We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory January 8, 2024
Japan - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Japan – Level 1: Exercise Normal Precautions
Reissued after periodic review without changes.
Exercise normal precautions in Japan.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Japan.
If you decide to travel to Japan:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Follow Embassy Tokyo’s American Citizen Services section on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Japan.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Duration of intended period of stay. Please note you cannot travel on a passport you have previously declared as lost or stolen even if you subsequently locate it
One page required for entry stamp
Amounts equivalent to ¥1,000,000 or above subject to declaration
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Tokyo 1-10-5 Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo 107-8420 Japan Telephone: 81-3-3224-5000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 81-3-3224-5000 Fax: 81-3-3224-5856 Our Navigator Assistant will guide you to the information you need.
U.S. Consulate General Osaka-Kobe 2-11-5, Nishitenma, Kita-ku, Osaka 530-8543, Japan Telephone: 81-6-6315-5900 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 81-3-3224-5000 Fax: 81-6-6315-5914 Our Navigator Assistant will guide you to the information you need.
U.S. Consulate General Naha 2-1-1 Toyama, Urasoe City, Okinawa, Japan Telephone: 81-98-876-4211 Emergency Telephone: 81-3-3224-5000 Fax: 81-98-876-4243 Our Navigator Assistant will guide you to the information you need.
U.S. Consulate General Sapporo Kita 1-jo Nishi 28-chome, Chuo-ku, Sapporo 064-0821, Japan Telephone: 81-11-641-1115 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 81-11-641-1115 Fax: 81-11-643-1283 Our Navigator Assistant will guide you to the information you need. All assistance at the Consulate General Sapporo is by appointment only.
U.S. Consulate Fukuoka 5-26 Ohori 2-chome, Chuo-ku, Fukuoka 810-0052, Japan Telephone: 81-92-751-9331 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 81-3-3224-5000 Fax: 81-92-713-9222 [email protected] Our Navigator Assistant will guide you to the information you need. Routine services are provided by appointment only.
U.S. Consulate Nagoya Nagoya International Center Bldg. 6th floor, 1-47-1 Nagono, Nakamura-ku, Nagoya 450-0001, Japan Telephone: 81-52-581-4501 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: 81-3-3224-5000 Fax: 81-52-581-3190 Our Navigator Assistant will guide you to the information you need. Emergency services are provided by U.S. Consulate General Osaka-Kobe.
Destination Description
See the Department of State’s Fact Sheet on Japan for information on U.S-Japan relations.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Visit the Embassy of Japan website for the most current visa information.
There are no COVID-related entry requirements for U.S. citizens.
Entry & Exit:
- You must have a valid passport and an onward/return ticket for tourist/business "visa free" stays of up to 90 days. Your passport must be valid for the entire time you are staying in Japan.
- You cannot work on a 90-day "visa free" entry.
- "Visa free" entry status may not be changed to another visa status without departing and then re-entering Japan with the appropriate visa, such as a spouse, work, or study visa.
- Visit the Embassy of Japan website for the most current information on all visa categories.
- Japanese immigration officers may deny you entry if you appear to have no visible means of support.
- All foreign nationals are required to provide fingerprint scans and to be photographed at the port of entry. Exceptions to this requirement include diplomatic and official visa holders, minors, and individuals covered under SOFA Article IX.2. For further information about landing procedures, please visit the Immigration Bureau of Japan’s website .
- Make sure your passport is valid. Note you cannot travel on a passport you have previously declared as lost or stolen even if you subsequently locate it. Japanese authorities will likely deny you entry into Japan if you attempt to do so. If you have reported your passport lost or stolen, you must apply for a new passport before travel.
Transiting Japan:
- Ensure that your passport and visa are valid and up-to-date before you leave the United States. Passport services are not available at the airport.
- Airlines in Japan may deny you boarding for transit if you do not have the required travel documents for an onward destination in another country or if your passport does not have six months of validity remaining. For the entry requirements of the country you are traveling to, visit the State Department's Country Specific Information website.
Military/SOFA Travelers: While active-duty U.S. military personnel may enter Japan under the Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA) with proper Department of Defense (DoD) identification and travel orders, all SOFA family members, civilian employees, and contractors must have valid passports to enter Japan. Please consult the DOD Foreign Clearance Guide before leaving the United States.
See the Immigration Bureau of Japan’s website for various immigration procedures.
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Japan.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
For police services in Japan, dial 110. For fire or ambulance services, dial 119.
Crime: Crime against U.S. citizens in Japan is generally low and usually involves personal disputes, theft, or vandalism. In addition:
- Robberies committed after a victim has been drugged from a spiked drink can occur, especially in nightlife districts.
- Sexual assaults are not often reported, but they do occur, and victims may be randomly targeted. Victim's assistance resources or shelters are difficult for foreigners to access.
- Hate-related violent crimes rarely occur, although some U.S. citizens have reported being the target of discrimination because of their nationality or their race.
- Pick pocketing can occur in crowded shopping areas, on trains, and at airports.
- Police reports must be filed before leaving Japan, as Japanese police will not accept reports filed from overseas.
- In instances involving credit card theft or fraud, Japanese police often provide a report number rather than a police report. You can provide this report number to your credit card company to confirm the incident with the police.
Entertainment and Nightlife Districts in Tokyo:
- Exercise caution in all entertainment and nightlife districts throughout Japan, especially Roppongi, Kabuki-cho, Shibuya, and Ikebukuro.
- Incidents involving U.S. citizens in these areas include physical and sexual assaults, drug overdoses, theft of purses, wallets, cash and credit cards at bars or clubs, and drugs slipped into drinks.
- Drink spiking at bars and entertainment venues, especially in areas such as Roppongi and Kabuki-cho, near Shinjuku, has led to robbery, physical and sexual assaults, and credit card fraud. Some victims regain consciousness in the bar or club; other victims may awaken on the street or other unfamiliar locations.
- U.S. citizens have reported being threatened with gun or knife violence in such venues so that they will pay exorbitant bar tabs or withdraw money. U.S. citizens have also reported being beaten when they have refused to pay or hand over money.
- There have been reports of U.S. citizens being forcibly taken to ATMs and robbed, or made to withdraw funds after being unable to pay exorbitant bar tabs.
- Please be aware that Roppongi, Kabuki-cho, and other entertainment and nightlife districts have also been the scenes of violence between criminal syndicates.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information on scams.
Police reports must be filed at the nearest police station prior to departure from Japan. The Japanese police cannot accept reports filed from overseas. Report crimes to the local police at 110 and contact the U.S. Embassy at 03-3224-5000 (011-81-3-3224-5000 from overseas). Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting the crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- help you find appropriate medical care;
- assist you in reporting a crime to the police;
- contact relatives or friends with your written consent;
- explain the local criminal justice process in general terms;
- provide a list of local attorneys;
- provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S. ;
- provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
- help you find accommodation and arrange flights home; and/or
- replace a stolen or lost passport.
Contacting Police, Fire and Ambulance Services: You can reach the police throughout Japan by dialing 110. Fire and ambulance services can be contacted by dialing 119. Note that English-speaking dispatchers may not be available. Please review advice on “Calling for Help” on our website . If you need assistance, you should be able to describe your address/location in Japanese or find someone who can do so, since few police officers speak English.
Domestic Violence: Victim's assistance resources or battered women's shelters exist in major urban areas, but are difficult for foreigners to access. These types of resources are also generally unavailable in rural areas. Investigations of sexual assault crimes are often conducted without female police officers present, and police typically ask about the victim's sexual history and previous relationships.
Tourism: The Victim's assistance resources or battered women's shelters exist in major urban areas, but are difficult for foreigners to access. These types of resources are also generally unavailable in rural areas. Investigations of sexual assault crimes are often conducted without female police officers present, and police typically ask about the victim's sexual history and previous relationships.
See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage.
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to Japanese law while you are in Japan. If you violate Japanese laws, even unknowingly, you may be arrested, imprisoned, or deported. If you are arrested in Japan, even for a minor offense , you may be held in detention without bail for several months or more during the investigation and legal proceedings.
Some offences are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of Japanese law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
The vast majority of arrests of U.S. citizens in Japan are for drug-related offenses. Japanese authorities aggressively pursue drug smugglers and users, including recreational users with sophisticated detection equipment, "sniffing" dogs, blood tests, “stop and frisk” tactics, and other methods. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking a drug that is illegal in Japan are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and fines. Please note that some drugs which may be legal in certain jurisdictions outside of Japan, including marijuana and synthetic drugs, remain illegal in Japan. This also applies to certain prescription drugs that doctors in the United States may prescribe. Japanese law makes no distinction between medical and recreational marijuana; therefore, having a prescription for medical marijuana will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. Even possession of a small amount of marijuana for personal medical or recreational use can result in a long jail sentence and fine. Japanese customs officials carefully screen incoming packages, and individuals who are mailed drugs can be arrested and prosecuted as drug traffickers.
Confiscation of Prescription Drugs and Other Medication: It is important to note that some medications that are routinely prescribed in the United States, including Adderall and marijuana, are strictly prohibited in Japan. The Japanese government decides which medications may be imported legally into Japan. The Embassy and Consulates of Japan in the United States have limited information available and do not have a comprehensive list of specific medications or ingredients. Please see more information on importing medicines into Japan.
You must carry your U.S. passport or Japanese Residence Card (Zairyu Kado) with you at all times. In Japan, you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have your passport or Japanese residence card to show your identity and status in Japan (e.g., as a visitor, student, worker, or permanent resident).
It is illegal to work in Japan while in tourist or visa-waiver status. Overstaying your visa or working illegally may lead to fines of several thousands of dollars, and in some cases, re-entry bans as long as 10 years, or indefinitely for drug offenders. For additional information, please see Japan’s Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act and contact the Japanese Embassy or nearest Japanese Consulate in the United States for more information.
Driving under the influence of alcohol could also land you immediately in jail. The blood-alcohol limit in Japan is 0.03%. Punishments can be up to 10,000 USD in fines and up to five years in prison.
Possession of a gun or ammunition is a crime in Japan. Carrying a knife with a locking blade, or a folding blade that is longer than 5.5 cm (a little more than two inches), is illegal in Japan. U.S. citizens and U.S. military personnel have been arrested and detained for more than 10 days for carrying pocket knives that are legal in the United States but illegal in Japan. The possession of lock-picking tools is illegal in Japan.
Establishing a Business : Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
A list of English-speaking lawyers located throughout Japan is available on our website .
Arrest Notification : If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See the Department of State’s webpage and the Embassy’s website for additional information.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice’s website for more information .
Faith-Based Travelers: See our following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTQI+ Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI+ events in Japan.
Laws governing rape, sexual commerce, and other activity involving sexual relations do not apply to same-sex sexual activity. This leads to lower penalties for perpetrators of same-sex rape and sexual assault and greater legal ambiguity surrounding same-sex prostitution.
See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers with Disabilities: The law in Japan prohibits discrimination against persons with disabilities. Japanese disability laws require the public sector to provide reasonable accommodations and the private sector to make best efforts in employment, education, access to health care, or the provision of other services; however, there are no penalties for noncompliance. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States.
Although Japan’s accessibility laws mandate that new construction projects for public use include provisions for persons with disabilities, older buildings are not likely to have been retrofitted for accessibility. At major train stations, airports, and hotels, travelers with disabilities should encounter few accessibility problems. Note that many smaller stations are inaccessible to those who cannot climb stairs. Information on travel in Japan for travelers with disabilities is available at Accessible Japan .
Travelers with disabilities can learn more about resources available in country from the Japan National Tourism Organization’s traveling with a disability page .
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Conditions at Prisons and Detention Facilities: Japanese prisons and detention facilities maintain internal order through a regime of very strict discipline. U.S. citizen prisoners often complain of stark, austere living conditions and psychological isolation. Heating in winter can be inadequate in some facilities, food portions can be significantly smaller than what many may be accustomed to, and access to specialized medical care, particularly mental health care, at detention facilities and prisons is sometimes limited. Additional information on arrests in Japan is available on our embassy website.
Customs Regulations: Please contact the Japanese Embassy or nearest Japanese consulate in the United States, or visit the Japanese Customs website for specific information regarding import restrictions and customs requirements.
Japanese customs authorities encourage the use of an Admission Temporaire/Temporary Admission (ATA) Carnet in order to temporarily import professional equipment, commercial samples, and/or goods for exhibitions and trade fairs into Japan. For additional information, please call (212) 354-4480, or email the U.S. CIB for details.
Pets: The Japanese Animal Quarantine Service (AQS) sets procedures for importing pets. At a minimum, the process will take seven to eight months, though the process can take up to a year before a pet may enter Japan. Advance planning is critical. You can find more information about importing a pet into Japan or information about exporting a pet from Japan on our Embassy website.
Employment Issues: U.S. citizens should not come to Japan to work without having the proper employment visa arranged ahead of time. Teaching English, even privately, and serving as hosts/hostesses are both considered "work" in Japan and are illegal without the proper visa.
Some U.S.-based employment agencies and Japanese employers do not fully or correctly represent the true nature of employment terms and conditions. A minimum requirement for effectively seeking the protection of Japanese labor law is a written and signed work contract. If there is no signed contract, Japanese authorities are not able to act on behalf of foreign workers. If you are coming to Japan to work, carefully review your contract and the history and reputation of your Japanese employer before traveling to Japan. Complaints against U.S.-based employment agencies or recruiters may be directed to the Better Business Bureau or the Office of the Attorney General in the relevant state(s).
Disaster Preparedness : Japan is prone to natural disasters, including earthquakes, typhoons, tsunamis, and landslides. See the Embassy’s webpage for recommendations and steps you can take to prepare for an emergency. The Japan Tourism Organization’s Safety Tips app and NHK World app provide Japanese government emergency “J-Alerts” to your cell phone in English through push notifications. “J-Alerts” can provide early warning emergency alerts on earthquakes predicted in a specific area, sometimes seconds before an earthquake hits.
Radiation: Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant : The Government of Japan continues to closely monitor the conditions at and around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. You should comply with all travel restrictions and cautions put into place by the Government of Japan for areas surrounding the plant. For more information, contact the Japan Nuclear Regulation Authority .
For police service in Japan, dial 110. For fire or ambulance, dial 119.
Ambulance services are widely available but receiving hospitals may decline to accept inbound patients unless they can provide proof of funds to pay for services.
COVID-19 Testing:
- Travelers should contact Japanese local health providers to determine the location of testing facilities within Japan. A non-comprehensive list of some COVID-19 testing facilities can be found here on the Embassy website.
COVID-19 Vaccines:
- The COVID-19 vaccine is available for U.S. citizens to receive in Japan.
- Review the Government of Japan’s English language website on COVID-19 vaccinations in Japan.
- Visit the FDA's website to learn more about FDA-approved vaccines in the United States.
The Department of State does not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Some care providers in Japan only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
If traveling with prescription medication, check with the government of Japan’s Ministry of Health website to ensure the medication is legal in Japan; possession, use, or importation of a prescription drug that is illegal in Japan may result in arrest and criminal prosecution. Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription. U.S. prescriptions are not honored in Japan, so if you need ongoing prescription medicine, you should arrive with a sufficient supply for your stay in Japan or enough until you are able to see a local care provider.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Japan has a national health insurance system which is available only to those foreigners with long-term visas for Japan. National health insurance does not pay for medical evacuation. Medical caregivers in Japan may require payment in full at the time of treatment or concrete proof of ability to pay before they will treat a foreigner who is not a member of the national health insurance plan.
U.S.-style and standard psychological and psychiatric care can be difficult to locate outside of major urban centers in Japan and generally is not available outside of Japan's major cities. Extended psychiatric care can be very difficult to obtain.
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety : Driving in Japan can be complicated and expensive. Traffic moves on the left side of the road. Those who cannot read the language will have trouble understanding road signs. Highway tolls can be very high, and city traffic is often very congested. A 20-mile trip in the Tokyo area may take two hours. There is virtually no legal roadside or curbside parking; however, traffic is commonly blocked or partially blocked by those illegally parked curbside. In mountainous areas, roads are often closed during the winter, and cars should be equipped with tire chains. Roads in Japan are much narrower than those in the United States.
Traffic Laws : Japanese law provides that all drivers in Japan are held liable in the event of an accident, and assesses fault in an accident on all parties. Japanese compulsory insurance (JCI) is mandatory for all automobile owners and drivers in Japan. Most short-term visitors choose not to drive in Japan. Turning right or left on red lights is not permitted in Japan, and all passengers are required to fasten their seat belts.
Japan has a national 0.03 percent blood-alcohol-level standard for driving, and drivers stopped for driving under the influence of intoxicants will have their licenses confiscated. If you are found guilty of driving under the influence, speeding, or blatantly careless driving resulting in injury, you are subject to up to 15 years in prison.
See our Road Safety page for more information. The National Police Agency (NPA) oversees the administration and enforcement of traffic laws in Japan. You can find further information in English on the NPA English website . Information about roadside assistance, rules of the road, and obtaining a Japanese driver's license is available in English from the Japan Automobile Federation (JAF) web site . See the Japan National Tourism Organization’s website for car rental and driving in Japan.
Emergency Assistance : For roadside assistance, please contact the Japan Automobile Federation (JAF) at 03-5730-0111 in Tokyo, 072-645-0111 in Osaka, 011-857-8139 in Sapporo, 092-841-5000 in Fukuoka, or 098-877-9163 in Okinawa.
International Driving Permits (IDPs): An international driving permit (IDP) issued in the United States by the American Automobile Association (AAA) or the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA) is required of short-term visitors who drive in Japan. You must obtain an IDP issued in your country of residence prior to arriving in Japan. The U.S. Embassy andU.S. consulates do not issue IDPs. IDPs issued via the Internet and/or by other organizations are not valid in Japan.
Foreign residents in Japan who use an IDP may be fined or arrested. In practice, the term “resident” involves more than simply visa status or length of stay in Japan and is determined by the police. In short, a driver license from country outside Japan is not a substitute for a valid Japanese license for foreign residents. See the U.S. Embassy’s website for more information on driving in Japan.
Aviation Safety Oversight : The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Japan’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Japan’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA's safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel : Mariners planning travel to Japan should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts in the Alerts section of the Embassy’s messages. Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) broadcast warnings website portal select “broadcast warnings.”
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Japan . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Travel to Japan
A record 24.04 million people visited Japan in 2016, welcomed by Japan's spirit of omotenashi . A nation where tradition and modernity share the same space, Japan offers an exciting, unique experience for everyone. From Tokyo’s urban sprawl to the peacefulness of Kyoto, from boisterous Osaka nightlife to Hiroshima's contemplative spirit, Japan’s attractions never fail to dazzle visitors. The amazing food, unique culture, and warm hospitality will keep you coming back!
To get you started, here are some useful tools for your trip: Convert US Dollars to Japanese Yen ・ Japan Weather Forecast ・ Japan train route finder (trip planner) ・ Another train route finder Download DC-based Japan Travel Agencies & JR Pass Distributors
Do I need to bring anything special?
Not usually - just a valid passport. If you are a US citizen, you do not need a visa to travel to Japan for up to 90 days with a roundtrip ticket. The purpose of your visit must be tourism, visiting relatives/acquaintances, attending a conference, etc.
Japan has made agreements to waive visa requirements for tourism with 61 countries and regions. You can find more information about this on the Embassy's visa section page . If you need to obtain a visa for your travels, please contact your nearest Consulate General of Japan or call the Visa Section of the Embassy at 202-238-6800.
Where should I visit in Japan?
What can i bring through customs, can i use a credit card, is japan a safe country, do japanese people speak english, what do i do if i need help or get lost, how can people call me while i'm in japan.
To call Japan from the U.S., dial 011 81 , followed by the area code and phone number. For Japanese cell phones, the area code is 80 or 90. Other common codes are 3 for Tokyo, 78 for Kobe, 75 for Kyoto, 6 for Osaka, and 82 for Hiroshima. If you're given a number that starts with 0, remove it and dial the rest. So, if the number is 080, just dial 80. You can also look up numbers via the Japan Phone Book.
Other options for calling abroad include VoIP services such as Skype .
How is Japan's public transportation system/How can I get a "JR Rail Pass"?
Excellent! Japan has an extremely modern subway and rail system, as well as the famous shinkansen bullet trains, and a large network of buses. Japan-Guide has an excellent guide to transportation in Japan, including information on the numerous tickets and passes available. You can also use the Japan train route finders at the top of this page.
The Japan Rail Pass is one of the most popular option if you'll be traveling long distances by train, or if you're looking for an economical solution for sightseeing. Japan-Guide has more information about the rail pass, but we also have a list of distributors in the DMV area available on our DMV Resources page . You must purchase an Exchange Order before you travel to Japan. You cannot buy a Japan Rail Pass in Japan.
For information about traveling on public transport system with a wheelchair or other disabilities, please check our special circumstances section below.
Can I use a drone/UAV in Japan for tourism?
UAVs are under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism. Their website has a guide in English for those who would like to use UAVs in Japan.
For laws in specific cities and prefectures, you can try and contact local film offices, who might be able to provide you with information on filming with UAV.
What about prescription medications?
Medications are restricted by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. Certain medications require a Yakkan Shoumei import/export certificate which can take over two weeks to process. For information and/or restrictions on specific medications, please check with Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare .
For more information, please check the main Embassy's guide to bringing Medications into Japan . The Embassy of the United States in Japan also has good information on bringing medication for personal use, although we are not affiliated with them.
What if I'm in a wheelchair or have another disability?
What if i have a medical device (cpap machines, etc.), what if i have dietary restrictions.
Although Japanese food is considered some of the healthiest in the world, it can be difficult to find appropriate foods if you have dietary restrictions such as gluten-free, vegan, vegetarian, and more. Many major restaurants now include pictorgrams on their menus to help, but smaller restaurants may not have them.
If you are gluten-free , Legal Nomads has provide a gluten-free card in Japanese on her website , and Celiac Travel has a different version on their website .
For vegans and vegetarians , HappyCow , Japan Vegan and Vege-Navi all have resources to help you find good restaurants. Additionally, Is it Vegan? Japan offers help with reading packaging.
For those with halal food restrictions, the JNTO provides a guide to Muslim friendly food stores as well as a travel guide. Additionally, Veg-Travel Tokyo is a vegetarian, halal, and kosher restaurant search. The Jewish Community of Japan also has helpful kosher guides.
If you have food allergies , be aware that any products containing eggs, milk, wheat, buckwheat, peanuts, shrimp and crab will be labeled by law. The JNTO's English Tourist's Language Handbook includes information on how to indicate what you are allergic to.

Ultimate Guide to Japan Travel Requirements: Everything You Need to Know
When it comes to traveling to Japan, there are certain requirements that you need to be aware of before you embark on your journey. From visas to essential documents, vaccinations to customs regulations, and transportation rules to travel tips, this ultimate guide will provide you with everything you need to know about Japan travel requirements. So, let’s dive right in!
Understanding the Visa Process for Traveling to Japan
Essential documents you must have before departure, important vaccinations and health precautions for japan, customs and entry regulations: what to expect upon arrival, transportation rules and regulations within japan, tips for a smooth travel experience in japan: dos and don’ts, q: do i need a visa to visit japan, q: how long can i stay in japan without a visa, q: what documents do i need to enter japan, q: are there any health precautions i should take before traveling to japan, q: can i drive in japan with my foreign driver’s license, expert advice on japan travel requirements.
If you are planning to visit Japan, one of the first things you need to consider is the visa process. The type of visa you require depends on the purpose and duration of your stay. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- For short-term visits, tourists from many countries can enter Japan without a visa for up to 90 days.
- If you plan to stay in Japan for more than 90 days, you will need to apply for a long-term visa, such as a work visa, student visa, or spouse visa.
- To apply for a visa, you will generally need to submit a valid passport, a completed visa application form, a recent photograph, and any additional documents required for your specific visa type.
- It is important to apply for your visa well in advance of your planned departure date, as processing times can vary.
Before you travel to Japan, make sure you have the following essential documents with you:
- A valid passport with at least six months of validity remaining.
- Your visa, if required.
- A copy of your travel itinerary and accommodation details.
- Proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay in Japan.
- Travel insurance that provides coverage for medical expenses and emergencies.
Prior to your trip to Japan, it is recommended to ensure that you are up-to-date on routine vaccinations. Additionally, there are a few specific vaccinations and health precautions to consider:
- Hepatitis A and B vaccines are recommended for all travelers.
- Japanese encephalitis vaccine is recommended for those planning to stay for an extended period, particularly in rural areas.
- It is advisable to check with your healthcare provider regarding any other recommended vaccinations based on your individual health status and travel plans.
- It is also important to take precautions against mosquito bites, as Japan is known to have cases of dengue fever and other mosquito-borne diseases.
- Carrying a basic first aid kit with essential medications and supplies is always a good idea.
When you arrive in Japan, you will go through customs and immigration. Here are some important customs and entry regulations to be aware of:
- Declare any items that are restricted or prohibited, such as firearms, drugs, or certain food products.
- Japanese customs regulations are strict, so make sure to familiarize yourself with the list of prohibited items before your trip.
- Upon arrival, you will be fingerprinted and photographed as part of the immigration process.
- It is important to comply with all customs and immigration procedures to ensure a smooth entry into the country.
Getting around in Japan is a breeze, thanks to the country’s efficient transportation system. However, there are a few rules and regulations to keep in mind:
- When using public transportation, like trains and buses, always follow the designated rules, such as giving up your seat to elderly or disabled passengers.
- Smoking is prohibited on most trains, buses, and in many public areas.
- It is important to obtain and activate a prepaid transportation card, such as the Suica or Pasmo card, for convenient use on trains, buses, and even for making purchases at some stores.
- When driving in Japan, make sure to have an International Driving Permit (IDP) in addition to your valid driver’s license from your home country.
To ensure a smooth and enjoyable travel experience in Japan, here are some dos and don’ts to keep in mind:
- Do respect local customs and traditions, such as bowing when greeting others.
- Don’t tip in Japan, as it is not customary.
- Do try traditional Japanese cuisine and explore local food markets.
- Don’t talk loudly or disturb others in public places.
- Do carry cash, as many smaller establishments may not accept credit cards.
- Don’t forget to pack comfortable shoes, as you will likely be doing a lot of walking.
Frequently Asked Questions about Japan Travel Requirements
Here are some commonly asked questions about Japan travel requirements:
A: The visa requirements for Japan depend on your nationality and the duration of your stay. Some countries are exempt from requiring a visa for short visits.
A: Visitors from many countries can stay in Japan without a visa for up to 90 days. However, it is important to check the specific requirements based on your nationality.
A: You will need a valid passport, a completed arrival card (which is typically provided on your flight), and any required visas or permits.
A: It is recommended to be up-to-date on routine vaccinations and consider additional vaccinations based on your travel plans. It is also important to take precautions against mosquito-borne diseases.
A: To drive in Japan, you need to have both a valid driver’s license from your home country and an International Driving Permit (IDP).
For expert advice on Japan travel requirements, it is always recommended to consult with the Embassy or Consulate of Japan in your home country. They will provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding visas, entry requirements, and any other travel-related queries you may have.
Izumi Kenta
Hi, I’m Izumi Kenta from Japan. By profession, I worked as a tourist guide and interpreter in Japan. Besides this profession, I’m a hobbyist blogger. I love to talk about different things about Japan and share them with a wider audience who wants to know about my country. To share my thoughts, I’ve created this site Visitjapan and brought some Japanese travel enthusiasts and tourists worldwide to share their experiences.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Why Does Japan Have So Many Earthquakes? Discovering the Secrets Behind Japan's Seismic Activity
Japan is a country that is known for its frequent earthquakes. The question of why Japan experiences so many earthquakes has intrigued scientists and researchers for years. In this article, we will...
Unlocking the Secrets: Kobe Beef Price per kg Revealed!
Unlocking the Secrets: Kobe Beef Price per kg Revealed! Understanding the Factors Affecting Kobe Beef Price per kg Kobe beef, renowned for its exceptional quality and flavor, is a delicacy that...

Do I need a visa for Japan?

Most travelers to Japan can enter the country without obtaining a visa in advance. These include nationals from 65 countries, including the USA , Australia , the United Kingdom and New Zealand. You'll automatically be granted a temporary visitor visa on arrival, which is valid for up to 90 days (as long as you don’t plan to work while you’re in Japan). Even if you are from one of these visa-exempt countries, you must have a passport that remains valid through the time you stay in Japan.
However, there are plenty of countries that do require their nationals to obtain a visa before their arrival in Japan. These countries include China , Vietnam , the Pacific Islands and Ukraine (among others). Luckily, the visa application process is relatively easy and stress-free as you can apply at your nearest Japanese embassy/consulate. The introduction of e-visas is expected to be launched in the near future, however, they're not available at this time.
Regardless of whether you need a tourist visa to visit Japan, it's important that you get your passport stamped on arrival as this is needed to secure a Japan Rail Pass. If you don't have a stamp, you won't get a pass and that could disrupt your travel plans if it's your preferred mode of transportation around Japan.
As well as having a valid passport with at least 6 months' validity, nationals that need to obtain a visa for tourism purposes have to show the following supporting documentation:
- recent passport-sized photo
- copy of your birth certificate
- travel details, including a return flight
- proof of financial stability for the duration of your stay in Japan
Once submitted, the visa approval process usually takes around 5 to 15 business days but it can take longer depending on the visa you're applying for and the Japanese embassy/consulate you're applying at so we recommend starting the process as soon as you figure out your travel plans to avoid any disruptions.
You'll need to pay for your visa upon application and this can be done at your nearest Japanese embassy/consulate. Please note the payment must be received in that country's currency and that fees are subject to change depending on your nationality and what type of visa you're applying for (a single-stay tourist visa, a multi-stay tourist visa etc). However, the average visa application fee is 3,000 Yen or USD$21. Once you've paid, you'll receive confirmation that your application has been submitted.
This page is for general information only and may be subject to change. It is your responsibility to obtain relevant visa and travel information required for entry, departure and travel to each country or region you visit on your trip. You should confirm these with the relevant embassies and/or consulates.
Last updated: 15 June, 2023
Let's create an exclusive trip for your group.
The top 7 destinations for travel in April 2024
10 awesome places to go for your 21st birthday
6 ways you can go beyond Asia’s hotspots in 2023
Japan or China: Where to travel next?
Now is the perfect time to visit Japan. This Intrepid leader explains why.
Japan or South Korea? How to choose your next holiday destination
The naked truth: a non-nudist’s guide to using a Japanese onsen
What is Japan famous for? The 11 things to seek out on your next trip
Inside Kyoto
A Kyoto Travel Guide
Do I Need A Visa For Japan?
Most tourists to Japan can get a temporary visitor’s visa on arrival in Japan. Here’s a rundown of what to expect at immigration and whether you’re eligible to extend your visa

Most nationalities visiting Japan are issued a 90-day visitor visa upon arrival in Japan that cannot be extended within Japan (first list). Obviously, 90 days is more than enough for most tourist purposes. Some lucky countries are issued a 90-day visitor visa upon arrival that can be extended for another 90 days within Japan (second list). Other countries are issued 15-day visitor visas on arrival (third list).
Check Hotel Availability
Destination, check-in date, check-out date.

Visitors from the following countries are issued 90-day temporary visitor visas upon arrival:
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Republic of Korea
Visitors from a few countries are issued 90-day temporary visitor visas upon arrival and can usually extend these for another 90 days at an immigration office in Japan (i.e., you do not have to leave Japan to do this):
- Switzerland
Visitors from the following countries are issued 15-day temporary visitor visas upon arrival:
Do I Need To Show Proof Of Onward Travel?
Technically, you must be able to show proof of onward travel when entering Japan. In practice, immigration officers rarely ask to see this. However, if they were looking for a reason to refuse you entry, this would be an easy way to do so (if indeed you didn’t have an onward ticket).
Proof Of Sufficient Funds
You should be able to show proof of sufficient funds to travel for the length of your stay in Japan. This could involve a credit card, a large wad of cash or a bank statement. Again, immigration officers rarely ask to see this, but it doesn’t hurt to be prepared.
Note that all foreign visitors to Japan are photographed and fingerprinted upon entry (when you show your passport).
How To Extend Your Visa
If you want to extend your visa or deal with any other immigration-related issue, visit the Osaka Immigration Bureau Kyoto Branch. It located on the 4th floor of the Dai Ni Chiho Godochosha Building at 34-12 Higashi Marutamachi, Kawabata Higashi-iru, Sakyo-ku. It’s a 5-minute walk from the Keihan line’s Marutamachi Station.
Kyoto Vacation Checklist
- For all the essentials in a brief overview, see my First Time In Kyoto guide
- Check Kyoto accommodation availability on Booking.com and Agoda.com - often you can book with no upfront payment and free cancellation
- You can buy shinkansen (bullet train) tickets online from Klook - popular routes include Tokyo to Kyoto , Kyoto to Osaka and Kyoto to Tokyo
- Need tips on where to stay? See my one page guide Where To Stay In Kyoto
- See my comprehensive Packing List For Japan
- Buy a data-only SIM card online for collection when you arrive at Kansai International Airport (for Osaka and Kyoto) or Tokyo's Narita Airport . Or rent an unlimited data pocket wifi router
- Compare Japan flight prices and timings to find the best deals
- If you're making frequent train journeys during your visit, you might save money with Japan Rail Pass – see if it's worth it for you
- A prepaid Welcome Suica card makes travelling around Kyoto easy – here's how
- World Nomads offers simple and flexible travel insurance. Buy at home or while traveling and claim online from anywhere in the world
Kyoto District Map

- Central Kyoto
- Northwest Kyoto
- Northern Higashiyama
- Southern Higashiyama
- Downtown Kyoto
- Kyoto Station Area
- South East Kyoto
Disclosure: InsideKyoto.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com and amazon.co.uk. World Nomads provides travel insurance for travellers in over 100 countries. As an affiliate, we receive a fee when you get a quote from World Nomads using this link. We do not represent World Nomads. This is information only and not a recommendation to buy travel insurance.
- General Information
- Do I need a visa to enter Japan?
Information regarding visas for Japan is summarized on the pages below.
Please contact the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan for individual inquiries.
Visa Information Websites of Japanese Embassies, Consulates and Permanent Missions
Have more questions?
Was this article helpful.
Search 10 out of 21 found this helpful
Articles in this section
- Is it necessary for overseas visitors to show their passport upon checking in at accommodations?
- When is peak travel season?
- When do the cherry blossoms bloom?
- When can we see autumn foilage in Japan?
- Will travel in Japan be difficult without Japanese language skills?
- Is Japan expensive?
- How can I find accommodations/hotels and reserve a room?
- What kind of accommodation is available in Japan?
- I have heard that I can only visit Katsura-rikyu Palace with a permit. How can I get this authorisation?
- When is the best time to visit Japan?
- Is a biometric passport necessary?
- Where are the JNTO offices located?
- What can I import into Japan?
- Which tour operators specialise in Japan?
- Climbing Mt. Fuji
- Pass/Tickets
- Safe Travel
- Maps & Brochure Request
- Novel coronavirus (COVID-19)
6 questions travelers need to ask before visiting Japan this year

Oct 5, 2022 • 5 min read

Unrestricted international tourism is returning to Japan on October 11 © Getty Images
On October 11, Japan will finally open its doors to independent travel following more than two years of some of the world’s toughest border restrictions. The country is also bringing back visa-free entry for visitors from more than 60 countries.
Does that mean it will be as easy to visit now as it was pre-pandemic? Sort of. There are still some pandemic-era rules in place, and you might find that locals are still taking many precautions against the virus compared to other nations. Yet at the same time, there’s much excitement on the ground about the return of international tourism, with Japan gearing up to welcome visitors back with exciting new attractions and events.
Eating on trains, embracing bidets and more tips for your Japan trip
1. Do I need to pack a mask?
Yes. Face masks have been a norm in Japan since before the pandemic. People often wear them year-round to protect their lungs from air pollution and to protect themselves and others from viruses, infections and allergens. While Japan has no official mask mandate in place, you’ll find that many businesses still require people to wear one indoors; you’ll also see people with a mask while on a bus, train or taxi, or in any sort of crowded indoor environment. They’re an everyday item for many, and it wouldn’t hurt to have one in your bag or pocket at all times. If you forget to pack one, it’s easy enough to find a surgical-style disposable face mask in airports and pharmacies all over Japan.

2. Have I checked which entry rules apply to me?
Japan has a color-coded classification entry scheme for all countries, which will continue even after travel rules ease on October 11. The system sets out distinct rules depending on what country you’re entering Japan from. Travelers coming from a “blue” country – a list that currently includes the United States, Canada, the UK, Australia, Mexico, Thailand and many EU nations – no longer have to quarantine and have the option to show proof of vaccination or negative test results before traveling. Travelers from “yellow” and “red” countries are subject to additional entry requirements, such as testing upon arrival and quarantine. You can view the complete list of countries and categories here .
The 10 most spectacular road trips in Japan
3. Have I downloaded the MySOS app?
MySOS is a smartphone app (available for Android and iOS ) that’s used to record your vaccine and health information for entry into Japan. It should help you get through airport security checks more quickly by being a one-stop shop for all of your essential documents. If you’re traveling with kids, their relevant information can be stored in your MySOS app, too.
4. Do I need to apply for a visa?
Japan will reinstate visa-free travel on October 11 for travelers from more than 68 countries, including the US, Canada, the UK, Ireland, Australia, Mexico, Argentina, Singapore, Thailand and more . If a passport holder a country on the visa-waiver list, you won’t need a visa to travel to Japan if you’re staying for less than 90 days.
The ultimate guide to karaoke in Japan

5. Should I reserve restaurants and museums in advance?
Japan has some of the most sophisticated, creative and celebrated restaurants on the planet. And for many travelers, its cuisine is one of Japan's biggest draws. Getting a table at the top spots has always been a challenge in the capital Tokyo (whether it's Kozue for seafood, Tamawarai for soba, or the two-star Michelin Den , you generally need to express your interest well before showing up), and in cities like Kyoto and Osaka – but since the pandemic, most restaurants across the country require advance reservation, a rule that hasn’t gone away even as the government relaxes its response to the pandemic.
Museums also have new entry systems in place as well, and you’ll likely need to book your spot before showing up. Check the website of the museum you wish to visit ahead of your trip to secure your preferred date and time.
8 unique places to stay in Tokyo
6. What new attractions can I add to my Japan itinerary?
Theme Parks
It feels like there’s always something exciting brewing in Japan. While the pandemic may have paused momentum, it’s now full speed ahead for the opening of some much-anticipated new attractions. After the world's first Super Nintendo World opened in Osaka during the pandemic, the next big thing is Ghibli Park , a theme park based on the works of animation legend Hayao Miyazaki set to open in Aichi Prefecture on November 1. Unlike traditional theme parks, you won’t find rides here: instead, you’ll walk through the dreamy, watercolor-style landscapes and architecture from Ghibli movies like My Neighbor Totoro and Howl's Moving Castle .
Earlier this year, Ishikawa’s New Prefectural Library opened, featuring 300,000 open stacks of books (and the capacity for two million). It’s quickly become a magnet for anyone who loves books, crafts, art and history, and anyone with even a passing interest in cutting-edge architecture. The building’s exterior resembles the pages of a book being turned, while inside you’ll find craftworks by Ishikawa’s master artisans.
Trying the traditional crafts of Ishikawa prefecture
Now that borders are open you can visit a new UNESCO site in northern Japan, open since May 2021. The Jomon Prehistoric Sites collectively form a Cultural Heritage Site, at which you’ll learn about the culture of the indigenous Jōmon people across 17 archaeological areas.
Bullet Trains
Japan’s public transport system is among the best in the world, its jewel the high-tech, high-speed bullet-train network, which is continuously expanding. If you want to test a new route on your travels, the Nishi- Kyūshū line opened in September, taking passengers on a 41-mile journey between the famous hot spring town of Takeo Onsen in the northwest and the city of Nagasaki (gateway to the Gotō Islands) in just 23 minutes.
Japan's best food and drink experiences
If you’re in Tokyo, check out Okushibu, the Japanese nickname for “Deep Shibuya.” This once well-kept secret within the shopping district of Shibuya has now become a go-to zone for late-night cafe culture, as well as some really unique and creative restaurants. Okushibu runs parallel to the new rooftop Miyashita Park , and you can stay in the heart of the action when the new Trunk Hotel Yoyogi Park opens in 2023. Expect a rooftop infinity pool with views across the park – and the city.
Explore related stories

Oct 25, 2019 • 6 min read
From blockbusters to Bollywood, here's how that movie makes it onto your plane.

May 3, 2024 • 14 min read

May 1, 2024 • 9 min read

Apr 14, 2024 • 6 min read

Apr 3, 2024 • 17 min read

Apr 2, 2024 • 10 min read

Mar 31, 2024 • 7 min read

Mar 28, 2024 • 7 min read

Mar 28, 2024 • 6 min read

Mar 28, 2024 • 11 min read
What you need to know for your first time in Japan

Puedes leer esta historia presionando aquí.
Japan is a bucket list destination for many tourists. Although there is a common notion that it is an expensive destination, there are many ways to save if you decide to take the trip to the land of the rising sun.
Here are some basic tools to prepare for your first trip to Japan on your own.
U.S. citizens do not need a visa to enter. However, you must complete an immigration declaration and another for Customs when entering the country. You can do it online to save time when arriving at some of its airports or ports of entry.
How do I move around in Japan?
The first thing you should do is download the official application of the Japanese Ministry of Tourism . It is a tool that will help you organize your trip. Although you can use Google Maps, I suggest downloading the Navitime app ( iOS and Android ). It is very efficient at identifying the best subway and public transportation routes and includes activity recommendations that will be of great help.
◾ Public transportation: The public transportation system is excellent. To pay on the subway, trains or buses, I recommend adding the Suica or Pasmo cards to your mobile device. You can download both to your Apple or Android wallets and pay directly from your device every time you need it. You just have to go to the transportation card area and search for them by name. You can add balance directly from your credit cards.
Save when traveling: How to use low-cost airlines without having to pay too much
Visa or vaccines? How to know your international travel requirements
Is the Japan Rail Pass worth it?
The answer will depend on the duration and plans of your trips in Japan, although I can tell you that it is expensive. For example, if you are only going to the cities of Tokyo, Osaka and Kyoto and the duration of your trip will not be more than 7-10 days, it will probably not be cost-effective to buy it since the greatest savings are when you use it on bullet trains between big cities.
If your plan is to stay for more than a week and you plan to move between several of its large cities, such as Tokyo, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, Nagoya, Osaka or Sapporo, it is very likely that it will be very cost-effective for you to acquire the JR Pass . I recommend that you do the mathematical exercise of comparing the cost of purchasing the individual passes versus the pass.
How do I find, book activities?
To book most activities in Japan you can use the Klook app ( iOS and Android ). In it, you can get everything from tickets to the Universal Studios parks to reservations at your cafes or immersive experiences. It is important that you know that most of the most famous restaurants require reservations. It is highly recommended that you book them at least two to six weeks before your trip.
Skip the line: 4 tools to help you move through airports faster
Off the beaten path: 4 spectacular (and cheap) European destinations
How do I communicate?
Google Translate ( iOS and Android ) can be your best ally in a country where you don't speak the local language. Although it is always recommended that you learn between 10 to 20 basic phrases of the language of the destination you are going to visit, the Japanese are distinguished by their kindness and service, and this will facilitate the communication process.
Wilson "Wil" Santiago Burgos is the founder of Mochileando.com , one of the largest travel platforms in Puerto Rico and the Latin American market in the U.S.
- Media & Industry
- Meetings & Events
- Select Language 简体中文 繁體中文(香港) 繁體中文(臺灣) India (English) Bahasa Indonesia 한국어 ภาษาไทย Tiếng Việt Singapore (English) Philippines (English) Malaysia (English) Australia/New Zealand (English) Français Deutsch Italiano Español United Kingdom (English) Nordic countries(English) Canada (English) Canada (Français) United States (English) Mexico (español) Português العربية Japan(日本語) Global (English)
- India (English)
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Singapore (English)
- Philippines (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- Australia/New Zealand (English)
- United Kingdom (English)
- Nordic countries(English)
- Canada (English)
- Canada (Français)
- United States (English)
- Mexico (español)
- Global (English)
- Fujiyoshida
- Shimonoseki
- Ishigaki Island
- Miyako Island
- Kerama Island
- Tokyo Island
- Koka & Shigaraki
- Hida Takayama
- Ginza, Nihonbashi
- Beppu & Yufuin (Onsen)
- Ginzan Onsen
- Nagasaki Islands

- Kumano Kodo
- Shikoku Karst
- Amami Oshima
- Hachimantai
- Omihachiman
- Aizuwakamatsu

- Diving in Japan
- Skiing in Japan
- Seasonal Flowers in Japan
- Sustainable Outdoors
- Off the Beaten Track in Japan
- Scenic Spots
- World Heritage
- Home Stays & Farm Stays

- Japanese Gardens
- Japanese Crafts
- Temple Stays
- Heritage Stays
- Festivals and Events
- Theater in Japan
- Japanese Tea Ceremony
- Cultural Experiences in Japan
- Culture in Japan

- Local Cuisine Eastern Japan
- Local Cuisine Western Japan
- Local Street Food
- Japan's Local Ekiben
- Japanese Whisky
- Vegetarian and Vegan Guide
- Sushi in Japan Guide
- Japanese Sake Breweries

- Art Museums
- Architecture
- Performing Arts
- Art Festivals
- Japanese Anime and Comics
- Japanese Ceramics
- Local Crafts

- Scenic Night Views
- Natural Wonders
- Theme Parks
- Samurai & Ninja
- Iconic Architecture

- Wellness Travel in Japan
- Japanese Ryokan Guide
- A Guide to Stargazing in Japan
- Relaxation in Japan
- Forest Bathing (Shinrin-yoku)

- Experiences in Japan
- Enjoy my Japan
- National Parks
- Japan's Local Treasures
- Japan Heritage
- Snow Like No Other
- Wonder Around Japan

- Visa Information
- Getting to Japan
- Airport Access
- COVID-19: Practical Information for Traveling to Japan
- Anime Tourism
- Countryside Stays
- Accessible Tourism
- Hokkaido Great Outdoors
- Scenic World Heritage in Tohoku
- Shikoku’s Nature and Traditions
- Southern Kyushu by Rail

- Traveling by Rail
- How to Travel by Train and Bus
- JR Rail Passes
- Scenic Railways
- Renting a Car
- Sustainable Travel in Japan
- Travel Brochures
- Useful Apps
- Online Reservation Sites
- Eco-friendly Accommodation
- Luxury Accommodations
- Traveling With a Disability
- Hands-free Travel
- How to Book a Certified Tour Guide
- Volunteer Guides
- Tourist Information Center

- Japanese Manners
- Spring in Japan
- Summer in Japan
- Autumn in Japan
- Winter in Japan
- Cherry Blossom Forecast
- Autumn Leaves Forecast

- Japan Visitor Hotline
- Travel Insurance in Japan
- Japan Safe Travel Information
- Accessibility in Japan
- Vegetarian Guide
- Muslim Travelers
- Safety Tips

- JAPAN Monthly Web Magazine
- Arts & Cultures
- Nature & Outdoor
- Festivals & Events
- Insider Blog
- Things to do
- Local Guides
- Food & drink
- Traditional
- Hokuriku Shinetsu

My Favorites
${v.desc | trunc(25)}
Planning a Trip to Japan?
Share your travel photos with us by hashtagging your images with #visitjapanjp

For Travelers Process Map and Checklist
All information here is gathered from the relevant authorities. Due to the regularly changing situation, it is essential for you to always check and follow the latest guidance.
Last updated: Wednesday, May 31st, 2023
Get ready for your dream trip to Japan! Japan is now open to travelers from all countries or regions! Those who enter Japan on or after April 29th 2023 are not be required to present a valid vaccination certificate or a Covid-19 negative test certificate.
Process Map -From April 29th 2023-

Checklist for Travelers
Before Departure
At the arrival airport in japan, after arrival, returning home, did this information help you.
out of found this information helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
Other useful information.

- For Travelers
Please Choose Your Language
Browse the JNTO site in one of multiple languages
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Japan travel advice
Latest updates: The Need help? section was updated.
Last updated: April 30, 2024 07:18 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, japan - take normal security precautions.
Take normal security precautions in Japan.
Back to top
Fukushima nuclear power plant and surrounding area
Following the 2011 incident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, Japanese authorities have placed restrictions, including travel and overnight stay bans, on the plant's surrounding area due to the risk of exposure to radiation. Restricted areas are clearly identified.
Follow the instructions of local authorities.
Assistance of Residents Affected by the Nuclear Incidents – Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry
Tensions on Korean Peninsula
The regional security situation on the neighbouring Korean Peninsula could deteriorate suddenly. Tensions may increase before, during and after North Korean nuclear and missile tests. Military exercises and activities may also escalate tension.
- Remain vigilant
- Monitor developments to stay informed on the current situation
- Follow the instructions of local authorities, including the Cabinet Secretariat's guidance on civil protection
Cabinet Secretariat Civil Protection Portal
Crime against foreigners is generally low. However, petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs from time to time. Be cautious in entertainment and nightlife districts throughout Japan, especially in these four in Tokyo:
If you are the victim of a crime, file a police report at the closest station of the incident. Occasionally, local police may be hesitant to prepare a report for foreigners. If this happens, contact the Embassy of Canada to Japan for assistance.
Drug trafficking
An increasing number of travellers report having been used as unwitting drug couriers.
Penalties for drug-related criminal activities are severe. Even unsuspecting individuals transporting packages containing narcotics can be criminally charged and face long jail sentences.
Be wary of individuals, even those you know, who ask you to carry a package to Japan on their behalf.
Useful links
Drugs, alcohol and travel
- International Drug Smuggling Scams
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
There are reports of incidents where staff, or other customers at bars and nightclubs, have mixed drugs and copious amounts of alcohol into drinks of unsuspecting clients. These incidents are particularly frequent in the districts of Kabukicho and Roppongi in Tokyo. The intend is usually to defraud, overcharge services, rob or assault the person.
Credit card and ATM fraud occurs. There have been incidents of overcharging at bars and clubs. Disputes over overcharging have led to violence.
Be cautious when using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements and contact your financial institution as soon as possible if irregularities
Overseas fraud
Women's safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse. Inappropriate physical contact may occur on busy subways and trains. There are women-only train cars during rush hour on some subway and train lines.
Advice for women travellers
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety are generally good throughout the country. However, roads may be narrow.
Japan Road Traffic Information Center (in Japanese)
Public transportation
Taxis are generally safe.
- Use only officially marked taxis
- Negotiate fares in advance, or insist that the driver use the meter, as you may be overcharged
- Have your destination written in Japanese as drivers may not understand English
Taxis in Japan – Japan National Tourism Organization
Train and subway
Travel by subway and train is quick and convenient. Signs are usually in Japanese but signage in English is becoming more common, especially in larger cities and at tourist destinations.
General safety information
Emergency information and advice for tourists is available from the Japan National Tourism Organization .
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Japanese authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for the expected duration of your stay in Japan. If you plan to travel to other countries in the region, check passport validity requirements for the countries you plan to visit.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays up to a maximum of 90 days Business visa: required Work visa: required Student visa: required
You can’t apply for a business, work or student visa if you have already entered Japan as a tourist.
Business travellers need a visa if they are to receive compensation in addition to their regular salary for work carried out while in Japan.
Overstaying the 90-day, tourist visa-free limit or any other visa time limit is a criminal offence. If you overstay, you may be subject to fines and deportation, and you may be barred from re-entry to Japan.
Other entry requirements
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket, confirmed accommodations arrangements and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
Japanese officials will photograph and fingerprint visitors upon arrival. Exceptions may apply.
Immigration Services Agency of Japan
Registration
Japanese regulations require that visiting foreigners give detailed information when checking in at hotels or other lodging facilities.
Foreigners must also allow their passports to be photocopied.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is not required to enter this country.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
* It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a risk in some areas of this destination. It is a viral disease that affects the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). It is spread to humans by the bite of infected ticks or occasionally when unpasteurized milk products are consumed.
Travellers to areas where TBE is found may be at higher risk during April to November, and the risk is highest for people who hike or camp in forested areas.
Protect yourself from tick bites . The vaccine is not available in Canada. It may be available in the destination you are travelling to.
In this destination, rabies may be present in some wildlife species, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who will be working directly with wildlife.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.

Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Medical services and facilities
Health care is very good. Service is available throughout the country.
Services in English could be limited, especially in rural areas. The cost of health-care services is similar to Canada. As a foreigner, you will likely have to pay in advance or provide a document proving that the bill will be paid prior to discharge.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Health insurance for foreign workers
As a Canadian working in Japan, you must have medical and health services coverage for the duration of your stay. If not provided by your Japanese employer, you must subscribe to the national health insurance plan.
If you need to consult medical professionals, the following organizations can refer you to medical facilities with English and other foreign language-speaking staff:
- Japan National Tourism Organization
- Tokyo Metropolitan Health and Medical Information Centre (in Japanese)
- AMDA International Medical Information Center
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
In many cases, arrested or detained suspects are denied oral or written communication with anyone other than their lawyer or a Canadian consular representative for an extended period.
If you are detained, even for a minor offence, you may be held without charge for up to 23 days. Police officers may begin their initial questioning before you see a lawyer. You could also be in detention for weeks or months during the investigation and legal proceedings.
- Overview of the criminal law system in Japan
- Arrest and detention
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect jail sentences and heavy fines. Japan has a zero-tolerance policy with respect to drugs, including recreational drugs and cannabis. Severe penalties are imposed for the possession of even a small quantity.
Medications
Certain medications are banned in Japan, including:
- amphetamines
- methamphetamines
- pseudoephedrine
You may bring a one-month supply of prescription medication or a two-month supply of non-prescription medication into Japan, as long as the medication does not contain narcotics (including codeine). You cannot bring banned substances with you, even with a prescription.
You must have a doctor’s note that states your full name, address, the reason for use, and dosage, along with your prescribed medication. Local authorities may also request a detailed listing of the contents of the medication.
If you wish to bring in larger supplies of medication or bring in prescription medication that contains narcotics, you must apply in advance for import certification. You should do so several months prior to arrival.
Bringing medicines for personal use into Japan – Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Japanese law doesn't prohibit sexual acts between individuals of the same sex. However, homosexuality is not widely socially accepted.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Japan.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Japan, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
If you acquire 2 or more citizenships at birth, you can keep them all, including Japanese citizenship, until the age of 18. At 18, you must choose between your Japanese citizenship or other citizenships within a 2-year period.
Japanese family law is different from Canadian family law.
In Japan, joint custody of a child after separation is not a legal option if one of the parents is a Japanese national. As a result, access rights for a non-custodial parent can be limited, if granted.
If you are involved in a custody or other family law dispute in Japan, consult a Japanese family lawyer.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. The convention applies between Canada and Japan.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Japan, and if the applicable conditions are met, you may apply for the return of your child to the Japanese court.
If you are in this situation:
- act as quickly as you can
- contact the Central Authority for your province or territory of residence for information on starting an application under The Hague Convention
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Japan to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- List of Canadian Central Authorities for the Hague Convention
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- The Hague Convention - Hague Conference on Private International Law
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
Identification
You must carry your passport or residence card at all times.
A photocopy will not satisfy authorities. Police officers in Japan may ask for your identification documents at any time.
If you fail to do so, you could face arrest or detention.
Working in Japan
Working without an appropriate visa is illegal. Offenders may be subject to imprisonment, a fine and deportation.
If you are considering employment offers in Japan, contact the Japanese embassy or consulate nearest you before coming to Japan.
Foreign diplomatic missions and consulates in Canada
Teaching English
You should carefully review a contract to teach English before you sign. There have been incidents of employers not adhering to their contractual obligations.
Ensure that all terms and conditions of employment are clearly stated in the contract and that you meet all requirements before accepting an offer.
More on teaching English in Japan
You may be denied entry to public establishments such as swimming pools, hot springs, beaches and some gyms if you have a tattoo.
Some establishments may ask that you cover your tattoo.
Traffic drives on the left.
You must carry an international driving permit along with your Canadian licence, or a Japanese driver’s licence.
International Driving Permit
You must also obtain Japanese insurance. There are two types of driving insurance available:
- compulsory insurance, which is basic government-mandated insurance covering your legal liability
- voluntary insurance, obtained on your own from a private company and designed for your needs
Should you have an accident, compulsory insurance may not be sufficient.
Drinking and driving
Penalties for drinking and driving are severe.
Under Japanese law, it’s forbidden to:
- drive if you have been drinking
- lend a car to someone who has been drinking
- serve alcohol to someone who has to drive
If you are a passenger in a car whose driver is under the influence of alcohol, you both are subject to prosecution.
The currency of Japan is the yen (JPY).
Credit cards are accepted in most major hotels and restaurants, but Japan is a predominantly cash-based society.
ATMs are widely available, but many don’t accept foreign debit cards.
Typhoons usually occur between June and October. During this period, even small storms can quickly develop into major typhoons. Southern areas, including Okinawa and surrounding islands, are more vulnerable.
These severe storms can put you at risk and hamper the provision of essential services.
If you decide to travel to Japan during the typhoon season:
- know that you expose yourself to serious safety risks
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
- Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
- Large-scale emergencies abroad
- Japan Meteorological Agency
Seismic activity
Japan is located in an active seismic zone and is prone to a multitude of natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, flooding, volcanic eruptions. Strong earthquakes occur, as well as tsunamis.
Earthquakes
Each year, Japan experiences thousands of earthquakes of varying magnitudes, some triggering tsunamis. Deaths, injuries and significant damage may occur.
Earthquakes - Government of Canada
Japan is prone to tsunamis. A tsunami can occur within minutes of a nearby earthquake. However, the risk of tsunami can remain for several hours following the first tremor. If you’re staying on the coast, familiarize yourself with the region’s evacuation plans in the event of a tsunami warning.
Tsunami alerts - U.S. Tsunami Warning System
There are a number of active volcanoes. The Japan Meteorological Agency lists active volcanoes and associated warnings.
If you are travelling near a volcano, check for the latest activity and warnings. Always follow the advice and instructions of local authorities.
Volcanic alert levels and warnings - Japan Meteorological Agency
Seasonal risks
Snowstorms occur in western Honshu and Hokkaido from December to March.
Avalanches can occur in mountainous areas, including at ski resorts. These can cause power disruptions, make roads impassable and limit the ability of responders to reach these areas in case of emergency.
- Information in case of natural disasters - Japan National Tourism Organization
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 110
- medical assistance: 119
- firefighters: 119
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Japan, in Tokyo, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
When calling from within Japan, the area code is preceded by a 0. There is no 0 when calling from outside Japan. If placing a call to a cellular phone number, you do not need to enter the code.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Japan set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Japanese Embassy in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Japan.
Travel in Japan
There are no official COVID-19 restrictions on travel, dining out or other activities. However, the Japanese government still recommends social distancing, mask wearing and other basic precautions. Public compliance with these recommendations is high.
Passport validity requirements
If you’re visiting Japan, your passport must be valid for the length of your stay. No additional period of validity is required.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Visa requirements
If you have a ‘British citizen’ passport, you can travel to Japan for tourism or business for up to 90 days. You will get a visa in your passport on arrival, and you do not need to apply before you travel. The Japanese immigration authorities may extend your visa by another 90 days at their discretion. You will need to apply for an extension.
If you have another type of British passport, you must get a visa.
To stay longer (to work or study, for or for other reasons), you must meet the Japanese government’s entry requirements. Check which type of visa or work permit you need with the Japanese Embassy in the UK .
It is illegal to work in Japan without the correct visa however informal or temporary the work.
If you overstay your permission to remain in Japan, you risk arrest, detention and a heavy fine.
For residency information, see the Japanese Immigration Services Agency website and living in Japan .
Vaccination requirements
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need in TravelHealthPro’s Japan guide .
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of Japan . You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
It is illegal to bring meat products (including sausages, bacon and ham) to Japan without permission from the Japanese Animal Quarantine Service . Penalties include a heavy fine and prison sentence.
Whale meat is available in Japan but importing it into the UK and EU is illegal. If you import whale meat to the UK, you can get a fine of up to £5,000 and a prison sentence. Customs officers will seize the meat.
Taking money into Japan
People mainly use cash in Japan.
You may have difficulty using credit and debit cards issued outside Japan. Cirrus, Maestro, Link and Delta cash cards are not widely accepted. Japanese post offices, 7-Eleven stores and JP Post Bank have cash machines that will accept some foreign cards during business hours.
Check with your bank before travelling and take alternative sources of money.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise normal safety precautions in Japan.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
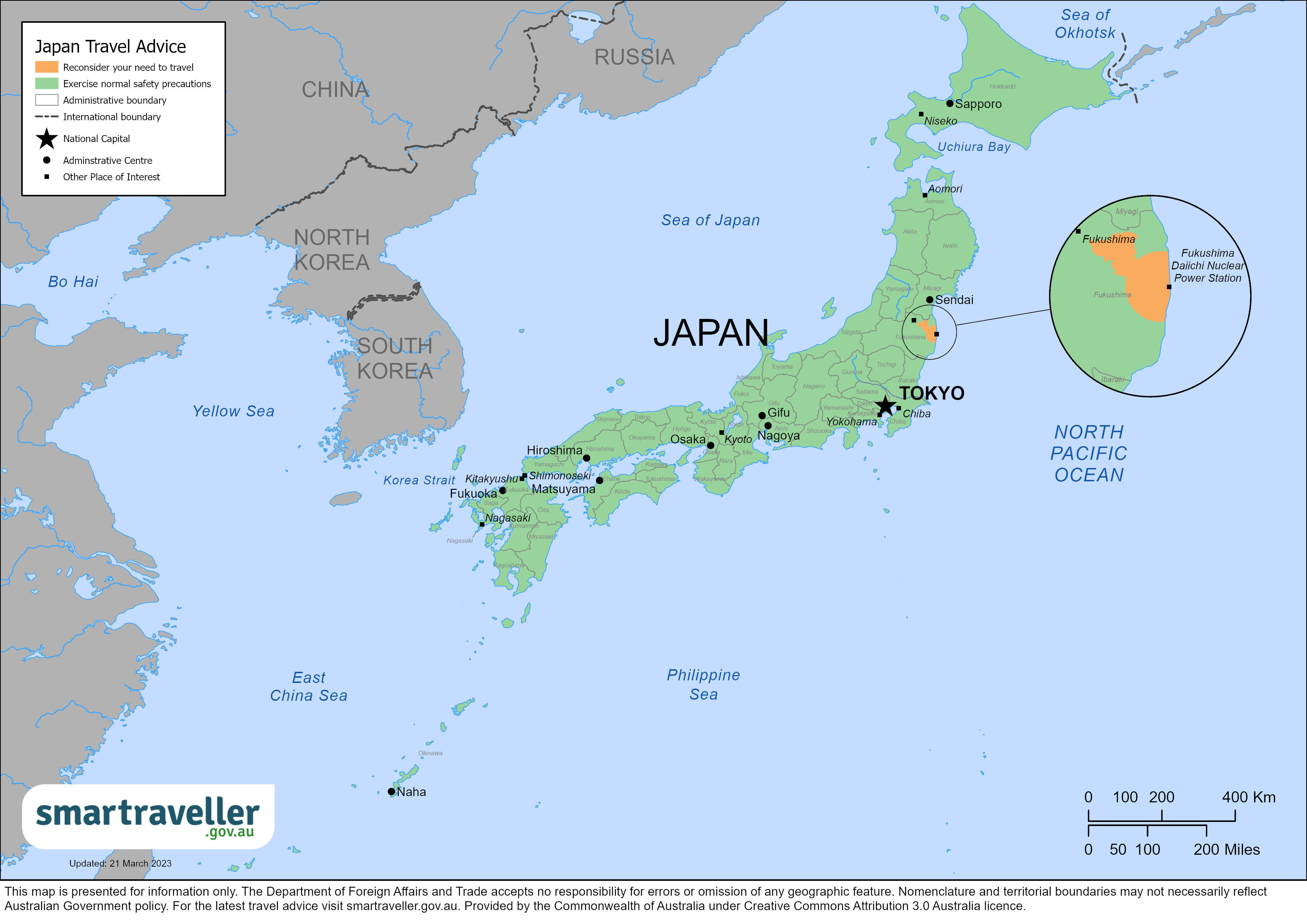
Japan (PDF 460.84 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 110 or contact the local police at the nearest police station.
For Tokyo English-speaking Police, call 3501 0110 (Monday to Friday 8:30am to 5:15pm).
Advice levels
Reconsider your need to travel to the restricted areas near the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant.
- Japan is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis. Japanese authorities have detailed plans to respond to natural disasters. In an earthquake, follow the advice of local authorities and emergency signage. Move to higher ground immediately if you're in a coastal region after a major earthquake. Check the Disaster Prevention Portal for more information.
- All major disaster warnings are published by the Japan Meteorological Agency . We recommend downloading NHK’s smart phone application to keep up to date with a natural disaster or other emergency alerts.
- A series of earthquakes occurred in Ishikawa Prefecture in Central Japan on and after 1 January 2024. Some infrastructure may remain impacted. Follow the advice of local authorities if travelling to affected areas.
- Regional tensions and the security situation, including with North Korea, could worsen with little warning. Tensions, which may affect Japan, could arise because of missile tests by North Korea. For advice see Japan's Civil Protection Portal Site .
- Japan has a low crime rate. Petty theft can happen, like bag snatching at popular tourist attractions. There's a risk of crime in bars and nightclubs. Crimes include overcharging, credit card fraud, forced withdrawal of large amounts of cash at ATMs, drink spiking and assault. Avoid taking large amounts of money and be vigilant in carrying your debit/credit card) when in bars or clubs and at parties.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Japan has strict rules about bringing medicine into the country, including some ingredients in ADHD and cold and flu medication. If you plan on bringing in medication, check if it's legal before you travel. See the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare website for more information.
- Restricted zones exist around the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant. The 2011 earthquake caused the release of lethal radiation. Radiation levels in most parts of Japan, including Tokyo, are within the normal range.
- Medical facilities are of a high standard. You can find English-speaking medical staff in most major cities. You may need to pay upfront before you're treated.
Full travel advice: Health
- You must carry your passport (or Japanese residency card) with you at all times.
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. Authorities can charge you if they find trace amounts of illegal drugs in your blood or urine.
- Japanese family law, including divorce and child custody, is very different to Australian law. For example, joint custody of a child after divorce is not a legal option, and there are limits to access for a non-custodial parent. The Family Courts in Japan generally consider that it is in a child's best interests for them to remain in their "usual place of residence". Courts, therefore, usually give sole custody to the parent who has taken care of the child most recently. If you're involved in custody or other family disputes, it is important to seek legal advice about your options both in Japan and in Australia. We have produced some general information about custody, child abduction and parental rights.
- Some employment agents mislead and encourage foreigners to work in Japan without the correct paperwork. If you want to work in Japan, verify the work offered and get the correct visa. Get legal advice before signing a contract.
- Japan has strict alcohol laws. The legal drinking age is 20. It's illegal to drive with any alcohol in your bloodstream. Allowing someone who has been drinking to drive is also illegal. Laws restrict alcohol consumption in specific areas on certain days, such as in Shibuya around Halloween night (31 October) and New Year's Eve. Smoking on the street is illegal in Tokyo and some other cities.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- Australians are eligible for Japan's visa exemption scheme for short-stay tourism and business travel. You don't need a visa to travel to Japan for up to 90 days. Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. It is your responsibility to verify visa requirements from the nearest embassy or consulate of Japan.
- If you're travelling for any other reason, contact your nearest Japanese embassy or consulate to check if you need a visa, especially if you plan to work in Japan. Penalties may apply if you work in Japan on a tourist visa.
- It's dangerous to climb Mount Fuji from September to June.
- You can drive for up to 1 year with an Australian driver's licence and an International Driving Permit. If you're staying longer, you will need to obtain a local licence. Heavy snowfalls and ice in winter can make driving dangerous. It's illegal to drive with any alcohol in your bloodstream.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what we can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Tokyo or the Consulate-General in Osaka .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy’s social media accounts
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Japan has security measures in place at key facilities, such as:
- public transport
- public event venues
- entry ports
More information:
- Terrorist threats
Regional Threats
Regional tensions and the security situation, including with North Korea, could worsen with little warning. Tensions, which may affect Japan, could arise because of missile tests by North Korea.
The Japanese Government has confirmed an increase in missile launch activity from North Korea towards Japan. At times, 'take shelter' alerts have been issued in some parts of Japan.
To stay safe:
- be alert to developments
- review the Civil Protection Portal Site advice from the Japanese Cabinet Secretariat for National Security Affairs and Crisis Management
- follow the instructions of local authorities
- check NHK World for the latest information
Japan has a low crime rate. Petty theft can happen, like bag snatching at popular tourist attractions from time to time.
There's a risk of crime in bars and nightclubs, especially in the Roppongi and Shinjuku (Kabuki-cho) entertainment areas of Tokyo. Both men and women have been targeted. You may be targeted with:
- overcharging
- fraudulent credit card charges
- forced withdrawal of large amounts of cash at ATMs
- drink spiking
- illegal drugs
You may be served drinks with higher alcohol content than normal. Some victims have woken in unknown places and discovered high credit card charges. Other victims have been taken to ATMs and forced to withdraw a large sum of cash while under the effects of drink spiking.
In these situations, you may find it hard to get a police report for your bank and travel insurer.
- never leave your drink unattended, and be cautious of accepting drinks from strangers or recent acquaintances
- don't take large amounts of cash to parties, bars, clubs or entertainment districts and be vigilant in carrying your debit/credit card
- Partying overseas
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Mountain climbing and trekking
Trekking and mountaineering can be dangerous. Register your plans with local police before you go into the mountains, and take an emergency locator beacon with you.
Every year, a number of people die while trying to climb Mount Fuji.
Japanese Emergency Services warn against climbing from September to June when it's most dangerous. Check the official Mount Fuji Climbing website for each trail's climbing season dates.
Check your travel insurance covers you for extreme activities, such as mountain climbing.
Hikers and other travellers may encounter bears in parts of rural Japan. There have been incidents of fatal bear attacks. Some prefectural governments provide safety advice regarding bears.
If you plan to hike or camp in rural and mountainous areas of Japan:
- follow local safety advice and pay attention to
- warning notices
Snow sport safety
Back-country skiing (off-piste) and snowboarding is dangerous in most parts of Japan. You should stay within the boundaries of the ski resort.
Take an emergency locator beacon with you if you plan to explore other areas of the mountains.
Many travellers have suffered serious head injuries they could've prevented by wearing the right equipment.
Check your insurance policy covers you for snow sports.
Local ski resorts govern rules in each ski region. You can be arrested and detained for unruly behaviour.
If you're skiing in Japan:
- use a helmet and protective gear
- learn local rules and get weather updates from your hotel, a local tourism centre or the local ski resort
- obey local ski region rules
- only visit areas that local authorities mark as safe
- know what your travel insurance policy covers you for
Climate and natural disasters
A series of earthquakes occurred in Ishikawa Prefecture in Central Japan on and after 1 January. Some infrastructure may remain impacted. Exercise caution and follow local authorities' advice if travelling to affected areas.
Japan experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- volcanic eruptions
- earthquakes
In an emergency, consular help may be severely limited.
Be prepared to deal with emergencies by:
- maintaining a basic emergency supply kit
- securing your passport in a safe, waterproof place
- follow the advice of local authorities, emergency services and local media updates. Make sure you react to any evacuation orders.
Disaster preparation
The Japan National Tourism Organization provides disaster preparation Safety Tips for visitors to Japan and other useful emergency information.
In any emergency or crisis, it's important to keep in contact with family and friends if possible.
The following stations broadcast emergency information in English:
- US Armed Forces station (810 AM)
- Inter FM (76.1 FM) in Tokyo
Japanese public broadcaster NHK provides a free smartphone app , which can be set to receive emergency notifications in English. This includes earthquake, tsunami, volcanic eruption, typhoon, and missile warnings.
If there's a natural disaster:
- follow local authorities' advice
- react to any evacuation orders
- monitor the media, other local information sources, and the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
- keep in contact with family and friends
Earthquakes and tsunamis
There's a constant risk of earthquakes and tsunamis.
The Japan Meteorological Agency provides information in English about earthquakes and tsunamis.
Know the dangers of a major earthquake and the emergency plan information in your area. Know where your local shelter is. This information is available from local or prefectural government offices, such as the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Disaster Prevention .
Local authorities are responsible during a crisis for helping people living or travelling within their jurisdictions.
If there's an earthquake:
- follow the advice of local authorities
- check the Japan Meteorological Agency for earthquake and tsunami information
- move to higher ground straight away if you're in a coastal region
Typhoons and severe weather
The typhoon season is from May to November, with most activity between July and September.
Local authorities broadcast current typhoon information through the local media and the Japan Meteorological Agency website.
If there's a typhoon approaching:
- check the latest typhoon information from the Japan Meteorological Agency’s website
- be alert to landslide risk areas
If there is heavy rain, stay indoors. If necessary, evacuate to a place on the second floor or higher. Find out the location of your nearest evacuation shelter and move there when safe to do so.
Keep away from areas with:
- steep hills at risk of landslides
- flooded streets
Be careful of fallen electrical lines.
Japan has 110 active volcanoes.
The Japan Meteorological Agency has a list of the latest volcano warnings.
If you plan to visit a volcanic area:
- be aware of alert levels, which can change at short notice
Winter weather
Parts of Japan experience heavy snowfalls and extremely low temperatures in winter.
Conditions can change suddenly.
Each year, people are injured or killed in snow-related incidents, including:
- motor vehicle accidents
- ice falling from roofs
- prolonged exposure to extreme cold
- ski accidents
Walking alone or under the effects of alcohol, or straying from marked trails, can be fatal.
Avalanches are common and heavy snowstorms can create deep powder snow drifts.
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you are travelling while pregnant, confirm that your policy covers both your pregnancy and your baby in the event of a premature birth. Medical services for premature babies can cost over $A 150,000. See the advice for pregnant travellers page for more information.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare, or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
Different environments, unfamiliar customs and language barriers may worsen existing mental health conditions. They may also trigger new issues.
Mental health treatment and services can differ to those in Australia.
If you need counselling services in English while in Japan:
- call TELL Lifeline (+81 3) 5774 0992
- call TELL Counselling (+81 3) 4550 1146
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (HealthDirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Japan has strict rules about bringing medication into the country. This affects both medication imports and medication you carry for personal use.
There are 4 categories (PDF 250 KB) of medicine. These are:
- psychotropic
You may need a permit or certificate to take medication into Japan. This will depend on the medication's classification, name and quantity.
Some medication is banned, including:
- the stimulant dexamphetamine, used to treat ADHD
- pseudoephedrine, found in some cold and flu tablets
Authorities could detain you if you're found with them.
For narcotic medications, including codeine, morphine and oxycodone, apply for a Narcotic Certificate. If you don't have this certificate when you enter Japan, authorities may confiscate the medication.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Japan. Take enough legal medication for your trip. See the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare for more information.
Carry a copy of your prescription and a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
- Bringing medication into Japan
Health risks
Restricted areas exist around the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant. The 2011 earthquake caused the release of lethal radiation. Radiation levels in almost all parts of Japan, including Tokyo, are within the normal range.
Monitor advice by the Japanese Government . There are ID checks points into the Restricted Areas . Do not enter without permission.
The Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA) provides details on radiation in Japan. ARPANSA has assessed the radiation levels in most parts of Japan, including Tokyo, to be within the normal range.
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry
- Nuclear Regulation Authority
Insect-borne diseases
Japanese encephalitis can occur in Japan's rural areas. Get vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis before you travel.
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Measles and rubella
Measles and rubella cases have been reported in Japan in recent years.
Make sure your vaccinations are up to date before you travel.
- Infectious diseases
- Measles immunisation service
- Rubella immunisation service
Medical care
Medical facilities.
Medical facilities are of a high standard. You can find medical facilities with English-speaking staff in most major cities, however, you may have difficulties finding English-speaking medical staff in some parts of Japan.
Medical care in Japan can be expensive. You may need to pay up-front or give a guarantee that you'll cover costs before you're treated.
The Japan National Tourism Organization lists hospitals with English and other foreign language-speaking staff.
There are many hospitals with decompression chambers in areas where diving is popular.
Medical information for Japan
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you within the scope of our Consular Services Charter , but we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
See the Australian Embassy Tokyo website for more information about arrests in Japan.
Be aware that you won't be allowed to make a phone call if you are arrested in Japan. You can also be detained for up to 23 days without any formal charge.
Authorities can arrest and charge you if they find trace amounts of illegal drugs in your blood or urine.
- Carrying or using drugs
- Tokyo Metropolitan Government
Japanese family law, including divorce and child custody, is very different to Australian law. For example, joint custody of a child after divorce is not a legal option, and there are limits to access for a non-custodial parent. The Family Courts in Japan generally consider that it is in a child’s best interests for them to remain in their “usual place of residence”. Courts therefore usually give sole custody to the parent who has taken care of the child most recently.
If you're involved in custody or other family disputes, consult a lawyer before you leave Australia or if you are already in Japan. We have produced some general information about custody, child abduction and parental rights.
Australia and Japan are both parties to The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction.
If you're concerned that your child has been wrongfully removed to or detained in Japan, contact the Attorney-General's Department in Australia.
- Travelling with children
Employment law
Some employment agents may mislead and encourage foreigners to work in Japan without:
- the correct visa
- financial arrangements in place
This could leave you open to exploitation and prosecution.
Authorities have arrested Australians for working in the entertainment industry while in Japan on tourist visas.
If you want to travel to Japan for work:
- check the true nature of the work offered
- get the correct visa before arriving in Japan
- get legal advice before signing any contract
Living or working overseas
Police powers
Police can stop you on the street, demand identification and search you and your belongings.
If you're in a public place, police can seize:
- knives longer than 5.5cm, including blades and penknives
- any other weapons or things you could use as weapons
- any item they reasonably suspect you stole or have unlawfully
If they find any of these items on you, it’s likely that police will detain you.
If you're arrested, police can detain you for up to 23 days without charge, including for offences you might think are minor. Police might hold you for weeks or months while they investigate and undertake legal proceedings.
The initial police interview could last several hours. Police might record it in writing rather than electronically.
Under Japanese law, you can:
- remain silent
- access legal representation
- have an interpreter provided
However, in Japan police can question you without your lawyer present.
English interpreters may be substandard. Get a list of English-speaking lawyers around Japan from the Australian Embassy website.
If you're visiting Japan short-term as a tourist or for business, you must always carry your passport.
If you live in Japan, you must always carry your residence card.
It's illegal to:
- buy or drink alcohol if you're under 20 years old
- drive with any alcohol in your bloodstream
- allow someone under the influence of alcohol to drive a vehicle in which you're a passenger
The following activities are also illegal:
- importing or possessing firearms or other weapons without a permit
- smoking on the streets in some parts of Tokyo and other cities
- using UHF-CB radios (walkie-talkies) that don't meet Japanese standards, such as those purchased outside Japan
- resisting arrest or other actions that obstruct an official's duties
- flying a drone without a permit in many areas of Japan. Strict regulations apply under aviation laws
- having illegal drugs in your body (detected by urine testing).
Penalties for serious crimes, such as murder, include the death penalty.
Other sentences can include:
- heavy fines
- lengthy jail terms with hard labour
- deportation
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law
Dual citizenship
Japan recognises dual nationality until the age of 20, after which the dual national must decide which nationality to retain.
- Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Australians are eligible for Japan's visa exemption scheme for short-stay tourism and business travel.
You don't need a visa if you're visiting for less than 90 days:
- as a tourist
- for a business trip or conference
- to visit friends and family
After entering under the visa exemption scheme, entry status cannot be changed to another visa status without departing and then re-entering Japan with the appropriate visa, such as a spouse, work, or study visa.
See the Embassy of Japan in Australia website for more information (including eligibility and required documents).
See the Ministry for Health, Labour and Welfare and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs websites for full details on entry requirements.
More information
- Immigration Bureau of Japan (Government of Japan)
- Customs and Tariff Bureau of Japan (Government of Japan)
Border measures
If you're transiting through Japan and your onward flight is leaving from a different airport, you must enter Japan. In order to transit between airports you will need to meet the entry requirements detailed above.
Please confirm any questions about transit directly with your airline.
Other formalities
You'll be photographed and fingerprinted electronically when you arrive, even if you're a permanent resident in Japan. If you refuse, immigration officers could deny you entry.
Travellers aged under 16 years, or who hold a diplomatic or official visa, are exempt.
If you'll be staying in Japan long term, you will need to register your details with the Immigration Bureau of Japan before arriving. Once you present the correct landing permission, you'll get a residence card. You must always carry it with you.
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- in Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- if you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
If you lose your passport while travelling in Japan, try retracing your steps. Lost items are often handed into hotels, shop owners, train stations and police boxes.
It's important to look after your passport carefully. Passports that have gone through a washing machine or exposed to heavy rain will likely need to be replaced.
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
More information:
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The Japanese currency is the Yen (JPY).
No restrictions apply to bringing foreign currency in or out of the country. Declare all amounts more than JPY 1 million or equivalent, when you arrive or leave. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
Cash is preferred in most places, but cards are becoming more widely used, especially in major cities.
Hotels accept major credit cards. Credit cards are still not widely accepted outside major cities.
Some ATMs at banks and convenience stores don't accept foreign cards.
Ask your bank if your cards will work in Japan.
Local travel
Check the Japan National Tourism Organization for emergency updates in English. The site also has advice on safe and hassle-free travel in Japan.
Fukushima and surrounding areas
There are some restricted areas around the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant. This is due to the 2011 earthquake that resulted in the release of lethal radiation. The Japanese Government specifies these areas.
If you must stay overnight in restricted areas, ask local authorities for advice on how to minimise health risks.
Monitor and follow the advice from local authorities.
- Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA)
Travelling in Japan with a Disability
Japan has a number of resources available online with tips and advice on travelling around Japan as a tourist with a disability.
- Japan Travel – Traveling with a disability
- Japan Accessible Tourism Center
- Accessible Travel Japan
- Advice for travellers with a disability
Driving permit
To drive in Japan, you must hold either:
- a valid Japanese driver's licence, or
- a valid International Driving Permit (IDP) and a current Australian driver's licence
After 365 days, you need to get a Japanese licence.
Get your IDP before leaving Australia.
- Driving in Japan
- Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department
Road travel
Roads and vehicles are mostly well-maintained and traffic is orderly.
Vehicles travel is on the left-hand side like in Australia. In Japan it's illegal to drive with any alcohol in your bloodstream.
Heavy snowfalls and ice in the winter can make driving dangerous, especially if you are unaccustomed to driving in these conditions. Ensure your vehicle has the necessary equipment, including snow tyres, chains, and a dig-out kit. More information:
Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check your travel insurance policy covers you for riding motorbikes.
Always wear a helmet.
It's safe to use taxis in Japan.
Taxi drivers usually open and shut the rear passenger doors remotely.
Public transport
Japan has modern and reliable rail and bus services.
Transport and getting around safely
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Japan's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Passenger ferries depart from Tokyo (Yokohama) to many destinations across Japan as well as Asia.
Several international cruises stopover in Japan.
- Going on a cruise
Japan National Tourism Organization (JNTO)’s Tourist Information Center accepts telephone enquiries 24 hours a day. Call (+81 3) 3201 3331.
Contact your provider with any complaints about tourist services or products.
You can also contact the National Consumer Affairs Center of Japan’s Consumer Hotline for Tourists. Call (+81 3) 5449 0906 from Monday to Friday 10am to 4pm, excluding national holidays.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
For Tokyo English-speaking Police, call (+81 3) 3501 0110 (Monday to Friday 8:30am to 5:15pm).
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
If a report is hard to get, seek advice from a lawyer or the English-speaking Police.
Your travel insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Mental health services
Call TELL Lifeline services in English (+81 3) 5774 0992.
Call TELL Counselling services in English (+81 3) 4550 1146.
Living in Japan
English information on living in Japan is available from the:
- Japanese Cabinet Office
- Council of Local Authorities for International Relations
- Tokyo International Communications Committee
In Tokyo, for advice from the Foreign Residents' Advisory Centre , call (+81 3) 5320 7744.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Tokyo or Australian Consulate-General in Osaka .
Australian Embassy, Tokyo
2-1-14 Mita, Minato-ku
Tokyo 108-8361
Phone: (+81 3) 5232 4111
Fax: (+81 3) 5232 4057
Website: japan.embassy.gov.au
Email: [email protected]
Facebook: Australian Embassy Japan
Instagram: @australianinjpn
X: @AustraliaInJPN
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian Consulate-General, Osaka
16th Floor, Twin 21MID Tower
2-1-61 Shiromi, Chuo-ku
Osaka 540-6116
Phone: (+81 6) 6941 9271 or (+81 6) 6941 9448
Fax: (+81 6) 6920 4543
Website: japan.embassy.gov.au/tkyo/location_osaka.html
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Japan?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs website uses JavaScript. Please turn on "JavaScript" and use it.

Multiple Entry Visa (for nationals of visa exemption countries/regions)
Currently, all foreign nationals who wish to newly enter Japan need to apply for a visa except for re-entry cases. Meanwhile, the visa exemption measures for passport holders of countries/regions eligible to visa exemption will be resumed from 0:00 am (JST) on October 11, 2022.
[For entrants until October 10, 2022]
Currently, all foreign nationals are required to obtain a visa before entering the country except for those with re-entry permit. Nationals of visa exemption countries/regions that are currently under temporary suspension will be able to apply for a multiple-entry short-term stay visa for the purposes of business affairs, etc (Note) and for the spouse or child of a Japanese national from September 7.
Target group
- Nationals of visa exemption countries/regions
Types of Visa
Multiple entry short-term stay visa with validity of 1 year and maximum stay of 90 days at a time (business affairs, etc., spouse or child of a Japanese national)
(Note) In some cases, single-entry visa may be issued after examination.
Documents required for application
Business, etc..
- (1) Visa application form
- (2) Passport
- (3) Photograph
- (4) Certificate issued by the ERFS (the one with "Your intention of applying for Multiple Entry Visa" item marked "desired")
Spouse or child of a Japanese national
- (4) Documents certifying that the applicant is a spouse or child of a Japanese national

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
U.S. citizens needing urgent assistance should contact us by using our inquiry form or phone (03-3224-5000). If you need after-hours assistance in an emergency, please call 03-3224-5000 and ask to speak with the Embassy's duty officer. Emergency Contact Information for U.S. citizens.
All you need to know about entering, leaving and staying in Japan. Any foreign visitor entering Japan must have a valid passport for the duration of their stay, and all visitors must comply with the conditions of their visas. See below for information about the current visa requirements for Japan. Visa Information. If you have any further ...
All foreign nationals/people who need to obtain a short-term visa to Japan AND currently reside in the following countries/region, are eligible to apply for a visa online: Australia, Brazil, Cambodia, Canada, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, Taiwan, United Arab Emirates (except areas with the jurisdiction of the Consulate-General of Japan ...
If you do NOT need a visa, skip to STEP #6. Prepare all the required documents: Types of Visas & Documents. Visit the Embassy of Japan and submit all the documents: Application Drop-off Hours. Visit the Embassy of Japan to pick up the visa and pay the visa fee: Pick-up/payment Hours & Fees.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
April 26, 2024. Japanese. Tweet. Foreign nationals/people who wish to travel to Japan for tourism for a short-term period can apply for a visa online and receive an electronic visa (eVISA) through the JAPAN eVISA system. As of April 26, 2024, the JAPAN eVISA system is available for nationals/people residing in the following countries/regions.
Japan has made agreements to waive visa requirements for tourism with 61 countries and regions. You can find more information about this on the Embassy's visa section page. If you need to obtain a visa for your travels, please contact your nearest Consulate General of Japan or call the Visa Section of the Embassy at 202-238-6800.
A1: People of some countries (or from some regions) do not need a visa if their period of stay in Japan is 90 days or less and they are not going to be engaged in income-earning activities. Refer to the List of Countries and Regions that have Visa Exemption Arrangements with Japan. Q2: I want to invite a foreign national to Japan.
Your passport should also be valid for the proposed duration of your stay. Travelers not from a visa-exempt country will need to apply for one via their nearest Japanese embassy in their home nation or organize one with an accredited travel agent approved by the Japanese Embassy. The cost of visas is approximately 3,000 yen for a single-entry ...
Before you travel to Japan, make sure you have the following essential documents with you: A valid passport with at least six months of validity remaining. Your visa, if required. A copy of your travel itinerary and accommodation details. Proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay in Japan.
Most travelers to Japan can enter the country without obtaining a visa in advance. These include nationals from 65 countries, including the USA, Australia, the United Kingdom and New Zealand. You'll automatically be granted a temporary visitor visa on arrival, which is valid for up to 90 days (as long as you don't plan to work while you're ...
Visa. Most nationalities visiting Japan are issued a 90-day visitor visa upon arrival in Japan that cannot be extended within Japan (first list). Obviously, 90 days is more than enough for most tourist purposes. Some lucky countries are issued a 90-day visitor visa upon arrival that can be extended for another 90 days within Japan (second list).
Do I need a visa to enter Japan? Information regarding visas for Japan is summarized on the pages below. Please contact the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan for individual inquiries. Visa Information. Websites of Japanese Embassies, Consulates and Permanent Missions.
4. Do I need to apply for a visa? Japan will reinstate visa-free travel on October 11 for travelers from more than 68 countries, including the US, Canada, the UK, Ireland, Australia, Mexico, Argentina, Singapore, Thailand and more. If a passport holder a country on the visa-waiver list, you won't need a visa to travel to Japan if you're ...
A3: It is a visa that is issued and recorded electronically. If you apply through JAPAN eVISA, an electronic visa (eVISA) will be issued. You will not have a visa sticker in your passport. When checking in at the airport, you will be asked to display a "visa issuance notice" on your device (e.g. smart-phone, tablet) to prove that you have a ...
The first thing you should do is download the official application of the Japanese Ministry of Tourism. It is a tool that will help you organize your trip. Although you can use Google Maps, I ...
-Register relevant information and get QR codes on Visit Japan Web for smooth entry into Japan. QR codes are generated after the registration. *Immigration and Customs procedures on Visit Japan Web are available at 7 major airports (Tokyo/Narita, Tokyo/Haneda, Kansai, Chubu, Fukuoka, New Chitose, Naha). About Visit Japan Web
Business travellers need a visa if they are to receive compensation in addition to their regular salary for work carried out while in Japan. Overstaying the 90-day, tourist visa-free limit or any other visa time limit is a criminal offence. ... If you decide to travel to Japan during the typhoon season: know that you expose yourself to serious ...
Visa requirements. If you have a 'British citizen' passport, you can travel to Japan for tourism or business for up to 90 days. You will get a visa in your passport on arrival, and you do not ...
Australians are eligible for Japan's visa exemption scheme for short-stay tourism and business travel. You don't need a visa to travel to Japan for up to 90 days. Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. It is your responsibility to verify visa requirements from the nearest embassy or consulate of Japan.
Currently, all foreign nationals who wish to newly enter Japan need to apply for a visa except for re-entry cases. Meanwhile, the visa exemption measures for passport holders of countries/regions eligible to visa exemption will be resumed from 0:00 am (JST) on October 11, 2022. [For entrants until October 10, 2022]
5. As the other answers suggest, you do not need a visa to transit at Narita, as stated by Timatic, the database used by airlines: Visa required, except for holders of onward tickets transiting on the same calendar day. Important to note, however, is that a transit visa is also not required for an overnight transfer (even though Narita's ...