Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
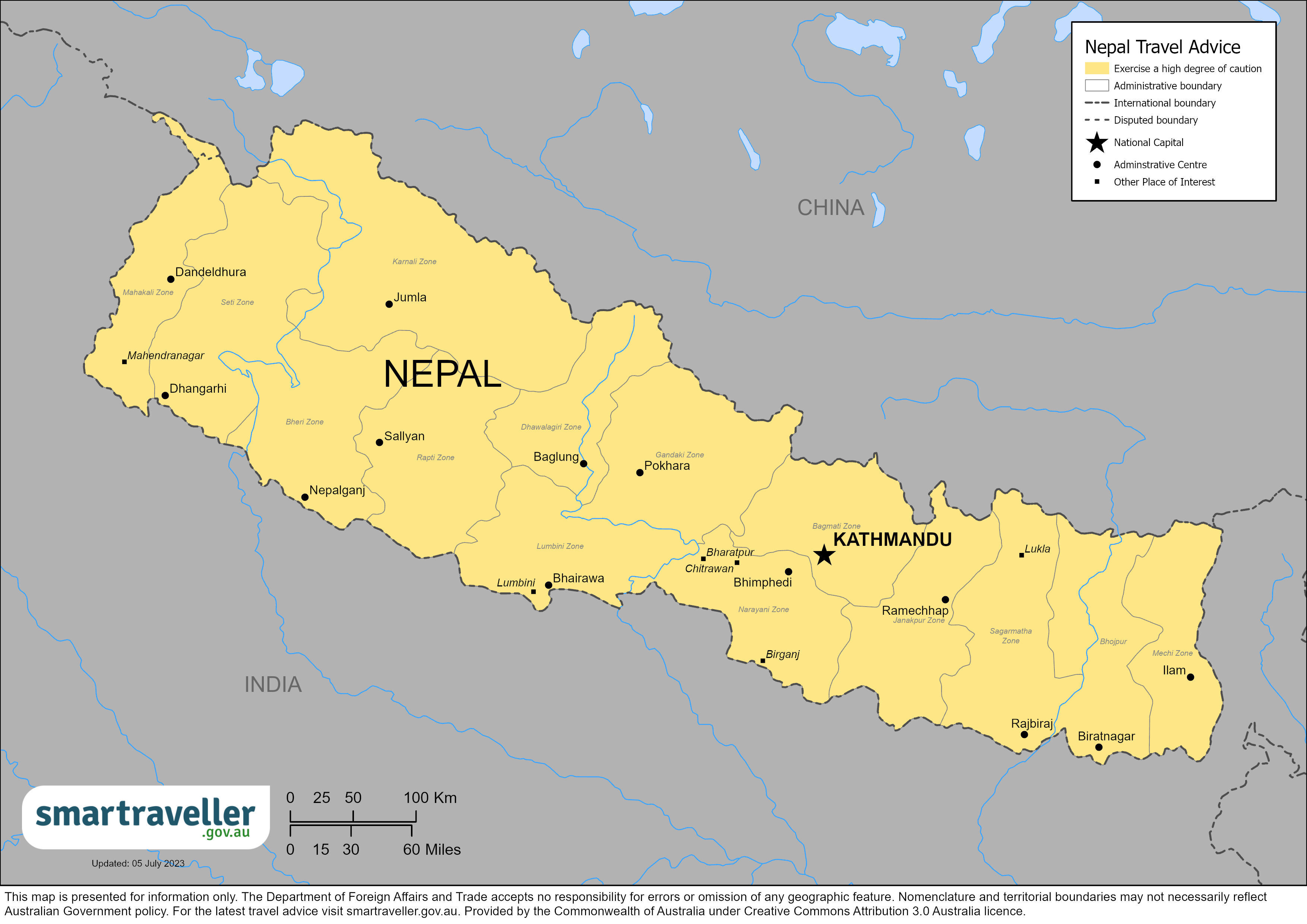
Nepal travel advice
Latest updates: The Need help? section was updated.
Last updated: April 5, 2024 07:23 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, nepal - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Nepal due to the fragile political and security situation.
Back to top
Petty theft is common, particularly near tourist sites, on buses and in hotel rooms.
Take particular care when walking around Kupandol, Sanepa and Thamel, popular tourist spots in Kathmandu, where pickpocketing is common.
- Do not leave personal belongings unattended. Armed robberies, particularly of solo trekkers, occur occasionally
- Exercise caution in and around Kathmandu and other cities
- Do not travel after dark
Festival season
There is a significant increase in crime, including thefts, purse and bag snatchings, pickpocketing and break-ins, during the festival season, which extends from September to November. Maintain a high level of personal security awareness and ensure that your personal belongings and your passports are secure.
Women’s safety
Women are vulnerable to harassment and verbal abuse. Dress conservatively, particularly in remote areas.
Female tourists travelling alone are more at risk of violent attacks.
Advice for women travellers
Political tensions
While Nepal continues its transition to a stable democracy, the political situation remains fragile and tensions can increase with little notice.
Acts of violence
Small-scale, politically-motivated attacks occasionally occur, especially in Kathmandu. Past attacks have led to injuries and sometimes caused deaths. Foreigners have not been targeted. Further attacks are likely.
Demonstrations
Political protests are common in Nepal and sometimes result in violence. Transport and public services may be disrupted at short notice.
Politically motivated protests have been particularly volatile in Kathmandu as well as in Nepal’s southern region bordering India, which has at times resulted in supply shortages and affected border crossings.
Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
General strikes (locally referred to as bandhs) are a popular form of political expression and can occur on short notice throughout the country. Such strike action can affect access to services. While bandhs are usually peaceful, riots and violence are possible. During a bandh, businesses and roads may close and transportation services may be unavailable or severely disrupted.
Avoid travelling on public transportation during or immediately preceding bandhs, as tourists have been injured. Transportation to and from airports throughout Nepal could be affected. Army and police checkpoints are frequent, especially at night.
Follow the advice of local authorities and respect curfews and roadblocks.
Trekking and mountain climbing
Many popular trekking trails ascend higher than 5,500 metres.
A number of hikers and guides have been stranded, injured or killed while trekking. You may experience acute mountain sickness at high altitudes and should be well informed on possible hazards in the high mountains.
Drops in temperature and changes in weather conditions, including blizzards and avalanches can occur suddenly in mountainous regions at any time of year.
If you intend to trek:
- never do so alone and always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you're properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back to camp
- know the symptoms of acute altitude sickness, which can be fatal
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes or ski slopes before setting out and do not venture off marked trails or slopes
Emergency services such as evacuations and rescues from remote areas are available but can be hindered by:
- the lack of immediate payment to helicopter rescue services
- a positive response from clients of their insurance companies
- limited access to regular phone service in many trekking areas
There have been helicopter rescue scams in the past. Ensure that you are dealing with reputable helicopter companies. Check with your trekking agency for updates on the security situation in the area.
Trekkers’ Information Management System
All trekkers must purchase a trekkers’ information management system (TIMS) card from one of the following entities:
- the Trekking Agencies’ Association of Nepal
- the Nepal Tourism Board
- an authorized trekking company
National park permit
You must obtain a national park entry permit before entering official trekking regions or routes such as those in the Annapurna, Everest and Langtang regions.
Permits may be obtained from the national tourism board after arrival in Kathmandu or Pokhara.
More about trekking permits - Trekking Agencies’ Association of Nepal
Organize white-water rafting excursions through reputable agencies only.
Due to an energy shortage, electric power cuts, termed “load shedding,” are a year-round occurrence. They occur frequently for short periods and without advance notice.
Public transportation
Most public buses are often poorly maintained and accidents involving buses, often causing injuries and fatalities, are common.
Avoid travelling on overnight buses.
Tourist buses are generally safe.
Boat accidents are common due to the overloading and poor maintenance of vessels. Do not board vessels that appear overloaded or unfit, especially where there are strong currents.
Road safety
Exercise caution when travelling by road as road conditions and driving standards are poor and traffic laws are not enforced.
Drivers often drive at excessive speed and often do not yield right-of-way to pedestrians.
Many mountain and hill roads, which can be hazardous even in the best weather, are intermittently impassable during the monsoon season due to landslides.
Traffic is congested in the Kathmandu Valley.
Landmines and unexploded ordnance constitute a risk in parts of the country, including in some trekking areas. Follow the advice of local authorities, and only travel on well-used roads and paths.
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Nepalese authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Nepal.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required (only issued in Nepal) Student visa: required
You can purchase a tourist visa, valid for up to 60 days, at:
- a Nepalese embassy or consulate
- the Tribhuvan International Airport in Kathmandu
- some border crossings, upon arrival
You will need to supply a recent passport-size photo. Ensure that you have the necessary amount of funds (Canadian and U.S. dollars are accepted) with you if you wish to obtain a visa upon arrival. Check with the closest Nepalese embassy or consulate for the latest visa fees.
Tourist Visa - Department of Immigration, Government of Nepal
Visa overstays
Overstaying your visa is an offence and immigration authorities can detain you until you pay a fine. In addition to fines and detention, overstays can result in a 7-year ban on re-entry.
Travel to Tibet
If you intend to travel to Tibet from Nepal, contact the Chinese embassy in Kathmandu for current entry regulations.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Travellers going to countries in South Asia should speak to a health care professional about getting vaccinated.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
Outside the Kathmandu Valley and Pokhara, medical services and facilities do not meet standards you might expect in Canada.
Most hospitals require up-front payment or confirmation of insurance coverage prior to commencing treatment. Following an incident or accident, you should contact your travel insurance company without delay.
Trekkers may experience frostbite and acute mountain sickness (AMS) at high altitudes. AMS can be deadly. Medical evacuation to Bangkok, Thailand, New Delhi, India, or Singapore is often necessary for serious conditions. Carry medical and first aid kits.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect jail sentences, including life imprisonment, and heavy fines.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Photography
Photography of military installations and personnel is prohibited.
You may not bring any kind of firearm into Nepal. Violators who bring in firearms or ammunition may be prosecuted. This includes firearm imitations or in jewellery form.
Traffic drives on the left.
There is zero tolerance for driving under the influence of alcohol.
Helmets are mandatory for motorcycle drivers.
You must carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
Dress and behaviour
Women should dress conservatively in public.
Public displays of affection are considered to be inappropriate at many of Nepal’s religious sites.
Commercial surrogacy
Commercial surrogacy services for foreigners is banned in Nepal. If you have already entered into such an arrangement, you should seek advice from a local lawyer on how this ban could affect your situation and, in particular, on any exit requirement.
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Nepal.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Nepal, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Nepal.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Nepal by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Nepal to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
The currency is the Nepalese rupee (NPR).
The economy is largely cash-based; however, credit cards can be used in major stores, hotels and restaurants. ATMs are available in larger cities such as Kathmandu and Pokhara.
It is illegal to take NPR banknotes out of the country.
Any amount over US$5,000 in cash (or equivalent in foreign currencies) must be declared at customs upon arrival in Nepal.
Earthquakes
Nepal is located in an active seismic zone and there is a continued risk of earthquakes, aftershocks and landslides.
Become familiar with local earthquake safety procedures. In the event of an earthquake, exercise caution, follow the advice of local authorities and monitor local media.
Monsoon season
The rainy (or monsoon) season extends from June to September. Severe rainstorms can cause flooding and landslides, resulting in significant loss of life and extensive damage to infrastructure, and hampering the provision of essential services.
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
In mountainous regions, avalanches present a risk and have resulted in fatalities. Monitor local media and weather forecasts and follow the advice of local authorities.
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 100
- tourist police: + 977 1 424 7041
- medical assistance: 102
- firefighters: 101
General assistance
- Tourist Police in Kathmandu: 1144 (hotline)
- Tourist Police in Pokhara: +977 61 462761
- Thamel Tourism Development Council: +977 1 4700750
More about the Tourist Police
Consular assistance
Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh, Chhattisgarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Delhi, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Pondicherry, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
For emergency consular assistance, call the Consulate of Canada in Nepal and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Attractions
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites
- Protected Areas
- Eight Thousanders
- Pilgrimage Sites
- Bungee Jumping
- Motor Biking
- Rafting & Kayaking
- Mountain Biking
- Paragliding
- Cave Exploration
- Bird Watching
- Mountain Viewing
- Jungle Discovery
- Butterfly Watching
- Nagarkot Sunrise and Sunset
- Traditional Crafts
- Meet the People
- Village Tours
- Food & Culinary
- Cultural Tours
- Heritage Walk
- Museum Tours
- Faith Healing
- Panchakarma Treatment
- Sound Meditation
- Natural Hot Water Springs in Nepal
- Pilgrimage Tours
- Destination Wedding
- Indra Jatra
- Chhat Parva
- Event Calendar
- Festival Highlights
- Travel with children
- Ganesh Himal Trek
- Chandragiri - Chitlang - Kulekhani
- Pilgrimage to Doleshwar mahadev Temple
About Nepal
Travel details.
- Tourist Visa
- Local Transportation
- Trekking Permit
- Park Entry Fees
- Heritage Site Entry Fees
- Tourist Police
- Safety in the Mountains
Book Your Trip
- Book Experience
- Travel Updates
Latest Travel Updates
Updates about latest rules and standard protocol for traveling and trekking in Nepal.
New Provision for Trekking in Nepal

FAQs about the new provision
The new rule will come into effect from April 1st, 2023. The trekkers who get the permits and start the trek before April 1st will not require a guide. But they'll need to have entered the trekking area before April 1st.
All the treks need to comply with the new rule. You can contact a trekking agency in Nepal for the guide to accompany you in mountain bikes.
Trekking Agencies in Nepal
What if I an experienced trekker and associated to a trekking/mountaineering association in home country?
The rule is applicable for all the foreign national trekkers.
Is this rule also applicable when I hike around Kathmandu? Or to Sarangkot? Where all are these rules applicable?
The Revised Provision for Trekking in Nepal must be followed only while trekking to areas where TIMS is applicable. It is applicable in all national park areas in the mountains. It is not applicable in Kathmandu Valley outskirts, Pokhara outskirts, and hiking areas in and around major cities.
Do I have to go via a trekking agency? Or is it OK so long as I have a guide?
It is mandatory to hire a licensed trekking guide through a government-registered trekking agency.
How can I find that out if the trekking agency is legit?
Trekking guide must be hired through government-registered trekking agency. You can verify information on the trekking agency from Department of Tourism and Trekking Agencies Association of Nepal .
What are the consequences if I do not follow this rule?
Not following the rule is a punishable offense.
I am a trail runner and fast packer, no agency specifically provided guides that can keep up with me. What should I do?
It is applicable to all. You must ascertain that the trekking agency can provide guide who matches your specific requirement.
I am an expat living in Nepal. Does this rule also apply to me?
Yes, the rule is applicable to Diplomats as well as Expats.
I am Nepali. Does this rule apply to me?
The rule is not applicable to Nepali citizens.
What if I go on a motorcycle ride to Muktinath?
The rule does not apply to motorcycle ride or the bus ride to Muktinath. TIMS and Annapurna area permit are required.
What are the areas requiring TIMS and permits?
Covid 19 Related Information
Useful links.
- Trekking Agencies Association of Nepal (TAAN)
- Nepal Mountaineering Association
- COVID-19 Crisis Management Center
- Ministry of Culture, Tourism and Civil Aviation
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Department of Immigration
- Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal
- Nepal Airline Corporation
- Diplomatic Missions in Kathmandu
Just in Case
NTB Crisis Cell: [email protected]
COVID Hotline: 9851255839,9851255837,9851255834
Tourist Police: 1144/014247041
Sukraraj Hospital, Ktm: 014253396
Gandaki Hospital, Pkr: 061520067

Nepal Tourism Board is a national tourism organization of Nepal established in 1998 by an Act of Parliament in the form of partnership between the Government of Nepal and private sector tourism industry to develop and market Nepal as an attractive tourist destination. The Board provides platform for vision-drawn leadership for Nepal’s tourism sector by integrating Government commitment with the dynamism of private sector.
Nepal Tourism Board
Other sites.
- Tenders & Trade
- Photo Nepal
Feedback Form

- Go to Travel Advice
Nepal Travel Restrictions COVID-19
Useful info? Why not share it;
Covid-19 Update and restrictions for Nepal
Last updated 15/03/2022, are tourists allowed to enter nepal yet do i need a vaccine what restrictions are in place.
The good news is that Nepal is now officially open for tourism once again!
– On-arrival visas are back
– Quarantine is no longer required
– Nepal is considered safe and has been removed from the majority of no-travel lists
– Both vaccinated and unvaccinated travelers can enter Nepal without quarantine, if they produce proof of vaccination or a negative PCR test (taken within 72 hours before arrival)
– Conditions apply, please read on for full details
Information courtesy of covidcontrols.co

Nepal travel restrictions COVID-19
Nepal hasn’t had an easy time with Covid-19 over the past couple of years, but today the picture is much more optimistic. Infection rates have declined dramatically and most of the population is now fully vaccinated. There is no lockdown in place and life is largely back to normal.
Are tourists allowed back to Nepal?
YES!!!! Tourists have been restricted by changes to entry requirements and quarantine rules since April 2021, but as of 23rd September 2022, the Government of Nepal have announced that on-arrival visas are now open to foreign travellers once again.
Vaccine Requirements
Nepal is open to both vaccinated and unvaccinated travelers. Proof of double vaccination (or equivalent) must be shown at immigration and jabs shouldn’t have been completed less that 14 days before entry.
Unvaccinated travelers must provide proof of a negative PCR coronavirus test taken no more than 72 hours before travel (Gene Expert or True NAAT tests also accepted). Rapid antigen tests may also be required at immigration.
All travelers, regardless of vaccination status, must have travel insurance covering health, crisis or rescue for the duration of the trip and proof of accommodation in Nepal.
(For departure, a PCR test is only necessary if your airline or destination country requires it.)
Tourist Entry: Allowed Testing: Negative PCR test results required unvaccinated travelers from all countries, taken no more than 72hrs before travel. Rapid antigen tests may also be required at the airport or once you reach your hotel. Quarantine Required: None Quarantine Details: N/A
CCMC form to travel Nepal
Since COVID-19 restrictions came into place in Nepal, this form has been required for entry. Discussions are underway to officially remove this requirement, with an announcement due shortly.
Local Restrictions
Lockdown in Effect: No lockdown Events: Partially Allowed Transport: Operational Shopping: Open Restaurants and Bars: Open with some minor restrictions
Facemasks are still recommended or required at some shops, venues and tourist attractions.
Official links
- Ministry of Culture Tourism & Civil Aviation: www.moctca.gov.np
- Nepal Tourism Board (NTB): www.welcomenepal.com
- Department of Immigration: www.immigration.gov.np
- Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal: https://caanepal.gov.np/
- For the latest information on COVID-19 vaccination data, you can visit: https://covid19.mohp.gov.np/
Regional news
Everest / Khumbu region
Manang district
Information correct at the time of writing, but please check official sources before making your travel plans.
Usual entry requirements still apply in addition the Covid-19 measures. For more information, please see our Nepal Visa and Arrivals page.
more super-useful Travel advice....

Nepal Weather

Nepal transport and getting around

Things to do in Nepal without trekking

Nepali Culture, Language and Religion
Join the mailing list, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

QUICK LINKS
- Travel Advice
- Stories of Nepal
Connect With Us
© copyright 2021 travel nepal & royal mountain travel. all rights reserved., privacy overview, please fill in the form below with as much information as you can provide, and one of our nepal travel advisors will get back to you within 48 hours.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Nepal due to the risk of civil unrest and natural disasters.
Nepal (PDF 733.49 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 100 or go directly to the hospital.
Call 100 or visit the nearest police station. Alternatively, call the Tourist Police.
Traffic Police
Tourist police.
- 1144 – headquarters
- 470 0750 – Kathmandu
- 146 2761 – Pokhara
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Nepal.
- A small number of incidents involving Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) occur annually, often associated with political events, such as election periods. Physical confrontations between rival political organisations can also occur. In November 2022, there were several small-scale explosions in Nepal.
Terrorism is a threat worldwide. An attack could happen anywhere and at any time.
- Political protests are commonplace and general strikes occasionally occur. Strikes can disrupt essential services. Don't visit government buildings during political unrest. Reconsider the need to operate a vehicle during strikes as it may be a target. Don't participate in public protests as it would breach your visa conditions, and you would be arrested and deported.
- Pickpocketing and petty theft are common. Bag-snatching and 'snatch-and-grab' attacks by thieves on motorbikes occur. Keep your belongings close. Don't travel alone; females are at a higher risk of assault.
- Travellers have been victims of armed robberies and assaults, including sexual assaults. Drink spiking often occurs before a sexual assault. Never accept food, drinks, gum or cigarettes from strangers. Don't leave your food or drinks unattended.
- Nepal experiences earthquakes, landslides, floods and severe weather. Be prepared for a major emergency. Keep an emergency kit that includes first aid supplies and bottled water.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Altitude sickness is a risk above 2,500m. It can be life-threatening. It can affect anyone, even people who are physically fit. Ensure your travel insurance covers medical evacuation from altitude. Some towns, including Kathmandu, have high levels of seasonal smog and pollution. Get medical advice if you have breathing difficulties.
- Malaria is a risk in the Terai (plains) and Hill districts and Chitwan National Park. Consider taking anti-malarial medicine for these areas. Other mosquito-borne diseases are becoming more common, including in Kathmandu. These include dengue and Japanese encephalitis. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof. Get vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis before you travel.
- Rabies is common. It's fatal without immediate treatment. Avoid dogs, monkeys and other mammals. Get medical help straight away if an animal bites or scratches you.
- HIV/AIDS is common. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
- Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are common. These include typhoid, cholera and hepatitis. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- Medical facilities in Nepal are very limited, especially outside Kathmandu. In Kathmandu, treatment at high-standard clinics is expensive. If you're seriously ill or injured, you'll need medical evacuation. Ensure your travel insurance covers this.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. You may be offered illegal drugs in tourist areas. Penalties for drug offences are severe, including for possessing small amounts.
- Be careful when taking photos. It's illegal to photograph army barracks, checkpoints and military personnel.
- Don't participate in public protests as it would breach your visa conditions, and you would be arrested and deported.
- It's illegal to convert people from their religion. Punishment can include jail. If you're suspected of trying to convert people, you will likely be deported and banned from re-entering Nepal.
- Same-sex relations are legal. However, society is conservative. LGBTI travellers have reported harassment and discrimination. Avoid public displays of affection.
- Nepal doesn't recognise dual nationality. Always travel on your Australian passport.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You need a visa to enter Nepal. Visas-on-arrival are available, but travellers should check with the nearest Nepal Embassy for details and conditions.
- You no longer need to complete a pre-departure COVID-19 (PCR) test or show a vaccination certificate on arrival in Nepal.
- Nepal is issuing trekking and mountaineering permits, but you should check with your intended tour provider on operations in the 2023 spring and autumn seasons.
- The local currency is the Nepalese Rupee (NPR). Exchange foreign currency for NPR at banks and exchange bureaus in major centres. Major hotels and commercial centres accept credit cards. ATMs are uncommon in remote areas. Carry enough cash to cover your needs.
- Only use registered taxis and authorised limousines. Taxi drivers often refuse to use meters and overcharge travellers. Negotiate the fare with the driver before you go. Avoid public buses and vans. They're overcrowded and poorly maintained. Intercity buses often have serious accidents. Women may be harassed on public buses.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what we can and can't do to help you overseas.
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Kathmandu .
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Civic unrest and political tension.
A small number of incidents involving Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) occur annually, often associated with political events, such as election periods. These attacks have caused deaths and serious injuries. Physical confrontations between rival political organisations can also occur.
These incidents usually don't target travellers, but you could get caught up in violence aimed at others.
Threats have been made against religious organisations in Nepal. This includes schools.
Demonstrations and protests
Calls for political protests, strikes and demonstrations sometimes are common. Violent clashes between protesters and authorities can occur. Avoid visiting government buildings during political unrest.
During strikes, authorities may enforce curfews at short notice in the areas that protests affect. This happens throughout Nepal.
Illegal roadblocks and enforced national or local strikes can occur. These happen without notice and continue for long periods.
Road travel can be dangerous. Protesters may forcibly stop vehicles, including taxis, or target them with projectiles.
Travel services may also be affected. This includes travel to trekking areas and outside of the Kathmandu valley.
To reduce your risks during strikes:
- limit your movements - don't go out unless you have to
During periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, protests and other public gatherings
- monitor the media for new threats, especially when political tensions are high
- avoid affected areas
- obey curfews
- follow the instructions of local authorities
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Petty crime
Pickpocketing and petty theft are common, especially:
- at tourist sites and airports
- from hotel rooms
Bag-snatching and 'snatch-and-grab' attacks by thieves riding motorcycles occur. Victims are often injured.
Police have increased their presence in Thamel and Durbar Marg to reduce crime in these areas.
To reduce your risk of petty crime:
- only carry a copy of the main pages of your passport, not the original
- walk on footpaths away from the curb, with your bag held on the opposite side to the traffic
- keep your personal belongings close, especially in crowded areas
- avoid travelling alone, especially if you're a woman
- never trek alone
- If you're the victim of fraud or a scam, report it to local police immediately.
Violent crime
Travellers have been victims of armed robberies and assaults, including sexual assaults .
Victims of sexual assault often have their drinks 'spiked' before the assault. This happens in popular areas of Kathmandu and Pokhara.
Women are at particular risk, especially when alone and at night.
To protect yourself from drink spiking:
- never accept food, drinks, gum or cigarettes from strangers
- don't leave drinks unattended
- if you aren't sure if a drink is safe, leave it
- stick with people you trust when you're out
Get urgent medical help if you think you or a companion have had your drinks spiked.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
To stay safe from terrorism:
- be alert to possible threats, especially in public places and places frequented by foreigners
- report any suspicious activity or items to the police
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the advice of local authorities
If there's an attack, leave the area immediately if you can.
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes adventure activities, such as trekking, paragliding, rafting or kayaking.
Paragliding accidents have caused serious injuries and deaths. Rivers can be unpredictable and dangerous, even for experienced kayakers and rafters.
Mountaineering can be dangerous. Some mountaineering expedition companies may hire inexperienced guides and save other costs in order to offer cheaper prices, including to climb Mount Everest. Carefully check a company's credentials and experience before you book.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Trekking and mountaineering
With conditions, foreign tourists are permitted to enter Nepal for mountain trekking and mountaineering. All foreigners require a permit for trekking and mountaineering. Solo foreign trekkers are required to have a licenced trekking guide. Trekking is managed through the Trekkers' Information Management System (TIMS) by:
- Trekking Agency Association of Nepal (TAAN)
- Nepal Tourism Board (NTB)
All foreign trekkers must have a valid TIMS card. This includes those not travelling with organised groups.
TIMS cards help authorities locate trekkers in case there's an emergency.
Get a TIMS card through:
- authorised trekking companies
- TAAN offices in Kathmandu or Pokhara
- the NTB office in Kathmandu
Special regulations apply to mountaineering expeditions. All expedition members must have permits.
Get a licenced trekking guide through authorised trekking companies.
Trekking risks
Some trekking companies or guides may offer condensed treks. This is to attract travellers with limited time or budgets.
Shorter treks may not give you enough time to get used to high altitude. This may cause excessive physical strain and lead to significant health problems or death. See Health .
Make sure you have travel and medical insurance that covers:
- the altitude you'll reach
- altitude sickness
- emergency evacuation by helicopter or other means
See Health
Research regulations that apply to trekking in the area, such as permits or registration. Confirm requirements through:
- reputable companies in Nepal or Australia
- an embassy or consulate of Nepal
Find out how long you need to safely complete your trek, especially at high altitudes.
A trek to Everest Base Camp should take at least 12 days from Lukla. This is the start and end points of treks in the Everest region.
Hire a trekking company with a good reputation and professional guides.
Don't trek alone. Solo foreign trekkers are required to have a licensed trekking guide.
Before you travel, check:
- the security situation
- route conditions
- likely weather in the area
Be ready to change your plans.
For more information on trail conditions, check the Himalayan Rescue Association .
Let family or friends know about your plans. Tell them how long your trek will take and your route.
Medical evacuation
Sometimes trekkers are pressured into taking expensive helicopter evacuations. This can happen at the first mild signs of ill health, without having had a proper medical consultation.
In such cases, insurance companies have declined to pay for the evacuation. The trekker must then pay the cost.
Some people have reported cases of dishonest trekking guides deliberately serving contaminated food or water. The aim was to make travellers sick to justify their evacuation.
Individuals who arrange helicopter evacuations sometimes falsely claim to have checked with a trekker's insurance company.
Some travellers have been encouraged to provide false or misleading information to insurance companies about an evacuation.
If you become ill while trekking, confirm if your insurance covers evacuation costs. Do this yourself, if possible, before you agree to a helicopter evacuation.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications facilities are limited and can be unreliable, especially outside major cities and towns.
Mobile phone coverage doesn't exist in many rural and remote areas.
Essential supplies
Electricity supplies can be unreliable, including in Kathmandu. Unreliability increases during winter and in the lead up to the monsoon season.
Shortages of essential supplies can happen with limited notice. Essential supplies include:
Shortages can affect businesses, including hotels and guesthouses.
Climate and natural disasters
Nepal experiences earthquakes , landslides, floods and severe weather .
Major natural disasters can lead to:
- injuries and deaths
- disruptions to transport and essential services
- damage to infrastructure
- food shortages
- health issues.
Be prepared for a major emergency. Keep an emergency kit that includes:
- first aid supplies
- water treatment tablets or stocks of bottled water.
If a natural disaster occurs:
- keep your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- monitor local media
- keep in touch with friends and family
- avoid unnecessary travel to affected regions.
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Earthquakes
Nepal is in an active earthquake zone. Earthquakes and tremors are common.

Landslides, floods and avalanches
Landslides and floods resulting in deaths occur regularly in Nepal. This happens especially during the monsoon season, from June to September.
Major roads and all trekking areas can be affected.
Avalanches can happen at any time of year.
Severe weather
Storms and blizzards can occur with little or no warning, especially in the Himalayas.
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away.
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need.
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring any medication, check if it's legal in Nepal. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription and a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medicine is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Air pollution.
Air quality in Nepal varies, especially in winter. Some towns, including Kathmandu, experience high levels of seasonal smog and pollution.
Get medical advice if you're worried about air pollution.
- Pollution levels in Kathmandu
Altitude sickness
If you travel to an area higher than 2,500m, you might develop altitude sickness .
Altitude sickness can be deadly. It can affect anyone, even if you're very physically fit.
Your risk of altitude sickness increases if you:
- ascend too quickly
- have had altitude sickness before
- exercise or drink alcohol before you can adjust to the altitude
- have health problems that affect your breathing.
If you'll be travelling above 2,500m, get advice from your doctor before you travel.
Insect-borne illnesses
Malaria is a risk in:
- the Terai (plains) and Hill districts
- Chitwan National Park.
Other insect-borne diseases are becoming more common, including in some areas of Kathmandu. These diseases include:
- Japanese encephalitis
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- get vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis before you leave
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria.
- Infectious diseases
HIV/AIDS is common.
Take precautions if engaging in activities that expose you to the virus.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are common. These include:
- swine flu (influenza A H1N1)
- bird flu (avian influenza)
- leptospirosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
Highly contagious eye problems, such as conjunctivitis , are common after the monsoon season.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
- avoid contact with dogs and other mammals and birds.
Get medical advice if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Animals may carry rabies in Nepal. If a stray dog, monkey or other mammal bites you:
- immediately wash the wound with soap and water
- get urgent medical treatment.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
Medical facilities and ambulances in Nepal are very limited, especially outside Kathmandu.
In Kathmandu, treatment at high-standard clinics is expensive. Up-front payment is usually needed.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you'll need to be evacuated to a place with better facilities. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
In tourist areas, it's common to be offered to buy drugs.
Penalties for drug offences are severe. Even if you're found with small quantities, authorities can convict and jail you.
- Carrying or using drugs
Surrogacy laws
Commercial surrogacy has been illegal since 2015.
- Going overseas for international surrogacy
- Going overseas to adopt a child
It's illegal to take photos or videos of:
- army barracks
- checkpoints
- military personnel.
It's illegal to convert people from their religion. Punishment can include jail.
If authorities suspect you're trying to convert people, you will likely be deported and banned from re-entering Nepal for years.
Same-sex relationships are legal. Nepali LGBTI+ people actively advocate for their rights. However, Nepal is a conservative and traditional society.
Some LGBTI+ travellers have reported harassment and discrimination. Avoid public displays of affection.
- LGBTI travellers
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law
Dual citizenship
Nepal doesn't recognise dual nationality.
If you're a dual citizen, this limits the consular services we can give if you're arrested or detained.
Always travel on your Australian passport .
- Dual nationals
Local customs
Dress codes are relaxed in tourist areas of Kathmandu and Pokhara. Other parts of the country are more conservative.
Dress modestly to avoid offending locals. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
You need a visa to enter Nepal. Visas-on-arrival are available but travellers should check with the nearest Nepal Embassy for details and conditions.
You need a valid visa in your passport to leave Nepal.
Maximum stays
Australians in Nepal may be able to extend their visas. Please consult Nepal's Department of Immigration for updates.
Expired visas
You must have a valid visa in your passport to leave Nepal.
If your visa has expired, extend it at the Department of Immigration before you leave.
If you overstay your visa, authorities can detain you until you pay a fine. The amount of the fine is based on the number of days you overstayed.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
Border measures
You no longer need to complete a pre-departure COVID-19 (PCR) test, show a vaccination certificate or quarantine on arrival in Nepal.
Nepal’s land borders are open to foreign nationals. Follow the Australian Embassy Facebook and Twitter accounts for regular updates.
Contact an embassy or consulate of Nepal for details.
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for six months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than six months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
If you get an emergency passport, you must also transfer your visa to your new passport before leaving Nepal.
To do this, present the following to the Department of Immigration :
- a police report
- two current passport-sized photographs
Passport with 'X' gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTI travellers
The local currency is the Nepalese Rupee (NPR).
Declare all amounts over $US5,000 or equivalent on arrival and departure. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
You can't take more than $NPR5,000 in or out of Nepal.
You can change foreign currency for NPR at banks and exchange bureaus in major centres.
Credit cards are accepted at major hotels and commercial places.
ATMs are not common in remote places. Carry enough cash to cover your needs.
Local travel
Monsoon season.
The monsoon season generally occurs from June to September but can be unpredictable.
Expect travel disruptions and be prepared to change your plans.
Road travel can be dangerous, especially in the low-lying Terai (plains), where the risk of flooding is higher.
Landslides are common in mountainous areas, including the Kathmandu valley.
Airports may close. Air travel disruptions are common.
Monitor Nepal weather information for up-to-date information on conditions. Contact your travel provider about possible disruptions to your travel plans.
Travel from Nepal to India
Nepal’s land borders are open to foreign nationals. For information on the entry requirements for India please refer to the Smartraveller India specific travel advice.
Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of India for up-to-date information.
- Travel advice for India
- Indian Ministry of Home Affairs
Travel from Nepal to Tibet
Generally, only travellers in organised tour groups get visas and permits for the Tibetan region of China.
If you're planning to travel to Tibet:
- check the travel advice for China
- contact an embassy or consulate of the People's Republic of China
If you're in Nepal, contact the Embassy of the People's Republic of China in Kathmandu.
Driving permit
To drive in Nepal, you need both:
- a valid Australian driver's licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Get your IDP before you leave Australia.
Your travel and vehicle insurance could be void if you drive without an IDP.
If you stay for longer than six months, you need a Nepali driver's licence.
The minimum driving age is 18 years.
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Nepal than in Australia.
Driving can be dangerous due to:
- crowded and poorly maintained roads
- poor driving standards
- aggressive drivers who ignore traffic laws.
Road travel is dangerous at night, especially in rural areas.
Landslides and flooding can damage or block rural roads. This is common during the monsoon season from June to September. Towns or areas are often cut off for days at a time.
Landslides and other disruptions can occur on the Mugling-Narayanghat highway, a section of the road between Kathmandu and Chitwan National Park, and the Prithvi Highway, the road between Kathmandu and Pokhara.
Road travel can be disrupted due to:
- demonstrations and strikes
- roadworks and infrastructure projects.
Significant delays on major roads within cities and towns, as well as on highways, are common.
Open drains and uncovered manholes are a risk to pedestrians and cyclists.
Locals often assume foreigners are at fault in car accidents, regardless of the situation. They may demand money. Crowds of onlookers can gather quickly after an accident and may turn hostile.
Car accidents resulting in injuries often lead to confrontations and road closures. Violence against drivers also happens.
If you plan to drive in Nepal:
- learn local traffic laws and practices
- monitor the media for road closures
- always keep your car windows up and doors locked
- avoid travel between cities after dark.
If you're involved in a traffic accident and are worried about your safety:
- stay in your locked vehicle
- phone 103 for the Traffic Police
- wait for the police.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check if your travel insurance policy covers you when using a motorbike, quad bike or similar vehicle.
Always wear a helmet. Helmets bought in Nepal may not meet Australian safety standards.
Only use registered taxis and authorised limousines. Arrange them through your hotel or resort.
Taxi drivers often refuse to use meters and overcharge travellers. Negotiate a fare with the driver before the trip.
Fuel shortages can make it hard to get local taxis and other forms of transport.
Public transport
Travel on public buses and vans is dangerous. These vehicles are overcrowded and poorly maintained.
There are frequent accidents with multiple deaths involving intercity buses.
Accidents involving private hire cars and jeeps travelling between cities regularly occur and can cause injuries or death. If you are concerned, ask your driver to slow down and drive safely.
Women are often harassed, including sexually, on public buses.
- Transport and getting around safely
Check with your airline or tour operator for updates on your flight.
In normal circumstances, cancellations and delays are common, especially during:
- tourist seasons when the airport is crowded
- bad weather (especially throughout the monsoon season).
Check weather conditions before travelling. Bad weather conditions in mountainous and hill regions could further increase the risk to your safety and cause lengthy delays. Airfields such as Lukla's, in the Solukhumbu (Everest) region, are among the most remote and difficult to land on. These airfields are challenging for even the most technically proficient pilots and well-maintained aircraft.
All carriers from Nepal have been refused permission to operate air services to the EU due to safety concerns.
There have been several air accidents in Nepal over the last 10 years, including:
- 15 January 2023, a Yeti Airlines flight from Kathmandu to Pokhara with 72 people on board crashed shortly before landing. All 68 passengers and four crew were killed.
- 29 May 2022, a Tara Air flight from Pokhara to Jomsom with 22 people on board crashed shortly after take-off in bad weather. All 16 passengers and six crew were killed.
- 12 March 2018, a US Bangla Airlines flight from Bangladesh with 71 passengers on board crashed on landing at Kathmandu International Airport. Fifty-one passengers were killed.
- 26 February 2016, an Air Kasthamandap flight with 11 passengers on board crashed while flying between Nepalgunj and Jumla. Two crew members were killed.
- 24 February 2016, a Tara Air flight with 20 passengers on board crashed while flying between Pokhara and Jomsom. Twenty-three passengers were killed.
Check Nepal's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Tourism complaints
Contact your provider with any complaints about tourist services or products.
You can also lodge a complaint with the Nepal Tourism Board .
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Traffic Police
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Kathmandu.
Australian Embassy, Kathmandu
300 metres north of Narayan Gopal Chowk Bansbari, Kathmandu Phone: (+977 1) 437 1678 Fax: (+977 1) 437 1533 Email: [email protected]
Website: nepal.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australian Embassy, Nepal X: @AusAmbNP
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Nepal?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Travel Advisory
All passengers travelling to Nepal by air or land route is no longer required a fully vaccinated proof OR Negative PCR test report.

गृह मन्त्रालय
अध्यागमन विभाग.
कालिकास्थान, काठमाडौँ
- नेपाल प्रवेशसम्बन्धी...
नेपाल प्रवेशसम्बन्धी सूचना
This is to notify that the notice regarding travel restriction (7 days mandatory hotel quarantine) published by the Department of Immigration on 17 th December 2021 has been postponed until further notice. Other notices relted to travel advisory published on 24 th September 2021 and 2 nd December 2021 are still active.
- 19 बैशाख बोलपत्र स्वीकृत गर्ने आशयको सूचना । (प्रकाशित मिति: २०८१।०१।१९) 3 दिन अगाडी
- 06 बैशाख बोलपत्र स्वीकृत गर्ने आशयको सूचना । 15 दिन अगाडी
- 02 बैशाख ट्रेकिंग एजेन्सीहरुलाई अनुरोध 20 दिन अगाडी
- 02 चैत्र सूचना । 1 महिना अगाडी
- 15 फाल्गुन लेख रचना उपलब्ध गराउने सम्बन्धमा । 2 महिना अगाडी
- 13 फाल्गुन Invitation for Bids 2 महिना अगाडी
Pinpoint Travel Health

Foreign Travel Advice Nepal
Table of Contents
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Foreign travel advice
Get advice about travelling abroad, including the latest information on coronavirus, safety and security, entry requirements and travel warnings.
Countries or territories
226 Countries or territories
Countries starting with A
- Afghanistan
- Antarctica/British Antarctic Territory
- Antigua and Barbuda
Countries starting with B
- Bonaire/St Eustatius/Saba
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
Countries starting with C
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Cook Islands, Tokelau and Niue
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
Countries starting with D
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
Countries starting with E
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
Countries starting with F
- Falkland Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
Countries starting with G
- Guinea-Bissau
Countries starting with H
Countries starting with i, countries starting with j, countries starting with k, countries starting with l.
- Liechtenstein
Countries starting with M
- Marshall Islands
- Myanmar (Burma)
Countries starting with N
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
Countries starting with O
Countries starting with p.
- The Occupied Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Island
Countries starting with Q
Countries starting with r, countries starting with s.
- São Tomé and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- St Kitts and Nevis
- St Martin and St Barthélemy
- St Pierre & Miquelon
- St Vincent and the Grenadines
- Switzerland
Countries starting with T
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
Countries starting with U
- United Arab Emirates
Countries starting with V
Countries starting with w.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara
Countries starting with Y
Countries starting with z, get updates for all countries, is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 10 - India
- Section 10 - Thailand
CDC Yellow Book 2024
Author(s): David Shlim
Destination Overview
Infectious disease risks, environmental hazards & risks, safety & security, availability & quality of medical care.
Home to >29 million people, Nepal stretches for 805 km (500 mi) along the Himalayan mountains that form its natural border with China (see Map 10-13 ). The topography rises from low plains at 70 m (≈230 ft) elevation to the highest point in the world at 8,848 m (≈29,029 ft), the summit of Mount Everest. Kathmandu, the capital city with a population of >2 million people, sits in a lush valley at 1,324 m (≈4,344 ft) elevation.
Nepal’s latitude of 28°N (the same as Florida) means that its non-mountainous areas are temperate year-round. Most annual rainfall comes during the monsoon season (June–September). The main tourist seasons are the spring (March–May) and fall (October–November). The winter months, December–February, are pleasant in the lowlands but can be too cold to make trekking enjoyable in the high mountains.
Approximately 30% of travelers to Nepal go to trek into the mountains; others go to experience the country’s culture and stunning natural beauty. Lumbini, in the Terai region, is the birthplace of the Buddha and has become an increasingly popular and beautifully developed pilgrimage destination for Buddhists from around the world. In recent years, trekkers have begun traveling to the Manaslu area, which offers a hiking experience featuring less-developed lodges and extended time away from roads. Notable in this area is the Nubri Valley, which also has many sacred Buddhist sites.
In addition to trekking, Nepal has some of the best rafting and kayaking rivers in the world. Jungle lodges in Chitwan National Park allow visitors to see a wide range of wildlife, including crocodiles, rhinoceros, tigers, and a huge variety of exotic birds. Less adventurous travelers can drive to comfortable hotels offering commanding views of the Himalayas, both near Kathmandu and near Pokhara. The airport near Lumbini is being upgraded to an international airport. Pokhara airport also is scheduled to become an international airport in the future, giving visitors more options for traveling in and out of Nepal.
Map 10-13 Nepal
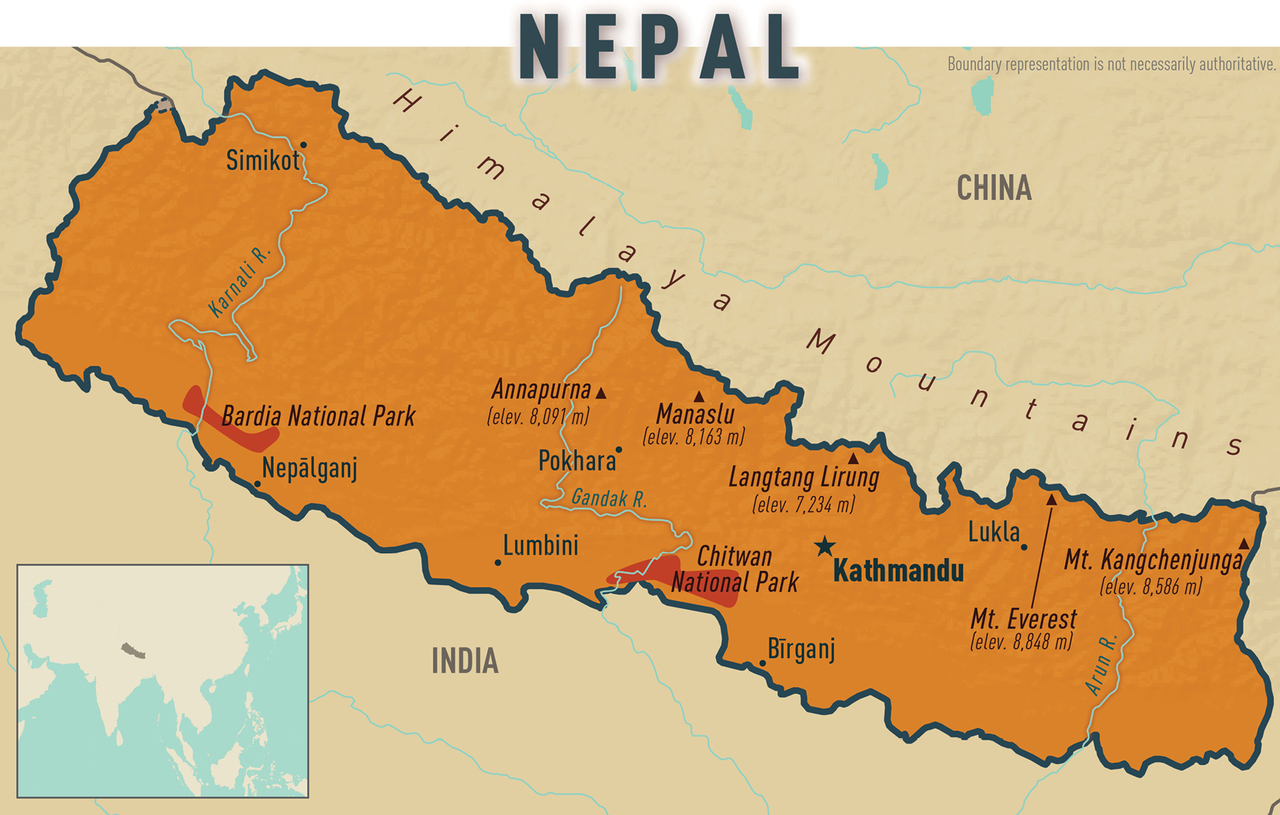
View Larger Figure
Enteric Infections & Diseases
Travelers to Nepal are at high risk for enteric diseases. Hepatitis A vaccine and typhoid vaccine are the 2 most important pretravel immunizations. The risk for typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever among visitors to Nepal is among the highest in the world, and the prevalence of fluoroquinolone resistance also is high (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 24, Typhoid & Paratyphoid Fever ). Tap water in Nepal is not considered safe for drinking, and travelers should only drink boiled or bottled water (see Sec. 2, Ch. 8, Food & Water Precautions , and Sec. 2, Ch. 9, Water Disinfection ).
Cyclosporiasis
Cyclospora cayetanensis , an intestinal protozoal pathogen, is highly endemic to Nepal (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 5, Cyclosporiasis ). Risk for infection is distinctly seasonal; transmission occurs almost exclusively during May–October, with a peak in June and July. Because transmission occurs outside the main tourist seasons, cyclosporiasis primarily effects expatriates who stay through the monsoon. In addition to watery diarrhea, profound anorexia and fatigue are the hallmark symptoms of Cyclospora infection. The treatment of choice is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; no highly effective alternatives have been identified.
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E virus is endemic in Nepal, and several cases each year are diagnosed in visitors or expatriates. No vaccine against hepatitis E is commercially available; travelers should follow safe food and water precautions (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 10, Hepatitis E ).
Travelers’ Diarrhea
Travelers’ diarrhea is a risk, and the risk during the spring trekking season (March–May) is double that of the fall trekking season (October–November). Because many visitors head to remote areas that do not have available medical care, provide travelers with medications for self-treatment (see Sec. 2, Ch. 6, Travelers’ Diarrhea ). Extensive resistance to fluoroquinolones has been documented among bacterial diarrheal pathogens in Nepal.
Respiratory Infections & Diseases
Respiratory illnesses among travelers are common, both in Kathmandu and on trekking routes. The advent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) makes it more difficult to assume the etiology of a respiratory infection. Prolonged symptoms beyond 7–10 days often requires a medical assessment.
Coronavirus Disease 2019
All travelers going to Nepal should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
Influenza is a risk in Nepal, particularly in crowded teahouses at higher elevations. Trekkers should receive a current influenza immunization before travel.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) disease that exists among local people can be due to drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Both multidrug-resistant and extensively–drug resistant TB have been reported in Nepal. Overall, however, risk to travelers is low.
Vectorborne Diseases
In 2019, the Ministry of Health in Nepal reported ≈18,000 cases of dengue, and in 2022, >46,000 cases. Counsel all travelers going to Nepal during the warmer, wetter months to pack an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent in their travel health kit and to practice insect bite precautions (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is endemic to Nepal; the greatest disease risk is in the Terai region during and immediately after monsoon season (June–October). JE has been identified in local residents of the Kathmandu Valley, but only 1 case of JE acquired in Nepal has been reported in a foreign traveler, a tourist who spent time in the Terai region in August. JE vaccine is not routinely recommended for people trekking to higher elevation areas or spending short periods in Kathmandu or Pokhara en route to such treks. JE vaccine is recommended for expatriates living in Nepal (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 13, Japanese Encephalitis ).
Although targeted for complete elimination of malaria by 2020, Nepal continues to report low (and decreasing) numbers of indigenous cases, primarily Plasmodium vivax . No malaria transmission occurs in Kathmandu or Pokhara, and all the main Himalayan trekking routes are free of malaria, but documented transmission persists in some areas of the country. For this reason (and until malaria is eliminated from Nepal), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention continues to recommend chemoprophylaxis for travelers visiting destinations below 2,000 m (≈6,500 ft) elevation.
Air Quality
Air pollution problems in the Kathmandu valley are frequent. People with underlying cardiorespiratory illness, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or congestive heart failure can suffer exacerbations in Kathmandu, particularly after a viral upper respiratory infection. Short-term exposure to these levels of air pollution can irritate the eyes and throat. In addition, exposure to high levels of air pollution greatly increases the risk for both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, including otitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia (see Sec. 4, Ch. 3, Air Quality & Ionizing Radiation ). Children and older people are the most vulnerable.
Altitude Illness & Acute Mountain Sickness
The destinations for most trekkers are the Annapurna region west of Kathmandu, the Langtang trekking area north of Kathmandu, and the Mount Everest region east of Kathmandu. In the Annapurna region, short-term trekkers can choose to hike to viewpoints in the foothills without reaching any high elevations. Others can undertake a longer trek around the Annapurna massif, going over a 5,416 m (≈17,769 ft) pass, the Thorung La.
The highest point in the Langtang region (the summit of Langtang Lirung) is 7,245 m (23,770 ft); overall, however, high-elevation exposure in Langtang National Park is generally less than in the Everest region. By contrast, trekkers in the Mount Everest region routinely sleep at elevations of 4,267–4,876 m (≈14,000–16,000 ft) and hike to elevations >5,486 m (≈18,000 ft). This prolonged exposure to very high elevations means that travelers must be knowledgeable about the risk for altitude illness and might need to carry specific medications to prevent and treat the problem (see Sec. 4, Ch. 5, High Elevation Travel & Altitude Illness ).
Most trekkers in the Mount Everest region arrive by flying to a tiny airstrip at Lukla at 2,860 m (≈9,383 ft) elevation; they then reach Namche Bazaar at 3,440 m (≈11,286 ft) elevation the next day. Acetazolamide prophylaxis can substantially decrease the chances of developing acute mountain sickness in Namche.
Animal Bites & Rabies
Rabies is highly endemic among the dogs in Nepal, but in recent years Kathmandu has had fewer stray dogs. Half of all traveler exposures to a possibly rabid animal occur near Swayambunath, a beautiful hilltop shrine also known as the monkey temple. Advise travelers to be extra cautious with dogs and monkeys in this area. Monkeys can be aggressive if approached, and will jump on a person’s back if they smell food in a backpack. Clinics in Kathmandu that specialize in the care of foreign travelers almost always have complete postexposure rabies prophylaxis, including human rabies immune globulin. Private helicopter companies in Nepal provide rescue; thus, most people can return to Kathmandu from a trek within 1–2 days. Even in the absence of helicopter rescue, trekkers bitten in the mountains have been able to return to Kathmandu in an average of 5 days.
Natural Disasters
In April 2015, a major earthquake in Nepal caused extensive damage and killed >9,000 people. Most of the damage occurred in non-tourist areas and the infrastructure for tourism has largely been repaired. The Langtang trekking area, north of Kathmandu, was virtually destroyed by a landslide triggered by the earthquake; since then, many services have been rebuilt, and tourism is returning to the area.
Large glacial lakes formed by melting glaciers can fail massively and cause intense downstream destructive flooding. Sudden snowstorms have occasionally occurred during trekking seasons, resulting in some deaths and numerous stranded trekkers. Ordinarily, though, the weather during the trekking seasons is mild.
Road Construction Issues
In recent years, Nepal has seen a frenzy of motorable road construction. Once the most roadless country in the world, much of Nepal is now connected by roads that vary in quality from well-constructed and maintained to terrifying. Hasty planning and construction have resulted in many road washouts and landslides, especially during the heavy rains of the monsoon, and road travel in general is an uncomfortable experience.
Motor roads have been constructed up the 2 major valleys of the Around-Annapurna Trek, shortening the trip from 21 to 5 days for people traveling by vehicle. In many cases, traditional trekking trails are no longer being maintained or have been subsumed by the road, substantially changing the nature of the experience and leading trekkers to seek out the few remaining roadless areas for a more traditional hiking experience. Encourage trekkers to inquire about road construction in areas where they intend to hike, because many have found that hiking on dusty or muddy roads, alongside buses, jeeps, and motorcycles, is not the experience they were anticipating.
Contact information for 2 clinics in Kathmandu specializing in the care of foreign travelers in Nepal is available on the International Society of Travel Medicine website. Hospital facilities have improved steadily over the years, and general and orthopedic emergency surgery are available and reliable in Kathmandu. Acute cardiac care also is available, including the placement of coronary artery stents. Modern hospitals tend to compete for foreign patients, and travelers should carry the names of reliable clinics and hospitals so they can request the hospital of their choice. Occasionally, patients are taken to an alternative hospital without their consent; when reaching a hospital, patients or their companions should ascertain whether they are indeed in the hospital they requested. Medical evacuation points providing definitive care outside of Nepal include locations in India and in Thailand.
Medical Evacuation
Helicopter evacuation from most areas is readily available. Communication has improved from remote areas because of satellite and cellular telephones, and private helicopter companies accept credit cards and are eager to perform evacuations for profit. Evacuation can often take place on the same day as the request, weather permitting. Helicopter rescue is usually limited to morning hours because of afternoon winds in the mountains. Helicopter rescue is billed at ≈$4,000 per hour, with an average total cost of $8,000–$10,000 US. Evacuation insurance policies generally require that rescues be arranged through the insurance provider; if not, the cost of the rescue will be borne by the traveler. Because of ready access to helicopter evacuation, trekkers have sometimes requested rescues for trivial conditions. Due to the potential for abuse of unnecessary helicopter rescue, some international evacuation insurance companies no longer provide coverage for Nepal or impose an additional surcharge for coverage there.
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: David R. Shlim
Bibliography
Cave W, Pandey P, Osrin D, Shlim DR. Chemoprophylaxis use and the risk of malaria in travelers to Nepal. J Travel Med. 2003;10(2):100–5.
Government of Nepal, Ministry of Health and Population, Department of Health Services, Epidemiology and Disease Control Division. Situation update of dengue 2022. Available from: http://edcd.gov.np/news/download/situation-update-of-dengue-2022 .
Hoge CW, Shlim DR, Echeverria P, Rajah R, Herrmann JE, Cross JH. Epidemiology of diarrhea among expatriate residents living in a highly endemic environment. JAMA. 1996;275(7):533–8.
Murphy H, Bodhidatta L, Sornsakrin S, Khadka B, Pokhrel A, Shakya S, et al. Traveler’s diarrhea in Nepal—changes in etiology and antimicrobial resistance. J Travel Med. 2019;26(8):taz054.
Pandey P, Lee K, Amatya B, Angelo KM, Shlim DR, Murphy H. Health problems in travellers to Nepal visiting CIWEC clinic in Kathmandu—a GeoSentinel analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2021;40:101999.
Schwartz E, Shlim DR, Eaton M, Jenks N, Houston R. The effect of oral and parenteral typhoid vaccination on the rate of infection with Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi A among foreigners in Nepal. Arch Intern Med. 1990;150(2):349–51.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more

Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
- Destinations
- Asia (East)
- Asia (Central)
- Australasia & Pacific
- Central America
- Europe & Russia
- Middle East
- North America
- South America & Antarctica
Nepal (Asia)
Advice for all destinations.
Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Vaccinations and malaria risk
Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
If you think you require vaccines and/or malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional:
- How to make an appointment with a travel health professional
A travel health risk assessment is also advisable for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets are not required.
- Do I need a travel health risk assessment?
Risk prevention advice
Many of the health risks experienced by travellers cannot be prevented by vaccines and other measures need to be taken.
Always make sure you understand the wider risks at your destination and take precautions, including:
- food and water safety
- accident prevention
- avoiding insect bites
- preventing and treating animal bites
- respiratory hygiene
- hand hygiene
Our advice section gives detailed information on minimising specific health risks abroad:
- Travel Health Advice A-Z
Other health considerations
Make sure you have travel insurance before travel to cover healthcare abroad.
Find out if there are any restrictions you need to consider if you are travelling with medicines .
Know how to access healthcare at your destination: see the GOV.UK English speaking doctors and medical facilities: worldwide list
If you feel unwell on your return home from travelling abroad, always seek advice from a healthcare professional and let them know your travel history.
Vaccinations
- Confirm primary courses and boosters are up to date as recommended for life in Britain - including for example, seasonal flu vaccine (if indicated), MMR , vaccines required for occupational risk of exposure, lifestyle risks and underlying medical conditions.
- Courses or boosters usually advised: Diphtheria; Hepatitis A; Tetanus; Typhoid.
- Other vaccines to consider: Hepatitis B; Rabies.
- Selectively advised vaccines - only for those individuals at highest risk: Cholera; Japanese Encephalitis.
Yellow fever vaccination certificate required for travellers aged 9 months or over arriving from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission and for travellers having transited for more than 12 hours through an airport of a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
Notes on the diseases mentioned above
Risk is higher during floods and after natural disasters, in areas with very poor sanitation and lack of clean drinking water.
- Diphtheria : spread person to person through respiratory droplets. Risk is higher if mixing with locals in poor, overcrowded living conditions.
Risk is higher where personal hygiene and sanitation is poor.
Risk is higher for long stays, frequent travel and for children (exposed through cuts and scratches), those who may require medical treatment during travel.
- Japanese Encephalitis : spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. This mosquito breeds in rice paddies and mainly bites between dusk and dawn. Risk is highest for long stay travellers to rural areas, particularly if unable to avoid mosquito bites.
- Tetanus : spread through contamination of cuts, burns and wounds with tetanus spores. Spores are found in soil worldwide. A total of 5 doses of tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK. Boosters are usually recommended in a country or situation where the correct treatment of an injury may not be readily available.
- Typhoid : spread mainly through consumption of contaminated food and drink. Risk is higher where access to adequate sanitation and safe water is limited.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes.You cannot be vaccinated against malaria.
Malaria precautions
- Malaria risk is present throughout the year with seasonal peaks from July to October in pockets of the low lying southern 'terai' districts bordering India. Risk is highest in the district of Kailali. In this area the risk is not high enough to warrant antimalarial tablets for most travellers, however, it may be considered for certain groups who may be at higher risk (see below under Low risk with additional advice)
- There is a low to no risk in all other areas.
- Malaria precautions are essential: avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers especially after sunset, using insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleeping under a mosquito net.
- Check with your doctor or nurse about suitable antimalarial tablets.
- See malaria map – additional information can be found by clicking on the Regional Information icon below the map.
- Low risk with additional advice: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised, however, they can be considered for certain travellers who may be at higher risk e.g. longer stay in rural areas, visiting friends or relatives, those with medical conditions, immunosuppression or those without a spleen. Atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline OR mefloquine is advised for those at risk.
- Low to no risk: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised.
- If you have been travelling in a malarious area and develop a fever seek medical attention promptly. Remember malaria can develop even up to one year after exposure.
- If travelling to an area remote from medical facilities, carrying standby emergency treatment for malaria may be considered.
Other Health Risks
Altitude and travel, dengue fever.
There is a risk of exposure to coronavirus (COVID-19) in this country.
Please be aware that the risk of COVID-19 in this country may change at short notice and also consider your risk of exposure in any transit countries and from travelling itself.
- The 'News' section on this page will advise if significant case increases or outbreaks have occurred in this country.
Prior to travel, you should:
- Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return.
- Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination.
- You can check this in the FAQ's.
- If you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 you should carefully consider your travel plans and consider seeking medical advice prior to making any decisions.
For further information, see Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel pages.
- 68 additional items in the news archive for this country
back to top

Travel Advice for Nepal
Going to Nepal and need to know about the latest government travel advice for Nepal? Find the updated travel advice and travel warnings for Nepal from governments around the world, here.
General Travel Advice and Warnings for Nepal
The decision to take a trip to Nepal is your choice and you are accountable for your personal health and safety whilst in Nepal.
The content on this page is given information only and pulled together from travel advice and warnings for Nepal by governments around the globe to their citizens.
While we make every effort to give you latest travel advice details, it is offered on an “as is” basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied.
This owners of this website does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information offered.
General Cautions You Need to Bear In Mind When Travelling in Nepal
Crime – Petty criminal offenses such as pick pocketing in a crowded environment to sexual assault and muggings do occur in bigger cities of Nepal. Ensure that all your personal possessions, including passports and other traveling documents, are secure at all times.
Terrorism – Always be aware of your surroundings when in public areas. Be particularly vigilant if participating in sporting events and during religious holidays and other public events, as terrorists often make use of such events to mount attacks.
Demonstrations and Protests – Demonstrations might take place. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any moment. They can also result in disruptions to traffic and public transport. It is in your interest of safety and security to keep away from locations where demonstrations and large events are occurring and follow the directions of local authorities. Monitor local media in Nepal for details on continuous demonstrations in Nepal.
Scams – Exercise caution in crowded tourist locations in Nepal, where scammers target foreigners. If you’ve been scammed in Nepal, get to a safe area immediately; make note, as soon as possible of the name and address of the facility where you were held; alert the cops in Nepal and acquire a record and if your credit card is used by the scammer call your credit card provider to report the scam; they will likely ask for a copy of the police report to cancel the financial transaction.
Spiked Food and Drinks – Never ever leave food or beverages unattended or in the care of strangers when taking a trip in Nepal or anywhere else. Watch out for accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items might contain drugs that could put you in danger of sexual assault and mugging.
What is the entry/exit conditions for Nepal?
Every nation or territory determines who can get in or exit through its borders, in the same manner Nepal chooses exactly who enter its territories. The Government of your home country cannot step in on your behalf if you do not satisfy your Nepal’s entry or exit requirements.
To find out more concerning the entry/exit requirement for Nepal go to visa requirements for Nepal or obtain the current info with the visa office at the Nepalese embassy in your home country.
Travel insurance coverage for Nepal
Travel health cover is one of the major reasons visitors get travel insurance policy. It will not prevent you getting sick or hurt, though it can prevent you being affected financially. Medical support overseas can be very expensive.
You should shell out for all healthcare you get overseas. You can not expect to get free or subsidised care through your Nepal’s public health system, like you would in your home country.
If you can’t pay, local authorities could jail you. The government from your home country can not pay you medical costs for you, loan you money or get you out of jail.
You need travel insurance coverage for travelling to Nepal . You also need to ensure you select a plan that is right for you.
Read through the fine print of your travel insurance policy.
Declare all pre-existing conditions to your travel insurance firm upfront. If you do not, you may void your travel insurance policy.
Inform your travel insurance provider the activities you intend to do, prior to you go. Many common activities like winter sports are omitted in basic policies. You might need to pay added.
Check if you have free credit card travel insurance policy. Some cards include travel insurance cover. Nonetheless, they typically have different conditions than paid policies. Understand the differences.
If you’re going to Nepal from a country that has a reciprocal health care arrangement, you still require travel health insurance. Agreements are restricted in what they’ll will cover.
If you have an incurable health problem, you might not have the ability to obtain standard travel insurance policy. However you may have the ability to find a specialised insurance company that covers you for health, mishaps or property troubles unassociated to your disease. Speak to your insurance company to learn.
Learn more about obtaining international travel insurance policy for Nepal prior to you go.
© 2021 Government Travel Advice
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
FCDO travel advice for Nepal. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Travel Advisory. December 18, 2023. Nepal - Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution. U. Reissued after periodic review with updates to risk indicators and "if you decide to travel" section. Exercise increased caution in Nepal due to the potential for isolated political violence . Country Summary: Political demonstrations intended to be peaceful can ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
As per the decision of the Government of Nepal, all fully vaccinated passengers travelling to Nepal by air or land route must submit a certificate of full vaccination against COVID-19 (Vaccine Certificate). Negative PCR test is no longer mandatory for the fully vaccinated passengers. Passengers who fail to submit vaccine certificate (including the children below 18 years and above
All fully vaccinated foreigners travelling to Nepal from the United Kingdom, Ireland and Malta must present the following documentation on arrival in Nepal in addition to those required for visa: a) Evidence of completion of 14 days of full vaccination against COVID-19, b) COVID-19 negative PCR test report obtained within 72 hours of the departure from first port of embarkation.
Guidelines to be followed by Nepali and foreign nationals travelling to Nepal, 2021 The Government of Nepal has issued these Guidelines on the basis of its earlier decisions regarding arrangements for the movement of Nepali and foreign nationals without adversely affecting the control and preventive measures of the new variant of COVID-19. 1.
Nepal Travel Advisory: Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution: December 18, 2023: Nicaragua Travel Advisory: Level 3: Reconsider Travel: January 11, 2024: ... You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Dosing info - Hep A. Hepatitis B. Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Nepal. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Nepal. Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book. Dosing info - Hep B. Japanese Encephalitis. Recommended for travelers who.
Avoid travelling on public transportation during or immediately preceding bandhs, as tourists have been injured. Transportation to and from airports throughout Nepal could be affected. Army and police checkpoints are frequent, especially at night. Follow the advice of local authorities and respect curfews and roadblocks.
Travel Details. Tourist Visa ... tourism organization of Nepal established in 1998 by an Act of Parliament in the form of partnership between the Government of Nepal and private sector tourism industry to develop and market Nepal as an attractive tourist destination. The Board provides platform for vision-drawn leadership for Nepal's tourism ...
Nepal is open to both vaccinated and unvaccinated travelers. Proof of double vaccination (or equivalent) must be shown at immigration and jabs shouldn't have been completed less that 14 days before entry. Unvaccinated travelers must provide proof of a negative PCR coronavirus test taken no more than 72 hours before travel (Gene Expert or True ...
Contact your travel provider about possible disruptions to your travel plans. Travel from Nepal to India. Nepal's land borders are open to foreign nationals. For information on the entry requirements for India please refer to the Smartraveller India specific travel advice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of India for up-to-date ...
Travel Advisory. All passengers travelling to Nepal by air or land route is no longer required a fully vaccinated proof OR Negative PCR test report.
Other notices relted to travel advisory published on 24th September 2021 and 2nd December 2021 are still... This is to notify that the notice regarding travel restriction (7 days mandatory hotel quarantine) published by the Department of Immigration on 17th December 2021 has been postponed until further notice. ... [email protected] ...
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions.Find out more about FCDO travel advice.. Before you travel. No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide as well as support for British nationals abroad which includes:. advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
Official U.S. government health recommendations for traveling. Provided by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). ... Nepal Healthy Travel Packing List. Pack items for your health and safety. You may not be able to purchase and pack all of these items, and some may not be relevant to you and your travel plans. Talk to your ...
Get advice about travelling abroad, including the latest information on coronavirus, safety and security, entry requirements and travel warnings.
Home to >29 million people, Nepal stretches for 805 km (500 mi) along the Himalayan mountains that form its natural border with China (see Map 10-13 ). The topography rises from low plains at 70 m (≈230 ft) elevation to the highest point in the world at 8,848 m (≈29,029 ft), the summit of Mount Everest. Kathmandu, the capital city with a ...
Prior to travel, you should: Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return. Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination. Check if you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19.
Travelling to Nepal and need to learn about the latest government travel advice for Nepal? Go here find the updated travel advice and travel warning for Nepal from governments around the world. Home / Choose Country