

What is leisure tourism, and what examples?
- March 2, 2023
Leisure tourism, a popular form of travel, refers to the act of taking a trip for the purpose of relaxation, recreation, or enjoyment. It involves participating in activities typically done during one’s free time, such as sightseeing, shopping, dining out, and engaging in cultural events. While leisure tourism can take many forms, it is often associated with vacations and getaways, allowing individuals to escape the stress of everyday life and explore new places.

Despite the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on travel, leisure tourism remains a popular choice for individuals looking to recharge and explore the world. From exploring famous landmarks in Paris to sunbathing on the beaches of Bali, there are countless examples of leisure tourism destinations and activities available worldwide. In this article, we will explore the concept of leisure tourism and provide several examples of popular destinations and activities you can add to your travel bucket list.
What is leisure travel?
Leisure travel refers to traveling for pleasure rather than business or work-related purposes. It is a type of travel that involves exploring new destinations, engaging in recreational activities, and relaxing and unwinding. Whether traveling alone or with friends and family, leisure travel provides a much-needed break from the daily routine and allows individuals to experience new cultures, environments, and experiences.
For the person traveling, leisure travel can provide a wide range of benefits, including learning about different cultures, making new friends, and creating lasting memories. It can also provide a sense of adventure, challenge, and excitement that can be hard to find in everyday life. Additionally, leisure travel can help reduce stress levels and improve mental health by providing a break from the daily routine.
As a tourist, leisure travel can also significantly impact the environment and local communities. Responsible tourism practices, such as supporting local businesses, using eco-friendly transportation, and being mindful of waste, can help minimize negative impacts and promote sustainable tourism.
Of course, finances are an essential consideration for leisure travel. Depending on the destination, activities, and accommodations chosen, leisure travel can be a costly endeavor. However, with careful planning, budgeting, and research, it is possible to enjoy leisure travel without breaking the bank. Many travel websites and apps offer discounts and deals on flights, hotels, and activities, making planning an affordable and enjoyable leisure travel experience easier than ever.
Types of leisure tourism
Adventure tourism.
One of the most popular types of adventure tourism is extreme sports. From bungee jumping to skydiving, there’s no shortage of heart-pumping activities to get your adrenaline flowing. These experiences are not for the faint of heart, but they offer a rush like no other and can be incredibly rewarding for those who take the plunge.
For those who prefer a slower pace, there are plenty of other adventure tourism options. Hiking, camping, and backpacking are all popular choices that allow you to explore the great outdoors and connect with nature. Whether traversing rugged mountain trails or pitching a tent in a remote wilderness area, these activities offer a chance to escape the hustle and bustle of everyday life and immerse yourself in the beauty of the natural world.
Of course, adventure tourism is only for some. Some people prefer to stick to more traditional types of leisure tourism, such as beach vacations or city breaks. However, you love a challenge and aren’t afraid to step outside your comfort zone. In that case, adventure tourism can be an incredibly rewarding and life-changing experience.
So, whether you’re looking to bungee jump off a bridge, hike through the wilderness, or explore a new city on foot, there’s an adventure tourism experience that’s perfect for you. So why not take the leap and try something new? You never know what amazing experiences and memories you might create!
Cultural tourism
One of the most exciting things about cultural tourism is that it can take you to places you never imagined. Whether exploring ancient ruins in Greece, visiting museums in Paris, or attending festivals in Japan, there are countless opportunities to learn and grow through cultural tourism.
Of course, cultural tourism doesn’t have to take you to far-flung destinations. There are plenty of opportunities to explore different cultures closer to home, whether visiting museums and art galleries, attending cultural events in your city, or trying new foods at ethnic restaurants.
For those who love to travel, cultural tourism offers a chance to see the world differently. Rather than just ticking off tourist attractions, cultural tourism allows you to connect with locals, learn about their way of life, and gain a deeper appreciation for the rich diversity of our planet.
So whether you’re a history buff, an art lover, or simply someone who wants to experience something new, cultural tourism has something for everyone. So why not step out of your usual environment and immerse yourself in the rich tapestry of cultures that make our world so fascinating? Who knows what incredible experiences and memories await you along the way!
Suppose you’re someone who cares deeply about the environment and wants to make a positive impact on the world. In that case, ecotourism might be the perfect choice for your next leisure tourism adventure. This tourism category is all about traveling responsibly and sustainably, focusing on preserving natural habitats and supporting local communities.
One of the main things to consider when it comes to ecotourism is your travel’s impact on the environment. This means choosing eco-friendly accommodations and activities, such as staying in lodges that use renewable energy, participating in wildlife conservation efforts, and using low-impact transportation methods like hiking or cycling.
Another important factor to consider is your travel’s impact on the local community. Ecotourism aims to support local economies and promote cultural exchange, so it’s important to choose tours and activities led by local guides and support local businesses.
Of course, ecotourism is not just about being responsible and sustainable – it’s also about having fun and experiencing the beauty of nature. Whether you’re exploring pristine forests, snorkeling in coral reefs, or observing wildlife in their natural habitats, there’s no shortage of amazing experiences to be had in ecotourism.
Suppose you’re passionate about the environment and want to positively impact the world while having fun and exploring new places. In that case, ecotourism might be the perfect fit for you. And as the tourism industry continues to grow and evolve, there are plenty of opportunities for jobs and careers in eco-tourism, making it a great choice for those who want to make a difference while pursuing their passions.
Beach tourism
Beach tourism is leisure tourism that revolves around visiting coastal destinations and enjoying the beach environment. This type of tourism is popular among people of all ages, from families with young children to solo travelers seeking relaxation and recreation.
Beach tourism destinations vary widely, from crowded beaches in popular tourist hotspots to secluded and pristine shorelines in remote locations. Some of the most popular beach tourism destinations include the Caribbean, Hawaii, the Maldives, and the Mediterranean.
Activities commonly associated with beach tourism include swimming, sunbathing, beach volleyball, surfing, and water sports such as jet skiing, parasailing, and snorkeling. Many beach tourism destinations also offer a range of amenities, such as beachfront restaurants, bars, cafes, and hotels and resorts catering to beachgoers.
Beach tourism can be a great way to escape the stresses of everyday life and enjoy some time in the sun and sand. It offers many experiences, from relaxing and soaking up the sun to more active pursuits such as water sports and beach games. For those who love the ocean and the beach environment, beach tourism is a must-try type of leisure tourism.
Health and wellness tourism
Health and wellness tourism is a type of leisure tourism that focuses on improving physical, mental, and emotional well-being through various activities and services. It involves traveling to destinations that offer specialized programs and services to help visitors achieve their health and wellness goals.
Some of the most common health and wellness tourism activities include spa treatments, yoga and meditation classes, fitness activities, healthy eating, and alternative medicine practices such as acupuncture and herbal remedies. Health and wellness tourism destinations can range from specialized wellness centers and retreats to traditional vacation spots that offer a variety of wellness-focused activities and services.
Health and wellness tourism has become increasingly popular in recent years as more people seek to prioritize their health and well-being. This type of tourism offers a range of benefits, including stress relief, improved physical health, and a renewed sense of energy and vitality.
In addition to the benefits for individual travelers, health and wellness tourism can also positively impact local communities. It can create job opportunities in the wellness industry and stimulate local economies through increased tourism.
Overall, health and wellness tourism is a great option for those seeking to prioritize their health and well-being while enjoying leisure travel’s benefits. With a wide range of activities and services available, there is something for everyone in the world of health and wellness tourism.
Can business travelers have leisure time on a business trip?
Yes, business travelers can have leisure time on a business trip, depending on their schedule and the purpose of their trip. Many business travelers often have free time during their trip, either before or after their work obligations are completed. During this time, they may choose to engage in leisure activities and explore the destination they are visiting.
Business travelers may also extend their trip for a few days or a weekend to have more time to explore the destination and engage in leisure activities. This is often called “bleisure” travel, a combination of business and leisure travel.
However, it is important to note that the amount of leisure time a business traveler can have may depend on the nature of their business trip and the expectations of their employer. Sometimes, the schedule may be tightly packed with meetings, and there may be little free time for leisure activities. Additionally, some employers may have policies restricting the amount of leisure time a business traveler can have or the type of activities they can engage in during their free time.
Ultimately, it is up to the individual business traveler to determine how much leisure time they can have on a business trip and to balance their work obligations with their desire to explore and engage in leisure activities.
What are the examples of leisure tourism?
There are many examples of leisure tourism, as it encompasses many activities and destinations. Some examples of leisure tourism include:
- Beach tourism – visiting coastal destinations for sun, sand, and water activities.
- Adventure tourism – engaging in activities such as hiking, skiing, and whitewater rafting in natural environments.
- Cultural tourism – visiting destinations to learn about the local culture, history, and customs.
- Health and wellness tourism – traveling to destinations that offer specialized programs and services to improve physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
- Ecotourism – visiting natural environments to observe and learn about the local flora and fauna while minimizing environmental impact.
- Rural tourism – visiting rural destinations to experience rural life and engage in farming, fishing, and hunting activities.
- Wine tourism is visiting destinations known for their wine production and touring vineyards and wineries.
- Sports tourism – traveling to participate in or observe events such as marathons, golf tournaments, and soccer matches.
- Food tourism – traveling to destinations to experience local cuisine and food traditions.
- Educational tourism is traveling to destinations to learn about specific subjects, such as art, history, or language.
These are just a few examples of leisure tourism, and many other types of tourism can fall under this category. Ultimately, leisure tourism is about enjoying the free time and engaging in activities that provide relaxation, entertainment, and personal enrichment.
In conclusion, leisure tourism encompasses various activities and destinations, from beaches to educational tourism. The purpose of leisure tourism is to provide individuals with opportunities for relaxation, entertainment, and personal enrichment. People engage in leisure tourism to escape from their usual environment, explore new destinations, and engage in activities that they enjoy or that interest them.
While there are many types of leisure tourism, all of them share a common goal of providing individuals with a break from their daily routines and an opportunity to have fun and create memorable experiences. As the tourism industry continues to grow and evolve, we can expect to see new types of leisure tourism emerge, and existing types become more popular.
Ultimately, leisure tourism plays an important role in the tourism industry and the lives of individuals who engage in it. It provides opportunities for personal growth, cultural exchange, and economic development. Whether it’s a relaxing beach vacation, an adventurous trek through the wilderness, or an educational trip to a historic site, leisure tourism has something to offer everyone.
David Stokes
Related posts.

8 Hacks to Never pay for Luggage
- March 24, 2023

Smart Hacks to Book Cheap Flights in 2023
- March 22, 2023

8 Famous Cities in the USA You Must Visit
- March 3, 2023
Trending now

Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Tips
What Does Leisure And Tourism Mean
Published: December 12, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Karna Choi
- Plan Your Trip
- Sustainability
Introduction
Leisure and tourism are two interconnected concepts that play a significant role in our lives. They are not only sources of relaxation and entertainment but also contribute to the growth of economies and the development of cultures. In this article, we will explore what leisure and tourism mean, how they are related, and why they are important.
Leisure refers to the time spent outside of work or other commitments, where individuals engage in activities that they enjoy and find fulfilling. It can be any activity that brings pleasure, such as hobbies, sports, reading, or socializing with friends and family. Leisure is crucial for maintaining a healthy work-life balance and overall well-being. It allows individuals to rejuvenate, recharge, and engage in activities that bring them joy and satisfaction.
Tourism, on the other hand, involves traveling to different places for recreational, educational, or business purposes. It is an industry that encompasses a wide range of activities, such as sightseeing, visiting cultural and historical sites, exploring natural wonders, participating in adventure sports, attending conferences, and experiencing different cuisines and lifestyles. Tourism provides an opportunity to discover new cultures, broaden horizons, and create lasting memories.
Definition of Leisure
Leisure can be defined as the discretionary time individuals have outside of their work and other necessary commitments. It is the time to engage in activities that bring joy, relaxation, and personal fulfillment. It provides a break from the daily routine and allows individuals to pursue their interests and passions.
Leisure activities can vary greatly depending on personal preferences and interests. Some individuals may find solace in engaging in physical activities such as swimming, hiking, or playing sports, while others may prefer more passive activities like reading, listening to music, or watching movies. Leisure can also include socializing with friends and family, exploring new hobbies, attending cultural events, or even simply resting and rejuvenating.
One important aspect of leisure is that it is not bound by obligations or tasks. It is a free and voluntary choice that individuals make to engage in activities that bring them pleasure and relaxation. Unlike work or other responsibilities, leisure provides a sense of freedom and autonomy, allowing individuals to make choices based on their personal preferences and desires.
Leisure is essential for personal well-being and mental health. It helps individuals to de-stress, recharge, and maintain a healthy work-life balance. Engaging in leisure activities can have numerous benefits, including reducing anxiety and depression, improving cognitive functions, boosting creativity, and enhancing social connections.
It is important to note that leisure is subjective and can vary from person to person. What one individual finds enjoyable and fulfilling may not be the same for another. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to identify activities that bring them joy and make time for those activities in their lives. By prioritizing leisure, individuals can enhance their overall quality of life and find a sense of fulfillment and happiness.
Definition of Tourism
Tourism is the act of traveling to different destinations for recreational, educational, or business purposes. It involves the exploration and experience of new places, cultures, and activities outside one’s usual environment. Tourism is a multi-faceted industry that encompasses various activities and services, including transportation, accommodation, attractions, and hospitality.
The primary motive behind tourism is usually leisure and entertainment. People travel to escape their daily routines, experience new things, and create lasting memories. However, tourism can also serve other purposes, such as business travel, educational or cultural exchanges, and even medical tourism for specialized treatments.
There are several different types of tourism, each catering to specific interests and preferences. Some of the common types include:
- Leisure tourism: This involves traveling for recreational purposes, such as beach vacations, adventure trips, or visiting theme parks.
- Cultural tourism: This focuses on exploring the heritage, customs, and traditions of different cultures, including visiting museums, historical sites, and attending cultural events.
- Eco-tourism: This promotes responsible travel to natural areas, with the aim of preserving the environment and supporting local communities.
- Business tourism: This involves traveling for business-related activities, such as attending conferences, meetings, or trade shows.
- Medical tourism: This refers to traveling to foreign countries to receive medical treatments or procedures that may be more affordable or of higher quality than in one’s home country.
Tourism plays a vital role in the global economy, contributing to employment generation, infrastructure development, and foreign exchange earnings. It stimulates local businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, and transportation services, creating a multiplier effect on the economy. Moreover, tourism has the potential to foster cultural exchange and understanding between different societies, promoting peace and mutual respect.
However, it is important to note that tourism can also have negative impacts, including over-tourism, environmental degradation, and disruption of local communities. Sustainable tourism practices are increasingly emphasized to minimize these negative effects and ensure the long-term viability of tourist destinations.
Relationship between Leisure and Tourism
Leisure and tourism share a close and interconnected relationship. While leisure refers to the activities individuals engage in during their free time, tourism provides an avenue for individuals to experience leisure in different locations and environments. In other words, tourism is one of the ways in which people seek leisure experiences beyond their usual surroundings.
Tourism encompasses a wide range of activities and experiences that are specifically designed to provide leisure and entertainment. When individuals go on vacation or travel to different destinations, they often engage in leisure activities as part of their overall tourism experience. This may include exploring tourist attractions, trying new foods, participating in adventure sports, or simply relaxing on a beach.
On the other hand, leisure can also act as a motivator for individuals to engage in tourism. People often plan trips or vacations to unwind, break away from their daily routines, and indulge in leisure activities that they may not have the opportunity to enjoy in their regular lives. The desire for leisure experiences can inspire individuals to embark on travel adventures and explore new destinations.
Furthermore, leisure and tourism can also have a reciprocal relationship, where they reinforce and support each other. For instance, the availability of leisure activities in a tourist destination can attract visitors and contribute to the growth of the tourism industry. Similarly, tourism development can lead to the creation of new leisure facilities and opportunities for both locals and visitors to enjoy.
The relationship between leisure and tourism is not limited to individual experiences but also extends to the societal level. The leisure and tourism industries collectively contribute to the economic growth of countries, generate employment opportunities, and stimulate local businesses. They also play a significant role in cultural exchange and understanding as individuals from different cultures engage in leisure and tourism activities together.
It is important to recognize and foster the relationship between leisure and tourism to cater to the diverse needs and desires of travelers. Tourism destinations and businesses often strive to provide a variety of leisure activities and experiences that appeal to different interests and preferences, ensuring that visitors can engage in meaningful and enjoyable leisure during their trips.
Importance of Leisure and Tourism
Leisure and tourism play a crucial role in both individual lives and the broader society. They provide numerous benefits and contribute significantly to personal well-being, economic growth, and cultural exchange. Here are some key reasons why leisure and tourism are important:
1. Personal Well-Being: Leisure activities give individuals the opportunity to relax, recharge, and engage in activities they enjoy. They help reduce stress, promote mental health, and enhance overall well-being. Leisure activities provide a sense of fulfillment, satisfaction, and happiness, allowing individuals to maintain a healthy work-life balance.
2. Economic Impact: The leisure and tourism industries have a substantial impact on economies worldwide. They create jobs, stimulate local businesses, and generate revenue through various sectors such as accommodation, transportation, food and beverage, and entertainment. Tourism also encourages infrastructure development, leading to improvements in transportation, communication, and public facilities.
3. Cultural Exchange: Tourism fosters cultural exchange by bringing people from different backgrounds together. Visitors have the opportunity to experience different traditions, customs, and ways of life, promoting understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures. Additionally, locals in tourism destinations can share their heritage and showcase their culture, which helps in preserving and celebrating their identity.
4. Environmental Preservation: Sustainable tourism practices promote the protection and conservation of natural resources and ecosystems. By emphasizing responsible travel and minimizing the negative impacts on the environment, tourism can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the overall health of our planet. Eco-tourism initiatives also support environmental education and local conservation efforts.
5. Educational Opportunities: Tourism provides opportunities for educational experiences. Visitors can learn about history, art, architecture, and other aspects of different cultures through museum visits, guided tours, and cultural events. Educational tourism can also include attending workshops, language classes, or participating in immersive experiences that help broaden knowledge and perspective.
6. Community Development: Tourism can play a significant role in community development, especially in less-developed areas. It creates employment opportunities and income streams for locals, which can improve their living standards. Additionally, tourism can help revitalize and preserve traditional industries, handicrafts, and cultural practices, supporting the sustainability of local communities.
Types of Leisure Activities
Leisure activities encompass a wide range of pursuits that individuals engage in during their free time. These activities serve as a means of relaxation, entertainment, and personal fulfillment. Here are some common types of leisure activities:
- Physical Activities: Engaging in physical activities is a popular form of leisure. This can include sports such as soccer, basketball, tennis, or swimming. Physical activities not only promote physical fitness but also provide an outlet for stress relief and a sense of accomplishment.
- Creative Pursuits: Many individuals find pleasure and fulfillment in creative leisure activities. This can include painting, drawing, writing, playing a musical instrument, or engaging in crafts such as knitting or woodworking. The act of creating something allows individuals to express themselves, tap into their imagination, and experience a sense of accomplishment.
- Socializing: Connecting with others is a fundamental aspect of leisure. Socializing can take various forms, such as meeting friends for a coffee or a meal, attending social events or parties, or participating in group activities like book clubs or sports teams. Engaging in social activities provides an opportunity for building relationships, sharing experiences, and fostering a sense of belonging.
- Exploring Nature: Many people find solace and rejuvenation in spending time in nature. Activities such as hiking, camping, birdwatching, or gardening allow individuals to connect with the natural world, experience tranquility, and appreciate the beauty of their surroundings. Outdoor leisure activities also contribute to physical fitness and overall well-being.
- Reading and Learning: Reading books, magazines, or articles is a favorite leisure activity for many. It allows individuals to escape into different worlds, expand their knowledge, and stimulate their imagination. Additionally, engaging in lifelong learning, whether through online courses, workshops, or educational programs, is a fulfilling leisure pursuit that promotes personal growth and intellectual development.
- Travel and Adventure: Exploring new places and embarking on travel adventures is a popular form of leisure. Whether it’s a weekend getaway to a nearby city or an international trip to a distant country, travel allows individuals to experience new cultures, cuisines, and landscapes. Adventure activities such as rock climbing, bungee jumping, or skydiving also provide an exhilarating form of leisure for thrill-seekers.
- Relaxation and Mindfulness: In today’s fast-paced world, relaxation and mindfulness activities are essential for mental well-being. These can include meditation, yoga, spa treatments, or taking soothing baths. Engaging in relaxation and mindfulness practices helps individuals to unwind, reduce stress levels, and achieve a state of inner calm.
Types of Tourism Activities
Tourism activities encompass a wide range of experiences and opportunities for travelers to engage in during their journeys. These activities cater to diverse interests and preferences, ensuring that individuals can immerse themselves in unique and memorable experiences. Here are some common types of tourism activities:
- Sightseeing and Cultural Exploration: One of the most popular tourism activities is sightseeing and exploring different cultures. This involves visiting famous landmarks, historical sites, museums, and cultural attractions. Travelers have the opportunity to learn about the history, art, and traditions of a particular destination, allowing for a deeper understanding of its heritage and identity.
- Nature and Adventure Tourism: For those seeking outdoor adventures and natural wonders, nature and adventure tourism is an ideal choice. Activities such as hiking, trekking, wildlife safaris, snorkeling, or zip-lining allow travelers to explore pristine landscapes, encounter unique flora and fauna, and experience adrenaline-pumping thrills.
- Beach and Resort Tourism: Many tourists are drawn to destinations with beautiful beaches and world-class resorts. Beach tourism offers relaxation, swimming, sunbathing, and water sports such as surfing, snorkeling, or jet skiing. Resorts provide luxurious accommodations, spa facilities, and a range of recreational activities for a truly indulgent vacation.
- Culinary and Food Tourism: Food enthusiasts often embark on culinary tourism, where they explore the local cuisine and indulge in gastronomic experiences. This can involve food tours, cooking classes, visiting food markets, or dining at renowned restaurants to savor authentic flavors and regional specialties.
- Heritage and Architectural Tourism: Heritage and architectural tourism focus on exploring historical buildings, monuments, and architectural gems. This can involve visiting ancient ruins, castles, temples, or exploring preserved historic neighborhoods. Travelers can appreciate the craftsmanship and cultural significance of these structures.
- Eco-tourism and Sustainable Tourism: With a growing focus on sustainability, eco-tourism has gained popularity. It involves responsible travel to natural areas, promoting conservation and sustainable practices. Activities can include wildlife conservation projects, eco-lodges, hiking in national parks, and participating in environmental education programs.
- Adventure and Extreme Tourism: Adventure-seekers often pursue extreme tourism activities that push their limits. This can include activities such as skydiving, bungee jumping, white-water rafting, paragliding, or mountain climbing. These adrenaline-pumping experiences provide a thrill and unique sense of achievement.
- Wellness and Health Tourism: Wellness tourism focuses on enhancing physical and mental well-being. Travelers can indulge in spa retreats, yoga and meditation retreats, detox programs, or health resorts. These activities promote relaxation, rejuvenation, and self-care.
Benefits of Leisure and Tourism
Leisure and tourism bring numerous benefits to individuals, communities, and societies as a whole. These benefits encompass various aspects of personal, economic, cultural, and environmental well-being. Here are some key advantages of leisure and tourism:
- Personal Well-being: Leisure and tourism activities contribute to personal well-being by providing opportunities for relaxation, stress relief, and enjoyment. Engaging in leisure activities helps individuals maintain a healthy work-life balance, reduce anxiety and depression, improve mood, and enhance overall mental and physical health.
- Cultural Exchange: Tourism promotes cultural exchange and understanding between people from different backgrounds. Visitors have the opportunity to immerse themselves in local cultures, traditions, and customs. This fosters mutual respect, broadens perspectives, and breaks down stereotypes, contributing to a more harmonious and interconnected world.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: The leisure and tourism industries have a significant impact on economies. They generate employment across various sectors, such as hospitality, transportation, and tourism services. Tourism also creates business opportunities for local entrepreneurs, stimulates infrastructure development, and generates revenue through visitor spending.
- Preservation of Natural and Cultural Heritage: Tourism plays a vital role in the preservation and conservation of natural and cultural heritage. It provides the necessary funds for the maintenance of historical sites, museums, national parks, and protected areas. Additionally, responsible tourism practices promote sustainability, environmental awareness, and the protection of delicate ecosystems.
- Community Development: Leisure and tourism contribute to community development in various ways. Local communities benefit from increased job opportunities, business growth, and infrastructure development. Tourism can also help revitalize traditional industries, preserve local crafts and cultural practices, and provide a platform for showcasing and celebrating local heritage and identity.
- Education and Learning: Leisure and tourism provide educational opportunities for travelers. Visiting museums, historical sites, and cultural attractions can enhance knowledge and understanding of different cultures, history, art, and architecture. Beyond formal education, tourism allows for experiential learning, providing insights into different ways of life and fostering personal growth and development.
- Quality of Life: Leisure and tourism contribute to an improved quality of life for individuals and communities. By providing opportunities for leisure and travel experiences, people can create lasting memories, build meaningful relationships, and pursue personal interests and hobbies. This leads to increased life satisfaction, happiness, and a sense of fulfillment.
Challenges in the Leisure and Tourism Industry
The leisure and tourism industry faces various challenges that can impact its sustainability, growth, and overall success. These challenges arise from internal and external factors, and the industry must navigate them effectively to thrive. Here are some key challenges in the leisure and tourism industry:
- Seasonality: Many tourism destinations experience significant fluctuations in visitor arrivals due to seasonal patterns. This creates a challenge in maintaining a stable flow of tourists and generating consistent revenue throughout the year. Destinations heavily reliant on specific seasons may struggle economically during off-peak periods.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: The leisure and tourism industry must constantly adapt to evolving consumer preferences. As travelers become more discerning, their demands and expectations shift. Meeting these changing preferences requires continuous innovation, investment in infrastructure, and ensuring high-quality service delivery.
- Competition: The leisure and tourism industry is highly competitive. Destinations and businesses must differentiate themselves and offer unique experiences to attract visitors. Furthermore, competition in the digital space has intensified with the rise of online travel agencies and platforms, making it necessary to have a strong online presence and effective marketing strategies.
- Security and Safety Concerns: Ensuring the safety and security of travelers is of paramount importance. Natural disasters, political instability, terrorism, and other security concerns can significantly impact tourism. Effective crisis management, stringent security measures, and proactive communication are essential to manage and mitigate such risks.
- Sustainable Practices: As environmental awareness grows, the leisure and tourism industry faces the challenge of adopting sustainable practices. Balancing tourism development with environmental protection is crucial to preserve destinations and minimize the industry’s ecological footprint. This involves minimizing waste, promoting responsible tourism, and supporting local communities.
- Infrastructure and Accessibility: Developing and maintaining adequate infrastructure can be a challenge, particularly in remote and less-developed areas. The lack of transportation networks, accommodation options, and tourist facilities can hinder tourism growth. Ensuring accessibility is crucial to attract and cater to a wide range of travelers.
- Social and Cultural Impacts: The influx of tourists can have both positive and negative impacts on local communities. Over-tourism can strain resources, cause cultural commodification, and disrupt traditional lifestyles. Finding the right balance between tourism development and preserving local cultures and identities presents a challenge.
The leisure and tourism industry must proactively address these challenges to sustain its growth and ensure long-term success. Collaboration between stakeholders, effective destination management, continuous innovation, and responsible practices are key to overcoming these challenges and maintaining a vibrant and sustainable leisure and tourism industry.
Future Trends in Leisure and Tourism
The leisure and tourism industry is constantly evolving and adapting to the changing needs and preferences of travelers. As we look to the future, several trends are expected to shape the industry and redefine the way people engage in leisure and travel. Here are some key future trends in leisure and tourism:
- Sustainable and Responsible Tourism: There is a growing emphasis on sustainable and responsible tourism practices. Travelers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly and socially conscious experiences. Future trends will focus on reducing carbon footprints, preserving natural and cultural heritage, and supporting local communities.
- Technology Integration: Technology will continue to play a significant role in the leisure and tourism industry. Advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence will enhance the overall travel experience. Technologies such as mobile apps, digital assistants, and smart devices will streamline processes and provide personalized recommendations to travelers.
- Experience-based Travel: Travelers are shifting towards a more experiential approach to travel. They seek immersive and authentic experiences that go beyond traditional sightseeing. Future trends will focus on curated experiences such as culinary tours, cultural workshops, adventure activities, and opportunities for meaningful connections with local communities.
- Wellness and Health Tourism: The importance of well-being and self-care is on the rise. Wellness tourism will continue to gain momentum, with travelers seeking destinations and experiences that promote relaxation, mental health, and physical fitness. Spas, yoga retreats, wellness resorts, and mindfulness activities will be in high demand.
- Customization and Personalization: Travelers are increasingly seeking personalized and tailored experiences. Future trends will focus on customization, allowing individuals to curate their itineraries based on their preferences and interests. Technology will play a crucial role in enabling personalized recommendations and immersive experiences.
- Multi-generational Travel: With longer life expectancy and changing family dynamics, multi-generational travel is becoming more popular. Families are seeking destinations and activities that cater to different age groups, ensuring a memorable experience for everyone. Future trends will focus on providing diverse offerings and amenities suitable for all generations.
- Workation and Digital Nomadism: The rise of remote work and digital nomadism has led to the emergence of workation trends. Travelers are combining work and travel, seeking destinations that offer a balance between work and leisure activities. Future trends will see destinations catering to the needs of digital nomads, providing infrastructure, coworking spaces, and networking opportunities.
The leisure and tourism industry needs to adapt to these future trends to stay relevant and meet evolving customer demands. Embracing sustainability, leveraging technology, providing personalized experiences, and recognizing the changing dynamics of travel will be key to success in the future.
Leisure and tourism are intertwined concepts that have a profound impact on individuals, communities, and societies worldwide. They provide opportunities for relaxation, exploration, personal growth, and cultural exchange. The diversity of leisure activities and the range of tourism experiences cater to the varied interests and preferences of travelers, ensuring that there is something for everyone.
Leisure activities offer individuals a break from their daily routines, allowing them to nurture their well-being, pursue their passions, and connect with others. Whether engaging in physical activities, creative hobbies, socializing, or embracing nature, leisure provides essential outlets for self-expression, enjoyment, and personal fulfillment.
Tourism, on the other hand, enables individuals to venture beyond their familiar surroundings and immerse themselves in new cultures, environments, and experiences. It contributes to economic growth, job creation, and the preservation of natural and cultural heritage. Tourism fosters intercultural understanding, promoting peace and harmony while supporting the development of local communities.
However, the leisure and tourism industry also faces challenges that require careful navigation and proactive management. Seasonality, changing consumer preferences, competition, security concerns, sustainable practices, and infrastructure development all present obstacles that need to be tackled for the industry’s sustainability and success.
Looking to the future, the leisure and tourism industry will continue to evolve and adapt to emerging trends. From sustainable and responsible tourism practices to technology integration, experiential travel, and wellness tourism, the industry will cater to the changing needs and desires of travelers. Customization, multi-generational travel, workation, and digital nomadism will shape the way individuals engage in leisure and travel, emphasizing personalization and flexibility.
In conclusion, leisure and tourism are integral parts of our lives. They promote personal well-being, economic growth, cultural exchange, and environmental preservation. By embracing the diverse range of leisure activities and promoting responsible tourism practices, we can create a more inclusive and sustainable world, where individuals can find joy, fulfillment, and connection through leisure and travel experiences.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

What is tourism? A definition of tourism
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Whilst most of us have been tourists at some point during our lives, you might find yourself asking ‘what is tourism?’ or ‘what is the definition of tourism’?

Having studied, worked in and taught tourism management for many years, I can tell you that there is no straight-cut answer to this question! In fact, I do tell you- in this YouTube video below!
The tourism industry is argued to be the largest industry in the world, providing more employment than any other industry. Note, however, the use of the word ‘argued’. You see, the tourism industry is somewhat grey in nature. Elements that some may consider ‘tourism’, others may not. Some people believe they are ‘ tourists ‘, when others do not. Some things are black and white, and others are not.
In this post I will explain why there is no simple explanation in answer to the question ‘what is tourism?’. I will explain the diversity of the tourism industry and provide a range of definitions of tourism that have been developed by academics and practitioners.
What is tourism?
Tourism is the generic term used to cover both demand and supply that has been adopted in a variety of forms and used throughout the world.
Tourism essentially refers to the activities undertaken by visitors, also known as the visitor economy. The tourism industry encompasses all activity that takes place within the visitor economy.
This includes activities that are directly related to the tourist, such as staying in a hotel, ordering a meal or visiting a tourist attraction. It also includes indirect activities, such as the transport company which delivers the food to the restaurant in which the tourist eats or the laundry company that has a contract with the hotel for cleaning bed sheets.
It is largely due to the indirect contributions to tourism, that defining and measuring the tourism industry is so difficult!
Tourism comes in many different shapes and sizes and there are many different types of tourism . There is mass tourism , niche tourism and special interest tourism. There is domestic tourism and international tourism . There is inbound tourism and outbound tourism .
Whilst there is a range of different forms of tourism, they all come under the broad tourism umbrella, nonetheless. This is because they all revolve around visitors and they all feed the visitor economy in one way or another.
A definition of tourism
Tourism is a phenomenon with no universally accepted definition, owing to the complexity and individualism of the travellers themselves and the activities that they choose to undertake.
The most widely utilised definition of tourism, proposed by the World Trade Organisation (WTO) and United States (UN) Nations Statistics Division (1994), prescribes that in order to qualify as a tourist one must travel and remain in a place outside of their usual residential environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business or other purposes.
Matheison and Wall (1982) on the other hand, do not impose a timeframe, simply stating that one must travel to a destination temporarily.
Leiper (1979) believed that defining tourism is more complex than this, proposing that there are three approaches that can be taken. The economic stance focuses on tourism as a business, the technical stance focusses on the tourist in order to provide a common basis by which to collect data and the holistic stance attempts to include the entire essence of the subject.
The Cambridge Dictionary define tourism quite simply as; ‘the business of providing services such as transport, places to stay or entertainment for people who are on holiday’.
Read also: – The importance of tourism – Types of tourism: A glossary – Outbound tourism | Understanding the basics – The structure of the tourism industry – Domestic tourism tourism explained – The history of tourism
Whilst such attempts to define the concept of tourism may be useful from a generic perspective, the practical application of such definitions is difficult when applied to specific tourism types, such as those outlined in this post outlining the different types of tourism.
In fact, Robinson and Novelli (2007), in their introduction to the niche tourism phenomena, postulate that tourists have developed as consumers, becoming increasingly sophisticated in their needs and preferences as a result of an emergent culture of tourism.
Despite such acknowledgements of the progressive and adaptive nature of tourism, particularly evident through the limitless introduction of new and niche tourism forms, there appear to have been no attempts to develop the commonly accepted definitions of tourism in parallel.
As such, I would argue that there is a need the definition of tourism to be revisited by academics and industry practitioner, to ensure that it is representative of the tourism industry that operates today.
How would you define the term tourism?
For more information on what makes up the tourism industry, I recommend the key text Tourism: Principles and Practice by John Fletcher, available from Amazon here .
Liked this article? Click to share!

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” [1] . The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
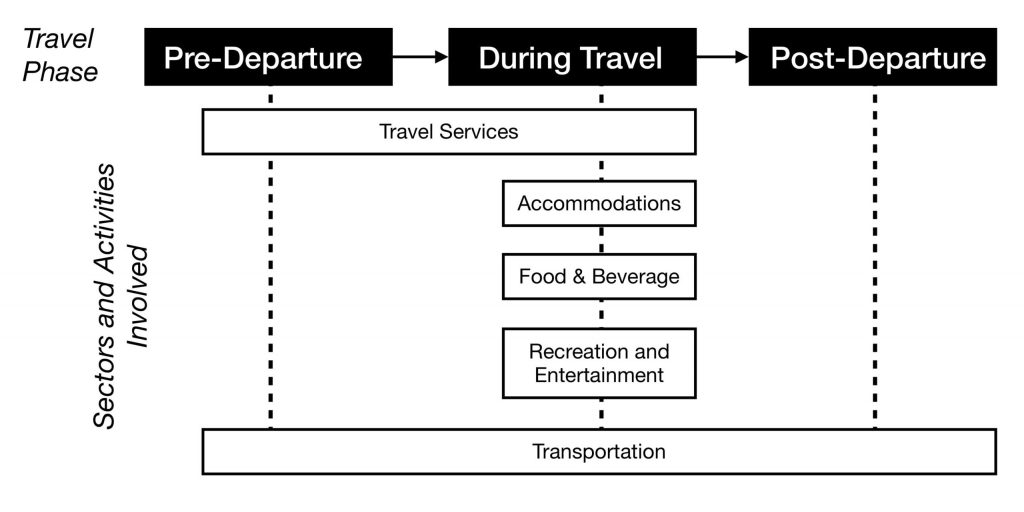
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Media Attributions
Front Desk © Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial) license
- (LinkBC, 2008, p.8) ↵
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism Copyright © 2020 by NSCC is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

What Is the Difference Between Tourism and Leisure?
By Robert Palmer
When it comes to taking a break from our daily lives, we often hear the terms ‘tourism’ and ‘leisure’ being used interchangeably. However, these two concepts are not the same. They differ in terms of purpose, activity, and duration.
What is Tourism? Tourism refers to the act of visiting a place for a specific purpose. It could be for recreation, cultural exploration, or business.
People who travel for tourism usually have a pre-planned itinerary that involves visiting different tourist attractions in the destination they are visiting. Tourism is more structured and organized than leisure.
The primary purpose of tourism is to explore and experience new cultures, gain knowledge about different places, and engage in leisure activities that are unique to the destination being visited. Tourists plan their trips well in advance and have set goals that they want to achieve during their visit.
Tourism involves engaging in activities that are designed to promote cultural exchange and education. These activities can include visiting museums, historical landmarks, attending cultural festivals, or participating in adventure sports like bungee jumping or zip-lining.
Tourism usually lasts for a short period of time ranging from a few days to a few weeks. Tourists generally have limited time available to them as they are often constrained by work schedules or other commitments.
What is Leisure? Leisure refers to free time that individuals have outside of their work or other responsibilities. It involves engaging in activities that one enjoys without any specific goals or objectives in mind. Leisure is more flexible than tourism as it allows individuals the freedom to do what they want when they want.
The primary purpose of leisure is to relax and unwind from daily life stressors. It provides an opportunity for individuals to engage in activities that they find enjoyable and satisfying. Leisure activities can be anything from reading a book, watching movies, or spending time with loved ones.
Leisure activities are not structured and can vary from person to person. The activities can be passive or active depending on the individual’s preference.
Passive activities include watching TV, listening to music, or reading a book. Active activities include exercise, sports, or hobbies like painting or photography.
Leisure time is not constrained by time limits and can last for as long as an individual wishes. It can be a few hours during the day or an entire weekend depending on the availability of free time.
6 Related Question Answers Found
What is the difference between leisure and recreation in tourism, what is difference between recreation and tourism, what is the difference between recreation and tourism, what is leisure travel and tourism, what are the importance of leisure in tourism, what is recreation and leisure in tourism, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva
Tourism – Definition, Types & Forms, History & Importance of Tourism
Tourism is one of the world’s fastest-growing industries and a major foreign exchange and employment generation for many countries. It is one of the most remarkable economic and social phenomena.
The word ‘tour’ is derived from the Latin word tornus, meaning ‘a tool for making a circle.’ Tourism may be defined as the movement of people from their usual place of residence to another place ( with the intention to return) for a minimum period of twenty-four hours to a maximum of six months for the sole purpose of leisure and pleasure.
According to WTO (1993), ” Tourism encompasses the activities of persons traveling and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes.”
The Rome conference on tourism in 1963 defined tourism as ‘ a visit to a country other than one’s own or where one usually resides and works. This definition, however, did not take into account domestic tourism, which has become a vital money-spinner and job generator for the hospitality industry.
The UNWTO defines tourists as ‘ people who travel to and stay in place outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes not related to the exercise of an activity remunerated from within the place visited.
According to the Tourism Society of Britain ,” tourism is the temporary short-period movement of people to destination outside the places where they usually live, work; and activities during their stay at these destinations.” This definition includes the movement of people for all purposes.
The development of technology and transportation infrastructure, such as jumbos jets, low-cost airlines, and more accessible airports, have made tourism affordable and convenient. There have been changes in lifestyle – for example, now retiree-age people sustain tourism around the year. The sale of tourism products on the internet, besides the aggressive marketing of the tour operators and travel agencies , has also contributed to the growth of tourism.
27 September is celebrated as world tourism every year. This date was chosen as on that day in 1970, the Statutes of UNWTO were adopted. The purpose of this day is to raise awareness of the role of tourism within the international community.
History of Travel and Tourism
Inbound tourism, outbound tourism, domestic tourism, forms of tourism, classification of tourism, nature of tourism, importance of tourism, economic impacts, social impacts, cultural impacts, environmental impact, industries related to tourism, tourism products.
Travel is as old as mankind on earth. At the beginning of his existence, man roamed about the planet’s surface in search of food, shelter, security, and better habitat. However, with time, such movements were transformed into wanderlust.
About five thousand years ago, climate changes, dwindling food and shelter conditions hostile invaders made the people leave their homes to seek refuge elsewhere like the Aryans left their homes in Central Asia due to climate changes. Perhaps, this leads to the development of commerce, trade, and industry.
Religion, education, and cultural movement began during the Hindu and Chinese civilizations. Christian missionaries, Buddhist monks, and others traveled far and wide carrying religious messages and returned with fantastic images and opinions about alien people.
For centuries movement of people continued to grow due to the efficiency of transport and the assistance and safety with which the people could travel. By the end of the 15th century, Italy had become Europe’s intellectual and cultural center. It represented the classical heritage both for the intelligentsia and the aristocracy.
During the 16th century, travel came to be considered an essential part of the education of every young Englishman. Travel thus became a means of self-development and education in its broadest sense. The educational travel was known as the ‘ Grand Tour .’
The industrial revolution brought about significant changes in the pattern and structure of British society. Thus, the economy of Britain was greatly responsible for the beginning of modern tourism. It also created a large and prosperous middle class. Because of remarkable improvement in transportation systems in the latter half of the 18th century and the first quarter of the 19th century, an increasing number of people began to travel for pleasure.
Travel was inspired initially by the need for survival (food, shelter, and security), the desire to expand trade, and the quest to conquer. As the transportation system improved, the curiosity for transforming the vast and virgin world into a close neighborhood created a new industry, i.e., Travel and Tourism .
However, the developments of rails, roads, steamships, automobiles, and airplanes helped to spread technology across the globe. Earlier travel was a privilege only for wealthy people, but with the industrial revolution, the scenario altogether changed. Transportation, as well as accommodation, became affordable to middle and working-class citizens.
Essentially, with the development of jet travel, communication, new technology, tourism, and travel became the world’s largest and fastest-growing industry.
Travel and tourism have recently emerged as a dominant economic force on the global scene, accounting for more than 12% of total world trade and growing at 8 percent annually.
Types of Tourism
Tourism has two types and many forms based on the purpose of visit and alternative forms of tourism. Tourism can be categorized as international and domestic tourism .
Tourism has two types and various forms. Based on the movement of people, tourism is categorized into two kinds. These are the following:
International Tourism
When people visit a foreign country, it is referred to as International Tourism . To travel to a foreign country, one needs a valid passport, visa, health documents, foreign exchange, etc.
International tourism is divided into two types; Inbound Tourism & Outbound Tourism.
This refers to tourists of outside origin entering a particular country. Traveling outside their host/native country to another country is called inbound tourism for the country where they are traveling. For example, when a tourist of Indian origin travels to Japan, it is Inbound tourism for Japan because foreign tourists come to Japan.
This refers to tourists traveling from the country of their origin to another country. When tourists travel to a foreign region, it is outbound tourism for their own country because they are going outside their country. For example, when a tourist from India travels to Japan, it is outbound tourism for India and Inbound tourism for Japan.
The tourism activity of the people within their own country is known as domestic tourism . Traveling within the same country is easier because it does not require formal travel documents and tedious formalities like compulsory health checks and foreign exchange. A traveler generally does not face many language problems or currency exchange issues in domestic tourism.
Tourism has various forms based on the purpose of the visit and alternative forms. These are further divided into many types according to their nature. Forms of tourism are the following:
Some most basic forms of tourism are the following:
- Adventure Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Beach Tourism
- Cultural Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Medical Tourism
- Religious Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Sex Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
- Wildlife Tourism
Tourism can be classified into six distinct categories according to the purpose of travel. These are the following:
1) Recreational : Recreational or leisure tourism takes a person away from the humdrum of everyday life. In this case, people spend their leisure time in the hills, sea beaches, etc.
2) Cultural tourism satisfies cultural and intellectual curiosity and involves visits to ancient monuments, places of historical or religious importance, etc.
3) Sports/Adventure : Trips taken by people with a view to playing golf, skiing and hiking, fall within this category.
4) Health : Under this category, people travel for medical, treatment or visit places where there are curative possibilities, for example, hot springs, spa yoga, etc.
5) Convention Tourism : It is becoming an increasingly important component of travel. People travel within a country or overseas to attend conventions relating to their business, profession, or interest.
6) Incentive Tourism : Holiday trips are offered as incentives by major companies to dealers and salesmen who achieve high targets in sales. This is a new and expanding phenomenon in tourism, These are in lieu of cash incentives or gifts, Today incentive tourism is a 3 billion dollar business in the USA alone.
Tourism as a socio-economic phenomenon comprises the activities and experiences of tourists and visitors away from their home environment and are serviced by the travel and tourism industry and host destination. The sum total of this activity experience and services can be seen as a tourism product.
The tourism system can be described in terms of supply and demand. Tourism planning should strive for a balance between demands and supply. This requires an understanding not only of market characteristics and trends but also of the planning process to meet the market needs.
Often tourists from core generating markets are identified as the demand side; the supply side includes all facilities, programs, attractions, and land uses designed and managed for the visitors. These supply-side factors may be under the control of private enterprises, non-profit organizations, and the government. New and innovative forms of partnerships are also evolving to ensure the sustainable development and management of tourism-related resources.
The supply and demand side can be seen to be linked by flows of resources such as capital, labor, goods, and tourist expenditures into the destination, and flows of marketing, promotion, tourist artifacts, and experiences from the destination back into the tourist generating region.
In addition, some tourist expenditures may leak back into the visitors generating areas through repatriation of profits of foreign tourism investors and payment for improved goods and services provided to tourists at the destination. Transportation provides an important linkage both to and from the destination.
For planning purposes, the major components that comprise the supply side are:
- Various modes of transportation and other tourism-related infrastructure.
- Tourist information.
- Marketing and promotion.
- The community of communities within the visitor’s destination area.
- The political and institutional frameworks for enabling tourism.
The tourism system is both dynamic and complex due to many factors linked to it and because of the existence of many sectors contributing to its success. These factors and sectors are linked to the provision of the tourist experience and the generation of tourism revenue and markets .
The dynamic nature of the tourism system makes it imperative to scan the external and internal environment of the destinations on a regular basis so as to make changes when necessary to ensure a healthy and viable tourism industry.
Thus, it is now an accepted fact that tourism development can no longer work in isolation of the environment and the local communities, nor can it ignore the social and cultural consequences of tourism.
Tourism and hospitality , which are inextricably linked to each other, are among the major revenue-earning enterprises in the world. They happen to be among the top employers too. There has been an upmarket trend in tourism over the last few decades as travel has become quite common. People travel for business, vacation, pleasure, adventure, or even medical treatments.
Tourism constitutes an important industry today. It has opened up new vistas for the play of economic emancipation. It provides a very potent contribution by strengthening and developing the financial resources of a country. Moreover, it is a process in which mutual material and mental benefits occur. Furthermore,
- Tourism fetches foreign exchange in the form of invisible exports, which results in the manifold progress of the nation.
- Tourism generates jobs. These employments are the main contribution of tourism to generating national income. But one should remember that employment in the tourism industry is often seasonal.
- Tourism often leads to the commercialization of art forms and especially handicrafts. Art items with cultural or religious meaning are sought by tourists as souvenirs. As more and more tourists visit a destination, souvenir production has increased, often leading to mass production. This production also generates income.
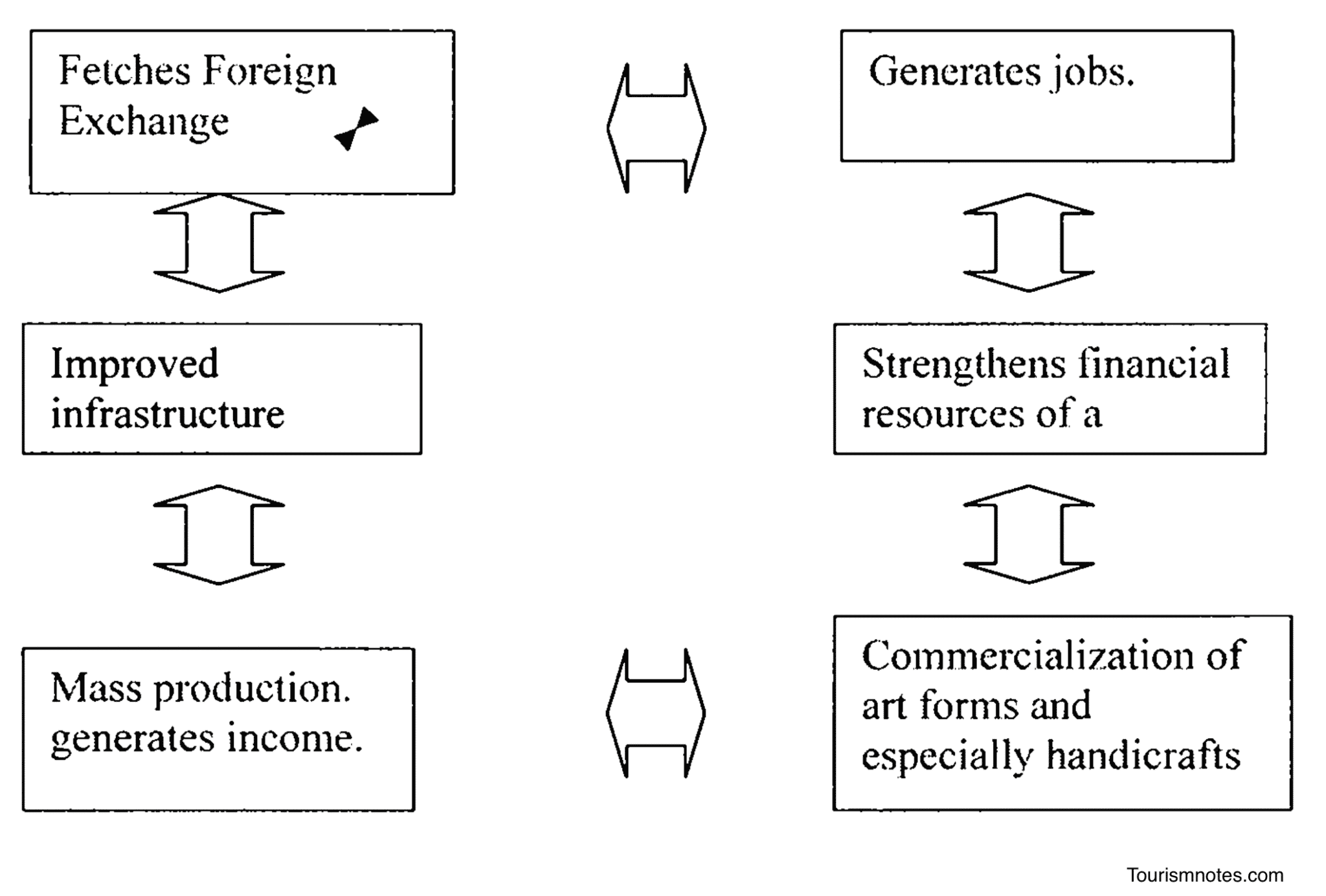
With several business-related activities associated with tourism, the industry has a tremendous potential to generate employment as well as earn foreign exchange. Many countries, such as Mauritius, Malaysia, Singapore, Fiji, and the Caribbean, whose economies are primarily driven by tourism. Tourism can contribute to the economic growth of a country in the followings ways:
Employment Generation
It creates a large number of jobs among direct services providers (such as hotels , restaurants, travel agencies , tour operators , guide and tour escorts, etc.) and among indirect services providers (such as suppliers to the hotels and restaurants, supplementary accommodation, etc.)
Infrastructure Development
Tourism spurs infrastructure development. In order to become an important commercial or pleasure destination, any location would require all the necessary infrastructure, like good connectivity via rail, road, and air transport , adequate accommodation, restaurants, a well-developed telecommunication network, and, medical facilities, among others.
Foreign Exchange
The people who travel to other countries spend a large amount of money on accommodation, transportation, sightseeing, shopping, etc. Thus, an inbound tourist is an important source of foreign exchange for any country.
The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) predict in 1997 that the twenty-first-century economy would be dominated by three industries: telecommunications, information technology, and tourism. The travel and tourism industry has grown by 500 percent in the last 25 years.
Now withstanding this bright outlook and prospects, the tourism and hospitality industries are very vulnerable to the fluctuations of national economies and happenings in the world, especially terrorist attacks that have at times dealt severe blows to business.
In recent years, there have been a few setbacks in tourism, such as the terrorist siege of the Taj and Oberoi in Mumbai, India (26 November 2008); the attack on the World Trade Centre in the United States of America (11 September 2001); bombing in a hotel on the Indonesian island of Bali (12 October 2002); tsunami in Southeast Asia and South Asia on 26 December 2004, in which thousands of the lives where lost and consequently tourism was hit. Nonetheless, the sector is now getting back to business.
Impacts of Tourism
Tourism is a multi-dimensional activity. The scope of tourism activities is so wide and varied that it cannot be restricted to any particular field of activity. Tourism has ramifications in almost all sectors and is influenced by the performance of each of these sectors directly or indirectly. Tourism in any country can be an apt reflection of the nation’s economic and social endowment apart from its natural wealth.
Tourism has vast potential to bring about changes in the country’s economic, environmental, societal, and cultural edifice. Tourism has two basics: the supply of facilities and the demand for participation. The twin market forces of supply and demand interact to produce tourism patterns. These patterns are associated with economic, social, cultural, environmental, and ecological impacts.
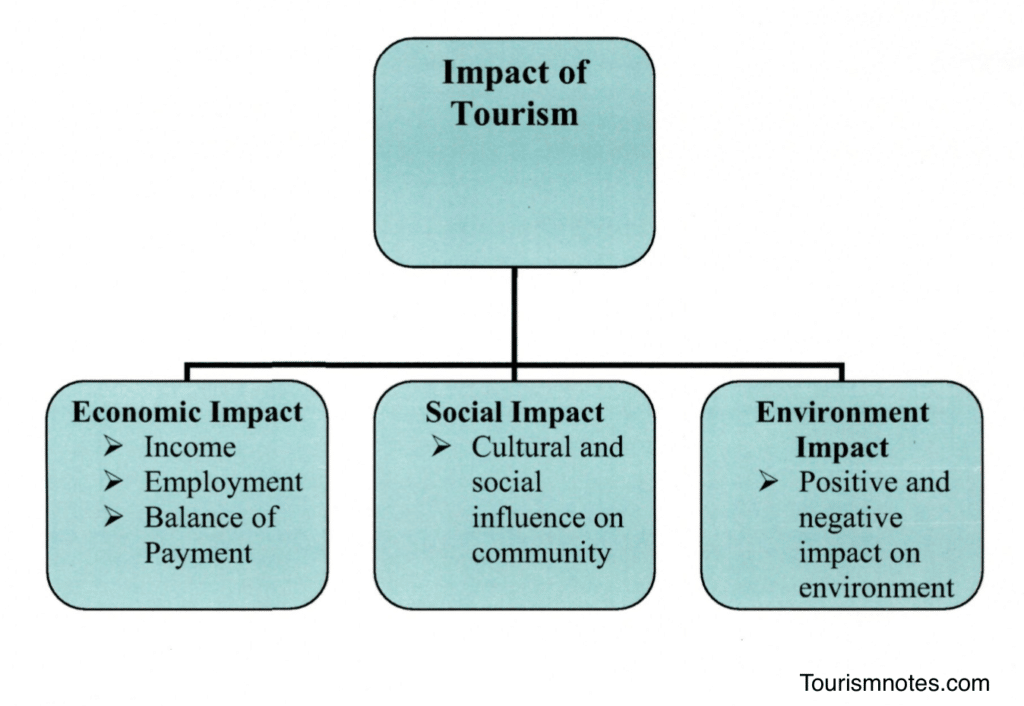
Establishing or developing a tourism industry involves expenditure, gains, costs, and benefits. If these impacts are considered from the outset of planning, strengths and opportunities can be maximized while weaknesses and threats can be minimized.
Each destination will be different in terms of tourism characteristics . The cost and benefits of tourism will vary in each destination and can change over time, depending on tourism and other activities in a destination’s local and regional context.
Tourism activities impact the economy of the country as well as the local economy of the destination.
Economics Benefits
- Tourism generates local employment, directly in the tourism sector and in the support and resource management sectors.
- Tourism stimulates profitable domestic industries, hotels and other lodging facilities, restaurants and food services, transportation systems, handicrafts, and guide services.
- Tourism generates foreign exchange for the country and injects capital and new money into the local economy.
- Tourism helps to diversify the local economy.
- Improved tourism infrastructure.
- Increase tax revenues from tourism.
Economic Costs
- Higher demand created by tourism activity may increase the price of land, housing, and a range of commodities necessary for daily life.
- Demands for health services provision and police service increase during the tourist seasons at the expense of the local tax base.
Tourism also affects the society of the destination in good as well as bad ways. It benefits and costs the local communities.
Social Benefits
- The quality of a community can be enhanced by economic diversification through tourism.
- Recreational and cultural facilities created for tourism can be used by local communities as well as domestic/international visitors.
- Public space may be developed and enhanced through tourism activity.
- Tourism Enhances the local community’s esteem and provides an opportunity for greater understanding and communication among people of diverse backgrounds.
Social Costs
- Rapid tourism growth can result in the inability of local amenities and institutions to meet service demands.
- Without proper planning and management, litter, vandalism, and crime often accompany tourism development.
- Tourism can bring overcrowding and traffic congestion.
- Visitors bring with them material wealth and apparent freedom. The youths of the host community are particularly susceptible to the economic expectations these tourists bring which can result in complete disruption of traditional community ways of life.
- The community structure may change, e.g. community bonds, demographics, and institutions.
- The authenticity of the social and cultural environment can be changed to meet tourism demands.
Tourism activities also affect the culture of the host country. There are many positive and negative cultural impacts of tourism.
Cultural Benefits
- Tourism can enhance local cultural awareness.
- Tourism can generate revenue to help pay for the preservation of archaeological sites, historic buildings, and districts.
- Despite criticism about the alteration of cultures to unacceptable levels, the sharing of cultural knowledge and experience can be beneficial for hosts and guests of tourism destinations and can result in the revival of local traditions and crafts.
Cultural Costs
- Youth in the community begin to emulate the speech and attire of tourists.
- Historic sites can be damaged through tourism development and pressures.
- There can be long-term damage to cultural traditions and the erosion of cultural values, resulting in cultural change beyond a level acceptable to the host destination.
Tourism impacts the environment in positive as well as negative ways. These impacts are following below.
Environmental Benefits
- Parks and nature preserves may be created and ecological preservation supported as a necessity for nature-based tourism.
- Improved waste management can be achieved.
- Increased awareness and concern for the environment can result from nature-based tourism activities and development.
Environmental Costs
- A negative change in the physical integrity of the area.
- Rapid development, over-development, and overcrowding can forever change the physical environment and ecosystems of an area.
- Degradation of parks and preserves.
Over the years, tourism has become a popular global activity. Depending upon the nature and purpose of their travel, tourists, need and demand certain facilities and services. This has given rise to a wide range of commercial activities that have acquired industry proportions. Thus travel and tourism nowadays represent a broad range of related industries.
Hotels are a commercial establishment that provides accommodation, meals, and other guest services. In the travel and tourism industry, the hotel industry plays a very significant role, as all tourists need a place to stay at their destinations, and require many more services and facilities to suit their specific needs and tastes.
Restaurants
Restaurants are retail establishments that serve prepared food and beverages to customers. In the travel and tourism industry, restaurants and other food and beverage outlets are very important as tourists like to experiment with the local cuisines of the places they are visiting.
Retail and Shopping
The retail industry is very important as tourists shop for their day-to-day necessities as well as look for mementos and souvenirs. In recent years, some cities in the world have been promoted as shopping destinations to attract people with a penchant for shopping by offering various products, such as garments, electronic goods, jewelry, and antiques. New York, Paris, London, and Milan in Italy are famous as fashion havens of the world.
Transportation
It is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. A well-developed transport industry, as well as infrastructure, is integral to the success of any travel and tourism enterprise.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a retailing business that sells travel-related products and services, particularly package tours, to customers on the behalf of suppliers such as airlines, car rentals, cruise liners, hotels, railways, and sightseeing.
Travel agencies play a very important role as they plan out the itinerary of their clients and make the necessary arrangements for their travel, stay, and sightseeing, besides facilitating their passport, visa, etc.
Tour Operators
A tour operator assembles the various elements of a tour. It typically combines tour and travel components to create a holiday. Tour operators play an important role in the travel and tourism industry.
Tourist Destinations
A tourist attraction is a place of interest for tourists, typically for its inherent or exhibited cultural value, historical significance, nature or building beauty or amusement opportunities. These are the basic fundamentals of the tourism industry.
Cultural Industries
Cultural or creative industries are responsible for the creation, production, and distribution of goods and services that are cultural in nature and usually protected by intellectual property rights. As tourists like to visit places of cultural significance and soak in the culture of the area, the cultural industry is very important to travel and tourism.
Leisure, Recreation, and Sport
Leisure or free time is a period of time spent out of work and essential domestic activity. Recreation or fun is spending time in a manner designed for therapeutic refreshment of the body or mind. While leisure is more like a form of entertainment or rest, recreation requires active participation in a refreshing and diverting manner.
As people in the world’s wealthier regions lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle, the need for recreation has increased. These play a significant role in the travel and tourism sector.
A tourism/tourist product can be defined as the sum of the physical and psychological satisfaction it provides to tourists, during their ‘traveling and sojourn’ en route at the destinations.
Since the travel and tourism industry is an agglomeration of too many sectors that promote travel-related services. These sectors are referred to as travel vendors and their services and goods are called ‘travel products’. A tourism product includes five main components such as physical plant, services, hospitality, freedom of choice, and a sense of involvement.
Thus, whatever the natural and man-made resources and services brought about the consumption of tourists are called tourism products .
Charecterstatics Of Tourism Products
By now, you must have understood what a tourism product is. Now let us look at some of its characteristics:-
1) Intangible : Tourism is an intangible product means tourism is such a kind of product that can not be touched or seen and there is no transfer of ownership, But the facilities are available for a specified time and for a specified use. For e.g. a room in the hotel is available for a specified time.
2) Psychological : The main motive to purchase a tourism products is to satisfy the psychological need after using the product, by getting an experience while interacting with a new environment. And experiences also motivate others to purchase that product.
3) Highly Perishable : Tourism product is highly perishable in nature means one can not store the product for a long time. Production and consumption take place while a tourist is available. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not purchase it.
A travel agent or tour operator who sells a tourism product cannot store it. Production can only take place if the customer is actually present. And once consumption begins, it cannot be stopped, interrupted, or modified. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not visit a particular place, the opportunity at that time is lost. It is due to tourism reason that heavy discount is offered by hotels and transport-generating organizations during the offseason.
4) Composite Product : Tourist product is a combination of different products. It has not a single entity in itself. In the experience of a visit to a particular place, various service providers contribute like transportation The tourist product cannot be provided by a single enterprise, unlike a manufactured product.
The tourist product covers the complete experience of a visit to a particular place. And many providers contribute to the tourism experience. For instance, the airline supplies seats, a hotel provides rooms and restaurants, travel agents make bookings for stay and sightseeing, etc.
5) Unstable Demand : Tourism demand is influenced by seasonal, economic political, and other factors. There are certain times of the year that see greater demand than others. At these times there is a greater strain on services like hotel bookings, employment, the transport system, etc.
Pleasure tourism
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2015
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Salvatore Bimonte 3
1994 Accesses
Pleasure is defined as a feeling of happiness, satisfaction, or enjoyment. Therefore, the pursuit of such feelings through travel is referred to as pleasure tourism. According to Currie ( 1997 ), “tourism” means pleasure travel, and according to the UNWTO ( 2007 ), pleasure represents the main purpose of tourism.
In the research literature, pleasure tourism is normally defined in opposition to business tourism. The classification is partly driven by statistical measurement conventions that mainly focus on the purpose of a trip rather than on its motivations. The UNWTO ( 2007 ) classifies tourism into two broad categories: personal and business/professional purposes. The former can be broken down into subcategories such as holidays, leisure, and recreation; visiting friends and relatives; education and training; health and medical care; religion and pilgrimages; shopping; and other pursuits.
The previous classifications do not distinguish between pleasure and non-pleasure tourism. In the...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Bimonte, S., and V. Faralla 2012 Tourist Types and Happiness: A Comparative Study in Maremma, Italy. Annals of Tourism Research 39:1929-1950.
Article Google Scholar
Bimonte, S., and V. Faralla 2013 Happiness and Outdoor Vacations: Appreciative versus Consumptive Tourists. Journal of Travel Research, DOI: 10.1177/0047287513513171.
Google Scholar
Currie, R. 1997 A Pleasure Tourism Behaviors Framework. Annals of Tourism Research 24:884-897.
Smith, V. 1989 Host and Guest: The Anthropology of Tourism. Philadelphia: The University of Pennsylvania Press.
UNWTO 2007 International Recommendations on Tourism Statistics. Madrid: World Tourism Organization.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics and Statistics, University of Siena, Via Banchi di Sotto, 55/4, 53100, Siena, Italy
Salvatore Bimonte
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Salvatore Bimonte .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Hospitality Leadership, University of Wisconsin-Stout, Menomonie, Wisconsin, USA
Jafar Jafari
School of Hotel and Tourism Management, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR
Honggen Xiao
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Bimonte, S. (2015). Pleasure tourism. In: Jafari, J., Xiao, H. (eds) Encyclopedia of Tourism. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_461-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_461-1
Received : 12 January 2015
Accepted : 12 January 2015
Published : 23 September 2015
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-01669-6
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Business and Management Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5. Recreation
Don Webster
Learning Objectives
- Differentiate between recreation, outdoor recreation, adventure tourism, and nature-based tourism
- Describe the significance, size, and economic contribution of this sector to the overall tourism industry in BC
- Identify key industry organizations in recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism
- Classify different subsectors of recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism
- Recognize the unique challenges facing recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism in BC
In this chapter, we discuss the concept of recreation in tourism and hospitality. Recreation can be defined as the pursuit of leisure activities during one’s spare time (Tribe, 2011) and can include vastly different activities such as golfing, sport fishing, and rock climbing. Defining recreation as it pertains to tourism, however, is more challenging.
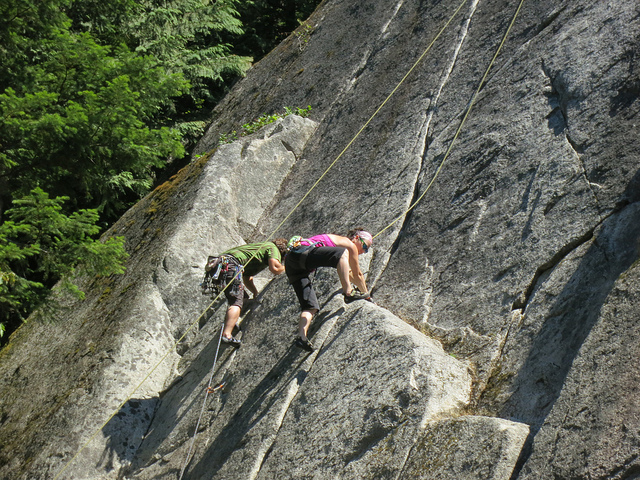

Let’s start by exploring some recreation-based terms that are common in the tourism industry. Outdoor recreation can be defined as “outdoor activities that take place in a natural setting, as opposed to a highly cultivated or managed landscape such as a playing field or golf course” (Tourism BC, 2013, p. 47). This term is typically applied to outdoor activities that individuals engage in and that are located close to their community. When these activities are further away, and people must travel some distance to participate in them, they are often described as adventure tourism.
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), adventure tourism is “a trip that includes at least two of the following three elements: physical activity, natural environment, and cultural immersion” (UNWTO, 2014, p.12). Examples of adventure tourism in BC include river rafting, helicopter skiing, and rock climbing.
Take a Closer Look: UNWTO Global Report
The Global Report on Adventure Tourism by UNWTO offers an in-depth analysis of the global adventure travel sector. It can be found at http://affiliatemembers.unwto.org/publication/global-report-adventure-tourism
Adventure tourism can be “soft” or “hard.” Differentiating between the two is somewhat subjective, but is loosely based on the level of experience required, the level of fitness required, and the degree to which the participant is exposed to risk (UNWTO, 2014). Examples of soft adventure include wildlife viewing or moderate hiking, whereas river rafting or rock climbing would usually be considered hard adventure.
Another term that is used, one that overlaps with the definitions of outdoor recreation and adventure tourism, is nature-based tourism, which refers to “those tourism experiences that are directly or indirectly dependent on the natural environment” (Tourism BC, 2005b, p.6). This term is often used to describe activities that are closely connected to nature, such as whale watching, birding, or self-propelled travel such as hiking and kayaking.
As you can see, there are challenges in classifying recreation in tourism. For instance, if people kayak near their home or community, it may be considered outdoor recreation. If they travel afar for that same activity, it likely is designated as adventure tourism. If the kayaking is done in protected, mild conditions, it would be considered soft adventure, but if done in a challenging and risky river descent, it may be classified as hard adventure.
Of course, each of the above scenarios of kayaking could be considered nature-based tourism if it is strongly linked to the natural environment. Ultimately, categorization is based on a combination of several factors, including manner of engagement in the activity (risk exposure, experience requirement, group or solo activity), the distance travelled to access the activity, and the type of environment (proximity to nature, level of challenge involved) that that the activity occurs in.
A 2013 adventure tourism market study discovered that people who travel for adventure experiences tend to be well-educated, with 48% holding a four-year degree or higher credential. They value natural beauty and rank this as the highest factor when choosing a destination, and the most cited reasons for their travel are relaxation “relaxation, exploring new places, time with family, and learning about different cultures” (UNWTO, 2014, p.15).
Globally, it is estimated that the continents of Europe, North America, and South America account for 69% of adventure tourism, or US$263 billion in adventure travel spending. Adventure tourists tend to be seen as high-value visitors, with as much of 70% of their expenditures remaining in the communities visited (UNWTO, 2014).
The size, extent, and economic contribution of recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism in British Columbia is also substantial. The rest of this chapter explores the sector in the province in more detail.
Recreation and Adventure Tourism in BC
Studies have shown that nearly all residents of BC partake in some kind of outdoor recreation activity during any given year. Approximately 85% of those participants indicate that these recreational activities were very important to them (Tourism BC, 2013).
Spotlight On: Outdoor Recreation Council of BC
The Outdoor Recreation Council of BC (ORC) describes itself as “promoting access to and responsible use of BC’s public lands and waters for public outdoor recreation” (Outdoor Recreation Council of BC, 2014). The Council promotes the benefits of outdoor recreation, represents the community to government and the general public, advocates and educates about responsible land use, provides a forum for exchanging information, and connects different outdoor recreation groups. For more information, visit the Outdoor Recreation Council of BC website : http://orcbc.ca

It is estimated that there are approximately 2,200 outdoor/adventure tourism operators in BC. In 2001, this accounted for 21,000 jobs and $556 million in direct wages. The last sector-wide study in 2005 estimated that business revenues in outdoor adventure tourism accounted for approximately $854 million in annual business revenues (Tourism BC, 2013). Given the growth of adventure tourism over the last decade, it is likely these numbers have risen.
Additionally, in the current five-year provincial tourism strategy, entitled Gaining the Edge, outdoor/adventure tourism is indicated as one of six key areas targeted for growth ( British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Innovation , 2012). This government support, combined with the rapid growth of the outdoor and adventure tourism industry, point to a strong future for this sector.
Take a Closer Look: Outdoor Adventure Sector Profile
Outdoor Adventure: Tourism Sector Profile, a report produced by Destination BC, includes information on the size, type, and characteristics of tourism companies in this sector. Also included is market demand for these activities and future challenges the sector faces. You can find the report at Outdoor Tourism Sector Profile [PDF] : http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Sector-Profiles/Outdoor-Adventure-Sector-Profile,-May-2014/Tourism-Sector-Profile_OutdoorAdventure_May2014.pdf.aspx
This section covers two key types of recreation and tourism, with a focus on British Columbia:
- Land-based recreation and tourism
- Water-based recreation and tourism
It’s not possible to detail all the recreational activities available in BC, but by the end of this section, you will have an understanding of the key unique activities available in the province.

Land-Based Recreation and Tourism
Golf courses and resorts.
A 2009 economic impact study found that more than six million Canadians participate in the game of golf each year, making this sport the number one outdoor recreational activity in Canada based on participation. Golf also directly employs more than 155,000 people and contributes more than $11 billion directly to Canada’s gross domestic product. BC has over 300 golf course facilities, and with over $2 billion annually in direct economic activity, the golfing industry in the province is the fourth largest in Canada (Strategic Networks Inc., 2009).
Golf is a significant tourism attraction in BC; in 2007 the province was chosen as the “Best Golf Course Destination in North America” by the International Association of Golf Tour Operators (Destination BC, 2014c). Part of the draw is the diverse environment; golfers can choose from lush coastal forests to desert environments, and many courses have a viewscape of mountains or the ocean.
A 2006 study by the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC) detailed both demographic and economic factors related to the Canadian golf industry. Significant findings included that there were more than 3.4 million golf travellers in Canada annually, and that of those travellers, approximately 34% travelled to BC. In addition, the Canadian golf participation rate (for the total Canadian population) was 21.5%, which is among the highest golf participation rates of any country in the world. Golfing provides an opportunity to attract significant tourism revenue as the average golf traveller has a much higher than average income level, with up to 50% of all golf travellers earning $100,000 or more per annum (Tourism BC, 2009b).
Spotlight On: British Columbia Golf Marketing Alliance
The British Columbia Golf Marketing Alliance is a strategic alliance that represents 58 regional and destination golf resorts in BC. The purpose of the alliance is to grow the game of golf in BC and achieve recognition nationally and internationally as a leading golf destination. The alliance supports and distributes information about research, lobbying efforts, and golf industry events. For more information, visit the Allied Golf Association of BC website : http://aga-bc.org/committees/recreational-golf-committee/
Mountain Resorts and Nordic Centres
Resorts in British Columbia range from smaller eco-lodges to large ski areas. Mountain resorts and nordic centres are part of the larger resort tourism sector, which in 2004 was valued at $1.9 billion (Tourism BC, 2011c).

Ski/Snowboard Mountain Resorts
BC’s many world-class facilities and high-quality snow conditions provide mass appeal for downhill skiing and snowboarding. Mountain resorts in BC can be separated into two principal categories: destination resorts and regional resorts. Destination mountain resorts are often significantly larger and offer a greater range of amenities such as on mountain accommodation and food services; they are also generally marketed to out-of-area and international visitors. Examples of a destination resort would include Whistler Blackcomb Ski Resort. On the other hand, regional mountain resorts are usually smaller in size and capacity, have fewer amenities, and often cater more directly to the local community (Tourism BC, 2011c) such as Whitewater Ski Resort in the Kootenay Rockies.
Spotlight On: Canada West Ski Areas Association
Ski areas in Western Canada (Alberta and BC) are represented by the Canada West Ski Areas Association (CWSAA), which has a diverse mandate that includes marketing, advocacy, environmental stewardship, and risk management. For more information, visit the Canada West Ski Areas Association website : http://www.cwsaa.org
The aggregate economic value of destination mountain resorts is significant; one study by Tourism BC found that 13 of these resorts were responsible for generating approximately 1.1 billion in revenue, or 8% of the total provincial tourism revenues in 2008. Additionally, they provided the equivalent of 14,267 full-time equivalent jobs (Tourism BC, 2011c). Furthermore, BC’s top mountain resorts have received many prestigious awards (Tourism BC, 2011c, p. 11):
- Whistler Blackcomb has consistently been named the #1 ski resort in North America.
- In 2009, Sun Peaks was named one of the “Top 20 Ski Resorts in North America” by Condé Nast Traveler.
- Big White Ski Resort was recognized in 2009 as a “Top 5 Family Resort” by the UK-based Sunday Times.
The publicity that these resorts receive has undoubtedly reflected positively on the rest of the BC tourism industry.
Spotlight On: “Ski It to Believe It”
Destination BC offers a specific mountain resort marketing website for 13 destination resorts in BC called “Ski It to Believe It.” The site features live updates on snow conditions, resort info, a map featuring all BC ski destinations, blogs, and dynamic content featuring visitors enjoying various skiing experiences including heli, cat, backcountry, and downhill skiing. For more information, visit the Ski It to Believe It website : http://skiittobelieveit.com
Nordic Centres
Nordic skiing, also commonly known as cross-country skiing, is a low-risk, low-impact winter sport popular across Canada. It differs from backcountry skiing in that participants ski on groomed trails typically maintained as part of an established facility (Cross Country BC, n.d.).
Spotlight On: Whistler Sport Legacies
Leading up to the 2010 Winter Olympics held in Vancouver and Whistler, there was much debate about the need for a continuing legacy from the event. Whistler Sport Legacies is an example of a recreational, tourism, and sport legacy that can emerge out of a mega event such as the Olympics. For more information, visit the Whistler Sport Legacies website : http://www.whistlersportlegacies.com
With more than 50 cross-country ski centres across BC, and a season that often exceeds that of downhill skiing (November to May in many areas), the sport attracts large numbers of local and inbound recreation enthusiasts. Trail networks have been developed in both stand-alone environments, as well as in partnership with large mountain resorts such as Silver Star in Vernon, Sun Peaks in Kamloops, Cypress Mountain above Vancouver, and Rossland in the Kootenays. Many of these trail networks offer both groomed and track-set trails, a number are lit for night skiing.
Spotlight On: Silver Star’s Sovereign Lake Nordic Centre
Located just outside Vernon, Sovereign Lake is Canada’s largest daily groomed trail network that includes 105 kilometres of trails varying from green (easy) to black diamond (most difficult); a further trail expansion is planned for 2015. For more information, visit Sovereign Lake’s website : http://www.sovereignlake.com
Backcountry Skiing and Snowboarding
Backcountry skiing and snowboarding offers a recreational activity in a wilderness setting, away from any established mountain resorts, lifts, or trails. BC is regarded as a world-class destination for backcountry access, and has recently seen considerable and sustained growth in this sector (Porteus, 2013). The motivator for pursuing this activity for most people is primarily the lure of fresh, untracked snow in a beautiful mountain setting. Some backcountry skiers and snowboarders combine this activity with helicopter or snowcat skiing.
Spotlight On: Backcountry Lodges Association of British Columbia
The Backcountry Lodges Association of British Columbia (BLABC) represents backcountry lodges in the province. Its consumer site features a find-a-lodge function, profiles for summer and winter lodges, the ability to check conditions in various backcountry areas, and consumer content including a blog and videos. For more information, visit the Backcountry Lodges Association of BC : www.backcountrylodgesofbc.com
Helicopter skiing transports skiers and snowboarders by helicopter to the backcountry. It is typically a professionally guided activity, with packages ranging in duration from a single day to weeks. The skiing/snowboarding is often packaged with a luxury lodge accommodation, gourmet meals, and access to spa treatments.
Heliskiing was pioneered in Canada by Swiss mountain guide Hans Gmoser, who founded the company Canadian Mountain Holidays, which has grown to be the largest heliskiing company in the world (Canadian Mountain Holidays, n.d.). Today, there are close to 20 helicopter skiing companies in BC, which represents the largest concentration of commercial operations in the world (HeliCat Canada, n.d.).
Snowcat skiing is alpine skiing accessed by travelling to the top of the ski area in a snowcat (an enclosed cab vehicle on tracks). As with heliskiing, this activity also has its commercial roots in BC. Snowcat skiing was pioneered in 1975 by Selkirk Wilderness Skiing as an alternative to both lift-serviced and helicopter-accessed riding and skiing (Selkirk Wilderness Skiing, n.d.). It is typically a guided activity due to the avalanche risk associated with the terrain. As with heliskiing, snowcat skiers have the option of choosing single-day or multi-day vacation packages. During the winter of 2015, there were 11 established snowcat skiing operations in BC (HeliCat Canada, n.d.).
Spotlight On: Avalanche Canada
This organization provides public avalanche forecasts and education for any backcountry travellers venturing into avalanche terrain. This vital service is provided to the public free of charge, as Avalanche Canada is a not-for-profit society dedicated to a vision of eliminating avalanche injuries and fatalities in Canada. In addition to the website, it provides training programs and shares safety best practice. For more information, visit Avalance Canada : http://www.avalanche.ca
Guides for these operations are typically certified by either the Association of Canadian Mountain Guides (ACMG) or the Canadian Ski Guide Association (CSGA). Both organizations assess the guides for their expertise in technical skills, avalanche forecasting, risk management and emergency response before issuing certification. The process is extensive and rigorous, taking much time and commitment for guides to become fully certified.
Spotlight On: HeliCat Canada
Based in Revelstoke, BC, HeliCat Canada is an industry organization that represents heliskiing and snowcat skiing operators in Canada. It provides regulation, advocacy, and marketing for the operators. Since 1978, the organization has worked closely with government and industry to develop operations guidelines. For more information, visit Helicat Canada : www.helicatcanada.com
Off-Road Recreational Vehicles
An off-road recreational vehicle (ORV) is any vehicle designed to be driven off road that is not included within any other vehicle classification framework. This includes snowmobiles, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), and dirt bikes (British Columbia Ministry of Forest, Lands and Natural Resource Operations, 2014). ORV use is recognized as a considerable contributor to the BC economy, owing primarily to recreational users, but also from tourist visits.

Recreational snowmobiling in BC is represented by the British Columbia Snowmobile Federation (BCSF). The BCSF’s mandate is to represent recreational snowmobile clubs through advocacy, education, and stewardship (BCSF, n.d.). Commercial snowmobiling is represented by the British Columbia Commercial Snowmobile Operators Association (BCCSOA), a group of snowmobile tour operators who have mobilized to support marketing, product development, and government advocacy initiatives (BCCSOA, n.d.).
ORV use has long been the subject of conflict between non-motorized and motorized recreational users of the wilderness. Non-motorized users claim that motorized users negatively impact the wilderness through noise pollution and environmental damage by degrading trails and scaring wildlife (Webster, 2013). Recently, wilderness tourism operators who hold Crown land tenure to operate in remote areas have complained that ORVs negatively affect their visitors’ experiences. Some of these conflicts may now be mitigated through the implementation of the Off-Road Vehicle Act, which was passed in 2014. This Act requires mandatory registration of ORVs, and includes elements that promote safety, enforcement of regulations, education, and outreach (British Columbia Ministry Forest, Lands and Natural Resource Operations, 2014).
Guest Ranchers and Hunting Outfitters
Guest and dude ranches.
Guest ranches and dude ranches offer personal and home-like vacation experiences centered on horseback riding and an authentic ranch experience. These operators typically offer accommodation in a ranch-type environment, and include as part of the experience the opportunity to participate in ranch activities such as horse riding and cattle wrangling. Other services and activities may also be available, such as spa treatments, hiking, canoeing, and fishing (BC Guest Ranchers Association, n.d.).
Spotlight On: The British Columbia Guest Ranchers Association
The British Columbia Guest Ranchers Association (BCGRA) represents guest and dude ranch operators in the province. It serves and represents its members through cooperative marketing, advertising, development of operational standards, and member pricing on liability insurance plans (BCGRA, n.d.). For more information, visit the British Columbia Guest Ranchers Association website : http://www.bcguestranches.com
A 2011 study of guest ranches by Tourism BC found that there were 57 operating ranches in the province. Most of these were small operations with one to five employees and serving fewer than 1,000 clients per year (Tourism BC, 2011a). There are also large operations such as the Hills Health Guest Ranch located near 100 Mile House, which can accommodate hundreds of guests at one time. The ranch features a full on-site spa and two dining rooms, and hosts a multitude of special events each year. Two other examples of unique guest ranch operations are the Siwash Lake Ranch in south-central BC, a “high-end” exclusive resort featuring executive-chef prepared meals, and the Echo Valley Ranch and Spa in the BC interior, offering an alternative therapy spa and gold-panning excursions.
Hunting Outfitters
Hunting is a traditional recreational activity in BC, and it is also one of the original tourism products in the province (GOABC, n.d.). BC is fortunate to have a vast amount of wilderness available for hunting activities. The exact size of the hunting market is difficult to quantify, but in 2003, a study found that 5,000 non-resident hunting licences were sold in BC, contributing $46 million to the provincial economy (CTC, 2012).
Some people choose self-guided hunting activities, but to hunt certain species, a guide outfitter must be hired. Guide outfitters are licensed by the BC Government to provide commercial hunting services for non-residents. This commercial hunt service directly employs more than 2,000 BC residents and generates approximately $116 million in economic activity annually (GOABC, n.d.). Many of these outfitters are small family operations based in rural areas; they are a source valuable economic activity in areas with limited resources (GOABC, n.d.).
Spotlight On: Guide Outfitters Association of BC
Guide Outfitters Association of BC (GOABC) was established in 1966 to promote and preserve the interests of guide outfitters who take hunters out into wildlife habitat. GOABC is also the publisher of Mountain Hunter magazine. Its website outlines a code of conduct and standards for guide outfitters as well as a wildlife DNA collection program to help provide insight into animal populations. For more information, visit the Guide Outfitters Association of BC website : http://www.goabc.org
Cycling is a popular recreational activity in BC thanks to a variety of terrain, spectacular scenery, and favourable weather conditions, with approximately 44% of residents participating each year (Tourism BC, 2013). Cycling also attracts out-of-province visitors. One study from 2008 reported that out of 5.6 million Canadians who travelled to BC over a two-year period, almost one million (17%) had participated in a cycling activity (Tourism BC, 2009).
Spotlight On: Cycling Destinations
Several BC destinations have developed cycling as a key tourism product. For example, the Salt Spring Island group Island Pathways helped make the island more bike-friendly in recent years by installing bike racks, developing a map with bike routes, encouraging local transportation to accommodate bikes, and establishing local bike rentals and service. For more information, visit Salt Spring Island Cycling : http://www.saltspringtourism.com/cycling/
Another great example of cycling tourism is the Kettle Valley Railway in the Okanagan, built on an abandoned railbed. This 600-kilometre trail network includes a multitude of tunnels and trestles, and is most often travelled by cycling. Sections of the trail system are also now included in the Trans Canada Trail. For more information, visit the Kettle Valley Railway website : http://www.kettlevalleyrailway.ca/
Cycling can be generalized into two styles: road cycling and mountain biking.
Road cycling appeals to those who want to travel on paved roads on bikes designed for travelling long distances efficiently and effectively. Road cycling may refer to racing, both recreational and professional, or cycle touring, where cyclists travel by bike on single- or multi-day trips. Given the multitude of rolling hills, mountain passes, and stunning vistas, BC is regarded as a premier cycle touring destination (Destination BC, 2014b).

Mountain biking generally involves riding on unpaved routes and trails either specially designed for biking or for multipurpose use. BC’s reputation as a prime mountain biking destination has grown because of the unique array of trails available, ranging from the steep, challenging routes of Vancouver’s North Shore, to the high alpine cross-country routes found in the South Chilcotin Mountains (Tourism BC, 2011b).
Take a Closer Look: Mountain Bike Tourism
The report Tourism Essentials Guide: Mountain Bike Tourism is a valuable resource for operators or communities seeking to develop or promote mountain biking tourism in their area. It can be found at Tourism Essentials Guide: Mountain Bike Tourism [PDF] : http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Programs/Guides-Workshops-and-Webinars/Guides/Tourism-Business-Essentials-Guides/TBE-Guide-Mountain-Biking-May2011.pdf.aspx
Over the years, mountain biking has grown from being a fringe activity to a mainstay of the tourism economy. In fact, the growth potential of mountain biking is so highly regarded that the BC Government now considers it as one of the top growth areas in the outdoor adventure sector (Tourism BC, 2011b).
Indeed, numerous mountain winter resorts such as Whistler Blackcomb, Silverstar, and Kicking Horse have developed mountain biking trail infrastructure and lift-accessed biking to provide off-season activities. World-class mountain biking races such as the Test of Metal and the BC Bike Race bring thousands of riders through small communities for mountain biking. The economic impact of these events is significant. Over the course of a single four-month season in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor in 2006 (including the communities of North Vancouver, Squamish, and Whistler), the economic contribution of mountain biking to local economies was $10.3 million (Western Canada Mountain Bike Tourism Association, 2006).
Spotlight On: Test of Metal and GranFondo
Two major bike races bring significant visitors to the Sea-to-Sky Corridor. The Test of Metal, held in Squamish, has sold out every year since 1998, and brings upward of 1,000 mountain bikers into the area for a one-day event each June. For more information, visit The Test of Metal : http://testofmetal.com/. The GranFondo Whistler is a road biking race from Vancouver to Whistler that now attracts upward of 7,000 participants each year. For more information, visit The GranFondo : http://granfondowhistler.com
Spotlight On: Western Canada Mountain Bike Tourism Association
Western Canada Mountain Bike Tourism Association (MBTA) is a not-for-profit organization working toward establishing BC, and Western Canada, as the world’s foremost mountain bike tourism destination. It has hosted a symposium on mountain bike tourism and works with Bike Parks BC to ensure terrain development. For more information, visit the Mountain Bike Tourism Association website : http://www.mbta.ca/
Camping and Hiking
In 2012, over 19.3 million people visited BC provincial parks, including 16.8 million day visitors, many of whom used the parks for hiking and exploration in addition to picnics, swimming, and other outdoor activities. Of these visitors, 2.3 million were overnight campers, generating $15.5 million in user fees, with an average guest satisfaction rating of 82% (BC Parks, 2012). As discussed in Chapter 3, there are also a number of private camping providers in the province.
Wildlife Viewing
Given the diversity and richness of our natural environment, it is not surprising that there is a thriving wildlife viewing industry in BC. This includes whale, bird, and bear watching as well as travelling to view the northern lights or alpine flowers (CTC, 2007). One study conducted by the Canadian Tourism Commission established that within BC, approximately 37% of tourists took part in wildlife viewing while visiting. Significantly, for 13% of visitors, the primary motivation for their travel to BC was wildlife viewing (CTC, 2007).
Spotlight On: Wilderness Tourism Association of British Columbia
The Wilderness Tourism Association of British Columbia (WTA) provides industry support and advocacy for those operators offering nature-based tourism products. For more information, visit the Wilderness Tourism Association of BC website : www.wilderness-tourism.bc.ca
Whale watching occurs along the coast of BC, with tours sometimes leaving from major urban centres, but more commonly from smaller communities such as Telegraph Cove on northern Vancouver Island. Tours are typically by boat, on vessels ranging from open, 10-passenger Zodiacs, to comfortable cabin cruisers with inside seating. The most commonly observed whale is the orca, one of the province’s most distinctive animals. Other whales like the humpback, minke, and Pacific grey are also frequently encountered. The province’s vast diversity of marine life is a key attraction of the tours; in addition to whale watching, a typical tour may encounter bald eagles, sea lions, porpoises, and a variety of sea birds (Destination BC, 2014,d).
Take a Closer Look: Mammal Viewing Guidelines
Marine mammal viewing in Canada has grown in popularity to the point where the federal government has established marine wildlife viewing guidelines. These establish parameters such as safe viewing distances and time limits. For more information, visit the marine wildlife viewing guidelines : http://www.pac.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/fm-gp/species-especes/mammals-mammiferes/view-observer-eng.html
Bear viewing — whether for black bears, grizzly bears, or the rare kermode bear — is also popular. Black bears are common across all regions of BC. Grizzly bears are more likely to be found in remote and mountainous regions; they have an estimated population in the province of approximately 16,000. Kermode bears, also called spirit bears, are a subspecies of black bears with a genetic trait that produces white fur instead of black. They are found primarily in the Great Bear Rainforest of the Central Coast, and figure prominently in the spiritual traditions of BC’s Coastal First Nations. The spirit bear is also BC’s official animal (Destination BC, 2014a).

Tourism operators that offer bear viewing typically operate in remote regions of BC. They may utilize raised viewing areas or operate from a boat-based platform, and offer accommodation at night. The season is typically limited to May through October, with the highest chances of viewing success during the salmon spawning season in the fall.
Spotlight On: Commercial Bear Viewing Association of BC
Bear viewing is a complex activity with potential for physical risk to visitors and impacts to the bears. The Commercial Bear Viewing Association of BC (CBVA) sets standards for operators offering bear viewing. For more information, visit the Commercial Bear Viewing Association website : http://www.bearviewing.ca
Now that we’ve explored some of the key land-based tourism and recreational experiences in BC, let’s turn to the water.
Water-Based Recreation and Tourism
Water-based recreation and tourism in BC is extensive and varied. The coastline of more than 25,000 kilometres in length provides ideal opportunities for recreation and tourism (BC Adventure, n.d.). Activities include scuba diving, boat tours, sport fishing, paddle sports, and more. Following is an overview of a few core water-based activities offered by BC tourism operators, as well as a brief description of their economic contributions and related industry organizations.

Scuba Diving
BC waters offer scuba divers a rich diversity of marine life such as giant Pacific octopuses, wolf eels, sixgill sharks, soft corals, and cloud sponges. As well, a variety of dive sites are available, including marine parks, protected natural areas, sunken naval vessels, artificial reefs, historic wrecks, and even a submerged fuselage of a Boeing 737 airliner (Dive Industry Association of BC, n.d.).
A 2004 study conducted by the Dive Industry Association of BC found that the dive industry in BC consisted of 116 operators offering services to tourists and residents alike. The many segments of the industry include manufacturers, distributers, dive charters, dive shops, and instructional centres. The study estimated that gross revenues from this industry at $15 million, although this number failed to account for other indirect spending such as trip-related accommodation and transportation. It is likely that the actual economic value of this subsector is actually significantly larger (Ivanova, 2004).
Spotlight On: Dive Industry Association of British Columbia
Established in 2002, the Dive Industry Association of British Columbia (DIABC) is a not-for-profit that represents and supports the recreational diving industry in BC. Funded in part by matching donations from Destination BC, their diverse membership includes dive shops, tour operators, and individual dive guides. For more information, visit the Dive Industry Association of BC : http://diveindustrybc.com
Sport Fishing and Lodges
There is a long and rich history of sport fishing in BC. Anglers are drawn to the province’s tidal waters (for salmon and halibut) and to freshwater rivers and lakes (for trout, steelhead, and sturgeon). The annual rate of recreational participation is significant; a 2009 study estimated that there are nearly 600,000 anglers (either fresh or saltwater) in any given year in BC (Tourism BC, 2009). Furthermore, non-resident anglers contributed almost $6 million by way of licensing fees, and an additional $46 million in non-fishing expenditures to the economy of BC. The British Columbia Fishing Resorts and Outfitters Association (BCFROA) represents commercial freshwater resorts and outfitters and delivers advocacy, conservation, and marketing efforts on behalf of its members (BCFROA, n.d.).
Paddle Sports
River rafting, canoeing, sea kayaking, and standup paddle boarding (SUP) are common activities for both recreationists and tourists alike in BC. Collectively, these sports fall under the paddle sports category, which encompasses any activity that takes place in small boats propelled by paddles (Education Scotland, n.d.). Although all paddle sports are popular recreational activities, two of the more sizable and commercially productive paddle sports subsectors are river rafting and sea kayaking.
River rafting operators can be found on many rivers across BC. Product offerings may range from a three-hour adrenaline-fuelled tour on the famous Fraser River to a 14-day wilderness exploration down the UNESCO World Heritage Tatshenshini-Alsek Rivers in northern BC. These trips consist primarily of three types of rafting: paddle rafting, motorized rafting, and float trips (Destination BC, n.d.).
Commercial rafting in BC is represented by the British Columbia River Outfitters Association (BCROA), which acts as a regulatory and marketing organization for river rafting in the province. Guides are required to be certified at one of three levels: guide, senior guide, or trip leader. Each river in BC that is commonly rafted has an extensive set of safety requirements called “provisions” listed by the BCROA. These provisions set out the minimum level of guide required, acceptable water levels ranges, and type of equipment needed for each river excursion (BCROA, n.d.).

A 2005 study conducted by Tourism BC identified 59 operators offering river rafting trips in the province. With an average of 5.5 employees, these operations are typically small in comparison to other industry subsectors. Collectively, however, they provided services to 216,000 customers and contributed almost $15 million in gross revenues to the BC economy in 2005. The same study also indicated that up to 75% of participants had travelled to join in the activity, indicating that they can predominantly be classified as adventure tourists (Tourism BC, 2007a).
Sea kayaking in BC has grown into a sizable recreational and commercial industry in recent years. The province is highly regarded internationally for its long coastline punctuated by many inlets and fjords. Kayaking trips may be as short as an afternoon harbour tour, or as long as a seven-day wilderness exploration to the remote regions of Vancouver Island. Noteworthy areas for sea kayakers include Pacific Rim National Park on western Vancouver Island, Johnstone Strait on northern Vancouver Island, and Gwaii Haanas National Park in Haida Gwaii.
A 2005 report entitled British Columbia’s Sea Kayaking Sector identified more than 114 operators offering rentals, instruction, day tours, or multi-day tours. These operators reported gross revenues of approximately $14 million in 2005 (Tourism BC, 2005a).
Spotlight On: The Sea Kayak Guides Alliance of BC
Commercial operators offering tours are represented by the Sea Kayak Guides Alliance of BC (SKGABC), which represents more than 600 individual and company members working in the commercial sea kayaking industry. It provides operating standards, guide certification, advocacy, and government liaison services for its members. For more information, visit the Sea Kayak Guides Alliance of BC website : www.skgabc.com
Trends and Issues
As shown throughout this chapter, recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism play predominant roles in the tourism and hospitality industry in BC. However, there are challenges that impact the viability of this sector, as well as barriers that limit the growth. These topics are discussed briefly here.
Access to wilderness areas for tourism operators is an ongoing challenge. Some zones across the province are set aside for recreation, such as provincial and national parks. However, when it comes to conducting commercial operations in these same places, gaining access often involves an extensive permitting process that may impose restrictions on the type of activity and the number of visitors allowed.
In addition, parks are generally limited to non-motorized activities, thus presenting barriers for tourism operators that seek to offer mechanized recreation. Operators using Crown land for commercial activities also require authorization from the provincial government; in some instances, priority may be given to resource extraction or development. The permitting process can be onerous and time consuming, which for small operators, may be a barrier to growth (Wilderness Tourism Association, 2005).
Environmental issues are discussed in detail in Chapter 10.
Environmental Impacts

Environmental impacts from climate change, deforestation, and resource extraction all have significant potential to affect this sector of the tourism economy. On a local scale, competition with resource extraction for wilderness areas is a vital issue; without reliable access to pristine wilderness, many operators are facing threats to their sustainability (Wilderness Tourism Association, 2005). Indeed, conflicts with the oil and gas industry, forestry, and mining are constant management challenges for wilderness tourism operators. On a global scale, climate change threatens tourism in BC in many ways, including irregular and insufficient snowfall for winter operations, the pine beetle epidemic sweeping through the province’s forests, and climate-related stress impacting prime wildlife viewing of species such as whales and bears. Environmental issues are discussed in detail in Chapter 10: Environmental Stewardship.
Risk Management
Concerns over risk management and litigation are ongoing for any operator that offers activities with an element of risk. When lawsuits in adventure tourism occur, they are often extensively publicized by the media, creating a perception of risky, dangerous, and irresponsible adventure operators. This can negatively affect the sector through rising insurance rates, increasing governmental regulation, challenging certification requirements, and permitting difficulties when interfacing with land management agencies.
With the popularity of backcountry skiing, snowboarding, snowmobiling, snowshoeing, and other winter sports on the rise in BC, the number of participants accessing backcountry areas is increasing (Mitsui, 2013). This is becoming a concern for long-time backcountry enthusiasts as well as safety monitors such as Avalanche Canada. As winter and summer backcountry equipment becomes more readily accessible, people are able to equip themselves without having received advanced safety training.
The increase of backcountry users will continue to expose users to possible dangerous situations. The best scenario is to ensure users receive proper training and education before they venture into the backcountry areas.
Other elements of risk and liability are discussed further in Chapter 11.
Despite some of the challenges faced by recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism, the industry as a whole remains an exciting, dynamic, and growing sector of the BC tourism economy. Employment opportunities abound, and the potential for economic contribution to the province, protection of wilderness areas, and diversification of rural economies away from resource extraction are exciting prospects. BC is uniquely positioned to maintain positive growth in this area, contingent upon government support to address the barriers and challenges listed above. Students looking to develop professionally in this field should strive to gain both hands-on experience in a specialized activity, and a strong tourism focused education; this combination will offer the best chance to open doors to a long-term career in this exciting industry.
Now that we understand the importance of recreation to the tourism industry, especially in BC, let’s explore Chapter 6, which looks at entertainment, the other half of this industry classification.
- Adventure tourism: outdoor activities with an element of risk, usually somewhat physically challenging and undertaken in natural, undeveloped areas
- Association of Canadian Mountain Guides (ACMG): Canada’s only internationally recognized guiding association, offering a range of certifications
- Avalanche Canada : a not-for-profit society that provides public avalanche forecasts and education for backcountry travellers venturing into avalanche terrain, dedicated to a vision of eliminating avalanche injuries and fatalities in Canada
- British Columbia Golf Marketing Alliance: a strategic alliance representing 58 regional and destination golf resorts in BC with the goal of having BC achieve recognition nationally and internationally as a leading golf destination
- British Columbia Guest Ranchers Association (BCGRA): an organization offering marketing opportunities and development support for BC’s guest ranch operators
- British Columbia Snowmobile Federation (BCSF): an organization offering snowmobile patrol services, lessons on operations, and advocating for the maintenance of riding areas in BC
- Canada West Ski Areas Association (CWSAA): founded in 1966 and headquartered in Kelowna, BC, CWSAA represents ski areas and industry suppliers and provides government and media relations as well as safety and risk management expertise to its membership
- Canadian Ski Guide Association (CSGA): founded in British Columbia, an organization that runs a training institute for professional guides, and a separate non-profit organization representing CSGA guide and operating members
- Commercial Bear Viewing Association of BC (CBVA): promoters of best practices in sustainable viewing, training, and certification for guides, and advocating for land use practices.
- Destination mountain resorts: large-scale mountain resorts where the draw is the resort itself; usually the resort offers all services needed in a tourism destination
- Dive Industry Association of BC: a marketing and advocacy organization protecting the interests of divers, dive shops, guides, dive instructors, and diving destinations in BC
- Guide Outfitters Association of BC (GOABC): established in 1966 to promote and preserve the interests of guide outfitters, who take hunters out into wildlife habitat; publishers of Mountain Hunter magazine
- Nature-based tourism: tourism activities where the motivator is immersion in the natural environment; the focus is often on wildlife and wilderness areas
- Off-road recreational vehicle (ORV): any vehicle designed to travel off of paved roads and on to trails and gravel roads, such as an ATV (all-terrain vehicle) or Jeep
- Outdoor recreation : recreational activities occurring outside; generally in undeveloped areas
- Outdoor Recreation Council of BC (ORC): a not-for-profit organization that promotes the benefits of outdoor recreation, represents the community to government and the general public, advocates and educates about responsible land use, provides a forum for exchanging information, and connects different outdoor recreation groups
- Recreation: activities undertaken for leisure and enjoyment
- Regional mountain resorts : small resorts where the focus is on outdoor recreation for the local communities; may also draw tourists
- Sea Kayak Guides Alliance of BC : representing more than 600 members in the commercial sea kayaking industry, providing operating standards, guide certification, advocacy, and government liaison services
- Western Canada Mountain Bike Tourism Association (MBTA): a not-for-profit organization working toward establishing BC, and Western Canada, as the world’s foremost mountain bike tourism destination
- Wilderness Tourism Association (WTA): an organization that advocates for over 850 nature-based tourism operators in BC, placing a priority on protecting natural resources for continued enjoyment by visitors and residents alike
- Compare and contrast the terms recreation, outdoor recreation , and adventure tourism . How can we differentiate between each of these terms?
- Do you believe that ORV tourism operators should be considered nature-based tourism? Explain.
- What is the difference between a regional mountain resort and a destination mountain resort?
- Of the smaller subsectors of tourism economy discussed in this chapter, name three that are commonly found in small, rural communities. What is their significance to the local community?
- Name a well-known destination for mountain biking in BC. What is the attraction of that area?
- Why is backcountry skiing/snowboarding sometimes considered a risky activity? Explain. How can these risks be mitigated?
- List three industry organizations described in this chapter that represent outdoor tourism subsectors. What general services do they offer to those they represent?
- What unique advantages does BC offer for recreation, outdoor recreation, and adventure tourism?
- Review the section Trends and Issues. What suggestions would you give to the BC Government to support tourism in this subsector?
Case Study: The Wind Within
In late 2014, Destination British Columbia launched a video and set of corresponding marketing materials that sought to expand on the “Super, Natural” brand promise for the province.
Watch the video here: “The Wild Within: British Columbia, Canada” : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dNFrZNjs2ng
On your own or as part of a team, consider the following:
- What natural elements are being promoted?
- What recreational activities are featured in the video?
- Which industry groups or associations are needed to support these activities? Name at least five.
- What are the advantages of promoting BC’s natural elements as a pillar of marketing campaigns?
- What are the disadvantages? How might these be mitigated?
BC Adventure. (n.d.) BC Adventure Planner . Retrieved from: http://www.bcadventure.com/adventure/planner/quick.htm
BC Fishing Resorts and Outfitters Association. (n.d.). About BCFROA . Retrieved from: http://bcfroa.ca/about-bcfroa
BC Guest Ranchers Association. (n.d.). Requirements . Retrieved from: www.bcguestranches.com
BC Parks. (2012). 2011/2012 Statistics Report . [PDF] Retrieved from http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/bcparks/research/statistic_report/statistic_report_2012.pdf
British Columbia Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations. (2014). Off-Road Vehicle Act. Retrieved from: https://www.leg.bc.ca/40th2nd/1st_read/gov13-1.htm
British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Innovation. (2012). Gaining the edge: A five-year strategy for tourism in BC. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.jtst.gov.bc.ca/tourismstrategy/documents/mjti_tourismstrategyreport_fnl.pdf
British Columbia River Outfitters Association. (n.d.). Provisions. [PDF] Retrieved from www.bcroa.com/sites/default/files/river_raft2002_revisedmanual.pdf
British Columbia Snowmobile Federation (n.d.). About BCSF . Retrieved from: http://bcsf.org
British Columbia Snowmobile Operators Association. (n.d.). About us – Snowmobile British Columbia. Retrieved from http://www.snowmobilebritishcolumbia.com/?page_id=450
Canadian Mountain Holidays. (n.d.). About us. Retrieved from: www.canadianmountainholidays.com/about-us.aspx
Canadian Tourism Commission. (2007). TAMS 2006-Canadian activity profile: Wildlife viewing while on trips . [PDF] Retrieved from: http://en-corporate.canada.travel/sites/default/files/pdf/Research/Product-knowledge/TAMS/Canadian%20Travellers%20Outdoor%20Activity/CDN_Wildlife_Viewing_en.pdf
Canadian Tourism Commission. (2012). Sport fishing and game hunting in Canada: An assessment on the potential international tourism opportunity. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://en-corporate.canada.travel/sites/default/files/pdf/Research/Product-knowledge/Product-research/07082013_the_hunting_landscape_rev1.pdf
Cross Country BC. (n.d.). About us. Retrieved from: http://www.crosscountrybc.ca/about
Destination BC. (2014a). Bear viewing. Retrieved from: www.hellobc.com/british-columbia/things-to-do/parks-wildlife/bear-watching.aspx
Destination BC. (2014b). Biking. Retrieved from: www.hellobc.com/british-columbia/things-to-do/outdoor-activities/biking.aspx
Destination BC. (2014c). Golfing. Retrieved from: http://www.hellobc.com/british-columbia/things-to-do/outdoor-activities/golf.aspx
Destination BC. (2014d). Whale watching. Retrieved from: www.hellobc.com/vancouver-island/things-to-do/parks-wildlife/whale-watching.aspx
Destination BC. (n.d.) River rafting British Columbia . Retrieved from http://www.hellobc.com/british-columbia/things-to-do/water-activities/river-rafting.aspx
Dive Industry Association of BC. (n.d.). About us. Retrieved from: www.diveindustrybc.com
Education Scotland. (n.d.). Paddlesports. Retrieved from: http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/learningteachingandassessment/approaches/outdoorlearning/healthandsafety/guides/activityguidance/paddlesports.asp
Guide Outfitters Association of BC. (n.d.). Economic contribution. Retrieved from: www.goabc.org/economic-contribution.aspx
HeliCat Canada. (n.d.). Our members. Retrieved from: http://www.helicatcanada.com/our-members/heliskiing-members.html
Ivanova, I. (2004). Recreational diving in British Columbia survey report. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/Water-based/Recreational_Scuba_Diving_in_British_Columbia-sflb.pdf.aspx
Mitsui, E. (2013). Popularity of backcountry skiing worries some in industry. CBC News. Retrieved from http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/popularity-of-backcountry-skiing-worries-some-in-industry-1.1313223
Outdoor Recreation Council of BC. (2014). About Us. Retrieved from: http://orcbc.ca/about_mission.htm
Porteus, S. (March 6, 2013). The growing business of the backcountry. BC Business. Retrieved from: www.bcbusiness.ca/tourism-culture/the-growing-business-of-the-backcountry
Selkirk Wilderness Skiing (n.d.). About us. Retrieved from: www.selkirkwilderness.com/about_us/
Strategic Networks, Inc. (2009). Economic impact for golf in Canada. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.pgaofcanada.com/Userfiles/SNG_NAGA_Impact%20GolfCanada_2009_KeyFindings_EN_Issued%20Aug17_09(1).pdf
Tourism BC. (2005a). British Columbia River Outfitters report . Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/Research/Research-by-Activity/Water-based.aspx#.VIYlbb4irzI
Tourism BC. (2005b). Characteristics of commercial nature-based tourism industry in British Columbia [PDF] . Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/Land-based/Economic_Impacts_of_Commercial_Nature-Based_Tourism_Report-sflb.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2007a). British Columbia’s sea kayaking sector 2005. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Research-by-Activity/British-Columbia-s-Sea-Kayakers-Report-(2005),-Dec/British_Columbia_s_Sea_Kayakers_Report_2005-sflb.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2007b). Travel activities and motivations of Canadian residents: An overview. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Travel-Motivations-(TAMS)/Canadian-Travel-Motivations/Canadian_TAMS_Overview_Report.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2009a). Fishing product overview. Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/Water-based/Fishing_Sector_Profile.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2009b). Golf sector profile [PDF] . Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/Land-based/Golf_Sector_Profile.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2009c). Wildlife viewing product overview . [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/Land-based/Wildlife_Viewing_Sector_Profile.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2011a). Guest ranchers business survey 2008/2009. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Research-by-Activity/Guest-Ranchers-Business-Survey-2008-2009,-January/GuestRanchersReport2008_2009.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2011b). Mountain bike tourism guide. Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/Research/Research-by-Activity/Land-based.aspx#.VIYqOr4irzI
Tourism BC. (2011c). The value of mountain resorts to the British Columbia economy. [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Research-by-Activity/Value-of-Mountain-Resorts-to-the-British-Columbia/Value_of_Mountain_Resort_Properties_Phase_One_June-2012.pdf.aspx
Tourism BC. (2013). 2009/2010 Outdoor recreation study . [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.destinationbc.ca/getattachment/Research/Research-by-Activity/All-Research-by-Activity/Outdoor-Recreation-Study-2009-2010,-January-2013/Outdoor-Recreation-for-Distribution-14Jan13-FINAL-DRAFT-(2).pdf.aspx
Tribe, J. (2011). The economics of recreation, leisure, and tourism. 4th Edition. Oxford, England: Elsevier.
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2014). Global report on adventure tourism. Retrieved from: http://affiliatemembers.unwto.org/publication/global-report-adventure-tourism
Webster, D. (2013). Adventure tourism operators and snowmobiles: Managing interactions. [PDF] Retrieved from: https://dspace.royalroads.ca/docs/bitstream/handle/10170/660/webster_donald.pdf?sequence=1
Western Canada Mountain Bike Tourism Association. (2006). Sea-to-sky mountain biking economic impact study . [PDF] Retrieved from: http://www.mbta.ca/assets/pdfs/S2S_E_I_Study.pdf
Wilderness Tourism Association. (2005). Characteristics of the commercial nature-based Tourism industry in British Columbia . [PDF] Retrieved from http://www.wilderness-tourism.bc.ca/docs/Commercial_Nature-Based%20Tourism.pdf
Attributions
Figure 5.1 Up and over by Ruth Hartnup is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 5.2 Row Your Boat by Matt Hosford is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 5.3 Blackcomb by Jeff Wilcox is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 5.4 Snowmobiling by Shazron is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 5.5 Cyclists by Jason Sager is used under a CC-BY-SA 2.0 license.
Figure 5.6 A bear in Bute Inlet, BC by John Critchley is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 5.7 Waiting in line by Ruth Hartnup is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 5.8 Rafting Adventure in Squamish, BC by Raj Taneja is used under a CC-BY-NC 2.0 license.
Figure 5.9 Absolutely Nothing is Allowed Here by Vicki & Chuck Rogers is used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 2.0 license.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC Copyright © 2015 by Don Webster is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Un standards for measuring tourism, share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Glossary of tourism terms
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which involve tourism expenditure.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y Z
Activity/activities : In tourism statistics, the term activities represent the actions and behaviors of people in preparation for and during a trip in their capacity as consumers ( IRTS 2008, 1.2 ).
Activity (principal): The principal activity of a producer unit is the activity whose value added exceeds that of any other activity carried out within the same unit ( SNA 2008, 5.8 ).
Activity (productive): The (productive) activity carried out by a statistical unit is the type of production in which it engages. It has to be understood as a process, i.e. the combination of actions that result in a certain set of products. The classification of productive activities is determined by their principal output.
Administrative data : Administrative data is the set of units and data derived from an administrative source. This is a data holding information collected and maintained for the purpose of implementing one or more administrative regulations.
Adventure tourism : Adventure tourism is a type of tourism which usually takes place in destinations with specific geographic features and landscape and tends to be associated with a physical activity, cultural exchange, interaction and engagement with nature. This experience may involve some kind of real or perceived risk and may require significant physical and/or mental effort. Adventure tourism generally includes outdoor activities such as mountaineering, trekking, bungee jumping, rock climbing, rafting, canoeing, kayaking, canyoning, mountain biking, bush walking, scuba diving. Likewise, some indoor adventure tourism activities may also be practiced.
Aggregated data : The result of transforming unit level data into quantitative measures for a set of characteristics of a population.
Aggregation : A process that transforms microdata into aggregate-level information by using an aggregation function such as count, sum average, standard deviation, etc.
Analytical unit : Entity created by statisticians, by splitting or combining observation units with the help of estimations and imputations.
Balance of payments : The balance of payments is a statistical statement that summarizes transactions between residents and non-residents during a period. It consists of the goods and services account, the primary income account, the secondary income account, the capital account, and the financial account ( BPM6, 2.12 ).
Bias : An effect which deprives a statistical result of representativeness by systematically distorting it, as distinct from a random error which may distort on any one occasion but balances out on the average.
Business and professional purpose (of a tourism trip): The business and professional purpose of a tourism trip includes the activities of the self-employed and employees, as long as they do not correspond to an implicit or explicit employer-employee relationship with a resident producer in the country or place visited, those of investors, businessmen, etc. ( IRTS 2008, 3.17.2 ).
Business tourism : Business tourism is a type of tourism activity in which visitors travel for a specific professional and/or business purpose to a place outside their workplace and residence with the aim of attending a meeting, an activity or an event. The key components of business tourism are meetings, incentives, conventions and exhibitions. The term "meetings industry" within the context of business tourism recognizes the industrial nature of such activities. Business tourism can be combined with any other tourism type during the same trip.
Business visitor : A business visitor is a visitor whose main purpose for a tourism trip corresponds to the business and professional category of purpose ( IRTS 2008, 3.17.2 ).
Central Product Classification : The Central Product Classification (CPC) constitutes a complete product classification covering goods and services. It is intended to serve as an international standard for assembling and tabulating all kinds of data requiring product detail, including industrial production, national accounts, service industries, domestic and foreign commodity trade, international trade in services, balance of payments, consumption and price statistics. Other basic aims are to provide a framework for international comparison and promote harmonization of various types of statistics dealing with goods and services.
Census : A census is the complete enumeration of a population or groups at a point in time with respect to well defined characteristics: for example, Population, Production, Traffic on particular roads.
Coastal, maritime and inland water tourism : Coastal tourism refers to land-based tourism activities such as swimming, surfing, sunbathing and other coastal leisure, recreation and sports activities which take place on the shore of a sea, lake or river. Proximity to the coast is also a condition for services and facilities that support coastal tourism. Maritime tourism refers to sea-based activities such as cruising, yachting, boating and nautical sports and includes their respective land-based services and infrastructure. Inland water tourism refers to tourism activities such as cruising, yachting, boating and nautical sports which take place in aquatic- influenced environments located within land boundaries and include lakes, rivers, ponds, streams, groundwater, springs, cave waters and others traditionally grouped as inland wetlands.
Coherence : Adequacy of statistics to be combined in different ways and for various uses.
Competitiveness of a tourism destination : The competitiveness of a tourism destination is the ability of the destination to use its natural, cultural, human, man-made and capital resources efficiently to develop and deliver quality, innovative, ethical and attractive tourism products and services in order to achieve a sustainable growth within its overall vision and strategic goals, increase the added value of the tourism sector, improve and diversify its market components and optimize its attractiveness and benefits both for visitors and the local community in a sustainable perspective.
Consistency : Logical and numerical coherence.
Country of reference : The country of reference refers to the country for which the measurement is done. ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Country of residence : The country of residence of a household is determined according to the centre of predominant economic interest of its members. If a person resides (or intends to reside) for more than one year in a given country and has there his/her centre of economic interest (for example, where the predominant amount of time is spent), he/she is considered as a resident of this country.
Country-specific tourism characteristic products and activities : To be determined by each country by applying the criteria of IRTS 2008, 5.10 in their own context; for these products, the activities producing them will be considered as tourism characteristic, and the industries in which the principal activity is tourism-characteristic will be called tourism industries ( IRTS 2008, 5.16 ).
Cultural tourism : Cultural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the tangible and intangible cultural attractions/products in a tourism destination. These attractions/products relate to a set of distinctive material, intellectual, spiritual and emotional features of a society that encompasses arts and architecture, historical and cultural heritage, culinary heritage, literature, music, creative industries and the living cultures with their lifestyles, value systems, beliefs and traditions.
Data checking : Activity whereby the correctness conditions of the data are verified. It also includes the specification of the type of error or of the condition not met, and the qualification of the data and their division into "error-free data" and "erroneous data".
Data collection : Systematic process of gathering data for official statistics.
Data compilation : Operations performed on data to derive new information according to a given set of rules.
Data confrontation : The process of comparing data that has generally been derived from different surveys or other sources, especially those of different frequencies, in order to assess and possibly improve their coherency, and identify the reasons for any differences.
Data processing : Data processing is the operation performed on data by the organization, institute, agency, etc., responsible for undertaking the collection, tabulation, manipulation and preparation of data and metadata output.
Data reconciliation : The process of adjusting data derived from two different sources to remove, or at least reduce, the impact of differences identified.
Destination (main destination of a trip): The main destination of a tourism trip is defined as the place visited that is central to the decision to take the trip. See also purpose of a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.31 ).
Destination management / marketing organization (DMO) : A destination management/marketing organization (DMO) is the leading organizational entity which may encompass the various authorities, stakeholders and professionals and facilitates tourism sector partnerships towards a collective destination vision. The governance structures of DMOs vary from a single public authority to a public/ private partnership model with the key role of initiating, coordinating and managing certain activities such as implementation of tourism policies, strategic planning, product development, promotion and marketing and convention bureau activities. The functions of the DMOs may vary from national to regional and local levels depending on the current and potential needs as well as on the decentralization level of public administration. Not every tourism destination has a DMO.
Documentation: Processes and procedures for imputation, weighting, confidentiality and suppression rules, outlier treatment and data capture should be fully documented by the survey provider. Such documentation should be made available to at least the body financing the survey.
Domestic tourism : Domestic tourism comprises the activities of a resident visitor within the country of reference, either as part of a domestic tourism trip or part of an outbound tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39 ).
Domestic tourism consumption : Domestic tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a resident visitor within the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Domestic tourism expenditure : Domestic tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a resident visitor within the economy of reference, (IRTS 2008, 4.15(a)).
Domestic tourism trip : A domestic tourism trip is one with a main destination within the country of residence of the visitor (IRTS 2008, 2.32).
Domestic visitor : As a visitor travels within his/her country of residence, he/she is a domestic visitor and his/her activities are part of domestic tourism.
Durable consumer goods : Durable consumer goods are goods that may be used repeatedly or continuously over a period of a year or more, assuming a normal or average rate of physical usage. When acquired by producers, these are considered to be capital goods used for production processes, as is the case of vehicles, computers, etc. When acquired by households, they are considered to be consumer durable goods ( TSA:RMF 2008, 2.39 ). This definition is identical to the definition of SNA 2008, 9.42 : A consumer durable is a goodthat may be used for purposes of consumption repeatedly or continuously over a period of a year or more.
Dwellings : Each household has a principal dwelling (sometimes also designated as main or primary home), usually defined with reference to time spent there, whose location defines the country of residence and place of usual residence of this household and of all its members. All other dwellings (owned or leased by the household) are considered secondary dwellings ( IRTS 2008, 2.26 ).
Ecotourism : Ecotourism is a type of nature-based tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to observe, learn, discover, experience and appreciate biological and cultural diversity with a responsible attitude to protect the integrity of the ecosystem and enhance the well-being of the local community. Ecotourism increases awareness towards the conservation of biodiversity, natural environment and cultural assets both among locals and the visitors and requires special management processes to minimize the negative impact on the ecosystem.
Economic analysis : Tourism generates directly and indirectly an increase in economic activity in the places visited (and beyond), mainly due to demand for goods and services thatneed to be produced and provided. In the economic analysis of tourism, one may distinguish between tourism's 'economic contribution' which refers to the direct effect of tourism and is measurable by means of the TSA, and tourism's 'economic impact' which is a much broader concept encapsulating the direct, indirect and induced effects of tourism and which must be estimated by applying models. Economic impact studies aim to quantify economic benefits, that is, the net increase in the wealth of residents resulting from tourism, measured in monetary terms, over and above the levels that would prevail in its absence.
Economic territory : The term "economic territory" is a geographical reference and points to the country for which the measurement is done (country of reference) ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Economically active population : The economically active population or labour force comprises all persons of either sex who furnish the supply of labour for the production of goods and services as defined by the system of national accounts during a specified time-reference period (ILO, Thirteenth ICLS, 6.18).
Economy (of reference): "Economy" (or "economy of reference") is an economic reference defined in the same way as in the balance of payments and in the system of national accounts: it refers to the economic agents that are resident in the country of reference ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Education tourism : Education tourism covers those types of tourism which have as a primary motivation the tourist's engagement and experience in learning, self-improvement, intellectual growth and skills development. Education Tourism represents a broad range of products and services related to academic studies, skill enhancement holidays, school trips, sports training, career development courses and language courses, among others.
Employees : Employees are all those workers who hold the type of job defined as "paid employment" (ILO, Fifteenth ICLS, pp. 20-22).
Employer-employee relationship : An employer-employee relationship exists when there is an agreement, which may be formal or informal, between an entity and an individual, normally entered into voluntarily by both parties, whereby the individual works for the entity in return for remuneration in cash or in kind ( BPM6, 11.11 ).
Employers : Employers are those workers who, working on their own account with one or more partners, hold the type of job defined as a "self-employment job" and, in this capacity, on a continuous basis (including the reference period) have engaged one or more persons to work for them in their business as "employee(s)" (ILO, Fifteenth ICLS, pp. 20-22).
Employment : Persons in employment are all persons above a specified age who, during a specified brief period, either one week or one day, were in paid employment or self-employment (OECD GST, p. 170).
Employment in tourism industries : Employment in tourism industries may be measured as a count of the persons employed in tourism industries in any of their jobs, as a count of the persons employed in tourism industries in their main job, or as a count of the jobs in tourism industries ( IRTS 2008, 7.9 ).
Enterprise : An enterprise is an institutional unit engaged in production of goods and/or services. It may be a corporation, a non-profit institution, or an unincorporated enterprise. Corporate enterprises and non-profit institutions are complete institutional units. An unincorporated enterprise, however, refers to an institutional unit —a household or government unit —only in its capacity as a producer of goods and services (OECD BD4, p. 232)
Establishment : An establishment is an enterprise, or part of an enterprise, that is situated in a single location and in which only a single productive activity is carried out or in which the principal productive activity accounts for most of the value added ( SNA 2008, 5.14 ).
Estimation : Estimation is concerned with inference about the numerical value of unknown population values from incomplete data such as a sample. If a single figure is calculated for each unknown parameter the process is called "point estimation". If an interval is calculated within which the parameter is likely, in some sense, to lie, the process is called "interval estimation".
Exports of goods and services : Exports of goods and services consist of sales, barter, or gifts or grants, of goods and services from residents to non-residents (OECD GST, p. 194)
Frame : A list, map or other specification of the units which define a population to be completely enumerated or sampled.
Forms of tourism : There are three basic forms of tourism: domestic tourism, inbound tourism, and outbound tourism. These can be combined in various ways to derive the following additional forms of tourism: internal tourism, national tourism and international tourism.
Gastronomy tourism : Gastronomy tourism is a type of tourism activity which is characterized by the visitor's experience linked with food and related products and activities while travelling. Along with authentic, traditional, and/or innovative culinary experiences, Gastronomy Tourism may also involve other related activities such as visiting the local producers, participating in food festivals and attending cooking classes. Eno-tourism (wine tourism), as a sub-type of gastronomy tourism, refers to tourism whose purpose is visiting vineyards, wineries, tasting, consuming and/or purchasing wine, often at or near the source.
Goods : Goods are physical, produced objects for which a demand exists, over which ownership rights can be established and whose ownership can be transferred from one institutional unit to another by engaging in transactions on markets ( SNA 2008, p. 623 ).
Gross fixed capital formation : Gross fixed capital formation is defined as the value of institutional units' acquisitions less disposals of fixed assets. Fixed assets are produced assets (such as machinery, equipment, buildings or other structures) that are used repeatedly or continuously in production over several accounting periods (more than one year) ( SNA 2008, 1.52 ).
Gross margin : The gross margin of a provider of reservation services is the difference between the value at which the intermediated service is sold and the value accrued to the provider of reservation services for this intermediated service.
Gross value added : Gross value added is the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 3.32 ).
Gross value added of tourism industries : Gross value added of tourism industries (GVATI) is the total gross value added of all establishments belonging to tourism industries, regardless of whether all their output is provided to visitors and the degree of specialization of their production process ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.86 ).
Grossing up : Activity aimed at transforming, based on statistical methodology, micro-data from samples into aggregate-level information representative of the target population.
Health tourism : Health tourism covers those types of tourism which have as a primary motivation, the contribution to physical, mental and/or spiritual health through medical and wellness-based activities which increase the capacity of individuals to satisfy their own needs and function better as individuals in their environment and society. Health tourism is the umbrella term for the subtypes wellness tourism and medical tourism.
Imputation : Procedure for entering a value for a specific data item where the response is missing or unusable.
Inbound tourism : Inbound tourism comprises the activities of a non-resident visitor within the country of reference on an inbound tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39 ).
Inbound tourism consumption : Inbound tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a non-resident visitor within the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Inbound tourism expenditure : Inbound tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a non-resident visitor within the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.15(b) ).
Innovation in tourism : Innovation in tourism is the introduction of a new or improved component which intends to bring tangible and intangible benefits to tourism stakeholders and the local community, improve the value of the tourism experience and the core competencies of the tourism sector and hence enhance tourism competitiveness and /or sustainability. Innovation in tourism may cover potential areas, such as tourism destinations, tourism products, technology, processes, organizations and business models, skills, architecture, services, tools and/or practices for management, marketing, communication, operation, quality assurance and pricing.
Institutional sector : An aggregation of institutional units on the basis of the type of producer and depending on their principal activity and function, which are considered to be indicative of their economic behaviour.
Institutional unit : The elementary economic decision-making centre characterised by uniformity of behaviour and decision-making autonomy in the exercise of its principal function.
Intermediate consumption : Intermediate consumption consists of the value of the goods and services consumed as inputs by a process of production, excluding fixed assets whose consumption is recorded as consumption of fixed capital ( SNA 2008, 6.213 ).
Internal tourism : Internal tourism comprises domestic tourism and inbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident and non-resident visitors within the country of reference as part of domestic or international tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(a) ).
Internal tourism consumption : Internal tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of both resident and non-resident visitors within the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism consumption and inbound tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Internal tourism expenditure : Internal tourism expenditure comprises all tourism expenditure of visitors, both resident and non-resident, within the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism expenditure and inbound tourism expenditure. It includes acquisition of goods and services imported into the country of reference and sold to visitors. This indicator provides the most comprehensive measurement of tourism expenditure in the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.20(a) ).
International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities : The International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) consists of a coherent and consistent classification structure of economic activities based on a set of internationally agreed concepts, definitions, principles and classification rules. It provides a comprehensive framework within which economic data can be collected and reported in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decision-taking and policymaking. The classification structure represents a standard format to organize detailed information about the state of an economy according to economic principles and perceptions (ISIC, Rev.4, 1).
International tourism : International tourism comprises inbound tourism and outbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident visitors outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips and the activities of non-resident visitors within the country of reference on inbound tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(c) ).
International visitor : An international traveller qualifies as an international visitor with respect to the country of reference if: (a) he/she is on a tourism trip and (b) he/she is a non-resident travelling in the country of reference or a resident travelling outside of it ( IRTS 2008, 2.42 ).
Job : The agreement between an employee and the employer defines a job and each self-employed person has a job ( SNA 2008, 19.30 ).
Measurement error : Error in reading, calculating or recording numerical value.
Medical tourism : Medical tourism is a type of tourism activity which involves the use of evidence-based medical healing resources and services (both invasive and non-invasive). This may include diagnosis, treatment, cure, prevention and rehabilitation.
Meetings industry : To highlight purposes relevant to the meetings industry, if a trip's main purpose is business/professional, it can be further subdivided into "attending meetings, conferences or congresses, trade fairs and exhibitions" and "other business and professional purposes". The term meetings industry is preferred by the International Congress and Convention Association (ICCA), Meeting Professionals International (MPI) and Reed Travel over the acronym MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions) which does not recognize the industrial nature of such activities.
Metadata : Data that defines and describes other data and processes.
MICE : See meetings industry.
Microdata : Non-aggregated observations, or measurements of characteristics of individual units.
Mirror statistics : Mirror statistics are used to conduct bilateral comparisons of two basic measures of a trade flow and are a traditional tool for detecting the causes of asymmetries in statistics (OECD GST, p. 335).
Mountain tourism : Mountain tourism is a type of tourism activity which takes place in a defined and limited geographical space such as hills or mountains with distinctive characteristics and attributes that are inherent to a specific landscape, topography, climate, biodiversity (flora and fauna) and local community. It encompasses a broad range of outdoor leisure and sports activities.
National tourism : National tourism comprises domestic tourism and outbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident visitors within and outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(b) ).
National tourism consumption : National tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of resident visitors, within and outside the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism consumption and outbound tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
National tourism expenditure : National tourism expenditure comprises all tourism expenditure of resident visitors within and outside the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism expenditure and outbound tourism expenditure ( IRTS 2008, 4.20(b) ).
Nationality : The concept of "country of residence" of a traveller is different from that of his/her nationality or citizenship ( IRTS 2008, 2.19 ).
Non-monetary indicators : Data measured in physical or other non-monetary units should not be considered a secondary part of a satellite account. They are essential components, both for the information they provide directly and in order to analyse the monetary data adequately ( SNA 2008, 29.84 ).
Observation unit : entity on which information is received and statistics are compiled.
Outbound tourism : Outbound tourism comprises the activities of a resident visitor outside the country of reference, either as part of an outbound tourism trip or as part of a domestic tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39(c) ).
Outbound tourism consumption : Outbound tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a resident visitor outside the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Outbound tourism expenditure : Outbound tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a resident visitor outside the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.15(c) ).
Output : Output is defined as the goods and services produced by an establishment, a) excluding the value of any goods and services used in an activity for which the establishment does not assume the risk of using the products in production, and b) excluding the value of goods and services consumed by the same establishment except for goods and services used for capital formation (fixed capital or changes in inventories) or own final consumption ( SNA 2008, 6.89 ).
Output (main): The main output of a (productive) activity should be determined by reference to the value added of the goods sold or services rendered (ISIC rev.4, 114).
Pilot survey : The aim of a pilot survey is to test the questionnaire (pertinence of the questions, understanding of questions by those being interviewed, duration of the interview) and to check various potential sources for sampling and non-sampling errors: for instance, the place in which the surveys are carried out and the method used, the identification of any omitted answers and the reason for the omission, problems of communicating in various languages, translation, the mechanics of data collection, the organization of field work, etc.
Place of usual residence : The place of usual residence is the geographical place where the enumerated person usually resides, and is defined by the location of his/her principal dwelling (Principles and recommendations for population and housing censuses of the United Nations, 2.20 to 2.24).
Probability sample : A sample selected by a method based on the theory of probability (random process), that is, by a method involving knowledge of the likelihood of any unit being selected.
Production account : The production account records the activity of producing goods and services as defined within the SNA. Its balancing item, gross value added, is defined as the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption and is a measure of the contribution to GDP made by an individual producer, industry or sector. Gross value added is the source from which the primary incomes of the SNA are generated and is therefore carried forward into the primary distribution of income account. Value added and GDP may also be measured net by deducting consumption of fixed capital, a figure representing the decline in value during the period of the fixed capital used in a production process ( SNA 2008, 1.17 ).
Production : Economic production may be defined as an activity carried out under the control and responsibility of an institutional unit that uses inputs of labour, capital, and goods and services to produce outputs of goods or services ( SNA 2008, 6.24. ).
Purpose of a tourism trip (main): The main purpose of a tourism trip is defined as the purpose in the absence of which the trip would not have taken place ( IRTS 2008, 3.10. ). Classification of tourism trips according to the main purpose refers to nine categories: this typology allows the identification of different subsets of visitors (business visitors, transit visitors, etc.) See also destination of a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 3.14 ).
Quality of a tourism destination : Quality of a tourism destination is the result of a process which implies the satisfaction of all tourism product and service needs, requirements and expectations of the consumer at an acceptable price, in conformity with mutually accepted contractual conditions and the implicit underlying factors such as safety and security, hygiene, accessibility, communication, infrastructure and public amenities and services. It also involves aspects of ethics, transparency and respect towards the human, natural and cultural environment. Quality, as one of the key drivers of tourism competitiveness, is also a professional tool for organizational, operational and perception purposes for tourism suppliers.
Questionnaire and Questionnaire design : Questionnaire is a group or sequence of questions designed to elicit information on a subject, or sequence of subjects, from a reporting unit or from another producer of official statistics. Questionnaire design is the design (text, order, and conditions for skipping) of the questions used to obtain the data needed for the survey.
Reference period : The period of time or point in time to which the measured observation is intended to refer.
Relevance : The degree to which statistics meet current and potential users' needs.
Reliability : Closeness of the initial estimated value to the subsequent estimated value.
Reporting unit : Unit that supplies the data for a given survey instance, like a questionnaire or interview. Reporting units may, or may not, be the same as the observation unit.
Residents/non-residents : The residents of a country are individuals whose centre of predominant economic interest is located in its economic territory. For a country, the non-residents are individuals whose centre of predominant economic interest is located outside its economic territory.
Response and non-response : Response and non-response to various elements of a survey entail potential errors.
Response error : Response errors may be defined as those arising from the interviewing process. Such errors may be due to a number of circumstances, such as inadequate concepts or questions; inadequate training; interviewer failures; respondent failures.
Rural tourism : Rural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activities, agriculture, rural lifestyle / culture, angling and sightseeing. Rural tourism activities take place in non-urban (rural) areas with the following characteristics:
- Low population density;
- Landscape and land-use dominated by agriculture and forestry; and
- Traditional social structure and lifestyle
Same-day visitor (or excursionist): A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Sample : A subset of a frame where elements are selected based on a process with a known probability of selection.
Sample survey : A survey which is carried out using a sampling method.
Sampling error : That part of the difference between a population value and an estimate thereof, derived from a random sample, which is due to the fact that only a subset of the population is enumerated.
Satellite accounts : There are two types of satellite accounts, serving two different functions. The first type, sometimes called an internal satellite, takes the full set of accounting rules and conventions of the SNA but focuses on a particular aspect of interest by moving away from the standard classifications and hierarchies. Examples are tourism, coffee production and environmental protection expenditure. The second type, called an external satellite, may add non-economic data or vary some of the accounting conventions or both. It is a particularly suitable way to explore new areas in a research context. An example may be the role of volunteer labour in the economy ( SNA 2008, 29.85 ).
SDMX, Statistical Data and Metadata Exchange : Set of technical standards and content-oriented guidelines, together with an IT architecture and tools, to be used for the efficient exchange and sharing of statistical data and metadata (SDMX).
Seasonal adjustment : Seasonal adjustment is a statistical technique to remove the effects of seasonal calendar influences on a series. Seasonal effects usually reflect the influence of the seasons themselves, either directly or through production series related to them, or social conventions. Other types of calendar variation occur as a result of influences such as number of days in the calendar period, the accounting or recording practices adopted or the incidence of moving holidays.
Self-employment job : Self-employment jobs are those jobs where remuneration is directly dependent upon the profits (or the potential of profits) derived from the goods or services produced.
Self-employed with paid employees : Self-employed with paid employees are classified as employers.
Self-employed without employees : Self-employed without employees are classified as own-account workers.
Services : Services are the result of a production activity that changes the conditions of the consuming units, or facilitates the exchange of products or financial assets. They cannot be traded separately from their production. By the time their production is completed, they must have been provided to the consumers ( SNA 2008, 6.17 ).
Social transfers in kind : A special case of transfers in kind is that of social transfers in kind. These consist of goods and services provided by general government and non-profit institutions serving households (NPISHs) that are delivered to individual households. Health and education services are the prime examples. Rather than provide a specified amount of money to be used to purchase medical and educational services, the services are often provided in kind to make sure that the need for the services is met. (Sometimes the recipient purchases the service and is reimbursed by the insurance or assistance scheme. Such a transaction is still treated as being in kind because the recipient is merely acting as the agent of the insurance scheme) (SNA 2008, 3.83).
Sports tourism : Sports tourism is a type of tourism activity which refers to the travel experience of the tourist who either observes as a spectator or actively participates in a sporting event generally involving commercial and non-commercial activities of a competitive nature.
Standard classification : Classifications that follow prescribed rules and are generally recommended and accepted.
Statistical error : The unknown difference between the retained value and the true value.
Statistical indicator : A data element that represents statistical data for a specified time, place, and other characteristics, and is corrected for at least one dimension (usually size) to allow for meaningful comparisons.
Statistical metadata : Data about statistical data.
Statistical unit : Entity about which information is sought and about which statistics are compiled. Statistical units may be identifiable legal or physical entities or statistical constructs.
Survey : An investigation about the characteristics of a given population by means of collecting data from a sample of that population and estimating their characteristics through the systematic use of statistical methodology.
System of National Accounts : The System of National Accounts (SNA) is the internationally agreed standard set of recommendations on how to compile measures of economic activity in accordance with strict accounting conventions based on economic principles. The recommendations are expressed in terms of a set of concepts, definitions, classifications and accounting rules that comprise the internationally agreed standard for measuring indicators of economic performance. The accounting framework of the SNA allows economic data to be compiled and presented in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decision-taking and policymaking ( SNA 2008, 1.1 ).
Total tourism internal demand : Total tourism internal demand, is the sum of internal tourism consumption, tourism gross fixed capital formation and tourism collective consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.114 ). It does not include outbound tourism consumption.
Tourism : Tourism refers to the activity of visitors ( IRTS 2008, 2.9 ).
Tourism characteristic activities : Tourism characteristic activities are the activities that typically produce tourism characteristic products. As the industrial origin of a product (the ISIC industry that produces it) is not a criterion for the aggregation of products within a similar CPC category, there is no strict one-to-one relationship between products and the industries producing them as their principal outputs ( IRTS 2008, 5.11 ).
Tourism characteristic products : Tourism characteristic products are those that satisfy one or both of the following criteria: a) Tourism expenditure on the product should represent a significant share total tourism expenditure (share-of-expenditure/demand condition); b) Tourism expenditure on the product should represent a significant share of the supply of the product in the economy (share-of-supply condition). This criterion implies that the supply of a tourism characteristic product would cease to exist in meaningful quantity in the absence of visitors ( IRTS 2008, 5.10 ).
Tourism connected products : Their significance within tourism analysis for the economy of reference is recognized although their link to tourism is very limited worldwide. Consequently, lists of such products will be country-specific ( IRTS 2008, 5.12 ).
Tourism consumption : Tourism consumption has the same formal definition as tourism expenditure. Nevertheless, the concept of tourism consumption used in the Tourism Satellite Account goes beyond that of tourism expenditure. Besides the amount paid for the acquisition of consumption goods and services, as well as valuables for own use or to give away, for and during tourism trips, which corresponds to monetary transactions (the focus of tourism expenditure), it also includes services associated with vacation accommodation on own account, tourism social transfers in kind and other imputed consumption. These transactions need to be estimated using sources different from information collected directly from the visitors, such as reports on home exchanges, estimations of rents associated with vacation homes, calculations of financial intermediation services indirectly measured (FISIM), etc. ( TSA:RMF 2008, 2.25 ).
Tourism destination : A tourism destination is a physical space with or without administrative and/or analytical boundaries in which a visitor can spend an overnight. It is the cluster (co-location) of products and services, and of activities and experiences along the tourism value chain and a basic unit of analysis of tourism. A destination incorporates various stakeholders and can network to form larger destinations. It is also intangible with its image and identity which may influence its market competitiveness.
Tourism direct gross domestic product : Tourism direct gross domestic product (TDGDP) is the sum of the part of gross value added (at basic prices) generated by all industries in response to internal tourism consumption plus the amount of net taxes on products and imports included within the value of this expenditure at purchasers' prices ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.96 ).
Tourism direct gross value added : Tourism direct gross value added (TDGVA) is the part of gross value added generated by tourism industries and other industries of the economy that directly serve visitors in response to internal tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.88 ).
Tourism expenditure : Tourism expenditure refers to the amount paid for the acquisition of consumption goods and services, as well as valuables, for own use or to give away, for and during tourism trips. It includes expenditures by visitors themselves, as well as expenses that are paid for or reimbursed by others ( IRTS 2008, 4.2 ).
Tourism industries : The tourism industries comprise all establishments for which the principal activity is a tourism characteristic activity. Tourism industries (also referred to as tourism activities) are the activities that typically producetourism characteristic products. The term tourism industries is equivalent to tourism characteristic activities and the two terms are sometimes used synonymously in the IRTS 2008, 5.10, 5.11 and figure 5.1 .
Tourism product : A tourism product is a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the potential customers. A tourism product is priced and sold through distribution channels and it has a life-cycle.
Tourism ratio : For each variable of supply in the Tourism Satellite Account, the tourism ratiois the ratio between the total value of tourism share and total value of the corresponding variable in the Tourism Satellite Account expressed in percentage form ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.56 ). (See also Tourism share).
Tourism Satellite Account : The Tourism Satellite Account is the second international standard on tourism statistics (Tourism Satellite Account: Recommended Methodological Framework 2008 –TSA:RMF 2008) that has been developed in order to present economic data relative to tourism within a framework of internal and external consistency with the rest of the statistical system through its link to the System of National Accounts. It is the basic reconciliation framework of tourism statistics. As a statistical tool for the economic accounting of tourism, the TSA can be seen as a set of 10 summary tables, each with their underlying data and representing a different aspect of the economic data relative to tourism: inbound, domestic tourism and outbound tourism expenditure, internal tourism expenditure, production accounts of tourism industries, the Gross Value Added (GVA) and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) attributable to tourism demand, employment, investment, government consumption, and non-monetary indicators.
Tourism Satellite Account aggregates : The compilation of the following aggregates, which represent a set of relevant indicators of the size of tourism in an economy is recommended ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.81 ):
- Internal tourism expenditure;
- Internal tourism consumption;
- Gross value added of tourism industries (GVATI);
- Tourism direct gross value added (TDGVA);
- Tourism direct gross domestic product (TDGDP).
Tourism sector : The tourism sector, as contemplated in the TSA, is the cluster of production units in different industries that provide consumption goods and services demanded by visitors. Such industries are called tourism industries because visitor acquisition represents such a significant share of their supply that, in the absence of visitors, their production of these would cease to exist in meaningful quantity.
Tourism share : Tourism share is the share of the corresponding fraction of internal tourism consumption in each component of supply ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.51 ). For each industry, the tourism share of output (in value), is the sum of the tourism share corresponding to each product component of its output ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.55 ). (See also Tourism ratio ).
Tourism single-purpose consumer durable goods : Tourism single-purpose consumer durables is a specific category of consumer durable goods that include durable goods that are used exclusively, or almost exclusively, by individuals while on tourism trips ( TSA:RMF 2008 , 2.41 and Annex 5 ).
Tourism trip : Trips taken by visitors are tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.29 ).
Tourist (or overnight visitor): A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Tourism value chain : The tourism value chain is the sequence of primary and support activities which are strategically fundamental for the performance of the tourism sector. Linked processes such as policy making and integrated planning, product development and packaging, promotion and marketing, distribution and sales and destination operations and services are the key primary activities of the tourism value chain. Support activities involve transport and infrastructure, human resource development, technology and systems development and other complementary goods and services which may not be related to core tourism businesses but have a high impact on the value of tourism.
Travel / traveller : Travel refers to the activity of travellers. A traveller is someone who moves between different geographic locations, for any purpose and any duration ( IRTS 2008, 2.4 ). The visitor is a particular type of traveller and consequently tourism is a subset of travel.
Travel group : A travel group is made up of individuals or travel parties travelling together: examples are people travelling on the same package tour or youngsters attending a summer camp ( IRTS 2008, 3.5 ).
Travel item (in balance of payments): Travel is an item of the goods and services account of the balance of payments: travel credits cover goods and services for own use or to give away acquired from an economy by non-residents during visits to that economy. Travel debits cover goods and services for own use or to give away acquired from other economies by residents during visits to other economies ( BPM6, 10.86 ).
Travel party : A travel party is defined as visitors travelling together on a trip and whose expenditures are pooled ( IRTS 2008, 3.2 ).
Trip : A trip refers to the travel by a person from the time of departure from his/her usual residence until he/she returns: it thus refers to a round trip. Trips taken by visitors are tourism trips.
Urban/city tourism : Urban/city tourism is a type of tourism activity which takes place in an urban space with its inherent attributes characterized by non-agricultural based economy such as administration, manufacturing, trade and services and by being nodal points of transport. Urban/city destinations offer a broad and heterogeneous range of cultural, architectural, technological, social and natural experiences and products for leisure and business.
Usual environment: The usual environment of an individual, a key concept in tourism, is defined as the geographical area (though not necessarily a contiguous one) within which an individual conducts his/her regular life routines ( IRTS 2008, 2.21 ).
Usual residence : The place of usual residence is the geographical place where the enumerated person usually resides (Principles and recommendations for population and housing censuses of the United Nations, 2.16 to 2.18).
Vacation home : A vacation home (sometimes also designated as a holiday home) is a secondary dwelling that is visited by the members of the household mostly for purposes of recreation, vacation or any other form of leisure ( IRTS 2008, 2.27 ).
Valuables : Valuables are produced goods of considerable value that are not used primarily for purposes of production or consumption but are held as stores of value over time ( SNA 2008, 10.13 ).
Visit : A trip is made up of visits to different places.The term "tourism visit" refers to a stay in a place visited during a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.7 and 2.33 ).
Visitor : A visitor is a traveller taking a trip to a main destination outside his/her usual environment, for less than a year, for any main purpose (business, leisure or other personal purpose) other than to be employed by a resident entity in the country or place visited ( IRTS 2008, 2.9 ). A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Wellness tourism : Wellness tourism is a type of tourism activity which aims to improve and balance all of the main domains of human life including physical, mental, emotional, occupational, intellectual and spiritual. The primary motivation for the wellness tourist is to engage in preventive, proactive, lifestyle-enhancing activities such as fitness, healthy eating, relaxation, pampering and healing treatments.
The magazine of Glion Institute of Higher Education
- What is tourism and hospitality?
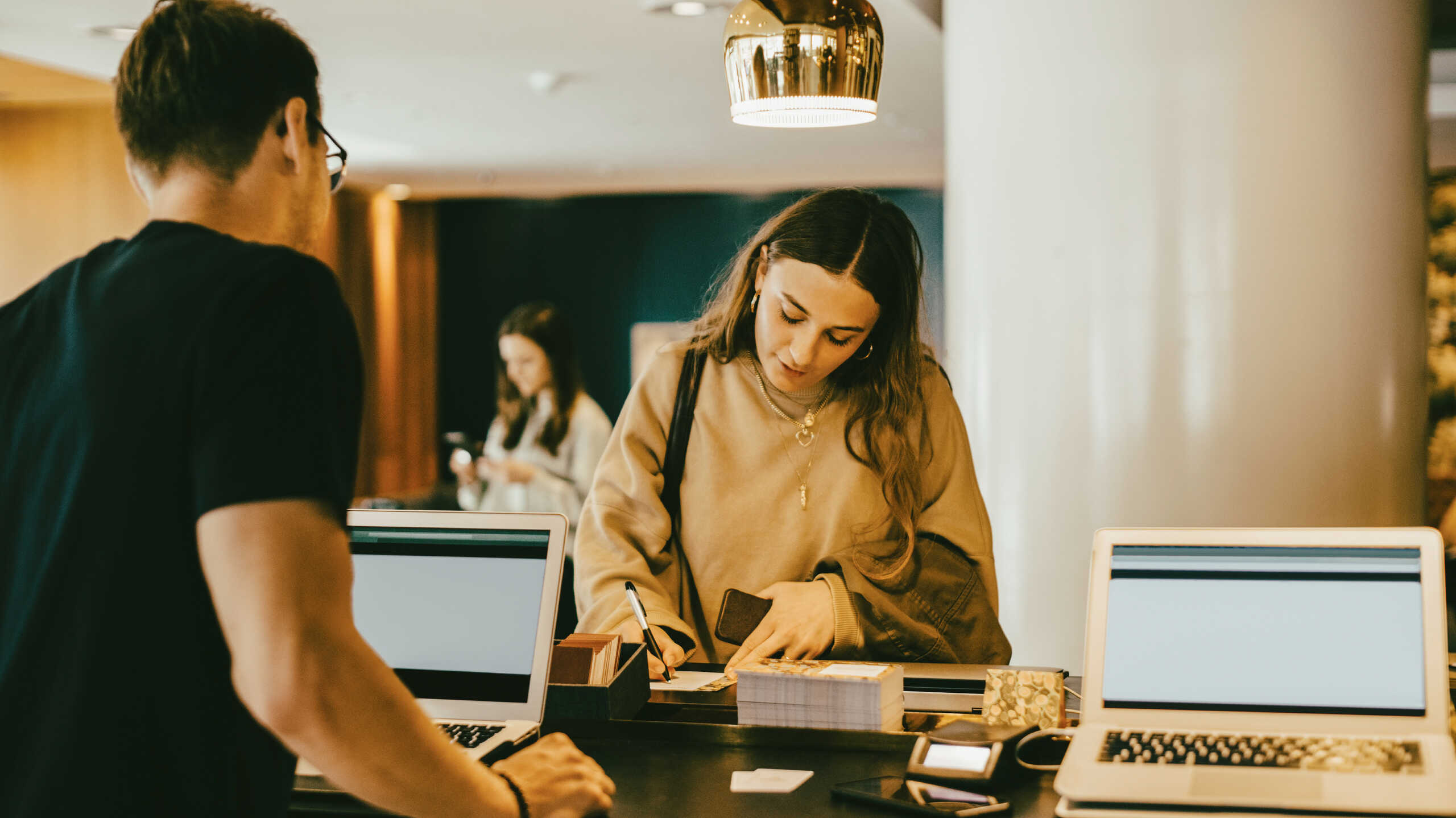

Tourism and hospitality are thriving industries encompassing many sectors, including hotels, restaurants, travel, events, and entertainment.
It’s an exciting and dynamic area, constantly evolving and adapting to changing customer demands and trends.
The tourism and hospitality industry offers a diverse range of career opportunities that cater to various interests, skills, and qualifications, with positions available from entry-level to executive management.
The booming tourism and hospitality industry also offers job security and career growth potential in many hospitality-related occupations.
What is tourism?
Tourism is traveling for leisure, pleasure, or business purposes and visiting various destinations, such as cities, countries, natural attractions, historical sites, and cultural events, to experience new cultures, activities, and environments.
Tourism can take many forms, including domestic, or traveling within your country, and international tourism, or visiting foreign countries.
It can also involve sightseeing, adventure tourism , eco-tourism, cultural tourism, and business tourism, and it’s a huge contributor to the global economy, generating jobs and income in many countries.
It involves many businesses, including airlines, hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, tour operators, and transportation companies.
What is hospitality?
Hospitality includes a range of businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, bars, resorts, cruise ships, theme parks, and other service-oriented businesses that provide accommodations, food, and beverages.
Hospitality is all about creating a welcoming and comfortable environment for guests and meeting their needs.
Quality hospitality means providing excellent customer service, anticipating guests’ needs, and ensuring comfort and satisfaction. The hospitality industry is essential to tourism as both industries often work closely together.
What is the difference between tourism and hospitality?
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries.
Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including transportation, accommodation, and attractions.
Transform your outlook for a successful career as a leader in hospitality management
This inspiring Bachelor’s in hospitality management gives you the knowledge, skills, and practical experience to take charge and run a business

Is tourism and hospitality a good career choice?
So, why work in hospitality and tourism? The tourism and hospitality industry is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world, providing a colossal number of job opportunities.
Between 2021 and 2031, employment in the hospitality and tourism industry is projected to expand faster than any other job sector, creating about 1.3 million new positions .
A tourism and hospitality career can be a highly rewarding choice for anyone who enjoys working with people, has a strong service-oriented mindset, and is looking for a dynamic and exciting career with growth potential.
Growth and job opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Tourism and hospitality offers significant growth and job opportunities worldwide. The industry’s increasing demand for personnel contributes to economic and employment growth, particularly in developing countries.
The industry employs millions globally, from entry-level to high-level management positions, including hotel managers, chefs, tour operators, travel agents, and executives.
It provides diverse opportunities with great career progression and skill development potential.
Career paths in tourism and hospitality

There are many career opportunities in tourism management and hospitality. With a degree in hospitality management, as well as relevant experience, you can pursue satisfying and fulfilling hospitality and tourism careers in these fields.
Hotel manager
Hotel managers oversee hotel operations. They manage staff, supervise customer service, and ensure the facility runs smoothly.
Tour manager
Tour managers organize and lead group tours. They work for tour companies, travel agencies, or independently. Tour managers coordinate a group’s transportation, accommodations, and activities, ensuring the trip runs to schedule.
Restaurant manager
Restaurant managers supervise the daily operations of a restaurant. They manage staff, ensure the kitchen runs smoothly, and monitor customer service.
Resort manager
Resort managers supervise and manage the operations of a resort. From managing staff to overseeing customer service, they ensure the entire operation delivers excellence.
Entertainment manager
Entertainment managers organize and oversee entertainment at venues like hotels or resorts. They book performers, oversee sound and lighting, and ensure guests have a great experience.
Event planner
Event planners organize and coordinate events, such as weddings, conferences, and trade shows. They work for event planning companies, hotels, or independently.
vent planners coordinate all aspects of the event, from the venue to catering and decor.
Travel consultant
Travel consultants help customers plan and book travel arrangements, such as flights, hotels, and rental cars. They work for travel agencies or independently. Travel consultants must know travel destinations and provide superb customer service.
What skills and qualifications are needed for a career in tourism and hospitality?

Tourism and hospitality are rewarding industries with growing job opportunities. Necessary qualifications include excellent skills in communication, customer service, leadership, problem-solving, and organization along with relevant education and training.
Essential skills for success in tourism and hospitality
A career in the tourism and hospitality industry requires a combination of soft and technical skills and relevant qualifications. Here are some of the essential key skills needed for a successful career.
- Communication skills : Effective communication is necessary for the tourism and hospitality industry in dealing with all kinds of people.
- Customer service : Providing excellent customer service is critical to the success of any tourism or hospitality business . This requires patience, empathy, and the ability to meet customers’ needs.
- Flexibility and adaptability : The industry is constantly changing, and employees must be able to adapt to new situations, be flexible with their work schedules, and handle unexpected events.
- Time management : Time management is crucial to ensure guest satisfaction and smooth operations.
- Cultural awareness : Understanding and respecting cultural differences is essential in the tourism and hospitality industry, as you’ll interact with people from different cultures.
- Teamwork : Working collaboratively with colleagues is essential, as employees must work together to ensure guests have a positive experience.
- Problem-solving : Inevitably, problems will arise, and employees must be able to identify, analyze, and resolve them efficiently.
- Technical skills : With the increasing use of technology, employees must possess the necessary technical skills to operate systems, such as booking software, point-of-sale systems, and social media platforms.
Revenue management : Revenue management skills are crucial in effectively managing pricing, inventory, and data analysis to maximize revenue and profitability
Master fundamental hospitality and tourism secrets for a high-flying career at a world-leading hospitality brand
With this Master’s degree, you’ll discover the skills to manage a world-class hospitality and tourism business.

Education and training opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Education and training are vital for a hospitality and tourism career. You can ensure you are prepared for a career in the industry with a Bachelor’s in hospitality management and Master’s in hospitality programs from Glion.
These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of the guest experience, including service delivery and business operations, while developing essential skills such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving. You’ll gain the knowledge and qualifications you need for a successful, dynamic, and rewarding hospitality and tourism career.
Preparing for a career in tourism and hospitality
To prepare for a career in tourism and hospitality management, you should focus on researching the industry and gaining relevant education and training, such as a hospitality degree . For instance, Glion’s programs emphasize guest experience and hospitality management, providing students with an outstanding education that launches them into leading industry roles.
It would help if you also worked on building your communication, customer service, and problem-solving skills while gaining practical experience through internships or part-time jobs in the industry. Meanwhile, attending industry events, job fairs, and conferences, staying up-to-date on industry trends, and networking to establish professional connections will also be extremely valuable.
Finding jobs in tourism and hospitality
To find jobs in tourism and hospitality, candidates can search online job boards, and company career pages, attend career fairs, network with industry professionals, and utilize the services of recruitment agencies. Hospitality and tourism graduates can also leverage valuable alumni networks and industry connections made during internships or industry projects.
Networking and building connections in the industry
Networking and building connections in the hospitality and tourism industry provide opportunities to learn about job openings, meet potential employers, and gain industry insights. It can also help you expand your knowledge and skills, build your personal brand, and establish yourself as a valuable industry professional.
You can start networking by attending industry events, joining professional organizations, connecting with professionals on social media, and through career services at Glion.
Tips for success in tourism and hospitality

Here are tips for career success in the tourism and hospitality industry.
- Gain relevant education and training : Pursue a hospitality or tourism management degree from Glion to gain fundamental knowledge and practical skills.
- Build your network : Attend industry events, connect with colleagues and professionals on LinkedIn, and join relevant associations to build your network and increase your exposure to potential job opportunities.
- Gain practical experience : Look for internships, part-time jobs, or volunteering opportunities to gain practical experience and develop relevant skills.
- Develop your soft skills : Work on essential interpersonal skills like communication, empathy, and problem-solving.
- Stay up-to-date with industry trends : Follow industry news and trends and proactively learn new skills and technologies relevant to tourism and hospitality.
- Be flexible and adaptable : The tourism and hospitality industry constantly evolves, so be open to change and to adapting to new situations and challenges.
- Strive for excellent guest service : Focus on delivering exceptional guest experiences as guest satisfaction is critical for success.
Tourism and hospitality offer many fantastic opportunities to create memorable guest experiences , work in diverse and multicultural environments, and develop transferable skills.
If you’re ready to embark on your career in tourism and hospitality, Glion has world-leading bachelor’s and master’s programs to set you up for success.
Photo credits Main image: Maskot/Maskot via Getty Images
LIVING WELL
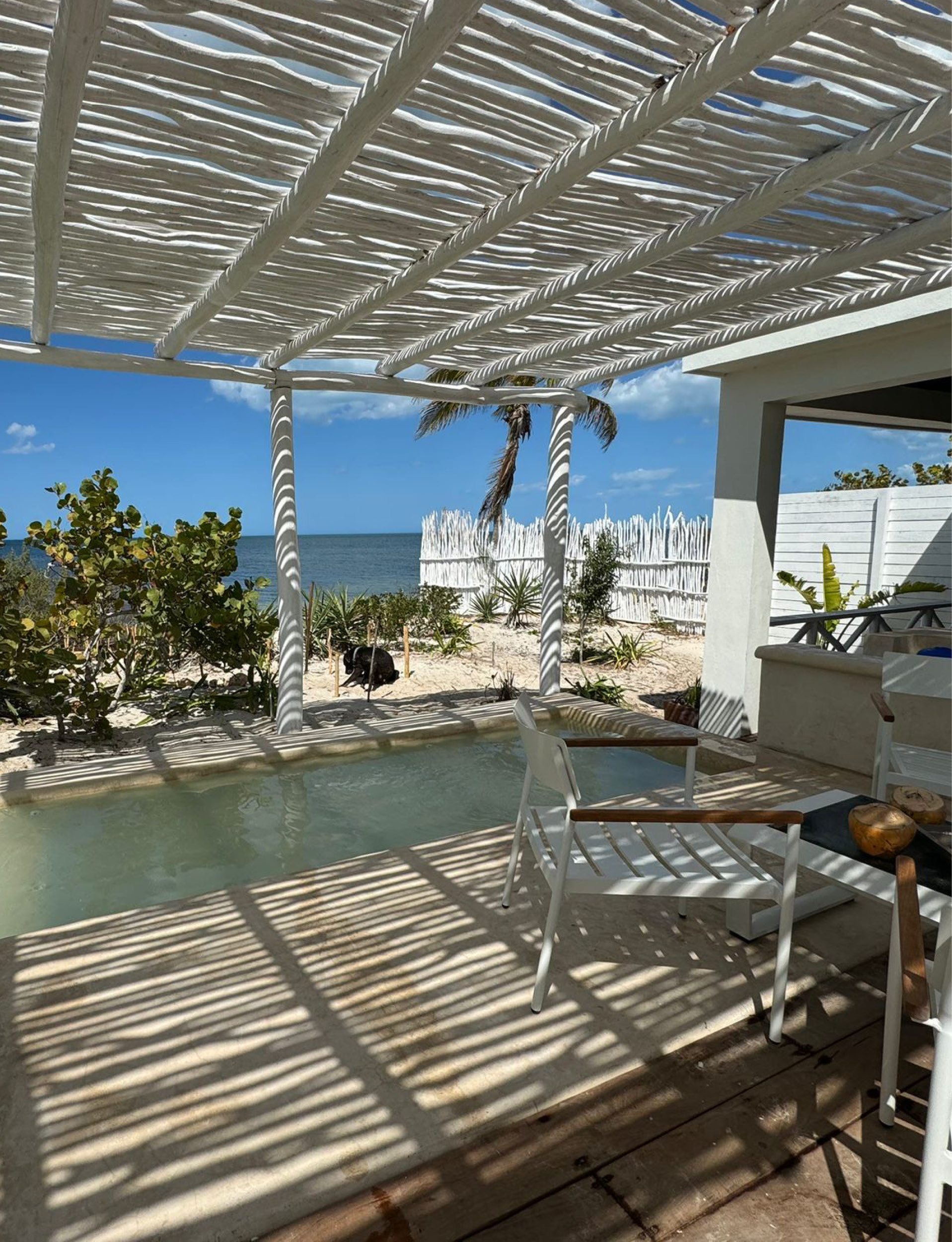

HOSPITALITY UNCOVERED

BUSINESS OF LUXURY

LISTENING TO LEADERS

WELCOME TO GLION.
This site uses cookies. Some are used for statistical purposes and others are set up by third party services. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you accept the use of cookies
Privacy Overview
- › Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
- › Leisure Travel
- Advertising & Marketing
- Agriculture
- Chemicals & Resources
- Construction
- Consumer Goods & FMCG
- Economy & Politics
- Energy & Environment
- Finance & Insurance
- Health, Pharma & Medtech
- Metals & Electronics
- Real Estate
- Retail & Trade
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology & Telecommunications
- Transportation & Logistics
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
- Accommodation
- Business Travel
- Food & Drink Services
- Leisure Travel
Travel & tourism is one of the biggest sectors in terms of global economic impact. In this respect, leisure travel represents by far the most important segment. In the United States and China – the leading countries based on travel & tourism contribution to the global GDP – leisure travel accounts for roughly 65 percent and 80 percent of the total tourism spending, respectively. Online travel agencies (OTAs) play a prominent role in the leisure travel market, with online sales channels representing over two-thirds of global travel and tourism revenue. While the onset of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic upended the OTA market, leading players such as Booking, Expedia, and Airbnb experienced a rebound in revenue in 2022.
Industry Insights
Market size, market segments, industry trends, industry leaders, regional overview, state of the industry, industry definition.
Leisure tourism spending worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Further details: Visit original statistic Leisure tourism spending worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leisure travel generates approximately 80 percent of global travel and tourism expenditure. While spending on vacation trips fell dramatically with the onset of the health crisis, the market is gradually recovering from the impact of COVID-19. As estimated by Statista, the package holidays segment, a key component of leisure travel, is expected to surpass pre-pandemic revenue in 2023.
Number of ocean cruise passengers worldwide from 2009 to 2023, with a forecast until 2027 (in millions)
Further details: Visit original statistic Number of ocean cruise passengers worldwide from 2009 to 2023, with a forecast until 2027 (in millions)
One of the travel and tourism segments worst hit by the COVID-19 pandemic, the global cruise industry breathed a sigh of relief in 2022, as the number of passengers carried by leading companies like Carnival, Royal Caribbean, and Norwegian Cruise Line bounced back. While the increase in global cruise revenue is cause for optimism for the major cruise lines, the financial losses accumulated during the health crisis and the costs related to investments in new vessels are not to be overlooked.
Revenue of the travel apps market worldwide from 2017 to 2027 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Further details: Visit original statistic Revenue of the travel apps market worldwide from 2017 to 2027 (in billion U.S. dollars)
During the last 15 years, the mobile segment has gradually gained momentum in the travel and tourism market, driven by an increase in smartphone users. Global travel app revenue is expected to rise steadily in the following years, reaching nearly two billion U.S. dollars by 2027. The U.S. and China, the leading markets in the travel apps segment, represent alone over 70 percent of this market’s earnings.
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide as of September 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Further details: Visit original statistic Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide as of September 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Booking Holdings and Expedia Group are the biggest online travel agencies based on global revenue. The two companies control a range of key brands in the online travel market, such as Booking.com, Priceline, Agoda, and KAYAK (Booking Holdings), then Vrbo, Hotels.com, and trivago (Expedia Group). While Airbnb and Trip.com rank among the global OTAs with the highest market cap, Tripadvisor is only second to Booking.com in terms of online traffic to travel websites.
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2005 to 2023, by region (in millions)
Further details: Visit original statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2005 to 2023, by region (in millions)
Europe is by far the most visited region worldwide based on international tourist arrivals, with Southern and Mediterranean Europe being the most popular subregion. While Asia and the Pacific reported the second-highest inbound tourism volume prior to the health crisis, this region has ranked behind the Americas since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, most likely due to China maintaining its quarantine measures up to early 2023.
Leisure travel refers to trips taken for relaxation and pleasure. It includes the segments of cruises, travel destinations, holiday activities, online travel market, tour operators and travel agencies. The cruise market mainly focuses on passenger movements, cruise ports and calls, occupancy rate, and bookings. The holiday destination and activities segments look at domestic and international tourism destinations, exploring tourist attractions, and trip purposes. The internet era meant the rise of the online travel market. This segment encompasses online travel agencies (OTAs), which allow tourists to book by themselves travel services on the web, and digital travel-related experiences, like online reviews. While brick-and-mortar travel agencies lost ground to OTAs, some consumers still prefer face-to-face support when booking trips. Apart from analyzing the state of such businesses, this market also looks at the online presence of travel agencies and tour operators.
More interesting topics from the industry "Leisure Travel"
- Cruise industry in Europe
- Cruise industry in Italy
- Cruise industry in the United Kingdom (UK)
- Cruise industry in the United States
- Cruise industry worldwide
- Luxury travel and tourism worldwide
- Travel and tourism in Malta
Destinations
- Chinese tourism in Europe
- Domestic tourism in European countries
- Hotels in Latin America
- Hotels in Spain
- Inbound tourism in Europe
- National park tourism in the U.S.
- Overtourism in European destinations
- Tourism in Barcelona
- Tourism in Italian cities
- Tourism in London
- Tourism in New York
- Tourism in Paris
- Tourism in Rome
- Tourism in Venice
- Tourism industry in Egypt
- Tourism industry in UAE
- Transport industry in UAE
- Travel and tourism in Croatia
- Travel and tourism in Iceland
- Travel and tourism in Portugal
- Travel and tourism in the Canary Islands
- Vacation travel behavior in the United Kingdom (UK)
- Visitor attractions in Paris
- Winter tourism in Europe
Holiday Activities
- Carnival in Brazil
- Recreational boating in the U.S.
- Spa industry
- Wellness industry
- Wellness industry in the U.S.
- Wellness industry in the UK
Online Travel Market
- Artificial intelligence (AI) use in travel and tourism
- Booking Holdings Inc.
- Digitalization of the travel industry
- Impact of technology on travel and tourism
- Mobile travel trends
- Online travel market
- Online travel market in Latin America
- Subscription model in the travel industry
- Travel agencies in the United Kingdom (UK)
- Travel agency industry
Tour Operators & Travel Agencies
- Package holidays in the United Kingdom (UK)
- Package travel in Japan
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)

- Get IGI Global News

- All Products
- Book Chapters
- Journal Articles
- Video Lessons
- Teaching Cases
Shortly You Will Be Redirected to Our Partner eContent Pro's Website
eContent Pro powers all IGI Global Author Services. From this website, you will be able to receive your 25% discount (automatically applied at checkout), receive a free quote, place an order, and retrieve your final documents .
What is Leisure Tourism

Related Books View All Books

Related Journals View All Journals

What Is Sports Tourism?
Senior Reporter, HuffPost Life

There’s been a lot of buzz lately in the travel industry about “gig-tripping,” as fans of Taylor Swift and other musical artists plan vacations all around the world just for the live concert experience.
Meanwhile, another experience-driven trend is also on the rise: sports tourism. Whether you’re an athlete yourself or just a big fan, you might want to consider this approach to travel.
So what exactly is sports tourism, and what does it involve? Below, industry experts break down the benefits and downsides.
What is sports tourism?
“‘Sports tourism’ refers to when individuals plan their travel tied to specific sporting events, typically to spectate but, depending on the event, it could include participation as well,” said Carolyn Addison, the head of product at travel company Black Tomato . “Some of the classic examples are the Olympics and we’ve often seen this type of travel for events like F1 [Formula One racing] or the Tour de France.”
Sports tourism can sometimes involve venturing to a different city to watch a regular-season away game for your favorite team. Or you might travel to participate in your own athletic endeavor, like a marathon or team competition.
“Sports tourism ranges all the way from youth sports to professional leagues,” said Nate Hardesty, the managing director of the Thompson Austin and Tommie Austin hotels in Texas. “For instance, we see so many families traveling around the country for tournaments that it’s become their spring break or summer trip. The same goes for collegiate and professional sports. We see so many fans follow their teams around the country and take the opportunity to check out the destination while they are here.”
If you live in a popular sports market, it might be easier to get good tickets to your team’s away game in another city. Some people also just like to merge their love of travel and sports into one experience.
Although taking a trip for a sporting event is not a brand-new phenomenon, more fans seem eager to have these kinds of experiences after being forced to stay at home amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
“People have been traveling for sports for years,” Hardesty noted. “However, experiential tourism has skyrocketed post-COVID.”
The popularity of shows like “Formula 1: Drive To Survive,” which gives a behind-the-scenes look at the world of auto racing, and “Welcome to Wrexham,” a docuseries about a Welsh soccer team, has also sparked greater interest in professional sports experiences.
The sports documentary movement has now expanded to golf with “Full Swing,” as well as to football with “Quarterback.” And with the buzz around the new sports drama “Challengers,” perhaps we’ll see more travelers planning trips around big tennis tournaments.

What are the benefits?
“We find that planning a trip around a sporting event gives a nice framework and intention to an itinerary,” Addison said. “Special events can also be a compelling way to interact with locals in a way that feels spontaneous and unforced.”
She pointed to the powerful energy in crowds at big events and the opportunity to bond with people who have similar interests. Sports tourism might take you to an exciting destination you wouldn’t have otherwise visited.
“You’re crafting your trip around a pivotal core memory and occasion which is supplemented by other local attractions, creating a comprehensive travel experience,” added Nikki Glass, the general manager at The Sawyer in Sacramento, California.
She noted that many sports tourism destinations have made efforts to ramp up various attractions and offerings around sporting events to give fans a multifaceted travel experience.
“These travelers tend to stay in their destination for extended periods to immerse themselves in the cultural tapestry and urban milieu, from vibrant dining scenes to museums and green spaces,” Glass said. “Sports tourists are tapping into it all.”
What are the downsides?
“There can be some additional challenges around planning travel during a major event,” Addison said. “Crowds and traffic can make the overall travel experience less enjoyable, and properties often impose higher rates and/or longer minimum stays.”
She emphasized the importance of advance planning to secure hotel reservations, airfare and tickets for sporting events.
“Sometimes the availability will be tight, and you need to book as soon as you can to get the best available rate,” echoed Lisa Bush, the director of sales and marketing at Thompson Nashville in Tennessee. “The last-minute booker usually learns that procrastination is not the best.”
Expect longer wait times and higher costs for things like accommodation and transportation. If you plan a trip based around sports tourism, you might find yourself in overcrowded areas that aren’t always equipped to deal with a surge of people. And you may have to put in extra effort to get an authentic local experience during times when so many tourists have taken over a destination.
Our 2024 Coverage Needs You
It's another trump-biden showdown — and we need your help, the future of democracy is at stake, your loyalty means the world to us.
As Americans head to the polls in 2024, the very future of our country is at stake. At HuffPost, we believe that a free press is critical to creating well-informed voters. That's why our journalism is free for everyone, even though other newsrooms retreat behind expensive paywalls.
Our journalists will continue to cover the twists and turns during this historic presidential election. With your help, we'll bring you hard-hitting investigations, well-researched analysis and timely takes you can't find elsewhere. Reporting in this current political climate is a responsibility we do not take lightly, and we thank you for your support.
Contribute as little as $2 to keep our news free for all.
Can't afford to donate? Support HuffPost by creating a free account and log in while you read.
The 2024 election is heating up, and women's rights, health care, voting rights, and the very future of democracy are all at stake. Donald Trump will face Joe Biden in the most consequential vote of our time. And HuffPost will be there, covering every twist and turn. America's future hangs in the balance. Would you consider contributing to support our journalism and keep it free for all during this critical season?
HuffPost believes news should be accessible to everyone, regardless of their ability to pay for it. We rely on readers like you to help fund our work. Any contribution you can make — even as little as $2 — goes directly toward supporting the impactful journalism that we will continue to produce this year. Thank you for being part of our story.
It's official: Donald Trump will face Joe Biden this fall in the presidential election. As we face the most consequential presidential election of our time, HuffPost is committed to bringing you up-to-date, accurate news about the 2024 race. While other outlets have retreated behind paywalls, you can trust our news will stay free.
But we can't do it without your help. Reader funding is one of the key ways we support our newsroom. Would you consider making a donation to help fund our news during this critical time? Your contributions are vital to supporting a free press.
Contribute as little as $2 to keep our journalism free and accessible to all.
Dear HuffPost Reader
Thank you for your past contribution to HuffPost. We are sincerely grateful for readers like you who help us ensure that we can keep our journalism free for everyone.
The stakes are high this year, and our 2024 coverage could use continued support. Would you consider becoming a regular HuffPost contributor?
The stakes are high this year, and our 2024 coverage could use continued support. If circumstances have changed since you last contributed, we hope you'll consider contributing to HuffPost once more.
Already contributed? Log in to hide these messages.
Popular in the Community
From our partner, huffpost shopping’s best finds, more in life.

Pasco County could soon be home to more 'sports tourism'
NEW PORT RICHEY, Fla. - On the heels of the wheelchair rugby tournament in Pasco County , Florida's Sports Coast continues to grow and leaders want to expand into leisure sports and ecotourism.
"We thought it was widely successful. We brought in over 50 athletes across 30 teams to compete for four days of just grinding wheelchair rugby matches," said Adam Thomas, the executive director of Florida Sports Coast.
Thomas said the U.S. Wheelchair Rugby Championship event was so successful that they’ve locked in the tournament again for next year, and they hope to bring more adaptive sports events to the area.
READ: Wheelchair rugby championships bringing competition, camaraderie to Wesley Chapel
They currently bring basketball, ice skating and more sporting events to their facilities while eyeing the unconventional.
"We look at unconventional sports that we don't currently have on our portfolio, but also what Florida is also not hosting. So, we look at boomerang tossing. We look at futsal. We look at indoor facility sports that really can pay dividends to the overall growth of our tourism economy," said Thomas.
But now they are looking to spotlight leisure sports and ecotourism along West Pasco’s waterways.
READ: Lakeland nurse delivers her own baby at home in surprise labor
"The estuaries really provide a visitor experience where they can get into the eco, natural Florida feel, just right in outside of a major metropolis in downtown Tampa," said Thomas.
Pasco boating captains Mark Dillingham, owner of Inshore Adventures, and Curt Romanowski, owner of Florida Backwater Charters, encourage ecotourism for visitors. Both captains run fishing charters with their respective businesses in the county.
"That's been a big interest. You know, we've got a great estuary up there. You've got 20 miles of shoreline in the county and a lot of mangrove shorelines, back areas. The fishery is really good," Romanowski said. "I think it's a good idea. The more people who know about what Pasco County has as far as the ecosystem, you know, the wildlife that they're in the water, we can educate them to do more… to not damage that area."
READ: Family of late firefighter moves into mortgage-free home: 'I'm speechless'
With about 1.5 million people visiting Pasco County every year, sharing what’s naturally special could keep paying off.
"Just recently, I just had a phone call from people that had just moved to the New Port Richey area and wanted to learn the area. They wanted to fish, but they also wanted to learn the area and kind of learn, like, the background of the area," said Dillingham, adding that nature is abundant in the area with freshwater springs, estuaries, manatees and dolphins. "As far as Pasco County, it is still the hidden gem."
Florida Sports Coast leaders said they will work with Florida Fish and Wildlife and the Coastal Conservation Association to share a sustainable vision of Pasco County for the years to come.
SIGN UP: Click here to sign up for the FOX 13 daily newsletter
WATCH FOX 13 NEWS

GPB Originals
Browse by genre, featured programs, featured programs & series, more gpb news, for kids & teachers, ghsa sports, high school football, browse by type, browse by category, for parents & caregivers, support gpb, gpb newsletter cta, banner image, section branding, header content, tagged as: , with 'bleisure' and fewer workers, the american hotel is in recovery.
May 13, 2024 8:12 AM
- Alina Selyukh
Share this page
Primary content.

Midday is quiet at a Hampton Inn & Suites near Dulles International Airport in Northern Virginia. Staff restock the snacks. A young dad bounces a baby among the grays, browns and teals of the lobby. Eventually, a couple of new arrivals roll a suitcase to the front desk, asking to check in early.
The hotel's owner, Vinay Patel, has noticed this interaction waning.
"People are now literally not wanting to go to the front desk," he says. "They'll check in online on the phone similar to the airlines and go straight to [the] room."
Technology has long been transforming hotels, and the pandemic accelerated that change.
It's Tuesday, and for this hotel, that used to mean a crush of business travelers. Instead, Patel has been welcoming a new type of guest: here not just for business or leisure, but a combination of both. "Bleisure" is a hot new term in hospitality, the product of remote-work culture.
All this is part of a big post-pandemic reset for the American hotel: It's shaken up travel habits, erased jobs and put the industry on a circuitous path to recovery.
Getting by with fewer workers
Today almost 200,000 fewer people work in hotels and other lodging than before the pandemic, federal data shows. That's a 9% drop. Lower employment often implies an industry in trouble — but hotels may actually never need as many workers as they once did.
When travel cratered in 2020, hotels were wiped out and over a million workers lost jobs. Housekeepers, front desk agents, maintenance staff went into construction, food, retail. Those who stayed trained to do new tasks. Hotels that offered extra services, like lunches, scaled them back.
Over time, guests learned to skip daily room cleanings for COVID precautions. Breakfasts got more self-served and automated, with waffles and pancakes tumbling out of machines. And in the long run, operating with fewer workers saves companies money.
"You know, like it or not ... the pandemic has kind of taught us a lot," says Patel, who owns 11 hotels around Virginia. "We've become a lot more efficient."
Less business, more "bleisure"
Vacationers surged back to hotels with " revenge travel ," but foreign tourists and corporate travelers are still not back in force.
"That's the biggest impact," says Miraj Patel, the chair of the Asian American Hotel Owners Association, whose members own the majority of U.S. hotels, and Vinay Patel's nephew. "The full recovery is still not there."
The "bleisure" travelers make up for some of the losses, says Vinay Patel. They come for meetings, and stay longer to visit the Virginia wineries. And at the Hampton, six miles from the airport, that's upended the ebb and flow.
Before the pandemic, "you do not mess with Tuesday-Wednesday," Patel recalls. "Business travelers come down on Tuesday-Wednesday."
And these days? "It's spread out a lot more," he says.
Questions about the industry's future
Major hotel chains, like Hilton and Marriott, have seen their stock price resurge to record highs this year. That's partly because luxury hotels have fared much better than the rest.
People stayed more often at upscale brands and less in economy lodging in early 2024 versus 2023, says Jan Freitag, who tracks hospitality analytics at the real estate data firm CoStar.
Overall hotel occupancy neared 64% in March compared to 68% in 2019, CoStar found. That suggests near-recovery from pandemic collapse, though the lag does obscure millions of rooms that got built, opened and not filled.
"We have more rooms available now, and we are selling fewer rooms than we did," says Freitag.
Price-wise, the average cost has jumped to $155 per room from $129 in 2019, Freitag says. That's a 20% increase. At the same time, overall U.S. inflation added up to almost 23% over those years. So hotel owners list plenty of higher costs, too: taxes, wages, insurance, coffee, cups, linens, detergent.
Add in high interest rates, plus banks being stingier with loans, and a new concern hovers overs the industry's future: Fewer people have been buying and building new hotels.
That includes Vinay Patel in Virginia, who keeps delaying construction on a lot where he originally planned to break ground when the pandemic began.
"I just can't make the numbers work right now," he says. "I have to wait another year to two years."
Still, he notes a silver lining: There's less competition for his existing hotels — for now.
NPR's Scott Horsley contributed to this report.
Bottom Content
Related news.

Sales are way down at a Florida flea market. A new immigration law could be to blame.
Florida's new strict immigration law threatens the state's economy and could hurt political ambitions for some GOP candidates. Vendors at a popular flea market are already seeing the impacts.
- Claudia Grisales

Netflix shows steady growth amid writers and actors strikes
The streamer said it added 5.9 million customers during the second quarter. Its share price has almost doubled over the past year.
- Chloe Veltman

Bed Bath & the great Beyond: How the home goods giant went bankrupt
The retailer once triumphed over rivals as a "category killer" with its blue coupons. Now, it's become rudderless, turbulent and broke. Here's what happened.

Support Quality Journalism
GPB is committed to bringing you comprehensive news coverage from Georgia, across the country and around the world. Your support makes this possible. Please consider making a gift today to support this vital public service.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Travel. Leisure tourism, a popular form of travel, refers to the act of taking a trip for the purpose of relaxation, recreation, or enjoyment. It involves participating in activities typically done during one's free time, such as sightseeing, shopping, dining out, and engaging in cultural events. While leisure tourism can take many forms, it ...
Leisure tourism: This involves traveling for recreational purposes, such as beach vacations, adventure trips, or visiting theme parks. Cultural tourism: This focuses on exploring the heritage, customs, and traditions of different cultures, including visiting museums, historical sites, and attending cultural events.
The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes". [28] The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that up to 500,000 people are in flight at any one time.
While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as "the ...
The main difference between leisure and tourism is that leisure is an activity that individuals engage in during their free time, while tourism involves traveling to new places and experiencing new activities. Leisure activities can be done at home or within one's local community, while tourism requires leaving one's home environment.
Tourism, as a form of leisure experience, produces positive emotions but how such emotions link to aspects of the tourist experience is largely unknown. Nawijn et al. ( 2012) found that individuals on 1- to 2-week vacation experienced substantial emotional changes over their trips.
Tourism essentially refers to the activities undertaken by visitors, also known as the visitor economy. The tourism industry encompasses all activity that takes place within the visitor economy. This includes activities that are directly related to the tourist, such as staying in a hotel, ordering a meal or visiting a tourist attraction.
While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as "the ...
Leisure is an essential aspect of tourism that cannot be overlooked. It is the time that tourists spend engaging in activities that are not work-related but rather for pleasure, relaxation, and enjoyment. Leisure activities in tourism can range from sightseeing, hiking, camping, swimming, shopping, and many more.
As tourists like to visit places of cultural significance and soak in the culture of the area, the cultural industry is very important to travel and tourism. Leisure, Recreation, and Sport. Leisure or free time is a period of time spent out of work and essential domestic activity.
Leisure has often been defined as a quality of experience or as free time. [1] [2] Free time is time spent away from business, work, job hunting, domestic chores, and education, as well as necessary activities such as eating and sleeping. Leisure as an experience usually emphasizes dimensions of perceived freedom and choice.
Pleasure is defined as a feeling of happiness, satisfaction, or enjoyment. Therefore, the pursuit of such feelings through travel is referred to as pleasure tourism. According to Currie ( 1997 ), "tourism" means pleasure travel, and according to the UNWTO ( 2007 ), pleasure represents the main purpose of tourism.
The relationship between leisure and tourism is analysed from the perspective of changes in the perception of time, including its division into free- and work-time, compression of time, moving ...
Leisure and tourism careers The possible paths are as diverse as the leisure and tourism topics in which you could choose to specialize. Many are outside of the nine to five office-job norm, often meaning unusual working hours, significant seasonal variation, travel to different locations and a fair amount of pressure - but for those with a passion for creating events or settings in which ...
Overview. In this chapter, we discuss the concept of recreation in tourism and hospitality. Recreation can be defined as the pursuit of leisure activities during one's spare time (Tribe, 2011) and can include vastly different activities such as golfing, sport fishing, and rock climbing. Defining recreation as it pertains to tourism, however ...
In its broadest sense, tourism is defined as when people travel and stay in places outside of their usual environment for less than one consecutive year for leisure, business, health, or other ...
Tourism is a social, ... Coastal tourism refers to land-based tourism activities such as swimming, surfing, sunbathing and other coastal leisure, recreation and sports activities which take place on the shore of a sea, lake or river. Proximity to the coast is also a condition for services and facilities that support coastal tourism.
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries. Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including ...
Leisure is often about events, sports centres, and multi-purpose venues. Tourism is about domestic and international travel, including sightseeing and attractions. All three will give you commercial and business skills, customer service experience, rapid thinking, working in high-pressure environments, and superb communication skills. You could ...
Leisure travel generates approximately 80 percent of global travel and tourism expenditure. While spending on vacation trips fell dramatically with the onset of the health crisis, the market is ...
As nouns the difference between leisure and tourism. is that leisure is freedom provided by the cessation of activities while tourism is the act of travelling or sightseeing, particularly away from one's home.
What is Leisure Tourism? Definition of Leisure Tourism: Leisure tourism refers to take a break from daily routine life. Leisure tourists usually enjoy beauty and nice hotels and resorts, enjoy atmosphere of beaches. The most popular activities of leisure tourism include social tours, cultural tours, religious tours, family tours, sports tours, and medical tours.
Sports tourism can sometimes involve venturing to a different city to watch a regular-season away game for your favorite team. Or you might travel to participate in your own athletic endeavor, like a marathon or team competition. "Sports tourism ranges all the way from youth sports to professional leagues," said Nate Hardesty, the managing ...
NEW PORT RICHEY, Fla. - On the heels of the wheelchair rugby tournament in Pasco County, Florida's Sports Coast continues to grow and leaders want to expand into leisure sports and ecotourism. "We ...
It's Tuesday, and for this hotel, that used to mean a crush of business travelers. Instead, Patel has been welcoming a new type of guest: here not just for business or leisure, but a combination of both. "Bleisure" is a hot new term in hospitality, the product of remote-work culture.
Combined with a massive drop in tourism - only 206,700 visitors entered Israel from January to March, compared with 966,200 during the same period in 2023 - the constrained supply has seen the ...