon
Amazon, the e-commerce giant , relies on customer journey mapping to enhance the online shopping experience. Their journey map encompasses the entire shopping process, from product discovery to delivery and customer support.
How Amazon Uses Journey Mapping:
- User-Friendly Interface: Amazon's website and mobile app are designed for ease of use, allowing customers to browse and purchase products effortlessly.
- Recommendation Engine: The company employs advanced algorithms to suggest products based on a customer's browsing and purchasing history.
- Efficient Fulfillment: Amazon's streamlined logistics and delivery services ensure prompt and reliable product deliveries.
Amazon's commitment to creating a frictionless shopping journey has made it a trusted and customer-centric e-commerce leader.
These examples showcase how diverse industries, from hospitality to entertainment and e-commerce, utilize customer journey mapping to create exceptional experiences. By examining their approaches, you can draw inspiration and adapt similar strategies to cater to your unique customer base and industry demands.
Remember, successful customer journey mapping is an ongoing process, so continue to refine and optimize based on customer feedback and evolving trends.
Continuous Customer Journey Optimization
Creating a customer journey map is not a one-and-done task; it's an ongoing process. To ensure your map remains relevant and effective in improving the customer experience, consider the following practices for continuous optimization:
- Regularly Update the Customer Journey Map: As your business evolves and customer preferences change, revisit and update your customer journey map accordingly. New touchpoints may emerge, and existing ones may evolve.
- Gather Customer Feedback and Data: Continue to collect feedback from your customers through surveys, reviews, and other channels. Use this data to refine your map and stay aligned with customer needs and expectations.
- Adapting to Changing Customer Behaviors and Trends: Keep a close eye on emerging trends, technologies, and shifts in customer behaviors. Be agile and ready to adjust your customer journey map to stay competitive and customer-focused.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Analyze the customer journeys of your competitors to identify areas where you can differentiate and excel. Learn from both their successes and their mistakes.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Ensure your team members across various departments are well-trained and aware of the customer journey map. Encourage a customer-centric culture within your organization.
- Regularly Review and Revise Metrics: Assess the KPIs you use to measure the effectiveness of your customer journey map. Make sure they remain relevant and align with your evolving goals.
- Experiment and Innovate: Don't be afraid to experiment with new strategies, technologies, or approaches to enhance the customer journey. Innovation can lead to breakthrough improvements.
By continuously optimizing your customer journey map and staying attuned to your customers' evolving needs, you'll be better equipped to provide exceptional experiences that drive loyalty and business growth. Remember that customer journey optimization is an ongoing journey in itself.
Conclusion for Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is your compass to providing remarkable experiences for your customers. Following the steps outlined in this guide, you can now create effective maps, identify opportunities, and continuously optimize the journey. Remember, it's all about putting your customers first and making their interaction with your brand a journey they'll cherish. As you embark on your journey mapping endeavors, remember that the customer experience is ever-evolving. Stay agile, gather feedback, and adapt to changing customer behaviors and expectations. By doing so, you'll not only meet but exceed your customers' needs, fostering loyalty and driving your business toward long-term success.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map in Minutes?
Unlock the full potential of customer journey mapping with Appinio , the real-time market research platform that empowers businesses to harness real-time consumer insights for smarter, data-driven decisions. In just minutes, you can conduct your market research effortlessly, making it an integral part of your daily decision-making process.
- Instant Insights: Move from questions to actionable insights in a matter of minutes, ensuring you have the most up-to-date information to shape your customer journey map.
- User-Friendly: No need for a PhD in research – our intuitive platform is designed for anyone to use, making it accessible to every member of your team.
- Global Reach: With access to over 90 countries and the ability to define the right target group from 1200+ characteristics, Appinio enables you to reach your desired audience wherever they are.
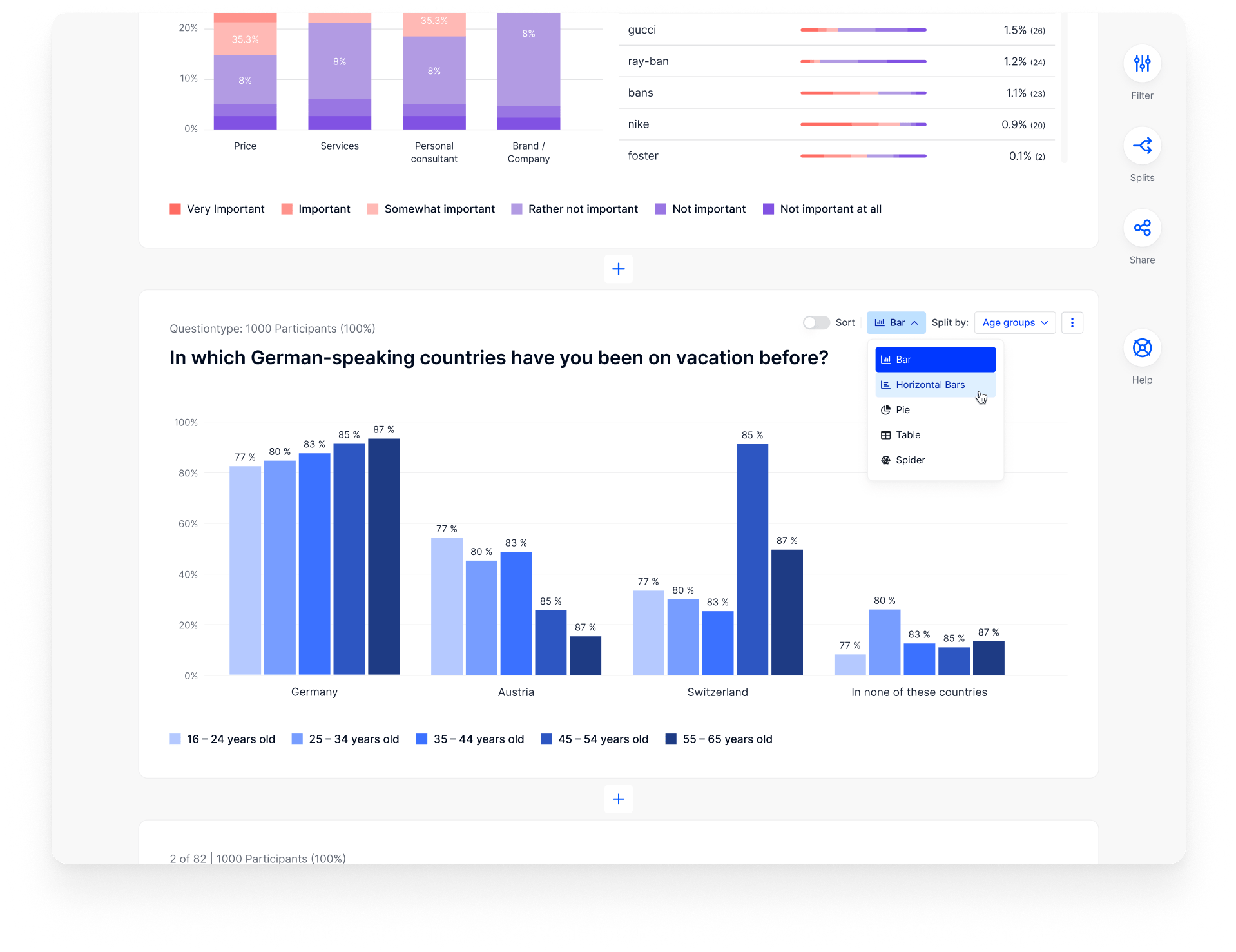
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more
09.04.2024 | 29min read
What is a Confidence Interval and How to Calculate It?

05.04.2024 | 27min read
What is Field Research? Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

03.04.2024 | 29min read
What is Cluster Sampling? Definition, Methods, Examples
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
Venngage Customer Journey Mind Maps
Learn the value of your user's pain points and needs, and improve the experience of your customers with Venngage's customer journey mind map templates.
Not a designer? Not a problem. With Venngage's beginner-friendly user journey map tool, making a journey map has never been easier. 40,000+ businesses trust Venngage to improve their marketing strategies!
Design from one of our customer journey mind map templates
Customize one of our professionally-designed templates. see all customer journey mind map templates, design an effective customer journey mind map on venngage by following these steps:.

Add different target customer profiles by accessing our library of illustrations and stock photos to represent different types of users.
Browse our library of 40,000+ icons and illustrations. Select the ones that emphasize key steps in your customer's journey.

Use a consistent theme. All of our user journey maps were designed with a central theme in mind, making it easy to create a professional-looking design.

Customize our customer journey mind map templates in a snap. Drag and drop new elements and share engaging visuals with your team using Venngage's smart editor.
How to create customer journey mind maps in 5 steps:
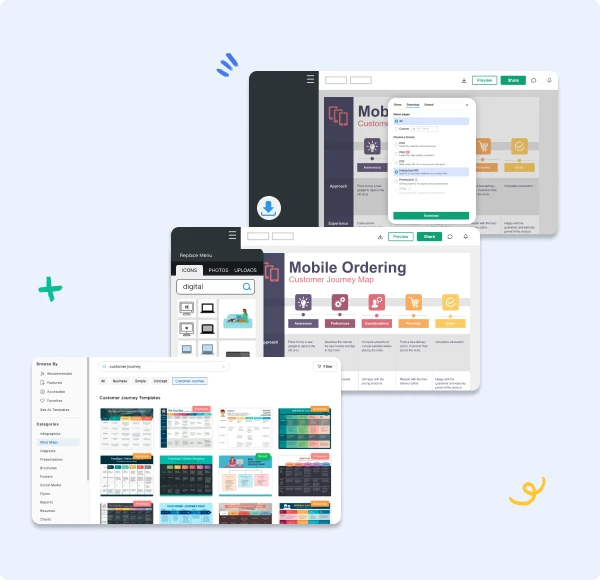
Understand how your clients interact with your brand
User Customer Journey Mind Map Templates
Plot this journey using Venngage's customer journey map tool. Our professional designs will help you create a resource that you and your team can refer to.

User-Friendly Editor
Venngage is an online drag-and-drop graphic design tool for people with little to no design experience. Swap out text, images, icons, and add data to your user experience map!

Share Your Customer Journey Mind Map
Download your user journey design in high-quality PNG or PDF formats, or share it on social media directly from Venngage with just a few clicks.

Customer Support 24/7
Running into any issues? Have questions about using a feature or need advice? Our support team is available around the clock.
Brand Identity
Build your brand through consistency. My Brand Kit lets you incorporate your branding into every asset you design in Venngage.
Team Collaboration
Working with a team? Make your teamwork seamless by having multiple people within the same design. Write comments and helpful feedback.

Choose the customer journey mind map that best represents your users' experiences
- Choose a template that best fits the process you want to improve. Also, you can ask our team to recommend one to you.
- Customize design assets by adding, editing, dragging or deleting shapes, lines and colors with a few clicks.
- Quickly add branding to any process map with My Brand Kit. Save your brand's color palette, fonts and images and apply them to every graph you create.
Design the perfect visual representation of your user journey
Collaborate with your team and stakeholders in real-time
Download or share your customer journey mind map with a click.
- Download your document as a PDF or Interactive PDF (to use hyperlinking).
- To print your document, apply print bleeds in the editor and then download it as a PDF.
- Share your completed design using a share link - no need to download a single thing.
How do I create a customer journey mind map on Venngage?
Click the green button below and sign up for Venngage using your email, Gmail or Facebook account. Then, click "Templates" to find the best design for you.
Can I add hyperlinks to my customer journey mind map?
Click any element (text, icon, images) in our templates to add a link. Then, download your file as an Interactive PDF (Business plan only).
Can I share, download or print my customer journey map?
Sure thing! Share a link to your design with your colleagues or clients. Or download your file as a PNG or PDF file to print it (Premium and Business plans only).
Try Venngage's Customer Journey Map Maker today. Sign up for free!

Get started with our customer journey map templates
How to Create a Customer Journey Map

A customer journey map is a visual representation of the process someone goes through to accomplish a goal with your product or service, as well as what they do and how they feel at each stage of that process.
Salesforce Staff
Share article.
- Link Copied
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the process someone goes through to accomplish a goal with your product or service, as well as what they do and how they feel at each stage of that process.
You’ll visualise the story of your customer so that you can include a lot of information succinctly. You’ll also be able to create a shared vision among the marketing organisation and between marketing and other stakeholders.
In creating the customer journey map, you’ll be able to see how your customer relates to your brand through interaction points. You’ll develop a deep understanding of how a customer engages with your product or service, see your brand from a customer perspective, and define the qualitative factors that shape their ability or willingness to engage.
Common types of customer journey maps
Current state : Based on the experiences you provide right now, this type identifies current pain points so that you can incrementally improve.
Future state : Based on the experiences you will provide in the future, this type helps communicate a vision and drive a defined change.
Day in the life : Current state, with a broader view of the customer, examining everything they do along the journey whether it involves your company or not. This is where marketers can uncover unmet needs and drive innovation that is not yet defined.
Service blueprint : A simplified current or future state journey map, with people, processes, policies and technologies that deliver that experience layered on, this type’s primary purpose is assigning ownership for specific experiences and interactions.
And there are many ways to present each type. At its simplest, a customer journey map is a table, with steps through time on the horizontal axis and themes for analysis on the vertical axis.
When to create a customer journey map
We create journey maps any time we need to understand our customers and their relationships with our company, particularly if we need to:
Drive customer-centricity, shifting perspective from inside-out to outside-in
Break down silos to create one shared, organisation-wide vision
Assign ownership of customer touchpoints and interactions
Target and speak to specific customers
Structure of a customer journey map
Keep it simple – you’ll have a header section that contains who the customer is and what their goal is. From there down, it’s a big grid. Moving left to right is simply the passage of time, usually broken into phases – think of each stage for your customers as they move from awareness to advocacy.
From top to bottom, there are commonly three more sections:
Their chronological journey with your brand
Their tasks, thoughts and emotions as they interact
Your opportunities to remove friction and improve experiences (a s well as, if applicable, responsibility for the touchpoint)
How to create a customer journey map
Start out by understanding that the point of creating a customer journey map is not actually ending up with the map. It’s also the discoveries along the way. You’re gathering data, deriving insights from it, and identifying actions to take based on those insights.
Put more nicely, you’re getting to know customers, their needs and how those needs are met, or not, through interactions with your brand. You’ll uncover insights, and form and test hypotheses. Those insights, brought together with your company goals, will provide moments of inspiration that springboard into your greatest creative campaigns, or form the basis for ongoing and cumulative improvement.
The first step, then, is discovery – conduct your research. The methods of enquiry will depend on your product or service, but should include at least quantitative research with customers and the public (within your target demographic), and qualitative research with internal stakeholders. You may also observe users interacting with your product if that’s relevant for your brand.
Using that research, you’ll identify your persona, the scenario in which they interact with your brand, the touchpoints, and insights from your research about their actions and emotions at each touchpoint.
This actual mapping should be conducted in collaboration with other stakeholders from all levels and functions of the organisation who can offer varying insights and expertise. In a three-hour workshop, for example, you might offer a recap of your research, propose a persona for discussion, refine it, and map the journey collaboratively.
After the workshop, design the customer journey map, with a focus on succinctly presenting the story. Distribute it to all stakeholders, and – very importantly – never let it gather dust. Use it, iterate, use it more.
How to use your customer journey map
You’ll want to create personalised omnichannel customer experiences for each of your personas, based on everything you found – and for that you’ll need Pardot.
It’s powerful marketing automation software, built on the world’s #1 CRM – when you’re ready, a demo’s waiting for you .
More than 7,000 marketing leaders told us the challenges, priorities, metrics and more for 2020. Check out the State of Marketing report to find out more .
Explore related content by topic
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Journey
- Customer Journeys
- Digital Transformation

The 360 Blog from Salesforce teaches readers how to improve work outcomes and professional relationships. Our content explores the mindset shifts, organisational hurdles, and people behind business evolution. We also cover the tactics, ethics, products, and thought leadership that make growth a meaningful and positive experience.
Get the latest articles in your inbox.

New to Salesforce?
- Why Salesforce
- What is CRM
- Explore all products
- Customer success
- Product pricing
About Salesforce
- Security & Performance
- Salesforce.org
- Best CRM Software
- Sustainability
- Give us your Feedback
Popular Links
- New Release Features
- Salesforce Mobile App
- Business App Store
- CRM Software
- Salesforce Live
- Salesforce for startups
- América Latina (Español)
- Brasil (Português)
- Canada (English)
- Canada (Français)
- United States (English)
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- España (Español)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- France (Français)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Nederland (Nederlands)
- Sverige (Svenska)
- United Kingdom (English)
- All other countries (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- ประเทศไทย (ไทย)
© Copyright 2024 Salesforce, Inc. All rights reserved . Various trademarks held by their respective owners. SFDC Australia Pty Ltd. ABN 91 109 182 989. Salesforce Tower 180 George St Sydney, NSW, 2000, Australia
- 1-800-553-8159 Expand Menu
- Subscribe to Our Emails Expand Menu
- Chat with Sales Expand Menu
- Contact Us Expand Menu

9 Best Real-life Customer Journey Map Examples

April 4, 2024
The customer journey mapping process is a visual representation of the experiences and interactions customers have with a company, from initial awareness to post-purchase evaluation.
These maps utilize infographics to showcase touchpoints across the customer-brand relationship, revealing strategies for personalized experiences that enhance consumer success and engagement.
By aiding businesses in understanding the customer journey, identifying pain points, and enhancing overall experiences, journey mapping contributes to increased sales, loyalty, cost savings, and team alignment.
How Customer Journey Maps Impact Business Performance?
Customer journey maps serve as invaluable tools for enhancing business performance by facilitating a smoother path to customer satisfaction.
They provide insights into the customer experience, allowing businesses to empathize with customers, identify pain points, and address challenges they encounter along the way.
By pinpointing inconsistencies between touchpoints, such as communication gaps across platforms or departments, customer journey mapping aids in improving service quality and retention. Leveraging customer journey contact center data, these maps optimize genuine customer engagements across all communication channels.
Key Elements of a Customer Journey Map
Numerous customer journey mapping software options exist in the market, each offering unique features. Here are the key elements that characterize these customer journey map templates.
Customer Personas
To create a customer journey map, you first need to know who your potential customer is. This begins with developing customer personas, which are fictional representations of typical customers based on demographics, behaviors, and customer needs.
For instance, Uber has two primary personas: passengers seeking seamless rides from A to B, and drivers desiring flexibility and supplemental income.
Touchpoints
Touchpoints encompass every interaction a customer has with your brand throughout their buying journey. When creating a customer journey map, it's essential to outline these points of contact, information gathering, or interactions with your brand. Typical touchpoints include:
- Marketing emails and newsletters
- Phone calls, service and support lines, online chatbots
- Store staff, checkout registers, service points
- Website, apps, social media platforms
- Packaging, shipping, delivery
Customer Emotions
In this step, you map out the specific emotional experience of the customer at each touchpoint. What are they thinking? What actions do they take? How are they feeling?
Avoid guesswork by gathering real feedback from customers through surveys and, ideally, direct interactions with your customer support team.
Critical Moments
Critical moments are the touchpoints that significantly influence the overall customer experience, whether positively or negatively. These moments of truth provide opportunities for innovation and growth as they represent instances, such as pain points, where people are willing to invest in addressing their critical needs.
Channels and Platforms
Channels and platforms encompass the diverse mediums through which customers engage with your business. These may include traditional channels like in-person visits or phone calls, alongside digital channels such as websites, social media, or mobile apps. Understanding the preferred communication channels of different customer segments helps in effectively engaging with your customers throughout their journey.
From Concept to Reality: Creating Your Customer Journey Map
Customer journey maps are not one size fits all; however, there are fundamental steps that you can take to create your own.
Step 1: Define customer touchpoints
Identify all customer interactions, from ads to website visits, forming the core of your user journey map, illustrating the path from awareness to purchase and beyond.
Step 2: Create customer buyer personas
Develop fictional representations of your target audience, considering demographics and behaviors.
Step 3: Set goals
Establish goals for each touchpoint on your map, whether it's increasing brand awareness, driving sales, or fostering customer loyalty.
Step 4: Conduct user studies and surveys
Conduct user studies and surveys to understand how customers discover products, interact with your brand, and identify pain points or challenges they encounter.
Step 5: Analyze your customer journey map
Evaluate key metrics such as repeat purchases, sales, and customer satisfaction to assess the effectiveness of your customer’s journey map. Use the data to optimize touchpoints and enhance the overall digital customer experience .
Real-life Application: 9 Customer Journey Map Examples Across Industries
Example 1: consumer saas- spotify.
Spotify, a leading audio streaming service, utilized a customer journey map to enhance its music-sharing experience for users. The objective was to determine the optimal integration of music-sharing features within the customer journey.
The map detailed the user experience from opening Spotify on a mobile device to interacting with shared songs. By analyzing each stage and touchpoint, including user actions, thoughts, and emotions, Spotify identified pain points and implemented improvements for a smoother music-sharing experience.
This comprehensive journey map prioritized customer engagement, considered user behavior, and aimed to enhance overall user satisfaction, ultimately encouraging more frequent music sharing among users.
Example 2: Entertainment - Netflix
Similar to Spotify, Netflix's customer journey map incorporates stages, emotions, and thoughts, albeit with a different approach. In Netflix's map, each touchpoint is described in a more goal-oriented manner, focusing on addressing the goals through rows such as 'motivations', 'pain points', and notably, 'opportunities'.
Additionally, this customer journey map is tailored with a clear target persona in mind, likely detailed in their marketing materials, along with a predefined scenario. This approach makes Netflix's customer journey more actionable and focused on achieving its objectives.
Example 3: E-commerce - Amazon
Amazon, a global e-commerce giant, employs sophisticated technology and custom systems to guide customers through the sales journey. While its customer journey map is complex and extensive, it can be broken down into manageable parts for analysis.
For instance, Amazon's customer conversion funnel illustrates how its products facilitate the customer journey, driving engagement and maximizing sales. When conducting your customer journey mapping , remember to incorporate key metrics to monitor success and gain deeper insights into the overall customer experience.
Example 4: B2B - Hubspot
HubSpot opted for a linear design for their customer journey map, organizing common experiences along a timeline and using color coding to denote pain points or moments of delight. This format made the map easy to interpret and actionable for other teams.
Additionally, they incorporated testimonials from customers, categorized based on their position in the journey, to provide firsthand perspectives on interactions. These stories humanized the map, making the identified issues feel more relevant and pressing to employees.
Example 5: SaaS- Zendesk
This customer journey map example from Zendesk uniquely emphasizes customer churn and reconsideration. While it doesn't delve into the specifics of customer activities, thoughts, or emotions, it distinguishes itself by accounting for a range of outcomes, including churn and reevaluation.
For teams prioritizing these aspects, this format offers a valuable framework for gaining deeper insights into the customer's mindset at each stage of their journey.
Example 6: Toy- Lego
LEGO has innovatively crafted a Customer Journey Map using a tool called the "experience wheel." This wheel analyzes a flight to New York City in a simplified manner.
At its core are the persona's characteristics, surrounded by three levels of experience representing the journey's goal achievement. The outer circle details each step of the journey, marked with emoticons reflecting positive, neutral, or negative experiences. This straightforward format allows for easy creation, making it suitable for discussions and idea-generation sessions. It offers a quick way to view products or services from the customer's perspective.
Example 7: SaaS - TurboTax
TurboTax, a leading online tax preparation software, developed a customer journey map to launch its new product, Personal Pro.
The map, created through a blend of data research, customer surveys, and discussions with tax professionals, tracks the customer experience from website entry to tax filing completion. By identifying and addressing customer pain points, the map enables TurboTax to enhance the overall experience, ensuring smoother and more satisfactory interactions.
Example 8: Transport - Uber
Uber's customer journey map not only includes clearly defined stages, emotional waves, and thoughts at each touchpoint but also incorporates additional visuals from their app and descriptive elements.
For instance, the persona is well-defined, eliminating the need to reference external marketing documents for details. Moreover, the critical analysis for action section provides a clear assessment of both positives and areas for improvement at each step of the journey.
Example 9: Retail - Starbucks
Starbucks’ customer journey map, using a timeline style, highlights diverse touchpoints and aims to enhance customer experience. It gathers feedback from outlet visits and categorizes experiences into three components:
- Poached experience: Customers are asked about their overall impression of the outlet they visited, particularly during peak hours.
- Enhanced experience: Starbucks also assesses any negative experiences encountered by customers and seeks resolutions to prevent their recurrence.
- Touchpoints: This refers to the level and extent of interaction the consumer has experienced with the brand, whether in person, through the website, app, etc.
How to Implement Customer Journey Maps Using Five9
Implementing customer journey maps using Five9 is a simple process. With Five9, agents gain access to a unified view of customer history, including interactions from email, web chat, and phone calls.
By integrating all channels into a single interface, Five9 ensures that agents have a clear understanding of the customer journey, enabling them to respond effectively at every stage.
Discover how using Five9 customer journey mapping can boost customer service, helping agents understand and meet customer expectations, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Related Articles

10 Essential Contact Center Metrics and KPIs to Measure in Healthcare

Four Healthcare Contact Center Trends in 2024

Step-by-step Guide to Creating the Perfect Customer Journey Map
Call 1-800-553-8159 to learn more about five9.
Get a Quote
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Service Safaris
What are service safaris.
Service safaris are an early qualitative research method where researchers walk in the customers' shoes to experience a service from the customers’ perspective. By experiencing the service directly, they can find strengths, weaknesses and more as they build empathy with customers early in the design process.
Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, provides an overview of service safaris:
- Transcript loading…
“To acquire knowledge, one must study; but to acquire wisdom, one must observe.” — Marilyn vos Savant, Magazine columnist, author, lecturer, playwright and Guinness-Book-of-Records holder of the highest-recorded IQ
In service design , designers optimize end-to-end experiences. They focus on user needs , touchpoints and seamless integration across the entire service. For example, when a customer takes the train, they encounter many service components . Some examples of components include:
They use an app to buy their train tickets .
They enter the station and look for directions to the ticket machines .
They use the ticket machine to collect their tickets .
They ask a customer service representative for information.
They look at the departure board for updated travel information .
They use their ticket to pass through the entry barriers .
They board the train and use the signs to find their seats .
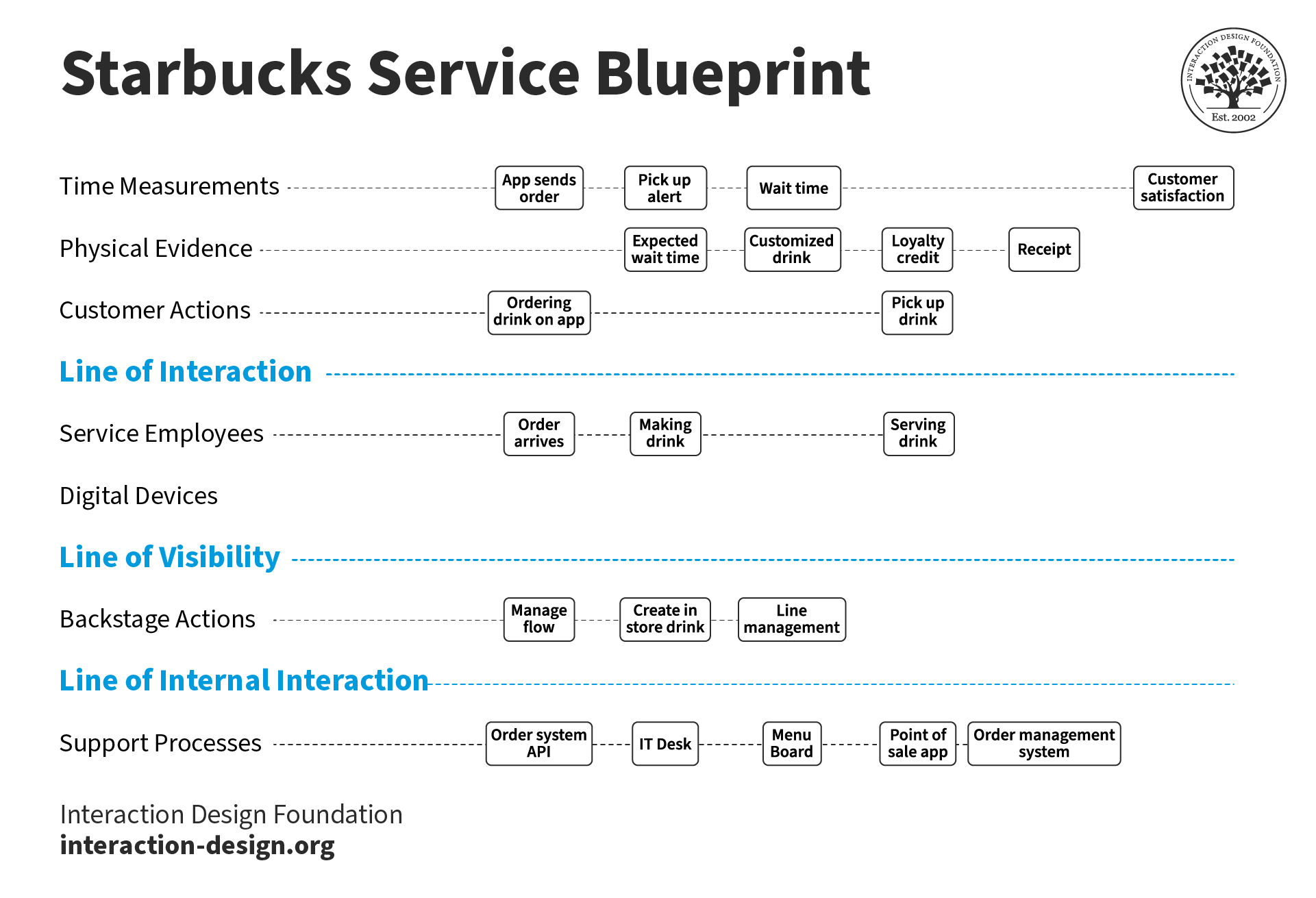
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
On a service safari, researchers perceive and interact with individual components and the service as a whole. Service safaris help researchers:
See, hear and feel the service's experience as a consumer, not a researcher.
Learn how a service works from the customer's perspective.
Review the service as a whole, not by individual components.
For example, in 2022 and 2023, Airbnb CEO Brian Chesky traveled across the US to stay in Airbnb rentals. He also made a room in his home available on Airbnb. Chesky discovered issues with the experience of being an Airbnb customer and a host. He used these insights to improve Airbnb’s service design.
How Do Service Safaris Improve Service Design?
Service safaris benefit service design in three primary ways:
They provide direct insight into how a service works and the customer experience . For example, a design team creates a café-oriented service involving an app. A “field trip” to Starbucks could offer a robust view of the many aspects of a well-branded coffee shop customer experience. Findings from safaris can directly inform design decisions. However, researchers must back up findings with actual user research .
They inform future research. Real-world insights help create hypotheses, guide user interviews and shape survey questions. Safaris turn observations into actionable research questions. These questions can further deepen researchers’ understanding of user needs and behaviors .
They build empathy within the design team. Researchers empathize with customers by experiencing the service as they do. This firsthand experience is invaluable for designing more intuitive and user-friendly services.
Direct Insights
When researchers venture out to get a first-hand experience as a customer, they can:
Observe real-world interactions. Researchers directly observe how customers interact with a service in their natural environment. Observations help identify pain points, moments of delight and areas for improvement. These observations might not be evident through other research methods.
Identify touchpoints . Researchers document every touchpoint where customers engage with the service. They note digital and physical interactions. Researchers must understand these touchpoints to map out the customer journey accurately.
Gather qualitative insights. Researchers collect qualitative data on their feelings, frustrations and satisfaction. This data deepens their understanding of the customer's emotional journey.
Analyze service flows. Researchers identify any inefficient processes or disconnects that could hinder the customer experience.
Influence management decisions . Researchers can present stakeholders with their findings to better convince them of the need for service design.
Future Research
Service safaris help form the basis of future user and ethnographic research . Safaris help researchers identify key customer behaviors and contexts . For example, insights from a service safari in a retail environment might highlight the following:
How consumers navigate the physical space.
The role of digital tools in their shopping experience.
Moments that lead customers to purchase decisions.
These observations can guide researchers to focus on specific behaviors, interactions or environmental factors.
Service safaris can uncover unspoken needs and pain points . For example, customers may repeatedly ask staff for directions in a supermarket. A positive experience with support staff may cause customers to overlook this as a pain point and not mention it in an interview or survey. This insight can inform the need for better signage in the supermarket.
Ann Blandford, professor of human-computer interaction (HCI), explains how user interviews help researchers discover the “why” but not the “how”:
Insights inform the recruitment of participants for ethnographic research. Service safaris can identify the most relevant user groups for a study, which allows researchers to get the most out of their research.
Observations can directly inform the development of research questions . For instance, a service safari in public transportation reveals challenges with buying tickets. Future research might explore the context and specificities of this challenge with customers.
When to Conduct Service Safaris?
Researchers conduct service safaris during the empathize stage of the design thinking process. Since safaris can form the basis of future research and help gain an overview of service, they are often the first method researchers use. They can be insightful and inspirational as researchers can research their own or other services.
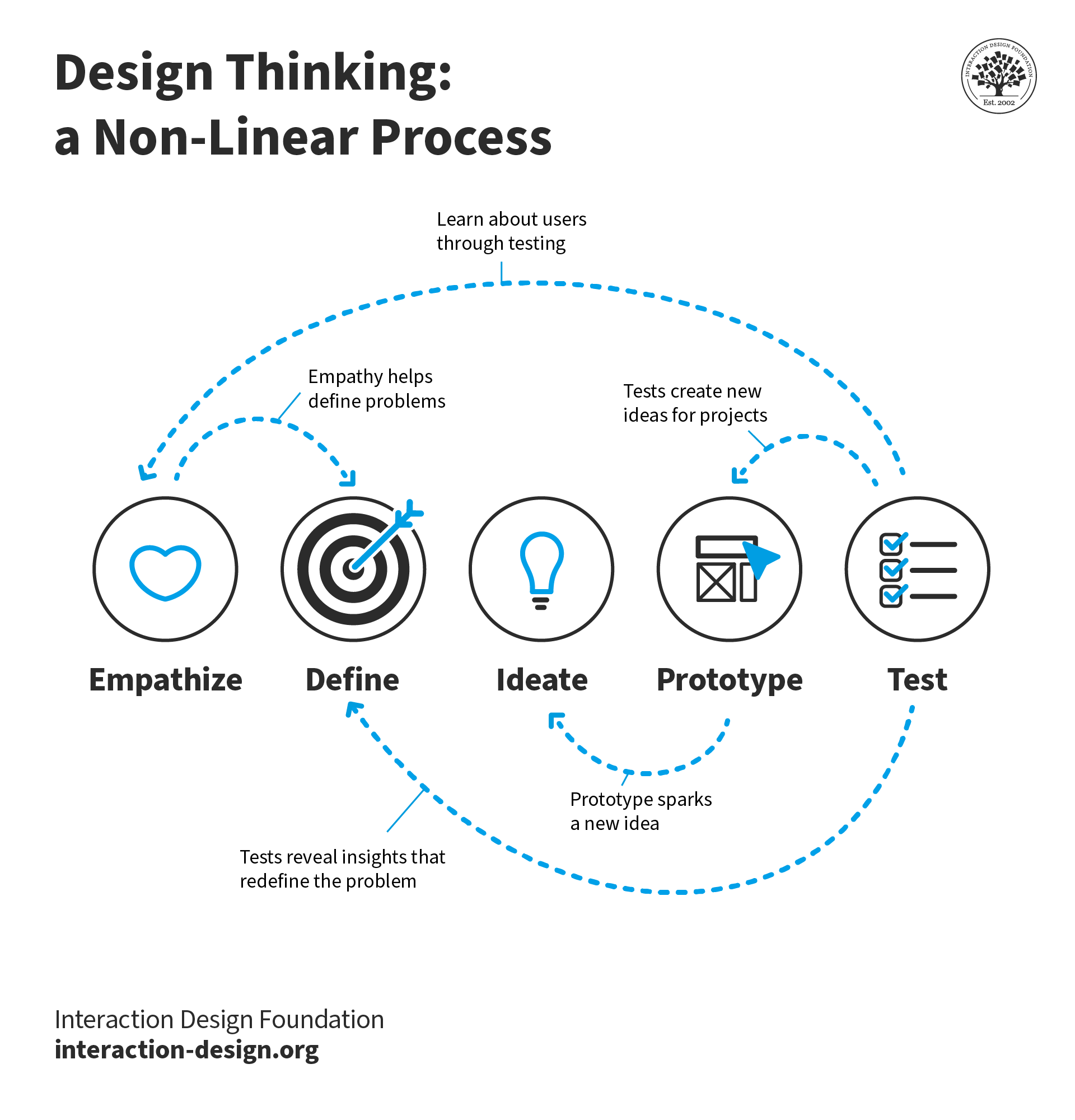
In the design thinking process, empathy helps define problems. This empathy fuels the entire design process and feeds into each stage. Early research methods like service safaris build empathy in a design team and are critical to user-centered design.
Some example scenarios in which a researcher might conduct a service safari include:
To begin the research process and map a previously unmapped service.
To research competitors or services from other industries to gain insights and inspiration.
To redesign or assess a specific aspect of a service.
To gather information that can convince stakeholders of the benefits of service design.
How To Conduct a Service Safari
Researchers conduct service safaris for both physical and digital services. For example, a digital service safari could follow the process of purchasing an item from an e-commerce website. Everything from a marketing email to delivery and contacting customer service should be part of the safari.
Required Resources
Safaris can be inexpensive and flexible.
For example, coffee shop and public transport safaris need little investment . Researchers can be reimbursed if they work for or with the service they are researching.
For some services, safaris are easy to set up and run. Researchers can conduct safaris as and when needed. Straightforward safari examples include coffee shops or digital-only safaris.
Recruiting users is unnecessary. Researchers and team members conduct the safari themselves.
Multiple team members and stakeholders can conduct service safaris for diverse insights .
Conversely, safaris can also be resource intensive:
High-cost services need more investment. Especially if the researcher is investigating rival or comparative services.
Some safaris are time-intensive —for example, a long-haul flight or a service in a remote location.
Researchers may need funding and permission from management regardless of the resources needed. Case studies and stories of successful safaris can be helpful for researchers who want to influence stakeholders.
Prepare for Your Service Safari
Once researchers have the funding and permission they need, they use the following process:
Set a goal or task a typical customer might have. In the coffee shop example, this might be to place an order in the app and pick it up at the shop.
Choose where to start the safari. While it may seem obvious where the safari will take place (e.g., a coffee shop), service design encompasses every service component. For example, when evaluating a coffee shop, the safari may begin with finding and accessing the shop. How well is its location advertised? Is its signage clear? Is it accessible to all customers?
Decide who should go. Multiple team members and stakeholders should conduct a service safari wherever possible. With several perspectives, researchers can better understand a typical experience. This approach improves empathy with and understanding of the service’s customers. However, each person must go alone. Researchers find it more challenging in a group to focus and put themselves in the customer's shoes. Group safaris can also result in groupthink , where the group’s identity overshadows individual opinions.
Decide what to bring. Researchers may take a smartphone or camera to take pictures and videos and a notebook to record observations. Items a customer would typically have are also essential. For example, researchers may take an umbrella if the service safari occurs in a restaurant and it’s raining. Researchers observe small details, like where customers can put their wet umbrellas.
Conduct the safari. Once you’ve planned your safari, the next step is to execute it. During the safari, pay close attention to the following (you can take pictures, videos and voice and written notes):
The service touchpoints and how they fit together. How do you interact with the service, and are there any problems? Do you notice any disconnects between parts of the service?
The service environment and any physical artifacts the service involves. e.g., coffee cups and seating.
Which digital interfaces do you use while you’re on safari?
Anytime you feel frustrated or confused by the service.
Crucial thoughts or feelings about the experience.
Tips and best practices
Service safaris may seem simple; however, researchers follow these best practices to get the best results:
Use empathy maps . Researchers often chart their observations on an empathy map, which can be helpful in later research and ideation. Empathy maps visually represent the researcher’s thoughts, feelings and actions. If you also spoke with other customers, you can include their thoughts, feelings and actions.
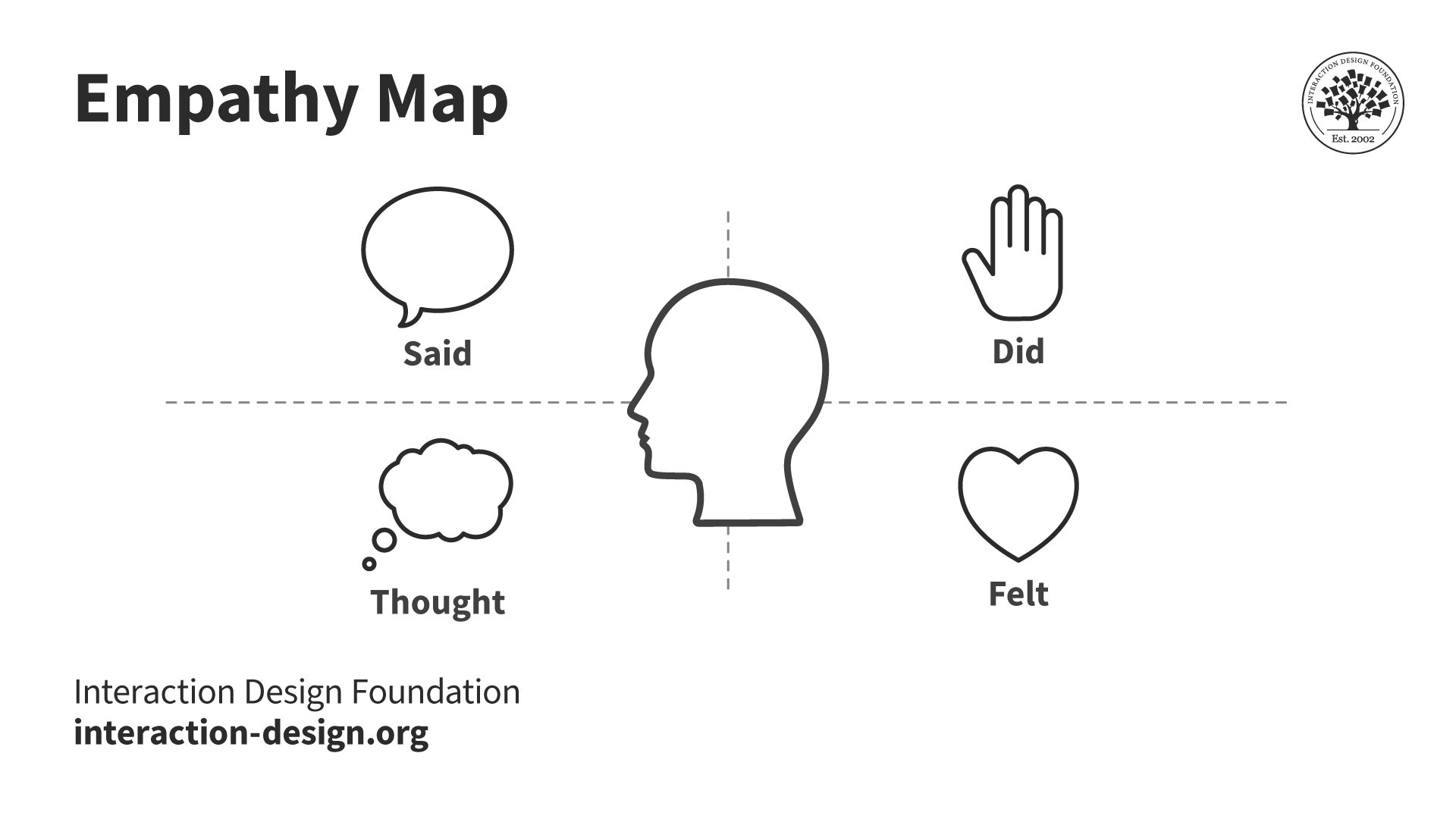
Design teams use empathy maps to inform further research, brainstorming and design decisions. Teams refer to the maps throughout the design process to stay empathetic and focus on the user.
Get comfortable with role play and prepare fictitious scenarios. Some service safaris involve everyday tasks, like buying a coffee. However, others, like applying for a loan at a bank, do not. Researchers must often role-play for a more accurate customer experience during service safaris. Prepare scenarios and backstories to ensure the service reacts to you as if you were a customer.
Immersion is key. Embody the customer or user as far as possible. Limit distractions and think deeply about the circumstances in which a customer would use the service.
Use observations to inform future research. A service safari is a foundation for ethnographic research, not a replacement. Safaris reveal issues that inform later research questions. If a service safari is the only research used, it will be biased and unreliable.
Keep an open and critical mind. An open mind is essential for stakeholders conducting service safaris of their services. Remain impartial and expect to find issues and disconnects.
Run a trial safari. A practice run can help prepare for the actual safari. A trial benefits those who’ve never done a service safari before. Trials can reveal the need for deeper role-play and better observation recording, among other pitfalls. This process will improve the outcomes of the actual safari.
Ensure privacy and consent. Service design often involves audio and video recordings. Ensure you get permission from the people you record (e.g., other customers standing in line). Secret audio or video recording violates privacy.
Service Safari Pitfalls
While service safaris are beneficial to service design, they do have some common challenges:
Familiarity with the service. It can be challenging for some team members and stakeholders to get into the customer’s mindset as they can anticipate what’s next. For example, a team member may be familiar with a train ticket machine and overlook its lack of user-friendliness because of expert knowledge. To combat this, take advantage of other team members' and customers' lack of experience and knowledge.
Bias and subjectivity. Service safaris involve personal observation and experience. While you can use techniques to limit bias, it is impossible to be completely objective. For this reason, it is vital you conduct further and deeper research with real customers.
Potential disruption. It is difficult for researchers to pretend to be a customer in some settings. For example, a researcher cannot entirely embody a patient in healthcare. Overtly observing or participating in the service as a “fake” customer can disrupt the normal service flow. Disruption can lead to less authentic observations.
Service Safari Deliverables
Service safaris provide insights that can contribute directly or indirectly (through future research) to several service design deliverables. These deliverables assist the design team throughout the service design process. They help the team build and retain empathy, make strategic decisions and maintain a holistic view of the whole service.
Customer journey maps visually represent a user's interactions with a product or service over time. Service safari insights can help researchers identify critical points within the user journey. However, researchers should create user journey maps with insights from real users, not only stakeholders. This detailed understanding allows researchers to pinpoint areas for improvement and innovation accurately.
Frank Spillers explains how journey maps fit into the service design process and how to approach them:
Personas are fictional characters researchers create based on research. They represent users who might use a product or service and help design teams remember who they are designing for. As with journey maps, service safaris should not solely inform personas. A holistic user research approach informs accurate and relatable personas.

Service blueprints chart the entire service process. Blueprints include “frontstage” and “backstage” components of a service. Blueprints also include “moments,” for example, when customers browse a menu or wait for their order.
As with journey maps, safaris can inform design teams when they create their service blueprints. While safaris focus on the customer’s point of view, researchers may observe other service components. They can include these observations in their service blueprints.
David Bill, service researcher at Amazon Web Services, explains the difference between “frontstage” and “backstage” in service design:
Learn More about Service Safaris
Take our course, Service Design: How to Design Integrated Service Experiences , to learn more about service safaris and other service design research methods.
Learn more about service safaris from Frank Spillers on the Experience Dynamics website .
UX and Service Design Agency Clockwork Belgium provides a wealth of great tips and additional considerations for service safaris.
Our Master Class, Going from UX to Service Design , is ideal for those who want to move into the field.
Listen to the Nielsen Norman Group podcast with Thomas Wilson, senior principal service researcher at United Healthcare, for service design and research insights.
Questions about Service Safaris
Researchers conduct service safaris remotely for digital-only services. For example, a researcher may take the following steps on an e-commerce service safari:
Click through from an advert on social media.
Sign up for the mailing list.
Read and review the emails they receive.
Click on a promotional email to purchase an item.
Review the website for purchasing information.
Contact customer service for extra information.
Purchase the product.
Review the order and delivery information emails.
Receive the order.
Experience the packaging, information provided and finally, the product.
Interact with after-sales support (help pages, customer support, etc.)
Researchers may conduct multiple safaris since digital services include many potential customer journeys .
Researchers must also consider the following adaptations for remote service safaris:
Note taking. Screenshots and screen recordings replace or accompany photos and videos.
Customer environment. Consider different situations in which customers use the service. Examples include at home, while commuting, on mobile, on desktop, etc.
Customer interaction. Forums and chatrooms can replace in-person interactions to get customer perspectives.
Photography and videography are crucial in service safaris because they capture what happens in real time. Photos and videos help researchers:
Capture interactions with the environment, including subtle moments that might go unnoticed.
Gain a comprehensive view of the entire service journey.
Spot problems , chances for new ideas and areas that need better solutions.
Create empathy for the whole design team, even those who weren't there in person.
Serve as references for creating customer journey maps and facilitating future ideation.
Researchers do not need to be expert photographers and videographers to capture valuable information. Similarly, professional equipment is not required. Most smartphone cameras or consumer equipment are enough for service safaris.
Ann Blandford, professor of human-computer interaction, covers the pros and cons of different research collection methods in this video:
Researchers use these methods to note their interactions and observations during service safaris:
Observational notes. Researchers keep written notes, either with digital devices or pen and paper. Notes should be understandable yet brief. This approach ensures you do not interrupt the immersion required in a service safari.
Photography and videography. Researchers use photos and videos to capture moments and details that are hard to express in words. These visuals can show the setting and interactions, providing a detailed context for analysis.
Audio recordings. Researchers record conversations and background sounds. These recordings offer insights into the service atmosphere and customer feedback. They are also helpful for accurately quoting users later on.
Sketches and diagrams. Researchers sketch the layout of service areas, user paths and interaction points. These drawings help illustrate the arrangement and relationships within service experiences.
Sticky notes and flashcards. Researchers use these to easily document thoughts, observations and insights. They are handy for sorting and prioritizing touchpoints and interactions during analysis.
Each method offers a different perspective on the service experience. Often, researchers combine these techniques to provide a complete view of the service safari. Remember, you must have permission from anyone you record or photograph.
Mike Rohde, researcher, teacher and illustrator, explains sketchnotes and how they can be useful to researchers:
Learn more from Mike in his Master Class, How to Become a Visual Thinker With Sketchnoting .
Researchers use a clear and structured method to share findings from a service safari effectively. An example process is:
Summary. Begin with a short overview. Highlight the main findings and their possible effects on the service design. Summaries let stakeholders quickly understand the research's core.
User journey maps. Show the user's journey with maps. These maps should cover interactions, key points, challenges and joyous moments. Develop these maps as you conduct further research with real customers. Maps make it easier to communicate user flow problems and areas for improvement.
Storytelling with visuals. Use photos and videos from your safari to share engaging stories about interactions and service settings. This method helps stakeholders feel more connected to what you found.
Data and insights. Support your findings with data where possible. Use quotes, numbers and analysis from the safari or other research to support the need for improvement.
Recommendations. State clear, actionable suggestions for innovation. Rank these by impact and how easy they are to implement.
Interactive session. Run a session where stakeholders can directly interact with your findings. For example, include a role-play session of certain service elements to show their positives and negatives.
Q&A time. Set aside time for questions and discussions. Q&As encourage stakeholders to get involved and offer a chance to gain insights and different viewpoints.
Storytelling plays an important role in effective communication. Learn from Ellen Lupton, writer, researcher, curator and educator, the role of paths and journeys in storytelling:
Learn more from Ellen in her Master Class, Storytelling Through Visual Design: A Practical Guide .
Unsuccessful service safaris are valuable learning experiences. Researchers use them to refine research processes and improve future design outcomes. Researchers learn from unsuccessful safaris in the following ways:
Reflect on objectives and outcomes. Begin by comparing the safari's objectives against the outcomes. Identify where they separated to reveal differences to your expectations.
Analyze the methodology. Review the research methodology to identify any weaknesses or biases that may have influenced the results. Consider whether different methods or tools might have yielded more insightful data.
Review data collection tools. Examine the effectiveness of the data collection tools and techniques used. Inadequate tools can hinder the capture of relevant data, pointing to areas for improvement.
Consider external factors. Reflect on external factors that could have affected the safari, like timing or unforeseen events. Understanding these influences can help plan more resilient future safaris.
Solicit feedback. Gather feedback from team members to gain diverse perspectives on what didn’t work and why. This feedback is crucial to identify blind spots and areas for growth.
Document lessons learned. Compile the insights gained from this reflection into a lessons-learned document. Use this document to refine future service safaris and avoid similar pitfalls.
Share findings with the team. Share the lessons learned with your team and stakeholders. Discuss what went wrong and how to improve to create a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Plan for flexibility. Recognize the importance of flexibility in research design. Incorporate contingency plans and be open to adapting the approach mid-safari to mitigate risks of failure.
Stay curious and resilient. Embrace a mindset of curiosity and resilience. Failures are stepping stones toward more effective and impactful design research.
Don Norman, emeritus professor of psychology, cognitive science and computer science, explains the importance of failure:
Researchers tailor the research focus, methodologies and participant engagement strategies for different industries. They do this in the following ways:
Customize research objectives. Define clear, industry-specific objectives. What works for a retail service safari might differ for a healthcare safari. For example, retail focuses on customer engagement and space layout. Healthcare prioritizes patient care and privacy.
Select relevant touchpoints. Identify industry-specific touchpoints and interactions critical to the service experience. For instance, digital interaction points in banking may be more relevant than in hospitality. In hospitality, personal service touchpoints are more important.
Adapt data collection methods. Use data collection methods suited to the context and goals of the industry. For example, indirect observation might be more appropriate than direct observation. Adaptability is critical in highly confidential environments like healthcare or legal services.
Incorporate expert insights . Researchers can involve industry experts or insiders in the safari. Experts help researchers understand the service context more profoundly.
Tailor reporting and analysis. Customize the analysis and reporting of findings to address the industry's strategic priorities. Highlight critical insights that can lead to competitive advantages.
Focus on sector-specific outcomes. Aim for outcomes that resonate with the industry's specific goals. Outcomes could be to streamline operations, enhance accessibility, or innovate service delivery.
Iterate and innovate. Be open to iterating the safari approach based on feedback and findings. Iteration allows for adaptations that could lead to better discoveries and deeper knowledge.
Researchers create or learn from business model canvases in new services or industries. Frank Spillers explains what business model canvases are and how to create them:
Service safaris stand out from other UX/UI design research methods because of their immersive, observational nature. This approach gives researchers deep insights into user interactions and service delivery processes. Key aspects that differentiate service safaris include:
Immersive observation. Methods like surveys and interviews rely on self-reported data. Conversely, service safaris allow researchers to witness firsthand how customers interact with services. Safaris capture nuances and behaviors other methods might not reveal.
Real-world context. Researchers conduct service safaris in the actual locations where services are delivered. This approach offers an unfiltered view of user experiences and environmental influences. Compare this to a method like usability testing. Usability testing often occurs in controlled environments and may not fully capture the use context.
Holistic service perspective. Service safaris give researchers a holistic view of the service ecosystem. This view includes touchpoints, interactions and the service environment. A broad perspective is essential for understanding complex service experiences. Meanwhile, methods like task analysis only focus on specific elements.
Empathy building. Researchers develop a more profound empathy for users as they engage directly with the service environment. This immersive experience can inspire innovative solutions grounded in real user needs. This approach contrasts with data-driven methods that might overlook a design's emotional aspects.
Service safaris can enhance the design process when combined with other research approaches. This comprehensive approach leads to more user-centered and effective service designs. Kendra Shimmell, vice president of design at Remitly, explains the importance of combining user and industry research in service design:
Researchers value observations that capture the entire customer experience and service delivery. Types of observations that are particularly insightful include:
User behaviors . Note both your actions and those of other customers. Pay attention to habits, routines and any workarounds users develop to cope with service shortcomings.
Emotional responses. Search for emotional cues that show satisfaction, frustration, confusion, or delight. Emotional responses can reveal unmet needs and areas for emotional engagement within the service.
Service touchpoints. Identify and assess all points of interaction between the customer and the service. Touchpoints include digital interfaces, physical spaces and human interactions. Understand these touchpoints to help pinpoint areas for improvement.
Pain points. Identify any difficulties or obstacles, including access barriers and usability issues you face. These insights are beneficial for future research.
Moments of delight. Record instances where the service exceeds customer expectations or provides pleasant surprises. These moments present opportunities to build upon.
User interactions. Pay attention to how customers interact with each other within the service context. Social dynamics can offer insights into user needs, behaviors and the service’s role in facilitating community.
Operational efficiencies. Note the effectiveness of the service’s operations. Observations include workflow, speed and quality of service delivery.
Comparative observations. If applicable, compare different service settings and times of day. This approach helps identify variability in the service experience. These comparisons can uncover opportunities for customization or targeted improvements.
Innovative uses. Look out for innovative or unintended ways users engage with the service. These observations can inspire new features or services.
Collectively, these observations provide a comprehensive view of the service experience. They highlight both strengths and areas for improvement. Document and analyze these insights to drive significant enhancements in service design.
To measure the effectiveness of a service safari, researchers evaluate the quality and impact of the insights gathered. Key ways researchers assess a safari’s effectiveness include:
Insight quality. Evaluate the depth, relevance and novelty of the insights obtained. When researchers conduct effective safaris, they uncover actionable insights. Insights reveal underlying user needs, pain points and opportunities for innovation.
Coverage of objectives. Measure how well the safari met its predefined objectives. Check if the safari sufficiently covered the service and customer experience and filled all knowledge gaps.
Follow-up research engagement. Check how well the safari has revealed new paths for research or found new questions to explore. An effective safari allows researchers to uncover questions and opportunities for deeper investigation.
Stakeholder feedback. Researchers gather feedback from stakeholders on how they presented the findings. Positive feedback indicates effectiveness, particularly about the insights' usefulness and presentation clarity.
Implementation rate. Track the number of insights translated into design improvements or strategic decisions. A high implementation rate shows researchers provided findings that were actionable and valued.
Impact on the design process. Evaluate how the safari influences the design process. Observe new team perspectives, empathy levels and new design practices or methodologies.
Design teams should evaluate these aspects step by step. This process helps them check how well their service safaris work and continue the improvement of their research methods.
One of the most important outcomes of a service safari is increased empathy with the customer. Learn how empathy affects good and bad design in this video:
Literature on Service Safaris
Here’s the entire UX literature on Service Safaris by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Service Safaris
Take a deep dive into Service Safaris with our course Service Design: How to Design Integrated Service Experiences .
Services are everywhere! When you get a new passport, order a pizza or make a reservation on AirBnB, you're engaging with services. How those services are designed is crucial to whether they provide a pleasant experience or an exasperating one. The experience of a service is essential to its success or failure no matter if your goal is to gain and retain customers for your app or to design an efficient waiting system for a doctor’s office.
In a service design process, you use an in-depth understanding of the business and its customers to ensure that all the touchpoints of your service are perfect and, just as importantly, that your organization can deliver a great service experience every time . It’s not just about designing the customer interactions; you also need to design the entire ecosystem surrounding those interactions.
In this course, you’ll learn how to go through a robust service design process and which methods to use at each step along the way. You’ll also learn how to create a service design culture in your organization and set up a service design team . We’ll provide you with lots of case studies to learn from as well as interviews with top designers in the field. For each practical method, you’ll get downloadable templates that guide you on how to use the methods in your own work.
This course contains a series of practical exercises that build on one another to create a complete service design project . The exercises are optional, but you’ll get invaluable hands-on experience with the methods you encounter in this course if you complete them, because they will teach you to take your first steps as a service designer. What’s equally important is that you can use your work as a case study for your portfolio to showcase your abilities to future employers! A portfolio is essential if you want to step into or move ahead in a career in service design.
Your primary instructor in the course is Frank Spillers . Frank is CXO of award-winning design agency Experience Dynamics and a service design expert who has consulted with companies all over the world. Much of the written learning material also comes from John Zimmerman and Jodi Forlizzi , both Professors in Human-Computer Interaction at Carnegie Mellon University and highly influential in establishing design research as we know it today.
You’ll earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you complete the course. You can highlight it on your resume, CV, LinkedIn profile or on your website.
All open-source articles on Service Safaris
Customer journey maps — walking a mile in your customer’s shoes.
- 1.1k shares
Service Design - Design is Not Just for Products

Understand the Service Design Process
- 2 years ago
Learn the Language of Service Design
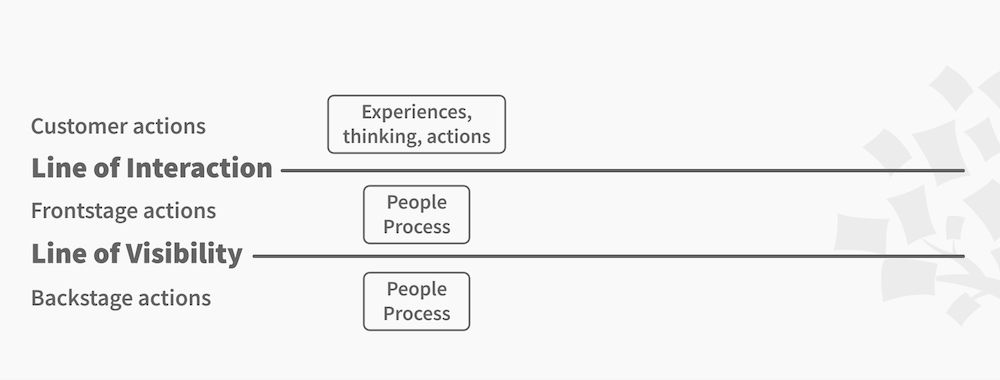
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Create a Customer Journey Map Plan to Prepare for Analysis and Design Phase
- Information Systems

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams. Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is a convenient way for cross-functional teams to provide feedback. Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team, so they always keep the customer top of mind.
Here's our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days: Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work. Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop. Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results.
Make customer journey mapping fun with a collaborative editor that your teams and multiple stakeholders can jump into anytime, anywhere. Canva Whiteboards lets you run workshops when you need to analyze your resources, build a customer persona, and map your customer journey. You can also use a template to start your journey mapping.
Customer journey maps are often visual representations showing you the customer's journey from beginning to end. They include all the touchpoints along the way. There are often four main stages in your sales funnel, and knowing these can help you create your customer journey maps: Inquiry or awareness.
Simply choose the touchpoints which accurately reflect a customer's journey with your brand. After you define your touchpoints, you can then start arranging them on your customer journey map. 4. Map the current state. Create what you believe is your as-is state of the customer journey, the current customer experience.
So, with that in mind, let's look at two ways that your journey maps can evolve…. 1. Adding Voice of the Customer insights to journey maps. The integration of Voice of the Customer (VoC) data into journey maps marks the first significant evolution in the approach to understanding customer experiences.
A customer journey map (also called a user journey map) shows your customer's experiences with your brand and company across all its touchpoints. In a customer journey map, interactions are placed in a timeline to map out the user flow. To sum it up, customer journey maps represent the journey a customer will experience.
Present the CJM's purpose & goals. Now it's time to kick off the customer journey map exercise. Start by speaking to the purpose and goals you've identified for the map. It's important to make sure your team understands what you're trying to accomplish, or else you run the risk of the session getting off track.
It's simple, professional and to-the-point, and covers all the basic elements that need to go into a journey map. 2. Gaming Customer Journey Map Template. This gaming customer journey map template is created with recreational mobile apps in mind, but you can use it for any tech, SaaS or other industry.
Identifying touchpoints is one of the most crucial steps when creating a customer journey map. Customer touchpoints represent any interaction that a customer has with your business and they can occur on any type of channel. For instance, customers may interact with: Your website. Your online store.
1. Review Goals. Consider organizational goals for the product or service at large, and specific goals for a customer journey mapping initiative. 2. Gather Research. Review all relevant user research, which includes both qualitative and quantitative findings to provide insights into the customer experience.
Customer journey maps can help teams create and manage customer-centric strategies. Benefits and challenges of customer journey mapping. Creating a customer journey map can provide businesses with invaluable insights into their customers' experiences, while also presenting some challenges in terms of gathering customer data and creating a ...
A customer journey map is a visual tool that helps you define your customers' needs, problems and engagement with your brand. Learn how to create a customer journey map, what elements to include, and how to validate it with your customers.
How to create a customer journey map (step-by-step) Here's how to create a user journey map in 6 steps: Choose a user journey map template (or create your own) Define your persona and scenario. Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions. Fill in the user's thoughts, emotions, and pain-points. Identify opportunities.
Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank. This free template is an example of a multi-persona, B2B customer journey. The key persona is a newly opened company looking for a bank to run their business. The CJM also visualizes interactions between the personas involved. Open a full-size image in a new tab.
Then, arrange each touchpoint sequentially so you can see the big picture. 4. Design a Visual Representation of the Customer Journey. After defining business goals, identifying key stages in the customer journey, and defining customer touchpoints, it's time to actually create your customer journey map.
Customer Journey Map: Understanding the Basics. How to Create a Customer Journey Map in 7 Steps: Determine Target Personas. Define Your Customer Touchpoints, Actions, and Reactions. Break Out Touchpoints and Actions Into Phases. Test the Customer Journey Map. Complete the Customer Journey Map with Persona Data.
3. Gather Relevant Data and Information. Data is the lifeblood of customer journey mapping. To create a comprehensive map, you need to gather as much relevant data as possible. Sources of data may include: Customer Surveys: Collect customer feedback to understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations.
Customer journey mapping can be modified to fit a specific need and help you better understand your customers' journey. Below are some types of customer journey maps and the customer journey map examples: Buyer's journey. The buyer's journey maps visualize the customer's journey from recognizing a need to making a purchase.
Using a flowchart, you can show the different stages of the customer journey and touchpoints at each stage. #4. Pinpoint The Key Touchpoints. The objective of this stage is to identify the crucial customer touchpoints, such as the first interaction, the decision-making process, and the post-purchase experience.
Create a Venngage account using your email, Gmail or Facebook account. 2. Browse our professional customer journey mind map examples. Choose a template that has the right look and feel for your needs. 3. Edit the text and add in your own images into the template. 4.
Structure of a customer journey map. Keep it simple - you'll have a header section that contains who the customer is and what their goal is. From there down, it's a big grid. Moving left to right is simply the passage of time, usually broken into phases - think of each stage for your customers as they move from awareness to advocacy.
The user journey is always evolving, and your user journey maps should too. Customer journey map examples. Because journey maps are a visual tool, seeing them in action helps cement how to make them and also just how beneficial they are. Here are three great examples of them in action. Spotify's sharing feature journey map
Step 1: Define customer touchpoints. Identify all customer interactions, from ads to website visits, forming the core of your user journey map, illustrating the path from awareness to purchase and beyond. Step 2: Create customer buyer personas. Develop fictional representations of your target audience, considering demographics and behaviors.
Learn how to create different types of journey maps, including service blueprints and experience maps in the course "Journey Mapping". User experience strategist, Paul Boag gives an overview of customer journey mapping in this article. Here is a checklist of everything you need to get started with customer journey mapping.
Case Study: Create a Customer Journey Map Plan to Prepare for Analysis and Design Phase RenewAgra is a large multi-national crop company focusing on growing cereals (primarily corn and wheat) and sugar (both sugar cane and sugar beets). RenewAgra consists of three businesses operating in the US, Brazil, Mexico, Germany, and India. Its first business, CropCo, is a crop services business that ...
Jan 01, 2010 — 4 min read. Sep 13, 2012 — 4 min read. Using automation and technology to grow Leveraging merchandise to create a unique customer experience Preparing to open location number 6. Mapping Broad Street Oyster Co.'s Journey From Pop-up Shop to Storefront Number 6. Copy.