
- Linkedin Weekly Newsletters
- RT Notes from the Field
- Travel Tomorrow
- Responsible Tourism enters its 3rd Decade.
- Why Responsibility?
- Accountability and Transparency
- Origins of the Cape Town Declaration
- About Responsible Tourism Partnership
- Harold Goodwin
- Media Links
- Privacy Policy
- 2022 Responsible Tourism Charter
- What is Responsible Tourism?
- What does Responsible mean?
- Addressing OverTourism
- Responsible Tourism at WTM London 2023
- WTM London 2022
- WTM London 2021
- WTM London 2020
- WTM London 2019
- WTM London 2018
- WTM London 2017
- WTM London 2016
- WTM London 2014
- WTM London 2013
- WTM Africa 2024
- WTM Africa 2023
- WTM Africa 2022
- WTM Africa 2021
- WTM Africa 2020
- WTM Africa 2018
- WTM Africa 2017
- WTM Africa 2016
- WTM Africa 2015
- WTM Latin America 2023
- Latin America Responsible Tourism 2023
- WTM Latin America 2022
- WTM Latin America 2020
- WTM Latin America 2018
- WTM Latin America 2017
- WTM Latin America 2015
- Arabian Travel Market 2023
- Arabian Travel Market 2022
- Arabian Travel Market 2021
- Arabian Travel Market 2020
- Arabian Travel Market 2016
- 2023 RT Awards Cycle
- 2022 WTM RT Awards Cycle
- Global Awards 2021
- WTM, Global Responsible Tourism Awards 2021
- World Responsible Tourism Awards 2020
- World Responsible Tourism Awards 2019
- World Responsible Tourism Awards 2018
- World Responsible Tourism Awards 2017
- World Responsible Tourism Awards 2004 to 2016
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2023
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2022
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2020
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2019
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2018
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2017
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2016
- Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 2015
- India Awards
- India ICRT Awards 2024
- India ICRT Awards 2023
- India ICRT Awards 2022
- ICRT India Responsible Tourism Awards 2021
- India Responsible Tourism Awards 2021
- India Responsible Tourism Awards 2020
- India Responsible Tourism Awards 2019
- India Responsible Tourism Awards 2018
- India Responsible Tourism Awards 2017
- India Responsible Tourism Awards 2016
- Latin America RT Awards 2023
- Latin America RT Awards 2022
- Rest of the World
- Why apply for an RT Award?
- RTP Library
- RT in India
- RT Awards 2024
- Cape Town Declaration
- Responsible Tourism Action
- Sustainable Tourism
- RT in Destinations – Introduction
- RTD17 Eswatini Responsible Tourism Matters
- RTD 16 The Gambia
- RTD 15 Finland & Summer School
- RTD 15 Helsinki
- RTD 14 Plymouth. Loved to Death?
- RTD 13 Iceland
- RTD 12 Finland
- RTD11- Cape Town
- RTD 10 Calvià, Mallorca, Spain
- RTD9 – Dublin, Ireland
- RTD 8 Day 1
- RTD 8 Day 2
- RTD7 - Barcelona
- RTD6 - Brazil
- RTD6 - London, UK
- RTD5 - Canada
- RTD4 - Oman
- RTD3 – Belize
- RTD2 - Kerala
- RTD1 - Cape Town
- Leaders in RT
- Awelani Lodge
- Blouberg Camp
- Modjadji Cultural Camp
- Mtomeni Camp
- Local Voices
- Creating shared value
- Village Ways
- CGH Earth Hotels
- RT Mission Kerala
- ICRT West Africa
- ICRT Southern Africa
- ICRT South East Asia
- Outstanding Awards India
- RT Awards Inbound Operators
- RT Awards Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- RT Awards Delhi
- RT Awards Goa
- RT Awards Gujarat
- RT Awards Himachal Pradesh
- RT Awards Karnataka
- RT Awards Kerala
- RT Awards Ladakh
- RT Awards Madhya Pradesh
- RT Awards Maharashtra
- RT Awards Odisha
- RT Awards Rajasthan
- RT Awards Sikkim
- RT Awards Tamil Nadu
- RT Awards Uttarakhand
- Travelling Responsibly Overview
- 2. The Problem: why are orphanage visits harmful?
- 3. Alternatives: what does good practise look like in principle?
- 4. Alternatives: what does good practice look like in practice?
- 5. Pitfalls: what should be avoided when developing alternatives to orphanage visits?
- 6. Transitions: advice on safely moving away from orphanage visits
- Child Protection
- Codes for Tourists
- Is Flying the problem?
- Places & Tips
- Volunteering
- Wildlife & Habitats
- Videos & Podcasts
If you'd like to know when new newsletters are published please register here to receive notifications

Overtourism Solutions: Strategies to Manage Mass Tourism
This pages have been created to enable the easy sharing of experience in managing overtourism and avoiding it. There is a typology of overtourism solutions which provides an index and wherever possible a link to where further information can be found along with a contact.
The limits to growth are not just an issue for travel and tourism as the Wall Street Journal has described tourism as currently “generating a global backlash”. Responsible Tourism is about using tourism to make better places for people to live in and to visit. Overtourism is the antithesis to this, tourism is using the place and degrading it.
Overtourism describes destinations where hosts or guests, locals or visitors, feel that there are too many visitors and that the quality of life in the area or the quality of the experience has deteriorated unacceptably. It is the opposite of Responsible Tourism which is about using tourism to make better places to live in and better places to visit. Often both visitors and guests experience the deterioration concurrently.
The problem is not going to go away – we need to work out how to cope with it. The challenge for businesses and destination marketing organisations is that they no longer have a free hand to use the places that people live and work in to attract visitors. The residents, whose place it is, are beginning to rebel and consumers are all too aware that some destinations are not what they were. The challenge now is to develop ways of “Coping with Success”, addressing overtourism.
Essential Preconditions
In many places, there is confusion about the roles of DMOs. The same acronym is used for both Destination Management Organisations and Destination Marketing Organisations with bodies composed primarily of private sector representatives spending private sector and public money on destination promotion.
In Barcelona the management of tourism is unequivocally the responsibility of the city council. It is significant that the “objectives and strategic lines” of Turisme de Barcelona, the public-private partnership organisation which markets the city include public policy objectives. Turisme de Barcelona recognises its “social and institutional responsibility” to “achieve a balance between tourist activity and everyday life in the city” and encouraging wider geographic distribution of tourism in the city.
- a) To boost the financial impact of the sector and to attract tourists with high spending power; b) To promote its own identity as a tourist attraction; c) To reconcile tourists/local community; d) To ensure the geographical and multi-sectorial distribution of tourism; e) To strengthen the public-private promotional model.
Overtourism is often attacked as tourismophobia . Barcelona has countered this view, as Ada Colau, now Mayor Barcelona said in 2014:
“Of course, the answer is not to attack tourism. Everyone is a tourist at some point in their life. Rather, we have to regulate the sector, return to the traditions of local urban planning, and put the rights of residents before those of big business.
The way of life for all Barcelonans is seriously under threat. And the only solution is to win back democracy for the city. This is precisely what the residents of La Barceloneta are doing – defending their neighbourhood, their city, from the free market and from the political elites that are putting our home up for sale.” more
Governance Barcelona & Kerala have effectively managed different sets or overtourism challenges by engaging the tourism sector and local communities in addressing the particular local issues and using a multi-stakeholder approach.
Barcelona's Strategy and Action Barcelona is using a wider range of mechanisms to address the challenge of overtourism than any other destination, their experience is important as others rise to the challenge.
Barcelona has sought, since 2004, to make tourist activities more sustainable, to increase the positive impacts of tourism in the city and to integrate visitors fostering coexistence, Barcelona aspires to treat visitors as temporary residents . The city is working to ensure that there are no tourist ghettos and that tourism contributes to the improvement of the quality of life and social cohesion. Barcelona has recognised that sustainability and competitiveness need to be used together in managing tourism. In Barcelona, a City and Tourism Council has been formed to advise the City Council on tourism policy and management. more
As in many sectors, the regulation moves more slowly than the growth of new business models. This has been evident in the growth of businesses like Airbnb and Uber where regulators have struggled to keep up. Similarly, the management of the public realm – streets, parks and squares - has been a major challenge as tourism numbers have grown and accelerated.
Shared/reliable common information Effective management action involving diverse stakeholders requires shared data. Dichter, a senior partner of McKinsey & Company consultancy, says that:
“We talk to so many people in the tourism ecosystem and no one has the same facts – not even close,” … “If you can’t even agree on how many tourists are showing up, it’s very difficult to have a proper debate.” More
Only with good data is it possible to identify benefits and costs and develop management strategies to rebalance tourism. Shared, publicly available, reliable data has been a major plank of Barcelona’s efforts to address overtourism. The UNWTO points to the importance of “monitoring and evidence-based decisions.”
Barcelona surveys its residents regularly to determine their views about tourism and other problems in the city.
Barcelona publishes monthly forecasts of volumes of visitor numbers for each day reporting all events or activities which involve 10,000 or more people, where the forecast goes over 70,000 the calendar shows red, residents can then avoid the congested areas or avoid the city altogether. In September 2018 there were three days over 200,000, one of which was close to 300,000. example
Strategies to manage overtourism
Limits of Acceptable Change
Identify key indicators for the destination which identify the emerging issues so that they can be addressed. The growth of unlicensed tourist accommodation and change of use for the housing stock, changing retail offer, rising local housing costs, litter, trampling, crowding... choose the locally significant issues and problems.
Preferential Access for Locals At Park Güell, in Barcelona access to the Monument Area (7.9% of its area) has been regulated. In 2013, an 8€ entry fee was imposed, local residents have unrestricted and free access
Barcelona publishes monthly forecasts of volumes of visitor numbers for each day reporting all events or activities which involve 10,000 or more people, where the forecast goes over 70,000 the calendar shows red, residents can then avoid the congested areas or avoid the city altogether. In September 2018 there were three days over 200,000, one of which was close to 300,000.
Temporary Residents Changing the nature of tourism and the visitor experience by managing the destination to attract visitors as temporary residents. This strategy can change the dynamics of tourism and the host-guest relationship.
Tourist Tax
Tourism Taxes are controversial. They are generally too low to deter visitors, but they do enable local authorities to raise money to fund the management of tourism, to repair damage to lawns and pay for the removal of litter.
If one of the aspirations of Responsible Tourism is that tourists should be treated as temporary residents then it is not unreasonable that overnight tourists and day visitors should contribute to the maintenance of the public realm which they are visiting and using. Tourism taxes are generally levied through accommodation providers and occasionally through tour companies. New Zealand has introduced a $35 tourism levy to protect tourist hot spots.
Amsterdam has introduced a Day Tourist Tax for TRANSIT sea cruise and river cruise passengers that moor within the municipal boundaries of Amsterdam.
Ensuring that local community’s benefit from tourism
In Kerala, India, the state government has established a Responsible Tourism Mission to ensure that local communities benefit through the creation of shared value.
Supply-side initiatives
Accommodation Deregulated housing markets can attract international investors causing inflation in housing costs, and holiday rentals can be far more lucrative than letting to residents and families. By restricting the availability of accommodation visitor arrivals can be restricted.
Issues arise where there are concentrations of tourism in particular areas where tourism comes to dominate, and where there is unlicensed and unregulated accommodation which may cause disturbance and raises issues of health and safety and taxation.
In July 2015, Barcelona's municipal government suspended the processing of new permits for tourist-accommodation, student-residences and youth-hostel establishments, to analyse the impact of tourist-accommodation activities in all its aspects and to draft a special urban-development plan to regulate it. Ciutat Vella now has a Usage Plan designed to restrict the growth of tourist accommodation, whether hotels or apartments and a Tourist Accommodation Working Group has been tasked to complement municipal efforts to reduce the numbers of unlicensed apartments.
Disintermediation Airbnb is most often the focus of attention; the internet has replaced small ads in newspapers, magazines and shop windows as a means of advertising accommodation. This has made it easier to market accommodation and this, coupled with the deregulation of housing in many jurisdictions, has led to a significant increase in the letting of accommodation to tourists and in many places a depletion in accommodation stock available to residents, often with negative social and economic impacts.
Barcelona and Dublin have regulated Airbnb. From June, 2019, in designated rent-pressure zones, which cover Dublin and major commuter towns as well as Galway and Cork cities and part of Limerick, councils will need to grant planning approval for any short-term letting of investment properties. Where a house or apartment is a person's principal private residence, they will be permitted to rent out a room (or rooms) within their home for short-term letting without restriction. However, they will only be allowed to sub-let their entire house without planning permission on the short-term market for a cumulative period of 90 days or less annually. Individuals who own a second property will no longer be allowed to arrange short-term lettings, unless the property already has permission to be used for such purposes or for tourism. more
Matching Demand to Supply Timed ticketing and seasonal pricing all help in matching demand to supply and can contribute to ensuring that visitors have a better experience. Praia das Catedrais or “Cathedrals Beach” on the Galician coast in northwest Spain requires an advance booking .
Spatial and Town Planning Local governments and national parks are generally able to control the siting of accommodation and other visitor services, depending on national planning policy frameworks.
The Amsterdam municipal authority introduced a zoning plan "Shop Diversity Center" prohibits new shops opening in the city center that mainly target tourists and day visitors, such as souvenir shops. The municipality argued that it wants to counteract a so-called monoculture in the city center and prevent tourist shops from gaining the upper hand in the streets. Tourism companies that existed before 2017 are excluded from the zoning plan rules. Building owners and companies objected to the restrictions imposed by the zoning plan, accusing the municipality of violating the European Services Directive, discrimination, and causing property values to fall. In April 2020, the Council of State found in favour of the municipality deciding that the Amsterdam city council could reasonably conclude that there is a monoculture of shops and facilities in the city center, and that banning new tourist shops was in the interest of the people who live and work in Amsterdam. The Council of State also saw no grounds for claims of discrimination and building depreciation. more
Transport Barcelona has experimented with moving coach parks, bus routes and pick-up and put-down points to change the way tourists move through an urban area. In rural areas and in national parks, parking has been used to control visitor movements and reduce dispersal to the sacrifice zone. Strategies like pedestrianisation and park-and-ride can benefit residents as well as assisting in managing tourism and the tourist experience.
Closure Closing areas to allow regeneration has long been a management practice in natural areas. Thai officials said Maya Bay needed an enforced break from the daytrippers who have flocked there since it was featured in 2000 film The Beach. more Thailand closed dozens of dive sites to tourists in 2011. Koh Yoong, in the Phi Phi island chain and Koh Tachai, in the Similan Islands National Park, have also been off-limits to visitors since mid-2016. more Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte announced that Boracay Island will also be closing for a few months, having, in his words, become an overcrowded "cesspool". more
Banning Second Home Building Banning the building of second homes may have unintended consequences as those outsiders wanting to purchase buy existing properties raising prices and damaging the local building and tourism industries.
Banning Motor Homes In the UK Swale Borough Council in Kent has used Section 43 of the anti-social behaviour, crime and policing act to ban overnight camping between 8pm and 8am as illegal and likely to have a "detrimental effect" on locals. The Council says that the council had received complaints "This conduct is unreasonable and must stop immediately." Continued use would result in a £100 fixed penalty notice. If unpaid, magistrates can issue a fine of up to £2,500 and require the "surrender of possessions" which could then be destroyed or disposed of by police.
Section 43: Power to issue notices (1)An authorised person may issue a community protection notice to an individual aged 16 or over, or a body, if satisfied on reasonable grounds that— (a)the conduct of the individual or body is having a detrimental effect, of a persistent or continuing nature, on the quality of life of those in the locality, and (b)the conduct is unreasonable.
In New Zealand, new legislation was introduced in August 2011 empowering local councils to issue fines to people freedom camping in non-designated places. Details
Demand-side initiatives
Ministers of Tourism and DMOs are generally judged by the visitor arrivals figures, and for national governments with their focus on exports, international arrivals are the key measure of the value of the marketing organisation. If you change the KPI of a marketer, they will deliver to it. A destination could choose to focus on visitor spend, length of stay, distribution and dispersal or on particular market segments. If you don't change the KPIs they will do the easy thing and sell the honeypots.
Attract tourists who fit the destination - change the destination's image Businesses and the destination marketers should focus their efforts on attracting the market segments which fit the destination. Barcelona has been explicit:
“What is good for citizens is good for the tourist. Places that are good to live in are also good to visit. Efforts will be made to improve the quality of life for local people by managing the friction between residents and visitors and to improve the interaction between hosts and guests…..” and that the “tourist that Catalunya wants to attract is the one who will respect the environment, the society and the local culture, eager to discover and share experiences.” more
Cap Arrivals Neither Barcelona nor Venice is able to manage tourist arrivals, both have good road links, airports, railway stations and ports, none of which are they able to manage. Dubrovnik, by contrast, has been able to limit cruise ship arrivals. In October 2018 it announced that it is limiting cruise ship arrivals from 2019 to two per day, allowing only 5,000 visitors to arrive by sea each day.
Bruges has placed a cap on the number of cruise ships and an end to all advertising campaigns encouraging daytrippers.

Change Tourist Behaviour through marketing and advice
a) Demarketing Demarketing can be used to discourage visitors in order to reduce negative impacts – as with marketing there is a range of methods available from price rises to reducing promotional activity and spreading the word that the quality of the experience has deteriorated to discourage visitors.
b) Discourage “Bad” Tourists and Tourism Banning stag nights and hen dos. In Barcelona, it is known as “turismo de Borrachera” travelling to another place to behave in ways you would not do where you are known. This does not always require travel across an international boundary.
Rome has outlawed men going topless in public and the practice of attaching “love padlocks” to bridges, both of which carry a fine if contravened. Eating messy foods around tourist attractions, touching your lips against the spout when drinking from Roman public water fountains, Ticket touts selling “skip the line” tickets at some of the Eternal City’s biggest attractions, such as the Vatican Museums and Colosseum, are prohibited, as well as those who dress up as Roman centurions around tourist hotspots and charge money for photos.
c) Pricing and Rationing Dynamic pricing charging higher prices at peak demand and lower prices when demand and crowding is less
Site Hardening
Constructing facilities and locating trails and roads to reduce the impacts of visitors on sensitive soils and vegetation, and to help meet the visitors' needs for user access.
Managing activity in the destination
Municipal Regulation Examples where a local government organisation has taken a holistic approach to the management of tourism in the destination as has been the case in, for example, Barcelona and Sagada in the Philippines.
Introducing guide and tour operator licenses. In Barcelona, there is a city task group working to prevent the spread of souvenir shops in Ciutat Vella, Sagrada Família, Park Güell
Dispersal – Spatial Spread the tourist out by encouraging them to visit less visited places, there may well be districts and areas where people would like to see more tourists, boost less popular attractions and develop new ones. Paris has done this effectively for many years. Barcelona has adopted spatial dispersal as part of its strategy and Helsinki has encouraged citizens to invite tourists to visit their favourite places.
Create new itineraries and guided tours to less visited areas Consider regulating group size and coach drop off points to manage visitor flows
In Ireland the Wild Atlantic Way
Dispersal - temporal Attracting tourists to visit at other times of the year, week and day to disperse the positive and negative impacts of tourism.
Timed Tickets and Differential Pricing
'Policing' Activities and Behaviour Since May 2017 in Florence:
"From today, we'll be experimenting with a very simple measure: pouring water over the church steps to clean the spaces, and hopefully discourage people from eating, drinking and making a mess there,"
Mayor Dario Nardella told reporters. "If tourists want to sit there, they'll get wet," he said. "Florence is full of cafes with outdoor seating, tables, and benches. The churches aren't restaurants; they are religious and cultural sites." more
Since 2018 in Amsterdam: Public consumption of alcohol will result in a fine of €95; public urination, disorderliness and littering, meanwhile, will draw fines of €140.
The council has also announced plans to tackle overcrowding in The Wallen, which residents say has become “unliveable” due to mass tourism. Streets there will be monitored in real time and coded green, orange or red, depending on how busy they are. If a code red is called, officials will be deployed and “if necessary, streets will be closed,” the council said. More
Closure Komodo, Indonesia The fight for Dragon Island Maya Bay "The Beach" Thailand
If you have solutions for overtourism which you would like to see included here please email [email protected] Your contribution will be acknowledged.
- EU (2018) Research for TRAN Committee - Overtourism: impact and possible policy responses
- Goodwin H (2018) Managing Tourism in Barcelona 2nd Edition
- Goodwin H (2017) The Challenge of Overtourism
- McKinsey & WTTC (2017) Coping with success: Managing overcrowding in tourism destinations
- UNWTO (2018) ‘Overtourism’? – Understanding and Managing Urban Tourism Growth beyond Perceptions, Executive Summary
Latest News Items

Harold on the Web

Get a sample of Harold Goodwin's Book "Responsible Tourism"

What is overtourism and how can we overcome it?

The issue of overtourism has become a major concern due to the surge in travel following the pandemic. Image: Reuters/Manuel Silvestri (ITALY - Tags: ENTERTAINMENT)
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Joseph Martin Cheer
Marina novelli.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Travel and Tourism is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, travel and tourism.
Listen to the article
- Overtourism has once again become a concern, particularly after the rebound of international travel post-pandemic.
- Communities in popular destinations worldwide have expressed concerns over excess tourism on their doorstep.
- Here we outline the complexities of overtourism and the possible measures that can be taken to address the problem.
The term ‘overtourism’ has re-emerged as tourism recovery has surged around the globe. But already in 2019, angst over excessive tourism growth was so high that the UN World Tourism Organization called for “such growth to be managed responsibly so as to best seize the opportunities tourism can generate for communities around the world”.
This was especially evident in cities like Barcelona, where anti-tourism sentiment built up in response to pent-up frustration about rapid and unyielding tourism growth. Similar local frustration emerged in other famous cities, including Amsterdam , Venice , London , Kyoto and Dubrovnik .
While the pandemic was expected to usher in a new normal where responsible and sustainable travel would emerge, this shift was evidently short-lived, as demand surged in 2022 and 2023 after travel restrictions eased.
Have you read?
Ten principles for sustainable destinations: charting a new path forward for travel and tourism.
This has been witnessed over the recent Northern Hemisphere summer season, during which popular destinations heaved under the pressure of pent-up post-pandemic demand , with grassroots communities articulating over-tourism concerns.
Concerns over excess tourism have not only been seen in popular cities but also on the islands of Hawaii and Greece , beaches in Spain , national parks in the United States and Africa , and places off the beaten track like Japan ’s less explored regions.
What is overtourism?
The term overtourism was employed by Freya Petersen in 2001, who lamented the excesses of tourism development and governance deficits in the city of Pompei. Her sentiments are increasingly familiar among tourists in other top tourism destinations more than 20 years later.
Overtourism is more than a journalistic device to arouse host community anxiety or demonize tourists through anti-tourism activism. It is also more than simply being a question of management – although poor or lax governance most definitely accentuates the problem.
Governments at all levels must be decisive and firm about policy responses that control the nature of tourist demand and not merely give in to profits that flow from tourist expenditure and investment.
Overtourism is often oversimplified as being a problem of too many tourists. While that may well be an underlying symptom of excess, it fails to acknowledge the myriad factors at play.
In its simplest iteration, overtourism results from tourist demand exceeding the carrying capacity of host communities in a destination. Too often, the tourism supply chain stimulates demand, giving little thought to the capacity of destinations and the ripple effects on the well-being of local communities.
Overtourism is arguably a social phenomenon too. In China and India, two of the most populated countries where space is a premium, crowded places are socially accepted and overtourism concerns are rarely articulated, if at all. This suggests that cultural expectations of personal space and expectations of exclusivity differ.
We also tend not to associate ‘overtourism’ with Africa . But uncontrolled growth in tourist numbers is unsustainable anywhere, whether in an ancient European city or the savannah of a sub-Saharan context.
Overtourism must also have cultural drivers that are intensified when tourists' culture is at odds with that of host communities – this might manifest as breaching of public norms, irritating habits, unacceptable behaviours , place-based displacement and inconsiderate occupation of space.
The issue also comes about when the economic drivers of tourism mean that those who stand to benefit from growth are instead those who pay the price of it, particularly where gentrification and capital accumulation driven from outside results in local resident displacement and marginalization.
Overcoming overtourism excesses
Radical policy measures that break the overtourism cycle are becoming more common. For example, Amsterdam has moved to ban cruise ships by closing the city’s cruise terminal.
Tourism degrowth has long been posited as a remedy to overtourism. While simply cutting back on tourist numbers seems like a logical response, whether the economic trade-offs of fewer tourists will be tolerated is another thing altogether.
The Spanish island of Lanzarote moved to desaturate the island by calling the industry to focus on quality tourism rather than quantity. This shift to quality, or higher yielding, tourists has been mirrored in many other destinations, like Bali , for example.
Dispersing tourists outside hotspots is commonly seen as a means of dealing with too much tourism. However, whether sufficient interest to go off the beaten track can be stimulated might be an immoveable constraint, or simply result in problem shifting .
Demarketing destinations has been applied with varying degrees of success. However, whether it can address the underlying factors in the long run is questioned, particularly as social media influencers and travel writers continue to give attention to touristic hotspots. In France, asking visitors to avoid Mont Saint-Michelle and instead recommending they go elsewhere is evidence of this.
Introducing entry fees and gates to over-tourist places like Venice is another deterrent. This assumes visitors won’t object to paying and that revenues generated are spent on finding solutions rather than getting lost in authorities’ consolidated revenue.
Advocacy and awareness campaigns against overtourism have also been prominent, but whether appeals to tourists asking them to curb irresponsible behaviours have had any impact remains questionable as incidents continue —for example, the Palau Pledge and New Zealand’s Tiaki Promise appeal for more responsible behaviours.
Curtailing the use of the word overtourism is also posited – in the interest of avoiding the rise of moral panics and the swell of anti-tourism social movements, but pretending the phenomenon does not exist, or dwelling on semantics won’t solve the problem .
Solutions to address overtourism
The solutions to dealing adequately with the effects of overtourism are likely to be many and varied and must be tailored to the unique, relevant destination .
The tourism supply chain must also bear its fair share of responsibility. While popular destinations are understandably an easier sell, redirecting tourism beyond popular honeypots like urban heritage sites or overcrowded beaches needs greater impetus to avoid shifting the problem elsewhere.
Local authorities must exercise policy measures that establish capacity limits, then ensure they are upheld, and if not, be held responsible for their inaction .
Meanwhile, tourists themselves should take responsibility for their behaviour and decisions while travelling, as this can make a big difference to the impact on local residents .
Those investing in tourism should support initiatives that elevate local priorities and needs, and not simply exercise a model of maximum extraction for shareholders in the supply chain.
How is the World Economic Forum supporting the development of cities and communities globally?
The Data for the City of Tomorrow report highlighted that in 2023, around 56% of the world is urbanized. Almost 65% of people use the internet. Soon, 75% of the world’s jobs will require digital skills.
The World Economic Forum’s Centre for Urban Transformation is at the forefront of advancing public-private collaboration in cities. It enables more resilient and future-ready communities and local economies through green initiatives and the ethical use of data.
Learn more about our impact:
- Net Zero Carbon Cities: Through this initiative, we are sharing more than 200 leading practices to promote sustainability and reducing emissions in urban settings and empower cities to take bold action towards achieving carbon neutrality .
- G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance: We are dedicated to establishing norms and policy standards for the safe and ethical use of data in smart cities , leading smart city governance initiatives in more than 36 cities around the world.
- Empowering Brazilian SMEs with IoT adoption : We are removing barriers to IoT adoption for small and medium-sized enterprises in Brazil – with participating companies seeing a 192% return on investment.
- IoT security: Our Council on the Connected World established IoT security requirements for consumer-facing devices . It engages over 100 organizations to safeguard consumers against cyber threats.
- Healthy Cities and Communities: Through partnerships in Jersey City and Austin, USA, as well as Mumbai, India, this initiative focuses on enhancing citizens' lives by promoting better nutritional choices, physical activity, and sanitation practices.
Want to know more about our centre’s impact or get involved? Contact us .
National tourist offices and destination management organizations must support development that is nuanced and in tune with the local backdrop rather than simply mimicking mass-produced products and experiences.
The way tourist experiences are developed and shaped must be transformed to move away from outright consumerist fantasies to responsible consumption .
The overtourism problem will be solved through a clear-headed, collaborative and case-specific assessment of the many drivers in action. Finally, ignoring historical precedents that have led to the current predicament of overtourism and pinning this on oversimplified prescriptions abandons any chance of more sustainable and equitable tourism futures .
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Travel and Tourism .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How Japan is attracting digital nomads to shape local economies and innovation
Naoko Tochibayashi and Naoko Kutty
March 28, 2024

Turning tourism into development: Mitigating risks and leveraging heritage assets
Abeer Al Akel and Maimunah Mohd Sharif
February 15, 2024

Buses are key to fuelling Indian women's economic success. Here's why
Priya Singh
February 8, 2024

These are the world’s most powerful passports to have in 2024
Thea de Gallier
January 31, 2024

These are the world’s 9 most powerful passports in 2024

South Korea is launching a special visa for K-pop lovers

7 Ways You Can Help Turn the Tide on Overtourism
- Last Updated: January 10, 2023
The ultimate guide to overtourism solutions and how you can beat this global issue!
Travel has never been easier.
With more and more people exploring the world though, some of our most well-loved destinations are feeling the strain.
What are the overtourism solutions and can you as an individual create an impact?
READ MORE: Check out our ultimate guide to sustainable tourism !
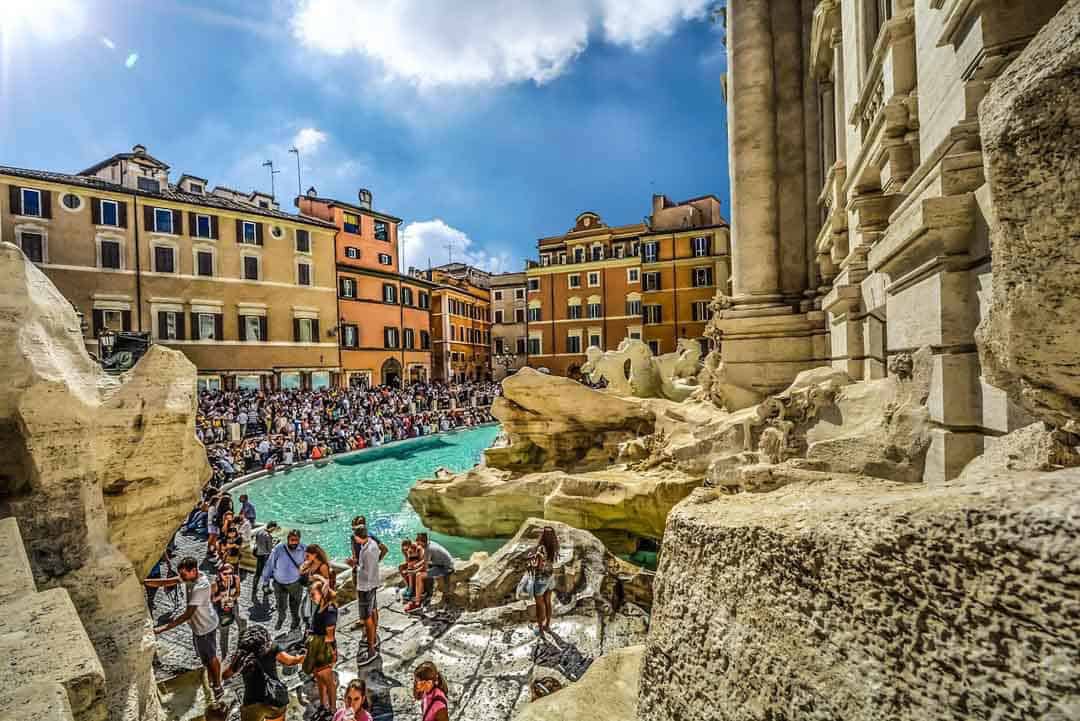

Table of Contents
What Is Overtourism?
Tourism is a good thing…isn’t it, some impacts are obvious, other impacts take place behind the scenes, what’s the solution to overtourism, 1. search out regional alternatives, 2. visit during off-peak periods, 3. support the local community with your time and money, 4. explore beyond the hotspots with a local guide, 5. be an eco-friendly, responsible traveler, 6. travel with responsible, ethical tour companies, 7. travel off the beaten track, overtourism solutions: here are 7 ways you can help turn the tide on overtourism.
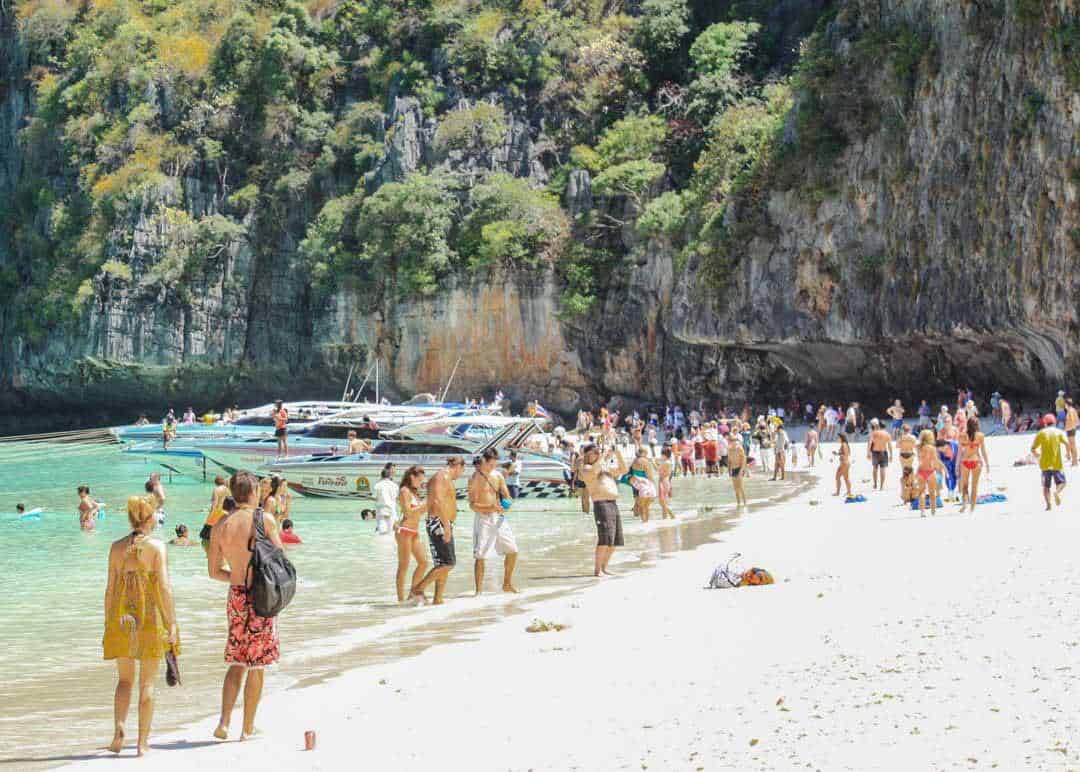
Our brightly painted long-tail boat motored around the curve of Koh Phi Phi Leh’s sheer karst walls.
I’d been waiting for this moment for years, ever since Leo stepped out from the palms and onto the shore of ‘The Beach’ at the movies.
Between the film, the internet, and my partner John’s nostalgic musings on Thailand in the ’90s, I could picture Maya Bay perfectly: an idyllic haven of pearly white sand lapped by turquoise water, surrounded by high cliffs.
Then the whining roar of a speed boat cut through my reverie, just as the bay opened up before us.
But in place of a peaceful cove, all I could see was an armada of boats.
The bay was a frenzy of activity. Speedboats packed one end of the beach, long-tail boats the other.
Hundreds of people wandered the sandy shore and splashed about in the shallows. Guides blew high-pitched whistles to gather their groups.
Empty beer cans floated in the water, alongside drifts of discarded plastic trash.
Stepping ashore, I felt an abject sense of disappointment and dismay.
I hadn’t been expecting a lost paradise. But the scene before me was more like a paradise lost.
This year, the Thai government took the drastic step of closing Maya Bay to tourists.
The move might be temporary, but this much-loved cove is just one more casualty in a line-up of destinations where an ever-rising wave of tourism is threatening to wash away the very charms that draw us to them in the first place.
There’s a buzzword for the phenomenon too: Overtourism.

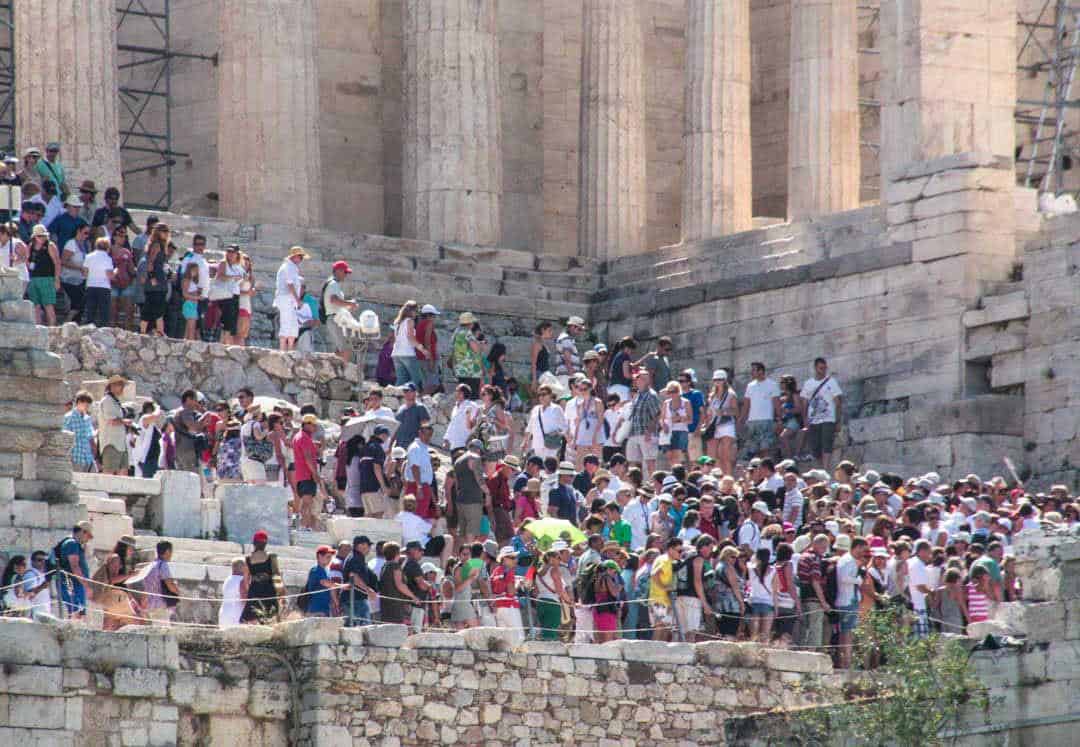
If you’ve ever experienced the heaving summer crush atop the ancient Acropolis in Athens, or elbowed your way through the high season hordes at the Trevi Fountain in Rome, then you’re familiar with overtourism. I
t’s what happens when a place attracts more tourists that it can reasonably sustain.
The problem of overtourism isn’t limited to cities or sights where mass tourism has taken hold either, though all-inclusive package holidays, big resorts and even bigger cruise ships all play a significant role.
Overtourism can also be an issue for fragile environments, ecosystems and wildlife, where even small increases in visitation can have a long-lasting impact.
Managed well, tourism can be a positive game-changer for destinations.
It creates jobs, attracts investment, drives infrastructure development.
Ethical, sustainable tourism can also improve livelihood, education levels and quality of life for local people.
It can refocus energy and action towards conservation, and help to preserve cultural traditions.
Without checks and balances though, unregulated tourism growth can sound a death knell for some destinations.
Or at the very least, our experience of them.

What Are The Impacts Of Overtourism?
When a destination takes on more tourists than it can cope with, the fallout can run deep.
Overcrowding is one glaring result.
On the Isle of Capri in Italy, peak season can see up to 15,000 visitors a day thronging the narrow, cobbled streets of the ancient holiday escape.
Enjoying a casual wander is almost impossible.
Excessive footfall and human interaction, plus all the extra waste that comes with many more people, can also have a detrimental effect on delicate historic sites and environments.
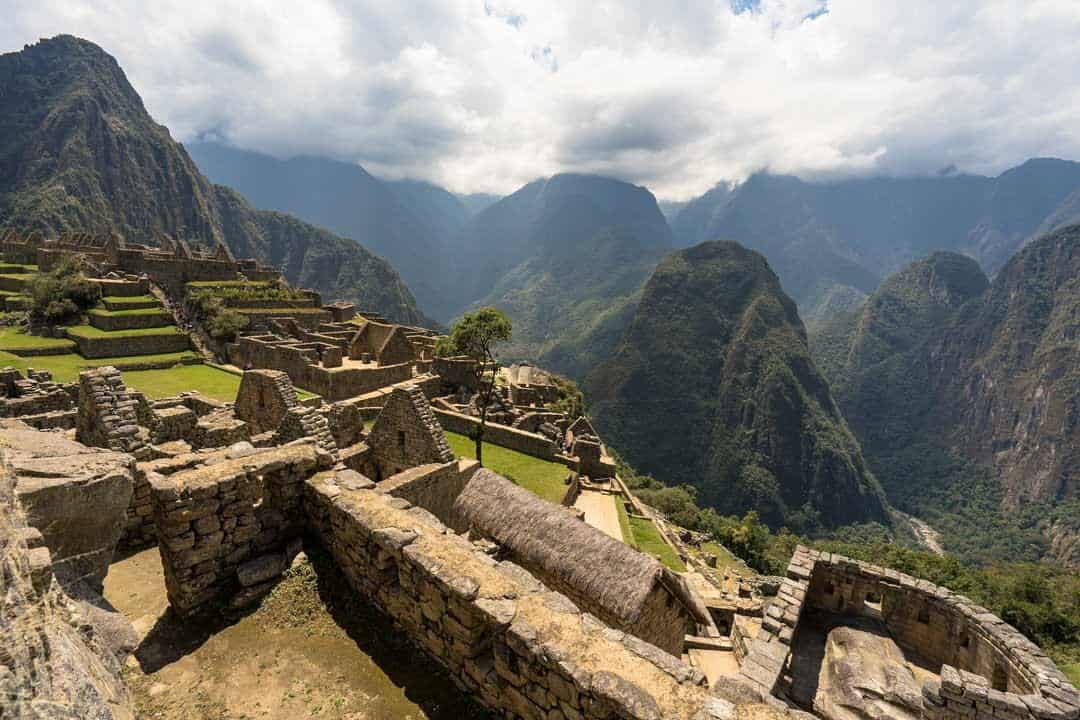
Machu Picchu , the mountaintop Incan citadel in Peru, is one destination at very real risk of crumbling under the pressure of too much tourist love.
In response, the Peruvian government has implemented morning and afternoon entry sessions and one-way circuits in a bid to control foot traffic, alleviate erosion and protect the 550-year-old stone buildings of this World Heritage jewel.

Unchecked tourism can also put wildlife at risk of harm and stress.
We felt this all too keenly on a trip to swim with whale sharks in Mexico .
Despite local efforts to regulate licensing and monitor boats, ever-increasing demand for the experience is driving a rise in unlicensed operators with little regard for rules, or the wildlife.
Overtourism can also wreak a more insidious havoc.
In Venice, for example, the massive tourist influx in peak has led to rent hikes and housing shortages that are effectively driving locals out of the city.
This creates a different issue altogether.
If you take the inhabitants out of a place, you lose the vibrant characters, stories and cultural idiosyncrasies that bring that destination to life.
Without locals, all you’re really left with is a pretty stage set.
What about all the money generated by that excess of tourism?
In reality, it doesn’t always make its way into local hands or programs.
What little does though can sometimes create an unsustainable reliance on tourism, driving negative behaviours like overzealous touting or begging.
It can also have devastating consequences for locals if tourism suddenly takes a tumble.

In the big picture, governments and the global tourism industry have a huge task ahead in the fight against overtourism.
Fortunately, many are starting to take note.
In Antarctica, an association-led system of protocols and practices – like collaborating on cruising itineraries, and daily caps on the number of people making shore landings per site – are designed to minimise the pressures of growing tourism on this pristine environment.
If you want to know more about travelling to Antarctica responsibly check out our article.
Likewise, in the Galapagos Islands , there are caps on the number of berths allowed in the cruising tour fleet.
This ensures tourist numbers are limited, at least to the archipelago’s more remote islands, which is critical for protecting their unique ecosystems and wildlife.
Options like tourist taxes and ticketing systems are being explored in some places, along with technological solutions.
In Italy’s hugely popular Cinque Terre, a phone app is being trialed that shows visitors real time congestion on the trails, and points them in the direction of alternatives.
Even one of the world’s most remote destinations, Easter Island , has recently changed the length of stay for tourist visas from 90 days to 30; an effort to curb the impacts of rising tourism on the tiny Pacific isle.
For some places though, like Maya Bay in Thailand, and Boracay Island in the Philippines, the strain of overwhelming visitation has led to the extreme measure of closing the destinations to tourists altogether: an enforced time out for clean-up and recovery.
The challenge will be ensuring that when these places reopen to visitors, they do so with responsible, sustainable tourism measures in place.

What Can You Do About Overtourism?
As one person, overtourism might feel like an issue that’s simply too big for you to have any real impact on.
The choices you make though, about where you go, what you do, and how you spend your tourist dollar, can actually go a long way to helping ease the pressures of overtourism.
Here are 7 steps you can take as a responsible traveller.
Places suffering overtourism are usually bucket list headliners for a reason: they’re special.
But while the hordes are pounding the well-trodden paths of these tourist hotspots, why not get off the tourist trail and search out a destination’s lesser known sights and experiences?
Take the island of Bali.
This relatively small corner of the Indonesian archipelago attracted more than 5 million tourists in 2017.
Visitors tend to congregate around the island’s south, in heaving tourist centres like Seminyak and Kuta, and much has been written on the challenges brought about by tourism in those places.
But there’s an entire island outside of Bali’s resort towns, and plenty of spots where you can still find a low-key patch of paradise, mingle with locals, and experience Bali’s distinctive island culture.
Or take the opportunity to explore another part of Indonesia.
From the jungles of Sumatra and the temples of Java, to the white- and black-sand beaches of Flores, there are literally dozens of destinations right across Indonesia that offer palm-fringed curves of sand, outdoor adventure and diverse culture.
Without the tourist crowds.
Taking yourself and your dollar off the tourist trail means you’ll meet more locals, experience more authentic culture, and take away memories and photos that don’t look like everyone else’s.
Better yet, you’ll be investing directly into local communities.

What if you really, really want to visit that hugely popular place though?
If that’s the case, try and visit outside of peak times.
Peak periods are different for every place and every experience.
If you want to avoid the worst of the crowds, you’ll need to do your research before you go.
There can be drawbacks to visiting out of peak.
The weather might be less than ideal.
You might have fewer daylight hours to play with.
Some tourist attractions and amenities could even be closed.
On the plus side, you’ll be contending with fewer tourists, and you’ll often be able to take advantage of cheaper flights, accommodation and experiences.
Plus, seasonal changes usually bring a whole new set of highlights and opportunities to seek out.
Even visiting a popular destination out of busy hours can make all the difference.
In Croatia, Dubrovnik’s Old Town turns into a tourist crush during the hot daylight hours of the cruise ship season.
But a morning stroll along the city walls before the crowds arrive, or an evening wander through its lantern-lit streets after they’ve shipped out?

While tourism can bring a much-needed boost to a local community, the reality is that large tour groups – particularly package and cruise ship tours – often spend little time, and even less money in the places they’re visiting.
By staying longer, sleeping in locally owned accommodations, eating at smaller, locally owned restaurants, and joining tours or experiences run by responsible local operators, you can feel more confident that your valuable tourist dollar is going directly into that community.
Likewise, if you’re keen to buy a souvenir or keepsake, keep an eye out for local artisans and, if you can, buy from them direct.

For many of our over-loved destinations, crowds are often concentrated around a handful of hotspots.
But what about the rest the place?
Exploring a destination with a responsible local guide can reveal an entirely different side to the place you’re visiting, and get you away from the over-touristed mainstream.
Local guides will often take you to places most tourists never get to see.
They’ll introduce you to real locals, and to the sights, tastes, customs and stories that give a place its character.
Joining small group tours like offbeat city walks, cycle tours, guided nature hikes and foodie strolls is one way you can help to shift tourism away from high traffic pressure points.
Plus, by choosing small local businesses, you’re supporting the local economy.
With a bit of research online, and using forums like TripAdvisor, it’s easy to find reputable, responsible guides and tour operators just about everywhere.

‘Leave no trace’ is a mantra these days for responsible travelers.
It becomes even more important in the context of overtourism, where ever-increasing numbers of tourists means ever-increasing volumes of waste for local communities to deal with.
By taking steps to minimise the waste you produce on your travels, and encouraging others to do the same, you can do your bit in helping to ease the pressures on this front.
Just having some key items in your backpack like a cloth shopping bag, a reusable water bottle, a keep cup, a biodegradable toothbrush and cutlery, and a reusable straw, will immediately reduce your environmental footprint as you travel.
Check out this article if you want more ideas on how to be a responsible traveler.
You can also find out if there are local clean-ups or other opportunities and volunteering programs where you can donate your time, and help give back to the communities you’re visiting.

Travelling as part of a tour can be a fantastic way of exploring a new destination without the hassle and uncertainty that sometimes accompanies independent travel.
Not only does someone else do the planning for you, but you’ll meet like-minded people, and visit places you might not otherwise get to on your own.
By opting for a tour company with a solid reputation for responsible, ethical tourism practice, you’ll be directly supporting sustainable tourism.
Responsible travel operators will often have a policy or set of core values on their website that defines what responsible travel means to them and their people, and how they achieve this through their tours.
While responsible tour companies may include tourism hotspots within their itineraries, they’ll usually find ways to visit those places sustainably, reduce their impact, and ensure that local people and businesses benefit from you being there.
At the end of the day, the most effective way of easing the pressure on our over-touristed destinations is to go somewhere else instead.
Ideally, somewhere that would benefit from more visitors.
The opportunities to get off the beaten track are better than ever, and many destinations are welcoming travellers with open arms.
Like Iran .
We traveled there for close to a month, and encountered a beautiful, safe and surprisingly diverse country.
The people were warm, kind and eager to spend time with us and share their stories.
Other travelers were few and far between, and there were times when we felt we had the place almost to ourselves.
It’s a country, a people and an experience unlike any other.
If you’re looking for inspiration on low-key destinations that could use a tourism boost, take a look at the Intrepid Adventure Index .
It offers a snapshot of places, like Iran, where you won’t feel like the tourists outnumber the locals.

So what does the future look like for our most beloved destinations?
For Maya Bay at least, the outlook is positive.
With time to recover and plans to reopen later in 2018 with boat limits, an annual low-season closure, and a long-view approach to tourism, this spectacular cove may once more be ‘The Beach’ of our dreams.
In the meantime, as responsible travellers, we too can do our bit to help turn the tide on overtourism, and support a new wave of sustainable tourism practice around the world.
Danielle And John
Hi, We’re Alesha and Jarryd!

We’ve been traveling the world together since 2008, searching for the planet’s best destinations and adventures.
Love Travel?
Sign up for our free weekly newsletter for the best travel tips, ideas and deals!
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at any time.
READ MORE...
10 Important Ways to be a RESPONSIBLE TRAVELLER in 2024
Sustainable Tourism in Thailand – Ecotourism, Wildlife and Culture Guide
What are Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Hotels?
Related posts, enchanting beauty and sustainability in yangshuo, china, why we didn’t do an elephant tour in sen monorom, from tan hoa village to tu lan caves – the local’s role, 7 thoughts on “7 ways you can help turn the tide on overtourism”.
Great info! Thank you! It helped so much with my assignment on over-tourism!
So glad it helped Lia. All the best with your assignment. 🙂
Do you not realize, that websites like yours contribute to the exact problems you are talking about? Insatiable travel has caused these problems and visiting the “Secret Spots” only opens them up to the same problems. We have all seen what lack of travel during the COVID 19 Pandemic has done to heal our earth. Search your hearts and ask yourself if it is ok to damage our planet just to make you happy or seem cool. Exchanging things for experiences may not be helping at all. Carbon exchange is a fallacy, just don’t do the carbon and fly all over the world. (Before the pandemic four billion people were flying each day). That is how you really help.
Thanks for the comment. So in your opinion, nobody who travels should be able to talk about overtourism? Is it better for us to simply not address the topic at all, simply because we own a website? We travel for a number of reasons, but trying to seem cool definitely isn’t one of them. You must be new to our website, or travel in general, if you think we are actively going out trying to destroy the planet by choosing to explore the world. If you would like to never leave your home country, that is your decision. We live on an island however and don’t have the luxury of not flying somewhere, unless we take cruise ship, which is actually worse for the environment. Also double-check your statistics, because it’s a rough estimate that 6 million fly on any given day, not 4 billion (more than half the planet’s entire population) like you suggested.
The previous post’s point about disadvantages of revealing new spots is valid but you are correct to have the discussion. I’m a Fil Am and aspiring Siargao, Philippines tourist to be- and those islanders have taken note of this very issue (lessons from Boracay and Bali). Perhaps, discussion can include eco tourist resort construction- storm resistance and tourist conduct. Resorts exist that reduce carbon footprint and water supply strain e.g. Bali has a Temple w/ accommodations- with eco-plumbing. Siargao has new residences with storm resilient construction. Easily adaptable to new resort building. Siargao is extreme storm prone like Florida, USA As for conduct, well Indonesia is culturally conservative Muslim. Latest news is their having discussion about tourism singles conduct. The surfing community Western well heeled was not appreciative. Indo, however, is home to the Mentawi islands- surfing Mecca and numerous “black diamond” surf spots. At least the air is now clear.
Look, I’ve been to Hawaii, I can feel the vibe of the locals. Sometimes, tourists misbehave and that has not gone over well with folks that live there. Great website:)
excellent post !!
Thanks so much
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

What's the problem with overtourism?
With visitor numbers around the world increasing towards pre-pandemic levels, the issue of overtourism is once again rearing its head.
When locals in the charming Austrian lakeside village of Hallstatt staged a blockade of the main access tunnel, brandishing placards asking visitors to ‘think of the children’, it highlighted what can happen when places start to feel overrun by tourists. Hallstatt has just 800 residents but has opened its doors to around 10,000 visitors a day — a population increase of over 1,000%. And it’s just one of a growing number of places where residents are up in arms at the influx of travellers.
The term ‘overtourism’ is relatively new, having been coined over a decade ago to highlight the spiralling numbers of visitors taking a toll on cities, landmarks and landscapes. As tourist numbers worldwide return towards pre-pandemic levels, the debate around what constitutes ‘too many’ visitors continues. While many destinations, reliant on the income that tourism brings, are still keen for arrivals, a handful of major cities and sites are now imposing bans, fines, taxes and time-slot systems, and, in some cases, even launching campaigns of discouragement in a bid to curb tourist numbers.
What is overtourism?
In essence, overtourism is too many people in one place at any given time. While there isn’t a definitive figure stipulating the number of visitors allowed, an accumulation of economic, social and environmental factors determine if and how numbers are creeping up.
There are the wide-reaching effects, such as climate change. Coral reefs, like the Great Barrier Reef and Maya Bay, Thailand, made famous by the Leonardo DiCaprio film, The Beach , are being degraded from visitors snorkelling, diving and touching the corals, as well as tour boats anchoring in the waters. And 2030 transport-related carbon emissions from tourism are expected to grow 25% from 2016 levels, representing an increase from 5% to 5.3% of all man-made emissions, according to the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO). More localised issues are affecting locals, too. Renters are being evicted by landlords in favour of turning properties into holiday lets, and house prices are escalating as a result. As visitors and rental properties outnumber local residents, communities are being lost. And, skyrocketing prices, excessive queues, crowded beaches, exorbitant noise levels, damage at historical sites and the ramifications to nature as people overwhelm or stray from official paths are also reasons the positives of tourism can have a negative impact.
Conversely, ‘undertourism’ is a term applied to less-frequented destinations, particularly in the aftermath of the pandemic. The economic, social and environmental benefits of tourism aren't always passed on to those with plenty of capacity and, while tourist boards are always keen for visitors to visit their lesser-known attractions, it’s a more sustainable and rewarding experience for both residents and visitors.

What’s the main problem with it?
Overcrowding is an issue for both locals and tourists. It can ruin the experience of sightseeing for those trapped in long queues, unable to visit museums, galleries and sites without advance booking, incurring escalating costs for basics like food, drink and hotels, and faced with the inability to experience the wonder of a place in relative solitude. The absence of any real regulations has seen places take it upon themselves to try and establish some form of crowd control, meaning no cohesion and no real solution.
Justin Francis, co-founder and CEO of Responsible Travel, a tour operator that focuses on more sustainable travel, says “Social media has concentrated tourism in hotspots and exacerbated the problem, and tourist numbers globally are increasing while destinations have a finite capacity. Until local people are properly consulted about what they want and don’t want from tourism, we’ll see more protests.”
A French start up, Murmuration, which monitors the environmental impact of tourism by using satellite data, states that 80% of travellers visit just 10% of the world's tourism destinations, meaning bigger crowds in fewer spots. And, the UNWTO predicts that by 2030, the number of worldwide tourists, which peaked at 1.5 billion in 2019, will reach 1.8 billion, likely leading to greater pressure on already popular spots and more objection from locals.
Who has been protesting?
Of the 800 residents in the UNESCO-listed village of Hallstatt, around 100 turned out in August to show their displeasure and to push for a cap on daily visitors and a curfew on tour coach arrivals.
Elsewhere, residents in Venice fought long and hard for a ban on cruise ships, with protest flags often draped from windows. In 2021, large cruise ships over 25,000 tonnes were banned from using the main Giudecca Canal, leaving only smaller passenger ferries and freight vessels able to dock.
In France, the Marseille Provence Cruise Club introduced a flow management system for cruise line passengers in 2020, easing congestion around the popular Notre-Dame-de-la-Garde Basilica. A Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA) spokesperson said, “Coaches are limited to four per ship during the morning or afternoon at the Basilica to ensure a good visitor experience and safety for residents and local businesses. This is a voluntary arrangement respected by cruise lines.”
While in Orkney, Scotland, residents have been up in arms at the number of cruise ships docking on its shores. At the beginning of 2023, the local council confirmed that 214 cruise ship calls were scheduled for the year, bringing around £15 million in revenue to the islands. Following backlash from locals, the council has since proposed a plan to restrict the number of ships on any day.

What steps are being taken?
City taxes have become increasingly popular, with Barcelona increasing its nightly levy in April 2023 — which was originally introduced in 2012 and varies depending on the type of accommodation — and Venice expects to charge day-trippers a €5 fee from 2024.
In Amsterdam this summer, the city council voted to ban cruise ships, while the mayor, Femke Halsema, commissioned a campaign of discouragement, asking young British men who planned to have a 'vacation from morals’ to stay away. In Rome, sitting at popular sites, such as the Trevi Fountain and the Spanish Steps, has been restricted by the authorities.
And in Kenya’s Maasai Mara, meanwhile, the Narok County governor has introduced on-the-spot fines for off-roading. He also plans to double nightly park fees in peak season.
What are the forecasts for global tourism?
During the Covid pandemic, tourism was one of the hardest-hit industries — according to UNWTO, international tourist arrivals dropped 72% in 2020. However, traveller numbers have since been rapidly increasing, with double the number of people venturing abroad in the first three months of 2023 than in the same period in 2022. And, according to the World Travel Tourism Council, the tourism sector is expected to reach £7.5 trillion this year, 95% of its pre-pandemic levels.
While the tourism industry is forecast to represent 11.6% of the global economy by 2033, it’s also predicted that an increasing number of people will show more interest in travelling more sustainably. In a 2022 survey by Booking.com, 64% of the people asked said they would be prepared to stay away from busy tourist sites to avoid adding to congestion.
Are there any solutions?
There are ways to better manage tourism by promoting more off-season travel, limiting numbers where possible and having greater regulation within the industry. Encouraging more sustainable travel and finding solutions to reduce friction between residents and tourists could also have positive impacts. Promoting alternative, less-visited spots to redirect travellers may also offer some benefits.
Harold Goodwin, emeritus professor at Manchester Metropolitan University, says, “Overtourism is a function of visitor volumes, but also of conflicting behaviours, crowding in inappropriate places and privacy. Social anthropologists talk about frontstage and backstage spaces. Tourists are rarely welcome in backstage spaces. To manage crowds, it’s first necessary to analyse and determine the causes of them.
Francis adds: “However, we must be careful not to just recreate the same problems elsewhere. The most important thing is to form a clear strategy, in consultation with local people about what a place wants or needs from tourism.”
As it stands, overtourism is a seasonal issue for a small number of destinations. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a range of measures are clearly an option depending on the scale of the problem. For the majority of the world, tourism remains a force for good with many benefits beyond simple economic growth.
Related Topics
- OVERTOURISM
- SUSTAINABLE TOURISM
You May Also Like

How can tourists help Maui recover? Here’s what locals say.

One of Italy’s most visited places is an under-appreciated wine capital
Free bonus issue.

In this fragile landscape, Ladakh’s ecolodges help sustain a way of life

Cinque Terre’s iconic ‘path of love’ is back. Don’t love it to death

25 breathtaking places and experiences for 2023

See the relentless beauty of Bhutan—a kingdom that takes happiness seriously

Is World Heritage status enough to save endangered sites?
- Perpetual Planet
- Environment
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Gory Details
- 2023 in Review
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

The "Good Tourism" Blog
For diverse perspectives on sustainable tourism & responsible travel ... because travel & tourism is everyone's business., what is ‘mass tourism’ and what’s the problem.

What is ‘mass tourism’? How do we think about it and talk about it? Do we consider all of its contexts, costs, and benefits?
Does mass tourism contribute to good lives? Or do ‘the masses’ only represent threat?
Does leisure travel for the many have its place in a ‘green’ future for us all? Or will it remain the privilege of a few?
Vilhelmiina Vainikka shared this “Good Tourism” Insight at the invitation of Tourism’s Horizon: Travel for the Millions , a “GT” Partner. (You too can write a “GT” Insight .)
Table of contents
What is ‘mass tourism’ .
Why would anyone ask such a question? Isn’t the answer obvious?
Presumably everyone using the term — in industry, academia, and in general — has some idea of what mass tourism might be. After all, it’s likely we have been tourists ourselves, many of us live in places that attract tourists, and many work in tourism.
Mass tourism is integral to our culture. But, as Raymond Williams argued in relation to the term ’culture’ itself, its ubiquity masks a range of contested understandings.
Don’t miss other “GT” posts tagged ‘Carrying capacity, mass tourism, & overtourism’
Researchers of tourism have probably had to define mass tourism in their publications. Tourism students have probably had to learn one or more definitions. We can say that most people — academics too, despite claimed expertise and authority — hold socially-constructed views of mass tourism.
There are many different definitions of and perspectives on mass tourism. My own doctoral research concentrated on the different ways professionals — academic researchers, package tour agents, and tour guides — think of mass tourism.
What is ‘mass tourism’? Quantitative vs qualitative definitions
When we define something, we are simultaneously part of creating that phenomenon. Language conveys meaning, but also constructs it. Definitions make something an understandable entity, drawing lines where it ends and something else begins.
One way to define mass tourism is as a quantitative notion. ‘Mass’ implies a large scale, involving many people (in relation to the global, regional, or local context in which mass tourism is perceived).
This quantitative notion is often tied to qualitative characteristics. Large numbers of tourists may be understood in a positive, neutral, or negative way. Today it is often understood as problematic, for example in the debates on ’overtourism’.
Mass tourism can also be approached in other, more qualitative ways:
- It can refer to a mode of production/consumption . So, for example, we might think of Fordist mass production, or economies of scale of mass production.
- It can refer to spatial specialisation . The resort as a space for mass tourism is an example of this.
- It can also carry a strong association with democratisation , such as access to tourism by sections of society; by social class , for example.
All of the categories mentioned above have changed — none are static — adding to the reality that mass tourism really needs thinking through.
Equally, mass tourism can also be understood as a ’super-umbrella term’ for tourism for ’the masses’, which combines the aforementioned perspectives. This suggests that numbers of tourists, the mode of production, the politics of consumption, physical manifestations such as the resort, and democratisation, are all part of a wider ideological and political infrastructure that we might call ’mass society’ or ’mass culture’.
The super-umbrella approach connects tourism to all of its historical, economic, and political contexts: the development of industrial society, political change, growth, (in)equality, technological advances, and infrastructures.
Notably in this framing, the niche modes of tourism (ecotourism, for example), which are often aesthetically and culturally counterposed to mass tourism, can be seen as being part of the mass phenomenon of tourism, just like the resort. This underlines the complexity of the phenomenon today.
Also read Sudipta K Sarkar’s “Good Tourism” Insight ‘Ecotourism for the masses, not the elite classes!’
Contexts for mass tourism: The ‘good life’
Context is important. Mass tourism is contextualised on spatial, temporal, and scalar terms; we experience it in space, time, and at a scale. Therefore, it is necessary to zoom in on different local, regional, and national contexts in which mass tourism is taking place. The histories of different communities with mass tourism, whether as destinations or as sources of tourists, are meaningful in understanding contemporary lifestyles and ideas of what constitutes a ’good life’.
Is mass tourism a singularity or a plurality?
The ‘mass’ in mass tourism is both a singular and a plural . The relationship between the two is key. In discussions of mass tourism, characterisations of the singular mass, or ’the masses’, can obscure the plurality of individuals, and individuality itself.
I have argued in my research that the usefulness of mass tourism as a concept is embedded in addressing this very relation; reflecting on what the ‘mass’ symbolises and what consequences it has for how we see our fellow humans.
Erik Cohen has urged more research on mass tourist experiences and underlined the possibility for both collective and individual experiences. We should allow space for both the singularity and the plurality in the discussions we have of mass tourism.
Are the masses a threat?
Seeing large numbers of people as a threat is not new, nor is it only a feature of debates about tourism. Christian Borch noted that crowds have often been perceived more as a threat than a solution in society .
Classical crowd theories hold that individual agency and individuality are lost in the mass mind, and that crowds threaten the social order. These theories emerged in part as an elite fear of unrest among the urban working masses. One could argue that these fears are sustained through contemporary prejudices.
Also read Jim Butcher’s “GT” Insight ‘Was this the European summer of terrible tourists? Give us a break, media!’
These ideas, and their modern manifestation, are often reductive. Rather than threatening, the crowd can be the very thing that is attractive about tourism experiences. For example, Jillian Rickly reminds us that part of the appeal in tourism are the events in which crowds gather and create an authentic experience.
Certainly, tourism is a form of competitive consumption. Often we wish there were no other tourists, and certainly no crowds, at the places we wish to admire and enjoy. But equally, in other contexts, crowds can be exciting, fun, human; the very essence of what anthropologists refer to as communitas .
Let’s talk about mass tourism … deterministically or flexibly?
Whether we are researchers, authorities, or tourism industry professionals, it matters how we discuss mass tourism . If we use a deterministic discourse, we liken mass tourism to a mould. Into that mould we pour the experiences of millions, but turn out a single, uniform entity: stereotypical mass tourism.
However, if we use a flexible discourse on mass tourism, we recognise that the phenomenon, including its production and consumption, changes over time and as technologies and knowledge are developed. This acknowledgement requires us to take a more dynamic conceptualisation and wider perspective on mass tourism. As a result, we get a more realistic portrayal of the phenomenon, which can lead to more fruitful discussions on its status and future.
Mass tourism vs the green transition
When we follow the discussion on the green transition for a sustainable future, we are challenged by the issue of ’quality over quantity’; a better type of tourism . It sounds reasonable because, of course, we wish tourism standards to be high in relation to the environment and local communities.
But as destinations seek to optimise benefits from tourism, ’quality over quantity’ can mean in practice ’the upper classes versus the masses’; ’quality’ tourism for the rich and better educated; ’quantity’ for the less enlightened ’mass tourist’ stereotype.
Also read Peter Smith’s “GT” Insight ‘For the sake of the world’s poor, might the risk of overtourism be worth it?’
Perhaps we should invest more in finding ways to accommodate as many as possible, while considering that tourism could be something different from what we have practiced so far. This may also make it easier to win support from ‘the masses’ — individuals seeking their own versions of the ‘good life’ — for reducing carbon emissions and addressing environmental concerns.
Ultimately, the masses vote, produce, and consume. Progressive, sustainable change needs to come through them. Caricatures of mass tourism are unlikely to win friends and influence people.
Mass mobilities
Finally, researchers have begun to investigate how climate change influences the mobilities of people, naming it ‘ climate mobilities ’. It is likely that we will face a blurring of the previous categories of mobility.
Climate change, and the impacts it has on different places, will likely increase migration and affect tourism. Categories of travel — voluntary/involuntary, leisure/residential, migration/refugee, short-term/long-term, etc — will be further complicated.
Therefore, we need to discuss how societies and mobilities will be constructed and for whom. Through it all we should remember that ‘the masses’ are the ’we’ and the ’us’; the ‘you’ and ‘I’; the prospective beneficiaries of true sustainable development.
What do you think?
What is ‘mass tourism’ to you? Share your own thoughts in a comment below. Or write a deeper “GT” Insight . The “Good Tourism” Blog welcomes diversity of opinion and perspective about travel & tourism, because travel & tourism is everyone’s business .
“GT” is where free thought travels.
About the author

Vilhelmiina Vainikka is a post-doctoral research fellow at Tampere University , Finland. She is working on the HUMANE-CLIMATE project (2022 – 2026), “the civic potential of climate mobility”, which is funded by the Academy of Finland.
Dr Vainikka contributed this “Good Tourism” Insight at the invitation of Tourism’s Horizon: Travel for the Millions , a “GT” Partner.
Featured image (top of post)
What is ‘mass tourism’? Is it, as this graffiti asserts, “human pollution”? Image by Mark de Jong (CC0) via Unsplash . “GT” cropped the image and added the dangling ‘?’.
Contents ^
Related posts

This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Privacy Overview
- Partners and Fundings
- events & news
- green hotels
- who’s talking about us
Overtourism: Causes, Consequences and Solutions

Overtourism : one of the words that people use most in recent years. In effect, more and more often, tourist destinations suffer from overtourism, tourism overcrowding . Places that everyone wants to see because they are “famous”. Movie scenes shot in locations (such as Lake Braies ) that now attract hordes of tourists looking for a short trip. Simply, they stop the time for a selfie and then leave for the next famous stage. This type of mass tourism causes pollution, the devastation of nature and distress of local populations. Let’s see in detail what is overtourism, what are its causes , what are the consequences , and what can be done to avoid it.

What is overtourism?
Overtourism is a neologism that indicates the overcrowding of tourists on a holiday destination. The term was first inserted in the Oxford dictionary in 2018 and nominated as the year’s word. Overtourism, literally “too much tourism” , is a complex phenomenon that we should analyze from various points of view. In essence, we could sum up the concept in one question. Is this place affected by the presence of more tourists than the place and the inhabitants can support?
When it comes to natural tourist destinations , tourism must respect flora, fauna, and microclimate. When the destination is a city , tourism must primarily r espect residents , as well as local culture and archaeological sites . The latter in particular are small microcosms blocked in time that tourism should protect. If this doesn’t happen, we talk about overtourism, or unsustainable tourism for the place, for nature, for the people who live there.

The Causes of overtourism
More than 1.4 billion people are moving around the world every year, and they are growing at an exponential rate. The World Tourism Organisation predicts that by 2030 the international flow of tourists will exceed 2 billion . This very high number of people focus on a few tourist destinations in the world, which suffer from the excessive presence of tourists . The causes of too much tourism are many. From the famous films that make tourist destinations famous to the ease with which you can reach any corner of the world. Also, we can name the cruises that bring large quantities around the seas. We talked about cruises and their environmental impact in this article .

Cultural tourism, a new trend
A trend of the moment is tourism i nfluenced by mass culture . According to this kind of tourism, people chose the destination based on social media , influencers, television programs and films. Tourism influenced by film and TV series products, also known as film tourism , has in some cases led to real disasters. An example is what is happening in the Pacific Islands : in Thailand at Maya Bay , where the film “The Beach” was shot with Leonardo Di Caprio. Over the years, tourists who wanted to see the film set invaded the small beach. This forced the Thai government to prohibit the entry of tourists to restore the delicate balance of the beautiful bay.
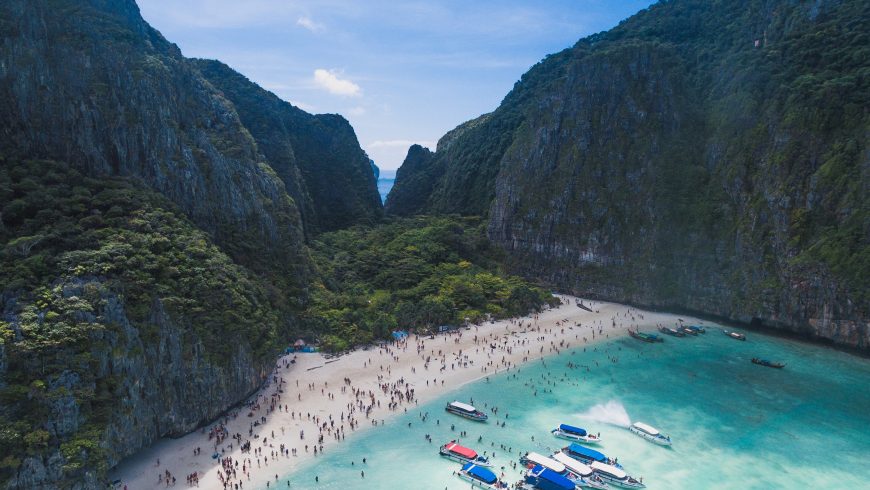

The increase in low-cost air flights and cruises is certainly one of the causes of Overtourism.
The numbers published by the World Tourism Organisation (Unwto) speak for themselves. Even in Italy , we have examples of how mass tourism damages the nature and residents of cities invaded by travelers. Venice , for example, is visited by about 20 million people a year. A number a little too high for such a delicate city, devastated also by cruise ships causing pollution .
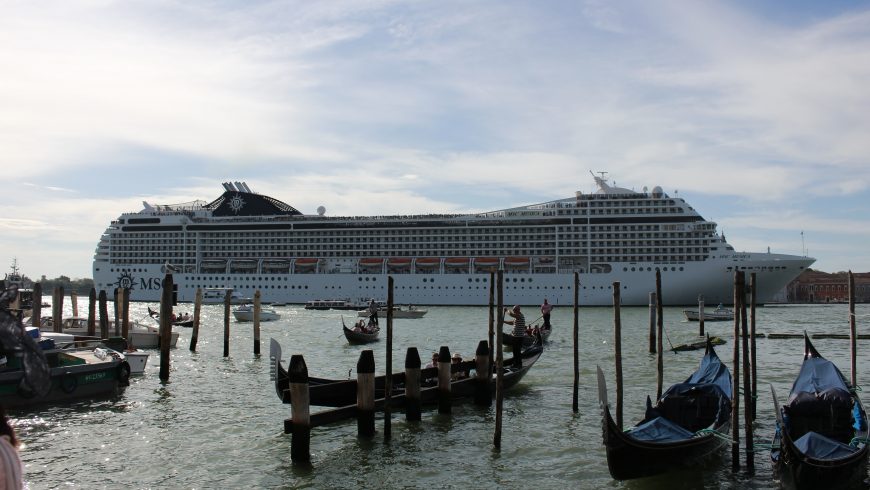

Even Florence , Capri and the Cinque Terre National Park in Liguria suffer from the excessive number of tourists arriving every year. This influx is leading the administrations of the various Italian municipalities to take steps to limit the number of revenues.

Consequences of overtourism
1 destruction of natural ecosystems.
The flora and fauna are usually the first to suffer overtourism in the most popular natural tourist destinations. In some natural destinations, environmental issues led to the destruction of entire ecosystems. Among these problems, we can mention deforestation, exploitation of the soil and pollution . But also, no policy of raising awareness and protecting natural environments. In some cases, this situation has no possibility of redemption, such as, for example, what happens to coral reefs around the world. As global warming and tourists irreparably ruined them, corals are part of a natural system that is becoming extinct.

2. Increase in the amount of waste
Another consequence of mass tourism is the large accumulation of waste that people don’t differentiate. Inevitably, it creates a major environmental problem of disposal and pollution. Boracay Island , in the Philippines, has been closed to restore the ecosystem after years of uncontrolled tourism. The waste problem is also very important on the island of Bali , which is trying to combat it thanks to the thought of Zero waste Bali.

3. Escape and malaise of residents
Too much tourism affects mainly the locals. Across Europe, in cities like Barcelona or Venice, the phenomenon of overtourism has unleashed strong tensions from the inhabitants. Residents complain about the rising of housing prices and rentals. In effect, they inflated them due to the spread of online platforms such as Airbnb. But also, they talked about the disappearance of small shops, replaced by tourist shops, and the inviolability of their cities. The last consequence is the escape of residents from their cities, which have become tourist theatres, thus losing their authenticity.
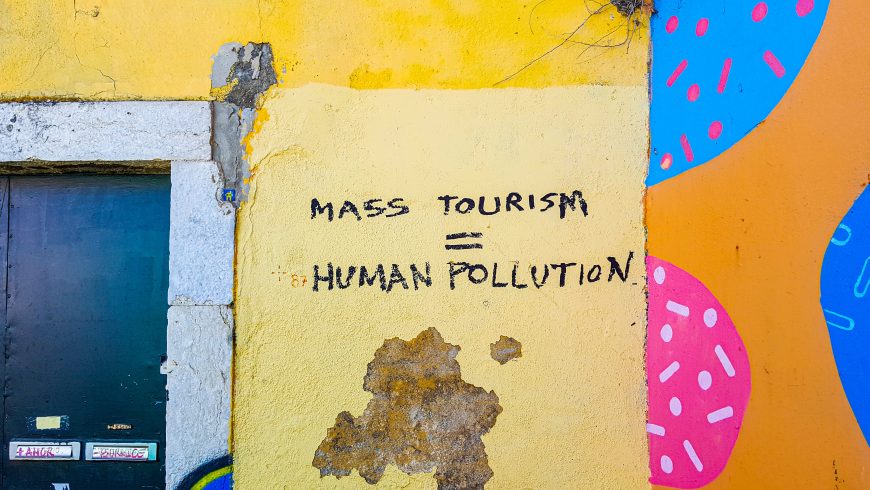
Solutions to overtourism for destinations
As tourist flows around the world increased, the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) has dedicated an entire Report to overtourism. Certainly, there is not one single solution, but many small things that we can do during our holidays . The Report thus proposes 11 strategies and 68 measures to combat excessive tourism.
Here are the 11 suggestions that tourist destinations can follow to counter the phenomenon of overtourism.
- Encourage the dispersion of tourists within the city, and even beyond the territory, suggesting the visit of lesser-known destinations and less touristic areas.
- Promote tourism in different periods (for example out of season) and at different times from the most popular.
- Create new and different itineraries and tourist attractions.
- Review and improve regulations , such as closing some overcrowded areas to traffic.
- Attract more responsible types of travelers.
- ensure the benefits of tourism to local communities, for example by increasing the number of inhabitants employed in tourism, and by involving residents in the creation of tourism experiences.
- Develop and promote experiences in the city or territory that benefit both tourists and residents.
- Increase the infrastructure and services of the resort.
- Involve the local community in tourist decisions and choices.
- Educate travelers and tell them how to be more responsible and respectful of the place.
- Monitor and measure changes.

And what can we do?
With Ecobnb we promote responsible tourism , avoiding overcrowded famous destinations and promoting the close destinations. Often we don’t know what surrounds us and which beauties we can find without necessarily taking planes that emit huge amounts of CO2. Slow and sustainable tourism offers authentic locations. These places enrich local communities and those who invest in eco-sustainable activities. The real holiday could also be for you the relaxing and unplugging holiday. You could simply recharge the energies in contact with nature. Nonetheless, remember to try and lessen as much as possible for your environmental impact.

The good news is that each of us can do our part to counteract overtourism and promote sustainable tourism.
Here’s your vademecum
Here are 5 simple ideas , a vademecum, to promote quality tourism, instead of quantity, every time we travel.
- Avoid air flights and cruises, move by train and public transport whenever you can.
- Don’t take your decisions following the mass. If everyone goes to the mountains on August 15, why don’t you choose a different date?
- Organize your holidays in an alternative way, choose authentic and less touristy destinations .
- Travel out of season : spring and autumn are beautiful and less expensive seasons.
- Respect the places you visit (here you find 40 tips to travel green ), try to live like a local”, immerse yourself in the culture of the place and make friends with the inhabitants.
Cover image: photo by Elizeu Dias via Unsplash
You might also like

How do cruise ships impact on the environment
The cruise ship is the holiday that has grown faster than any other in the last 20 years. Despite the disaster of the Costa Concordia near the island of Giglio (Italy), cruises are becoming increasingly popular, coming to carry each year about 20 million passengers worldwide and 800,000 in Italy. But it is also the […]

A Cruise Ship Pollutes as One Million Cars
Cruise ships are often associated with luxury and total relaxation, but in reality, they represent huge damage to the environment and the health of passengers and port cities. Cruise ships not only create significant environmental damage but are extremely harmful to health due to their exhaust gases. This is what emerges from the 2016 Environmental […]

Save our cities from overtourism!
SET (Sud-Europe facing Overtourism): a network created by 15 European cities to denounce the destructive effects of mass tourism and promote the research for a new touristic system. Mass tourism brings enormous amounts of tourists in the main cities. The effects of the so-called overtourism are indeed severe. Cities lost their original artistic, natural and cultural heritage: […]

Pacific Islands: the Paradises ruined by ‘Overtourism’
‘Overtourism’: too much mass tourism threatens fragile ecosystems, such as the Pacific Islands. Philippines, Indonesia, and Thailand the most affected countries. Strategies to preserve destinations and promote responsible tourism are essential Admiring the photos of the dream beaches of some islands of Polynesia or the Philippines is not surprising if in the last few years […]
Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Tips
What Is Mass Tourism
Published: December 12, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Hermione Trull
- Plan Your Trip
- Sustainability
Introduction
Travel and tourism have become increasingly popular in recent years, experiencing a significant growth in numbers. This surge in travel can be attributed to various factors, such as increased disposable income, improved transportation systems, and the growing desire for new experiences and adventure. However, with this exponential growth comes the concept of mass tourism, which has both positive and negative implications.
Mass tourism is a term used to describe the phenomenon of large numbers of people traveling to and visiting the same destinations at the same time. It involves the mass movement of tourists to popular hotspots, often resulting in overcrowding, strain on local resources, and potential negative impacts on the environment, society, and local economies.
This article will delve into the concept of mass tourism, exploring its definition and the factors that contribute to its rise. We will also discuss the environmental, social, and economic impacts of mass tourism, as well as consider sustainable tourism as an alternative approach to travel. By understanding the issues associated with mass tourism and exploring sustainable solutions, we can work towards a more responsible and balanced approach to travel and tourism.
Definition of Mass Tourism
Mass tourism can be defined as a form of tourism that involves the movement of large numbers of people to the same tourist destinations, typically popular and well-known places. It is characterized by the concentration of visitors in specific areas and the simultaneous arrival of tourists during peak seasons.
The key aspect of mass tourism is the sheer volume of tourists visiting a particular location, often resulting in overcrowding. These destinations are often marketed as must-visit places, attracting visitors from all over the world. Examples of popular mass tourism destinations include iconic landmarks like the Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Taj Mahal in India, or the Great Wall of China.
Mass tourism is facilitated by various factors, such as affordable transportation options, the availability of budget accommodations, and the influence of media and advertising. With the rise of social media and travel influencers, certain destinations have experienced a surge in popularity, contributing to the phenomenon of mass tourism.
It is important to note that mass tourism is not inherently negative. It can bring economic benefits to local communities, creating jobs and generating revenue through visitor spending. However, it is essential to recognize and address the potential negative impacts that mass tourism can have on the environment, local culture, and the well-being of residents in these destinations.
The concept of mass tourism is closely related to the idea of overtourism, which refers to the point at which the number of tourists overwhelms the capacity and limits of a destination. When a destination experiences overcrowding and is unable to sustain the influx of tourists, it can lead to negative consequences for both the visitors and the local community.
Overall, the definition of mass tourism revolves around the movement of a large number of people to specific destinations, resulting in overcrowding and potential negative impacts. By understanding this concept, we can explore strategies to mitigate the challenges associated with mass tourism and promote more sustainable and responsible travel practices.
Factors Contributing to Mass Tourism
Mass tourism is influenced by a variety of factors that contribute to its growth and popularity. Understanding these factors can help shed light on the reasons behind the rise of mass tourism and the challenges it presents.
1. Accessibility: Improved transportation systems, including affordable flights, high-speed trains, and cruise ships, have made travel more accessible to people around the world. This increased connectivity has made it easier for individuals to reach popular destinations, resulting in higher tourist numbers.
2. Globalization: The interconnectedness of the world through technology and communication has made travel more appealing and feasible. People are exposed to different cultures, destinations, and attractions, fueling their desire to explore the world and check off popular destinations from their bucket lists.
3. Marketing and Advertising: Effective marketing campaigns and advertising play a crucial role in promoting destinations and attracting tourists. Through enticing visuals, persuasive narratives, and strategic branding, destinations are positioned as must-visit places, driving the demand for mass tourism.
4. Social Media and Influencers: The advent of social media platforms has revolutionized the way people travel. Travel influencers and bloggers provide inspiration, recommendations, and firsthand experiences, creating a desire among their followers to visit the same destinations. The viral nature of content on social media has contributed to the rapid growth of mass tourism.
5. Economic Factors: Economic considerations also play a significant role in mass tourism. Affordable accommodation options, discounted travel packages, and competitive prices make travel more accessible and appealing to a larger audience. Additionally, the economic benefits that tourism brings to local communities, such as job creation and increased revenue, further incentivize destinations to cater to mass tourism.
6. Political Stability: Political stability and the absence of conflicts or security concerns in a destination can greatly influence the growth of mass tourism. Tourists are more likely to visit places that are perceived as safe and stable, leading to increased visitor numbers.
While these factors contribute to the rise of mass tourism, it is important to recognize the potential negative impacts that can arise from the overwhelming influx of tourists. Balancing the desire for travel with sustainability and responsible tourism practices is crucial in managing the growth of mass tourism and its associated challenges.
Environmental Impacts of Mass Tourism
Mass tourism can have significant environmental impacts on the destinations it attracts. The sheer volume of tourists, coupled with unsustainable practices, can put a strain on natural resources, ecosystems, and contribute to climate change. Here are some key environmental impacts of mass tourism:
1. Overcrowding: Popular tourist destinations often experience overcrowding during peak seasons, which can lead to congestion and pressure on infrastructure. This can result in increased pollution, waste generation, and stress on local ecosystems.
2. Loss of Biodiversity: In some cases, mass tourism can lead to the destruction of natural habitats and loss of biodiversity. The development of hotels, resorts, and tourist infrastructure can encroach upon sensitive ecosystems, displacing wildlife and disrupting their habitats.
3. Pollution: The increased number of visitors brings with it an increase in pollution. Air pollution from transportation, such as planes and cars, and water pollution from cruise ships and recreational activities, can have detrimental effects on the environment. Improper waste management and littering can also degrade natural ecosystems.
4. Resource Depletion: The high demand for resources by tourists, including water, energy, and food, can deplete local resources. The extraction of water for hotels and resorts can strain water sources, especially in regions with limited water availability. The consumption of energy and non-renewable resources can contribute to environmental degradation.
5. Climate Change: Mass tourism is a significant contributor to carbon emissions due to transportation, accommodation, and recreational activities. Air travel, in particular, emits greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. The increased carbon footprint from mass tourism can exacerbate the effects of global warming and impact local ecosystems.
6. Disturbance of Natural Ecosystems: Activities associated with mass tourism, such as hiking, snorkeling, and wildlife viewing, can disrupt natural ecosystems. Trampling on delicate flora and fauna, disturbing nesting sites, and stressing wildlife can have long-term consequences on the biodiversity and ecological balance of the destination.
Addressing these environmental impacts requires a concerted effort from both tourists and destinations. Implementing sustainable practices, such as promoting responsible tourism, investing in renewable energy, managing waste effectively, and preserving natural habitats, can help mitigate the negative effects of mass tourism on the environment. Additionally, raising awareness among tourists about their role in minimizing their ecological footprint and respecting natural resources is essential for long-term sustainable tourism.
Social and Cultural Impacts of Mass Tourism
Mass tourism can have profound social and cultural impacts on the destinations and local communities it attracts. While tourism can bring economic opportunities and cultural exchange, the rapid growth and influx of tourists can also have negative consequences. Here are some key social and cultural impacts of mass tourism:
1. Crowding and Displacement: The sheer numbers of tourists can result in overcrowding in popular tourist destinations. This can lead to a loss of quality of life for local residents, as public spaces become crowded and potentially inaccessible. Local communities may also face difficulties accessing essential services due to the prioritization of catering to tourists. In extreme cases, the displacement of locals from their homes and neighborhoods to make way for tourism infrastructure can occur.
2. Loss of Authenticity: Mass tourism can lead to the commodification and commercialization of local cultures and traditions. Tourist areas may be transformed to cater to the desires of visitors, eroding the authentic character of the destination. This can result in the loss of traditional practices, language, and customs, as local communities adopt tourist-friendly activities and performances.
3. Cultural Appropriation: The rise of mass tourism can bring with it the risk of cultural appropriation. Tourists may engage in activities or wear clothing that is significant to the local culture without appropriately understanding or respecting their significance. This can lead to the exploitation of cultural heritage and the misrepresentation of local traditions.
4. Strain on Infrastructure and Services: The influx of tourists can strain local infrastructure, including transportation, healthcare, and public facilities. Local communities may find it challenging to cope with the increased demands on resources, resulting in inadequate services for both tourists and residents.
5. Social Tensions: The presence of mass tourism can create social tensions between tourists and local communities. Differences in language, behavior, and cultural expectations can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts. Additionally, the economic disparities between tourists and locals can create a sense of inequality and resentment.
6. Loss of Community Identity: The transformation of a destination into a mass tourism hotspot can alter the identity and dynamics of local communities. Traditional livelihoods and community structures may be disrupted, and young generations may choose tourism-related jobs over traditional occupations, leading to the erosion of community cohesion and local identity.
Addressing these social and cultural impacts of mass tourism requires a collaborative approach between tourists, local communities, and governments. Measures such as promoting community-based tourism, encouraging cultural exchange, respecting local customs and traditions, and implementing sustainable tourism practices can help maintain the social fabric and cultural integrity of destination communities.
Economic Impacts of Mass Tourism
Mass tourism can have significant economic impacts on the destinations it attracts, bringing both benefits and challenges to local economies. The influx of visitors can generate revenue, create employment opportunities, and stimulate economic growth. However, it can also lead to a reliance on tourism, income inequalities, and the exploitation of resources. Here are some key economic impacts of mass tourism:
1. Job Creation: Mass tourism can provide employment opportunities for local communities, directly and indirectly. From hotel and restaurant staff to tour guides, drivers, and artisans, the tourism industry creates a diverse range of jobs, contributing to economic stability and reducing unemployment rates.
2. Economic Growth: The spending of tourists can have a positive impact on local economies. Tourists contribute to the local economy through accommodation bookings, dining at restaurants, purchasing souvenirs, and participating in activities and excursions. This expenditure can result in increased business revenues, tax revenues for the government, and overall economic growth.
3. Infrastructure Development: The growth of mass tourism often necessitates the development of infrastructure, such as hotels, resorts, restaurants, and transportation systems. This infrastructure development can boost local construction industries, stimulate investment, and improve the overall quality of life for residents.
4. Income Inequality: The economic benefits of mass tourism are not always distributed equally among the local community. In some cases, income inequality can arise, with a small portion of the population reaping the majority of the benefits while others struggle to access the opportunities created by tourism. This can contribute to social tensions and disparities within the destination.
5. Seasonality and Dependency: Mass tourism can lead to seasonality in employment and visitor numbers. Destinations may experience peak seasons with high visitor numbers and demand for services, followed by periods of low tourism activity. This seasonality can create challenges, as businesses and communities become dependent on the income generated during peak times, leading to economic instability during off-peak periods.
6. Resource Exploitation: The mass influx of tourists can put pressure on local resources, including water, energy, and natural landscapes. In some cases, resources may be overexploited to meet the demands of tourism, potentially harming the environment and impacting the long-term sustainability of the destination.
It is important for destinations to carefully manage the economic impacts of mass tourism, considering the sustainability and long-term viability of the local economy. This can include diversifying the tourism product, investing in infrastructure that benefits both visitors and residents, promoting responsible tourism practices, and prioritizing the well-being and inclusion of the local community in the tourism industry.
Sustainable Tourism as an Alternative
In response to the challenges posed by mass tourism, sustainable tourism has emerged as an alternative approach that aims to mitigate the negative impacts and promote responsible travel practices. Sustainable tourism focuses on the triple bottom line of economic, environmental, and social sustainability. Here are some key aspects of sustainable tourism:
1. Environmental Conservation: Sustainable tourism prioritizes the preservation and protection of natural resources and ecosystems. This includes promoting eco-friendly practices such as waste reduction, energy efficiency, water conservation, and the preservation of biodiversity. Destinations can implement sustainable infrastructure, promote sustainable transportation options, and encourage visitors to engage in environmentally responsible activities.
2. Community Empowerment: Sustainable tourism seeks to empower local communities by involving them in decision-making processes and ensuring their voices are heard. It emphasizes community participation, fair distribution of economic benefits, and the preservation of local cultures, traditions, and heritage. Community-based tourism initiatives can provide opportunities for direct engagement between tourists and local residents, fostering cultural exchange and mutual understanding.
3. Economic Benefits for Local Communities: Sustainable tourism emphasizes the importance of equitable economic benefits for local communities. It encourages the development of small and medium-sized enterprises, supporting local artisans, farmers, and service providers. By promoting local businesses and products, sustainable tourism aims to reduce leakages and ensure more of the tourism revenue stays within the destination community.
4. Education and Awareness: Sustainable tourism promotes education and awareness among tourists, residents, and industry stakeholders. By educating visitors about responsible travel practices, environmental conservation, and cultural sensitivity, they can make informed choices that contribute to sustainable tourism. Engaging local communities in educational initiatives can also help build support and understanding for sustainable tourism practices.
5. Responsible Tourism Behavior: Sustainable tourism encourages tourists to engage in responsible and mindful behavior while traveling. This includes respecting local cultures and traditions, minimizing waste and pollution, supporting local businesses, and being mindful of their impact on the environment. Sustainable tourism also encourages tourists to seek off-the-beaten-path experiences, reducing the strain on overtouristed destinations.
6. Collaboration and Partnerships: Sustainable tourism requires collaboration and partnerships among various stakeholders, including local communities, governments, tourism operators, and non-profit organizations. By working together, destinations can develop and implement sustainable tourism strategies, share best practices, and monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of initiatives.
By embracing sustainable tourism practices, destinations can strike a balance between the economic benefits of tourism and the preservation of their environment, culture, and community. Sustainable tourism offers an alternative approach that ensures the long-term viability and resilience of destinations, allowing future generations to continue enjoying the wonders of travel while protecting the planet and its people.
Mass tourism brings opportunities and challenges to destinations around the world. While it offers economic benefits, the rapid growth and influx of tourists can have negative impacts on the environment, local communities, and cultural heritage. It is crucial to address these challenges and promote sustainable tourism practices.
By understanding the factors contributing to mass tourism and its impacts, we can work towards finding solutions that balance the economic benefits of tourism with the preservation of natural resources, cultural integrity, and the well-being of local communities. Sustainable tourism offers an alternative approach that prioritizes economic, environmental, and social sustainability.
Destinations can adopt sustainable practices such as promoting eco-friendly initiatives, involving local communities in decision-making processes, preserving cultural heritage, and educating tourists about responsible travel behavior. By diversifying tourism offerings, managing visitor flow, and investing in sustainable infrastructure, destinations can mitigate the negative effects of mass tourism.
Furthermore, tourists also play a vital role in the transition to sustainable tourism. Choosing responsible and mindful travel practices, supporting local businesses, respecting local cultures, and minimizing environmental impact are essential for promoting sustainable tourism. By embracing sustainable tourism as individuals, we can contribute to the preservation and ethical enjoyment of destinations for generations to come.
In conclusion, mass tourism presents us with an opportunity to rethink how we travel and experience the world. By focusing on sustainable tourism practices, we can create a more balanced and harmonious relationship between tourism, the environment, local communities, and cultural heritage. It is through our collective efforts that we can ensure that travel remains a positive force for both present and future generations.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Mass tourism, biosecurity and sustainability challenges: prospects illustrated by the current COVID-19 pandemic
Journal of Tourism Futures
ISSN : 2055-5911
Article publication date: 23 March 2023
Using COVID-19 pandemic as a more immediate empirical reference, this paper aims to understand the biosecurity risks arising from tourist activities and, through a more prospective analysis, to consider the relevance of public health issues in the context of tourism-sustainability nexuses.
Design/methodology/approach
The text assumes a hybrid format, incorporating elements resulting from empirical research and essayistic viewpoints. The collection of empirical elements was based on documental research in several sources, such as newspapers, international institutions of an intergovernmental nature and the discussion forum of the travel platform TripAdvisor.
By assuming mobility and large agglomerations of people from different origins, mass tourism has fostered multiple outbreaks of COVID-19 and the rapid global spread of contagion chains. The pandemic clearly exemplified the responsibility of tourism in the dispersion of biotic agents with severe ecological, economic, social and public health repercussions. It is, therefore, urgent to rethink the tourism growth trajectory and more effectively consider the biosecurity risks associated with mobility in discussions on tourism and sustainability. At the same time, tourism must be delineated in terms of the great aims of sustainability, and this transversal purpose to which it contributes should be considered an intrinsic condition of its own sectorial sustainability as an economic activity.
Originality/value
The biosecurity challenges posed by mass tourism are a very topical issue, still little considered in sustainability policies and on which there is a marked deficit in scientific research.
- Mass tourism
- COVID-19 pandemic
- Biosecurity
- Sustainability
Sacramento, O. (2023), "Mass tourism, biosecurity and sustainability challenges: prospects illustrated by the current COVID-19 pandemic", Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/JTF-07-2022-0173
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2023, Octávio Sacramento
Published in Journal of Tourism Futures . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
1. Introduction
Mass tourism produces a very negative ecological and social impact, and although it generates substantial economic benefits, they are generally unevenly distributed ( Chong, 2019 ; Fang et al. , 2021 ). It could have been expected that the COVID-19 pandemic might have constituted a decisive tipping point for a deprioritising of the economy, considering the tourism system as a means to serve society and the sustainable development goals (SDGs) that foresee the viability of our common future ( Gössling et al. , 2021 ; Higgins-Desbiolles, 2018 ). However, instead of considering the current crisis of the pandemic, together with the climate crisis, as imperative reasons for urgent structural changes in global mass tourism ( Jamal and Budke, 2020 ), it is quite likely – among other possible scenarios of “survival of the fittest” (collapse), “business as unusual” (transition) and “responsible tourism” (transformation) ( Postma et al. , 2020 ; Yeoman et al ., 2022 ) – that there will be a return to “business as usual” (growth) and the old normality of unsustainable tourism as soon as the health crisis is overcome ( Hall et al. , 2020 ; Ioannides and Gyimóthy, 2020 ; Vărzaru et al. , 2021 ). In fact, the dominant concern has been the profound negative economic impact of COVID-19, especially in regard to tourism ( Sharma and Nicolau, 2020 ; Uğur and Akbıyık, 2020 ; United Nations, 2020 ; Yeh, 2021 ), with a constant reiteration of the urgency of resuming stimulating activity, based on a “boosterist”, expansionary and pro-growth motivation ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2021 ).
With this materialist immediacy, the fact that tourism is falling victim to itself as one of the main causes of the pandemic tends to be relegated to the background, being overlooked that he is suffering the consequences of a health crisis to which it contributed greatly. Something very similar has been happening for many years in the context of the climate crisis, which has also had very profound negative effects in the field of tourism, as the so-called pro-limits critics of tourism have been warning ( Bramwell and Lane, 2011 ; Gössling et al. , 2021 ; Hall et al. , 2020 ; Higgins-Desbiolles, 2021 ). Inspired by these standpoints, I discuss here the role of mass tourism flows in the development of the COVID-19 pandemic and, from there, I try to reflect on the future of tourism's sustainability. The theoretical framework of this analysis integrates several perspectives and contributions, predominantly sociological, that make up the so-called “critical tourism studies”: a set of approaches devoted to socioeconomic and political critique that seek to make tourism a more equitable and sustainable social space ( Ateljevic et al. , 2012 ; Pritchard et al. , 2011 ). Based on this conceptual lens, the analysis is guided by two central objectives: understand how tourism activities and mobility have contributed to generating epidemiological risks – raising enormous challenges in the field of biosecurity ( Chen et al. , 2021 ; Iaquinto, 2020 ; Hall, 2015 ) – and projecting the urgency of give greater visibility to public health issues in discussions about tourism and sustainability.
The article is written in a hybrid format, incorporating both empirical research and essayistic viewpoints through which I seek to develop some prospective reflections on the public health challenges in the context of tourism sustainability. The empirical research was predominantly directed towards the collection of data on mass tourism as a vector of the rapid globalization of COVID-19. To this end, I chose documentary research – mainly secondary data analysis and policy research ( Tight, 2019 ) – as the most appropriate methodological approach to collect data (documentary elements, statistical information, reports and written statements) that would enable sound analytical connections to be made between international tourism and biosecurity threats. Through this documentary research, I access mainly media sources (e.g. newspapers), information associated with large international institutions of an intergovernmental nature (e.g. World Tourism Organization [WTO]) and the discussion forum of the travel platform TripAdvisor. The triangulation of empirical content resulting from these sources enabled the development of sustained inferences about the tourism-pandemic nexus. At the same time, provided a factual basis for problematizing the challenges and conceptualizations around sustainability, seeking to show the relevance of including bio-risks and public health issues more effectively in this discussion. The aim is to point towards a desirable (and urgent) future in which the biosecurity risks associated with tourist mobility are consistently considered as sustainability risks, leading to policies and tourism governance strategies aimed at minimising these risks.
2. Tourism as a powerful contagion vector
In the 21st century, tourism has asserted itself as a strong sector in global expansion, in which more and more countries are investing to diversify or boost their economies, as well as promote rural areas in demographic decline ( Cheer et al. , 2019 ; Croce, 2018 ; Khan, 2020 ). Immediately before the COVID-19 pandemic crisis and the consequent mobility restrictions, the year 2019 ended with a record of 1,460 billion international tourist arrivals – around 60 times more than in 1950 ( WTO, 2021 ). Tourist mobility in 2019 represented 10.4% of the global gross domestic product (GDP), with a turnover comparable, for example, to that of oil production ( World Travel and Tourism Council [WTTC], 2021 ). The economic performance of world tourism has been celebrated by many, namely by the major international organizations of the sector (e.g. WTO, WTTC), as an unquestionable success and reason to continue to grow, without giving the due attention to the multiple risks arising from tourism and its global expansion.
Some of these risks – for tourists and their respective places of origin and destination – are located in the field of biosecurity and public health, with particular emphasis on the spread of infectious diseases such as COVID-19 ( Chen et al. , 2021 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hall, 2015 , 2019a ; Hall and Baird, 2013 ; Iaquinto, 2020 ; Melly and Hanrahan, 2021 ; Sabin et al. , 2020 ; Sacramento, 2022 ). As highlighted by Gössling et al. (2021, p. 13) , “tourism is about movement, and transport does act as a vector for the distribution of pathogens at regional and global scales”. Today tourism is, to a large extent, driven by global air transport networks which create conditions conducive to rapid and widespread contagion and epidemiological dispersion processes ( Brockmann, 2018 ; Brockmann and Helbing, 2013 ). Air transport implies large concentrations of people, closed spaces and many health challenges (e.g. air filtration), generating increased risks in terms of transmission of infectious agents ( Grout et al. , 2017 ). It can also facilitate the circulation of infectious arbovirus vectors, such as mosquitoes ( Kraemer et al. , 2015 ; Wilson, 2020 ). Air mobility constitutes a powerful macro-vector for the amplification and acceleration of contagions, not only because of the material conditions of the transport itself but also because of the diversity of itineraries of those who cross at airports and planes ( Brown et al. , 2016 ; Findlater and Bogoch, 2018 ; Tatem et al. , 2012 ).
Tourism and its associated transport networks are the results of socio-material, more-than-human assemblages, in which multiple actors (e.g. humans, non-humans, technology, institutions and natural resources) interact contingently, contributing to the generation of unforeseen vitalities that pose serious risks of biocontamination and can even create epidemic scenarios ( Brito-Henriques, 2020 ; Hall, 2015 ; Lupton, 2021 ). The responsibility of tourism in the geographical dispersion of biotic agents is processed in two ways: (1) directly, through the tourists themselves, with luggage, food, transport and other material elements associated with the trip; (2) indirectly, because tourist activities are associated with industrial food production prone to outbreaks of zoonotic diseases, are responsible for the invasion of wildlife habitats and contribute to the emission of climate-changing pollutants that disrupt ecosystems ( Gössling et al. , 2021 ; Hall, 2019a ; Melly and Hanrahan, 2021 ).
The Ministry of Health and the Directorate-General for Health confirmed this Monday the first cases of infection by Covid-19 in Portugal. One patient was on vacation in northern Italy and another in Valencia [Spain]. Both are hospitalized in Oporto ( Diário de Notícias, 2020a );
On January 31, Italy detected the first two cases of Covid-19 in the country. They were two Chinese tourists from the birthplace of the new coronavirus, Wuhan, who had arrived on the 23rd and visited several Italian cities. That same day, on the remote Spanish island of La Gomera, in the Canary Islands, a German tourist became the first case diagnosed in Spain ( Diário de Notícias, 2020b );
France confirms the first death in Europe from coronavirus. The death of an 80-year-old Chinese tourist in a Paris hospital was the first known fatality from the new virus outside Asia ( The New York Times, 2020 );
There have now been four reported cases of novel coronavirus infection found in Thailand: three Chinese tourists and one Thai ( Bangkok Post, 2020 );
Brazil confirms that a new strain [of SARS-CoV-2] detected in Japan is circulating in the Amazon. The variant arrived in Japan after four Japanese travellers visited the Brazilian Amazon and presented a series of unprecedented mutations ( Público, 2021 ).
By accumulating large numbers of people from different origins in small compacted spaces and infrastructures with shared material elements, international tourism scenarios fostered multiple outbreaks of COVID-19 and boosted the rapid global spread of the infection, as has happened in other infectious disease events. Regardless of its scales, typologies and specific configurations, mass tourism presumes a high density of transit and coexistence of people. The “mobilities are made with the encapsulation of bodies in mobile closed spaces – planes, buses, cruises, etc. – and flows converge and compress as they pass through nodes – airports, hotels, congress centres, museums, etc. – that stimulate interactions and human contact with each other and with different forms of materiality” ( Brito-Henriques, 2020, p. 207 ). It is precisely this intense density of movement that caused the most immediate physical conditions to make tourism a phenomenon inseparable from the instigators that boosted the COVID-19 pandemic.
From January 2020, up until the generalization of travel restrictions, there were several contexts in which tourist mobilities were intrinsically associated with the geographic expansion of contagion chains ( Sacramento, 2022 ). As an example, I address one of these tourist contexts of super-spreading of SARS-CoV-2: the ski resort of Ischgl, in the Alps.
2.1 A paradigmatic tourism scenario of SARS-CoV-2 global dissemination: the Ischgl ski resort
During the 2020 and 2021 ski seasons, there were major outbreaks of COVID-19 in resorts in several countries, especially in the Alpine region (Austria, Switzerland and Italy) and North America. In the USA, the disease outbreaks in the first months of 2021 in around 15 resorts in the state of Colorado are the most noteworthy, particularly in Winter Park, which has recorded more than 100 positive cases of the disease among the respective workers alone ( CPR News, 2021 ). In neighbouring Canada, the Whistler Blackcomb resort, the largest in North America, closed in late March 2021, was linked to 200 of the 877 cases of the “Brazilian variant” (P1) in the province of British Columbia, at the time the largest outbreak of this variant outside Brazil ( The Guardian, 2021 ). Arguably the most problematic situation, however, occurred about a year earlier, in the first months of 2020, in the centre of the European continent, in the Alps, particularly in Ischgl (Paznaun, Austrian Tyrol). As such, this will be the example I give the most attention.
Before the outbreak of Covid-19, in the winter season of 2018–2019, the ski resort of Ischgl, famously known as the “Ibiza of the Alps”, registered 300,414 arrivals of tourists from different origins and 1,409,478 overnight stays ( Tyrol Provincial Government, 2019, p. 28 ). Its association with the Samnaun resort (Ischgl/Samnaun Silvretta Arena) places this ski destination among the 10 largest in Europe and among the 50 largest in the world ( Vanat, 2020 ). These resorts staged the scene of one of the largest global events of super-spreading of SARS-CoV-2. During the “peak” of the high ski season, between the end of February and the beginning of March 2020, it was estimated that more than 6,000 people from about half a hundred of nations may have been infected in Ischgl and transported the virus to their respective countries [1] , quickly dispersing it worldwide. The initial contagion was so massive that, according to a serological study carried out by the Innsbruck University of Medicine, at the end of April 2020 more than 42% of residents in Ischgl already had antibodies to the virus ( Van Laer et al. , 2020 ). Not only because of the number of infections, but also because of the multinationality of the infected and the fact that contagions occurred at an early stage of the pandemic, Ischgl played a very significant role, along with other alpine resorts, to the speed with which COVID-19 took hold in the European continent and its spread worldwide ( Correa-Martínez et al. , 2020 ; Kreidl et al. , 2020 ).
The specific question that remains is what socio-material conditions have fostered the viral outbreak in Ischgl and other ski resorts? There are immediate visible reasons of a structural nature, inherently characteristic to most touristic contexts: the sharp reduction in air travel costs and the unconditional “open doors” positioning of destinations – presented as free territories ready to be consumed –, which led to a spiral of hyper-massification of tourism with the potential to create epidemic scenarios. The photographs that follow ( Plates 1 and 2 ) illustrate the many directions that opened Ischgl to the rest of the world and brought thousands of people to it, who settled there in a compact and active way, living in (almost) “a state of exception” and transforming the resort into a “post-national zone”: “a space of which the traditional nation-state is not in complete control, meshing together, as it does, various kinds of ‘circulating’ populations with different kinds of ‘locals’. […] a space densely and continuously connected to places beyond the nation” ( Inda, 2000, pp. 92–99 ).
Besides the more general and structural conditions related to the wide concentration of people from different geographic origins, common to many other tourist destinations, the set of specific circumstances directly responsible for the massive contagion processes in ski resorts has not yet been unequivocally identified. However, some possibilities are already considered as quite probable, such as (1) the high weekly turnover of thousands of tourists; (2) socially intense après-ski recreational activities, which presuppose close contacts, especially in closed spaces; (3) the long queues and crowds that form on cable cars, lift lines, restaurants, shops and many other facilities; (4) sharing accommodation between groups of resort employees and between groups of tourists, which often result in situations of high concentration of people in the same dwelling; (5) frequent physical contact with a wide variety of shared surfaces (e.g. cable cars, perches, rented equipment, handrails and doors), facilitating possible contagion through fomites; (6) the presence of nasal secretions on gloves resulting from constant cold-induced rhinorrhoea ( Dalton et al ., 2020 ; Felbermayr et al ., 2021 ; Gianfredi et al. , 2021 ; Kreidl et al. , 2020 ).
Our only other comment is that it really is becoming too busy. You used to go out sure you’d not have to wait for lifts and sure the slopes would be safe. Last week (admittedly a holiday week when there was bad weather at times) there were times when the queues built up at bottlenecks and when some slopes were lethal because of the crowding, number of people on slopes they couldn’t handle and general idiocy of groups of young lads skiing recklessly. It’s also now really difficult to find a place to eat or drink for a pit stop - you have to reserve tables for lunch which never used to be the case and is really annoying. The self service restaurants are all far too busy. We’ll not be going back at peak season (LondonFriday, Gurugram-Índia, 01/03/2020).
This resort is huge and caters to the glitzy and well-healed skiers who like the party scene. The huge line-ups for the gondolas (at the base) set the tone for our stay. Everything was busy (the runs, the lifts and the restaurants). We had a mixed bag of skiing largely dependent on weather-which is to be expected. Some of the runs and lifts were closed down due to bad weather which made it challenging to get down to the bottom. Some people got stuck on the Swiss side during a storm and had to take long bus ride back to Ischgl (Sue S., Kingston-Canadá, 26/04/2020).
From these excerpts, a set of rhetorical elements (short, but significant) stand out to characterize Ischgl as a tourist destination and, to a certain extent, to qualify the experience of the tourists themselves. Through brief discursive descriptions – “becoming too busy”, “queues built up at bottlenecks”, “crowding”, “restaurants are all far too busy”, “glitz party scene”, “everything was busy” – the testimonies highlight several situations that describe a routine of crowd compression in the spaces and the constant frenetic atmosphere and partying, whether in large concerts with international bands ( Plate 2 , back) or in the day-to-day life in the various and not very large après ski bars existing in the resort. The result was a social ecology that turned out to be convenient for a pathogenic entity that, to a large extent, subsists and circulates based on what, ontologically, defines the human condition: proximity and interpersonal contact.
The analysis of the Ischgl ski resort case allows us to deduce that the rapid internationalisation and growth of mass tourism tends to exceed the ecological, social and organisational capacities of the receiving contexts in terms of welcoming tourist flows and providing unconstrained and pleasant stays for the visitors. This results in scenarios and challenges of over-tourism which, among many other impacts, generate biosecurity risks of a transnational scale and situations of health unsustainability, potentially responsible for severe public health emergencies such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
3. Biosecurity and public health: questioning tourism (and) sustainability
Around the world, in countries at all development levels, many millions of jobs and businesses are dependent on a strong and thriving tourism sector. Tourism has also been a driving force in protecting natural and cultural heritage, preserving them for future generations to enjoy (in https://www.unwto.org );
Tourism is far more than tourism alone. From infrastructure and communication to food production and transport, tourism’s considerable economic weight gives it the responsibility and the power to play a key role in the sustainable and responsible development of economies and societies. Not only has tourism been a sector of consistently above-average growth for eight straight years, with 1.3 billion international tourist arrivals recorded in 2017, but the sector’s cross-cutting nature and wide global reach make it an effective tool to contribute to all of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (in Fair Observer, 2019 ).
In the boosterism that characterizes the approach of the WTO and other entities and agents, the evaluation of tourism (and its success) is almost always done according to the numbers that reflect its expression as a market force and its influence on economic growth (e.g. GDP, % of total exports), assuming that the continuous expansion of tourist activities automatically assures a factor of well-being, development and sustainability ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2021 ). However, this assumption is based more on wishful thinking than on real measures, results and concrete situations beyond those that fulfil a merely tokenistic function, as was the case of the proclamation of the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, in 2017, by the United Nations (UN). In fact, “the idea of tourism being a responsible and sustainable industry is still a far-to-reach goal, as some of the game-changing and promising attempts quickly face the harsh reality of a highly competitive market” ( Stankov et al. , 2020, p. 708 ).
In general, the sector has shown the little capacity and/or willingness to implement structural changes and adopt procedures to face the great contemporary ecological and social challenges, thus becoming less and less sustainable as it expands economically ( Andria et al. , 2021 ; Hall, 2019b ; Moscardo and Murphy, 2014 ; Scott et al. , 2019 ; Sharpley, 2020 ). The inertia in truly facing the many negative impacts of tourist activity results, in the first place, from the blindness induced by market logics and by the unconditional search for growth. But it also results from the semantic complexity of the notion of “sustainable tourism” and the consequent divergence of understandings between academics, tourist agents and technicians about sustainability and the respective forms of operationalization and evaluation ( Andria et al. , 2021 ; Cernat and Gourdon, 2012 ; Gibson, 2012 ; Sørensen and Grindsted, 2021 ).
the potential for disease spread will only increase further as international tourism expands in terms of the number of tourists that travel, as well as the distance travelled. In addition, the risk of biological invasion is only likely to increase further in the future as a result of climate change […], while the potential lag between invasion, population growth on the new range, and impact on indigenous species and the physical environment, may mean that the effects of the rapid growth in tourism mobility from the late 1960s on, may only now be starting to become obvious in some destinations (p. 89).
As we have seen above, based on the example of the Ischgl ski resort, the responsibility of tourist flows in the rapid spread of the COVID-19 pandemic unequivocally proves the relevance of drawing attention to the fact that tourism induces multiple risks of biosecurity and is responsible for the dispersion of organisms with severe ecological, economic, social and public health repercussions at local and transnational scales ( Hall, 2015 ; Hall and Baird, 2013 ; Kim et al. , 2022 ; Mackay et al. , 2021 ; Melly and Hanrahan, 2021 ; Robinson and McNeill, 2022 ). Given the evident role of tourism in the viral globalization of SARS-CoV-2, it is to be expected that the biosecurity challenges raised by tourist mobilities will gain greater attention and be subject to more consistent and effective policy frameworks at international, national and local levels ( Melly and Hanrahan, 2021 ). To this end, it is essential to consider biosecurity and public health as even more relevant dimensions in the SDG ( Kim et al. , 2022 ), bringing to the forefront of the debate on (tourism) sustainability the biohazards generated by mass tourism and valuing health issues as another important pillar to consider in the conceptualisation of sustainability and in the respective policies. At the same time, it is fundamental to question the relationship between tourism and sustainability, assuming that “with the magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic, there is an urgent need not to return to business-as-usual when the crisis over, rather than an opportunity to reconsider a transformation of the global tourism system more aligned to the SDGs” ( Gössling et al. , 2021, p. 15 ).
Recognizing the responsibility of tourist activities in the production of risks and perverse impacts should lead to a rethinking of the tourism-sustainability nexus. In this sense, it is essential to start by clarifying whether tourism and its sustainability (i.e. future viability, mainly economic, in a given context) are an end in themselves or a means of transversally promoting the sustainable development of societies ( Butler, 1999 ; Postma et al. , 2017 ; Saarinen, 2020 ; Simão and Partidário, 2012 ). Given that tourist activities are, by definition, manifestations densely embedded in the social fabric, they must be viewed clearly as part of a much larger whole and positioned in their proper place, “at the service of local communities and societies. Tourism is not an end in itself; thus sustaining tourism is not the ultimate goal” ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2021, p. 565 ). Only in this way, through its contributions to face the great contemporary social and ecological challenges can tourism truly assert itself as an agent of sustainability; and this transversal purpose to which it contributes is an intrinsic condition of its own sectorial sustainability as an economic activity ( Postma et al. , 2017 ).
The COVID-19 pandemic showed us these links in their most negative manifestations: tourism played a decisive role in the rapid viral circulation on a global scale, which, in turn, implied a kind of shutdown of tourist activities as a strategy of virus containment. The unsustainability of tourism in terms of biosecurity contributed significantly to a scenario of health crises that, in a reverse effect, ended up severely affecting the economic sustainability of the sector. For all these reasons, the eventual critical reconsideration of the tourism growth trajectory (i.e. more tourism equals more benefits) and its greater convergence with the SDGs could even be considered as one of the few “positive aspects” resulting from the pandemic crisis ( Gössling et al. , 2021 ). However, will the post-COVID in fact constitute the end of over-tourism ( Koh, 2020 ) and the emergence of meta-economic modes of tourism, organized primarily according to the social and natural contexts of which they are a part? If something has indeed been learned over the last two years of the pandemic, an increased concern for sustainability issues and responsible tourism models is quite likely ( Postma and Yeoman, 2021 ). In this sense, and taking into account the four post-COVID-19 scenarios for global tourism in 2025 that Yeoman et al. (2022) outlined, let us hope that will come true the scenario of “responsible tourism”, characterised by “A rethinking of the relationship of tourism with the ecosystem; a sustainable and balanced future; a conscious, well-informed and responsible holiday behaviour; rethinking capitalism” ( Yeoman et al. , 2022, p. 186 ).
4. Conclusion
Tourist mobilities are one of the greatest expressions of the fluidity of the contemporary world system that SARS-CoV-2 took advantage of to quickly reach large distances and spread into a pandemic. Increasingly associated with a broad global structure of air mobility, international tourism has become an influential socio-technical vector in the process of the sudden spread of the virus on a planetary scale ( Iaquinto, 2020 ). This was due to the fact that it provided contexts of epidemiological risk resulting from the formation of large transnational clusters of people who, in a matter of days, covered distances of thousands of kilometres and came into close contact with hundreds of other people between the contexts of origin, transit and tourist destination. The case of the Ischgl ski resort presented here – as an example of the coronavirus super-spreading – is paradigmatic of tourism's ability to mobilize and concentrate large numbers of people from multiple origins in rotation in the same destination, providing social configurations and complex more-than-human assemblages with obvious implications in terms of biosecurity, among many others.
Mass tourism is undoubtedly a relevant phenomenon in the multiplicity of causes of the initial spread of the virus, despite it being portrayed in various discourses as (singularly) one of the main socio-economic “victims” of COVID-19. Prior to suffering the profound and serious impacts of the pandemic, it contributed decisively to this same pandemic. For the future, it is essential to avoid head-in-the-sand behaviour and keep this perspective in mind. If we limit ourselves to looking at COVID-19 as an exogenous manifestation, lingering on the outer limits of the tourist economy with its values and practices, we run a serious risk of perpetuating situations that lead to new epidemiological emergency scenarios and postponing impingent changes ( Sigala, 2020 ). Therefore, an effective (self)criticism of tourist activities is required to assess their social, environmental and biosafety impacts, while seeking to build tourism models that generate economy(ies) at the service of the common good, in which poverty, climate change, biosecurity and health and well-being constitute factors to be considered unconditionally as a priority. Only in this way will it truly be possible the alignment with the SDGs goals and, inherently, the sustainability of tourism itself. If it persists in clinging to the old obsessive spiral of unrelenting growth, tourism will hardly have a future.
A “totem” pole celebrating Ischgl as a multi-national space
Thousands of people at one of the usual concerts organised in the resort of Ischgl before the pandemic
The estimate of the number of people infected in Ischgl is based on data from the Consumer Protection Association (VSV), which is coordinating a class action lawsuit against the Austrian government for negligence in terms of public health responses to the COVID-19 outbreak. The signatures of more than 6,000 tourists from 47 countries who believe they have been infected with the virus in Ischgl have already been gathered ( The Guardian, 2020 ).
Dissemination of pathogens, disease vectors and animal and plant alien species.
Journalistic sources
Bangkok Post ( 2020 ), “ First Thai infected with coronavirus”, January 22, available at : https://www.bangkokpost.com/thailand/general/1841199/first-thai-infected-with-coronavirus (by Apinya Wipatayotin) .
CPR News ( 2021 ), “ Winter Park reports largest Colorado ski area coronavirus outbreak with 109 cases”, February 11, available at : https://www.cpr.org/2021/02/11/winter-park-reports-largest-colorado-ski-area-coronavirus-outbreak-with-109-cases/ (by Sarah Mulholland) .
Diário de Notícias ( 2020a ), “ Portugal confirma dois casos de Covid-19 com ligações a Itália e Espanha ”, March 2 , available at: https://www.dn.pt/pais/confirmados-dois-primeiros-casos-de-coronavirus-em-portugal-11805920.html (by Graça Henriques, Rita Nunes and Susete Henriques).
Diário de Notícias ( 2020b ), “ Espanha vs. Itália. Das semelhanças na 1. a vaga às diferenças na segunda ”, September 11 , available at: https://www.dn.pt/edicao-do-dia/11-set-2020/espanha-vs-italia-das-semelhancas-na-primeira-vaga-as-diferencas-na-segunda-12710407.html (by Susana Salvador).
Fair Observer ( 2019 ), “ Tourism is an effective tool for the SDGs ”, February 13, available at: https://www.fairobserver.com/culture/tourism-industry-sustainable-development-goals-world-tourism-organization-news-today-33480/ (by Kourosh Ziabari) .
Público ( 2021 ), “ Brasil confirma que nova estirpe detectada no Japão circula na Amazónia”, January 13, available at : https://www.publico.pt/2021/01/13/ciencia/noticia/covid19-brasil-confirma-circulacao-amazonia-nova-estirpe-detectada-japao-1946100 (by Lusa) .
The Guardian ( 2020 ), “ Everyone was drenched in the virus”: was this Austrian ski resort a Covid-19 ground zero?”, September 5, available at : https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/sep/05/everyone-was-drenched-in-the-virus-was-this-austrian-ski-resort-a-covid-19-ground-zero (by Philip Oltermann e Lois Hoyal) .
The Guardian ( 2021 ), “ Canada ski resort linked to largest outbreak of P1 Covid variant outside Brazil”, April 11, available at : https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/apr/11/canada-ski-resort-p1-covid-variant-whistler (by Leyland Cecco) .
The New York Times ( 2020 ), “ France confirms first death in Europe from coronavirus”, February 15, available at : https://www.nytimes.com/2020/02/15/world/europe/france-coronari vus-death.html (by Elian Peltier) .
Ali , S. and Keil , R. ( 2008 ), Networked Disease: Emerging Infections in the Global City , Blackwell , Chichester .
Andria , J. , Tollo , G. and Pesenti , R. ( 2021 ), “ Fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making: an entropy-based approach to assess tourism sustainability ”, Tourism Economics , Vol. 27 No. 1 , pp. 168 - 186 .
Ateljevic , I. , Morgan , N. and Pritchard , A. (Eds) ( 2012 ), The Critical Turn in Tourism Studies: Creating an Academy of Hope , Routledge , London and New York .
Bramwell , B. and Lane , B. ( 2011 ), “ Critical research on the governance of tourism and sustainability ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 19 Nos 4-5 , pp. 411 - 421 .
Brito-Henriques , E. ( 2020 ), “ Covid-19, turismo e sustentabilidade: tudo está interligado ”, Finisterra – Revista Portuguesa de Geografia , Vol. 55 No. 115 , pp. 205 - 210 .
Brown , A. , Ahmad , S. , Beck , C. and Nguyen-Van-Tam , J. ( 2016 ), “ The roles of transportation and transportation hubs in the propagation of influenza and coronaviruses: a systematic review ”, Journal of Travel Medicine , Vol. 23 No. 1 , tav002 .
Brockmann , D. ( 2018 ), “ Human mobility, networks and disease dynamics on a global scale ”, in Bunde , A. , Caro , J. , Kärger , J. and Vogl , G. (Eds), Diffusive Spreading in Nature, Technology and Society , Springer , Cham , pp. 375 - 396 .
Brockmann , D. and Helbing , D. ( 2013 ), “ The hidden geometry of complex, network-driven contagion phenomena ”, Science , Vol. 342 No. 6164 , pp. 1337 - 1342 .
Buckley , R. ( 2012 ), “ Sustainable tourism: research and reality ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 39 No. 2 , pp. 528 - 546 .
Butler , R.W. ( 1999 ), “ Sustainable tourism: a state-of-the-art review ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 1 No. 1 , pp. 7 - 25 .
Cernat , L. and Gourdon , J. ( 2012 ), “ Paths to success: benchmarking cross-country sustainable tourism ”, Tourism Management , Vol. 33 No. 5 , pp. 1044 - 1056 .
Cheer , J. , Milano , C. and Novelli , M. ( 2019 ), “ Tourism and community resilience in the Anthropocene: accentuating temporal overtourism ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 27 No. 4 , pp. 554 - 572 .
Chen , L. and Wilson , M. ( 2008 ), “ The role of the traveler in emerging infections and magnitude of travel ”, The Medical Clinics of North America , Vol. 92 No. 6 , pp. 1409 - 1432 .
Chen , S. , Law , R. and Zhang , M. ( 2021 ), “ Review of research on tourism-related diseases ”, Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , Vol. 26 No. 1 , pp. 44 - 58 .
Chong , K.L. ( 2019 ), “ The side effects of mass tourism: the voices of Bali islanders ”, Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , Vol. 25 No. 2 , pp. 157 - 169 .
Correa-Martínez , C. , Kampmeier , S. , Kümpers , P. , Schwierzeck , V. , Hennies , M. , Hafezi , W. , Kühn , J. , Pavenstädt , H. , Ludwig , S. and Mellmanna , A. ( 2020 ), “ A pandemic in times of global tourism: superspreading and exportation of COVID-19 cases from a ski area in Austria ”, Journal of Clinical Microbiology , Vol. 58 No. 6 , pp. 005888 - 20 , doi: 10.1128/JCM.00588-20 .
Croce , V. ( 2018 ), “ With growth comes accountability: could a leisure activity turn into a driver for sustainable growth? ”, Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 4 No. 3 , pp. 218 - 232 .
Dalton , C. , Katelaris , A. and Wilson , N. ( 2020 ), “ Open with care: minimising COVID-19 superspreading settings in Australia ”, SSRN , 3625655 , pp. 1 - 12 , doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3625655 .
Dauvergne , P. and Lister , J. ( 2013 ), Eco-Business: A Big-Brand Takeover of Sustainability , The MIT Press , Cambridge and London .
Fang , J. , Gozgor , G. , Paramati , S.R. and Wu , W. ( 2021 ), “ The impact of tourism growth on income inequality: evidence from developing and developed economies ”, Tourism Economics , Vol. 27 No. 8 , pp. 1669 - 1691 .
Felbermayr , G. , Hinz , J. and Chowdhry , S. ( 2021 ), “ Après-ski: the spread of coronavirus from Ischgl through Germany ”, German Economic Review , Vol. 22 No. 4 , pp. 415 - 446 .
Findlater , A. and Bogoch , I. ( 2018 ), “ Human mobility and the global spread of infectious diseases: a focus on air travel ”, Trends in Parasitology , Vol. 34 No. 9 , pp. 772 - 783 .
Gianfredi , V. , Mauer , N.S. , Gentile , L. , Riccò , M. , Odone , A. and Signorelli , C. ( 2021 ), “ Covid-19 and recreational skiing: results of a rapid systematic review and possible preventive measures ”, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , Vol. 18 No. 8 , p. 4349 , doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084349 .
Gibson , K. ( 2012 ), “ Stakeholders and sustainability: an evolving theory ”, Journal of Business Ethics , Vol. 109 No. 1 , pp. 15 - 25 .
Gössling , S. ( 2002 ), “ Global environmental consequences of tourism ”, Global Environmental Change , Vol. 12 No. 4 , pp. 283 - 302 .
Gössling , S. , Scott , D. and Hall , C.M. ( 2021 ), “ Pandemics, tourism and global change: a rapid assessment of COVID-19 ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 29 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 20 .
Grout , A. , Howard , N. , Coker , R. and Speakman , E. ( 2017 ), “ Guidelines, law, and governance: disconnects in the global control of airline-associated infectious diseases ”, The Lancet Infectious Diseases , Vol. 17 No. 4 , pp. e118 - e122 .
Hall , C.M. ( 2005 ), “ Biosecurity and wine tourism ”, Tourism Management , Vol. 26 No. 6 , pp. 931 - 938 .
Hall , C.M. ( 2011 ), “ Biosecurity, tourism and mobility: institutional arrangements for managing tourism-related biological invasions ”, Journal of Policy Research in Tourism, Leisure and Events , Vol. 3 No. 3 , pp. 256 - 280 .
Hall , C.M. ( 2015 ), “ Tourism and biological exchange and invasions: a missing dimension in sustainable tourism? ”, Tourism Recreation Research , Vol. 40 No. 1 , pp. 81 - 94 .
Hall , C.M. ( 2019a ), “ Biological invasion, biosecurity, tourism, and globalization ”, in Dallen , T. (Ed.), Handbook of Globalisation and Tourism , Edward Elgar , Cheltenham and Northampton , pp. 114 - 125 .
Hall , C.M. ( 2019b ), “ Constructing sustainable tourism development: the 2030 agenda and the managerial ecology of sustainable tourism ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 27 No. 7 , pp. 1044 - 1060 .
Hall , C.M. and Baird , T. ( 2013 ), “ Ecotourism, biological invasions and biosecurity ”, in Ballantyne , R. and Packer , J. (Eds), International Handbook on Ecotourism , Edward Elgar , Cheltenham and Northampton , pp. 66 - 77 .
Hall , C.M. , Scott , D. and Gössling , S. ( 2020 ), “ Pandemics, transformations and tourism: be careful what you wish for ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 22 No. 3 , pp. 577 - 598 .
Higgins-Desbiolles , F. ( 2018 ), “ Sustainable tourism: sustaining tourism or something else? ”, Tourism Management Perspectives , Vol. 25 , pp. 157 - 160 .
Higgins-Desbiolles , F. ( 2021 ), “ The ‘war over tourism’: challenges to sustainable tourism in the tourism academy after COVID-19 ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 29 No. 4 , pp. 551 - 569 .
Higgins-Desbiolles , F. , Carnicelli , S. , Krolikowski , C. , Wijesinghe , G. and Boluk , K. ( 2019 ), “ Degrowing tourism: rethinking tourism ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 27 No. 12 , pp. 1926 - 1944 .
Iaquinto , B. ( 2020 ), “ Tourist as vector: viral mobilities of COVID-19 ”, Dialogues in Human Geography , Vol. 10 No. 2 , pp. 174 - 177 .
Inda , J. ( 2000 ), “ A flexible world: capitalism, citizenship, and postnational zones ”, PoLAR – Political and Legal Anthropology Review , Vol. 23 No. 1 , pp. 86 - 102 .
Ioannides , D. and Gyimóthy , S. ( 2020 ), “ The COVID-19 crisis as an opportunity for escaping the unsustainable global tourism path ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 22 No. 3 , pp. 624 - 632 .
Jamal , T. and Budke , C. ( 2020 ), “ Tourism in a world with pandemics: local-global responsibility and action ”, Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 6 No. 2 , pp. 181 - 188 .
Khan , K. , Memish , Z. , Chabbra , A. , Liauw , J. , Hu , W. , Janes , D. , Sears , J. , Arino , J. , Macdonald , M. , Calderon , F. , Raposo , P. , Heidebrecht , C. , Wang , J. , Chan , A. , Brownstein , J. and Gardam , M. ( 2010 ), “ Global public health implications of a mass gathering in Mecca, Saudi Arabia during the midst of an influenza pandemic ”, Journal of Travel Medicine , Vol. 17 No. 2 , pp. 75 - 81 .
Khan , U. ( 2020 ), “ Does tourism boost economic growth: evidence from Italy ”, International Journal of Economics and Business Administration , Vol. 8 No. 4 , pp. 214 - 222 .
Kim , M.J. , Bonn , M. and Hall , C.M. ( 2022 ), “ Traveler biosecurity behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic: effects of intervention, resilience, and sustainable development goals ”, Journal of Travel Research , Vol. 61 No. 7 , pp. 1599 - 1618 . doi: 10.1177/00472875211034582 .
Koh , E. ( 2020 ), “ The end of over-tourism? Opportunities in a post-Covid-19 world ”, International Journal of Tourism Cities , Vol. 6 No. 4 , pp. 1015 - 1023 .
Kraemer , M. , et al. ( 2015 ), “ The global distribution of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae . Albopictus ”, eLife , No. 4 , p. e08347 .
Kreidl , P. , Schmid , D. , Maritschnik , S. , Richter , L. , Borena , W. , Genger , J.-W. , Popa , A. , Penz , T. , Bock , C. , Bergthaler , A. and Allerberger , F. ( 2020 ), “ Emergence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Austria ”, Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift , Vol. 132 No. 21 , pp. 645 - 652 .
Lupton , D. ( 2021 ), “ Contextualising COVID-19: sociocultural perspectives on contagion ”, in Lupton , D. and Willis , K. (Eds), The COVID-19 Crisis: Social Perspectives , Routledge , London , pp. 14 - 24 .
Mackay , M. , Henwood , R. , Nelson , T. , Perkins , H.C. and Wilson , J. ( 2021 ), “ Tourism and biosecurity: a content analysis of Aotearoa New Zealand news media reporting 2009-2019 ”, Tourism Recreation Research . doi: 10.1080/02508281.2021.1981072 .
Melly , D. and Hanrahan , J. ( 2021 ), “ Tourism biosecurity risk management and planning: an international comparative analysis and implications for Ireland ”, Tourism Review , Vol. 76 No. 1 , pp. 88 - 102 .
Moscardo , G. and Murphy , L. ( 2014 ), “ There is no such thing as sustainable tourism: reconceptualizing tourism as a tool for sustainability ”, Sustainability , Vol. 6 No. 5 , pp. 2538 - 2561 .
Postma , A. , Cavagnaro , E. and Spruyt , E. ( 2017 ), “ Sustainable tourism 2040 ”, Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 3 No. 1 , pp. 13 - 22 .
Postma , A. , Heslinga , J. and Hartman , S. ( 2020 ), Four Futures Perspectives of the Visitor Economy after Covid-19 , Centre of Expertise in Leisure, Tourism and Hospitality , Breda .
Postma , A. and Yeoman , I.S. ( 2021 ), “ A systems perspective as a tool to understand disruption in travel and tourism ”, Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 7 No. 1 , pp. 67 - 77 .
Pritchard , A. , Morgan , N. and Ateljevic , I. ( 2011 ), “ Hopeful tourism: a new transformative perspective ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 38 No. 3 , pp. 941 - 963 .
Rasoolimanesh , S.M. , Ramakrishna , S. , Hall , C.M. , Esfandiar , K. and Seyfi , S. ( 2020 ), “ A systematic scoping review of sustainable tourism indicators in relation to the sustainable development goals ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , pp. 1 - 21 , doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1775621 .
Robinson , A.P. and McNeill , M.R. ( 2022 ), “ Biosecurity and post-arrival pathways in New Zealand: relating alien organism detections to tourism indicators ”, NeoBiota , No. 71 , pp. 51 - 69 .
Saarinen , J. (Ed.) ( 2020 ), Tourism and Sustainable Development Goals: Research on Sustainable Tourism Geographies , Routledge , Abingdon .
Sabin , N. , Calliope , A. , Simpson , S. , Arima , H. , Ito , H. , Nishimura , T. and Yamamoto , T. ( 2020 ), “ Implications of human activities for (re)emerging infectious diseases, including COVID-19 ”, Journal of Physiological Anthropology , Vol. 39 No. 29 , pp. 2 - 12 .
Sacramento , O. ( 2022 ), “ Vírus em viagem: fluxos turísticos globais e propagação pandêmica da Covid-19 ”, Tempo Social , Vol. 34 No. 2 , pp. 257 - 276 .
Sigala , M. ( 2020 ), “ Tourism and COVID-19: impacts and implications for advancing and resetting industry and research ”, Journal of Business Research , No. 117 , pp. 312 - 321 .
Simão , J.N. and Partidário , M.R. ( 2012 ), “ How does tourism planning contribute to sustainable development? ”, Sustainable Development , Vol. 20 No. 6 , pp. 372 - 385 .
Scott , D. , Hall , C.M. and Gössling , S. ( 2019 ), “ Global tourism vulnerability to climate change ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 77 , pp. 49 - 61 .
Sharma , A. and Nicolau , J. ( 2020 ), “ An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry ”, Annals of Tourism Research , No. 83 , 102990 .
Sharpley , R.A. ( 2020 ), “ Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 28 No. 11 , pp. 1932 - 1946 .
Sørensen , F. and Grindsted , T.S. ( 2021 ), “ Sustainability approaches and nature tourism development ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 91 , 103307 .
Stankov , U. , Filimonau , V. and Vujičić , M.D. ( 2020 ), “ A mindful shift: an opportunity for mindfulness-driven tourism in a post-pandemic world ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 22 No. 3 , pp. 703 - 712 .
Tanguay , G.A. , Rajaonson , J. and Therrien , M.C. ( 2013 ), “ Sustainable tourism indicators: selection criteria for policy implementation and scientific recognition ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 21 No. 6 , pp. 862 - 879 .
Tatem , A. , Huang , Z. , Das , A. , Qi , Q. , Roth , J. and Qiu , Y. ( 2012 ), “ Air travel and vector-borne disease movement ”, Parasitology , Vol. 139 , pp. 1816 - 1830 .
Tight , M. ( 2019 ), Documentary Research in the Social Sciences , Sage , London .
Tyrol Provincial Government ( 2019 ), “ Der tourismus im Winter 2018/2019 ”, Innsbruck, Planning and Statistics Department of the TPG, available at: https://www.tirol.gv.at/filead min/themen/statistik-budget/statistik/downloads/Tourismus/Der_Tourismus_im_ Winter_18_19.pdf
Uğur , N. and Akbıyık , A. ( 2020 ), “ Impacts of COVID-19 on global tourism industry: a cross-regional comparison ”, Tourism Management Perspectives , Vol. 36 , 100744 .
United Nations ( 2020 ), “ Policy brief: COVID-19 and transforming tourism ”, available at: https://unsdg.un.org/sites/default/files/2020-08/sg_policy_brief_covid-19_touri sm_august_2020.pdf
Vanat , L. ( 2020 ), International Report on Snow & Mountain Tourism. Overview of the Key Industry Figures for Sky Resorts , Genebra , available at: https://www.vanat.ch/RM-world-report-2020.pdf
Van Laer , D. , Fleischhacker , W. and Willeit , P. ( 2020 ), “ Ischgl-Studie. 42,4 prozent sind antikörper-positiv ”, Medizinische Universität Innsbruck News , 25 June, available at: https://www.i-med.ac.at/mypoint/news/746359.html
Vărzaru , A. , Bocean , C. and Cazacu , M. ( 2021 ), “ Rethinking tourism industry in pandemic COVID-19 period ”, Sustainability , Vol. 13 No. 12 , pp. 1 - 19 .
Wilder-Smith , A. ( 2006 ), “ The severe acute respiratory syndrome: impact on travel and tourism ”, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease , Vol. 4 No. 2 , pp. 53 - 60 .
Wilson , M. ( 2020 ), “ What goes on board aircraft? Passengers include Aedes, Anopheles, 2019-nCoV, Dengue, Salmonella, Zika, et al ”, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease , No. 33 , 101572 .
World Tourism Organization – WTO ( 1993 ), Indicators for the Sustainable Management of Tourism , WTO , Winnipeg .
World Tourism Organization – WTO ( 1998 ), Guide for Local Authorities on Developing Sustainable Tourism , WTO , Madrid .
World Tourism Organization – WTO ( 2004 ), Indicators of Sustainable Development for Tourism Destinations: A Guidebook , WTO , Madrid .
World Tourism Organization – WTO ( 2021 ), International Tourism Highlights , 2020 Edition , WTO , Madrid .
World Travel and Tourism Council – WTTC ( 2021 ), “ Global economic impact and trends 2021 ”, available at: https://wttc.org/Portals/0/Documents/Reports/2021/Global%20Economic%20Impact%20and%20Trends%202021.pdf?
Yeoman , I.S. , Postma , A. and Hartman , S. ( 2022 ), “ Scenarios for New Zealand tourism: a COVID-19 response ”, Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 8 No. 2 , pp. 177 - 193 .
Zimmermann , F. ( 2018 ), “ Does sustainability (still) matter in tourism (geography) ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 20 No. 2 , pp. 333 - 336 .
Yeh , S.-S. ( 2021 ), “ Tourism recovery strategy against COVID-19 pandemic ”, Tourism Recreation Research , Vol. 46 No. 2 , pp. 188 - 194 .
Further reading
Ischgl.com® ( 2018 ), “ Multitalented Artist Lenny Kravitz to rock out season finale in Ischgl ”, October 10, available at: https://www.ischgl.com/en/More/Service-area/Press/Press-releases/Multitalented-Artist-Lenny-Kravitz-to-rock-out-season-finale-in-Ischgl_ pt_281867
Spiegel International ( 2020 ), “ Chronicle of failure. A corona hotspot in the Alps spread virus across Europe ”, March 31, available at: https://www.spiegel.de/international/world/ischgl-austria-a-corona-hotspot-in-the-alps-spread-virus-across-europe-a-32b17b7 6-14df-4f37-bfcf-39d2ceee92ec (by Jürgen Dahlkamp et al. ) .
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements: to the Centre for Transdisciplinary Development Studies (CETRAD-UTAD), an entity financed by Portuguese national funds through FCT - Foundation for Science and Technology, I.P., within the scope of the UIDB/04011/2020 project; and to the Centre for Research in Anthropology (CRIA-IUL), an interuniversity R&D unit funded by Portuguese national funds through FCT, under the UIDB/04038/2020 project.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

Overtourism, Technology Solutions and Decimated Destinations pp 203–215 Cite as
Alternative Tourism as a Solution of Overtourism
- Yesim Koba 3
- First Online: 03 January 2022
757 Accesses
Since the twentieth century, package tours that consisted ‘sea, sun and sand’ trio became fashionable. Over time, mass tourism caused rapid and unplanned use of natural, cultural, and environmental resources. This has damaged the natural, cultural and environmental resources in a way that is not possible to renew and reaches a level that is dangerous for future generations. The existence of the phenomenon of tourism continues to depend largely on the quality of the environment (Kozak, Akoğlan Kozak, & Kozak General tourism. Detay Publishing, 2014). Lankford and Howard (Ann Tour Res 21:121–139, 1994) and Butler (Prog Tour & Hosp Res 2:283–293, 1996) describe the harmful effects of overcrowding, noise, damage to physical assets, and reductions in tourist satisfaction. According to Doğan, mass tourism reduces communication between tourists and local people (Doğan, Socio-cultural foundations of tourism. Ofis Ofset Publications, Izmir, 1987, 123). Such negative effects can be reduced by developing customized holiday addressing the special interests of the consumers. Therefore, in addition to the sea-sand-sun trio, alternative tourism types that consist of special interest trips have gained importance. The damage caused by mass tourism on natural, cultural, and environmental resources and the casualization over time has created changes in consumers’ travel (holiday) expectations. As consumers started to opt for personalized, high-quality products and services, tourism product providers started to create alternatives that could meet different expectations. Also, the local people living in the regions where tourism is developing want to get a share from the tourism revenues, which has spread the tourism activity to the whole year, and it has started to increase the diversity of tourism products. Sustainable tourism has gained importance in order to minimize the negative effects of tourism. Alternative tourism is seen as an ideal way to eliminate the problems posed by mass tourism and to ensure sustainability. This chapter focuses on alternative tourism as a solution to the aforementioned problems of mass tourism.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Akis, S., Peristianis, N., & Warner, J. (1996). Residents’ attitudes to tourism development: The case of Cyprus. Tourism Management, 17 (7), 481–494.
Article Google Scholar
Bahçe, S. (2013). Introduction to alternative tourism. In S. Bahçe (Ed.), Alternative tourism (pp. 3–24). TC Anadolu Universty Publications.
Google Scholar
Bjork, P. (2000). Ecotourism from a conceptual perspective, an extended definition of a unique tourism form. International Journal of Tourism Research, 2 , 189–202.
Bramwell, B. (2004). Mass tourism, diversification and sustainability in southern Europe’s coastal regions. In B. Bramwell (Ed.), Coastal mass tourism: Diversification and sustainable development in southern Europe (pp. 1–31). Channel View Publications.
Chapter Google Scholar
Britton, R. A. (1977). Making tourism more supportive of small state development : The case of St. Vincent. Annals of Tourism Research, 5 , 269–278.
Butler, R. W. (1996). The concept of carrying capacity for tourism destination: Dead or merely buried? Progress in Tourism and Hospitality Research, 2 , 283–293.
Conway, D., & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for ‘slow tourism’. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 10 (4), 329–344.
Dernoi, L. (1981). Alternative tourism: Towards a new style in north-south relations. Tourism Management, 2 , 253–264.
Dowling, R. K. (1993). Tourist and resident perceptions of the environment–tourism relationship in the Gascoyne region, Western Australia. GeoJournal, 29 (3), 243–251.
Dowling, R. K. (2006). Cruise ship tourism . CABI.
Book Google Scholar
Egres, I. (2016). Post-Fordism, alternative tourism and sustainability. In I. Egresi (Ed.), Alternative tourism in Turkey role, potential development and sustainability (pp. 271–283). Springer International Publishing AG.
Goodwin, H. (2017). The challenge of overtourism . Responsible Tourism Partnership.
Gossling, S., Hall, C. M., & Weaver, D. B. (2009). Sustainable tourism futures: Perspectives on systems, restructuring and innovations. In S. Gossling, C. M. Hall & D. B. Weaver (Eds.), Sustainable tourism futures: Perspectives on systems, restructuring and innovations (pp. 1–8). Routledge.
Hacıoğlu, N., & Avcıkurt, C. (2008). Turistik Ürün ÇeĢitlendirmesi . Nobel Yayın Dagıtım.
Hall, C. M., Scott, D., & Gössling, S. (2020). Pandemics, transformations and tourism: Be careful what you wish for. Tourism Geographies . https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2020.1759131
Insch, A. (2020). The challenges of over-tourism facing New Zealand: Risks and responses. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 15 , 100378.
Isaac, R. K. (2010). Alternative tourism: New forms of tourism in Bethlehem for the Palestinian tourism industry. Current Issues in Tourism, 13 (1), 21–36.
Jacobsen, J. K. S. (2000). Anti-tourist attitudes. Annals of Tourism Research, 27 , 284–300.
Kozak, M. A., & Bahçe, A. S. (2012). Special interest tourism (2nd ed.). Detay Publishing.
Kozak, N., Akoğlan Kozak, M., & Kozak, M. (2014). General tourism . Detay Publishing.
Krebs, A., Petr, C., & Surbled, C. (2007). La gestion de l’hyper fréquentation du patrimoine: D’une problématique grandissante à ses réponses indifférenciées et segmentées. In Proceedings of the 9th international conference on arts & cultural management . University of Valencia.
Lane, B. (2009). Thirty years of sustainable tourism: Drivers, progress, problems—And the future. In S. Gossling, C. M. Hall, & D. B. Weaver (Eds.), Sustainable tourism futures: Perspectives on systems, restructuring and innovations (pp. 19–32). Routledge.
Lankford, S. V., & Howard, D. R. (1994). Developing a tourism impact attitude scale. Annals of Tourism Research, 21 (1), 121–139.
Li, J., Nguyen, T. H. H., & Coca-Stefaniak, J. A. (2020). Coronavirus impacts on post-pandemic planned travel behaviours. Annals of Tourism Research . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2020.102964
MacDonald, K. (2011). Expression and emotion: Cultural diplomacy and nation branding in New Zealand (masters of international relations) . Victoria University of Wellington.
Marson, D. (2011). From mass tourism to niche tourism. In P. Robinson, S. Heitman, & P. Dieke (Eds.), Research themes for tourism (pp. 1–11). CABI.
Mieczkowski, Z. (1995). Envrionmental issues of tourism and recreation . University Press of America.
Morwforth, M., & Munt, I. (2016). Tourism and sustainability: Development, globalisation and new tourism in the Third World . Routledge.
Noveli, M., & Benson, A. (2005). Niche tourism: A way forward to sustainability? In M. Noveli (Ed.), Niche tourism: Contemporary issues, trends and cases (pp. 247–250). Elsevier.
O’Reilly, A. M. (1986). Tourism carrying capacity. Tourism Management, 7 (4), 254–258.
Obrador Pons, P., Crang, M., & Travlou, P. (2009). Introduction: Taking Mediterranean tourists seriously. In P. Obrador Pons, M. Crang & P. Travlou (Eds.), Cultures of mass tourism: Doing the mediterranean in the age of banal mobilities (pp. 1–20). Ashgate.
Oriade, A., & Evans, M. (2011). Sustainable and alternative tourism. In P. Robinson, S. Heitmann & P, Dieke (Eds.), Research themes for tourism (pp. 69–86). CABI International.
Oklevik, O., Gössling, S., Michael Hall, C., Jens Kristian, S. J., Ivar Petter, G., & McCabe, S. (2019). Overtourism, optimisation, and destination performance indicators: A case study of activities in Fjord Norway. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 27 , 1–21.
Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “organic, incremental and induced path to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David Weaver. Tourism Management, 33 , 1038–1041.
Petr, C. (2009). Fame is not always a positive asset for heritage equity! Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 26 (1), 1–18.
Poon, A. (1993). Tourism, technology and competitive strategy . CABI.
Robinson, M., & Noveli, M. (2005). Niche tourism: An introduction. In M. Noveli (Ed.), Niche tourism: Contemporary issues, trends and cases (pp. 1–11). Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Romeril, M. (1985). Tourism and the environment: Towards a symbiotic relationship. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 25 , 215–218.
Sheivachman, A. (2016, 16 August). Iceland and the trials of 21st century tourism. Skift . Retrieved from: https://skift.com/iceland-tourism/ . Accessed: 23 Dec 2020.
Smith, V. L., & Eadington, W. R. (Eds.). (1992). Tourism alternatives: Potentials and problems in the development of tourism . University of Pennsylvania Press.
Spilanis, I., & Vayanni, H. (2004). Sustainable tourism: Utopia or necessity? The role of new forms of tourism in the Aegean Islands. In B. Bramwell (Ed.), Coastal mass tourism: Diversification and sustainable development in Southern Europe (pp. 269–291). Channel View Publications.
UNESCO. (n.d.). World Heritage in Danger . Retrieved from: https://whc.unesco.org/en/158/ . Accessed: 1 Aug 2020.
UNWTO. (2018). ‘Overtourism’? – Understanding and managing urban tourism growth beyond perceptions: Executive summary. Retrieved from: https://www.e-unwto.org/doi/pdf/10.18111/9789284420070/. Accessed: 23 December, 2020.
Urry, J. (1990). The ‘consumption’ of tourism. Sociology, 24 (1), 23–35.
Vanhove, N. (1997). Mass tourism: Benefits and costs. In S. Wahab & J. J. Pigram (Eds.), Tourism, development and growth: The challenge of sustainability (pp. 46–71). Routledge.
Wachyuni, S. S., & Kusumaningrum, D. A. (2020). The effect of COVID-19 pandemic: How are the future tourist behavior? Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science, 33 (4), 67–76.
Walter, J. A. (1982). Social limits to tourism. Leisure Studies, 1 (3), 295–304.
Wearing, S., & Neil, J. (2009). Ecotourism: Impacts, potentials and possibilities (2nd ed.). Elsevier, Butterworth-Heinemann.
Yeoman, I., & McMahon-Beattie, U. (2011). The future challenge. In N. Morgan, A. Pritchard & R. Pride (Eds.), Destination brands: Managing place reputation (3rd ed., pp. 169–182). Butterworth-Heinemann.
Zenker, S., & Kock, F. (2020). The coronavirus pandemic: A critical discussion of a tourism research agenda. Tourism Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.10416
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Dokuz Eylül, İzmir, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Tourism Consultants Network, The Tourism Society, London, UK
Azizul Hassan
Department of Commerce and Management, University of Kota, Kota, Rajasthan, India
Anukrati Sharma
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Koba, Y. (2021). Alternative Tourism as a Solution of Overtourism. In: Hassan, A., Sharma, A. (eds) Overtourism, Technology Solutions and Decimated Destinations. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2474-2_13
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2474-2_13
Published : 03 January 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-2473-5
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-2474-2
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- General Information
Moscow CityPass
The Moscow CityPass is a tourist card that gives you free entry to more than 40 top attractions in the Russian capital, including the Kremlin and Saint Basil's Cathedral.
Included attractions
The 10 most popular attractions included with the Moscow CityPass are:
- Saint Basil's Cathedral
- Bunker-42 Museum
- Tretyakov Gallery
- Tsaritsyno Palace Museum
- Museum of the Patriotic War 1812
- State Historical Museum
- Great Wooden Palace of Tsar Alexis I in Kolomenskoye
- Moscow Sightseeing Bus Pass
- Moscow River Cruise
Moscow CityPass Prices
You can buy the Moscow CityPass for a duration of 1, 2, 3 or 5 days depending how long you're planning to spend in the city.
Is it worth it?
Entrance into these attractions is worth much more than the cost of the CityPass, yet it offers even more, for example, the Pushkin Museum , the Museum of the History of Vodka and the Museum of Contemporary History , among others, plus discounts at restaurants, shows and shops. If you're already planning to visit these sights, then it's well worth buying the CityPass to save money on tickets.
Where to buy the Moscow CityPass?
You can buy your Moscow CityPass online in advance via our website . Then, all you need to do is collect it from the Komsomolskaya Tourist Information Centre (Komsomolskaya Square, 5-1), near the Komsomolskaya metro station. The office is open from 9 am until 8 pm.
You may also be interested in

Moscow has seen its fair share of history, from invasions to revolutions: these days it is home to a wealth of culture and is one of the most populated capitals in the world.

Russian National Ballet
Ballet is one of the most emblematic symbols of Russian culture, a dance that has infiltrated countries the world over. Watch a performance in Moscow!
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
COMMITTEE FOR TOURISM - MOSCOW CITY GOVERNMENT
Country: Russian Federation
Website: https://www.mos.ru/tourism/

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Overtourism Solutions: Strategies to Manage Mass Tourism. January 5, 2019. Harold Goodwin. This pages have been created to enable the easy sharing of experience in managing overtourism and avoiding it. There is a typology of overtourism solutions which provides an index and wherever possible a link to where further information can be found ...
Sustainable Tourism and Solutions to Overtourism. Photo via Canva. Luckily today even the supply and demand of sustainable tourism are increasing. ... SET (Sud-Europe facing Overtourism): a network created by 15 European cities to denounce the destructive effects of mass tourism and promote the research for a new touristic system. Mass tourism ...
Adopt a wise-travel mindset. When you arrive in a place, you become part of that place. Where you go, what you do, how you spend, whom you talk to: It all makes a difference. Try to get out of the ...
Here we outline the complexities of overtourism and the possible measures that can be taken to address the problem. The term 'overtourism' has re-emerged as tourism recovery has surged around the globe. But already in 2019, angst over excessive tourism growth was so high that the UN World Tourism Organization called for "such growth to be ...
The World Tourism and Travel Council says that of 1.4 billion international tourist trips in 2018, more than 36%, or half a billion, involved a visit to one of the planet's 300 most popular ...
Managed well, tourism can be a positive game-changer for destinations. It creates jobs, attracts investment, drives infrastructure development. Ethical, sustainable tourism can also improve livelihood, education levels and quality of life for local people. It can refocus energy and action towards conservation, and help to preserve cultural ...
This is mass tourism 4.0, an alarming phenomenon that sees the gradual but systematic destruction of the most beautiful places in the world, without understanding its essence.
60-Second Vacation: Machu Picchu. 01:00 - Source: CNN. In Iceland, explains Reynisdóttir, the situation is different again. "The growth has been very fast - especially since 2010: we've had ...
And 2030 transport-related carbon emissions from tourism are expected to grow 25% from 2016 levels, representing an increase from 5% to 5.3% of all man-made emissions, according to the United ...
This book presents new research on this emerging phenomenon and discusses the main causes and implications before putting forward possible solutions. The authors take an interpretivist approach in order to unveil aspects of overtourism that have not yet been discussed. It provides case studies and explores topics such as tourism education ...
As Florence braces for the return of mass tourism, Schmidt wants the Uffizi Diffusi project to take the heat off Florence, and is promising works by "household names" to help disperse the crowds.
This article will cover my top 10 overtourism solutions: Stay longer at your destination. Stay in central accommodation (and avoid using Airbnb) Explore off the beaten path. Support local businesses. Respect locals going about their day-to-day lives. Respect private property.
The 'mass' in mass tourism is both a singular and a plural. The relationship between the two is key. In discussions of mass tourism, characterisations of the singular mass, or 'the masses', can obscure the plurality of individuals, and individuality itself.
Mass tourism is premised on the social and economic changes associated with the advent of modern, mass society. It is distinctive to modern society culturally too - the need to escape the city to the liminal space of the beach perhaps (Preston-Whyte, 2004), to spend one's wages earned from an employer on consumption beyond necessities, to utilise free time (away from wage labour) and ...
Cultural tourism, a new trend. A trend of the moment is tourism influenced by mass culture.According to this kind of tourism, people chose the destination based on social media, influencers, television programs and films.Tourism influenced by film and TV series products, also known as film tourism, has in some cases led to real disasters.An example is what is happening in the Pacific Islands ...
Over-tourism is a new-found word to be introduced in the tourism lexicon. Only Collins online dictionary describes it as 'a phenomenon of popular destinations or sights becoming overrun by tourists in an unsustainable way'. It is different from mass tourism or the concept of crowding. Gathering a large number of people/tourists at a ...
Mass tourism is facilitated by various factors, such as affordable transportation options, the availability of budget accommodations, and the influence of media and advertising. ... By understanding the factors contributing to mass tourism and its impacts, we can work towards finding solutions that balance the economic benefits of tourism with ...
1. Introduction. Mass tourism produces a very negative ecological and social impact, and although it generates substantial economic benefits, they are generally unevenly distributed (Chong, 2019; Fang et al., 2021).It could have been expected that the COVID-19 pandemic might have constituted a decisive tipping point for a deprioritising of the economy, considering the tourism system as a means ...
Sustainable tourism has gained importance in order to minimize the negative effects of tourism. Alternative tourism is seen as an ideal way to eliminate the problems posed by mass tourism and to ensure sustainability. This chapter focuses on alternative tourism as a solution to the aforementioned problems of mass tourism.
Moscow CityPass Prices. You can buy the Moscow CityPass for a duration of 1, 2, 3 or 5 days depending how long you're planning to spend in the city. Duration. Adults. Children under 16 years old. 1 day. € 60 ( US$ 64.90) € 45 ( US$ 48.70) 2 days.
Moscow's burgeoning gastronomic scene has been causing a stir locally and internationally. Published for the first time in 2021, the Michelin Moscow Guide awarded its prestigious stars to no ...
Global Code of Ethics for Tourism; World Committee on Tourism Ethics; Ethics Convention; Accessibility; Tourism and Culture; Women's Empowerment and Tourism; COVID-19: Sociocultural Impact; Technical Cooperation. Silk Road; UN Tourism Academy. Courses, Webinars & Resources; UN Tourism Executive Education; UN Tourism.QUEST; UN Tourism.TedQual ...
In 2022, tourism contributed RUB 120 billion to the Moscow budget, which is approximately four times more than in 2010 accounting for RUB 31 billion of total revenues. The city's income from tourism, among other things, makes it possible to improve socially significant infrastructure; for example, the amount can be spent on building 40 ...